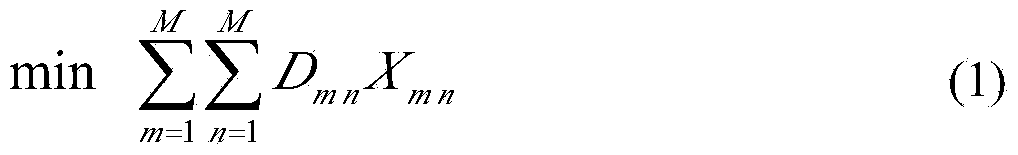
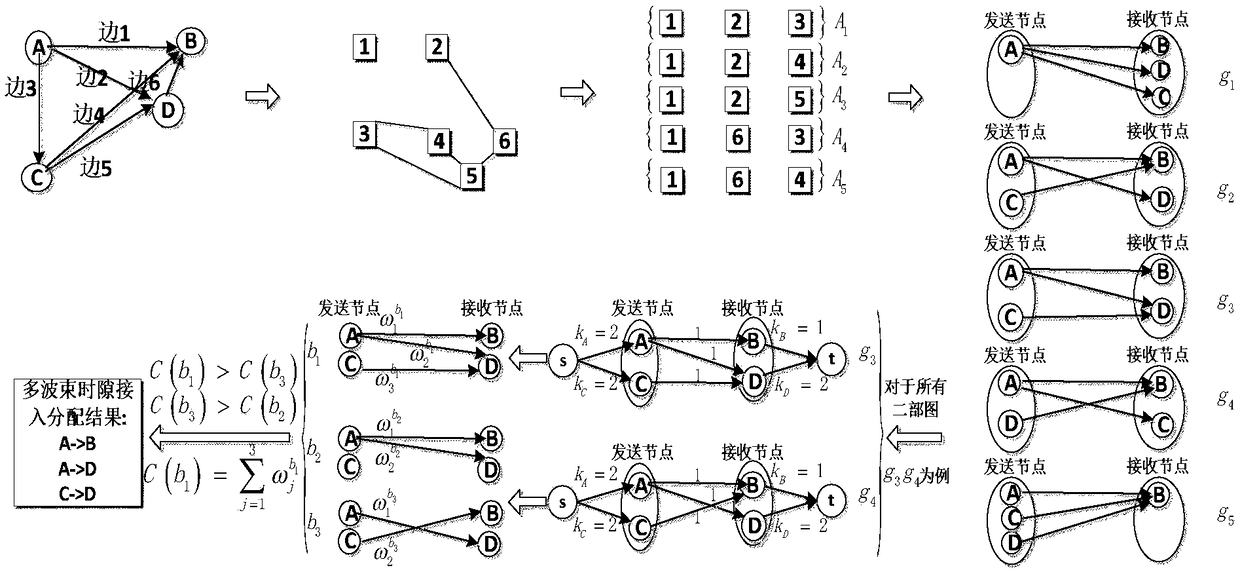
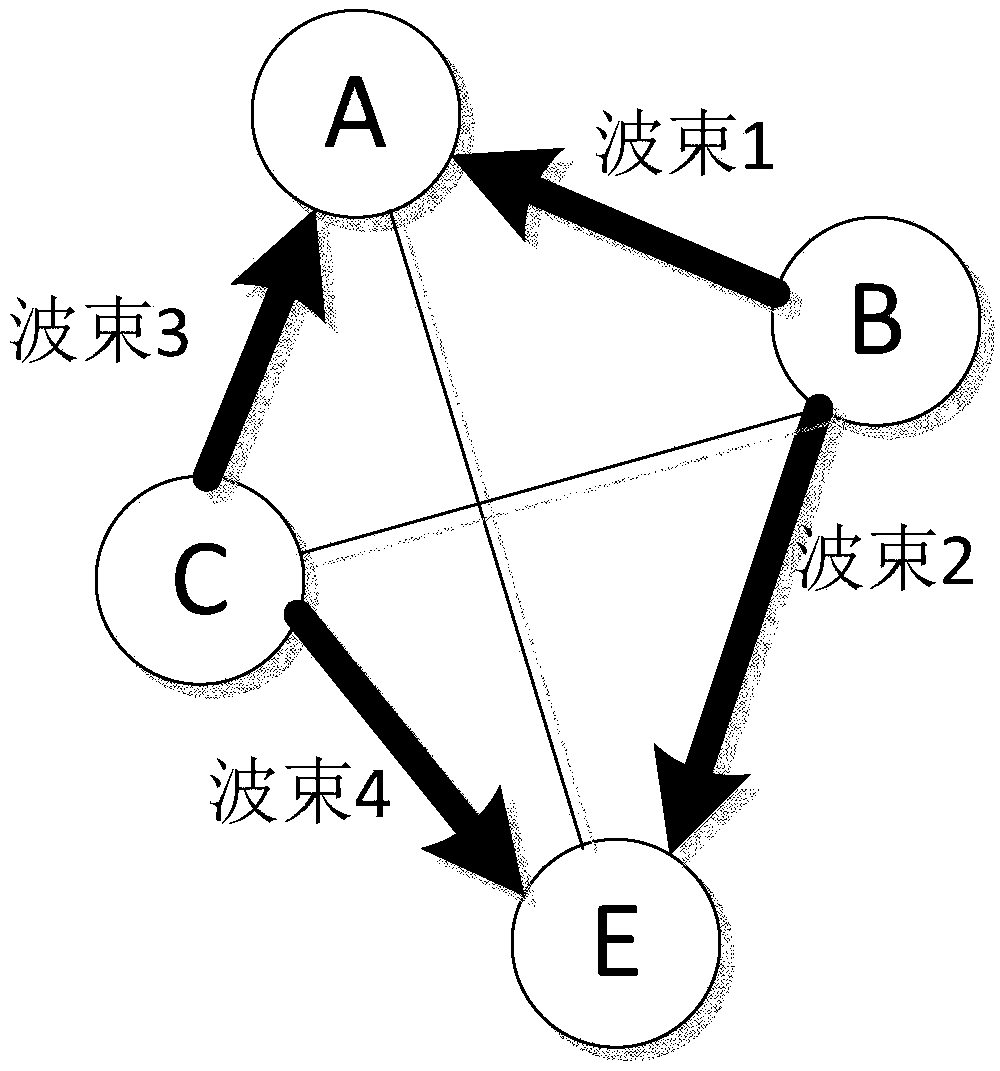
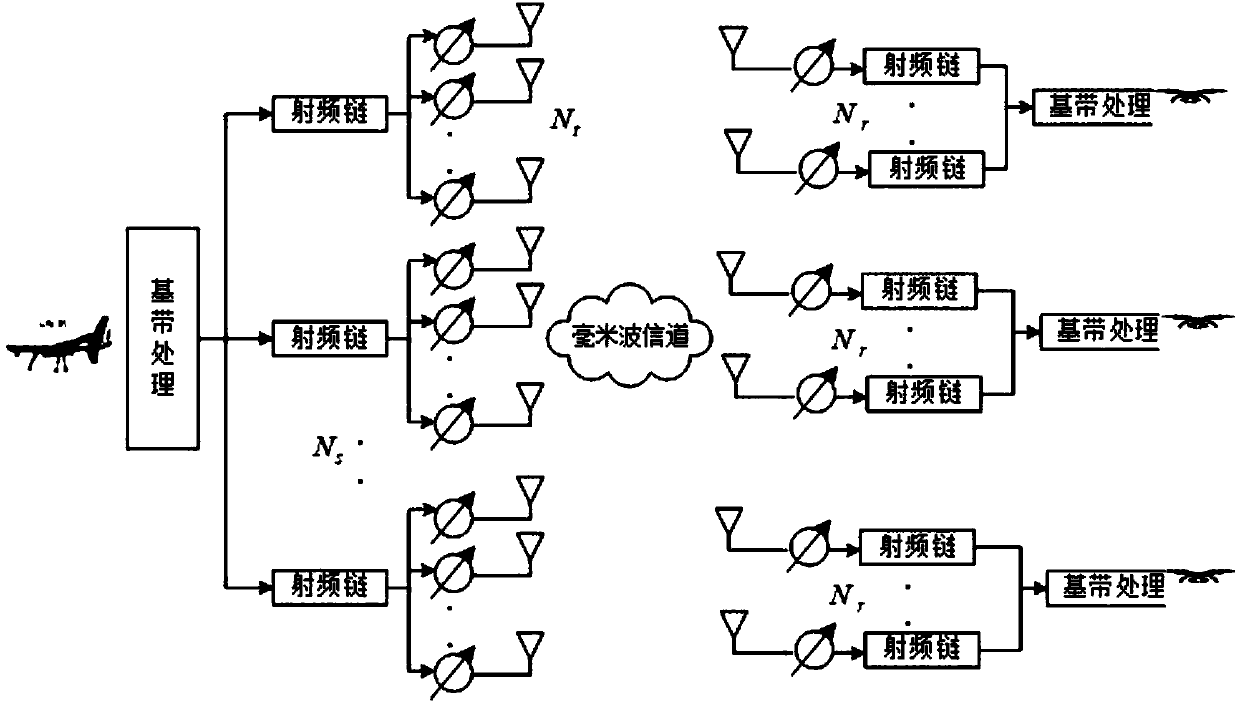
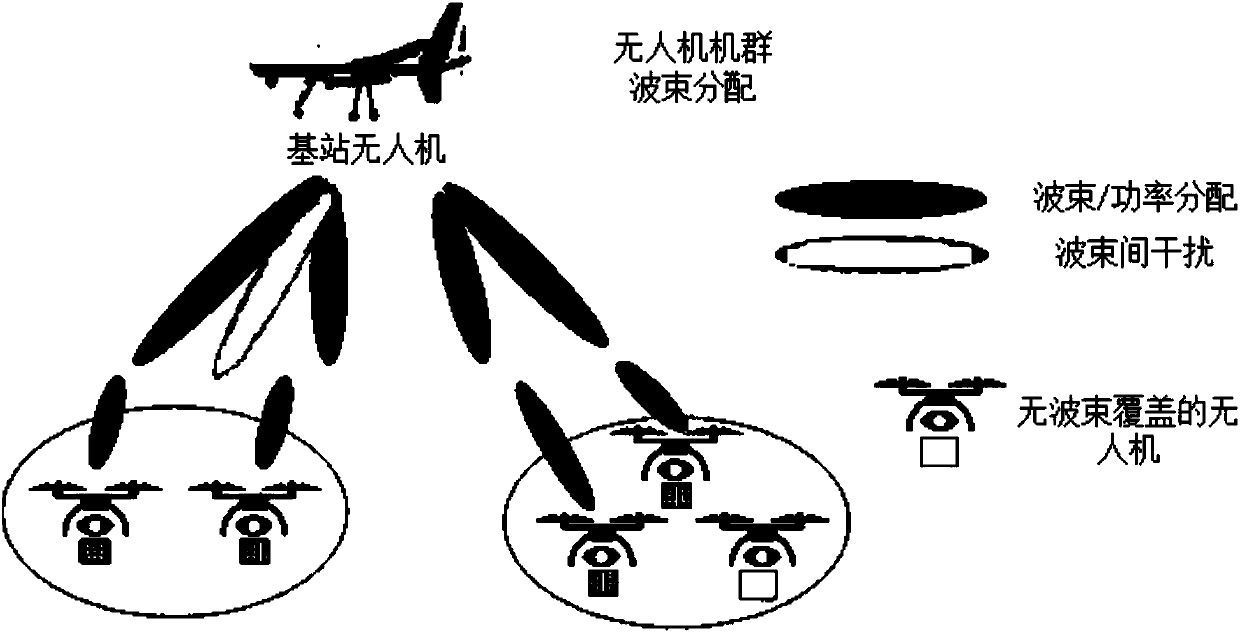
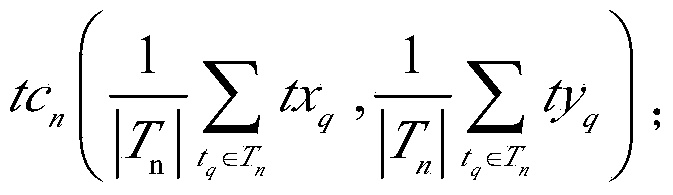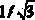Patents
Literature
747 results about "Allocation algorithm" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
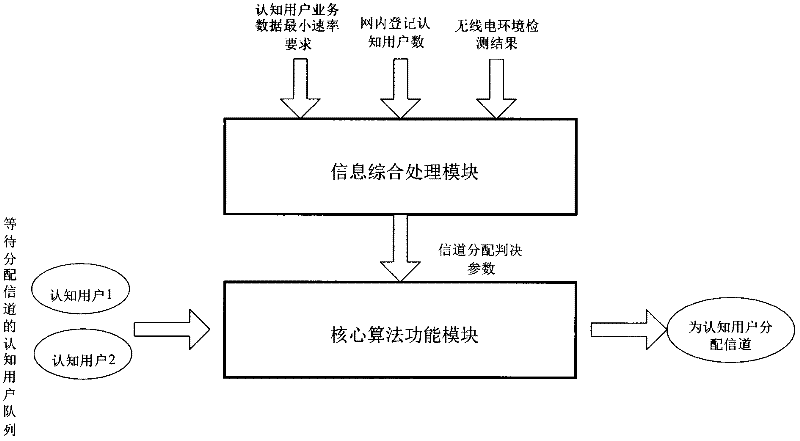
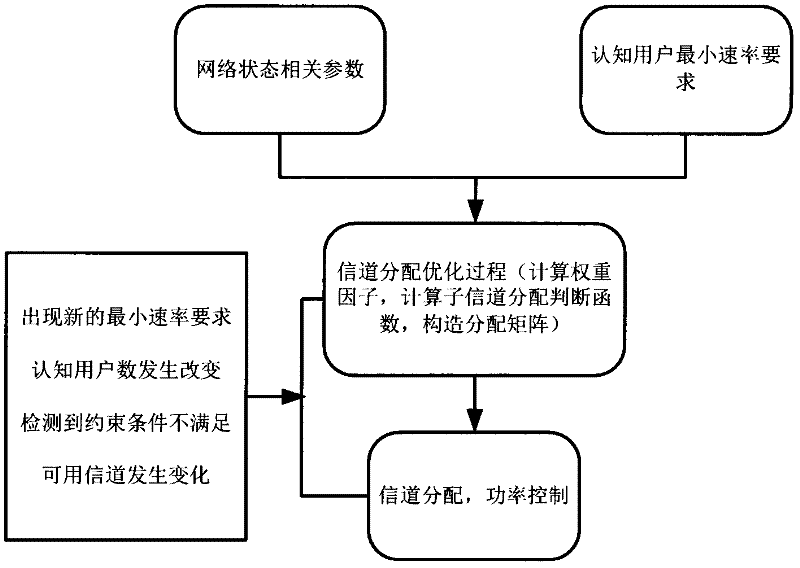
The two algorithms commonly used to allocate frames to a process are: Equal allocation: In a system with x frames and y processes, each process gets equal number of frames, i.e. x/y. Proportional allocation: Frames are allocated to each process according to the process size.
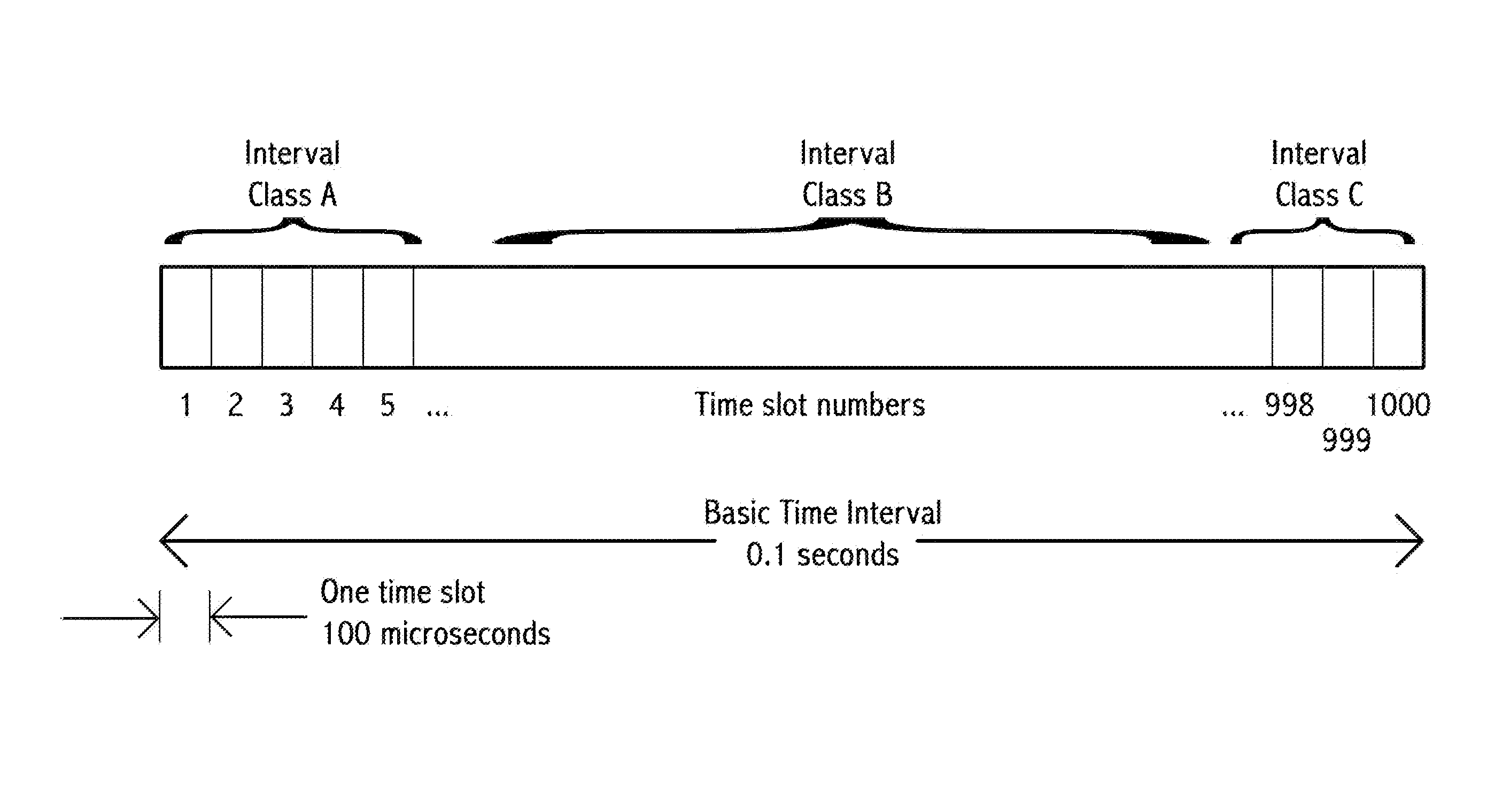
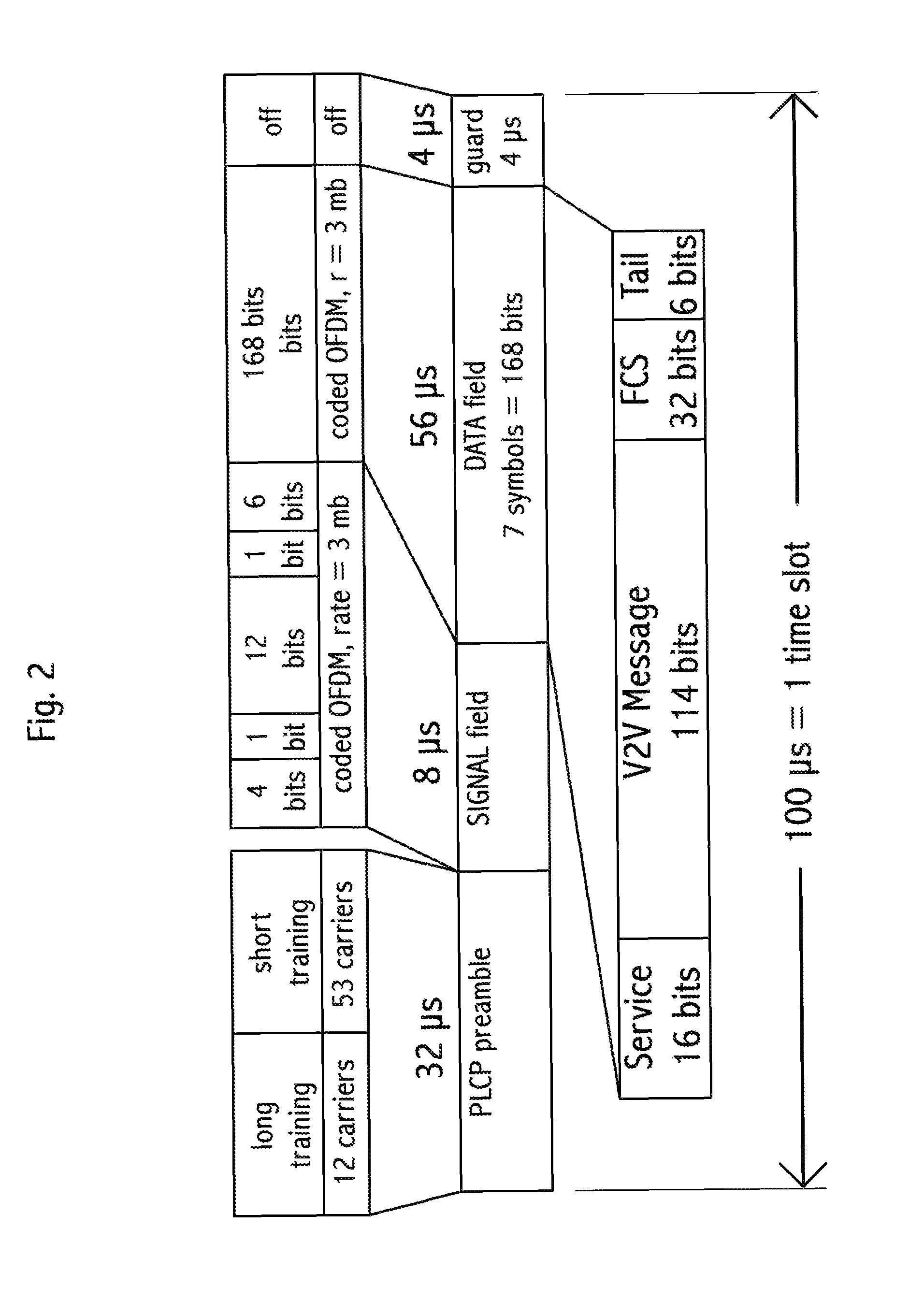
Time-slot-based system and method of inter-vehicle communication
ActiveUS8520695B1Efficient communicationEfficient codingInstruments for road network navigationArrangements for variable traffic instructionsWireless transmissionCommunications system
Device, system and method, in a vehicle communication system, to transmit wirelessly a message comprising the position, heading and speed of a vehicle or other moving object, wherein the transmission is repeated at regular intervals in a temporarily fixed time slot within a predetermined basic time interval. In a key embodiment the message duration is equal to or less than a predetermined time slot duration. Embodiments use generally the same time slot in a contiguous sequence of basic time intervals. Algorithms are described to resolve wireless interference within a time slot. Embodiments divide the basic time interval in multiple durations, “class regions,” for different message classes. Embodiments use different wireless bandwidth allocation algorithms for the class regions.
Owner:ZETTA RES & DEV - FORC SERIES
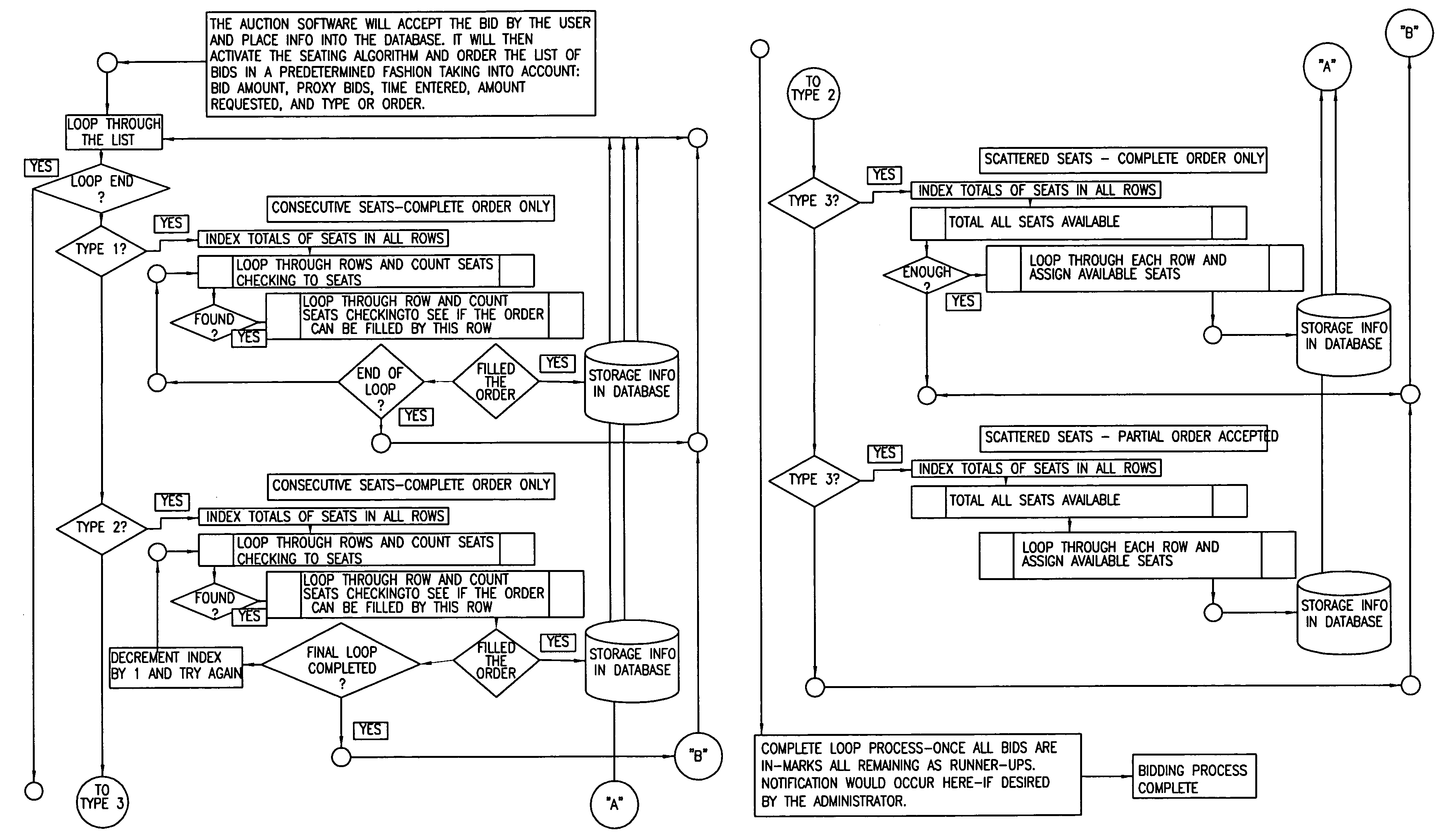
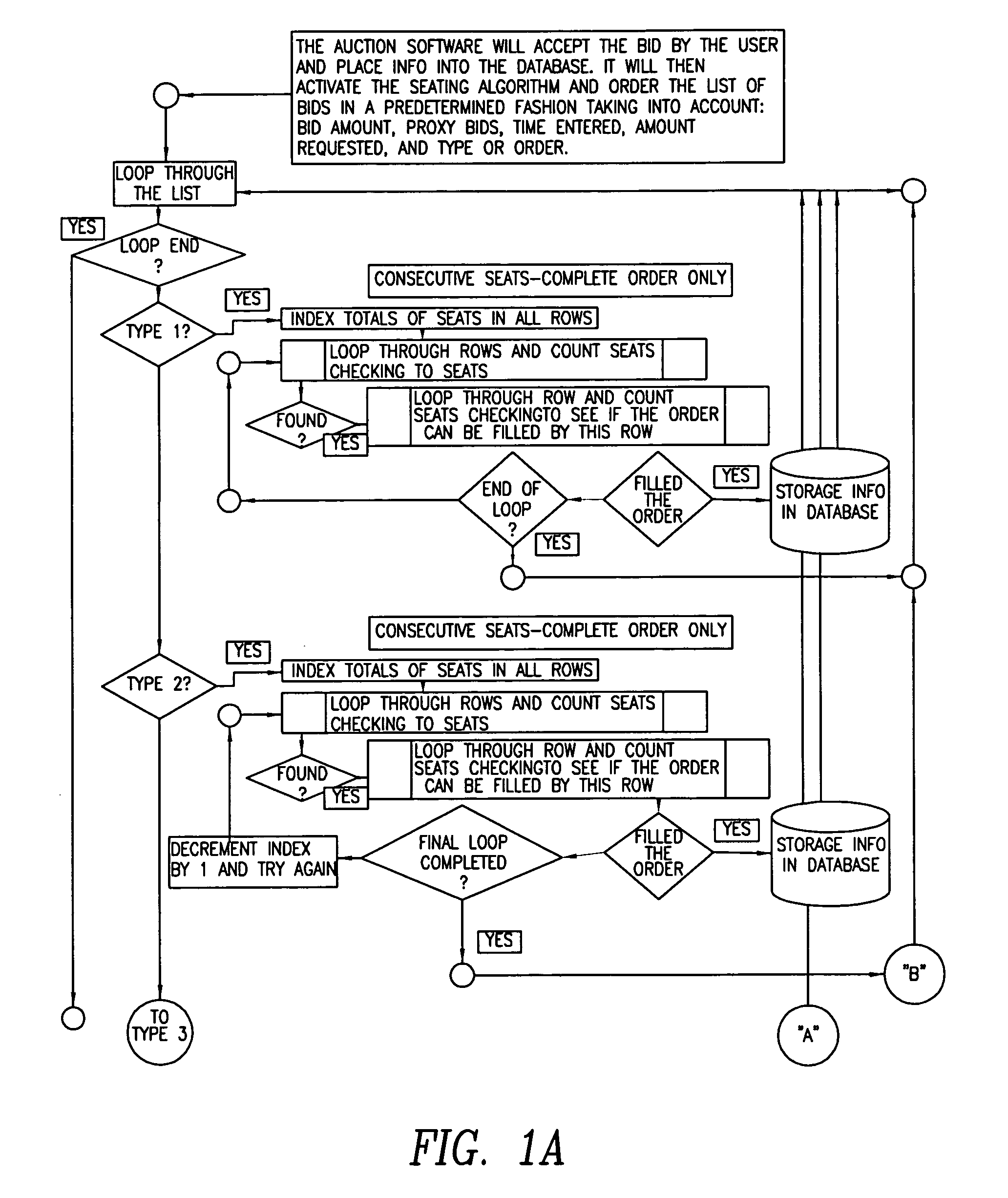
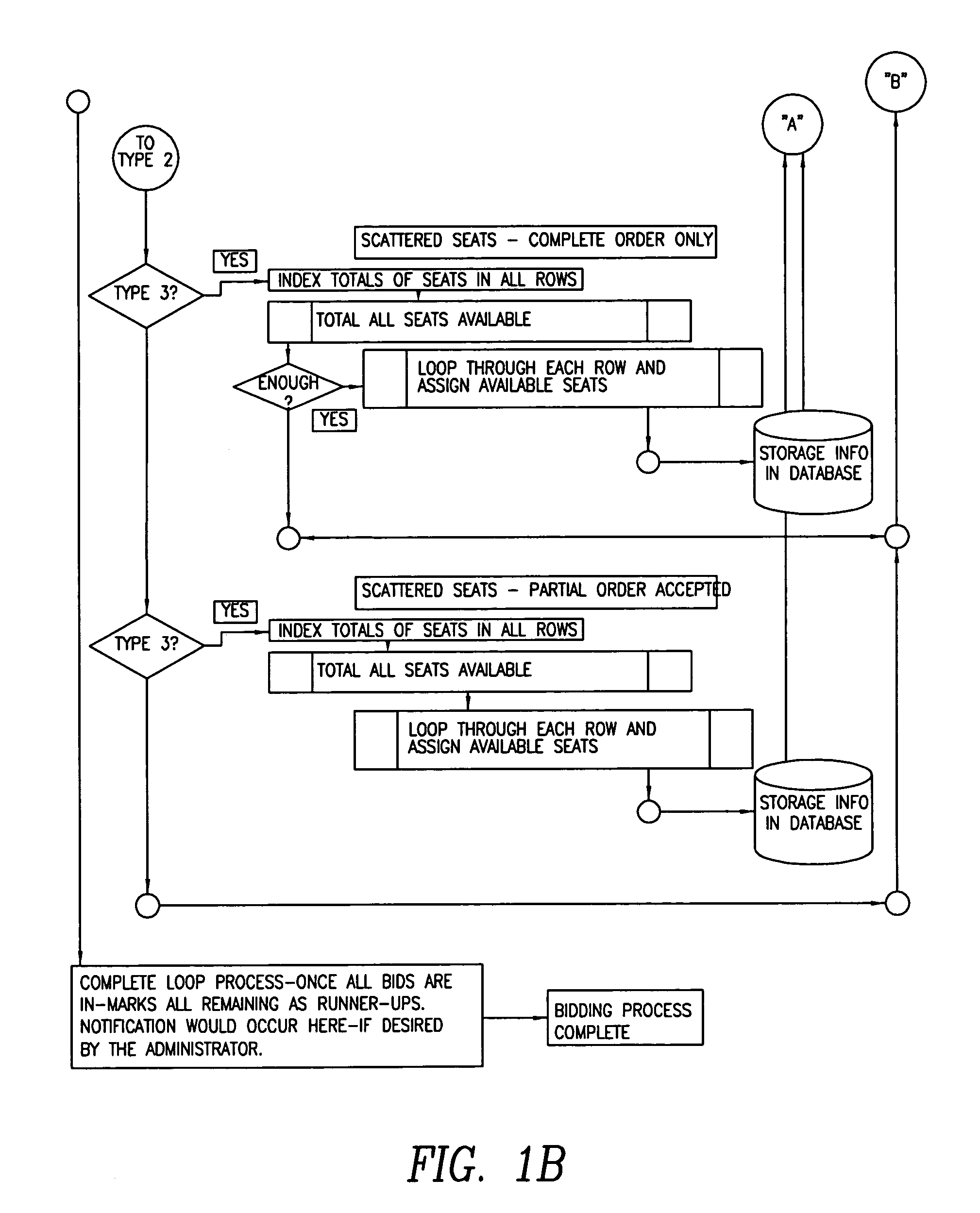
Ticket auction
InactiveUS7003485B1Eliminates chaosIncrease opportunitiesFinanceCommerceAllocation algorithmThe Internet
This computer-based Internet ticket auctioning method preregisters potential bidders and advises them that all bids are conditional offers to purchase tickets, and therefore cannot be lowered or canceled at will. The auction's organizer programs the computer that runs the auction with dates and locations of various events, and with auditoria layout and locations of seats to be auctioned. Each registered customer can view the layout of a particular auditorium and submit a bid for one or more seats. The bidder specifies whether a partially filled order and noncontiguous seat assignments are acceptable. The bidder is also provided with an option to engage a “proxy bid” that will increase the bid amount up to a limit set by the bidder, in order to ensure purchase of tickets. Each customer can also choose to bypass the auction process entirely, by submitting a purchase order at a high, preset price. This preset price is automatically accepted and purchase of tickets is guaranteed. At the conclusion of the auction, the computer runs a seat allocation algorithm that assigns the seats to the bidders so as to maximize the total amount realized from the auction. The seat assignment algorithm is also run periodically during the auction in order to determine which bidders have already being outbid, and to allow them to raise their bids.
Owner:F POSZAT HU
Wireless communication system with dynamic channel allocation
InactiveUS6023622AFacilitate communicationReduce distractionsNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsDynamic channelTransceiver
A plurality of base stations communicate with a plurality of mobile units. Each base station includes a base station transceiver that receives inbound information from the mobile units and transmits outbound information to the mobile units. A mobile switching center (MSC) is coupled to the base stations and communicates the inbound information and outbound information with the base stations. The base stations each include signal detectors that detect signal strength of the inbound information, co-channel information and adjacent channel information. The MSC maintains a table of signal strength per communication channel and allocates communication channels to the base stations based on the signal strength information. The inventive dynamic channel allocation includes several channel allocation algorithms that can be active at the same time. Only one of the algorithms is active at a time. The choice of the algorithm is based on current interference conditions and traffic load. The invention is implemented in the MSC and base stations of a digital cellular network using wideband technology for its air interface. While the decision-making mechanism and the channel allocation algorithms are implemented in the MSC, the protocol between the MSC and base stations is extended to support the proposed concept for dynamic channel allocation. Advantages of the invention includes improved communication and reduced interference.
Owner:WJ COMM
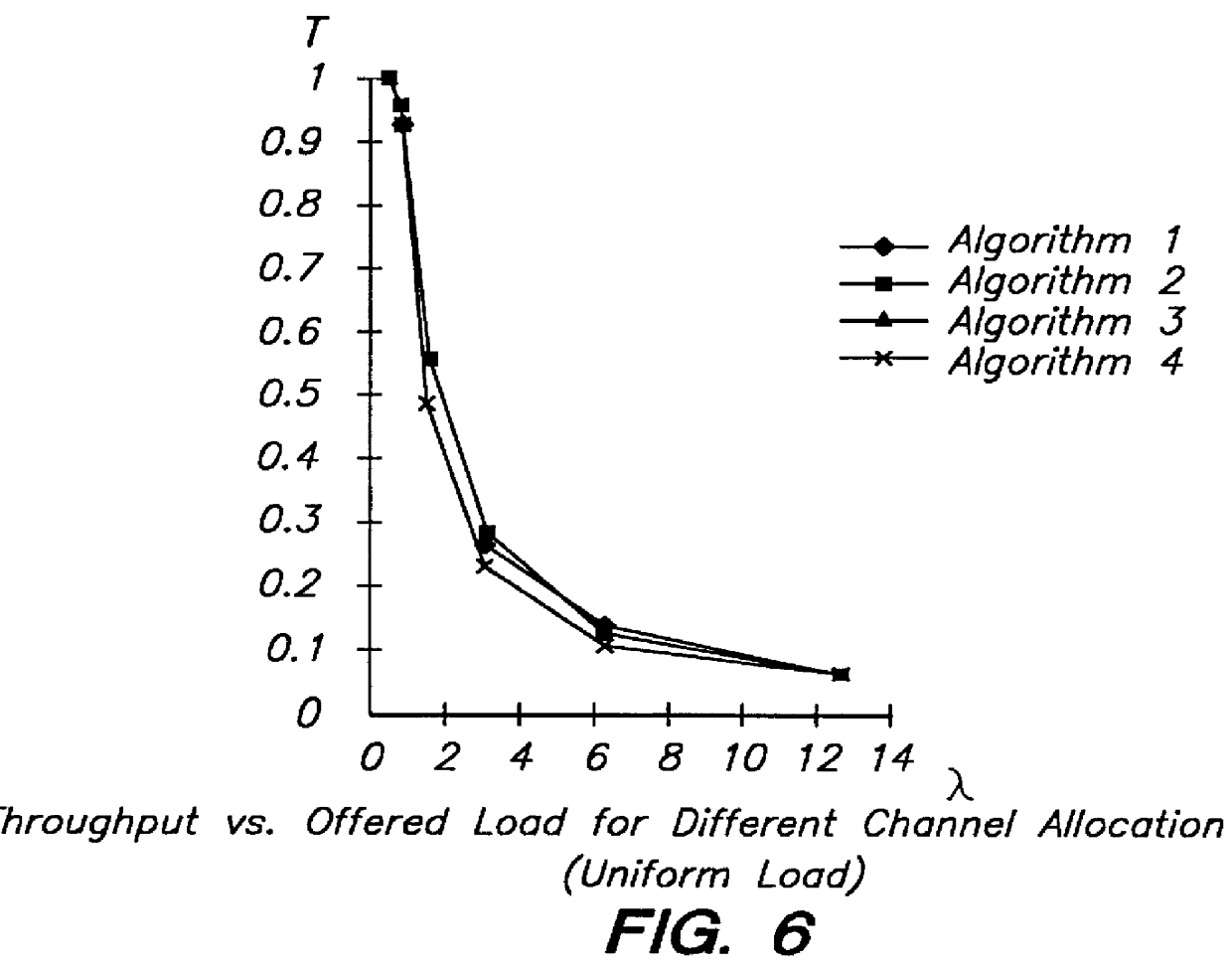
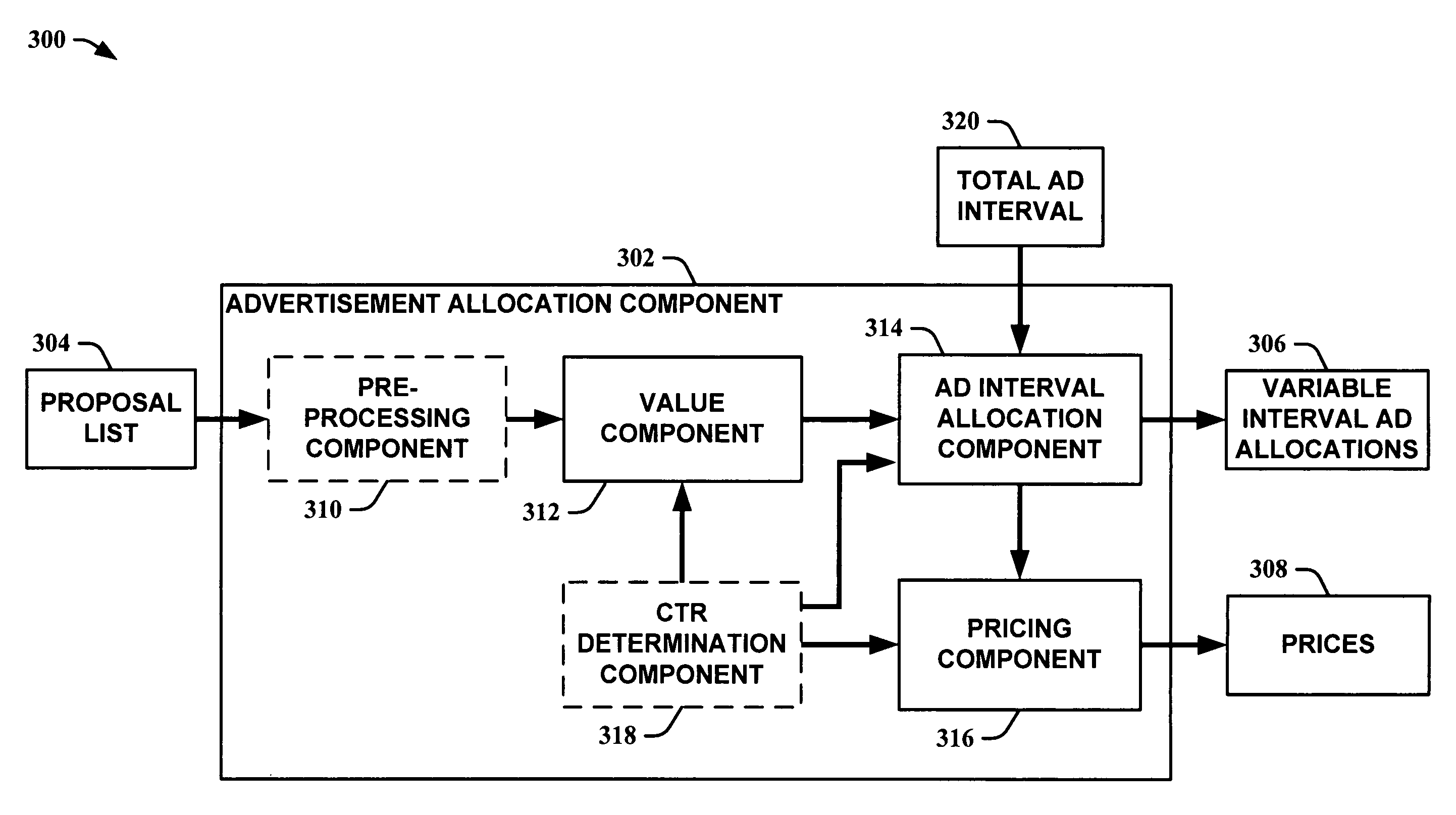
Mechanism for allocating advertisements of varying intervals
InactiveUS20060253319A1Easy to determineImprove performanceAdvertisementsAllocation algorithmData mining
The subject invention leverages determined values of auction advertisement proposals to facilitate in determining advertisement interval allocations for the proposals. The advertisement “interval” can include, but is not limited to, physical dimensions or time. Instances of the subject invention further utilize allocation algorithms and auctioning mechanisms to provide for allocation of ads of varying intervals and to improve performance of ad auctions, including employing algorithms that automate the ad interval layout to maximize revenue. Other instances of the subject invention provide pricing for the allocated intervals as well.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
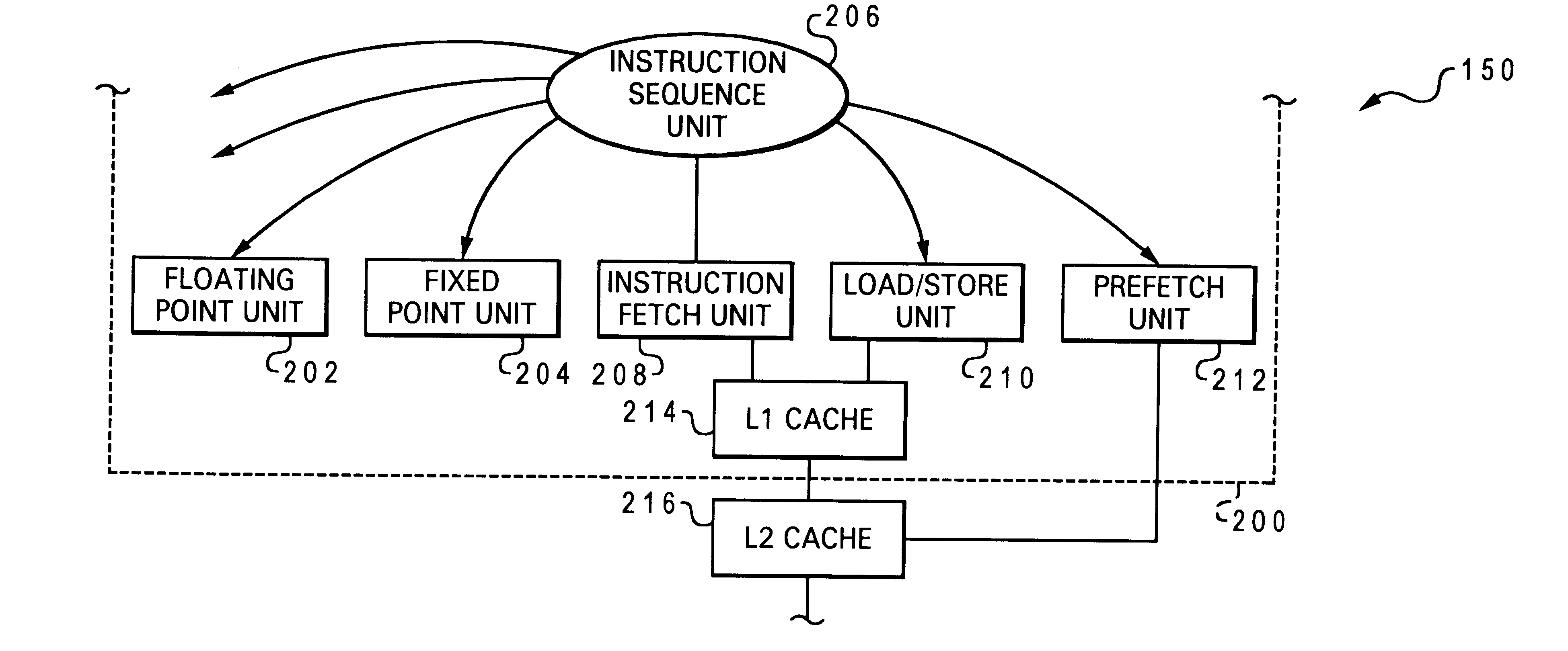
Optimized cache allocation algorithm for multiple speculative requests
A method of operating a computer system is disclosed in which an instruction having an explicit prefetch request is issued directly from an instruction sequence unit to a prefetch unit of a processing unit. In a preferred embodiment, two prefetch units are used, the first prefetch unit being hardware independent and dynamically monitoring one or more active streams associated with operations carried out by a core of the processing unit, and the second prefetch unit being aware of the lower level storage subsystem and sending with the prefetch request an indication that a prefetch value is to be loaded into a lower level cache of the processing unit. The invention may advantageously associate each prefetch request with a stream ID of an associated processor stream, or a processor ID of the requesting processing unit (the latter feature is particularly useful for caches which are shared by a processing unit cluster). If another prefetch value is requested from the memory hiearchy and it is determined that a prefetch limit of cache usage has been met by the cache, then a cache line in the cache containing one of the earlier prefetch values is allocated for receiving the other prefetch value.
Owner:IBM CORP
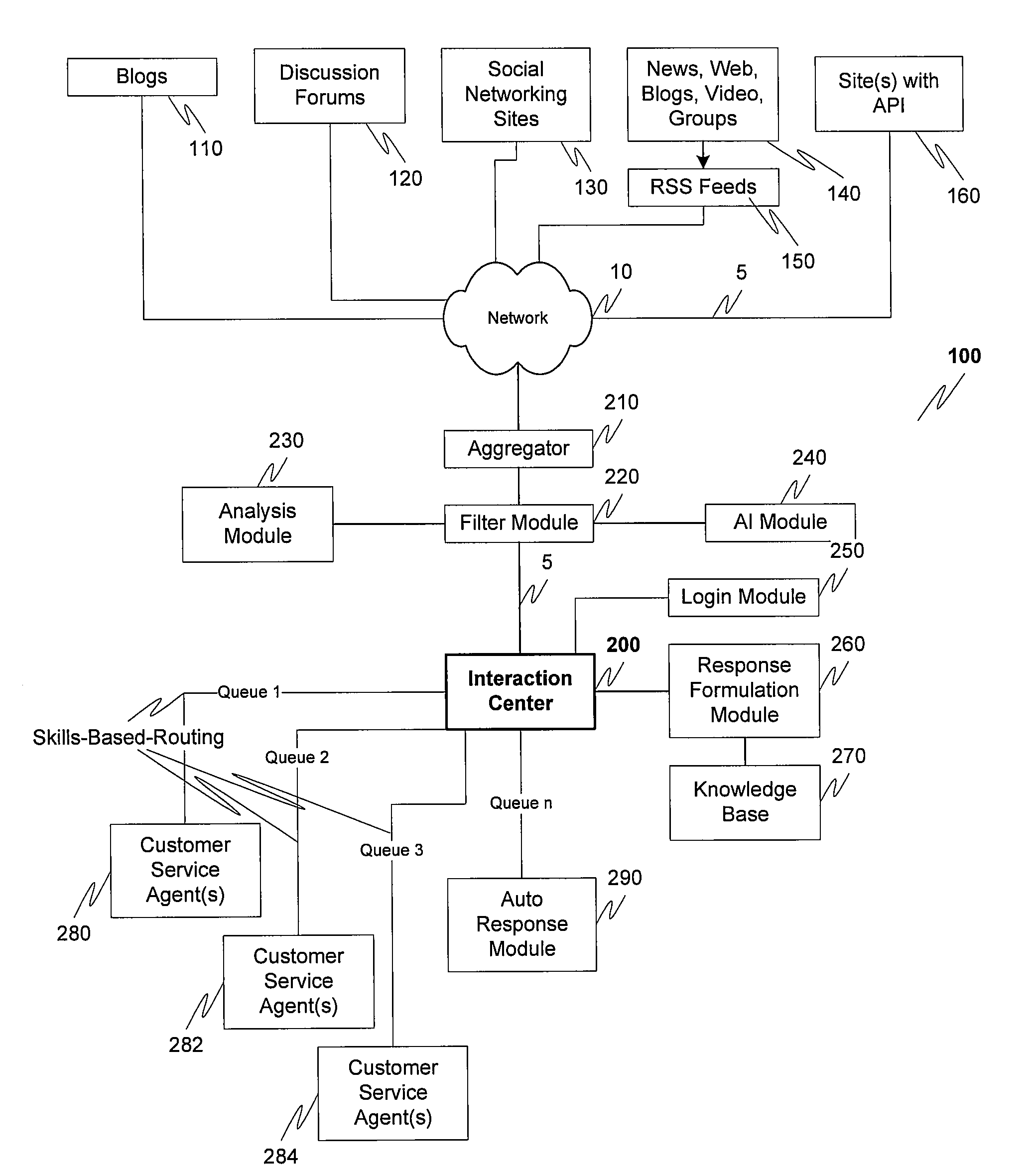
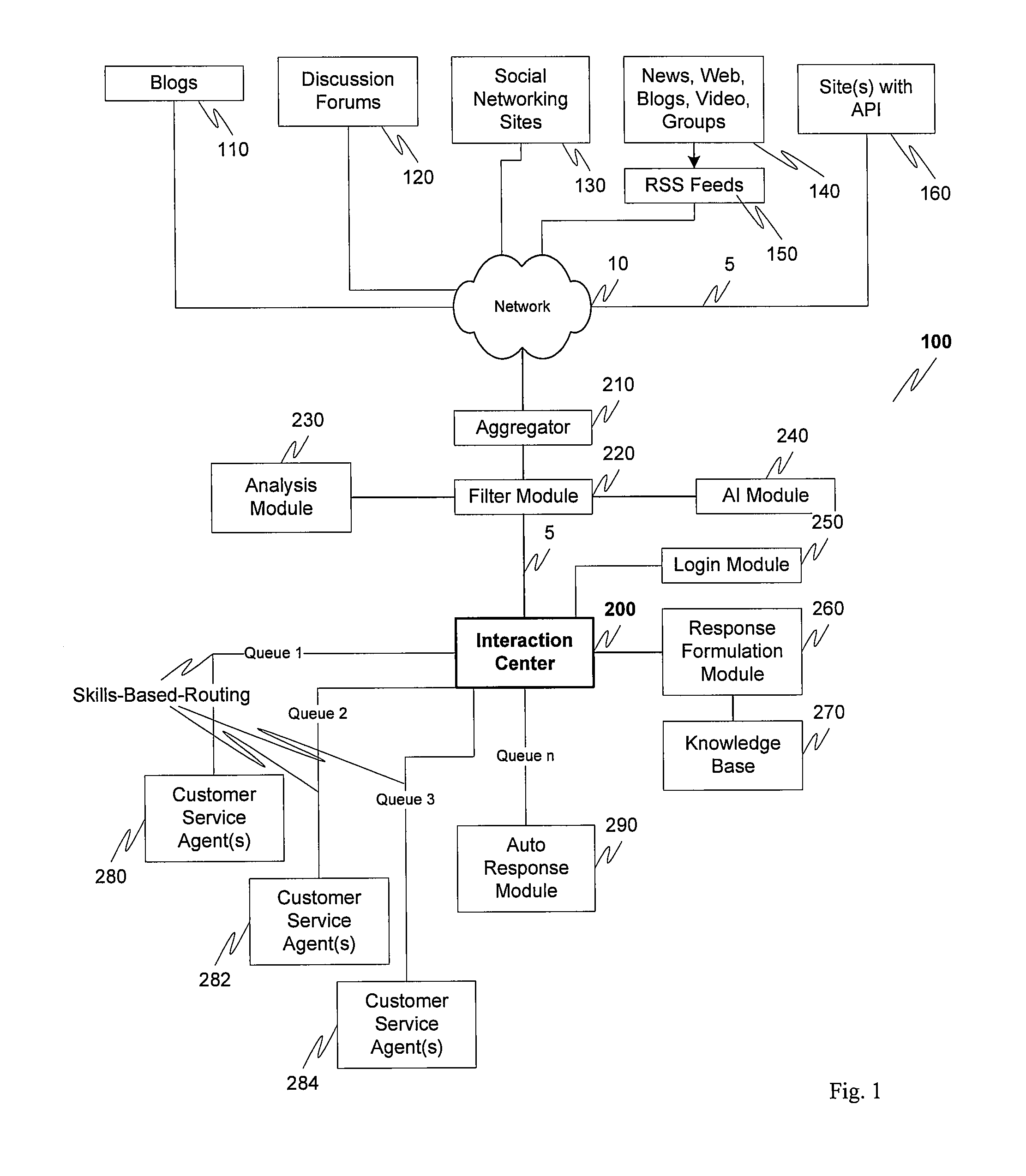
Treatment of web feeds as work assignment in a contact center
ActiveUS20100293560A1Eliminates and significantly reduces of and qualificationEnhance data gatheredDigital computer detailsCommerceWork distributionService experience
To provide an enhanced customer service experience, various combinations of web searches, site-specific filtering tools and syndicated feed readers can be used to find relevant posts on the internet. Internal email, IM, phone, and the like can cooperate with an appropriately equipped expert-finding solution to assist with help in locating the experts qualified to respond to the post(s). The leveraging of RSS / Atom feeds or similar technology, content analysis, and contact center work distribution algorithms are leveraged to monitor the feeds from multiple sites and automatically distribute messages to appropriately skilled contact center agents. Each message discovered is analyzed to determine which contact center queue it is to be routed to, and then the contact center assigns it to an appropriate agent. This eliminates or significantly reduces the amount of manual searching and qualification of posts.
Owner:AVAYA INC
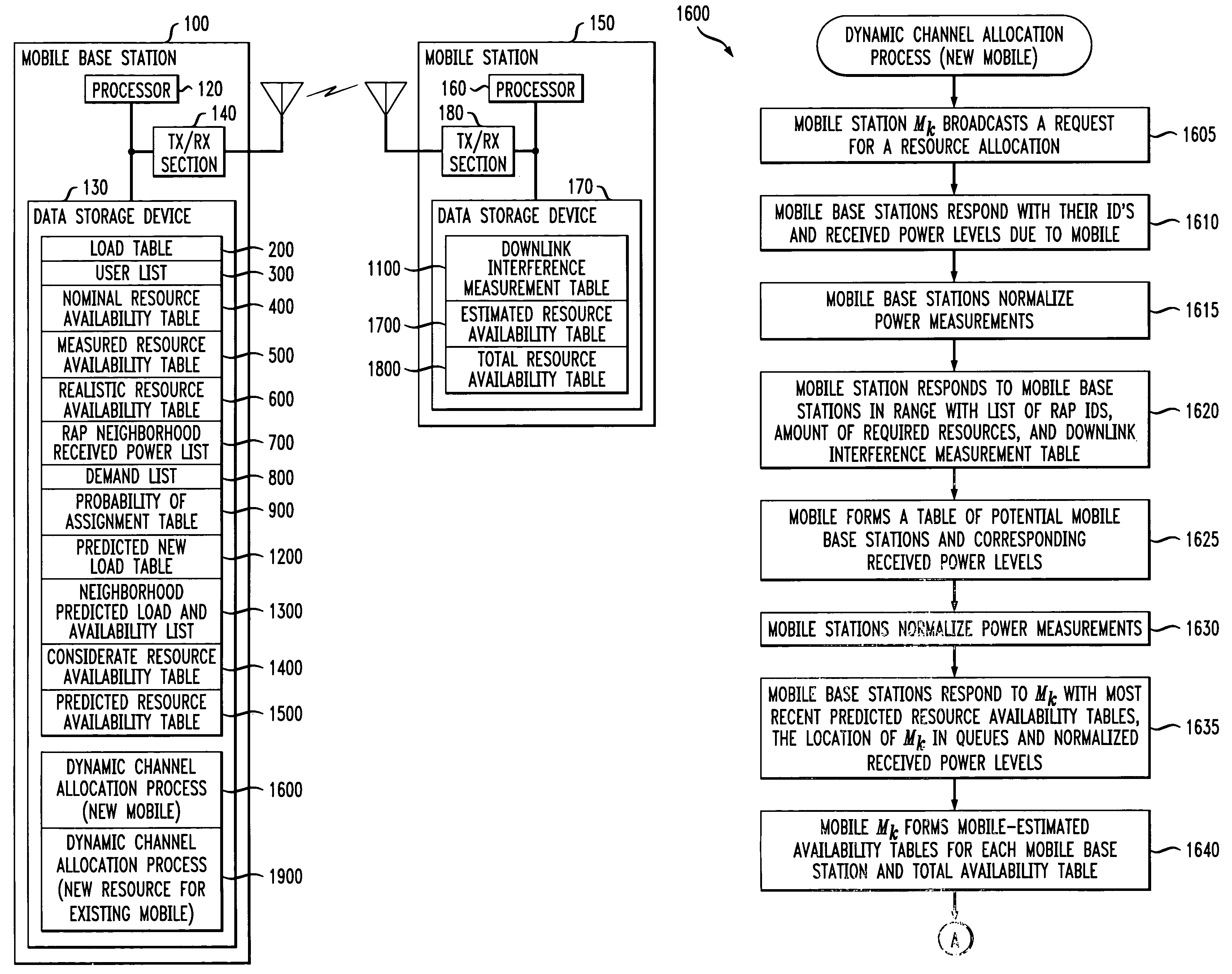
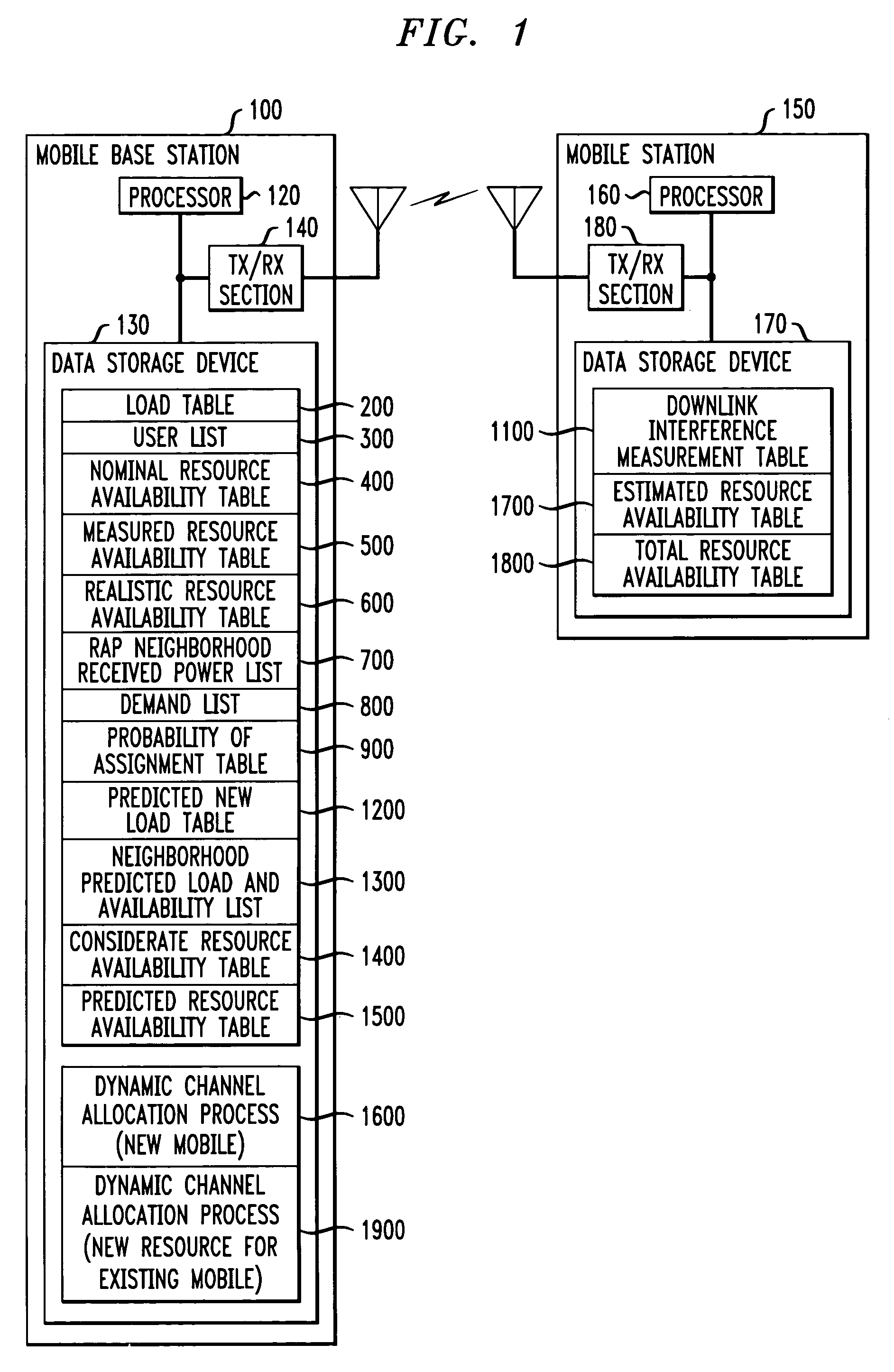
Distributed dynamic channel allocation technique for multi-carrier CDMA cellular systems with mobile base stations
InactiveUS7373151B1Light loadNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsChannel powerDynamic channel
A distributed dynamic channel allocation algorithm for a multi-carrier CDMA cellular system having at least one mobile base station. The distributed dynamic channel allocation algorithm uses channel power measurements from both the requesting mobile station and the mobile base station attempting to allocate an available resource to the mobile station. The distributed dynamic channel allocation algorithm attempts to allocate the best available resource for the requesting mobile station, in terms of interference, while minimizing the amount of interruption that the allocated resource may cause to existing connections in neighboring cells. Thus, the distributed dynamic channel allocation algorithm follows a “least-interference, least-interruption” strategy. The distributed dynamic channel allocation algorithm is load balancing, since it tends to assign new resources to mobile base station with lighter loads.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
Method and apparatus for minimizing near end cross talk due to discrete multi-tone transmission in cable binders
InactiveUS20010055332A1Minimize the total transmit powerMinimize cross-talkFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission path divisionModem deviceProximal point
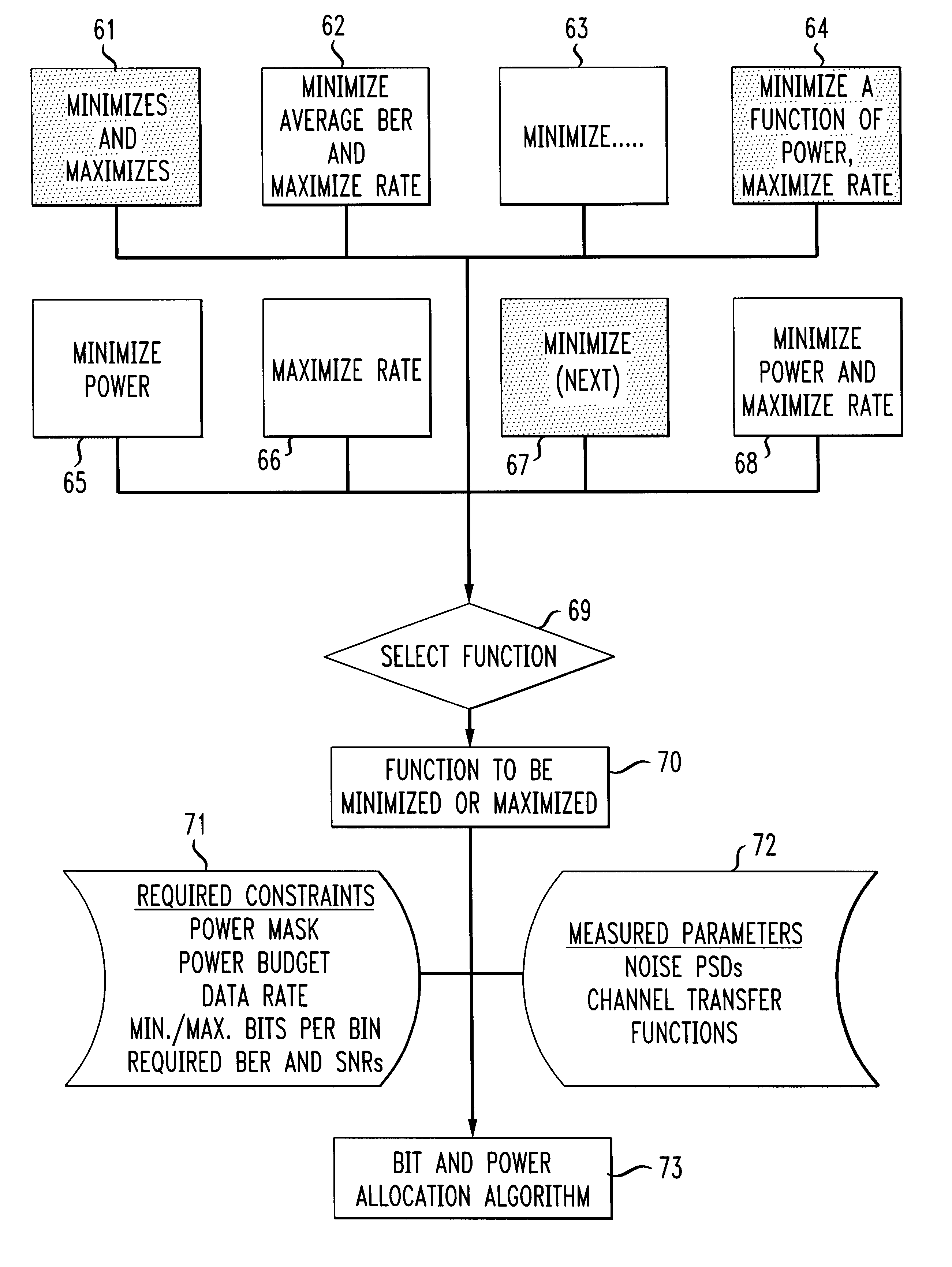
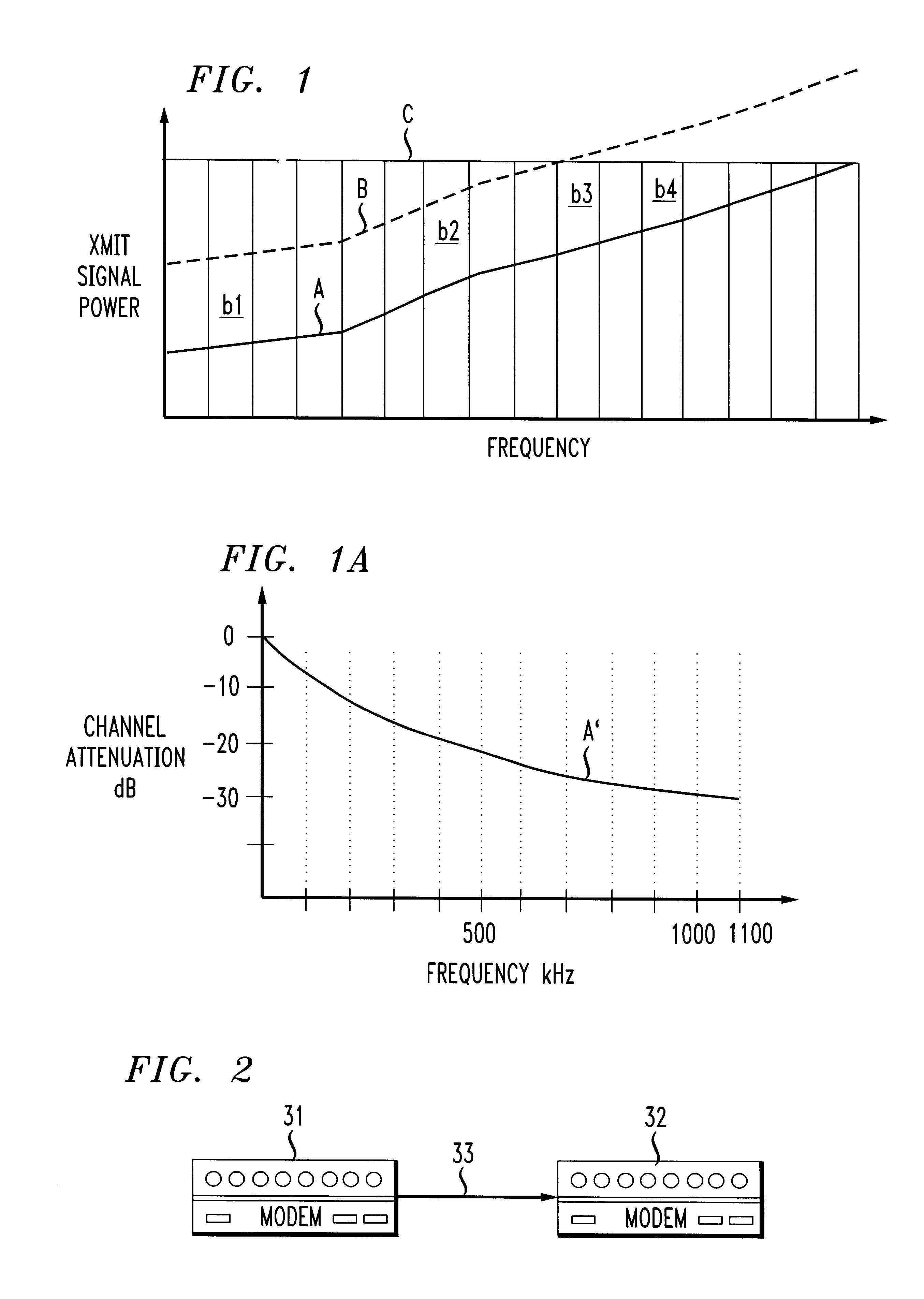
In a discrete multi-tone modem, a method of minimizing cross talk over a twisted pair of a twisted pair cable binder in which discrete multi-tone data transmission is utilized comprises the steps of one of jointly minimizing near end cross talk while maximizing total data rate, jointly minimizing an arbitrary function of total power while maximizing total data rate and minimizing total near end cross talk for a given data rate, selecting a function to be optimized and performing a bit and power allocation algorithm responsive to the selected function. The process may be combined with known optimization functions such as jointly minimizing an average bit error rate while maximizing the data rate. As a result, the process is considerably more flexible and adaptable to changing parameters such as environmental parameters impacting data transmission performance in the presence of cross talk. Either a telecommunications central office modem or a remote terminal modem may be so adapted to apply such a cross talk minimization method.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
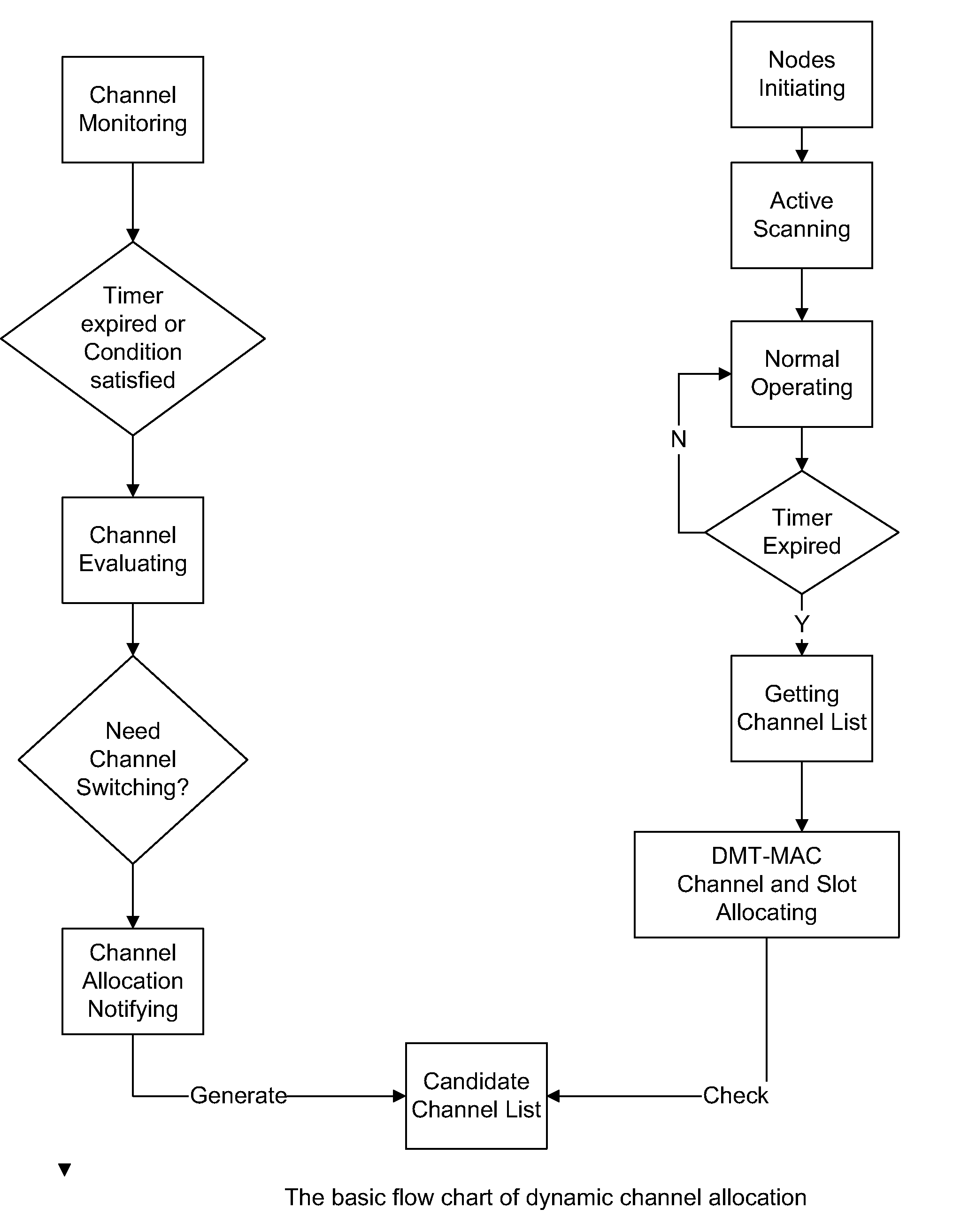
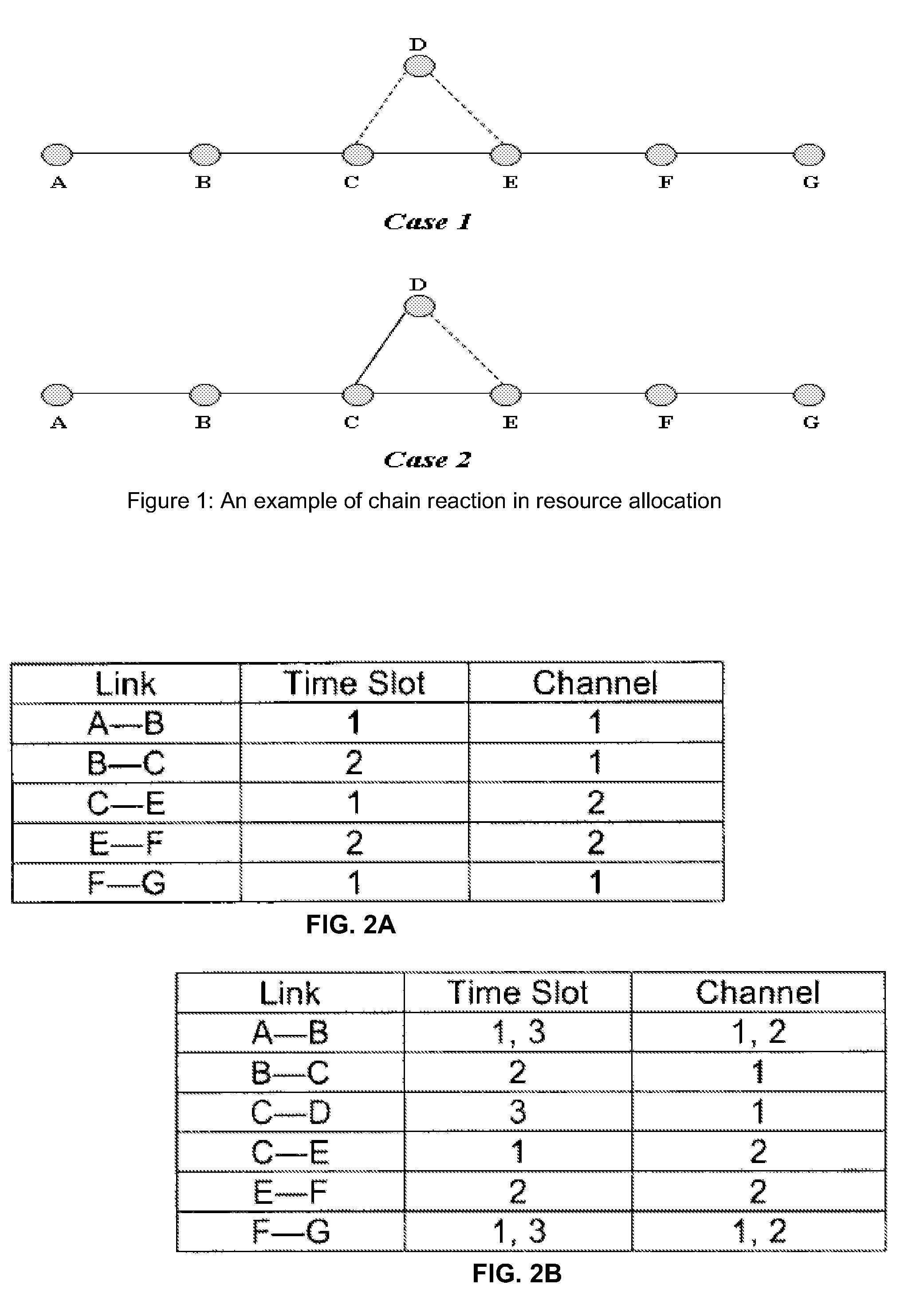
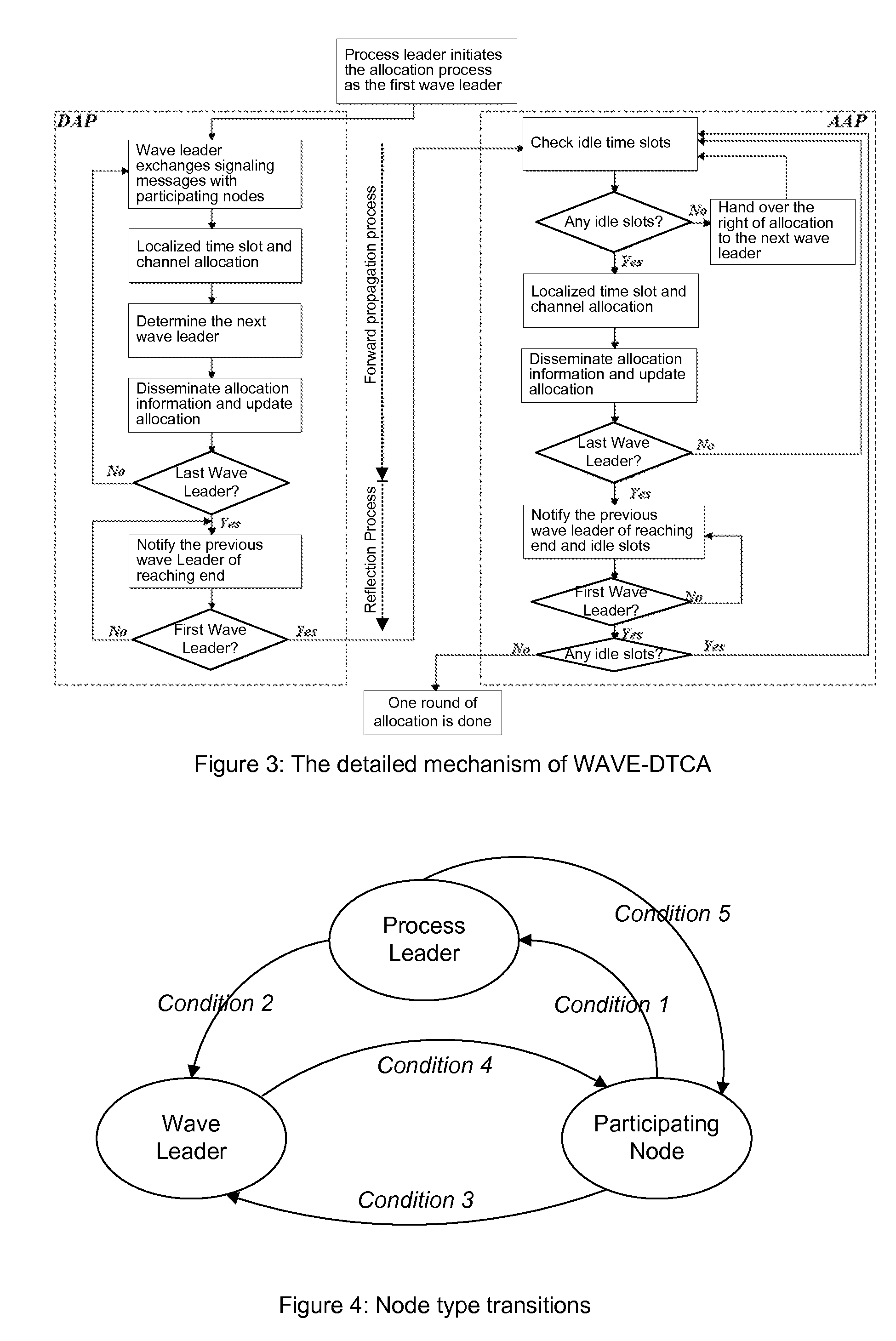
System and Method for Timeslot and Channel Allocation
ActiveUS20080137620A1Readily apparentError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTime-division multiplexTelecommunicationsAllocation algorithm
A distributed multi-channel TDMA MAC time slot and channel allocation algorithm for wireless networks is provided. The time slot and channel allocation includes a distributed allocation phase and an allocation adjustment phase. Each phase begins allocation at a first node and continues node-by-node until the last node in the network. The allocation then reflects back from the last node to the first node. At each node in the path, the node can initiate resource allocation between itself and its neighbor nodes. Nodes that are within range of the wireless network but are not on the path do not initiate resource allocation but instead participate in the resource allocation initiated from other nodes.
Owner:OL SECURITY LIABILITY CO
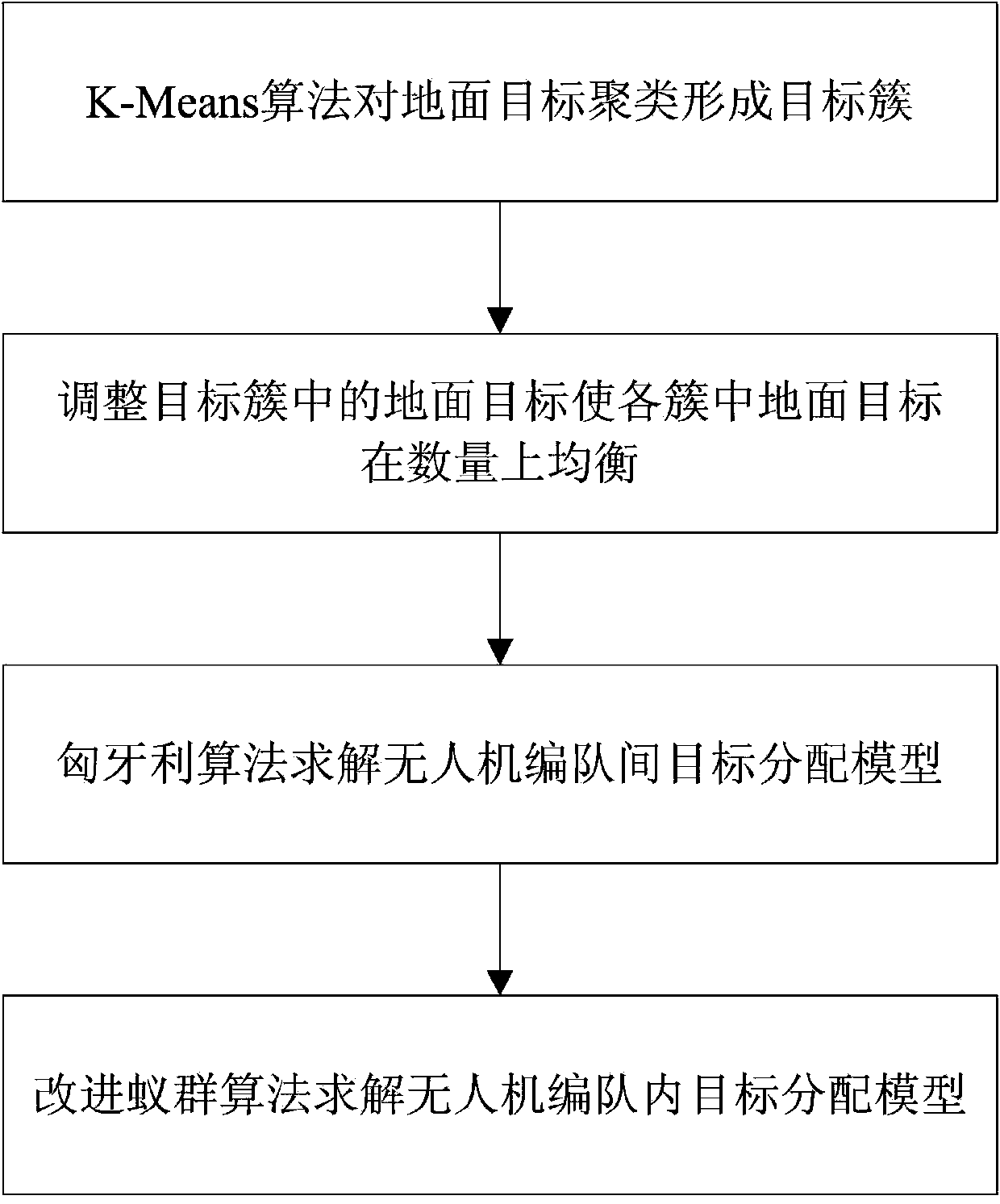
Hierarchical target allocation method for multiple unmanned aerial vehicle formations
The invention discloses a hierarchical target allocation method for multiple unmanned aerial vehicle formations. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of 1, clustering a plurality of ground targets to form a plurality of target clusters according to the number of the unmanned aerial vehicle formations; 2, regulating the obtained target clusters to keep the number of the ground targets in each target cluster consistent; 3, allocating the target clusters to the unmanned aerial vehicle formations in a one-to-one correspondence way by using an inter-unmanned aerial vehicle formation target allocation model and an inter-unmanned aerial vehicle formation target allocation algorithm; 4, allocating the ground targets to each unmanned aerial vehicle in the unmanned aerial vehicle formations by using an intra-unmanned aerial vehicle formation target allocation model and an intra-unmanned aerial vehicle formation target allocation algorithm. According to the method, the target allocation efficiency can be improved, and the problem of excessively long calculation time during large-scale target allocation for the multiple unmanned aerial vehicle formations can be effectively solved, so that the requirements of an application scenario such as a battlefield with a higher requirement on real-time performance are met.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Method and apparatus of dynamic spectrum allocation in coexisting heterogeneous wireless networks
InactiveUS20070281710A1Improve spectrum utilizationNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesFrequency spectrumTelecommunications
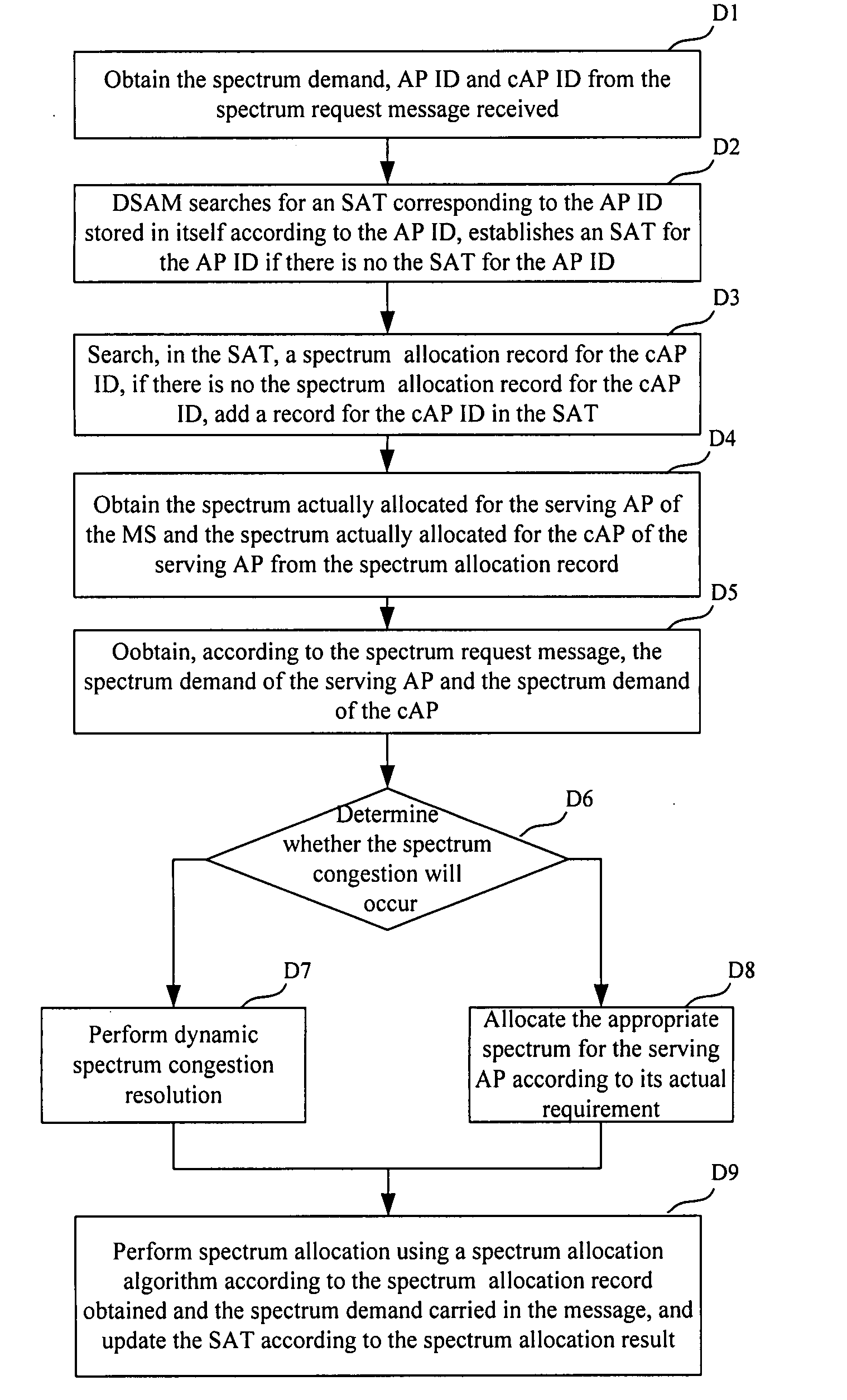
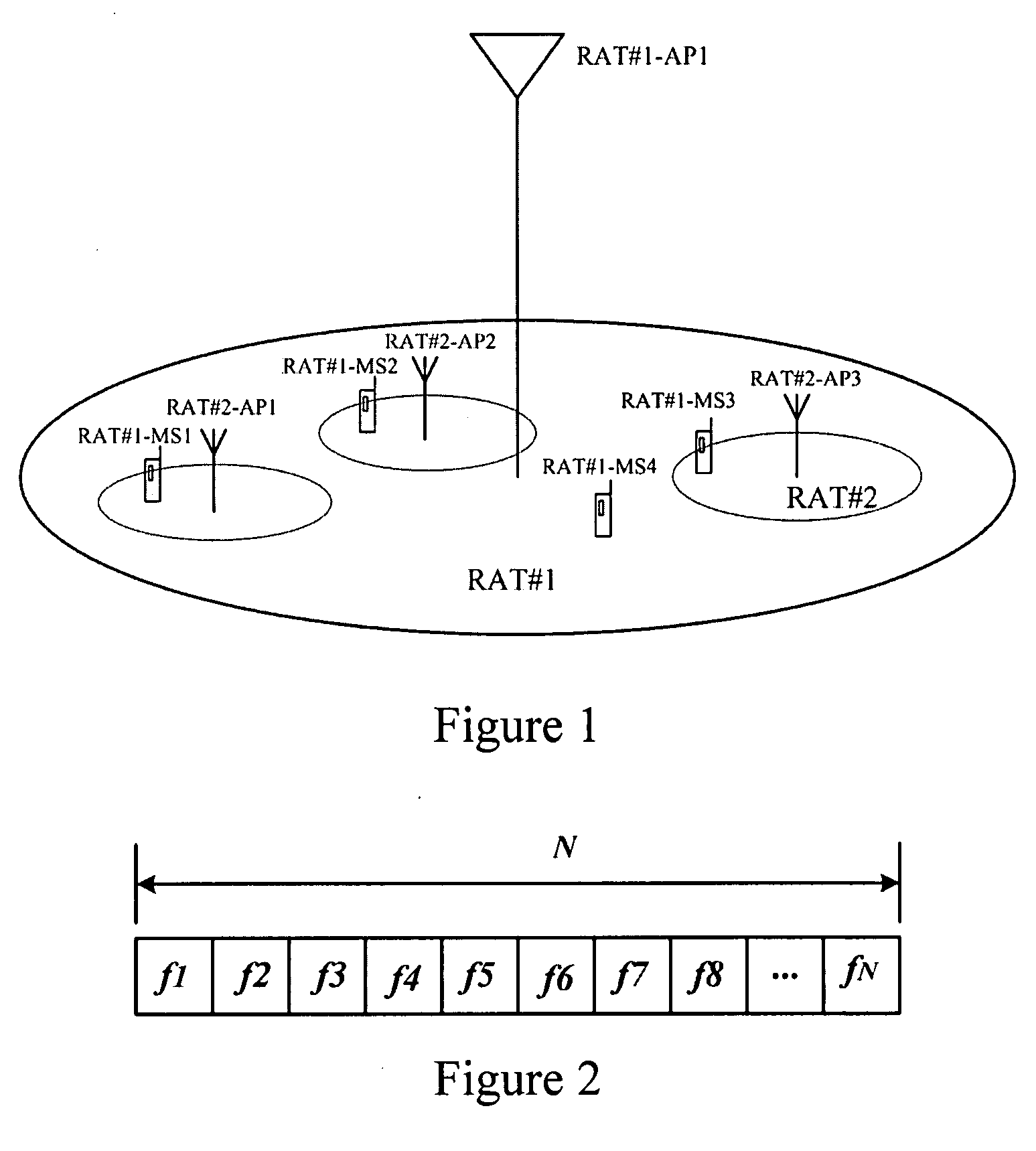
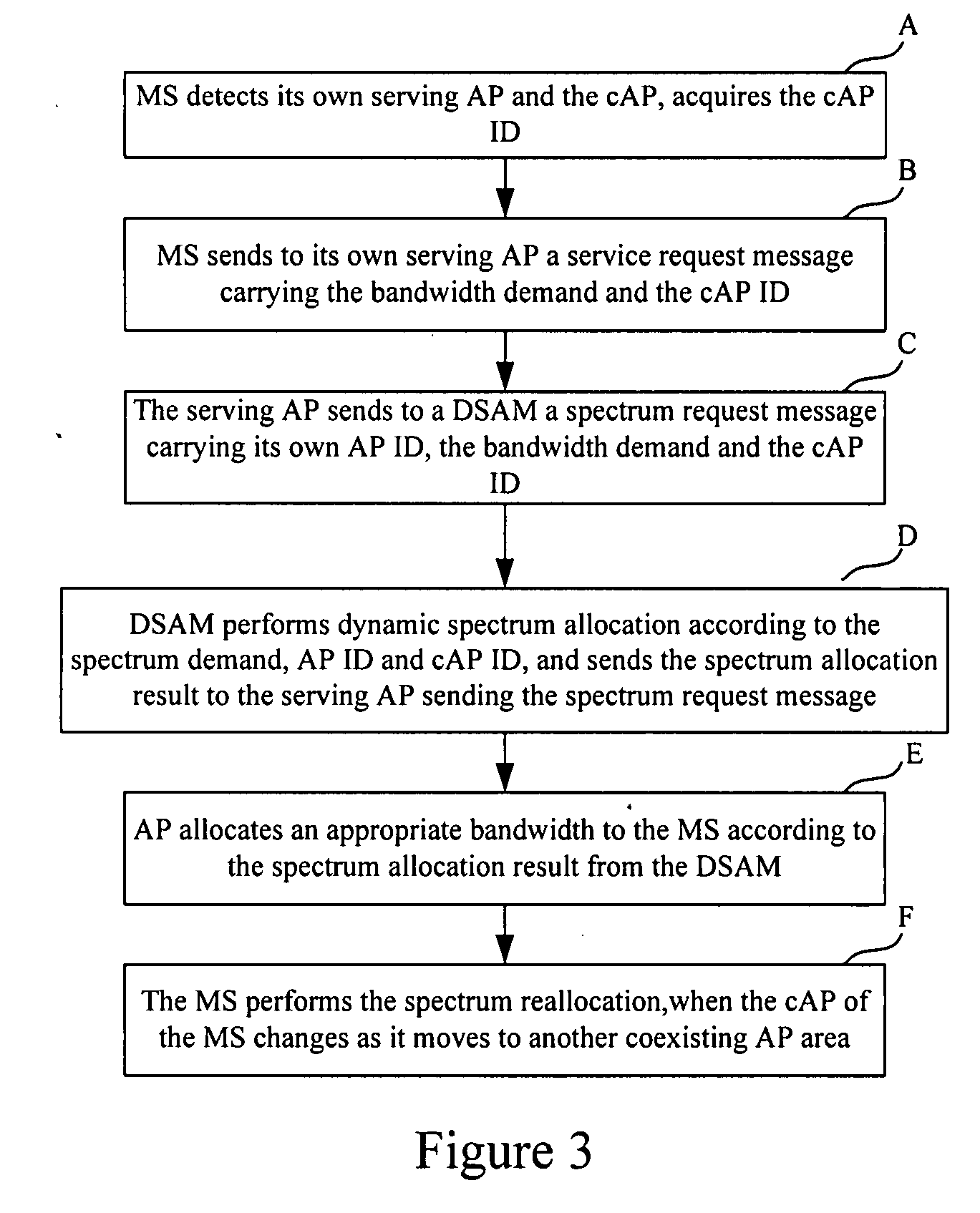
Embodiments of this disclosure include a method and apparatus of dynamic spectrum allocation in coexisting heterogeneous wireless networks. A Mobile Station (MS) detects its own serving Access Point (AP) and a coexisting AP (cAP) of the serving AP, sends to the serving AP a service request message carrying a bandwidth demand and a cAP ID. The serving AP sends to a Dynamic Spectrum Allocation Module (DSAM) a spectrum request message carrying its own AP ID, the cAP ID and the spectrum demand. The DSAM allocates the spectrum dynamically using a dynamic spectrum allocation algorithm according to the spectrum demand, AP ID and cAP ID, and sends a spectrum allocation result to the serving AP, which allocates an appropriate bandwidth to the MS according to the spectrum allocation result. Thus, sharing spectrum dynamically between multiple coexisting wireless networks can be achieved, and spectrum utilization can be improved.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
System and method of allocating bandwith to a plurality of devices interconnected by a plurality of point-to-point communication links
InactiveUS20020083233A1Data switching networksInput/output processes for data processingTelecommunications linkAllocation algorithm
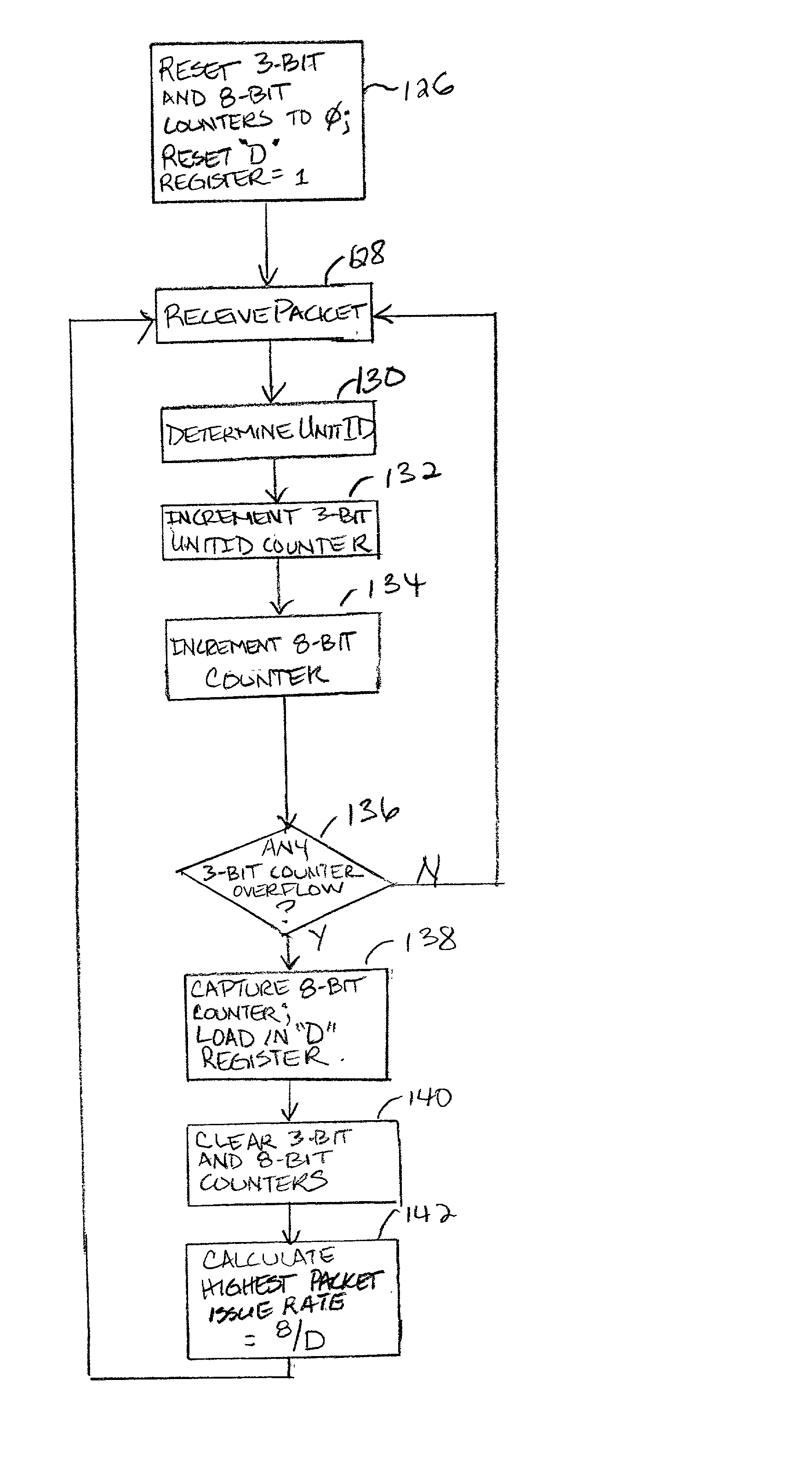
A method is provided for fairly allocating bandwidth to a plurality of devices connected to a communication link implemented as a plurality of point-to-point links. The point-to-point links interconnect the devices in a daisy chain fashion. Each device is configured to transmit locally generated packets and to forward packets received from downstream devices onto one of the point-to-point links. The rate at which each device transmits local packets relative to forwarding received packets is referred to as the device's insertion rate. A fair bandwidth allocation algorithm is implemented in each (upstream) device to determine the highest packet issue rate of the devices which are downstream of that (upstream) device. The packet issue rate of a downstream device is the number of local packets associated with the downstream device that are received at the upstream device relative to the total number of packets received at the upstream device. By monitoring the total flow of packets received at the upstream device, the highest packet issue rate of the respective packet issue rates of the downstream devices may be determined. Each upstream device then matches its insertion rate to the highest packet issue rate of its downstream devices. The determination of the highest packet issue rate may be performed dynamically such that the insertion rate of the upstream device can adapt to changes in communication traffic patterns. Further, the fair bandwidth allocation algorithm may include a priority algorithm to arbitrate between local and received packets transmitted at the insertion rate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Data transmission scheme using channel group and DOCSIS implementation thereof
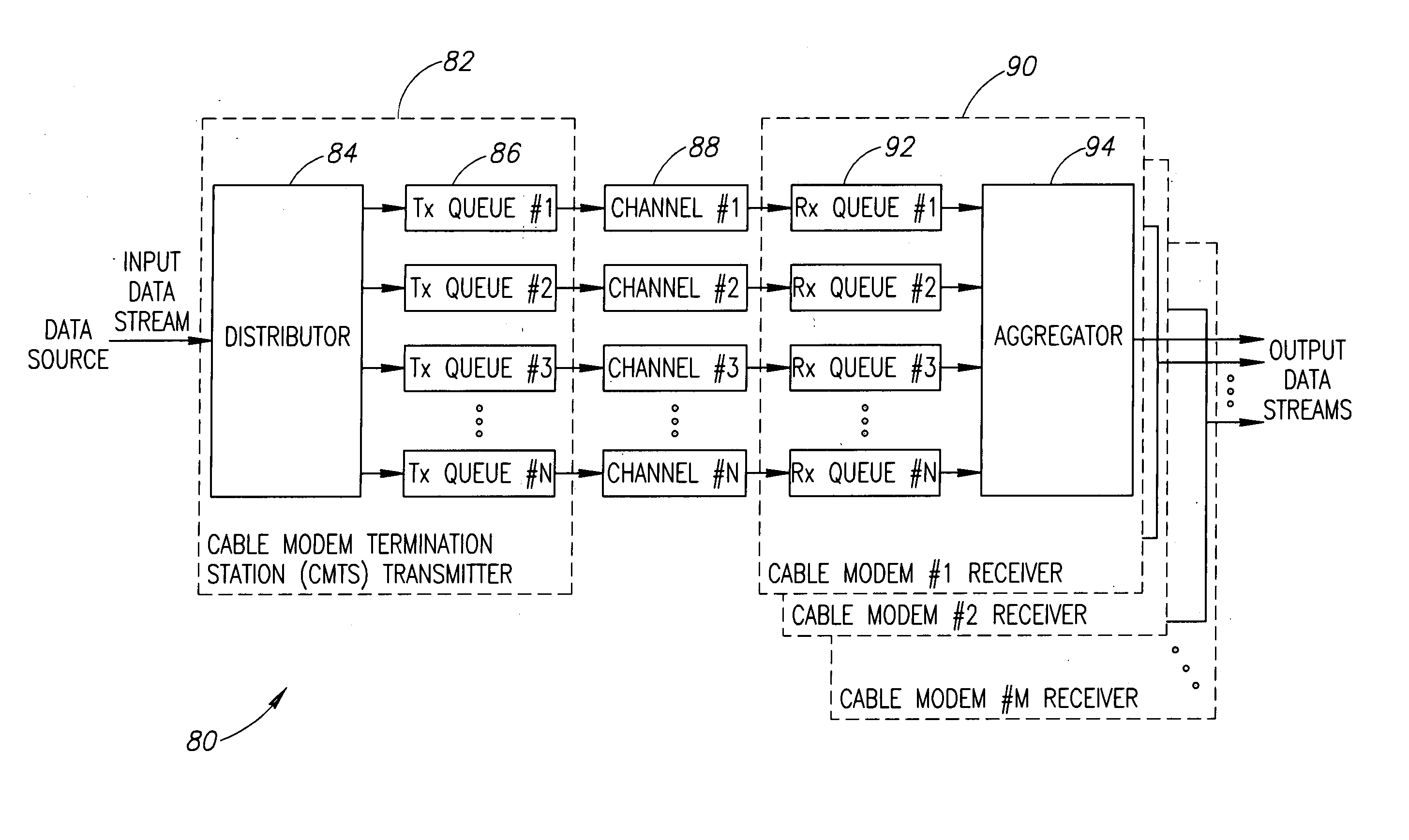
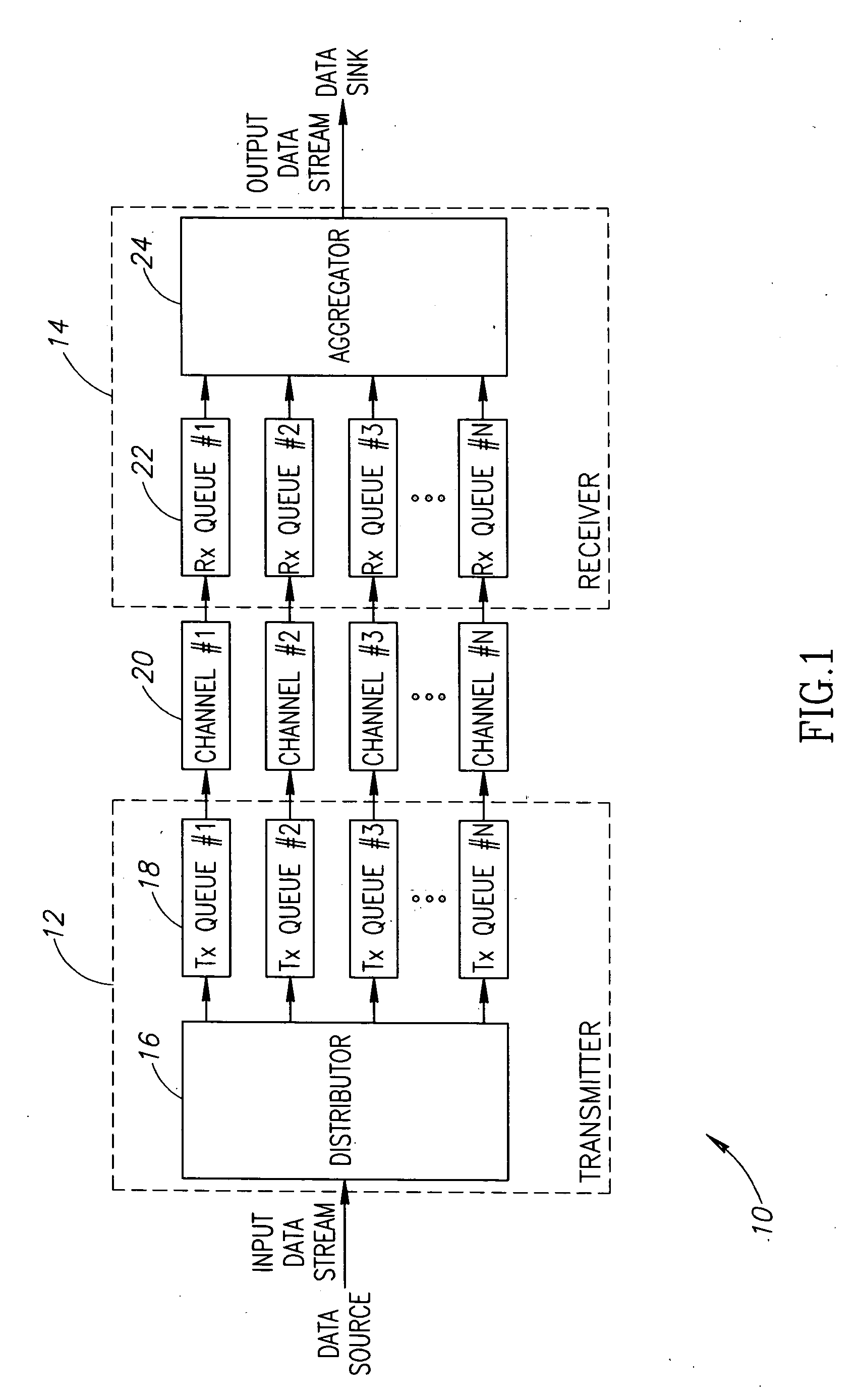
ActiveUS20060015917A1Flexible distribution of dataVariable lengthEnergy efficient ICTBroadband local area networksData streamCurrent channel
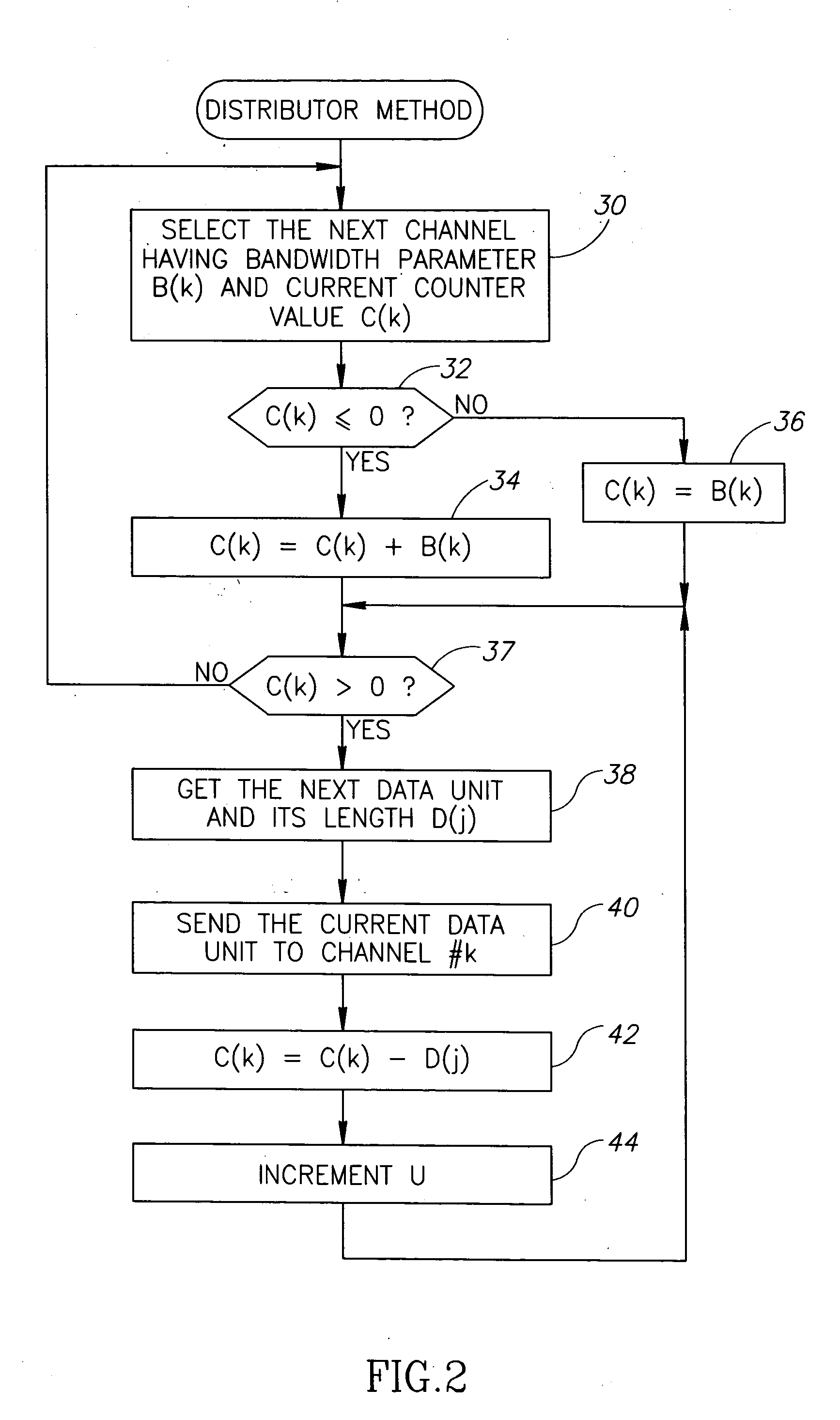
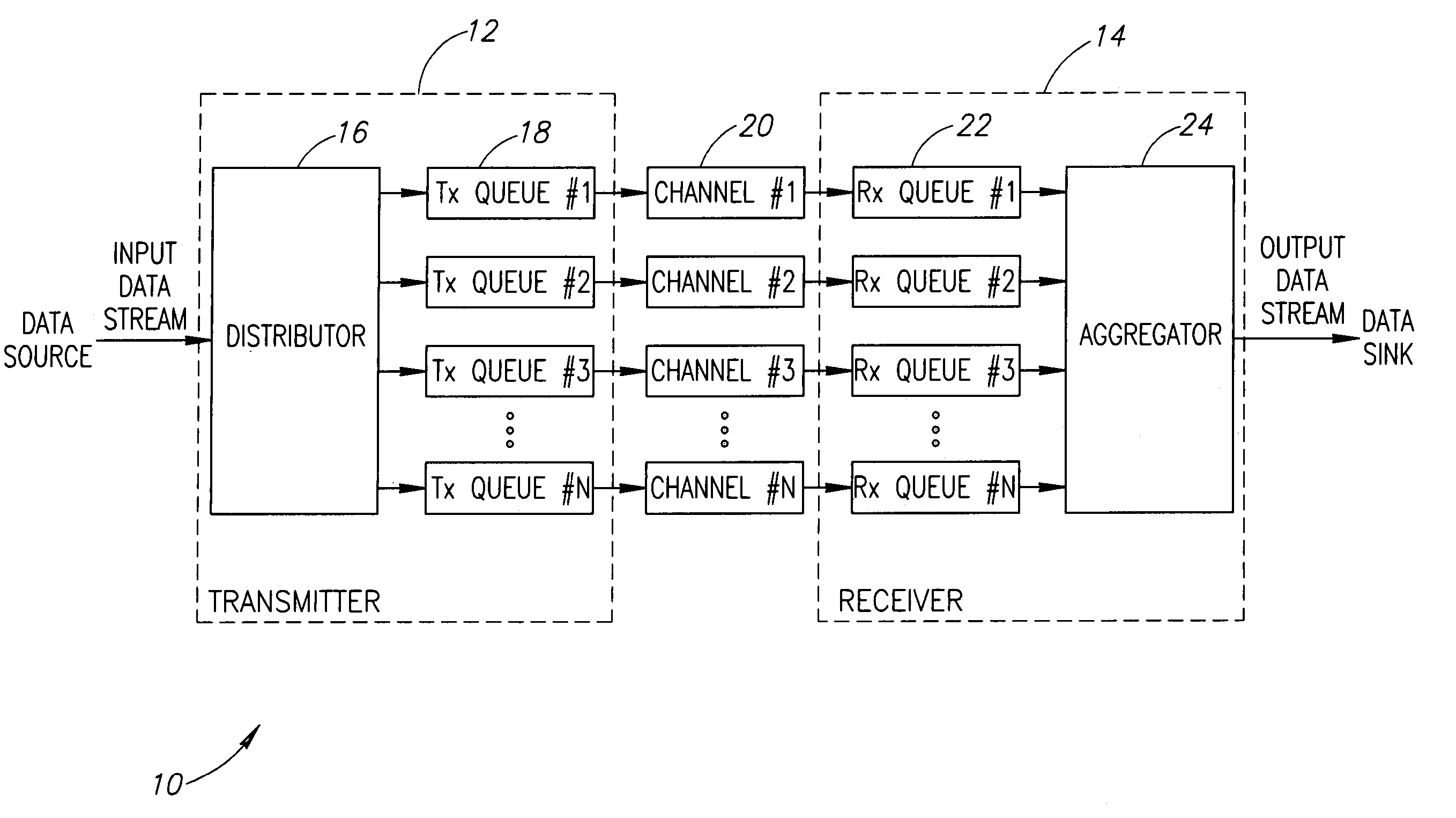
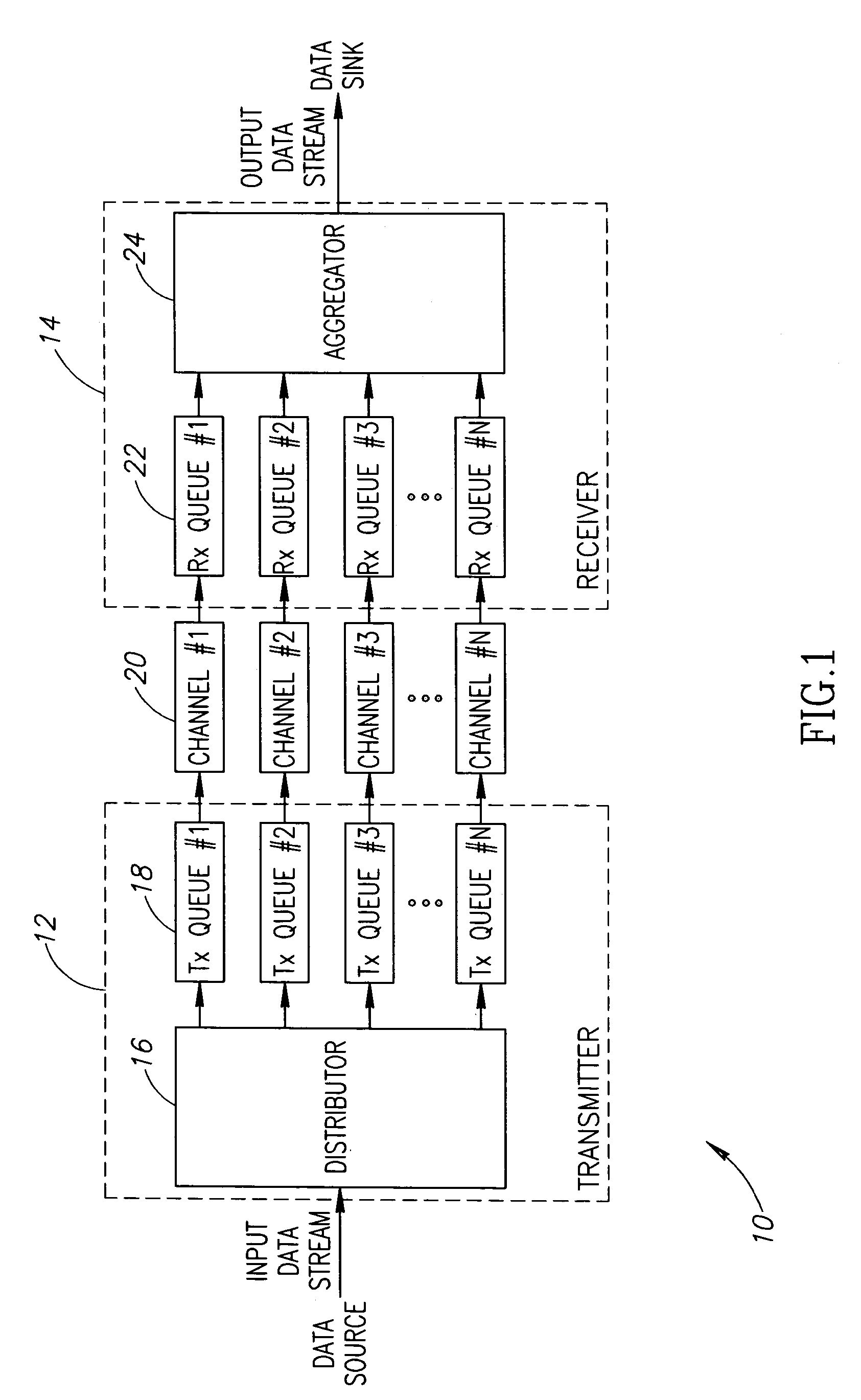
A novel apparatus for and a method of data transmission whereby an input data stream is distributed over a plurality of physical channels within a logical channel group. Transmission of data over the channel group appears as transmission over a single logical channel having a bandwidth approximately equal to the sum of the physical channel bandwidths. The physical channels making up the logical channel group may have different bandwidth capacities. The invention comprises a method of data unit distribution among a plurality of physical channels including the consideration of the bandwidth capacities of the individual physical channels in implementing the distribution algorithm, and the capability of reproducing the order of the transmission of the data units on the receiving side without the need for additional fields or modification of existing fields of the data units. The method of the present invention performs an algorithm whereby the transmitter and the receiver only need to decide to transmit / receive a data unit using the current channel or to switch to the next channel in the channel pool (i.e. the channel group). This decision is made considering the value of a bandwidth parameter and current ‘credit’ counter associated with each channel.
Owner:MAXLINEAR INC
Cluster task resource allocation method for multi-core processor
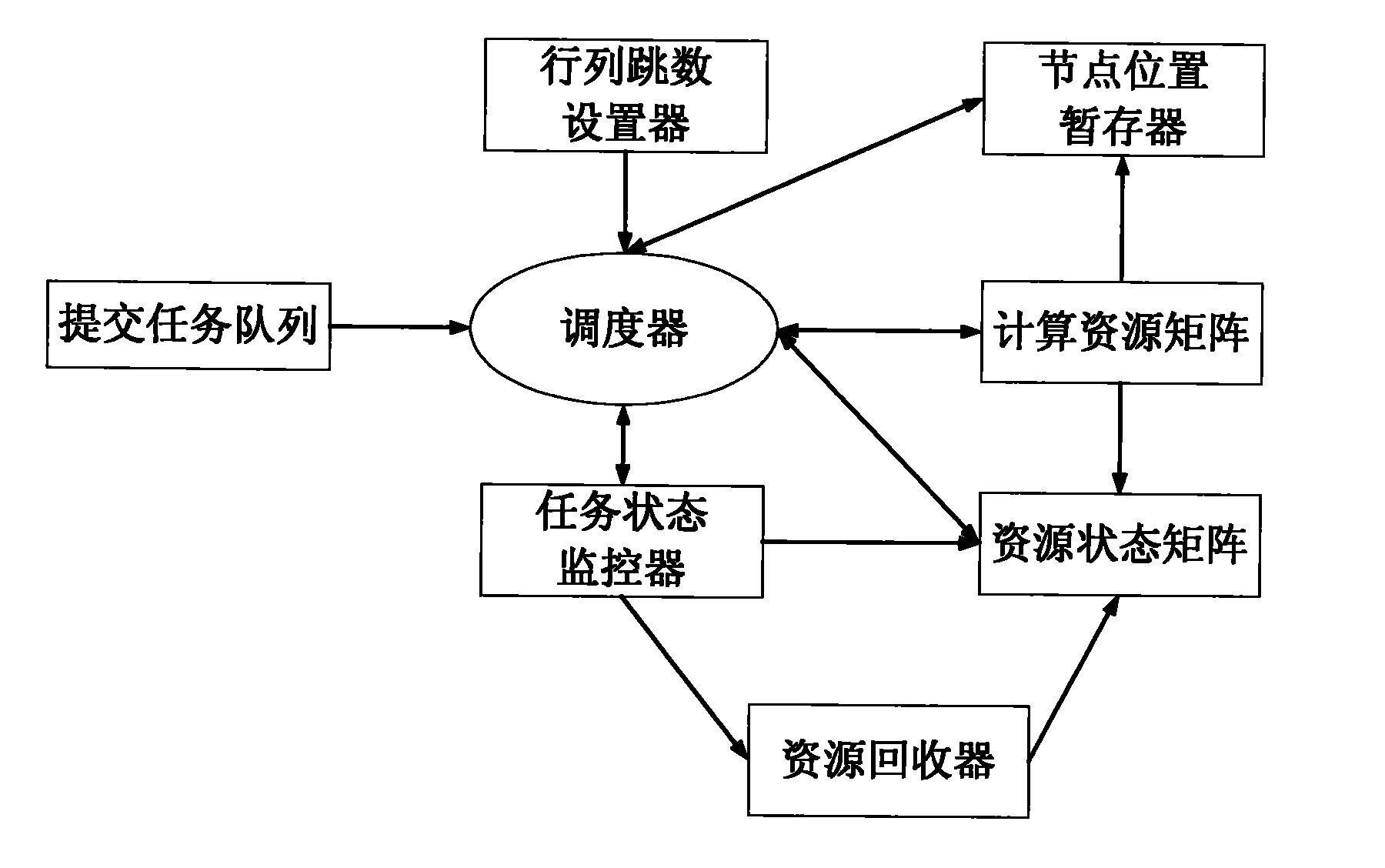
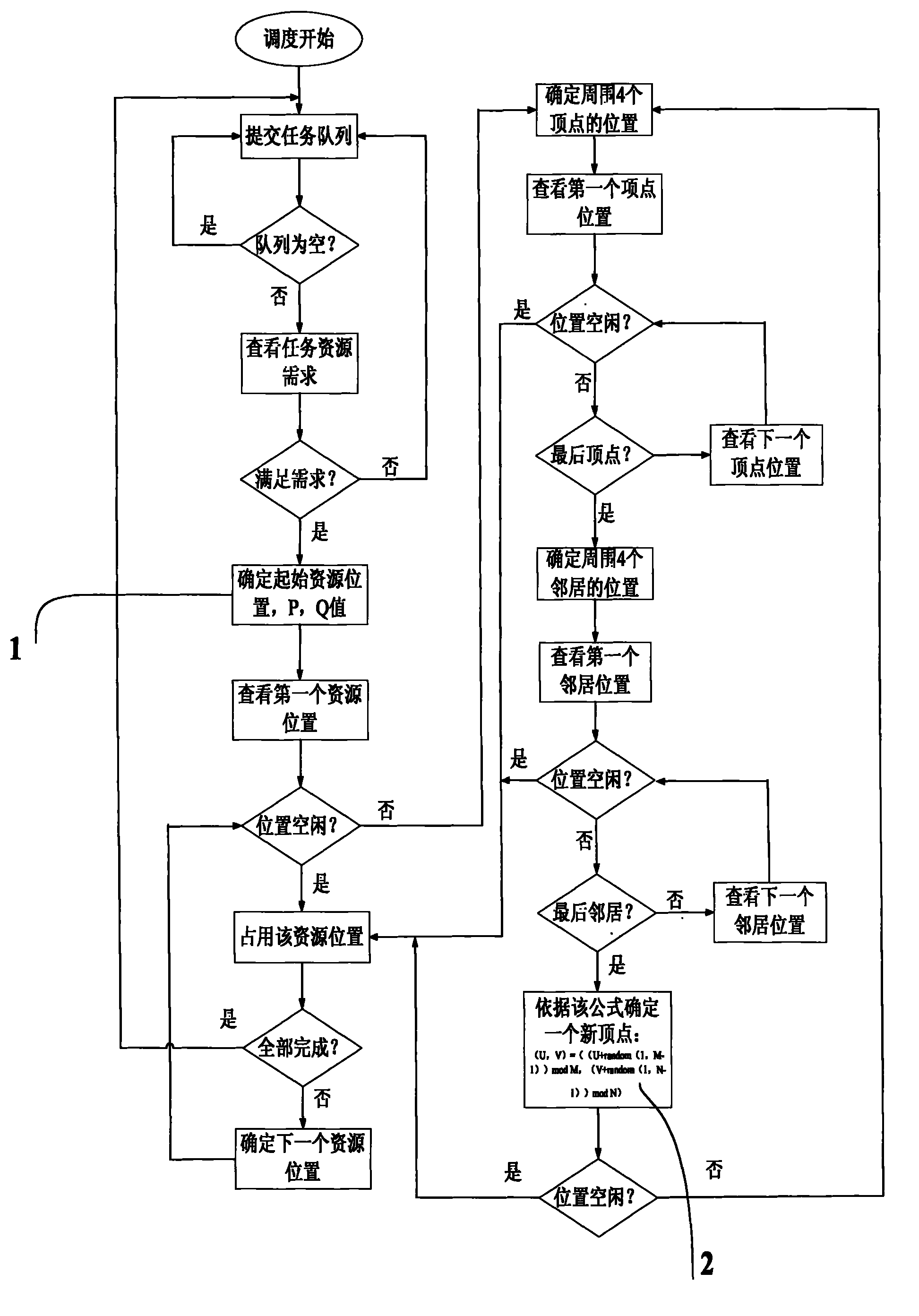
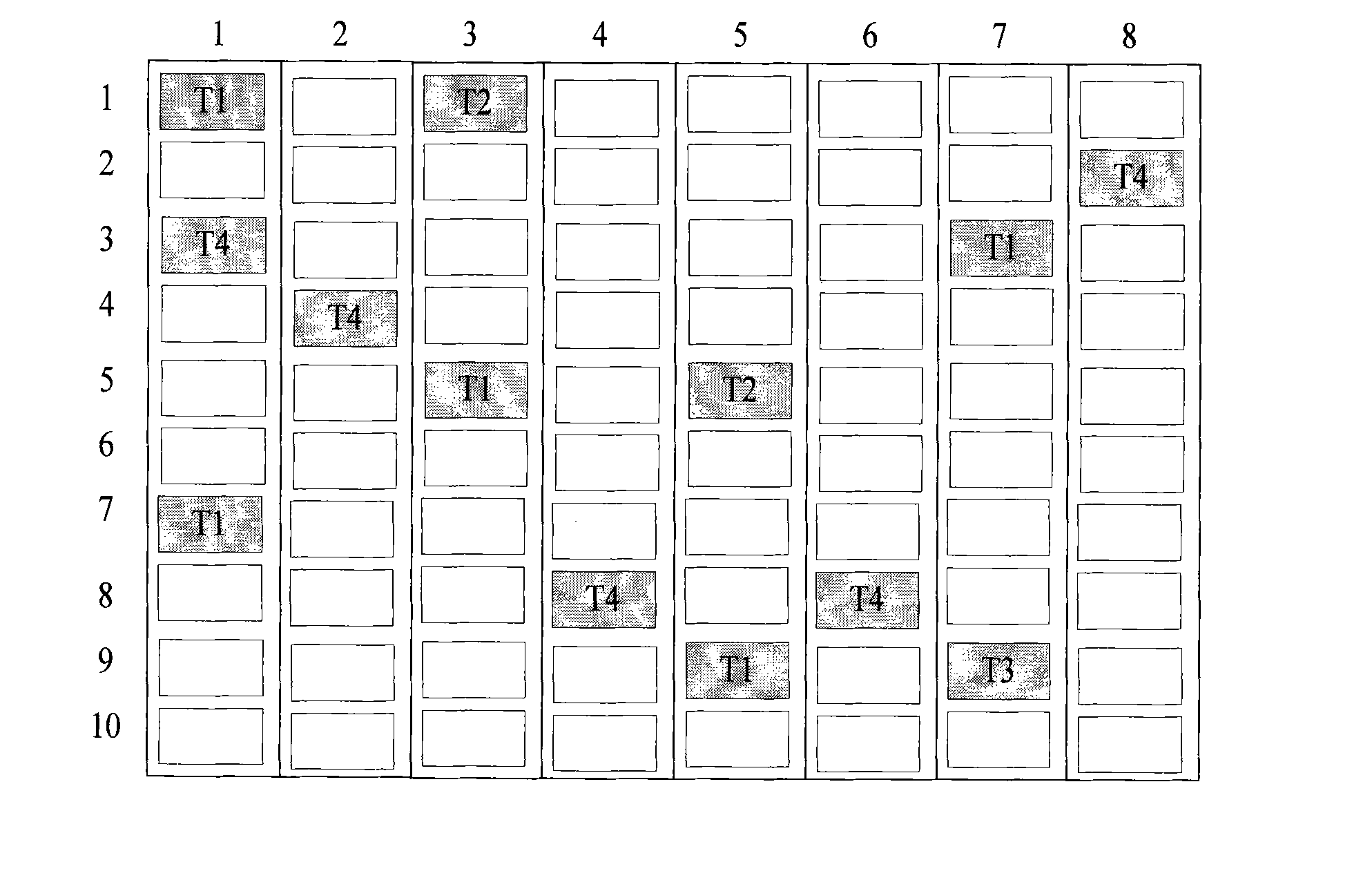
InactiveCN101916209AAdequate heat dissipationReduced thermal effectsResource allocationDigital data processing detailsCluster systemsAllocation algorithm
The invention relates to a cluster task resource allocation method for a multi-core processor. In the method, CPU resource nodes are used as basic allocation units for task allocation according to operation tasks submitted by receiving users to a cluster, and a task resource allocator is formed. The task resource allocator maps resources on the cluster to an M*N matrix AR. When idle resource positions are searched for the tasks, in the method, the tasks are uniformly dispersed and required resources are allocated to the nodes, so that the resource node positions occupied by all tasks are spaced. The method avoids the problem that tasks are excessively concentrated in one certain area, a large amount of heat energy is concentrated in the area as time goes by, the temperature of a local chip is too high, and the normal operating efficiency of a computer is influenced in the traditional task allocation algorithm. The task scheduling algorithm adopted by the method is an online real-time task scheduling algorithm and has good application prospects in the operation and task management of a multi-core processor cluster system.
Owner:EAST CHINA JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
Time-sensitive task dynamic allocation algorithm in battlefield environment for multiple unmanned aerial vehicles
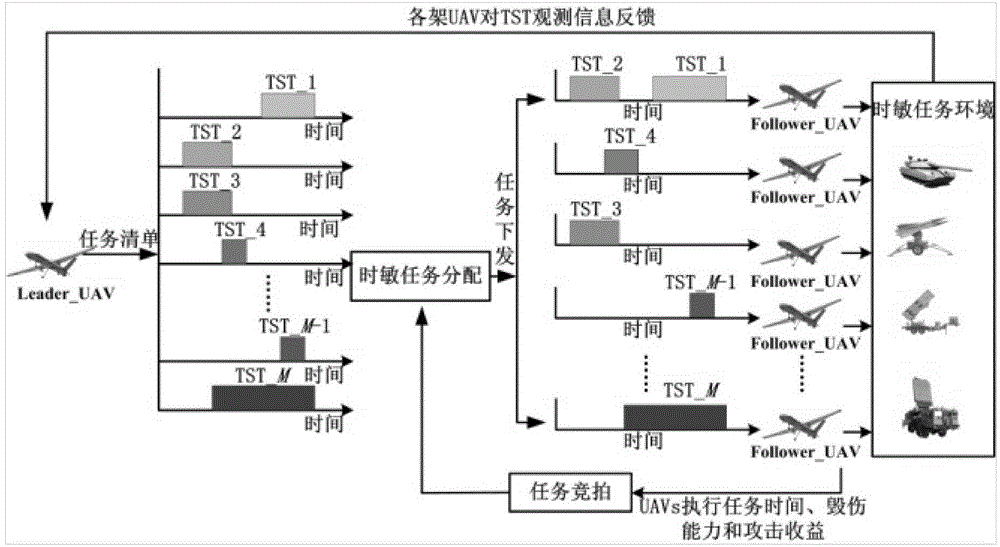
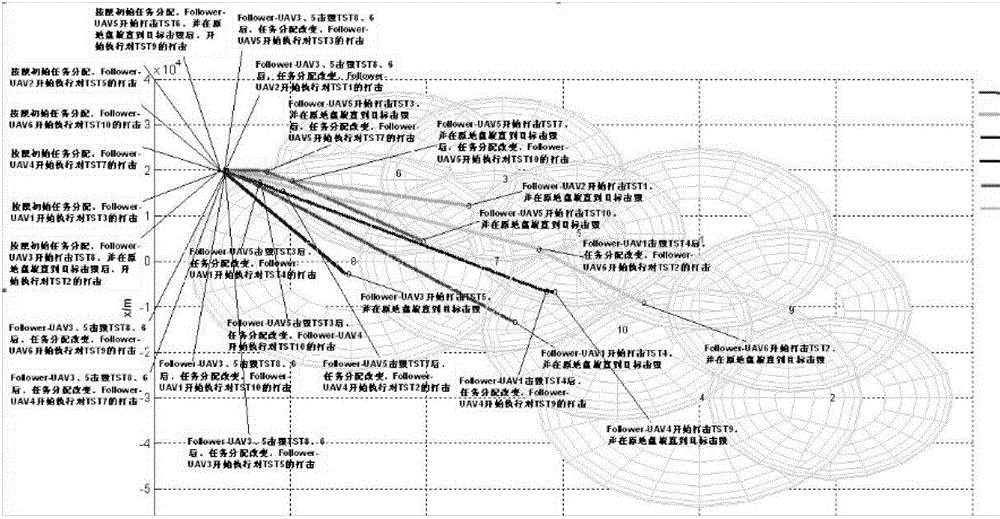
InactiveCN104155999ASolve the strike problemEffective strikeTarget-seeking controlAllocation algorithmModel predictive control
The invention discloses a time-sensitive task dynamic allocation algorithm in the battlefield environment for multiple unmanned aerial vehicles. The algorithm can realize that multiple unmanned aerial vehicles strike multiple time-sensitive targets in the battlefield environment; according to the algorithm, a task auction idea is used to construct a time-sensitive task dynamic allocation model, and the task execution time, damage ability and strike earnings as well as the influences of the execution of the current task on time-sensitive task time window width and threat degree are mainly considered by the model; the strike path planning of the unmanned aerial vehicles is realized by adopting a model predictive control algorithm, and that the strike paths of unmanned aerial vehicles are optimized under the condition that the unmanned aerial vehicles keep away from threat regions is mainly completed.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
Heterogeneous multi-core system-oriented process scheduling method
The invention discloses a process scheduling method for heterogeneous multi-core system. The method is implemented in the way that all the processes share the same queue for ready processes. Each process has a flag to indicate that the process is running in the main core or assistant core. The operating system in the method uses client-management structure. The core of the operating system runs in the main process, other processes deal with a variety of applications that only can run on it. When applications request the operating system services, the request would be passed on to the procedure on the main operating system. The process scheduler uses a split load scheduling algorithm and the processor allocation algorithm to achieving a reasonable process scheduling.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
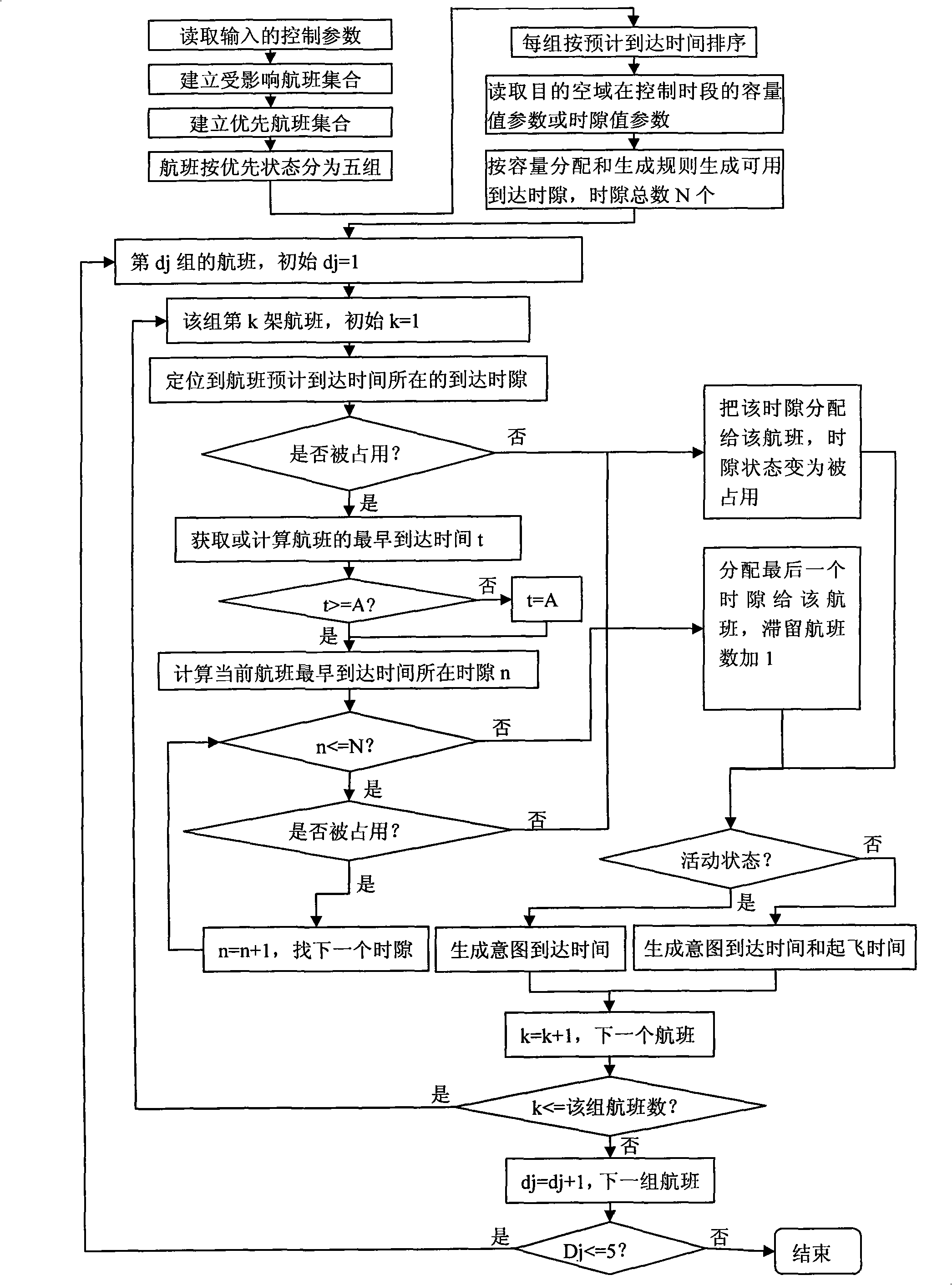
Method for implementing flight time slot allocation
The invention relates to a method for implementing flight time slot allocation. The method is realized through the assistance of a computer management system, and the system also comprises a flow management program generating / evaluating subsystem which is used as an operation platform for the method for implementing the flight time slot allocation. Based on statistics and prediction of flow and capacity, the method discovers the arisen or possibly arisen flow problems in time, assists flow managers to propose various proposals for solving the flow problems and corresponding implement effects, assists the flow managers to make a final decision, allocates take-off time slots meeting integrally optimal, impartial and just principles for flights needing ground delay through take-off time slot allocation algorithm in particular in a ground delay program, and has innovation, practicability and higher promotional value in improving the current situation of the domestic air traffic flow technology field.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
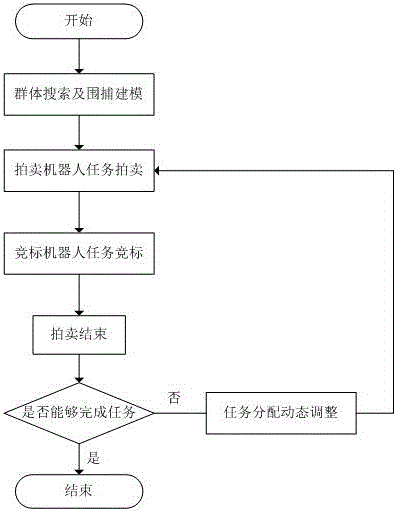
Task intensity dynamic adjustment based multiple robots cooperating task hunting allocation algorithm
InactiveCN105843227AImprove distribution efficiencyCutting costsPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesAssignment methodsAllocation algorithm
The invention provides a task intensity dynamic adjustment based multiple robots cooperating task hunting allocation algorithm, which belongs to the technical field of task allocation. The method comprises group searching, hunting model building and task allocation strategies. According to the invention, the conception of hunting experience obtained from an intensified learning method is introduced into a task allocation algorithm; the method can make dynamic adjustments to an initial task allocation scheme obtained from an auction algorithm so that the method can better adapt to a dynamic changing hunting environment and reduce the communication quantity and calculation quantity among systems. In the task allocation auction algorithm, the solutions for the cost function for a bidding robot are optimized, and the conception of task intensity is raised. As a result, task allocation efficiency for a multiple robots cooperating system is improved while cost is reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Multi-cell coordination large-scale MIMO pilot frequency multiplexing transmission method
InactiveCN103997394AReduce overheadNet Spectral Efficiency ImprovementError prevention/detection by diversity receptionFrequency spectrumSpectral efficiency
The invention provides a multi-user large-scale MIMO pilot frequency multiplexing transmission method based on multi-cell coordination. According to the transmission method, all base stations provided with a large-scale antenna array wirelessly communicate with several users on the same time-frequency resource, it is not required that the users in the same cell use complete orthogonal pilot frequency, it is not required either that different cells completely multiplex the same pilot frequency, and the users in the same cell or the different cells can multiplex the same pilot frequency. Multi-cell coordination communication is adopted, and a cell cluster is formed by the multiple cells. The transmission method includes the steps that all the cell base stations obtain statistics channel information of all the users in the cell cluster and send the information to a central control unit which takes charge of coordinating all the cells in the cell cluster; according to the statistics channel information, the central control unit allocates pilot frequency to all the users in the cell cluster and feeds back a result to all the base stations; all the base stations obtain all user channel estimations and statistical characteristics of errors of the user channel estimations by using pilot frequency signals sent by all the users, and the base stations perform uplink robust receiving and downlink robust pre-coding according to all the user channel estimations and the statistical characteristics of the errors of the user channel estimations. The transmission method can reduce the pilot frequency overhead substantially and improve net spectrum efficiency of a system and is high in adaptability to pilot frequency allocation algorithms, and uplink receiving and downlink pre-coding transmission has robustness.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Data transmission scheme using channel group and DOCSIS implementation thereof
ActiveUS7567620B2Flexible distribution of dataVariable lengthEnergy efficient ICTBroadband local area networksCurrent channelData stream
A novel apparatus for and a method of data transmission whereby an input data stream is distributed over a plurality of physical channels within a logical channel group. Transmission of data over the channel group appears as transmission over a single logical channel having a bandwidth approximately equal to the sum of the physical channel bandwidths. The physical channels making up the logical channel group may have different bandwidth capacities. The invention comprises a method of data unit distribution among a plurality of physical channels including the consideration of the bandwidth capacities of the individual physical channels in implementing the distribution algorithm, and the capability of reproducing the order of the transmission of the data units on the receiving side without the need for additional fields or modification of existing fields of the data units. The method of the present invention performs an algorithm whereby the transmitter and the receiver only need to decide to transmit / receive a data unit using the current channel or to switch to the next channel in the channel pool (i.e. the channel group). This decision is made considering the value of a bandwidth parameter and current ‘credit’ counter associated with each channel.
Owner:MAXLINEAR INC
Method and apparatus for minimizing near end cross talk due to discrete multi-tone transmission in cable binders
InactiveUS6393052B2Frequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission path divisionModem deviceProximal point
In a discrete multi-tone modem, a method of minimizing cross talk over a twisted pair of a twisted pair cable binder in which discrete multi-tone data transmission is utilized comprises the steps of one of jointly minimizing near end cross talk while maximizing total data rate, jointly minimizing an arbitrary function of total power while maximizing total data rate and minimizing total near end cross talk for a given data rate, selecting a function to be optimized and performing a bit and power allocation algorithm responsive to the selected function. The process may be combined with known optimization functions such as jointly minimizing an average bit error rate while maximizing the data rate. As a result, the process is considerably more flexible and adaptable to changing parameters such as environmental parameters impacting data transmission performance in the presence of cross talk. Either a telecommunications central office modem or a remote terminal modem may be so adapted to apply such a cross talk minimization method.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Method for distributing optimum rate for extensible video stream multi-rate multi-cast communication
InactiveCN101568026AEfficient use ofImprove throughputSpecial service provision for substationPulse modulation television signal transmissionHeterogeneous networkOptimization problem
The invention relates to a method for distributing optimum rate for an extensible video stream multi-rate multi-cast communication. In order to maximum whole user efficiency under a heterogeneous network environment, the invention comprises the following steps of: (1) carrying out combined optimization to the network codes and network flux control of multi-rate and multi-path route and relay node; (2) when selecting the optimum multi-cast transmission path and distributing all layers of video stream transmission rates, considering the code stream priority problem of the video coding layer simultaneously; for the one hand, searching the transmission network of the minimum cost for each video coding layer; and for the other hand, simultaneously meeting the requirement of dependency of the extensile video codes layers; and (3) realizing the optimum distribution of the resource and facilitating the distribution-type solution by adopting a complete distribution-type rate distribution arithmetic, namely adopting a Lagrange dual method to decompose the original convex optimization problem into two sub-optimization problems of high-order and low-order. The introduction of network codes not only improves the whole throughput of the network but also provides better video quality for the receiving terminals simultaneously.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
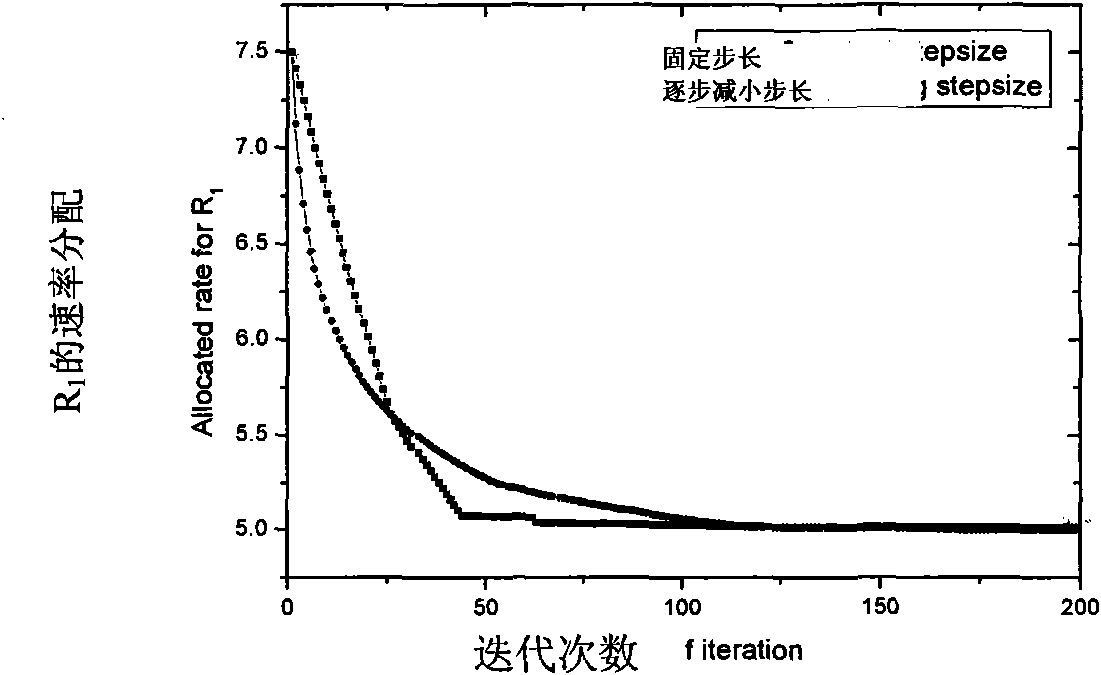
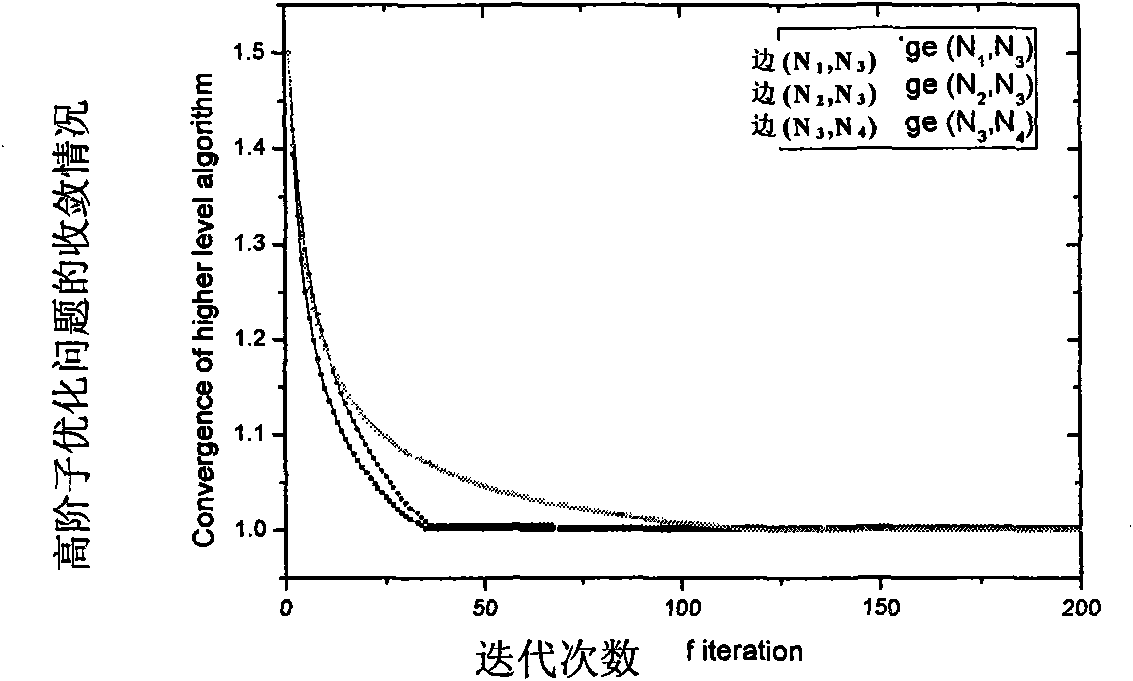
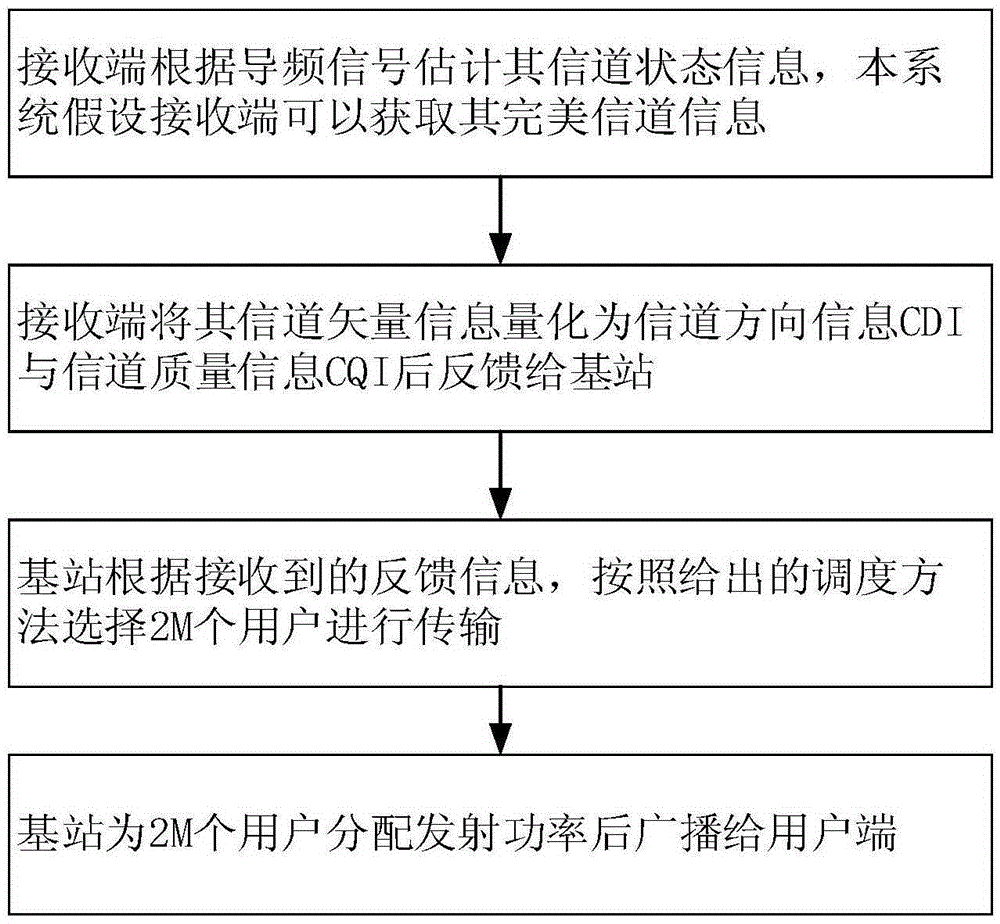
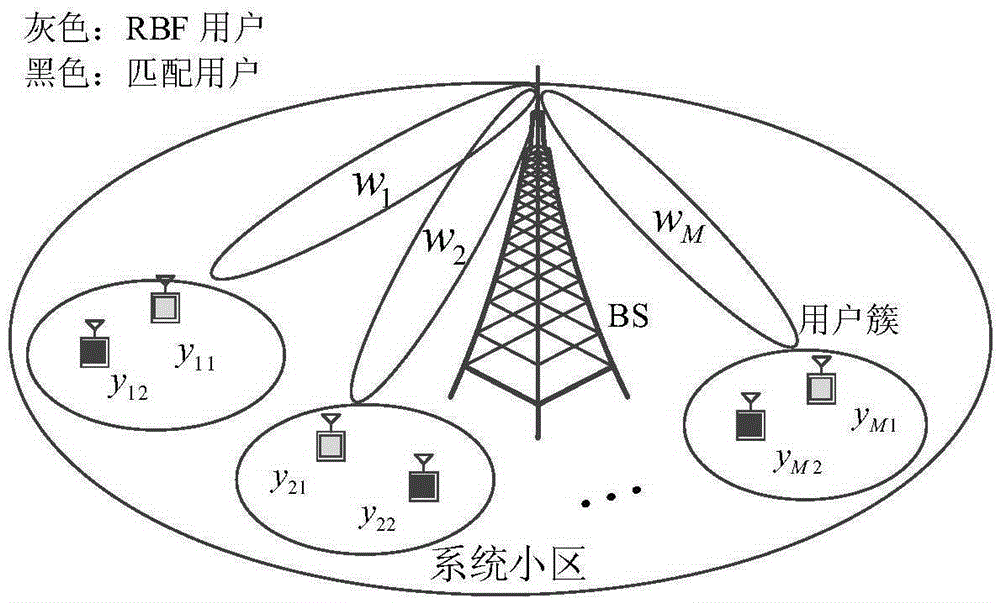
User selection method of non-orthogonal multiple access system downlink under limited feedback
InactiveCN105337651AOverall Throughput AdvantageGuaranteed service needsSpatial transmit diversitySignal allocationChannel state informationAllocation algorithm
The invention provides a user selection method of a non-orthogonal multiple access system downlink under limited feedback. M antennas are arranged at a base station side. K single antenna users are distributed in a cell. All users of a receiving side acquire channel state information via pilot frequency signals broadcasted by a transmitting end, and channel vectors are quantified as channel direction information CDI and channel quality information CQI and then the channel direction information CDI and the channel quality information CQI are fed back to the base station via a limited rate channel. The base station schedules 2M users from K candidate users to perform transmission of the downlink according to the CDI and the CQI fed back by the users, wherein every two of the 2M users form a user cluster, and M user clusters are formed in total. M wave beam forming vectors are adopted to transmit M user clusters in the system and equal power P is allocated for each cluster, wherein each wave beam vector supports one user cluster, each cluster includes two non-orthogonal users, and each user performs intra-cluster power allocation via a power allocation algorithm. The overall throughput of the system is enabled to have obvious advantages in comparison with that of conventional non-orthogonal transmission.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Task allocation method for formation of unmanned aerial vehicles in certain environment
ActiveCN103279793AEasy to operateEasy to understandBiological modelsSpecial data processing applicationsAllocation algorithmTabu search
The invention discloses a task allocation method for formation of unmanned aerial vehicles in a certain environment, belonging to the technical field of unmanned aerial vehicles. The task allocation method comprises the following steps of determining a coding sequence of a task allocation algorithm; determining a preponderant function of the unmanned aerial vehicles formed to execute a task; determining a speed update formula and a position update formula of a discrete particle swarm optimization; determining the flow of a tabu search; and determining the flow of hybrid optimization. According to the task allocation method for the formation of the unmanned aerial vehicles in the certain environment, the continuous particle swarm optimization is discretized, the algorithm is simply and conveniently operated on the premise that optimizing property can be guaranteed, and the effectiveness of the discrete particle swarm method is indicated through simulation. According to the task allocation method for the formation of the unmanned aerial vehicles in the certain environment, a supplement strategy of the tabu search algorithm is provided, and the local optimizing capacity of the algorithm is enhanced when the inertia weight [omega] of the particle swarm optimization is larger, i.e. the particle swarm embodies stronger variety, so that the original two algorithms realize complementing each other's advantages, the searching performance can be improved, and the judgment can be verified in multiple groups of simulated tests.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Multi-beam ad hoc network channel access control method
ActiveCN109348537AIncrease capacityMaximize capacityRadio transmissionHigh level techniquesHigh rateOmni directional
The invention discloses a multi-beam ad hoc network channel access control method, aiming at providing an access control method which has a high channel utilization rate and can improve the network performance. The method of the invention is implemented through the following technical scheme: for a distributed multi-beam scene, combining the characteristics of multi-beams, utilizing the broadcastchannel characteristics of an omni-directional network and the high bandwidth and high directivity characteristics of a directional network, using the short message protocol interaction between nodes,and assisting to complete the high-rate parallel transmission of multiple nodes on a directional link; using space division multiplexing among the nodes to achieve the concurrent communication between multiple transmission nodes and multiple receiving nodes; when a network cluster head node receives RTS frames of all other nodes, running a multi-beam ad hoc network channel access allocation algorithm; and searching an optimal transceiving node pair set in each time slot, finding an edge set with the maximum network capacity as a channel access allocation result of each node in the next directional link time slot, and further implementing the simultaneous multi-transmission and multi-reception of the multiple nodes at the same frequency.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
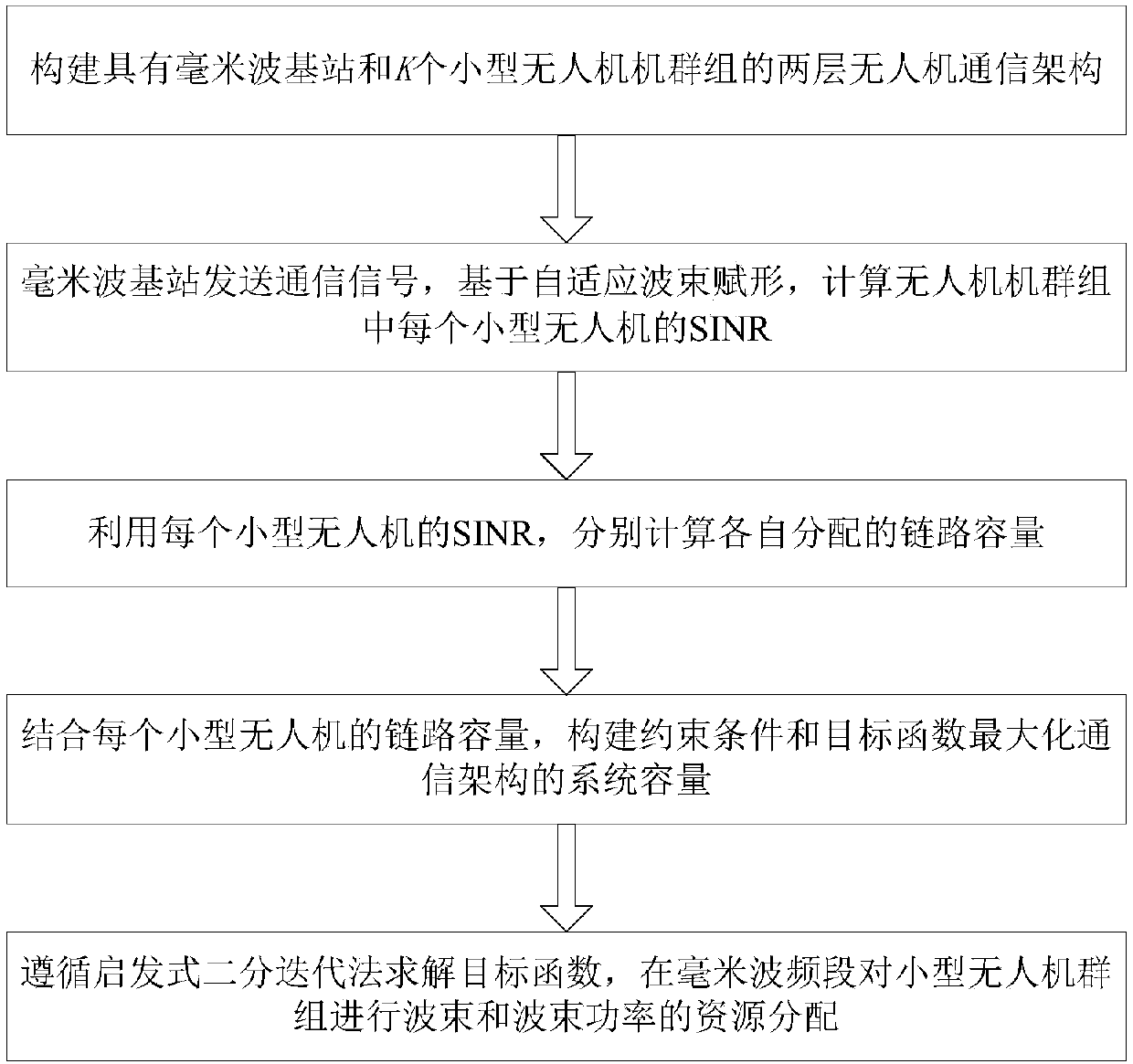
Allocation algorithm of joint beam and power for 5G unmanned aerial vehicle communication
ActiveCN108419286AIncrease capacityReduce the number of iterationsPower managementSpatial transmit diversitySystem capacityUncrewed vehicle
The invention provides an allocation algorithm of joint beam and power for 5G unmanned aerial vehicle communication, and belongs to the field of communication. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, constructing unmanned aerial vehicle communication architecture, sending, by a millimeter wave base station, a communication signal, calculating an SINR of each miniature unmanned aerial vehicle in an unmanned aerial vehicle group based on adaptive beam forming, and separately calculating the respective allocated link capacity; then, in combination with the link capacity of each miniature unmanned aerial vehicle, constructing constraint conditions and an objective function to maximize the system capacity of the communication architecture; and finally solving the objective function,and performing beam and beam power resource allocation on the miniature unmanned aerial vehicle group within a millimeter wave band. By adoption of the allocation algorithm provided by the invention,the number of iterations is reduced, the fast beam and power joint allocation is achieved, the fairness of the unmanned aerial vehicles is ensured, and the system capacity is also improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
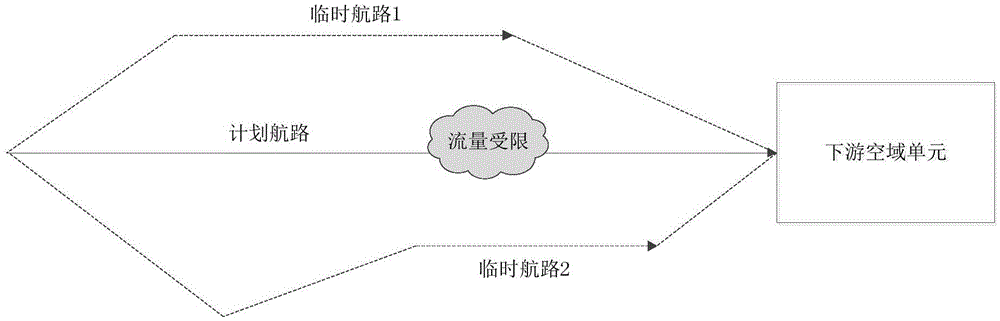
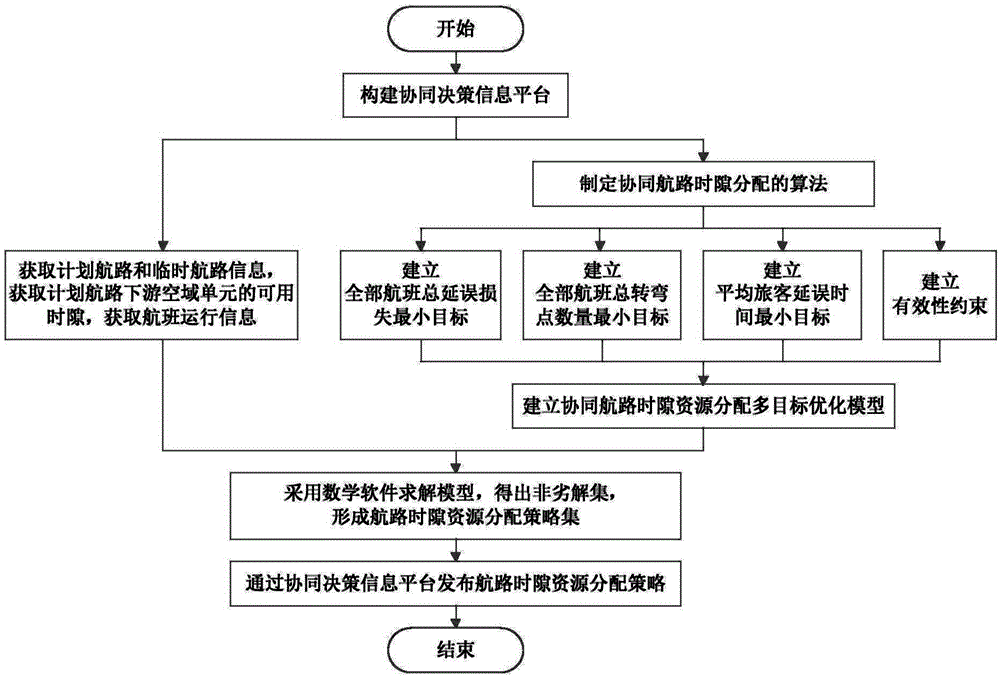
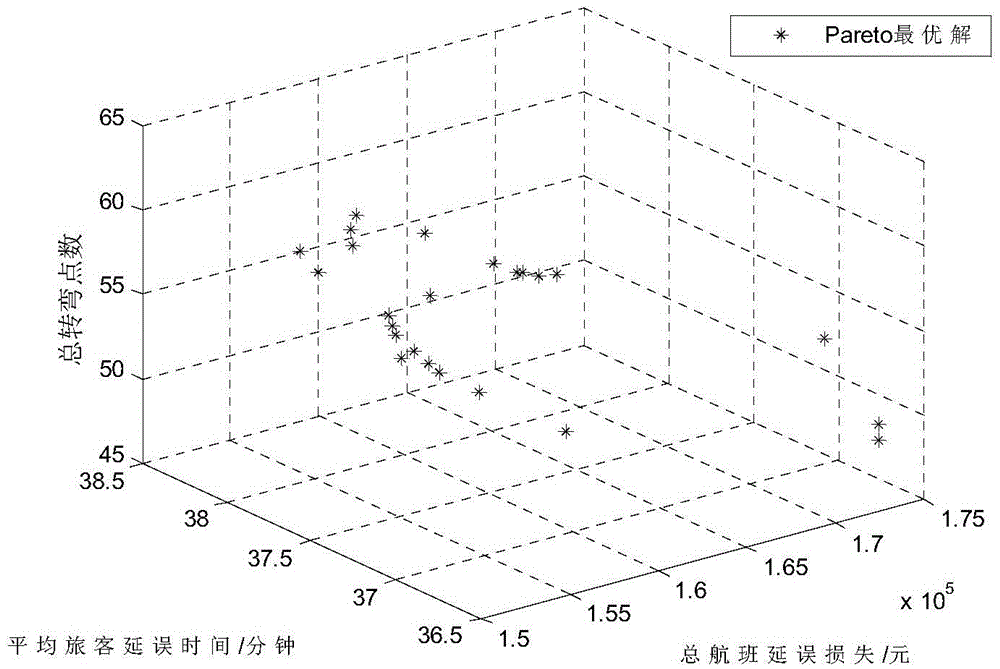
Collaborative multi-objective optimal allocation method for airway time slot resources
The invention discloses a collaborative multi-objective optimal allocation method for airway time slot resources. The method includes the steps that an airway time slot resource collaborative decision-making information platform is established, planned airway and temporary airway information in a flow-limited airspace and available time slot information and flight operation information of a planned airway downstream airspace unit are acquired, a collaborative airway time slot allocation algorithm is made, objective functions and constraint conditions meeting the requirement for validity are established with the minimum total delay loss of all flights, the minimum total number of turning points of all the flights and the minimum average delay time of passengers as objectives respectively, a multi-objective optimization model for collaborative airway time slot resource allocation is established, a non-inferior solution set is obtained by solving the model, an airway time slot resource allocation strategy set is formed, and airway time slot resource allocation strategies are issued through the airway time slot resource collaborative decision-making information platform.
Owner:THE 28TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
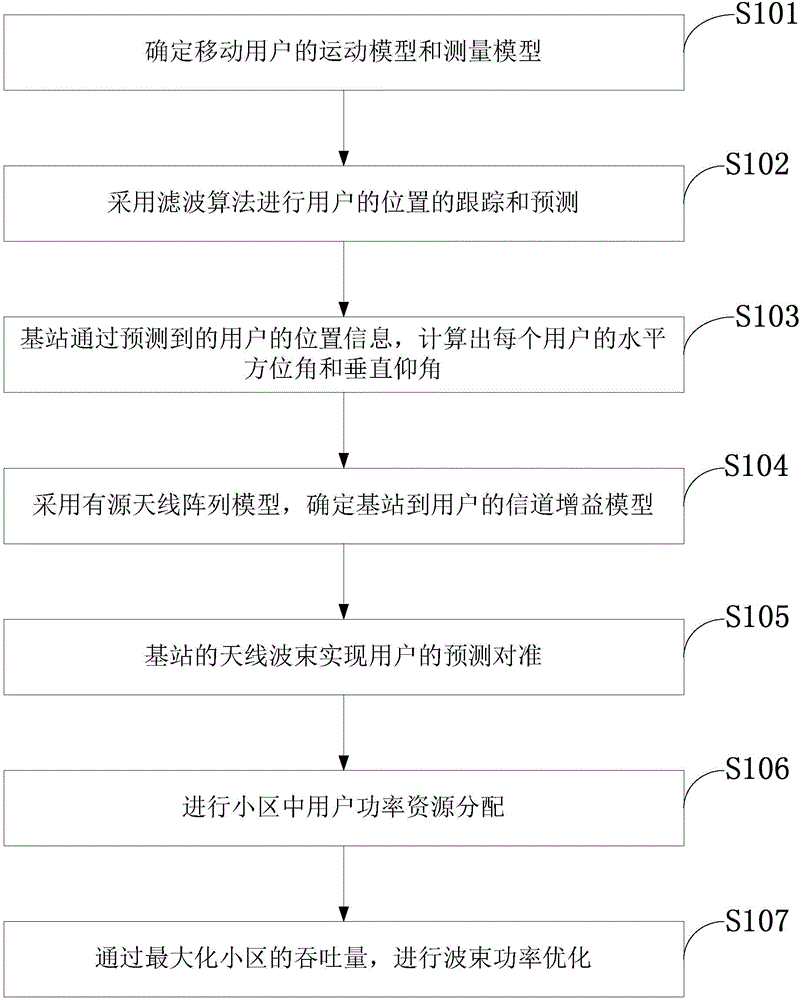
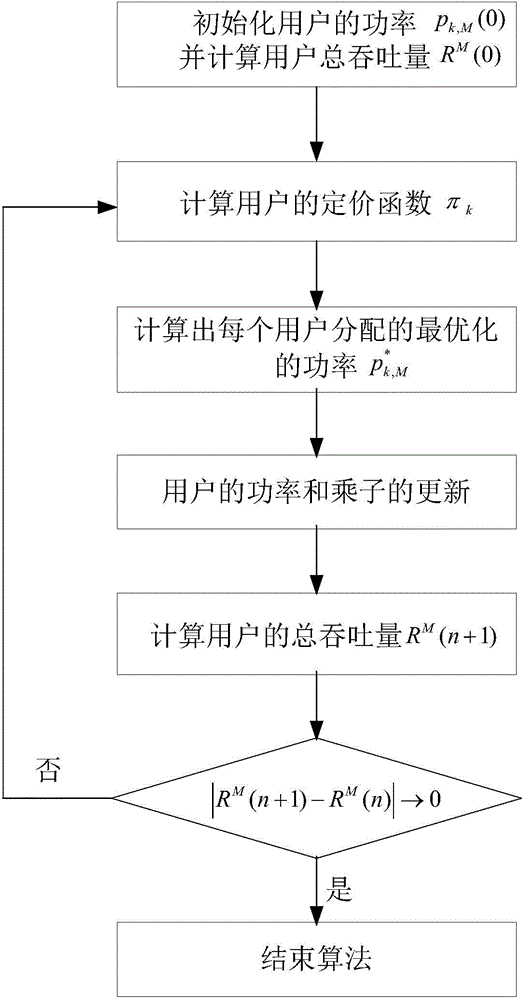
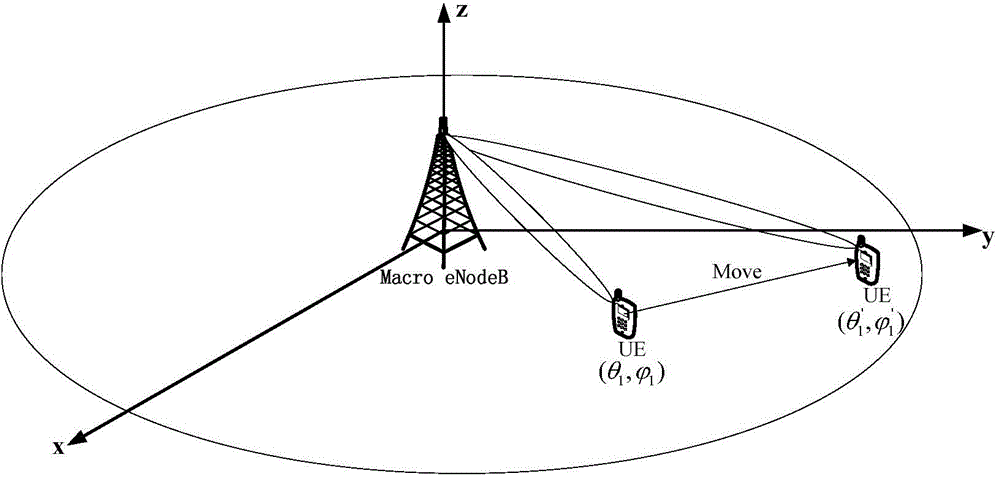
Active antenna array beam optimization method based on tracking and prediction of user position
ActiveCN104486775AAccurate trackingAccurate predictionNetwork planningHigh level techniquesSystem capacityFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses an active antenna array beam optimization method based on tracking and prediction of a user position. Based on the active antenna user level beam forming technology, the accurate prediction and tracking of the user position are achieved, the information interaction between a base station of a user is effectively reduced, and the handling capacity of a system is improved though a beam optimization algorithm. By means of the active antenna array beam optimization method based on tracking and prediction of the user position, the tracking and prediction of the user position are accurately achieved, the information interaction between the base station and the user is reduced, the utilization rate of spectrum resources is increased, the system capacity and the user performance are improved, and the large user performance improvement is achieved. Meanwhile, beam optimization is conducted based on the total handling capacity in a cell, an optimized beam power allocation algorithm is proposed, and the system capacity is increased.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
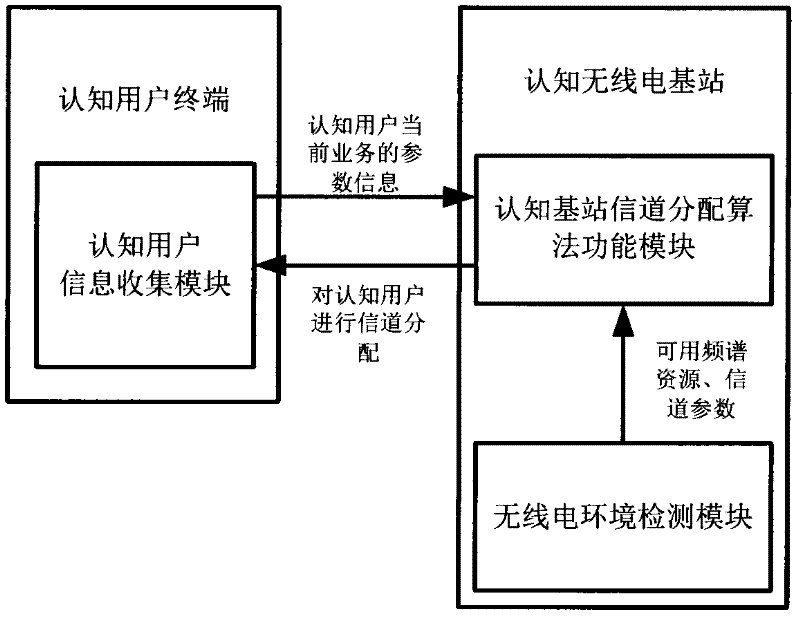
A Joint Channel and Power Allocation Method for Cognitive Radio Networks
InactiveCN102271338AEnsure fairnessFull consideration of fairnessNetwork planningCognitive userTelecommunications
The invention discloses a channel and power joint allocation method for a cognitive radio network. This method starts from the cognitive user's speed requirement and user fairness, uses the Nash coordination solution in the cooperative game to construct the target utility function, and fully considers the cognitive user's fairness and the Avoidance of primary user interference. Through step-by-step analysis and derivation, a heuristic sub-channel allocation algorithm is established. This method not only has the advantage of meeting the rate requirements of cognitive users, but also fully guarantees the fairness of cognitive users.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Method and system for allocating file in clustered file system
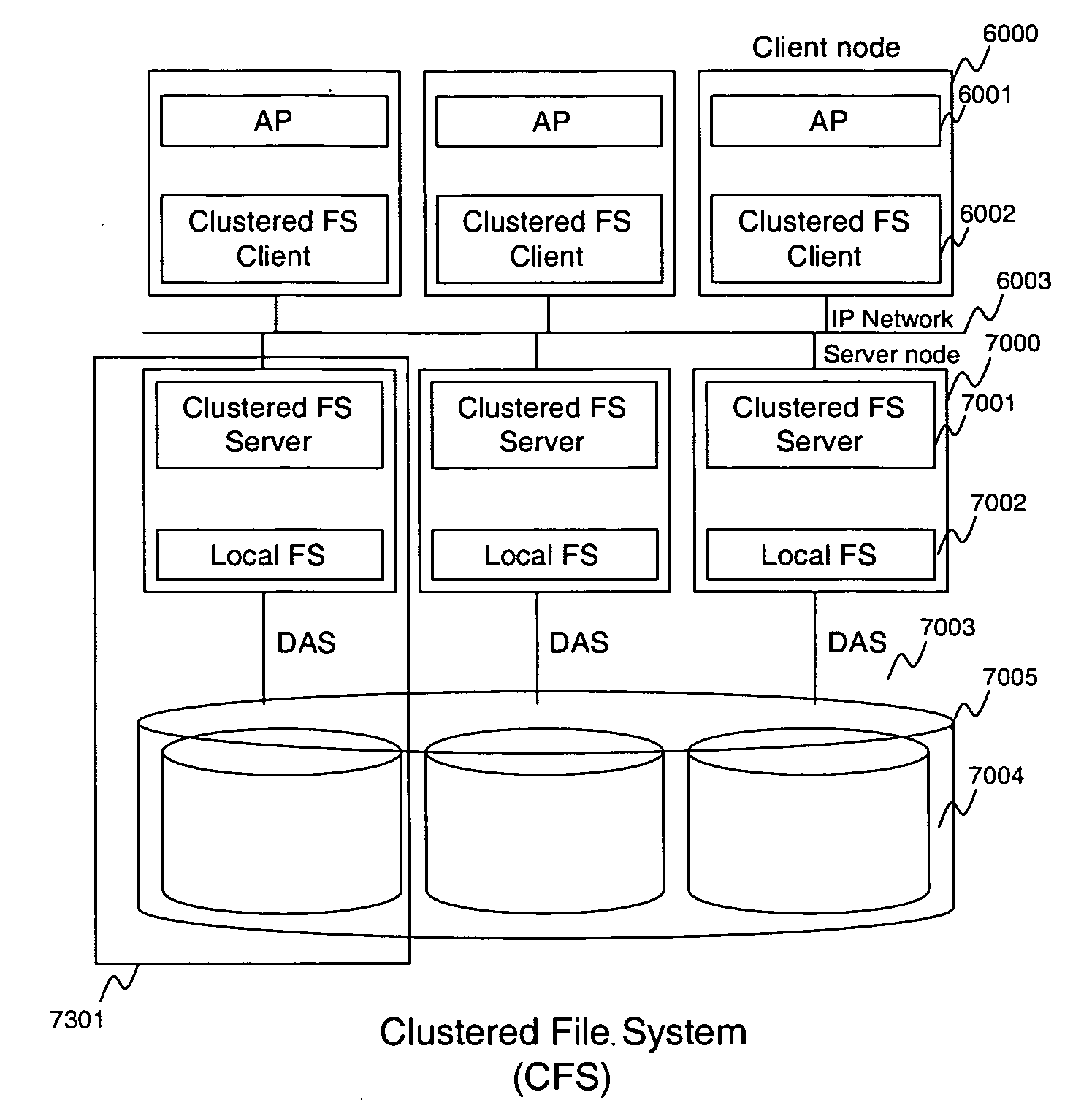
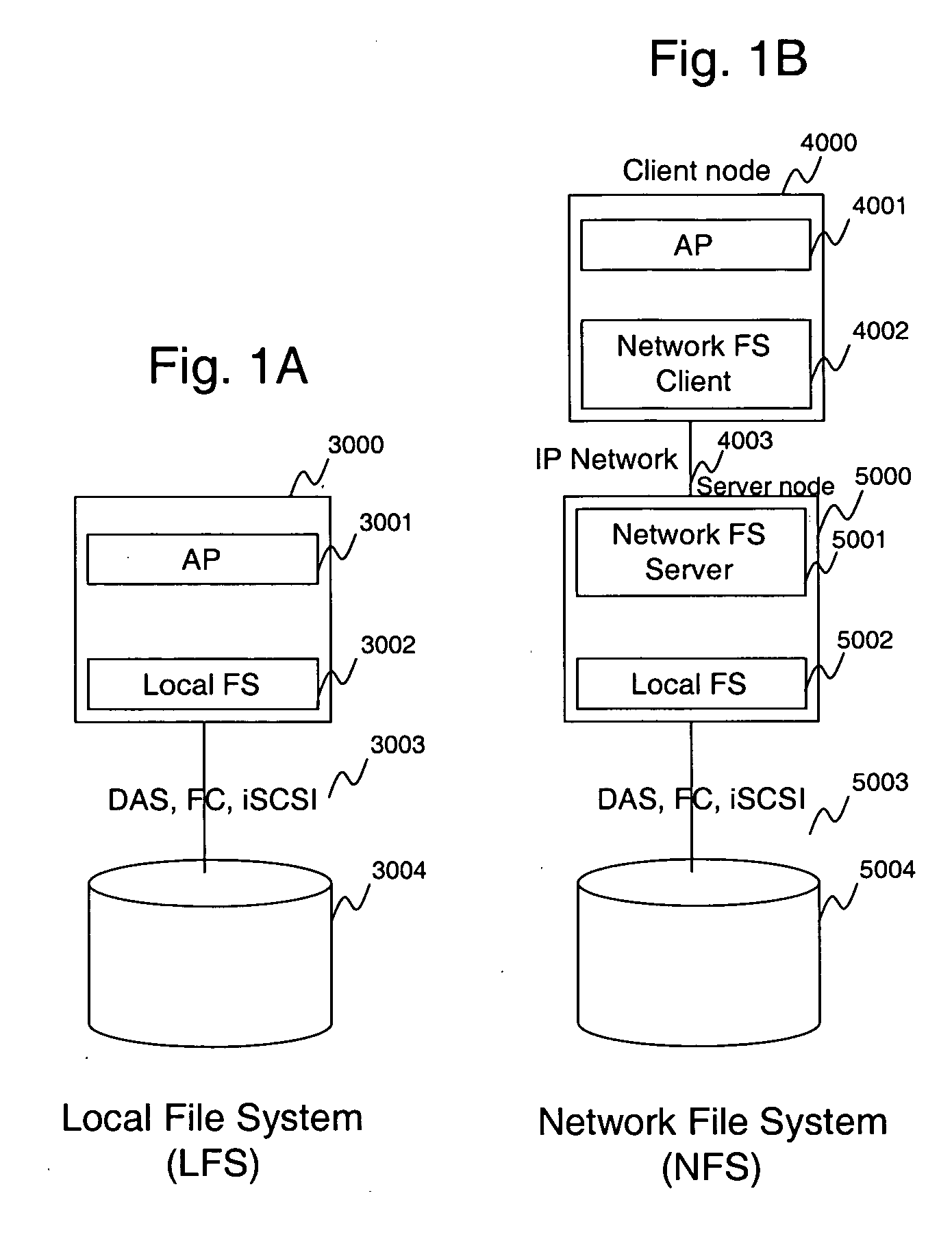
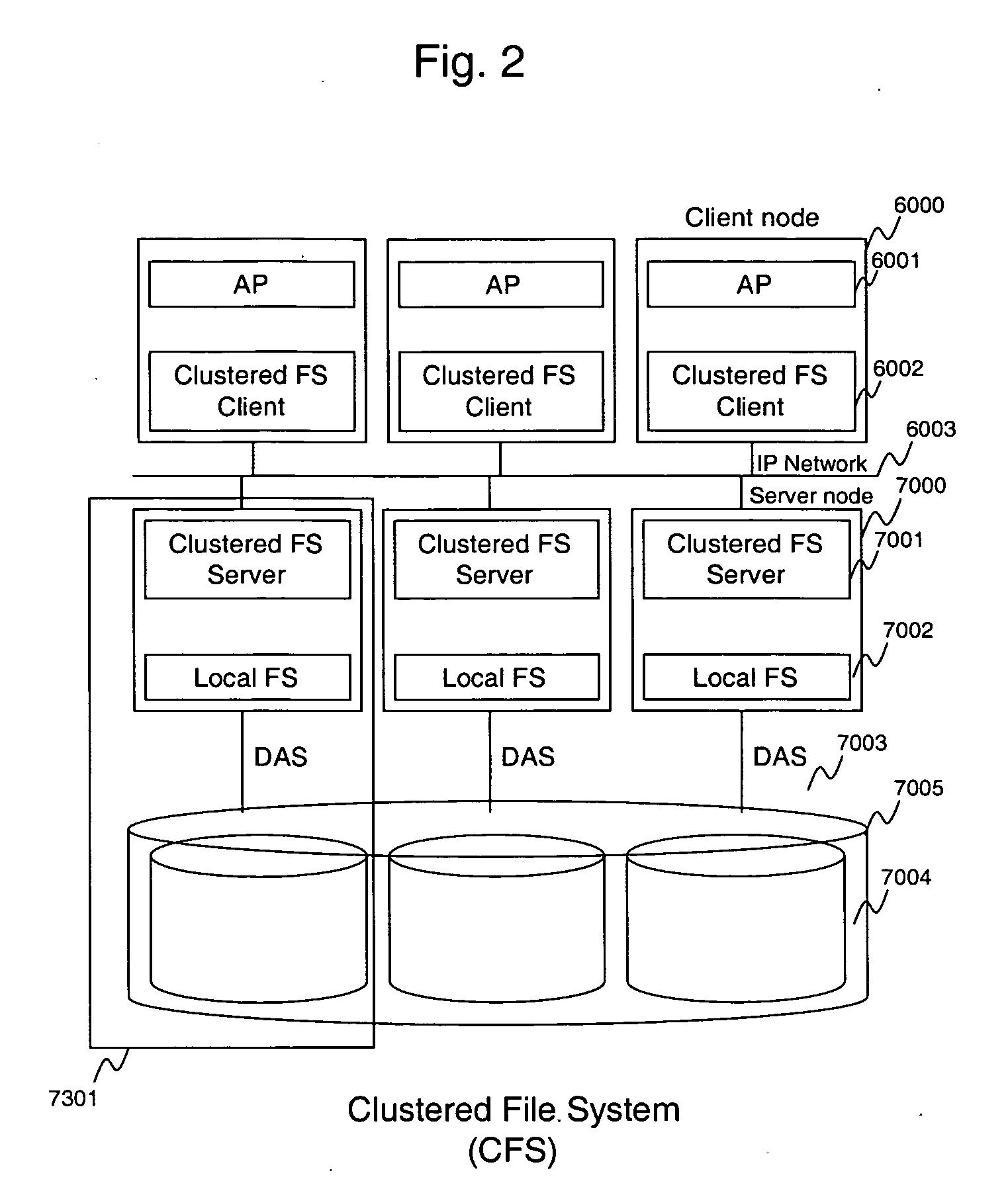
InactiveUS20070150492A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsFile allocationFile system
Described is a system and algorithm for allocating files in various storage units available within the CFS, as well as a technique for enabling storage system administrator(s) to control the file allocation in Clustered File Systems (CFS). The CFS server may execute one or more file allocation algorithms, which enable the storage system administrator(s) to establish a flexible file allocation policy for allocating storage resources among various storage units in the CFS. To this end, each file server in the CFS includes a file locator module, which operates in accordance with one or more file allocation algorithms, and inter-operates with other similar modules of other file servers in the CFS to exchange information on available storage resources and allocate storage resources within various storage units in the CFS. CFS may be configured to support multiple file allocation policies, which may be selected either automatically or by the storage system administrator(s). The file locator module enables the inventive CFS to implement these file allocation policies. Once the appropriate policy has been selected, the file allocation module performs various file allocation operations according to the selected file allocation policy, and issues the file creation requests to the appropriate CFS server(s).
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com