Patents
Literature
930 results about "Fixed interval" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
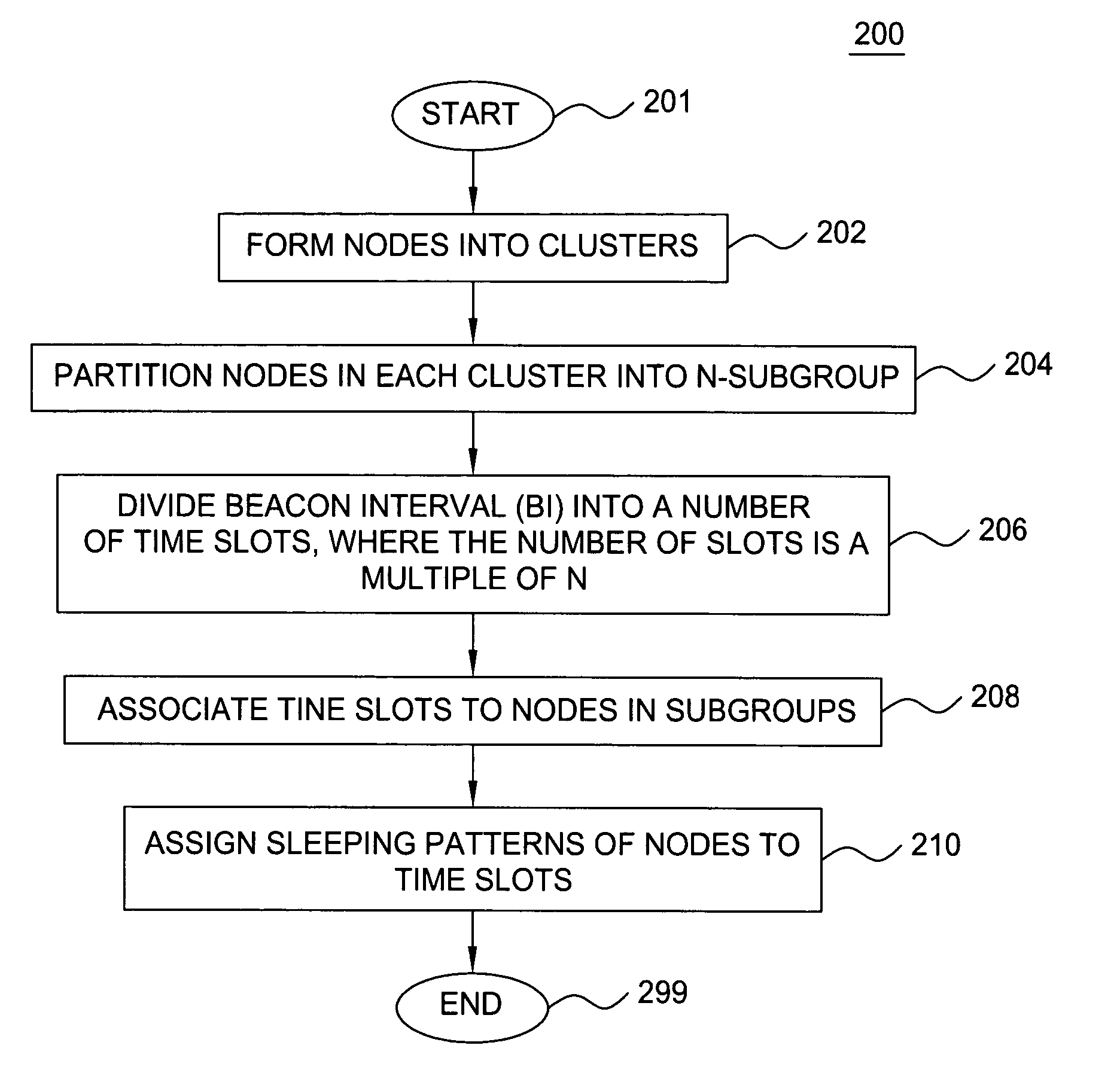
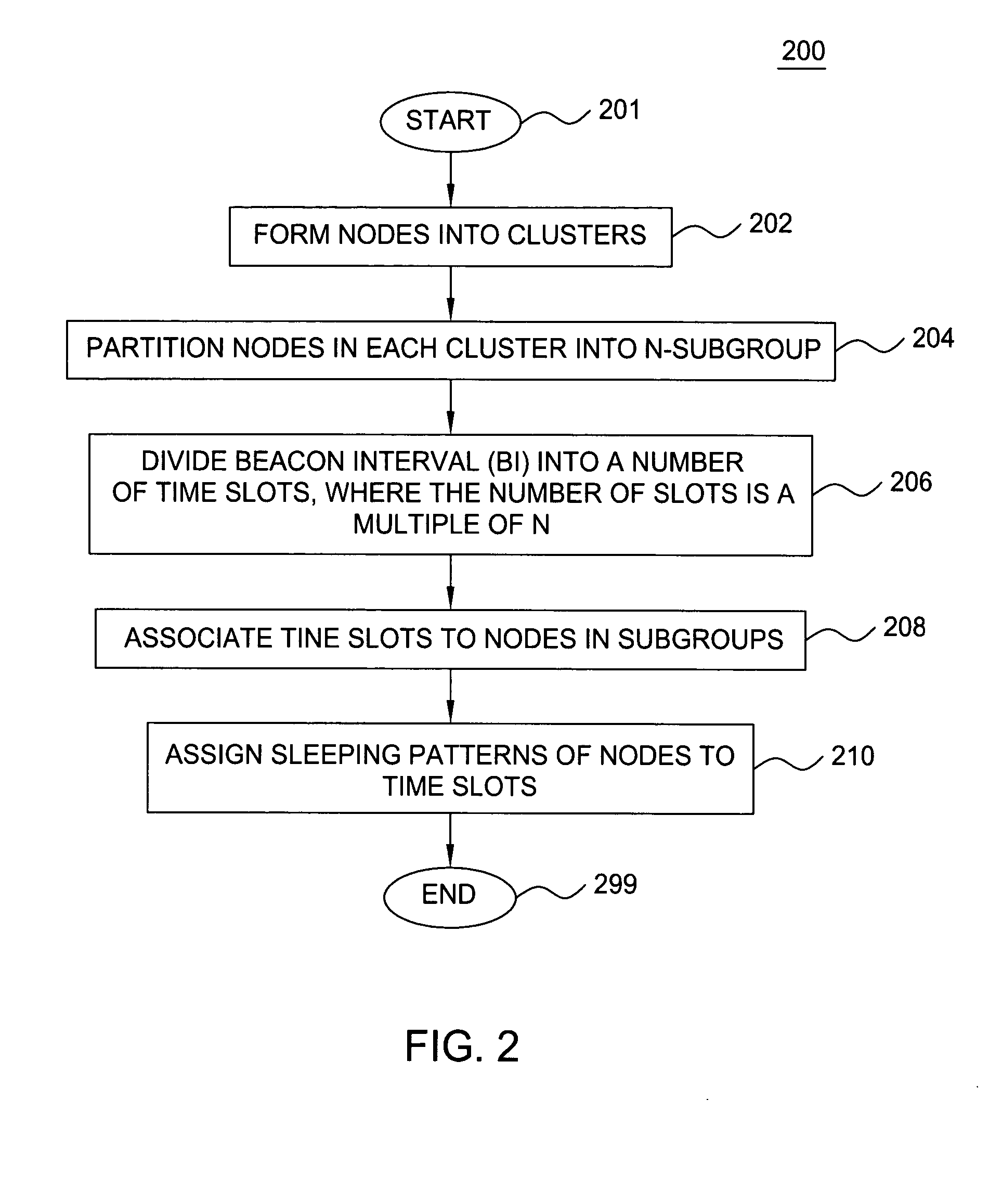
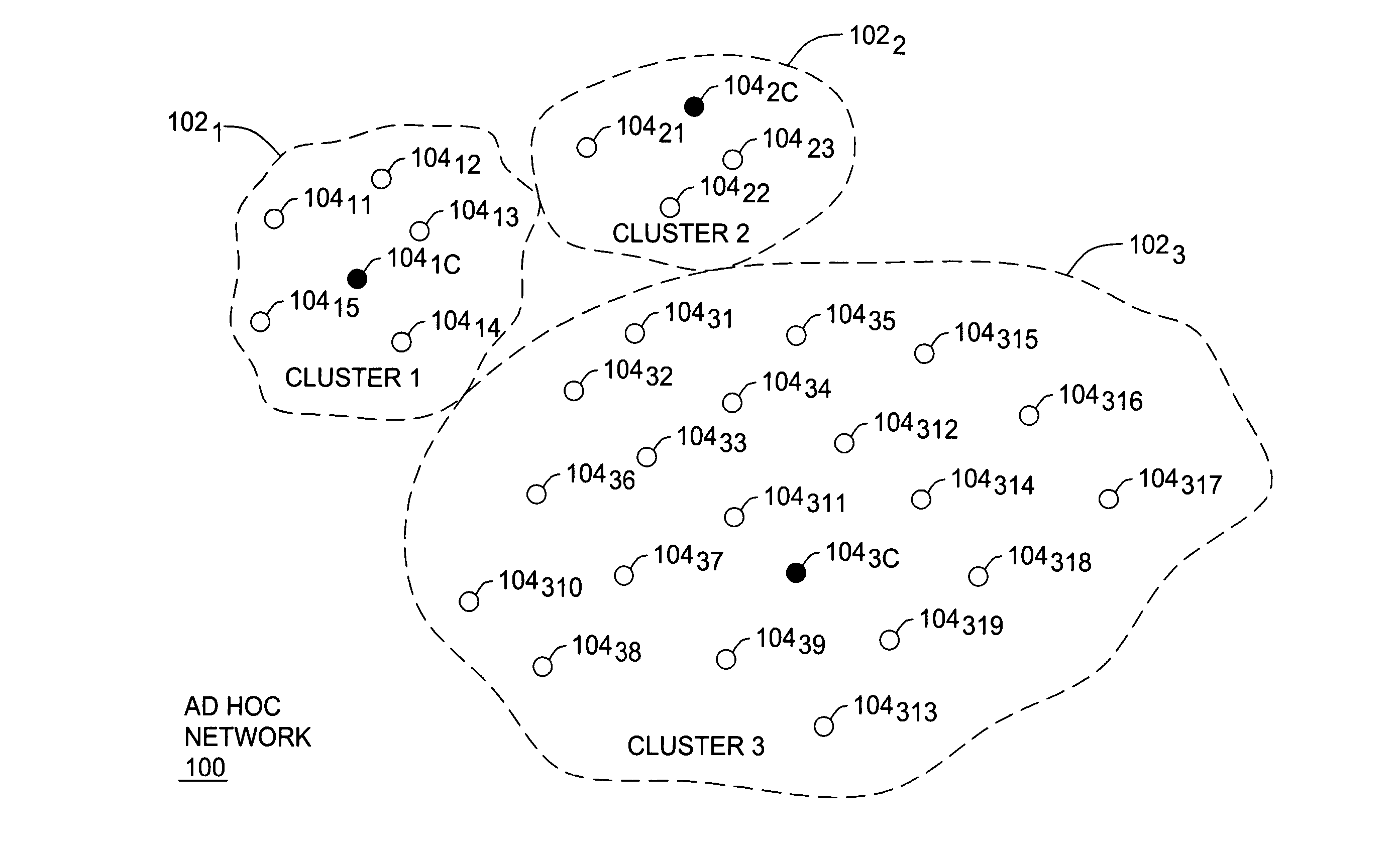
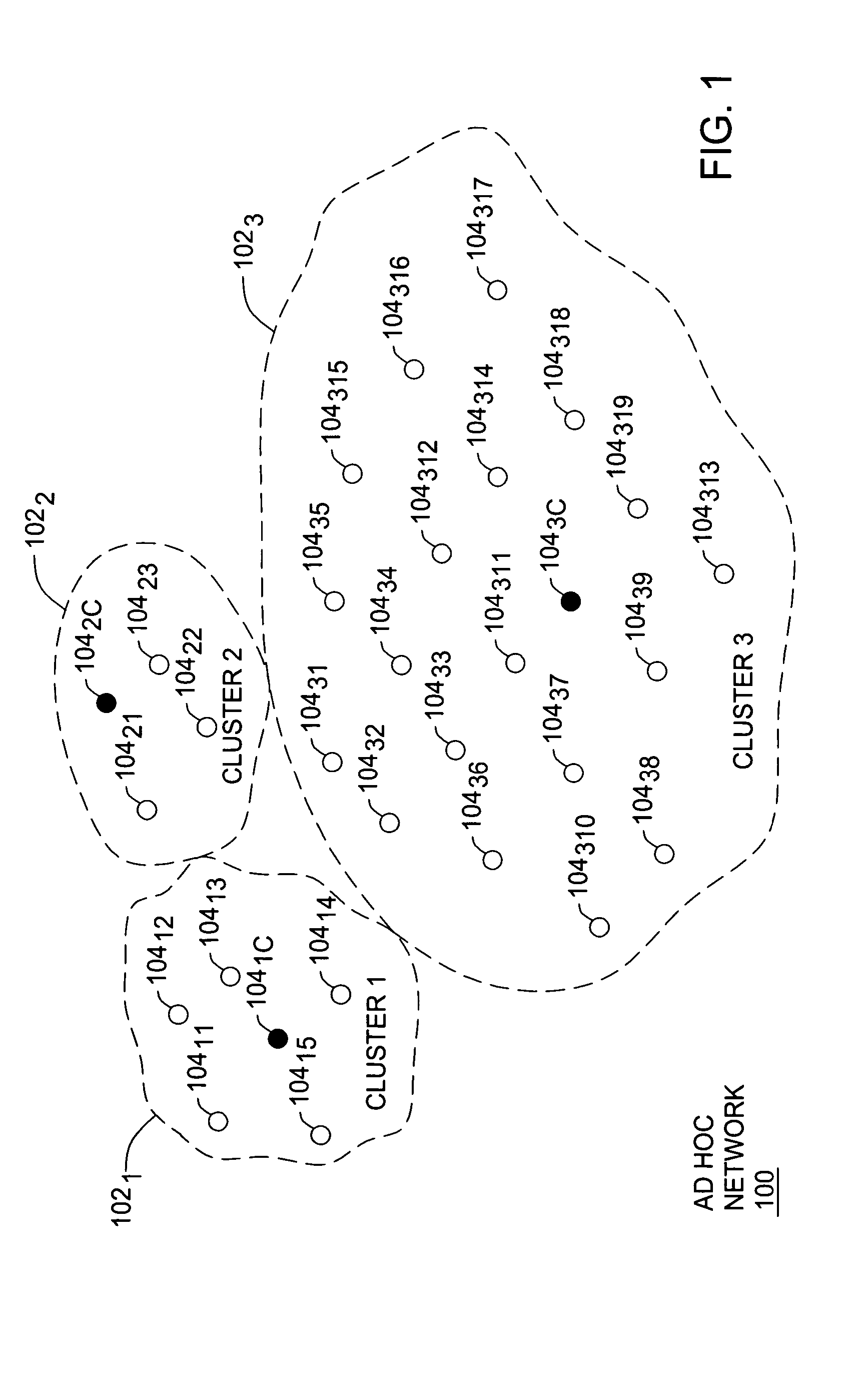
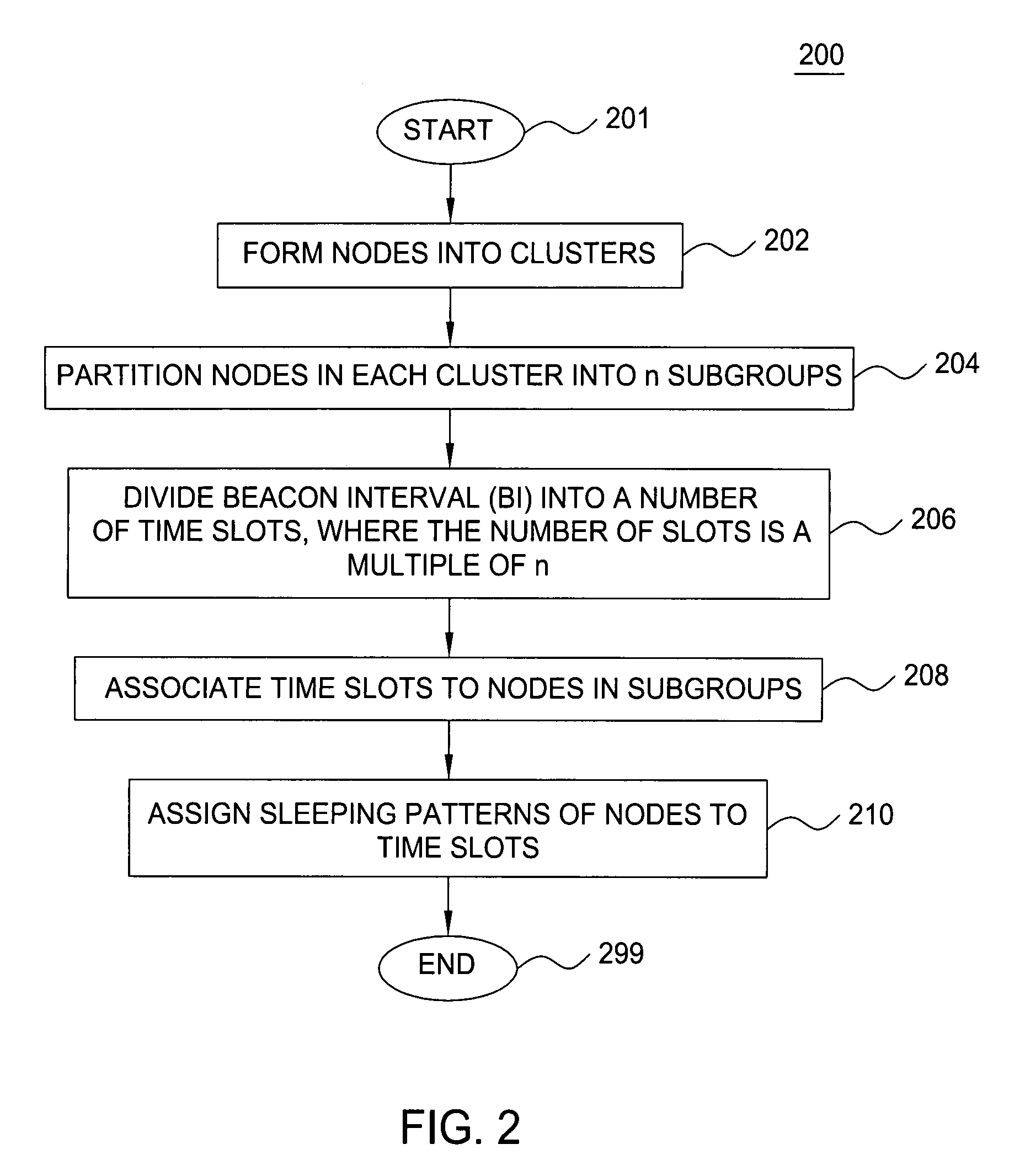
Clustering based load adaptive sleeping protocol for ad hoc networks
InactiveUS20050117530A1Sleep longerNeed to synchronizePower managementSynchronisation arrangementSleep patternsBiological activation
A clustering based load adaptive sleeping protocol for ad hoc networks includes a plurality of nodes forming a cluster, where the nodes in the cluster are partitioned into n groups. This partitioning is performed based on the node ID (e.g. node_id modulo n). The cluster head transmits a beacon at fixed intervals. The beacon interval is divided into N slots, where N is a multiple of n. Node sleep / activation times are synchronized to the beacon interval slots. The node's group number is used to determine the slots within a beacon interval that a node begins it s sleep cycle. Therefore, no additional signaling is required between nodes to indicate sleep patterns. The sleeping time of each node may be increased when extended periods of inactivity are detected according to an adaptive procedure.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
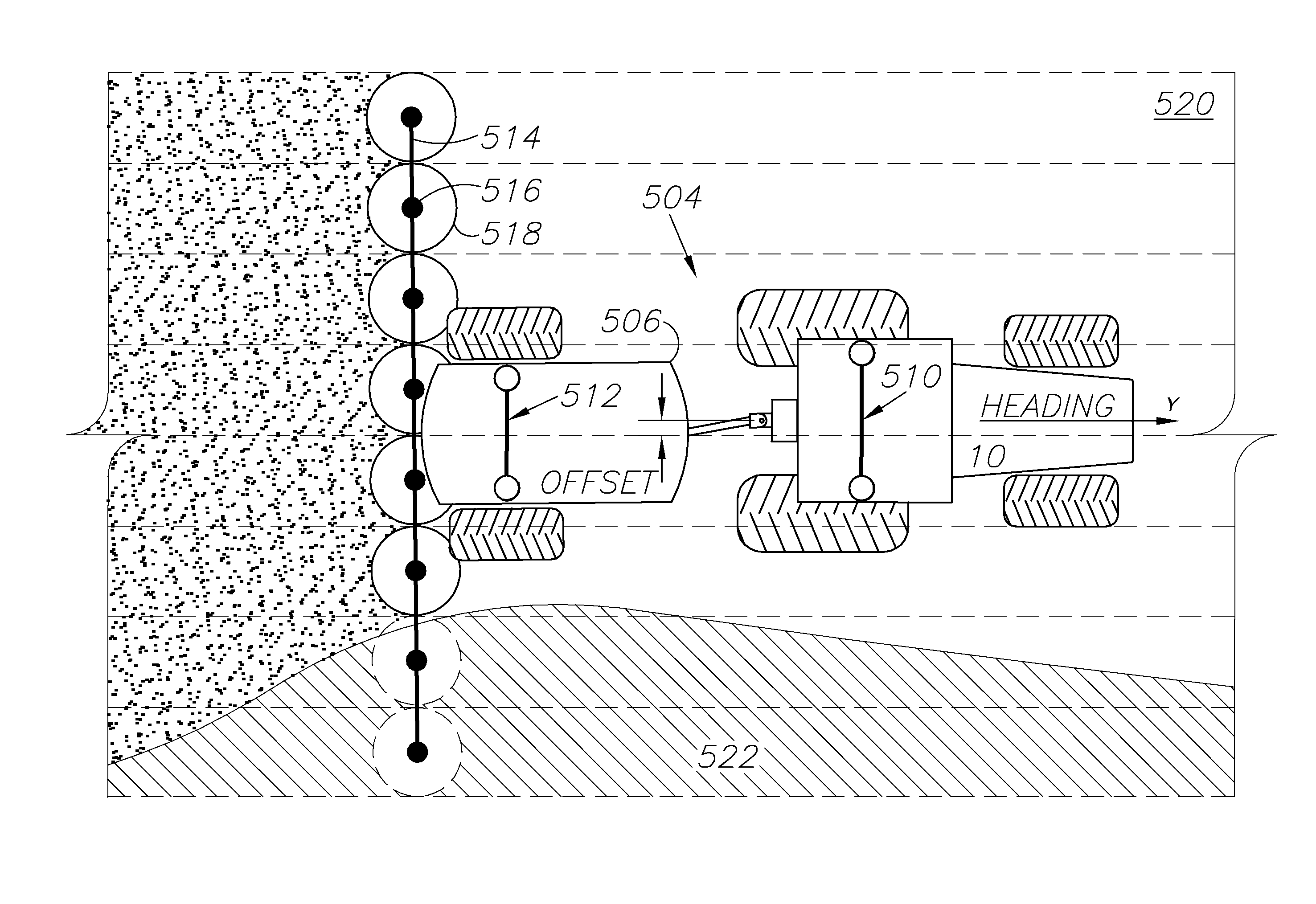
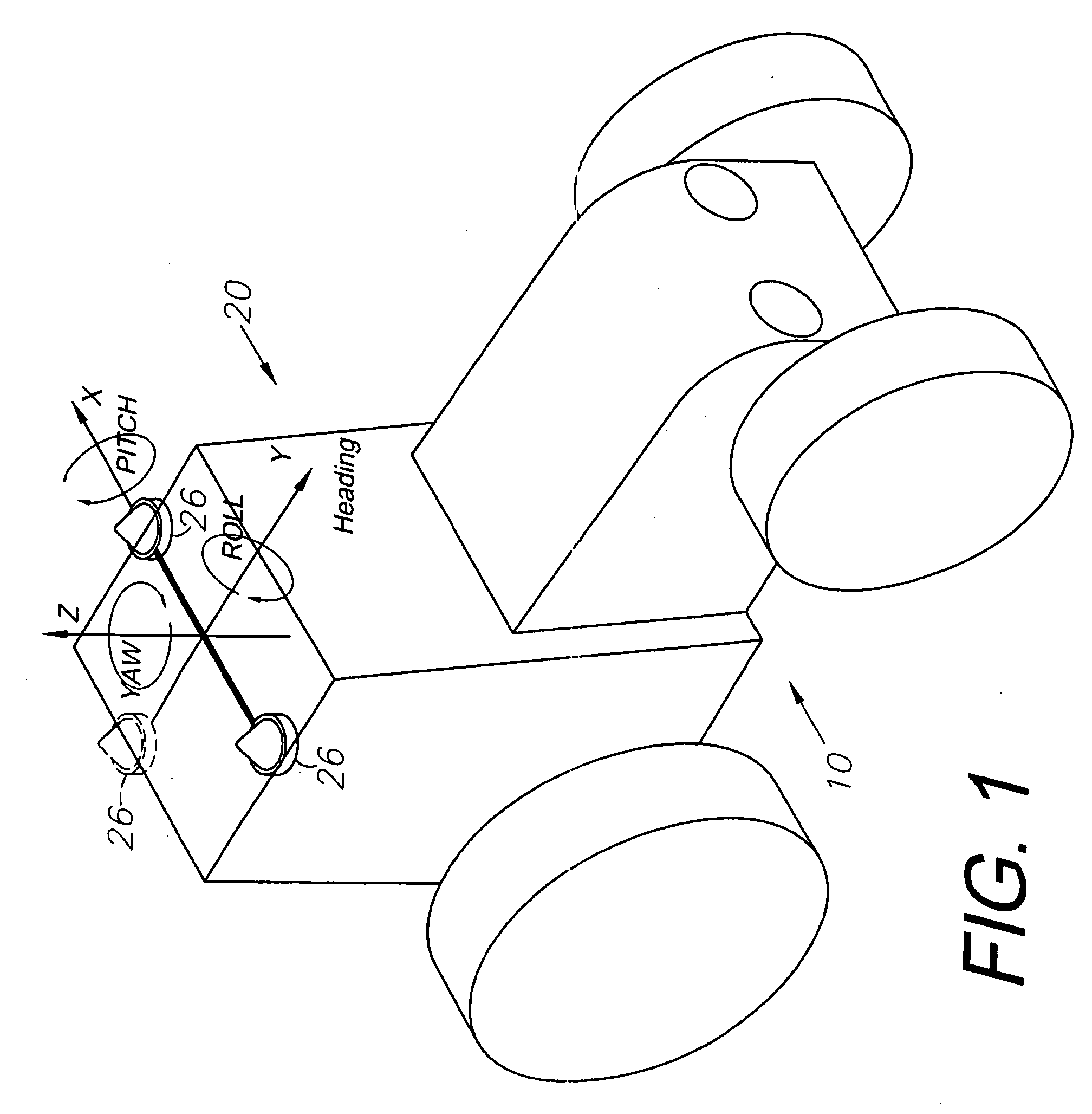
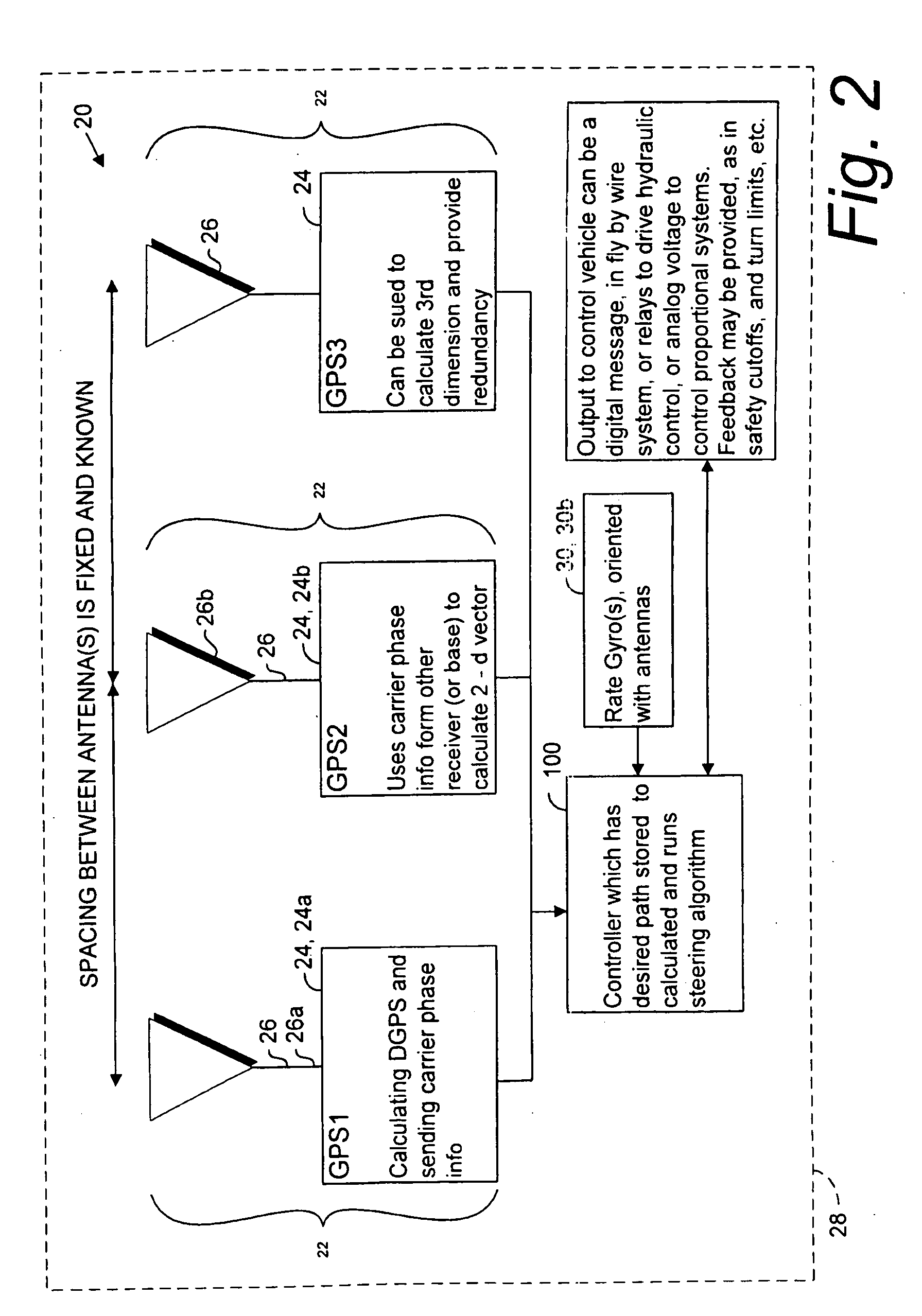
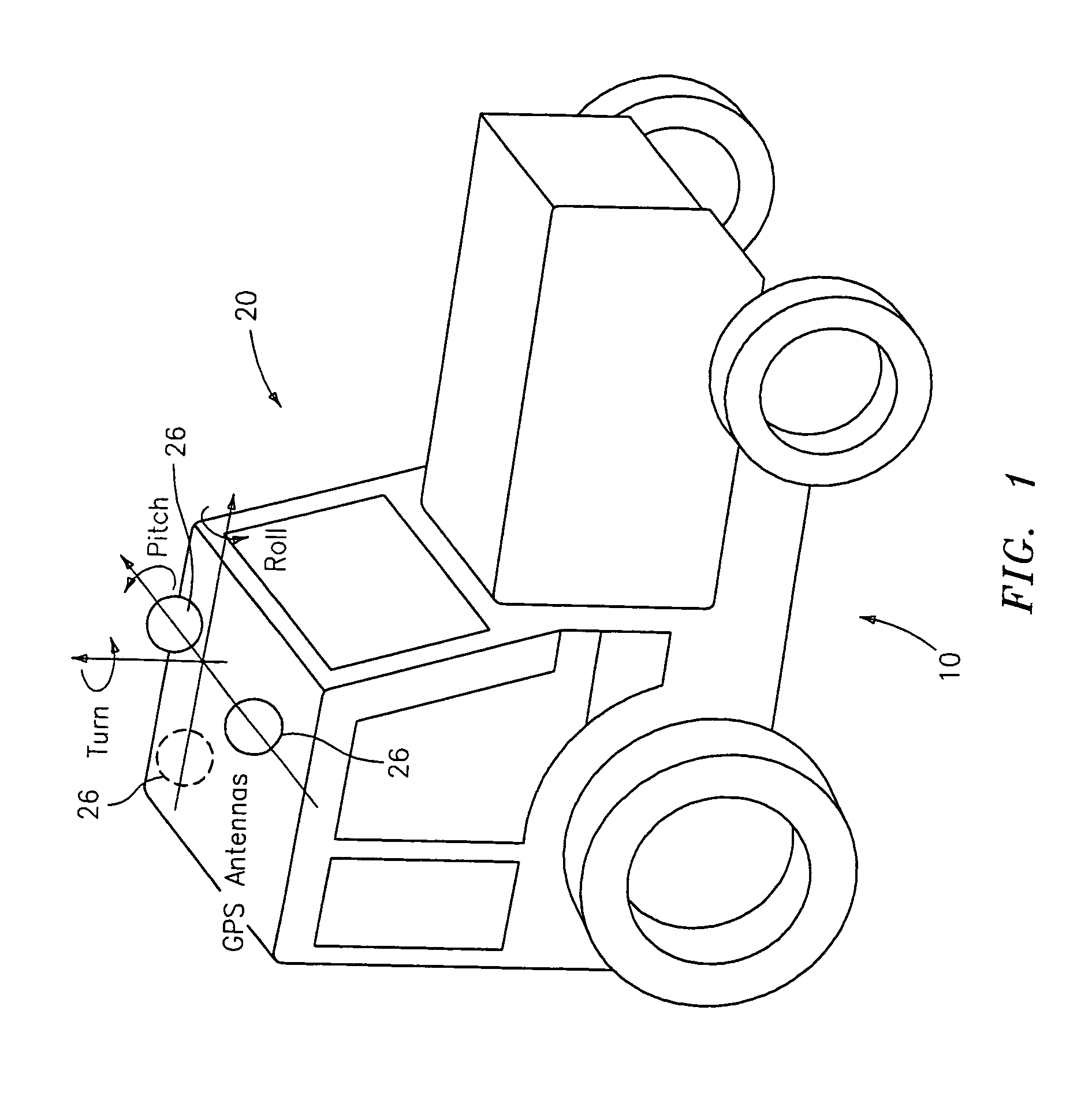
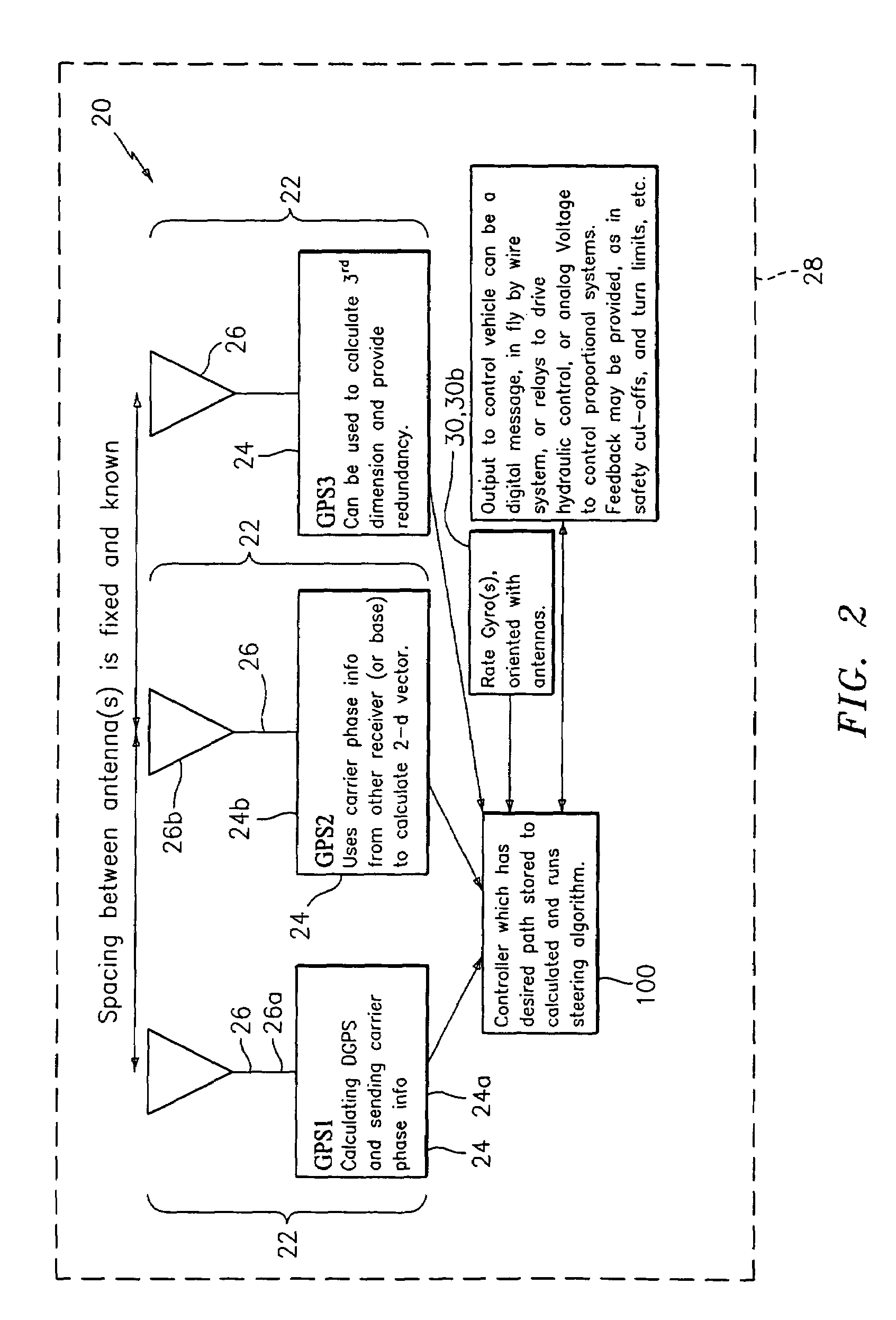
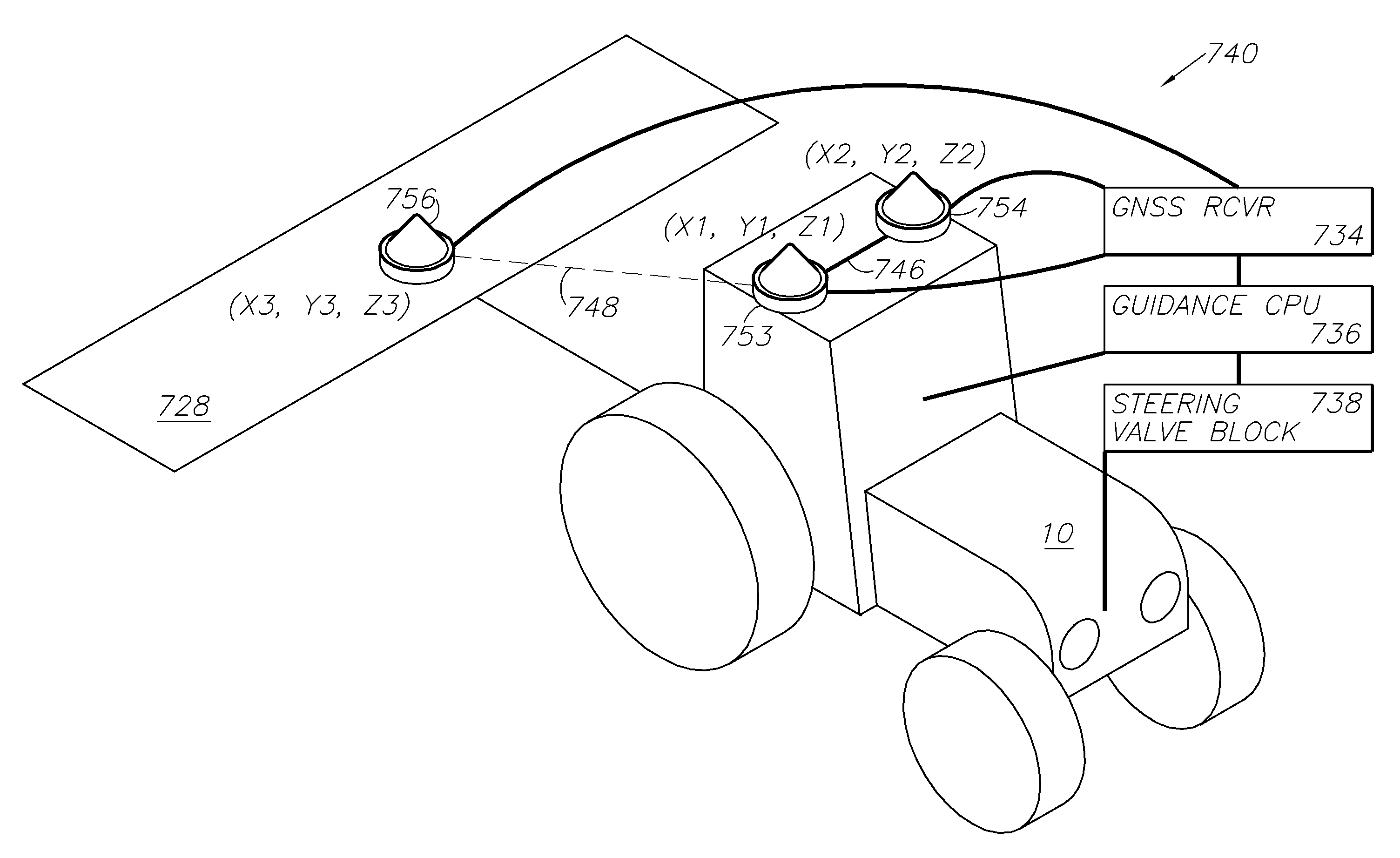
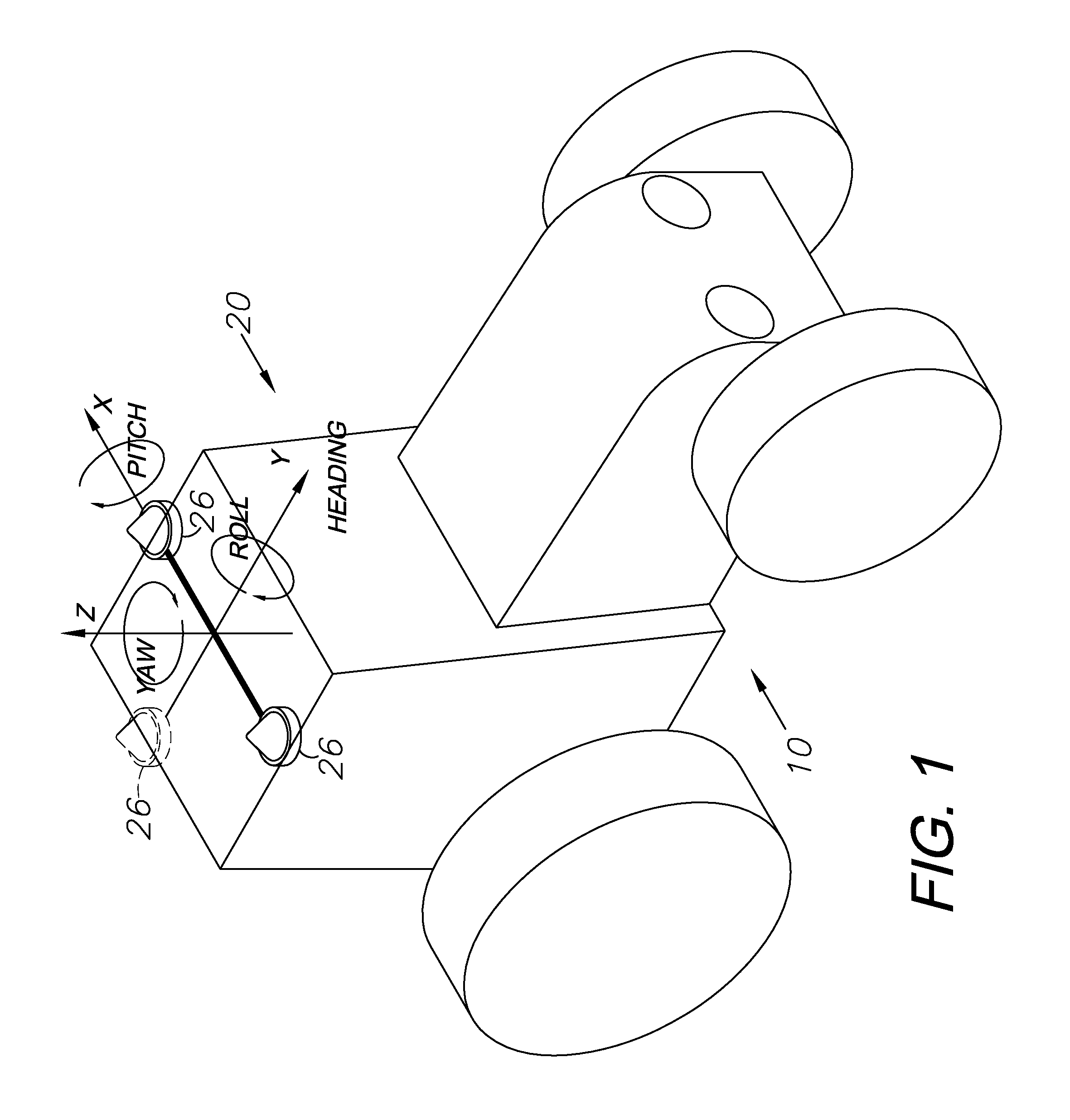
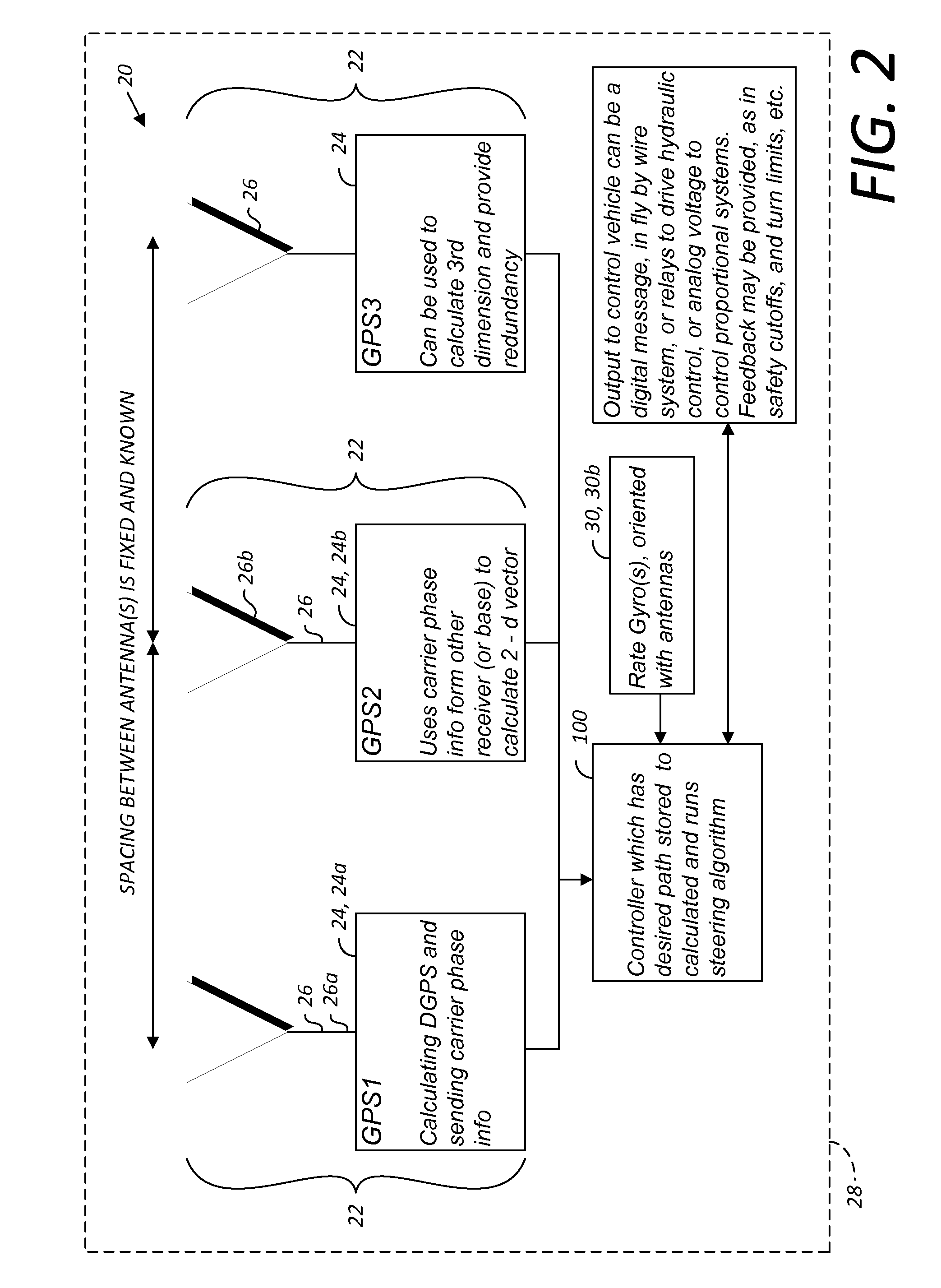
GNSS and optical guidance and machine control
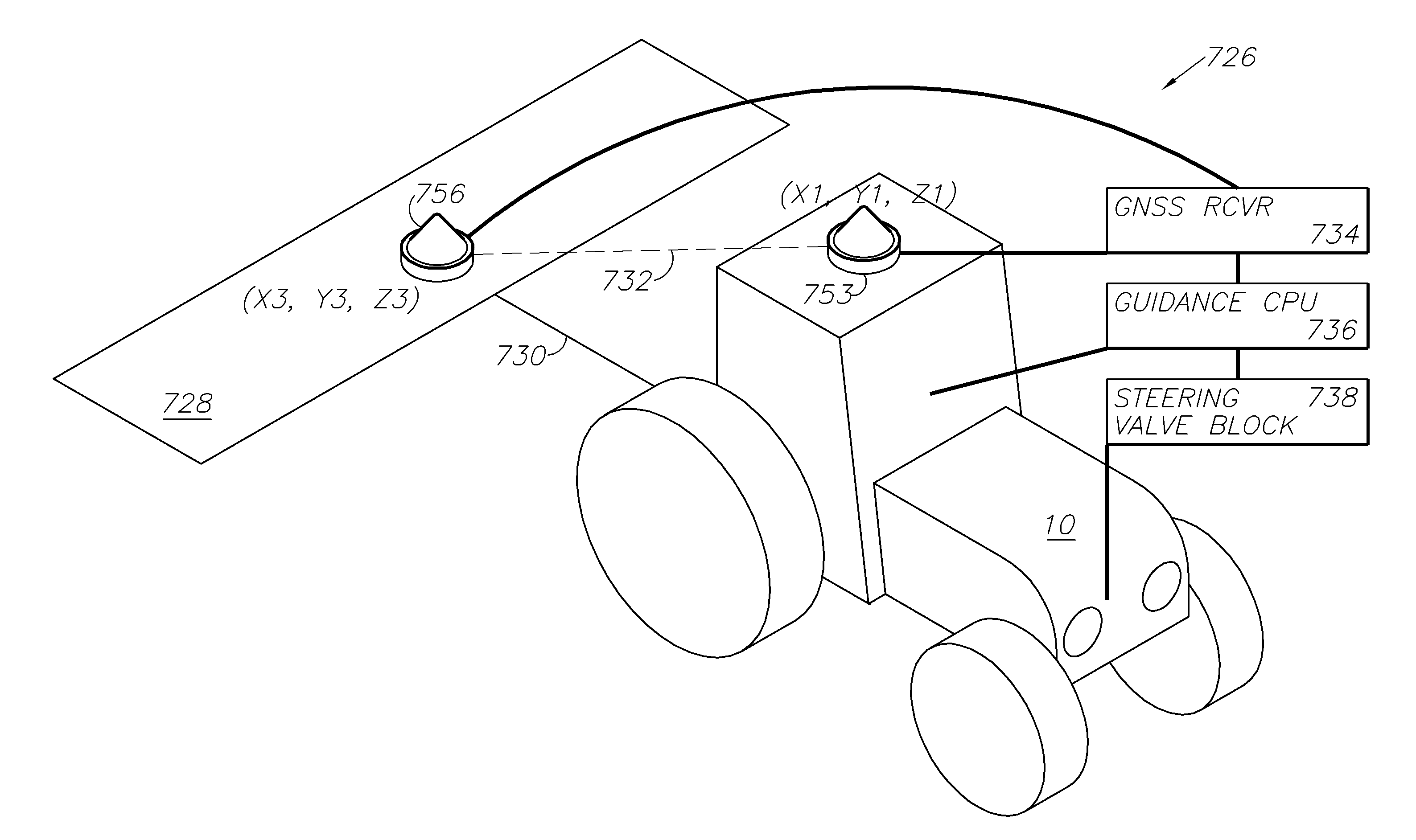
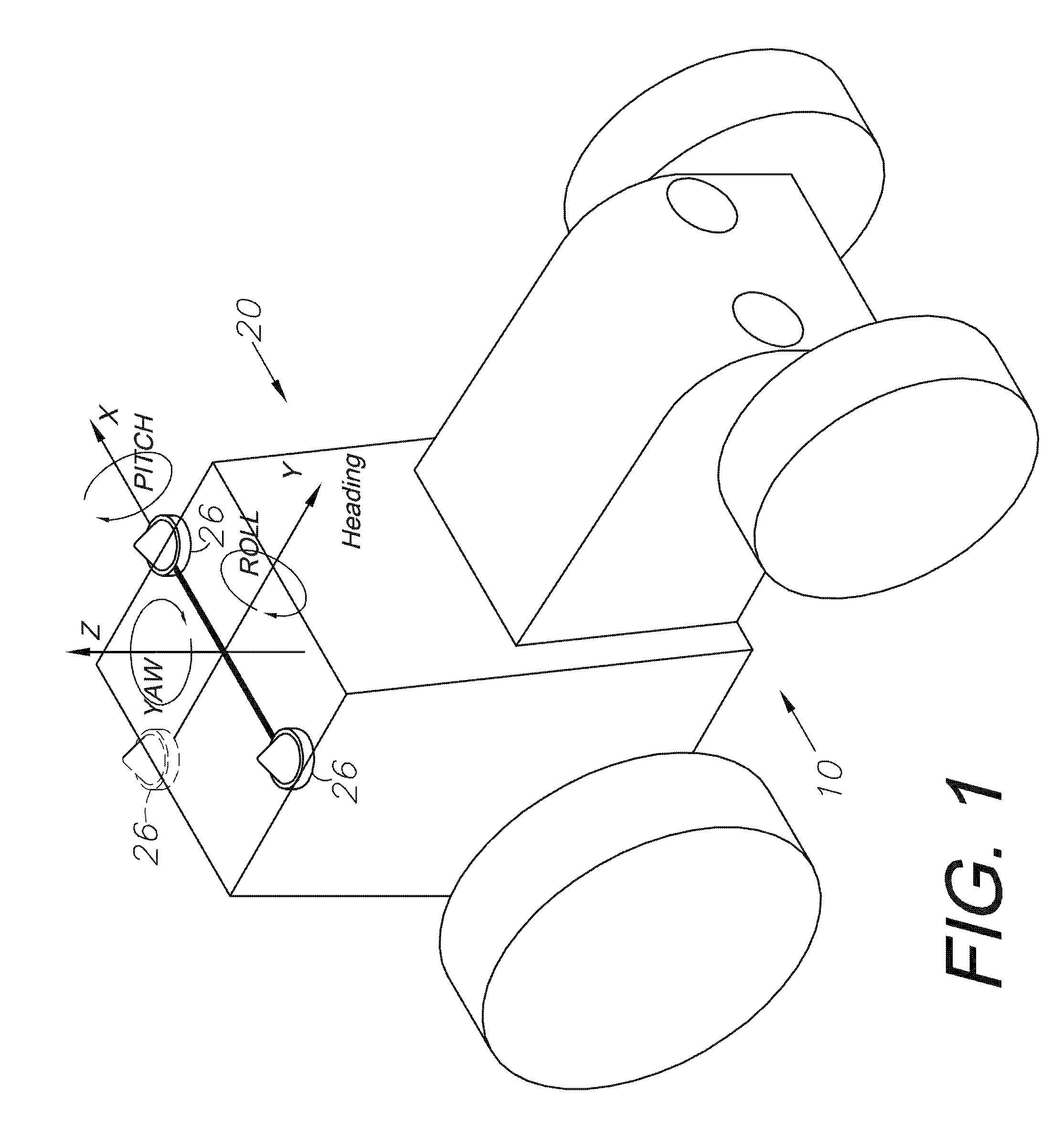
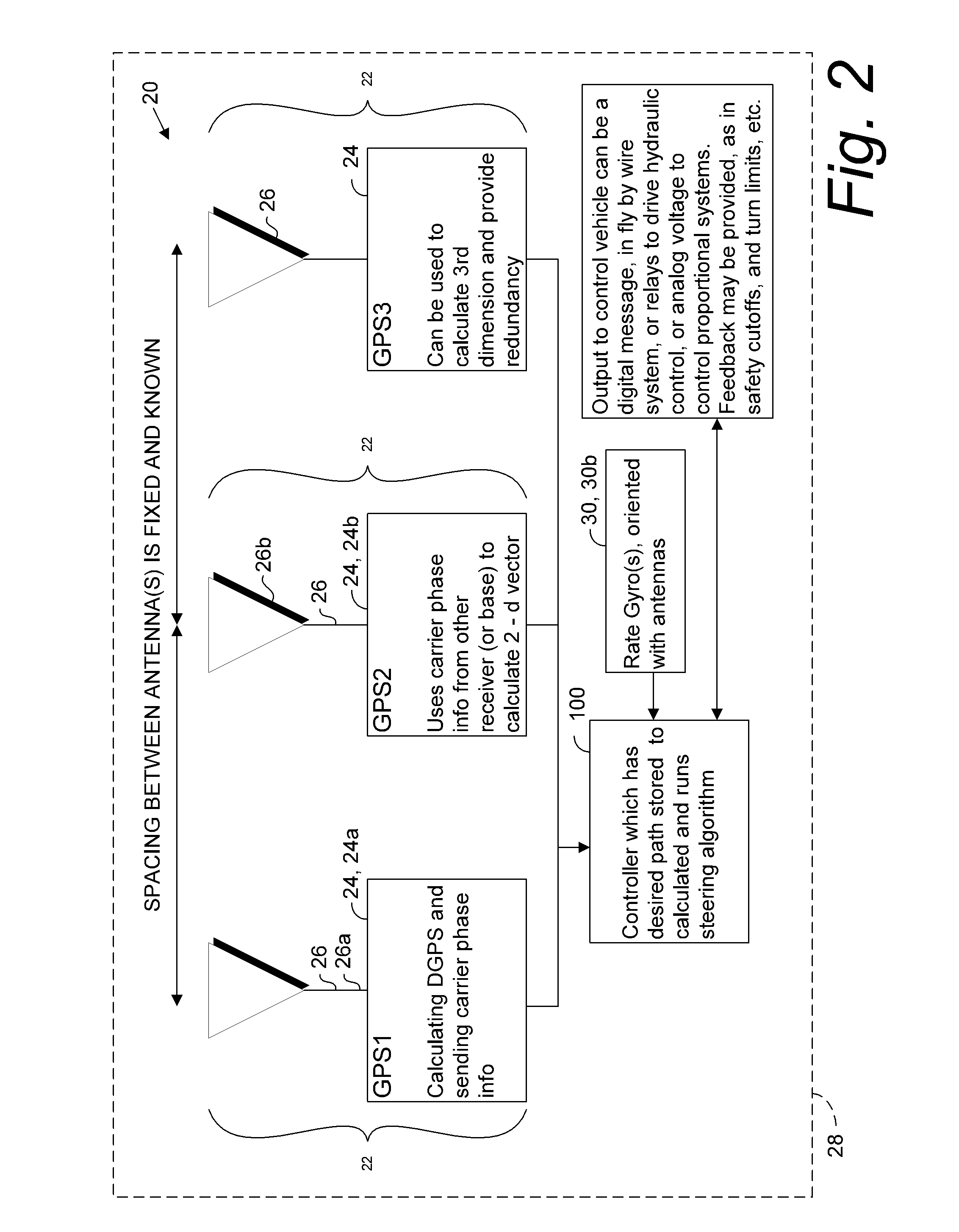
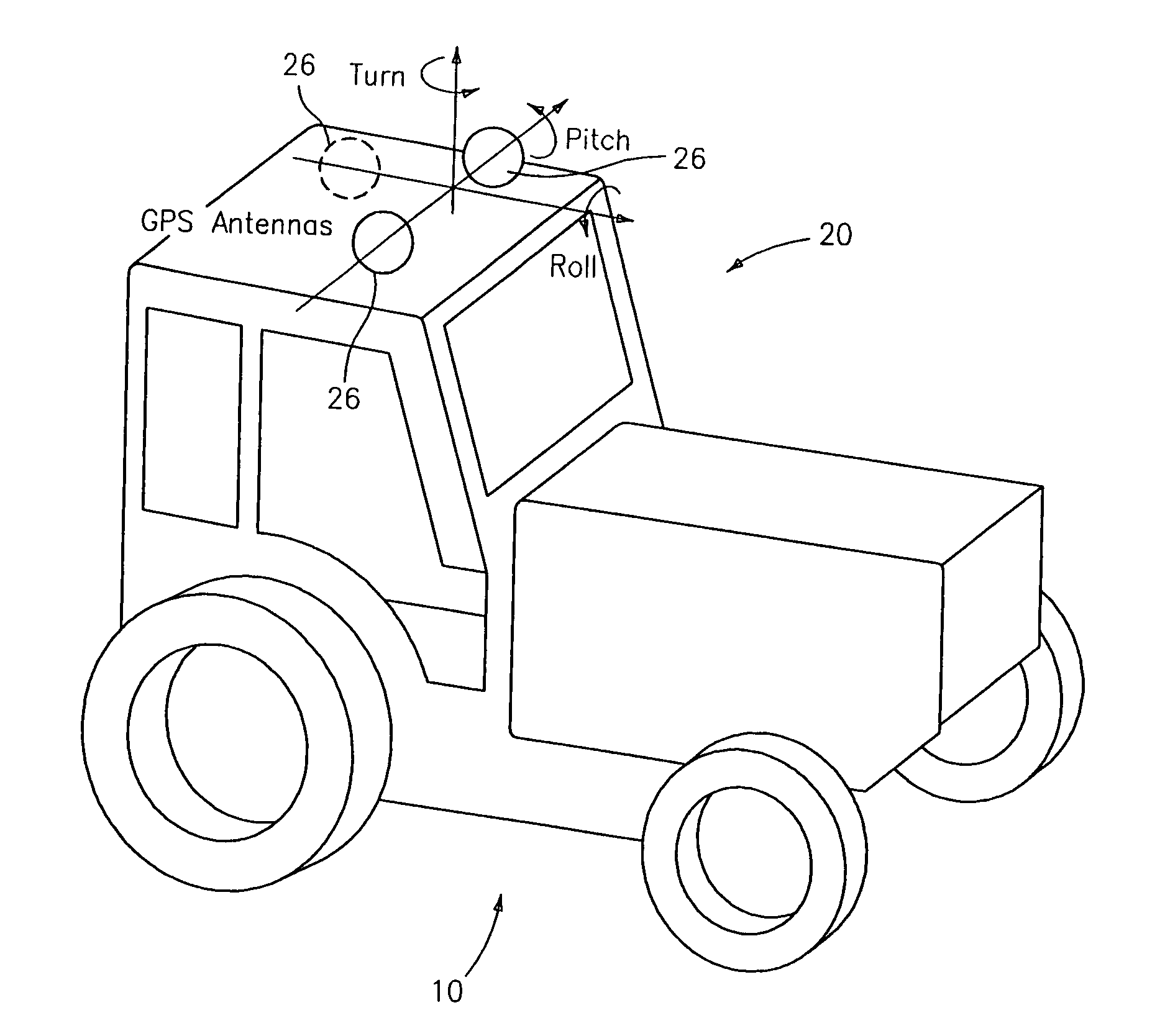
ActiveUS20140324291A1Accurate and economical preplannedEasy to correctDigital data processing detailsNavigation instrumentsCarrier signalSteering control
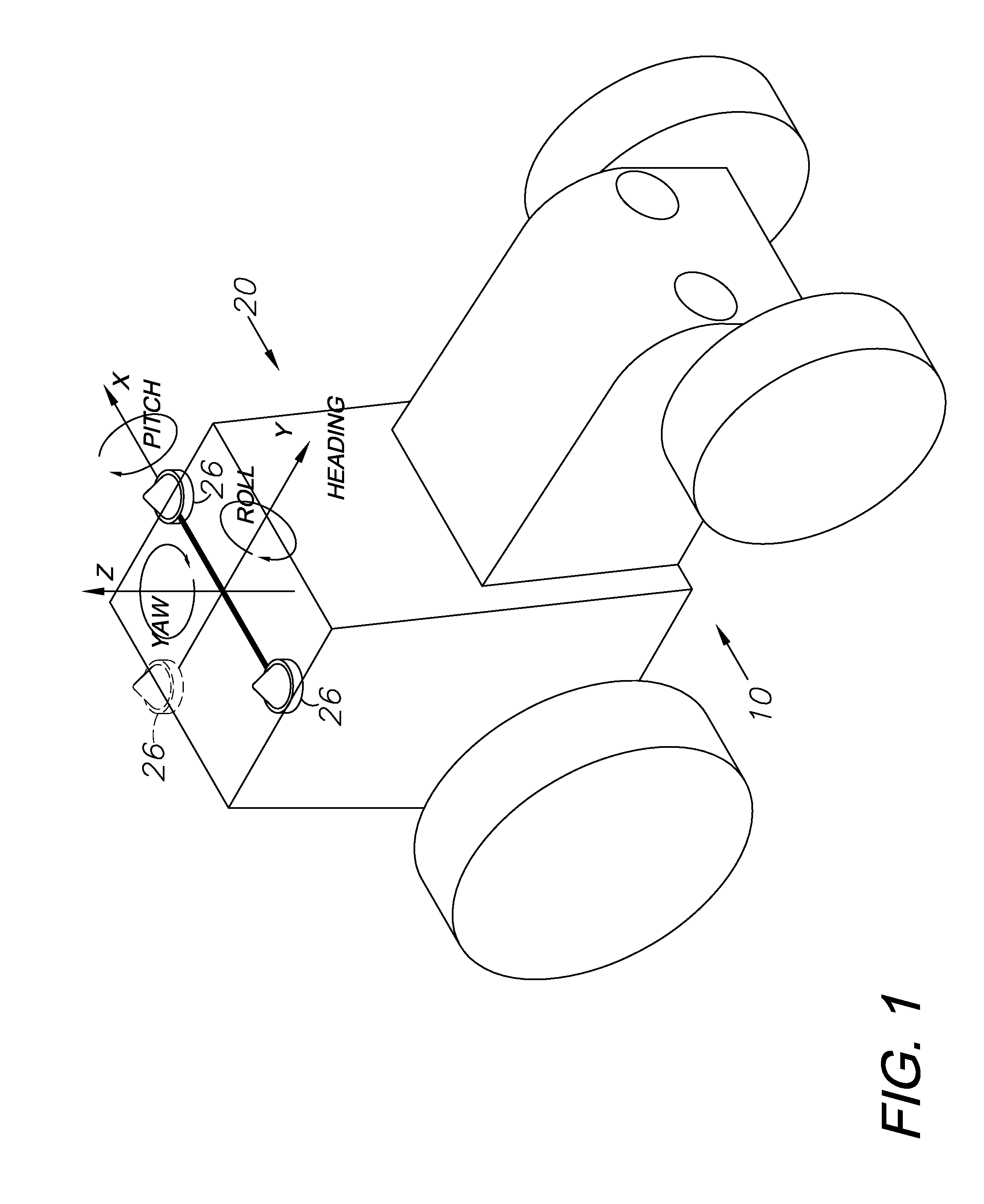
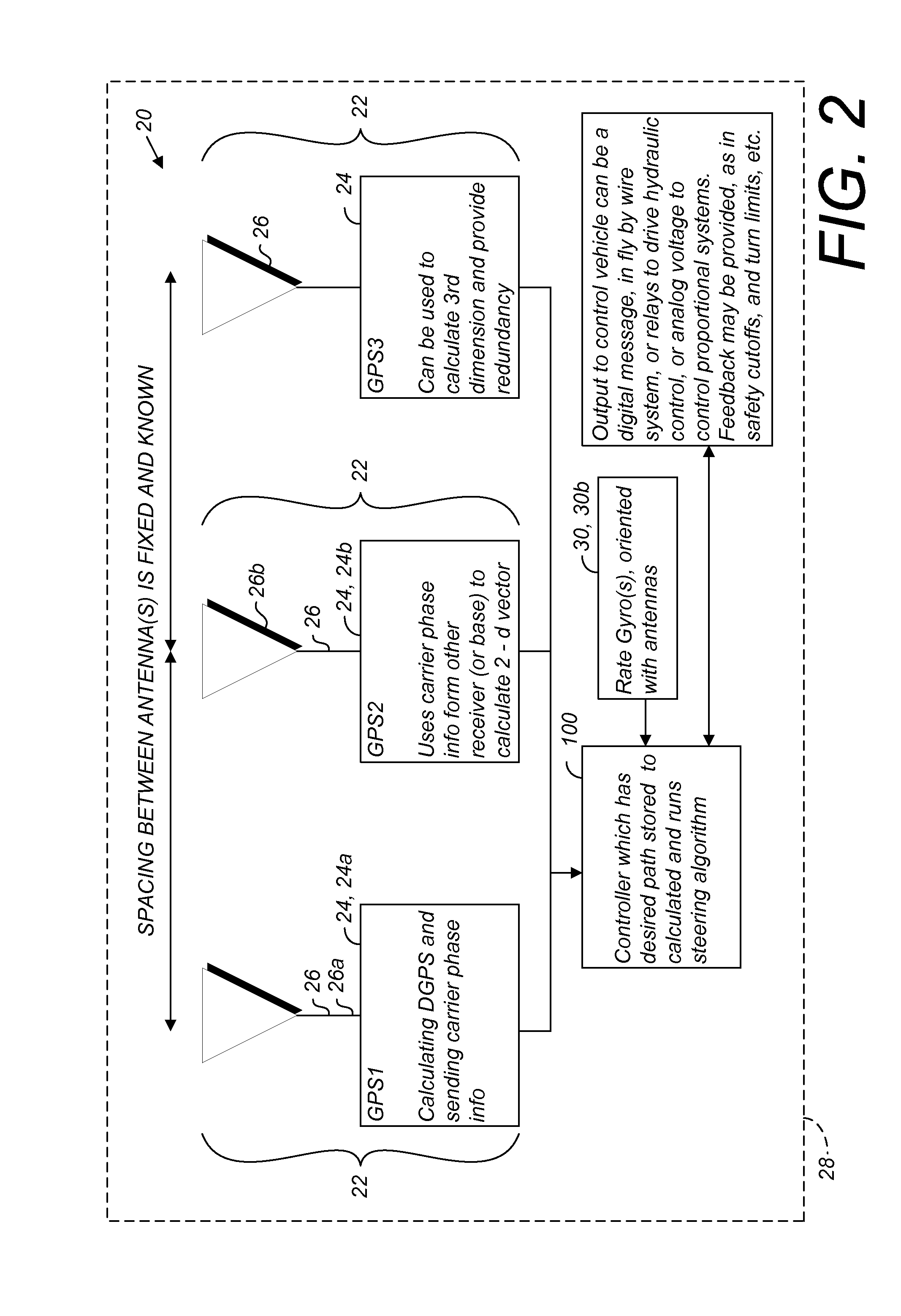
A global navigation satellite system (GNSS) and gyroscope control system for vehicle steering control comprising a GNSS receiver and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase position differences. The system also includes a control system configured to receive the vehicle position, heading, and at least one of roll and pitch, and configured to generate a steering command to a vehicle steering system. A vehicle control method includes the steps of computing a position and a heading for the vehicle using GNSS positioning and a rate gyro for determining vehicle attitude, which is used for generating a steering command. Relative orientations and attitudes between tractors and implements can be determined using optical sensors and cameras. Laser detectors and rangefinders can also be used.
Owner:AGJUNCTION
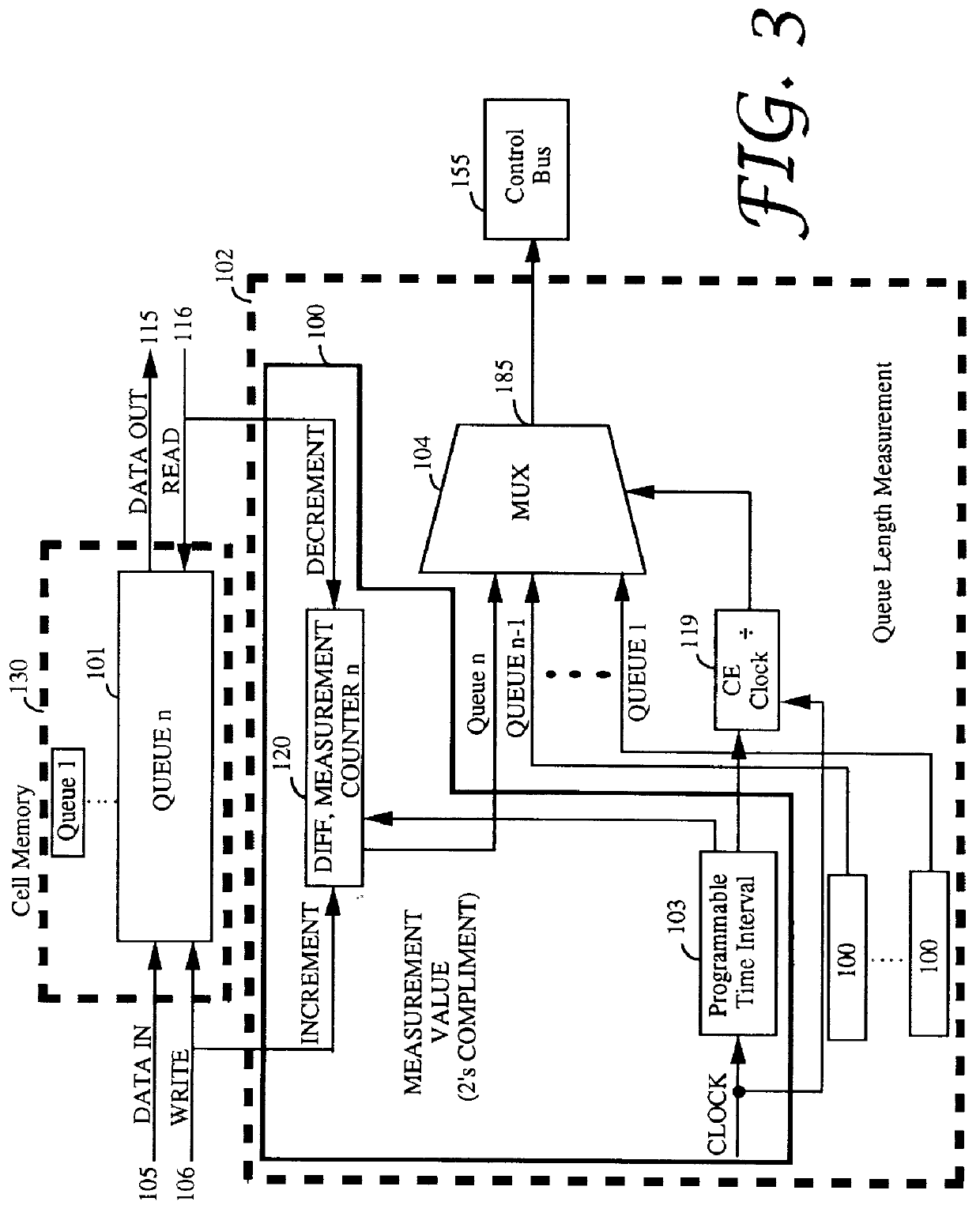
Closed loop congestion control using a queue measurement system
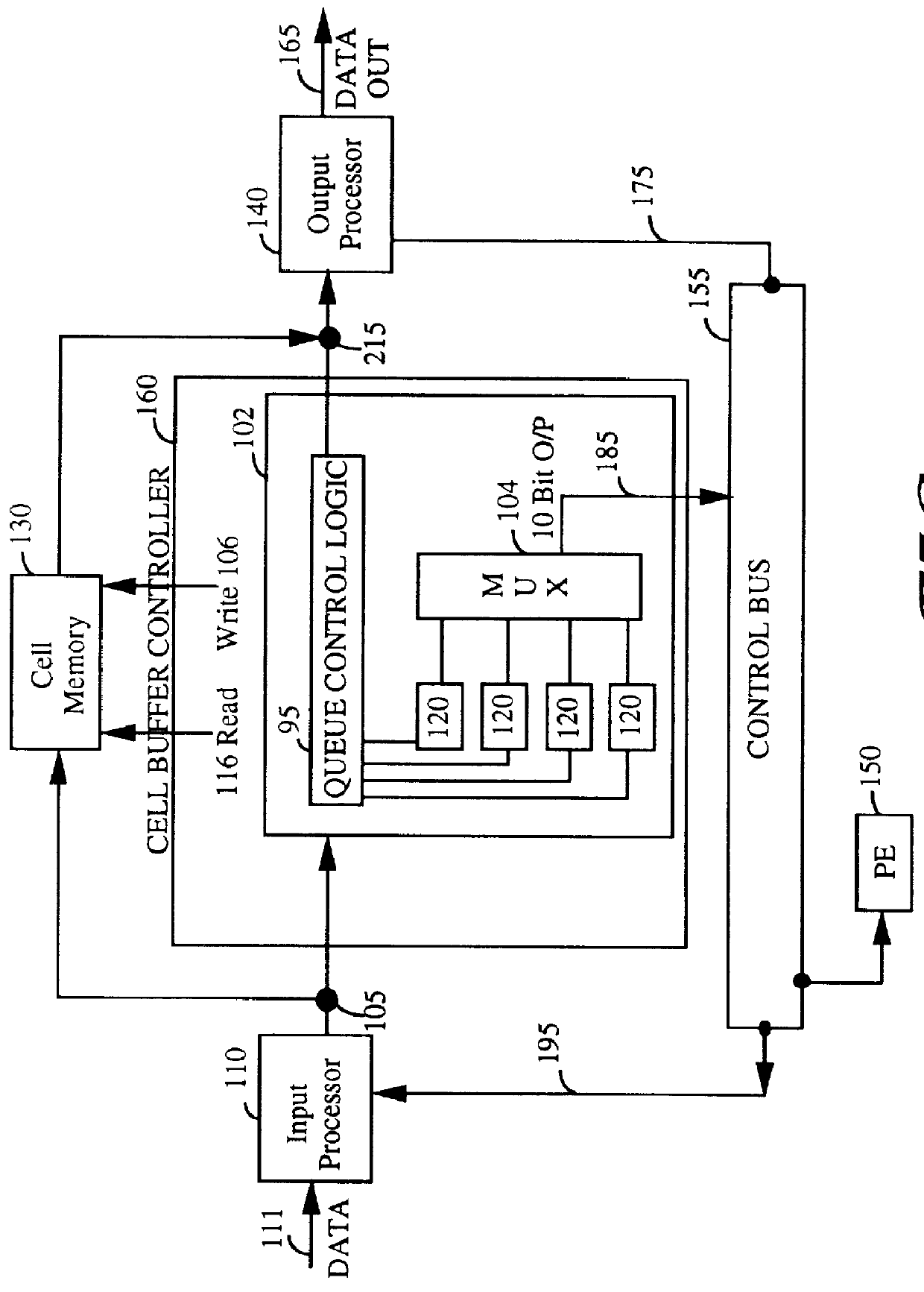
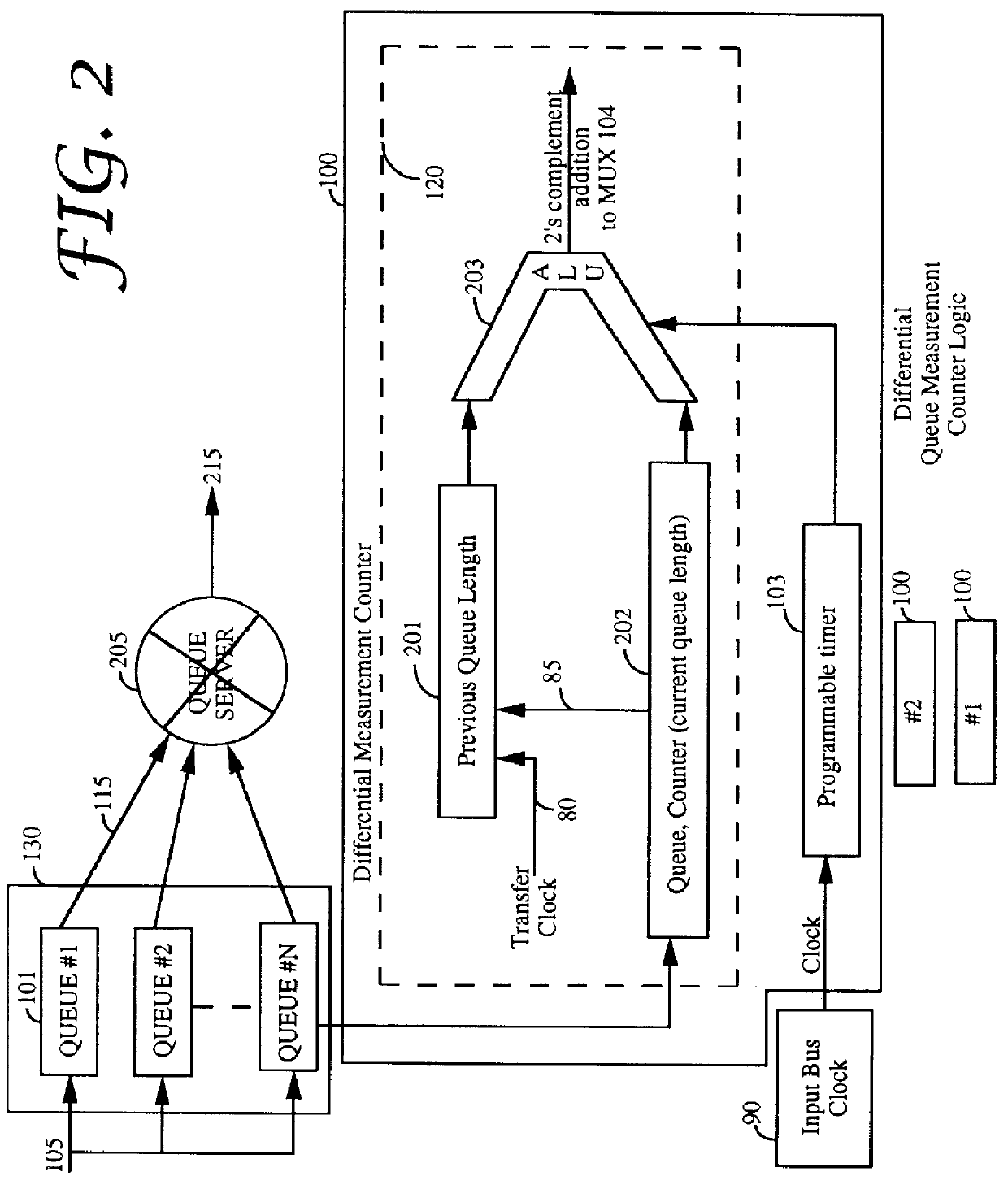
A queue length measurement device that is comprised of a number of queues that are capable of holding data cells. A differential counter is coupled to each queue. The counter is incremented when a cell is written into the queue and decremented when a cell is read from the queue. An interval measurement device, coupled to the differential counter, generates a pulse to reset the counter at fixed intervals equivalent to n cells time (where n is the maximum number of cells the queue counter can measure). A multiplexer is coupled to the multiple differential counters. A transfer control circuit coupled to the interval measurement device selects the appropriate queue measurement to be output from the multiplexer to the other switch elements. A system and methodology provide for queue flow statistics and closed loop control of cell flow into the queue. A congestion control system is provided comprising a queue (having an input and an output, and capable of storing and outputting a plurality of data cells), an input processor (for coupling a plurality of data cells to the queue input), an output processor, an interval measurement device (generating a pulse at predetermined intervals), and differential queue length generation logic. The output processor, couples to the queue output, for receiving a plurality of data cells from the queue, which generates a queue change in size signal in response to determining for each of the predefined intervals of the difference between a present and a previous queue length.
Owner:WHITTAKER COMM
Combined GNSS gyroscope control system and method
ActiveUS20080269988A1Avoid crossingEasy to correctSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsSteering controlLateral movement
A global navigation satellite sensor system (GNSS) and gyroscope control system for vehicle steering control comprising a GNSS receiver and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase position differences. The roll angle facilitates correction of the lateral motion induced position errors resultant from motion of the antennae as the vehicle moves based on an offset to ground and the roll angle. The system also includes a control system configured to receive the vehicle position, heading, and at least one of roll and pitch, and configured to generate a steering command to a vehicle steering system. The system includes gyroscopes for determining system attitude change with respect to multiple axes for integrating with GNSS-derived positioning information to determine vehicle position, velocity, rate-of-turn, attitude and other operating characteristics. A vehicle control method includes the steps of computing a position and a heading for the vehicle using GNSS positioning and a rate gyro for determining vehicle attitude, which is used for generating a steering command.
Owner:HEMISPHERE GNSS
GNSS guidance and machine control
ActiveUS20100312428A1Accurate fillingEasy to correctGuiding agricultural machinesSatellite radio beaconingSteering controlFixed interval
A global navigation satellite sensor system (GNSS) and gyroscope control system for vehicle steering control comprising a GNSS receiver and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase position differences. The roll angle facilitates correction of the lateral motion induced position errors resultant from motion of the antennae as the vehicle moves based on an offset to ground and the roll angle. The system also includes a control system configured to receive the vehicle position, heading, and at least one of roll and pitch, and configured to generate a steering command to a vehicle steering system. The system includes gyroscopes for determining system attitude change with respect to multiple axes for integrating with GNSS-derived positioning information to determine vehicle position, velocity, rate-of-turn, attitude and other operating characteristics. A vehicle control method includes the steps of computing a position and a heading for the vehicle using GNSS positioning and a rate gyro for determining vehicle attitude, which is used for generating a steering command. Alternative aspects include multiple-antenna GNSS guidance methods for high-dynamic roll compensation, real-time kinematic (RTK) using single-frequency (L1) receivers, fixed and moving baselines between antennas, multi-position GNSS tail guidance (“breadcrumb following”) for crosstrack error correction, guiding multiple vehicles and pieces of equipment relative to each other and earth-moving equipment and method applications.
Owner:AGJUNCTION
Satellite position and heading sensor for vehicle steering control
ActiveUS7400956B1Avoid crossingEasy to correctInstruments for road network navigationGuiding agricultural machinesControl systemCarrier signal
A sensor system for vehicle steering control comprising: a plurality of global navigation satellite sensor systems (GNSS) including receivers and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase corrected real time kinematic (RTK) position differences. The roll angle facilitates correction of the lateral motion induced position errors resultant from motion of the antennae as the vehicle moves based on an offset to ground and the roll angle. The system also includes a control system configured to receive the vehicle position, heading, and at least one of roll and pitch, and configured to generate a steering command to a vehicle steering system.
Owner:AGJUNCTION INC
Clustering based load adaptive sleeping protocol for ad hoc networks
InactiveUS7298716B2Sleep longerNeed to synchronizePower managementSynchronisation arrangementSleep timeSleep patterns
A clustering based load adaptive sleeping protocol for ad hoc networks includes a plurality of nodes forming a cluster, where the nodes in the cluster are partitioned into n groups. This partitioning is performed based on the node ID (e.g. node_id modulo n). The cluster head transmits a beacon at fixed intervals. The beacon interval is divided into N slots, where N is a multiple of n. Node sleep / activation times are synchronized to the beacon interval slots. The node's group number is used to determine the slots within a beacon interval that a node begins it s sleep cycle. Therefore, no additional signaling is required between nodes to indicate sleep patterns. The sleeping time of each node may be increased when extended periods of inactivity are detected according to an adaptive procedure.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
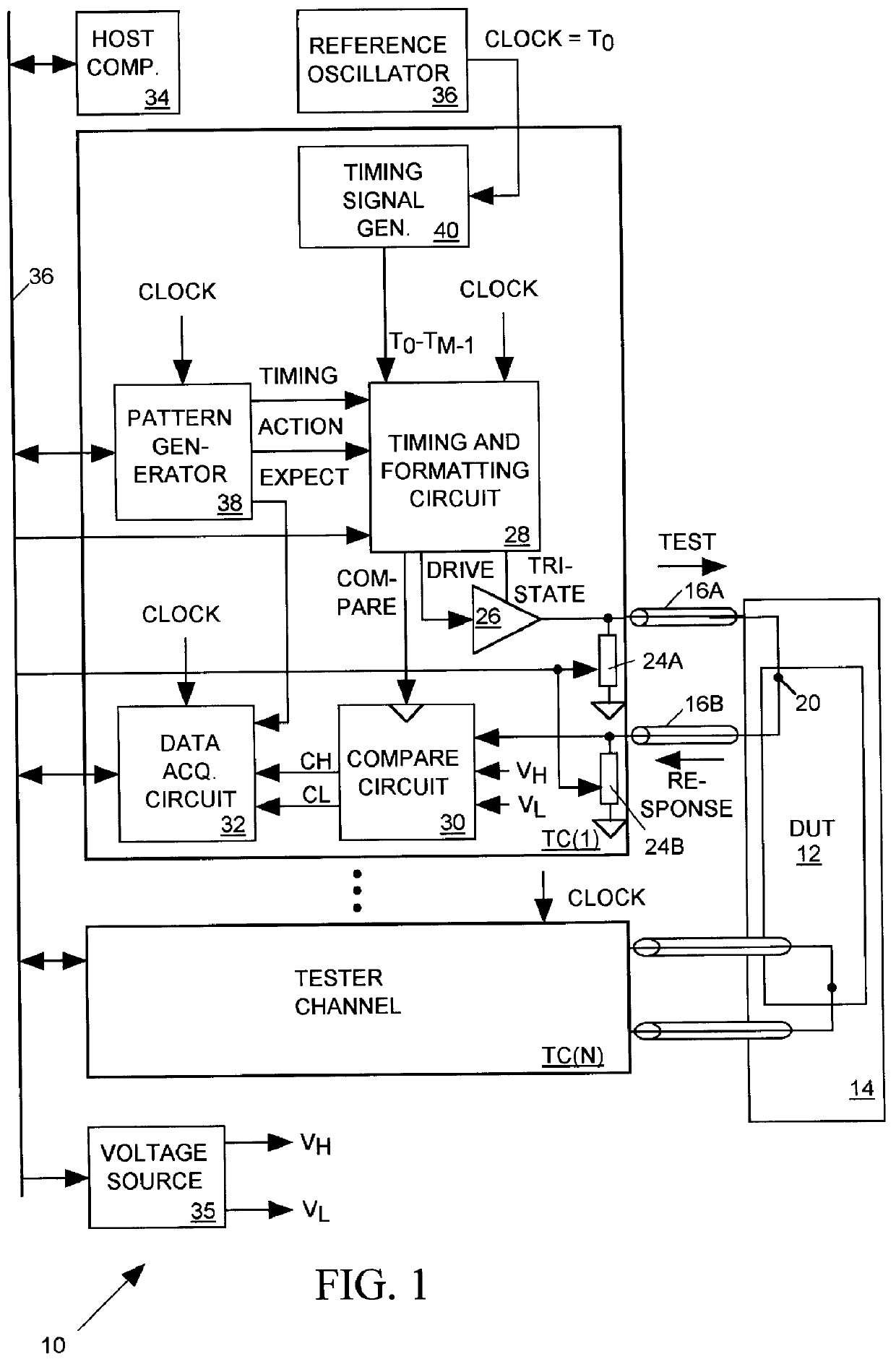
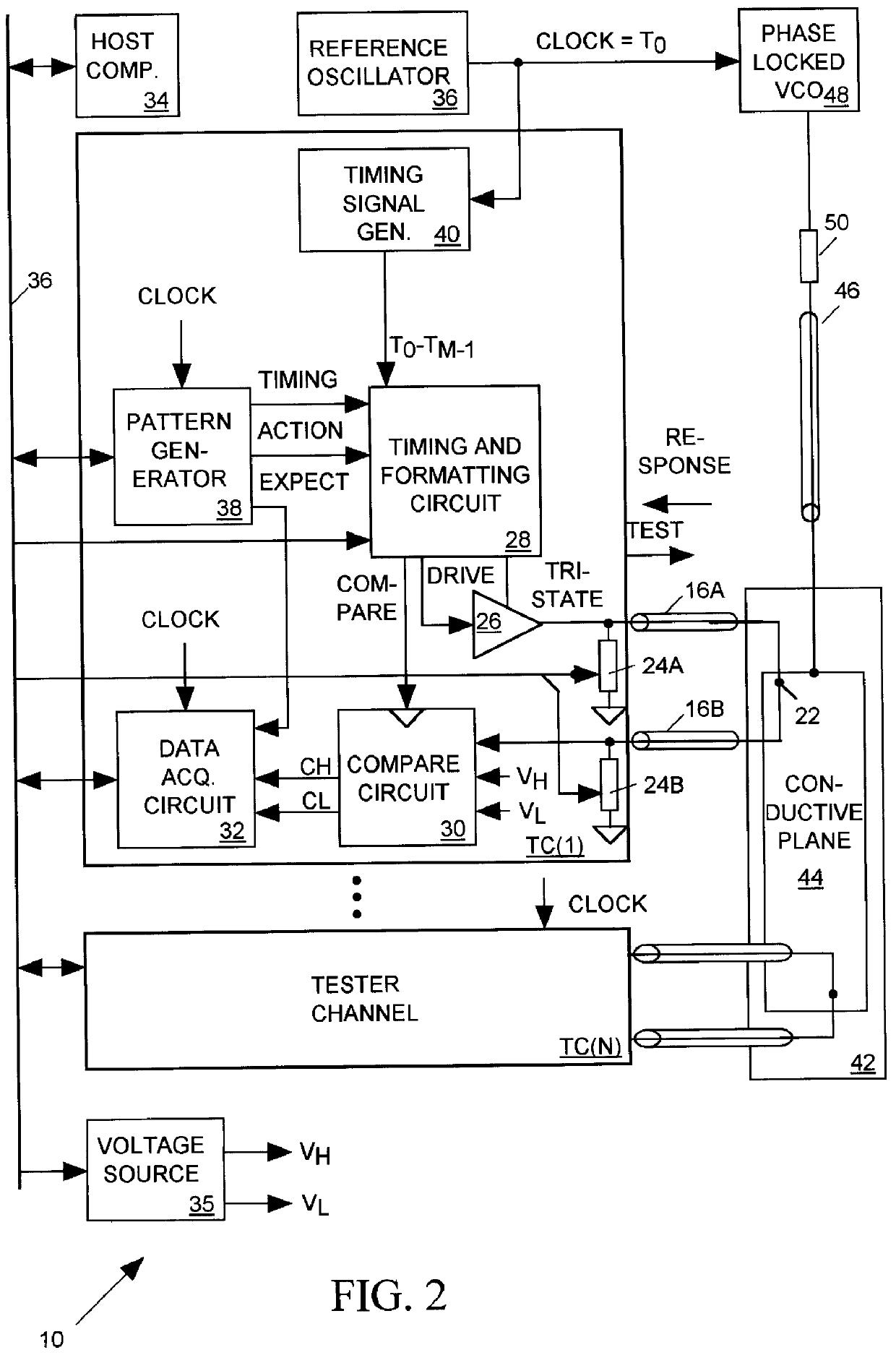
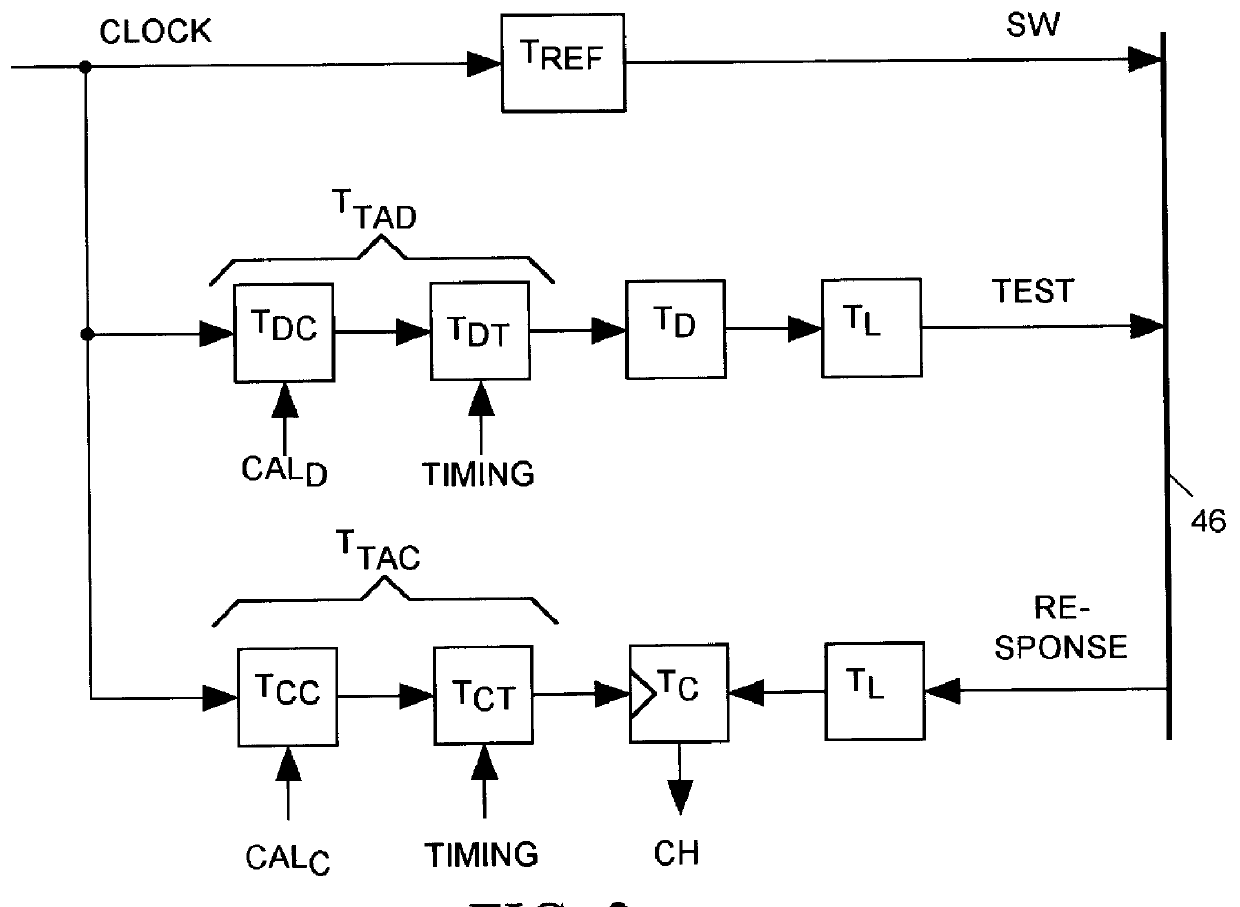
Salphasic timing calibration system for an integrated circuit tester
InactiveUS6105157AQuickly and easily calibratingDigital circuit testingError detection/correctionTester deviceEngineering
An integrated circuit tester produces an output TEST signal following a pulse of a reference CLOCK signal with a delay that is a sum of an inherent drive delay and an adjustable drive delay. The tester also samples an input RESPONSE signal following a pulse of the reference CLOCK signal with a delay that is a sum of an inherent compare delay and an adjustable compare delay. The inherent drive and compare signal path delays within an integrated circuit tester are measured by first connecting a salphasic plane to transmission lines that normally convey signals between the tester and terminals of an integrated circuit device under test. A standing wave signal appearing on that salphasic plane is phase locked to the CLOCK signal so that a zero crossing of the standing wave occurs at a fixed interval after each pulse of the CLOCK signal. Each transmission line concurrently conveys the standing wave to the tester to provide timing references for measuring the inherent drive and compare signal path delays within the tester. Transmission line signal paths are also measured. Delays are added to the drive and compare signal paths to compensate for the measured inherent drive, compare and transmission line delays.
Owner:CREDENCE SYSTEMS
Method and apparatus for analyzing call history data derived from execution of a computer program
InactiveUS20060218543A1Data is very largeReduce overheadError detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsGraphicsGraphical user interface
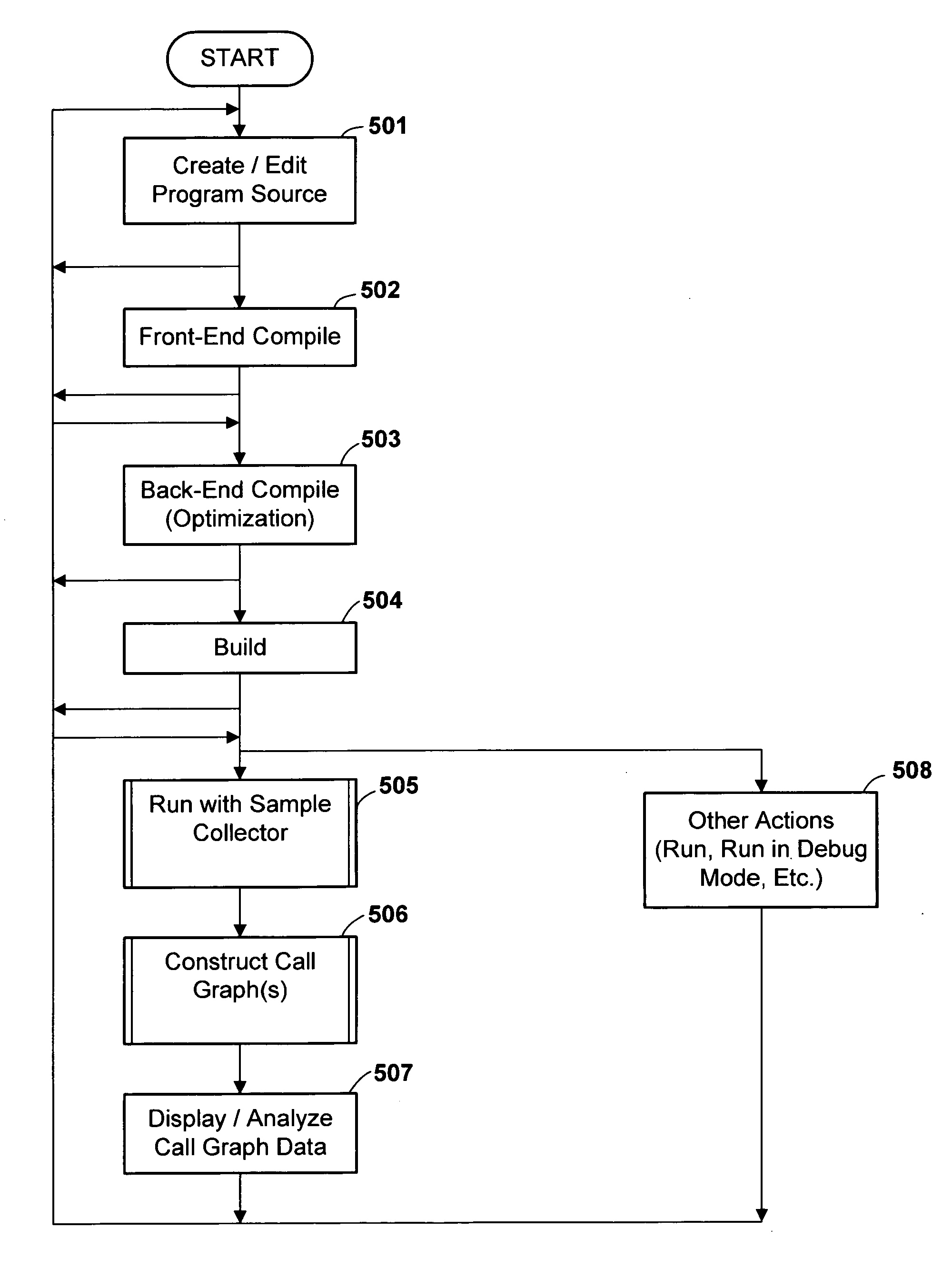
Call history data is sampled at fixed intervals during run-time, each sample representing only a limited portion of the stack. These data samples are subsequently automatically analyzed by merging overlapping sampled call history sequences to build larger call graphs, according to some pre-specified merge criterion. Preferably, the call history graphs are annotated with counts of the execution frequency (number of times a particular procedure was executing when the sample was collected) and the stack frequency (number of times the procedure appeared in the sampled stack portion) associated with each respective called procedure. Preferably, a graphical user interface presents the user with a graphical representation of the call graph(s) and annotations.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for implementing online tests of stream flow based on video images
ActiveCN102564508AHigh spatio-temporal resolutionGood followabilityTelevision system detailsVolume/mass flow measurementImaging processingStream flow
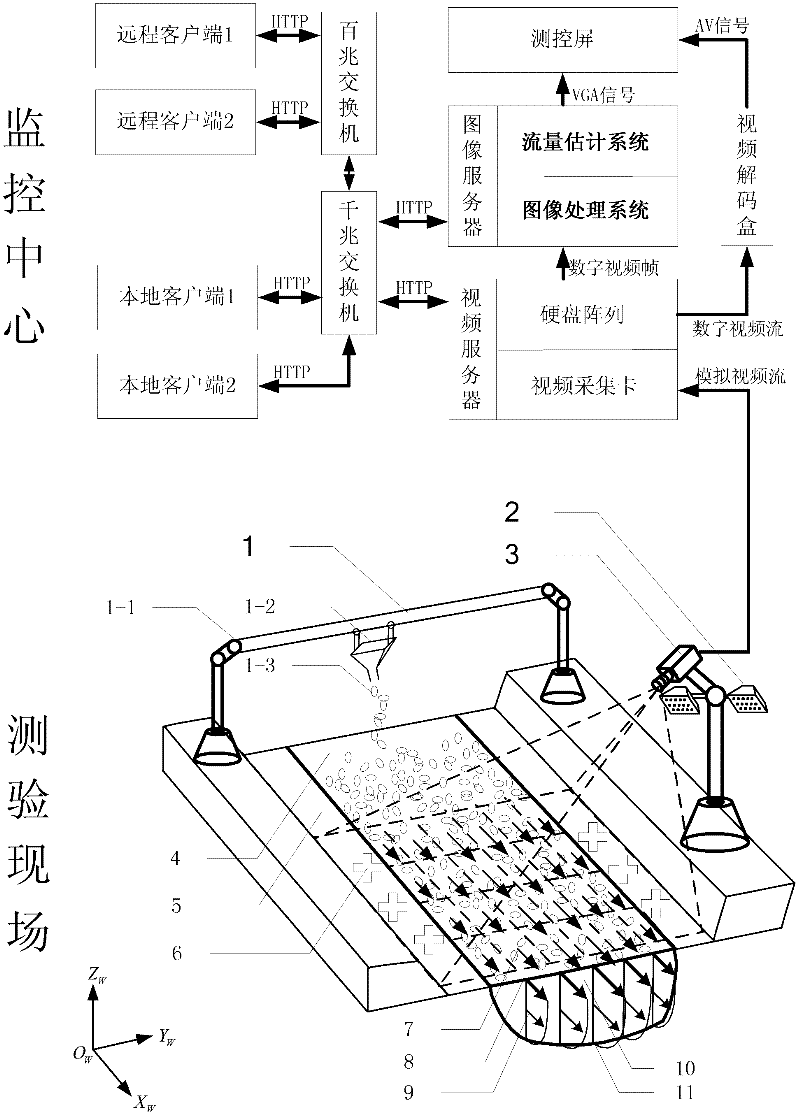
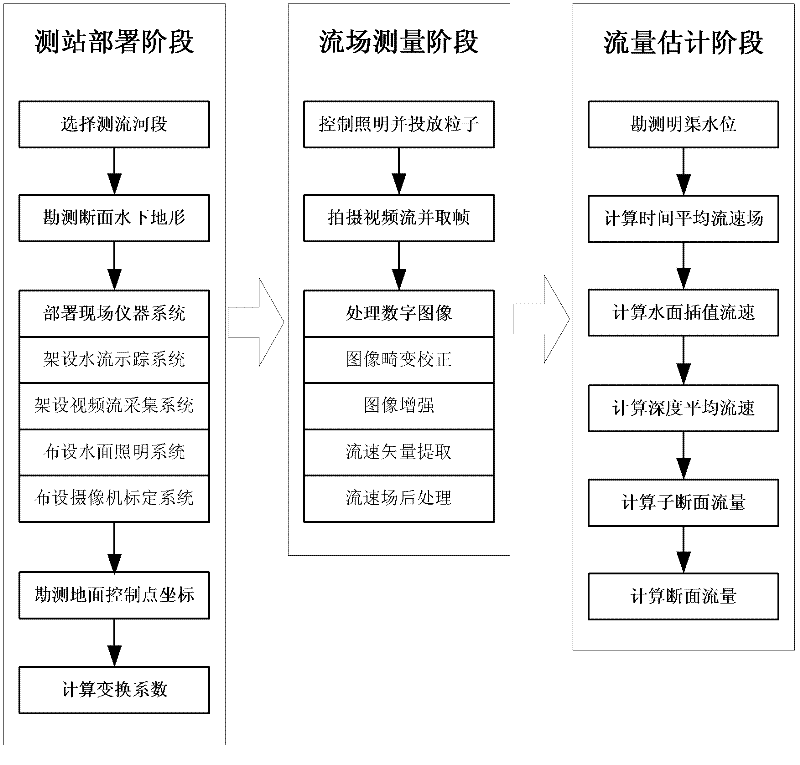
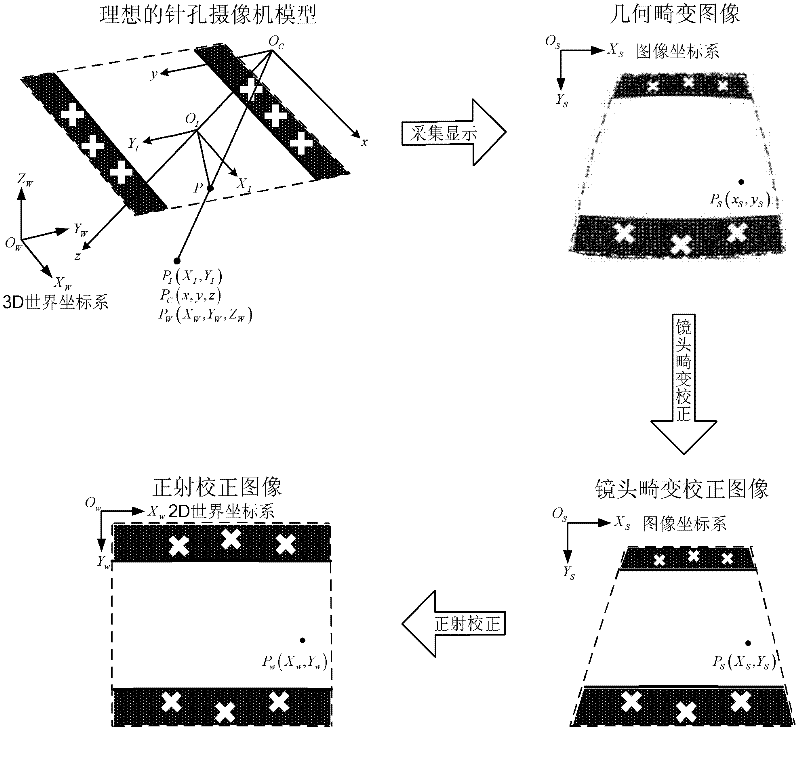
The invention discloses a method for implementing online tests of stream flow based on video images, and belongs to the technical field of non-contact open channel flow measurement. The method relates to a water flow tracing system, a water surface illuminating system, a video flow acquisition system, a camera calibrating system, an image processing system and a flow estimating system, trace particles are thrown in a flow measuring stream segment by the water flow tracing system, a camera shoots a water surface video stream, frames are extracted at fixed intervals and are processed digitally, the image processing system processes digital images according to ground control point coordinate information provided by the camera calibrating system, and finally, the stream flow is computed by the aid of the flow estimating system according to a flow rate and area method. By the aid of the method, complicity of stream flow measurement is reduced, simultaneously, high measurement precision can be guaranteed, and the stream flow can be dynamically monitored in extreme environments.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
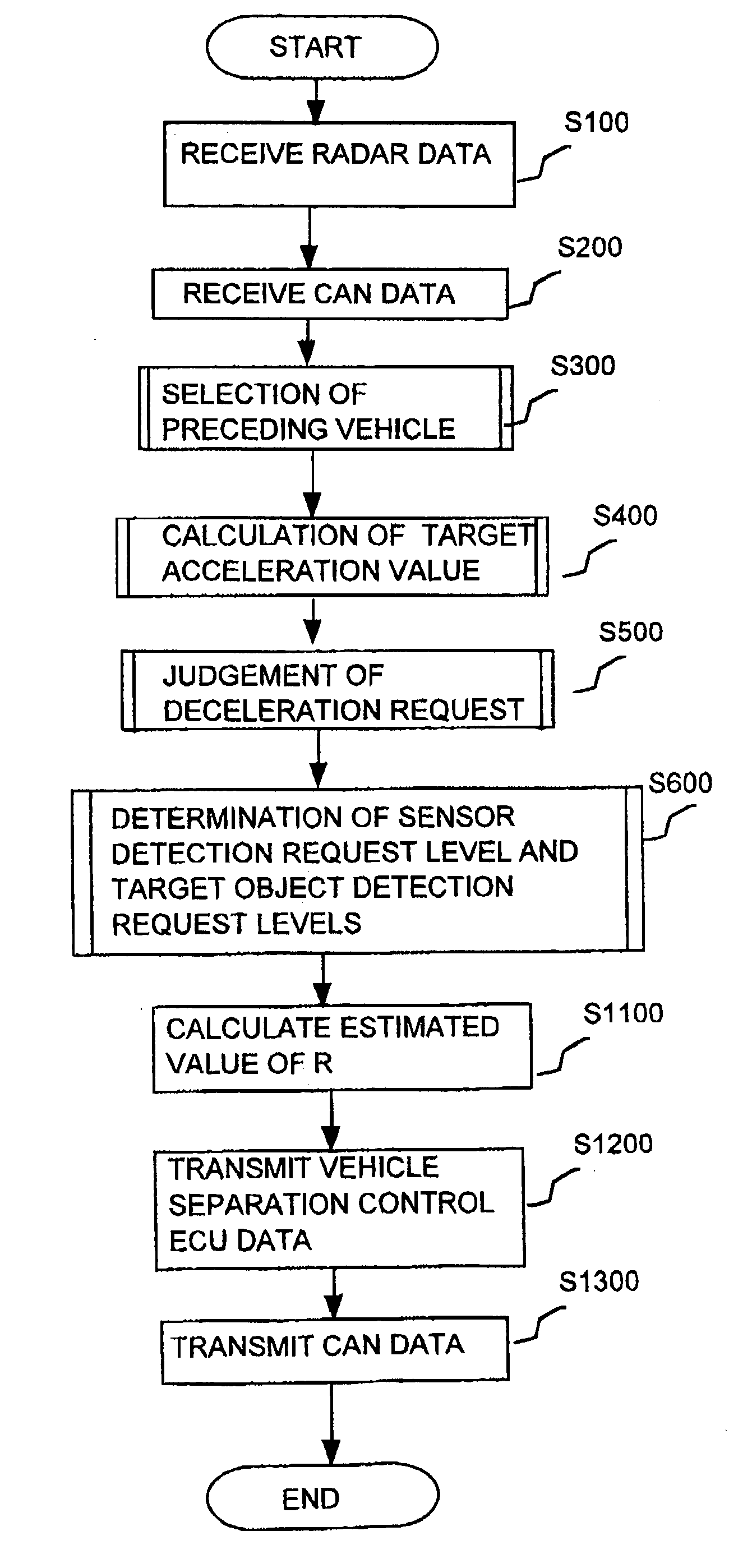
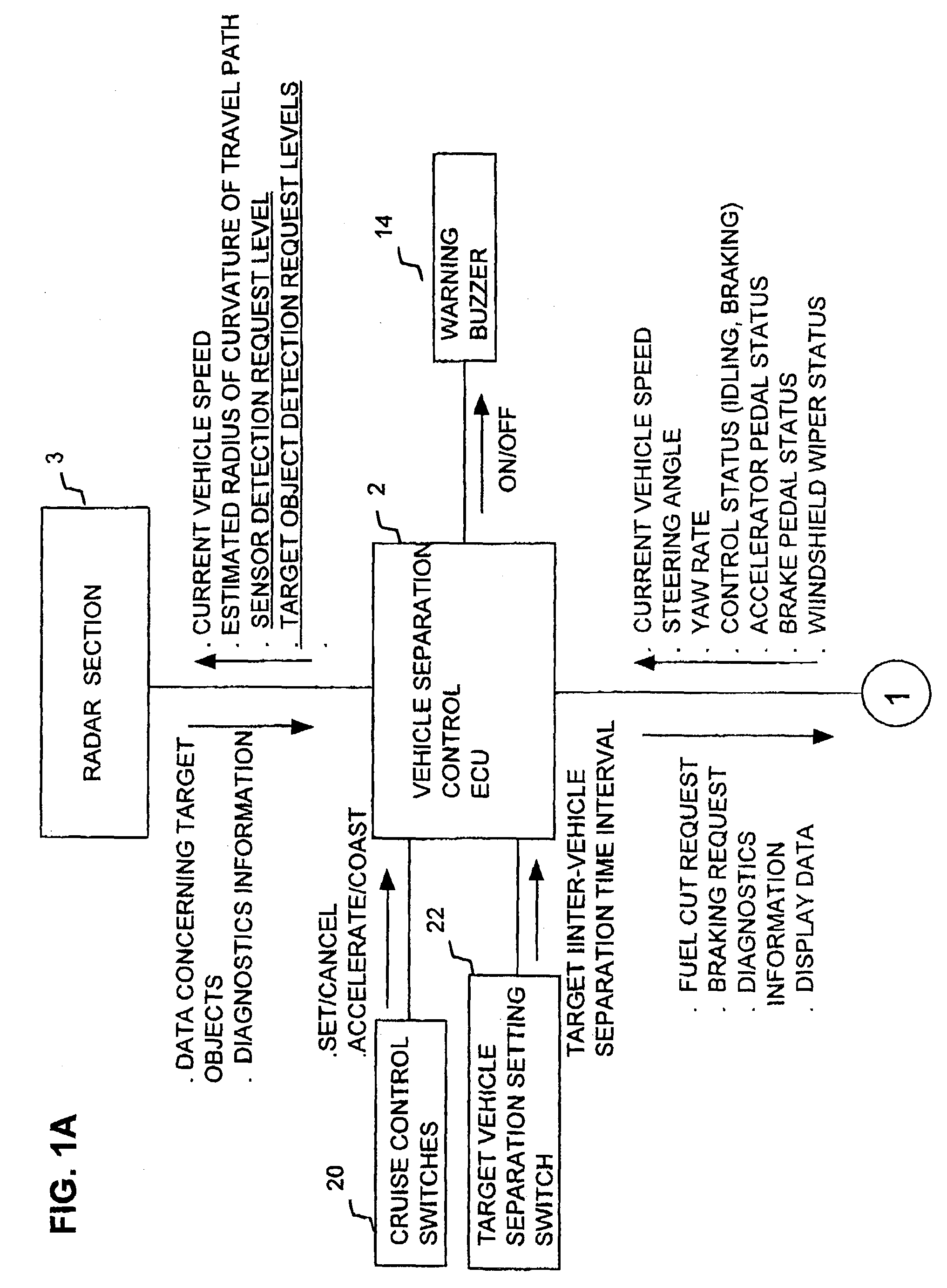
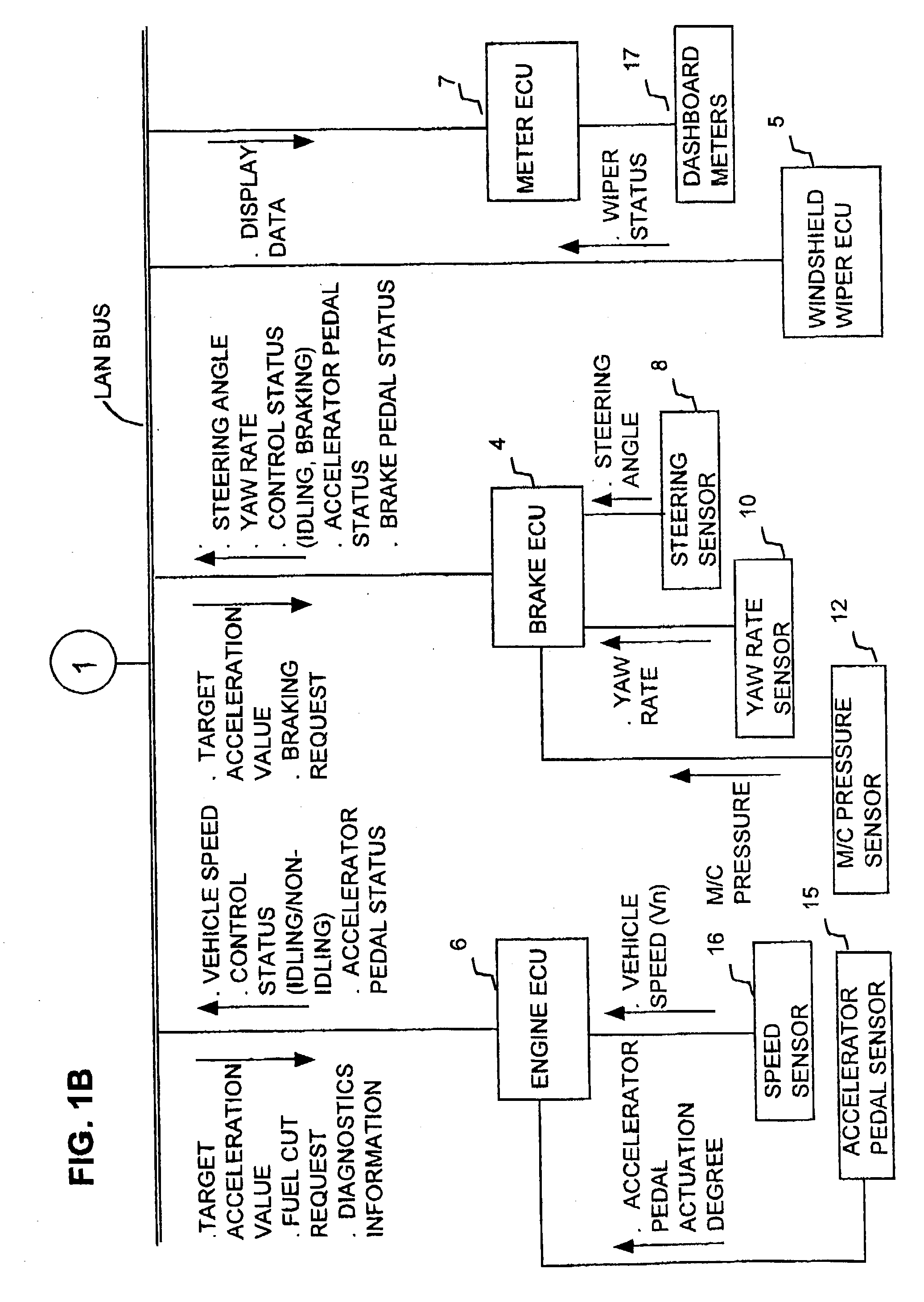
Cruise control apparatus performing automatic adjustment of object recognition processing in response to driver actions relating to vehicle speed alteration
InactiveUS6941216B2Improve abilitiesIncrease choiceVehicle fittingsDigital data processing detailsDriver/operatorCruise control
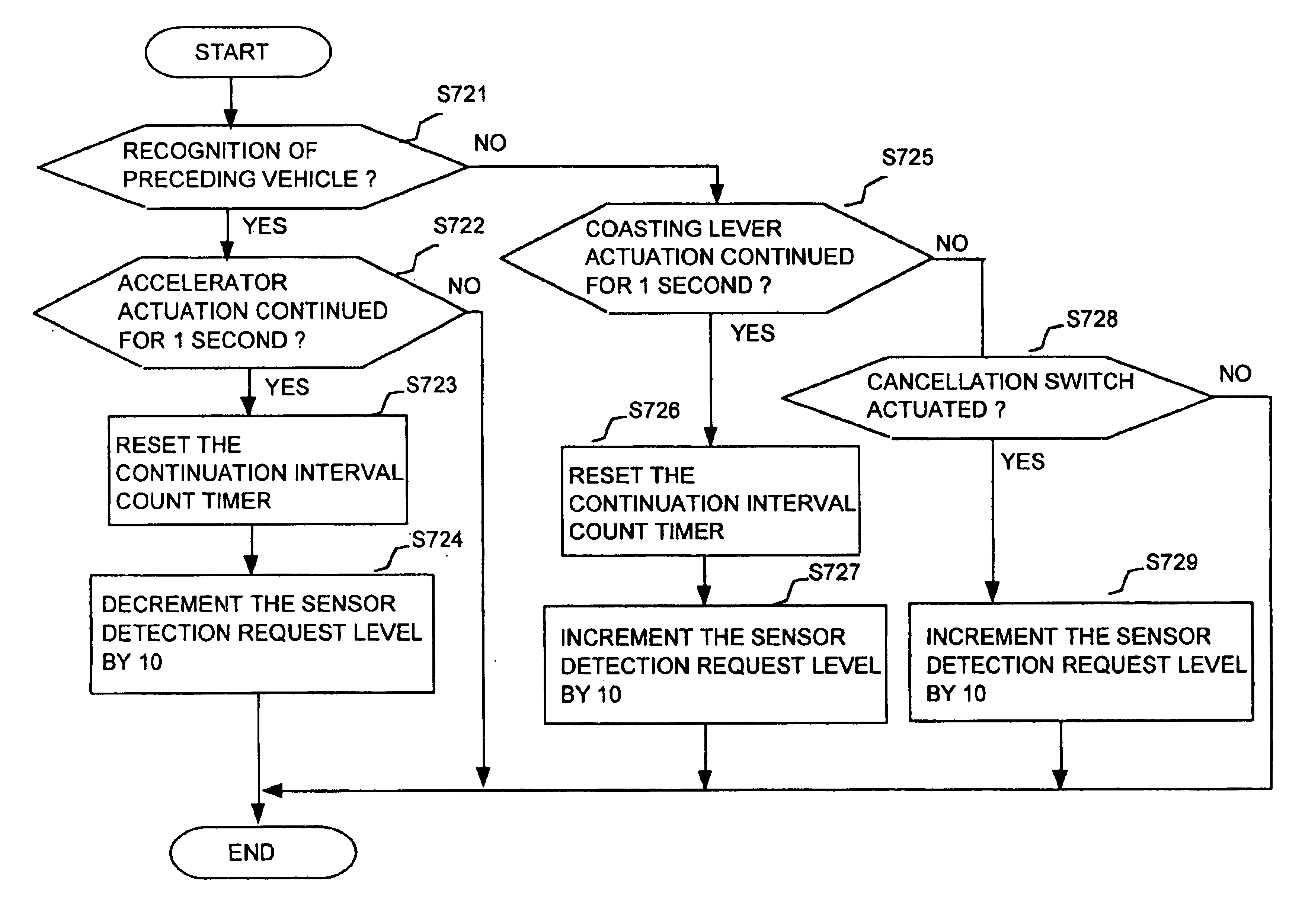
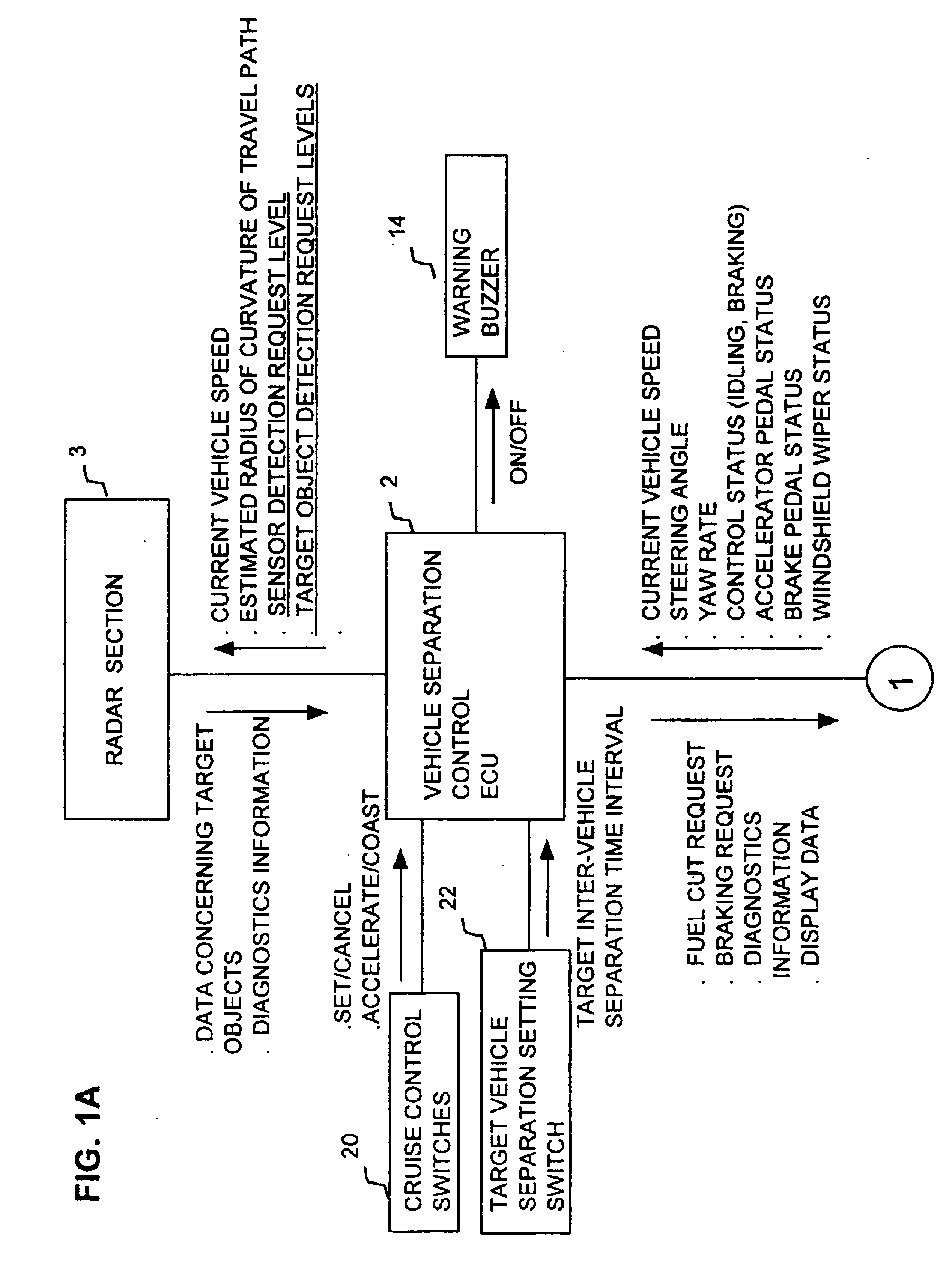
A cruise control apparatus can control a host vehicle to run with a fixed separation from a preceding vehicle when such a preceding vehicle is detected based on received radar signals and to run at a preset fixed speed when no preceding vehicle is detected. The cruise control apparatus is configured to respond to one of a set of predetermined actions by the vehicle driver, which indicate an intention to change the vehicle speed, by making it easier or more difficult for a preceding vehicle to be detected, in accordance with whether the indicated intention may signify that an actual preceding vehicle is not being detected or may signify that a non-existent preceding vehicle is being detected and that the host vehicle speed has been reduced accordingly. Improved performance is thereby achieved by utilizing the cognitive abilities of the driver to augment the detection operation of the cruise control apparatus.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Method and system for data-structure management
InactiveUS20080016216A1Efficient methodMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionTimerDistributed computing
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to computationally efficient methods and systems for managing connection-associated and exchange-associated resources within network proxies. In one embodiment of the present invention, a circular connection-switch queue is employed for allocating, de-allocating, and maintaining connection-based or exchange-based data resources within a proxy. The connection-switch queue includes a free pointer that identifies a next connection-switch queue entry for allocation, and an idle pointer that is incremented continuously or at fixed intervals as timers associated with connection-switch entries expire. In an alternate embodiment, the connection-switch queue includes a free pointer, an idle pointer, and a clear pointer.
Owner:SECURE64 SOFTWARE
Multi-antenna GNSS control system and method
ActiveUS8583315B2Easy to correctEconomical and accurateVehicle testingAnalogue computers for trafficControl systemSteering control
A global navigation satellite sensor system (GNSS) and gyroscope control system for vehicle steering control comprising a GNSS receiver and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase position differences. A vehicle control method includes the steps of computing a position and a heading for the vehicle using GNSS positioning and a rate gyro for determining vehicle attitude, which is used for generating a steering command.
Owner:AGJUNCTION
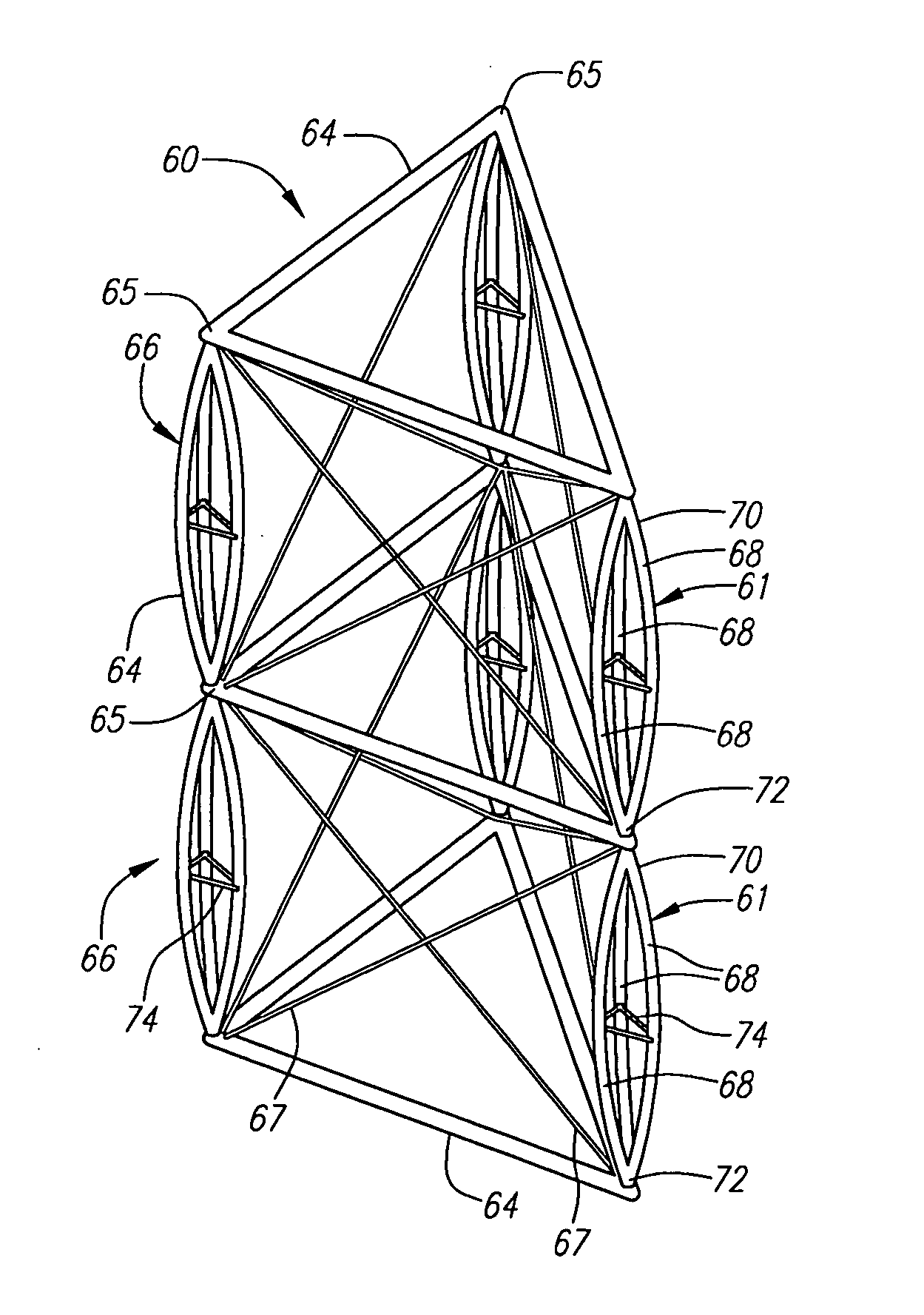
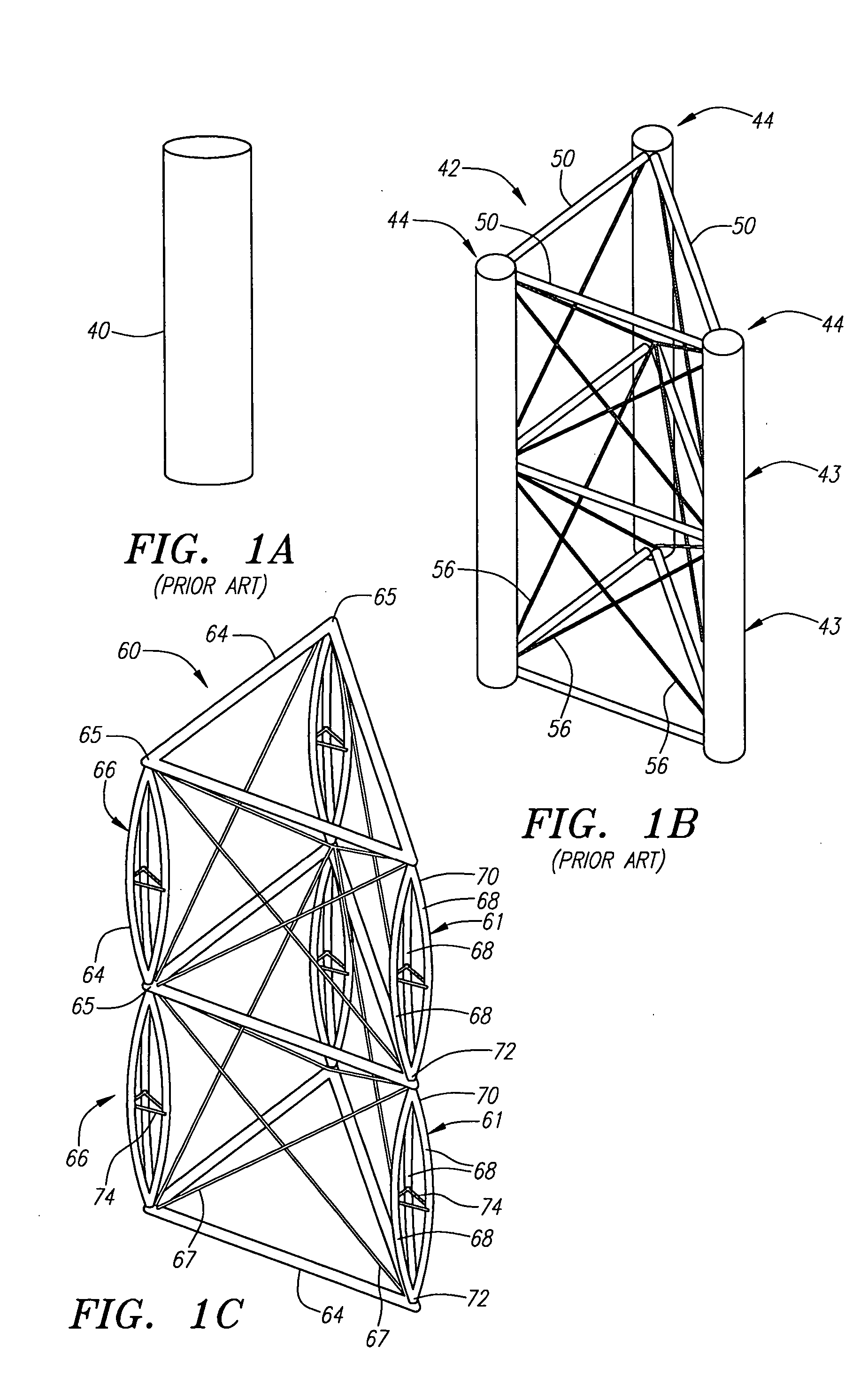
Deployable truss having second order augmentation
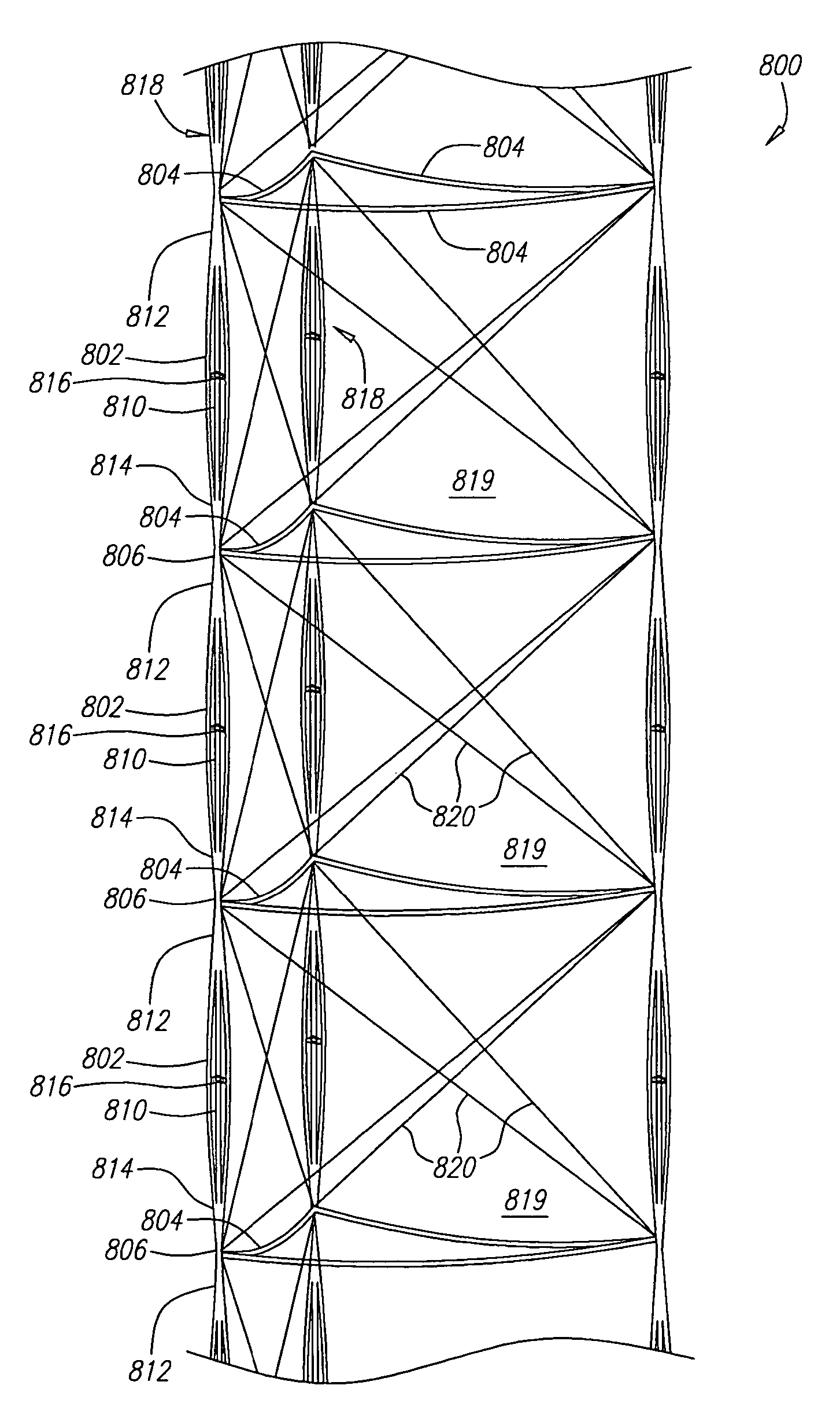
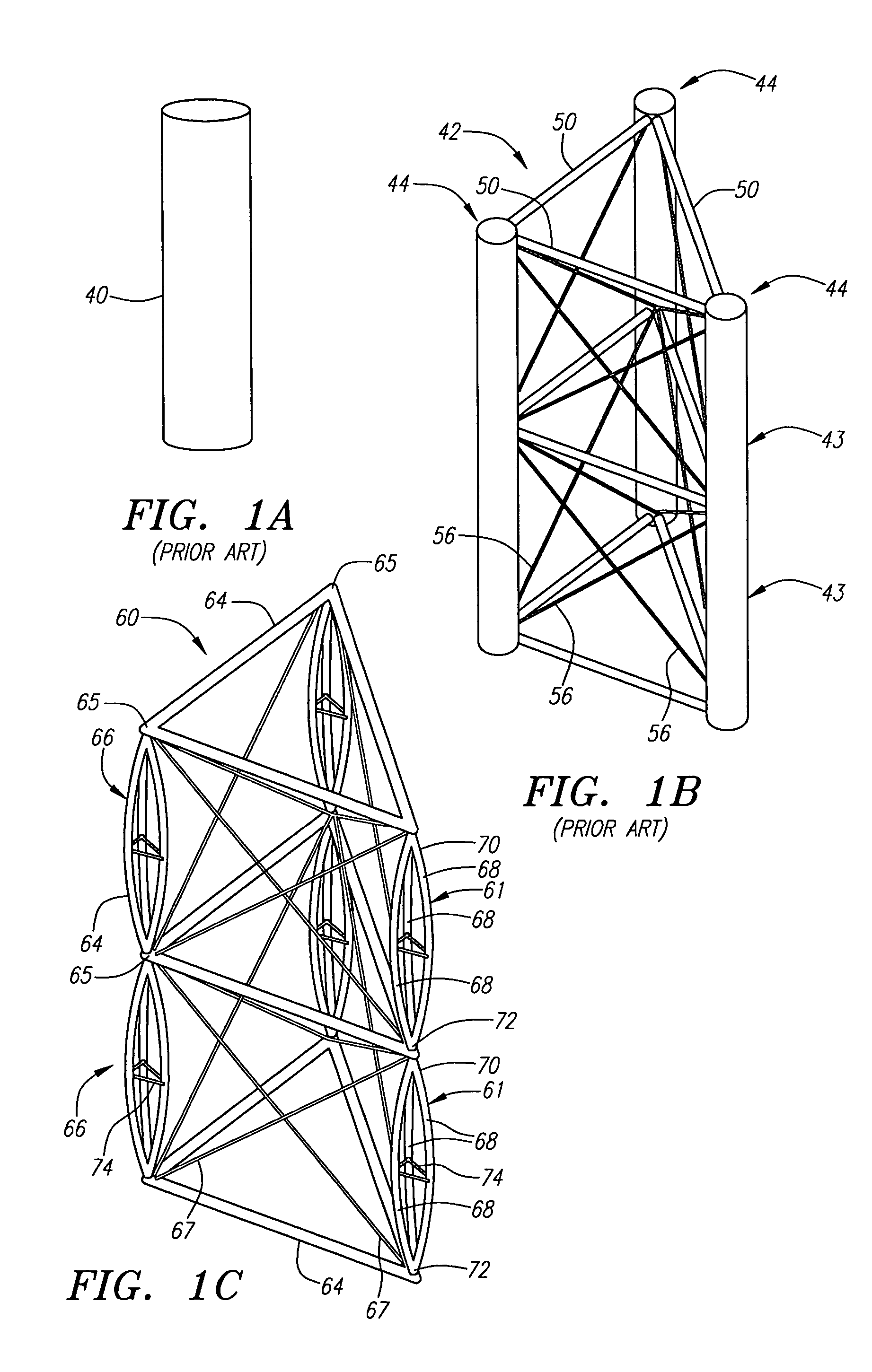
ActiveUS20050126106A1Decreases free buckling lengthIncrease its moment of inertiaCollapsable antennas meansCosmonautic vehiclesEngineeringMoment of inertia
A deployable truss is formed from a plurality of column members connected at their ends where at least some of the column members are formed from column assemblies, each including a plurality of strut members that are at least connected to each other at a first and second end of the column assembly. For added rigidity, strut members of a column assembly may be connected to each other between the first and second ends using, for example, a rigidizable resin, a fixed spacer, or a deployable spacer. Connecting strut members between the ends of the column assembly provides mutual bracing to the strut members and decreases the free buckling length of the individual strut members. Spacers are preferably configured to radially space the strut members away from the longitudinal centerline of the column assembly to increase its moment of inertia, and hence its buckling strength.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
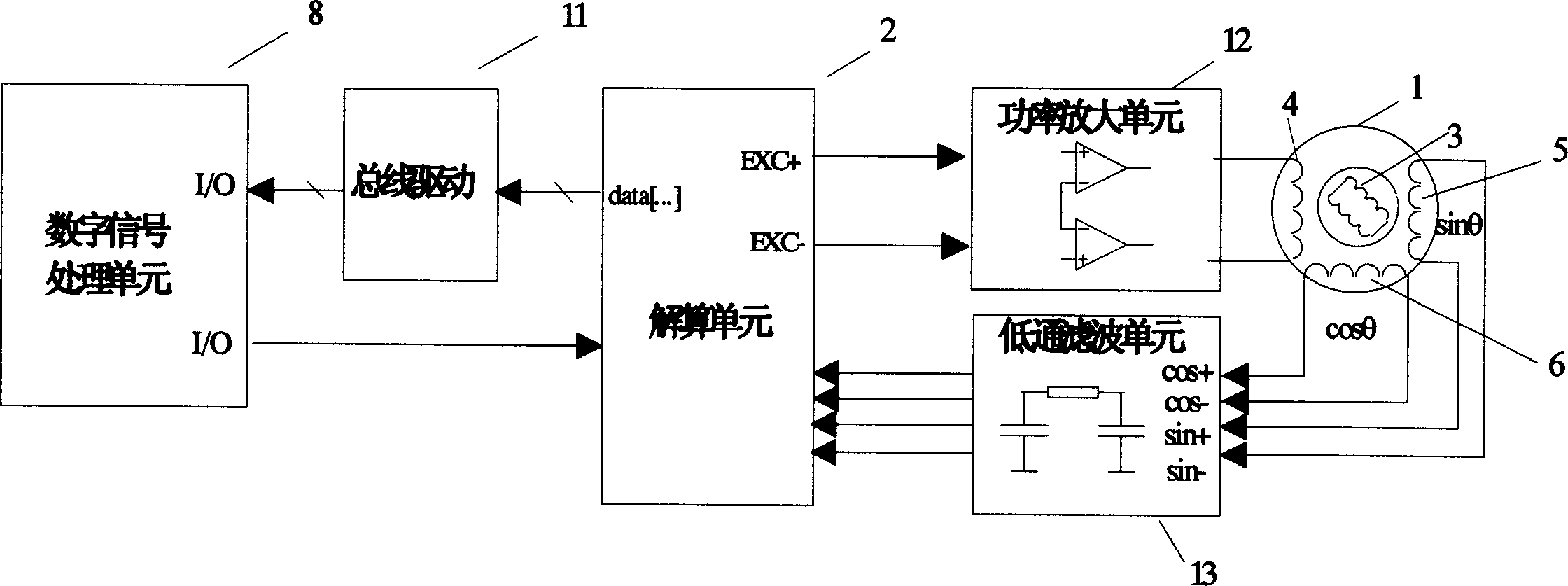
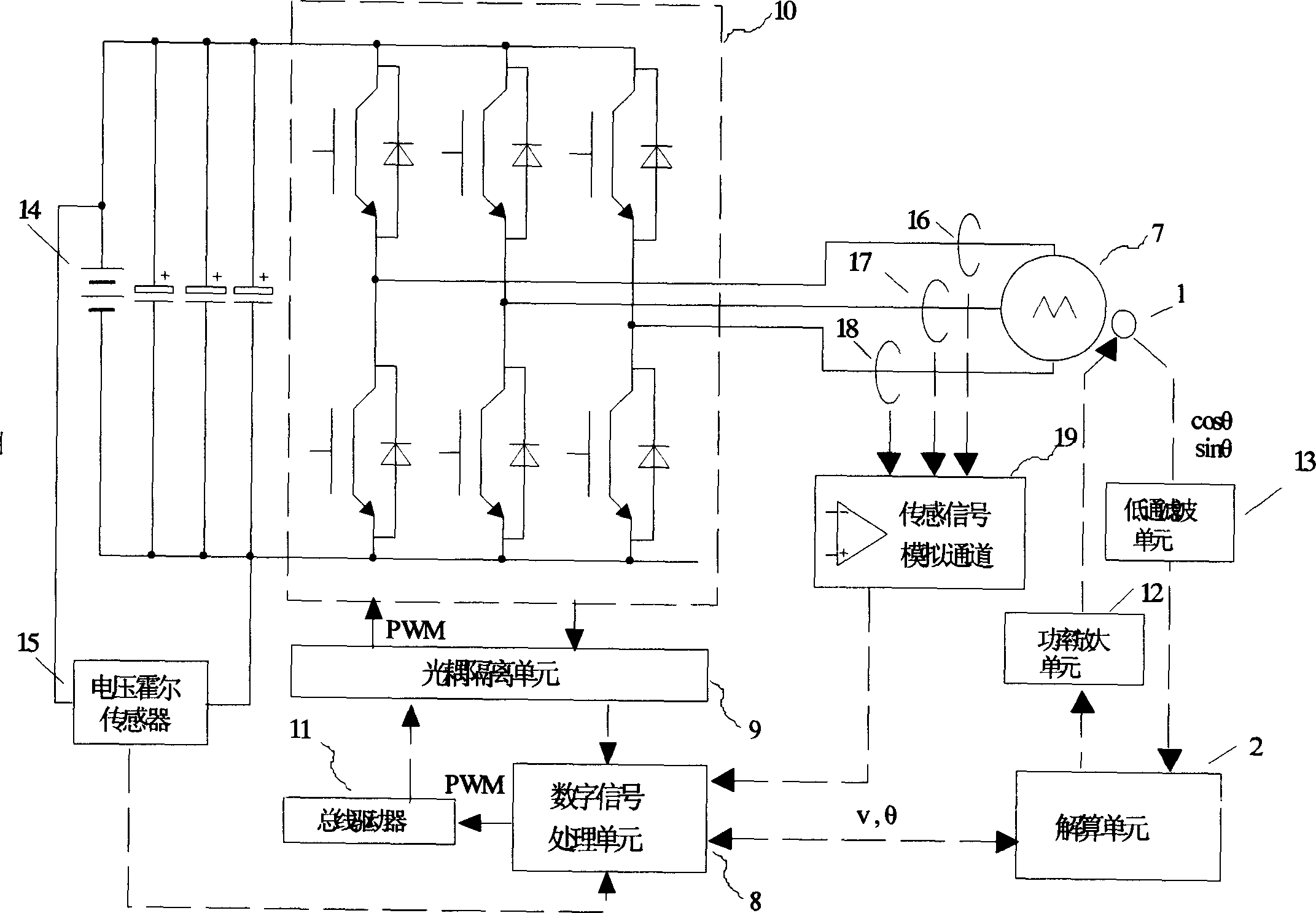
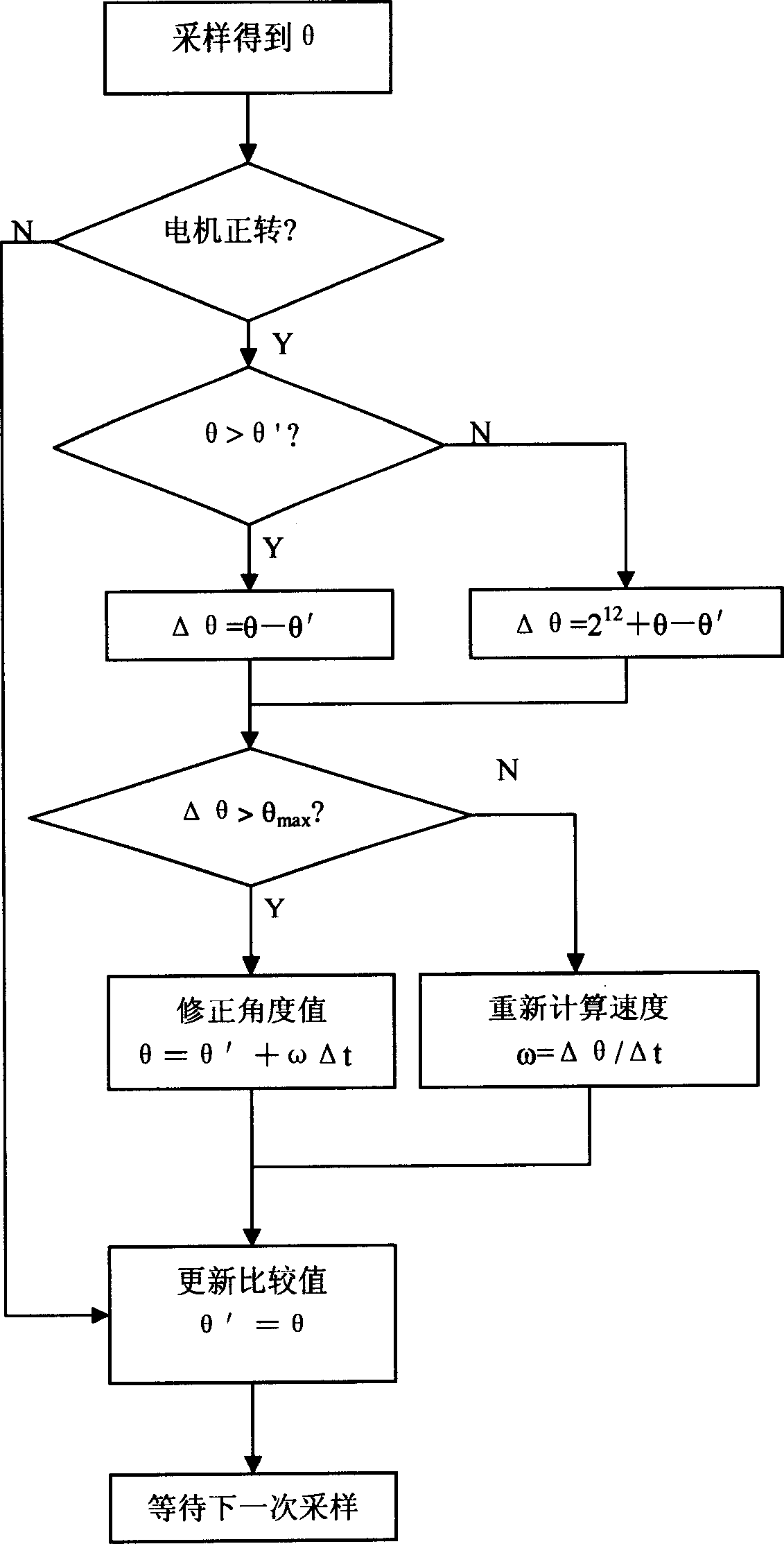
Permanent-magnet synchronous motor rotor position sensing method and position sensing device
ActiveCN1838523AHigh precisionImprove performanceElectronic commutatorsDigital signal processingPermanent magnet synchronous motor
This invention discloses a permanent synchronous generator rotor location sensing method and location sensing device, which uses rotary transformer and solving cell as sensor, and it has digit signal dealing cell, where the solving cells samples detection generator location angle in real time and fixing time interval, and it judges the change of the generator location angle after each sampling to determine whether to complement and correction. If the solving cell checks out that the extent of the rotary transformer's sensing signal of the output exceeds the allowing range, then it sends the demand to control the permanent synchronous generator to stop running to the digit signal dealing cell. This invention also discloses a permanent synchronous rotor location sensing device, which is compatible with bad magnetic environment of motor car or mixed motor car, and it can keep the generator running stably under the environment that the rotary transformer or solving cell has big error or invalidate. So this invention can be applied extensively in electric servo system of middle or small power including electric automobile and mixing motor car' driving part.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
Backlight unit and liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20060092666A1Eliminate the problemShow cabinetsImpedence networksLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
A backlight unit and an LCD device are provided, in which an LED (light emitting diode) is used as a light source of the backlight unit, and the heat generated from the LED is rapidly discharged to the outside. The backlight unit includes in one embodiment a cover bottom; at least one heat pipe located on the cover bottom; and a plurality of light sources located on the at least one heat pipe at fixed intervals.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
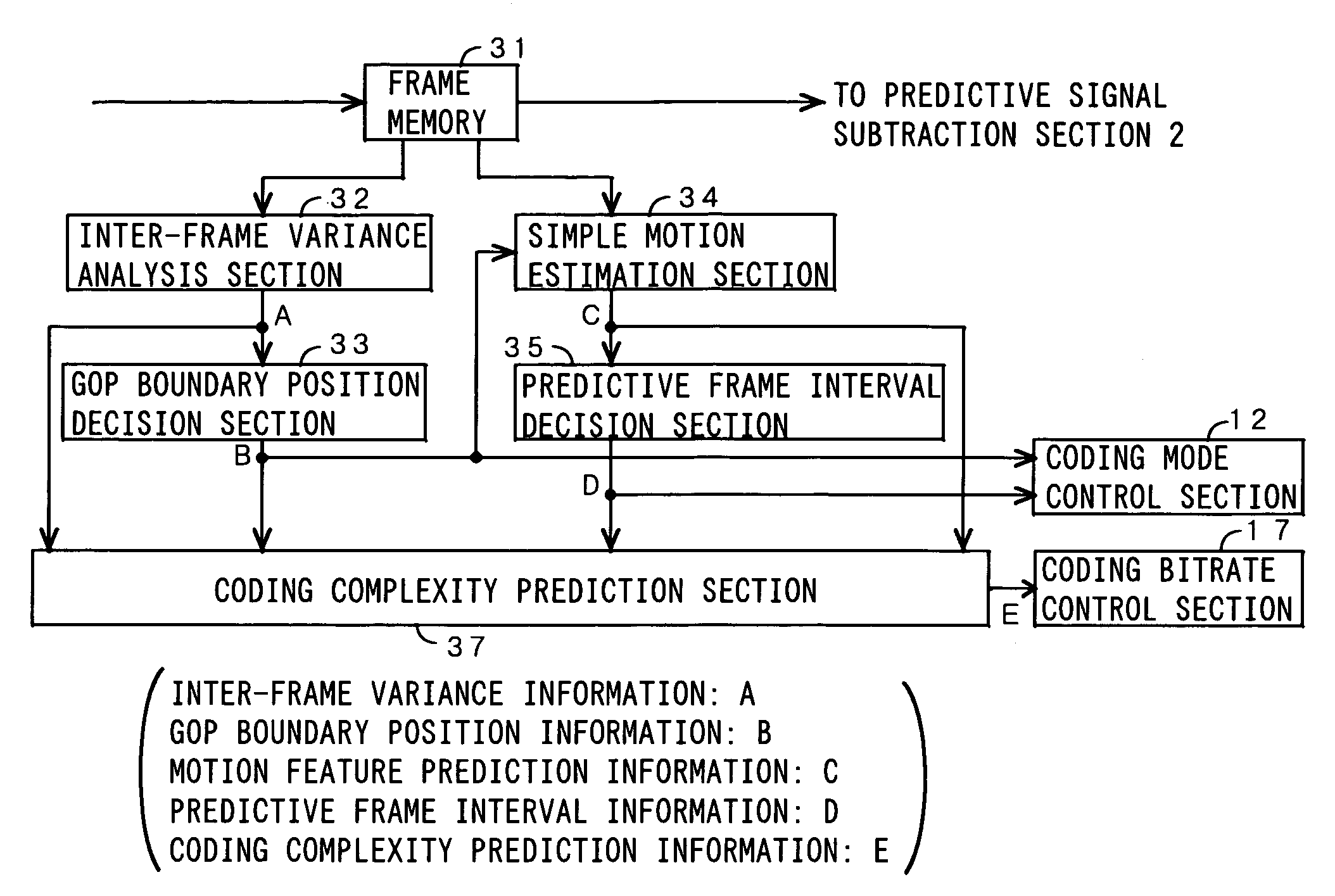
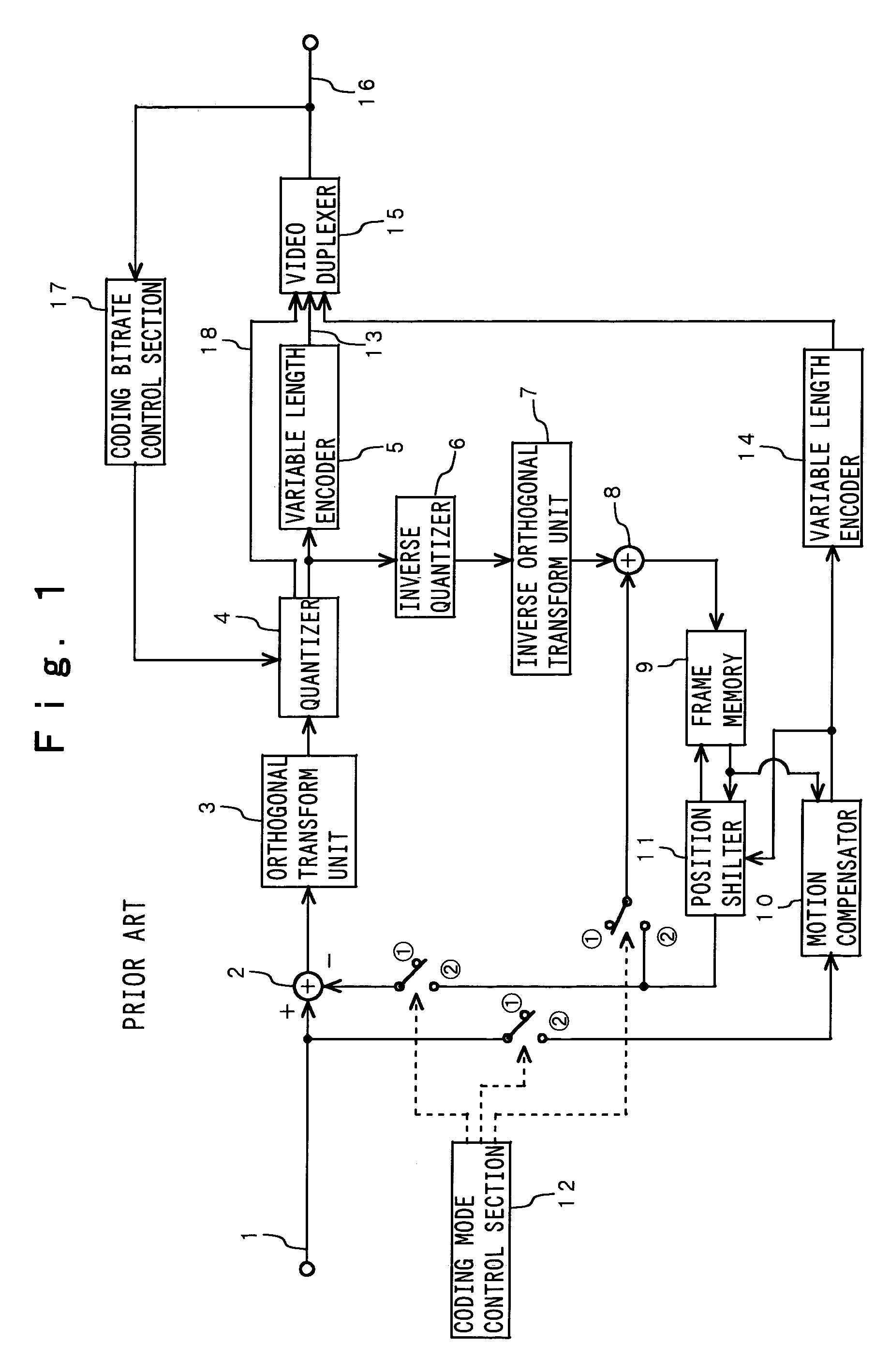
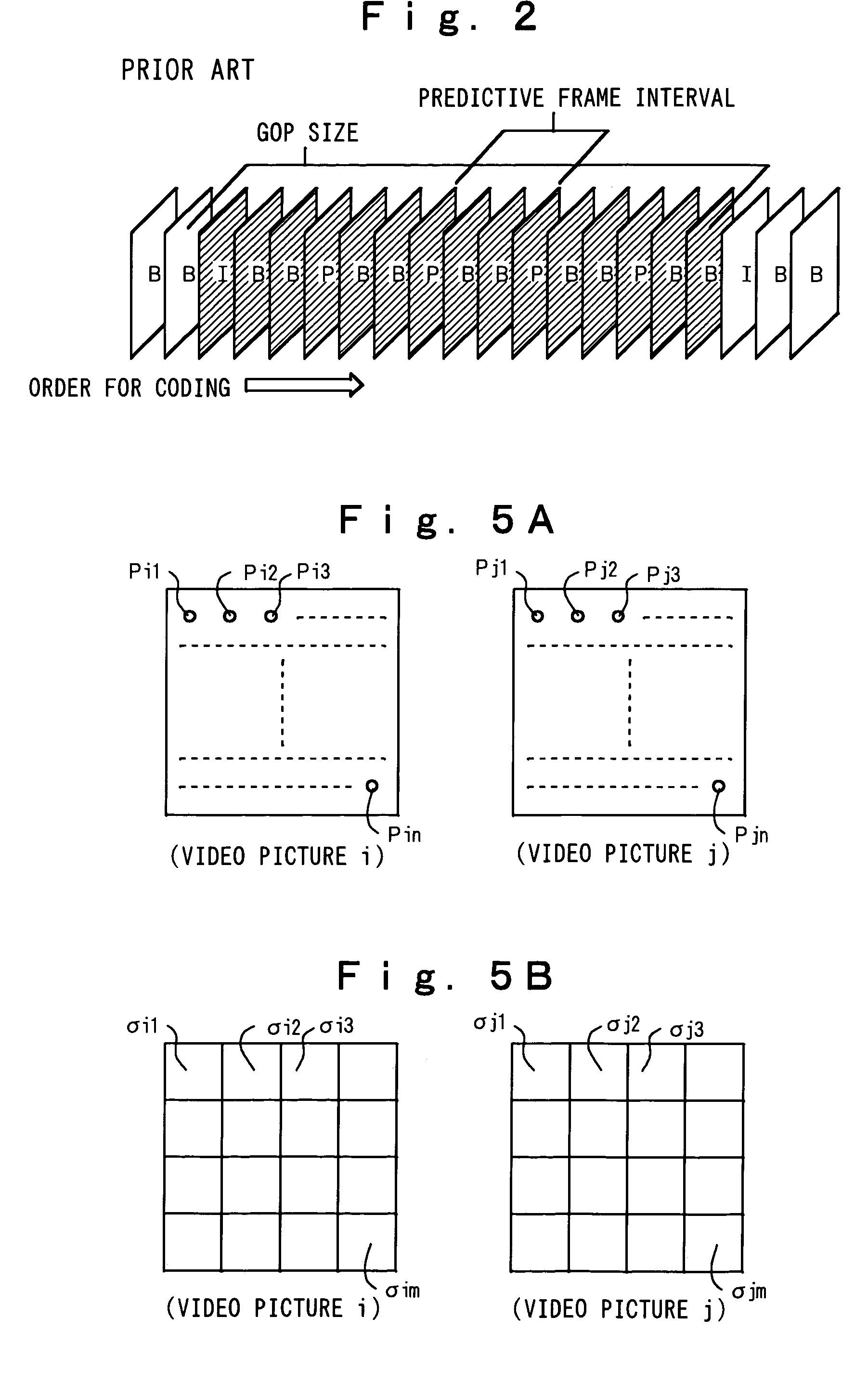
Video coding apparatus according to a feature of a video picture
InactiveUS6973126B1Prevent degradationValid encodingImage codingTelevision signal transmission by single/parallel channelsPattern recognitionInterlaced video
A variance between sequential video pictures is extracted, and then, a GOP boundary position is decided based on inter-frame variance information. Furthermore, simple motion estimation is carried out with respect to video pictures inside one GOP. If a motion variation between the video pictures is large, a small predictive frame interval is taken; to the contrary, if the motion variation is small, a large predictive frame interval is taken. The simple motion estimation is carried out between two downscaled feature planes at a timewise fixed interval with respect to a video picture which is discriminated to be an interlaced video picture, wherein a motion compensatory prediction error at that time is output as image variance information. If the image variance is small, coding is conducted by a frame structure; to the contrary, if the image variance is large, the coding is conducted by a field structure. With the above-described processing, it is possible to provide a video coding apparatus for deciding a GOP size and the predictive frame interval according to the feature of the input video picture, and another video coding apparatus for adaptively switching the coding by the frame / field structures according to the feature of the input video picture.
Owner:KDD CORP
Insulation assembly including a spacing element
InactiveUS6067764ASmooth and reliable movementEasy to manufactureConstruction materialWallsMechanical engineeringFixed interval
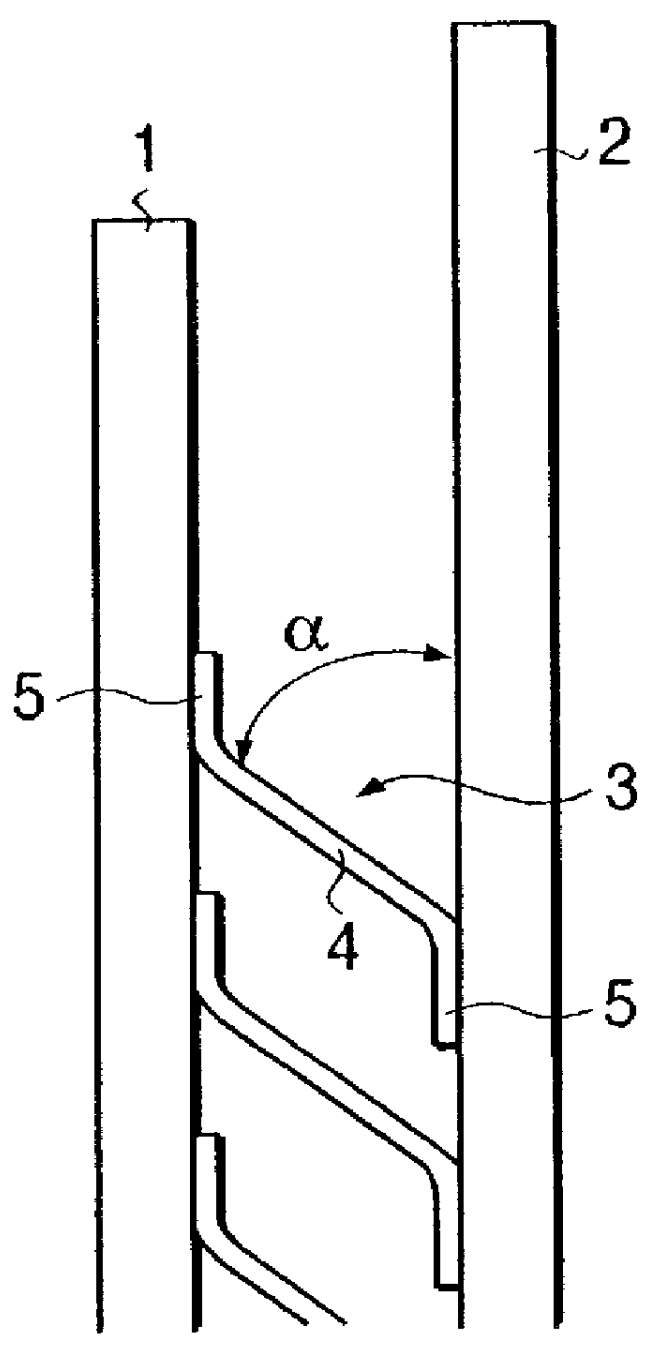
PCT No. PCT / DK96 / 00357 Sec. 371 Date Feb. 24, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Feb. 24, 1998 PCT Filed Aug. 27, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 08404 PCT Pub. Date Mar. 6, 1997The invention is an assembly for providing insulation. An assembly which provides ventilation in accordance with the invention includes a planar element; insulation positioned proximate to the planar element; and at least one space element, each space element being positioned between the planar element and the insulation, the space element including two parallel straight plate members and at least one distance member which interconnects the two parallel straight plate members which respectively face the planar element and the insulation, each distance member including two spaced apart bendable sections attached to zones of attachment to the plate members and a displacement part connected to the bendable sections and defining an angle ( alpha ) with one plate member with the angle ( alpha ) being variable by parallel displacement of the plate members away from or towards each other and defining a separation which is fixable between the parallel straight plate members with a fixed separation defining a ventilation space between the planar element and the insulation.
Owner:JOHANSEN KNUD ERIK
Calibrated surgical probe
A microsurgical probe tip and method of using same are disclosed. One embodiment of the microsurgical probe tip comprises: an outer cutting member, comprising a first tube having a wall, a closed end and a port formed in the wall near the closed end; an inner cutting member, comprising a second tube coaxial with and operable to move in a reciprocating motion within the first tube and having a first end operable to be coupled to a driving mechanism and a second end with a cutting edge for cutting tissue; a first alignment mark on the outer cutting member at a first predetermined position adjacent to the port; and a second alignment mark on the inner cutting member at a second predetermined position adjacent to the cutting edge of the inner cutting member, wherein the second alignment mark is visible through the port and operable to be aligned with the first alignment mark such that when the first and second alignment marks are aligned, a preferred relative positioning between the inner and outer cutting members is achieved. The microsurgical probe tip can further comprise one or more radial alignment marks on the inner cutting member, wherein the radial alignment marks are parallel to one another at fixed intervals from one another and positioned so that one or more of the radial alignment marks are visible through the port so as to indicate the relative lateral positioning between the inner cutting member and the outer cutting member. The radial alignment marks can be made by a method, or combination of methods, such as laser cutting, inkjet printing, and mechanical scribing. The driving mechanism can be a pneumatic driving mechanism, an electro-mechanical driving mechanism, and / or a magnetic driving mechanism. The microsurgical probe tip can further comprising a plurality of gauge marks on an outer surface of the outer cutting member, wherein the gauge marks are parallel to one another at a fixed interval (e.g., 1 millimeter) from one another and positioned so that the gauge marks can be used as a measuring tool in a surgical environment
Owner:ALCON INC
Synchronous memory read data capture
ActiveUS20080005518A1Simple and low latencyDigital storageMemory systemsLatency (engineering)Computer science
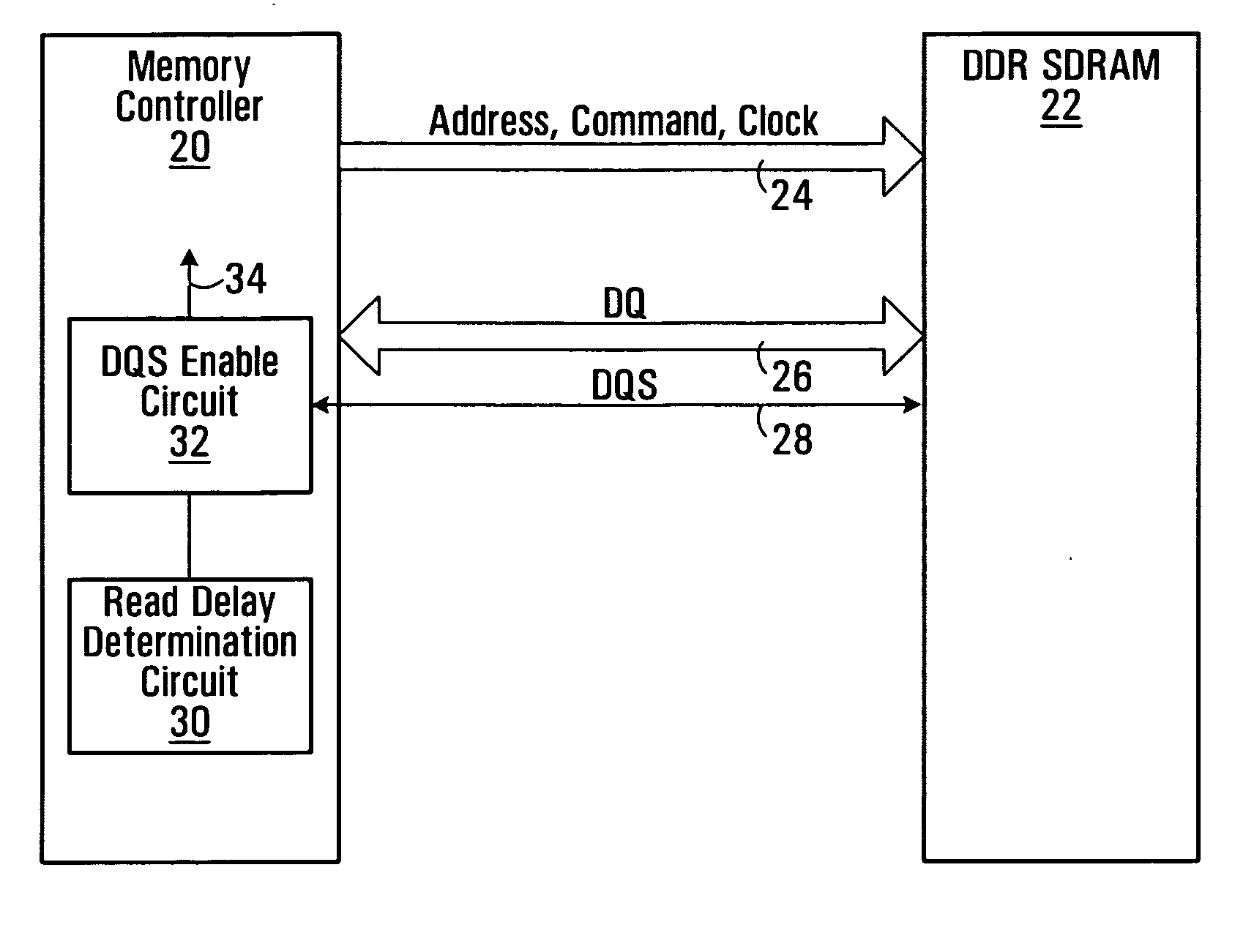
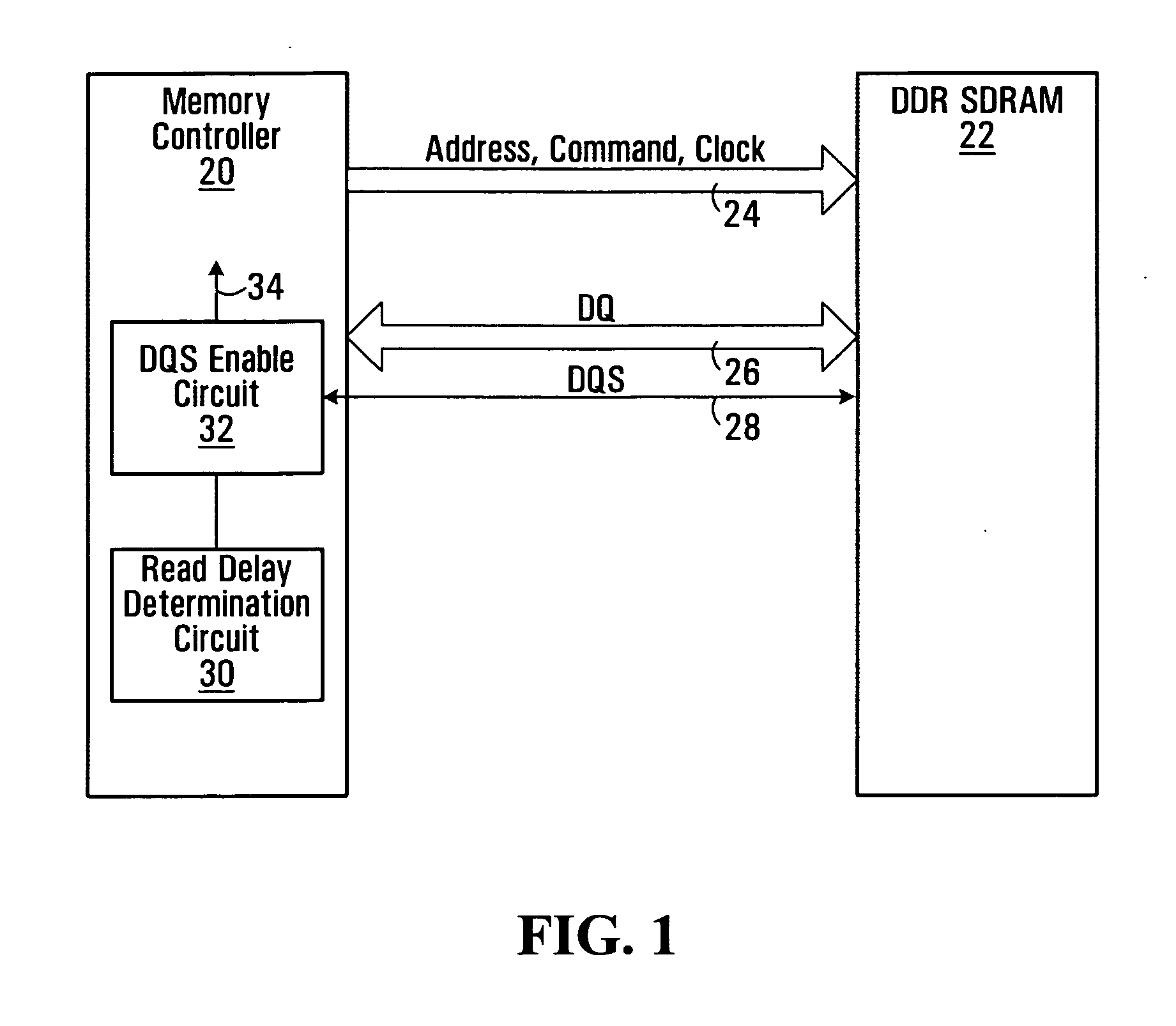
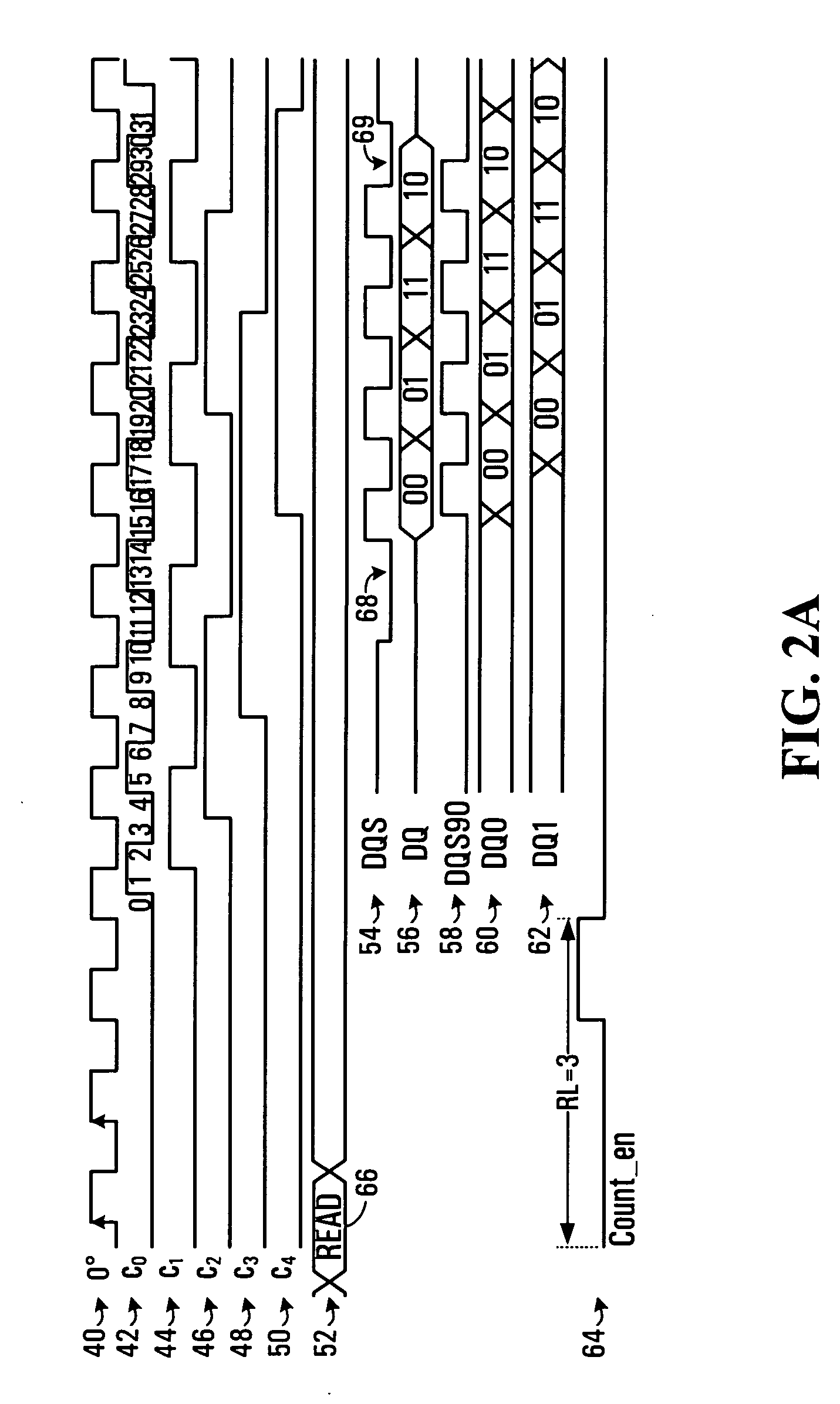
A method of snap-shot data training to determine the optimum timing of the DQS enable signal in a single read operation is provided. This is accomplished by first writing a Gray code count sequence into the memory and then reading it back in a single burst. The controller samples the read burst at a fixed interval from the time the command was issued to determine the loop-around delay. A simple truth table lookup determines the optimum DQS enable timing for normal reads. Advantageously, during normal read operations, the first positive edge of the enabled DQS signal is used to sample a counter that is enabled every time a command is issued. If the counter sample changes, indicating timing drift has occurred, the DQS enable signal can be adjusted to compensate for the drift and maintain a position centered in the DQS preamble. This technique can also be applied to a system that uses the iterative approach to determining DQS enable timing on power up. Another embodiment of the invention is a simple, low latency clock domain crossing circuit based on the DQS latched sample of the counter.
Owner:MOSAID TECH
Deployable truss having second order augmentation
ActiveUS7694486B2Decreases free buckling lengthIncrease its moment of inertiaCollapsable antennas meansCosmonautic vehiclesMoment of inertiaEngineering
A deployable truss is formed from a plurality of column members connected at their ends where at least some of the column members are formed from column assemblies, each including a plurality of strut members that are at least connected to each other at a first and second end of the column assembly. For added rigidity, strut members of a column assembly may be connected to each other between the first and second ends using, for example, a rigidizable resin, a fixed spacer, or a deployable spacer. Connecting strut members between the ends of the column assembly provides mutual bracing to the strut members and decreases the free buckling length of the individual strut members. Spacers are preferably configured to radially space the strut members away from the longitudinal centerline of the column assembly to increase its moment of inertia, and hence its buckling strength.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
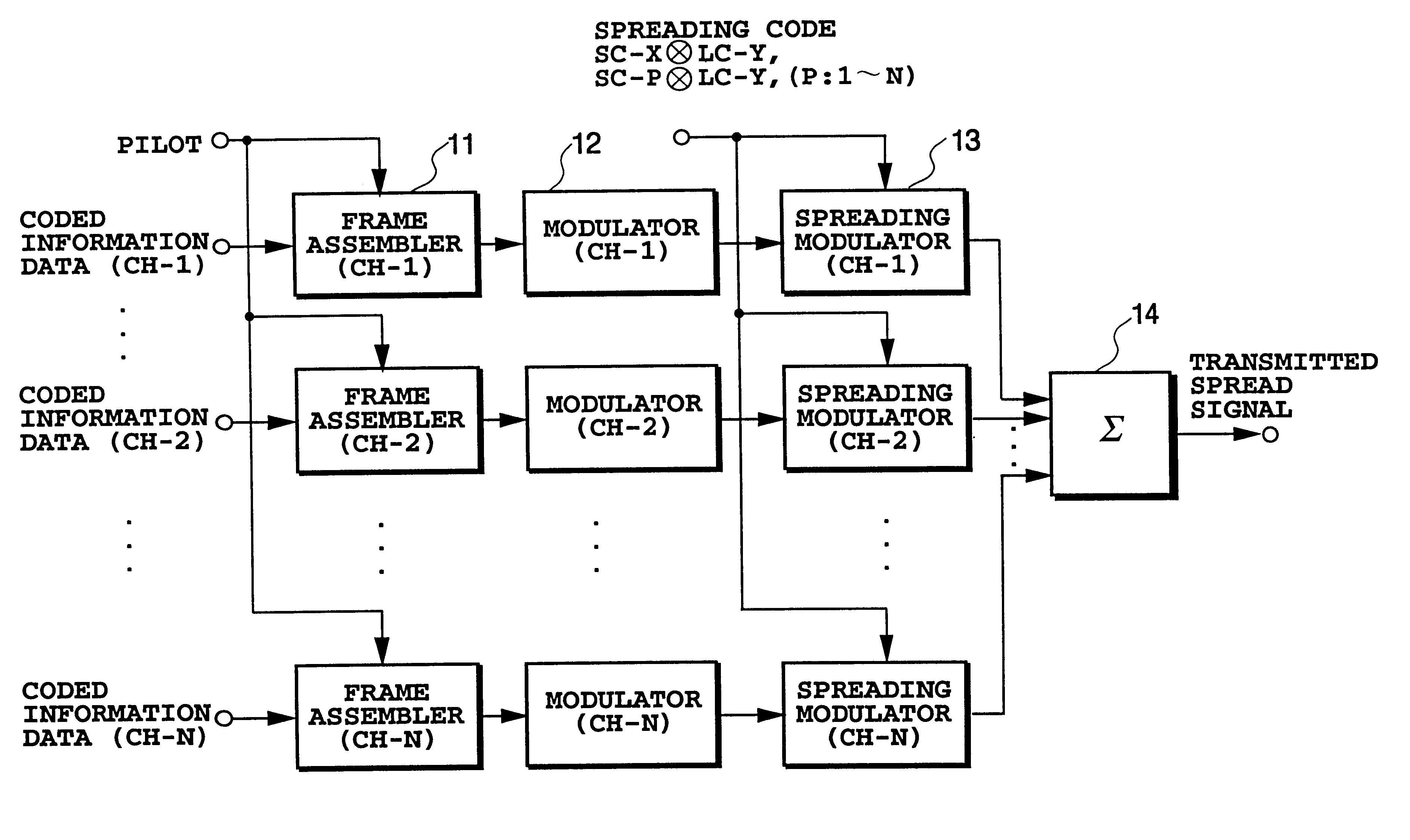
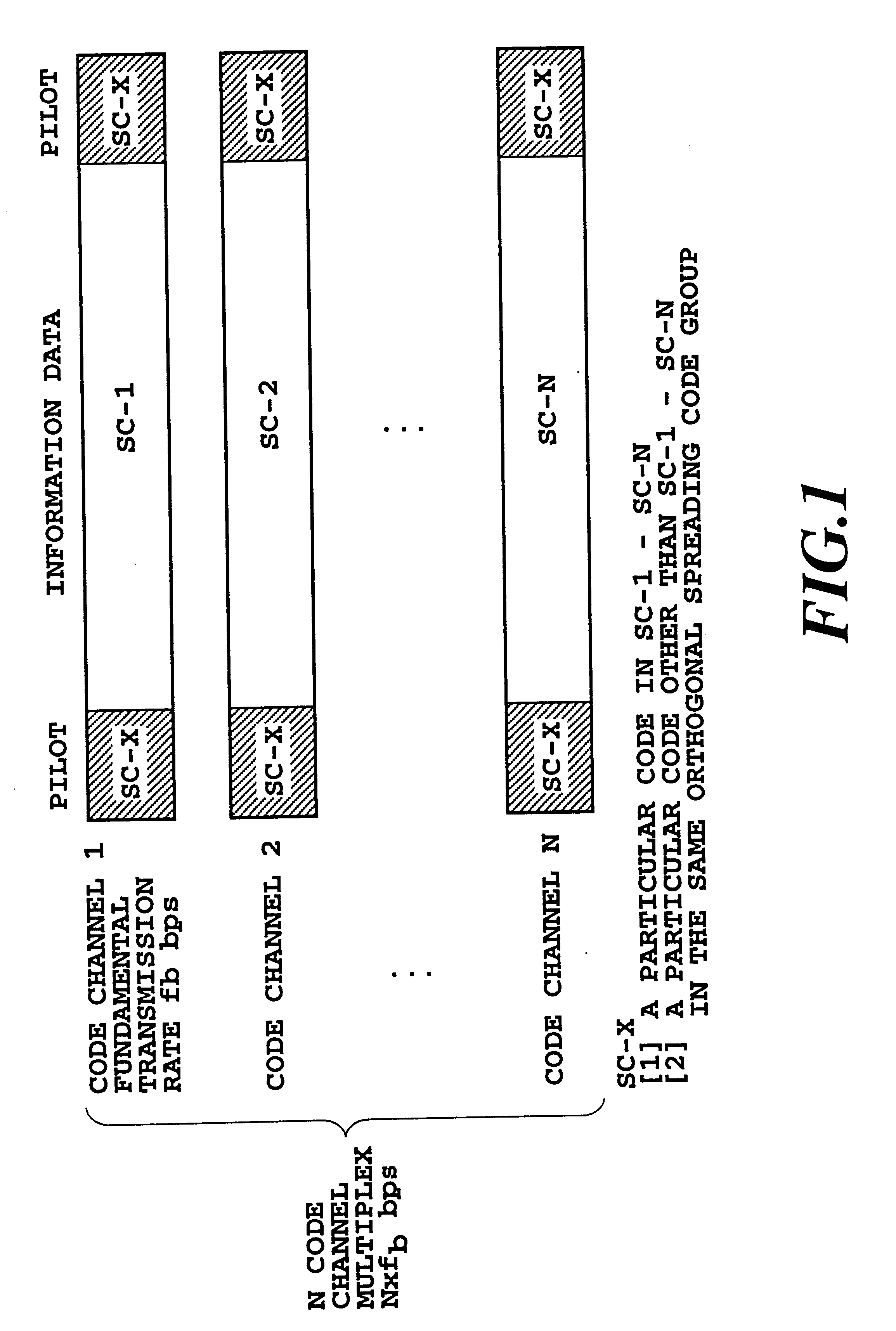
DS-CDMA transmission method
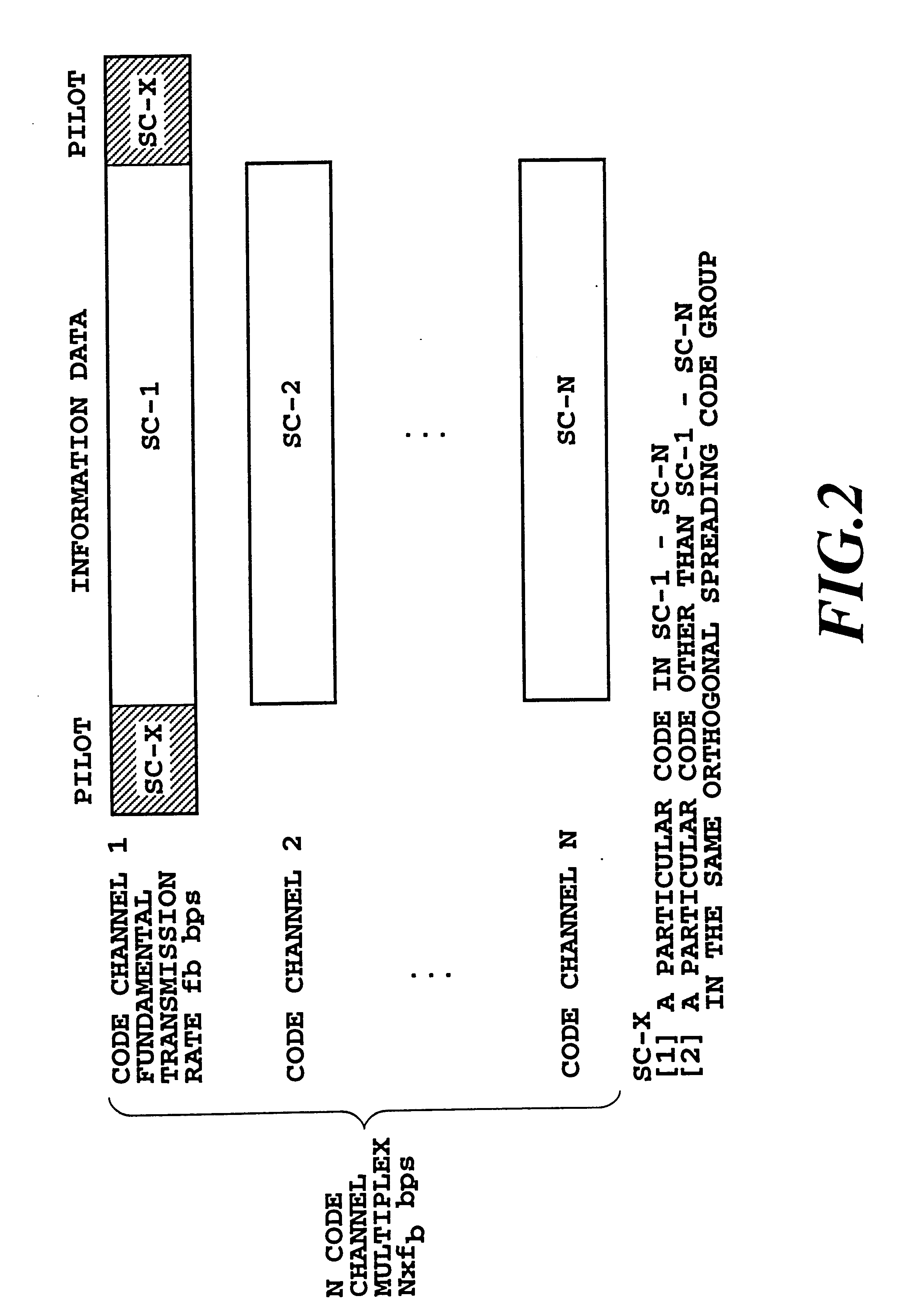
InactiveUS6842442B2Improve accuracyIncrease in circuit sizeTime-division multiplexRadio transmission for post communicationMultiplexingInformation data
A DS-CDMA transmission method capable of improving the accuracy of channel estimation using pilot symbols by eliminating cross-correlation between pilot symbols inserted into code channels in CDMA multiplexing carrying out fast signal transmission. In each frame assembler, the pilot symbols, which are used for channel estimation for coherent detection, are inserted into coded information data on code channels at fixed intervals, and then the data is modulated by the modulator. The modulated data symbols in each code channel from the modulator are spread by the spreading modulator, the pilot symbols are spread using a spreading code, whereas the information symbols are spread using different spreading codes assigned to respective code channels. The spread signals of the code channels are summed up by the adder to be transmitted.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Cruise control apparatus performing automatic adjustment of object recognition processing in response to driver actions relating to vehicle speed alteration
InactiveUS20030217880A1Avoid difficult choicesIncrease probabilityVehicle fittingsDigital data processing detailsAuto regulationDriver/operator
A cruise control apparatus can control a host vehicle to run with a fixed separation from a preceding vehicle when such a preceding vehicle is detected based on received radar signals and to run at a preset fixed speed when no preceding vehicle is detected. The cruise control apparatus is configured to respond to one of a set of predetermined actions by the vehicle driver, which indicate an intention to change the vehicle speed, by making it easier or more difficult for a preceding vehicle to be detected, in accordance with whether the indicated intention may signify that an actual preceding vehicle is not being detected or may signify that a non-existent preceding vehicle is being detected and that the host vehicle speed has been reduced accordingly. Improved performance is thereby achieved by utilizing the cognitive abilities of the driver to augment the detection operation of the cruise control apparatus.
Owner:DENSO CORP
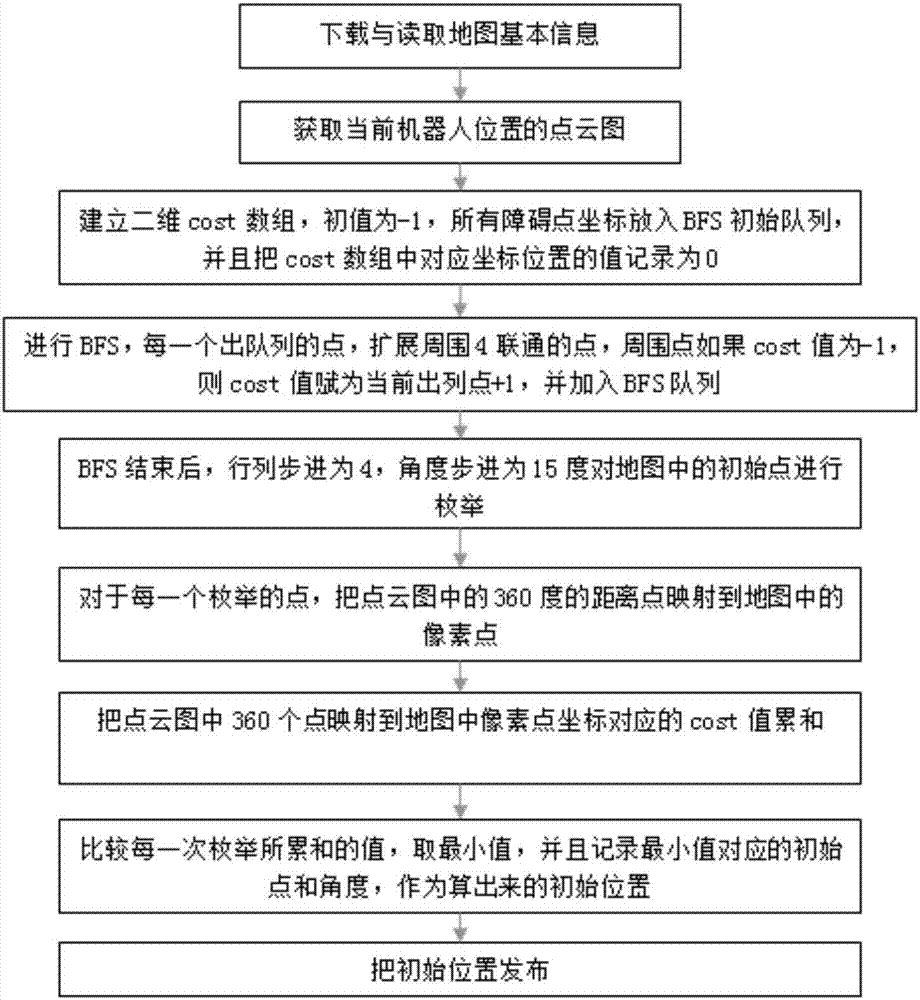
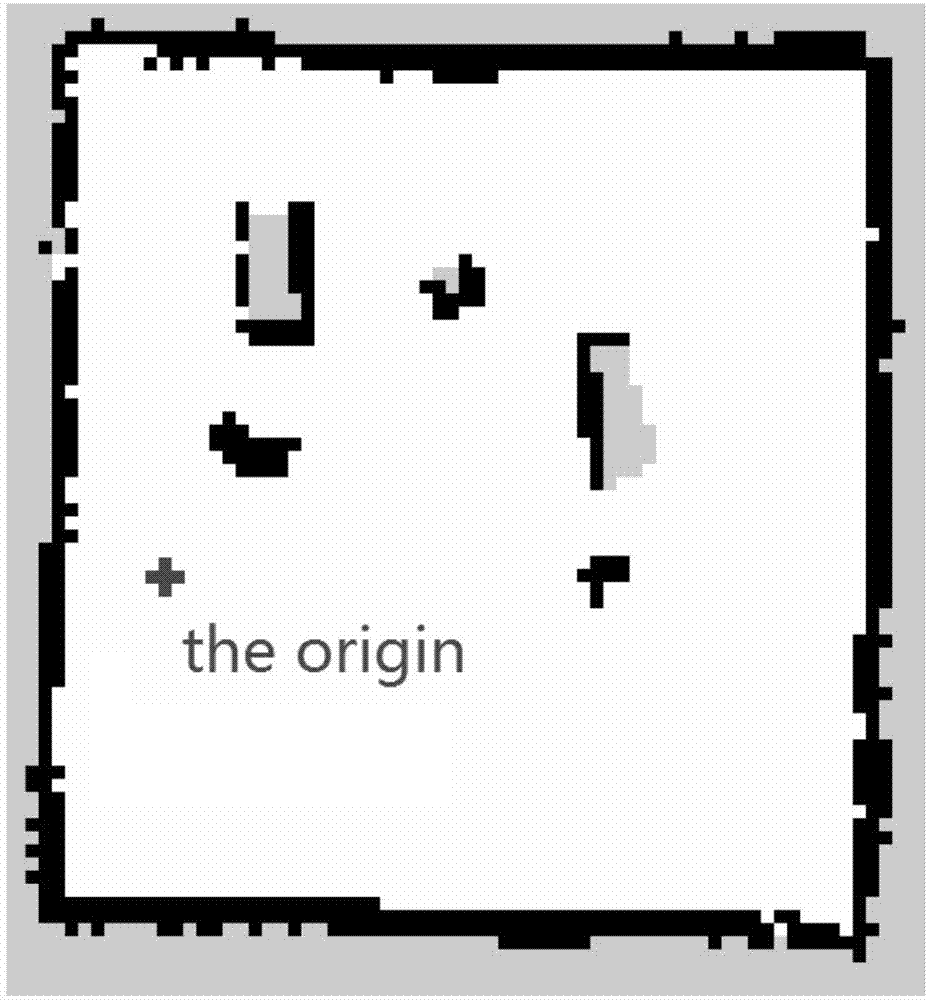
Mobile robot real-time positioning method based on laser radar and map matching
ActiveCN107390681AImprove matchWide applicabilityOptical rangefindersNavigational calculation instrumentsPoint cloudRadar
The invention discloses a mobile robot real-time positioning method based on laser radar and map matching. The method comprises the steps that a 2D map of the environment is established; transverse and longitudinal checkerboard average blocking is performed on the 2D map according to the fixed interval distance; assumption deduction is performed on each block of the map, assuming that the upper left position of the block is the initial position of the robot, direction enumeration is performed on the basis of each block; as for each assumption, the point cloud data of laser radar are mapped to the map pixels; a matching degree model is established to judge the score of each assumption, and the sum of the pixel distance "obstacle pixel" Manhattan distance corresponding to all the point cloud data of the laser radar is accumulated as for each assumption; the block and the direction of the minimum sum are selected to act as the initial position and the direction of the robot; and the real-time position of the robot is tracked by using the Monte Carlo method in the movement of the robot. The robot is enabled to perceive its position only through the built-in laser sensor and the known map without assistance of artificial intervention or environmental markers.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
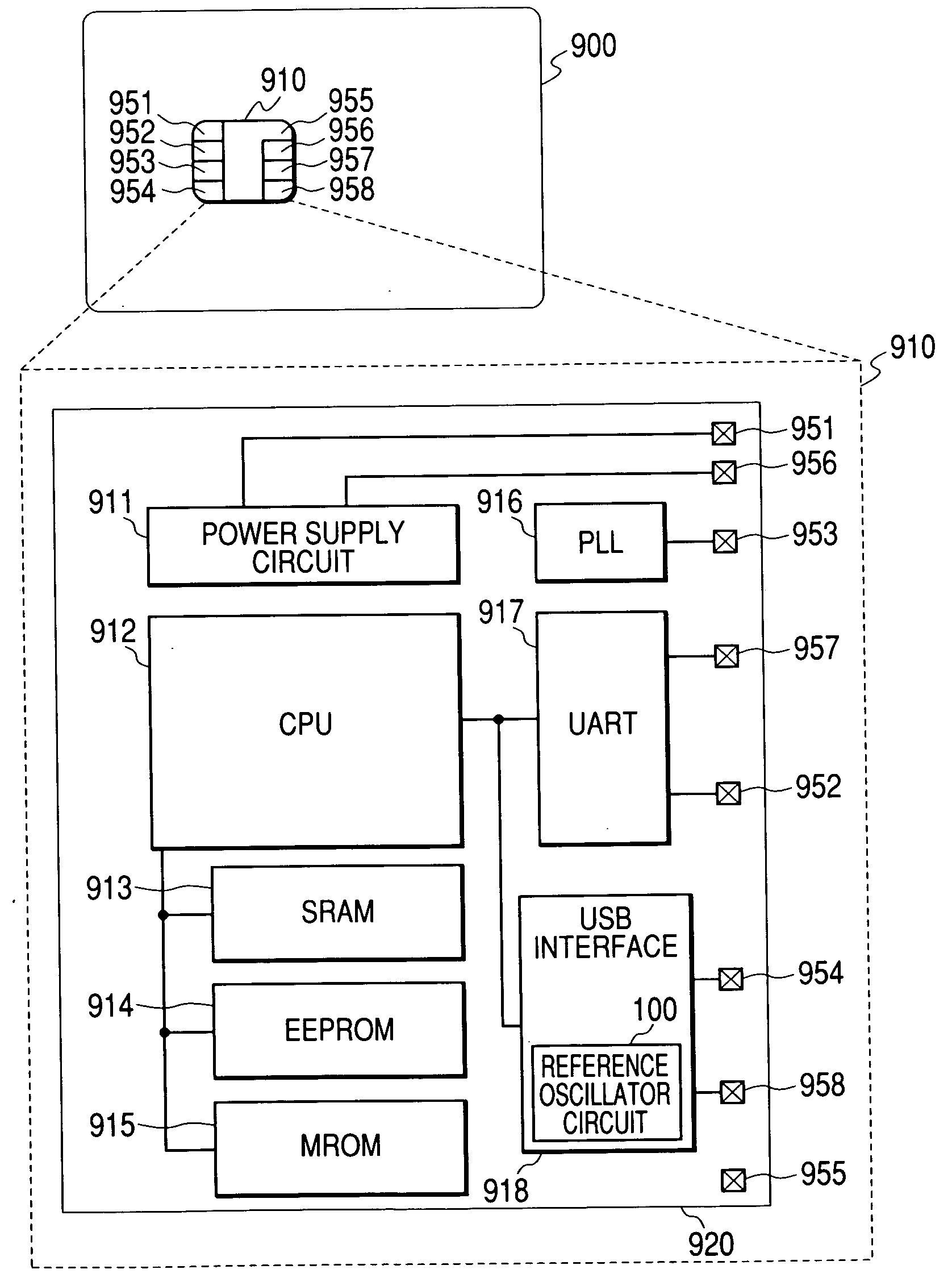
Semiconductor integrated circuit
InactiveUS20050081076A1Sufficient supplyLow costPulse automatic controlVolume/mass flow measurementSelf excitedEngineering
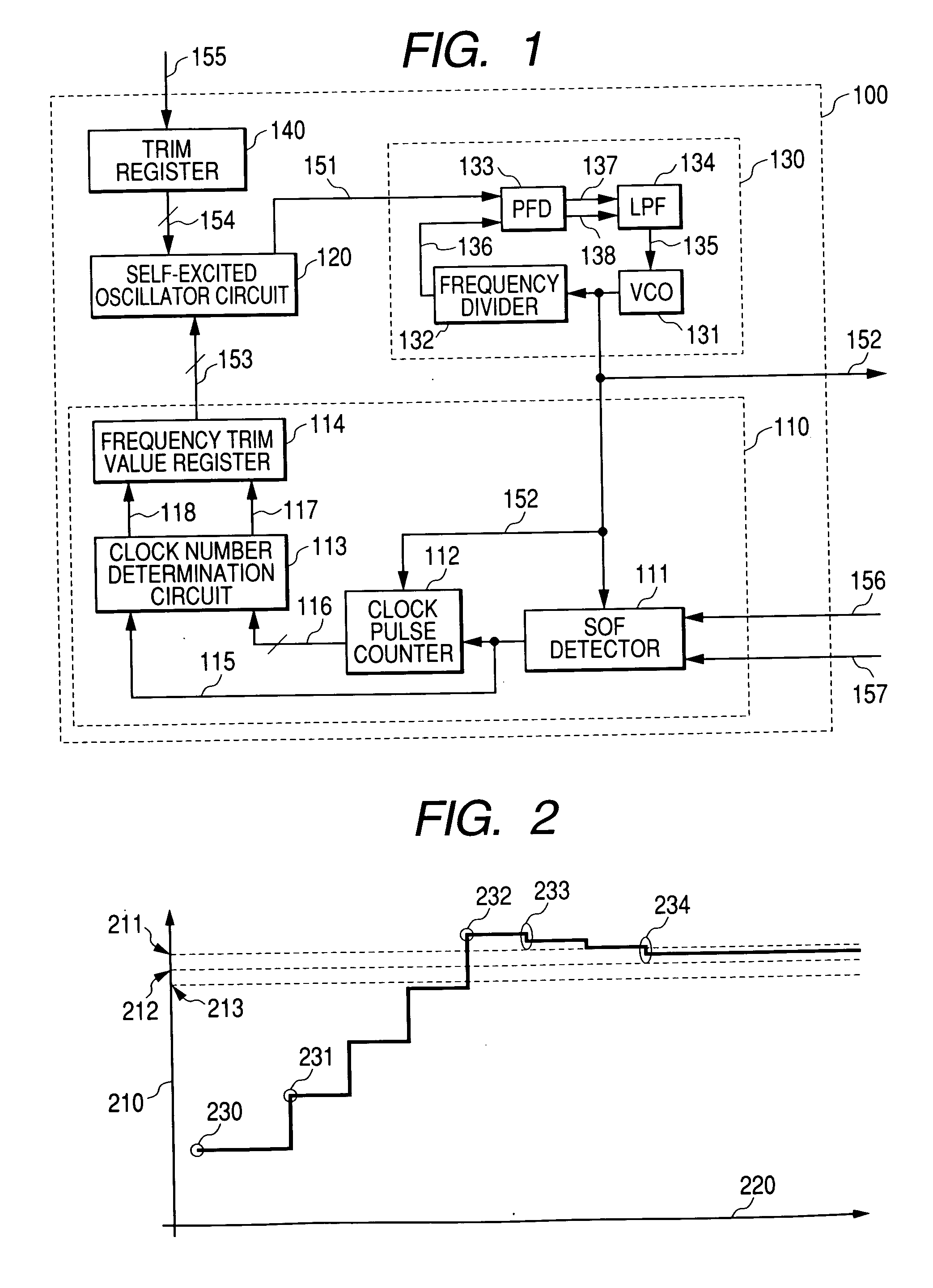
A semiconductor integrated circuit is provided with an external interface circuit, which includes a clock generation circuit for generating a synchronous clock signal to establish synchronization between data input and output through input and output of a data string sectioned at fixed intervals. The clock generation circuit includes a self-excited oscillator circuit serving as an oscillation source for the synchronous clock signal, and a control circuit for trimming the oscillation frequency of the self-excited oscillator circuit. The control circuit detects the sections made at the fixed intervals to the data string, measures the section interval based on an oscillation output of the self-excited oscillator circuit, and controls the oscillation frequency of the self-excited oscillator circuit to match the measurement value to a target value. With such a structure, any required frequency can be oscillated in a self-excited manner using a data string sectioned at fixed intervals using SOF packets or others instead of an oscillator.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
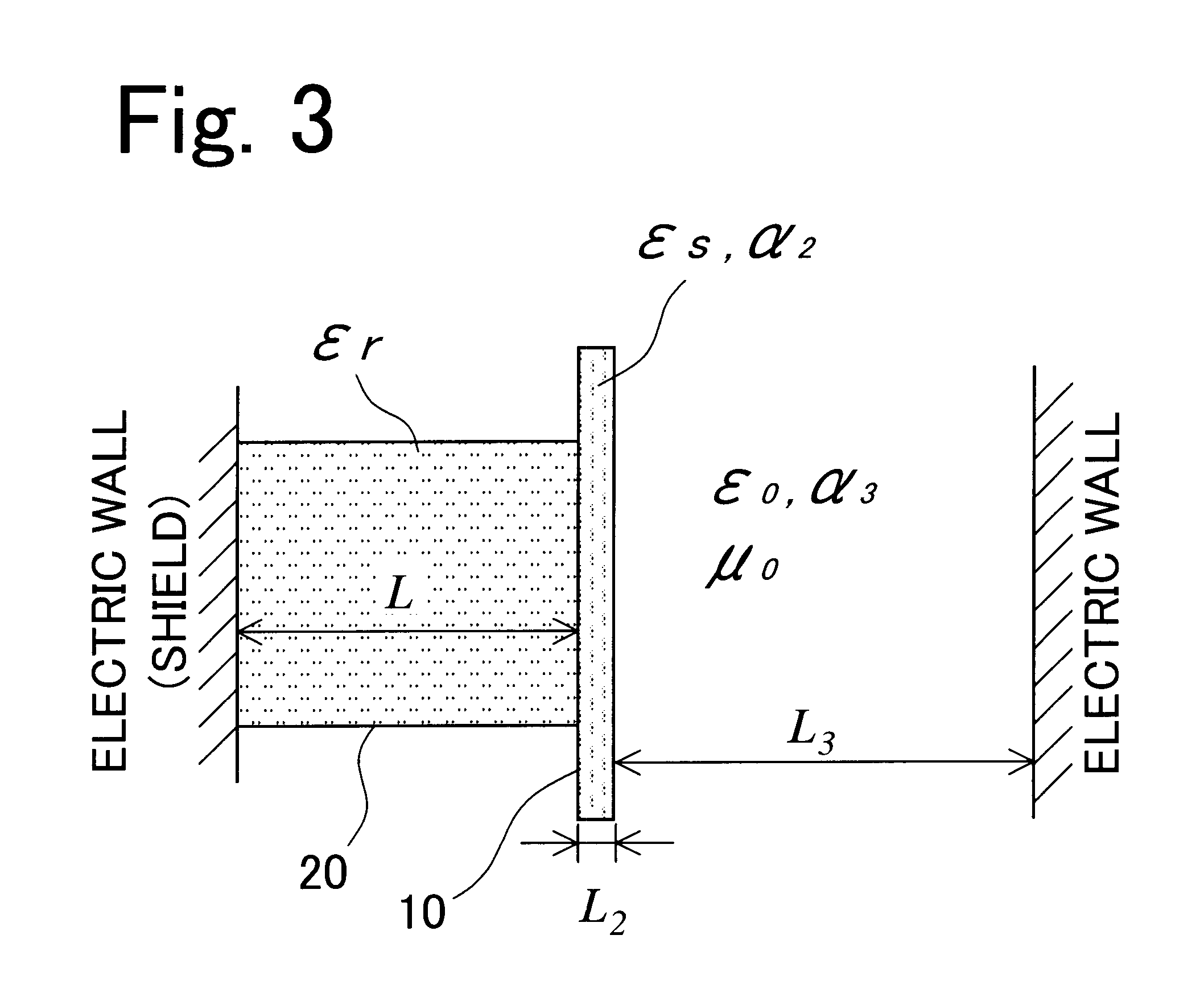
Method and device for measuring dielectric constant
InactiveUS6496018B1Dielectric property measurementsMaterial analysis using microwave meansSample MeasureResonance
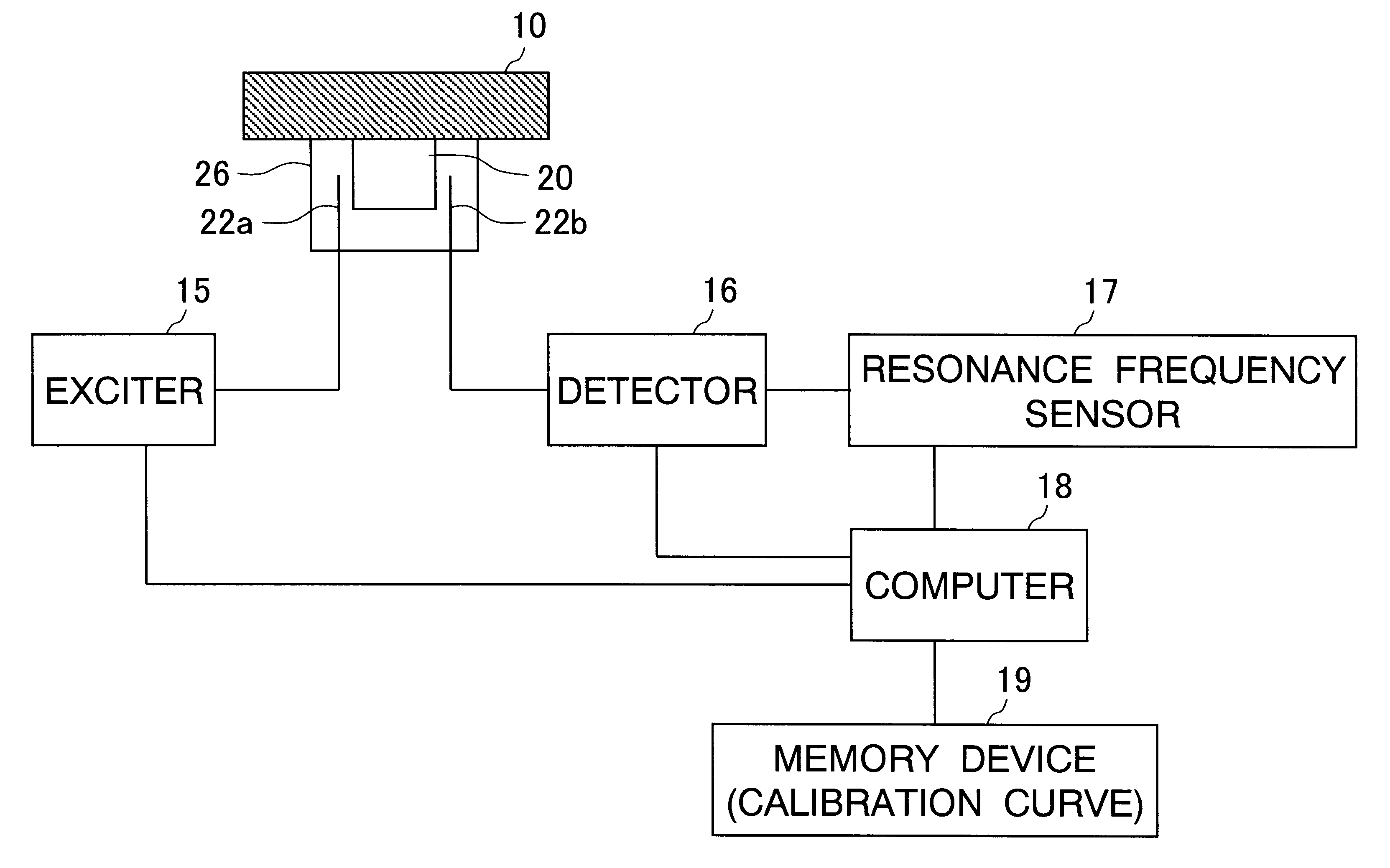
The sample measuring face of a dielectric resonator (20) is placed near a standard sample having a known dielectric constant at a fixed interval D. While appropriately varying the dielectric constant and thickness of the standard sample under the above condition, the variation of the resonance frequency of the dielectric resonator (20) is measured for each varied dielectric constant and thickness to draw a calibration curve of the varied resonance frequency depending on the dielectric constant and thickness. Under the same condition where calibration curve is drawn, the variation of the resonance frequency of the dielectric resonator (20) for a sample having a known thickness is measured. The dielectric constant of the sample is found from the measurement value and the calibration curve. The dielectric constant of not only a sheetlike sample but also a three-dimensional molded article or a liquid sample can be measured easily.
Owner:OJI PAPER CO LTD
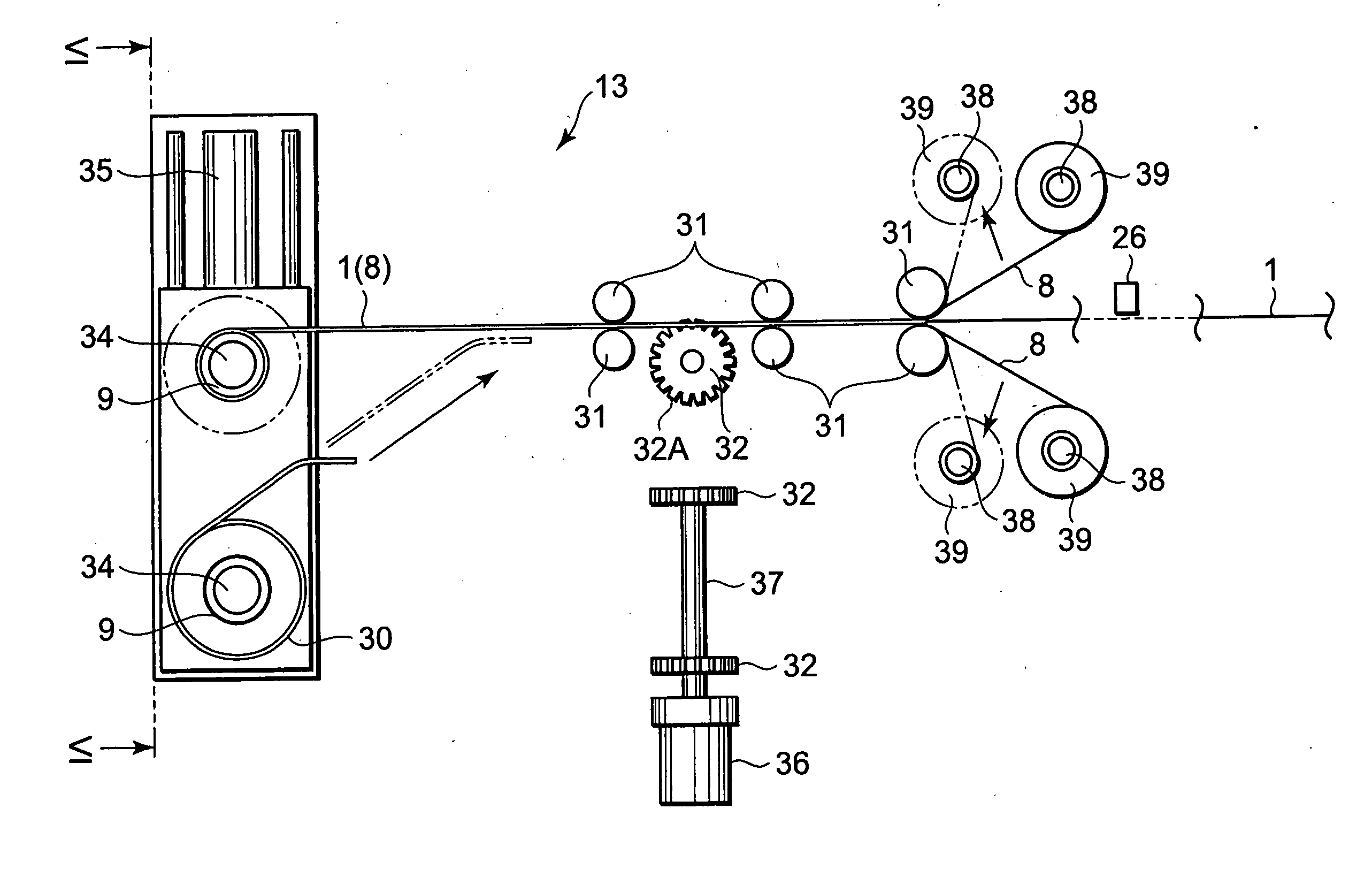
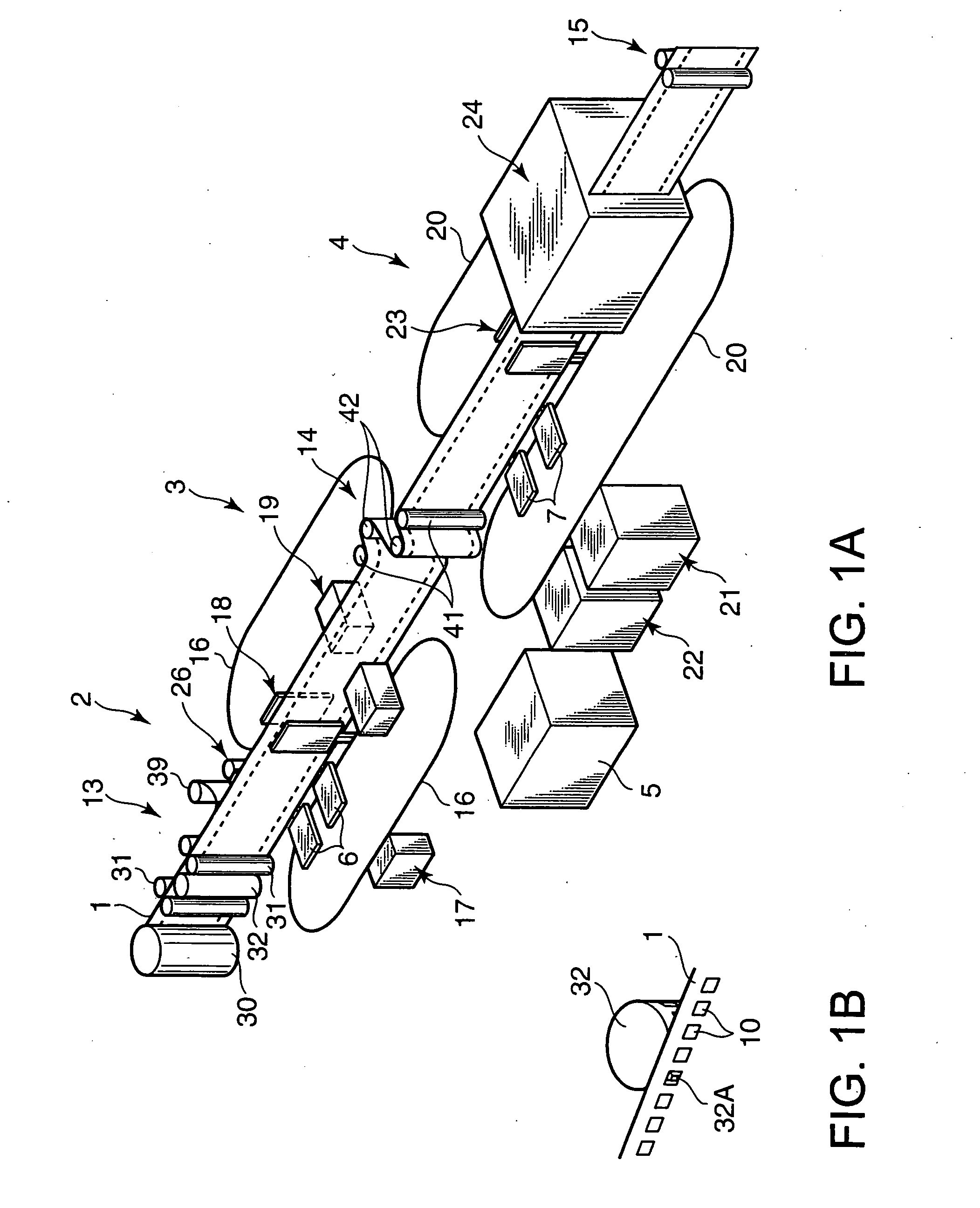
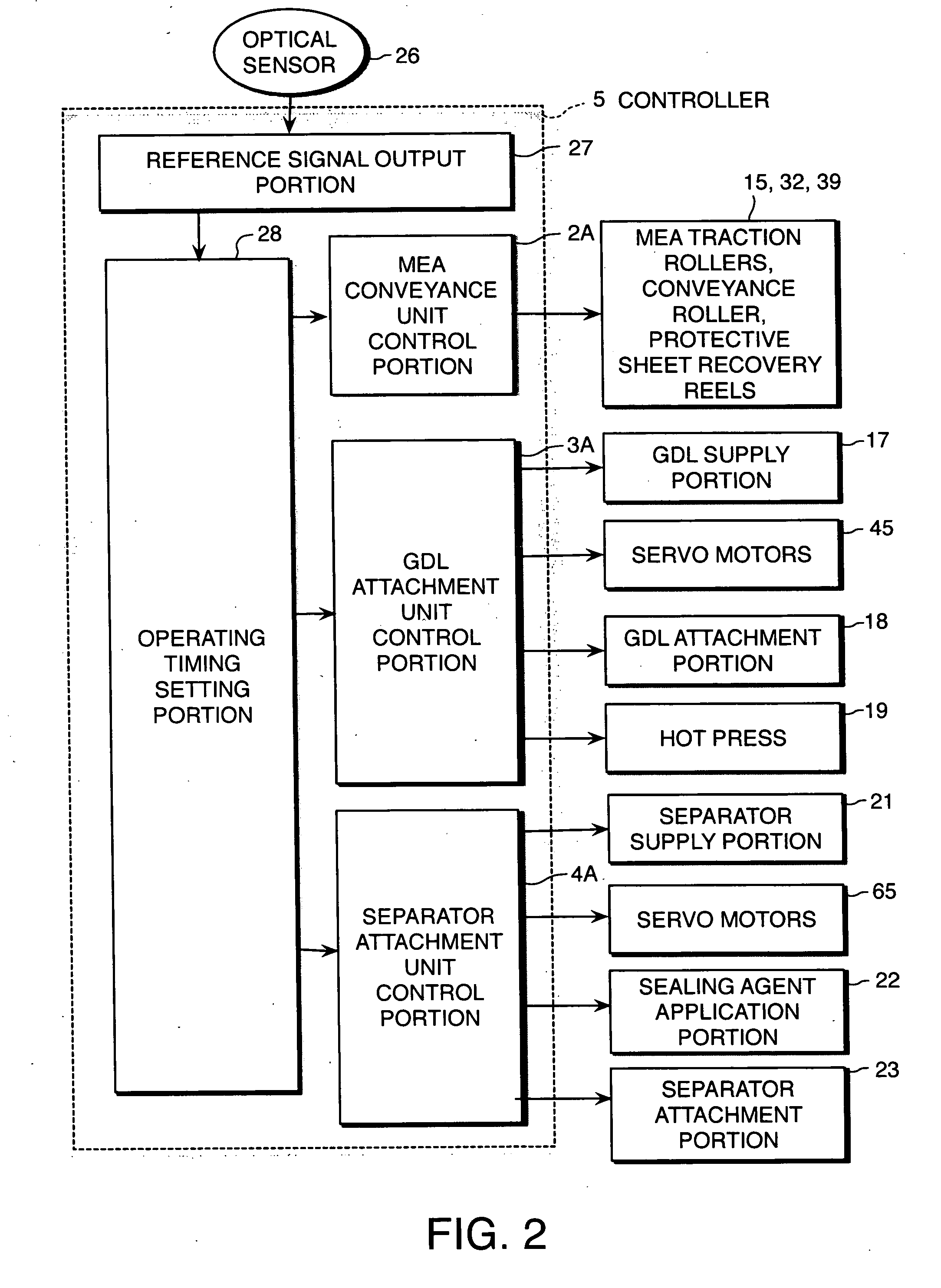
Manufacture of fuel cell
ActiveUS20070116999A1High feed accuracyPrecise positioningLamination ancillary operationsFuel cells groupingPolymer electrolytesFuel cells
A fuel cell is manufactured using a polymer electrolyte membrane (1). A catalyst layer (12) is formed at fixed intervals on the surface of the strip-form polymer electrolyte membrane (1) in the lengthwise direction thereof, and conveyance holes (10) are formed in series at fixed intervals on the two side portions thereof. By rotating a conveyance roller (32) comprising on its outer periphery projections which engage with the holes (10), the polymer electrolyte membrane (1) is fed from a reel (9). A GDL (6) and a separator (7) are adhered to the fed polymer electrolyte membrane (1) at a predetermined processing timing based on the rotation speed of the conveyance roller (32), and thus the fuel cell is manufactured efficiently while the GDL (6) and separator (7) are laminated onto the catalyst layer (12) accurately.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
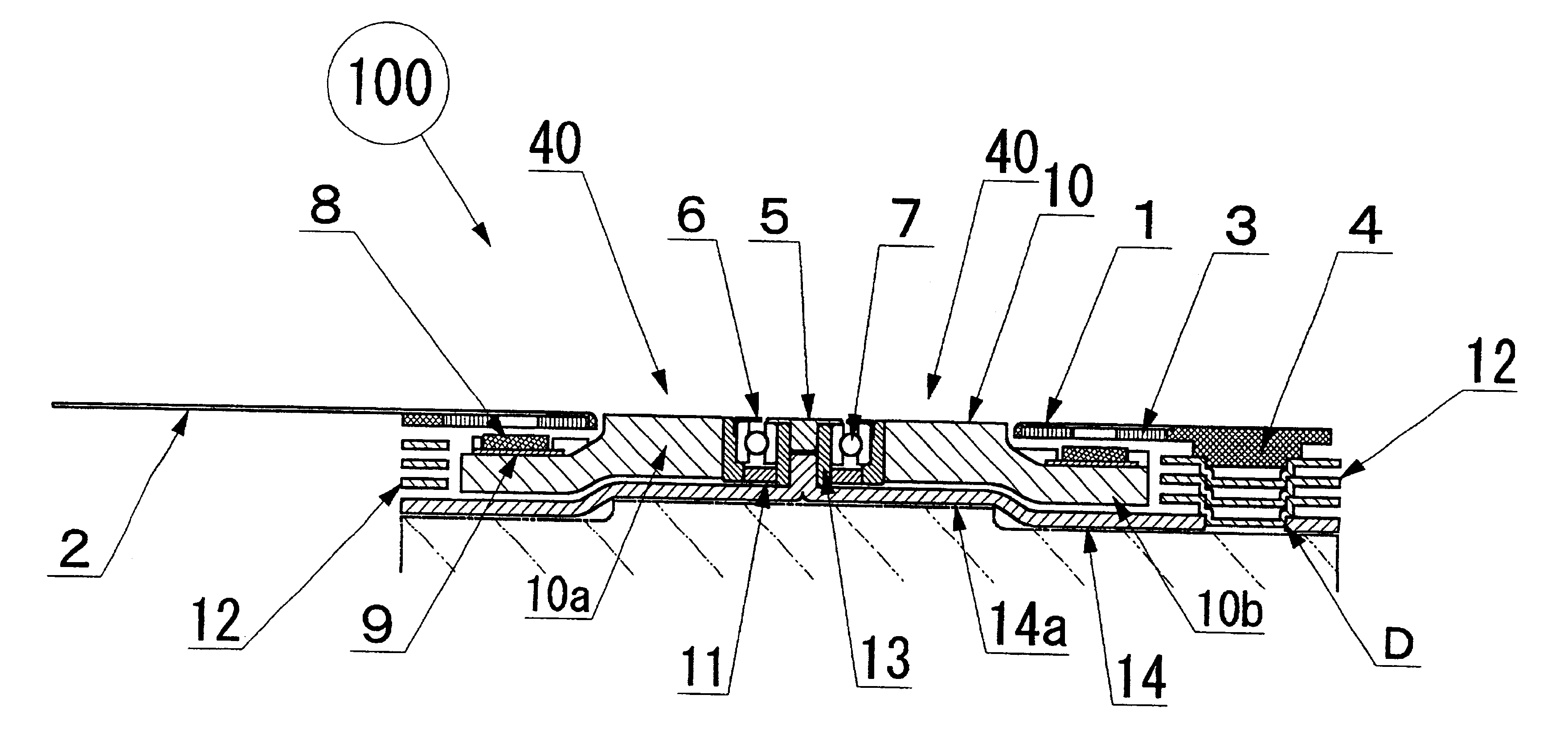
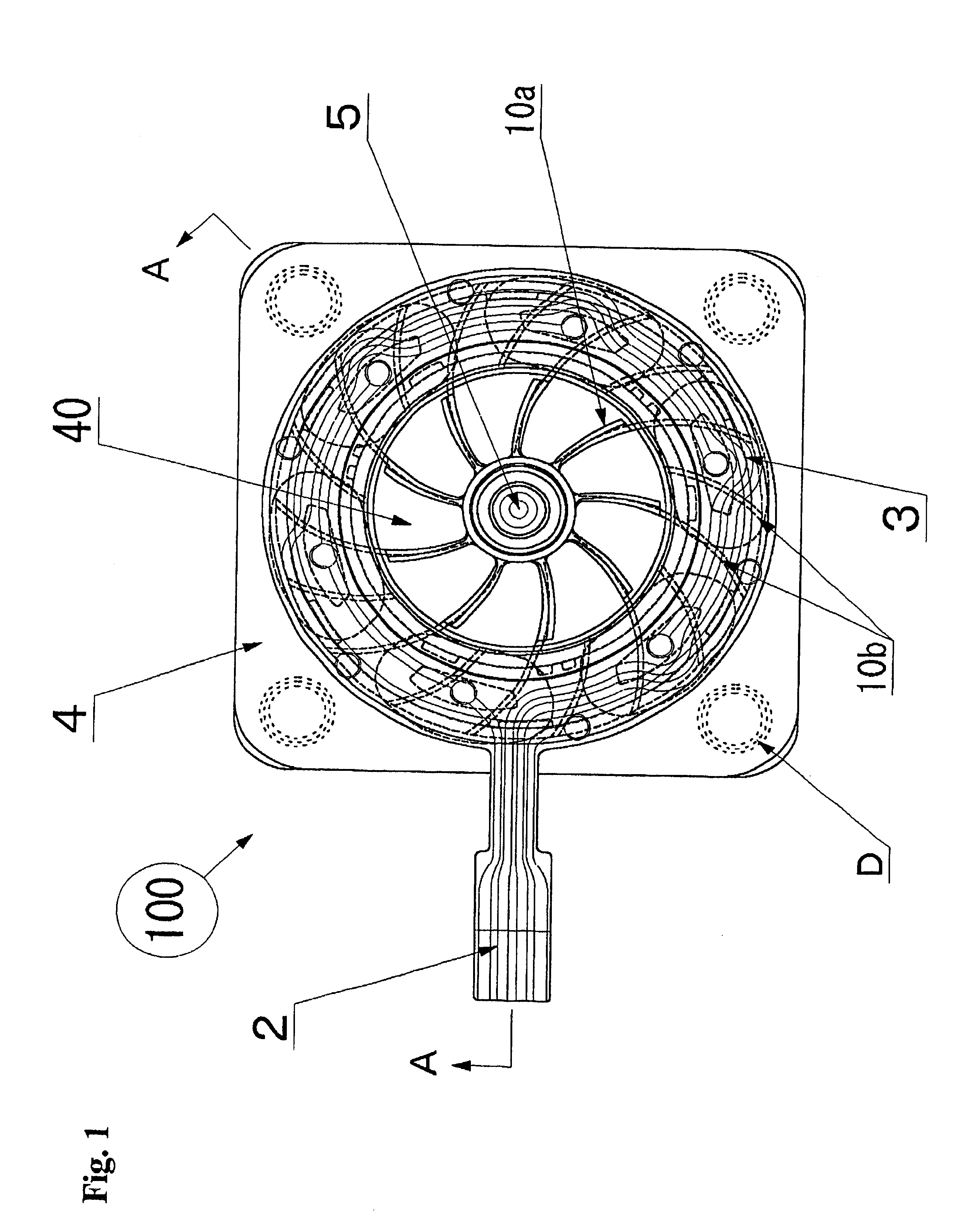
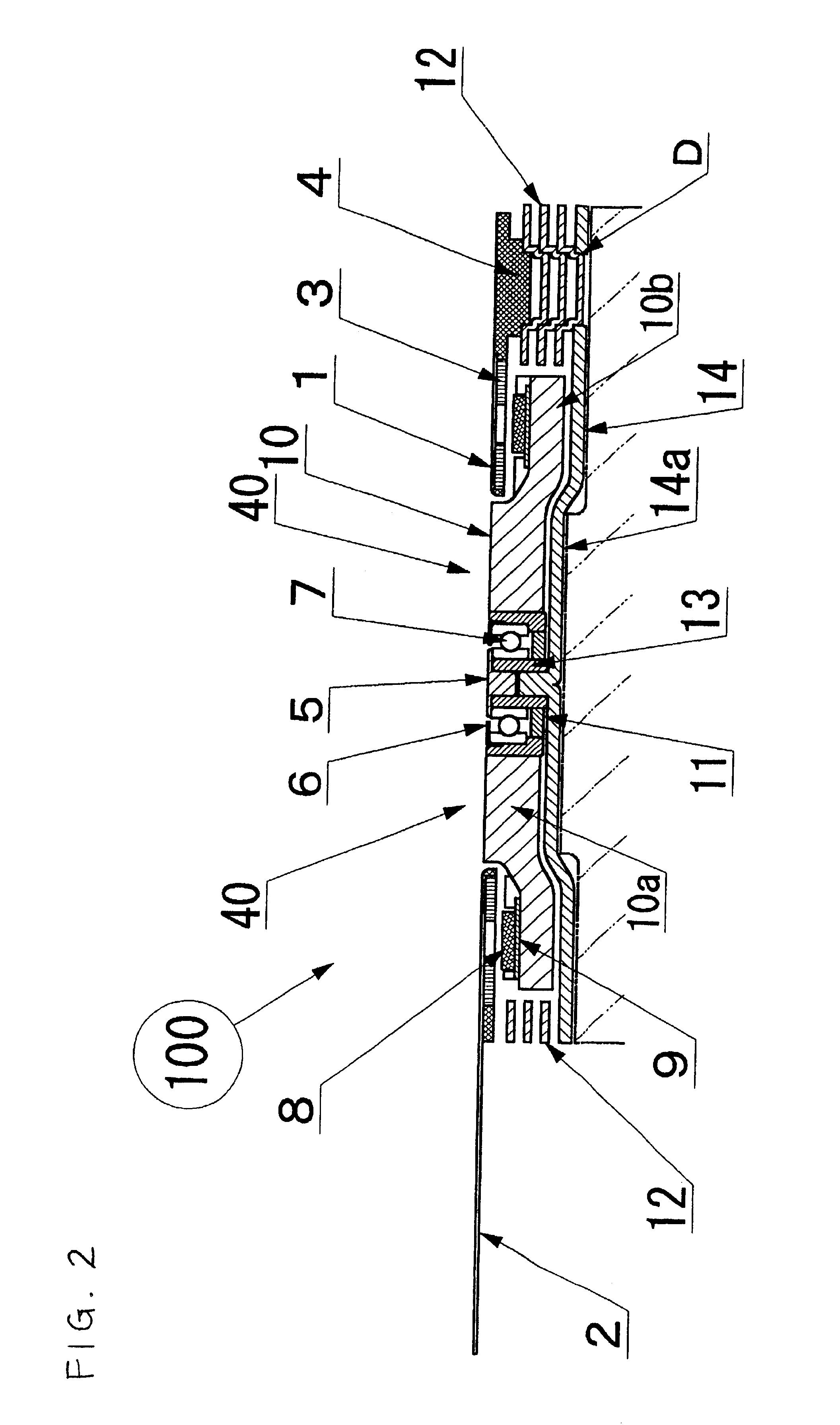
Very thin fan motor with attached heat sink
InactiveUS6873069B1Improve performanceStable speedPump componentsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsStator coilCooling effect
A very thin fan motor with an attached heat sink that has high heat radiation and air cooling effects in a small, flat, thin package, that has a simple and easily assembled overall structure as a fan motor, and that has superior cooling efficiency. A flat fan mounted in various kinds of electronic equipment that need to radiate heat, and particularly mounted directly on the CPU, characterized by having a fan motor mechanism that comprises a heat plate that supports a rotor fan that can rotate in a central position and that has a contact surface that matches the shape of the external surface of the item (such as a CPU) to be cooled, rotor magnets that are part of the rotor fan and are positioned around the periphery on the surface of the heat plate, and a stator coil substrate, by having multiple metal heat radiation fins with excellent thermal conductivity, which are thin heat-radiating fins, arranged in parallel at a fixed interval on the heat plate pointing outward from the rotor fan as cooling heat-radiation fins, and by combining the function of cooling heat sink with the heat radiation fins that conduct the heat absorbed from the heat plate and radiate it away by the action of the air moved by the rotor fan.
Owner:NAMIKI PRECISION JEWEL CO LTD
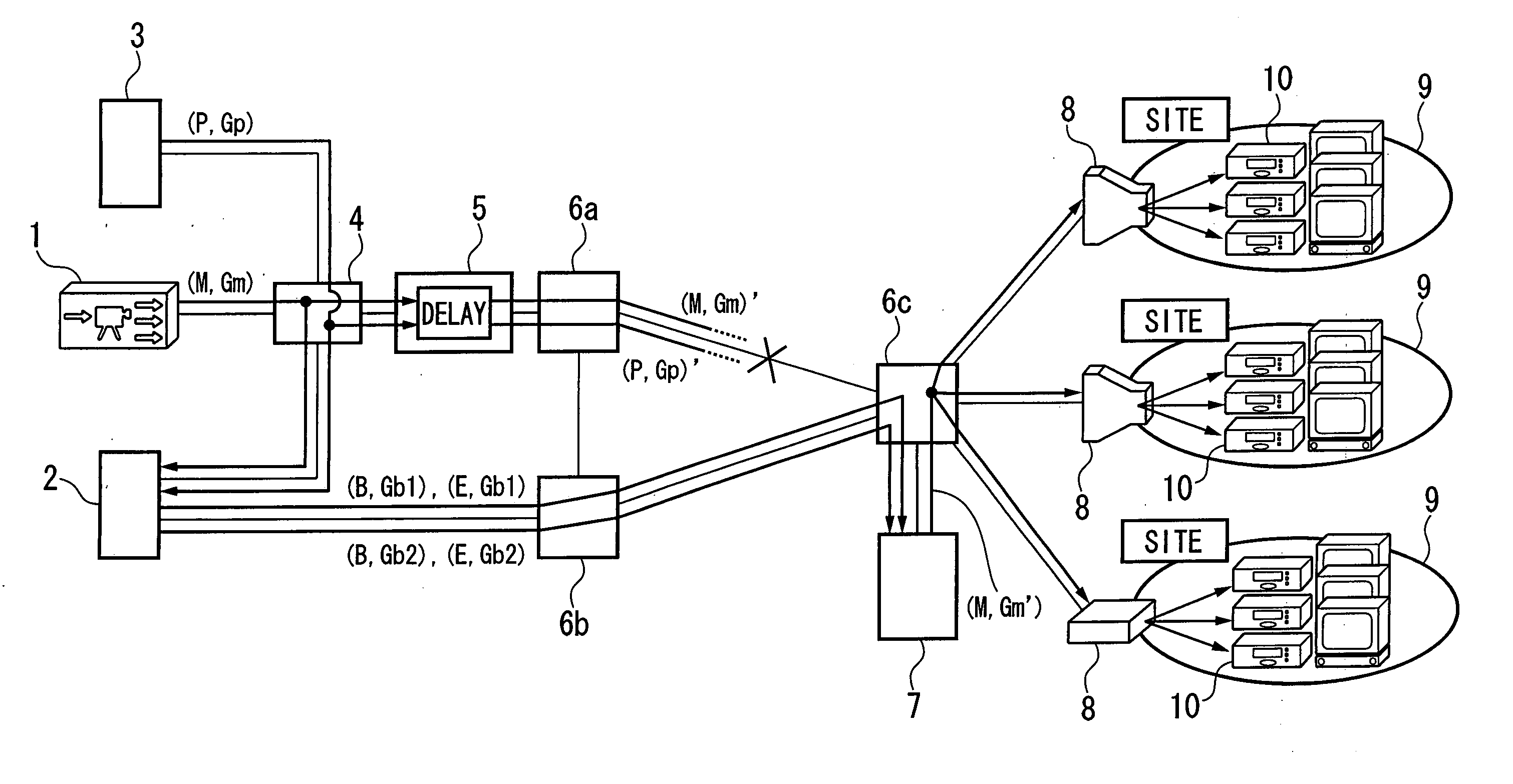
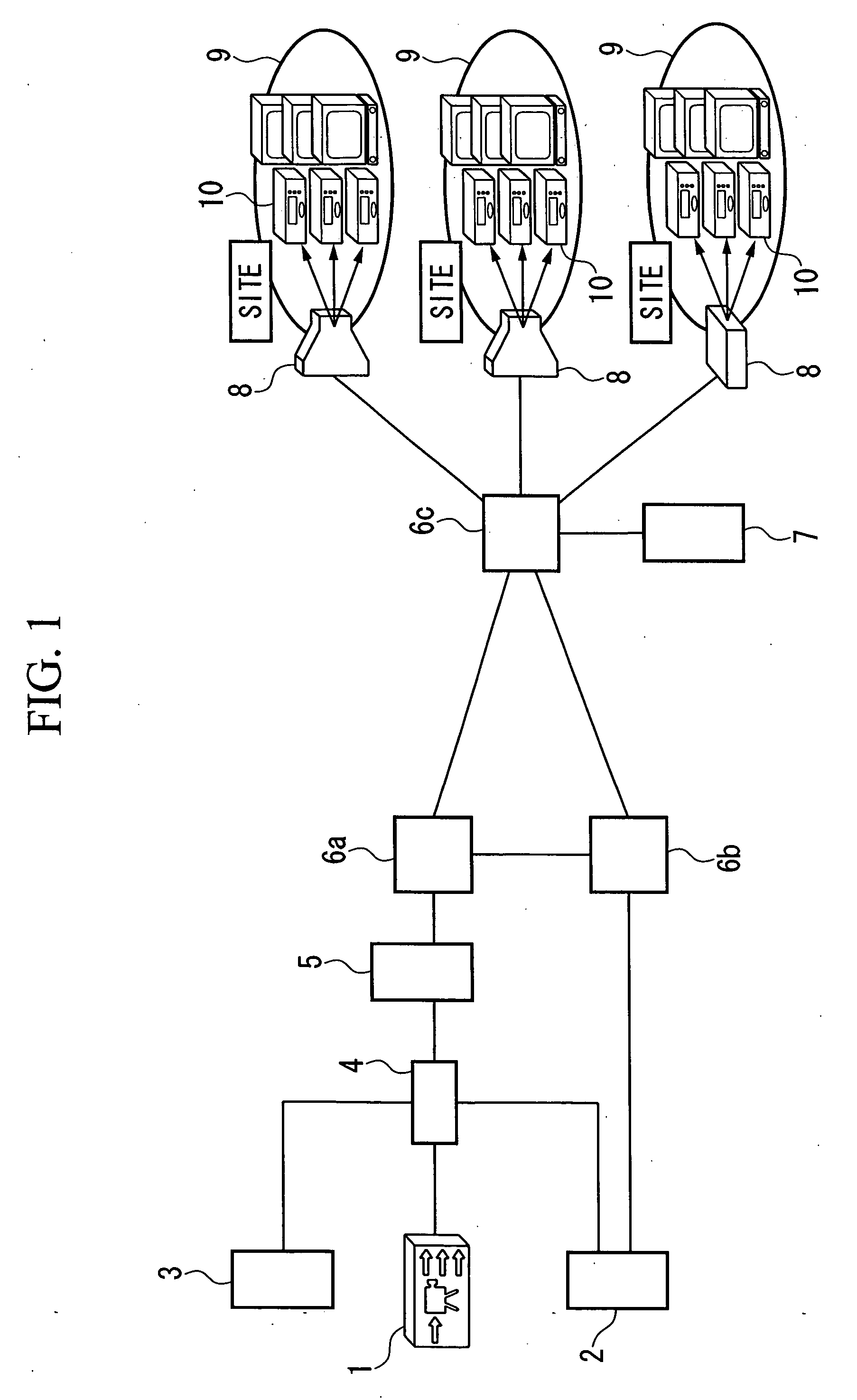
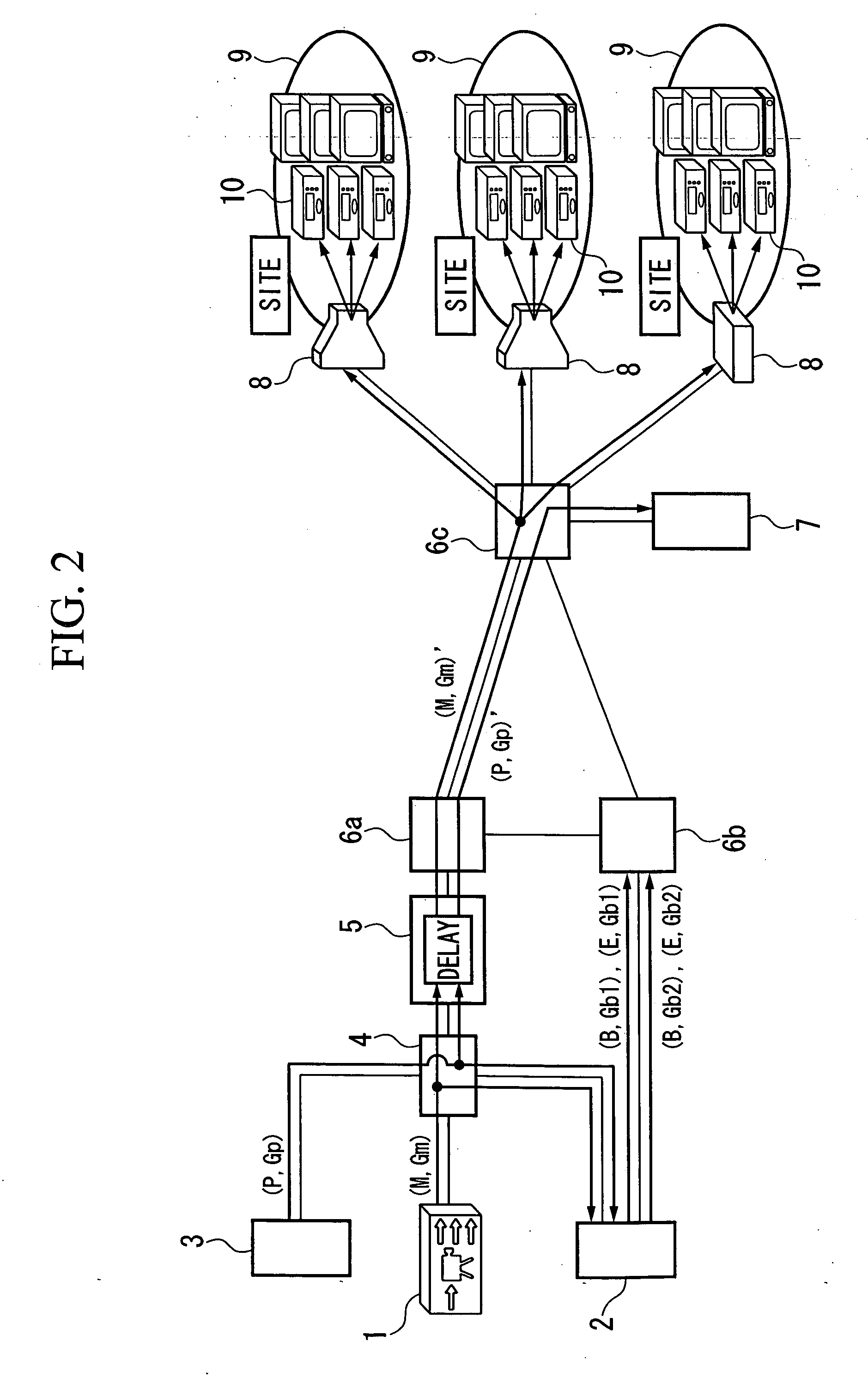
Communication system, delay insertion server, backup server and communication control apparatus
InactiveUS20060120396A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityCommunications system
A communication system includes a probe transmission server 3 which transmits at fixed intervals of time a probe multicast packet distributed along the same path as a main multicast packet, a delay insertion server 5 which appends the same fixed delay time to each of the main multicast packet and the probe multicast packet, a backup server 2 which generates synchronism and delay backup multicast packets from the main multicast packet and transmits them, and a communication control device 7 which determines the communication of the main multicast packet based on a reception interval of the probe multicast packet, generates a backup main multicast packet from the backup multicast packet when a communication break is detected, and transmits it. The communication system, upon implementing a broadcast-type multicast service, enhances compensation of communication breaks when detecting and recovering from a fault in an IP network, and reduces the network traffic.
Owner:KDDI CORP
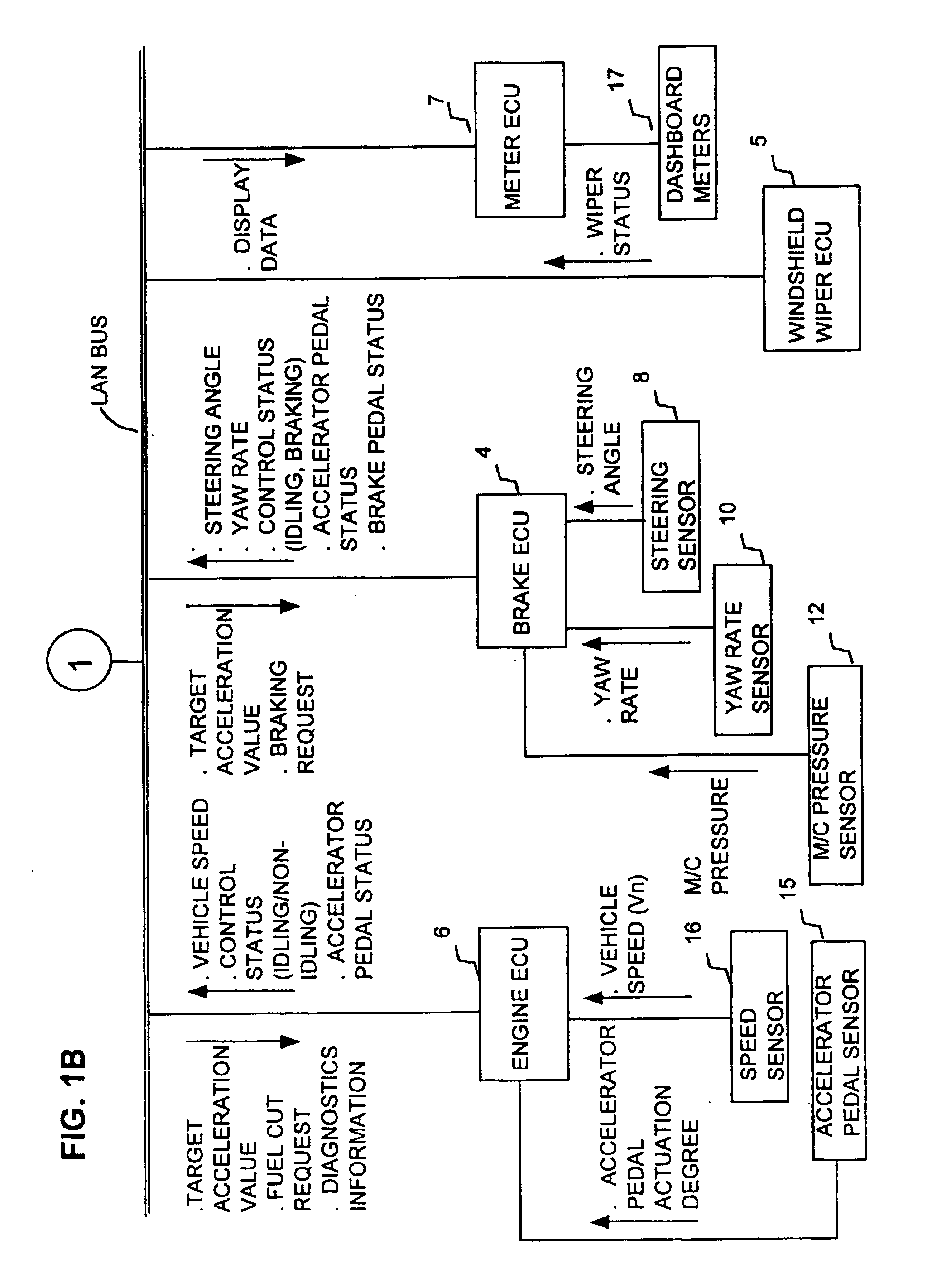
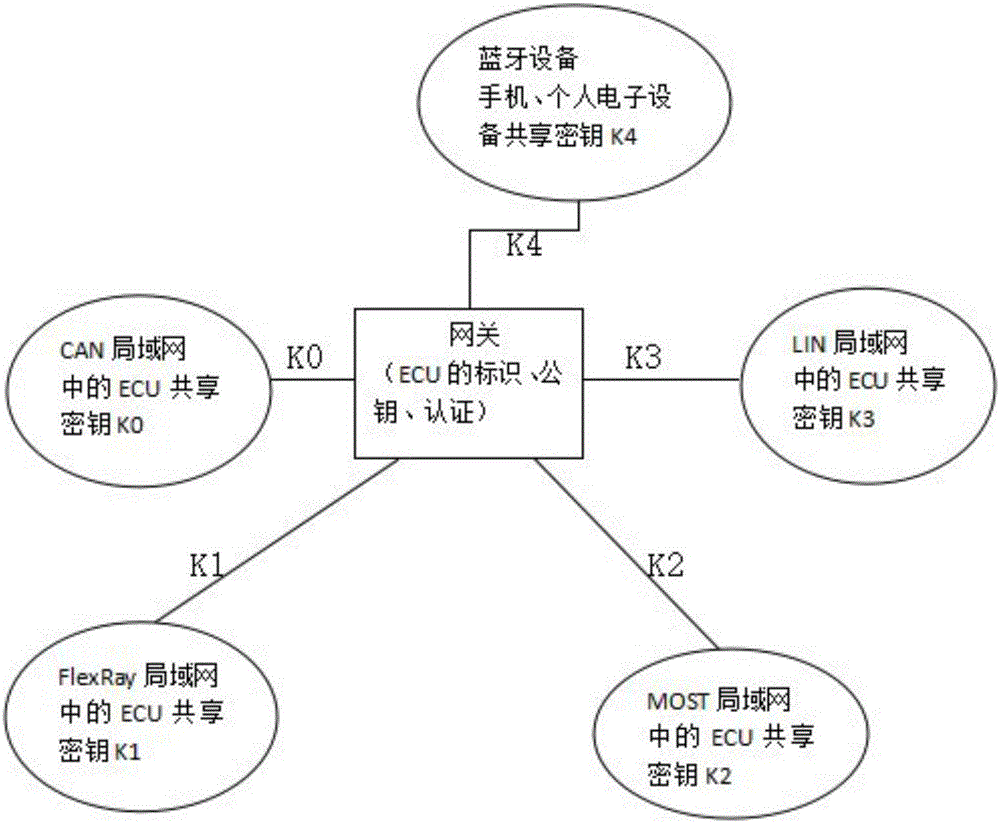
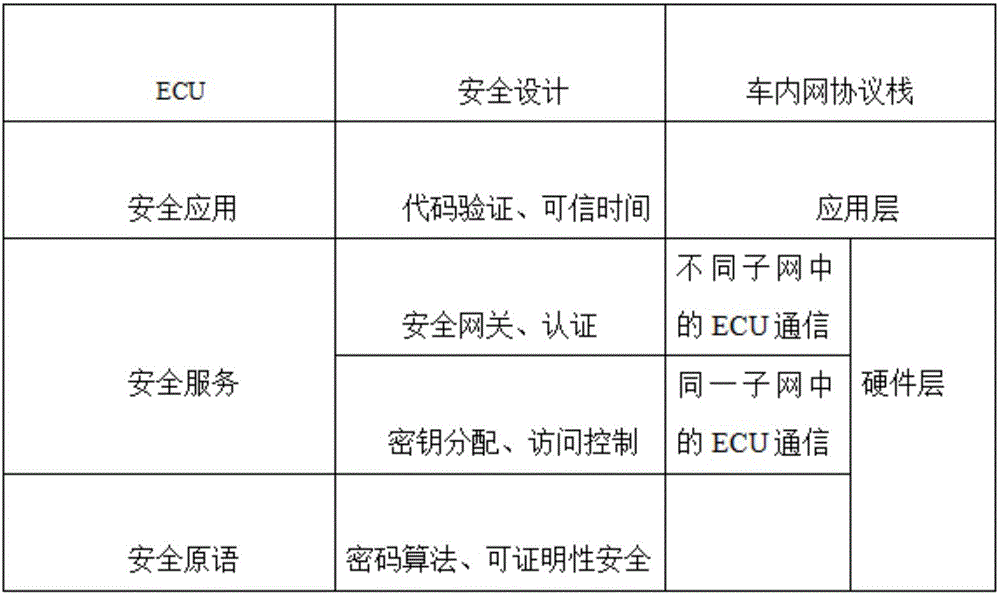
Method for secure communication of ECUs (Electronic control unit) in a vehicle network
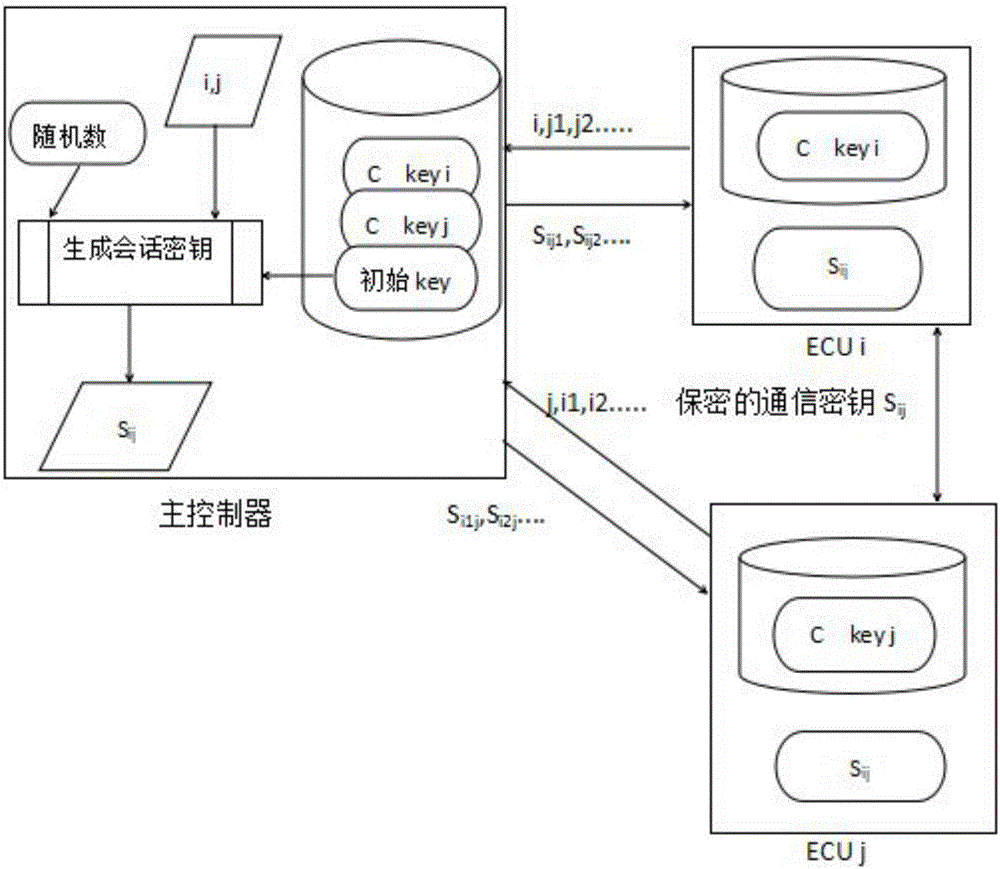
ActiveCN106533655AReduce the number of authenticationsAvoid communicationGeometric CADKey distribution for secure communicationHash functionKey generator
The invention discloses a method for secure communication of ECUs in a vehicle network, comprising: 1) establishing a system model: including the main controller inside the vehicle, ECUs installed on the vehicle and a gateway for the vehicle network; 2) initializing the system wherein the main controller uses a secure Hash function to generate a discrete value and takes the most significant bit from its binary system to obtain shared session keys; 3) distributing the keys to the ECUs in the same sub-network by the main controller; and securely transmitting the session keys between the triggered ECUs and the main controller wherein prior to the communications, the session keys are transmitted among the ECUs in need of communication; 4) authenticating the accessed ECUs into the different sub-networks by the gateway for the vehicle network wherein the private key generator in the gateway determines whether to authenticate the accessed ECUs or not through one signature and sending private keys to the authorized ECUs after successful identity verification; and 5) updating the private keys at fixed interval. The private keys are generated from main keys that are generated randomly to trigger the gateway at fixed time. As the private keys are dynamically updated, attacks can be avoided.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com