Constructing a statistical shape model from two-dimensional or three-dimensional data
a statistical shape model and data technology, applied in the field of statistical shape models, can solve problems such as manual defining landmarks, model failure to correctly determine whether, and difficulty in defining shape constraints
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
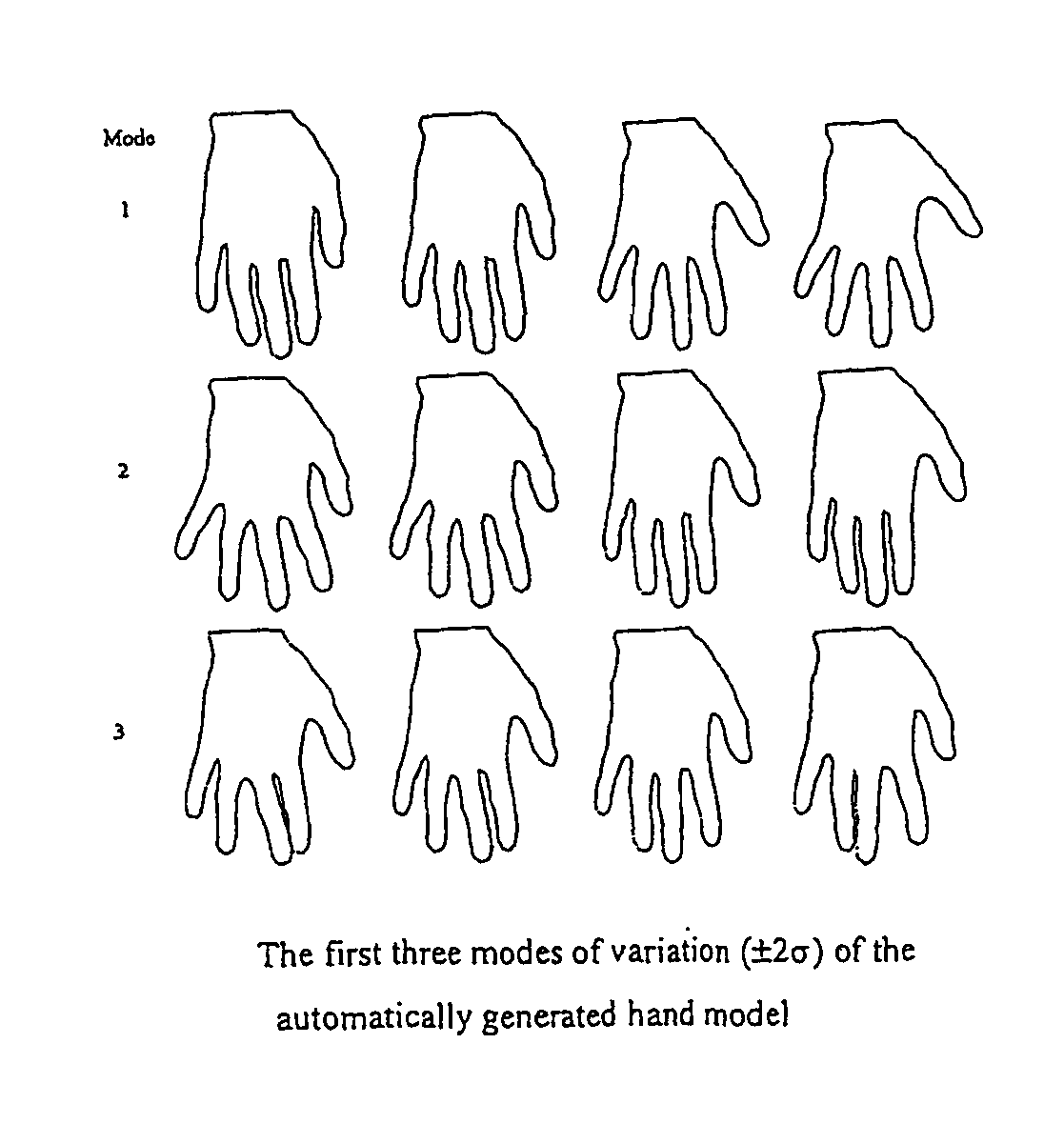
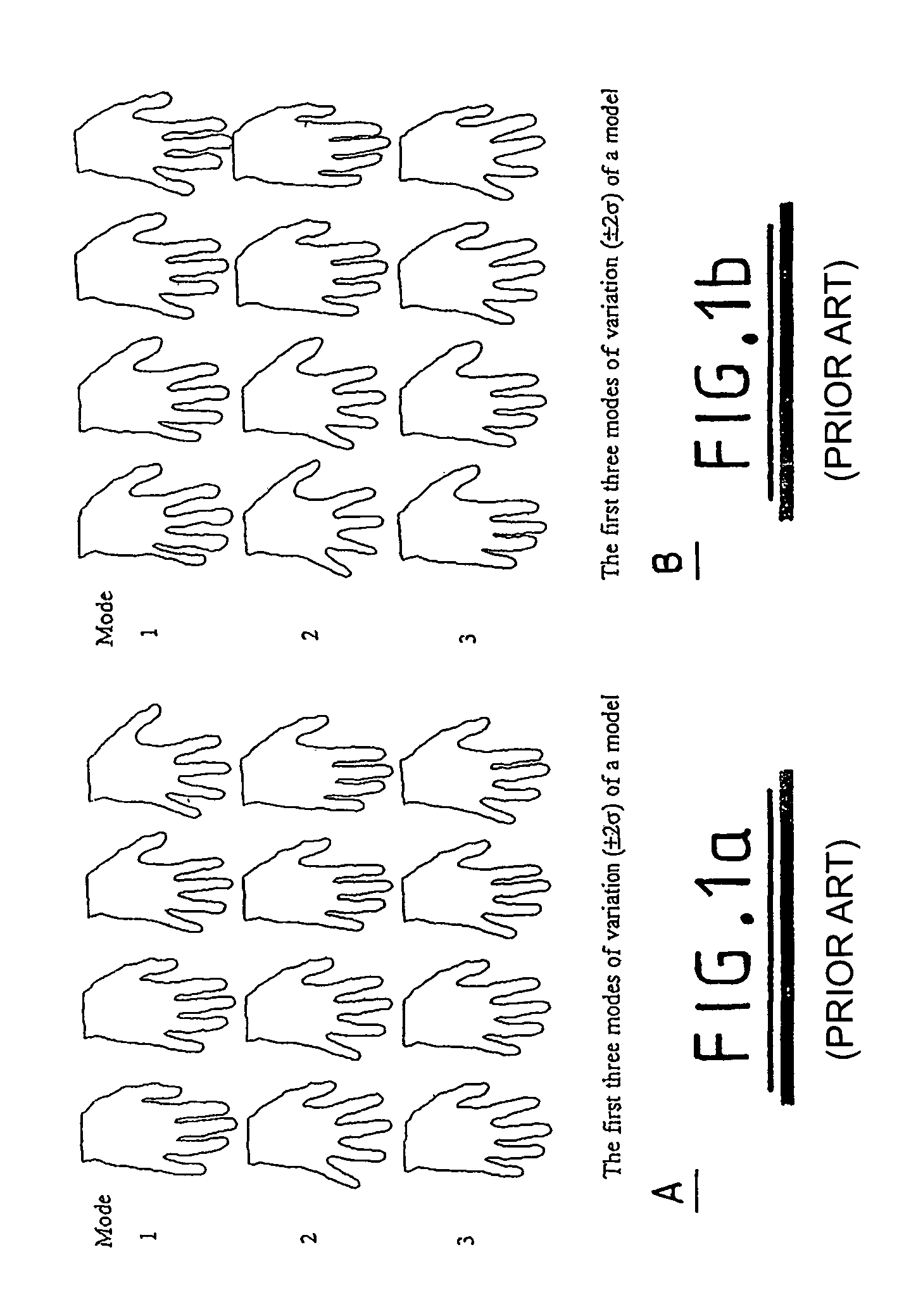
[0086]The illustrated embodiment of the invention is based upon a two dimensional (2-D) statistical shape model.
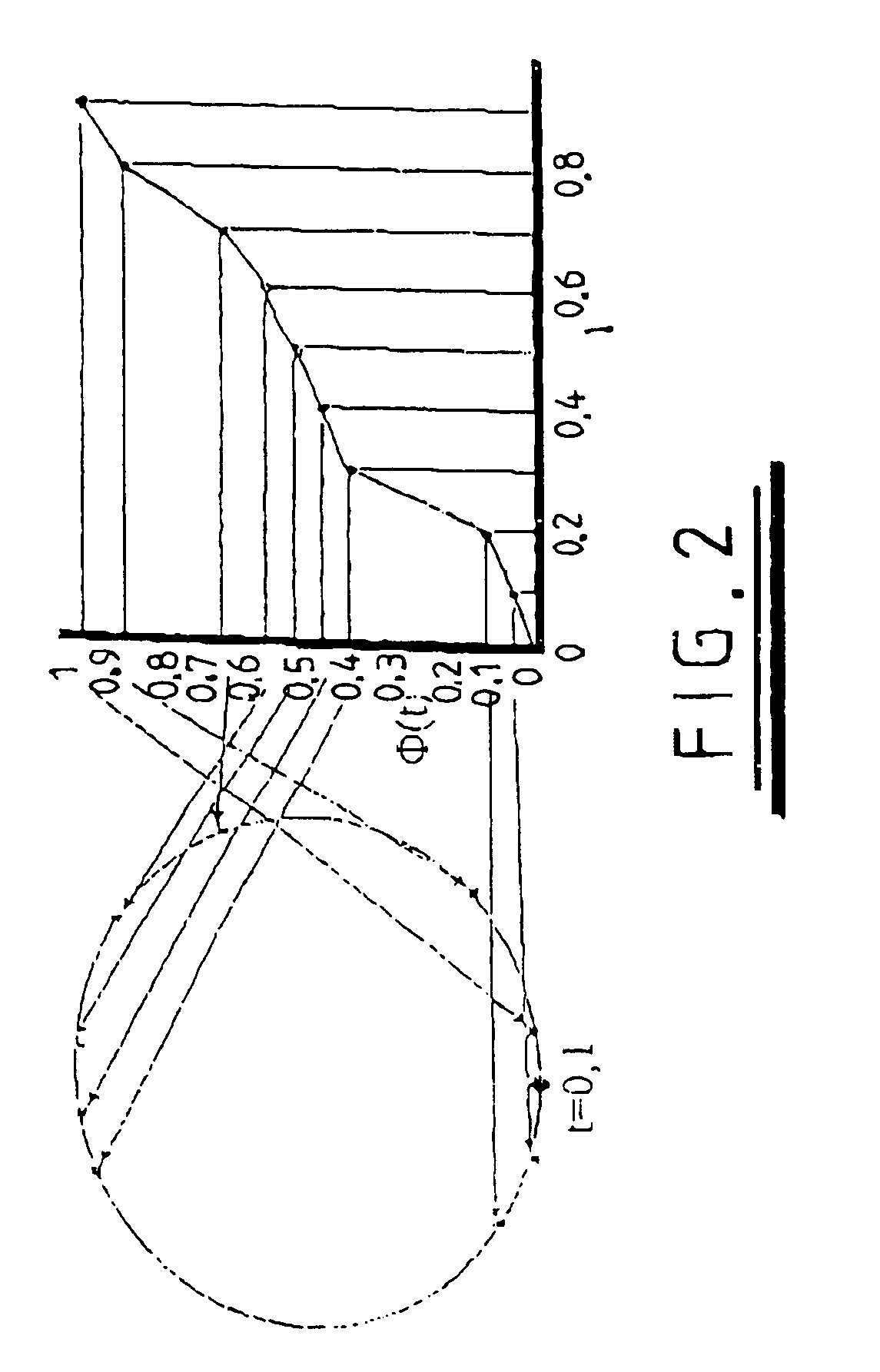
[0087]As previously described in the introduction, a 2-D statistical shape model is built from a training set of example shapes / boundaries. Each shape, Si, can (without loss of generality) be represented by a set of (n / 2) points sampled along the boundary at equal intervals, as defined by some parameterisation Φi of the boundary path (the term parameterisation refers to the separation of the boundary path into the set of distances along the boundary between the sampled points).
[0088]Using Procrustes analysis [12] the sets of points can be rigidly aligned to minimise the sum of squared differences between corresponding points. This allows each shape Si to be represented by a n-dimensional shape vector xi, formed by concatenating the coordinates of its sample points, measured in a standard frame of reference. Using Principal Component analysis, each shape vector can be appro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com