Method for feeding back ACK/NACK information
A technology for feedback information and channels, applied in the field of feedback ACK/NACK information, can solve problems such as failure to detect loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
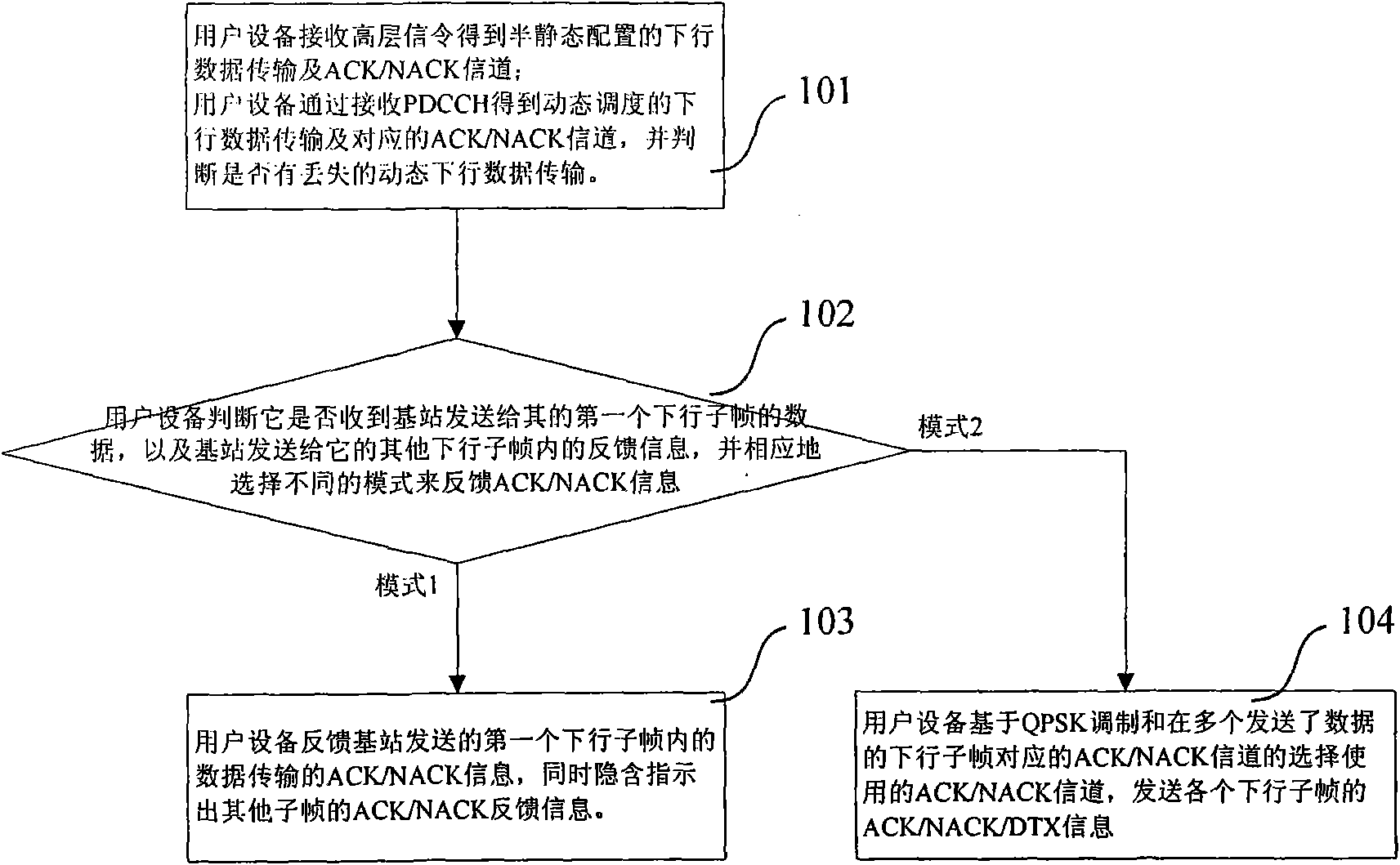
[0051] The first mode is used to deal with the following data transmission situation: the user equipment judges that it has received the data in the first downlink subframe sent by the base station, and the index of this subframe is k, but the k+1~ In the N-1 downlink subframes, either the base station does not send data to the user equipment; or the user equipment does not receive the data sent by the base station; or the user equipment receives the data sent by the base station but decodes it incorrectly. Specifically divided into the following three situations. The first situation is that the base station only sends data to the user equipment in one downlink subframe, and the user equipment receives this data. The second case is that the base station sends data for the user equipment in multiple downlink subframes, and the user equipment receives the data in the first downlink subframe sent to it by the base station, and the base station sends data to it in other downlink s...
Embodiment 2
[0077] The first mode is used to deal with the following data transmission situation: the user equipment judges that it has received the data in the first downlink subframe sent by the base station, and the index of this subframe is k, but the k+1~ In the N-1 downlink subframes, either the base station does not send data to the user equipment; or the user equipment does not receive the data sent to it by the base station. Including the following two situations. The first situation is that the base station only sends data for the user equipment in one downlink subframe, and the user equipment receives the data of this downlink subframe. The second case is that the base station sends data for the user equipment in multiple downlink subframes, and the user equipment receives the data in the first downlink subframe sent to it by the base station, and the base station sends data to it in other downlink subframes None of the data was received.
[0078] In this way, in the first mo...
Embodiment 3
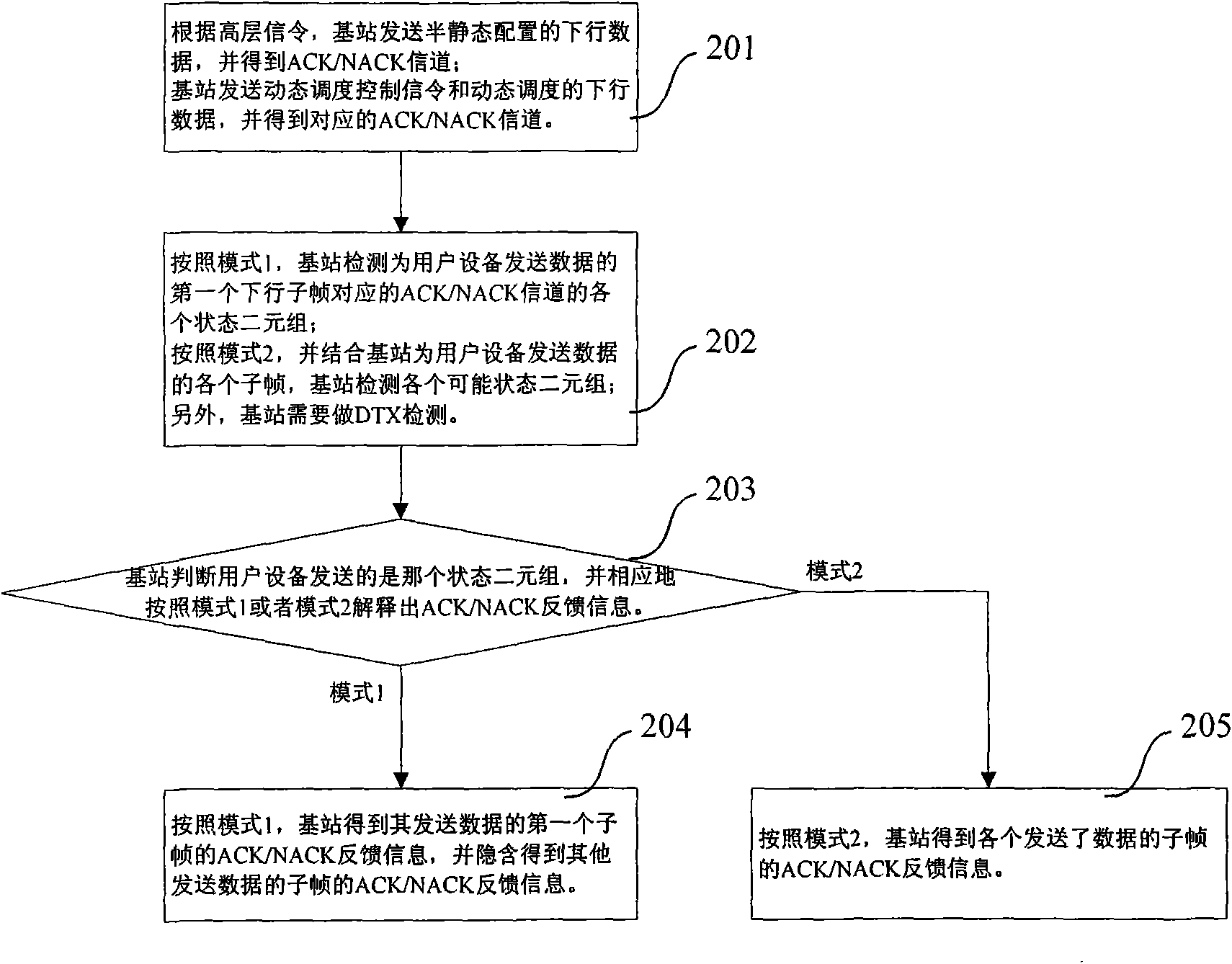
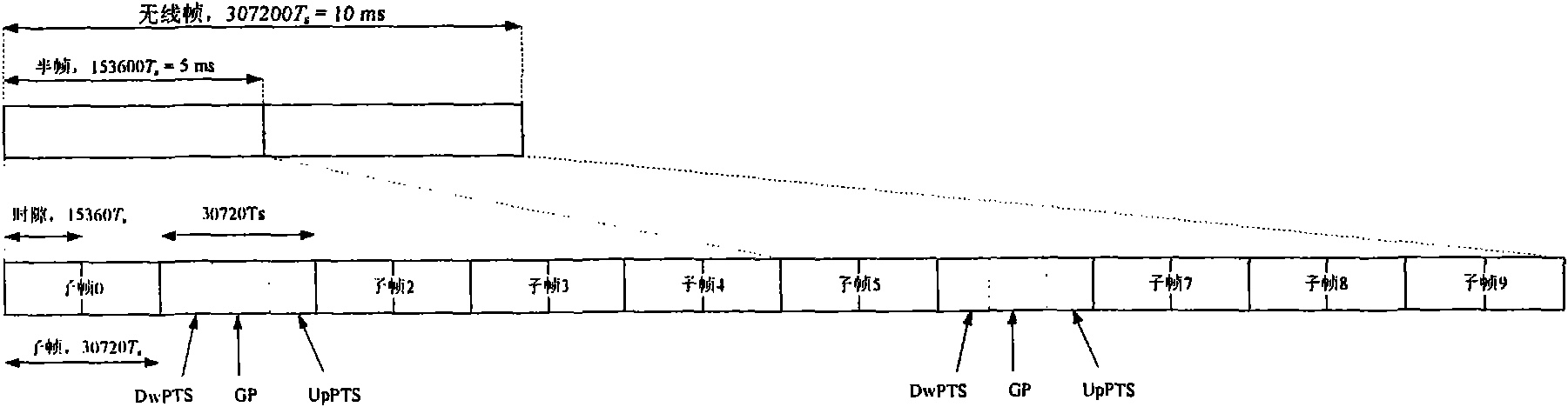
[0084] It is assumed here that in the first mode, it is specified that the first subframe in which the base station sends data refers to the first subframe in which the base station sends dynamic data. In LTE TDD, the DAI of the dynamic downlink control channel in this subframe is 0. The following two cases are handled in the second mode, that is, the case where the base station only sends semi-static downlink data; or although the base station sends both dynamic downlink data and semi-static downlink data, the user equipment does not detect the dynamic scheduling control channel, thus From the perspective of the user equipment, currently there is only semi-static downlink data transmission.
[0085] The first mode is used to deal with the following data transmission situations: the user equipment determines that it has received the data in the first dynamic downlink subframe sent to it by the base station, and the index of this subframe is k, and in other downlink subframes ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com