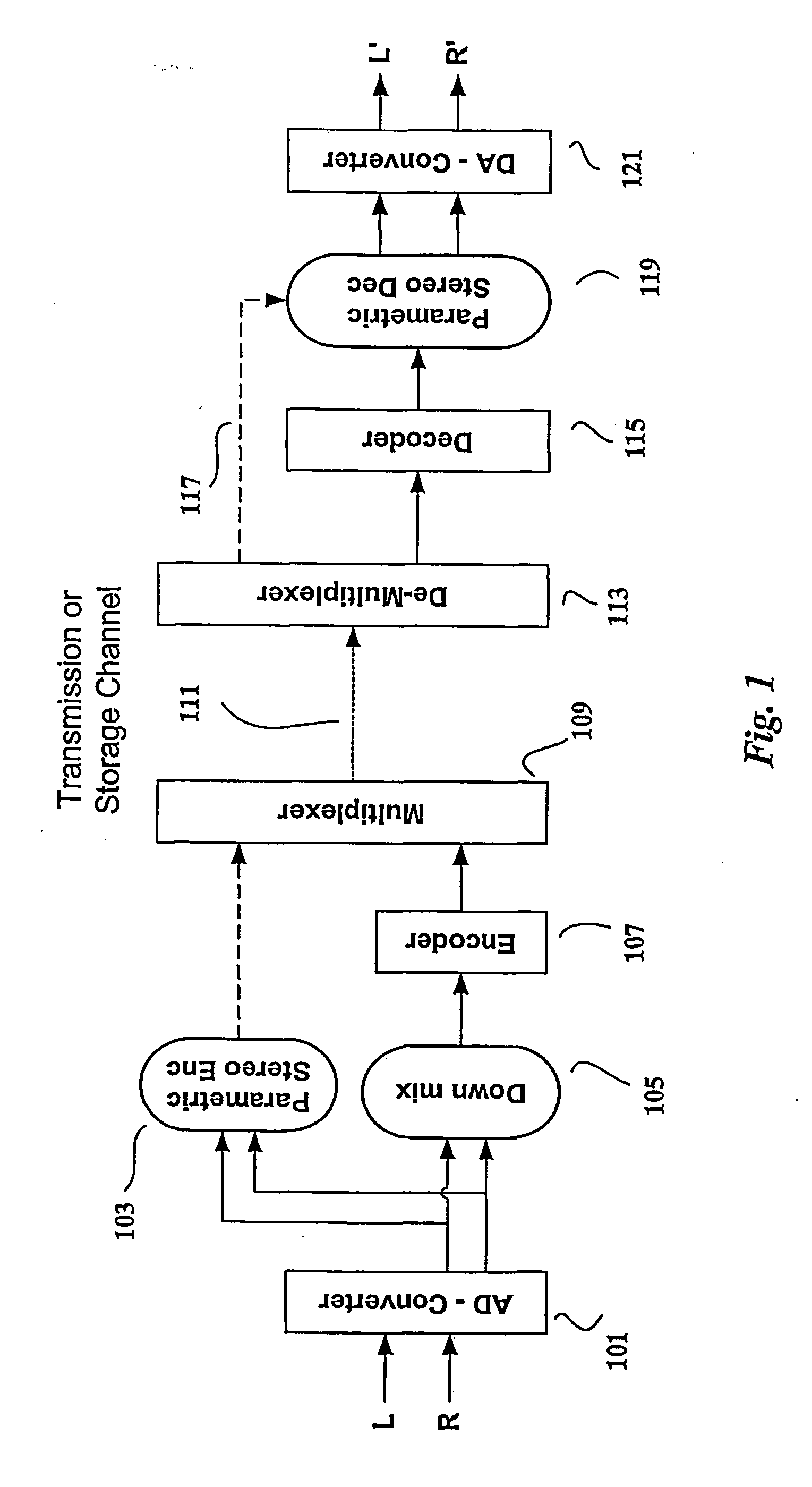
Patents
Literature
53 results about "Parametric Stereo" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
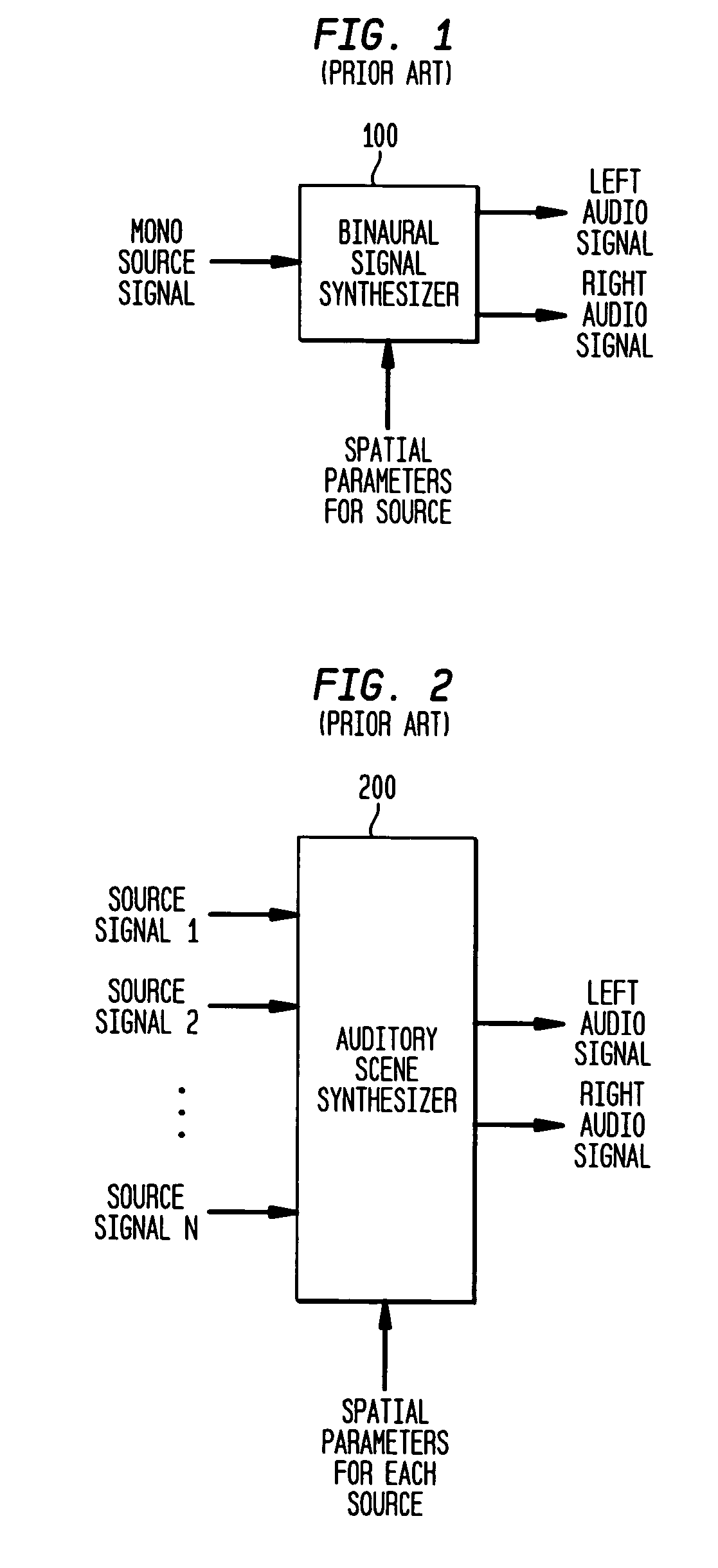
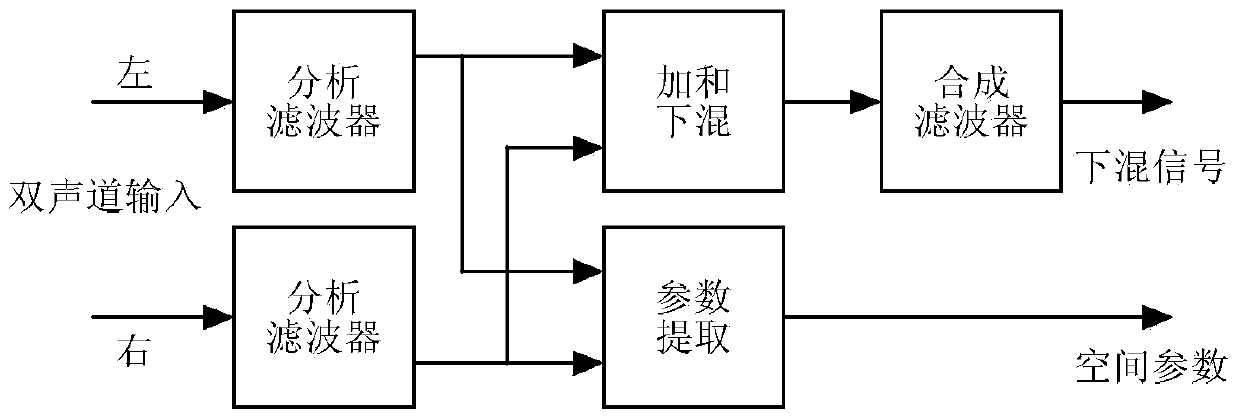
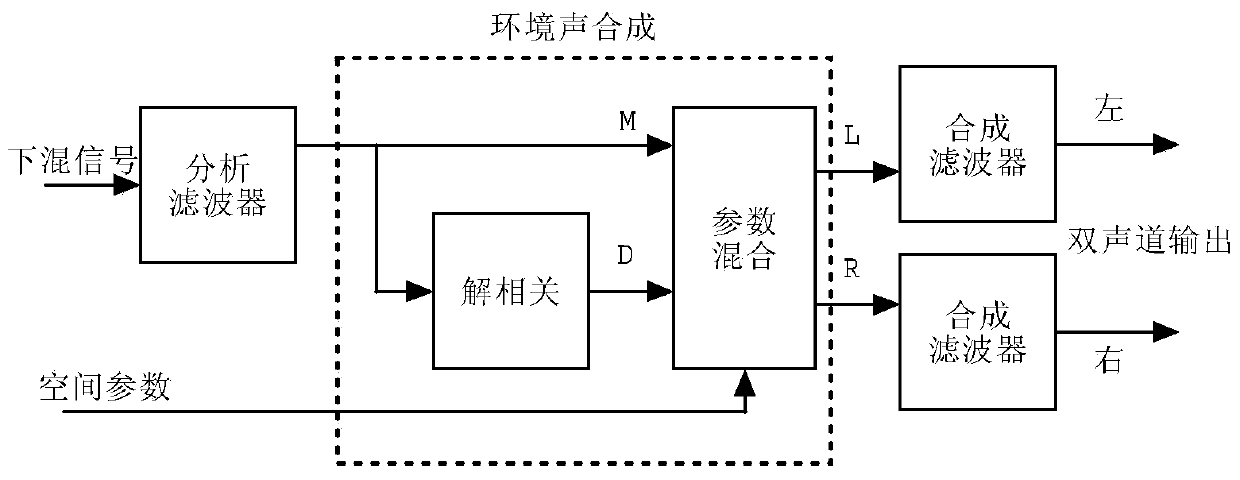
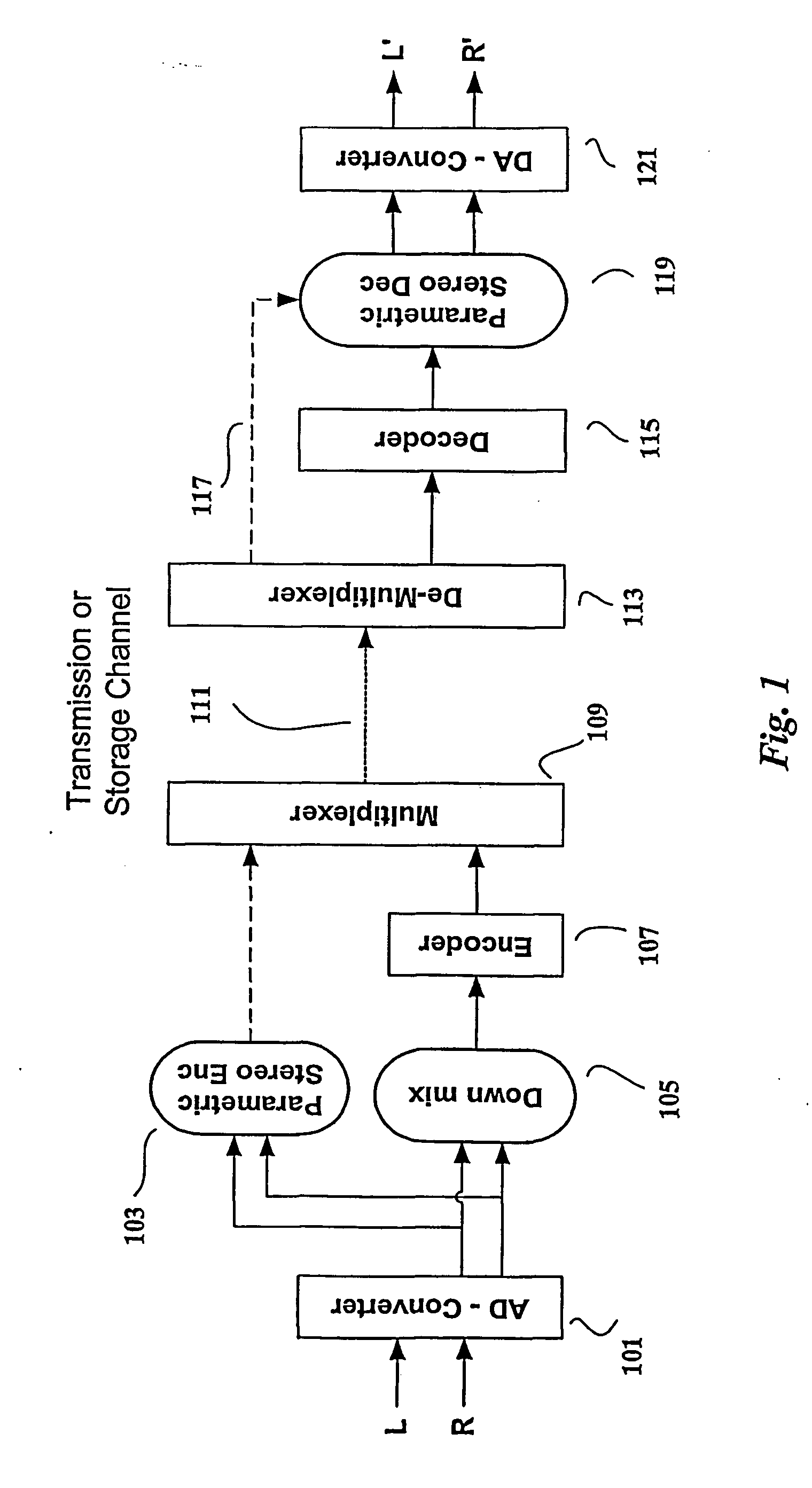
Parametric Stereo (PS) is lossy audio compression algorithm and a feature and an Audio Object Type (AOT) defined and used in MPEG-4 Part 3 (MPEG-4 Audio) to further enhance efficiency in low bandwidth stereo media. Advanced Audio Coding Low Complexity (AAC LC) combined with Spectral Band Replication (SBR) and Parametric Stereo (PS) was defined as HE-AAC v2. An HE-AAC v1 decoder will only give mono sound when decoding an HE-AAC v2 bitstream. Parametric Stereo performs sparse coding in the spatial domain, somewhat similar to what SBR does in the frequency domain.
Late reverberation-based synthesis of auditory scenes
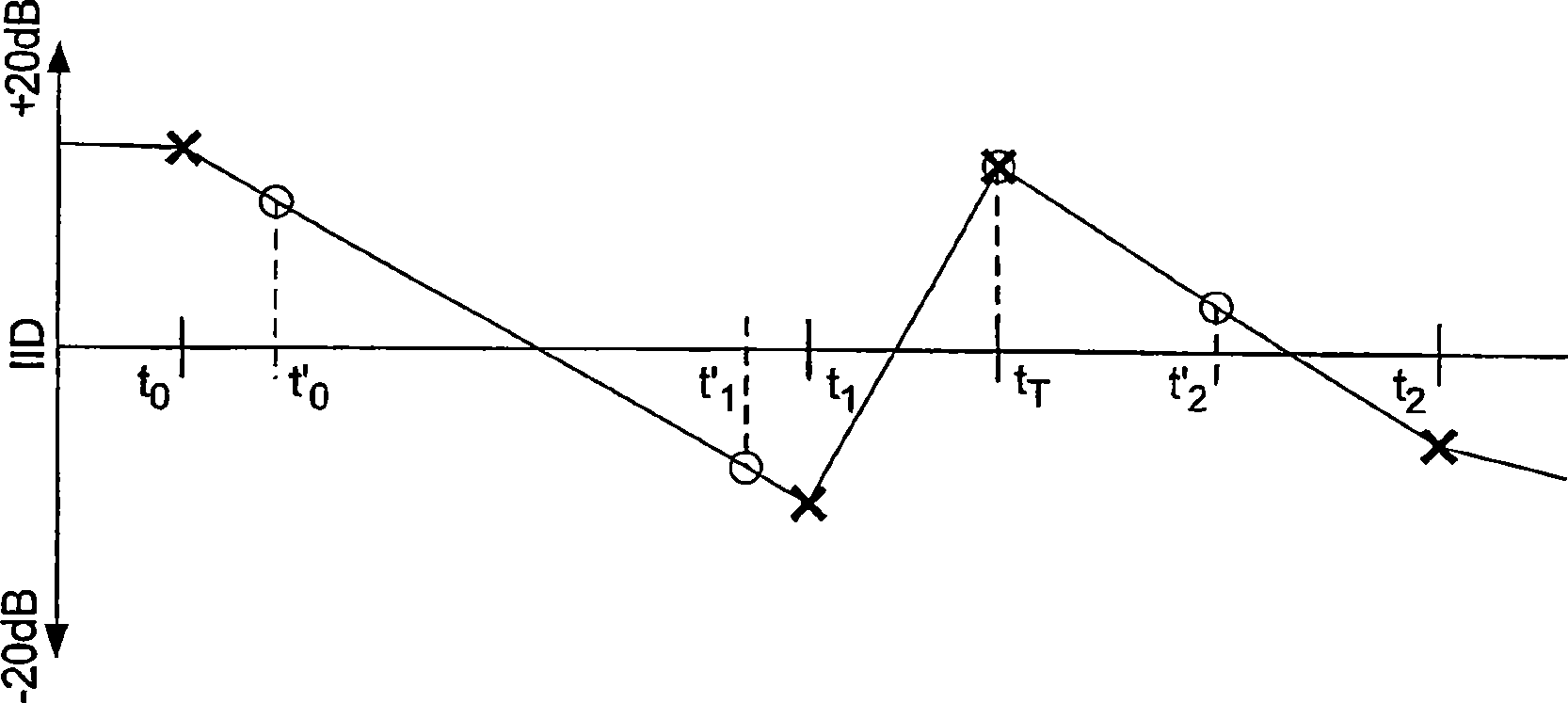
ActiveUS20050180579A1Reduce transmission bandwidth requirementsReduce bandwidth requirementsGain controlSpeech analysisComputation complexityChannel correlation
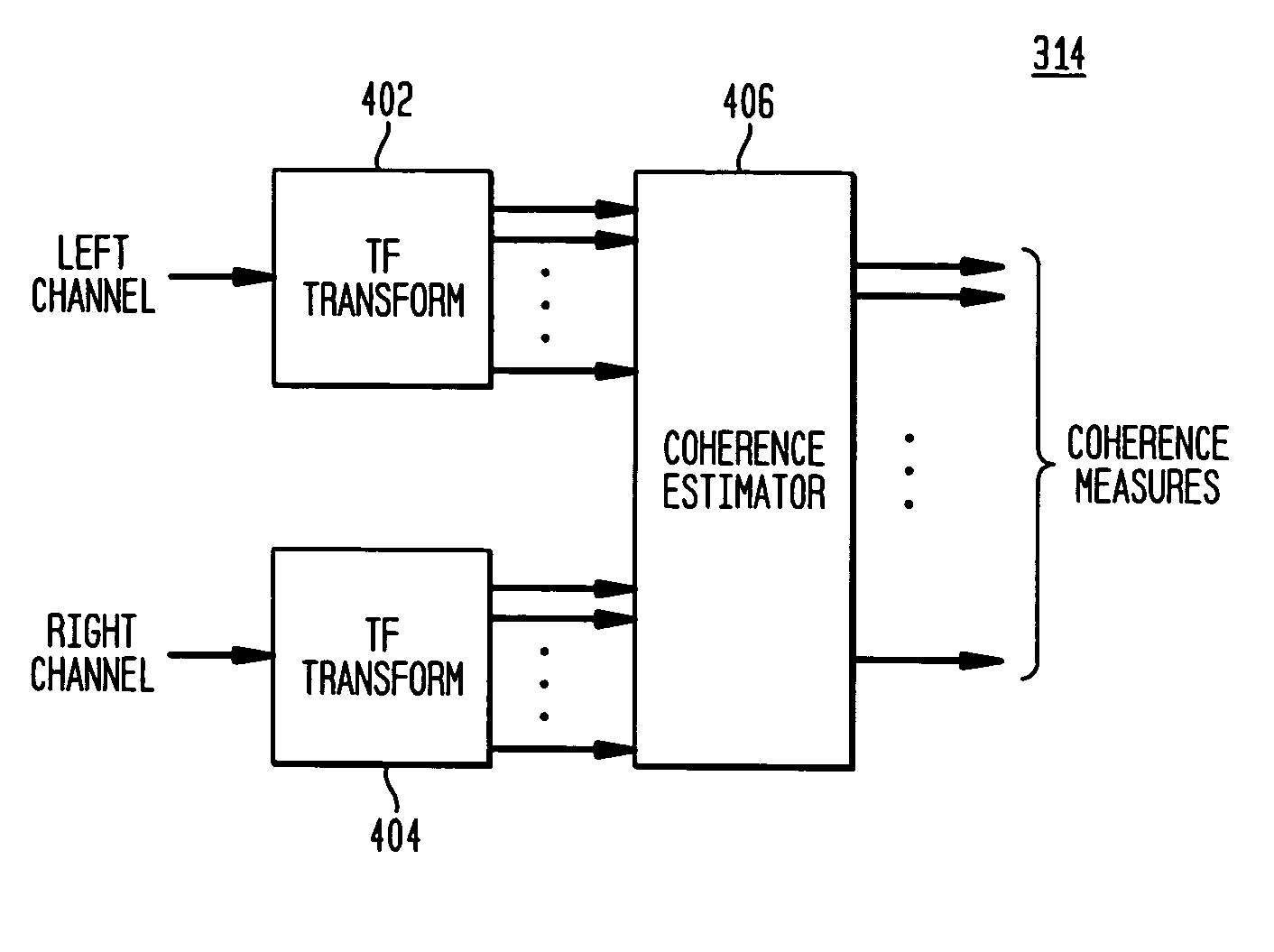
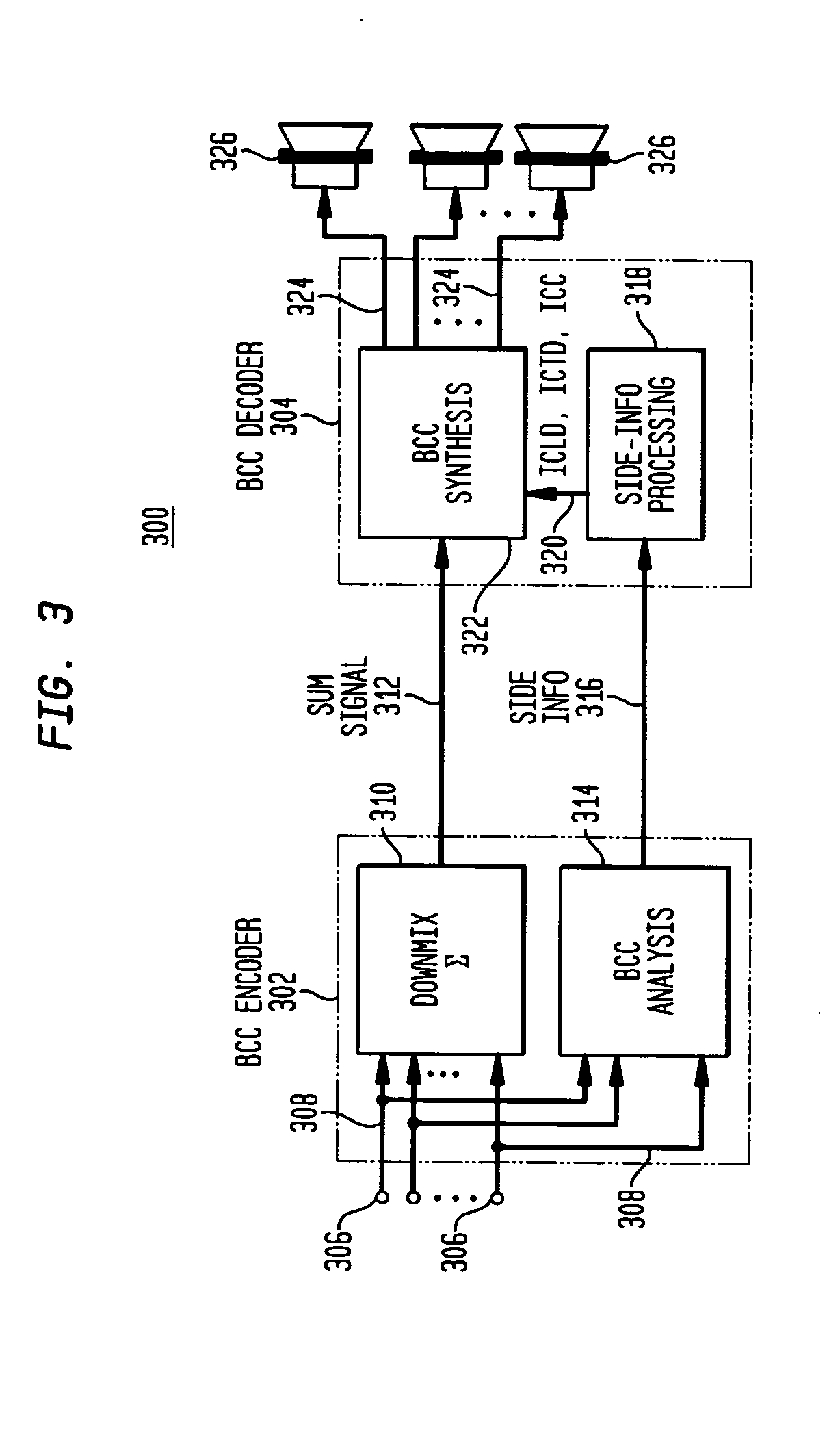
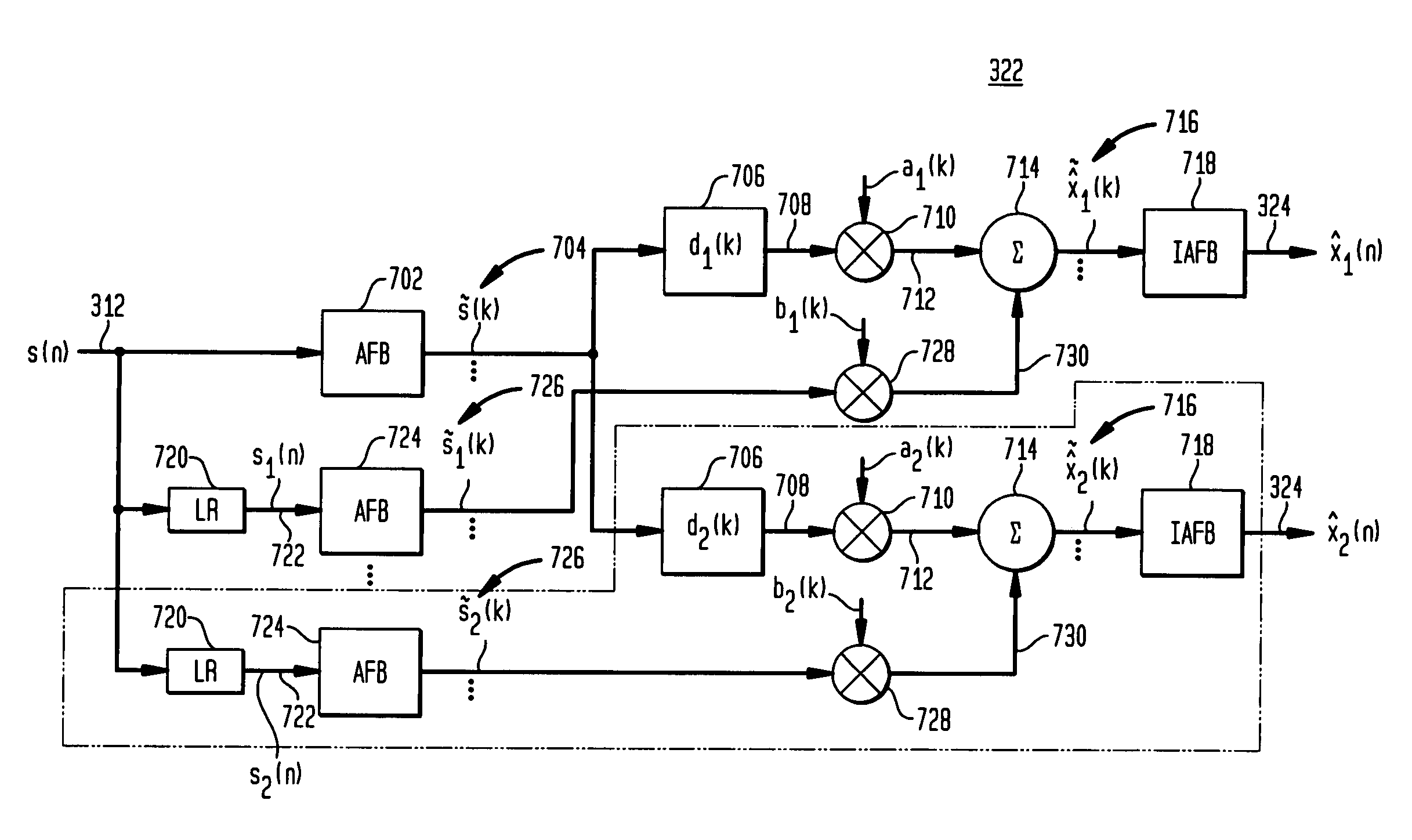
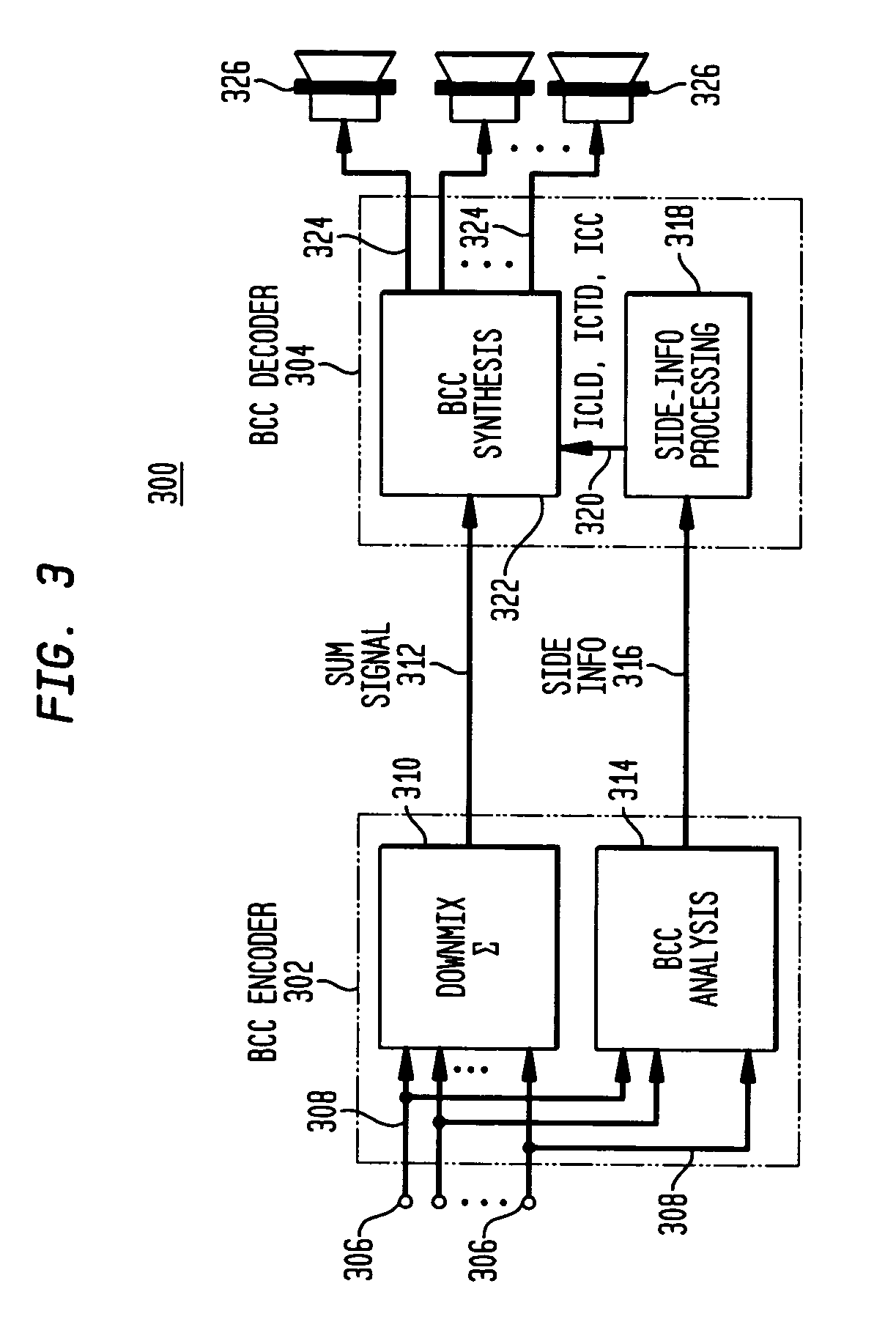
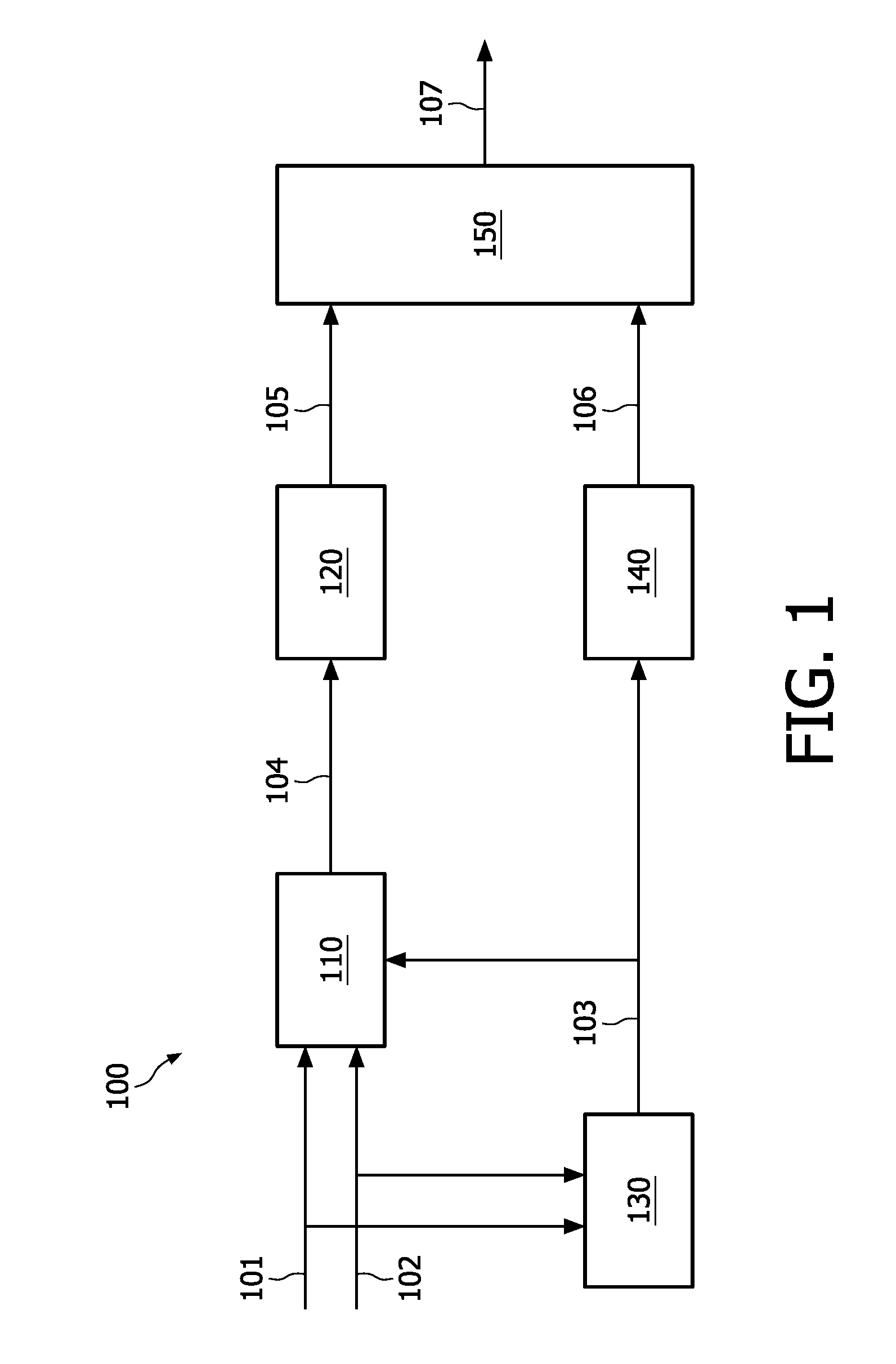
A scheme for stereo and multi-channel synthesis of inter-channel correlation (ICC) (normalized cross-correlation) cues for parametric stereo and multi-channel coding. The scheme synthesizes ICC cues such that they approximate those of the original. For that purpose, diffuse audio channels are generated and mixed with the transmitted combined (e.g., sum) signal(s). The diffuse audio channels are preferably generated using relatively long filters with exponentially decaying Gaussian impulse responses. Such impulse responses generate diffuse sound similar to late reverberation. An alternative implementation for reduced computational complexity is proposed, where inter-channel level difference (ICLD), inter-channel time difference (ICTD), and ICC synthesis are all carried out in the domain of a single short-time Fourier transform (STFT), including the filtering for diffuse sound generation.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Efficient and scalable parametric stereo coding for low bitrate applications
ActiveUS20050053242A1Reduce riskGuaranteed normal transmissionSpeech analysisPseudo-stereo systemsVocal tractStereo image
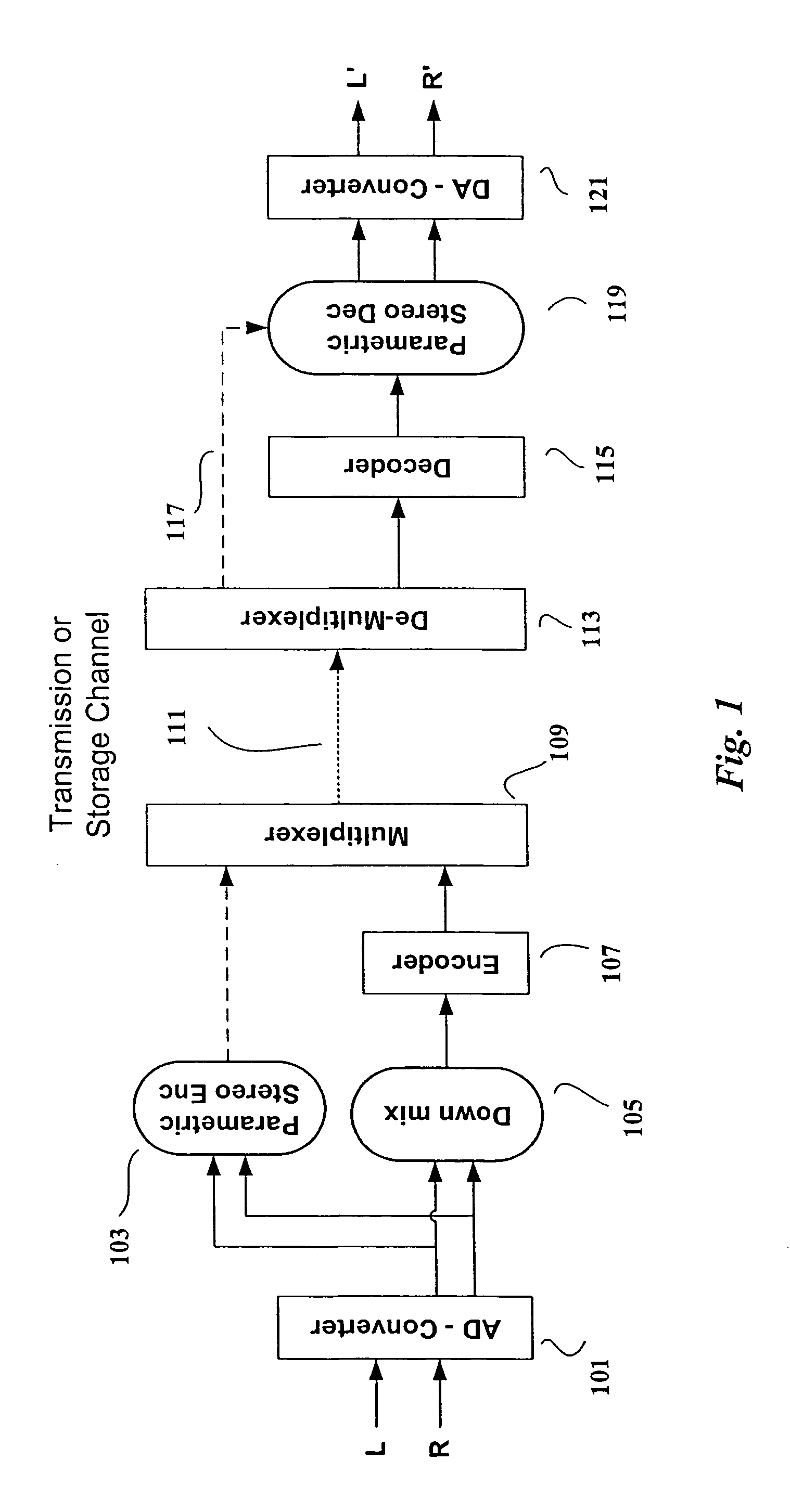
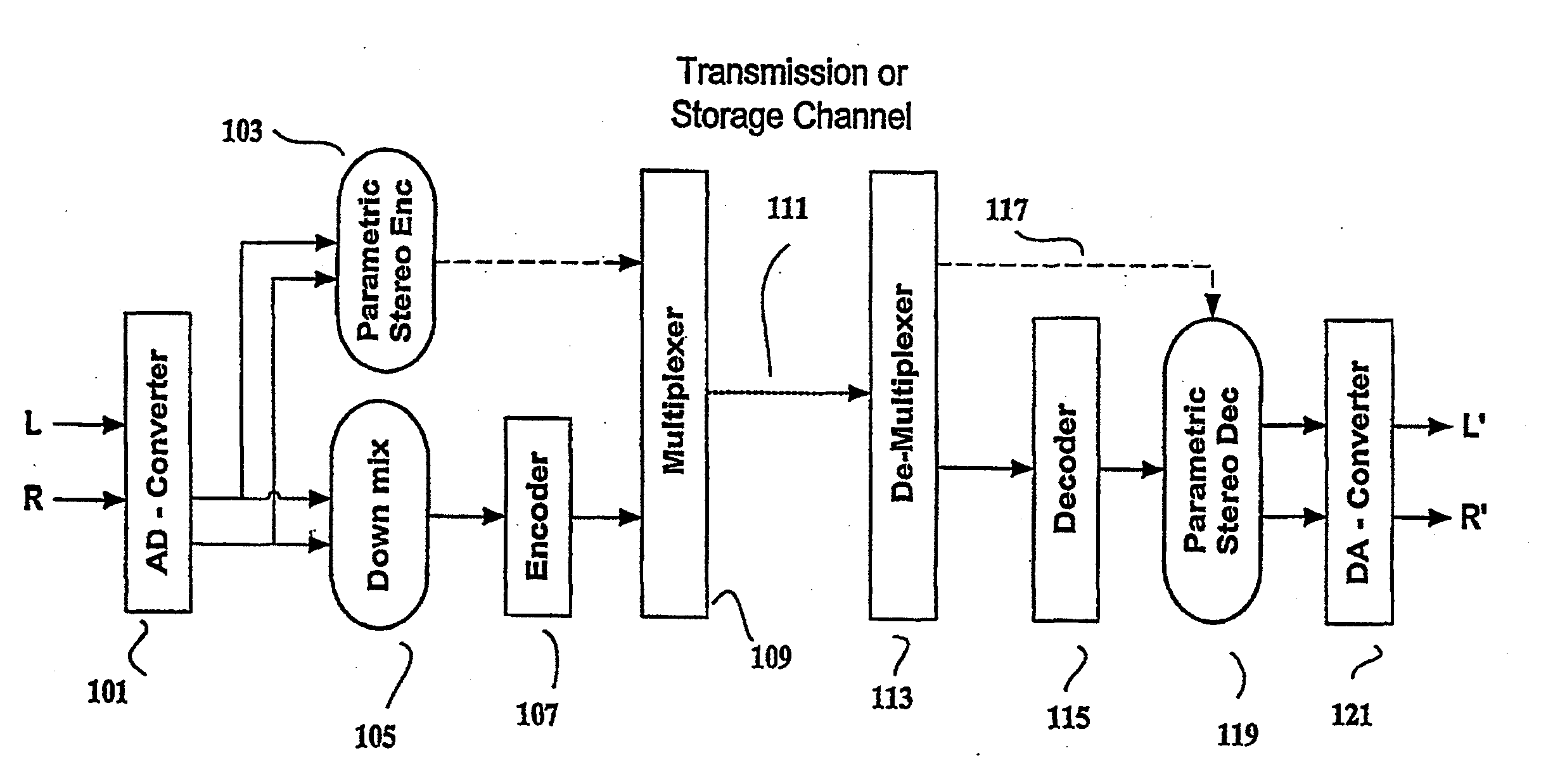
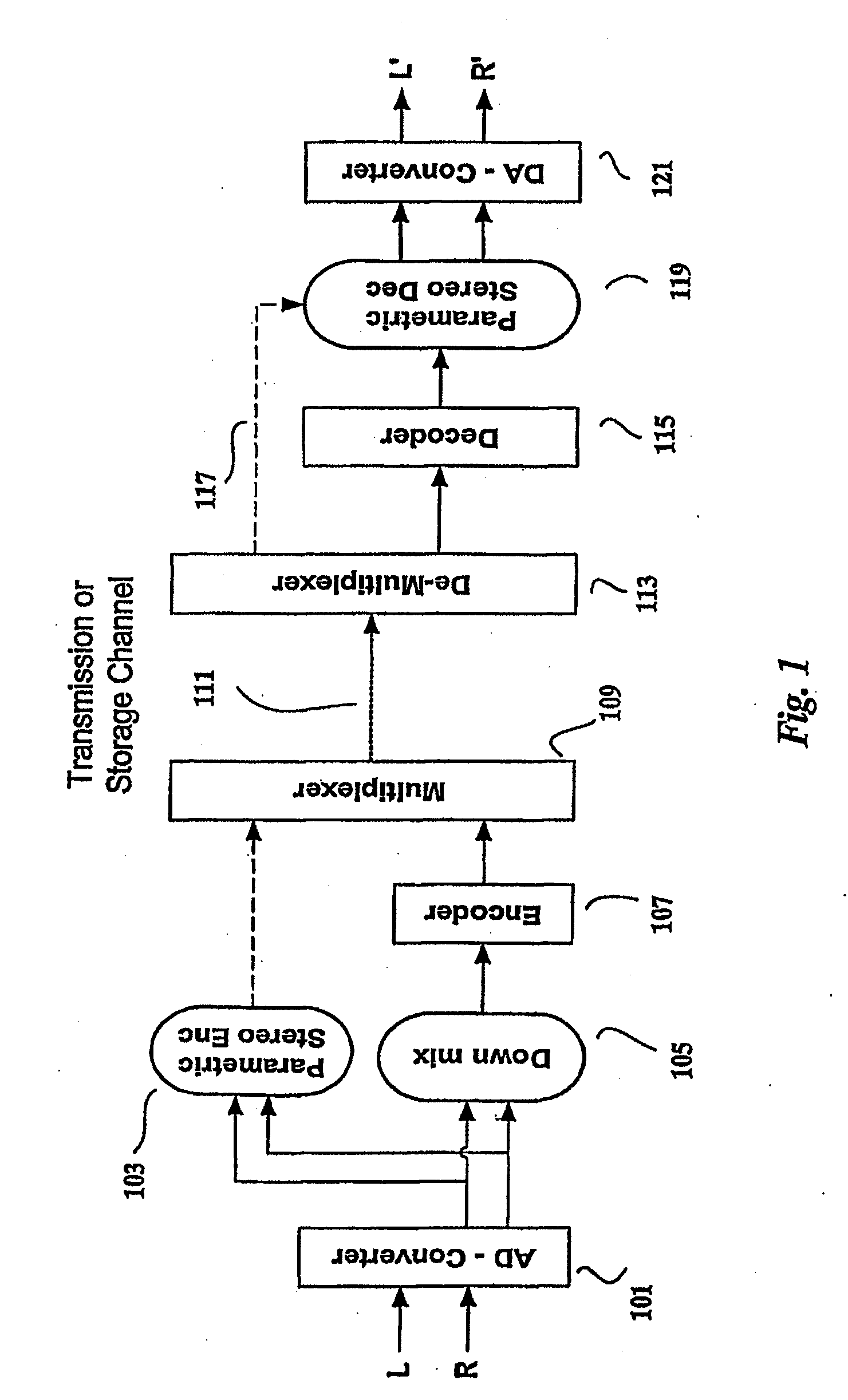
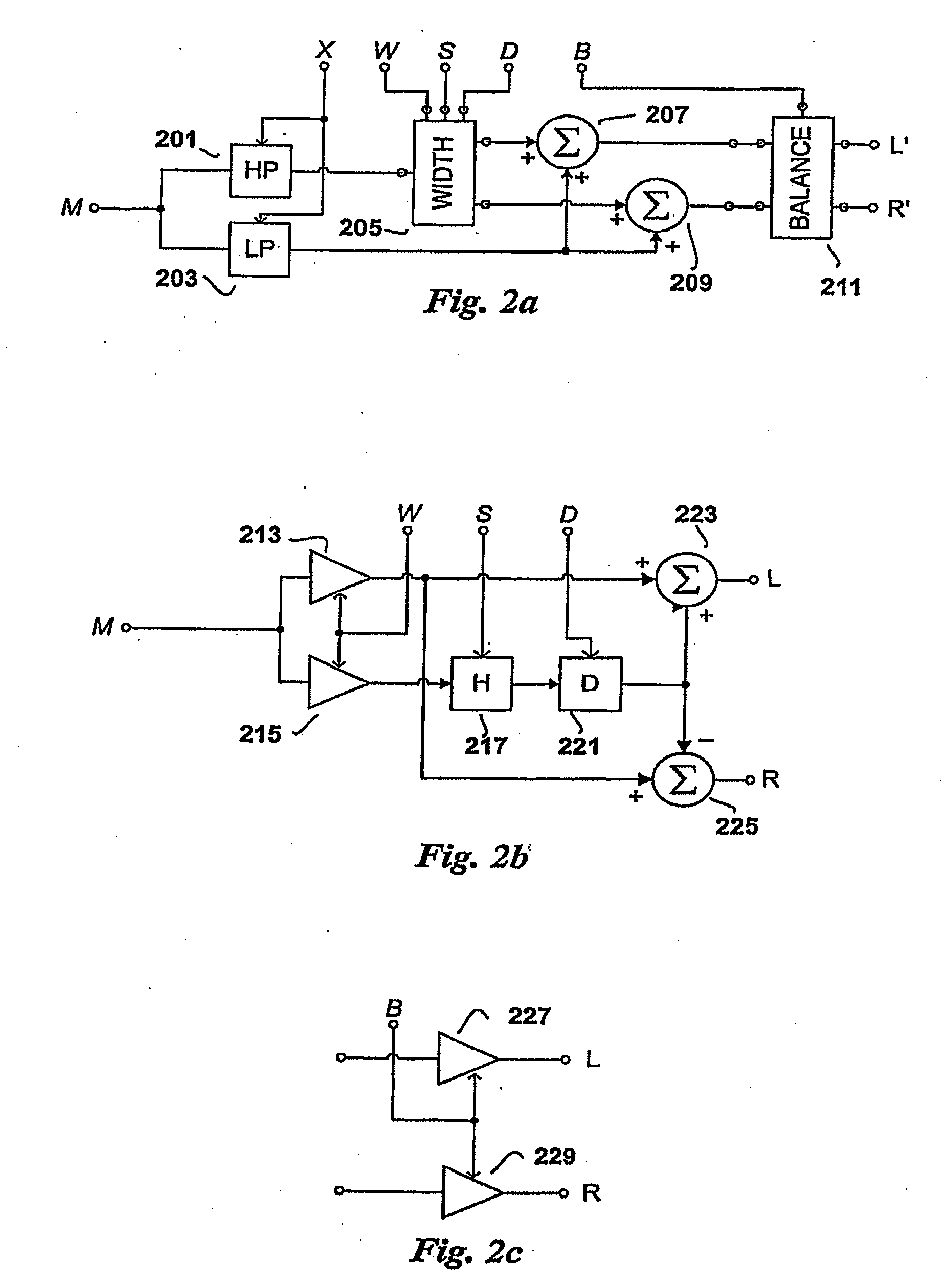
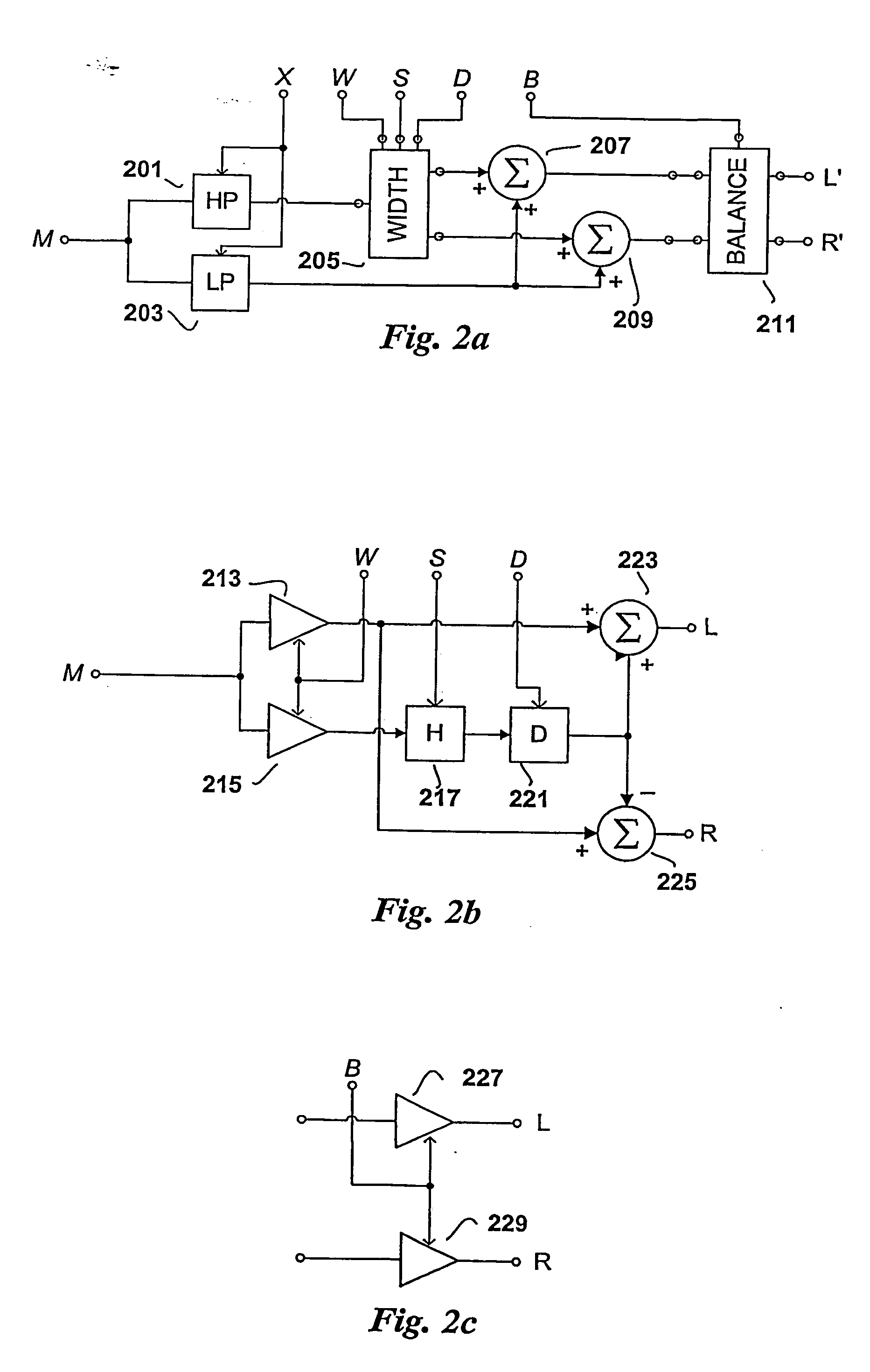
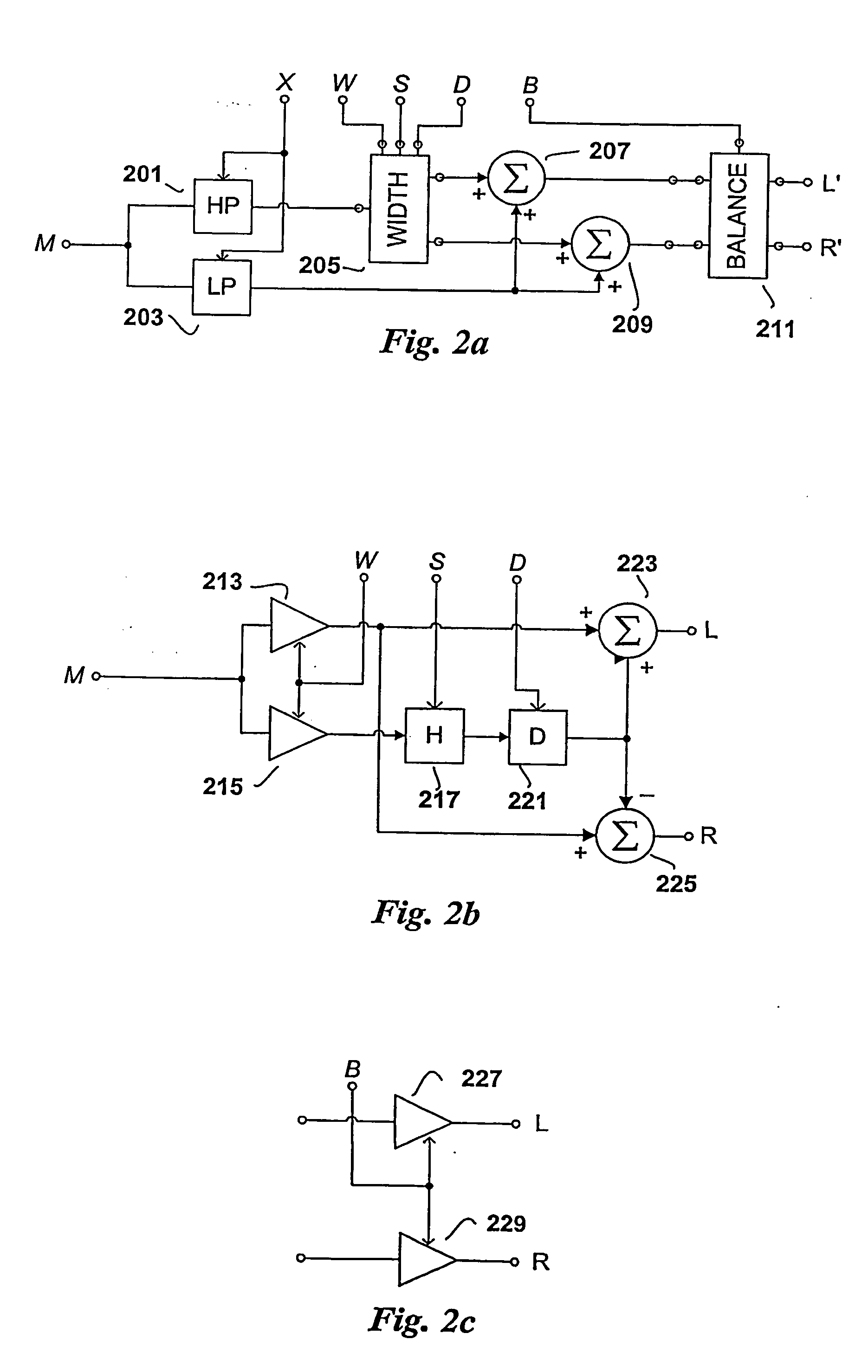
The present invention provides improvements to prior art audio codecs that generate a stereo-illusion through post-processing of a received mono signal. These improvements are accomplished by extraction of stereo-image describing parameters at the encoder side, which are transmitted and subsequently used for control of a stereo generator at the decoder side. Furthermore, the invention bridges the gap between simple pseudo-stereo methods, and current methods of true stereo-coding, by using a new form of parametric stereo coding. A stereo-balance parameter is introduced, which enables more advanced stereo modes, and in addition forms the basis of a new method of stereo-coding of spectral envelopes, of particular use in systems where guided HFR (High Frequency Reconstruction) is employed. As a special case, the application of this stereo-coding scheme in scalable HFR-based codecs is described.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Late reverberation-based synthesis of auditory scenes
ActiveUS7583805B2Reduce bandwidth requirementsExact widthGain controlSpeech analysisComputation complexityFourier transform on finite groups
A scheme for stereo and multi-channel synthesis of inter-channel correlation (ICC) (normalized cross-correlation) cues for parametric stereo and multi-channel coding. The scheme synthesizes ICC cues such that they approximate those of the original. For that purpose, diffuse audio channels are generated and mixed with the transmitted combined (e.g., sum) signal(s). The diffuse audio channels are preferably generated using relatively long filters with exponentially decaying Gaussian impulse responses. Such impulse responses generate diffuse sound similar to late reverberation. An alternative implementation for reduced computational complexity is proposed, where inter-channel level difference (ICLD), inter-channel time difference (ICTD), and ICC synthesis are all carried out in the domain of a single short-time Fourier transform (STFT), including the filtering for diffuse sound generation.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
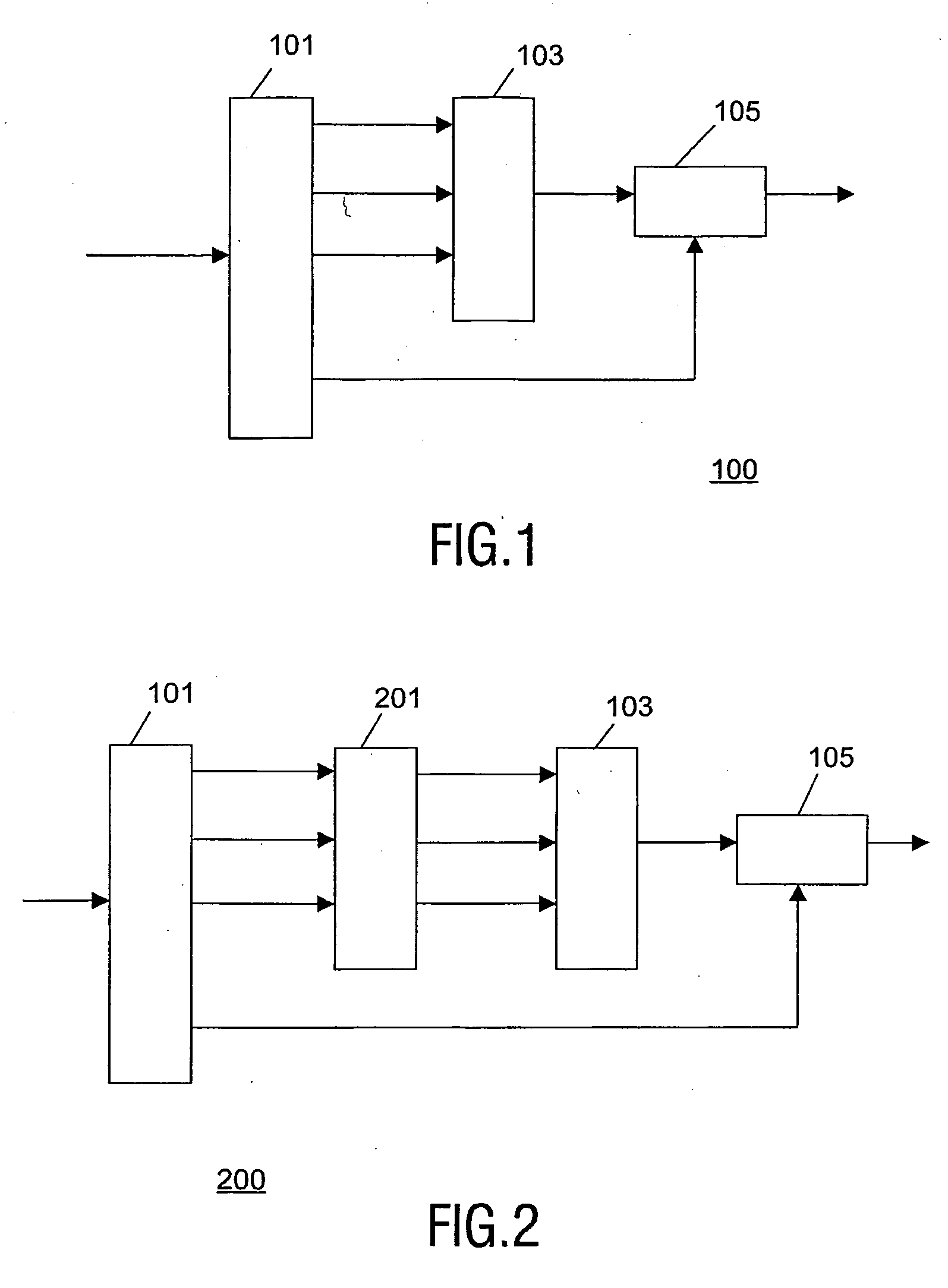
Transcoder and Method of Transcoding Therefore
InactiveUS20080260048A1Quality improvementImprove high frequency performanceSpeech analysisCode conversionComputer hardwareFrequency spectrum
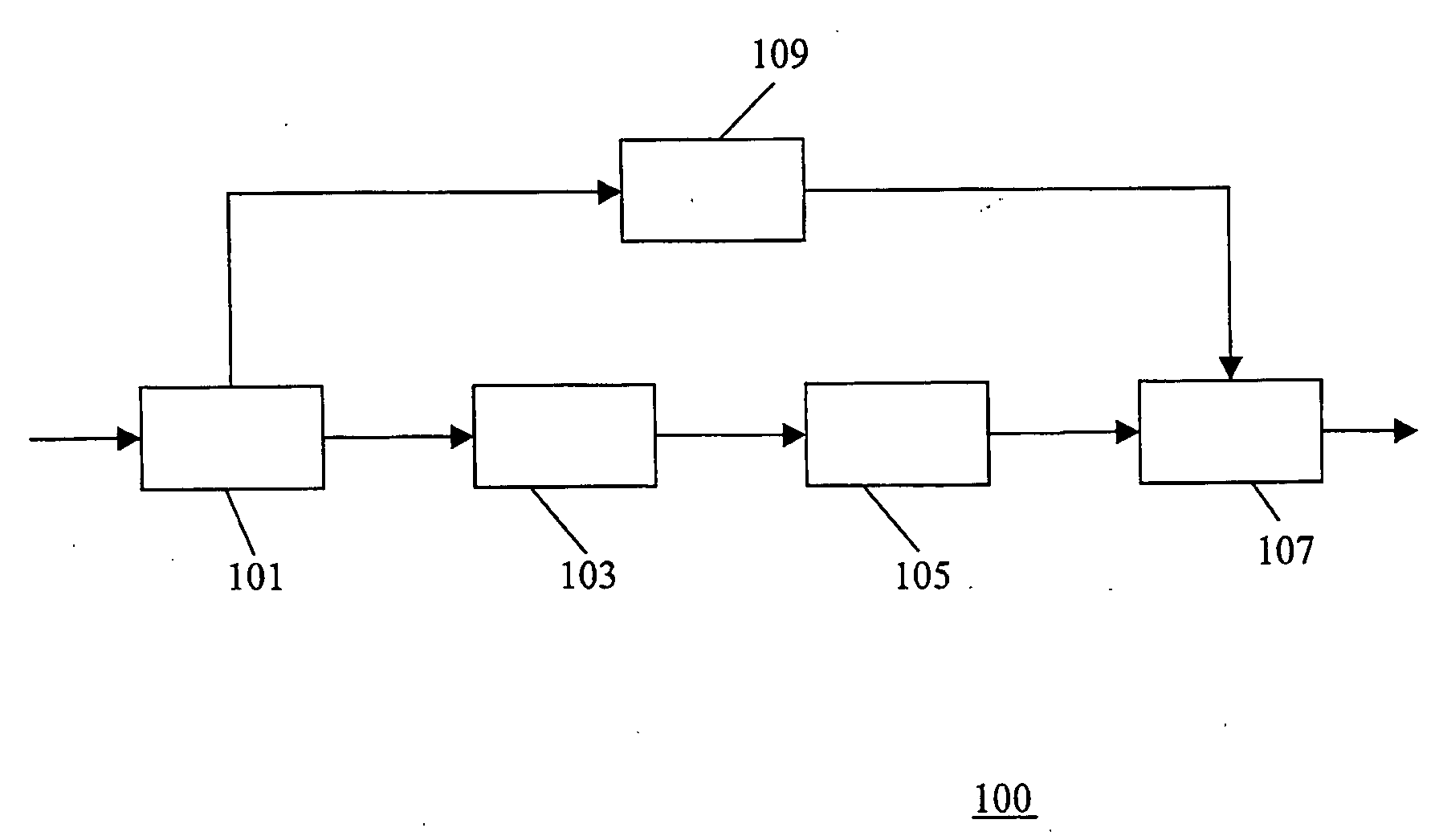
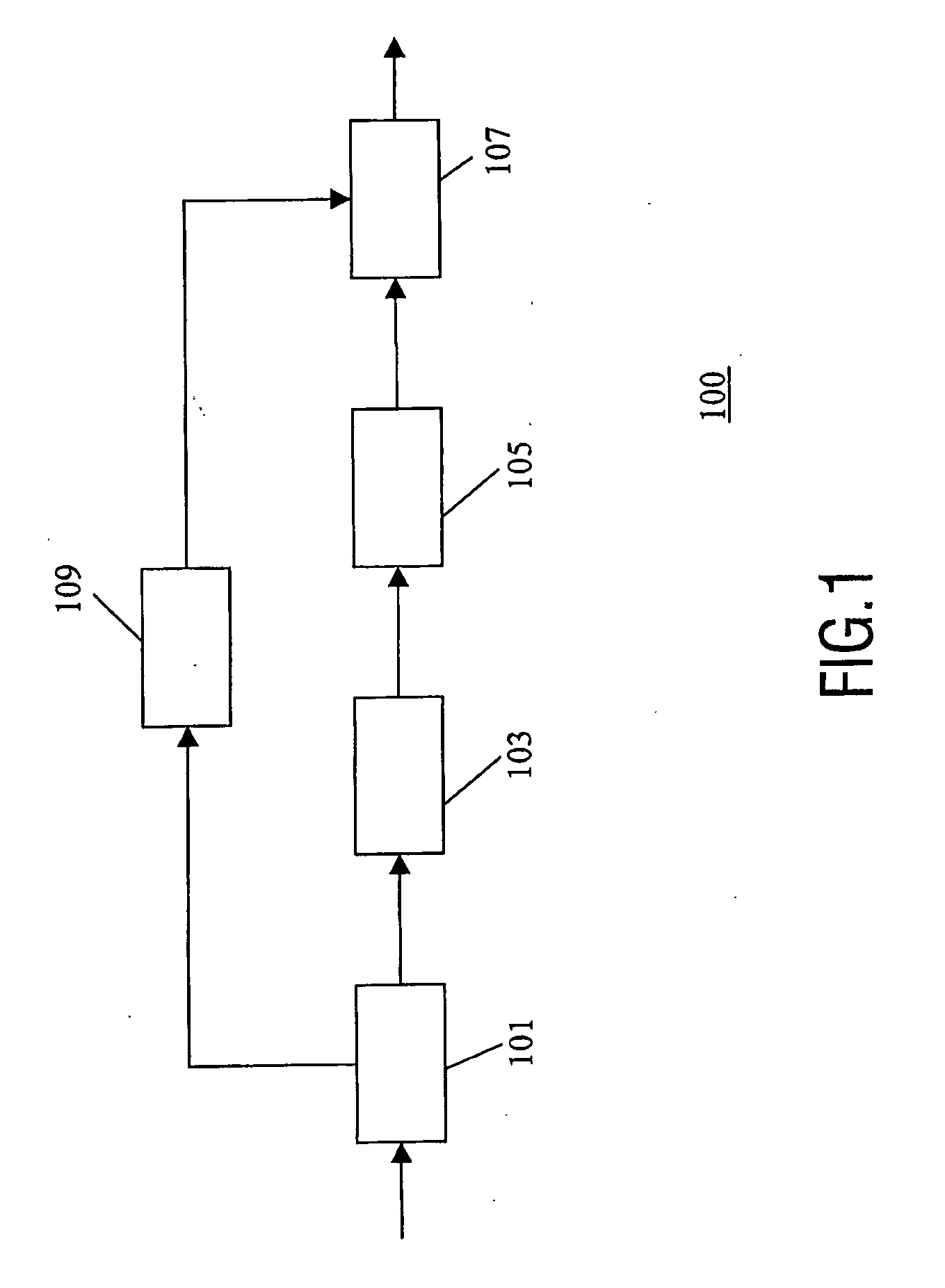
A transcoder comprises a receiver (101) which receives input data representing an encoded signal and comprising first encoding data and first parametric extension data. The encoded data is fed to a decoder (103). The output of the decoder (103) is fed to an encoder (105) which generates second encoded data according to a different encoding protocol or with different encoding parameters. The first parametric extension data is fed to an extension data processor (109) which generates second parametric extension data directly from the first parametric extension data. The second encoded data and the second parametric extension data is combined in an output processor (107) to generate a transcoded signal comprising separately determined parametric extension data. The parametric extension data may be Spectral Band Replication (SBR) or Parametric Stereo (PS) extension data for an audio bitstream. Improved quality and reduced complexity is achieved by the separate transcoding of the parametric extension data.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
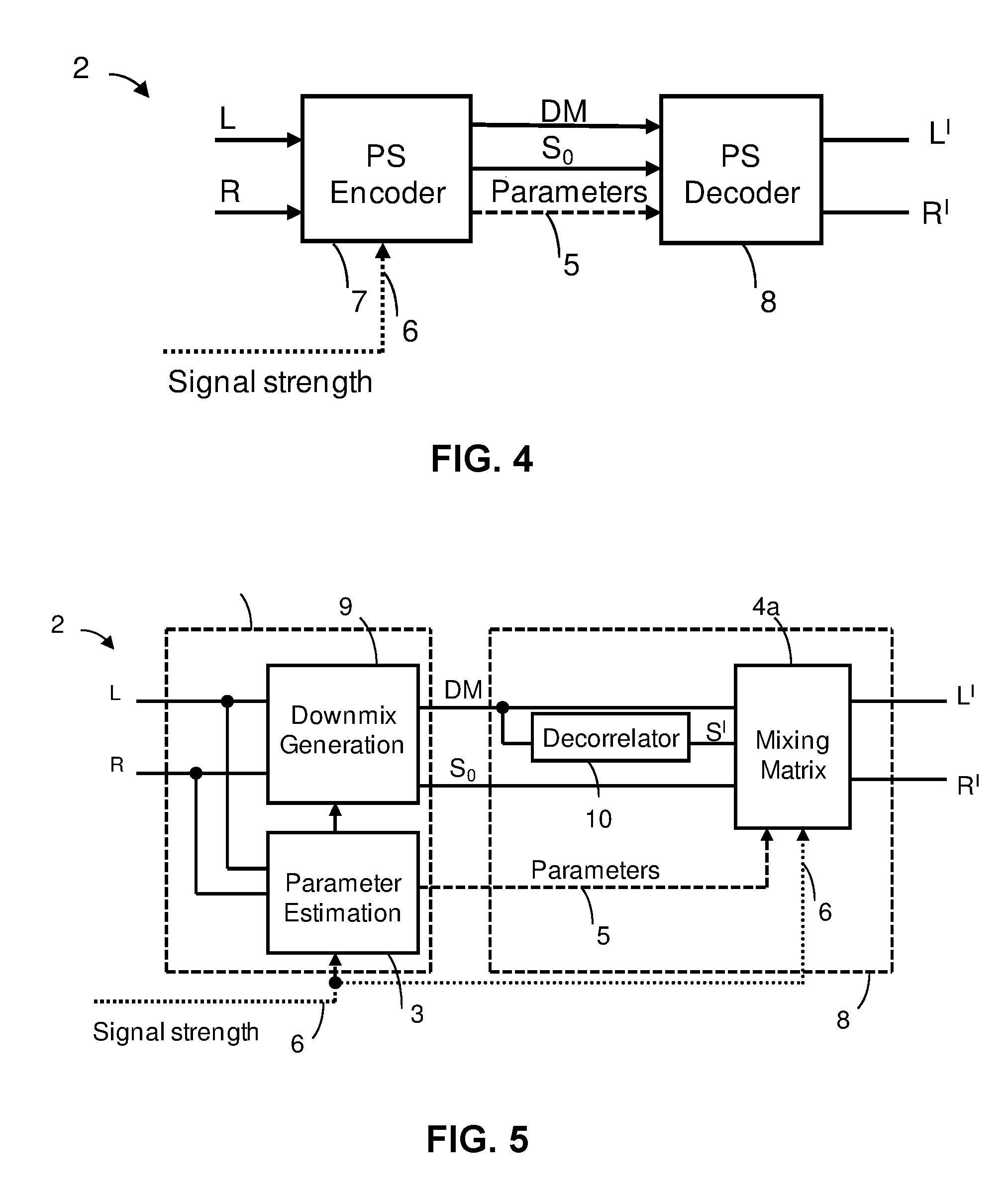
Parametric stereo upmix apparatus, a parametric stereo decoder, a parametric stereo downmix apparatus, a parametric stereo encoder
ActiveUS8811621B2Quality of left and rightLeft and right signalsSpeech analysisPseudo-stereo systemsVocal tractComputer vision
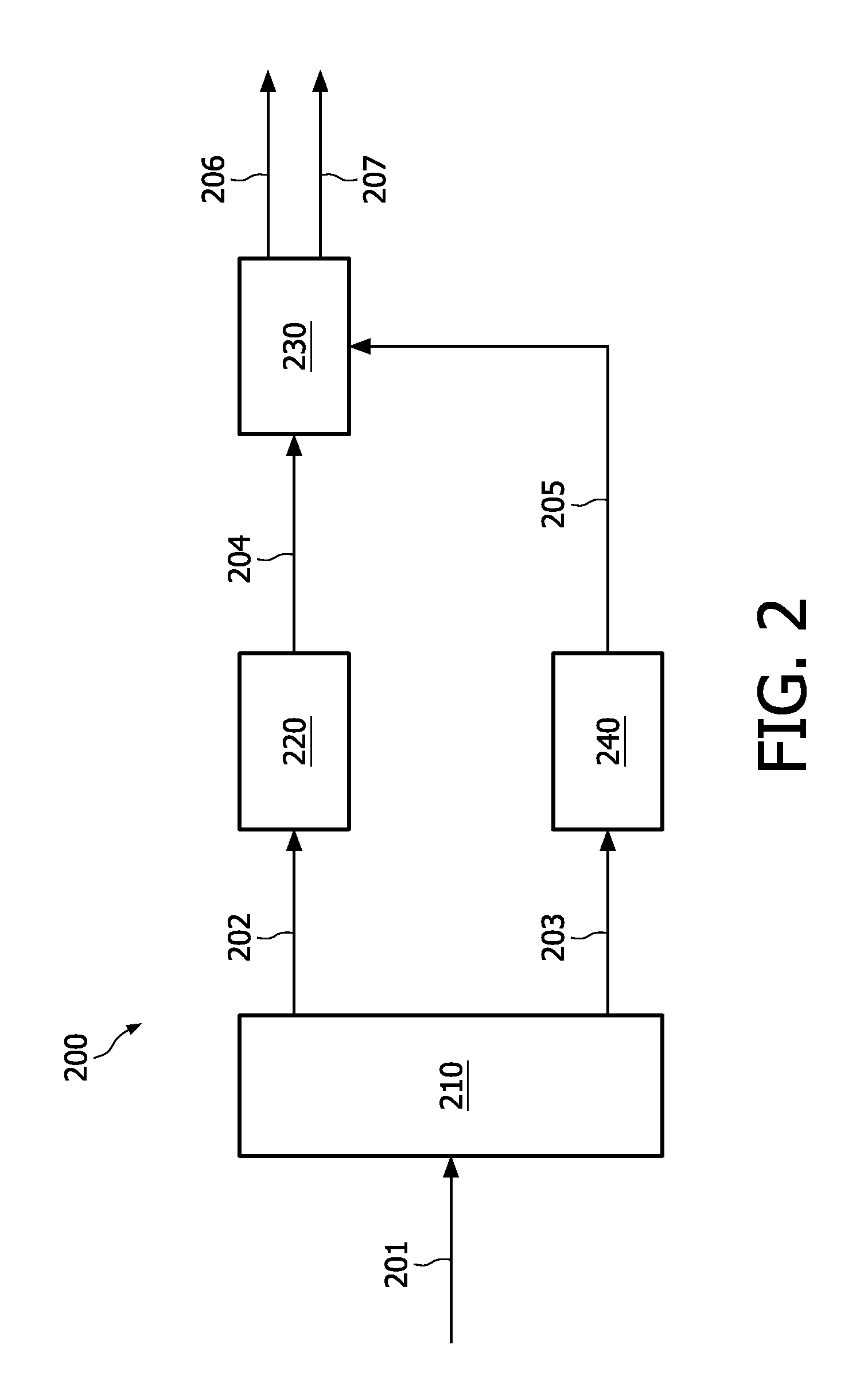
A parametric stereo upmix apparatus generates left and right signals from a mono downmix signal based on spatial parameters. The parametric stereo upmix includes a predictor configured to predict a difference signal including a difference between the left and right signals based on the mono downmix signal scaled with a prediction coefficient. The prediction coefficient is derived from the spatial parameters. The parametric stereo upmix apparatus further includes an arithmetic unit configured to derive the left and right signals based on a sum and a difference of the mono downmix signal and the difference signal.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Parametric stereo upmix apparatus, a parametric stereo decoder, a parametric stereo downmix apparatus, a parametric stereo encoder
ActiveUS20110096932A1Improve audio qualityQuality of left and rightSpeech analysisPseudo-stereo systemsPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
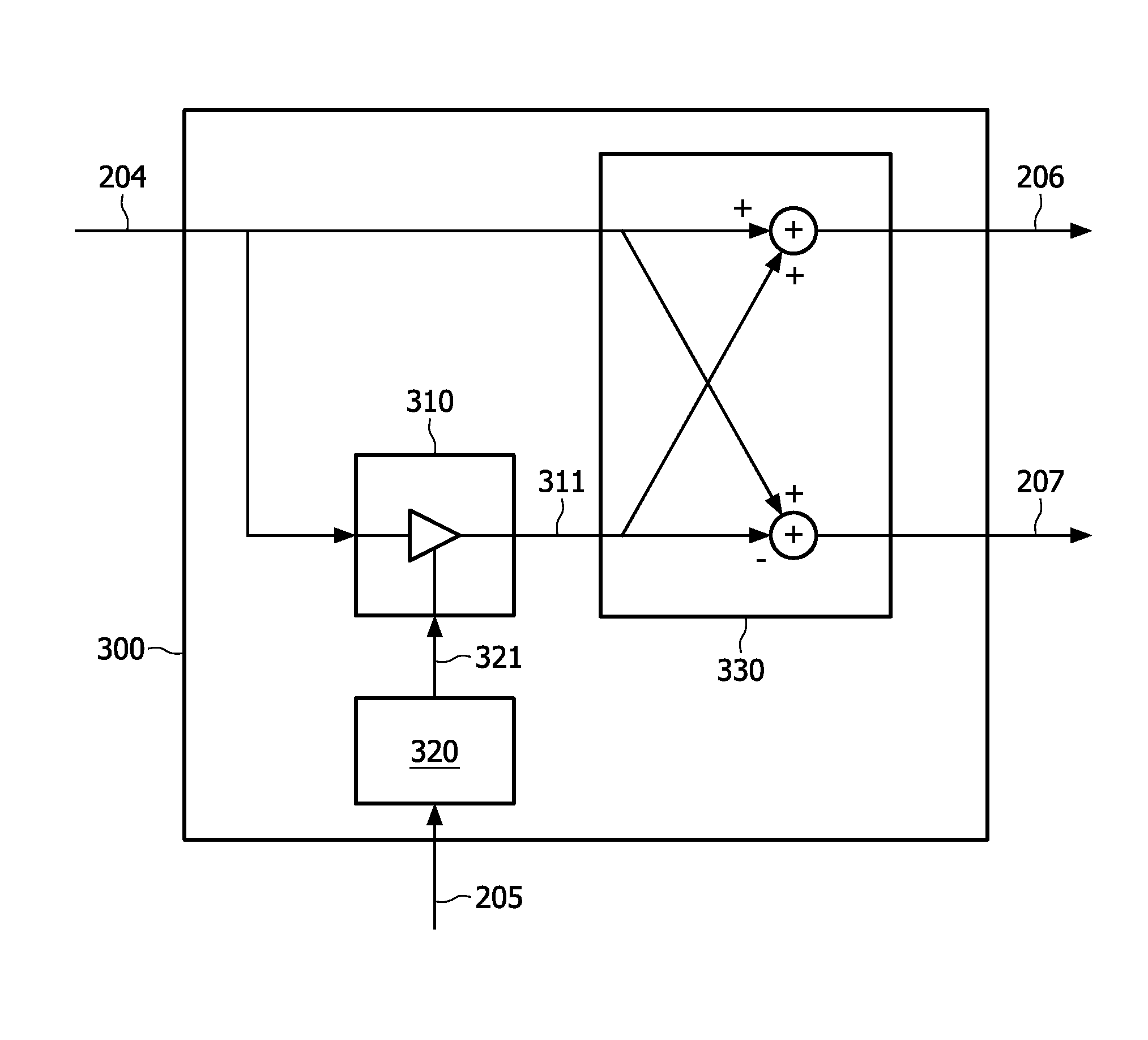
A parametric stereo upmix apparatus (300, 400) generating a left signal (206) and a right signal (207) from a mono downmix signal (204) based on spatial parameters (205). Said parametric stereo upmix being characterized in that it comprises a means (310) for predicting a difference signal (311) comprising a difference between the left signal (206) and the right signal (207) based on the mono downmix signal (204) scaled with a prediction coefficient (321). Said prediction coefficient is derived from the spatial parameters (205). Said parametric stereo upmix apparatus (300, 400) further comprises an arithmetic means (330) for deriving the left signal (206) and the right signal (207) based on a sum and a difference of the mono downmix signal (204) and said difference signal (311).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
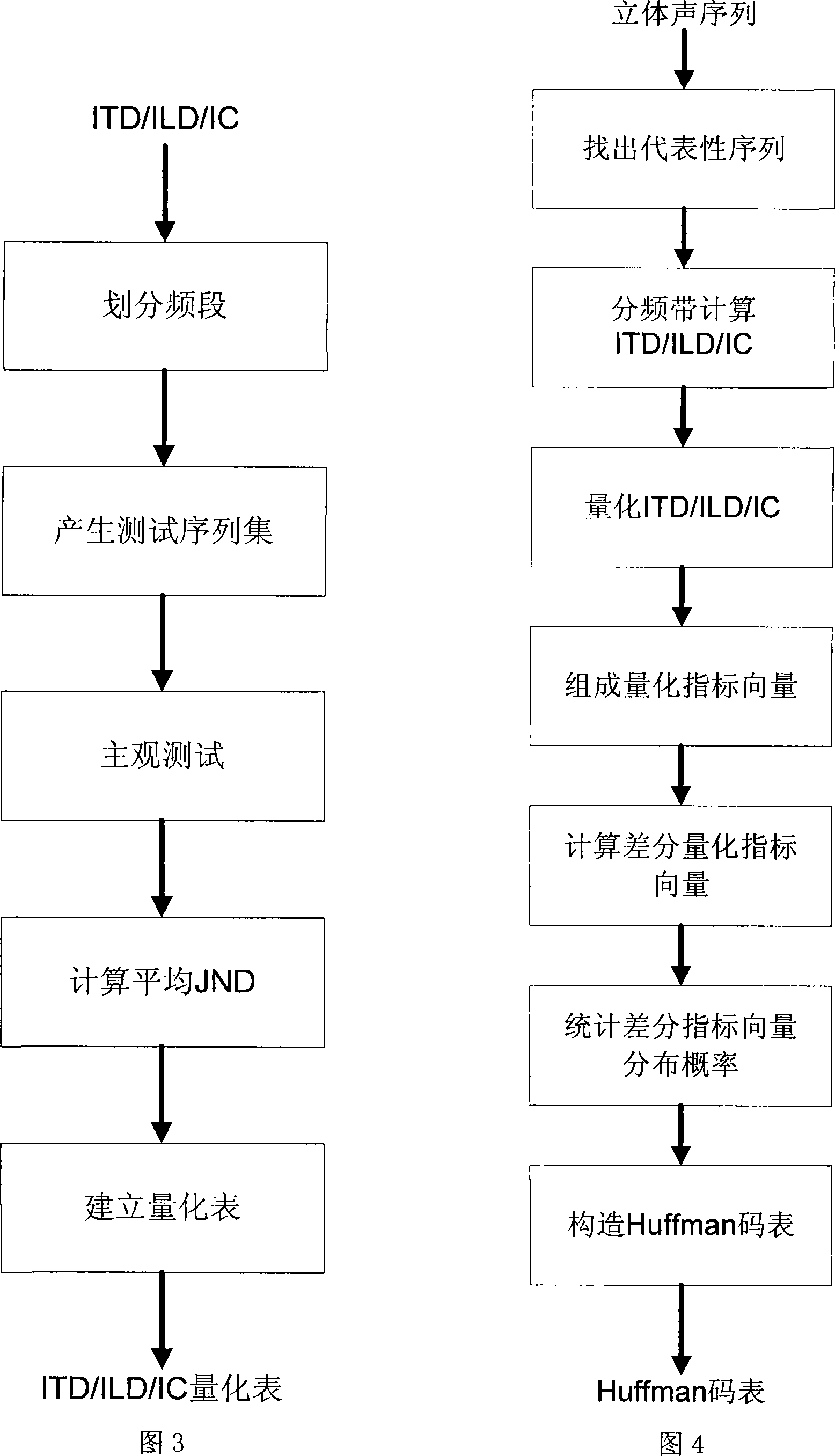
A space parameter quantification and entropy coding method for 3D audio signals and its system architecture
InactiveCN101188878AImprove sound qualityReduce code rateSpeech analysisPseudo-stereo systemsAlgorithmSound quality
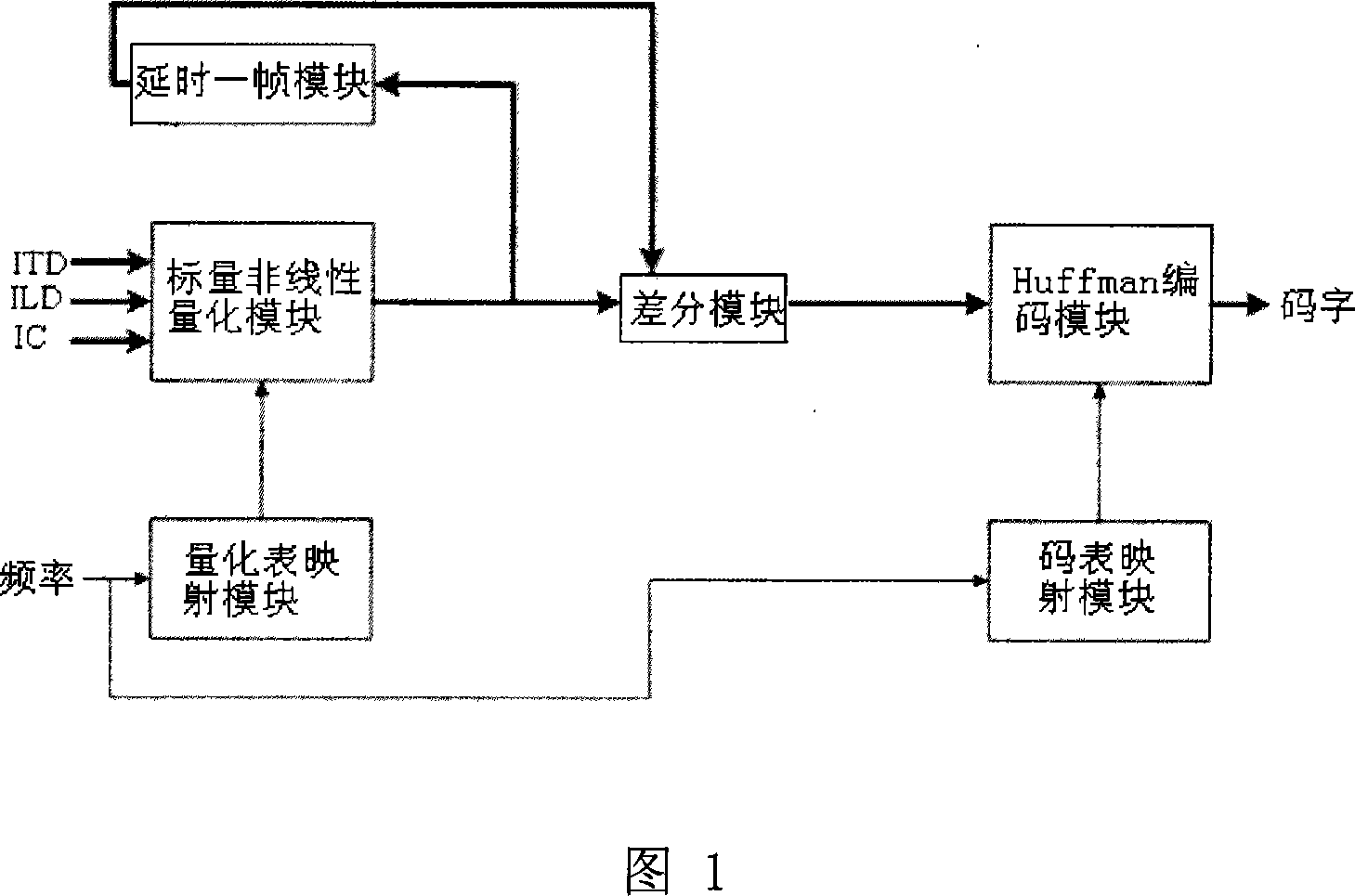
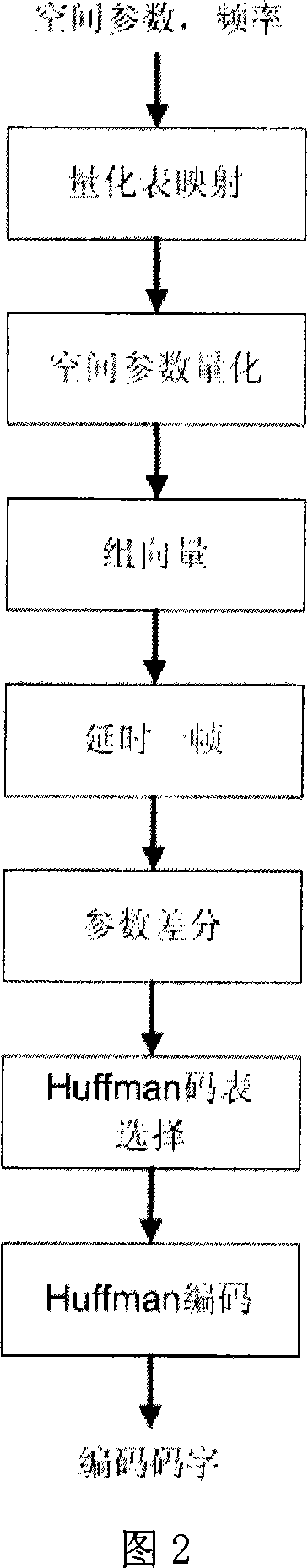
The invention discloses a space parameter quantification and entropy encoding method for a stereo voice-frequency signal, and a system structure thereof. Firstly, the space parameter quantification for the stereo voice-frequency signal uses different quantization tables in different frequency bands to perform the nonlinear scalar quantification by table search; then quantification indexes of each obtained space parameter are combined into a vector which executes a finite difference with the vector of the former quantification indexes; finally, the obtained finite difference quantification index vector acts the Huffman entropy encoding according to a Huffman code table corresponding to each present frequency band. The invention utilizes the dependency relationship between the hearing and esthesia of the space parameter and the frequency bands as well as the pertinency among the space parameters, thus the subjective and objective redundancy of the space parameter is effectively removed, the tone of the space parameter stereo code is enhanced under the same encoding rate, or the encoding rate is reduced under the same encoding tone.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Efficient and scalable parametric stereo coding for low bitrate audio coding applications
ActiveUS20060023891A1Reduce riskGuaranteed normal transmissionSpeech analysisPseudo-stereo systemsVocal tractStereo image
The present invention provides improvements to prior art audio codecs that generate a stereo-illusion through post-processing of a received mono signal. These improvements are accomplished by extraction of stereo-image describing parameters at the encoder side, which are transmitted and subsequently used for control of a stereo generator at the decoder side. Furthermore, the invention bridges the gap between simple pseudo-stereo methods, and current methods of true stereo-coding, by using a new form of parametric stereo coding. A stereo-balance parameter is introduced, which enables more advanced stereo modes, and in addition forms the basis of a new method of stereo-coding of spectral envelopes, of particular use in systems where guided HFR (High Frequency Reconstruction) is employed. As a special case, the application of this stereo-coding scheme in scalable HFR-based codecs is described.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Efficient and scalable parametric stereo coding for low bitrate audio coding applications
InactiveUS20100046762A1Reduce riskGuaranteed normal transmissionSpeech analysisTransmissionFrequency spectrumVocal tract
The present invention provides improvements to prior art audio codecs that generate a stereo-illusion through post-processing of a received mono signal. These improvements are accomplished by extraction of stereo-image describing parameters at the encoder side, which are transmitted and subsequently used for control of a stereo generator at the decoder side. Furthermore, the invention bridges the gap between simple pseudo-stereo methods, and current methods of true stereo-coding, by using a new form of parametric stereo coding. A stereo-balance parameter is introduced, which enables more advanced stereo modes, and in addition forms the basis of a new method of stereo-coding of spectral envelopes, of particular use in systems where guided HFR (High Frequency Reconstruction) is employed. As a special case, the application of this stereo-coding scheme in scalable HFR-based codecs is described.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
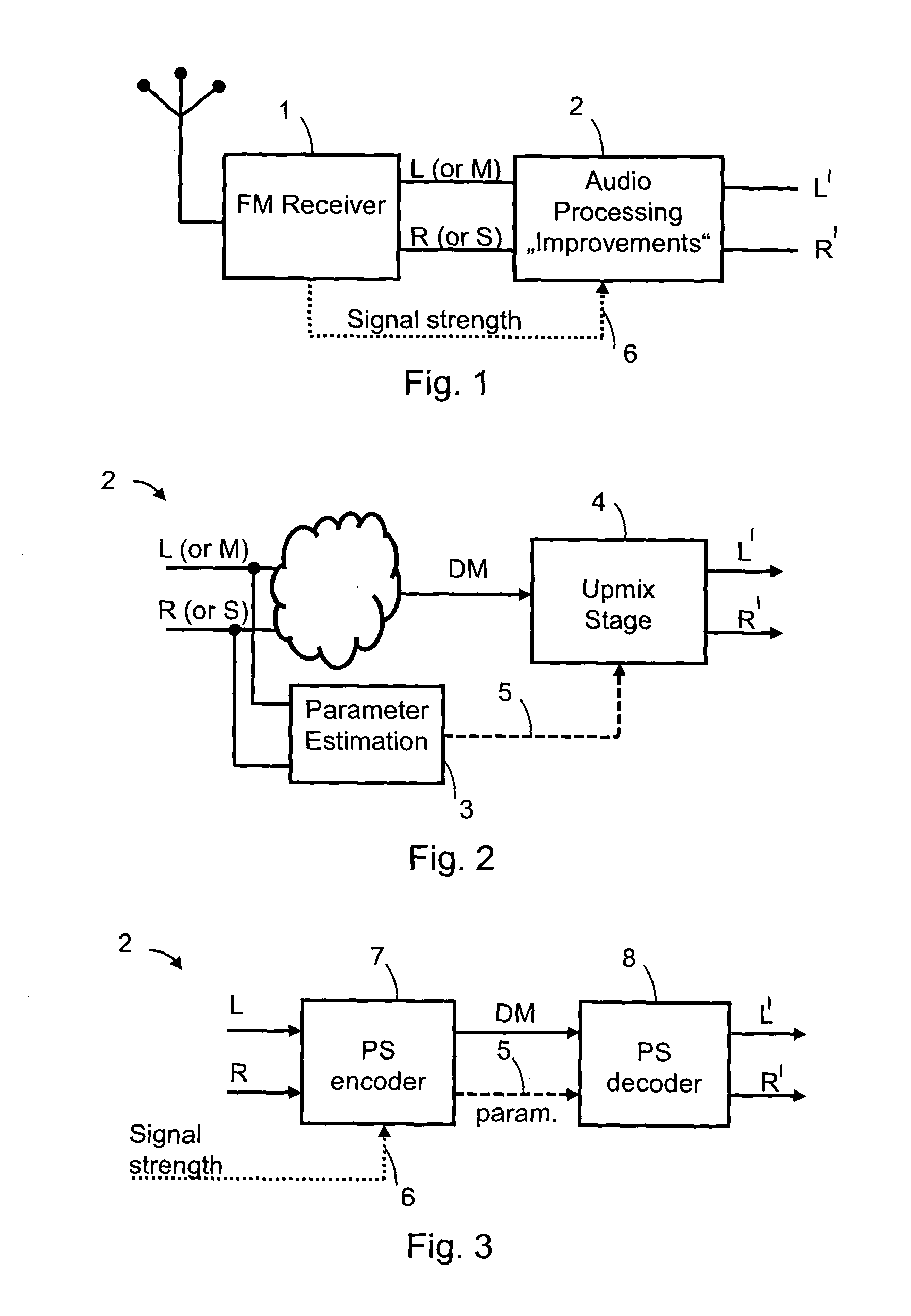
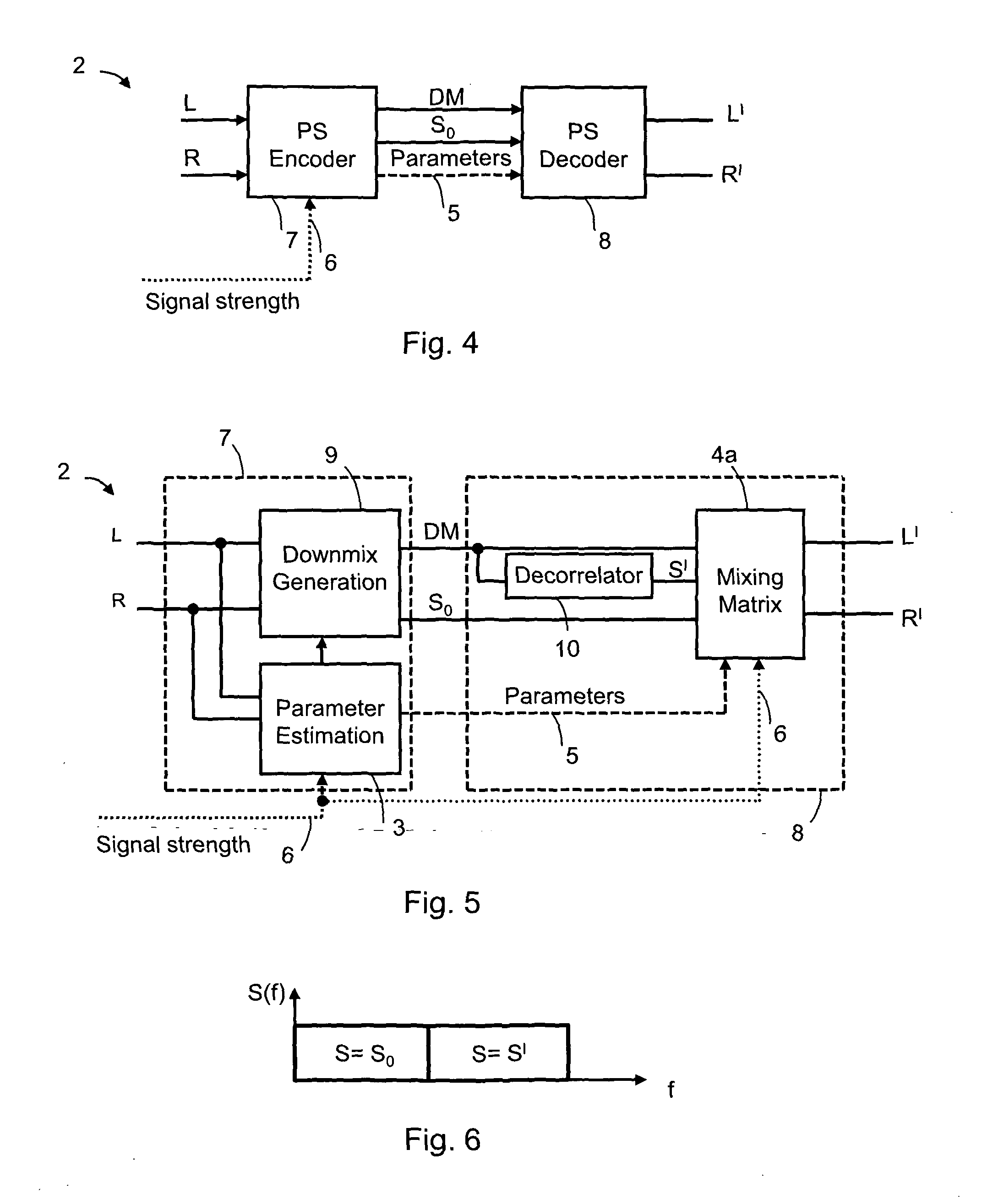
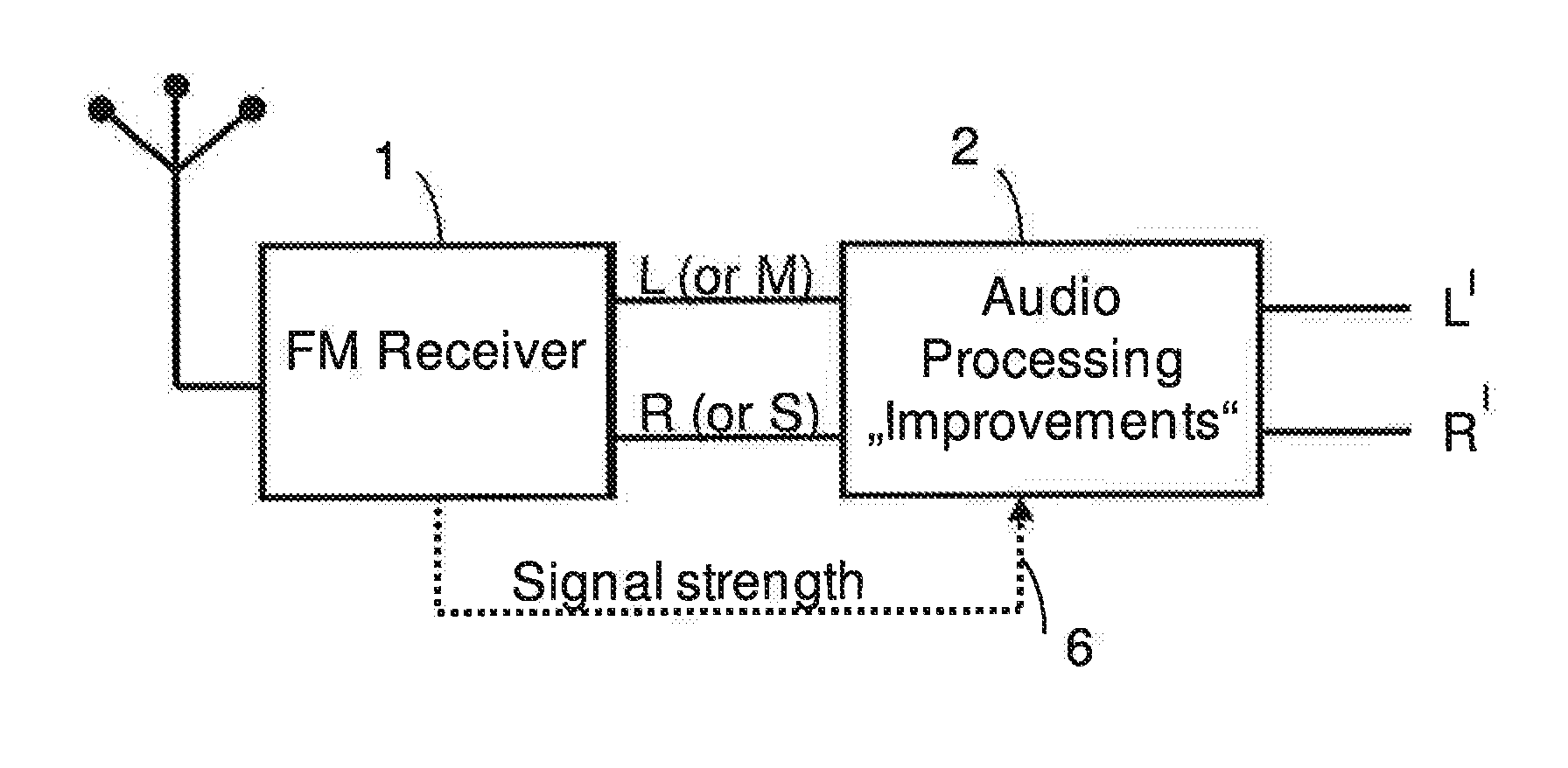
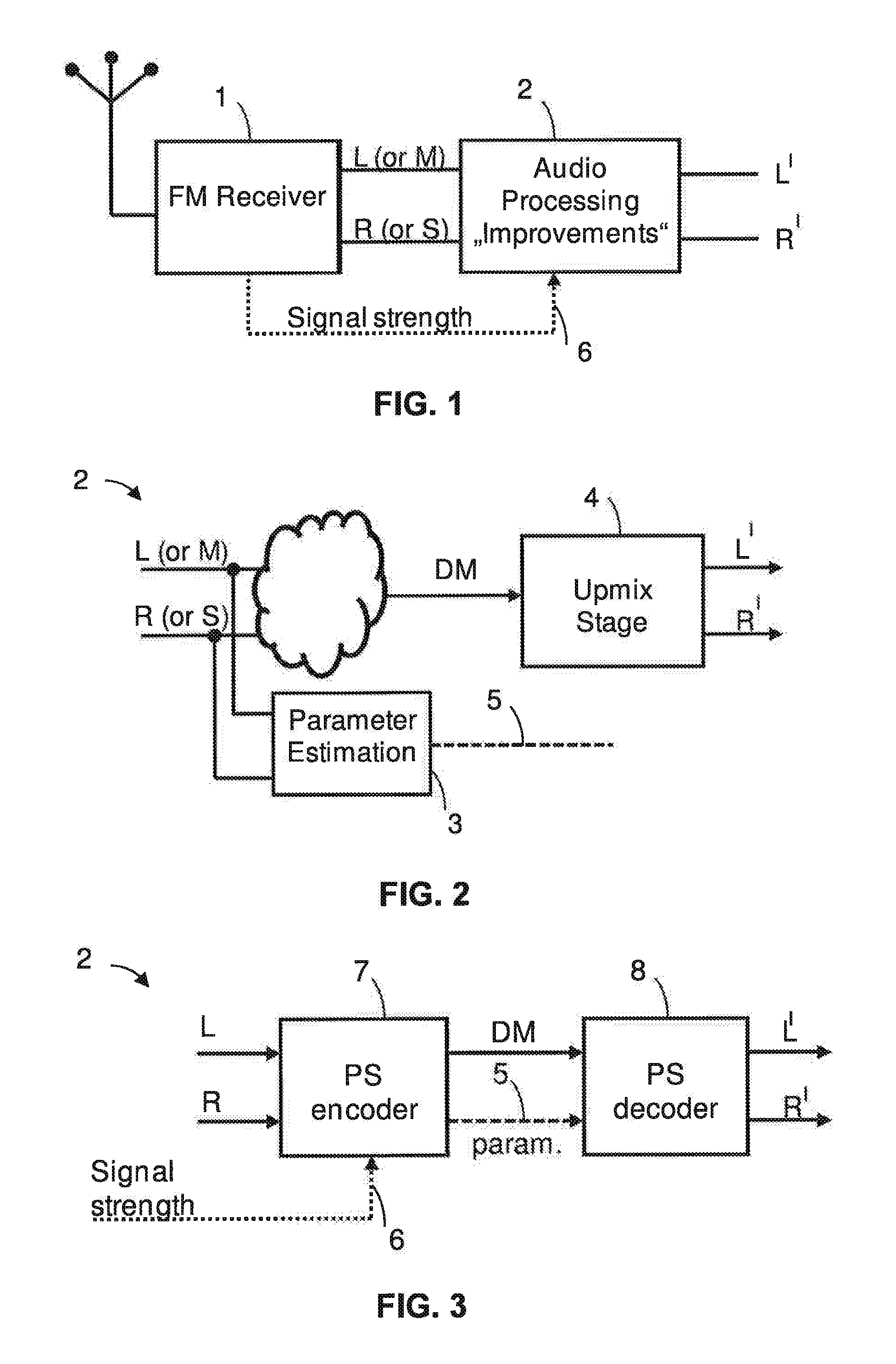
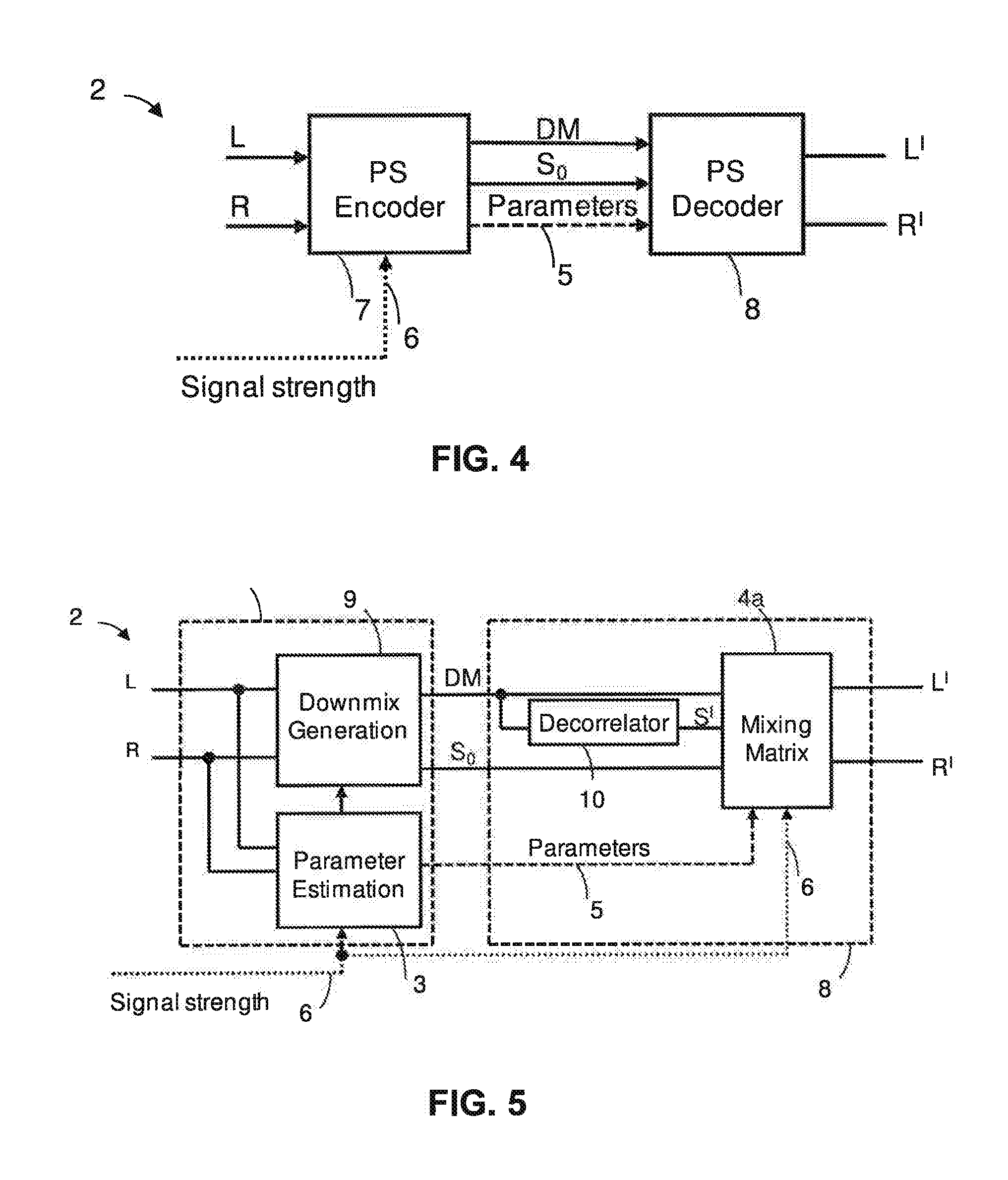
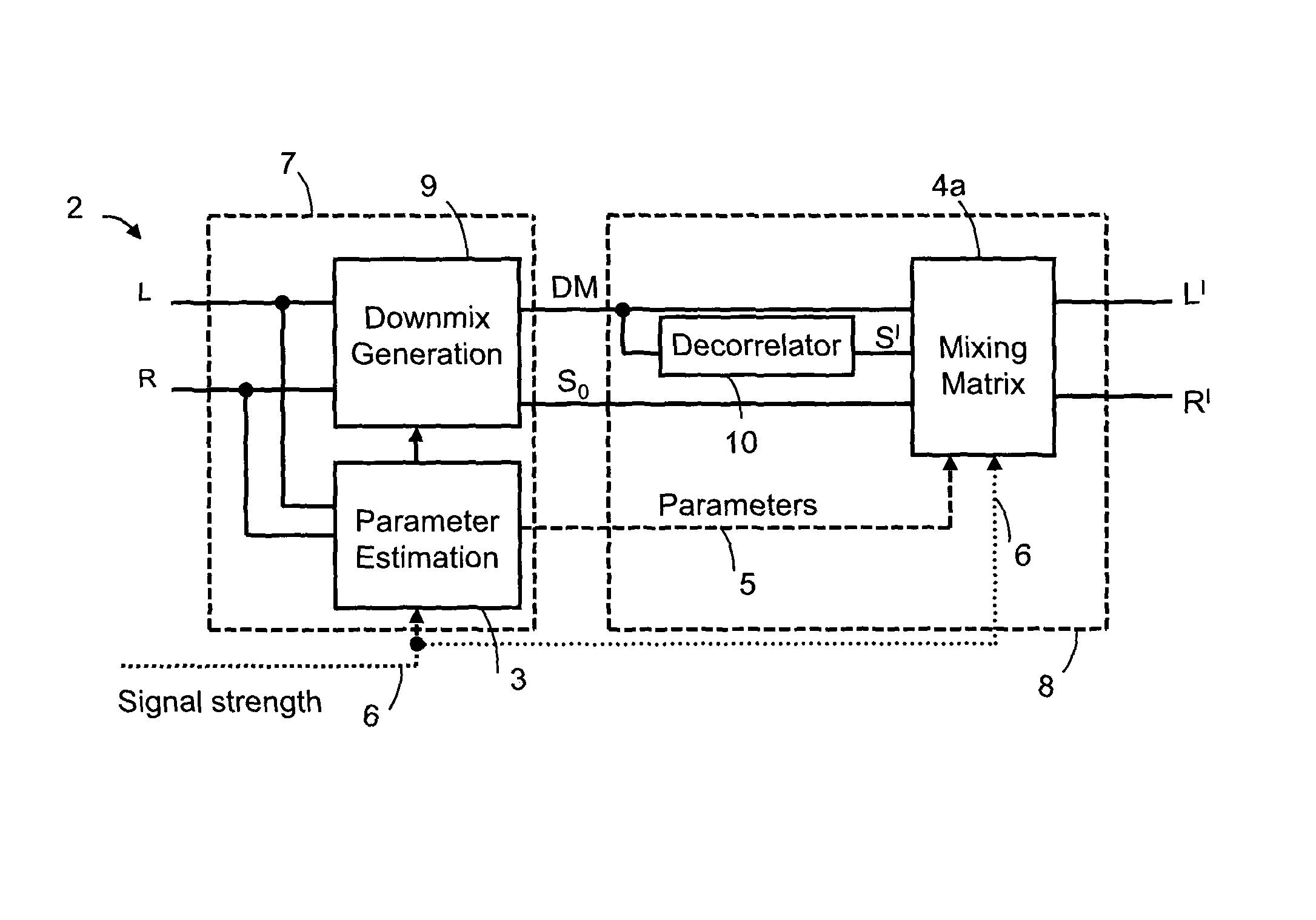
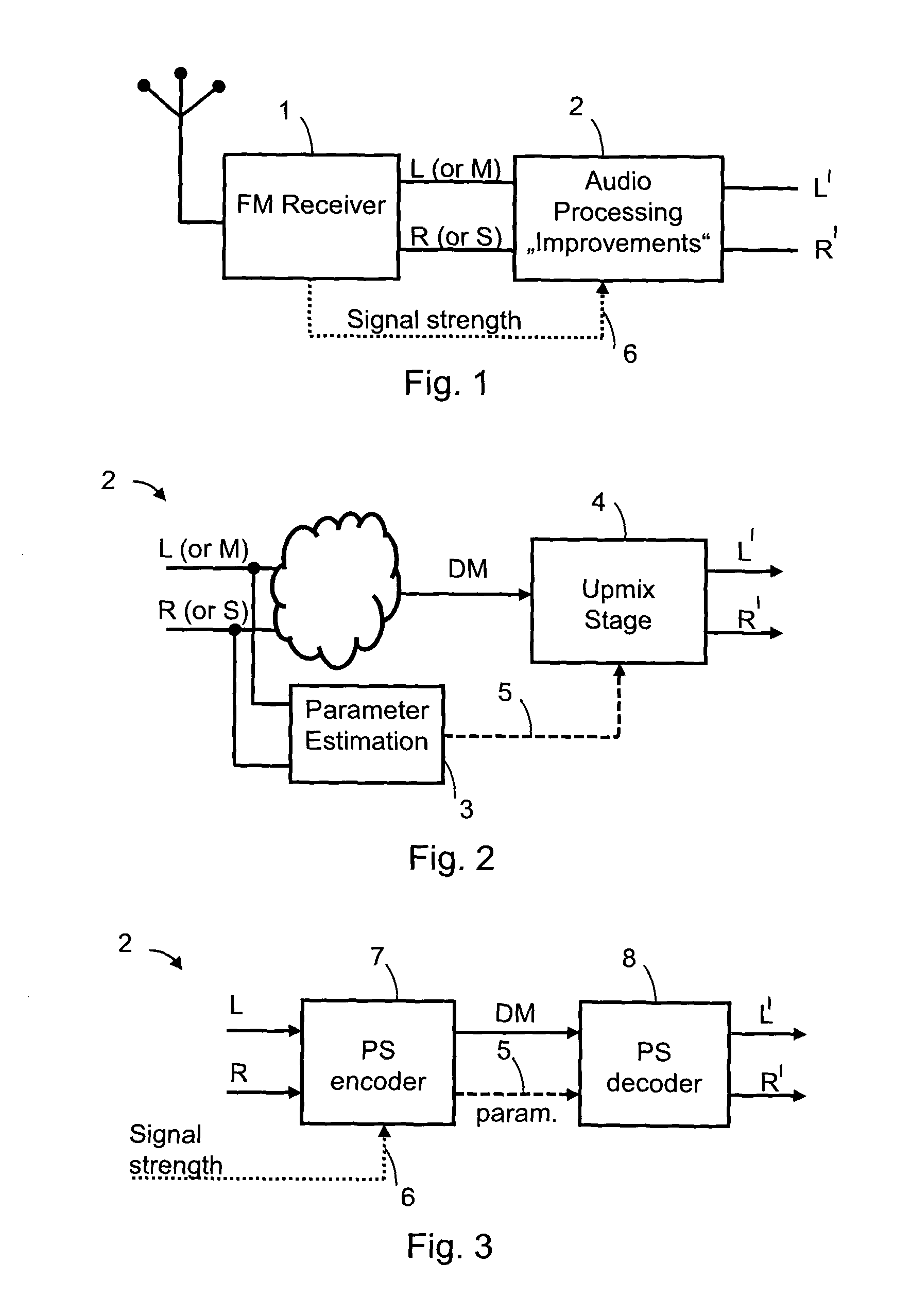
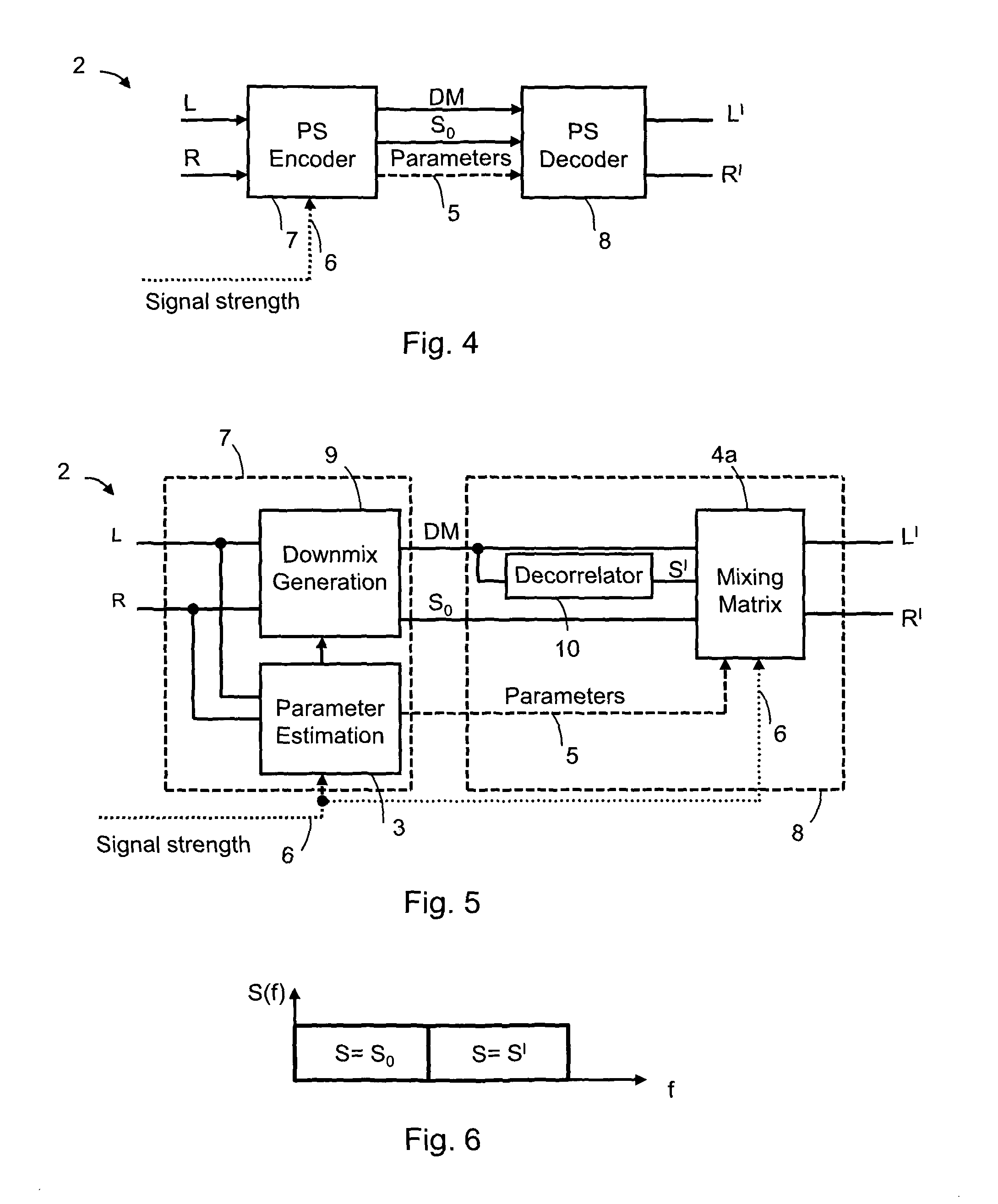
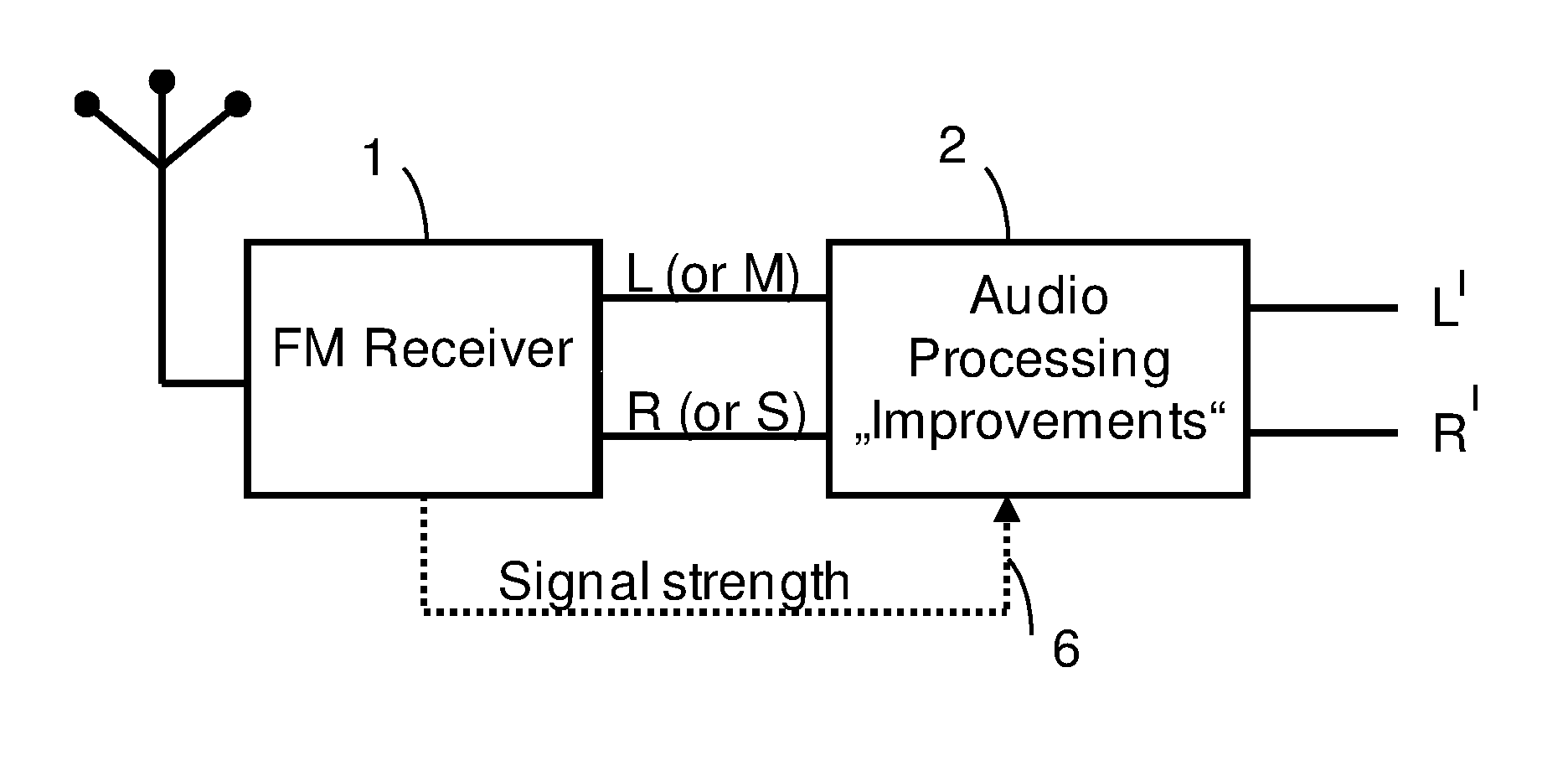
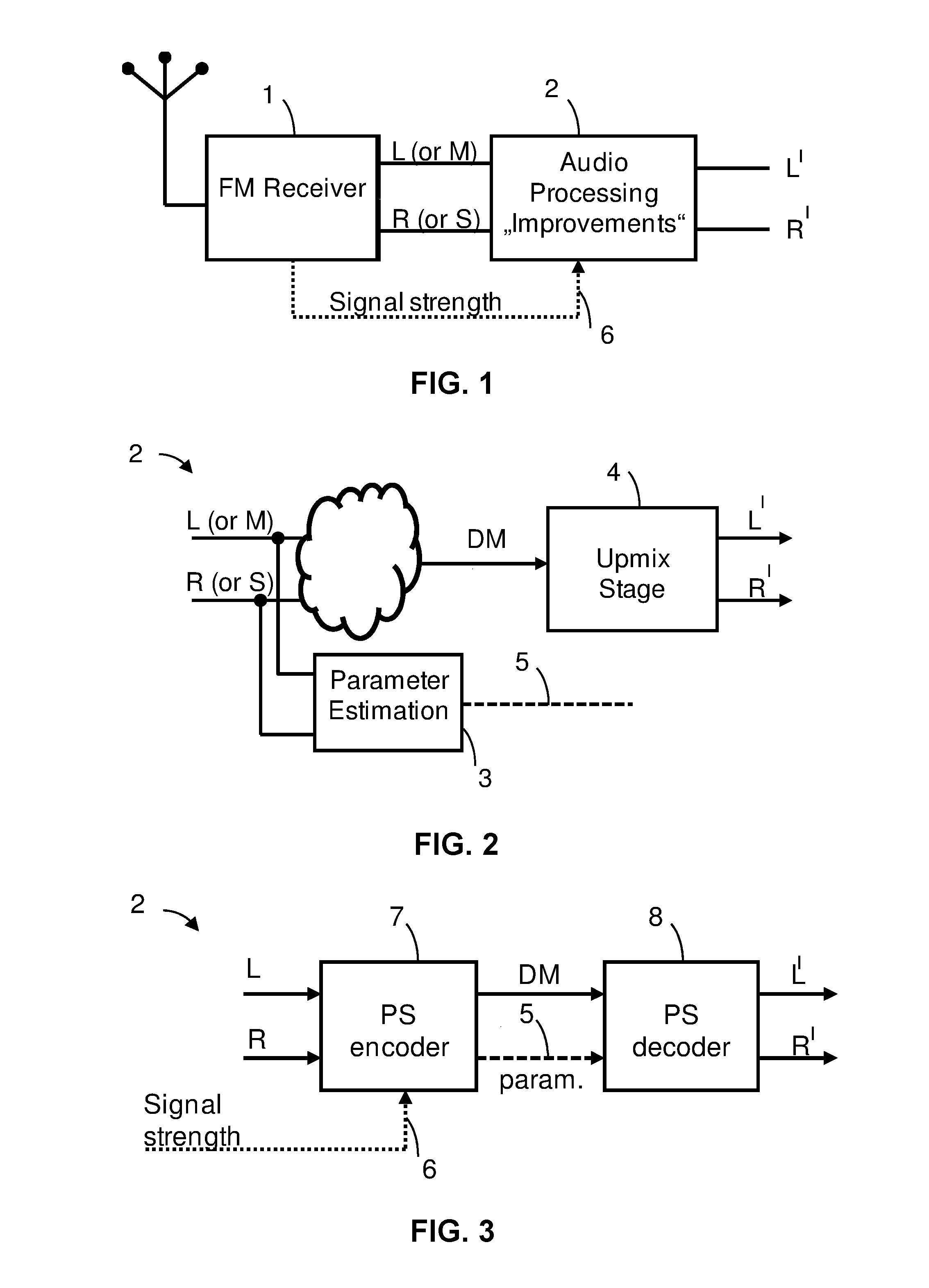
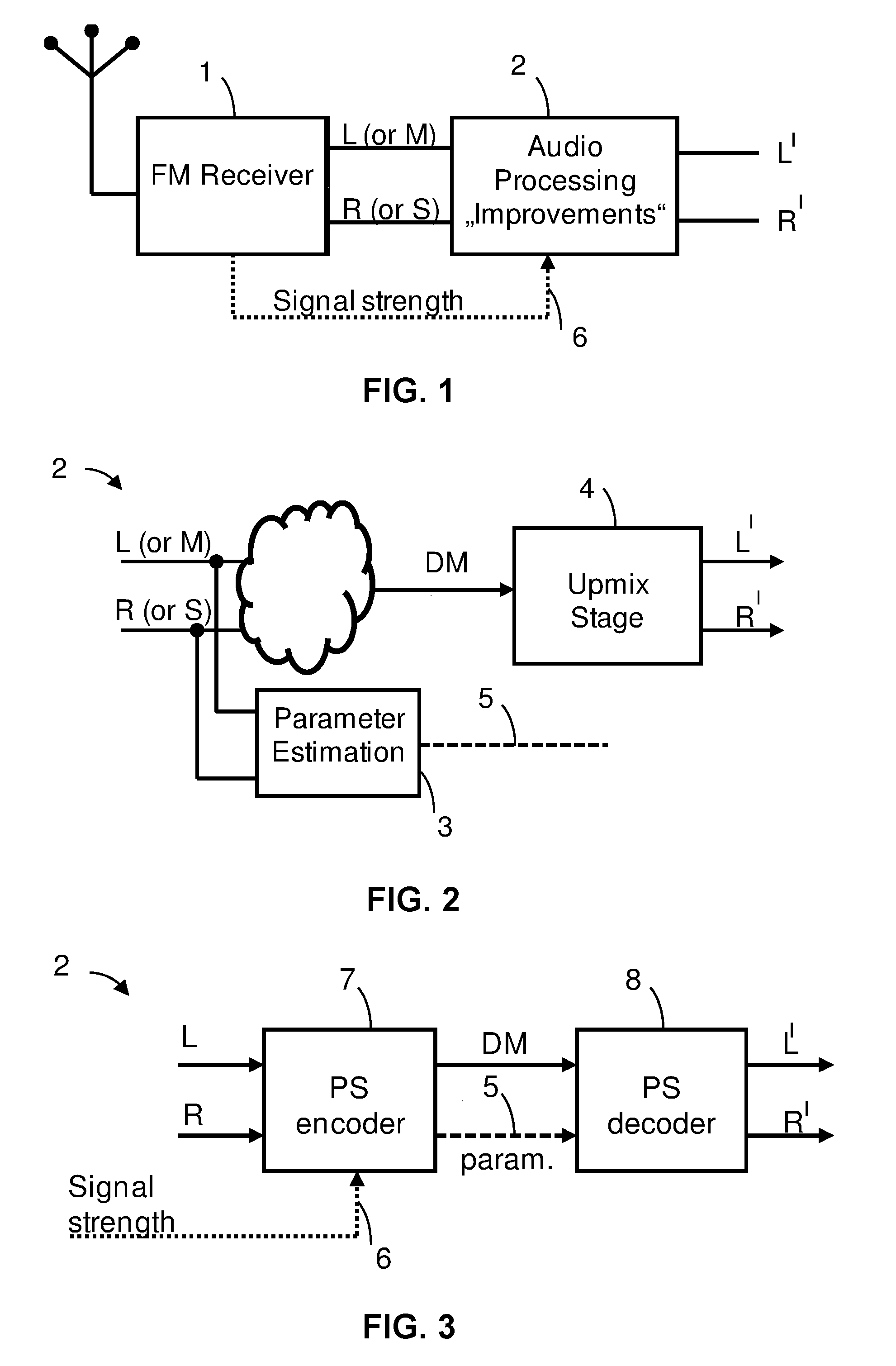
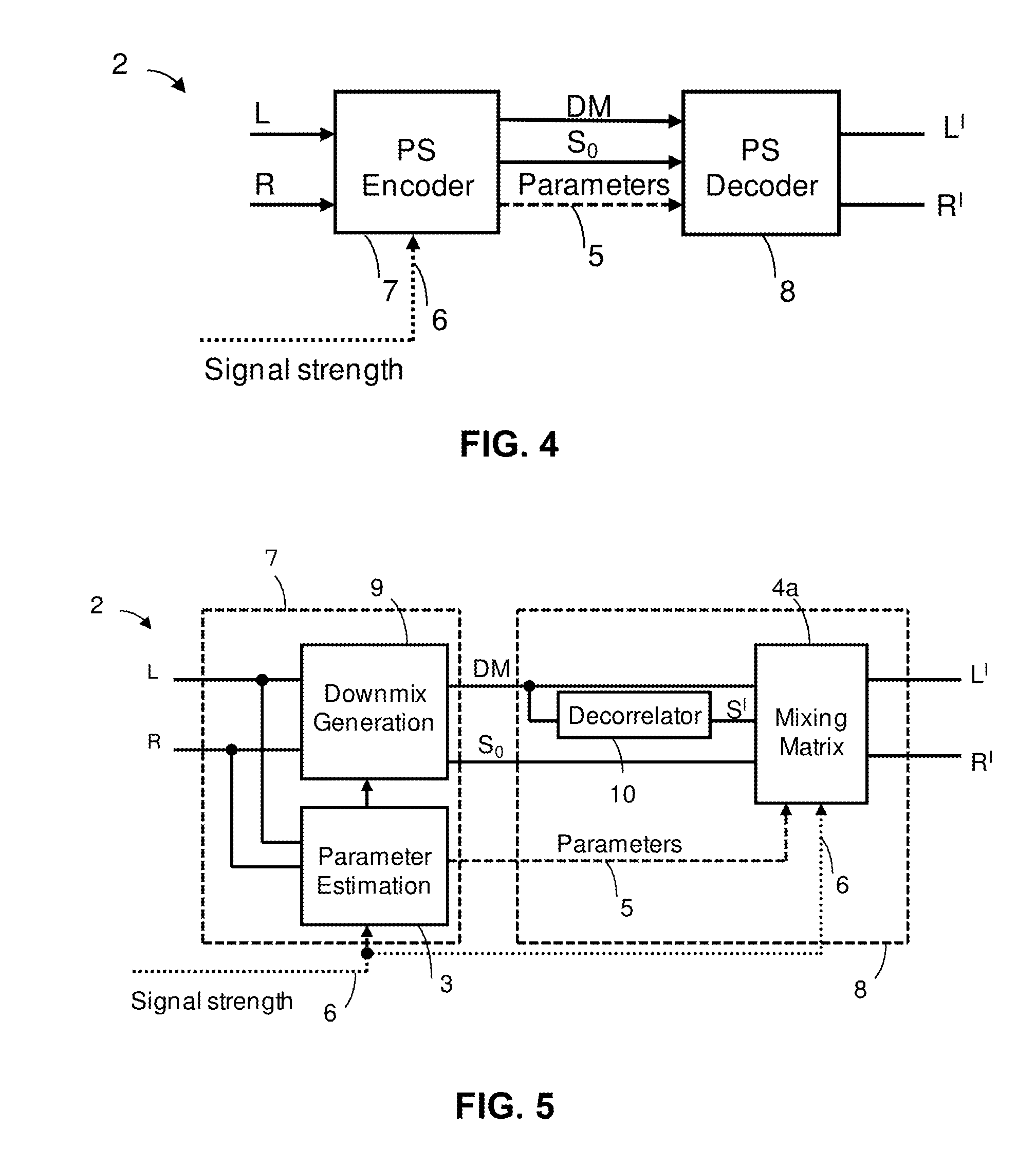
Audio signal of an FM stereo radio receiver by using parametric stereo
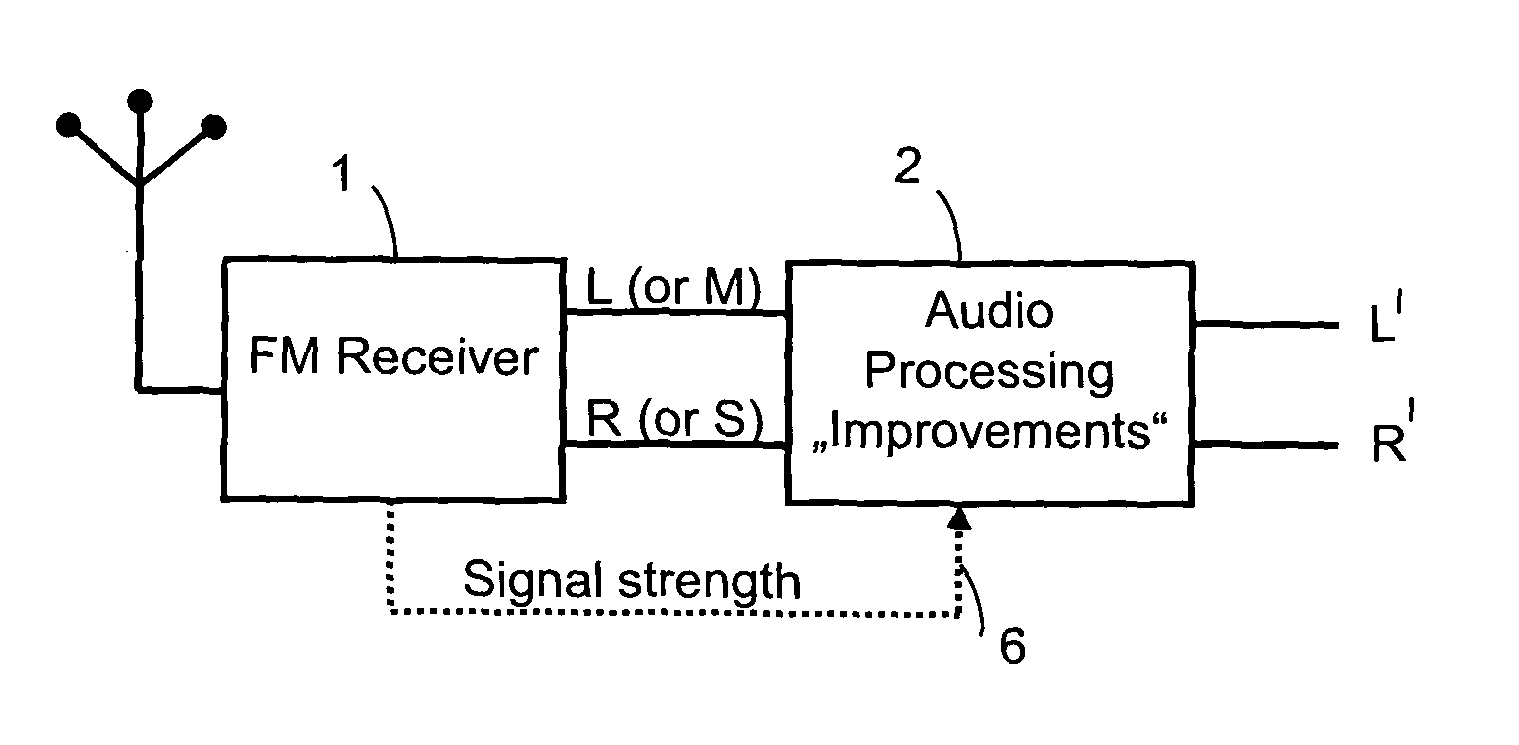
ActiveUS20120207307A1Improved stereo receptionEasy to receiveSpeech analysisBroadcast circuit arrangementsRadio receptionRadio receiver
The invention relates to an apparatus for improving a stereo audio signal of an FM stereo radio receiver. The apparatus comprises a parametric stereo (PS) parameter estimation stage. The parameter estimation stage is configured to determine one or more parametric stereo parameters based on the stereo audio signal in a frequency-variant or frequency-invariant manner. Preferably, these PS parameters are time- and frequency-variant. Moreover, the apparatus comprises an upmix stage. The upmix stage is configured to generate the improved stereo signal based on a first audio signal and the one or more parametric stereo parameters. The first audio signal is obtained from the stereo audio signal, e.g. by a downmix operation in a downmix stage. The PS parameter estimation stage may be part of a PS encoder. The upmix stage may be part of a PS decoder.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
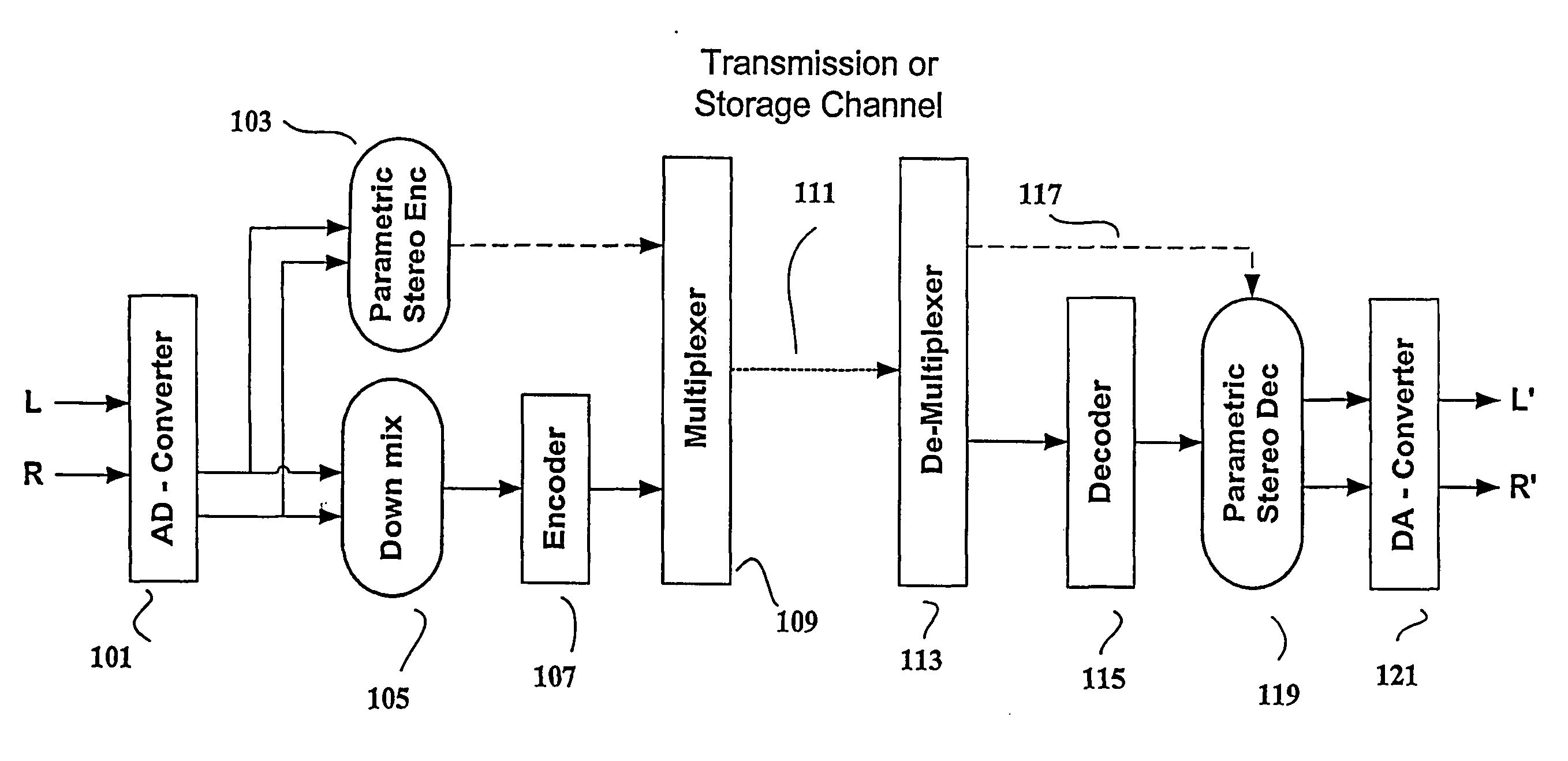
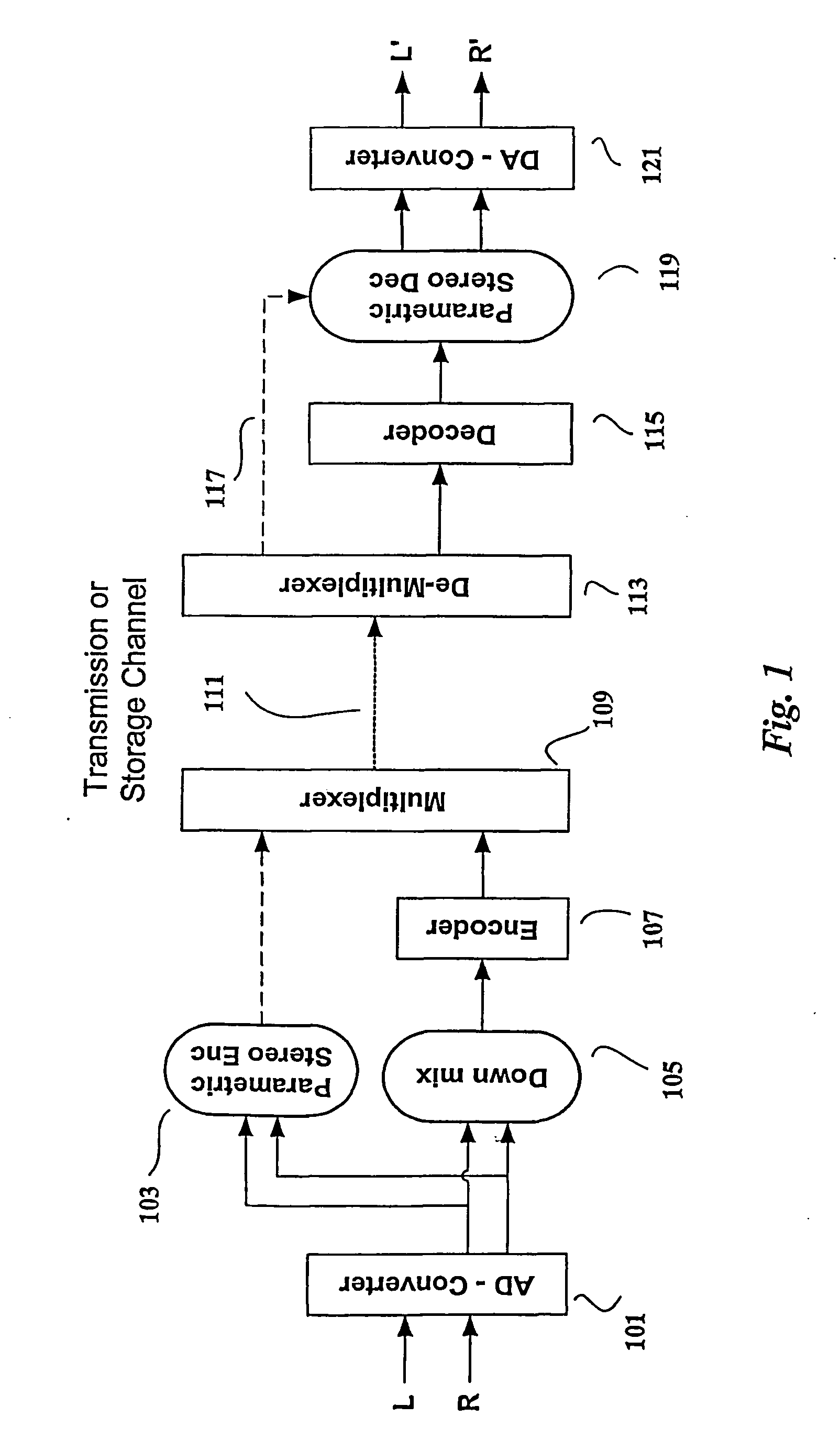
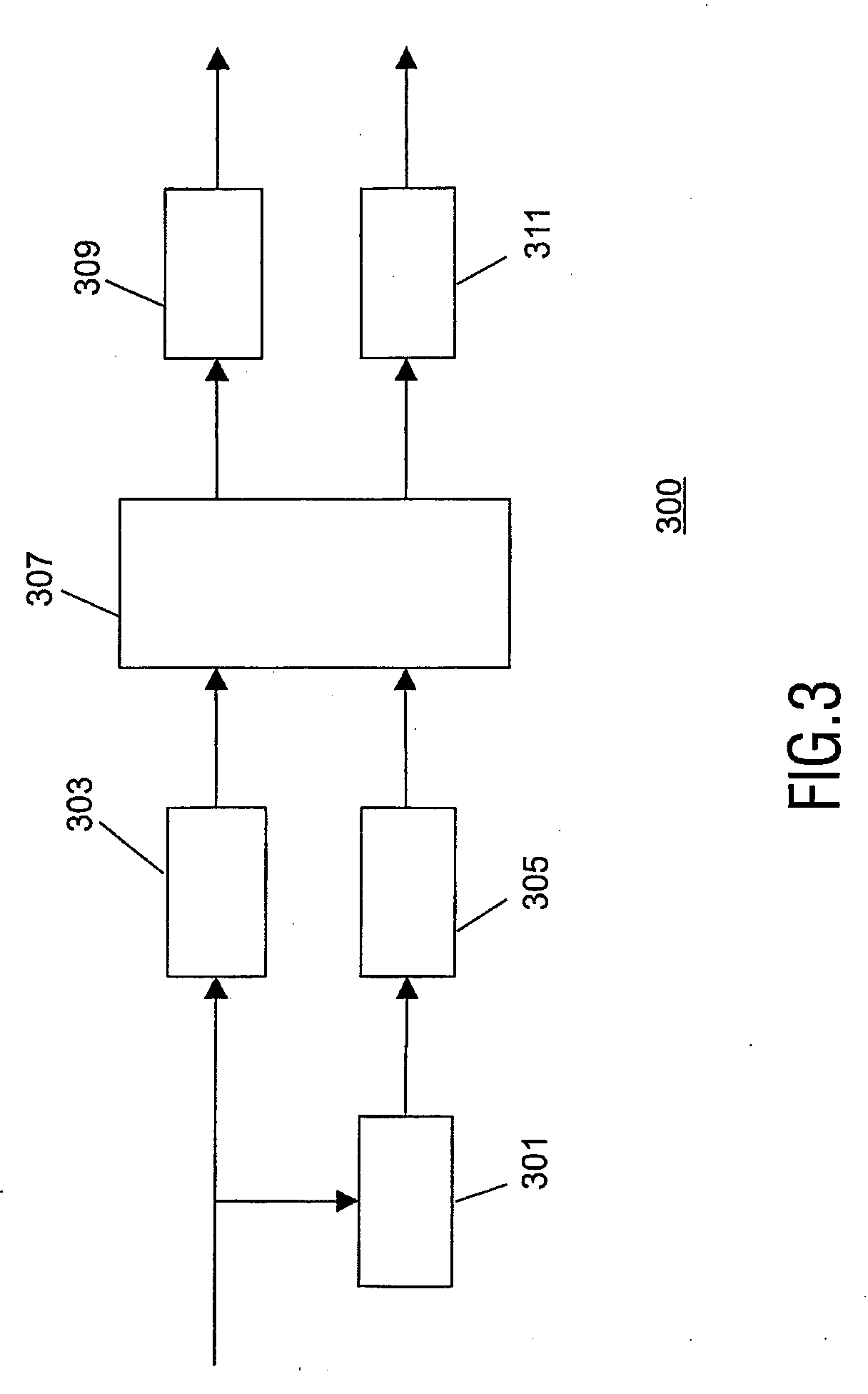
Audio distribution system, an audio encoder, an audio decoder and methods of operation therefore
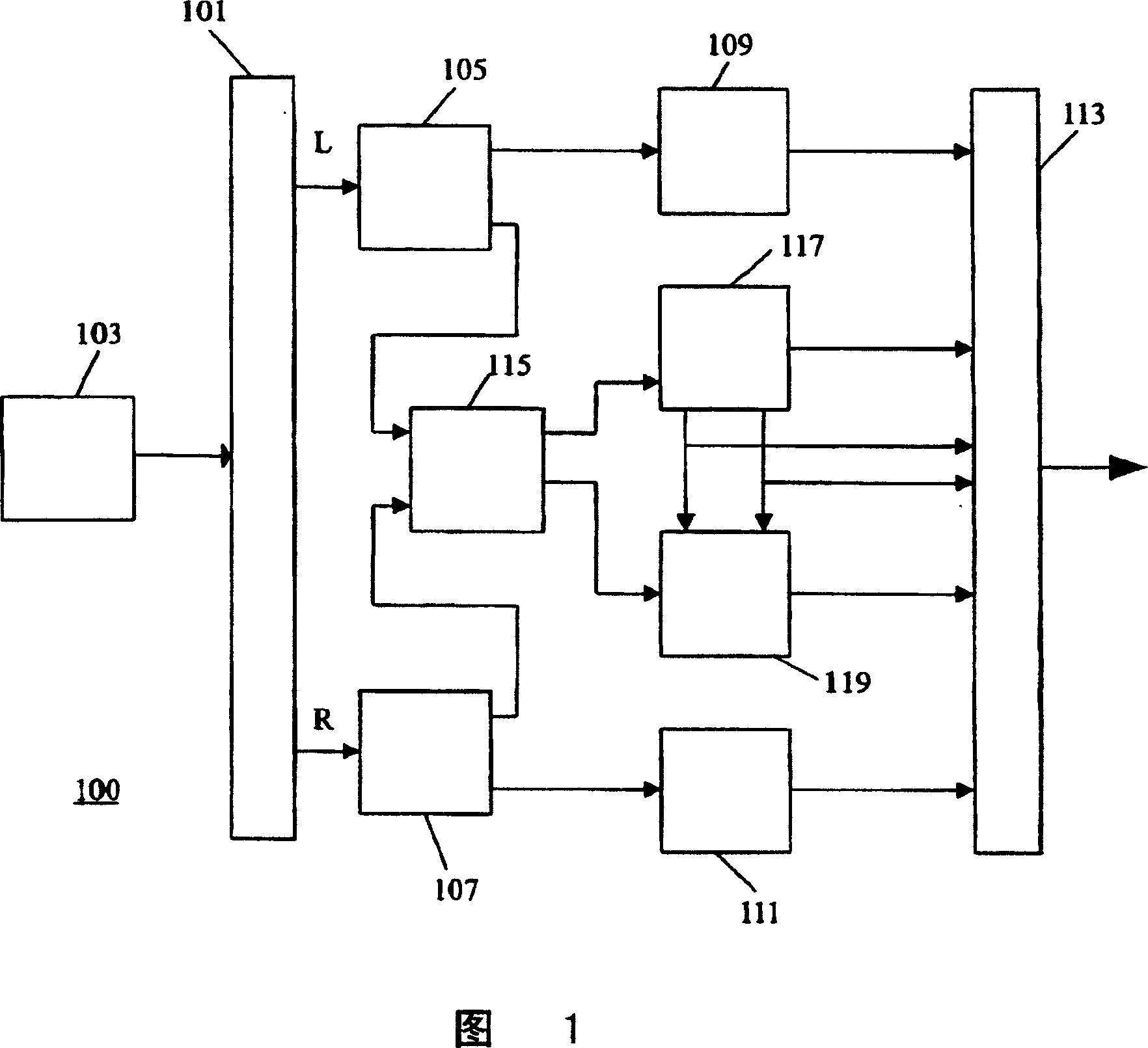
InactiveUS20070168183A1Efficient and high quality multi channel encodingQuality improvementSpeech analysisCode conversionDistribution systemVocal tract
A stereo audio encoder (100) comprises a parametric stereo encoder (115) which generates a mono signal and parametric stereo parameters for at least a high frequency part of an input stereo signal. A stereo intensity encoder (117) generates stereo intensity data for the mono signal. The mono signal and intensity data are encoded in accordance with an encoding standard such as MPEG Layer II and the parametric stereo parameters are included in the ancillary data sections by an output processor (113). Thus, a legacy decoder (such as an MPEG Layer II decoder) may generate a stereo signal using the stereo intensity data whereas a higher complexity decoder may generate a high quality audio signal using the parametric stereo parameters. A stereo decoder (200) receives the encoded data from the encoder (100). An intensity decoder (203) generates a stereo signal using intensity data. This is fed to a parametric stereo decoder (207) which processes the stereo signal in accordance with extracted parametric stereo data.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
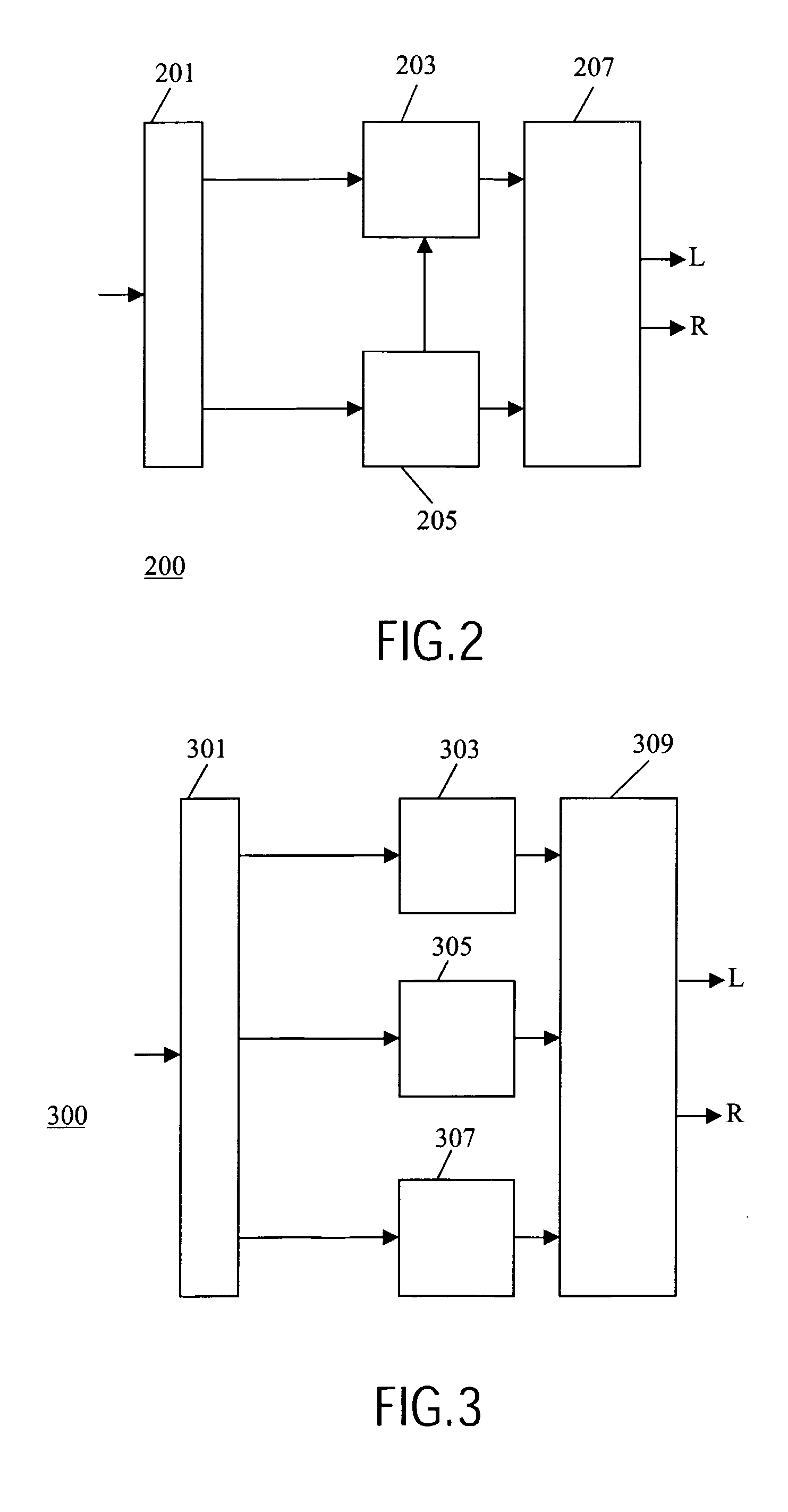
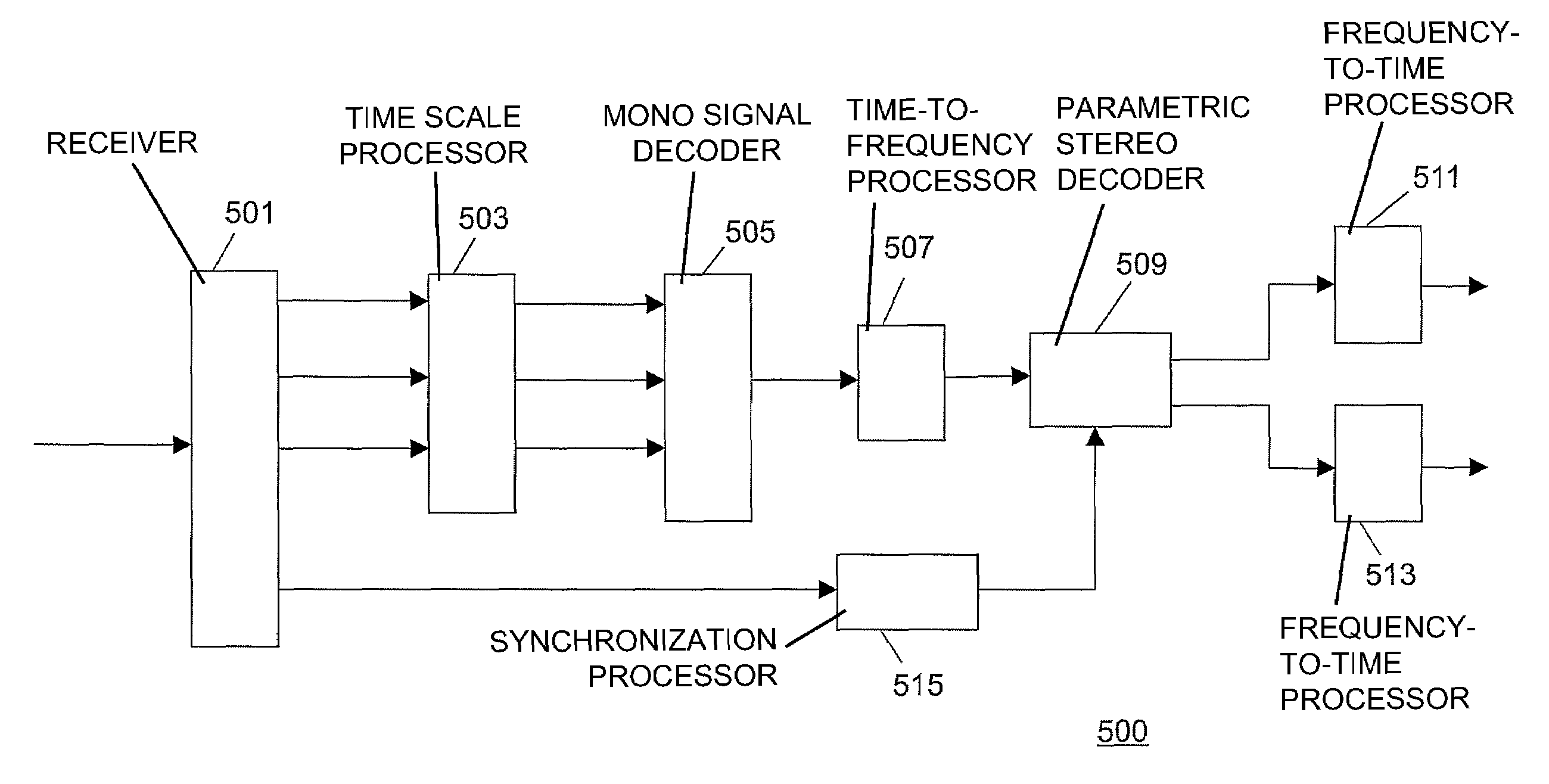
Method and apparatus for time scaling of a signal
InactiveUS7734473B2Efficient time scalingEfficient low complexity generationSpeech analysisTime domainComputer science
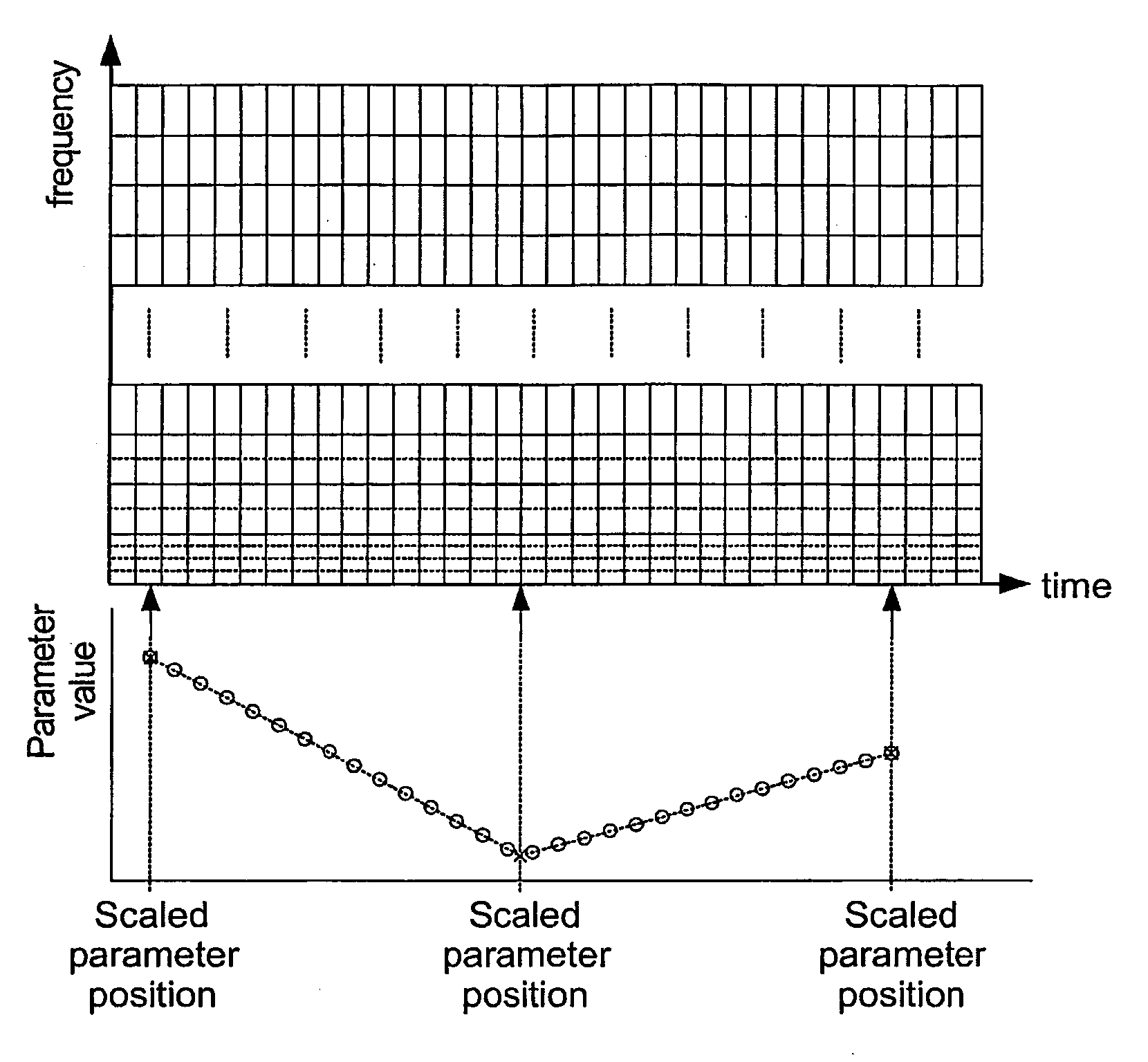
A decoder receives (501) a bitstream comprising an encoded mono signal and stereo data. A time scale processor (503) generates a time scaled mono signal. A time-to frequency processor generates frequency sample blocks of the time scaled signal, the block length being fixed and independent of the time scaling. A parametric stereo decoder (509) generates a stereo signal for the frequency sample blocks and these are converted to the time domain by a frequency-to-time processor (511). A synchronization processor (515) synchronizes the stereo data with the time scaled signal by determining a time association between a parameter value and a frequency sample block. The parameter value and time association is used to determine synchronized stereo parameter values for that and other frequency sample blocks. The invention is particularly suitable for low complexity generation of time scaled stereo signals from MPEG-4 encoded signals.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
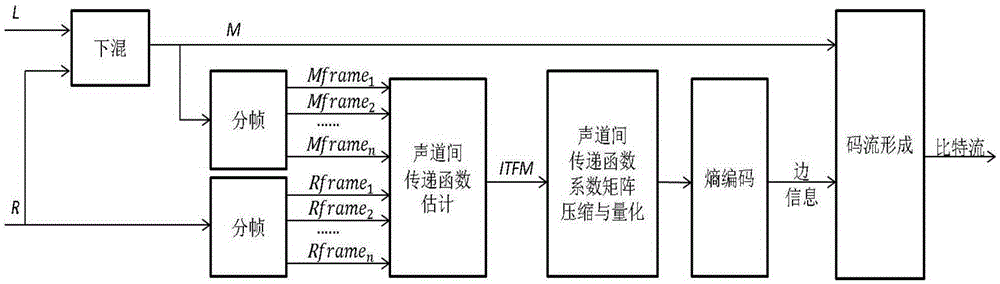
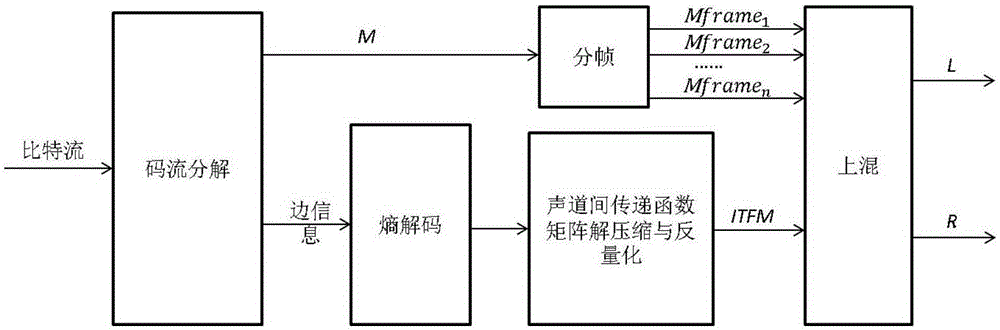
Parameter stereo coding, decoding method based on inter-channel transfer function
ActiveCN105405445AAchieve compressionPreserve low and high frequency spatial informationSpeech analysisDecoding methodsSide information
The invention discloses a parameter stereo coding, decoding method based on inter-channel transfer function. The parameter stereo coding, decoding method is characterized in that 1) a lower mixed signal can be generated by a coding end using a left track signal and a right track signal; 2) after the respective framing of the input lower mixed signal and the single track signal, the inter-channel transfer function coefficient of every frame can be extracted, and then the extracted transfer function coefficients can be used to form a two-dimensional matrix, and in addition, the single track signal can be the left track signal or the right track signal; 3) the two-dimensional compression, the run coding, and the entropy coding of the two-dimensional matrix can be carried out sequentially, and the coefficients of the two-dimensional matrix can be compressed to form the side information, and then the side information and the lower mixed signal can be used to form the bit stream. The lower high-power space information of the signals can be retained, and the inner-frame compression and the inter-frame compression can be realized at the same time.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method and apparatus for time scaling of a signal
InactiveUS20090192804A1Efficient low complexity generationEfficient time scalingSpeech analysisTime domainComputer science
A decoder receives (501) a bitstream comprising an encoded mono signal and stereo data. A time scale processor (503) generates a time scaled mono signal. A time-to frequency processor generates frequency sample blocks of the time scaled signal, the block length being fixed and independent of the time scaling. A parametric stereo decoder (509) generates a stereo signal for the frequency sample blocks and these are converted to the time domain by a frequency-to-time processor (511). A synchronization processor (515) synchronizes the stereo data with the time scaled signal by determining a time association between a parameter value and a frequency sample block. The parameter value and time association is used to determine synchronized stereo parameter values for that and other frequency sample blocks. The invention is particularly suitable for low complexity generation of time scaled stereo signals from MPEG-4 encoded signals.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Concealment of intermittent mono reception of FM stereo radio receivers
ActiveUS20130142340A1High degreeInhibition transitionSpeech analysisTransmissionRadio receiverVocal tract
The present invention relates to audio signal processing. In particular, it relates to a method and system for reliably concealing intermittent mono reception of FM stereo radio receivers. The system comprises a parametric stereo parameter estimation stage configured to determine a first parametric stereo parameter based on a first frame of the received two-channel audio signal. The system further comprises a concealment detection stage configured to determine an energy of a side signal within the first signal frame; determine a number of following successive signal frames during which the energy of the side signal drops from a value above the high threshold to a value below a low threshold; determine that the two-channel audio signal following the first signal frame is a forced mono signal if the number of successive signal frames is below a frame threshold; and determine the parametric stereo parameter based on the first parametric stereo parameter.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Audio signal of an FM stereo radio receiver by using parametric stereo
ActiveUS8929558B2Easy to receiveSpeech analysisBroadcast circuit arrangementsRadio receiverAudio frequency
The invention relates to an apparatus for improving a stereo audio signal of an FM stereo radio receiver. The apparatus comprises a parametric stereo (PS) parameter estimation stage. The parameter estimation stage is configured to determine one or more parametric stereo parameters based on the stereo audio signal in a frequency-variant or frequency-invariant manner. Preferably, these PS parameters are time- and frequency-variant. Moreover, the apparatus comprises an upmix stage. The upmix stage is configured to generate the improved stereo signal based on a first audio signal and the one or more parametric stereo parameters. The first audio signal is obtained from the stereo audio signal, e.g. by a downmix operation in a downmix stage. The PS parameter estimation stage may be part of a PS encoder. The upmix stage may be part of a PS decoder.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
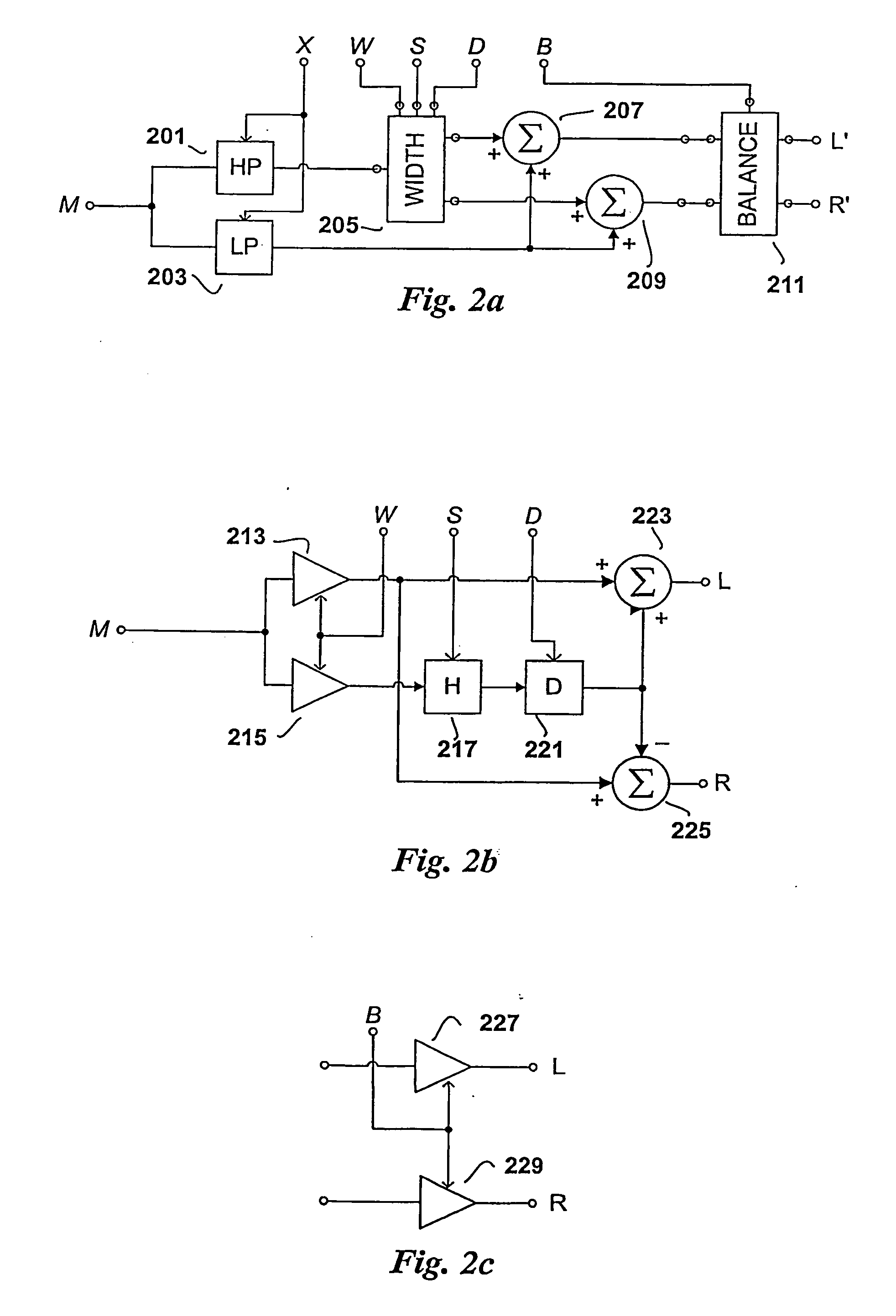
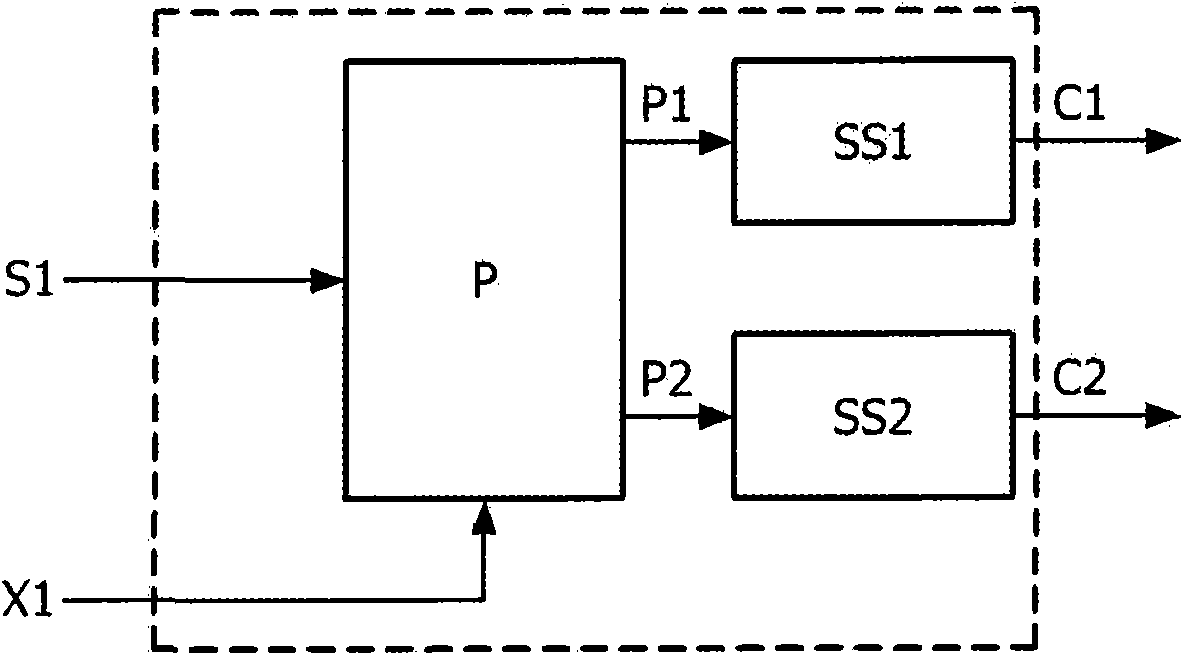
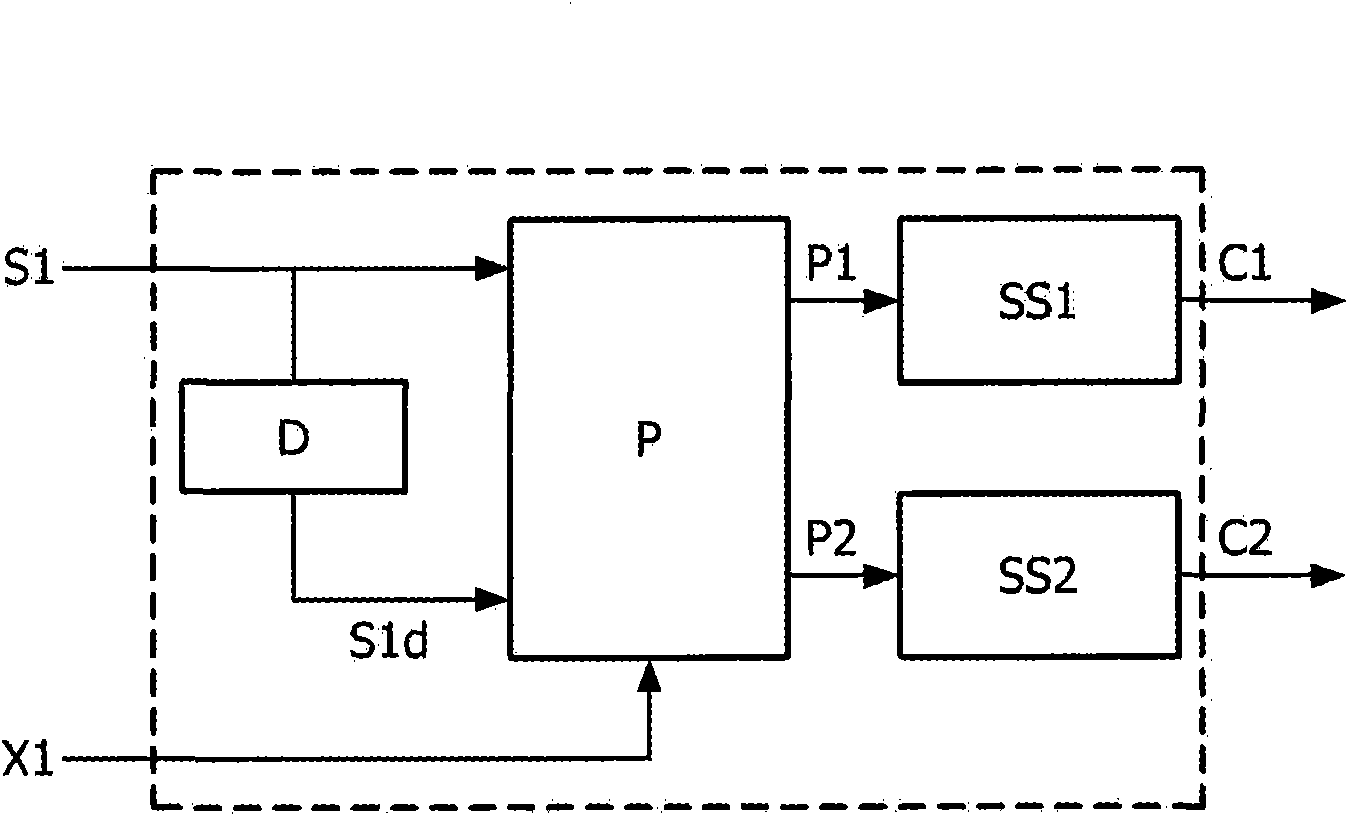
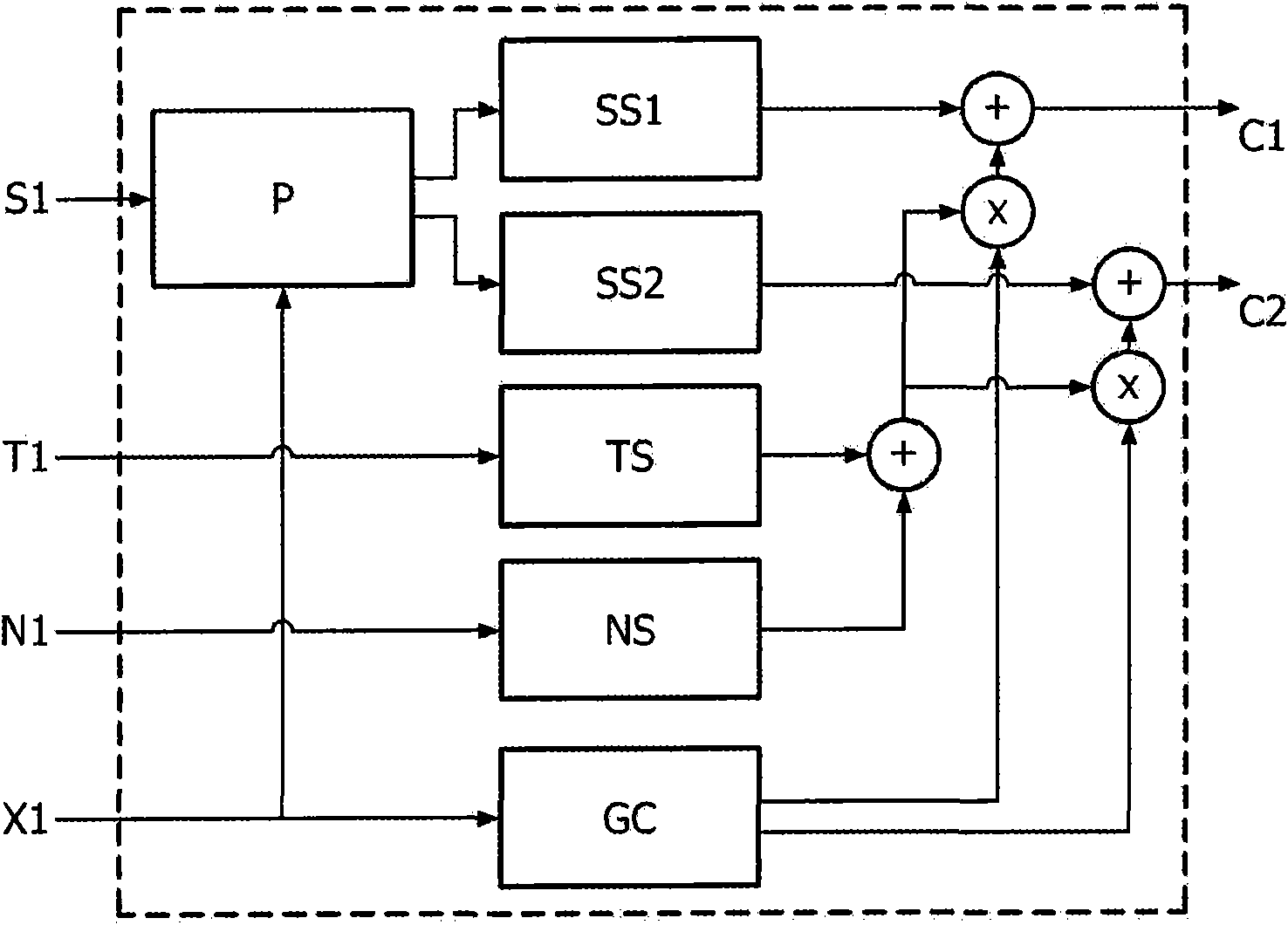
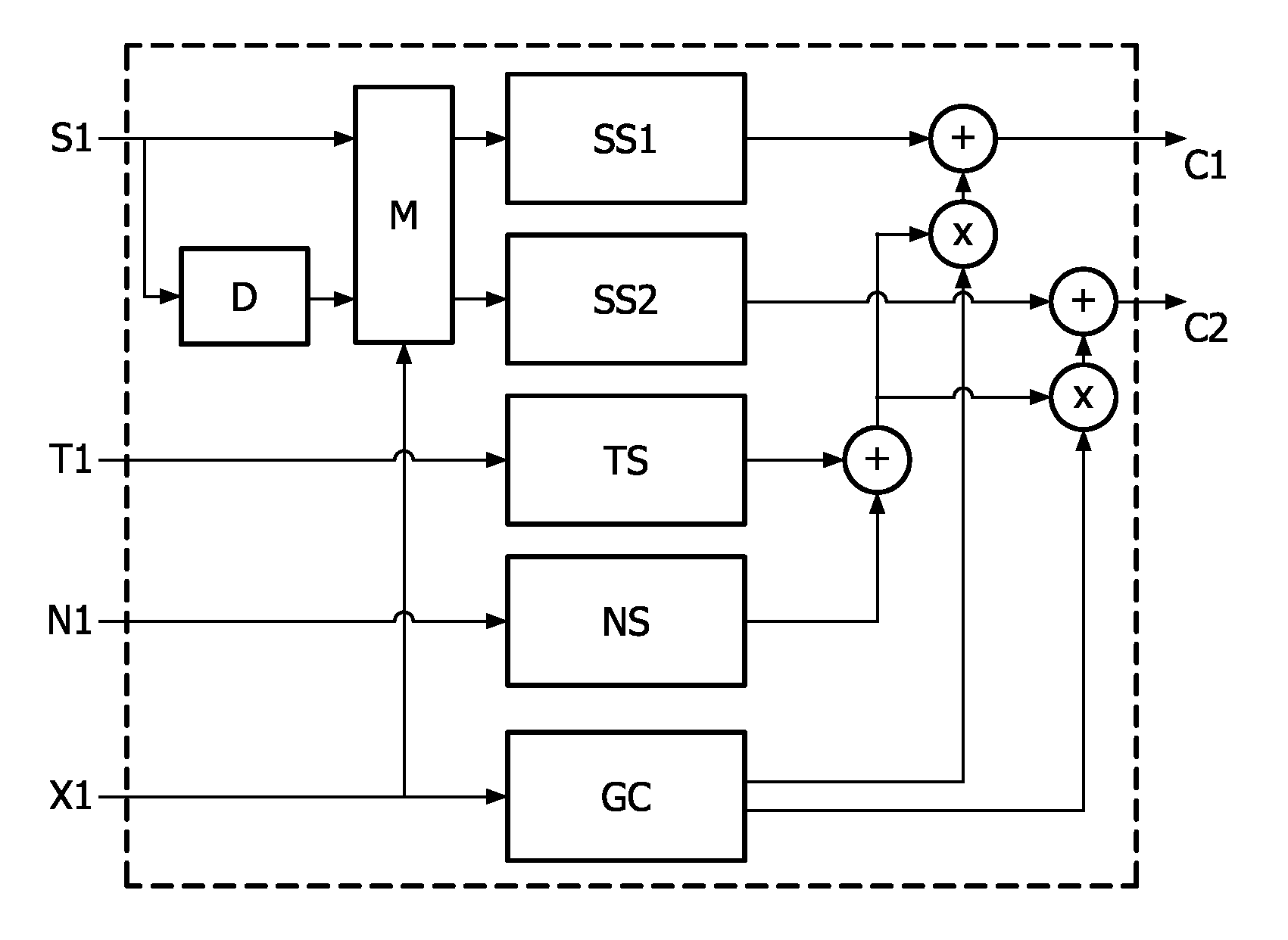
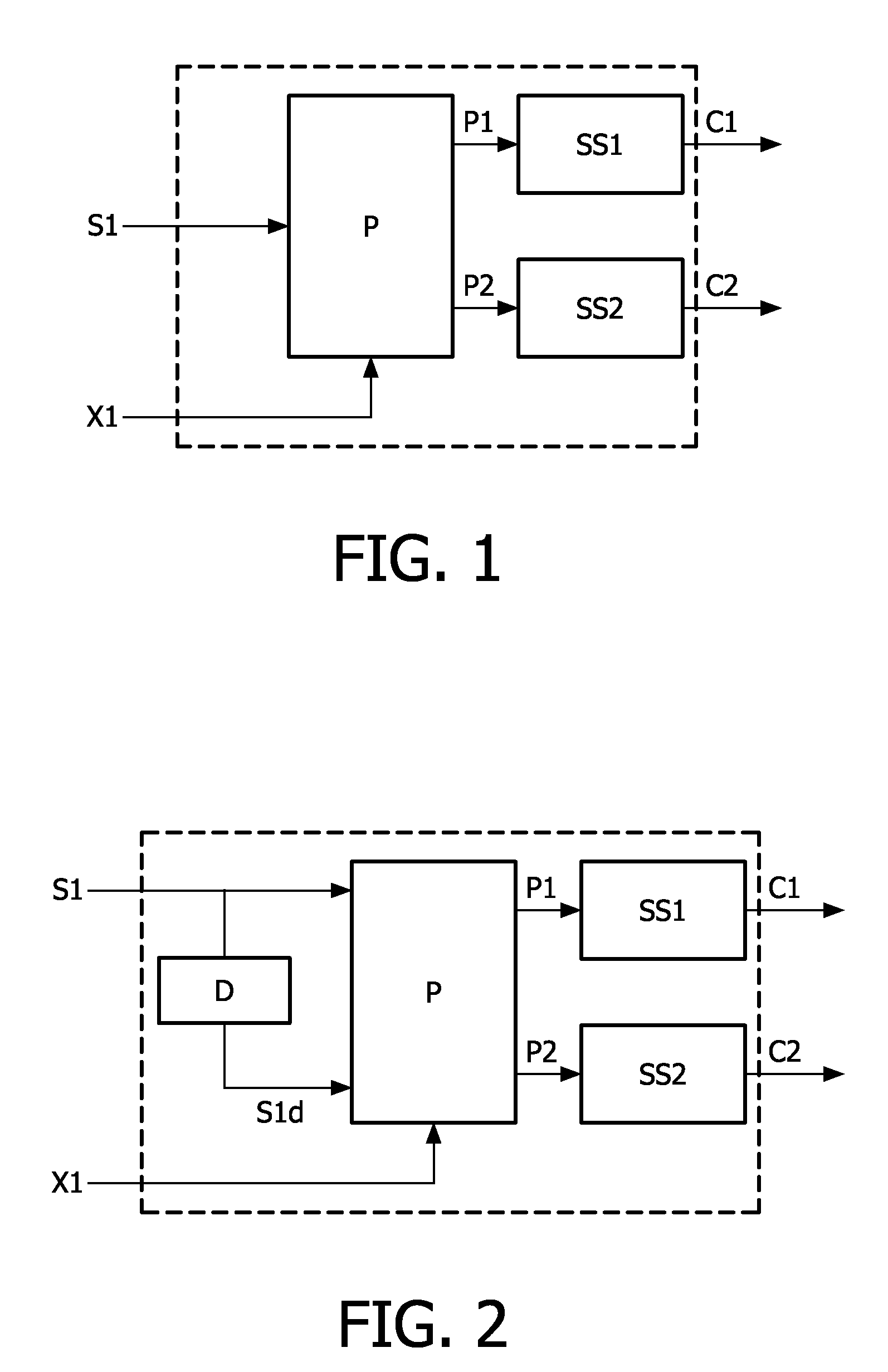
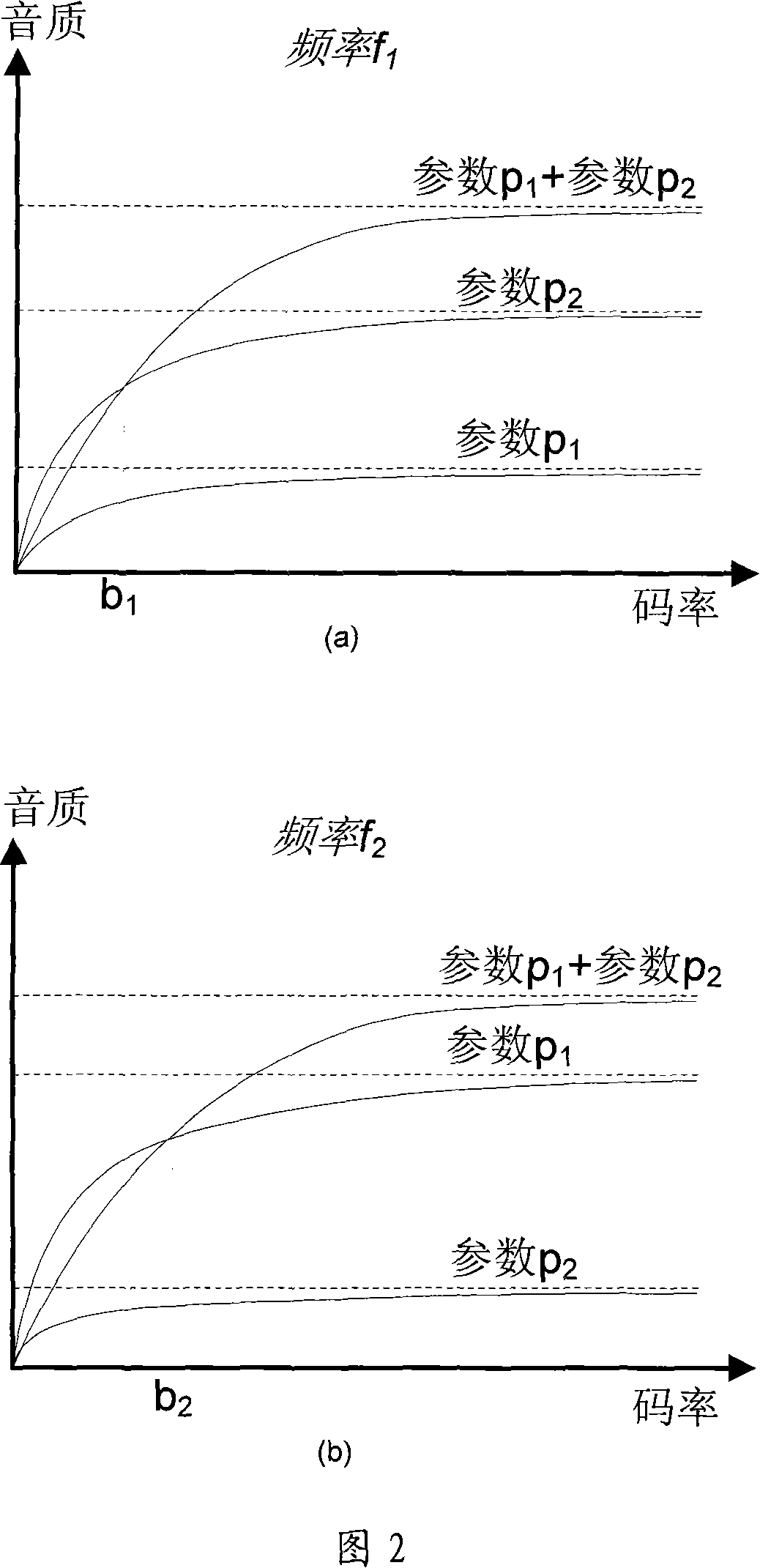
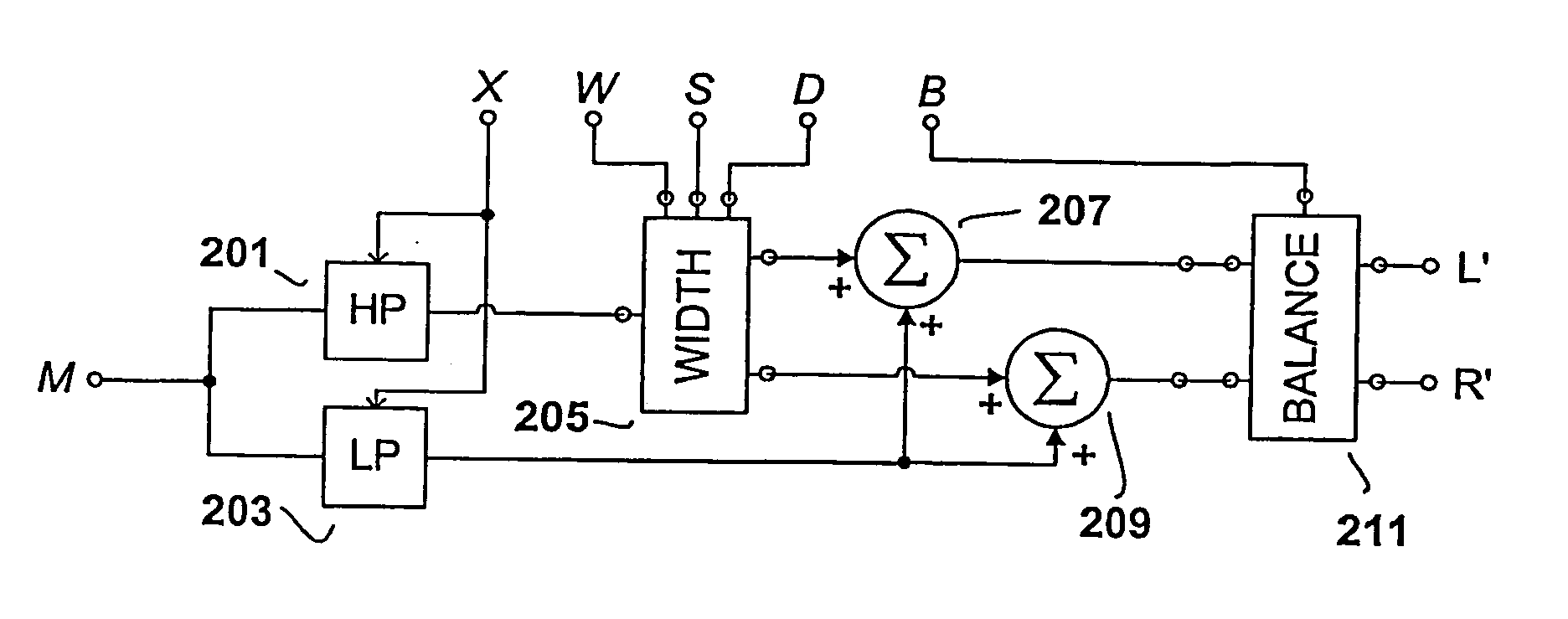
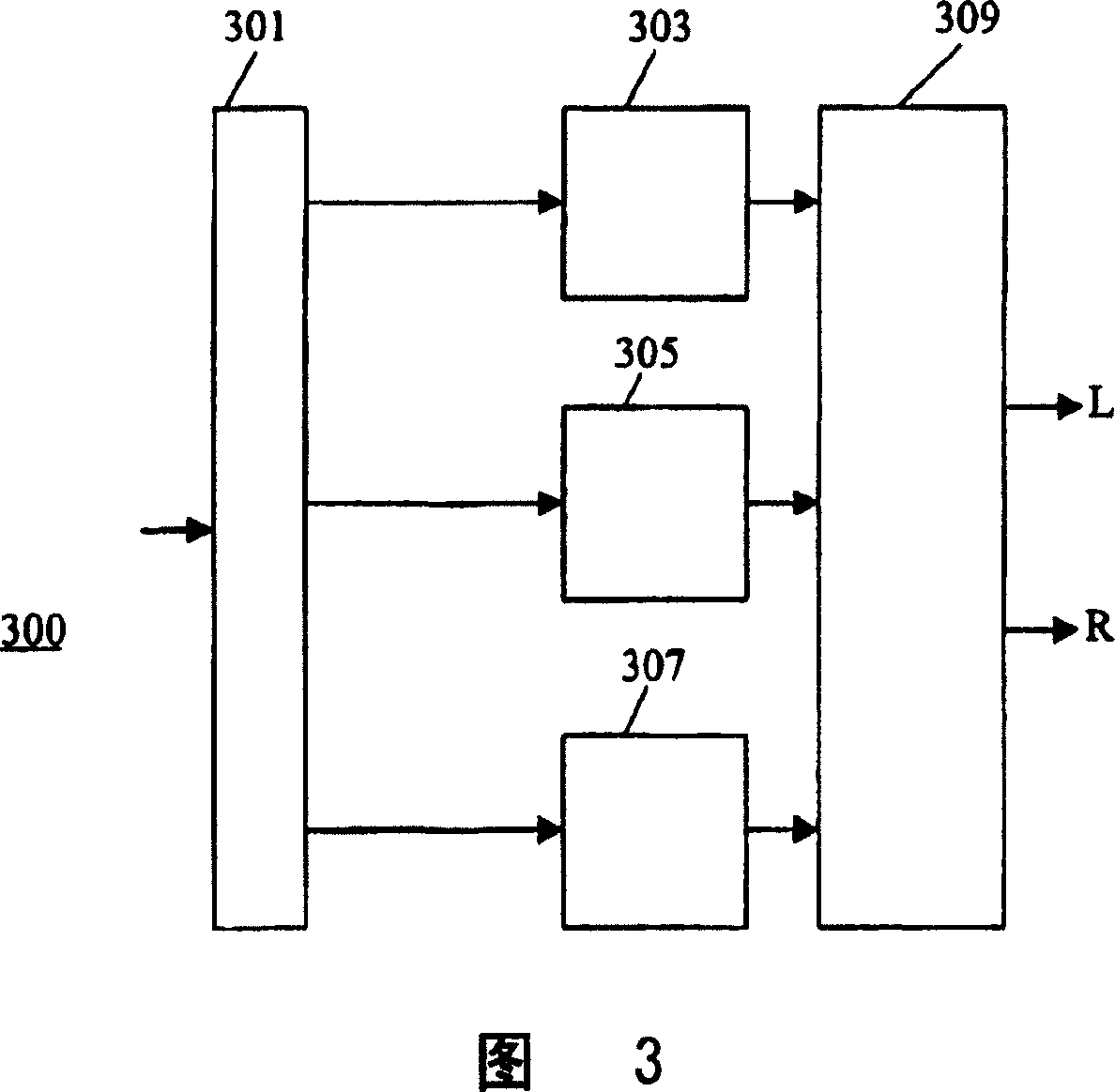
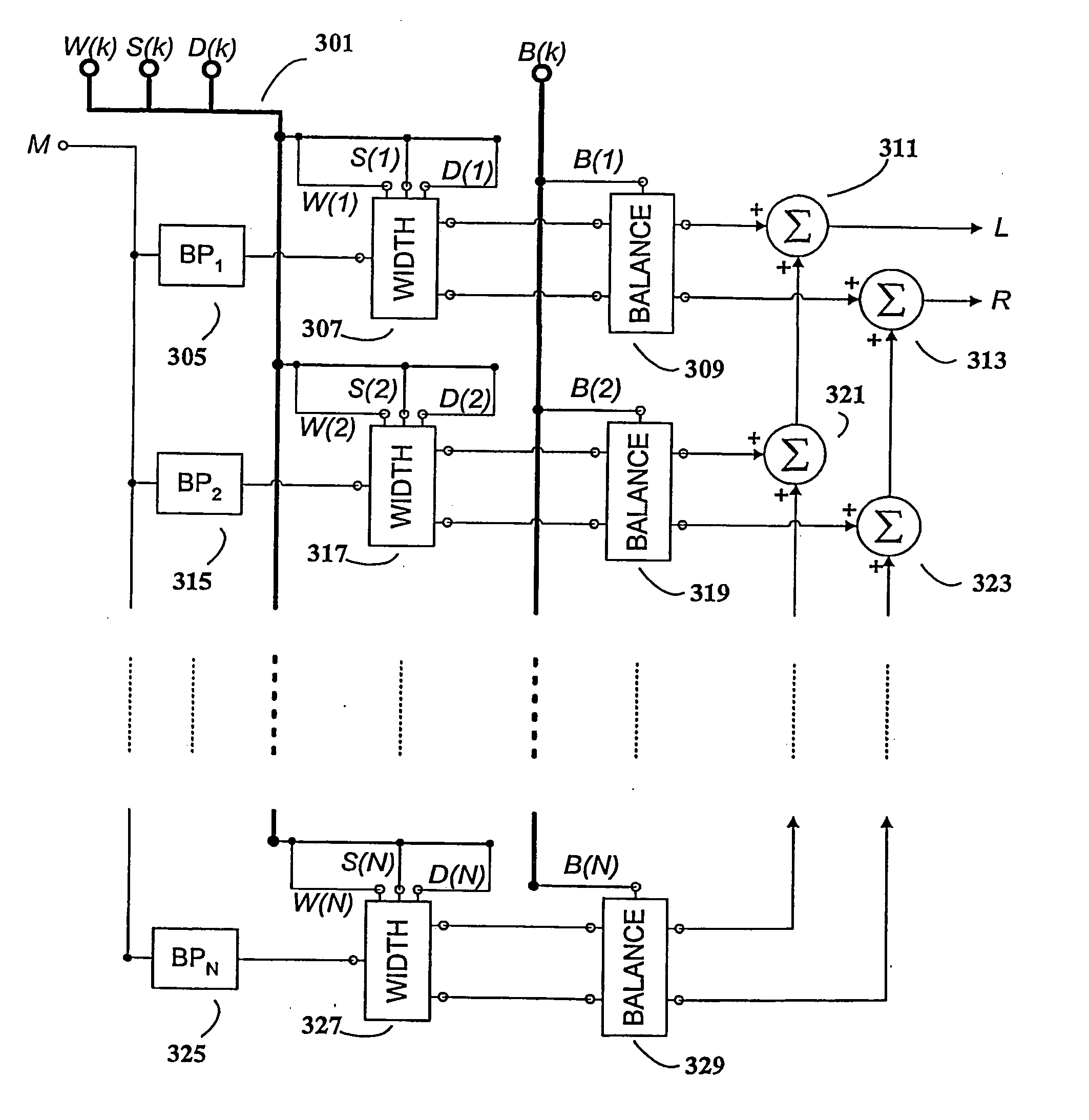
Low complexity parametric stereo decoder
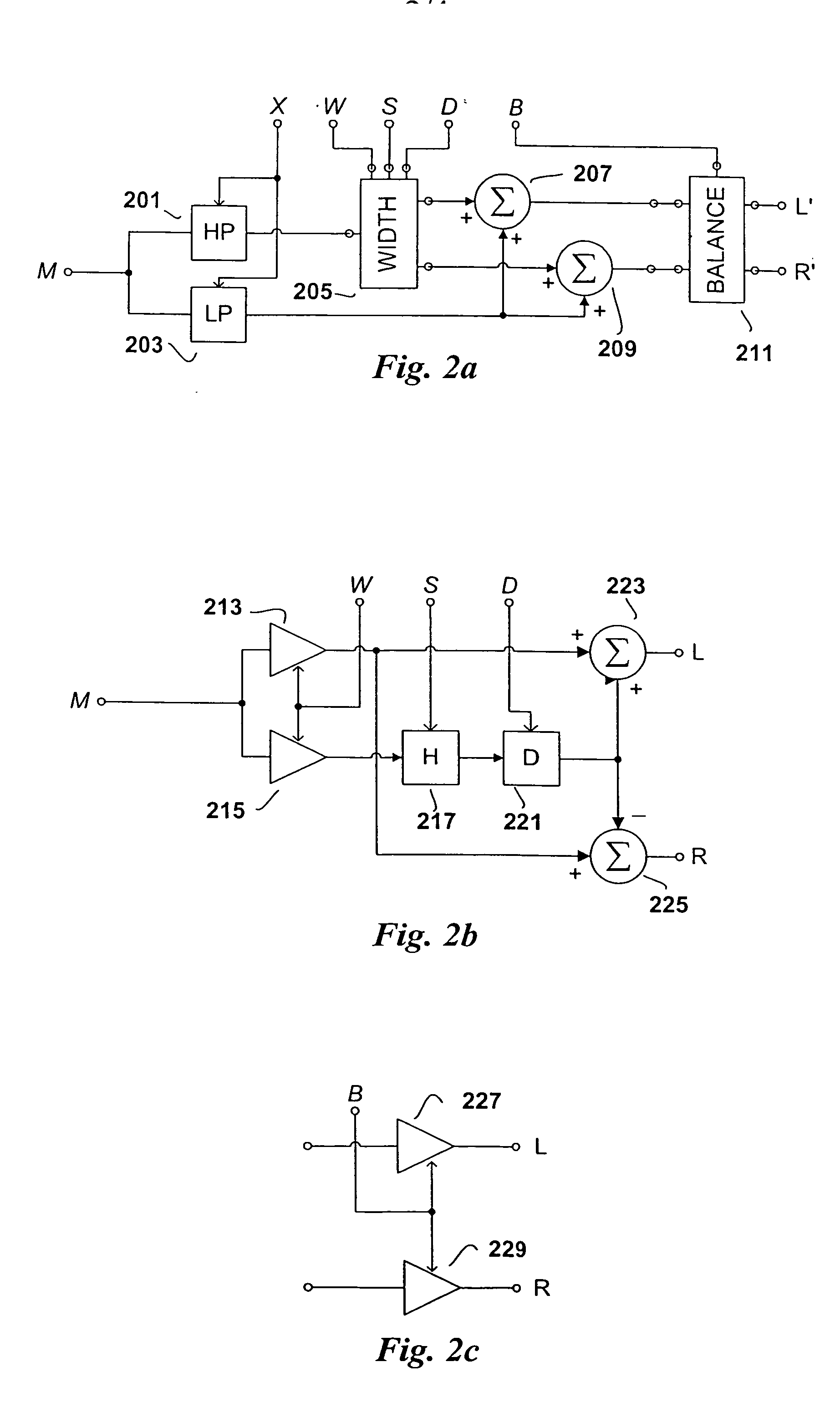
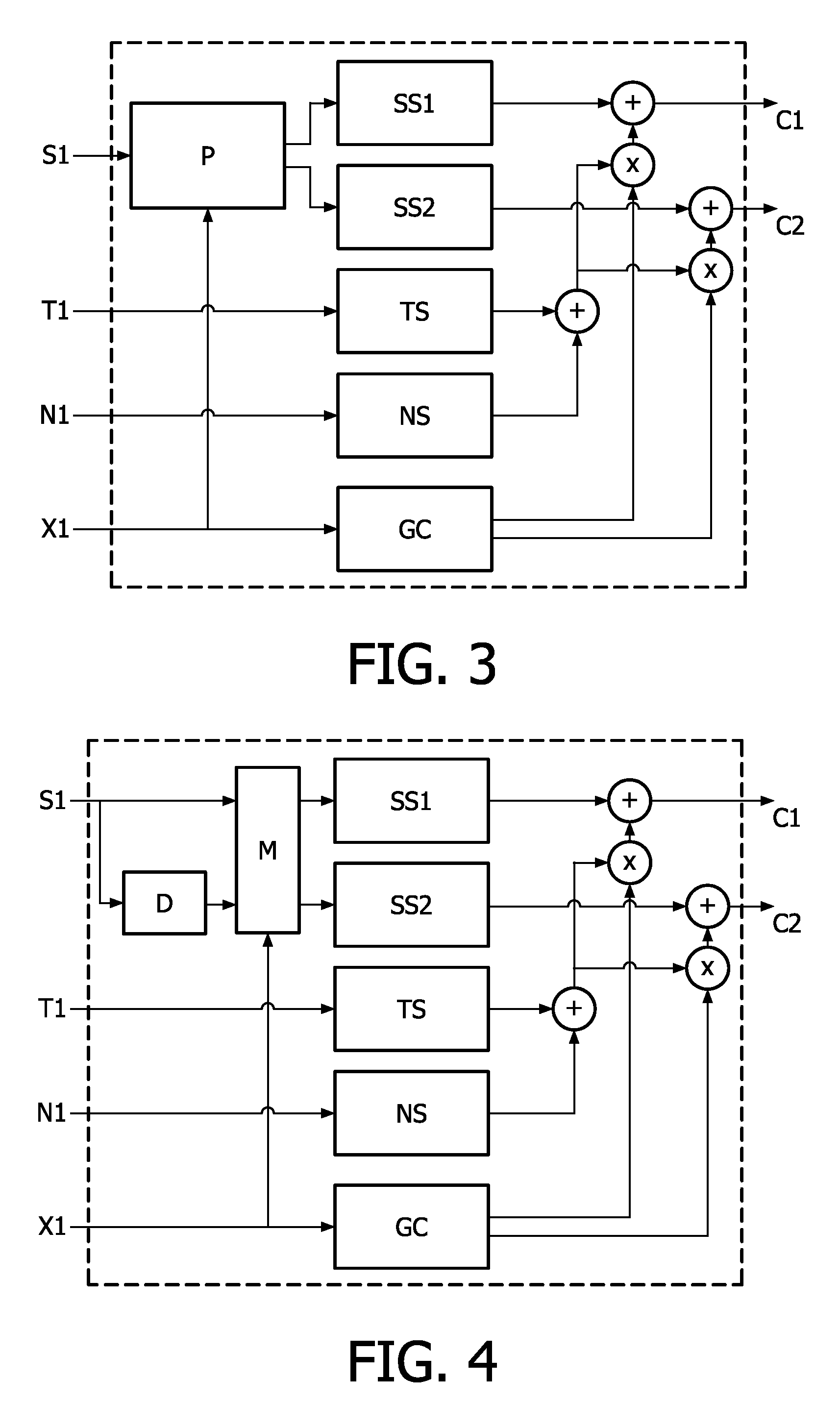
A stereo audio decoder with low complexity is provided. A high stereo sound quality can be obtained with a limited computational power and is thus suitable for miniature and mobile equipment. The stereo decoder generates a set of stereo output channels (C1, C2) in response to a parametric audio input including signal parameters (S1) and stereo related parameters (X1). A parameter processor (M) generates two different set of parameters (P1, P2) based on the input signal parameters (S1) thus up-mixing the signal parameters (S1) by altering or manipulating the signal parameters (S1) corresponding to the stereo related parameters (X1). The two different parameters (P1, P2) are finally synthesized by separate signalsynthesizers (SS1, SS2) to form respective stereo output channels (C1, C2). Since the stereo decoding can be performed in the parameter domain instead ofthe spectral domain, the required computational burden is reduced compared to what is known in prior art. Preferably the signalsynthesizers (SS1, SS2) are sinusoidal synthesizers, and preferably the decoder also includes transient and noise synthesizers to generate transient and noise signal portions to be applied to the stereo output channels (C1, C2). Further, different transient and noise signalportions to the output channels (C1, C2) may be provided by applying different gains based on the stereorelated parameter (X1). In preferred embodiments the two parameters (P1, P2) are determined from a current as well as a previous signal parameter input, e.g. by means of an input delay line.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS NV
Reduction of spurious uncorrelation in FM radio noise
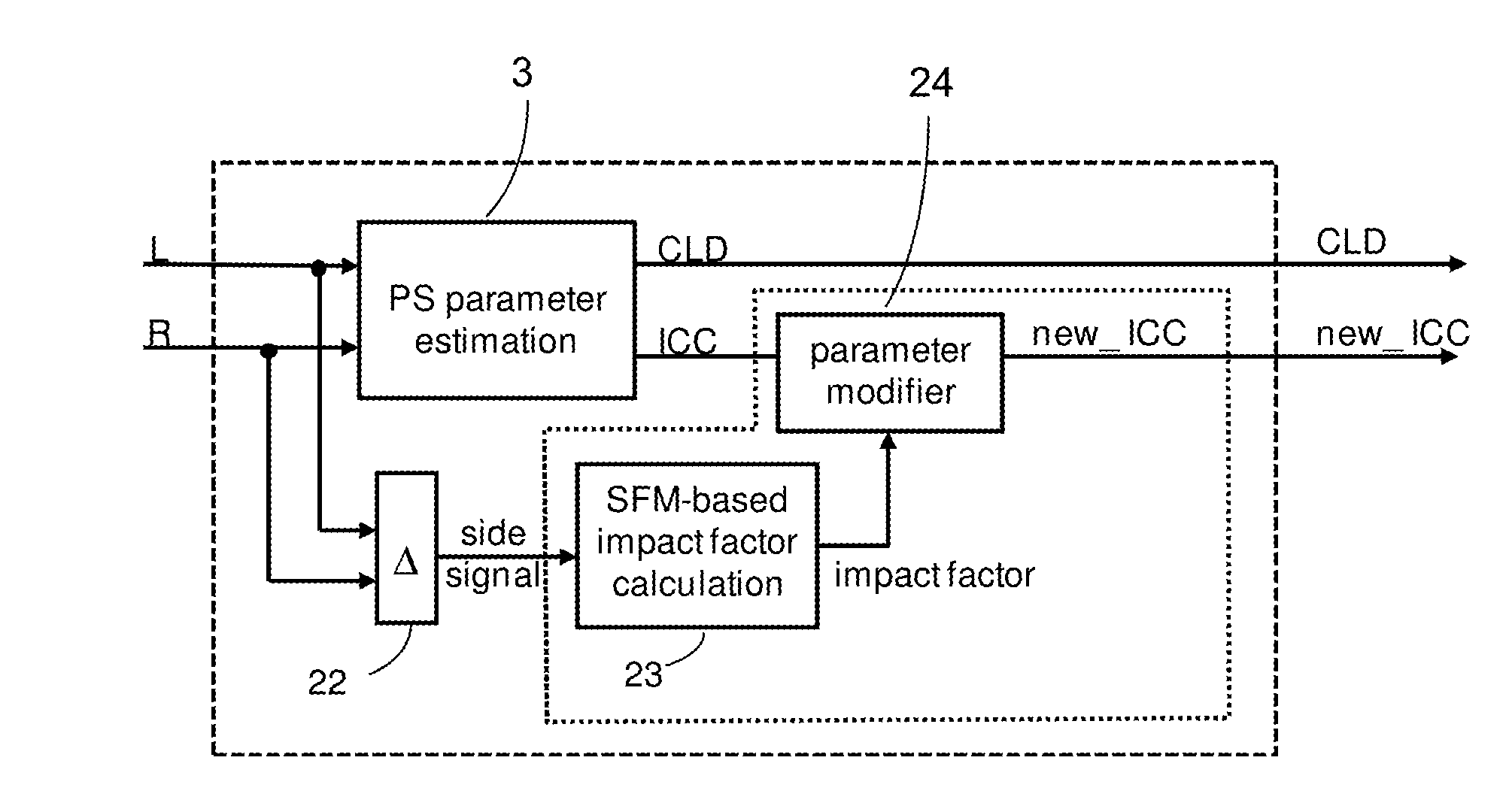
InactiveUS20130142339A1Easy to detectStereophonic circuit arrangementsSpeech analysisNoiseRadio receiver
The document relates to audio signal processing, in particular to a system and a corresponding method for improving an audio signal of an FM stereo radio receiver, in this context, one aspect relates to the estimation of noise in a received side signal and the compensation of such noise in parametric stereo parameters. A system for generating a parametric stereo parameter from a two-channel audio signal is described. The two-channel audio signal is presentable as a mid signal and side signal representative of a corresponding left and right audio signal. The system comprises a noise estimation stage configured to determine an impact factor characteristic for the noise of the side signal; and a parametric stereo parameter estimation stage configured to determine the parametric stereo parameter; wherein the determining is based on the two-channel audio signal and the impact factor.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Low complexity parametric stereo decoder
InactiveUS20100023335A1Low computing performanceReduce complexityStereophonic circuit arrangementsSpeech analysisSpectral domainSound quality
A stereo audio decoder with low complexity is provided. A high stereo sound quality can be obtained with a limited computational power and is thus suitable for miniature and mobile equipment. The stereo decoder generates a set of stereo output channels (C1, C2) in response to a parametric audio input including signal parameters (S1) and stereo related parameters (X1). A parameter processor (M) generates two different set of parameters (P1, P2) based on the input signal parameters (S1) thus up-mixing the signal parameters (S1) by altering or manipulating the signal parameters (S1) corresponding to the stereo related parameters (X1). The two different parameters (P1, P2) are finally synthesized by separate signalsynthesizers (SS1, SS2) to form respective stereo output channels (C1, C2). Since the stereo decoding can be performed in the parameter domain instead of the spectral domain, the required computational burden is reduced compared to what is known in prior art. Preferably the signalsynthesizers (SS1, SS2) are sinusoidal synthesizers, and preferably the decoder also includes transient and noise synthesizers to generate transient and noise signal portions to be applied to the stereo output channels (C1, C2). Further, different transient and noise signal portions to the output channels (C1, C2) may be provided by applying different gains based on the stereorelated parameter (X1). In preferred embodiments the two parameters (P1, P2) are determined from a current as well as a previous signal parameter input, e.g. by means of an input delay line.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Stereo Audio Encoder and Decoder
The present disclosure provides methods, devices and computer program products for encoding and decoding a stereo audio signal based on an input signal. According to the disclosure, a hybrid approach of using both parametric stereo coding and a discrete representation of the stereo audio signal is used which may improve the quality of the encoded and decoded audio for certain bitrates.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Orthogonal decoding related technology-based parametric stereo coding and decoding methods
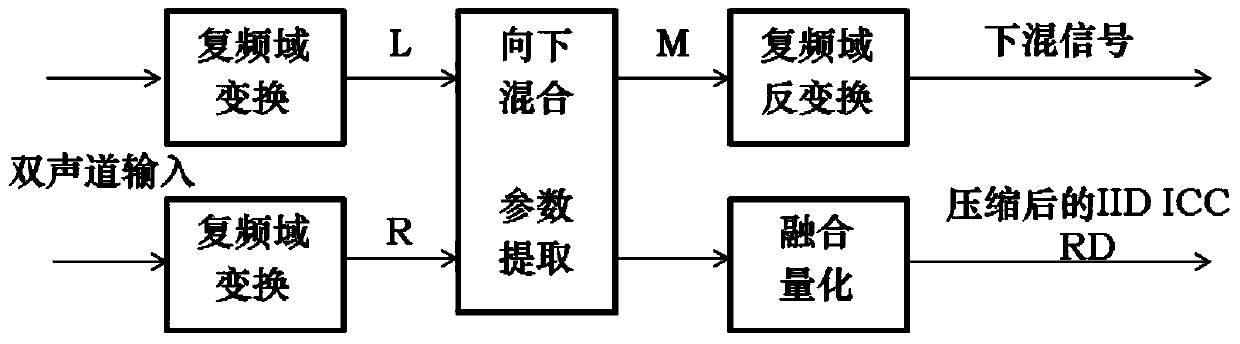
ActiveCN103700372AEncoding speed reductionImprove decoding speedSpeech analysisDecoding methodsTime domain
The invention discloses an orthogonal decoding related technology-based parametric stereo coding method and an orthogonal decoding related technology-based parametric stereo decoding method. The coding method comprises the following steps of (1) transforming input left-channel and right-channel time-domain signals to a complex frequency domain to obtain two complex frequency-domain signals L and R respectively; (2) processing L and R to output a down-mixed signal M; (3) estimating side information by utilizing L and R, and performing fusion quantification on the side information, wherein the side information comprises ICC (intra-channel cross-correlation), an IID (inter-channel intensity difference) and an RD (rotating direction); (4) performing time-domain inverse transform, coding and output on M, and compressing, coding and outputting the side information. The decoding method comprises the following steps of transforming an input time-domain down-mixed signal to the complex frequency domain, and outputting a signal M; decoding input side information; solving an output signal D which has amplitude equal to that of M and is orthogonal with M according to the RD; calculating a rotating matrix H according to the ICC and the IID; obtaining the complex frequency-domain signals L and R by utilizing H, M and D, and transforming the complex frequency-domain signals L and R to the time domain for output. According to the methods, the decoding speed is greatly increased.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
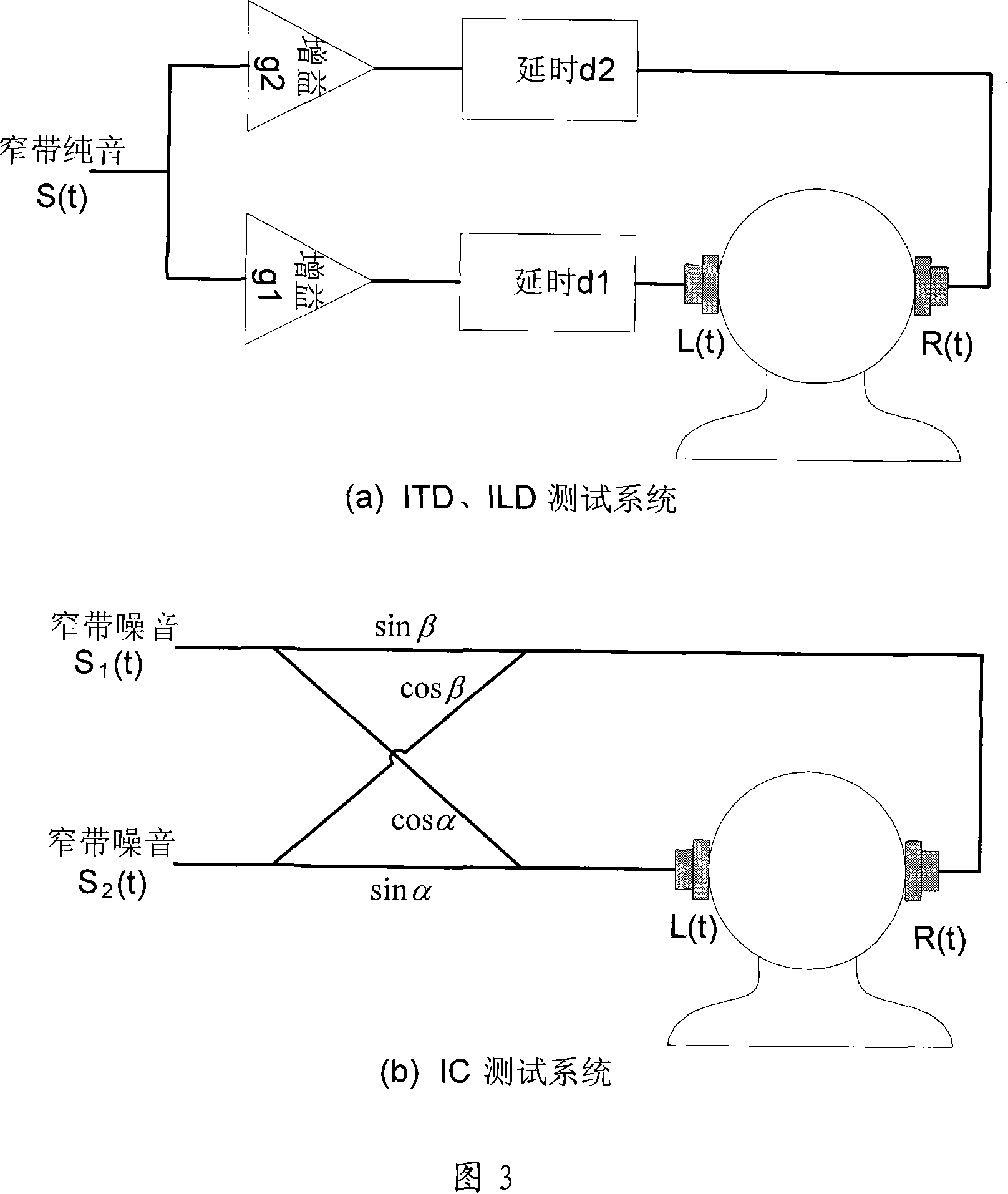
Space parameter selection method for parameter stereo coding
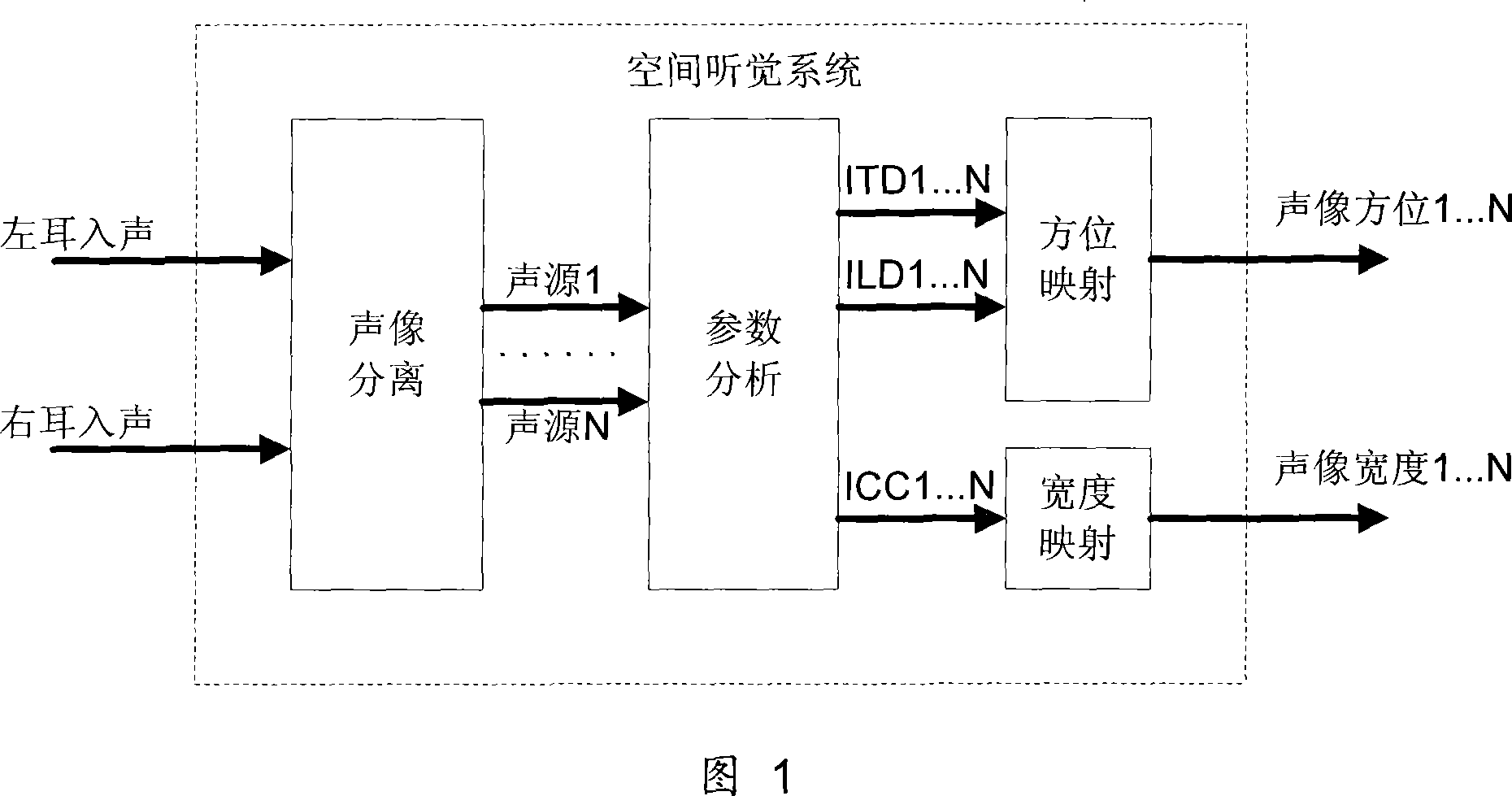
InactiveCN101149925AGuaranteed stereo sound qualityGuaranteed sound qualitySpeech analysisStereophonic systemsInteraural time differenceComputer science
The space parameter selection method for parameter stereo coding is disclosed. Three space parameters of interaural time difference, interaural intensity difference and interaural correlation degree are used for describing the space information in stereo signals. Signals are classified into three frequency ranges of low, middle and high frequency. According to the coding rate of the space parameters, different space parameter combinations are selected in each frequency range to describe space information. Advantage: raised effect of space information expression and coding efficiency of parameter stereo.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Efficient and scalable parametric stereo coding for low bitrate audio coding applications
ActiveUS20060023888A1Reduce riskGuaranteed normal transmissionSpeech analysisBroadcast circuit arrangementsVocal tractStereo image
The present invention provides improvements to prior art audio codecs that generate a stereo-illusion through post-processing of a received mono signal. These improvements are accomplished by extraction of stereo-image describing parameters at the encoder side, which are transmitted and subsequently used for control of a stereo generator at the decoder side. Furthermore, the invention bridges the gap between simple pseudo-stereo methods, and current methods of true stereo-coding, by using a new form of parametric stereo coding. A stereo-balance parameter is introduced, which enables more advanced stereo modes, and in addition forms the basis of a new method of stereo-coding of spectral envelopes, of particular use in systems where guided HFR (High Frequency Reconstruction) is employed. As a special case, the application of this stereo-coding scheme in scalable HFR-based codecs is described.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Low delay modulated filter bank
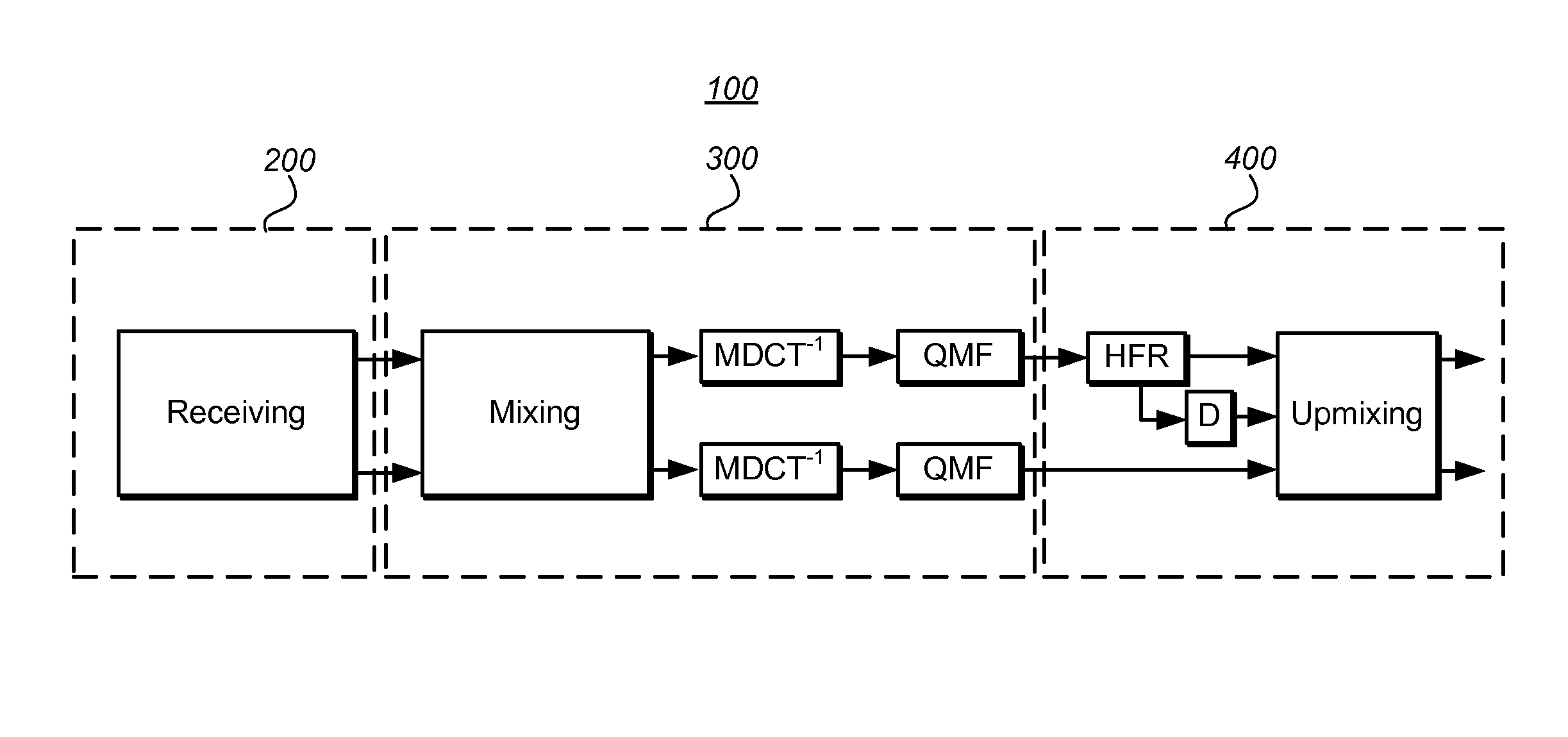
The document relates to modulated sub-sampled digital filter banks, as well as to methods and systems for the design of such filter banks. In particular, the present document proposes a method and apparatus for the improvement of low delay modulated digital filter banks. The method employs modulation of an asymmetric low-pass prototype filter and a new method for optimizing the coefficients of this filter. Further, a specific design for a (64) channel filter bank using a prototype filter length of (640) coefficients and a system delay of (319) samples is given. The method substantially reduces artifacts due to aliasing emerging from independent modifications of subband signals, for example when using a filter bank as a spectral equalizer. The method is preferably implemented in software, running on a standard PC or a digital signal processor (DSP), but can also be hardcoded on a custom chip. The method offers improvements for various types of digital equalizers, adaptive filters, multiband companders and spectral envelope adjusting filterbanks used in high frequency reconstruction (HFR) or parametric stereo systems.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
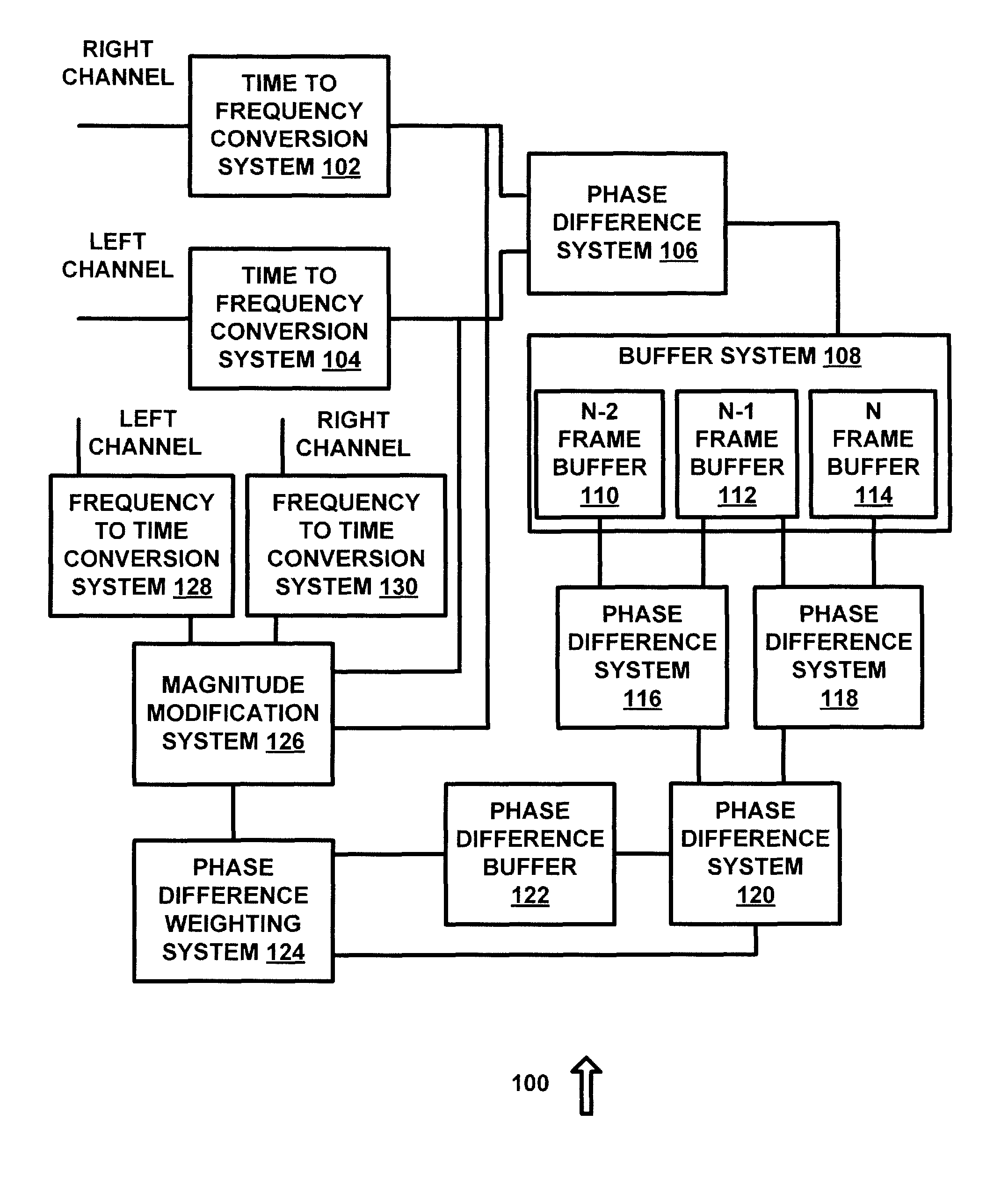
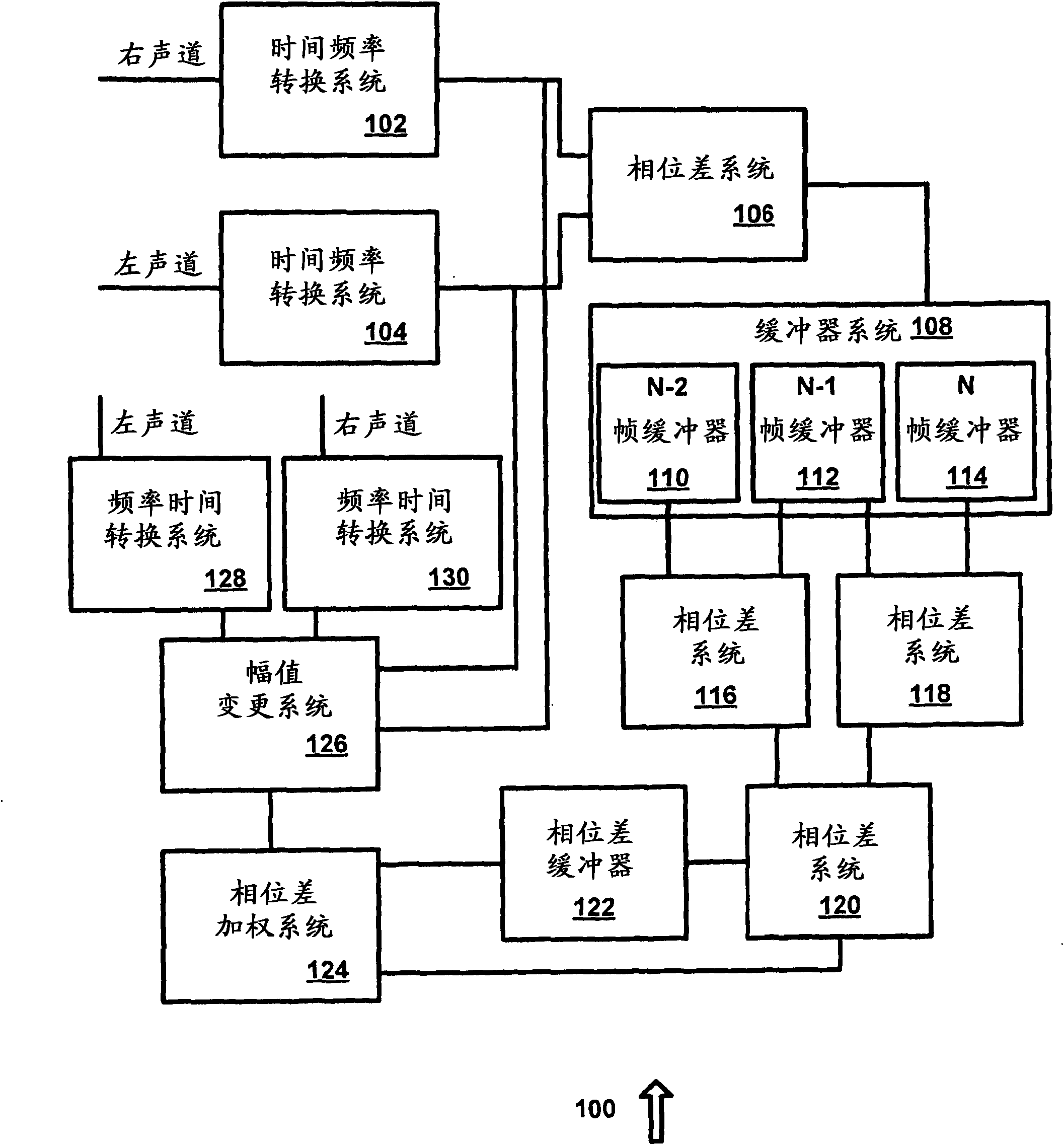
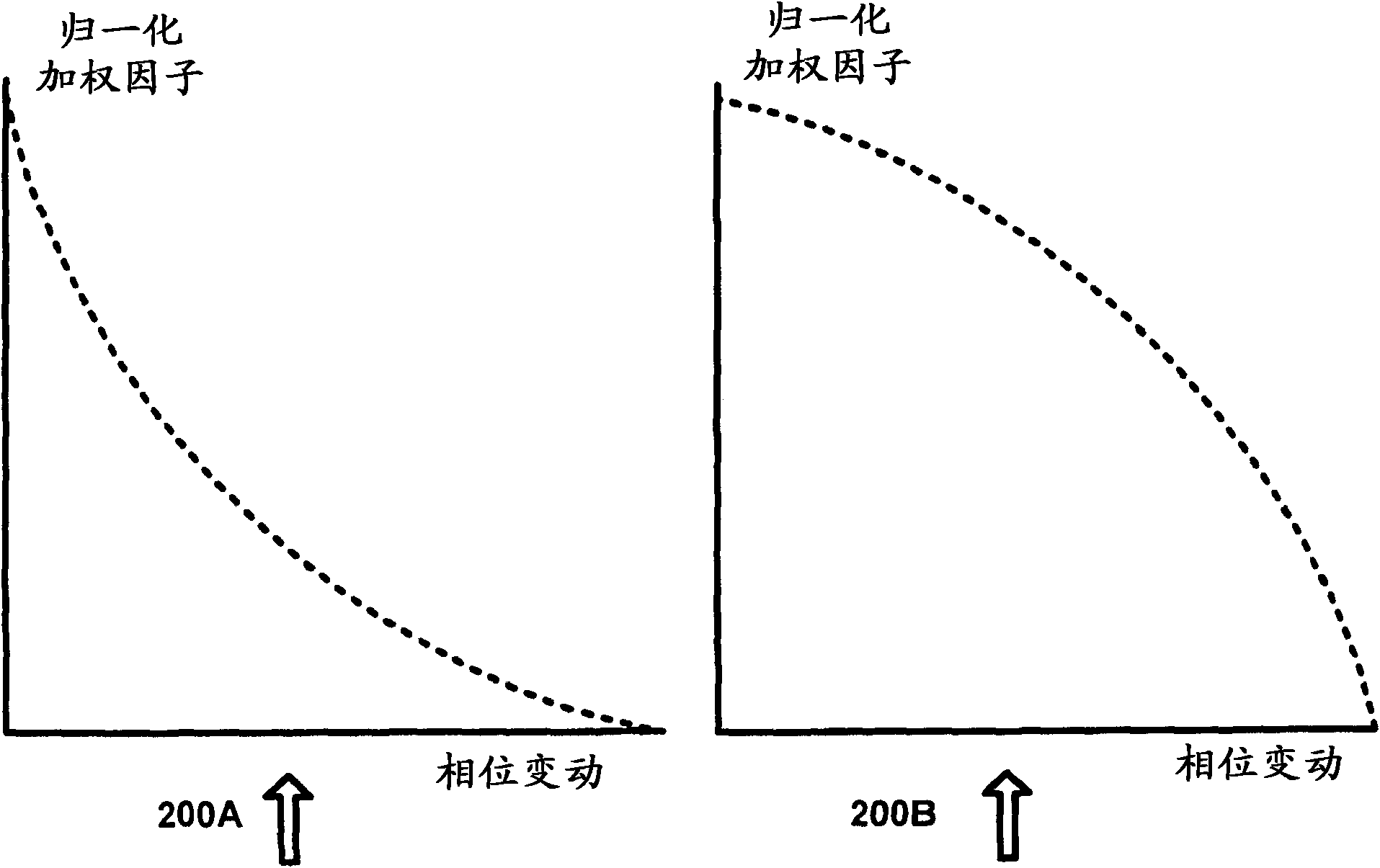
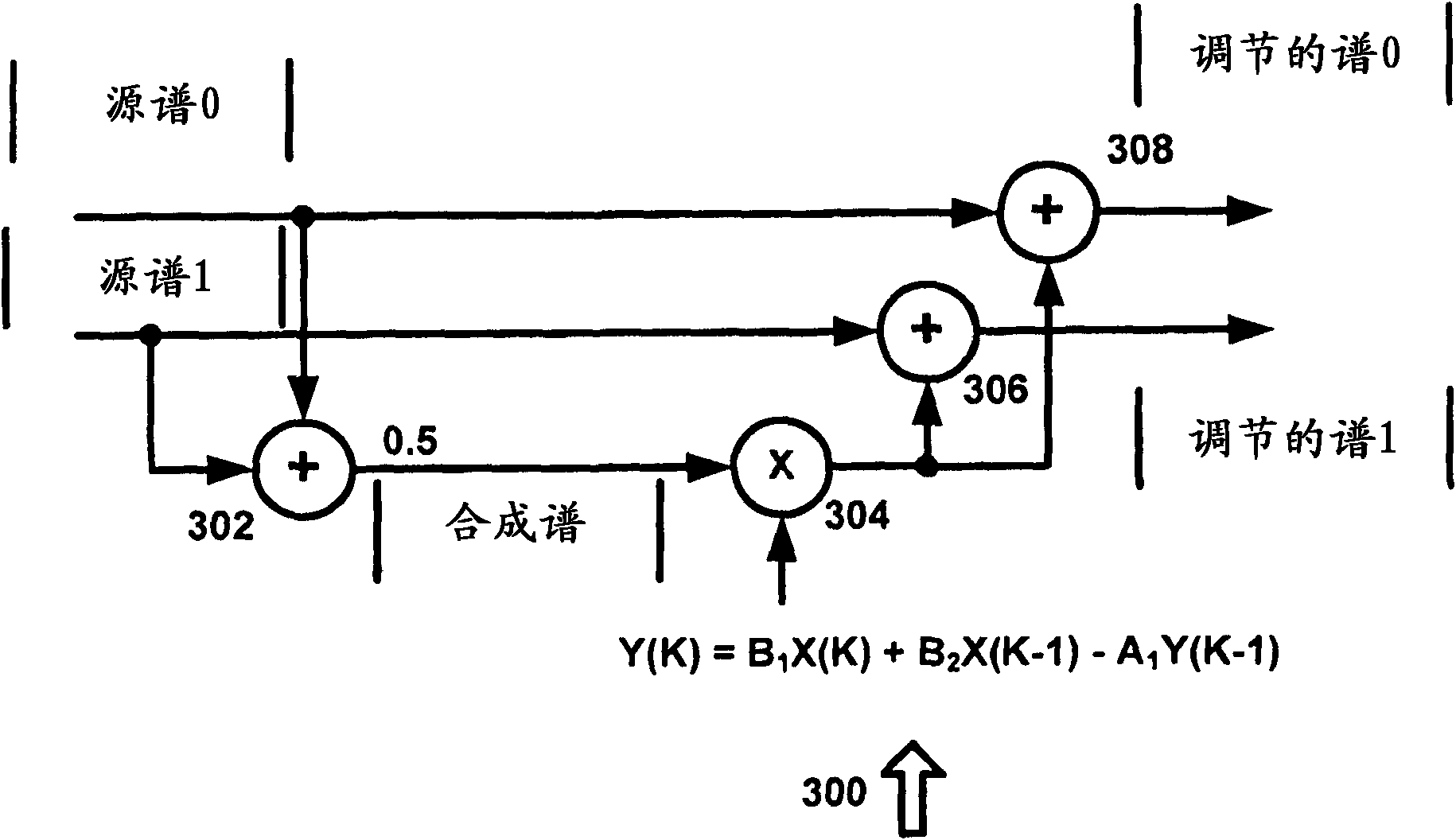
Parametric stereo conversion system and method
InactiveUS8385556B1Avoid it happening againSpeech analysisVolume compression/expansionChannel dataPhase difference
A system for generating parametric stereo data from phase modulated stereo data is provided. A phase difference system receives left channel data and right channel data and determines a phase difference between the left channel data and the right channel data. A phase difference weighting system receives the phase difference data and generates weighting data to adjust left channel amplitude data and right channel amplitude data based on the phase difference data. A magnitude modification system adjusts the left channel amplitude data and the right channel amplitude data using the weighting data to eliminate phase data in the left channel data and the right channel data.
Owner:DTS
Reduction of spurious uncorrelation in FM radio noise
InactiveUS9094754B2Easy to detectStereophonic circuit arrangementsSpeech analysisRadio receiverVocal tract
The document relates to audio signal processing, in particular to a system and a corresponding method for improving an audio signal of an FM stereo radio receiver, in this context, one aspect relates to the estimation of noise in a received side signal and the compensation of such noise in parametric stereo parameters. A system for generating a parametric stereo parameter from a two-channel audio signal is described. The two-channel audio signal is presentable as a mid signal and side signal representative of a corresponding left and right audio signal. The system comprises a noise estimation stage configured to determine an impact factor characteristic for the noise of the side signal; and a parametric stereo parameter estimation stage configured to determine the parametric stereo parameter; wherein the determining is based on the two-channel audio signal and the impact factor.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
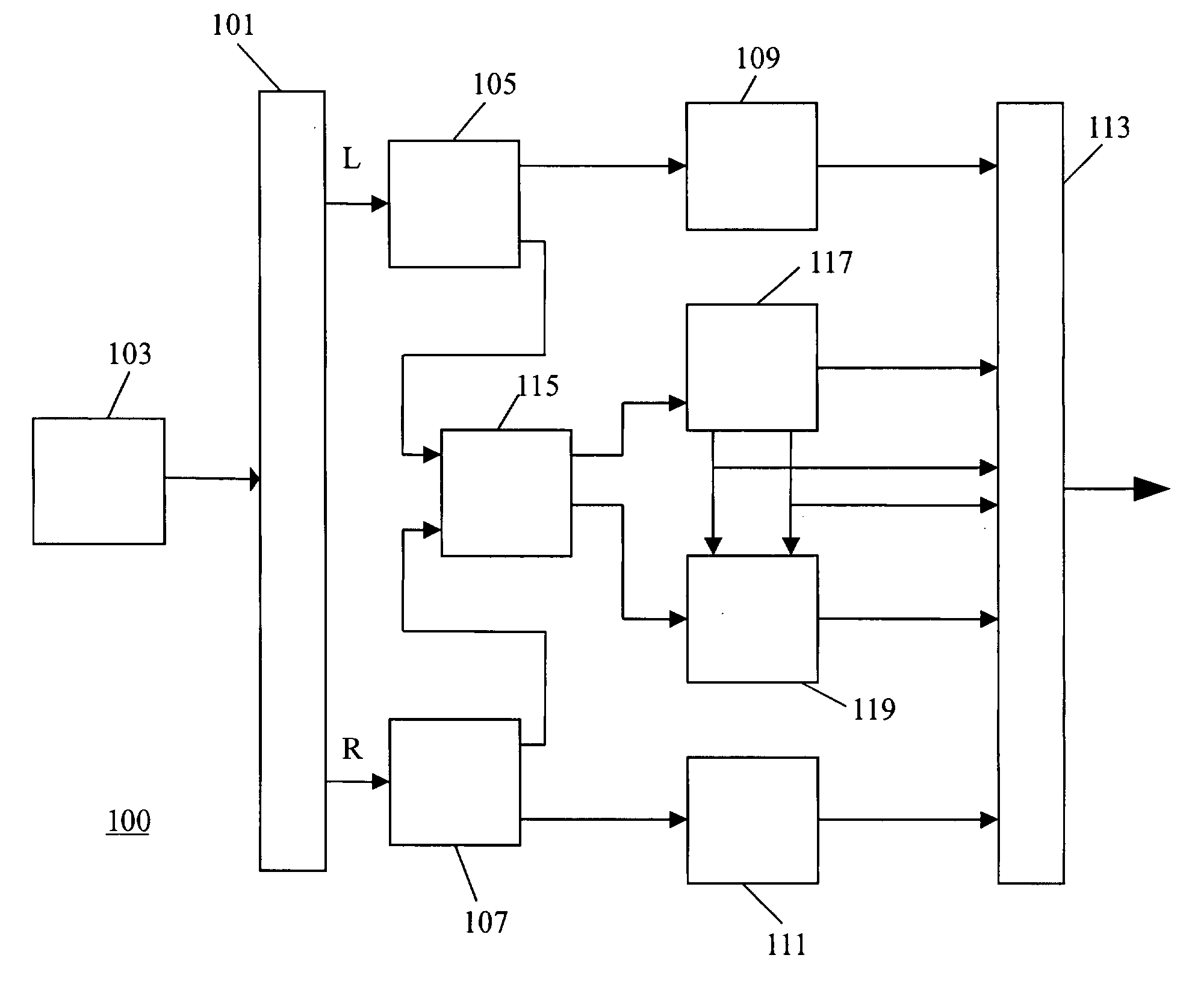
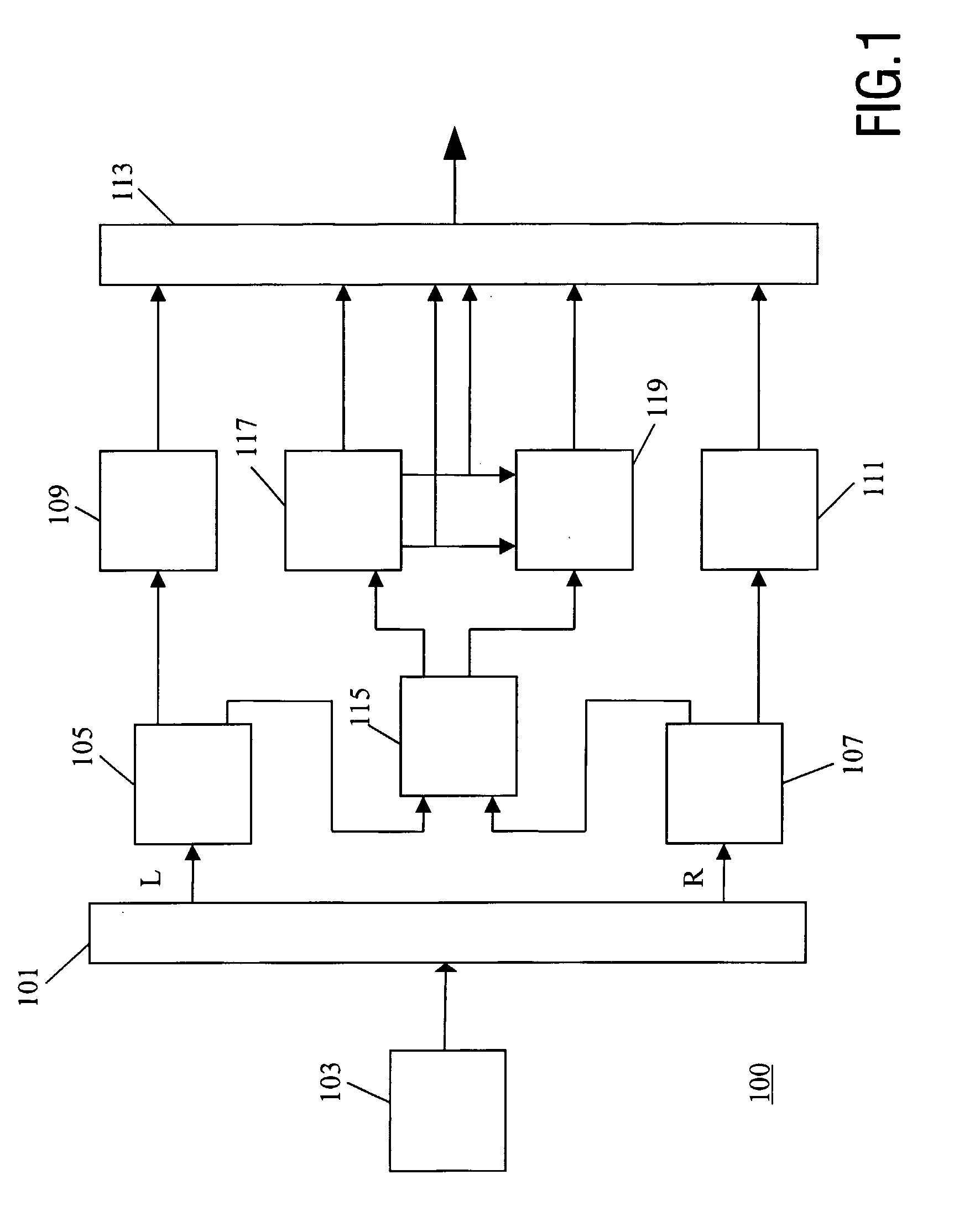
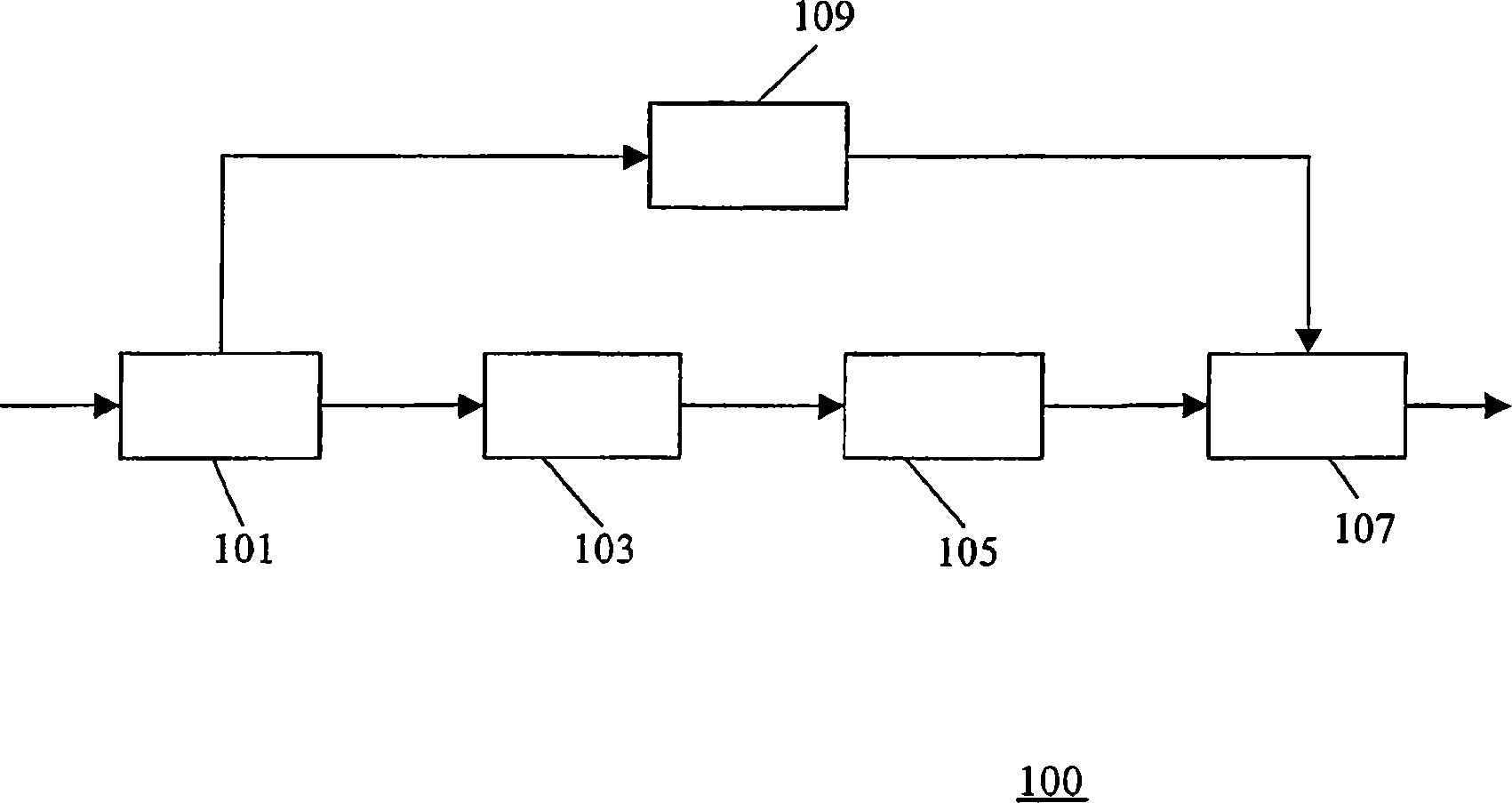
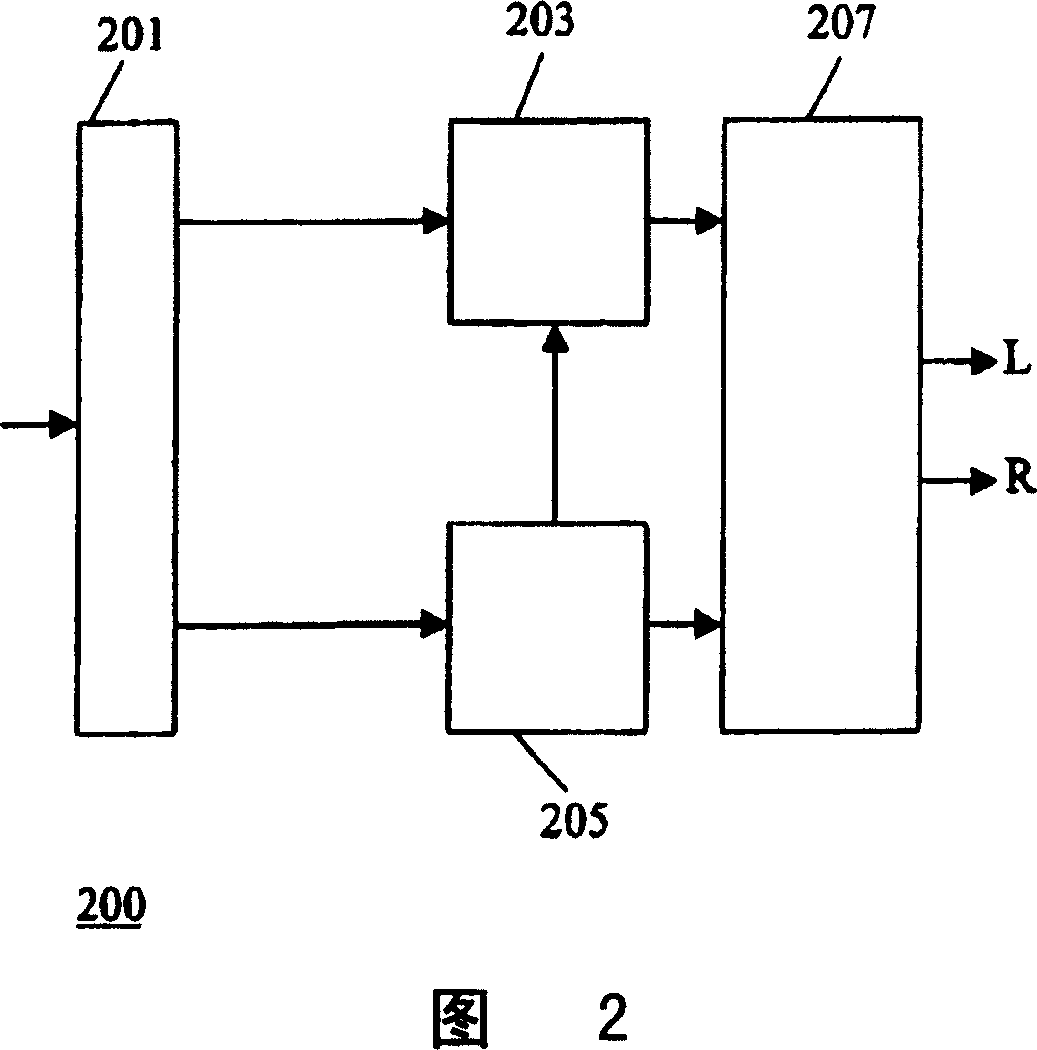
A transcoder and method of transcoding therefore
A transcoder comprises a receiver ( 101 ) which receives input data representing an encoded signal and comprising first encoding data and first parametric extension data. The encoded data is fed to a decoder ( 103 ). The output of the decoder ( 103 ) is fed to an encoder ( 105 ) which generates second encoded data according to a different encoding protocol or with different encoding parameters. The first parametric extension data is fed to an extension data processor ( 109 ) which generates second parametric extension data directly from the first parametric extension data. The second encoded data and the second parametric extension data is combined in an output processor ( 107 ) to generate a transcoded signal comprising separately determined parametric extension data. The parametric extension data may be Spectral Band Replication (SBR) or Parametric Stereo (PS) extension data for an audio bitstream. Improved quality and reduced complexity is achieved by the separate transcoding of the parametric extension data.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
An audio distribution system, an audio encoder, an audio decoder and methods of operation therefore
A stereo audio encoder ( 100 ) comprises a parametric stereo encoder ( 115 ) which generates a mono signal and parametric stereo parameters for at least a high frequency part of an input stereo signal. A stereo intensity encoder ( 117 ) generates stereo intensity data for the mono signal. The mono signal and intensity data are encoded in accordance with an encoding standard such as MPEG Layer II and the parametric stereo parameters are included in the ancillary data sections by an output processor ( 113 ). Thus, a legacy decoder (such as an MPEG Layer II decoder) may generate a stereo signal using the stereo intensity data whereas a higher complexity decoder may generate a high quality audio signal using the parametric stereo parameters. A stereo decoder ( 200 ) receives the encoded data from the encoder ( 100 ). An intensity decoder ( 203 ) generates a stereo signal using intensity data. This is fed to a parametric stereo decoder ( 207 ) which processes the stereo signal in accordance with extracted parametric stereo data.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Parametric stereo conversion system and method
A system for generating parametric stereo data from phase modulated stereo data is provided. A phase difference system receives left channel data and right channel data and determines a phase difference between the left channel data and the right channel data. A phase difference weighting system receives the phase difference data and generates weighting data to adjust left channel amplitude data and right channel amplitude data based on the phase difference data. A magnitude modification system adjusts the left channel amplitude data and the right channel amplitude data using the weighting data to eliminate phase data in the left channel data and the right channel data.
Owner:DTS BVI
Efficient and scalable parametric stereo coding for low bitrate audio coding applications
ActiveUS20060023895A1Less precisionValid encodingSpeech analysisPseudo-stereo systemsVocal tractStereo image
The present invention provides improvements to prior art audio codecs that generate a stereo-illusion through post-processing of a received mono signal. These improvements are accomplished by extraction of stereo-image describing parameters at the encoder side, which are transmitted and subsequently used for control of a stereo generator at the decoder side. Furthermore, the invention bridges the gap between simple pseudo-stereo methods, and current methods of true stereo-coding, by using a new form of parametric stereo coding. A stereo-balance parameter is introduced, which enables more advanced stereo modes, and in addition forms the basis of a new method of stereo-coding of spectral envelopes, of particular use in systems where guided HFR (High Frequency Reconstruction) is employed. As a special case, the application of this stereo-coding scheme in scalable HFR-based codecs is described.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com