Patents
Literature
390 results about "Passive cooling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
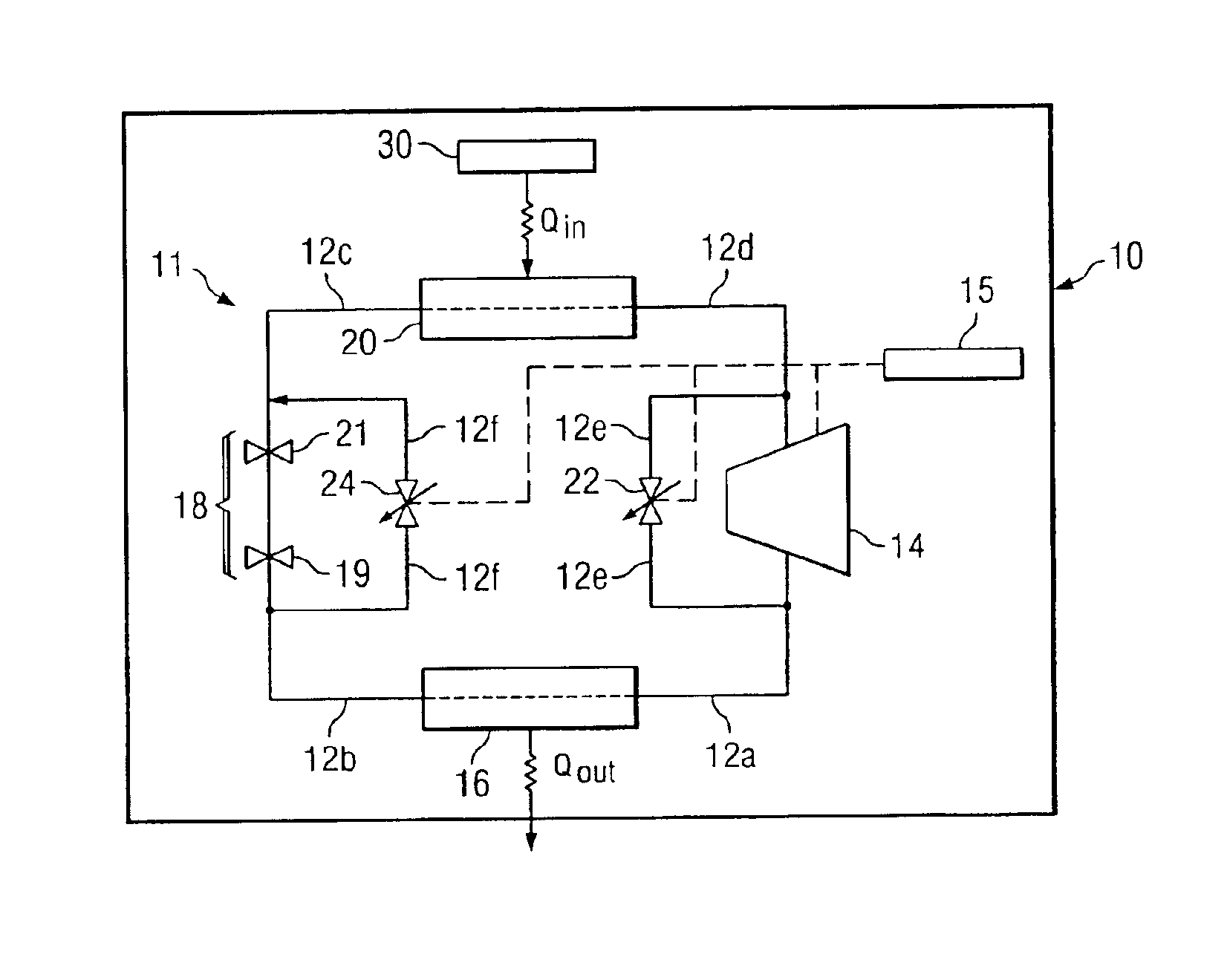
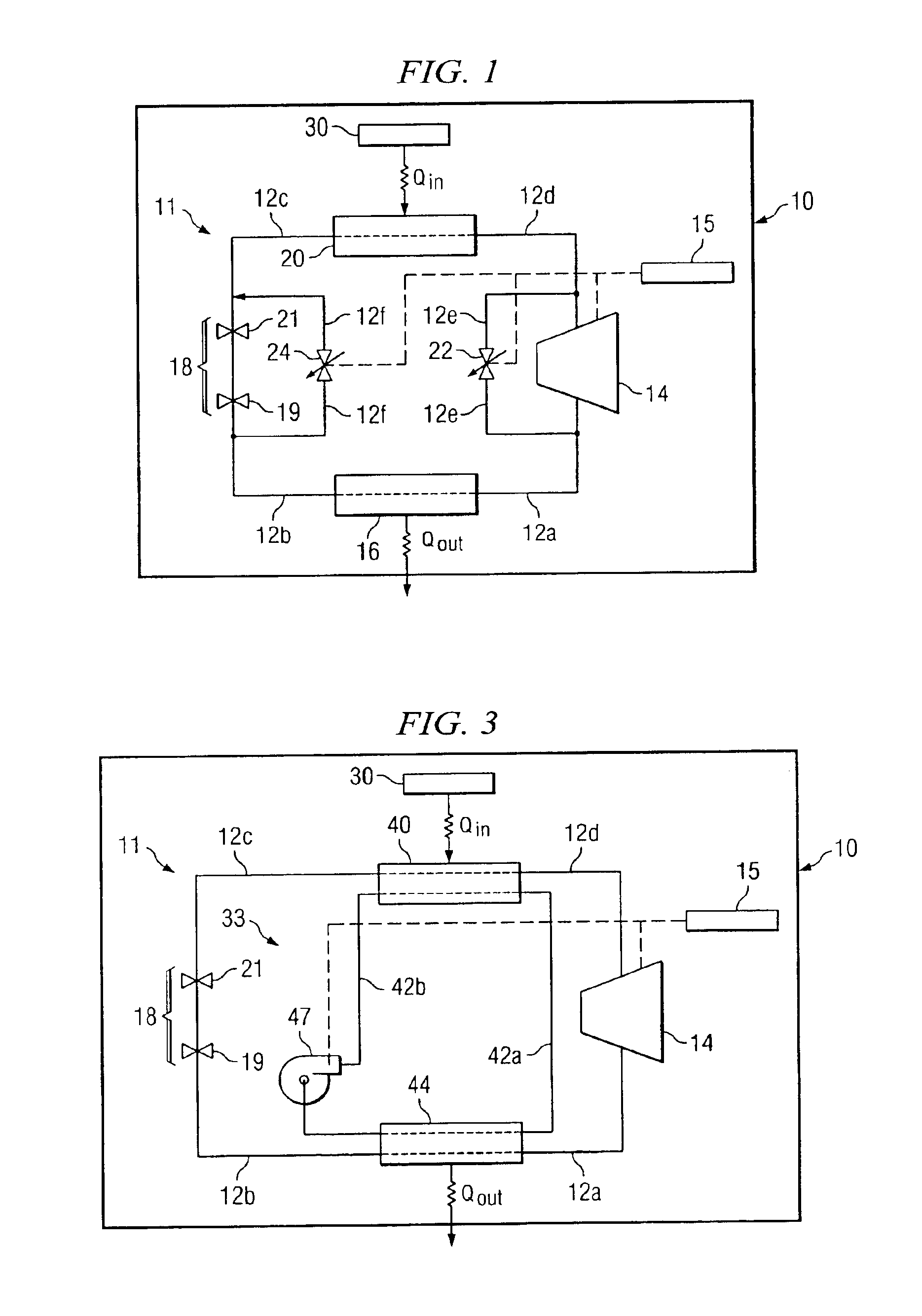
Passive cooling is a building design approach that focuses on heat gain control and heat dissipation in a building in order to improve the indoor thermal comfort with low or no energy consumption. This approach works either by preventing heat from entering the interior (heat gain prevention) or by removing heat from the building (natural cooling). Natural cooling utilizes on-site energy, available from the natural environment, combined with the architectural design of building components (e.g. building envelope), rather than mechanical systems to dissipate heat. Therefore, natural cooling depends not only on the architectural design of the building but on how the site's natural resources are used as heat sinks (i.e. everything that absorbs or dissipates heat). Examples of on-site heat sinks are the upper atmosphere (night sky), the outdoor air (wind), and the earth/soil.
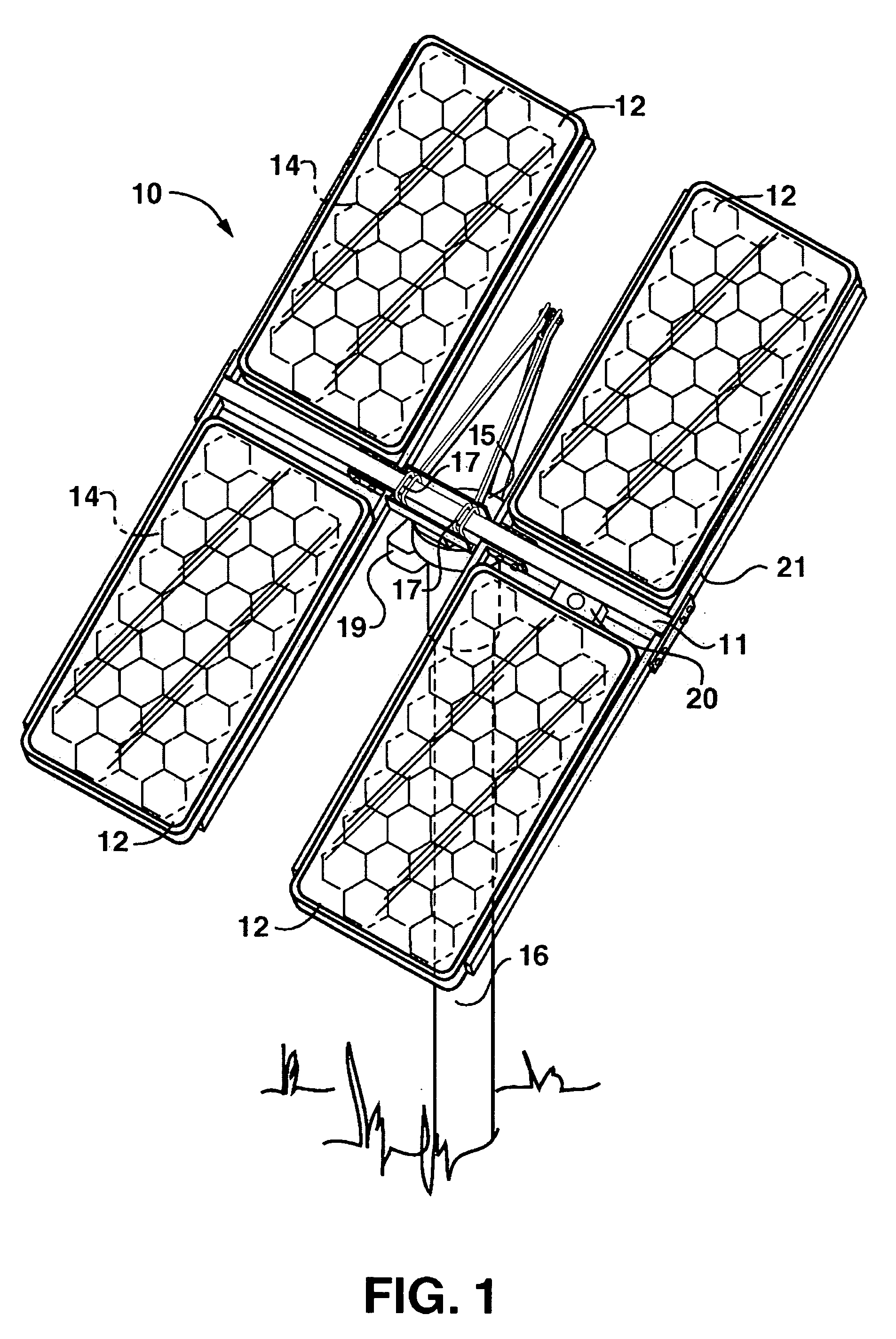
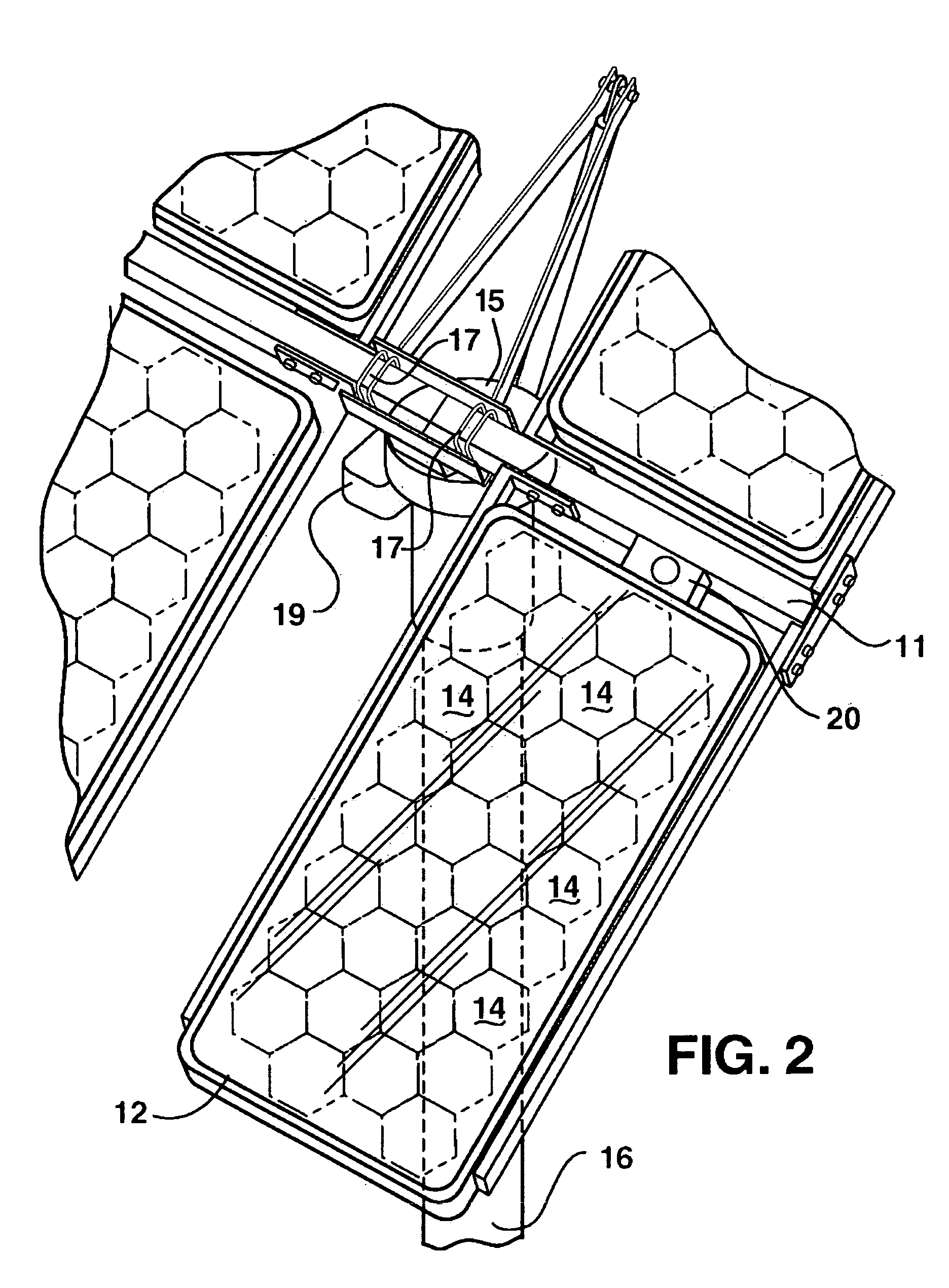
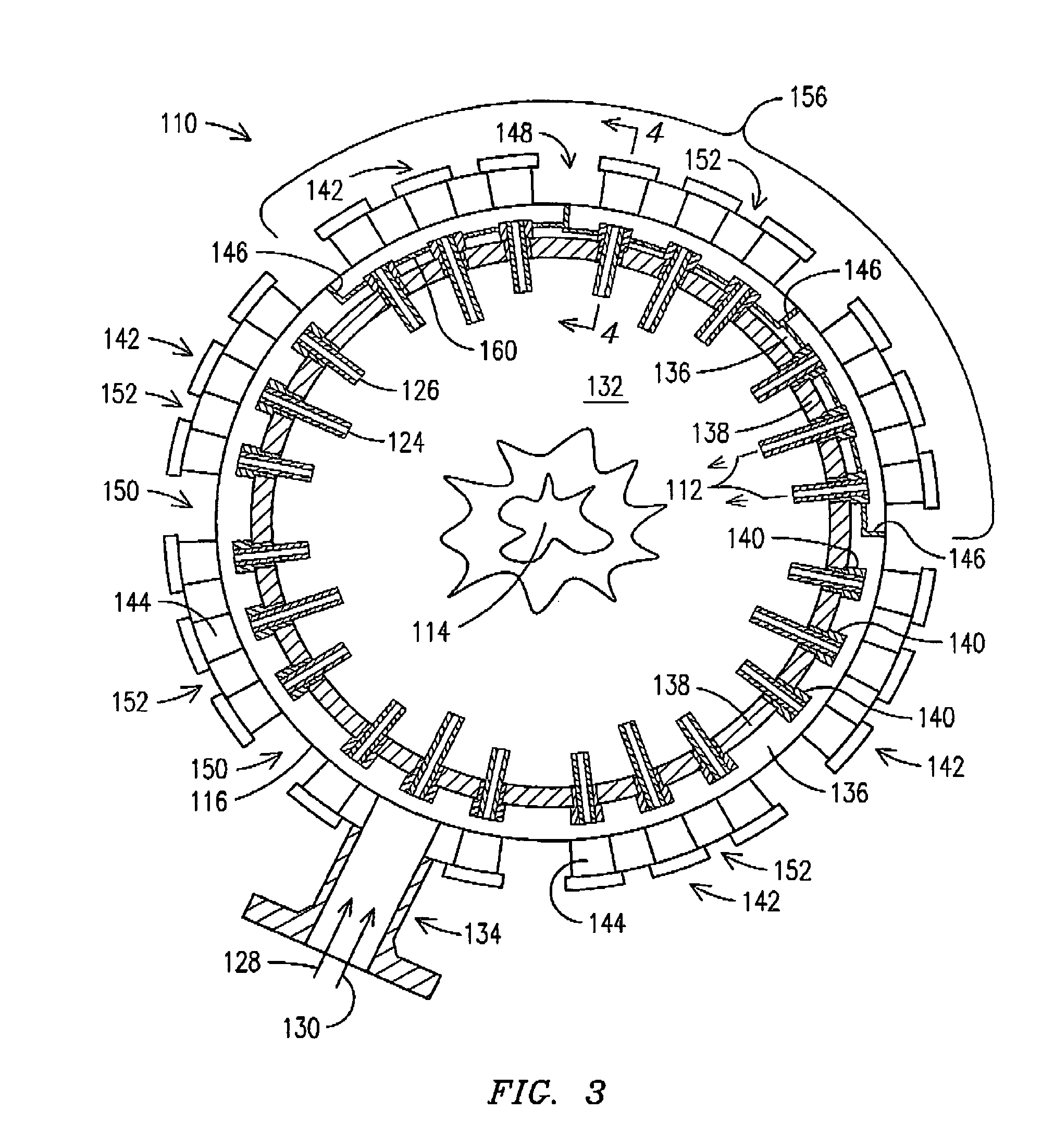
Concentrator solar photovoltaic array with compact tailored imaging power units
InactiveUS20060266408A1Low costEasy to assembleSolar heating energyMirrorsMechanical componentsEngineering
Solar panels and assembled arrays thereof include a collection of relatively compact, high-capacity power units. Optical components of each power unit include a front window or surface glazing, a primary mirror, secondary mirror and receiver assembly. Primary and secondary mirrors are defined by respective perimeters, at least a portion of which may be substantially coplanar and in contact with the front window. Some primary mirrors are configured with a perimeter of alternating full and truncated sections, and are curved to a base portion forming a pilot hole therein. Receiver assembly mechanical components include an alignment tube for mating with the primary mirror's pilot hole and for housing a photovoltaic solar cell. A base plate provided adjacent to the alignment tube serves to radiate heat emitted by the solar cell, and in some embodiments an additional heat sink provides further passive cooling. A tapered optical rod also provided within the receiver assembly directs received sunlight to the solar cell where electrical current is generated.
Owner:H2GO
Concentrator solar photovol taic array with compact tailored imaging power units
InactiveUS20070089778A1Low costReduced dimensionSolar heating energySolar heat devicesMechanical componentsEngineering
Solar panels and assembled arrays thereof include a collection of relatively compact, high-capacity power units. Optical components of each power unit include a front window or surface glazing, a primary mirror, secondary mirror and receiver assembly. Primary and secondary mirrors are defined by respective perimeters, at least a portion of which may be substantially coplanar and in contact with the front window. Some primary mirrors are configured with a perimeter of alternating full and truncated sections, and are curved to a base portion forming a pilot hole therein. Receiver assembly mechanical components include an alignment tube for mating with the primary mirror's pilot hole and for housing a photovoltaic solar cell. A base plate provided adjacent to the alignment tube serves to radiate heat emitted by the solar cell, and in some embodiments an additional heat sink provides further passive cooling. A tapered optical rod also provided within the receiver assembly directs received sunlight to the solar cell where electrical current is generated.
Owner:HORNE STEPHEN JOHN +1
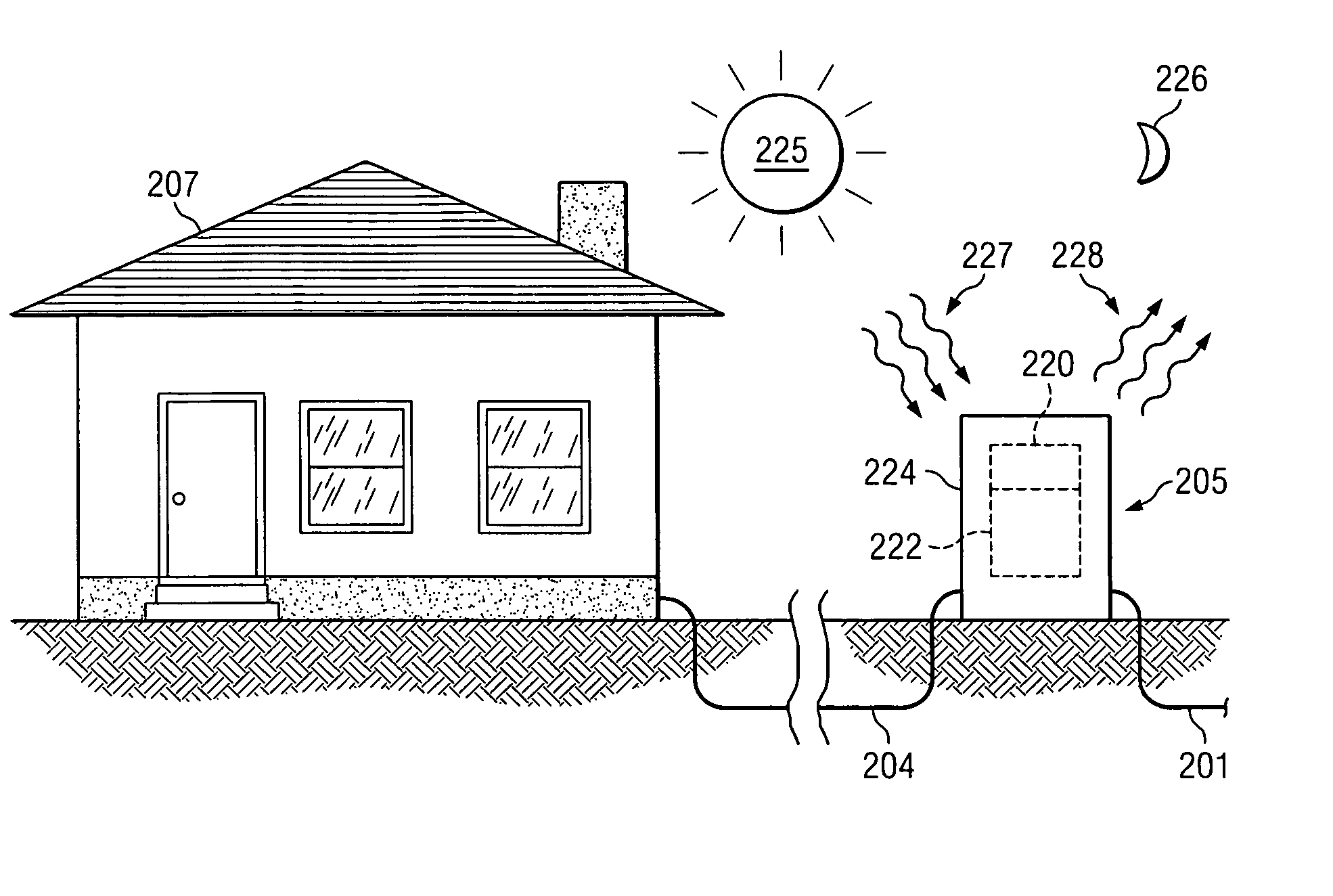
Passive cooling for fiber to the premise (FTTP) electronics
InactiveUS20070115635A1Indirect heat exchangersCooling/ventilation/heating modificationsFiberEngineering
A phase change material, including multiple phase change materials of different formulations, is placed in heat transfer association with an electronics enclosure (e.g., a sealed enclosure) deployed in an environment that causes the electronics and the phase change material to experience periods of heating and periods of cooling. During the periods of heating, the phase change material absorbs heat and changes at least partially from a first state to a second state to maintain the temperature of the electronics at a desirable level. During the periods of cooling, the phase change material reverts at least partially back to the first state for future heat absorption. The phase change material is cooled by a thermally cooler body such as the night sky. The electronics enclosure and phase change material may be placed in a second enclosure covered with a paint having a paint additive that reflects solar radiation.
Owner:TELLABS BEDFORD
Gas-discharge lamp replacement with passive cooling
An illumination device comprises a solid-state lighting device and a heat sink. The heat sink is configured to be attachable to a fixture for a gas-discharge lamp to retrofit existing gas-discharge fixtures. The heat sink is conductively thermally coupled to the solid-state lighting device to dissipate heat generated by the solid-state lighting device.
Owner:EXPRESS IMAGING SYST
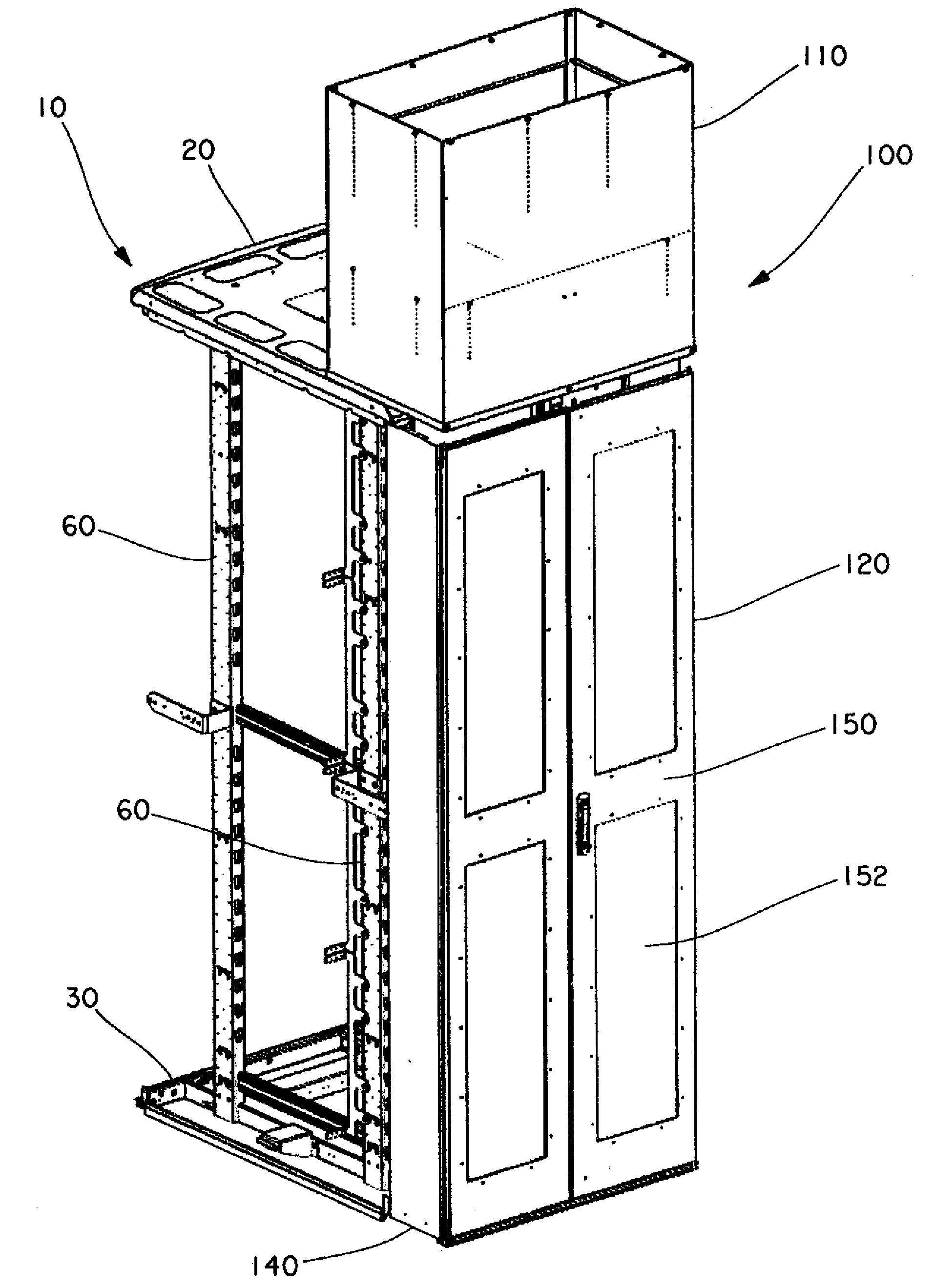
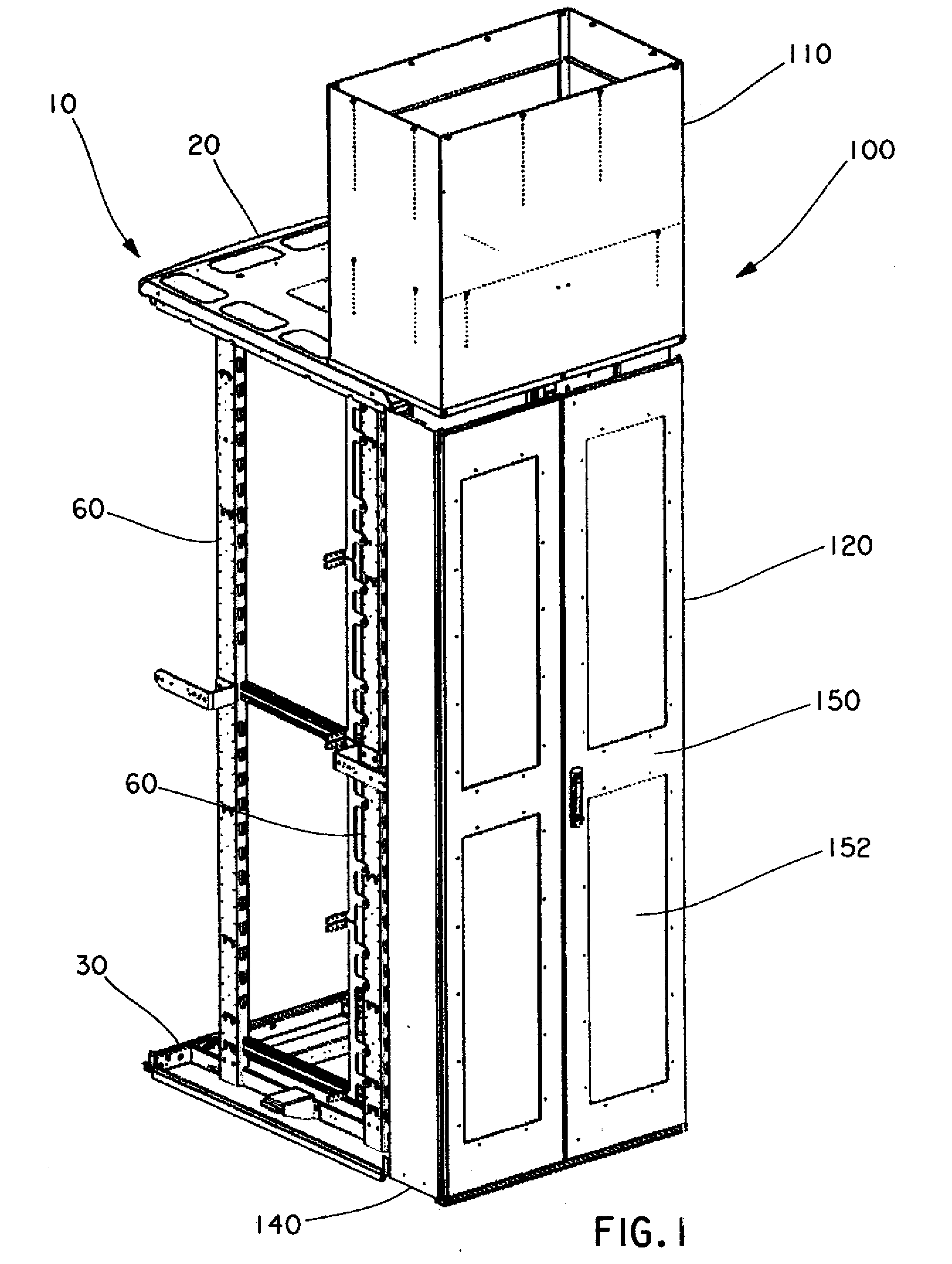
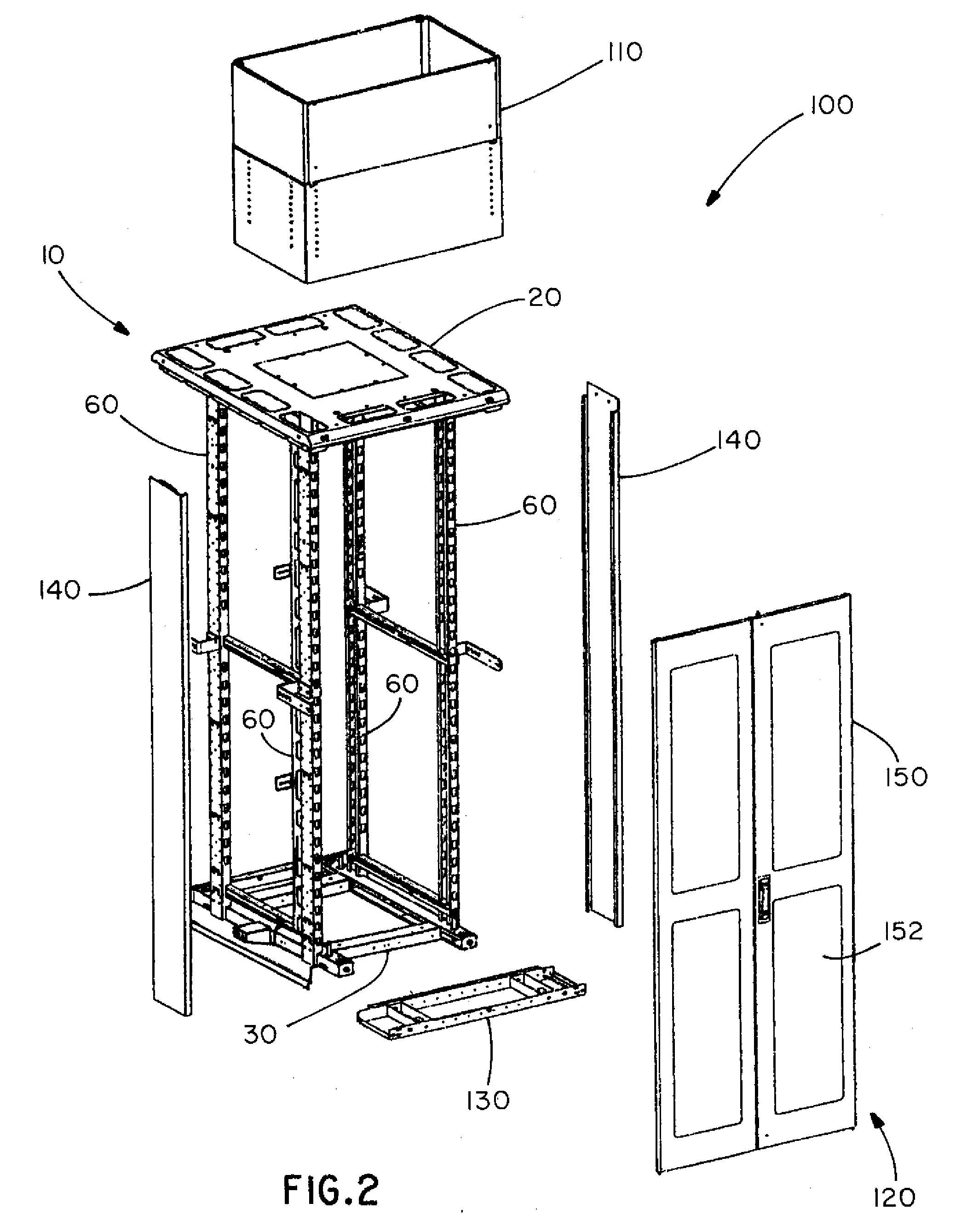
Passive Cooling Systems for Network Cabinet
ActiveUS20100003911A1Easy to installEasy to shareDucting arrangementsLighting and heating apparatusCold airEngineering
Certain embodiments of the present invention provide a cooling duct assembly for electronic equipment installed in a cabinet. The cooling duct assembly comprises at least one main duct in fluid communication with a front portion of the cabinet. The at least one main duct receives cold air from the front portion of the cabinet and routes the cold air toward a back portion of the cabinet. Additionally, the cooling duct assembly comprises at least one side duct in fluid communication with the at least one main duct. The at least one side duct receives the cold air from the at least one main duct and routes the cold air to at least one side air intake opening on the electronic equipment.
Owner:PANDUIT
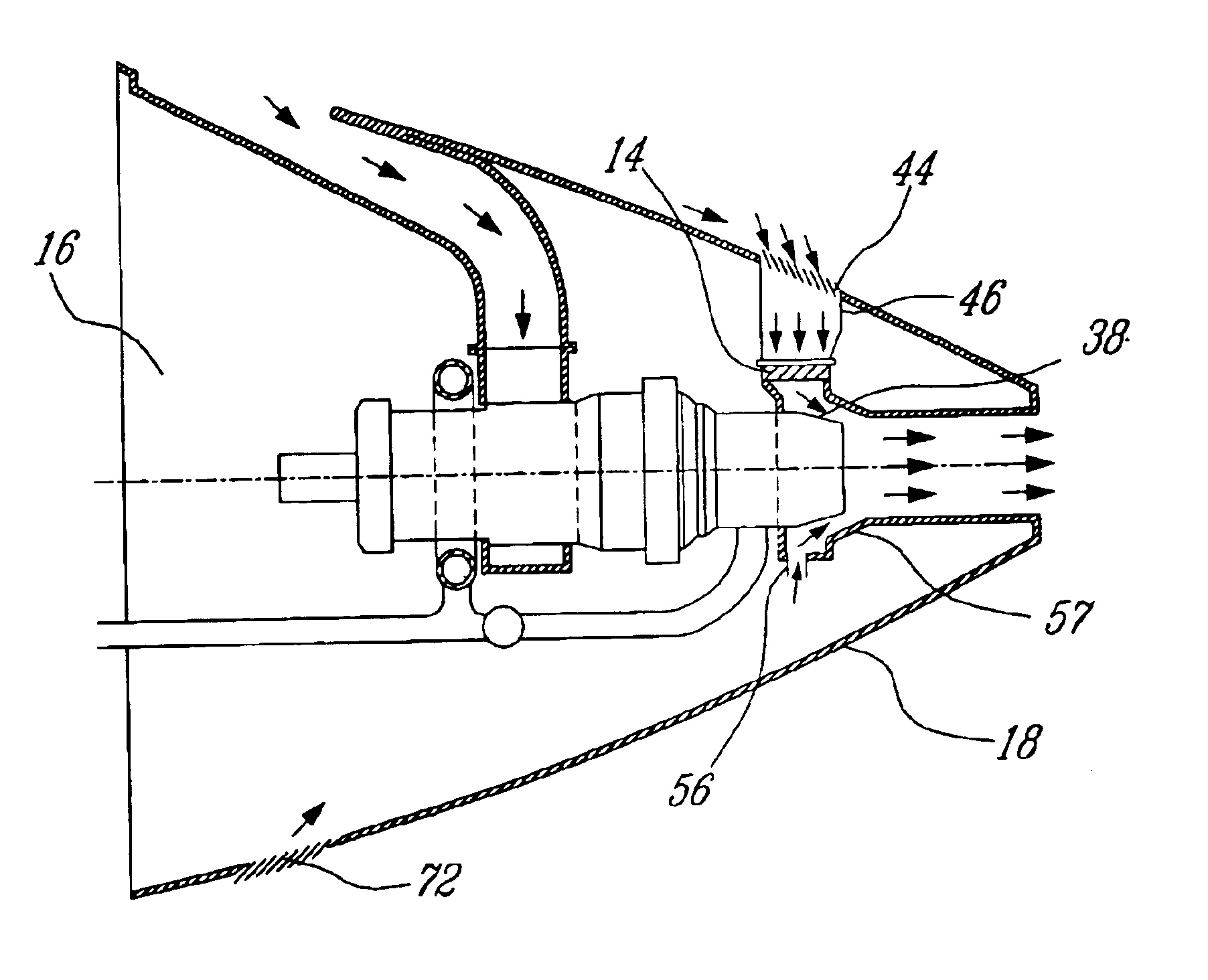
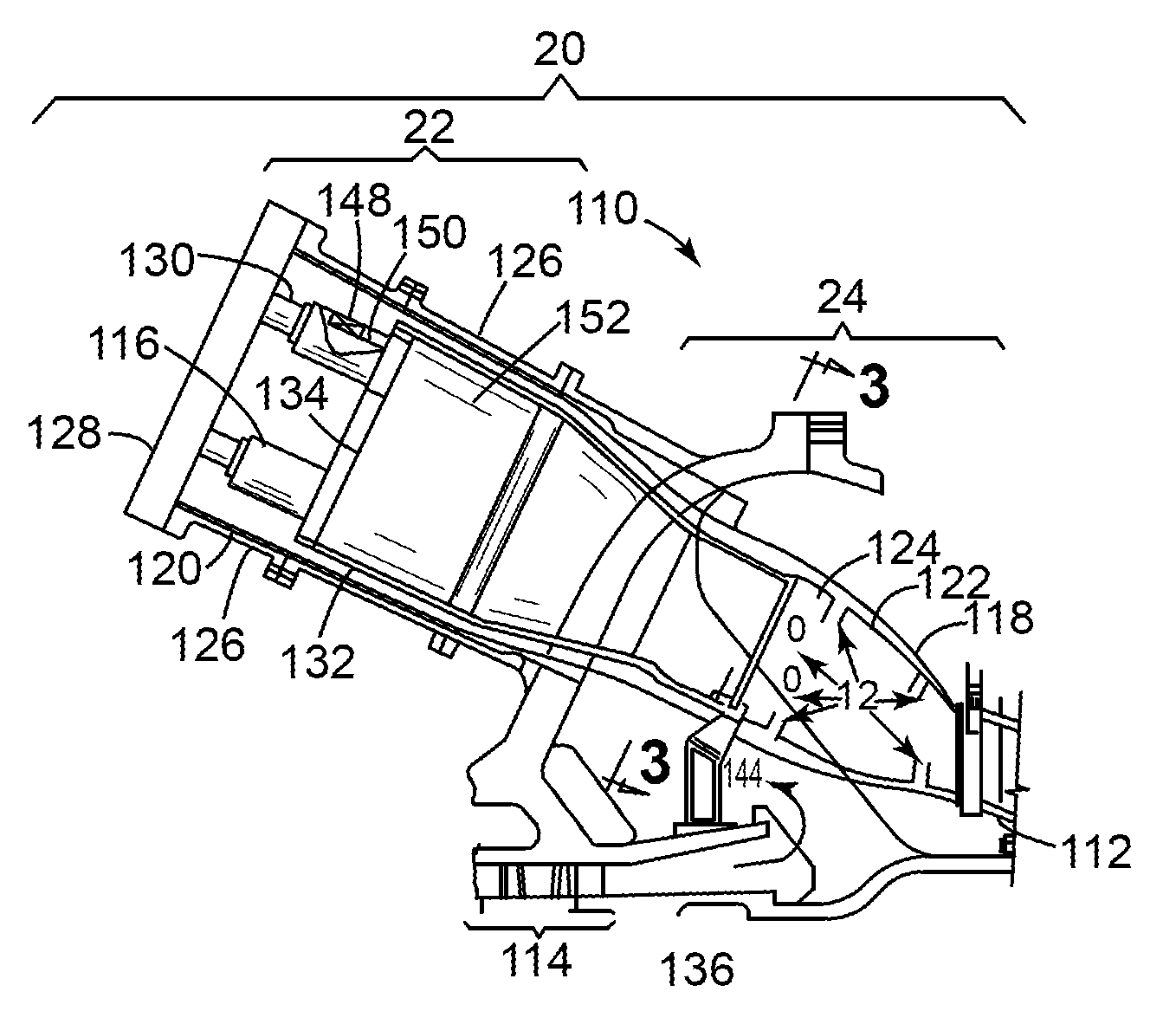
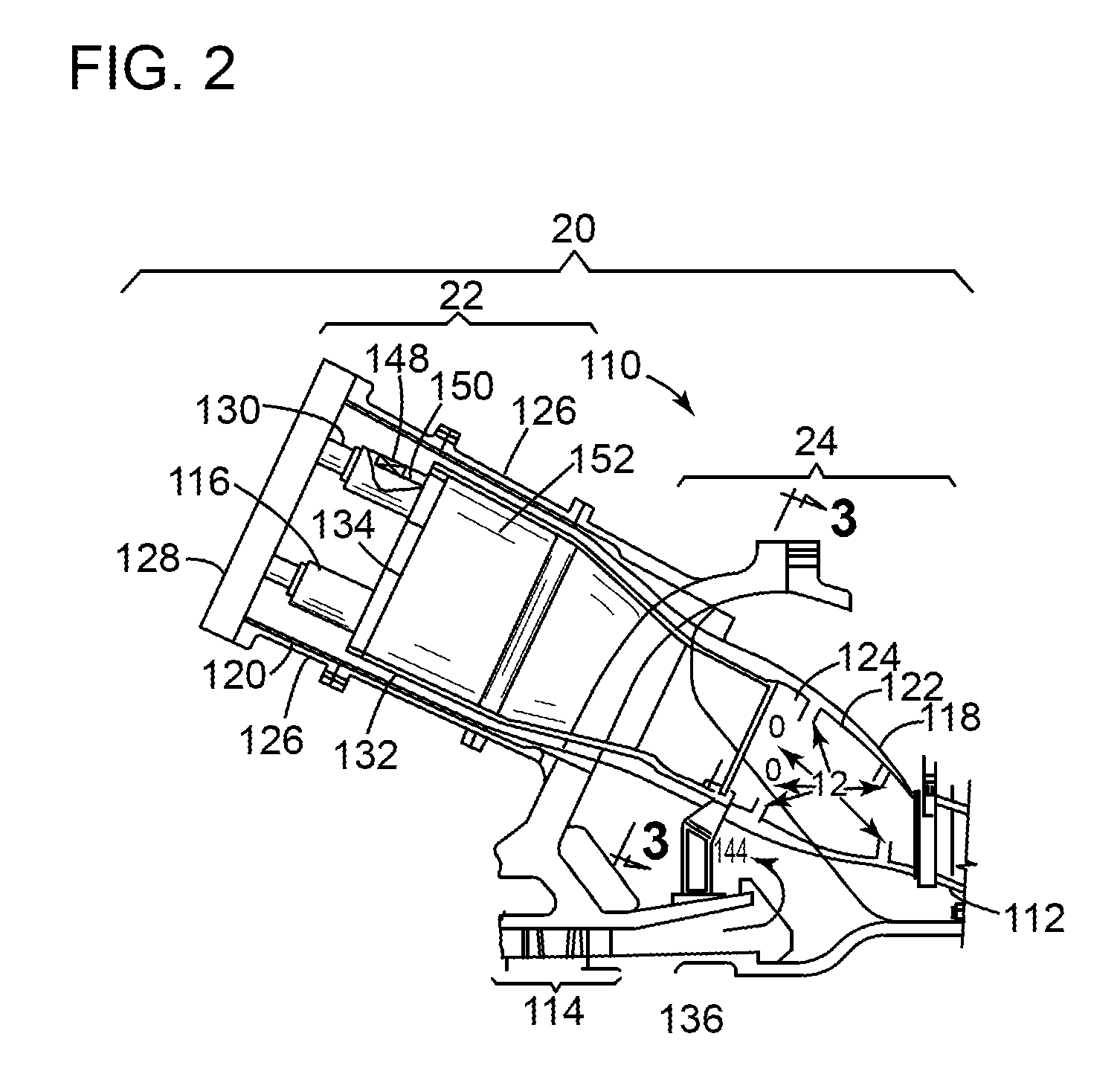
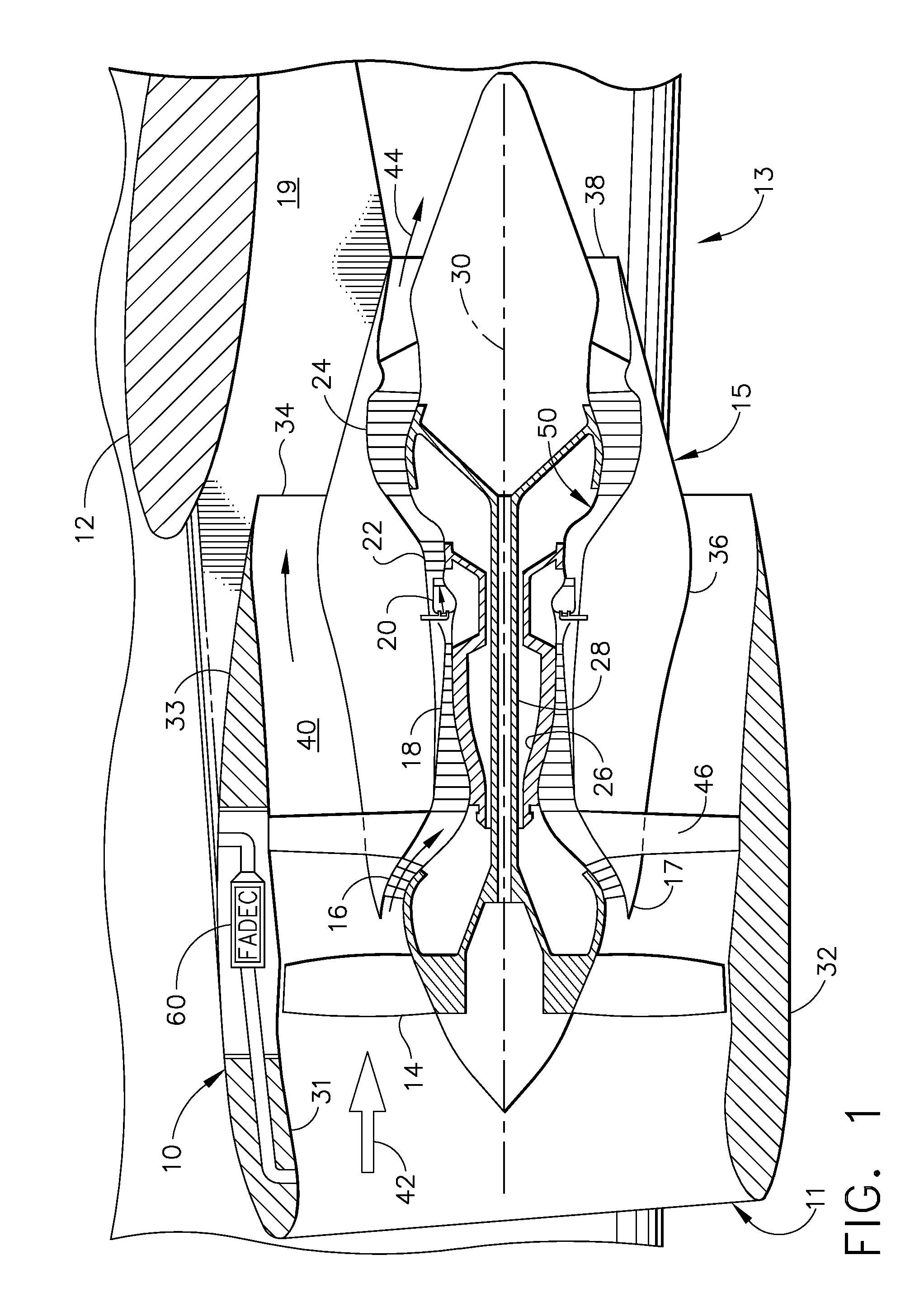
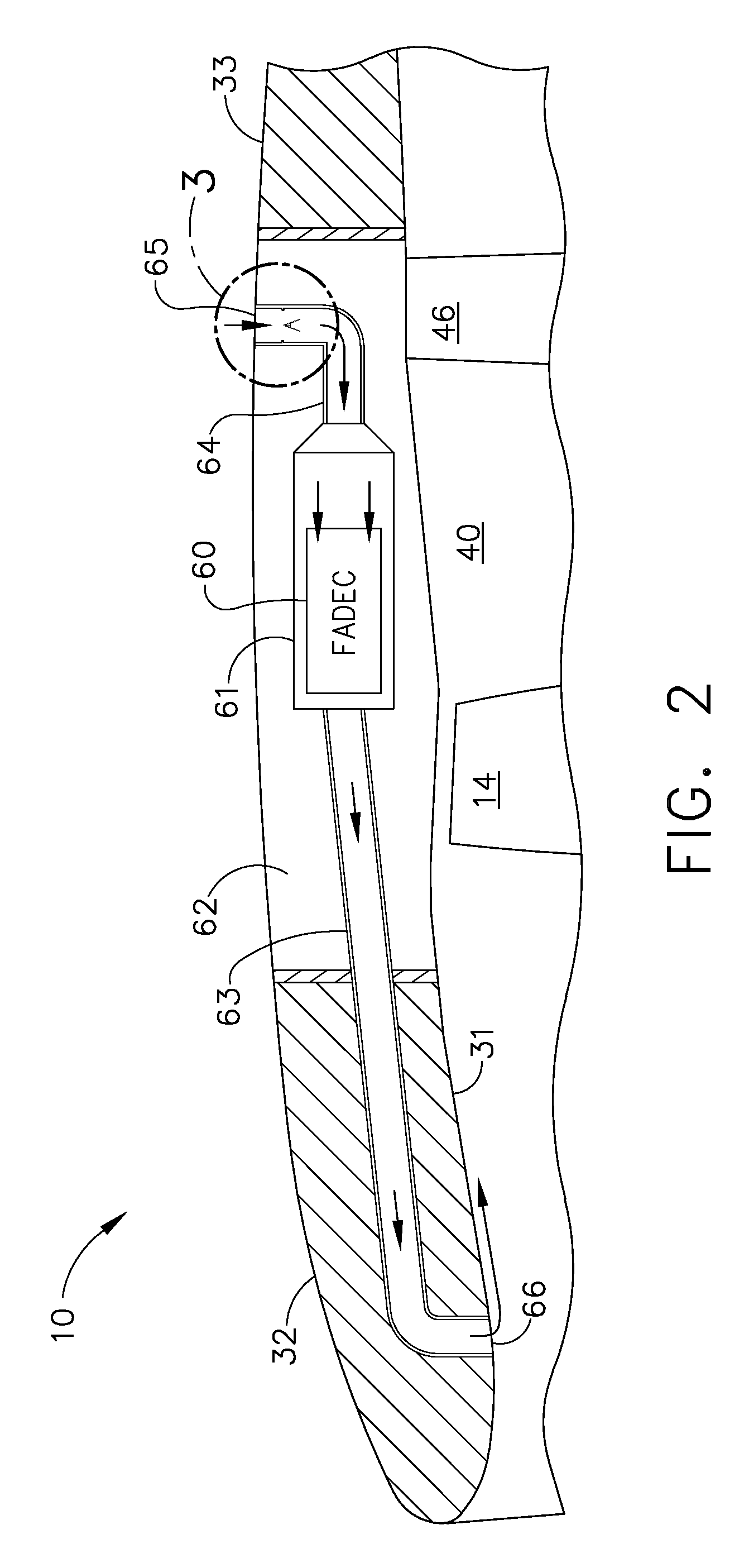
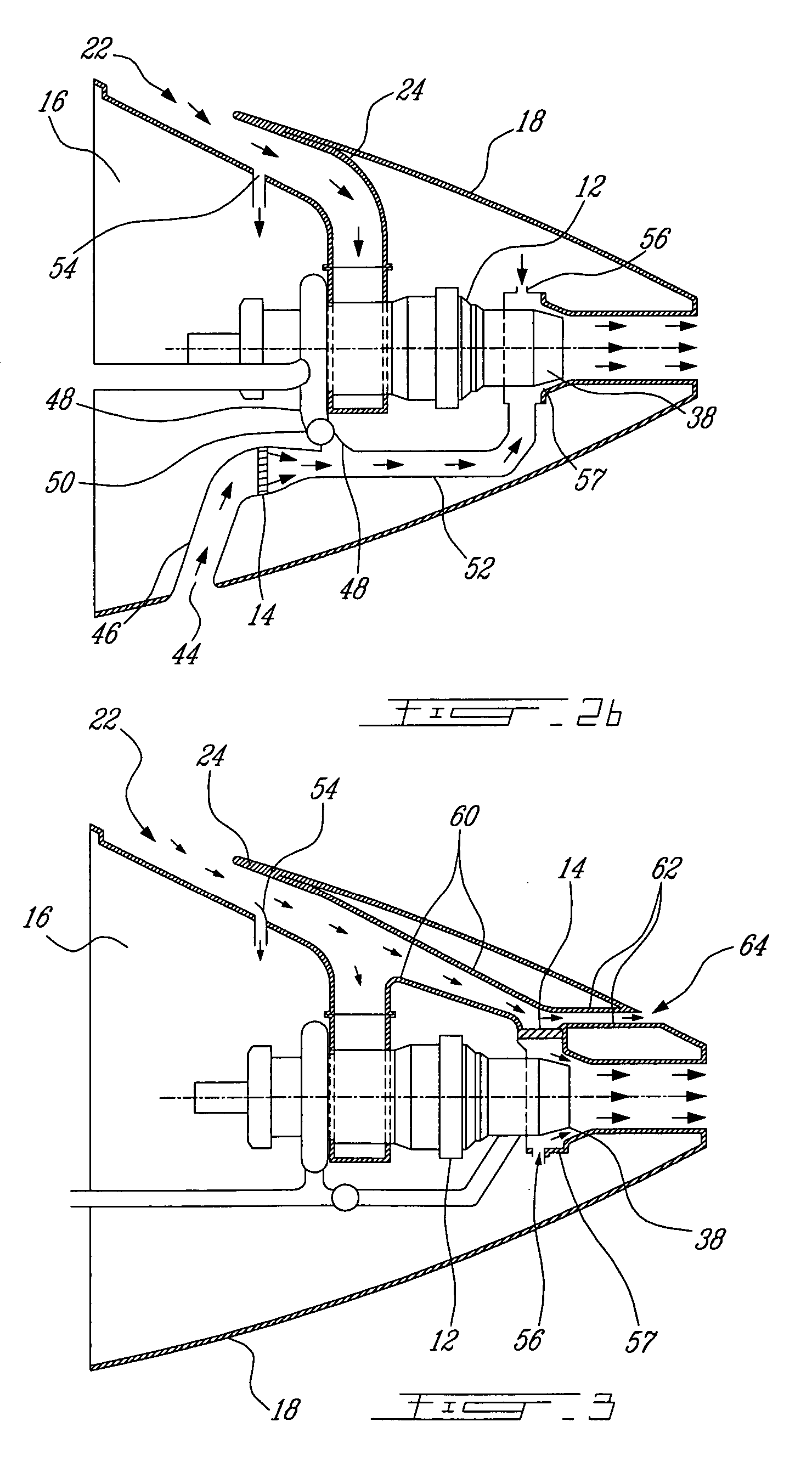
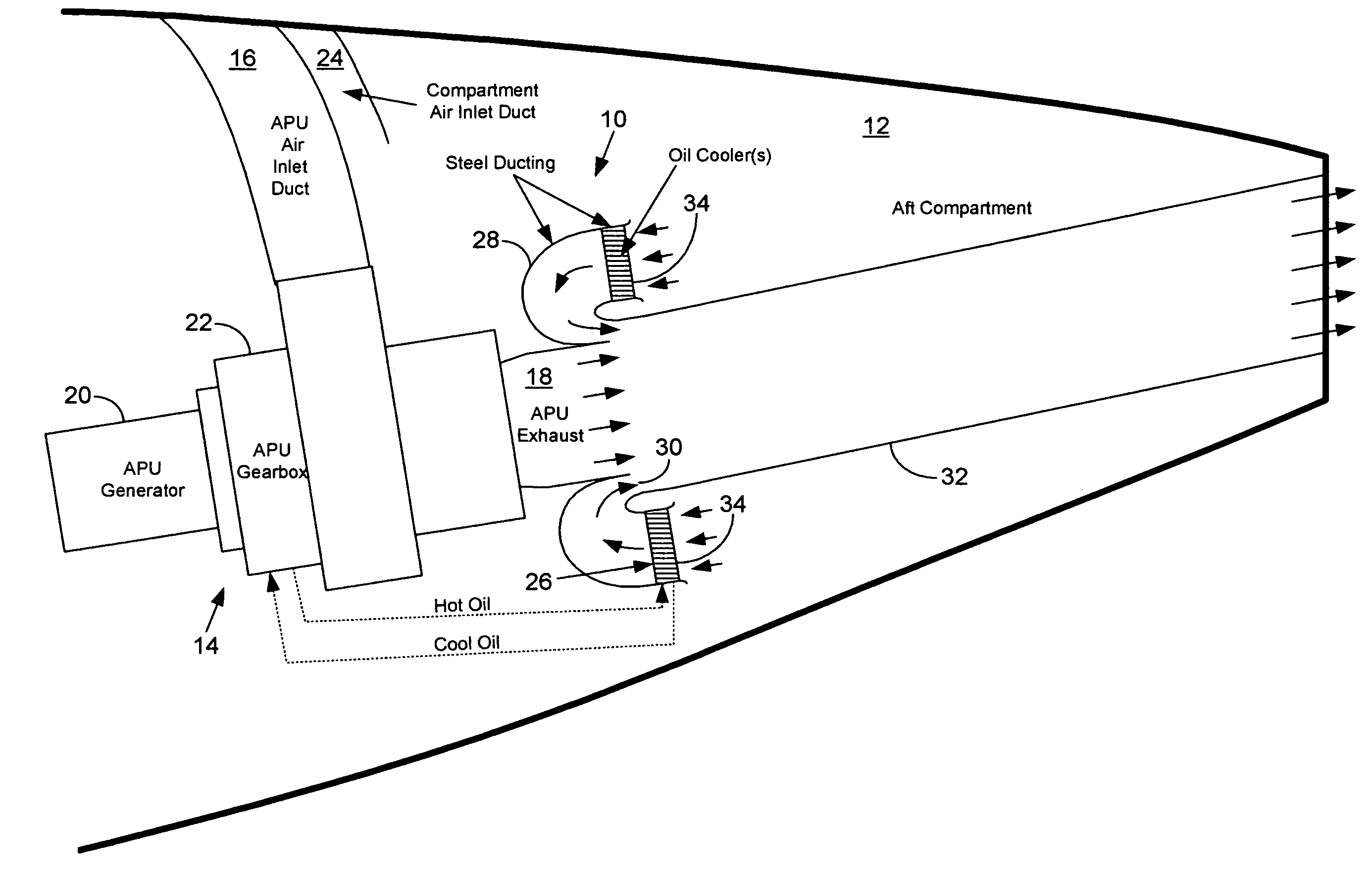
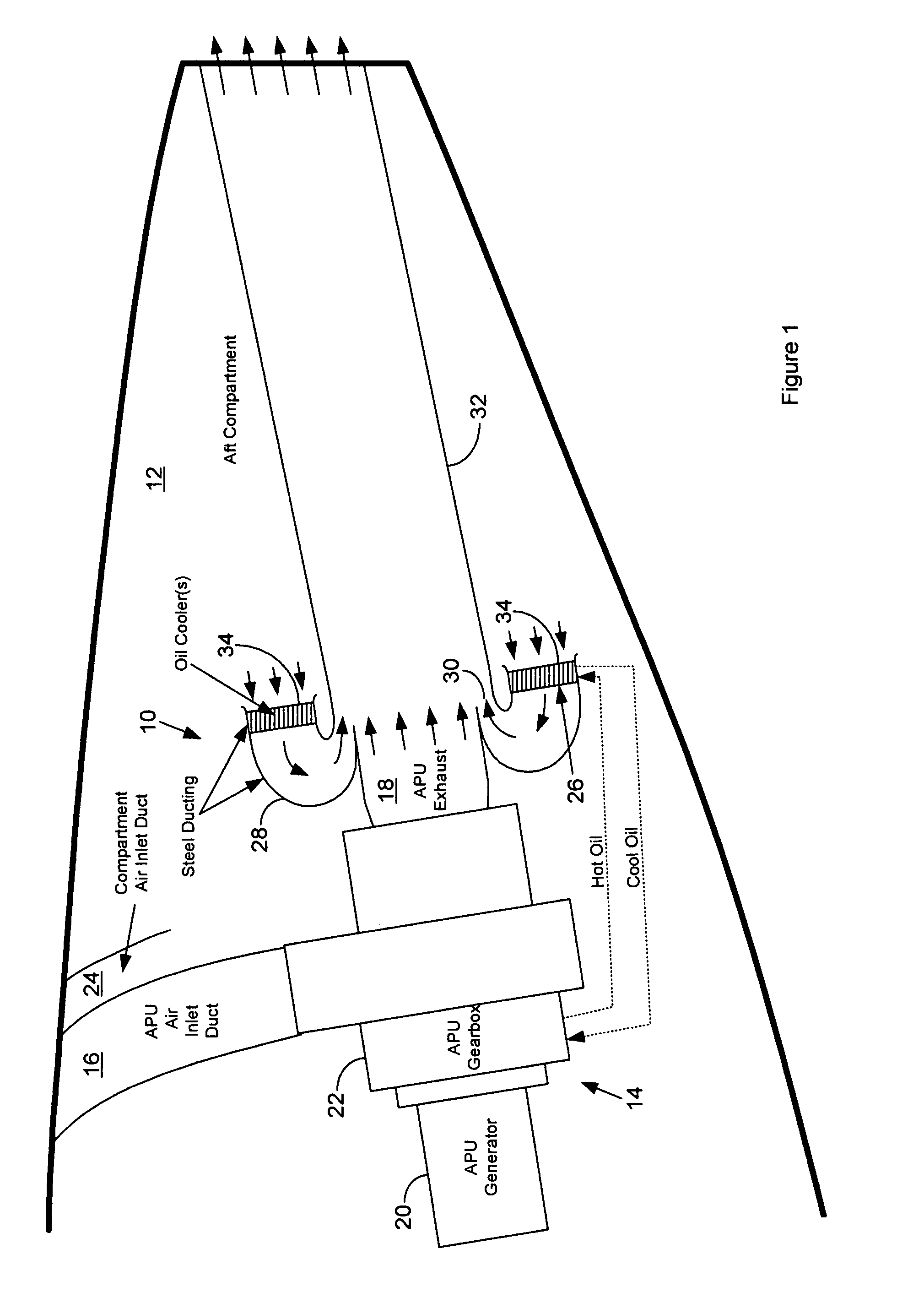
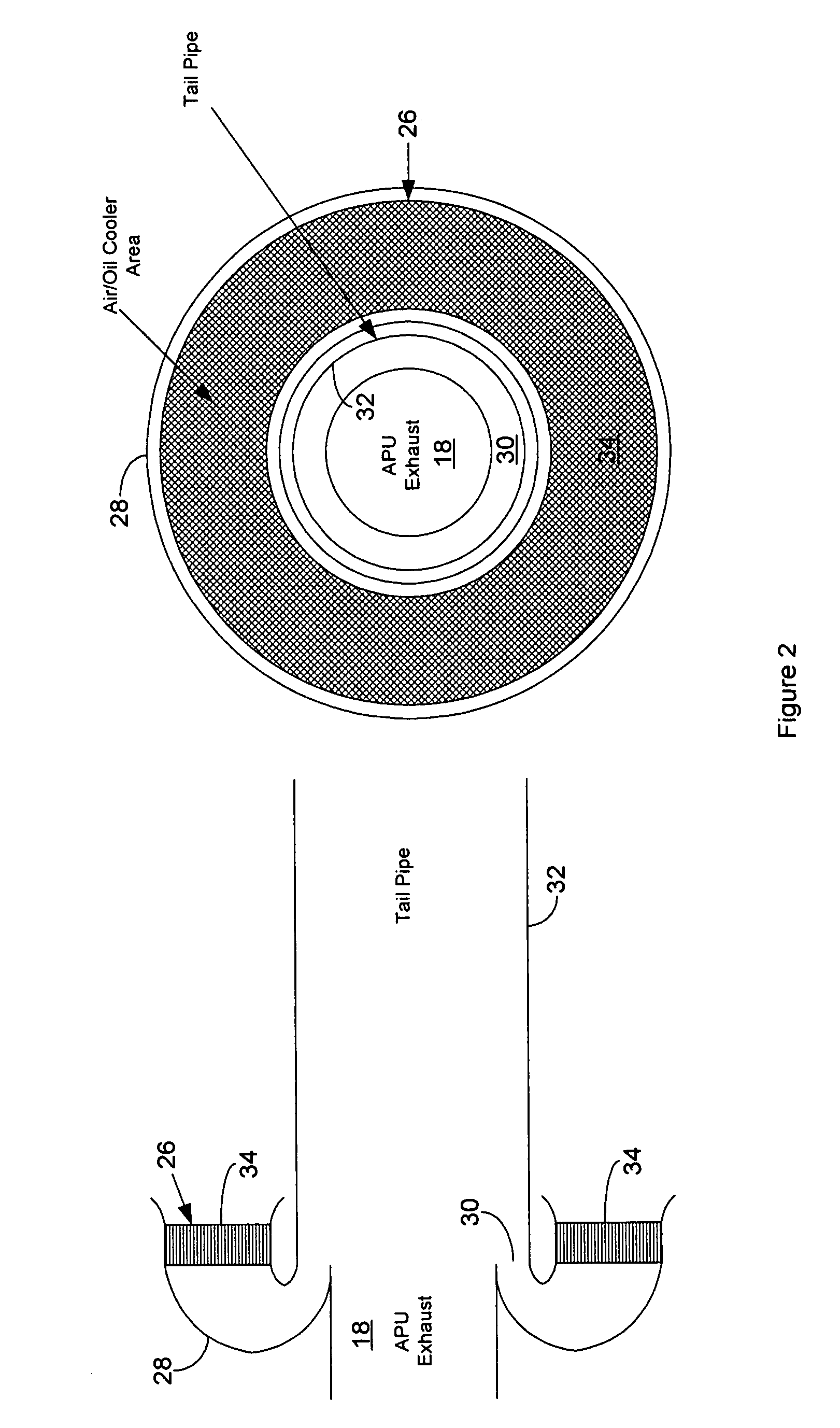
Passive cooling system for auxiliary power unit installation
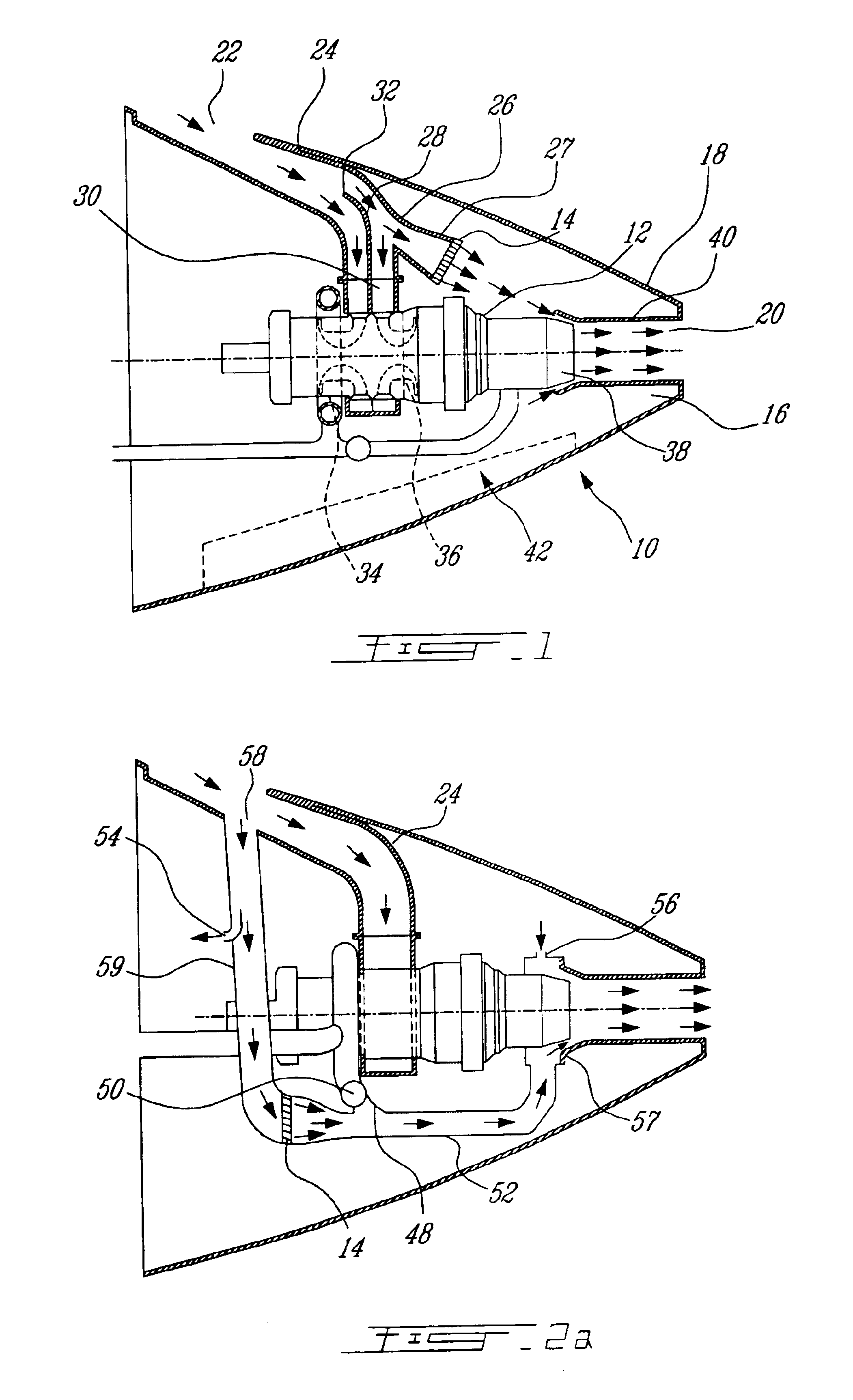
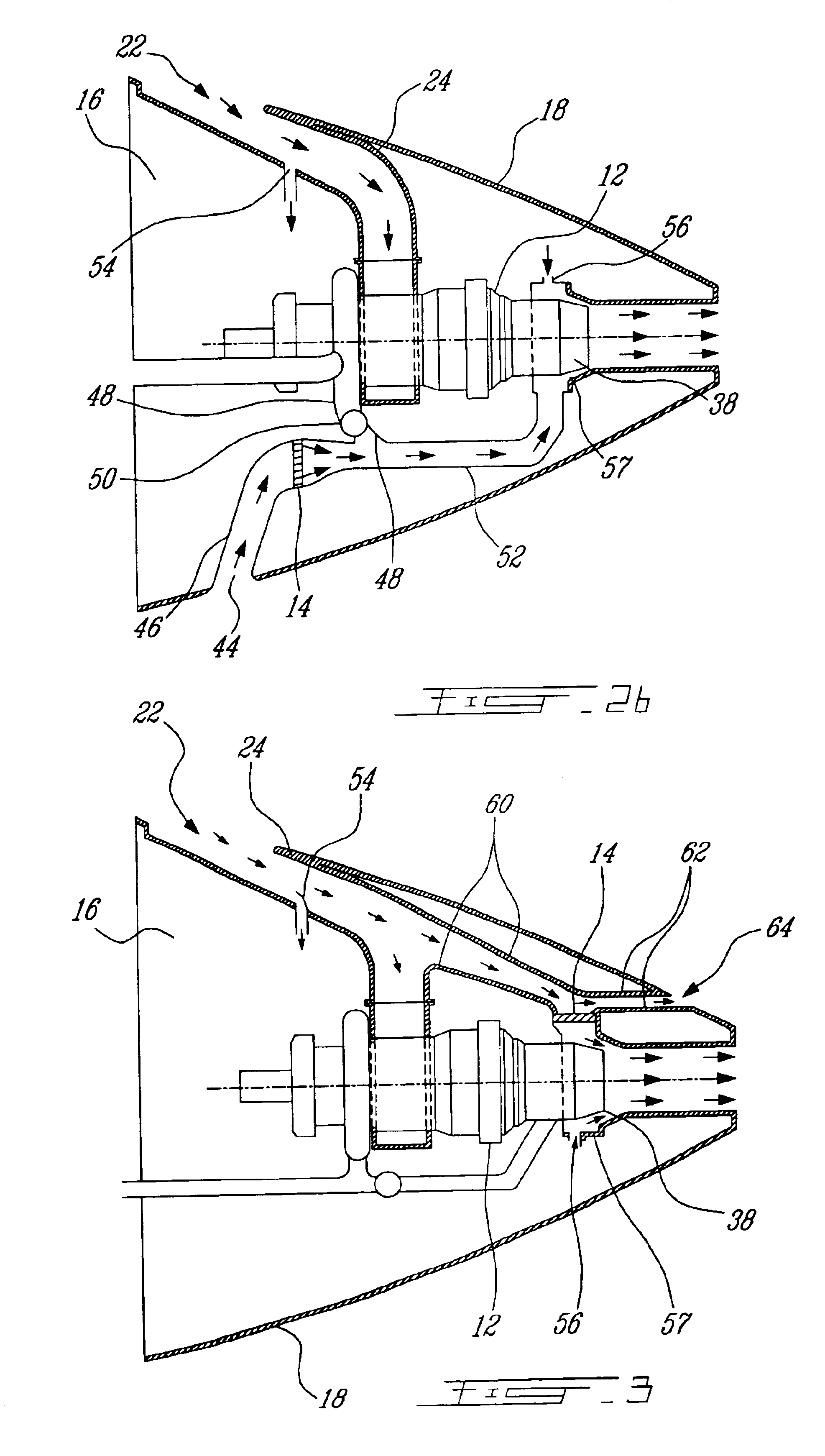
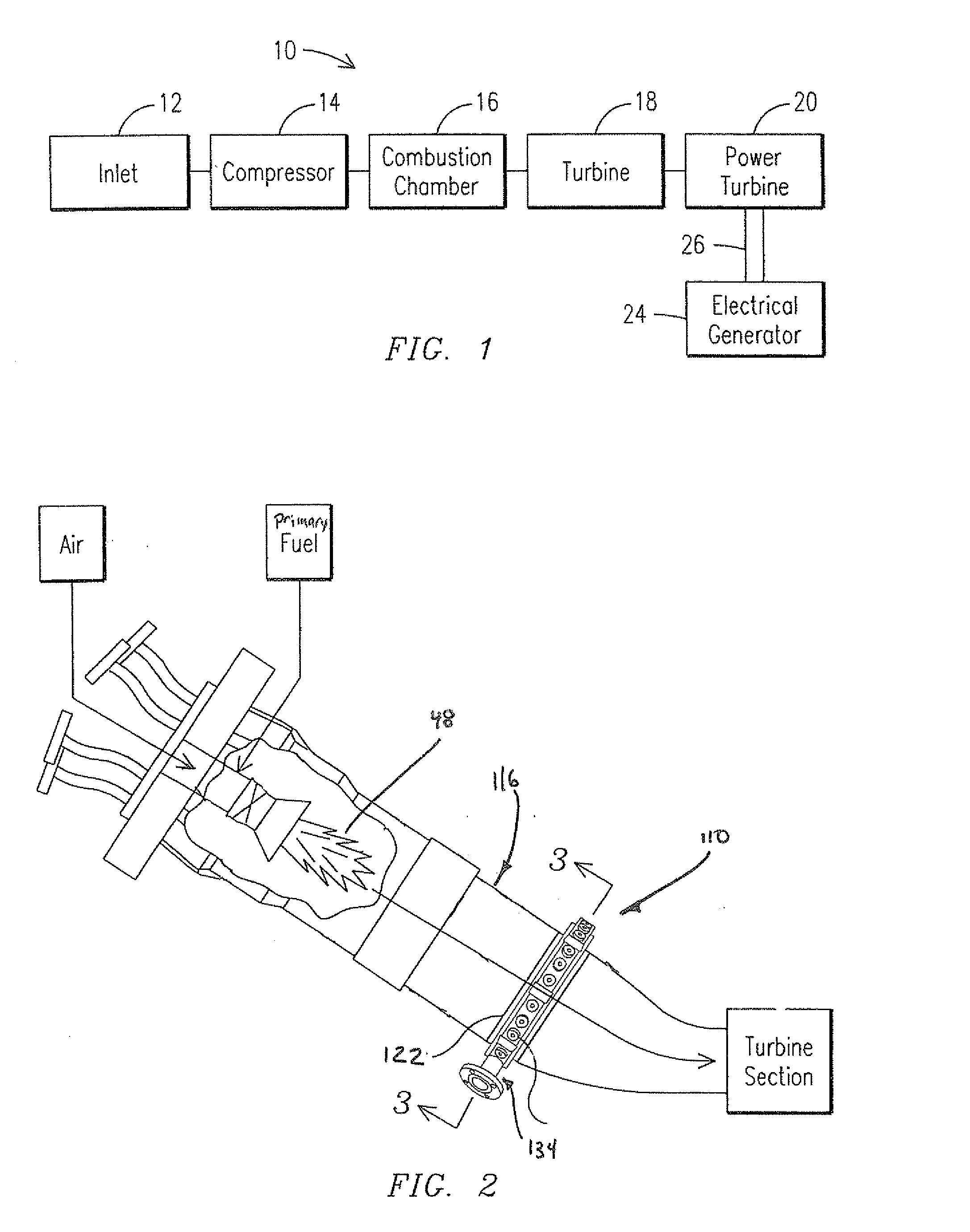
InactiveUS6942181B2Improve cooling effectEnhanced cooling airflowPower plant cooling arrangmentsAir-treating devicesAuxiliary power unitOil cooling
A passive cooling system for an auxiliary power unit (APU) installation on an aircraft is provided. The system is for an auxiliary power unit having at least a compressor portion of a gas turbine engine and an oil cooler contained separately within a nacelle. The system includes the auxiliary power unit housed within the nacelle of the aircraft, an engine exhaust opening defined in the aft portion of the nacelle and communicating with the gas turbine engine, at least a first air inlet duct communicating with a second opening defined in said nacelle and with said compressor portion and the oil cooler is located within a second duct communicating with an opening other than the engine exhaust opening of said nacelle and with the engine exhaust opening. Exterior cooling air and engine exhaust ejected through said engine exhaust opening entrain cooling air through said second duct to said oil cooler, and thus provide engine oil cooling. An exhaust eductor is also provided.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Secondary fuel delivery system
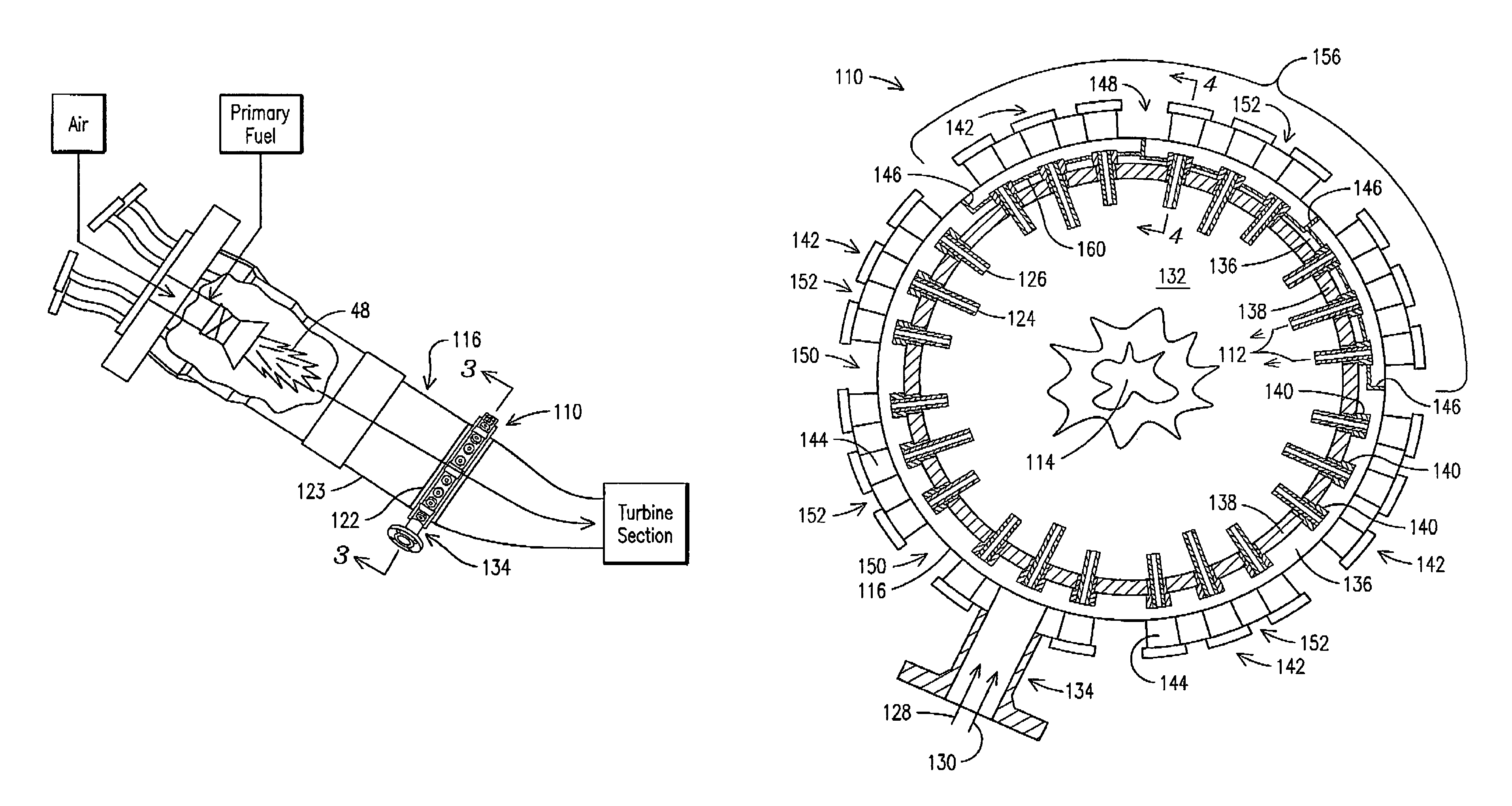
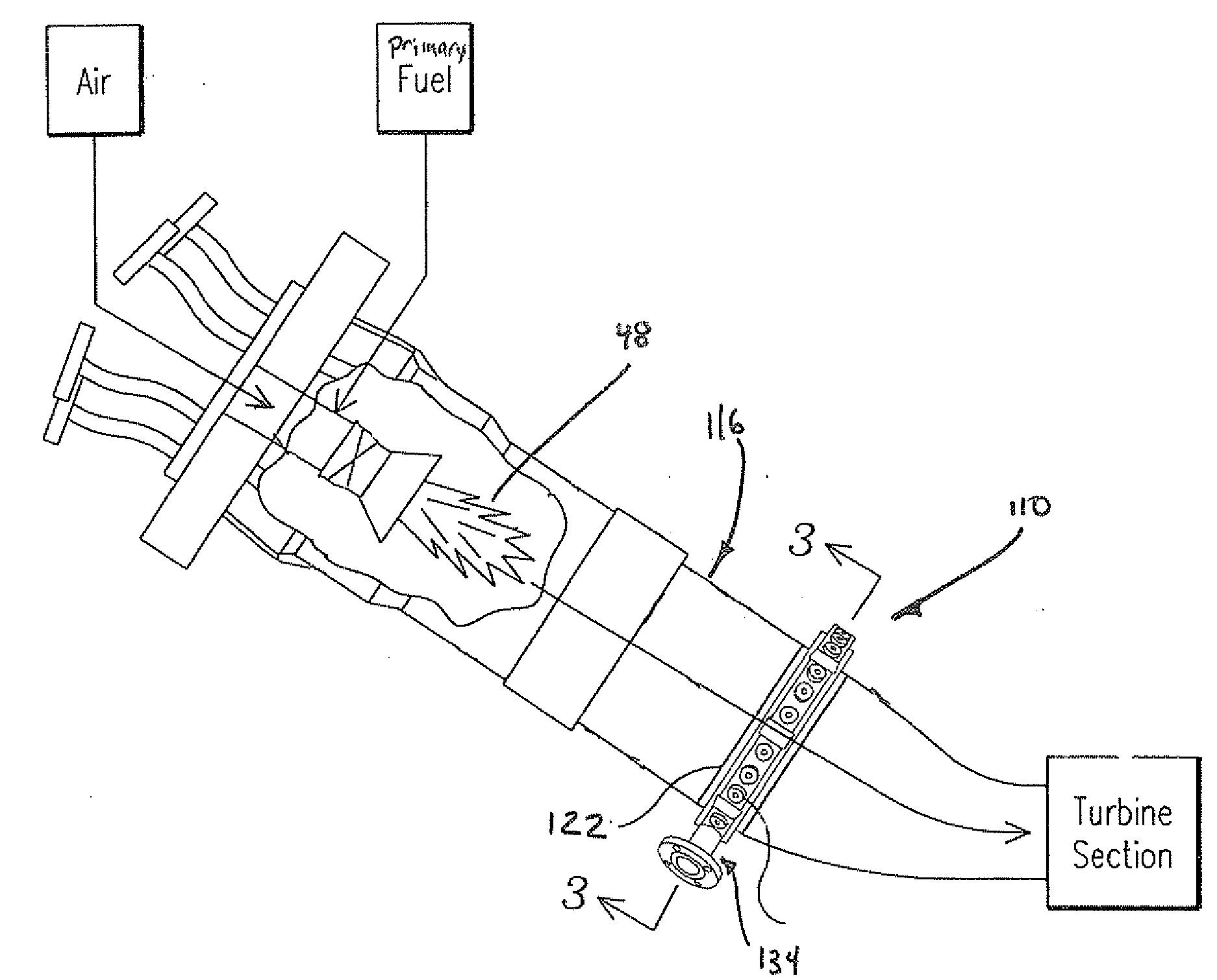
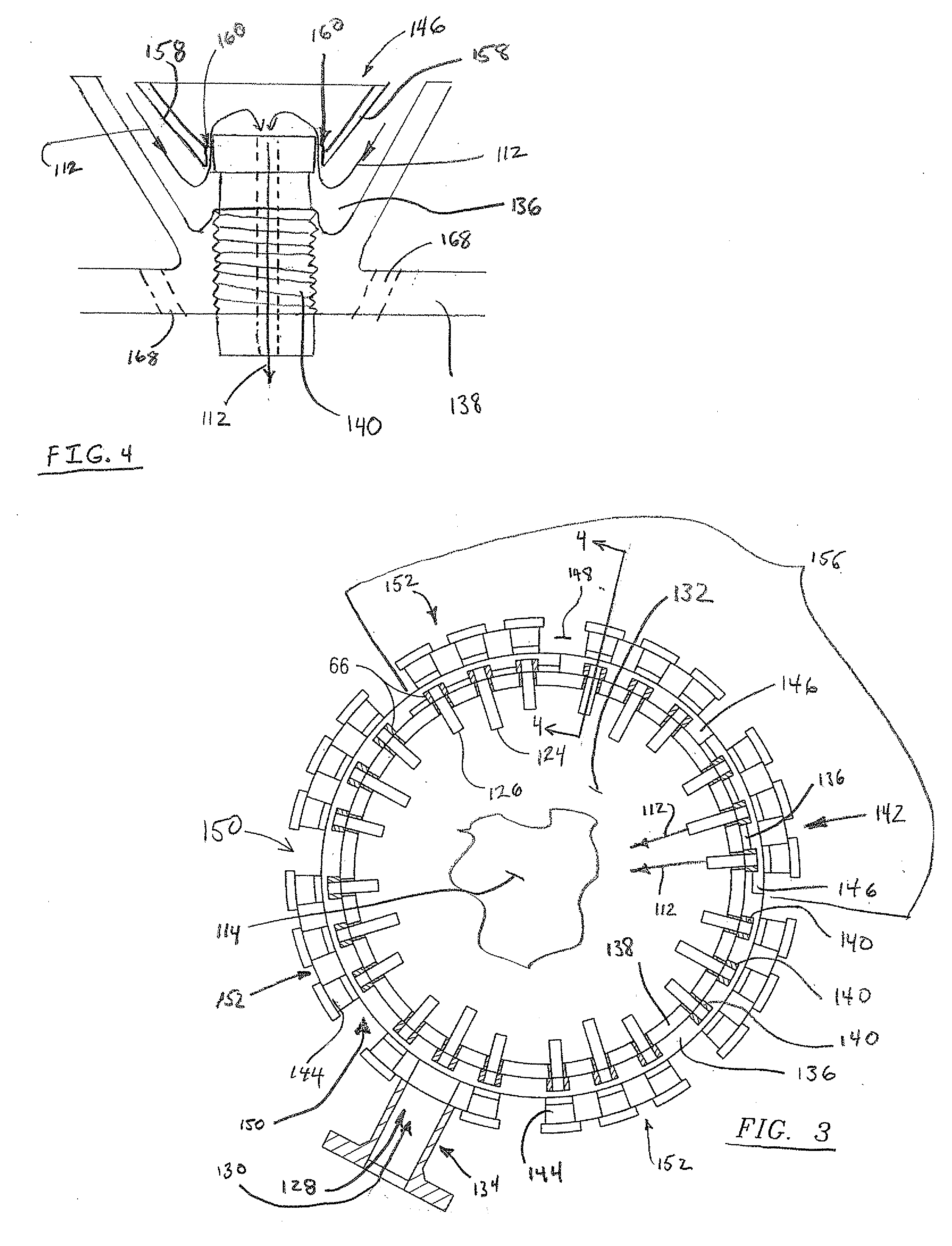
ActiveUS7665309B2Reduce impactAvoid heat dissipation difficultiesContinuous combustion chamberTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsCombustionDiluent
A secondary fuel delivery system for delivering a secondary stream of fuel and / or diluent to a secondary combustion zone located in the transition piece of a combustion engine, downstream of the engine primary combustion region is disclosed. The system includes a manifold formed integral to, and surrounding a portion of, the transition piece, a manifold inlet port, and a collection of injection nozzles. A flowsleeve augments fuel / diluent flow velocity and improves the system cooling effectiveness. Passive cooling elements, including effusion cooling holes located within the transition boundary and thermal-stress-dissipating gaps that resist thermal stress accumulation, provide supplemental heat dissipation in key areas. The system delivers a secondary fuel / diluent mixture to a secondary combustion zone located along the length of the transition piece, while reducing the impact of elevated vibration levels found within the transition piece and avoiding the heat dissipation difficulties often associated with traditional vibration reduction methods.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Active and passive cooling for an energy storage module
InactiveUS20140158340A1Protecting/adjusting hybrid/EDL capacitorElectrolytic capacitorsControl systemCoolant flow
The present disclosure relates to cooling an energy storage module using passive and active cooling techniques. Passive cooling is provided by storing heat in a phase change material that is contact with the energy storage cells of the energy storage module. Active cooling is provided by circulating coolant through coolant passages that are in thermal contact with the energy storage cells. A control system for determining the temperature of the energy storage module and controlling coolant flow when the temperature reaches a predetermined threshold is disclosed.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
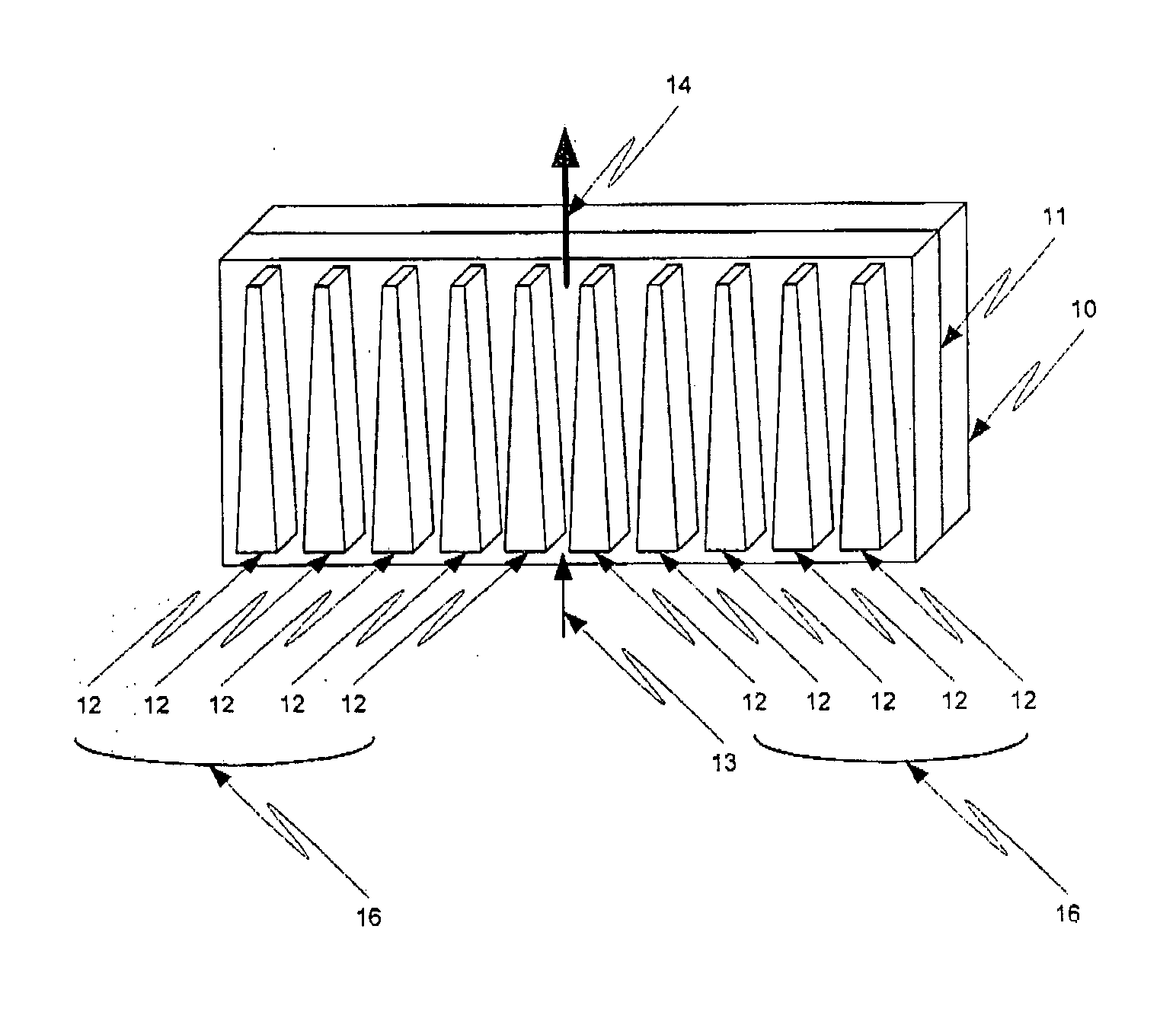
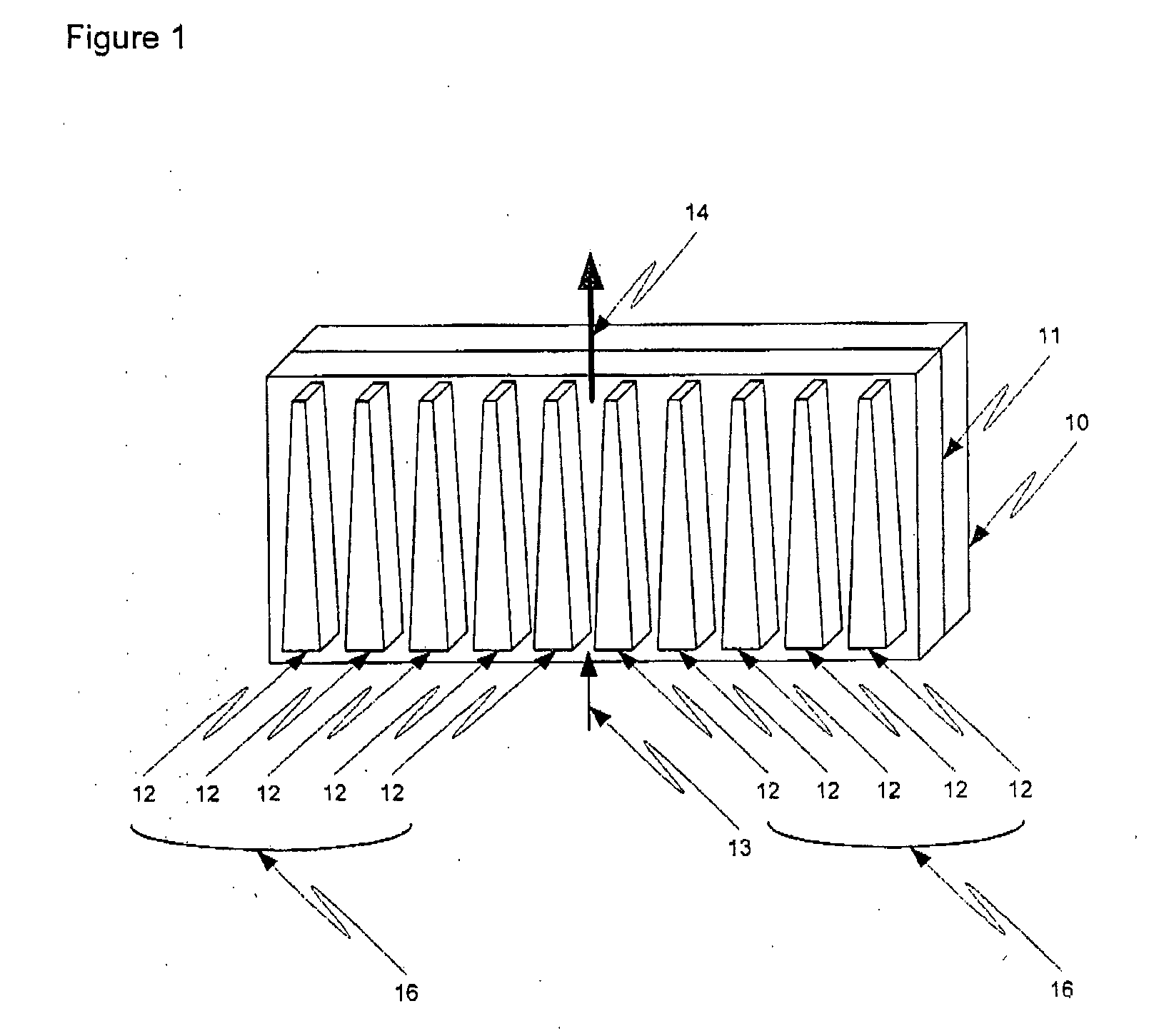
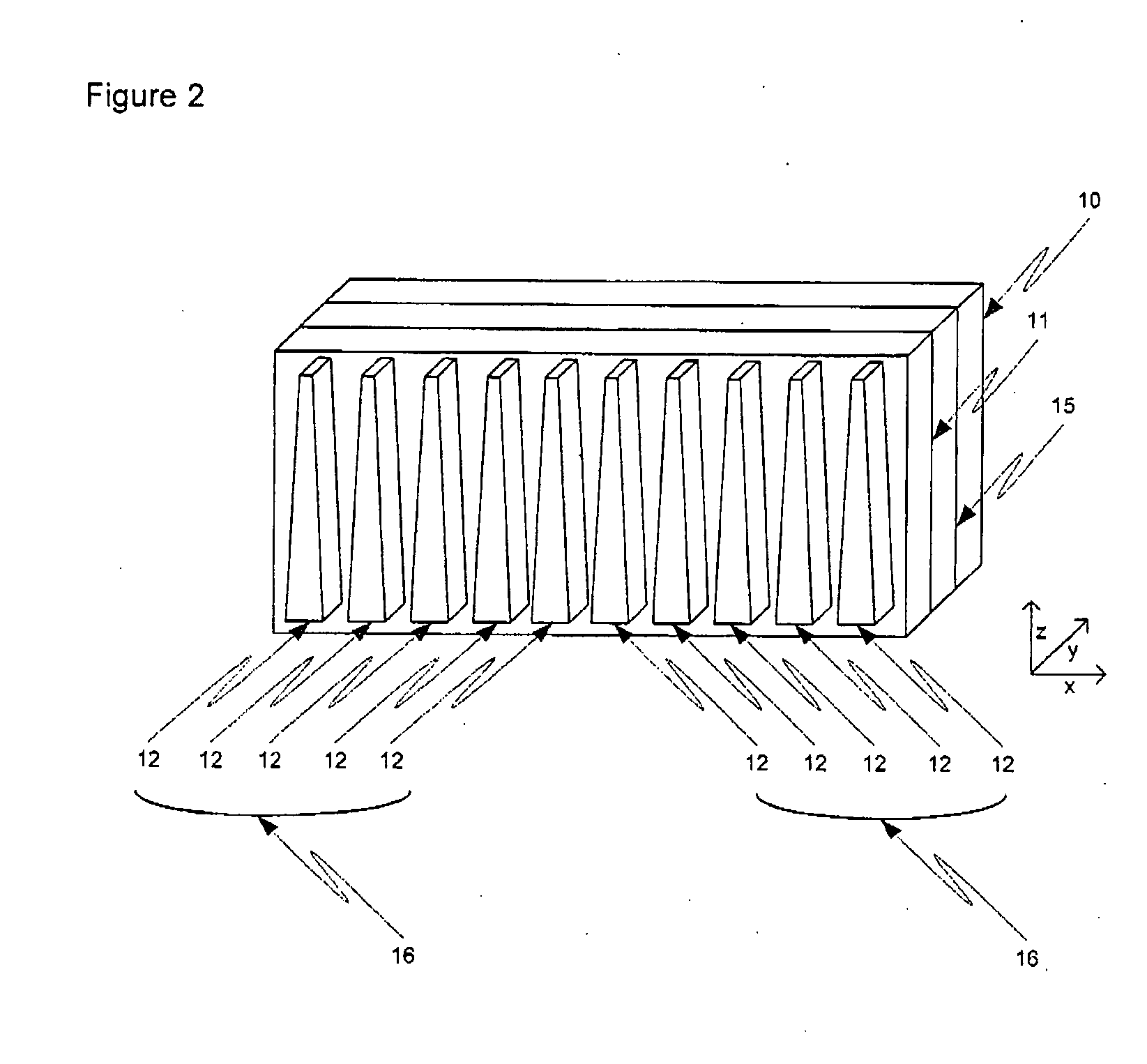
Heatsink method and apparatus
InactiveUS20060250776A1Improve cooling efficiencyDecrease resistance to rarificationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesConductive polymerEngineering
The invention relates to a heatsink. More particularly, the invention relates to a heatsink having tapered geometry that improves passive cooling efficiency. A tapered geometry between heatsink heat dissipation elements, as a function of distance along a z-axis opposing gravity, decreases resistance to rarification of passively flowing cooling gas upon heating. Thus, the tapered heatsink elements result in higher velocity of gas flow and increased cooling efficiency of the heatsink. Optionally, the heatsink is made from a thermally conductive polymer allowing the heatsink to be created in complex shapes using injection molding.
Owner:GLT ACQUISITION
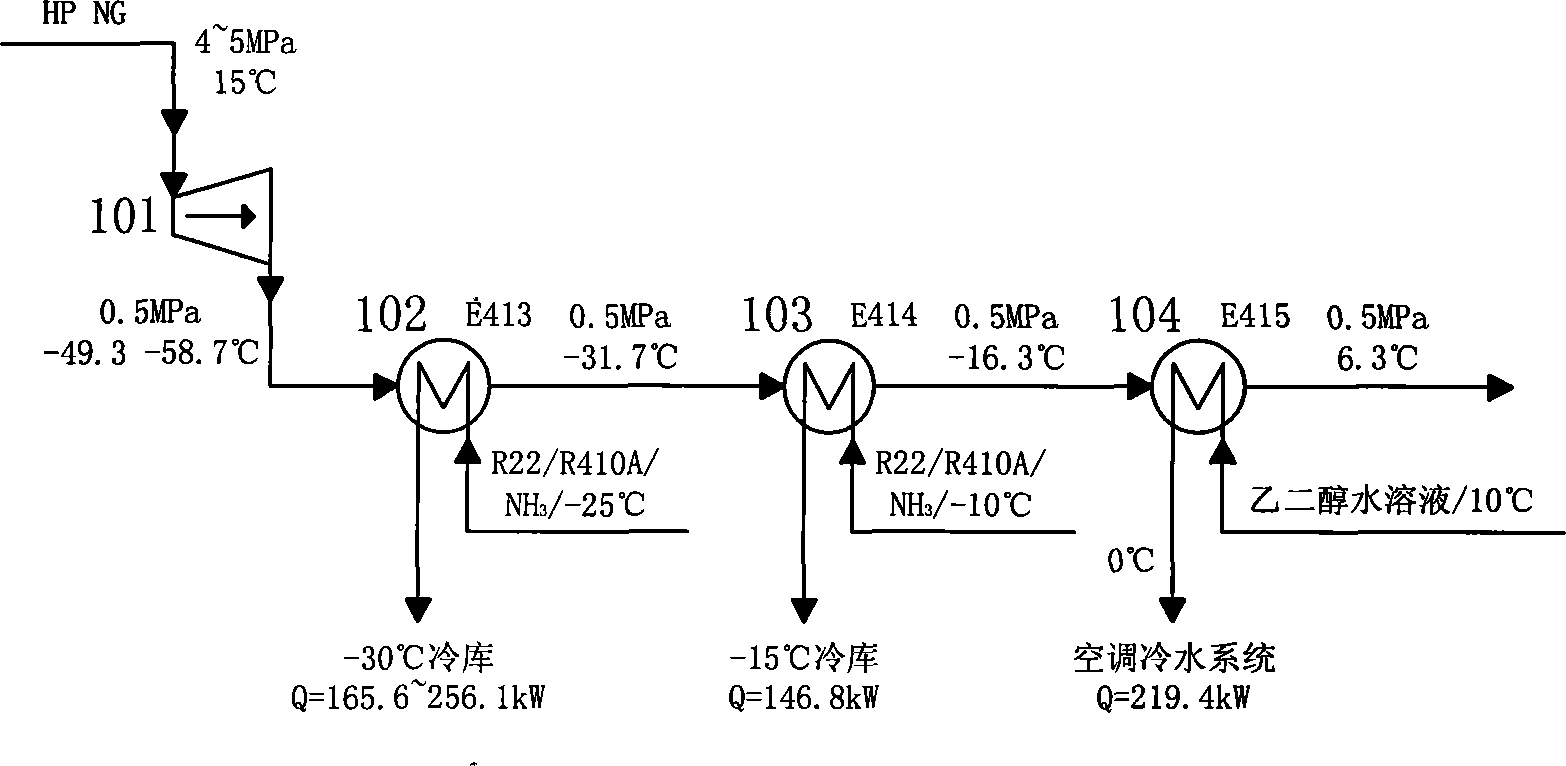
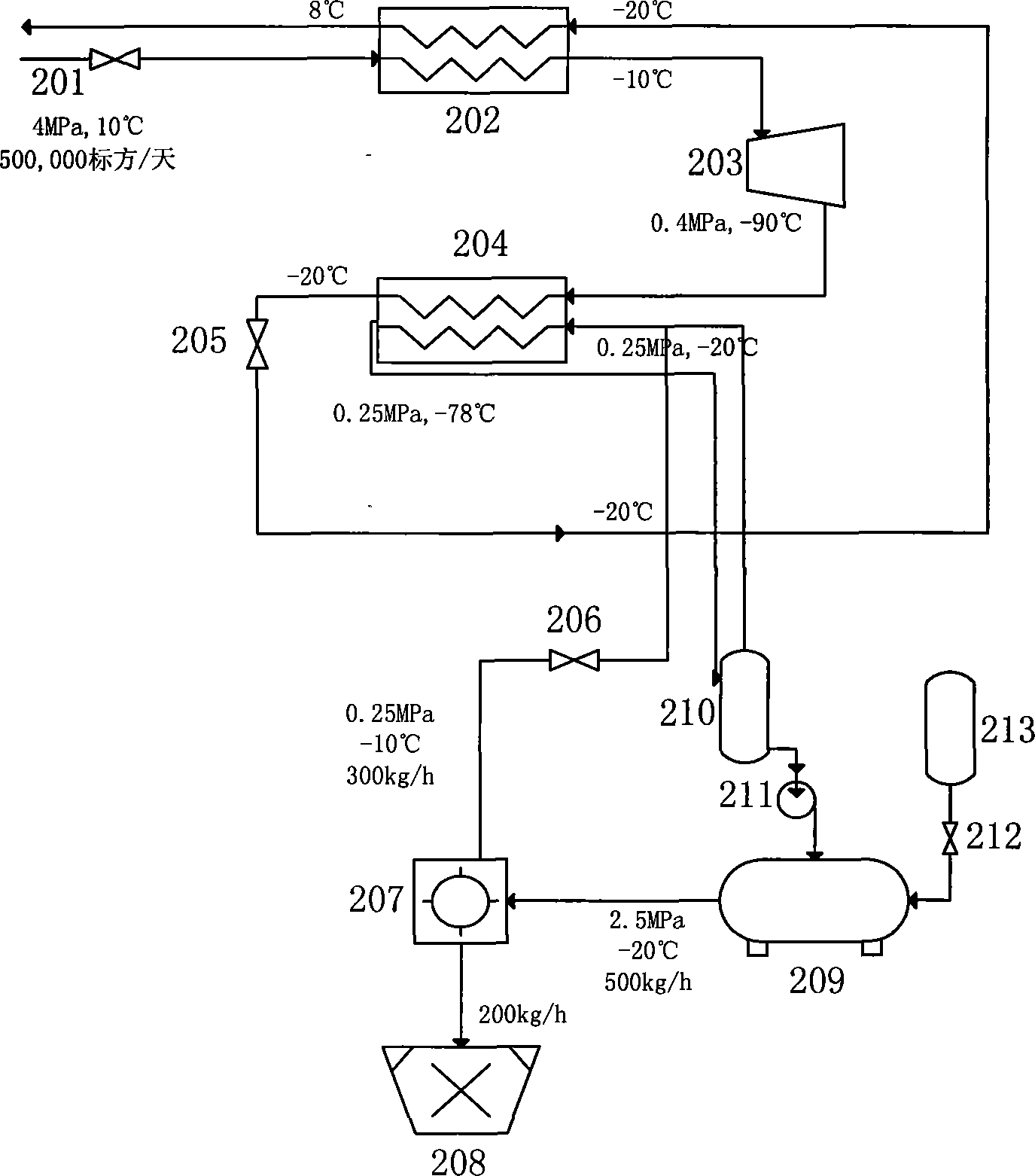
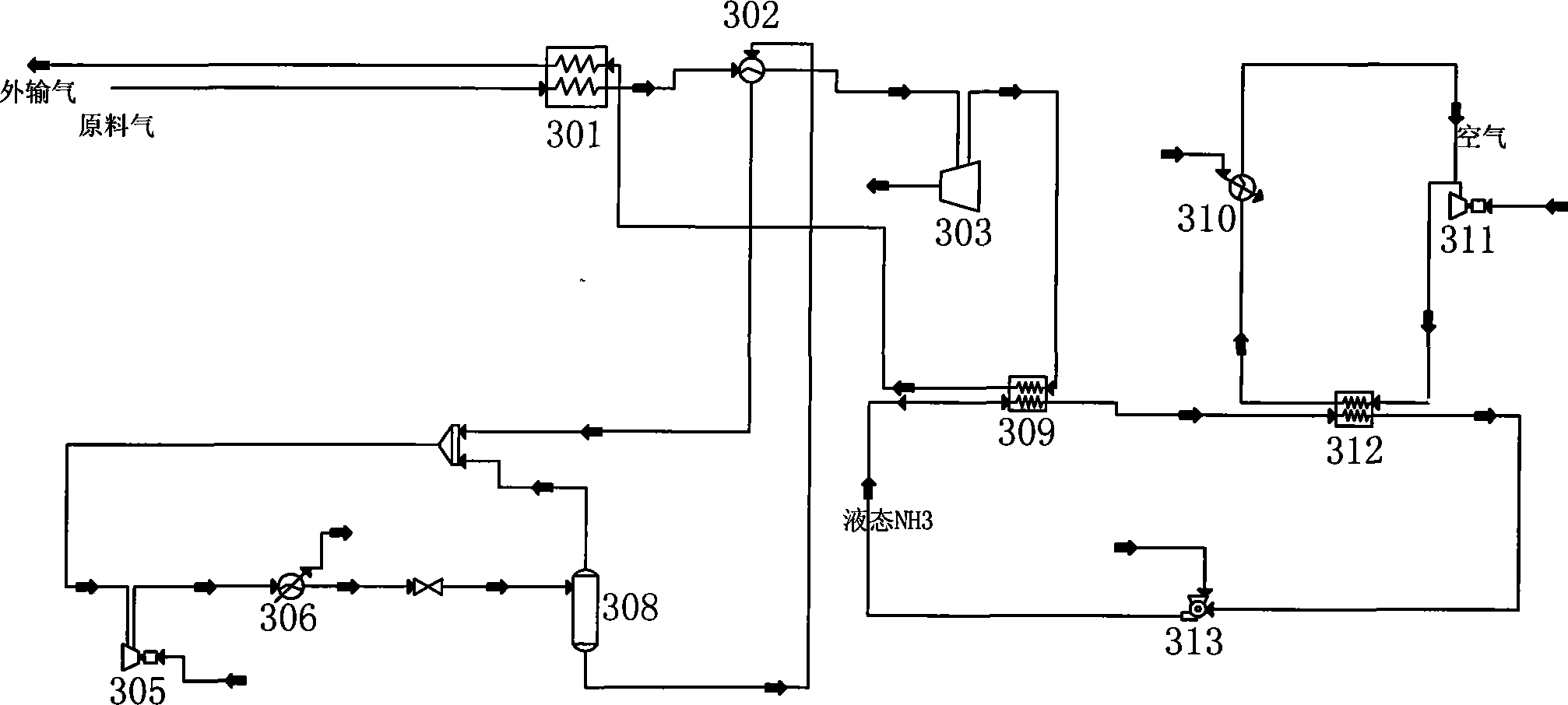
Method for utilizing pressure energy of natural gas
InactiveCN101245956AImprove utilization efficiencySimple processing technologyCompression machinesStationary plate conduit assembliesWaste rubberEngineering
The invention discloses a method which utilizes natural gas pressure energy; namely, the pressure and the temperature of the natural gas in a high pressure pipeline are reduced by a no-power refrigerator so as to gain low temperature natural gas which then exchanges the heat with a normal-temperature refrigerant which is sent by a normal-temperature tank; the low temperature refrigerant with temperature reduced enters a refrigerant storage tank for standby and is finally delivered to a cold energy user; the normal-temperature natural gas with temperature increased enters the pipeline. The method which utilizes natural gas pressure energy has convenient and practical whole process technique and high efficiency, spends little investment on the self-pressure energy in the pressure reduction process of the high pressure natural gas which is recovered by a pressure modulating station, converts the pressure energy into the cold energy with low operation cost, leads the cold energy to be used by cold quantity users of cold storages, cold water air conditioners, wasted rubber deep-cold crushing round the pressure modulating station by means of the refrigerant, etc., or to be made into ice blocks and dry ice products for abroad sale, etc., thus gaining huge economic benefits, improving the utilization ratio of the energy resource and eliminating the safe hidden trouble which is generated by sudden coolness of the equipment in the normal pressure modulating process.
Owner:GUANGZHOU GAS
Power management of a computer with vapor-cooled processor
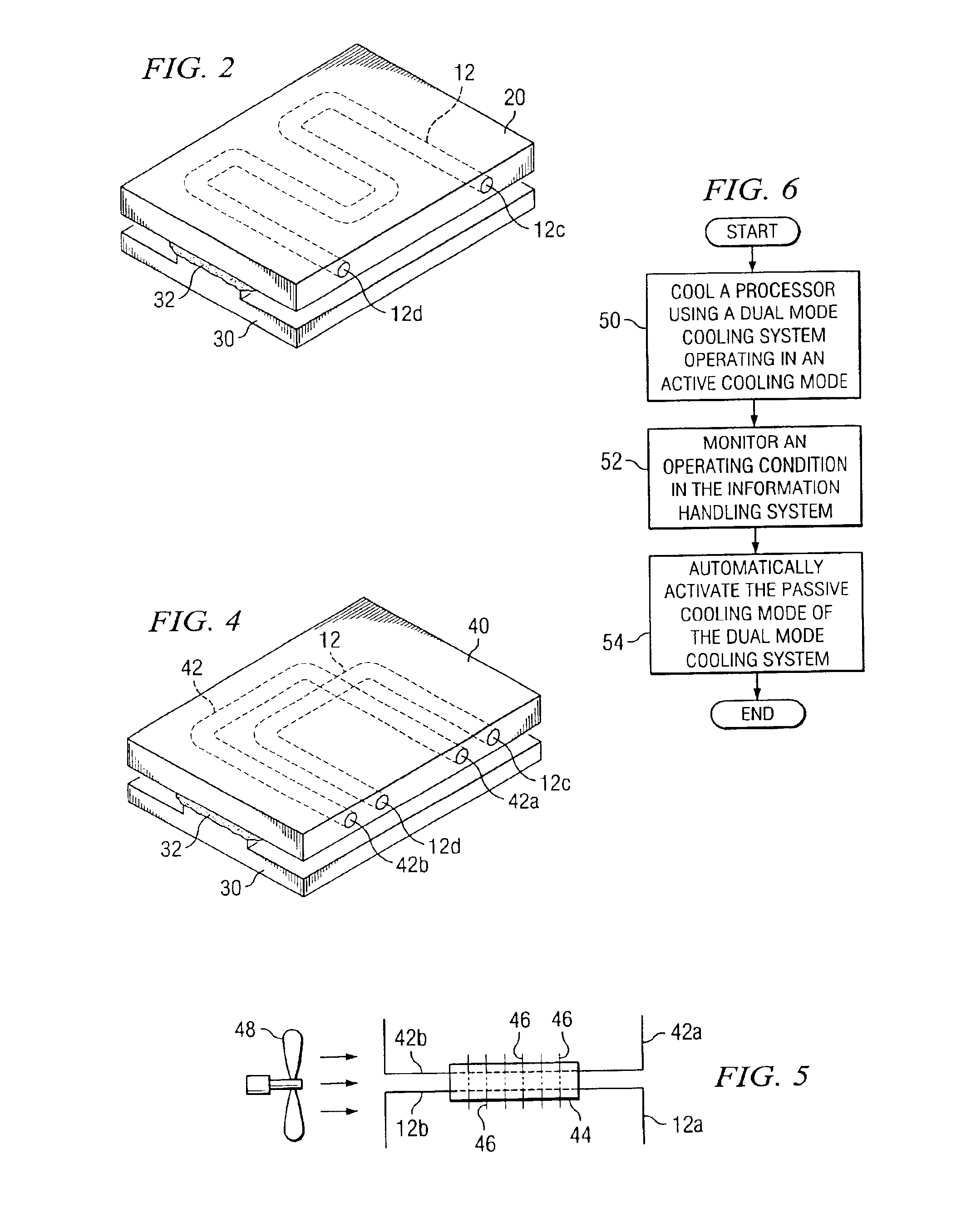
InactiveUS6837063B1Reduce consumptionReduce noiseEnergy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsNuclear engineeringActive cooling
A system and method for power management of a computer with a vapor-cooled processor is disclosed. A dual mode cooling system for an information handling system includes a heat exchanger for receiving heat generated by the information handling system. The system further includes a condenser in communication with the heat exchanger such that the heat received at the heat exchanger is transferred to the condenser. The heat exchanger and the condenser are able to selectively operate in an active cooling mode and a passive cooling mode.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
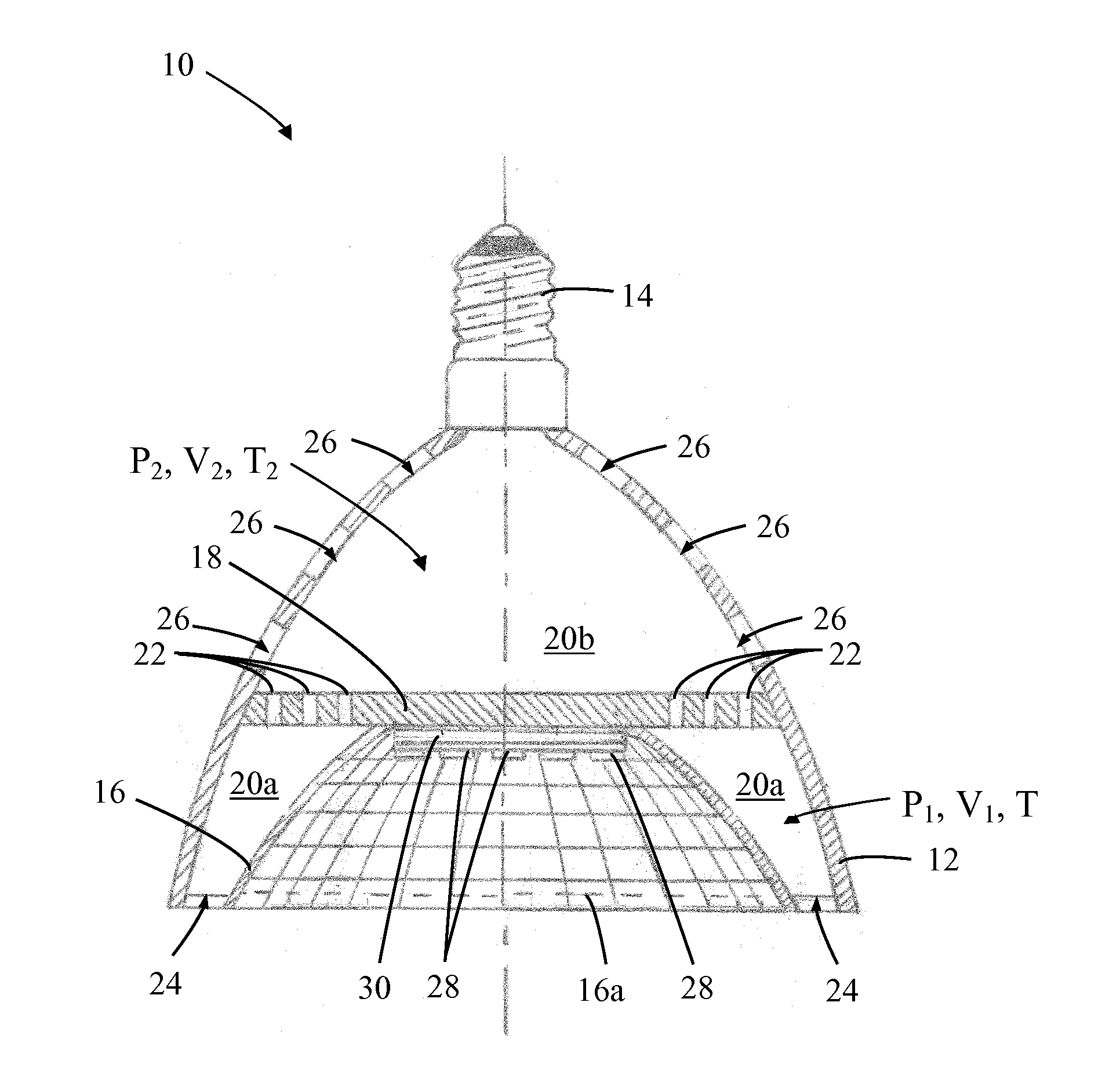
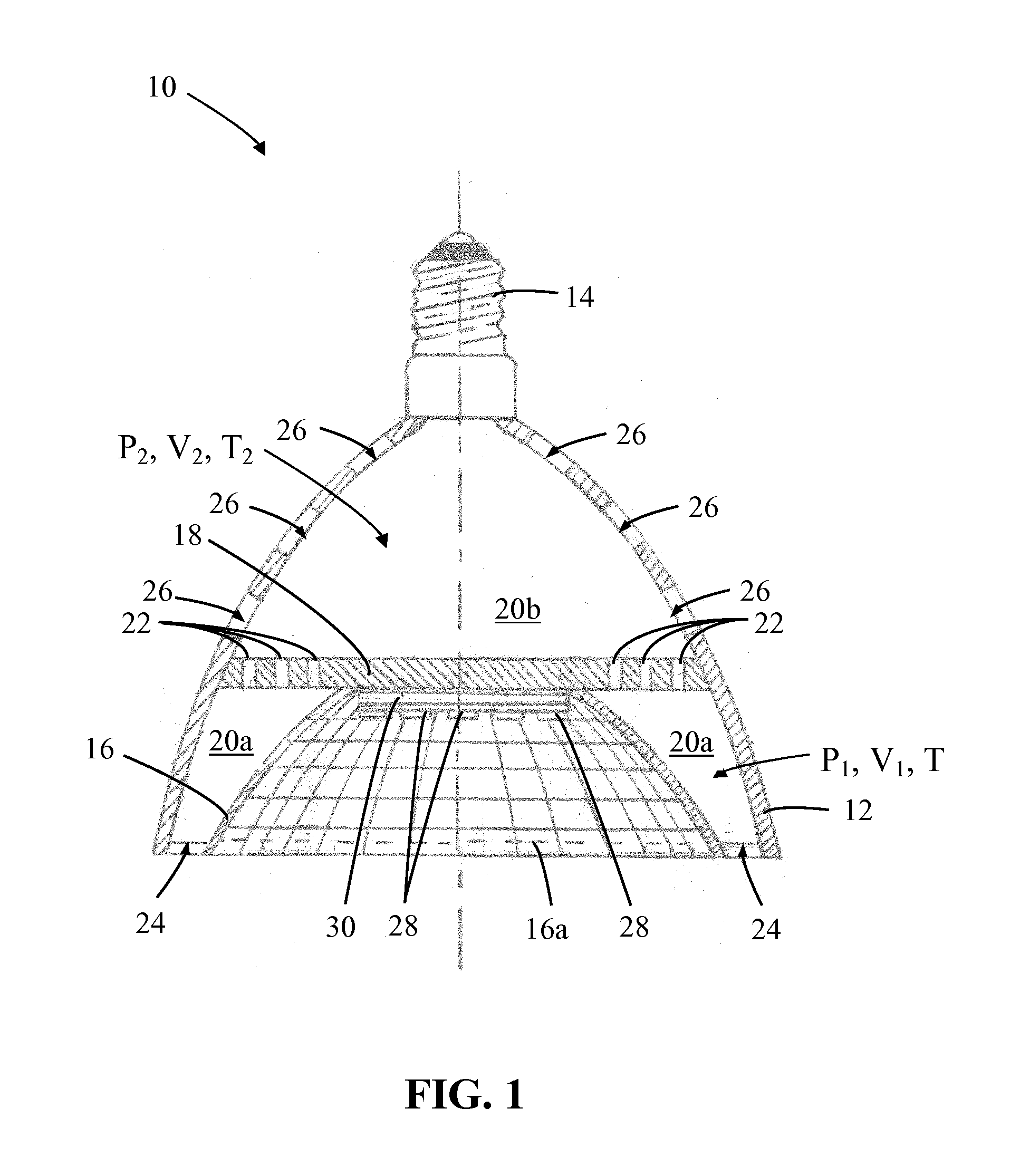
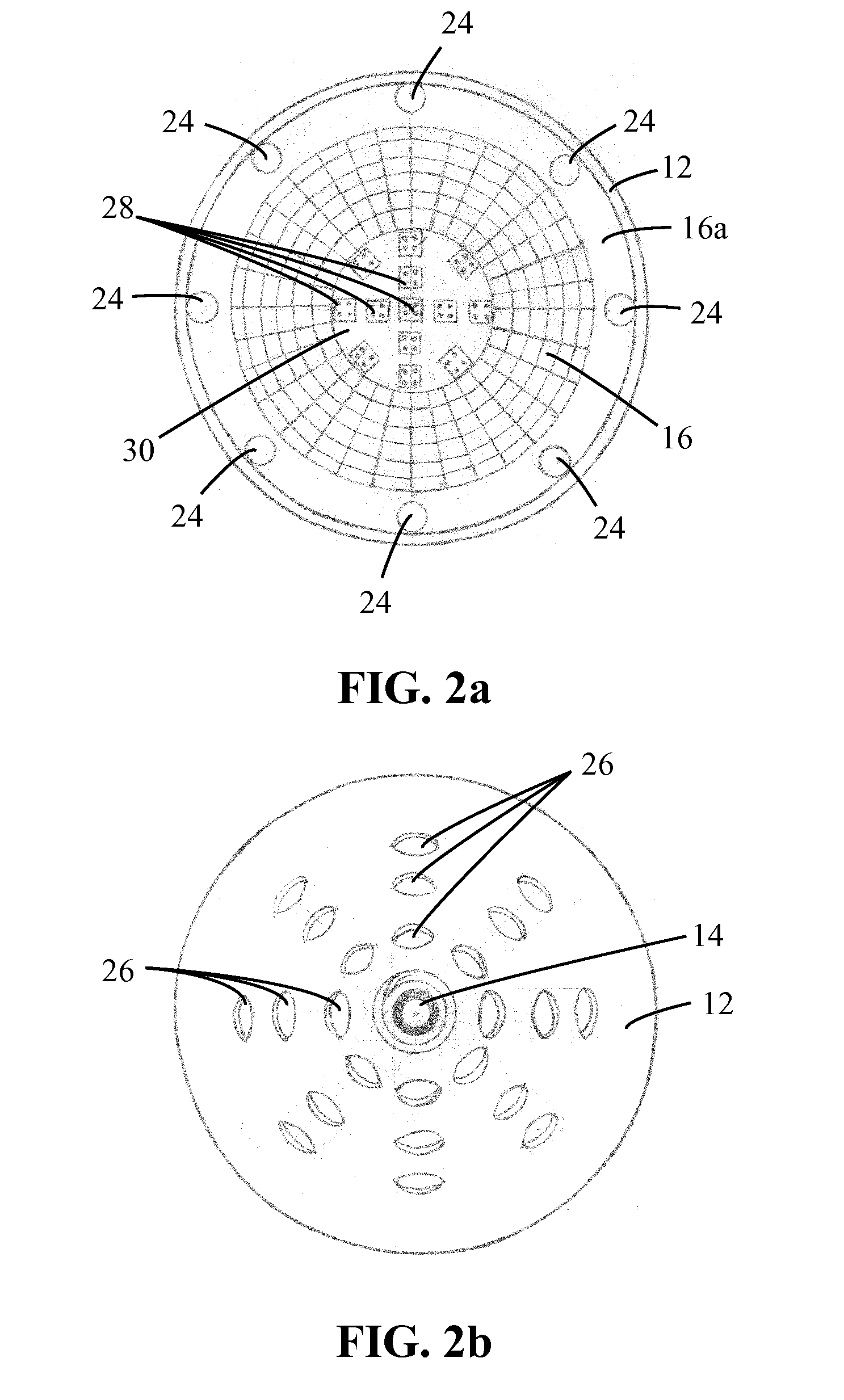
Solid-state lamps with passive cooling
InactiveUS20110110095A1Easy to movePoint-like light sourceLighting heating/cooling arrangementsEngineeringThermal radiation
A solid-state lamp comprises a body having a first chamber with inlet apertures and a second chamber with outlet apertures. The chambers are interconnected in fluid communication by one or more passages. The lamp further comprises a thermally conductive substrate having a heat radiating surface located within at least one chamber and one or more solid-state light emitters, typically LEDs, mounted in thermal communication with the thermally conductive substrate. The lamp is configured such that in operation heat generated by the LEDs is radiated by the substrate into one or both chambers causing a difference in air pressure between the chambers that results in surrounding air being drawn into the inlet apertures, flowing through the chambers via the interconnecting passages in the substrate and exiting through the outlet apertures thereby cooling the substrate and LEDs.
Owner:INTEMATIX
Method and system for reducing the level of emissions generated by a system
ActiveUS20100242482A1Lower emission levelsFuel supply regulationContinuous combustion chamberCombustion systemEmbedded system
An embodiment of the present invention provides a method and system of operating a combustion system that has Lean direct injection (LDI) functionality. The method and system provides a passive cooling system for an injector of the LDI system. The method and system may also provide a means to direct the flow of the fluid exiting the injector of the LDI system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for passive cooling of gas turbine engine control components
InactiveUS20090175718A1Satisfactory temperature rangePump componentsTurbine/propulsion engine coolingAtmospheric airGas turbines
A system for cooling a gas turbine engine control component comprises a control component, at least one duct in fluid communication with the component and the atmosphere, and a valve assembly located with the duct for modulating airflow to the component. A method for cooling a gas turbine engine control component comprises the steps of: a) providing a system for cooling the component, the system comprising at least one duct in fluid communication with the component and the atmosphere and a valve assembly located with the duct for modulating airflow to the component; b) exposing the system to a first condition where cooling of the component is required; c) opening the valve assembly in response to the first condition; d) exposing the system to a second condition where cooling of the component is not required; and e) closing the valve assembly in response to the second condition.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
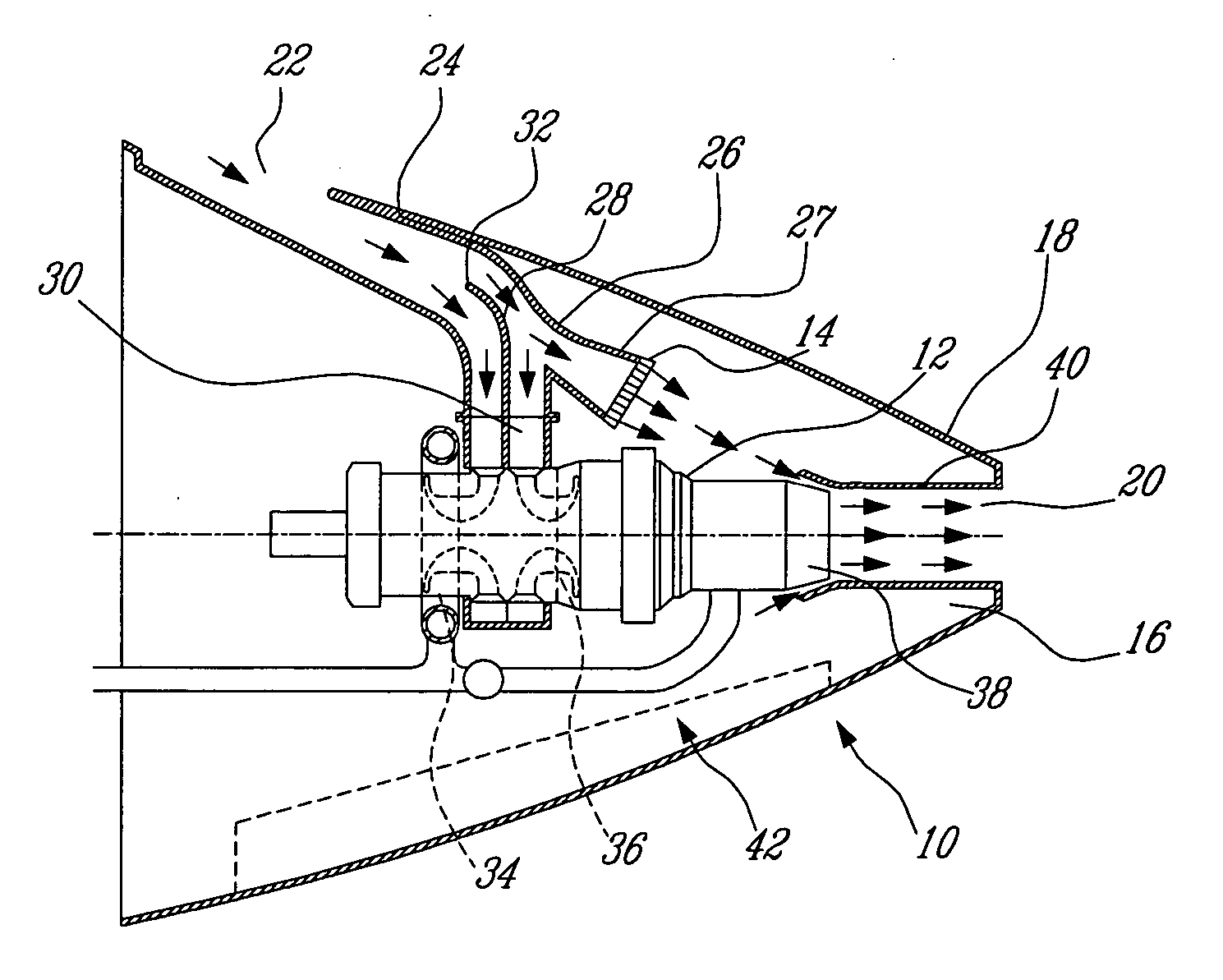
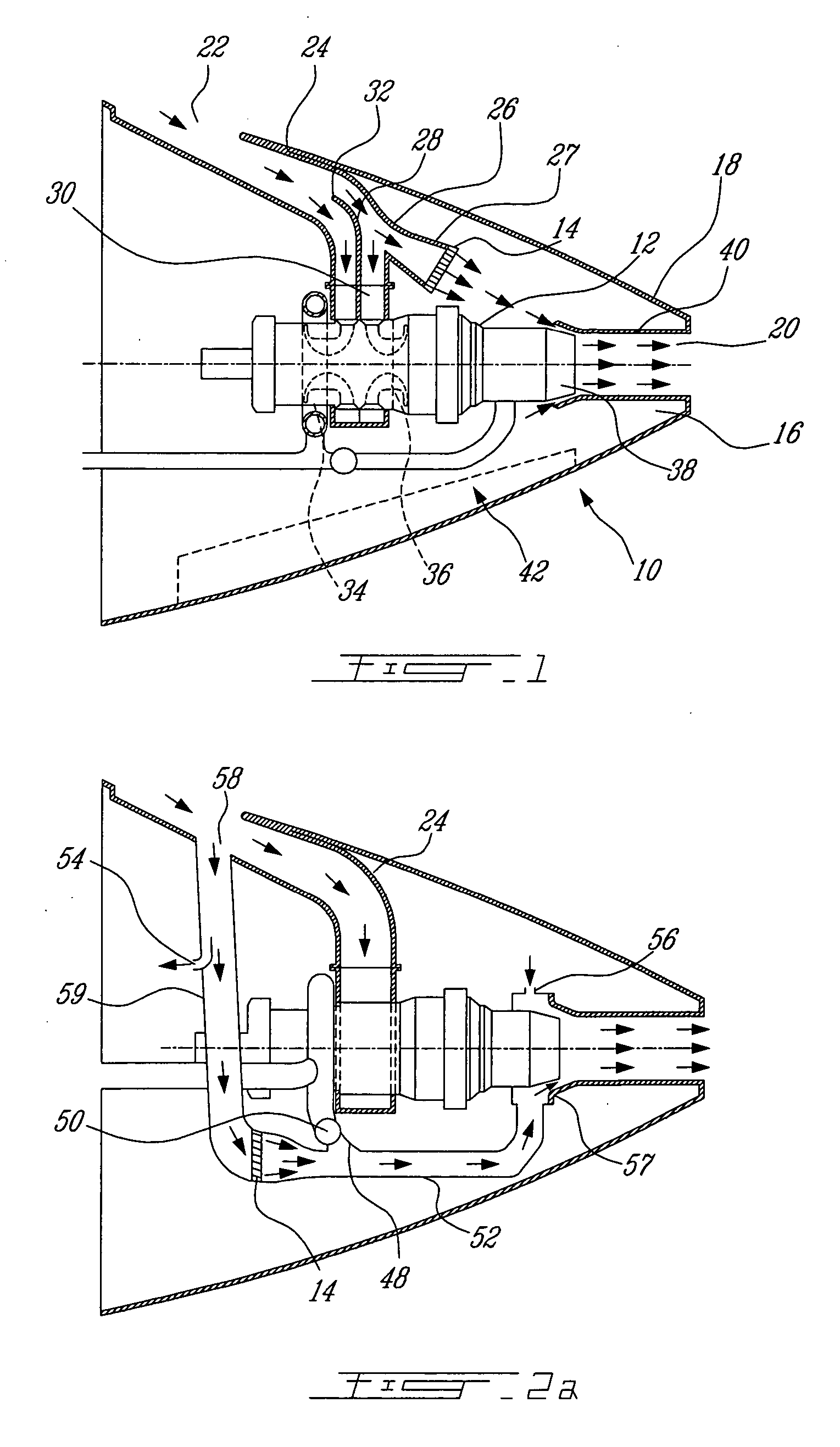
Passive cooling system for auxiliary power unit installation
InactiveUS20070063098A1Improve cooling effectEnhanced cooling airflowPower plant cooling arrangmentsPower installationsNacelleAir entrainment
A passive cooling system for an auxiliary power unit (APU) installation on an aircraft is provided. The system is for an auxiliary power unit having at least a compressor portion of a gas turbine engine and an oil cooler contained separately within a nacelle. The system includes the auxiliary power unit housed within the nacelle of the aircraft, an engine exhaust opening defined in the aft portion of the nacelle and communicating with the gas turbine engine, at least a first air inlet duct communicating with a second opening defined in said nacelle and with said compressor portion and the oil cooler is located within a second duct communicating with an opening other than the engine exhaust opening of said nacelle and with the engine exhaust opening. Exterior cooling air and engine exhaust ejected through said engine exhaust opening entrain cooling air through said second duct to said oil cooler, and thus provide engine oil cooling. An exhaust eductor is also provided.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Thermal management for aircraft auxiliary power unit compartment
An improved passive cooling system for an aircraft APU compartment that includes a lightweight annular air-cooled oil cooler that is strategically oriented and shrouded to face its annular inlet away axially downstream from the exhaust of the APU to make it inherently fireproof to flames from the APU or any location within the APU compartment that fuel can accumulate.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
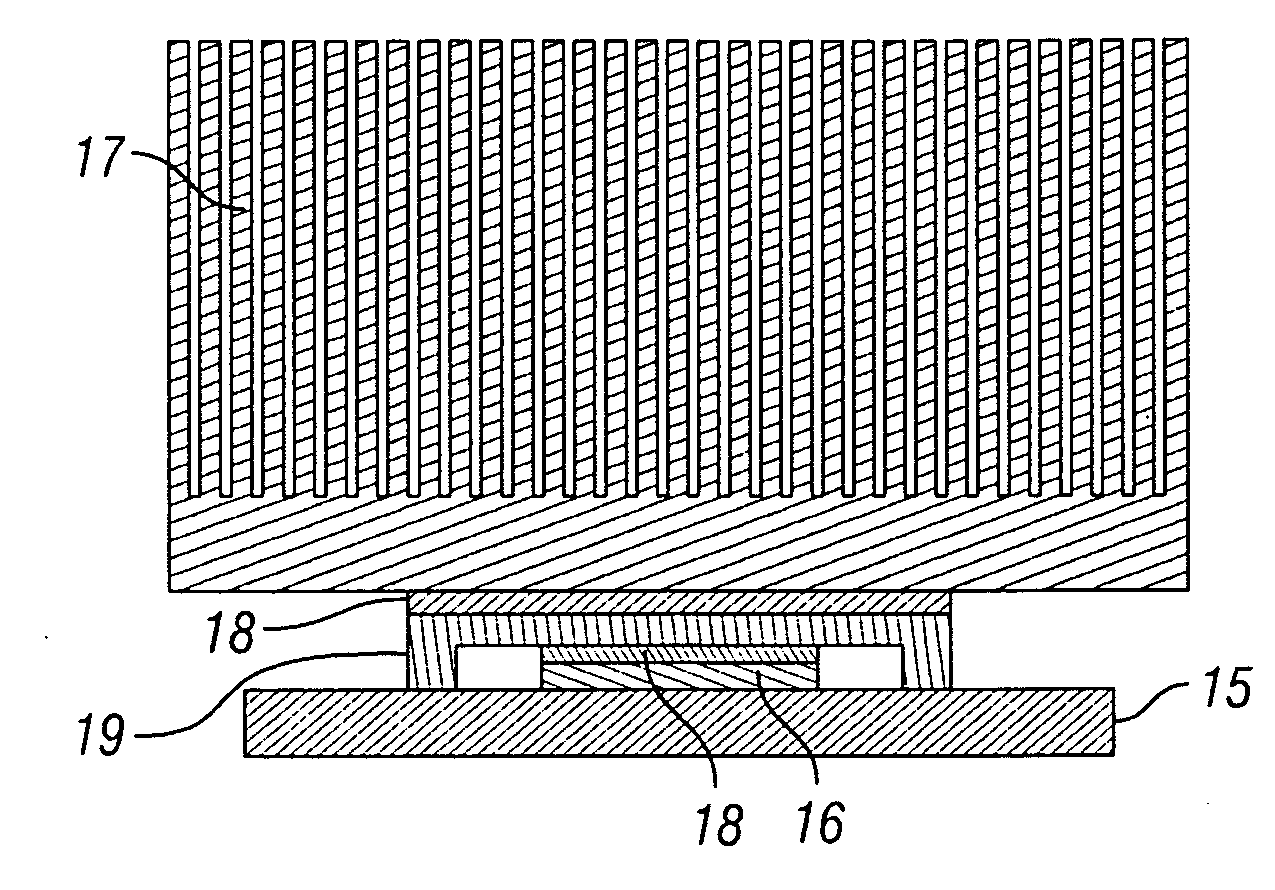
Thin, passive cooling system
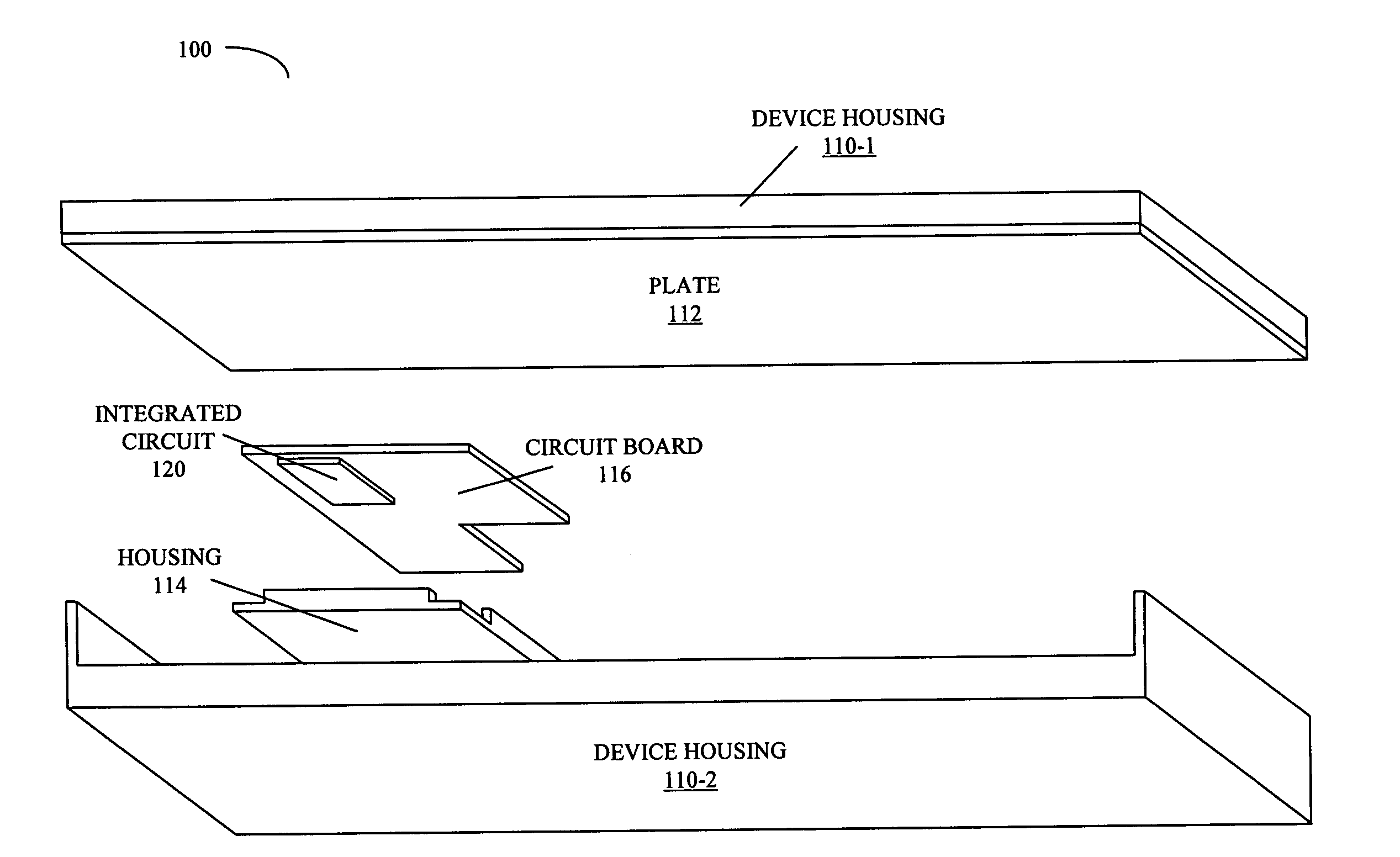
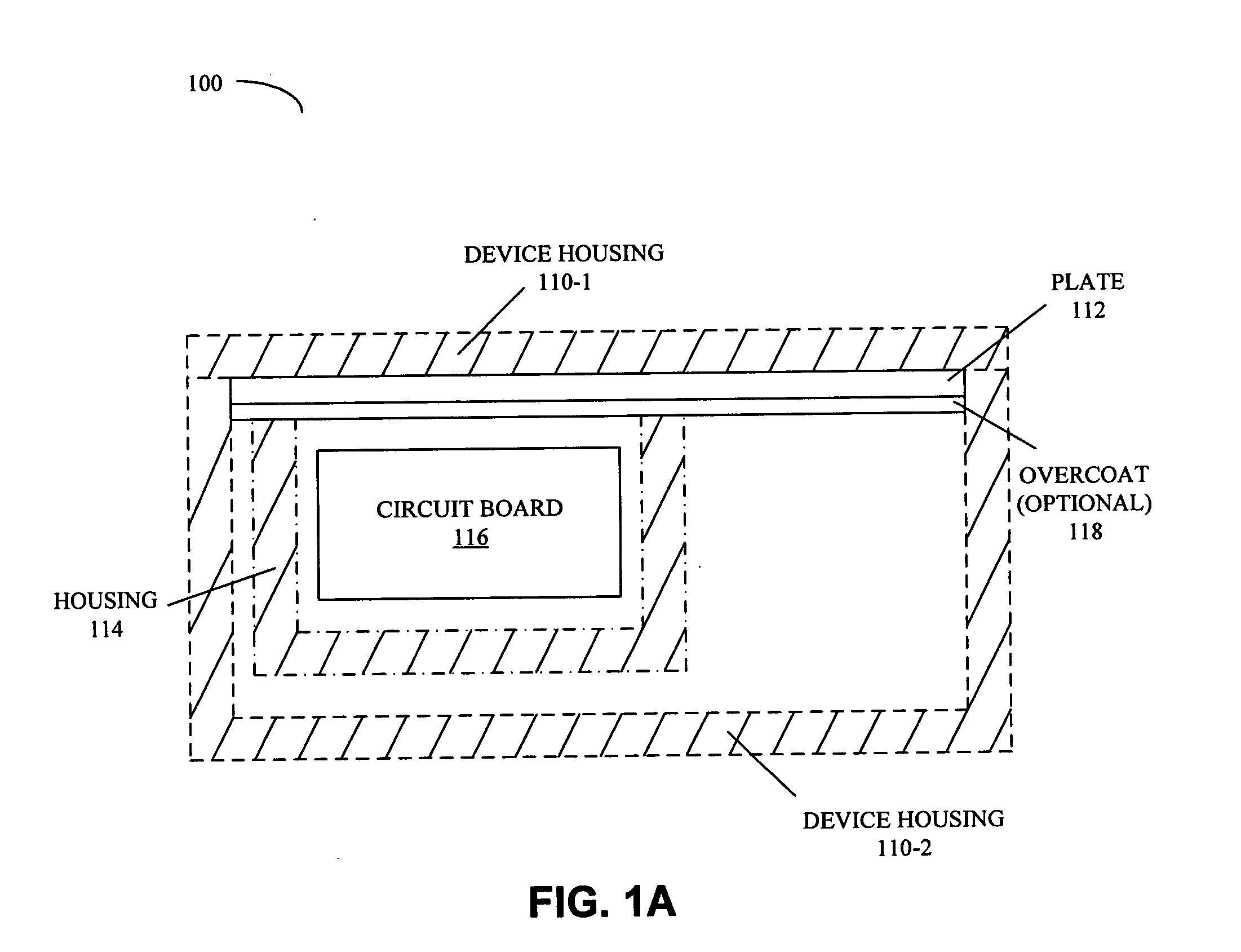
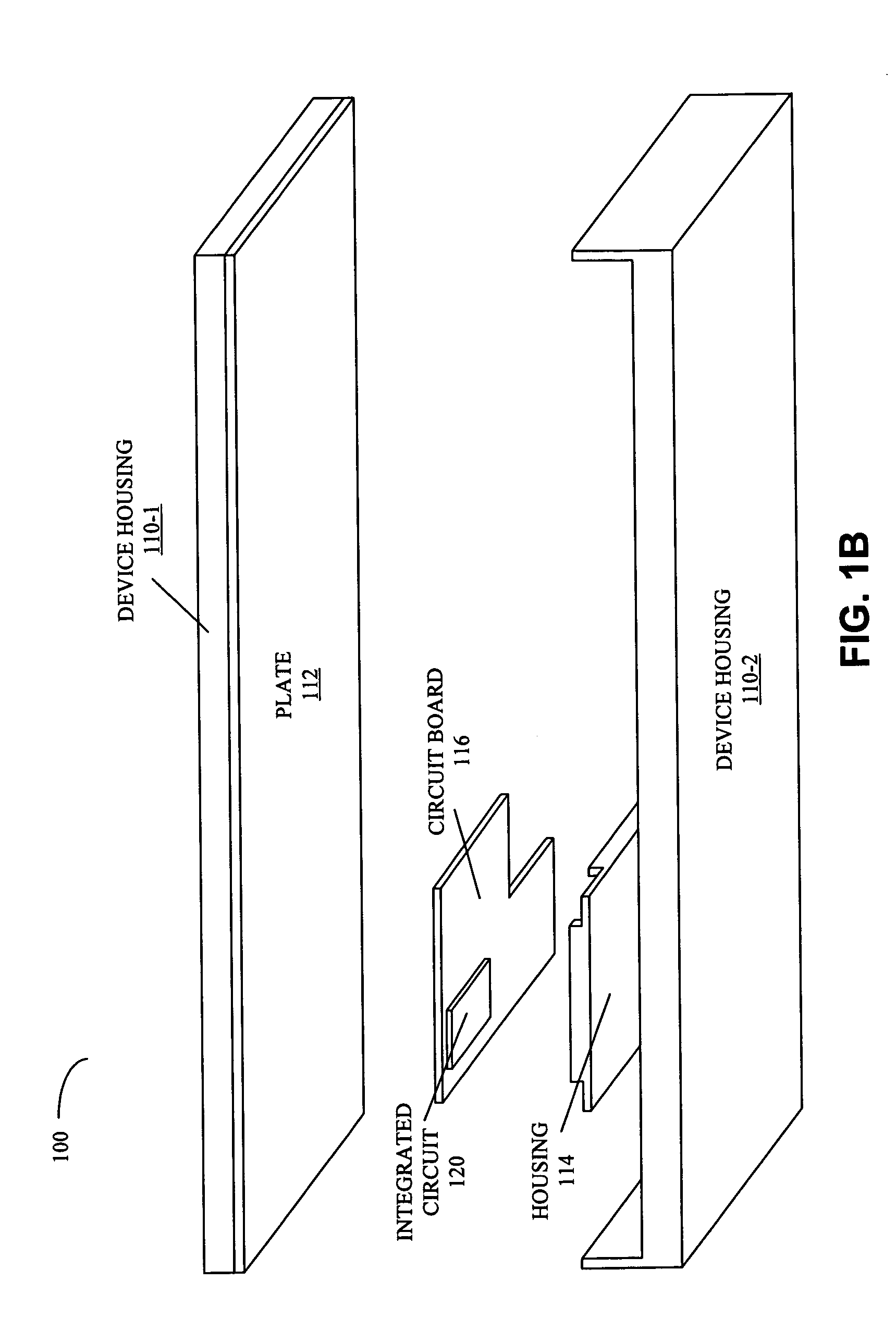
ActiveUS20080101026A1Lose weightDigital data processing detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHeat shieldPassive cooling
A system includes a power source and a heat-shield mechanism which encloses the power source. This heat-shield mechanism includes a 3-dimensional housing that defines a cavity in which the power source resides, and a plate that is positioned to cover an opening to the cavity that is defined by an edge of the housing. Note that the housing contains three layers in which a second layer is sandwiched between a first layer and a third layer. This second layer has a first anisotropic thermal conductivity. Furthermore, the plate includes a material having a second anisotropic thermal conductivity.
Owner:APPLE INC
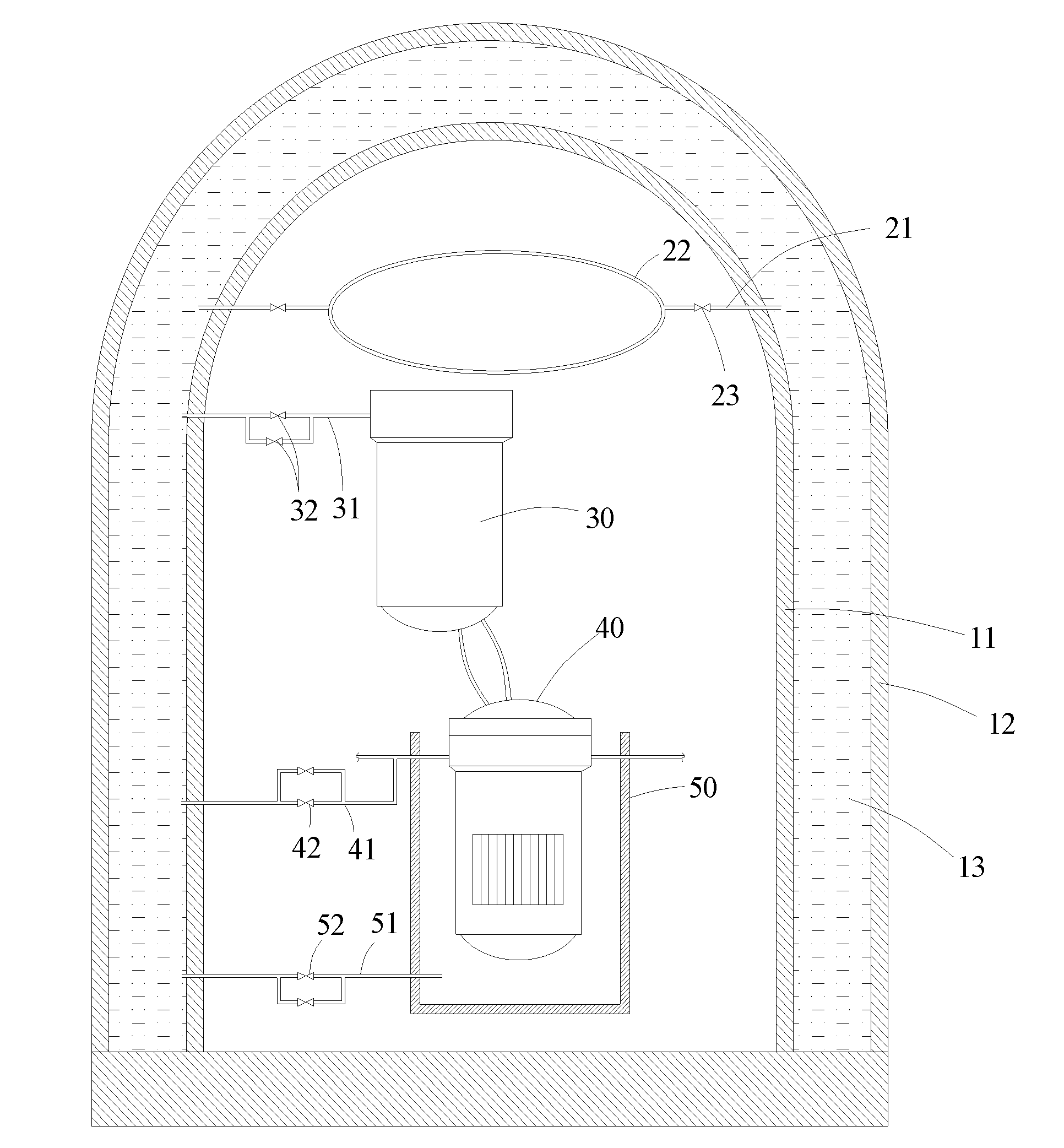
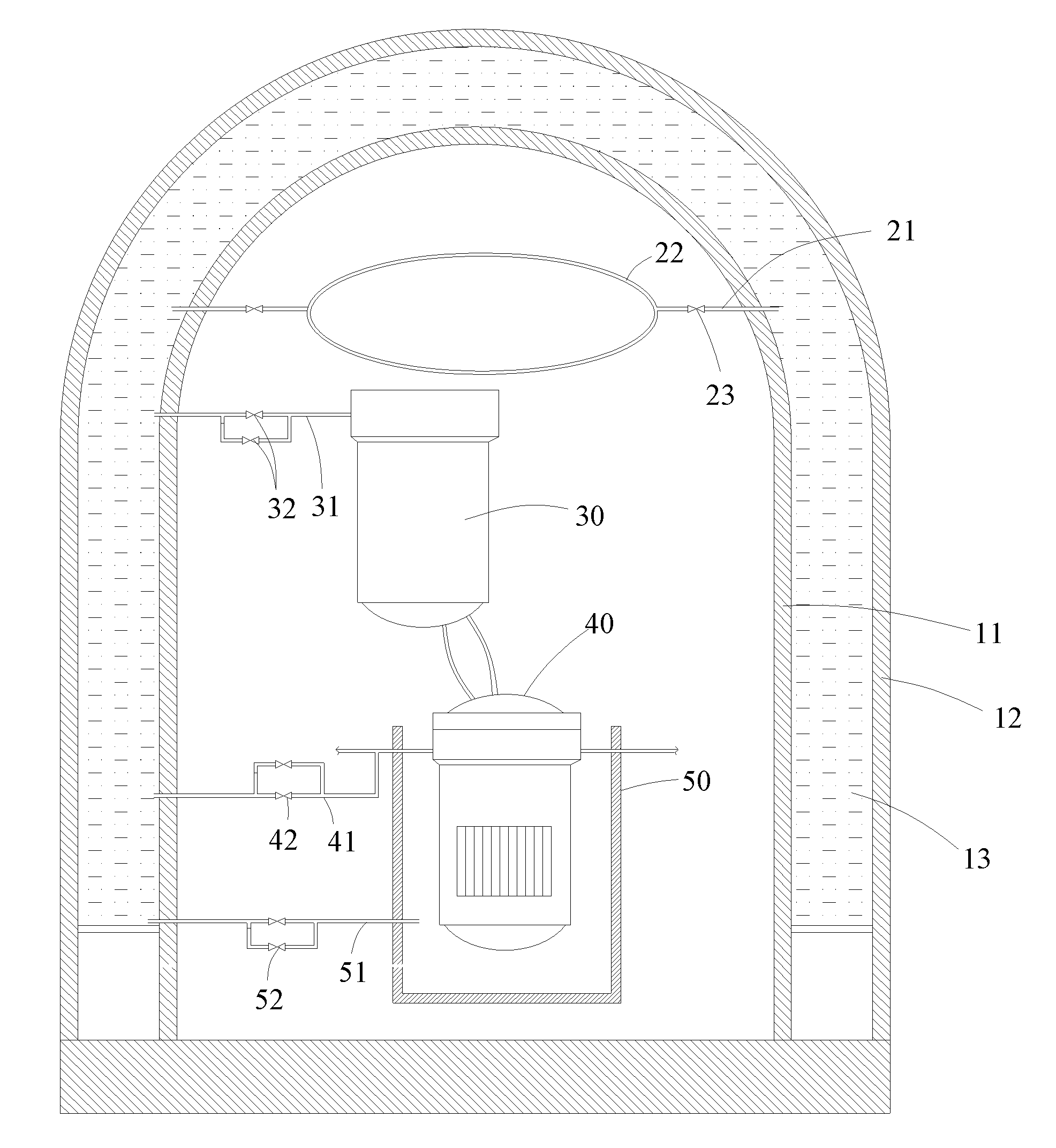
Device combining in-core and out-of-core dwelling of molten material of large-scale passive nuclear power plant
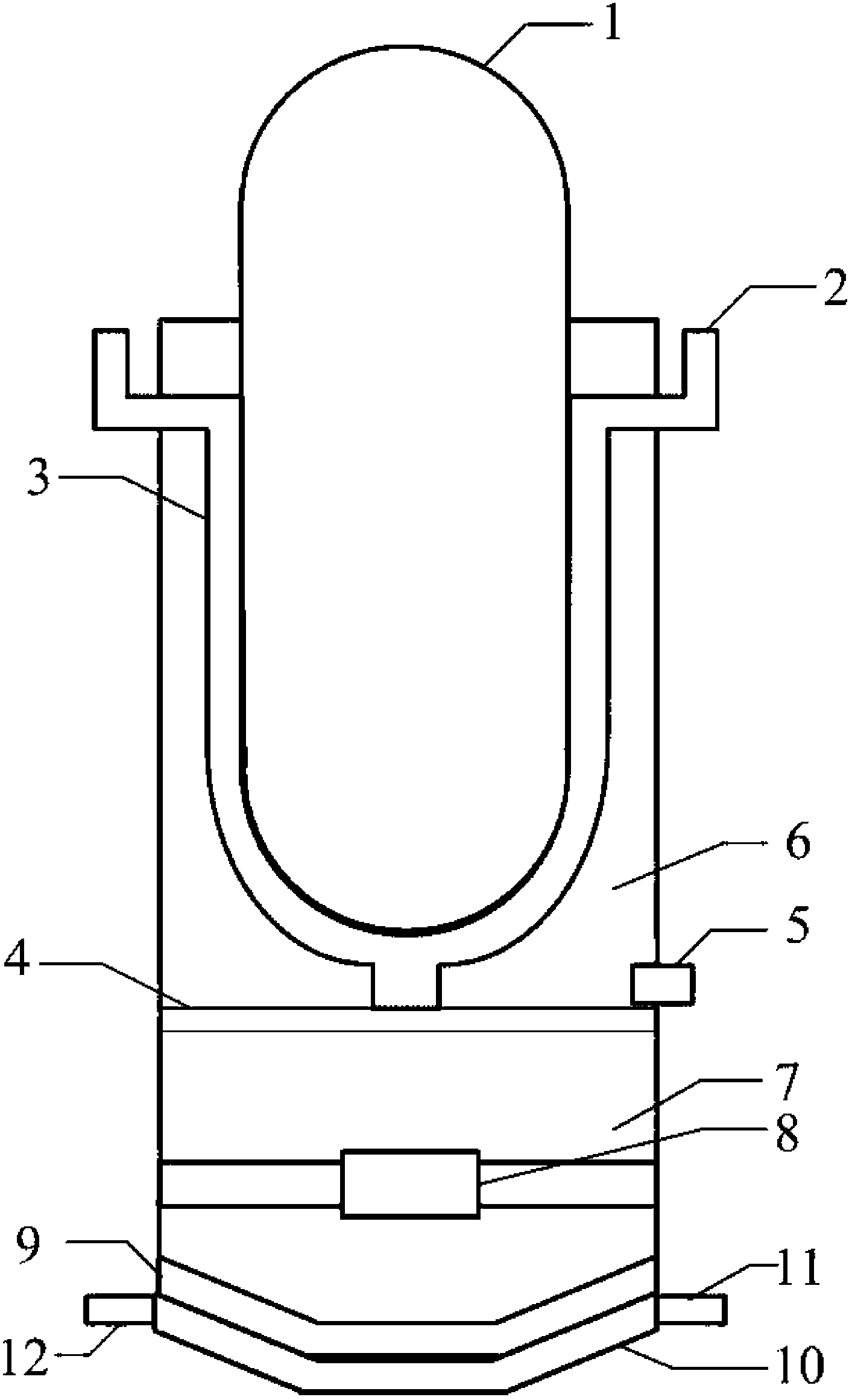
InactiveCN103578580AImplementation of off-stack coolingImplement in-heap retentionNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsCore catcherPressurized water reactor
The invention provides a device combining in-core and out-of-core dwelling of a molten material of a large-scale passive nuclear power plant. The device comprises a concrete sacrificial layer (4), a core catcher chamber (7), a core catcher refractory layer (8), a cooling channel inlet (9), a cooling channel outlet (10) and a core catcher bottom cooling channel (11). The invention provides a set of device organically combining molten material out-of-core cooling with an IVR (interactive voice response) system, when IVR succeeds, in-core dwelling of the molten material can be realized; and after the IVR fails, out-of-core dwelling of the molten material is realized by passive cooling of the core catcher bottom cooling channel, and the capability of mitigating severe accidents of the large-scale passive pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant is further enhanced.
Owner:SHANGHAI NUCLEAR ENG RES & DESIGN INST CO LTD
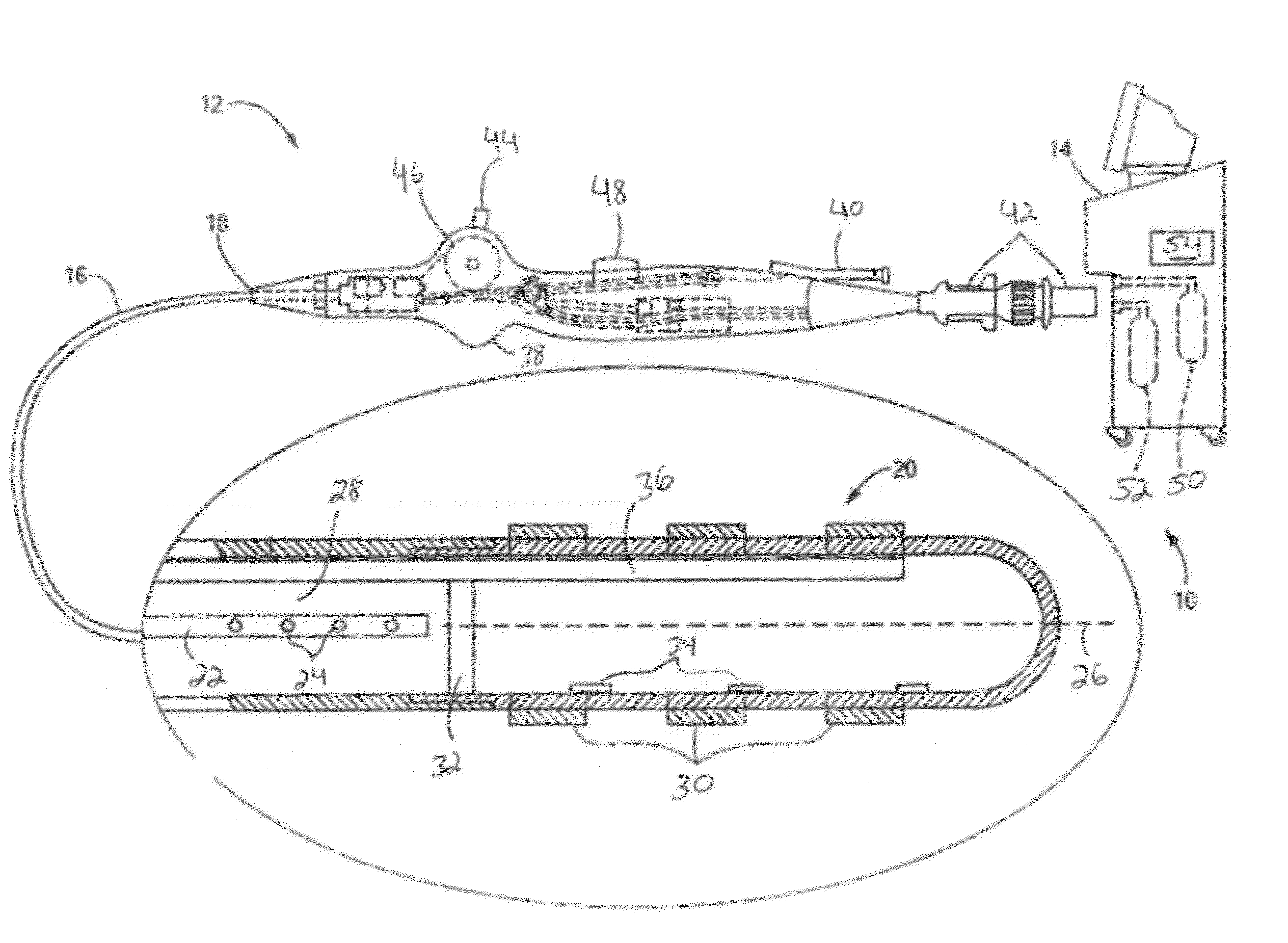
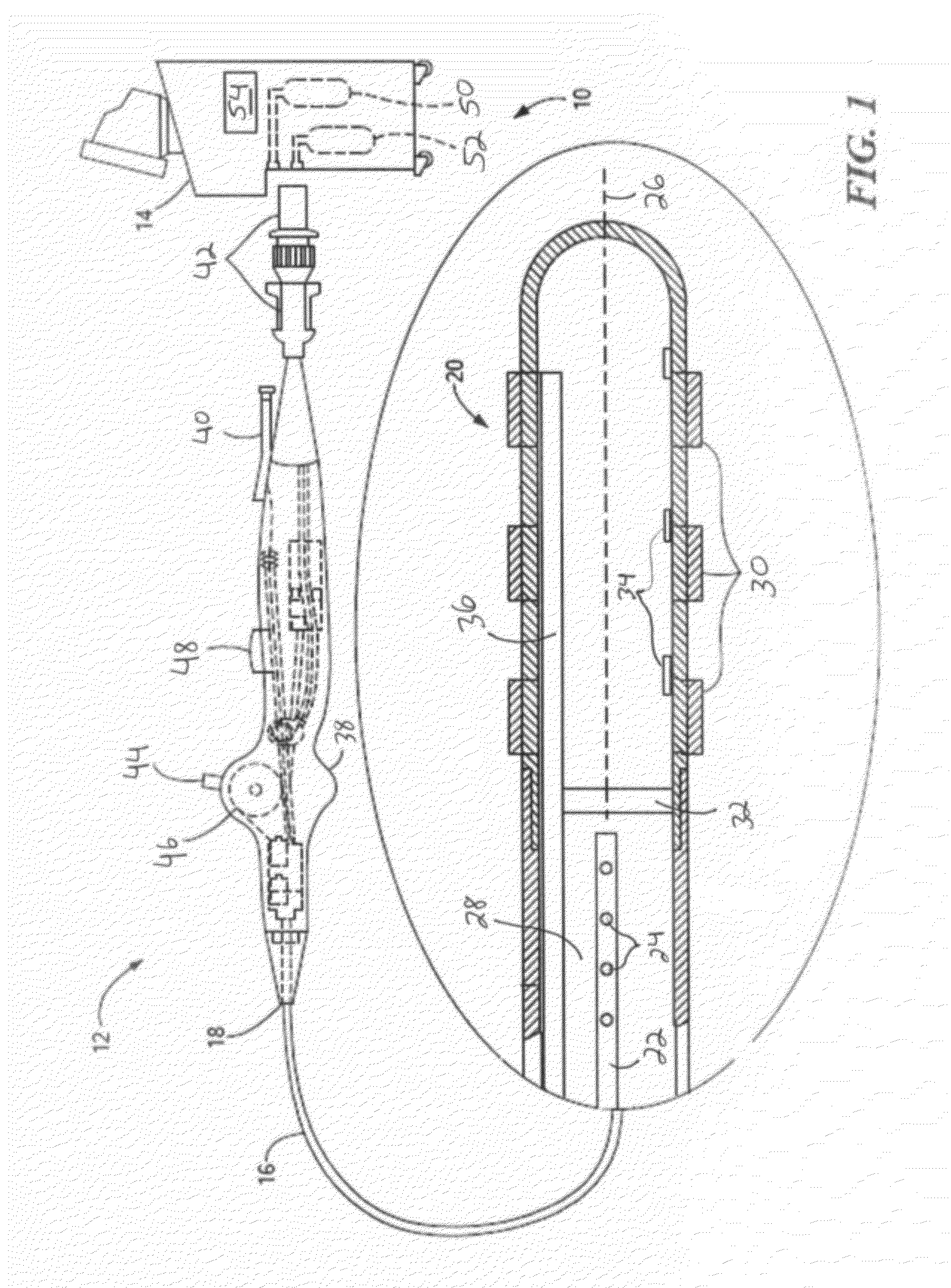
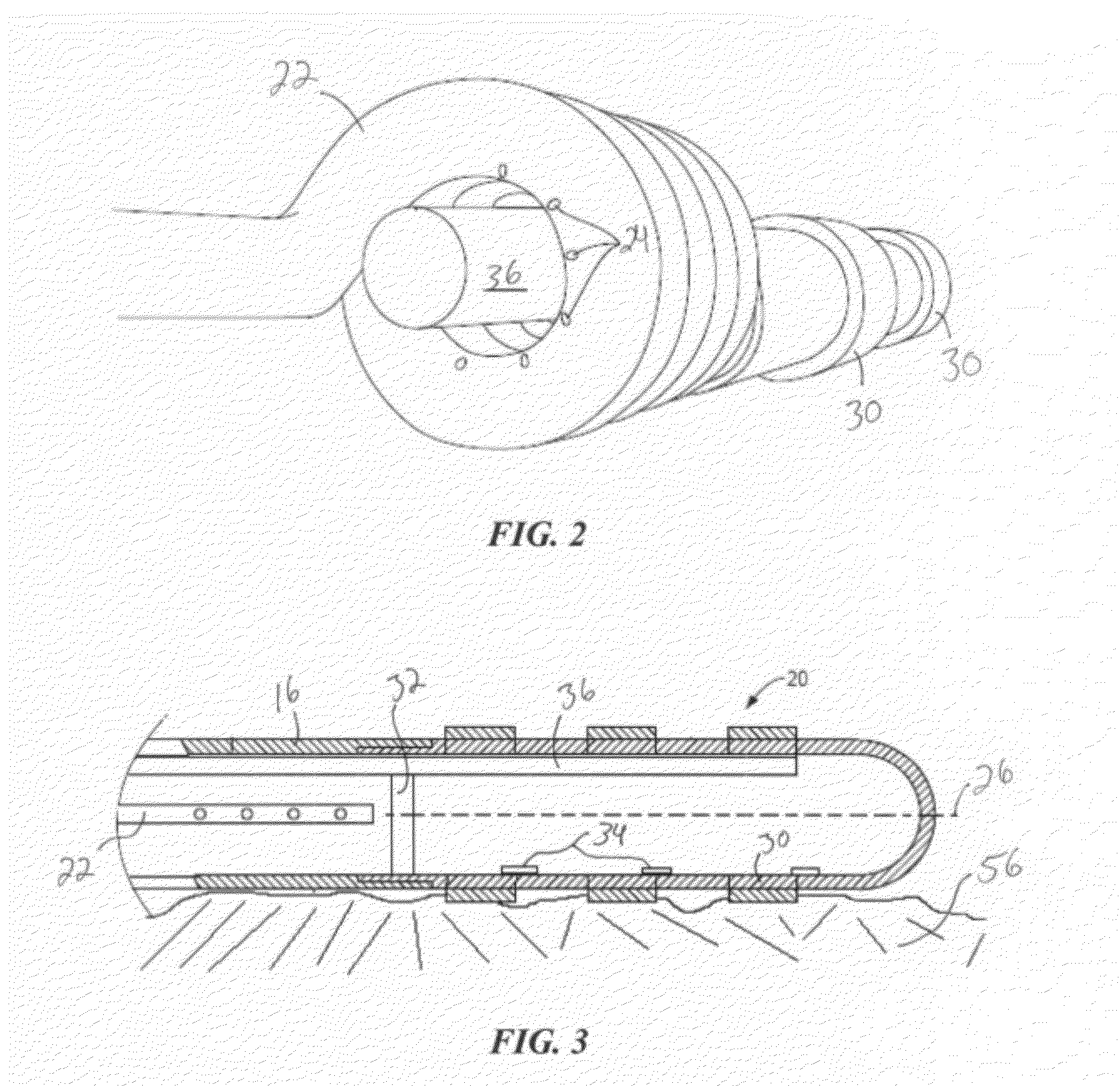
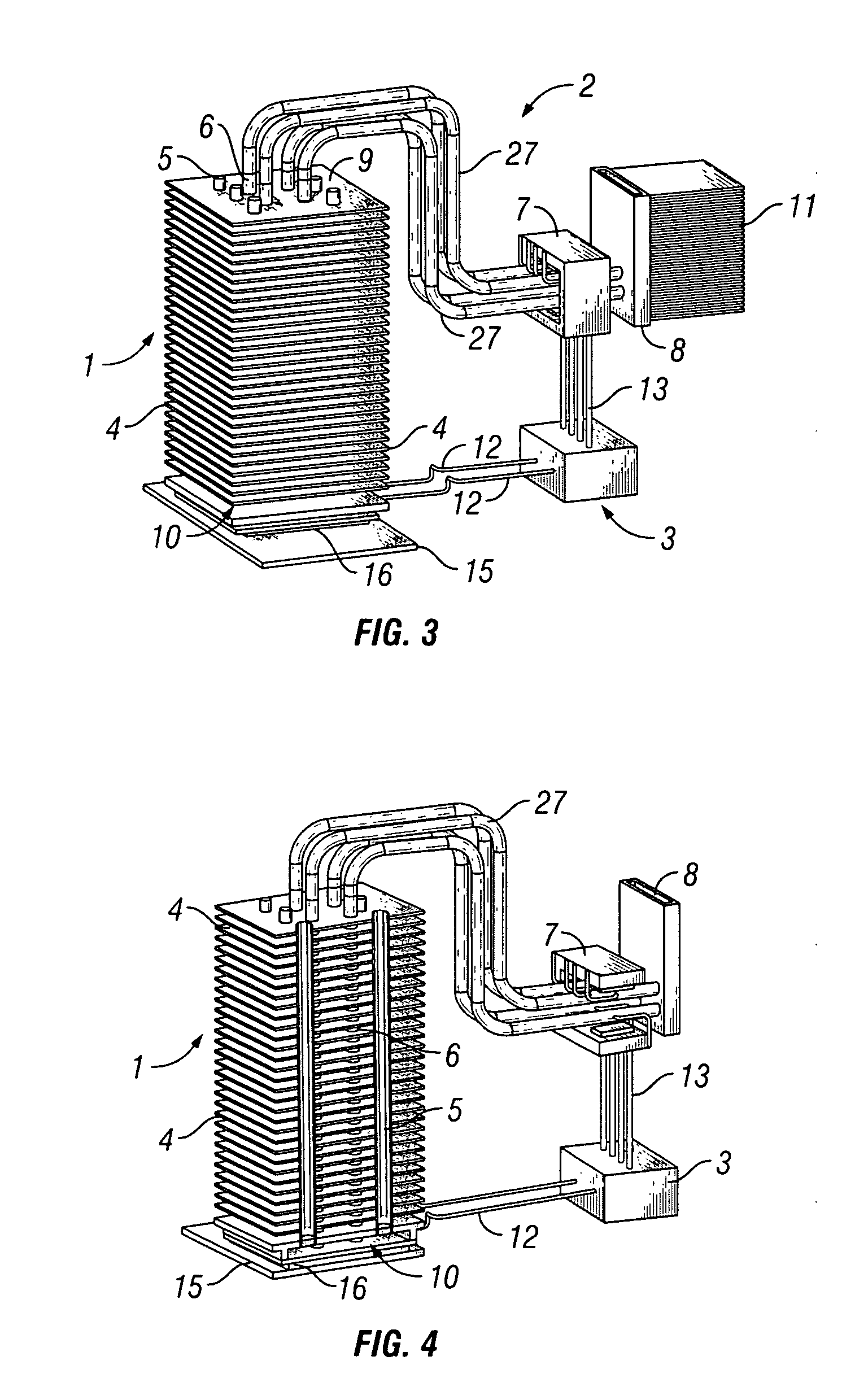
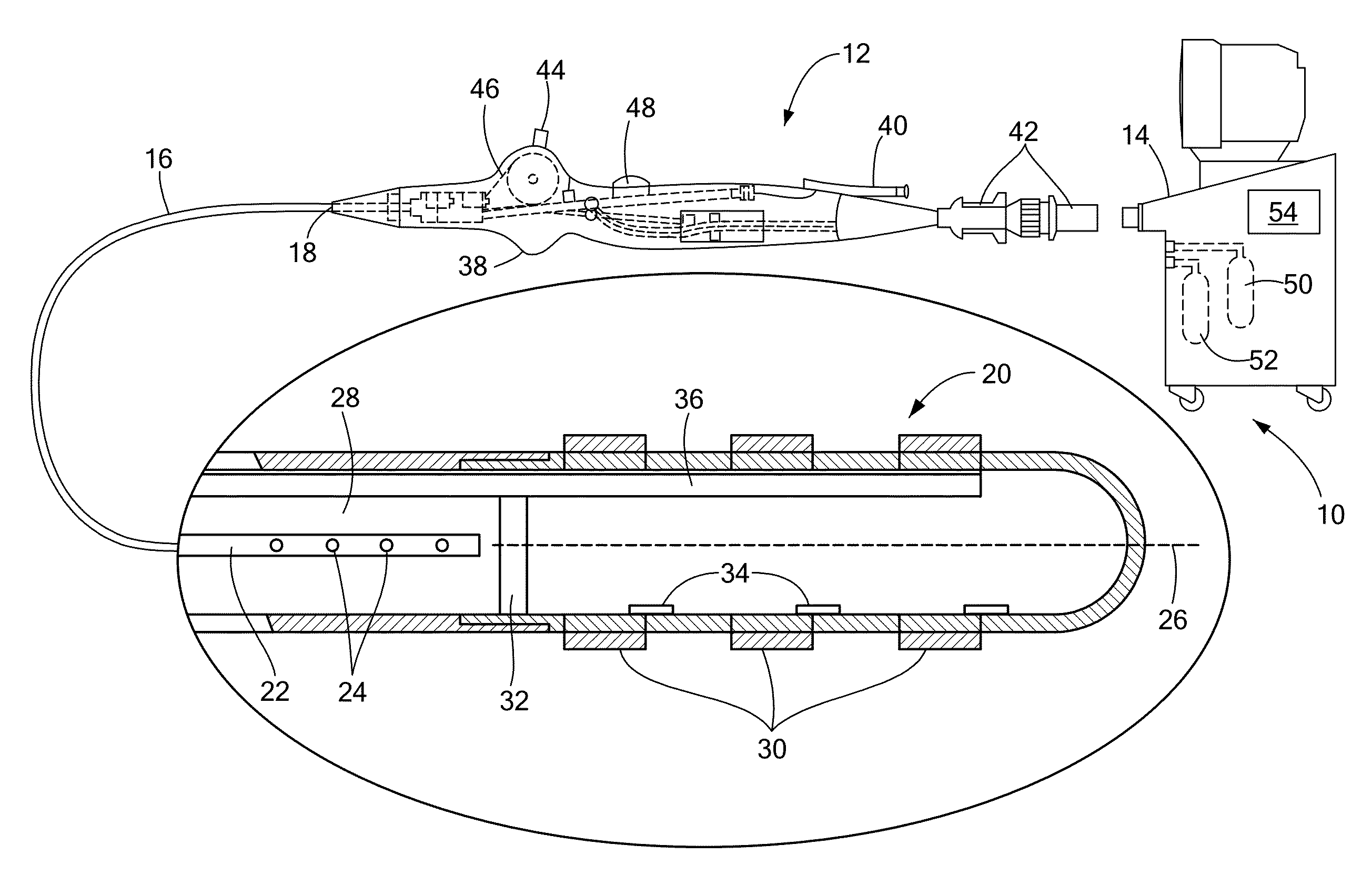
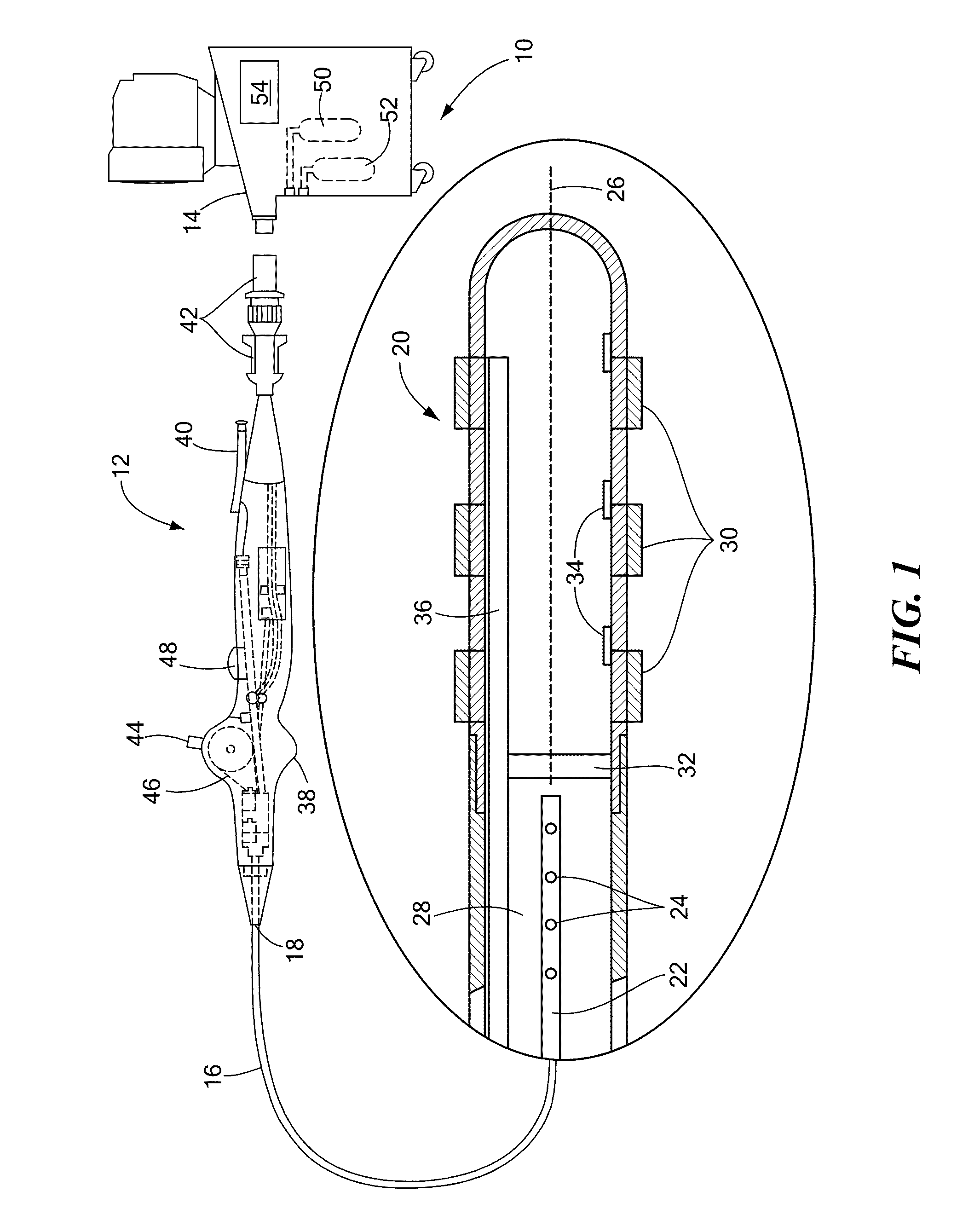
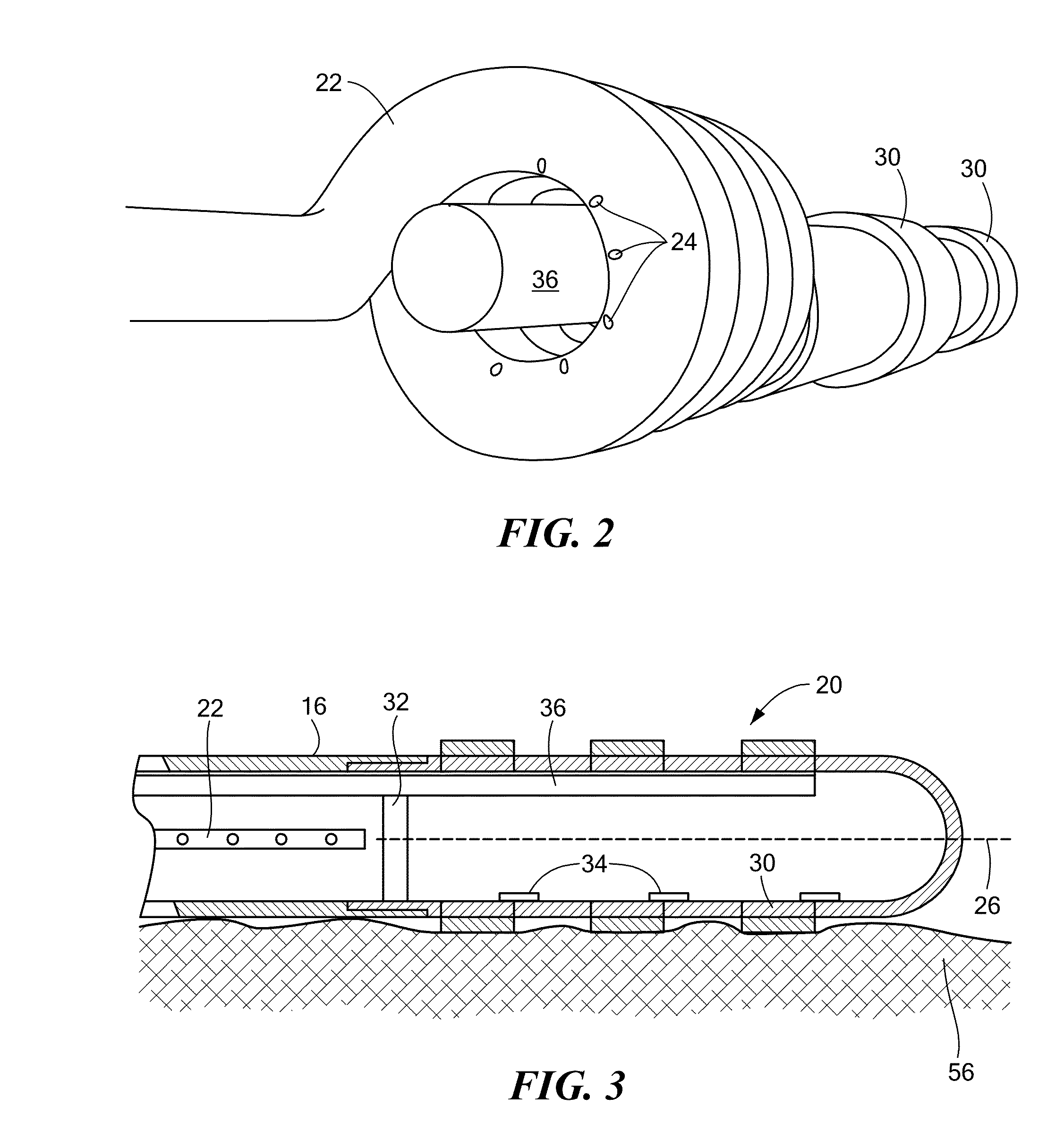
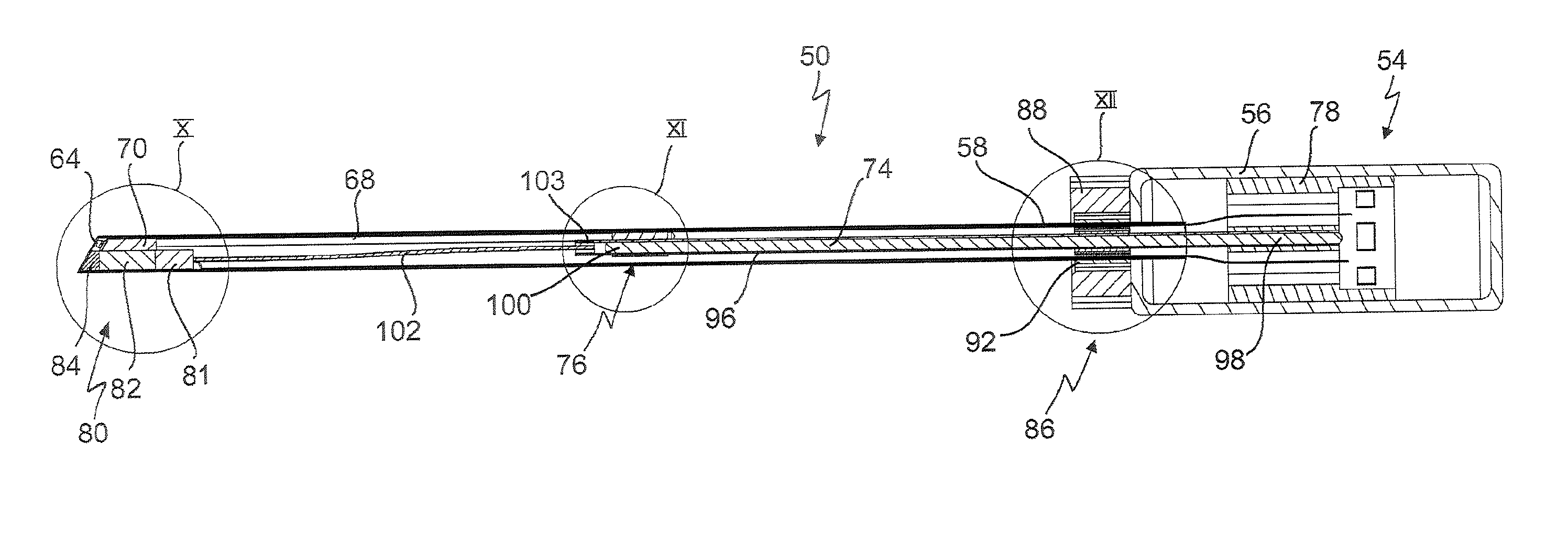
Independent passive cooling design for ablation catheters
ActiveUS20120239019A1Accurate measurementAccurate temperatureSurgical instruments for heatingDistal portionBiomedical engineering
Owner:MEDTRONIC ABLATION FRONTIERS
Secondary Fuel Delivery System
ActiveUS20090071159A1Reduce the impactAvoid heat dissipation difficultiesTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsContinuous combustion chamberCombustionEffusion
A secondary fuel delivery system for delivering a secondary stream of fuel and / or diluent to a secondary combustion zone located in the transition piece of a combustion engine, downstream of the engine primary combustion region is disclosed. The system includes a manifold formed integral to, and surrounding a portion of, the transition piece, a manifold inlet port, and a collection of injection nozzles. A flowsleeve augments fuel / diluent flow velocity and improves the system cooling effectiveness. Passive cooling elements, including effusion cooling holes located within the transition boundary and thermal-stress-dissipating gaps that resist thermal stress accumulation, provide supplemental heat dissipation in key areas. The system delivers a secondary fuel / diluent mixture to a secondary combustion zone located along the length of the transition piece, while reducing the impact of elevated vibration levels found within the transition piece and avoiding the heat dissipation difficulties often associated with traditional vibration reduction methods.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Intelligent cooling method combining passive and active cooling components
ActiveUS20080036076A1Temperatue controlSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsTemperature controlActive cooling
A method for cooling a semiconductor including passive cooling including transferring heat via passive cooling components; active cooling including transferring heat via active cooling components; and controlling the active cooling based on temperature of the semiconductor. A cooling system for a semiconductor including: a passive component in thermal contact with the semiconductor; an active cooling component in thermal contact with the semiconductor; and a controller controlling the active cooling component.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Independent passive cooling design for ablation catheters
ActiveUS8858548B2Accurate measurementAccurate temperatureSurgical instruments for heatingDistal portionCatheter
A medical system, including a catheter having a fluid flow path and a distal portion separated from the fluid flow path; a plurality of electrodes coupled to the distal portion; at least one temperature sensor coupled to the distal portion; a heat sink in thermal communication with each electrode and in fluid communication with the fluid flow path; a radiofrequency signal generator in communication with the plurality of electrodes; and a fluid source in fluid communication with the fluid flow path.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ABLATION FRONTIERS
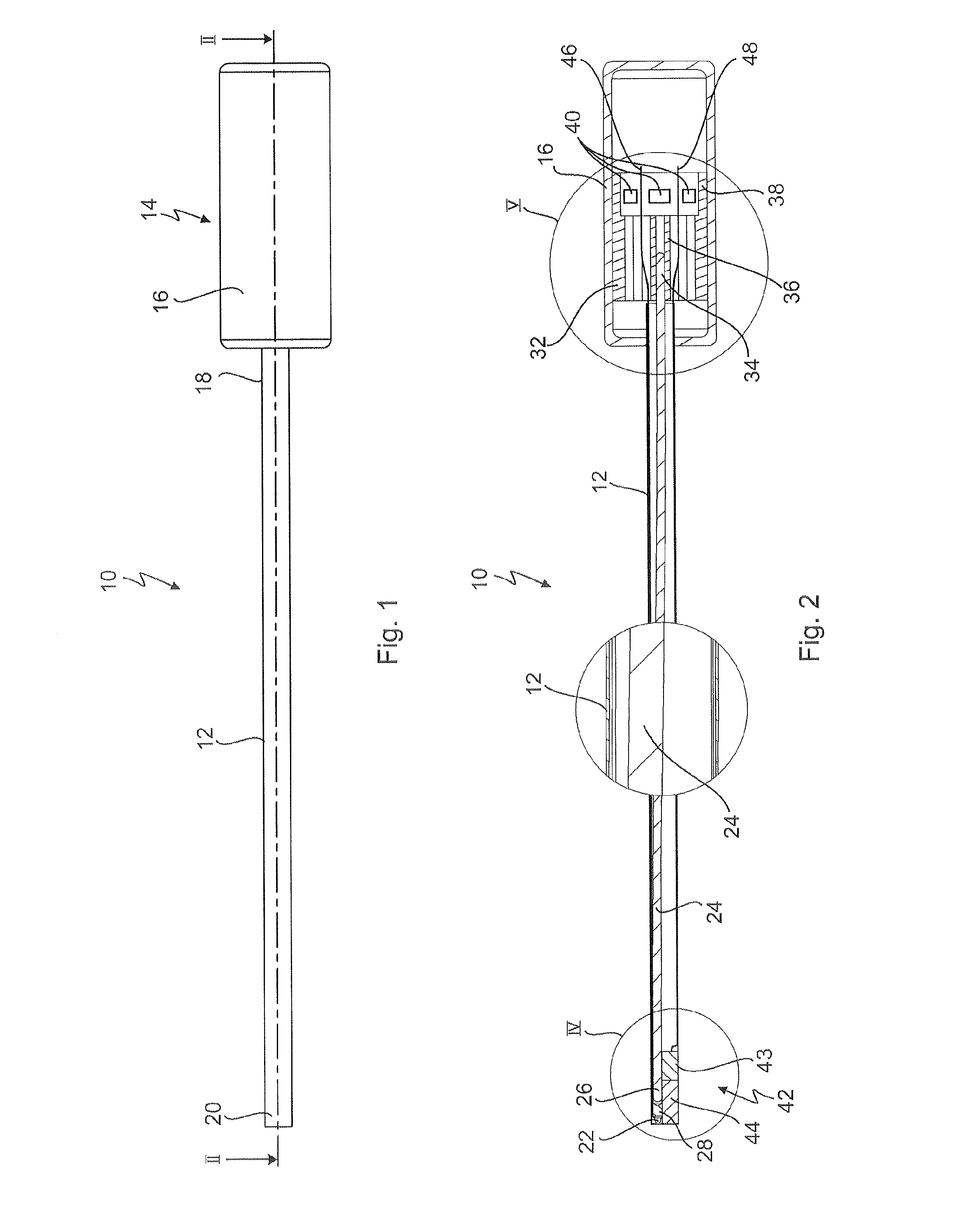
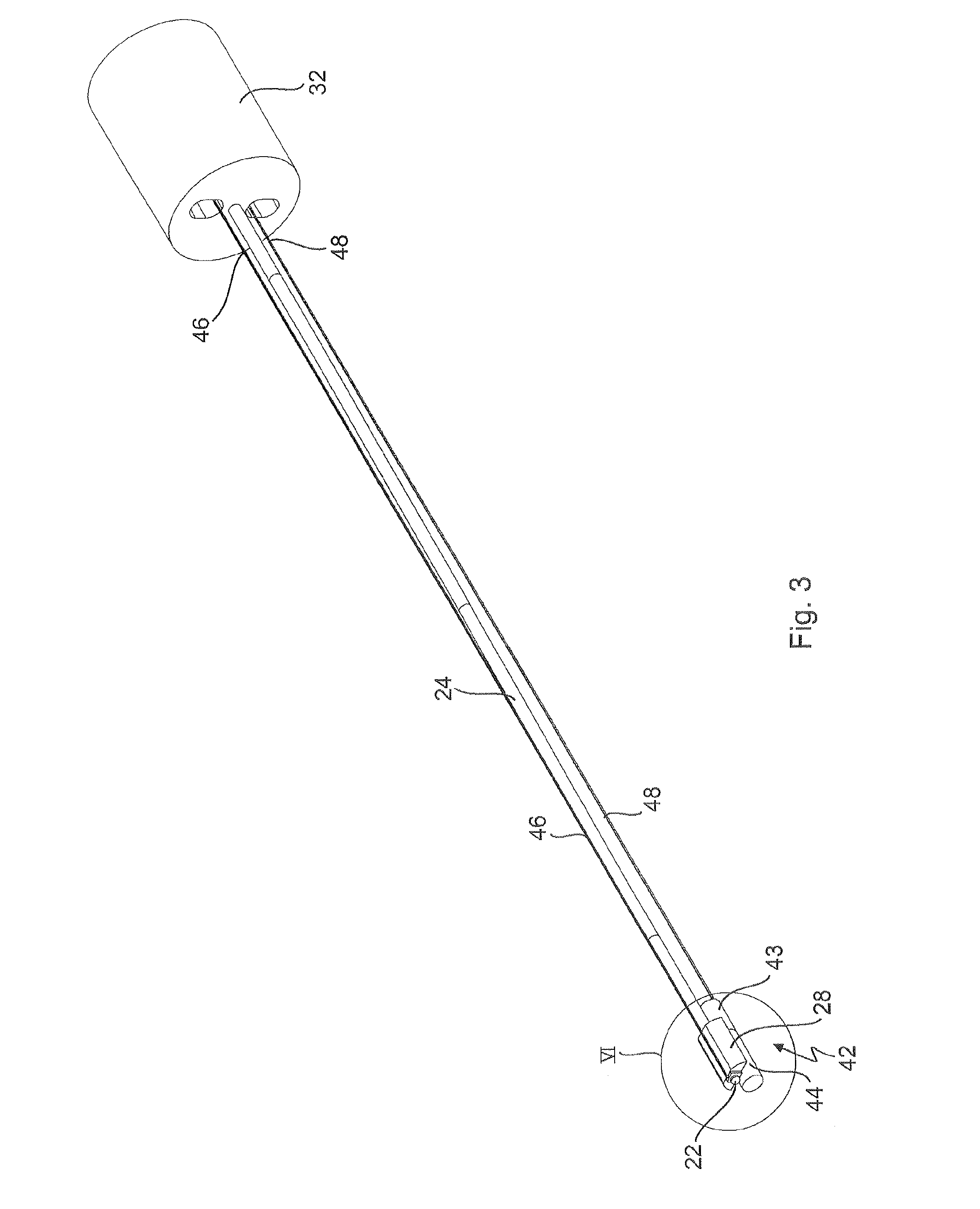
Endoscope
An endoscope comprises an elongated shaft, a headpiece at a proximal end of the shaft, the headpiece having a housing, at least one light source which is arranged in the shaft in a distal area thereof, and produces lost heat, and a passive cooling which has at least one heat pipe which is arranged in the shaft and is thermally coupled to the at least one light source in order to lead away the lost heat in the proximal direction. The at least one heat pipe extends into the headpiece, and a heat sink body is arranged in the headpiece, to which heat sink body the at least one heat pipe is thermally coupled, and which absorbs the lost heat from the at least one heat pipe and emits the lost heat to the environment directly or via the housing of the headpiece.
Owner:KARL STORZ GMBH & CO KG
Gas-discharge lamp replacement with passive cooling
An illumination device comprises a solid-state lighting device and a heat sink. The heat sink is configured to be attachable to a fixture for a gas-discharge lamp to retrofit existing gas-discharge fixtures. The heat sink is conductively thermally coupled to the solid-state lighting device to dissipate heat generated by the solid-state lighting device.
Owner:EXPRESS IMAGING SYST
Housing for a passively cooled computer
InactiveUS7095611B2Avoid large buildupNoise is generatedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPassive coolingPetroleum engineering
Owner:KONTRON
Multi-mode cooling garment
InactiveUS20090264969A1Longer lasting and more rapid cooling of a personReduce temperature differenceTherapeutic coolingTherapeutic heatingLiquid waterEvaporation
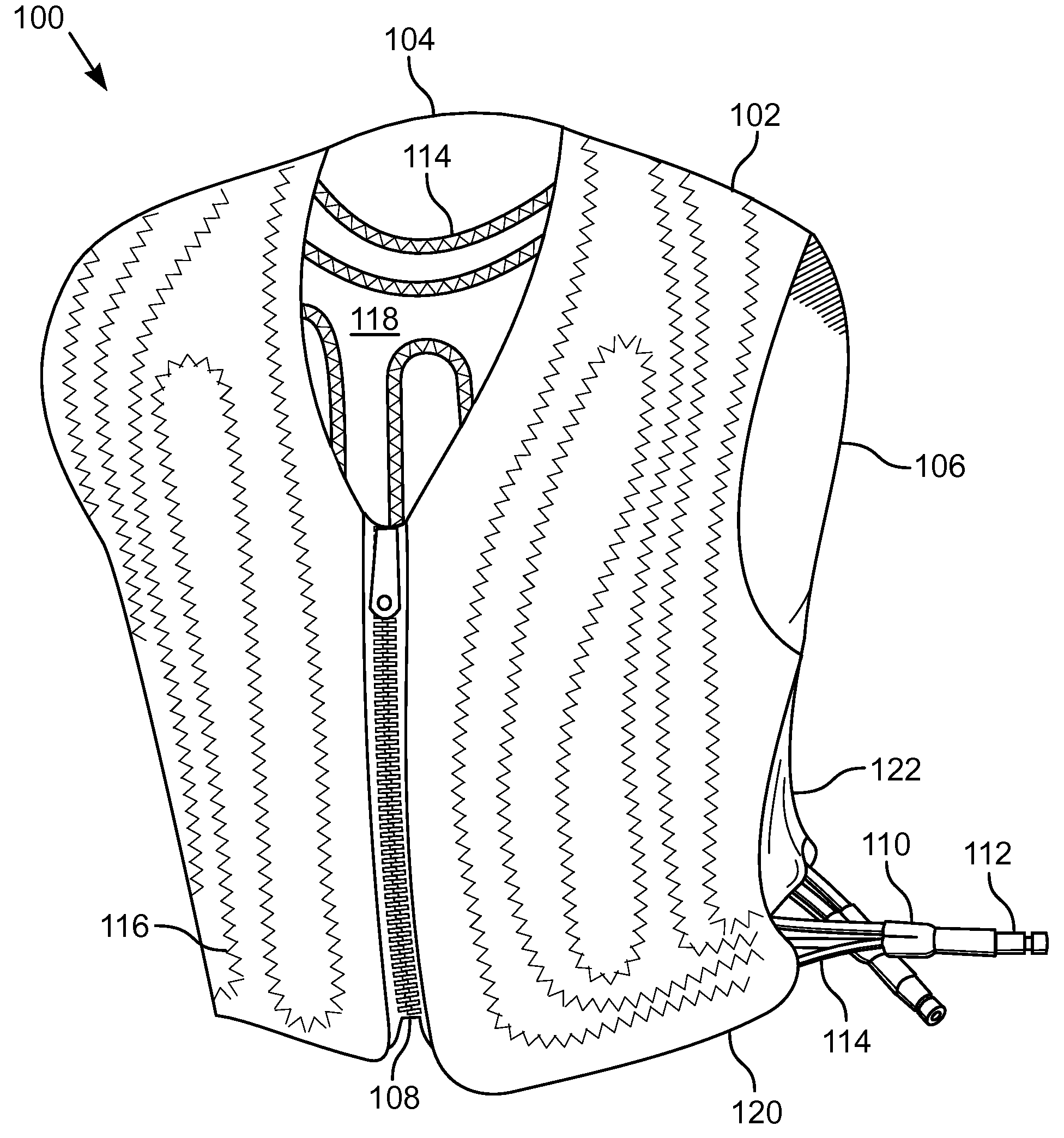
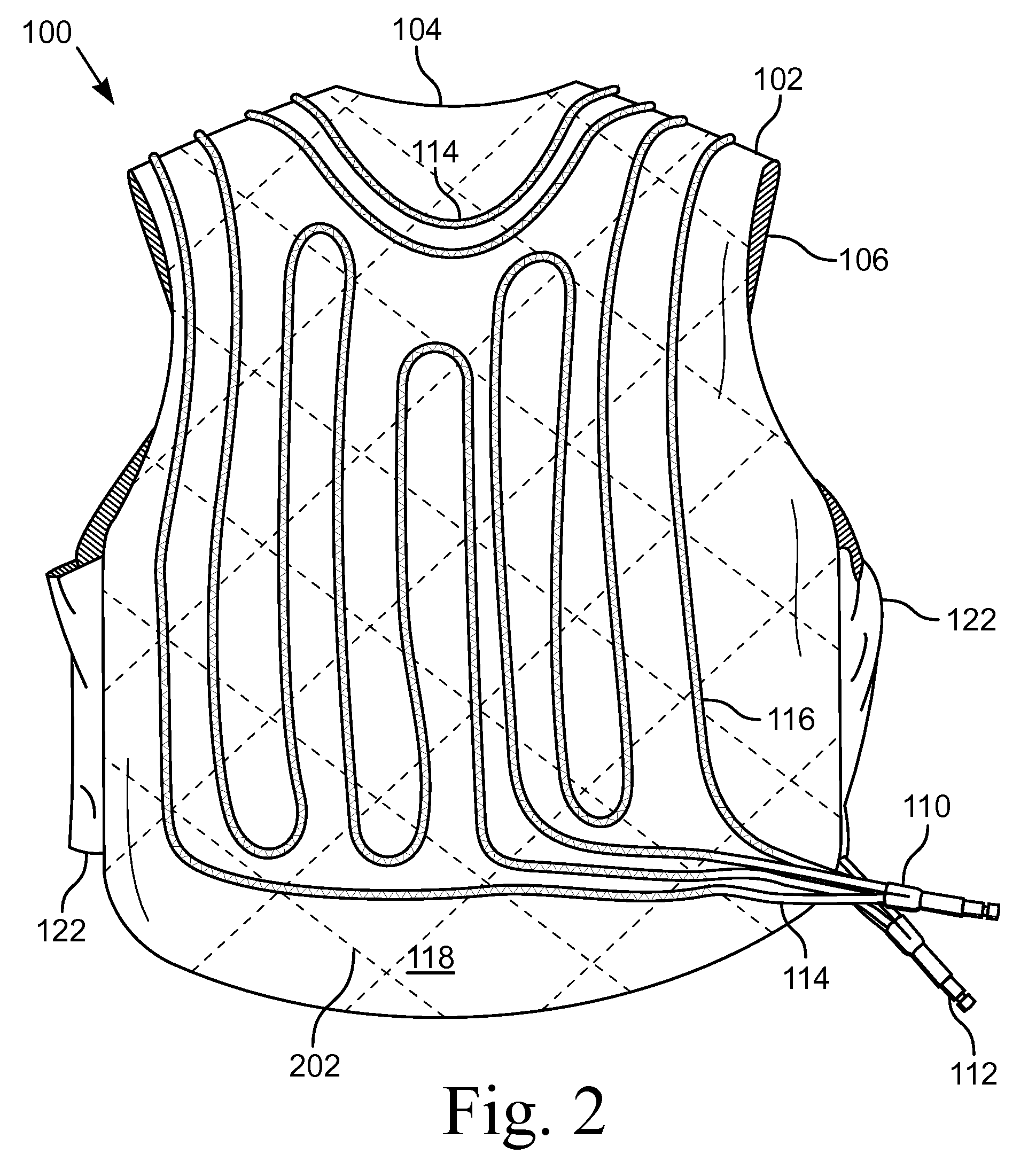
Apparatus for cooling a person in extreme environments. The apparatus includes a garment having a vest with attached tubing. The vest includes an evaporative cooling device and the tubing is configured to circulate chilled water. The vest includes a material that is able to receive and absorb an amount of liquid water with a mass greater than the material. When liquid water is applied to the vest, the vest absorbs the water for later evaporation. The tubing enables the garment to have a lower differential temperature between the inside surface and the outside surface, thereby reducing the rate of evaporation, which enables the passive cooling to be operable for an extended period of time. When the heat load does not permit the differential temperature to be reduced, the tubing removes additional heat, thereby providing additional heat removing capacity beyond the passive cooling.
Owner:ADROIT MEDICAL SYST
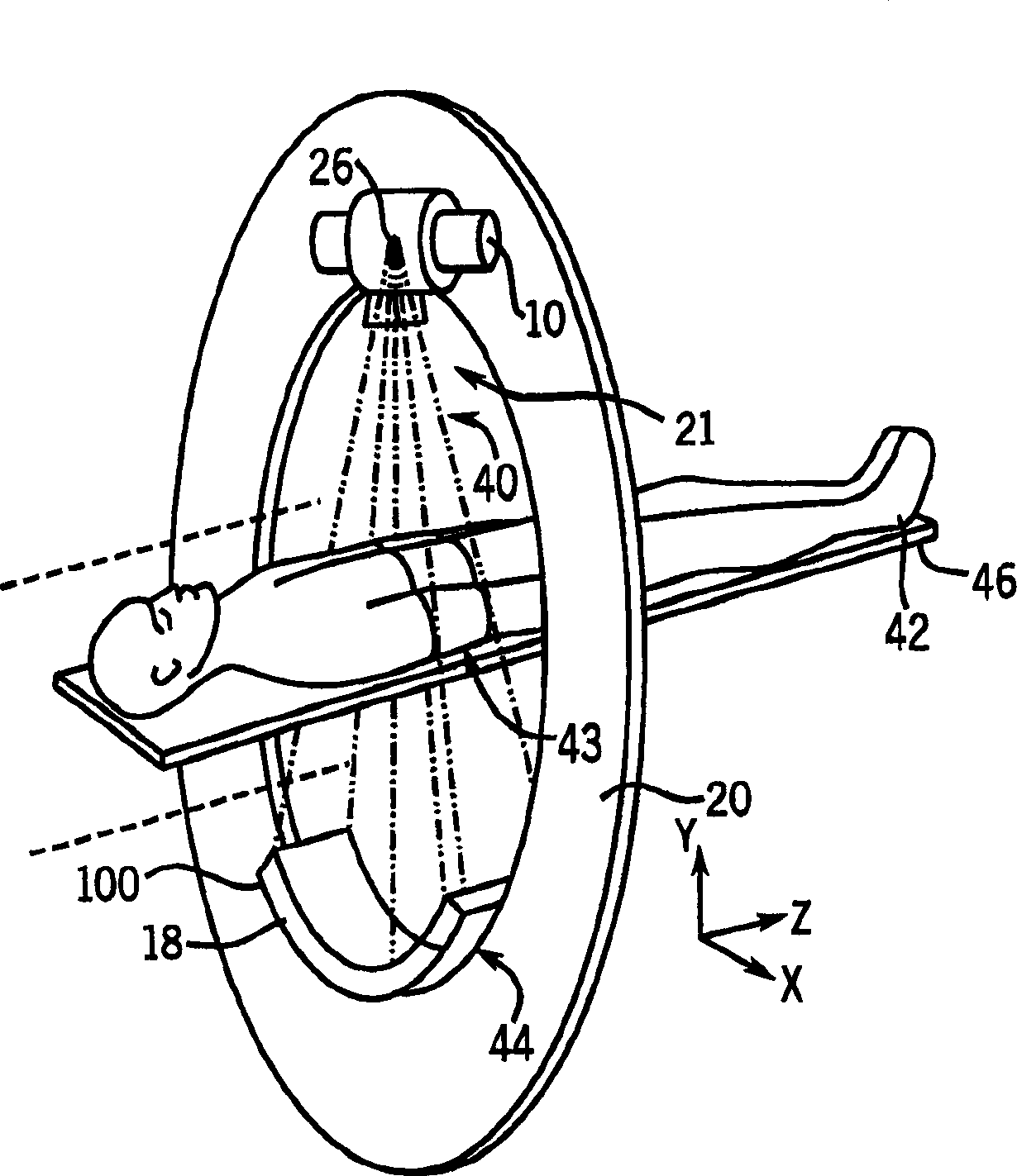
Thermoelectric controlled x-ray detector array
InactiveCN1475192ARadiation measurementComputerised tomographsThermoelectric coolingComputed tomography
Disclosed is an X-ray detector assembly for use in a computed tomography system. The X-ray detector assembly comprises an array of detector cells coupled between two rails. A thermoelectric cooler is coupled to an end of each of the rails, and is controlled to alternatively heat or cool the detector array to maintain the array in a substantially isothermal and thermally stable condition. The detector assembly preferably includes both passive and active cooling devices and insulation materials for controlling the temperature of the detector assembly. An electrical heater coupled at the center of the detector array can be used in conjunction with the TEC's to control the temperature profile of the detector array, and to minimize changes in the temperature gradients.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
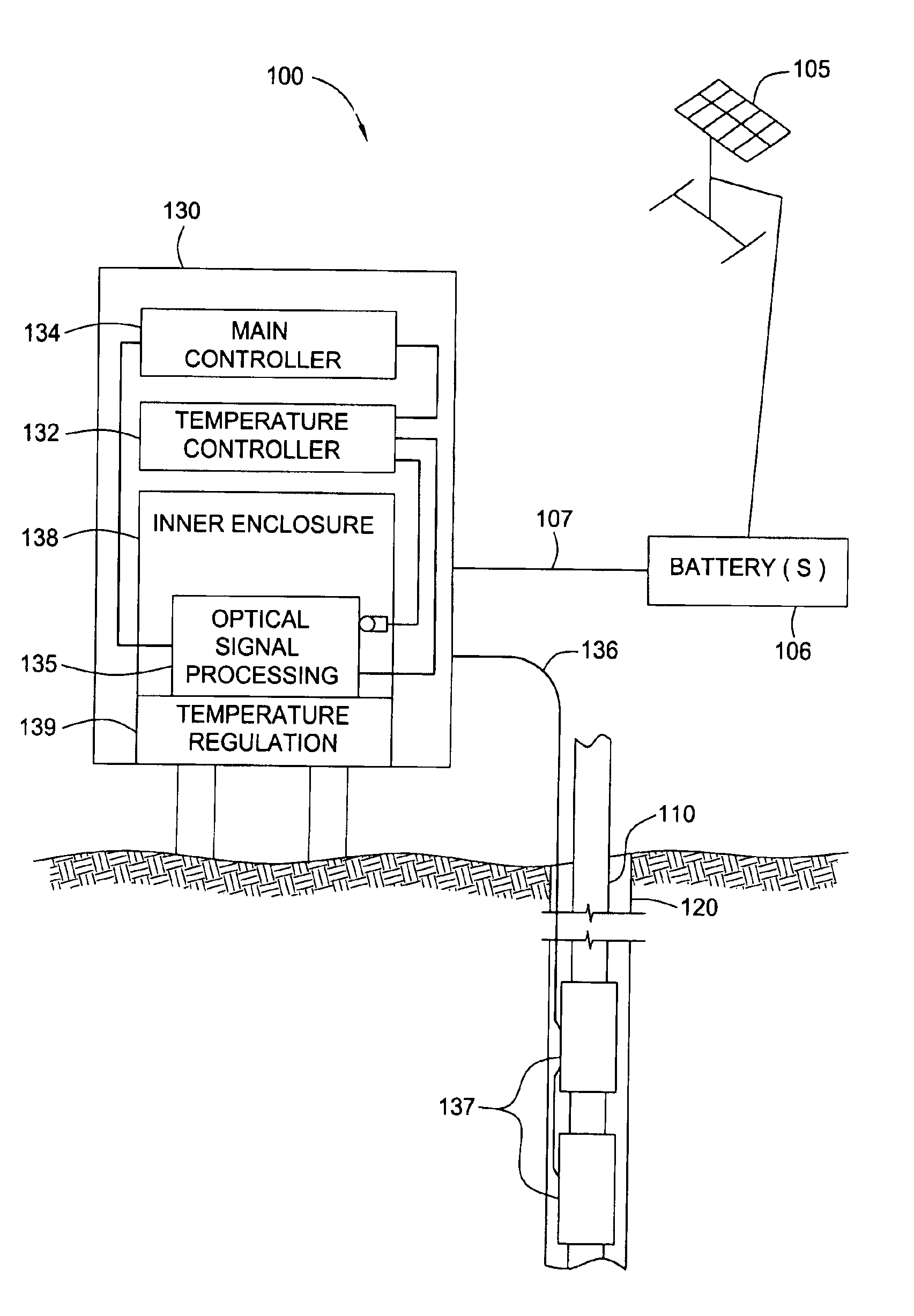
Reliable outdoor instrument cooling system
ActiveUS6951114B2Machines using electric/magnetic effectsTemperature control using electric meansThermoelectric coolingTemperature control
A method, system, and apparatus for controlling the temperature within a remotely located enclosure that contains temperature sensitive equipment is provided. For some embodiments, the system includes an array of thermoelectric cooling (TEC) devices that act as an active cooling device and an active heating device. The system may also include a temperature controller that receives signals from a temperature sensor located at or near the temperature sensitive equipment. The controller may be configured to supply DC power to the thermoelectric coupling devices based on the output signal of the temperature sensor. The polarity of the DC power can be reversed by the controller in order to cause the thermoelectric device to heat or to cool the enclosure. The system also contains a passive cooling device. The system includes an independent electrical power source with a battery and solar cell to supply power to the temperature control devices and the equipment contained in the enclosure.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Rechargeable battery pack with active or passive cooling
InactiveUS20180358664A1Battery isolationSecondary cells servicing/maintenanceActive coolingElectrical battery
A rechargeable battery pack having a housing, a plurality of cells located within the housing, a heat sink for dissipating heat from the plurality of cells, wherein the plurality of cells are encapsulated by the heat sink, and at least one elongated cooling channel to provide for active cooling, wherein the elongated cooling channel is within the housing and at least partially defined by the heat sink. A rechargeable battery pack having a housing, a plurality of cells located within the housing, wherein no single cell is completely surrounded by adjacent cells, a heat sink for dissipating heat from the plurality of cells, wherein the plurality of cells are encapsulated by the heat sink, and at least one elongated cooling channel to provide for active cooling, wherein the elongated cooling channel is located within the housing and is at least partially defined by the heat sink.
Owner:MTD PRODUCTS
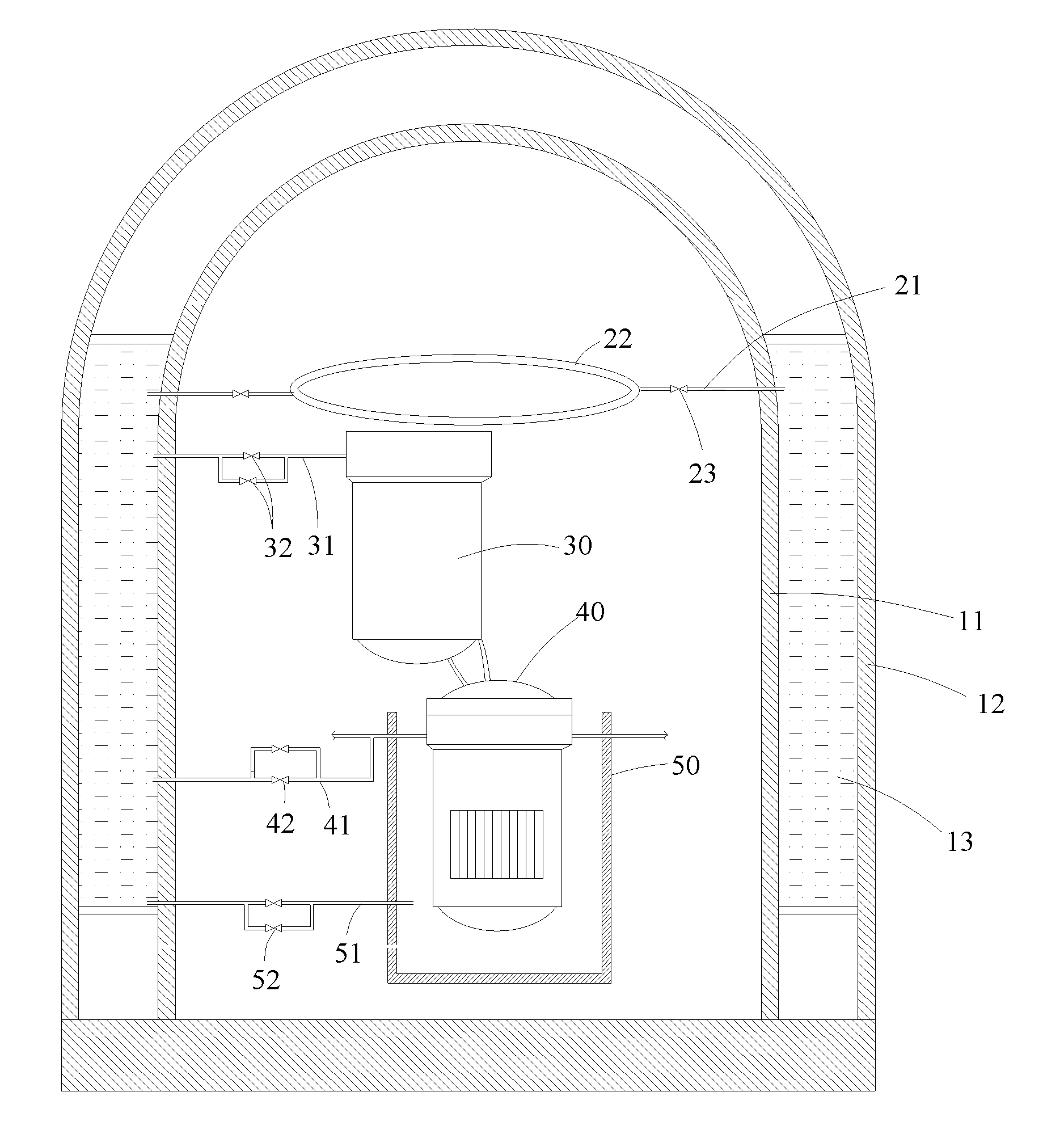
Reactor safety system
ActiveCN102194533AInhibition releaseAvoid coolingNuclear energy generationCooling arrangementNuclear powerReactor safety
The invention relates to a reactor safety system, which comprises a safety shell, a steam generator arranged in the safety shell, a reactor core, a reactor cavity and a cooling pipeline; the safety shell comprises an inner safety shell wall and an outer safety shell wall arranged at the periphery of the inner safety shell wall; an accommodating space is formed between the inner safety shell wall and the outer safety shell; and the accommodating space is filled with cooling liquid to form a passive cooling water tank; and the cooling pipeline is communicated with the accommodating space and injects the cooling liquid into the safety shell. The system can be used as a containment spraying system, and is used for injecting into the steam generator and the reactor core to carry away heat fromthe reactor core, and injecting into the reactor cavity to carry way heat outside a pressure vessel so as to prevent the pressure of the safety shell from rising, the reactor core from damage and thepressure vessel from out of work. Moreover, the system has the functions of preventing radioactive release and cooling the safety shell, so that the reliability and the safety of a nuclear power station are greatly improved.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER TECH RES INST CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com