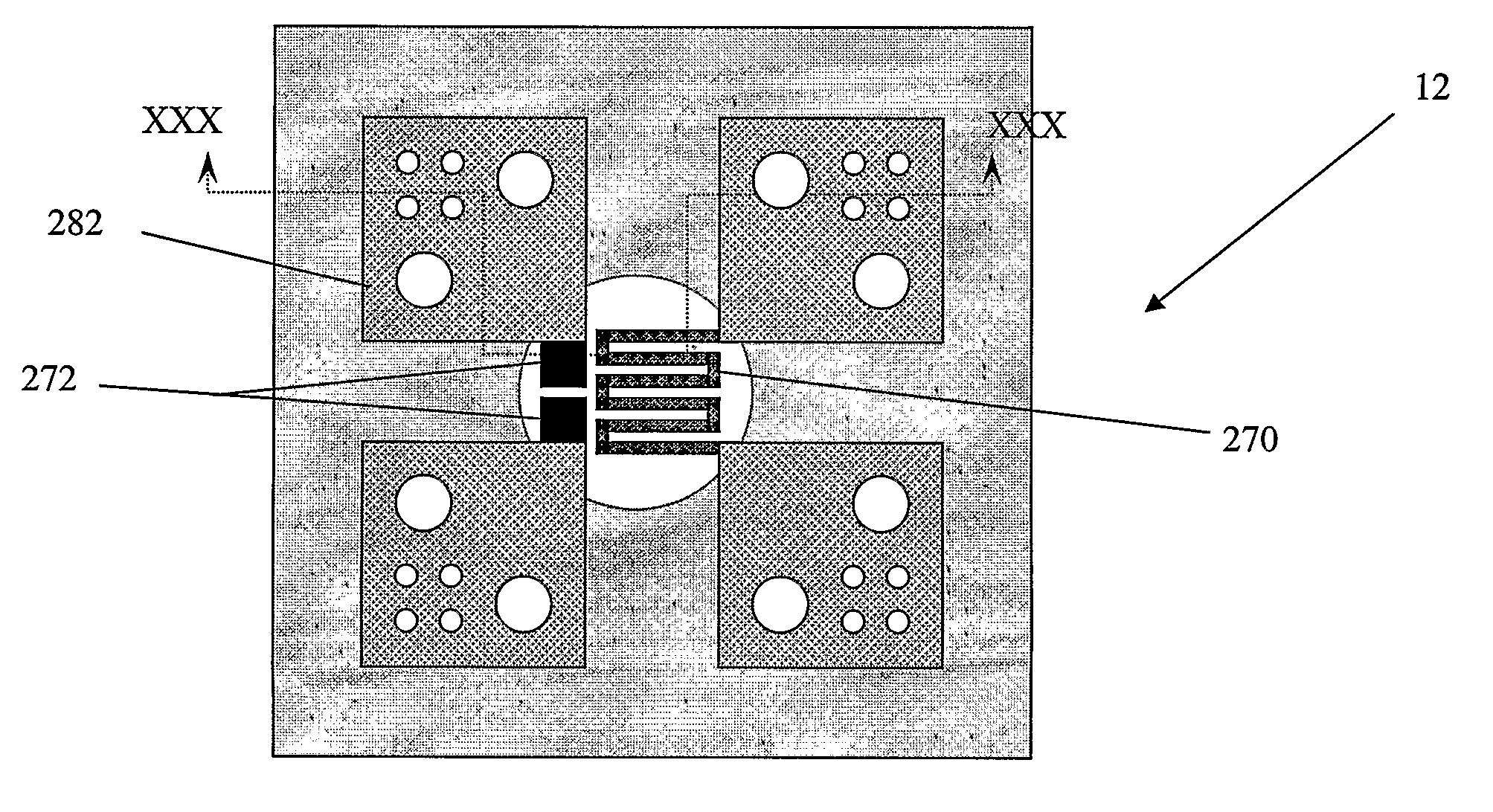
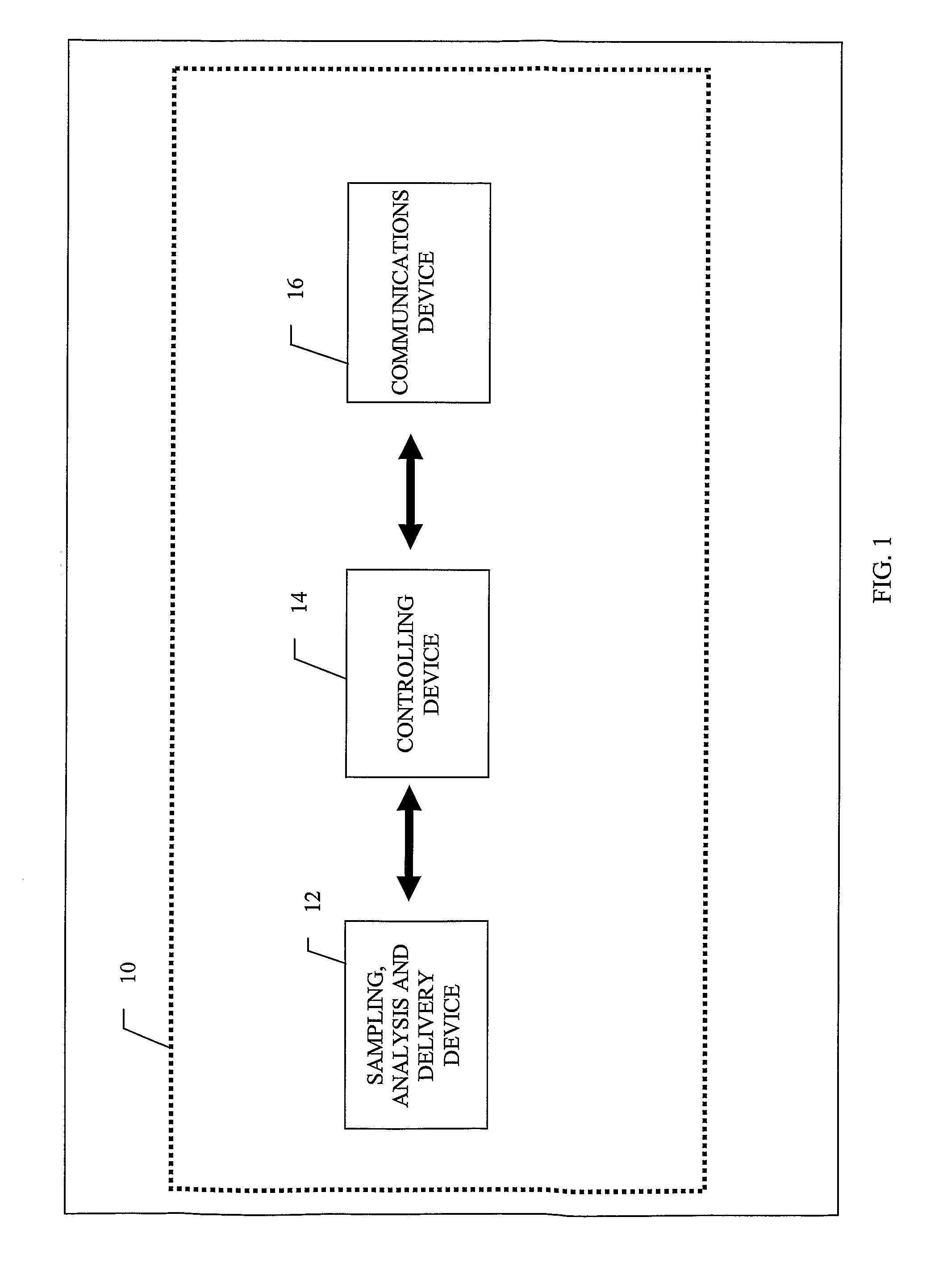
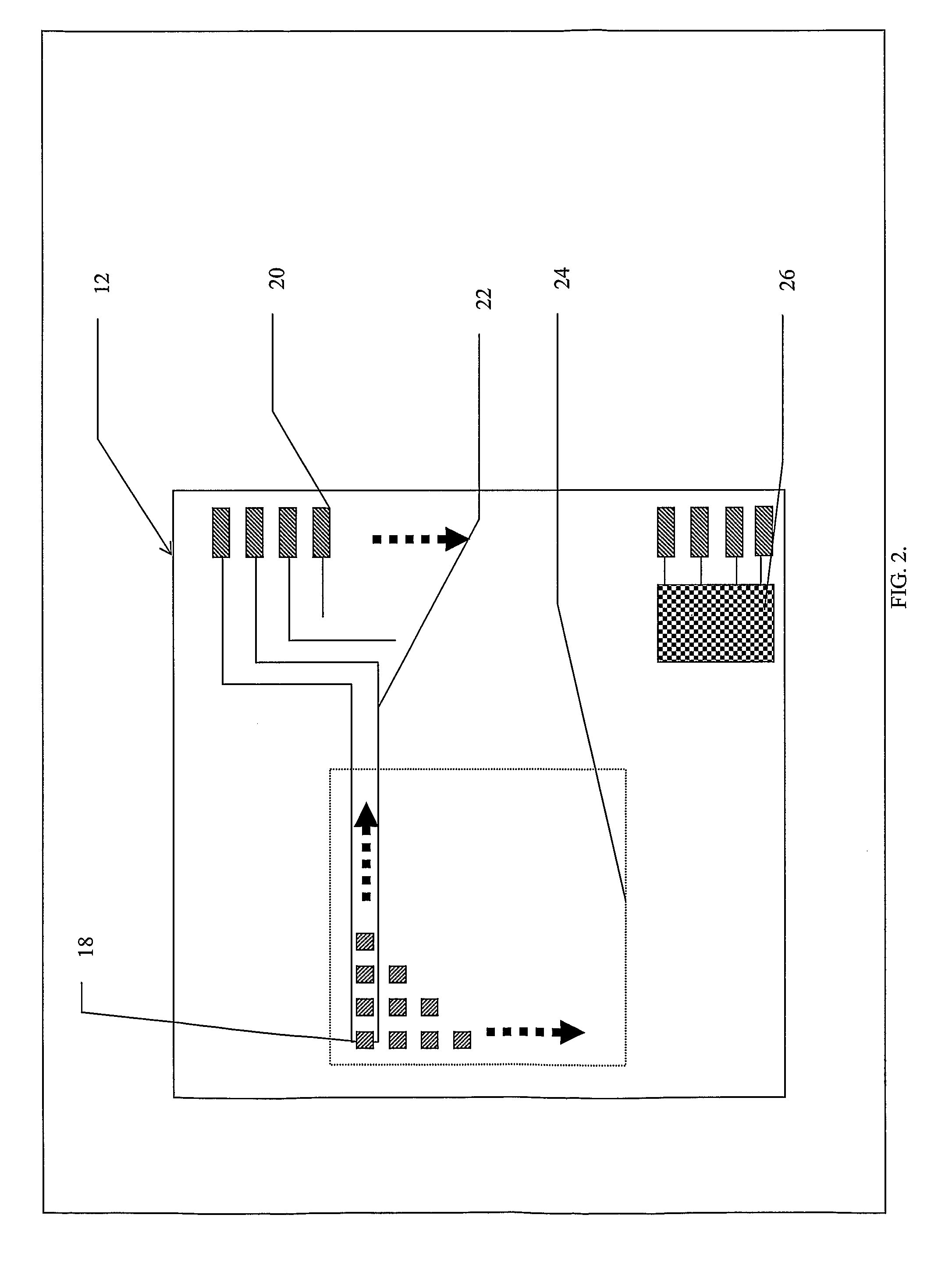
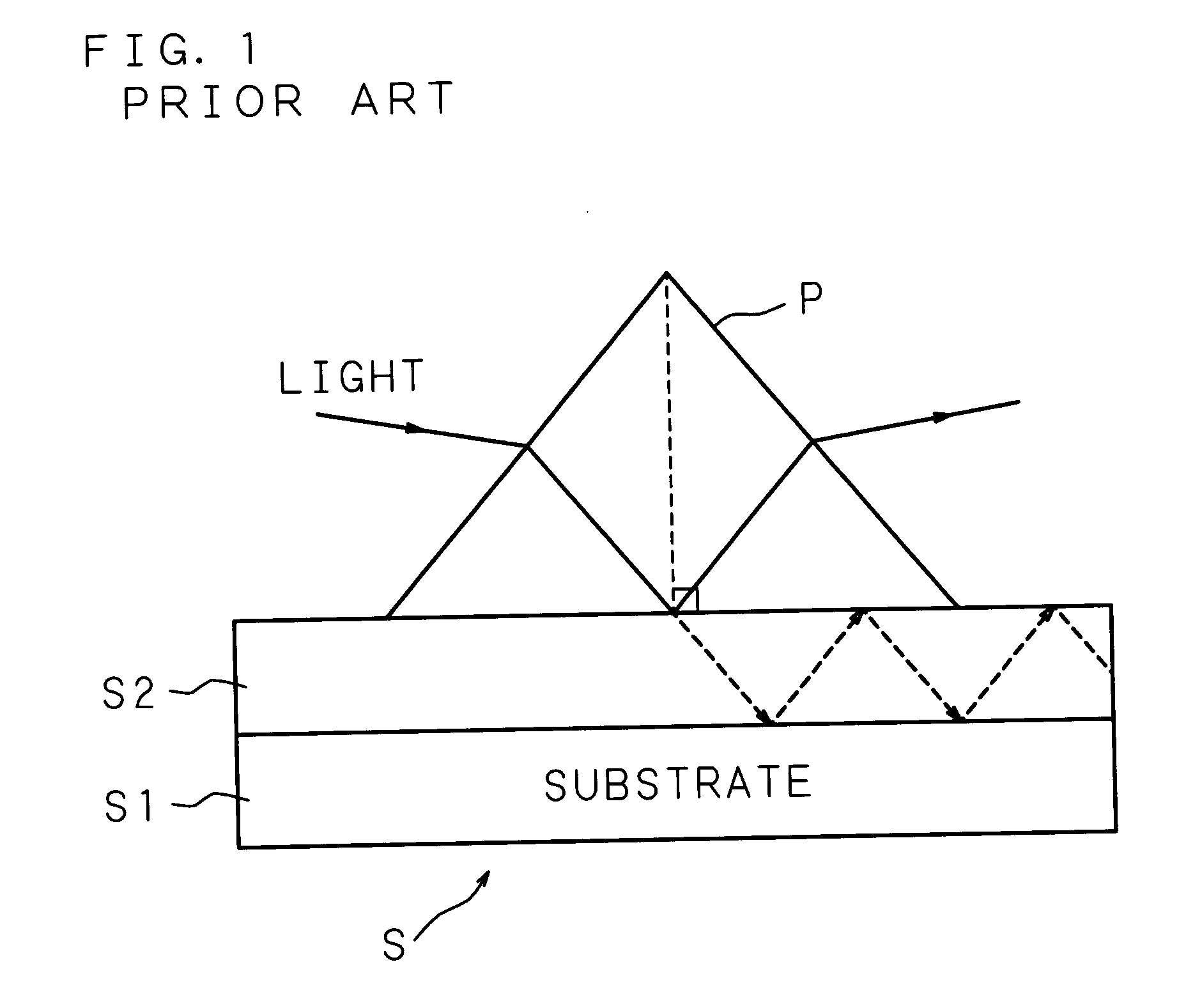
Patents
Literature
282 results about "Sample Measure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
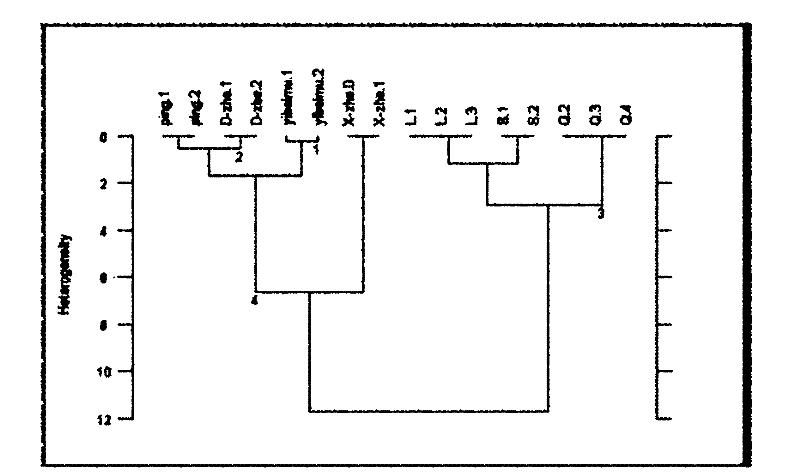
A minimum sample size is three, since in a sample of two, a bad measurement cannot be distinguished from the good one. 30 observations or less is generally considered a small sample. ... sample and population refer to the items or to the corresponding sets of measurements.
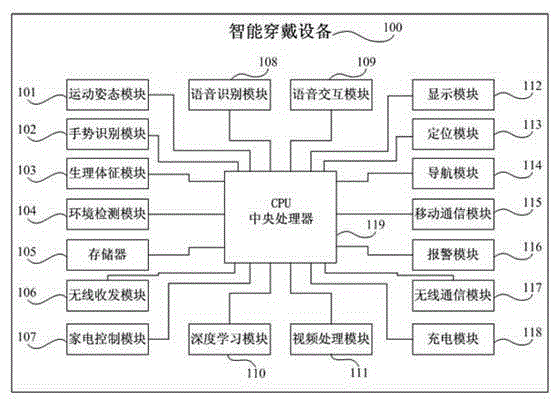
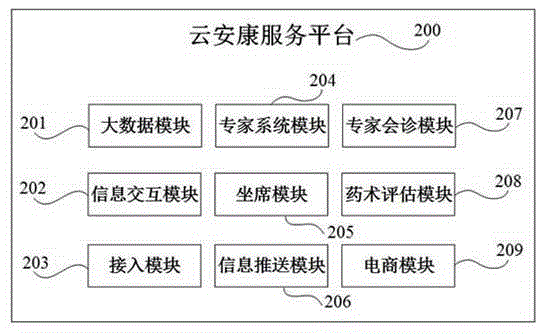
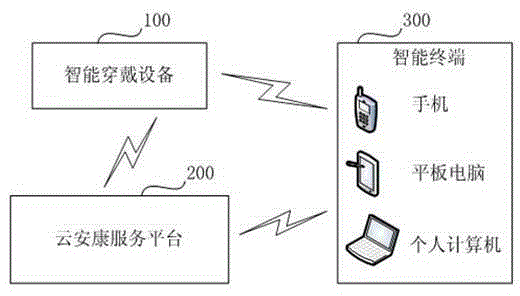
Cloud good health service platform of elderly people and big data processing method
InactiveCN104796485AImprove accuracyImprove scienceData processing applicationsTransmissionSample MeasureHealth history
The invention discloses a cloud good health service platform of elderly people and big data processing method. The platform comprises an access module, a big data module, an expert system module and an information pushing module. The big data module is used to store and check personal information, general information and safety and health record data of a wearer to process big data analyzing to obtain a standard data reference supported by samples measured data, and store health measurement results, health care plans and / or treatment regimes. The expert module is used to obtain the health measurement results, health care plans and / or treatment schemes according to the personal information, general information and safety and health record data of the wearer. The information pushing module sends the health measurement results, health care plans and / or treatment generator Transmitter optical subassembly to an intelligent terminal. The health service platform for cloud good rehabilitation allows the accuracy, scientificity and universality of health assessment, diagnostic report, health care plans and treatment schemes to be more applicable by big data analysis.
Owner:SHENZHEN GLOBAL LOCK SAFETY SYST ENG +1
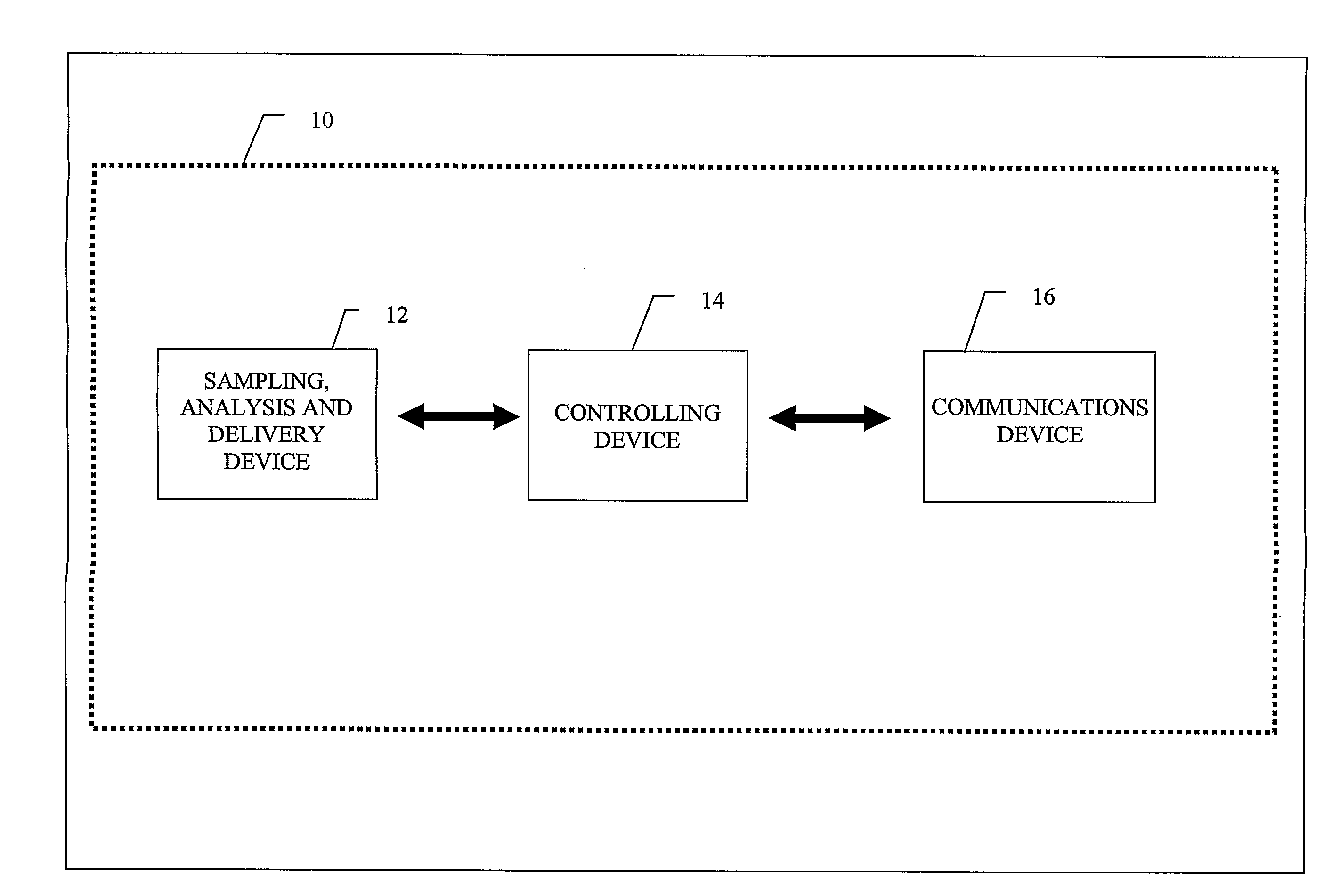
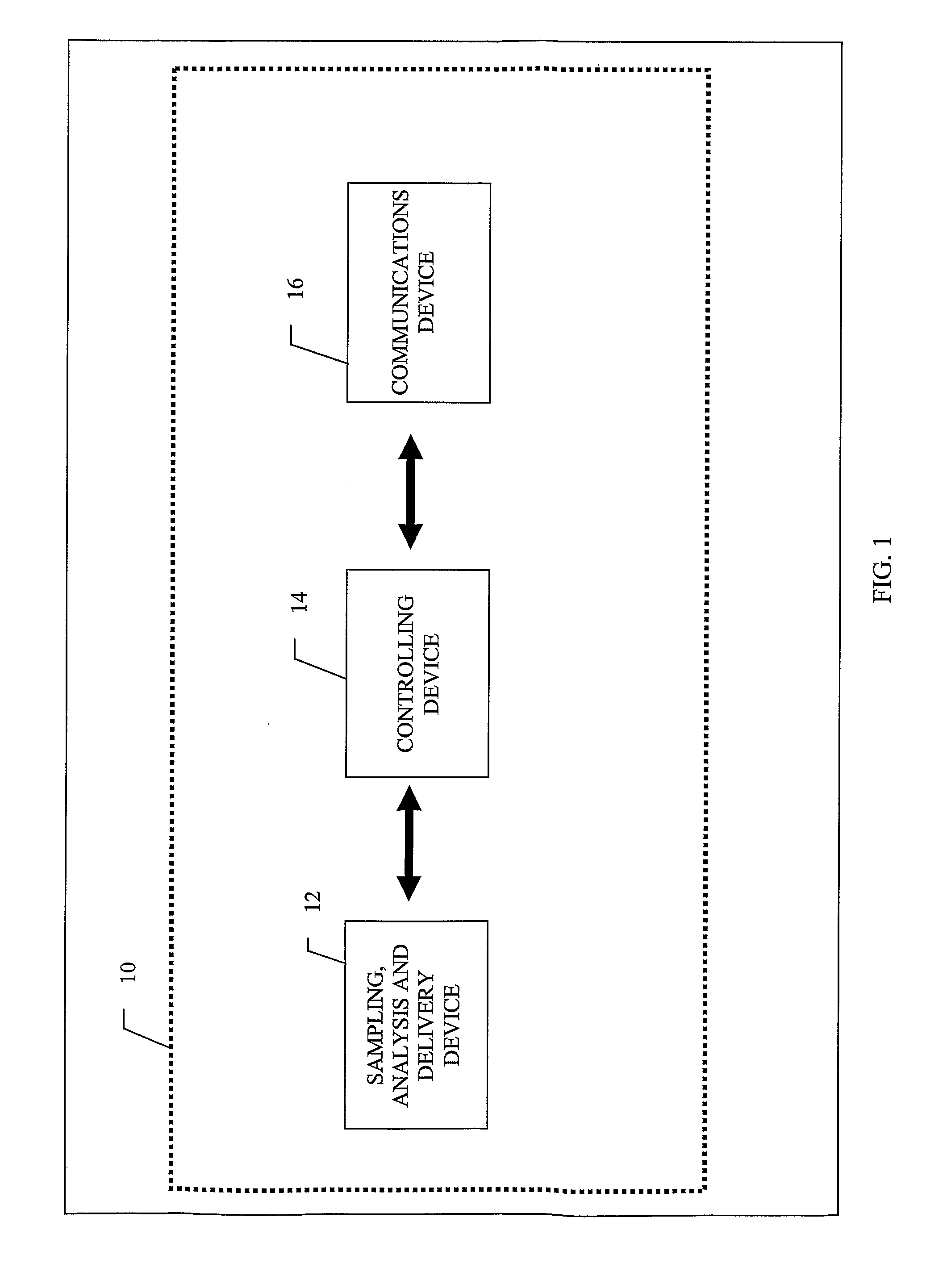
Flexible Apparatus and Method for Monitoring and Delivery
The present invention generally relates to a system and method that co-locates in a small flexible, configurable system and multi-level substrate sampling, rapid analysis, bio-sample storage and delivery functions to be performed on living tissues or matter obtained from living organisms. The types of the sampling may include chemical, biochemical, biological, thermal, mechanical, electrical, magnetic and optical sampling. In general, the analysis performed at the point of sampling measures the sample taken and records its value. The bio-sample storage function encapsulates a small sample of analyte and preserves it for subsequent examination or analysis, either on the organism by the system or at a remote location by an independent analysis system. Once stored, the sample can provide a record of a biological state at the precise time of sampling. The delivery at the point of sampling can include chemical, biochemical, thermal, mechanical, electrical, magnetic and optical stimuli.
Owner:FISH & RICHARDSON P C
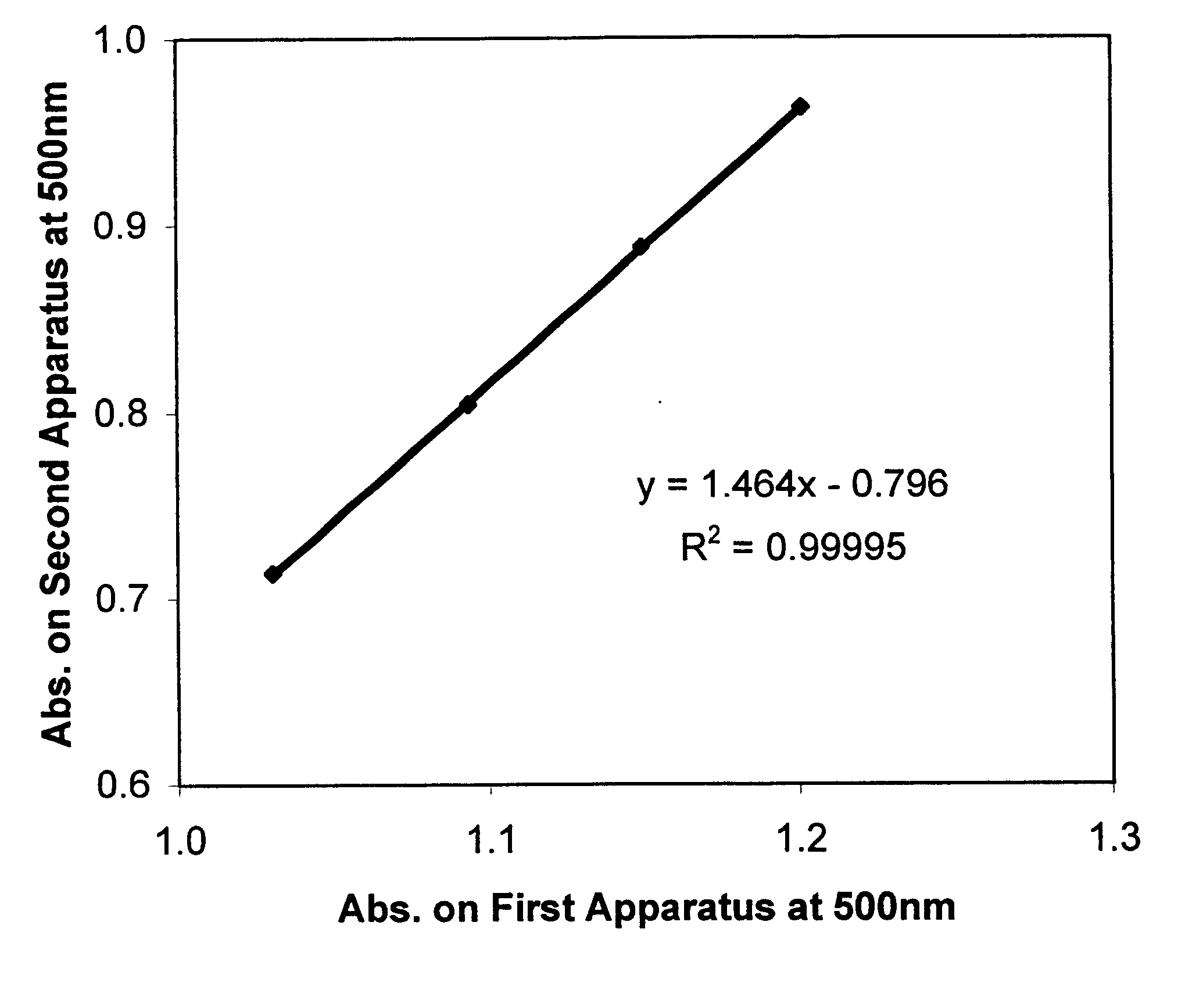
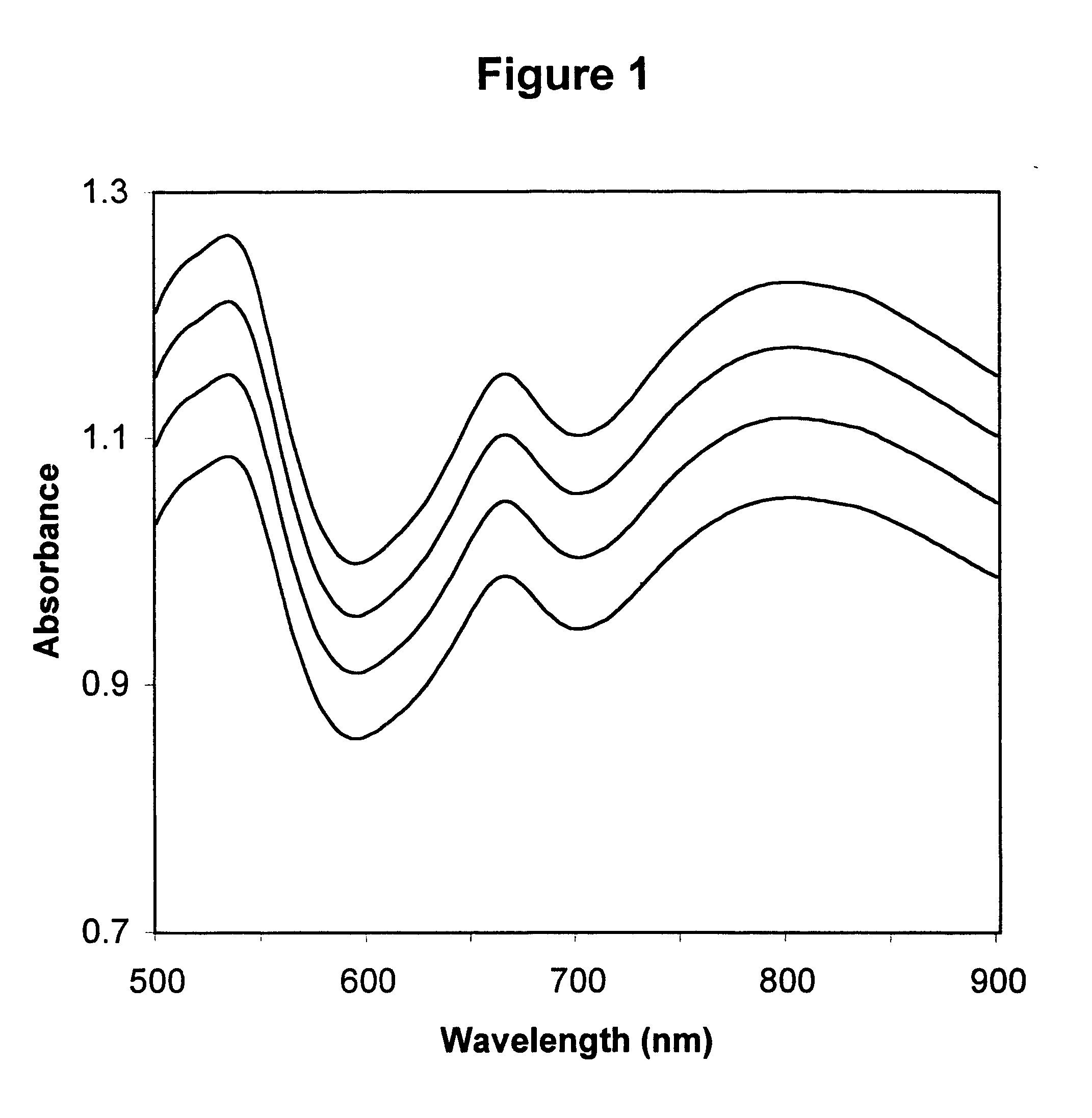
Method for calibrating spectrophotometric apparatus with synthetic fluids to measure plasma and serum analytes
InactiveUS6470279B1Testing/calibration apparatusScattering properties measurementsSample MeasureAnalyte
Described is a method for calibrating a spectrophotometric apparatus which is used to measure analytes in plasma and / or serum samples based on the calibration of a First Apparatus, and for recalibrating such apparatus, including recalibration of the First Apparatus all using synthetic calibrators. These apparatus use absorption of radiation to measure analytes in serum or plasma samples. The method described includes using synthetic calibrators which are submitted to the First Apparatus for measurement and compared with measurements of similar calibrators in a Second Apparatus and using the comparison to derive concentrations of analytes in samples measured on the Second Apparatus. As an alternative to making all apparatus identical, in terms of wavelength calibration, the absorbances of all apparatus should be mapped onto a standard set of wavelengths.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Real time determination of gas solubility and related parameters in manufacturing processes
InactiveUS6847898B1Easy to controlEasy to handleTesting beveragesSpecific gravity by measuring pressure differencesSolubilityApparent density
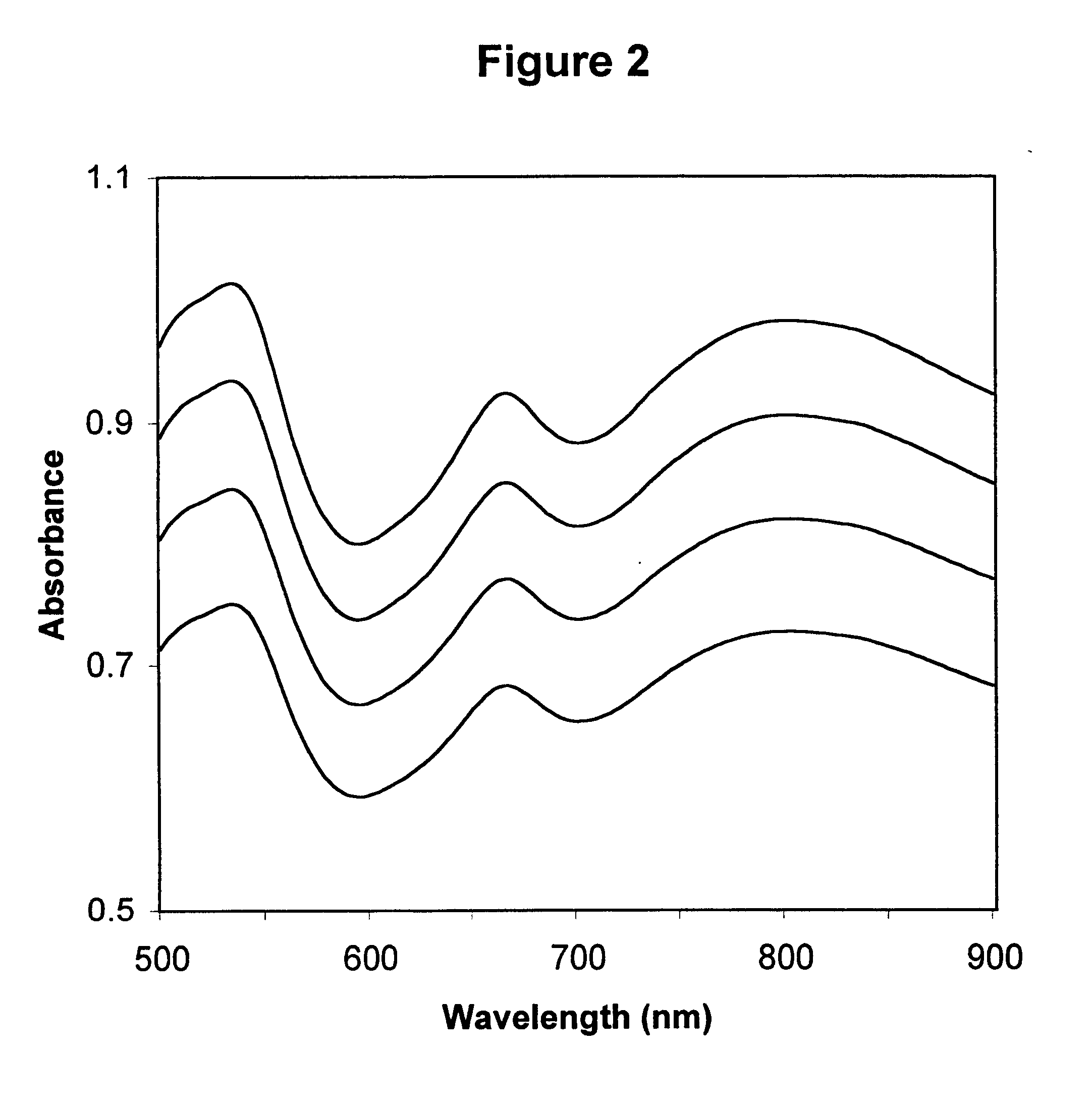
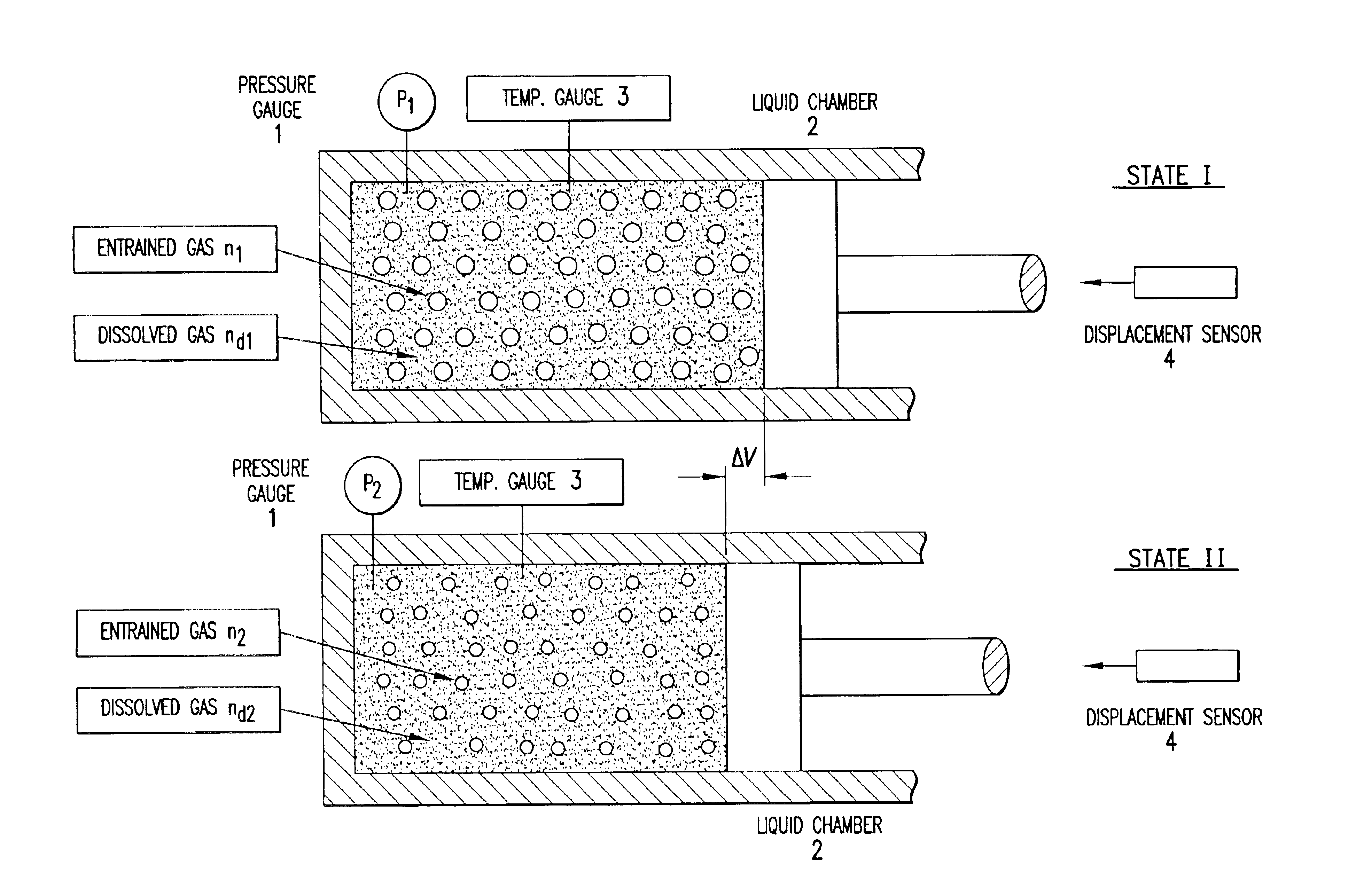
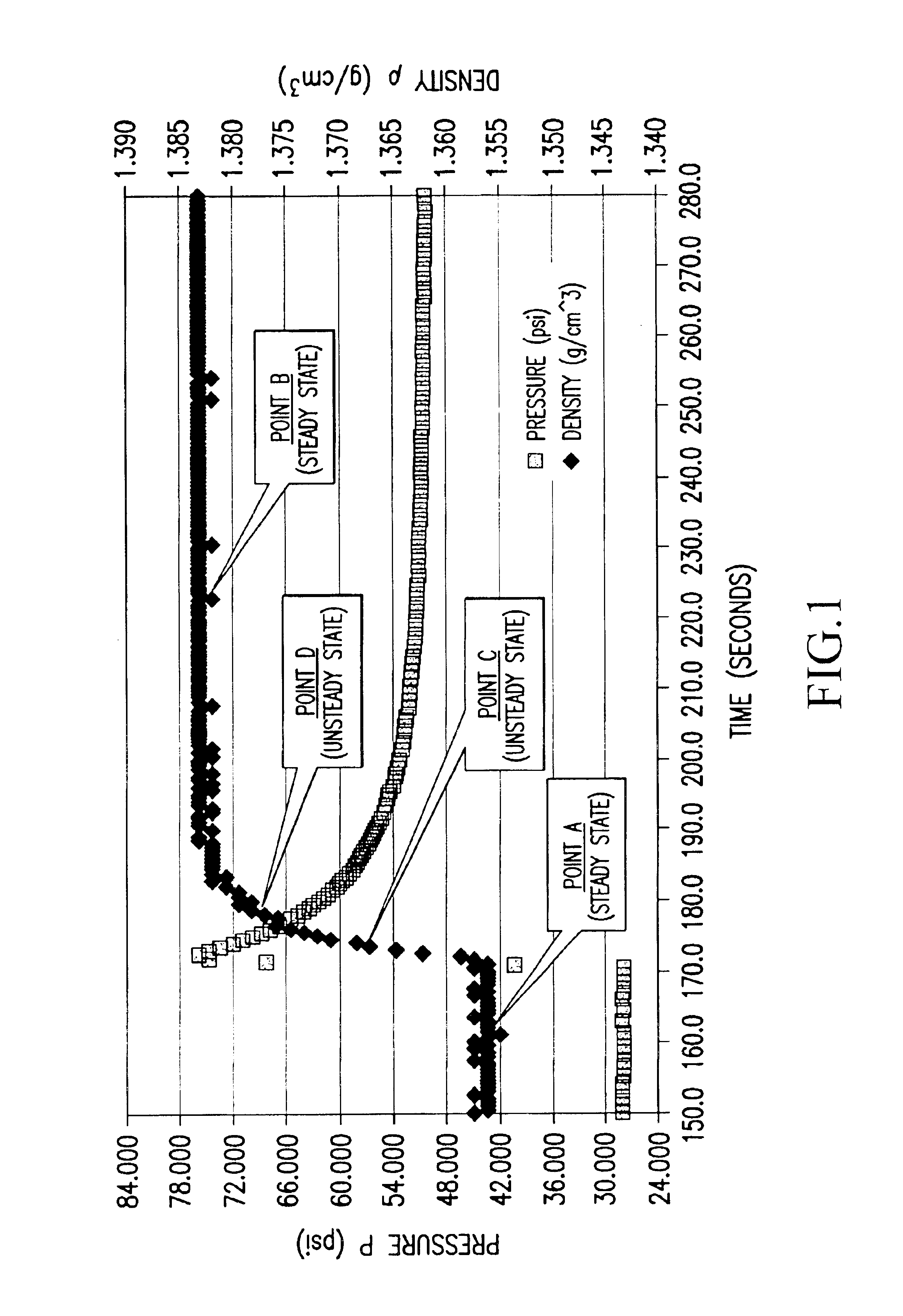
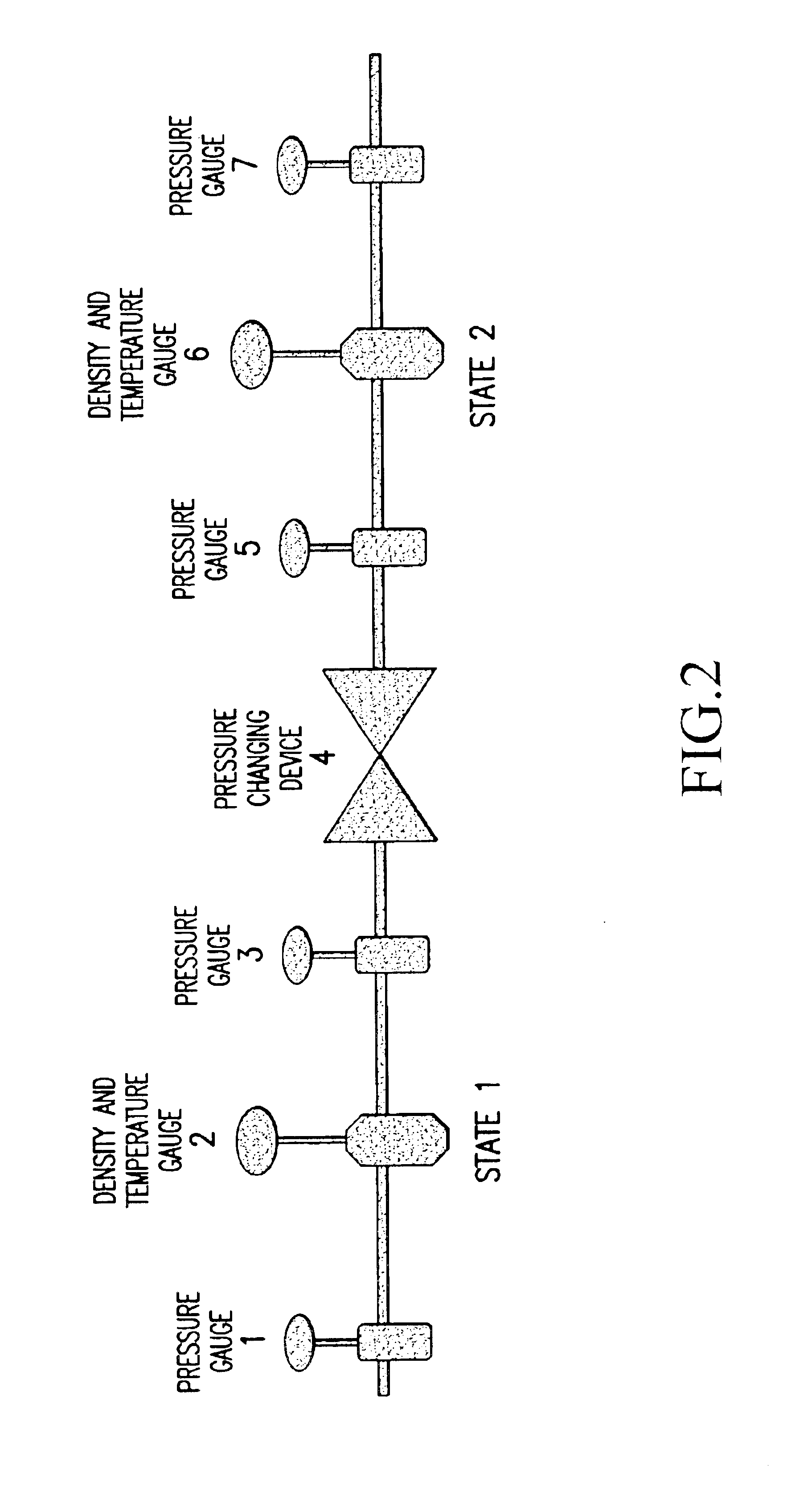
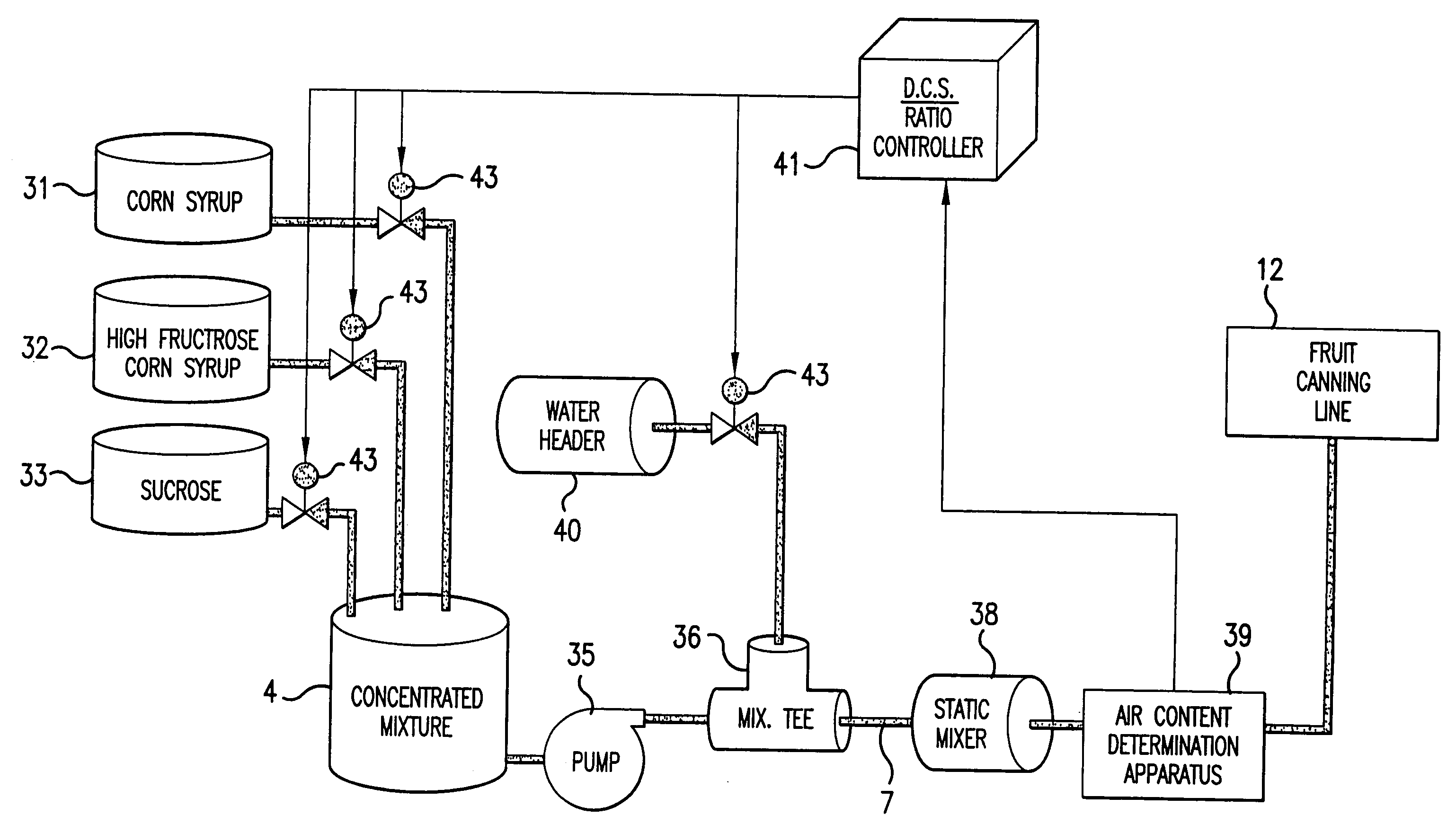
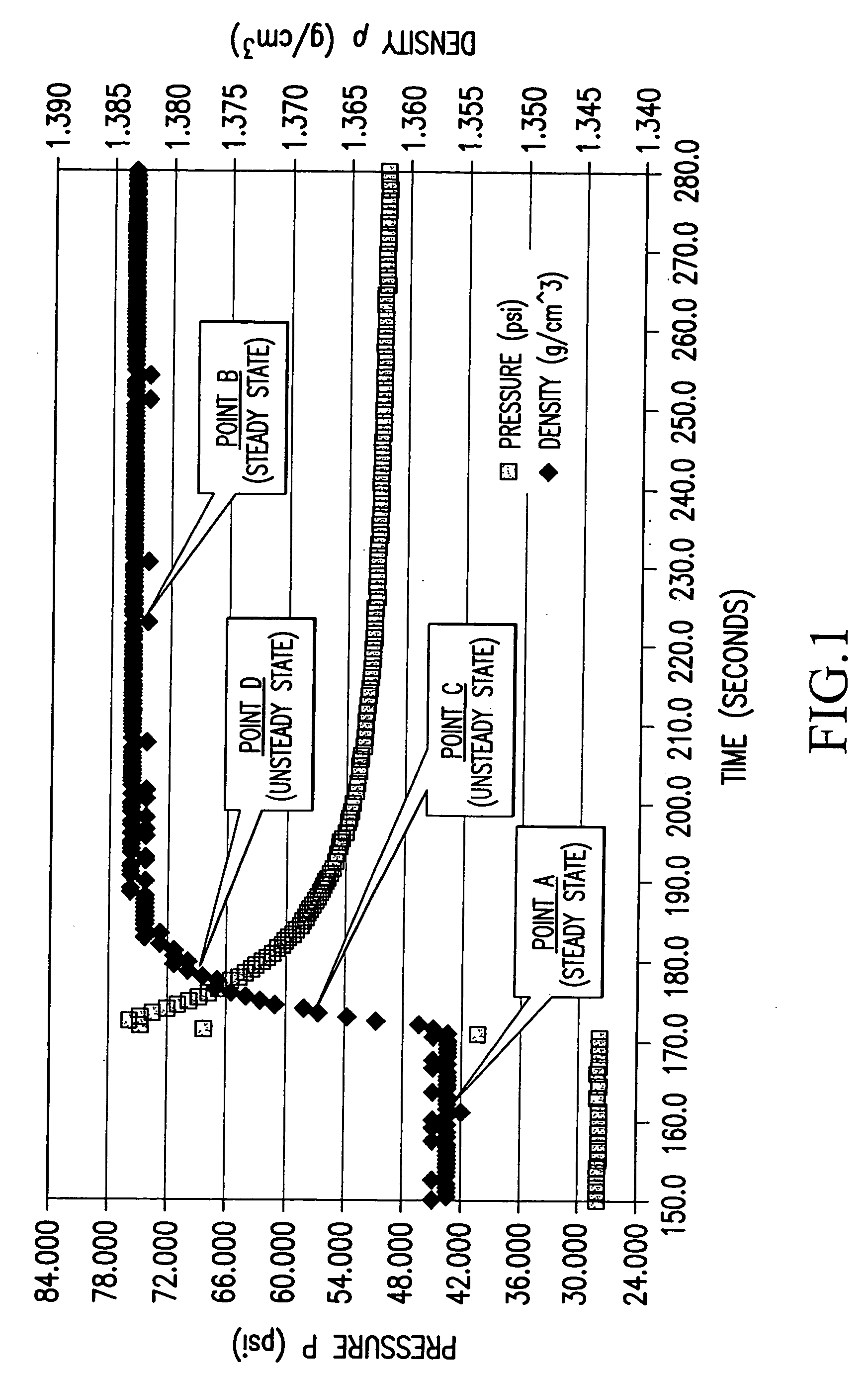
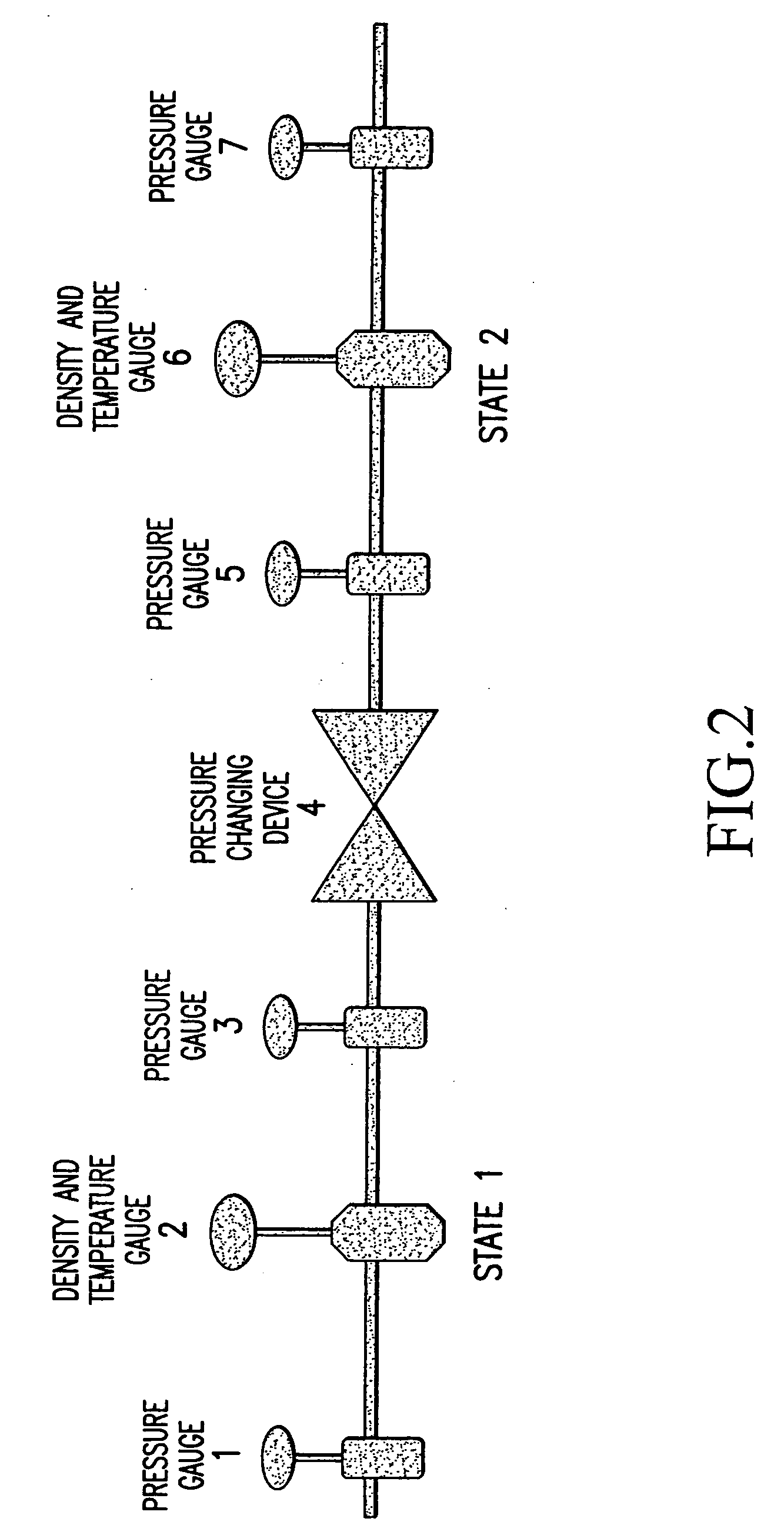
Methods and apparatuses for determining entrained and / or dissolved gas content of gas-liquid mixtures. Data generated is used to control the True (air-free) or Apparent (air-containing) Density or Entrained Air content of liquids within optimum ranges, e.g. in paper coating processes and in the manufacture of food products, personal care products, pharmaceutical products, paints, petroleum blends, etc. For example, an indirect method of continuously determining the amount of gas entrained in a liquid, by: continuously measuring the temperature, flow rate, and apparent density of the mixture at two different pressure states, and calculating the volume percentage of the gas in the liquid by using equation (28) x%=VsVs+V(28)wherein V is the volume of the gas-free liquid calculated by equation (23) V=1ρ1-[P2P2-P1(1ρ1-1ρ2)-RTP2-P1g(Δ PQa)](23)in which P1 and P2 are two different ambient pressures and ΔP=P2−P1, ρ1 and ρ2 are apparent densities of the liquid sample measured at P1 and P2, respectively, R is the constant of the Ideal Gas Law, T is the liquid temperature, Q is the flow rate, g(ΔP / Qa) is a function for determining the amount of gas being dissolved between P2 and P1, and Vs is determined by equation (27) Vs=TsTP1P2Ps(P2-P1)(1ρ1-1ρ2)-RTsPs(P1P2-P1g(Δ PQa)-g(P1-PsQa)).(27)
Owner:APPVION INC
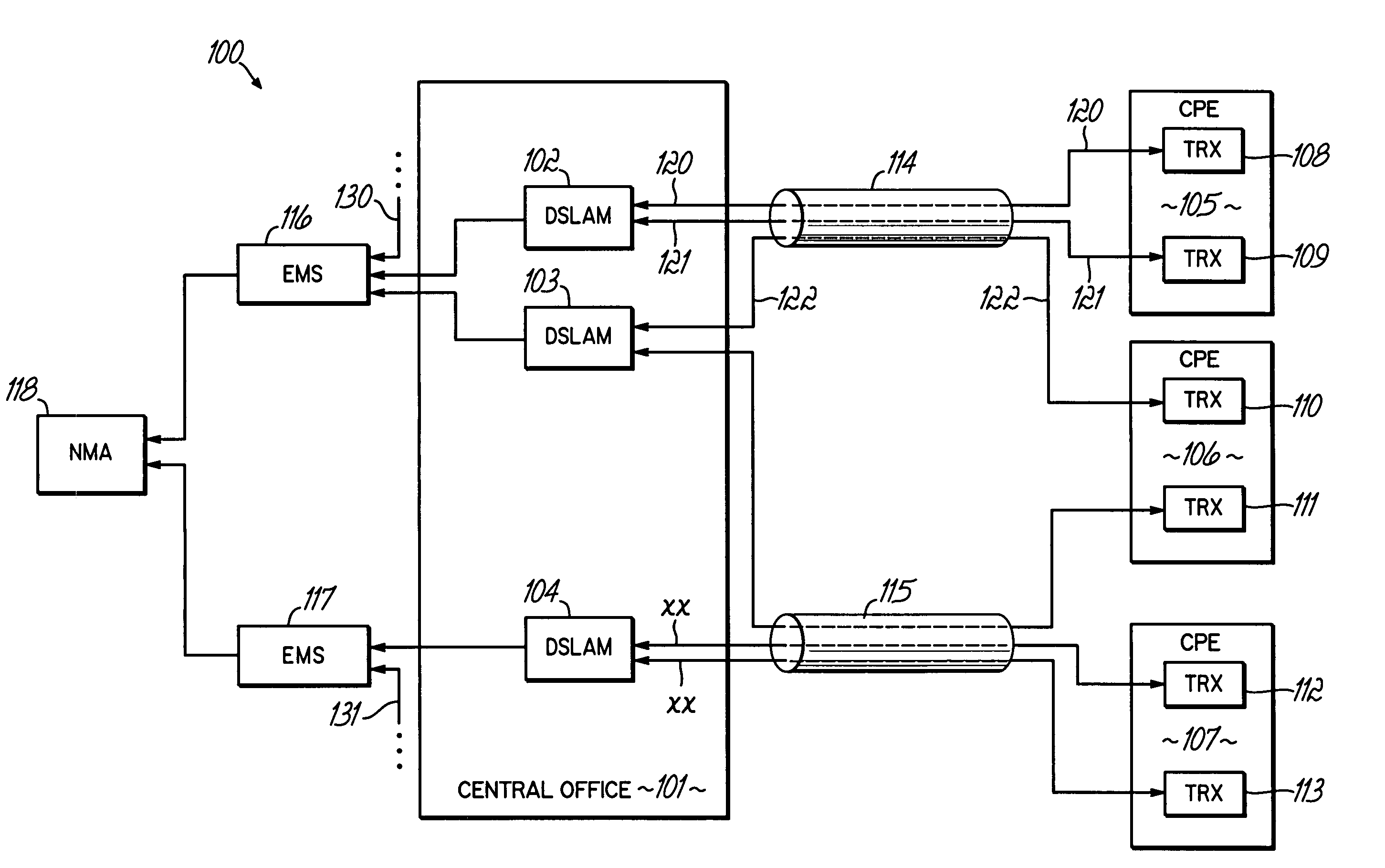
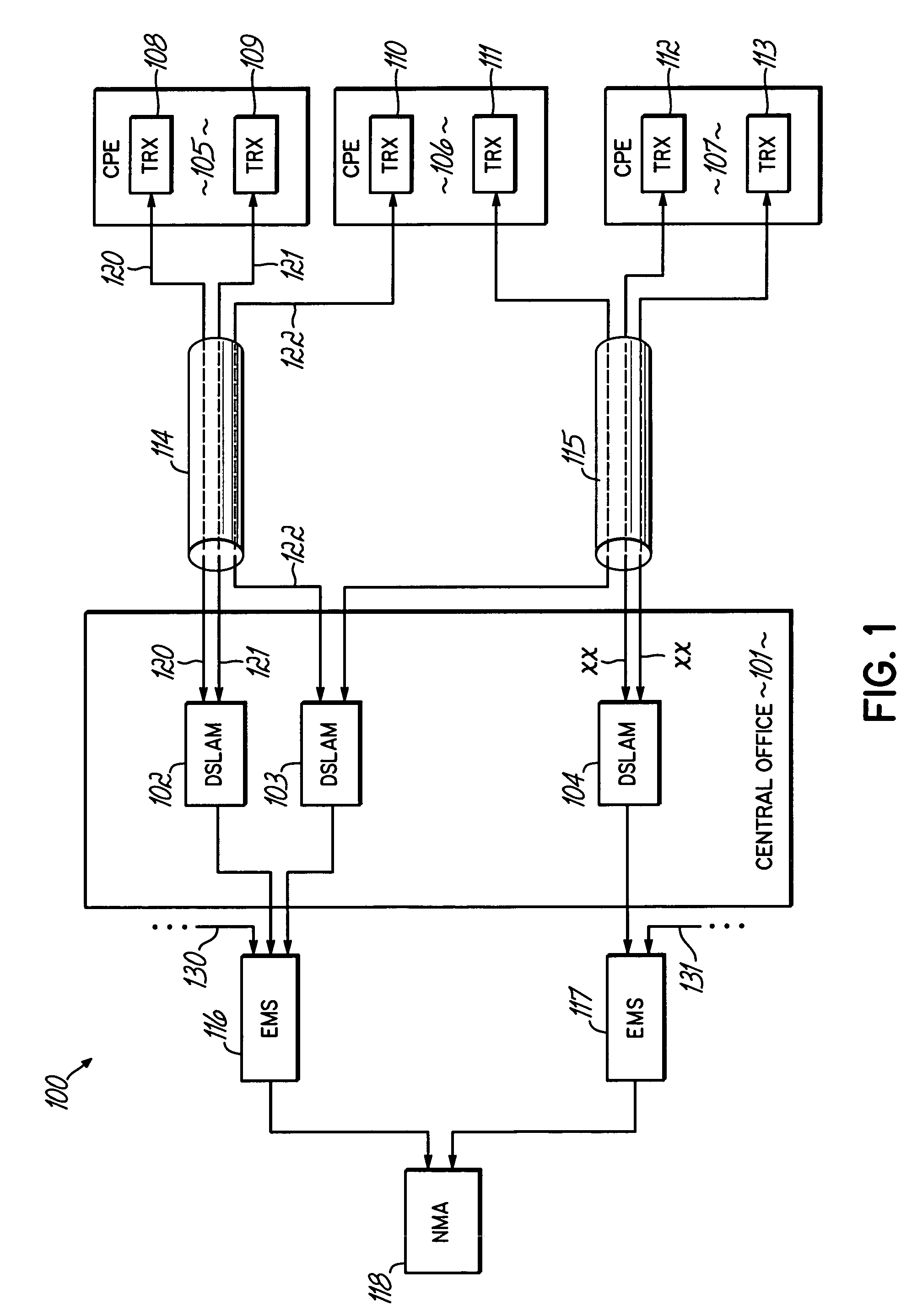
Method and apparatus for cooperative diagnosis of impairments and mitigation of disturbers in communication systems
InactiveUS6978015B1Interconnection arrangementsSubstations coupling interface circuitsSample MeasureCommunications system
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
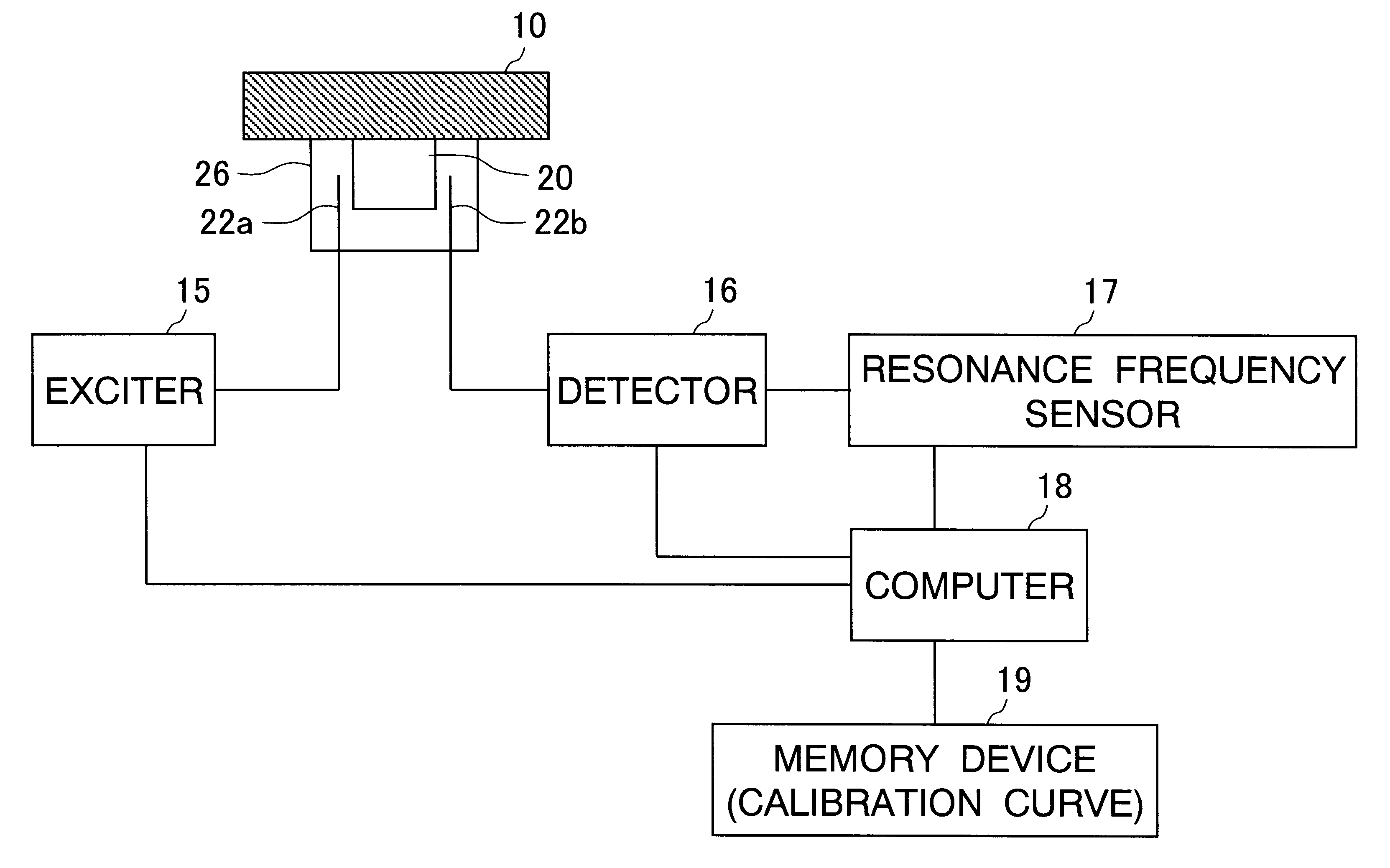
Method and device for measuring dielectric constant
InactiveUS6496018B1Dielectric property measurementsMaterial analysis using microwave meansSample MeasureResonance
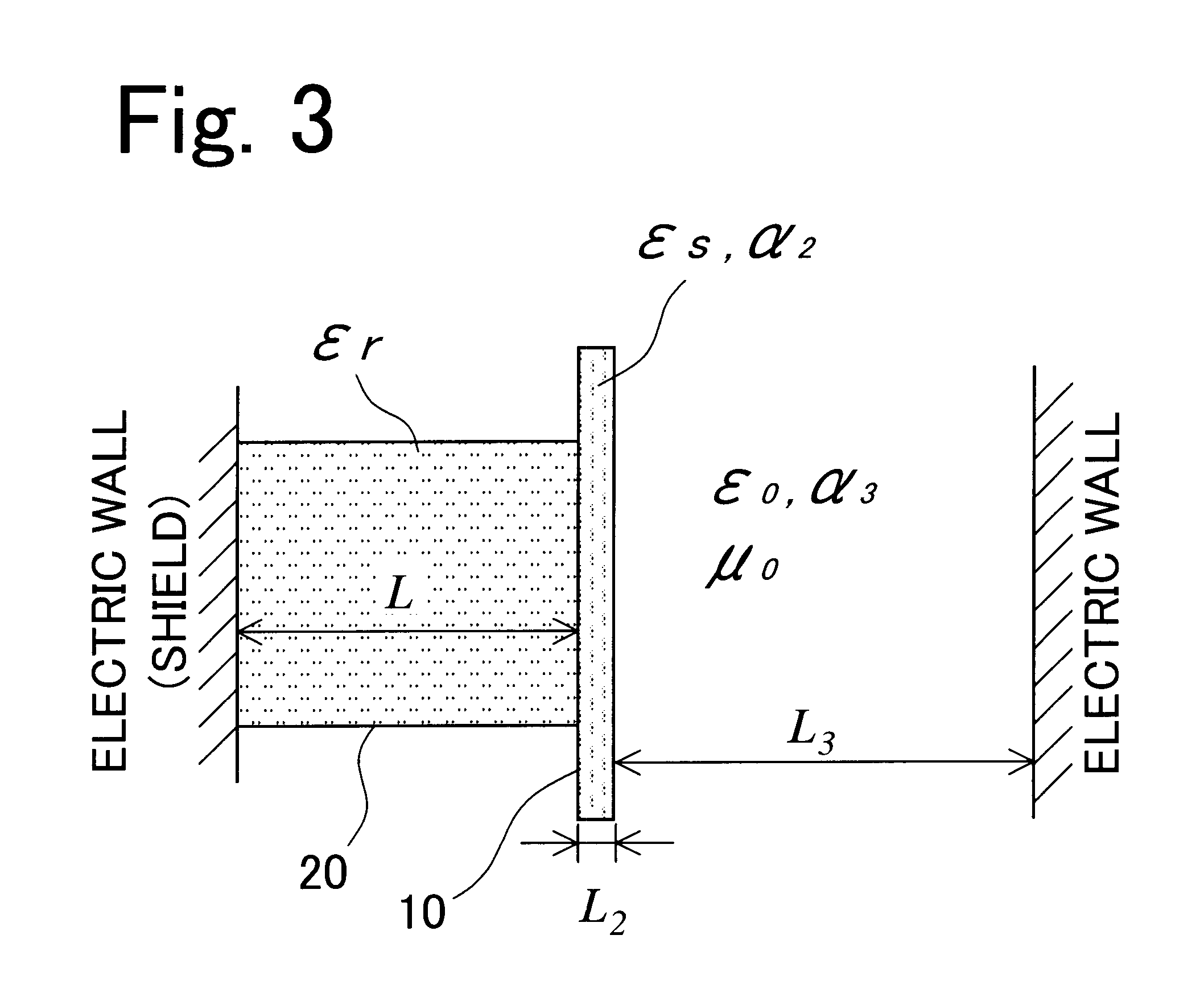
The sample measuring face of a dielectric resonator (20) is placed near a standard sample having a known dielectric constant at a fixed interval D. While appropriately varying the dielectric constant and thickness of the standard sample under the above condition, the variation of the resonance frequency of the dielectric resonator (20) is measured for each varied dielectric constant and thickness to draw a calibration curve of the varied resonance frequency depending on the dielectric constant and thickness. Under the same condition where calibration curve is drawn, the variation of the resonance frequency of the dielectric resonator (20) for a sample having a known thickness is measured. The dielectric constant of the sample is found from the measurement value and the calibration curve. The dielectric constant of not only a sheetlike sample but also a three-dimensional molded article or a liquid sample can be measured easily.
Owner:OJI PAPER CO LTD
Device for measuring thermal diffusivity
InactiveCN101929968AMonitor strength in real timeCorrect response timeMaterial thermal conductivityMaterial heat developmentSample MeasureMeasurement device
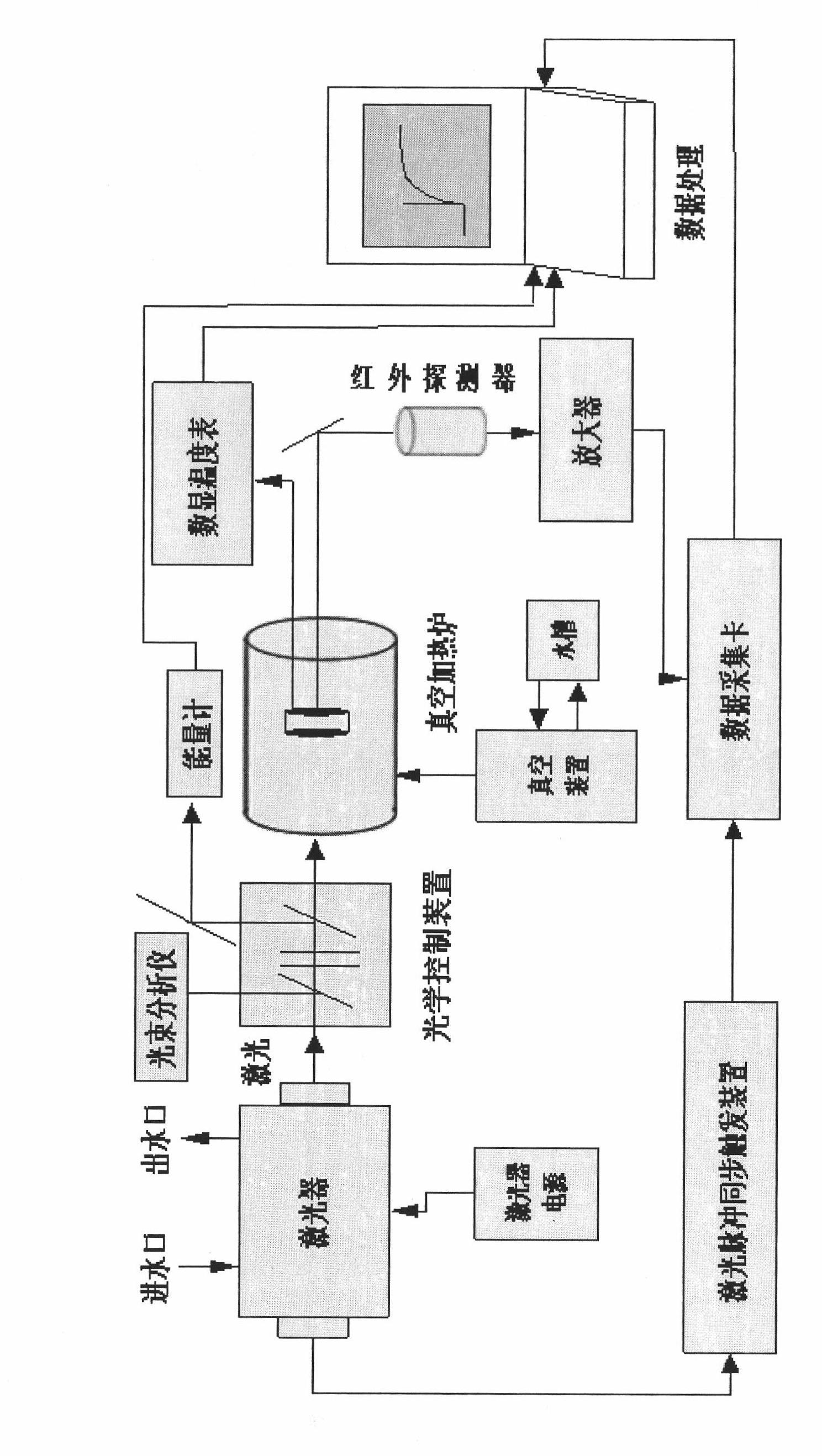
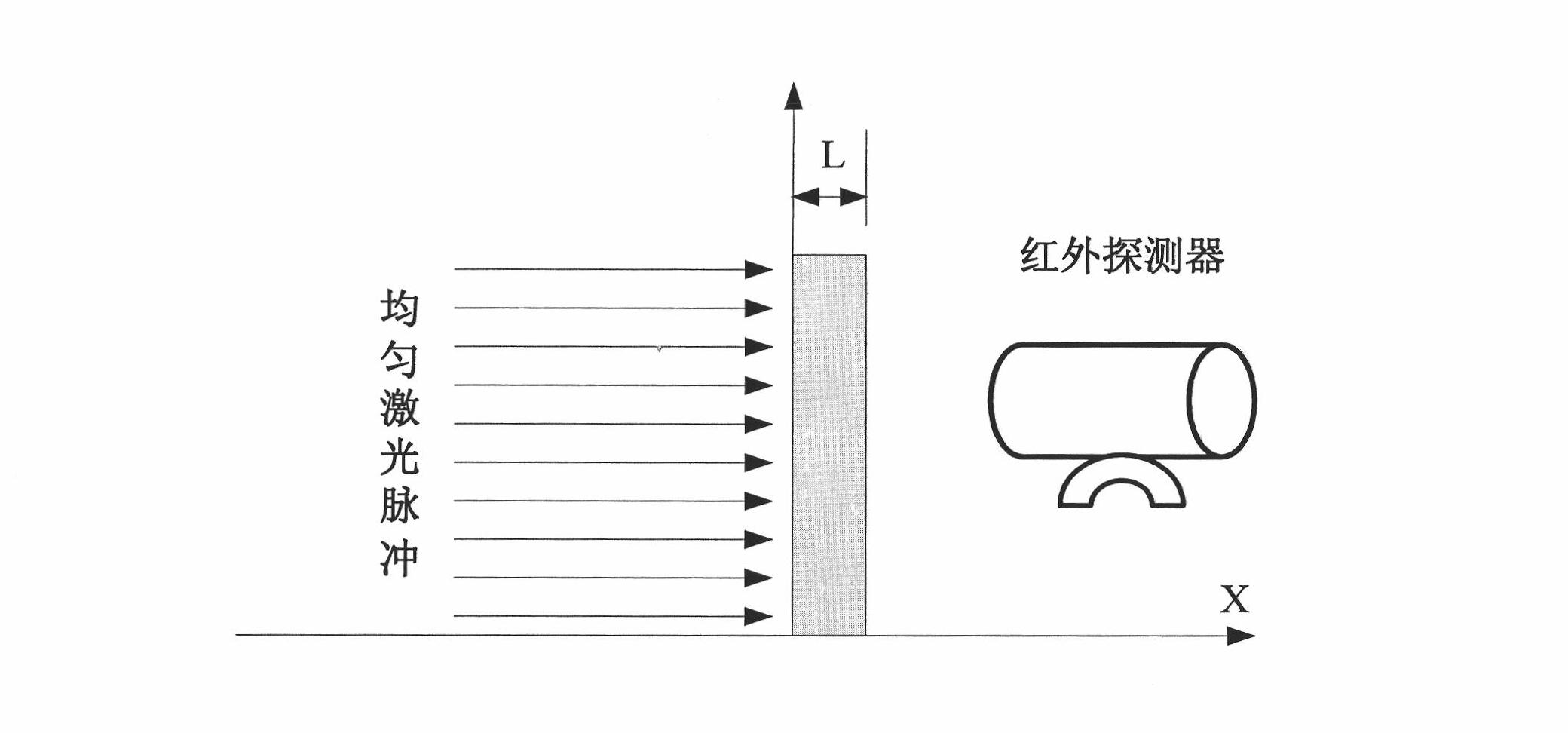
The invention provides a device for measuring a thermal diffusivity. The device comprises an excitation light source, an optical control device, a vacuum heating furnace, a temperature controlling device, a temperature measuring device and a data acquiring and processing device, wherein the excitation light source generates excitation light beams; the optical control device is provided with an optical component group, a light beam mass spectrometer and an energy meter and regulates the energy of the excitation light beams through a replaceable optical element in the optical component group; a heating element for heating a sample is arranged in the vacuum heating furnace; the temperature controlling device is used for controlling the heating temperature of the vacuum heating furnace; the temperature measuring device amplifies a temperature rise signal of the sample measured by a detector through a pre-amplifier and transmits the amplified signal to the data acquiring and processing device; the data acquiring and processing device comprises a data acquiring system and a data processing system; the data acquiring system transmits all acquired data signals to the data processing system; and the data processing system analyzes and repeatedly and theoretically corrects the data signals. The device for measuring the thermal diffusivity designed by the invention has the advantages of reducing the measuring repeatability of the thermal diffusivity of a material to be less than 1 percent, lowering uncertainty of measurement, improving the level of thermal diffusivity measurement and laying foundations for the establishment of a standard thermal diffusivity device in China, the preparation of a standard thermal diffusivity substance and the establishment of a standard thermal diffusivity database.
Owner:NAT INST OF METROLOGY CHINA +1
Flexible apparatus and method for monitoring and delivery
The present invention generally relates to a system and method that co-locates in a small flexible, configurable system and multi-level substrate sampling, rapid analysis, bio-sample storage and delivery functions to be performed on living tissues or matter obtained from living organisms. The types of the sampling may include chemical, biochemical, biological, thermal, mechanical, electrical, magnetic and optical sampling. In general, the analysis performed at the point of sampling measures the sample taken and records its value. The bio-sample storage function encapsulates a small sample of analyte and preserves it for subsequent examination or analysis, either on the organism by the system or at a remote location by an independent analysis system. Once stored, the sample can provide a record of a biological state at the precise time of sampling. The delivery at the point of sampling can include chemical, biochemical, biological, thermal, mechanical, electrical, magnetic and optical stimuli.
Owner:FISH & RICHARDSON P C
Sample measuring device
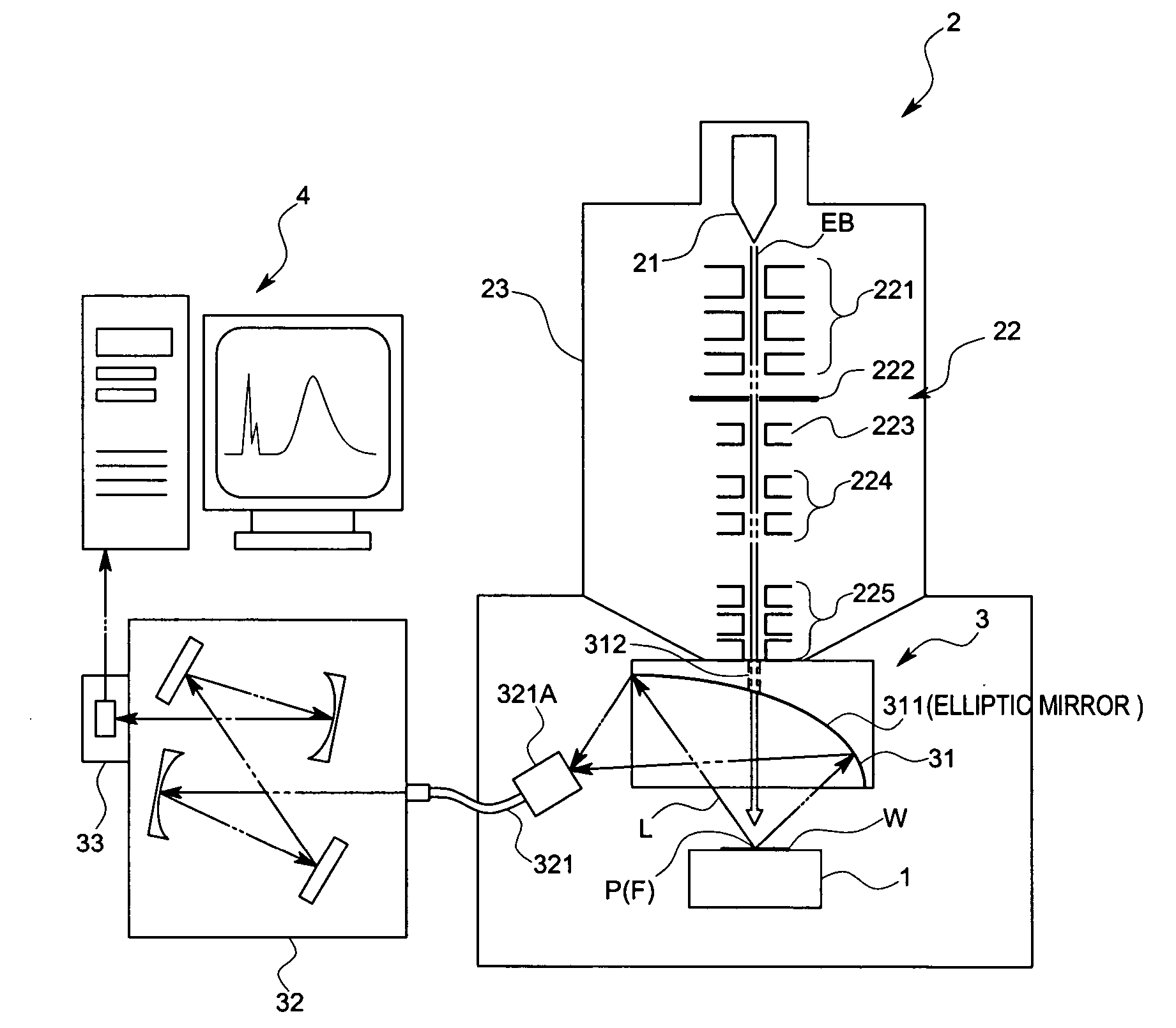
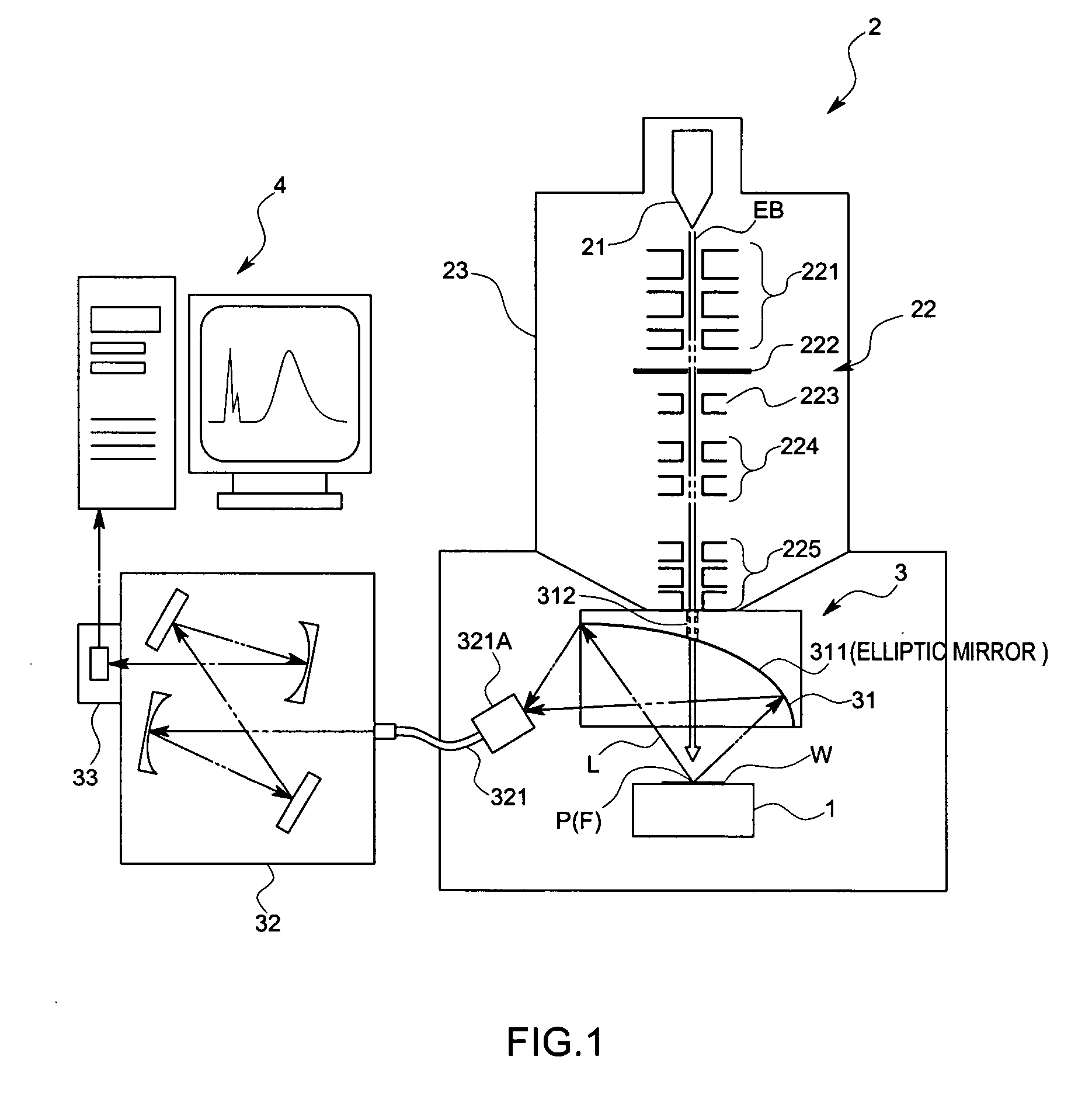
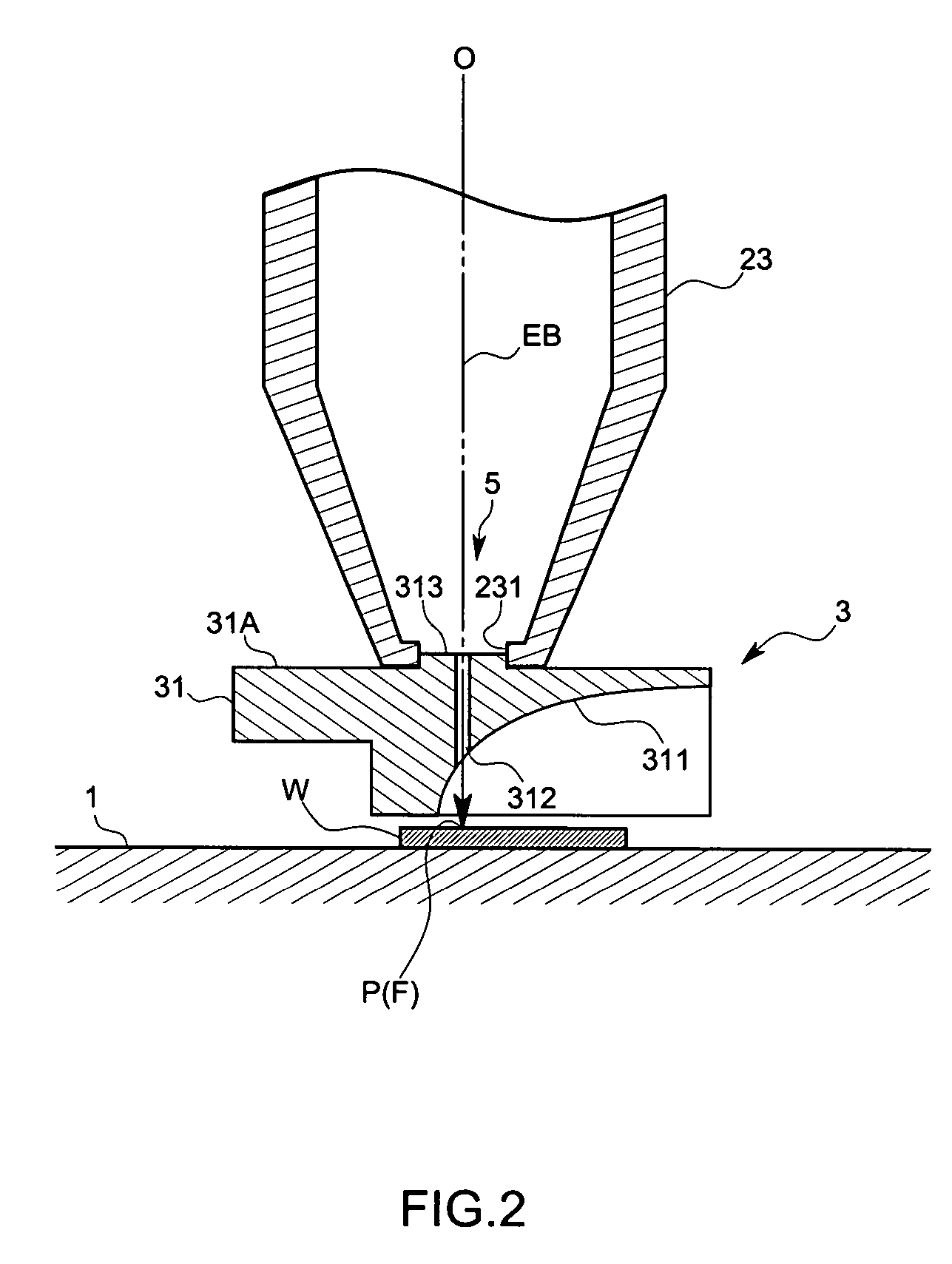
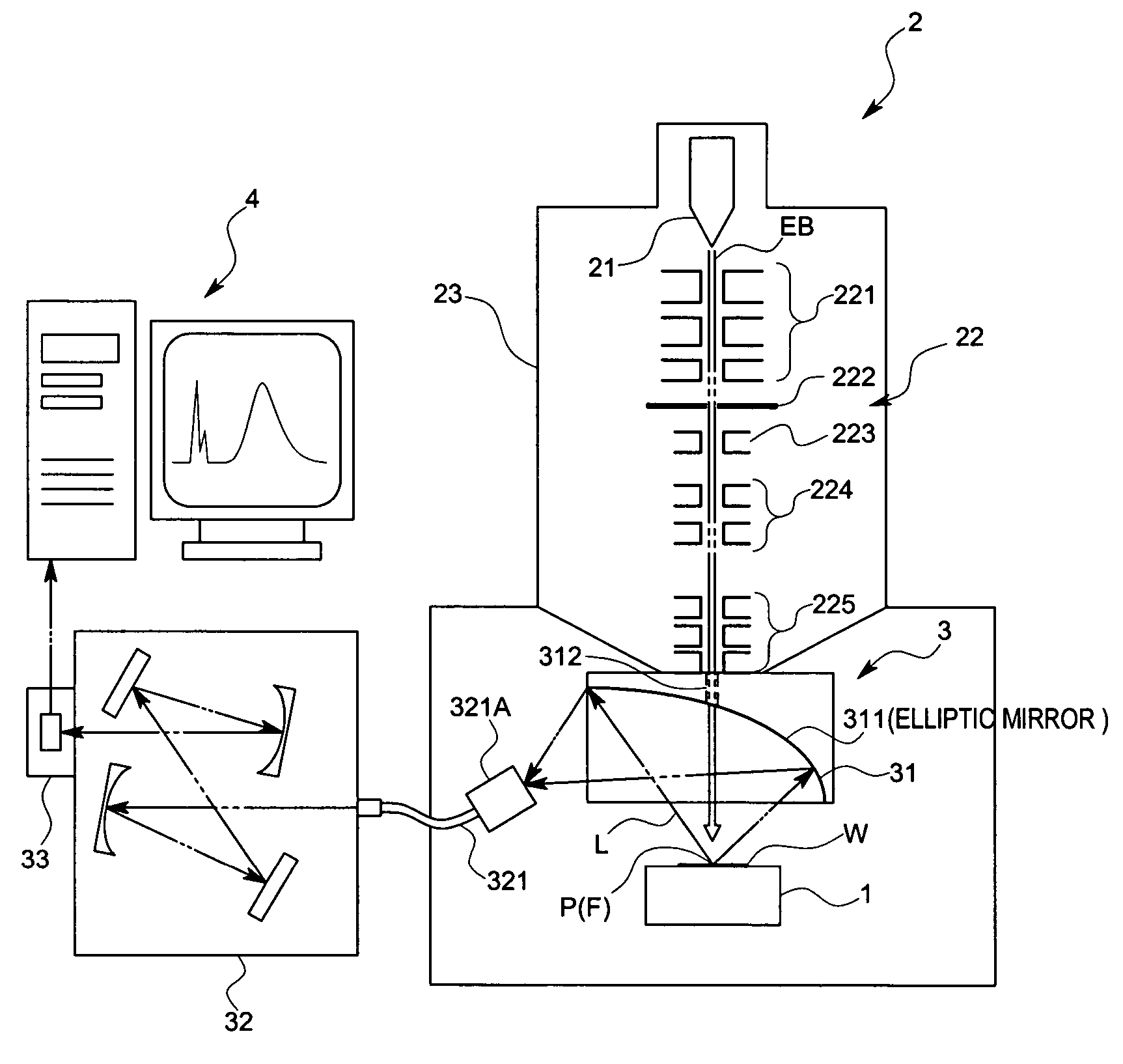
InactiveUS20070023655A1Shorten working distanceMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesSample MeasureMeasurement device
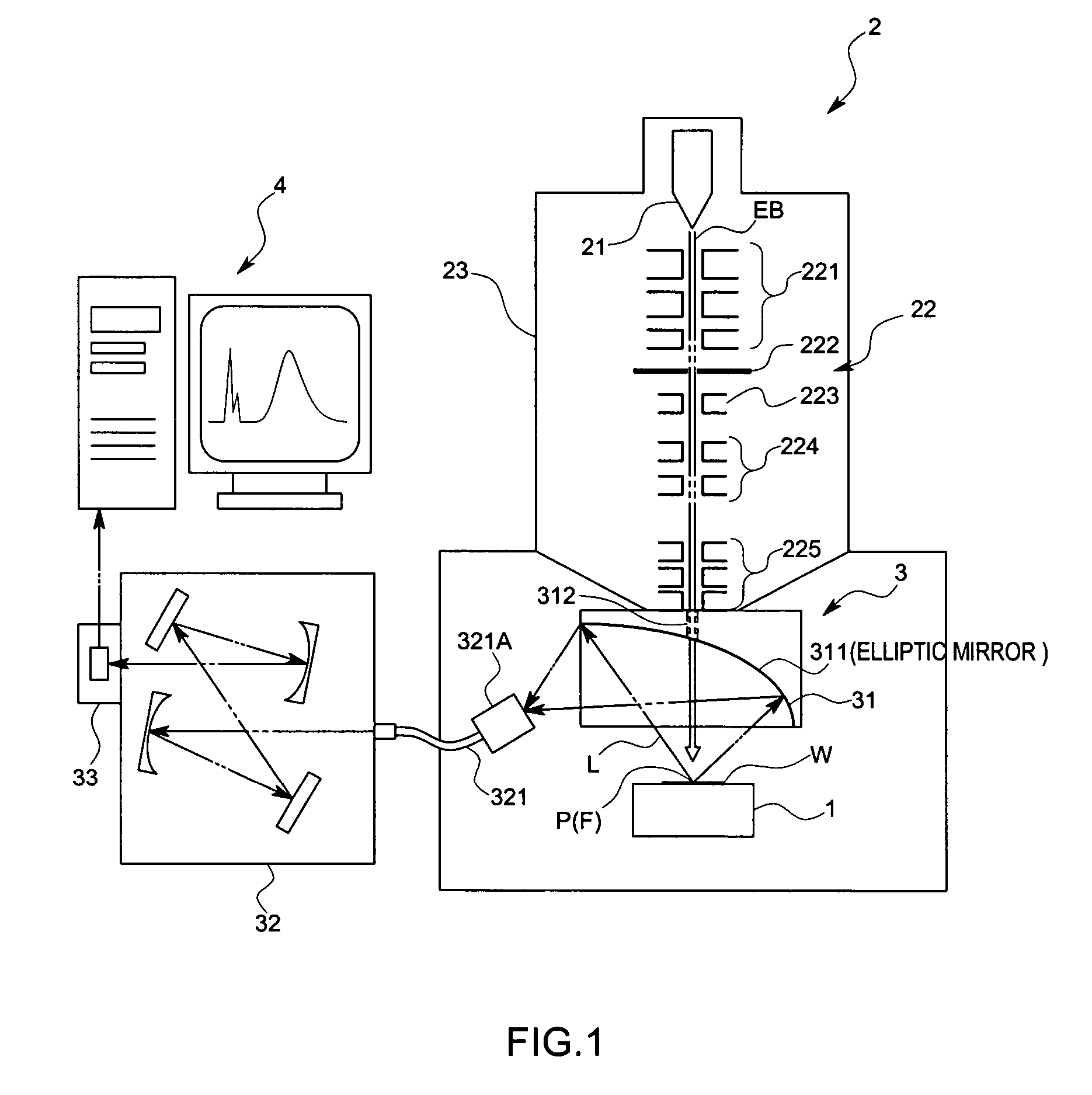
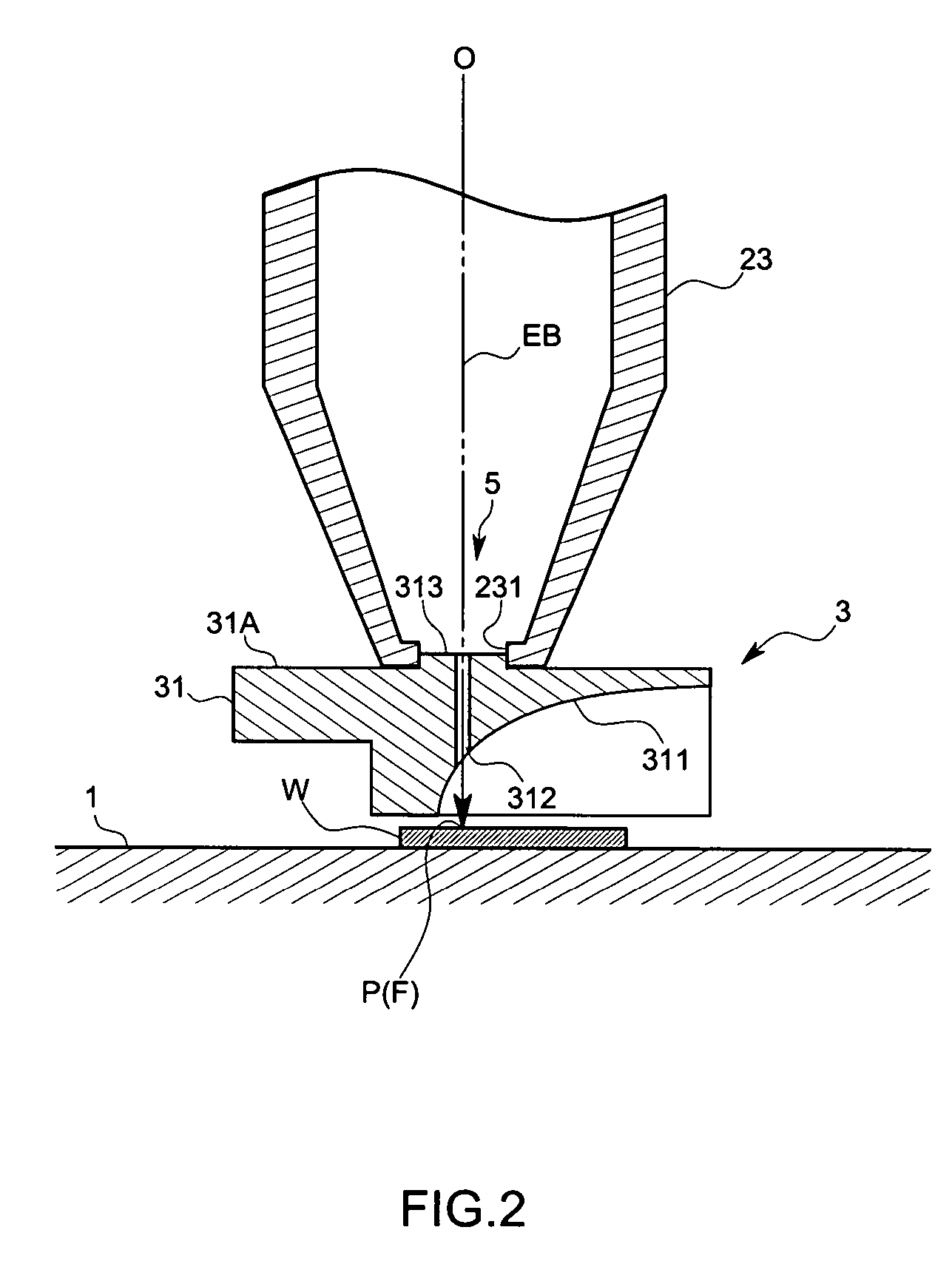
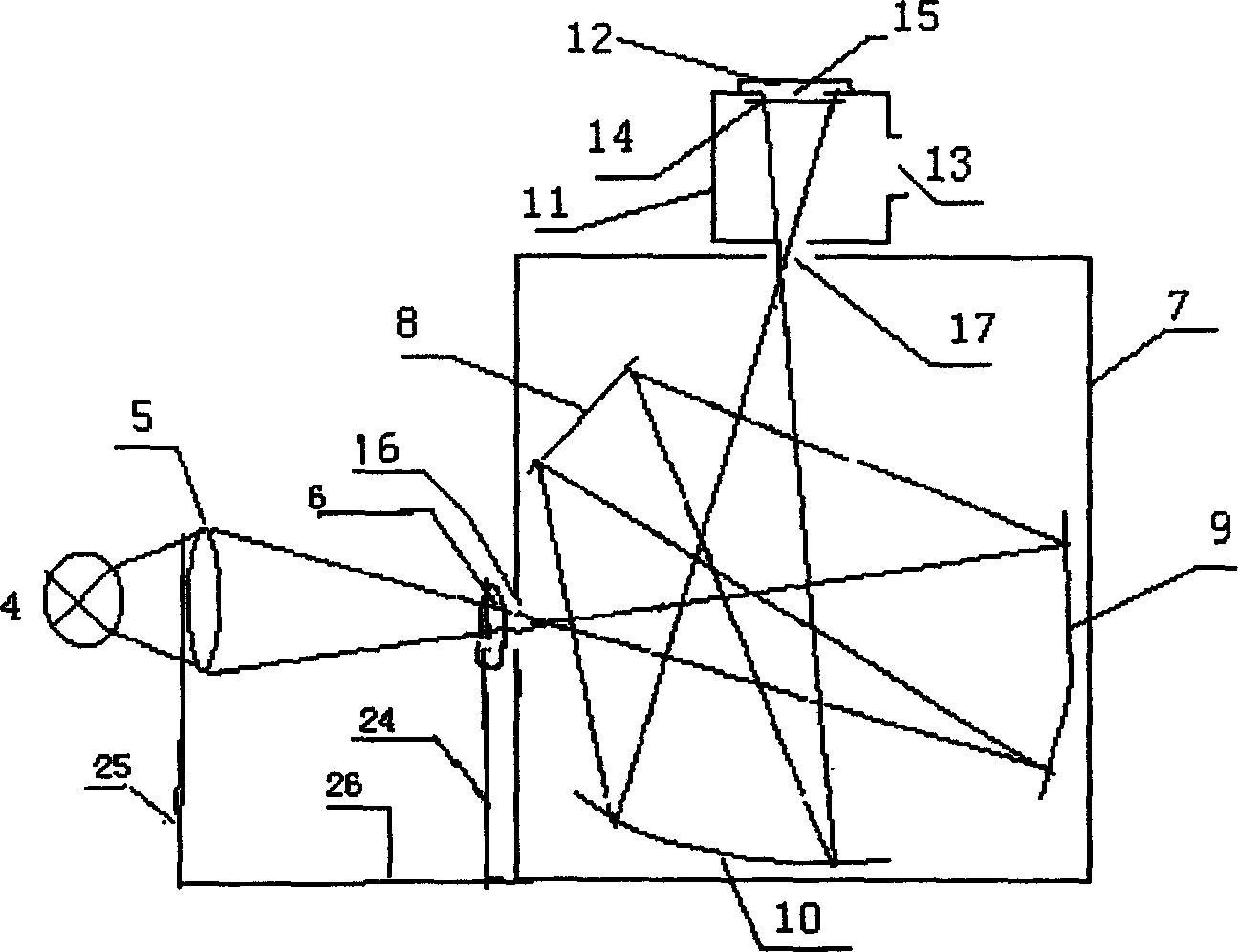
An object of this invention is to make it easy to adjust a position of the energy beam to irradiate and a position of a focal point of a light collecting mirror part, and to prevent displacement of the light collecting part due to vibration with a simple arrangement. A sample measuring device in accordance with this invention is to measure light generated from a sample W by irradiating electron beams EB on the sample W, and comprises a electron optical column part 23 that converges the electron beams EB, and a light collecting mirror part 31 that is arranged between the electron optical column part 23 and the sample W and that has an energy beam path 312 to pass the electron beams EB converged by the electron optical column part 23 and to irradiate the electron beams EB on the sample W and a mirror face 311 whose focal point F is set on an axis of the energy beam path 312 and that collects the light L generated from the sample W by means of the mirror face 311, wherein the light collecting mirror part 31 is supported by the electron optical column part 23 so that the axis of the electron beams EB coincides with the focal point F.
Owner:HORIBA LTD
Sample measuring device
InactiveUS7589322B2Shorten working distanceMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesSample MeasureAtomic physics
An object of this invention is to make it easy to adjust a position of the energy beam to irradiate and a position of a focal point of a light collecting mirror part, and to prevent displacement of the light collecting part due to vibration with a simple arrangement. A sample measuring device in accordance with this invention is to measure light generated from a sample W by irradiating electron beams EB on the sample W, and comprises a electron optical column part 23 that converges the electron beams EB, and a light collecting mirror part 31 that is arranged between the electron optical column part 23 and the sample W and that has an energy beam path 312 to pass the electron beams EB converged by the electron optical column part 23 and to irradiate the electron beams EB on the sample W and a mirror face 311 whose focal point F is set on an axis of the energy beam path 312 and that collects the light L generated from the sample W by means of the mirror face 311, wherein the light collecting mirror part 31 is supported by the electron optical column part 23 so that the axis of the electron beams EB coincides with the focal point F.
Owner:HORIBA LTD
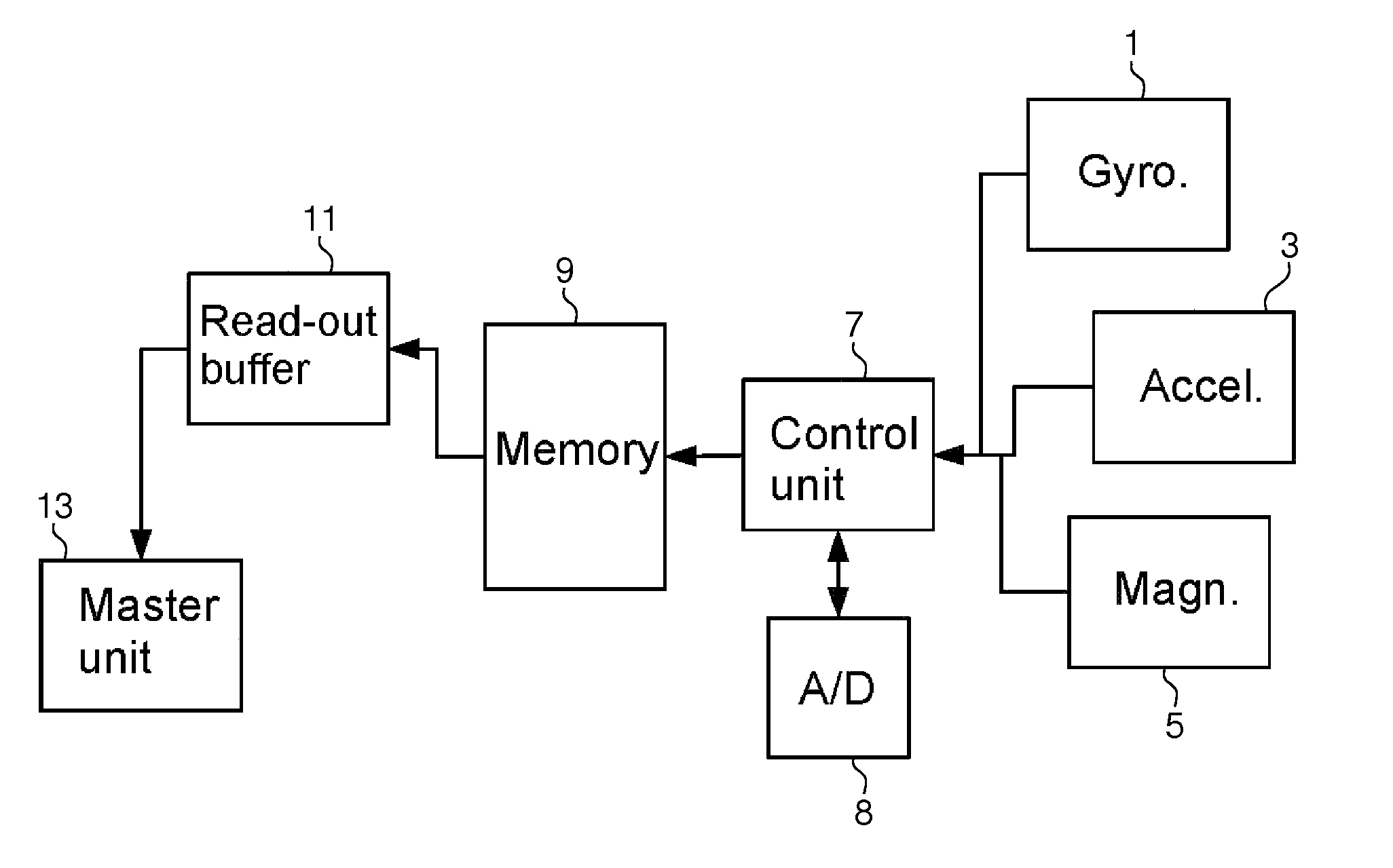
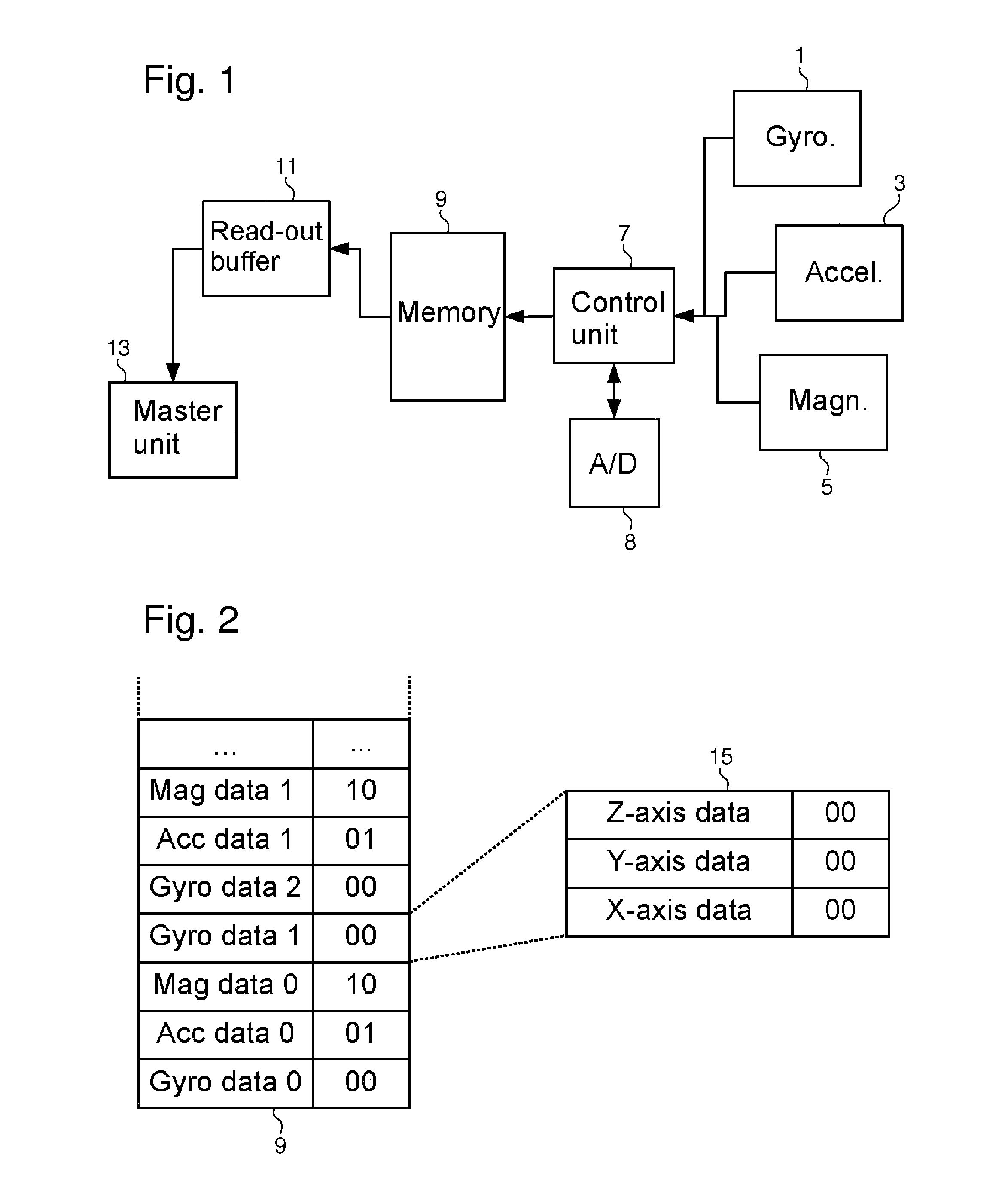
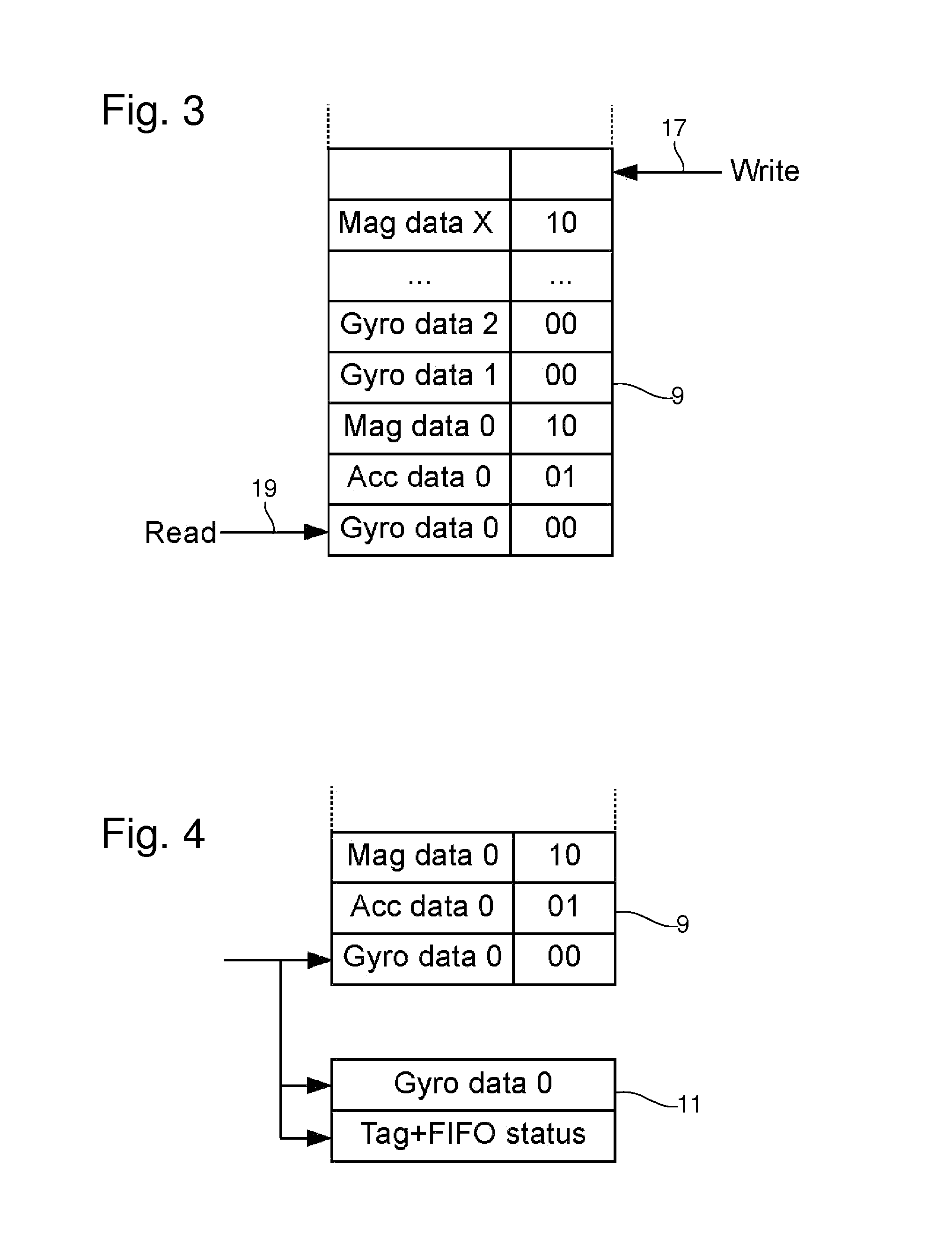
Operating a FIFO memory
ActiveUS20150331805A1Memory space can be efficientlyMinimize power consumptionMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer hardwareSample Measure
Owner:EM MICROELECTRONIC-MARIN
Solid phase extraction sample bottle and thermal analysis apparatus
ActiveCN1721850AImprove preprocessing efficiencyGood data repeatabilityComponent separationSample MeasureBottle
The invention relates to a solid phase extract sampling bottle and heat analysis device in the field of sample measuring technology. It is a liquid-solid extraction and gas-solid absorption technology, which is used to pre-treat gas sample, liquid sample and isotropy sample and to extract and collect the objecting component, especially in color analysis and instrumental analysis. The solid phase extract sampling bottle and heat analysis device comprises an extract sampling bottle which is like a cylinder with one open end and one sealed end as bottom, and a casing and one layer extracting fixed phase on the middle part of the cylinder's inner wall, a heat analysis device and an extract sampling bottle cleaning device.
Owner:QINGDAO SHENGHAN CHROMATOGRAPH TECH CO LTD
Modified Y-type molecular sieve and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103073024AReduce yieldIncrease profitCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieveLattice defects
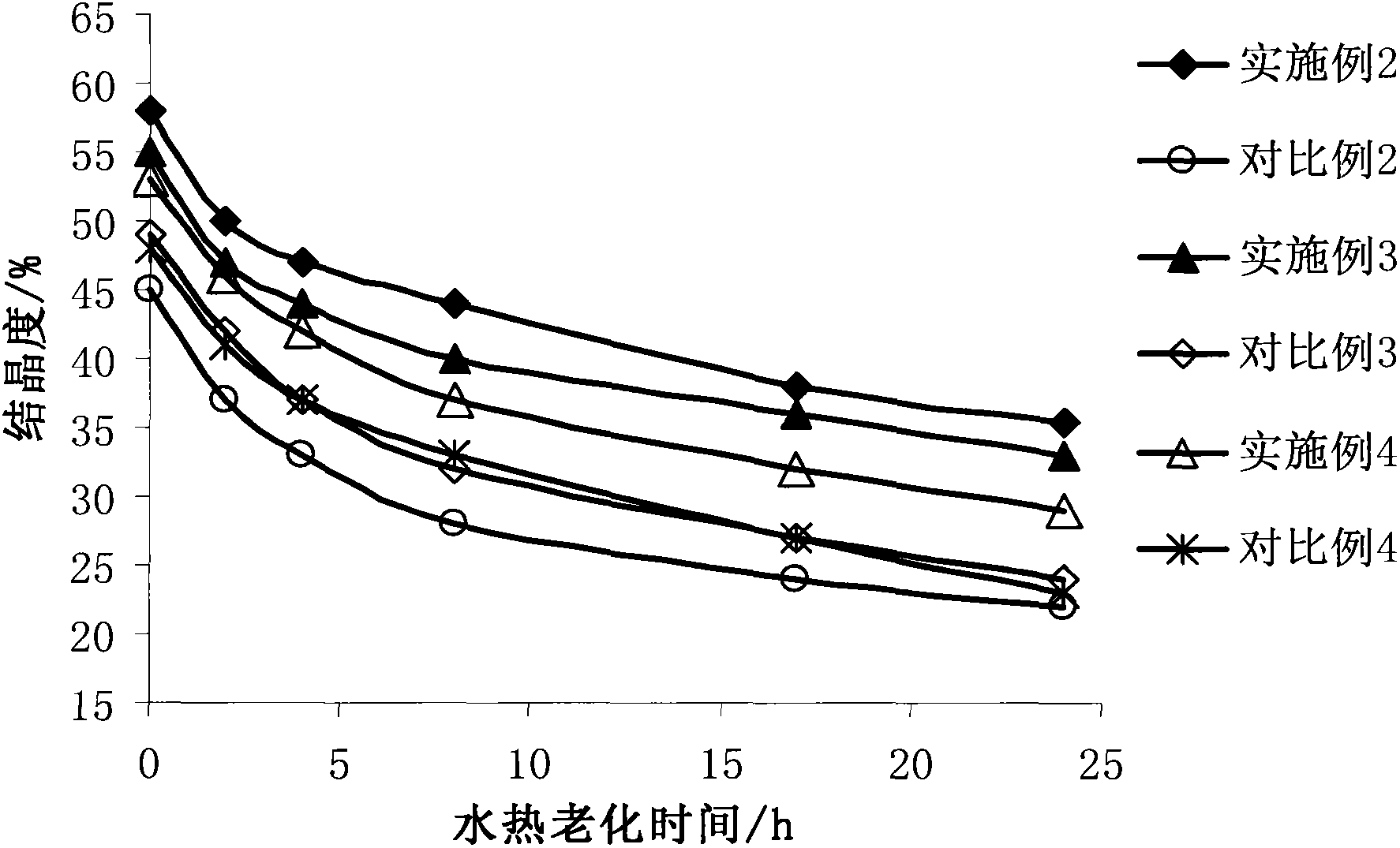
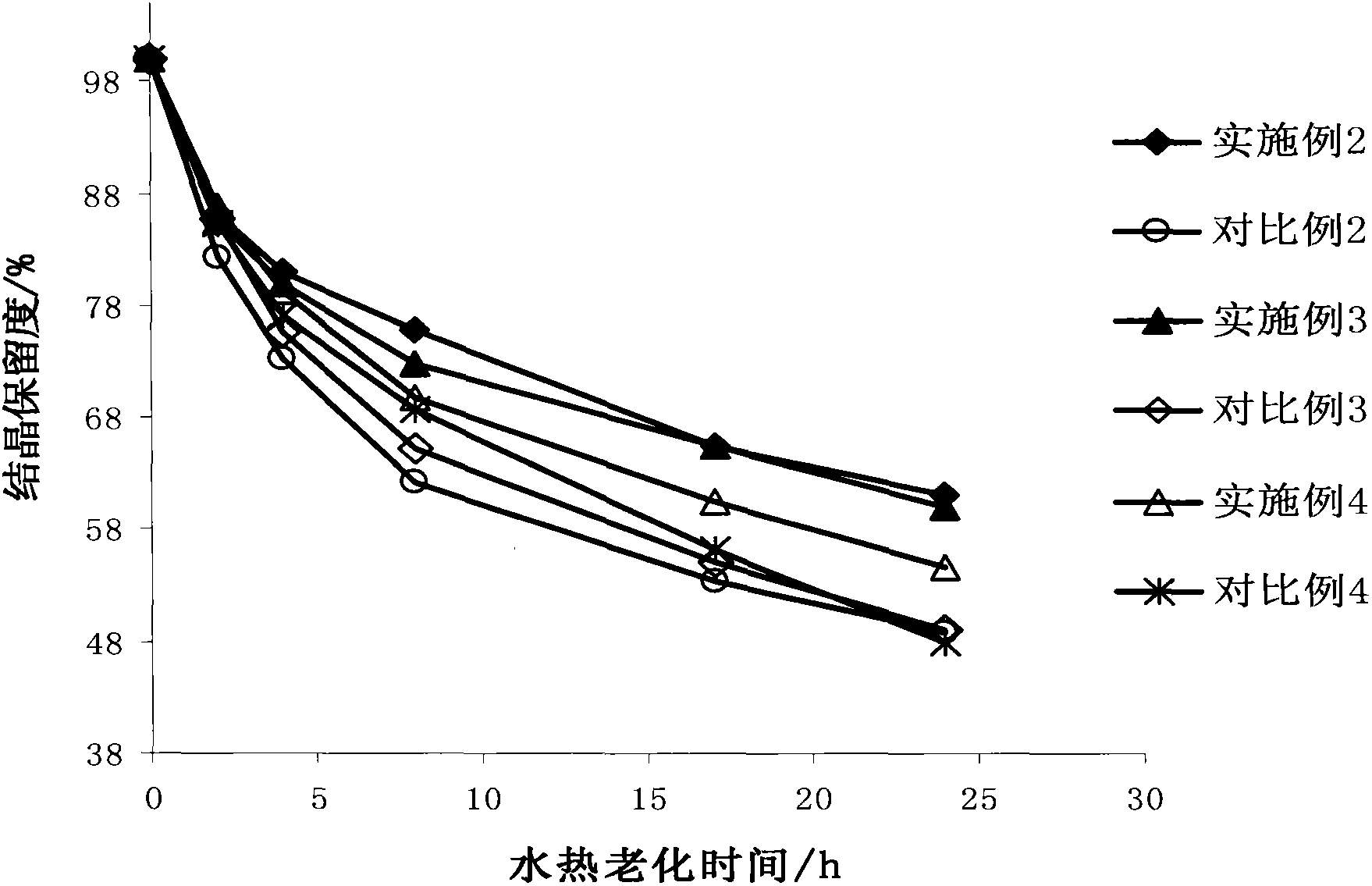
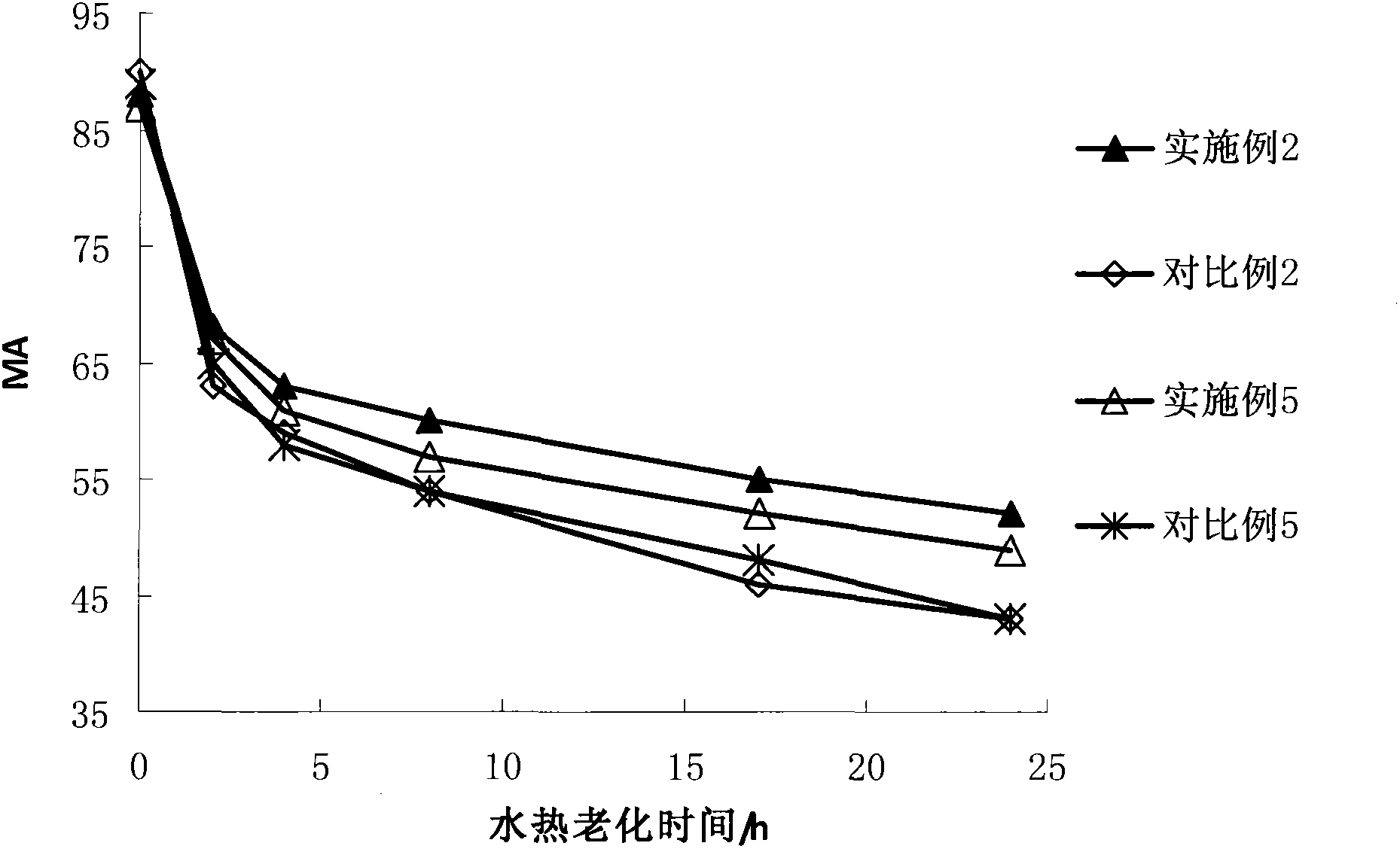
The invention discloses a modified Y-type molecular sieve which is characterized in that a cell constant is 2.420-2.440nm. According to weight percentages, the molecular sieve comprises 0.05-6% of P, 0.03-10% of RE2O3, and less than 22% of alumina. A specific hydroxyl nest concentration is smaller than 0.35mmol / g. In a formula, M200 DEG C, M500 DEG C and M800 DEG C t respectively represent weight loss percentages of the sample measured at 200 DEG C, 500 DEG C and 800 DEG C. C is sample crystallinity degree. The molecular sieve provided by the invention has low lattice defect, and can be used in a catalytic cracking catalyst as an active component. With the molecular sieve, long-period stable activity can be maintained, coke yield can be effectively controlled, and heavy oil utilization rate can be improved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Multi-section earth-pillar for simulating soil in petroleum hydrocarbon polluted aeration zone
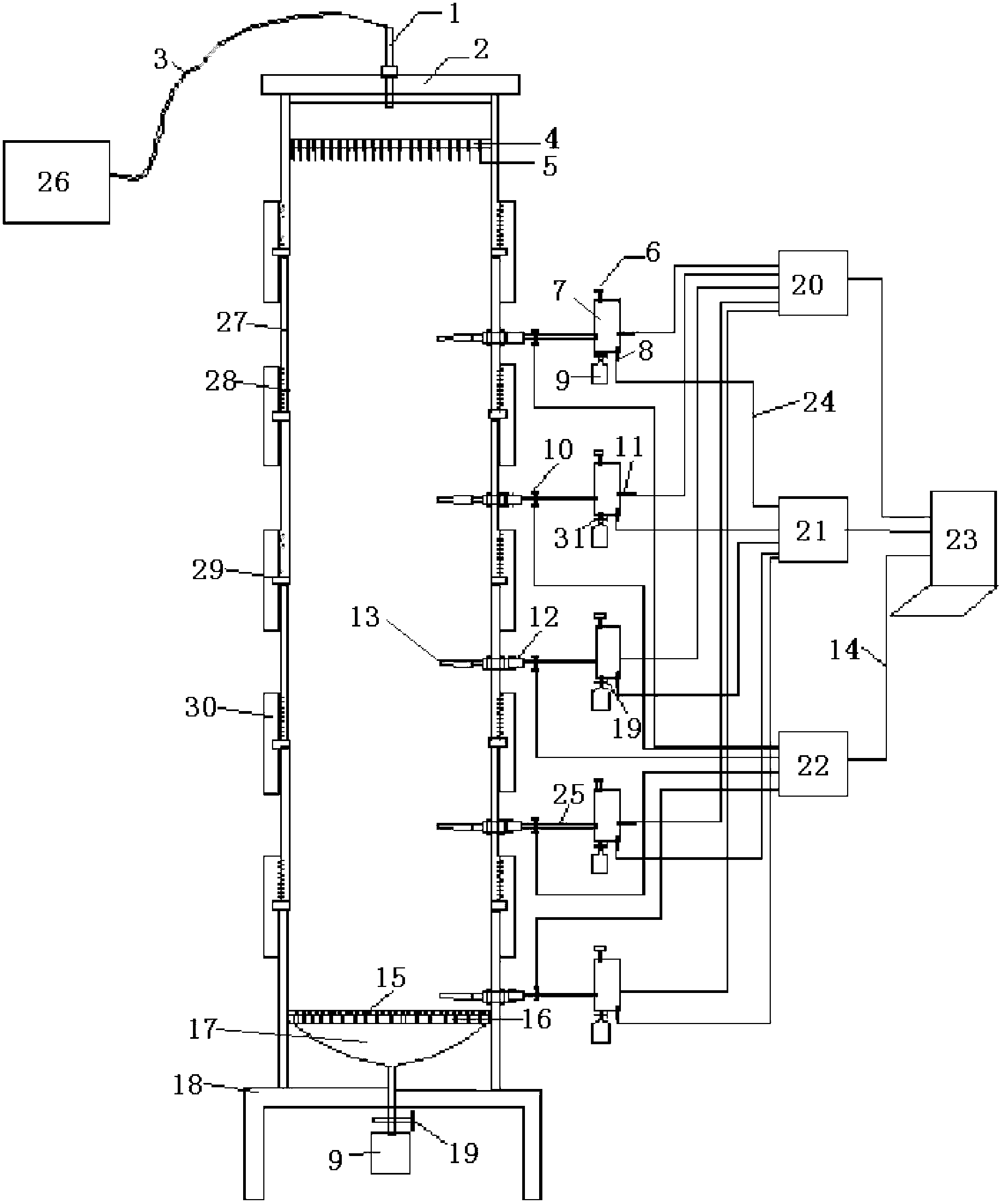
InactiveCN103018421AFlexible control of vertical heightReduce churnWithdrawing sample devicesEarth material testingPeristaltic pumpSample Measure
The invention provides a multi-section earth-pillar for simulating soil in a petroleum hydrocarbon polluted aeration zone. The multi-section earth-pillar at least comprises a base, a rotatable earth-pillar device, a sampling and sample-measuring device and a leaching device, wherein the rotatable earth-pillar device is arranged and fixed on the base; the leaching device is arranged on the top of the rotatable earth-pillar device, wherein the rotatable earth-pillar device comprises three or more rotatable earth-pillar units, a compact gauze element, an organic glass plate A with holes and a sample-collecting cavity of a sand-core funnel; the leaching device comprises a peristaltic pump, a glass rotator flow meter, an organic glass plate B with holes, a top cover and a rubber tube; the sampling and sample-measuring device comprises a sampling unit and a sample-measuring unit, wherein sampling heads which are arranged in the rotatable earth-pillar units are arranged on the sampling unit; and the sample-measuring unit is connected with the sampling unit and used for detecting the samples taken out by the sampling unit. The multi-section earth-pillar provided by the invention solves the defects in the prior art, can automatically sample in a quantitative manner, can get the soil in a layered manner to measure the content of petroleum hydrocarbons in the soil, and also can reduce the influence of sampling on the flow fields.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Integrated method and integrated device of SCD (System Configuration Document) of transformer station
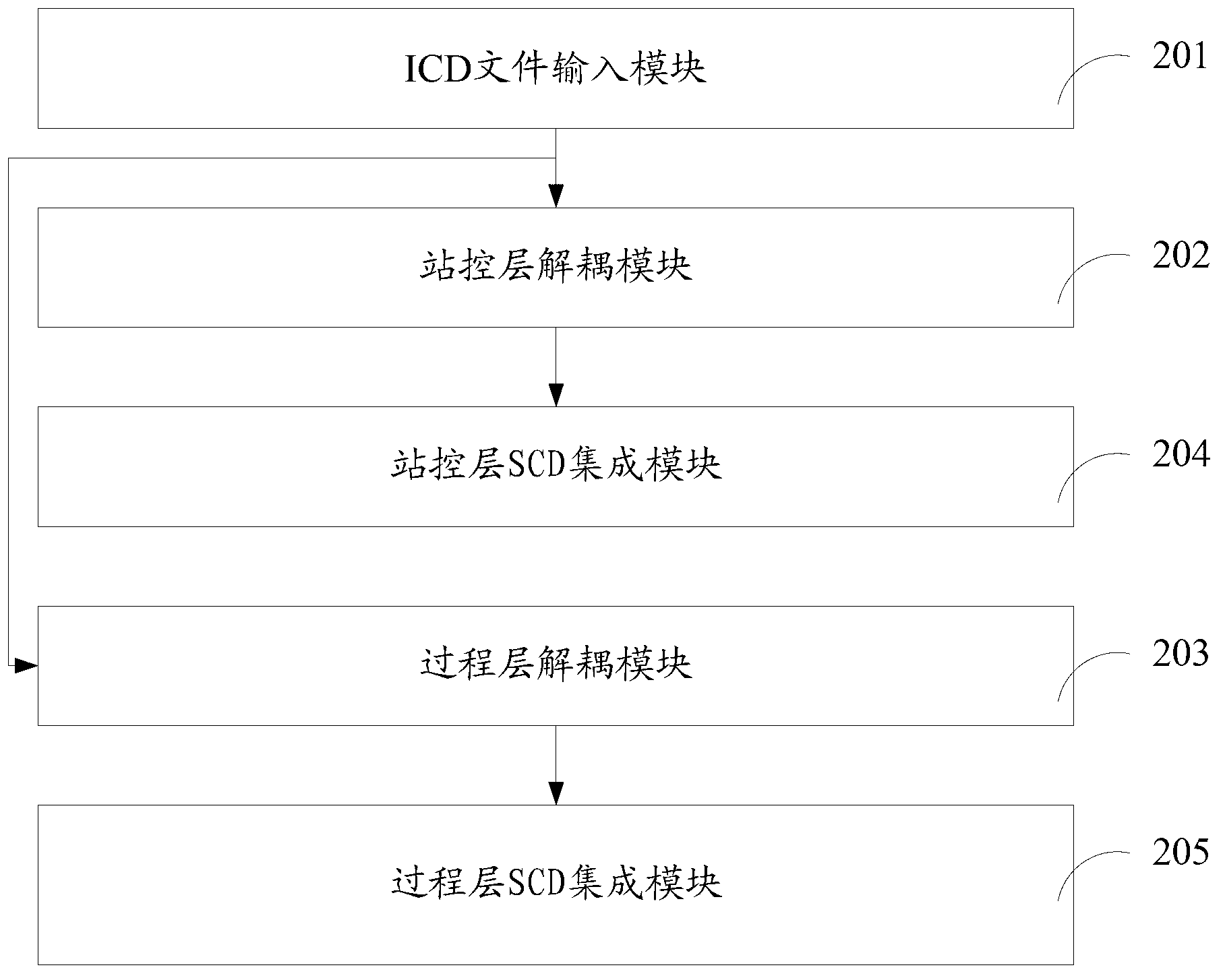
ActiveCN102801213AAddressing integration inefficienciesCircuit arrangementsInformation technology support systemCommunications systemSample Measure
The invention provides an integrated method of an SCD (System Configuration Document) of a transformer station. The integrated method comprises the steps of inputting an ICD (Interface Control Document), wherein the ICD comprises a header, a communication, a substation, an IED (Intelligent Electronic Device) and a data type template; decoupling a station level according to the ICD, and obtaining a station level ICD; decoupling a process level according to the ICD, and obtaining a process level ICD; inputting the station level ICD, configuring a station level communication parameter and a record control block, and obtaining a station level SCD; and inputting the process level ICD, configuring a GSE (Generis Substation State Event) of the process level, an AMV (Sampled Measured Value), a GOOSE (General Object Oriented Substation Event) and SV (Sample Value) control blocks and inputs, and obtaining a process level SCD. The invention also provides an integrated device of the SCD of the transformer station. According to the integrated device provided by the invention, the integrated efficiency of the SCD can be increased.
Owner:POWER DISPATCHING CONTROL CENT OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID CO LTD
X-ray fluorescence analyzer and X-ray fluorescence analysis method
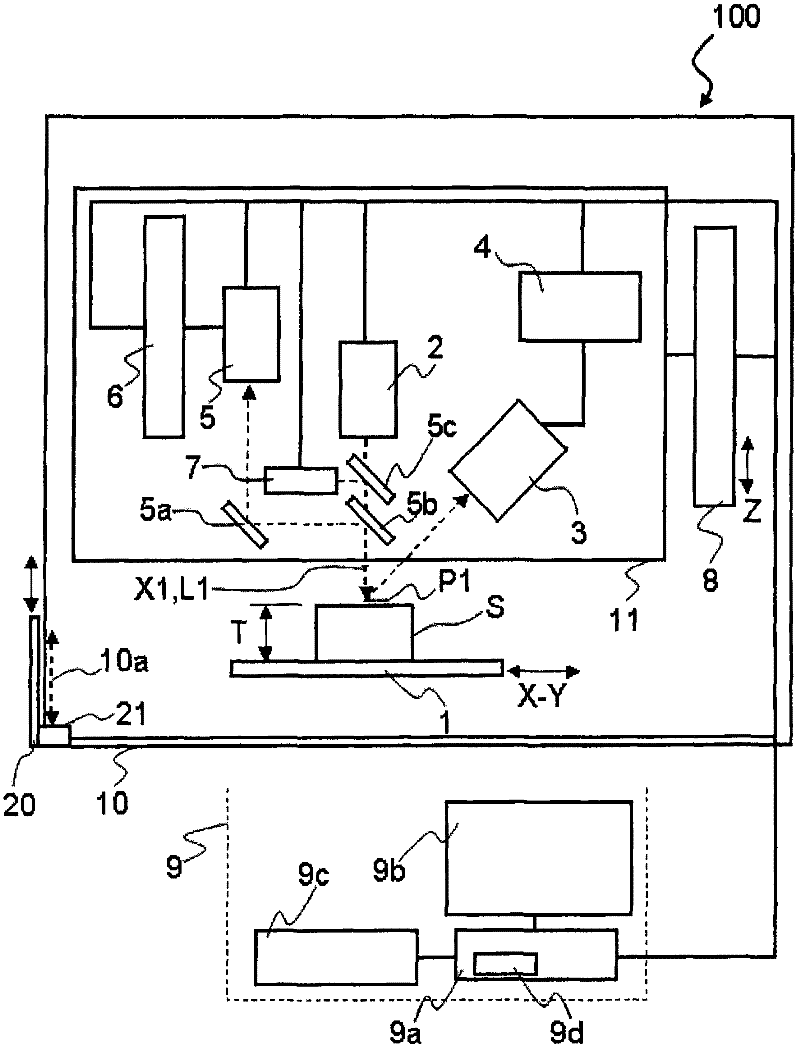
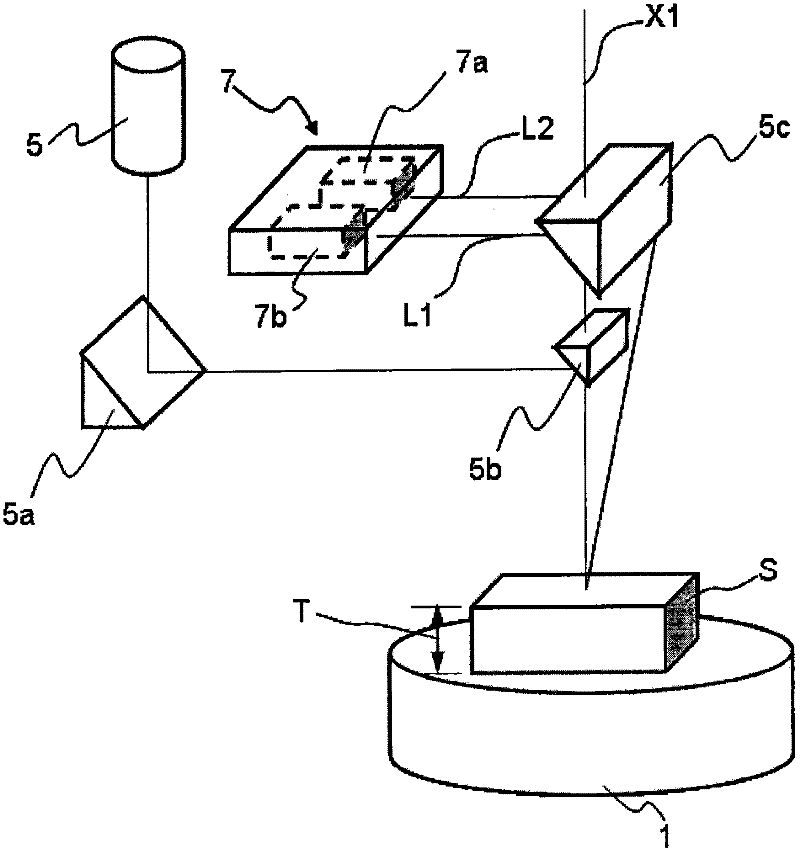
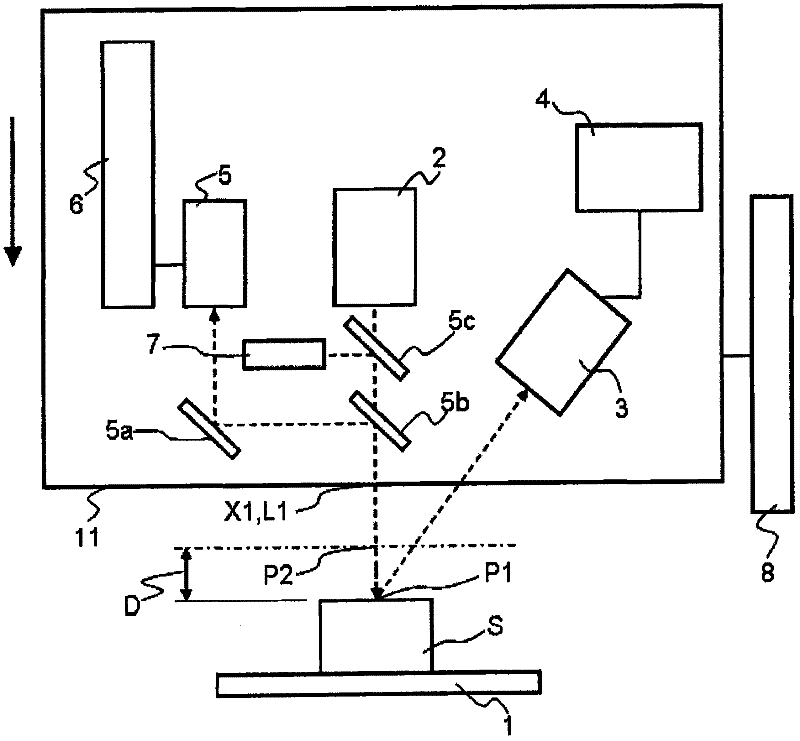
ActiveCN102384924AImprove work efficiencyDetermination of safety samplesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSample MeasureX ray analysis
The invention provides an X-Ray fluorescence analyzer and an X-ray fluorescence analysis method advantaged by high operating efficiency and safe sample measuring. The fluorescence analyzer (100) includes: a radioactive ray source (2) illuminating radioactive rays upon a radioactive point (P1) on a smapel (S); an X-ray detector (3); a moving mechanism (8) capable of moving the sample with respect to the radioactive ray source and the X-ray detector;an enclosure (10); a door (20) for opening and closing an opening (10a) for the sample into and out of the enclosure; a height measurement mechanism (7) capable of measuring a height at the irradiation point; a moving mechanism control unit (9) for adjusting a distance between the sample and the radiation source as well as the X-ray detector based on the measured height at the irradiation point; a laser unit (7) for irradiating the irradiation point with a visible light laser beam; a laser start control unit (9) for irradiating the visible light laser beam by the laser unit (7) when the door is open state; and a height measurement mechanism start control unit (9) for starting the height measurement mechanism to measure the height at the irradiation point when the door is opened.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH TECH SCI CORP
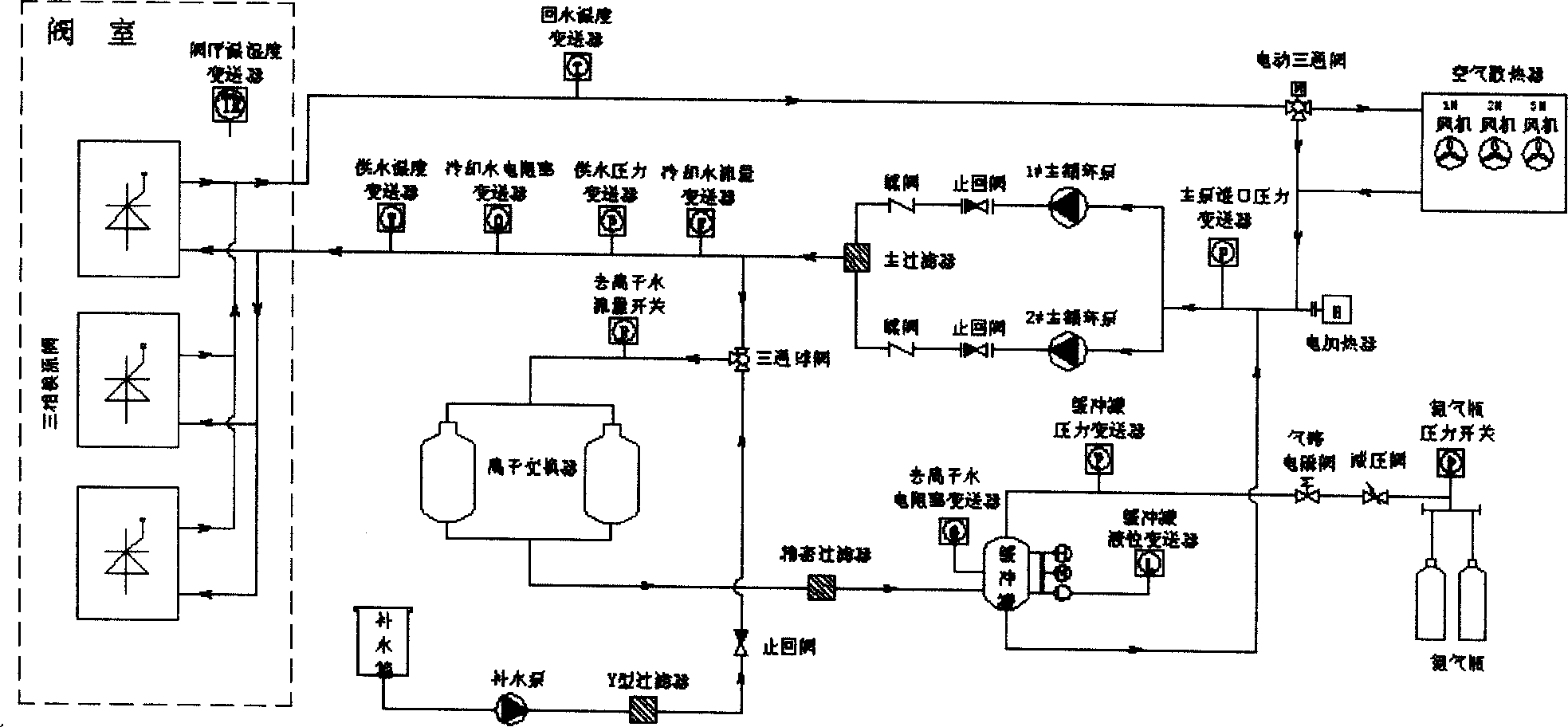
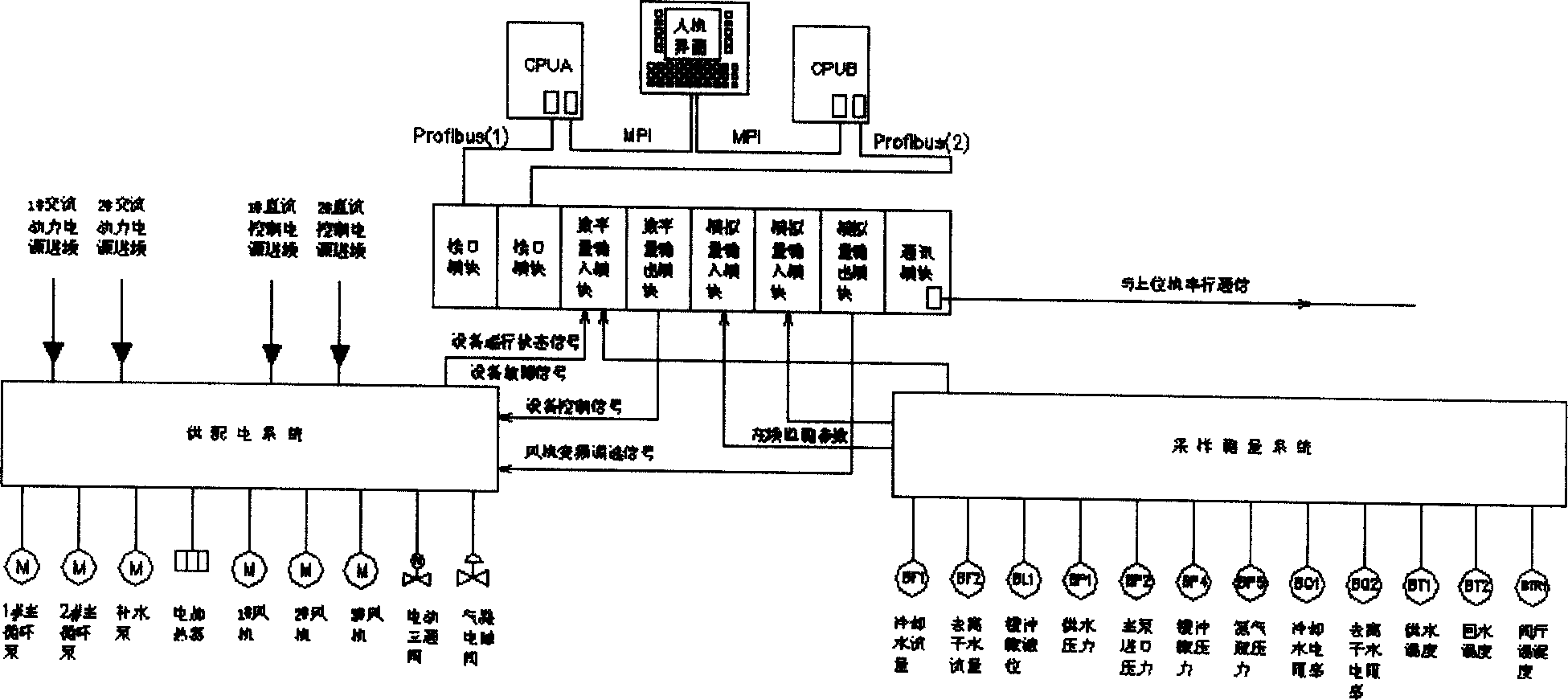
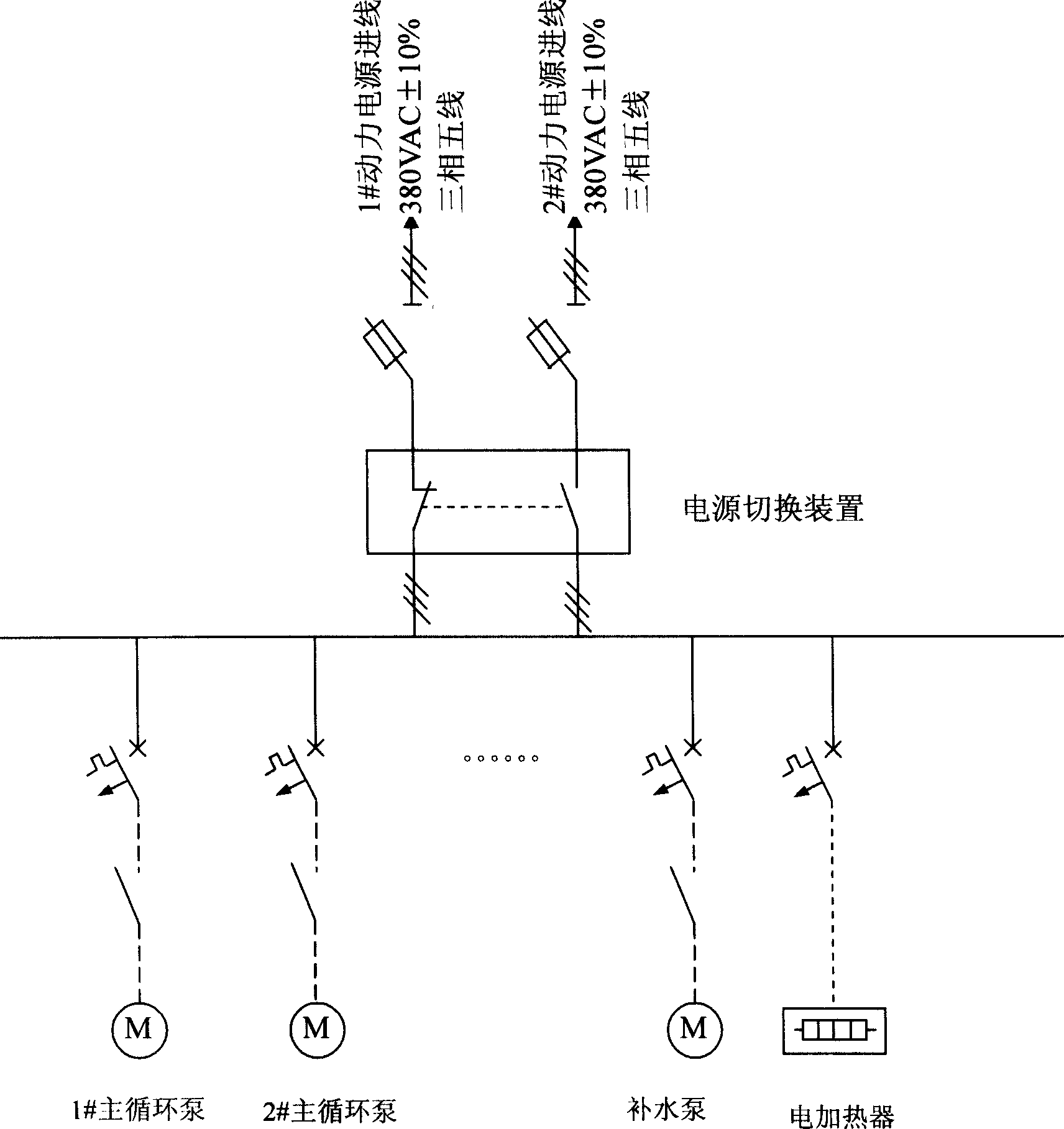
Control system of hermetic circulating type pure water cooling device for thyristor valve set
ActiveCN1766768AAvoid damageExpand the scope of the accidentComputer controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsHuman–machine interfaceSample Measure
The invention relates to a thyristor valve group closed cooling water recalculated apparatus control system, which relates to the electricity system and the thyristor valve group cooling apparatus of the electron apparatus. The system is mainly formed by a power distribution system, a sample measuring system, a controller and a human-machine interface. The system adopts dc power couple design to do redundancy design to the CPU and the key instrument and dose temperature control by high, middle and low three sections; it adopts dual node to ascertain the starting logic of the water cooling apparatus, which can to continuous sample to the buffer pot liquid to achieve the leakage preserving of the system; it also adopts electromagnetic compatible design to the system.
Owner:GUANGZHOU GOALAND ENERGY CONSERVATION TECH +1
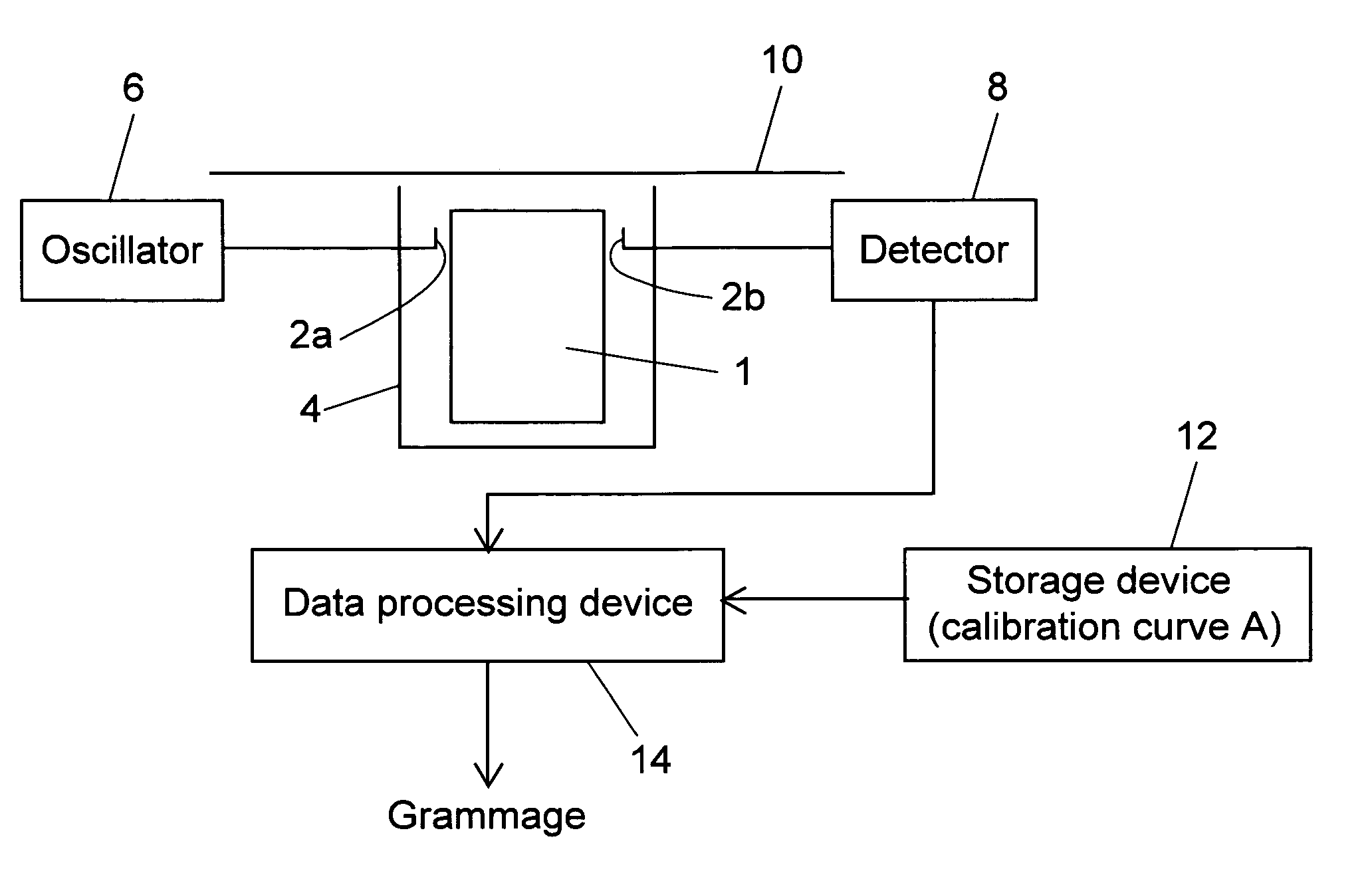
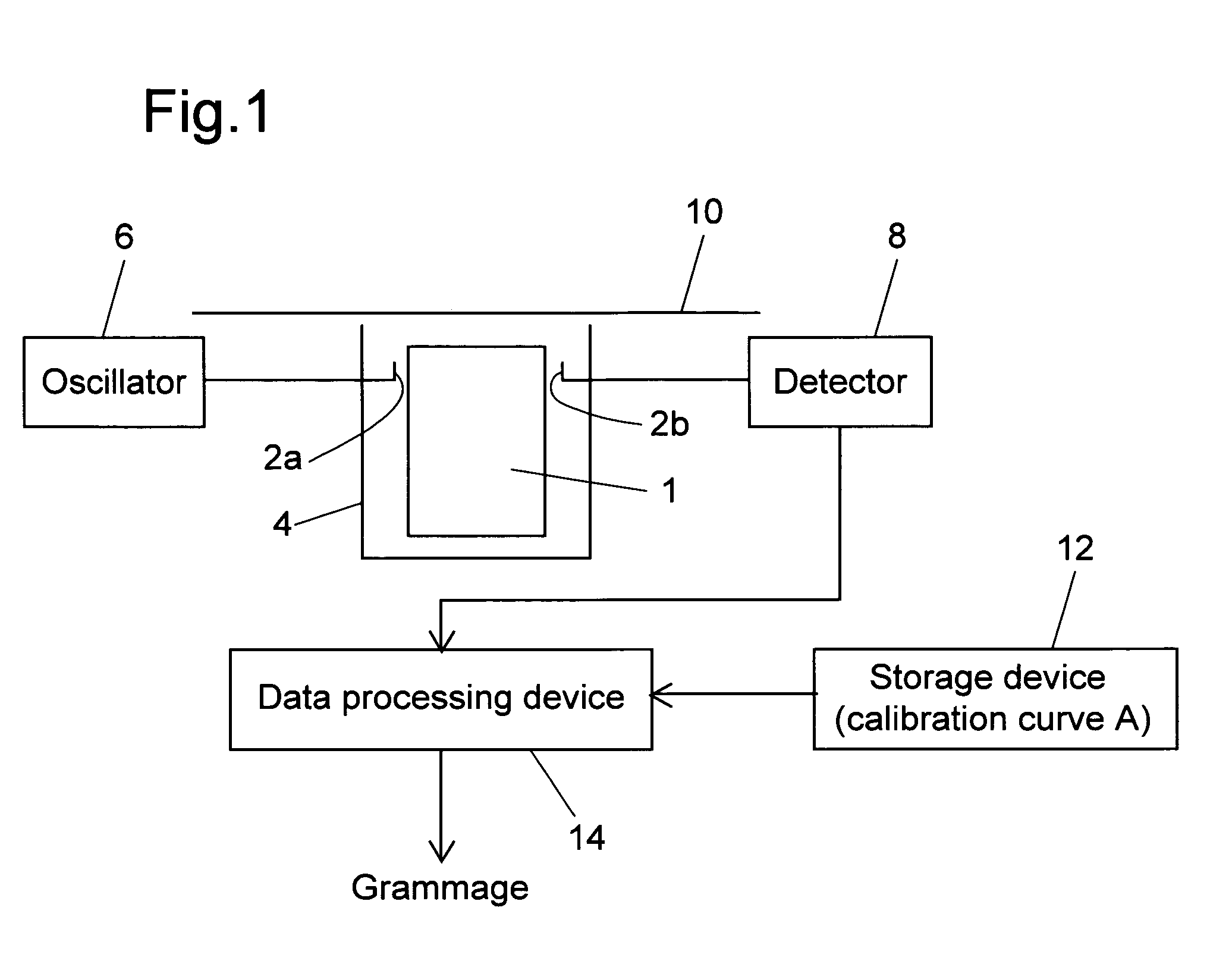
Method and apparatus for measuring grammage
InactiveUS7423435B2Easy to handleMeasure securityResistance/reactance/impedenceMoisture content investigation using microwavesMicrowaveSample Measure
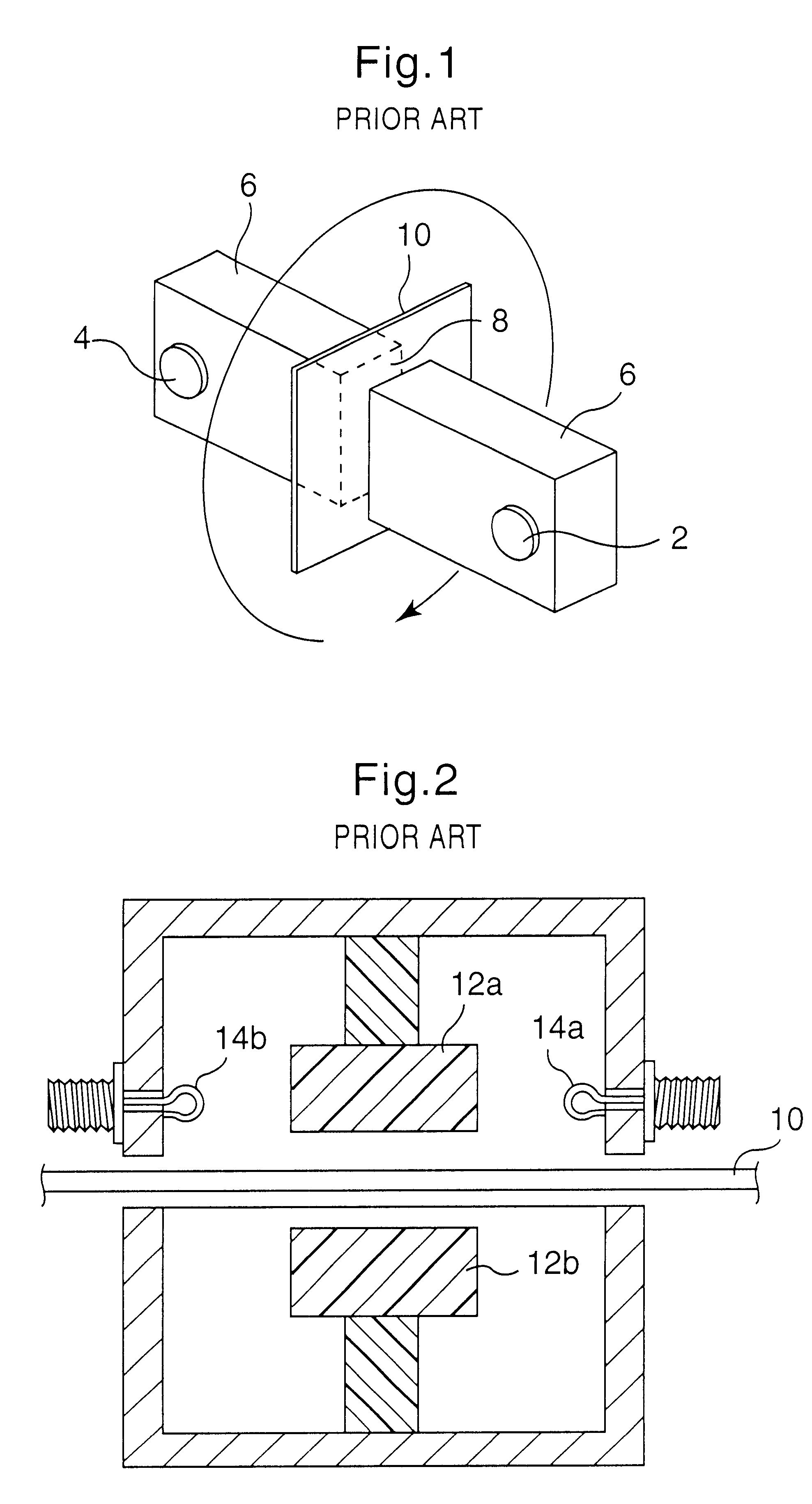
A grammage measuring apparatus including a dielectric resonator which is arranged only at one side surface of a sample; a shielding container with which the dielectric resonator is substantially covered except for a sample measuring surface; a microwave excitation device which causes the dielectric resonator to generate an electric field vector; a detection device which detects transmission energy or reflection energy by the dielectric resonator; a storage device in which a calibration curve indicating a resonance frequency shift amount for a grammage is stored; and a data processing device which calculates the grammage of a measuring sample from the calibration curve and measurement result of the resonance frequency shift amount of the measuring sample.
Owner:OJI PAPER CO LTD
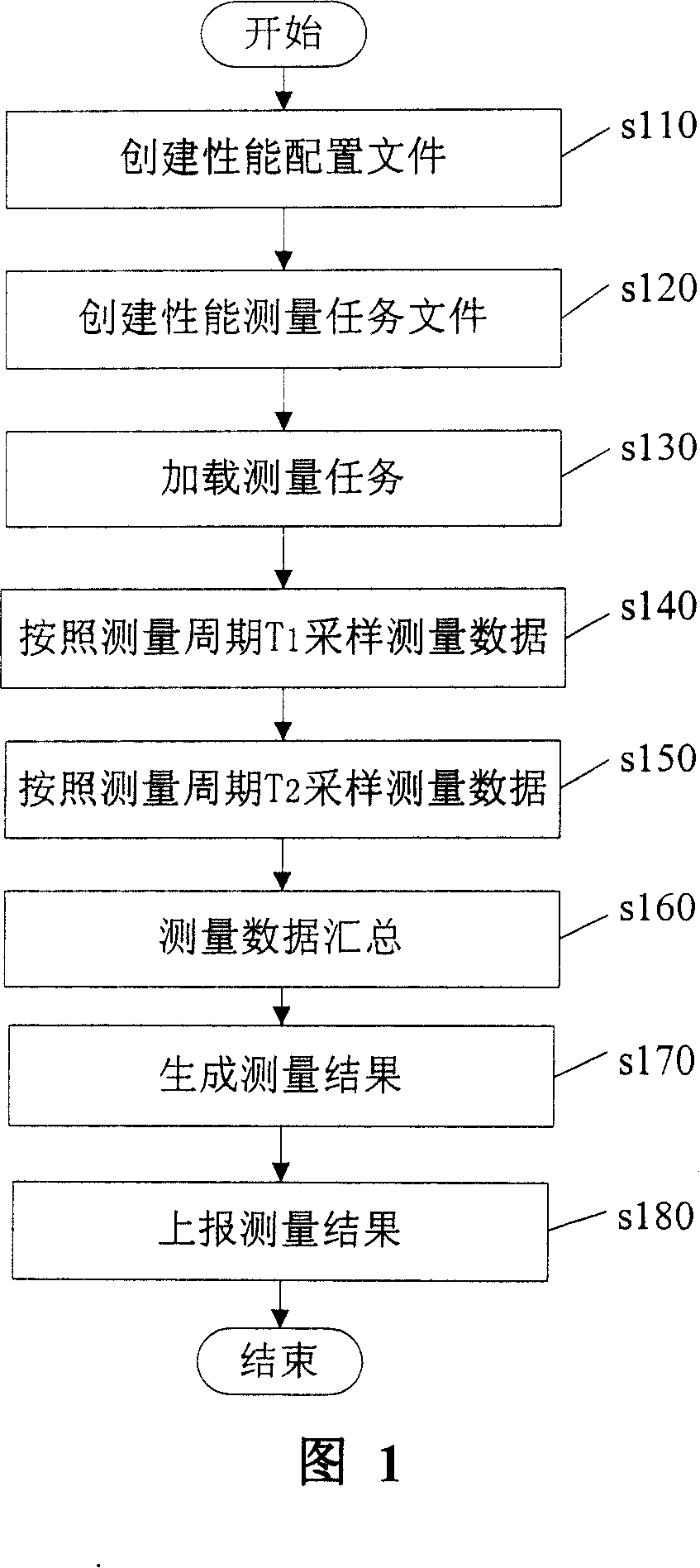
Network performance measuring method and system
InactiveCN101072130AComplete measurement dataPowerful means of observationData switching networksSample MeasureData acquisition
The method includes following steps: configuring measurement task, creating measurement task in task reporting mode (TRM) based on measurement in full index reporting mode (FIRM); according to measurement period T1, data acquisition point samples measured data of network performance index in TRM, otherwise, samples data according to measurement period T2; measured data are reported to master control board of net element; based on measured data of measurement task in TRM, the master control board of net element generates measured data corresponding to the measurement task; the master control board collects measured data in TRM and measured data of measurement task in FIRM so as to generate measured result of measurement task corresponding to FIRM. Advantages are: integrated data for measuring network performance, measuring object self-adaptive to change of configuration, and obtainable data of measured performance of network device in short time.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
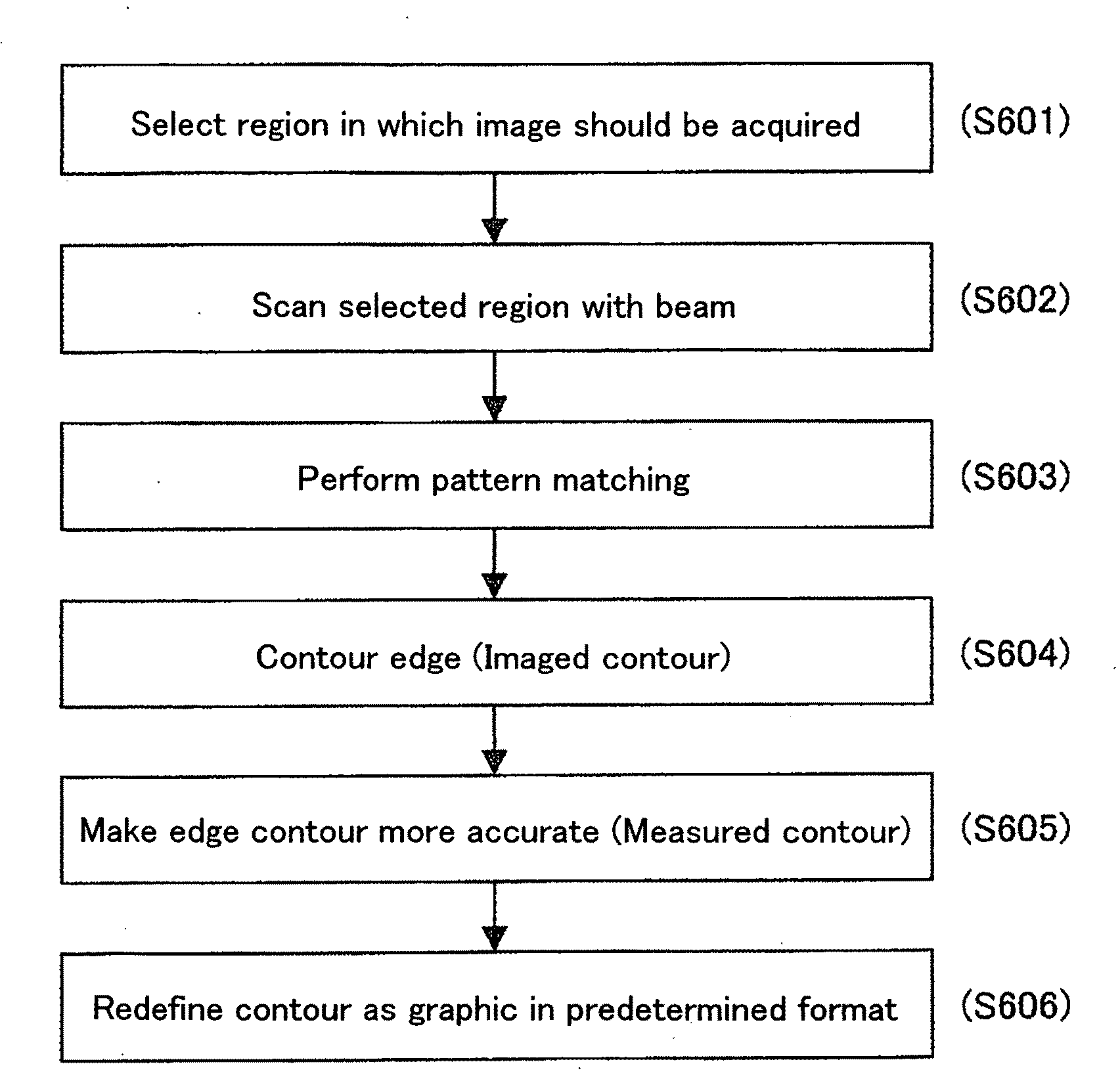
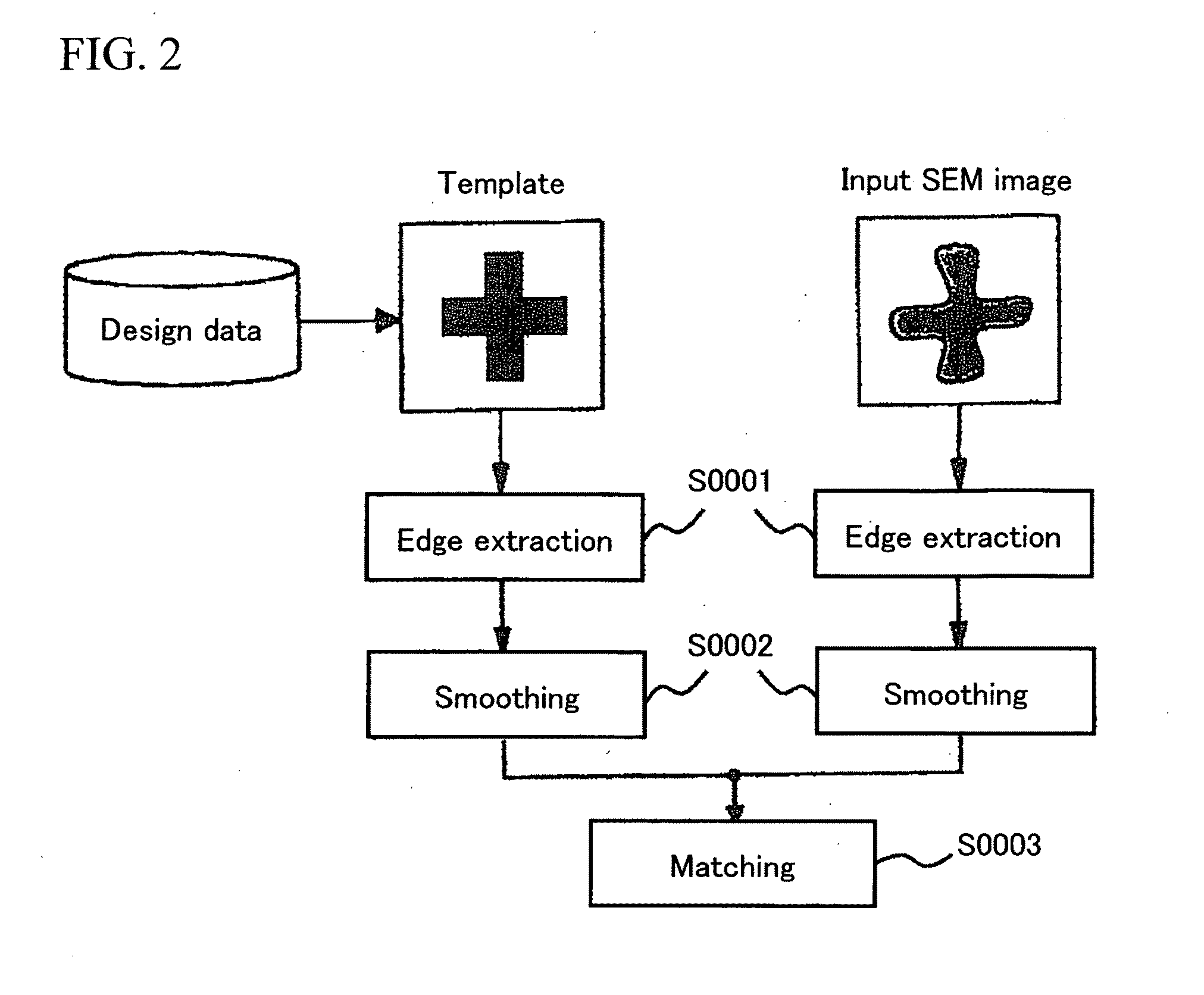
Pattern measuring method and pattern measuring device
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
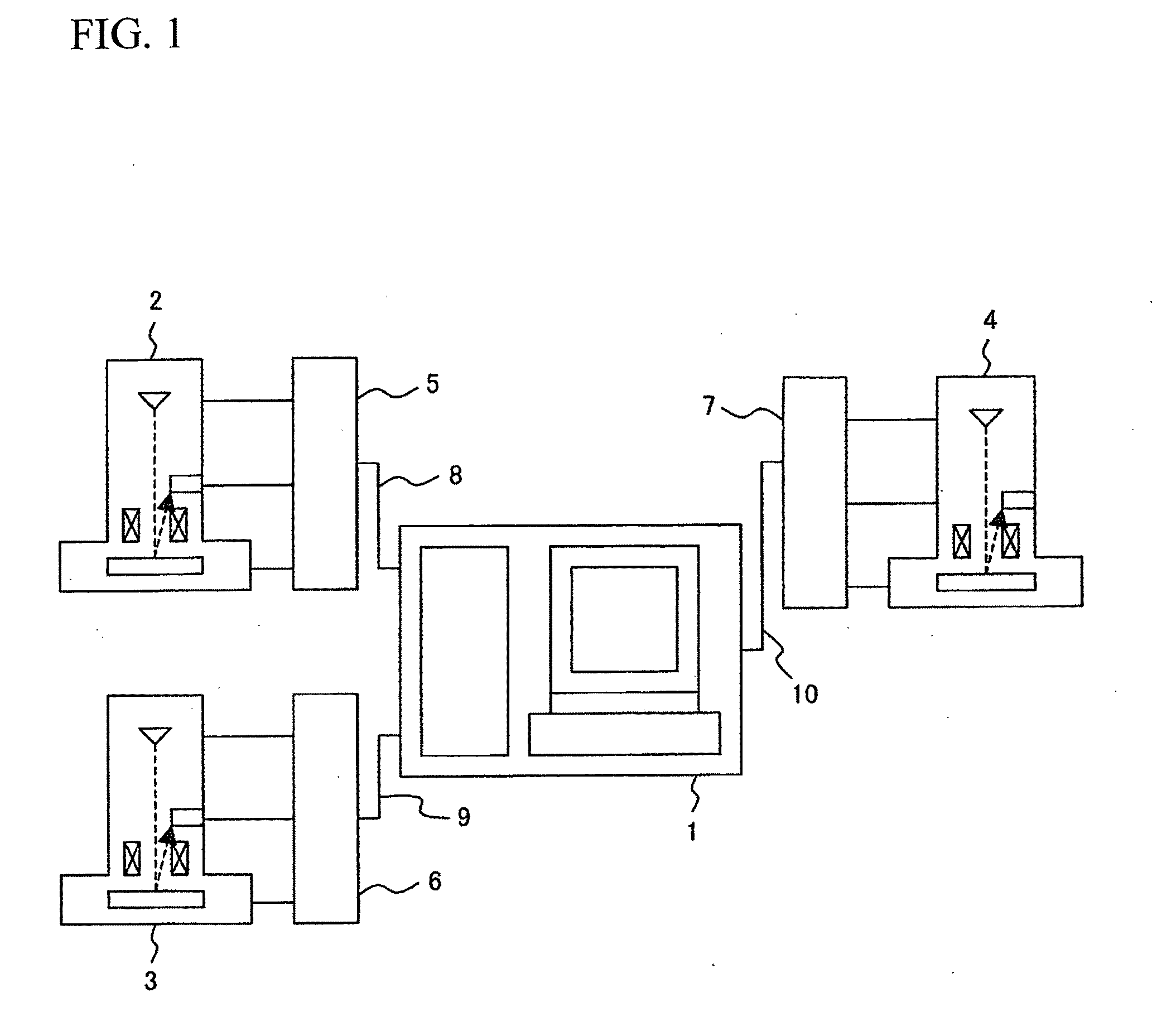
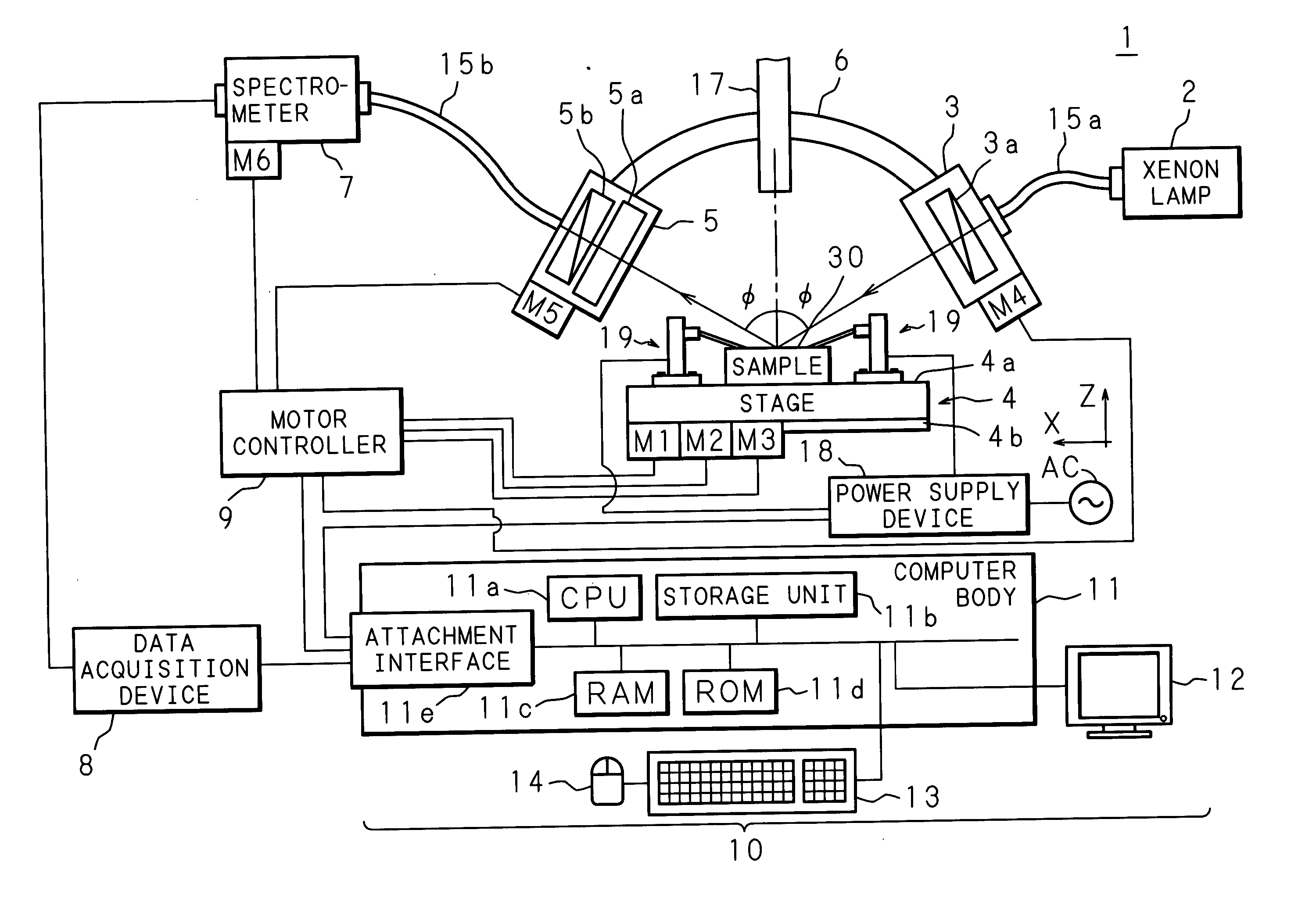
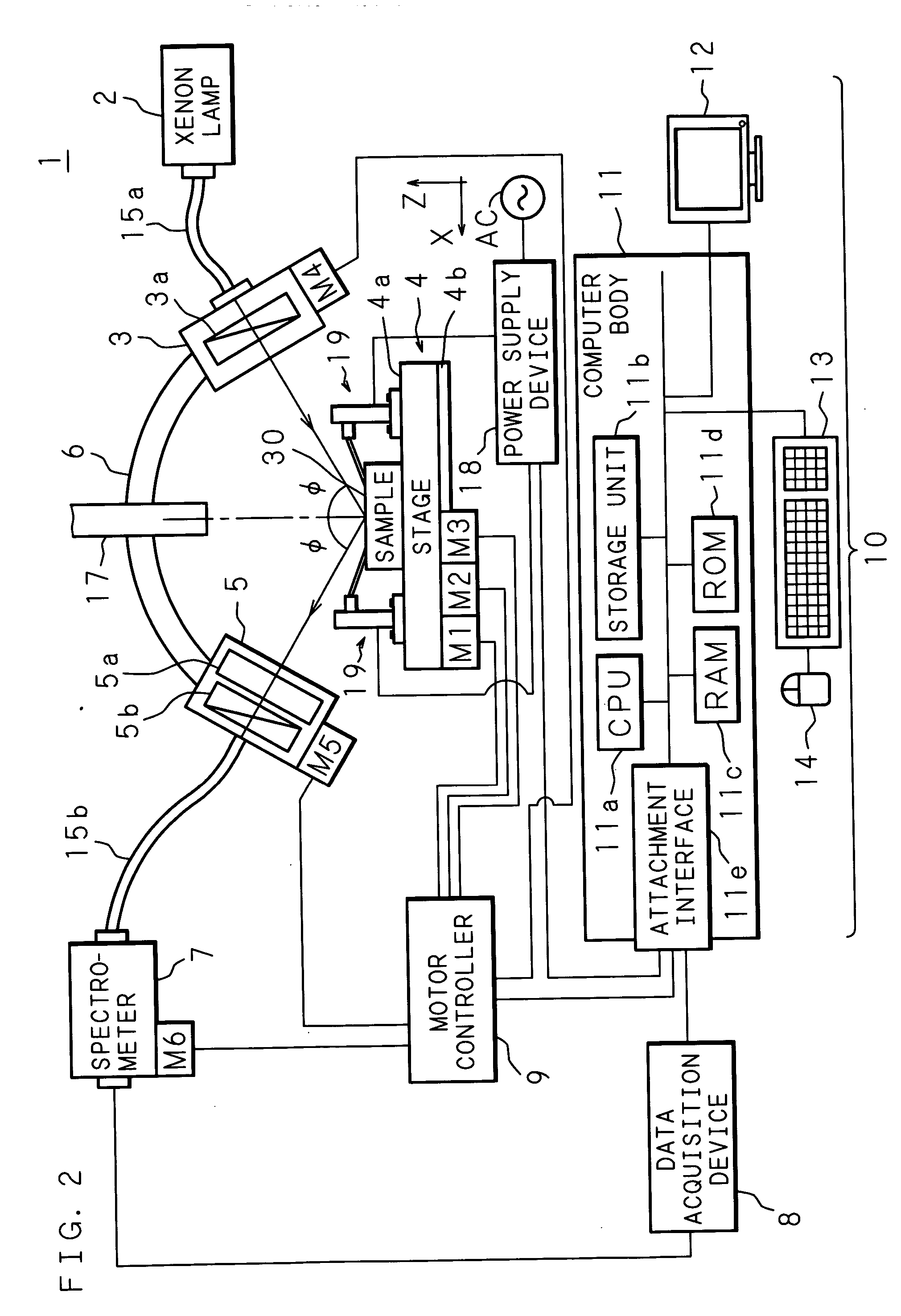
Optical characteristic analysis method, sample measuring apparatus and spectroscopic ellipsometer
InactiveUS20060023213A1Accurate analysisEfficient analysisMaterial analysis by optical meansLight polarisation measurementSample MeasureMeasurement device
The spectroscopic ellipsometer, by a computer program incorporated therein, applies voltage to a sample placed on a stage, with a power supply device and conducting probe stands, polarizes multi-wavelength light, with a light polarizer, generated by a xenon lamp and irradiates the polarized light to the sample. The sample is provided with a multilayer film and electrodes formed on a substrate and the sample's surface, and light reflected from the sample is received by the light receiver and measured by the spectrometer. The computer analyzes the optical characteristic of the sample individually for each layer of the multilayer film on the basis of the measurement result and a value calculated from a model which is formed according to the sample structure.
Owner:HORIBA LTD
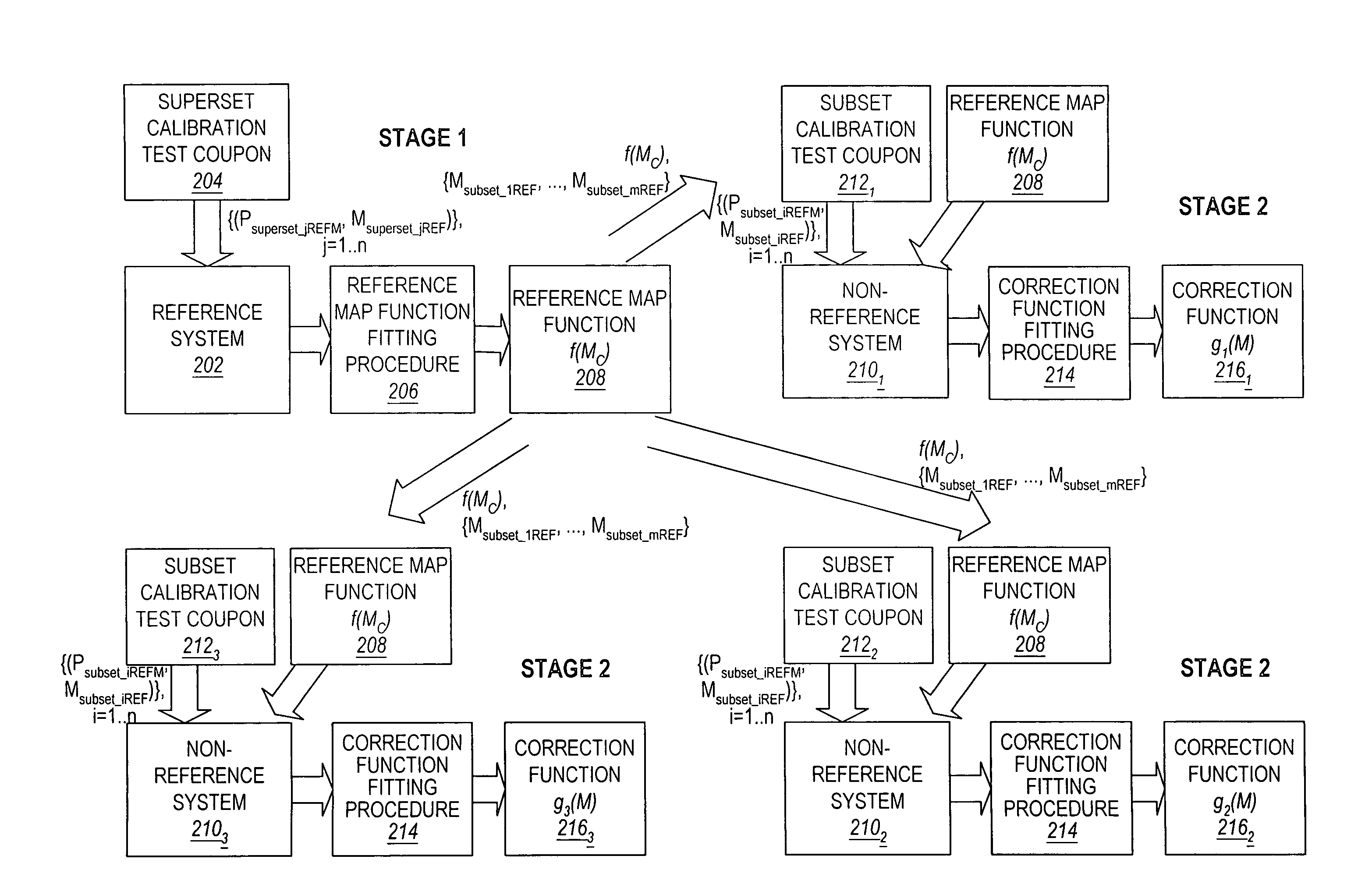
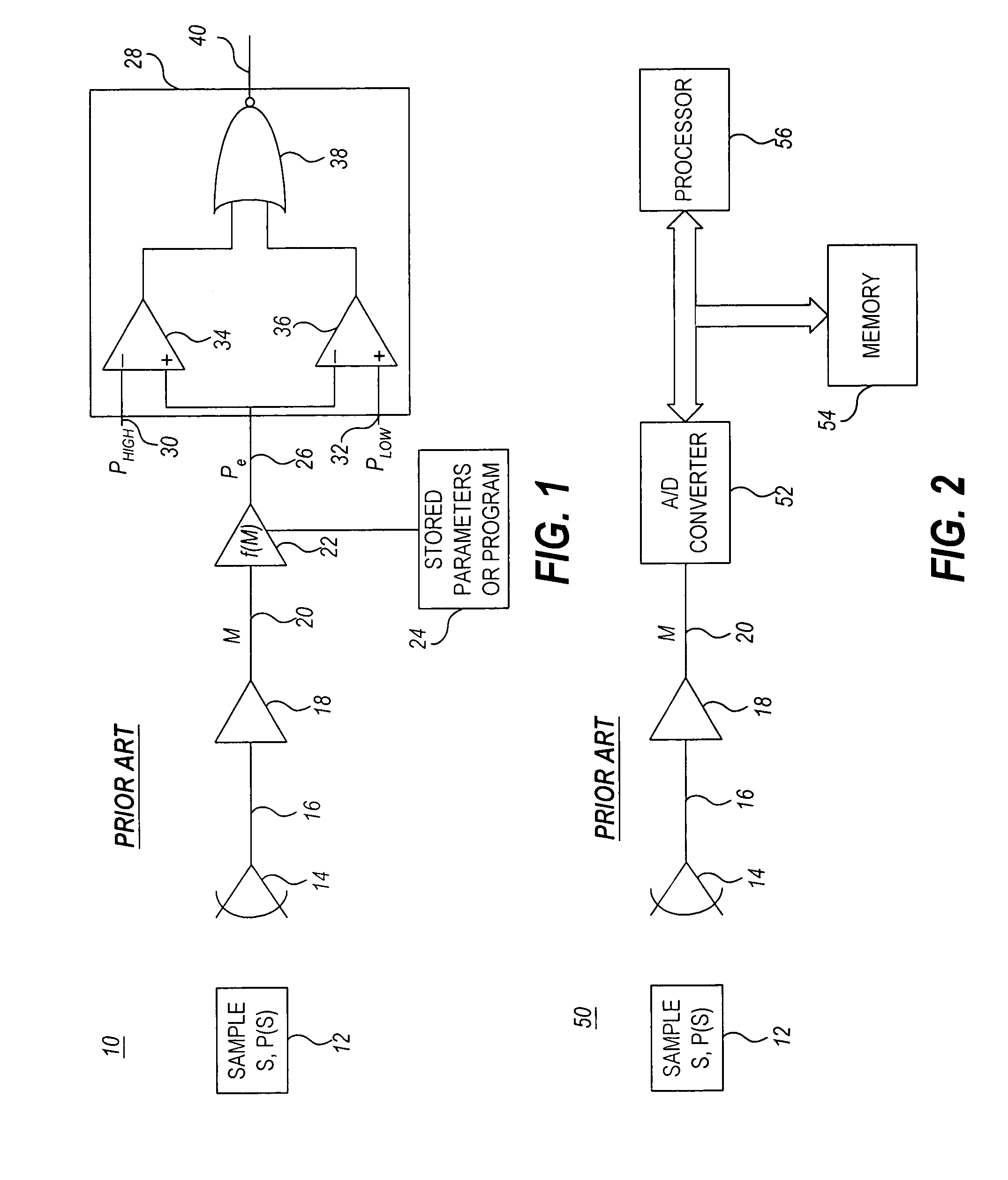
Method and apparatus for calibration of indirect measurement systems
InactiveUS7108424B2Minimize the differenceImprove accuracyThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsDigital computer detailsReference mapSample Measure
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Automatic calibration system and method of resistance absorbing instrument
InactiveCN101413869AAvoid human interferenceReal-time calibrationPermeability/surface area analysisSample MeasureAutomatic control
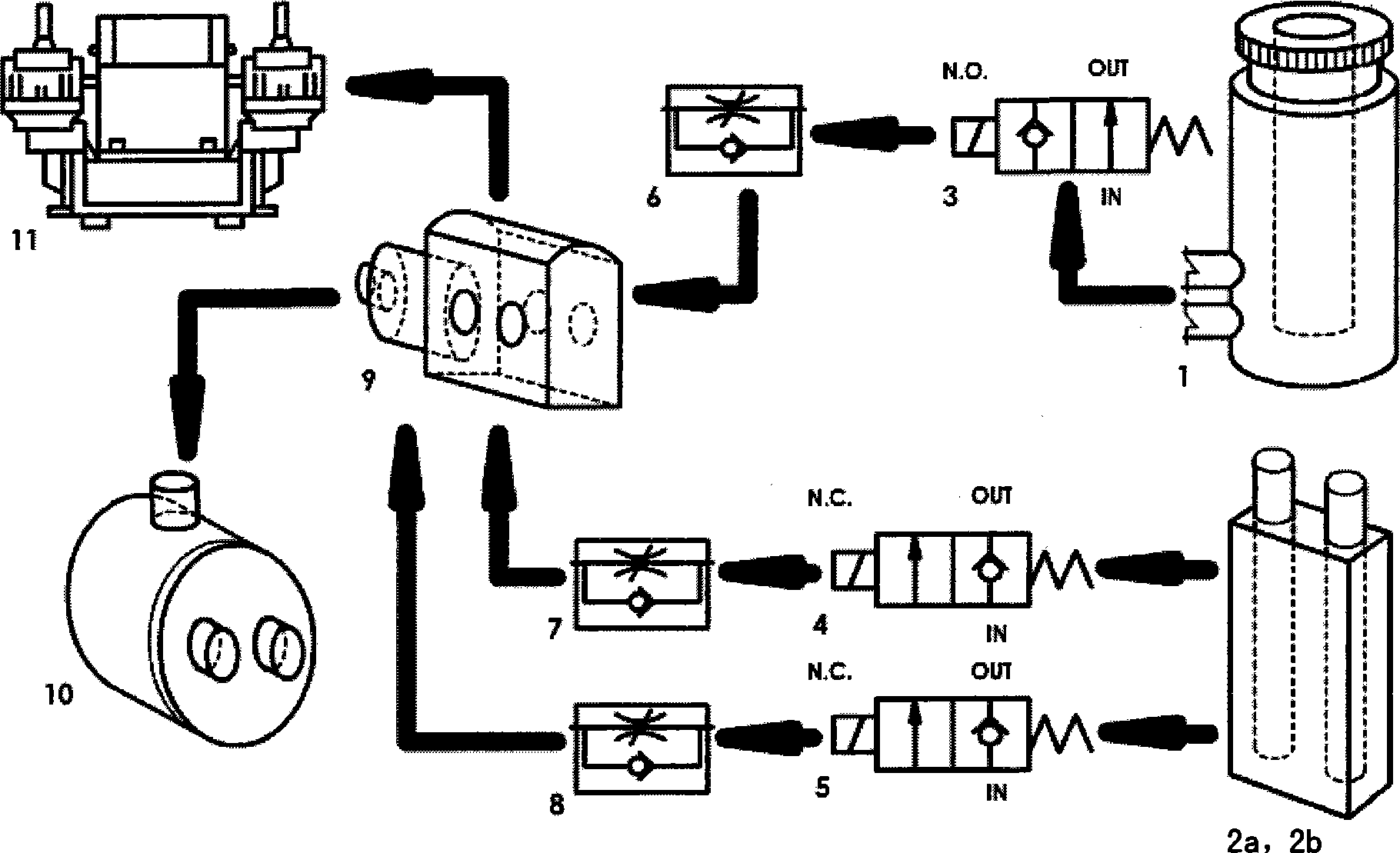
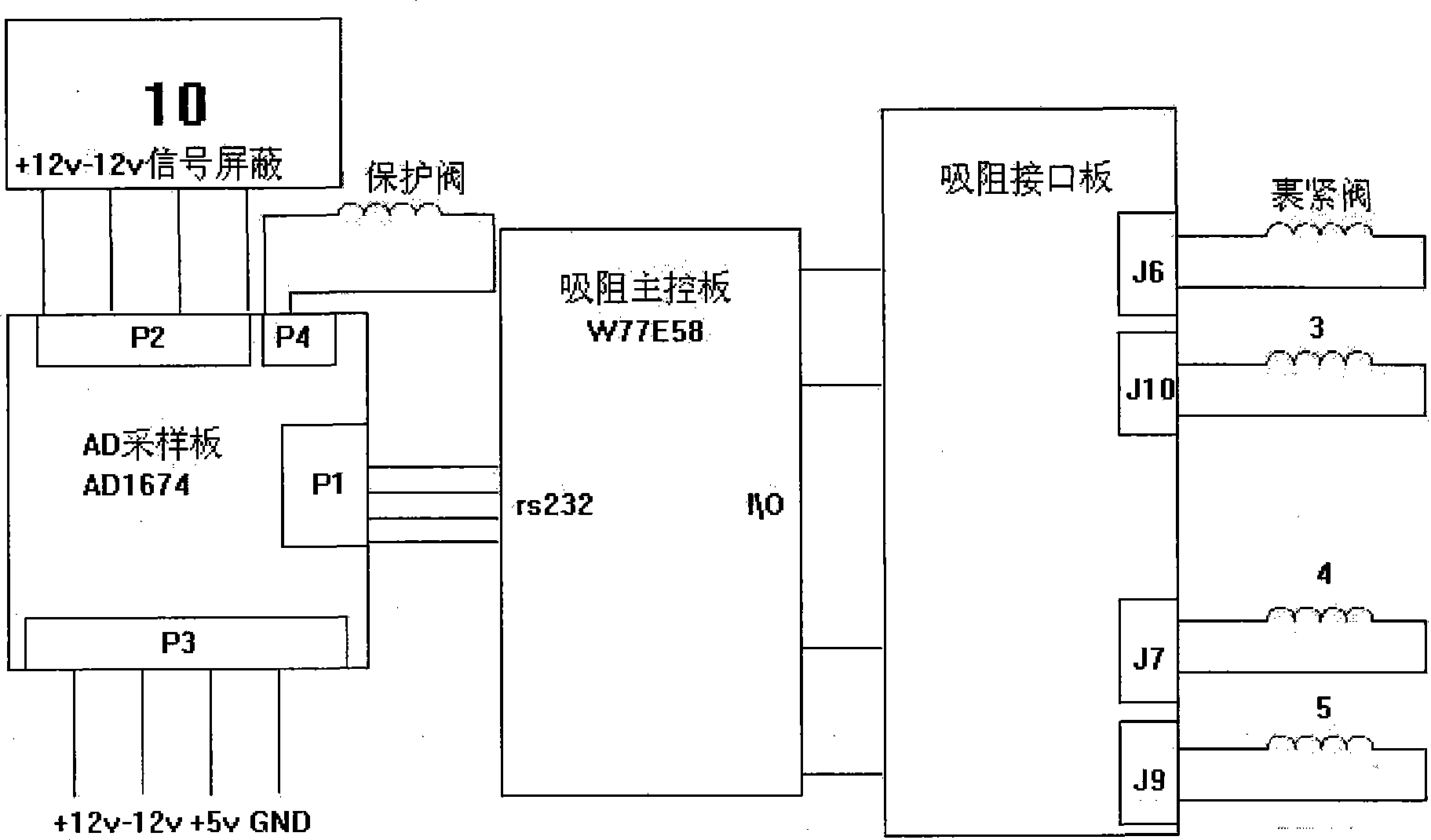
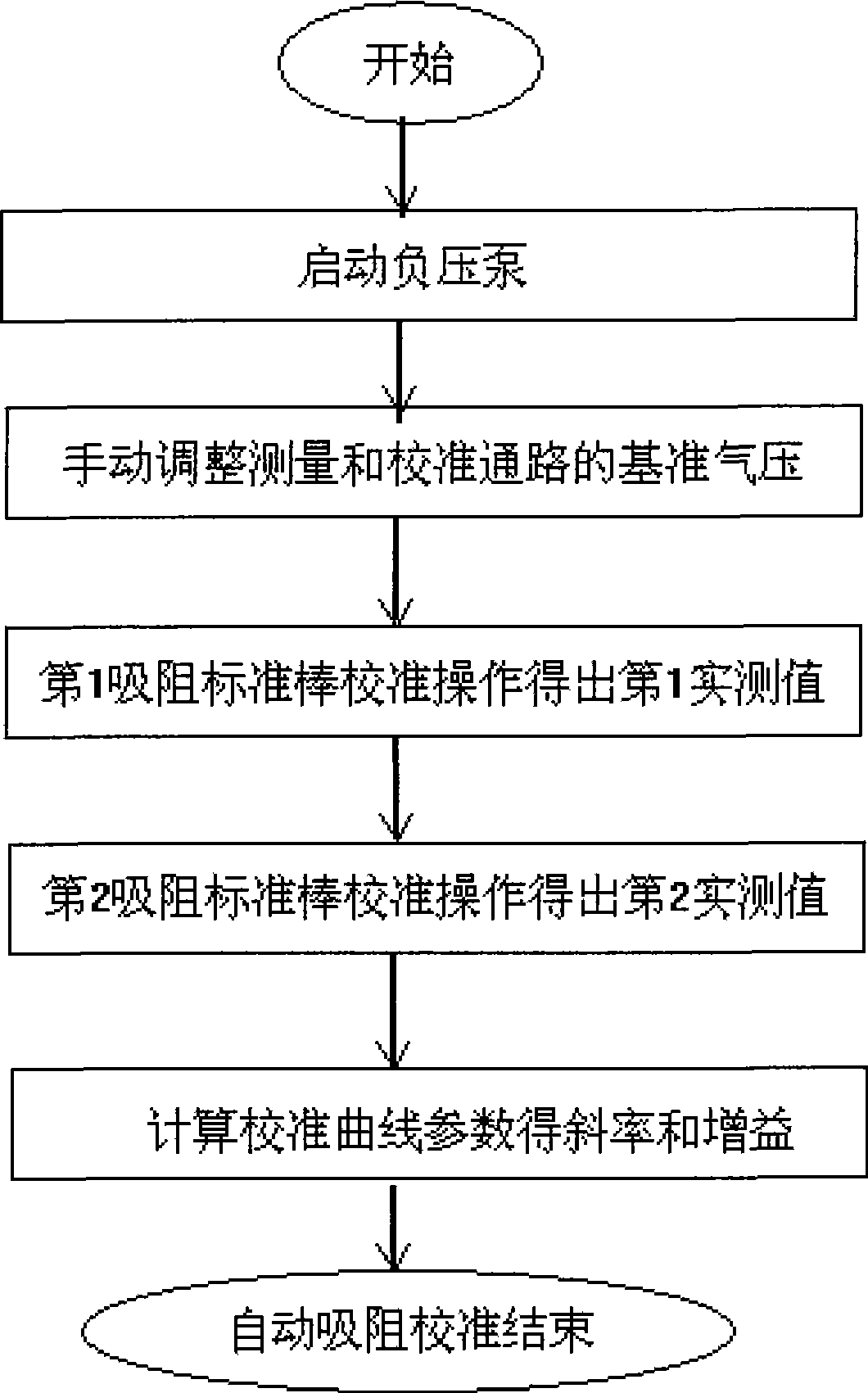
The invention relates to an absorbing resistance instrument automatic calibration system, which is provided with a gas circuit device and an electric control gear. The gas circuit device comprises a calibration gas circuit and a measuring gas circuit. The calibration gas circuit is provided with two absorbing resistance rod gauge measuring heads. The measuring gas circuit is provided with a sample measuring head. The calibration gas circuit and the measuring gas circuit respectively pass through a motorized valve and a hand-operated valve, and then are connected with a negative pressure vacuum air pump by the same constant flow element and a surge chamber. The constant flow element and the surge chamber are internally provided with a gas differential pressure pickup. The electric control gear is provided with a drawing resistance main control panel, the output end of which is respectively connected with the motorized valve in each gas circuit by a drawing resistance interface board; a serial communication interface of the drawing resistance main control board is connected with a drawing resistance sensor by an AD sampling panel. The method is as follows: the negative pressure vacuum air pump is started; the benchmark pressure of the measuring gas circuit and the calibration gas circuit are regulated; a first drawing resistance rod gauge is calibrated; a second drawing resistance rod gauge is calibrated; the calibration cure parameter is calculated to obtain the rate of slope of the specification curve and the gain. The system avoids artificial interference, realizes automatically controlled real time calibration, and is suitable for batch test.
Owner:SHENYANG SCI INSTR RES CENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Real time determination of gas solubility and related parameters in manufacturing processes
InactiveUS20050109078A1Easy to controlEasy to handleAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTesting beveragesApparent densitySolubility
Owner:APPVION OPERATIONS INC
Method for distinguishing variety of fritillaria and detecting total alkaloid content of fritillaria by virtue of near infrared spectrum
InactiveCN102175648ASmall absorption coefficientEasy to collectScattering properties measurementsSample MeasurePrincipal component regression
The invention provides a method for distinguishing variety of fritillaria and detecting total alkaloid content of the fritillaria by virtue of near infrared spectrum. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: (1) collecting a fritillaria sample; (2) measuring the near infrared diffuse reflection spectrogram of the fritillaria sample, preprocessing the 4000-5000cm<-1> wave band in the spectrogram, and performing cluster analysis on the pre-processed near infrared spectrogram to build a qualitative model; or preprocessing the 4000-7000cm<-1> wave band in the spectrogram, so as to obtain an absorbance, associating the absorbance with the alkaloid content of the sample measured by virtue of bromothymol blue colorimetry, and building a quantitative correction model for detecting alkaloid by one or more methods of a partial least squares method, a principal component regression method and a multiple linear regression method; (3) collecting the near infrared spectrogram of the sample to be measured, after the corresponding preprocessing is performed, distinguishing the variety of the fritillaria and detecting total alkaloid content of the fritillaria by utilizing the built qualitative model or quantitative correction model. The method provided by the invention has the characteristics of fast speed, no damage, environment friendliness and low cost.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
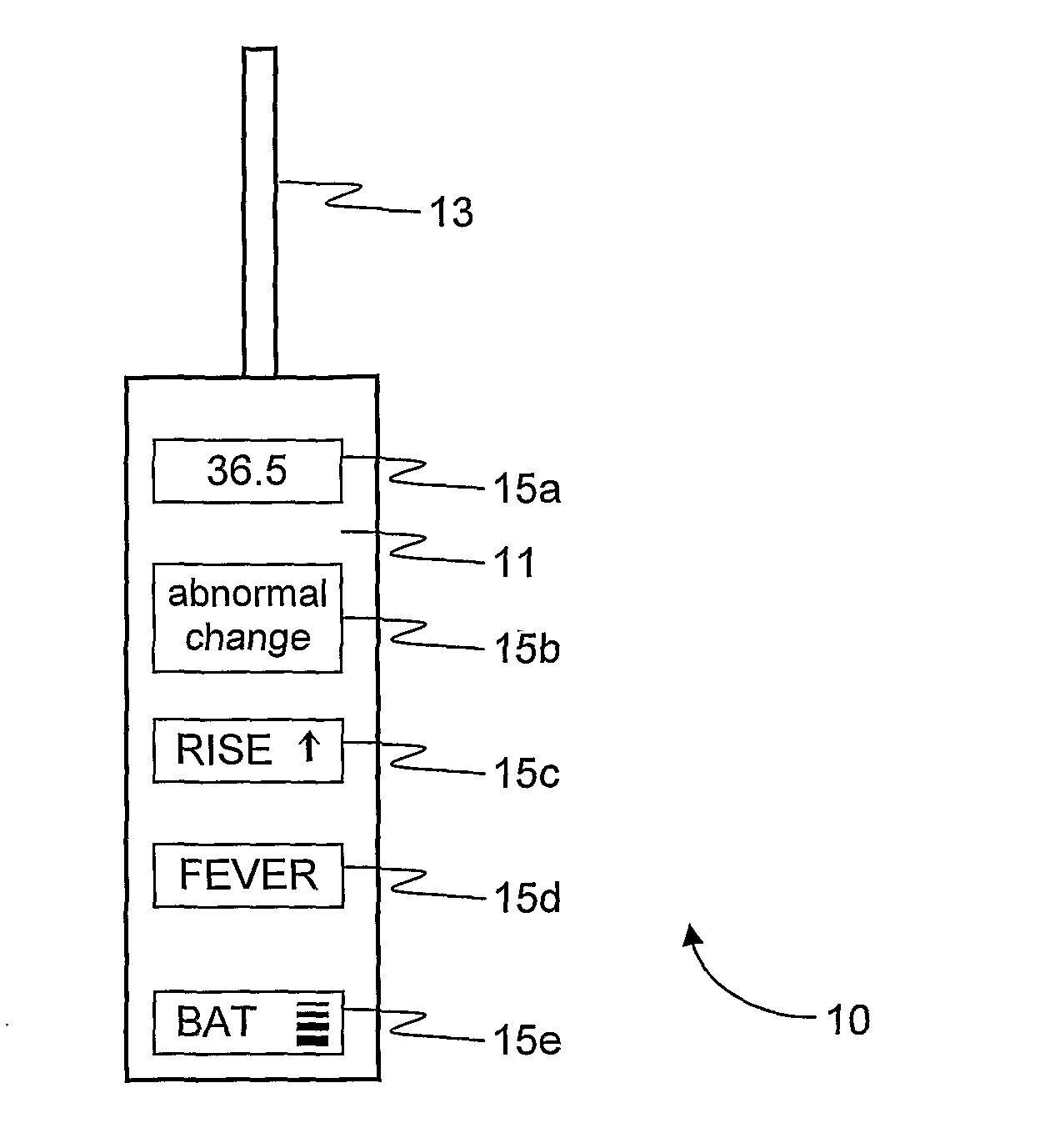
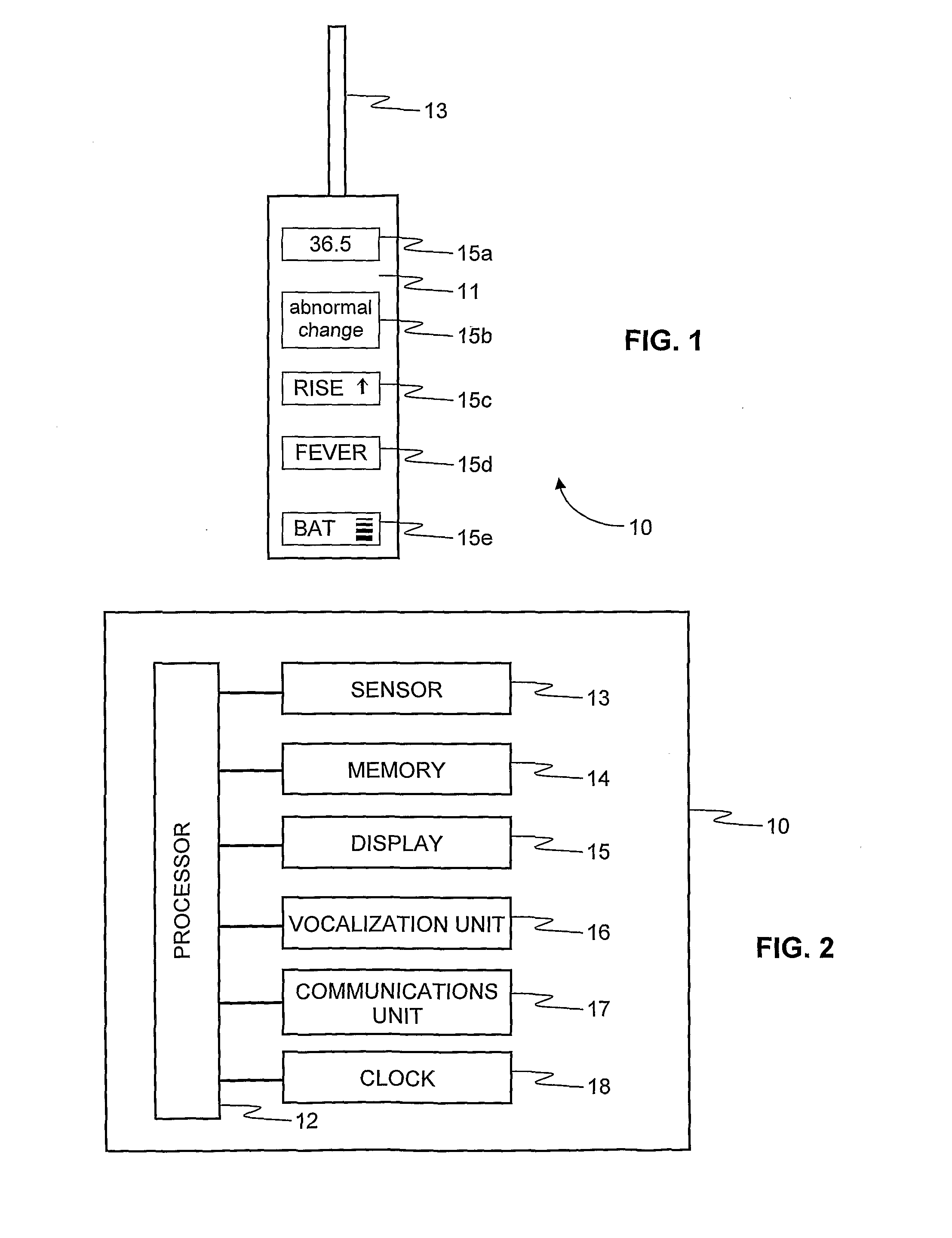
Digital thermometer
InactiveUS20100152606A1Eliminate needGood indicationThermometers using material expansion/contactionBody temperature measurementSample MeasureDigital thermometers
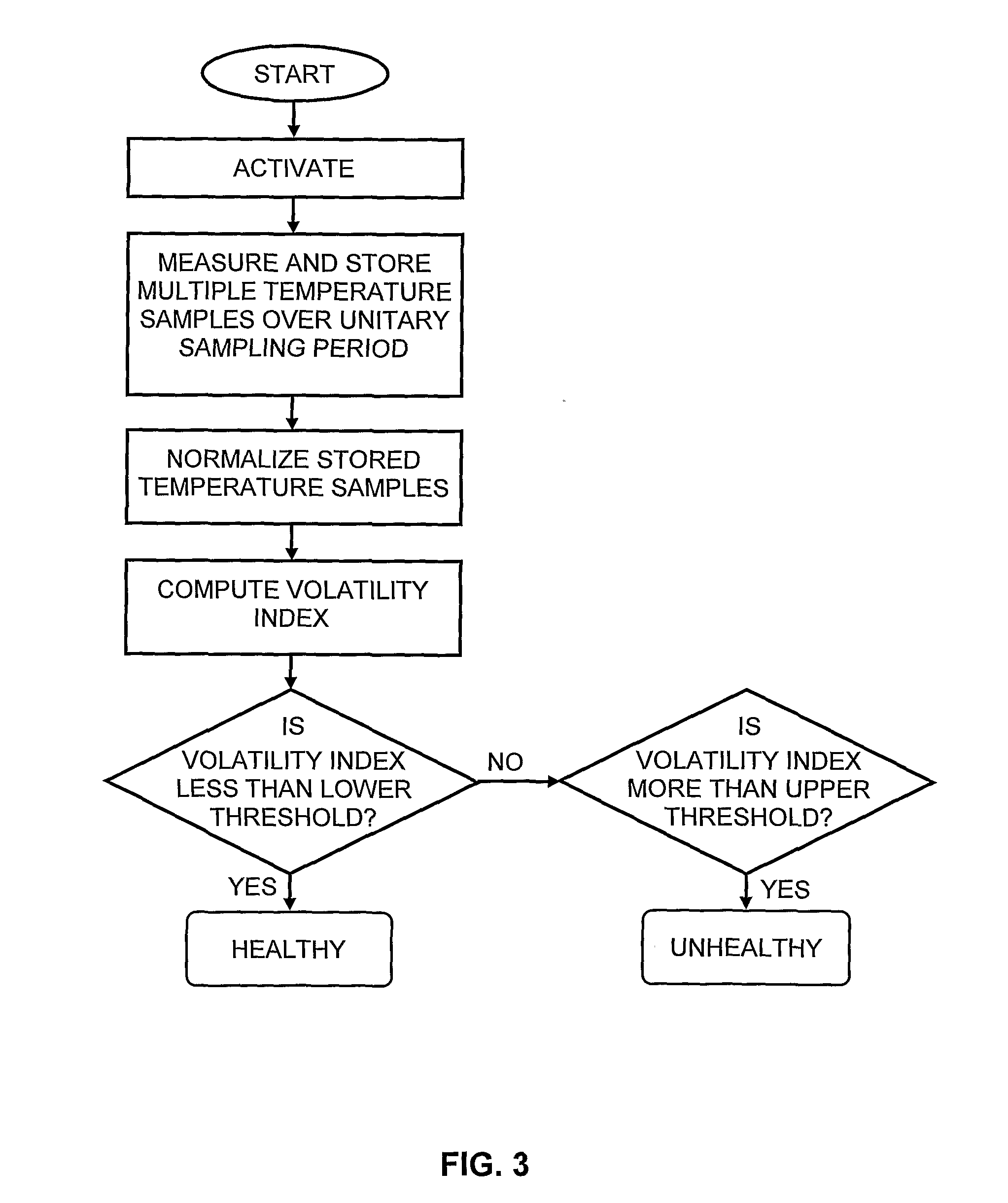
A digital thermometer (10) includes a temperature measuring device (13) for measuring temperature of an examinee. A microprocessor (12) is coupled to the temperature measuring device for processing a sequence of temperature samples measured during a unitary measuring interval and is responsive to the measured temperature samples or a function thereof for determining at least one health property other than temperature of the examinee or for predicting a change in at least one health property of the examinee such as an onset of an abnormal health condition. According to one embodiment, volatility of the temperature-time characteristic is used to indicate whether the examinee is healthy or not, even when no fever is registered. ‘Volatility’ is a measure of the extent to which temperature samples fluctuate with time, such as the number of temperature rises and falls during the sampling period.
Owner:HOW R YOU TECH
Portable type near infrared mineralogical analyser
InactiveCN1480721ALow priceEasy to carryColor/spectral properties measurementsInfraredSample Measure
The analyzer is composed of optical system, signal acquisition system and computer. Design of integrating sphere is utilized in the optical system of the analyzer. The procedure of the signal acquisition system is as follows. Incident light controlled by computer passes through optical modulator becomes varied light alternated intensity in high and low. Continuously, with being passed through grating spectrum analyzer, the light irradiates on a sample to be tested. Near infrared reflected back from the sample passing through the integrating sphere irradiates on a sensor so as to measure out the intensity of the light. Processing the measured intensity, computer obtains each component of sample measured and contents of each component. The portable analyzer can test rock and mine directly without need of specimen preparation. The measured data can be obtained in 70 second. Thus, it is suitable for use in field.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
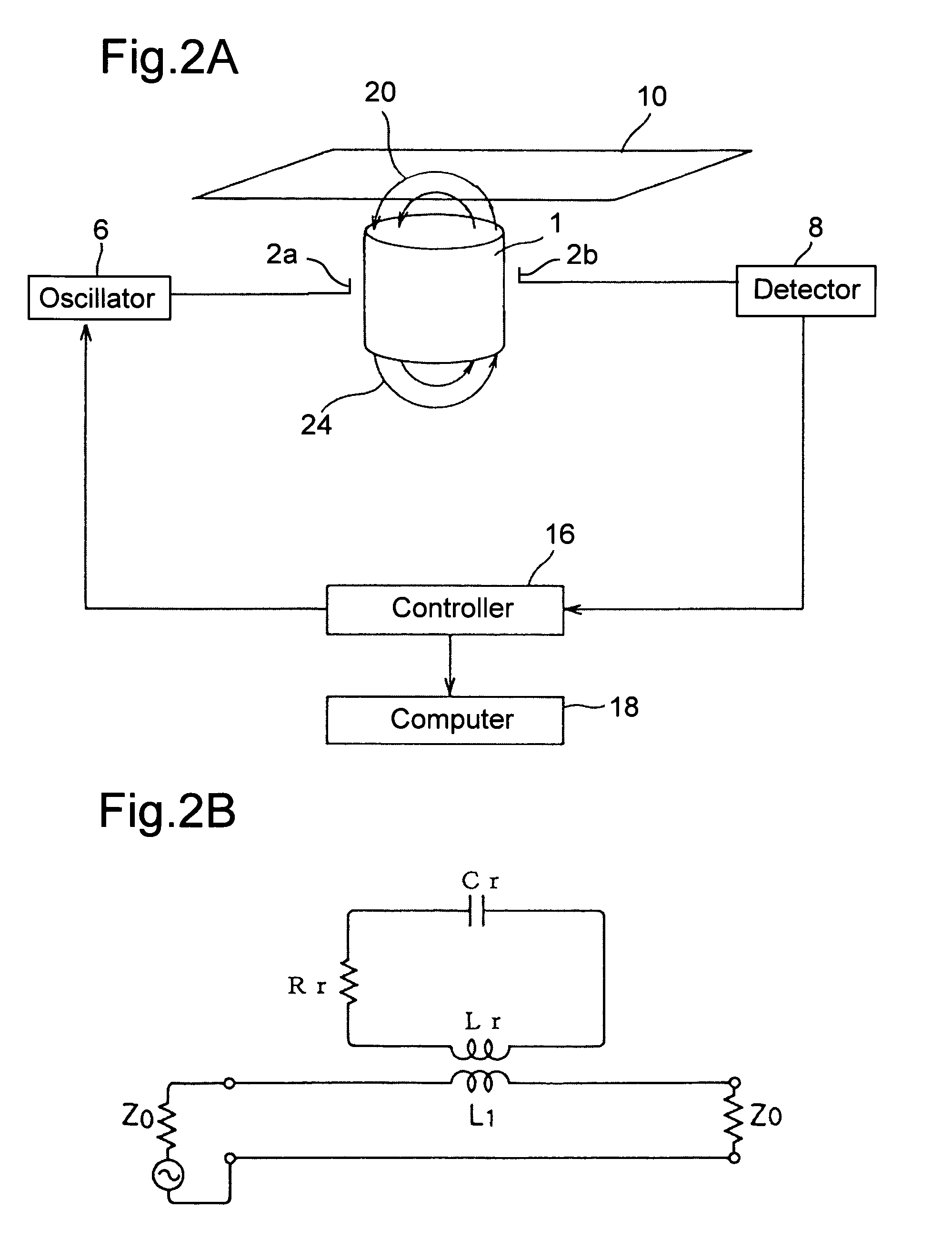
Method and device for measuring grammage
InactiveCN1880947ASafe and easy to measureResistance/reactance/impedenceUsing wave/particle radiation meansMicrowaveSample Measure
A grammage measuring apparatus includes a dielectric resonator (1) which is arranged only at one surface side of a sample (10); a shielding container (4) with which the dielectric resonator (1) is substantially covered except for a sample measuring surface; a microwave excitation device (6,2a) which causes the dielectric resonator (1) to generate an electric field vector; a detection device (8,2b) which detects transmission energy or reflection energy by the dielectric resonator (1); a storage device (12) in which a calibration curve indicating a resonance frequency shift amount for a grammage is stored; and a data processing device (14) which calculates the grammage of a measuring sample from the calibration curve and measurement result of the resonance frequency shift amount of the measuring sample.
Owner:OJI PAPER CO LTD
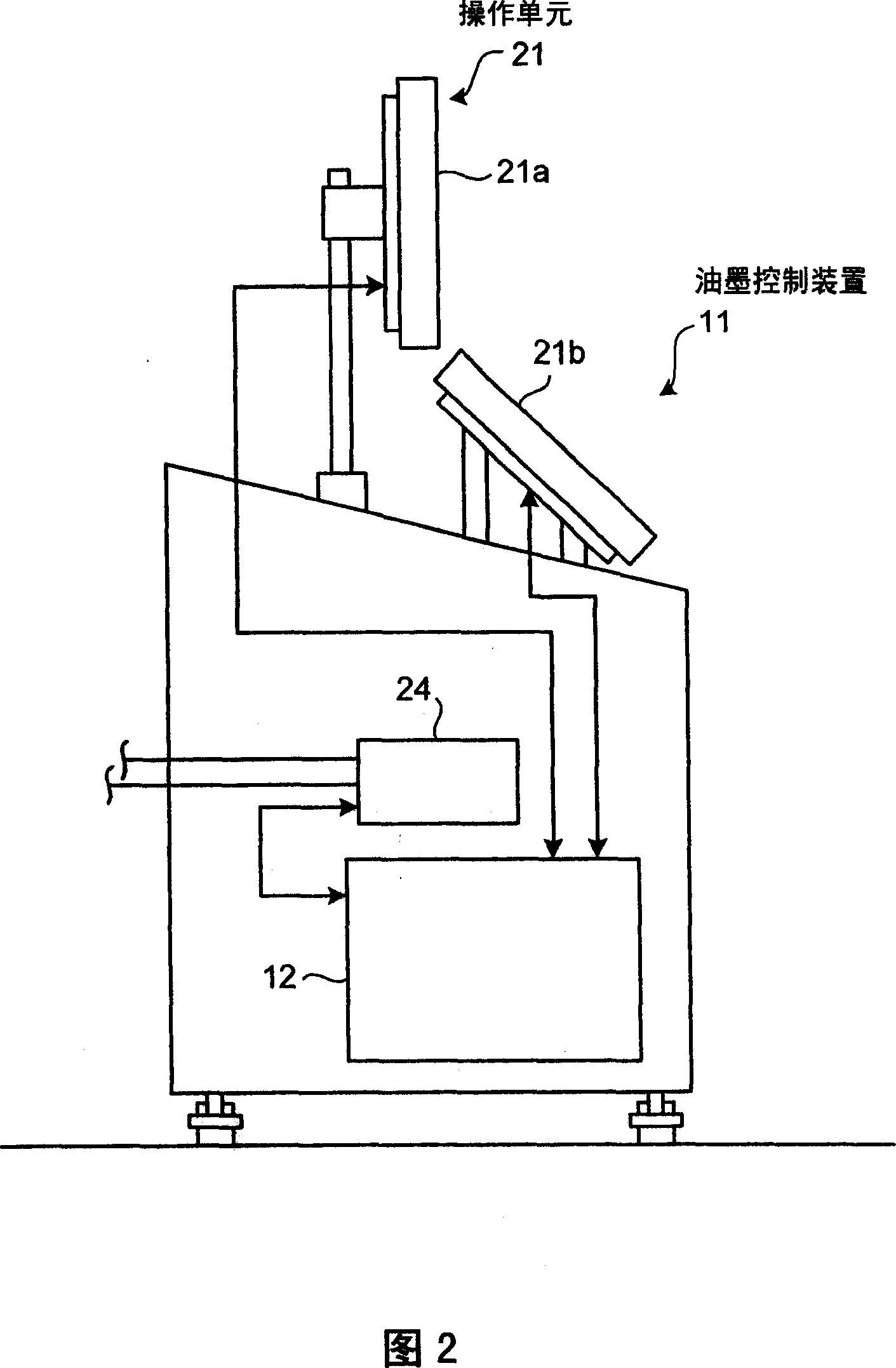
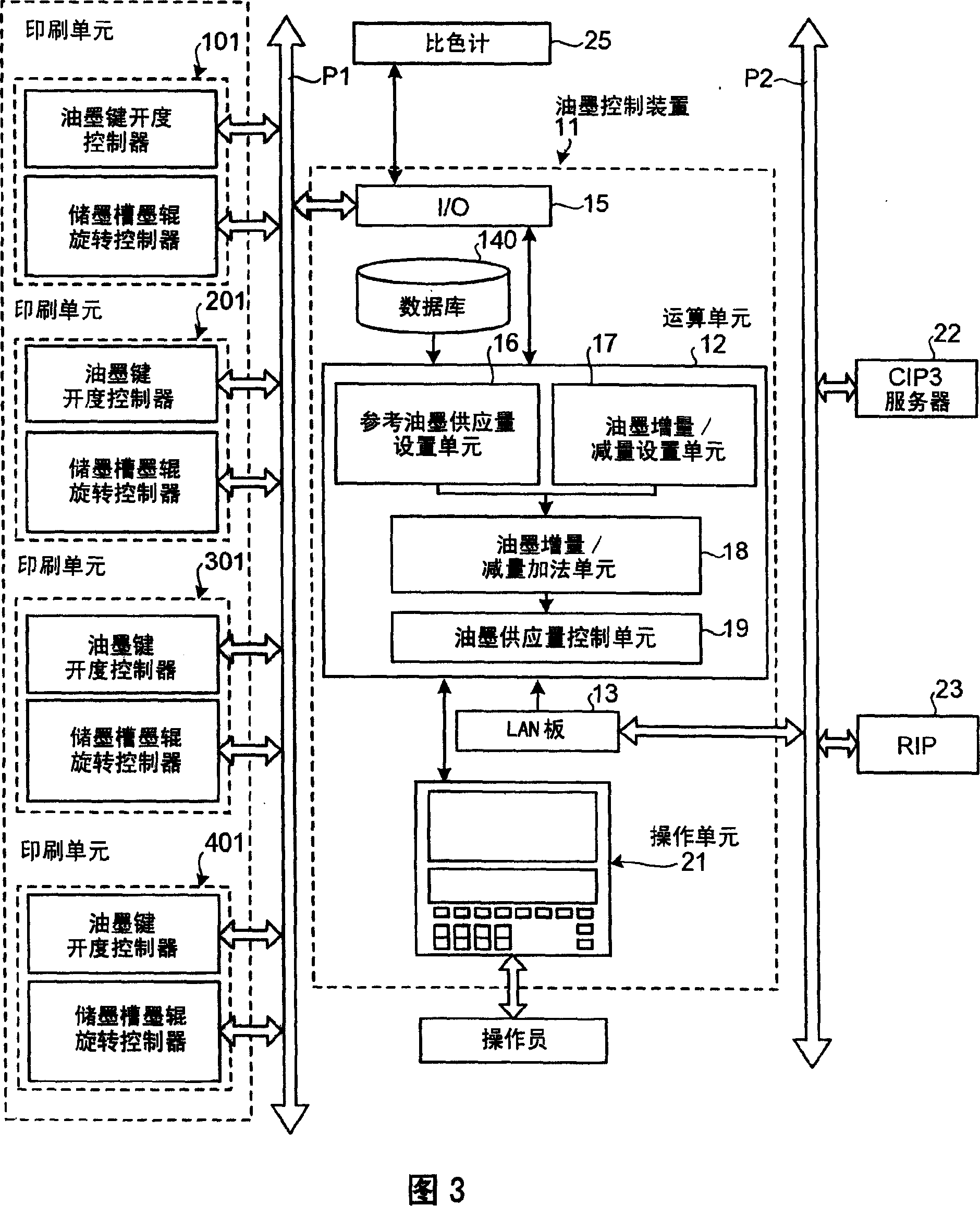
Ink control apparatus, printer, and printing method
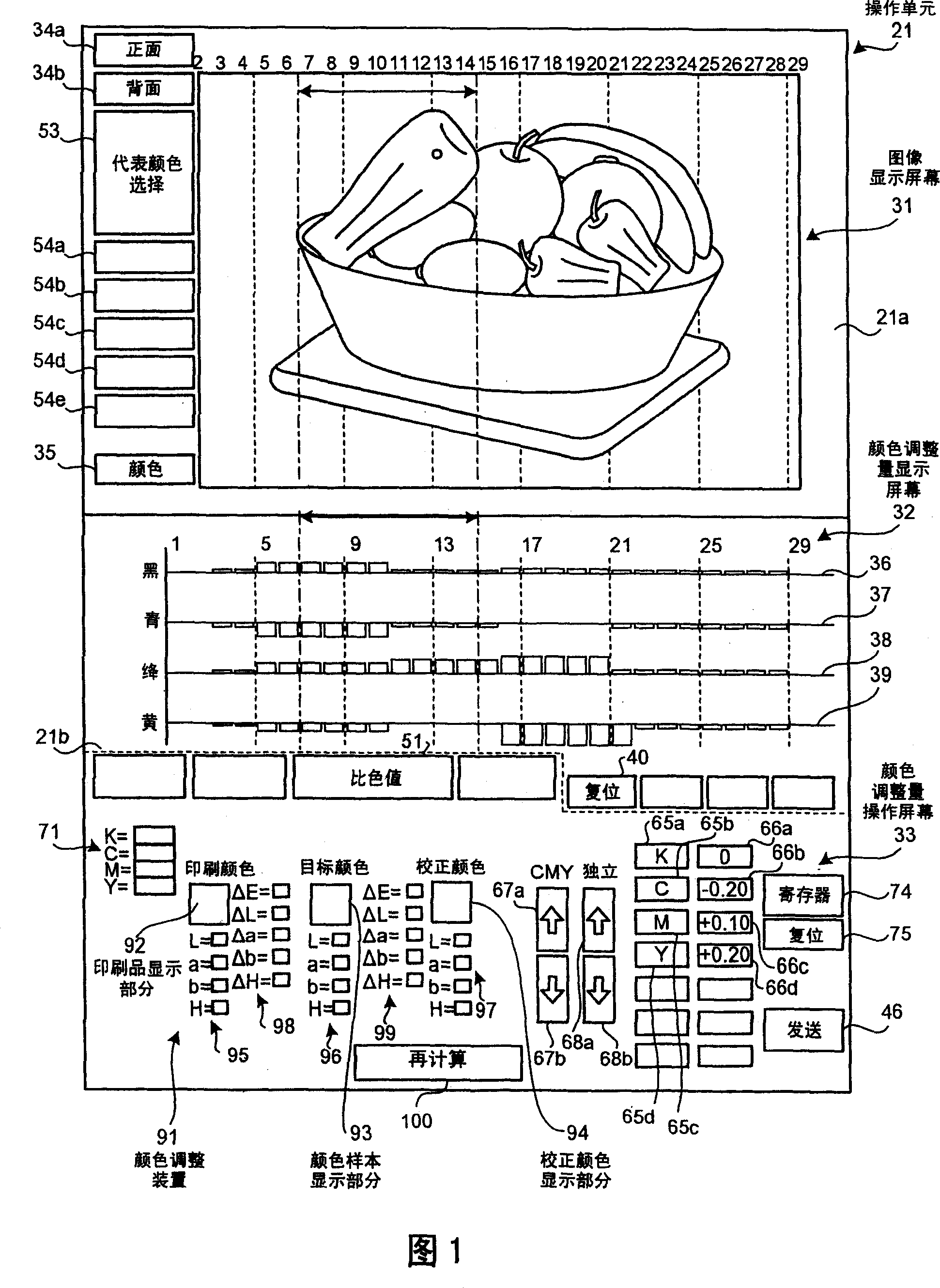
An image is created from PPF data and the image is displayed. An operator inputs a pre-set value of color adjustment from a color-adjustment-quantity operation screen. The color-adjustment-quantity operation screen includes a print display unit that displays a print color in a print measured by a colorimeter, a color-sample display unit that displays a target color in a color sample measured by the colorimeter, and a corrected-color display unit that displays a corrected color corresponding to a deviation between a colorimetric value of the print and a colorimetric value of the color sample.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
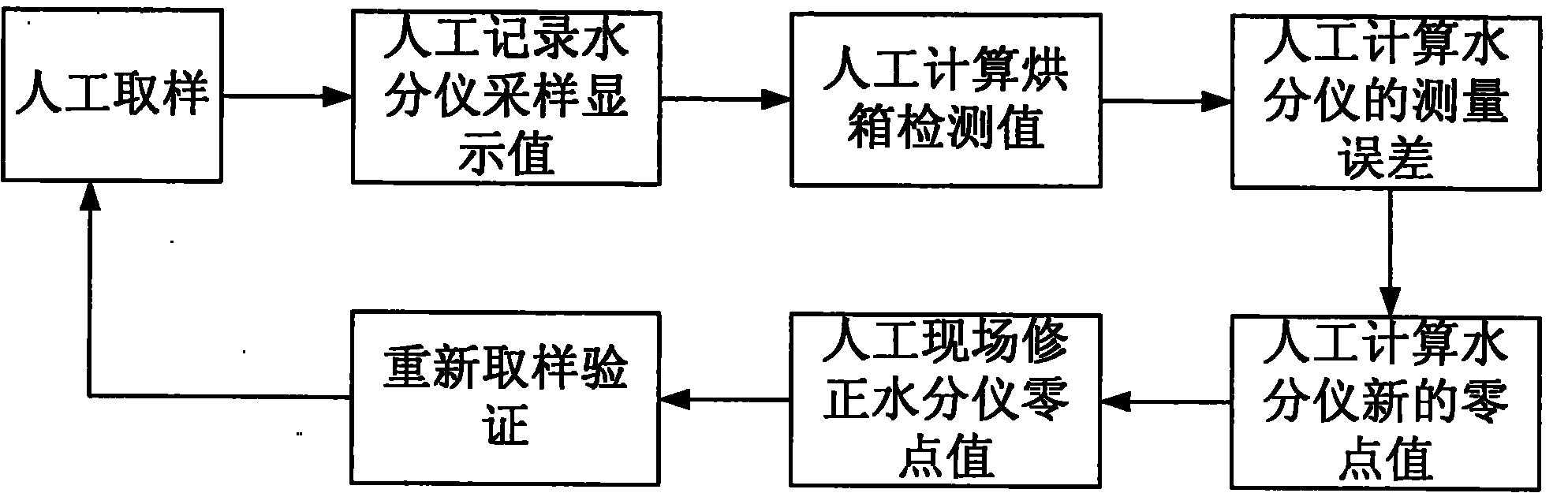
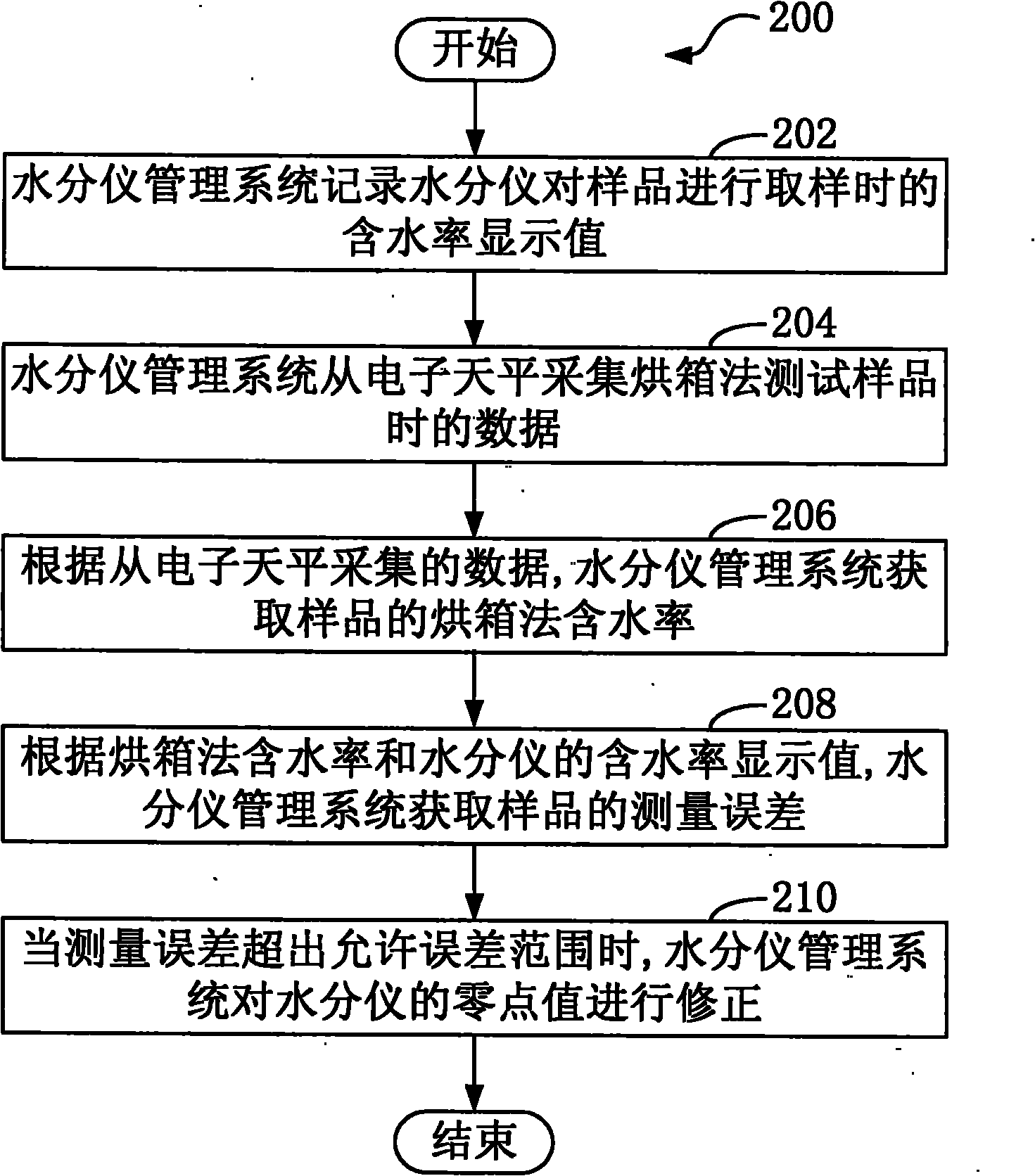
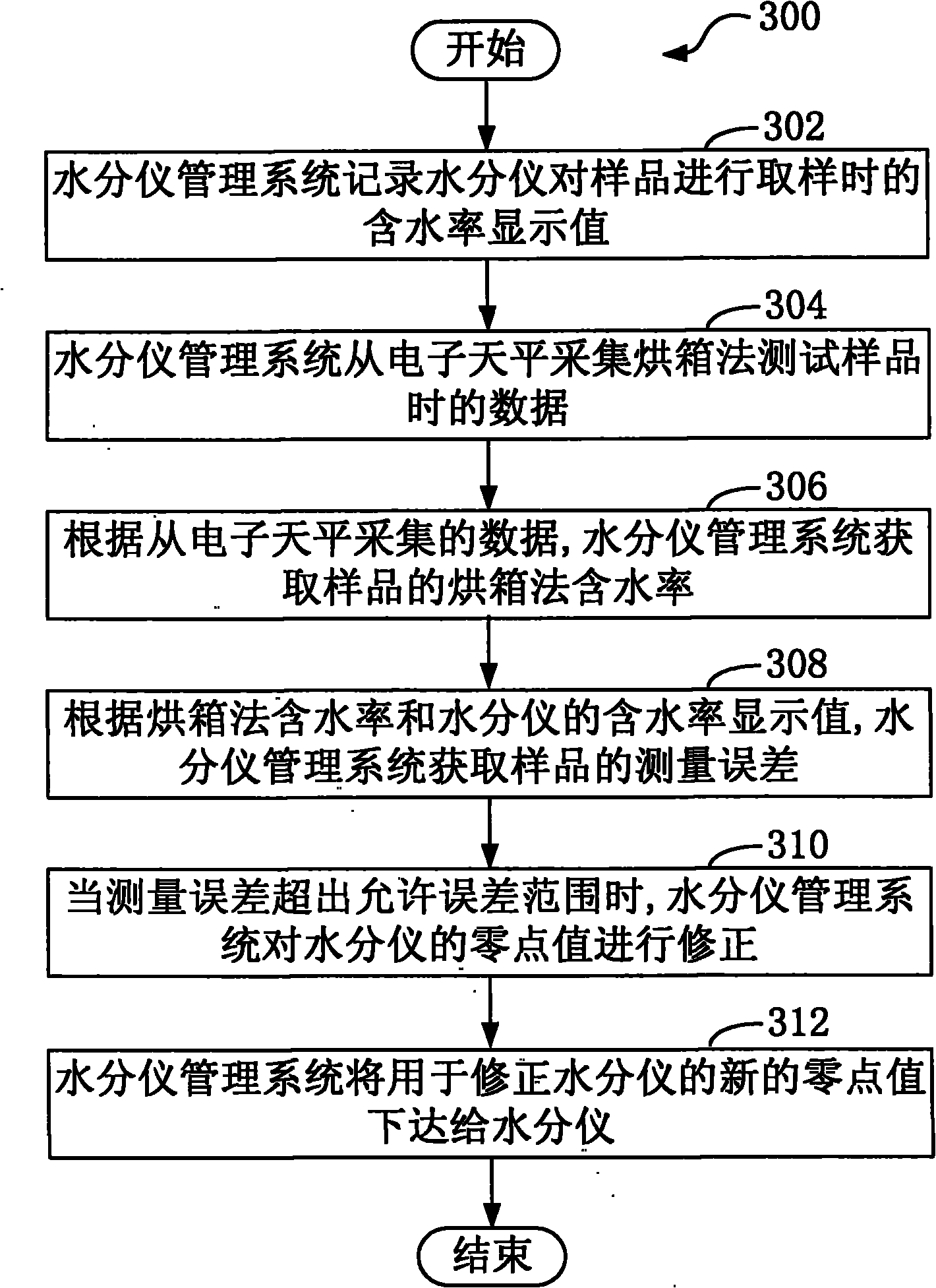
Moisture meter management method and system
InactiveCN102095831AImprove accuracyRealize automatic collectionMaterial analysisObservational errorSample Measure
The invention provides a moisture meter management method and system, relating to measuring equipment and a measuring method. The moisture meter management method comprises the following steps: the moisture meter management system records a moisture content display value when a sample is sampled by a moisture meter; the moisture meter management system collects data from an electronic balance when the sample is tested by utilizing a drying oven method; according to the data collected from the electronic balance, the moisture meter management system obtains the moisture content of the sample measured by the drying oven method; according to the moisture content measured by the drying oven method and the moisture content display value of the moisture meter, the moisture meter management system obtains the measuring error of the sample; and when the measuring error exceeds a permissible error range, the moisture meter management system corrects the zero value of the moisture meter. The moisture meter is controlled by the moisture meter management system, so that the data of the moisture meter is automatically collected and calculated, the zero value is automatically corrected, and the accuracy of the moisture meter is improved.
Owner:LONGYAN CIGARETTE FACTORY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com