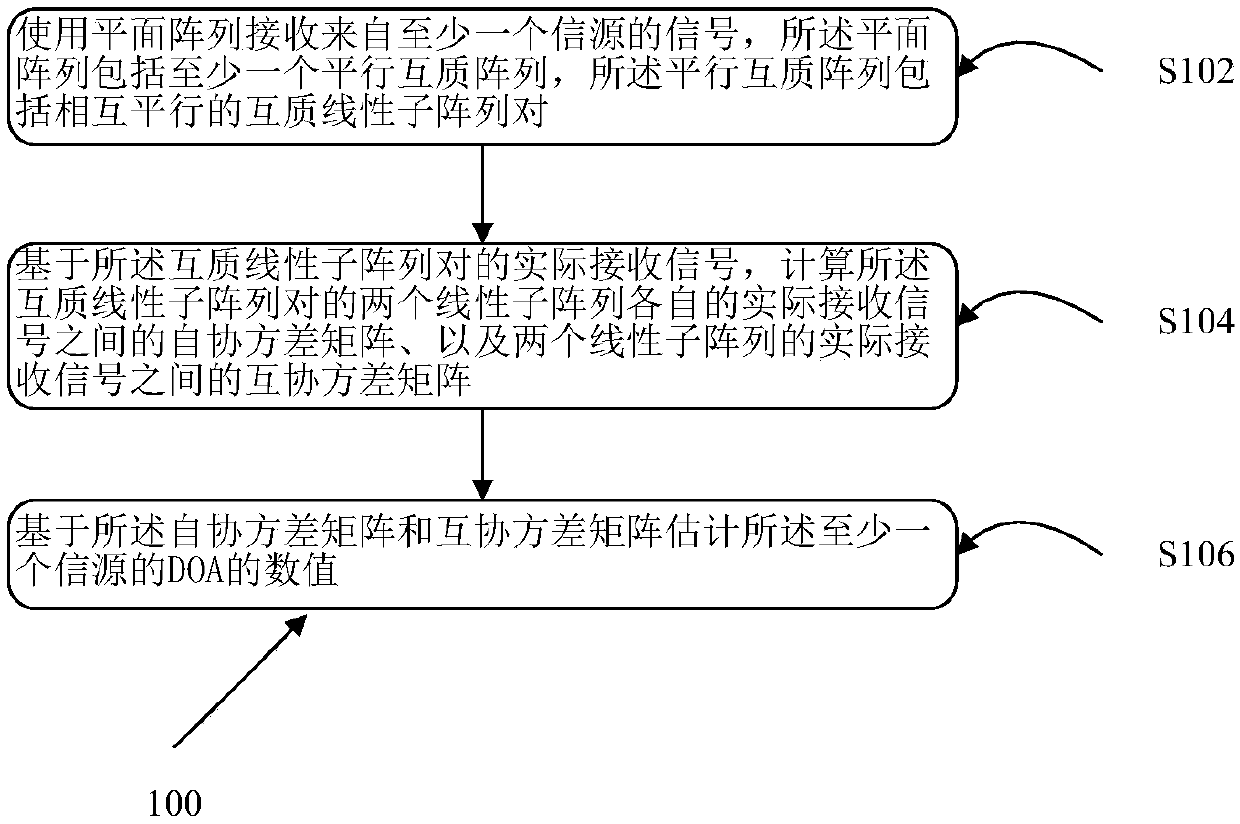
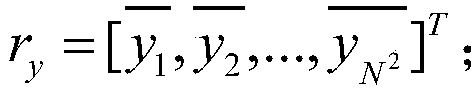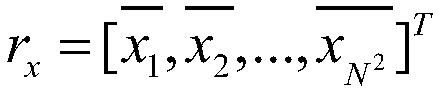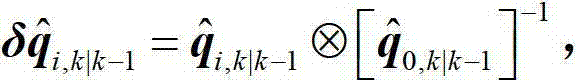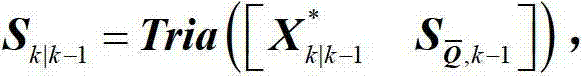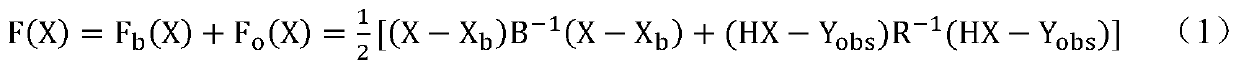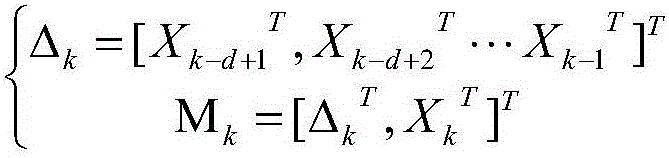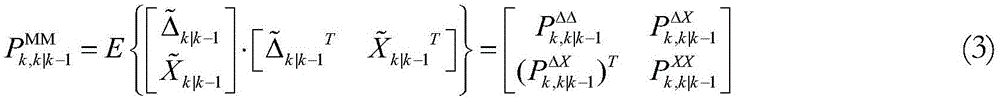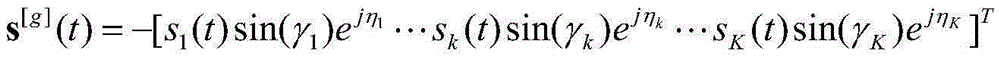Patents
Literature
125 results about "Cross-covariance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In probability and statistics, given two stochastic processes {Xₜ} and {Yₜ}, the cross-covariance is a function that gives the covariance of one process with the other at pairs of time points. With the usual notation E; for the expectation operator, if the processes have the mean functions μX(t)=E[Xₜ] and μY(t)=E[Yₜ], then the cross-covariance is given by KXY(t₁,t₂)=cov(Xₜ₁,Yₜ₂)=E[(Xₜ₁-μX(t₁))(Yₜ₂-μY(t₂))]=E[Xₜ₁Yₜ₂]-μX(t₁)μY(t₂).
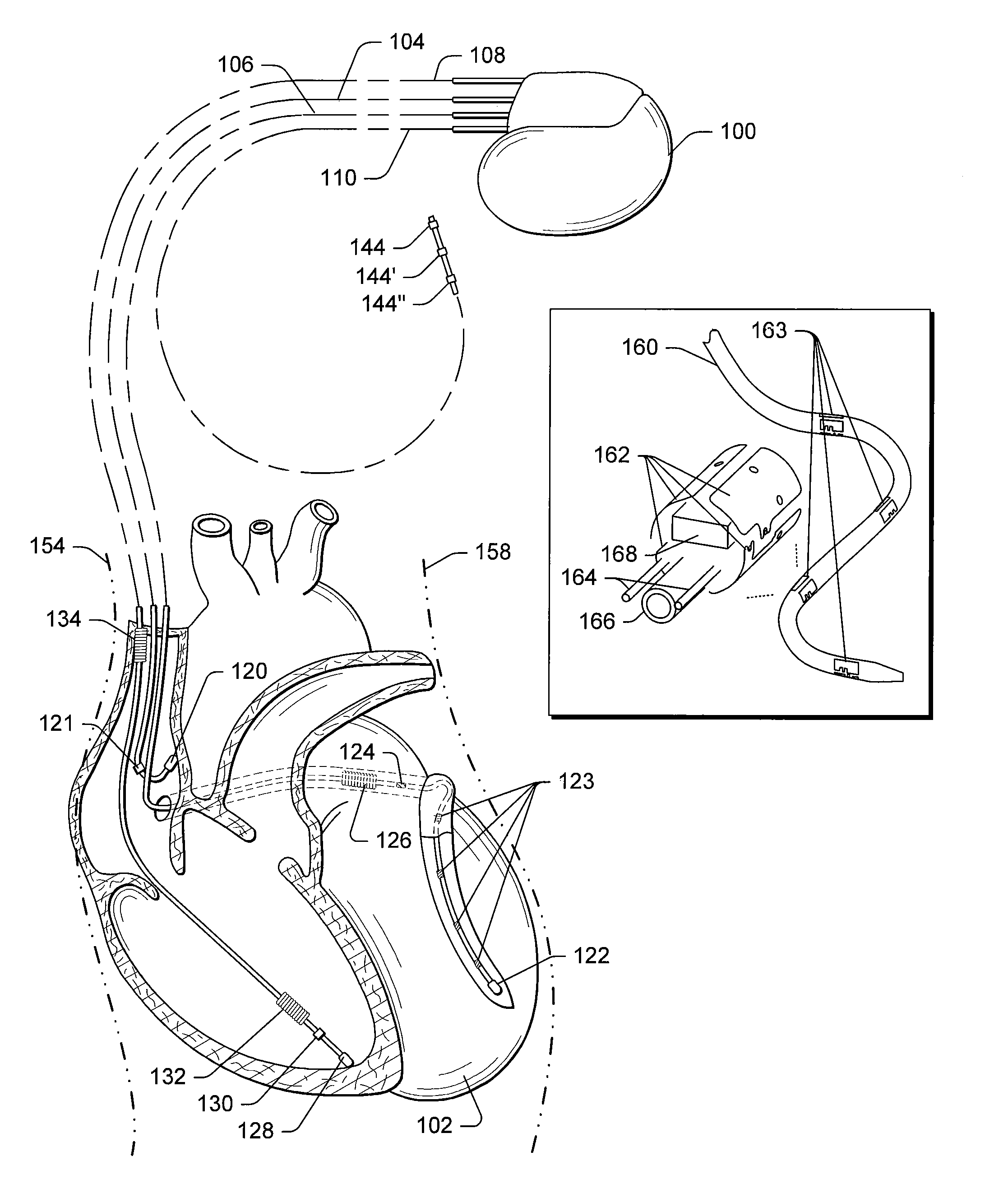
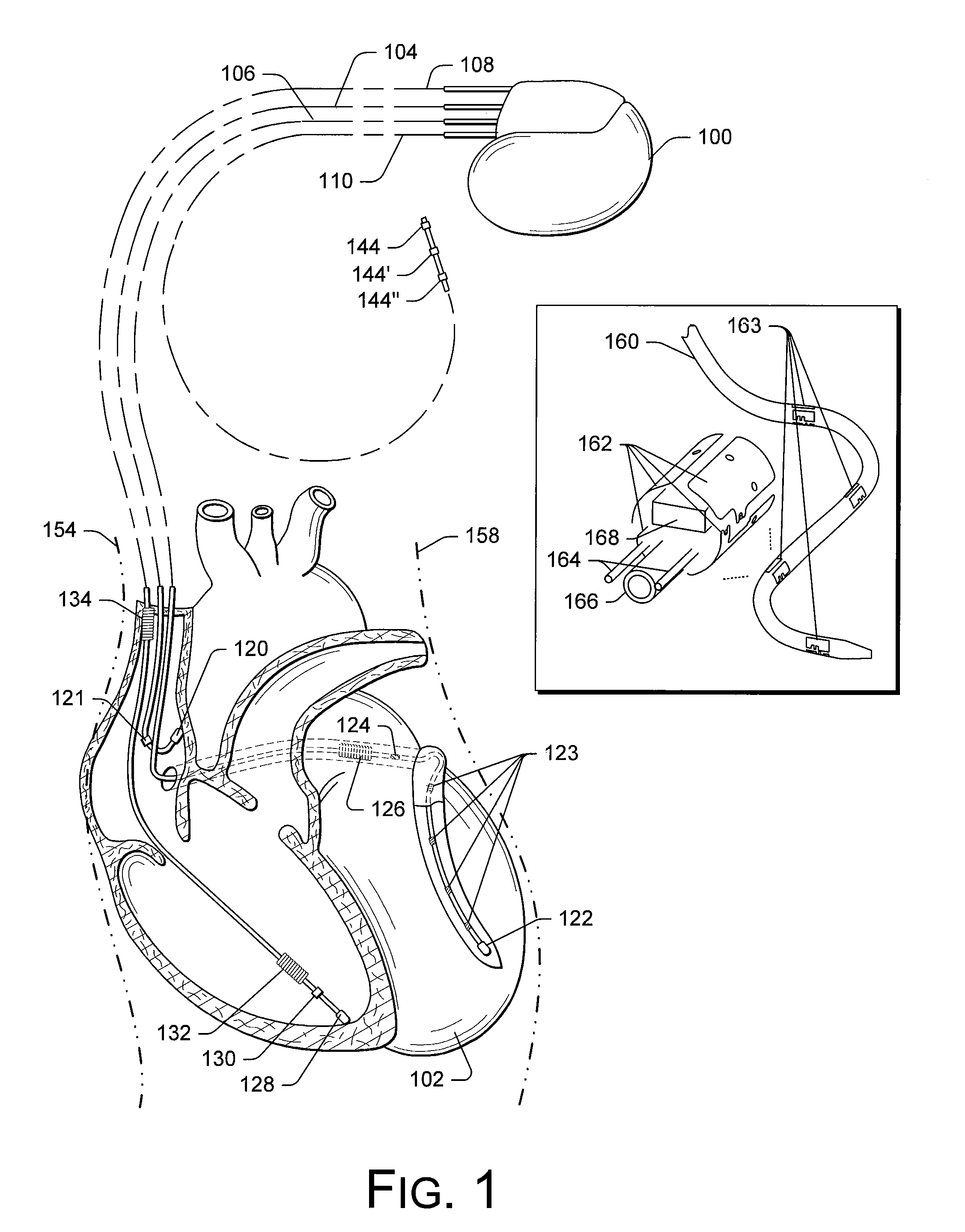
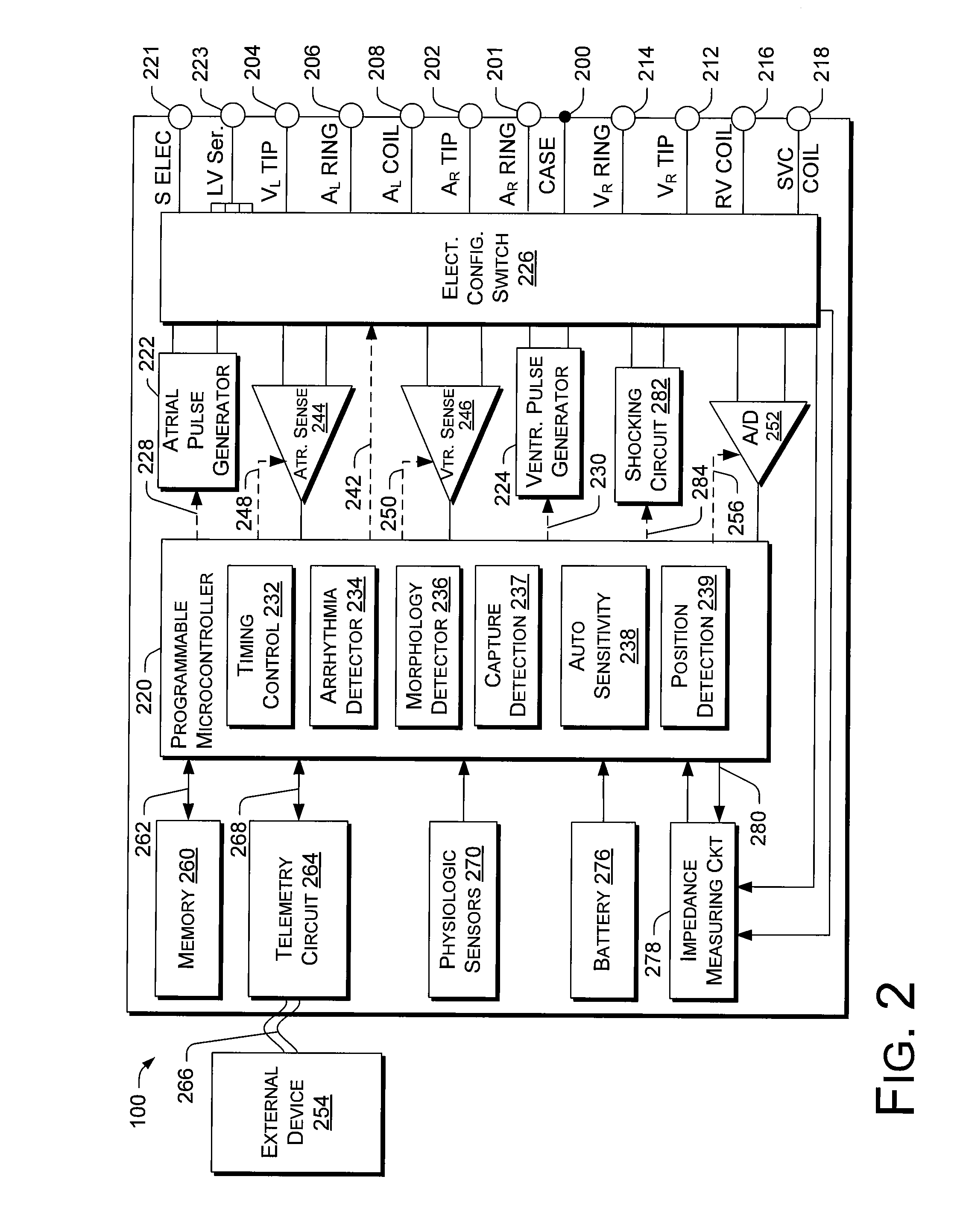
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Optimization Using Vector Measurements Obtained From Realtime Electrode Position Tracking
An exemplary method includes selecting a first pair of electrodes to define a first vector and selecting a second pair of electrodes to define a second vector; acquiring position information during one or more cardiac cycles for the first and second pairs of electrodes wherein the acquiring comprises using each of the electrodes for measuring one or more electrical potentials in an electrical localization field established in the patient; and determining a dyssynchrony index by applying a cross-covariance technique to the position information for the first and the second vectors. Another method includes determining a phase shift based on the acquired position information for the first and the second vectors; and determining an interventricular delay based at least in part on the phase shift.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
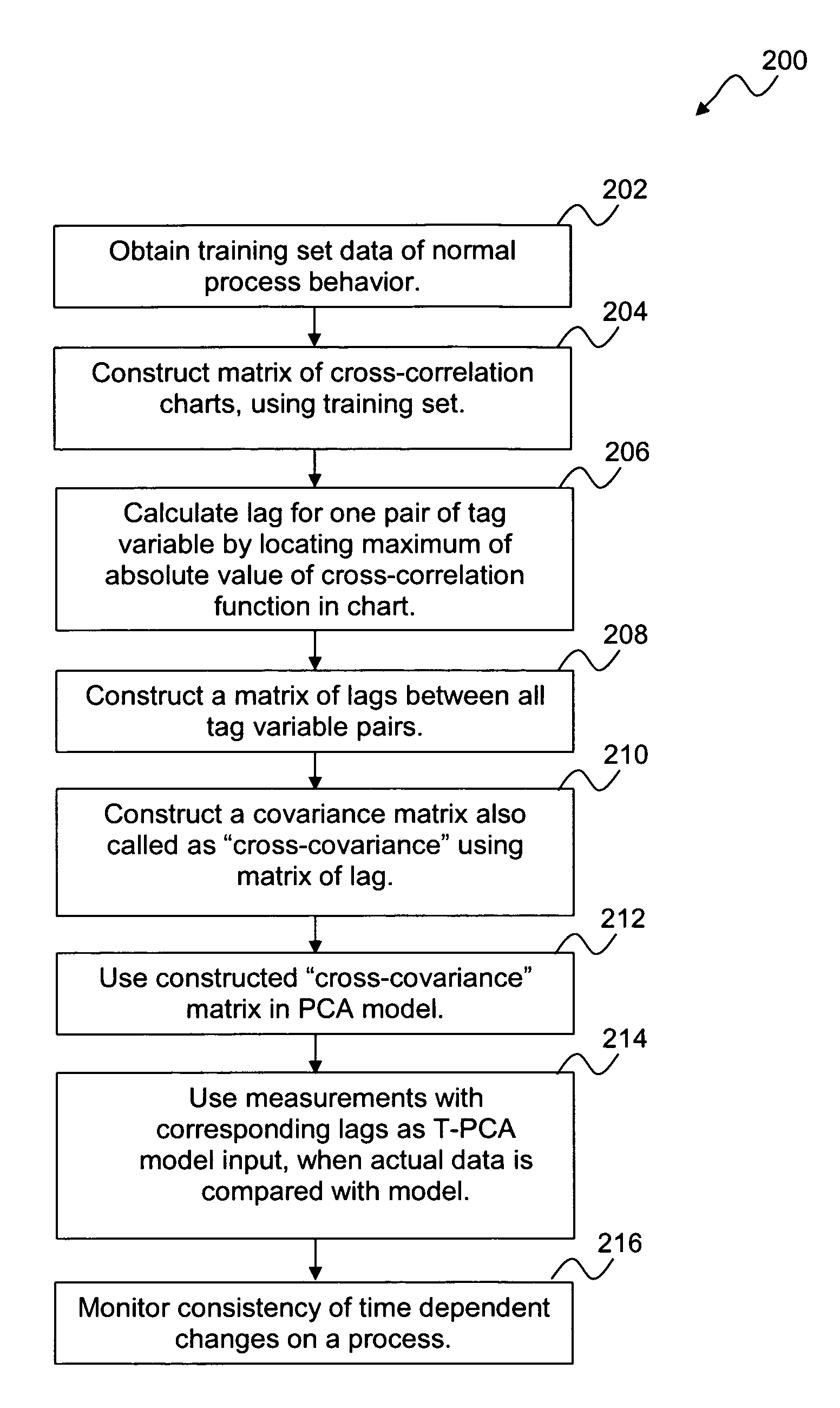
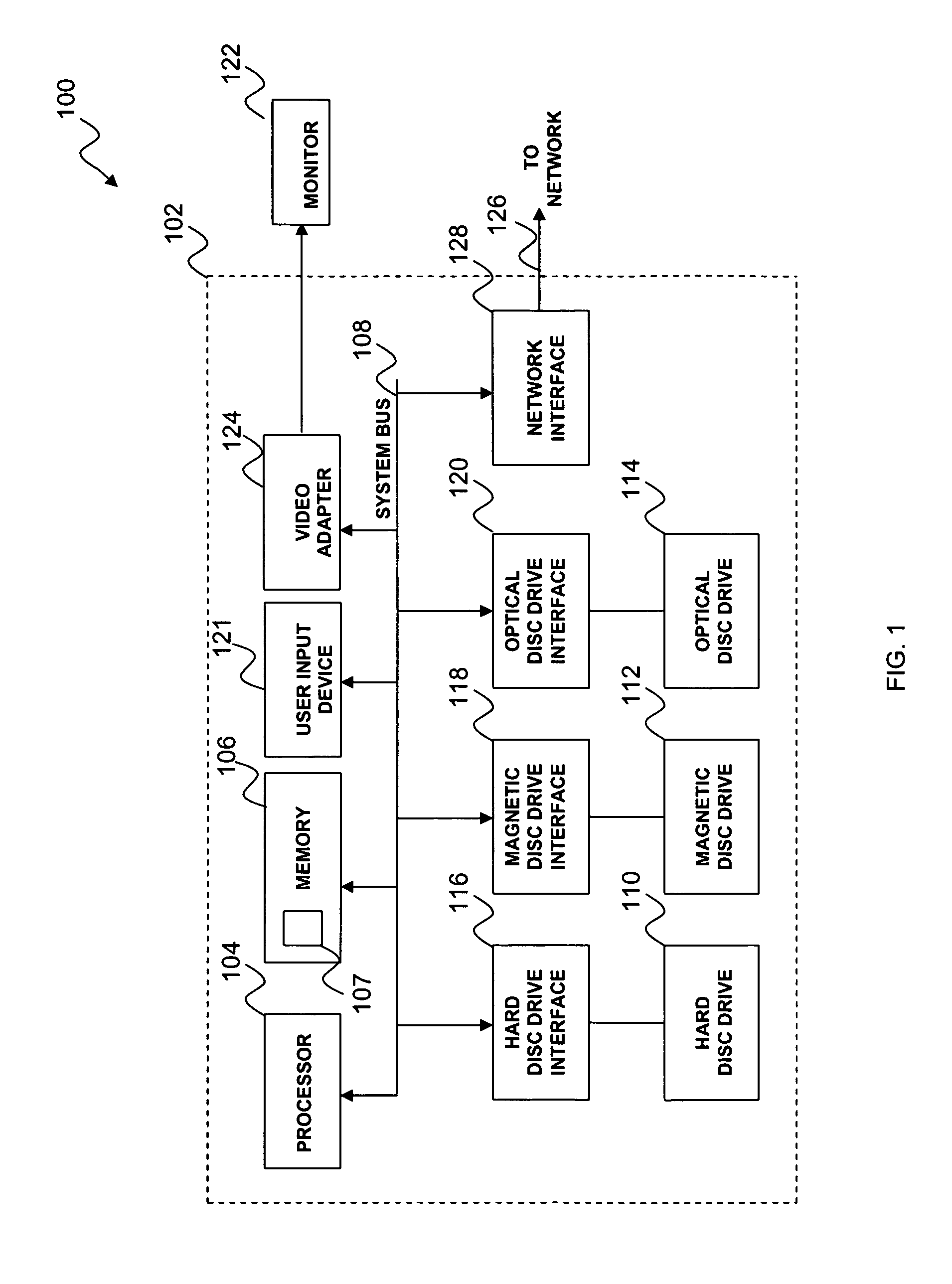
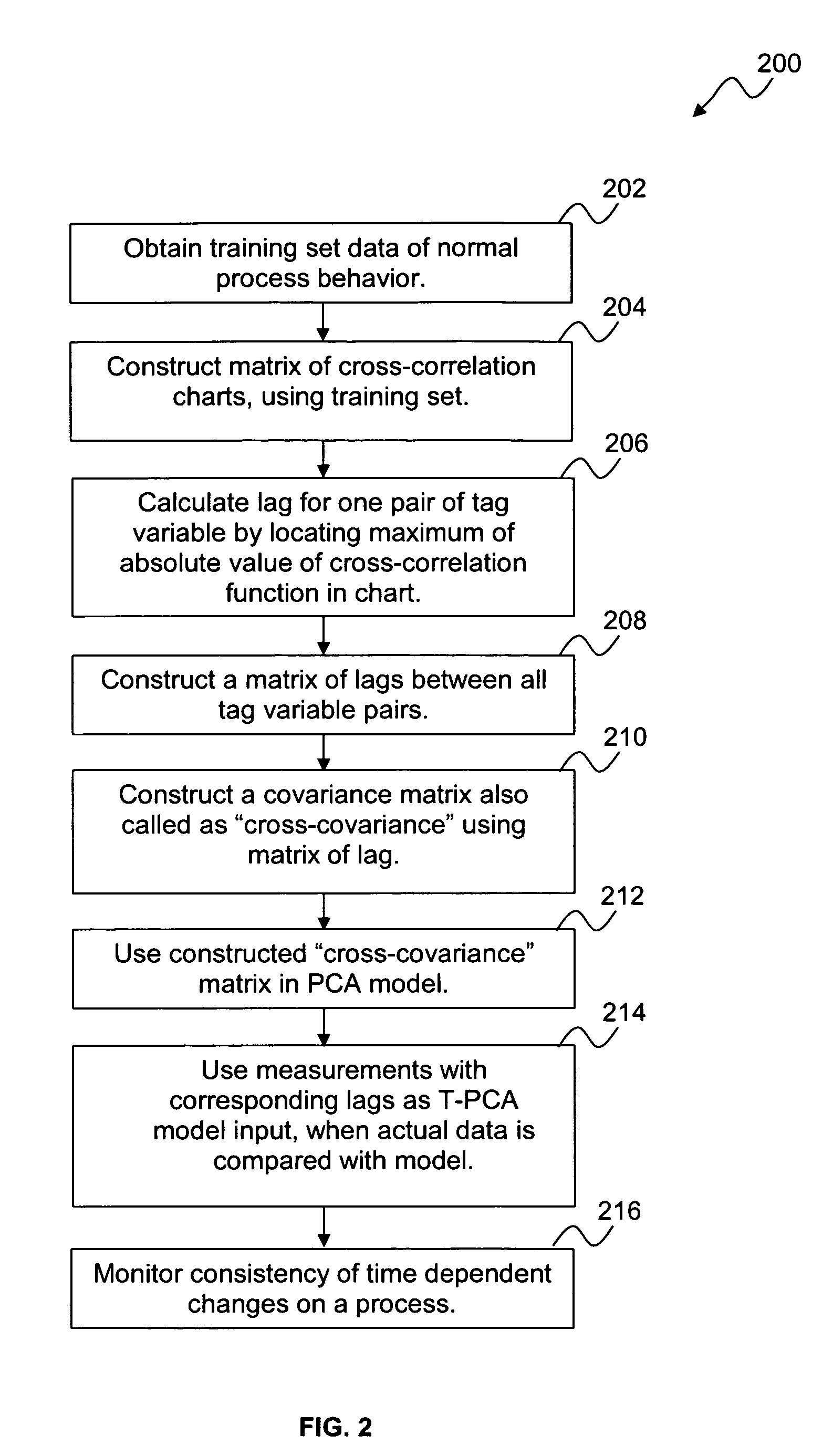
Monitoring and fault detection in dynamic systems
ActiveUS7421351B2Easily implemented/re-turnedAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceTesting/monitoring control systemsPrincipal component analysisData mining
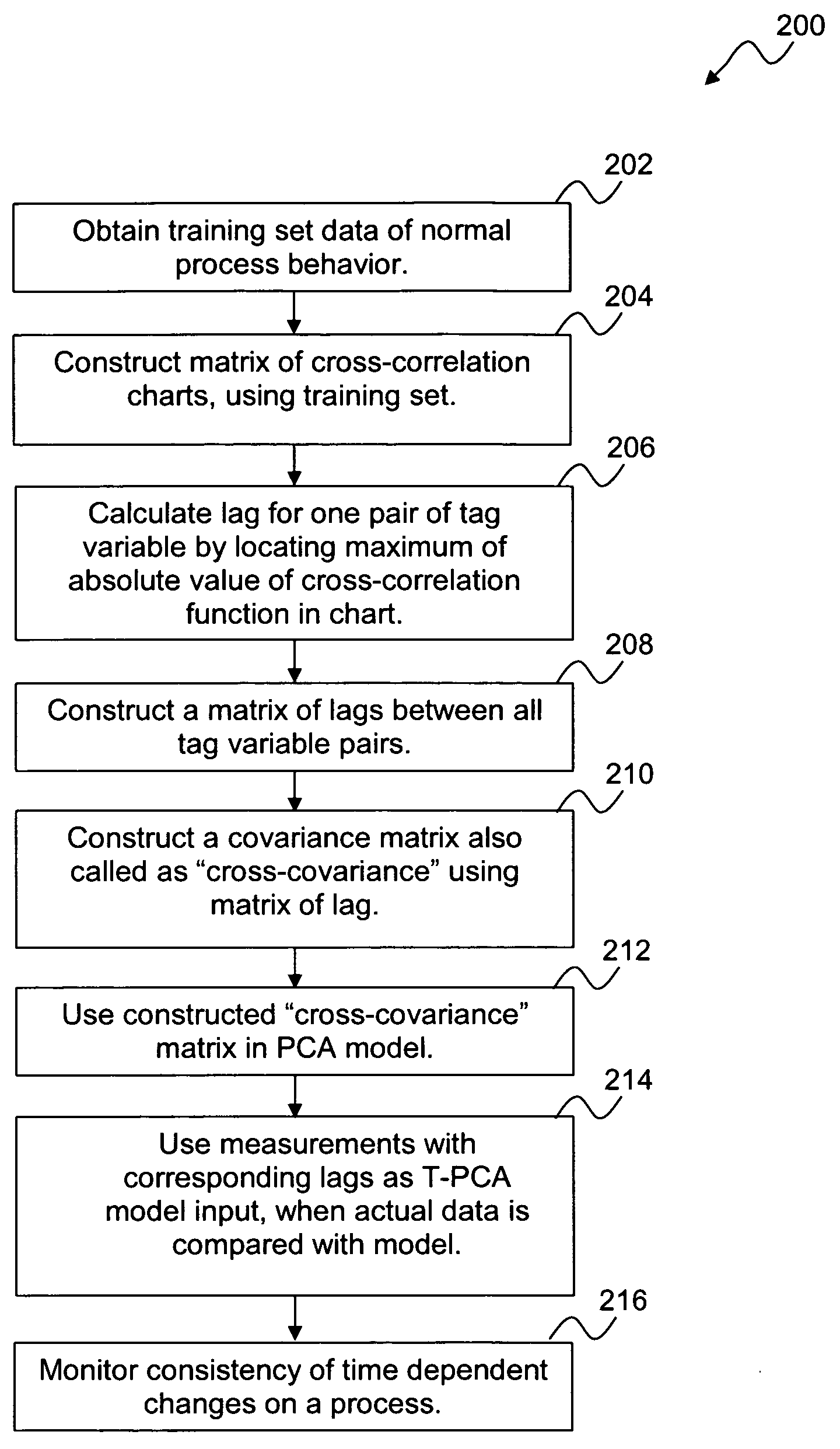
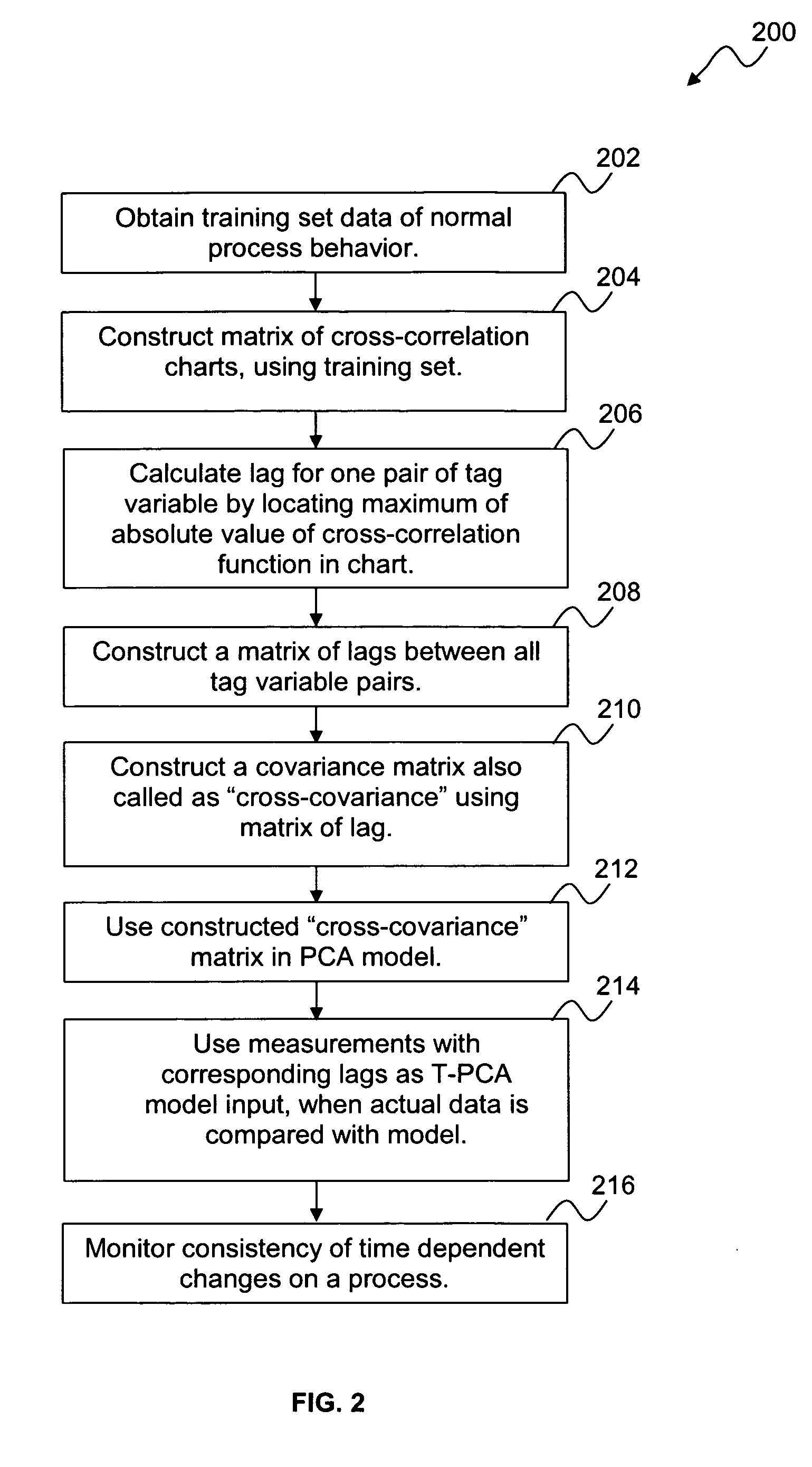
A system and method for monitoring and fault detection in dynamic systems. A “cross-covariance” matrix is used to construct and implement a principle component analysis (PCA) model and / or partial least squares (PLS) model. This system is further utilized for monitoring and detecting faults in a dynamic system. Time series information is synchronized, with respect to a set of training data. Based on historical data, consistency of correlations between variables can be checked with respect to a given time stamp.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
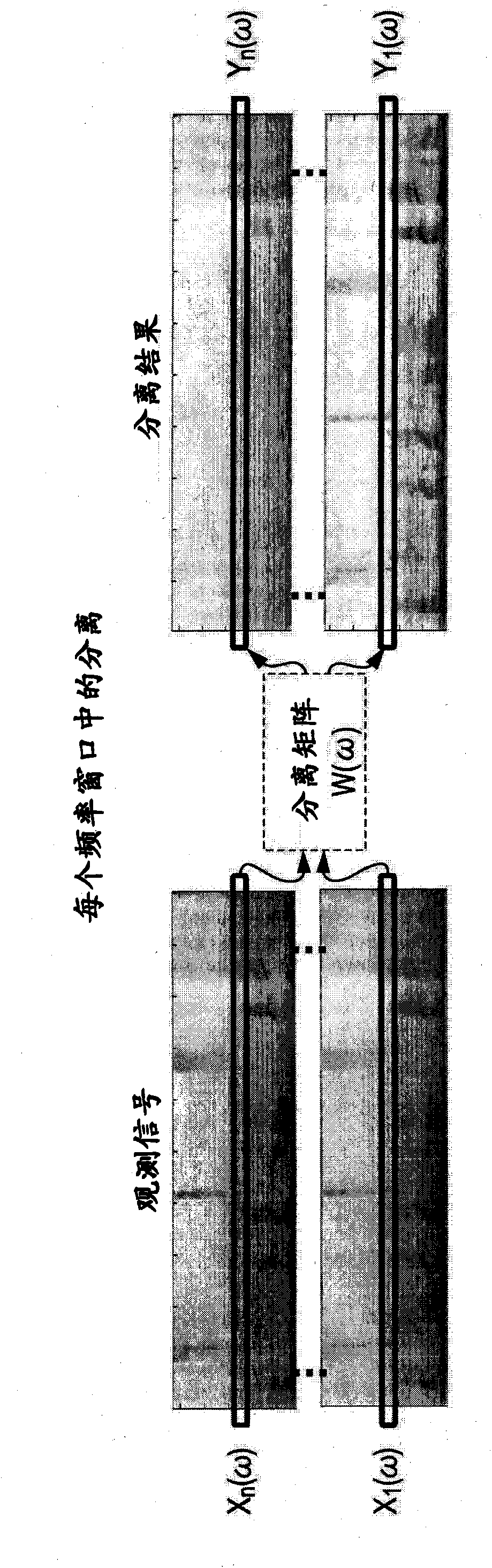
Signal processing apparatus, signal processing method, and program
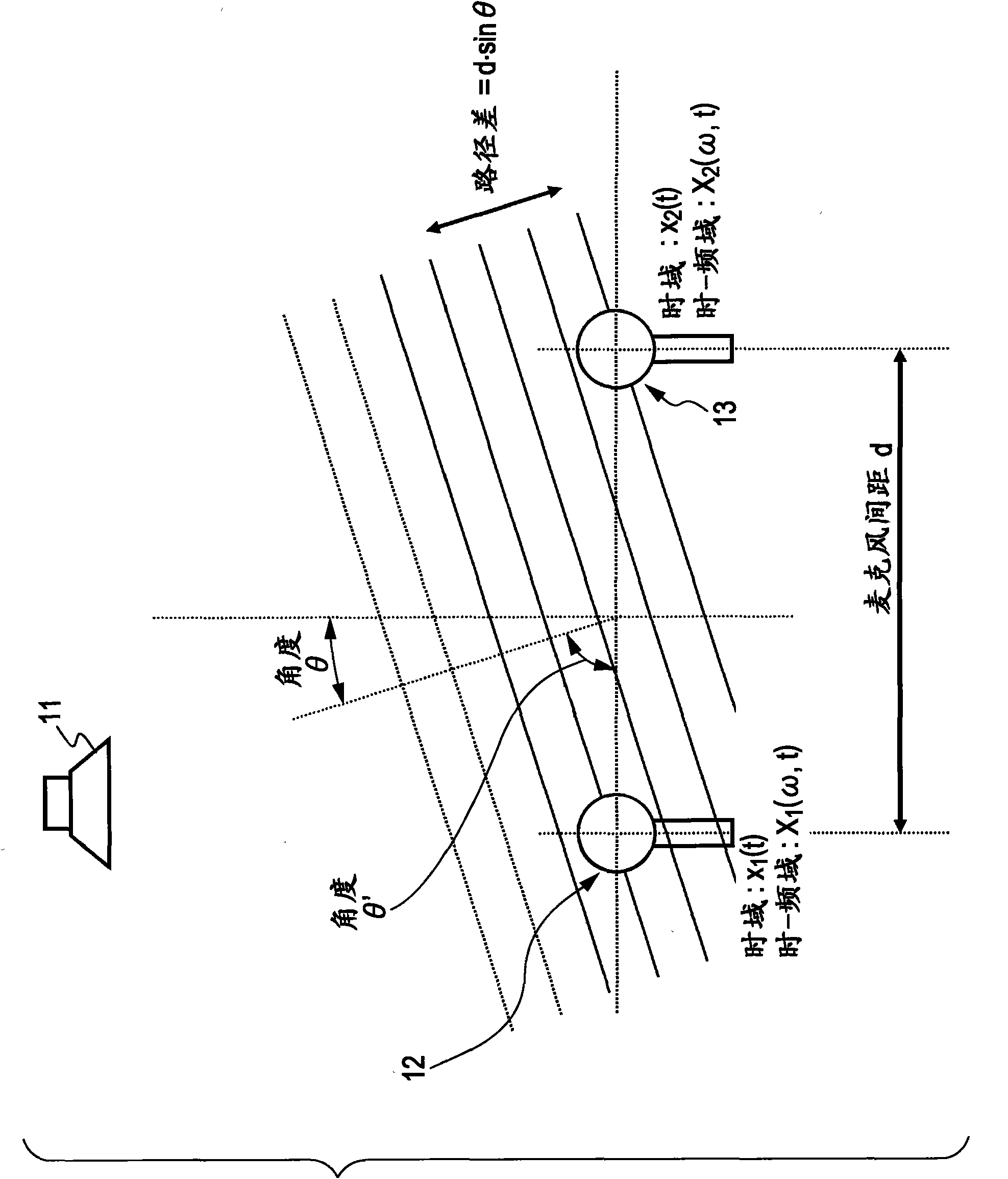
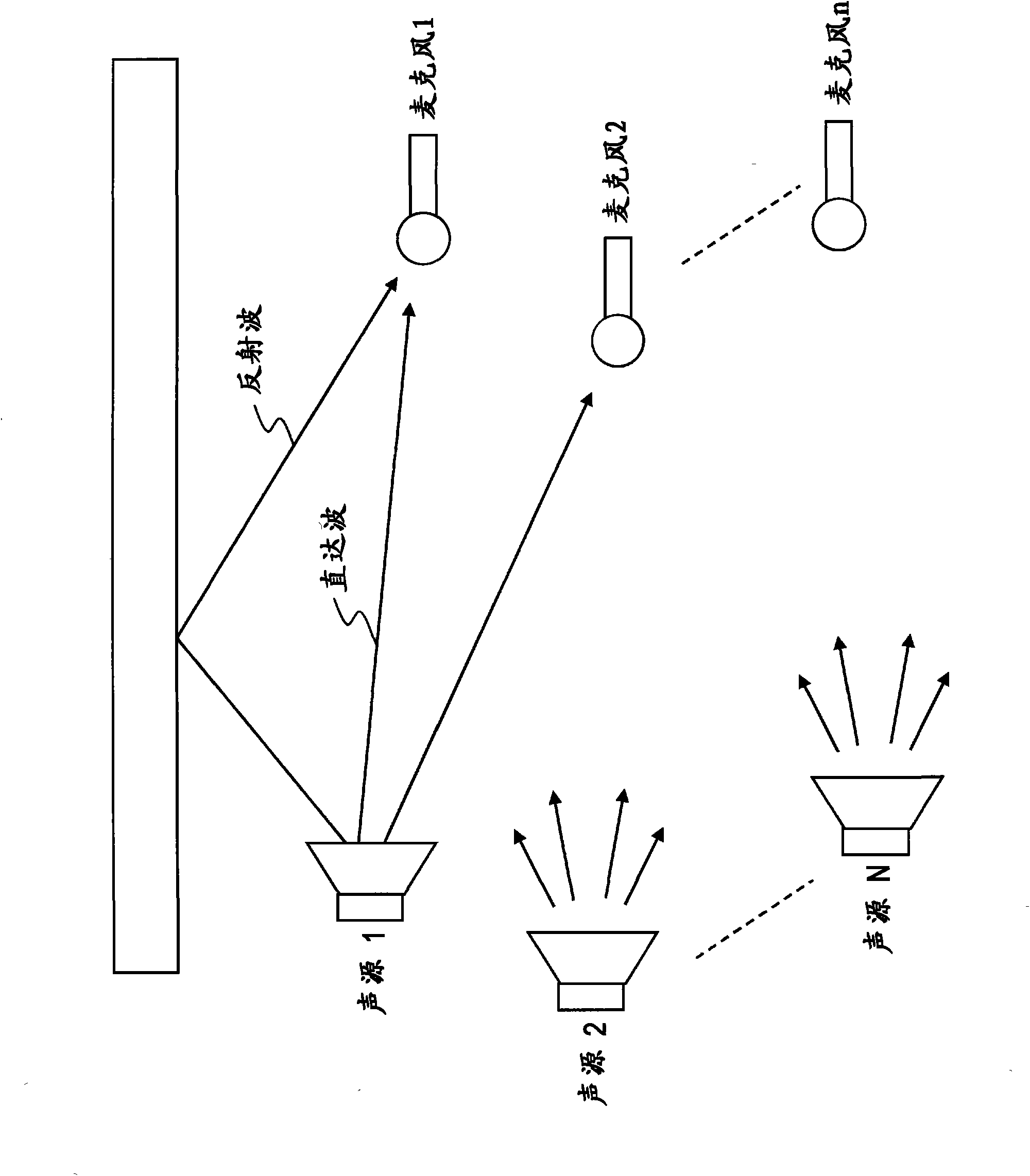
The invention provides a signal processing device, a signal processing method and program thereof. The signal processing apparatus includes: a learning processing unit that finds a separating matrix for separating mixed signals in which outputs from a plurality of sound sources are mixed, by a learning process that applies ICA (Independent Component Analysis) to observed signals including the mixed signals; a separation processing unit that applies the separating matrix to the observed signals to separate the mixed signals and generate separated signals corresponding to each of the sound sources; and a sound source direction estimating unit that computes a sound source direction of each of the generated separated signals. The sound source direction estimating unit calculates cross-covariance matrices between the observed signals and the separated signals in corresponding time segments in time-frequency domain, computes phase differences between elements of the cross-covariance matrices, and computes a sound source direction corresponding to each of the separated signals by applying the computed phase differences.
Owner:SONY CORP
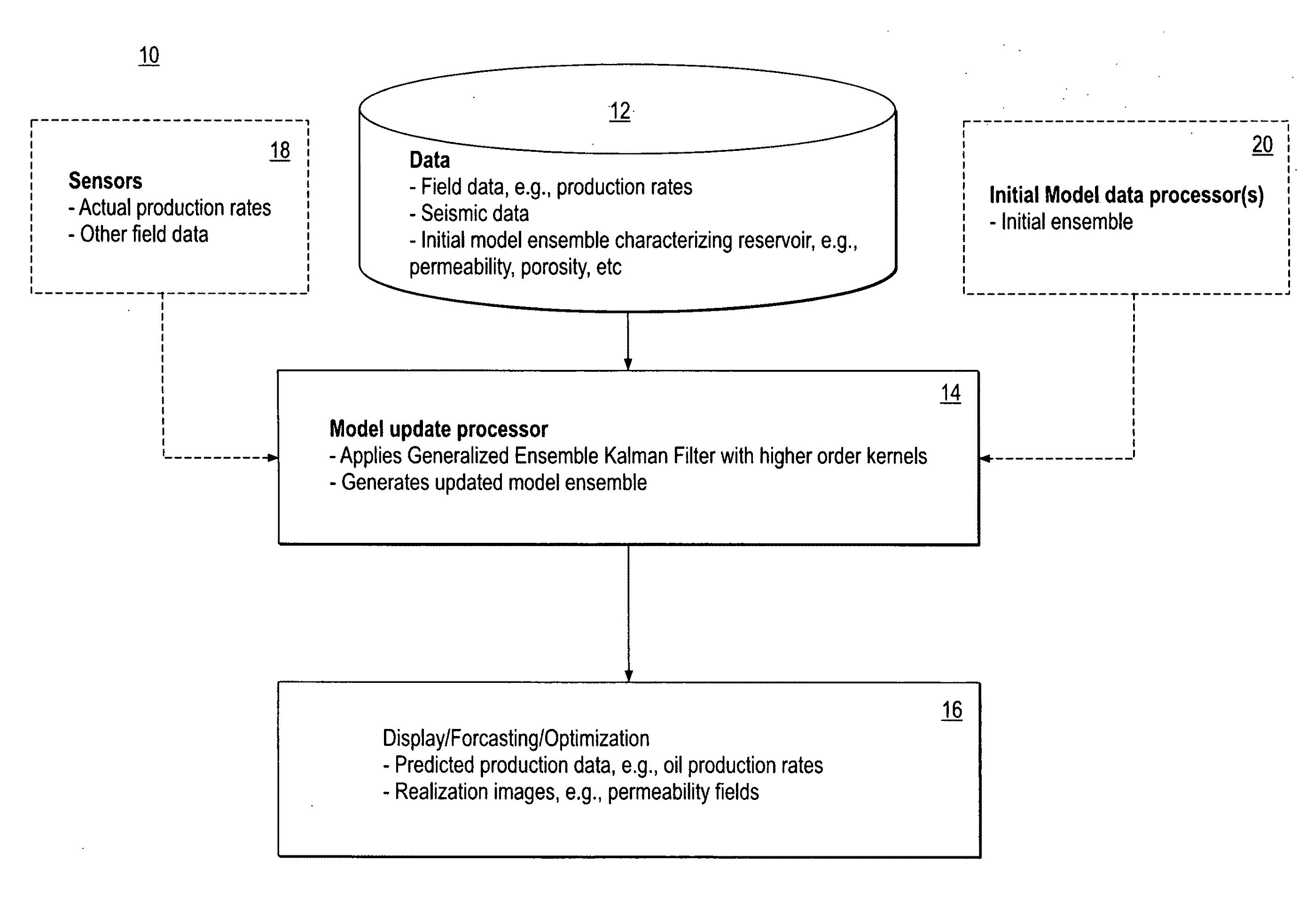
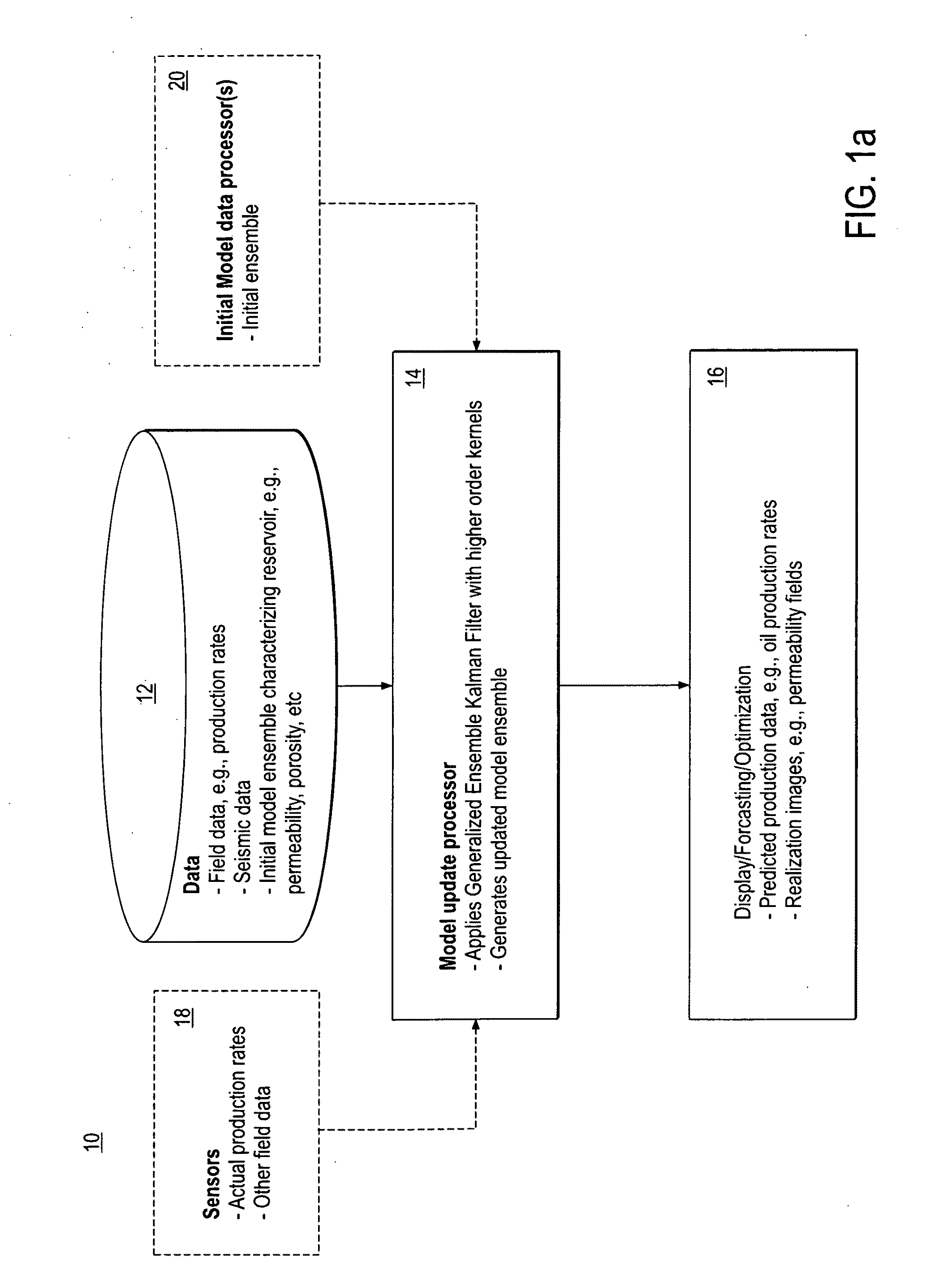
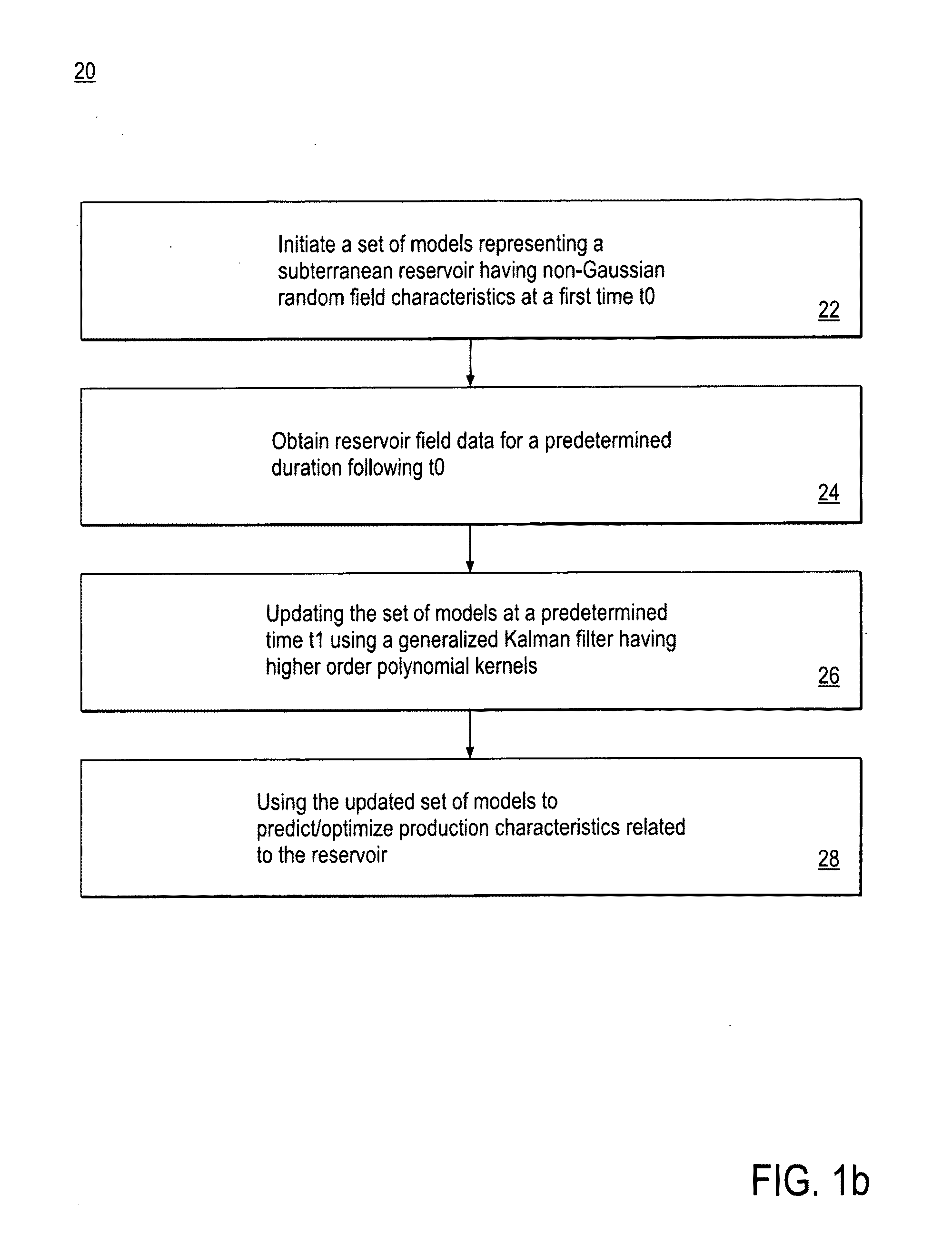
System and method for predicting fluid flow in subterranean reservoirs
ActiveUS20100198570A1Maximize accuracyGeomodellingCAD circuit designGaussian random fieldPrediction system
A reservoir prediction system and method are provided that use generalized EnKF using kernels, capable of representing non-Gaussian random fields characterized by multi-point geostatistics. The main drawback of the standard EnKF is that the Kalman update essentially results in a linear combination of the forecasted ensemble, and the EnKF only uses the covariance and cross-covariance between the random fields (to be updated) and observations, thereby only preserving two-point statistics. Kernel methods allow the creation of nonlinear generalizations of linear algorithms that can be exclusively written in terms of dot products. By deriving the EnKF in a high-dimensional feature space implicitly defined using kernels, both the Kalman gain and update equations are nonlinearized, thus providing a completely general nonlinear set of EnKF equations, the nonlinearity being controlled by the kernel. By choosing high order polynomial kernels, multi-point statistics and therefore geological realism of the updated random fields can be preserved. The method is applied to two non-limiting examples where permeability is updated using production data as observations, and is shown to better reproduce complex geology compared to the standard EnKF, while providing reasonable match to the production data.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Distributed multi-sensor fusion algorithm based on AMDs
ActiveCN106291533AAchieve integrationFusion simpleRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAlgorithmHigh dimensional
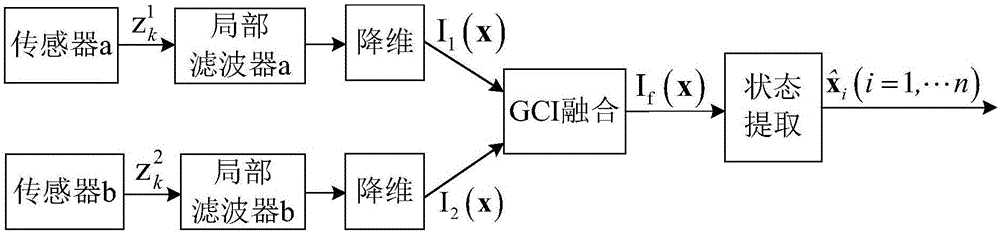
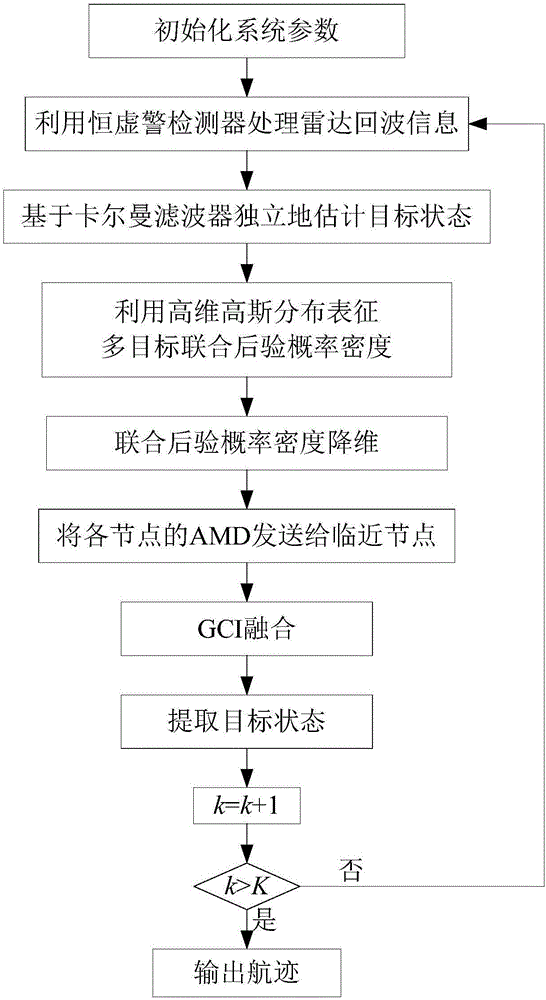
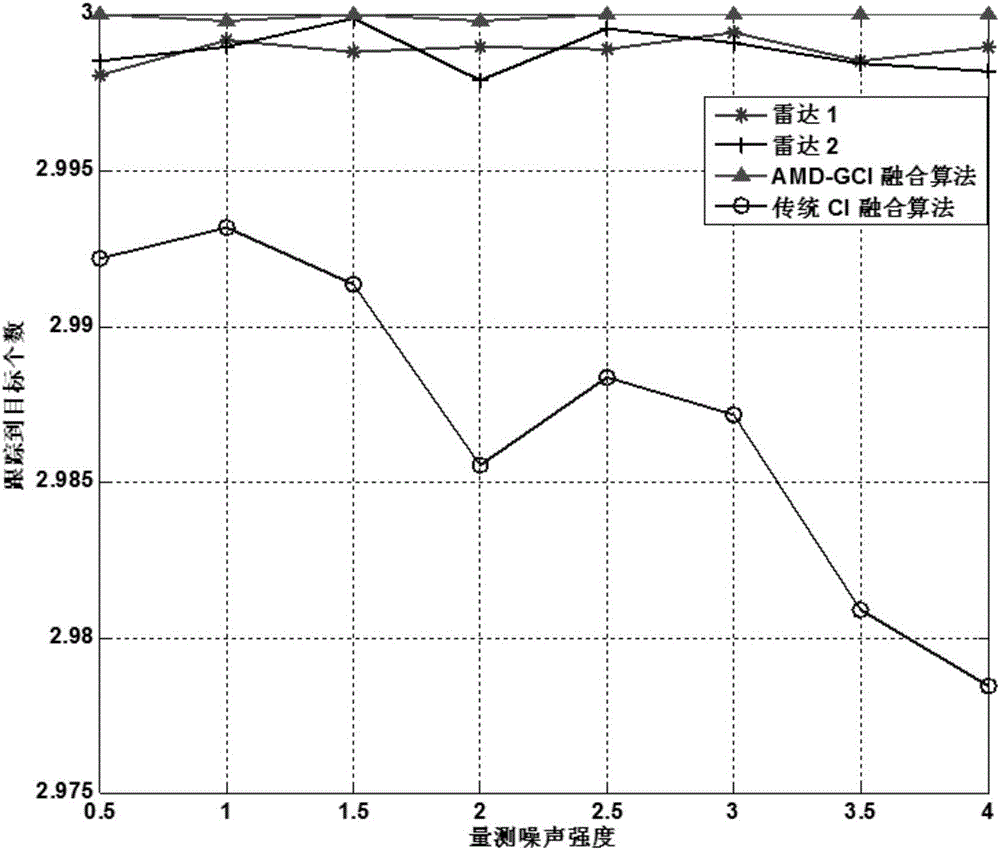
The invention discloses a distributed multi-sensor fusion algorithm based on AMDs. The algorithm comprises the following steps: S1, initializing system parameters; S2, using a constant false alarm detector to process radar echo information to obtain a measurement information set; S3, independently estimating a target state based on a kalman filter, S4, using high dimensional Gaussian distribution to represent the multi-objective joint posterior probability density; S5, carrying out the dimensionality reduction operation on the joint posterior probability density; S6, sending the AMD of each node to the adjacent nodes; S7, fusing the AMDs by using a generalized cross-covariance algorithm; S8, extracting the target state; S9, setting k = k + 1, if k>K, outputting the target state extracted in the S8 as a track; otherwise, returning to step S2. The distributed multi-sensor fusion algorithm realizes the joint fusion of a plurality of targets under the condition that the estimation errors of the different sensors are considered cross-correlated, has higher adaptability and better robustness, and effectively solves the problem of multi-target joint posteriori fusion in the traditional tracking system.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Two-dimensional direction of arrival estimation method for nested array based L-shaped antenna array
ActiveCN108957391ACancel noiseImprove robustnessRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsArray elementSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The invention discloses a two-dimensional direction of arrival estimation method for a nested array based L-shaped antenna array, and belongs to the field of array signal processing. The implementation method includes the following steps: constructing a nested array based L-shaped antenna array, calculating a cross-covariance matrix by using signals received by different sub arrays of the constructed L-shaped nested array; correcting the obtained cross-covariance matrix, performing vectorization on the corrected cross-covariance matrix to generate a virtual array, constructing a plurality of equivalent covariance matrices by using the virtual array, calculating the signal azimuth angle Theta and the pitch angle Phi by using the rotation invariance between different equivalent covariance matrices, and achieving multi-target and high-precision two-dimensional direction of arrival estimation with few snapshots at a low signal-to-noise ratio. The technical problem to be solved by the invention is to realize multi-target and high-precision two-dimensional direction of arrival estimation by using fewer array elements at a low signal-to-noise ratio and with few snapshots, and to solve related engineering technical problems by using two-dimensional direction of arrival estimation results.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
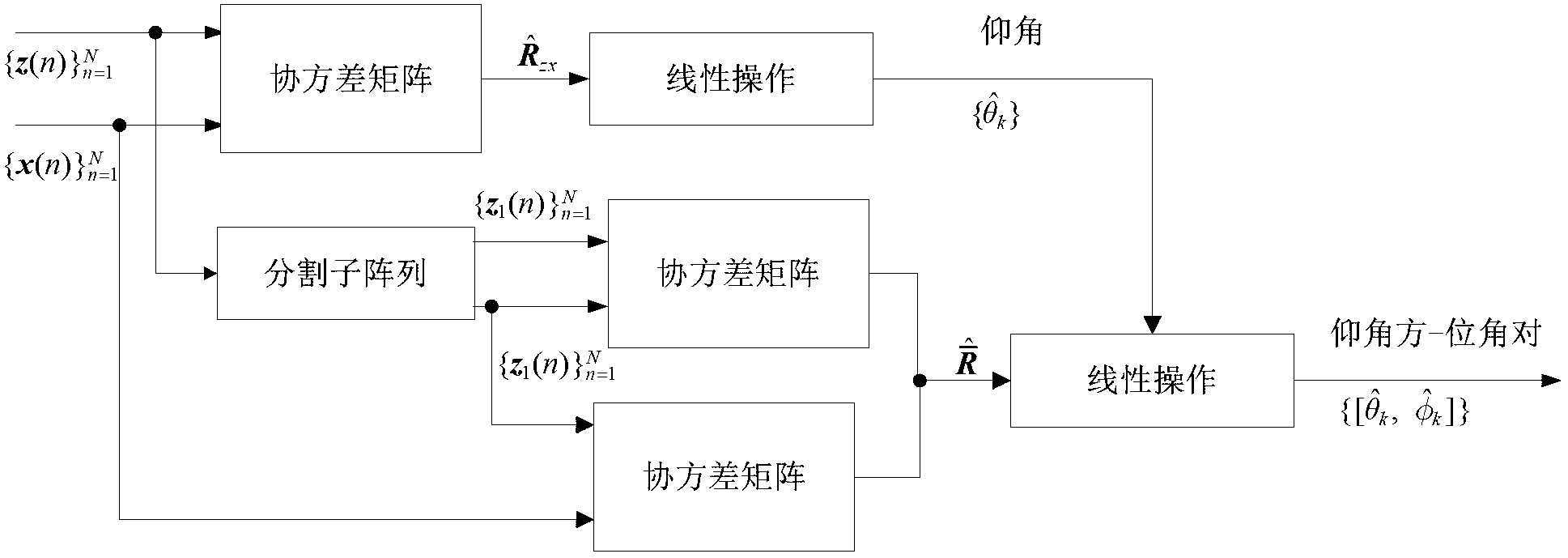
Joint estimation method for azimuth angle and elevation angle of signal on basis of L-type sensor array
ActiveCN102707258AAvoid the pairing processOvercoming pairing failuresRadio wave finder detailsRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsSensor arrayElevation angle
The invention discloses a joint estimation method for an azimuth angle and an elevation angle of a signal on the basis of an L-type sensor array. The joint estimation method is used for estimating a direction of arrival of an incidence signal emitted onto the L-type sensor array, wherein the L-type sensor array is placed on an x-z plane and is provided with two mutually vertical uniform linear arrays, and M omnidirectional sensors are equidistantly arranged in different spatial positions along a straight line on each of the uniform linear arrays. The joint estimation method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) estimating a covariance matrix of signals received by two rows of uniform linear arrays on x axis and z axis, and then obtaining an M*2M expanding cross covariance matrix by calculating according to the covariance matrix of the signals received by the two rows of uniform linear arrays; (2) cutting the uniform linear array on the z axis or x axis into two rows of non-coincident forward / backward sub-arrays, and then estimating the elevation angle by utilizing the expanding cross covariance matrix of data received by the two rows of uniform linear arrays according to a linear operation one-dimensional subspace method; and (3) estimating a corresponding azimuth angle by linearly operating by utilizing feasible regions of the azimuth angle and the elevation angle, the two rows of sub-arrays on the z axis or x axis and the cross covariance between one of the sub-array and the uniform linear array on the x axis or z axis.
Owner:RES INST OF XIAN JIAOTONG UNIV & SUZHOU
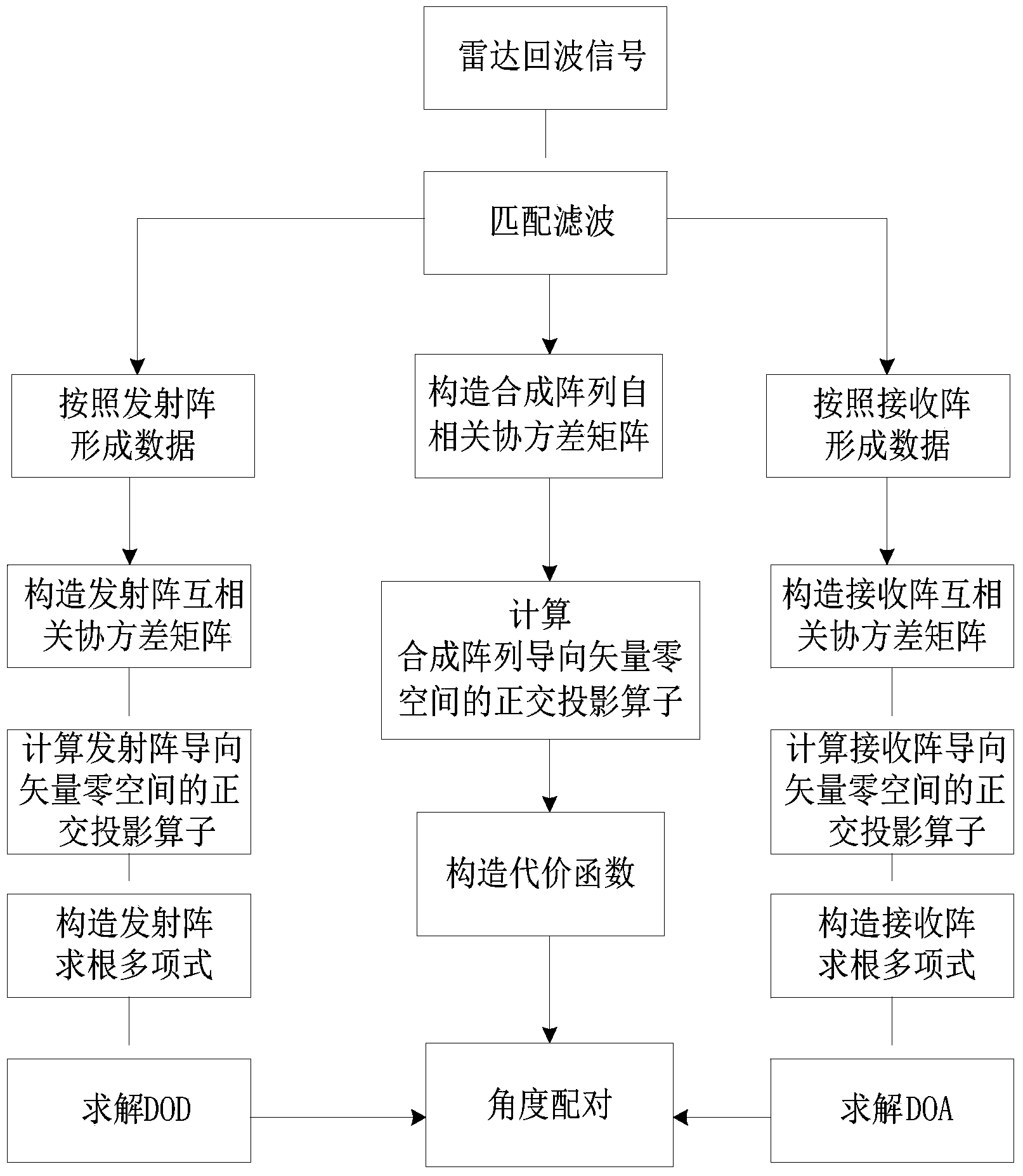
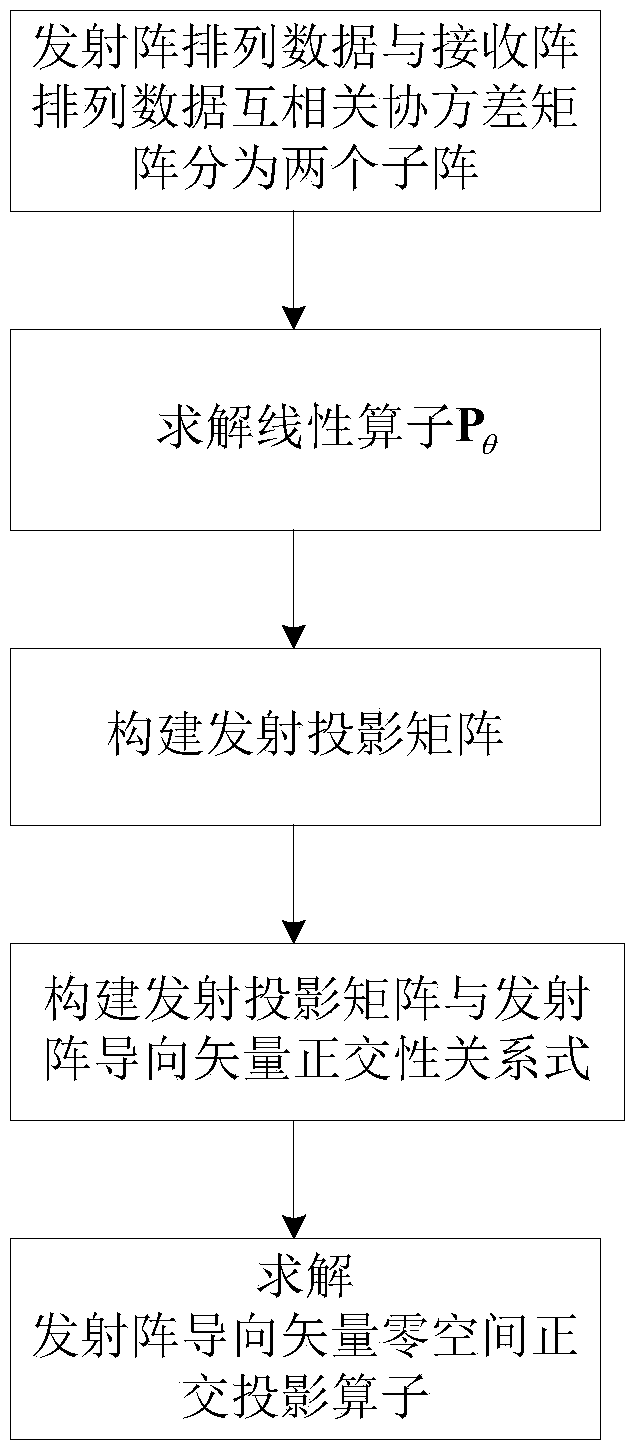
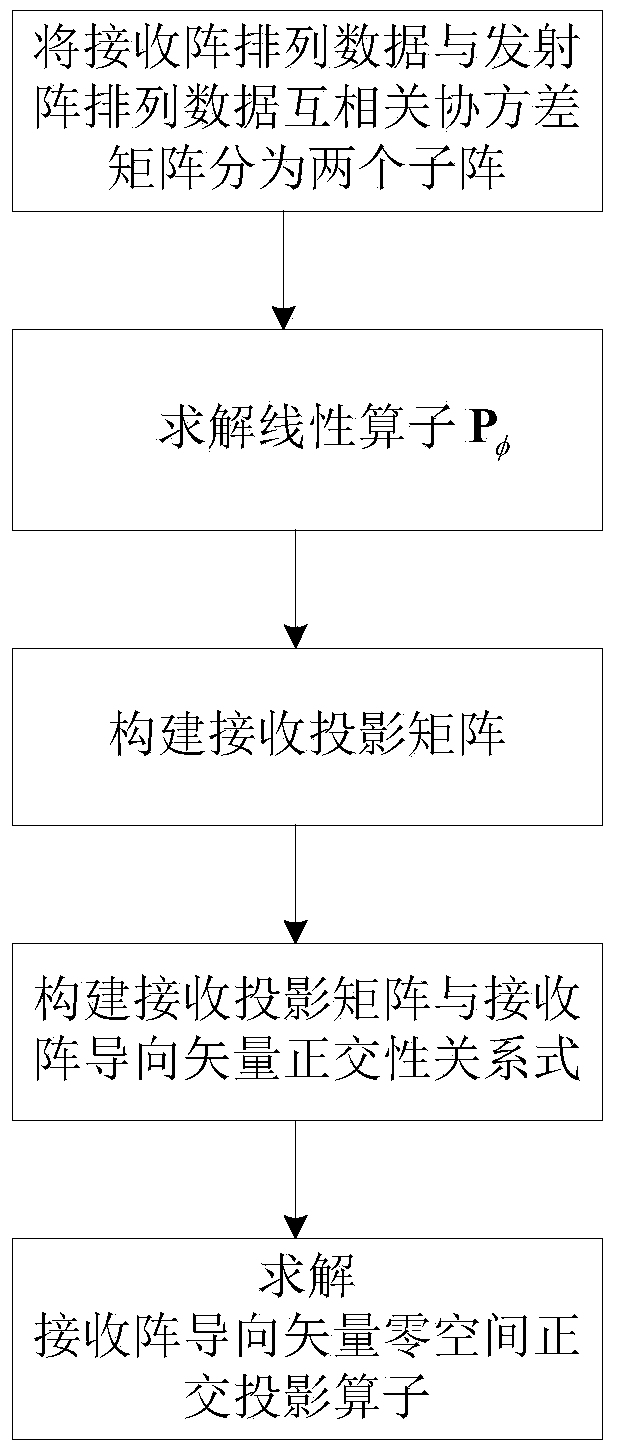
Double-base MIMO radar angle estimating method based on cross-correlation matrixes
InactiveCN103760547AReduce the influence of angle estimationImprove estimation accuracyDirection findersRadio wave reradiation/reflectionCross correlation matrixFiltration
The invention discloses a double-base MIMO radar angle estimating method based on cross-correlation matrixes. The method mainly solves that problem that a double-base MIMO radar angle is large in calculation and complex in computation. The achieving steps are as follows: (1) conducting matching and filtering on a radar echo signal, and forming data according to an emission array and a receiving array; (2) respectively constructing cross covariance matrixes by utilizing the formed data; (3) respectively obtaining rectangular projection operators in guide vector null space of the emission array and the receiving array through linear independence of a covariance matrix row vector; (4) obtaining the position of a target relative to the emission array and the receiving array; (5) respectively obtaining rectangular projection operators in guide vector null space of a synchronized array through linear independence of an autocorrelation covariance matrix row vector of the data after matching and filtration, and constructing a cost function for matching angles. The double-base MIMO radar angle estimating method based on cross-correlation matrixes achieves high-precision MIMO radar target angle estimation with small calculation and can be used for locating a target in a radar and communication.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Monitoring and fault detection in dynamic systems
ActiveUS20080154544A1Easily implemented/re-turnedRobust configurationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceTesting/monitoring control systemsPrincipal component analysisDynamic system model
A system and method for monitoring and fault detection in dynamic systems. A “cross-covariance” matrix is used to construct and implement a principle component analysis (PCA) model and / or partial least squares (PLS) model. This system is further utilized for monitoring and detecting faults in a dynamic system. Time series information is synchronized, with respect to a set of training data. Based on historical data, consistency of correlations between variables can be checked with respect to a given time stamp. Temporal PCA (T-PCA) can be used for clearly monitoring changes in tags (time series) synchronization, even when the temporal behaviors of the dynamic system are not clear.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
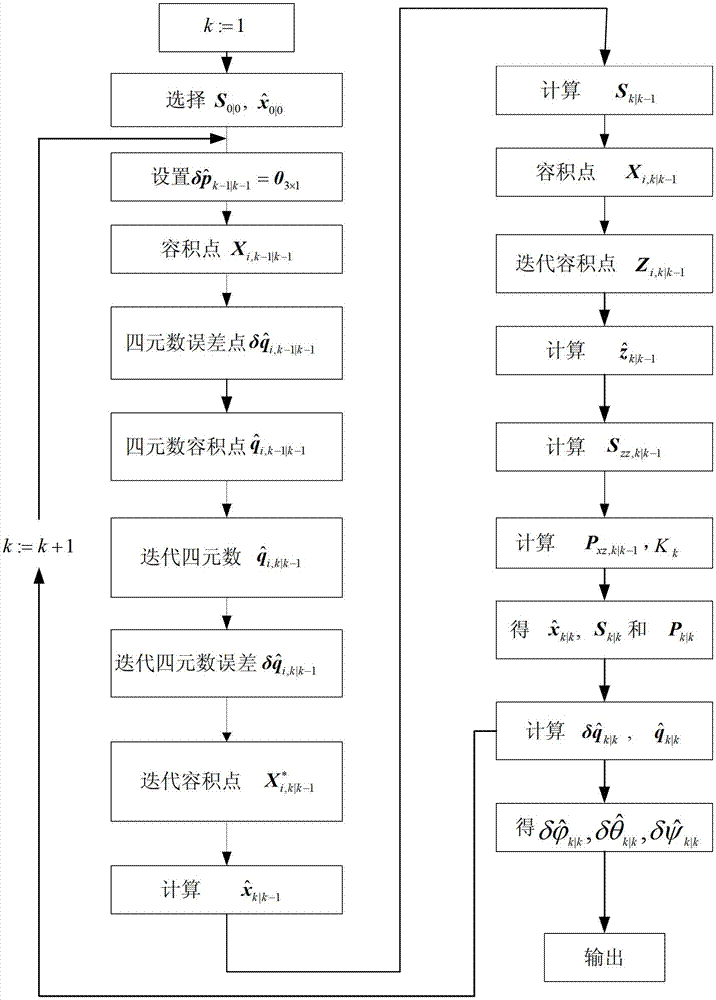
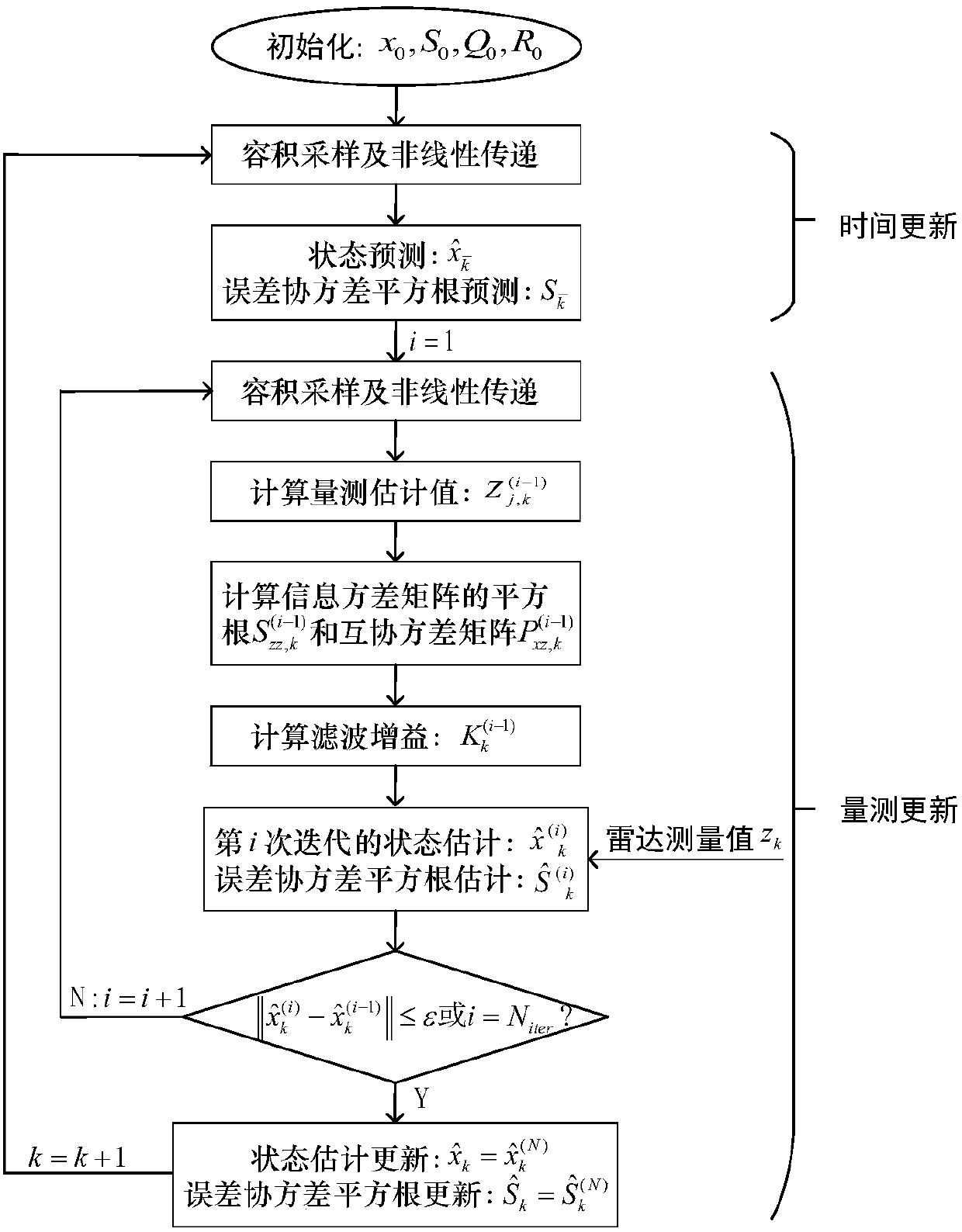
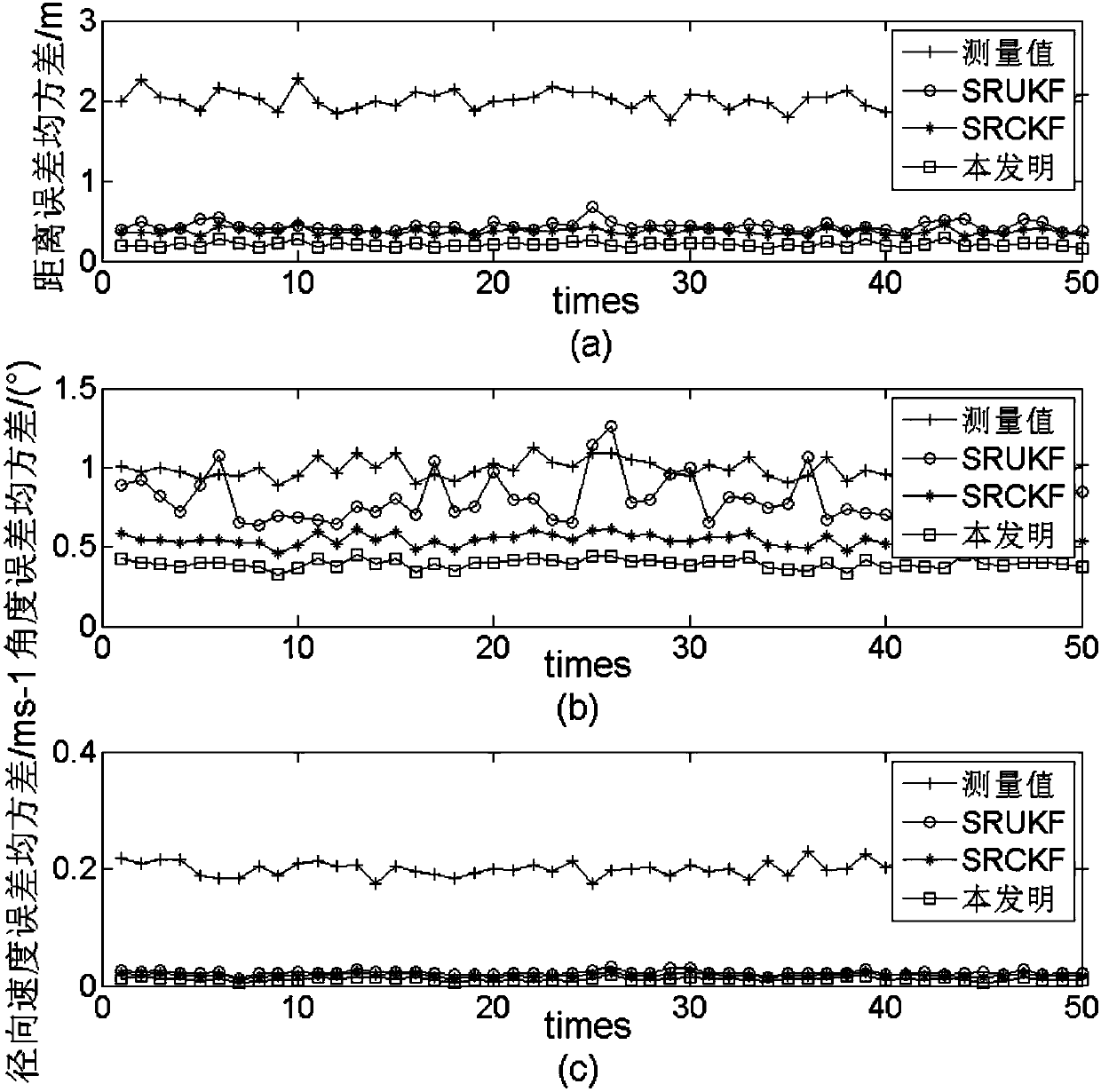
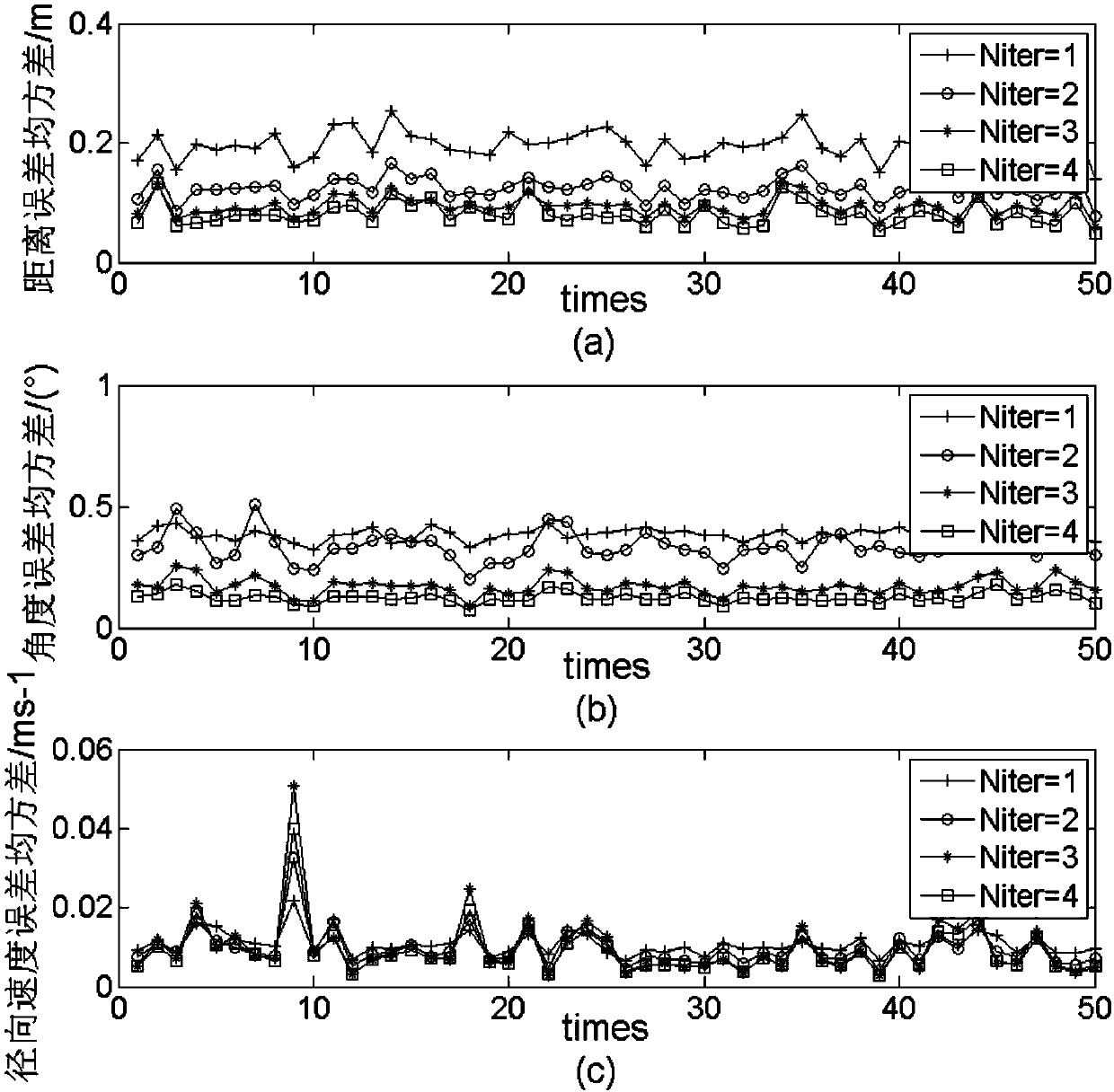
Square root cubature Kalman filter-based aircraft attitude estimation method
InactiveCN104121907AAvoid destructionHigh precisionNavigational calculation instrumentsKaiman filterEstimation methods
The invention relates to a square root cubature Kalman filter-based aircraft attitude estimation method which comprises the steps of setting an initial value and a Rodriguez parameter when calculating time updating, calculating a volume point value, calculating a quaternion error point, calculating a quaternion volume point, calculating an iteration quaternion and an iteration quaternion error, calculating an iteration volume point, estimating a one-step prediction state, estimating a square root factor prediction error covariance matrix, calculating a volume point in measurement updating, calculating an iteration volume point value, calculating prediction measurement estimation, calculating square root factor innovation covariance matrix estimation, calculating a cross covariance matrix, carrying out Kalman gain, estimating state updating, calculating an estimated error covariance matrix and a corresponding square root factor, updating the quaternion, and calculating a corresponding estimated error euler angle. According to the square root cubature Kalman filter-based aircraft attitude estimation method, the precision and the stability of aircraft attitude can be improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Method for carrying out fusion processing on meteorological data and generating numerical weather forecast
ActiveCN110020462AImprove the accuracy of eigenvaluesImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionDesign optimisation/simulationNumerical weather predictionData type
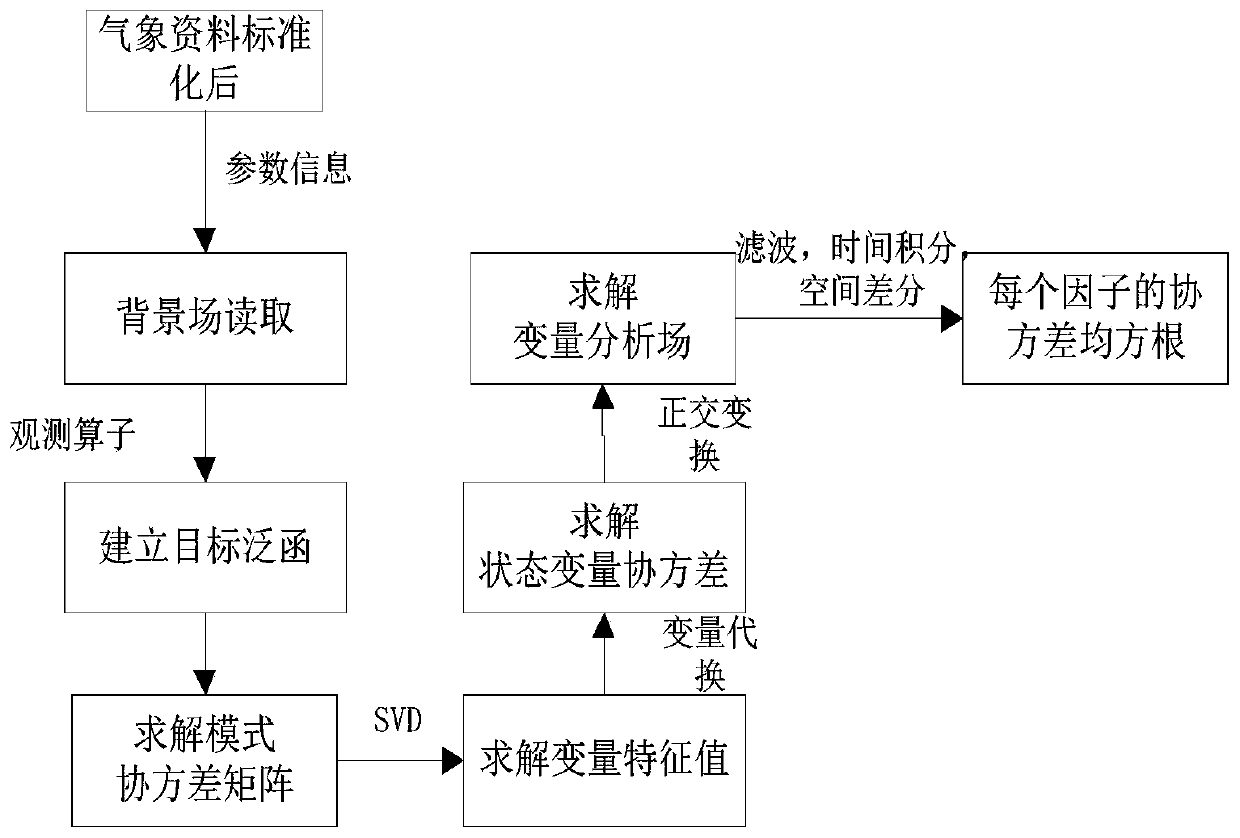
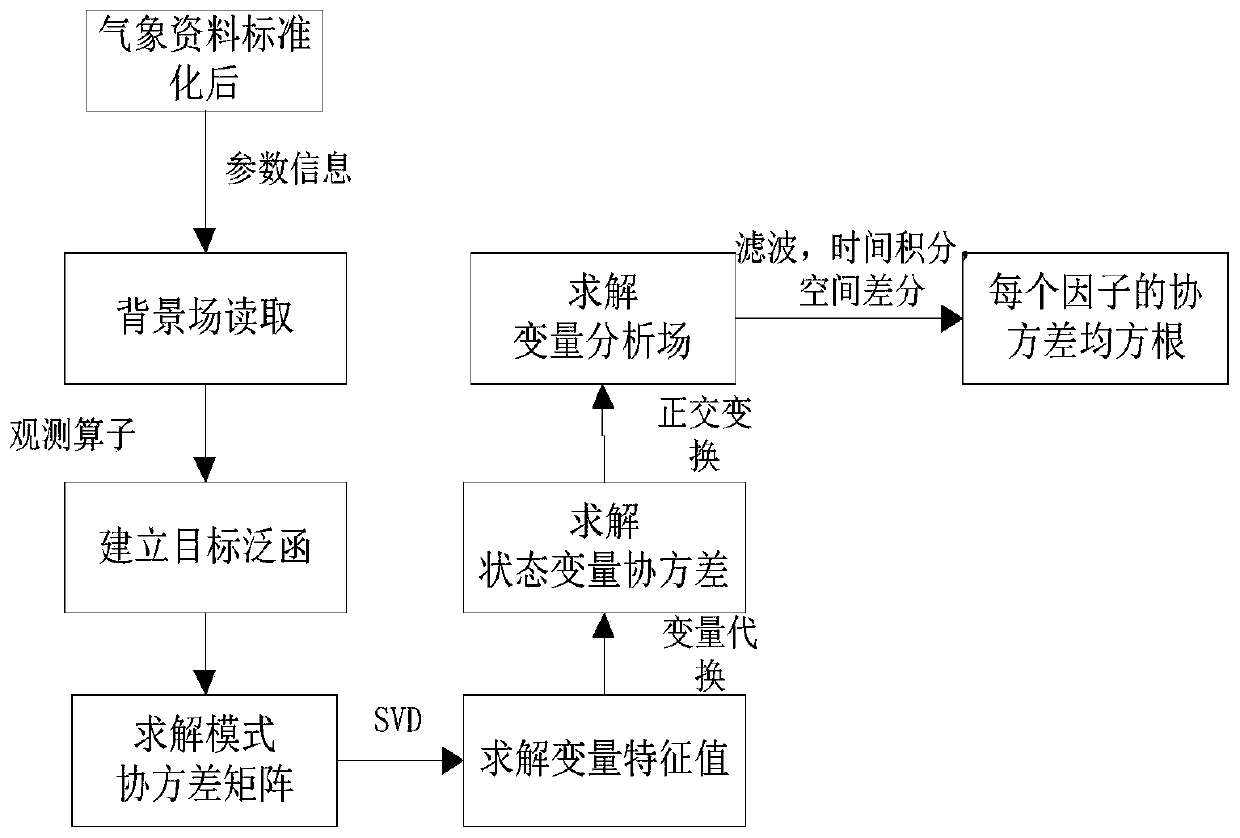
The invention discloses a method for carrying out fusion processing on meteorological data and generating a numerical weather forecast, which comprises the following steps: step 1, collecting and receiving various meteorological element data from meteorological observation detection equipment or CCTV to obtain a meteorological element set X1; step 2, performing standardized preprocessing on the acquired meteorological element data to obtain a standardized meteorological element set X; step 3, performing three-dimensional data variation assimilation on the meteorological element set X, performing characteristic error analysis and cross covariance analysis on the data in the meteorological element set X to obtain a covariance error root mean square of each data in the meteorological elementset X, and obtaining an optimal meteorological element data type according to the covariance error root mean square; step 4, performing WRF numerical weather forecast mode compiling according to the optimal meteorological element type; and step 5, performing forecast post-processing on the WRF mode result to generate meteorological element numerical forecast.
Owner:江苏无线电厂有限公司
Automotive radar target tracking method of iterative square root CKF (Cubature Kalman Filtering) on the basis of noise compensation
ActiveCN108304612AHigh precisionImprove stabilitySustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationSeries compensationCubature kalman filter
The invention discloses an automotive radar target tracking method of iterative square root CKF (Cubature Kalman Filtering) on the basis of noise compensation. The method comprises the following stepsthat: firstly, setting a system initial value, and calculating a cubature point value in a time update stage; spreading the cubature point; estimating a one-step prediction state and an error covariance square root factor; in a measurement update stage, importing a Gauss-Newton nonlinear iteration method to carry out iteration update, and calculating the cubature point during each-time iteration;spreading the cubature point; calculating measurement estimation; calcauting the square root factor of an innovation covariance and a cross covariance matrix; calculating Kalman gain; updating a current iteration state, and estimating the square root factor of an error covariance; judging whether an iteration termination condition is achieved or not; updating a current state, and estimating the error covariance square root; and in the measurement update process, regulating the noise compensation factor to optimize state estimation. By use of the method, accuracy and stability in an automotiveradar target tracking process can be effectively improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
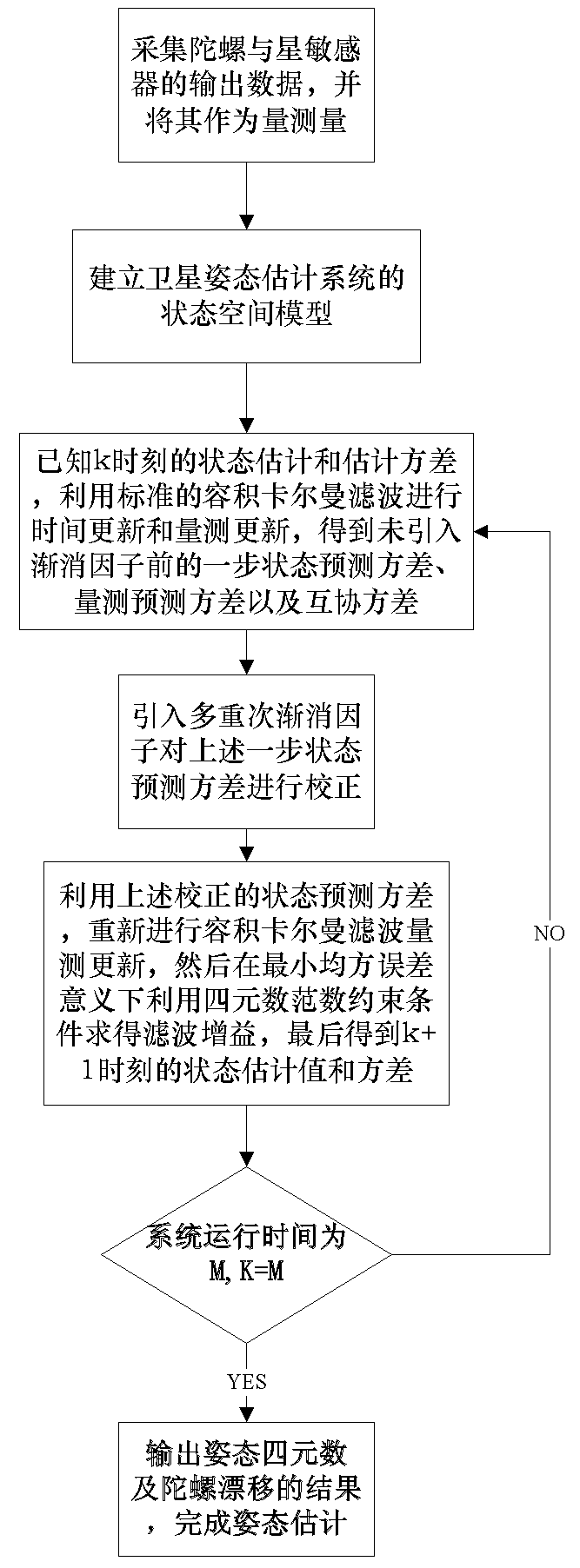
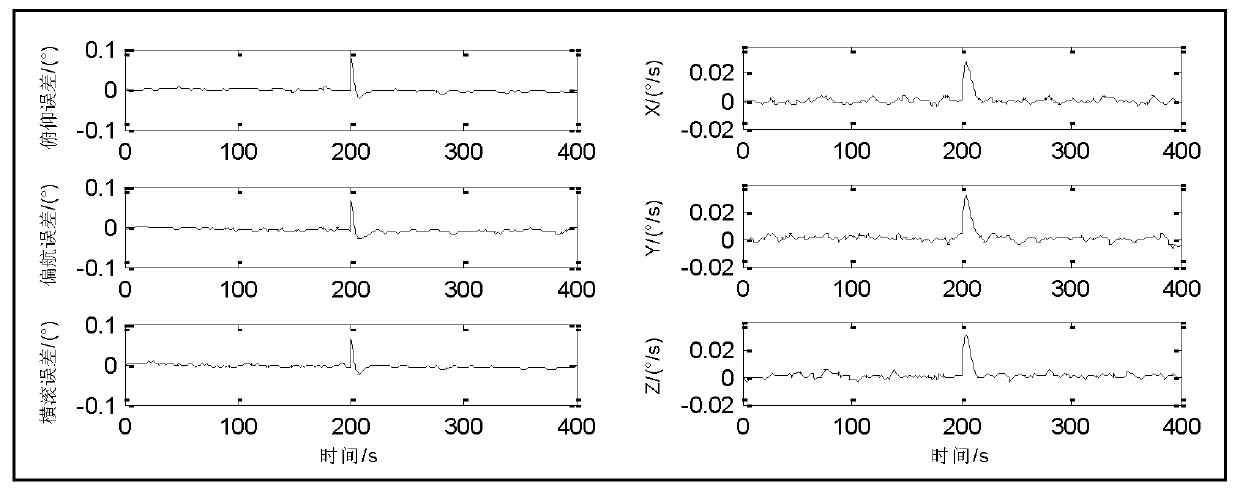
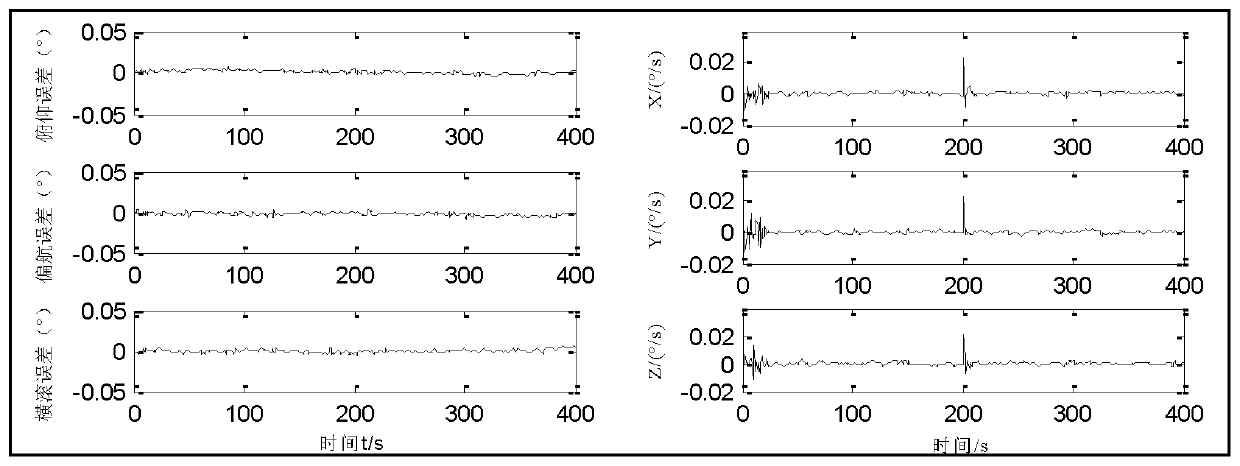
Norm constraint strong tracking cubature kalman filter method for satellite attitude estimation
InactiveCN104019817AAvoid calculationImprove estimation accuracyInstruments for comonautical navigationState predictionQuaternion
The invention discloses a norm constraint strong tracking cubature kalman filter method for satellite attitude estimation. The norm constraint strong tracking cubature kalman filter method comprises the following steps: 1, acquiring output data of a gyro and a star sensor; 2, determining state variables and measuration amount of a satellite attitude estimation system; 3, performing cubature kalman filter time updating and measuration updating at the moment of k to obtain one-step state prediction variance, one-step measuration prediction variance and cross covariance; 4, using a multiple gradual-fading factor for correction of the one-step prediction variance; 5, performing cubature kalman filter measuration updating again, acquiring state variance and state estimation variance at the moment of k +1; 6 if K + 1 = M (M is end moment of an attitude estimation nonlinear discrete system), outputting attitude quaternion and gyroscopic drift of state estimation of the moment of k +1 to complete the attitude estimation, if K + 1 < M, and k = K + 1, repeating steps 3, 4,and 5. The a norm constraint strong tracking cubature kalman filter method has the advantages of high estimation accuracy and strong robustness.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Signal number detection method applied on condition of incoherent signal and coherent signal mixing
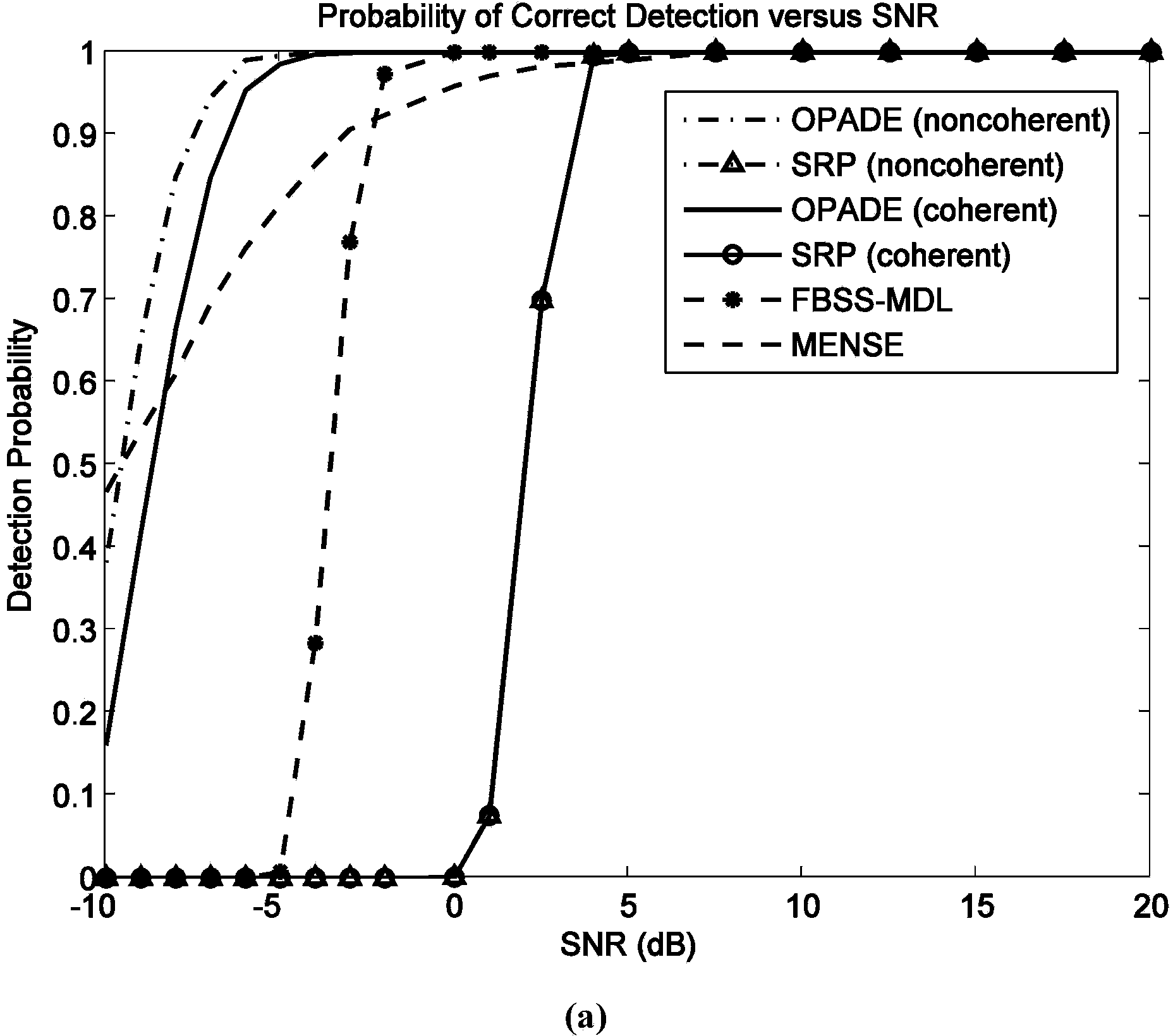
The invention discloses a signal number estimation method applied in incidence of incoherent signals and multiple groups of coherent signals on the basis of uniform linear arrays. After an outer-product matrix based on a cross covariance matrix of received signals of two linear arrays is acquired, a first combined matrix is constructed by the cross covariance matrix and a transformation matrix thereof, and an outer-product matrix of the combined matrix is acquired, the number of the incoherent signals and the number of the groups of coherent signals can be acquired according to the rank of the two outer-product matrixes. Further, a new oblique projector is estimated to suppress the incoherent signals of data of the received array, a series of cross covariance matrixes composed of data of one uniform linear array and a series of sub-arrays of the other uniform linear array form a new combined matrix, and the rank of the outer-product matrix of the combined matrix is equal to the number of the coherent signals. According to great quantities of experiments, the signal number estimation method with less snapshots and low signal-to-noise ratio is superior to the MDL / AIC method, the MENSE method and the SRP(smoothed rank profile test) which are subjected to the FBSS (front-rear space smooth) preprocess.
Owner:RES INST OF XIAN JIAOTONG UNIV & SUZHOU
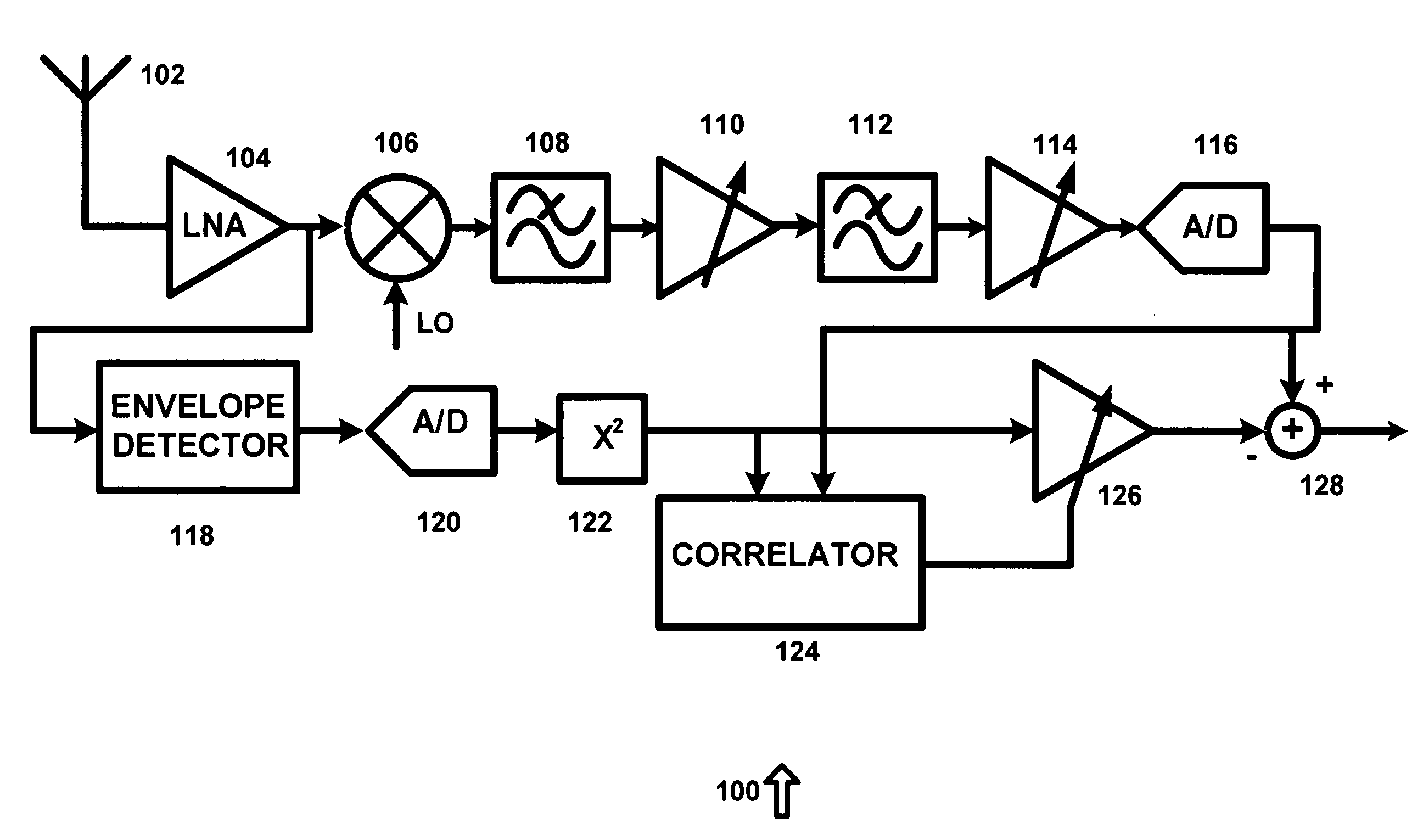
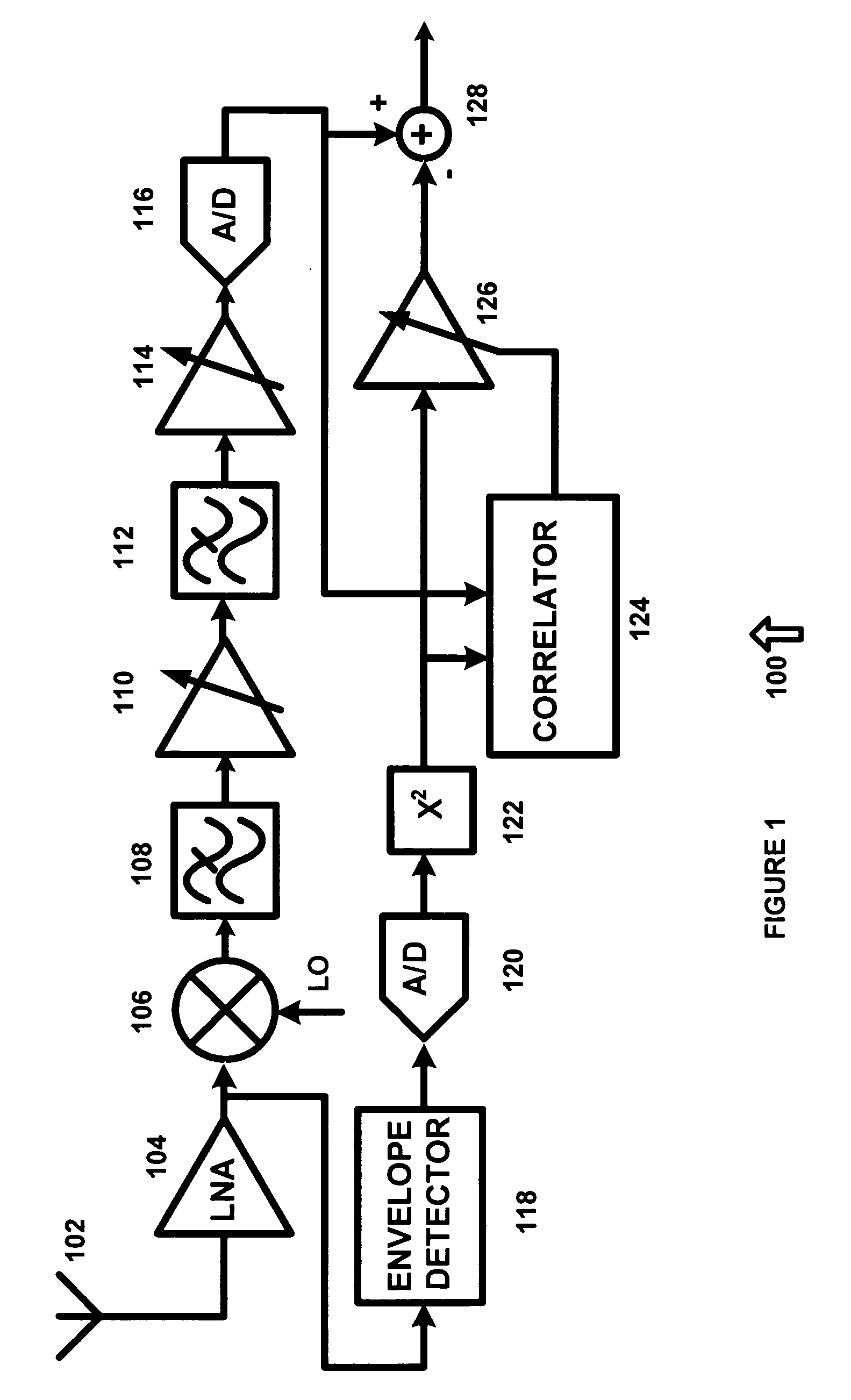
Receiver second order intermodulation correction system and method
ActiveUS20090181633A1Eliminate needSinusoidal oscillation interference reductionDirect-conversion receiverData signal
A system for correcting a second order intermodulation product in a direct conversion receiver is provided. The system includes a cross-covariance system receiving a data signal and a second order intermodulation estimate signal and generating a cross-covariance value. An auto-covariance system receives the second order intermodulation estimate signal and generates an auto covariance value. A buffer system stores a second order intermodulation product correction factor. A divider receives the cross-covariance value, the auto-covariance value and the second order intermodulation product correction factor and generates a running average second order intermodulation product correction factor.
Owner:AXIOM MICRODEVICES
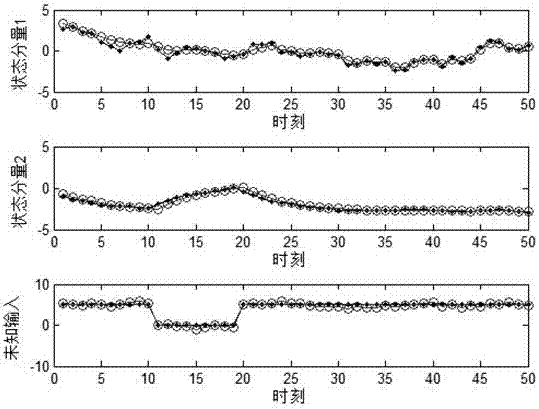
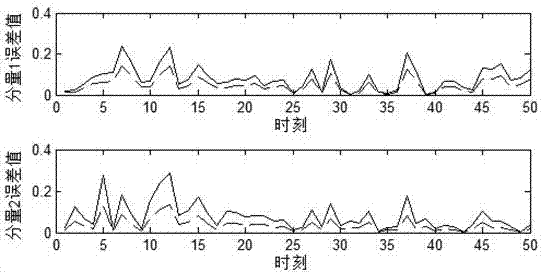
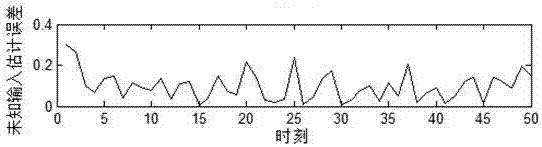
Distributed fusion filtering method for simultaneously estimating unknown input and state
ActiveCN107994885AImprove estimation accuracyDigital technique networkFilter algorithmEquation of state
The invention discloses a distributed fusion filtering method for simultaneously estimating an unknown input and a state, which is used for solving a problem that an existing distributed filter does not give out a state equation for estimating the unknown input. The distributed fusion filtering method comprises the following steps of: establishing a discrete linear time-varying system with a plurality of sensors; based on an observed quantity of each sensor, designing a three-step recursive filter; and deducing a cross-covariance matrix between any two local estimations, and then according tothe acquired local estimations and the cross-covariance matrix, giving out a distributed scalar weighting fusion filter of each component of the state by utilizing a linear minimum variance componenton the basis of a scalar weighting fusion estimation algorithm. The distributed fusion filtering method disclosed by the invention is superior to an existing distributed fusion filtering method in estimation accuracy on the state, and gives out unbiased estimation on the unknown input by utilizing the filtering algorithm for simultaneously estimating the unknown input and the state when the systemhas the unknown input with unknown statistic characteristics, and yet no estimation on the unknown input is given out in existing literatures.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
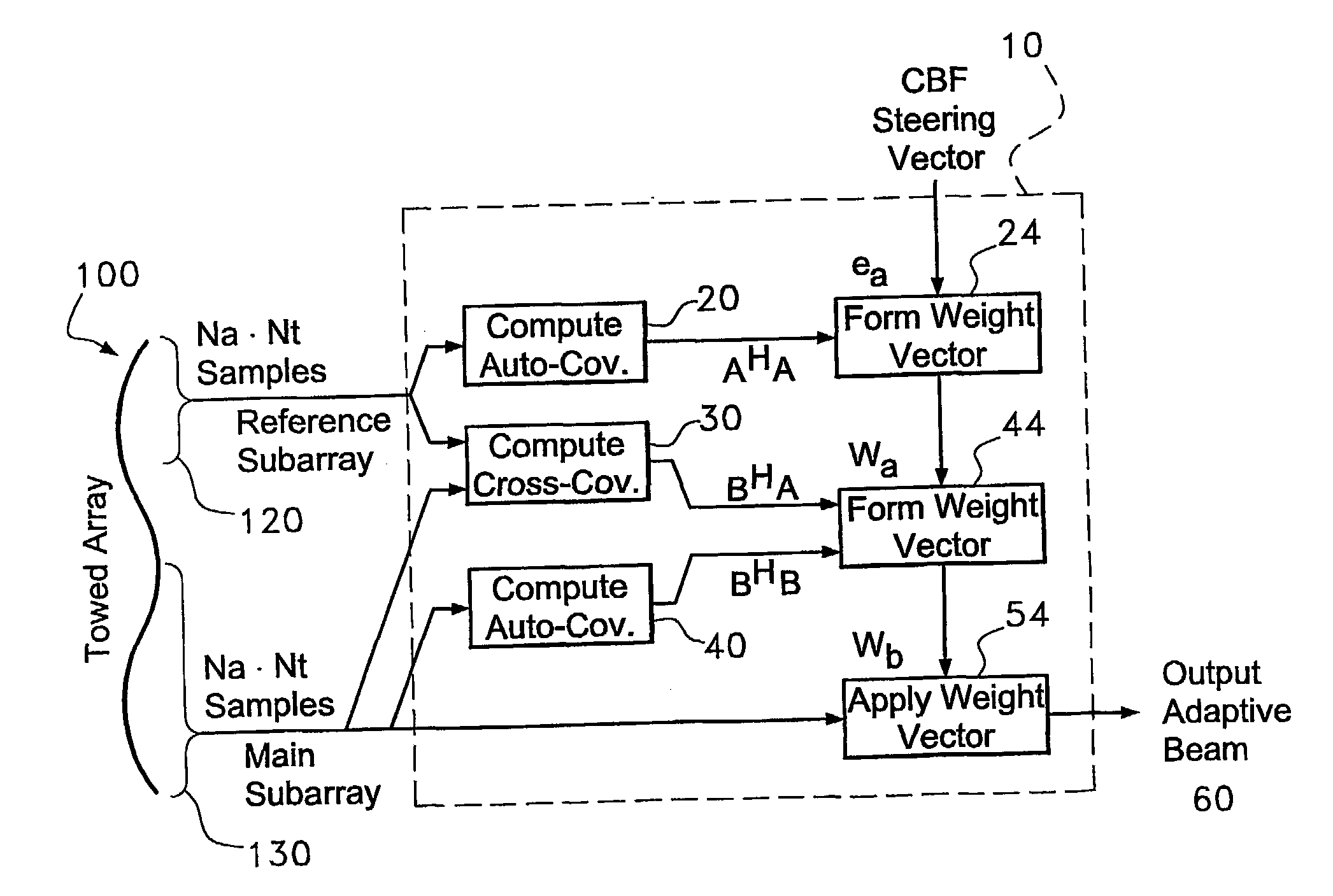
Subarray matching beamformer apparatus and method
InactiveUS20060241914A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsData signalEngineering
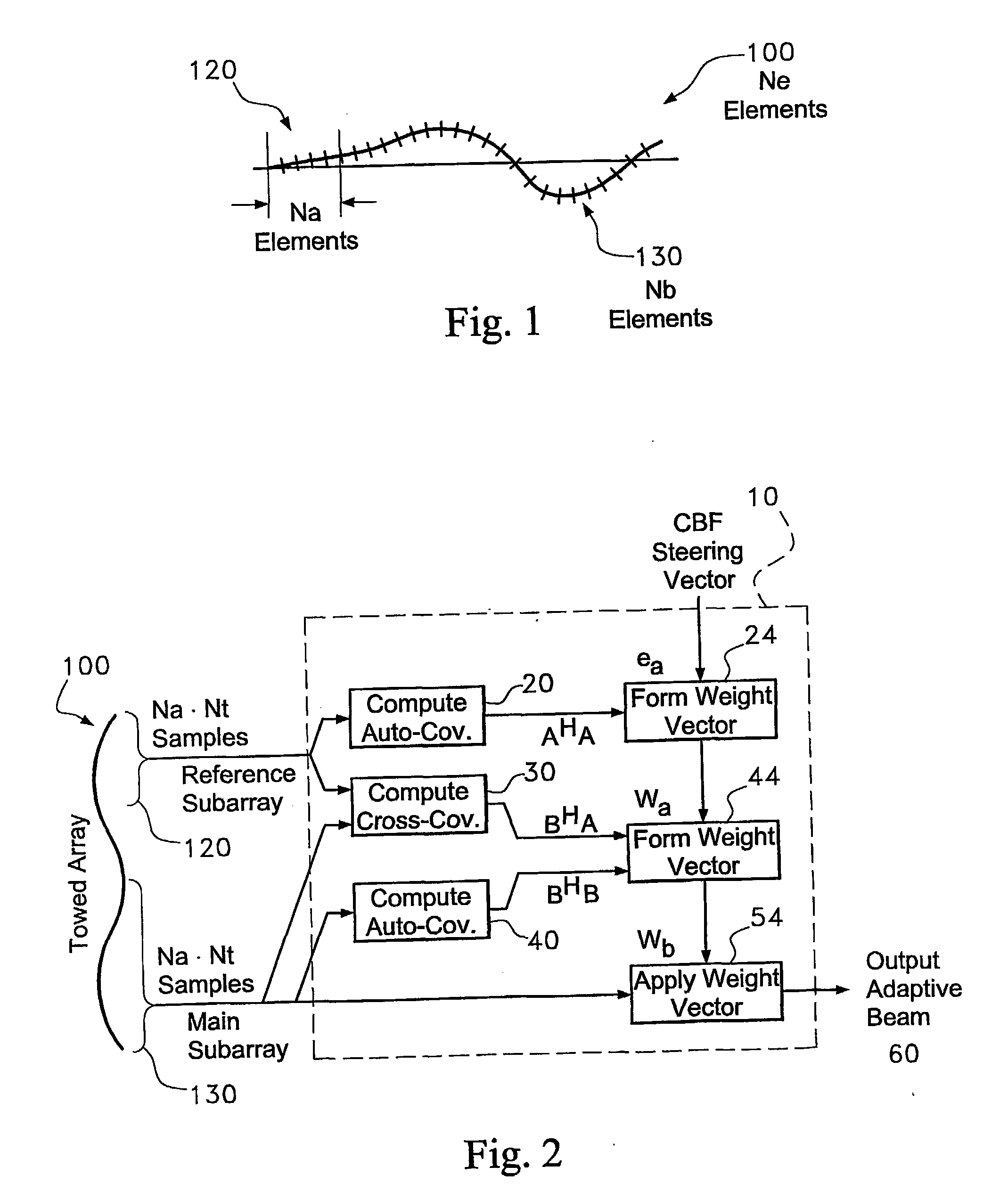
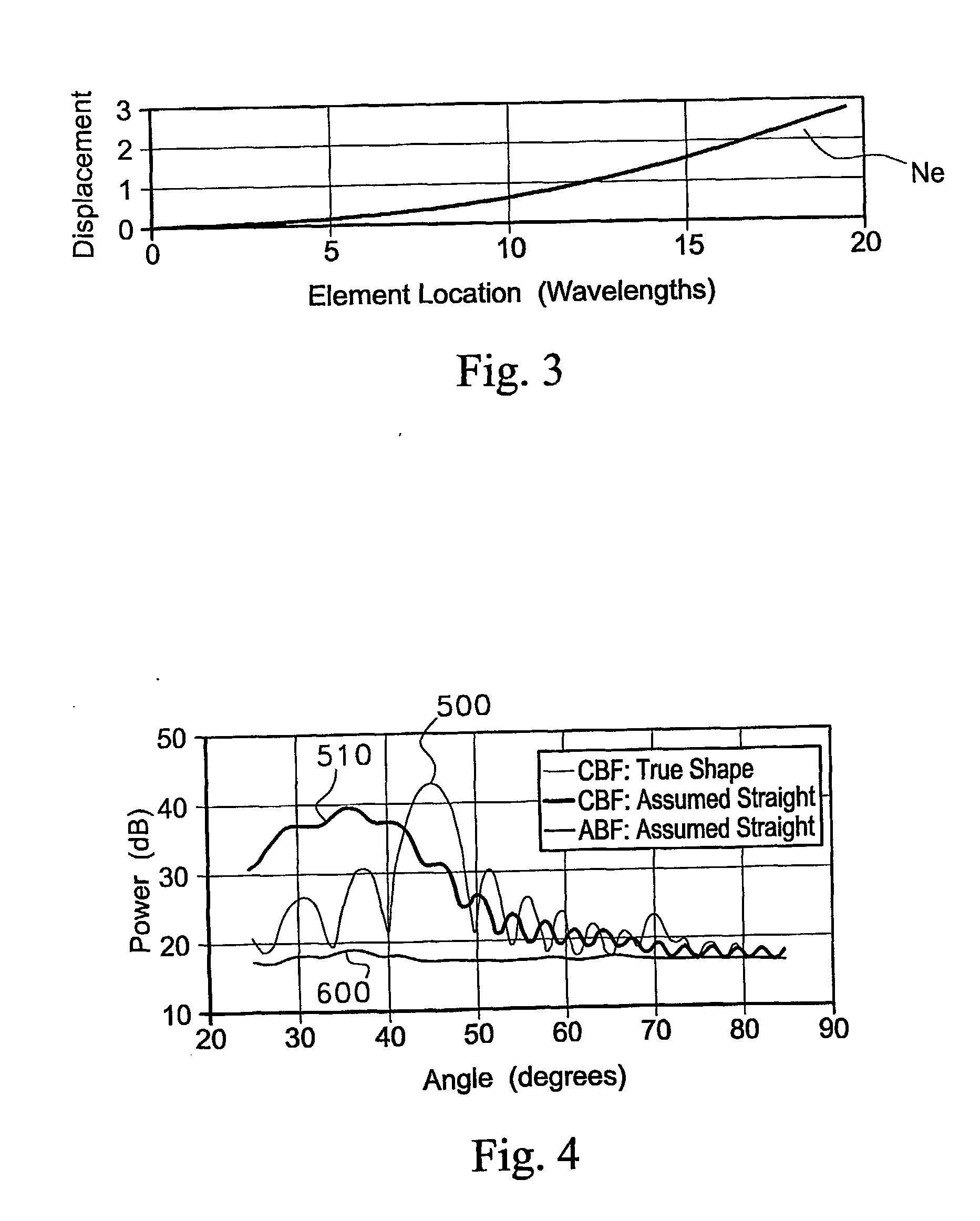
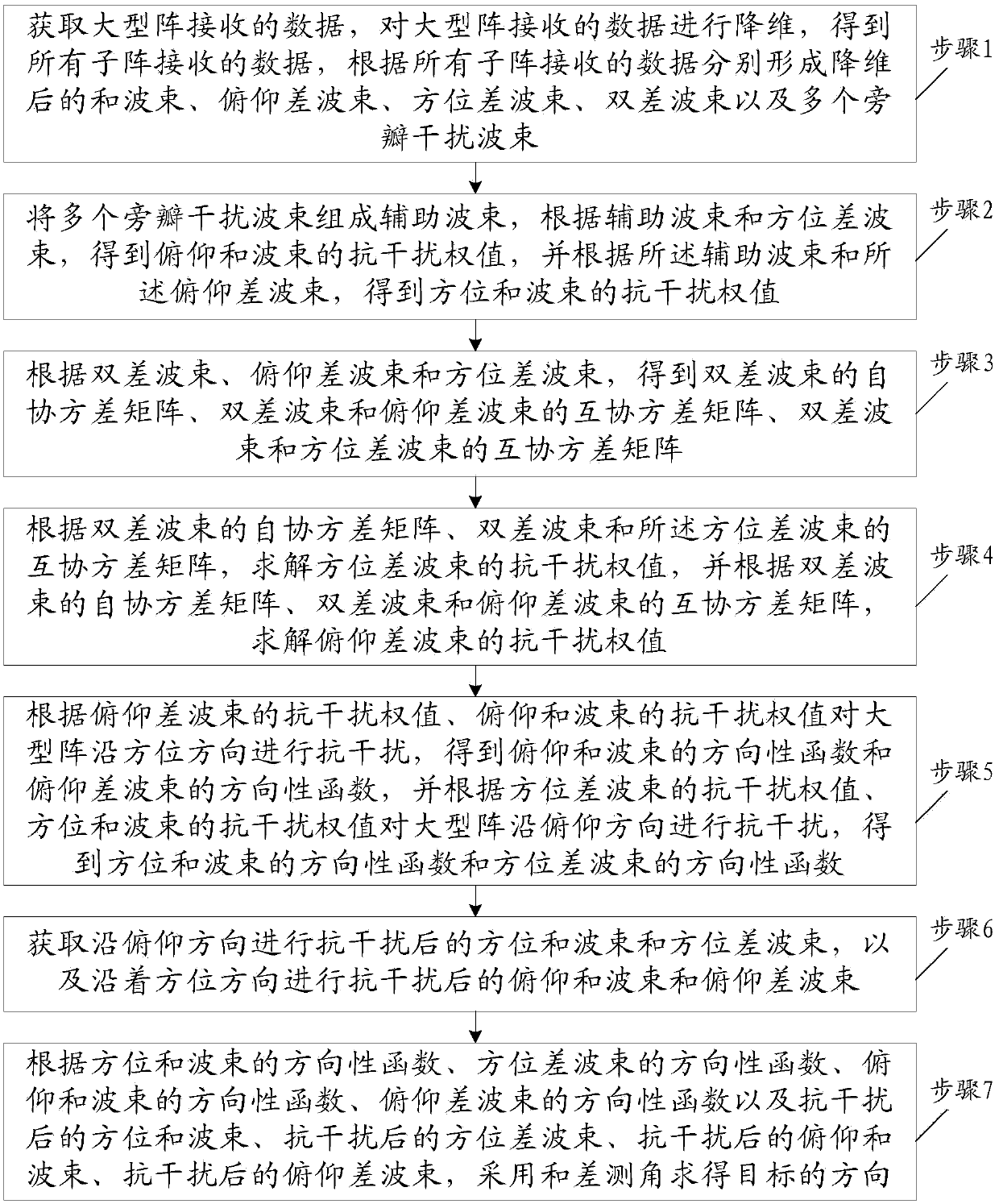
A method of beam forming an array (60), by computer processing a cross covariance (30), of the reference sub array seismic signal data signal (120), by having an unknown shape comprising receiving acoustic signals (120), via the aray (100), and computing the date (20) and segmenting the array into an initial segment of a known shape and at least a second segment (44), and beam forming the initial segment to provide a beam formed output (60), and using the beam formed output to obtain weights (24), for the second segment of the array.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
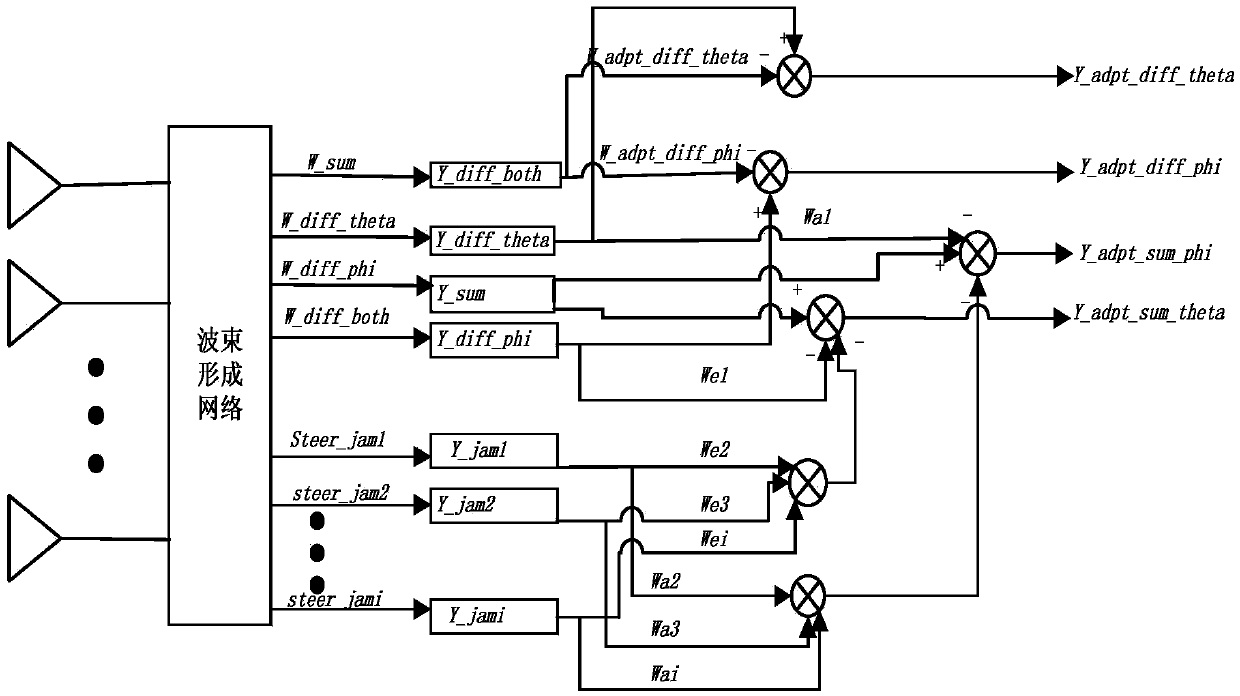
Phased array radar dimension reduction four-channel mainlobe sidelobe interference-resisting method
ActiveCN105372633ARealize simultaneous anti-jammingReduce complexityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterference resistanceDimensionality reduction
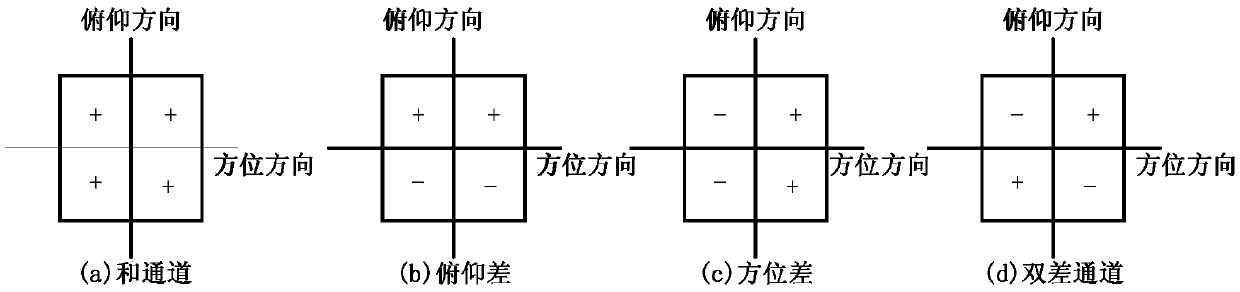
The invention belongs to the field of signal processing, and discloses a large dimension reduction four-channel mainlobe sidelobe interference-resisting method. The method comprises steps: according to data received by all subarrays, a sum beam, a pitch difference beam, an azimuth difference beam, a dual-difference beam and multiple sidelobe interference beams after dimension reduction are formed respectively; interference-resisting weights of the pitches and beams are obtained, and interference-resisting weights of the azimuths and the beams are obtained; according to the dual-difference beam, the pitch difference beam and the azimuth difference beam, an auto-covariance matrix for the dual-difference beam, a cross-covariance matrix for the dual-difference beam and the pitch difference beam and the cross-covariance matrix for the dual-difference beam and the azimuth difference beam are obtained; and the interference-resisting weight of the azimuth difference beam and the interference-resisting weight of the pitch difference beam are solved; and the azimuths, the beams and the azimuth difference beam after interference resistance along the pitch direction are acquired, and the pitches, the beams and the pitch difference beam after interference resistance along the pitch direction are acquired; and sum difference angle measurement is adopted to obtain the target direction.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
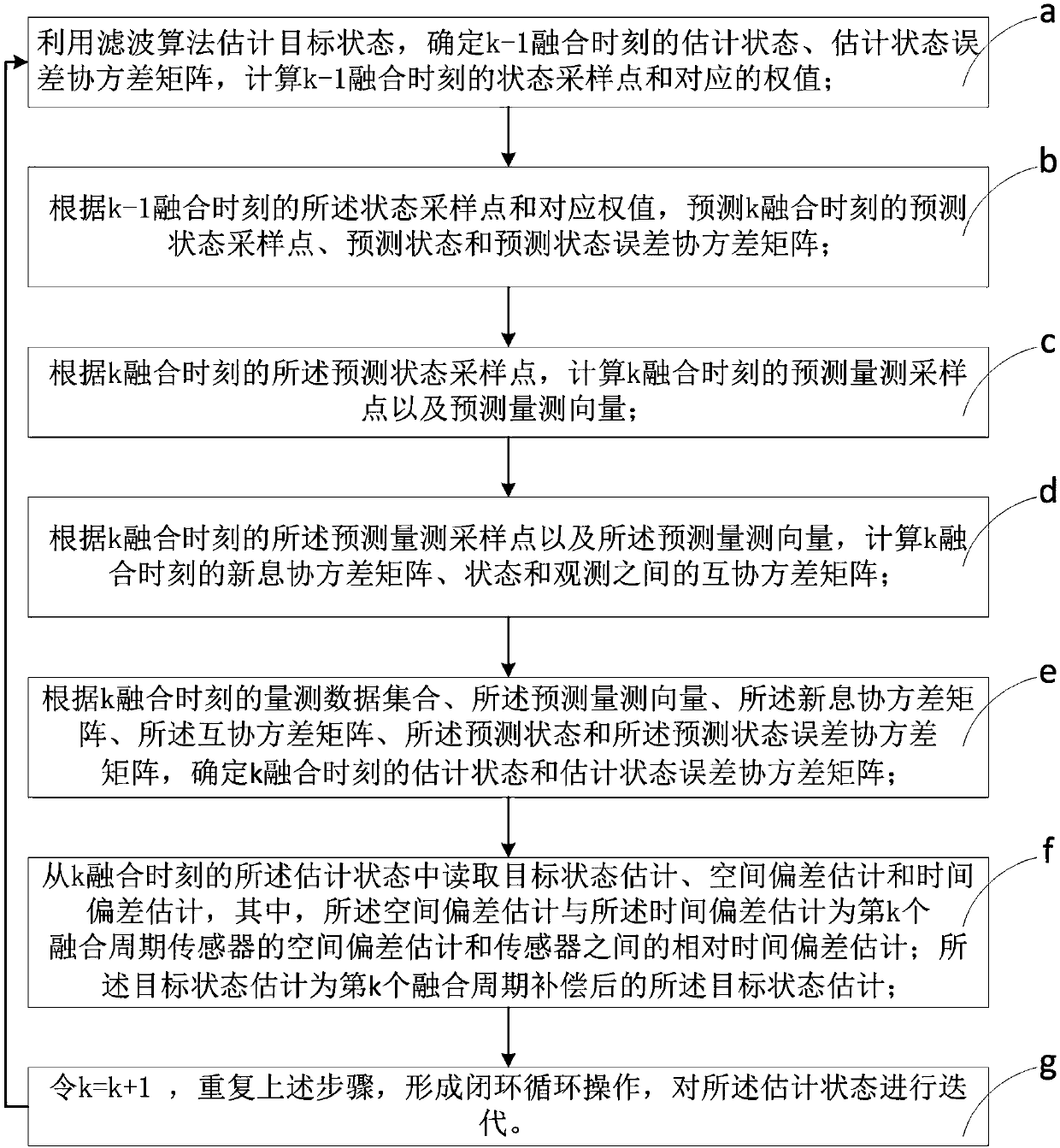
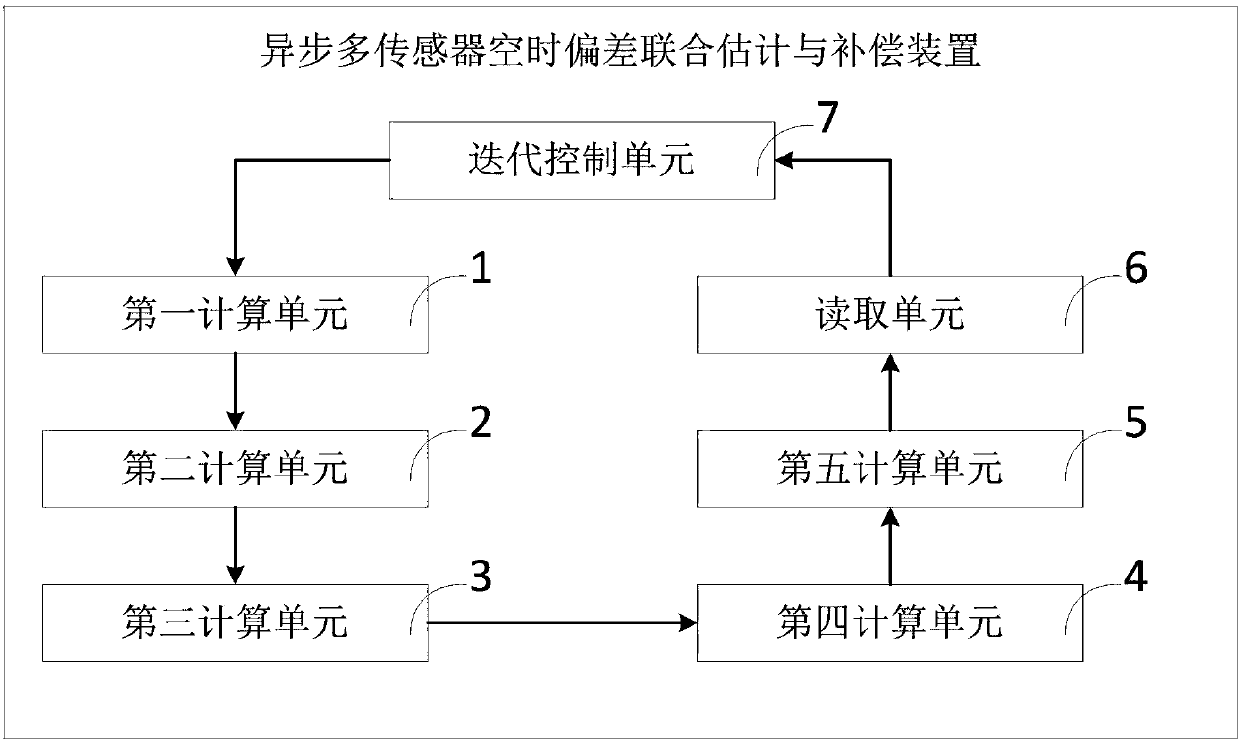
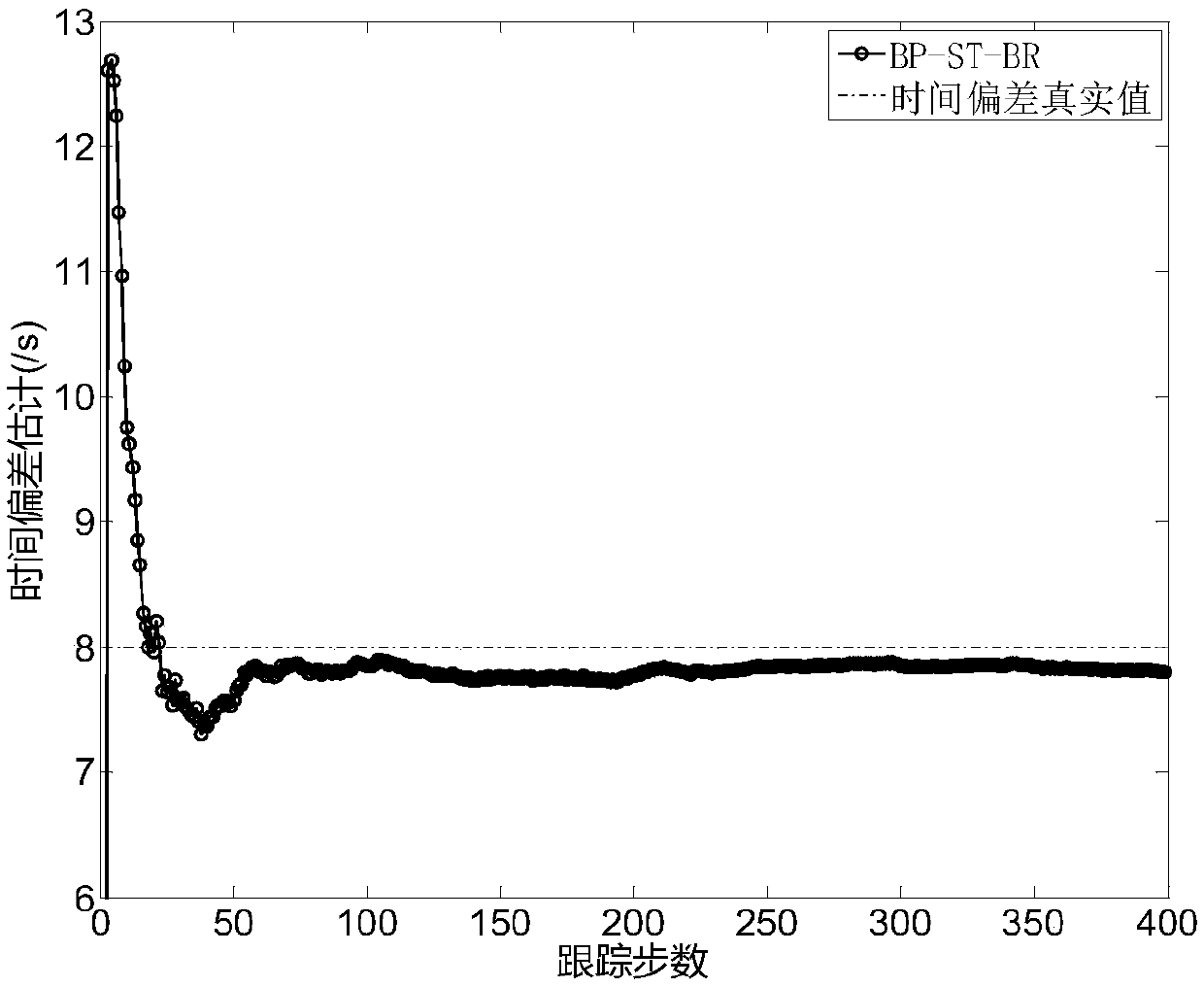
Asynchronous multi-sensor space-time deviation joint estimation and compensation method and device
ActiveCN108319570AEffective estimateEffective compensationComplex mathematical operationsTime deviationAlgorithm
The invention discloses an asynchronous multi-sensor space-time deviation joint estimation and compensation method and device. The method includes the steps of a, calculating a state sampling point and a corresponding weight value at a k-1 fusion moment; b, calculating a prediction state sampling point, a prediction state and a prediction state deviation covariance matrix at a k fusion moment; c,calculating a predicted measurement sampling point and a predicted measurement vector; d, calculating an innovation covariance matrix and a cross covariance matrix between states and observation; e, determining an estimation state and an estimation state deviation covariance matrix at the k fusion moment; f, reading target state estimation, space deviation estimation and time deviation estimation;g, making k equal to the sum of k and 1 and repeating the procedures above to form a closed-loop cyclic operation, wherein the device corresponds to the method. In this way, under the situation thatthe data rates of sensors are different, state vectors after dimensional expansion are estimated, and the target state estimation is obtained through iteration while effective estimation and compensation of space-time deviations are achieved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
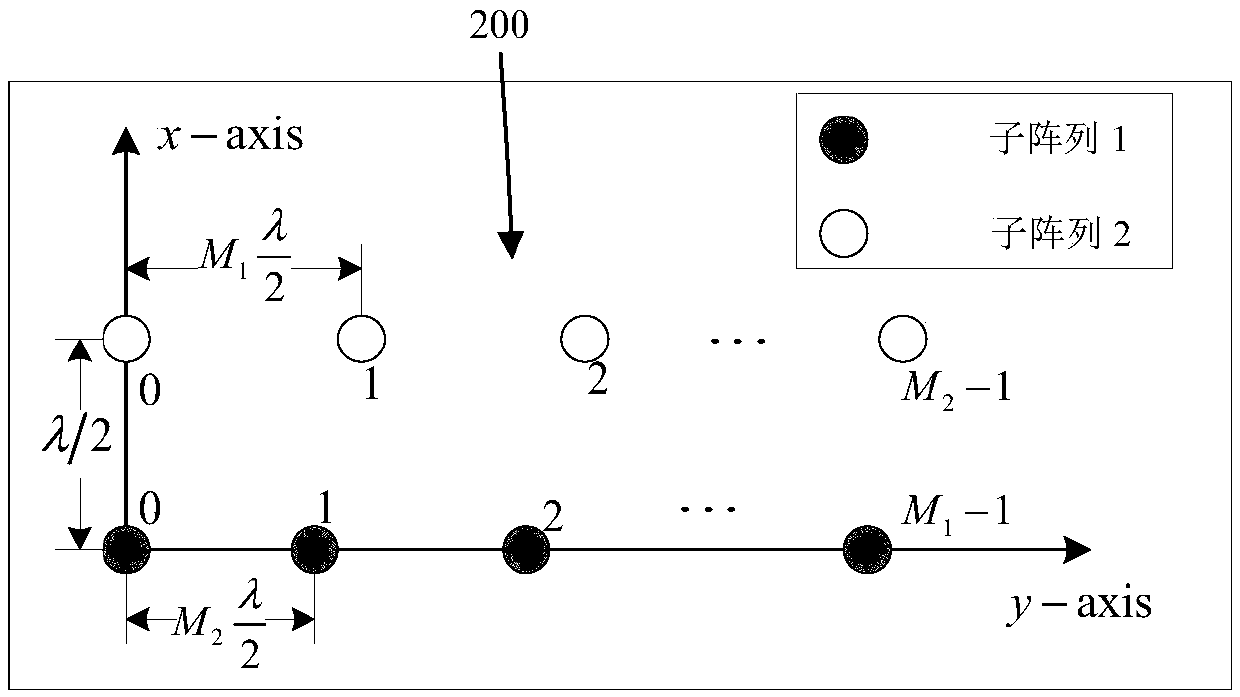
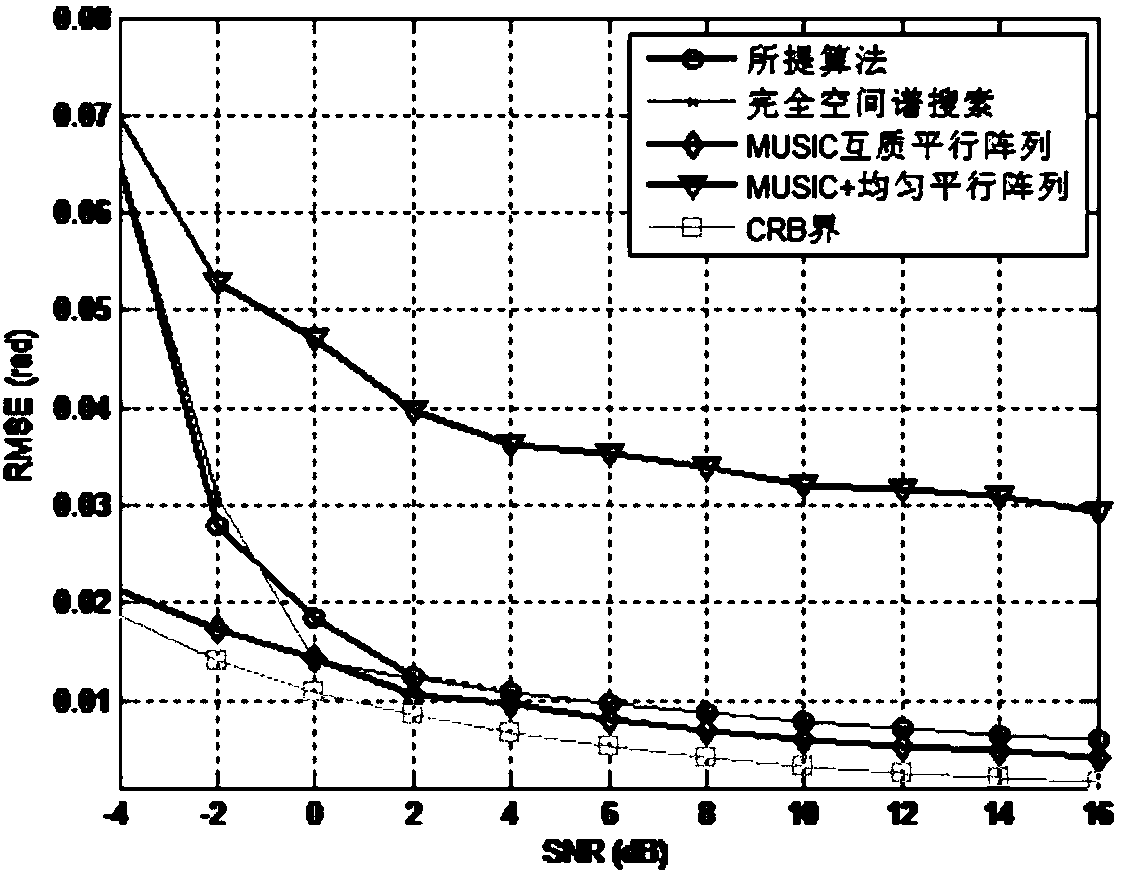
Planar array DOA estimation method and equipment thereof
ActiveCN108120967AHigh complexityReduce complexityWave based measurement systemsCoprime arrayEstimation methods
The invention discloses a planar array DOA estimation method and equipment thereof. The planar array DOA estimation method comprises the following steps of 1, receiving a signal from at least one signal source by means of a planar array, wherein the planar array comprises at least one parallel coprime array, and the parallel coprime array comprises coprime linear subarray pairs which are parallelwith each other; 2, based on an actually received signal of the coprime linear subarray pairs, calculating an autocovariance matrix of actually received signals of two linear subarrys of the coprime linear subarray pairs, and a cross-covariance matrix between the actually received signals of the two linear subarrys; and 3, estimating the DOA value of at least one signal source based on the autocovariance matrix and the cross-covariance matrix. The planar array DOA estimation method and the equipment thereof settle a problem of high algorithm complexity caused by factors such as two-dimensionalspatial spectrum searching and angle pairing and can realize high-precision wave arrival direction estimation with relatively low complexity. The method and the equipment are suitable for the occasion with high real-time performance requirement.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Multi-AUV collaborative navigation wave filtering method under communication delay
ActiveCN105910603AInhibit the growth of positioning errorsHigh positioning accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsPosition fixationFilter algorithmOne step prediction
The invention provides a multi-AUV collaborative navigation wave filtering method under communication delay, which includes the following steps: (S1) performing dimension expansion at a t<k> time from status X<k> to M<k> of a sub AUV; (S2) calculating one-step prediction and an error variance thereof at the t<k> time of the sub AUV status M<k> after the dimension expansion; (S3) calculating one-step prediction and a covariance and a cross covariance of the one-step prediction of distance measurement of the sub AUV at the t<k> time after the dimension expansion; and (S4) substituting the parameters calculated in the steps (S2) and (S3) into Kalman filtering principle to obtain to-be-estimated status X(estimate)<k|k>, and status estimation error variance P<xx><k,k|k>, thereby achieving multi-AUV collaborative navigation wave filtering. The method, according to communication time delay among AUVs, the status of the sub AUV is subjected to the dimension expansion, and status estimation after the dimension expansion is used for predicting delay measurement, thereby solving a problem of positioning failure caused by communication delay in a conventional wave filtering algorithm (EKF).
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
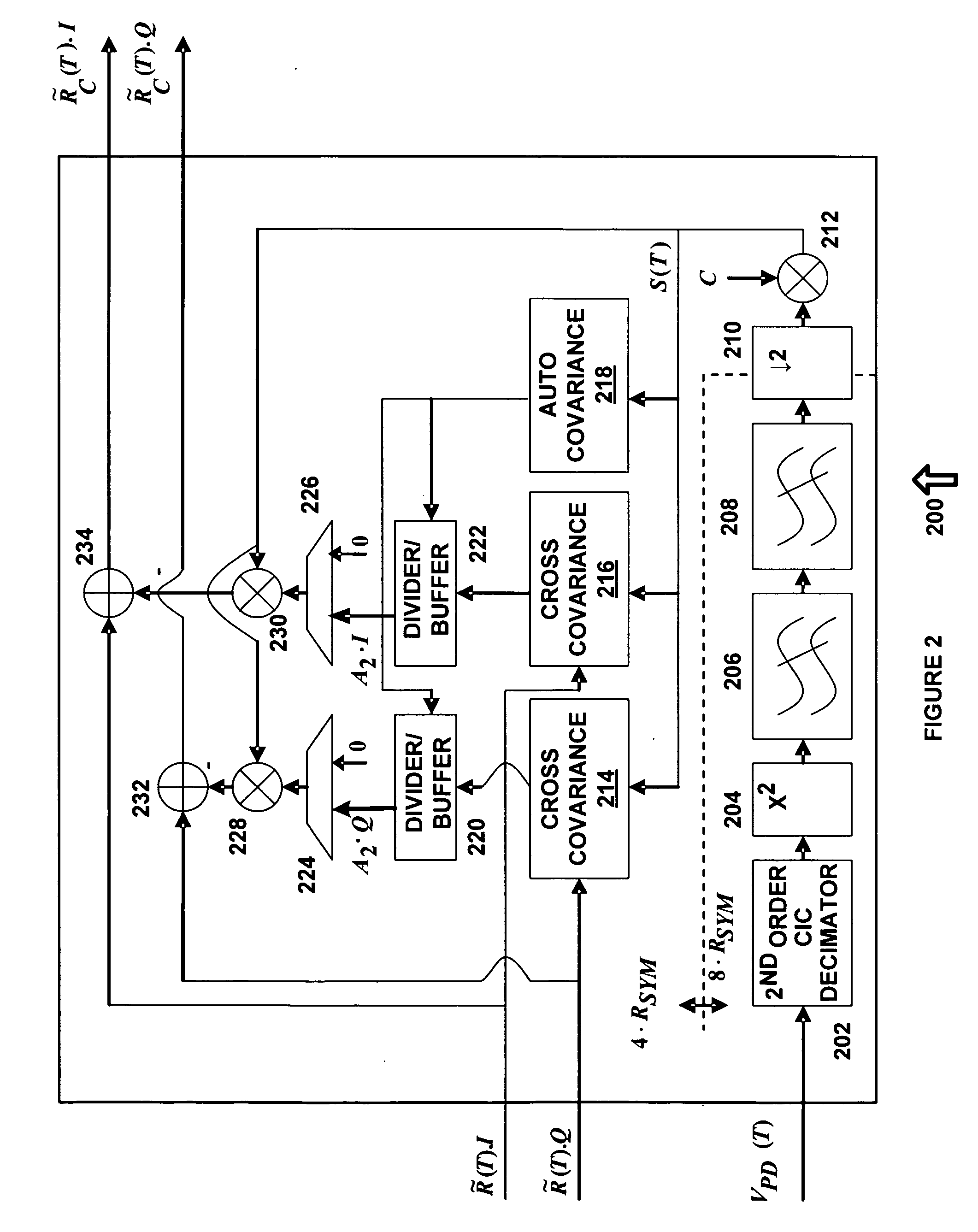
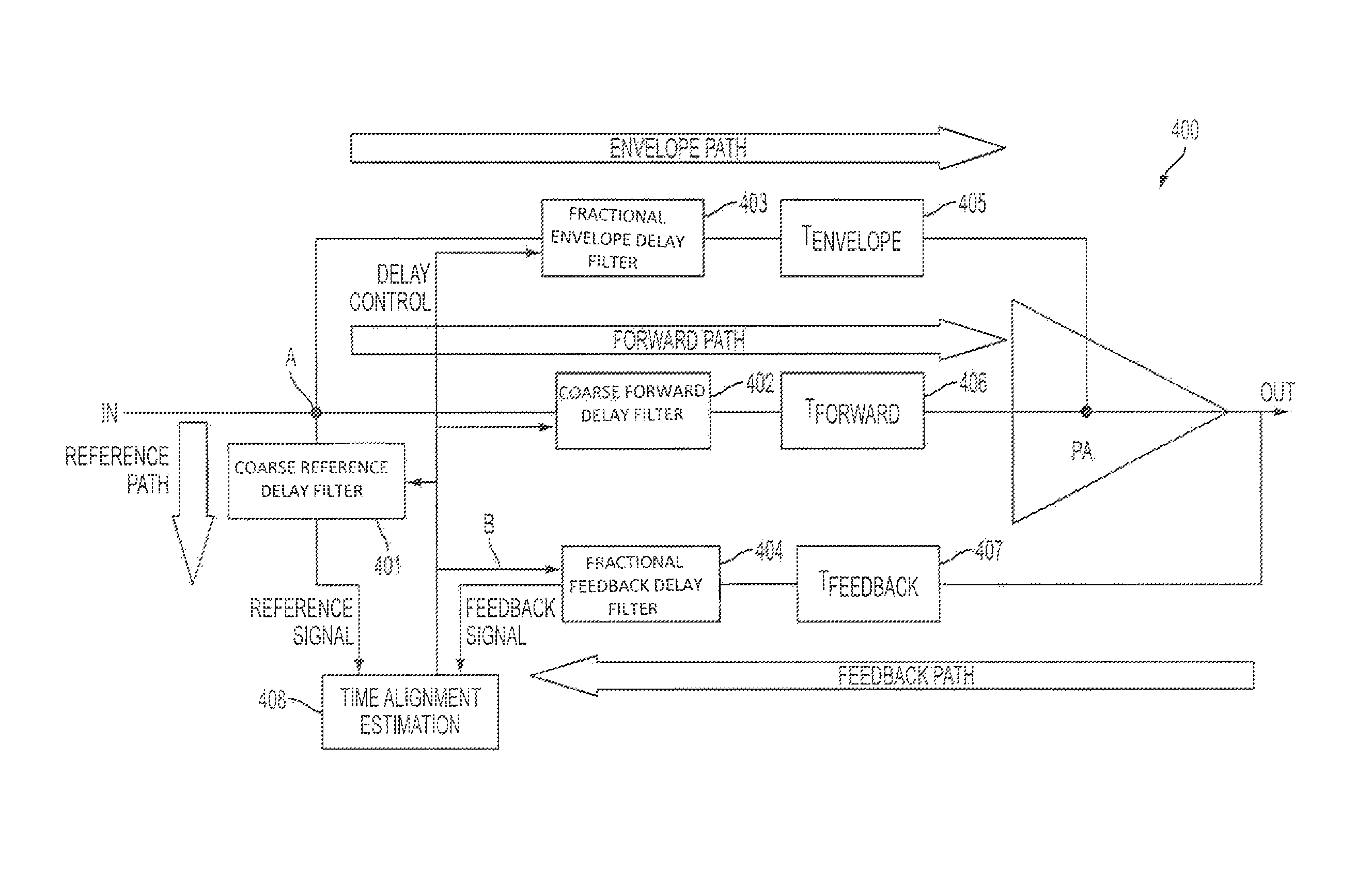
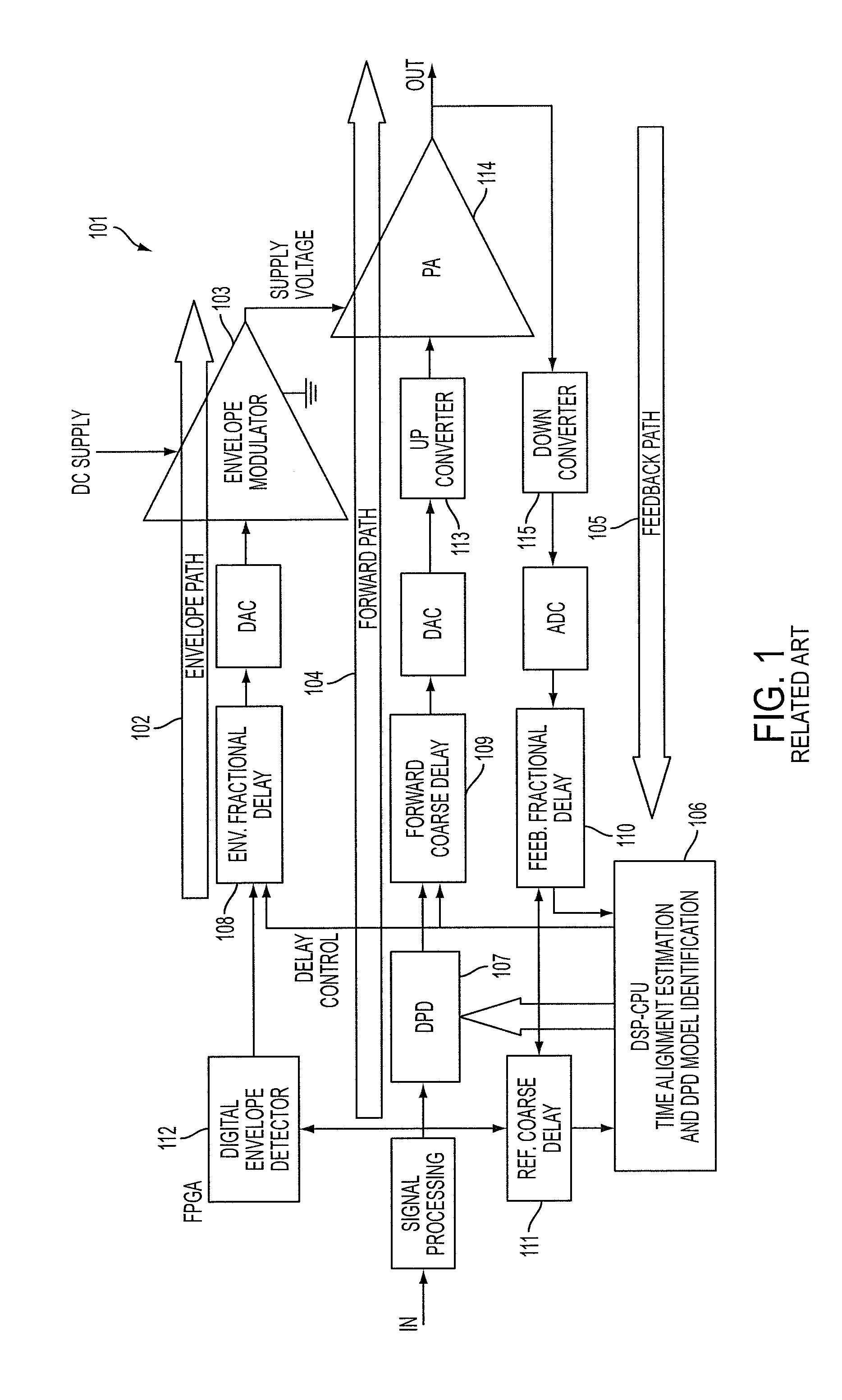
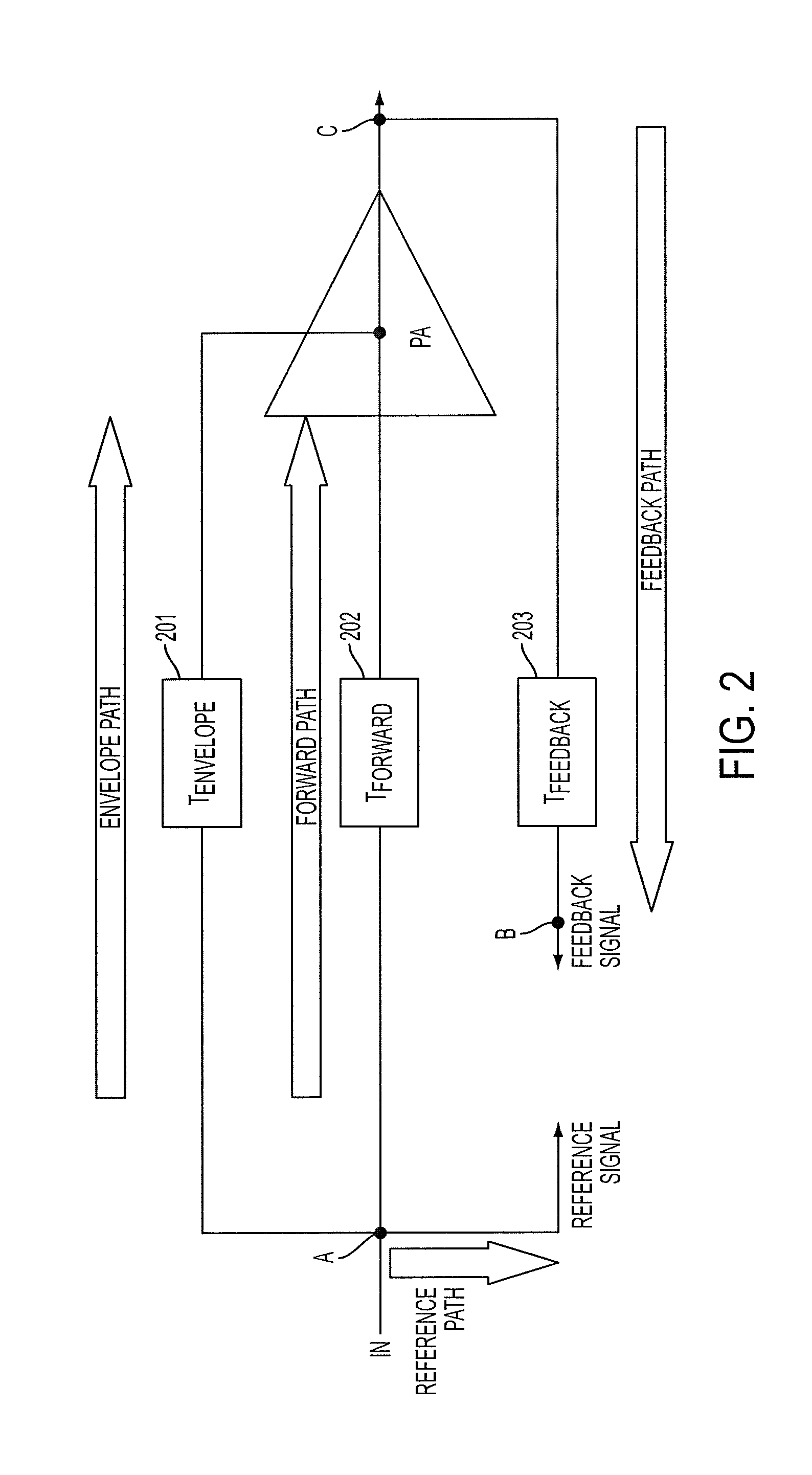
Apparatus and method for time alignment of an envelope tracking power amplifier
ActiveUS8908797B2Modulated-carrier systemsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierTime delays
An apparatus and method for a Time Alignment (TA) operation used by an Envelope Tracking (ET) Radio Frequency (RF) Power Amplifier (PA) that amplifies RF signals are provided. The ET RF PA has an input signal including complex, reference, and feedback signals. The apparatus includes a fast convolution unit for receiving the reference signal and the feedback signal, fore extracting respective envelopes of the reference signal and the feedback signal, for generating a cross-covariance vector for the reference signal envelope and the feedback signal envelope, a delay estimation unit for receiving the cross-covariance vector from the fast convolution unit, for determining peak values of the cross-covariance vector, for performing a fine time delay estimation, and for generating time delay settings according to the fine time delay estimation, and delay filters respectively delaying a timing of the reference signal and the feedback signal according to the generated time delay settings.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
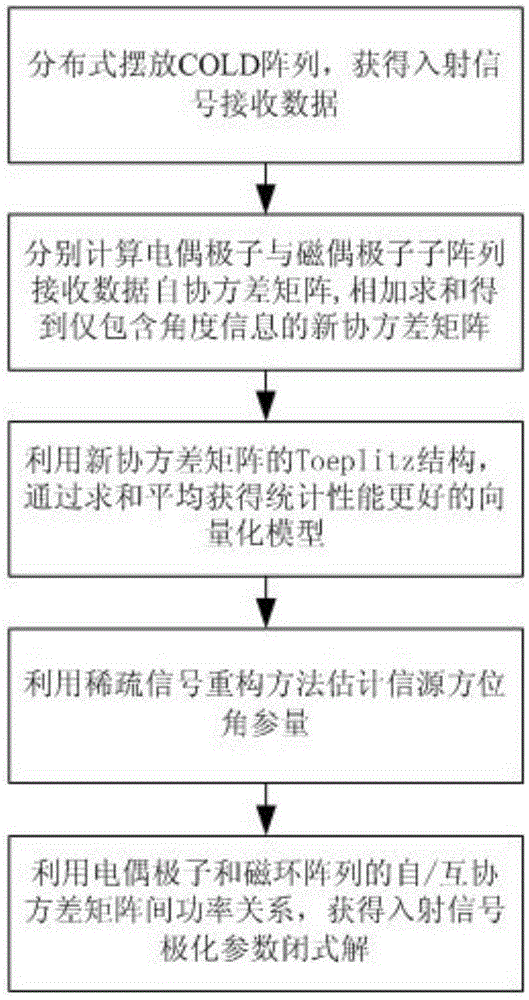
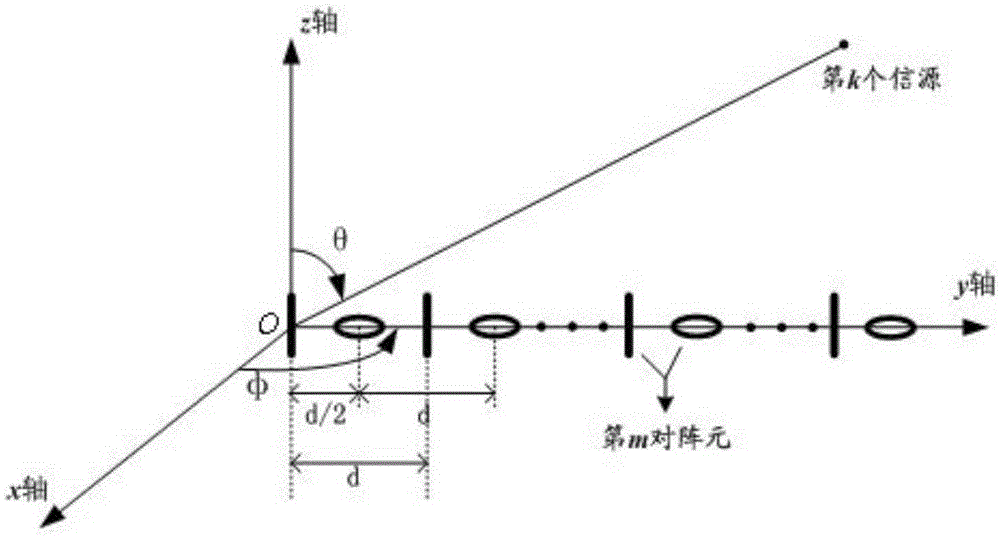
Method for multi-parameter joint estimation of distributed type electromagnetic vector sensor array
ActiveCN105334489AReduce the influence of mutual coupling effectImprove estimation performanceRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsComputation complexityArray element
The invention relates to a method for multi-parameter joint estimation of a distributed type electromagnetic vector sensor array and belongs to the field of array signal processing. Received data of the distributed type electromagnetic vector sensor array are constructed, covariance matrixes are performed on received data of an electric dipole and a magnetic dipole respectively and adding summation is performed, a covariance matrix sum only containing an information source azimuth parameter is obtained, a sparse signal reconstruction method is utilized to estimate the information source incident azimuth; and the estimation of polarization parameters is obtained by utilizing maxtrix relations of autocovariance and cross covariance of an electric dipole array and a magnetic dipole array. According to the method, the joint estimation of multi-dimensional parameters is converted into substep estimation of a plurality of one-dimensional parameters, the calculation complexity of the method is lowered; by distributed placing of electric dipole and magnetic dipole sensors, not only is the cross coupling influence between array elements reduced, but also the array physical pore diameter is extended effectively, and the parameter estimation accuracy is improved greatly.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
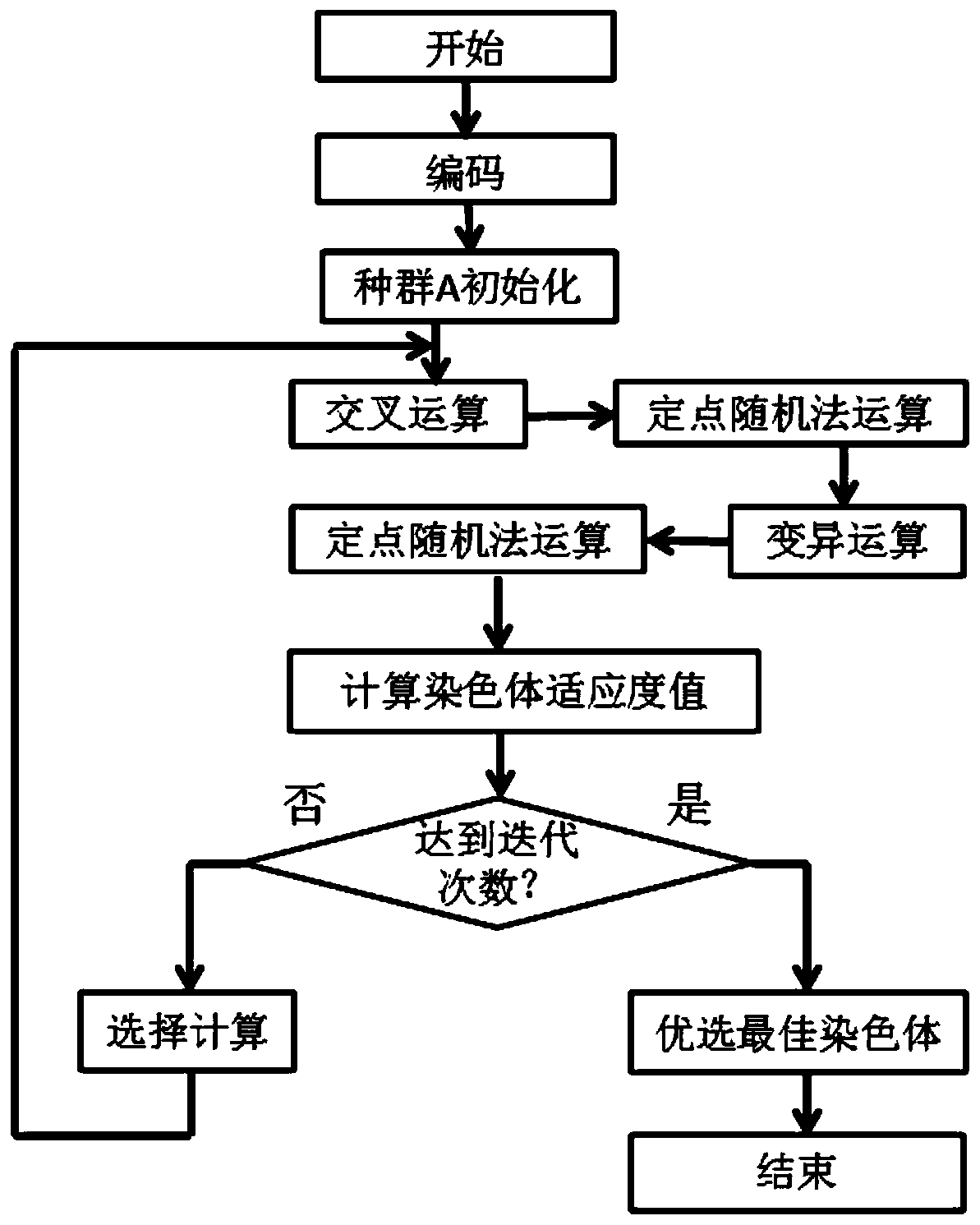
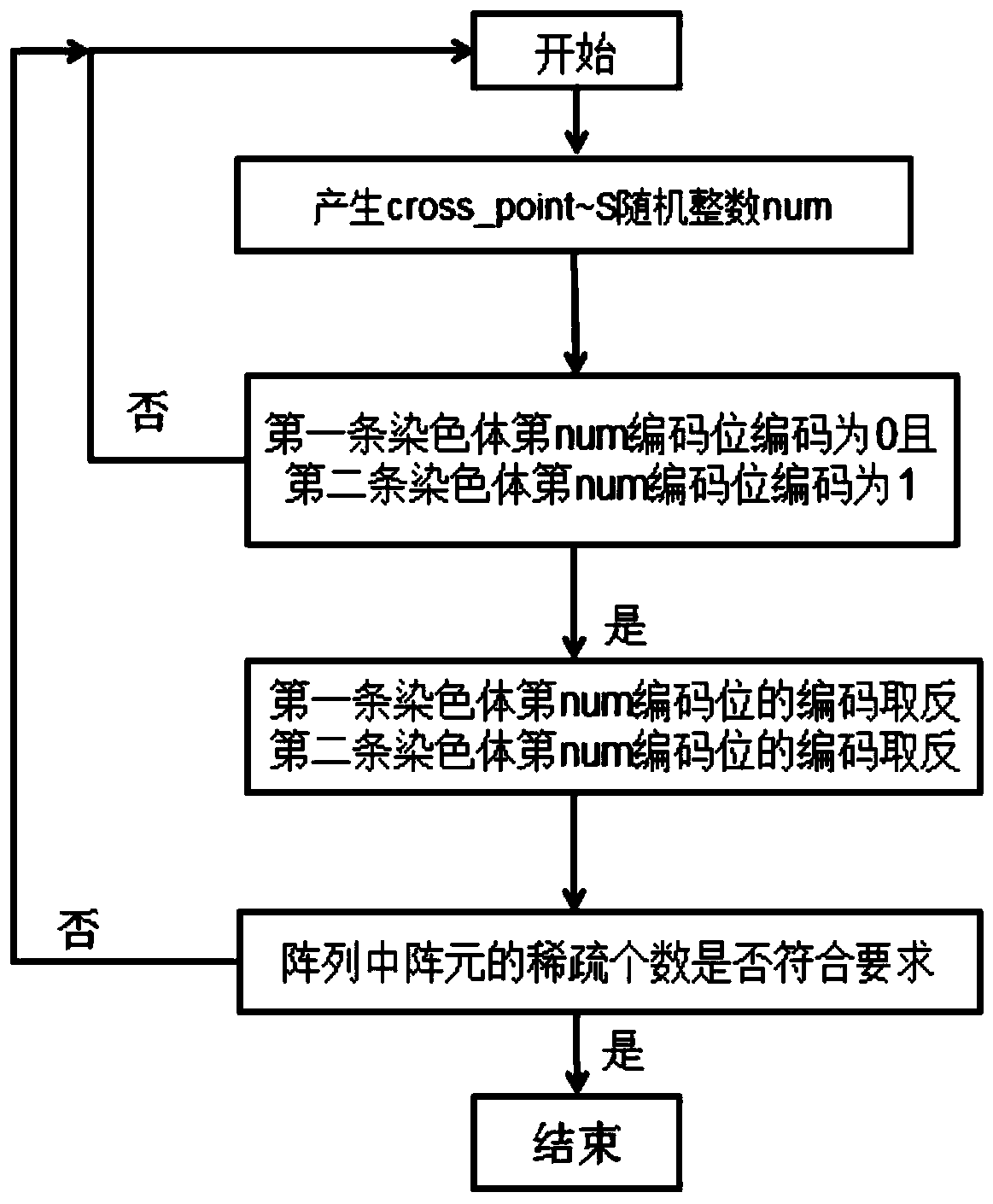
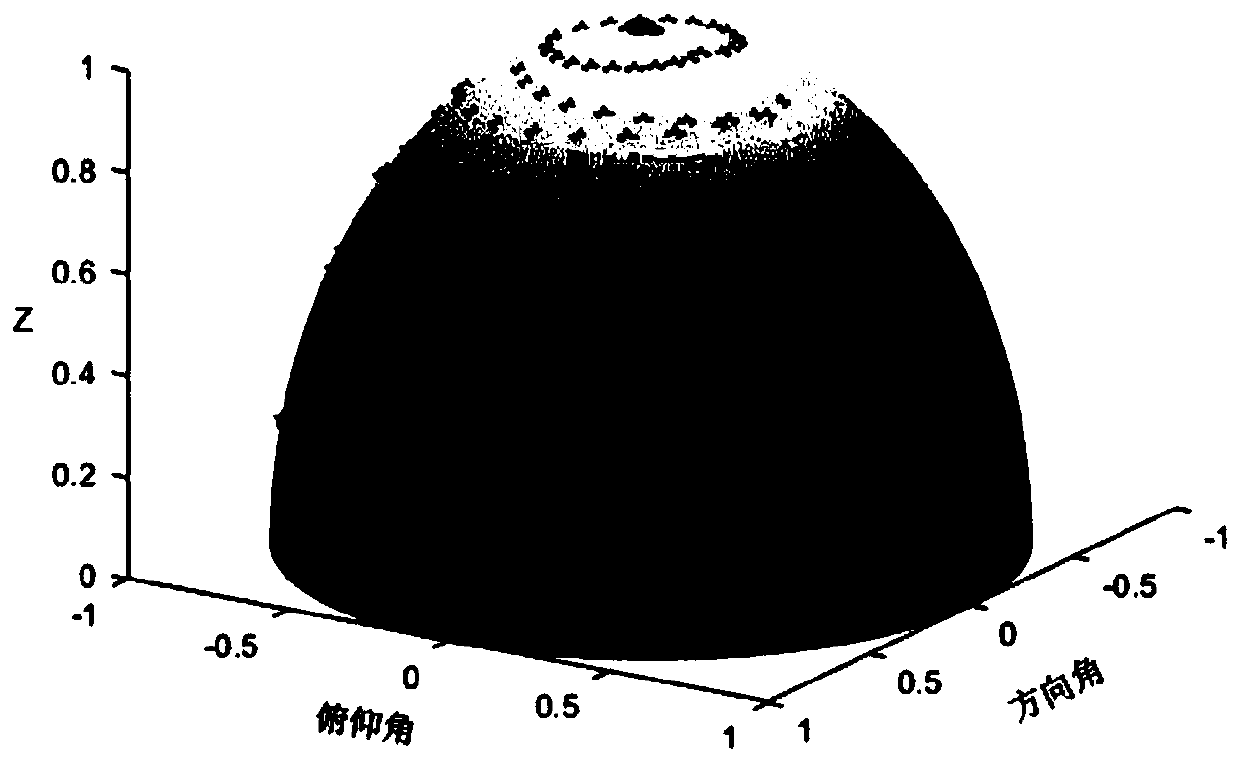
Radar array sparse optimization method based on improved genetic algorithm
ActiveCN109725294ASimple formationEasy to implementWave based measurement systemsGenetic modelsRadarMathematical model
The invention discloses a radar array sparse optimization method based on an improved genetic algorithm. The mathematical model of the genetic algorithm is established, the population is initialized,and the cross-covariance arithmetic is performed on the chromosomes in the population; the best chromosome is selected, and the array element sparse mode corresponding to the best chromosome is used as the optimal arrangement of the array elements in the radar array because the radar array is a hemispherical array with spiral distribution, the array elements in the array are encoded. The radar array sparse optimization method based on the improved genetic algorithm has the advantages of simple layout, simple engineering implementation, and effective reduction of the complexity of the subsequent signal processing part, and ensures the spatial performance of the radar array since the array element sparse mode is used and the 3dB beamwidth is used as a constraint.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
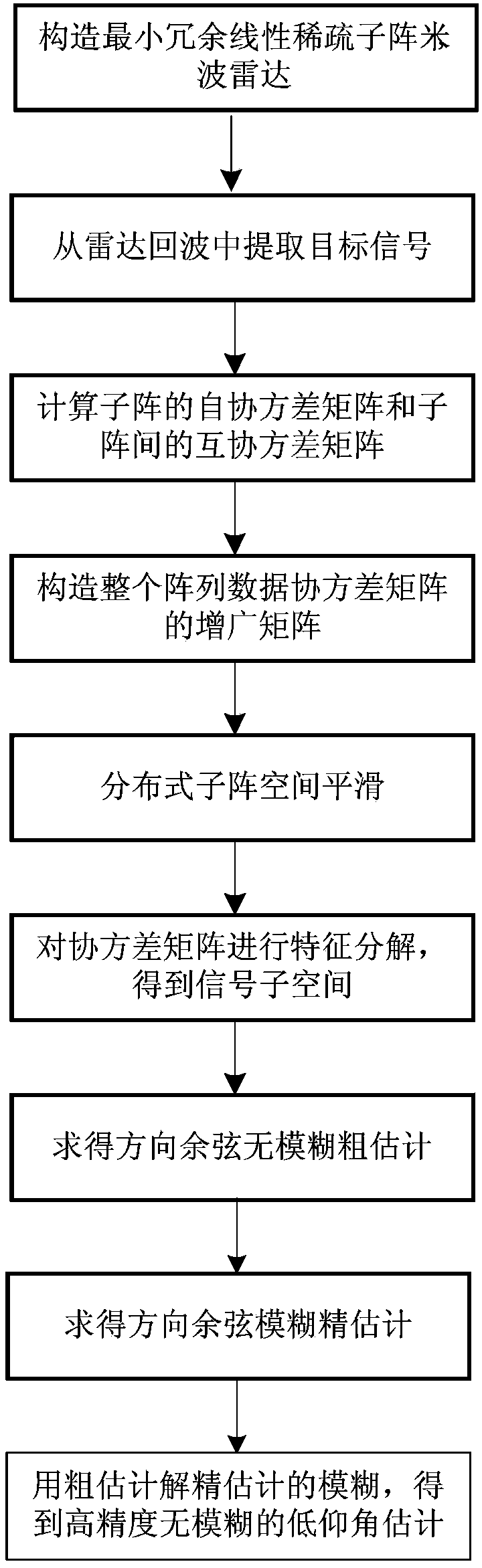
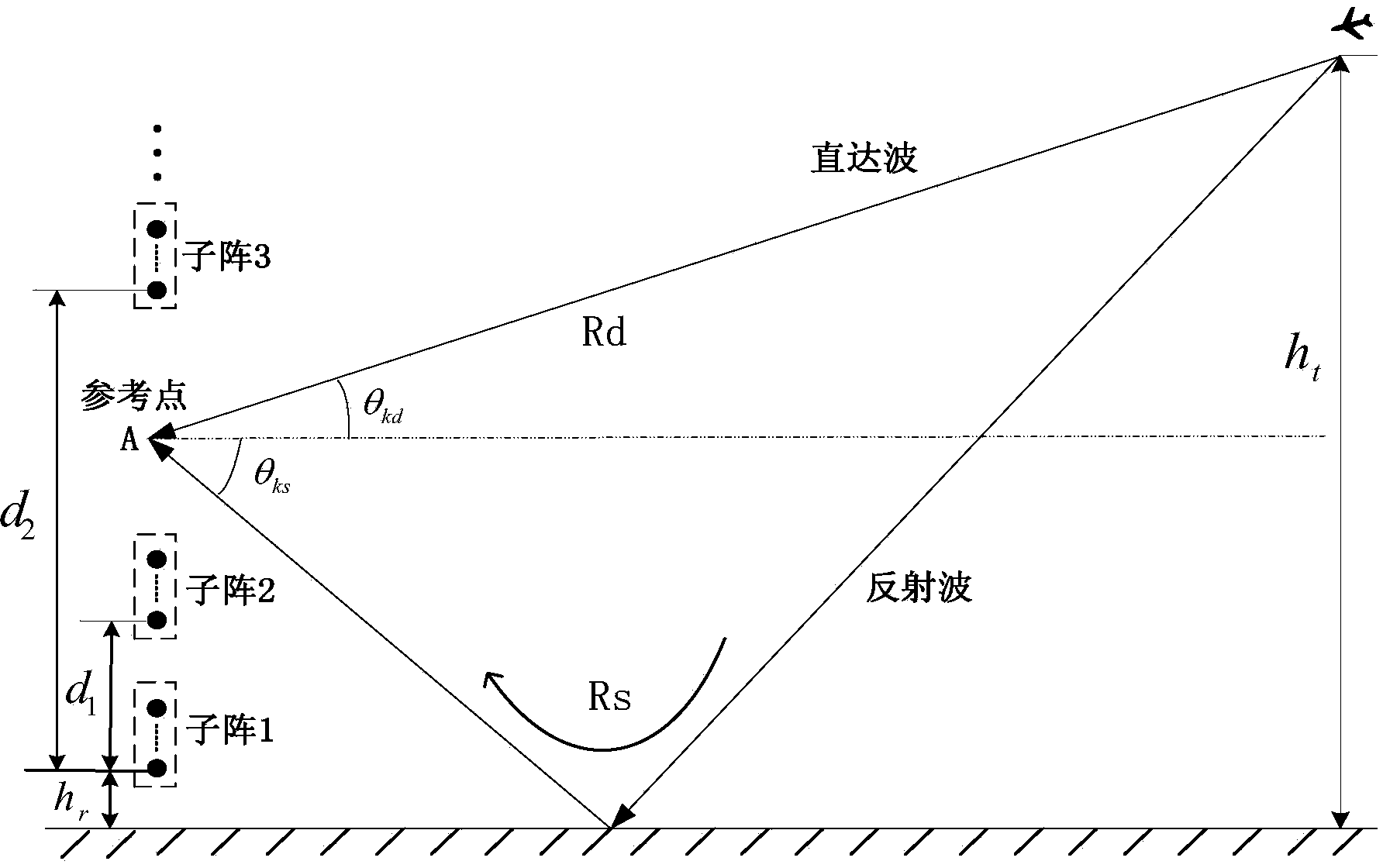
Meter-wave radar low elevation estimating method based on minimum redundancy linear sparse submatrix
ActiveCN103885049AGood angle measurement performanceIncrease the number ofWave based measurement systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Target signal
The invention discloses a meter-wave radar low elevation estimating method based on a minimum redundancy linear sparse submatrix. The meter-wave radar low elevation estimating method based on the minimum redundancy linear sparse submatrix mainly solves the problem that errors of estimation of meter-wave radar low elevations are large in the prior art. The meter-wave radar low elevation estimating method based on the minimum redundancy linear sparse submatrix comprises the implementation steps of (1) structuring a minimum redundancy linear sparse submatrix meter-wave radar, (2) extracting target signals from radar echoes, (3) calculating auto-covariance matrixes of submatrixes and cross covariance matrixes among the submatrixes, (4) structuring an augmented matrix of whole array data covariance matrixes, (5) restoring the rank of the augmented matrix by applying a spatial smoothing algorithm of distributed submatrixes, (6) carrying out characteristic decomposition on the covariance matrixes to obtain signal subspaces, (7) obtaining direction cosine non-fuzziness coarse estimation, (8) obtaining direction cosine fuzziness fine estimation, and (9) solving the fuzziness of the fine estimation by using the coarse estimation to obtain low elevation estimation with high precision and without fuzziness. According to the meter-wave radar low elevation estimating method based on the minimum redundancy linear sparse submatrix, the aperture of the meter-wave radar is expanded, the threshold of the signal to noise ratio is lowered, the precision of the lower elevation estimation is improved, and the method can be used for positioning and tracking targets.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Multi-method fusion based Kalman filtering quantization method
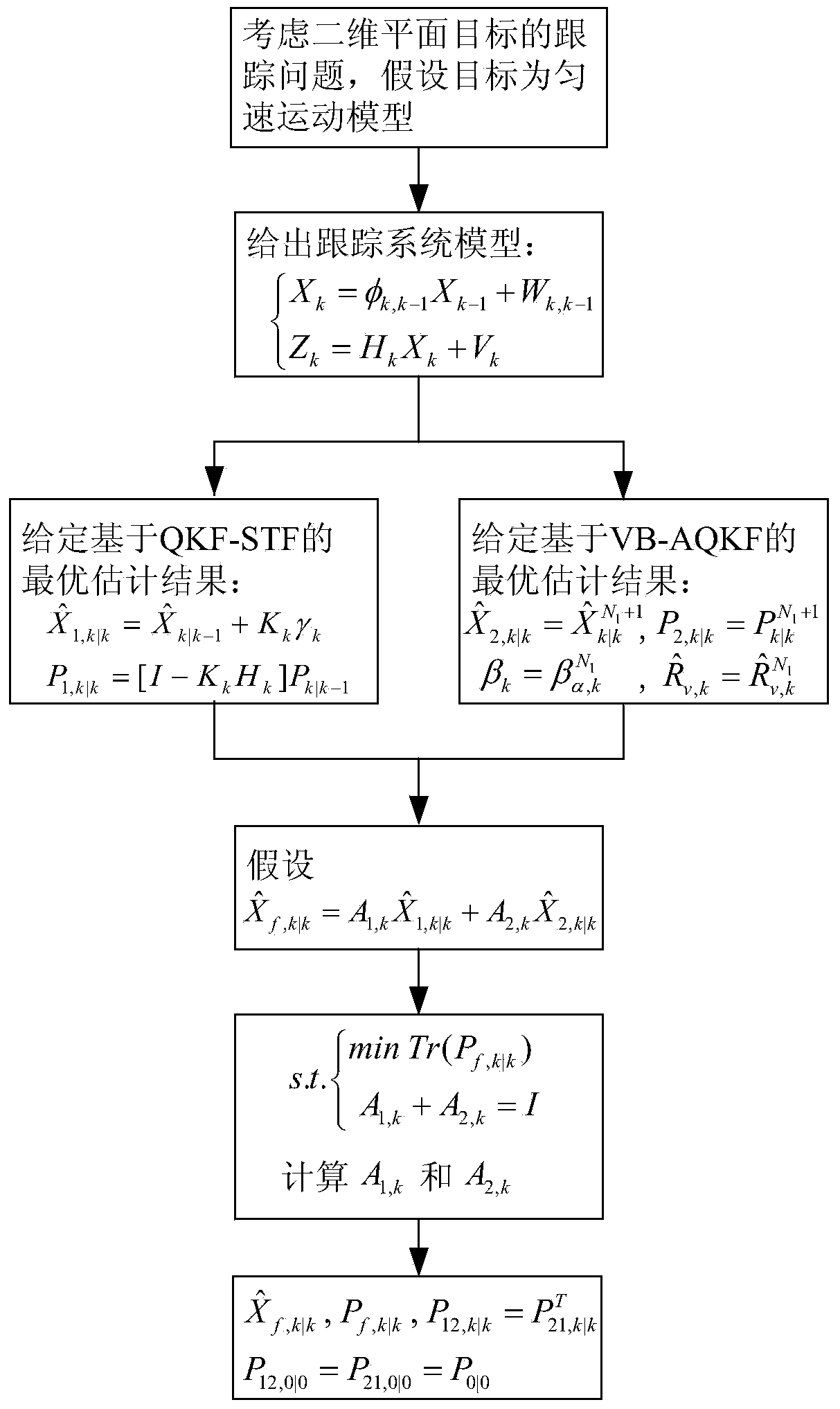
The invention relates to a multi-method fusion based Kalman filtering quantization method. The multi-method fusion based Kalman filtering quantization method comprises three parts of contents. The first part comprises performing system modelling according to real target motions; a second part comprises consulting pertinent literatures and giving optimal estimation results to QSK-STF and VB-AQKF; a third part comprises achieving optimal linear weighing fusion through the QSK-STF, wherein the optimal linear weighing fusion comprises calculating an optimal weighing matrix, estimating a final target state weighing fusion state and fusion estimating error covariance and a cross covariance matrix. The multi-method fusion based Kalman filtering quantization method has a strong trace function, can perform dynamic estimation on unknown covariance, achieves online real-time estimation and improves the target trace accuracy and accordingly the multi-method fusion based Kalman filtering quantization method can accurately estimate motion states of a target at any moment according to the existing data measured by a radar and achieves a target trace function.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
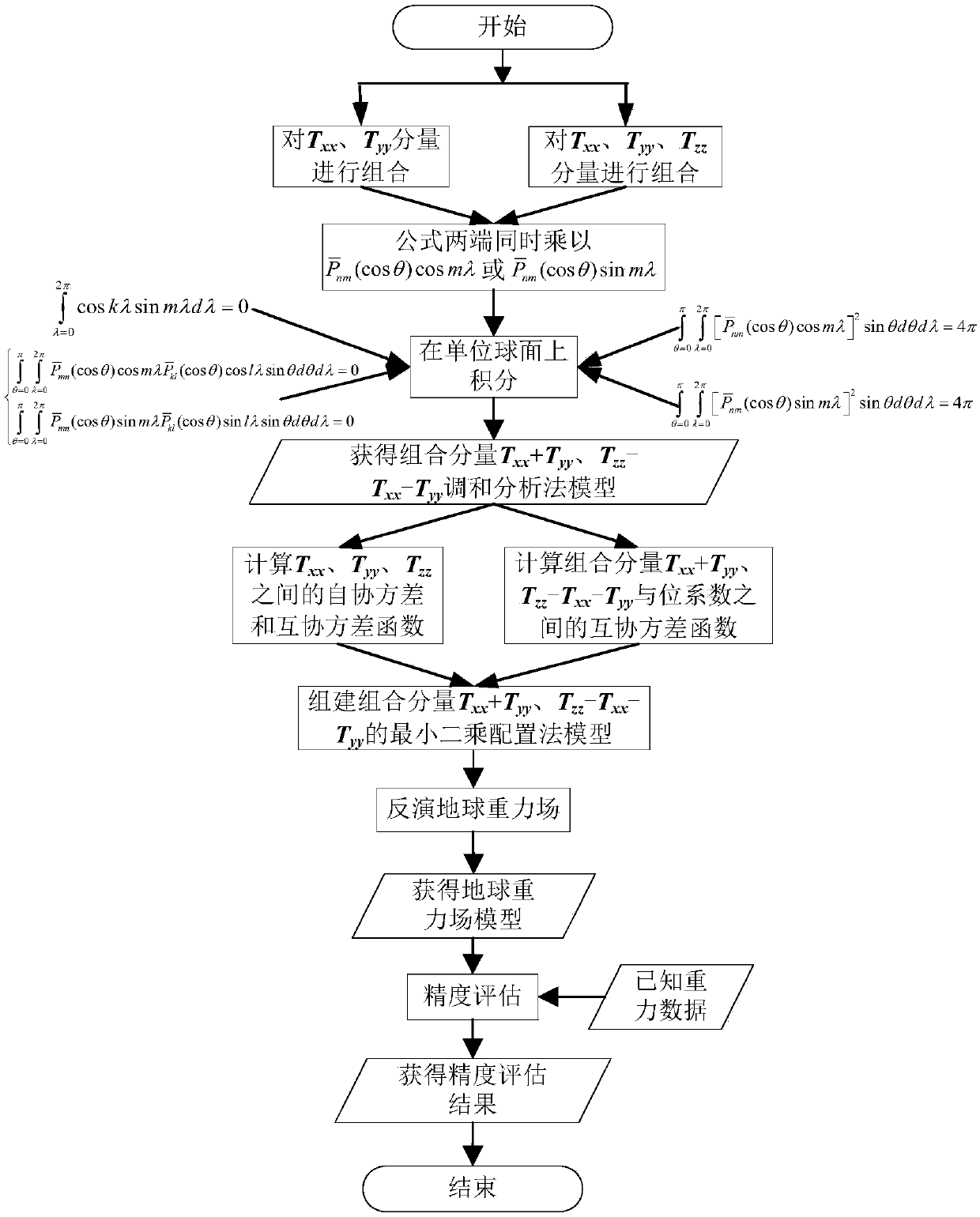
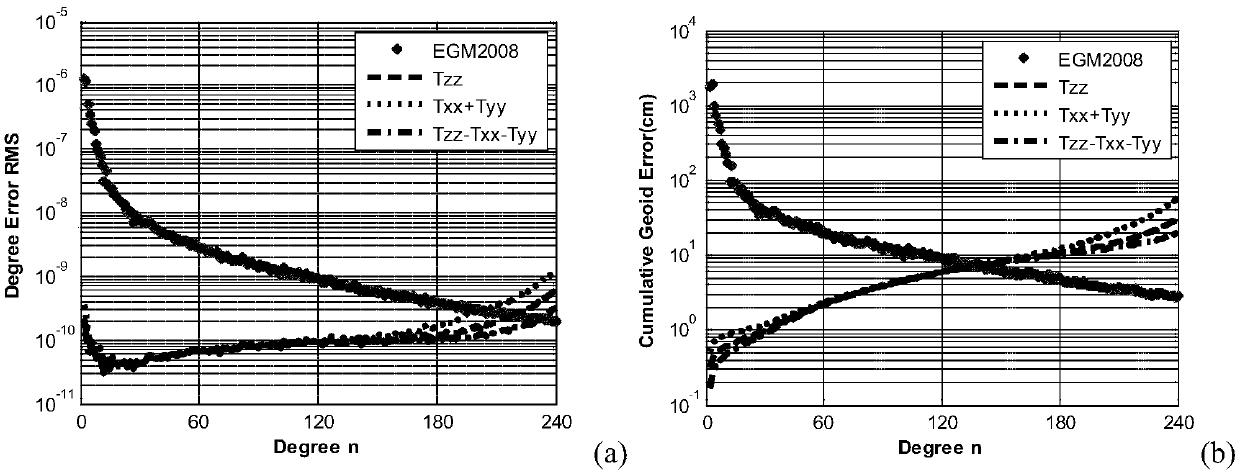
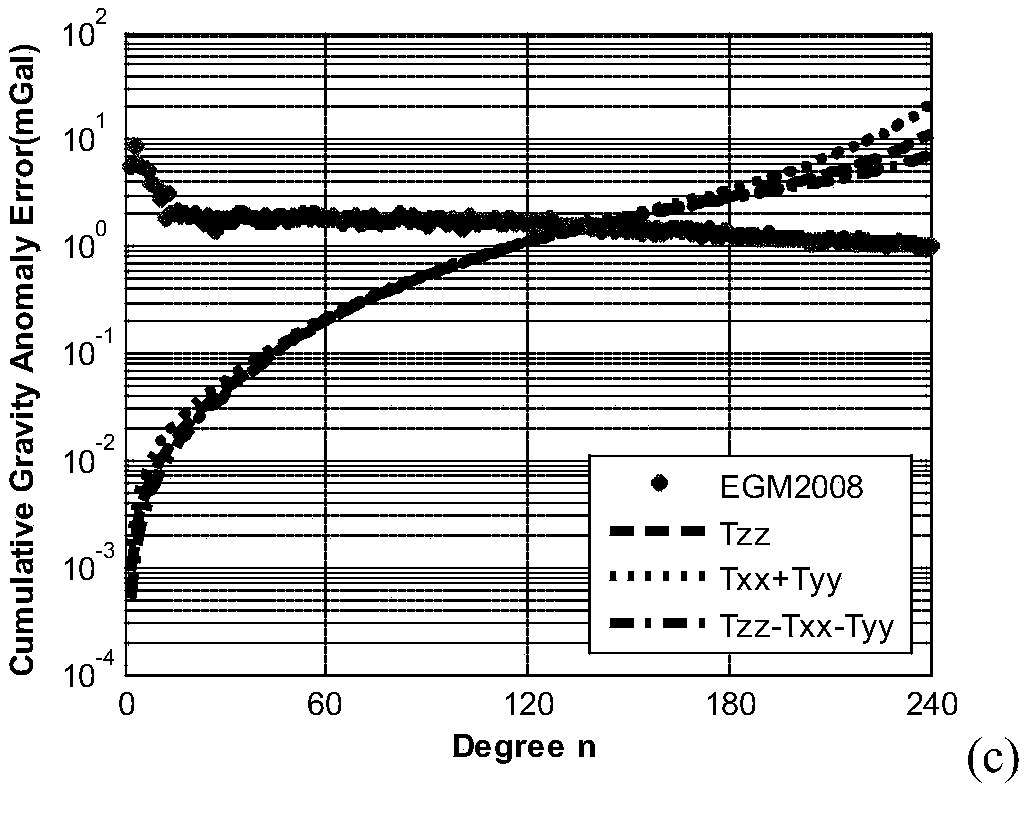
Least-square collocation model of satellite gravity gradient tensor diagonal three-component inversion earth gravity field and modeling method
InactiveCN108663718AIncrease contentVerify validityGravitational wave measurementGravitational potentialGravity gradient
The invention discloses a least-square collocation model of a satellite gravity gradient tensor diagonal three-component inversion earth gravity field and a modeling method, and belongs to the field of satellite gravity measurement. The method comprises the steps that starting from an orthogonality rule of a spherical harmonics function, Txx and Tyy components and Tzz, Txx and Tyy components are combined separately, practical calculation formulas of auto-covariance and cross covariance functions among the satellite gravity gradient tensor diagonal three-components and covariance functions of the components and gravitational potential coefficients are derived, and then the least-square collocation model of the Txx and Tyy two-component and Tzz, Txx and Tyy three-component inversion earth gravity fields is obtained. Accordingly, the theoretical basis is provided for fully utilizing the satellite gravity gradient tensor diagonal three-component inversion earth gravity field, and data resources of a gravity gradient measurement satellite GOCE launched by the ESA are fully utilized.
Owner:中国人民解放军61540部队
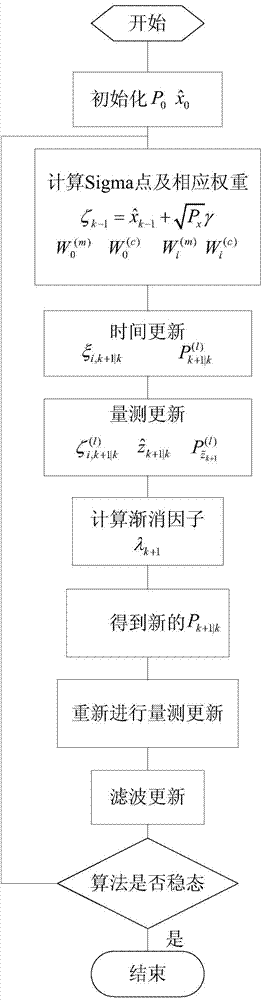
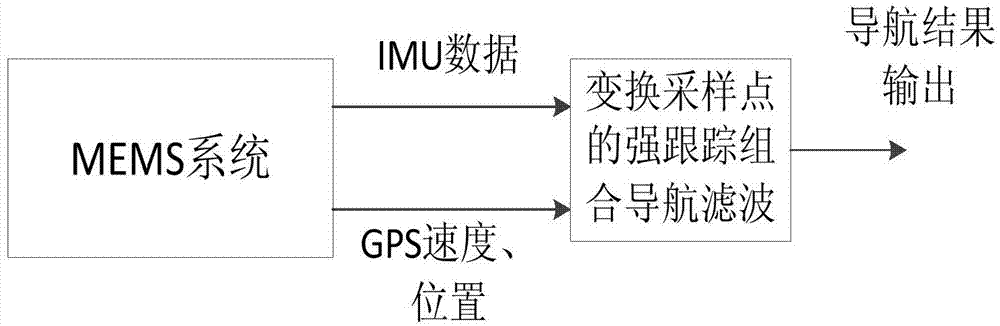
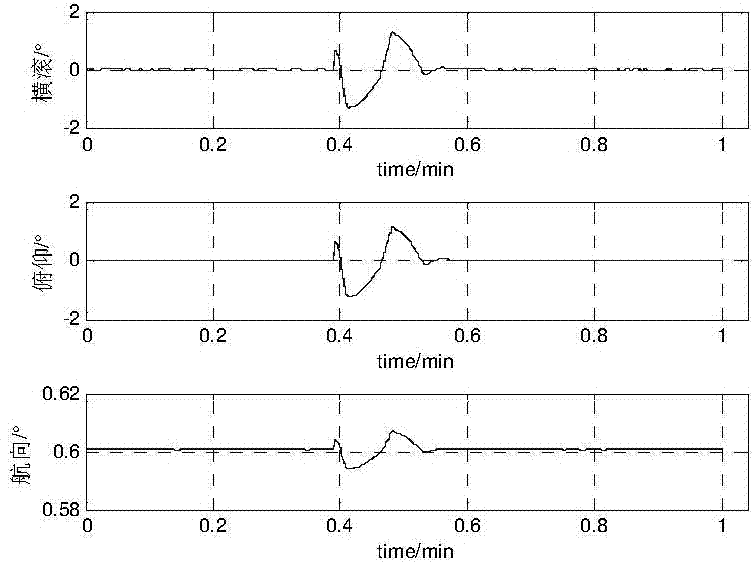
Strong tracking UKF filter method based on sampling point changing
InactiveCN103792562AGuaranteed numerical stabilitySolve the problem of non-local samplingNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSigma pointNon local
The invention provides a strong tracking UKF filter method based on sampling point changing. The strong tracking UKF filter method based on the sampling point changing comprises the steps that (1) initial parameter setting is carried out on a system; (2) Sigma points are sampled according to an orthogonal transformation sampling point method, a corresponding prediction equation is determined, and time and measurement are updated; (3) fading factors are calculated; (4) new one-step prediction covariance is calculated by using the fading factors, the Sigma points are recalculated, and auto-covariance and cross covariance after the fading factors are introduced are obtained through nonlinear measurement function propagation; (5) filter updating is carried out to the end. According to the strong tracking UKF filter method based on the sampling point changing, the problem of non-local sampling of the system is solved effectively, the precision of the system is improved, and the system is made to have certain strong tracking capability. The strong tracking UKF filter method based on the sampling point changing can be used for solving the problems of poor robustness and filtering divergence when a model of the system is uncertain, solves the problem of the non-local sampling in the high-dimensional system, and expands the application range of strong tracking filter. In an MEMS / GPS combined navigation system, the positioning and attitude determination performance of the MEMS / GPS combined navigation system can be improved through the method.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
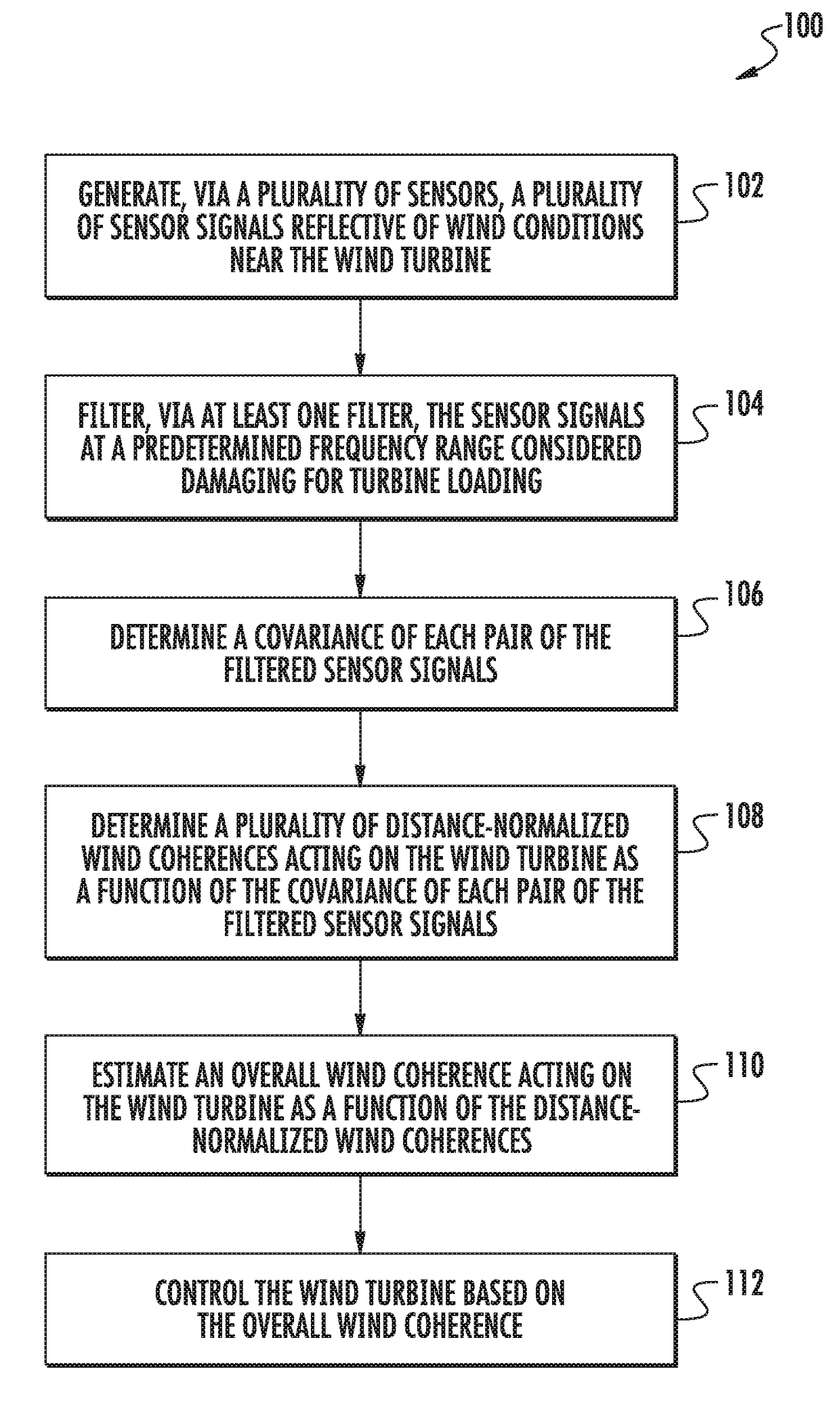
System and method for estimating wind coherence and controlling wind turbine based on same
The present disclosure is directed to a system and method for estimating an overall wind coherence acting on a wind turbine and using same to dynamically adapt the gain or bandwidth of pitch or torque or yaw control logic within a wind turbine. The method includes generating, via sensors, a plurality of sensor signals reflective of wind conditions near the wind turbine. The method also includes filtering, via at least one filter, the sensor signals at a predetermined frequency range considered damaging for turbine sub-system loading. Thus, the method also includes estimating an overall damaging wind coherence acting on the wind turbine as a function of distance-normalized wind coherences, which themselves are derived from auto and cross-covariances of pairs of filtered signals. The distance normalization uses a model of natural coherence dissipation with distance.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
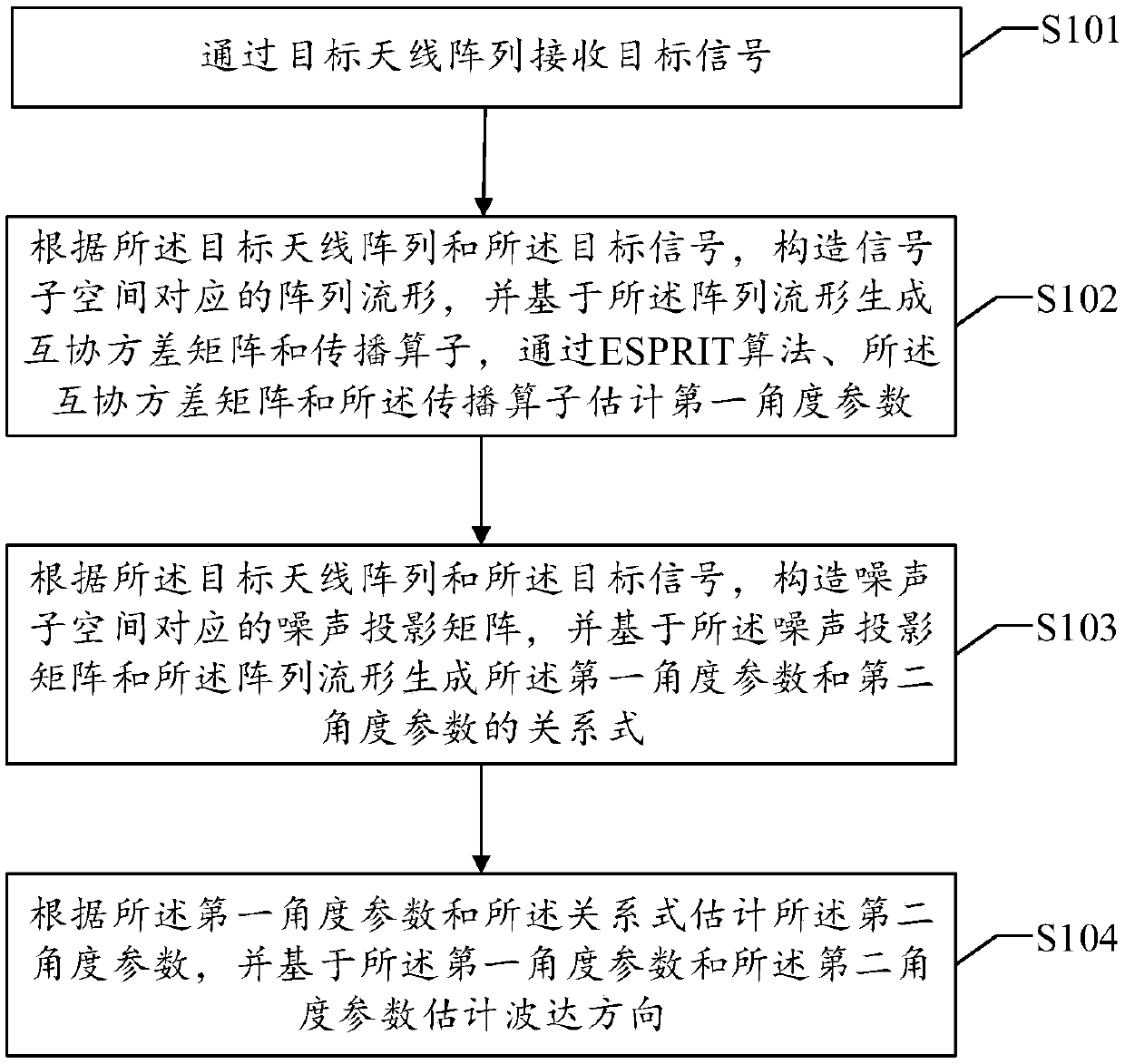
Two-dimensional wave arrival direction estimation method and device
The invention discloses a two-dimensional wave arrival direction estimation method. The method comprises the steps that after a target signal is received, an array manifold corresponding to a signal subspace is constructed according to a target antenna array and a target signal, a cross-covariance matrix and a propagation operator are generated on the basis of the array manifold, and a first angleparameter is estimated through an ESPRIT algorithm, the cross-covariance matrix and the propagation operator; meanwhile, a noise projection matrix corresponding to a noise subspace is constructed, and a relational expression of the first angle parameter and a second angle parameter is generated on the basis of the noise projection matrix and the array manifold; the second angle parameter is estimated according to the first angle parameter and the relational expression, and then the wave arrival direction is estimated. Therefore, according to the method, the second angle parameter is estimatedon the basis of the first angle parameter, and matching of two-dimensional angle parameters is avoided, so that the calculation complexity is reduced, and meanwhile good universality is achieved. Accordingly, the invention discloses a two-dimensional wave arrival direction estimation device which also has the technical effects.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com