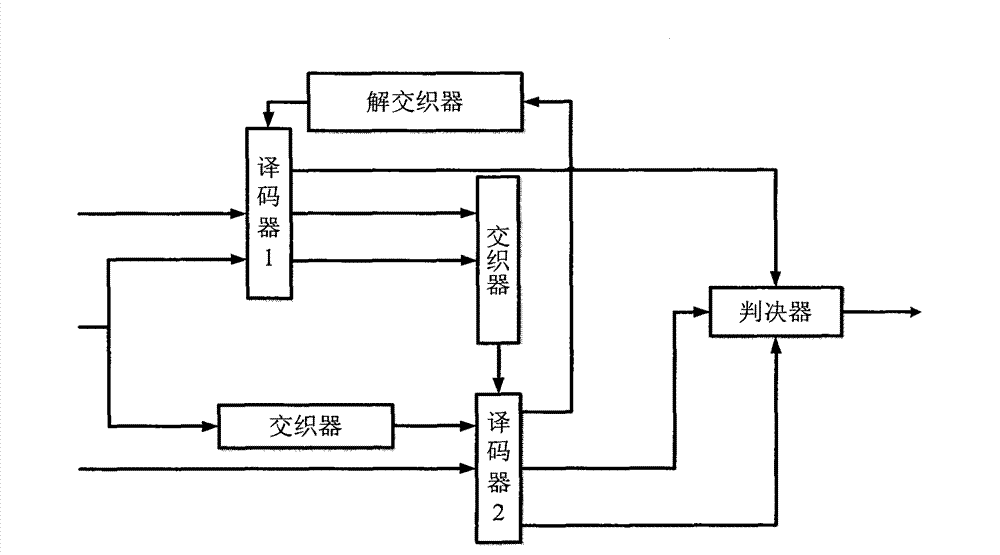
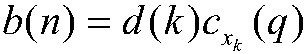Patents
Literature
293 results about "Qpsk modulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
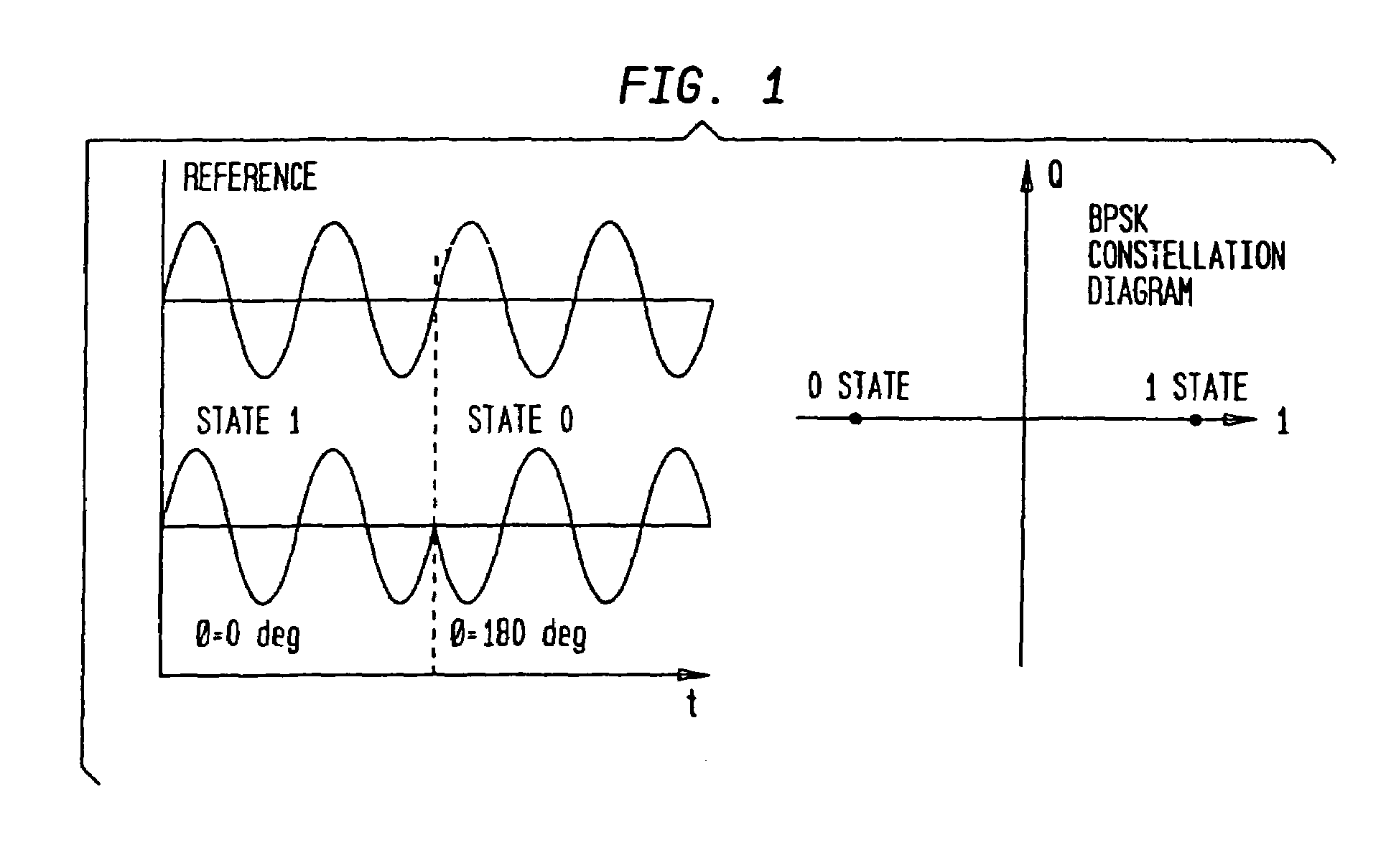
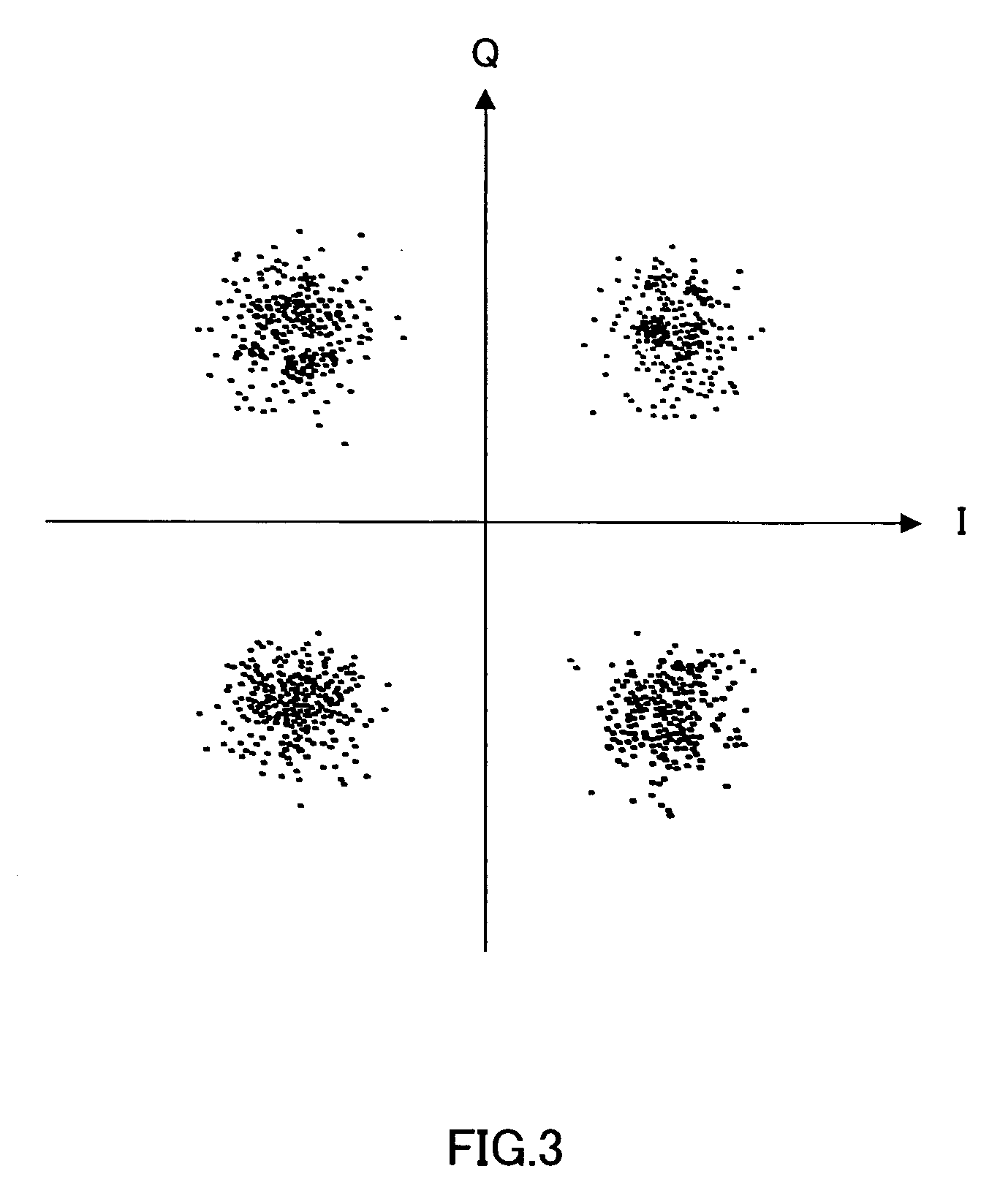
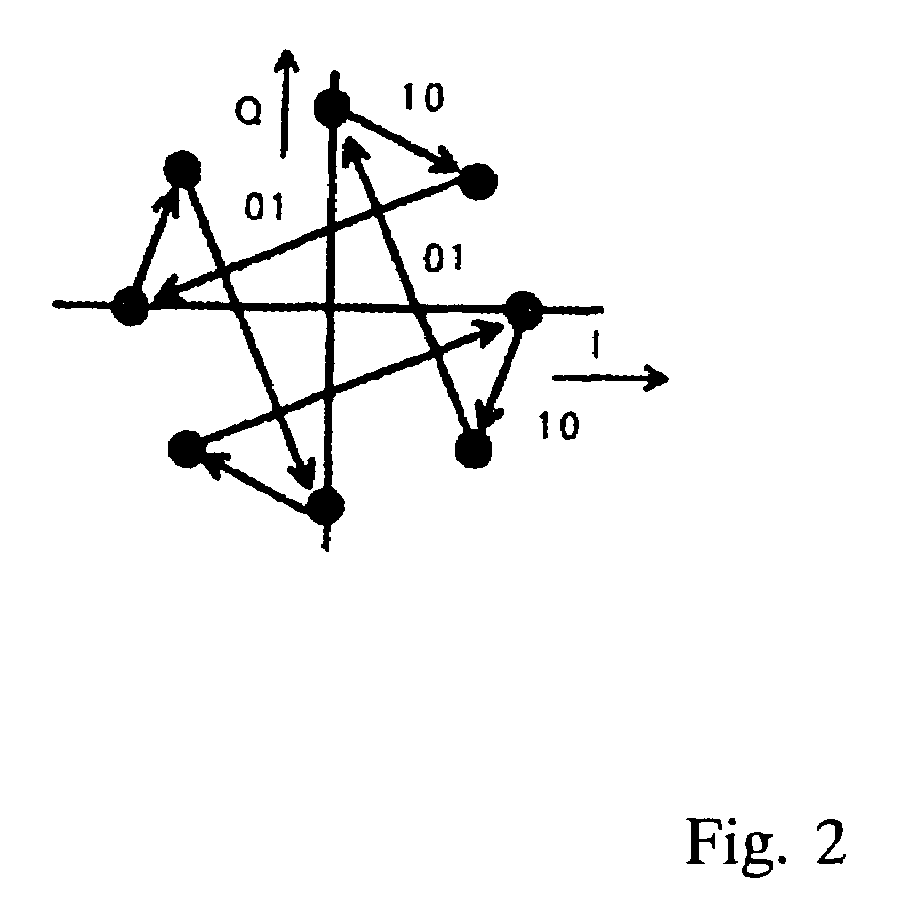
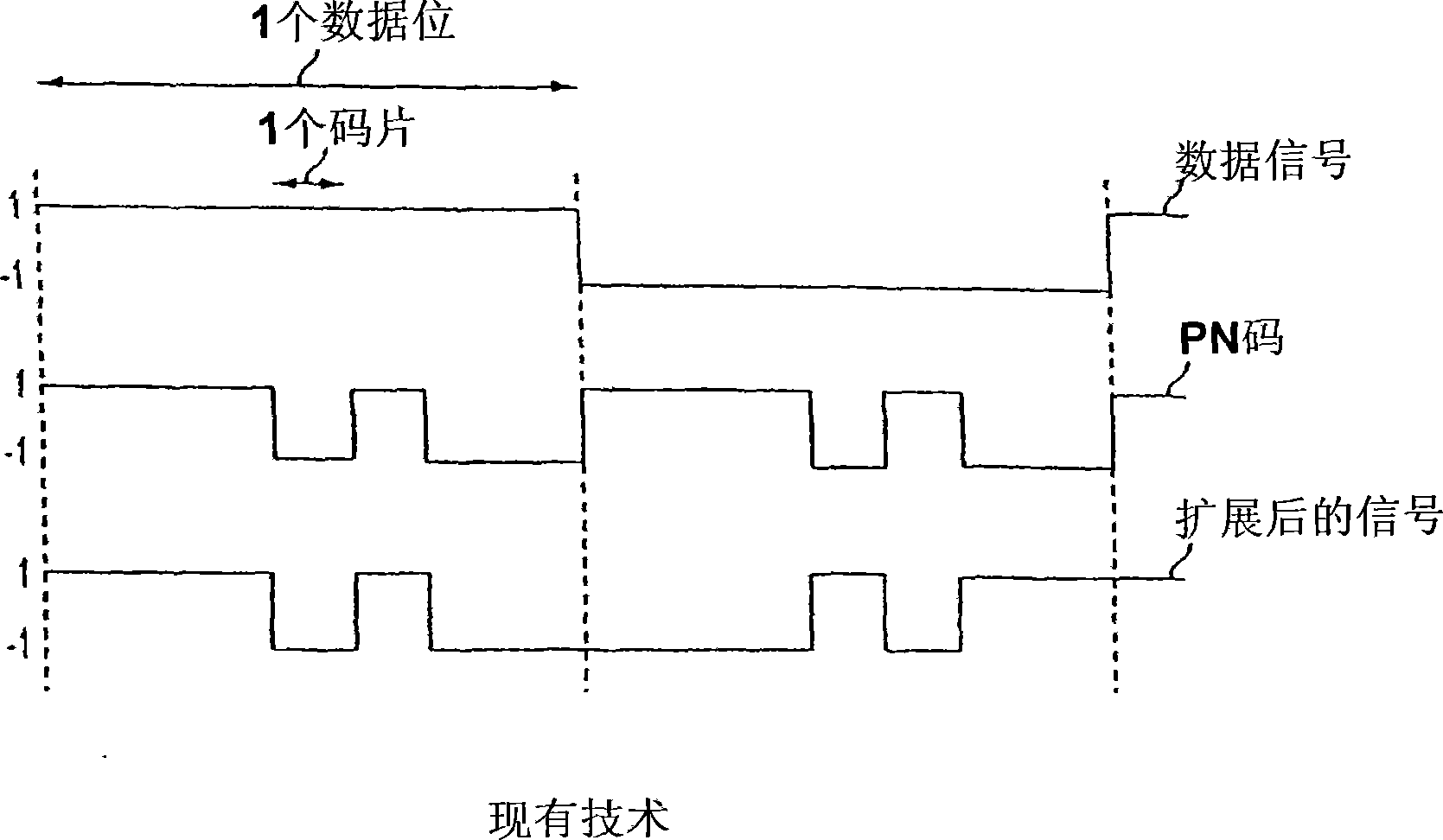
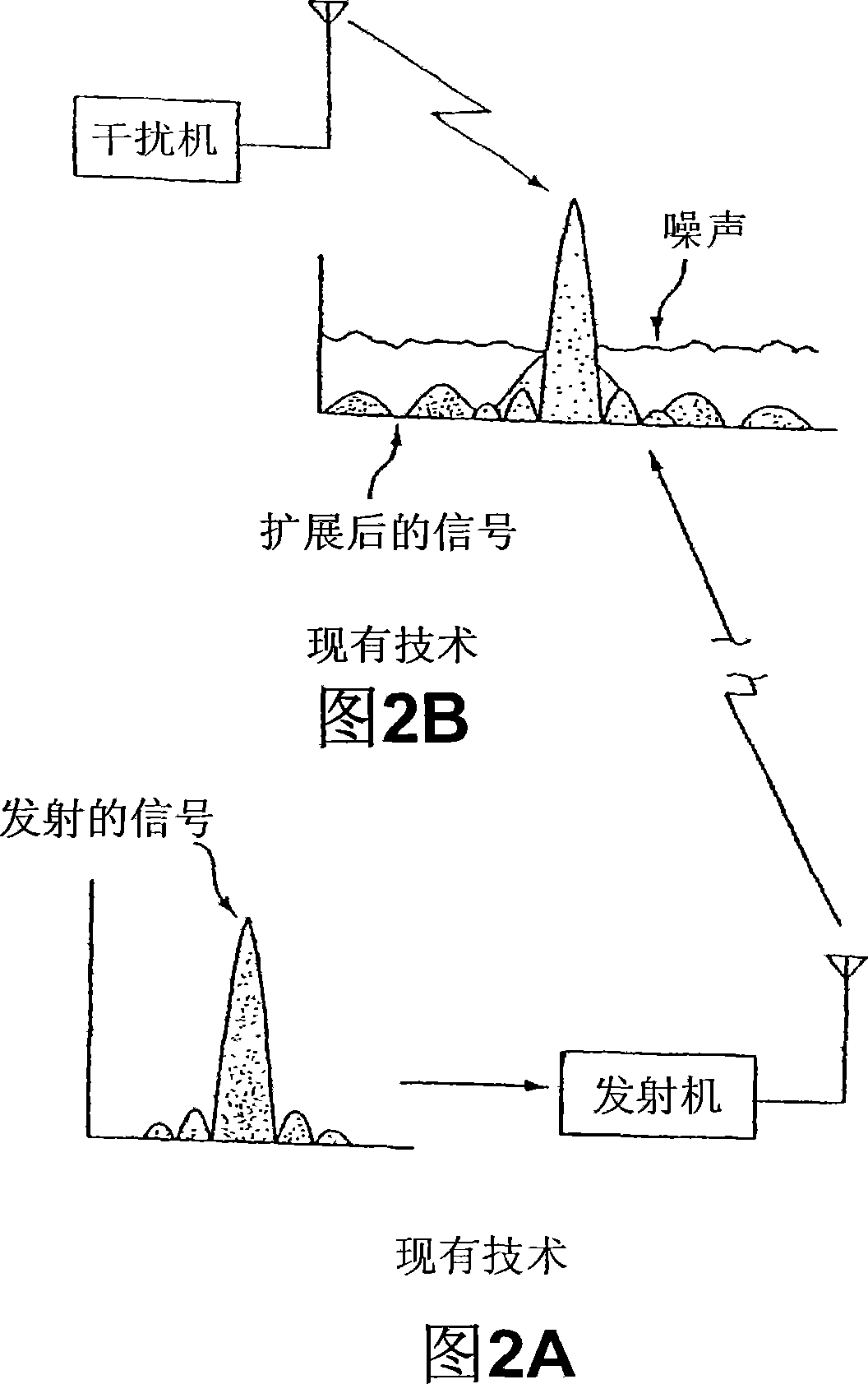
Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK) QPSK is a form of phase modulation technique, in which two information bits (combined as one symbol) are modulated at once, selecting one of the four possible carrier phase shift states.
FMOD transceivers including continuous and burst operated TDMA, FDMA, spread spectrum CDMA, WCDMA and CSMA
InactiveUS6928101B2Improve performanceLow costAsymmetric modulation circuitsPhase-modulated carrier systemsModem deviceFrequency spectrum
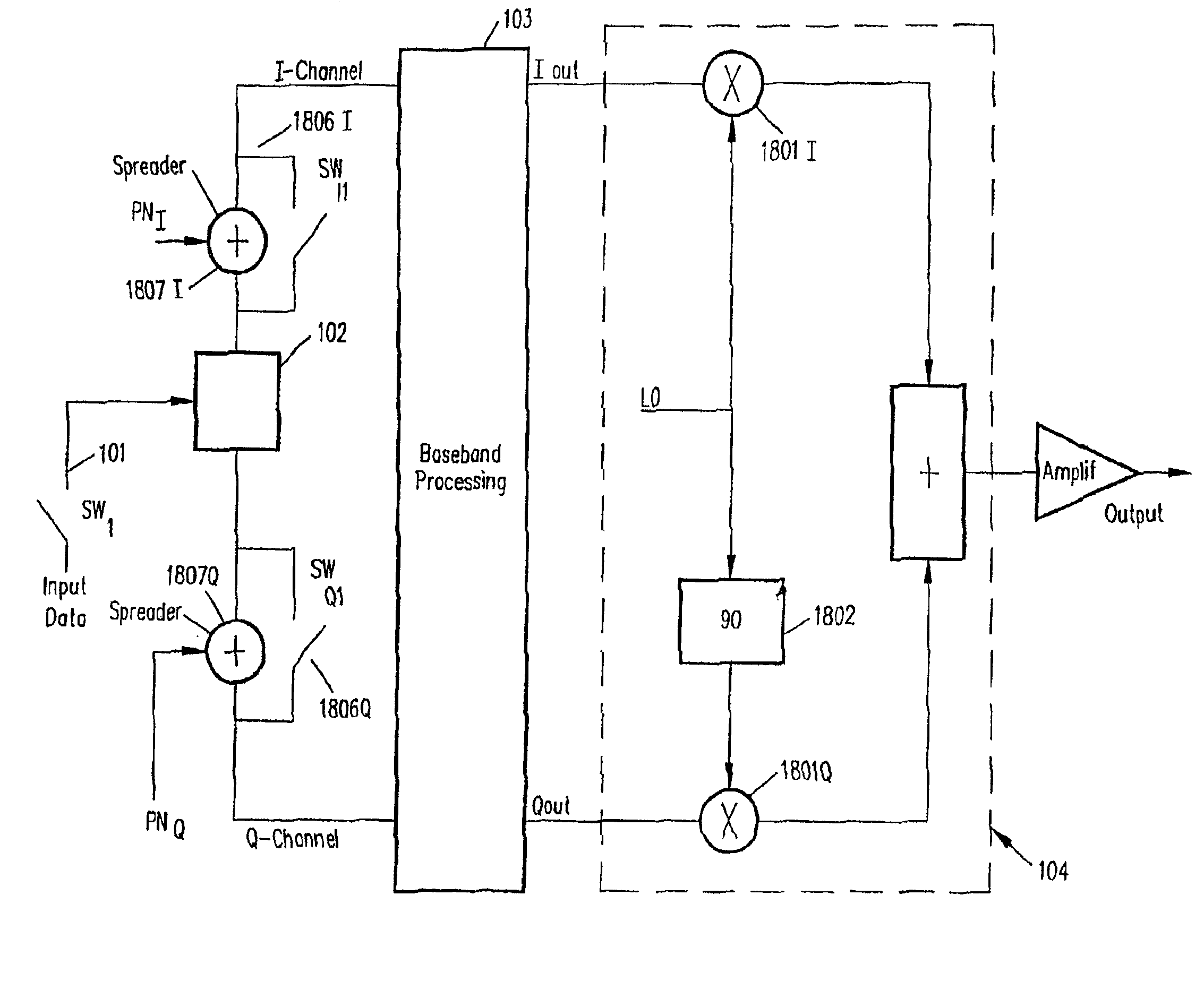
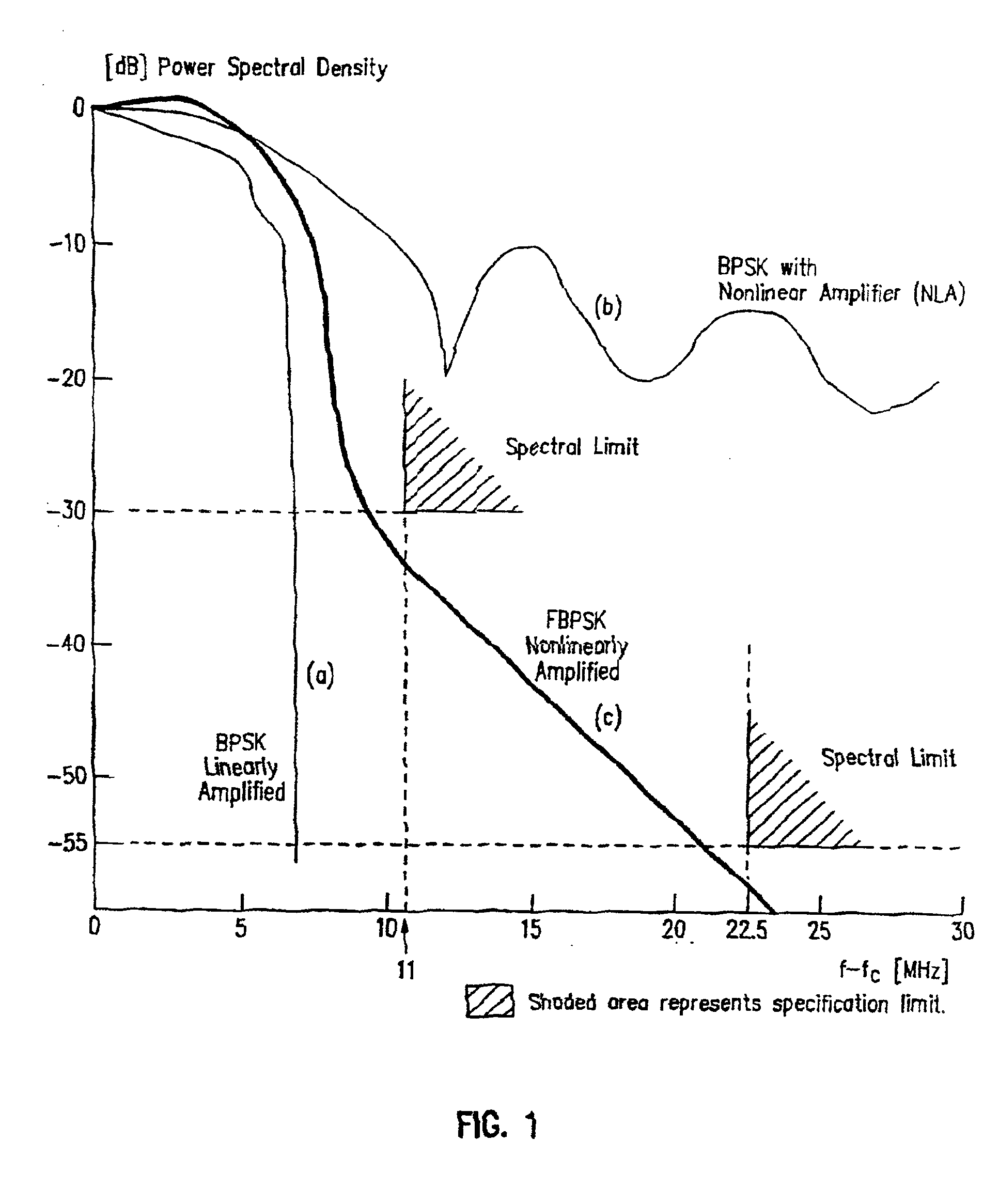
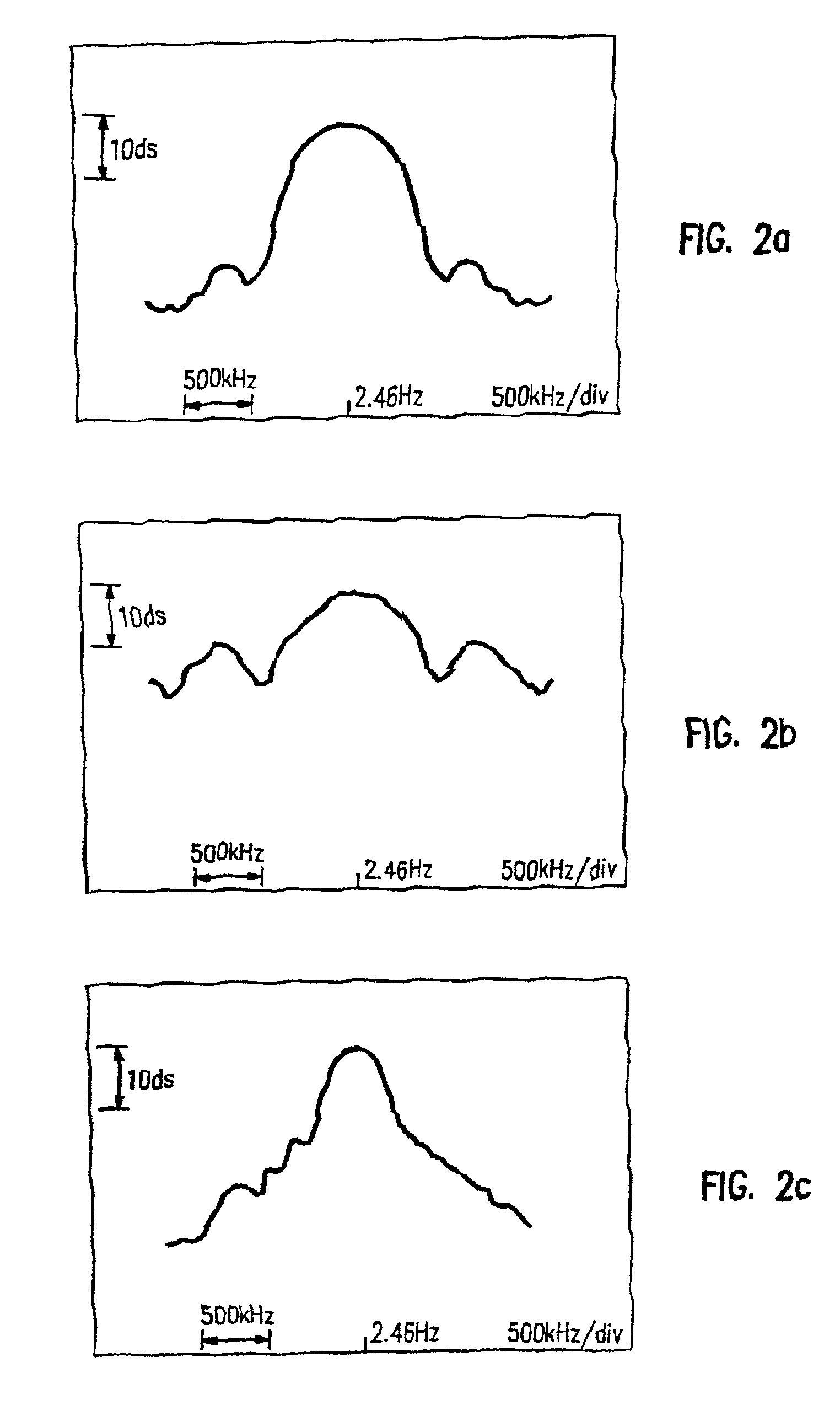
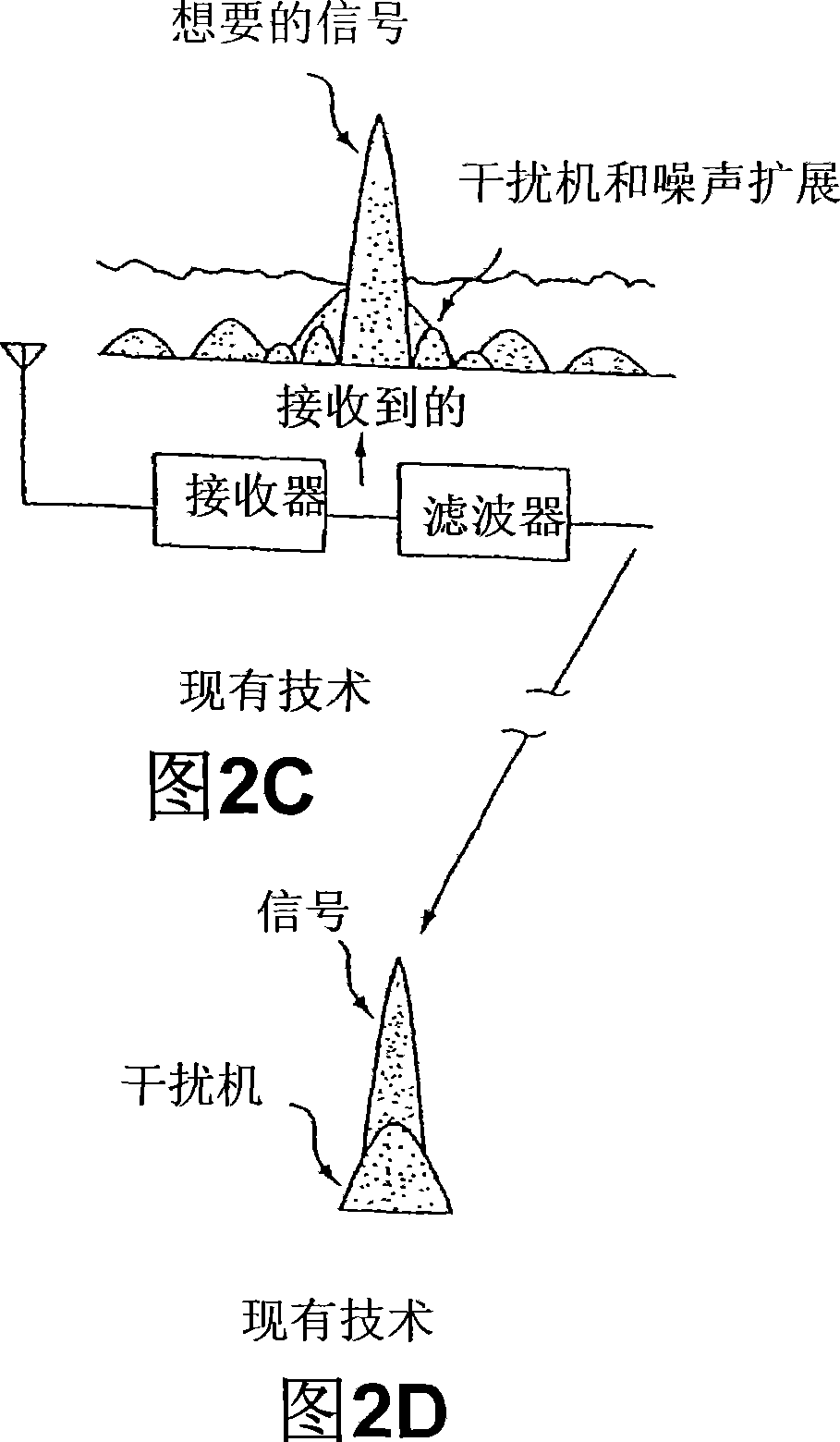
Binary and Quadrature Feher's Modulation (F-Modulation, or FMOD) Transmitter-Receiver systems and circuits exhibit reduced envelope fluctuation and peak radiation, and increased efficiency. A subclass of these systems has a constant envelope. They advantageously provide lower power operation with improved performance including robust BER performance, and compatibility with both linearly and nonlinearly amplified narrow spectrum, and without disadvantages of conventional BPSK, DBPSK QPSK and pi / 4-QPSK. Feher's BPSK (FBPSK) is an improved efficiency transmitter which is compatible with conventional BPSK receivers. FBPSK modems are based on using quadrature structure where Q-channel data is inserted in quadrature with I-channel data for certain applications. The Q-channel data may be “offset” from the I-channel data by an amount selectable between zero and a specified time. Further improvement in the spectrum is attained using correlation between I and Q channels. FBPSK modem is shown to meet the IEEE 802.11 specified spectral direct sequence spread spectrum mask (−30 dB point) for wireless LAN, and leads to an output power gain of 6.5 dB over conventional BPSK modems. The cross-coupled quadrature FMOD structure is also suitable for continuous mode and for burst operated TDMA, FDMA, CDMA, WCDMA and CSMA Frequency Modulation Quadrature AM (QAM), QPSK and offset QPSK, as well as pi / 4-shifted QPSK modems / processors. Reduced modulation index Gaussian FSK (GFSK), multilevel FM and cross-coupled Quadrature Amplitude Modulated (QAM) transmitters and combinations of these modulations and corresponding coherent demodulators are disclosed. Controlled rise and fall time descriptions of burst operated systems are included.
Owner:INTEL CORP
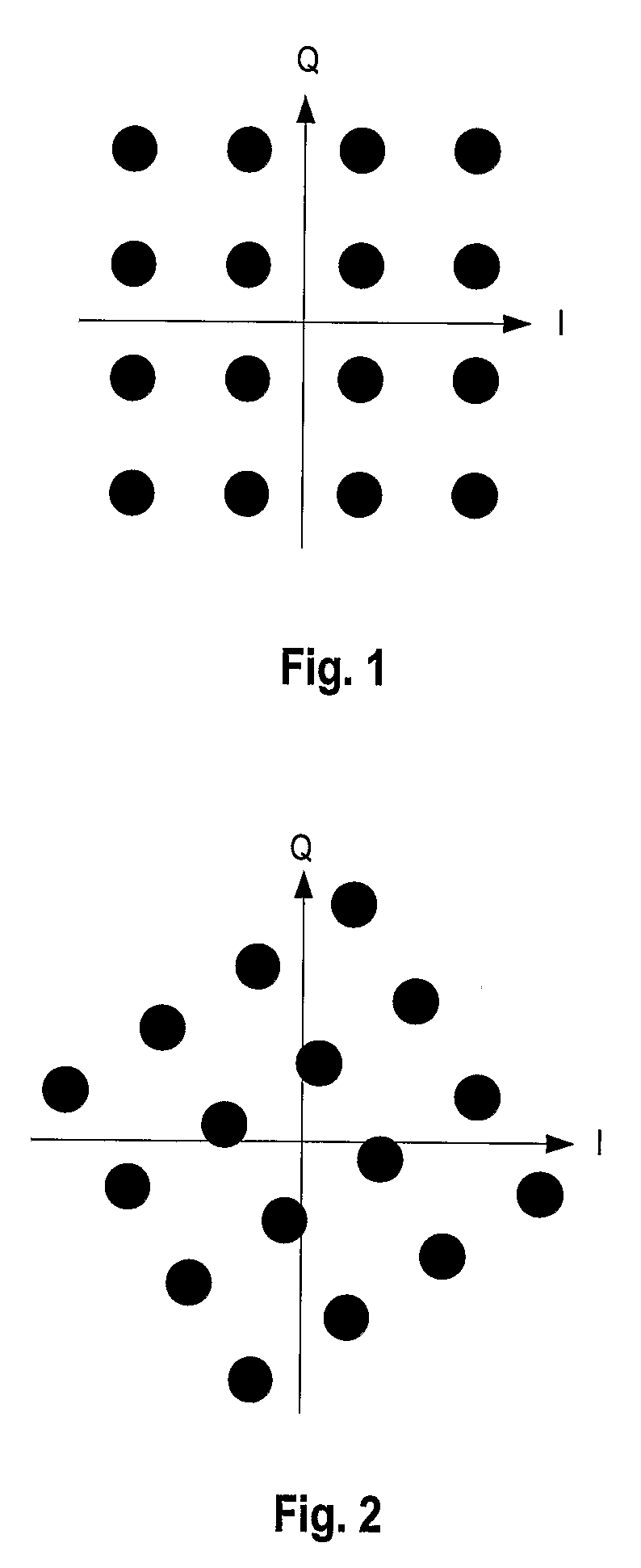
16 QAM modulator and method of 16 QAM modulation
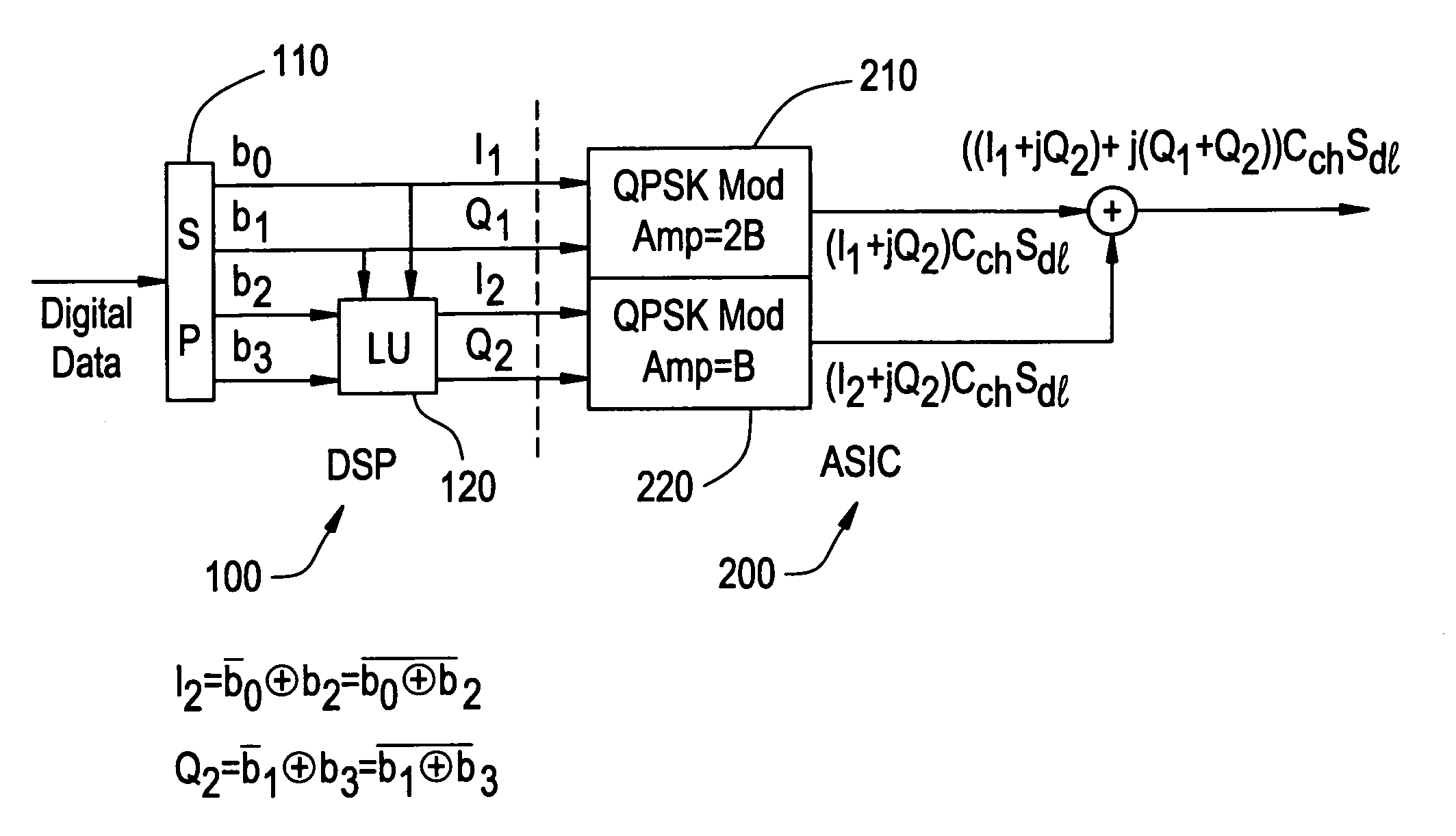
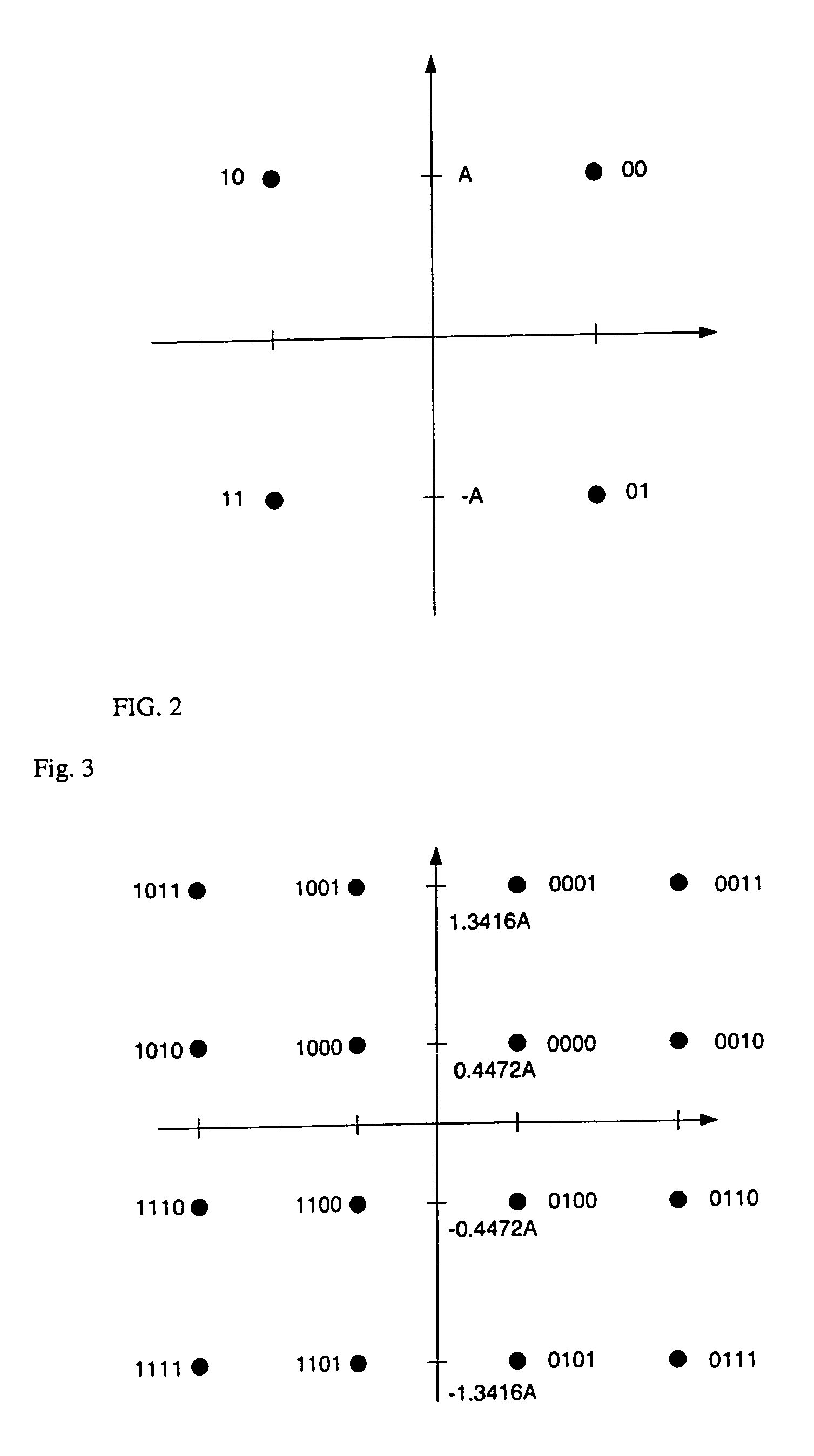
In one embodiment, the 16-quadrature amplitude modulation QAM modulator includes a logic operation device performing a logic operation on first-fourth bits of received data to generate first and second logic outputs. A first quadrature phase shift keying QPSK modulator receives the first and second bits of received data and generates a first QPSK signal. A second QPSK modulator receives the first and second logic outputs and generates a second QPSK signal. A combiner combines the first and second QPSK signals to generate a 16-QAM signal.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Communication quality estimation method, communication quality estimation apparatus, and communication system
ActiveUS7130587B2Accurate qualityHigh rateError prevention/detection by using return channelError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorCommunication qualityCommunications system
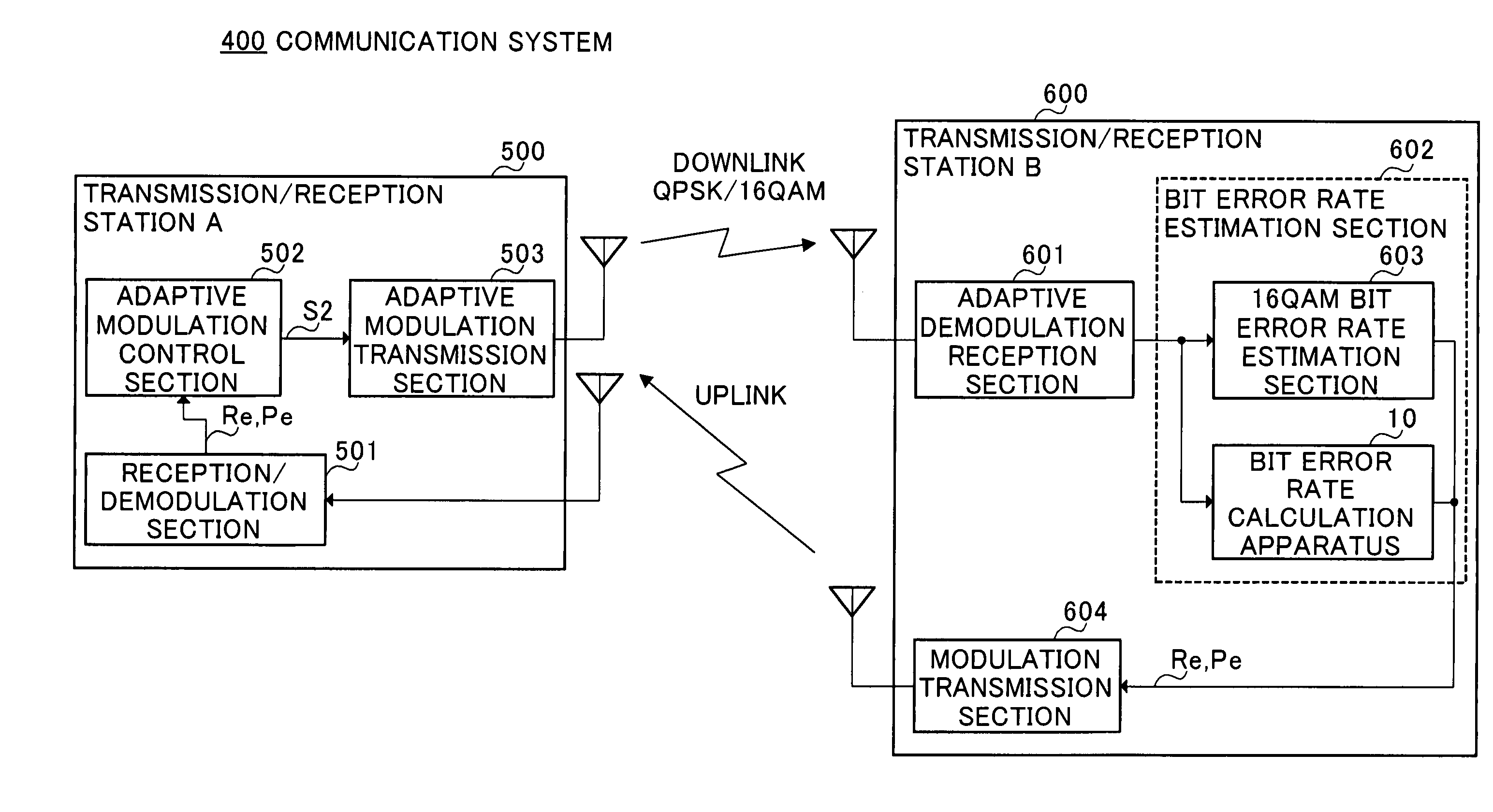
An average signal point amplitude detection section 15A determines an average position of I and Q components when a received QPSK modulated signal is demodulated and a threshold calculation section 15B determines threshold ths on an IQ plane based on the average signal point position of the received QPSK modulated signal and a theoretical distribution position on the IQ plane of signal points of a 16-value QAM signal. Then, a threshold decision section 14A makes a threshold-decision on the I and Q components of sequentially received QPSK modulated signals using this threshold ths and thereby calculates a simulated bit error rate of the 16-value QAM signal.
Owner:TELECOMM ADVANCEMENT ORG OF JAPAN +2
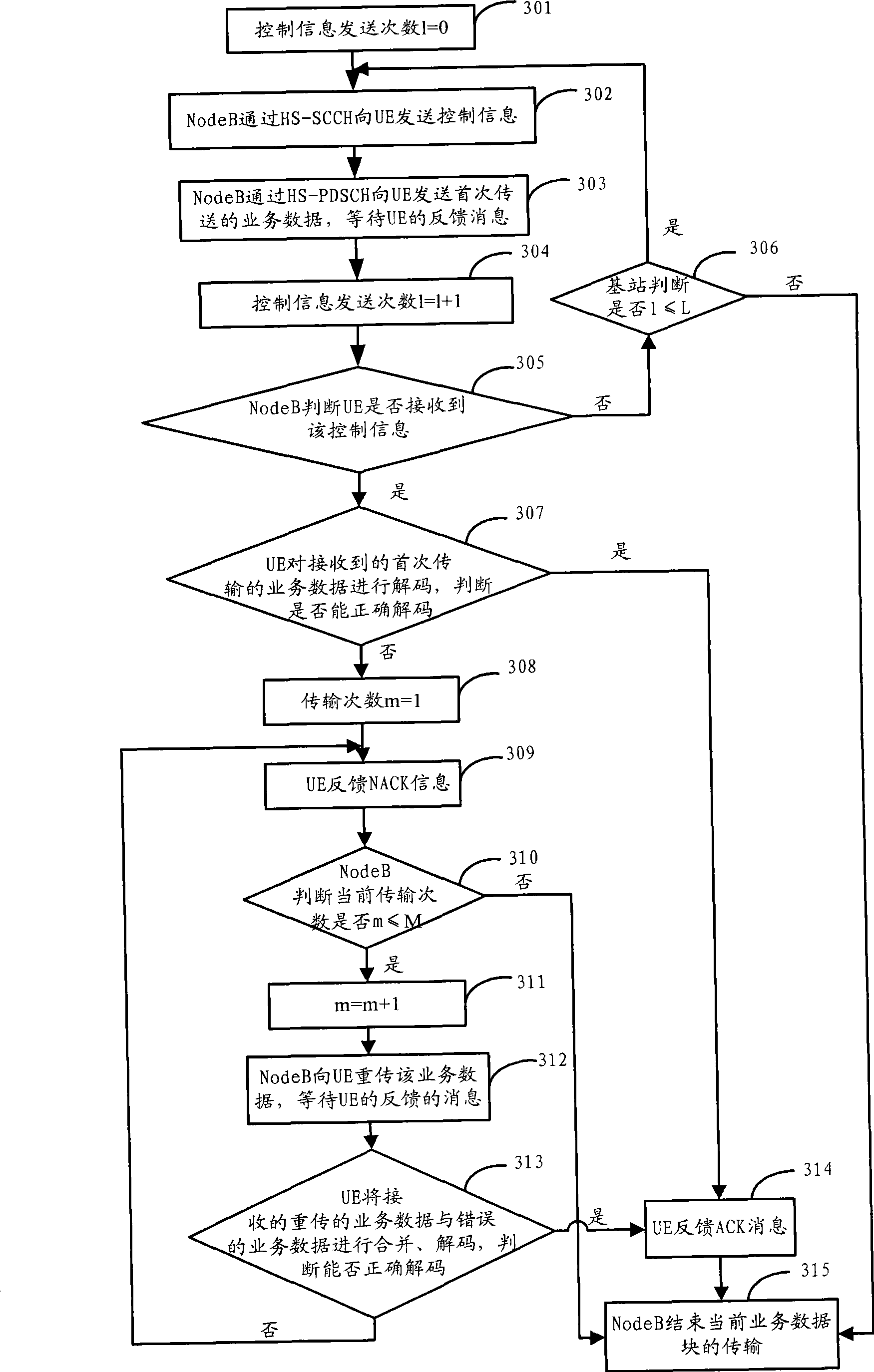
Method and apparatus for sending physics uplink control signal in TDD system
ActiveCN101227233ASolve highFulfil requirementsError preventionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTime domainSignal on
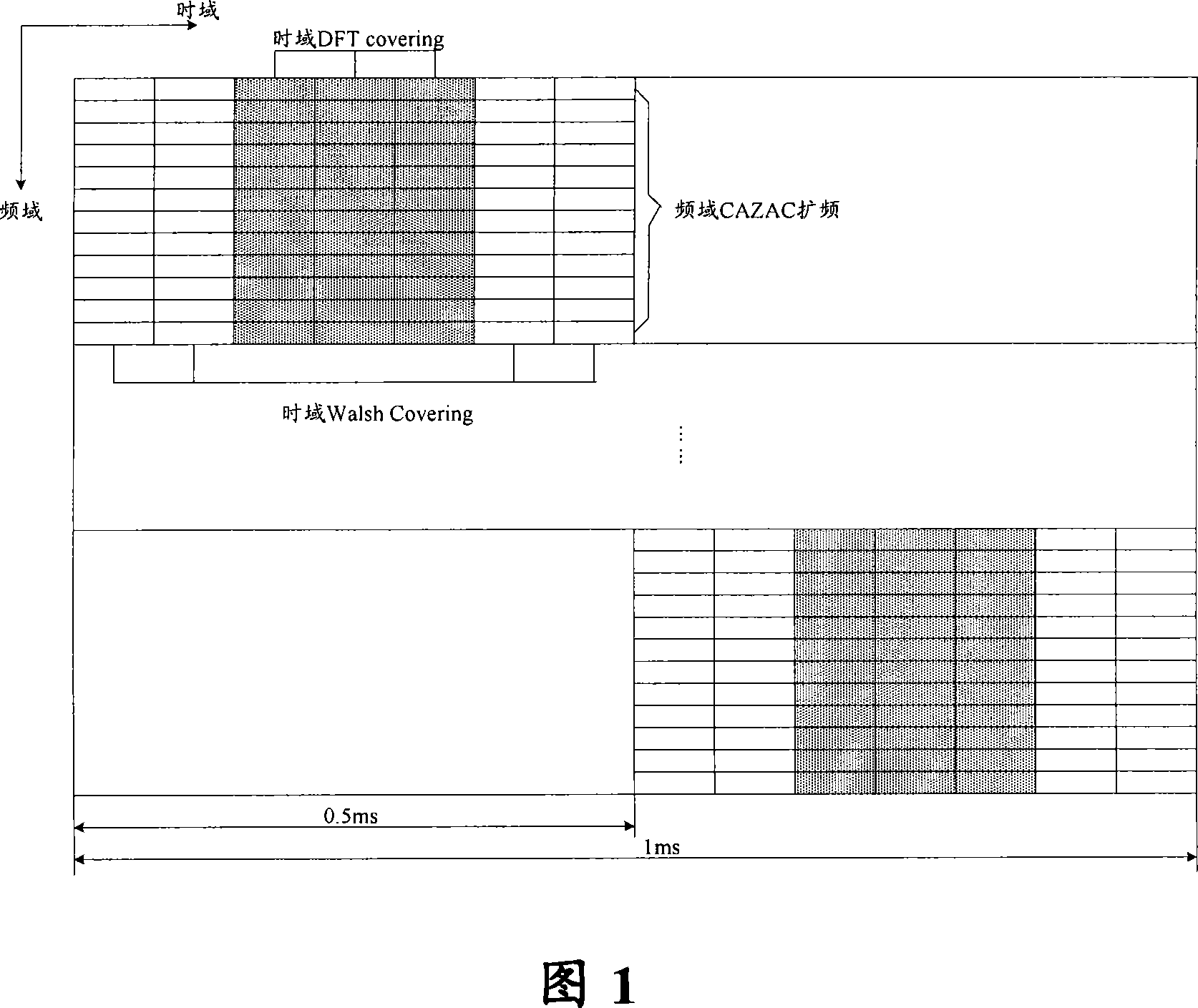
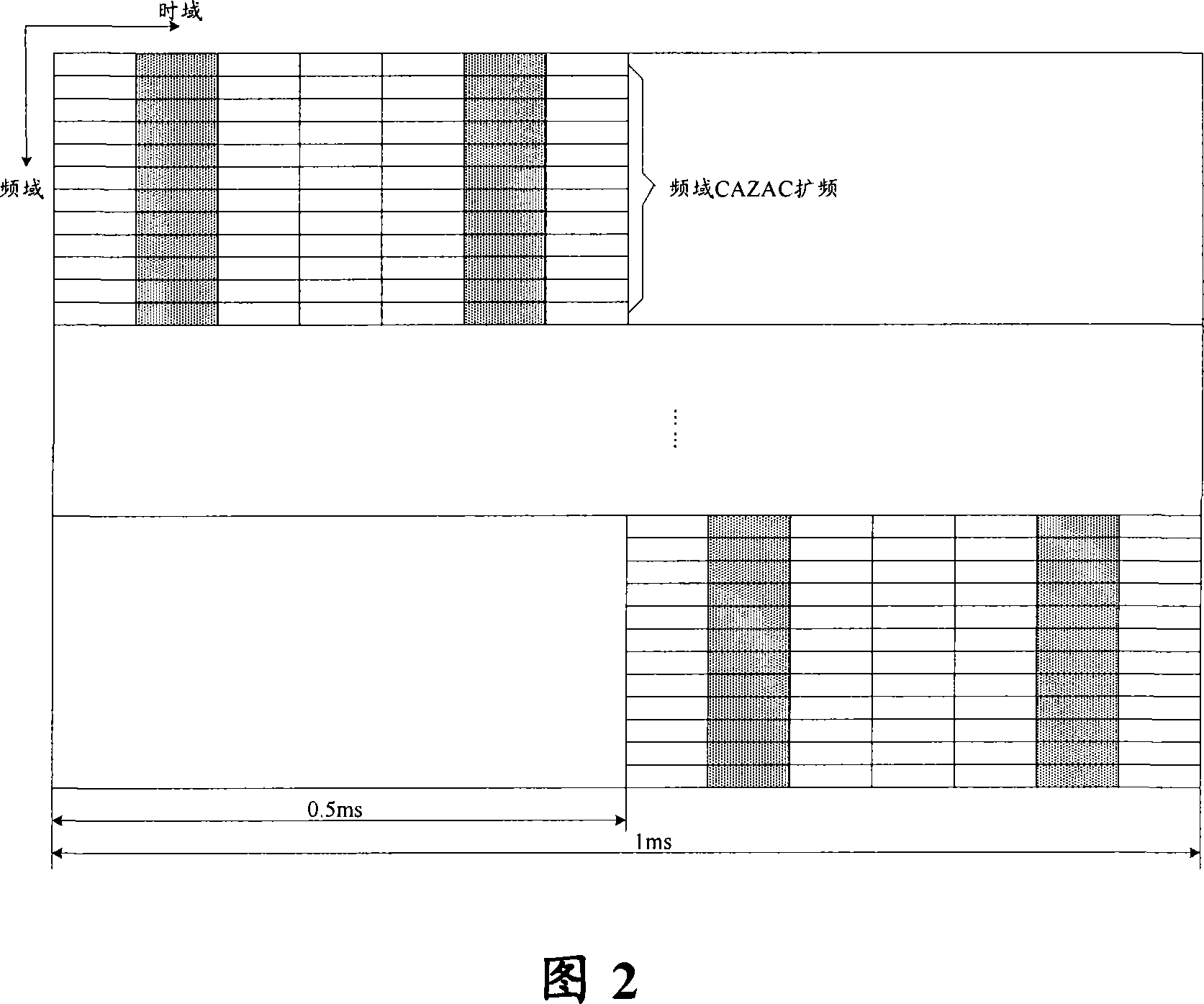
The invention provides a method and a device for sending physical uplink control signals in a time-division duplex system, the method comprises following steps: encoding the uplink control signals with a communication channel to obtain coded bits, modulating the coded bits with QPSK to obtain modulation symbols, transforming the modulation symbols with DFT to obtain symbols on a frequency domain,expanding the symbols on the frequency domain with time-domain through adopting a CAZAC root sequence to respectively obtain a first signal and a second signal which are sent on two time slots, mapping the first signal and the second signal on an information symbol which is corresponded with a PUCCH reference signal structure 2, and combining the information symbol and the reference signal into asignal which will be sent by a sub-frame. The invention can well satisfy the performance requirement and the covering requirement that a plurality of ACK / NACK can be sent on an uplink sub frame.
Owner:ZTE CORP
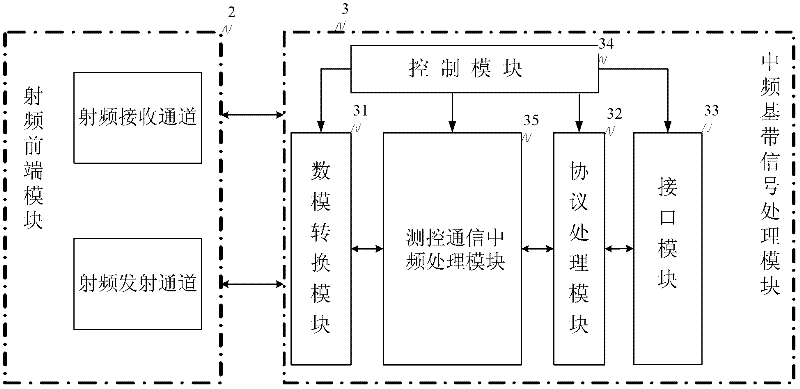
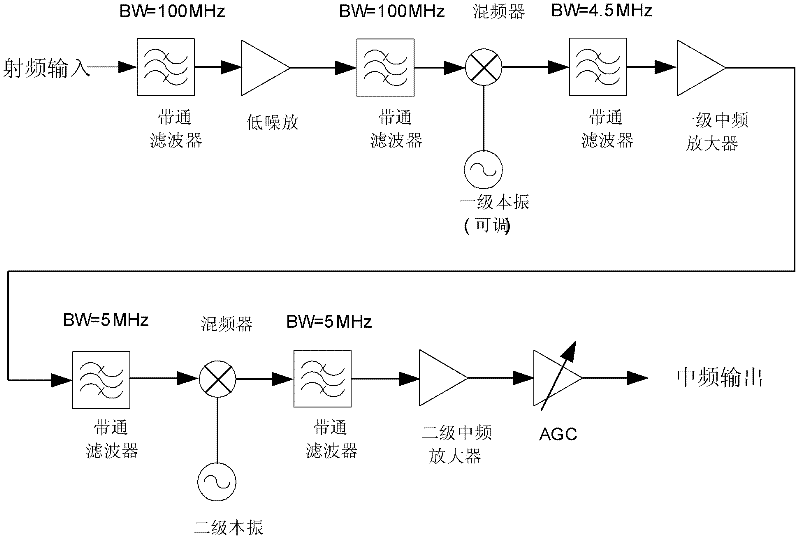
Micro/nano satellite measure and control communication integral transmitting and receiving system and realization method thereof
InactiveCN102333057AReduce the numberHighly integratedTransmission systemsPhase-modulated carrier systemsEngineeringNano satellite
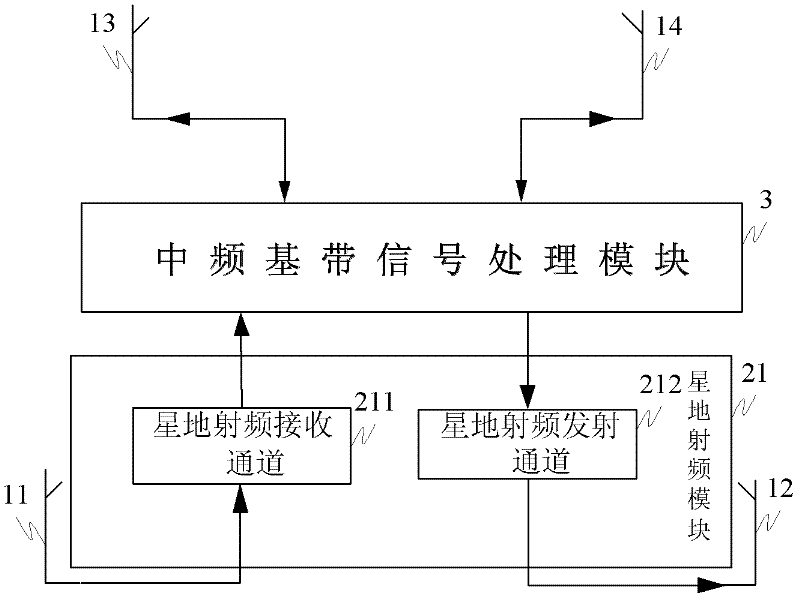
The invention discloses a micro / nano satellite measure and control communication integral transmitting and receiving system and a realization method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: 1) uplink signal processing: 11) receiving and processing radio-frequency signals to obtain analog intermediate-frequency signals; and 12) carrying out analog to digital conversion and digital underlocking on the analog intermediate-frequency signals and dividing into two paths of uplink digital intermediate-frequency signals, namely, one path of the signals is sent to a satellite-mounted computer by QPSK (quadrate phase shift keying) demodulation and uplink protocol processing so as to finish uplink data transmission, and the other path of the signals is subjected to the PM (phase modulation) demodulation to obtain side sound signals and PSK (phase shift keying) remote signals, and the PSK remote signals are subjected to BPSK (binary phase shift keying) demodulation to convert into a remote control command which is sent to the satellite-mounted computer so as to finish the remote control; and 2), downlink signal processing: 21), acquiring two paths of data from the satellite-mounted computer and a storage unit, namely, one path of data which is subjected to downlink protocol processing, BPSK modulation, combination with the side sound signals and downlink measure and control carrier PM modulation is combined with the other path of data which is subjected to the downlink protocol processing and the QPSK modulation to enter a satellite-ground radio-frequency emission channel; and 22) converting into radio-frequency signals to finish the remote measure and the downlink data transmission.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method and system for providing visually related content description to the physical layer
InactiveUS20080025196A1Network traffic/resource managementWireless network protocolsPhysical layerForward error correction
Aspects of a method and system for providing visually related content description to physical layer are provided. A MAC layer and / or a PHY layer in a wireless communication device may be controlled for processing at least one media object in an audiovisual scene based on metadata information that corresponds to the audiovisual scene. The metadata information may result from, for example, MPEG-4 encoding of the audiovisual scene. Each media object may be forward error corrected based on a determined priority level, such as foreground and background priorities, that results from the metadata information. In this regard, the number of bits utilized for protection and / or the RF modulated scheme may be selected in accordance with the priority level. The RF modulation may be, for example, QPSK modulation or 16 QAM modulation. The metadata information and the processed media objects may then be wireless communicated.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Phase Shift Keyed Modulation of Optical Signal Using Chirp Managed Laser
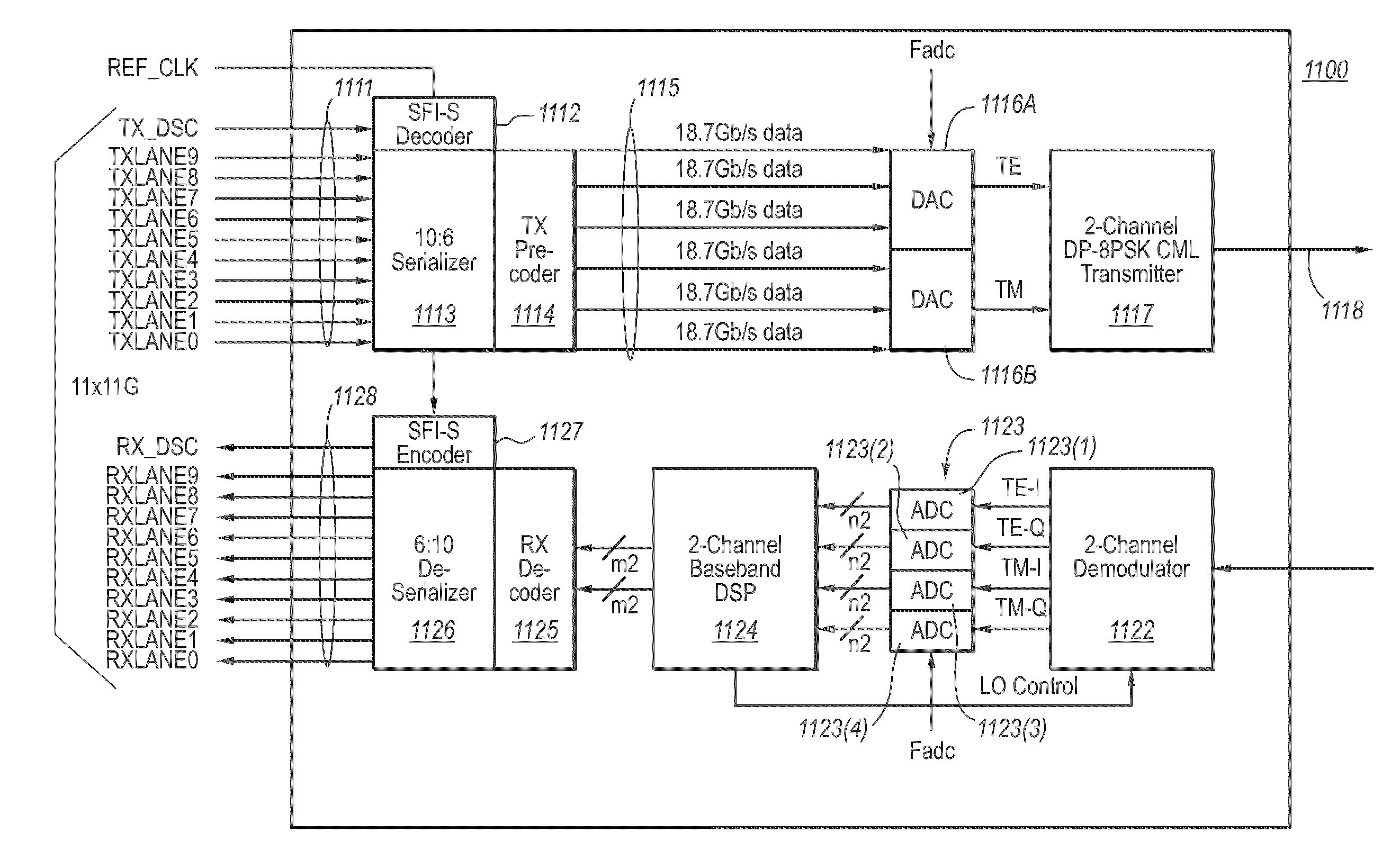
ActiveUS20100008679A1Reduce complexityMore manageable electrical bit rateElectromagnetic transmittersElectromagnetic receiversEngineeringAnalog-to-digital converter
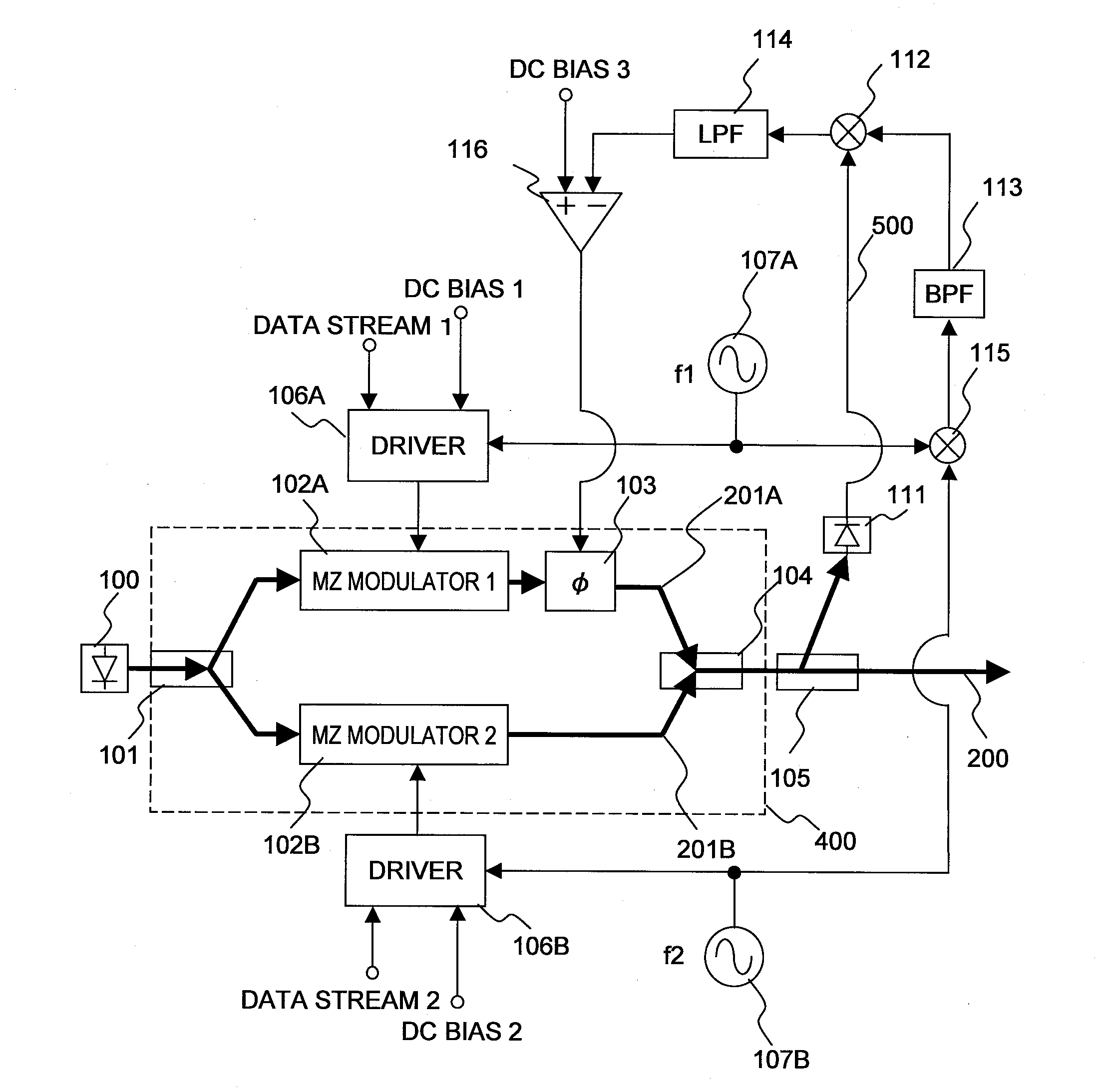
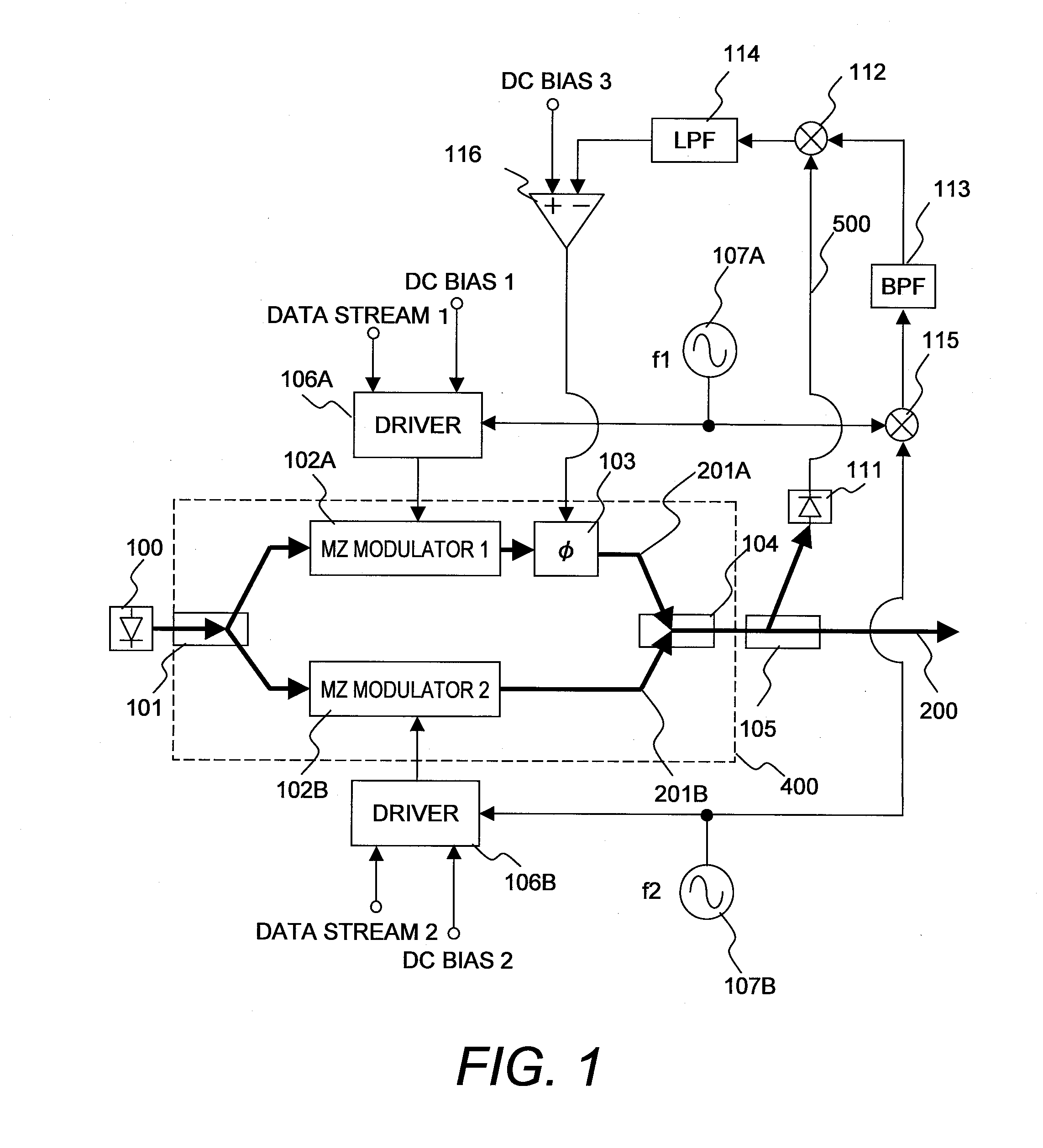
A high-speed optical transmitter comprises multiple digital lanes that are provided to a bank of digital-to-analog converters. The analog signals are then used to Phase Shift Keyed (PSK) modulation using a Chirp Managed Laser (CML)-based transmitter, and potentially using dual polarization. A corresponding optical receiver receives the sequence of optical signals at a demodulator. For each polarization, the demodulator includes a corresponding demodulation channel that is configured to demodulate that polarization component of the optical signal into one or more signal components. Each of these signal components is converted into a corresponding digital signal using a corresponding analog-to-digital converter. In the case of higher-order PSK modulation (e.g., 8PSK or higher), for each polarization, the analog converter has a lower sampling rate than for QPSK modulation.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Rf ID Tag Device
ActiveUS20090033462A1Maximize efficiencyElectromagnetic wave systemCircuit arrangementsResonanceBpsk modulation
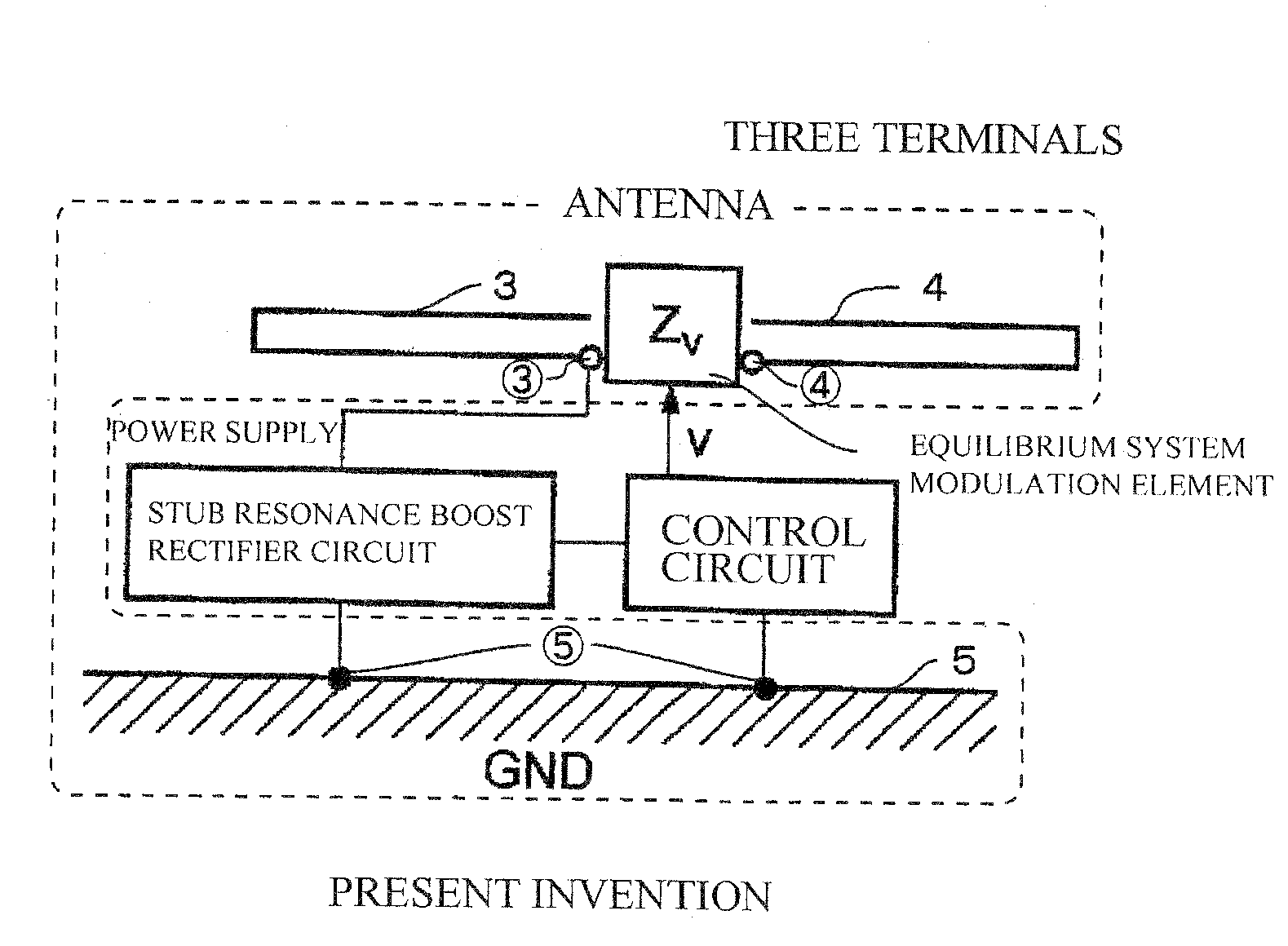
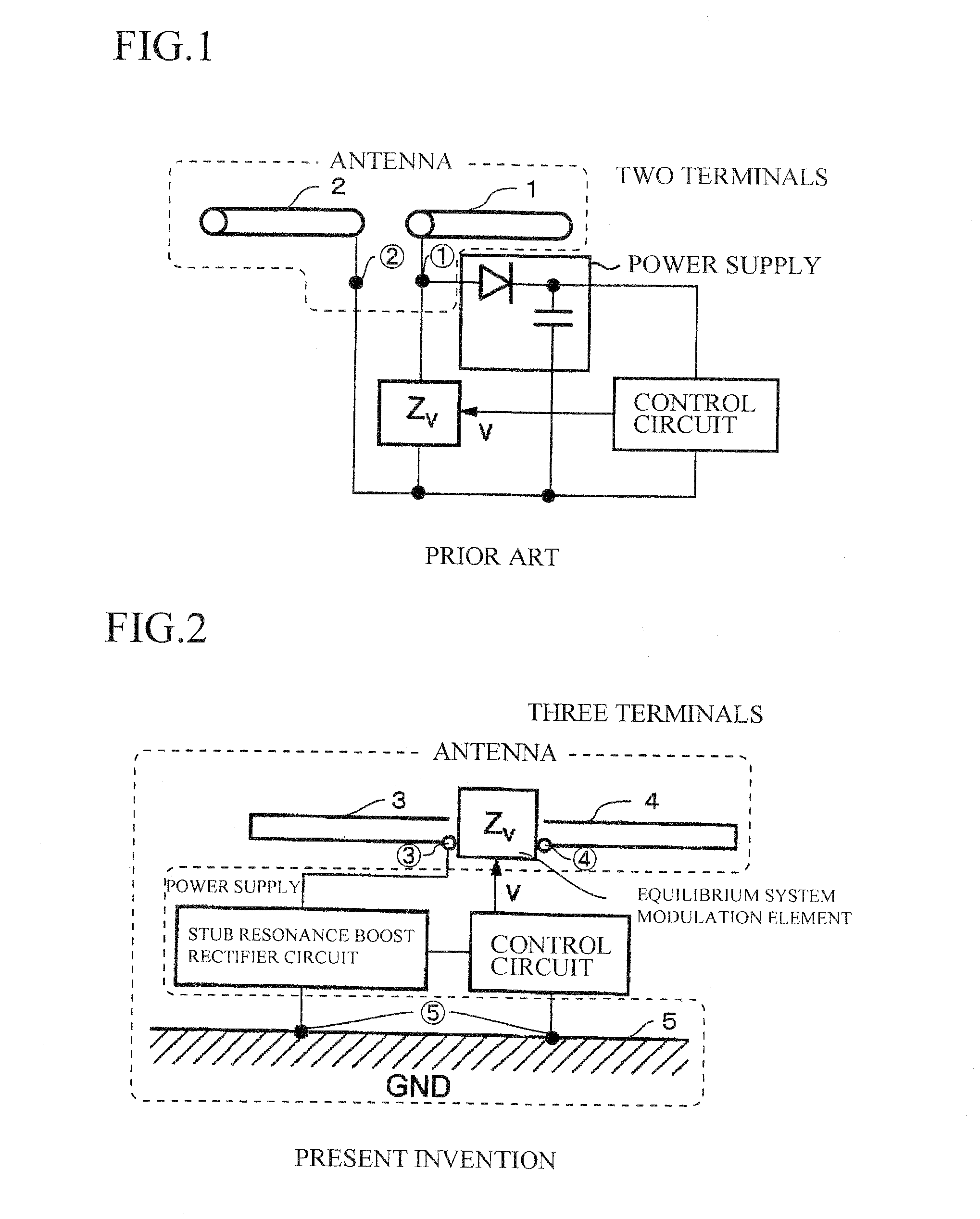
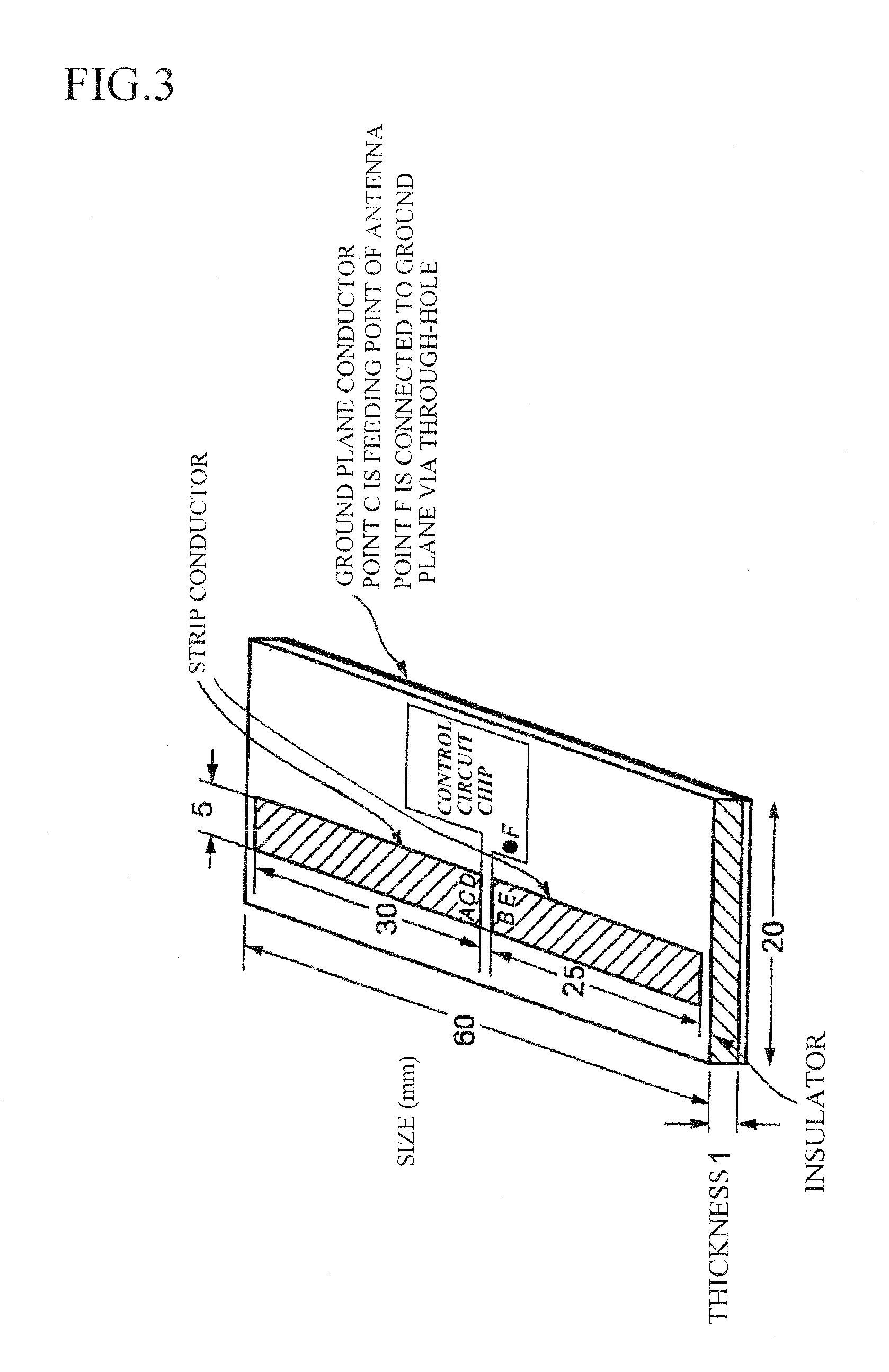
The present invention aims to overcome the drawback with conventional RFID tag devices having a short communication range, and expand the communication range to several times or more that in the conventional scheme. The conventional scheme is based on equilibrium feeding / equilibrium modulation (a two-terminal circuit for antenna operation), whereas the present invention is based on disequilibrium feeding / equilibrium modulation (a three-terminal circuit for antenna operation). The conventional scheme is based on simple rectification of received RF signals, whereas the present invention employs a circuit based on a combination of a stub resonance-based, impedance transformation boosting scheme and a ladder boosting scheme. The conventional scheme is based on ASK or BPSK modulation, whereas the present invention is based on passive modulation, but can employ a QPSK modulation circuit.
Owner:KITAYOSHI HITOSHI
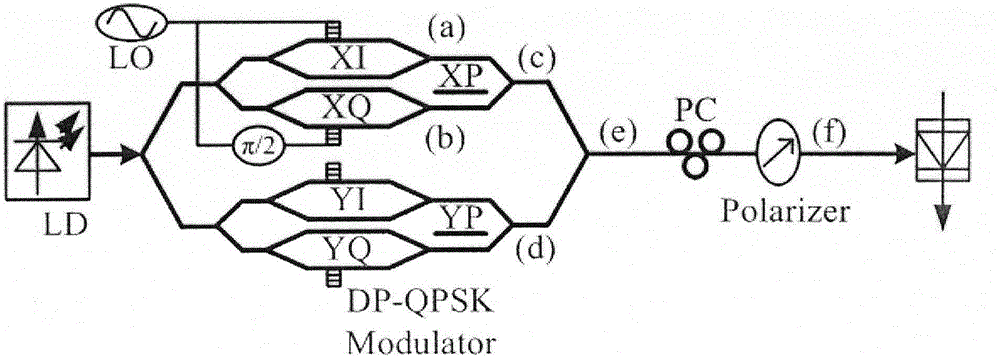
Frequency octupling millimeter wave generation device by means of DP-QPSK modulator and method thereof
InactiveCN105099558AReduce response frequency requirementsEasy to operateFibre transmissionPhase-modulated carrier systemsFrequency spectrumPolarizer
The invention discloses a frequency octupling millimeter wave generation device by means of a double polarization-quadrature phase shift keying (DP-QPSK) modulator and a method thereof, relates to the technical fields of microwave and optical communication, and is mainly applied to generation of high-frequency millimeter wave. According to the method shown in the appended drawings, the device comprises a light source, a radio frequency signal source, the DP-QPSK modulator, a phase shifter, a power divider, a polarization controller, a polarizer and a photoelectric detector. The nonlinear characteristics and the interference superposition characteristics of the two sub-modulators X-QPSK and Y-QPSK of the DP-QPSK modulator are utilized, and polarization controller is properly adjusted when the two sub-modulators XI and XQ of X-QPSK and a main modulator work at the maximum point so that frequency octupling millimeter wave signals can be generated, the radio frequency index required by generation of high-frequency / extremely-high-frequency signals can be greatly reduced and thus system cost can be reduced. Use of a filter is avoided by the method, and frequency adjustment performance is great. Meanwhile, the generated signals are great in phase noise and frequency spectrum purity.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV +1
Phase shift keyed modulation of optical signal using chirp managed laser
ActiveUS8068742B2Reduce difficultyReduce complexityElectromagnetic transmittersElectromagnetic receiversEngineeringAnalog-to-digital converter
A high-speed optical transmitter comprises multiple digital lanes that are provided to a bank of digital-to-analog converters. The analog signals are then used to Phase Shift Keyed (PSK) modulation using a Chirp Managed Laser (CML)-based transmitter, and potentially using dual polarization. A corresponding optical receiver receives the sequence of optical signals at a demodulator. For each polarization, the demodulator includes a corresponding demodulation channel that is configured to demodulate that polarization component of the optical signal into one or more signal components. Each of these signal components is converted into a corresponding digital signal using a corresponding analog-to-digital converter. In the case of higher-order PSK modulation (e.g., 8PSK or higher), for each polarization, the analog converter has a lower sampling rate than for QPSK modulation.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Control method for optical phase modulation
InactiveUS20080181620A1Stable characteristicsGuaranteed uptimePhase-modulated carrier systemsElectromagnetic transmittersMultiplexingPhase shifted
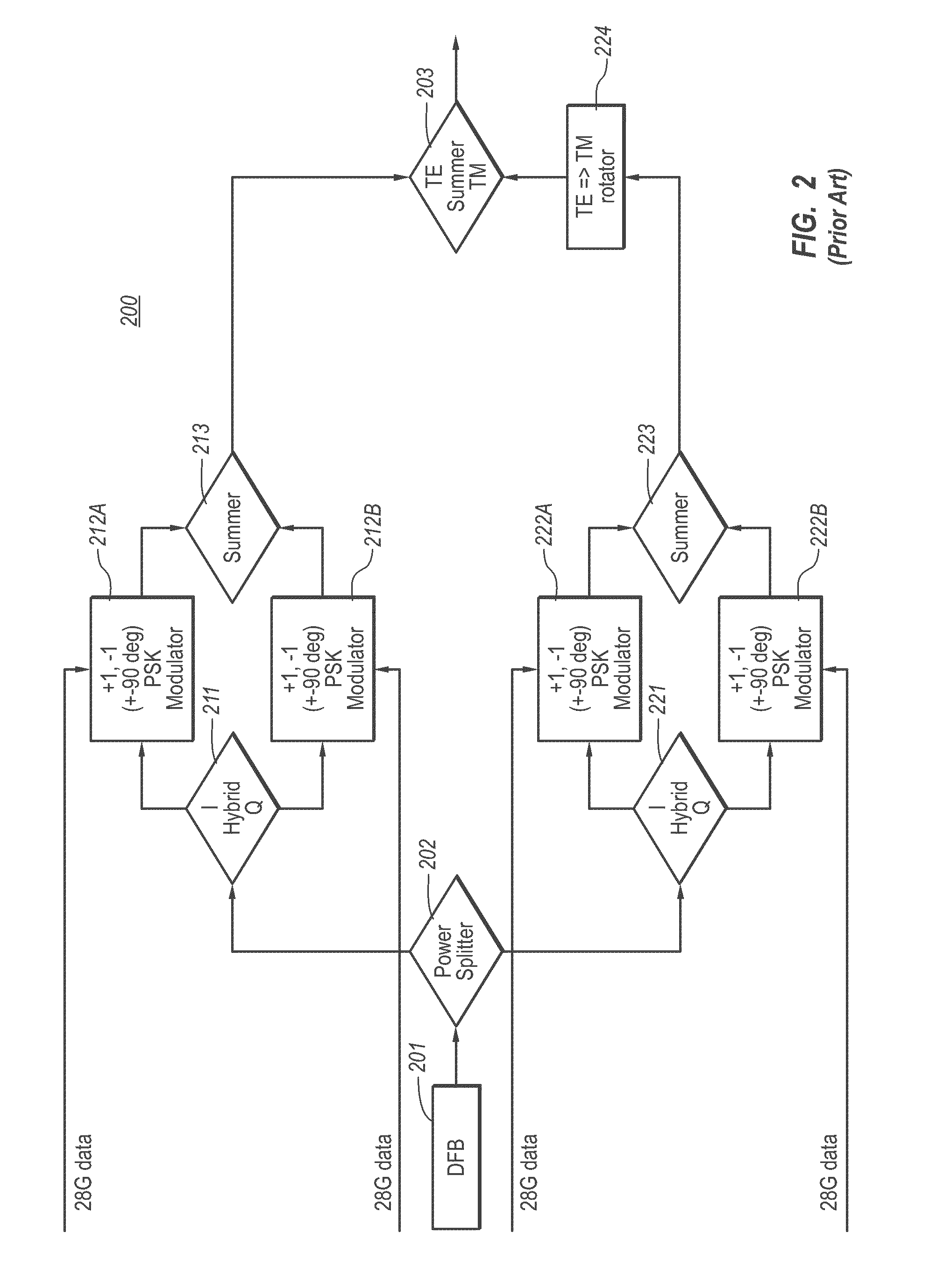
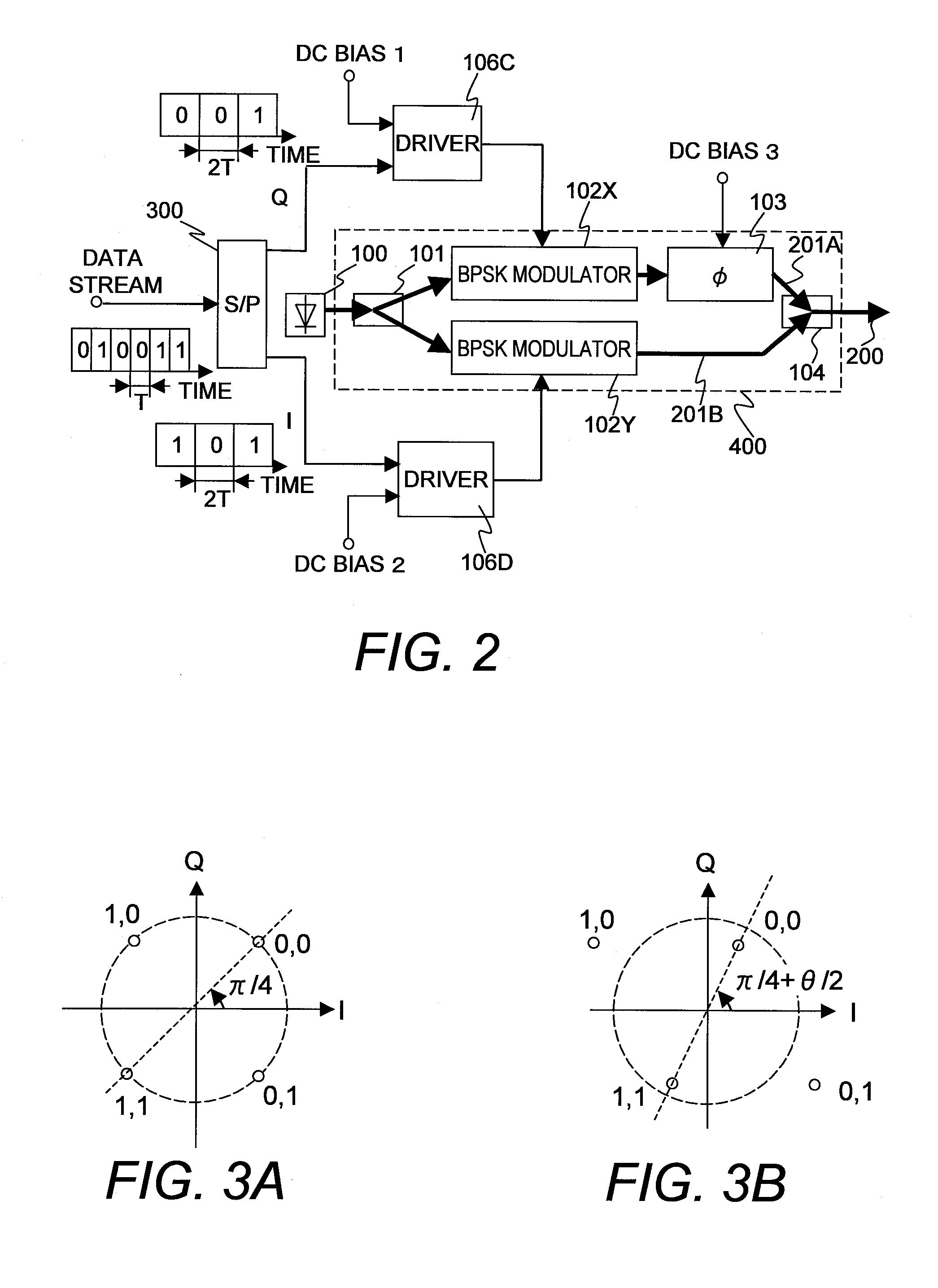
A QPSK modulator comprising: two phase modulators implemented in parallel for outputting the light phase-modulated with an information signal; a phase shifter for shifting the phase of the light phase-modulated with the first phase modulator of the two phase modulators and for outputting the phase-shifted light; and a combiner for combining output light of the phase shifter and output light of the second phase modulator, in which a drive signal generated by multiplexing a signal of a first and second frequencies and the information signal is inputted into the first and second phase modulators, and in which the QPSK modulator feeds back a detected amount to a voltage applied to the phase shifter so that the phase shift amount may be π / 2, the detected amount of signals having the frequency of the difference between or the sum of the first and second frequency which are extracted from the modulated light.
Owner:HITACHI COMM TECH
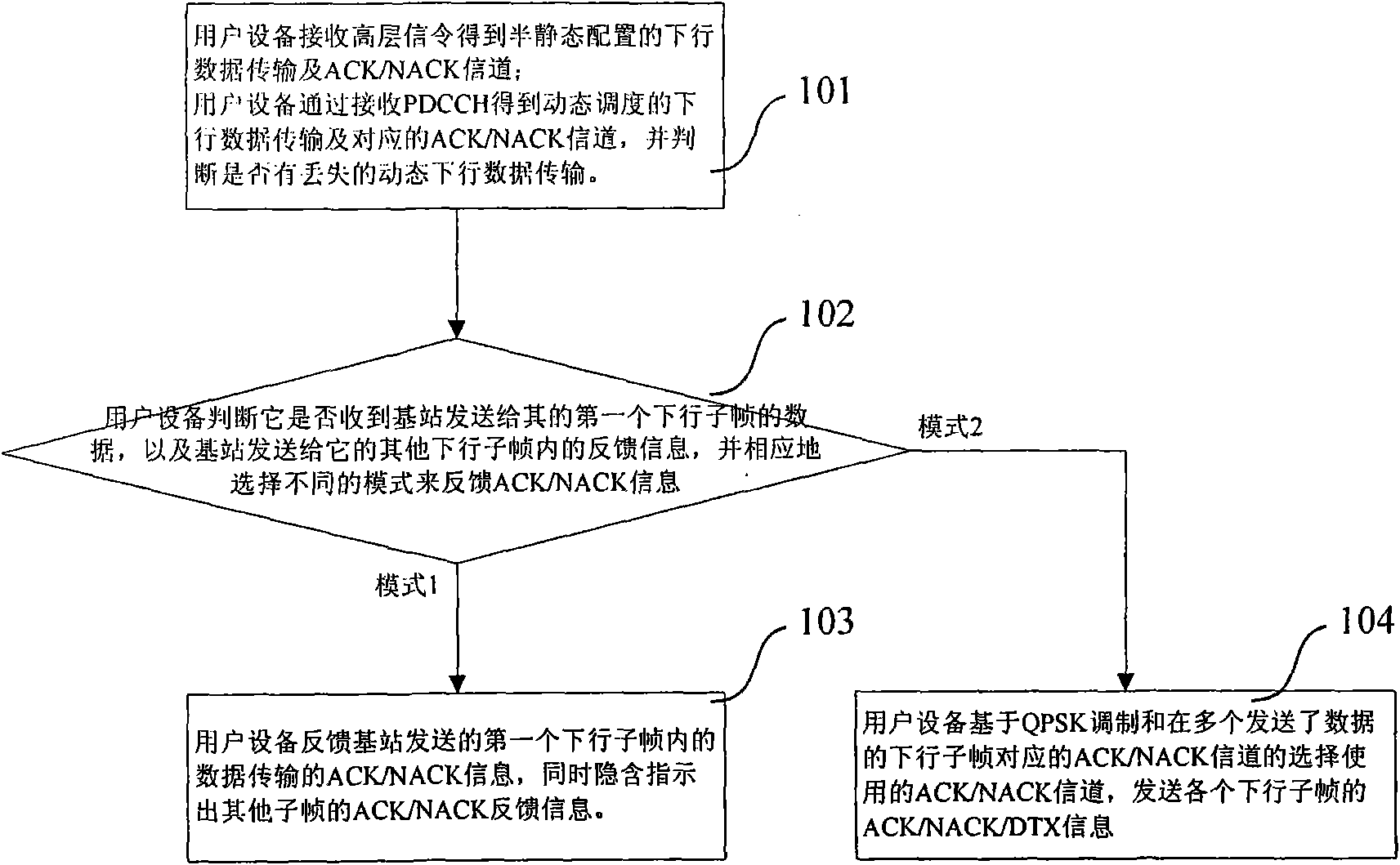
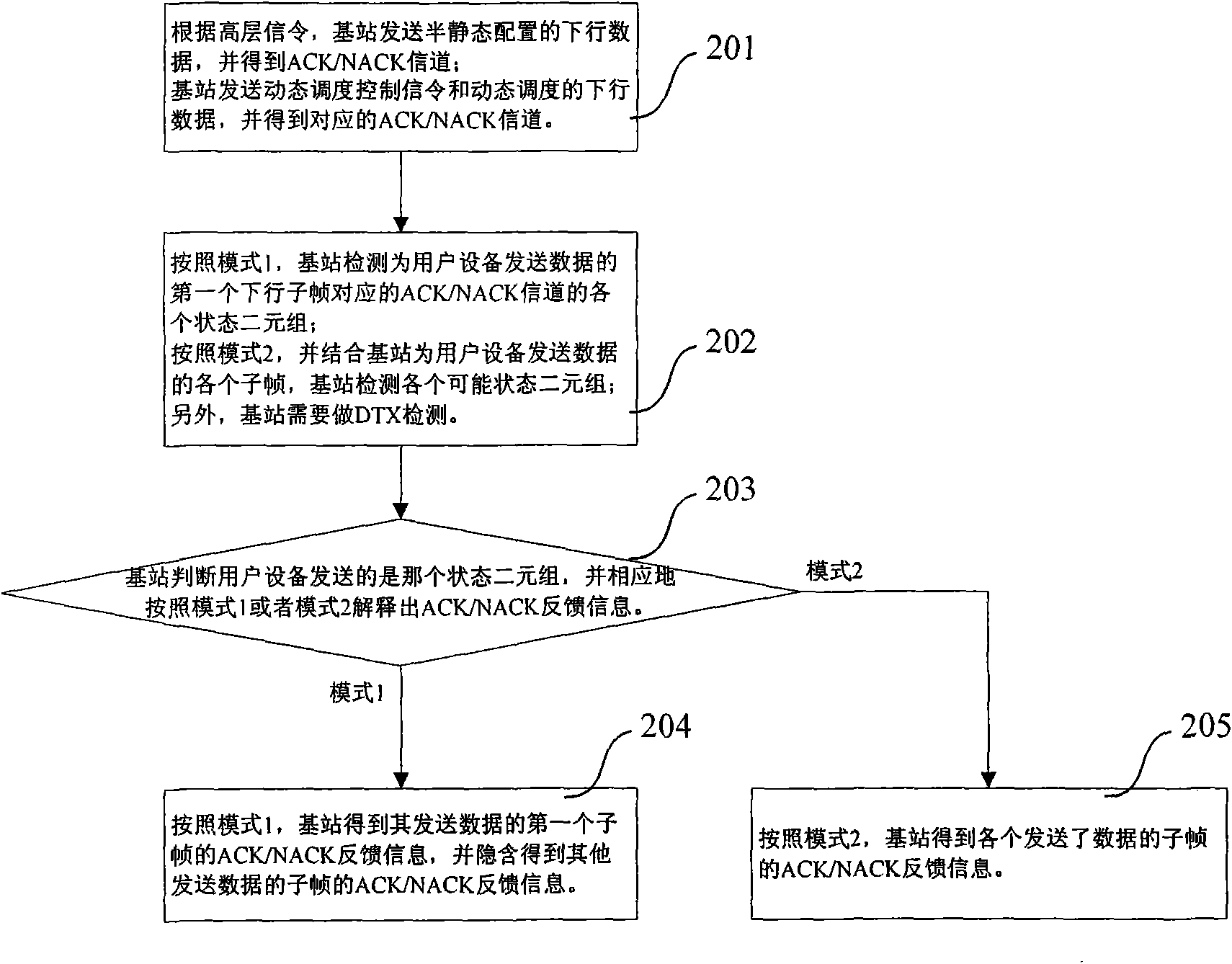
Method for feeding back ACK/NACK information
The invention relates to a method for feeding back ACK / NACK information. The method comprises the following steps that: when user equipment (UE) correctly receives the data of a first downlink subframe sent by a base station and the ACK / NACK feedback information on other subframes is NACK or DTX, the UE sends the ACK / NACK feedback information on the first subframe, and indicates at the same time that the ACK / NACK feedback information on other subframes is NACK or DTX and records the information as a first mode; and when the UE dost not correctly receive the data of the first downlink subframesent by the base station or the ACK / NACK feedback information on other subframes is ACK, the UE selects a used ACK / NACK channel from a plurality of ACK / NACK channels on the basis of QPSK modulation totransmit the ACK / NACK information on a plurality of downlink subframes and records the information as a second mode. The method utilizes a mechanism for detecting missed data transmission to supporta multi-bit feedback method of ACK / NACK information on multiple subframes, and can be converted into a feedback method for feeding back the ACK / NACK information on a single subframe without confusion.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
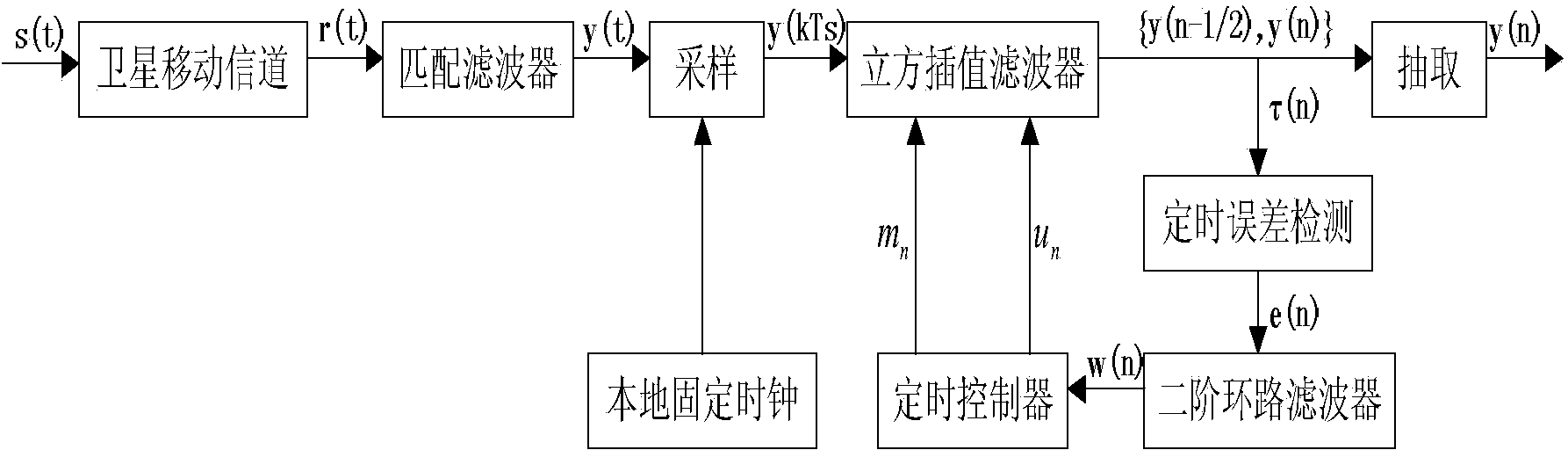
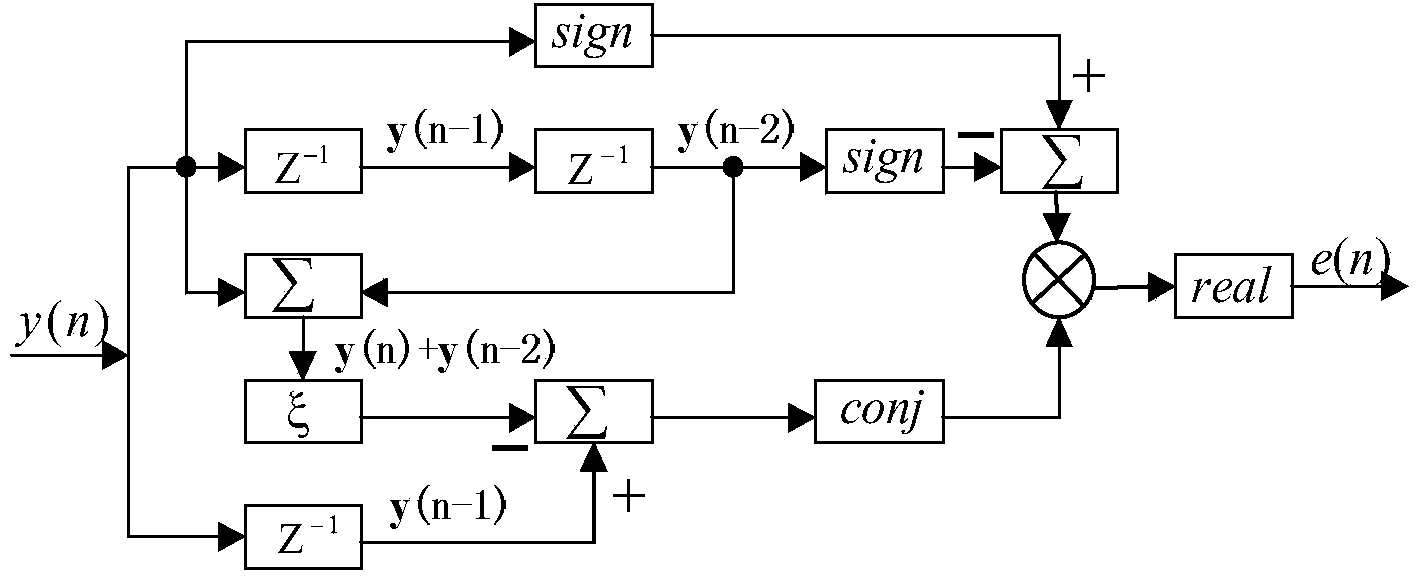
Satellite communication timing synchronization error detection method based on full-digital receiving
ActiveCN103457680AEliminate timing error skewEasy to lockReceivers monitoringSynchronising arrangementTime informationCoded element
Disclosed is a satellite communication timing synchronization error detection method based on full-digital receiving. In view of wide application of a Gardner algorithm in a timing synchronization loop and the limitation of the Gardner algorithm to band-limited signals, when polarity jump happens to two adjacent symbols, after two adjacent code elements are utilized for cosine roll-off forming filtering, the relation between samples of two best sampling points and the sample of a middle point of the two best sampling points is utilized, the effect of different adjacent symbols to the middle value is firstly taken into consideration and the effect value is calculated according to the minimum mean-square error criterion, and is then eliminated; when polarity jump does not happen to the adjacent symbols, how to reduce self noise generated by the situation that timing information can not be acquired is taken into consideration. A sign function sign (.) in an E-Gardner algorithm is utilized to solve the problem. Under the satellite channel environment, the enhancing algorithm is simple in structure, under the condition of a small roll-off coefficient, the performance of QPSK modulating signal clock capturing and error detection is improved, and the satellite communication timing synchronization error detection method based on full-digital receiving can effectively eliminate self-noise and reduce system resource consumption.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
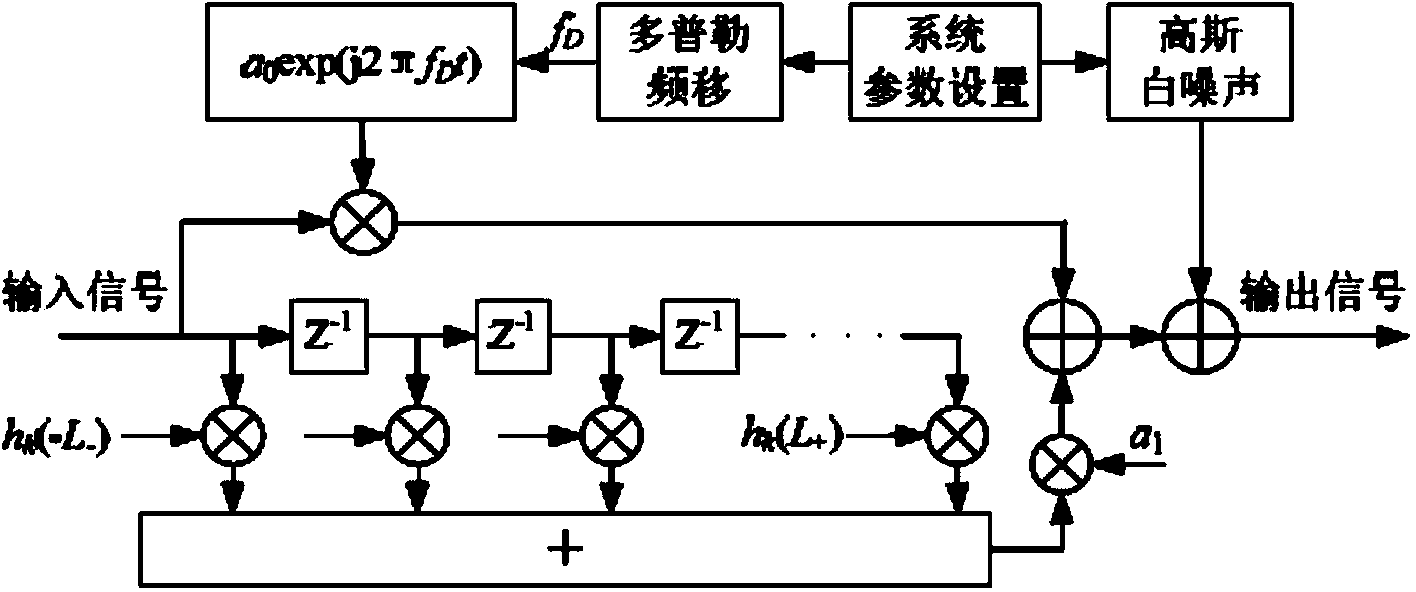
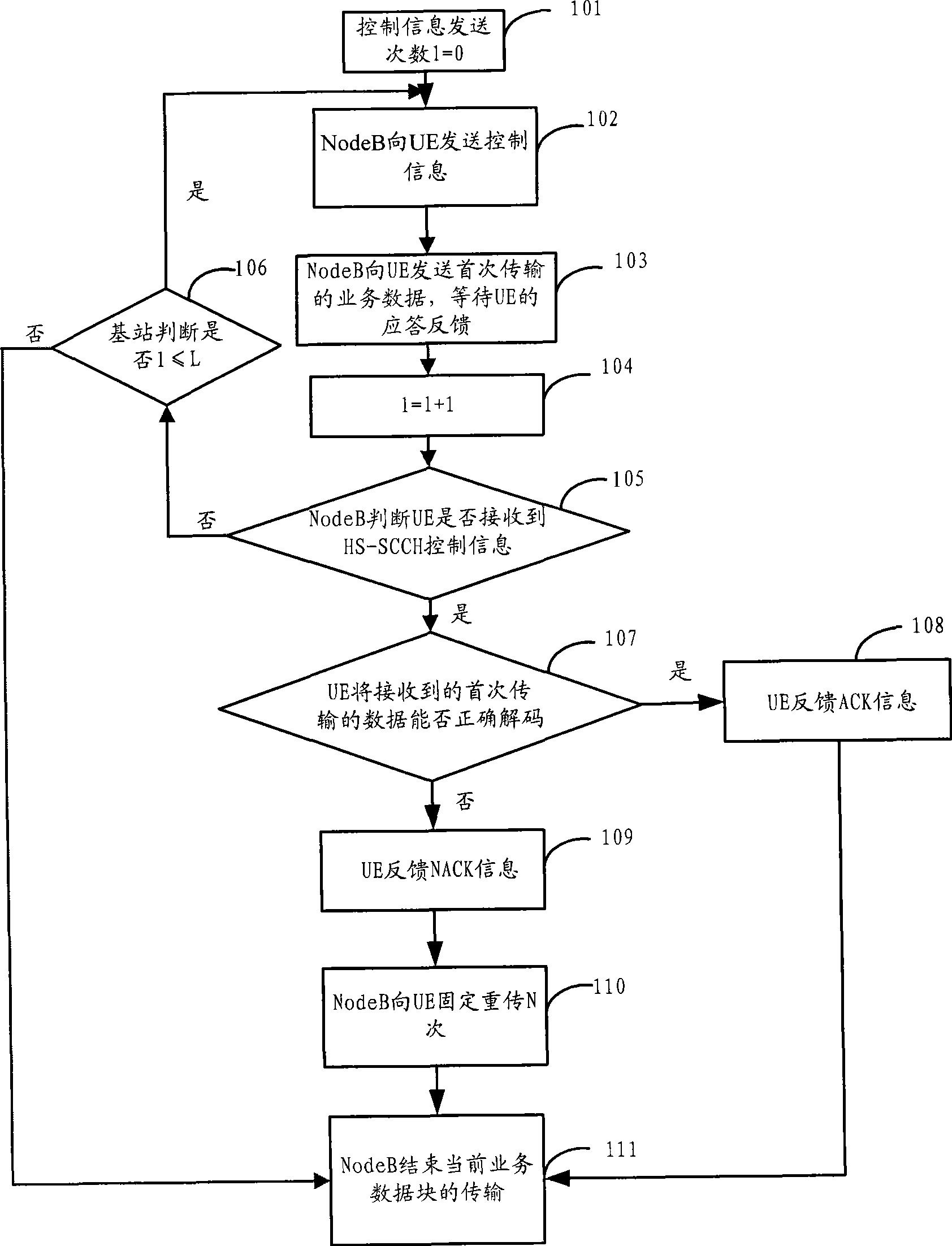
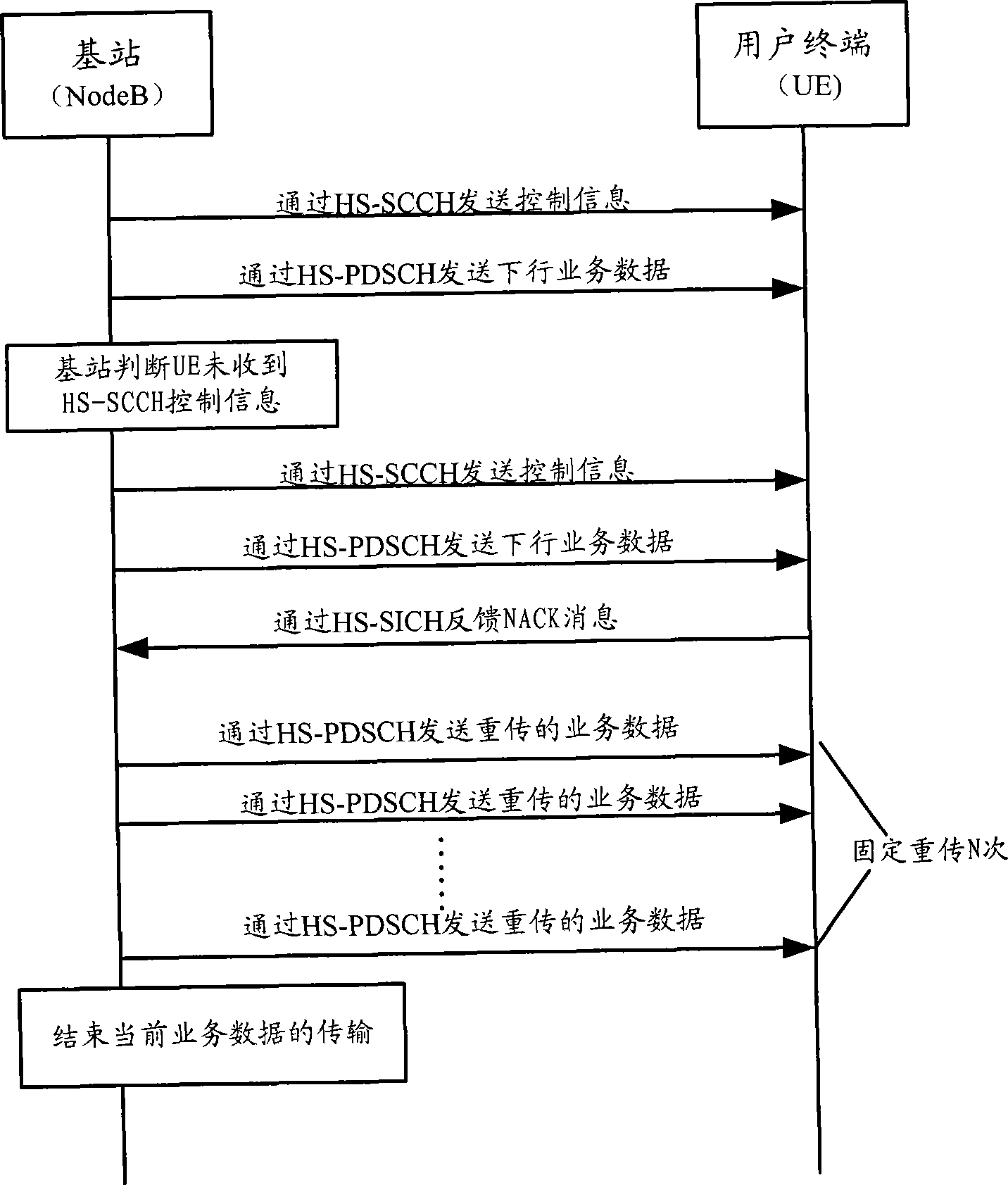
Method, apparatus and system for service data transmission in HSDPA
InactiveCN101399651AReduce overheadReduce the amount of informationError prevention/detection by using return channelPhase-modulated carrier systemsTransfer procedureNetwork packet
The invention discloses a method for transmitting service data in HSDPA, a device and a system thereof. UE time slot track is notified to distribute information by high-level signaling, by adopting synchronous mode of hybrid automatic repeat request, permanently adopting incremental redundancy versions of QPSK modulation and predefinition used during different transmission times. A base station only transmits control information including cyclical sequence number of a high-speed shared control channel, size index of transmission blocks and user identifications to UE on a physical control channel in the first transmission of data. Regarding small data packet service, such as transmission of VoIP service, information content of the control information is reduced, and transmission times of the control information during transmitting process can be greatly reduced, therefore, network load is reduced, and transmission efficiency of data of the small data packet service in HSDPA is improved.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
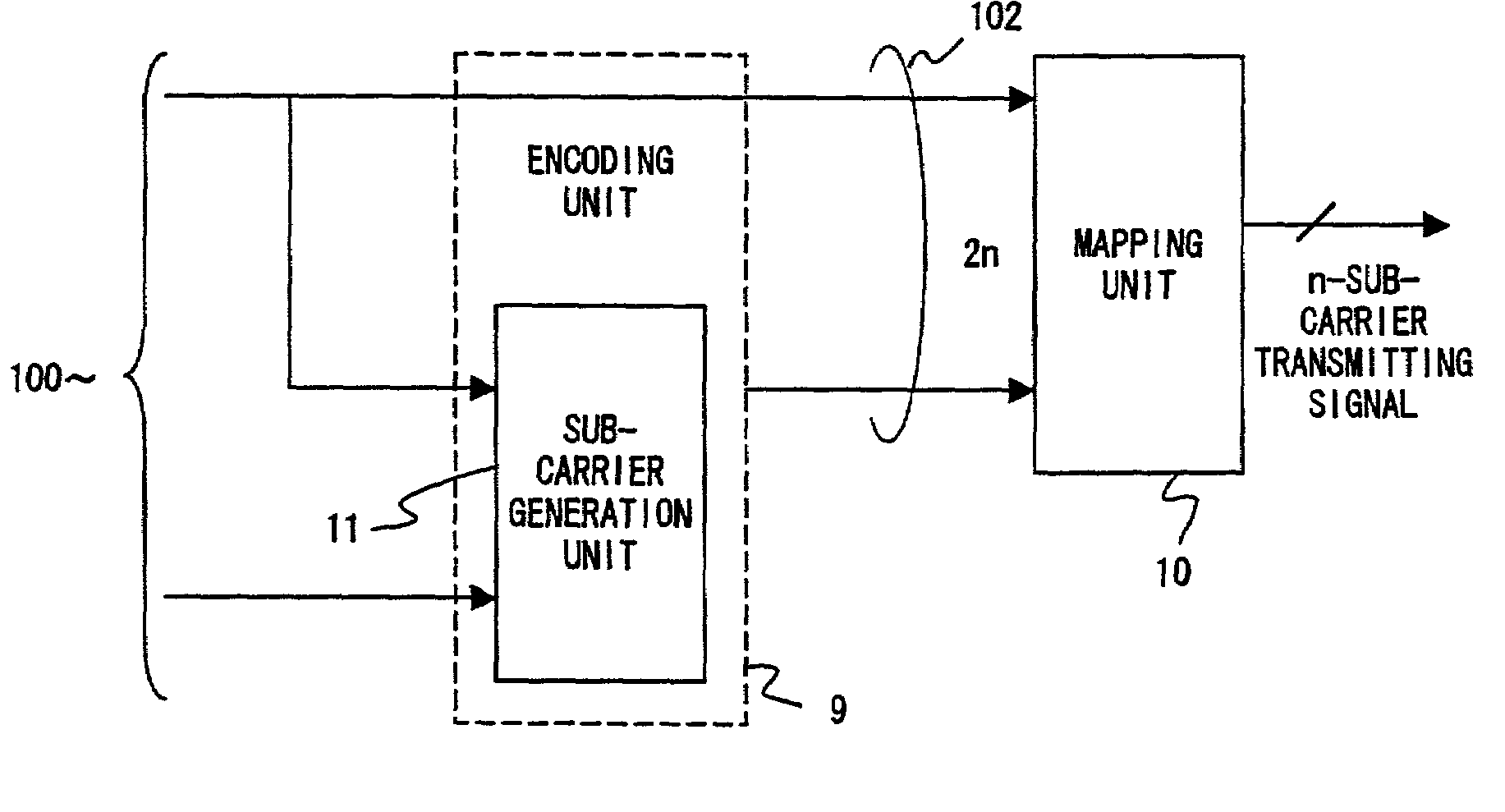
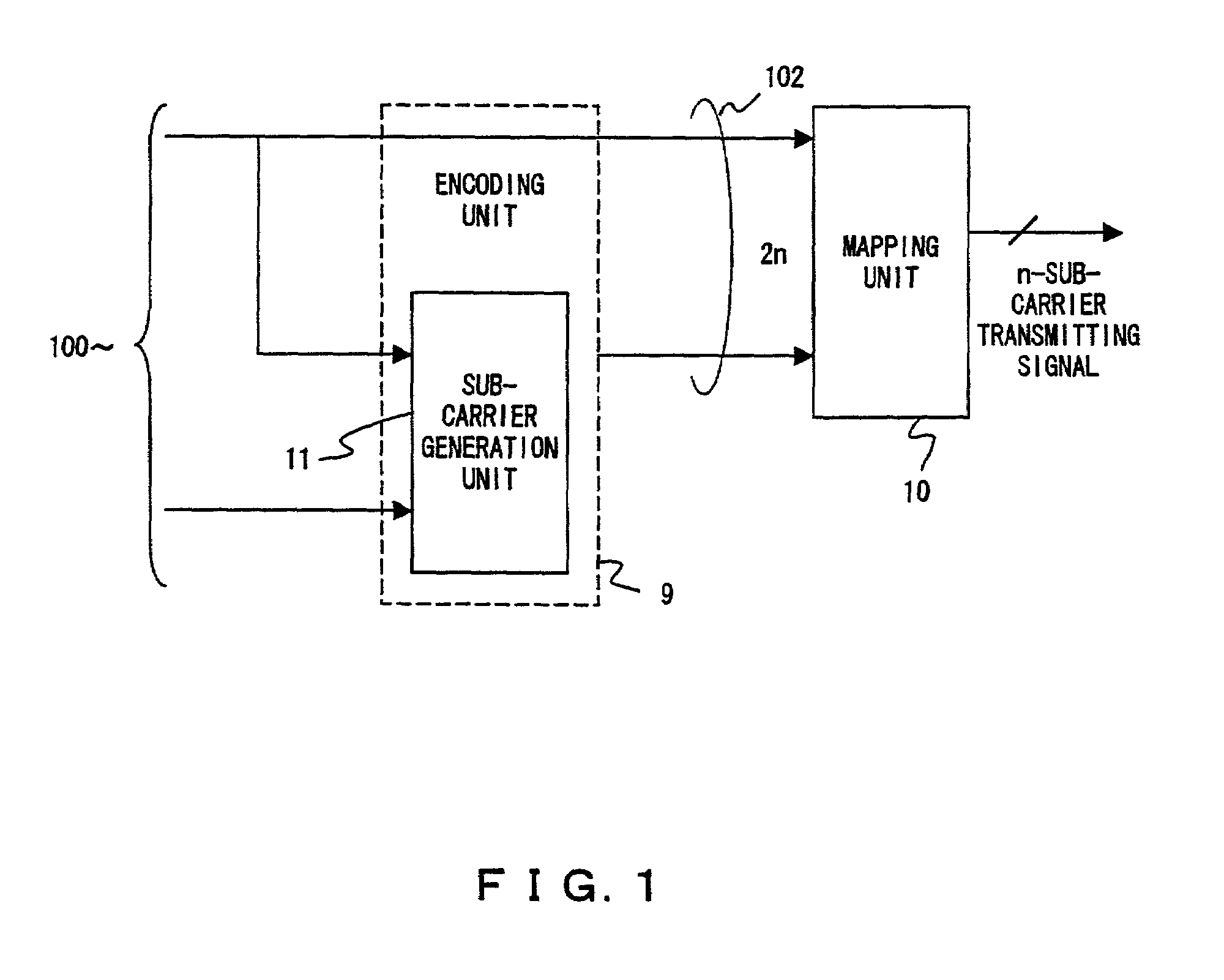
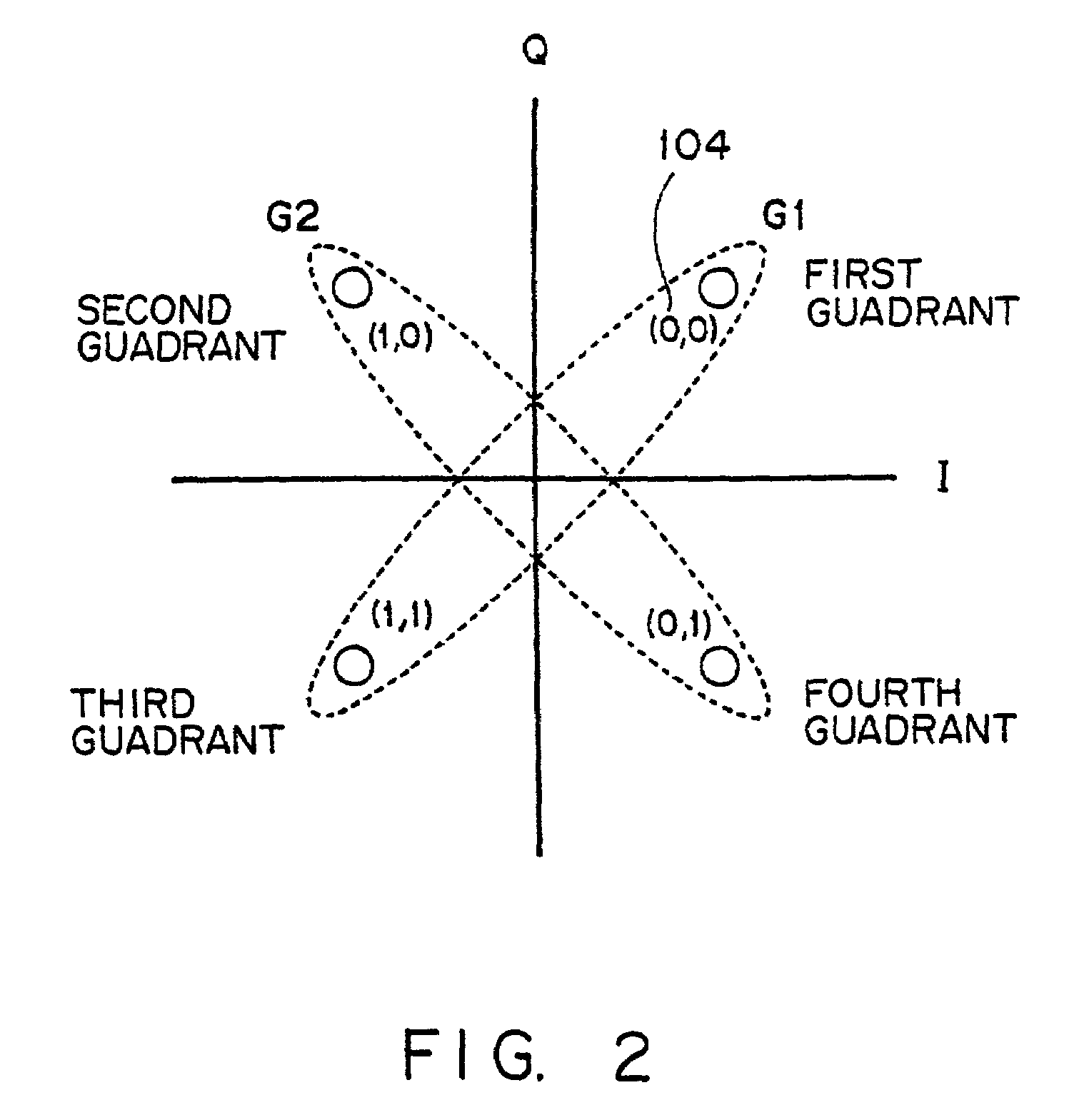
Transmitter, receiver and transmitting method in multi-carrier transmission system
InactiveUS7006429B2Improve encoding rateData switching by path configurationSecret communicationTelecommunicationsCarrier signal
An object of the present invention is to provide a method for suppressing peak power at a high encoding rate in a multi-carrier transmission system.The present invention provides a transmitter for transmitting a multi-carrier signal, in which when generating 128 patterns used to suppress the peak power of 8-bit sub-carrier mapping signals from 7-bit information bits in a encoding unit 9, a sub-carrier generation unit 11, for example, divides the signal point of QPSK modulation into orthogonal groups, generates a sub-carrier mapping signal in which a part of sub-carriers is dependent on the signal point of another sub-carrier and a receiver for receiving such a multi-carrier signal.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
System and method for adaptive modulation and power control in a wireless communication system
InactiveUS20080159362A1Power managementDuplex signal operationCommunications systemTransmitted power
A system for adaptive modulation and power control in a wireless communication system includes a downlink from a base station to a remote unit and an uplink from the remote unit to the base station. The base station incorporates adaptive modulation on the downlink while power control is not utilized. In contrast, the remote unit utilizes a fixed modulation level and power control to control transmit power levels. In an exemplary embodiment, the remote unit uses QPSK modulation. The header of uplink messages include data from the remote unit to instruct the base station which modulation level to utilize on downlink transmissions. This provides closed-loop, non-iterative modulation control. In an exemplary embodiment, the modulation selection data is included in all uplink messages so that adaptive modulation can be communicated on a frame-by-frame basis.
Owner:CLEARWIRE IP HLDG
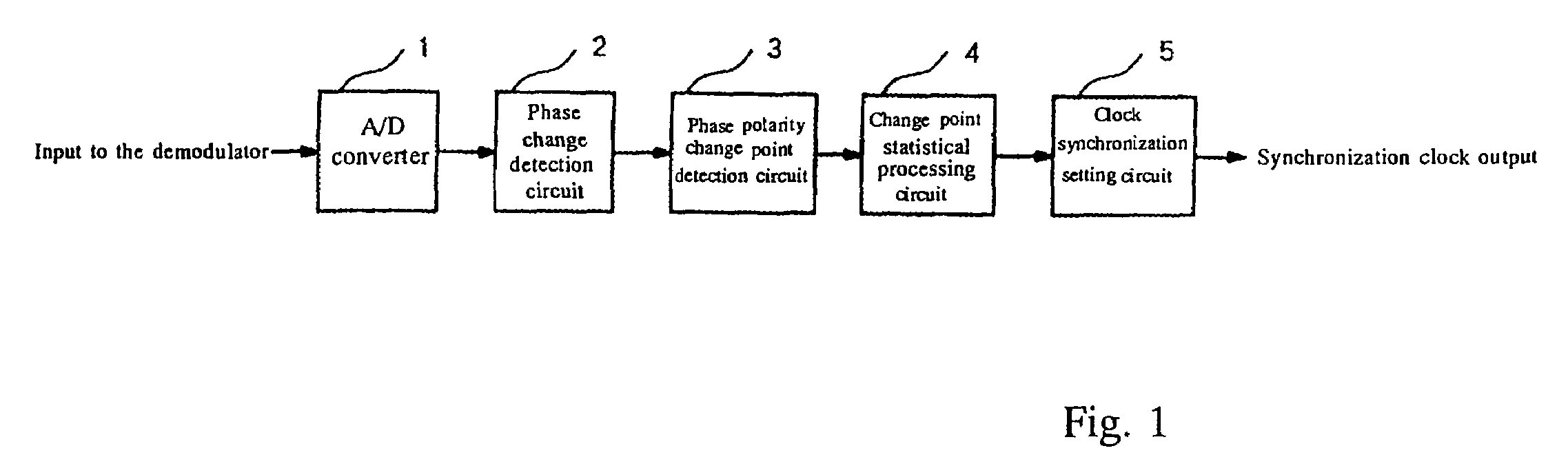
Demodulation and synchronization establishment apparatus
InactiveUS7023940B2Establish synchronizationShort timeSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlPhase-modulated carrier systemsDemodulationClock synchronization
A demodulation method for establishing clock synchronization within a short period of time from a received signal modulated by π / 4-shift QPSK modulation that contains a synchronization establishment signal wherein the change in phase periodically alternates between positive and negative, and for demodulating the received signal. The method includes establishing synchronization from the received signal based on the timing of changes in the positive / negative polarity of the change in phase of the synchronization establishment signal contained in the received signal, and demodulating the received signal.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Communication link used for telemetry and telecontrol communication system
ActiveCN104579416ARealize wireless communicationAvoiding Carrier Synchronization ProblemsModulated-carrier systemsTelecommunications linkCommunication link
The invention provides a communication link used for a telemetry and telecontrol communication system. An uplink broadcasing and downlink TDMA (time division multiple access) mode is adopted to solve the measurement and control problems of a single ground station for multiple aircrafts. A downlink adopts hybrid spread spectrum BPSK (binary phase shift keying) with multiple stages of adjustable gain for modulation, an uplink adopts coded spread spectrum QPSK (quadrature phase shift keying) with fixed gain for modulation, so that the anti-interference, anti-interception and anti-capturing capacity of a wireless link is improved, and asymmetry of the uplink and the downlink is considered. Both the uplink and the downlink adopt a single-pulse modulation symbol packet transmission mode, a fixed interval is inserted into every two adjacent symbol pulses, and accordingly, the spread spectrum signal capturing, tracking and synchronizing complication of receivers is reduced. Non-coherent demodulation is adopted, a complicated carrier synchronization problem is avoided, and the design and project realization of the receivers are further simplified. The complicated carrier synchronization problem is avoided, and wireless communication between a single ground station device and multiple telecontrol terminal devices is realized.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE MEASUREMENT & CONTROL TECH
Multi-carrier communication apparatus
InactiveUS20060128323A1Increase the number ofIncrease the amount of dataDiversity/multi-antenna systemsMulti-frequency code systemsCarrier signalPattern generation
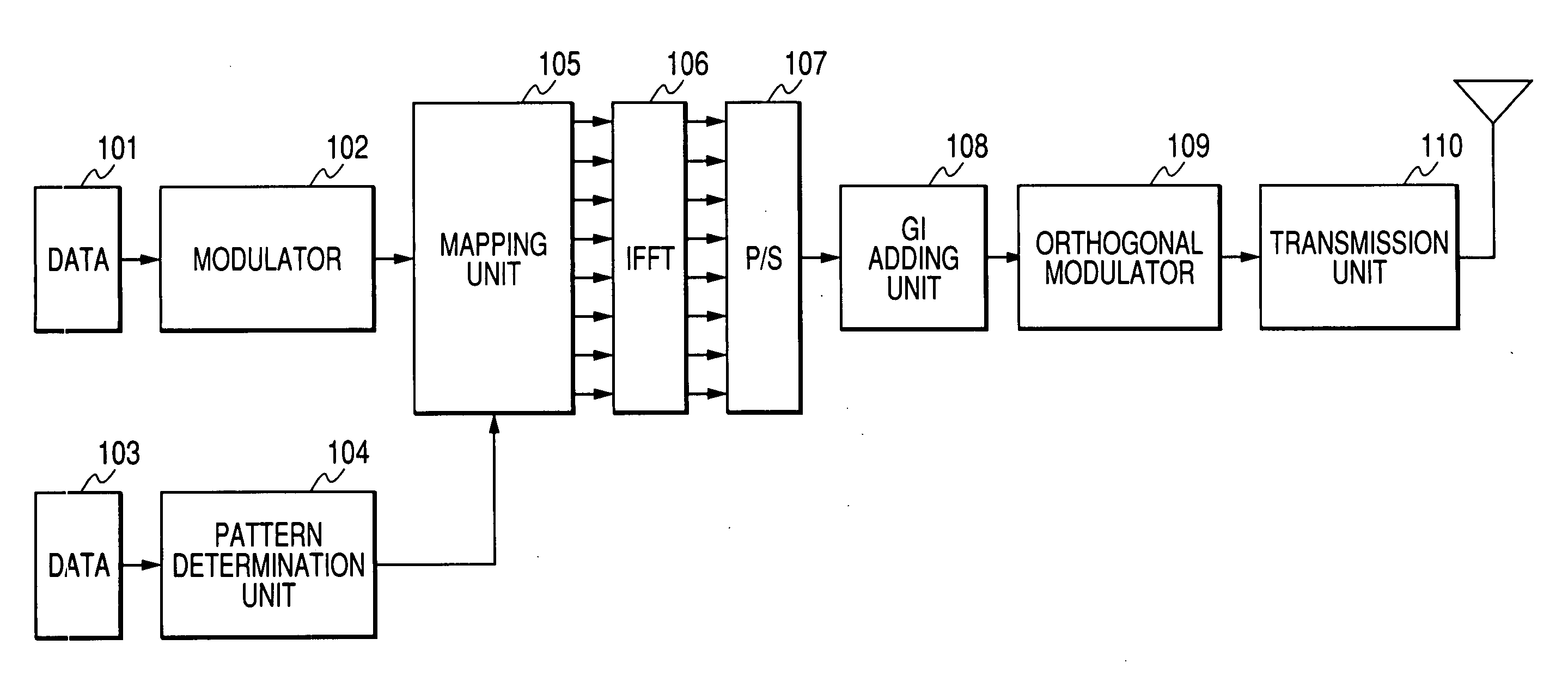
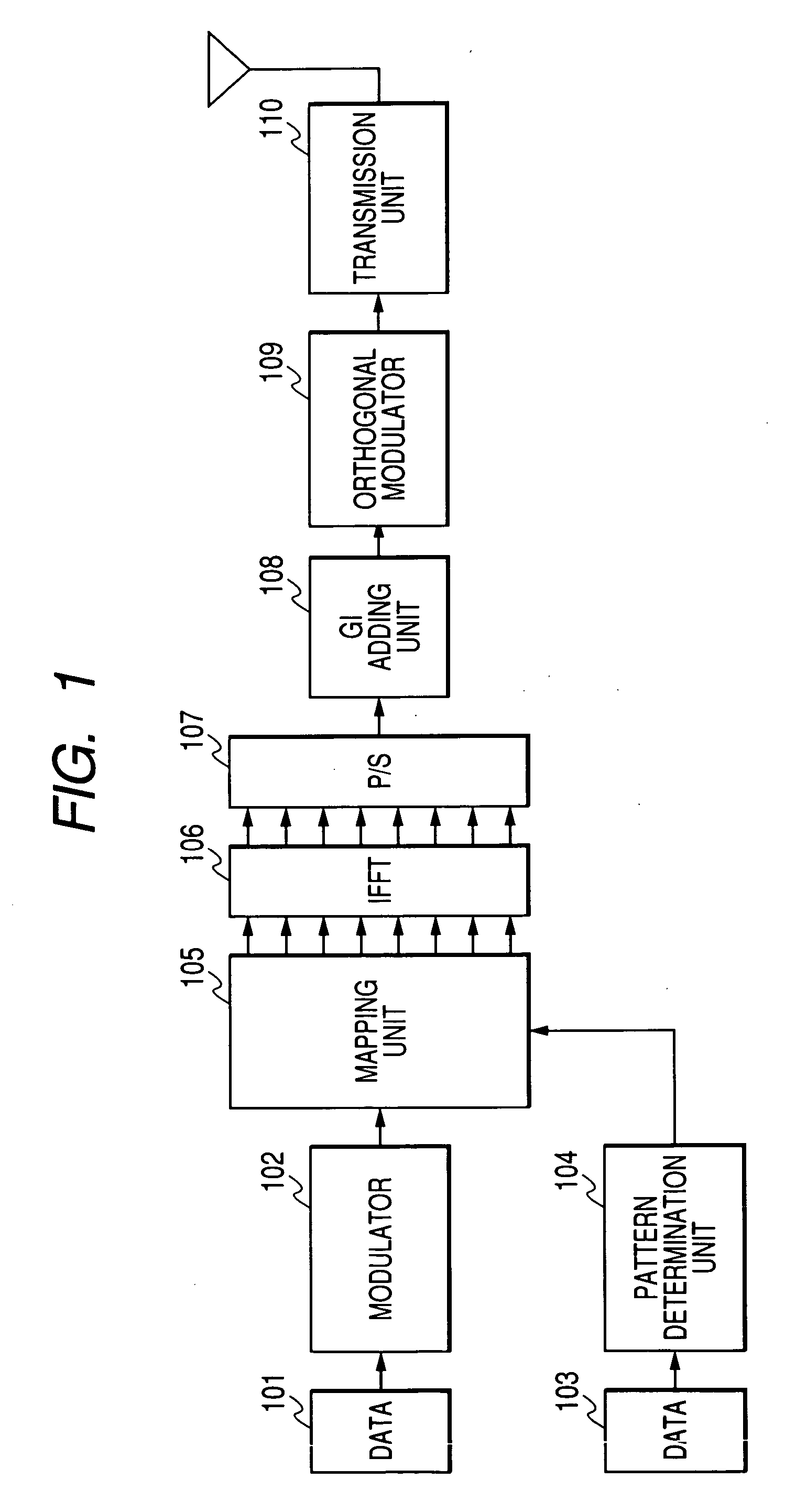
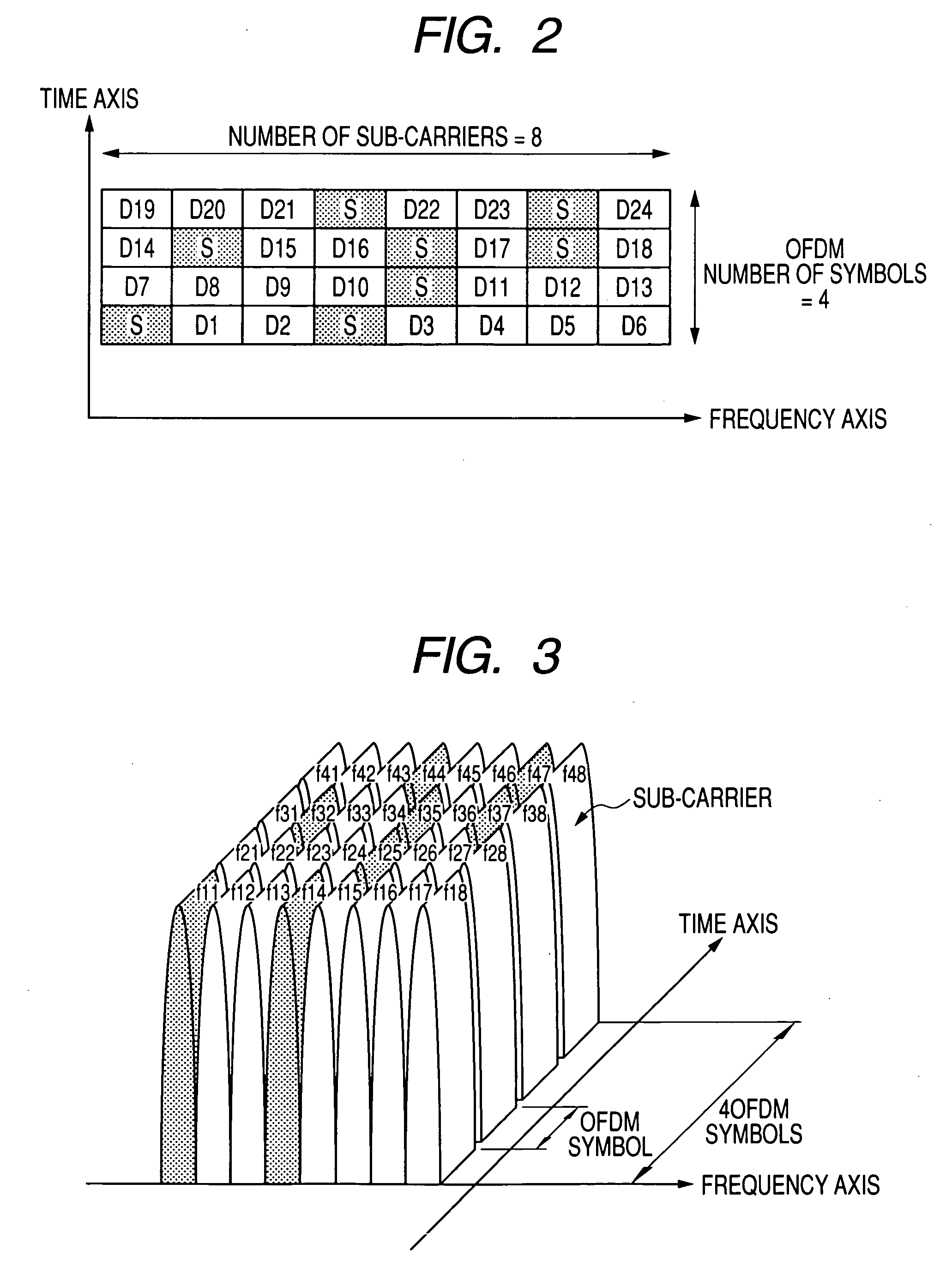
In a multi-carrier communication apparatus, it is an object of the invention to increase the amount of data per unit time greatly with the band width kept unchanged. A modulator (102) sequentially performs primary modulation of data (101) which are first transmitted data on the basis of, for example, QPSK modulation. A pattern generating unit (104) generates a pattern of particular signals which is to be allocated to sub-carriers of a matrix formed by arranging a plurality of sub-carriers arranged in the direction of a frequency axis into a plurality of symbols in the direction of a time axis. The pattern is determined based on data (103) which are second transmitted data. A mapping unit (105) allocates the sub-carriers modulated by the data (101) at the modulator (102) and the pattern of the particular signals to the sub-carriers of the matrix.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
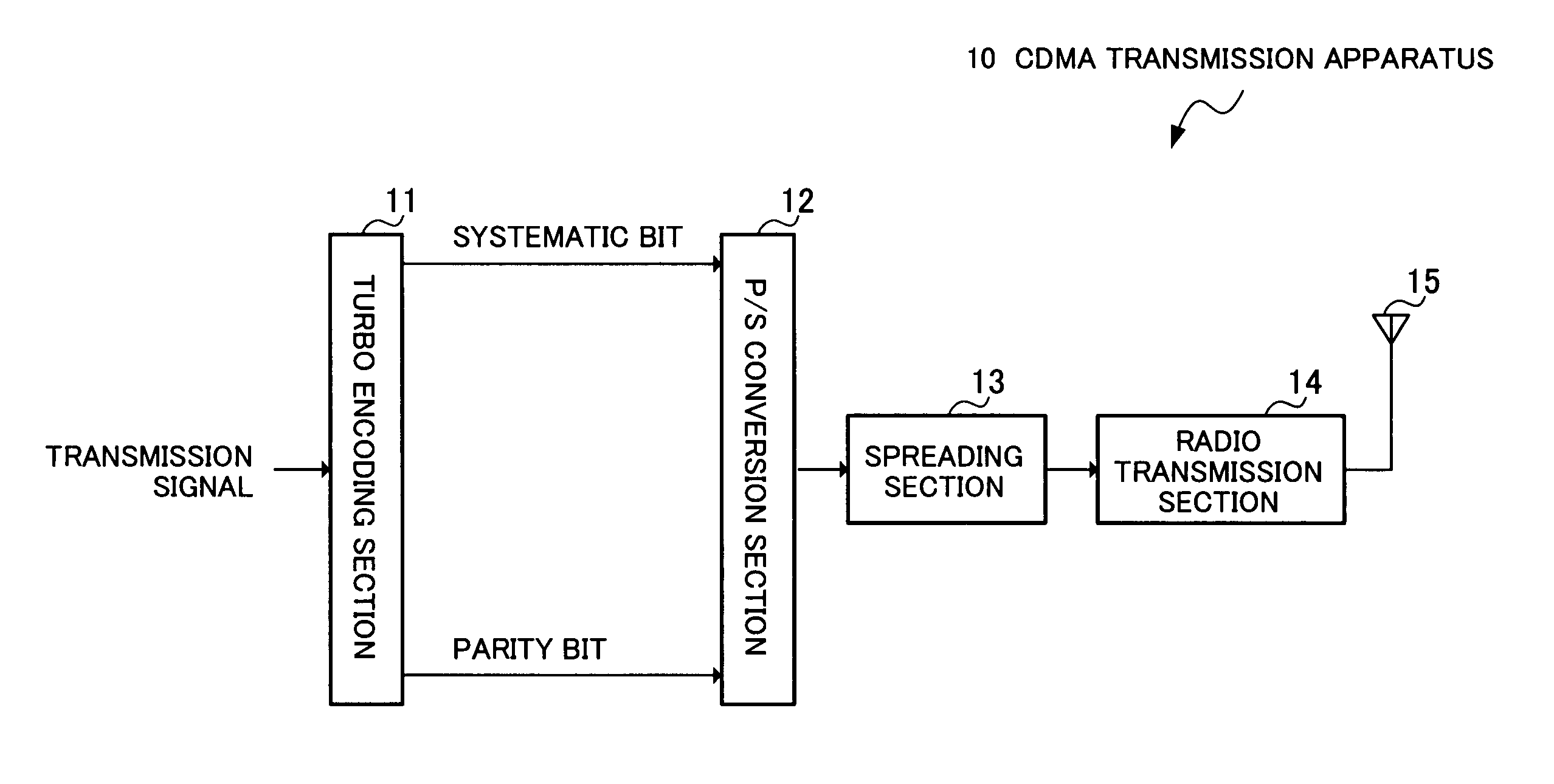
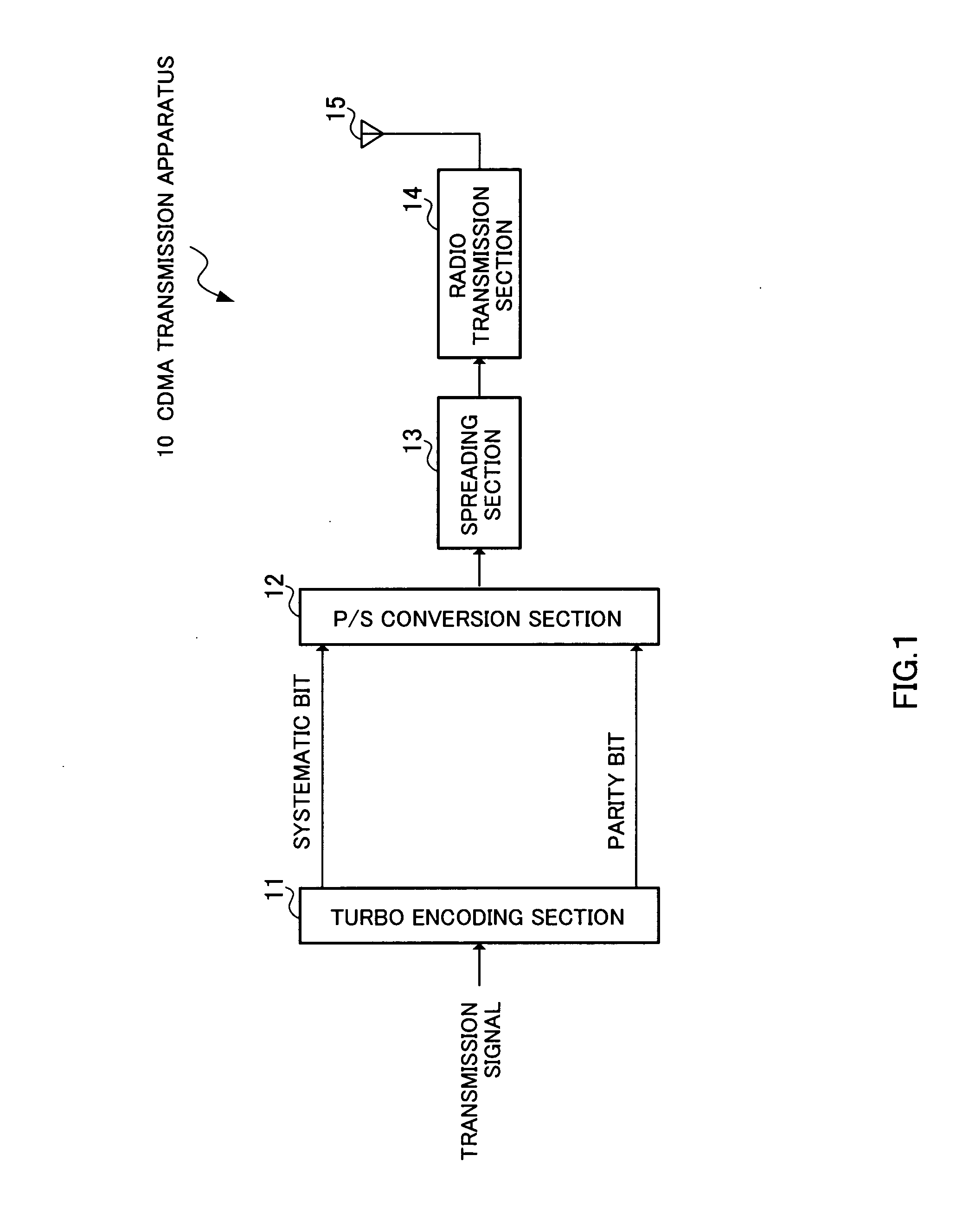
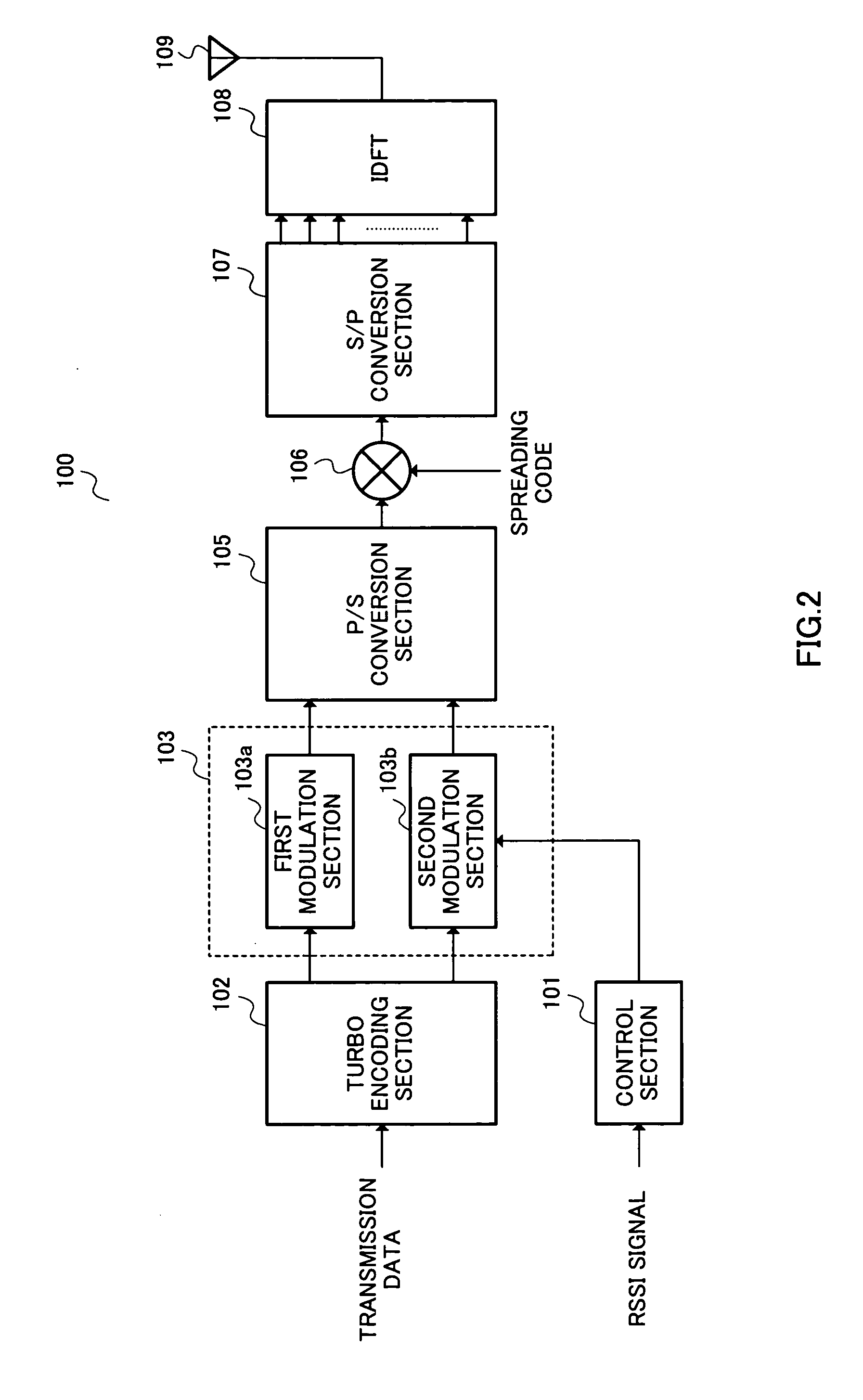
Transmitting device and transmitting method
InactiveUS20050229073A1Error characteristicError efficiencyError prevention/detection by using return channelError correction/detection using trellis codingControl signalComputer science
A turbo encoding section 102 turbo-encodes transmission data, outputs systematic bit data to a first modulation section 103a and outputs parity bit data to a second modulation section 104. The first modulation section 103a always QPSK-modulates systematic bit data. The second modulation section 103b adaptively modulates parity bit data. The control section 101 outputs a control signal for carrying out 16 QAM modulation to the second modulation section 103b when the RSSI value is equal to or higher than a threshold and outputs a control signal for carrying out QPSK modulation to the second modulation section 103b when the RSSI signal value is less than the threshold. In this way, it is possible to further make the error rate characteristic compatible with the transmission efficiency.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Parallel spread spectrum communication system and method
InactiveCN1846357AReduce the required transmitted powerLow powerMultiplex code allocationOrthogonal multiplexDigital dataData stream
The invention involves a parallel spread spectrum ('PSS') technique of spreading orthogonal encoded data. In a preferred embodiment, a method and system for communicating data comprises encoding and spreading a data stream using a scheme employing orthogonal Walsh functions, and thereby segmenting the data stream into multiple bit data packets representing one of a number of true or inverted Walsh codes. The data stream is then differentially encoded for either BPSK or QPSK modulation, and spread using a PN-sequence. The parallel spread data stream is modulated for transmission to a receiver. At the receiver, the data stream is recovered by computing a cross correlation between the digitized data stream and a programmed sequence. One of the benefits of the PSS techniques over conventional communication systems is that additional processing gain plus data forward error correction can be simultaneously achieved.
Owner:开普兰奇无线电马来西亚有限公司
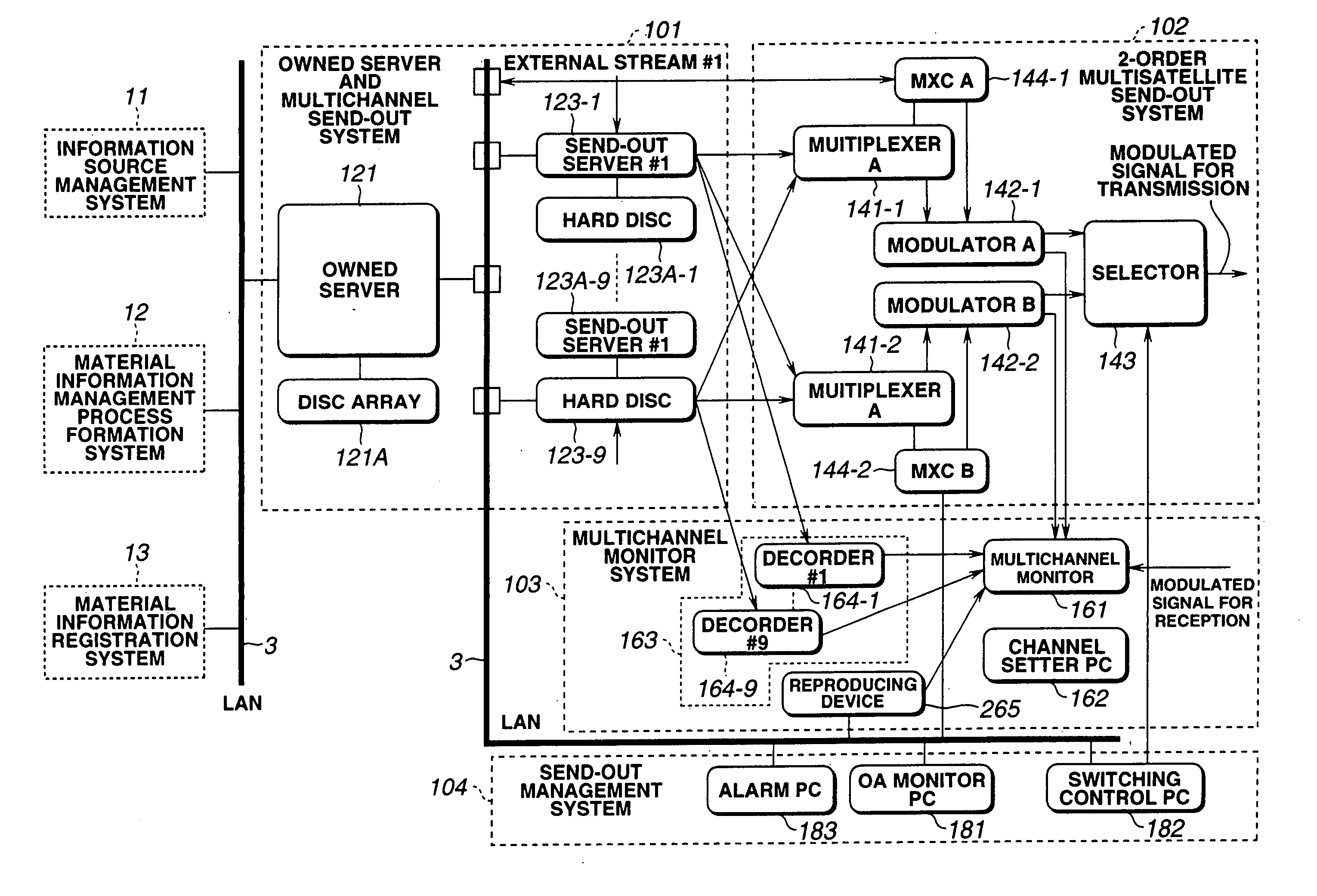
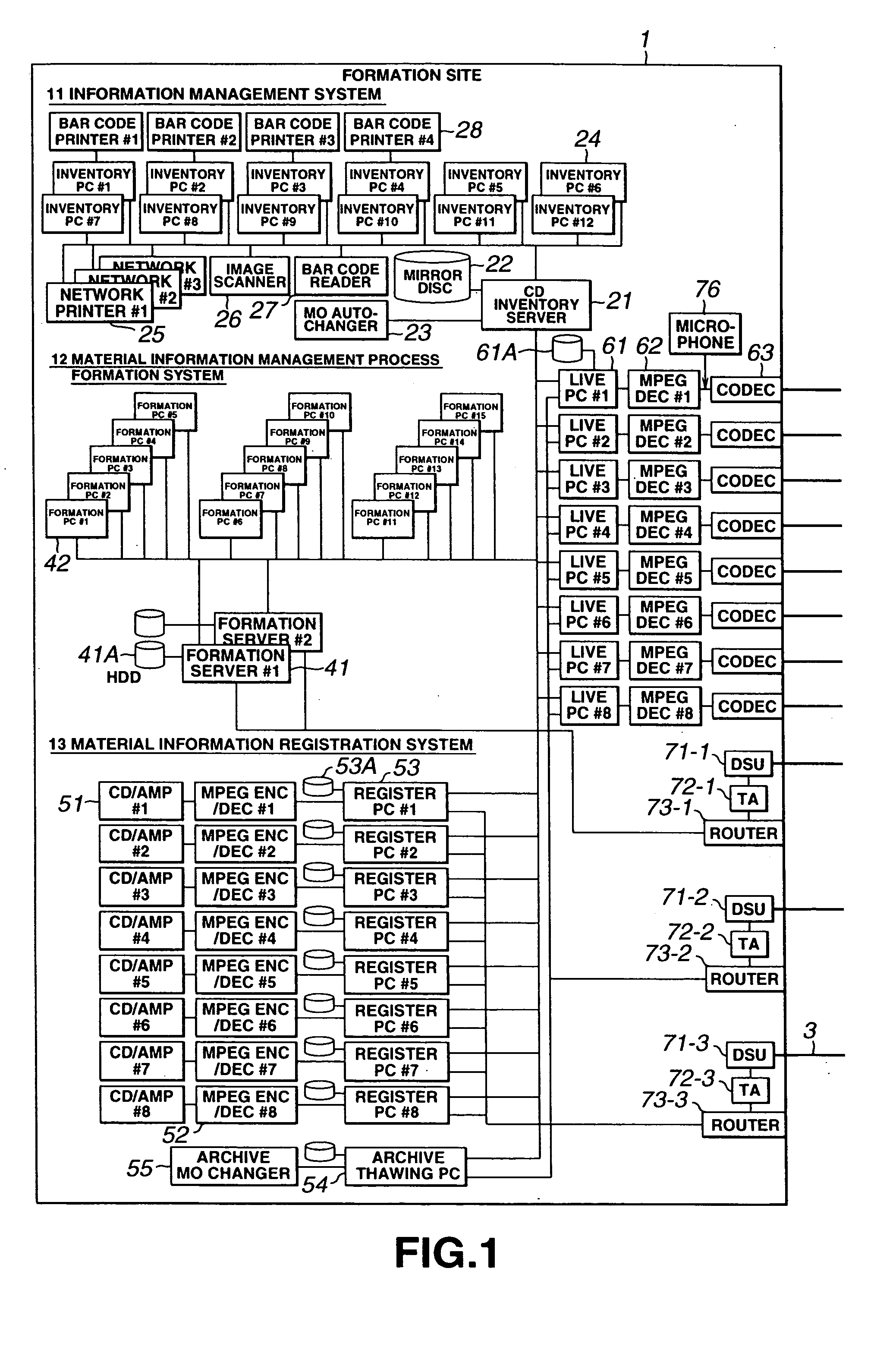
Method and apparatus for sending out multi-channel digital data, method and apparatus for programming the information and method and apparatus for managing multi-channel digital data
InactiveUS20050233694A1Automatically and efficiently broadcastShort timeTelevision system detailsFrequency-division multiplexDigital dataMultiplexing
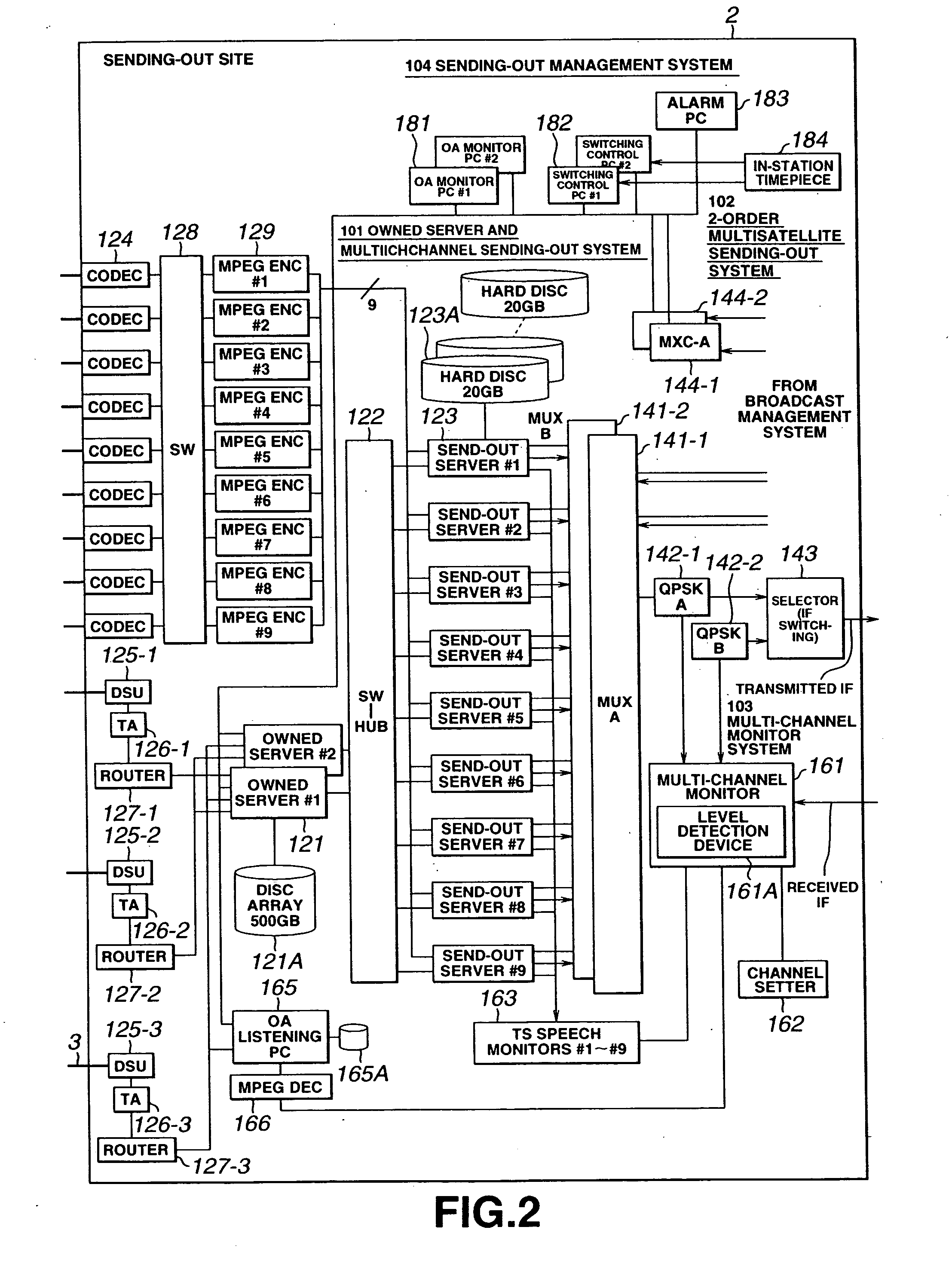
An information source management system 11 performs inventory management for CDs and a material information management progress programming system 12 performs programming. An material information registration system 13 compresses the musical numbers of the CDs for holding on a proprietary server and a proprietary server 121 of a multi-channel sending-out system 101. A large number of materials are held on the proprietary server 121 and read out from it. The read-out materials are converted in its format to a transmission format by a sending-out server 123 so as to be multiplexed by a multiplexer 141. The multiplexed data is QPSK-modulated by a modulator 142 and sent out via a selector 143. From the proprietary server 121 are read out data which is sent out via dedicated network 3 to a live PC where it is reproduced. This data is furnished again via dedicated network 3 and encoded by an MPEG encoder 129 so as to be sent out at the sending-out server 123.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Remote underwater acoustic communication method based on soft-demodulation soft-decoding joint iteration
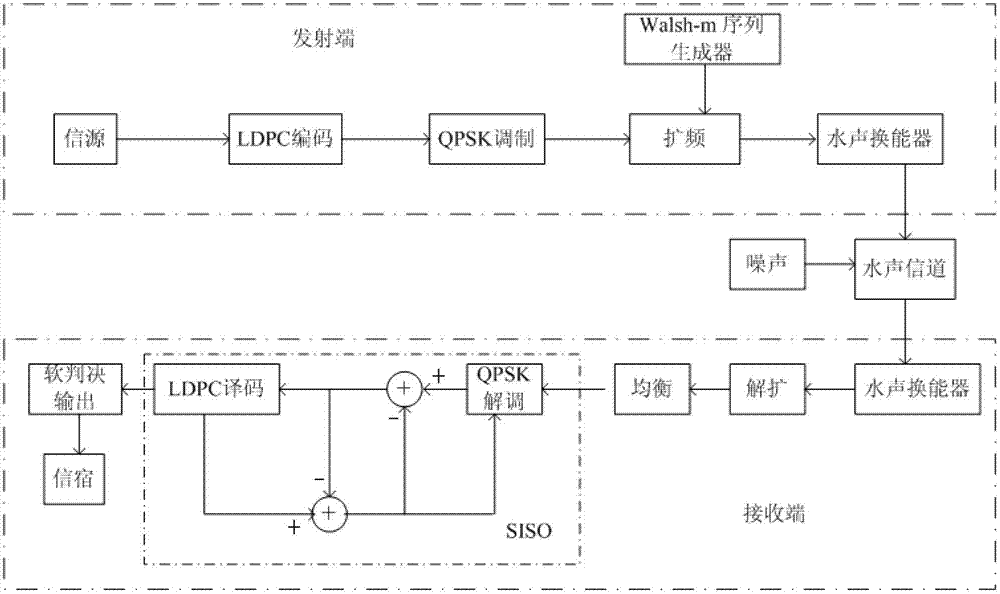
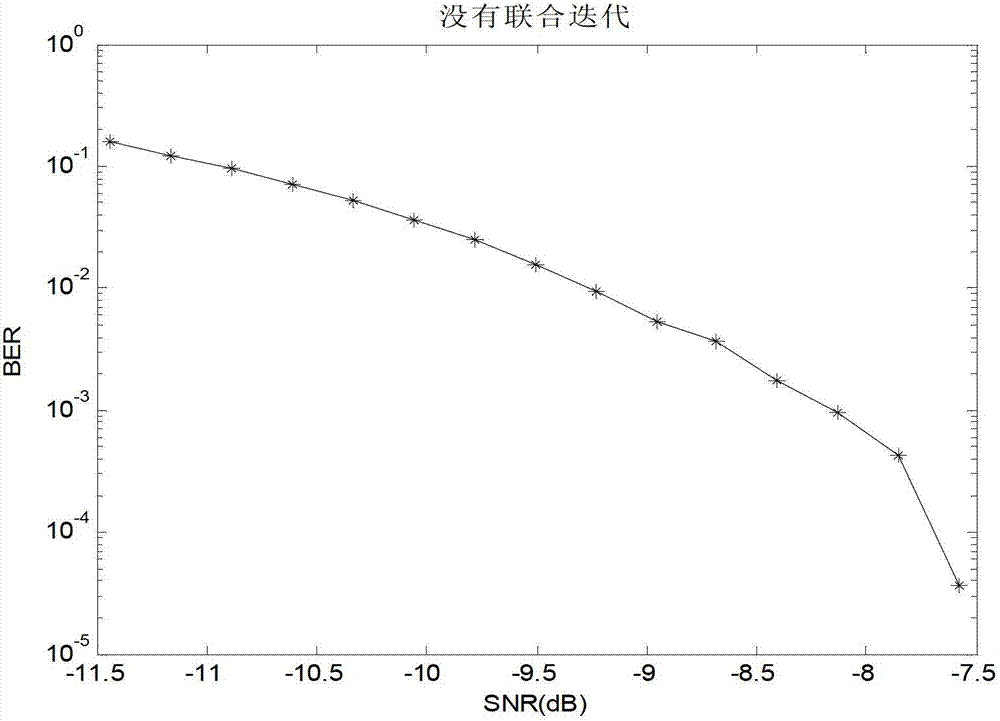
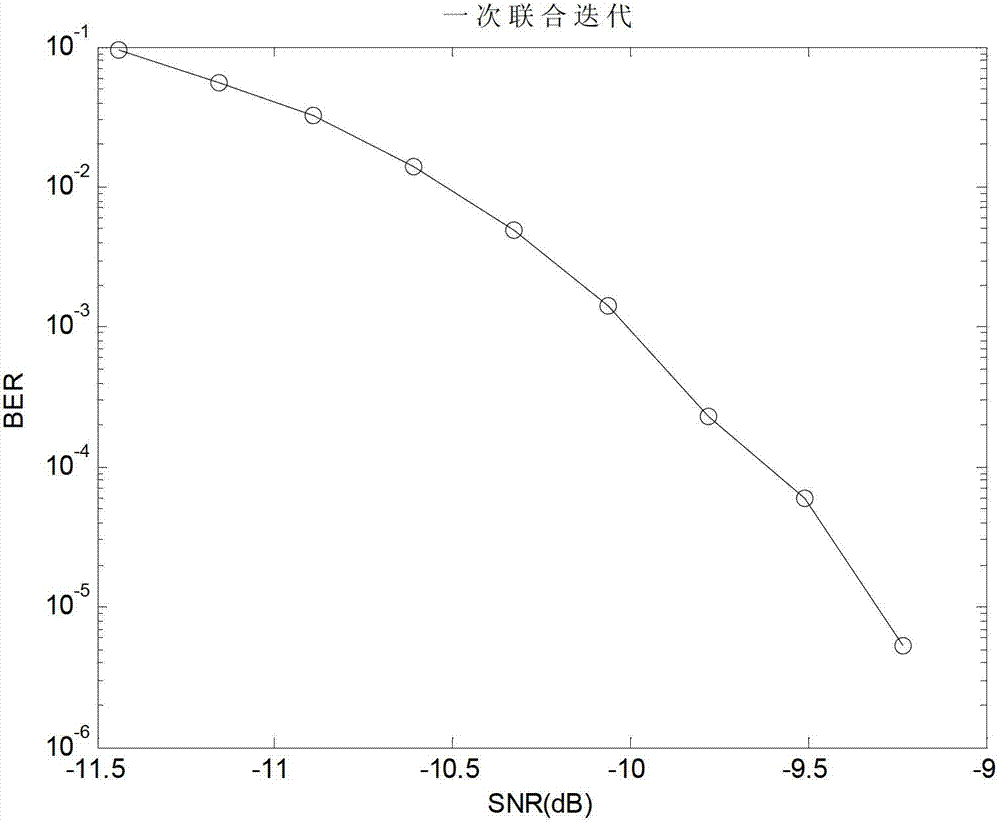
InactiveCN102739322AImprove real-time performanceIncrease independenceError preventionPhase-modulated carrier systemsBinary informationCoded element
The invention provides a remote underwater acoustic communication method based on soft-demodulation soft-decoding joint iteration. The method comprises the following steps that: a transmitting end performs low density parity check (LDPC) coding on a binary information sequence which is sent by a signal source, performs quaternary phase shift keying (QPSK) modulation and Gray mapping, maps code elements to one of four positions in a constellation diagram by taking two code elements as a group, performs Walsh-m composite sequence spectrum spreading to obtain a signal to be transmitted, and converts a digital signal to be transmitted into an underwater acoustic signal; and an underwater acoustic transducer at a receiving end converts the received underwater acoustic signal, de-spreads by using a composite sequence which is the same as that of the transmitting end to obtain a receiving signal, performs self-adaptation decision feedback equalization to obtain an amplitude fading complex signal, performs soft-demodulation soft-decoding joint iteration on the signal, stops joint iteration after set iteration frequency is reached, performs belief propagation (BP) decoding on an LDPC decoder and outputs a bit value to a sink. By the method provided by the invention, the reliability of remote underwater acoustic communication is improved. The method is applicable to the remote underwater acoustic communication.
Owner:三亚哈尔滨工程大学南海创新发展基地
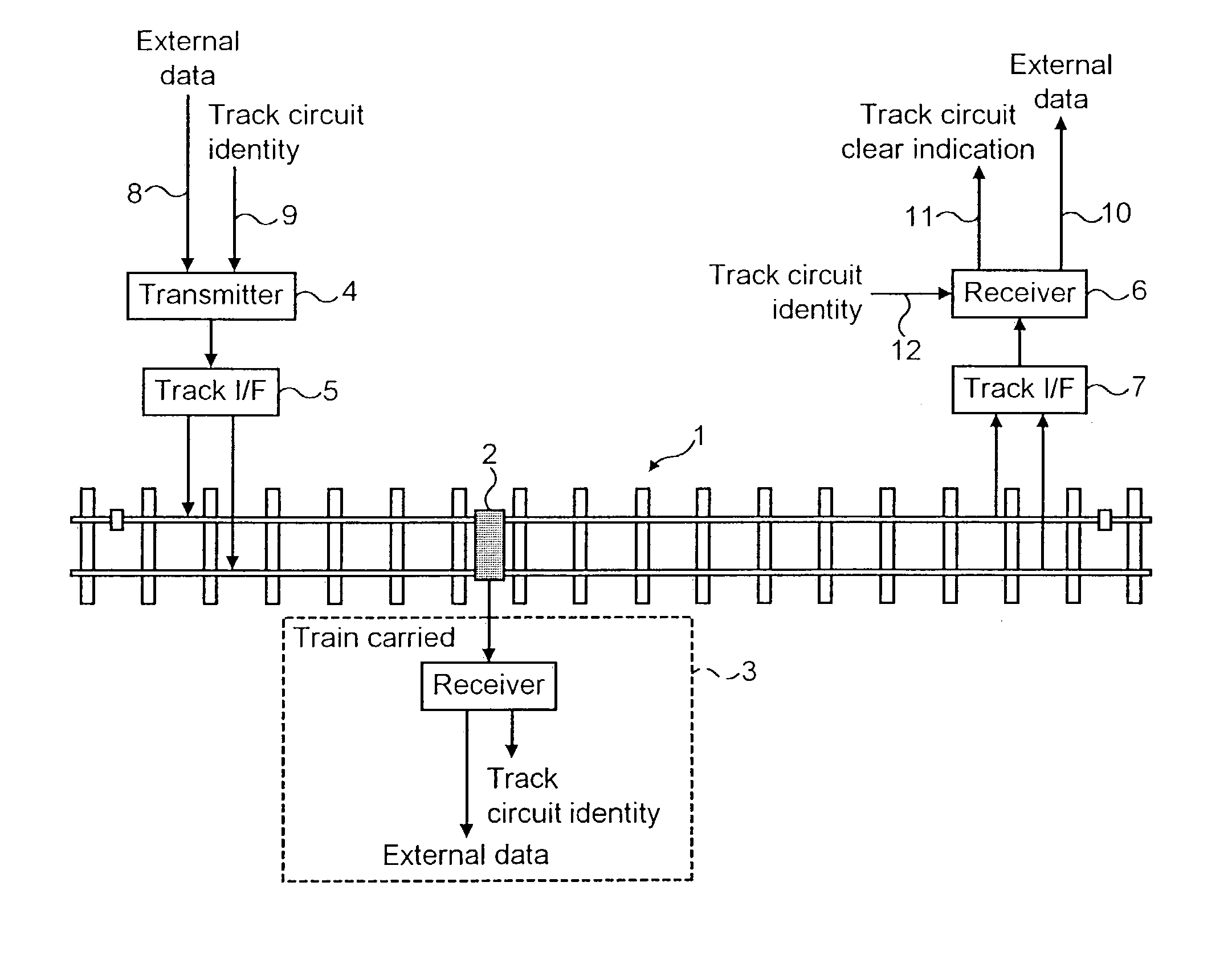
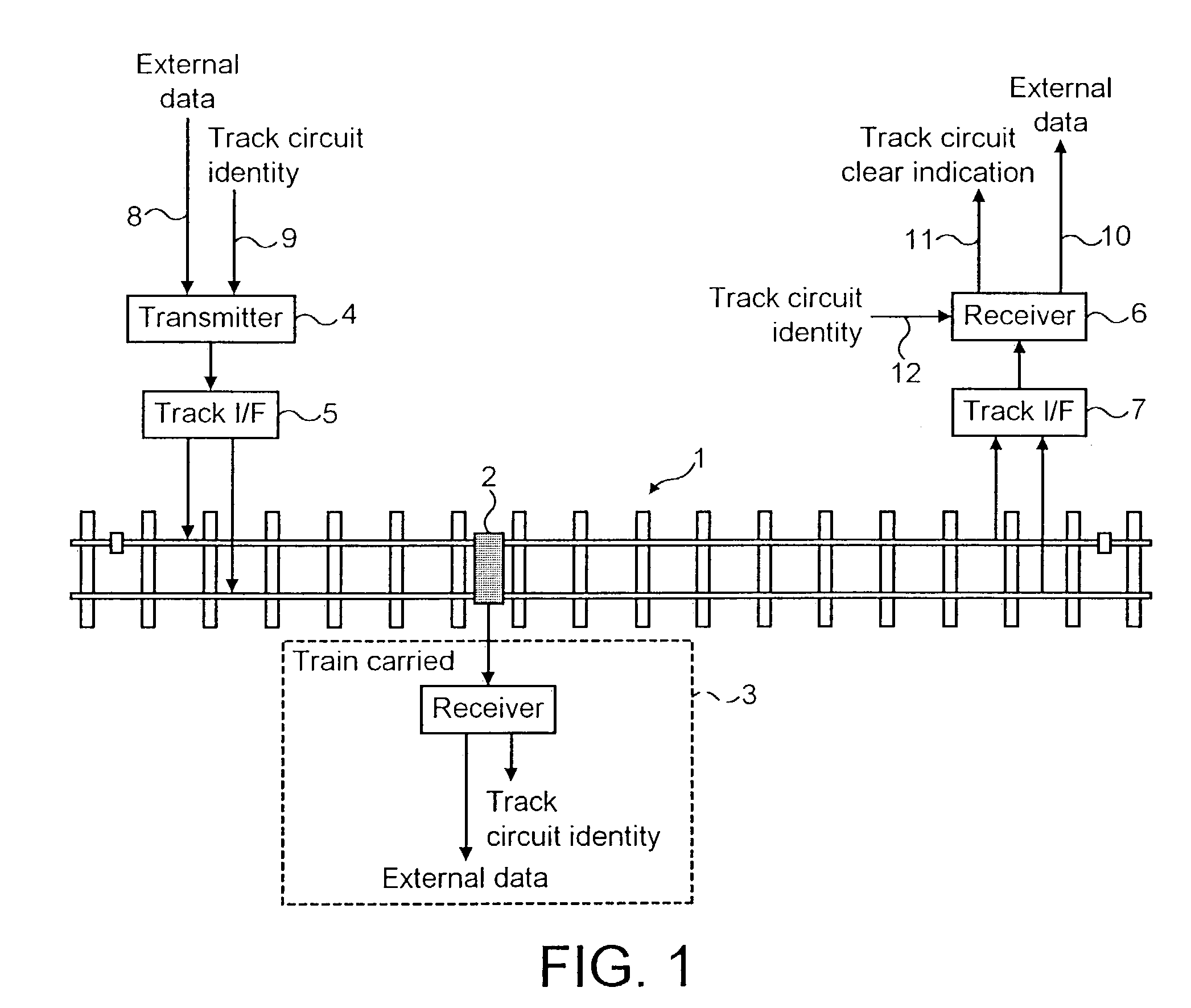
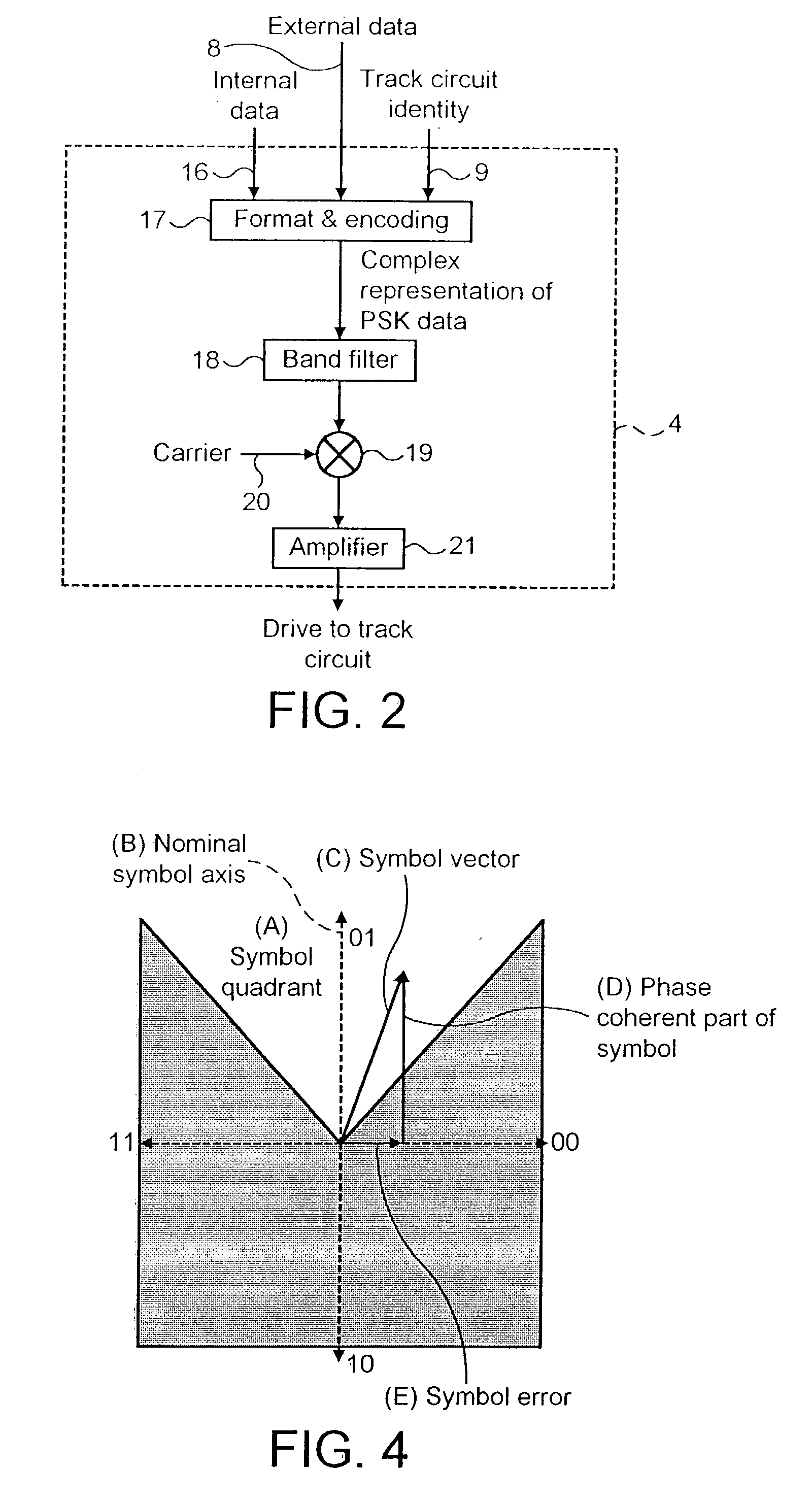
Railway track circuits
InactiveUS7017864B2Easy to shapeElectric signal transmission systemsMultiple keys/algorithms usageEngineeringTransmitter
Railway track circuit apparatus for train detection comprises a track circuit transmitter and a receiver, wherein the transmitter generates a QPSK modulated signal that is transmitted into a track circuit and which is detected by the receiver.
Owner:SIEMENS RAIL AUTOMATION HLDG
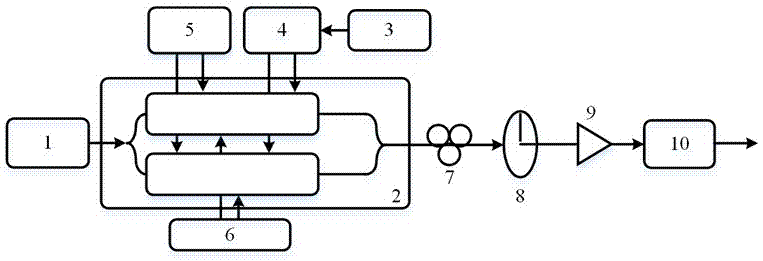
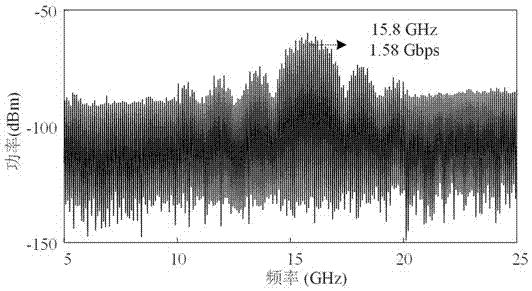
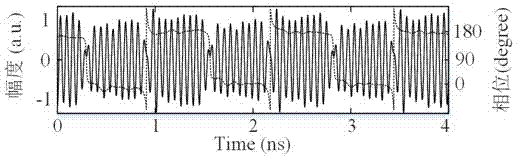
Generating device and method for QPSK mm wave of radio frequency optical fibre transmission system
InactiveCN101047448ALow costAdjustableElectromagnetic transmissionBand-pass filterMillimeter wave amplifiers
A device used for generating QPSK millimeter wave of radio frequency optical fiber transmission system consists of semiconductor laser of central station, polarization controller, optical phase modulator, optical comb fiber, optical QPSK modulator, optical branching unit / combining unit, optical detector of base station, narrow band band-pass filter, millimeter wave amplifier and millimeter wave antenna. Its optical modulating method for obtaining QPSK modulated millimeter wave signal is also disclosed.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Non-local-oscillator low-phase-noise microwave signal optical frequency-doubling generation device and method
ActiveCN107395284ARealize generationTunable microwave signal frequencyRing-type electromagnetic networksElectromagnetic transmittersPhase noiseMicrowave resonance
The invention discloses a non-local-oscillator low-phase-noise microwave signal optical frequency-doubling generation device and method, and belongs to the technical field of microwave signal generation. According to the device and the method, a narrow-band microwave photonic filter is formed by utilizing an equivalent phase modulation characteristic of one double parallel Mach-Zehnder modulator (DP-MZM) integrated in a polarized multiplexed double parallel Mach-Zehnder modulator (DP-QPSK modulator) and a phase shifting fiber bragg grating (PS-FBG); and in an optoelectronic oscillator, generation of a frequency tunable low-phase-noise microwave resonance signal is implemented. Signal frequency doubling of the generated microwave resonance signal is implemented by the other DP-MZM integrated in the DP-QPSK modulator so as to generate a high-frequency microwave signal. The non-local-oscillator low-phase-noise microwave signal optical frequency-doubling generation device and method disclosed by the invention can overcome the defect of limitation of the electronic bottleneck of an electronic system in the aspect of generating the high-frequency low-phase-noise microwave signal, and implement generation of the low-phase-noise microwave signal with a magnitude of dozens of GHz and even hundreds of GHz.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
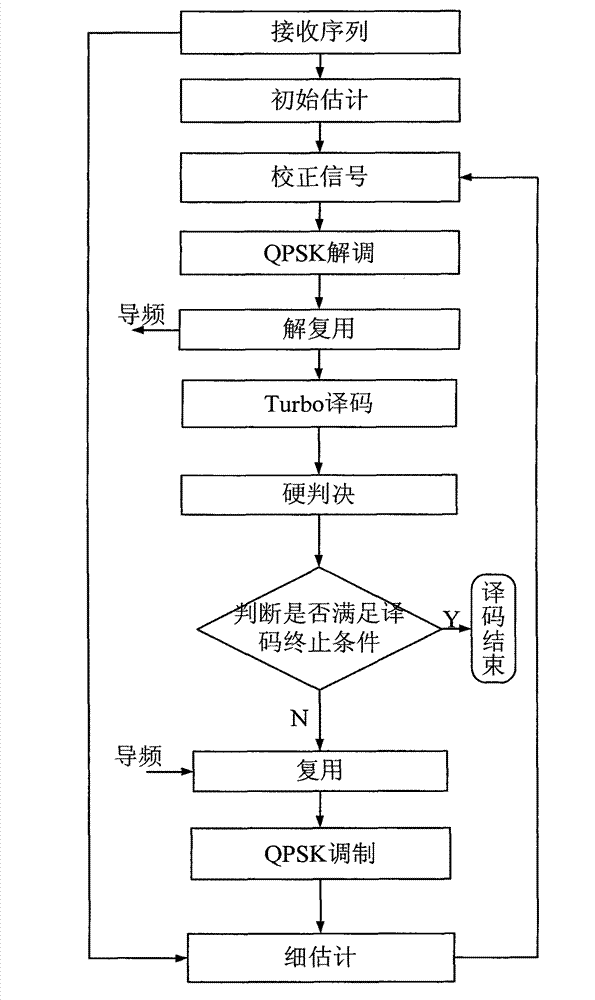
Carrier synchronization system and method of combining pilot frequency and iterative decoding
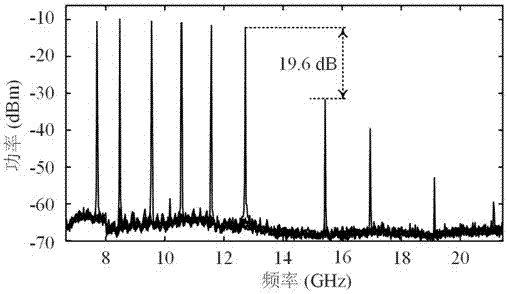
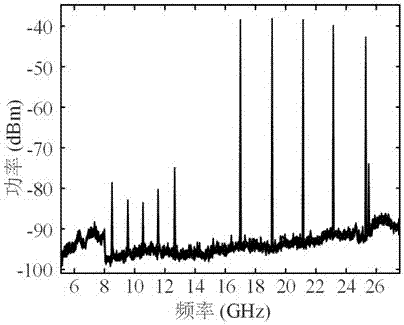
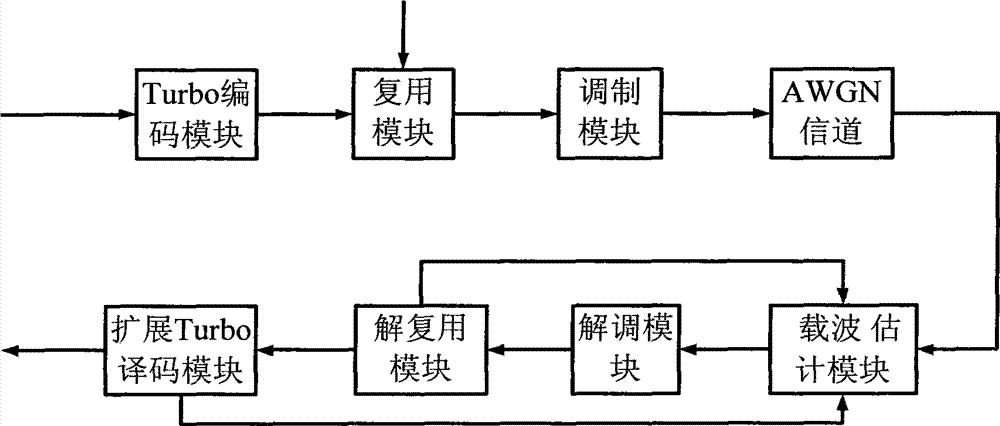
InactiveCN102932309AOvercome the disadvantage of low frequency estimation accuracyImprove estimation accuracyError preventionBaseband system detailsMultiplexingTurbo coded
The invention discloses a carrier synchronization system and a method of combining pilot frequency and iterative decoding. The system comprises a Turbo coding module, a multiplex module, a modulation module, a carrier estimation module, a demodulation module and an extension Turbo decoding module. The method includes the steps of receiving sequences, initial estimation, correcting signals, quadrature phase shift keying (QPSK) demodulation, data demultiplexing, Turbo decoding, hard decision, decoding termination conditions, data multiplexing, QPSK modulation and fine estimation. The carrier synchronization system and the method of the combining the pilot frequency and the iterative decoding have the advantages that the defect that in prior art, the frequency estimation accuracy is low caused by the fact that pilot frequency with the same number and maximum likelihood algorithm are utilized is overcome, the carrier frequency estimation accuracy is improved, simultaneously the disadvantage that in prior art, the output of a Turbo decoder is required to be recoded or subjected to nonlinear transformation is overcome, and the algorithm complexity of combining Turbo decoding and carrier synchronization process is reduced.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
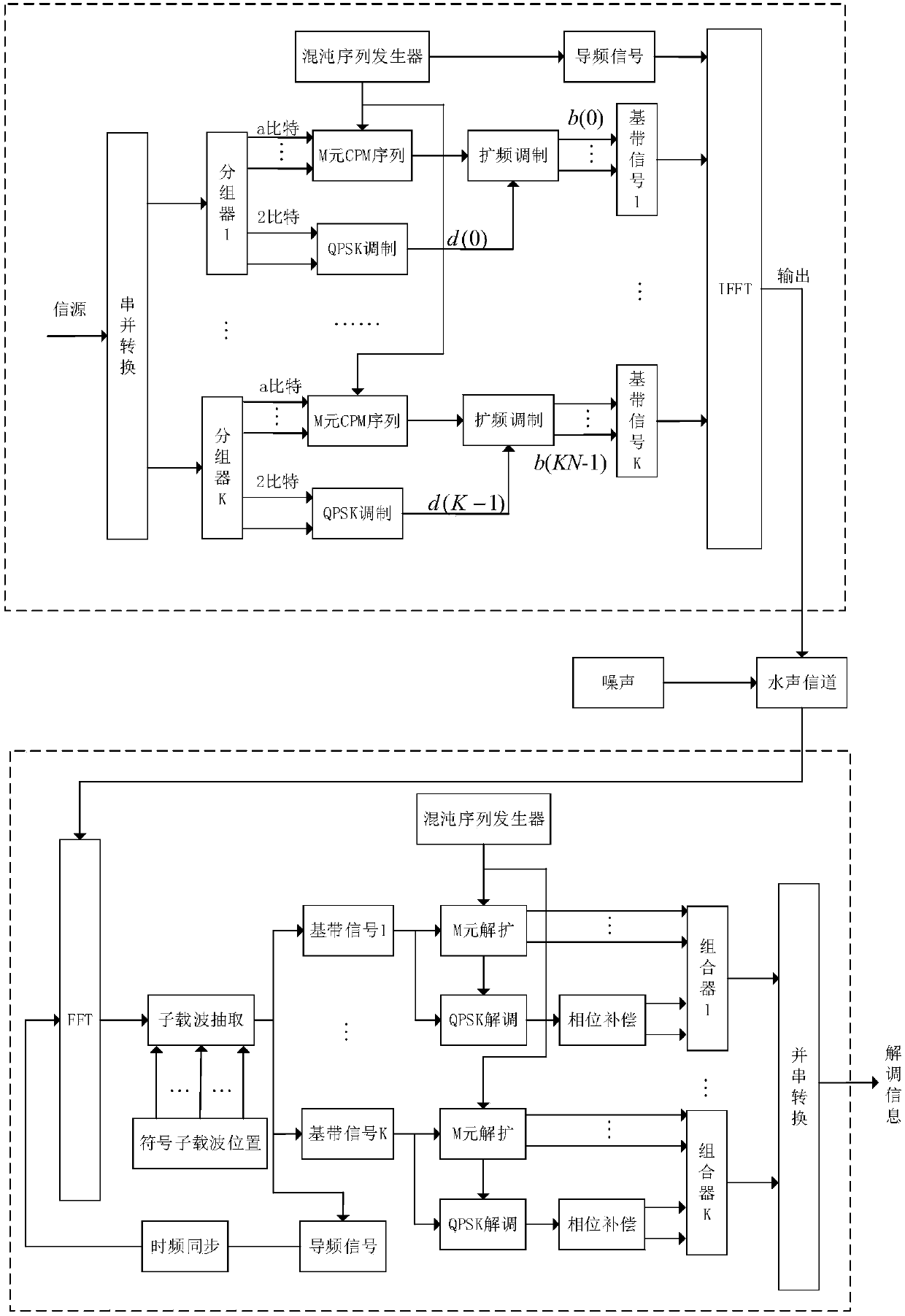
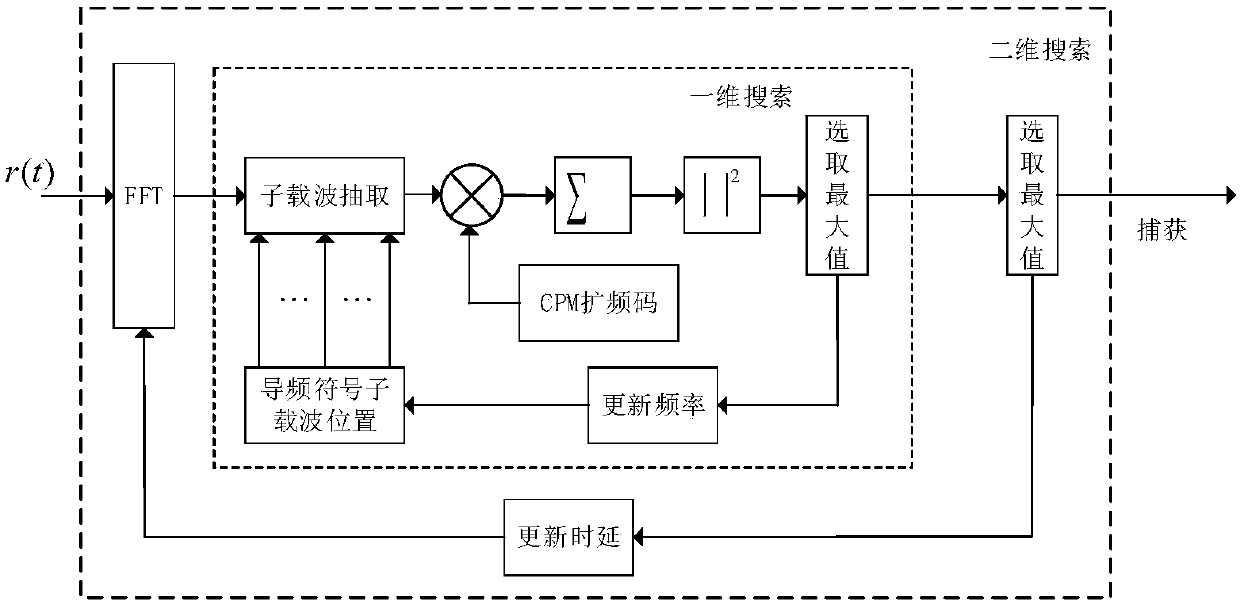
Orthogonal multi-carrier M-element chaotic phase modulation spread spectrum underwater acoustic communication method
ActiveCN110266622AOvercoming the disadvantage of poor cross-correlationHigh communication ratePhase-modulated carrier systemsMulti-frequency code systemsMulti carrierComputer science
The invention discloses an orthogonal multi-carrier M-element chaotic phase modulation spread spectrum underwater acoustic communication method. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) dividing an input information sequence sent by an information source into K groups of information sequences with the length of a + 2 by a transmitting end, respectively feeding the information sequences into K grouping devices; using each grouping device to carry out M-element chaotic phase modulation spread spectrum mapping on the previous a bits to obtain a chaotic phase modulation spread spectrum code, performing QPSK modulation on two rear bits, performing spread spectrum modulation by using the obtained chaotic phase modulation spread spectrum code to obtain baseband signals, and respectively mapping K groups of baseband signals to subcarriers of OFDM symbols to perform OFDM modulation to obtain a digital signal to be transmitted and transmitting the digital signal to be transmitted; and 2) enabling the receiving end to adopt a section of chaotic phase modulation spread spectrum signal in OFDM symbols as a pilot signal, performing time-frequency two-dimensional search on the received digital signal to complete time-frequency synchronization, then performing OFDM demodulation to obtain K groups of baseband signals, and inputing the K groups of baseband signals into K combiners to complete despreading and QPSK demodulation to obtain a binary sequence.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Signal Space Expansion For a 16 Qam Scheme
InactiveUS20080192851A1Improve bit error rateReduce complexityModulation with suppressed carrierMultiple carrier systemsData streamCommunications system
The invention relates to methods for transmitting and receiving a data bit stream in a communication system using a 16-QAM constellation. Further, an apparatus for performing the methods is provided. To provide a modulation and coding scheme using a signal space expansion and 16-QAM which improves the bit-error rate in comparison to QPSK modulated signals and still provides the possibility to implement coders and decoders with low complexity the invention suggests the use a 16-QAM constellation with specially selected mapping rules together with repetition coding (signal space expansion) and interleaving of the data stream to be transmitted.
Owner:OPTIS WIRELESS TECH LLC
Optical generation device and method for phase coding signal with tunable multiplication factor
ActiveCN107547138AReduce bandwidth requirementsHigh multiplication factorElectromagnetic transmittersElectromagnetic receiversPhase CodePolarizer
The invention relates to an optical generation device and method for a phase coding signal with a tunable multiplication factor. The device comprises a laser, a DP-QPSK modulator, a microwave signal generator, an electric amplifier, a coding signal generator, a direct current power, a polarization controller, a polarizer, an optical amplifier, and a photo detector. The method comprises the step ofgenerating binary phase coding signals with different multiplication factors according to needs by using a non-linear modulation characteristic of the DP-QPSK modulator, wherein the multiplication factors can be any one of one to four, and the frequencies of the generated signals are tuned by adjusting the frequency of an input microwave signal. The device is based on an integrated modulator structure, has a simple system, has stable performance, overcomes defects that a traditional manner of generating a pulse compression signal in the frequency domain is limited by the rate and bandwidth ofan electronic device, has difficulty in generating a high-frequency signal or cannot generate the high-frequency signal and the generated signal cannot be tuned flexibly in frequency, greatly improves the frequency of generating the phase coding signal, and can produce phase coding signals with very large frequency tuning range.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com