Patents
Literature
207results about How to "Valid encoding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
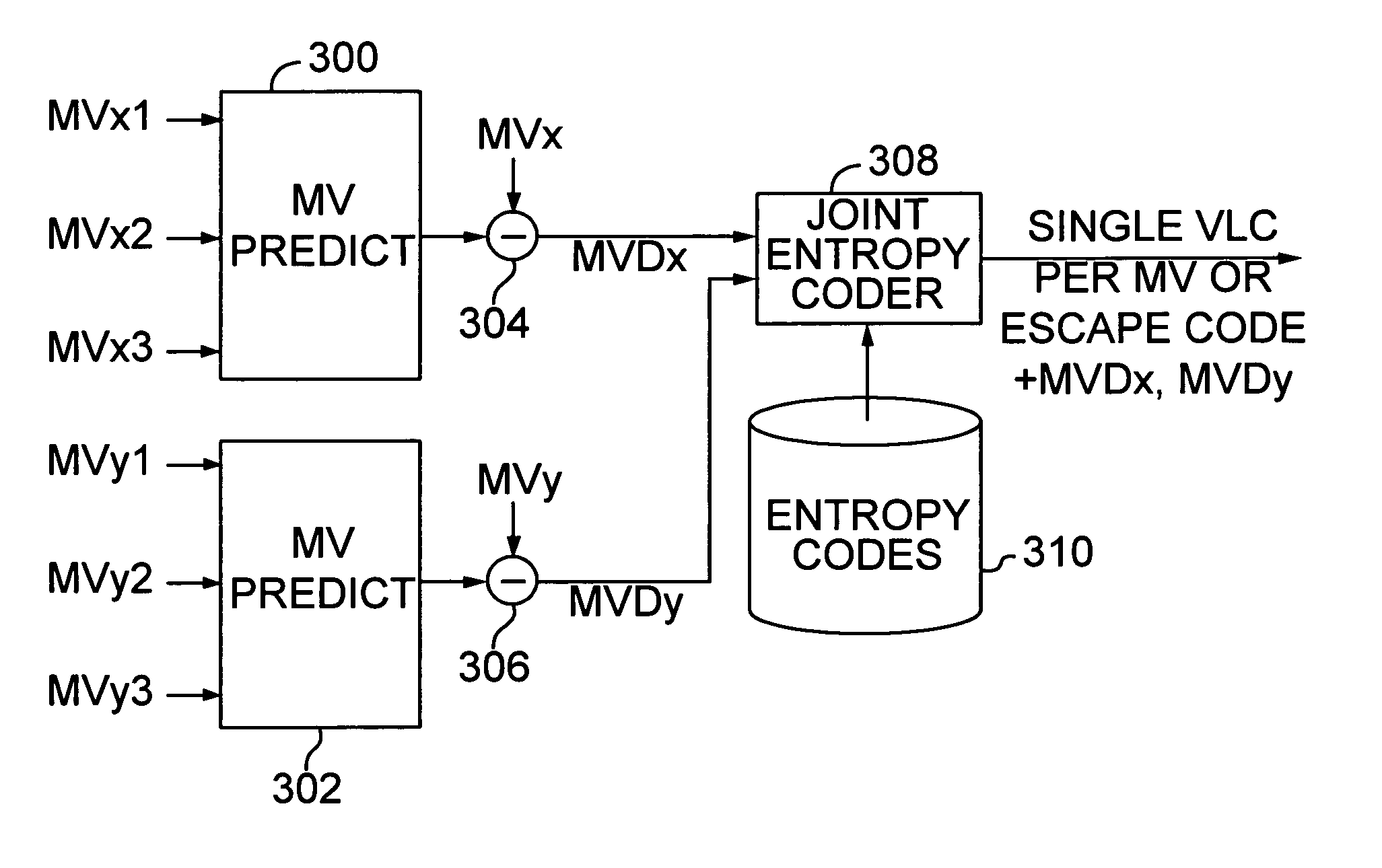
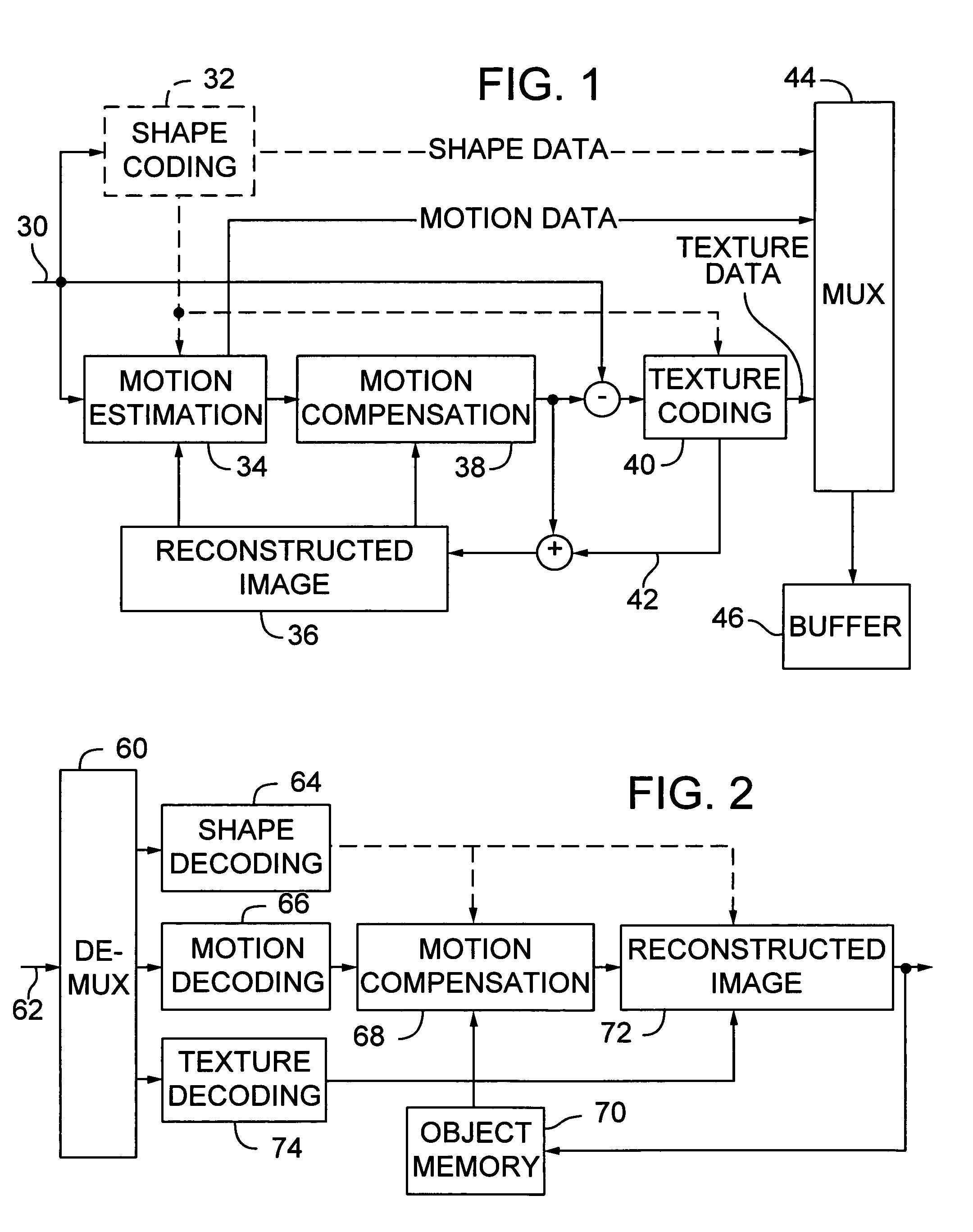
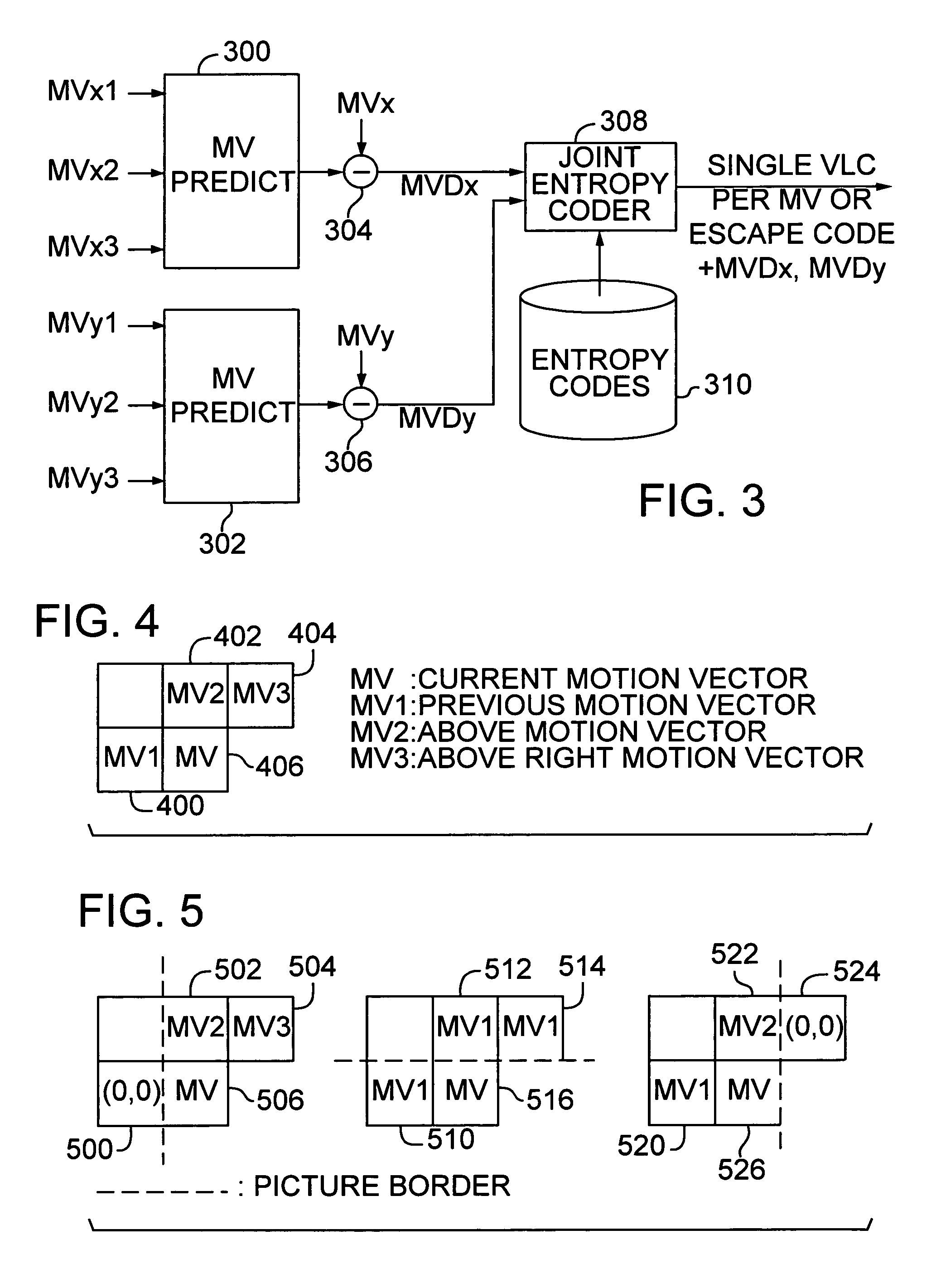
Efficient motion vector coding for video compression
InactiveUS6983018B1Code motion vectors more efficientlyLengthen codePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionVariable-length codeVideo encoding
Video coding efficiency is improved by jointly coding the x and y components of motion vectors with a single variable length code. The motion vector components for a block of pixels are predicted based on motion vectors of neighboring blocks of pixels. The predicted x and y components are then jointly coded by assigning a single variable length code corresponding to the pair of components, rather than a separate code for each component. If the x and y components do not have a corresponding entry in the coding table, they are coded with an escape code followed by fixed length codes.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
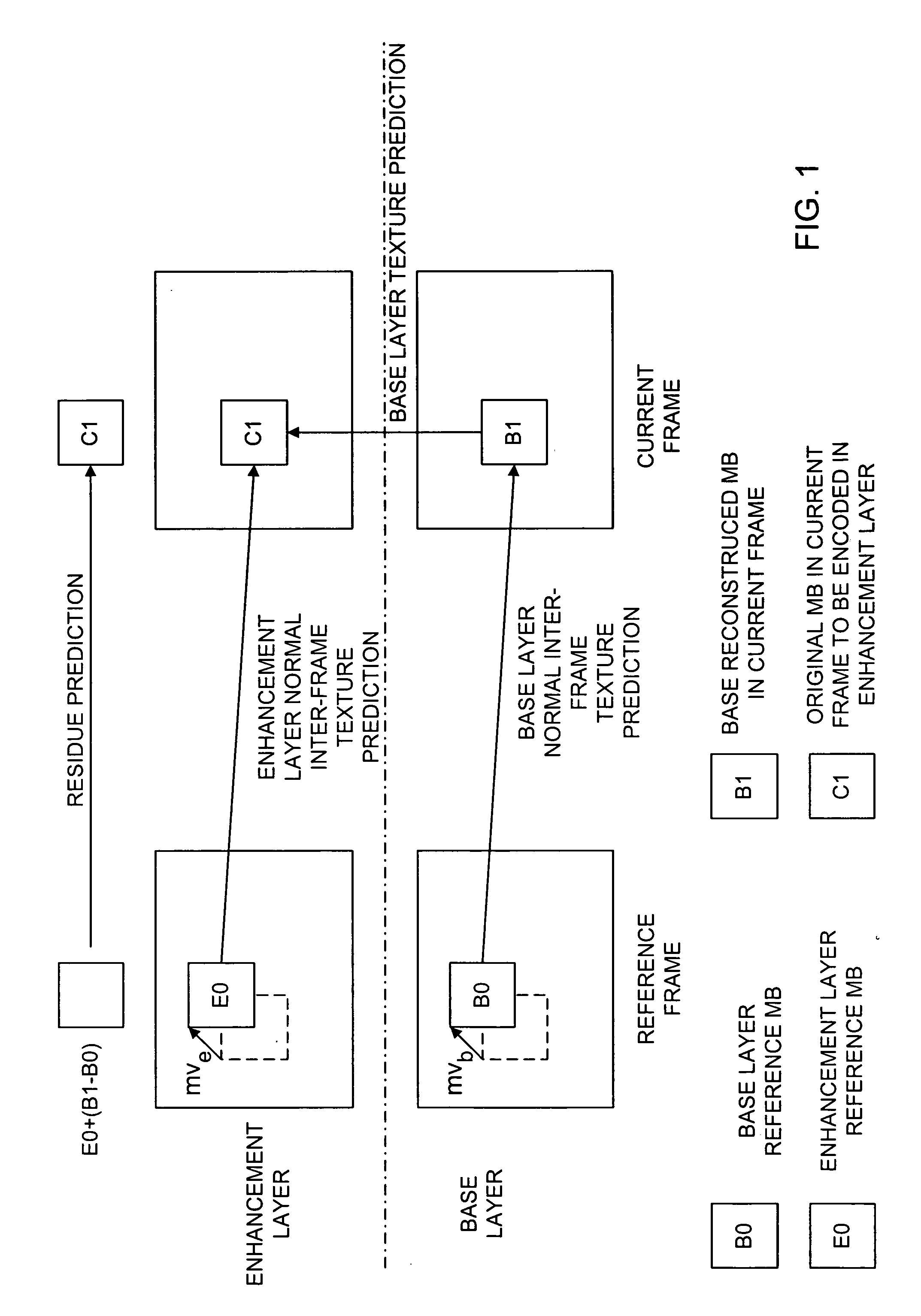
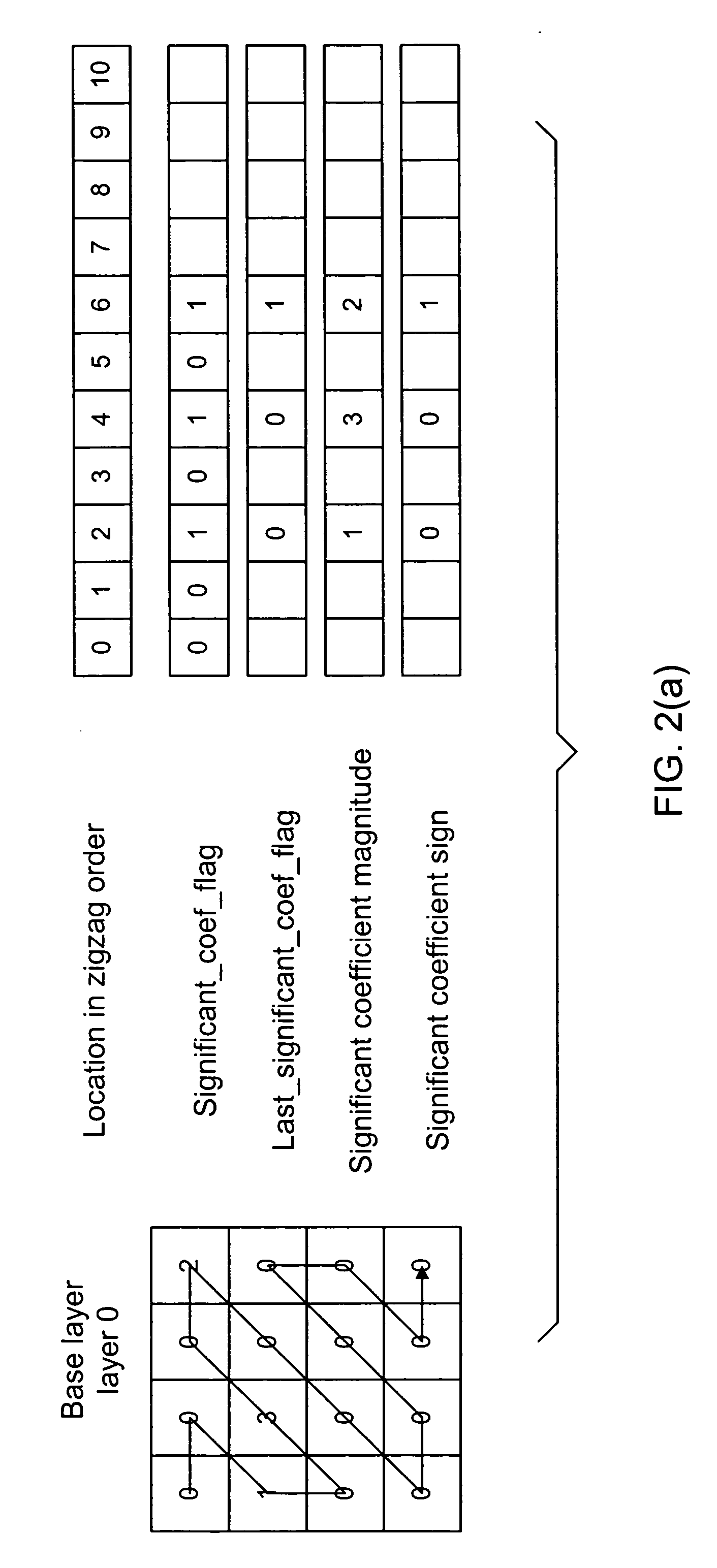
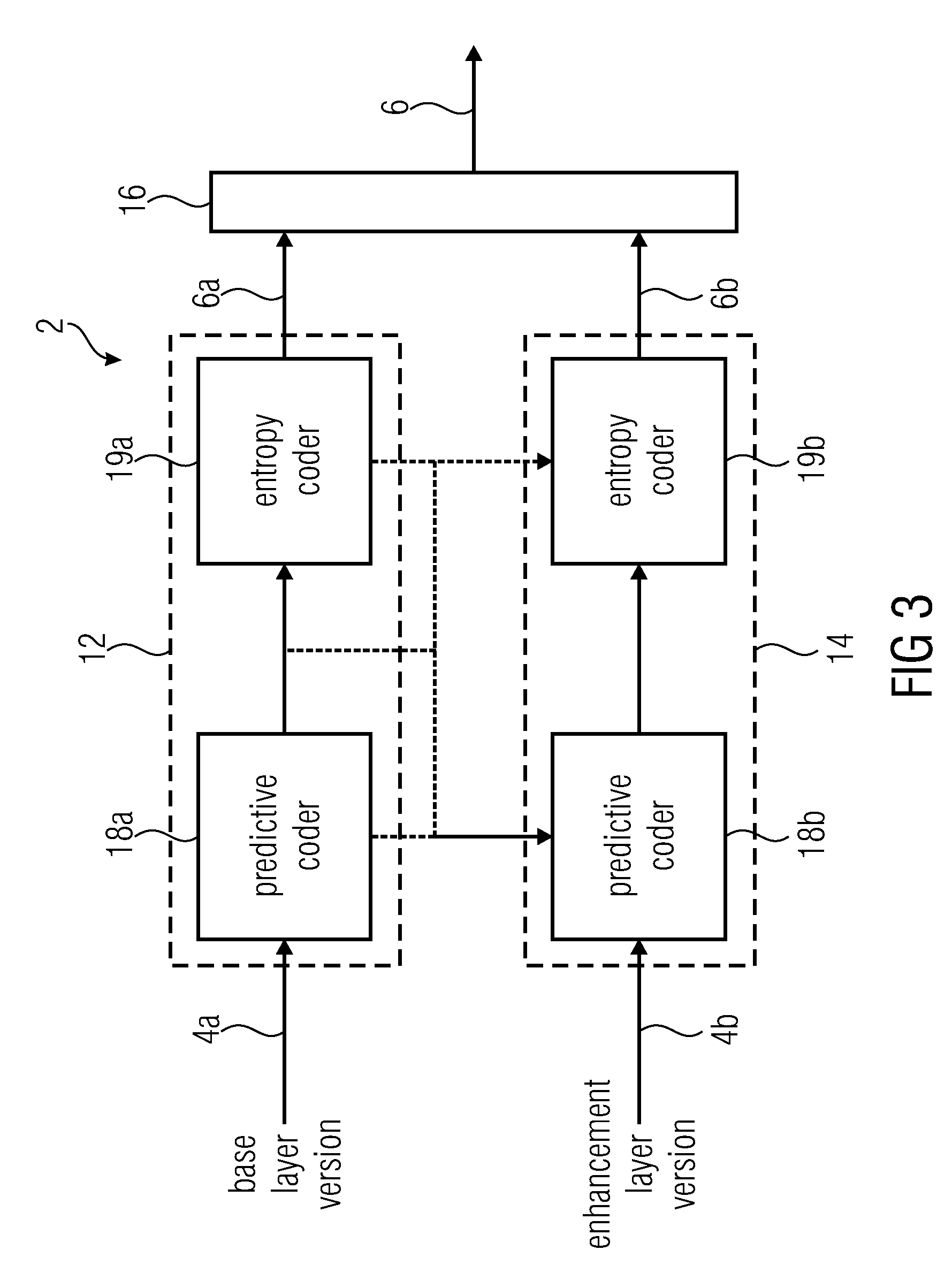
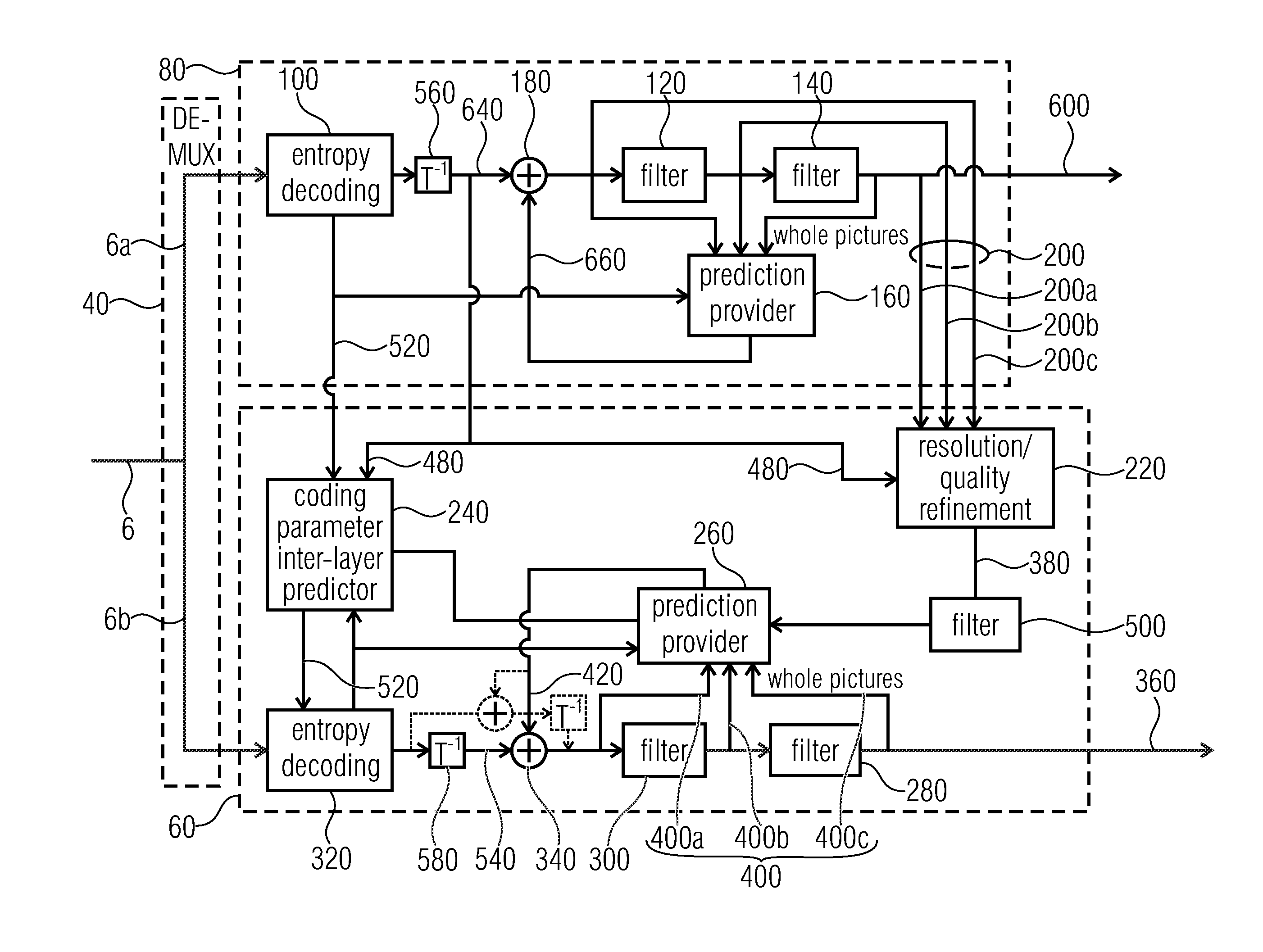
Inter-layer coefficient coding for scalable video coding
InactiveUS20060153294A1Pixel predictorImprove the overall coefficientColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionInter layerComputer architecture
A scalable video coding method and apparatus for coding a video sequence, wherein the coefficients in the enhancement layer is classified as belonging to a significant pass when the corresponding coefficient in the base layer is zero, and classified as belonging to a refinement pass when the corresponding coefficient in the base layer is non-zero. For coefficients classified as belonging to the significance pass, an indication is coded to indicate whether the coefficient is zero or non-zero, and if the coefficient is non-zero, coding an indication of the sign of the coefficient. A last_significant_coeff_flag is used to indicate the coding of remaining coefficients in the scanning order can be skipped. For coefficients classified as belonging to the refinement pass, a value to refine the magnitude of the corresponding coefficient in the base layer is coded, and if the coefficient is non-zero, a sign bit may be coded.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
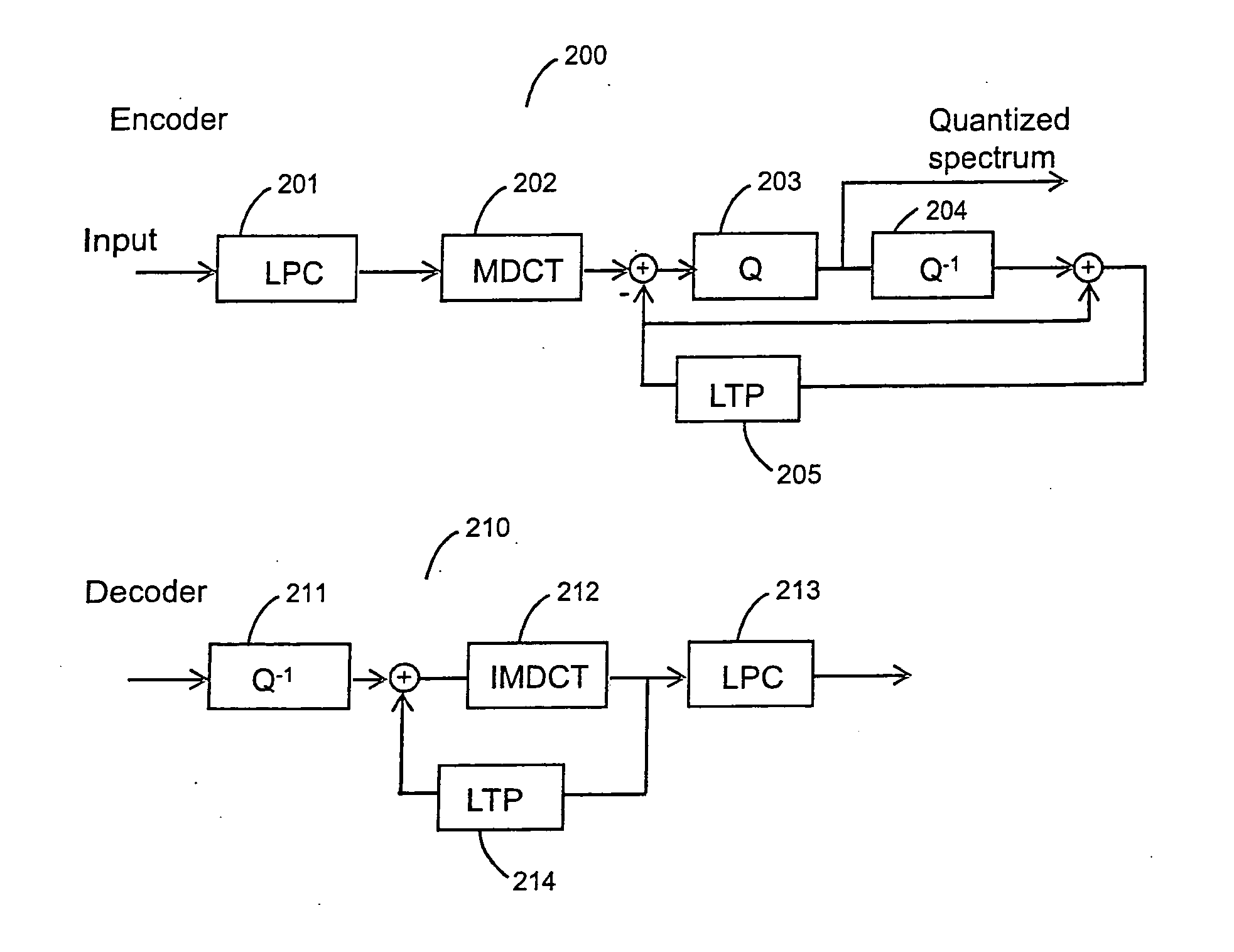
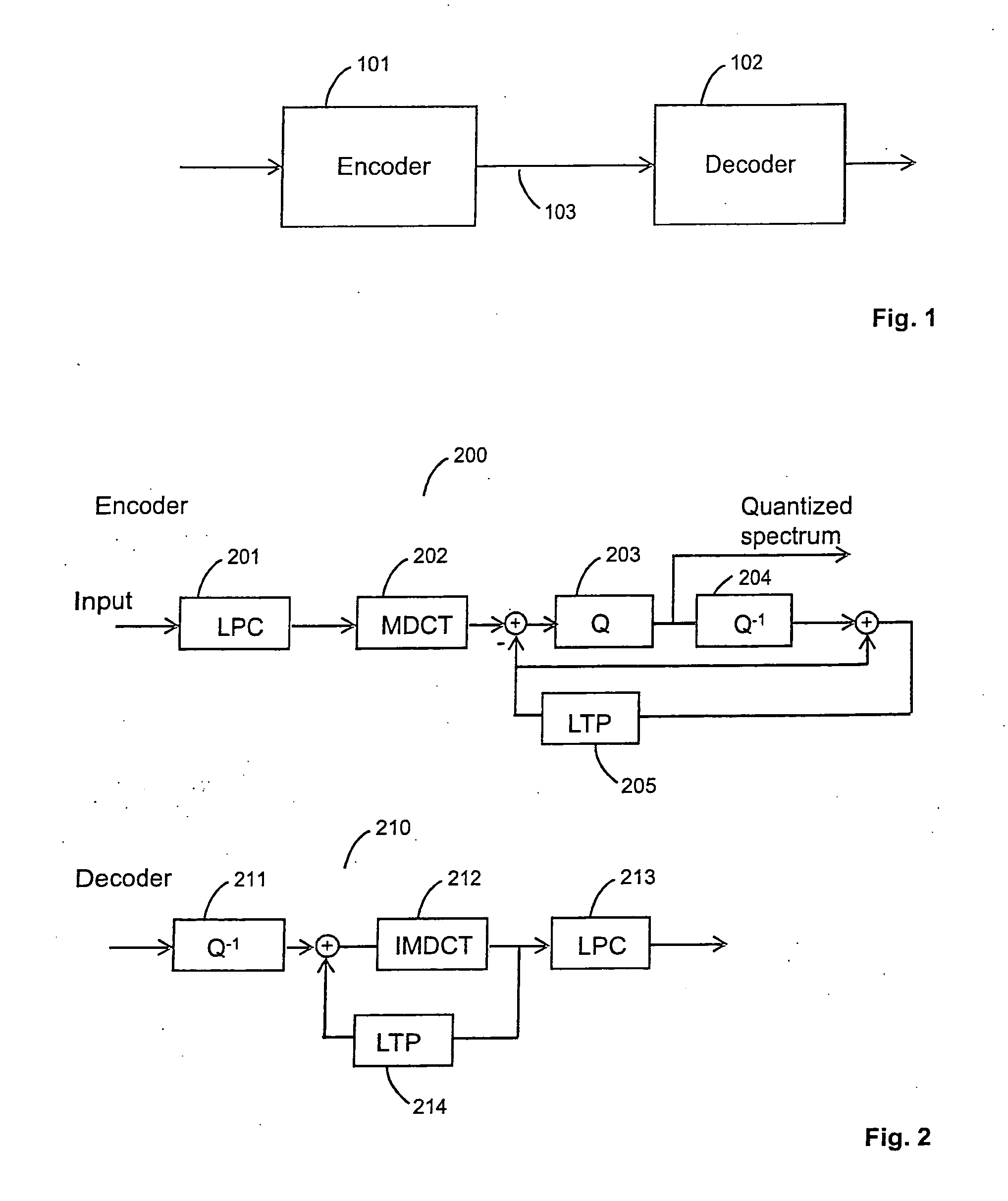
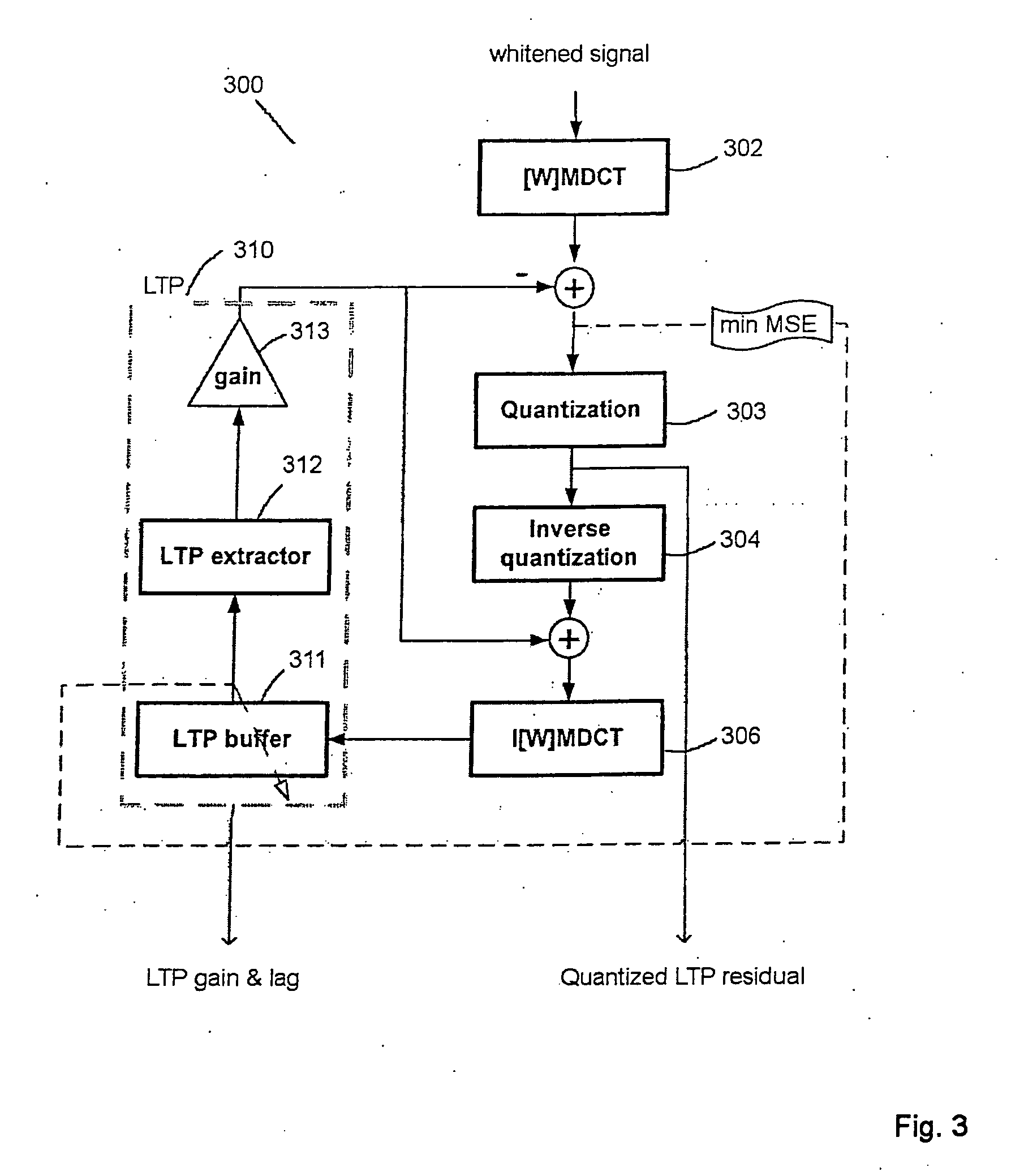
Audio encoder and decoder
The present invention teaches a new audio coding system that can code both general audio and speech signals well at low bit rates. A proposed audio coding system comprises a linear prediction unit for filtering an input signal based on an adaptive filter; a transformation unit for transforming a frame of the filtered input signal into a transform domain; a quantization unit for quantizing a transform domain signal; a long term prediction unit for determining an estimation of the frame of the filtered input signal based on a reconstruction of a previous segment of the filtered input signal; and a transform domain signal combination unit for combining, in the transform domain, the long term prediction estimation and the transformed input signal to generate the transform domain signal.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
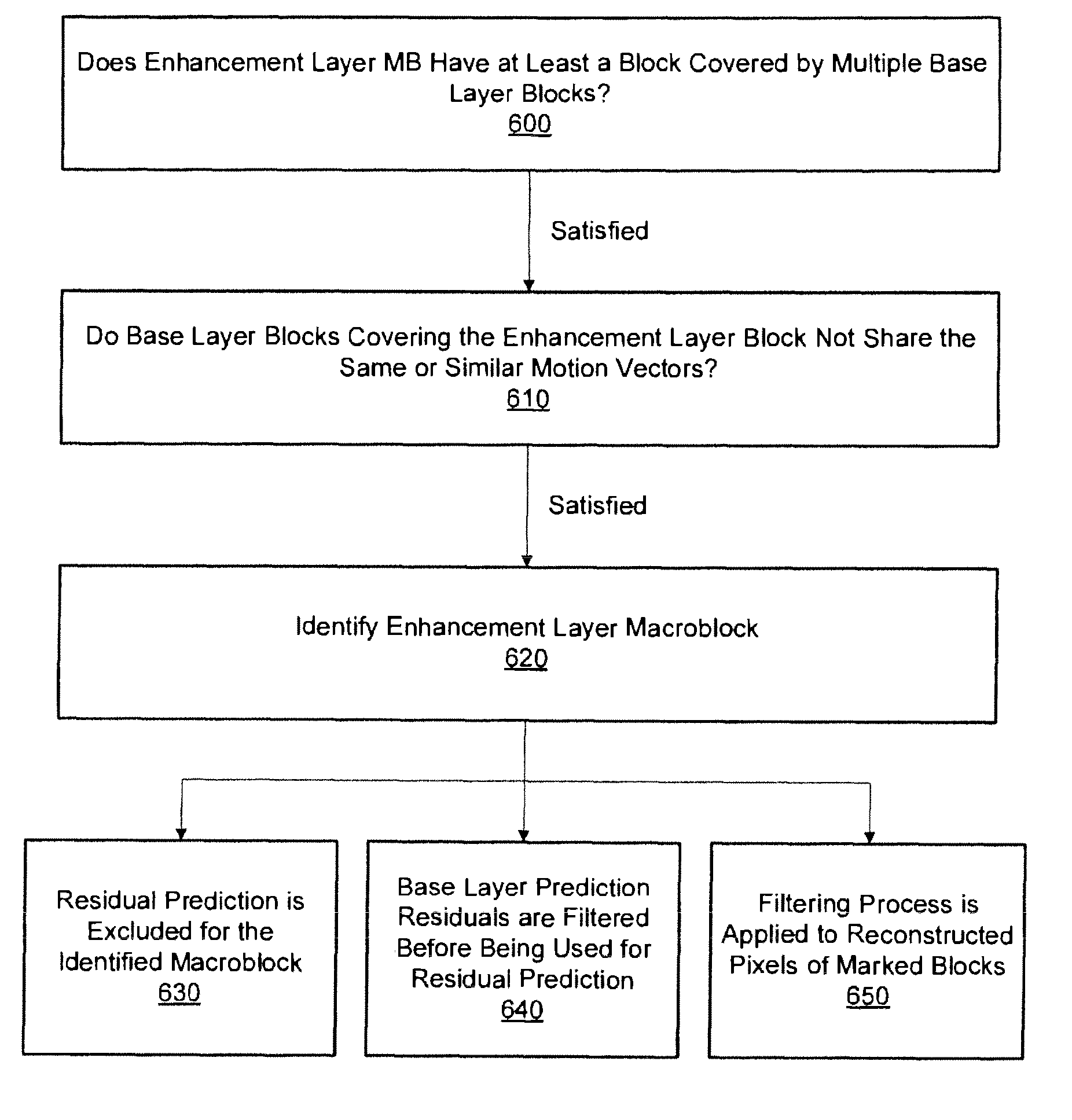
System and method for providing improved residual prediction for spatial scalability in video coding
InactiveUS20080225952A1Improving residual predictionAvoid introducingColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMultiple criteriaVisual artifact
A system and method for providing improved residual prediction for spatial scalability in video coding. In order to prevent visual artifacts in residual prediction in extended spatial scalability (ESS), each enhancement layer macroblock is checked to determine if the macroblock satisfies a number of conditions. If the conditions are met for an enhancement layer macroblock, then it is likely that visual artifacts will be introduced if applying residual prediction on the macroblock. Once such locations are identified, various mechanisms may be used to avoid or remove the visual artifacts.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
System and method for capture and rendering of performance on synthetic string instrument
ActiveUS20120174736A1Facilitate performanceImprove performanceElectrophonic musical instrumentsInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringComputer graphics (images)
Owner:SMULE
Moving Picture Coding Method And Moving Picture Decoding Method
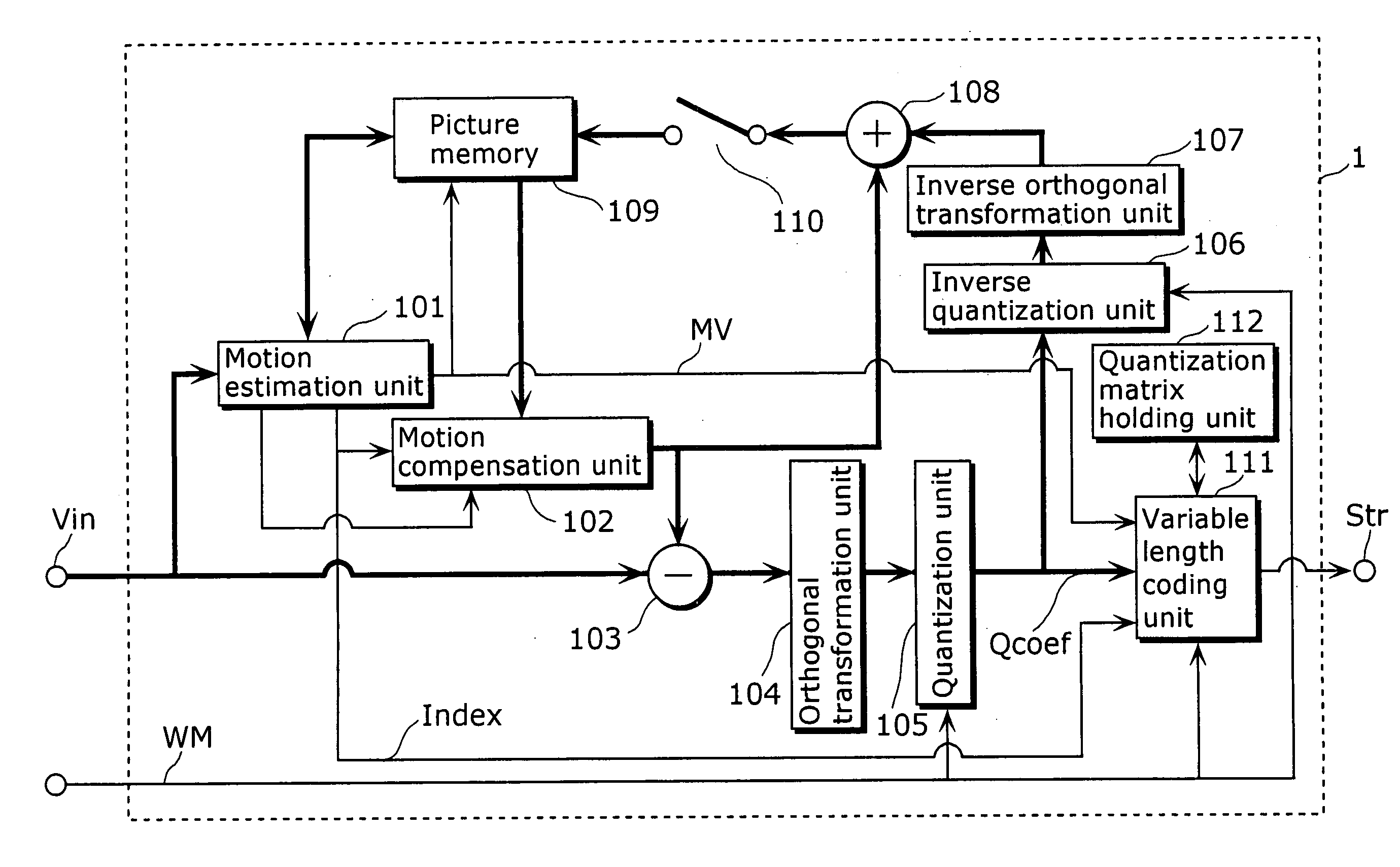
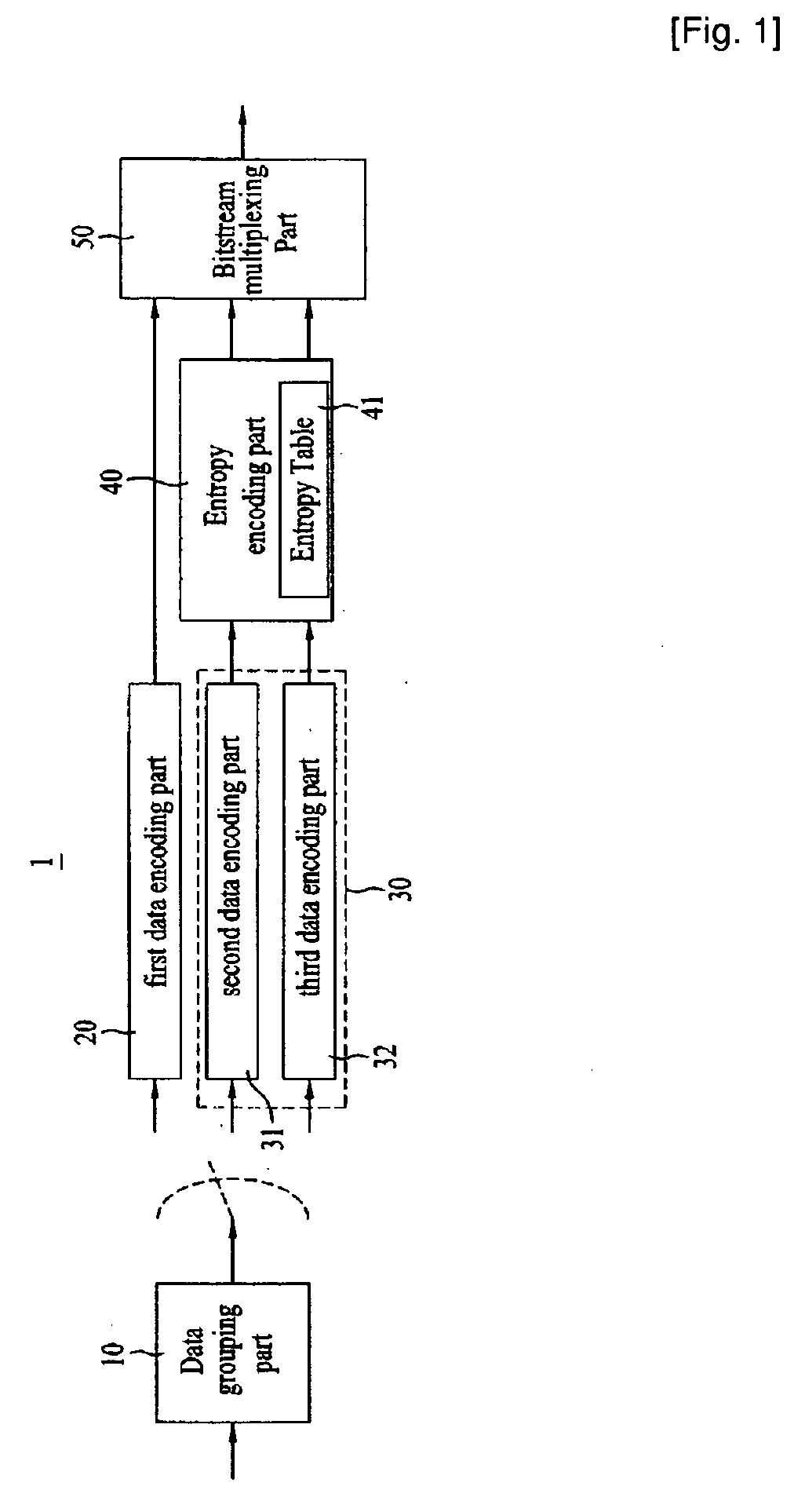
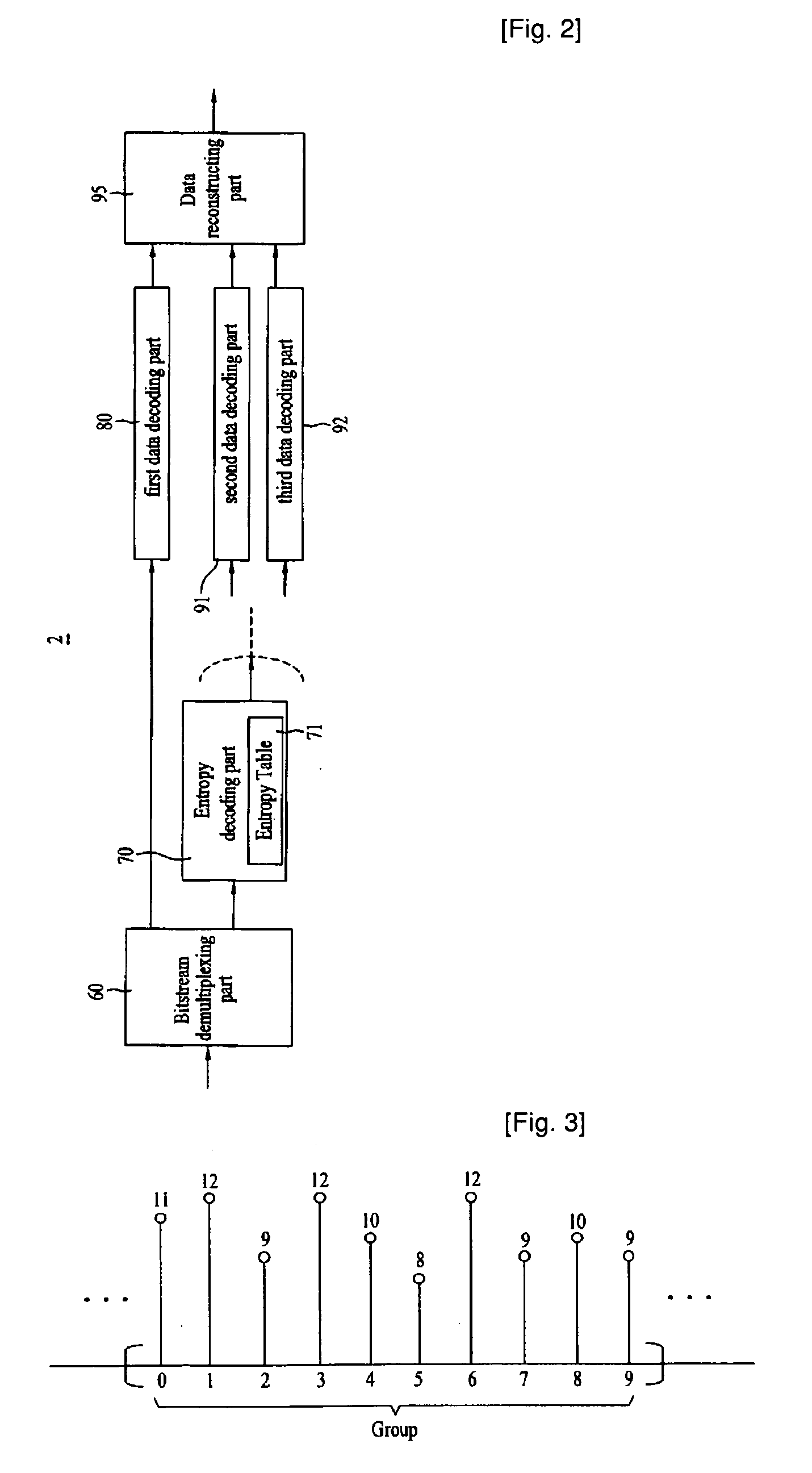
ActiveUS20080089410A1Reduce data volumeEfficient decodingPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesVariable-length codeQuantization matrix
A moving picture coding apparatus 1 includes: a quantization matrix holding unit (112) that holds a quantization matrix (WM) which has already been transmitted in a parameter set and a matrix ID for identifying the quantization matrix (WM), which are associated with each other; and a variable length coding unit (111) that obtains the matrix ID corresponding to the quantization matrix (WM) used for quantization from the quantization matrix holding unit (112) and places the matrix ID in a coded stream Str.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
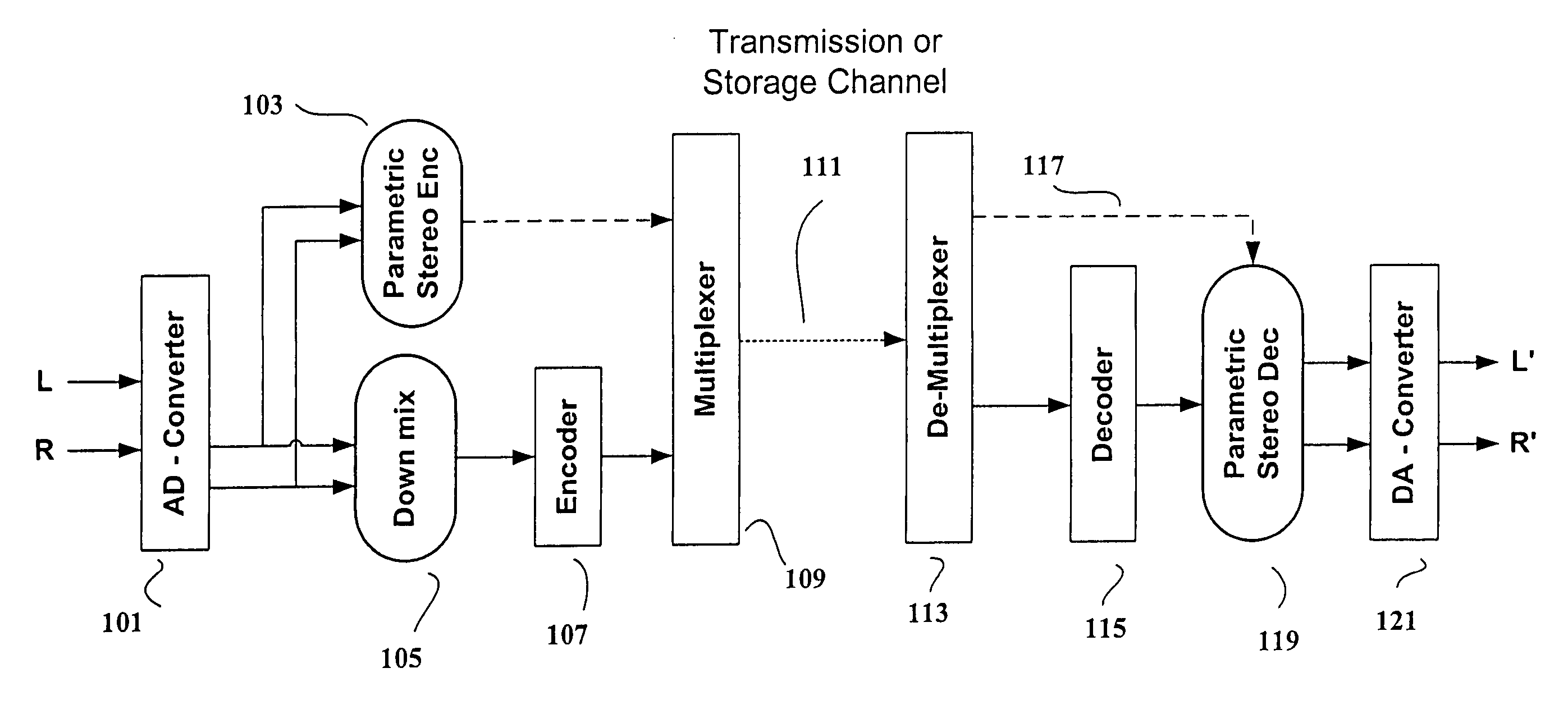
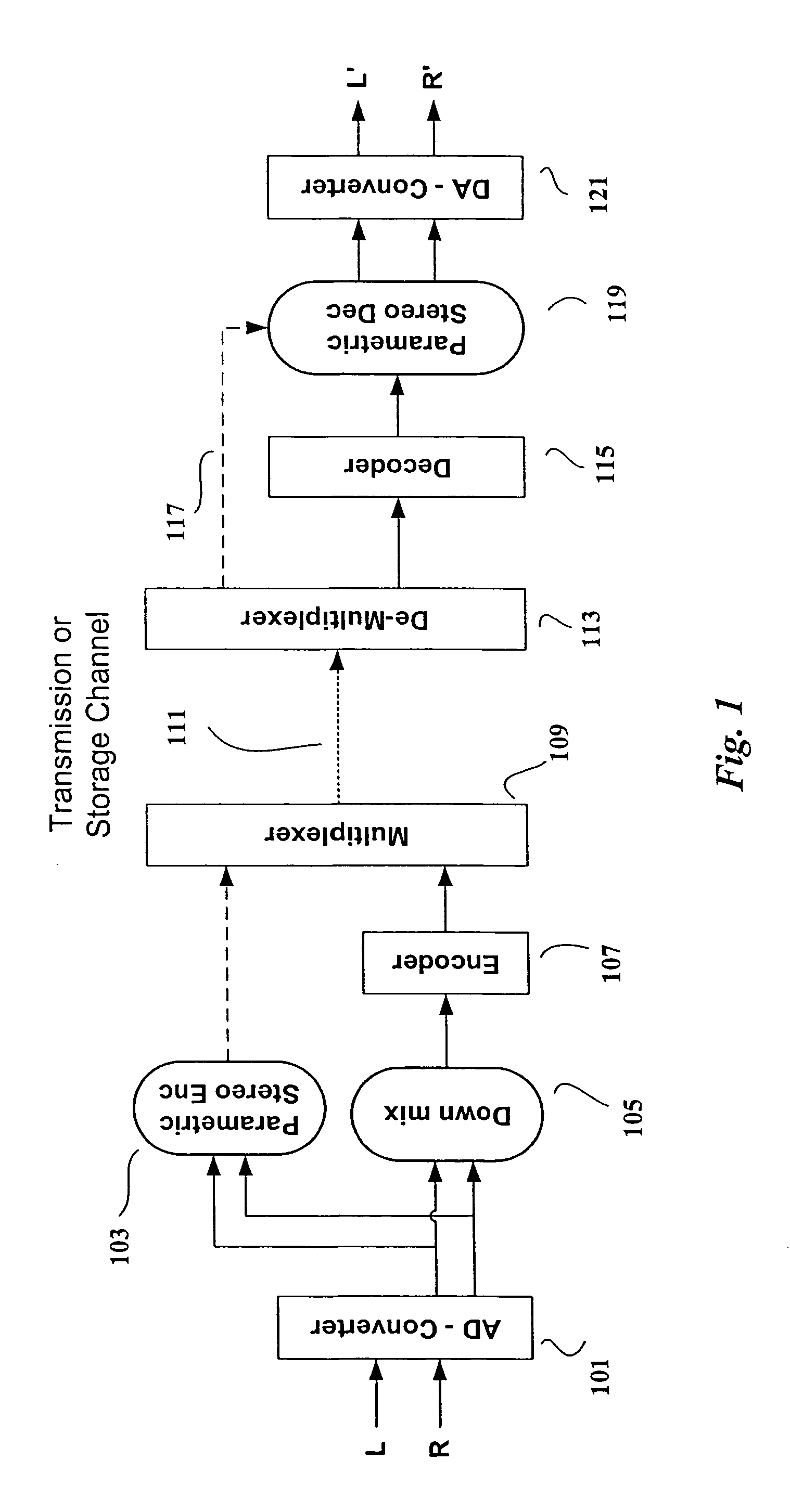
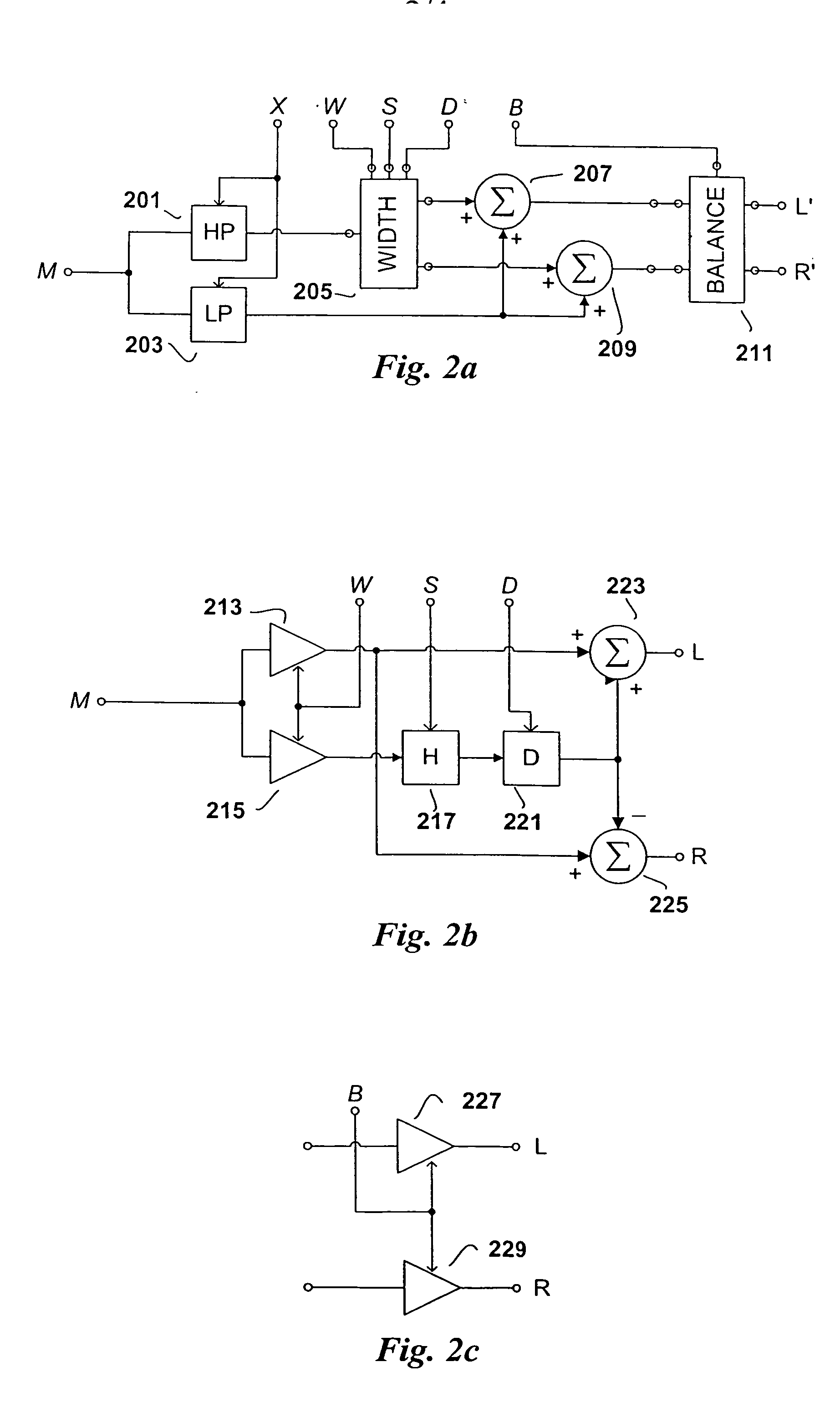
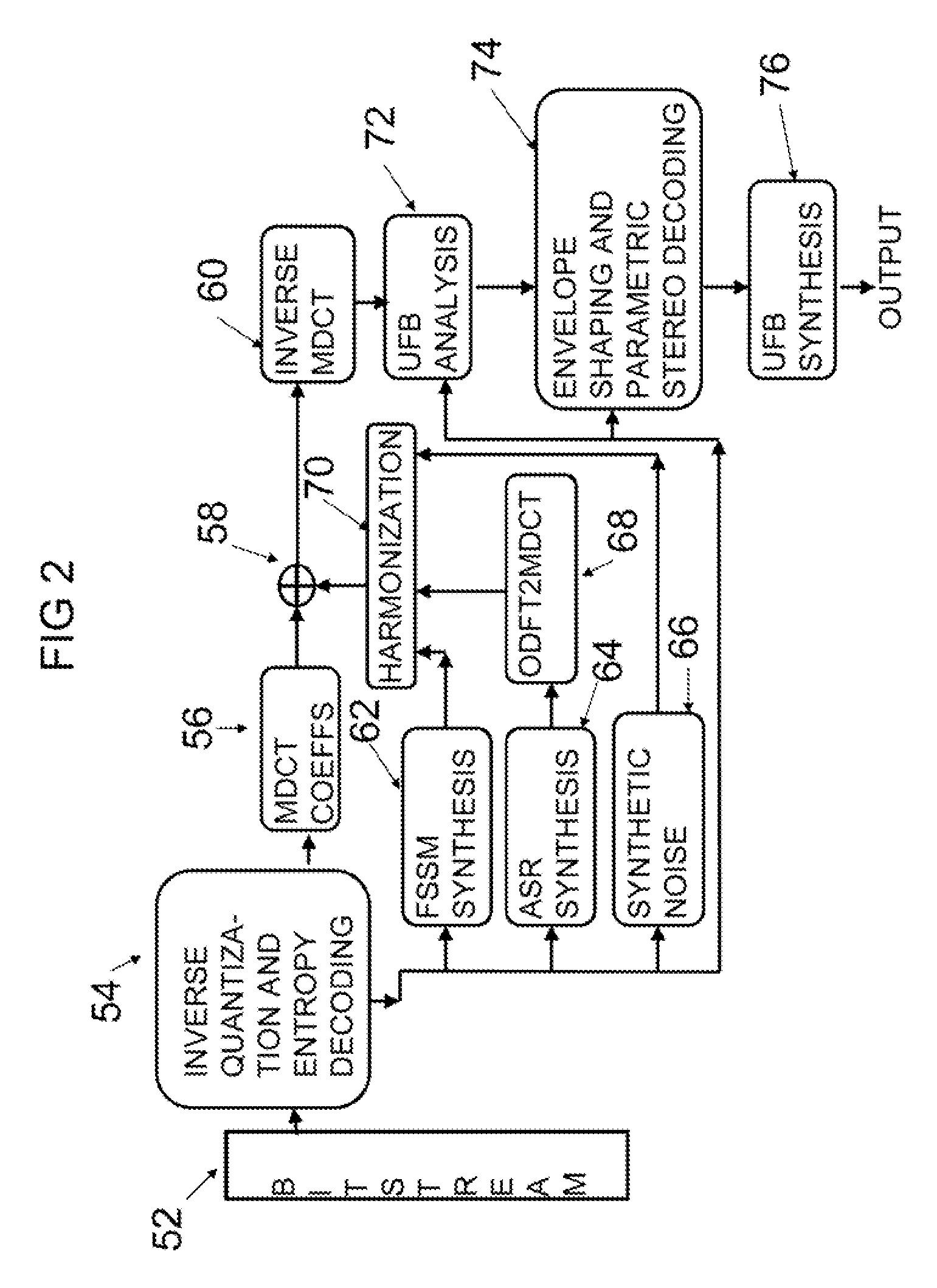
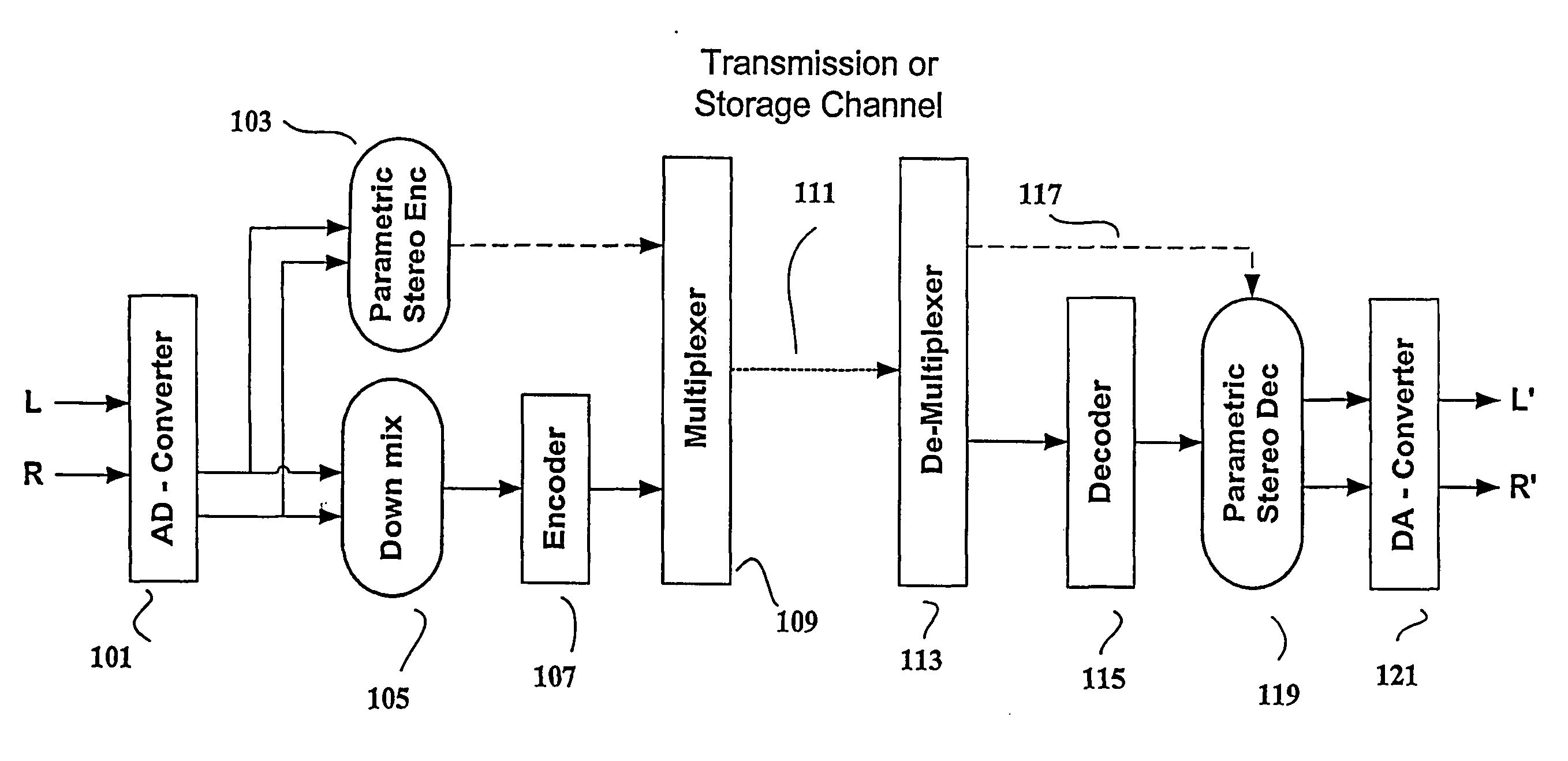
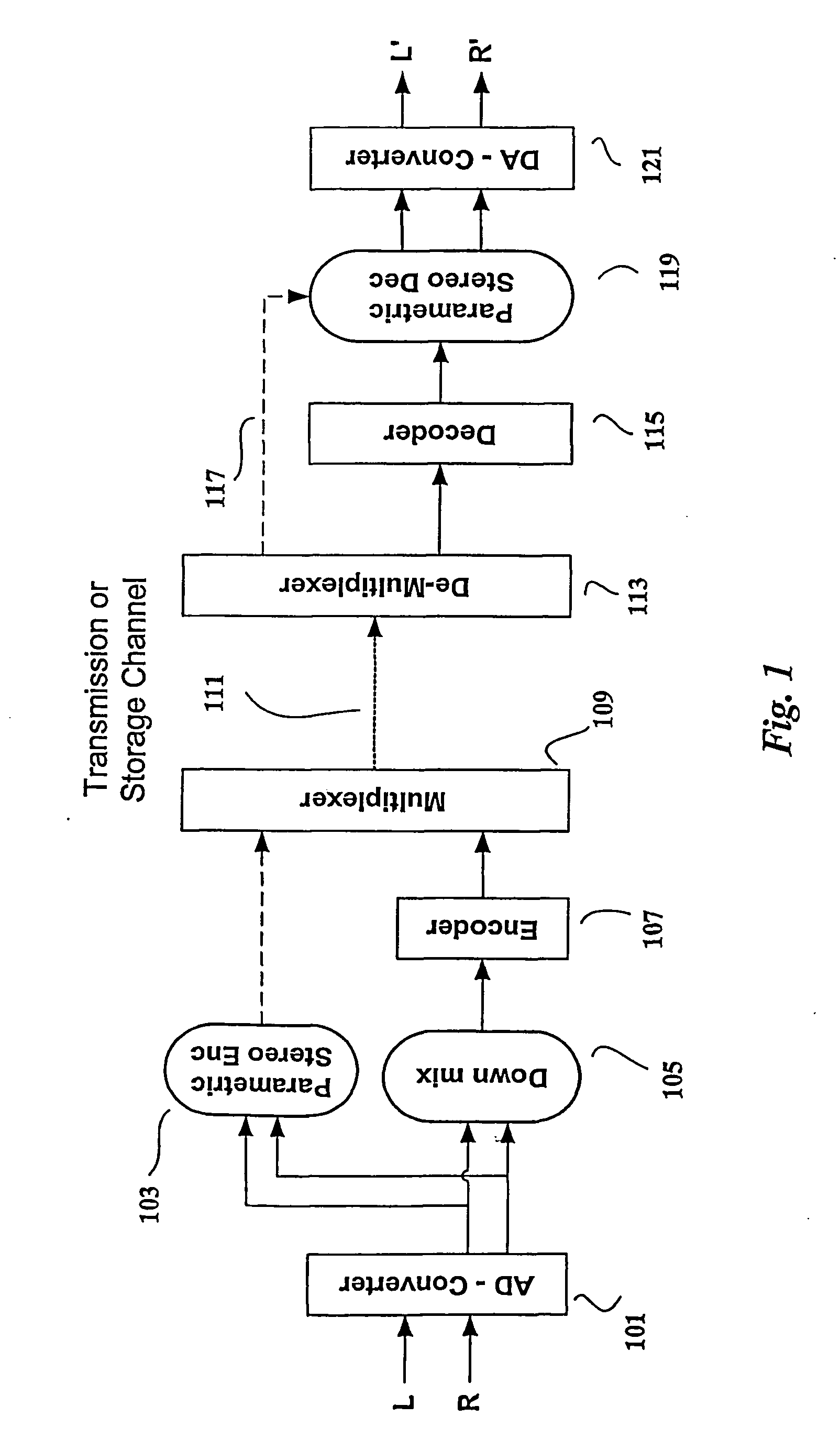
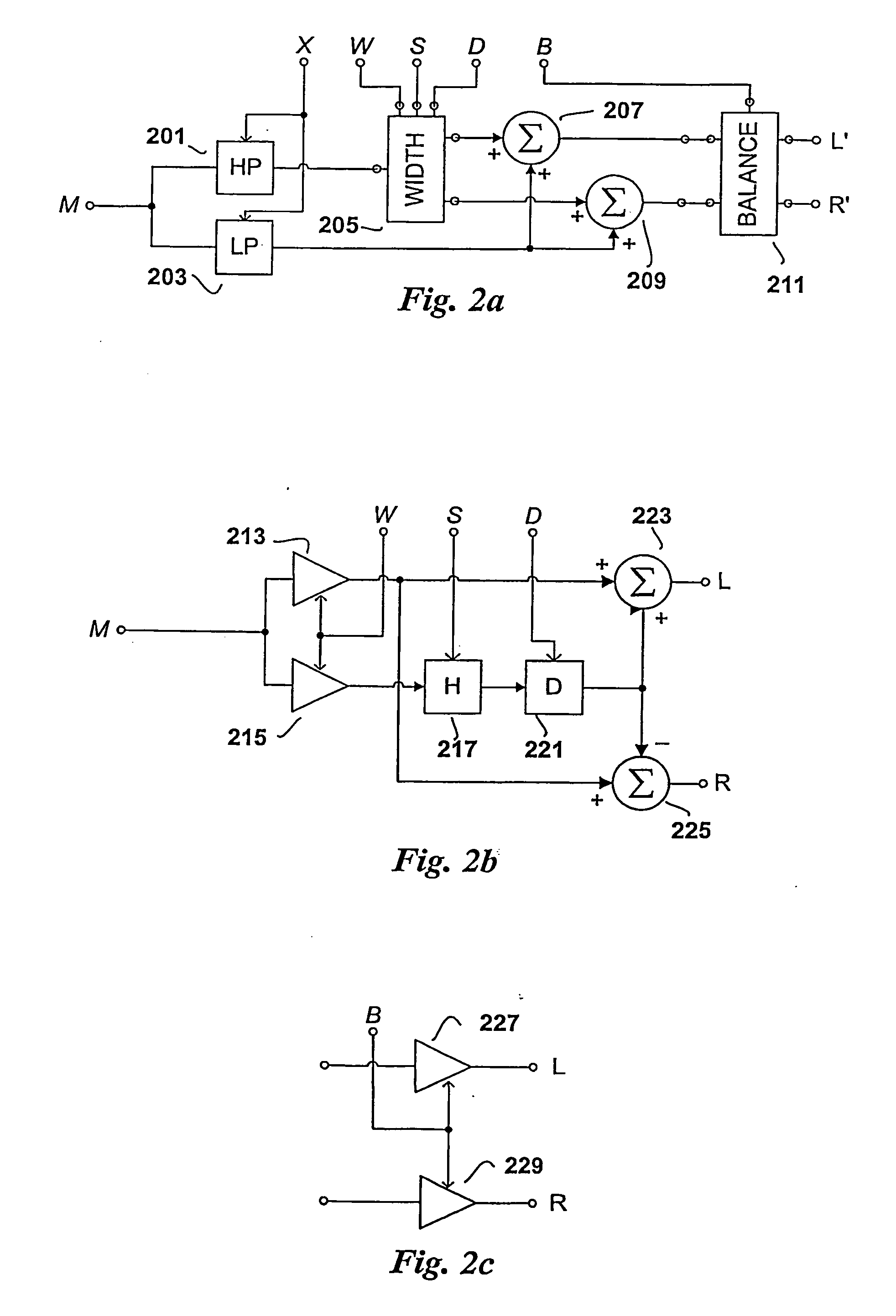
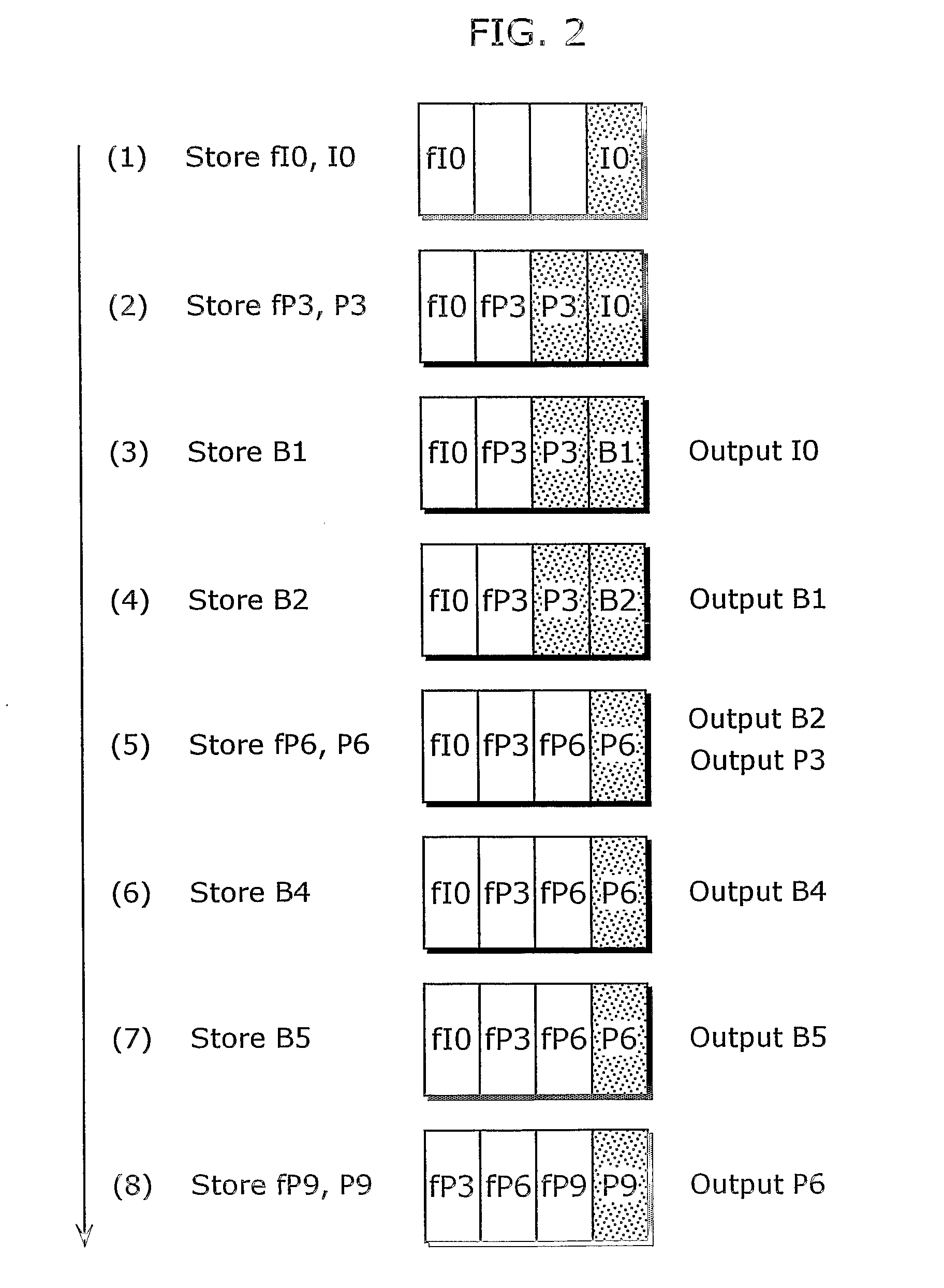
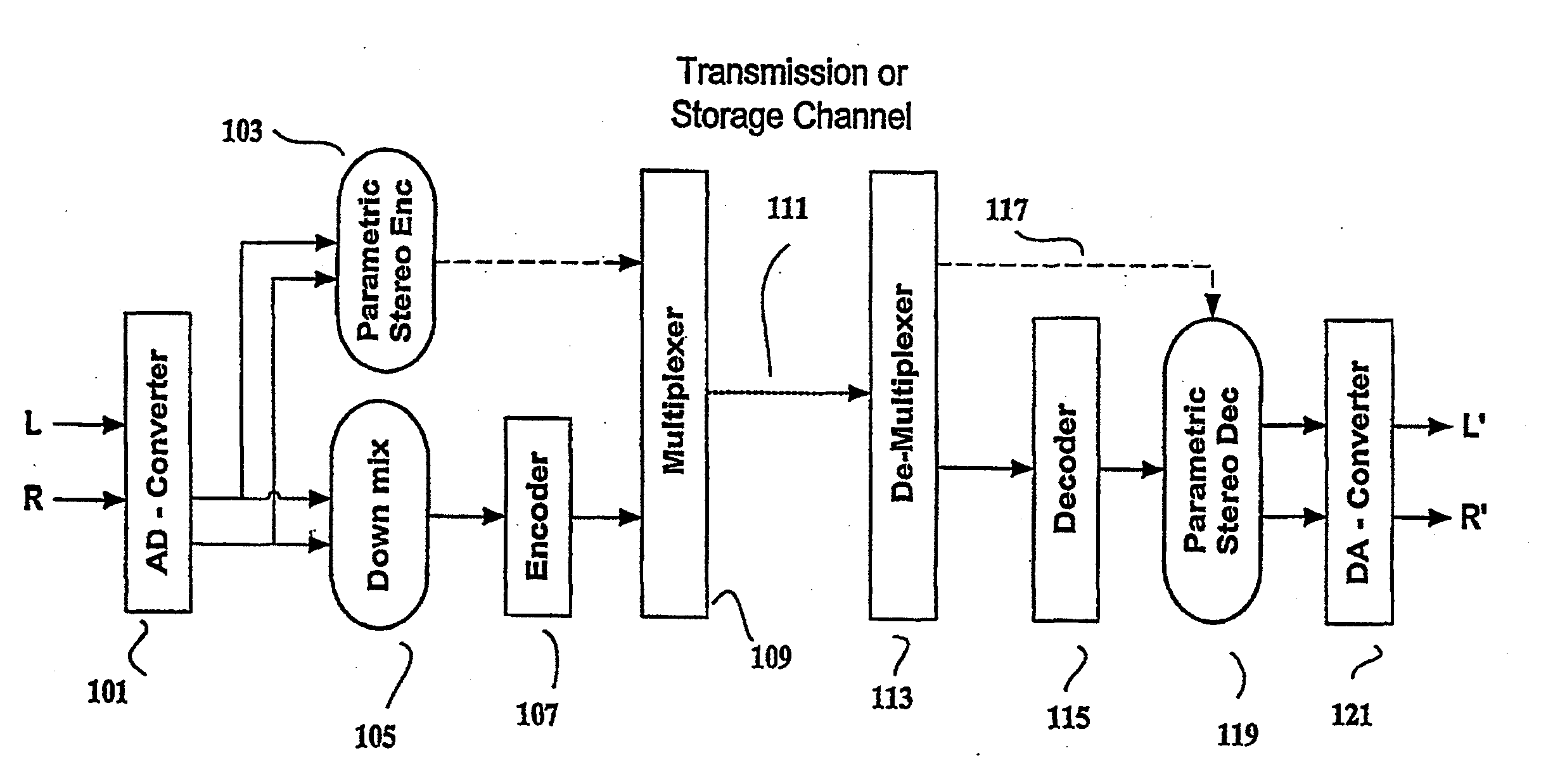
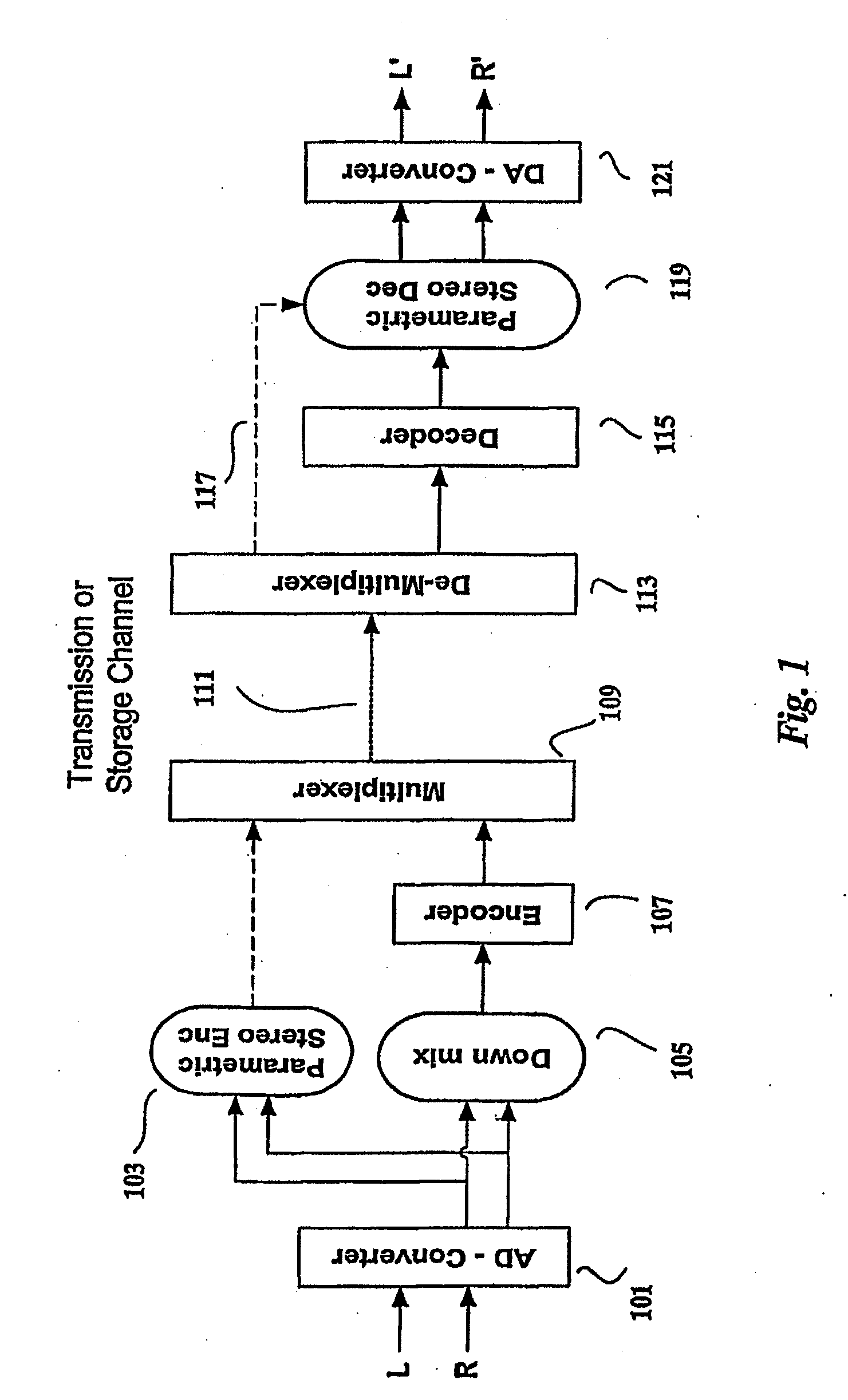
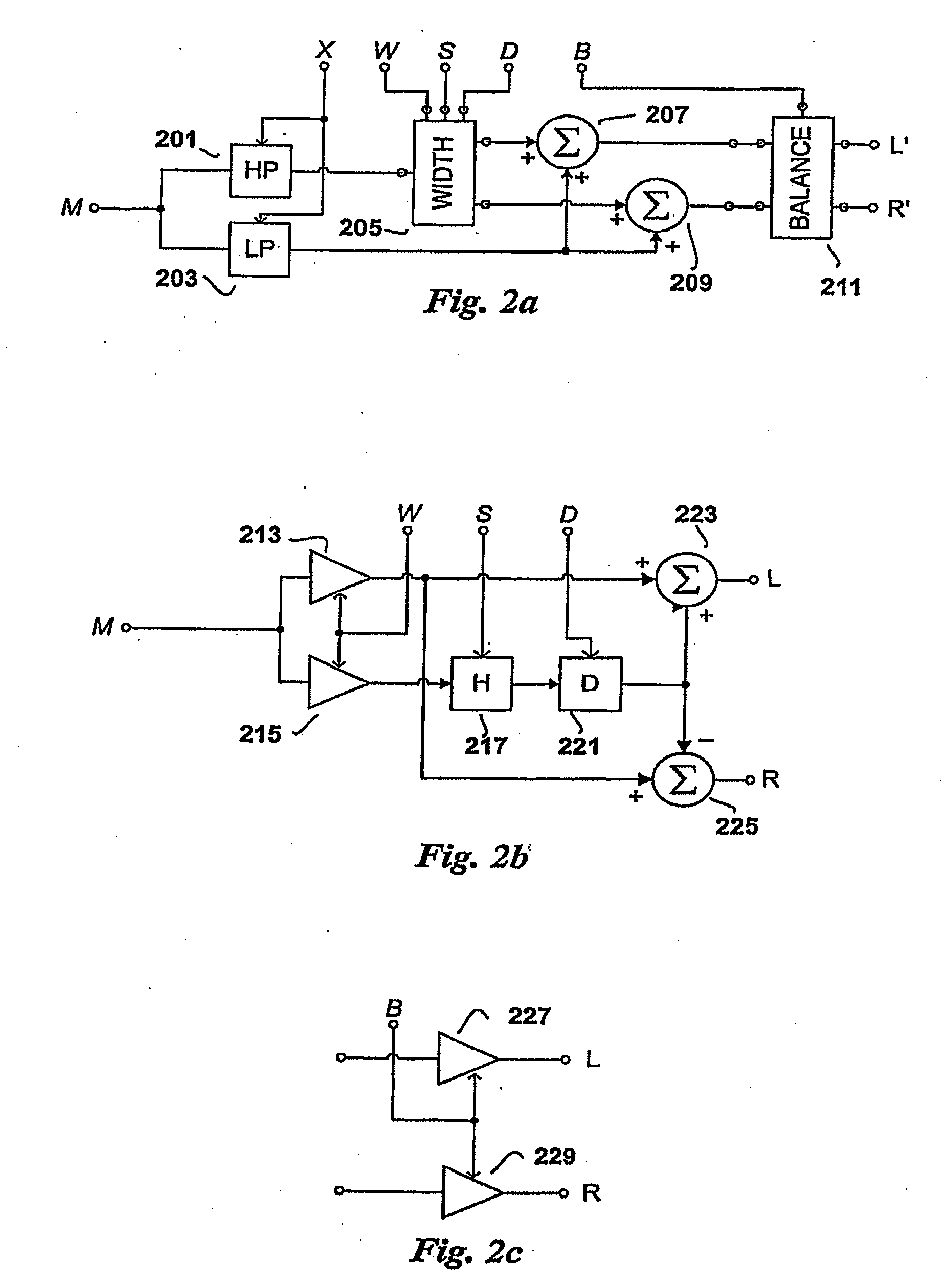
Efficient and scalable parametric stereo coding for low bitrate applications
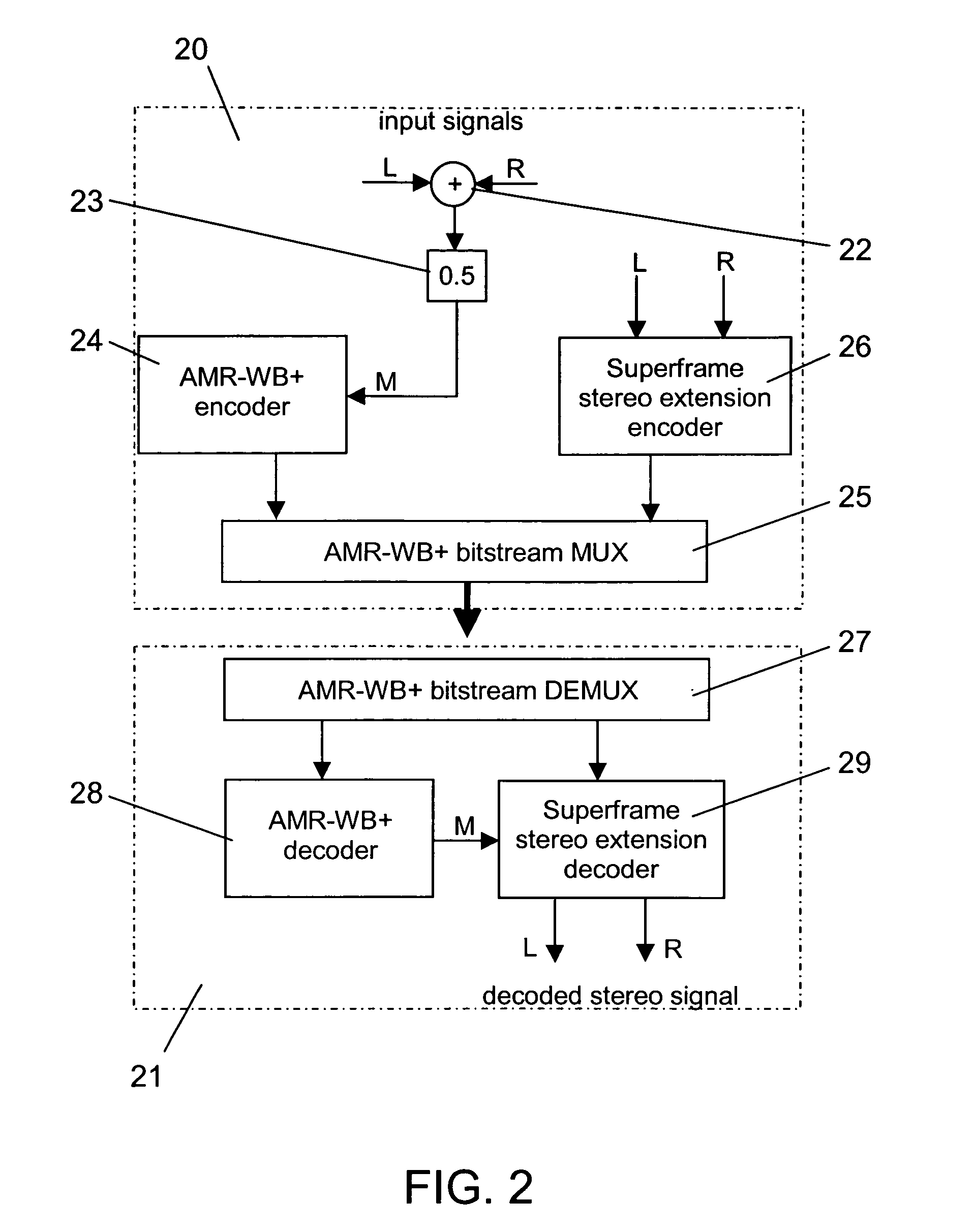
ActiveUS20050053242A1Reduce riskGuaranteed normal transmissionSpeech analysisPseudo-stereo systemsVocal tractStereo image
The present invention provides improvements to prior art audio codecs that generate a stereo-illusion through post-processing of a received mono signal. These improvements are accomplished by extraction of stereo-image describing parameters at the encoder side, which are transmitted and subsequently used for control of a stereo generator at the decoder side. Furthermore, the invention bridges the gap between simple pseudo-stereo methods, and current methods of true stereo-coding, by using a new form of parametric stereo coding. A stereo-balance parameter is introduced, which enables more advanced stereo modes, and in addition forms the basis of a new method of stereo-coding of spectral envelopes, of particular use in systems where guided HFR (High Frequency Reconstruction) is employed. As a special case, the application of this stereo-coding scheme in scalable HFR-based codecs is described.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Scalable video coding using derivation of subblock subdivision for prediction from base layer
ActiveUS20150195566A1Improving available qualityMotion-compensated predictionColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionData streamVideo encoding
Scalable video coding is rendered more efficient by deriving / selecting a subblock subdivision to be used for enhancement layer prediction, among a set of possible subblock subdivisions of an enhancement layer block by evaluating the spatial variation of the base layer coding parameters over the base layer signal. By this measure, less of the signalization overhead has to be spent on signaling this subblock subdivision within the enhancement layer data stream, if any. The subblock subdivision thus selected may be used in predictively coding / decoding the enhancement layer signal.
Owner:GE VIDEO COMPRESSION LLC
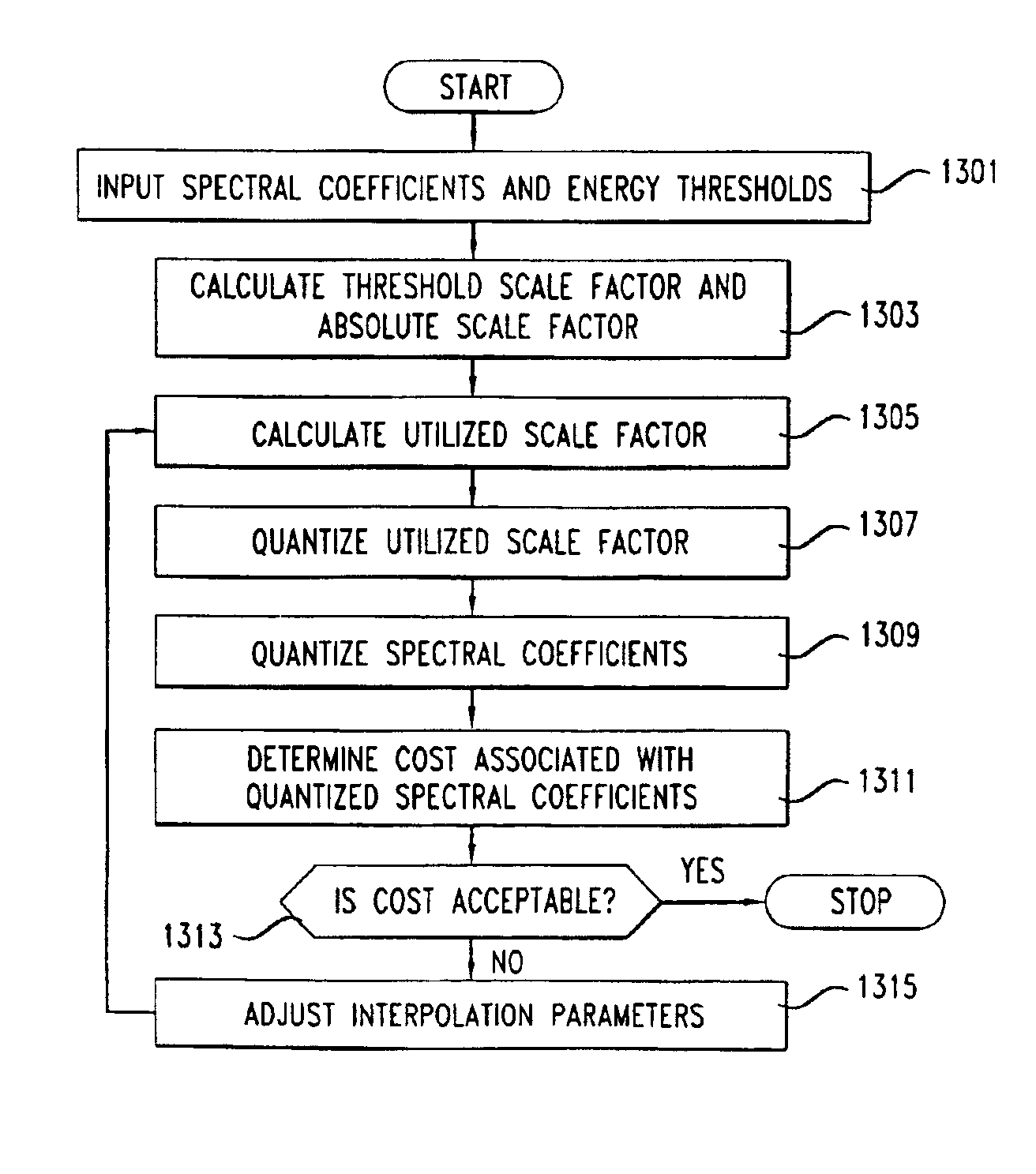
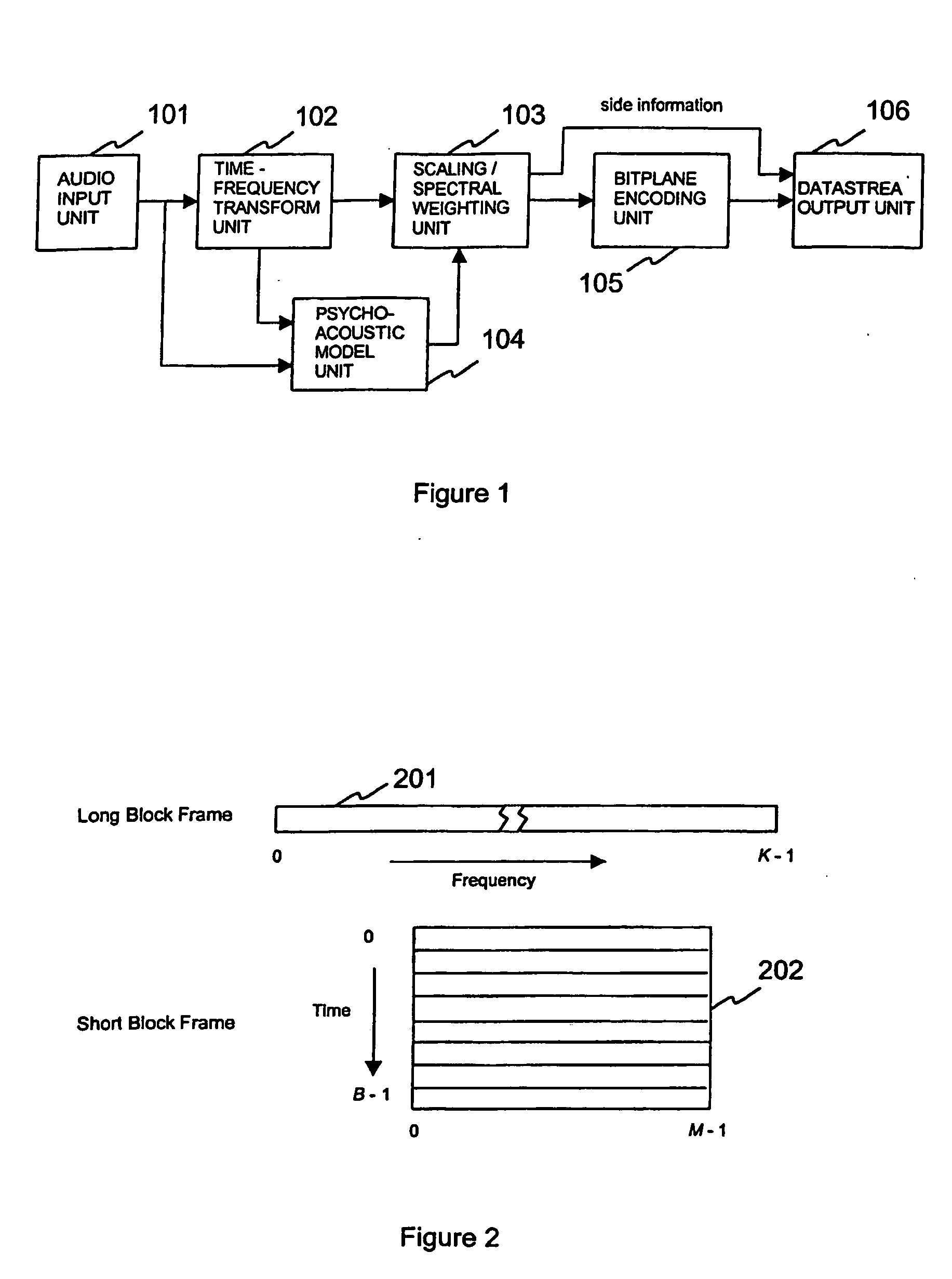
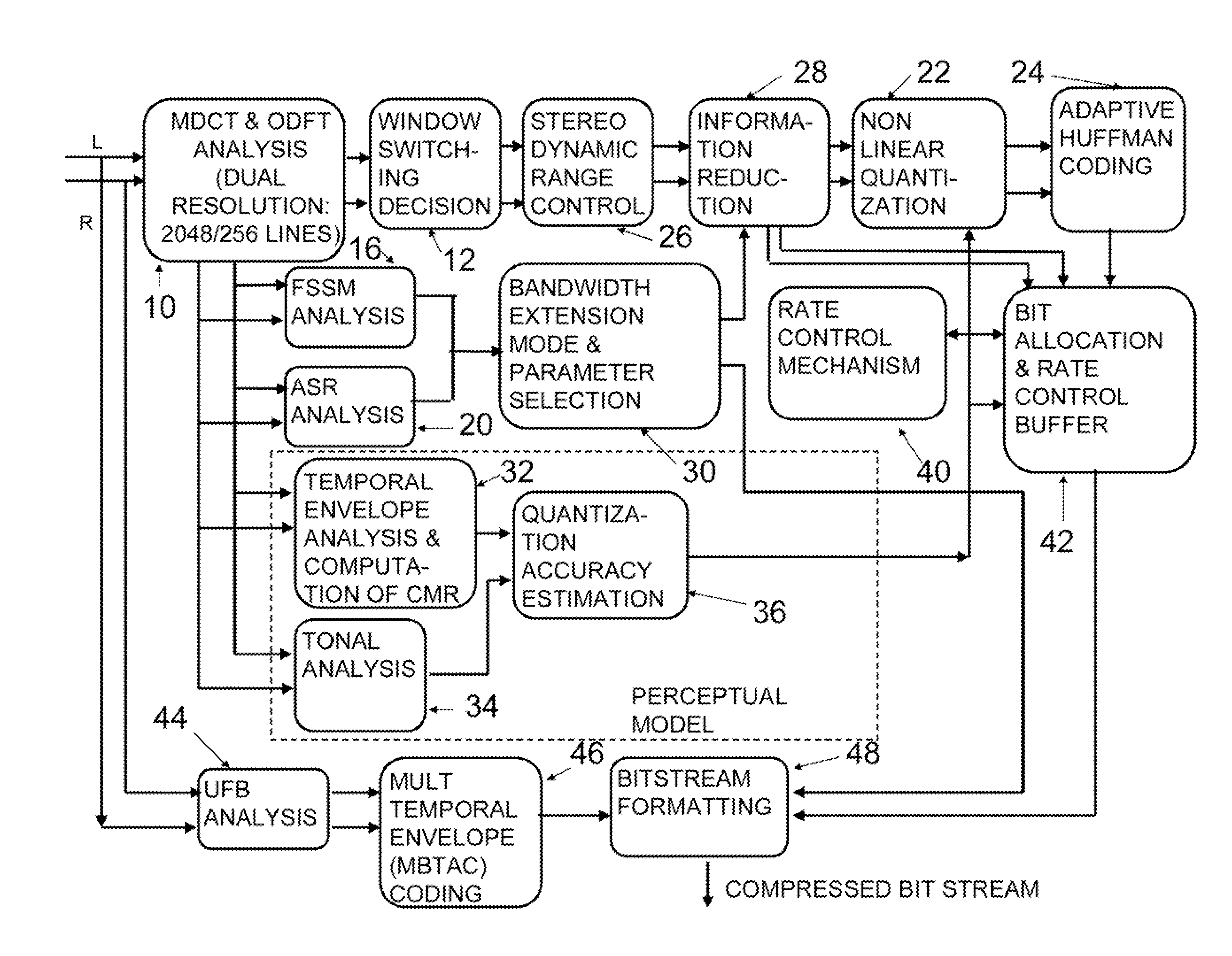
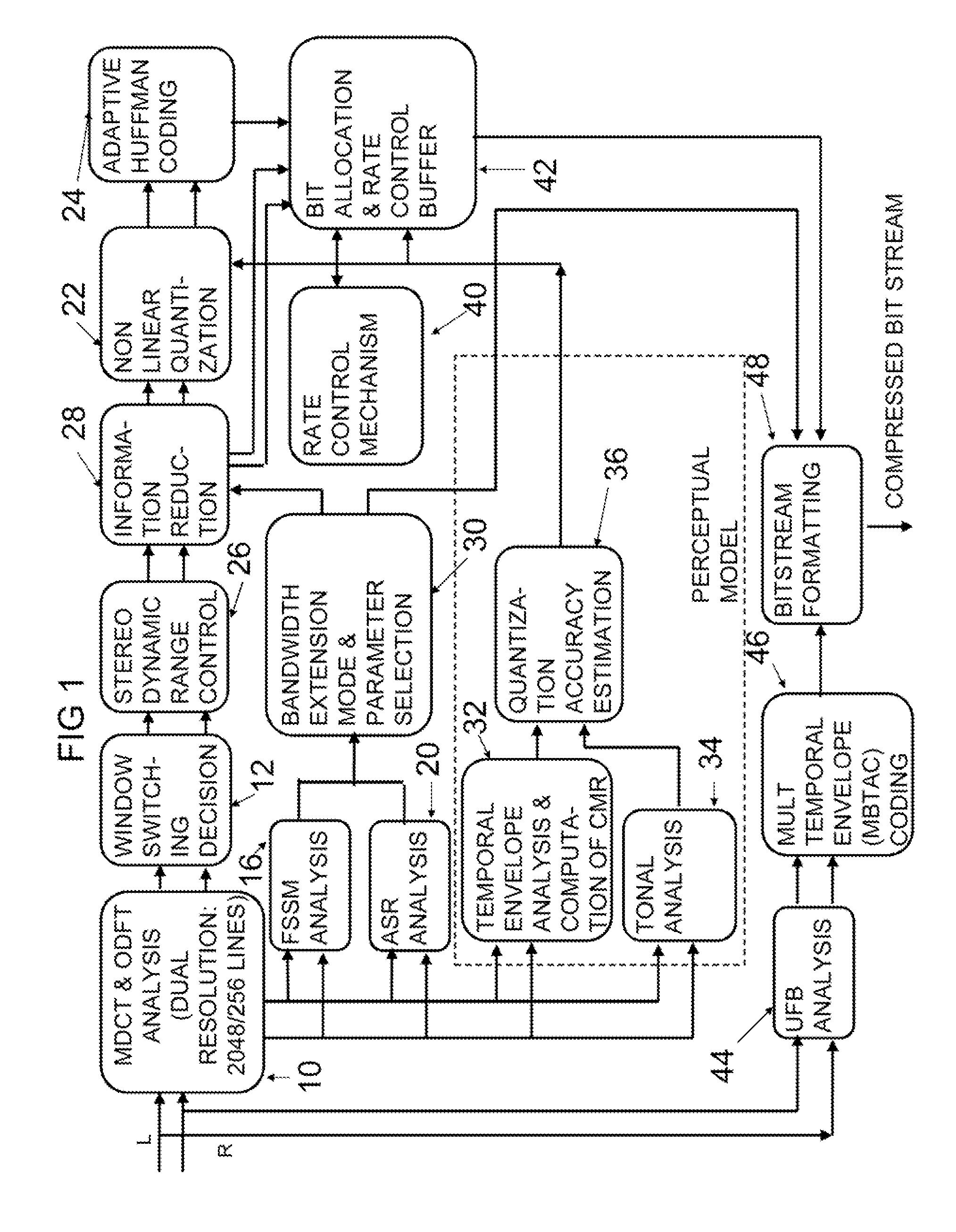
Rate loop processor for perceptual encoder/decoder
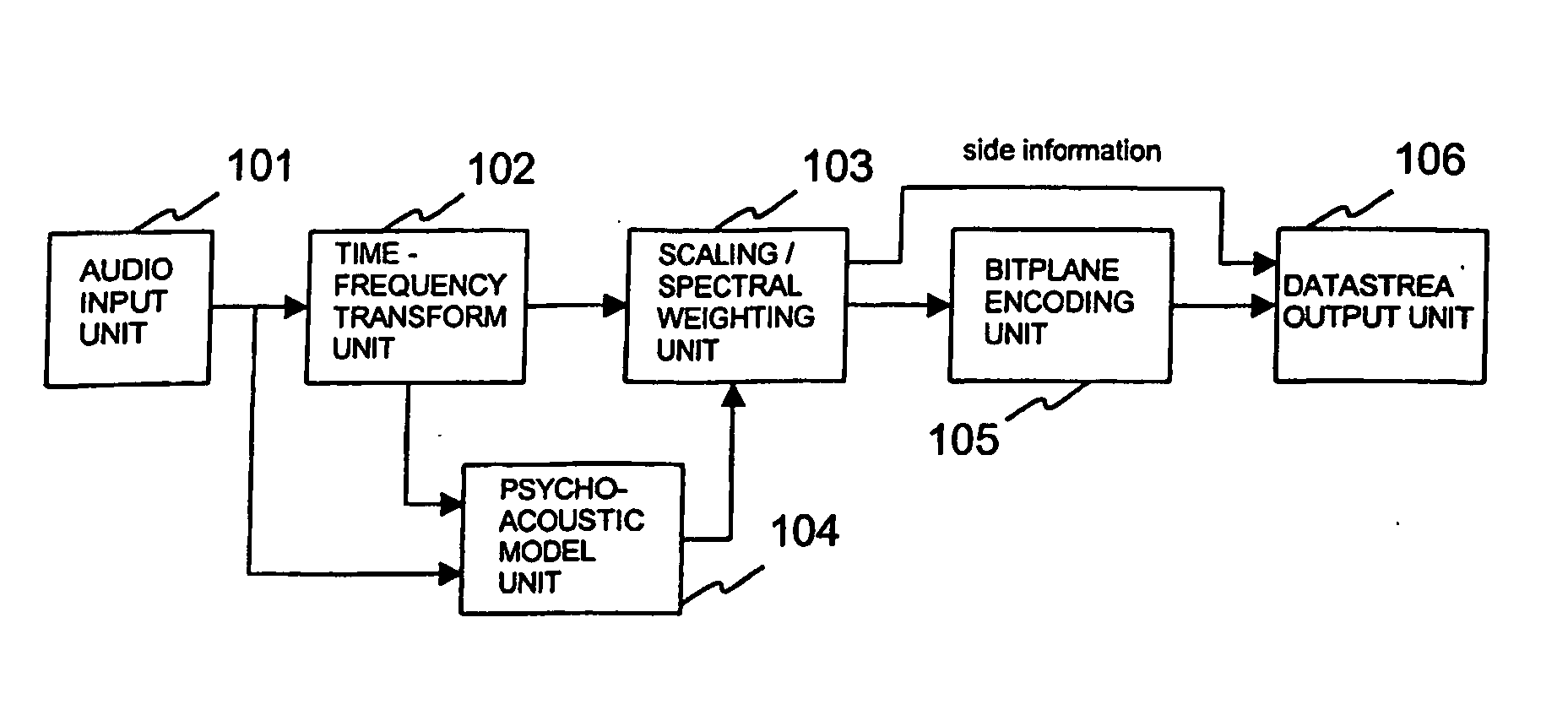
InactiveUSRE39080E1Easy to compressWithout degrading audio qualitySpeech analysisAnalogue-digital convertersHearing perceptionComputer science
A method and apparatus for quantizing audio signals is disclosed which advantageously produces a quantized audio signal which can be encoded within an acceptable range. Advantageously, the quantizer uses a scale factor which is interpolated between a threshold based on the calculated threshold of hearing at a given frequency and the absolute threshold of hearing at the same frequency.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
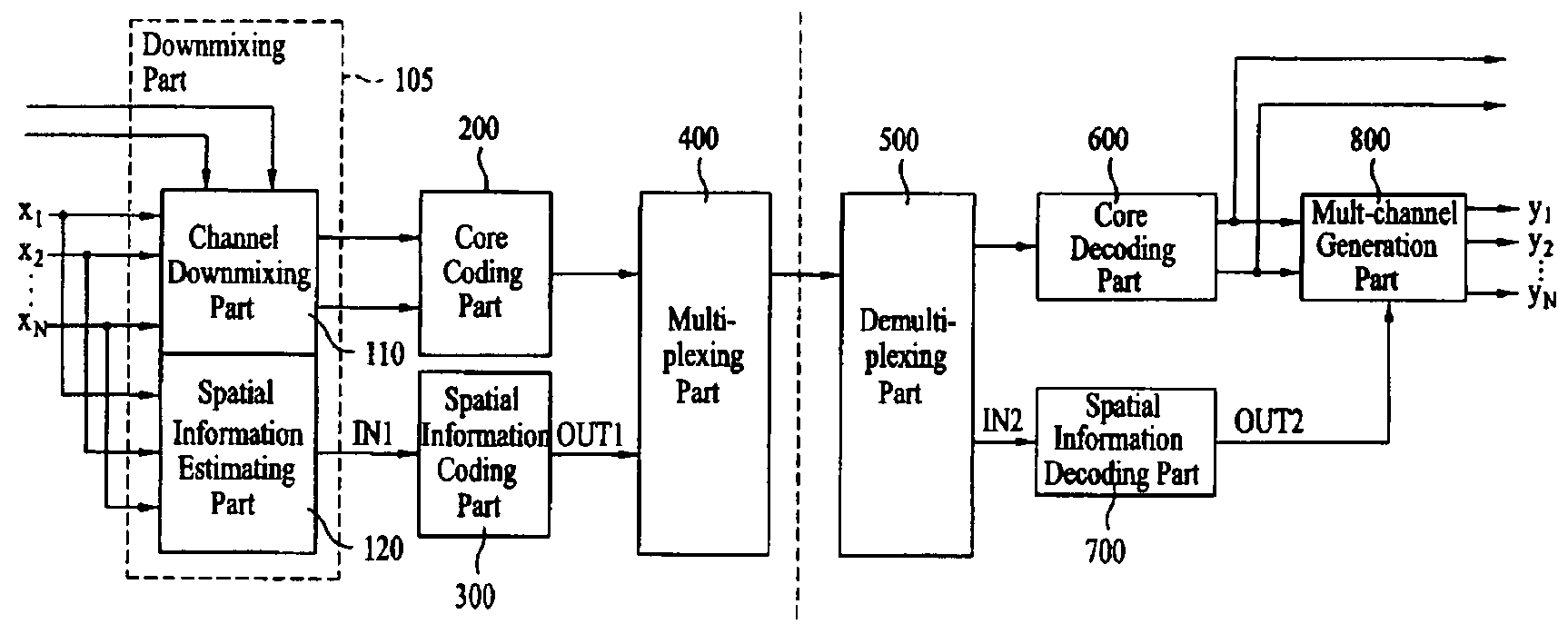
Multichannel audio extension
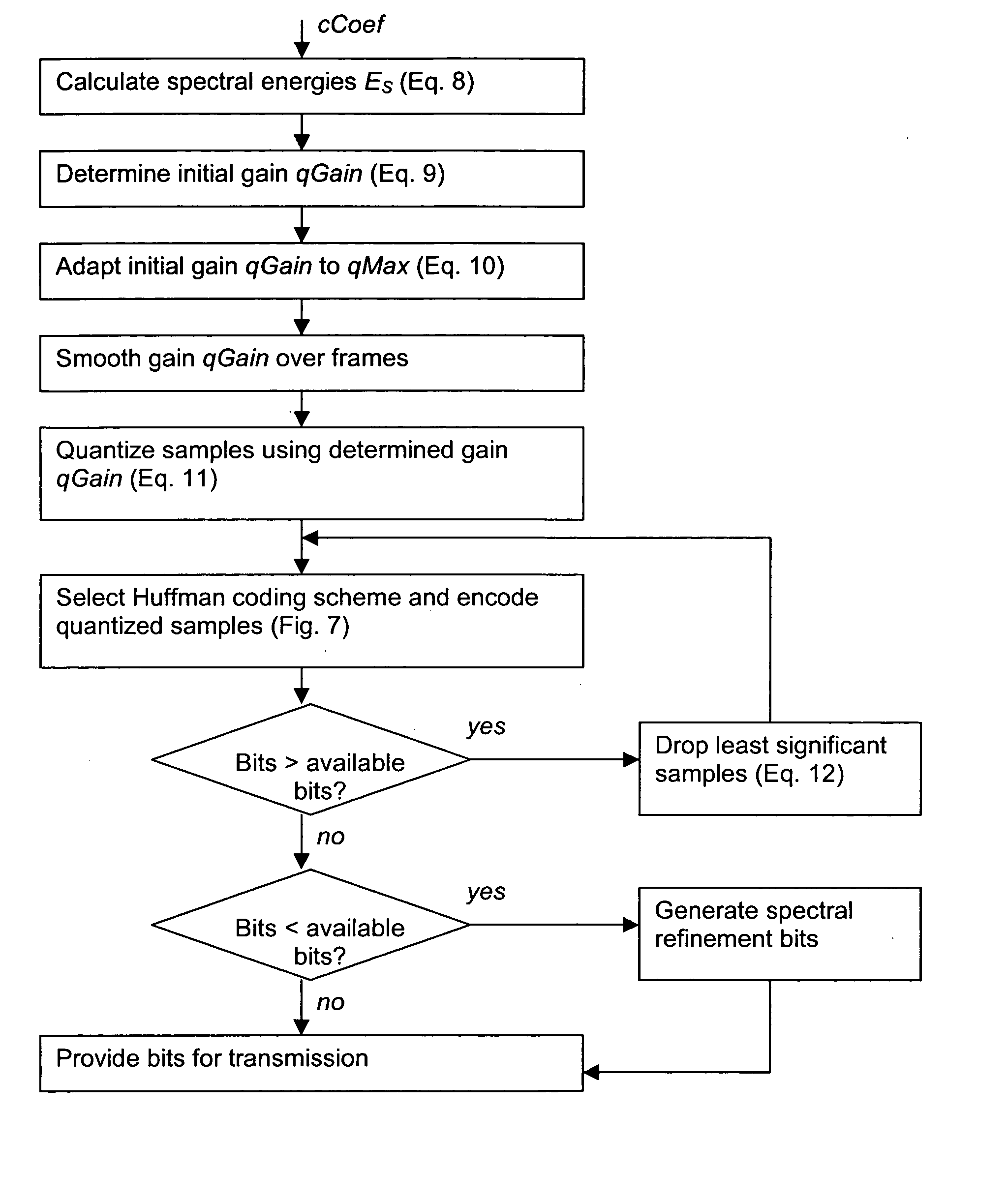
InactiveUS20050267763A1Valid encodingPromote reconstructionSpeech analysisStereophonic arrangmentsVocal tractAudio frequency
A method is shown for supporting a multichannel audio extension at an encoding end of a multichannel audio coding system. In order to improve the audio quality over a large frequency range, the method comprises transforming each channel of a multichannel audio signal into the frequency domain and dividing a bandwidth of the frequency domain signals into a first region of lower frequencies and at least one further region of higher frequencies. Then, the frequency domain signals are encoded in each of the frequency regions with another type of coding to obtain parametric multichannel extension information for the respective frequency region. The invention relates equally to a method for supporting in a corresponding manner a multichannel audio extension at a decoding end. Also shown are a corresponding encoder, a corresponding decoder, and corresponding devices, systems and software program products.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Audio compression
InactiveUS20050231396A1Low compute complexityHigh efficiencySpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency domainAudio frequency
Owner:SCALA TECH
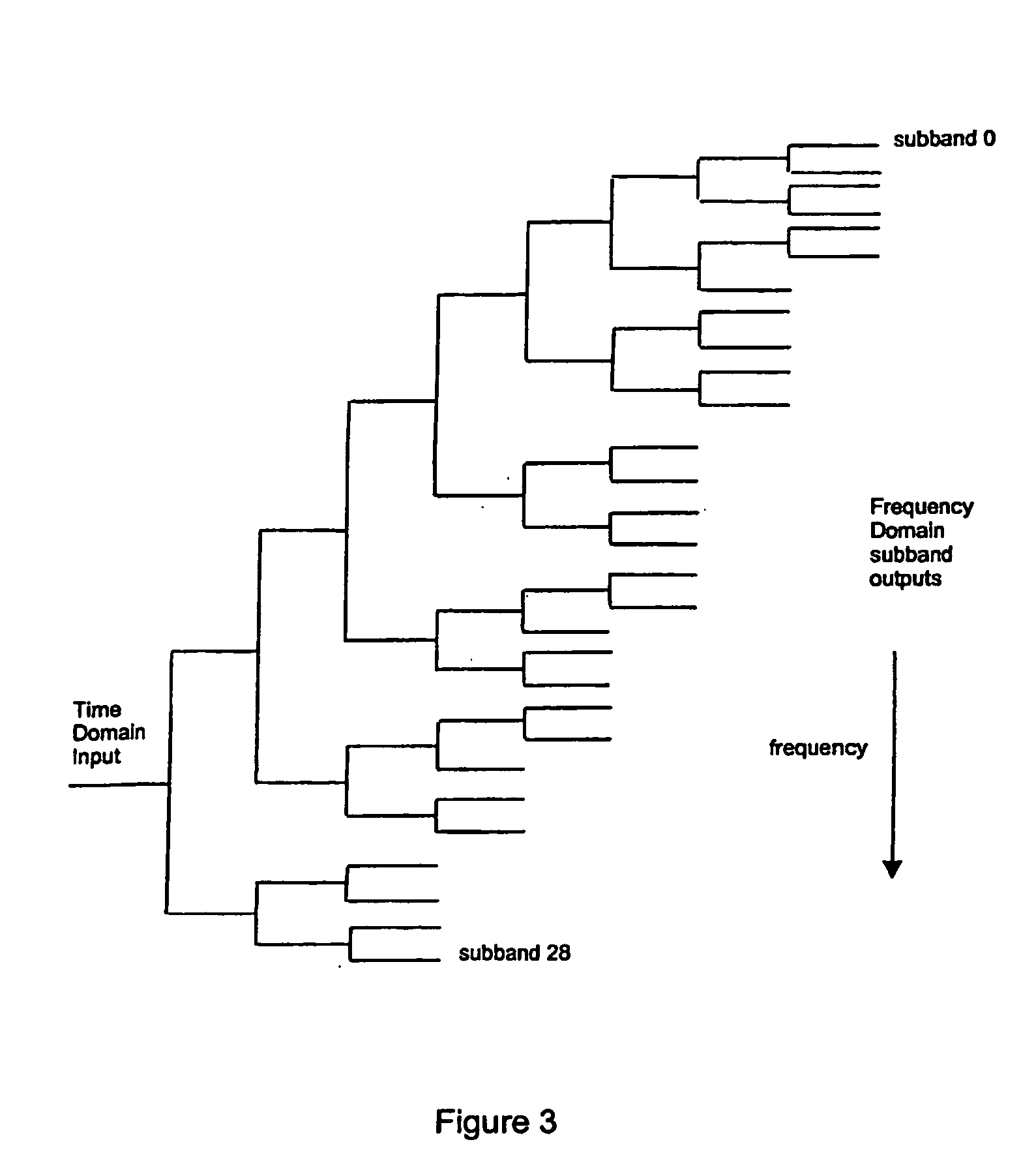
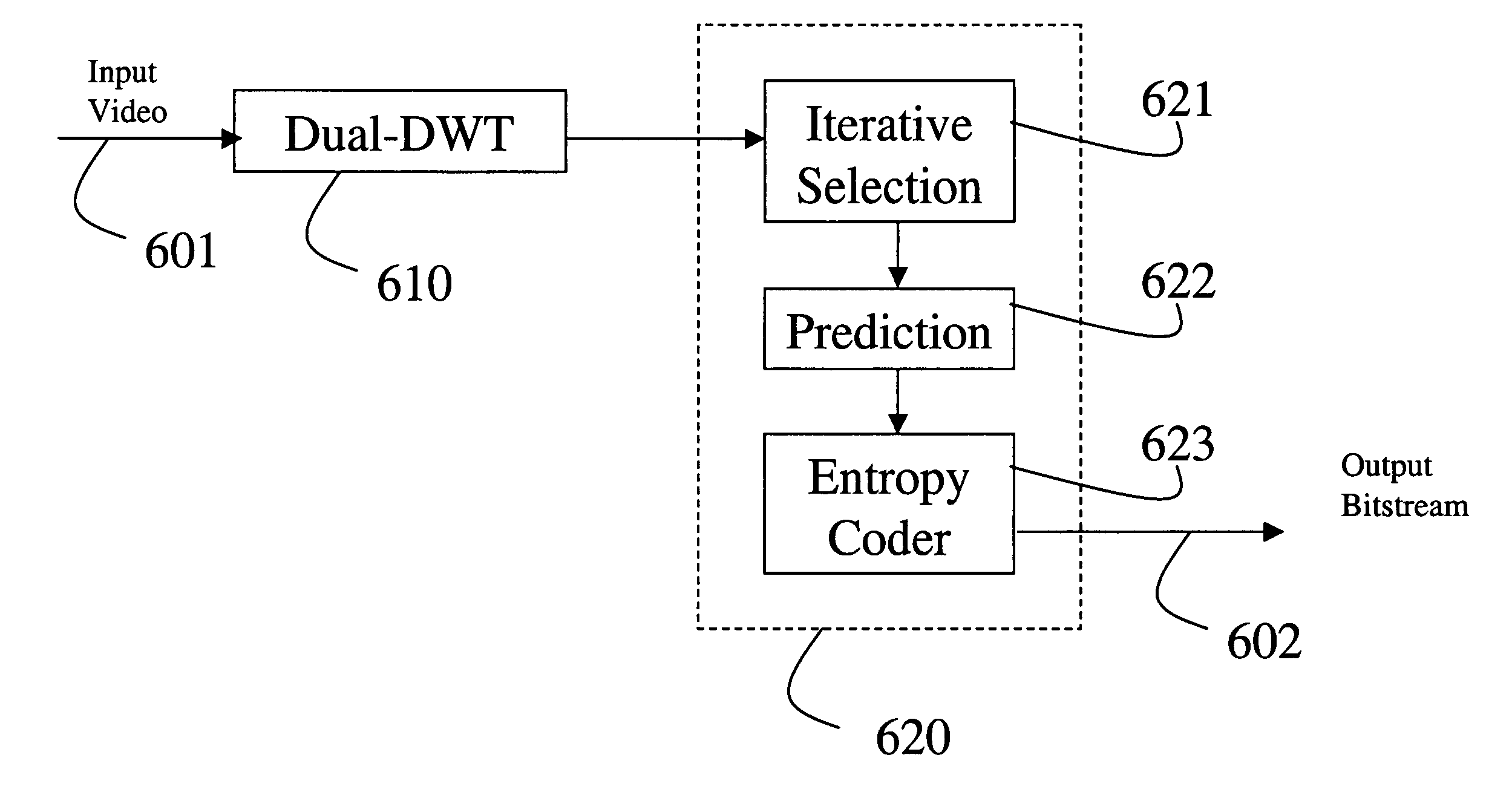
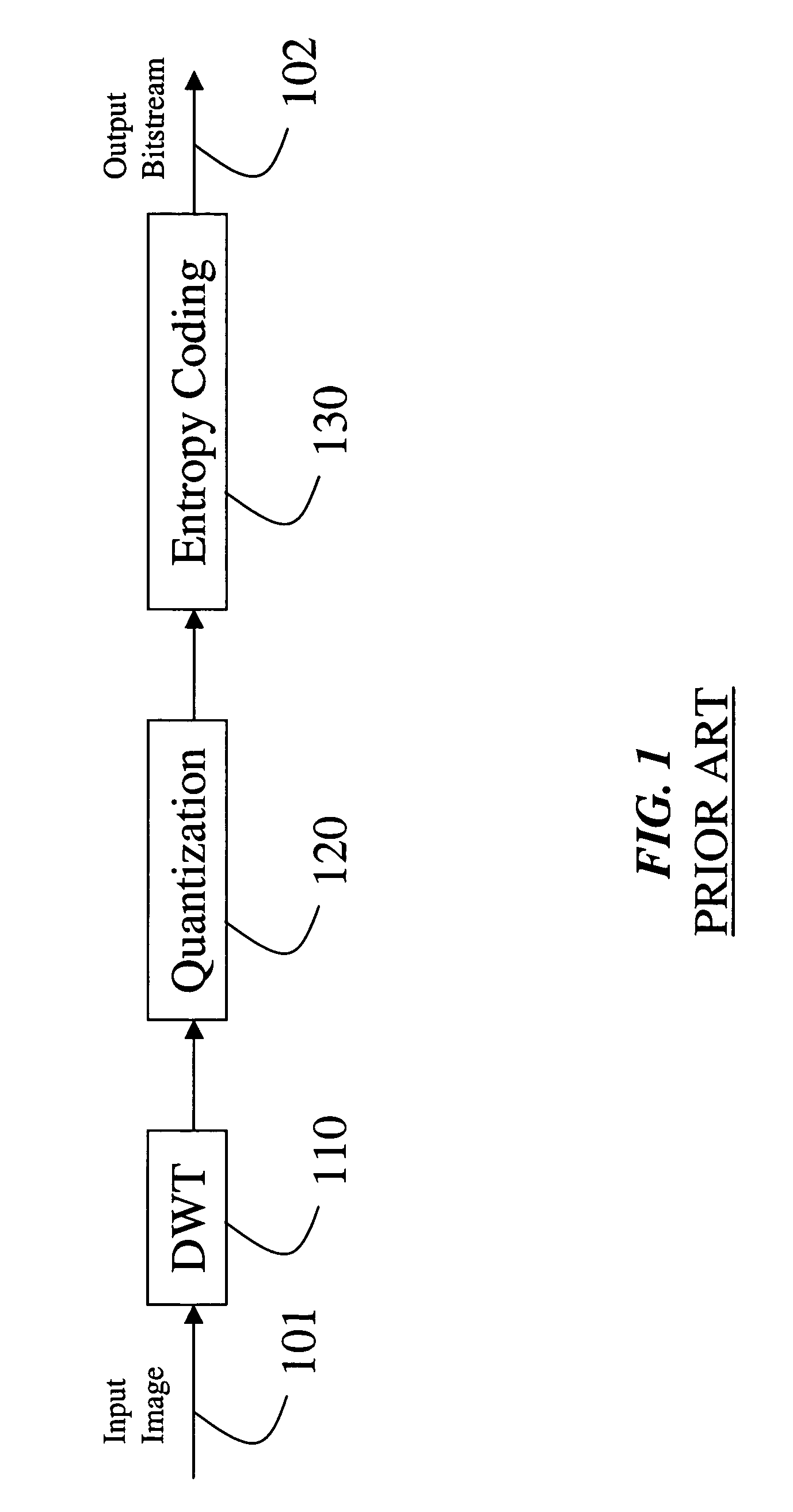
Video encoding with motion-selective wavelet transform
InactiveUS20050084014A1Increase in numberReduce numberColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionEntropy encodingCompression ratio
A method encodes a video by applying a dual-tree discrete wavelet transform to the video to generate sequences of wavelet coefficients. The sequences are compressed to produce a compressed bitstream corresponding to the video. The compression iteratively selects the wavelet coefficients in a large to small order, and entropy encodes the selected wavelet coefficient.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LABK
Object shape exploration using topology matching
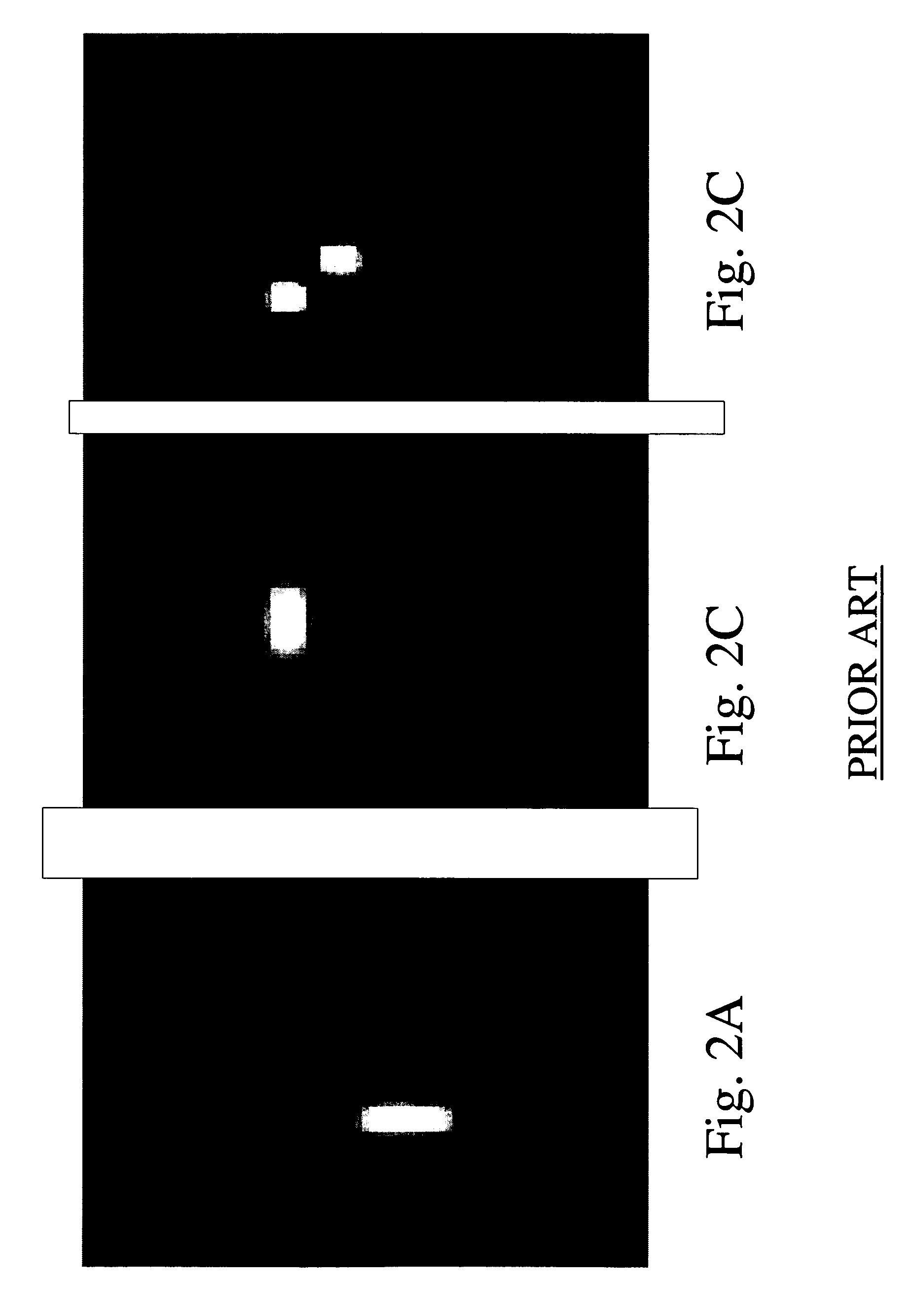
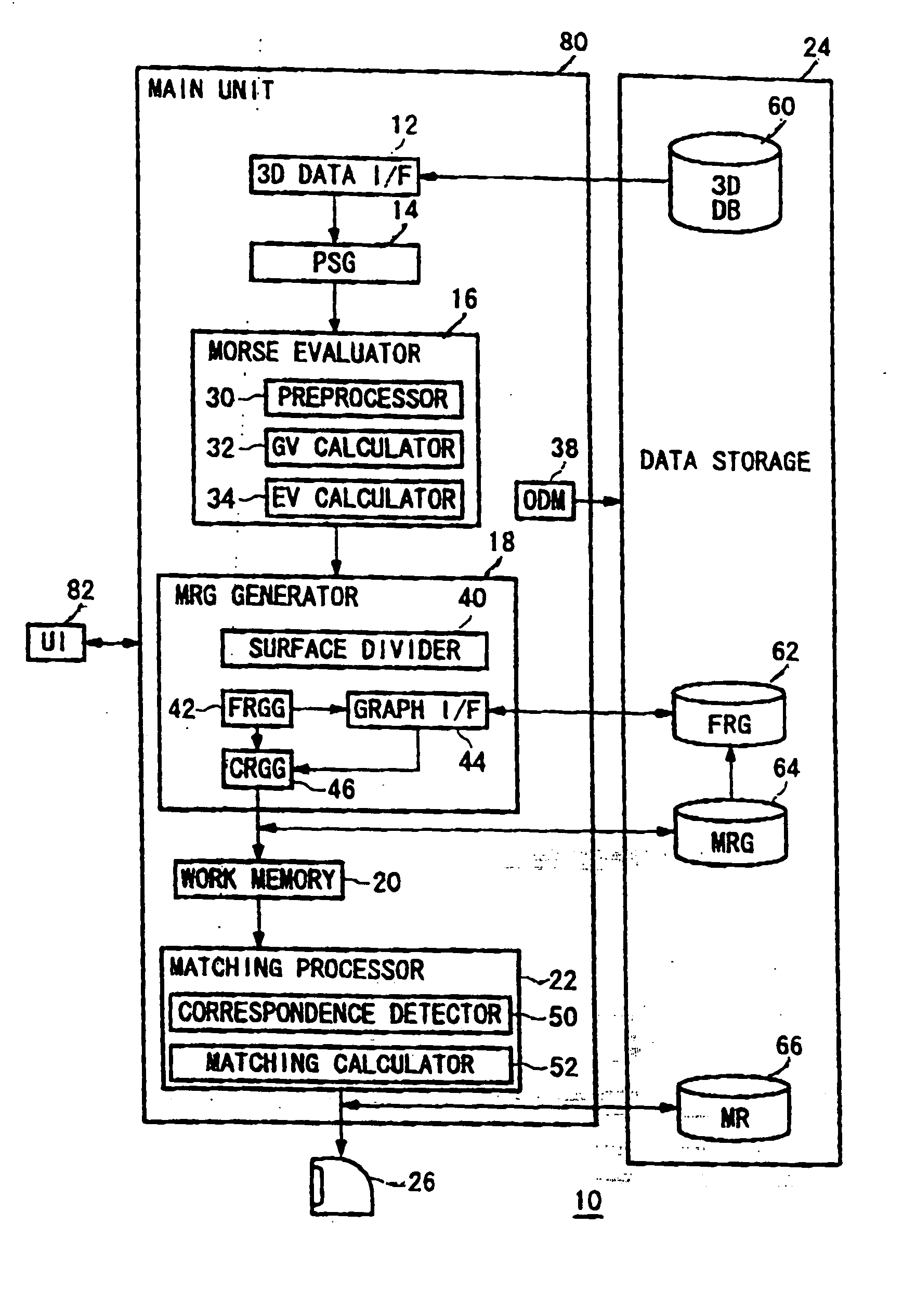
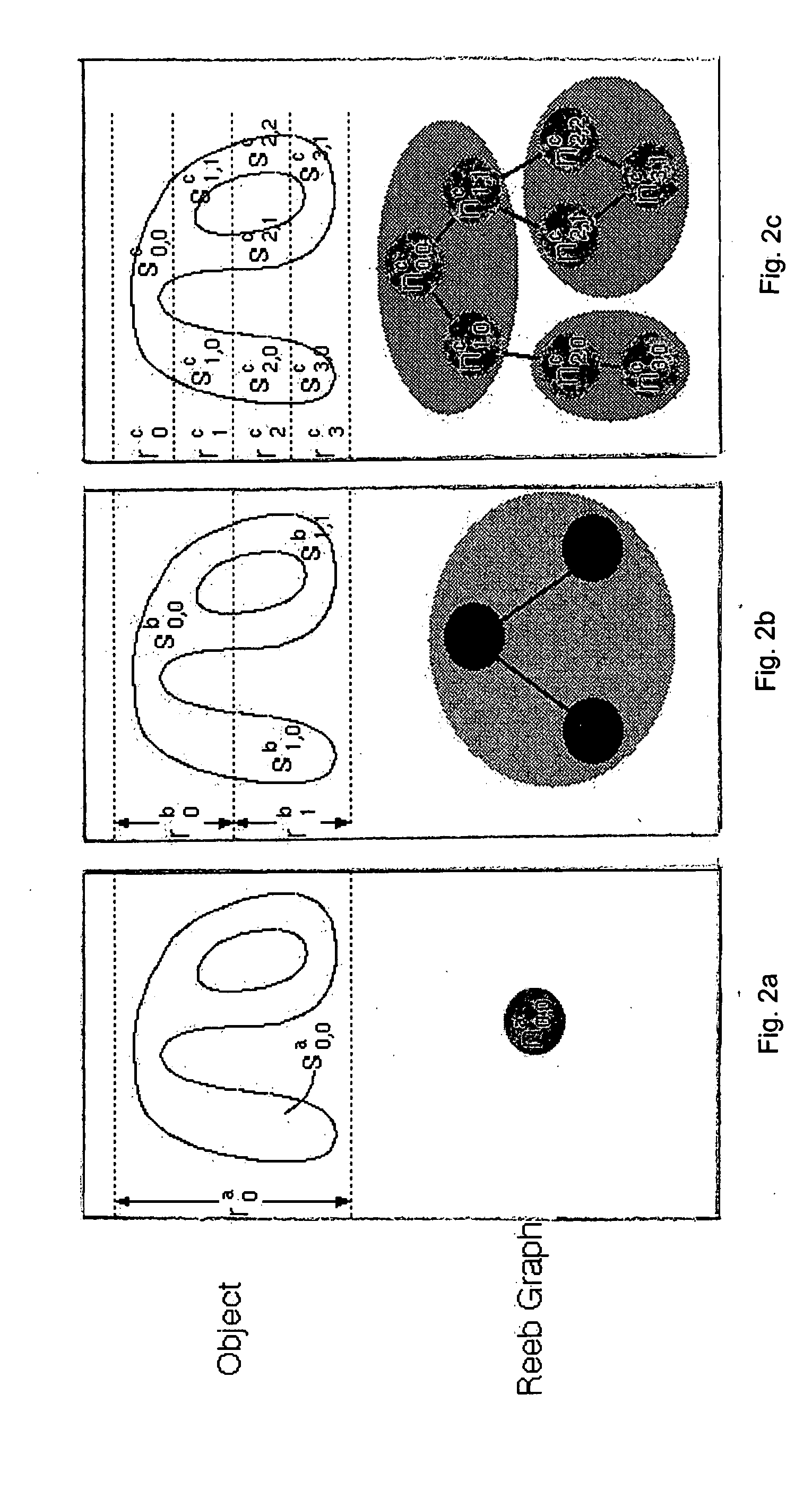
InactiveUS20050002571A1Efficient searchReduce computing costImage analysisDigital data information retrievalGraphicsComputer science
A shape analyzer is provided. The analyzer inputs a 3D representation of an object such as merchandise. The structural graph of the object is constructed by defining a continuous function on the surface of the object. The surface is then partitioned into plural areas according to the function values at the points on the surface. The areas are associated with nodes of the graph. By choosing a function that returns values invariant to rotation of the objects, the constructed graph also becomes invariant to rotation. This feature is important when searching for objects by shape from a shape database, as the postures of the objects are unknown when searched for. The analyzer is applicable to search engines for online shopping, where a user seeks goods by designating the general shape of the target.
Owner:MONOLITH
Constructing a statistical shape model from two-dimensional or three-dimensional data
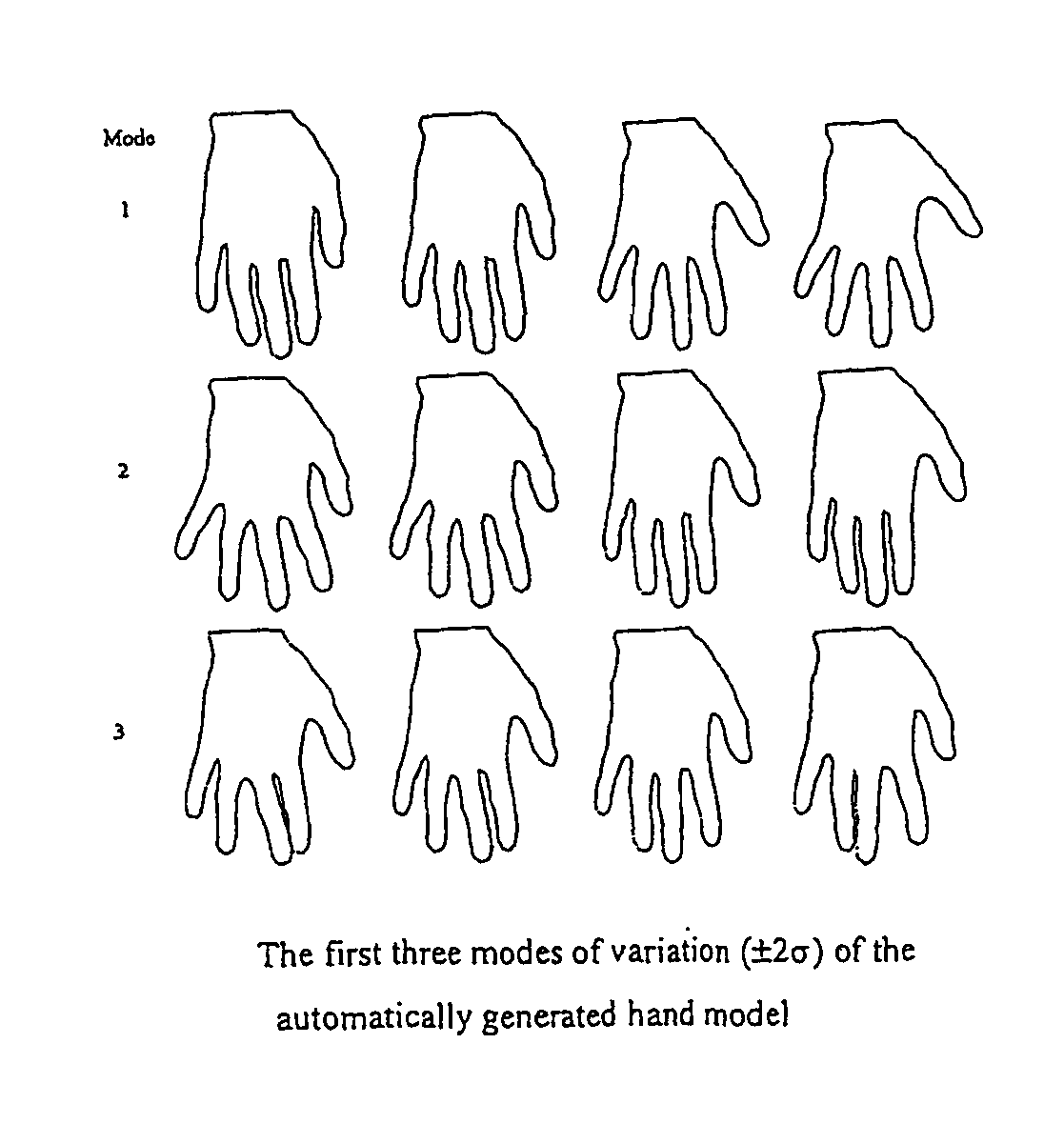
InactiveUS7584080B2Easy to compareValid encodingCharacter and pattern recognitionComputation using non-denominational number representationThree dimensional shapeComputer science
Owner:UNIV OF MANCHESTER
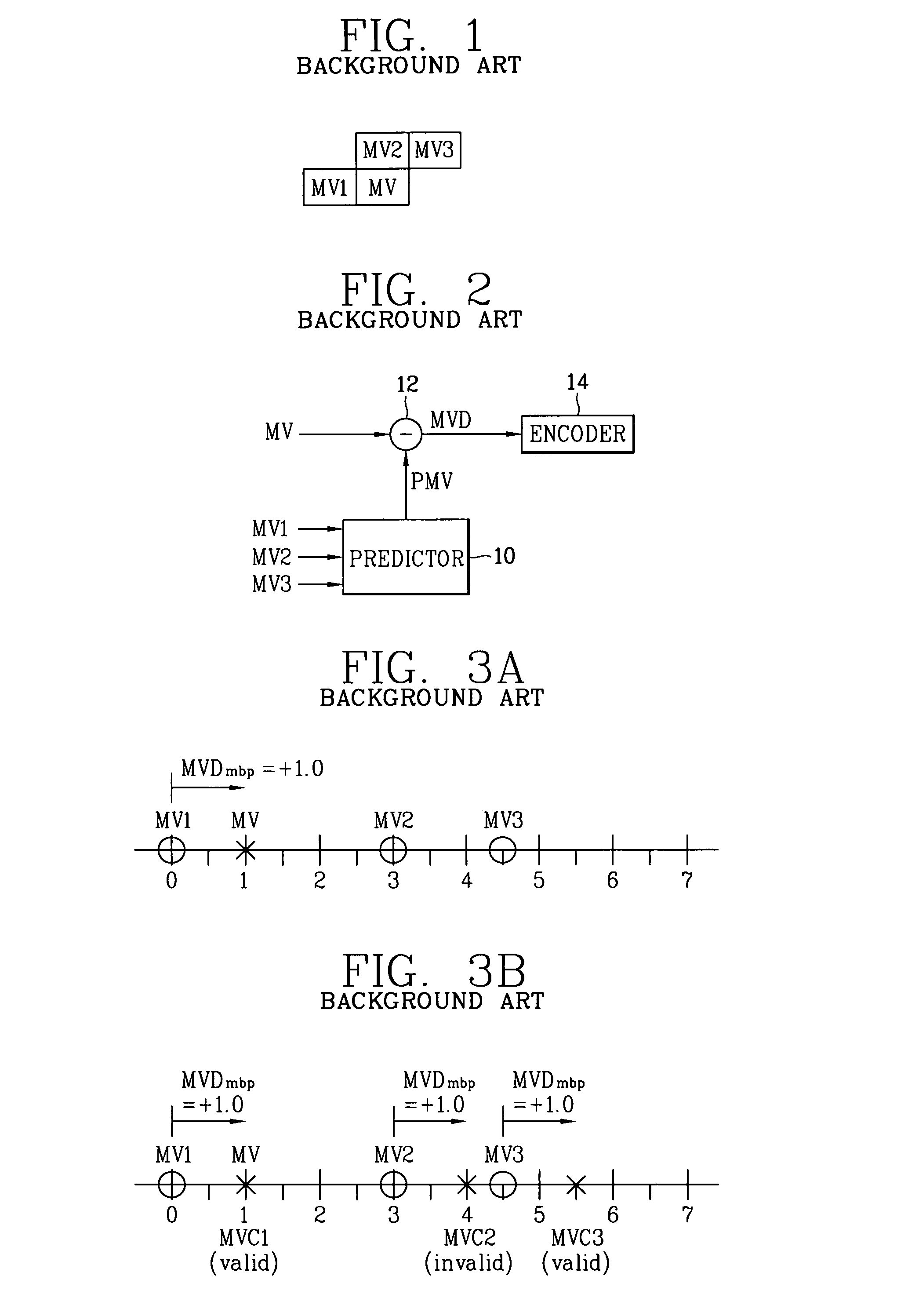
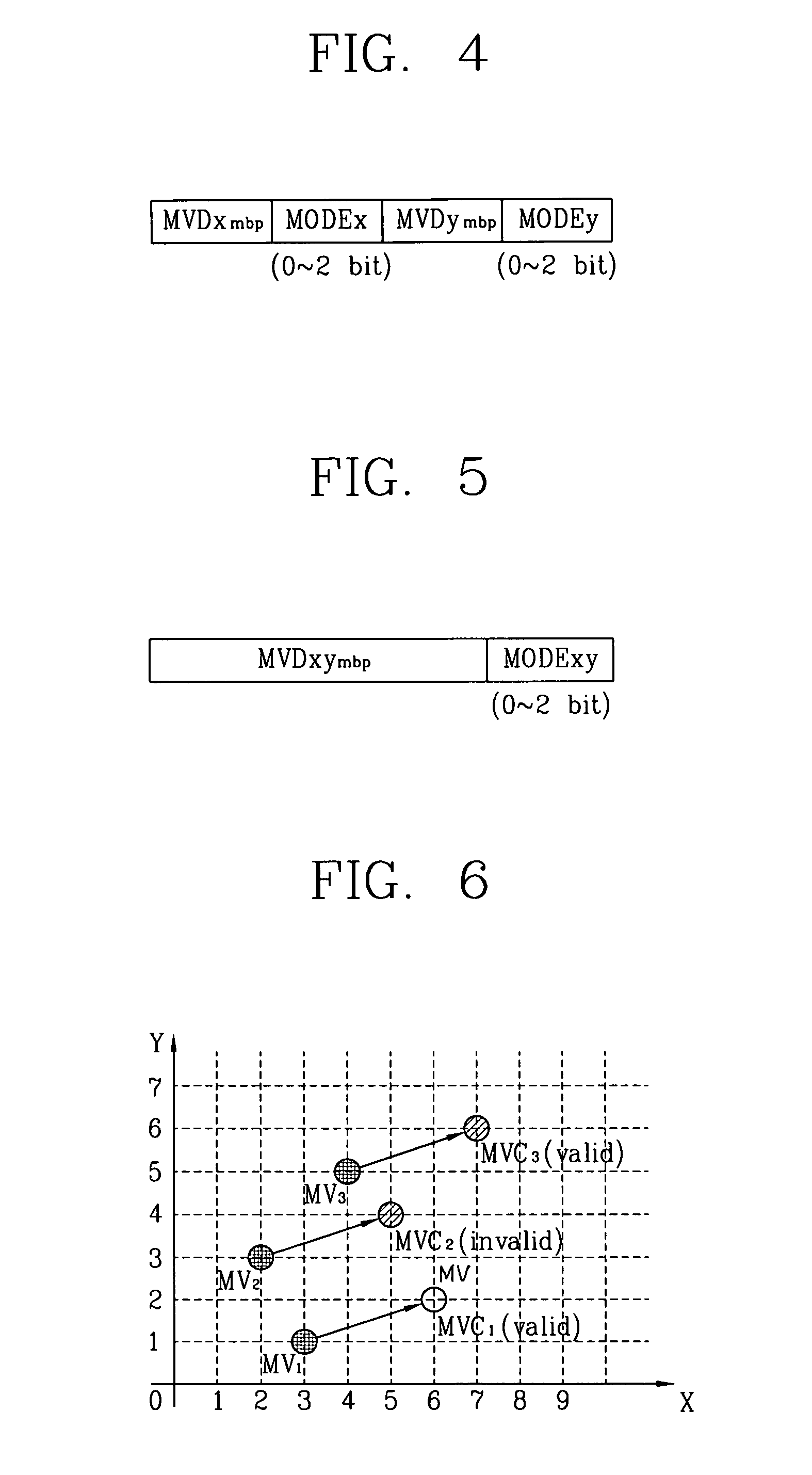
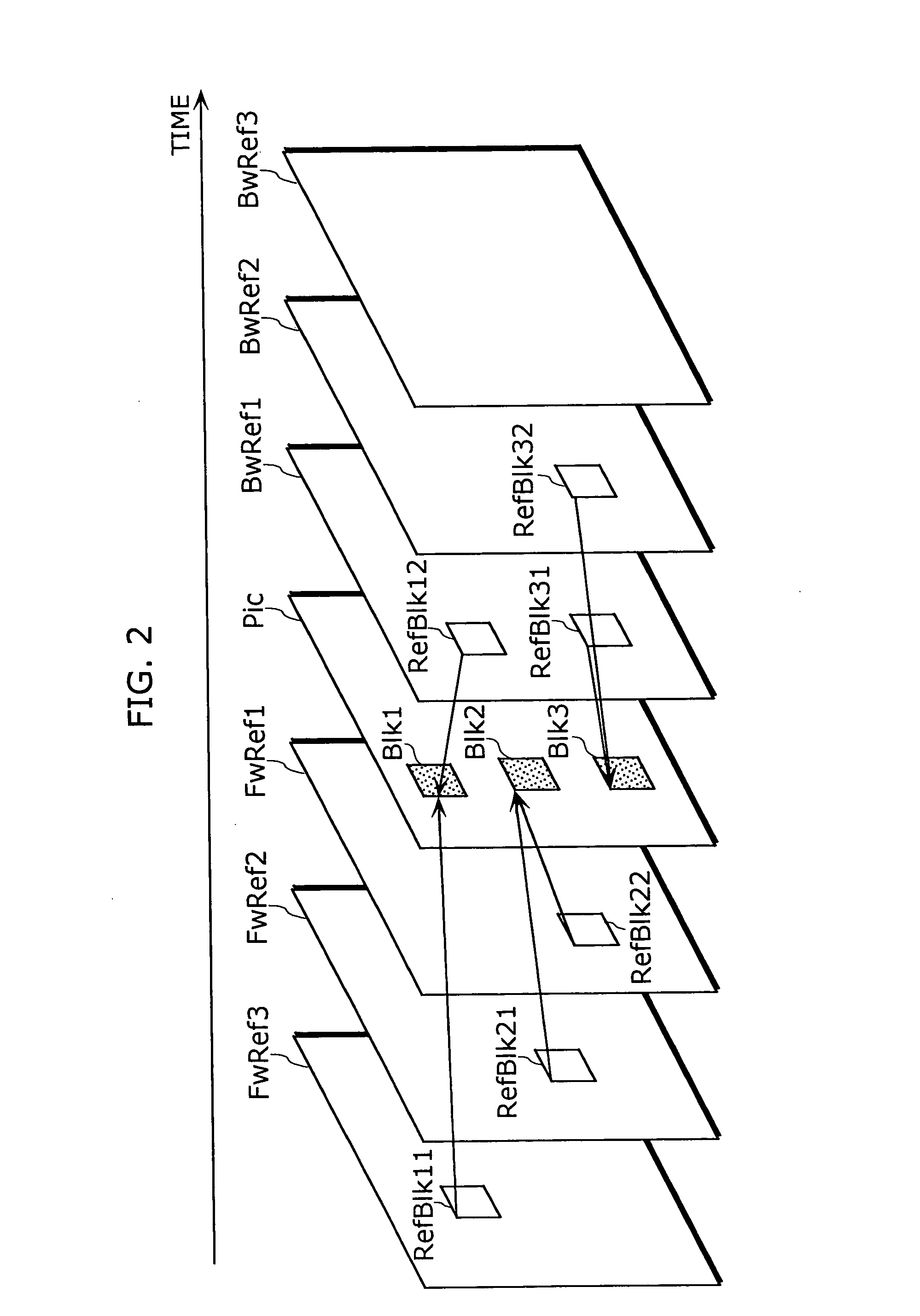
Method for coding motion vector using 2-dimensional minimum bitrate predicting technique
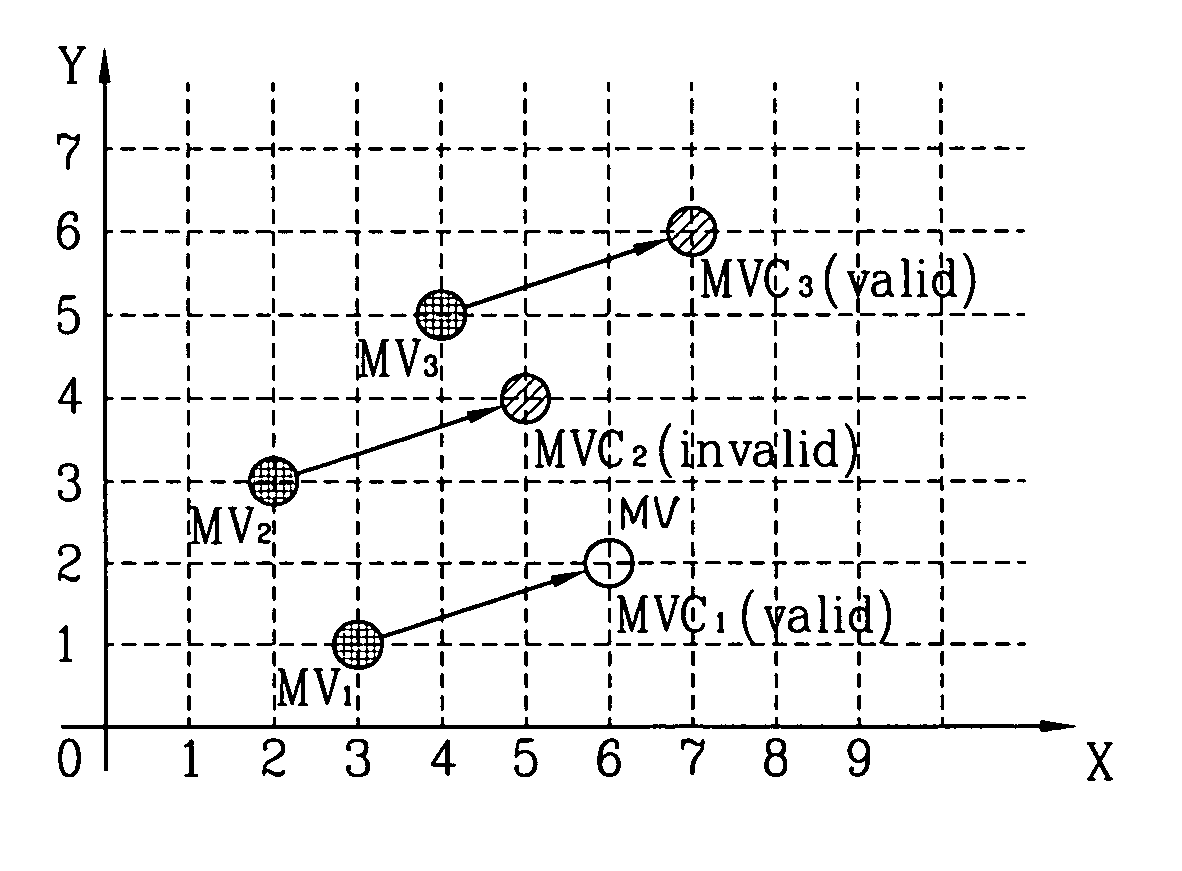
InactiveUS7023919B2Improve coding efficiencyValid encodingTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesMotion vectorDistribution characteristic
A method for coding a motion vector using a 2-dimensional minimum bitrate predicting technique is disclosed. A mode information (MODE) commonly adopted to the factors ‘X’ and ‘Y’ are transmitted to thereby reduce its transmission burden by using the two-dimensional minimum bitrate predicting technique, so that a coding efficiency of a motion vector can be improved. In addition, the two-dimensional MVD information coding method is proposed for the low transfer rate mobile image which is very small and has very small motion, so that even if a distribution characteristic of the MVD information is changed according to the minimum bitrate prediction, a coding efficiency of a major motion vector can be improved.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
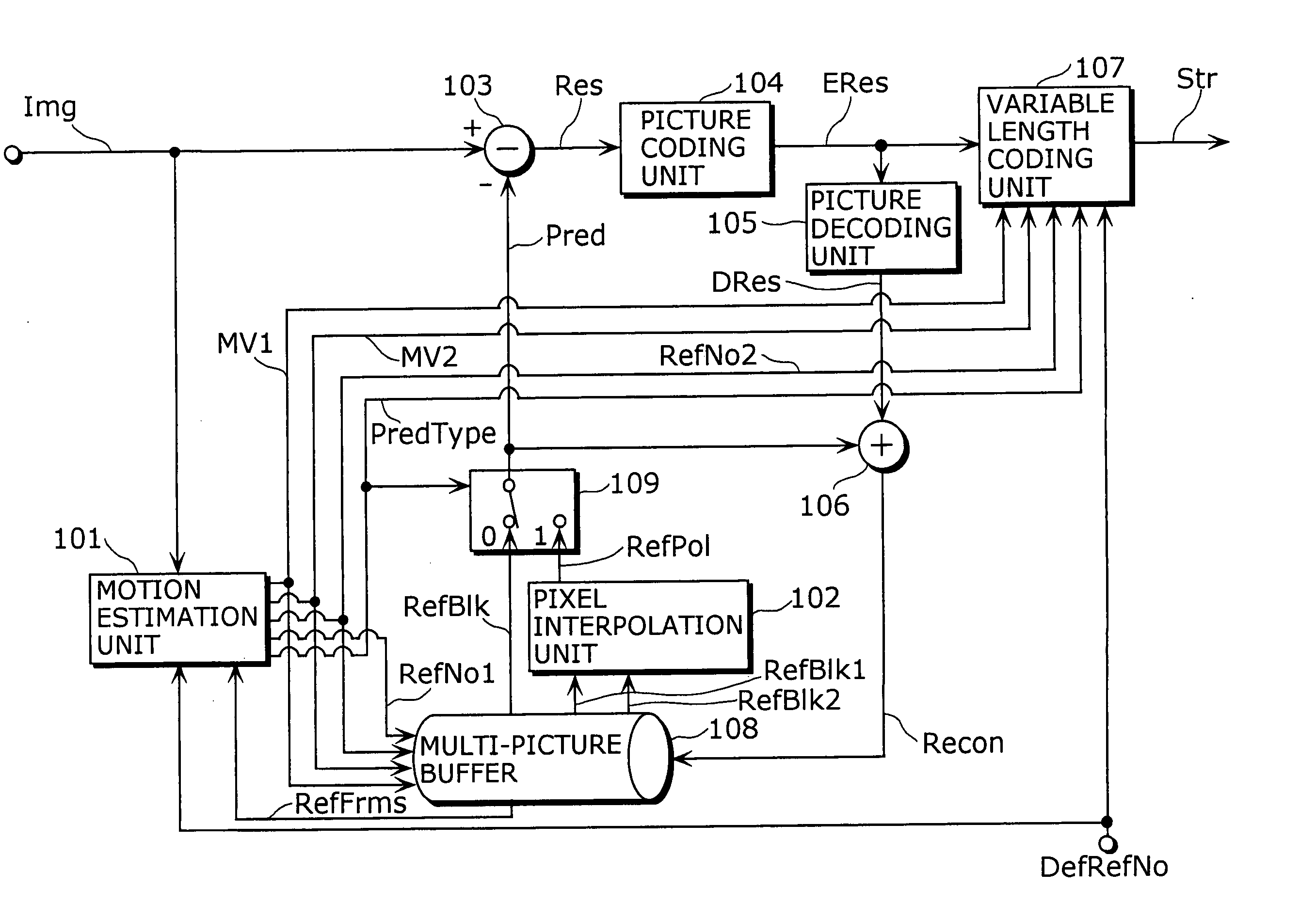
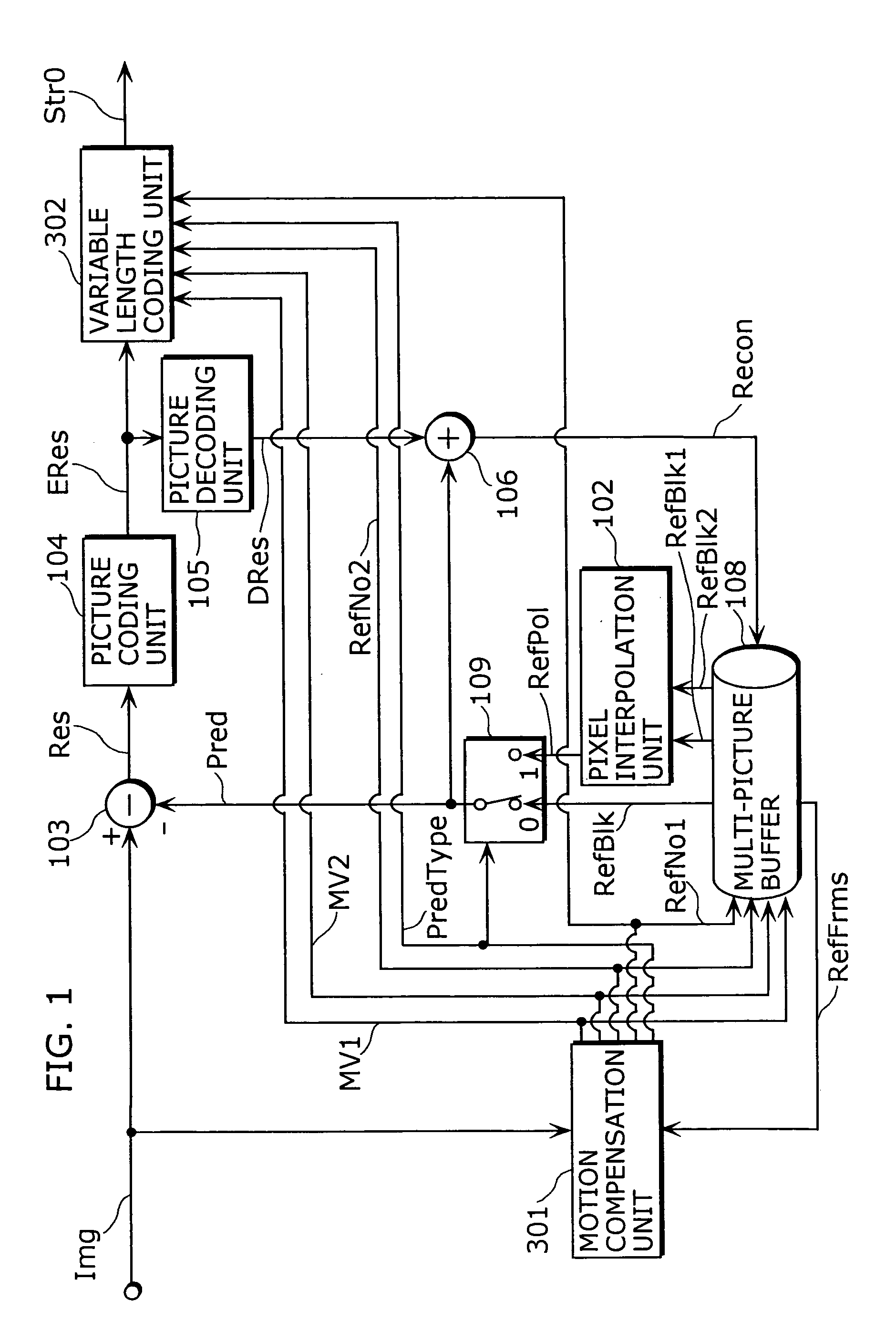
Moving picture coding method and a moving picture decoding method
ActiveUS20040146105A1Valid encodingReduce processing burdenColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVariable-length codePattern recognition
A moving picture coding apparatus includes a motion estimation unit (101) for performing motion estimation by fixing the one of two reference pictures as a reference picture indicated by an inputted default reference picture number DefRefNo and a variable length coding unit (107) for performing variable length coding on coded residual data ERes, a prediction type PredType, a reference picture number RefNo2 and motion vectors MV1, MV2 on a block-by-block basis, and outputting them as coded moving picture data Str.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
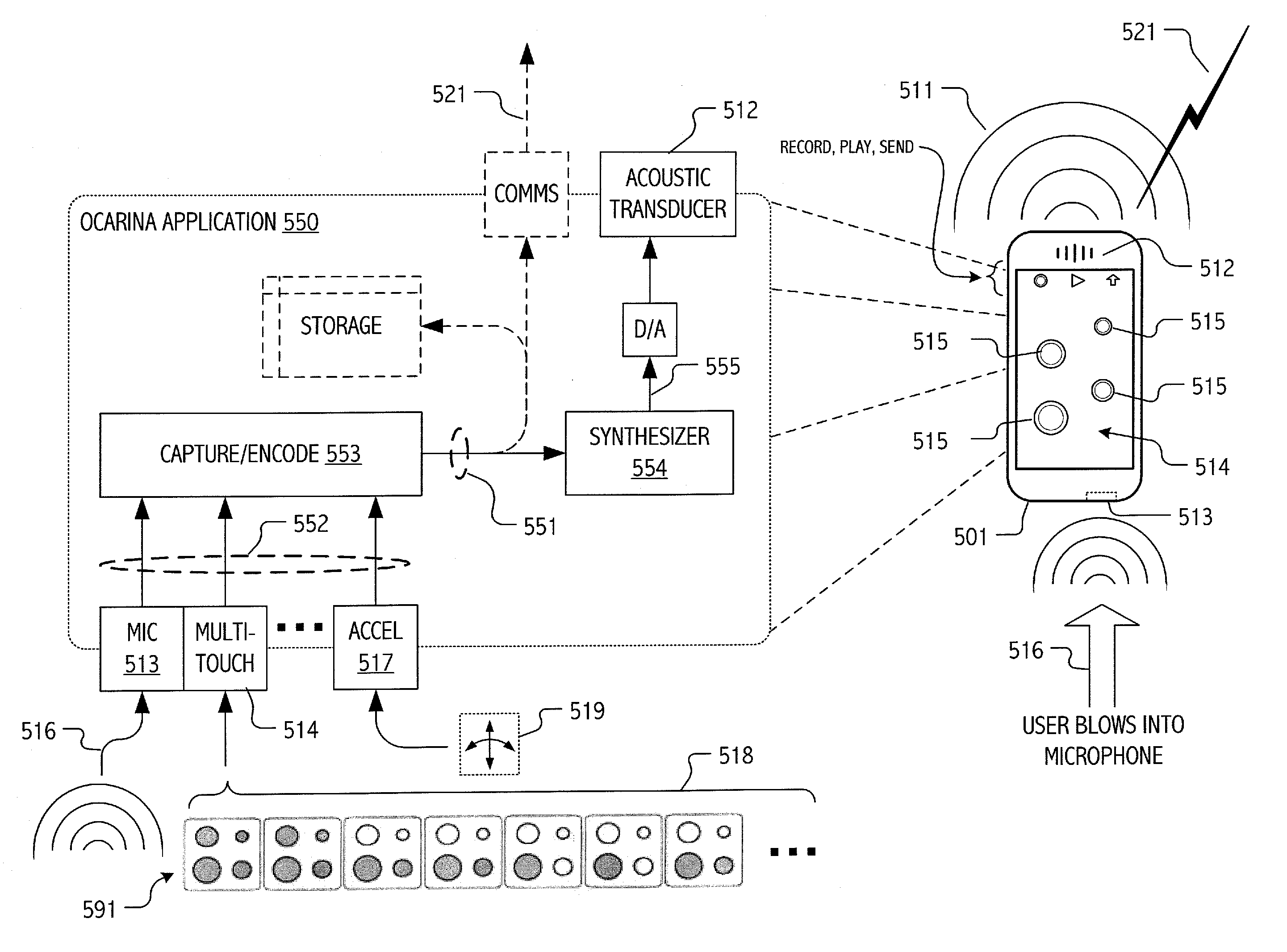
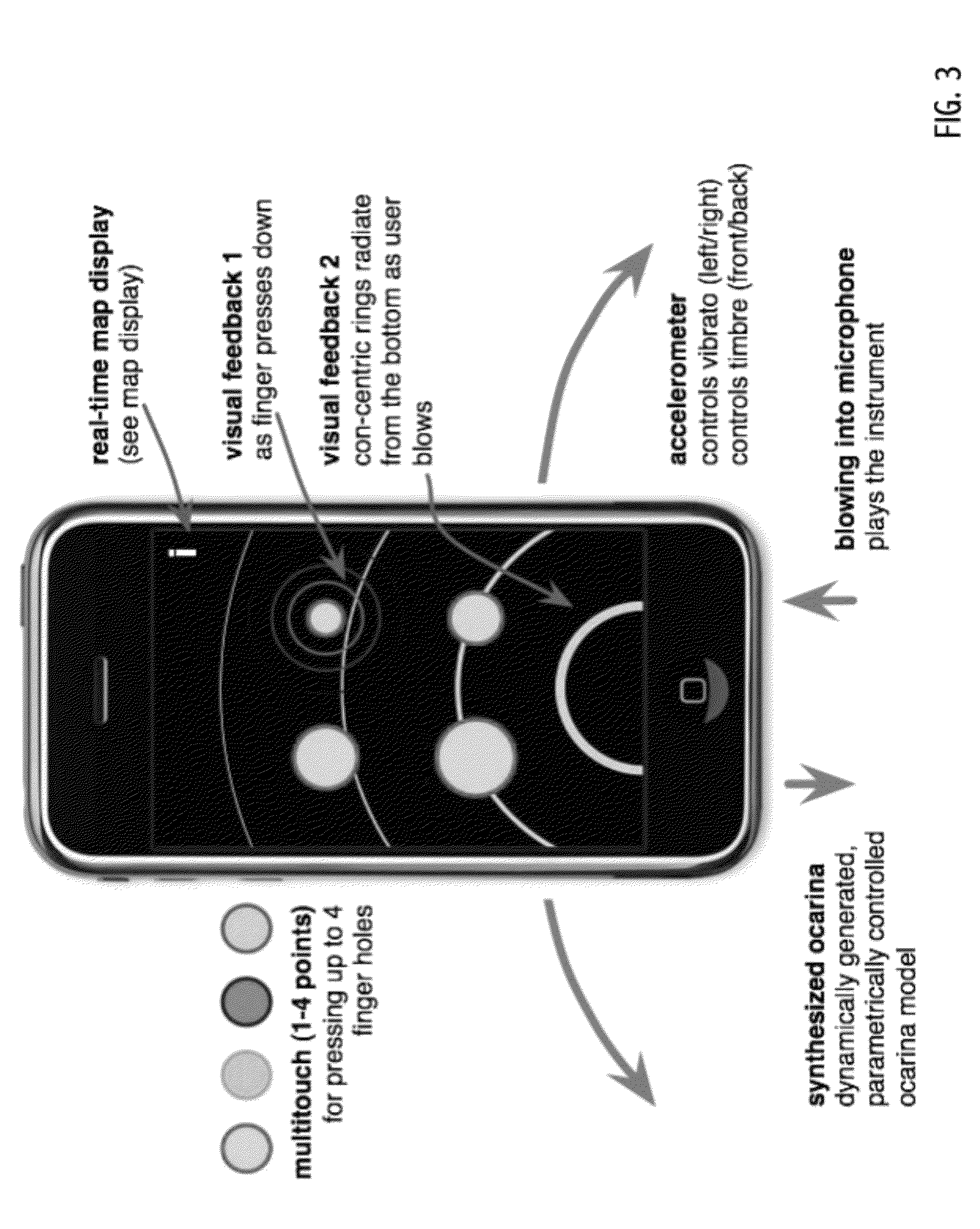
System and method for capture and rendering of performance on synthetic musical instrument
ActiveUS8222507B1Improve performanceFacilitate efficient encoding and communicationElectrophonic musical instrumentsComputer scienceHandheld equipment
Techniques have been developed for capturing and rendering musical performances on handheld or other portable devices using signal processing techniques suitable given the somewhat limited capabilities of such devices and in ways that facilitate efficient encoding and communication of such captured performances via wireless networks. The developed techniques facilitate the capture, encoding and use of gesture streams for rendering of a musical performance. In some embodiments, a gesture stream encoding facilitates audible rendering of the musical performance locally on the portable device on which the musical performance is captured, typically in real time. In some embodiments, a gesture stream efficiently codes the musical performance for transmission from the portable device on which the musical performance is captured to (or toward) a remote device on which the musical performance is (or can be) rendered. Indeed, is some embodiments, a gesture stream so captured and encoded may be rendered both locally and on remote devices using substantially identical or equivalent instances of a digital synthesis of the musical instrument executing on the local and remote devices.
Owner:SMULE
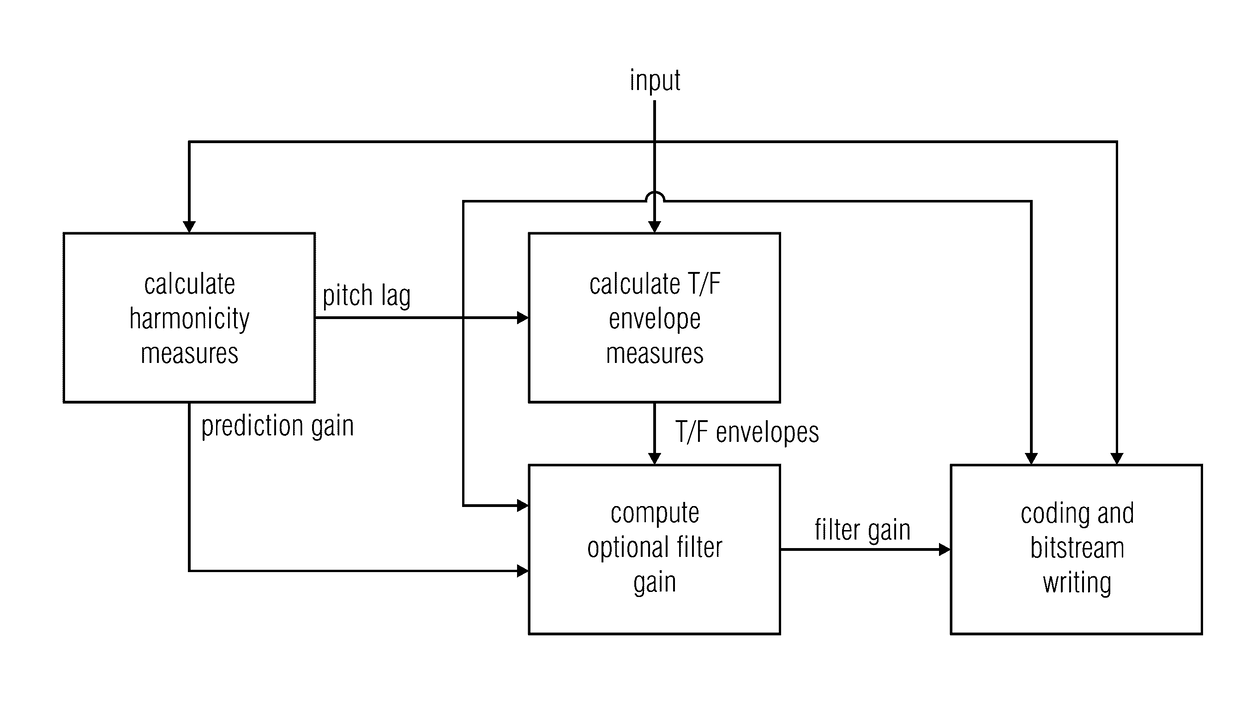
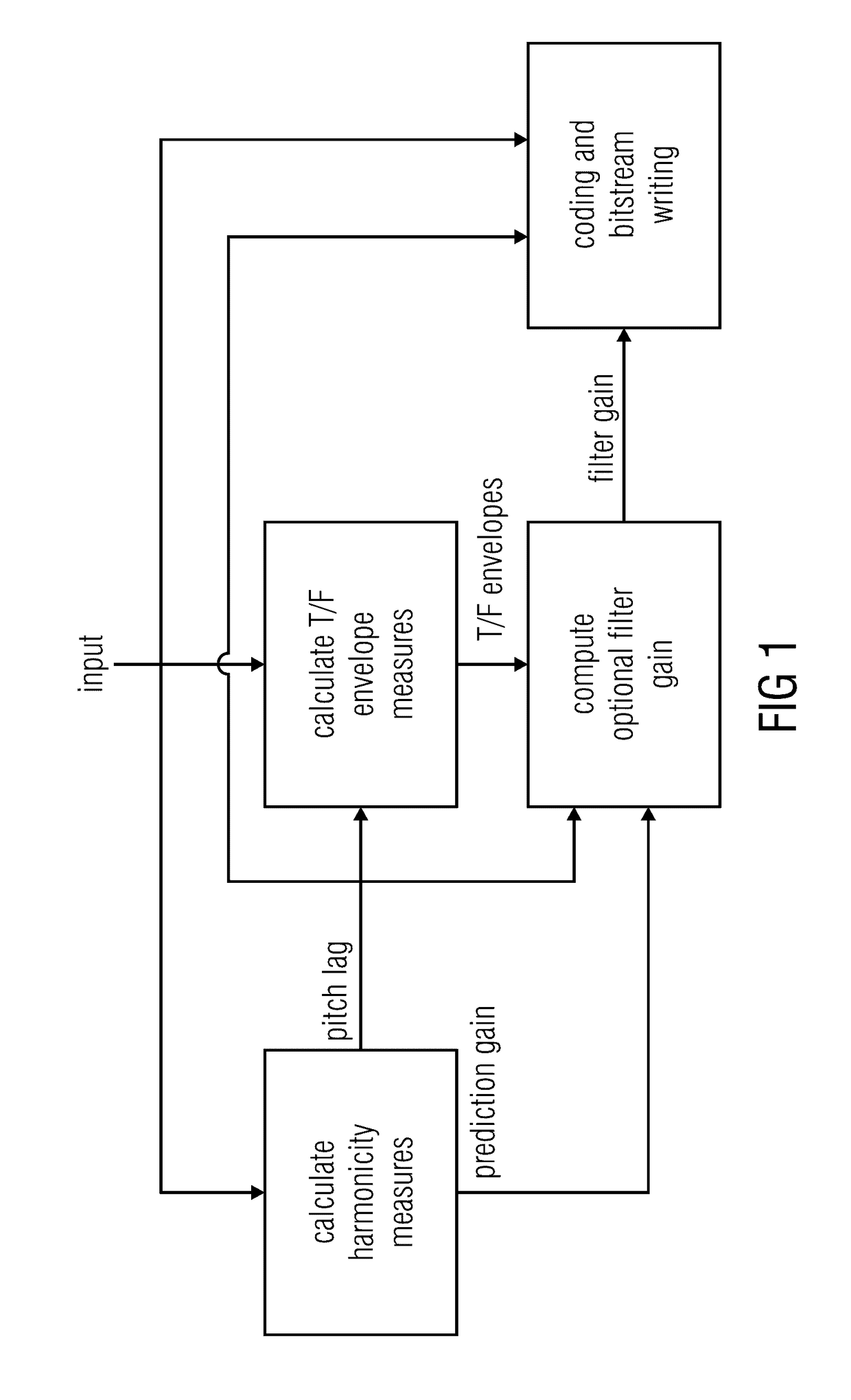
Harmonicity-dependent controlling of a harmonic filter tool
The coding efficiency of an audio codec using a controllable—switchable or even adjustable—harmonic filter tool is improved by performing the harmonicity-dependent controlling of this tool using a temporal structure measure in addition to a measure of harmonicity in order to control the harmonic filter tool. In particular, the temporal structure of the audio signal is evaluated in a manner which depends on the pitch. This enables to achieve a situation-adapted control of the harmonic filter tool so that in situations where a control made solely based on the measure of harmonicity would decide against or reduce the usage of this tool, although using the harmonic filter tool would, in that situation, increase the coding efficiency, the harmonic filter tool is applied, while in other situations where the harmonic filter tool may be inefficient or even destructive, the control reduces the appliance of the harmonic filter tool appropriately.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
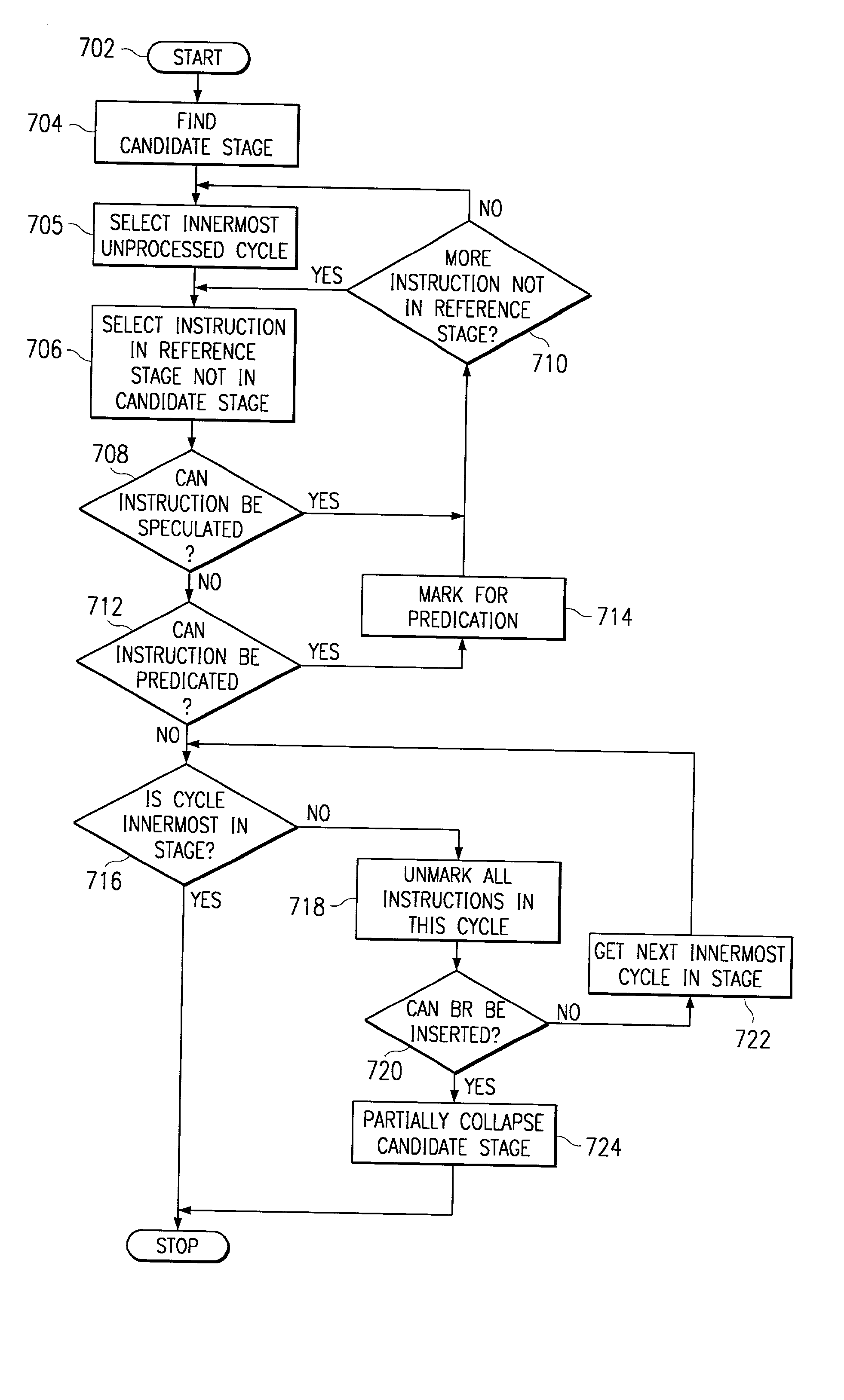
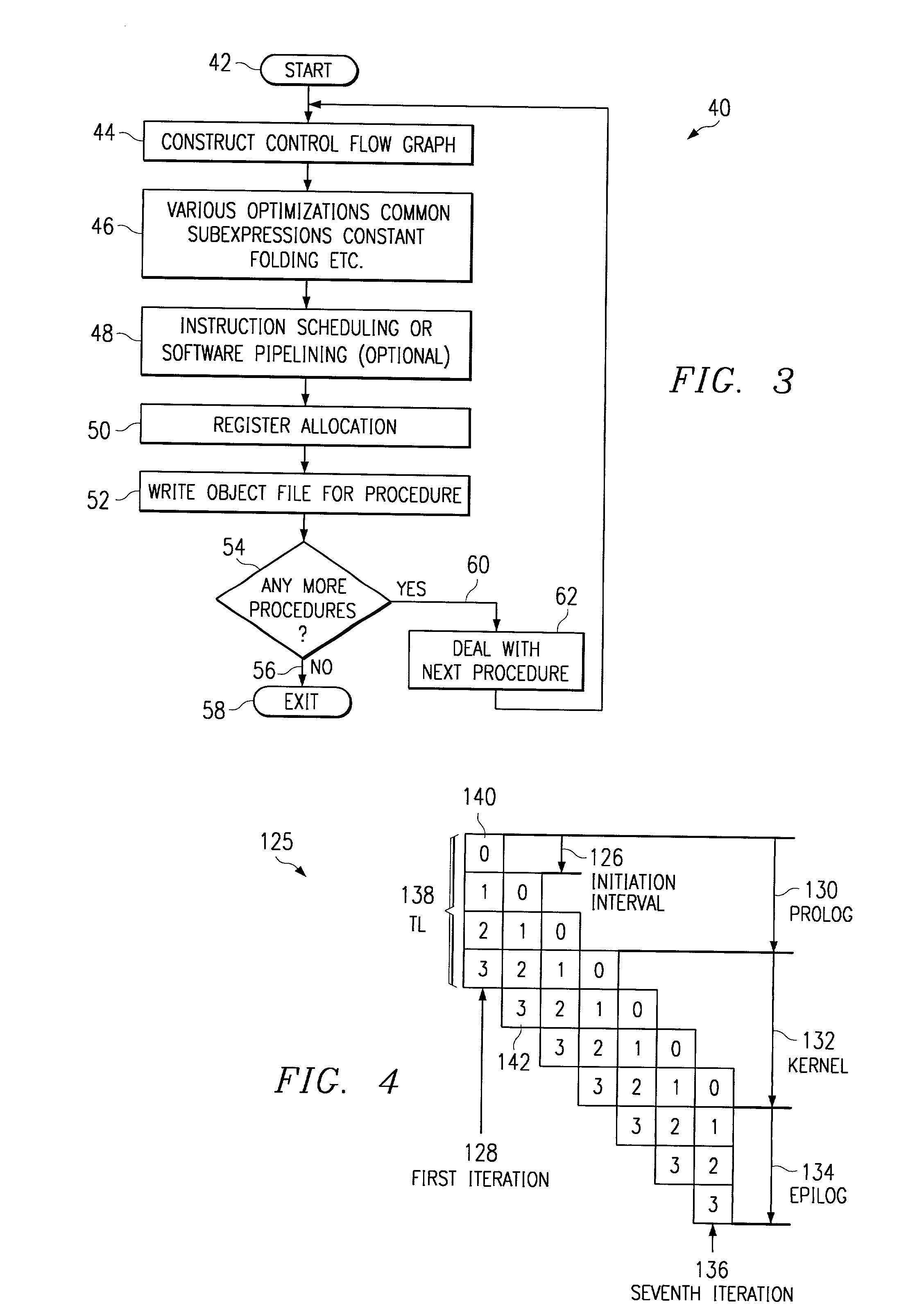
Method for collapsing the prolog and epilog of software pipelined loops
InactiveUS20020112228A1Suppresses increase in code sizeValid encodingSoftware engineeringProgram controlParallel computingSoftware
A method for reducing a code size of a software pipelined loop, the software pipelined loop having a kernel and an epilog. The method includes first evaluating a stage of the epilog. This includes selecting a stage of the epilog to evaluate (504) and evaluating an instruction in a reference stage. This includes identifying an instruction in the reference stage that is not present in the selected stage of the epilog (506) and determining if the identified instruction can be speculated (508). If the identified instruction can be speculated, such is noted. If the instruction cannot be speculated, it is determined whether the identified instruction can be predicated (512). If the instruction can be predicated, it is marked as needing predication (514). Next, it is determined if another instruction in the reference stage is not present in the selected stage of the epilog (510). If there is, the instruction evaluation is repeated. If there is another stage of the epilog to evaluate, the evaluation is repeated (518).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Scalable video coding using base-layer hints for enhancement layer motion parameters
ActiveUS20160014430A1Improving available qualityMotion-compensated predictionColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureMotion parameter
Owner:GE VIDEO COMPRESSION LLC
Method and apparatus for transmitting channel quality control information in wireless access system
ActiveCN102647248AValid encodingSend efficientlyError prevention/detection by using return channelSignal allocationTelecommunicationsComputer network
Provided is a method for transmitting channel quality control information using two transport blocks in a wireless access system that supports hybrid automatic retransmit request (HARQ). The method may include the steps of receiving a physical downlink control channel (PDCCH) signal including downlink control information (DCI); calculating the number of coded symbols, Q', required to transmit the channel quality control information using the DCI; and transmitting the channel quality control information through a physical uplink shared channel (PUSCH) on the basis of the number of coded symbols.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Image encoding method, image decoding method, image encoding device, image decoding device, integrated circuit, and program
InactiveCN102197651AValid encodingEfficient decodingPulse modulation television signal transmissionDigital video signal modificationDecoding methodsImaging quality
Provided is an image encoding method which can effectively encode an image while maintaining the image quality at a certain level. The image encoding method encodes an image in a block unit. The method includes: a conversion step (S1201) which converts a two-dimensionally arranged pixel value in the block to be encoded into a two-dimensionally arranged conversion coefficient according to the two-dimensionally arranged conversion coefficient; a scan order determination step (S1202) which determines the scan order for scanning the two-dimensionally arranged conversion coefficient; a scan step (S1203) which successively scans the two-dimensionally arranged conversion coefficient in accordance with the scan order so as to generate a one-dimensionally arranged conversion coefficient string; and an encoding step (S1204) which encodes the one-dimensionally arranged conversion coefficient string.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and device for coding residual signal in video coding system
ActiveUS20180288409A1Improve coding efficiencyReduce data volumeDigital video signal modificationInter frameBitstream
An image decoding method according to the present invention comprises the steps of: deriving quantized transform coefficients by unit of sub-blocks in a transform unit on the basis of residual information included in a bitstream; deriving transform coefficients on the basis of the quantized transform coefficients; generating a residual sample on the basis of the transform coefficients; generating a prediction sample on the basis of an inter prediction or an intra prediction; and restoring an image on the basis of the residual sample and the prediction sample. According to the present invention, a quantity of data required for a residual signal can be reduced, and an overall coding efficiency can be improved.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Integrated development environment for the development of electronic signal testing strategies
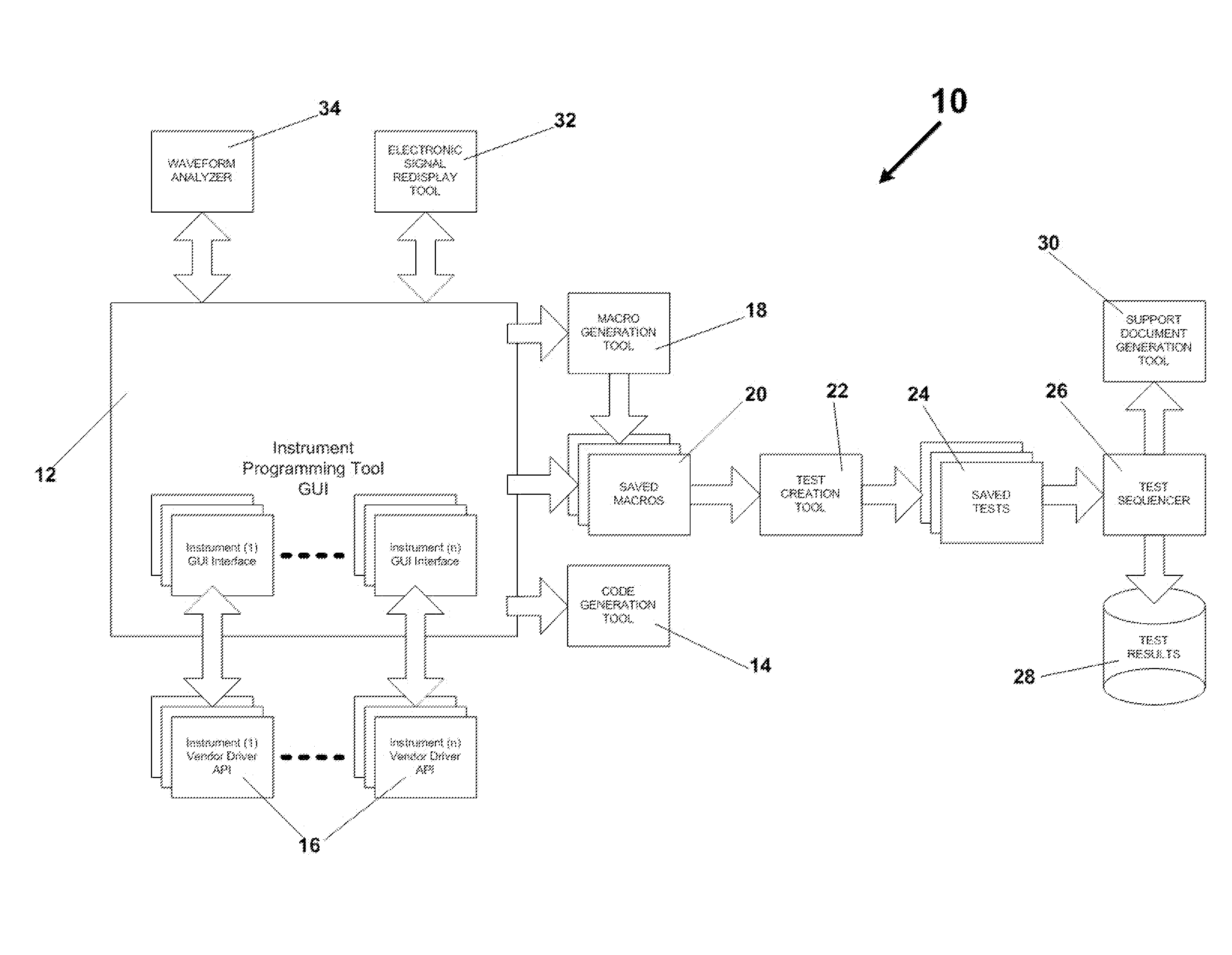
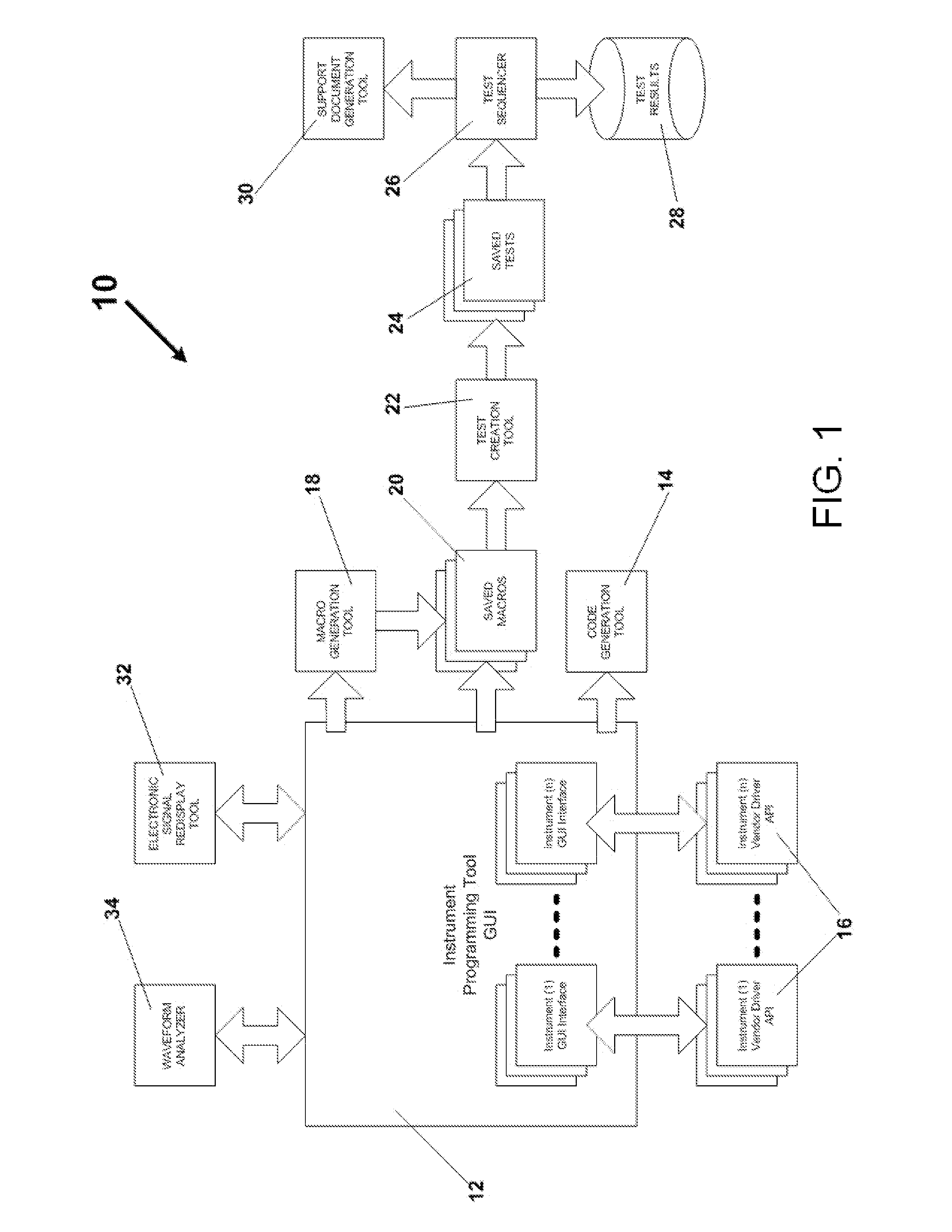
ActiveUS8356282B1Eliminating unnecessary replicationOptimize test throughputError detection/correctionVisual/graphical programmingData loggerInstrumentation
Integrated application of specific CASE tools that allow a user to accomplish instrument programming and control when generating, capturing and / or analyzing electronic signals, and in doing so automatically generate automation code to replicate a desired instrument setup, acquisition, analysis and sequence control. The CASE tools include, but are not limited to, GUI instrument programming tools, an electronic signal redisplay tool, a waveform analyzer tool, automated code generation tools, macro generation tools, macro and sequence playback tools, a test creation tool, a test sequencer tool, a decision engine that may be part of the test sequencer tool, and test result data logger. A method for analyzing electronic signals that enables multiple tests to be performed after a single signal acquisition, and enables results from the multiple tests to be analyzed is also disclosed.
Owner:ADVANCED TESTING TECH
Method and apparatus for audio encoding and decoding using wideband psychoacoustic modeling and bandwidth extension
ActiveUS7953605B2High frequency resolutionAccurate reconstructionSpeech analysisRadio transmissionMulti bandBandwidth extension
Owner:AUDIO TECH & CODECS
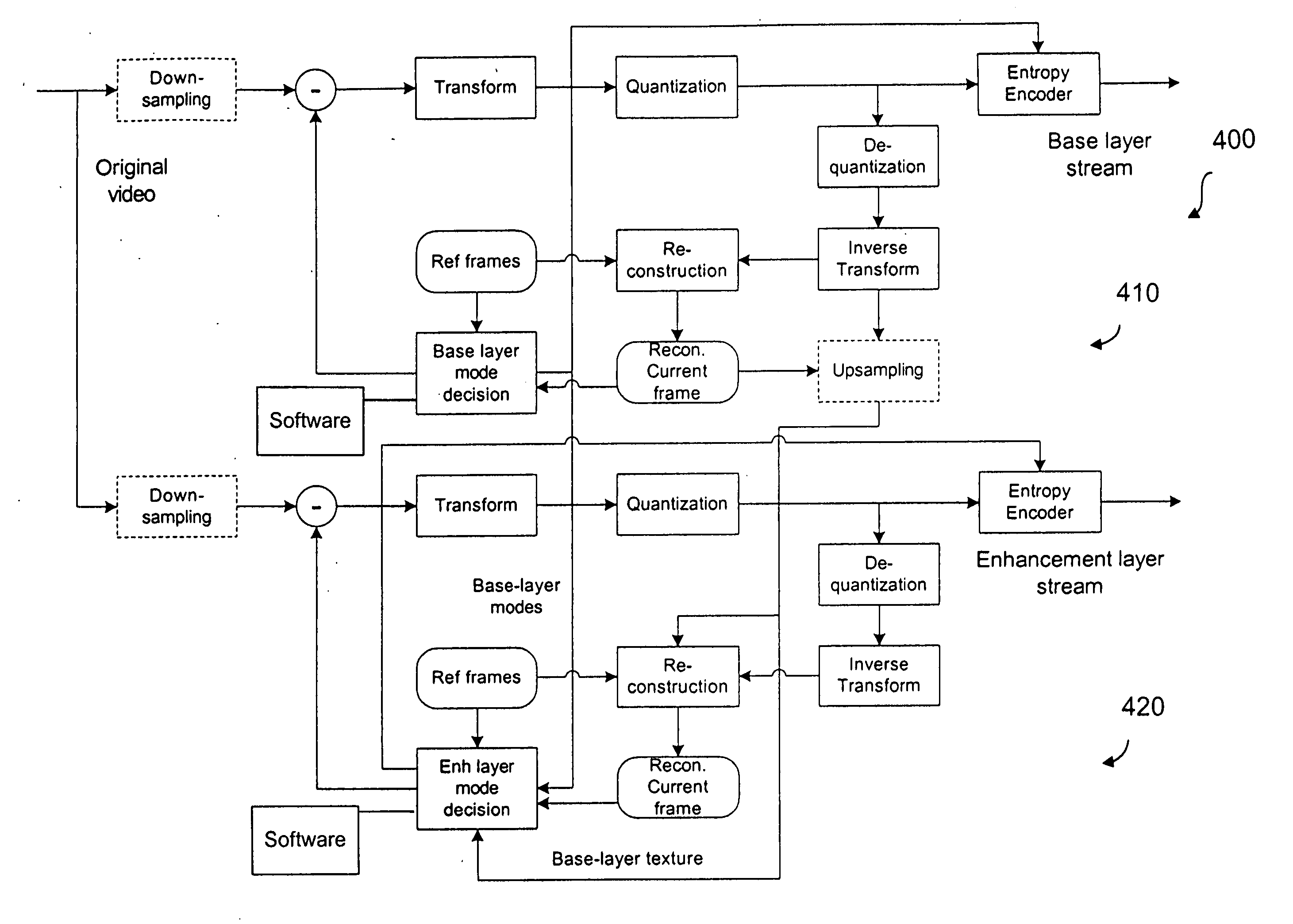
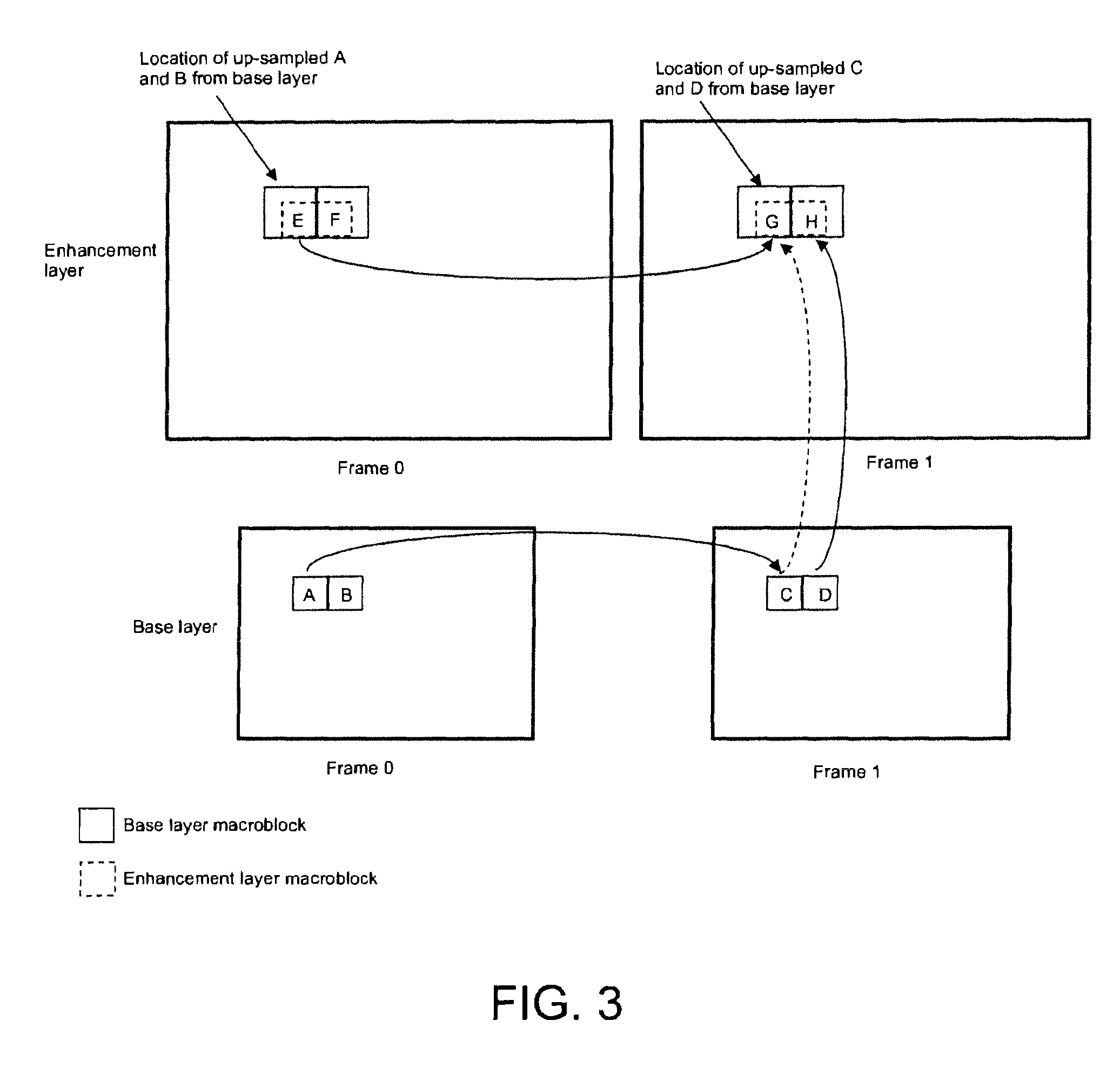
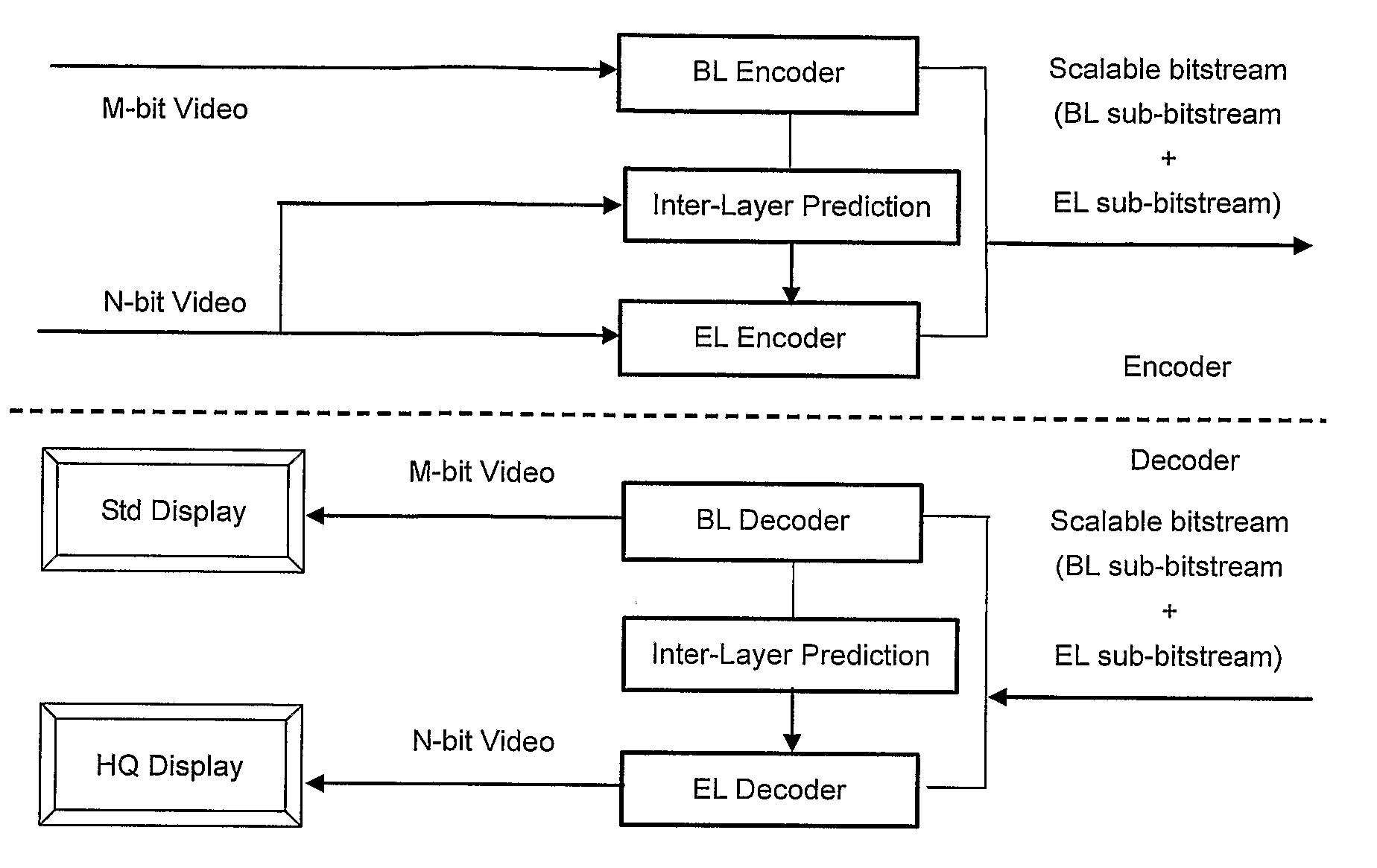
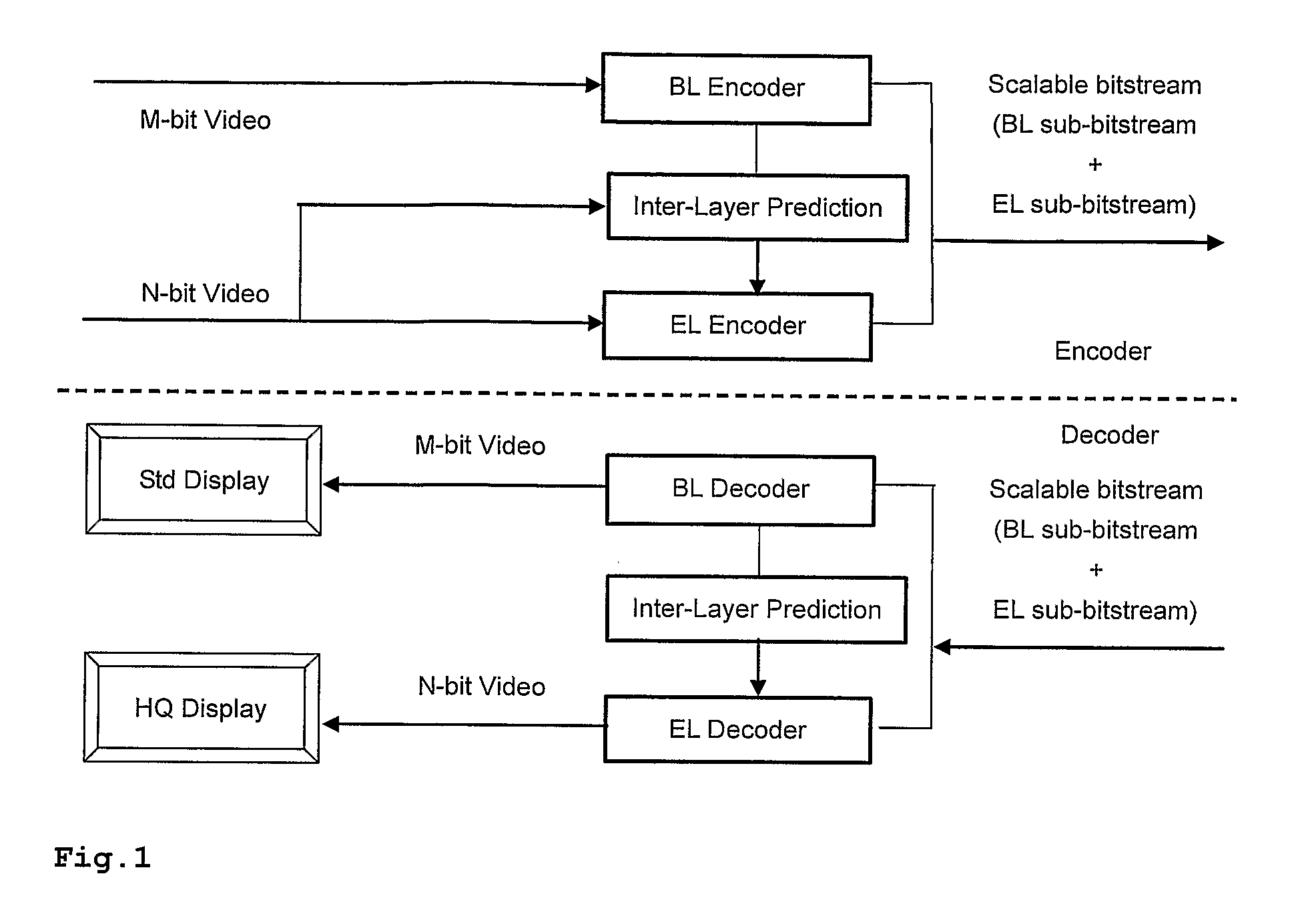
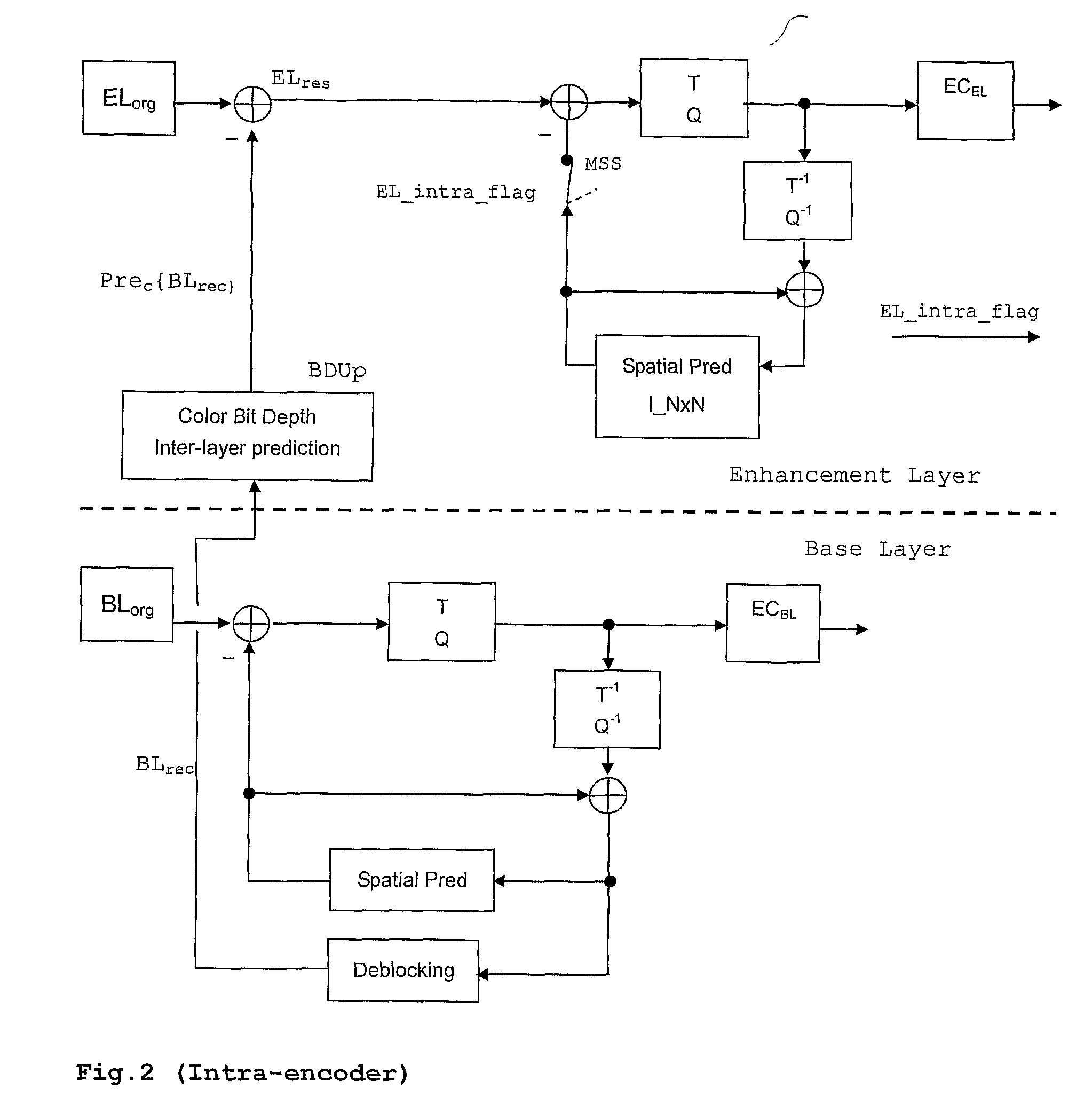
Method and apparatus for encoding and/or decoding bit depth scalable video data using adaptive enhancement layer prediction
InactiveUS20100111167A1Increase the number ofRaise the possibilityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionSelf adaptiveMode selection
A scalable video bitstream may have an H.264 / AVC compatible base layer (BL) and a scalable enhancement layer (EL), where scalability refers to color bit depth. The SVC standard allows spatial inter-layer prediction, wherein a residual in the EL is generated which is then intra coded. Another spatial intra-coding mode for EL is pure intra coding (I_N×N). The invention discloses a new intra-coding mode and two new inter coding modes, particularly for bit depth scalability. The new intra coding mode uses encoding of the residual between upsampled reconstructed BL and original EL, using mode selection. Two possible modes are residual prediction from BL and additional intra-coding of this residual. The new inter coding modes use also prediction of EL from reconstructed BL. In a first inter coding mode, the residual is encoded using Motion Estimation based on this residual. In a second inter coding mode, the residual is encoded using upsampled motion information from the BL.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL VC HLDG INC
Efficient and scalable parametric stereo coding for low bitrate audio coding applications
ActiveUS20060023891A1Reduce riskGuaranteed normal transmissionSpeech analysisPseudo-stereo systemsVocal tractStereo image
The present invention provides improvements to prior art audio codecs that generate a stereo-illusion through post-processing of a received mono signal. These improvements are accomplished by extraction of stereo-image describing parameters at the encoder side, which are transmitted and subsequently used for control of a stereo generator at the decoder side. Furthermore, the invention bridges the gap between simple pseudo-stereo methods, and current methods of true stereo-coding, by using a new form of parametric stereo coding. A stereo-balance parameter is introduced, which enables more advanced stereo modes, and in addition forms the basis of a new method of stereo-coding of spectral envelopes, of particular use in systems where guided HFR (High Frequency Reconstruction) is employed. As a special case, the application of this stereo-coding scheme in scalable HFR-based codecs is described.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Method and Apparatus for Processing a Signal
ActiveUS20090161795A1Valid encodingMaximize transfer efficiencyTelevision system detailsModulated-carrier systemsAudio frequencyBroadcast transmission
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for processing a signal. An object of the present invention devised to solve the problem lies on a method and apparatus for processing a signal, which allows a signal having optimized signal transmission efficiency to be transmitted / received. According to an aspect of the present invention, there is provided a method of processing a signal including receiving a broadcasting signal including audio data coded using a pilot reference value and a pilot difference value, demodulating the broadcasting signal in consideration of a scattered pilot which varies over time and a continual pilot which is fixed over time in a frame of the received broadcasting signal and decoding the demodulated signal to obtain a broadcasting transmission stream, demultiplexing the broadcasting transmission stream to obtain coded audio data in an Internet protocol (IP) packet and an identifier for identifying a method of decoding the audio data, obtaining the pilot reference value corresponding to a plurality of data and the pilot difference value corresponding to the pilot reference value from the coded audio data and obtaining the audio data using the pilot reference value and the pilot difference value.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Moving picture coding method, moving picture decoding method and program
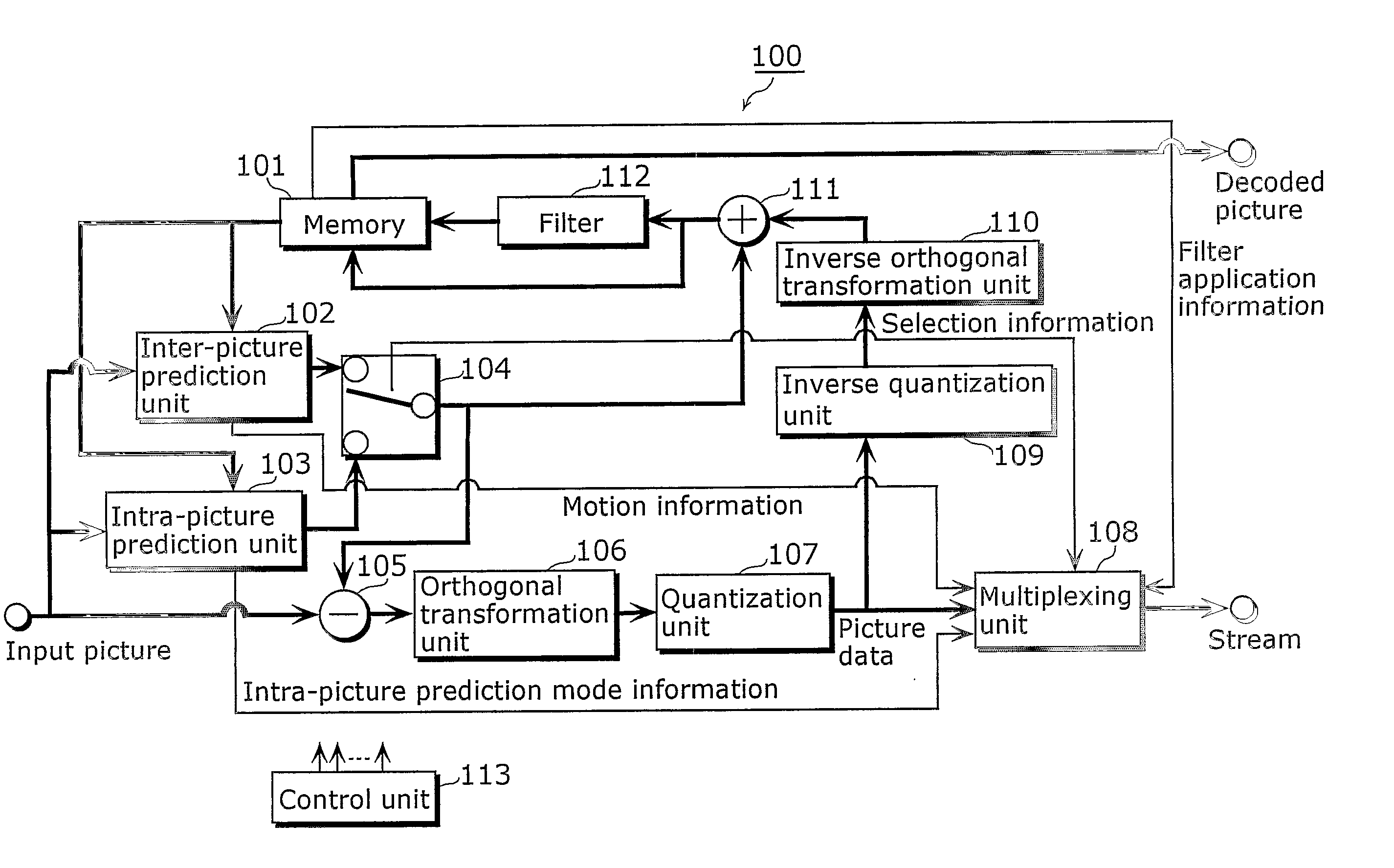
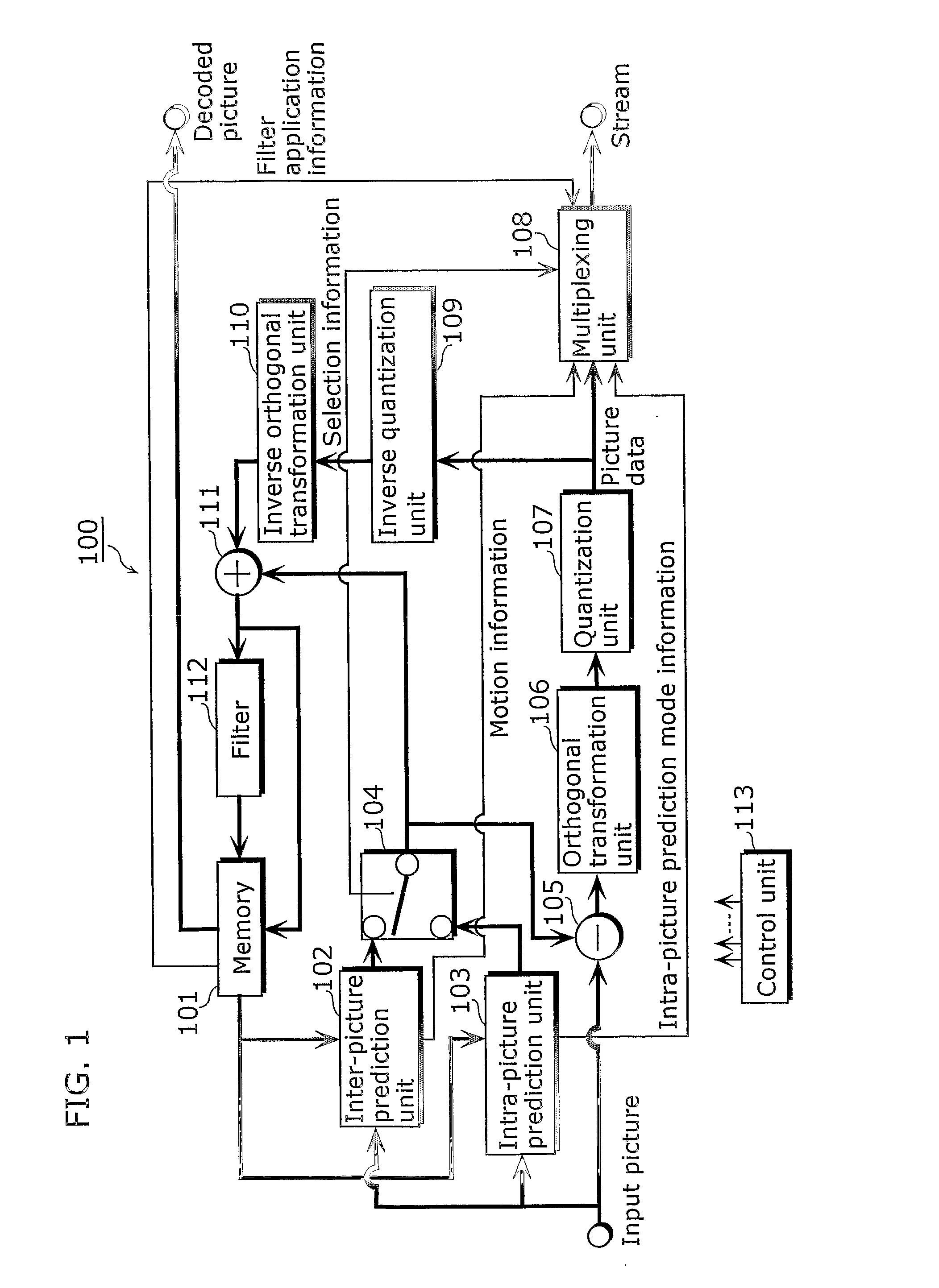
InactiveUS20070002947A1Without impairing quality of pictureQuality improvementColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDecoding methodsComputer graphics (images)
The present invention provides a picture coding method for predictively coding a picture with reference to a picture obtained from pictures which are coded and decoded; performing filtering processing (112) on a decoded picture; storing a filtered picture in a memory as a reference picture, out of two pictures: a filtered picture and an unfiltered picture, said filtered picture being a filtered decoded picture and said unfiltered picture being the decoded picture; and storing an unfiltered picture in the memory as a picture for output out of the two pictures.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Efficient and scalable parametric stereo coding for low bitrate audio coding applications
InactiveUS20100046762A1Reduce riskGuaranteed normal transmissionSpeech analysisTransmissionFrequency spectrumVocal tract
The present invention provides improvements to prior art audio codecs that generate a stereo-illusion through post-processing of a received mono signal. These improvements are accomplished by extraction of stereo-image describing parameters at the encoder side, which are transmitted and subsequently used for control of a stereo generator at the decoder side. Furthermore, the invention bridges the gap between simple pseudo-stereo methods, and current methods of true stereo-coding, by using a new form of parametric stereo coding. A stereo-balance parameter is introduced, which enables more advanced stereo modes, and in addition forms the basis of a new method of stereo-coding of spectral envelopes, of particular use in systems where guided HFR (High Frequency Reconstruction) is employed. As a special case, the application of this stereo-coding scheme in scalable HFR-based codecs is described.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com