Patents
Literature
1388results about How to "Stable characteristics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
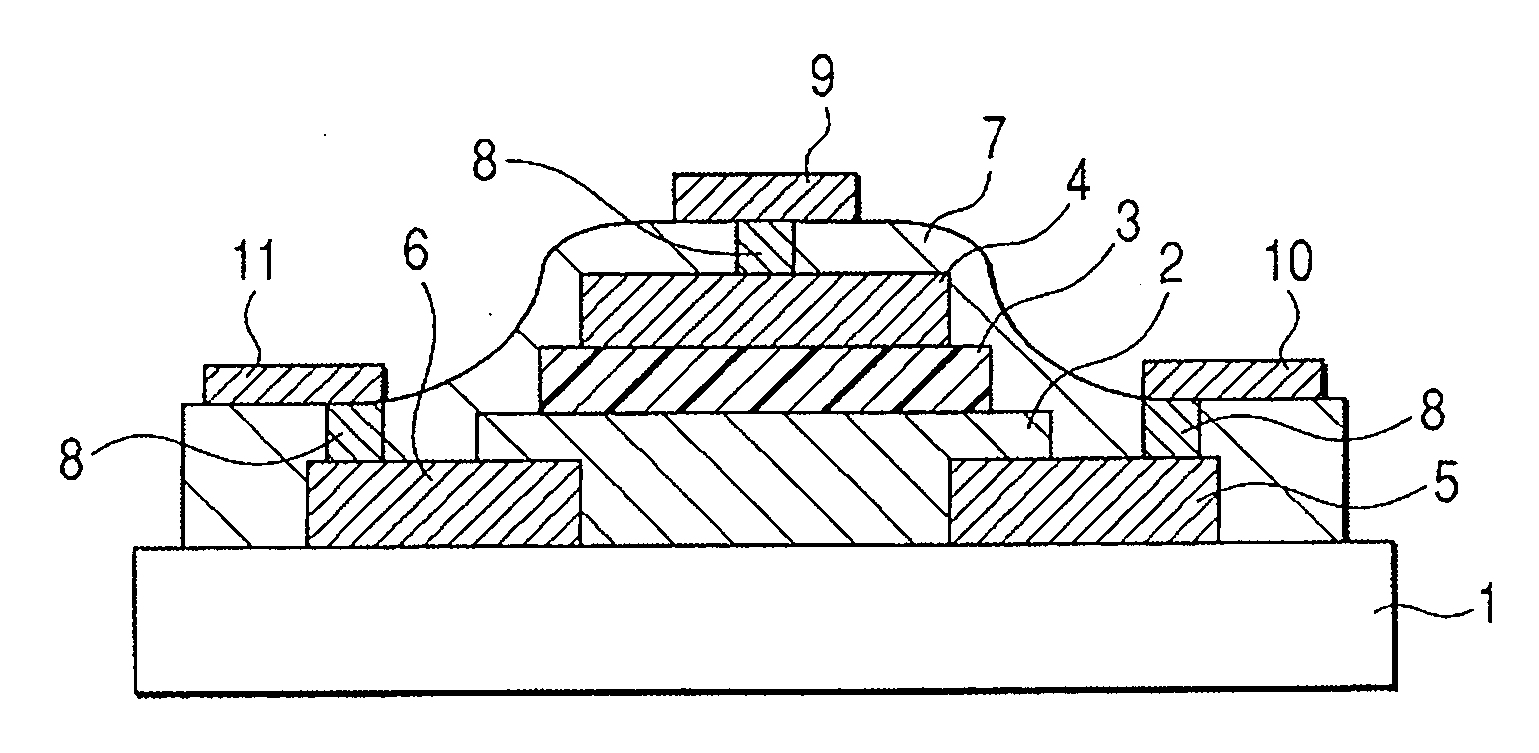
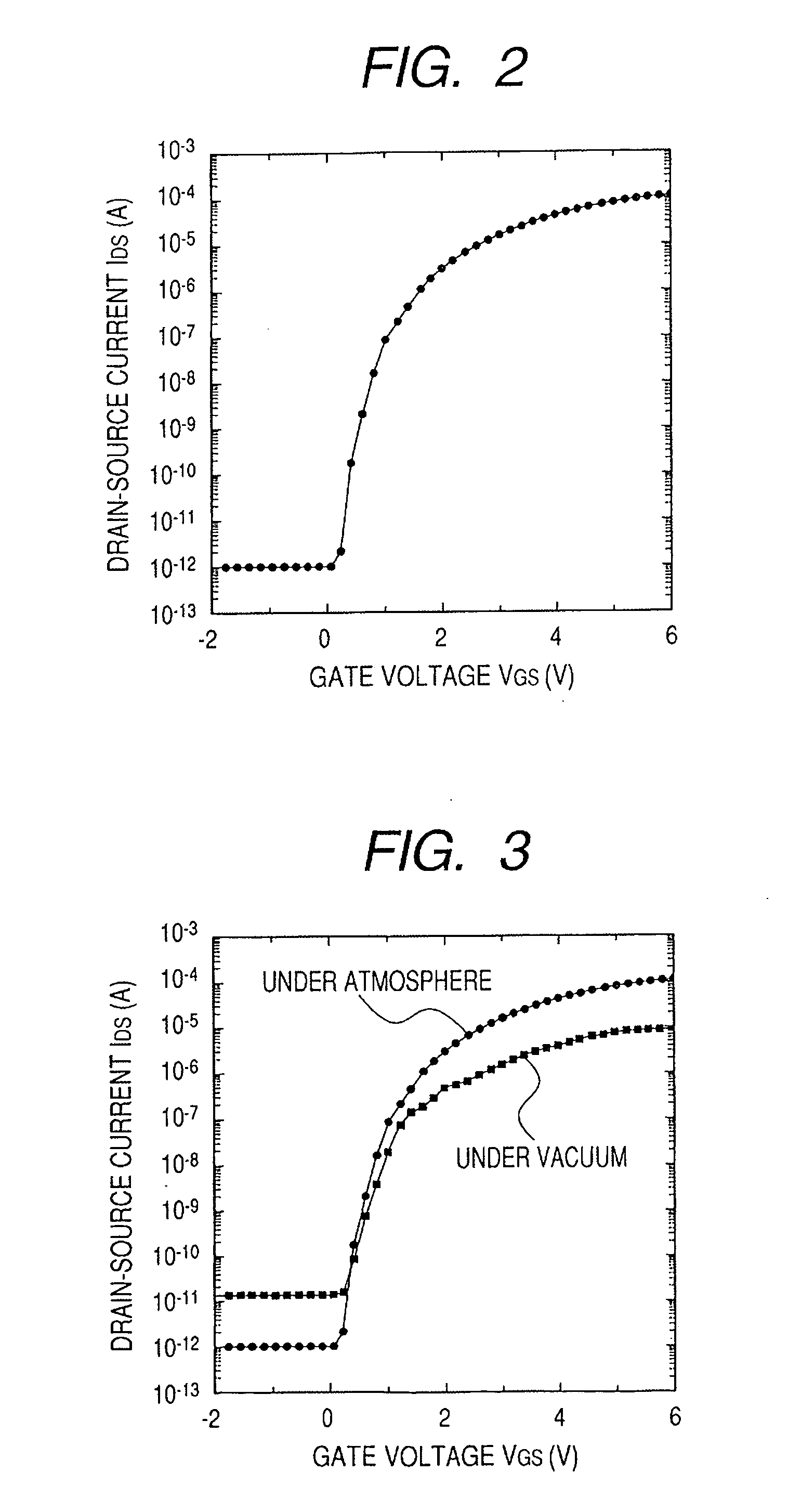
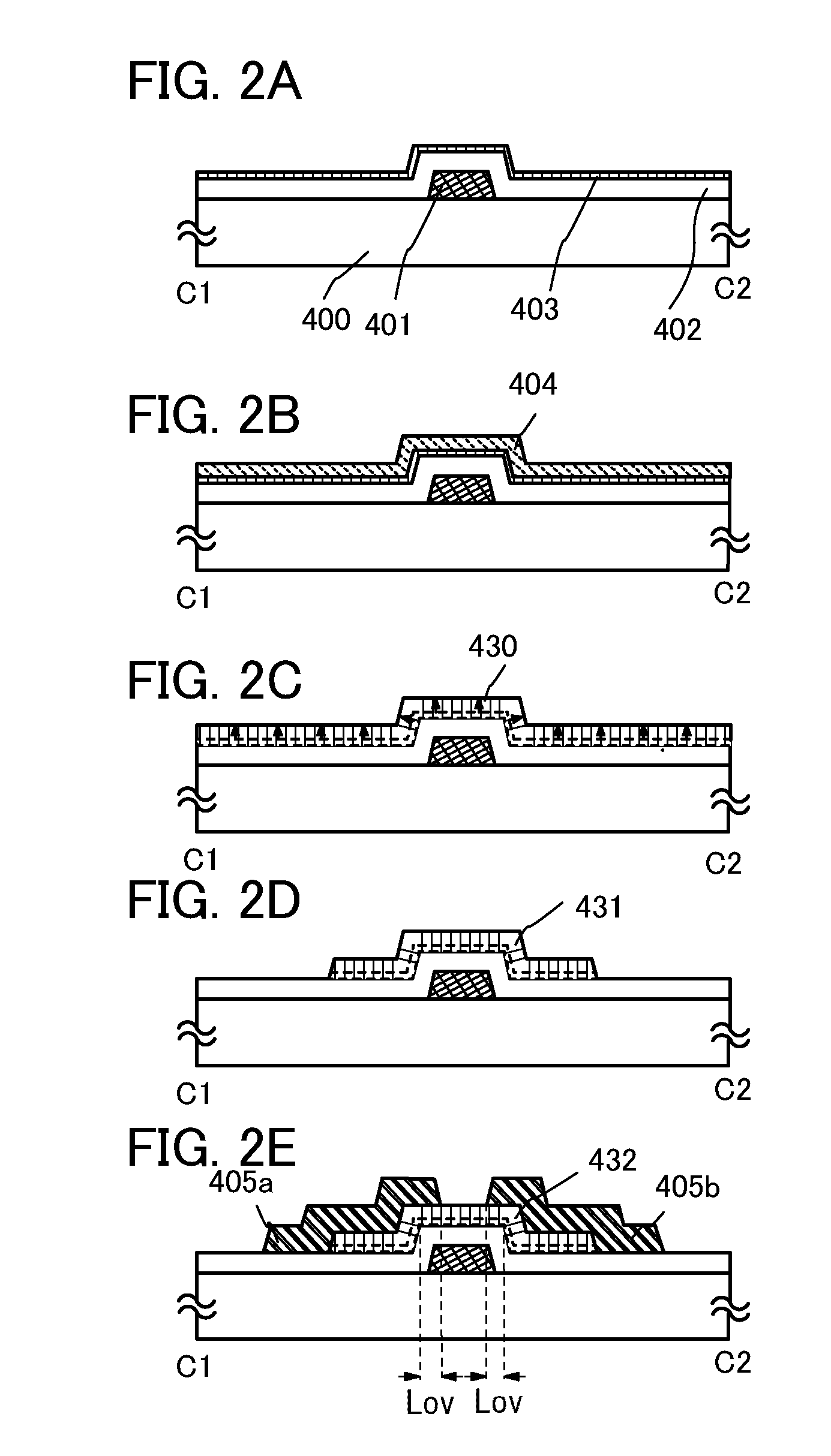
Oxide semiconductor thin film transistor and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20070052025A1Improve reliabilityUnstability of may lessenSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSemiconductor
Provided is a thin film transistor comprising a channel layer comprised of an oxide semiconductor containing In, M, Zn, and O, M including at least one selected from the group consisting of Ga, Al, and Fe. The channel layer is covered with a protective film.
Owner:CANON KK
Memory device utilizing carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS7015500B2Increase in malfunctionIncrease resistanceTransistorIndividual molecule manipulationDevice formCarbon nanotube
A fast, reliable, highly integrated memory device formed of a carbon nanotube memory device and a method for forming the same, in which the carbon nanotube memory device includes a substrate, a source electrode, a drain electrode, a carbon nanotube having high electrical and thermal conductivity, a memory cell having excellent charge storage capability, and a gate electrode. The source electrode and drain electrode are arranged with a predetermined interval between them on the substrate and are subjected to a voltage. The carbon nanotube connects the source electrode to the drain electrode and serves as a channel for charge movement. The memory cell is located over the carbon nanotube and stores charges from the carbon nanotube. The gate electrode is formed in contact with the upper surface of the memory cell and controls the amount of charge flowing from the carbon nanotube into the memory cell.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Stacked oxide material, semiconductor device, and method for manufacturing the semiconductor device
ActiveUS20110127579A1Improve mobilityReduced shutdown currentVacuum evaporation coatingSolid-state devicesDevice materialEngineering
One embodiment is a method for manufacturing a stacked oxide material, including the steps of forming a first oxide component over a base component, causing crystal growth which proceeds from a surface toward an inside of the first oxide component by first heat treatment to form a first oxide crystal component at least partly in contact with the base component, forming a second oxide component over the first oxide crystal component; and causing crystal growth by second heat treatment using the first oxide crystal component as a seed to form a second oxide crystal component.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Field effect transistor and process for production thereof
InactiveUS20100084655A1Improves uniformity and reliabilitySuppress mutationTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsField-effect transistorOxide semiconductor
A field effect transistor has a gate electrode, gate-insulating layer, a channel and a source and drain electrodes connected electrically to the channel, the channel comprising an oxide semiconductor, the source electrode or the drain electrode comprising an oxynitride.
Owner:CANON KK
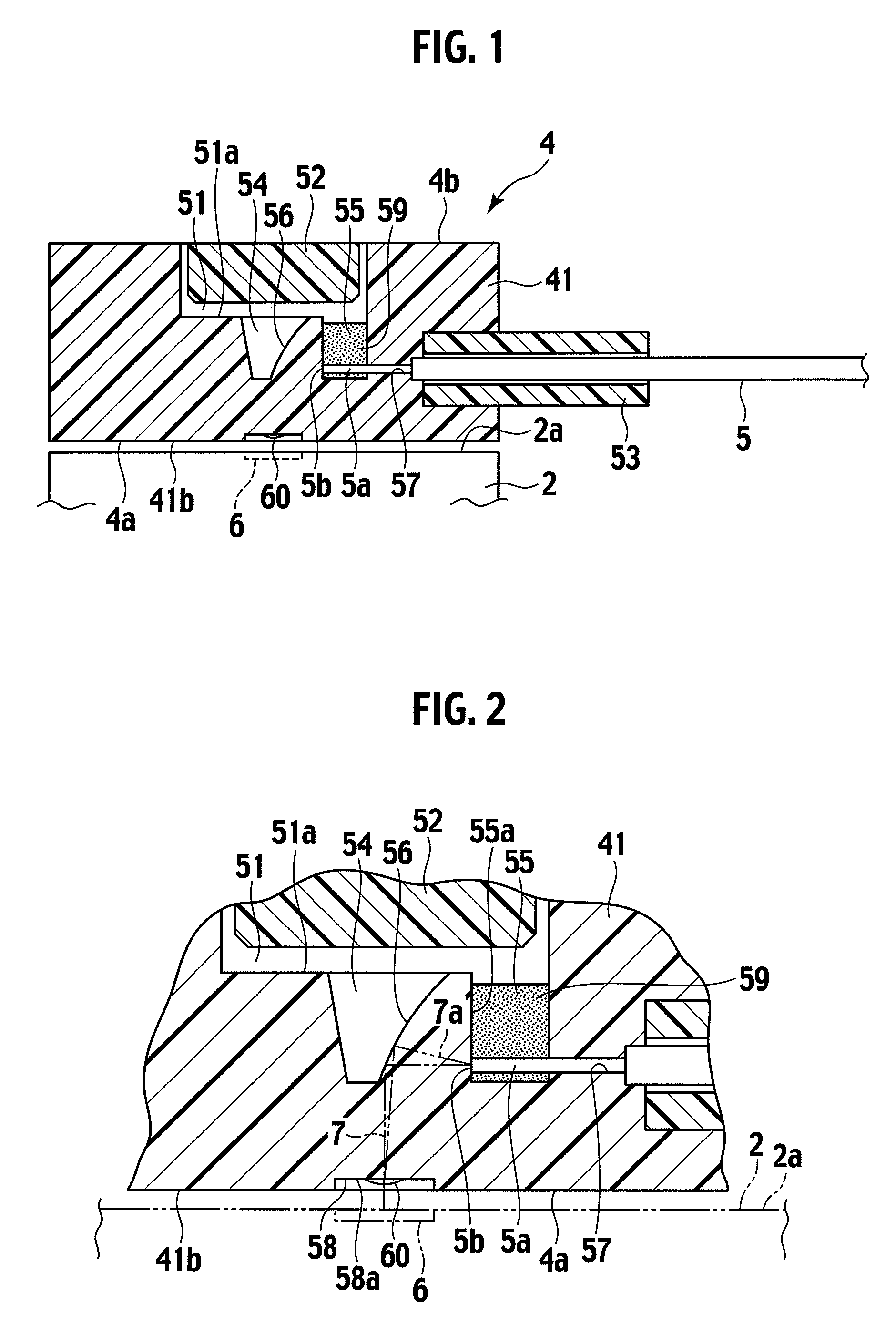
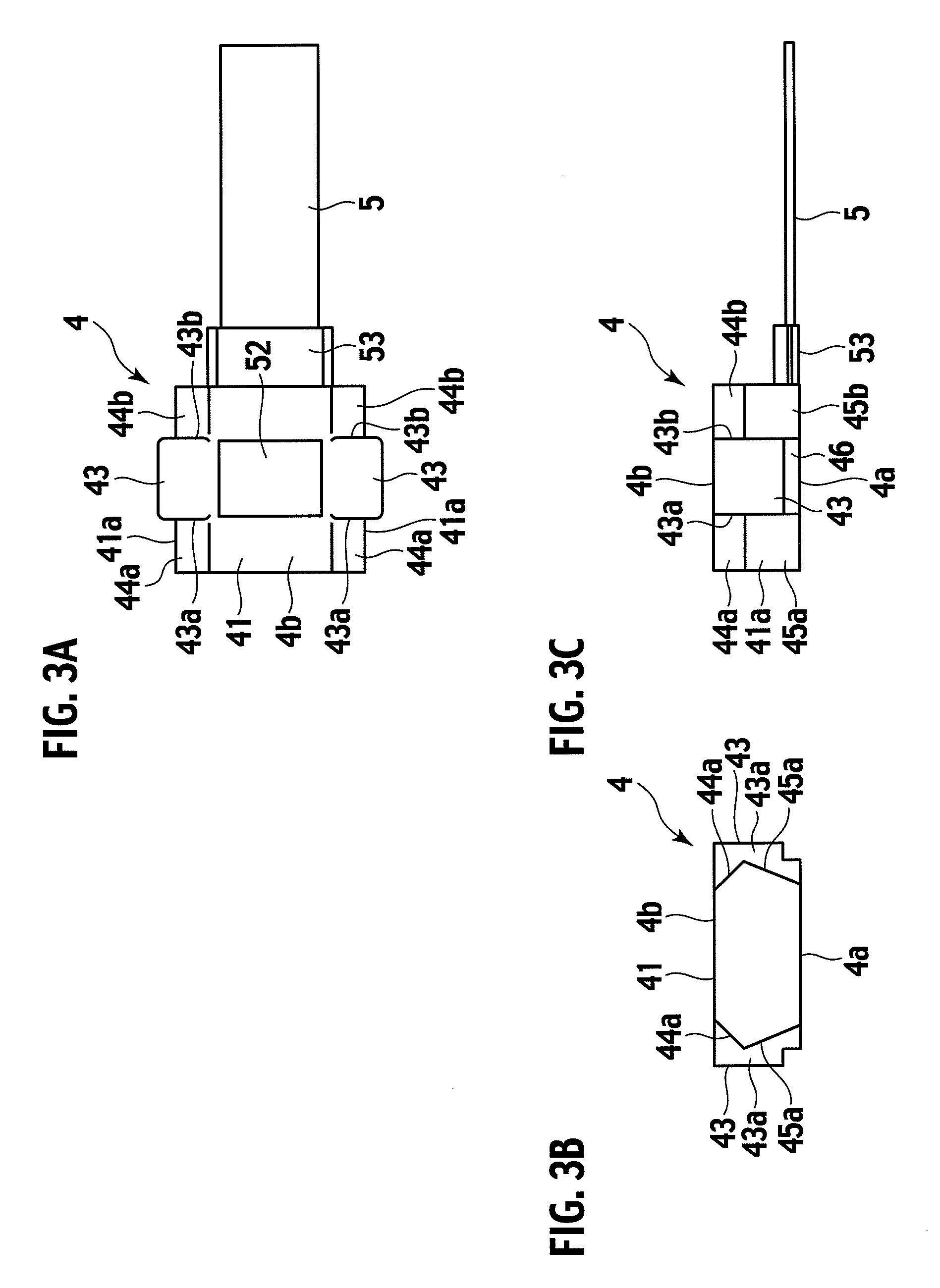
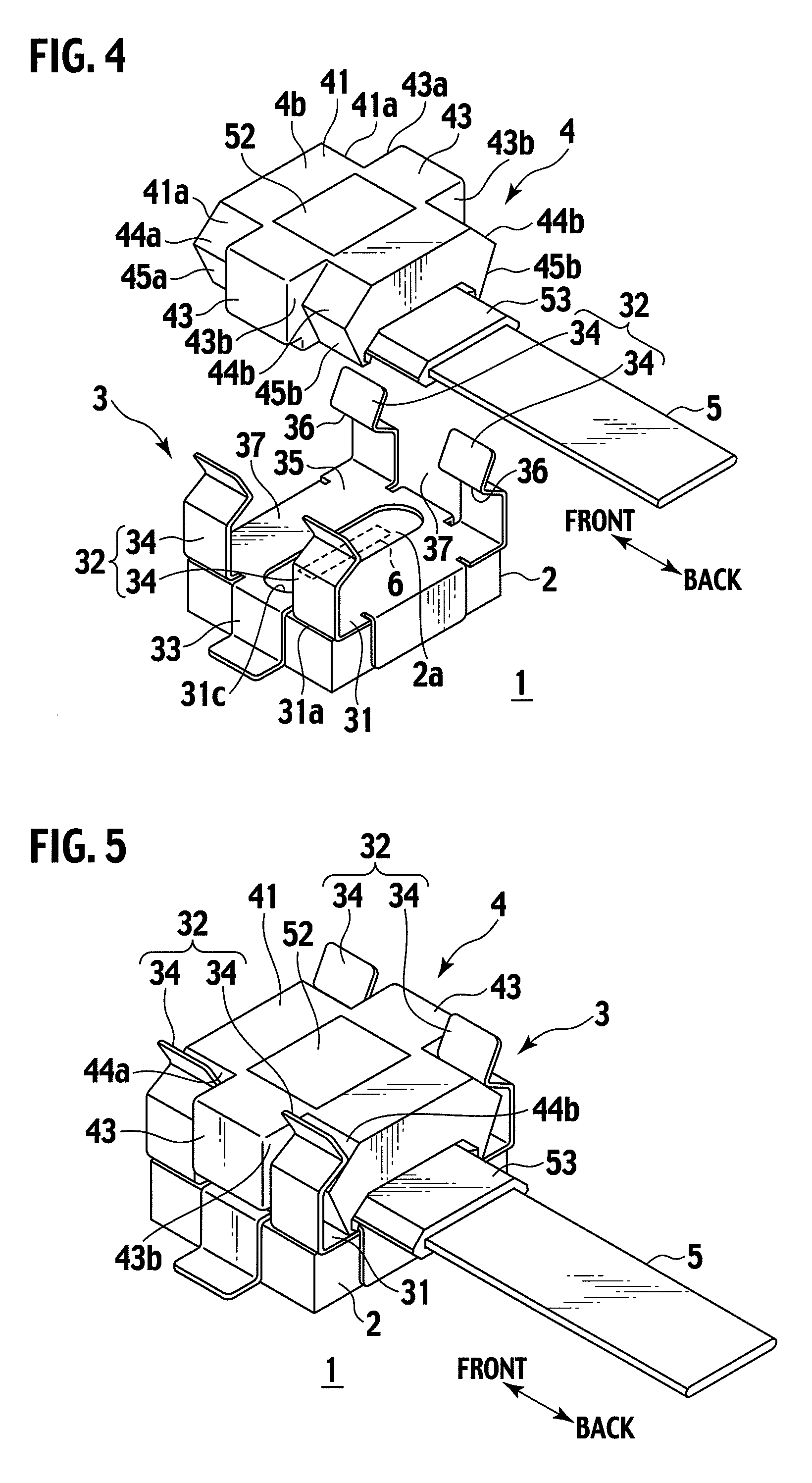
Electrostatic actuator and liquid droplet ejecting head having stable operation characteristics against environmental changes
InactiveUS20050104941A1Eliminate disadvantagesStable characteristicsFlexible member pumpsPrintingEngineeringElectrostatic actuator
A liquid droplet ejecting head includes: one or more nozzle holes ejecting liquid droplets; one or more pressure liquid chambers communicating with the nozzle holes and containing liquid to be ejected; a common liquid chamber communicating with the pressure liquid chambers; one or more diaphragms each forming a wall face of the corresponding pressure liquid chamber; one or more vibration chambers containing air gaps provided in contact with the diaphragms on the opposite side from the pressure liquid chambers; and one or more electrodes provided to oppose the diaphragms through the air gaps. The liquid droplet ejecting head further includes: a deformable plate whose deformation is greater than the total deformation of the diaphragms, the deformable plate forming a wall face of the common liquid chamber, and a pressure correcting chamber provided across the deformable plate from the common liquid chamber so as to communicate with the vibration chambers.
Owner:RICOH KK
Method for manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveUS20120064664A1Stable electrical characteristicsReduce the amount of variationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectroluminescent light sourcesCrystalline oxidePower semiconductor device
An object is to manufacture a semiconductor device including an oxide semiconductor film, which has stable electric characteristics and high reliability. A crystalline oxide semiconductor film is formed, without performing a plurality of steps, as follows: by utilizing a difference in atomic weight of plural kinds of atoms included in an oxide semiconductor target, zinc with low atomic weight is preferentially deposited on an oxide insulating film to form a seed crystal including zinc; and tin, indium, or the like with high atomic weight is deposited on the seed crystal while causing crystal growth. Further, a crystalline oxide semiconductor film is formed by causing crystal growth using a seed crystal with a hexagonal crystal structure including zinc as a nucleus, whereby a single crystal oxide semiconductor film or a substantially single crystal oxide semiconductor film is formed.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
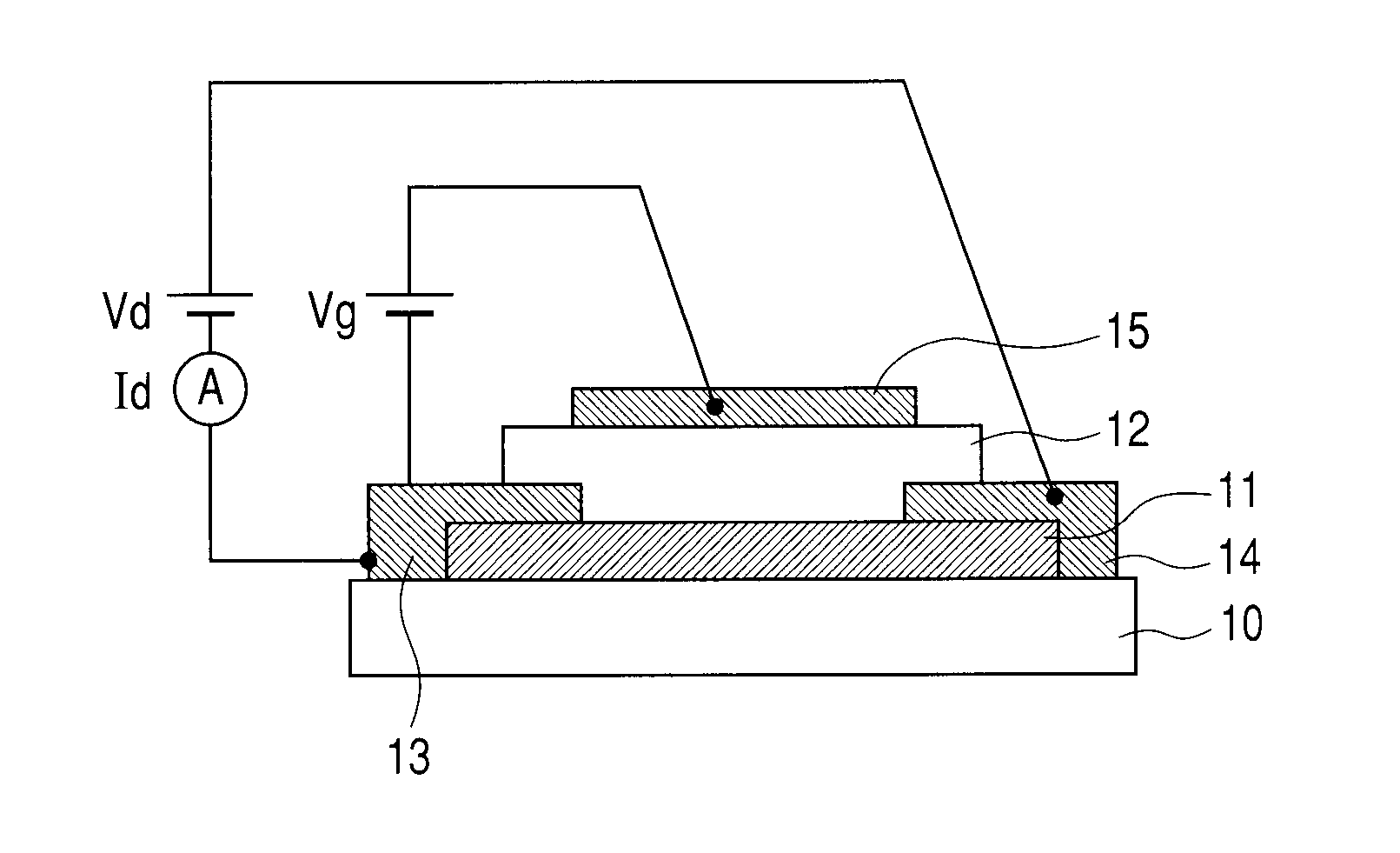
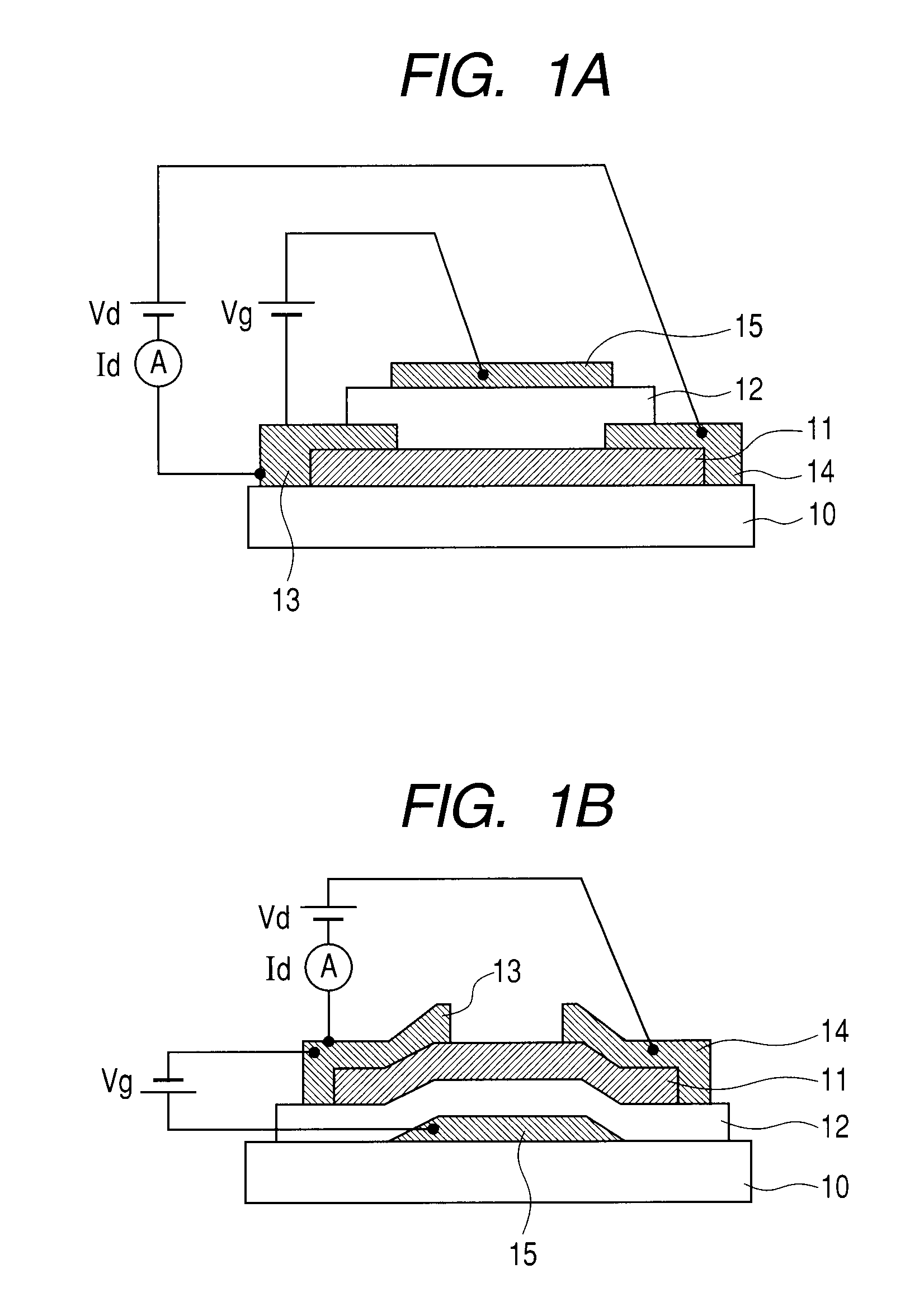
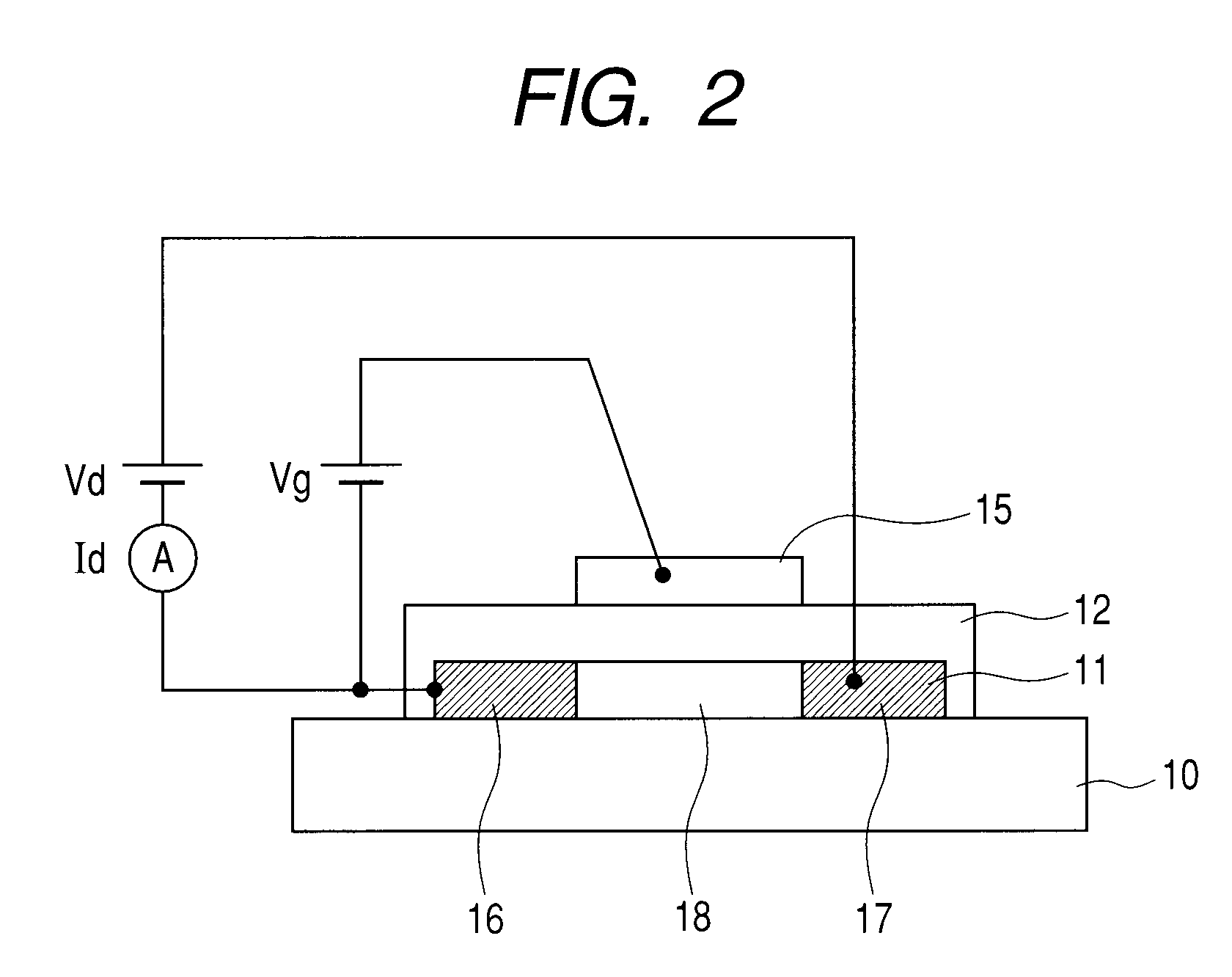
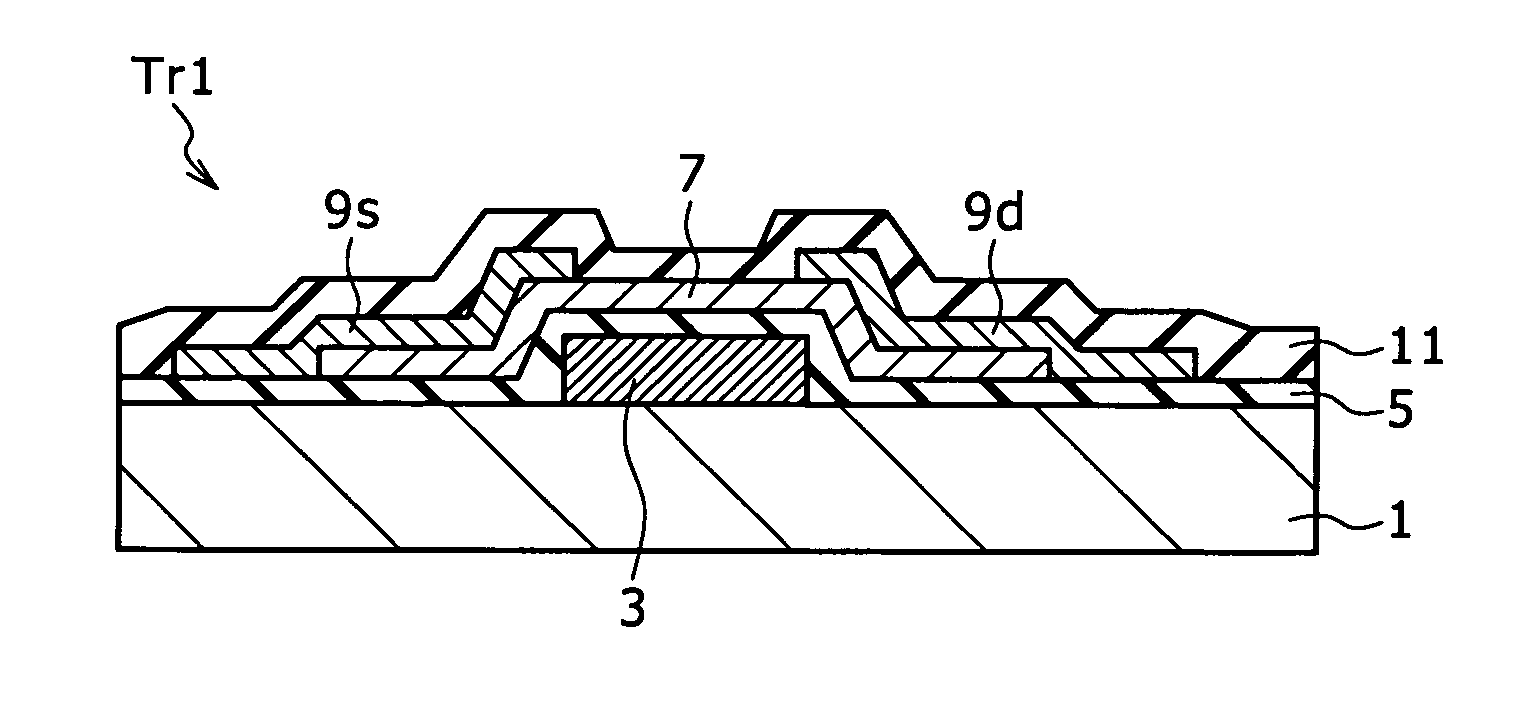
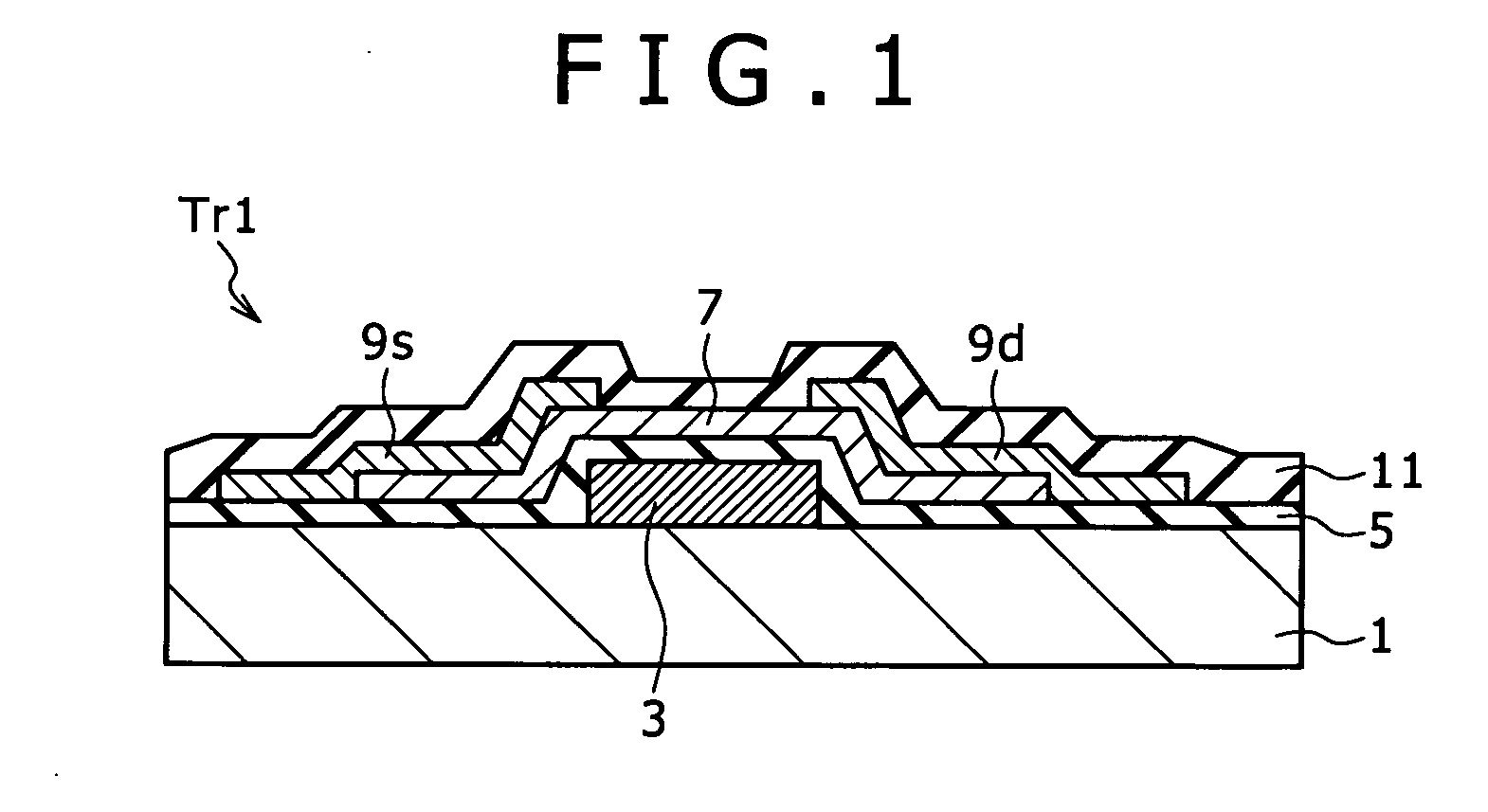
Semiconductor device and method for fabricating such device
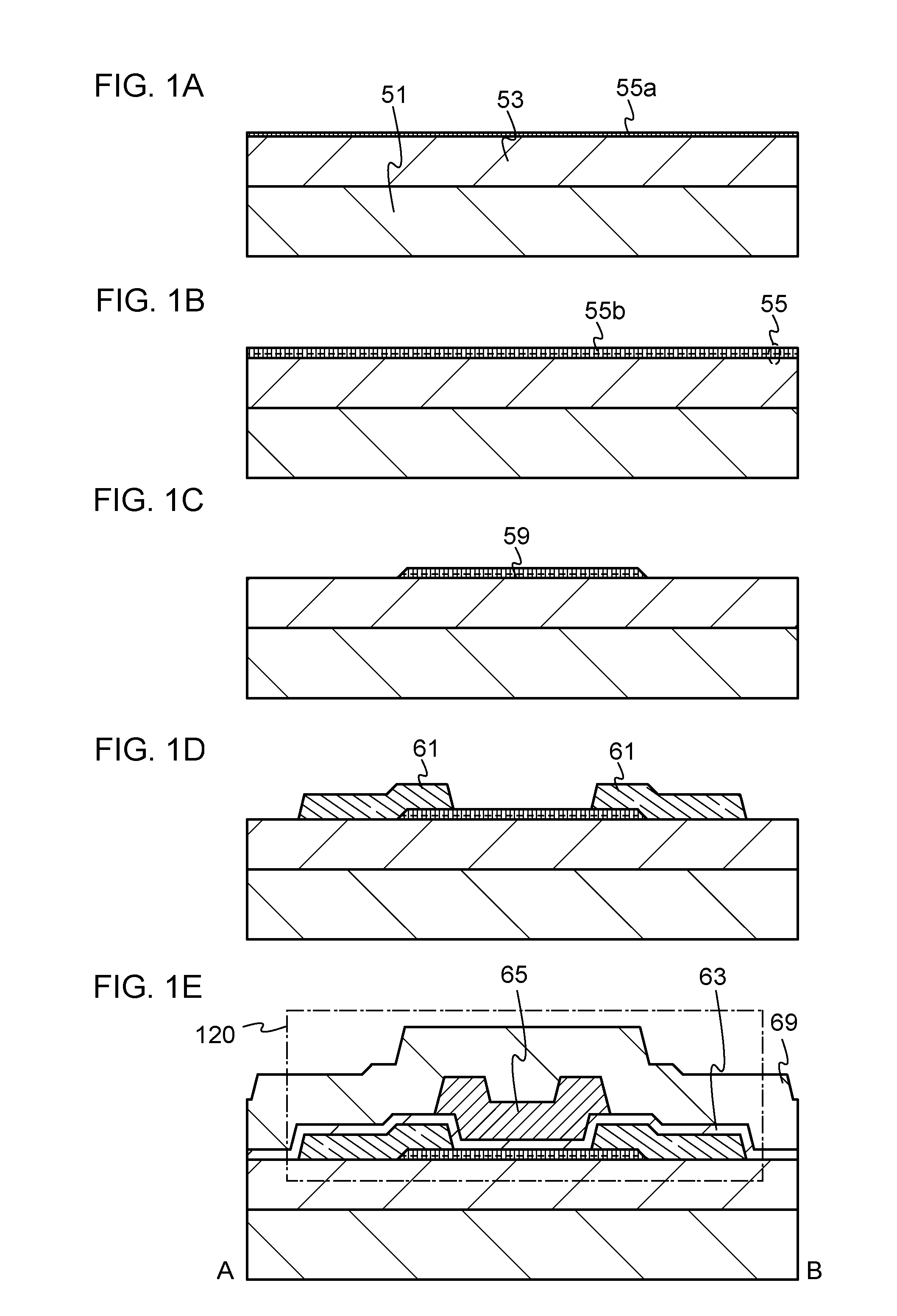
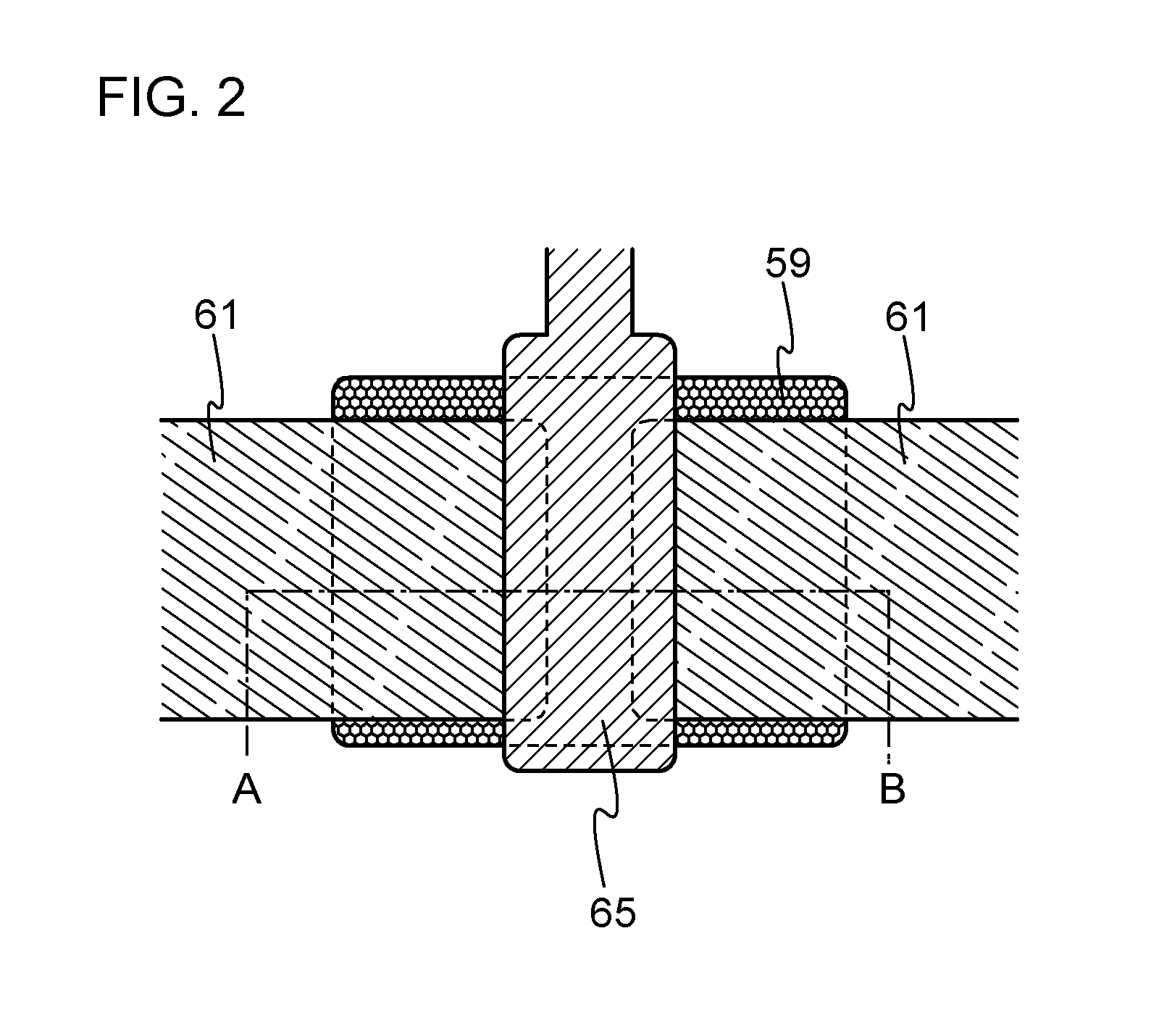
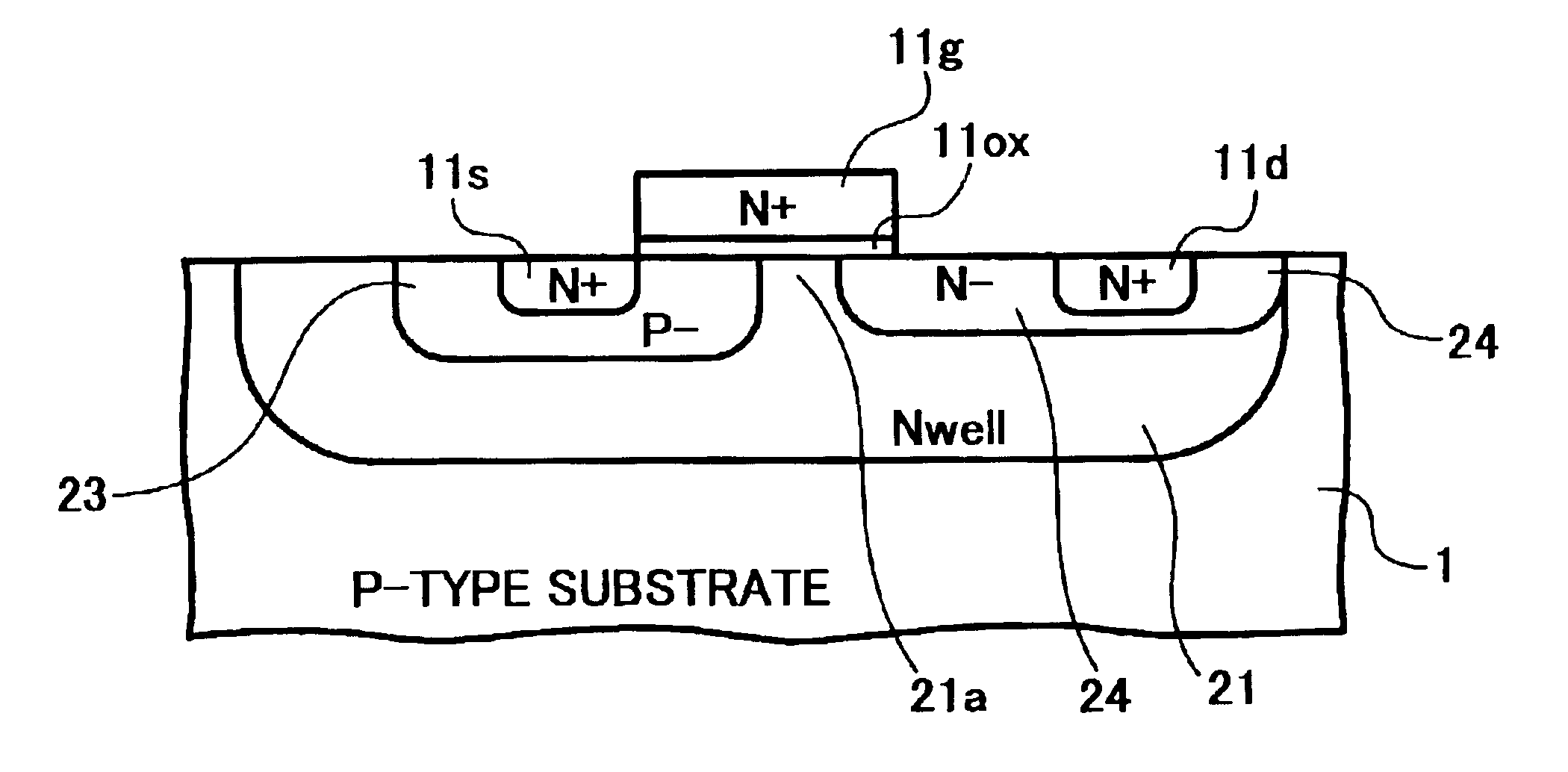
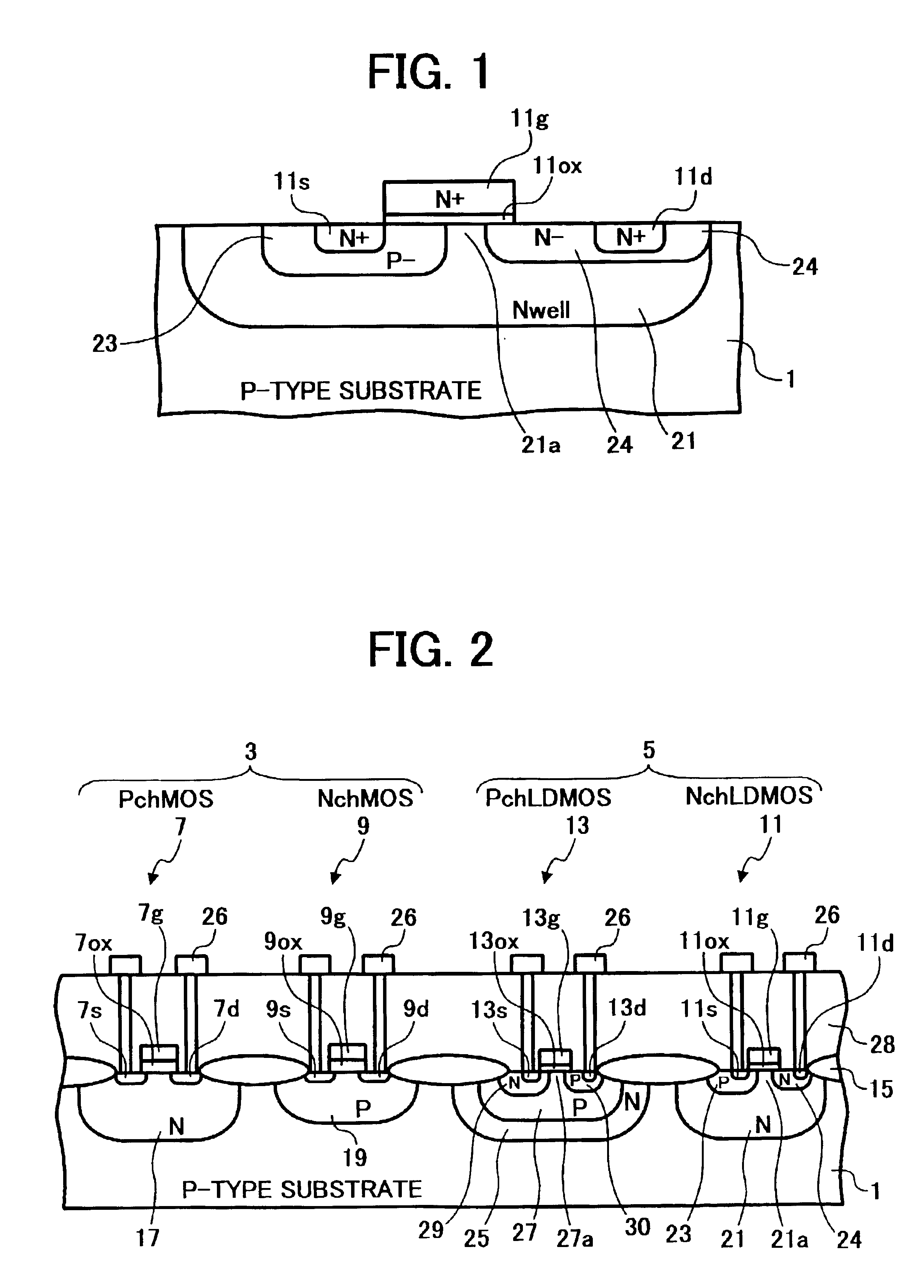
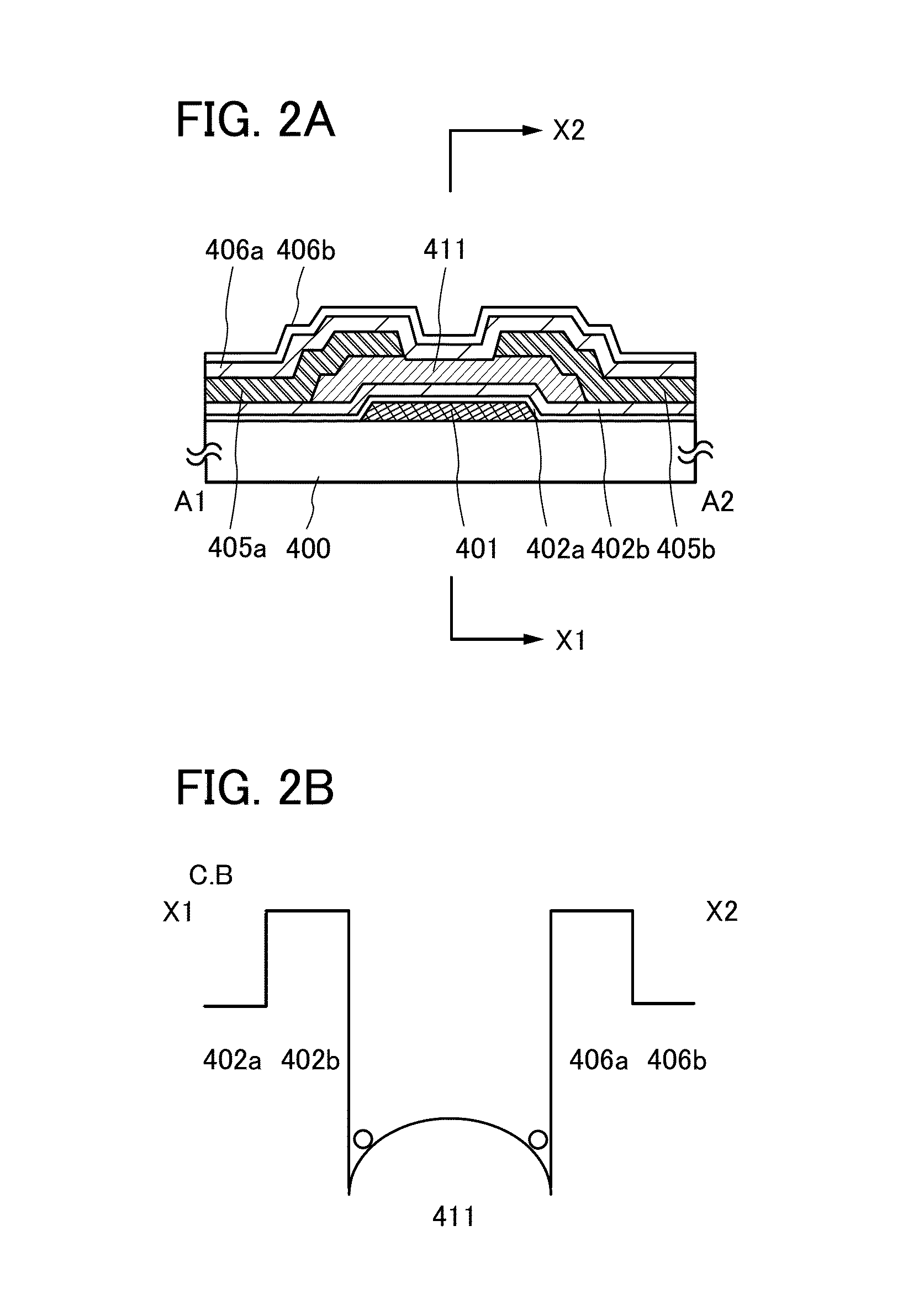
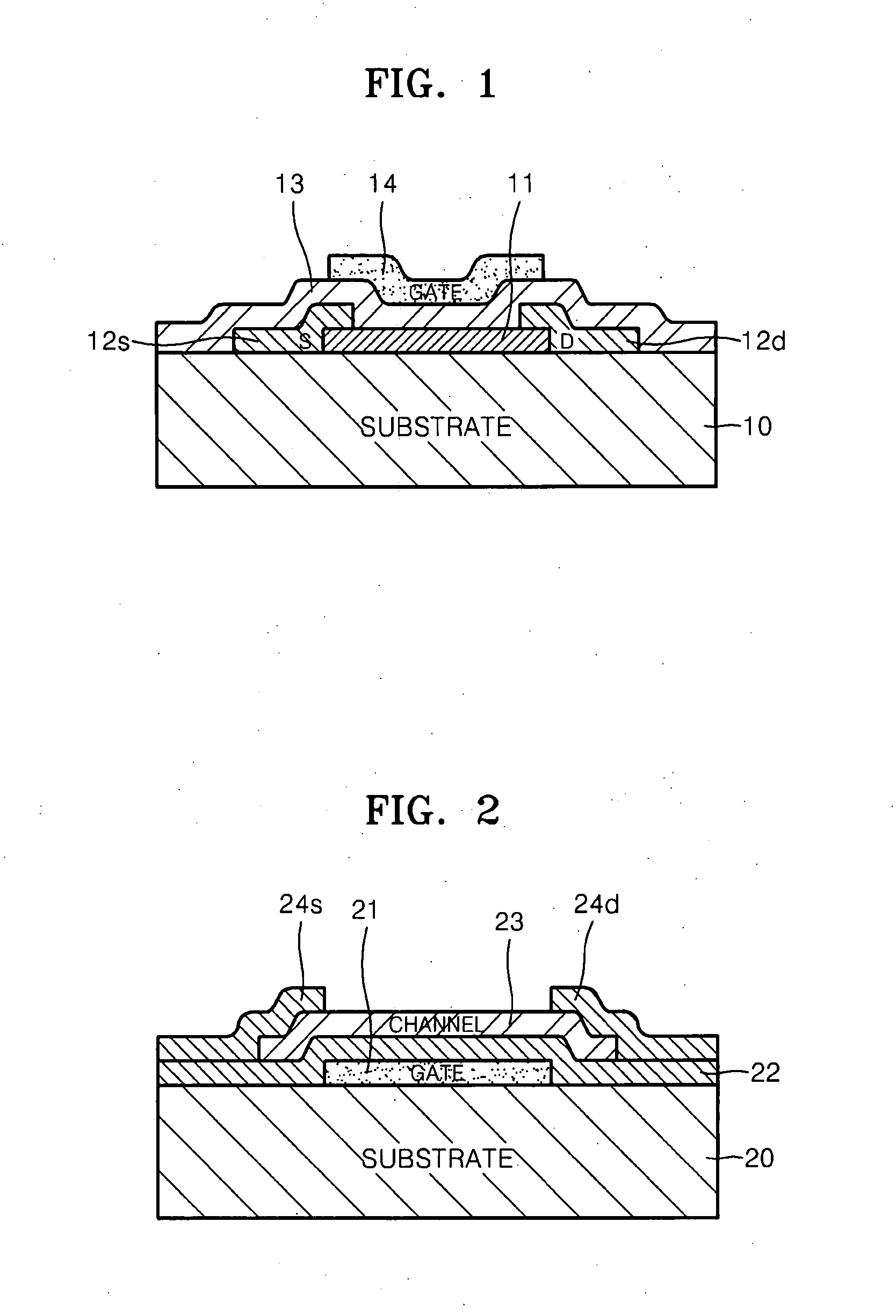
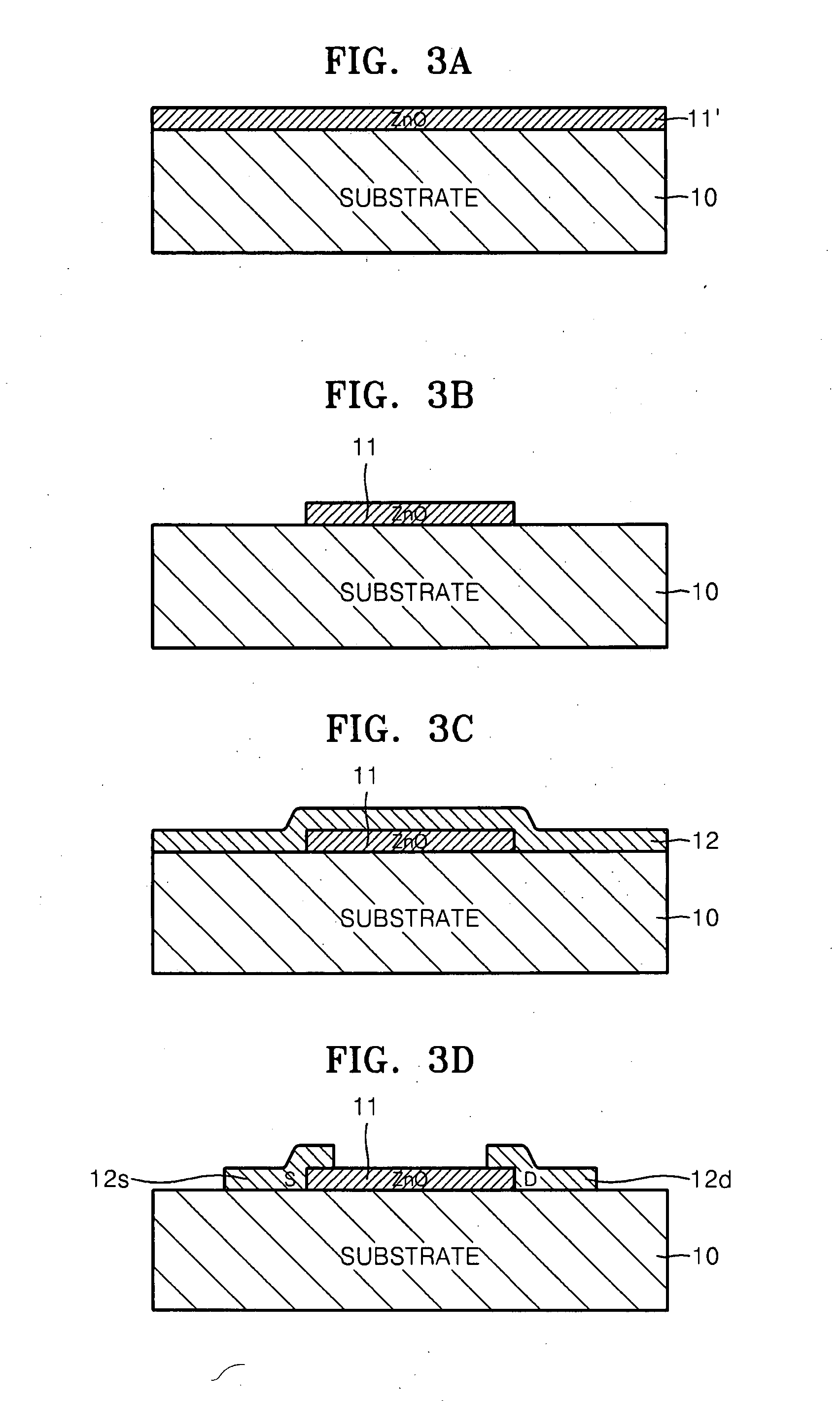
InactiveUS6911694B2Stable operational characteristicAvoid layeringTransistorSolid-state devicesLDMOSGate dielectric
An LDMOS transistor and a bipolar transistor with LDMOS structures are disclosed for suitable use in high withstand voltage device applications, among others. The LDMOS transistor includes a drain well region 21 formed in P-type substrate 1, and also formed therein spatially separated one another are a channel well region 23 and a medium concentration drain region 24 having an impurity concentration larger than that of drain well region 21, which are simultaneously formed having a large diffusion depth through thermal processing. A source 11s is formed in channel well region 23, while a drain 11d is formed in drain region 24 having an impurity concentration larger than that of drain region 24. In addition, a gate electrode 11g is formed over the well region, overlying the partially overlapped portions with well region 23 and drain region 24 and being separated from drain 11d. Since the source 11s, well region 23, and drain region 24 are respectively self-aligned to the gate electrode 11g, resultant transistor characteristics are stabilized, and the decrease in the on resistance and improved drain threshold voltages can be achieved. Also disclosed herein are bipolar transistors with LDMOS structures, which are capable of obviating the breakdown of gate dielectric layers even at high applied voltage and achieving improved stability in transistor characteristics.
Owner:RICOH KK
Antireflective member and electronic equipment using same
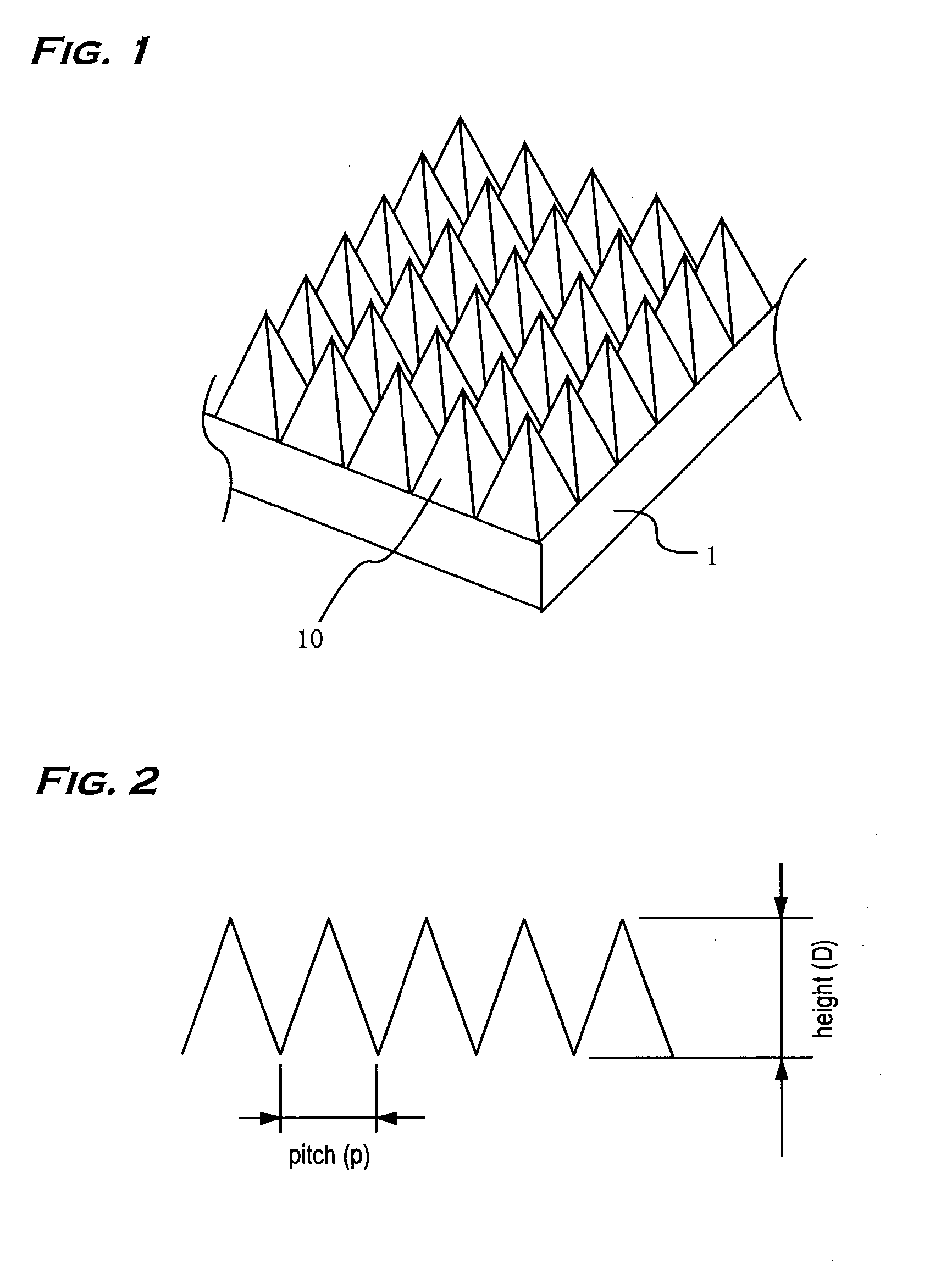
InactiveUS20030180476A1Stable characteristicsLiquid crystal compositionsDiffusing elementsZeroth orderOptoelectronics
This invention has an object to provide an antireflective member with stability and a low reflectance at low cost by performing an antireflective treatment to the substrate in the molding process of the substrate. In the invention a roughened surface with a continuous pattern in a fine pyramidal shape 10 is formed on a surface of a transparent substrate 1, the roughened surface is a diffraction surface with zeroth-order diffraction to visible light, and the pattern of the roughened surface is transferred from a mold at a transfer rate of not less than 70%.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Field effect transistor and process for production thereof
InactiveUS8164090B2Improves uniformity and reliabilitySuppress mutationTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsField-effect transistorSemiconductor
A field effect transistor has a gate electrode, gate-insulating layer, a channel and a source and drain electrodes connected electrically to the channel, the channel comprising an oxide semiconductor, the source electrode or the drain electrode comprising an oxynitride.
Owner:CANON KK
Microfabrication of organic optical elements
InactiveUS6855478B2Good optical stabilityConsistent optical performanceAdditive manufacturing apparatusPhotosensitive materialsMicrofabricationPhotoinitiator
Method of fabricating an optical element. A photodefinable composition is provided that includes (i) a hydrophobic, photodefinable polymer, said photodefinable polymer having a glass transition temperature in the cured state of at least about 80° C.; and (ii) a multiphoton photoinitiator system comprising at least one multiphoton photosensitizer and preferably at least one phtoinitiator that is capable of being photosensitized by the photosensitizer. One or more portions of the composition are imagewise exposed to the electromagnetic energy under conditions effective to photodefinably form at least a portion of a three-dimensional optical element.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20140042438A1Stable characteristicsImprove reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesIndiumEngineering
The present invention provides a transistor having electrically stable characteristics. In addition, the reliability of a semiconductor device including such a transistor is increased. The semiconductor device includes a gate electrode layer, a gate insulating film over the gate electrode layer, an oxide semiconductor stacked film overlapping with the gate electrode layer with the gate insulating film provided therebetween, and a pair of electrode layers in contact with the oxide semiconductor stacked film. In the semiconductor device, the oxide semiconductor stacked film includes at least indium and includes a first oxide semiconductor layer, a second oxide semiconductor layer, and a third oxide semiconductor layer which are sequentially stacked. Further, the first oxide semiconductor layer has an amorphous structure, the second oxide semiconductor layer and the third oxide semiconductor layer include a crystal part whose c-axis is substantially perpendicular to a top surface of the oxide semiconductor stacked film.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
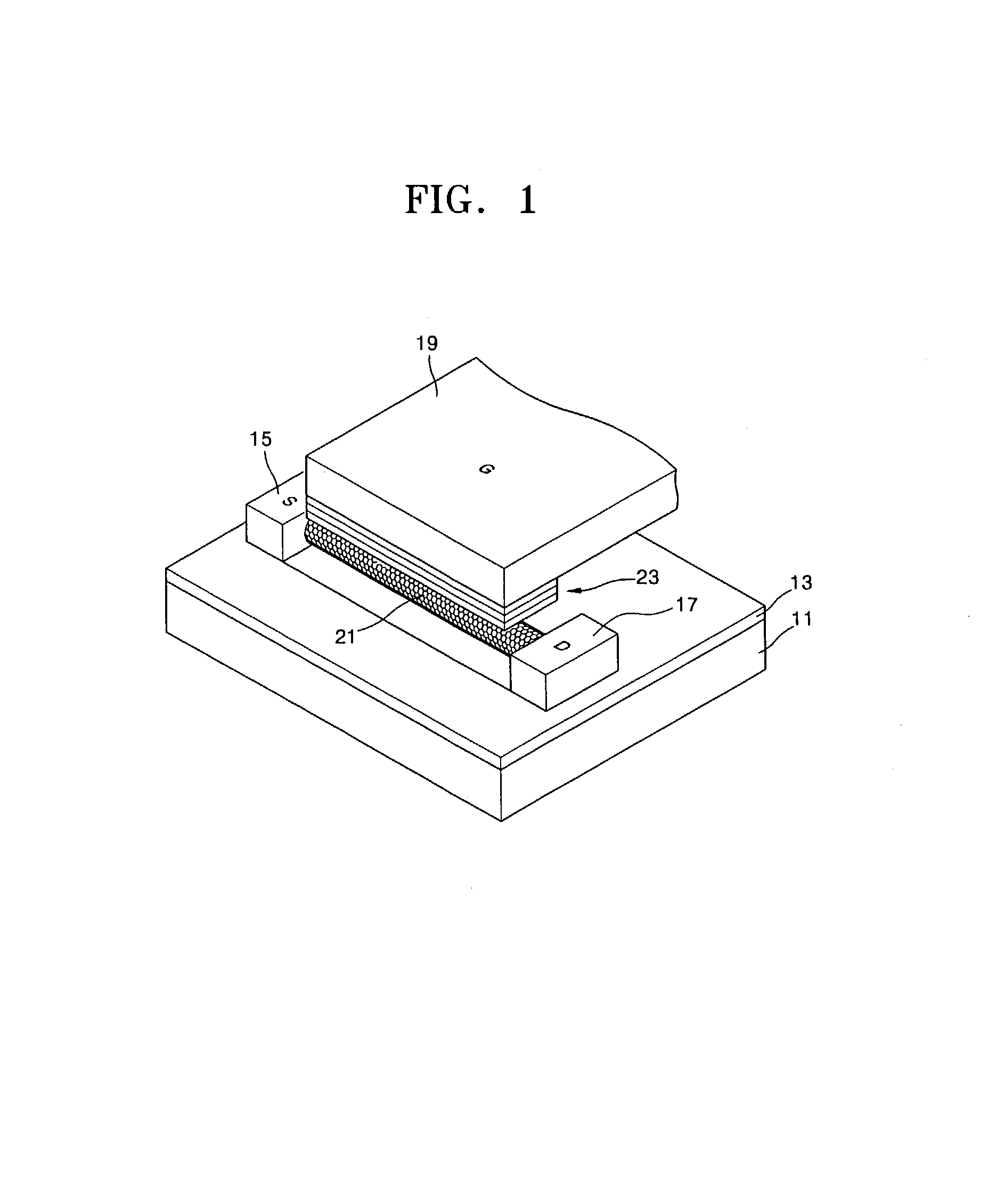
ActiveUS20070252147A1Improved optical sensitivityStable characteristicsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumOxide
A semiconductor device may include a composite represented by Formula 1 below as an active layer. x(Ga2O3)·y(In2O3)·z(ZnO) Formula 1wherein, about 0.75≦x / z≦about 3.15, and about 0.55≦y / z≦about 1.70. Switching characteristics of displays and driving characteristics of driving transistors may be improved by adjusting the amounts of a gallium (Ga) oxide and an indium (In) oxide mixed with a zinc (Zn) oxide and improving optical sensitivity.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
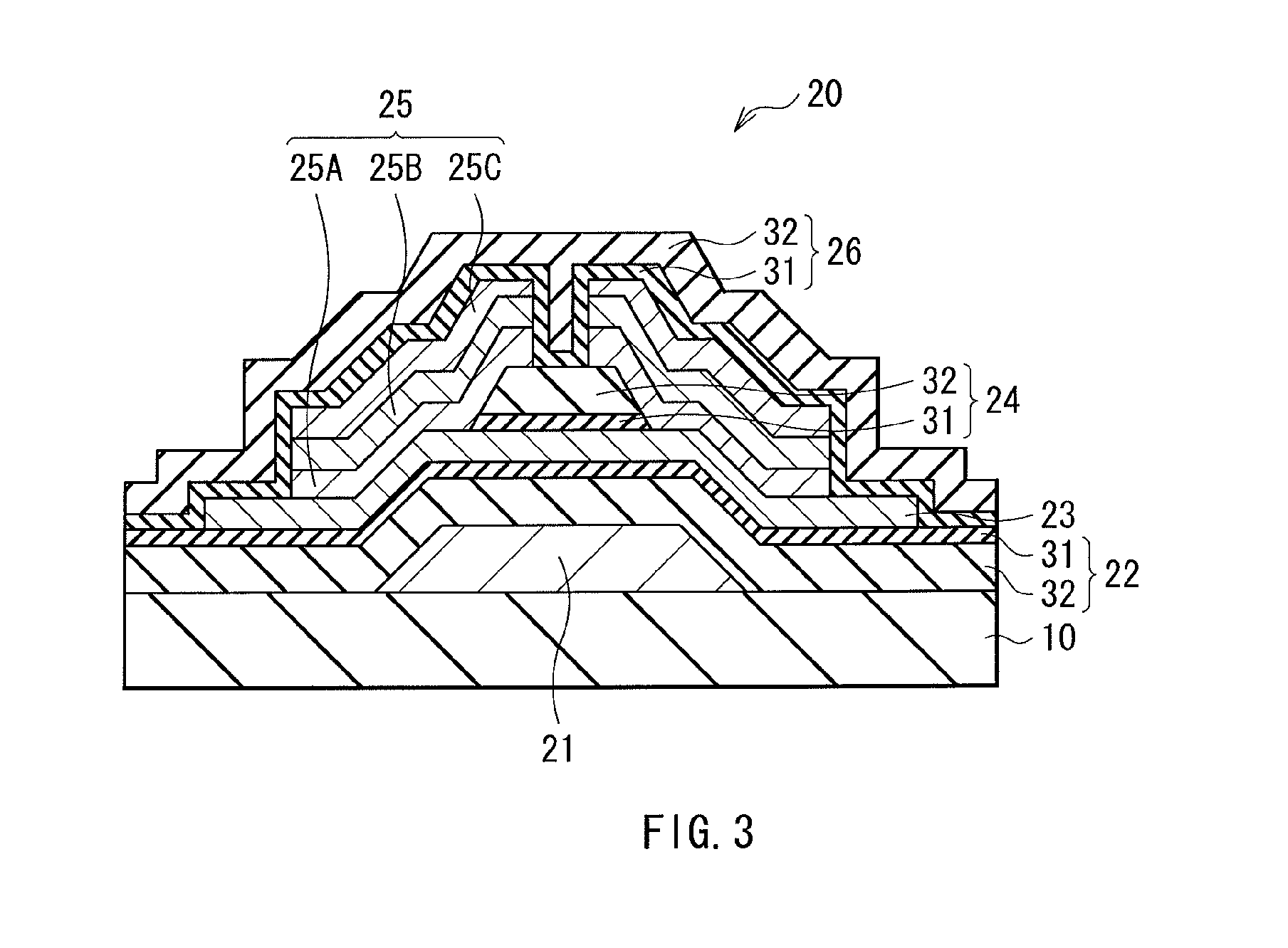
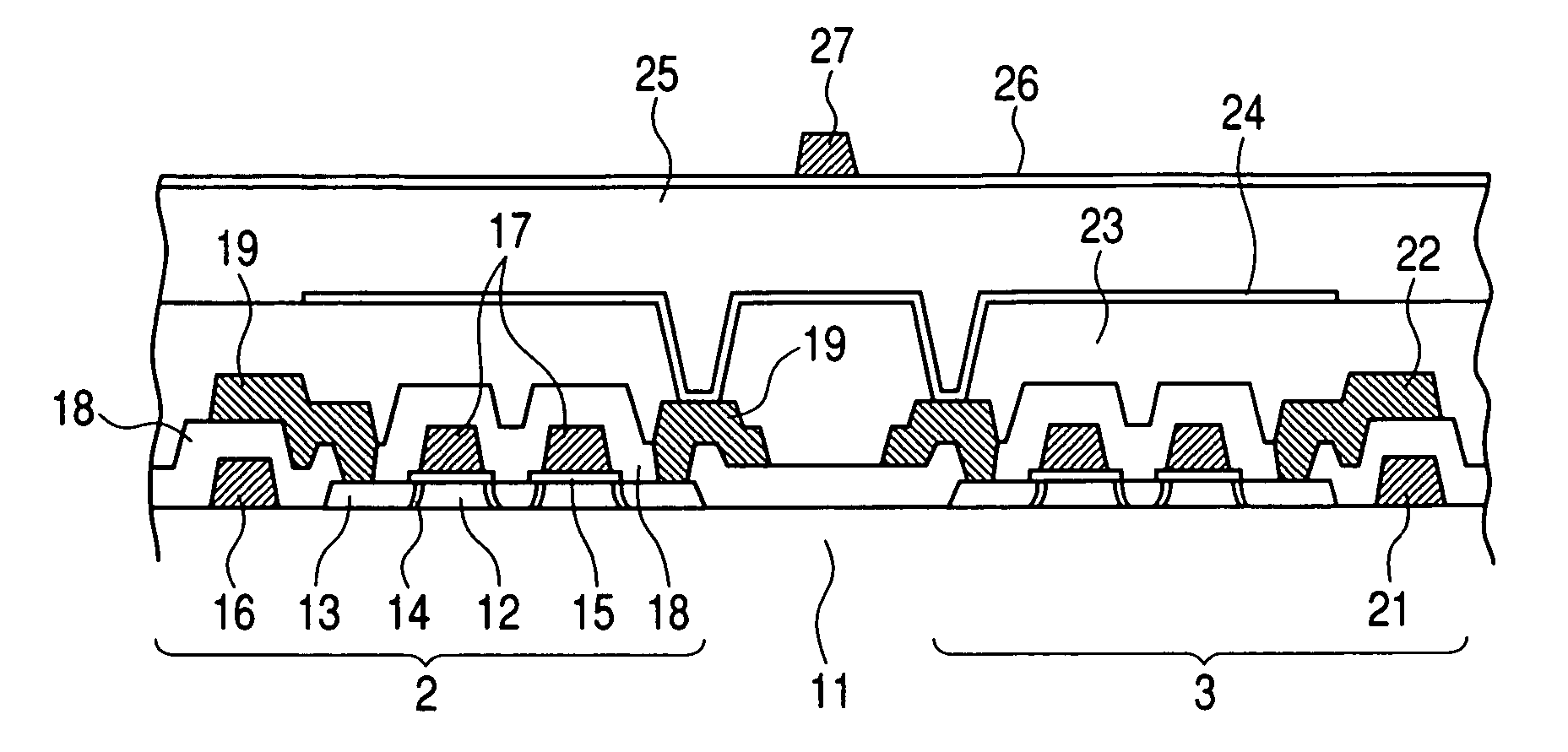
Thin film transistor and display device
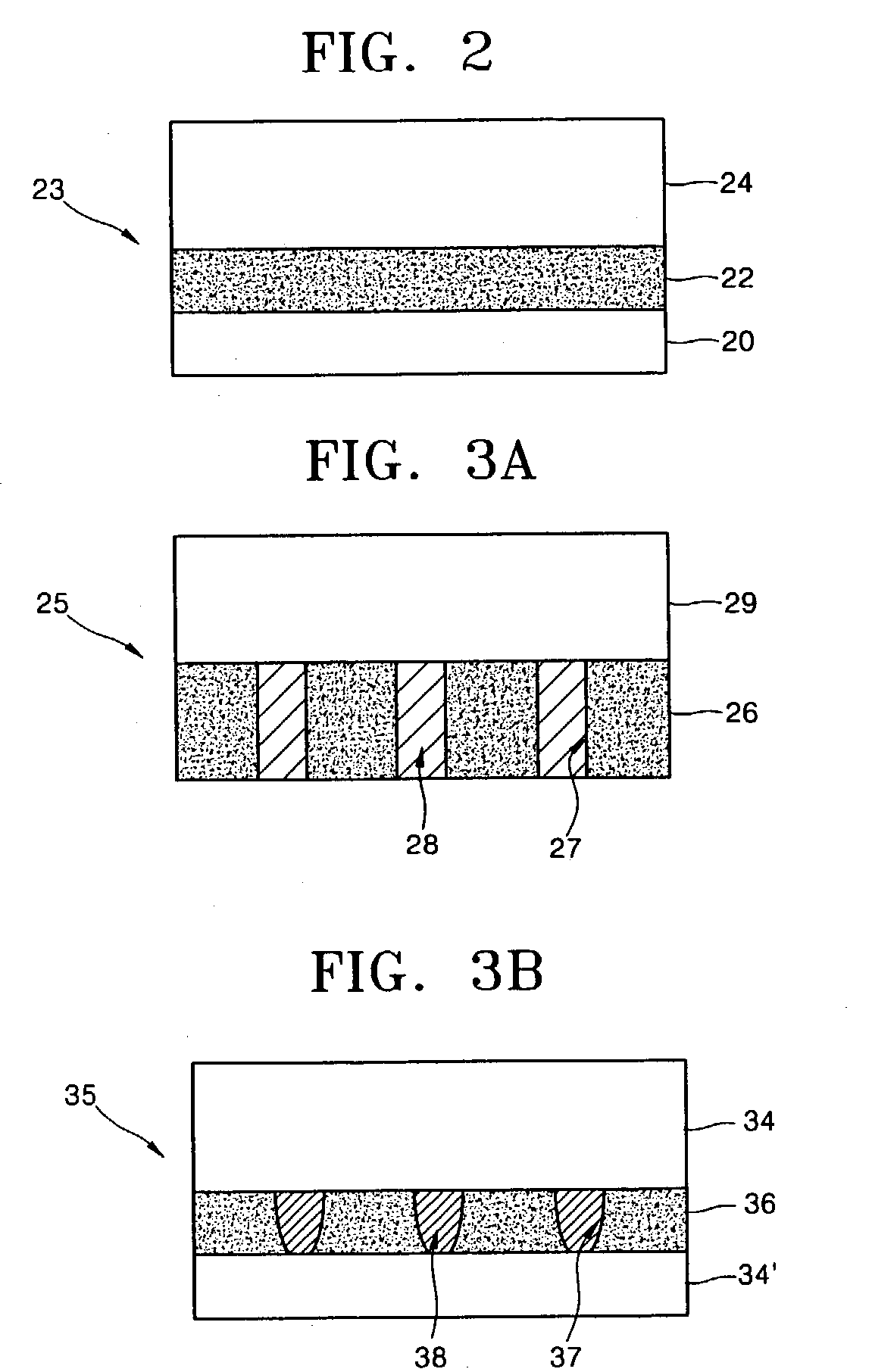
ActiveUS20110180802A1Inhibition of desorptionShorten the timeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesDesorptionDisplay device
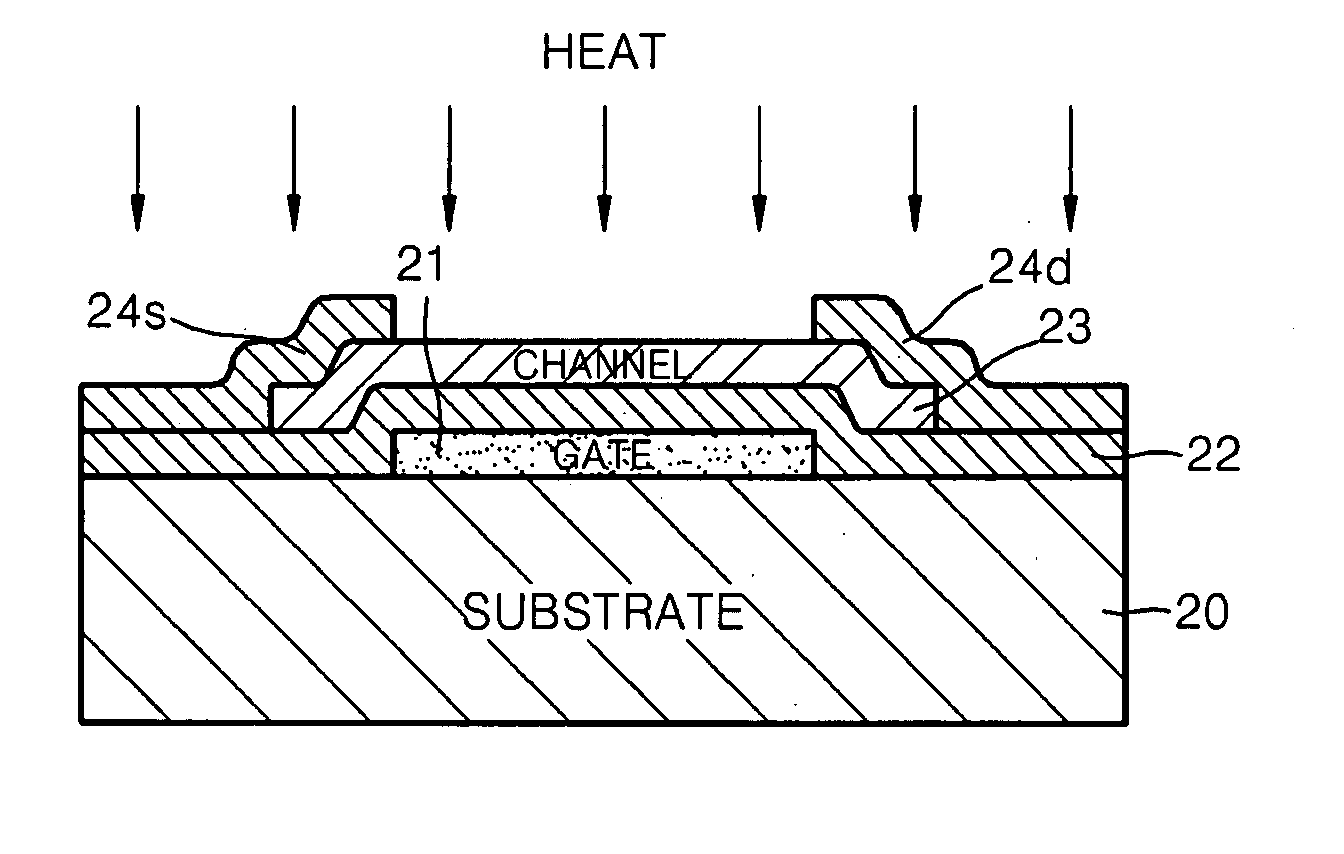
Provided are a thin film transistor that is capable of suppressing desorption of oxygen and others from an oxide semiconductor layer, and reducing the time to be taken for film formation, and a display device provided therewith. A gate insulation film 22, a channel protection layer 24, and a passivation film 26 are each in the laminate configuration including a first layer 31 made of aluminum oxide, and a second layer 32 made of an insulation material including silicon (Si). The first and second layers 31 and 32 are disposed one on the other so that the first layer 31 comes on the side of an oxide semiconductor layer 23. The oxide semiconductor layer 23 is sandwiched on both sides by the first layers 31 made of aluminum oxide, thereby suppressing desorption of oxygen and others, and stabilizing the electrical characteristics of a TFT 20. Moreover, since the second layer 32 is made of an insulation material including silicon (Si), the time to be taken for film formation can be reduced compared with a single layer made of aluminum oxide.
Owner:JOLED INC
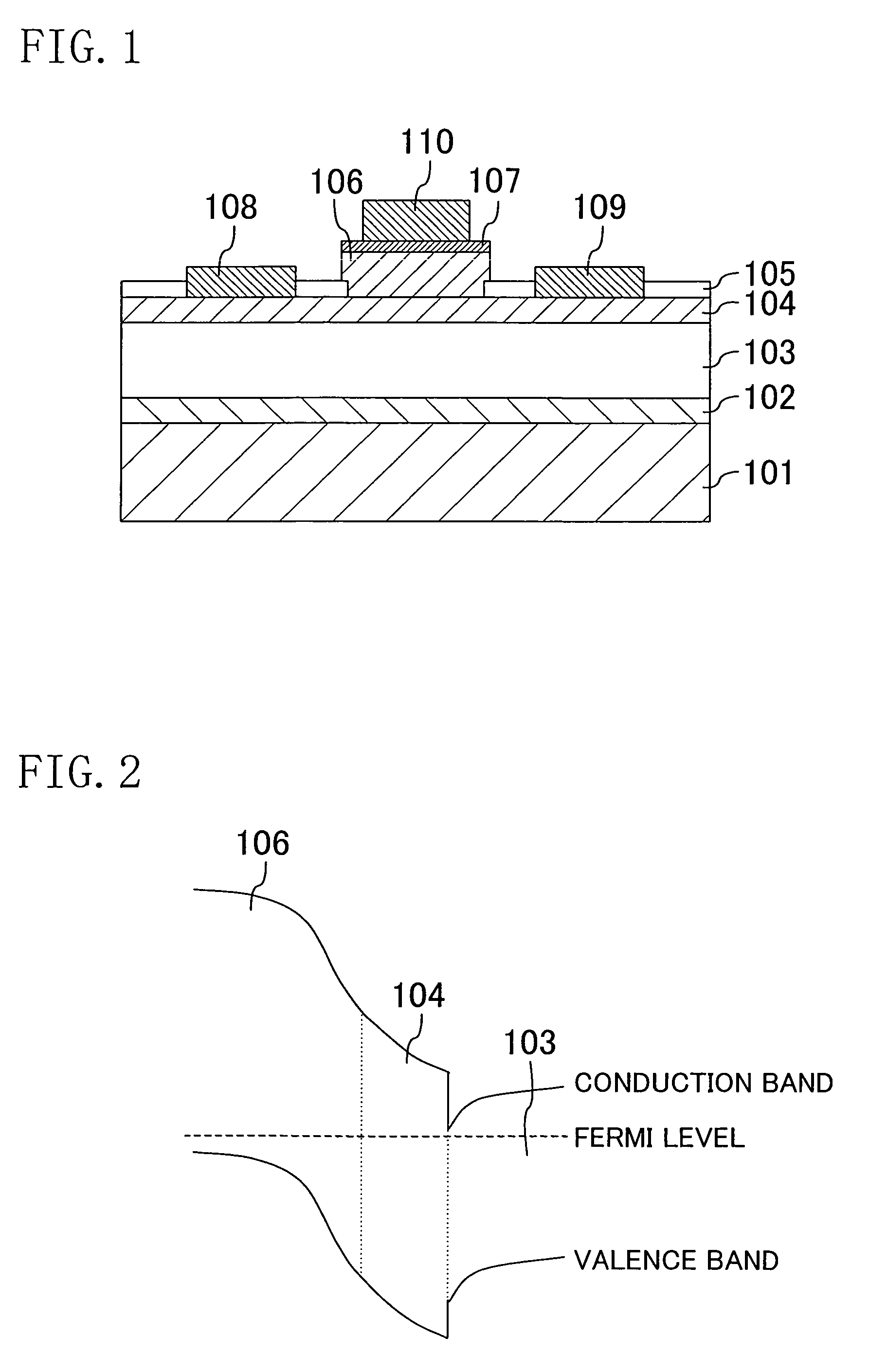
Radiation image pickup device
InactiveUS20060249763A1High sensitivityStable characteristicsTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesImaging qualityGate effect
In a radiation image pickup device including: a sensor element for converting radiation into an electrical signal; and a thin film transistor connected to the sensor element, an electrode of the sensor element connected to the thin film transistor is disposed above the thin film transistor, and that the thin film transistor has a top gate type structure in which a semiconductor layer, a gate insulating layer, and a gate electrode layer are laminated in this order on a substrate, so that a channel portion of the thin film transistor is protected by a gate electrode, thereby providing stable TFT characteristics without undesirable turning ON any of the TFT elements due to the back gate effect by the fluctuation in electric potentials corresponding to outputs from the sensor electrodes, and thereby greatly improving image quality.
Owner:CANON KK
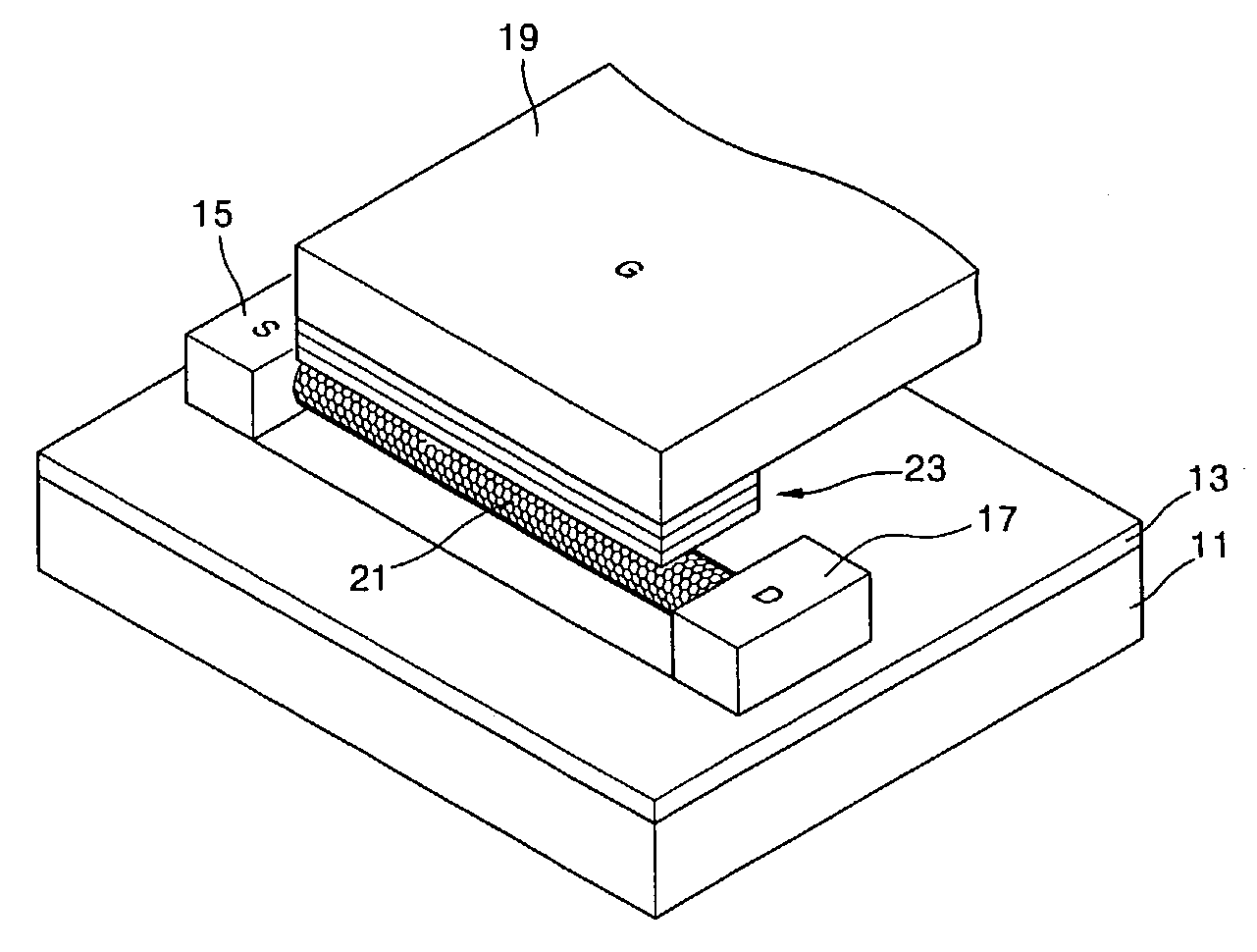
Organic field effect transistor and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050263756A1Characteristic changeExtend your lifeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharge injectionContact formation
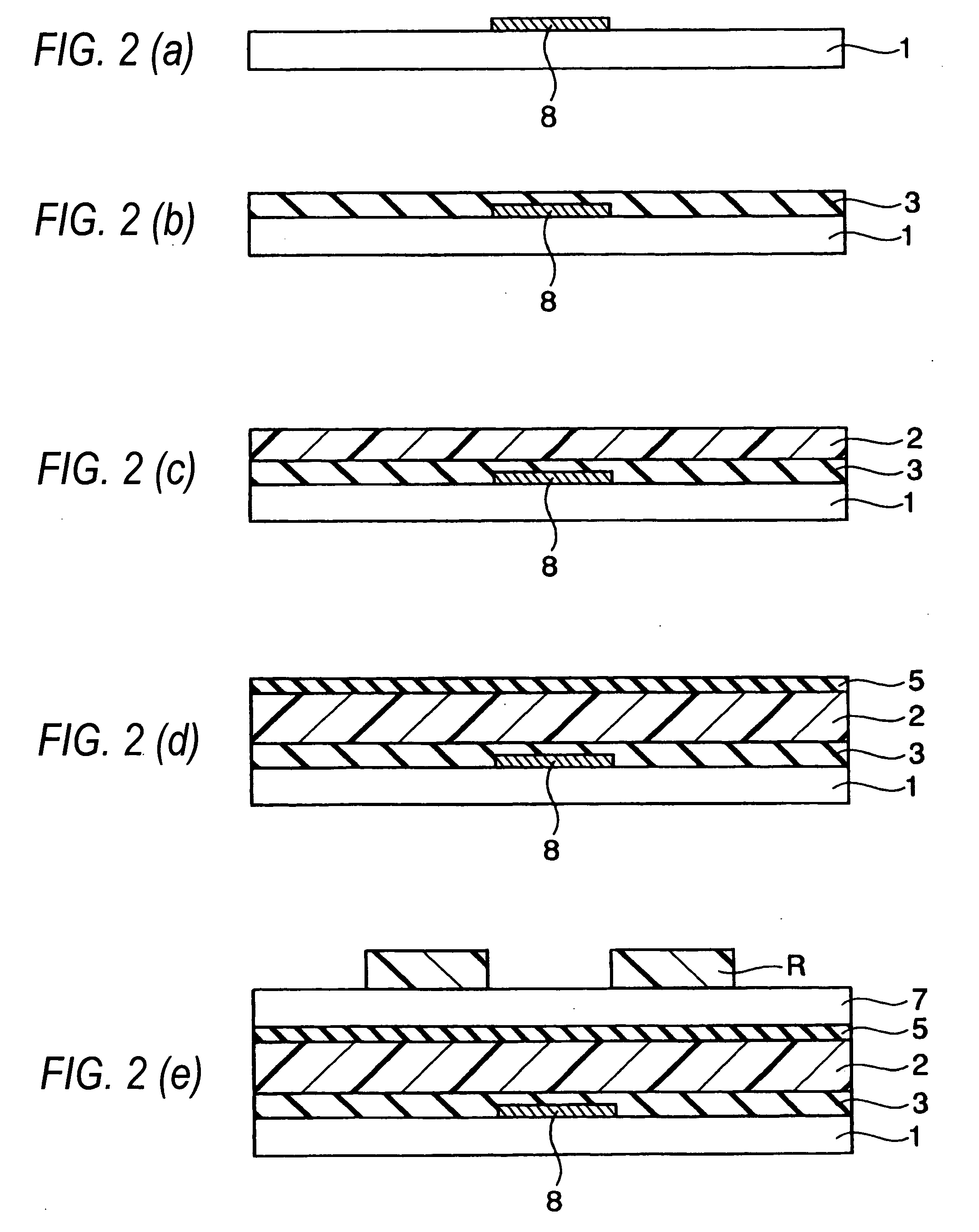
To provide an organic field effect transistor with stable characteristics and a long life span, an organic field effect transistor includes a gate electrode 8 formed on an organic semiconductor film 2 made of an organic semiconductor material with a gate insulating film 3 interposed therebetween; and a source electrode 6 and a drain electrode 7 provided so as to come in contacts with the organic semiconductor film with the gate electrode 8 interposed therebetween. At least one of the source electrode 6 and the drain electrode 7 is formed in contact with the organic semiconductor film 2 with charge injection layers 4 and 5 made of an inorganic material interposed therebetween.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Wireless communication device with two internal antennas
InactiveUS7069043B2Less numberCost reductionCordless telephonesResonant long antennasEngineeringCommunication quality
A portable wireless communication terminal device has a data communications function and a telephone function and includes a casing, a display having a display section exposed through an opening of the casing, a circuit board installed in the casing and having the display on one surface of the circuit board, a first antenna electrically connected to the circuit board and disposed on an opposite side to the display inside the casing, and a second antenna electrically connected to the circuit board and mounted on a periphery of the display inside the casing. The device maintains a stable antenna characteristic and communication quality even if it is placed on a table or if the fingers of a user cover the backside of the device.
Owner:SONY CORP
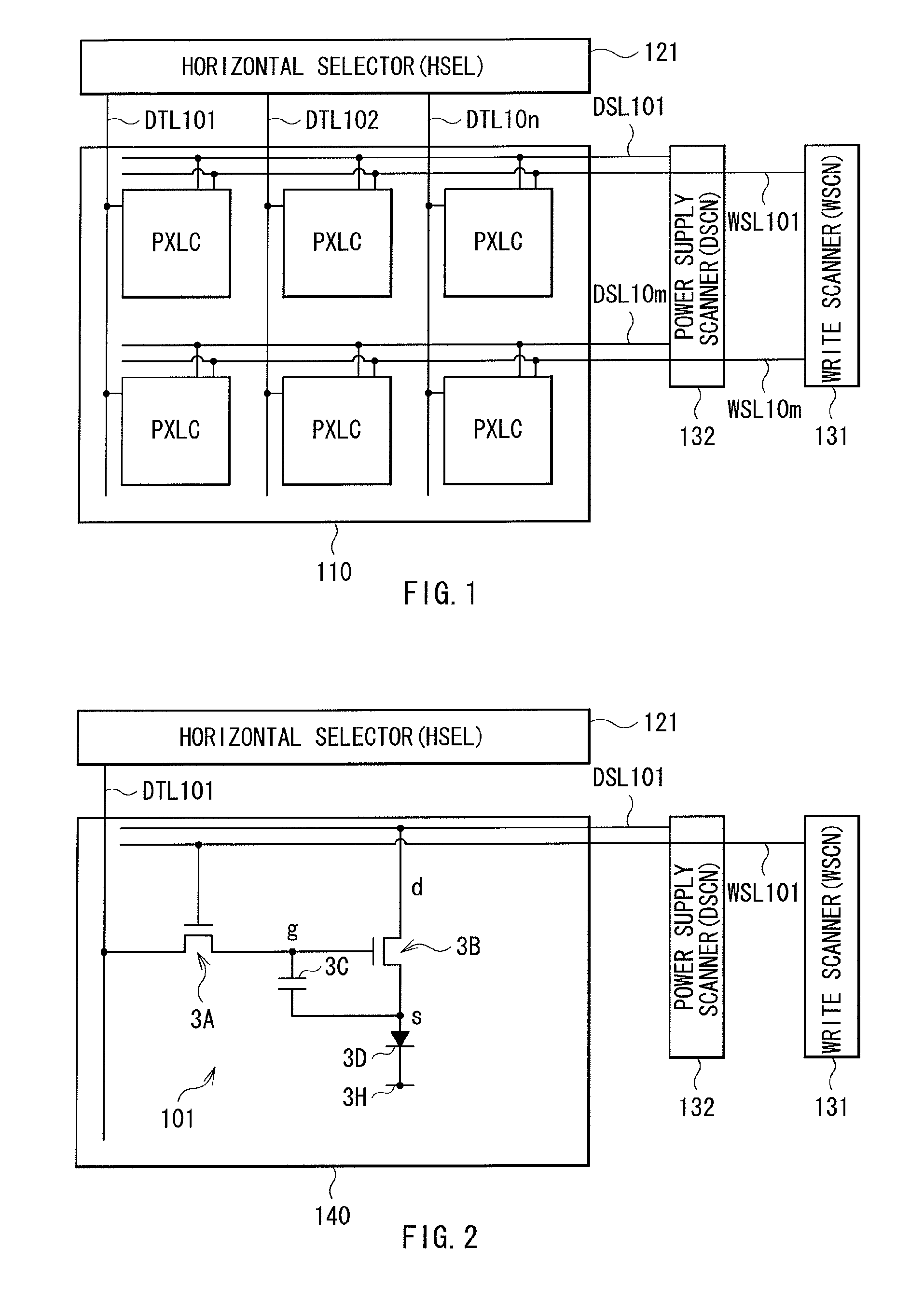
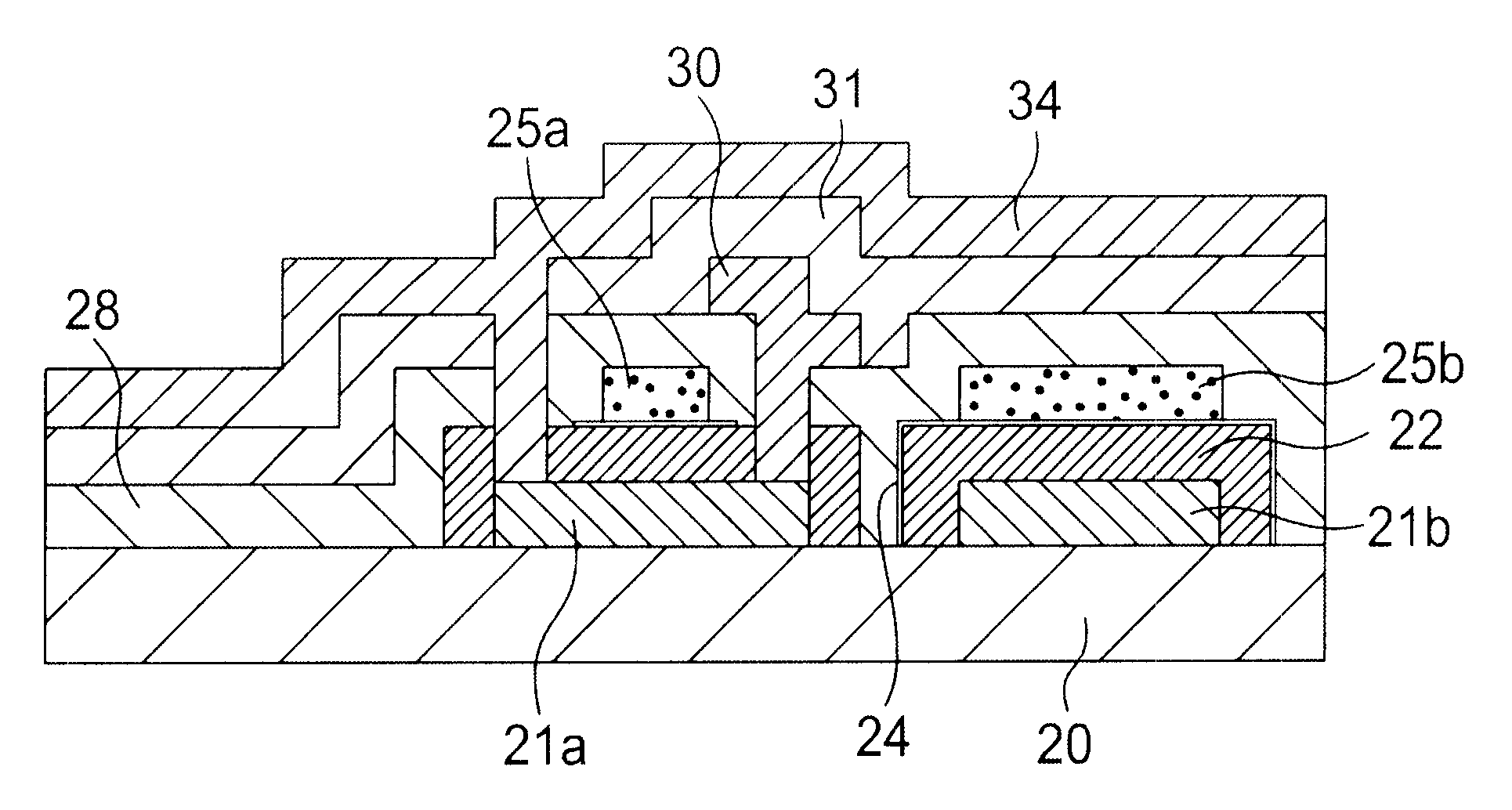
Liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS6556257B2Stable characteristicsThin is prevented degradationSolid-state devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
A liquid crystal display device of the monolithic type which comprises a first substrate, a plurality of display elements arranged in a matrix on the first substrate to define a display area of the liquid crystal display device, each of the display elements comprising a picture element or pixel electrode and a switching or pixel transistor associated with the picture element or pixel electrode, a driving circuit formed on the first substrate and connected to the display area. The driving circuit includes a horizontal driver and a vertical driver. The device further includes a second substrate substantially entirely opposed to the first substrate, and a liquid crystal layer disposed between the first and second substrates. A passivation layer is provided to cover the display area or pixel transistors and driving circuit.
Owner:SONY CORP
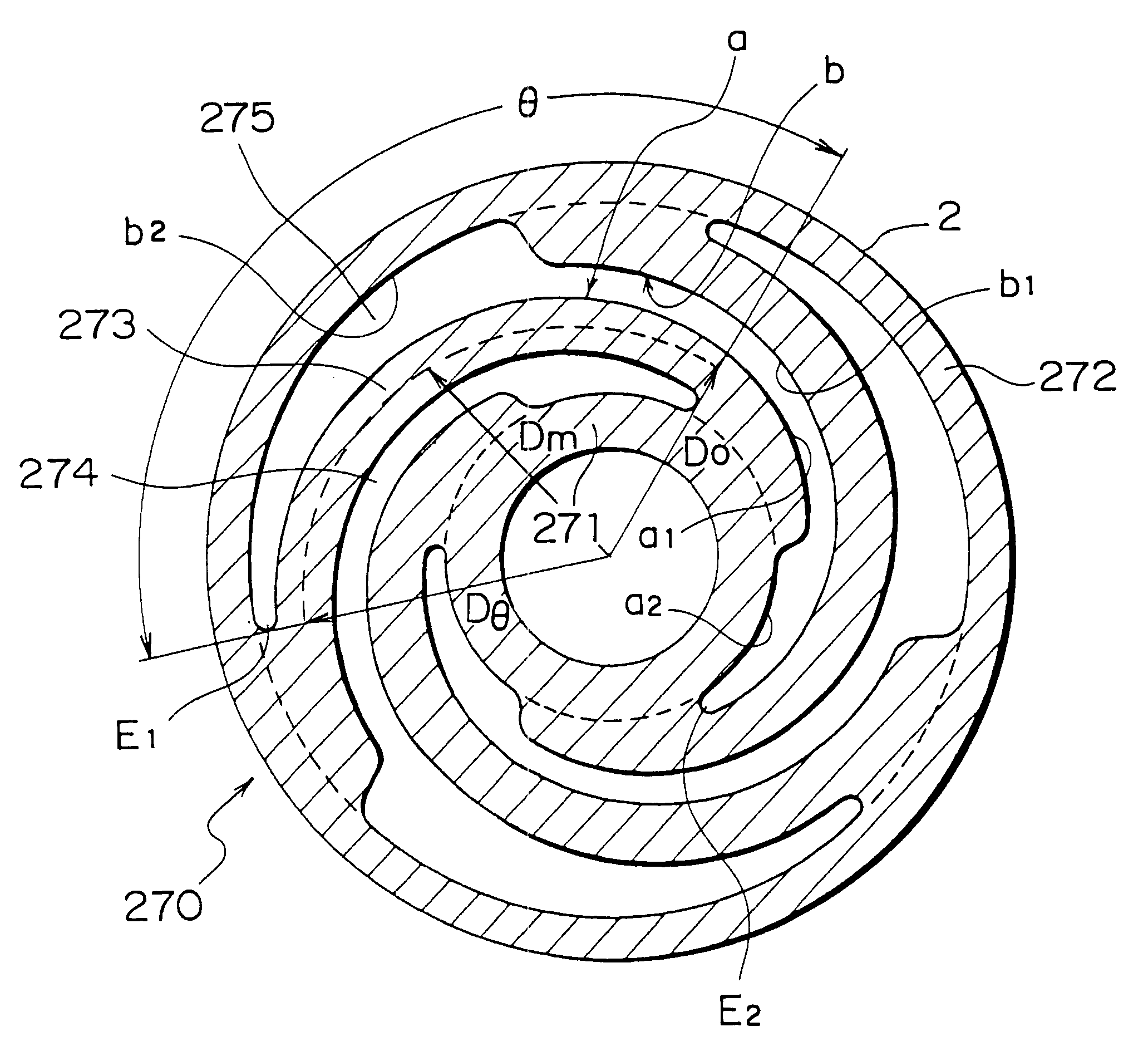
Vibration actuator having magnetic circuit elastically supported by a spiral damper with increased compliance
InactiveUS6377145B1Improve seismic performanceStable characteristicsTransducer detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesAngular degreesCoil spring
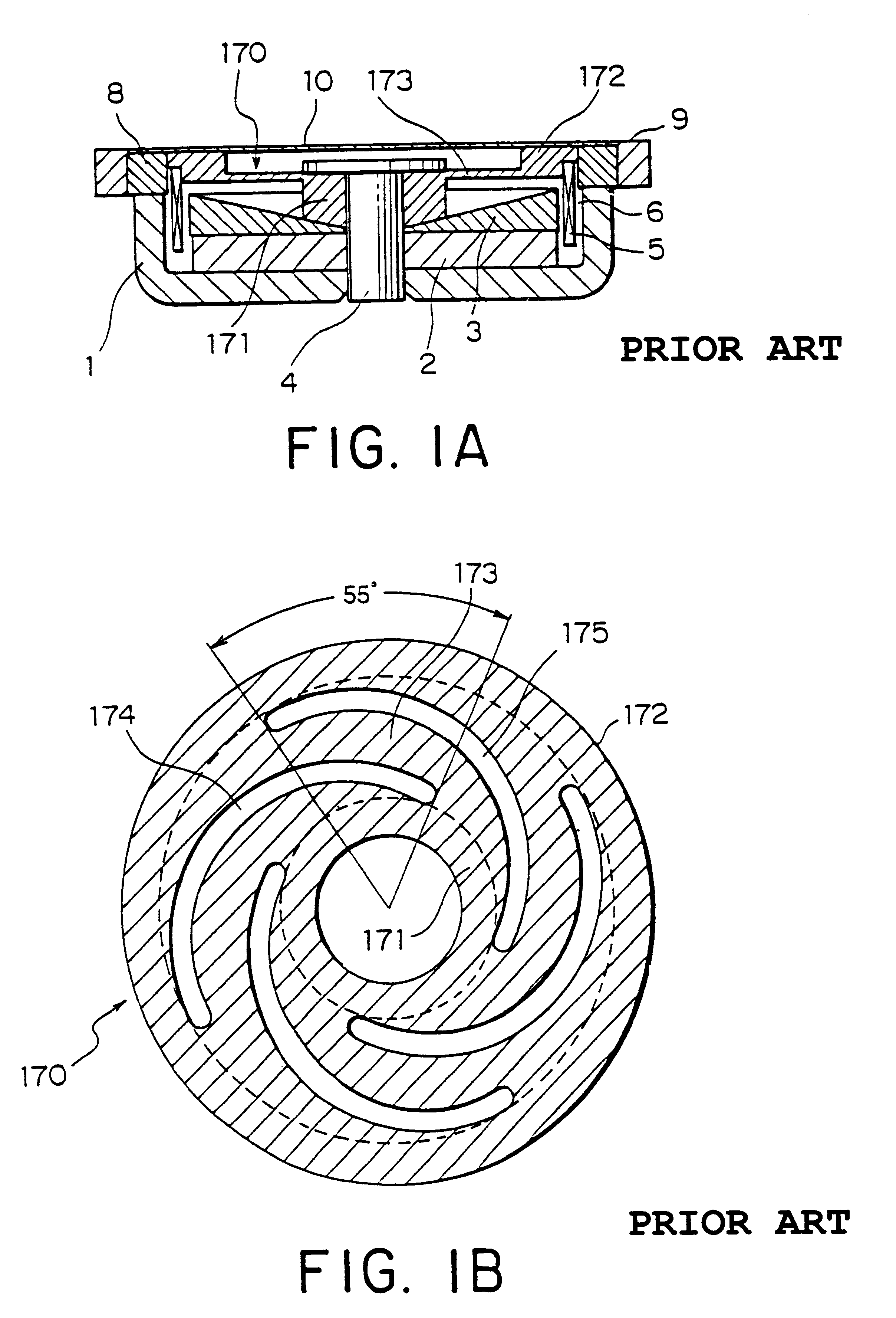
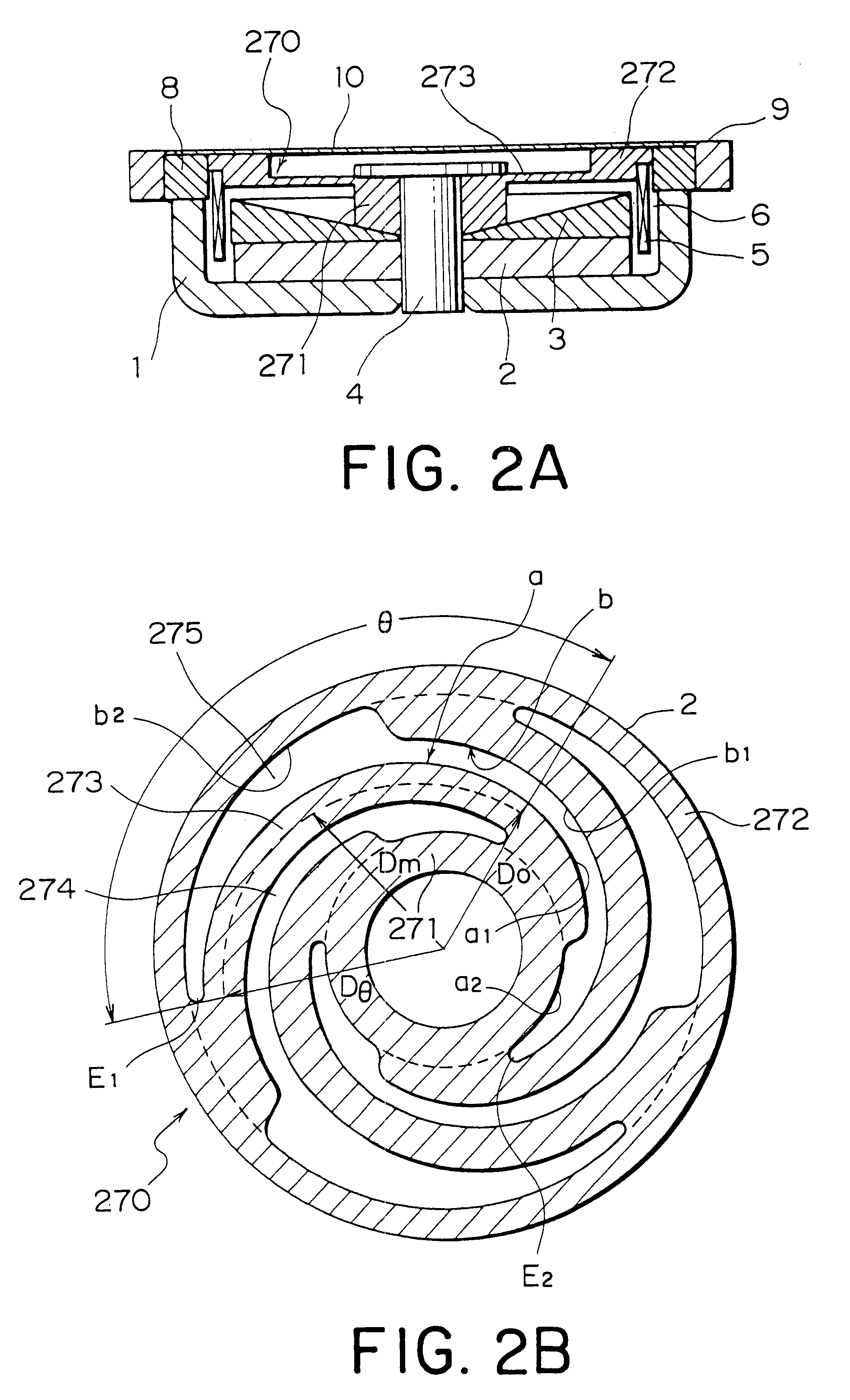
A vibration actuator includes an electromechanical transducer having a magnetic circuit (1-4) and a driving coil (5), a support frame (9), and a damper (270) elastically supporting the magnetic circuit onto the support frame to flexibly damp the vibration of the magnetic circuit when a driving AC current is supplied to the coil (5). The damper (270) comprises inner and outer ring portions (271, 272) and a plurality of spiral spring portions (273) determined by a plurality of spiral slits (274, 275) formed in the damper. In order to reduce the spiral spring portion determined by the adjacent two spiral slits in its compliance, each of the spiral spring portions has an effective spring length determined by an effective angle (theta) which is determined as an angle (by angular degree) from an inner end of the inner spiral slit to an outer end of the outer spiral slit defining each respective spiral spring portion around a center of the damper. The effective angle is 55 angular degree or more. In a preferable example, the effective spring length is determined by a product (r.theta) of an average radius (r) value by the unit of "mm" and the effective angle (theta) value by unit of the angular degree. The effective spring length is selected to 320 or more, and preferably 400 or more.
Owner:TOKIN CORP
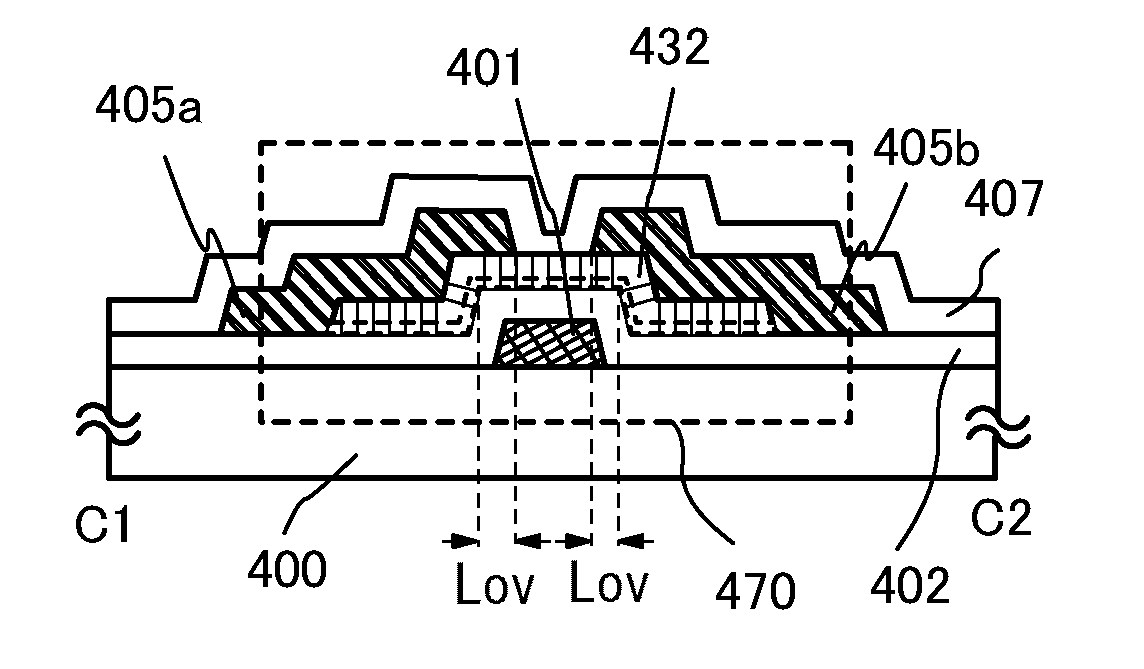
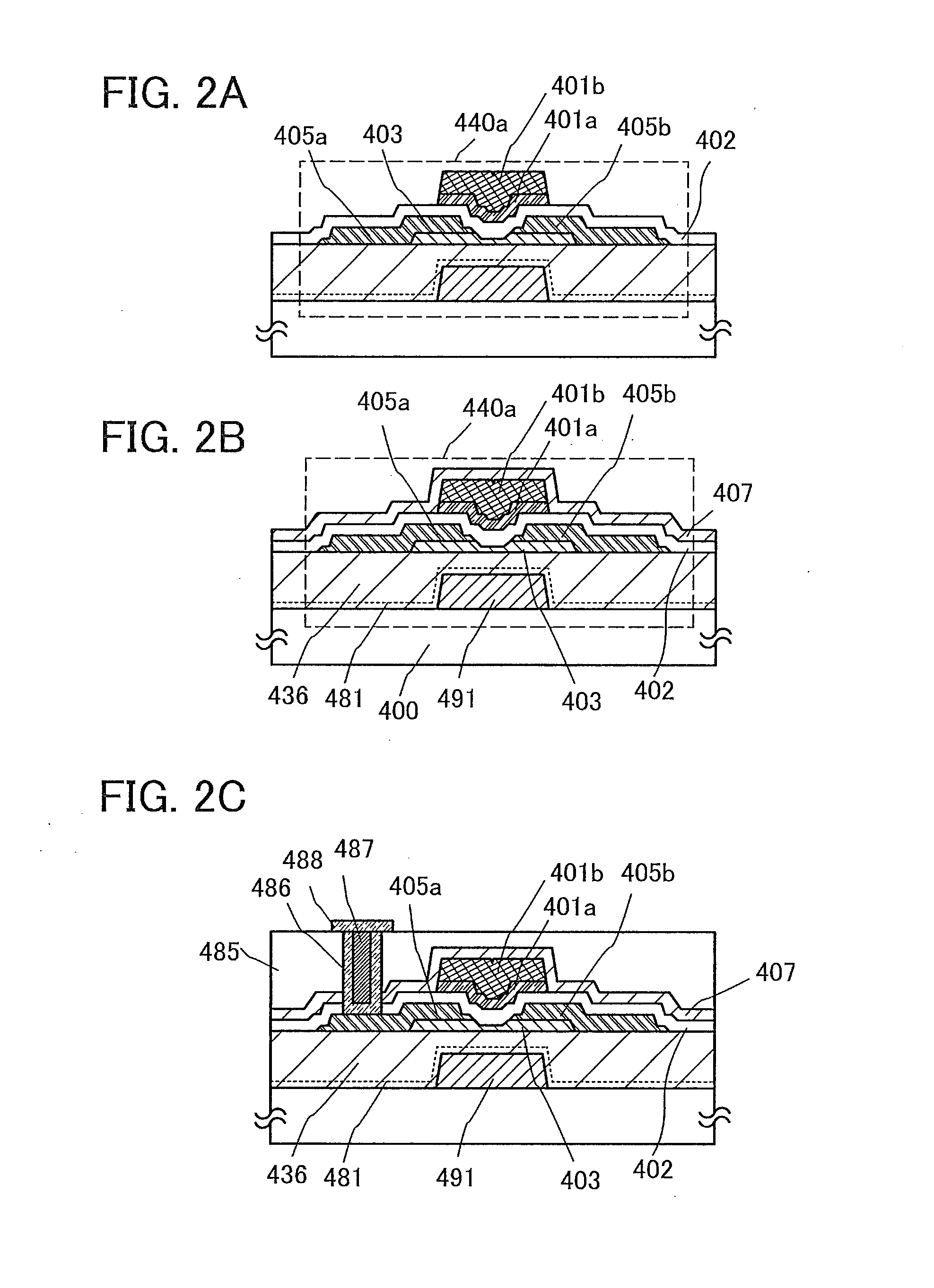
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100117074A1Stable electrical characteristicsImprove dynamic characteristicsTransistorSolid-state devicesIndiumNiobium
It is an object to provide a highly reliable semiconductor device including a thin film transistor whose electric characteristics are stable. In addition, it is another object to manufacture a highly reliable semiconductor device at low cost with high productivity. In a semiconductor device including a thin film transistor, a semiconductor layer of the thin film transistor is formed with an oxide semiconductor layer to which a metal element is added. As the metal element, at least one of metal elements of iron, nickel, cobalt, copper, gold, manganese, molybdenum, tungsten, niobium, and tantalum is used. In addition, the oxide semiconductor layer contains indium, gallium, and zinc.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
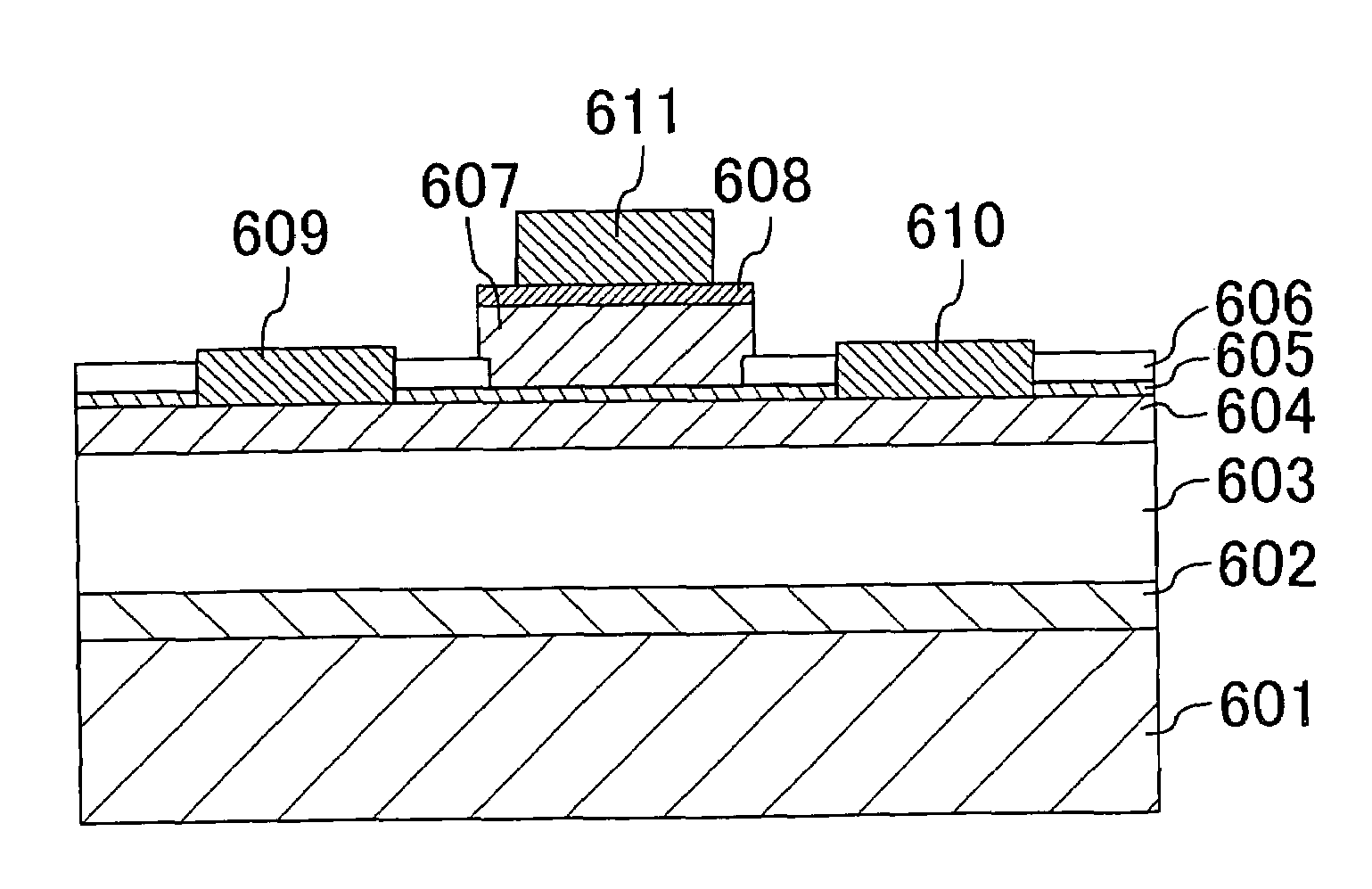
Thin film transistor, display, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20100295037A1Inhibit deteriorationMaintain stabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesIridiumDisplay device
Disclosed herein is a thin film transistor including: a semiconductor layer including an amorphous oxide, and a source electrode and a drain electrode which are provided in contact with the semiconductor layer. The source electrode and the drain electrode are formed by use of iridium or iridium oxide.
Owner:JOLED INC
External cavity tunable laser module
InactiveUS20120099611A1Reliably tunedImprove production yieldLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersGratingLength wave
Provided is a wavelength tunable external cavity semiconductor laser module by a thermo-optic effect of a semiconductor optical waveguide. The wavelength tunable external cavity semiconductor laser module includes: a light source generating wideband light; a semiconductor optical waveguide having one end optically coupled to the light source; a Bragg grating formed on the optical waveguide; a thin film heater provided at an upper portion of the Bragg grating and controlling a reflection band of the Bragg grating by a thermo-electric effect; a first temperature sensor provided at an upper portion of the optical waveguide; a thermoelectric cooler (TEC) provided at a lower portion of the optical waveguide; a heat insulating layer provided between the optical waveguide and the TEC; and an optical fiber optically coupled to the other end of the optical waveguide.
Owner:MEL TELECOM
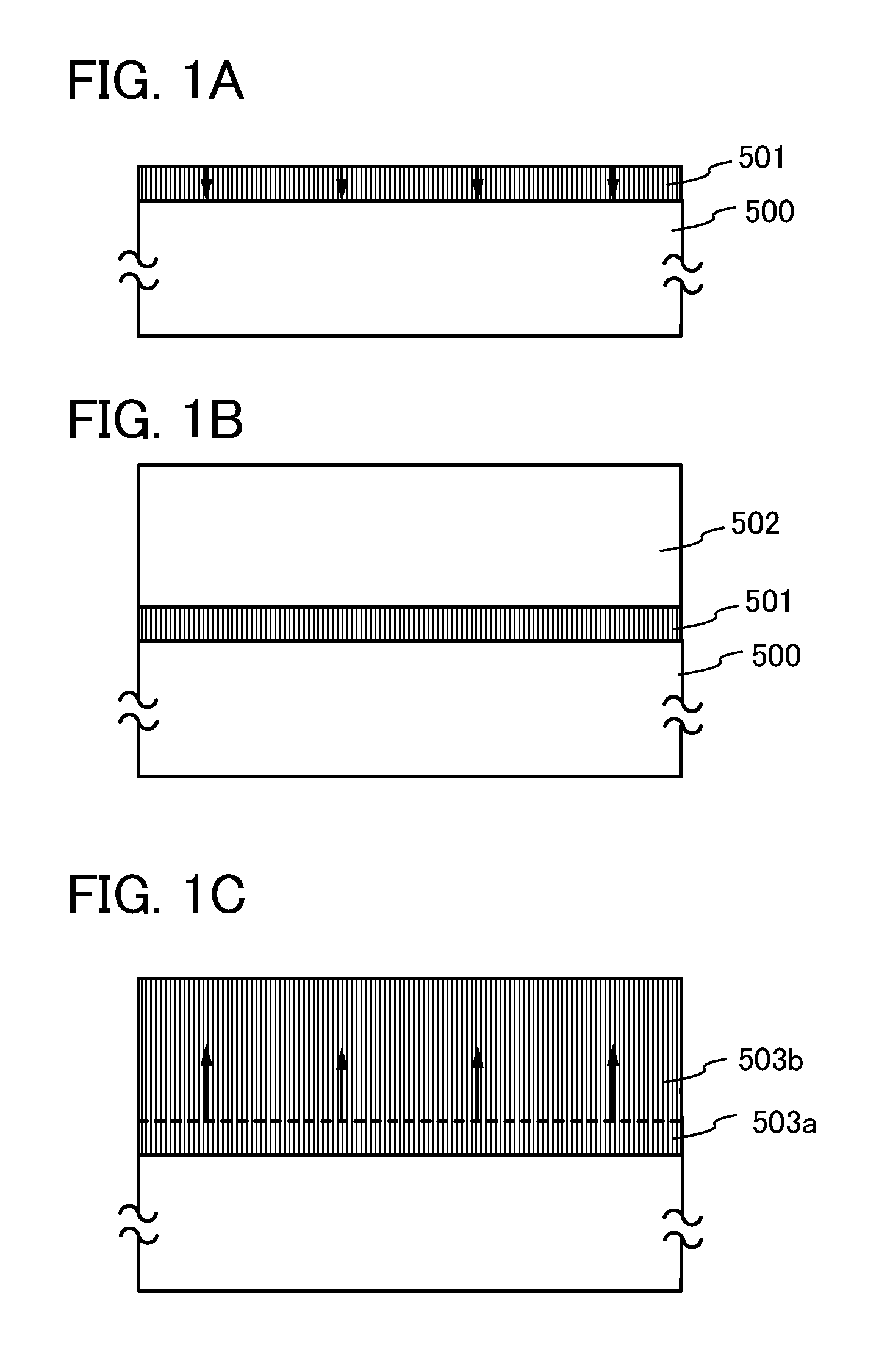
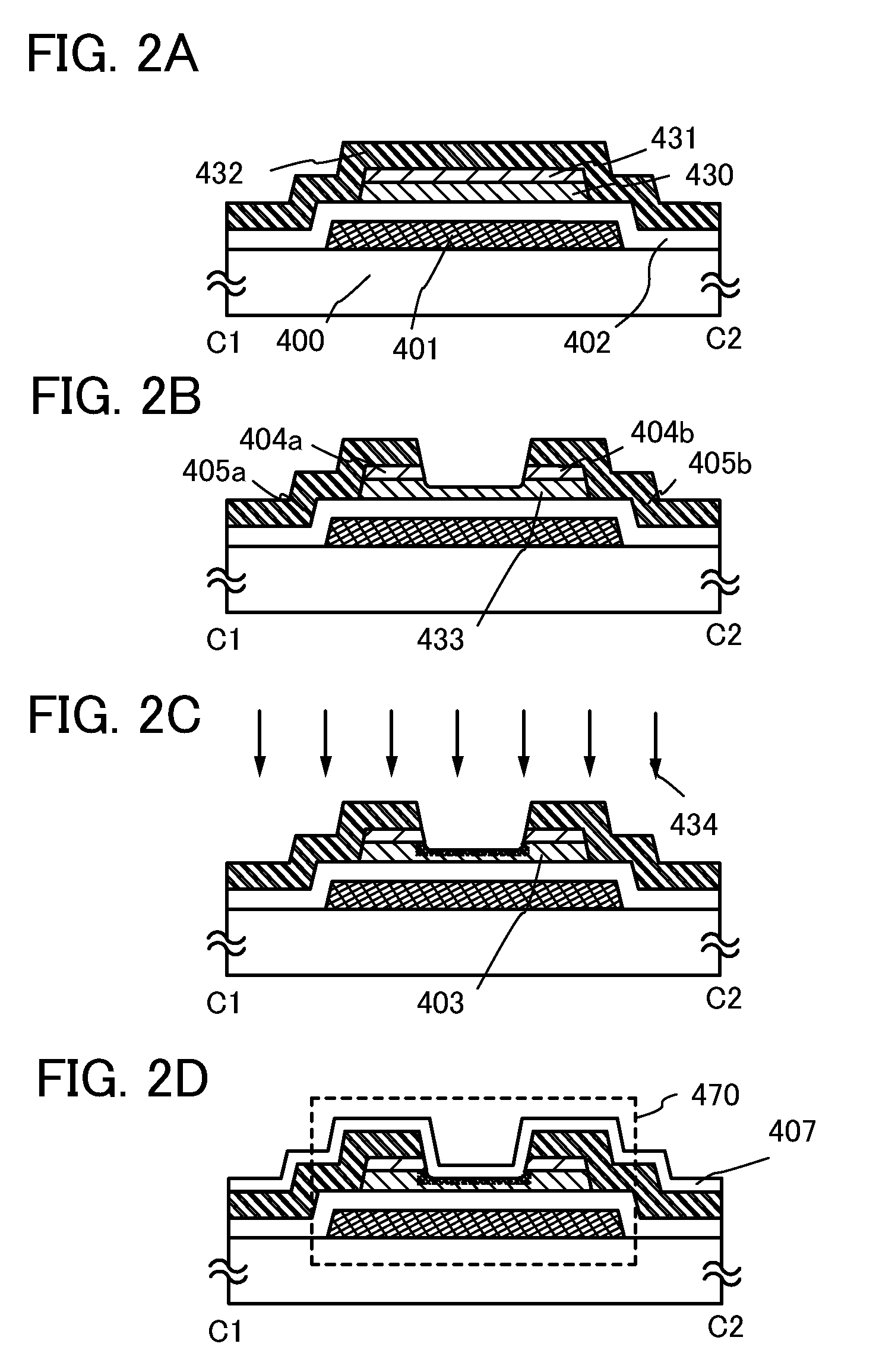
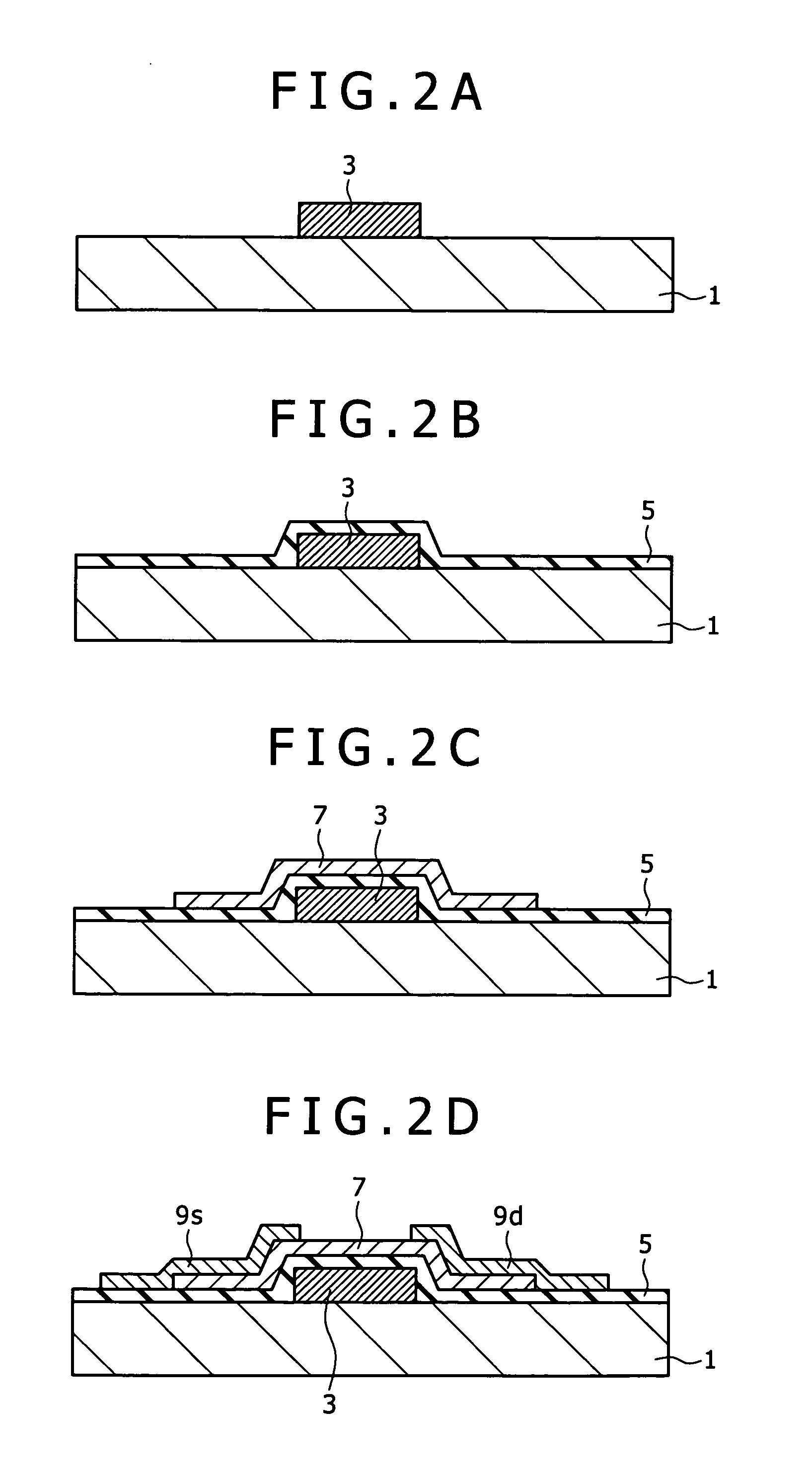
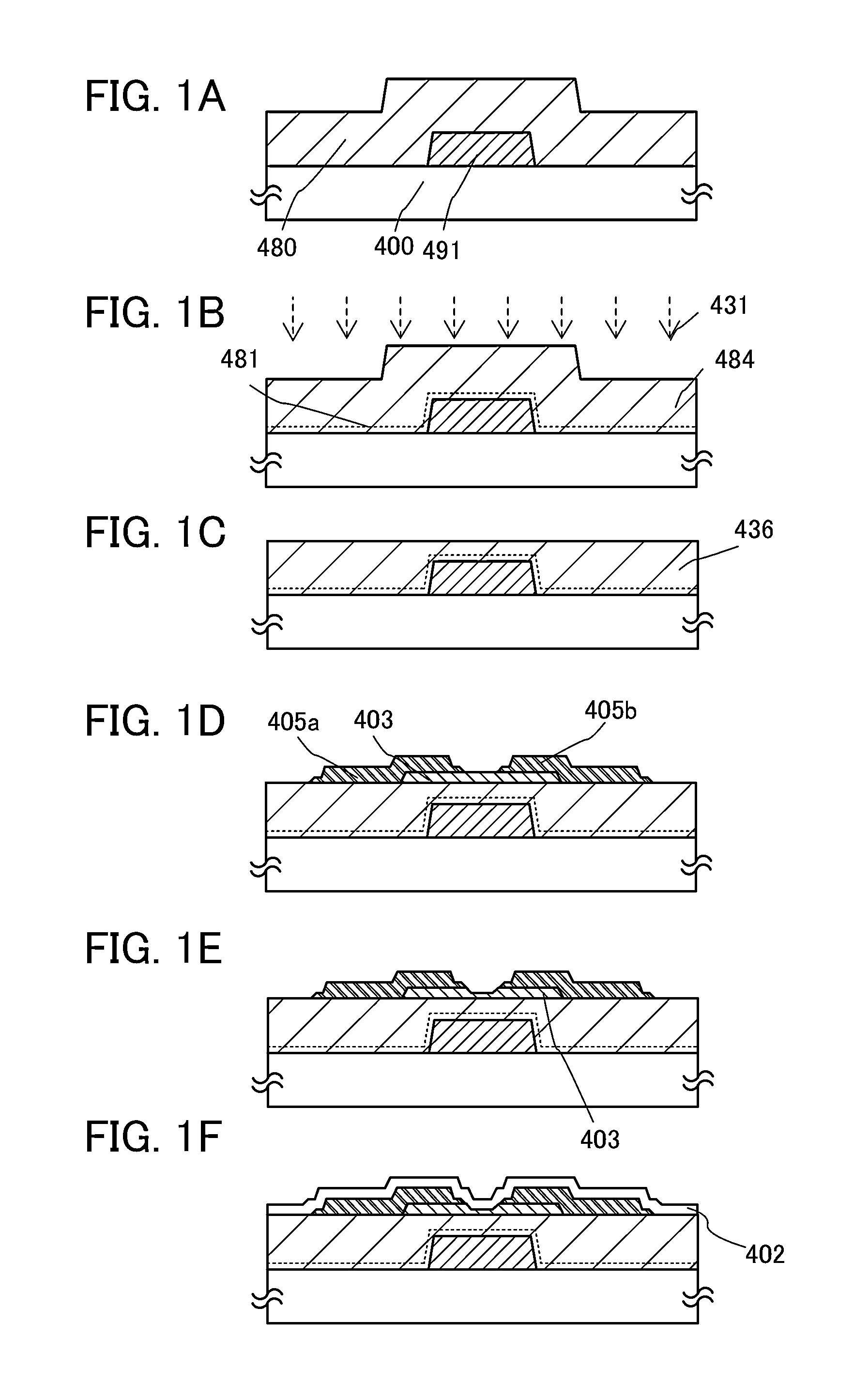
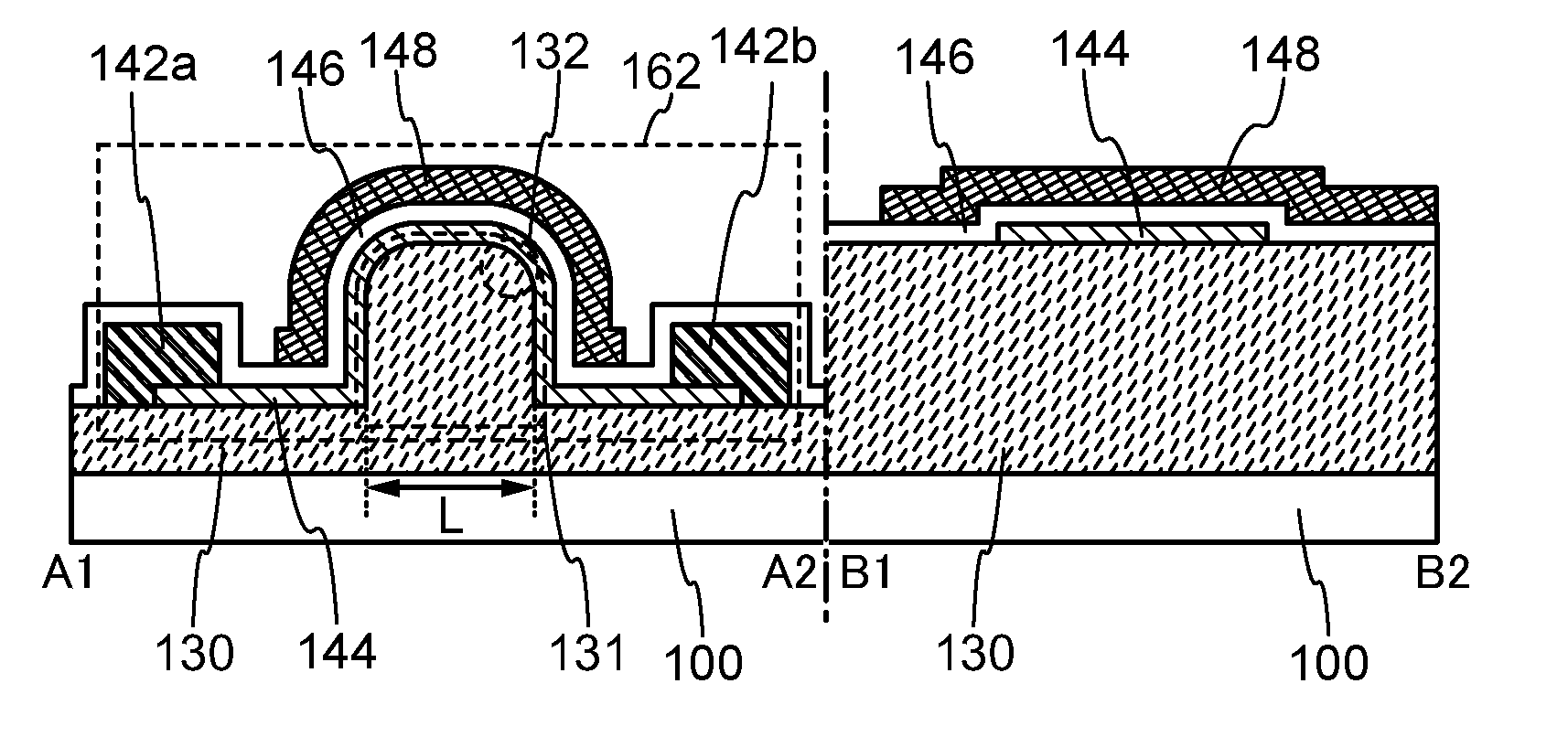
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveUS20140004656A1Stable characteristicsImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHydrofluoric acidCrystal structure
Provided is a method for manufacturing a transistor by which the defective shape of a semiconductor device is prevented in the case where a source electrode layer and a drain electrode layer are formed on an oxide semiconductor film. A source electrode layer and a drain electrode layer are formed each having a cross-sectional shape with which disconnection of a gate insulating film is unlikely to occur even when the gate insulating film over the source electrode layer and the drain electrode layer has a small thickness. An oxide semiconductor film having a crystal structure over an insulating surface is formed; an electrode layer on the oxide semiconductor film is formed; and a thickness of an exposed portion of the oxide semiconductor film is reduced by exposing the oxide semiconductor film to dilute hydrofluoric acid with a concentration higher than 0.0001% and lower than or equal to 0.25%.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
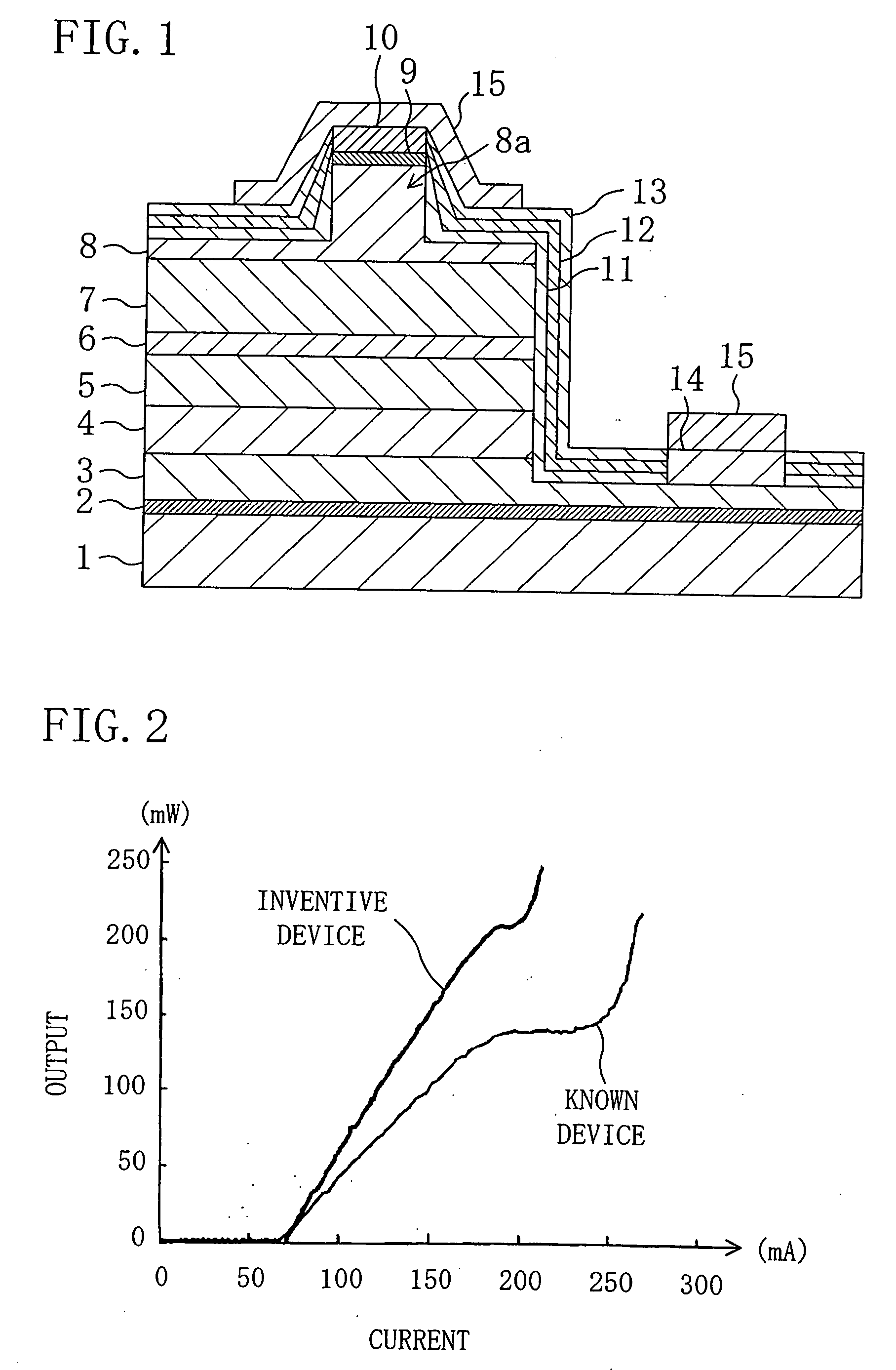
Nitride semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS7576373B1Stable characteristicsImprove productivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh concentrationOhmic contact
An AlN buffer layer, an undoped GaN layer, an undoped AlGaN layer, a first p-AlGaN layer, a second p-AlGaN layer and a high concentration p-GaN layer are formed in this order on a substrate. A gate electrode establishes ohmic contact with the high concentration p-GaN layer. A source electrode and a drain electrode are formed on the undoped AlGaN layer. Two-dimensional electron gas generated at the interface between the undoped AlGaN layer and the undoped GaN layer and the first and second p-AlGaN layers form a pn junction in a gate region. The second p-AlGaN layer covers a SiN film in part.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Loop antenna unit and radio communication medium processor
InactiveUS20070139285A1Variation of resonance frequency of be suppressExcellent in it convenience and extensibilityResonant long antennasIndividually energised antenna arraysElectricityEngineering
It is an object of the present invention to provide a radio communication medium processor having a stable performance that does not receive a limitation for an installed place, especially, the influence of a metallic structure, does not need to adjust the resonance frequency of an antenna or an impedance, is excellent in its convenience and extensibility upon installation and strong for unnecessary noise from a periphery. In electric current fed loop antenna units, non-electric current fed loop antenna are arranged in doughnut shapes outside the substantially same planes of electric current fed loop antennas so as to surround the electric current fed loop antennas. Thus, when non-electric current fed loop antenna units are installed linearly, in radial directions and in arrays adjacently to electric current fed loop antenna units, the influence of the non-electric current fed loop antenna units to the antenna characteristics of the electric current fed loop antenna units can be suppressed. When the non-electric current fed loop antenna units are extended and increased, the antennas of the electric current fed loop antenna units do not need to be adjusted.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Optical path changing member
An optical path changing member is assembled at ends of optical fibers and placed to face a substrate including an optical input / output terminal having optical axes inclined with respect to optical axes of the ends. The optical path changing member is made of a transparent material and includes a member body having a reflection surface for optically connecting the ends to the optical input / output terminal. The member body has optical fiber insertion holes and an end placement portion to which the insertion holes are open and in which the end faces of the optical fibers are placed. The reflection surface is formed so that light entering from the end faces of the optical fibers into the member body will be internally reflected toward the optical input / output terminal in the member body. The end placement portion is filled with an adhesive by which the ends are fixed to the member body.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing thereof
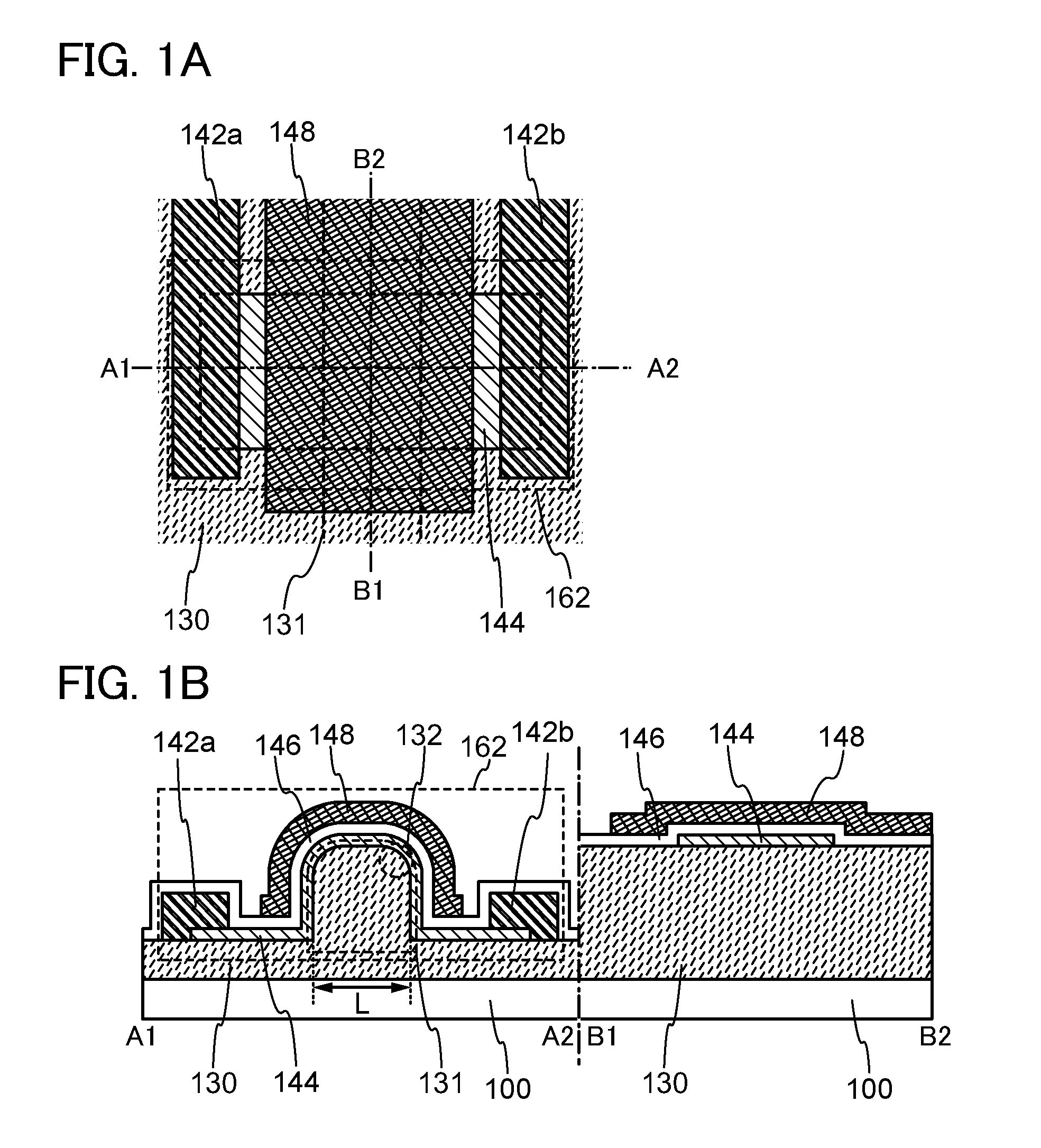
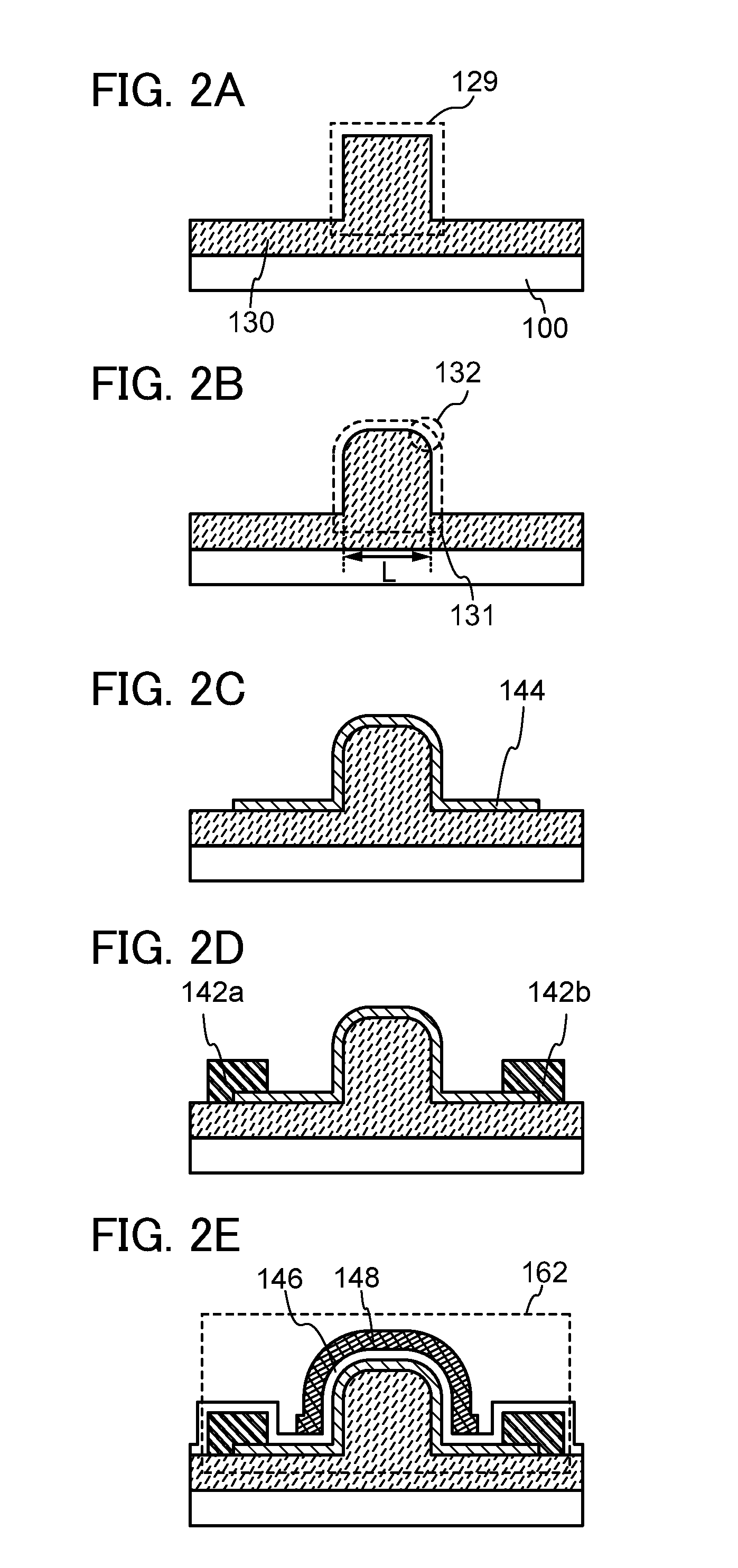
ActiveUS20120267624A1Suppress defectsStable electrical characteristicsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMiniaturizationEngineering
An insulating layer is provided with a projecting structural body, and a channel formation region of an oxide semiconductor layer is provided in contact with the projecting structural body, whereby the channel formation region is extended in a three dimensional direction (a direction perpendicular to a substrate). Thus, it is possible to miniaturize a transistor and to extend an effective channel length of the transistor. Further, an upper end corner portion of the projecting structural body, where a top surface and a side surface of the projecting structural body intersect with each other, is curved, and the oxide semiconductor layer is formed to include a crystal having a c-axis perpendicular to the curved surface.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor laser device and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20050281304A1Reduce waveguide lossReduce operating currentOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsRefractive indexActive layer
A semiconductor laser device includes a MQW active layer, a p-type cladding layer formed on the MQW active layer, having a ridge portion and having a smaller refractive index than that of the MQW active layer, a plurality of dielectric films formed at least on part of the p-type cladding layer extending from each side of the ridge portion.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Non-volatile memory devices including variable resistance material
ActiveUS20070252193A1The overall structure is simplified and improvedStable electrical characteristicsTransistorSolid-state devicesAlloyMaterials science
A non-volatile memory device comprises a first oxide layer, a second oxide layer and a buffer layer formed on a lower electrode. An upper electrode is formed on the buffer layer. In one example, the lower electrode is composed of at least one of Pt, Ru, Ir, IrOx and an alloy thereof, the second oxide layer is a transition metal oxide, the buffer layer is composed of a p-type oxide and the upper electrode is composed of a material selected from Ni, Co, Cr, W, Cu or an alloy thereof.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Nonvolatile memory element, nonvolatile memory apparatus, nonvolatile semiconductor apparatus, and method of manufacturing nonvolatile memory element
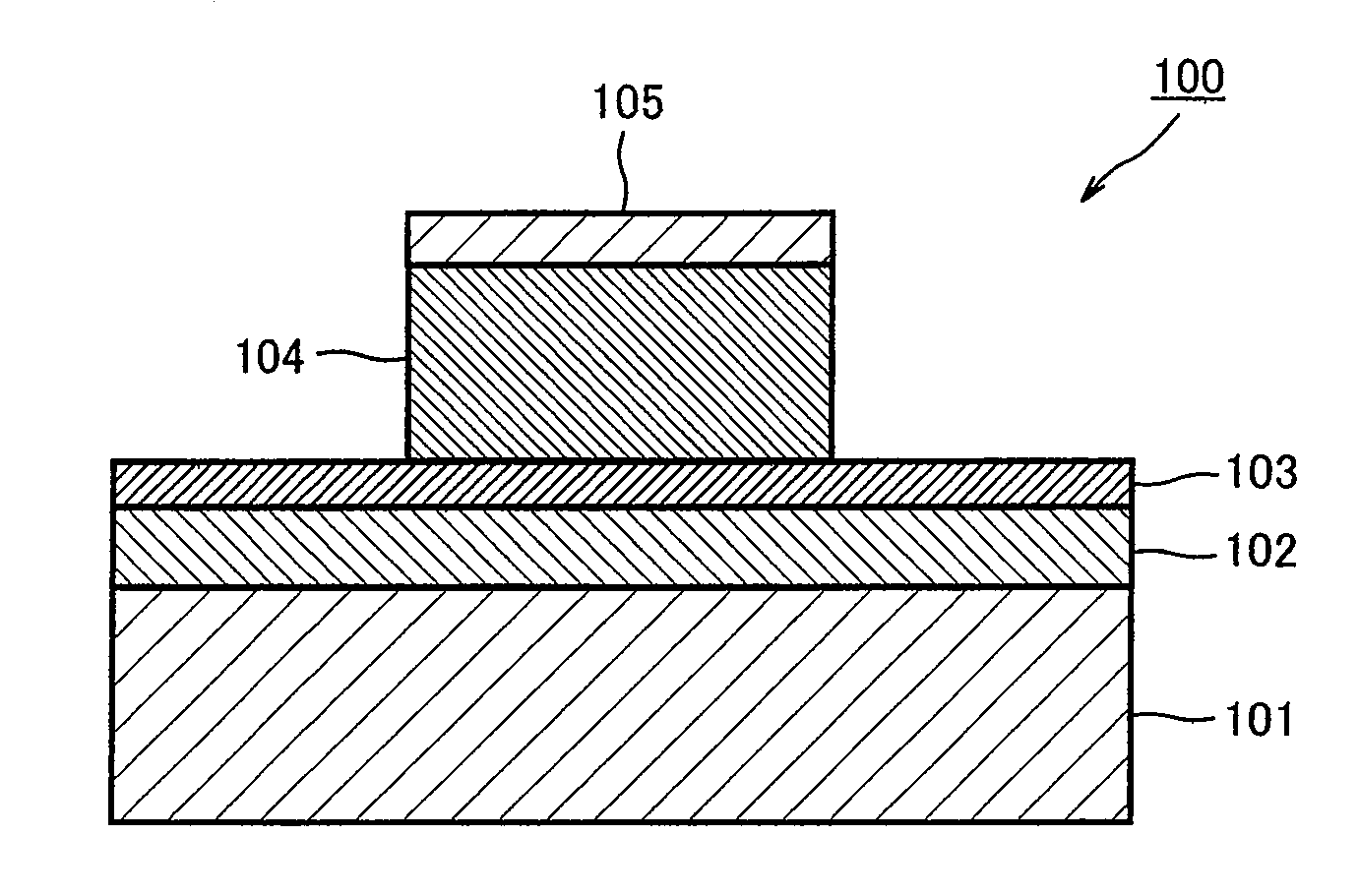
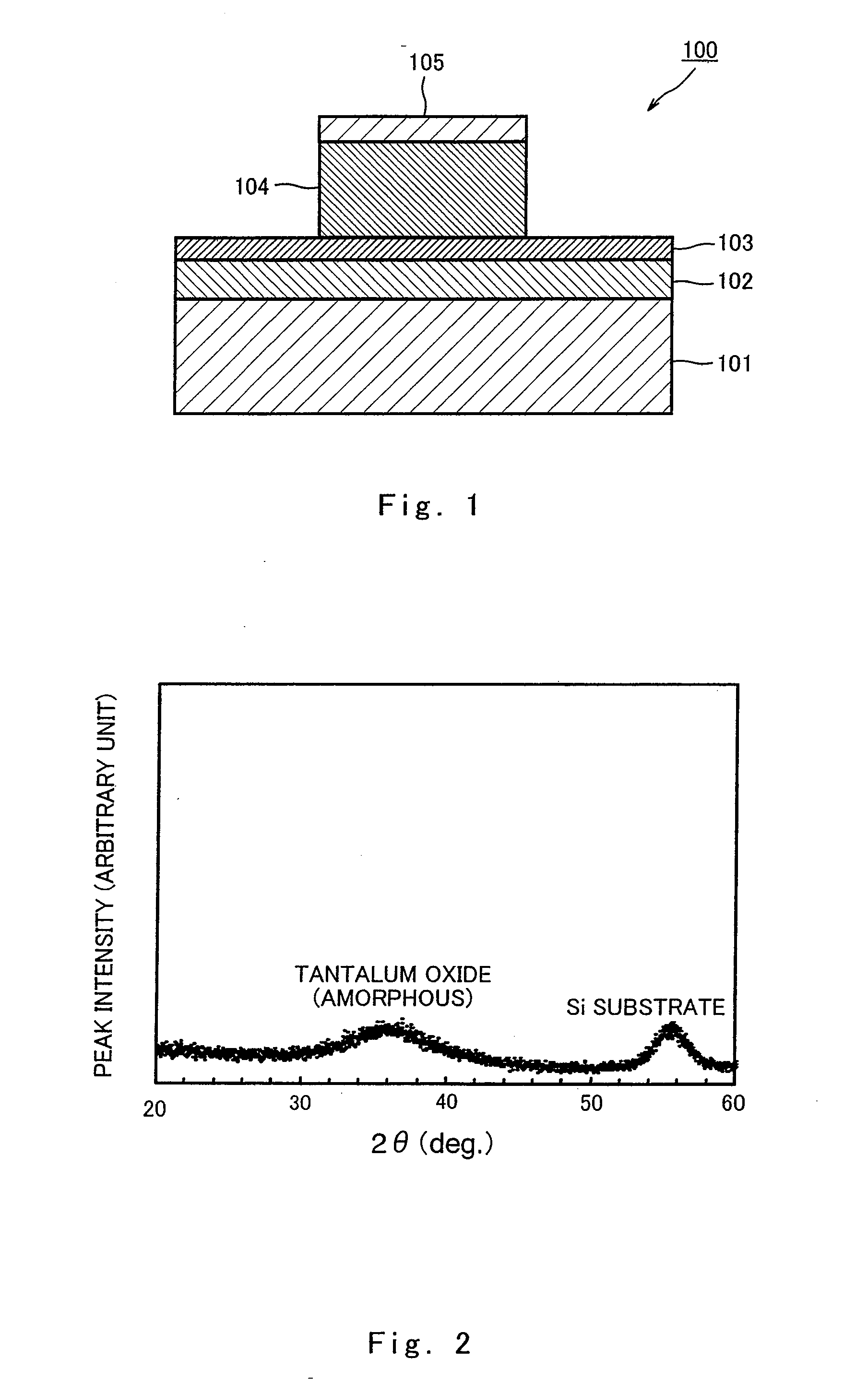
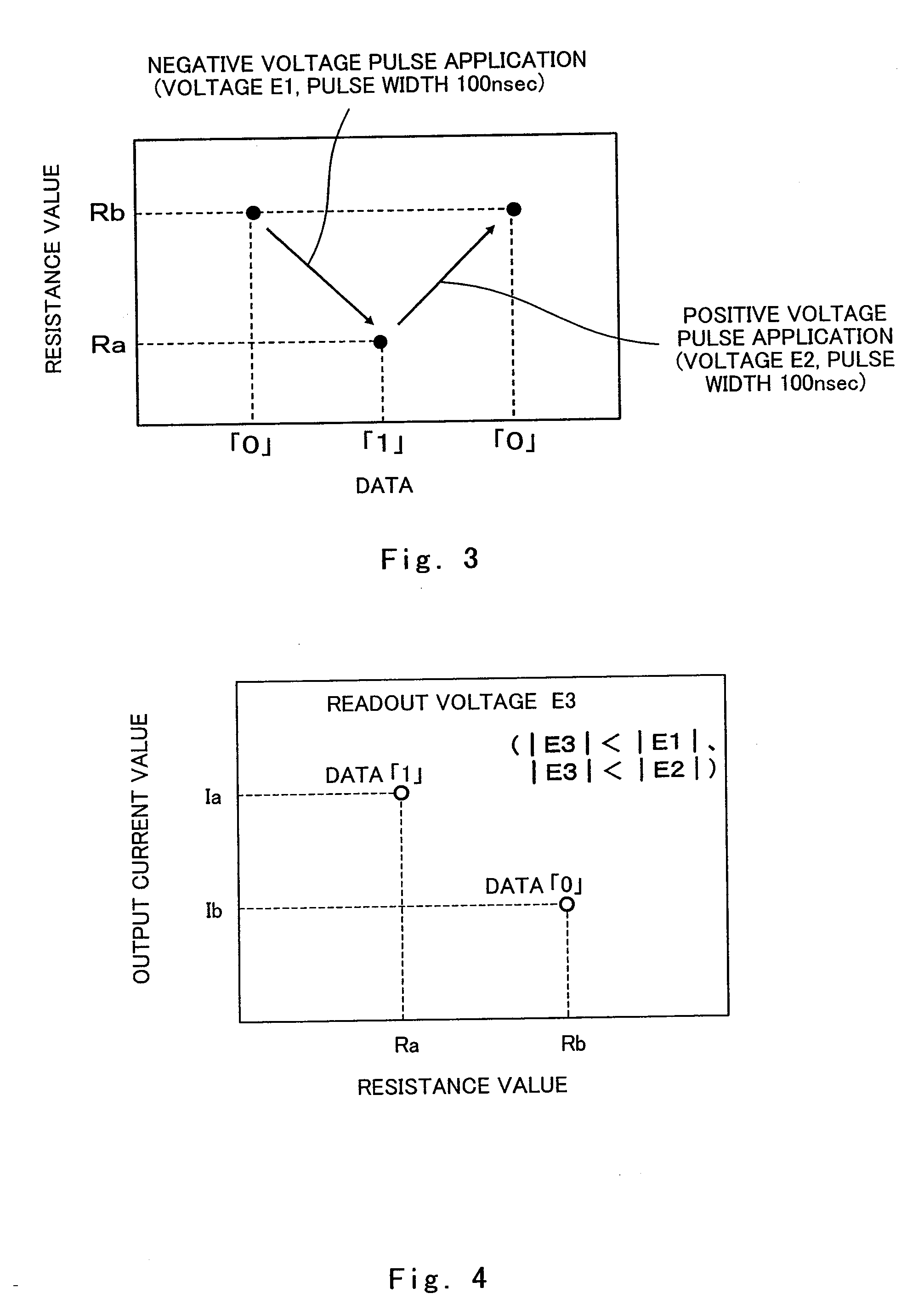
ActiveUS20090224224A1Stable characteristicsHigh affinitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsElectric signal
A nonvolatile memory element of the present invention comprises a first electrode (103), a second electrode (105), and a resistance variable layer (104) disposed between the first electrode (103) and the second electrode (104), a resistance value of the resistance variable layer varying reversibly according to an electric signal applied between the electrodes (103),(105), and the resistance variable layer (104) comprises at least a tantalum oxide, and is configured to satisfy 0<x<2.5 when the tantalum oxide is represented by TaOx.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
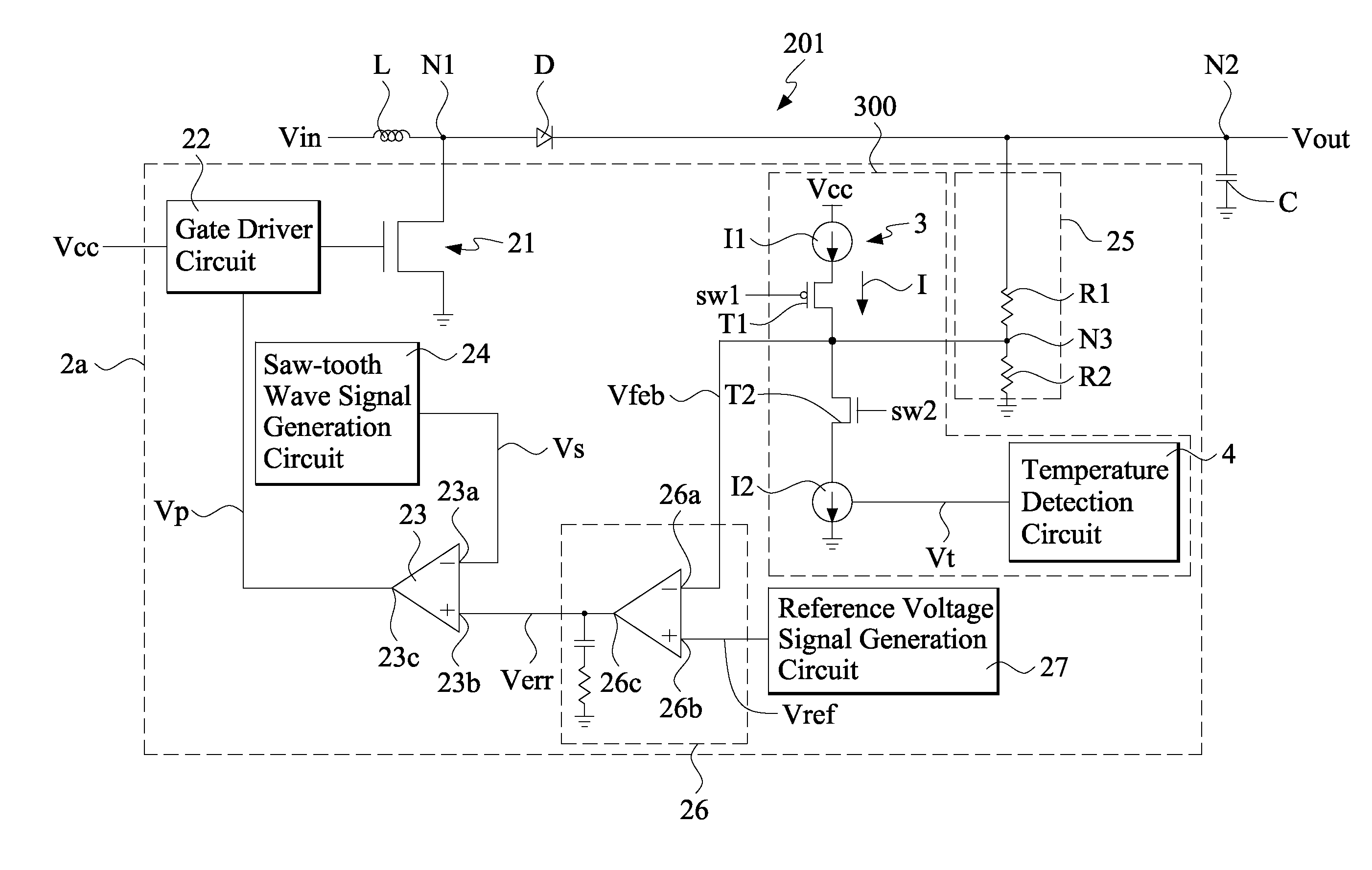
DC-DC converter with temperature compensation circuit
InactiveUS7859511B2Stable characteristicsEfficient supplyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDc dc converterNegative temperature
A DC-DC converter includes a temperature compensation circuit arranged between a feedback differential amplification circuit and an output voltage detection circuit to compensate the variation of the voltage level of the DC output voltage of the converter caused by ambient temperature changes. The temperature compensation circuit includes a temperature detection circuit that detects the ambient temperature and, in response thereto, generates a temperature signal; and a current source circuit that is connected between a feedback signal input terminal of the feedback differential amplification circuit and the output voltage detection circuit. The current source circuit, based on the temperature signal, generates an electrical current and a compensation voltage proportional to the electrical current. The compensation voltage is applied to the DC output voltage to thereby regulate the voltage level of the DC output voltage. The temperature signal is a temperature signal of positive temperature characteristics and / or a temperature signal of negative temperature characteristics.
Owner:VASTVIEW TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com