Patents
Literature
235 results about "Quantization matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
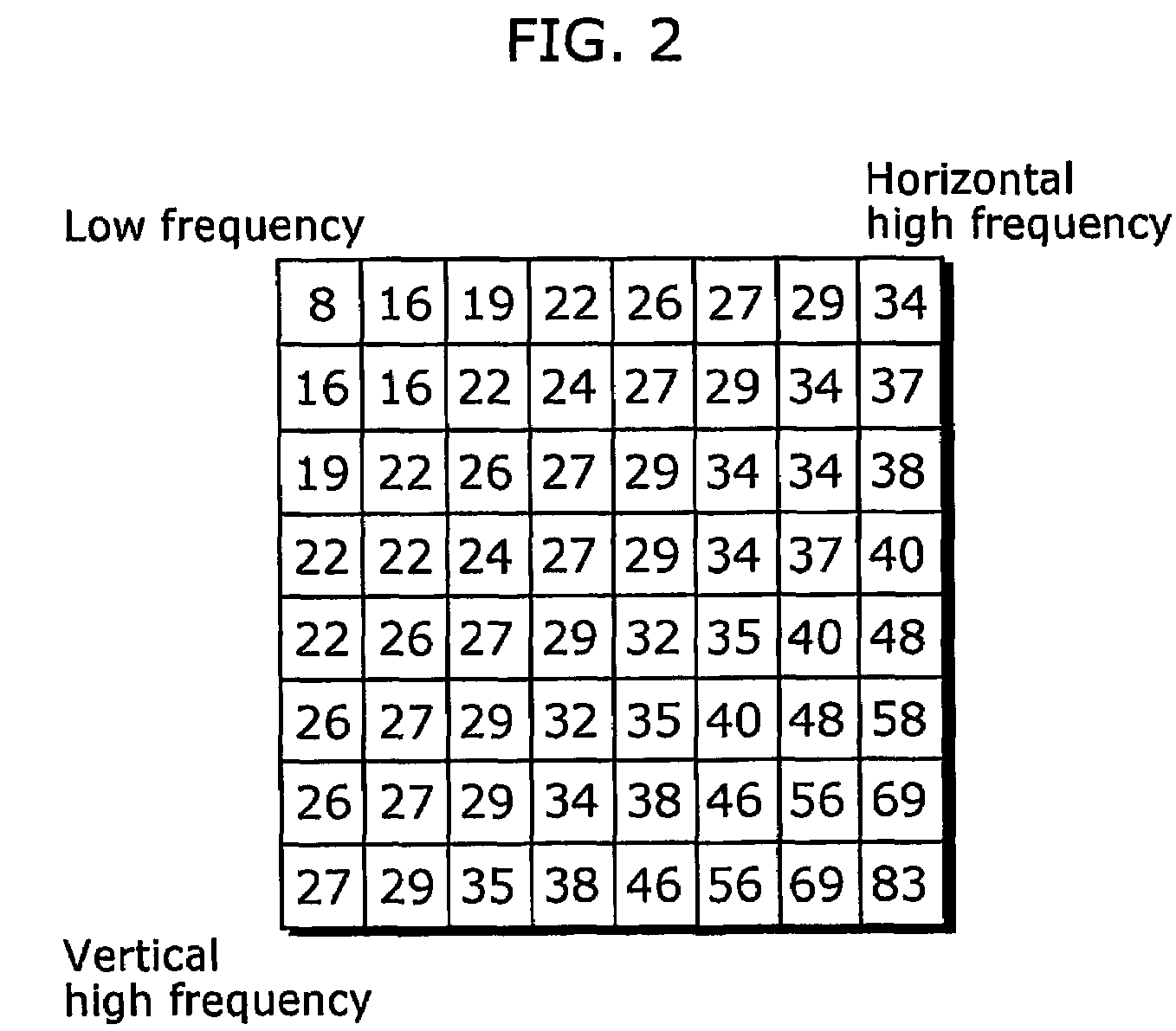
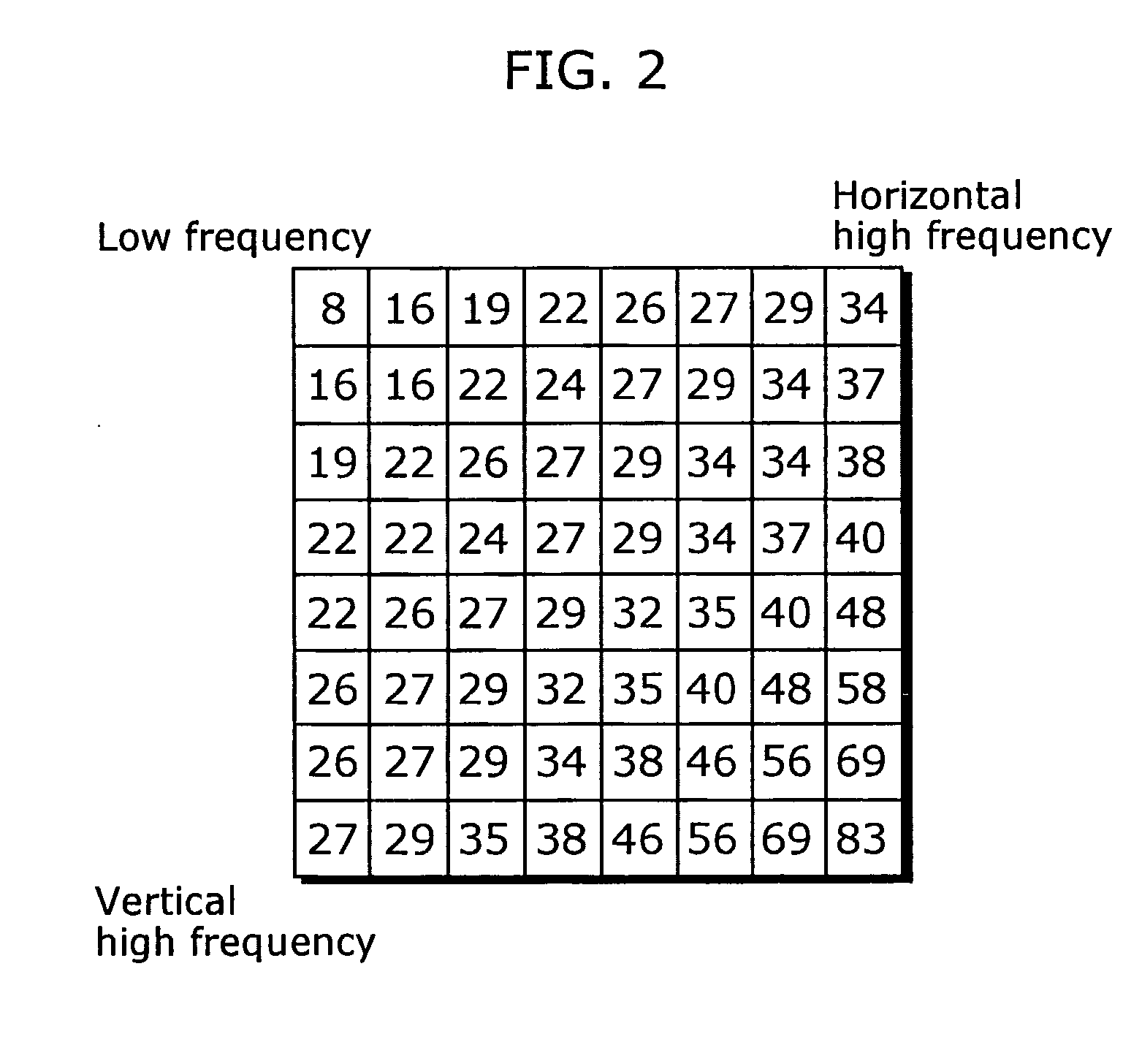
The quantization matrix is designed to provide more resolution to more perceivable frequency components over less perceivable components (usually lower frequencies over high frequencies) in addition to transforming as many components to 0, which can be encoded with greatest efficiency.
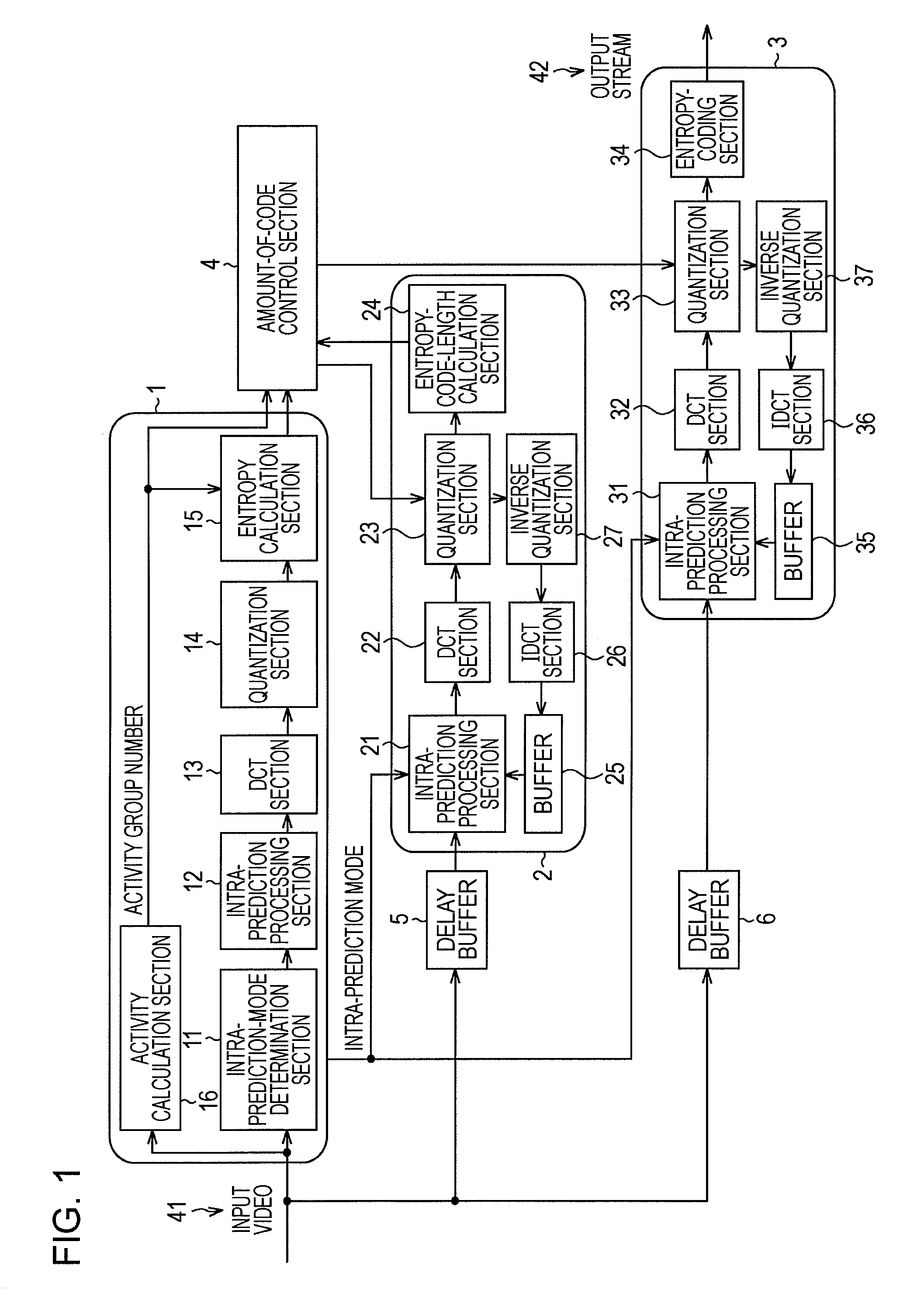
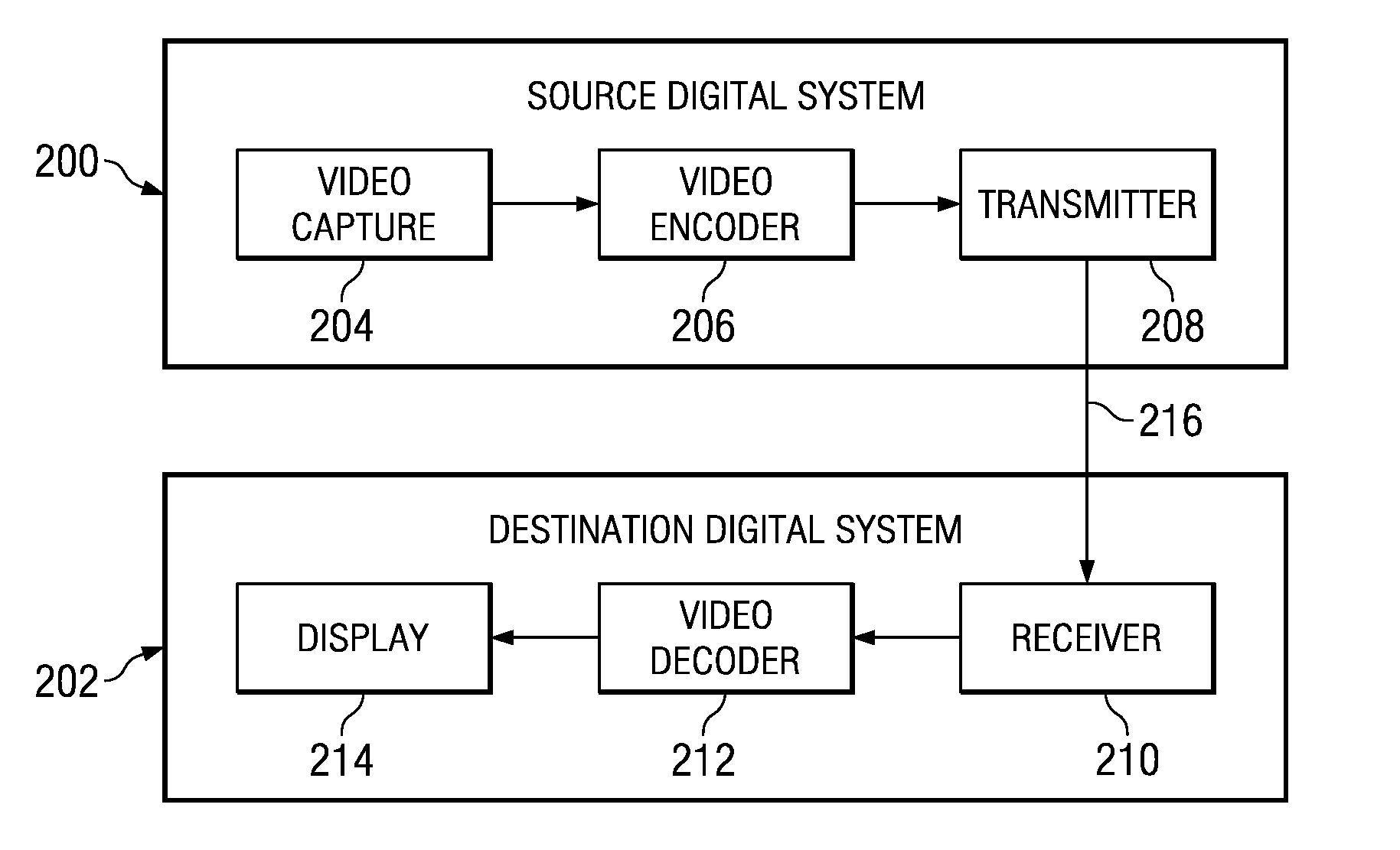
Video compression and decompression using dynamic quantization and/or encoding
InactiveUS6249614B1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionQuantization matrix
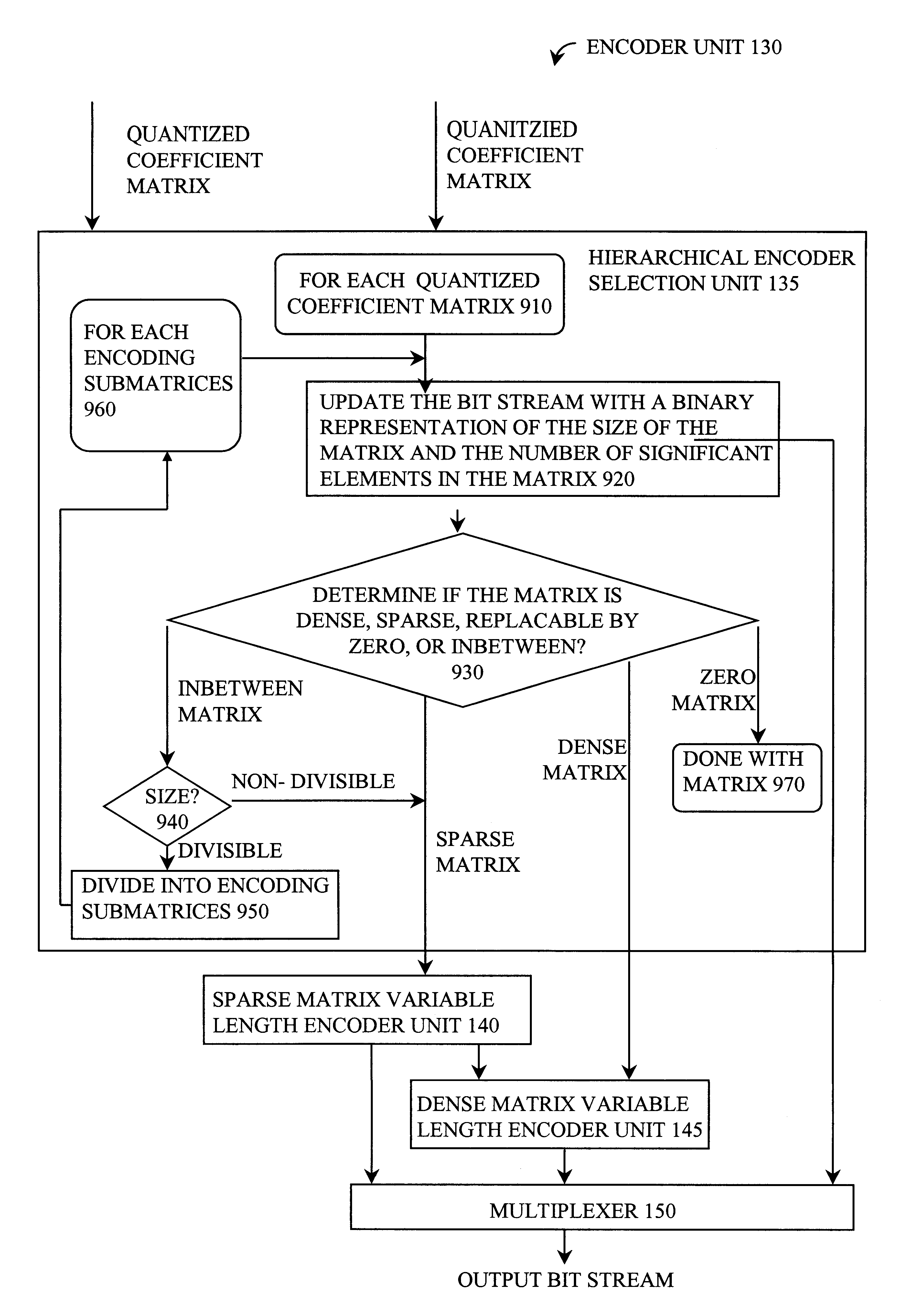
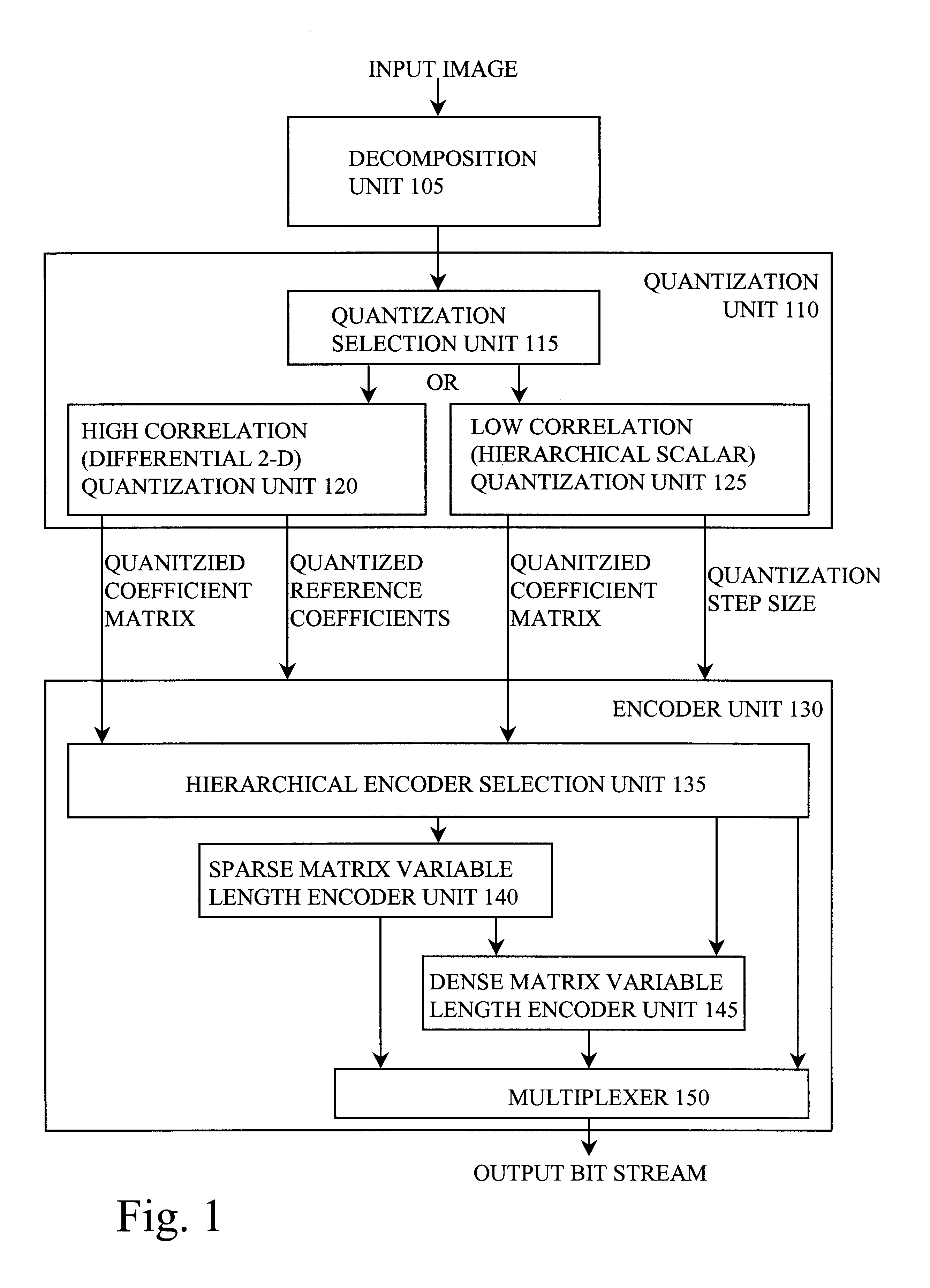
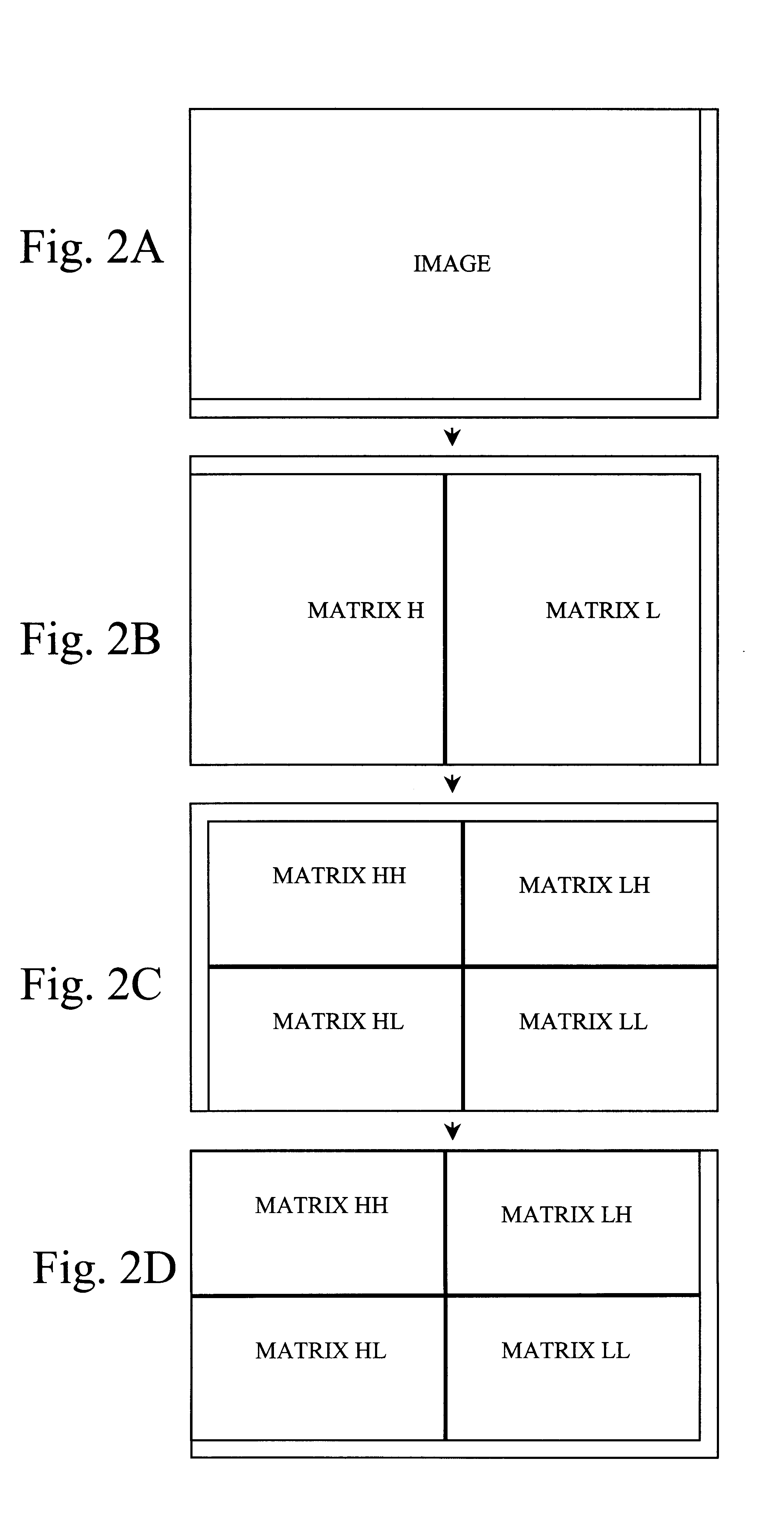
A method and apparatus for performing video compression and decompression using dynamic quantization and / or encoding. According to one aspect of the compression method, an image is recursively filtered into its constituent components each represented by a matrix of coefficients. Next, the level of correlation of a first of the matrices of coefficients is determined. Based on the level of correlation of this first coefficient matrix, one of a first quantization technique and a second quantization technique is selected. The first coefficient matrix is then quantized using the selected quantization technique.According to another aspect of the compression method, an image is digitally filtered into its constituent components, each represented by a matrix of coefficients. At least certain matrices are quantized to generated a first quantized matrix. The first quantized matrix is then recursively divided until the first quantized matrix or each of the resulting submatrices is sufficiently dense or sufficiently sparse. Each of the sufficiently dense matrices are encoded using a first technique, while each of the sufficiently sparse matrices are encoded a second technique.
Owner:XVD TECH HLDG LTD IRELAND
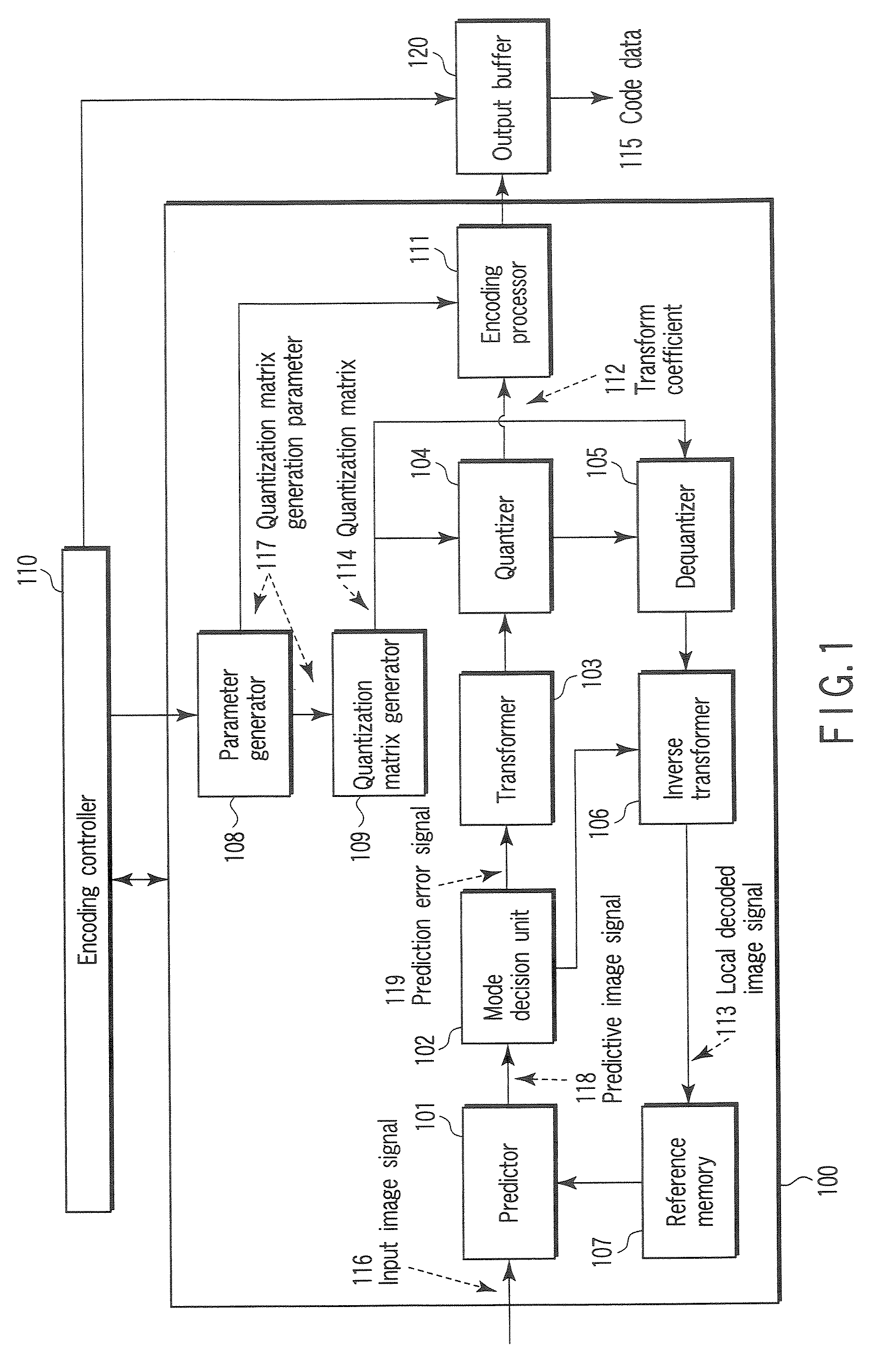
Video encoding/decoding method and apparatus
InactiveUS20070189626A1Character and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionVideo encoding
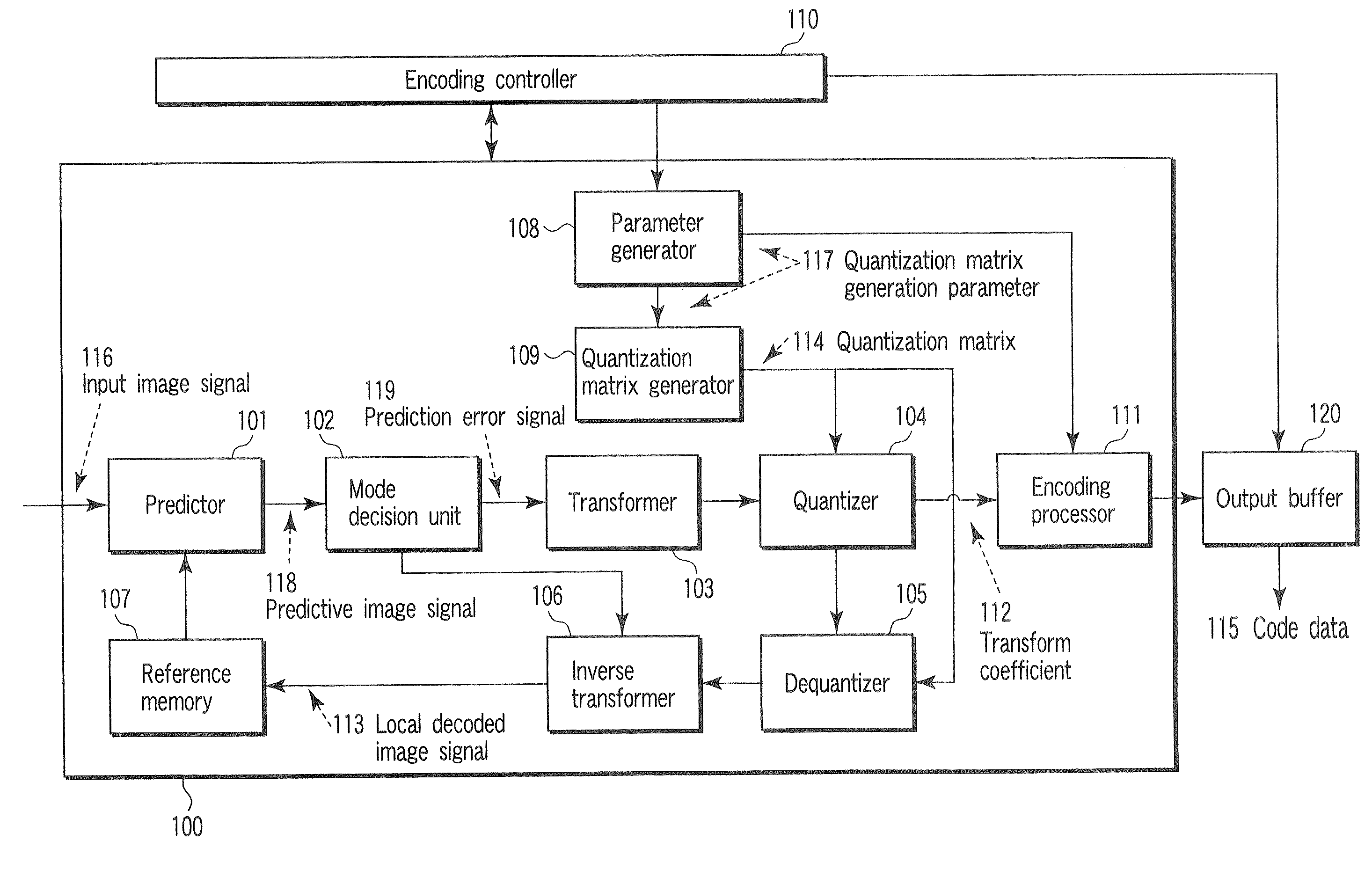
A video encoding method includes generating a quantization matrix using a function concerning generation of the quantization matrix and a parameter relative to the function, quantizing a transform coefficient concerning an input image signal using the quantization matrix to generate a quantized transform coefficient, and encoding the parameter and the quantized transform coefficient to generate a code signal.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
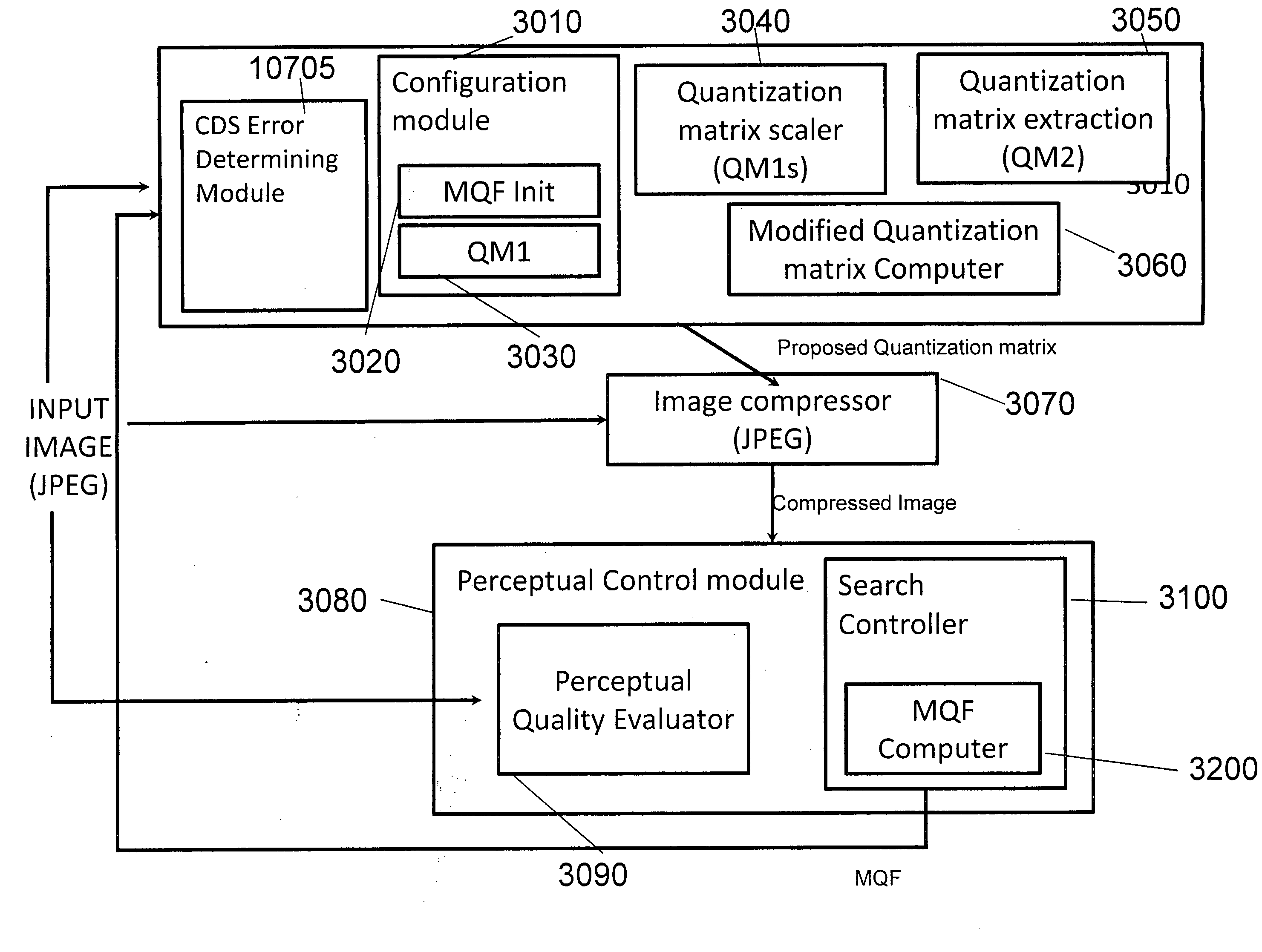
Apparatus and methods for recompression of digital images
ActiveUS20120201476A1Substantial size reductionSmall sizeCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationCoding blockReduced size
A system and method for generating a second reduced size digital image from a first digital image, the method including iteratively compressing the first digital image to an extent determined by a quality measure comprising at least a blockiness measure quantifying added artifactual edges along coding block boundaries of the second image and / or use of a quantization matrix generated by computing a weighted average of the quantization matrix of the first digital image and a scaled second quantization matrix.
Owner:BEAMR IMAGING LTD
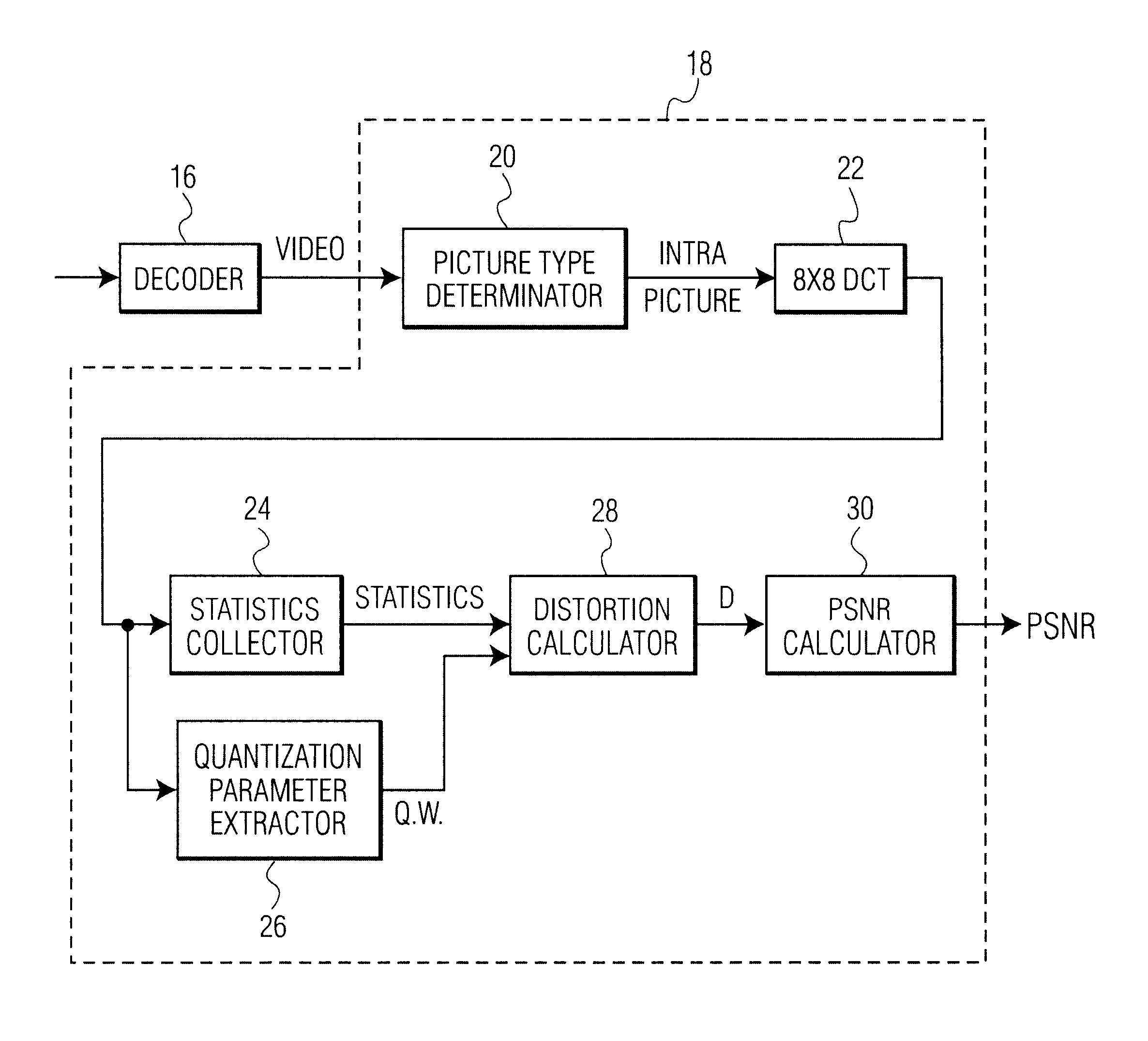
Method and system for estimating objective quality of compressed video data
InactiveUS6810083B2Image analysisPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPattern recognitionVideo bitstream
Owner:UNILOC 2017 LLC
Moving Picture Coding Method And Moving Picture Decoding Method
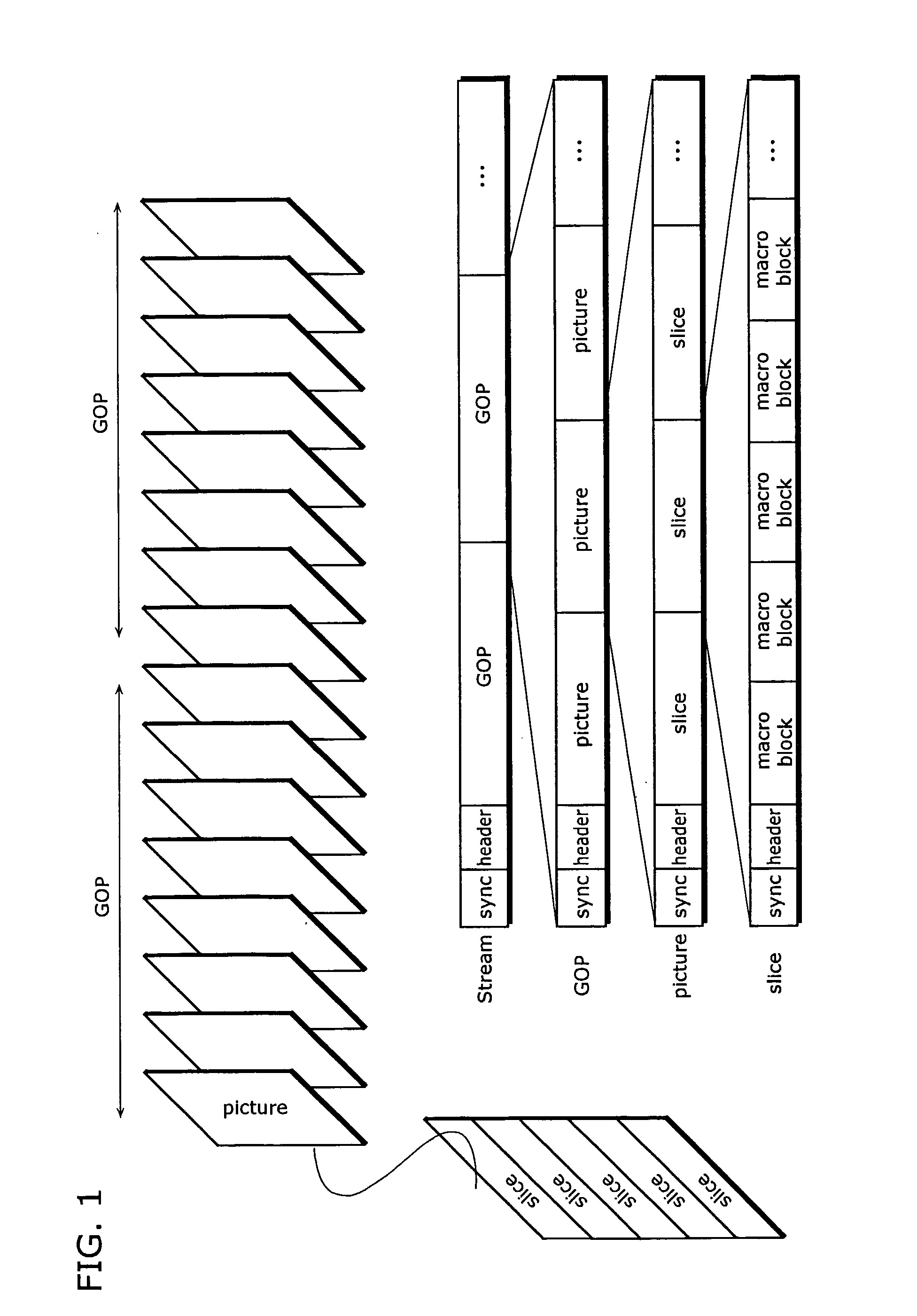
ActiveUS20080089410A1Reduce data volumeEfficient decodingPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesVariable-length codeQuantization matrix
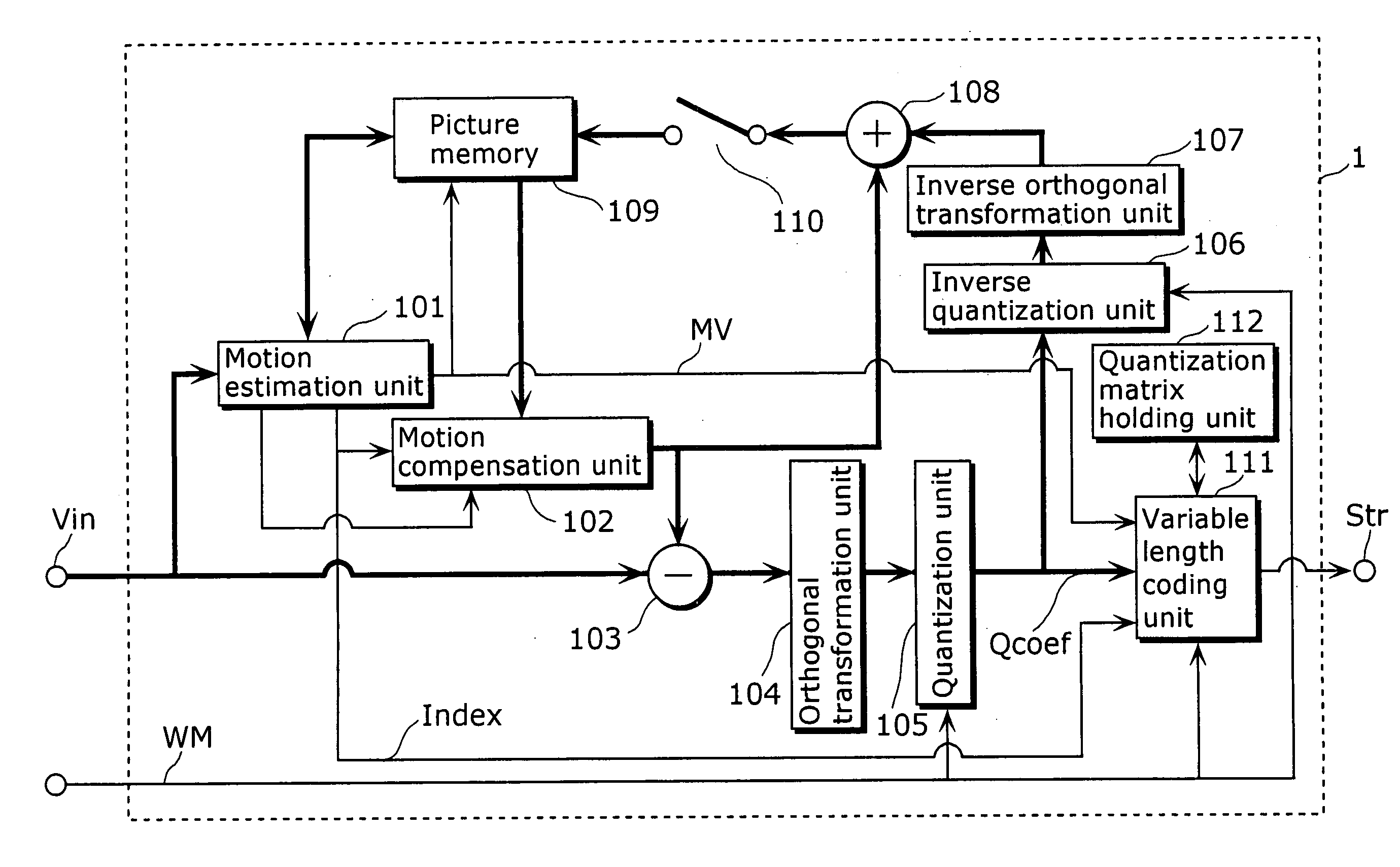
A moving picture coding apparatus 1 includes: a quantization matrix holding unit (112) that holds a quantization matrix (WM) which has already been transmitted in a parameter set and a matrix ID for identifying the quantization matrix (WM), which are associated with each other; and a variable length coding unit (111) that obtains the matrix ID corresponding to the quantization matrix (WM) used for quantization from the quantization matrix holding unit (112) and places the matrix ID in a coded stream Str.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Method and system for estimating objective quality of compressed video data
InactiveUS20030112333A1Image analysisPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPattern recognitionVideo bitstream
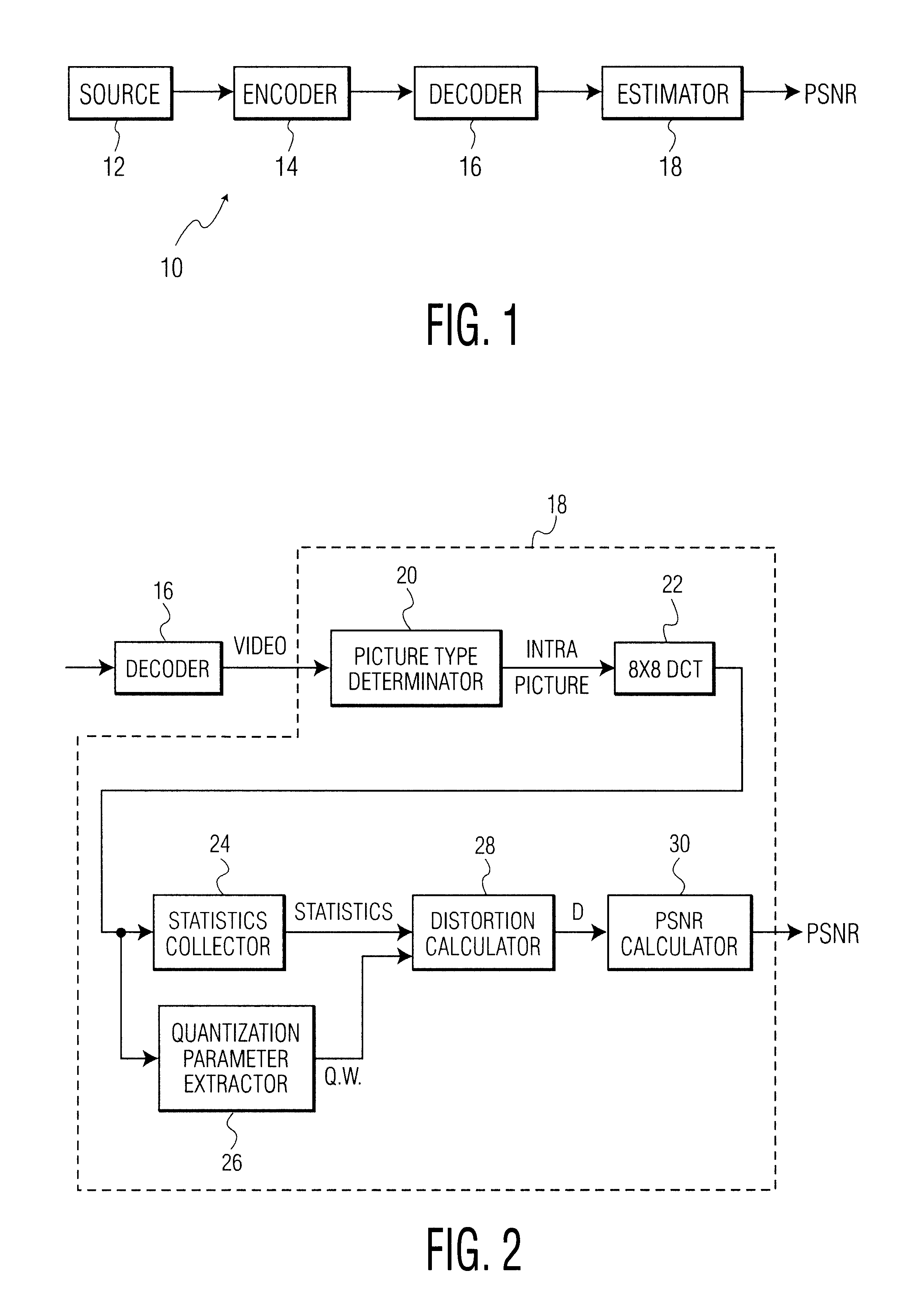
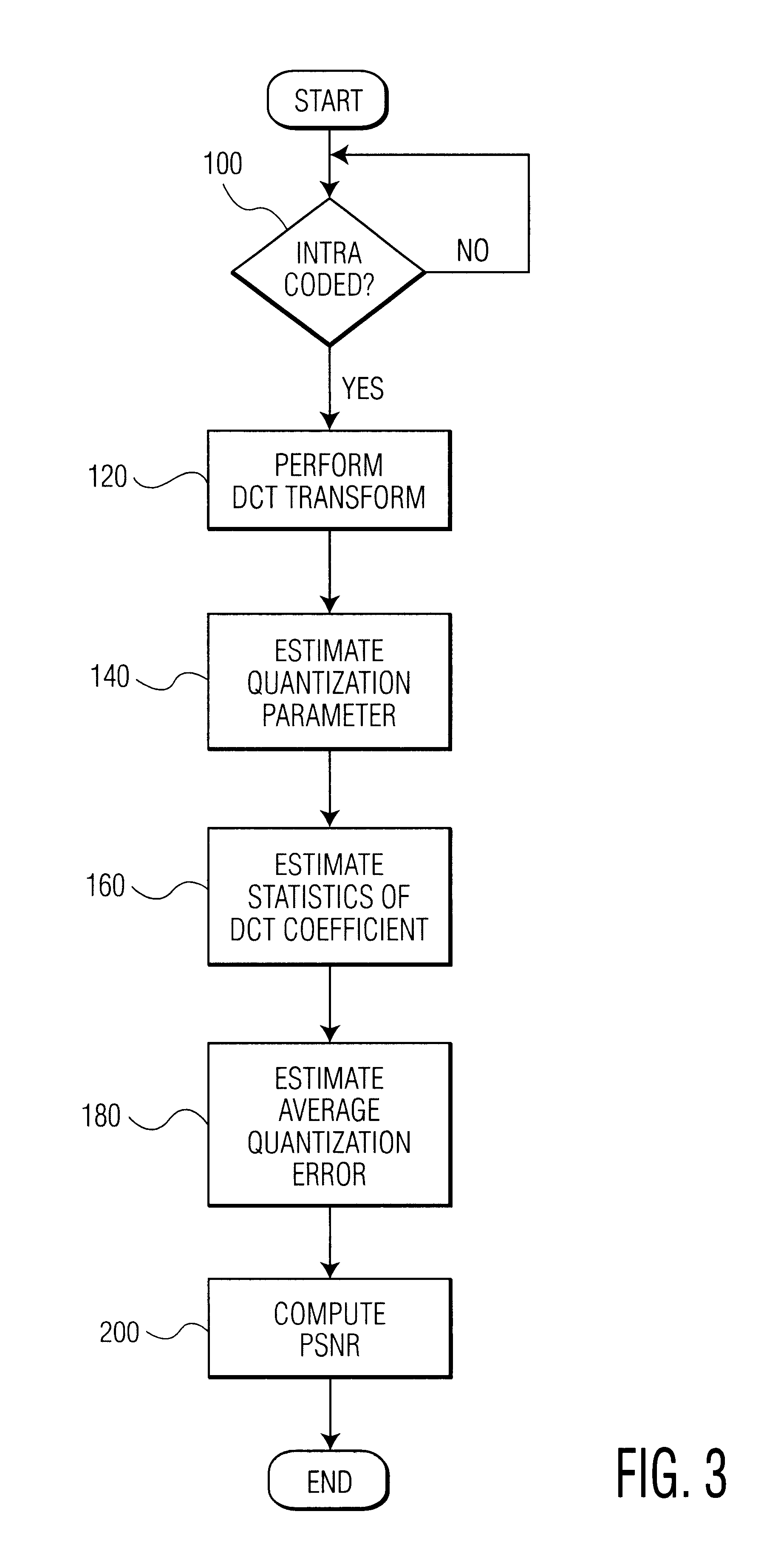
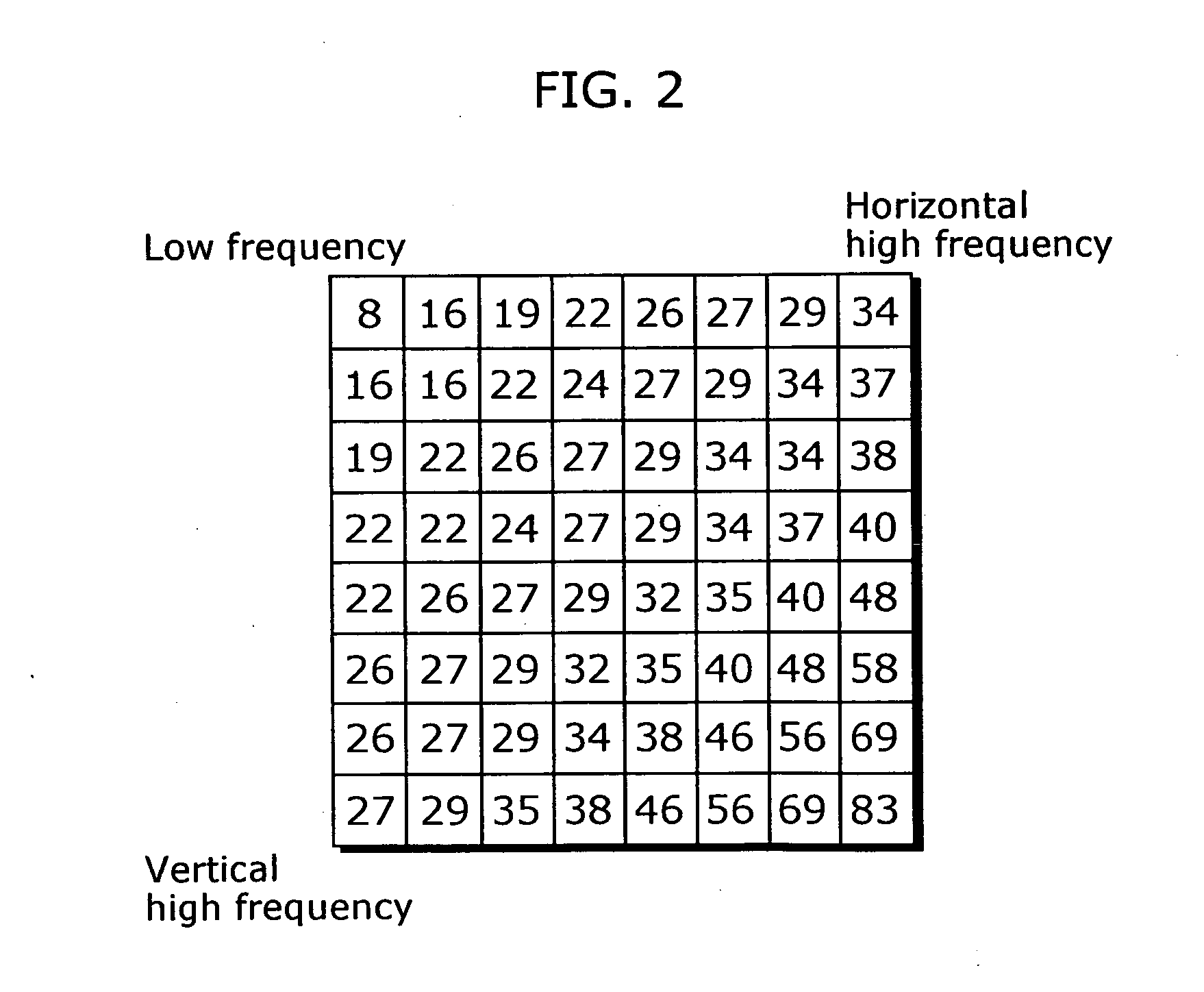
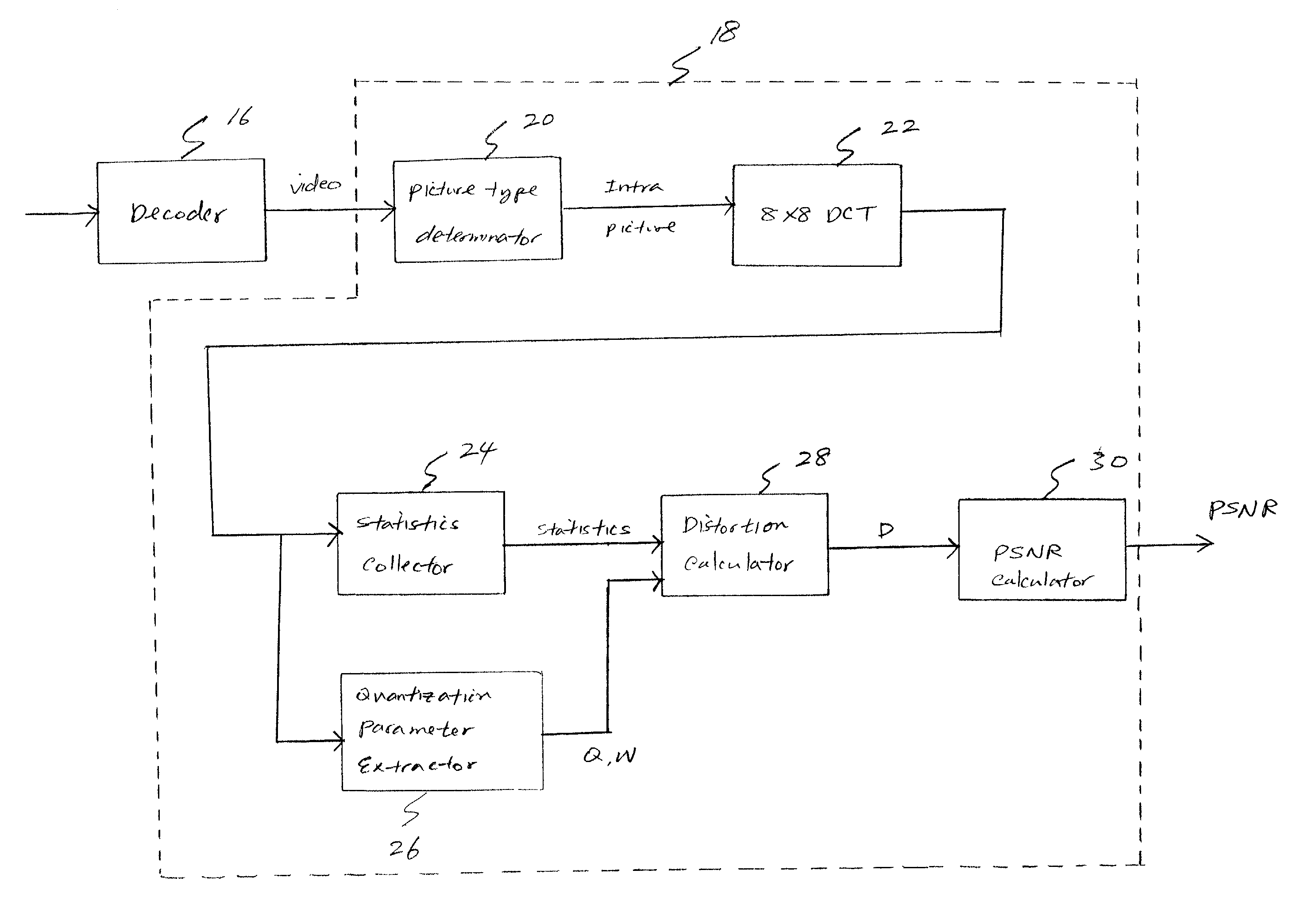
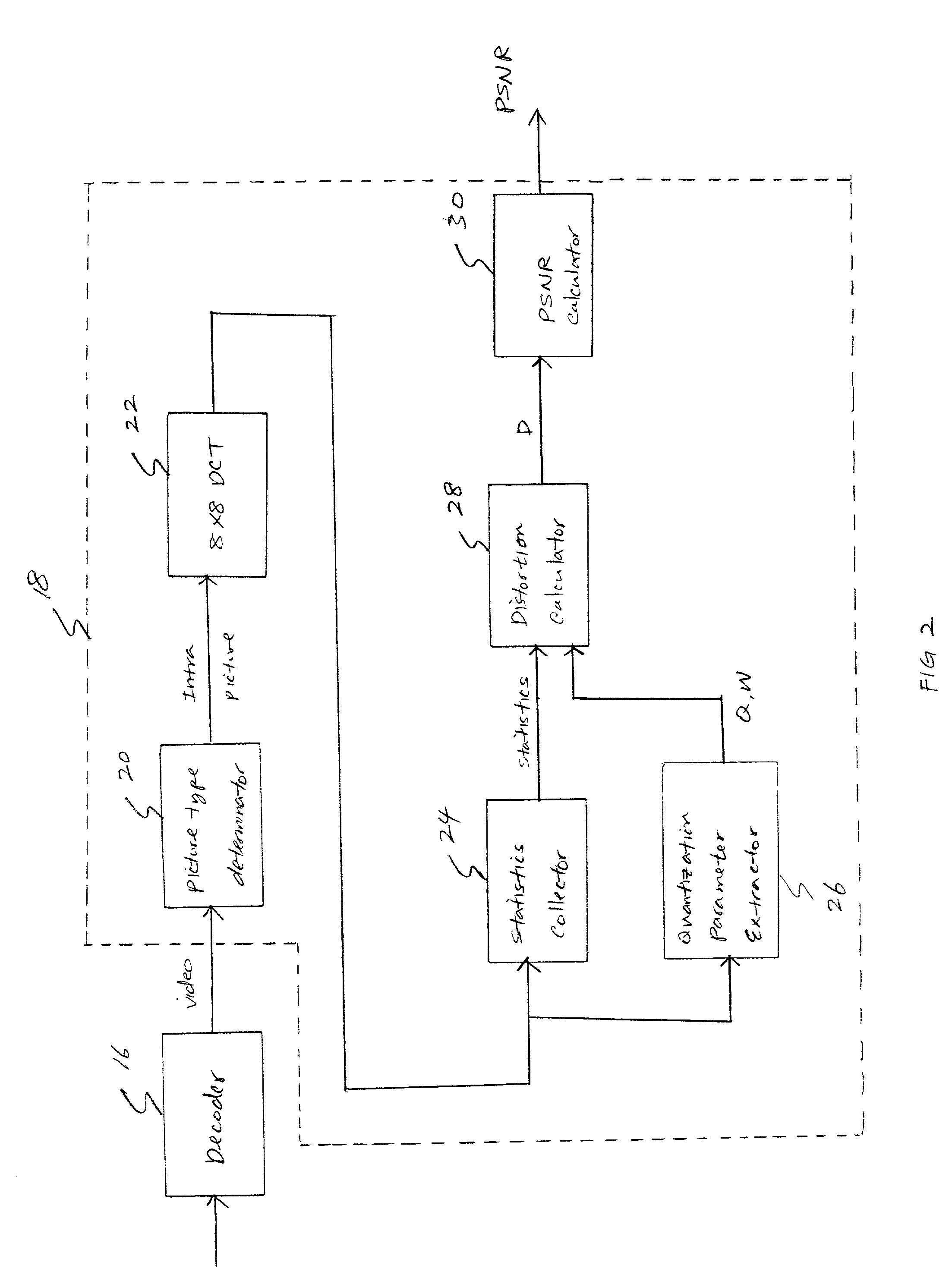
The present invention relates to a method and system for evaluating the quality of encoded video data without gaining access to the source data or the compressed video bitstream. The system is configured to decode compressed video data using an MPEG decoder to produce decompressed video data. The decoded data is analyzed to determine whether the decompressed video data is intra-coded. If so, a discrete cosine transform (DCT) is performed to produce a set of DCT coefficients for at least one AC frequency band in the decompressed video data. At the same time, quantization matrix data of a frame of the decompressed video data as well as a quantizer scale for each block of the decompressed video data are extracted. Thereafter, the variance of the converted DCT coefficients is obtained, and then an average quantization error for each set of said DCT coefficients is determined based on the variance, the quantization matrix, and the quantizer scale. Lastly, a peak signal to noise ratio (PSNR) is calculated based on the resultant average quantization error.
Owner:UNILOC 2017 LLC
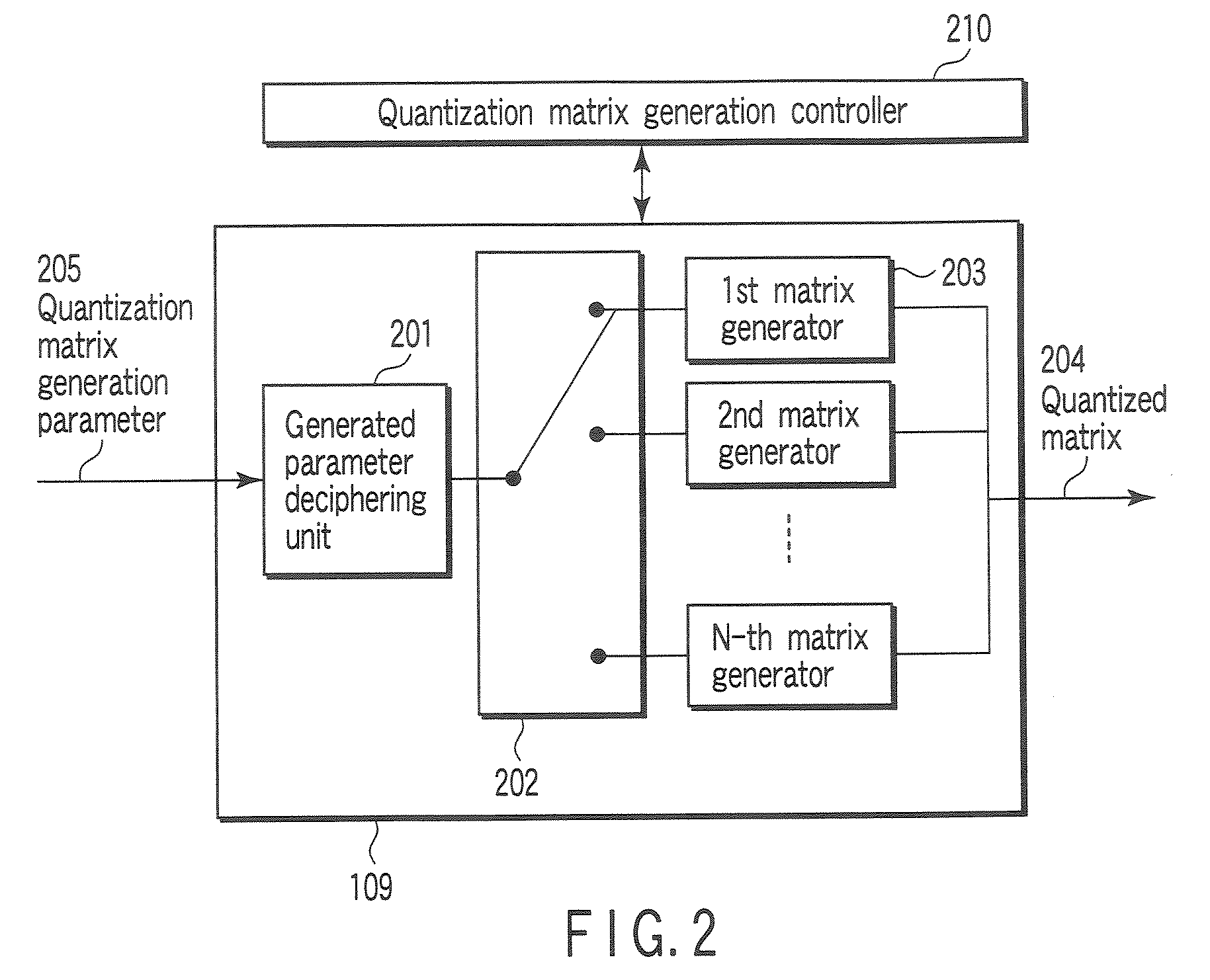
Method and apparatus for generating a quantisation matrix that can be used for encoding an image or a picture sequence
InactiveUS20060133479A1Promote resultsEfficient designColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo encodingAlgorithm
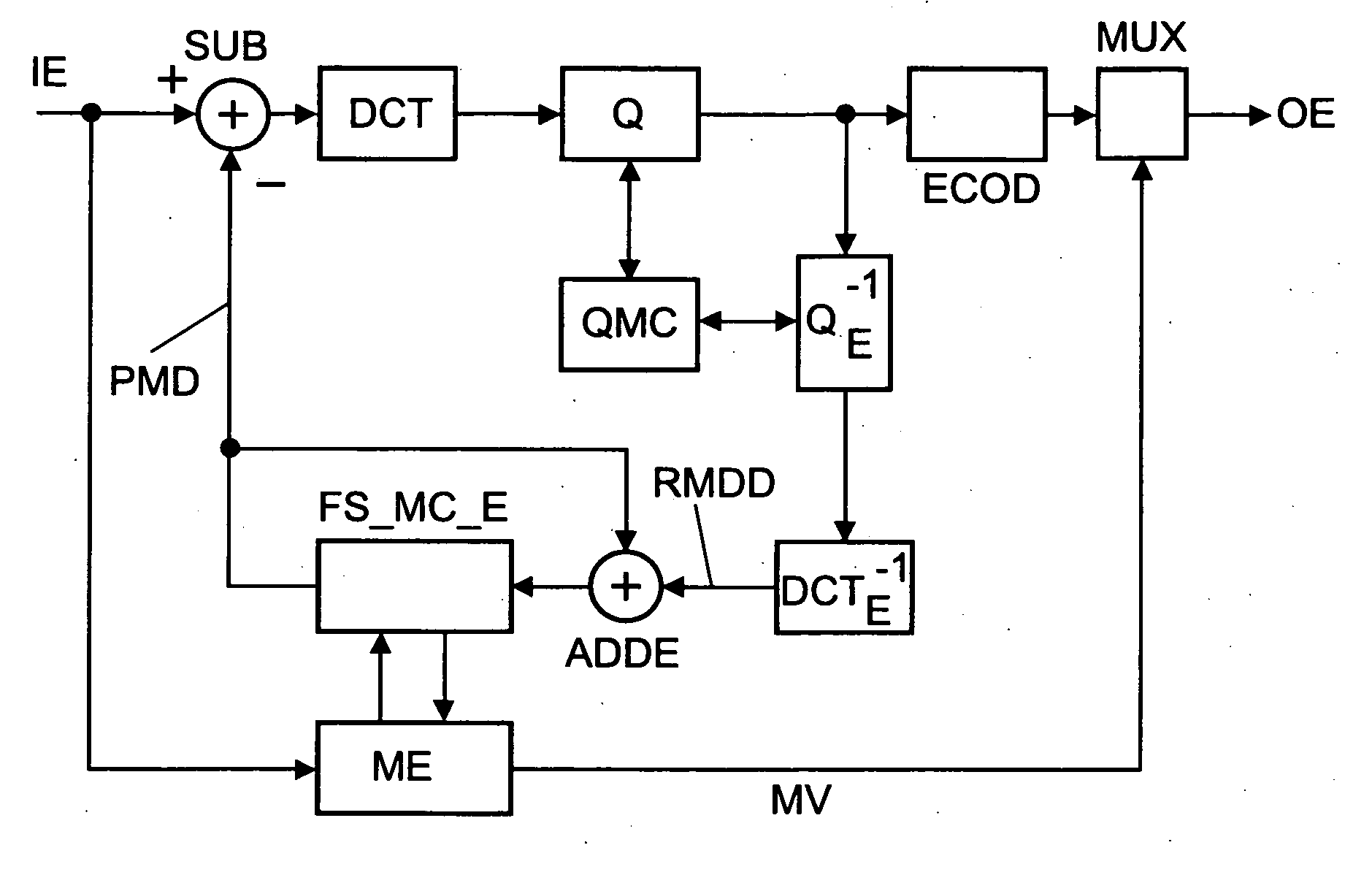
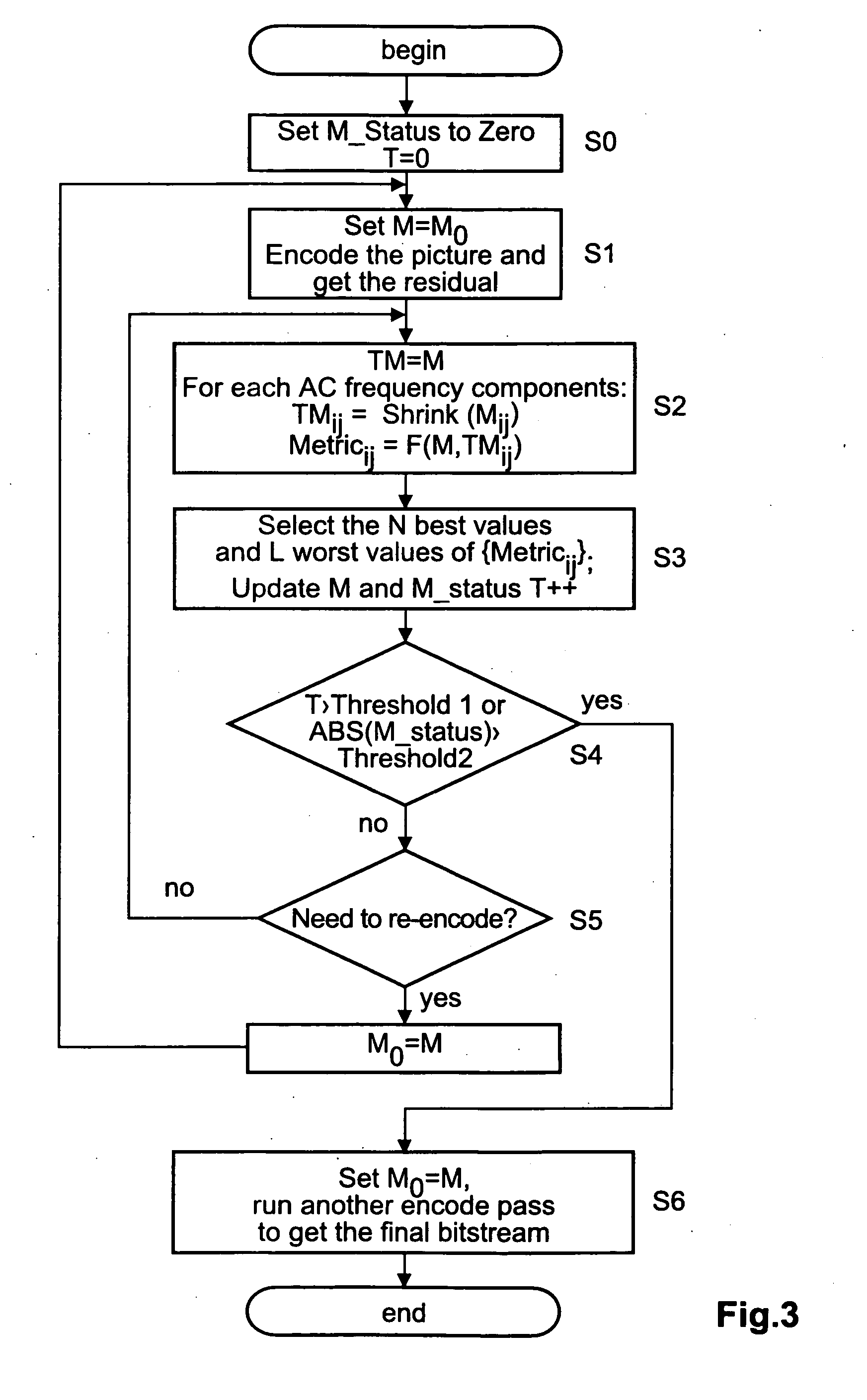
A significant data rate reduction effect in video coding is acchieved by quantizing the transformed frequency coefficients or components of a pixel block so that thereafter fewer amplitude levels need to be encoded and part of the quantised amplitude values becomes zero and need not be encoded as quantised amplitude values. Many transform based video coding standards use a default quantization matrix to achieve better subjective video coding / de-coding quality. A quantization matrix assigns smaller scaling values to some frequency components of the block if the related horizontal and / or vertical frequencies are believed to be the less important frequency components with respect to the resulting subjective picture quality. The inventive quantization matrix generation starts from default quantization matrices and derives therefrom a perceptually optimum quantization matrix for a given picture sequence. In a first pass the candidate quantization matrix for a given picture sequence is iteratively constructed by simultaneously increasing scaling values for some coefficient positions and decreasing scaling values for other ones of the coefficient positions. In a second pass the generated quantization matrix is applied for re-encoding the picture sequence.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
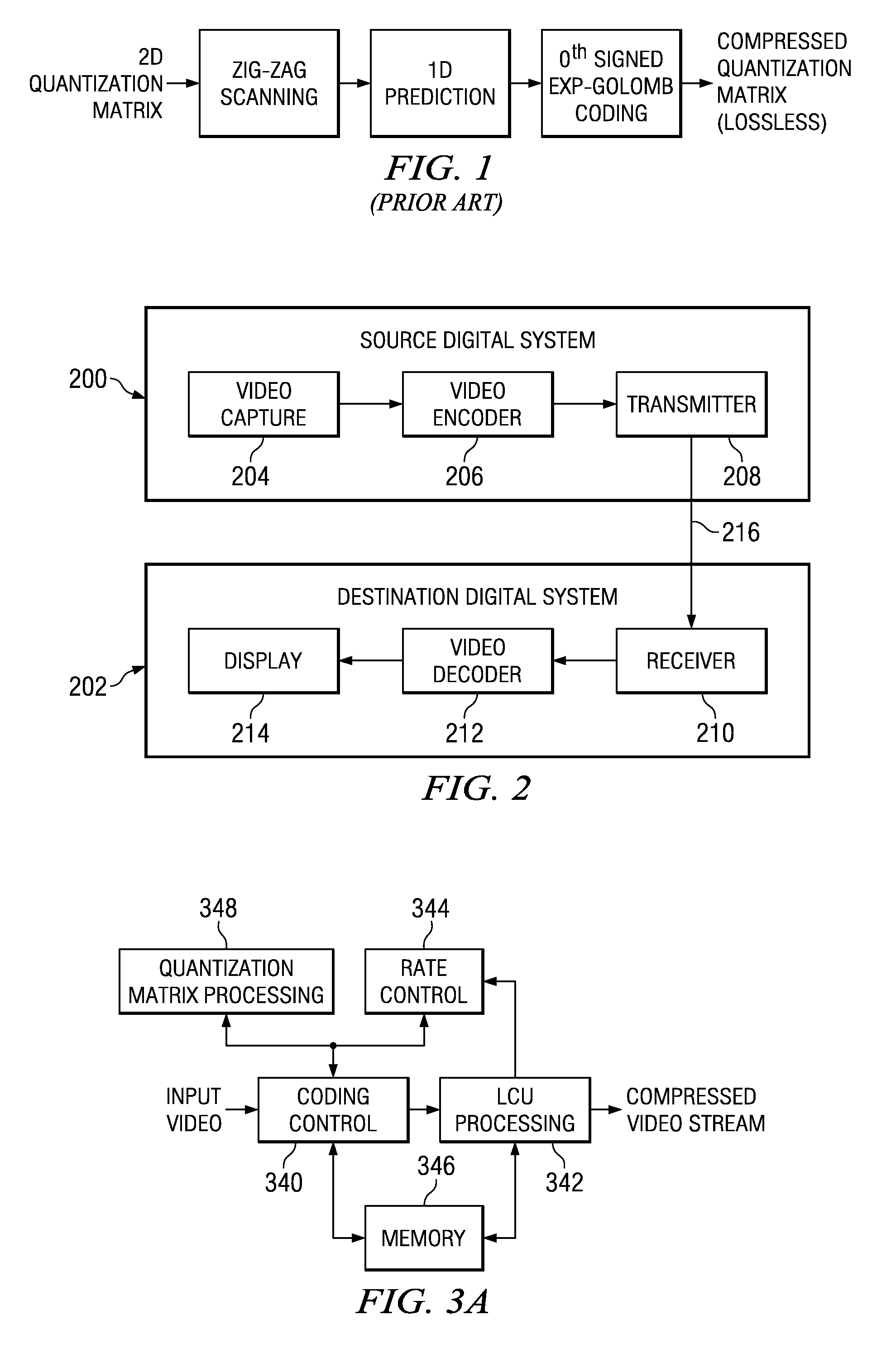
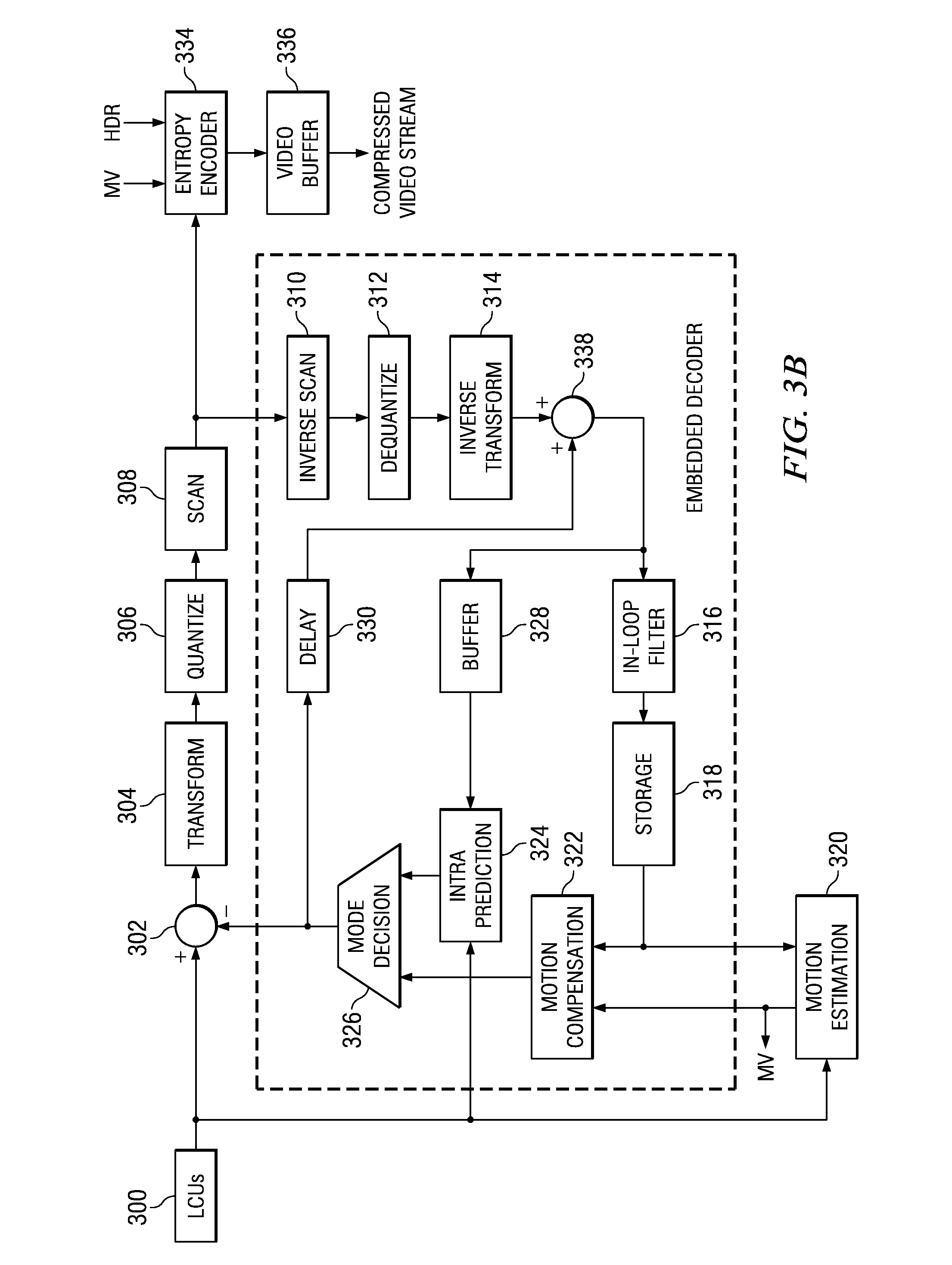
Quantization Matrix Compression in Video Coding
ActiveUS20120140815A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionAlgorithmQuantization matrix
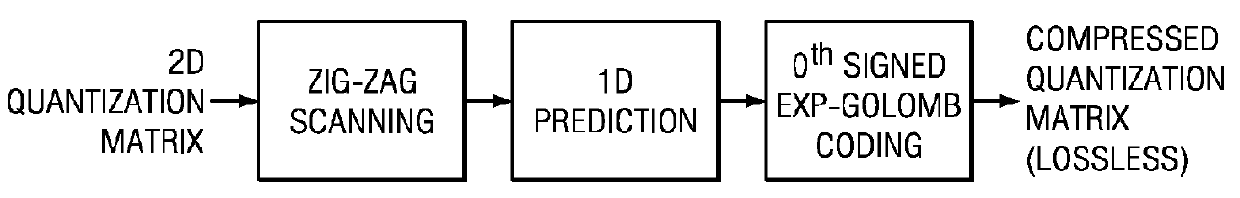
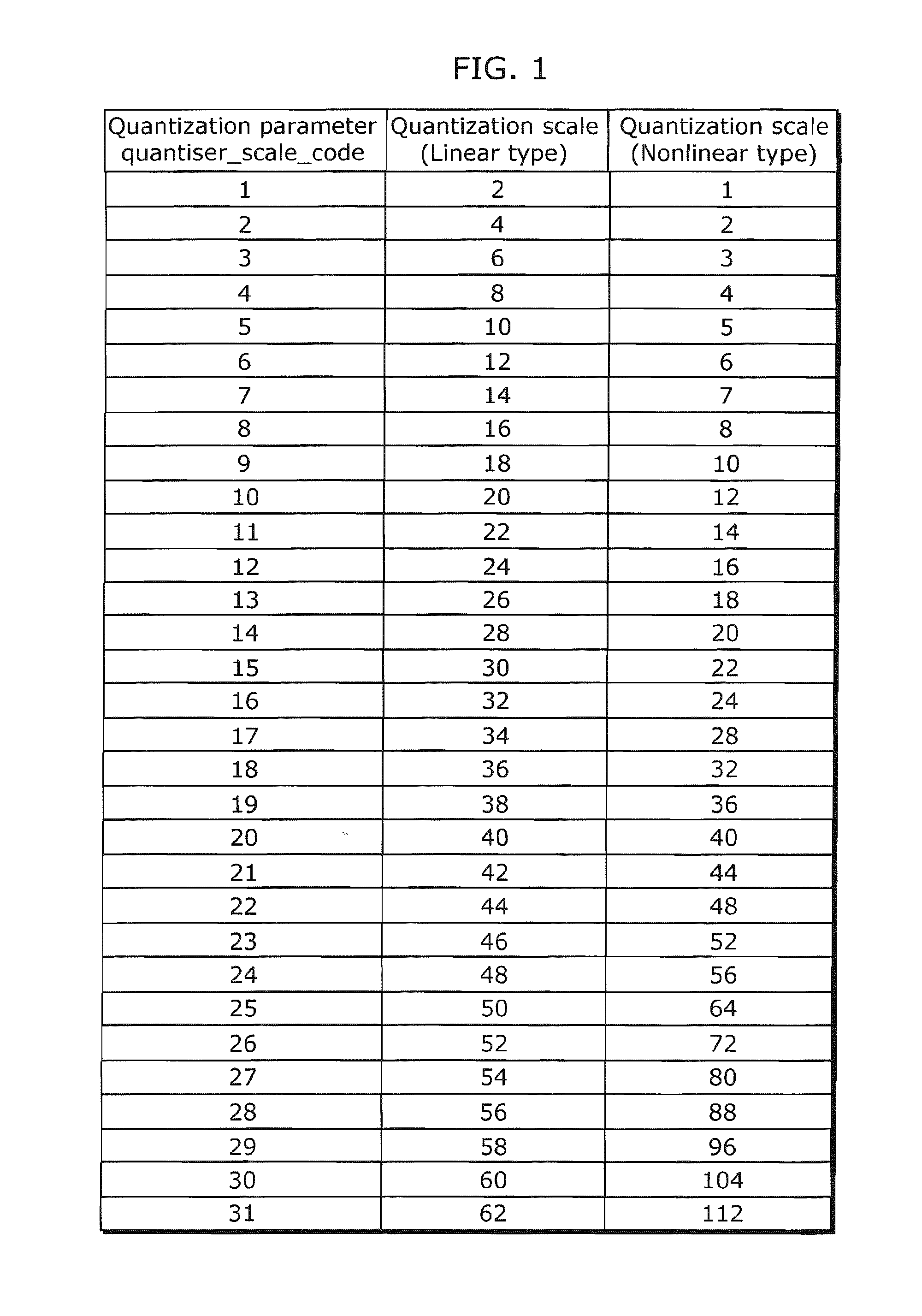
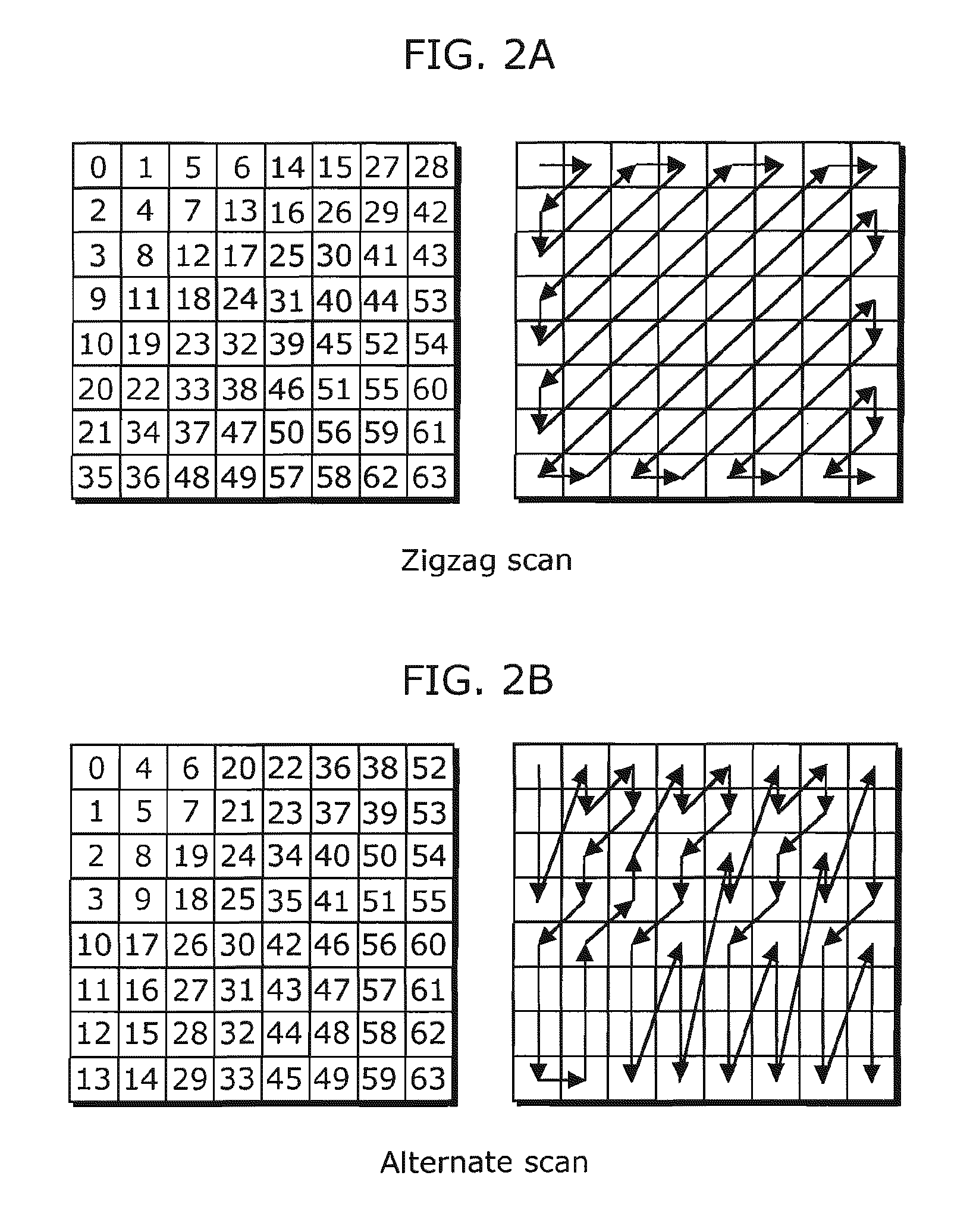
A method of quantization matrix compression in a video encoder is provided that includes preprocessing a quantization matrix by performing at least one selected from down-sampling the quantization matrix and imposing 135 degree symmetry on the quantization matrix, performing zigzag scanning on the pre-processed quantization matrix to generate a one dimensional (1D) sequence, predicting the 1D sequence to generate a residual 1D sequence, and coding the residual 1D sequence using kth order exp-Golomb coding to generate a compressed quantization matrix, wherein k≧0.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Image processing device and image processing method
ActiveUS20130251032A1Low efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionImaging processingAlgorithm
An image processing device including an acquiring section configured to acquire quantization matrix parameters from an encoded stream in which the quantization matrix parameters defining a quantization matrix are set within a parameter set which is different from a sequence parameter set and a picture parameter set, a setting section configured to set, based on the quantization matrix parameters acquired by the acquiring section, a quantization matrix which is used when inversely quantizing data decoded from the encoded stream, and an inverse quantization section configured to inversely quantize the data decoded from the encoded stream using the quantization matrix set by the setting section.
Owner:SONY CORP
Efficient de-quantization in a digital video decoding process using a dynamic quantization matrix for parallel computations
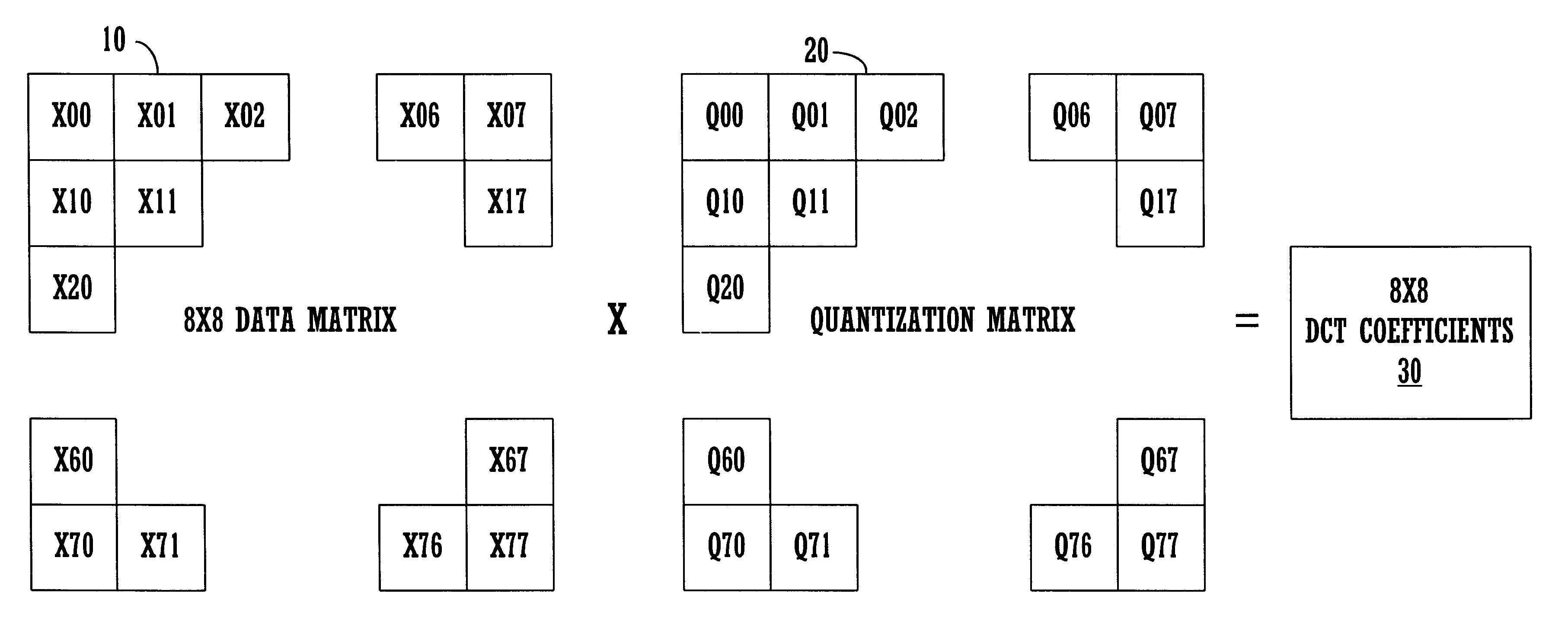
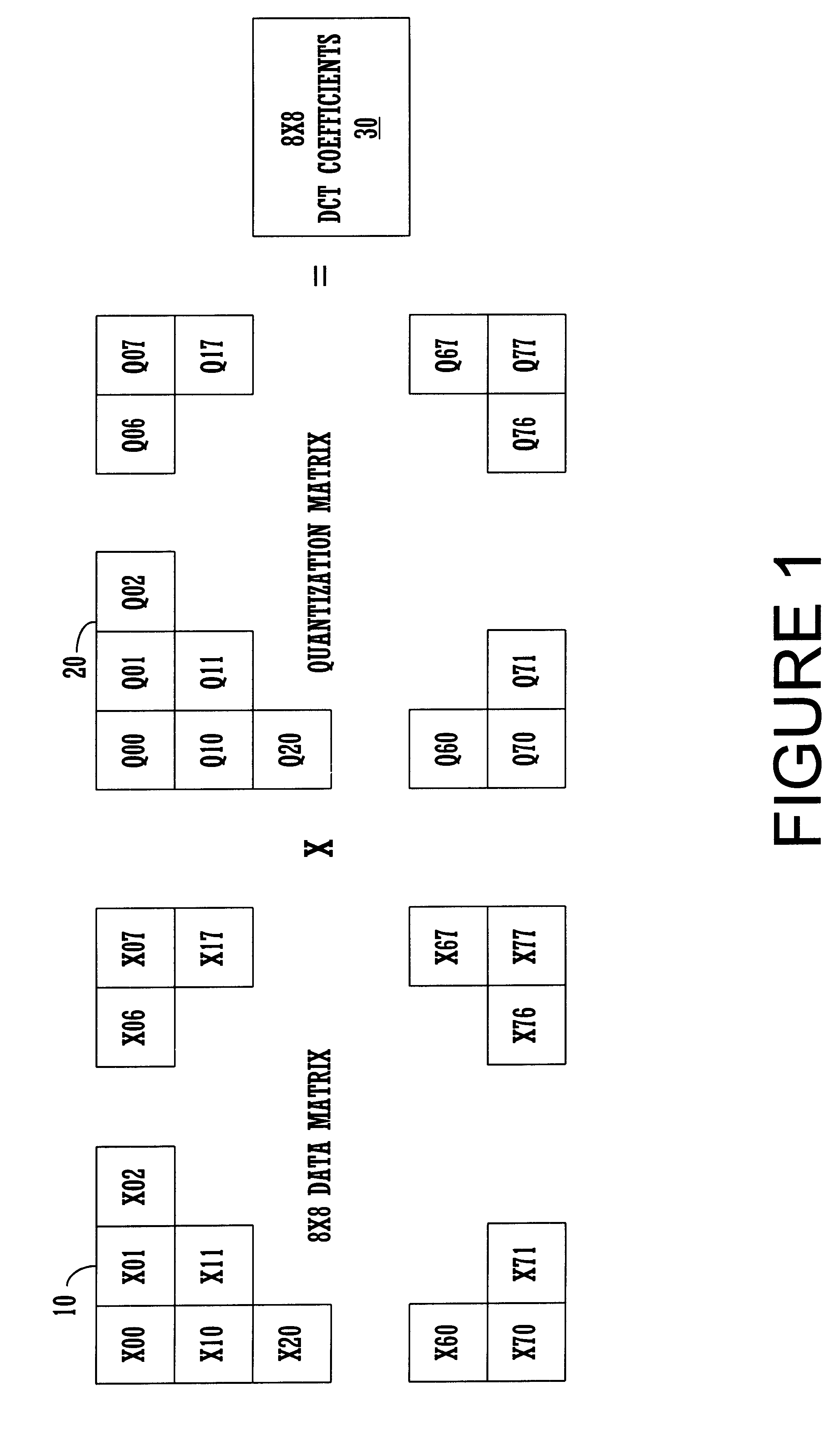
InactiveUS6507614B1Efficient productionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningDigital videoArray data structure
An efficient digital video (DV) decoder process that utilizes a specially constructed quantization matrix allowing an inverse quantization subprocess to perform parallel computations, e.g., using SIMD processing, to efficiently produce a matrix of DCT coefficients. The present invention utilizes a first look-up table (for 8x8 DCT) which produces a 15-valued quantization scale based on class number information and a QNO number for an 8x8 data block ("data matrix") from an input encoded digital bit stream to be decoded. The 8x8 data block is produced from a deframing and variable length decoding subprocess. An individual 8-valued segment of the 15-value output array is multiplied by an individual 8-valued segment, e.g., "a row," of the 8x8 data matrix to produce an individual row of the 8x8 matrix of DCT coefficients ("DCT matrix"). The above eight multiplications can be performed in parallel using a SIMD architecture to simultaneously generate a row of eight DCT coefficients. In this way, eight passes through the 8x8 block are used to produce the entire 8x8 DCT matrix, in one embodiment consuming only 33 instructions per 8x8 block. After each pass, the 15-valued output array is shifted by one value position for proper alignment with its associated row of the data matrix. The DCT matrix is then processed by an inverse discrete cosine transform subprocess that generates decoded display data. A second lookup table can be used for 2x4x8 DCT processing.
Owner:SONY ELECTRONICS INC +1
Adaptive quantization using code length in image compression
InactiveUS6882753B2Low memory and bus bandwidth requirementImprove processing efficiencyPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningPattern recognitionLandau quantization
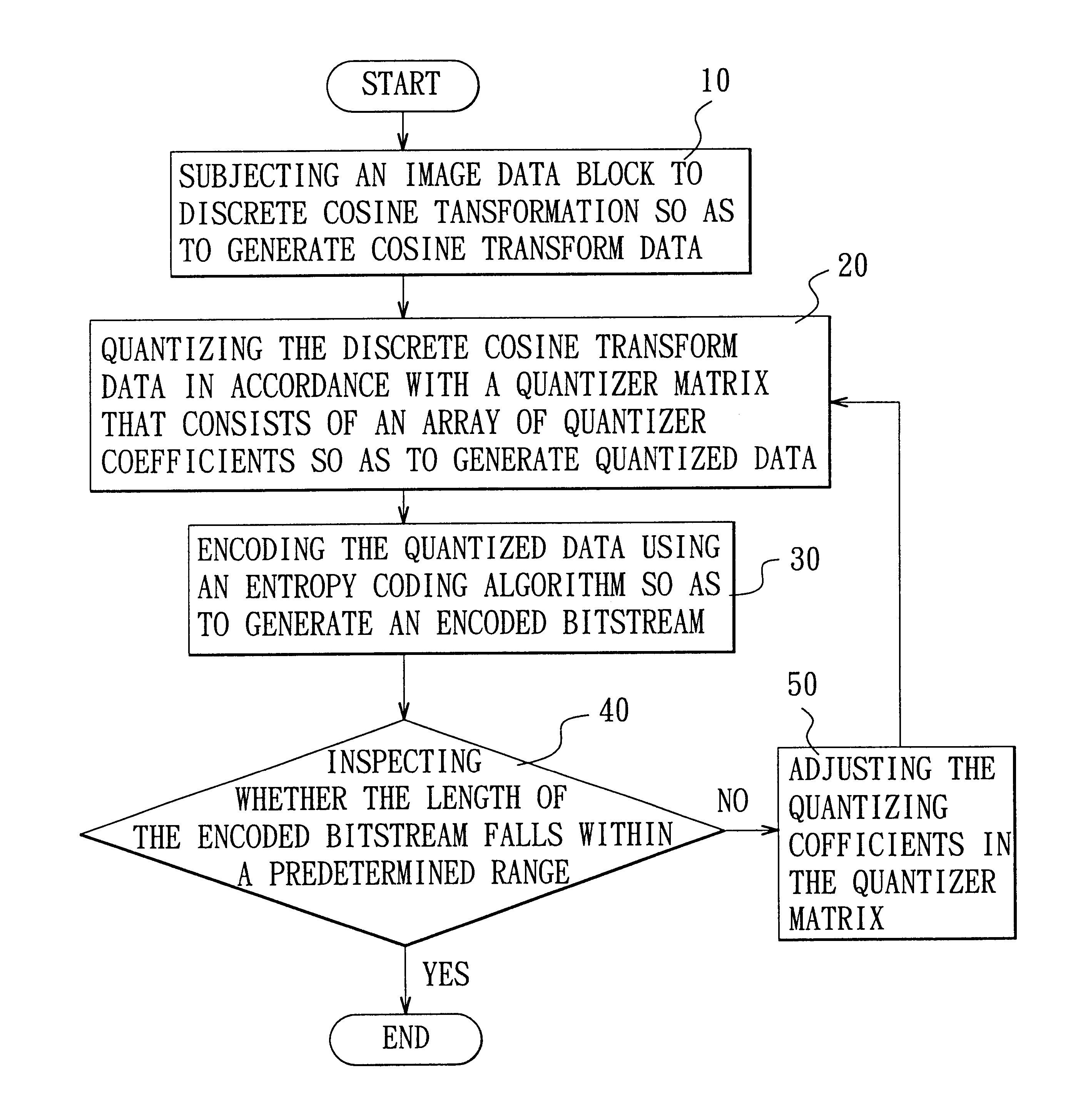
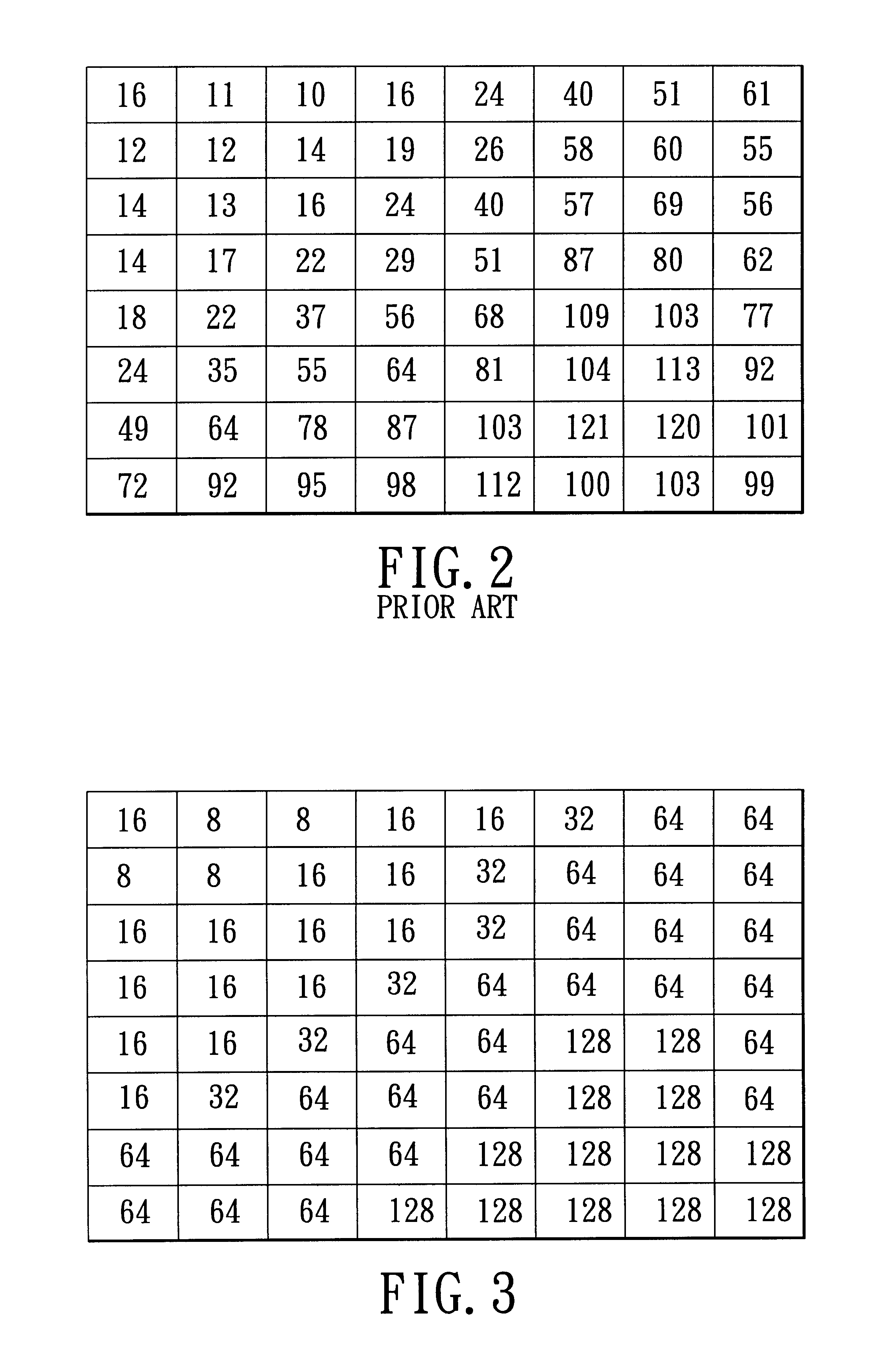
A method is adapted for compressing an image data block, and includes the steps of:(a) subjecting the image data block to discrete cosine transformation so as to generate discrete cosine transform data;(b) quantizing the discrete cosine transform data in accordance with a quantizer matrix that consists of an array of quantizing coefficients so as to generate quantized data;(c) encoding the quantized data using an entropy coding algorithm so as to generate an encoded bitstream; and(d) when the length of the encoded bitstream does not fall within a predetermined range, adjusting the quantizing coefficients in the quantizer matrix and repeating steps (b) and (c) until the length of the encoded bitstream falls within the predetermined range.
Owner:SILICON INTEGRATED SYSTEMS
Apparatus and methods for recompression of digital images
ActiveUS8908984B2Small sizeQuality improvementColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionCoding blockReduced size
A system and method for generating a second reduced size digital image from a first digital image, the method including iteratively compressing the first digital image to an extent determined by a quality measure comprising at least a blockiness measure quantifying added artifactual edges along coding block boundaries of the second image and / or use of a quantization matrix generated by computing a weighted average of the quantization matrix of the first digital image and a scaled second quantization matrix.
Owner:BEAMR IMAGING LTD
Coding rate conversion apparatus, coding rate conversion method, and integrated circuit
InactiveUS20100091842A1Suppresses image quality degradationSuppress errorColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionAlgorithmQuantization matrix
A plurality of macroblocks constituting coded data are inverse quantized using a first quantization matrix that is used when coding a picture, to obtain a plurality of sets of coefficient data. The first quantization matrix is converted to a second quantization matrix using a first conversion value and a second conversion value, where the first conversion value is for converting a low frequency coefficient corresponding to a frequency lower than a predetermined frequency among a plurality of coefficients shown by the first quantization matrix, and the second conversion value is for converting a high frequency coefficient among the plurality of coefficients and is larger than the first conversion value (Step S408). When the second quantization matrix is a matrix for increasing a coding rate of the coded data, a converted scale is calculated by multiplying a quantization scale corresponding to at least one macroblock by β1 (≧1). At least one part of the plurality of sets of coefficient data is quantized using the second quantization matrix and a calculated converted scale that corresponds to a macroblock corresponding to the at least one part of the plurality of sets of coefficient data.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Image processing device and image processing method
ActiveUS20130322525A1Low efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionImaging processingAlgorithm
Provided is an image processing device including an acquiring section configured to acquire quantization matrix parameters from an encoded stream in which the quantization matrix parameters defining a quantization matrix are set within a parameter set which is different from a sequence parameter set and a picture parameter set, a setting section configured to set, based on the quantization matrix parameters acquired by the acquiring section, a quantization matrix which is used when inversely quantizing data decoded from the encoded stream, and an inverse quantization section configured to inversely quantize the data decoded from the encoded stream using the quantization matrix set by the setting section.
Owner:SONY CORP
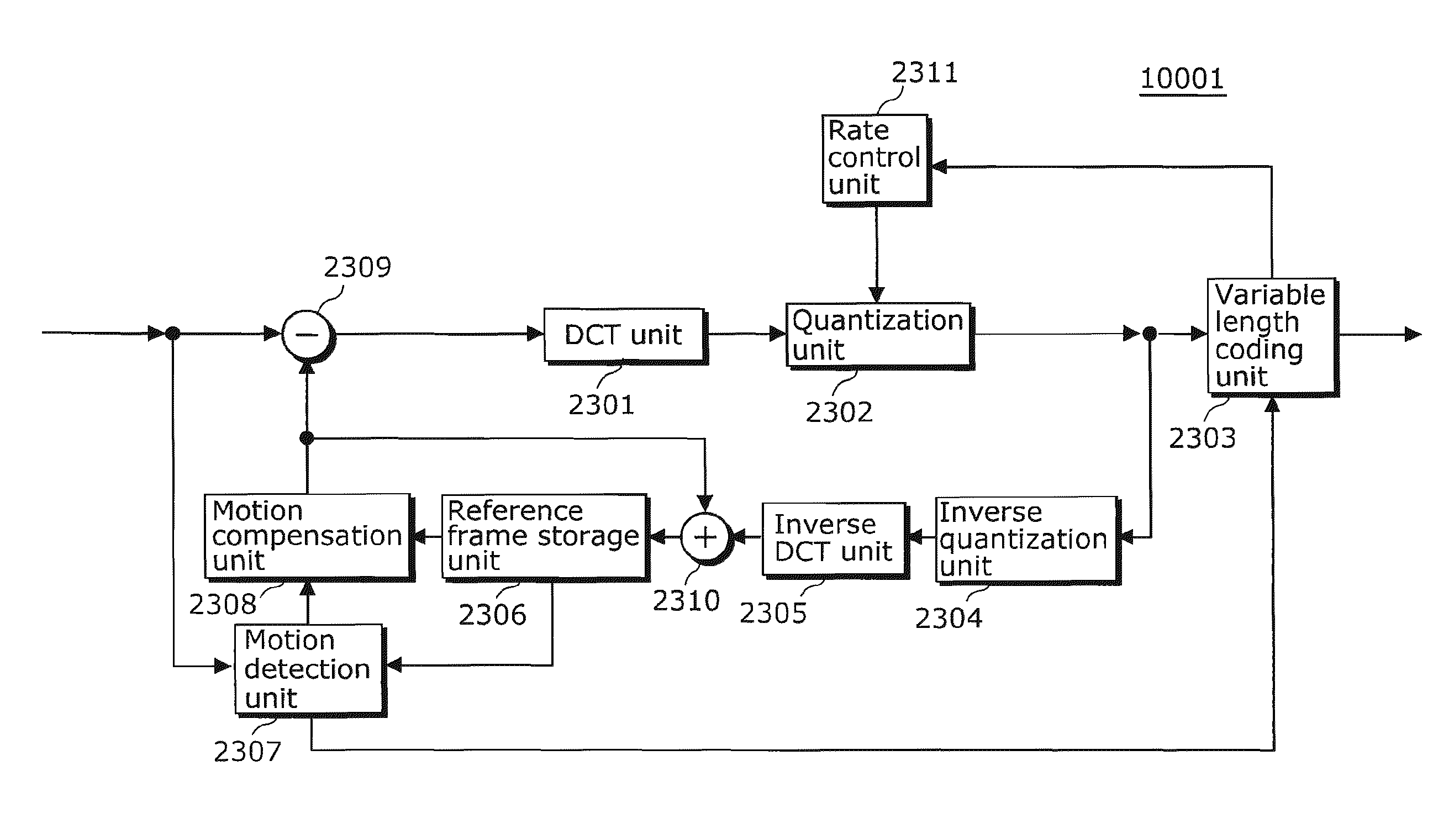
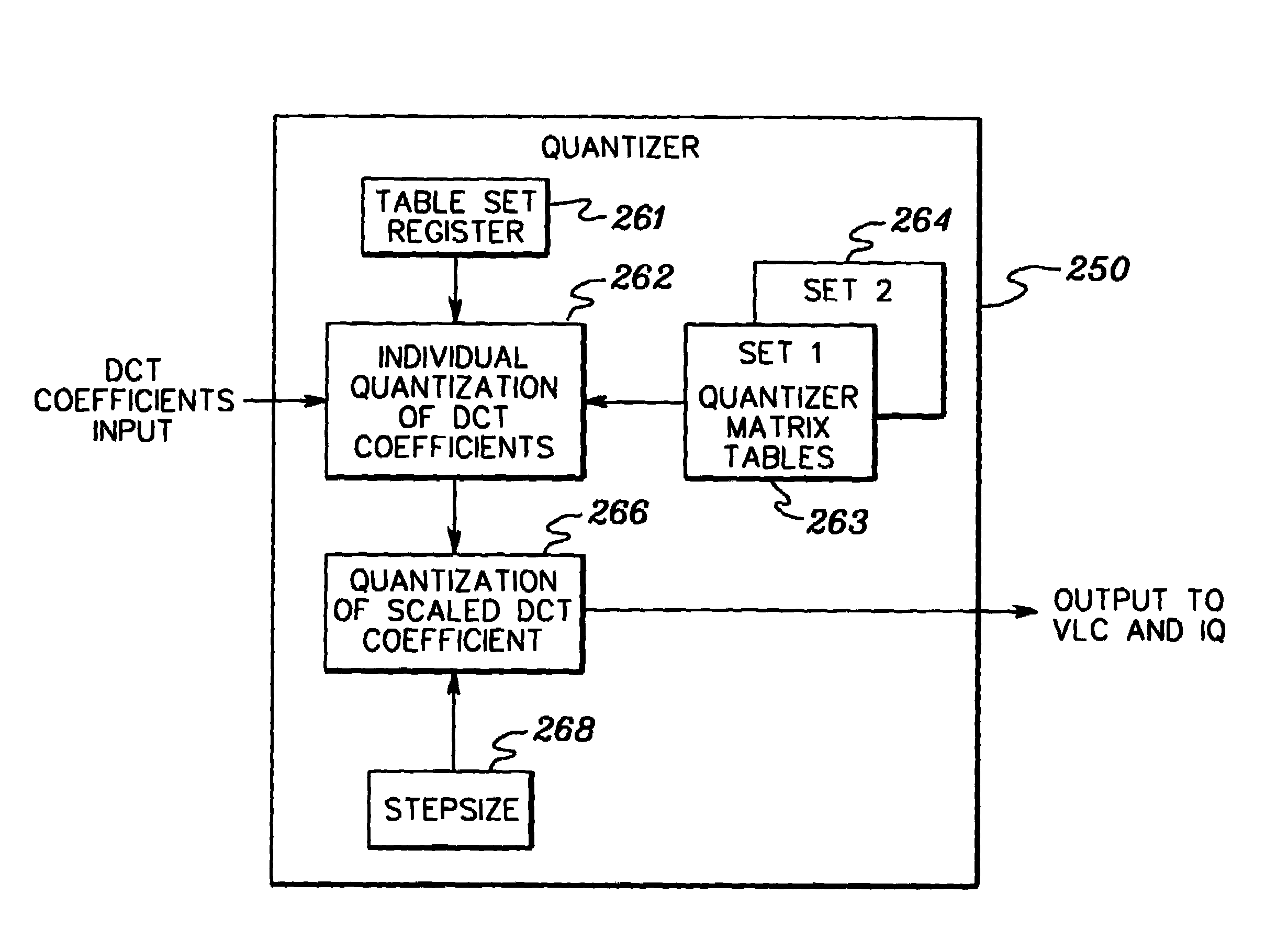
Dynamically switching quant matrix tables within an MPEG-2 encoder
InactiveUS6999511B1Maximum flexibilityImprove picture qualityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDigital videoComputer architecture
A digital video encoder is presented adapted for dynamically switching between sets of quantizer matrix tables without pausing encoding of a stream of video data. Two or more sets of quantizer matrix tables are held at the encoder's quantization unit and compressed store interface for dynamically switching between sets of quant matrix tables at a picture boundary of the sequence of video data, i.e., without stopping encoding of the sequence of video data. Further, while one set of matrix tables is being employed to quantize the stream of video data, the encoder can be updating or modifying another set of quantization matrix tables, again without stopping encoding of the sequence of video data.
Owner:IBM CORP
Picture Coding Method, Picture Decoding Method, Picture Coding Apparatus, Picture Decoding Apparatus, and Program Thereof
ActiveUS20080192838A1Reduce loadDegradation is multipliedColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureQuantization matrix
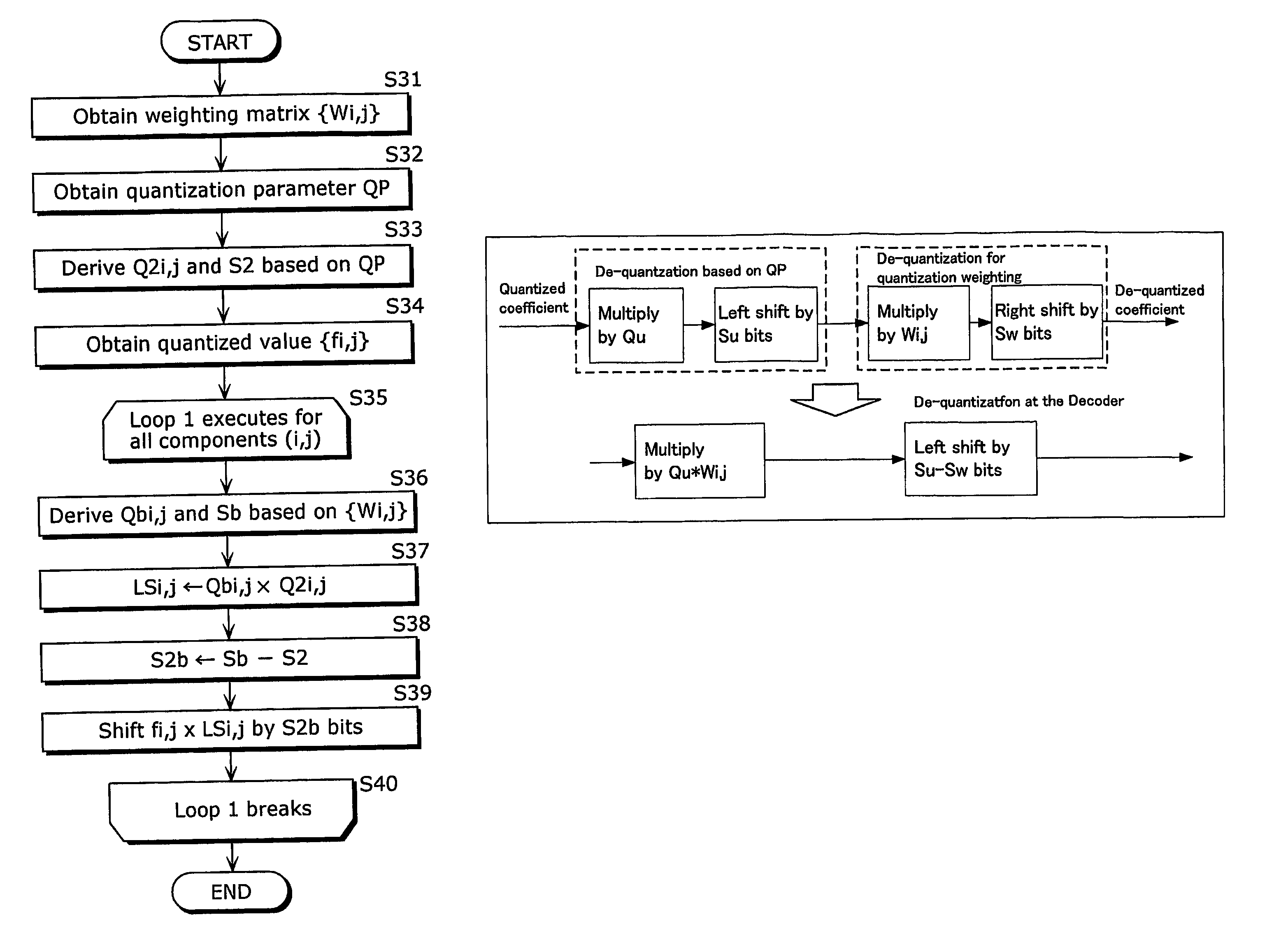
The picture decoding method according to the present invention is a decoding method for decoding coded pictures by inverse quantization and inverse orthogonal transformation, in which a quantization matrix which defines a scaling ratio of a quantization step for each component is multiplied by a multiplier, which is a coefficient for frequency transformation or a quantization step, and also, a result of the multiplication is multiplied by a quantized value, as a process of inverse quantization.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Method and device for transcoding images
InactiveUS20060050784A1Reduce complexityIncrease speedTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesJPEGDigital image
A method and device for transcoding digital images where at least portions of a first image coded according to a first method is decoded for obtaining first coefficients of a luminance component and chrominance components of the first image, where the chrominance components are subjected to a combined inverse quantization according to the first method and quantization according to a second method. The combined inverse quantization and quantization respectively uses a chrominance quantization matrix and a luminance quantization matrix for obtaining second coefficients for chrominance components of the second image having the same chroma format as the JPEG image. Finally, the first coefficients of the luminance component of the first image and the second coefficients of the chrominance components of the second image are coded for obtaining the second image decodable according to the second method.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
System and method for performing optimized quantization via quantization re-scaling
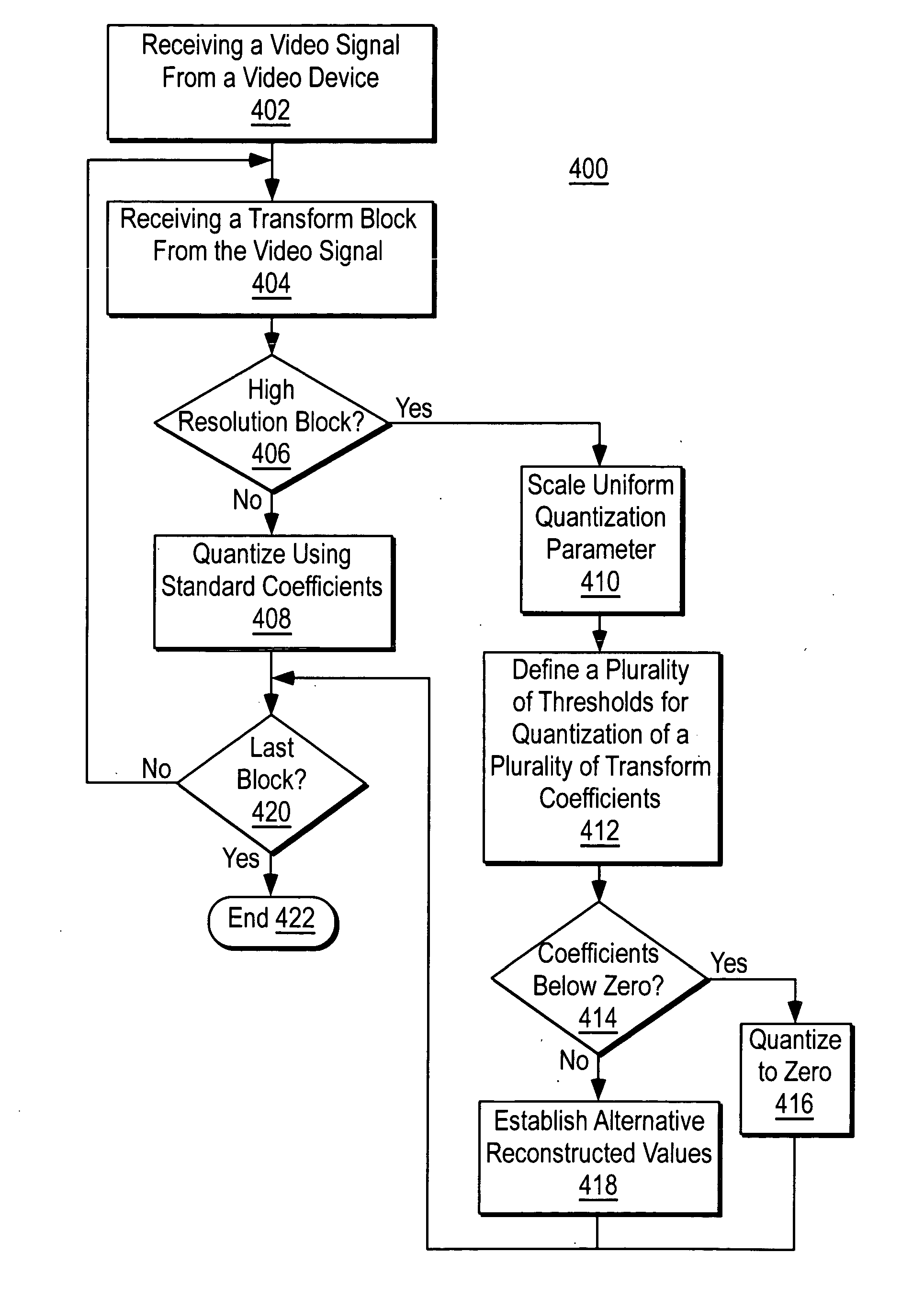
ActiveUS20060133478A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionQuantization matrixUniform quantization
A method, system, and program product for quantizing discrete cosine transform coefficients, e.g., for MPEG compression, with minimal bit rate overhead and without using a quantization matrix. This is done by scaling a uniform quantization parameter for the entire discrete cosine transform block, defining a variety of thresholds for the quantization of discrete cosine transform coefficients below which the corresponding coefficient will be quantized to zero, and setting different normative reconstructed values for coefficients that have not been quantized to zero as the decoder will still use the original, unmodified reconstructed values as long as the corresponding coefficient is not zero.
Owner:GEO SEMICONDUCTOR INC
Picture coding method, picture decoding method, picture coding apparatus, picture decoding apparatus, and program thereof
ActiveUS7630435B2Reduce loadDegradation is multipliedColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureQuantization matrix
The picture decoding method according to the present invention is a decoding method for decoding coded pictures by inverse quantization and inverse orthogonal transformation, in which a quantization matrix which defines a scaling ratio of a quantization step for each component is multiplied by a multiplier, which is a coefficient for frequency transformation or a quantization step, and also, a result of the multiplication is multiplied by a quantized value, as a process of inverse quantization.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Image coding apparatus and image coding method
ActiveUS20090067738A1Character and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationComputer architectureObject code
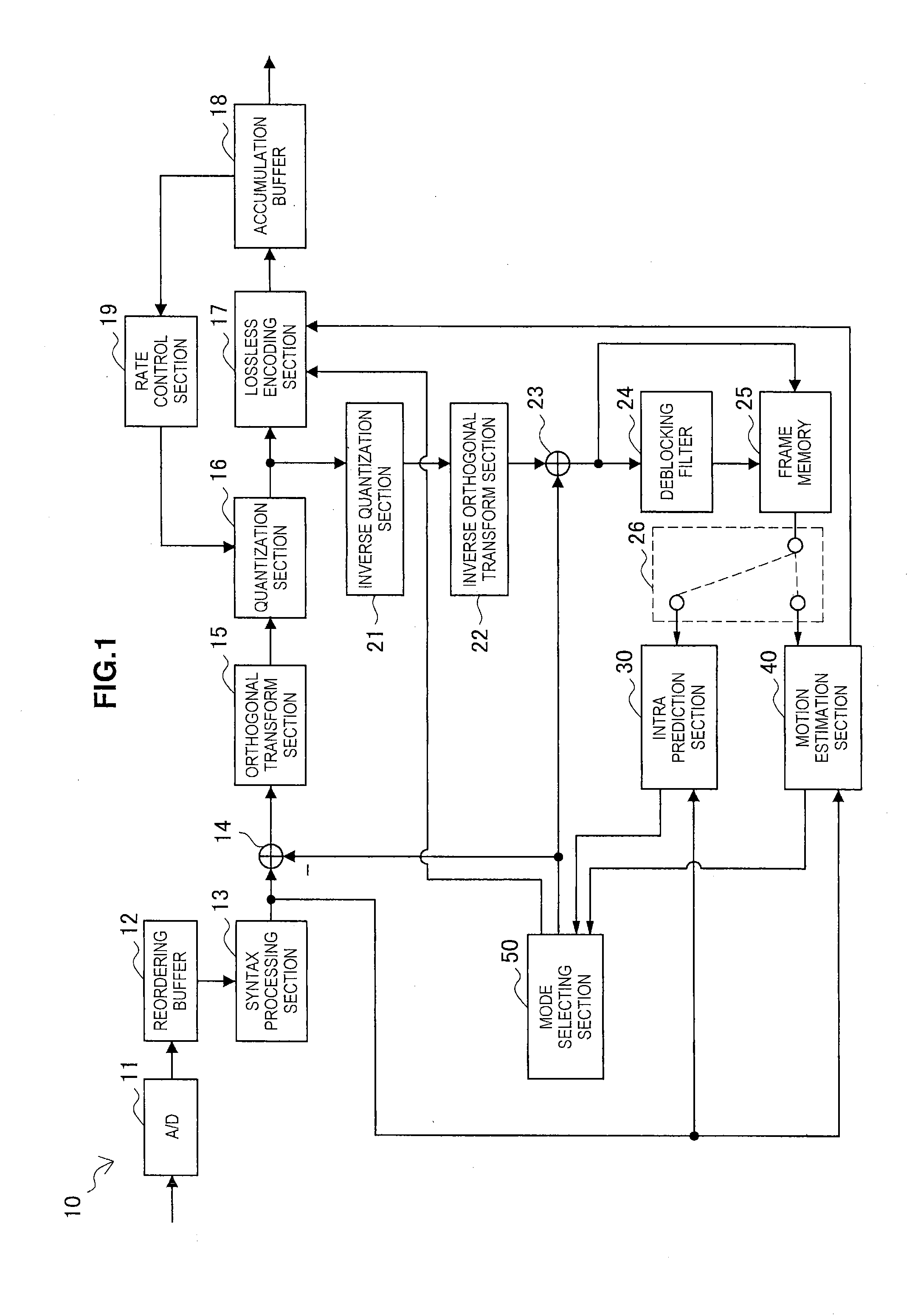
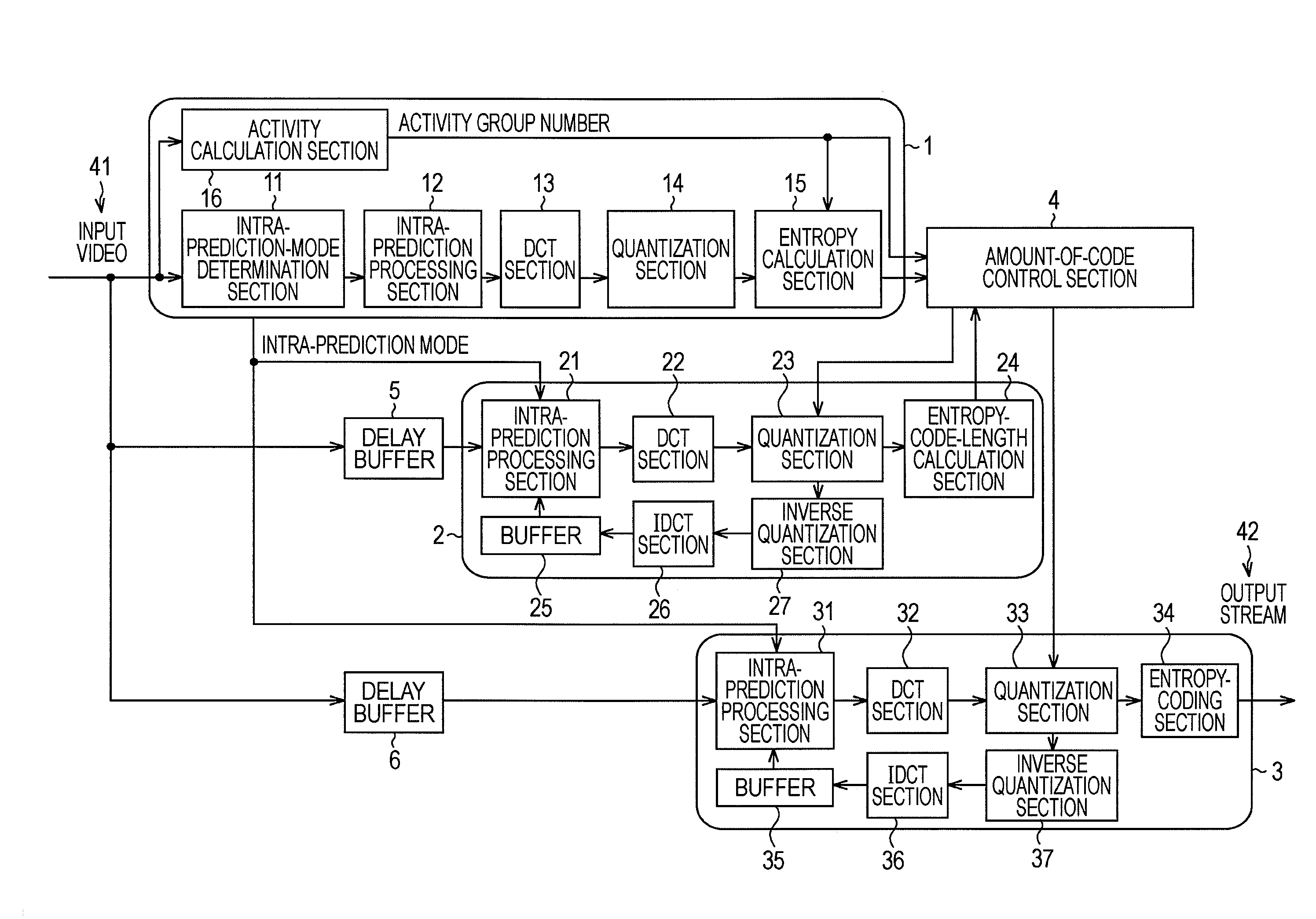
An image coding apparatus for coding image data. The image coding apparatus includes: a first coding mechanism predicting a quantization parameter and a quantization matrix to be used for calculating a target amount of code for the image data by coding the image data; a second coding mechanism correcting the quantization parameter predicted by the first coding means from an error between an amount of generated code produced by coding using the quantization parameter and the quantization matrix predicted by the first coding mechanism and the target amount of code; and a third coding mechanism coding the image data using the quantization parameter corrected by the second coding mechanism.
Owner:SONY CORP
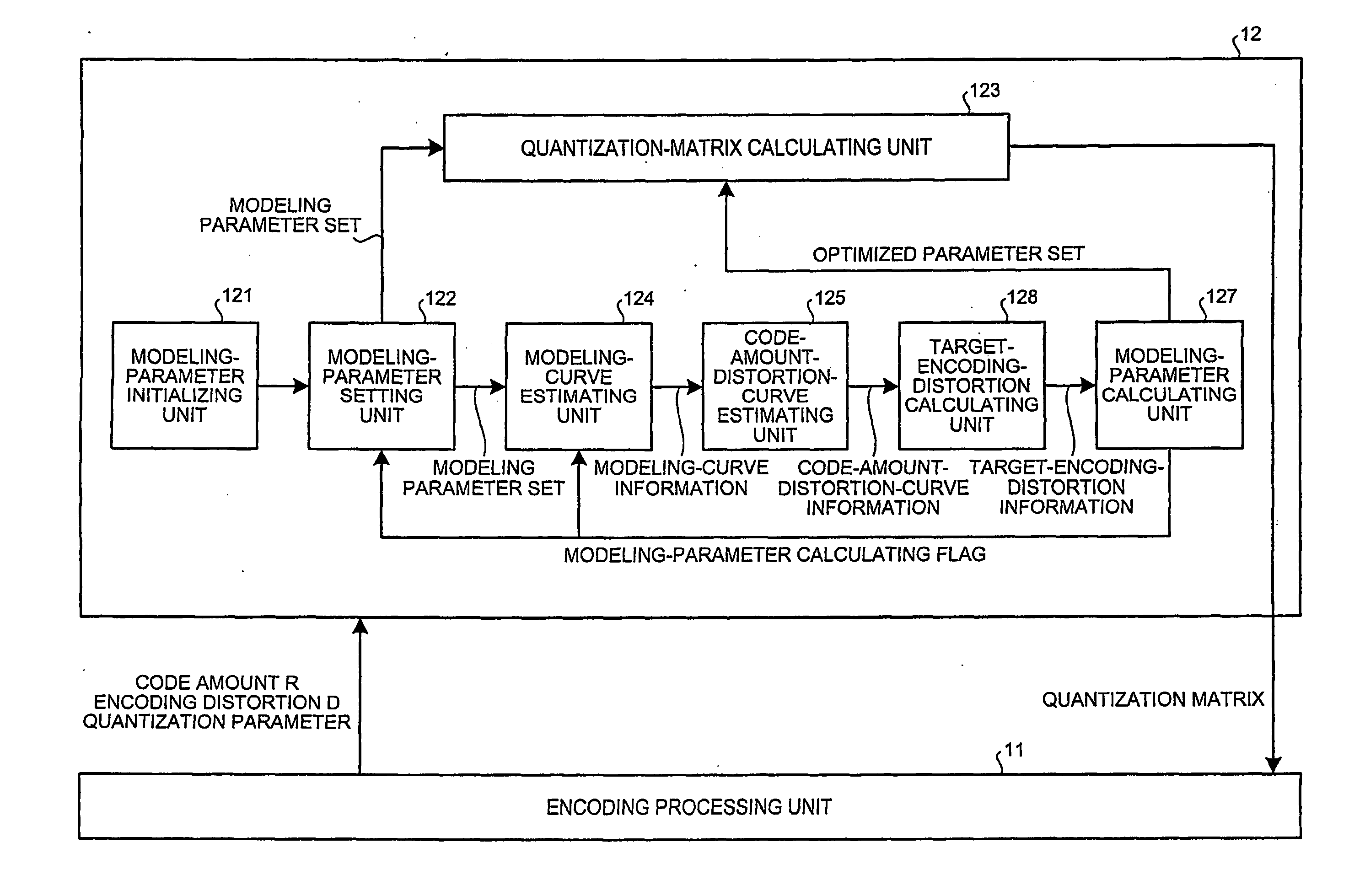
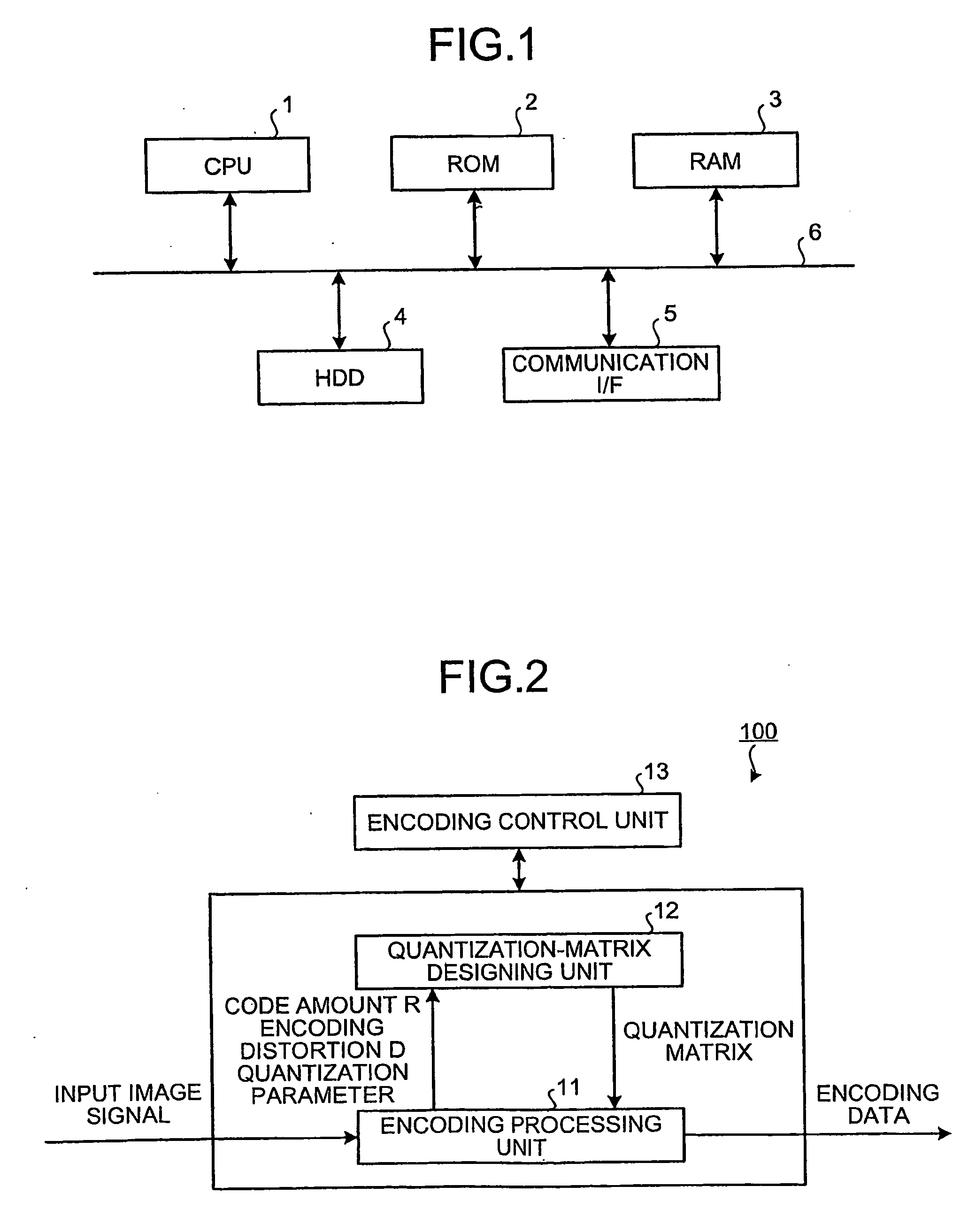
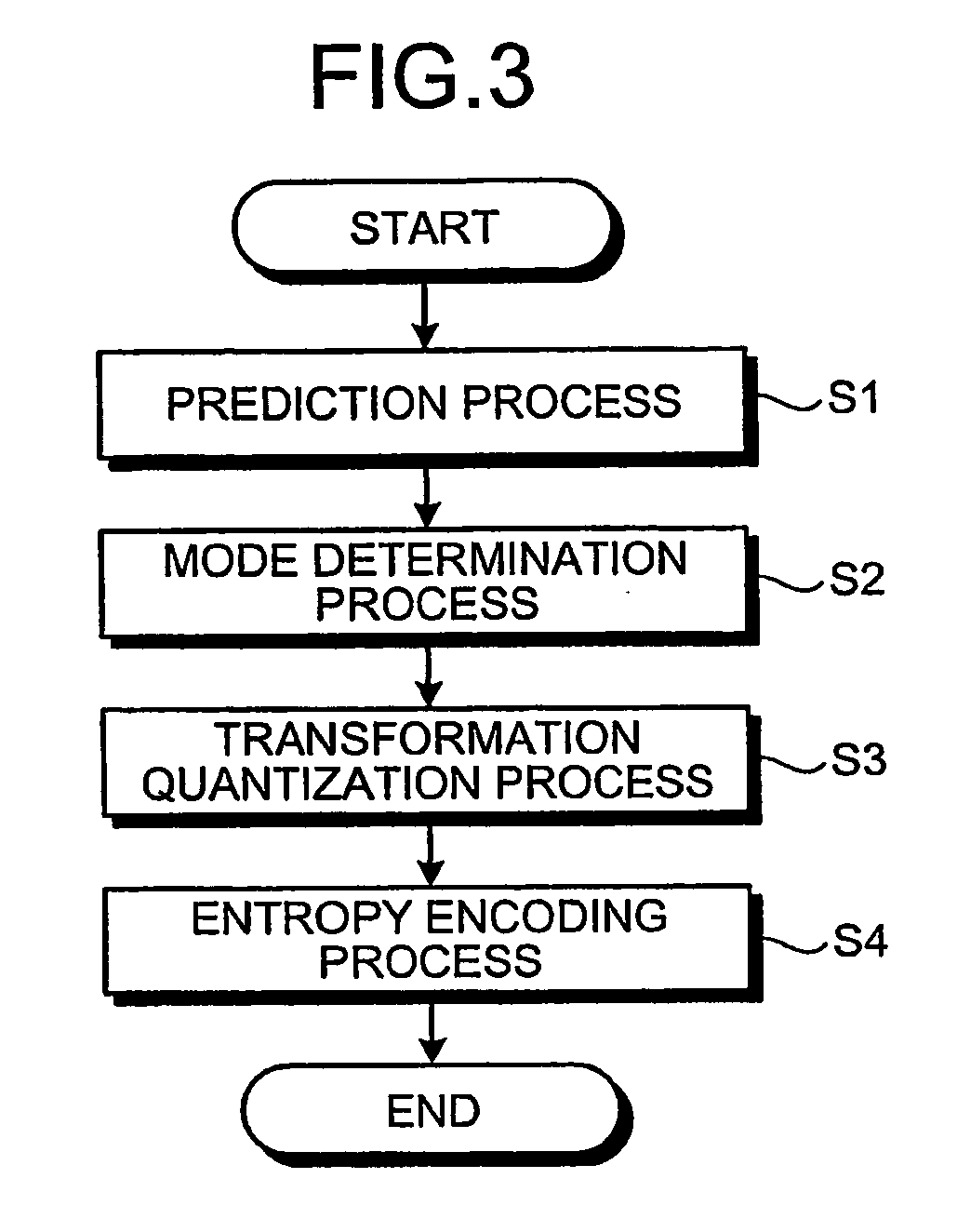
Method and apparatus for encoding image
InactiveUS20100074518A1Character and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationAlgorithmQuantization matrix
A value of a selection parameter is sequentially set from among a plurality of parameters included in a modeling equation to derive a quantization matrix. A value of each of the parameters is sequentially derived based on a code amount and an encoding distortion obtained from an encoding using a quantization matrix generated from an updated parameter set.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
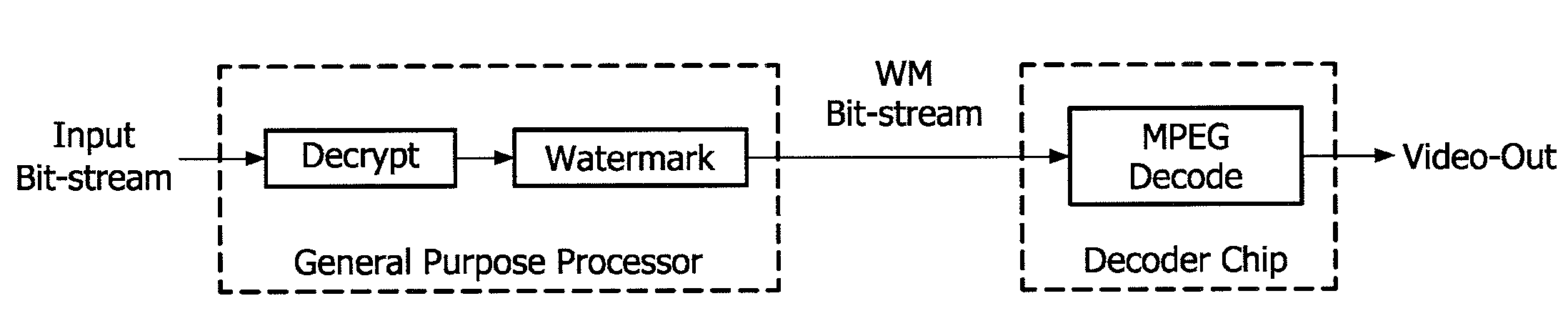
Video watermarking
ActiveUS20100046606A1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesUser identity/authority verificationTemporal changeSoftware update
A method of watermarking a video signal includes encoding the video signal using at least one encoding parameter that is time-varied according to a watermarking pattern. The parameter affects information lost while encoding the signal. The parameter may be a quantization factor corresponding to a particular coefficient of an encoding transform. The parameter may be an element of a quantization matrix corresponding to a particular coefficient in a block DCT transform. The method may be implemented in devices with limited processing resources by means of a software update. The method enables the devices to imprint an encoded signal with a robust watermark, which may survive subsequent decompression and recompression. Alternatively, a video signal may be watermarked by modifying a magnitude of a non-dc spatial frequency component in a manner which varies with time according to a watermarking pattern. Corresponding watermark detection methods and watermarking devices also are disclosed.
Owner:NAGRAVISION SA
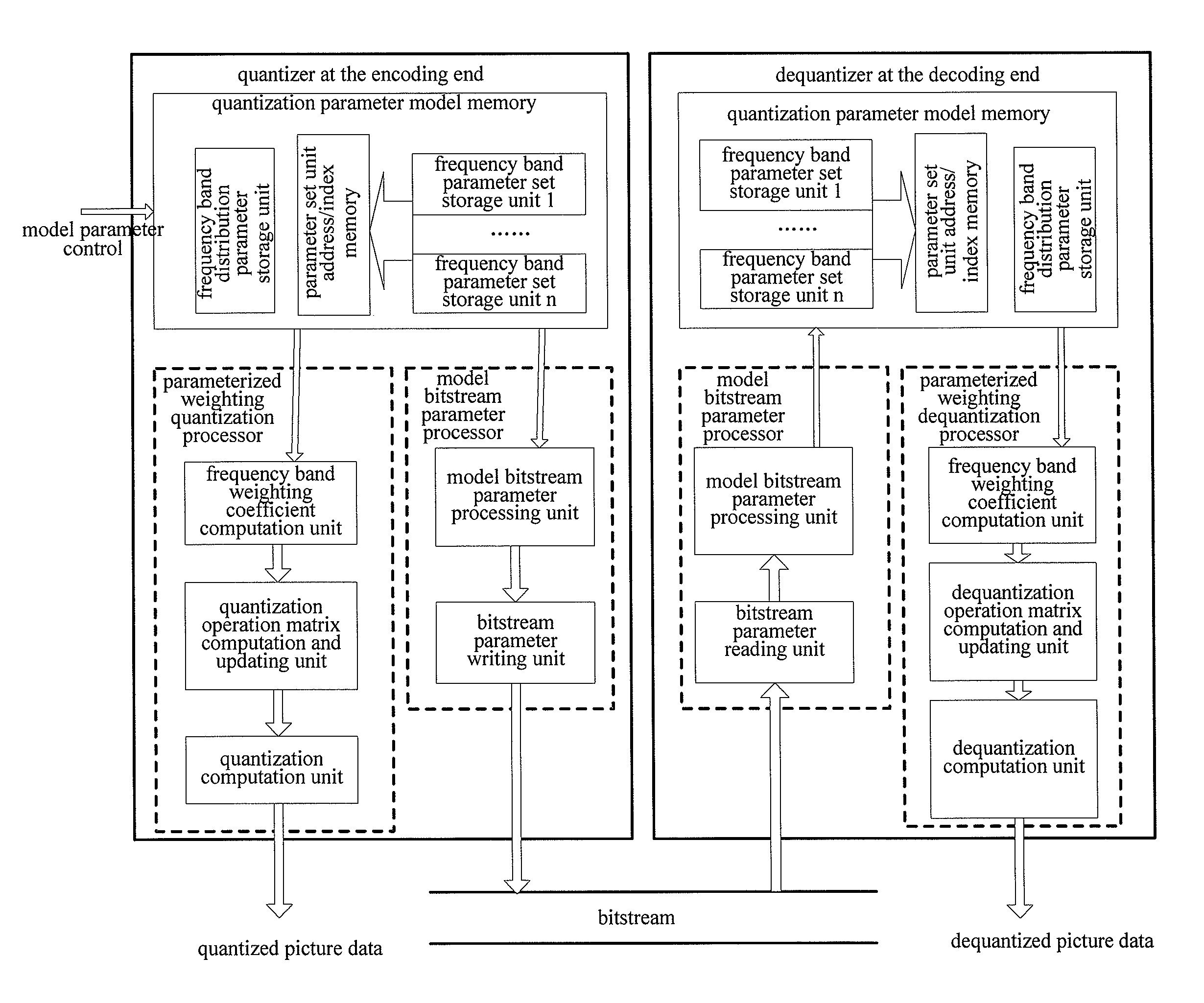
Quantization method and apparatus in encoding/decoding
ActiveUS20090034612A1Improve efficiencyImprove subjective qualityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionAlgorithmModel parameters
A method and apparatus is provided for implementing quantization in encoding / decoding. Firstly, the quantization on the picture transformed coefficient matrix is performed using a quantization parameter model, that is, the coefficient matrix is modeled as a parameter model represented by only several parameters, in which the parameter model includes two sorts of parameters, frequency band distribution parameters and frequency band weighting parameters. Thus, a quantization matrix conforming to the human vision system can be obtained by controlling the model parameters and the subjective quality of the encoded picture can be easily controlled. Secondly, the method does not need to store or transfer the quantization matrix in the bitstream which help to improve the encoding efficiency. Finally, the quantization on picture transformed coefficients using the method is well adapted to the content information of the picture to be encoded. Therefore, the present invention can improve the subjective quality of the encoded picture.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
Image encoding apparatus and method, computer program, computer-readable storage medium, and image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20060023957A1Efficient codingCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationSequence controlQuantization matrix
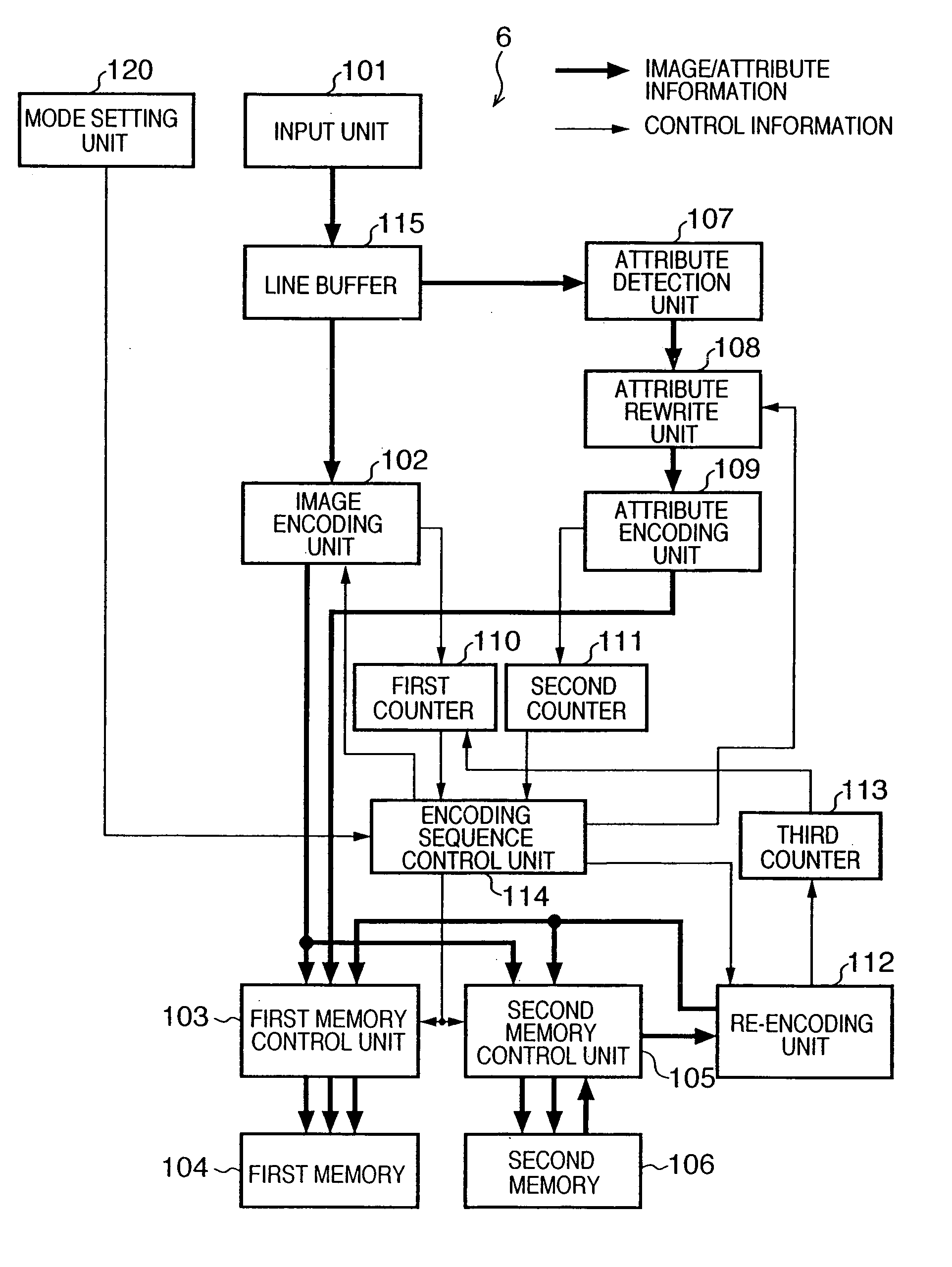
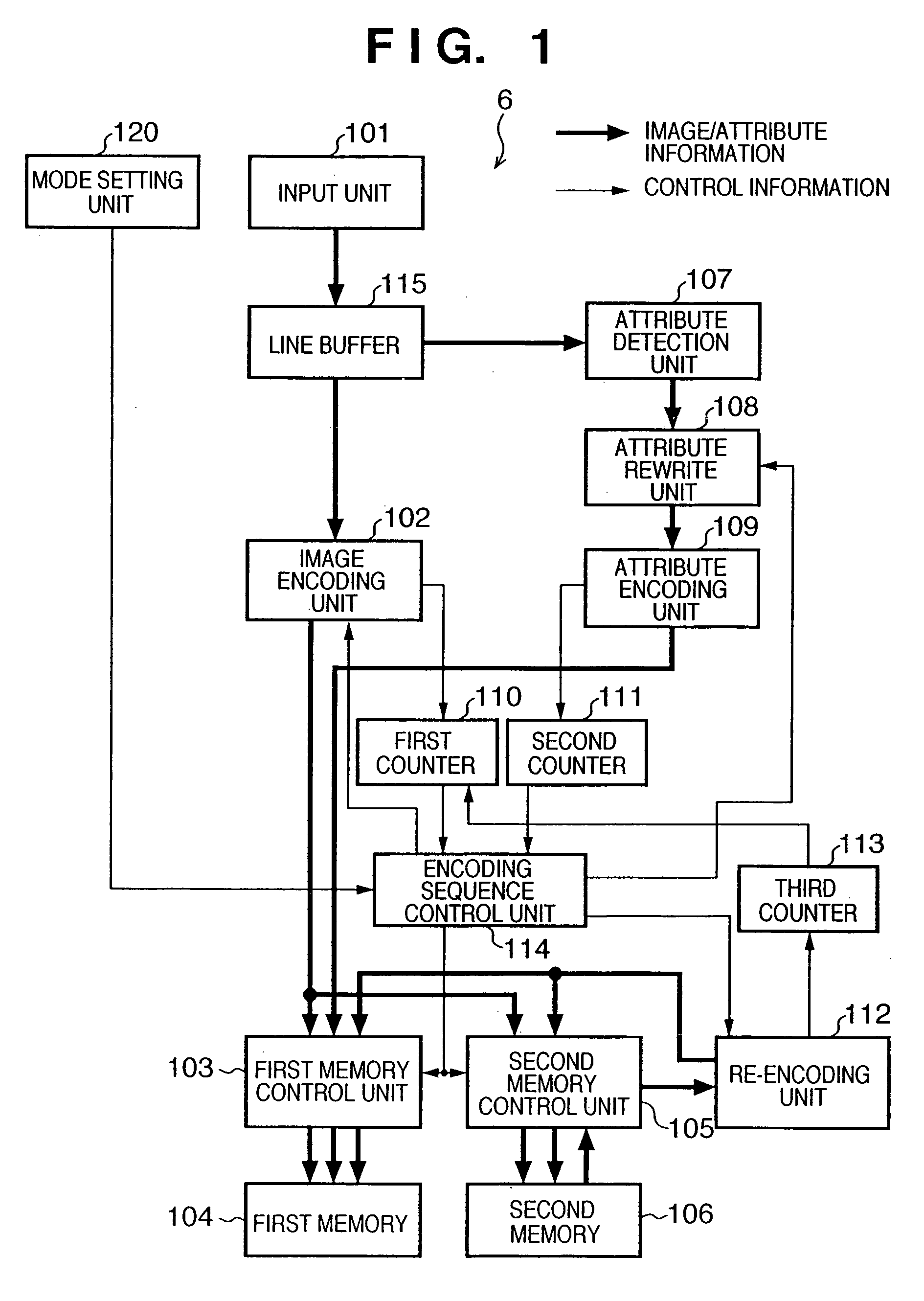
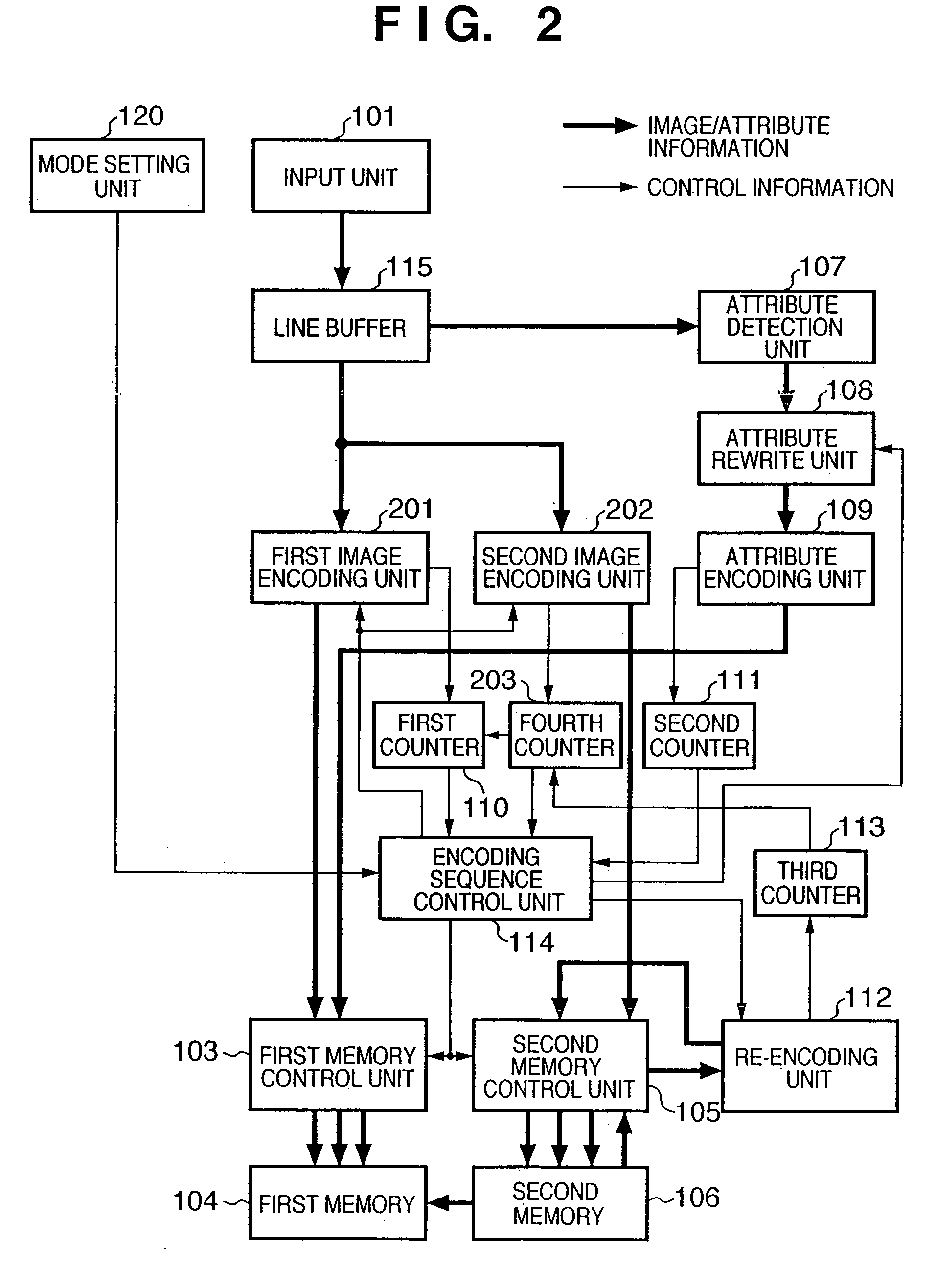
According to this invention, the encoded data amount of an image and its area attribute information can be encoded to a target amount or less by one input operation of image data, and an input image can be efficiently encoded in accordance with the property of the image. For this purpose, an encoding sequence unit sets an initial quantization matrix table for an image encoding unit in accordance with a mode set by a mode setting unit, and sets parameters associated with attribute rewrite for an attribute rewrite unit. When an image is input, encoded image data generated by the image encoding unit is stored in a memory. Attribute-encoded data generated by an attribute encoding unit is also stored in the memory. The first counter counts an encoded-image data amount, and the second counter counts an attribute-encoded data amount. When the sum of these encoded data exceeds a target amount, the encoding sequence control unit updates the quantization matrix table for the image encoding unit, and causes the image encoding unit to continue encoding. The updated quantization matrix table is set for a re-encoding unit, and encoded data stored in the memory is re-encoded.
Owner:CANON KK
Video signal coding apparatus and video signal coding method
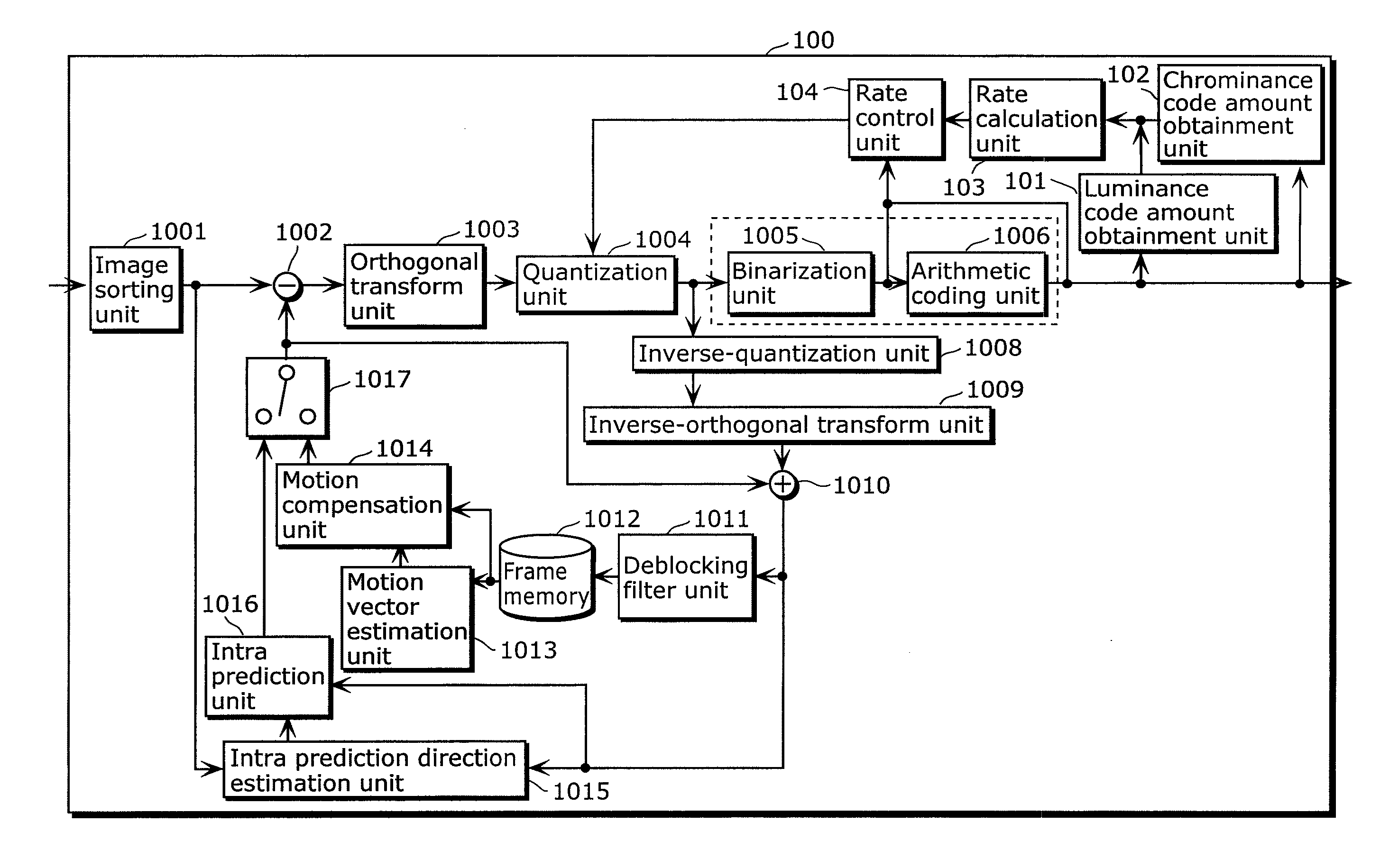
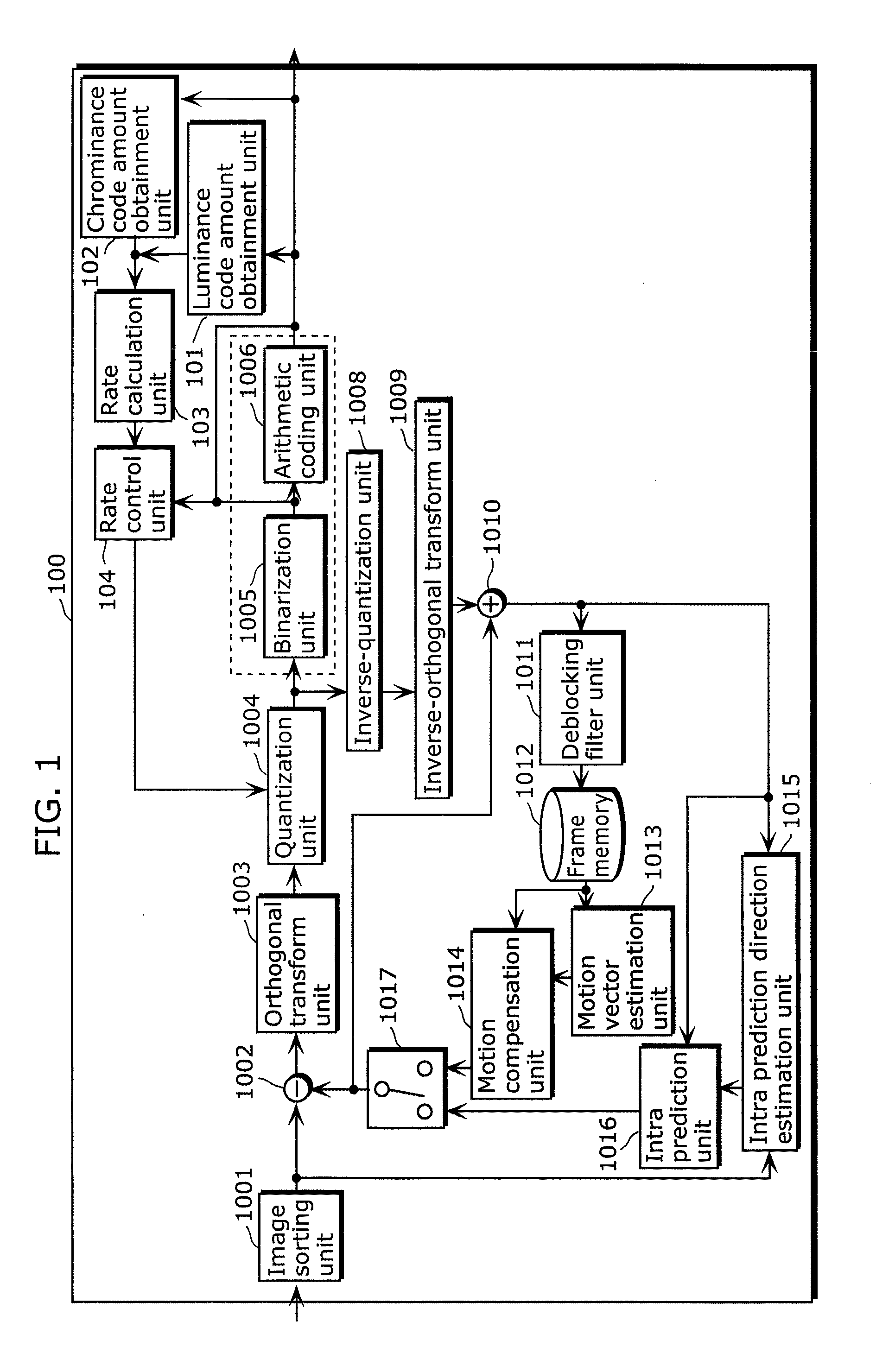
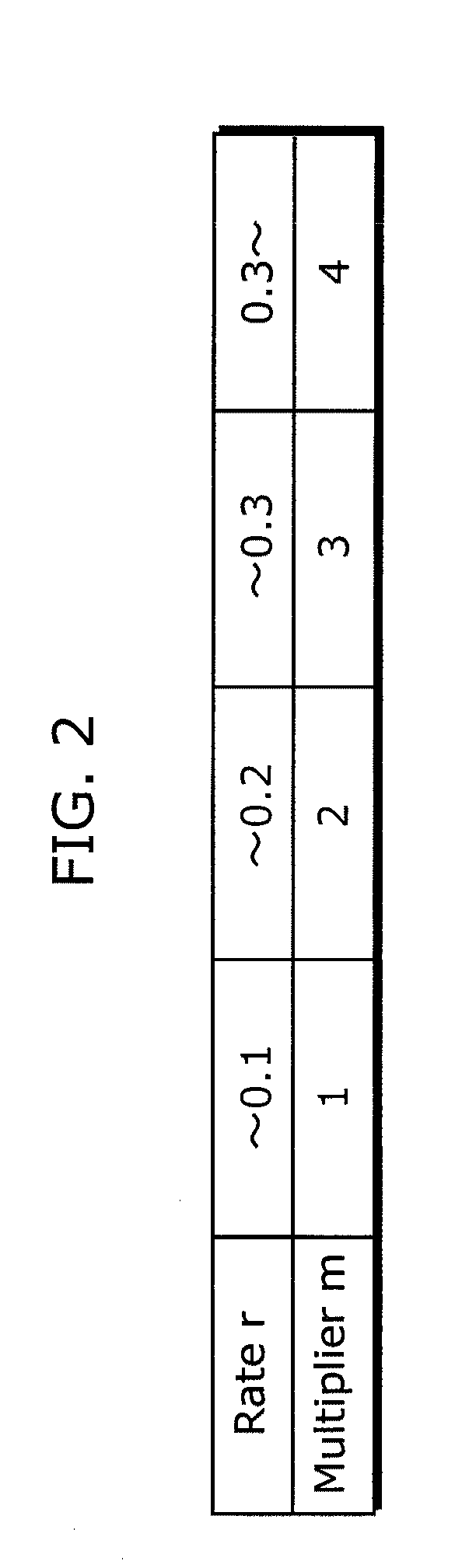
ActiveUS20100202513A1Improve image qualityAmount of codeColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionParallel computingQuantization matrix
Video signal coding apparatus includes: a quantization unit which quantizes, using coefficient values in a first quantization matrix, a luminance signal of each of a first picture and a second picture coded after the first picture, and quantizes, using coefficient values in a second quantization matrix, a chrominance signal of each of the first picture and the second picture; a code amount obtainment unit which obtains a luminance code amount and a chrominance code amount of each of the first picture and the second picture; a rate calculation unit which calculates a rate of the chrominance code amount with respect to the luminance code amount for each of the first picture and the second picture, obtained by the code amount obtainment unit; and a rate control unit which changes a coefficient value of at least one of the first matrix and the second matrix used in quantizing the second picture, before the quantization unit quantizes the second picture, so that the rate for the second picture becomes smaller than the rate for the first picture.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Quantization matrix compression in video coding
ActiveUS20150103892A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo encodingAlgorithm
A method of quantization matrix compression in a video encoder is provided that includes preprocessing a quantization matrix by performing at least one selected from down-sampling the quantization matrix and imposing 135 degree symmetry on the quantization matrix, performing zigzag scanning on the pre-processed quantization matrix to generate a one dimensional (1D) sequence, predicting the 1D sequence to generate a residual 1D sequence, and coding the residual 1D sequence using kth order exp-Golomb coding to generate a compressed quantization matrix, wherein k≧0.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Picture Coding Method, Picture Decoding Method, Picture Coding Apparatus, Picture Decoding Apparatus
ActiveUS20070292039A1Improve efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsVariable-length codeQuantization matrix
The picture coding method according to the present invention is a picture coding method for coding a picture on a block-by-block basis through orthogonal transformation and quantization, and coding a quantization matrix that is used to derive quantization steps for frequencies of orthogonal transformation coefficients, the method comprising: calculating a difference value between each of frequency components included in the quantization matrix and a predetermined value corresponding to said each of the frequency components; and coding the difference value into a variable length code, wherein a code length of the variable length code is shorter as the difference value is smaller, or equal to a code length of a neighboring difference value of said difference value.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
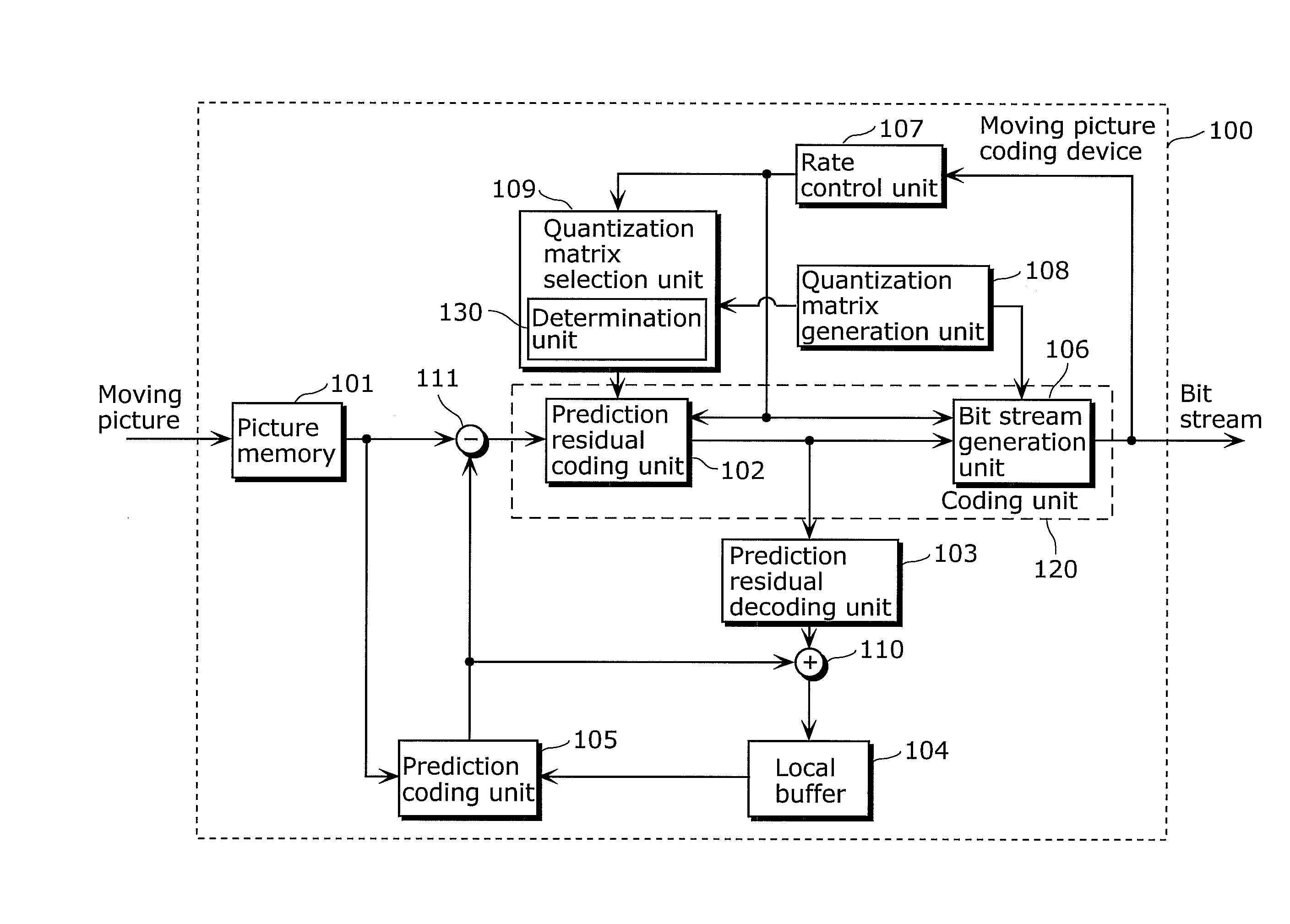
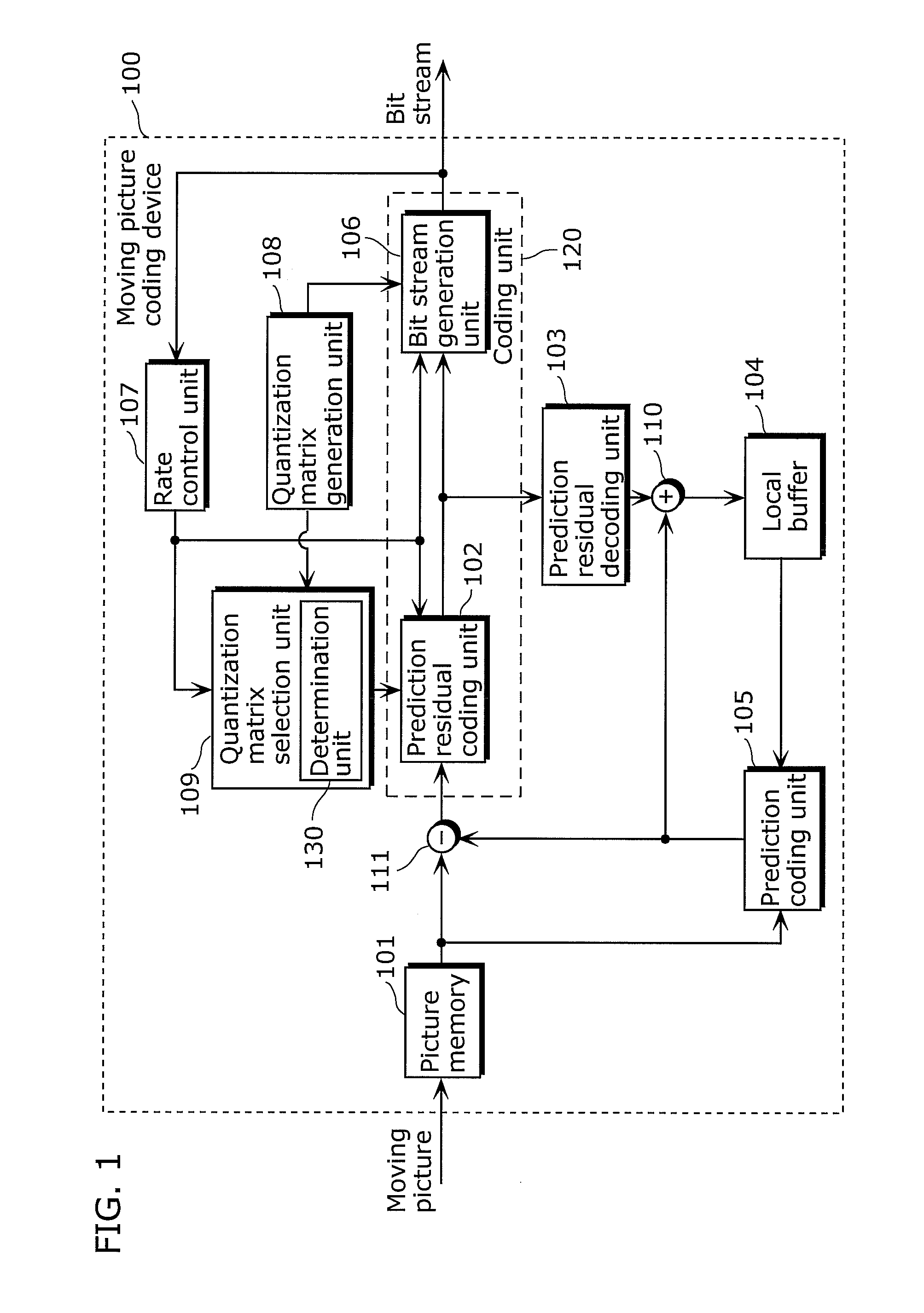
Moving picture coding device and broadcast wave recording device
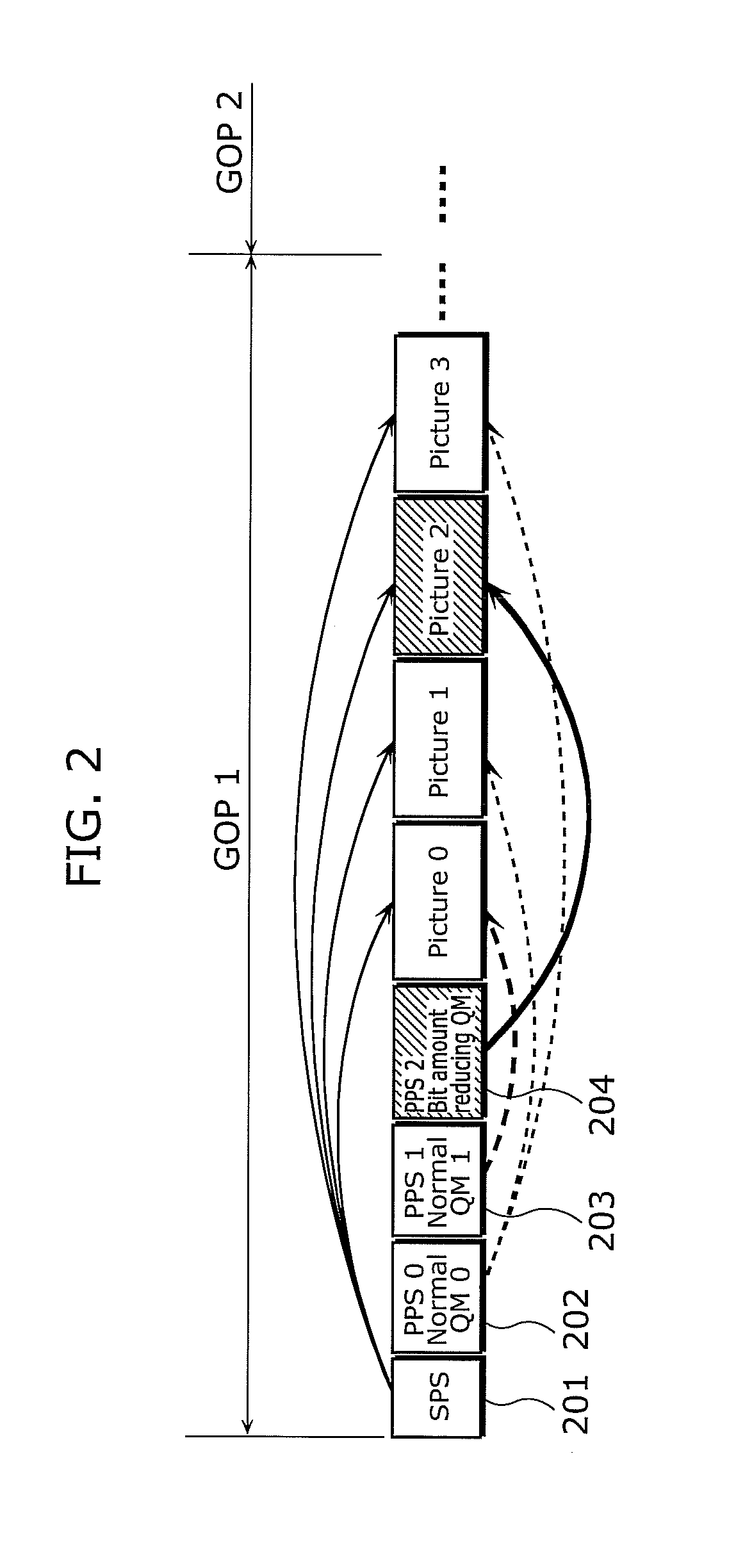
InactiveUS20100316120A1Reduce amountImprove image qualityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureSimulation based
A device coding a moving picture in units of a group including pictures, including: a generation unit generating quantization matrices; a selection unit selecting a quantization matrix for a current picture; a unit storing the quantization matrices in a header part of the group, and coding the current picture; a unit including a virtual buffer, and performing buffer simulation based on an amount of bits to be outputted; and a unit determining whether bit amount reducing is required for the current picture, based on a result of the buffer simulation, wherein the generation unit generates a normal quantization matrix used in common for at least one of the pictures, and a quantization matrix for bit amount reducing used only when the bit amount reducing is required, and the selection unit selecting the quantization matrix for bit amount reducing used for the current picture, when the bit amount reducing is required.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
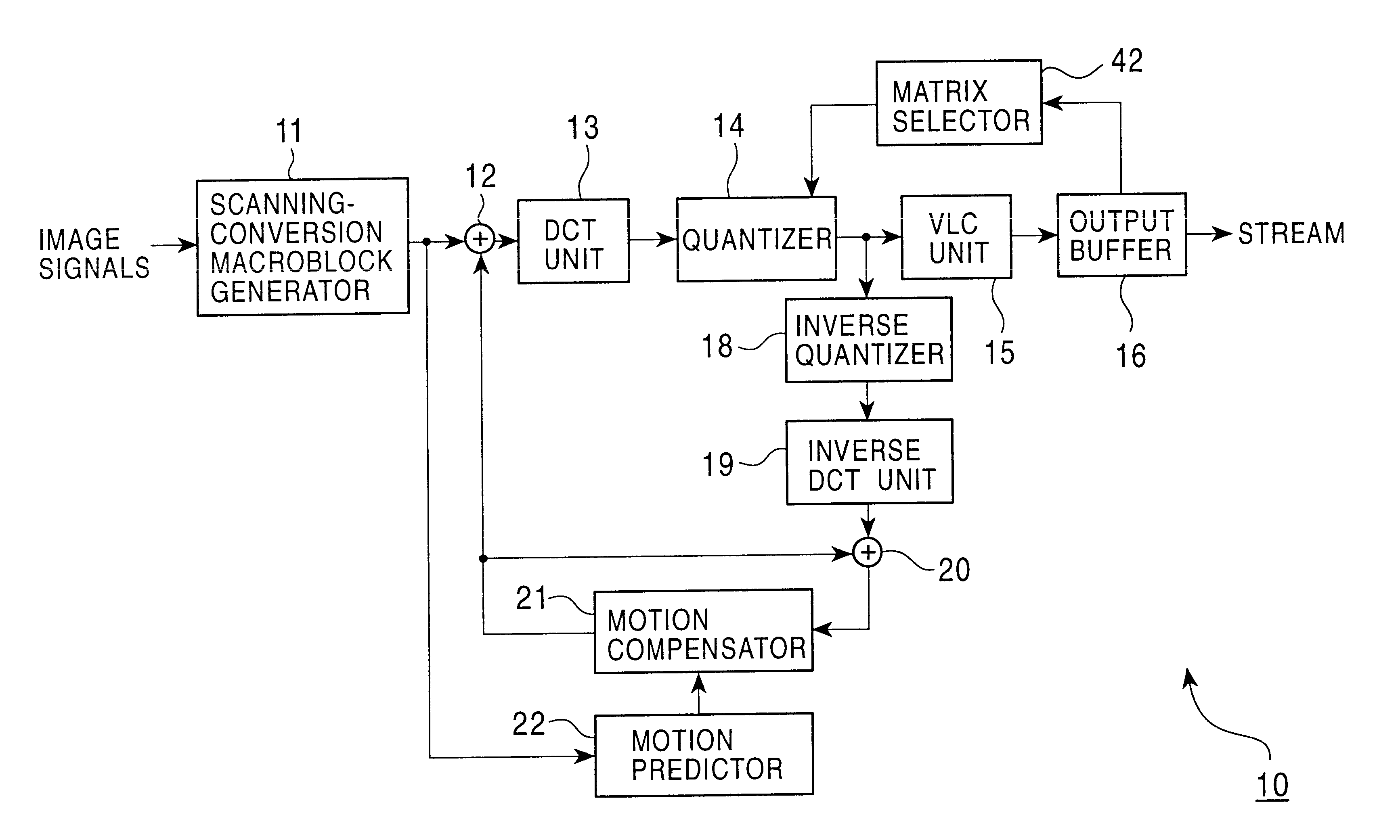
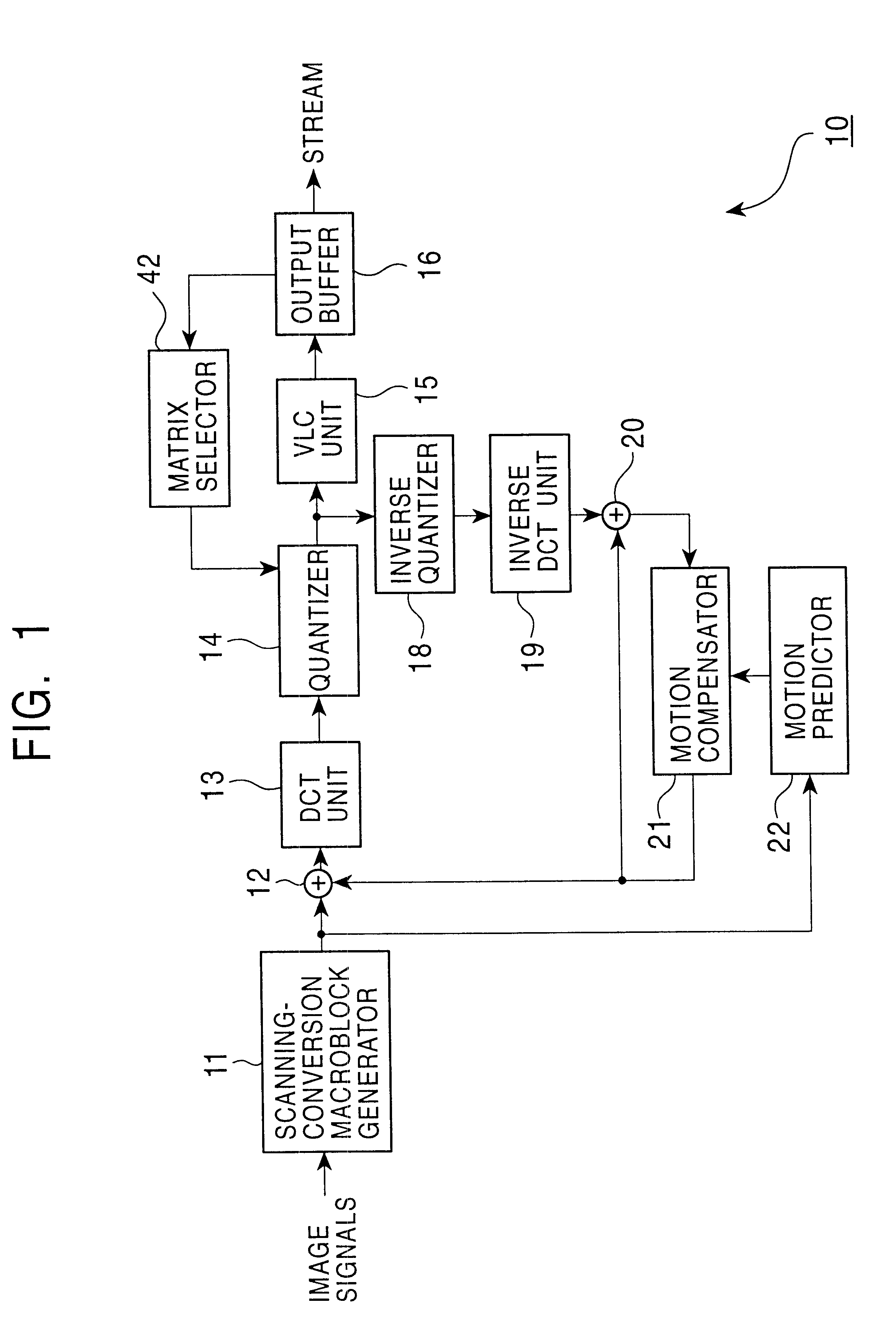
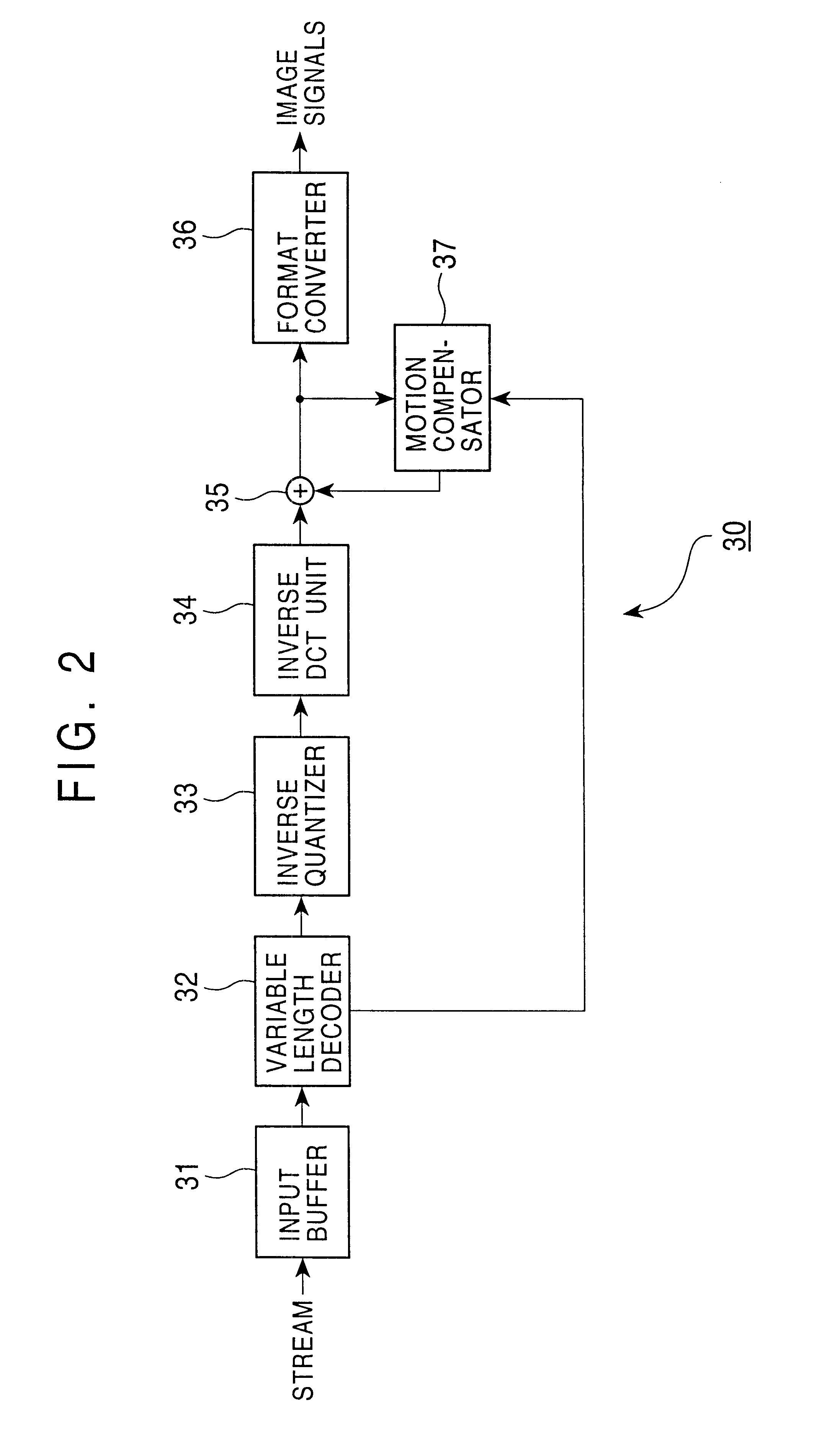
Encoding apparatus and method
InactiveUS6928113B1Quality improvementHigh frequencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVariable-length codeAlgorithm
An encoding apparatus and method prevents image deterioration generated by repeatedly performing encoding and decoding by using a quantization matrix for quantization which is different from a quantization matrix for inverse quantization. In the encoding apparatus, a matrix selector selects a first quantization matrix in accordance with the complexity of an encoded picture pattern, and supplies a quantizer with information on the selected first quantization matrix. A matrix unit rewrites, by information on a second quantization matrix, the information described in an encoded stream output from a variable length code unit so that a quantization matrix to be used for inverse quantization is a second quantization matrix different from the first quantization matrix.
Owner:SONY CORP
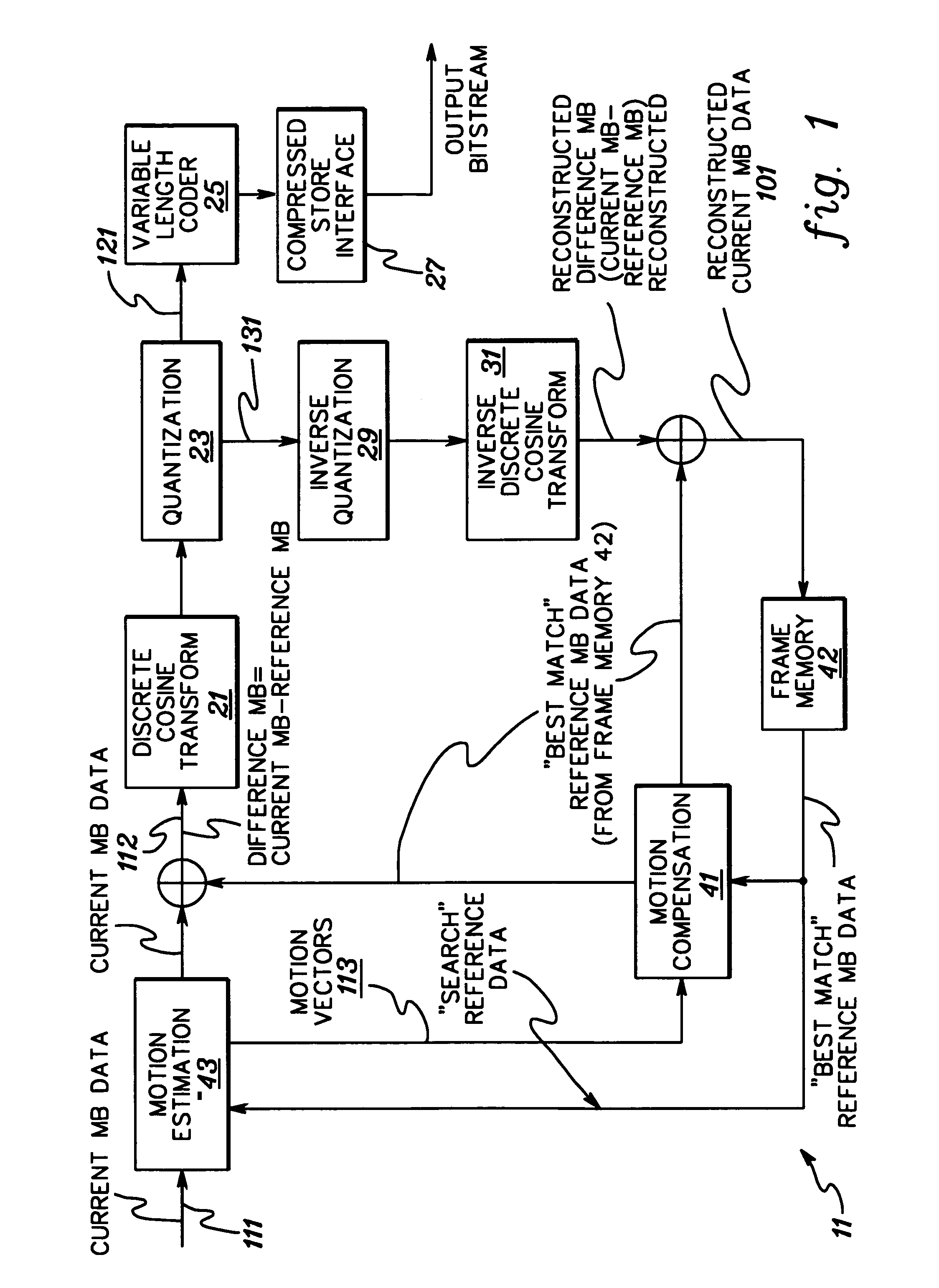
Dynamic image compression coding apparatus
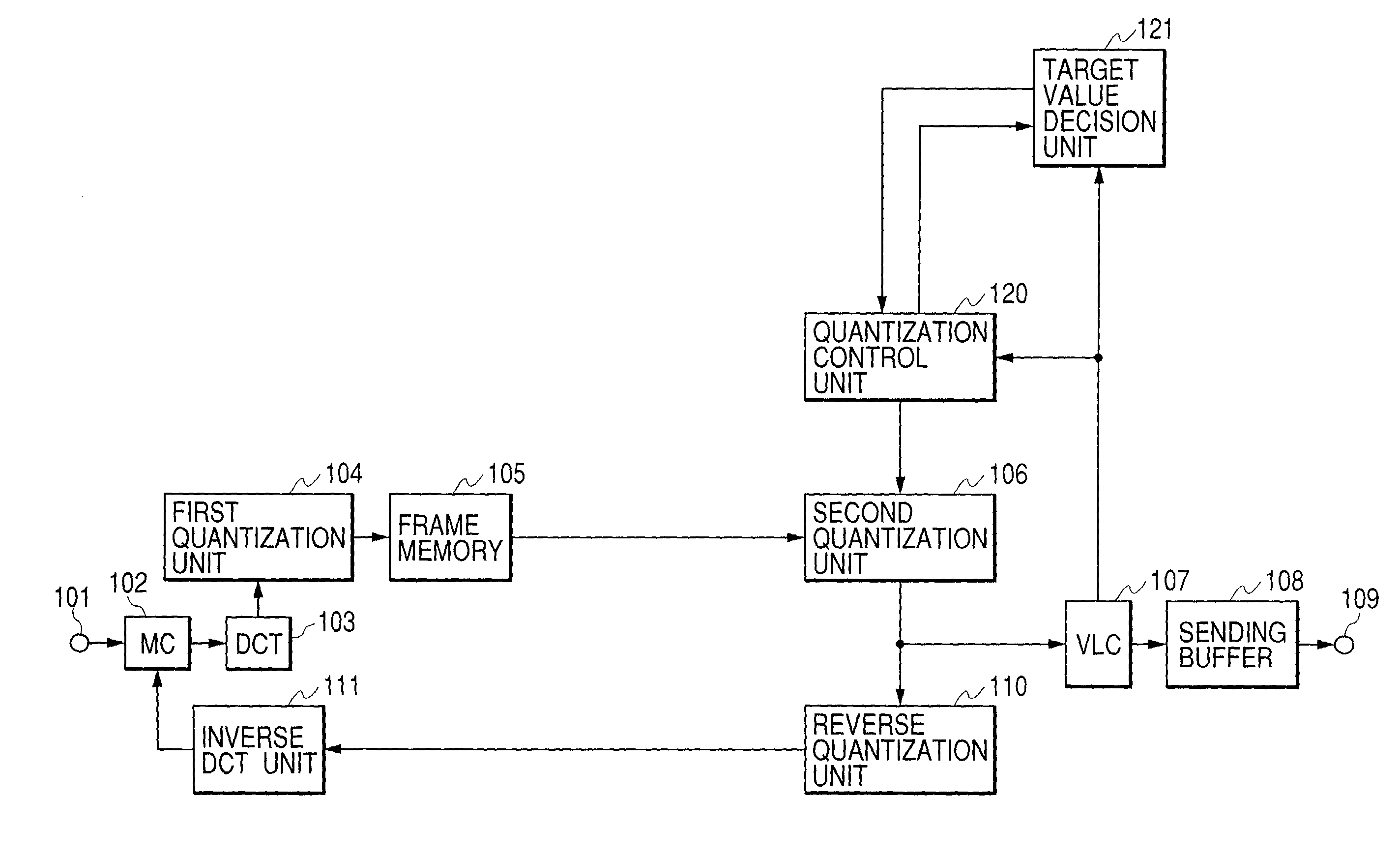
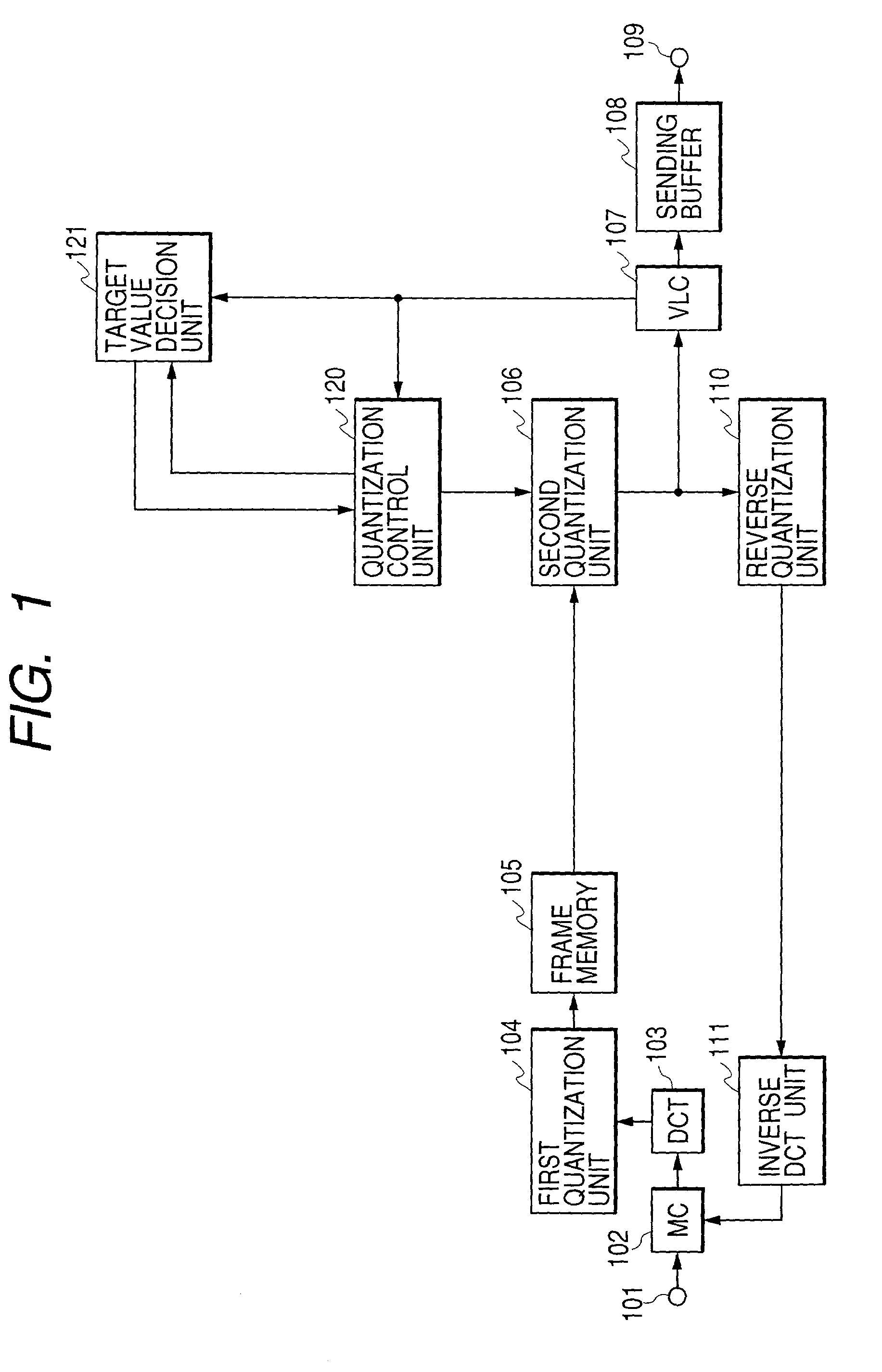
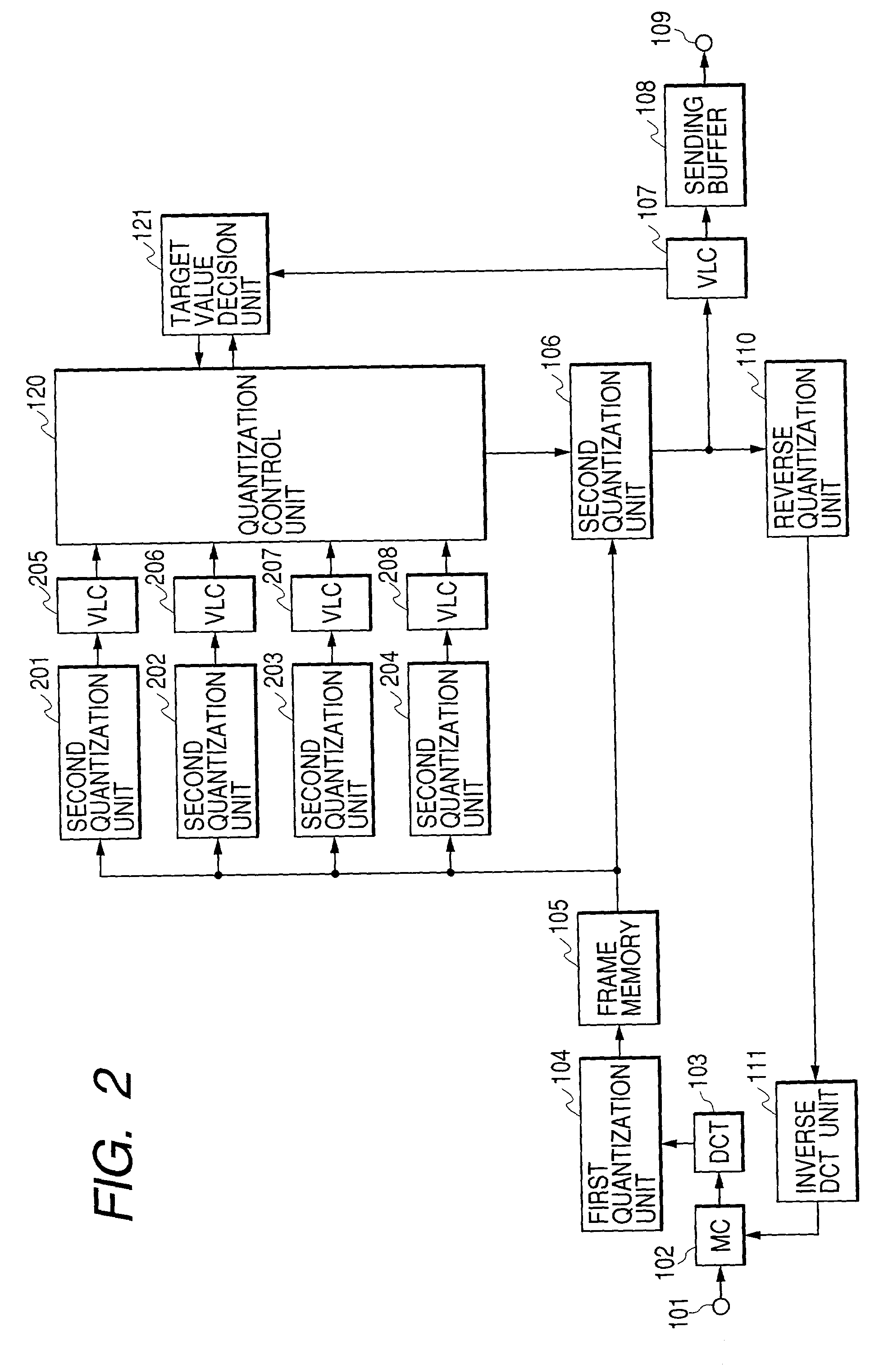
In the coding of a dynamic image signal that conforms to the MPEG-2 Standard, when one-picture two-path coding is performed, the capacity of a memory for storing one-picture image data is reduced while lowering a throughput to be executed repetitively. Further, a throughput for estimating a generated code amount is reduced. This dynamic image compression coding apparatus has a memory that splits quantization processing into division processing using a quantization matrix and division processing using a quantization scale and temporarily stores one-picture data after quantization using the quantization matrix. In the first coding performed for estimating a code amount generated every macro block, the quantization processing is performed using a bit shift instead of division. Further, round-off processing in the quantization processing is substituted for round-down processing.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com