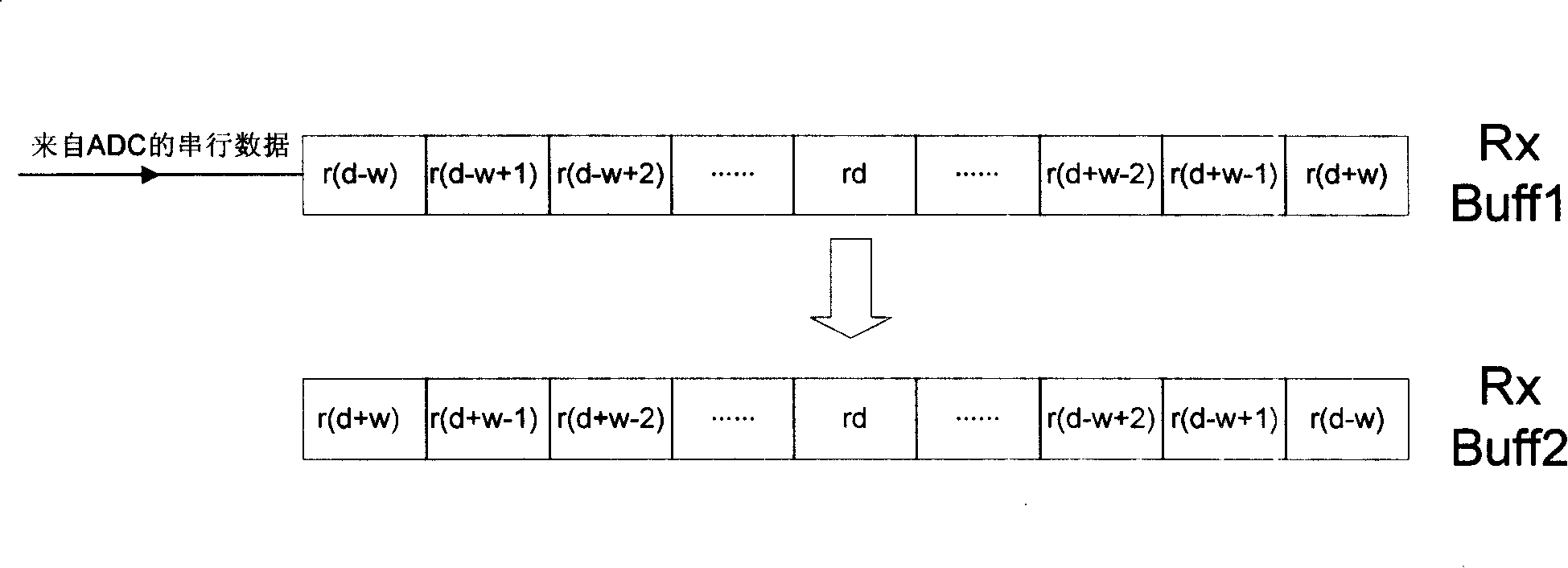
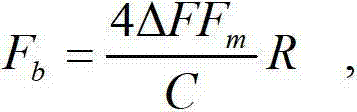Patents
Literature
213 results about "Bpsk modulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The BPSK modulation is a very basic technique used in various wireless standards such as CDMA, WiMAX (16d, 16e), WLAN 11a, 11b, 11g, 11n, Satellite, DVB, Cable modem etc. It is considered to be more robust among all the modulation types due to difference of 180 degree between two constellation points.
FMOD transceivers including continuous and burst operated TDMA, FDMA, spread spectrum CDMA, WCDMA and CSMA
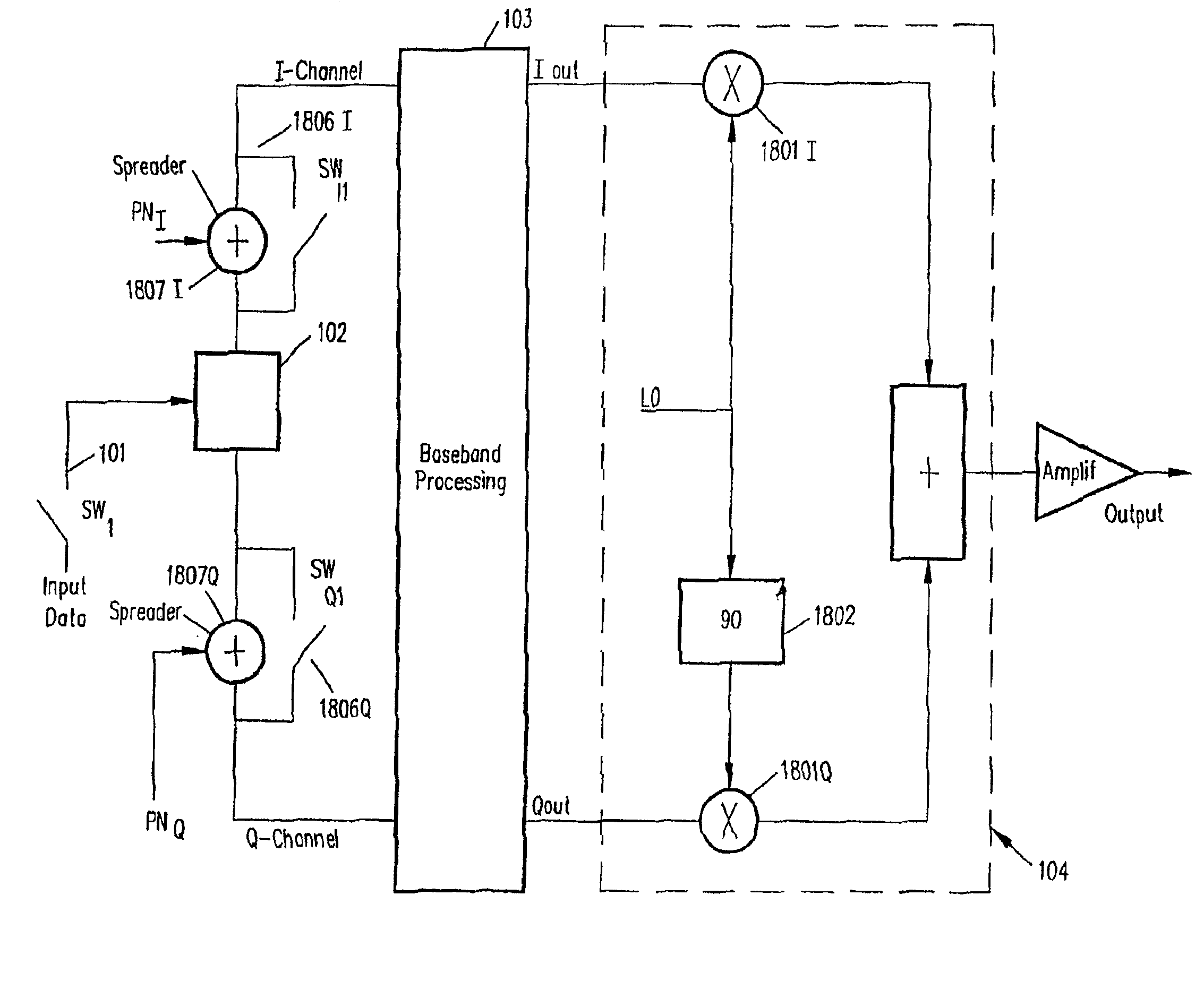
InactiveUS6928101B2Improve performanceLow costAsymmetric modulation circuitsPhase-modulated carrier systemsModem deviceFrequency spectrum
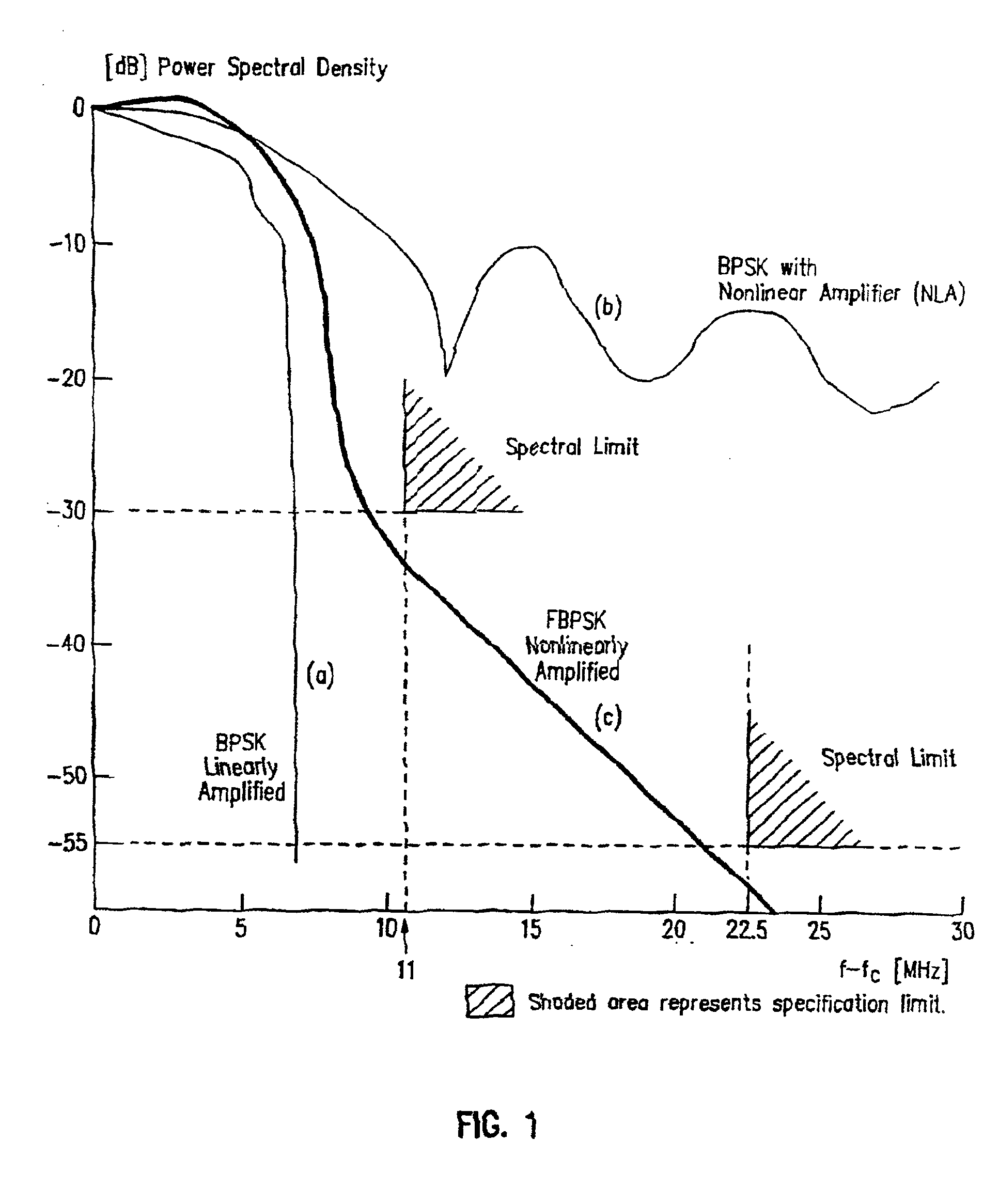
Binary and Quadrature Feher's Modulation (F-Modulation, or FMOD) Transmitter-Receiver systems and circuits exhibit reduced envelope fluctuation and peak radiation, and increased efficiency. A subclass of these systems has a constant envelope. They advantageously provide lower power operation with improved performance including robust BER performance, and compatibility with both linearly and nonlinearly amplified narrow spectrum, and without disadvantages of conventional BPSK, DBPSK QPSK and pi / 4-QPSK. Feher's BPSK (FBPSK) is an improved efficiency transmitter which is compatible with conventional BPSK receivers. FBPSK modems are based on using quadrature structure where Q-channel data is inserted in quadrature with I-channel data for certain applications. The Q-channel data may be “offset” from the I-channel data by an amount selectable between zero and a specified time. Further improvement in the spectrum is attained using correlation between I and Q channels. FBPSK modem is shown to meet the IEEE 802.11 specified spectral direct sequence spread spectrum mask (−30 dB point) for wireless LAN, and leads to an output power gain of 6.5 dB over conventional BPSK modems. The cross-coupled quadrature FMOD structure is also suitable for continuous mode and for burst operated TDMA, FDMA, CDMA, WCDMA and CSMA Frequency Modulation Quadrature AM (QAM), QPSK and offset QPSK, as well as pi / 4-shifted QPSK modems / processors. Reduced modulation index Gaussian FSK (GFSK), multilevel FM and cross-coupled Quadrature Amplitude Modulated (QAM) transmitters and combinations of these modulations and corresponding coherent demodulators are disclosed. Controlled rise and fall time descriptions of burst operated systems are included.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Magnetic field communication method for managing node with low power consumption
ActiveUS20110243267A1Reduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTCombined modulated pulse demodulationArea networkBpsk modulation
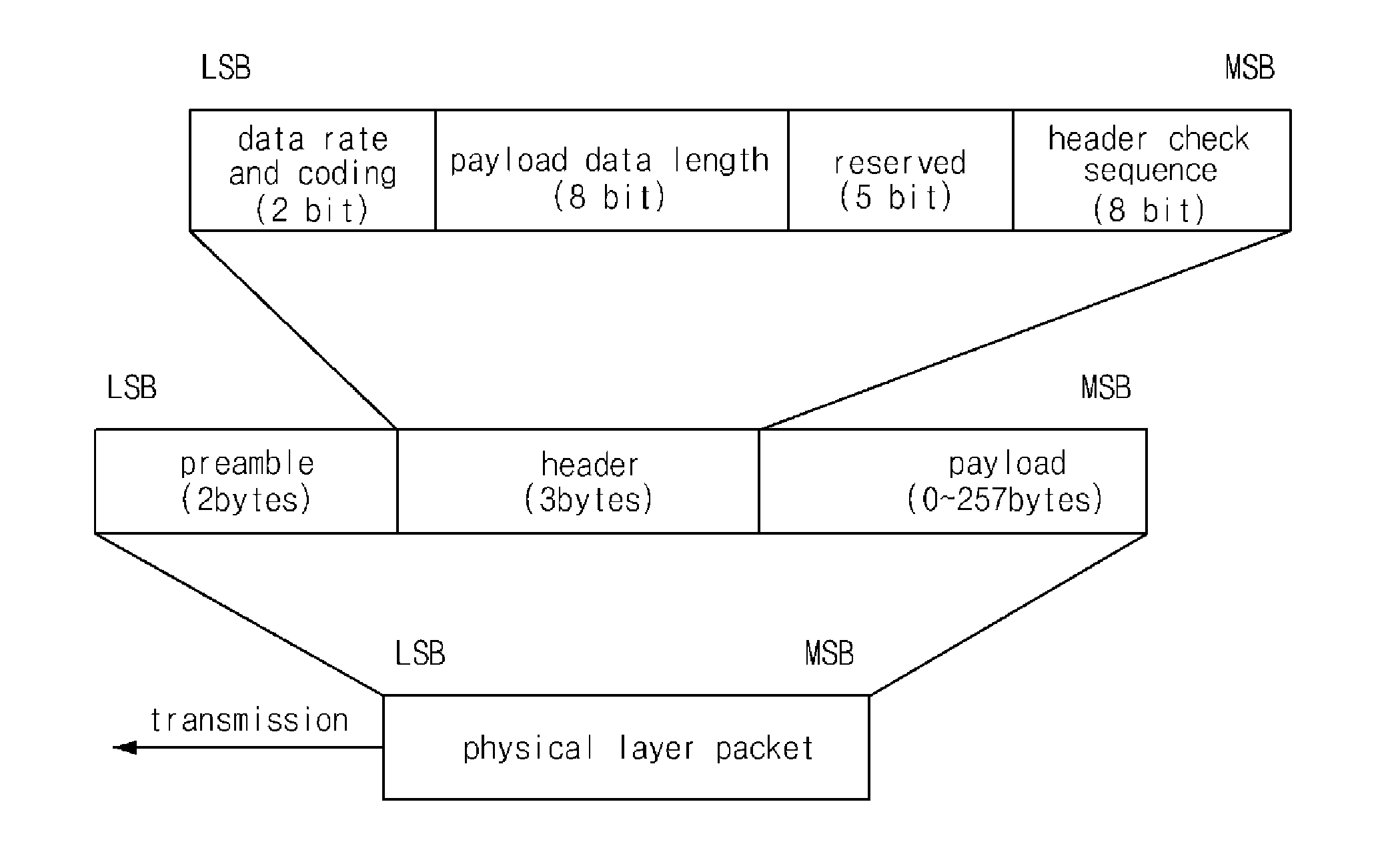
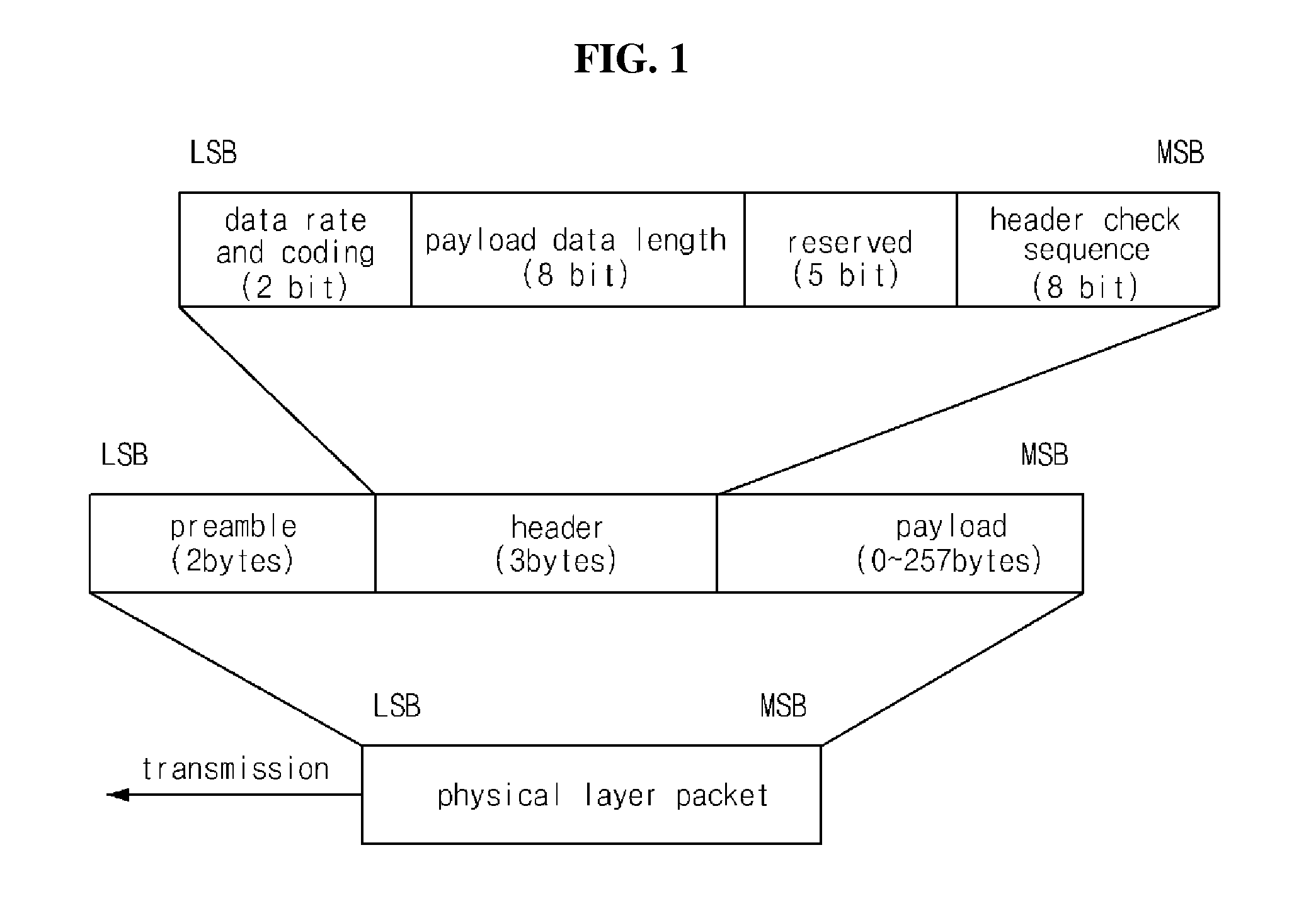
A magnetic field communication method is provided for managing node with low power consumption which enhances performance and efficiency of a magnetic field area network in the low frequency region. The magnetic field communication method for managing node with low power consumption of the present invention is accomplished in a low-frequency wireless network that is comprised of a MFAN-C and at least one MFAN-N wherein a physical layer is comprised of a preamble, a header, and a payload, and the preamble is comprised of a wake-up sequence and a synchronization sequence. The wake-up sequence is only added to the preamble of the frame that is transmitted from the MFAN-C when the MFAN-N is being activated from the hibernation mode. The wake-up sequence is modulated using ASK modulation, and the synchronization sequence is modulated using BPSK modulation.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOBIS CO LTD
Micro/nano satellite measure and control communication integral transmitting and receiving system and realization method thereof
InactiveCN102333057AReduce the numberHighly integratedTransmission systemsPhase-modulated carrier systemsEngineeringNano satellite
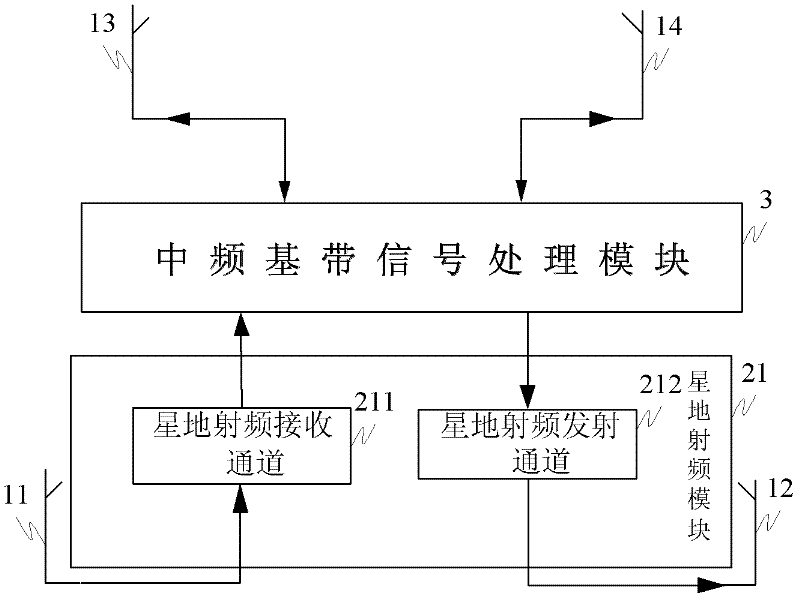
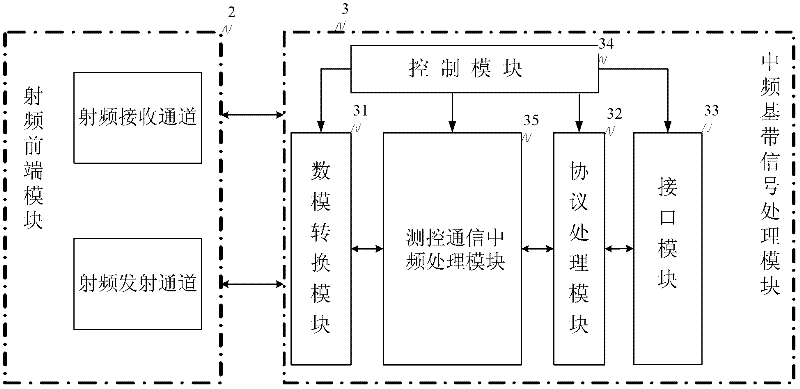
The invention discloses a micro / nano satellite measure and control communication integral transmitting and receiving system and a realization method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: 1) uplink signal processing: 11) receiving and processing radio-frequency signals to obtain analog intermediate-frequency signals; and 12) carrying out analog to digital conversion and digital underlocking on the analog intermediate-frequency signals and dividing into two paths of uplink digital intermediate-frequency signals, namely, one path of the signals is sent to a satellite-mounted computer by QPSK (quadrate phase shift keying) demodulation and uplink protocol processing so as to finish uplink data transmission, and the other path of the signals is subjected to the PM (phase modulation) demodulation to obtain side sound signals and PSK (phase shift keying) remote signals, and the PSK remote signals are subjected to BPSK (binary phase shift keying) demodulation to convert into a remote control command which is sent to the satellite-mounted computer so as to finish the remote control; and 2), downlink signal processing: 21), acquiring two paths of data from the satellite-mounted computer and a storage unit, namely, one path of data which is subjected to downlink protocol processing, BPSK modulation, combination with the side sound signals and downlink measure and control carrier PM modulation is combined with the other path of data which is subjected to the downlink protocol processing and the QPSK modulation to enter a satellite-ground radio-frequency emission channel; and 22) converting into radio-frequency signals to finish the remote measure and the downlink data transmission.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
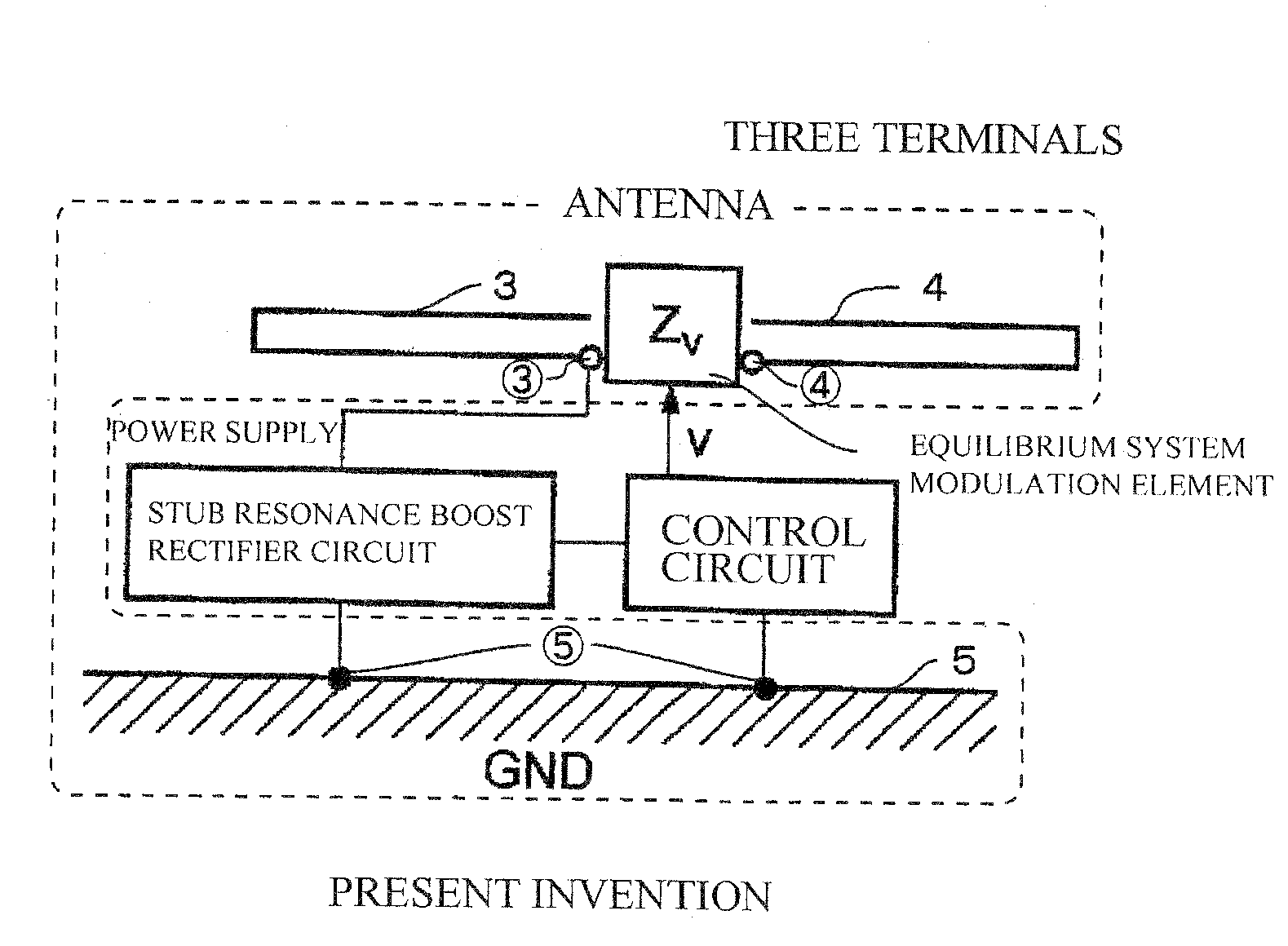
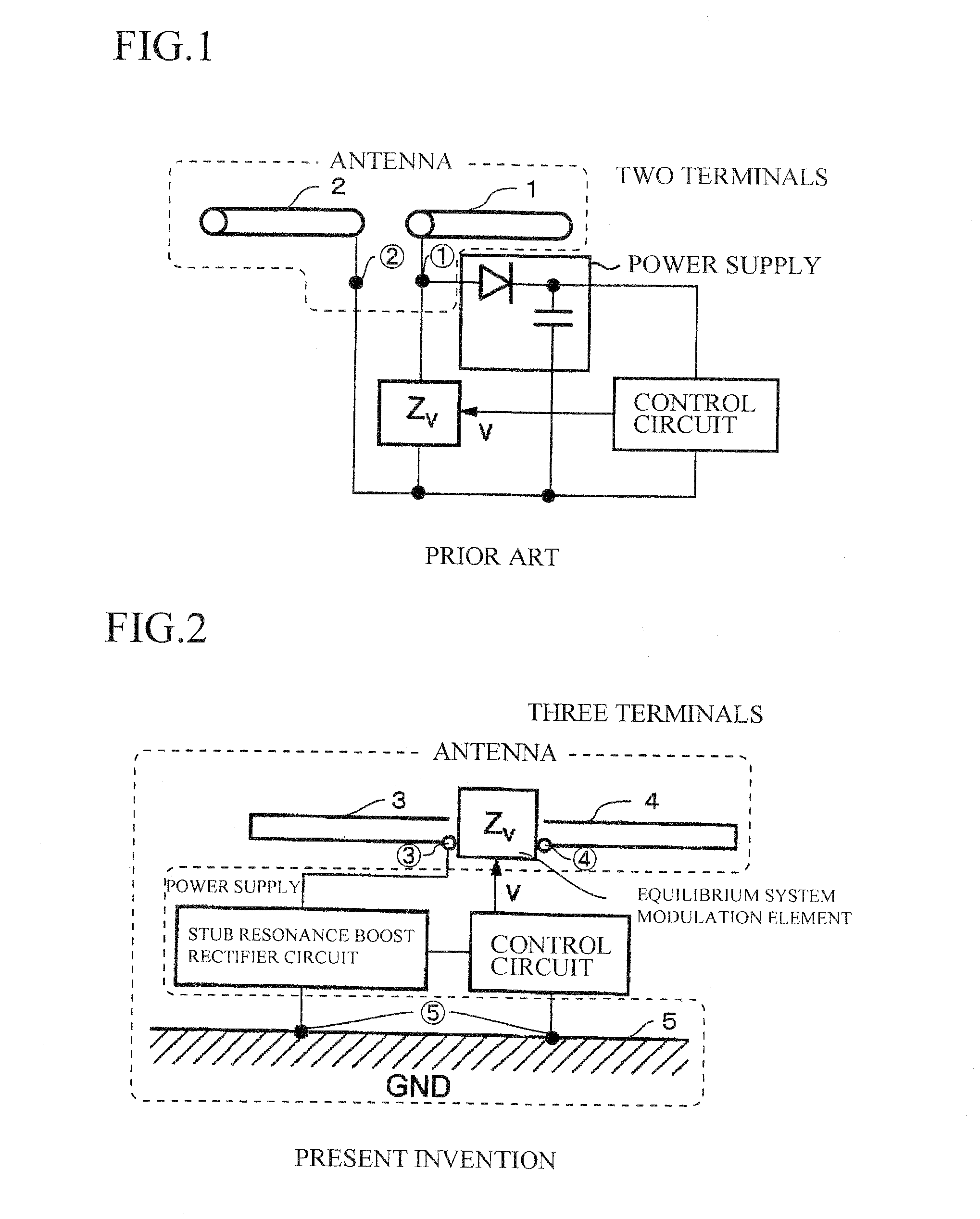
Rf ID Tag Device
ActiveUS20090033462A1Maximize efficiencyElectromagnetic wave systemCircuit arrangementsResonanceBpsk modulation
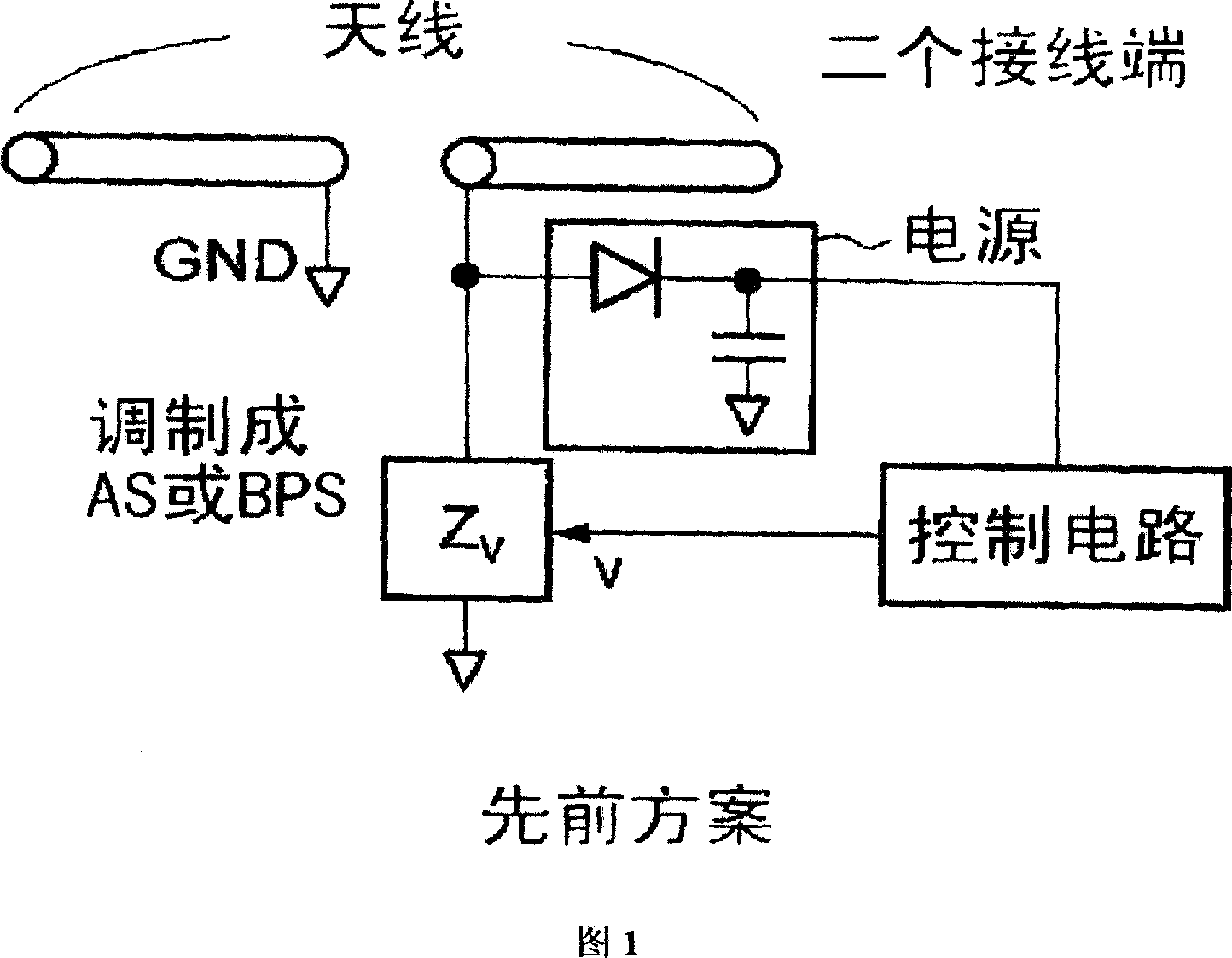
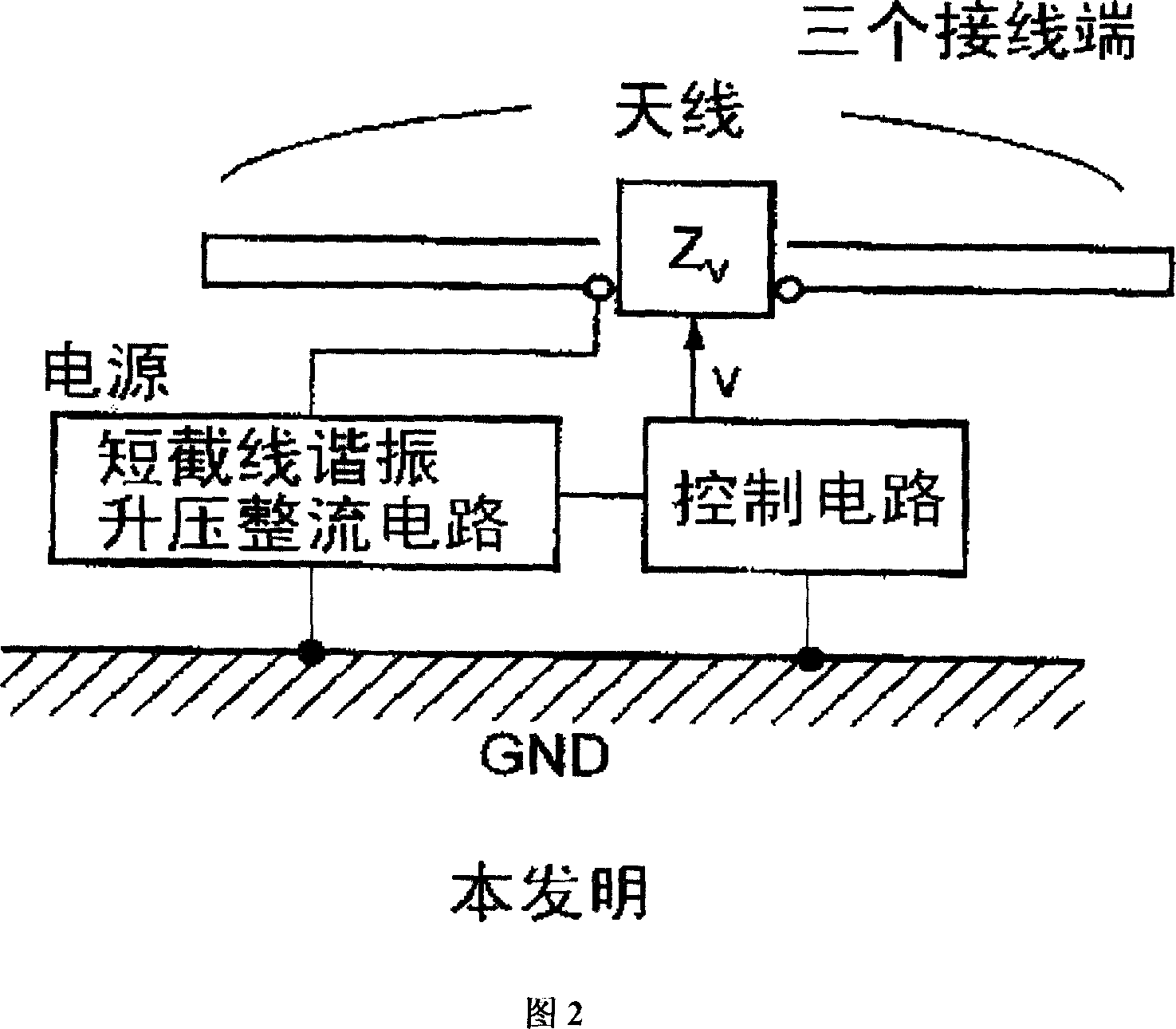
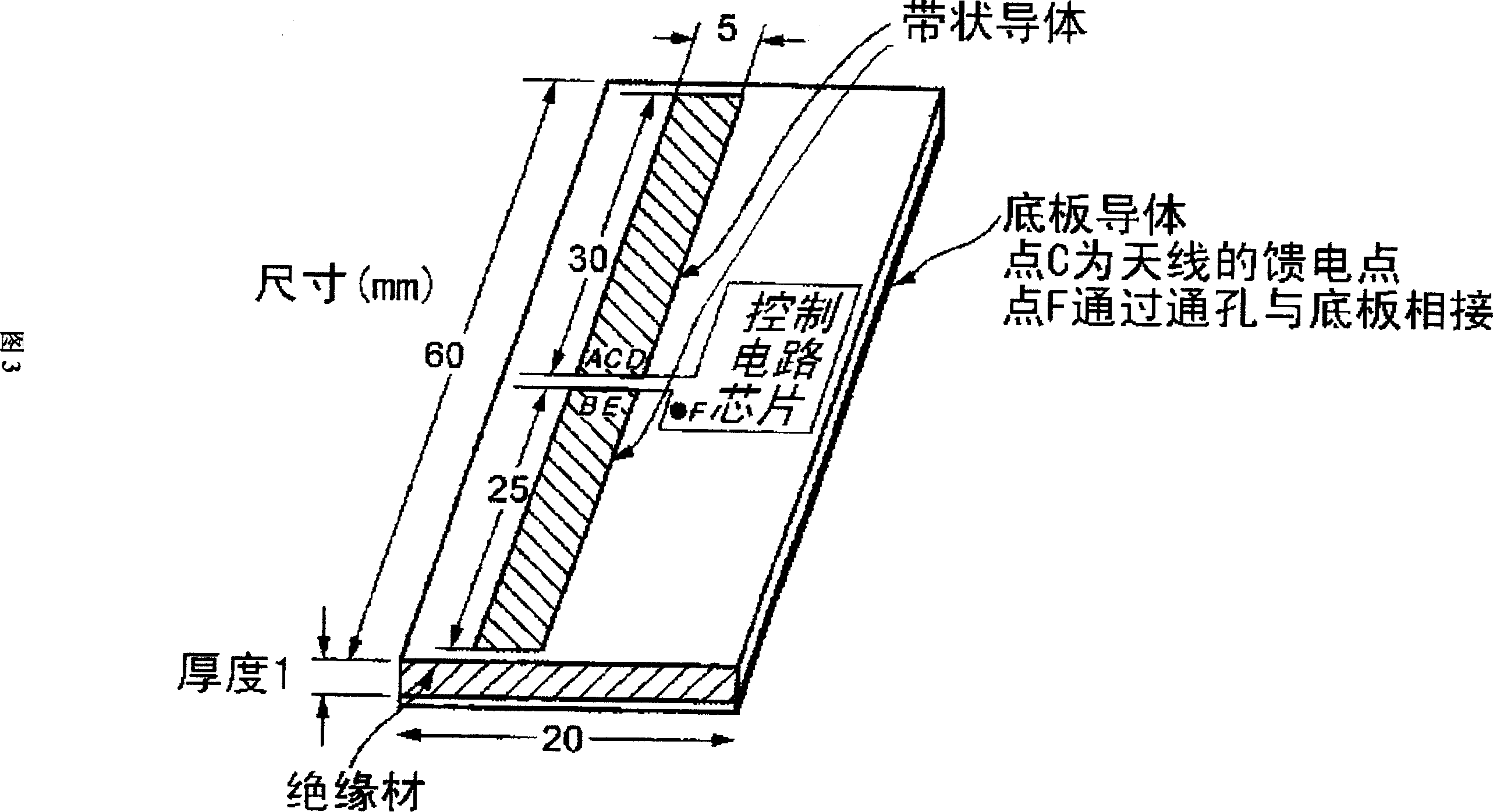
The present invention aims to overcome the drawback with conventional RFID tag devices having a short communication range, and expand the communication range to several times or more that in the conventional scheme. The conventional scheme is based on equilibrium feeding / equilibrium modulation (a two-terminal circuit for antenna operation), whereas the present invention is based on disequilibrium feeding / equilibrium modulation (a three-terminal circuit for antenna operation). The conventional scheme is based on simple rectification of received RF signals, whereas the present invention employs a circuit based on a combination of a stub resonance-based, impedance transformation boosting scheme and a ladder boosting scheme. The conventional scheme is based on ASK or BPSK modulation, whereas the present invention is based on passive modulation, but can employ a QPSK modulation circuit.
Owner:KITAYOSHI HITOSHI
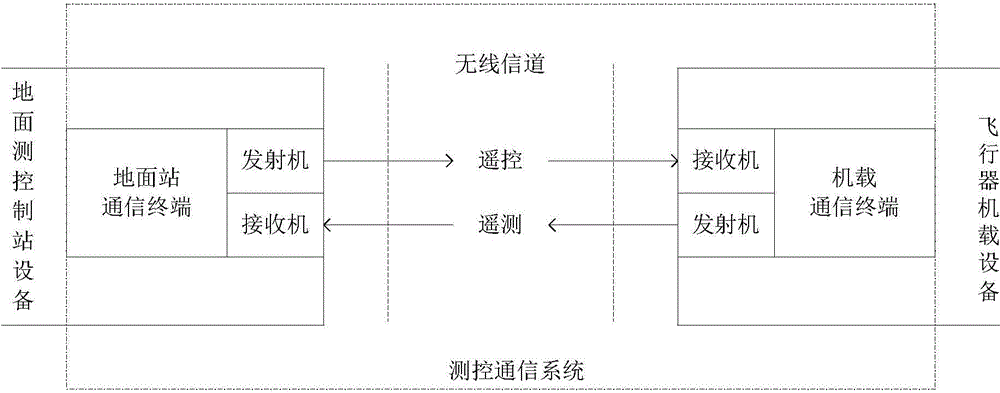
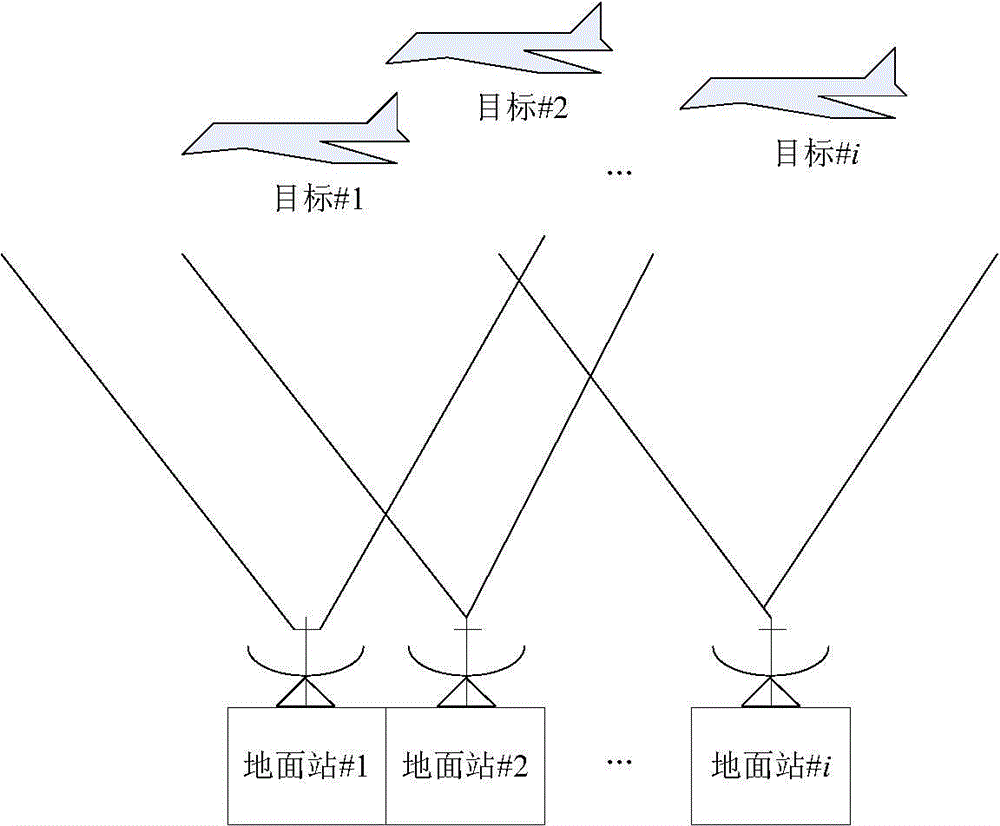
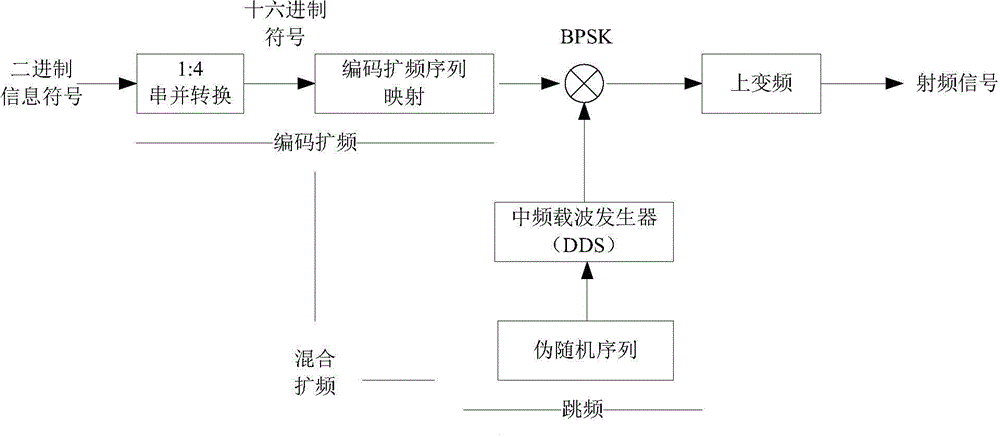
Communication link used for telemetry and telecontrol communication system
ActiveCN104579416ARealize wireless communicationAvoiding Carrier Synchronization ProblemsModulated-carrier systemsTelecommunications linkCommunication link
The invention provides a communication link used for a telemetry and telecontrol communication system. An uplink broadcasing and downlink TDMA (time division multiple access) mode is adopted to solve the measurement and control problems of a single ground station for multiple aircrafts. A downlink adopts hybrid spread spectrum BPSK (binary phase shift keying) with multiple stages of adjustable gain for modulation, an uplink adopts coded spread spectrum QPSK (quadrature phase shift keying) with fixed gain for modulation, so that the anti-interference, anti-interception and anti-capturing capacity of a wireless link is improved, and asymmetry of the uplink and the downlink is considered. Both the uplink and the downlink adopt a single-pulse modulation symbol packet transmission mode, a fixed interval is inserted into every two adjacent symbol pulses, and accordingly, the spread spectrum signal capturing, tracking and synchronizing complication of receivers is reduced. Non-coherent demodulation is adopted, a complicated carrier synchronization problem is avoided, and the design and project realization of the receivers are further simplified. The complicated carrier synchronization problem is avoided, and wireless communication between a single ground station device and multiple telecontrol terminal devices is realized.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE MEASUREMENT & CONTROL TECH
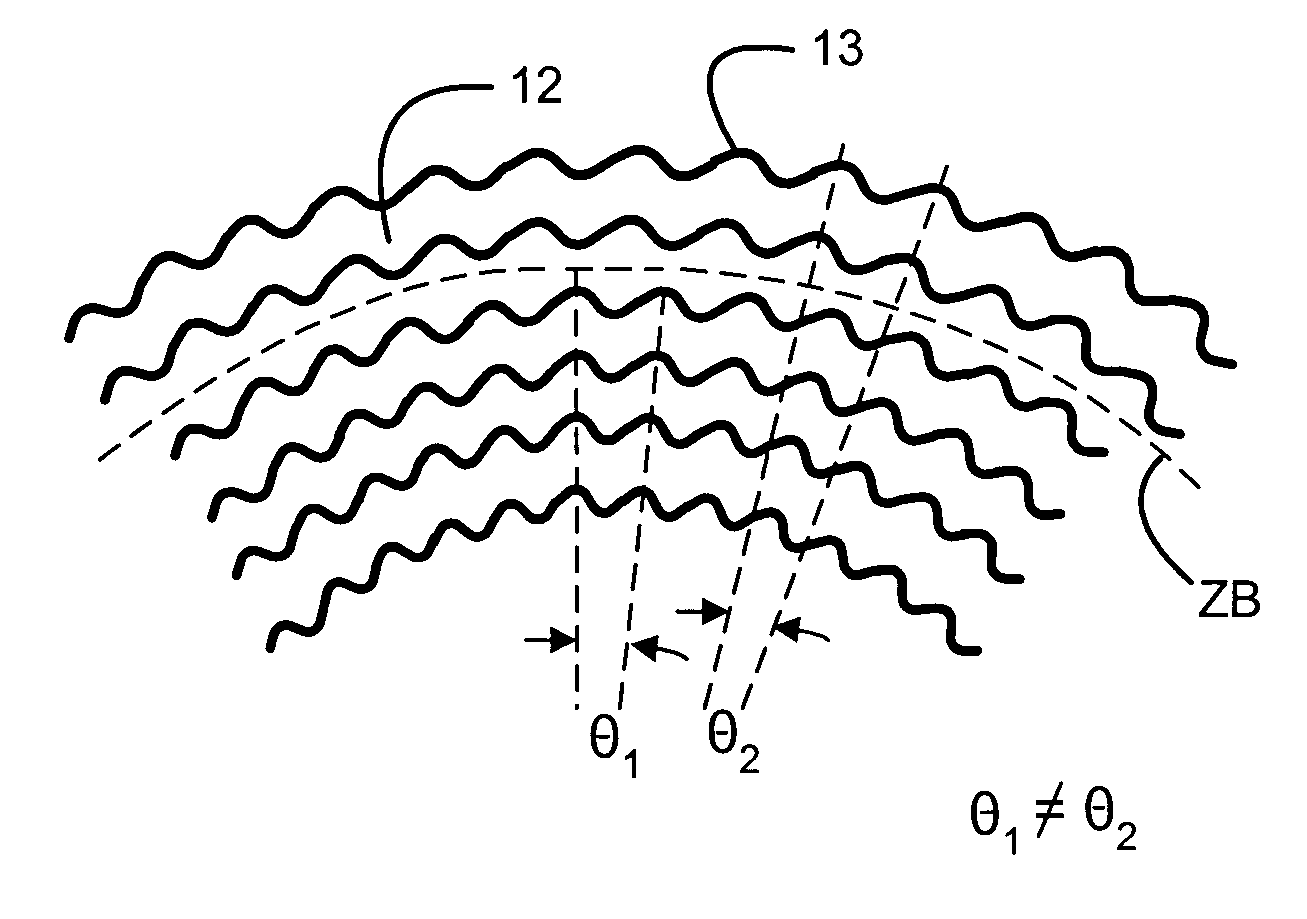
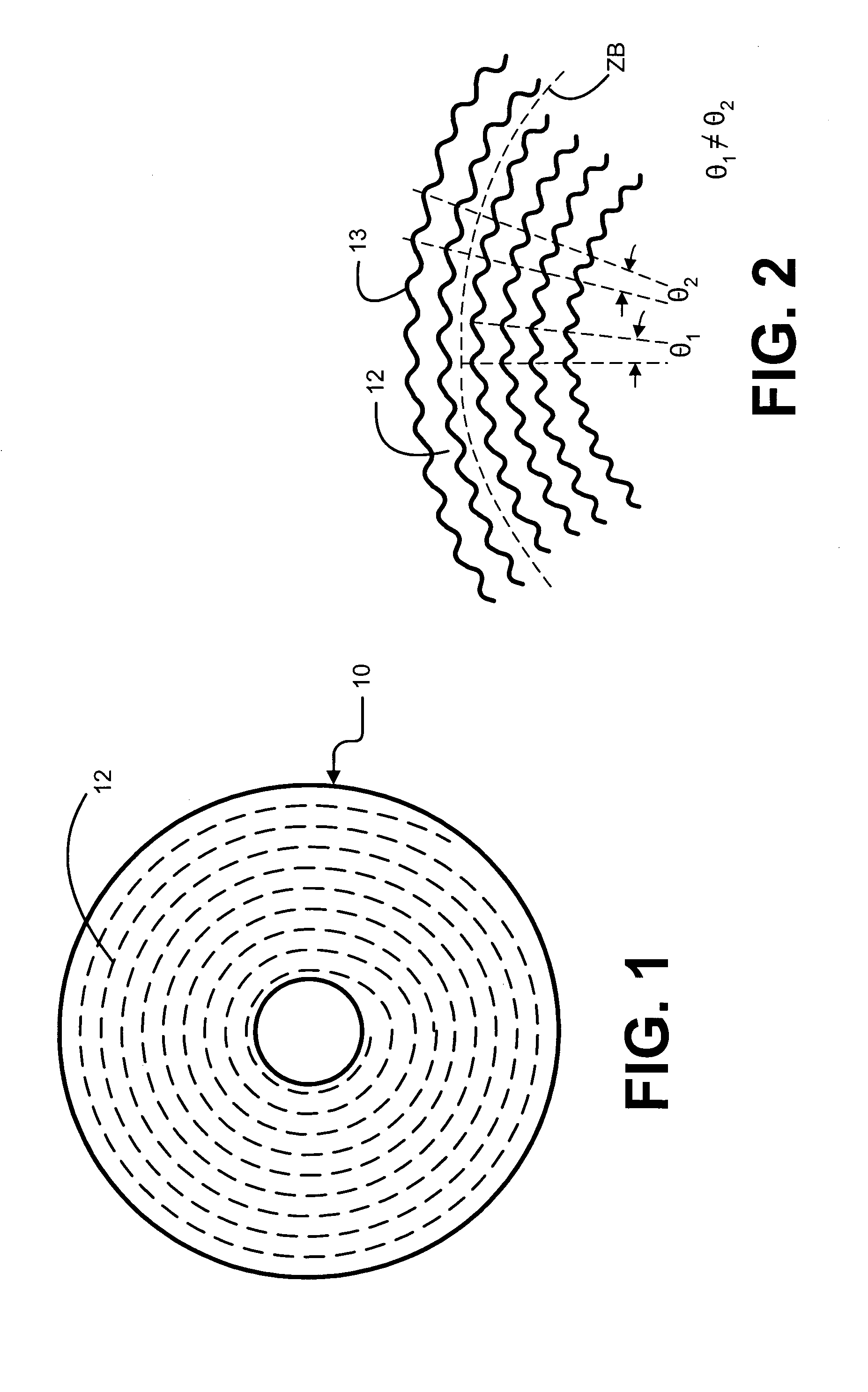
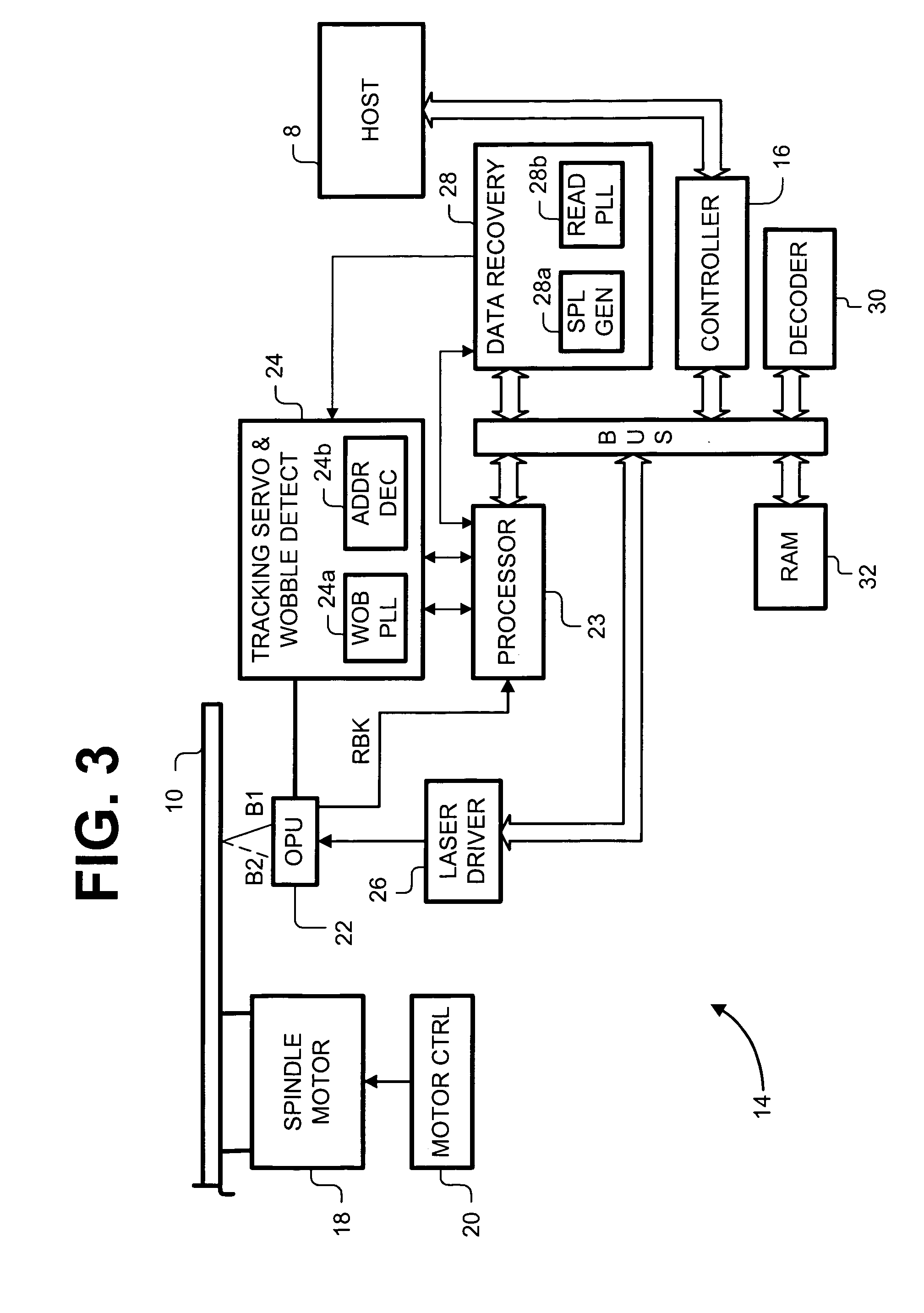
Optical disk having zone constant angular velocity wobble
InactiveUS7002895B1Reduce jitterConstant angular velocity wobbleInformation arrangementRecord information storageClassical mechanicsBpsk modulation
An optical disk has a groove in a recordable medium. The groove has a constant angular velocity wobble that is BPSK-modulated. Such a wobble provides timing and address information.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
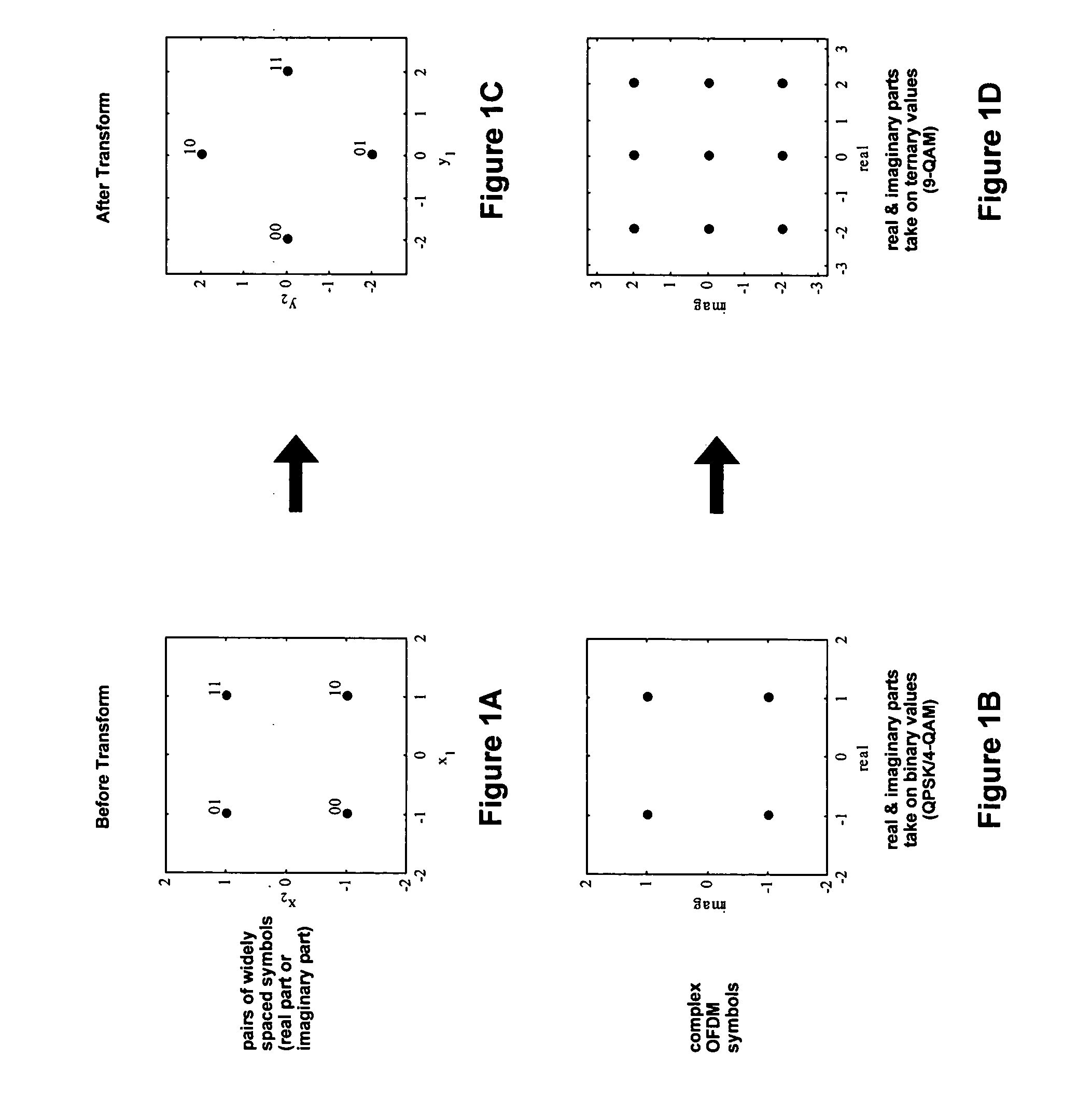
System & method for spreading on fading channels
InactiveUS20050220203A1Phase-modulated carrier systemsMulti-frequency code systemsRound complexityBpsk modulation
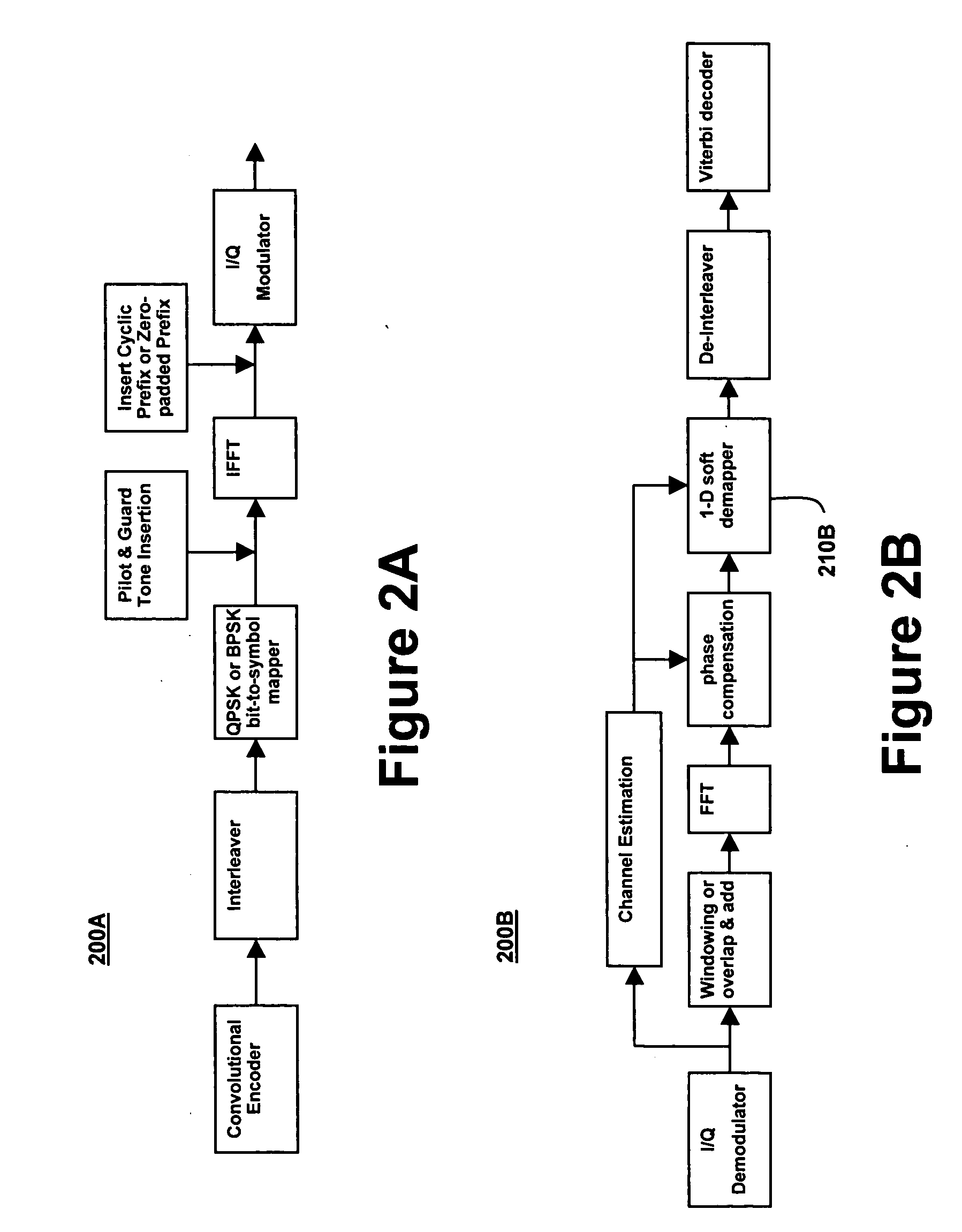
This disclosure describes a simple spreading technique that improves performance for communication over fading channels with QPSK or BPSK modulation. The technique may comprise combining two symbols at the transmitter by applying a 2×2 transform, resulting in a 4-PAM or 16-QAM constellation. The receiver may utilize a 2-dimensional soft de-mapper to provide inputs to a soft-input decoder. This scheme can offer significant performance gains over fading channels with minimal additional complexity. This technique is most beneficial on systems with a weak code or no code at all. One application of this technique is for coded OFDM systems that experience frequency-selective fading. An example of such a system is the MBOA draft specification for UWB wireless communications.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Pulse ultra-wideband transmitter with adjustable amplitude and spectrum
InactiveCN101924574AReduce power consumptionSimple structureTransmissionProcess deviationsUltra-wideband
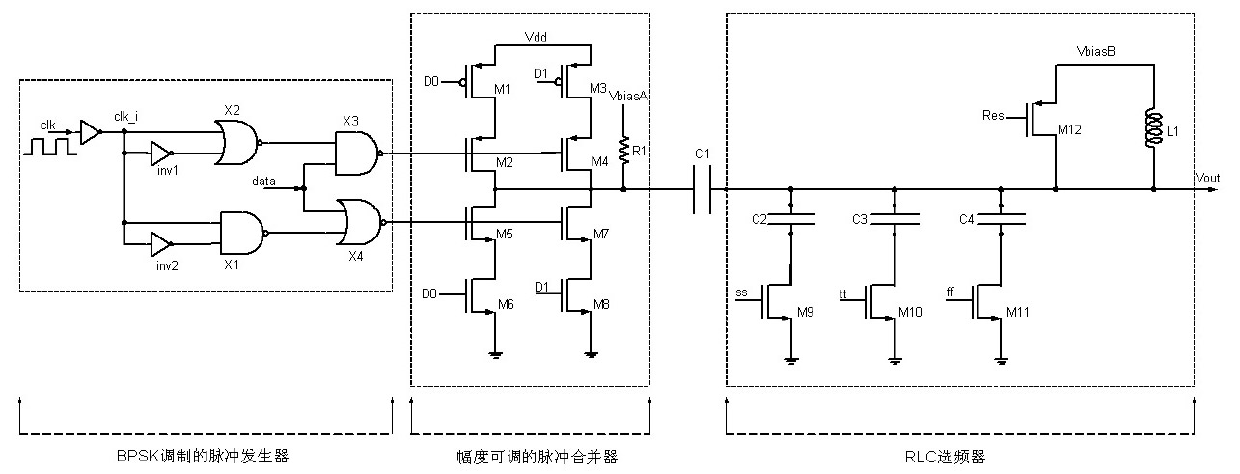
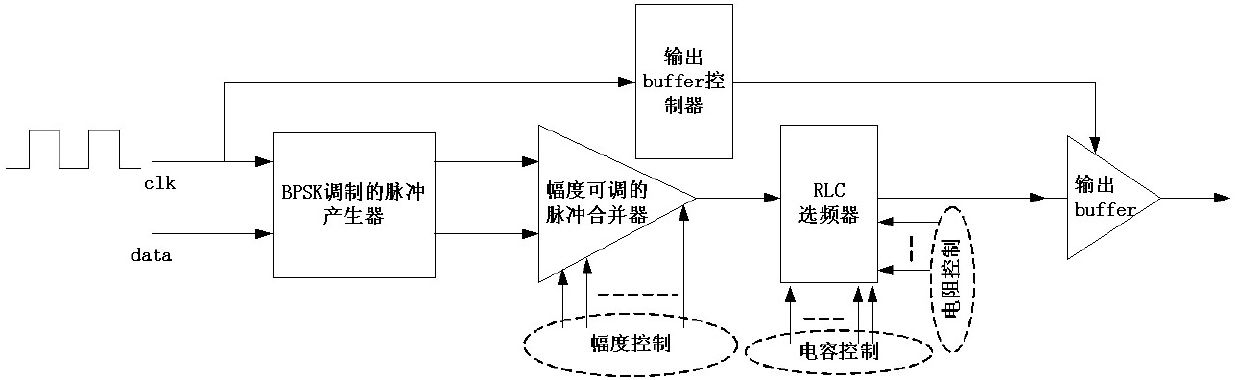
The invention belongs to the ultra-wideband communication technical field, and in particular relates to a pulse ultra-wideband transmitter with adjustable amplitude and spectrum. The transmitter is composed of four-stage modules which are sequentially connected together, wherein, the former two-stage modules generate pulse signals modulated by BPSK, an intermediate RLC frequency-selective network realizes adjustment of amplitude, length and spectrum of pulse, and finally the pulse is output by an ultra-wideband output buffer. The transmitter is modulated by adopting the BPSK, and an RLC network is taken as a core module of the whole system to realize adjustment of pulse parameters and compensation of process variation. By virtue of the characteristics of low duty cycle of an IR-UWB transmission signal, the output buffer is switched off in the case of no pulse to lower power consumption. The transmitter has the advantage of adjustable pulse parameters, thus meeting the requirements of UWB standards in different countries for spectrum and transmission power.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Sending terminal, receiving terminal directly realizing spread-spectrum ultra-wideband and method thereof
InactiveCN101291159AReduced sampling rate requirementsReduce difficultyError preventionPhase-modulated carrier systemsUltra-widebandUp conversion
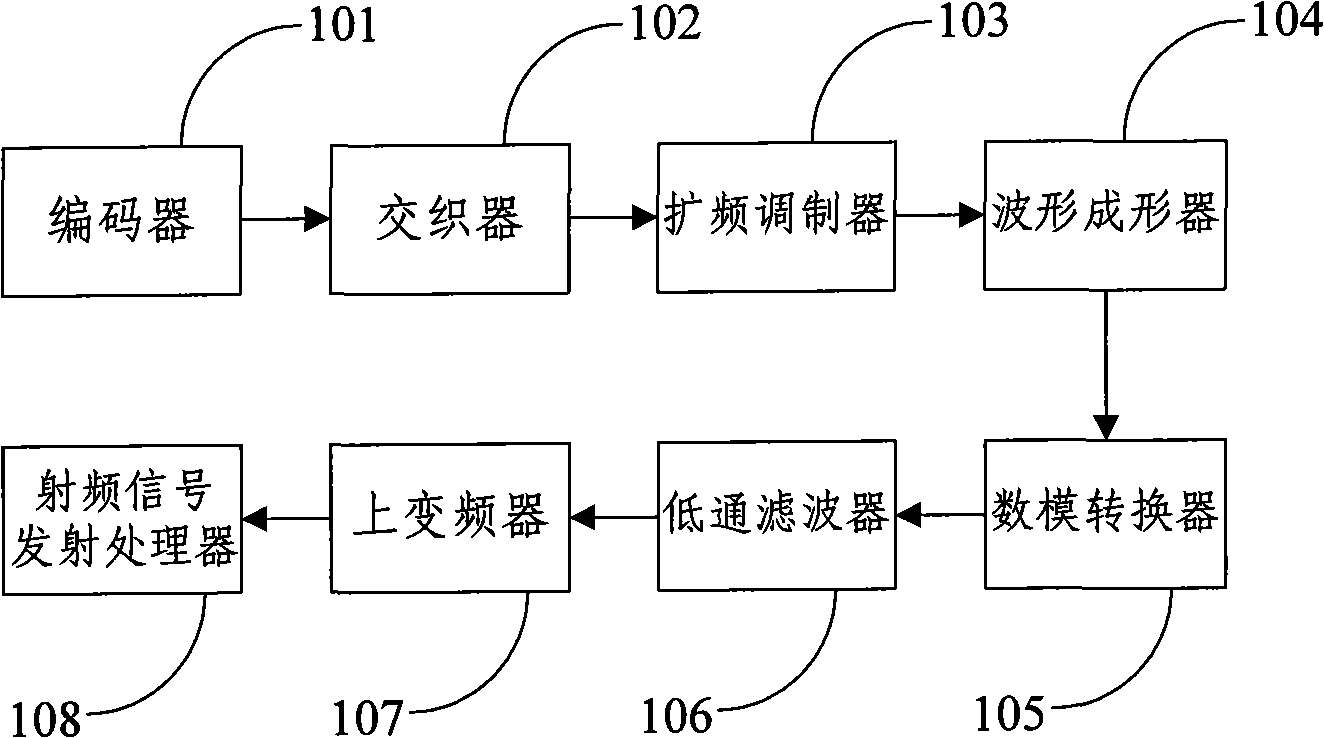
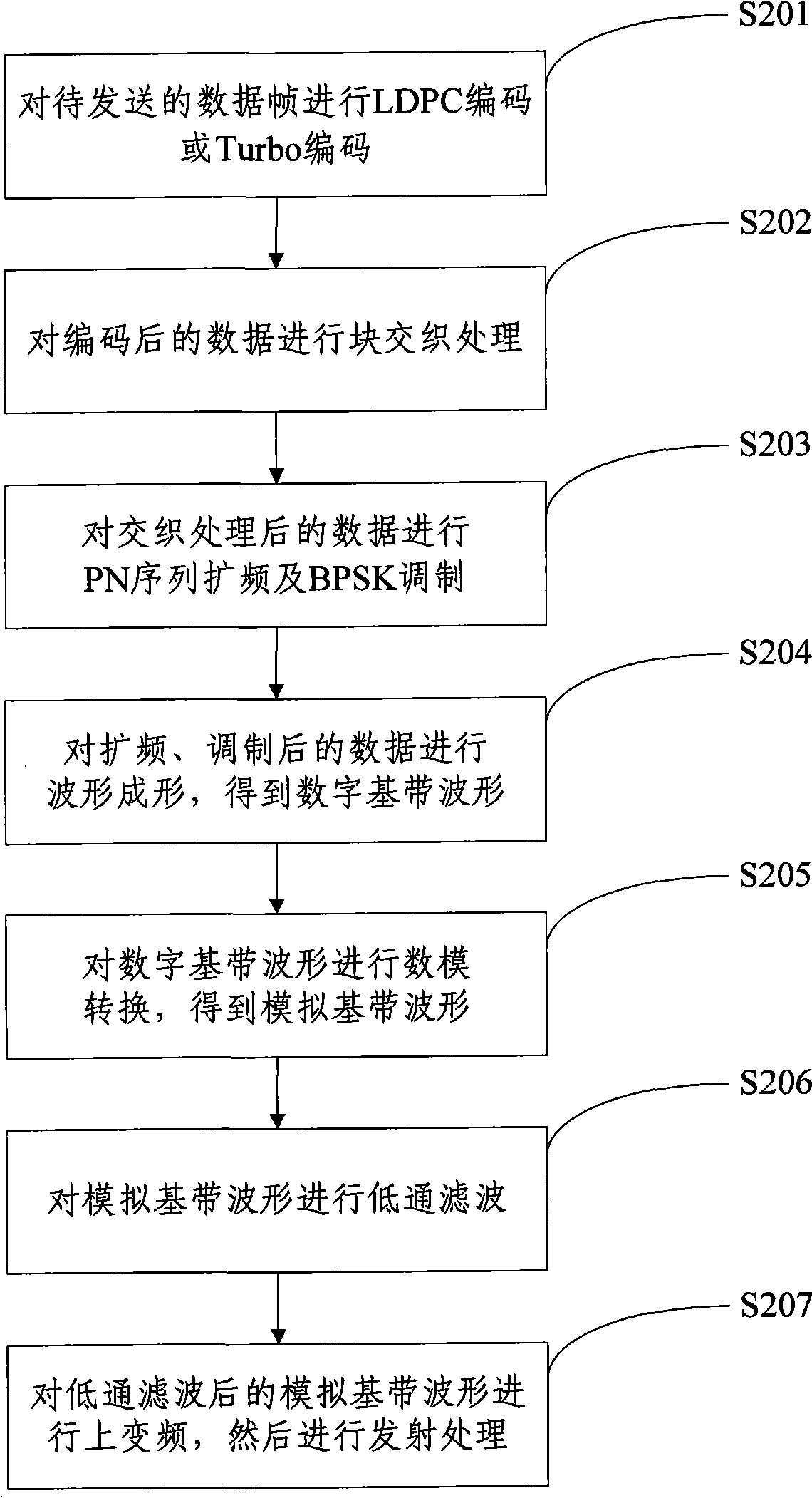
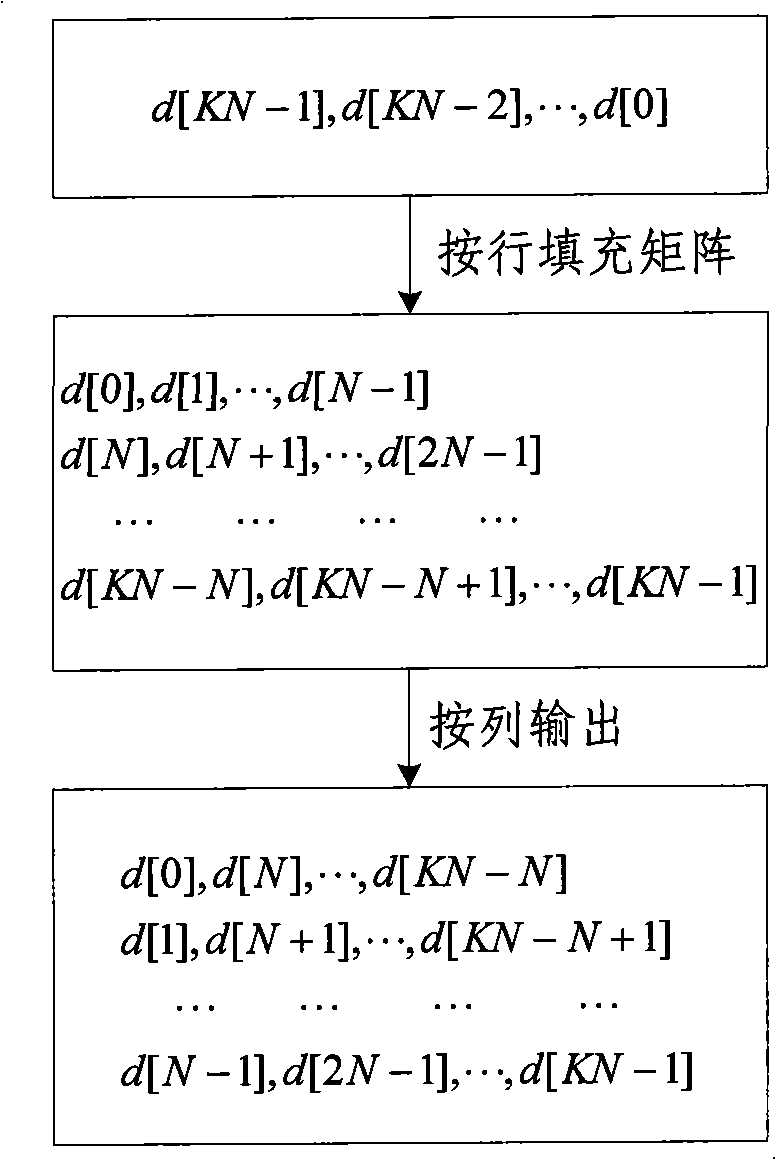
The invention relates to a sending terminal for implementing DS-UWB. The invention comprises: an encoder for decoding data frames to send, a spread spectrum modulator capable of performing PN sequence spectrum spreading and BPSK modulating to the data outputted by the decoder, a waveshaper capable of performing wave shaping to the data outputted by the spread spectrum modulator to get digital baseband waveshape, a digital-to-analog converter capable of performing digital-to-analog conversion to the digital baseband waveshape outputted by the waveshaper to get simulative baseband waveshape, a low pass filter capable of performing low pass filtering to the simulative baseband waveshape outputted by the digital-to-analog converter; an up-converter capable of performing up conversion to the simulative baseband waveshape outputted by the low pass filter, and an RF signal emission processor capable of performing emission processing to the signal outputted by the up-converter. The sending terminal for implementing DS-UWB also comprises a corresponding transmitting method, a receiving terminal and receiving method of the receiving terminal, which can overcome the difficulties in chipping DS-UWB technology in the prior art.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
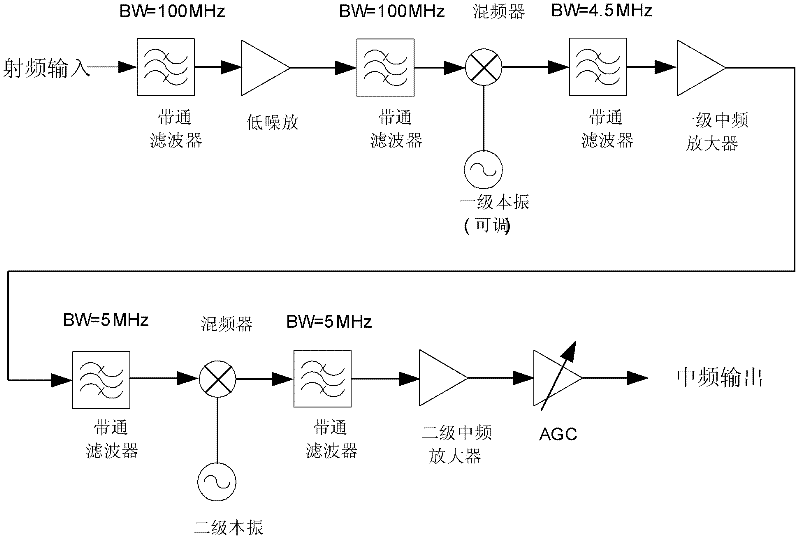
S-band multi-channel high-precision space ranging transponder
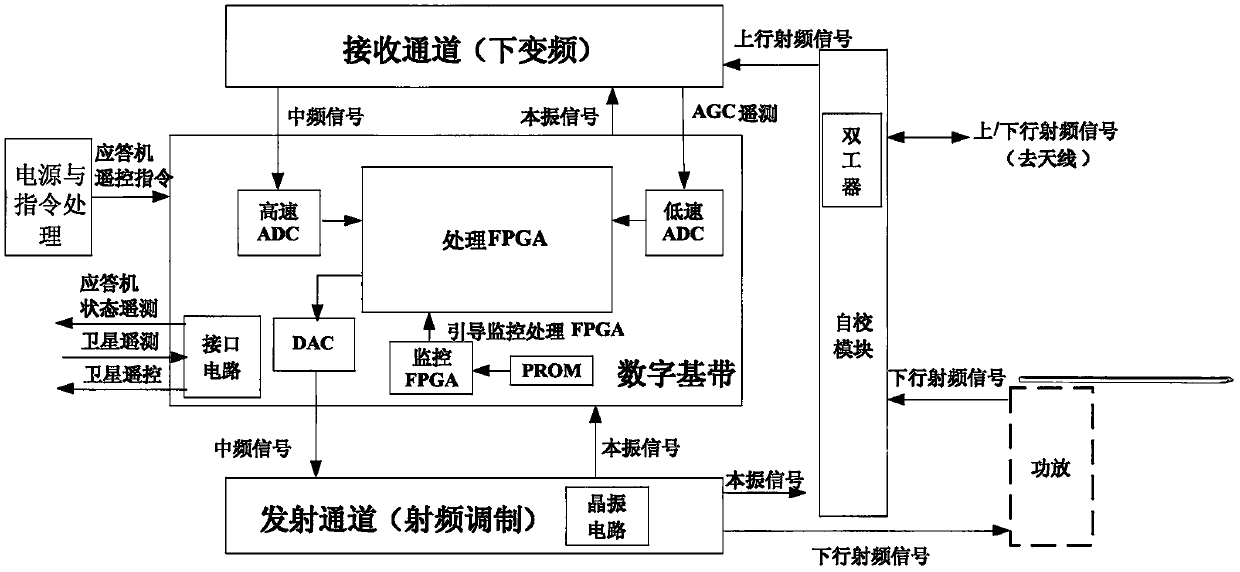
ActiveCN109765527AFunction increaseImprove ranging accuracyWave based measurement systemsLow noiseIntermediate frequency
The invention discloses an S-band multi-channel high-precision space ranging transponder. The S-band multi-channel high-precision space ranging transponder comprises a power supply, a command module,a receiving channel, a digital baseband, a transmission channel, an interface module, and a self-calibration module, wherein the receiving channel is used for receiving an uplink radio-frequency signal and performing low noise amplification, down conversion, intermediate frequency filtering, intermediate frequency signal amplification, and AGC telemetry control; the digital baseband is used for sampling and outputting calculated PCM telemetry code, synchronous clock, and strobe pulse after acquisition and tracking of a spreading code, acquisition and tracking of a carrier wave, and remote control information bit synchronization are conducted on the uplink telemetry channel; the PCM telemetry code is subjected to spectrum spreading and BPSK modulation in a downlink telemetry channel, and amodulated downlink spread spectrum signal is outputted; a range zero value of a transponder is calculated; the transmission channel is used for performing uplink frequency conversion, radio frequencyfiltering, and power amplification, and then a radio frequency signal is obtained and transmitted; the interface module is used for interacting with an on-board computer for satellite telemetry data,transponder telemetry data, and satellite remote control data; and the self-calibration module calculates the range zero value of the self-calibration module according to the digital baseband for self-calibration. The S-band multi-channel high-precision space ranging transponder has the advantages that the function is complete, ranging precision is high, and the structure is simple.
Owner:NO 63921 UNIT OF PLA
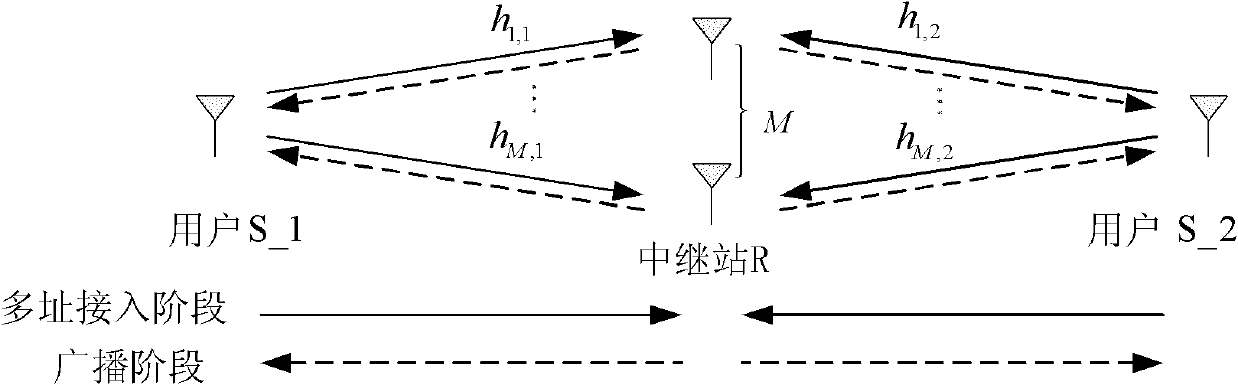
Space diversity method for physical layer network coding in communication system
InactiveCN102055565AImprove reliabilityImprove spectrum utilizationError prevention/detection by diversity receptionFrequency spectrumCommunications system
The invention relates to a space diversity method for physical layer network coding in a communication system, and belongs to the technical field of wireless communication. The method comprises the following steps of: arranging a plurality of distributed relay station antennas between two single antenna users, sending data to a relay station by a user, estimating channel information between the relay station and a user antenna by the relay station, acquiring a channel matrix, selecting a binary phase shift keying modulation mode by the user, sending interactive information among the users to the relay station, performing combined detection on the received superposed signals by the relay station to acquire network coding symbols, selecting an antenna set, performing space-time coding on the network coding symbols, then sending the coded network coding symbols to the user, performing space-time decoding on the space-time coded symbols by the user, and decoding the estimation values of the network coding symbols according to the interactive information to acquire data information of an opposite user. The method improves the frequency spectrum utilization rate and energy utilization efficiency of a bidirectional relay network and remarkably improves the bidirectional communication reliability of the users.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
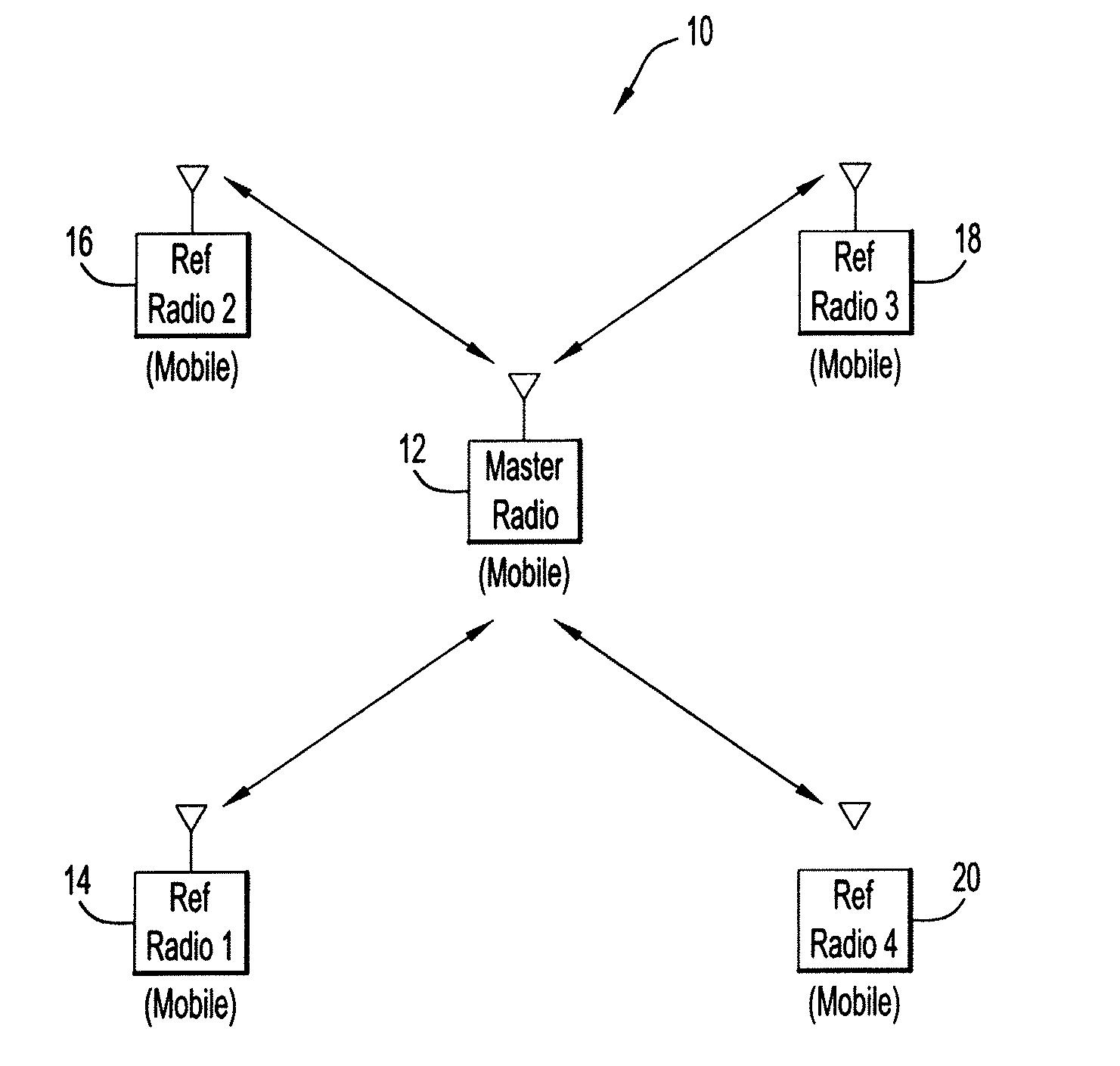
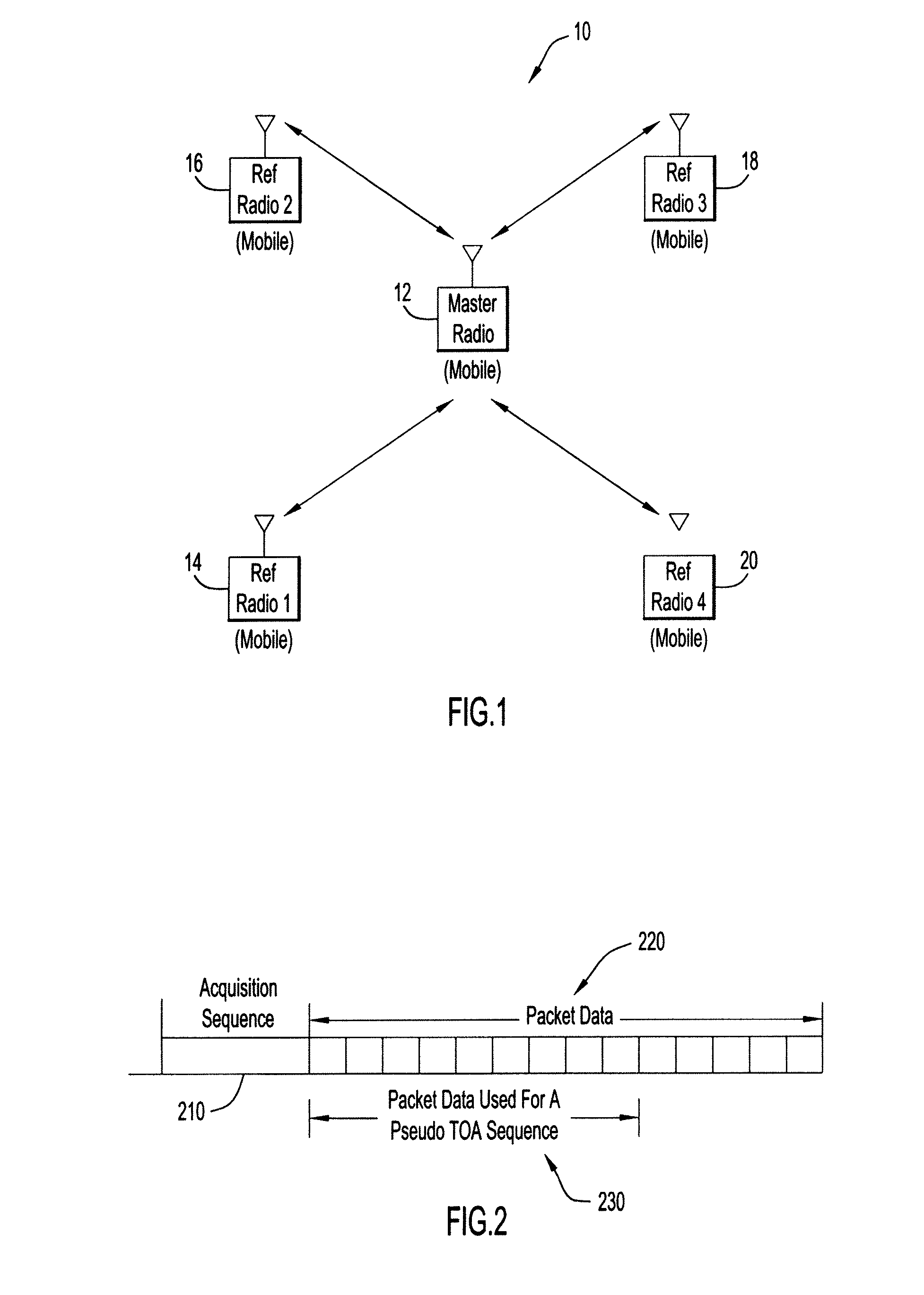
Ranging Between Radios Using Pseudo Time of Arrival Sequence
ActiveUS20100260207A1Accurately determineExpand the radio rangePosition fixationTime-division multiplexBpsk modulationCurve fitting
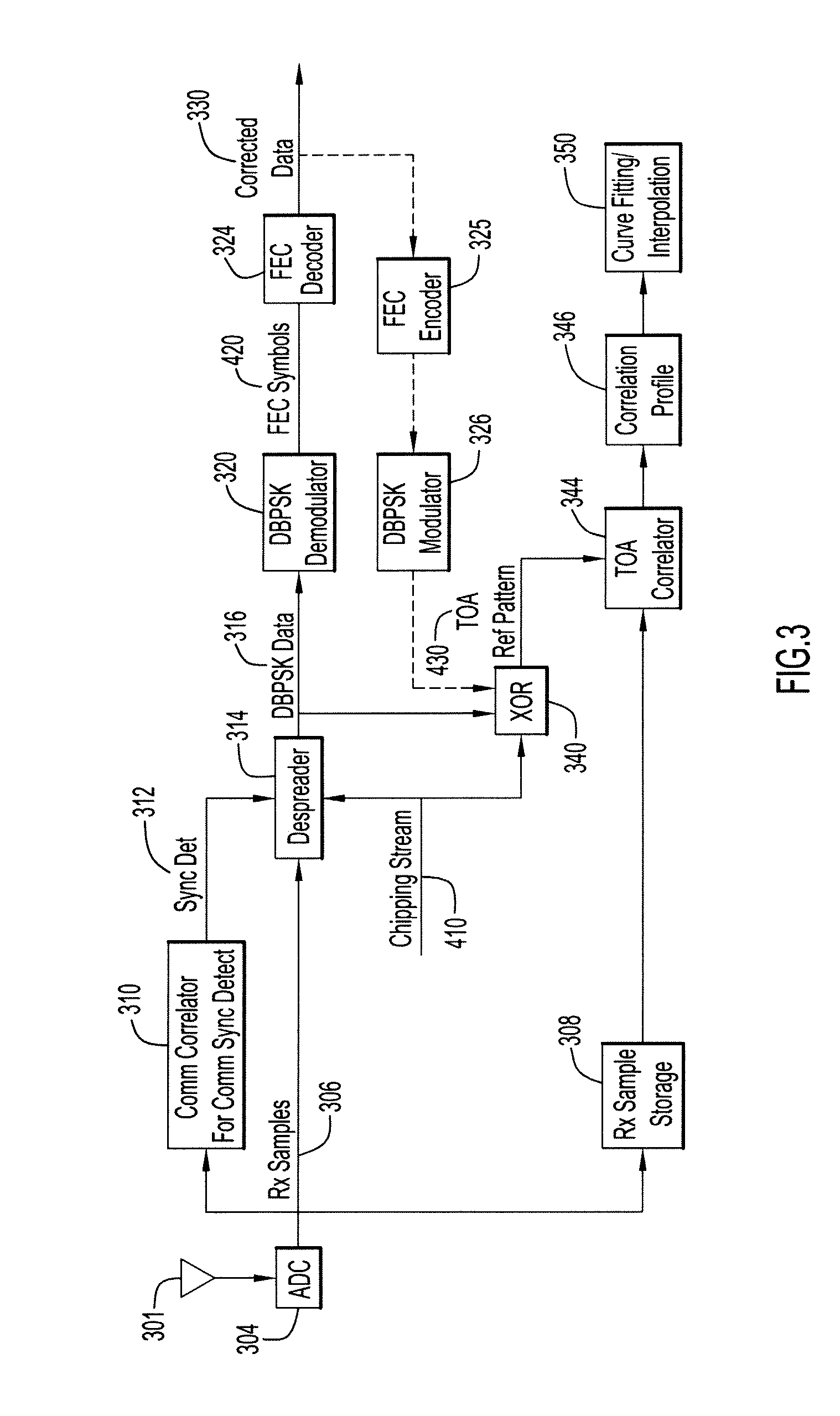
Systems and methods for refining the determination of the time of arrival (TOA) of given data. A portion of packet data is designated to be used as a pseudo TOA sequence. The packet information is modulated using, e.g., BPSK, and thereafter spread with a chipping stream known at both source and destination radios. The resulting stream includes a TOA reference pattern. On the receive side (destination radio), receive samples are despread and demodulated. The despread data is then XOR'ed with the chipping stream to re-create the TOA reference pattern. The re-created TOA reference pattern and original receive samples (previously stored) are passed through a correlator to obtain a correlation profile, which is then used for curve fitting / interpolation to accurately determine the TOA of the given received sample. Embodiments may be used in conjunction with a radio ranging system.
Owner:HARRIS GLOBAL COMMUNICATIONS INC
PN SN blind estimation method and device
InactiveCN101079653AGood effectRealized Blind EstimationPhase-modulated carrier systemsEstimation methodsBpsk modulation
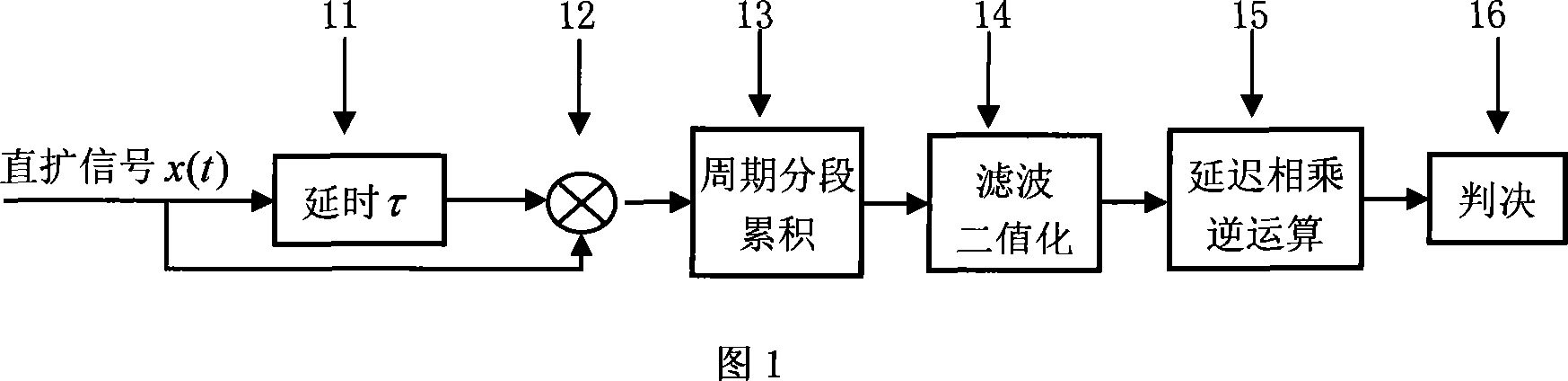
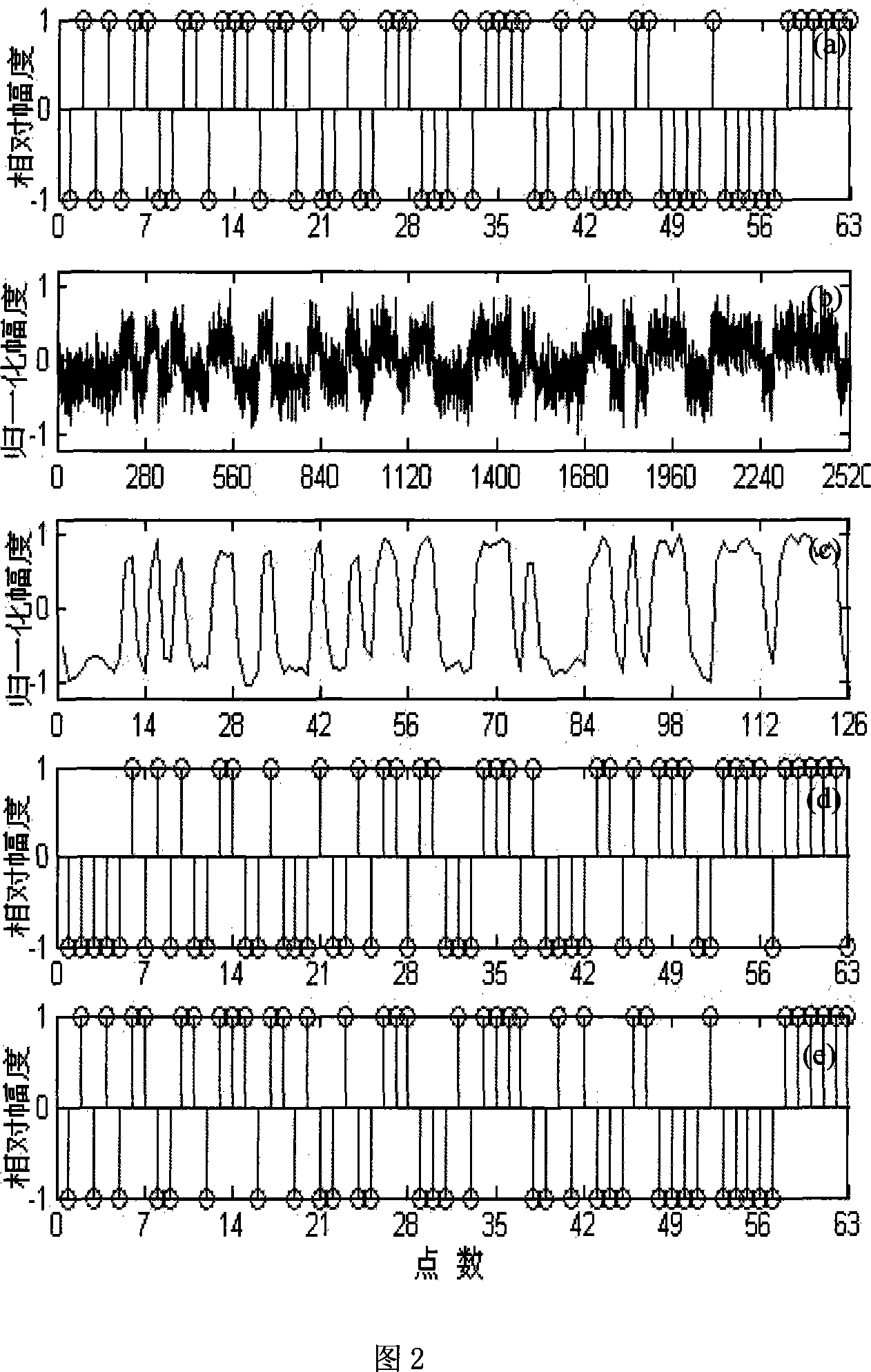
The invention discloses a PN sequent code typed blind estimating method and device, which is characterized by the following: multiplying the spread-spectrum communicating signal modulated by input BPSK directly; segmenting periodically; filtering; proceeding two valuing; delaying inverse operation of multiplying and decision; proceeding blind estimation for pseudorandom sequence (PN) in the spread-spectrum communicating signal; realizing blind estimation for long-code or short-code PN sequence with rapid speed.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Implementation method for preventing forwarding interference of frequency modulation radio fuze
InactiveCN103095334AFlexible change of fuze action distanceIncrease lethalityTransmission18-bitInterference resistance
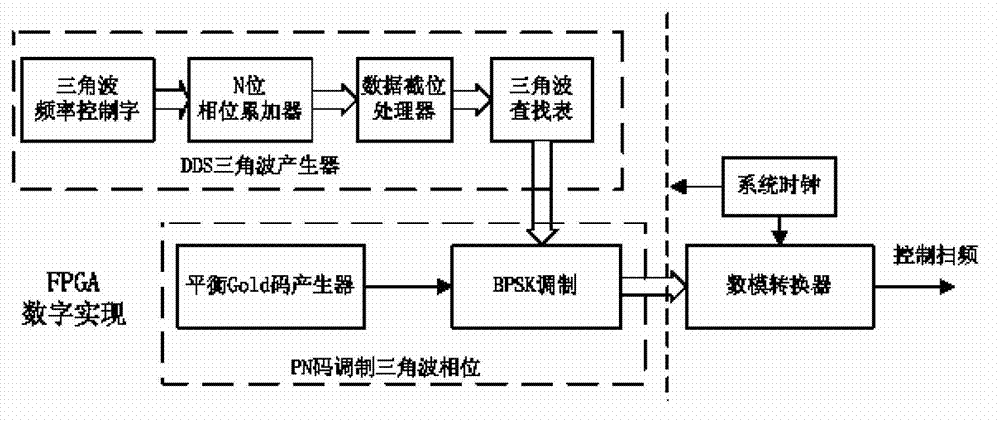
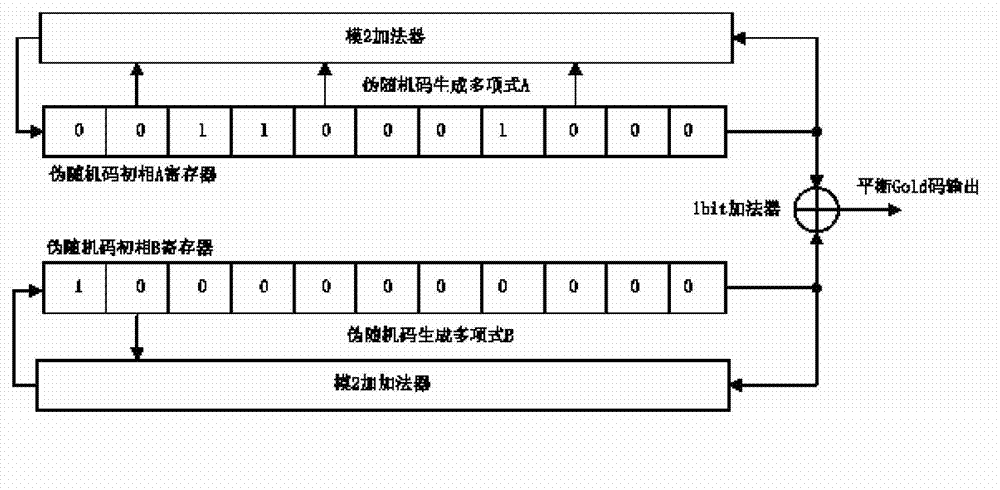
The invention provides an implementation method for preventing forwarding interference of a frequency modulation radio fuze and aims to provide a digitalized interference prevention fuze implementation method with which triangular wave frequency can be flexibly adjusted, fuze operating distance can be changed, and forwarding interference prevention capacity of fuze equipment can be improved. The implementation method is realized by the following technical scheme. A triangular wave generator formed by a triangular wave frequency control word, an N-bit phase accumulator, a data bit cut processor and a triangular wave phase lookup table in sequence and a BPSK (Binary Phase Shift Keying) modulator crosslinked between a balance GOLD code generator and a digital-to-analog converter are designed in a programmable gate array chip FPGA (Field Programmable Gata Array). After the triangular wave generator frequency is given, the computational formula of the triangular wave frequency control word is adopted in the DDS triangular wave generator. The calculated triangular wave frequency control word is sent to the N-bit phase accumulator to be accumulated, the lower 18 bits of the data are cut and the higher 14 bits of the data are maintained. The data is sent to the triangular wave lookup table, and phase-to-range conversion of triangular wave signals is achieved.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Chip millimeter-wave transceiver system and application thereof on fixed-distance proximity fuse
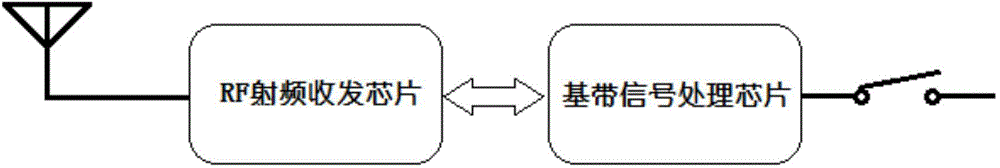
InactiveCN104596370ALow costImprove consistencyAmmunition fuzesBand-pass filterAnalog signal processing
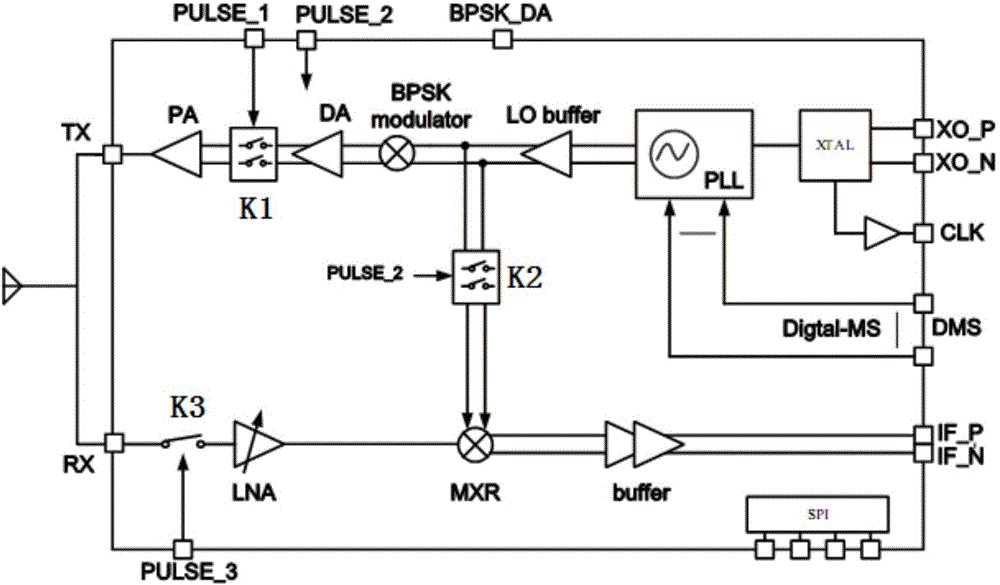
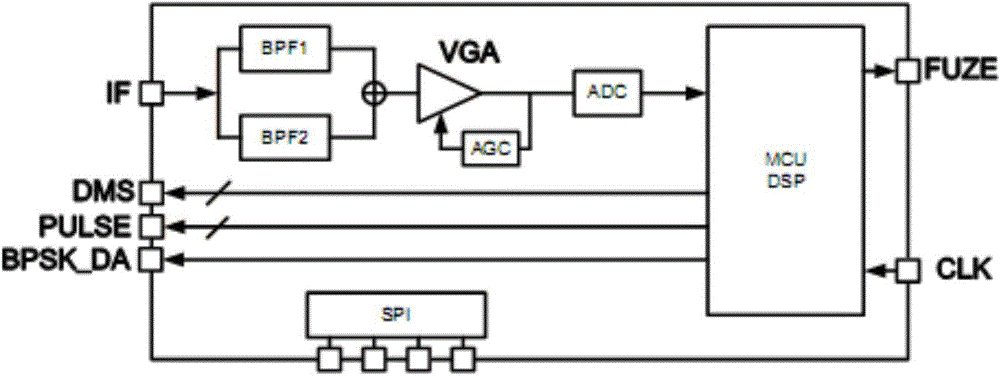
The invention discloses a chip millimeter-wave transceiver system, which comprises a radio frequency transceiver chip and a baseband signal processing chip, wherein the radio frequency transceiver chip is divided into a TX pat and an RX part; a TX transmitting main part comprises a VCO voltage-controlled oscillator, a DA drive amplifier, a PA power amplifier, a BPSK modulator and a PLL loop; an RX receiving main part comprises an LNA low-noise amplifier, an MIX mixer and a Buffer driver; the baseband signal processing chip mainly comprises an analogue signal processing unit and a digital signal processing unit; the analogue signal processing unit mainly comprises a BPF band-pass filter, an AGC variable-gain control loop and an ADC digital-to-analogue converter; and the digital processing unit mainly comprises a DSP and an MCU. Two fully integrated chips of the system finish all functions; the power consumption, the volume, the cost and the development difficulty of an overall machine are reduced; the number of circuits is reduced; the size is reduced; the chips are easy to integrate; and the system can be applied to fixed-distance proximity fuse, anti-collision radars, distance measurement and the like.
Owner:叶松
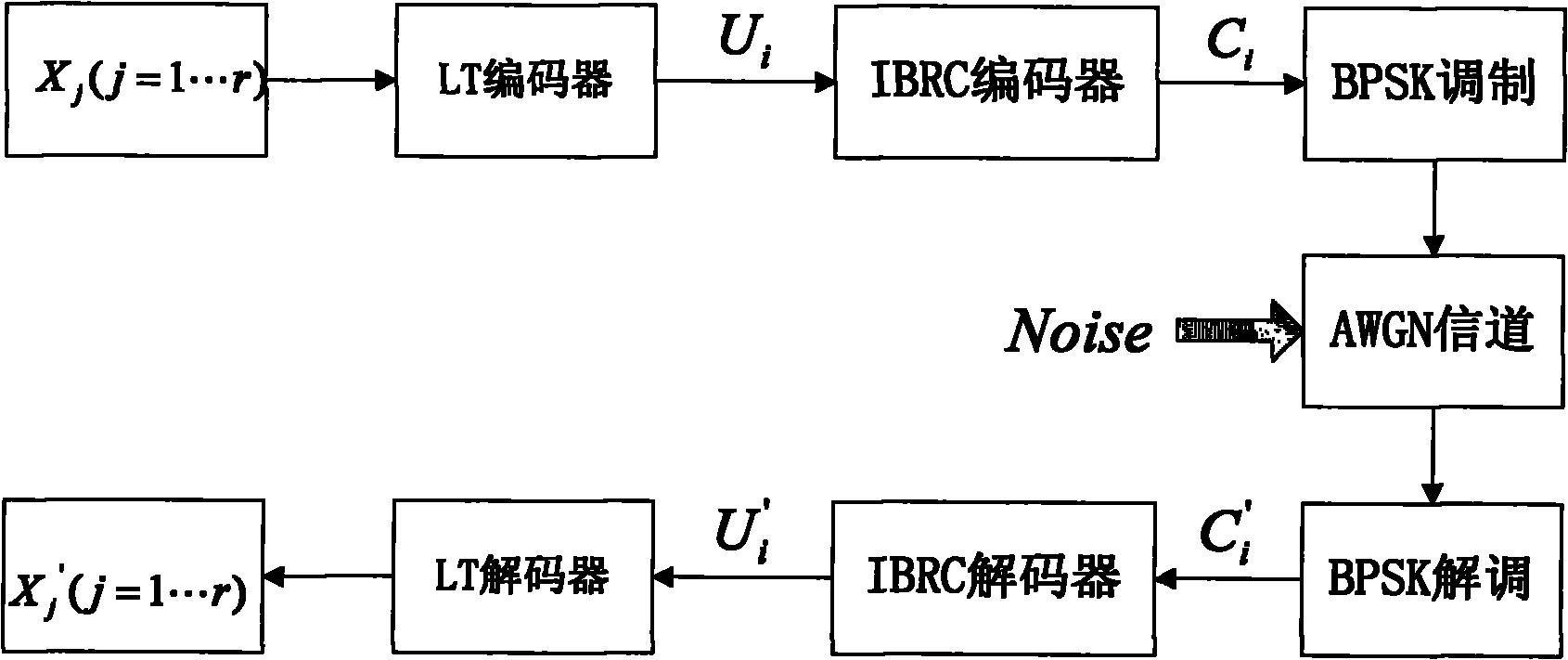
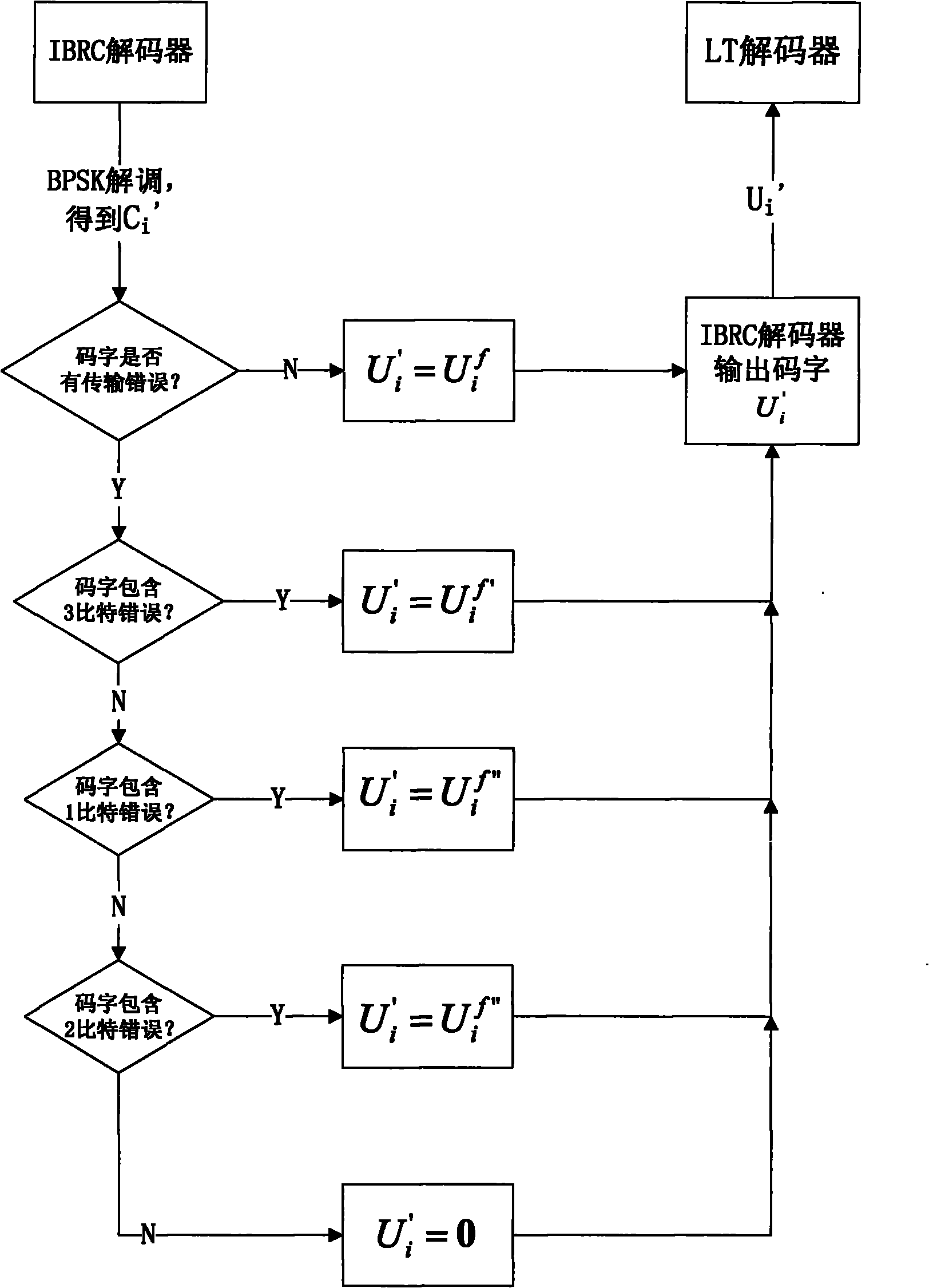
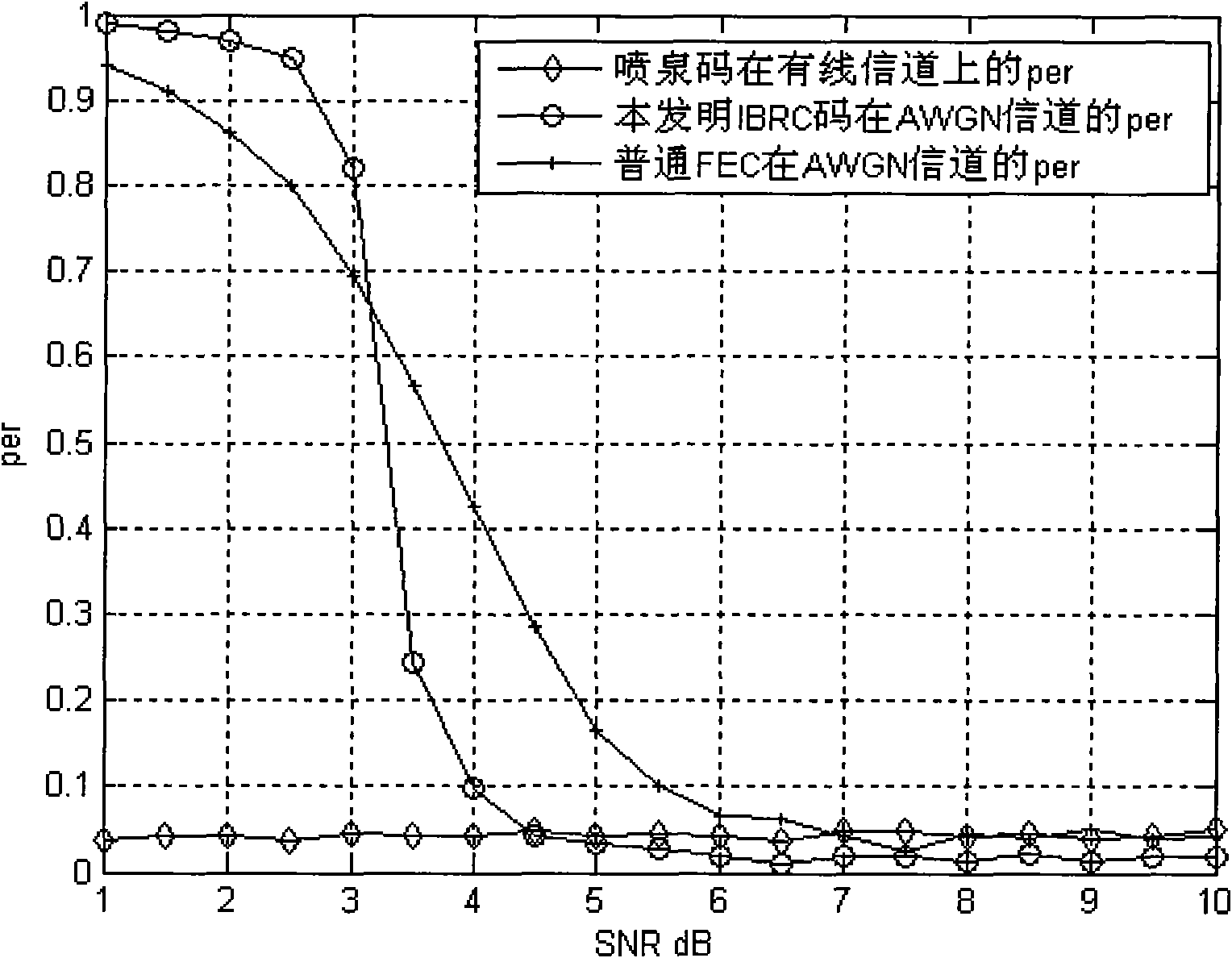
Channel coding method for enhancing transmission quality of fountain code on wireless channel
The invention discloses a channel coding method for enhancing the transmission quality of a fountain code on a wireless channel, which comprises the following steps of: when coding an IBRC channel, sequentially displacing input code words firstly by an IBRC coder circularly through taking each element in two displacement vectors as the amplitude of the circular displacement of each time sequentially, then carrying out modular two addition on all the obtained code words after displacing circularly to obtain two code words totally, afterwards cascading the two code words to obtain coding code words, modulating by using BPSK and transmitting; when decoding the IBRC channel, dividing the received code words into a front section and a back section after carrying out BPSK demodulation on the received code words by an IBRC decoder, then carrying out modular two addition, afterwards carrying out reverse circular displacement, determining whether IBRC code words are erroneous in the transmission process or not on the basis of the code words obtained after displacing circularly, and outputting the code words directly if the IBRC code words are not erroneous; otherwise, setting an erroneous bit number sequentially within a certain range, decoding under the setting, and outputting a decoding result if the decoding is successful; and if the set erroneous bit number is still not decoded successfully after the set erroneous bit number samples all integers in the range, outputting all-zero code words by the IBRC decoder.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Nano-antenna apparatus and method
InactiveUS7068225B2Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsOblate spheroidBpsk modulation
A nano-antenna apparatus (or equivalently a nano-antenna device) comprises a first conducting surface, a second conducting surface, a gap region between a first conducting surface and a second conducting surface and at least one discharge switch at least one discharge switch cooperates with first conducting surface, a second conducting surface to form a substantially continuous closed surface enclosing a volume. This volume may be substantially similar to a spheroid, a prolate spheroid, an oblate spheroid, a Cartesian rectangular solid or other shape. This volume may enclose at least one electric device. A dimension of the volume and a dielectric constant characterizing a dielectric layer may be chosen so as to yield a desired frequency response. Further, this volume may partition outside energy from inside energy, causing the former energy to radiate away.This invention further teaches a method for transmitting UWB impulse. This method comprises the steps of charging a first conducting surface with respect to a second conducting surface, and discharging a first conducting surface with respect to a second conducting surface such that the discharging forms a substantially continuous closed conducting shell from a first conducting surface and a second conducting surface. In alternate embodiments the discharging or charging may be adiabatic. Discharging may be positioned in time in accordance with a pulse position modulation scheme. Charging may be polarized in accordance to a flip or BPSK modulation scheme. Discharging may be effected by diodes, transistors, or MEMS devices.
Owner:NEXT RF
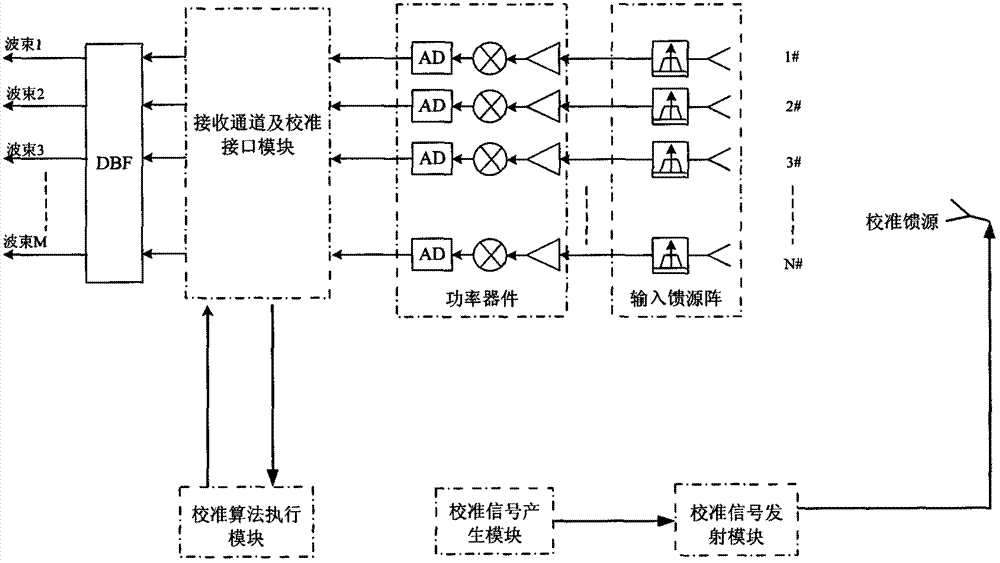
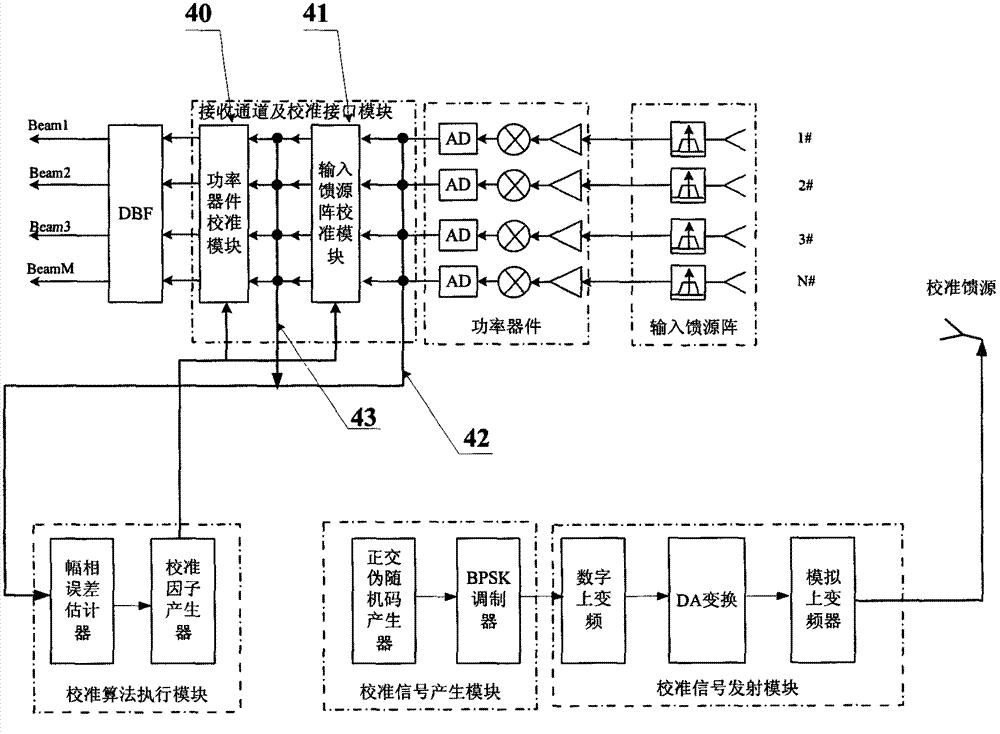
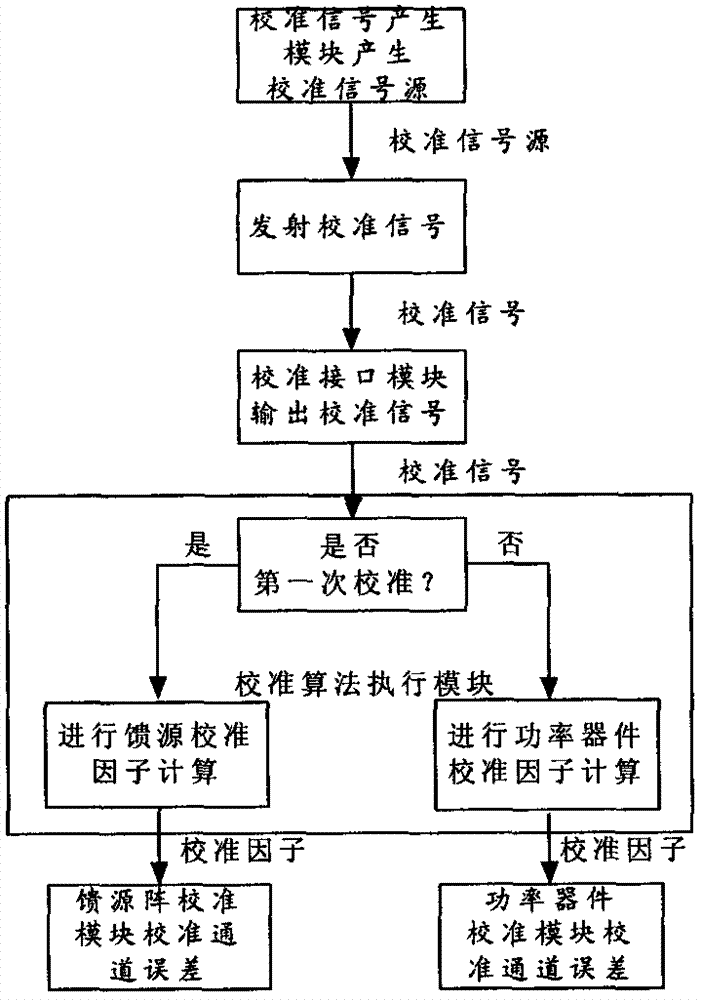
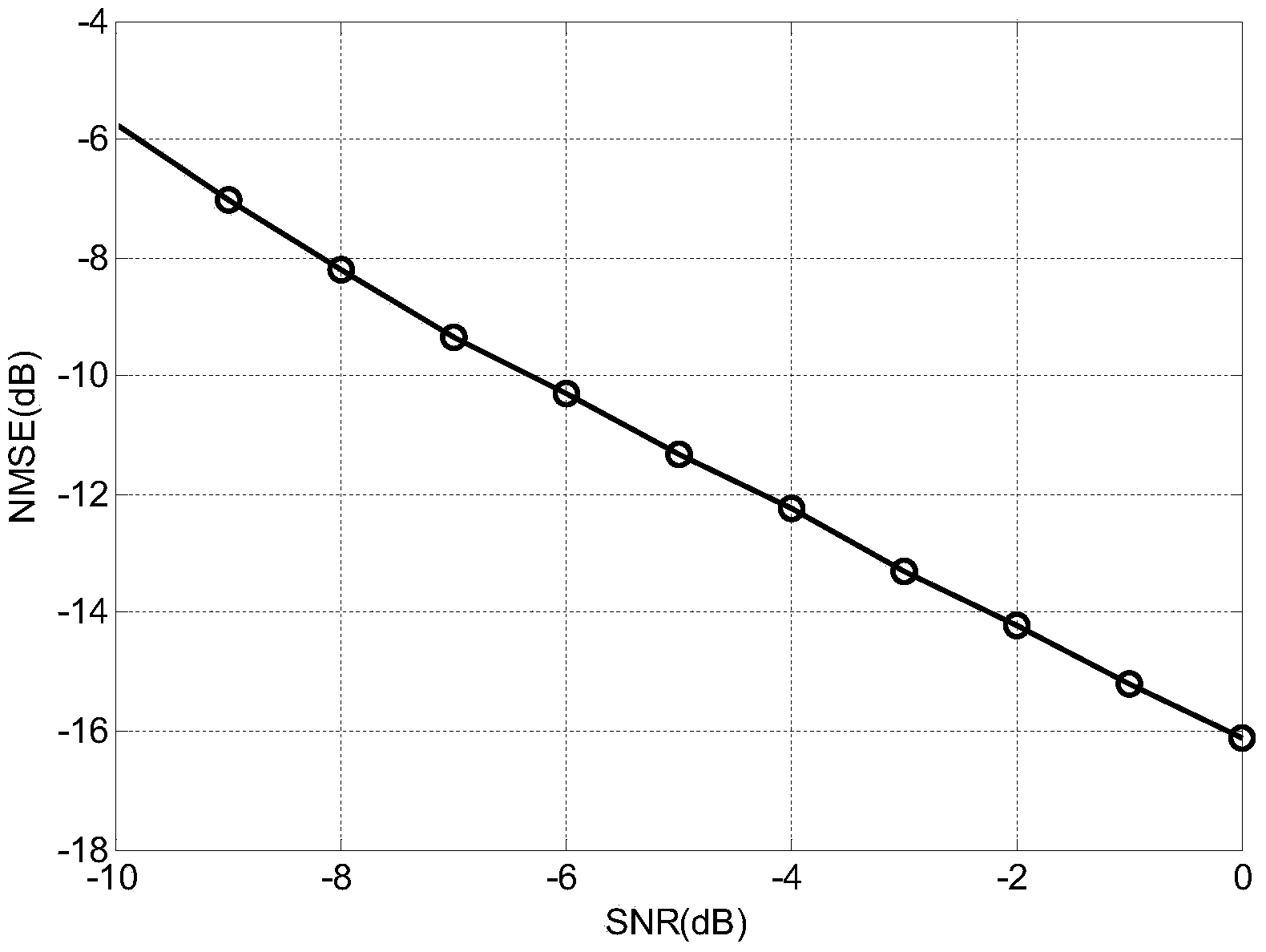
Calibration system and method for amplitude-phase error of receiving channel of spaceborne DBF network
ActiveCN102769601AEliminate distractionsGuaranteed stabilityBaseband system detailsMultiple carrier systemsCoding blockDigital up converter
The invention discloses a calibration system and method for the amplitude-phase error of a receiving channel of a spaceborne DBF (Digital Beam Forming) network. The system comprises a calibration signal generating module, a calibration signal transmitting module, a receiving channel and calibration interface module, and a calibration algorithm execution module, wherein the calibration algorithm execution module comprises an amplitude-phase error estimator and a calibration factor generator; the calibration signal generating module comprises an orthogonal pseudo random code block generator and a BPSK (Binary Phase Shift Keying) modulator; the calibration signal transmitting module comprises a digital up converter, a DA inverter, an analog up converter and a calibration feed source; the calibration signal generating module is connected with the calibration signal transmitting module; and the calibration algorithm execution module is connected with the receiving channel and calibration interface module. The system and the method provided by the invention have the advantages of strong real-time performance, high precision and high stability, and save satellite resources.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
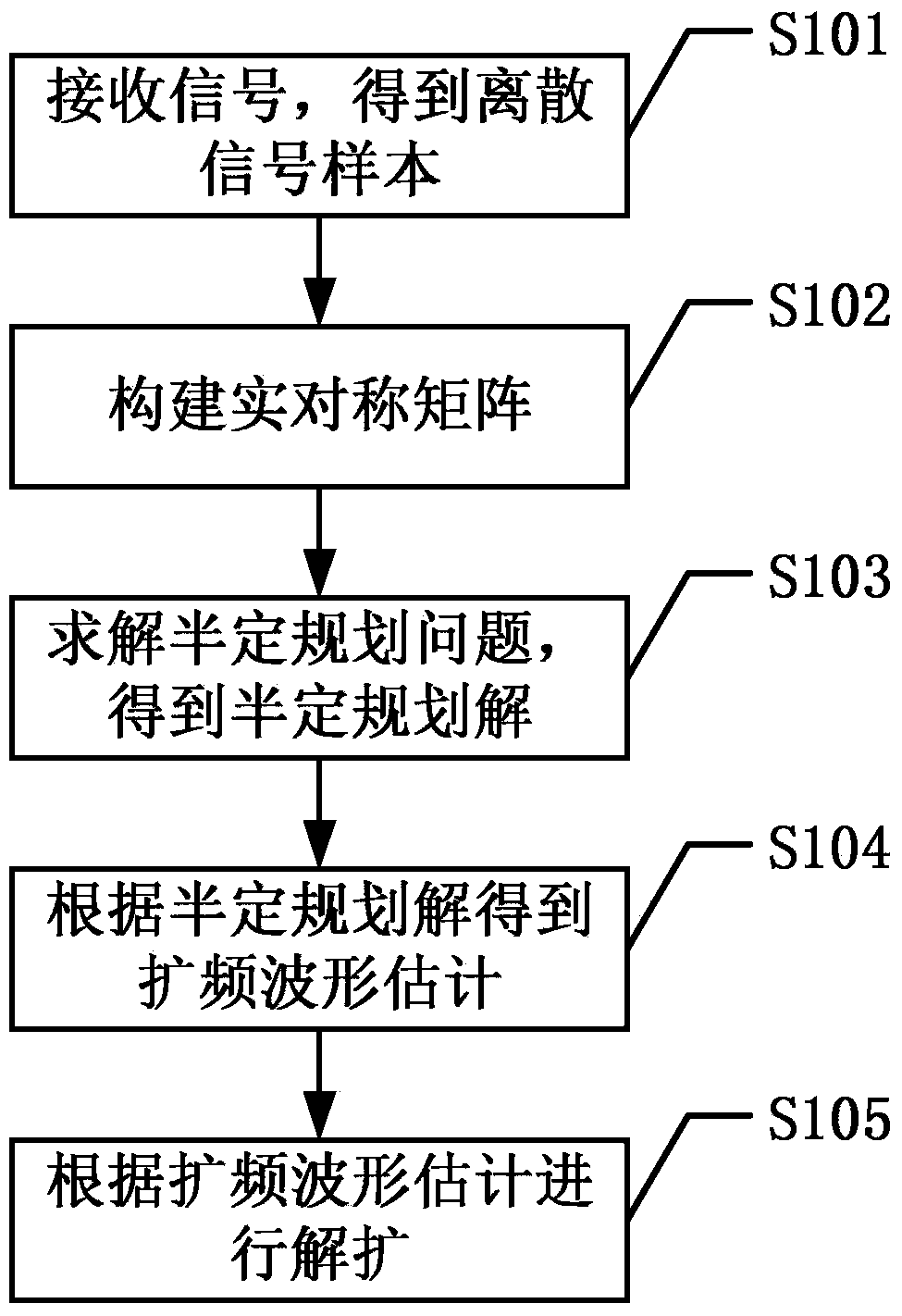
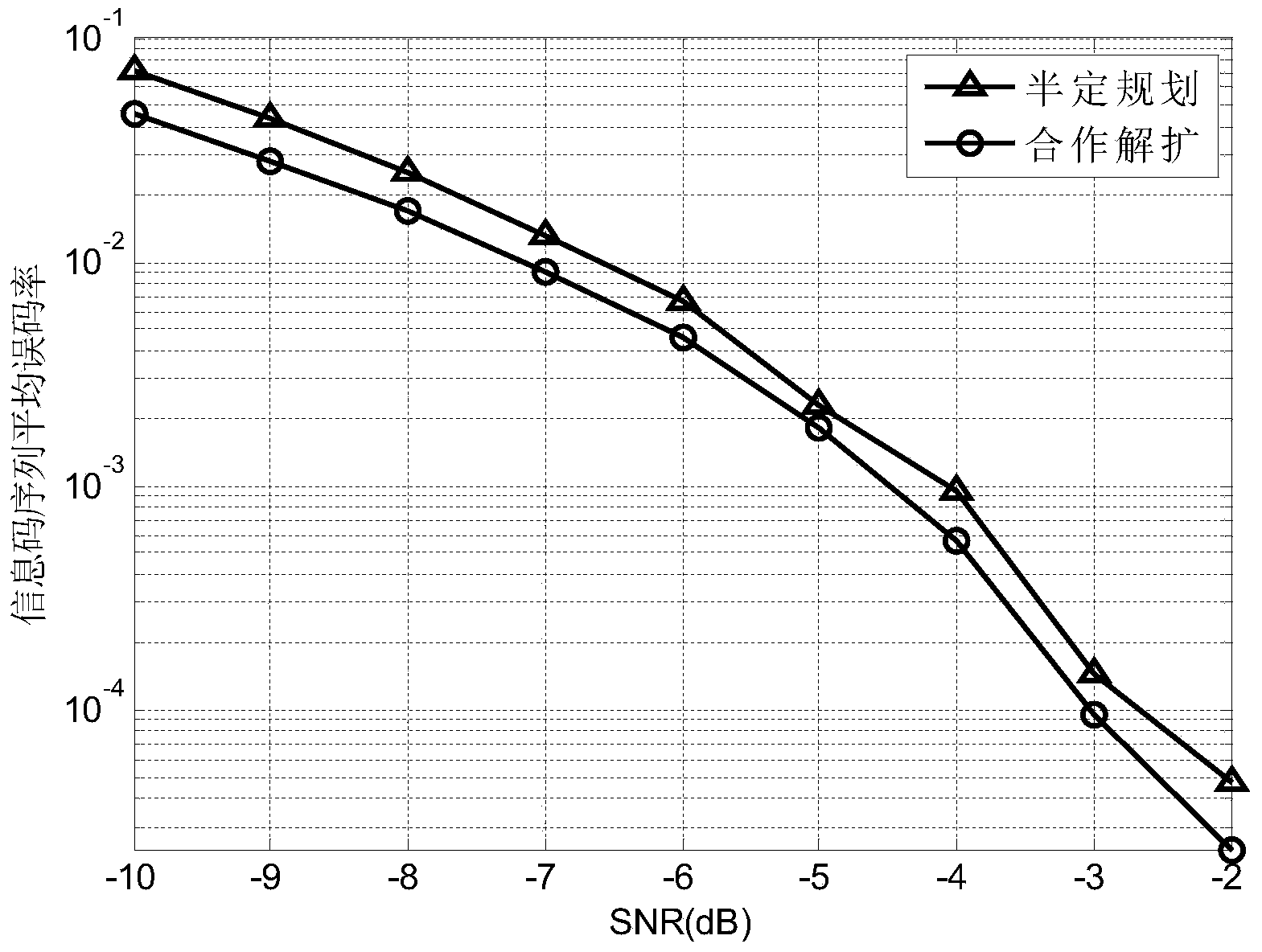
Long code DSSS signal blind dispreading method based on semi-definite programming
InactiveCN103414670ASpread Spectrum Waveform ReducedTransmitter/receiver shaping networksSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Computation complexity
The invention discloses a long code DSSS signal blind dispreading method based on semi-definite programming. A long code DSSS signal spread-spectrum waveform maximum likelihood estimation problem with exponential growth calculation complexity is converted to a semi-definite programming problem with polynomial calculation complexity, the semi-definite programming problem is then solved, the approximate solution of the spread-spectrum waveform maximum likelihood estimation problem is acquired, the spread-spectrum waveform estimation is acquired, and accordingly long code DSSS signal blind dispreading is finally finished. Regarding to long code DSSS signals modulated by BPSK under the multi-path channel condition, the long code DSSS signal blind dispreading method greatly reduces calculation complexity of spread-spectrum waveform maximum likelihood estimation through the adoption of semi-definite programming, can still have good performance even under low signal to noise ratio or short data conditions, and is particularly suitable for blind estimation of long code DSSS signals in the non-cooperative communication field.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Iteration demodulation decoding method of encoded modulation signals based on climax frequency deviation compensation
InactiveCN101854229AEfficient decodingImprove performanceError preventionTransmitter/receiver shaping networksLow-density parity-check codeBpsk modulation
The invention relates to an iteration demodulation decoding method of encoded modulation signals based on climax frequency deviation compensation, effectively solving the problem of iteration demodulation decoding of an LDPC (Low Density Parity Check Codes) encoded BPSK (Binary Phase Shift Keying) modulation system under frequency deviation and an unknown-phase channel. The method comprises the following steps of: receiving one frame of a full frame of encoded modulation signals, and dividing the full frame into a plurality of signal subblocks; initializing the external information of encodedbits; carrying out frequency deviation estimation by adopting a revised M&M arithmetic according to the external information of the encoded bits and the sample value of the received one-frame signals; carrying out a Tikhonov demodulation arithmetic to complete signal demodulation according to the structure of the signal subblocks and the frequency deviation estimation, and outputting a demodulation soft value of the encoded bits; receiving the demodulation soft value by a decoder, completing decoding once according to a confidence coefficient transmission decoding arithmetic, and outputting the external information of the encoded bits; and outputting a decoded value when the iteration demodulation times reach the preset times, and otherwise, increasing the length of the signal subblocks and repeating the operation until decoding is successful or iteration times achieve the regulated value.
Owner:PLA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Measurement and control signal and OFDM signal integrated waveform coexistence transmission system
ActiveCN111884971AFlexibleGood streamingMulti-frequency code systemsMultiple carrier systemsControl signalCarrier signal
The invention discloses a measurement and control signal and OFDM signal integrated waveform coexistence transmission system, and aims to provide a high-speed, real-time and reliable-transmission waveform coexistence transmission system, which is realized through the following technical scheme: in a data link, data information bits generated by a data information module are subjected to amplitudemodulation through an LDPC encoding module and a QAM module; an OFDM module generates an orthogonal multiplexing signal, and the OFDM signal and the measurement and control signal are subjected to rate adjustment by a power adjustment module to complete superposition of a power domain in a channel superposition module; a measurement and control information module on a measurement and control linkmaps a BPSK signal flow to a carrier after being modulated by a convolutional encoding module and a BPSK modulation module and spread by a spread spectrum module, and the power domain superposition ofthe BPSK signal flow and a data signal is completed in a channel superposition module after power adjustment. An integrated waveform signal in which the spread spectrum measurement and control signaland the OFDM signal coexist is formed through superposing.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
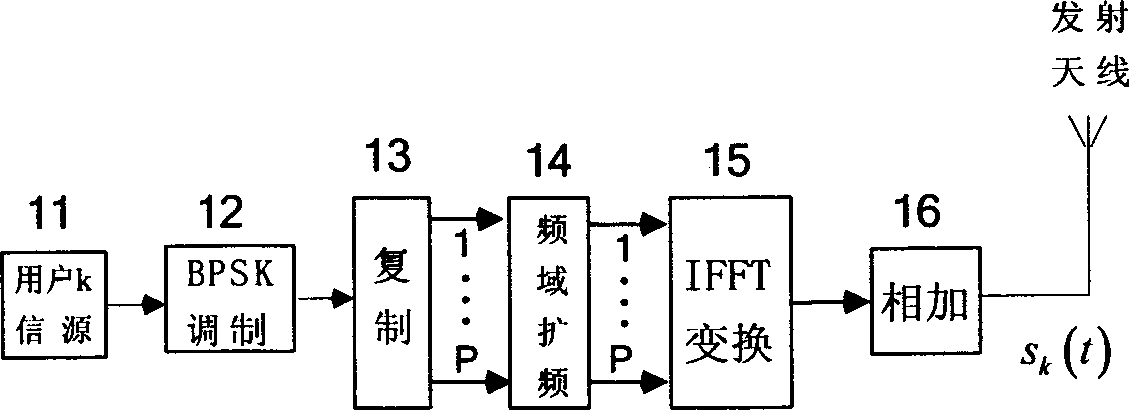
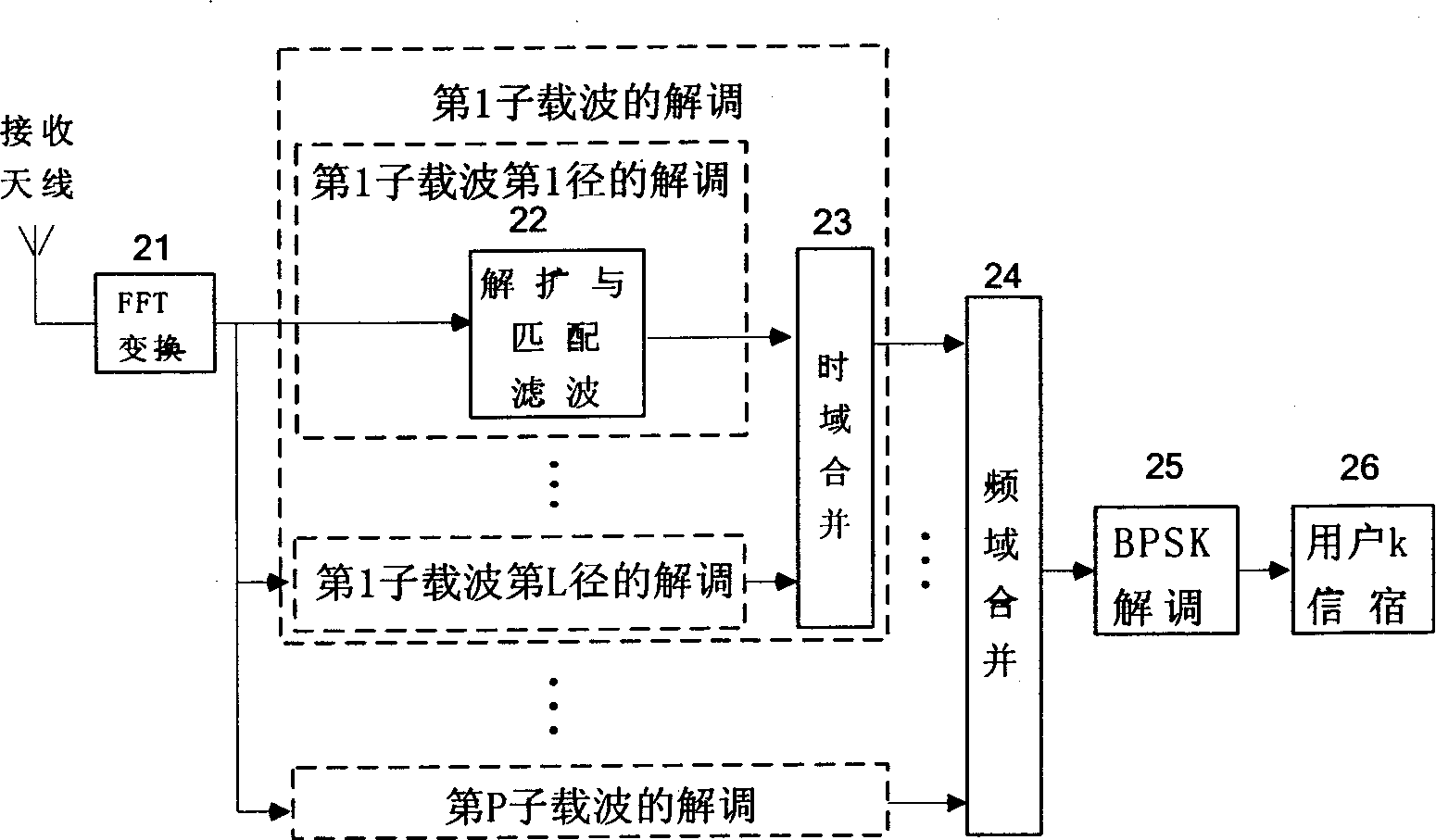
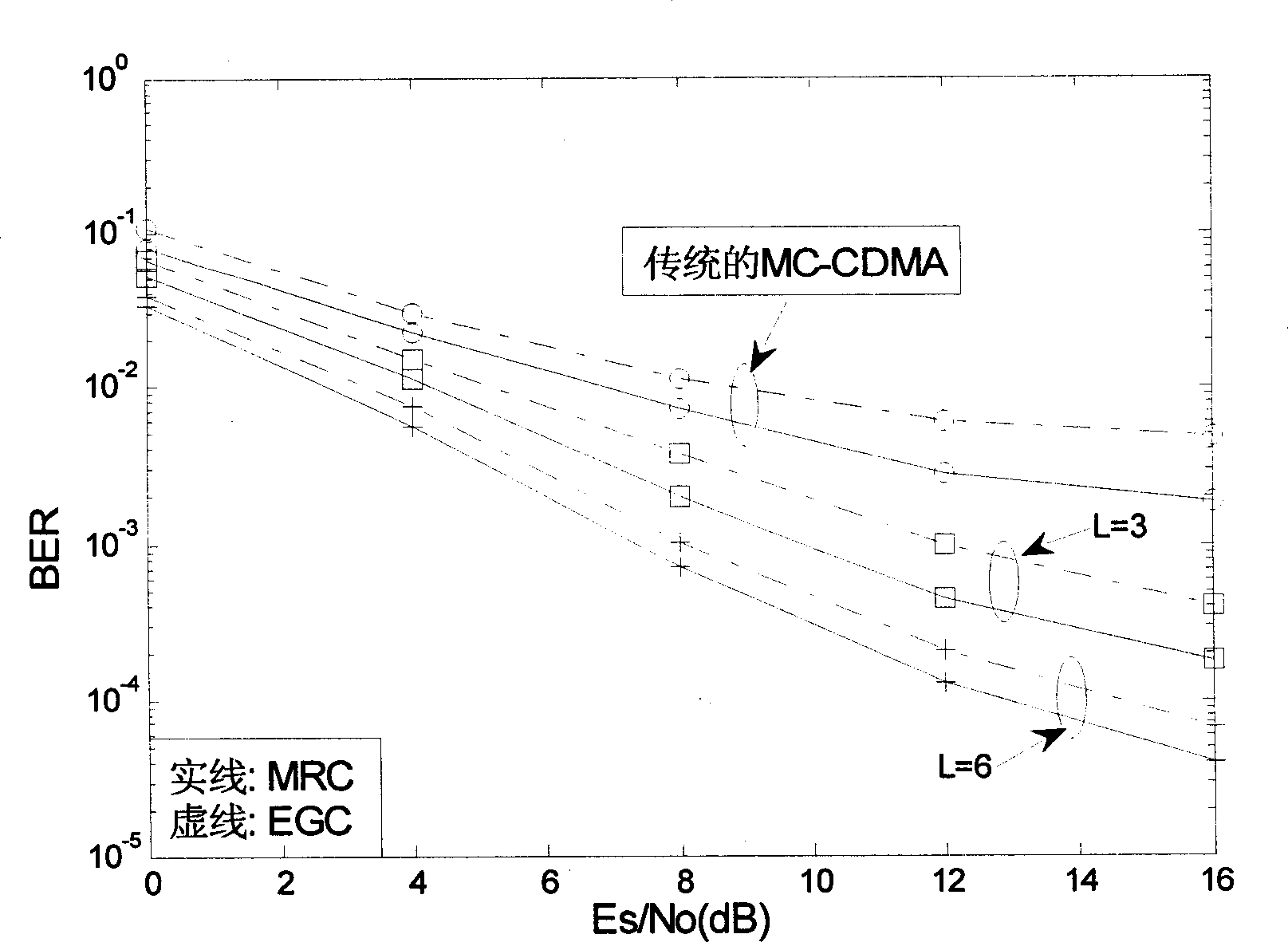
MC-CDMA system transmitting and receiving method
InactiveCN1777087AEliminate Inherent LimitationsEfficient separationSignal channelsTime domainData stream
The transmitting procedure includes steps: reproducing data stream modulated through BPSK from user so as to form parallel data stream identical in P routes; carrying out spread spectrum in frequency domain for reproduced parallel data stream in P routes, taking symbol period of transmission as integral multiple of í«Qiepuí» period; inverse FFT is carried out for parallel signal in P routes after spread spectrum; transmitting added modulated sub carrier signals in P routes. The receiving procedure includes steps: FFT is carried out for signal received from antenna to recover signals of each sub carrier; carrying out de-spread and matched filtering processes for signals in each path, each sub carrier and each user so as to obtain de-spread signal; uniting multipath signal in time domain so as to obtain signal of united each sub carrier in multipath; after combination in frequency domain obtains final judging variable; BPSK modulating the judging variable to recover userí»s data stream.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Frame synchronization detection method and device for OFDM system
InactiveCN101242259AResolve synchronizationConvenience to workData switching by path configurationSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlConjugate symmetryStart time
A frame synchronization detecting method in an orthogonal frequency division multiplex system comprises: conjugating correlation calculation to data signals in a fore and aft conjugate correlation window of data signal in a data signal sequence to obtain a correlation calculation accumulate result by accumulating; calculating an average energy of data signals in the fore and aft conjugate correlation window; taking a metric value of a data signal as a ratio between the correlation calculation accumulate result and the average energy, and in a detecting period, such as in a length of 1.5 frame, determining a frame starting time based on a data signal with a metric value maximal. The method, based on a character that predecessor using BPSK modulate conjugates symmetry, performs a frame synchronization detect, solves the synchronization problem in the orthogonal frequency division multiplex system.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES CENT FOR WIRELESS TECH
RFID tag device
InactiveCN1943126AGood effectHigh electromagnetic wave reception efficiencyElectromagnetic wave systemCircuit arrangementsResonanceBpsk modulation
The present invention aims to overcome the drawback with conventional RFID tag devices having a short communication range, and expand the communication range to several times or more that in the conventional scheme. The conventional scheme is based on equilibrium feeding / equilibrium modulation (a two-terminal circuit for antenna operation), whereas the present invention is based on disequilibrium feeding / equilibrium modulation (a three-terminal circuit for antenna operation). The conventional scheme is based on simple rectification of received RF signals, whereas the present invention employs a circuit based on a combination of a stub resonance-based, impedance transformation boosting scheme and a ladder boosting scheme. The conventional scheme is based on ASK or BPSK modulation, whereas the present invention is based on passive modulation, but can employ a QPSK modulation circuit.
Owner:INTELLIGENT UNIVERSE RES INST
Lead insulating fault detecting method and device based on frequency spreading reflection
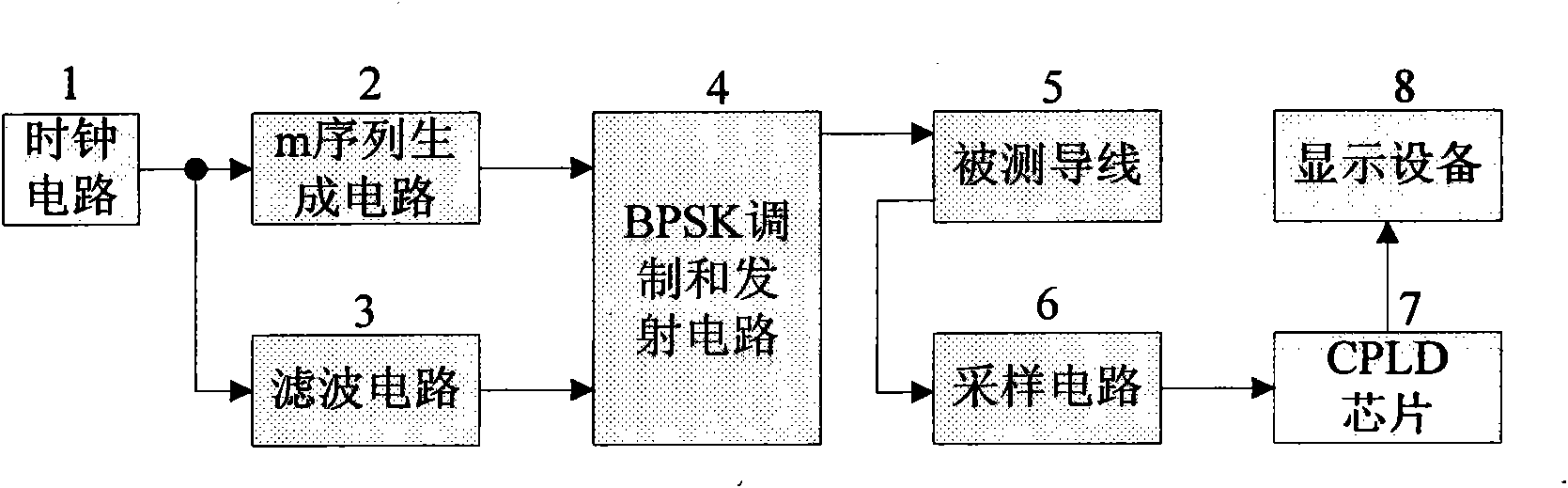
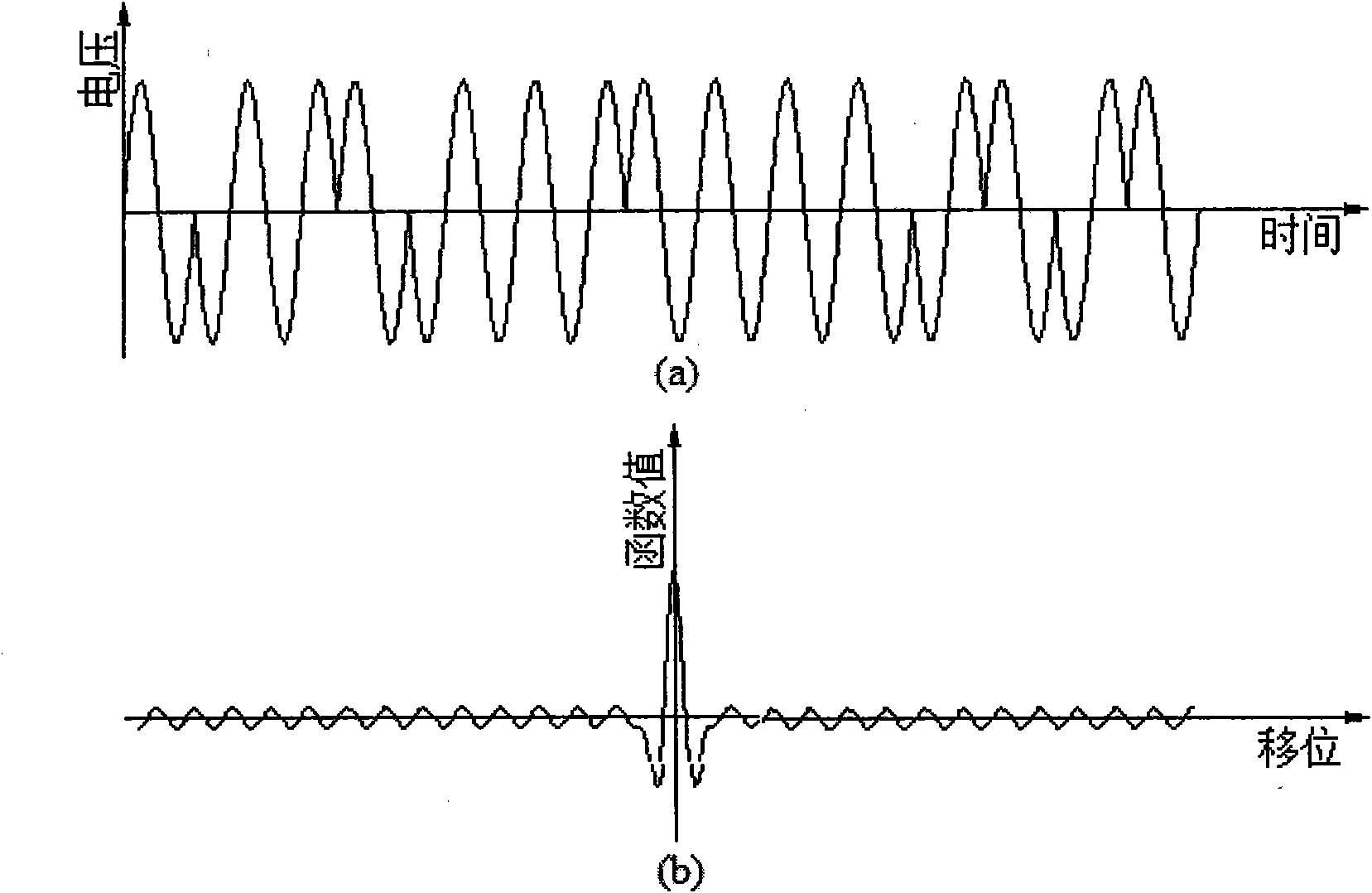
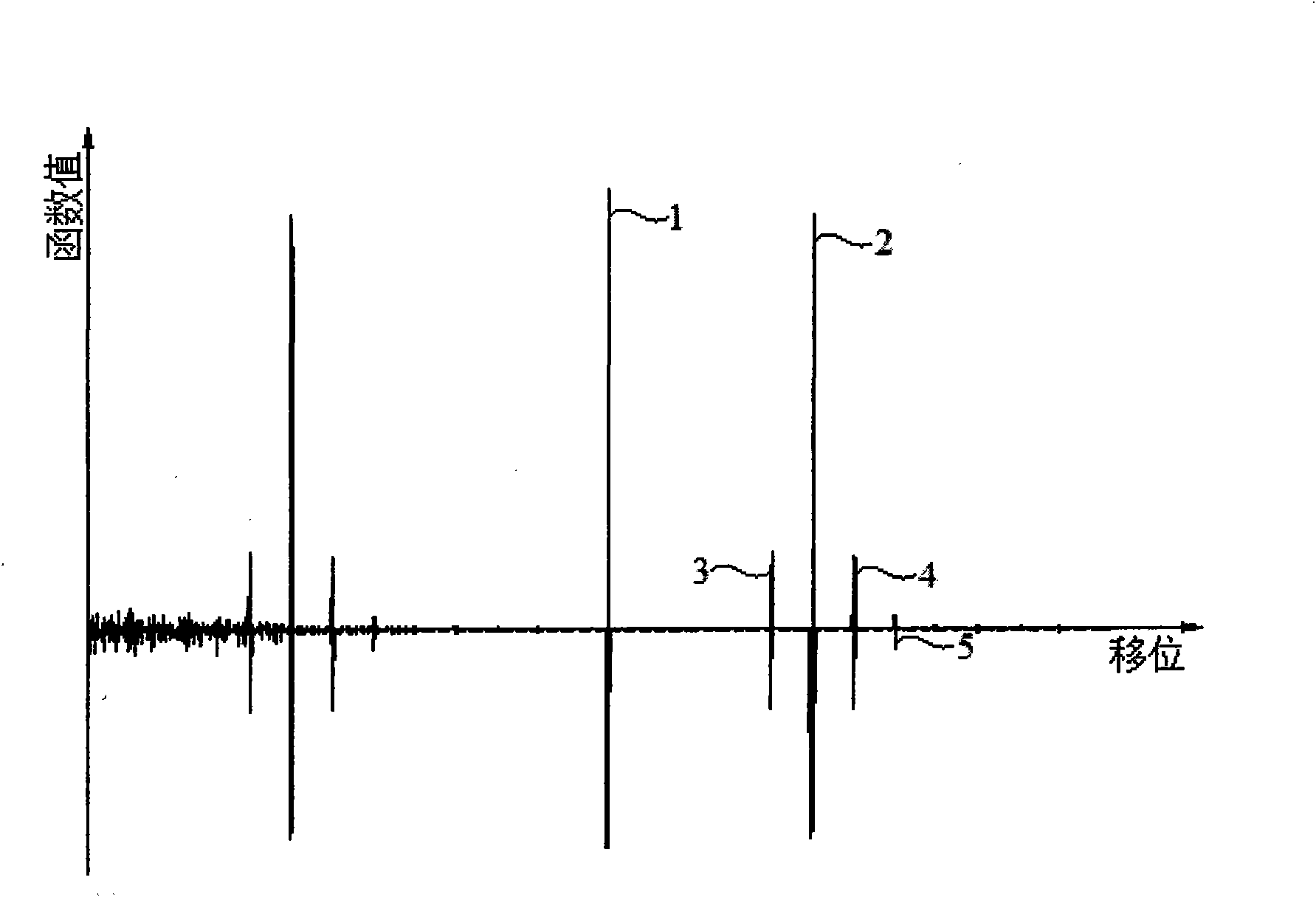
InactiveCN101900776AExcellent binary autocorrelation propertiesSuppress noiseFault location by pulse reflection methodsInterference resistanceBpsk modulation
The invention discloses lead insulating fault detecting method and device based on frequency spreading reflection. By using a BPSK (Binary Phase Shift Keying) modulated m sequence as a detecting signal of a lead fault and calculating the cross-correlation function of the detecting signal and a reflecting signal, the position and severity of the fault are confirmed. The device designed according to the method comprises a clock circuit, a filter circuit, an m sequence generating circuit, a BPSK modulating and emitting circuit, a sampling circuit, a CPLD (Complex Programmable Logic Device) chip and display equipment. The invention has the characteristics of high interference resistance and high positioning precision and can be used for the real-time detection of the lead fault.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Iterative joint source channel decoding method based on arithmetic coding and low-density parity-check
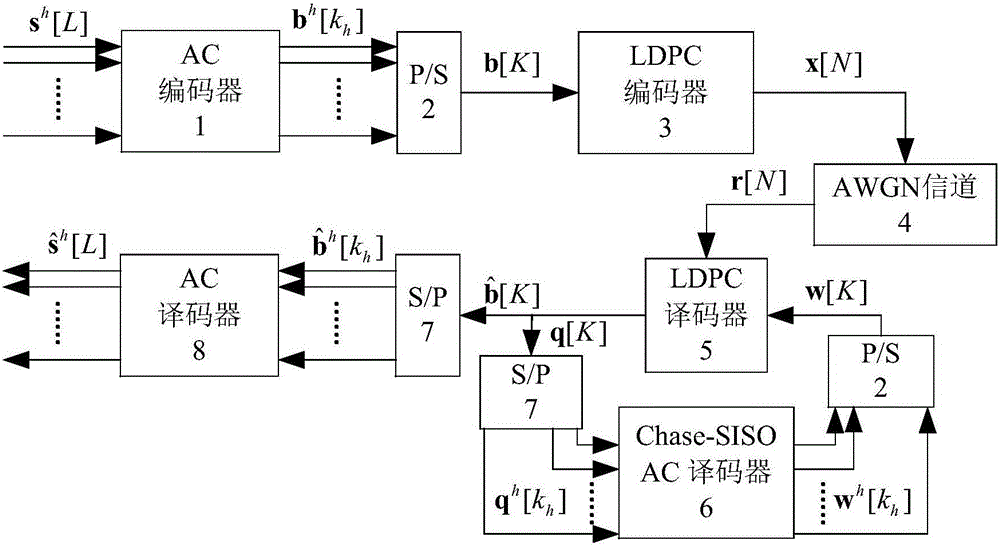
ActiveCN105846827ACoding efficiency has no effectSmall amount of calculationError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionBpsk modulationLow density
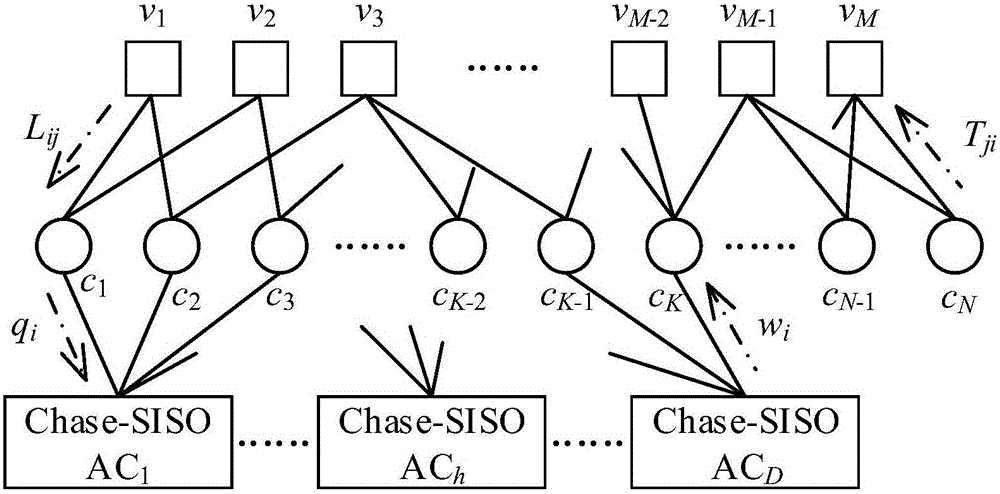
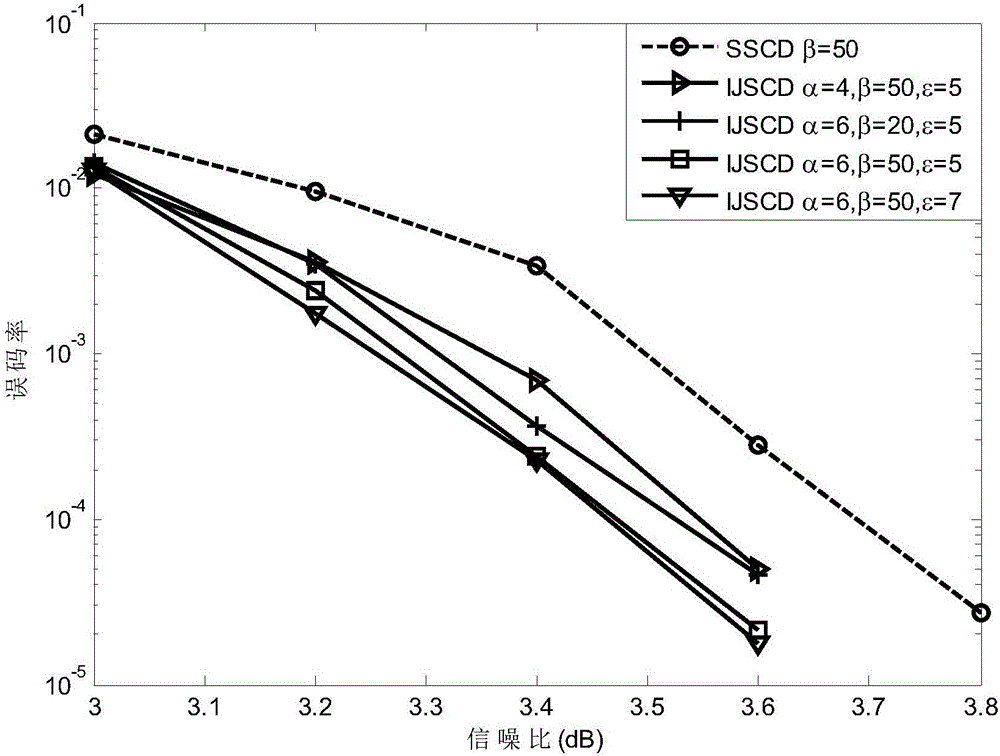
The invention provides an iterative joint source channel decoding (JSCD) method based on arithmetic coding (AC) and low-density parity-check (LDPC). In the method, an encoding sequence b<h> is obtained by processing a source symbol sequence s<h> through an AC encoder, an input information sequence b of an LDPC encoder is obtained by processing D encoding sequences b<h>, a code word sequence x is generated by processing the b through the LDPC encoder, and is sent to an AWGN channel after being modulated by a BPSK, a receiving sequence r is input to a closed ring formed by an LDPC decoder and a Chase-SISO AC decoder to be subjected to iterative decoding, after a plurality of times of iterations, a decoding sequence shown in the description is output by the LDPC decoder, the sequence is converted by a serial-parallel converter to obtain a sequence shown in the description, and the former sequence is processed by the AC decoder to obtain a decoding symbol sequence shown in the description. According to the method, the AC very efficient in lossless compression and the LDPC coding very high in error resistance are combined, so that the system validity and the reliability are very high; and meanwhile, an IJSCD (Iterative Joint Source Channel Decoding) method is utilized, so that the reliability is further improved on the premise of ensuring the validity.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Low-density parity check code-based relay cooperative transmission method
InactiveCN101826935AInnovative designSimple transfer methodError preventionResource consumptionLow-density parity-check code
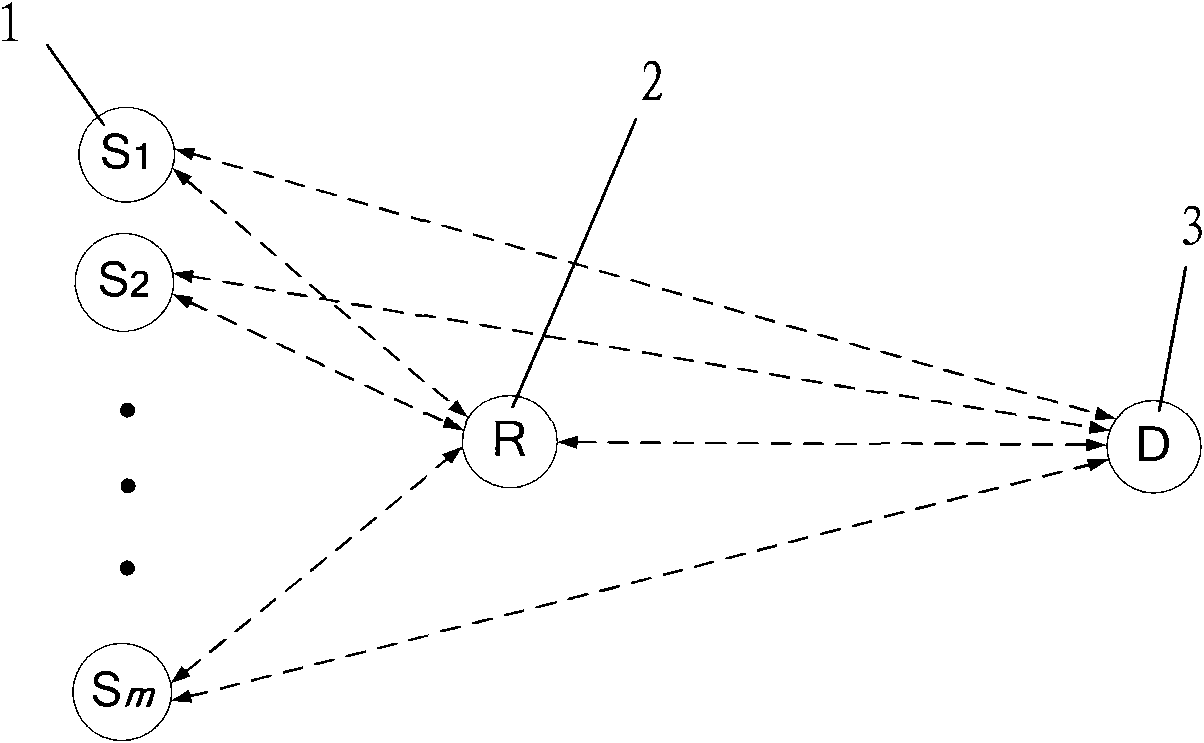
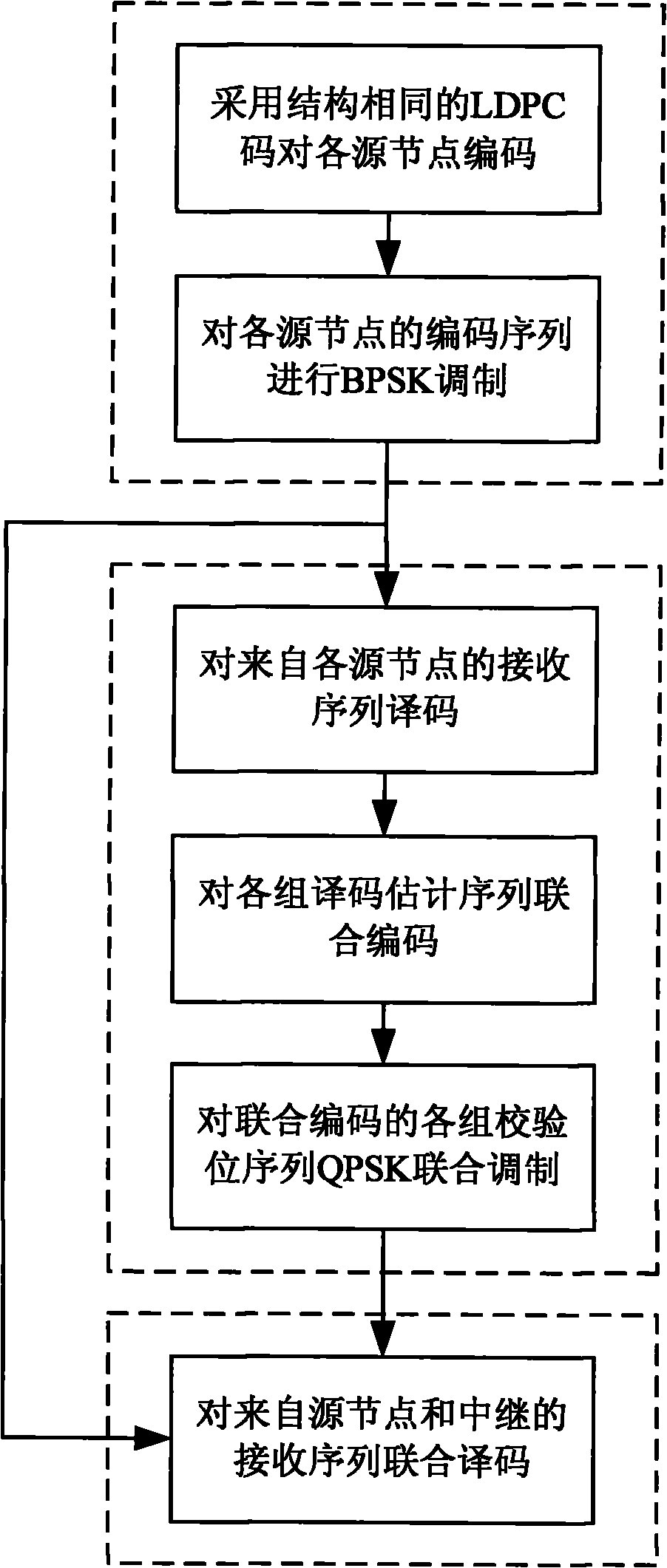
The invention discloses a low-density parity check code-based (LDPC) relay cooperative transmission method. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, performing LDPC encode processing on a source node; secondly, performing BPSK modulation processing on the source node and transmitting the result to a relay node and a destination node, namely, a base station; thirdly, decoding the relay node; fourthly, performing joint encoding processing on the relay node and correspondingly acquiring a plurality of joint encoding sequences and a plurality of corresponding check bit sequences; fifthly, performing joint modulation processing on the relay node and transmitting a plurality of check bit modulation sequences acquired by the joint modulation to the destination node; and finally, performing joint decoding processing on the destination node. The transmission method has the advantages of improving the performance of a receiving end and effectively solving the actual problems of low relay forwarding efficiency, high resource consumption and the like in the traditional wireless communication, along with novel design, simple implementation and good using effect.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
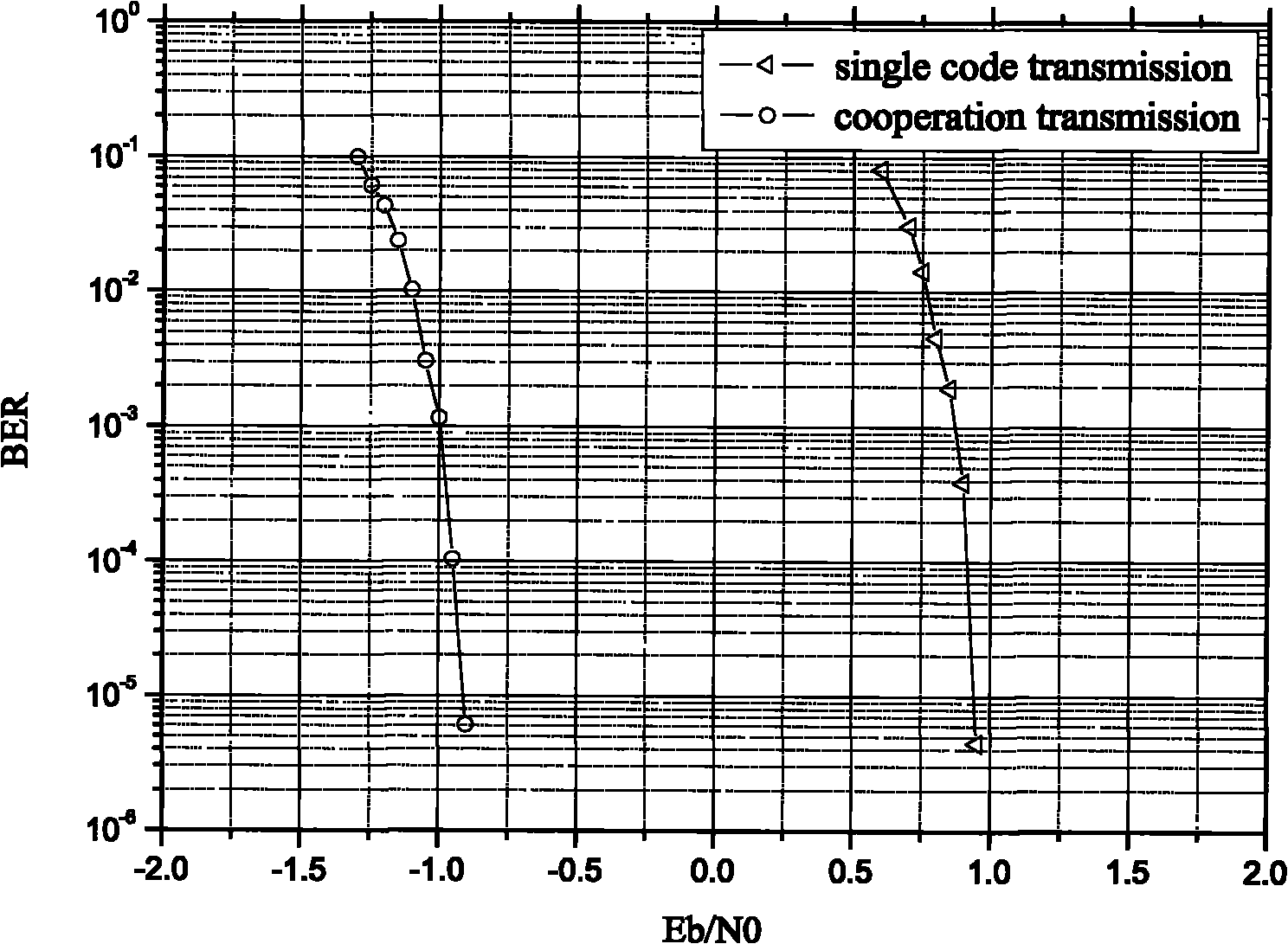
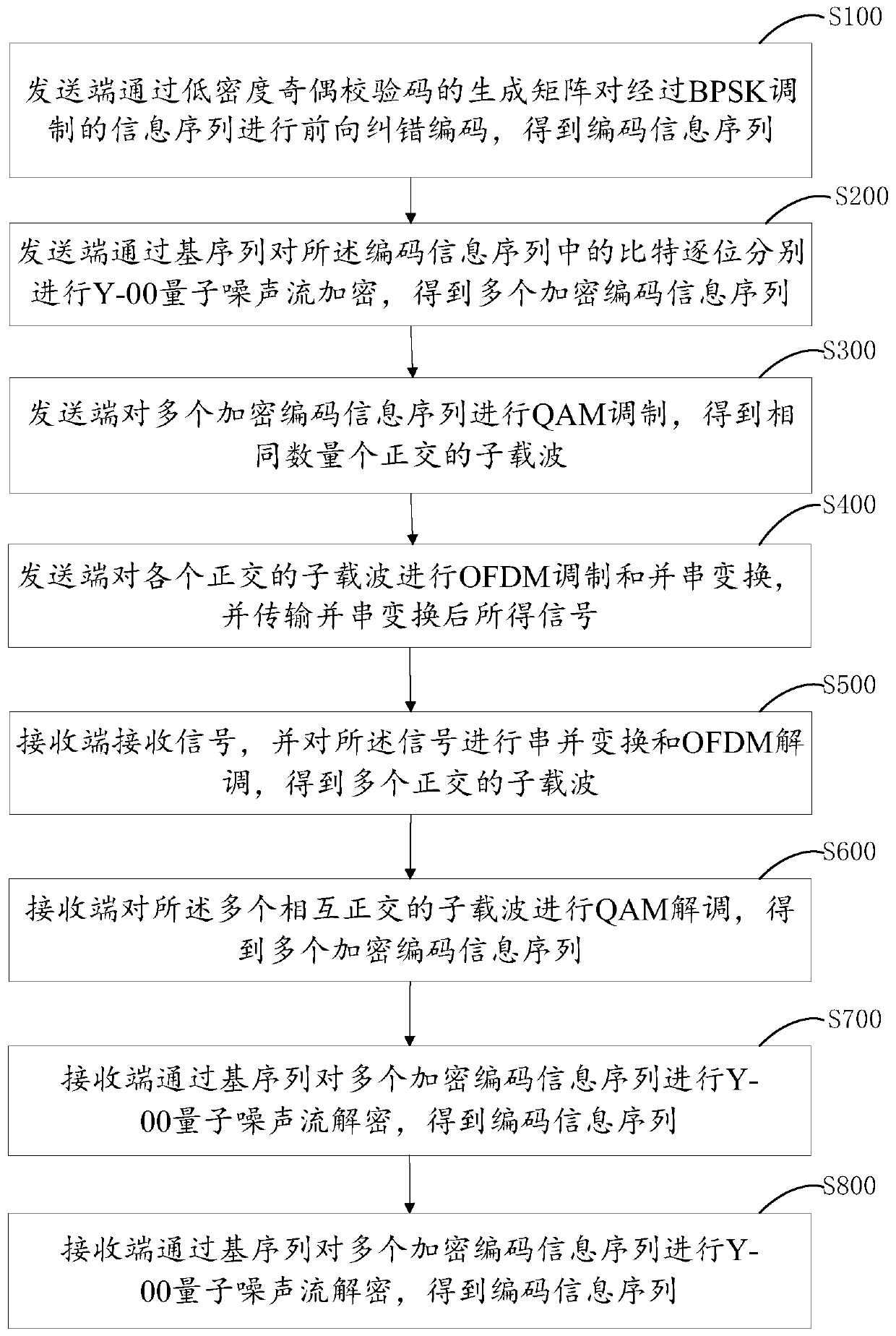
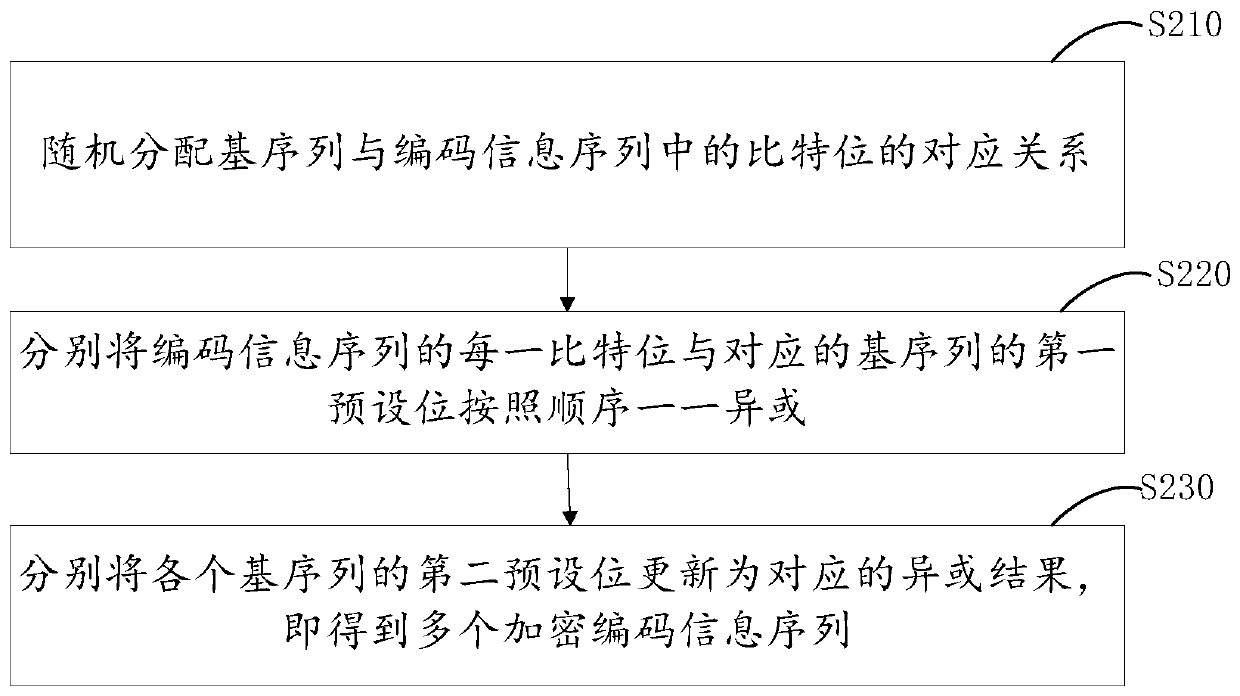
Y-00 quantum noise stream encryption transmission method with low bit error rate
ActiveCN111342958AReduce energy consumptionReduce bit error rateKey distribution for secure communicationError preventionQam modulationCarrier signal
The invention provides a Y-00 quantum noise stream encryption transmission method with a low bit error rate. The method comprises the steps that a transmitting end carries out the forward error correction coding of an information sequence modulated by BPSK through a generation matrix of a low-density parity check code, and obtains a coded information sequence; the sending end performs Y-00 encryption on bits in the coded information sequence bit by bit through the base sequence to obtain a plurality of encrypted coded information sequences; the sending end performs QAM modulation on the plurality of encrypted coded information sequences; the sending end performs OFDM modulation and parallel-serial conversion on each orthogonal subcarrier and transmits the orthogonal subcarriers; a receiving end receives the signals, and performs serial-parallel conversion and OFDM demodulation; the receiving end demodulates the plurality of orthogonal subcarriers QAM to obtain a plurality of encryptedcoded information sequences; the receiving end performs Y-00 decryption on the plurality of encrypted coded information sequences through the base sequence to obtain an information sequence subjectedto BPSK modulation; and the receiving end performs iterative computation through an LDPC FEC decoder to obtain an information sequence to be transmitted.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Distributed type combined information source-channel superposition coding and combined decoding method
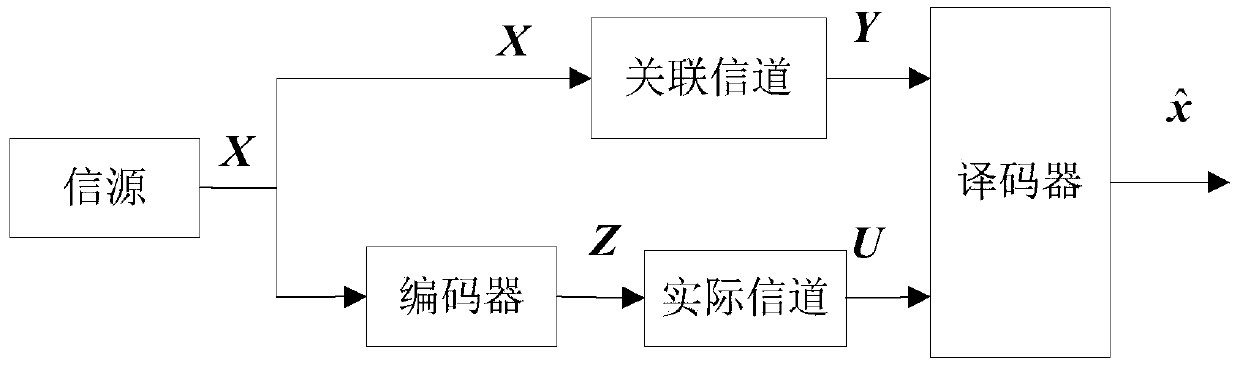
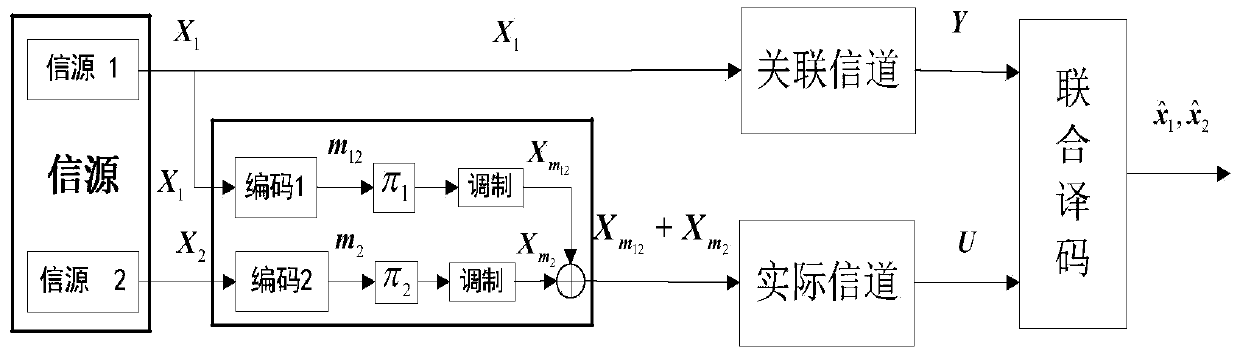
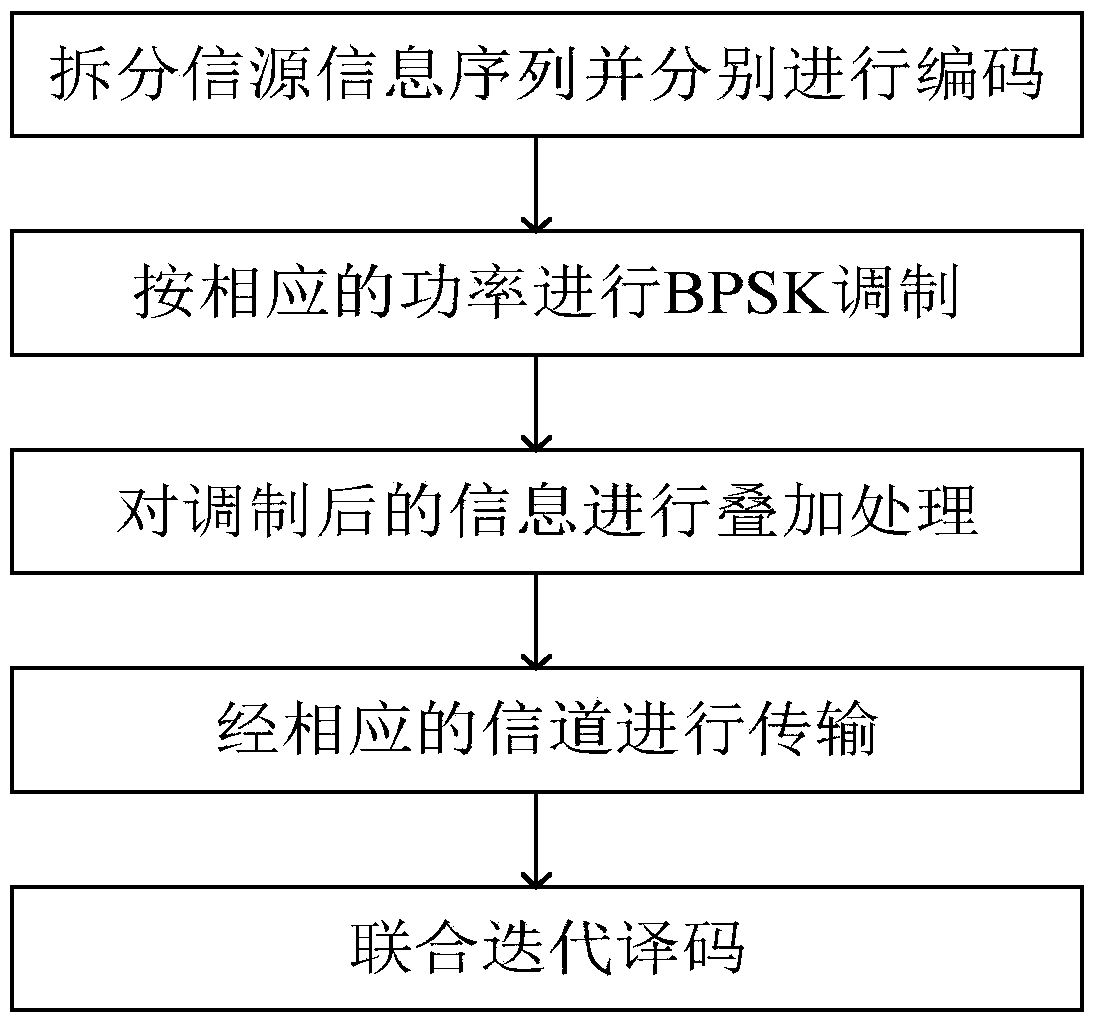
ActiveCN104079380AEasy to implementReduce complexityError preventionSuperposition codingBpsk modulation
The invention discloses a distributed type combined information source-channel superposition coding and combined decoding method. The method mainly solves the problem that the combined decoding performance is poor under the situation that an associated channel and an actual channel are not matched in existing related source coding. The method comprises the implementation steps that (1), a sending end codes a first information source information sequence and a second information source information sequence generated by information source information, and interleaving processing is carried out on coded codons; (2), BPSK modulation and superposition processing are carried out on the two parts of codons generated after the interleaving processing according to the corresponding power; (3), the signals generated after the superposition processing are transmitted through the actual channel, and the first information source information sequence is transmitted through the associated channel; (4), a decoding end carries out iteration processing on the received information in the mode that soft information is transmitted between two decoders until more accurate information source information is decoded out. The distributed type combined information source-channel superposition coding and combined decoding method can effectively restrain error spreading and improve the error rate performance, thereby being more suitable for wireless channel scenes with large channel random fluctuation.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Chaotic hybrid spread spectrum secure underwater acoustic communication method
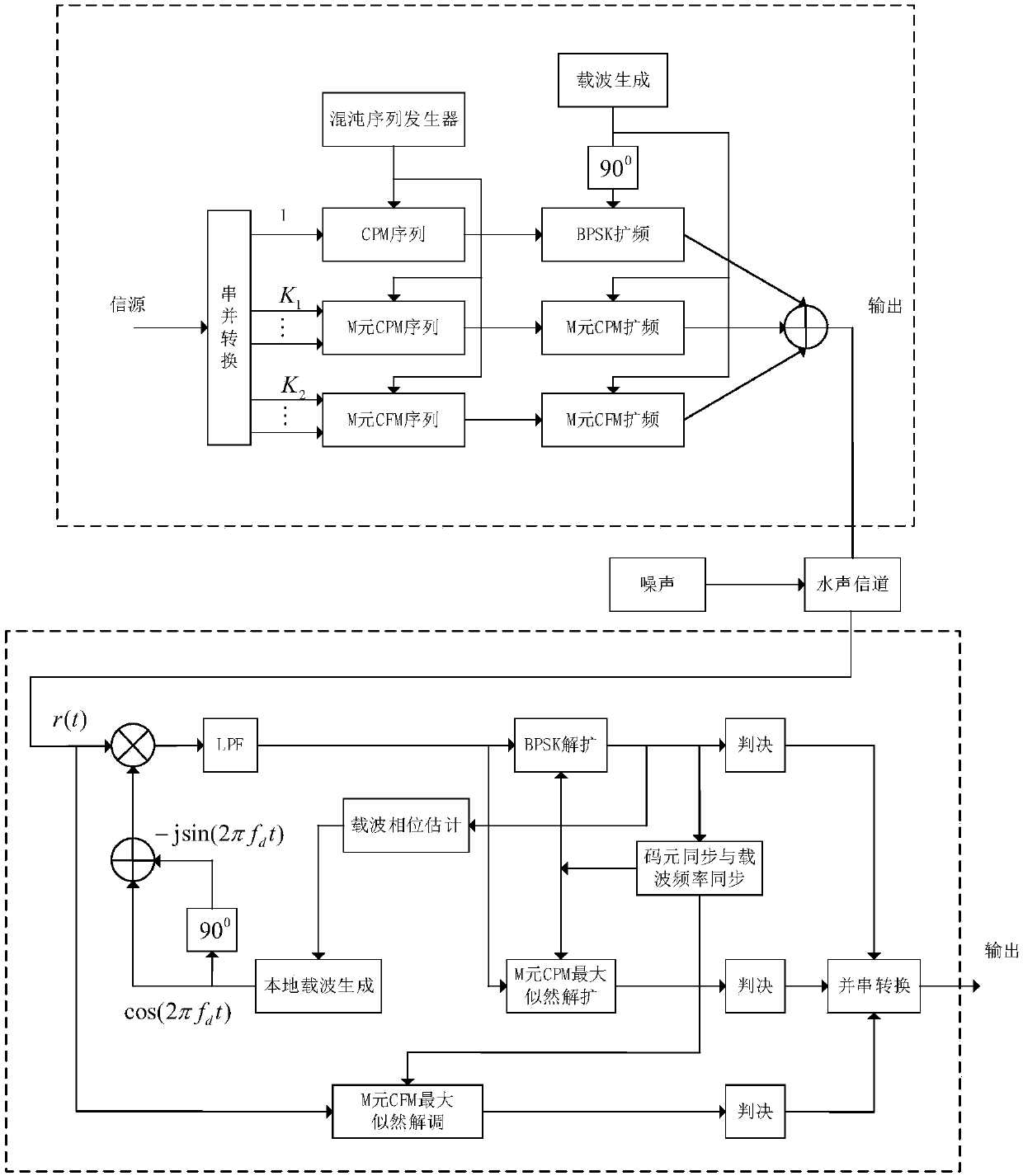
ActiveCN110266344AReduce distractionsGuaranteed Bit Error Rate PerformanceModulated-carrier systemsSecuring communication by chaotic signalsFrequency modulationDigital signal
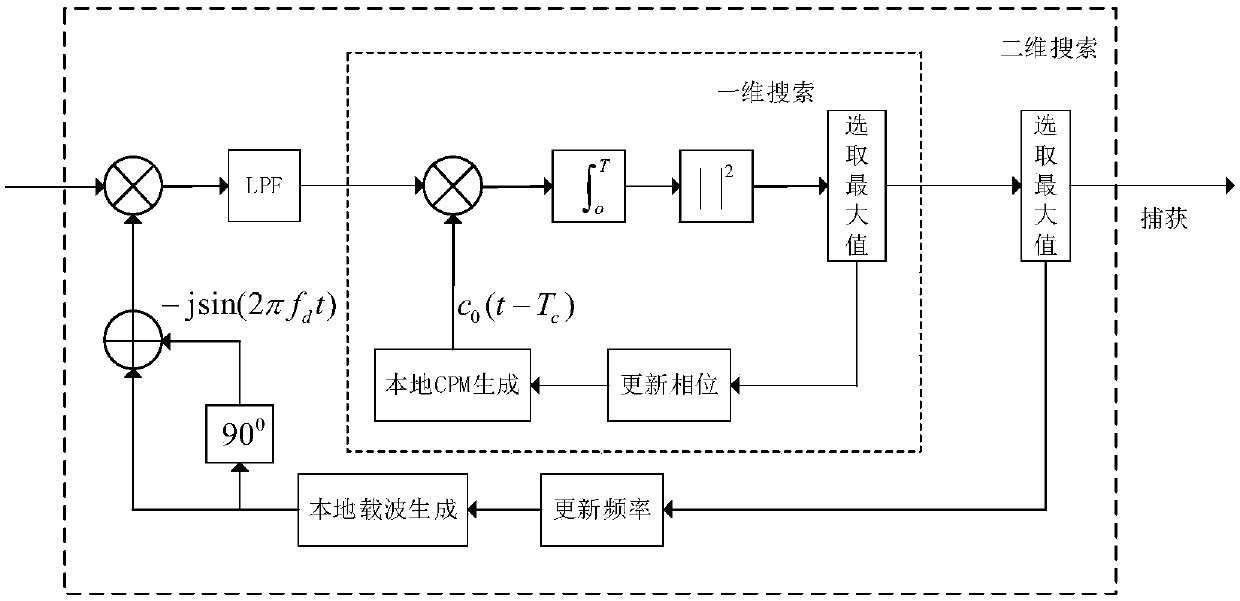
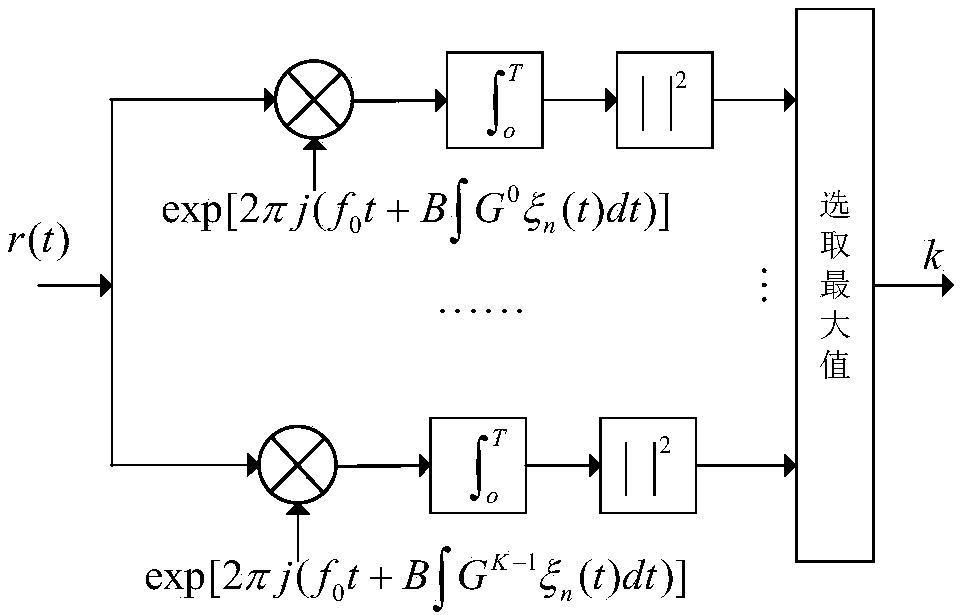
The invention discloses a chaotic hybrid spread spectrum secure underwater acoustic communication method. The method comprises the following steps: 1) a transmitting end uniformly groups a binary sequence sent by an information source, each group is divided into three blocks, the first block is subjected to BPSK modulation and Gray mapping, the second block is subjected to M-element chaotic phase modulation CPM spread spectrum sequence mapping, and the third block is modulated into a chaotic frequency modulation spread spectrum CFM signal; mixing and modulating the output three types of orthogonal signals to obtain a chaotic mixed spread spectrum CHSS signal to be transmitted, and converting the CHSS signal into an analog signal for transmission; 2) converting the received underwater acoustic analog signal into a digital signal by the receiving end, using an in-phase branch BPSK spread spectrum signal in chaotic phase modulation spread spectrum as a pilot signal, and performing time-frequency two-dimensional search on the signal by using the spread spectrum gain of the chaotic phase modulation spread spectrum code to complete time-frequency synchronization; and demodulating the signal after time-frequency synchronization, adopting an incoherent maximum likelihood demodulation algorithm for M-element CPM and CFM spread spectrum, and adopting a coherent demodulation algorithm for BPSK to complete M-element despreading and coherent demodulation, thereby obtaining a binary sequence.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com