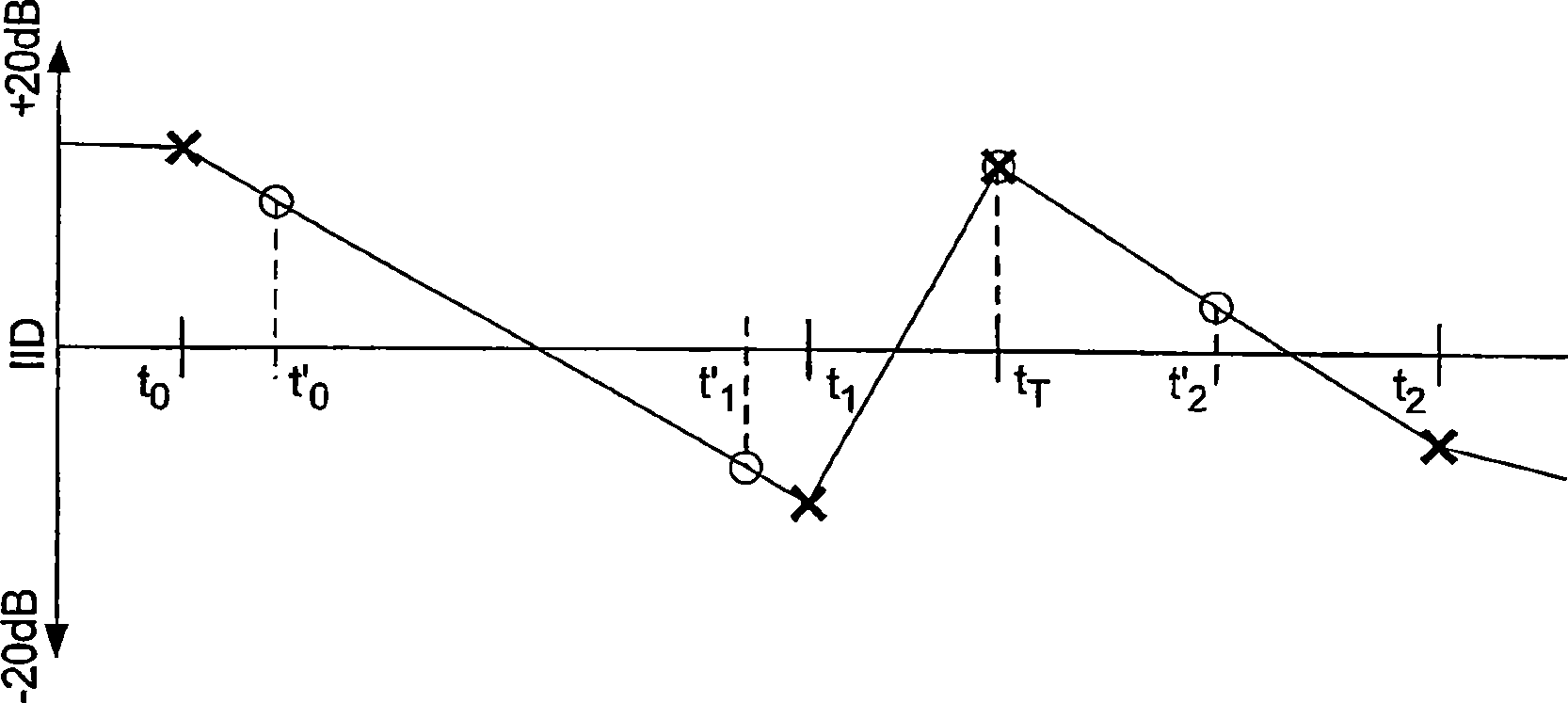
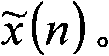Patents
Literature
47 results about "Spectral band replication" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Spectral band replication (SBR) is a technology to enhance audio or speech codecs, especially at low bit rates and is based on harmonic redundancy in the frequency domain. It can be combined with any audio compression codec: the codec itself transmits the lower and midfrequencies of the spectrum, while SBR replicates higher frequency content by transposing up harmonics from the lower and midfrequencies at the decoder. Some guidance information for reconstruction of the high-frequency spectral envelope is transmitted as side information.
Source coding enhancement using spectral-band replication
InactiveUS7283955B2Improvements of audio codecsImprove perceived qualitySpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumComputer science
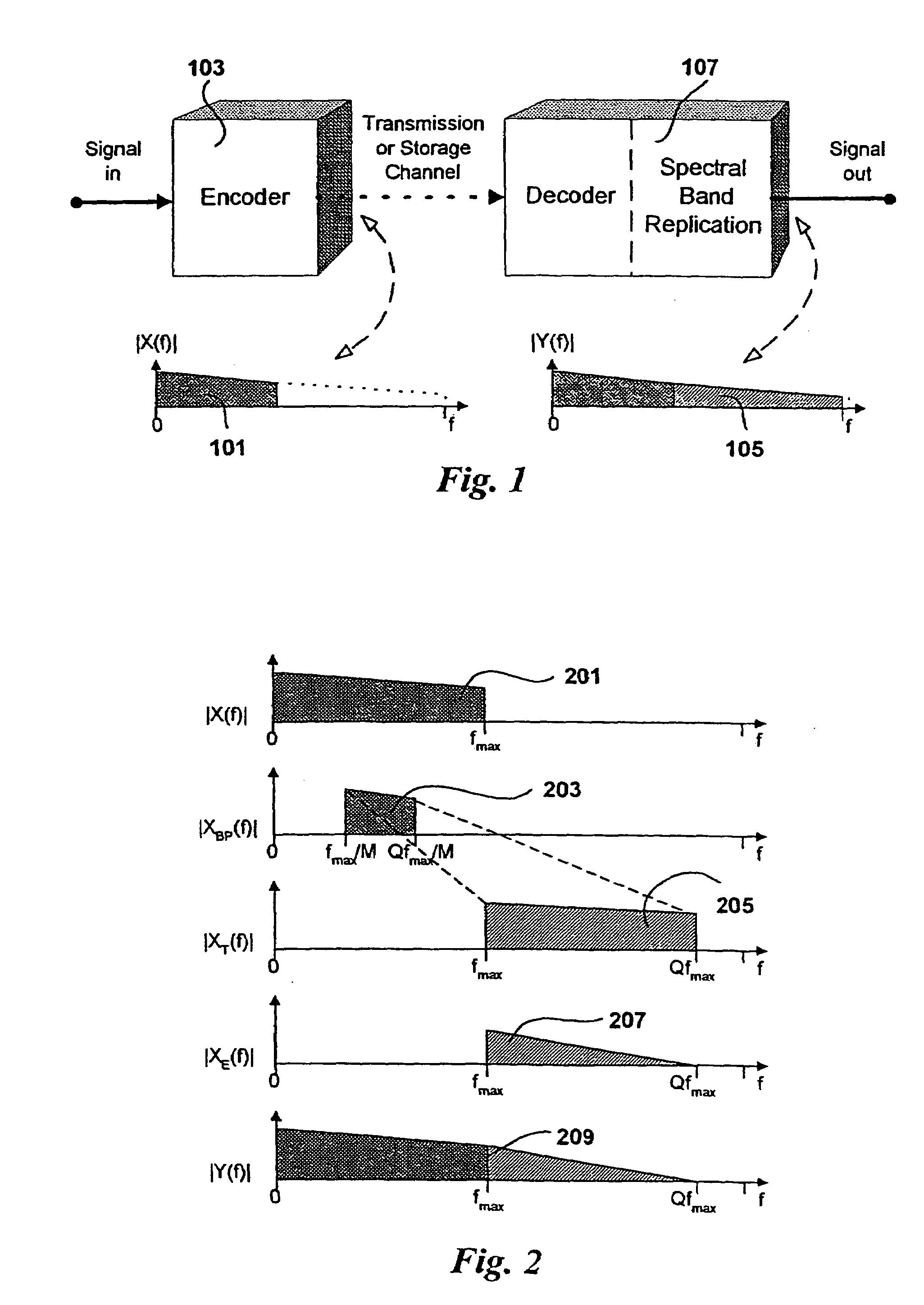
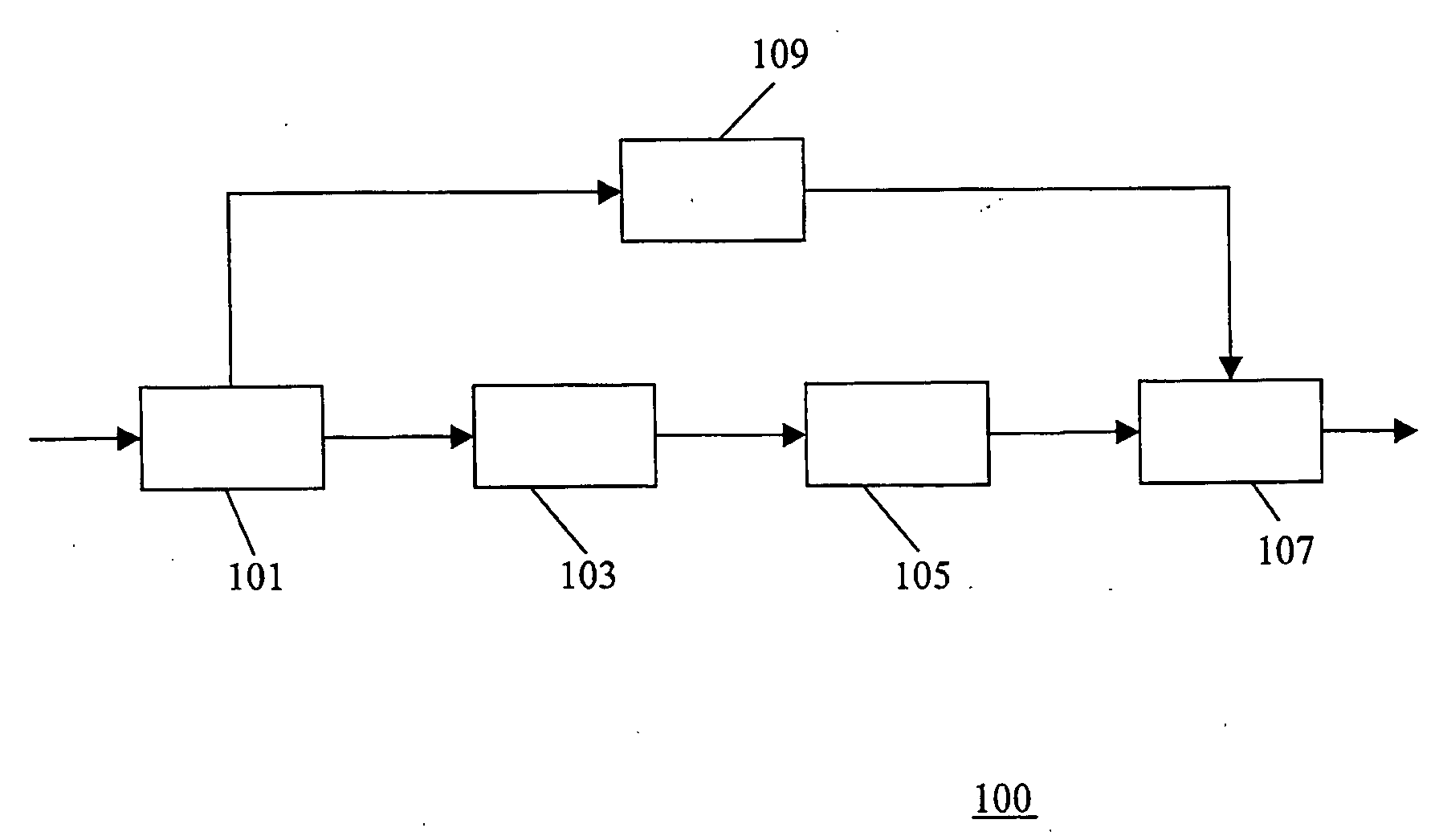
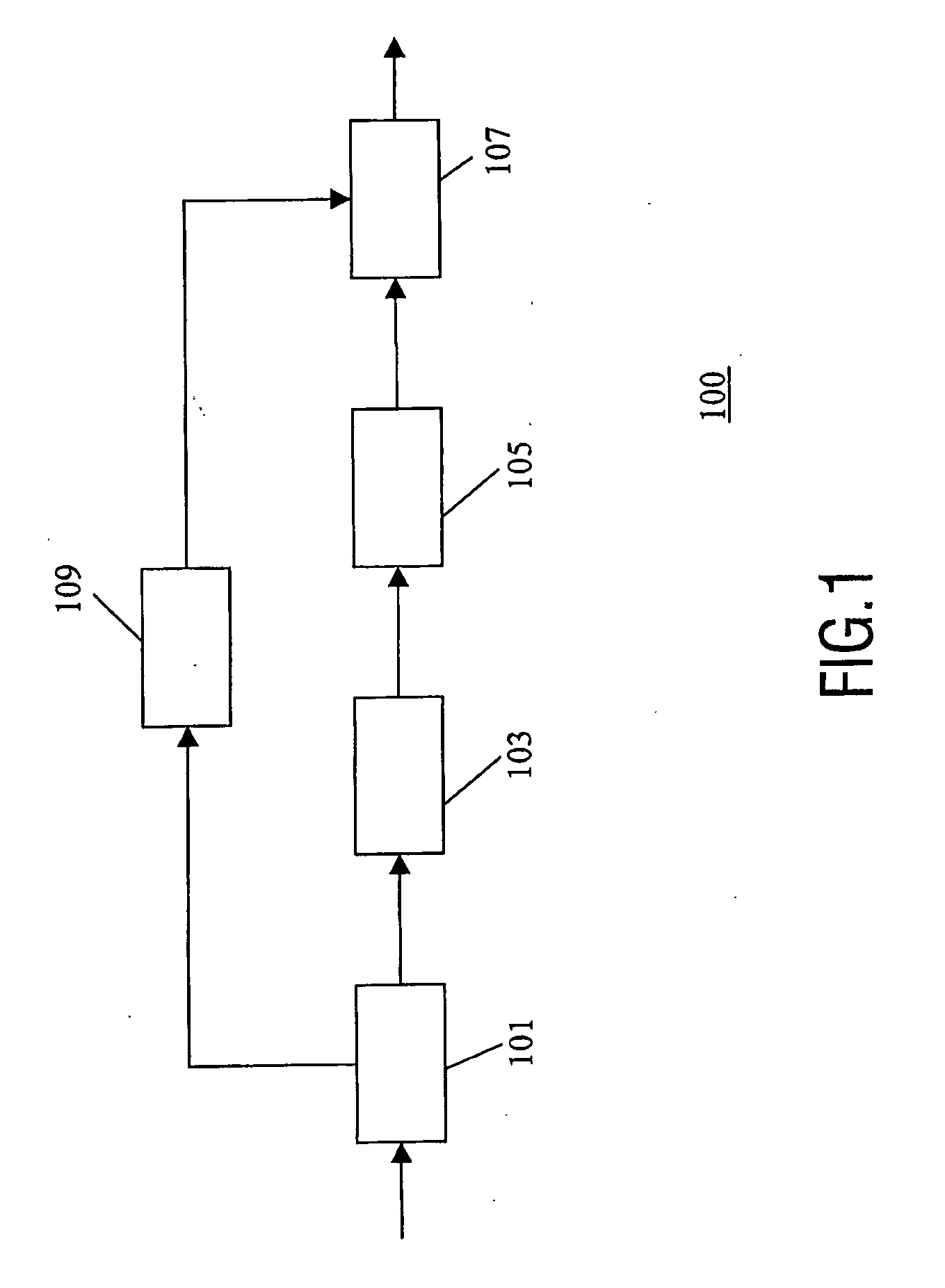
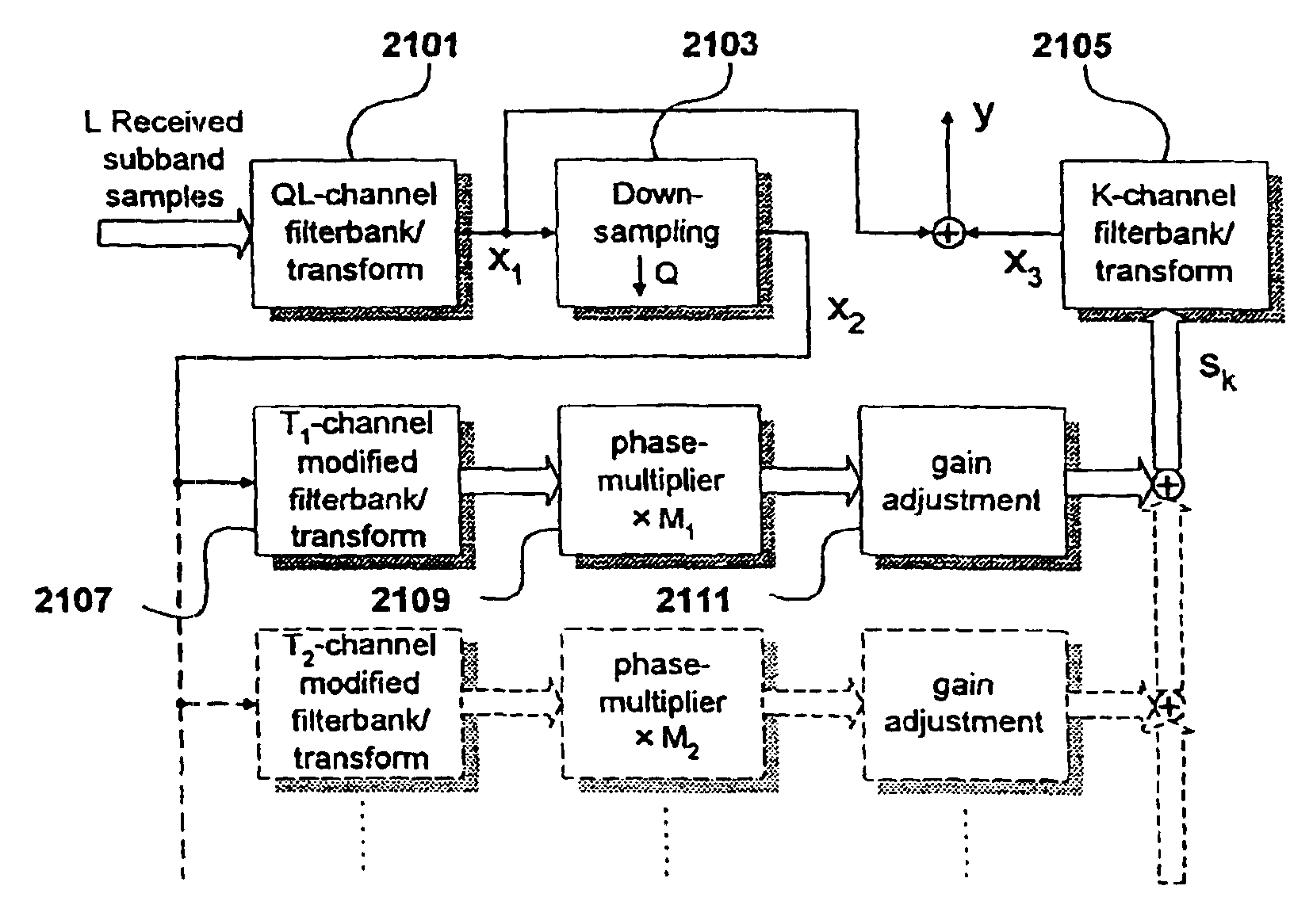
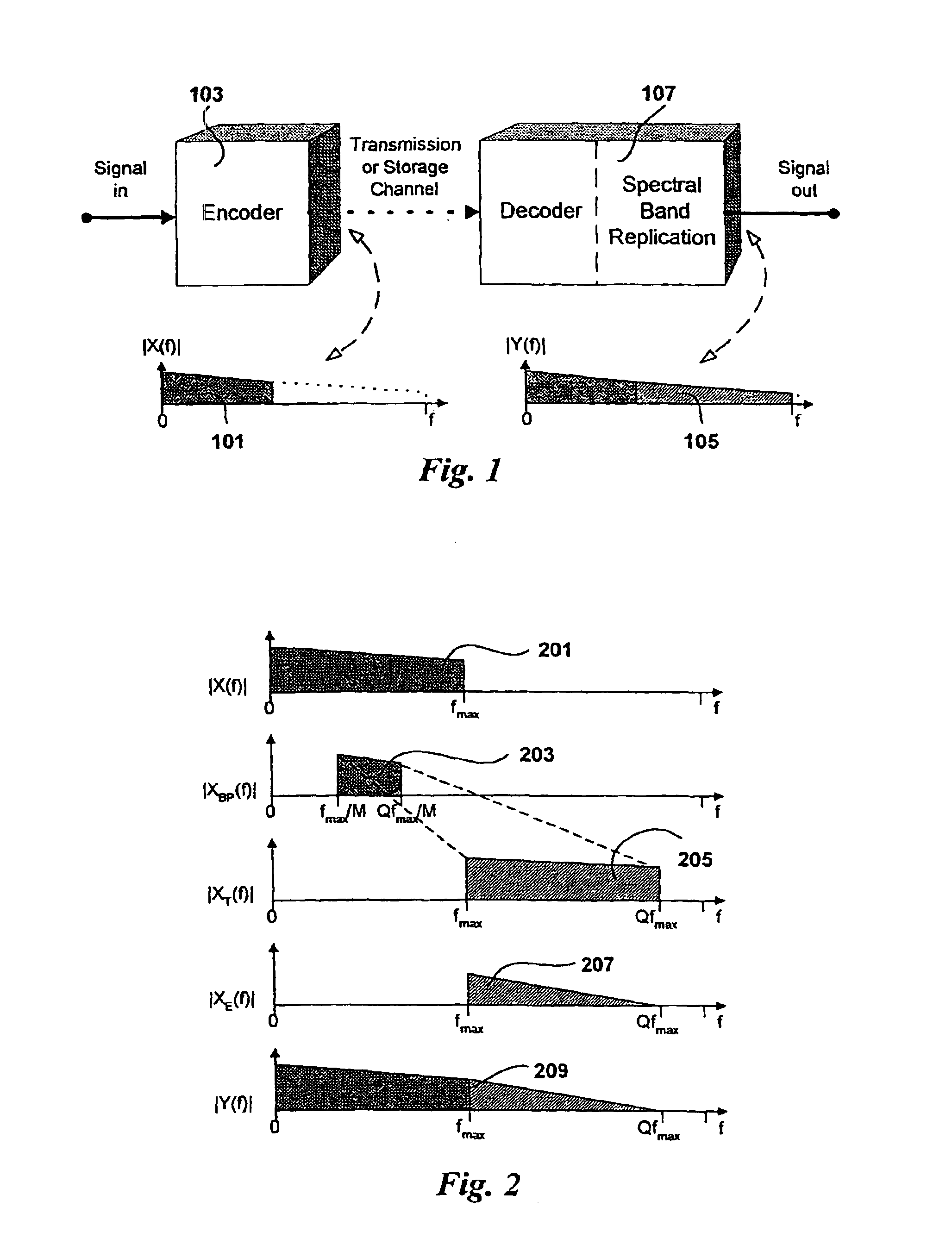
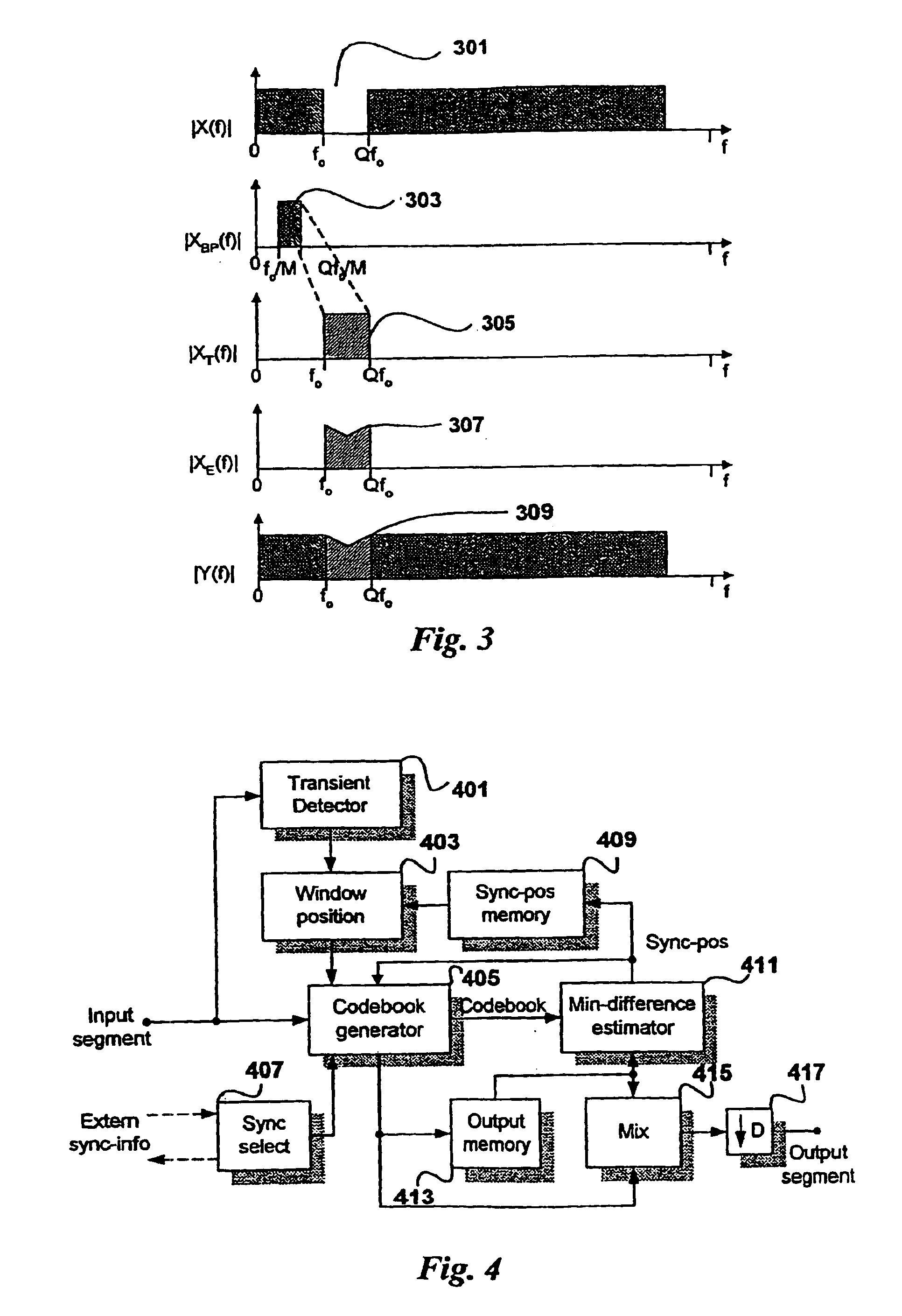
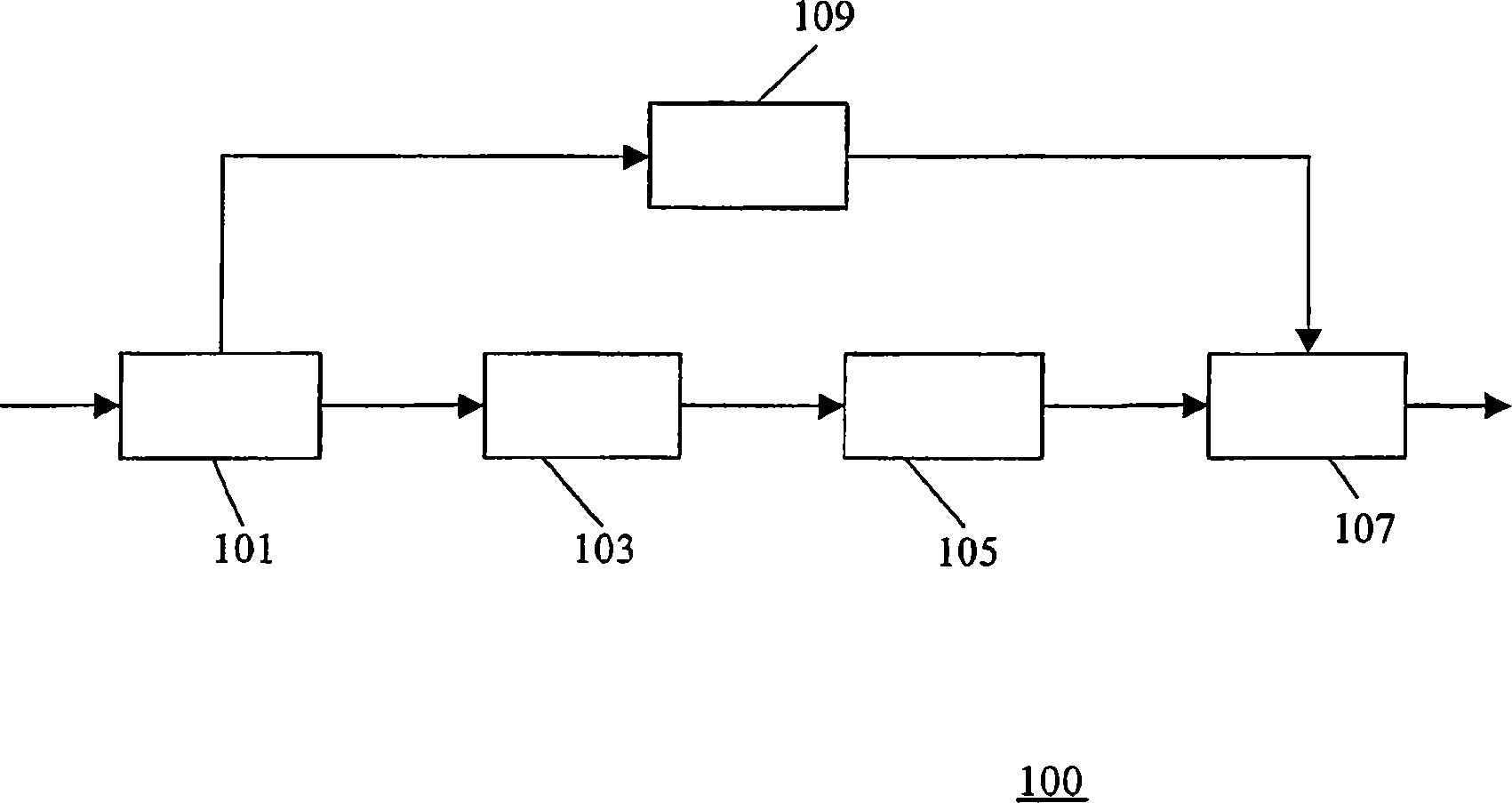
The present invention proposes a new method and apparatus for the enhancement of source coding systems. The invention employs bandwidth reduction (101) prior to or in the encoder (103), followed by spectral-band replication (105) at the decoder (107). This is accomplished by the use of new transposition methods, in combination with spectral envelope adjustments. Reduced bitrate at a given perceptual quality or an improved perceptual quality at a given bitrate is offered. The invention is preferably integrated in a hardware or software codec, but can also be implemented as a separate processor in combination with a codec. The invention offers substantial improvements practically independent f codec type and technological progress.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Audio Signal Synthesizer and Audio Signal Encoder
ActiveUS20110173006A1Quality improvementAvoid artifactsSpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumSpectral domain
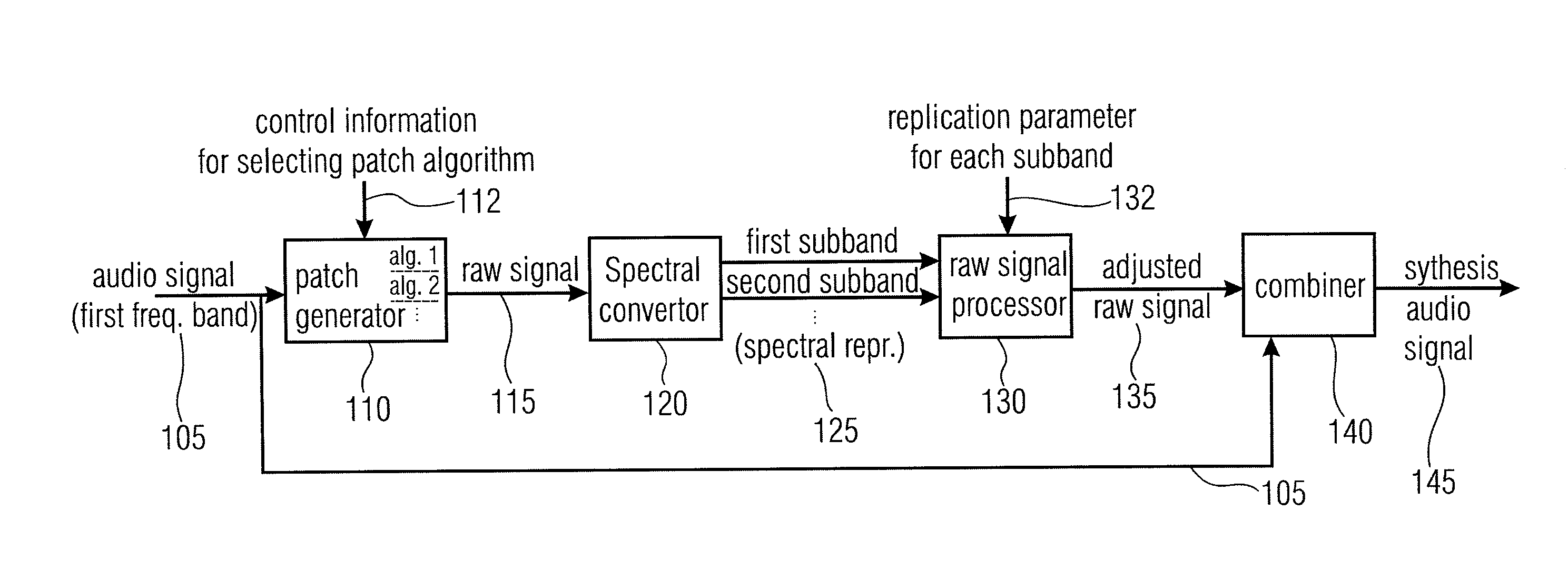
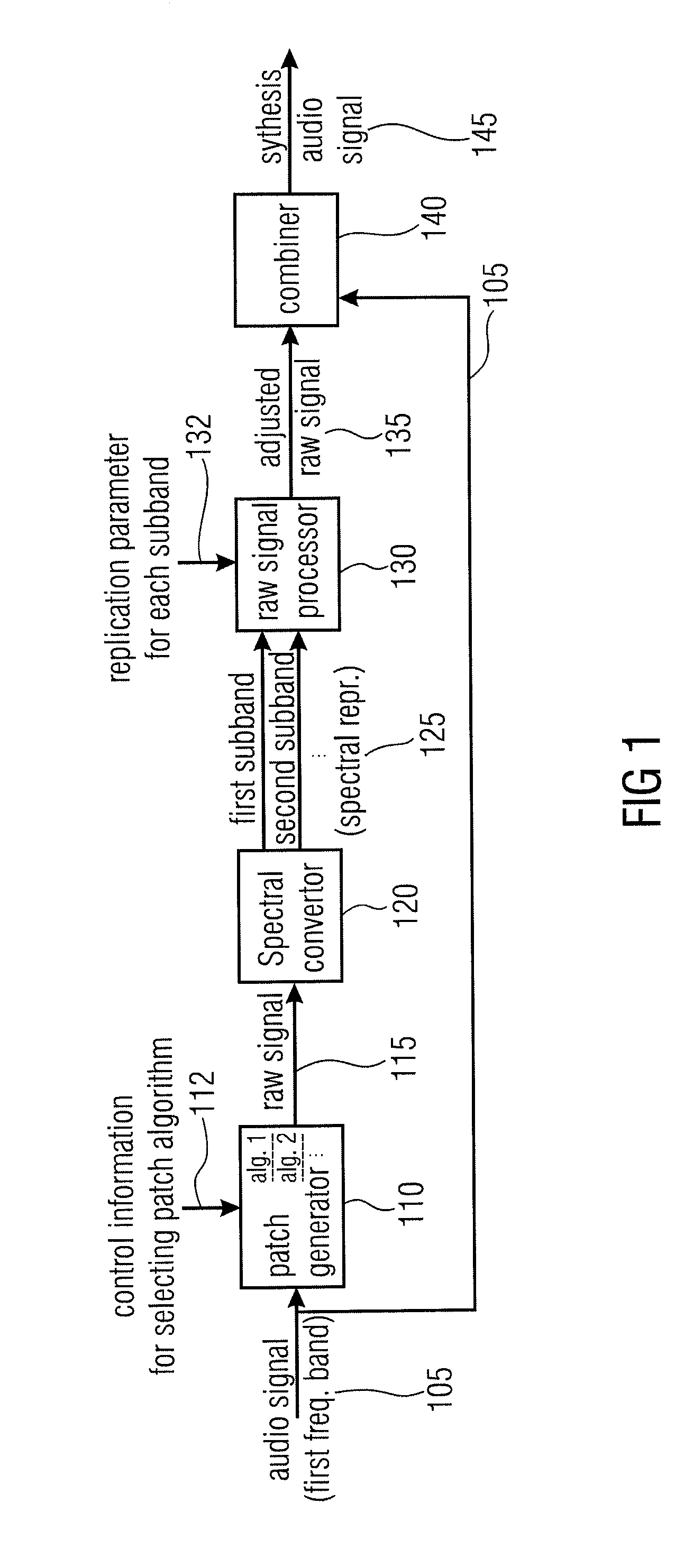
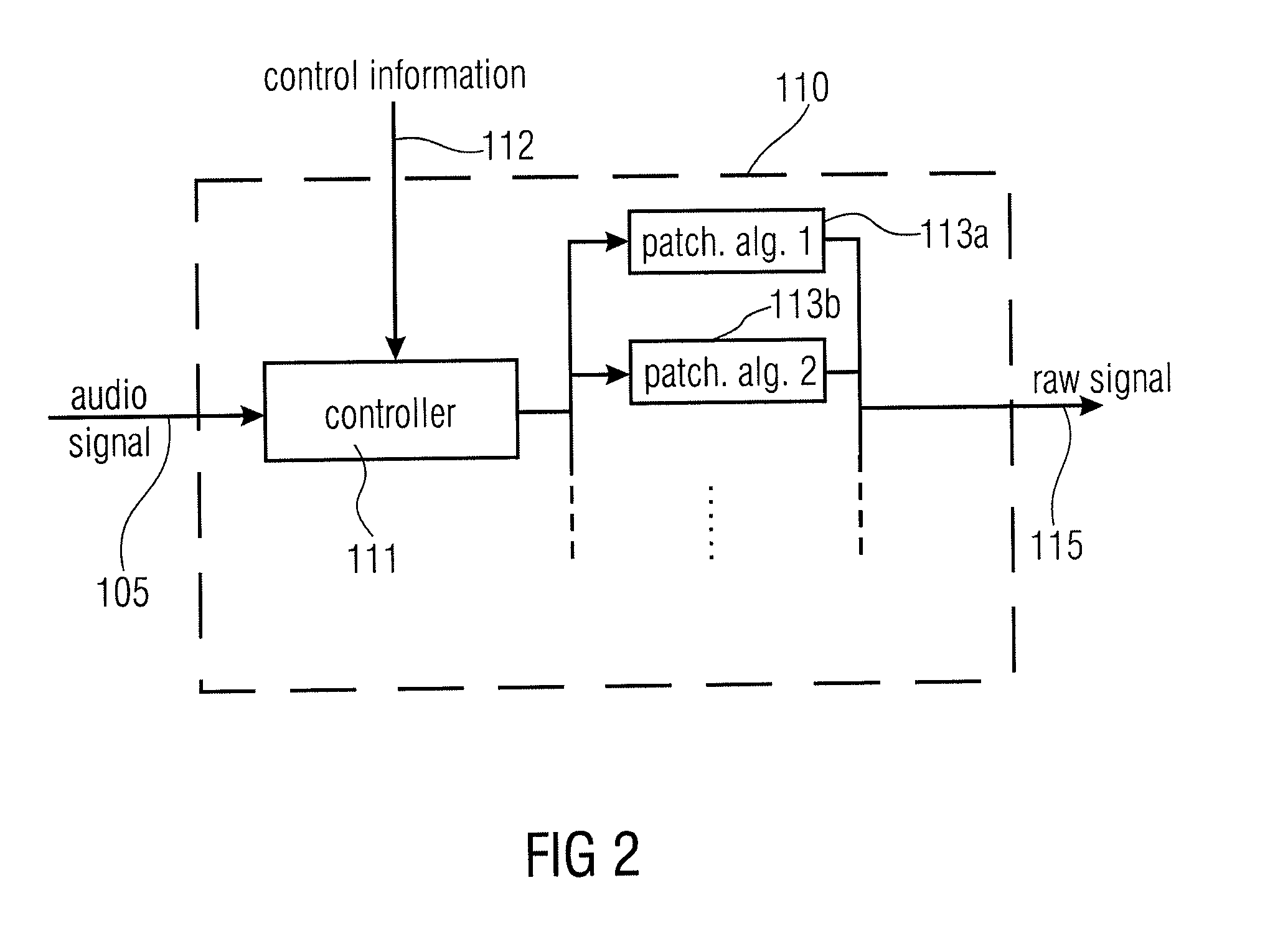
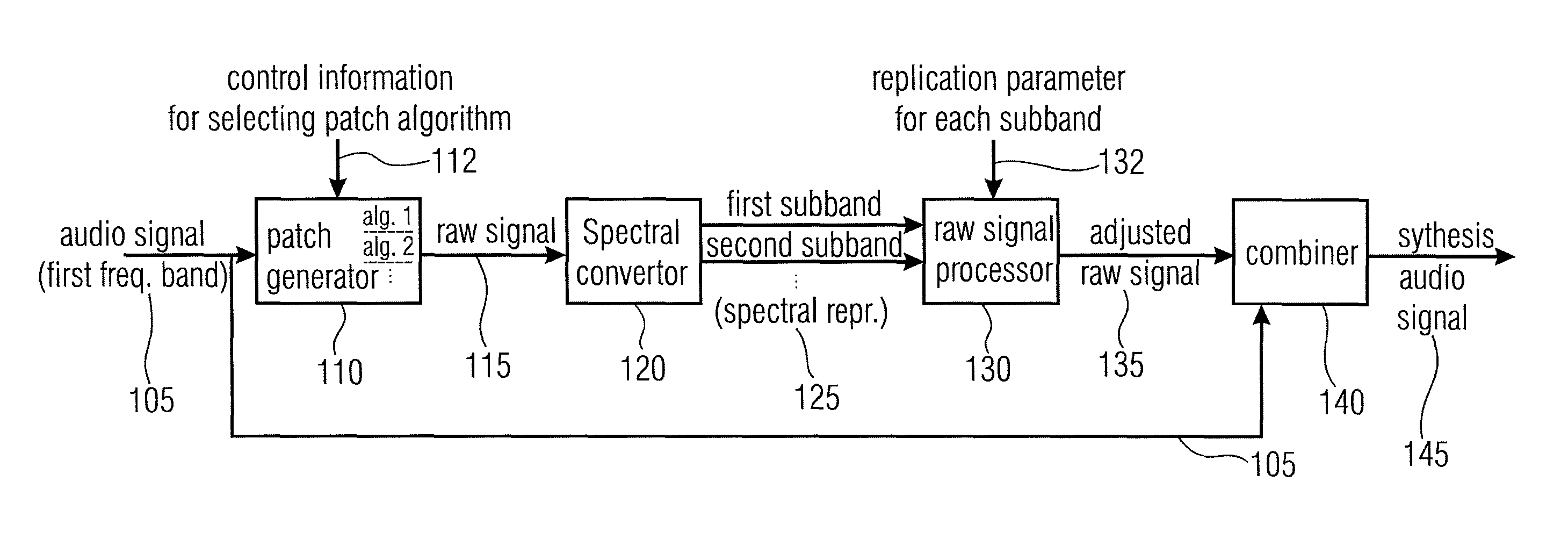
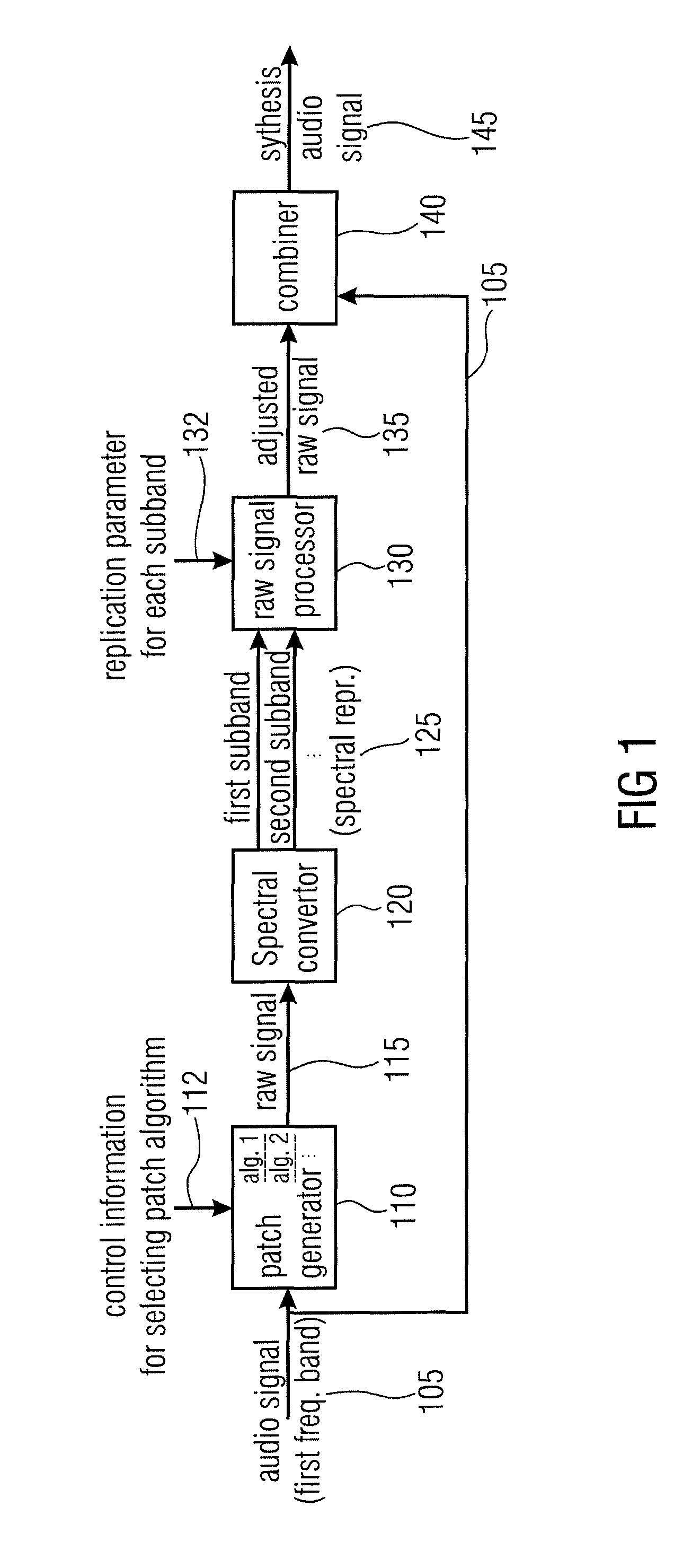
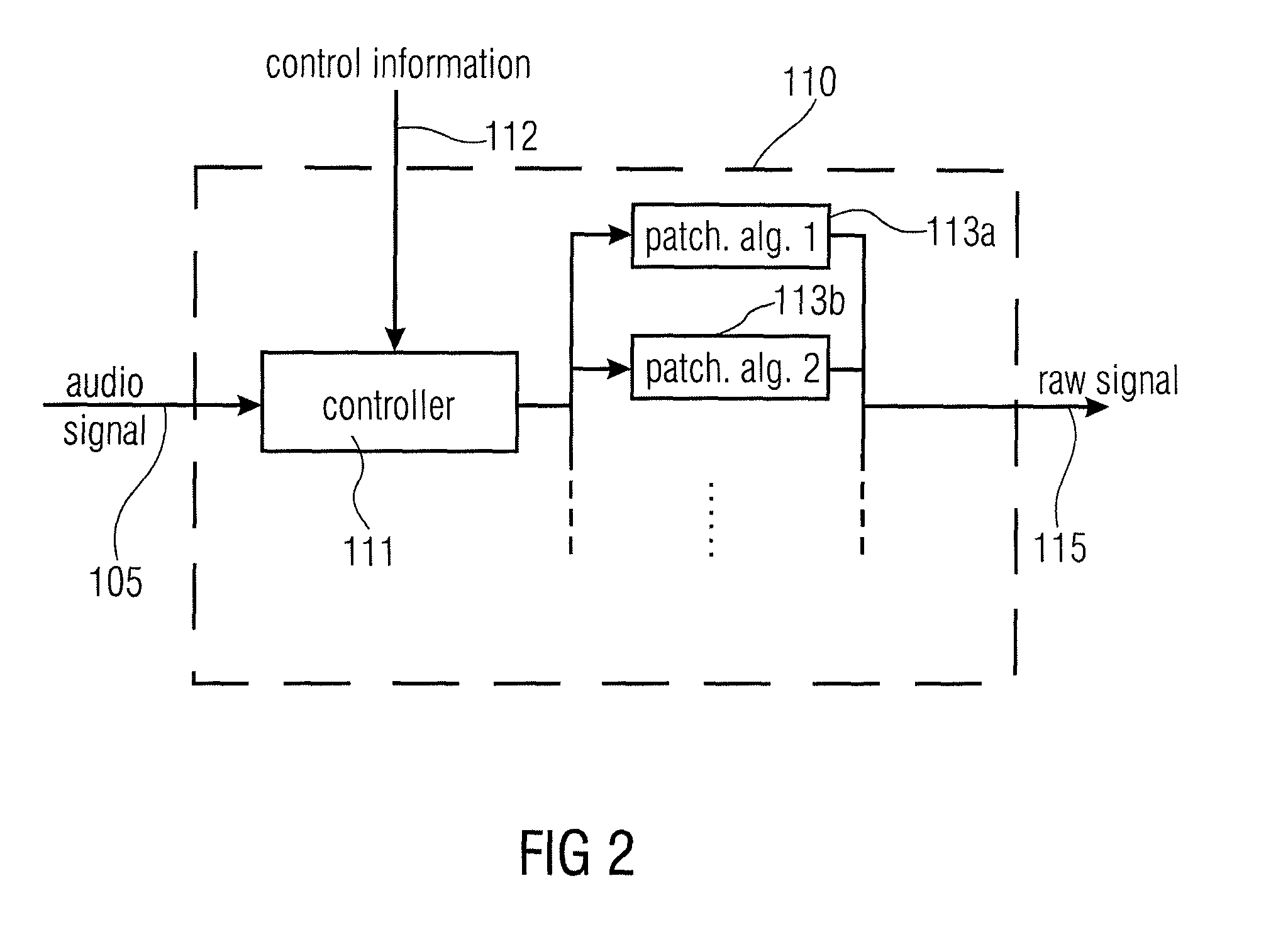
An audio signal synthesizer generates a synthesis audio signal having a first frequency band and a second synthesized frequency band derived from the first frequency band and comprises a patch generator, a spectral converter, a raw signal processor and a combiner. The patch generator performs at least two different patching algorithms, each patching algorithm generating a raw signal. The patch generator is adapted to select one of the at least two different patching algorithms in response to a control information. The spectral converter converts the raw signal into a raw signal spectral representation. The raw signal processor processes the raw signal spectral representation in response to spectral domain spectral band replication parameters to obtain an adjusted raw signal spectral representation.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Transcoder and Method of Transcoding Therefore
InactiveUS20080260048A1Quality improvementImprove high frequency performanceSpeech analysisCode conversionComputer hardwareFrequency spectrum
A transcoder comprises a receiver (101) which receives input data representing an encoded signal and comprising first encoding data and first parametric extension data. The encoded data is fed to a decoder (103). The output of the decoder (103) is fed to an encoder (105) which generates second encoded data according to a different encoding protocol or with different encoding parameters. The first parametric extension data is fed to an extension data processor (109) which generates second parametric extension data directly from the first parametric extension data. The second encoded data and the second parametric extension data is combined in an output processor (107) to generate a transcoded signal comprising separately determined parametric extension data. The parametric extension data may be Spectral Band Replication (SBR) or Parametric Stereo (PS) extension data for an audio bitstream. Improved quality and reduced complexity is achieved by the separate transcoding of the parametric extension data.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
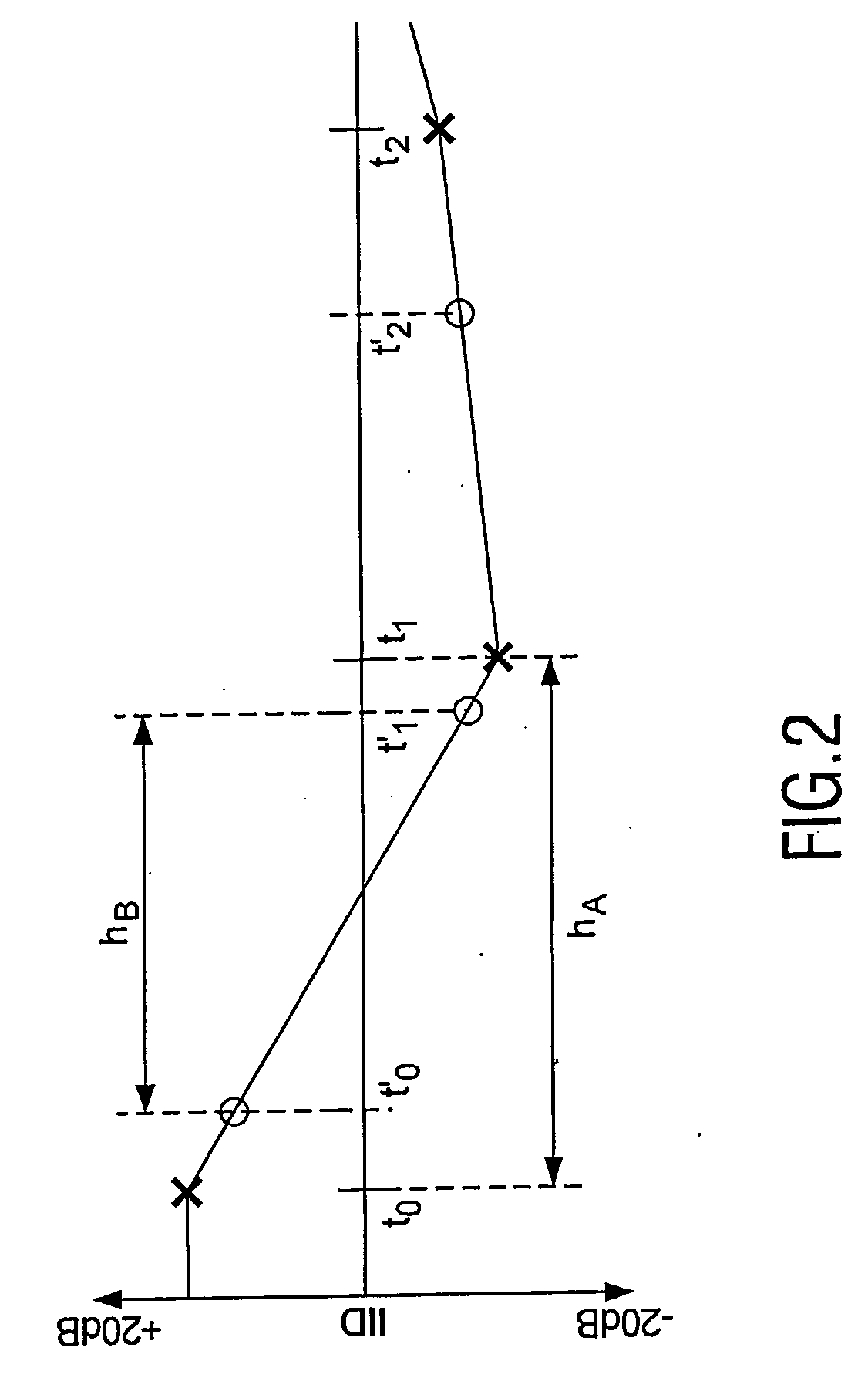
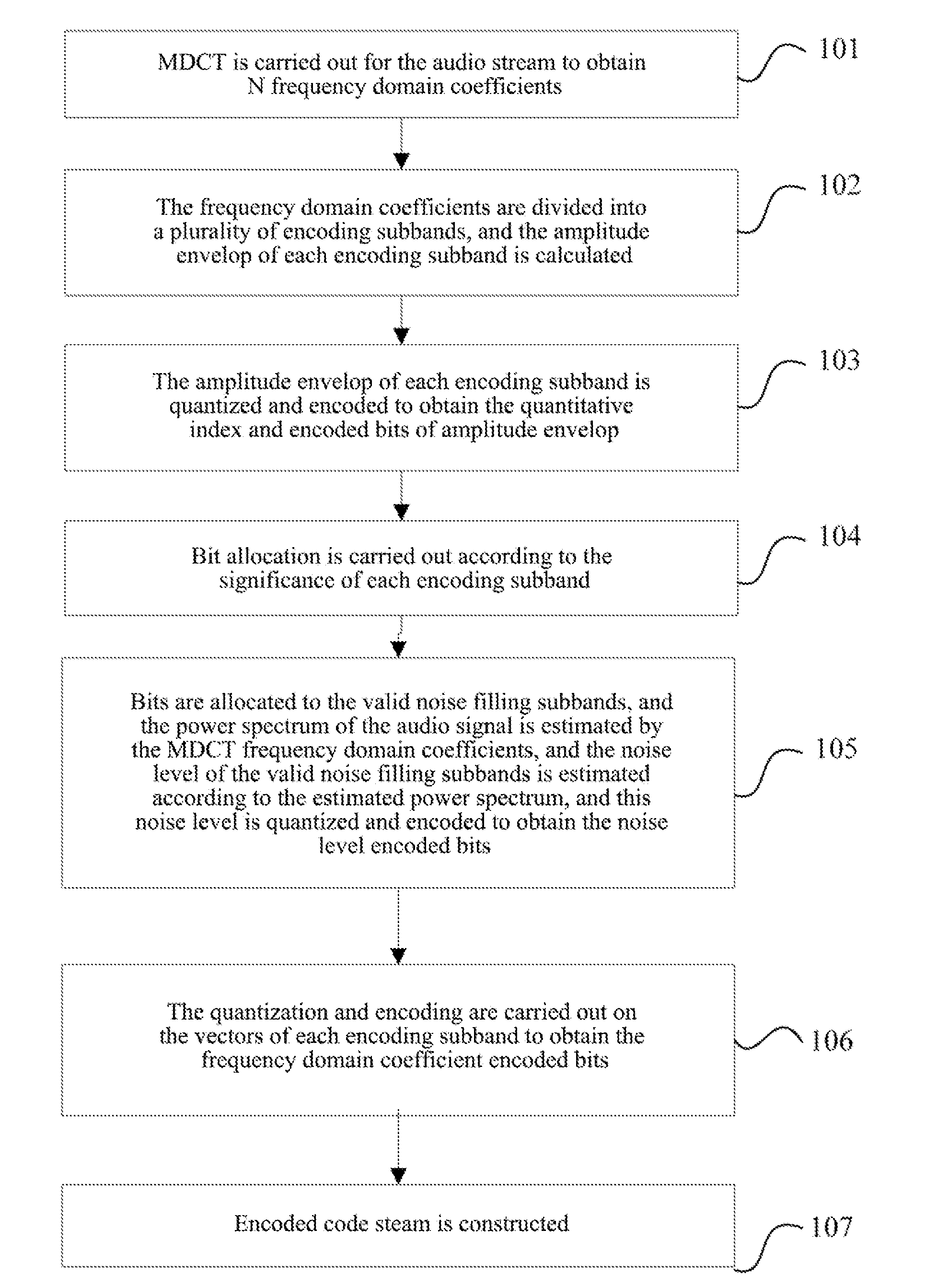
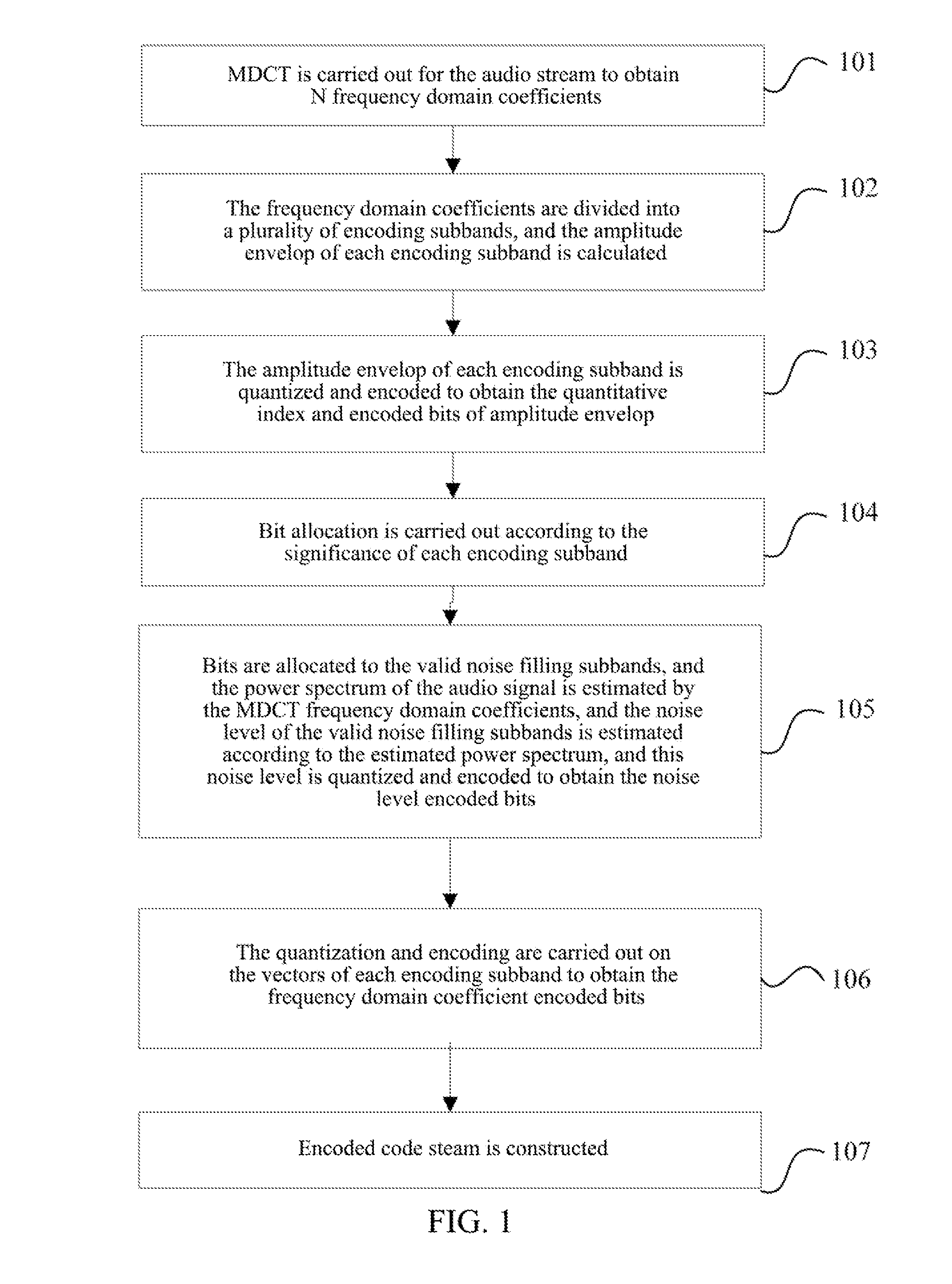
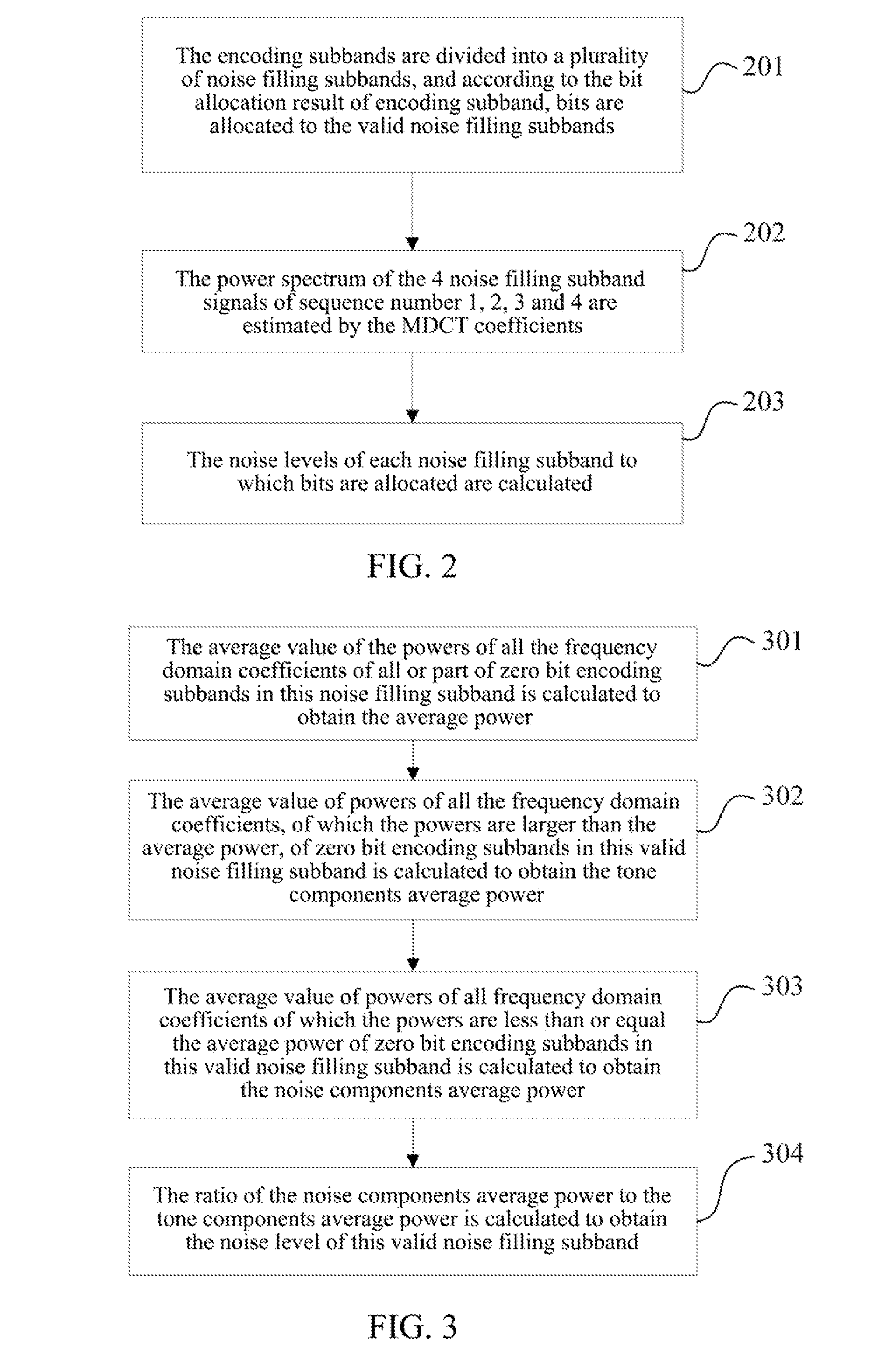
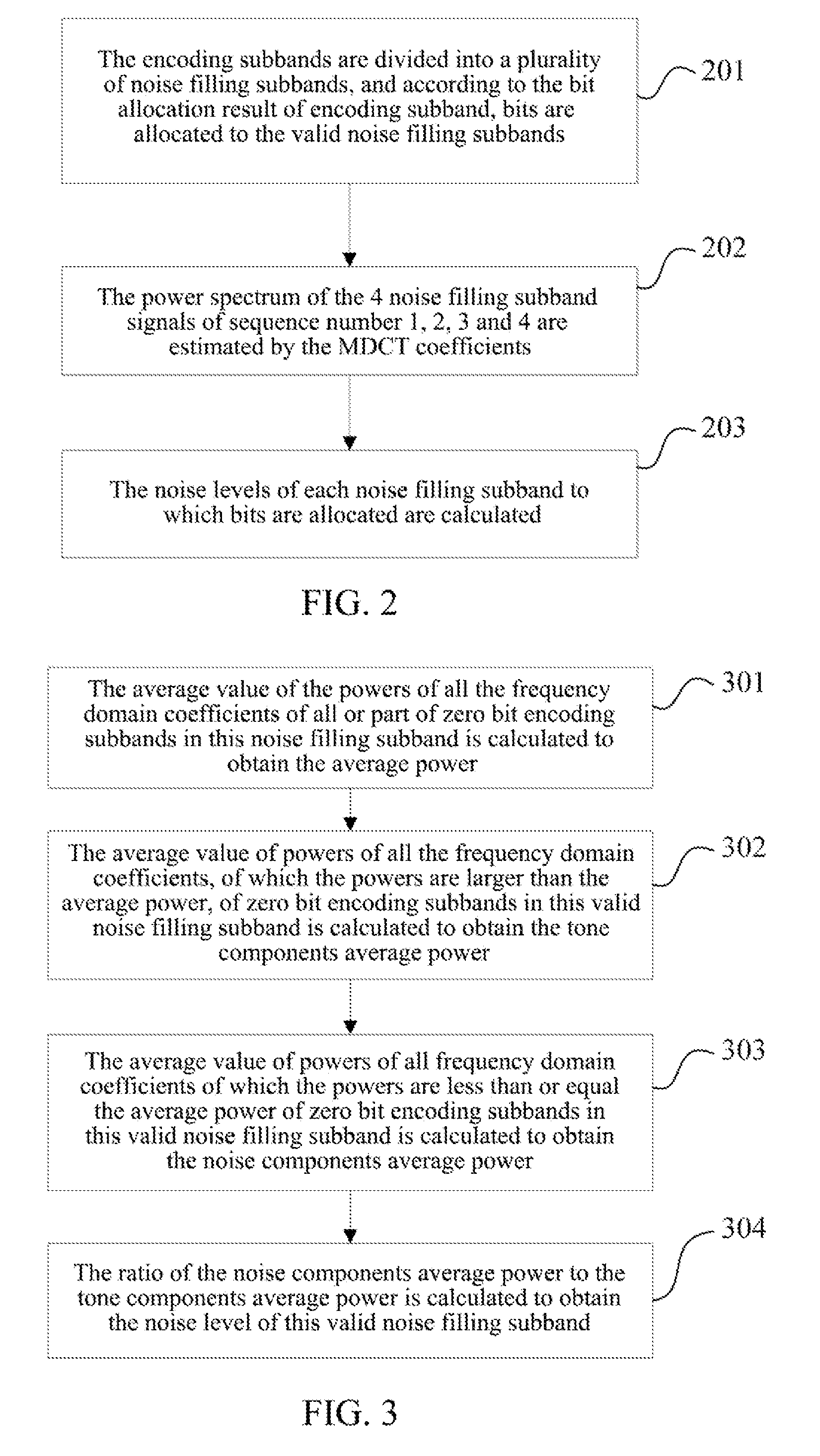
Method and system for audio encoding and decoding and method for estimating noise level
ActiveUS20130006645A1Improve listening effectSpeech analysisCode conversionNoise levelAudio frequency
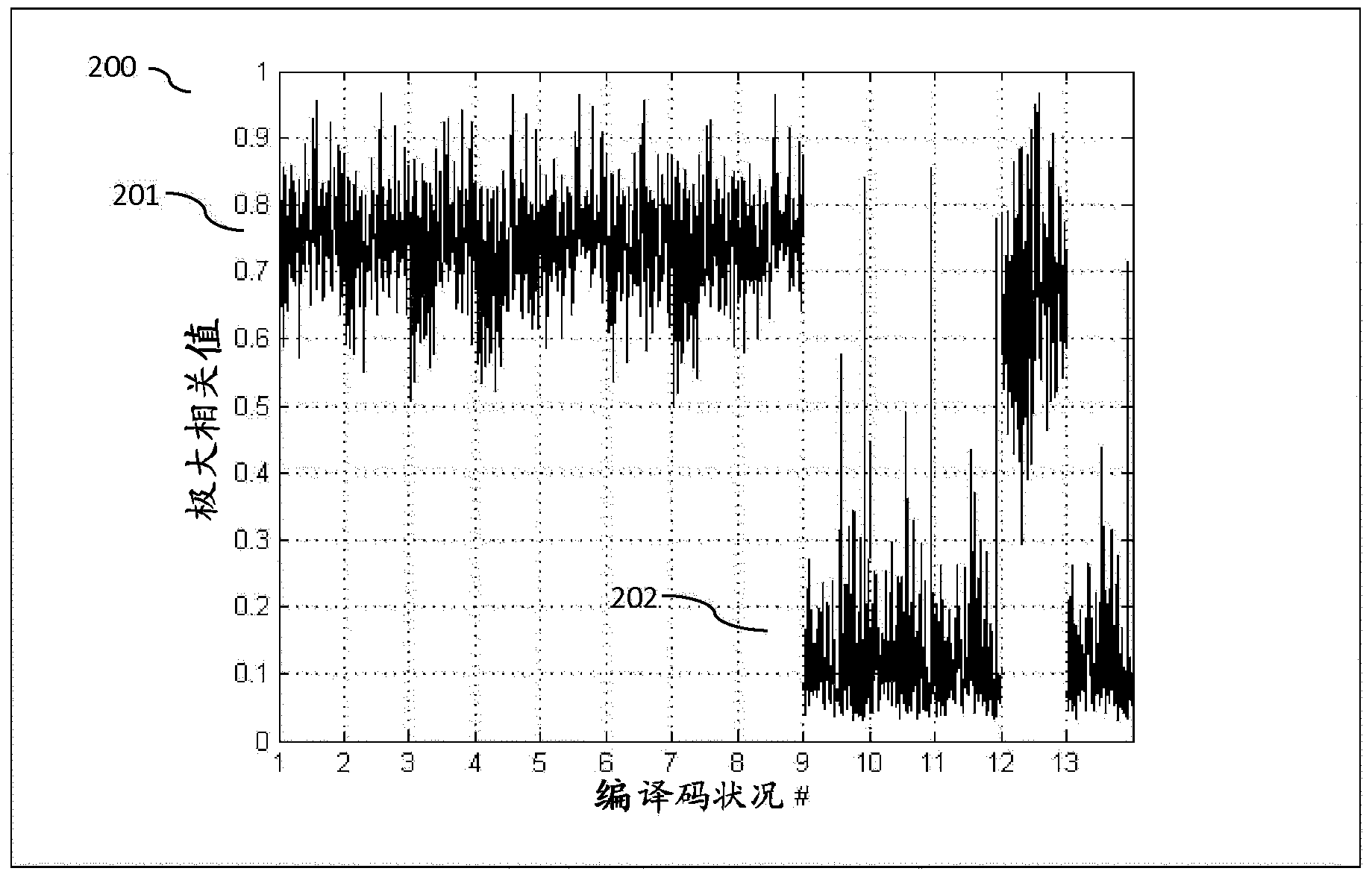
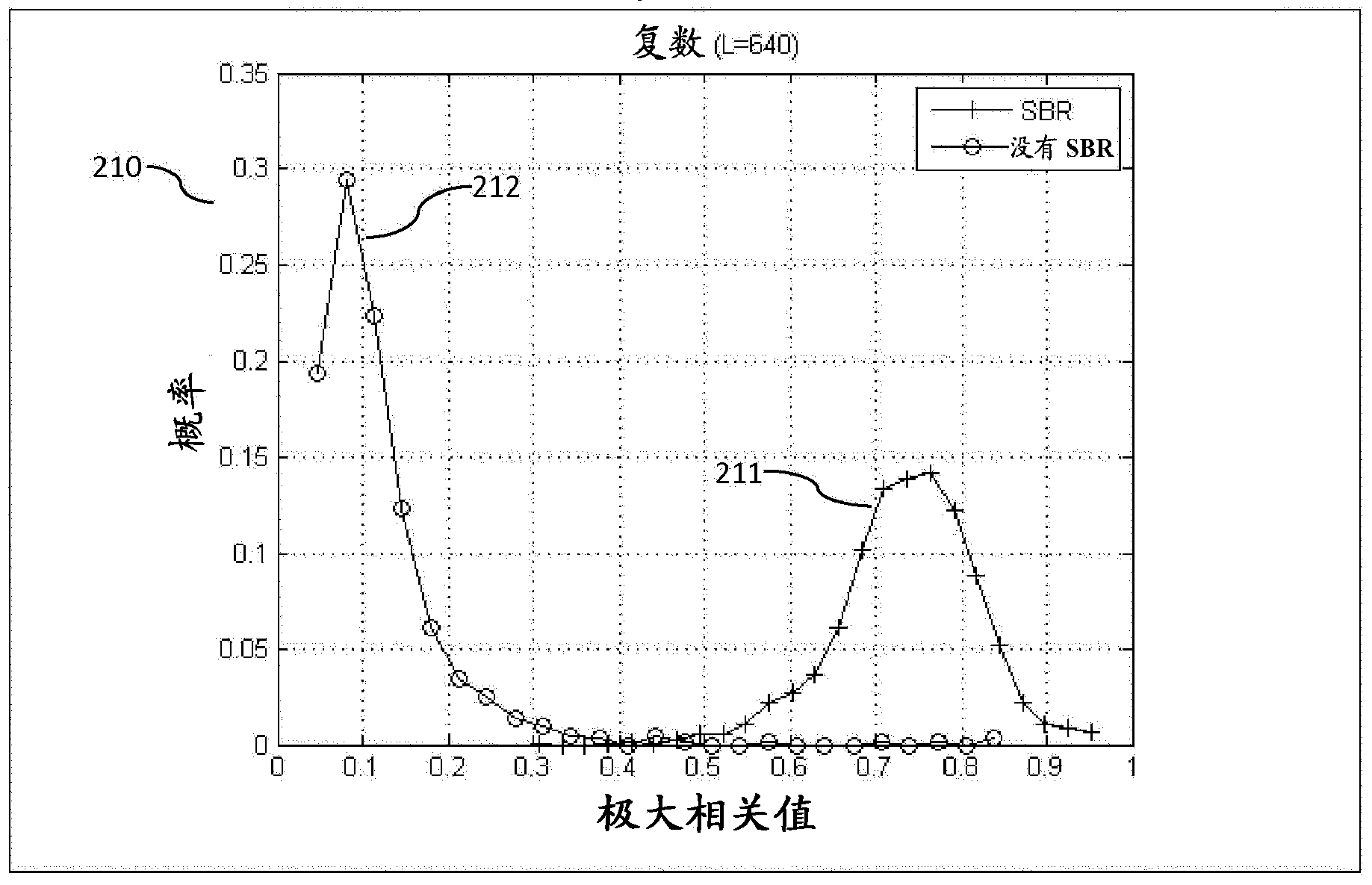
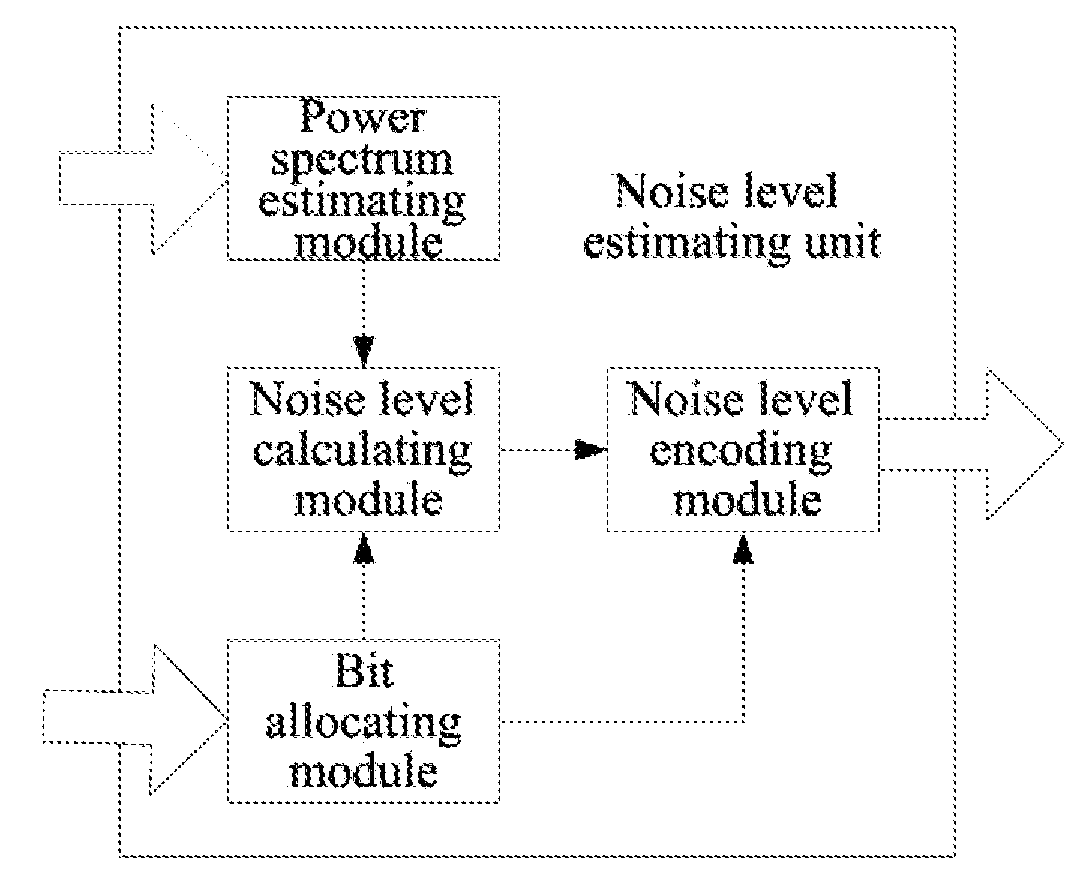
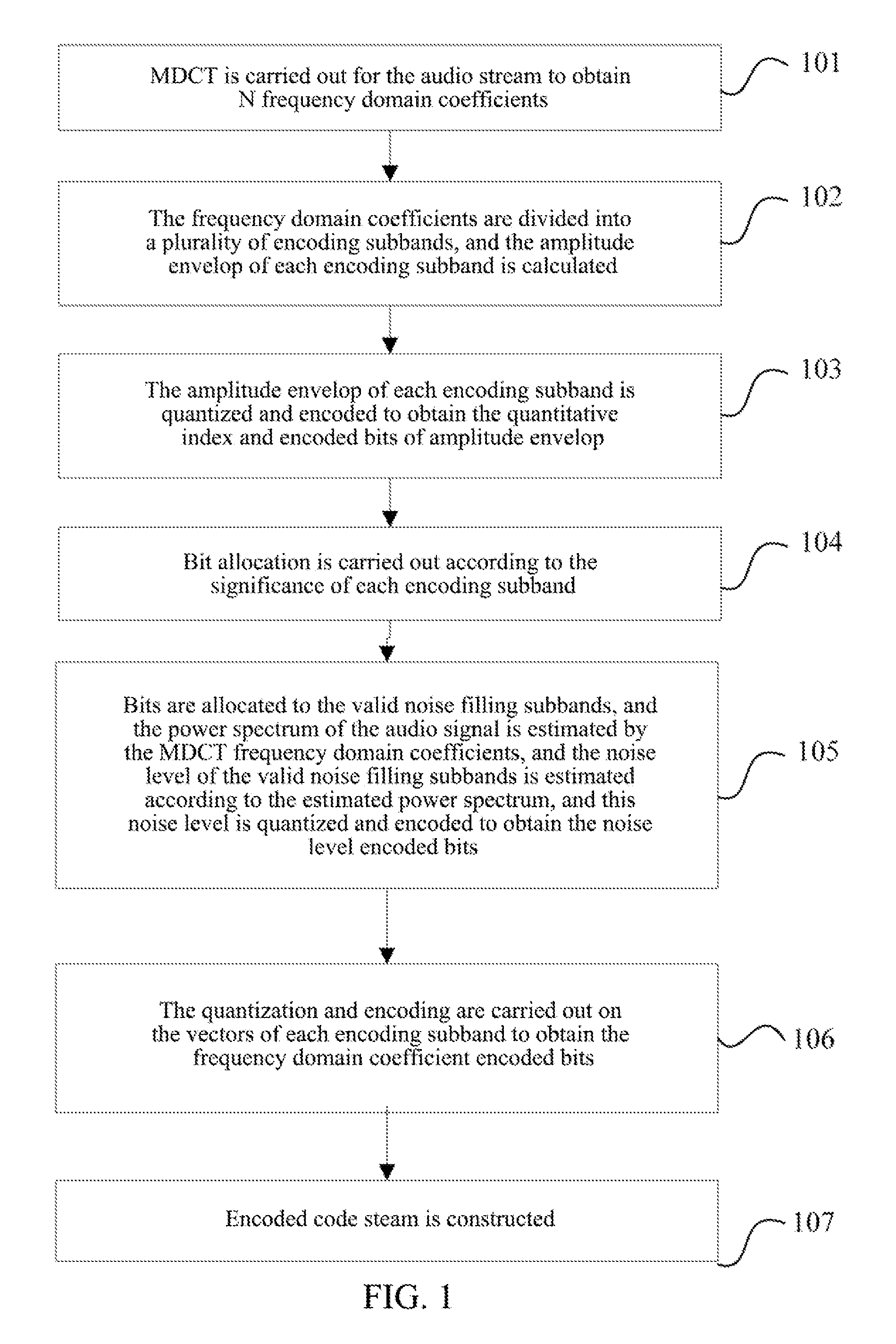
The present invention relates to a method and system for audio encoding and decoding and a method for estimating a noise level, and the method for estimating a noise level in the present invention comprises: estimating a power spectrum of an audio signal to be encoded according to a frequency domain coefficient of the audio signal to be encoded; and estimating a noise level of a zero bit encoding subband audio signal according to the power spectrum obtained by calculating, and this noise level for controlling an energy proportion of noise filling to spectral band replication during decoding; wherein a zero bit encoding subband refers to an encoding subband of which allocated bit number is zero. The present invention can well reconstruct the uncoded frequency domain coefficients.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Source coding enhancement using spectral-band replication
InactiveUS6925116B2Improvements of audio codecsImprove perceived qualitySpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumComputer science
The present invention proposes a new method and apparatus for the enhancement of source coding systems. The invention employs bandwidth reduction (101) prior to or in the encoder (103), followed by spectral-band replication (105) at the decoder (107). This is accomplished by the use of new transposition methods, in combination with spectral envelope adjustments. Reduced bitrate at a given perceptual quality or an improved perceptual quality at a given bitrate is offered. The invention is preferably integrated in a hardware or software codec, but can also be implemented as a separate processor in combination with a codec. The invention offers substantial improvements practically independent of codec type and technological progress.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Sbr bitstream parameter downmix
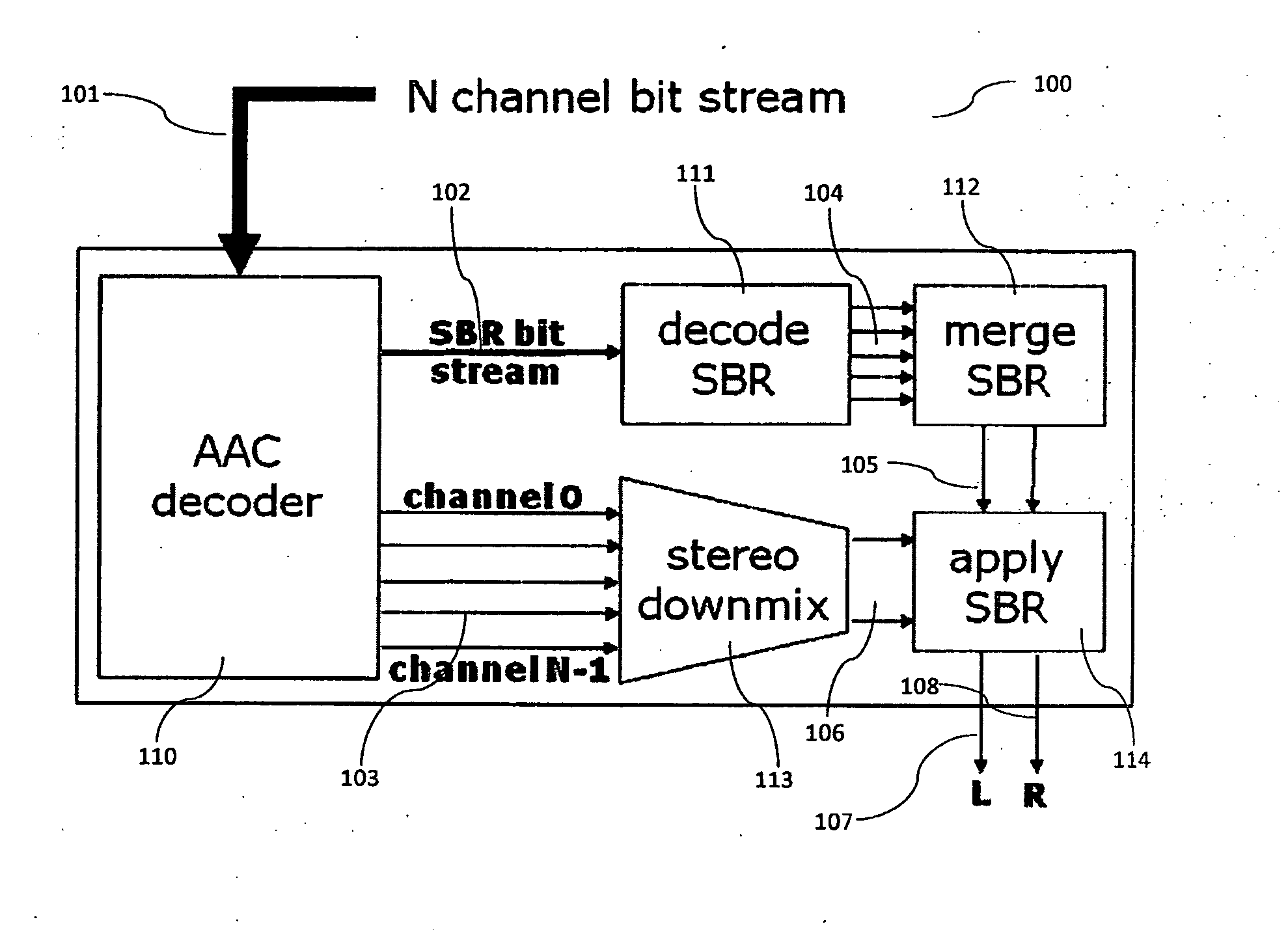
ActiveUS20120275607A1Reduce in quantityReduce computational complexitySpeech analysisStereophonic arrangmentsTranscodingAudio frequency
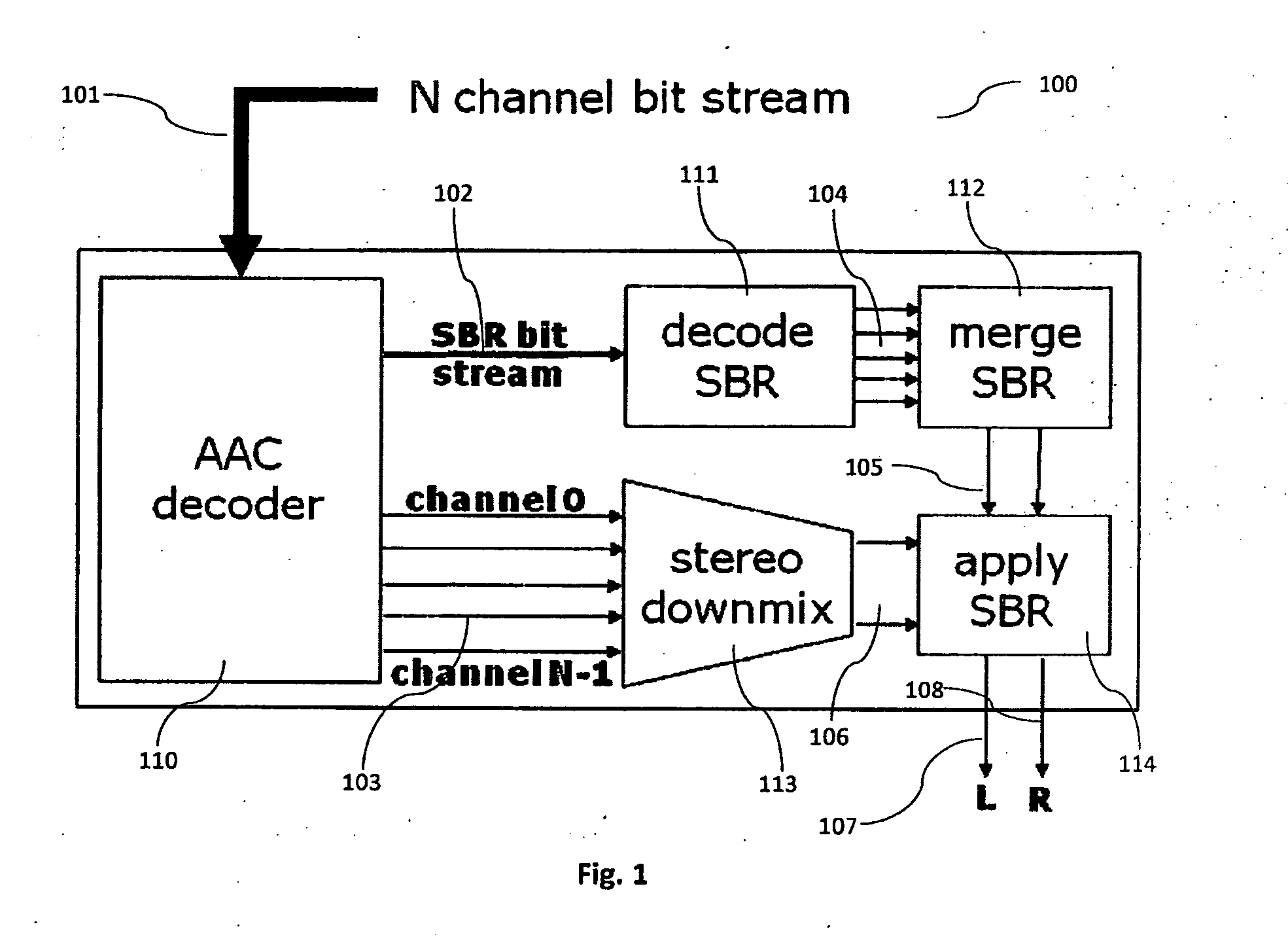
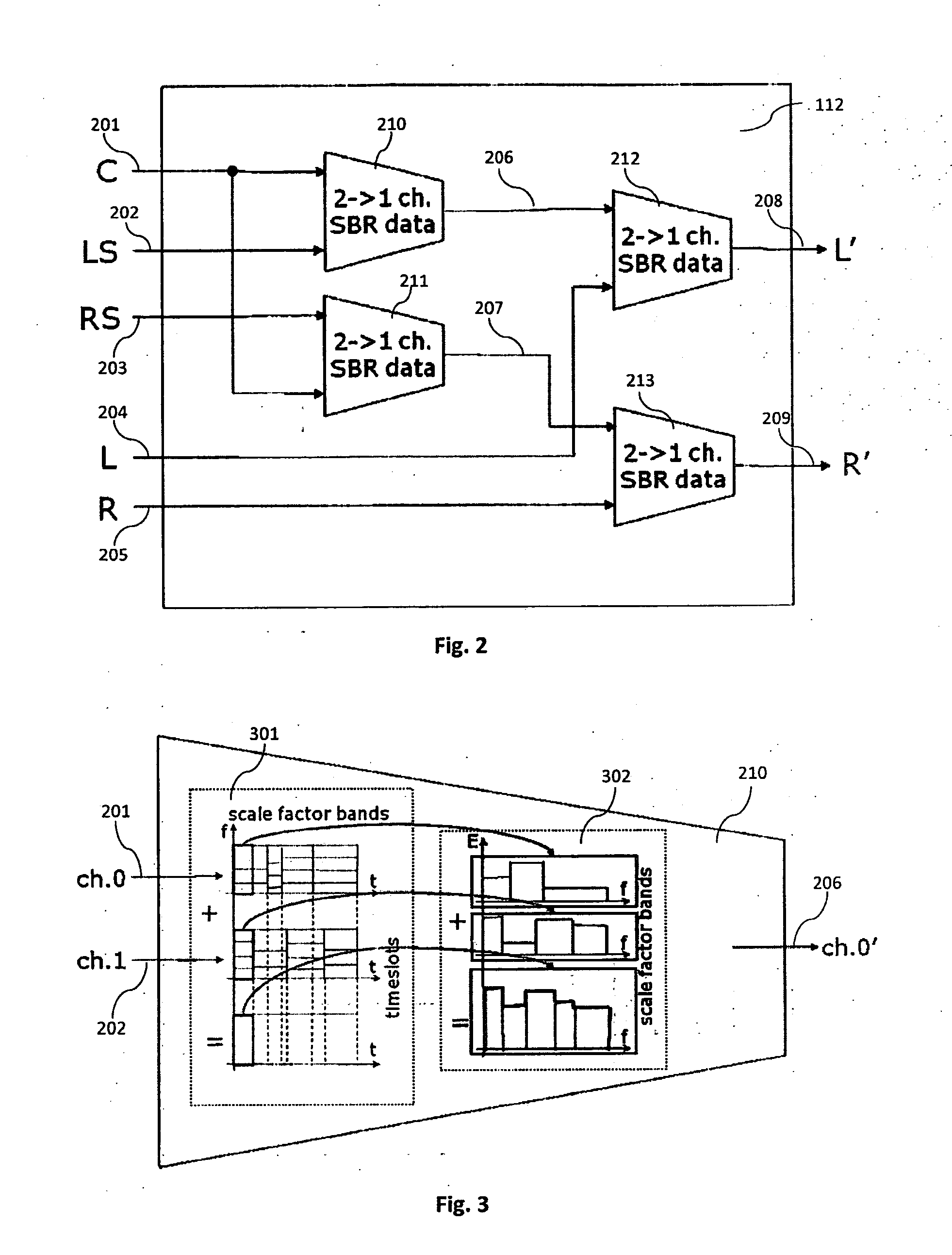
The present document relates to audio decoding and / or audio transcoding. In particular, the present document relates to a scheme for efficiently decoding a number M of audio channels from a bitstream comprising a higher number N of audio channels. In this context a method and system for merging a first and a second source set of spectral band replication (SBR) parameters to a target set of SBR parameters is described. The first and second source set comprise a first and second frequency band partitioning, respectively, which are different from one another. The first source set comprises a first set of energy related values associated with frequency bands of the first frequency band partitioning. The second source set comprises a second set of energy related values associated with frequency bands of the second frequency band partitioning. The target set comprises a target energy related value associated with an elementary frequency band. The method comprises the steps of breaking up the first and the second frequency band partitioning into a joint grid comprising the elementary frequency band; assigning a first value of the first set of energy related values to the elementary frequency band; assigning a second value of the second set of energy related values to the elementary frequency band; and combining the first and second value to yield the target energy related value for the elementary frequency band.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Processor extensions for accelerating spectral band replication
Owner:INTEL CORP
Apparatus and method of encoding audio data and apparatus and method of decoding encoded audio data
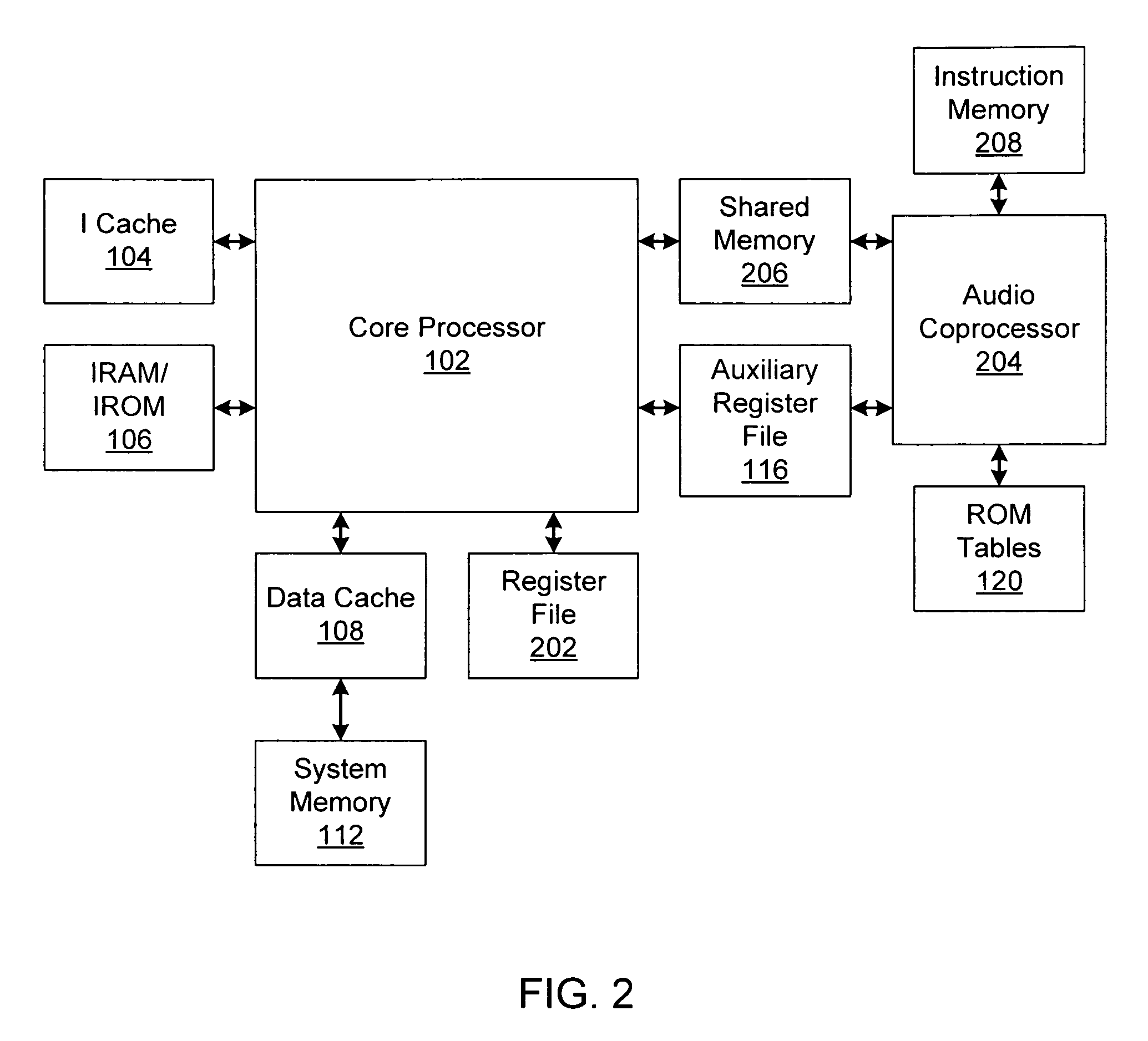
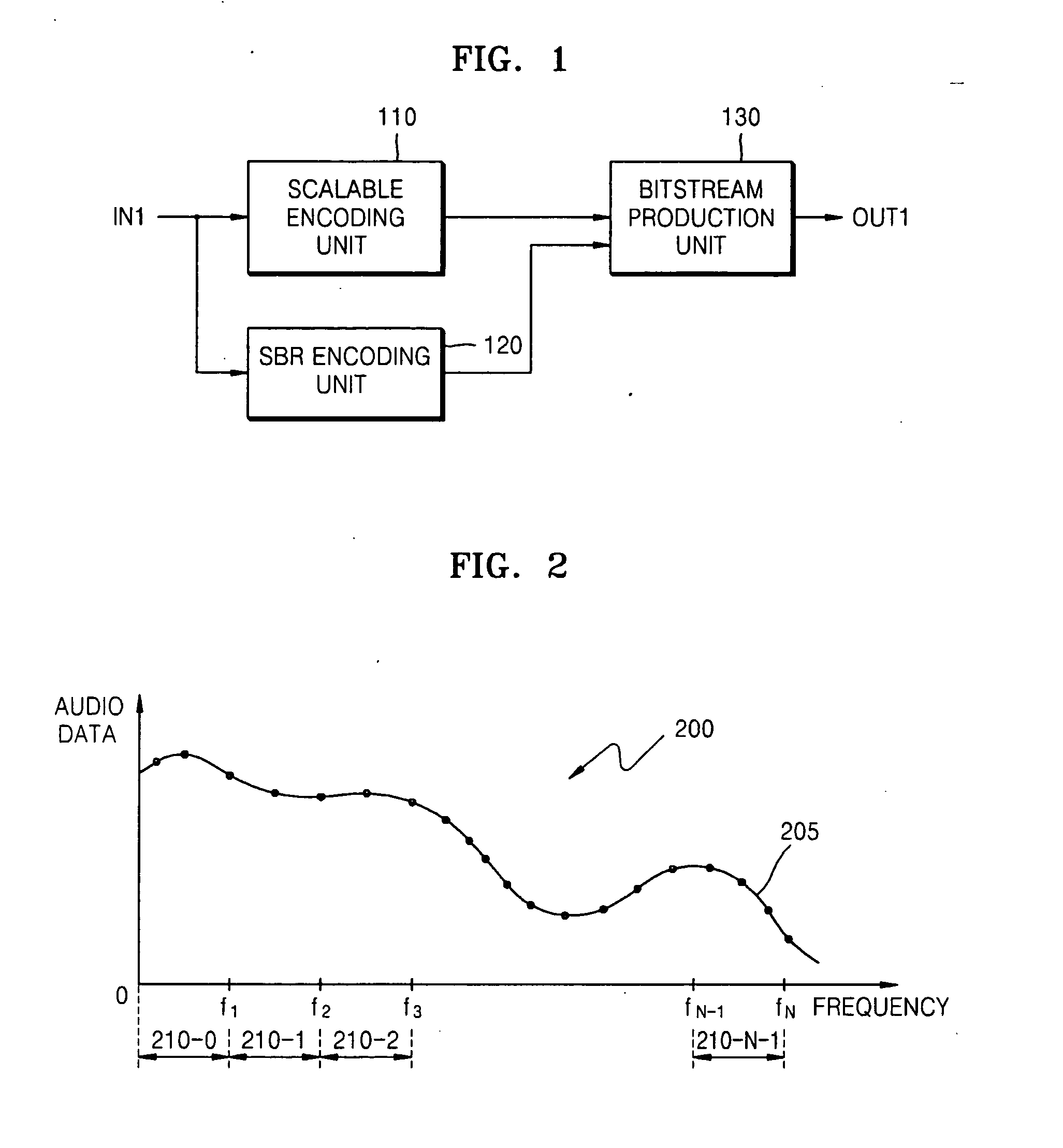
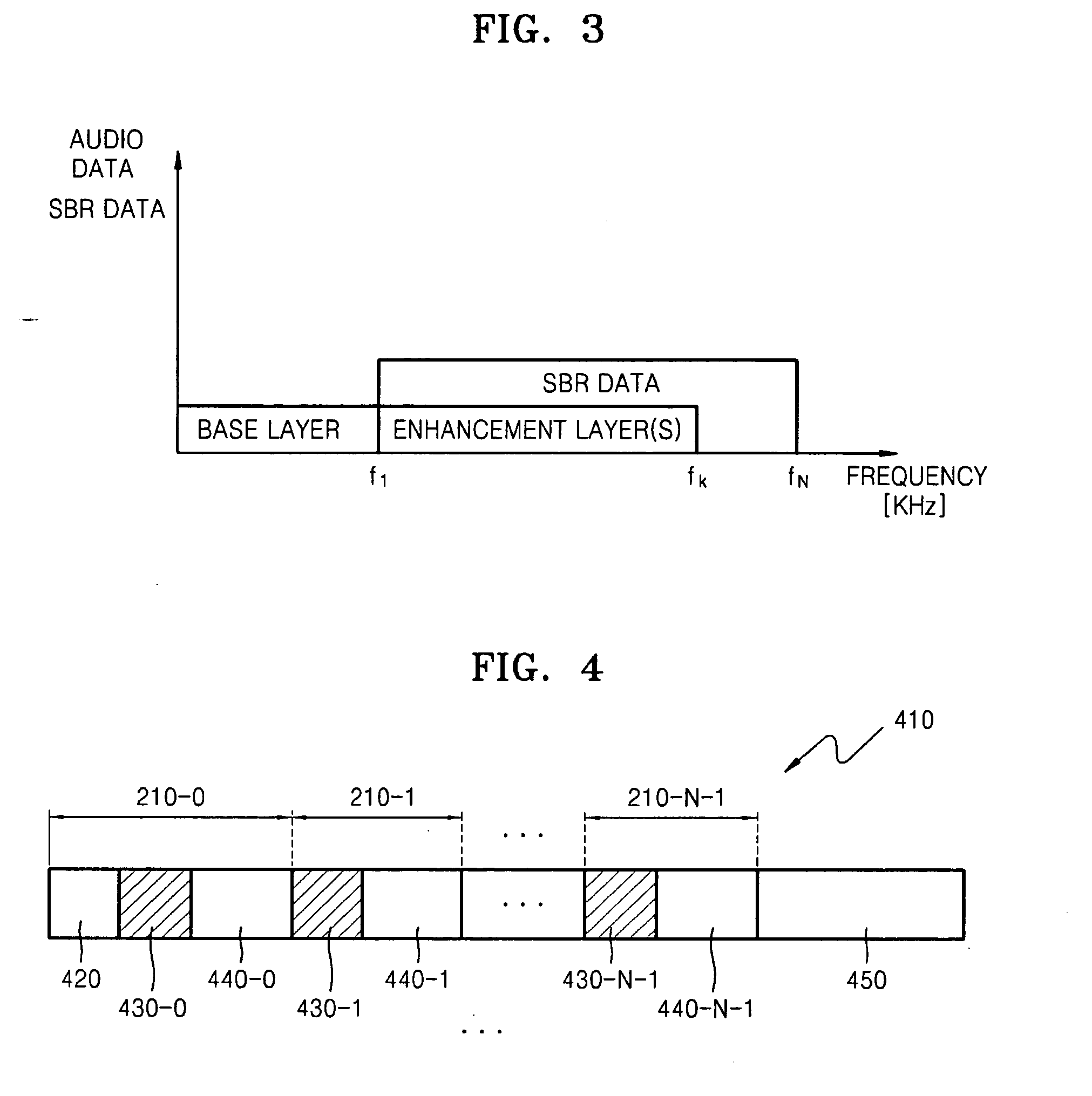
An apparatus and method encode audio data, and an apparatus and method decode encoded audio data. An audio data encoding apparatus includes: a scalable encoding unit dividing audio data into a plurality of layers, representing the audio data in predetermined numbers of bits in each of the plurality of layers, and encoding a lower layer prior to encoding an upper layer and an upper bit of each layer prior to encoding a lower bit of each layer; an SBR encoding unit generating spectral band replication (SBR) data that has information with respect to audio data in a frequency band of frequencies equal to or greater than a predetermined frequency among the audio data to be encoded, and encoding the SBR data; and a bitstream production unit generating a bitstream using the encoded SBR data and the encoded audio data corresponding to a predetermined bitrate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
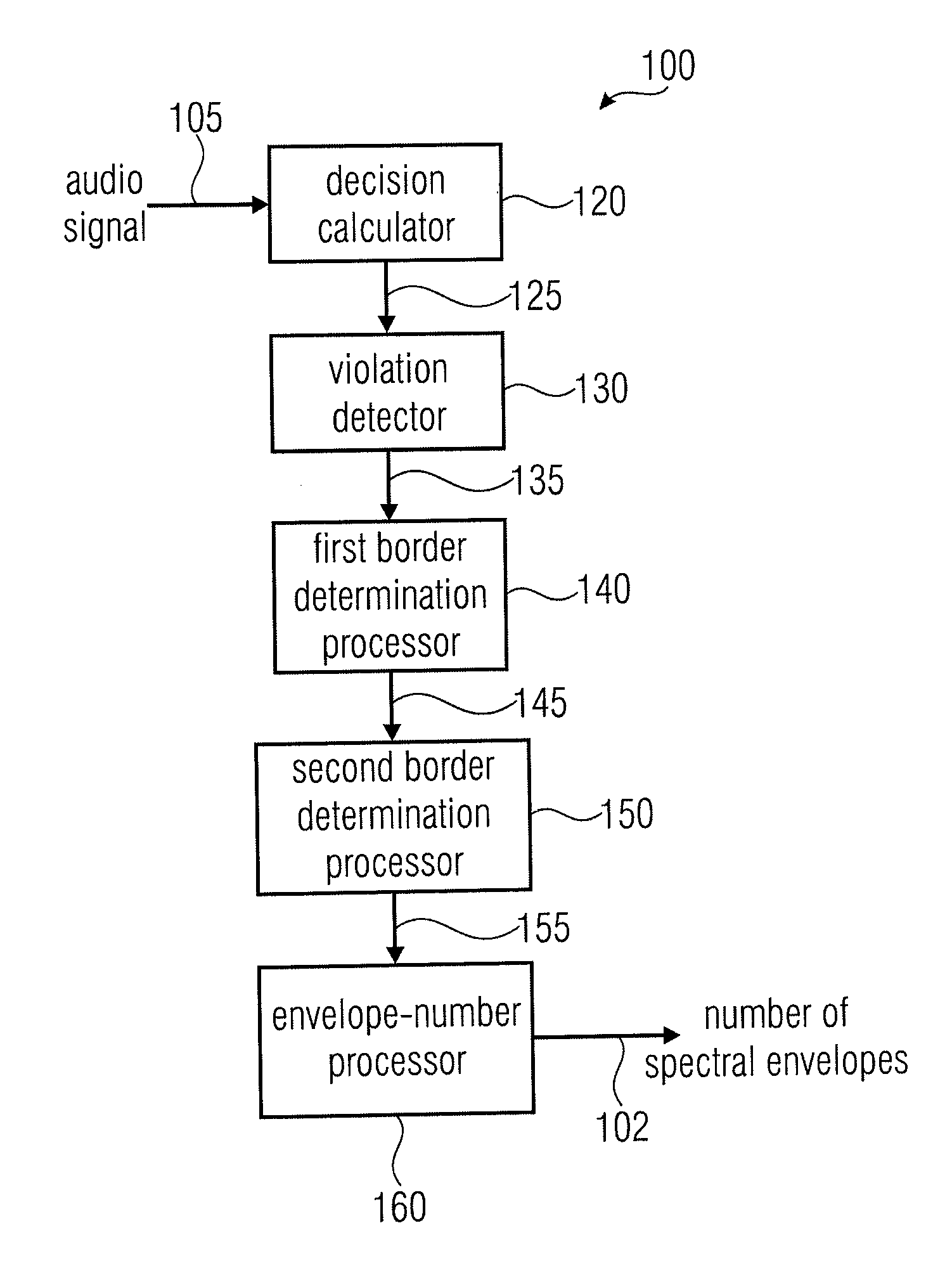
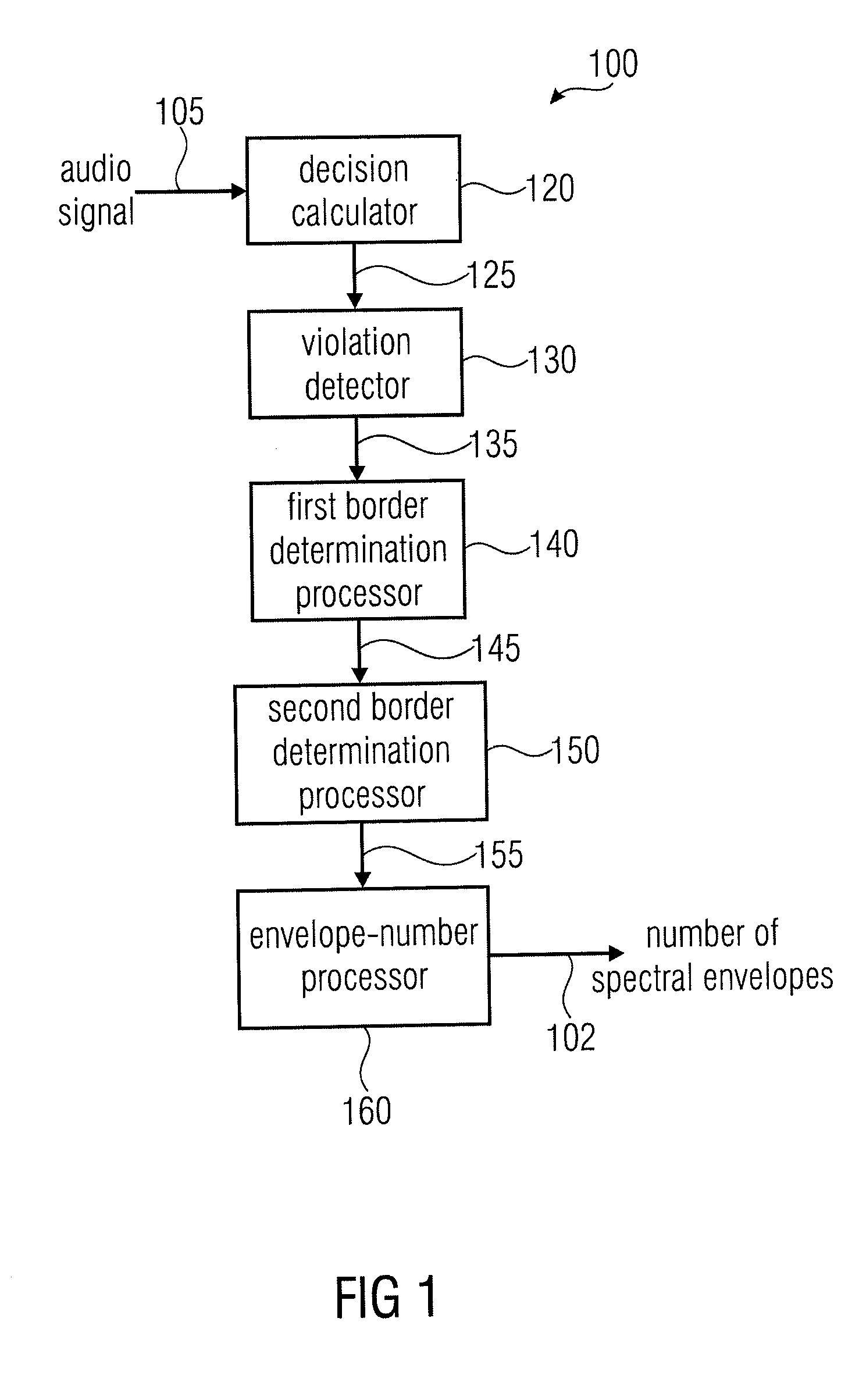
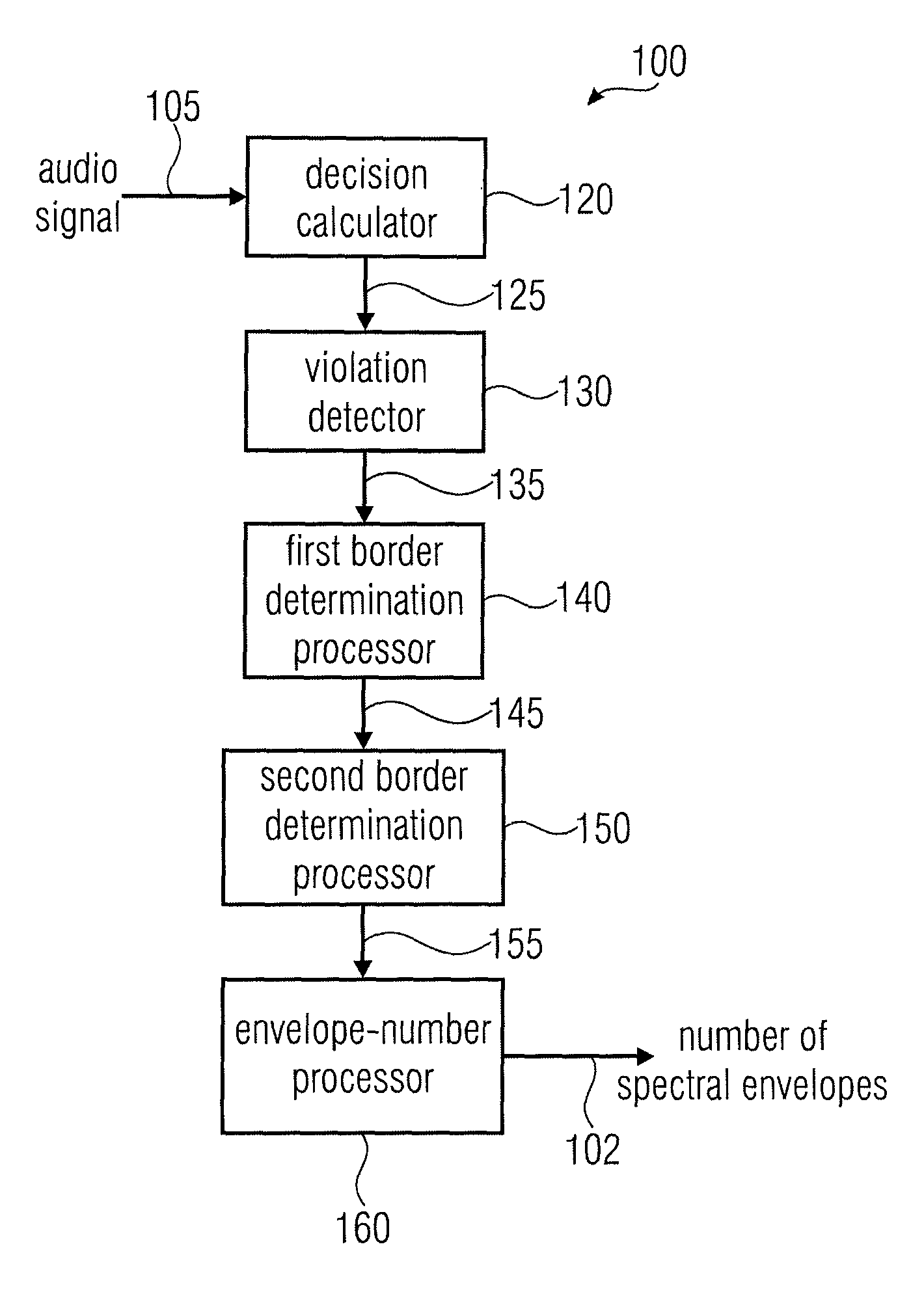
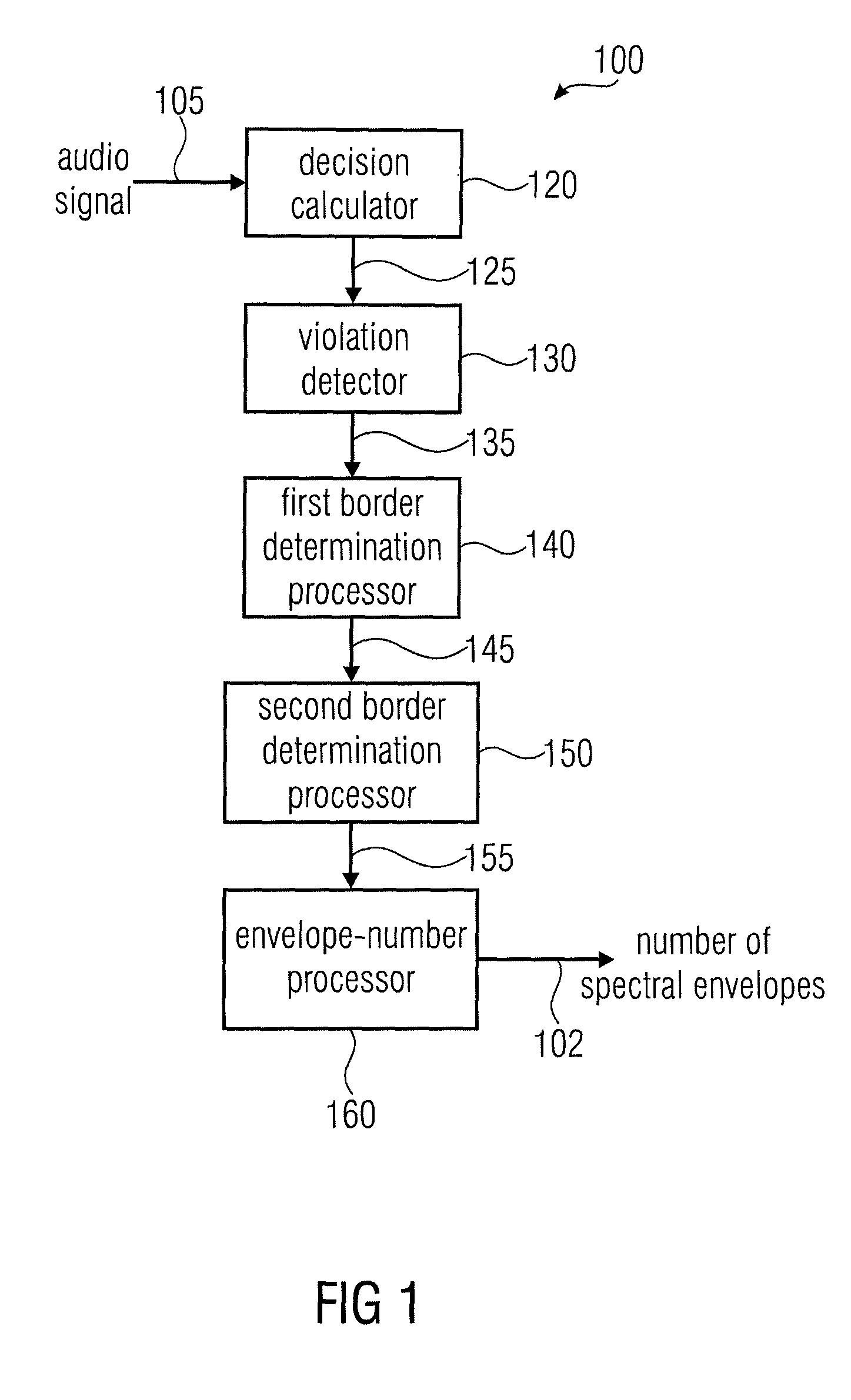
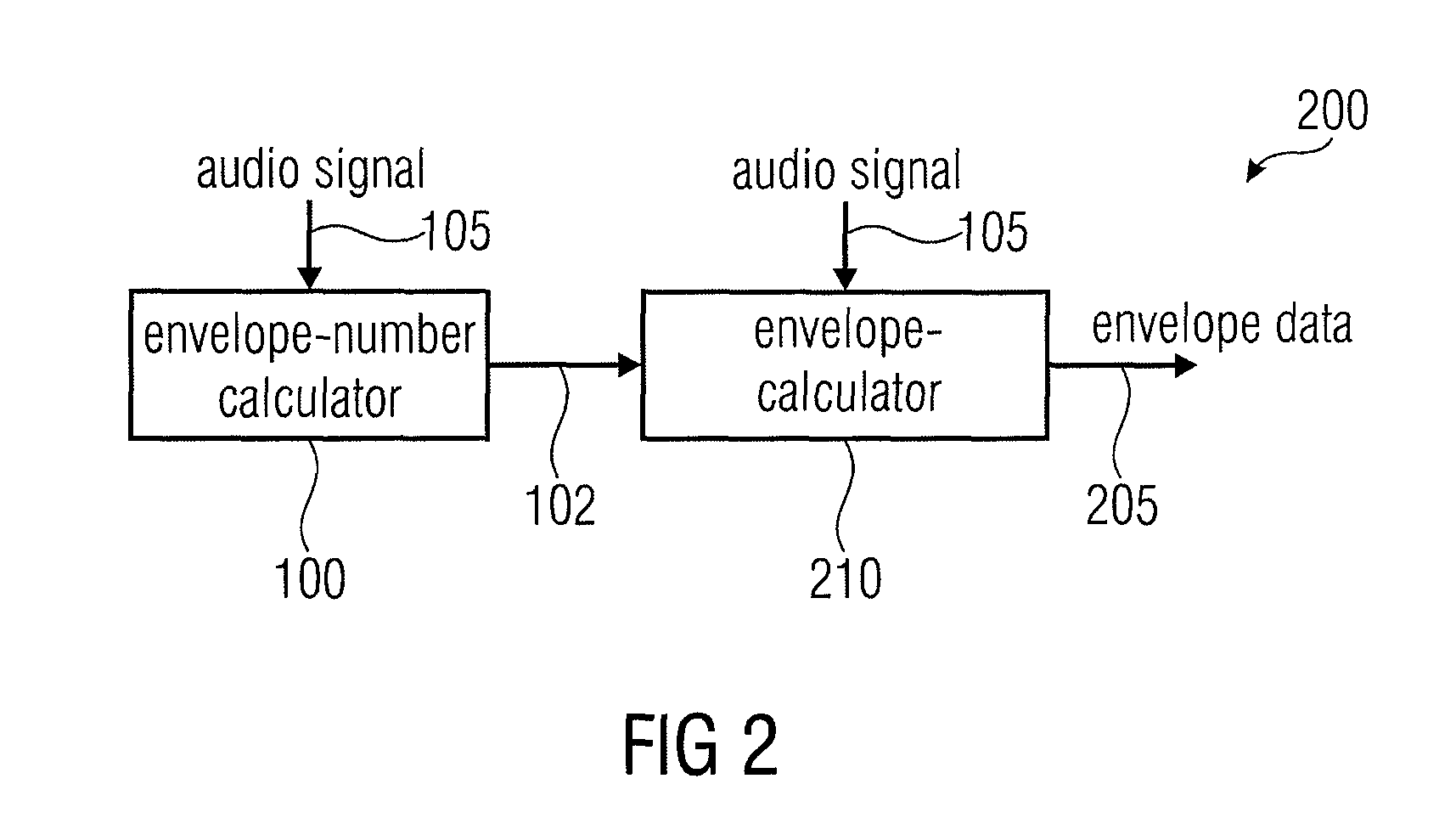
Apparatus and a Method for Calculating a Number of Spectral Envelopes
ActiveUS20110202358A1Easy to shapeFast enough to causeSpeech analysisDigital computer detailsFrequency spectrumChronological time
An apparatus calculates a number of spectral envelopes to be derived by a spectral band replication (SBR) encoder, wherein the SBR encoder is adapted to encode an audio signal using a plurality of sample values within a predetermined number of subsequent time portions in an SBR frame extending from an initial time to a final time, the predetermined number of subsequent time portions being arranged in a time sequence given by the audio signal. The apparatus has a decision value calculator for determining a decision value, the decision value measuring a deviation in spectral energy distributions of a pair of neighboring time portions. The apparatus further has a detector for detecting a violation of a threshold by the decision value and a processor for determining a first envelope border between the pair of neighboring time portions when the violation of the threshold is detected.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
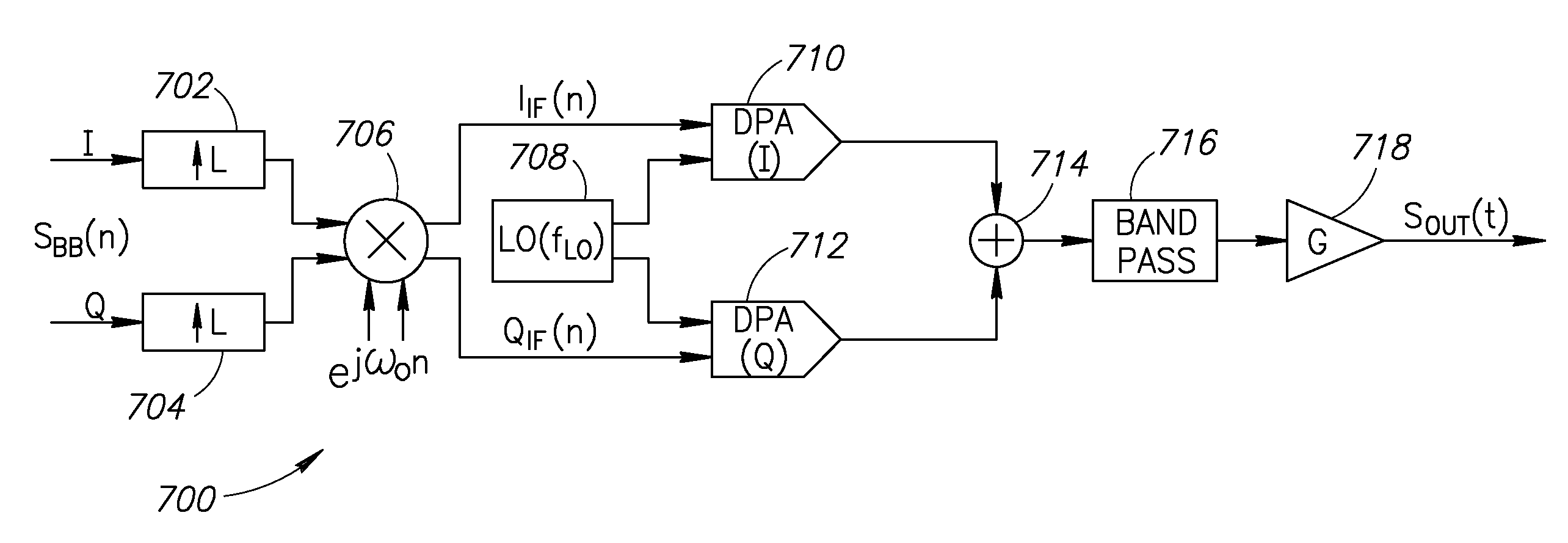
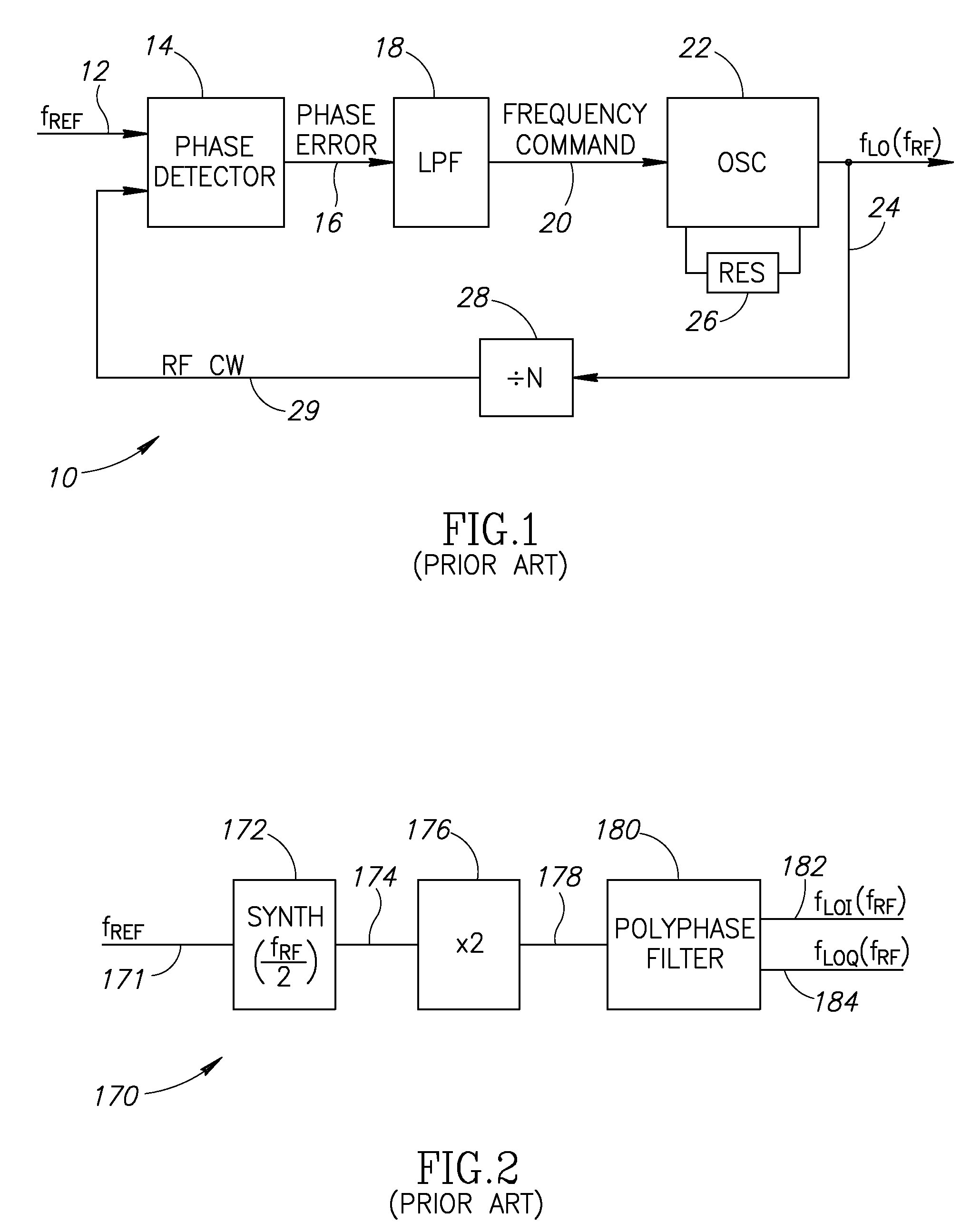
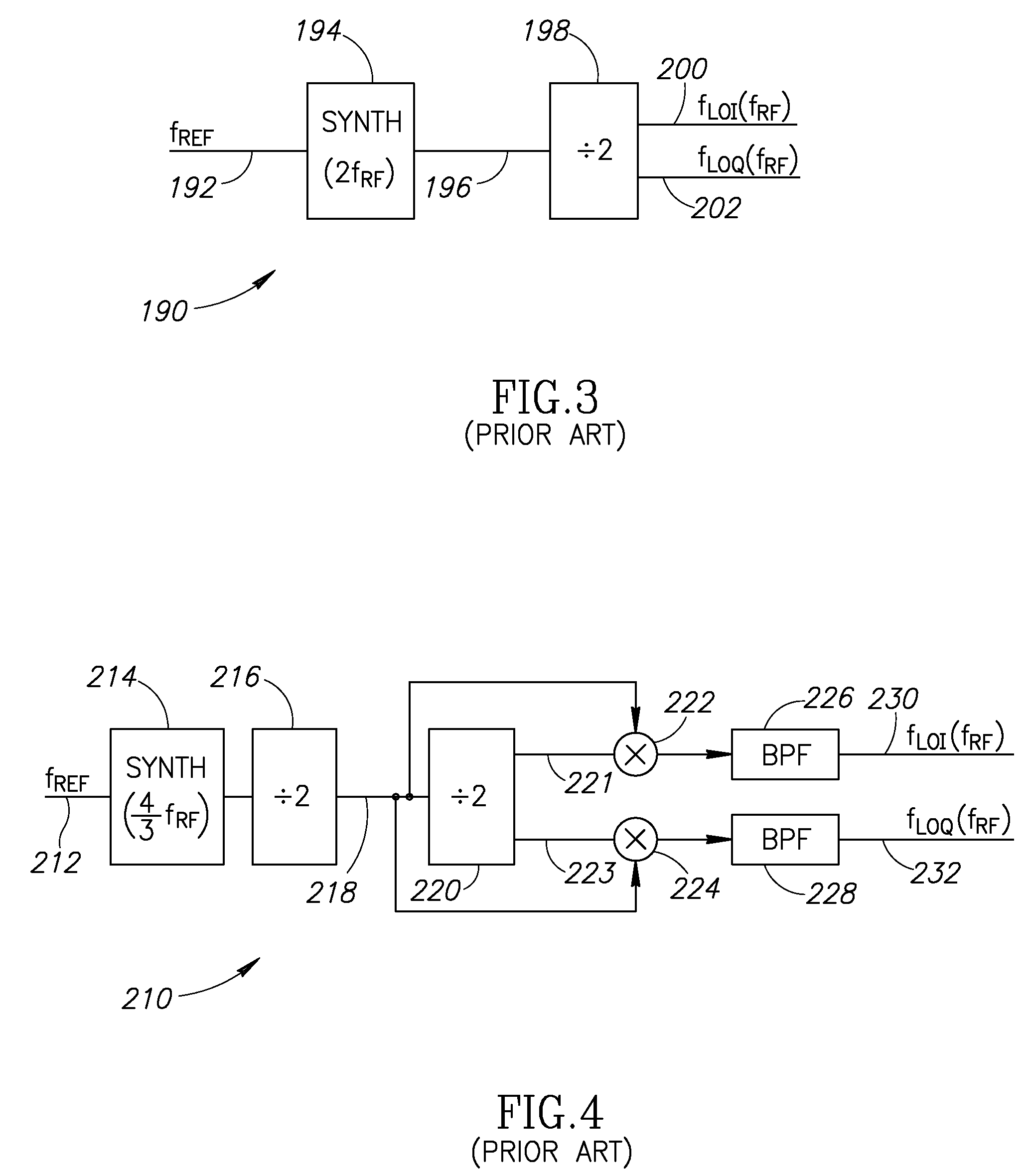
Local oscillator with non-harmonic ratio between oscillator and RF frequencies using wideband modulation spectral replicas
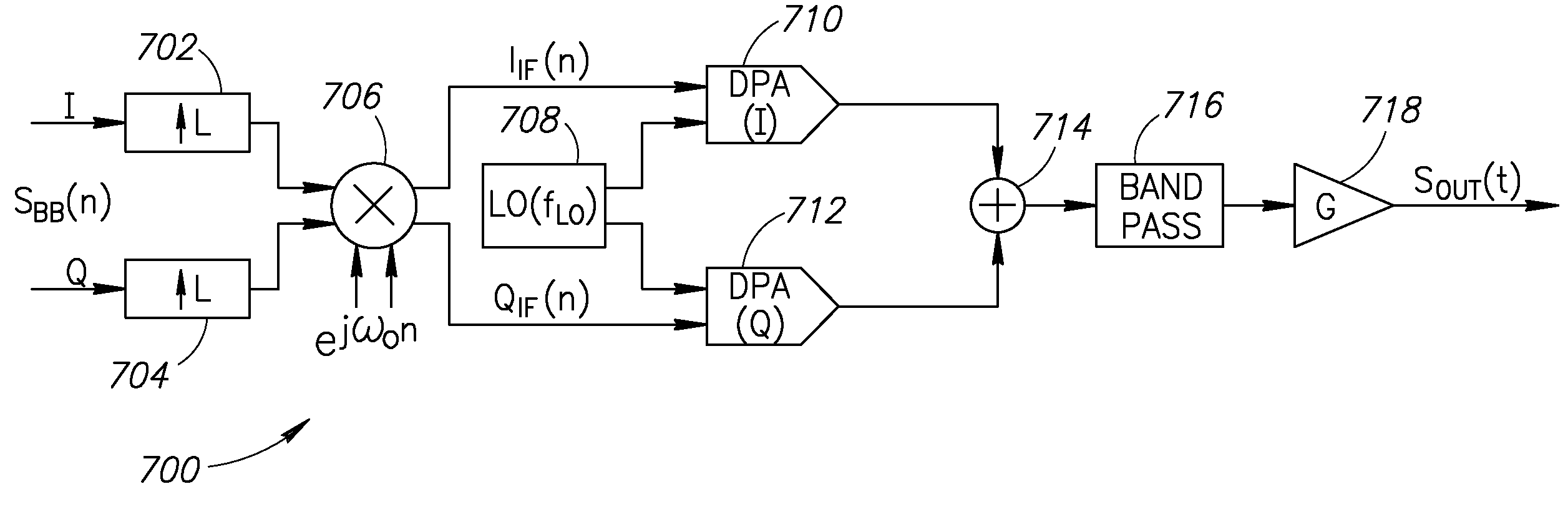
ActiveUS20080055014A1Easy to implementAvoid serious problemsModulation transferencePulse automatic controlBandpass filteringFrequency spectrum
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of local oscillator (LO) generation with non-integer multiplication ratio between the local oscillator and RF frequencies. The LO generation schemes presented are operative to generate I and Q square waves at a designated frequency while avoiding the well known issue of harmonic pulling. An input baseband signal is interpolated and upconverted in the digital domain to an IF. The LO operates at a frequency which is a n / m division of the target RF frequency fRF. The IF frequency is configured to ½ of the LO frequency. The upconverted IF signal is then converted to the analog domain via digital power amplifiers followed by voltage combiners. The output of the combiners is band pass filtered to extract the desired replica.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
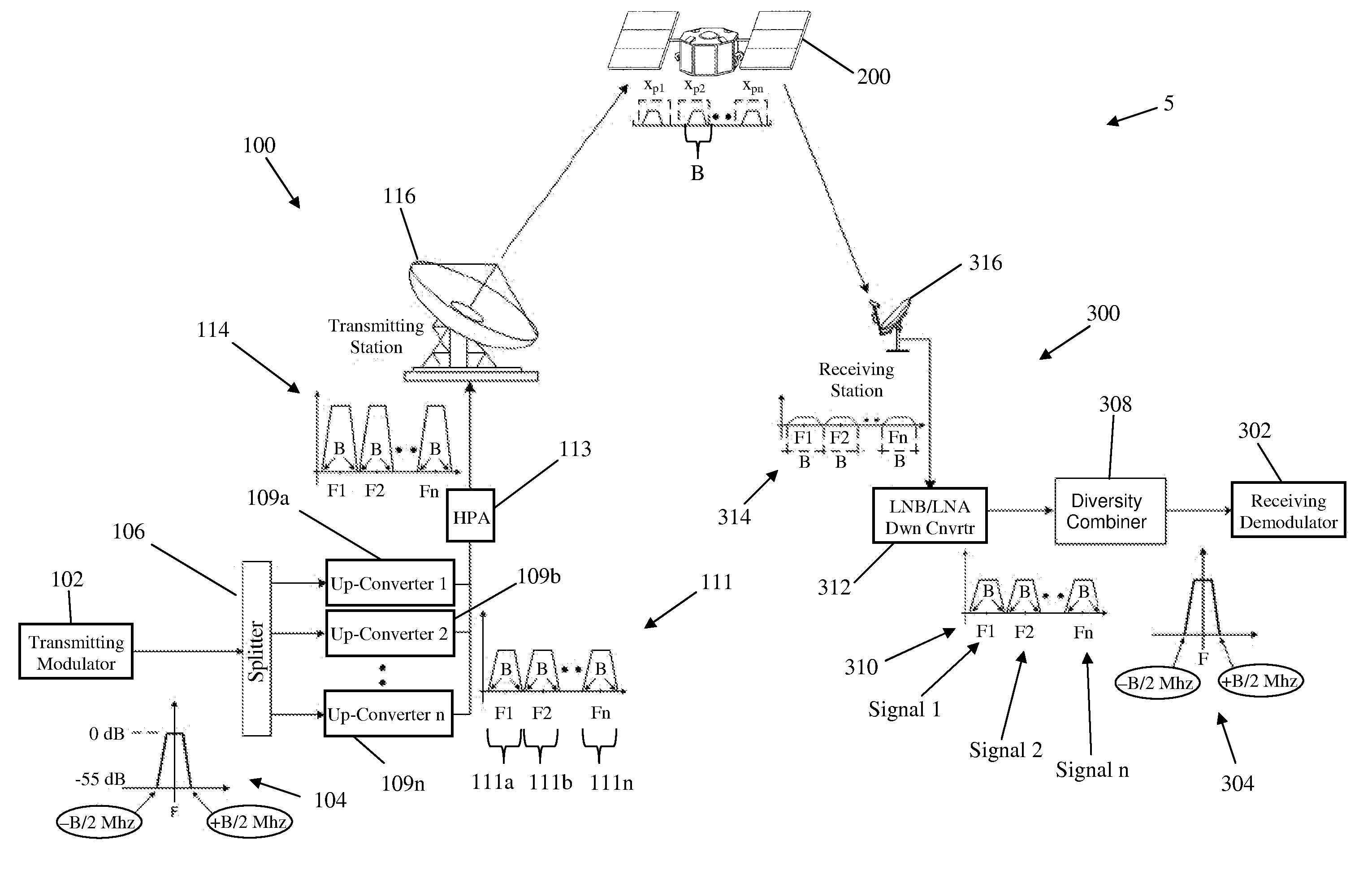
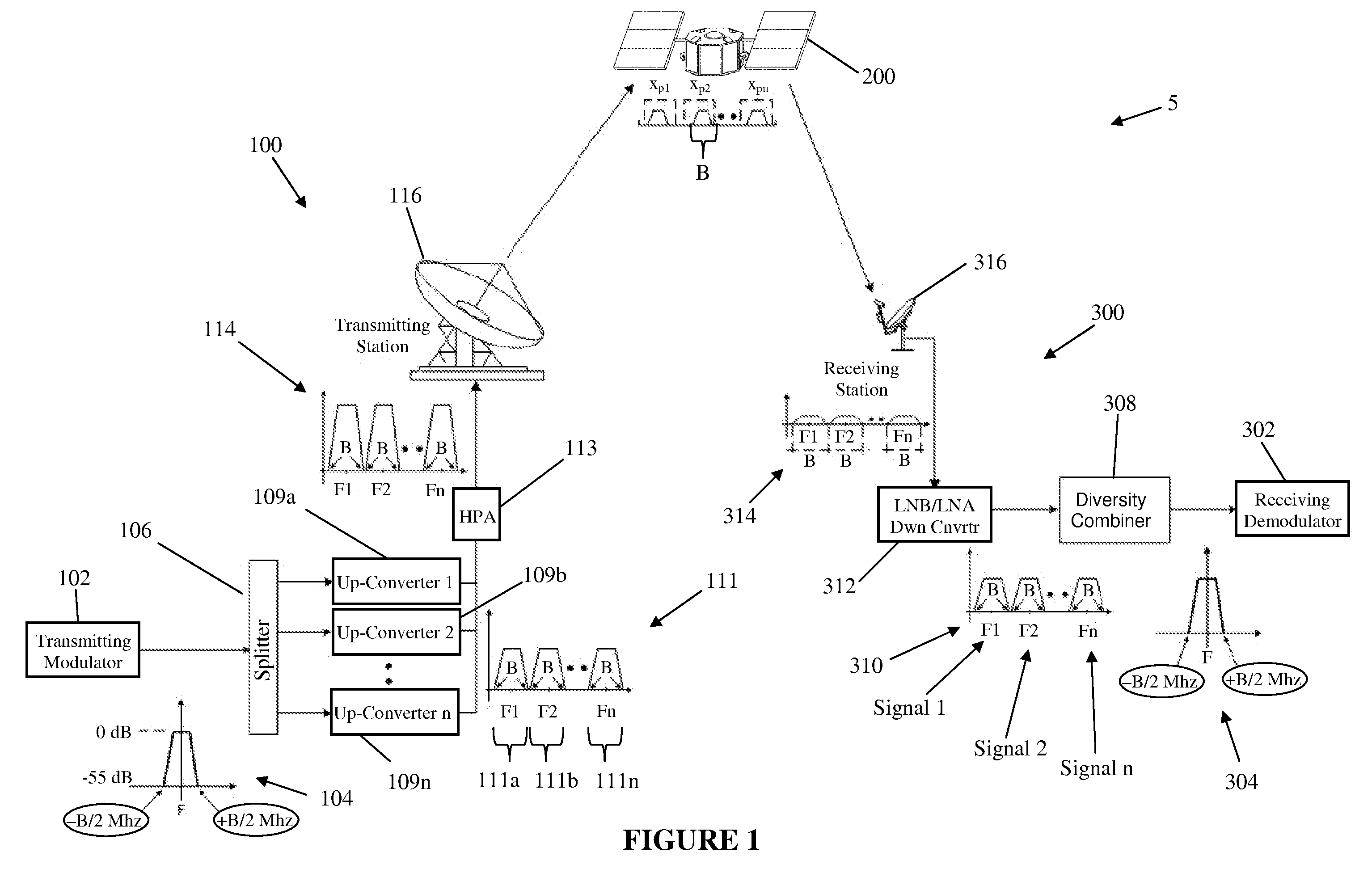
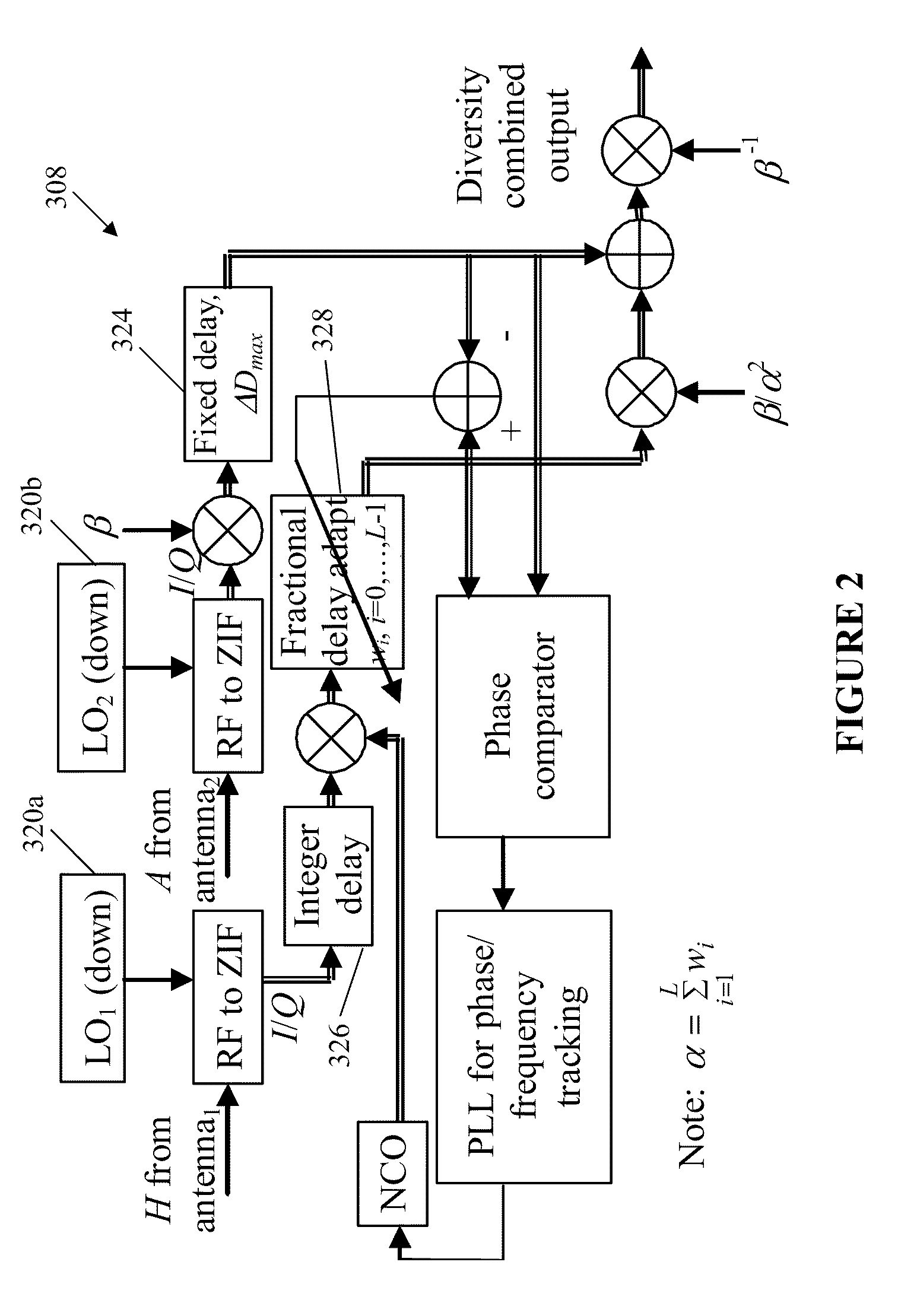
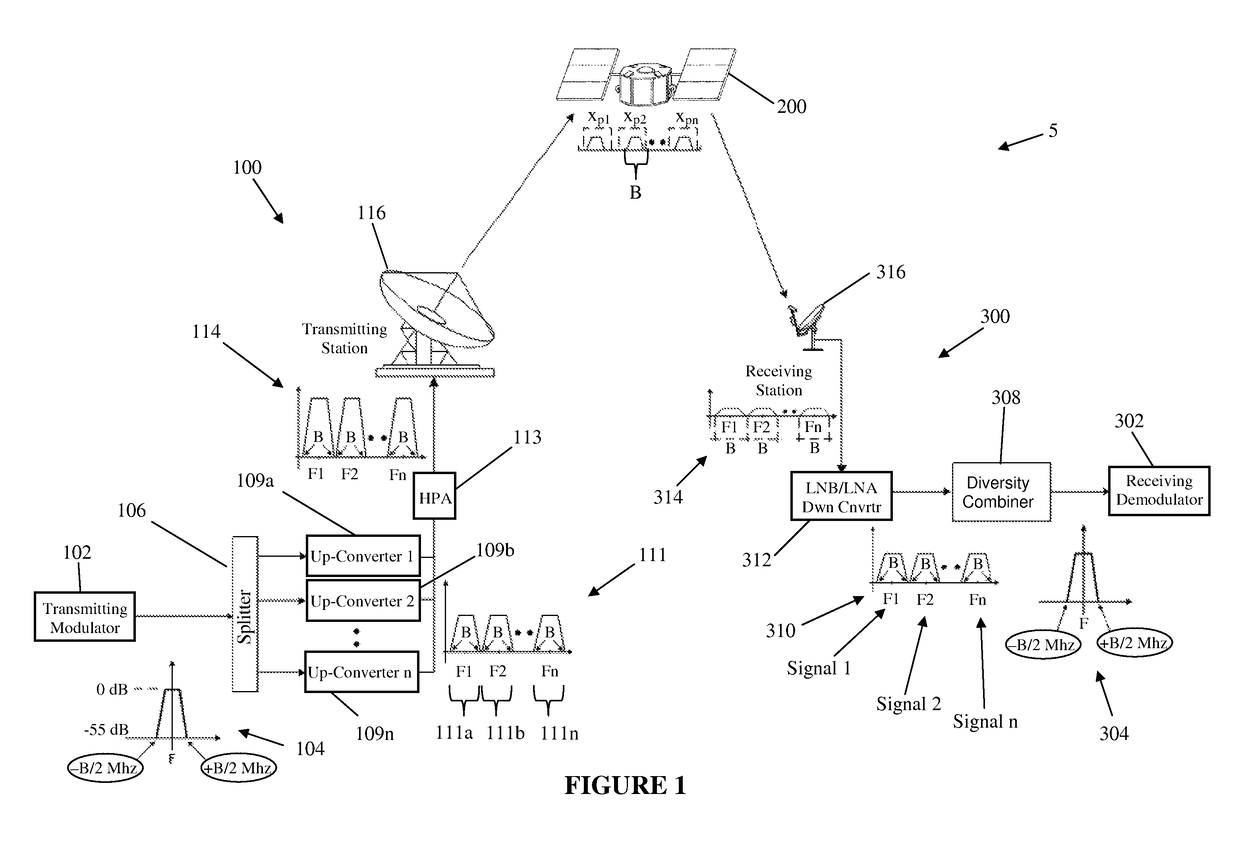
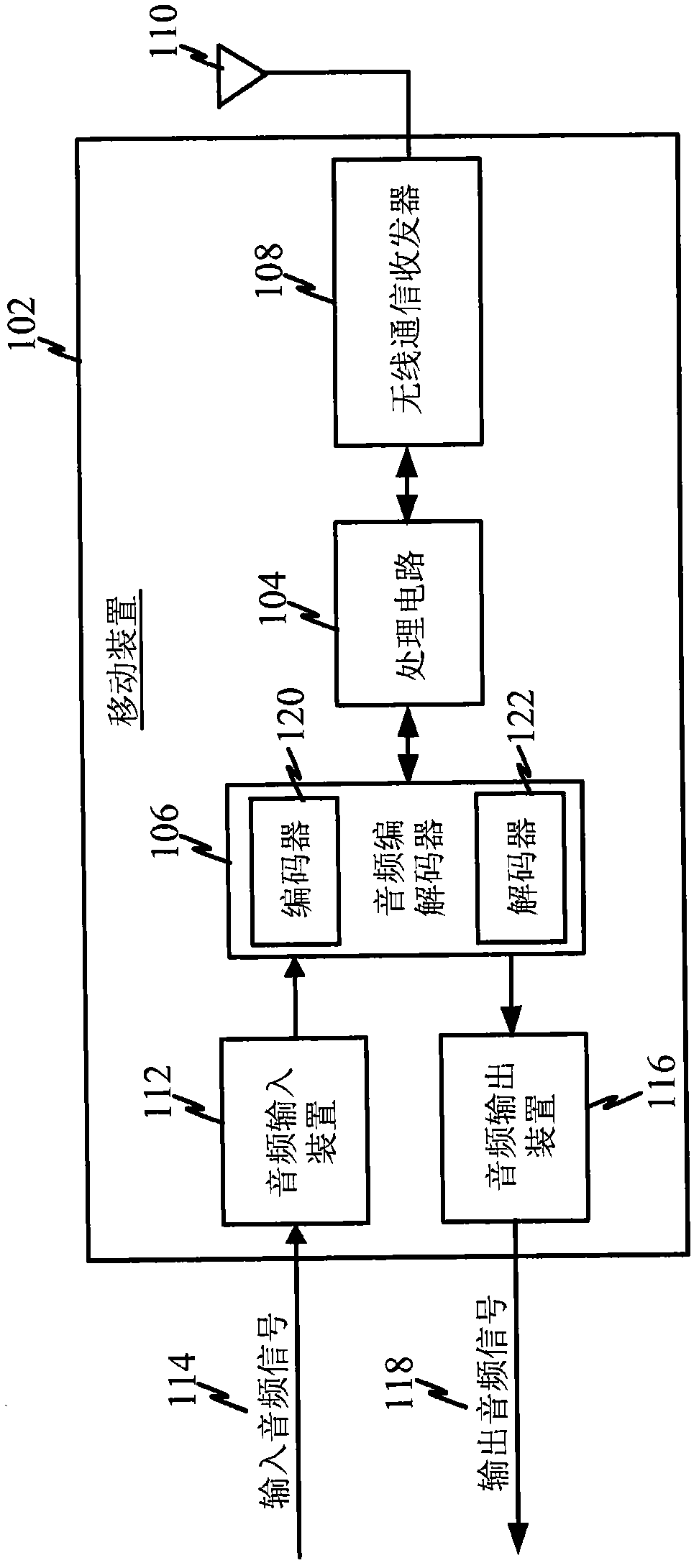
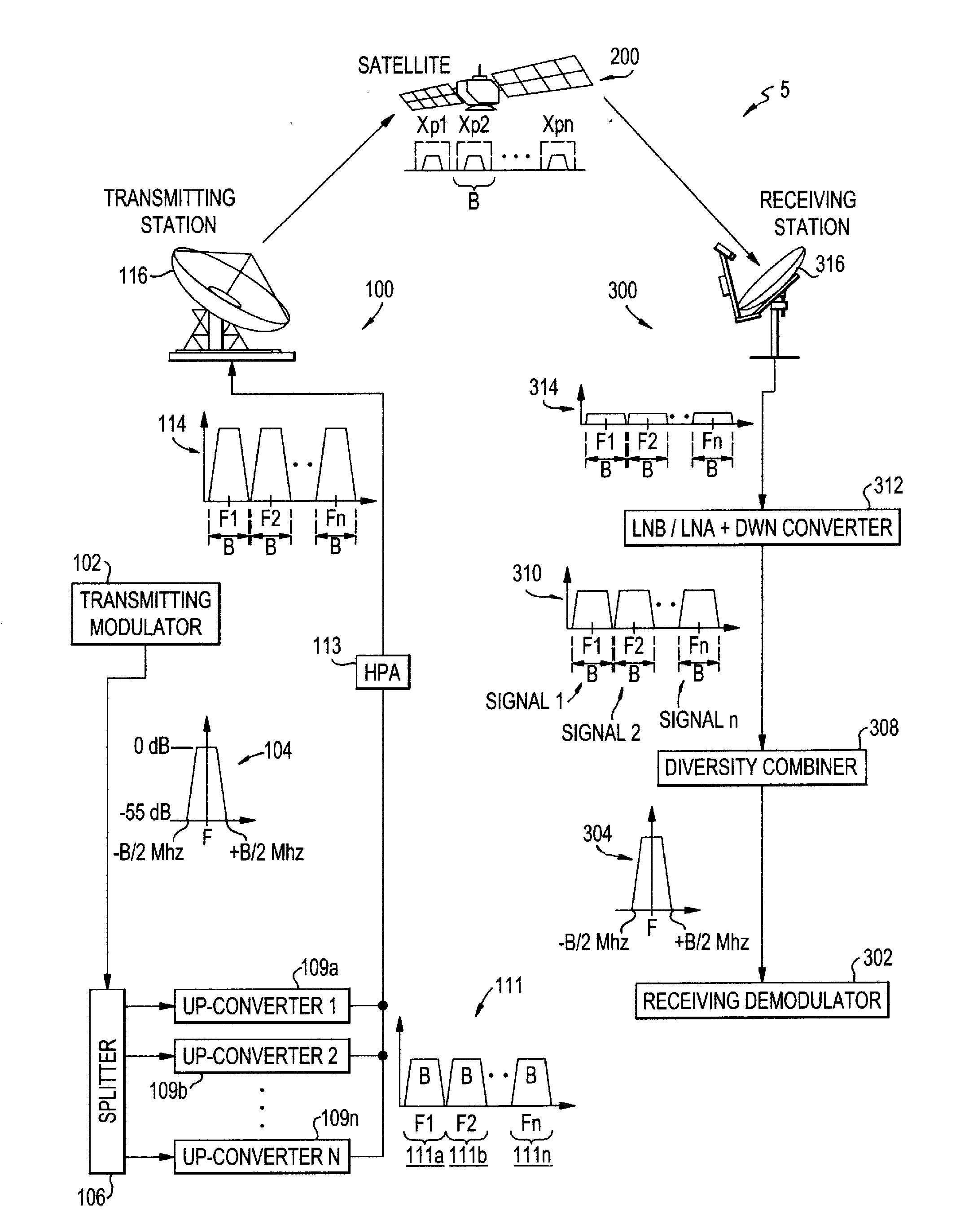
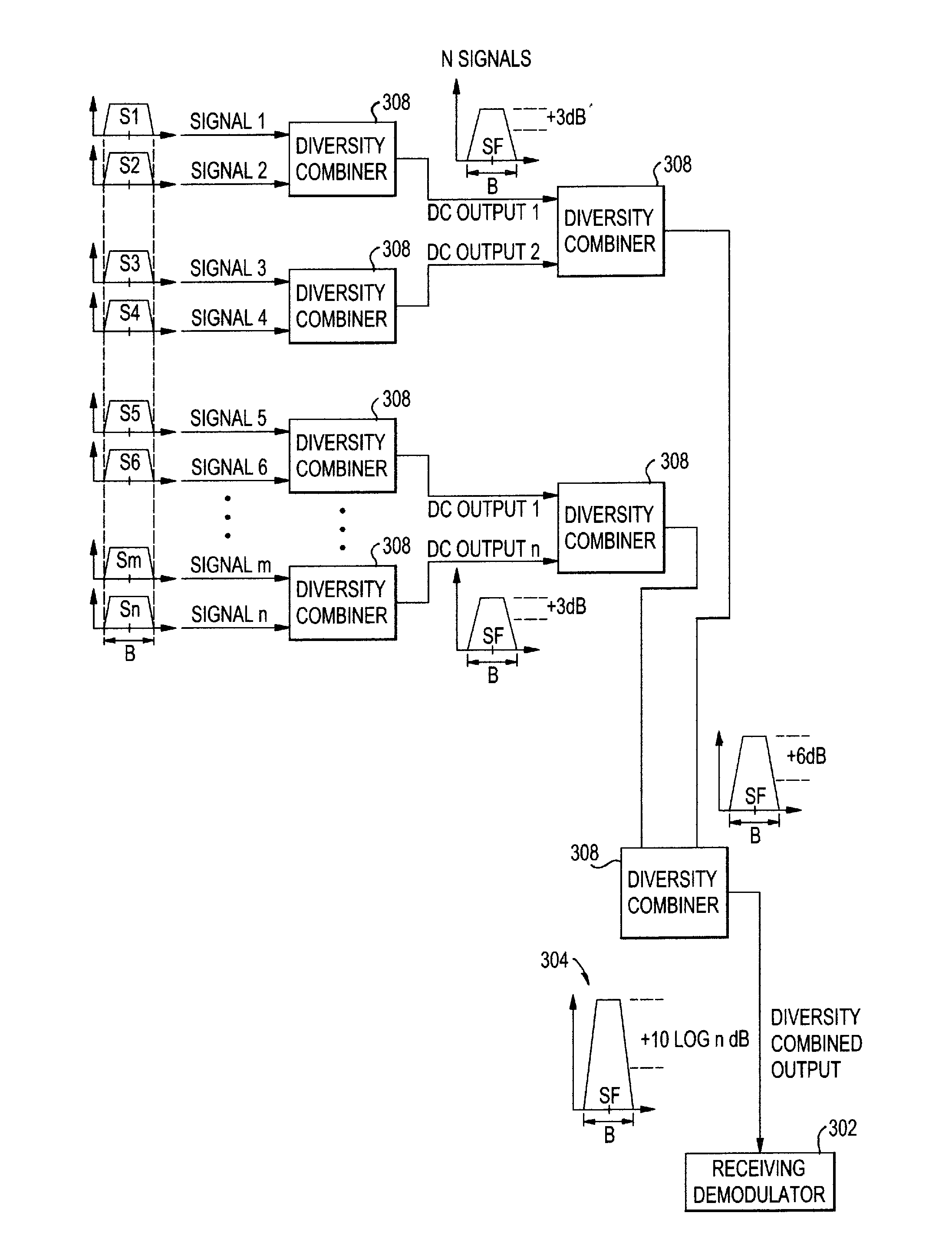
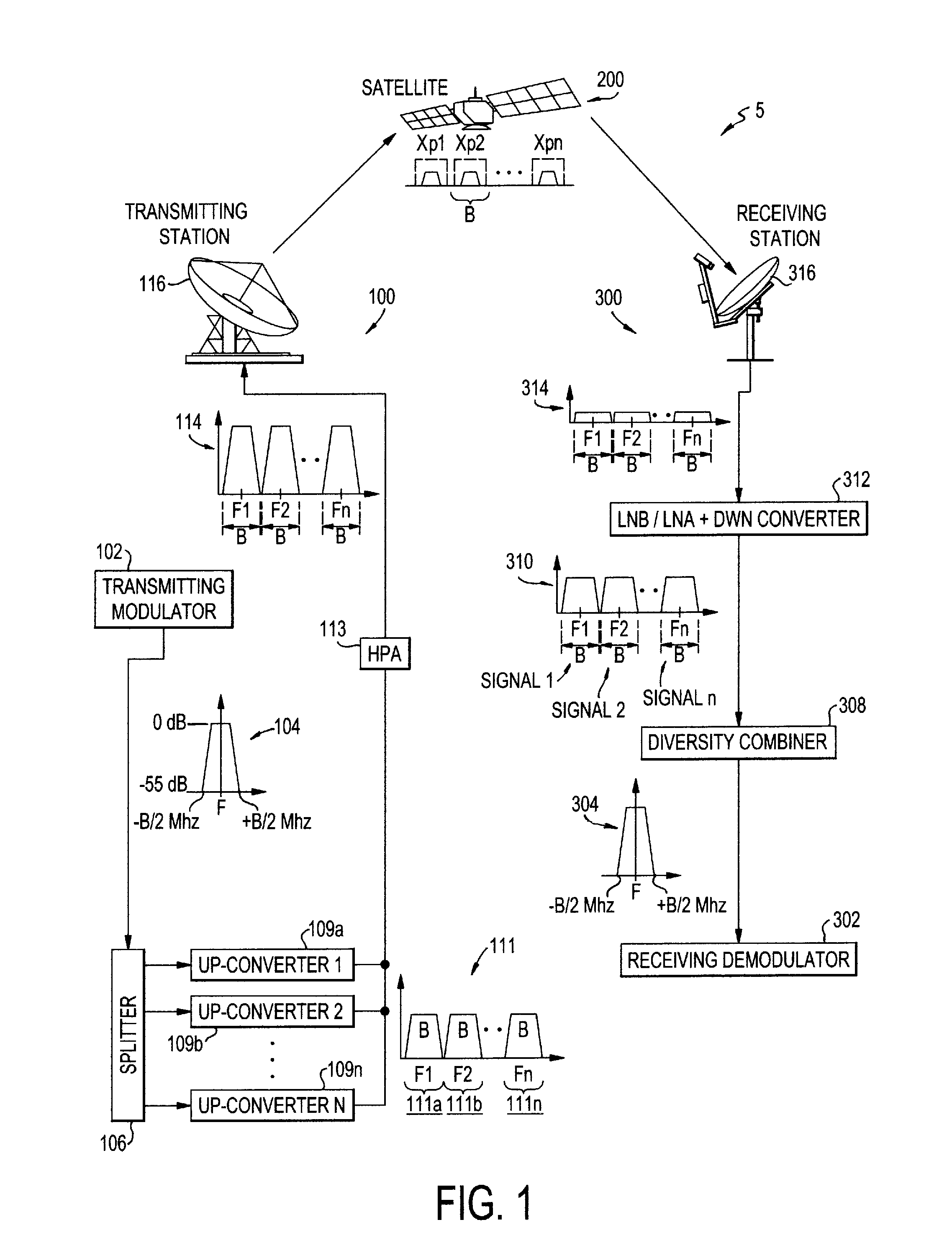
System and method for enabling ultra small aperture communication antenna using spectral replication and coherent frequency and phase combining
ActiveUS20110028088A1Increase power providedIncrease powerActive radio relay systemsWireless commuication servicesFrequency spectrumTransponder (satellite communications)
A system for enabling use of ultra-small aperture terminals in satellite communications is provided. The system comprises a transmitter configured to receive an input signal having information, a bandwidth, and an amplitude, replicate the input signal into two or more replications of the input signal, convert each of the two or more replications to have a frequency tuned to two or more corresponding satellite transponders while maintaining the bandwidth and all the information of the input signal, and combine the two or more replications into a single uplink signal. A transmit antenna is configured to transmit the uplink signal to the two or more satellite transponders.
Owner:ANUVU IP HLDG LLC
Local oscillator with non-harmonic ratio between oscillator and RF frequencies using wideband modulation spectral replicas
ActiveUS7809338B2Avoid serious problemsEasy to implementModulation transferencePulse automatic controlBandpass filteringFrequency spectrum
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of local oscillator (LO) generation with non-integer multiplication ratio between the local oscillator and RF frequencies. The LO generation schemes presented are operative to generate I and Q square waves at a designated frequency while avoiding the well known issue of harmonic pulling. An input baseband signal is interpolated and upconverted in the digital domain to an IF. The LO operates at a frequency which is a n / m division of the target RF frequency fRF. The IF frequency is configured to ½ of the LO frequency. The upconverted IF signal is then converted to the analog domain via digital power amplifiers followed by voltage combiners. The output of the combiners is band pass filtered to extract the desired replica.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Apparatus and a method for calculating a number of spectral envelopes
ActiveUS8296159B2Quality improvementLimits the core coder bandwidth—itSpeech analysisDigital computer detailsFrequency spectrumChronological time
An apparatus calculates a number of spectral envelopes to be derived by a spectral band replication (SBR) encoder, wherein the SBR encoder is adapted to encode an audio signal using a plurality of sample values within a predetermined number of subsequent time portions in an SBR frame extending from an initial time to a final time, the predetermined number of subsequent time portions being arranged in a time sequence given by the audio signal. The apparatus has a decision value calculator for determining a decision value, the decision value measuring a deviation in spectral energy distributions of a pair of neighboring time portions. The apparatus further has a detector for detecting a violation of a threshold by the decision value and a processor for determining a first envelope border between the pair of neighboring time portions when the violation of the threshold is detected.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
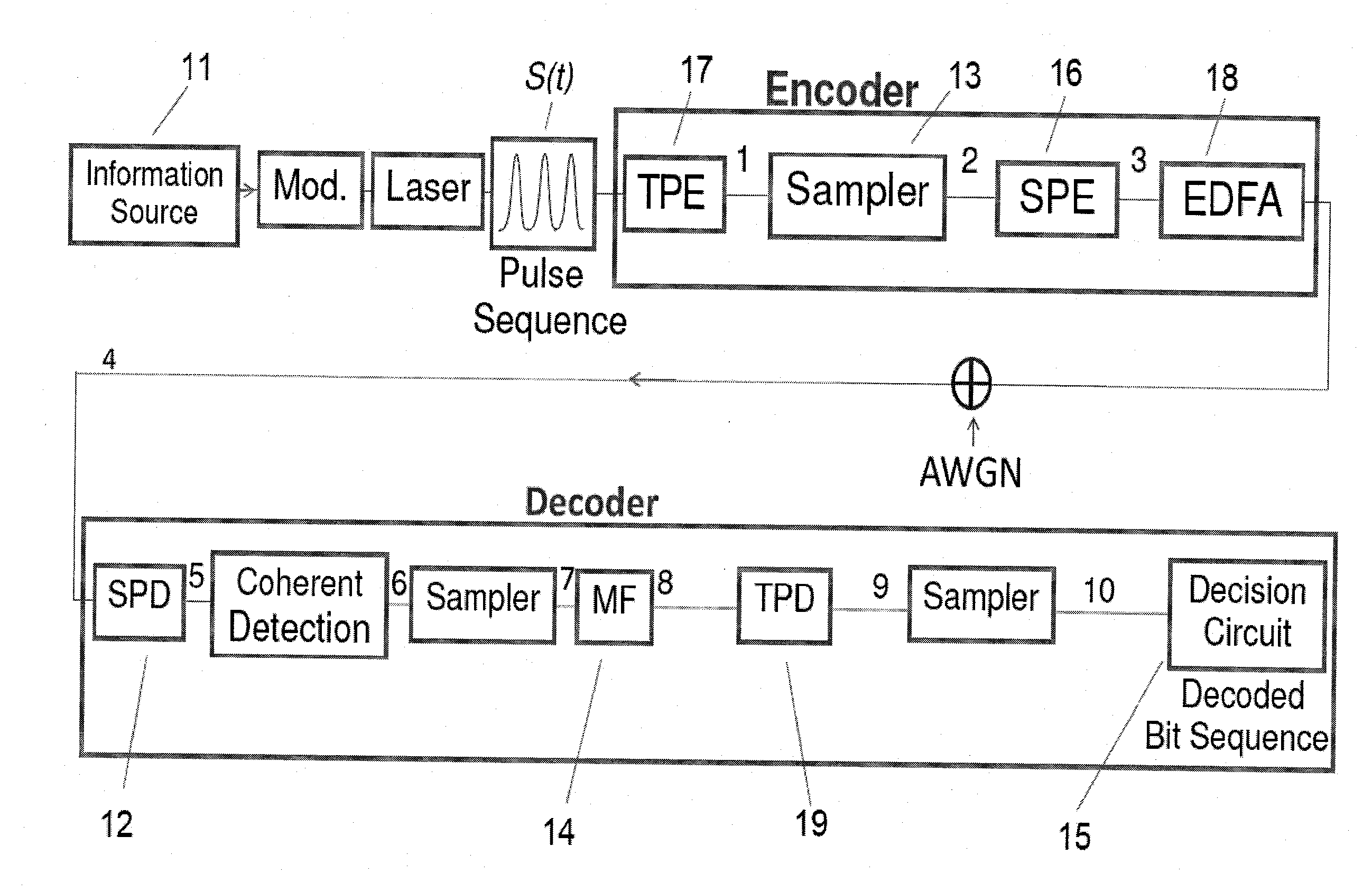
Spectral and temporal stealthy fiber optic communication using sampling and phase encoding detection system
ActiveUS20140146969A1Low power spectral densityEasy to solveKey distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationFrequency spectrumNoise level
A method for providing spectral and temporal stealthy information transmitted over an optical communication channel, according to which, at the transmitting side, the power spectral density of a pulse sequence bearing the information is reduced by encrypting the temporal phase of the pulse sequence. The power of the pulse sequence is spread in the frequency domain, to be below the noise level, by sampling the pulse sequence. Spectral phase encoding is used to temporally spread the pulse sequence and to prevent coherent addition of its spectral replicas in frequency domain. The resulting signal, encrypted both in time and frequency domains, is then transmitted. Spectral phase decoding is performed at the receiving side by performing coherent detection and folding all the spectral replicas of the transmitted signal to the baseband by means of sampling. The temporal phase of the signal is decrypted and the information which is delivered by the pulse sequence is decoded.
Owner:BAR ILAN UNIV +1
Complexity Scalable Perceptual Tempo Estimation
InactiveUS20120215546A1Improve the level ofLower Level RequirementsElectrophonic musical instrumentsSpeech analysisFrequency bandSpectral band replication
The present document relates to methods and systems for estimating the tempo of a media signal, such as audio or combined video / audio signal. In particular, the document relates to the estimation of tempo perceived by human listeners, as well as to methods and systems for tempo estimation at scalable computational complexity. A method and system for extracting tempo information of an audio signal from an encoded bit-stream of the audio signal comprising spectral band replication data is described. The method comprises the steps of determining a payload quantity associated with the amount of spectral band replication data comprised in the encoded bit-stream for a time interval of the audio signal; repeating the determining step for successive time intervals of the encoded bit-stream of the audio signal, thereby determining a sequence of payload quantities; identifying a periodicity in the sequence of payload quantities; and extracting tempo information of the audio signal from the identified periodicity.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Enhanced Chroma Extraction from an Audio Codec
InactiveUS20140310011A1Extension of timeReduce frequencyElectrophonic musical instrumentsSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumAudio frequency
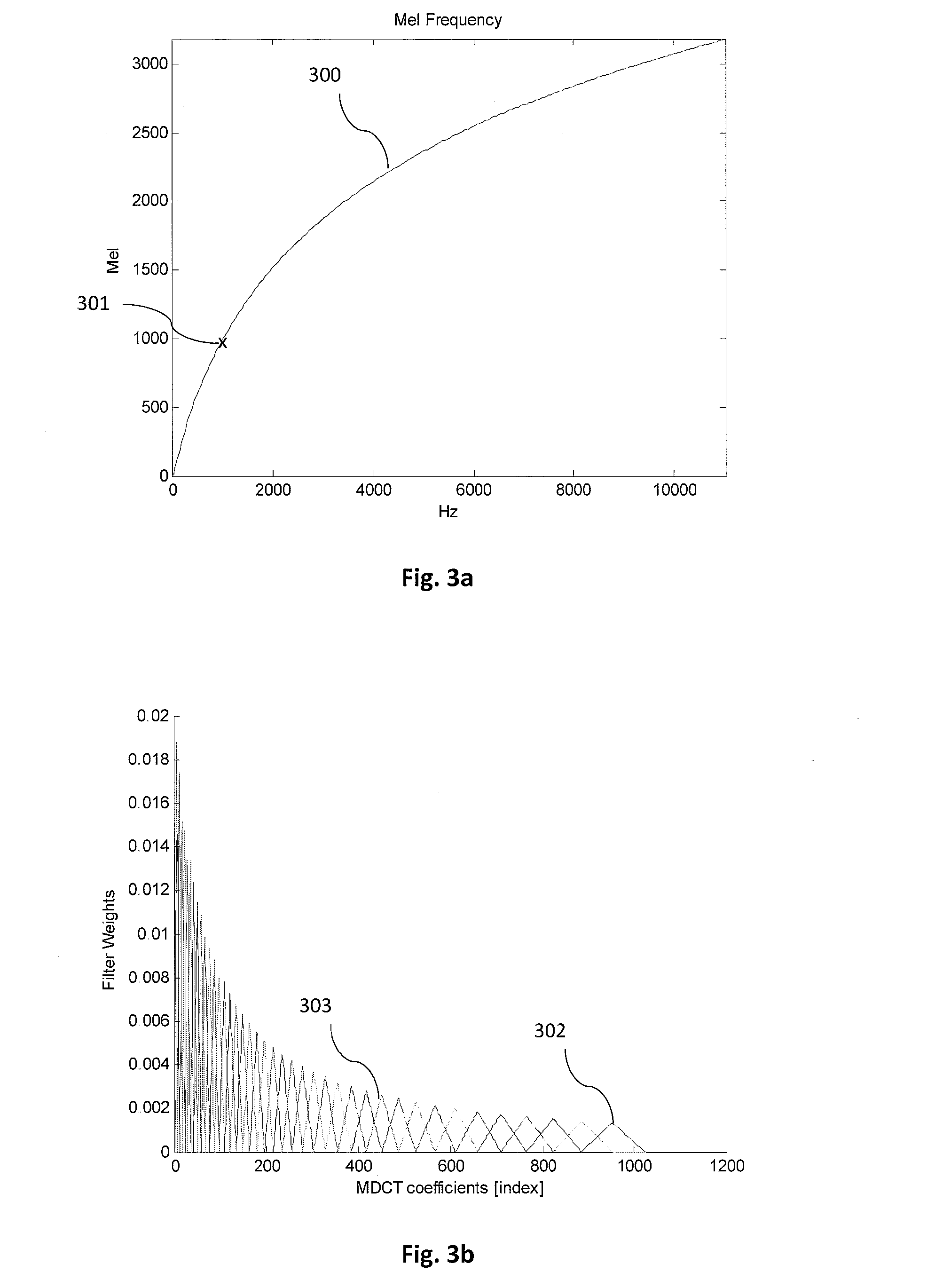
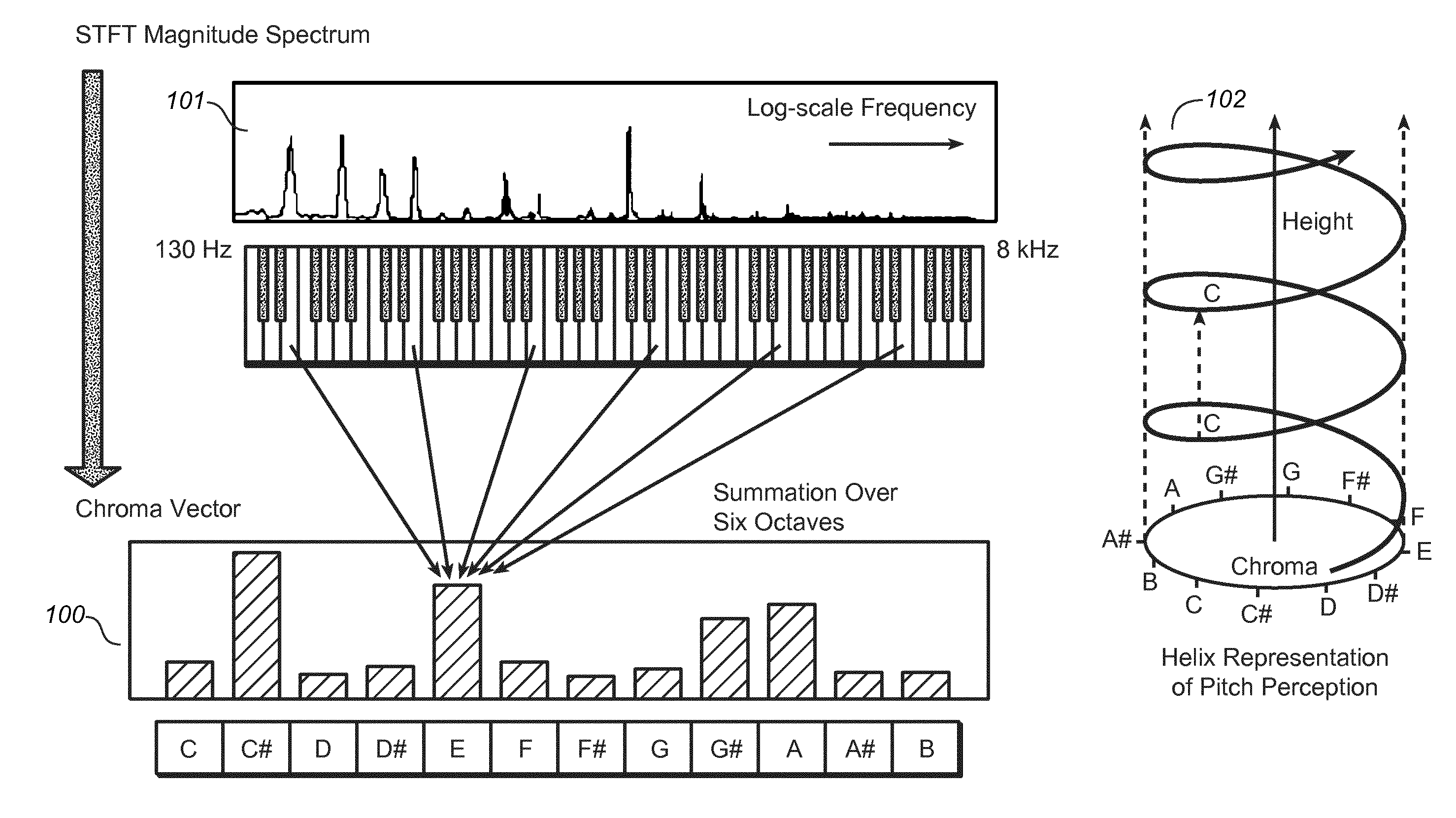
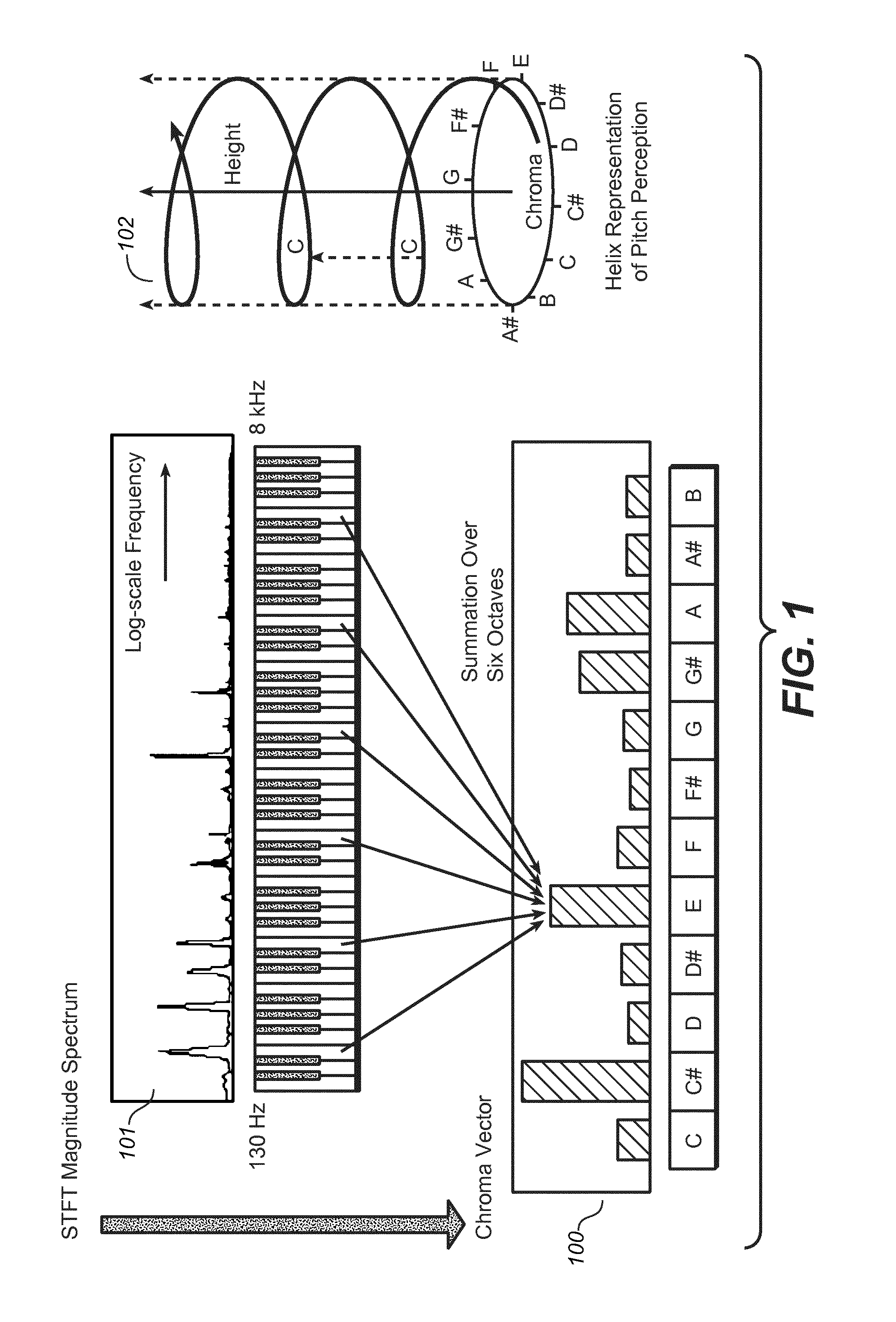
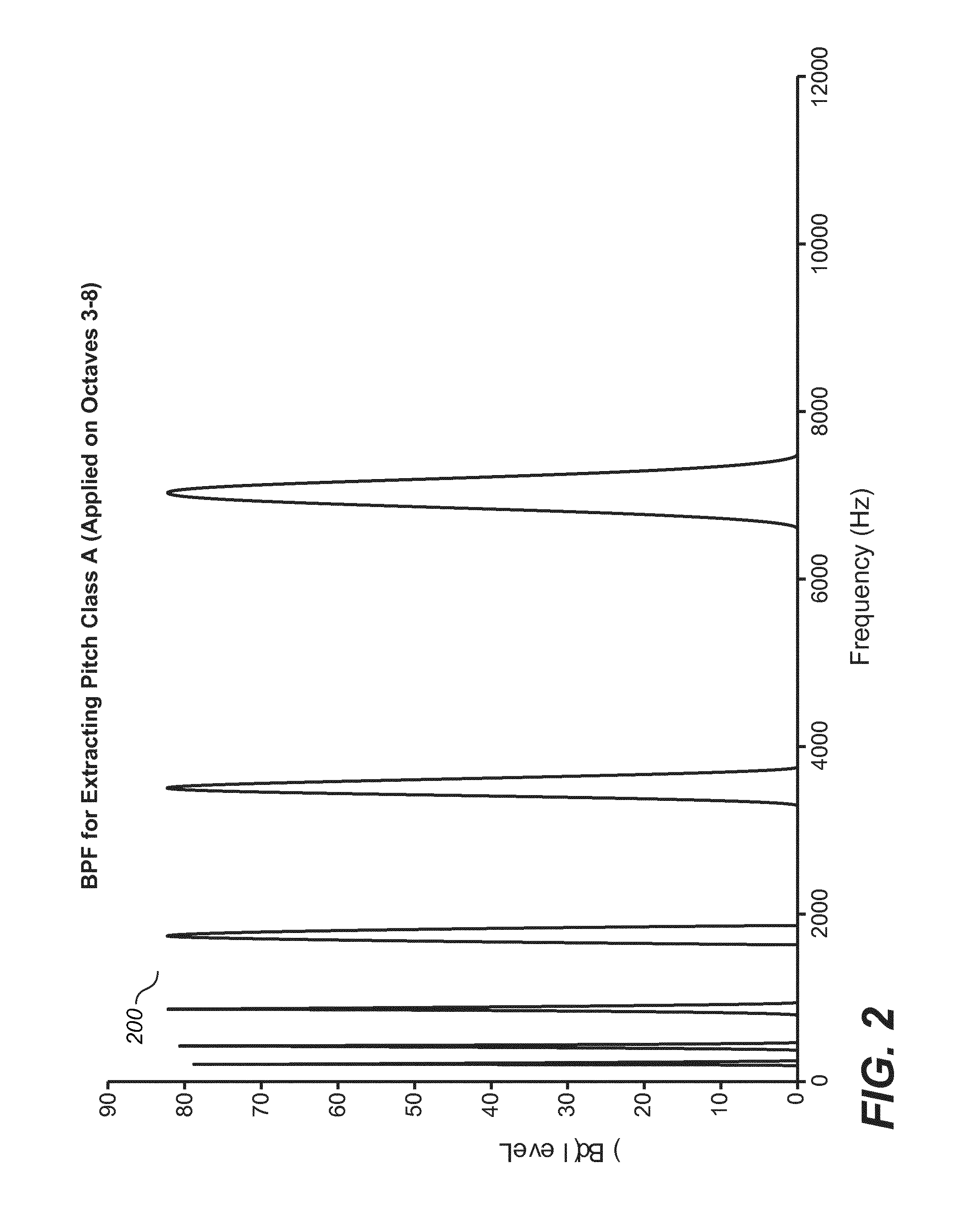
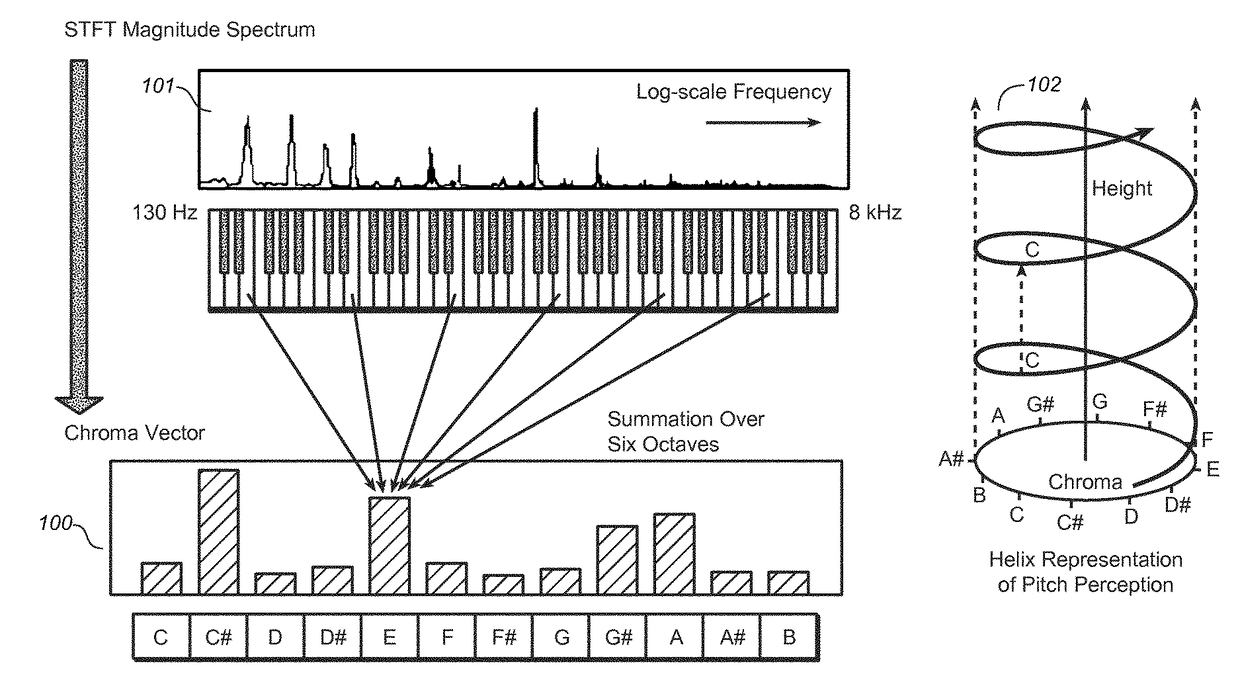
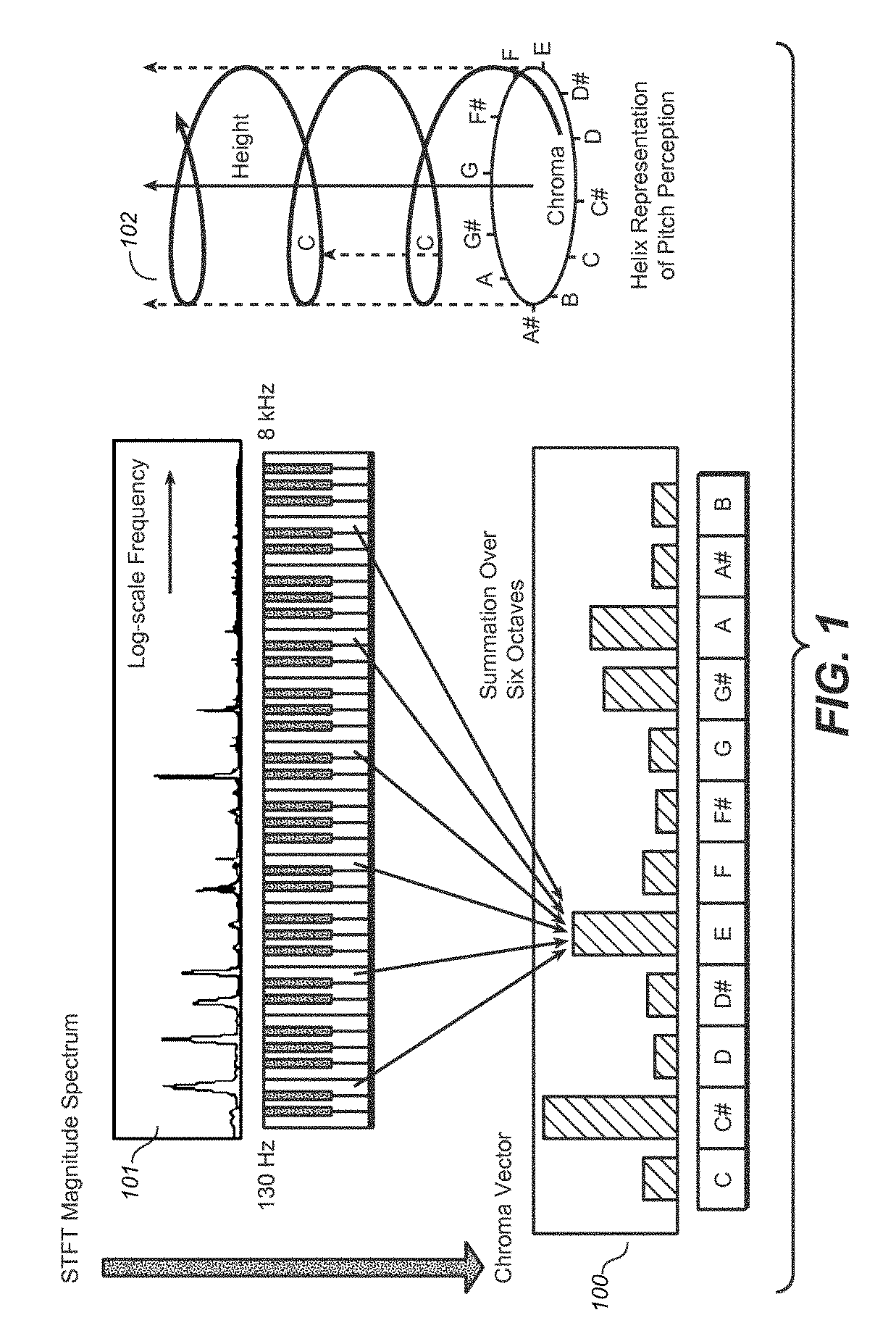
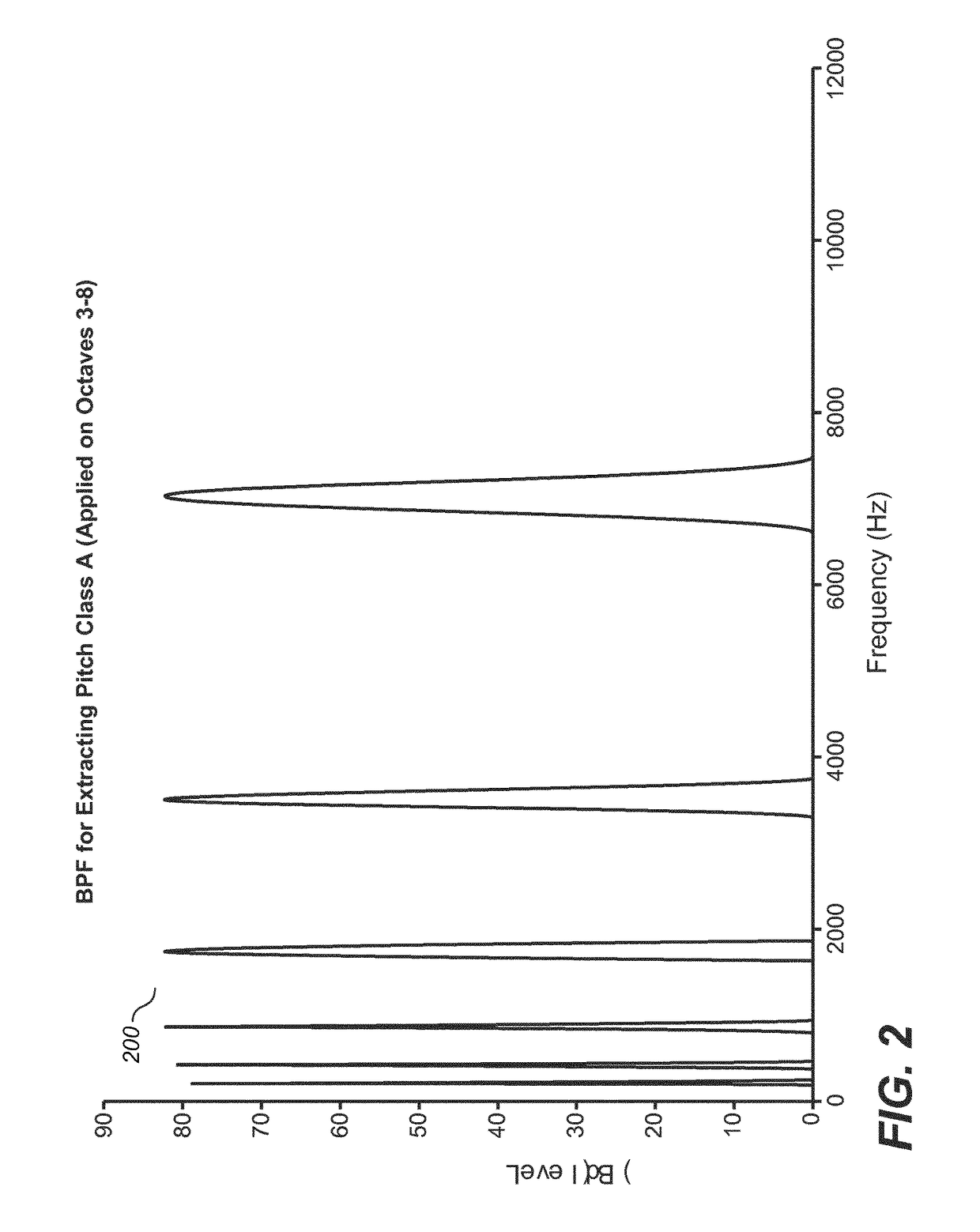
The present document relates to methods and systems for music information retrieval (MIR). In particular, the present document relates to methods and systems for extracting a chroma vector from an audio signal. A method (900) for determining a chroma vector (100) for a block of samples of an audio signal (301) is described. The method (900) comprises receiving (901) a corresponding block of frequency coefficients derived from the block of samples of the audio signal (301) from a core encoder (412) of a spectral band replication based audio encoder (410) adapted to generate an encoded bitstream (305) of the audio signal (301) from the block of frequency coefficients; and determining (904) the chroma vector (100) for the block of samples of the audio signal (301) based on the received block of frequency coefficients.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
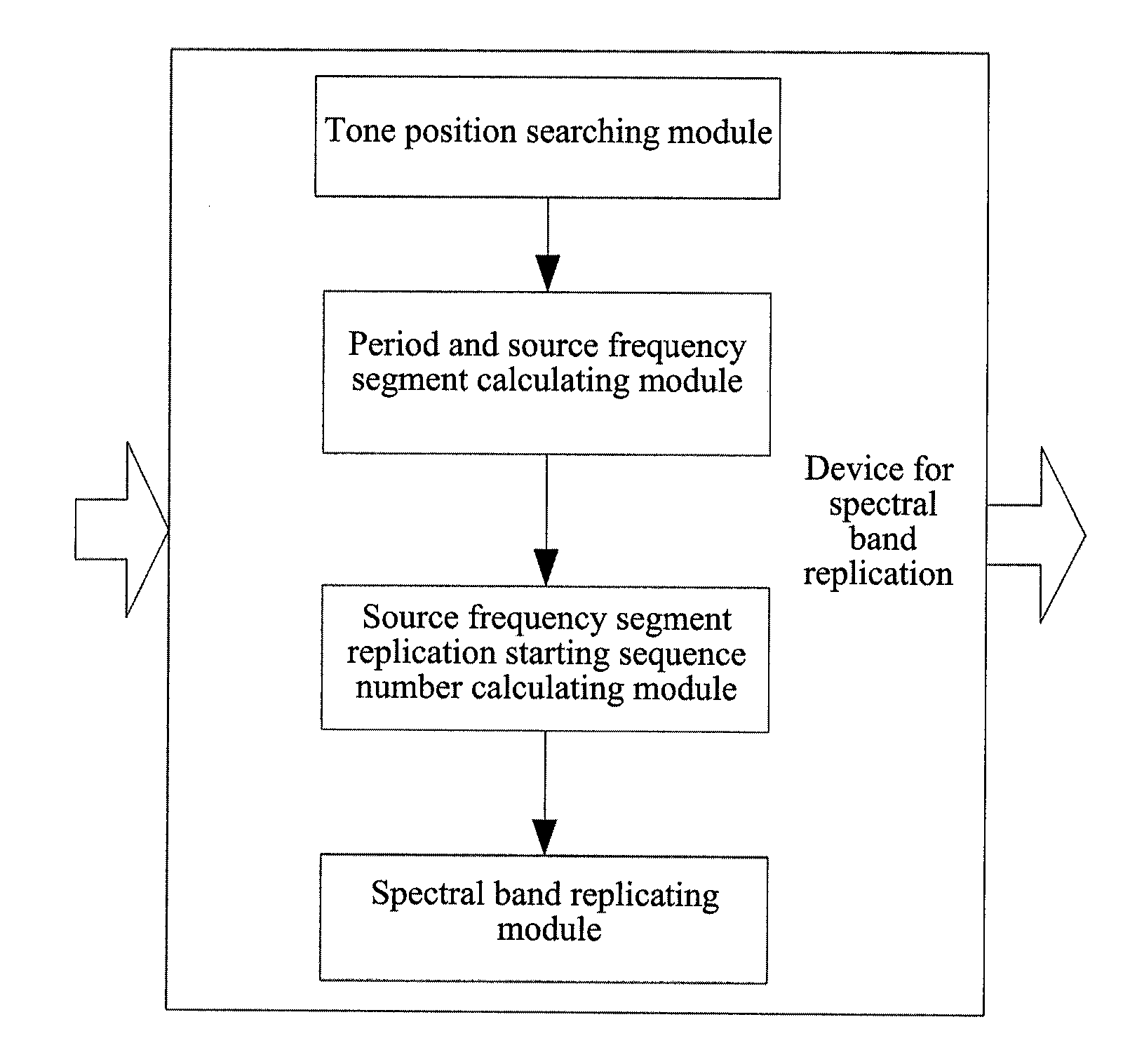
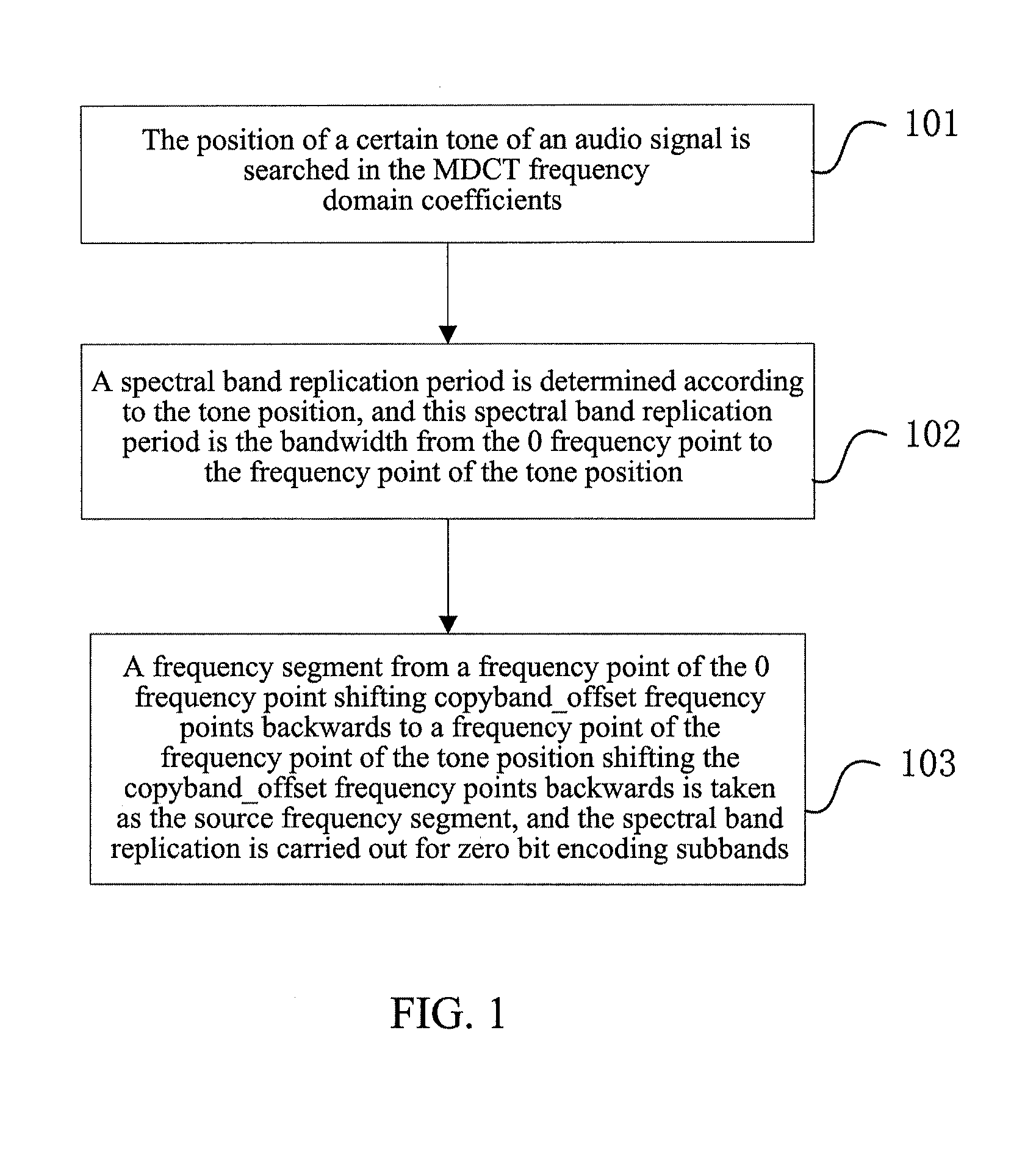
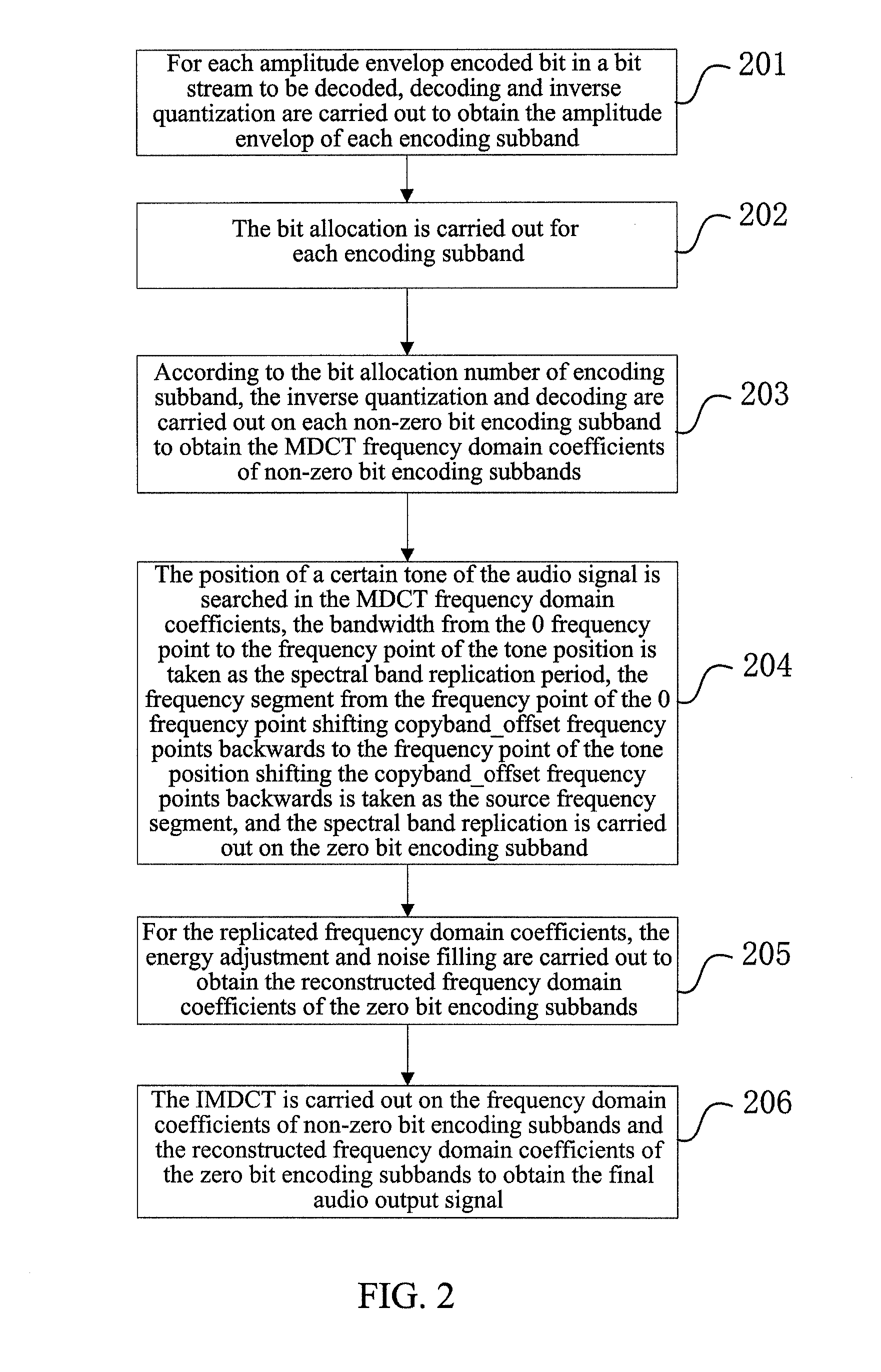
Method and device for spectral band replication, and method and system for audio decoding
InactiveUS20130006644A1Subjective listening effectImprove listening effectSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumAudio frequency
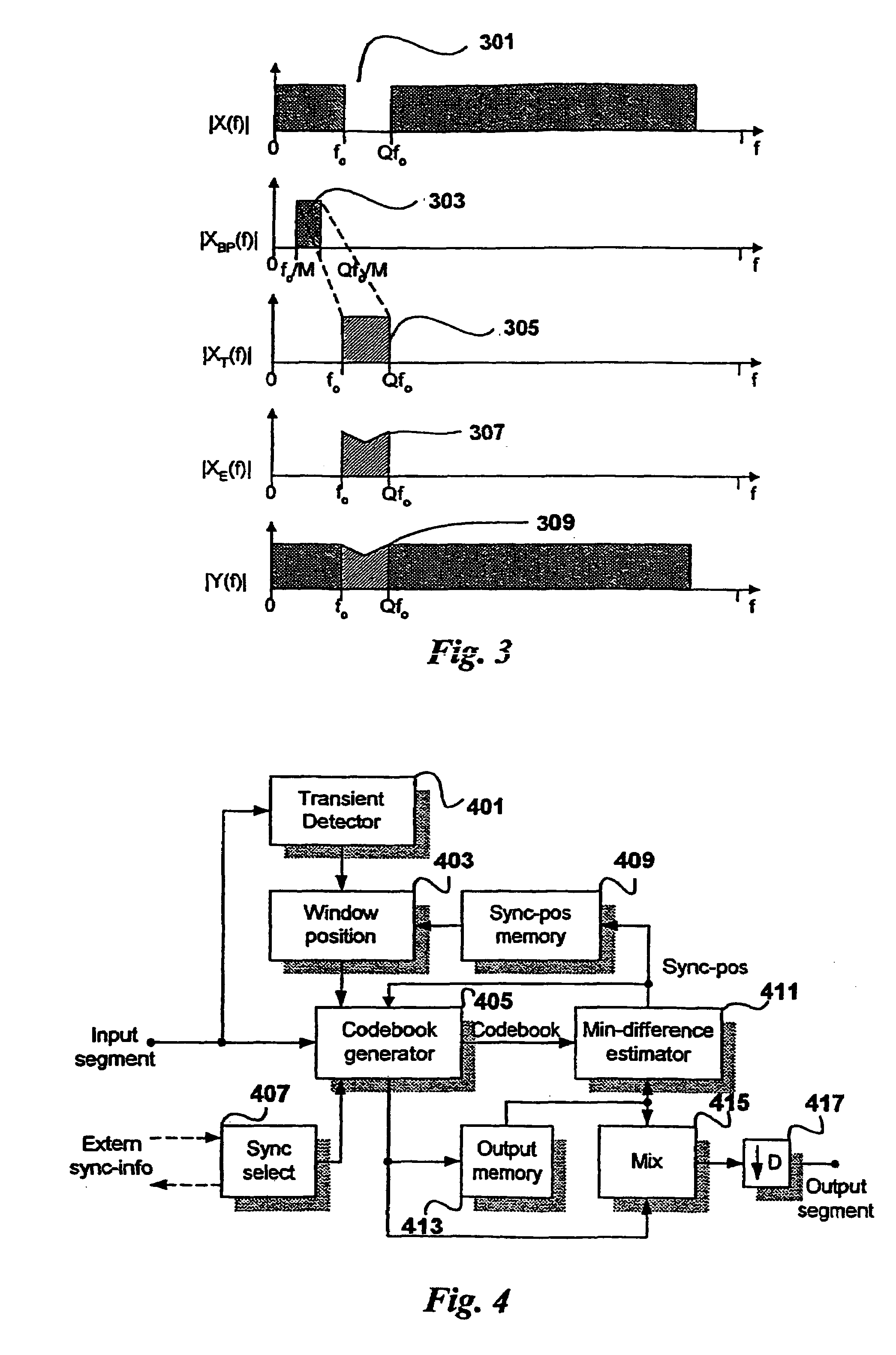
The present invention relates to a method and device for spectral band replication, and a method and system for audio decoding, and the method for spectral band replication comprises: A. searching for the position of a certain tone of an audio signal in MDCT frequency domain coefficients; B. according to the tone position, determining a spectral band replication period which is a bandwidth from a 0 frequency point to a frequency point of tone position, and a source frequency segment which is a frequency segment from a frequency point of the 0 frequency point shifting copyband_offset frequency points backwards to a frequency point of the frequency point of the tone position shifting the copyband_offset frequency points backwards, wherein said offset copyband_offset is greater than or equal to 0; and C. according to the spectral band replication period, carrying out spectral band replication on zero bit encoding subbands.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Forensic detection of parametric audio coding schemes
The present document relates to audio forensics, notably the blind detection of traces of parametric audio encoding / decoding. In particular, the present document relates to the detection of parametric frequency extension audio coding, such as spectral band replication (SBR) or spectral extension (SPX), from uncompressed waveforms such as PCM (pulse code modulation) encoded waveforms. A method for detecting frequency extension coding history in a time domain audio signal is described. The method may comprise transforming the time domain audio signal into a frequency domain, thereby generating a plurality of subband signals in a corresponding plurality of subbands comprising low and high frequency subbands; determining a degree of relationship between subband signals in the low frequency subbands and subband signals in the high frequency subbands; wherein the degree of relationship is determined based on the plurality of subband signals; and determining frequency extension coding history if the degree of relationship is greater than a relationship threshold.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP +1
Method and system for audio encoding and decoding and method for estimating noise level
ActiveUS8731949B2Improve listening effectCode conversionSpeech recognitionNoise levelComputer science
Owner:ZTE CORP
System and method for enabling ultra small aperture communication antenna using spectral replication and coherent frequency and phase combining
ActiveUS7907894B2Increase powerBroadcast transmission systemsRadio transmissionFrequency spectrumComputer terminal
Owner:ANUVU IP HLDG LLC
Audio processing method in mobile digital television recording
ActiveCN102254560ASmooth playbackBit error noTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionComputer hardwareData transport
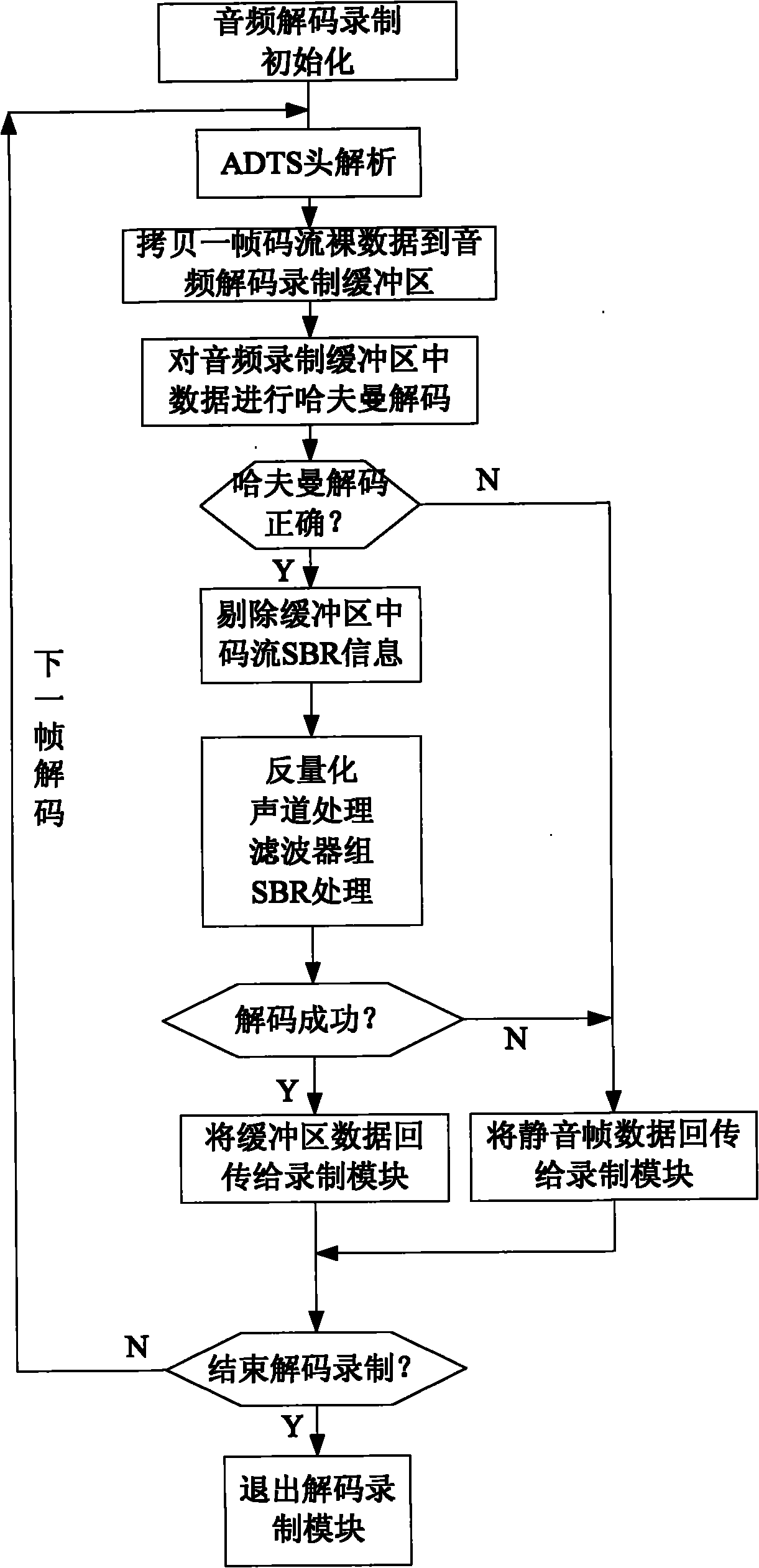
The invention discloses an audio processing method in mobile digital television recording. The method comprises the following steps of: packaging each advanced audio coding + (AAC+) code stream naked data frame which is received from the air into a frame in an audio data transport stream (ADTS) format; analyzing an ADTS frame head to find the original AAC+ code stream naked data of the frame; decoding the AAC+ code stream naked data, removing spectral band replication (SBR) information from the AAC+ code stream naked data in an audio decoding, recording and buffering area, and converting the AAC+ code stream naked data in the audio decoding, recording and buffering area into AAC naked data; and performing a subsequent decoding process by using an AAC+ decoder, and transmitting the AAC naked data to a recording module to record video and audio files. By the method, the mobile digital television recording also can be performed even if the signal is poor, and a recorded video file can benormally played on a computer by mainstream video play software, and severe abnormal phenomena such as harsh noise, silence, player breakdown, system crash and the like are avoided.
Owner:ANYKA (GUANGZHOU) MICROELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Speech encoding/decoding device
ActiveUS8655649B2Increase bitrateImprove subjective qualitySpeech analysisFrequency spectrumCovariance method
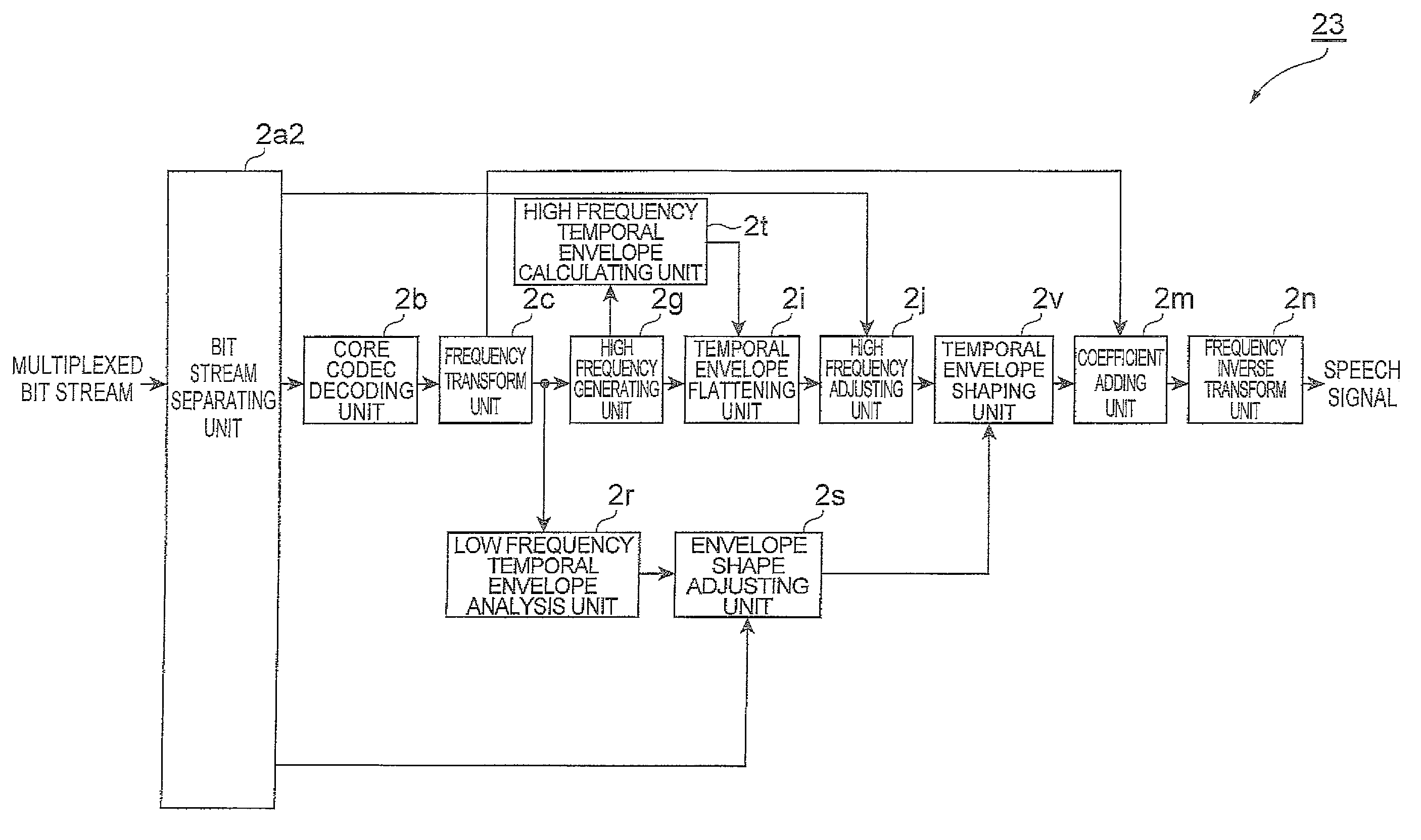
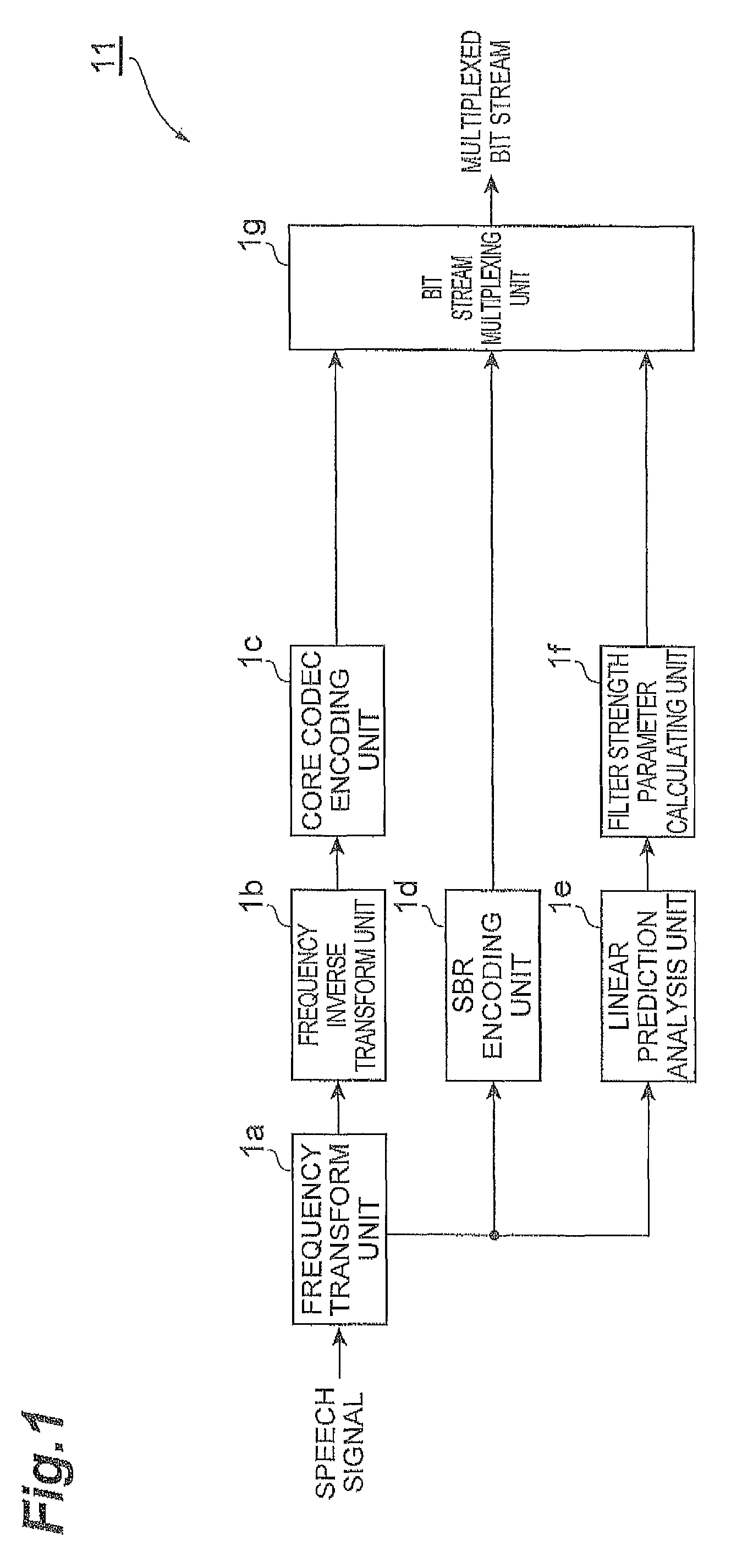
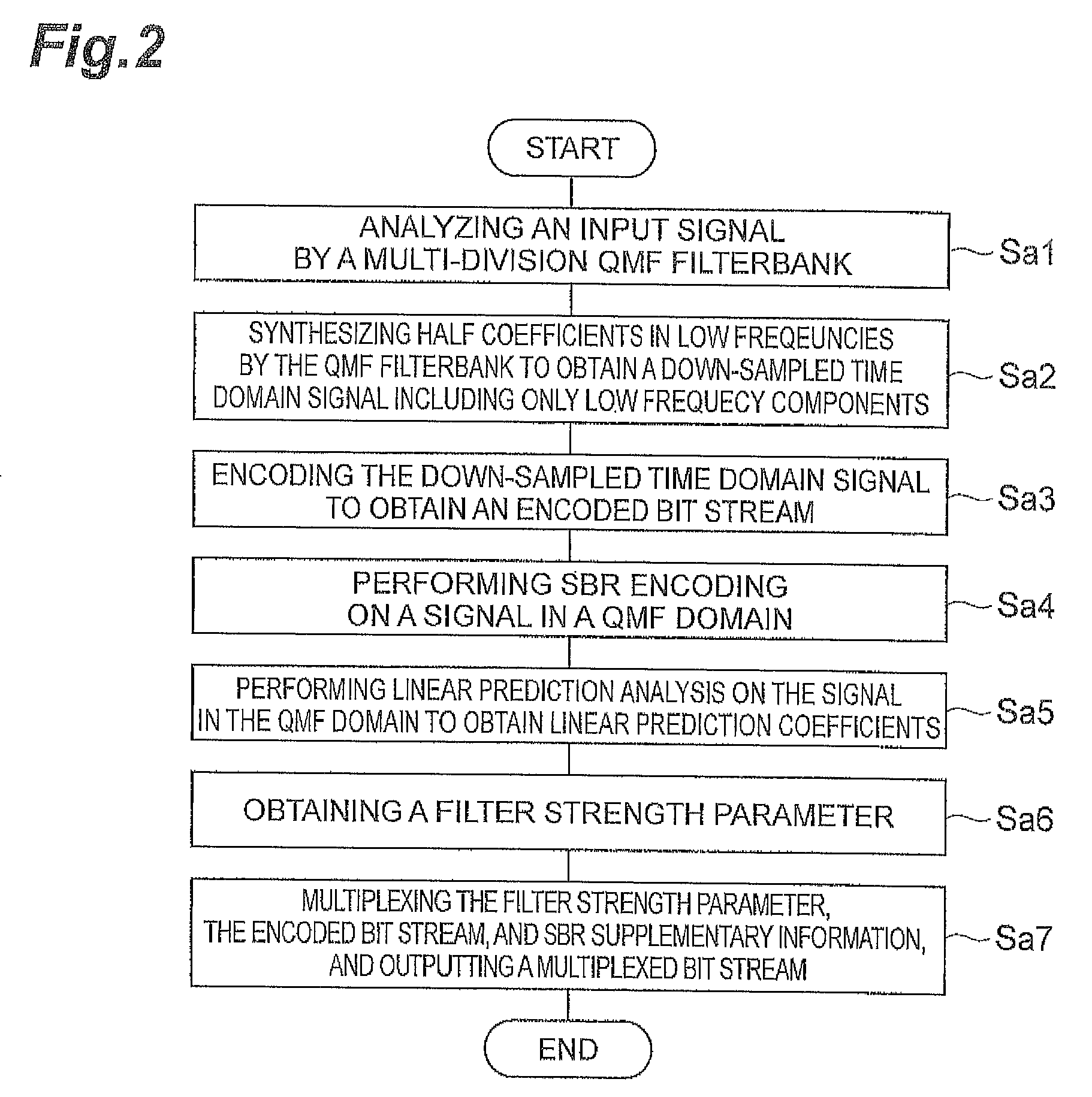
A linear prediction coefficient of a signal represented in a frequency domain is obtained by performing linear prediction analysis in a frequency direction by using a covariance method or an autocorrelation method. After the filter strength of the obtained linear prediction coefficient is adjusted, filtering may be performed in the frequency direction on the signal by using the adjusted coefficient, whereby the temporal envelope of the signal is shaped. This reduces the occurrence of pre-echo and post-echo and improves the subjective quality of the decoded signal, without significantly increasing the bit rate in a bandwidth extension technique in the frequency domain represented by spectral band replication.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
A transcoder and method of transcoding therefore
A transcoder comprises a receiver ( 101 ) which receives input data representing an encoded signal and comprising first encoding data and first parametric extension data. The encoded data is fed to a decoder ( 103 ). The output of the decoder ( 103 ) is fed to an encoder ( 105 ) which generates second encoded data according to a different encoding protocol or with different encoding parameters. The first parametric extension data is fed to an extension data processor ( 109 ) which generates second parametric extension data directly from the first parametric extension data. The second encoded data and the second parametric extension data is combined in an output processor ( 107 ) to generate a transcoded signal comprising separately determined parametric extension data. The parametric extension data may be Spectral Band Replication (SBR) or Parametric Stereo (PS) extension data for an audio bitstream. Improved quality and reduced complexity is achieved by the separate transcoding of the parametric extension data.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Enhanced chroma extraction from an audio codec
InactiveUS9697840B2Extension of timeReduce frequencyElectrophonic musical instrumentsSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumAudio frequency
The present document relates to methods and systems for music information retrieval (MIR). In particular, the present document relates to methods and systems for extracting a chroma vector from an audio signal. A method (900) for determining a chroma vector (100) for a block of samples of an audio signal (301) is described. The method (900) comprises receiving (901) a corresponding block of frequency coefficients derived from the block of samples of the audio signal (301) from a core encoder (412) of a spectral band replication based audio encoder (410) adapted to generate an encoded bitstream (305) of the audio signal (301) from the block of frequency coefficients; and determining (904) the chroma vector (100) for the block of samples of the audio signal (301) based on the received block of frequency coefficients.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Audio signal synthesizer for selectively performing different patching algorithms
ActiveUS8731948B2Without any changeIncrease resourcesSpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumSpectral domain
An audio signal synthesizer generates a synthesis audio signal having a first frequency band and a second synthesized frequency band derived from the first frequency band and comprises a patch generator, a spectral converter, a raw signal processor and a combiner. The patch generator performs at least two different patching algorithms, each patching algorithm generating a raw signal. The patch generator is adapted to select one of the at least two different patching algorithms in response to a control information. The spectral converter converts the raw signal into a raw signal spectral representation. The raw signal processor processes the raw signal spectral representation in response to spectral domain spectral band replication parameters to obtain an adjusted raw signal spectral representation.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Low complexity spectral band replication (SBR) filterbanks
A complex analysis filterbank is implemented by obtaining an input audio signal as a plurality of N time-domain input samples. Pair-wise additions and subtractions of the time-domain input samples is performed to obtain a first and second groups of intermediate samples, each group having N / 2 intermediate samples. The signs of odd-indexed intermediate samples in the second group are then inverted.A first transform is applied to the first group of intermediate samples to obtain a first group of output coefficients in the frequency domain. A second transform is applied to the second group of intermediate samples to obtain an intermediate second group of output coefficients in the frequency domain. The order of coefficients in the intermediate second group of output coefficients is then reversed to obtain a second group of output coefficients. The first and second groups of output coefficients may be stored and / or transmitted as a frequency domain representation of the audio signal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
System and method for enabling ultra small aperture communication antenna using spectral replication and coherent frequency and phase combining
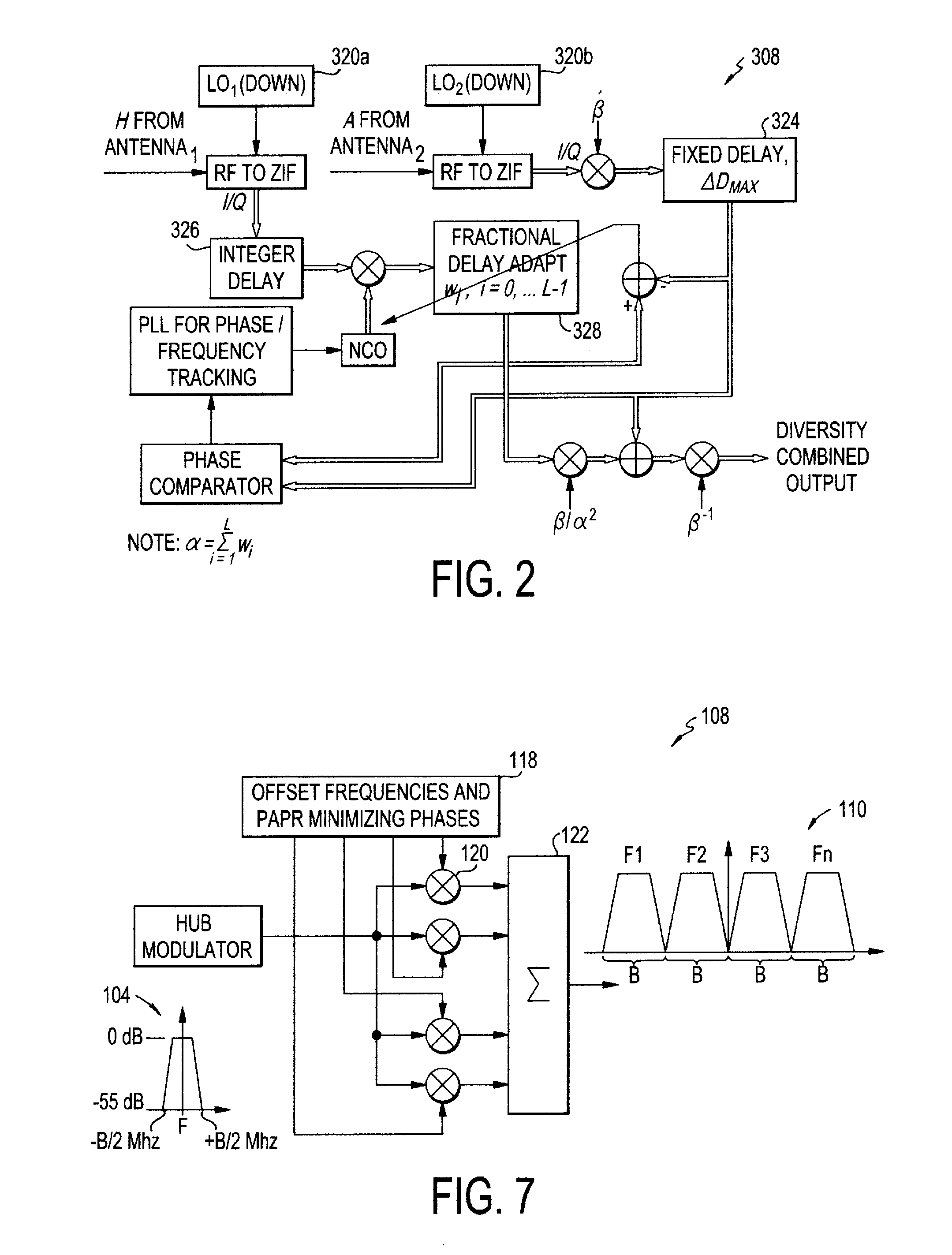
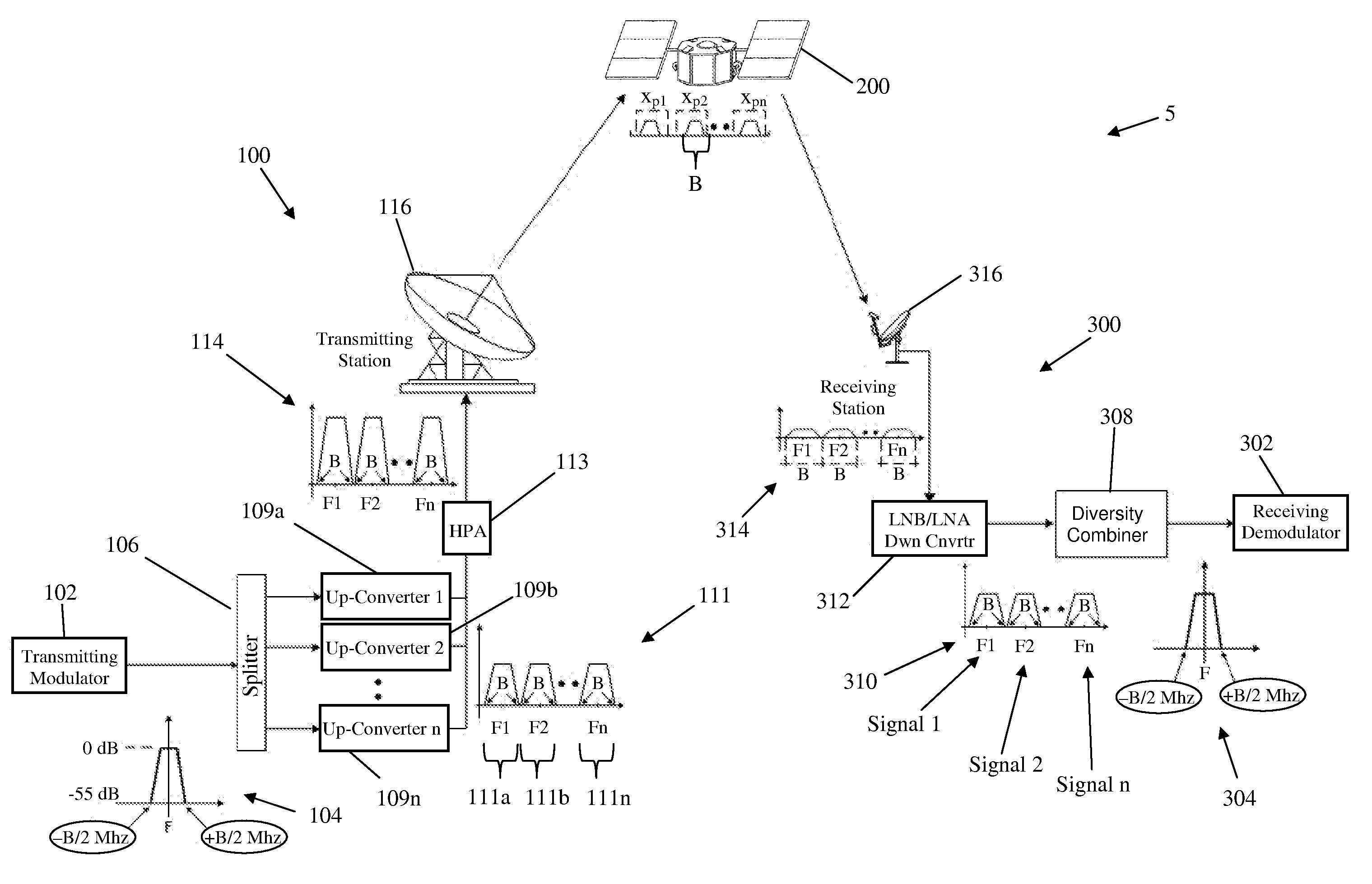
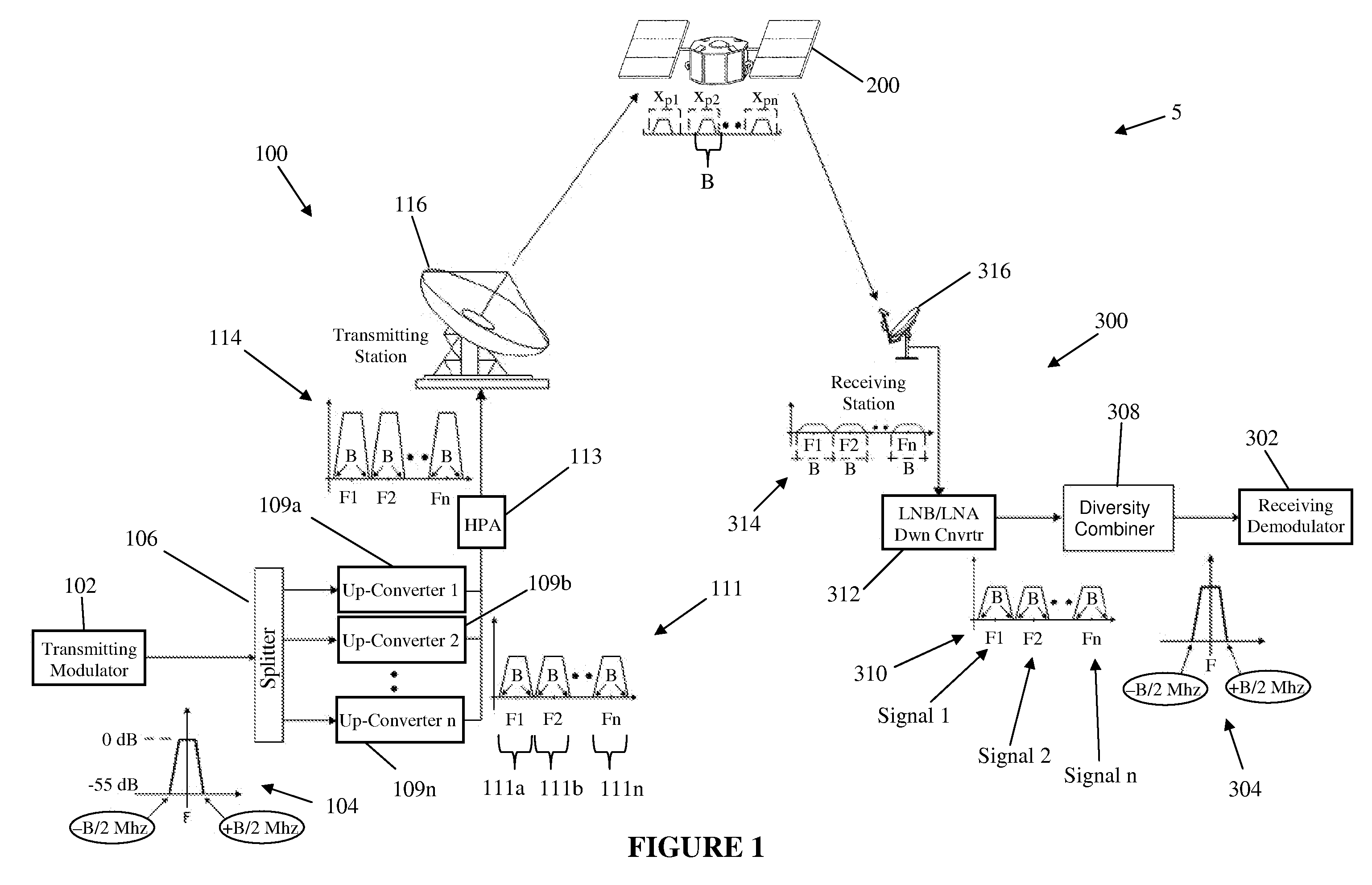
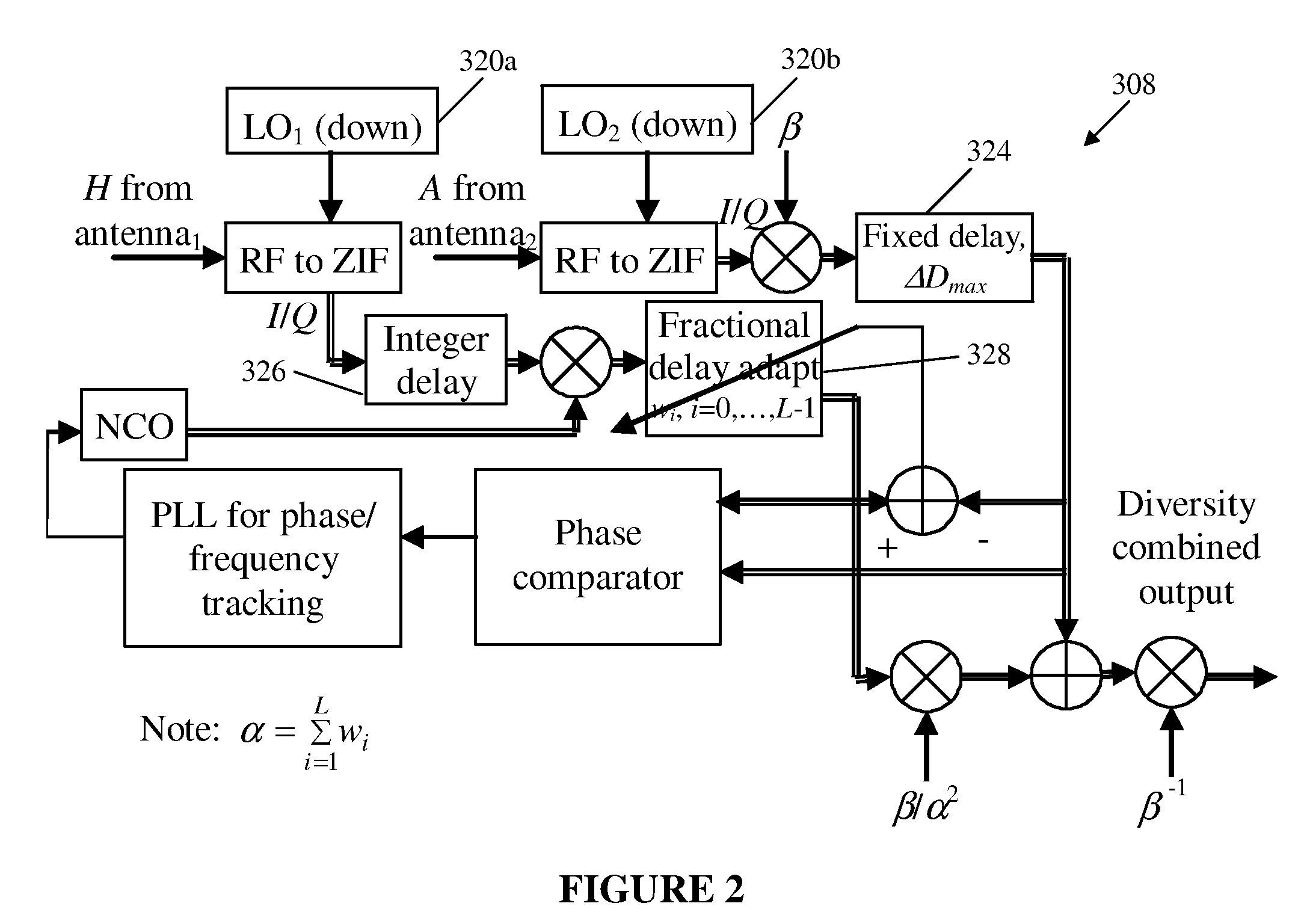
ActiveUS20110028086A1Increase power providedIncrease powerDiversity/multi-antenna systemsWireless commuication servicesFrequency changerFrequency spectrum
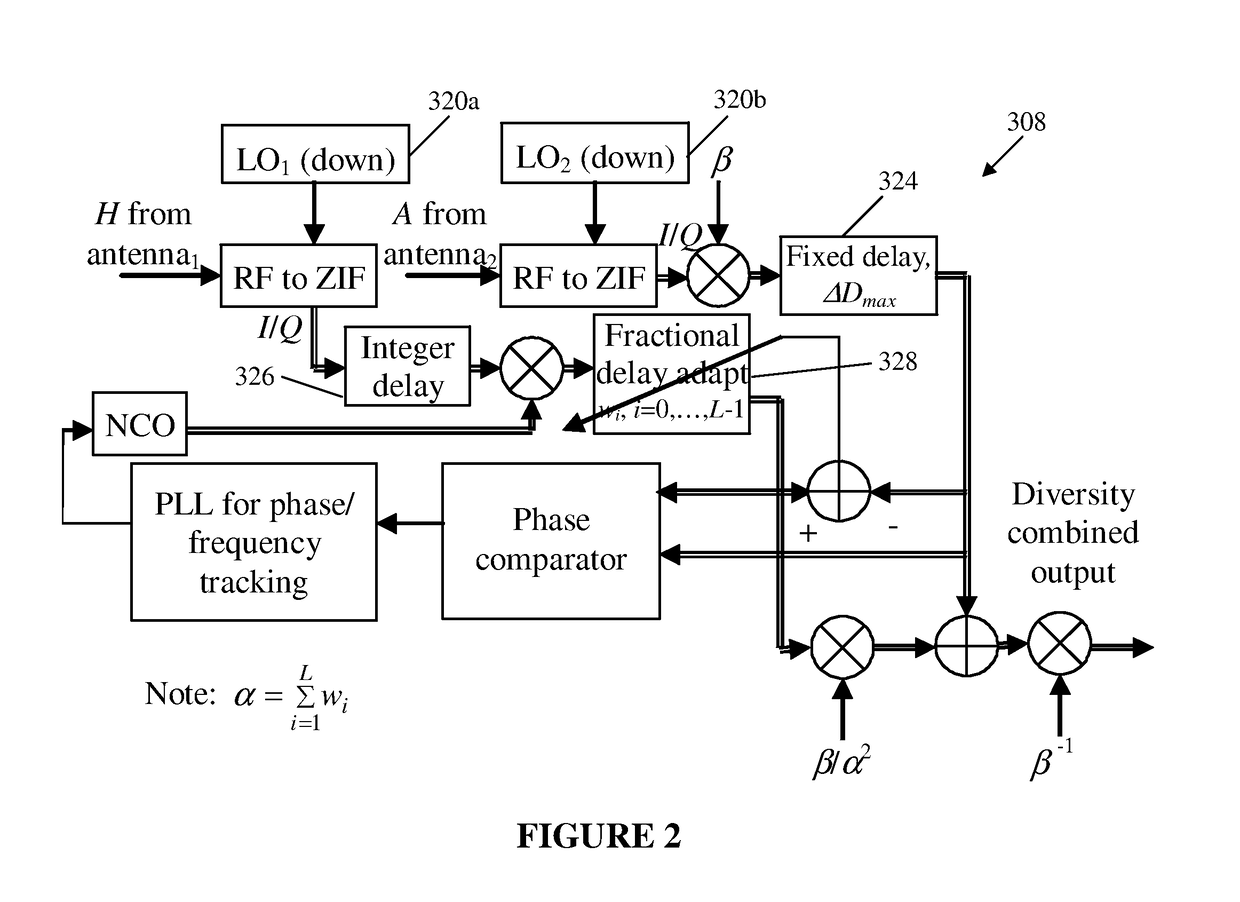
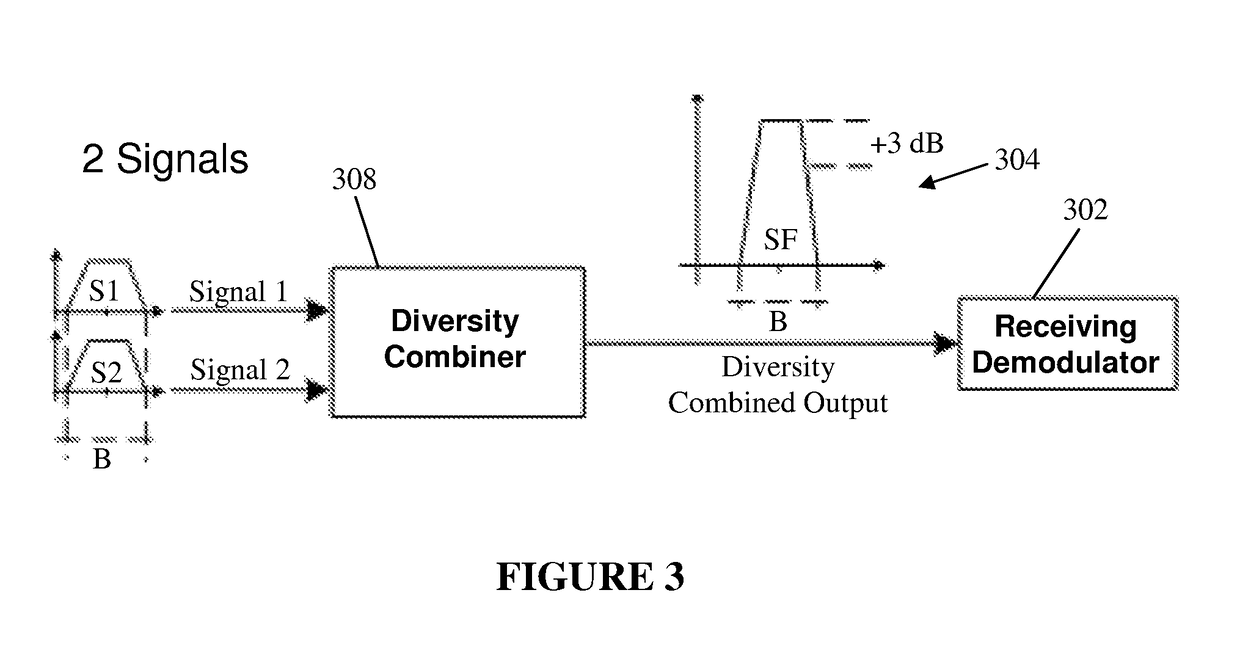
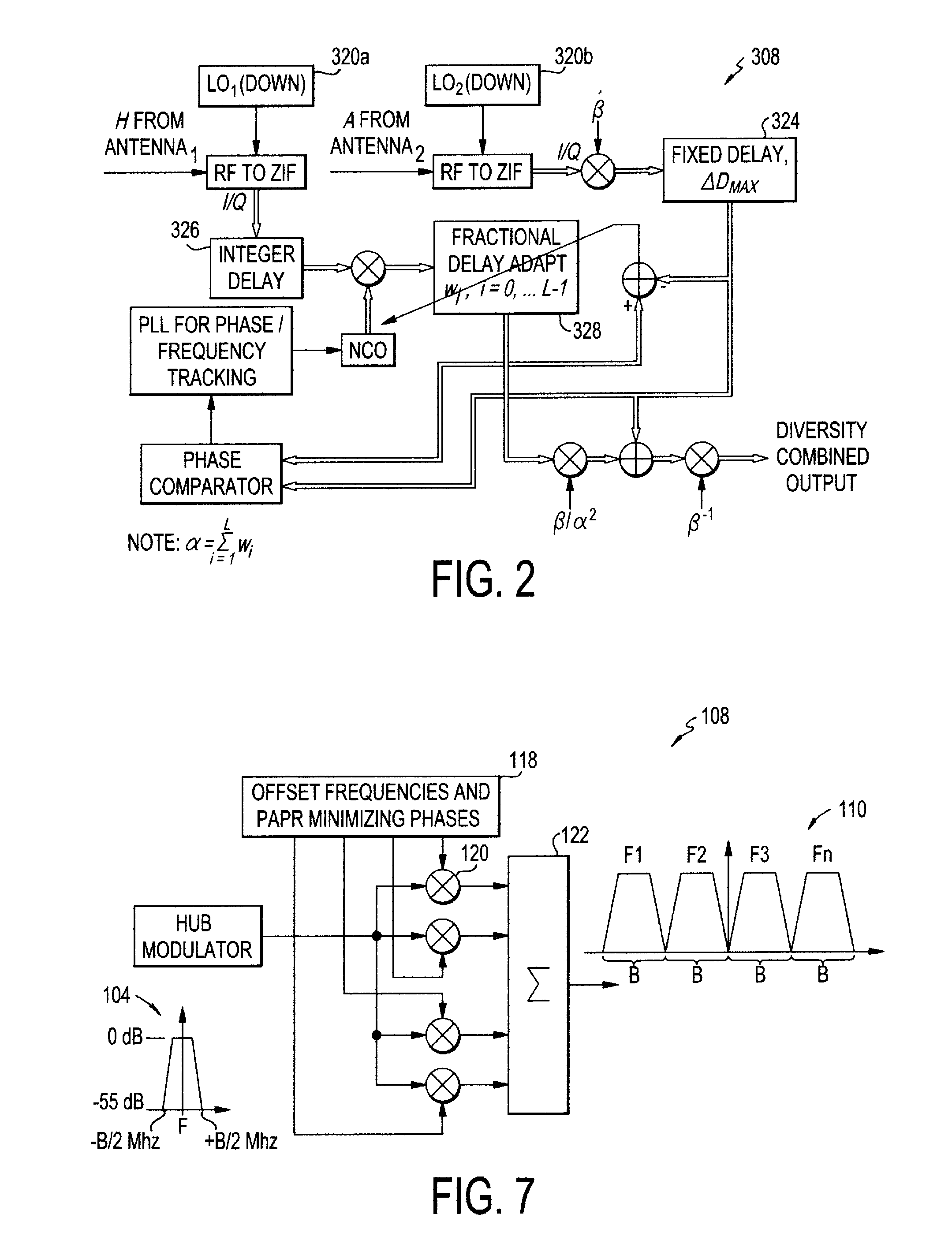
A satellite communications system has a hub terminal which communicates with a remote terminal through a satellite. The hub terminal 100 includes a transmitting modulator, power booster, up-converter and Power Amplifier (PA), and a transmitting station. The transmitting modulator generates a modulated signal, which is output to the power booster. The power booster receives the modulated signal and generates a spectral replication of the signal. The signal is then up-converted and amplified, and transmitted as an uplink signal to the satellite via a transmitting antenna. A remote station antenna receives the corresponding downlink signal. Following LNB / LNA and down-conversion, the signal is passed to a diversity combiner. The diversity combiner aligns the replicated signals by frequency and phase and generates a power-boosted signal. Accordingly, the system enables the use of ultra small antennas by providing increased power.
Owner:ANUVU IP HLDG LLC
System and method for enabling ultra small aperture communication antenna using spectral replication and coherent frequency and phase combining
ActiveUS20110028087A1Increase power providedIncrease powerRadio transmissionWireless commuication servicesFrequency spectrumTransmitter
A system for enabling use of ultra-small aperture terminals in satellite communications is provided. The system comprises a transmitter configured to receive an input signal having information, a bandwidth, and an amplitude, replicate the input signal into two or more replications of the input signal, convert each of the two or more replications to have a frequency tuned to two or more corresponding satellite transponders while maintaining the bandwidth and all the information of the input signal, and combine the two or more replications into a single uplink signal. A transmit antenna is configured to transmit the uplink signal to the two or more satellite transponders.
Owner:ANUVU IP HLDG LLC
System and method for enabling ultra small aperture communication antenna using spectral replication and coherent frequency and phase combining
ActiveUS8285203B2Increase powerBroadcast transmission systemsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsFrequency changerFrequency spectrum
A satellite communications system has a hub terminal which communicates with a remote terminal through a satellite. The hub terminal 100 includes a transmitting modulator, power booster, up-converter and Power Amplifier (PA), and a transmitting station. The transmitting modulator generates a modulated signal, which is output to the power booster. The power booster receives the modulated signal and generates a spectral replication of the signal. The signal is then up-converted and amplified, and transmitted as an uplink signal to the satellite via a transmitting antenna. A remote station antenna receives the corresponding downlink signal. Following LNB / LNA and down-conversion, the signal is passed to a diversity combiner. The diversity combiner aligns the replicated signals by frequency and phase and generates a power-boosted signal. Accordingly, the system enables the use of ultra small antennas by providing increased power.
Owner:ANUVU IP HLDG LLC
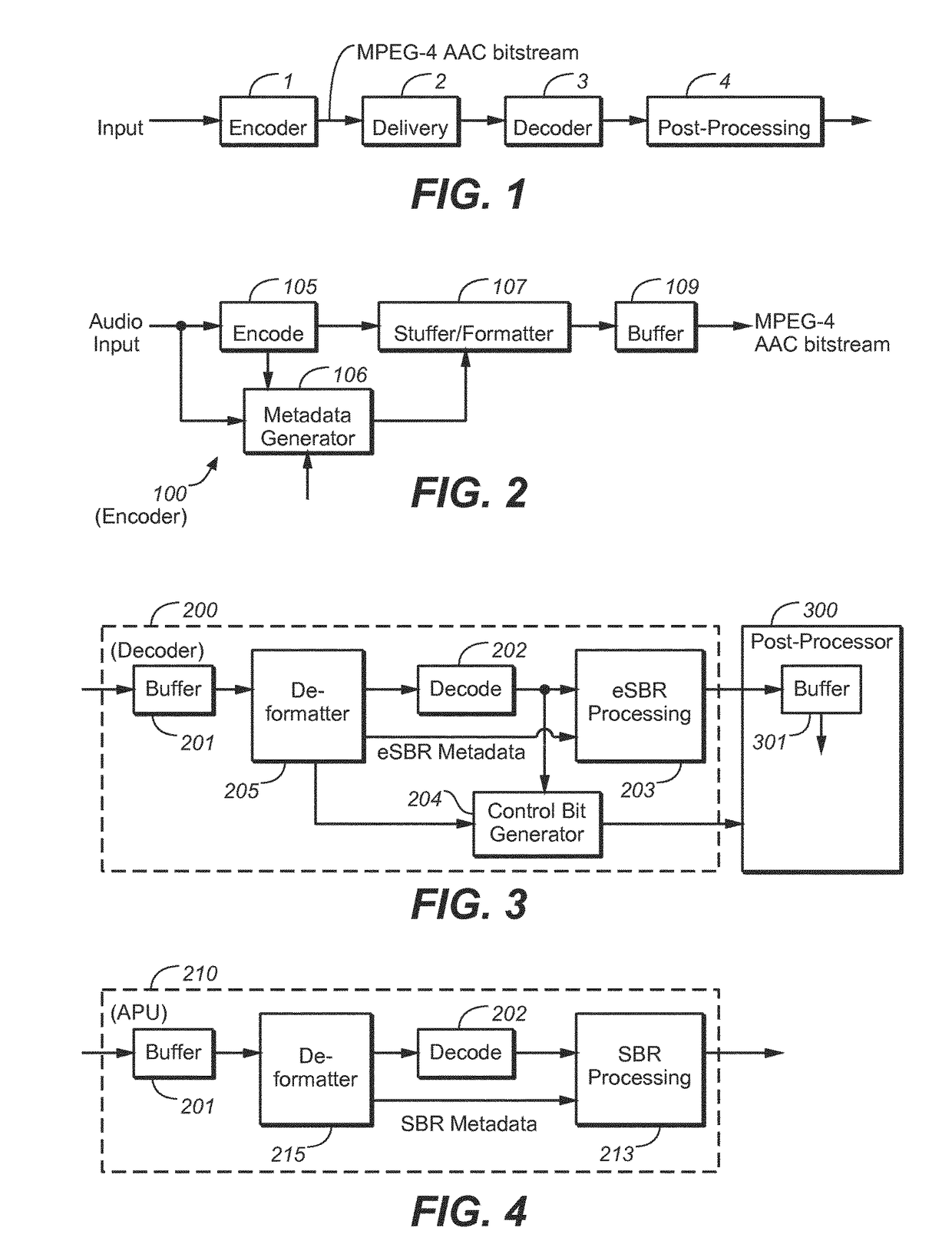
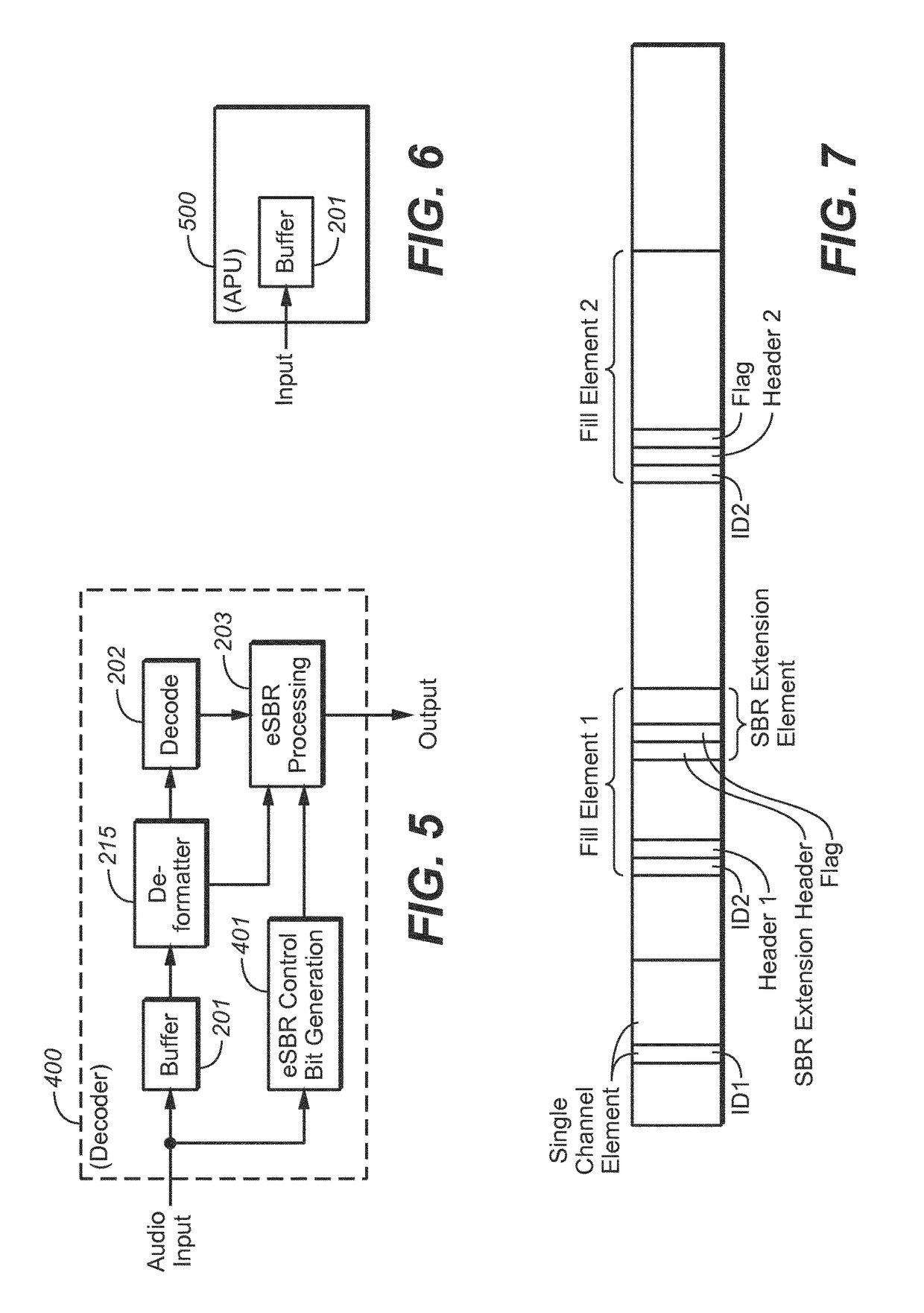
Decoding audio bitstreams with enhanced spectral band replication metadata in at least one fill element
Embodiments relate to an audio processing unit that includes a buffer, bitstream payload deformatter, and a decoding subsystem. The buffer stores at least one block of an encoded audio bitstream. The block includes a fill element that begins with an identifier followed by fill data. The fill data includes at least one flag identifying whether enhanced spectral band replication (eSBR) processing is to be performed on audio content of the block. A corresponding method for decoding an encoded audio bitstream is also provided.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com