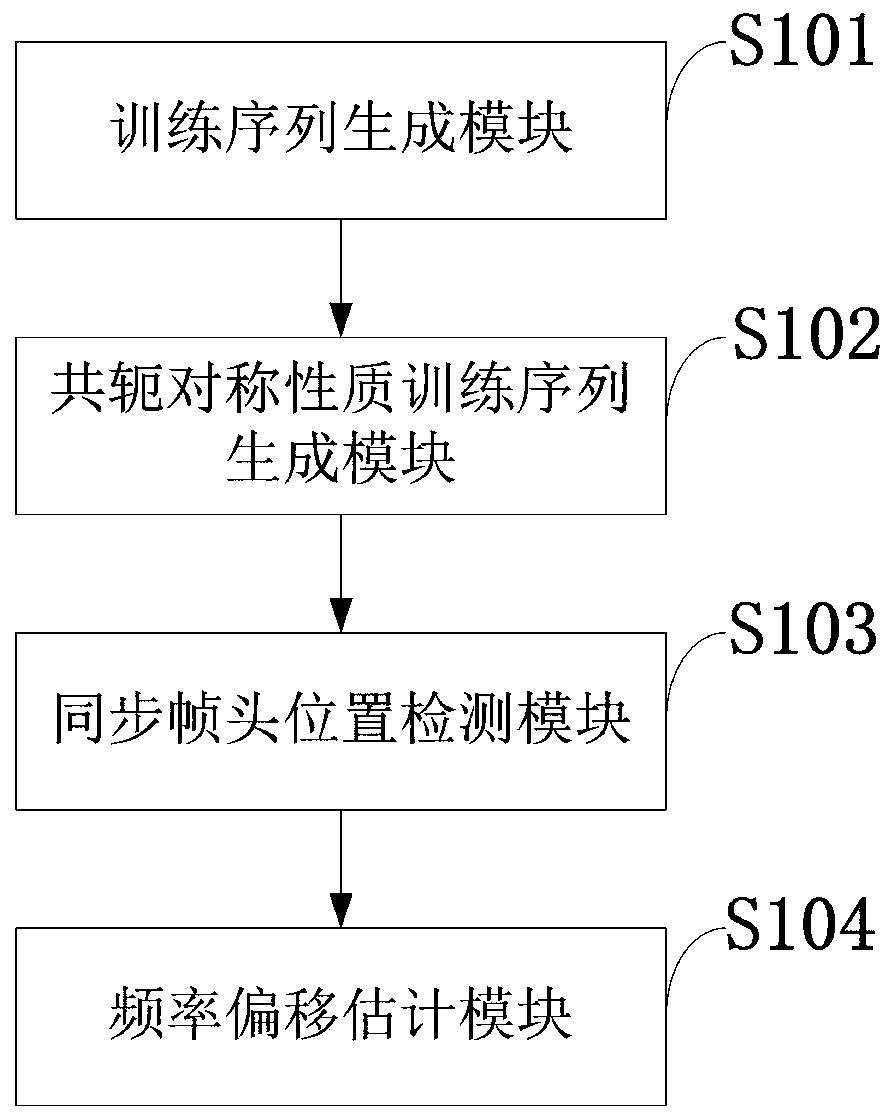
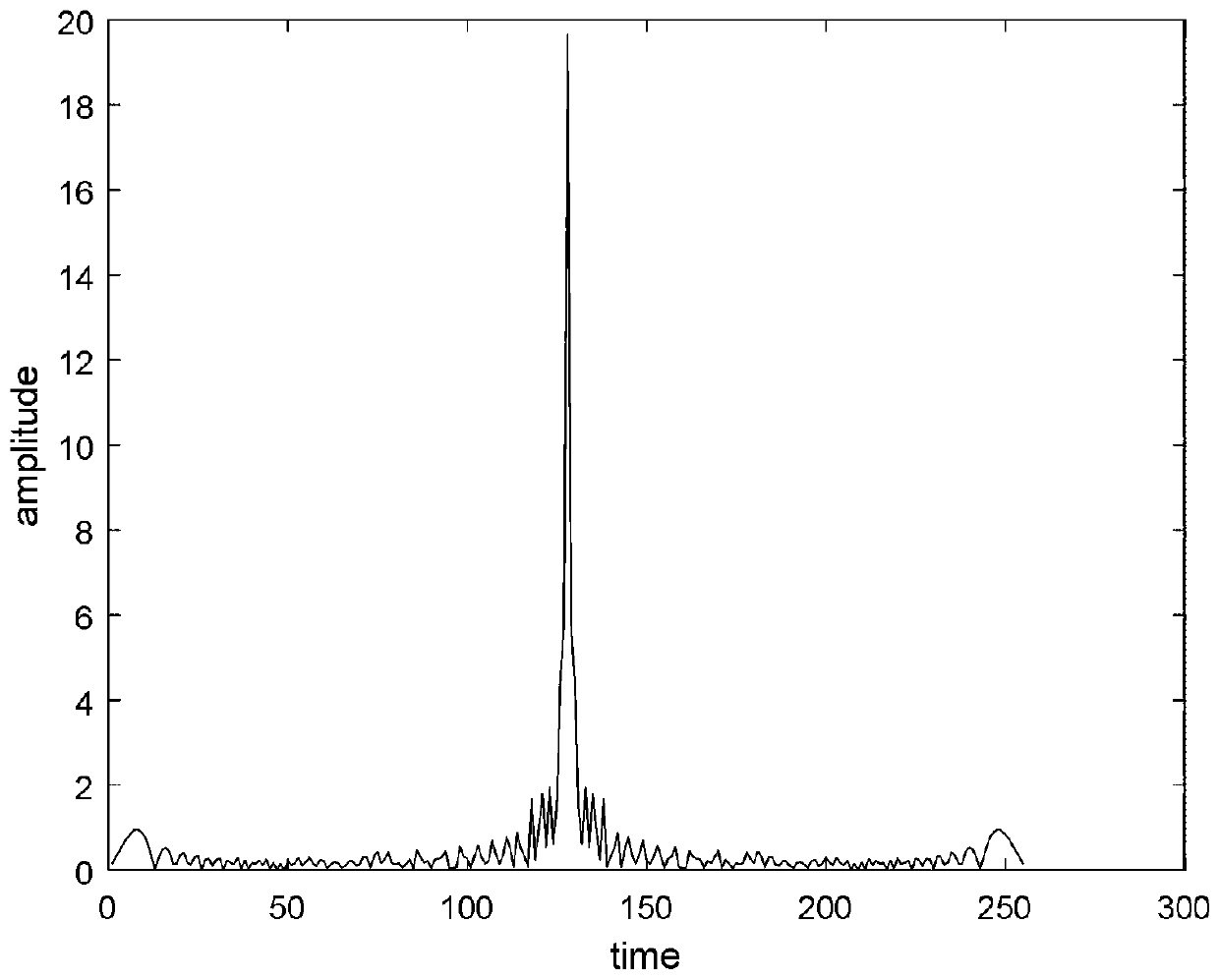
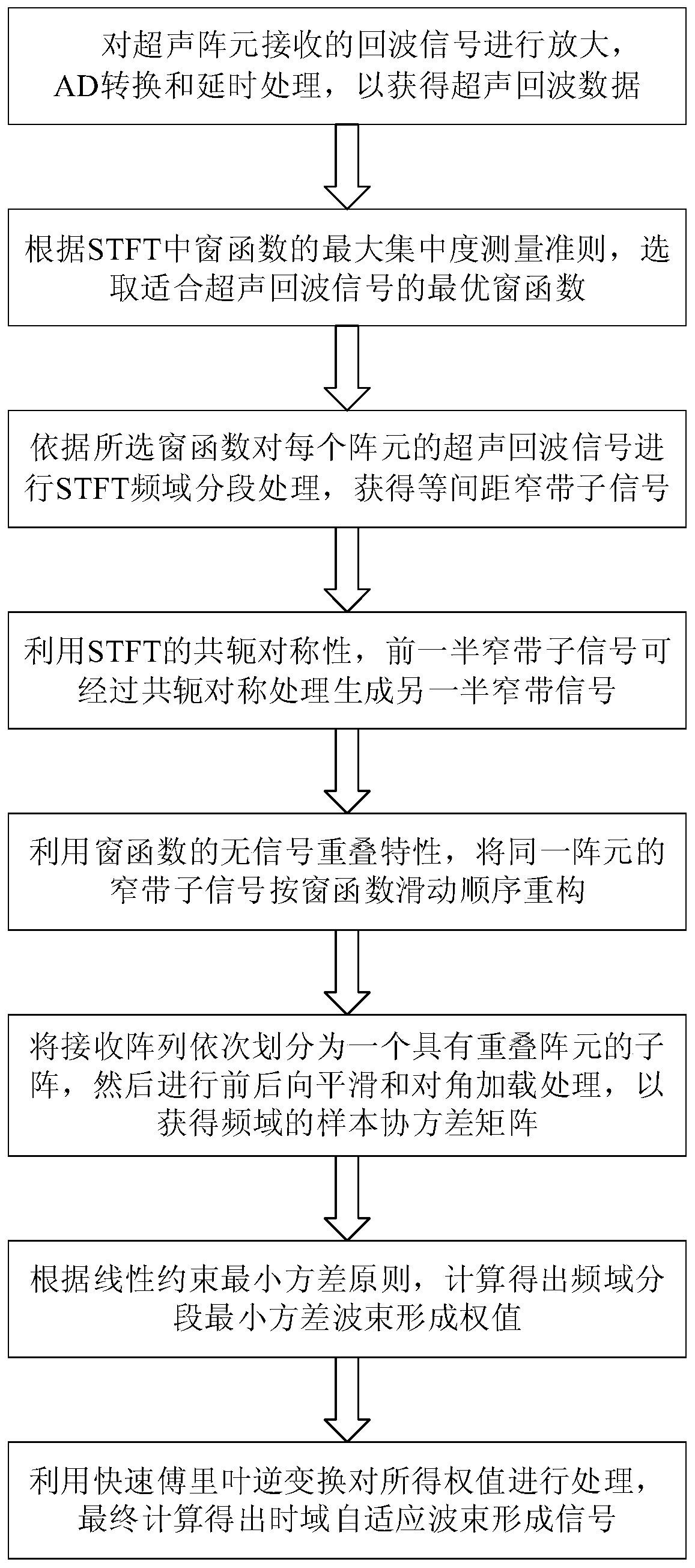
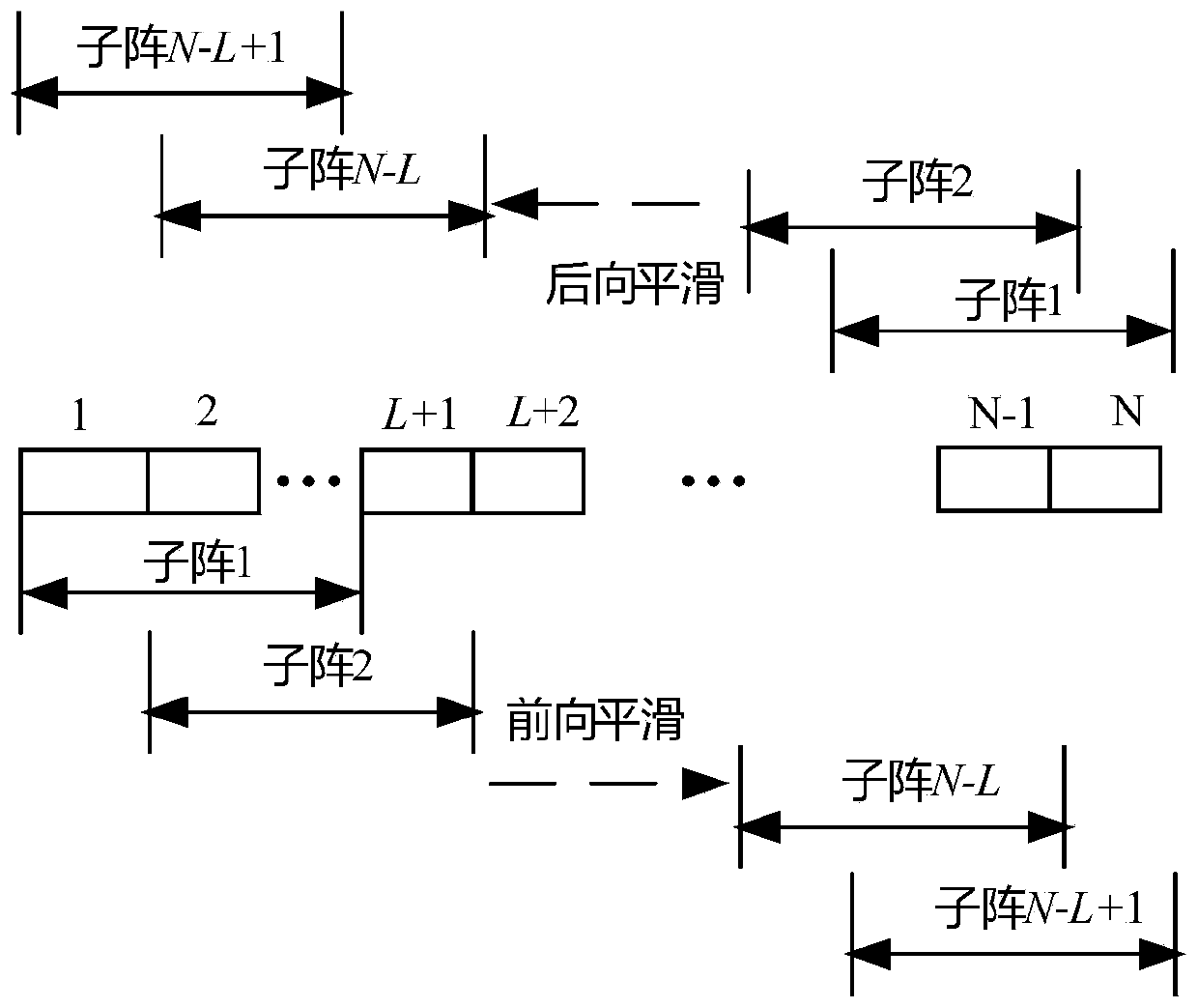
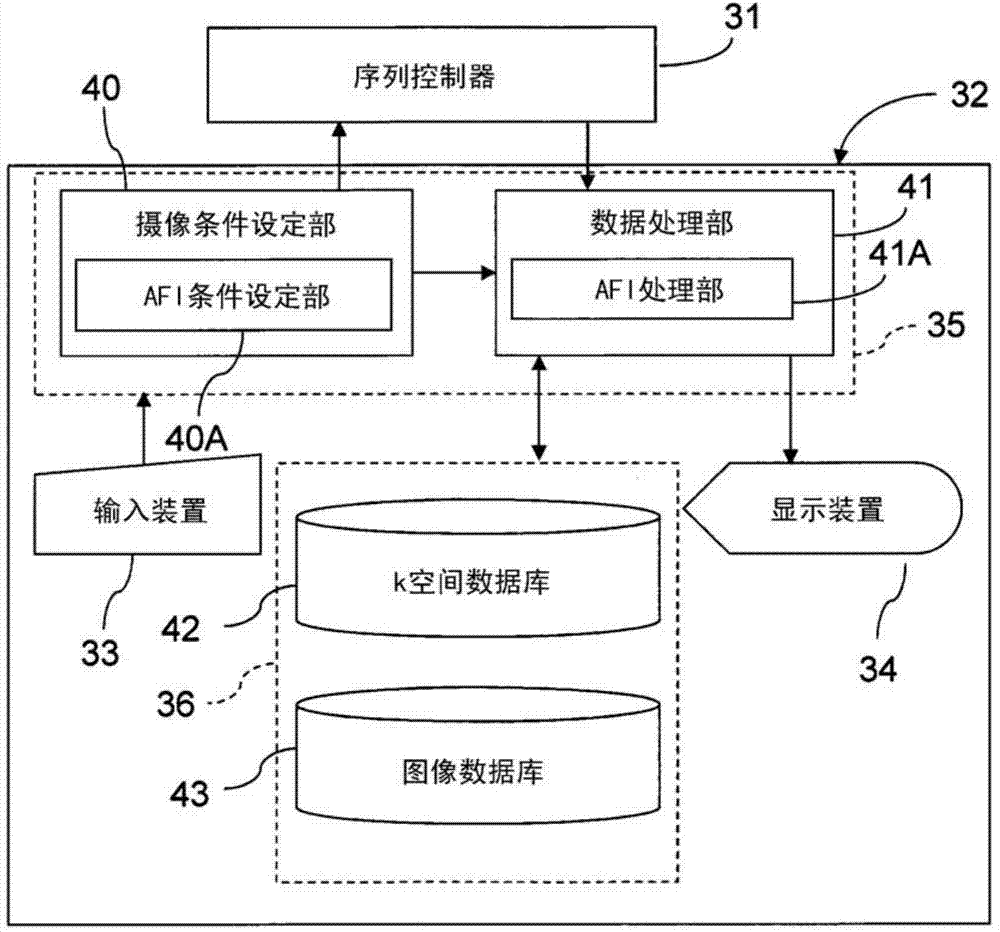
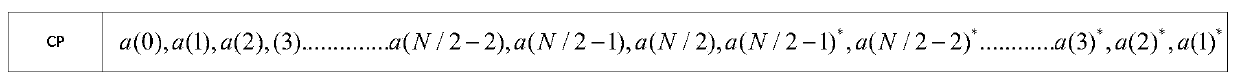Patents
Literature
67 results about "Conjugate symmetry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Conjugate symmetry. Abstract. Conjugate symmetry is an entirely new approach to symmetric Boolean functions that can be used to extend existing methods for handling symmetric functions to a much wider class of functions. These are functions that currently appear to have no symmetries of any kind.
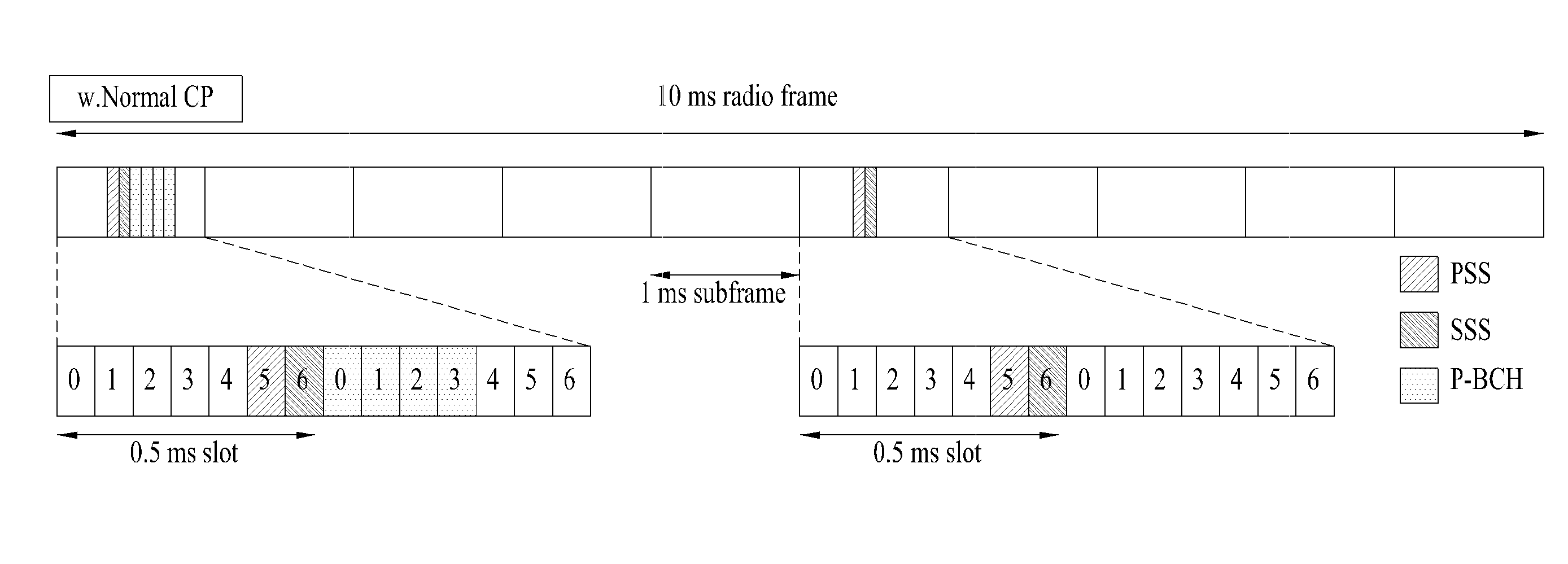
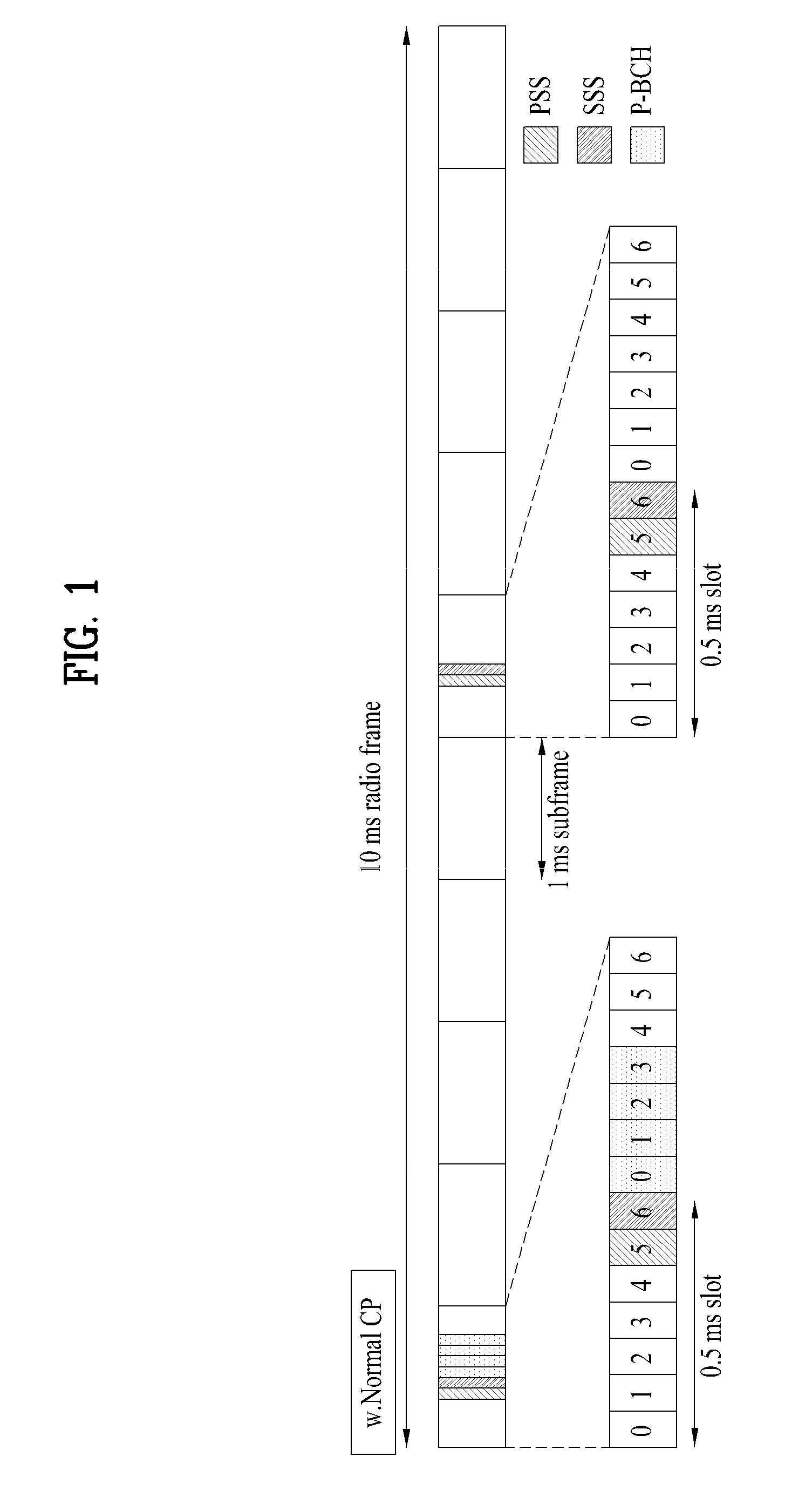
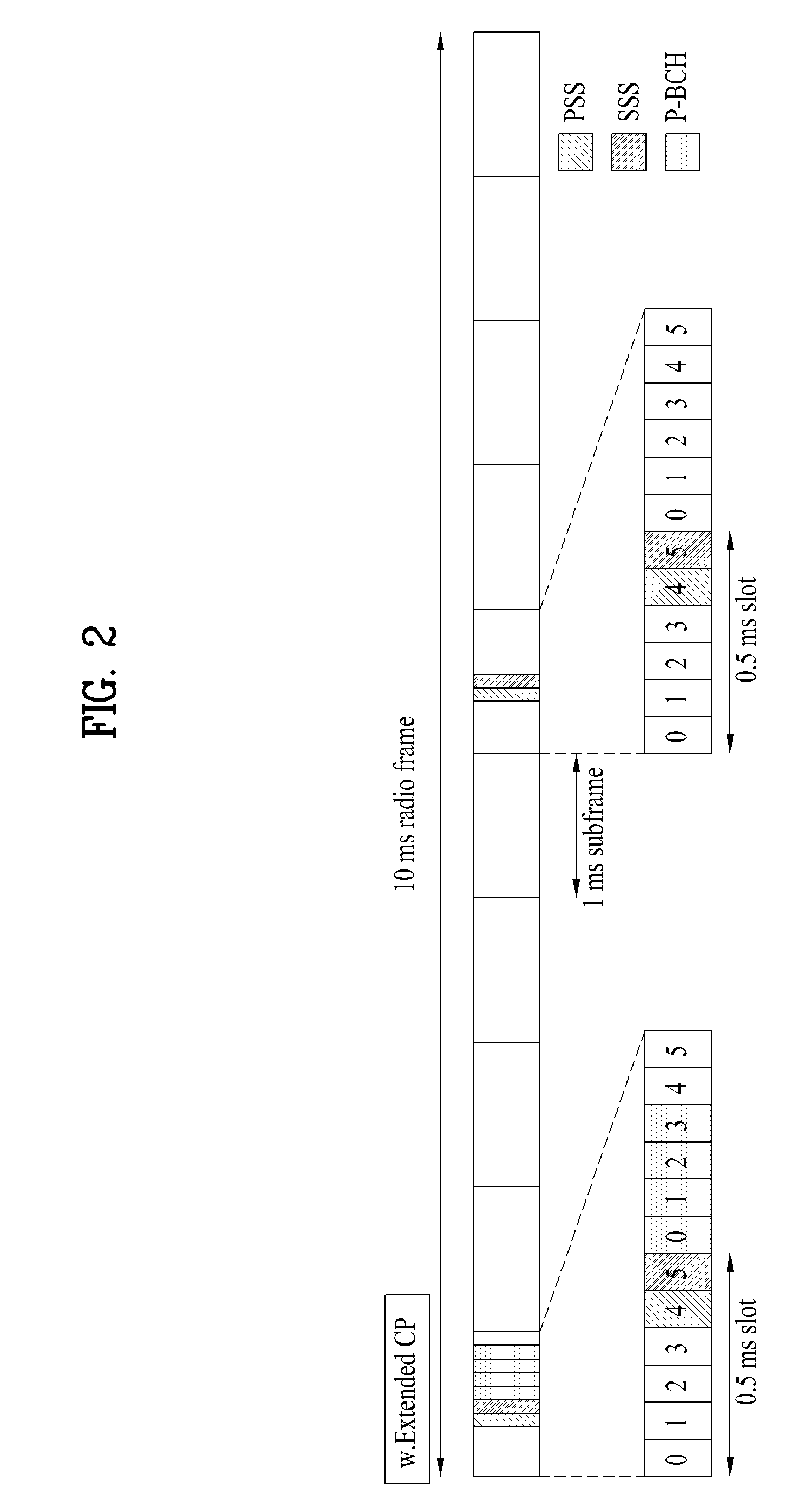
Method, apparatus and computer program product providing synchronization for OFDMA downlink signal
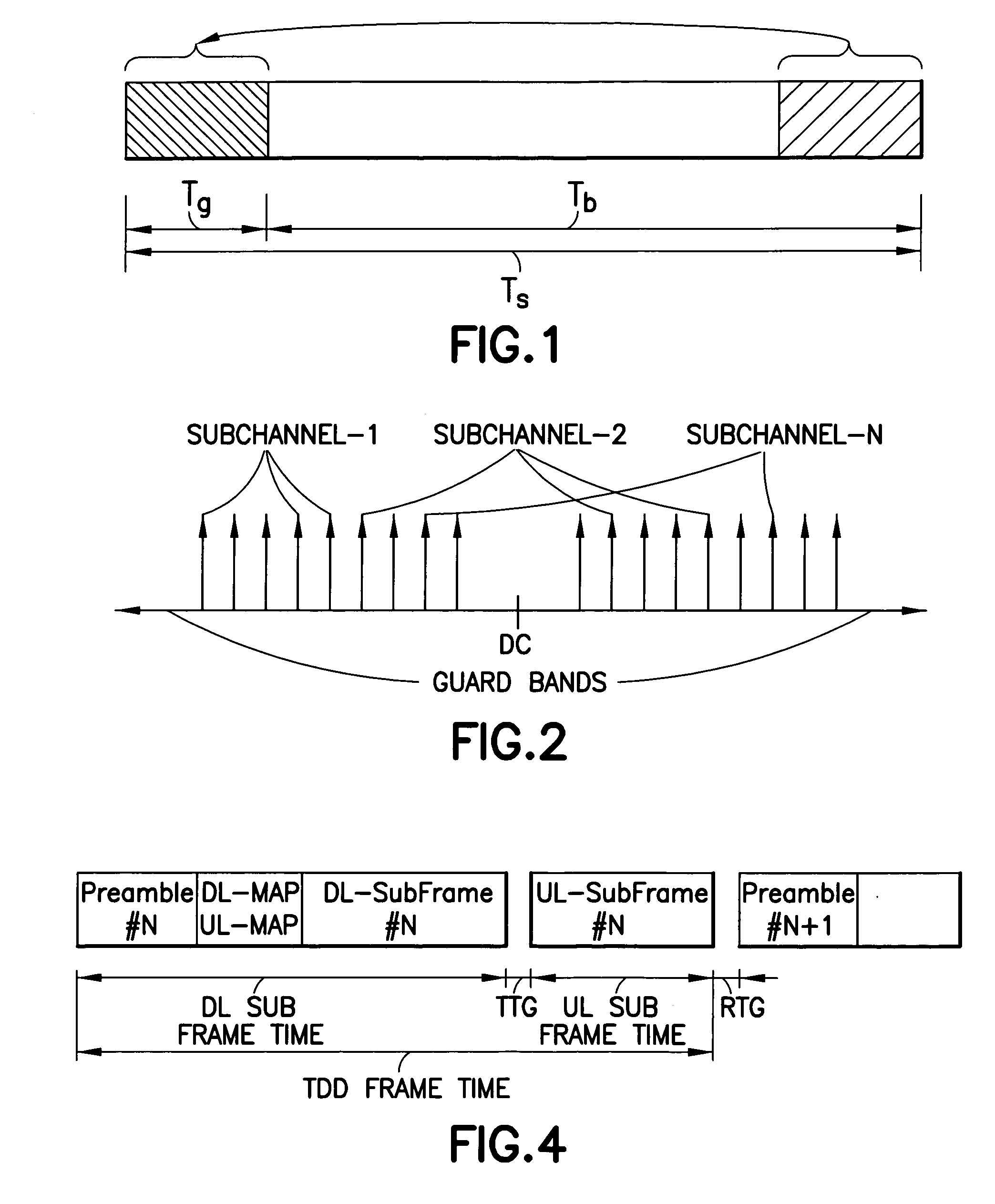
InactiveUS20070280098A1Good precisionModulated-carrier systemsTime-division multiplexCell specificCarrier frequency offset
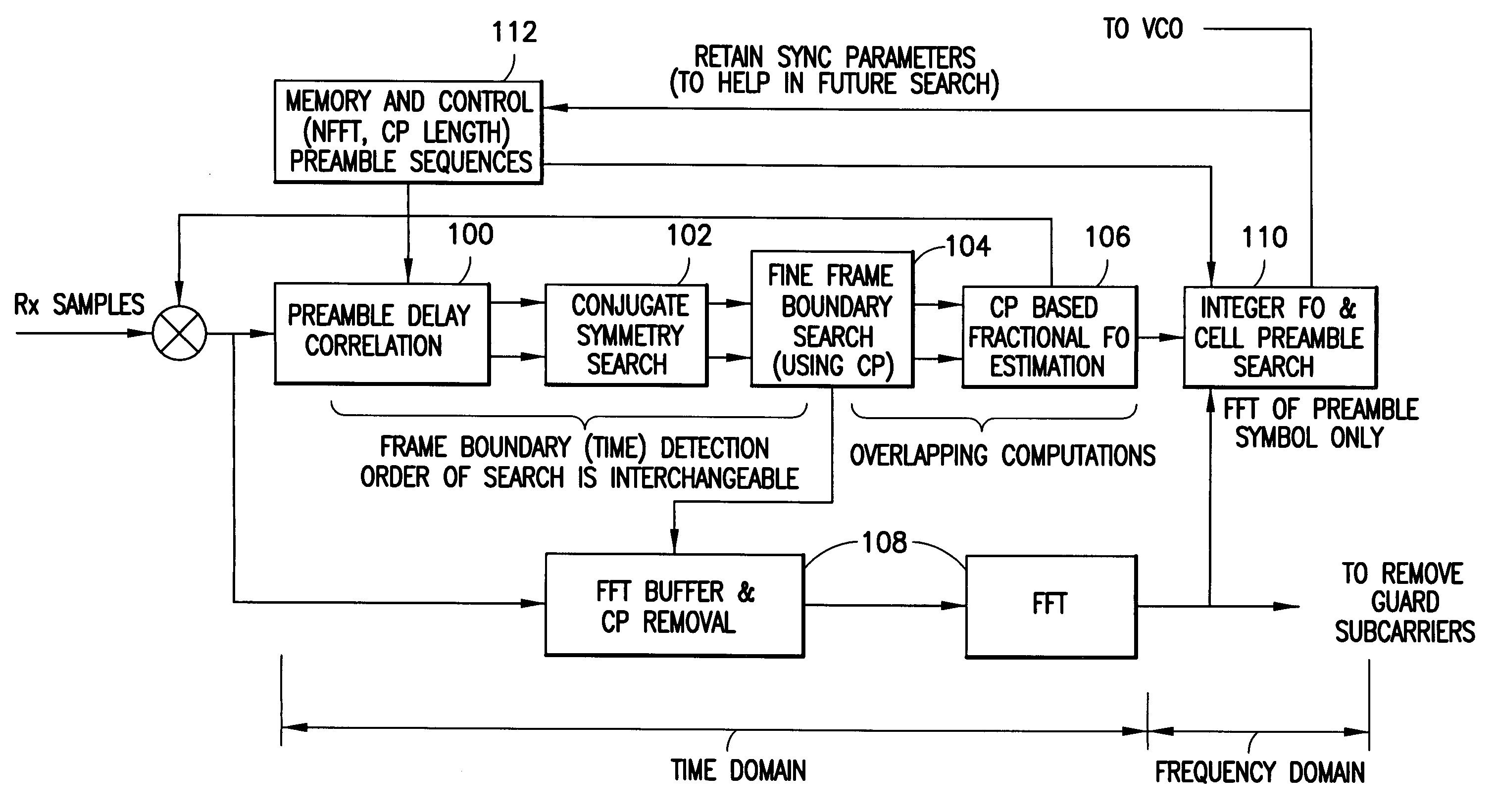
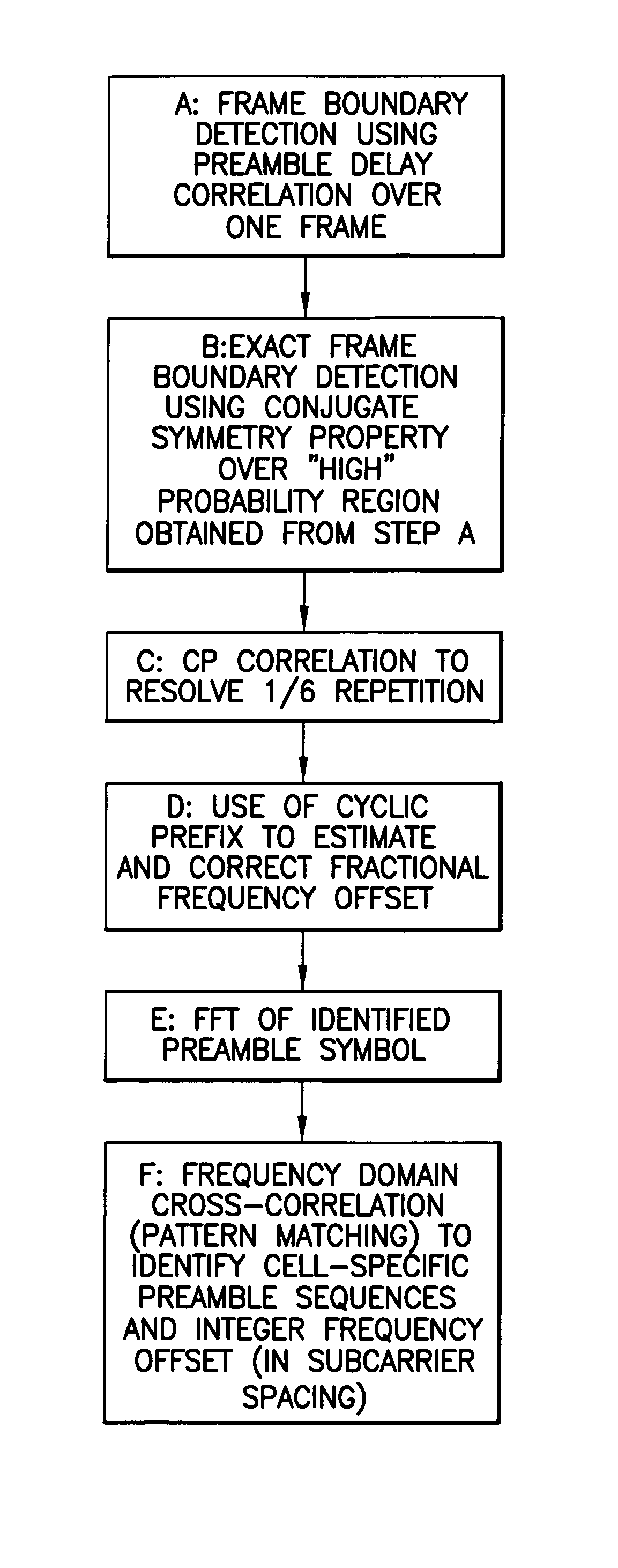
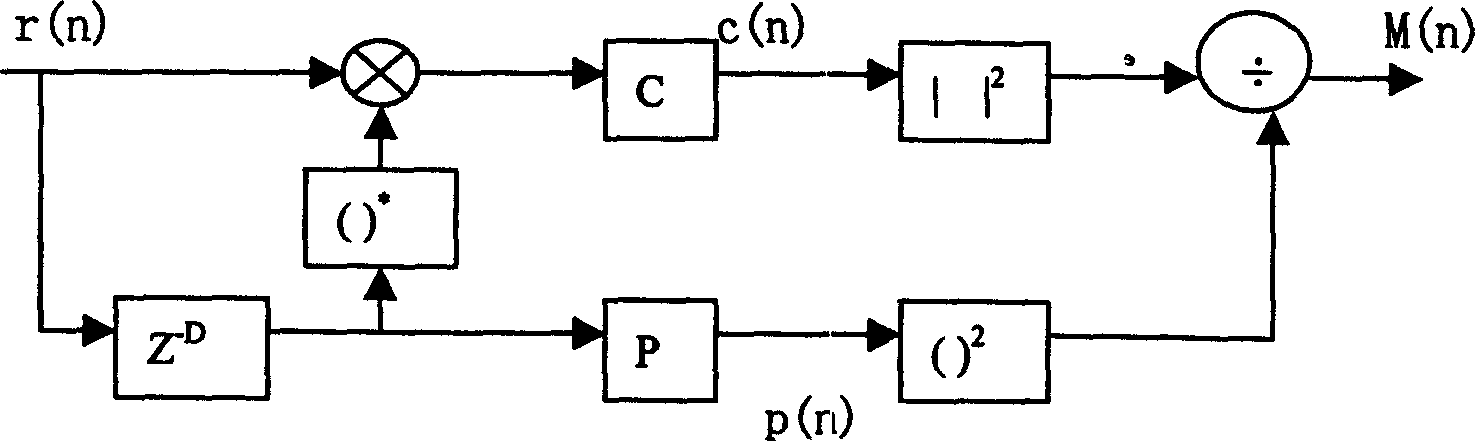
Disclosed is a method, a computer program product and a device that includes a receiver for receiving a downlink signal transmitted into a cell. The receiver is operable to obtain time, carrier frequency and cell-specific preamble synchronization to the received signal and includes a plurality of synchronization units that include a first detector to detect a frame boundary using preamble delay correlation; a second detector to detect the frame boundary with greater precision using a conjugate symmetry property over a region identified by the first detector; a cyclic prefix correlator to resolve symbol boundary repetition; an estimator, using the cyclic prefix, to estimate and correct a fractional carrier frequency offset; an operator to perform a Fast Fourier Transform of an identified preamble symbol and a frequency domain cross-correlator to identify cell-specific preamble sequences and an integer frequency offset in sub-carrier spacing. The transmitted signal may be a downlink signal transmitted into the cell from a base station that is compatible with IEEE 802.16e (WiMAX).
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Method, apparatus and computer program product providing synchronization for OFDMA downlink signal
InactiveUS7613104B2Modulated-carrier systemsTime-division multiplexCell specificCarrier frequency offset
Disclosed is a method, a computer program product and a device that includes a receiver for receiving a downlink signal transmitted into a cell. The receiver is operable to obtain time, carrier frequency and cell-specific preamble synchronization to the received signal and includes a plurality of synchronization units that include a first detector to detect a frame boundary using preamble delay correlation; a second detector to detect the frame boundary with greater precision using a conjugate symmetry property over a region identified by the first detector; a cyclic prefix correlator to resolve symbol boundary repetition; an estimator, using the cyclic prefix, to estimate and correct a fractional carrier frequency offset; an operator to perform a Fast Fourier Transform of an identified preamble symbol and a frequency domain cross-correlator to identify cell-specific preamble sequences and an integer frequency offset in sub-carrier spacing. The transmitted signal may be a downlink signal transmitted into the cell from a base station that is compatible with IEEE 802.16e (WiMAX).
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
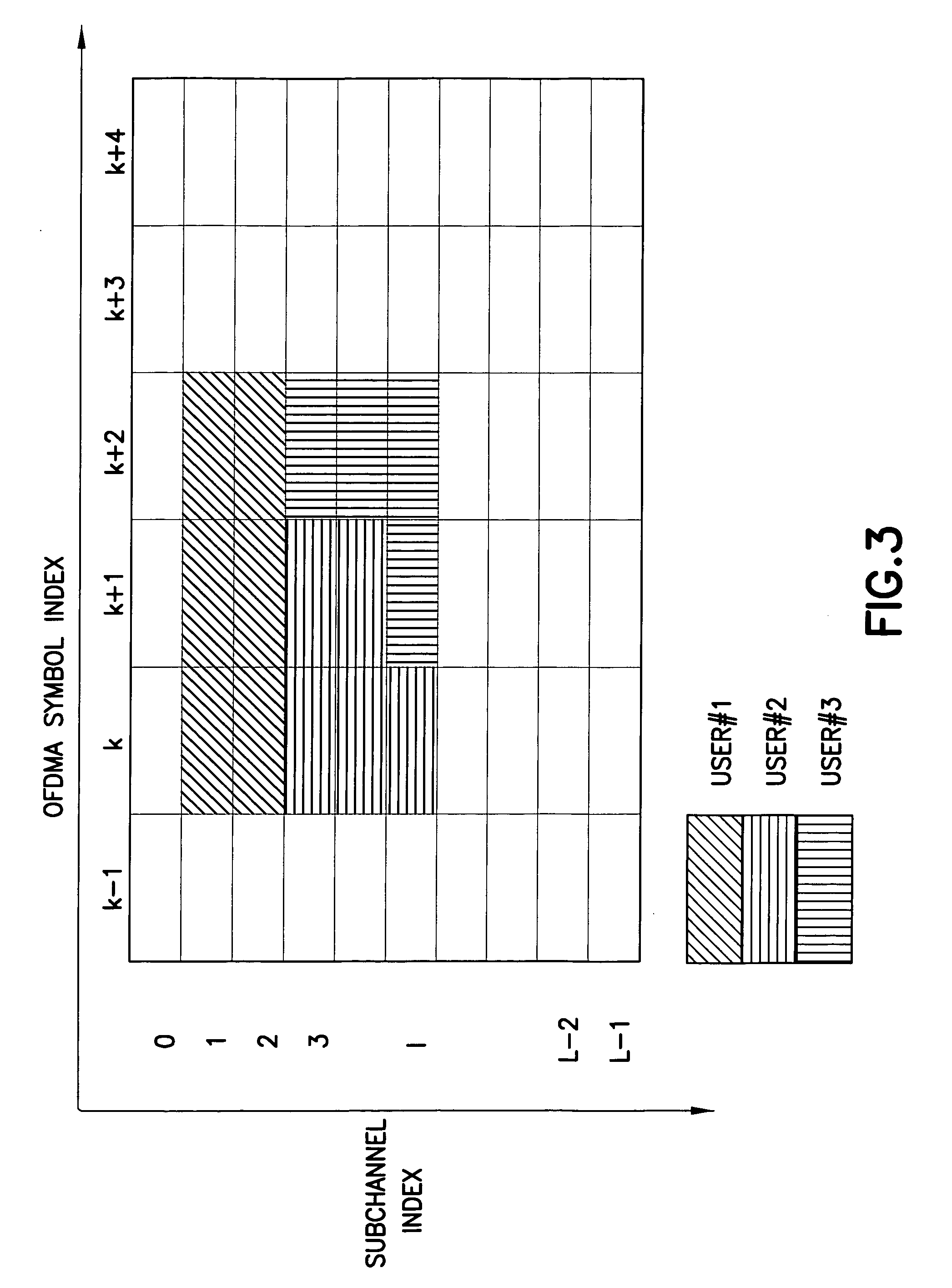
Sequence generating method for efficient detection and method for transmitting and receiving signals using the same
ActiveUS20080240285A1Improve featuresEasily detect sequenceSynchronisation arrangementTransmission path divisionConjugate symmetryOfdm communication system
A sequence generation method for allowing a reception end to effectively detect a sequence used for a specific channel of an OFDM communication system, and a signal transmission / reception method using the same are disclosed. During the sequence generation, an index is selected from among the index set having the conjugate symmetry property between indexes, and a specific part corresponding to the frequency “0” is omitted from a transmitted signal. In addition, a reception end can calculate a cross-correlation value between a received (Rx) signal and each sequence using only one cross-correlation calculation based on the conjugate symmetry property.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
Wireless optical orthogonal multi-carrier communication method with low peak to average power ratio
InactiveCN103618687ANo waste of frequency resourcesReduce peak-to-average power ratioClose-range type systemsMulti-frequency code systemsNonlinear distortionCyclic prefix
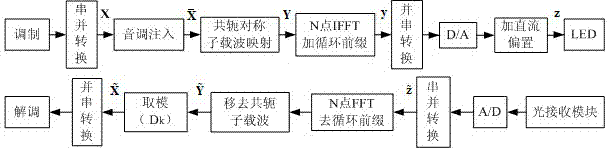
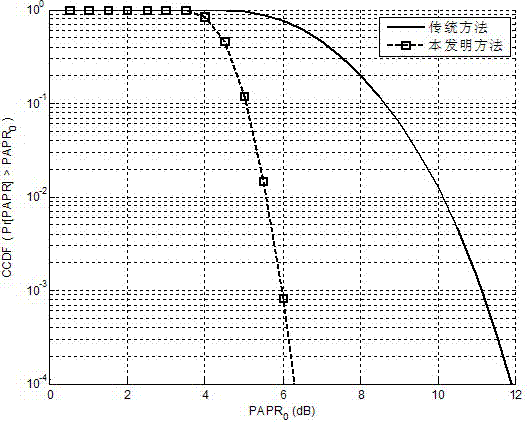
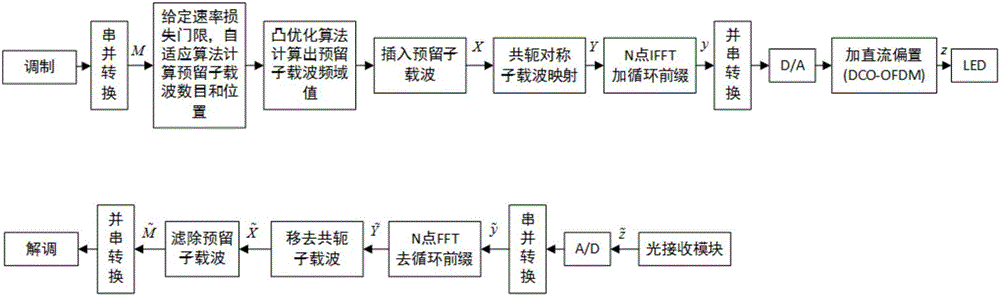
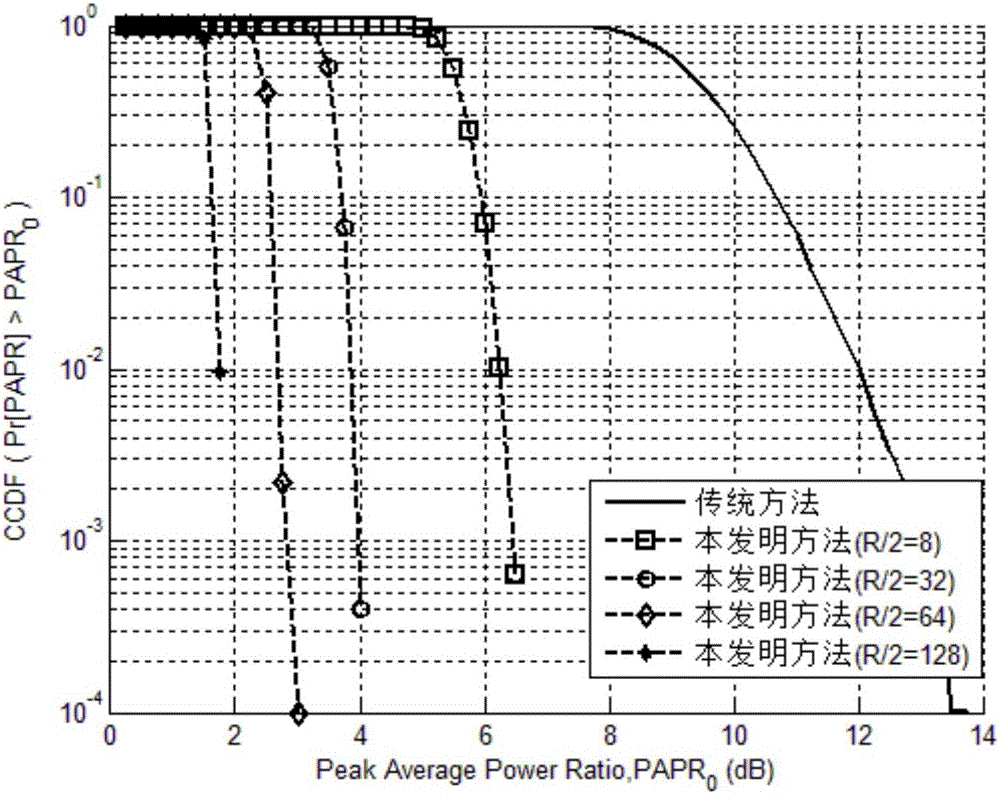
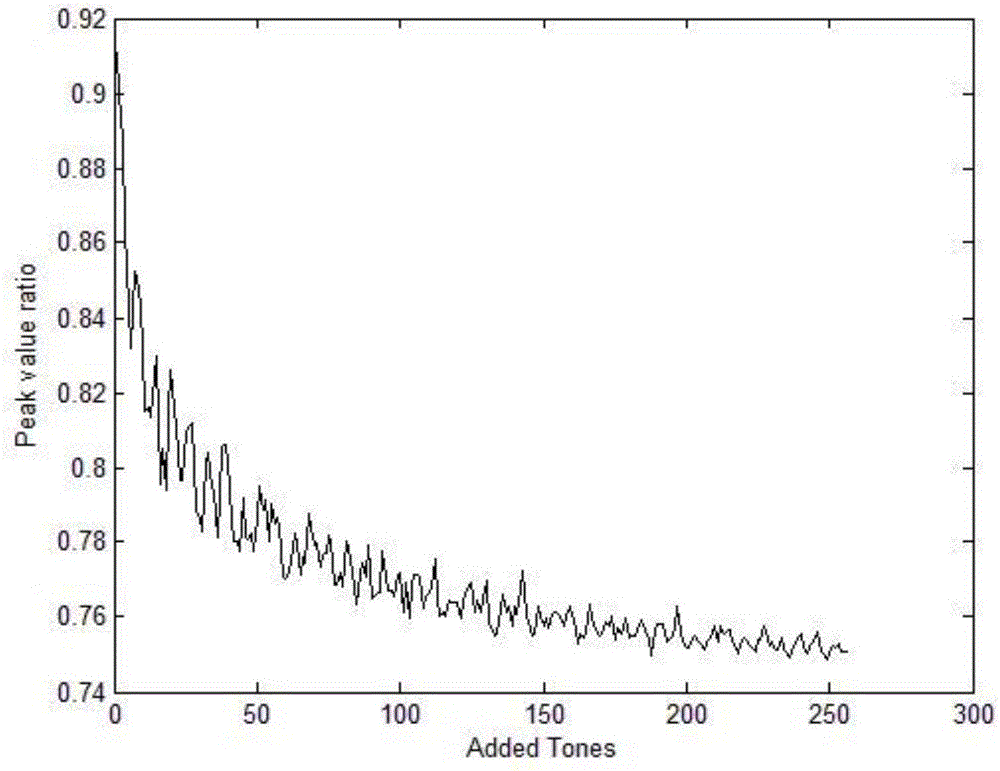
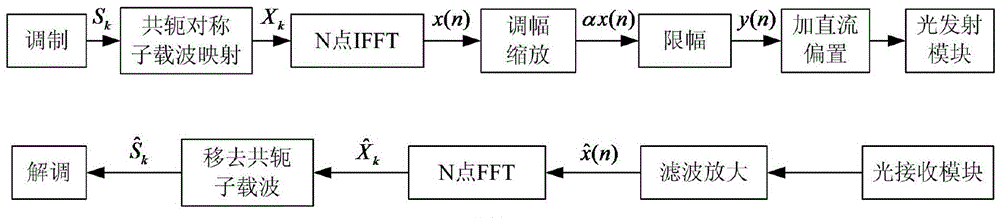
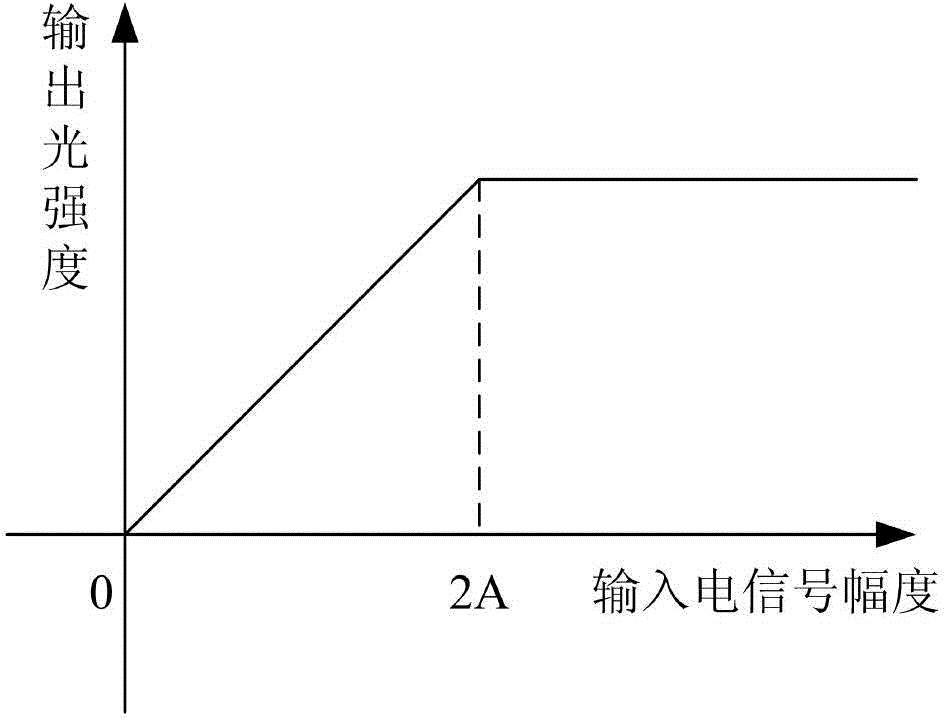
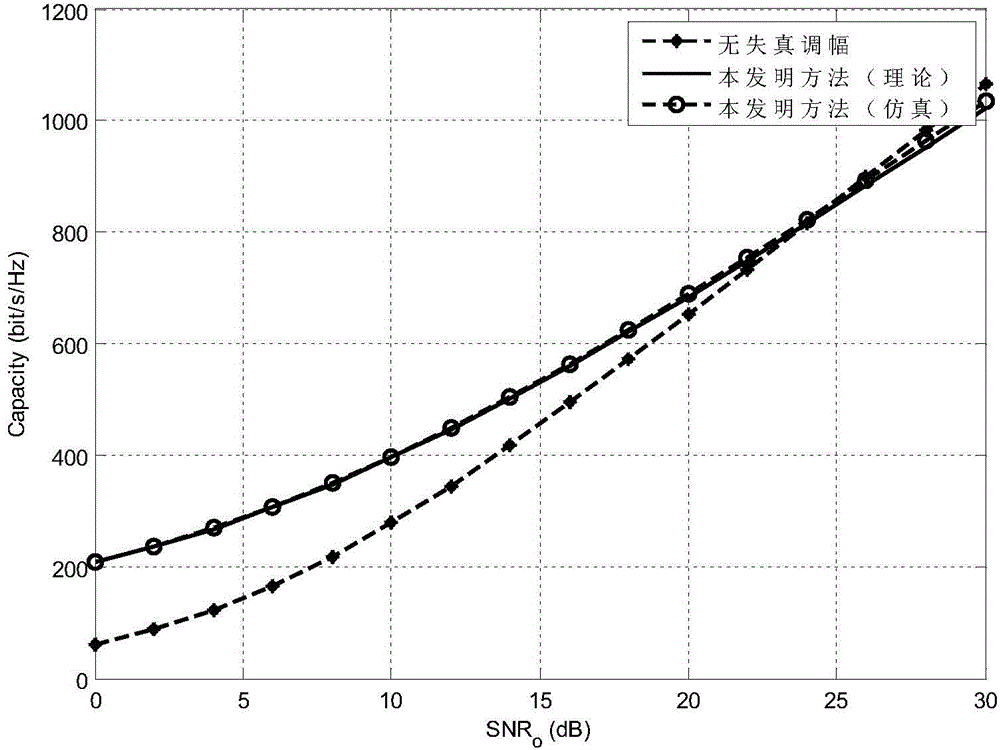
The invention discloses a wireless optical orthogonal multi-carrier communication method with a low peak to average power ratio. The wireless optical orthogonal multi-carrier communication method comprises the following steps that at a transmitting end, firstly, modulated frequency domain signals are converted into a semi-positive definite planning convex optimization problem by adopting a tone injection algorithm via a relaxation method, and solving is carried out through general convex optimization and randomized methods; secondly, the frequency domain signals are symmetrically mapped to subcarriers in a conjugate mode, and a cyclic prefix is added after reverse fast Fourier transformation; at last, time domain transmission signals are added into direct-current offset to drive a light-emitting diode to emit light. At a receiving end, photovoltaic conversion is achieved through a photodiode; signals are removed from the cyclic prefix and conjugate symmetry parts after amplification, filtering, analog-digital conversion and fast Fourier transformation; the signals are modulated to be recovered in an original planisphere; at last, receiving symbols are obtained through demodulation. According to the wireless optical orthogonal multi-carrier communication method, the peak to average power ratio of a wireless optical communication PFDM system can be effectively reduced, requirements of a power amplifier and an LED for linear degrees are reduced, non-linear distortion is reduced, and receiving performance is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
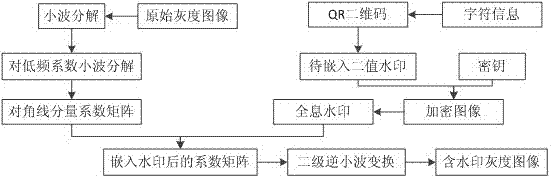
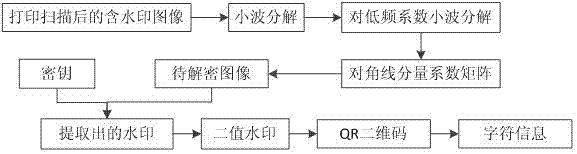
Transformation domain printing-scanning resistant digital watermarking method based on computer-generated holography
The invention relates to a transformation domain printing-scanning resistant digital watermarking method based on computer-generated holography. The method integrates QR two-dimension codes, double random phase modulation encryption technique, a conjugate symmetry prolongation Fourier computer-generated holography technique and a wavelet transform technique, adopts the QR two-dimension codes as original watermarking information, preprocessed QR two-dimension code information is used for two-value watermarking so as to perform double random phase modulation encryption, finally the conjugate symmetry prolongation Fourier computer-generated holography technique is utilized to calculate amplitudes and phase information of complex images so as to obtain a watermarking hologram after holography technique records are encrypted. An image obtained by performing holographic decryption and double random phase modulation decryption on the hologram generated in the mode is free of noise, and the robustness of a watermarking algorithm is improved. The safety of the watermarking algorithm is improved by using the double random phase modulation encryption technique. The QR two-dimension codes form a two-value image and can carry copyright information and enable accurate copyright owner or group positioning to be possible.
Owner:SHANGHAI PUBLISHING & PRINTING COLLEGE +1
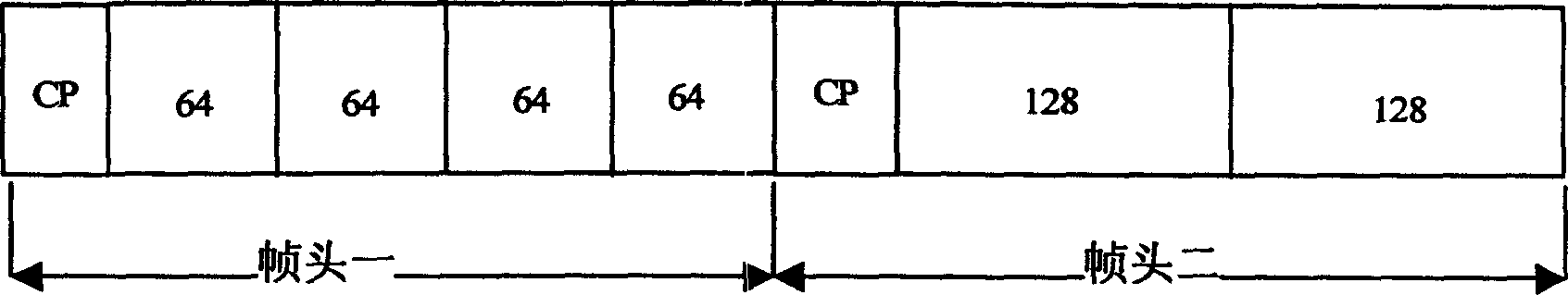
Synchronous method of orthogonal freuency division multiplex in broadband radio insertion system
InactiveCN1599367AReduce complexityImprove performanceSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlMulti-frequency code systemsConjugate symmetrySynchronous motor
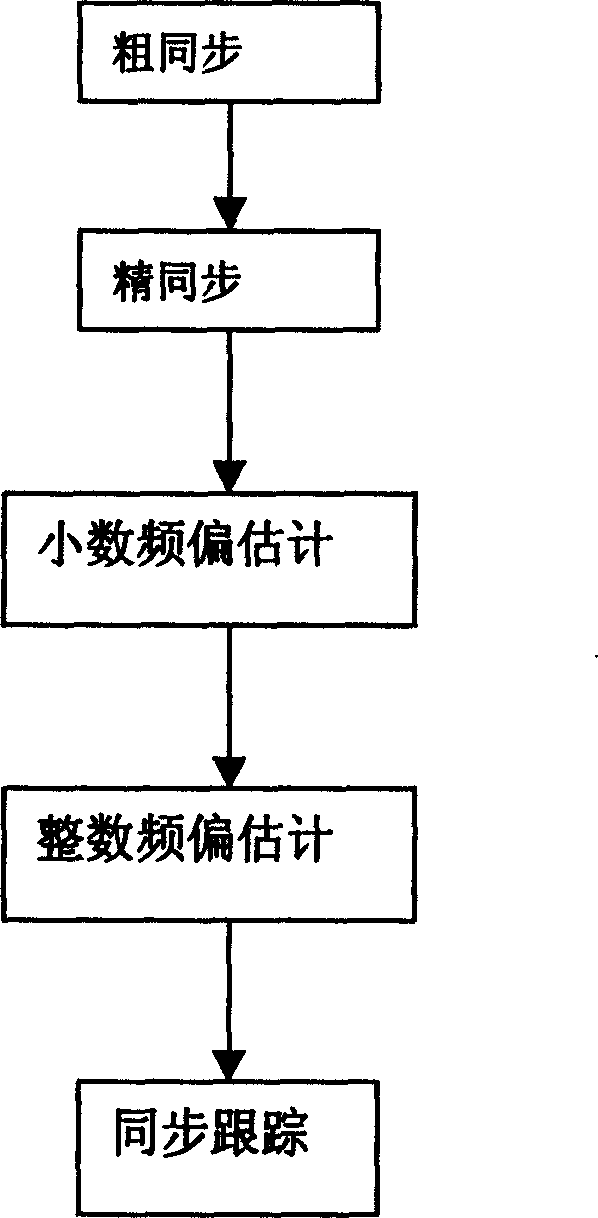
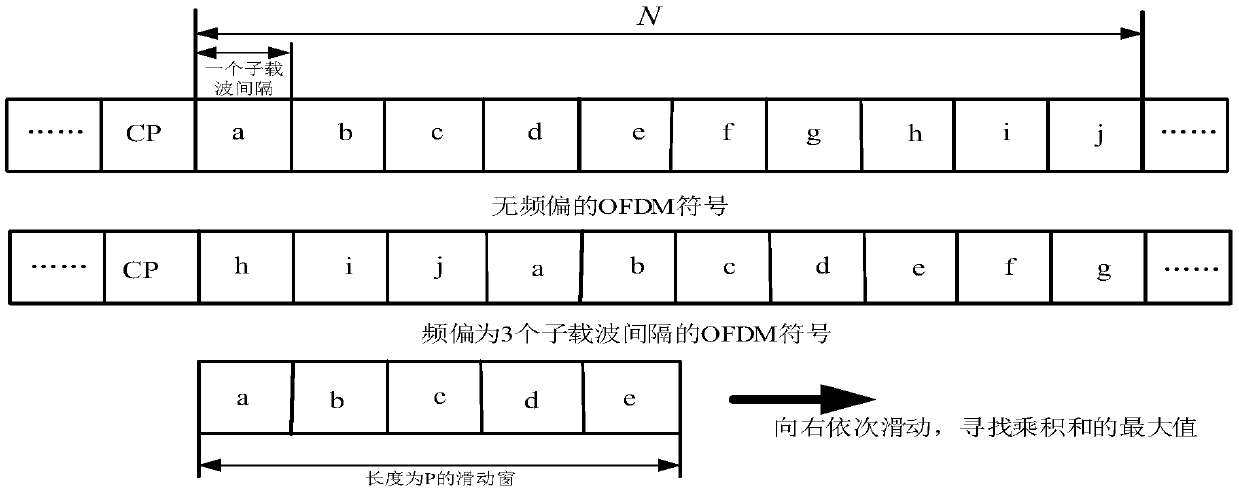
A synchronization method in OFDM broadband wireless access system includes such steps as utilizing NO.1 frame head as a delay related decision to realize rough synchronization, using the conjugate symmetry of No.2 frame head to realize accurate timing, the frame heads roughly and accurately estimate the decimal frequency deviation separately, the frequency field sequences of the two heads are used to estimate the integer frequency bias and finally synchronous tracing.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Sequence generating method for efficient detection and method for transmitting and receiving signals using the same
ActiveCN101641924AEasy to detectLow PAPR characteristicsTransmission path divisionConnection managementConjugate symmetryOfdm communication system
A sequence generation method for allowing a reception end to effectively detect a sequence used for a specific channel of an OFDM communication system, and a signal transmission / reception method using the same are disclosed. During the sequence generation, an index is selected from among the index set having the conjugate symmetry property between indexes, and a specific part corresponding to the frequency '0' is omitted from a transmitted signal. In addition, a reception end can calculate a cross-correlation value between a received (Rx) signal and each sequence using only one cross-correlation calculation based on the conjugate symmetry property.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
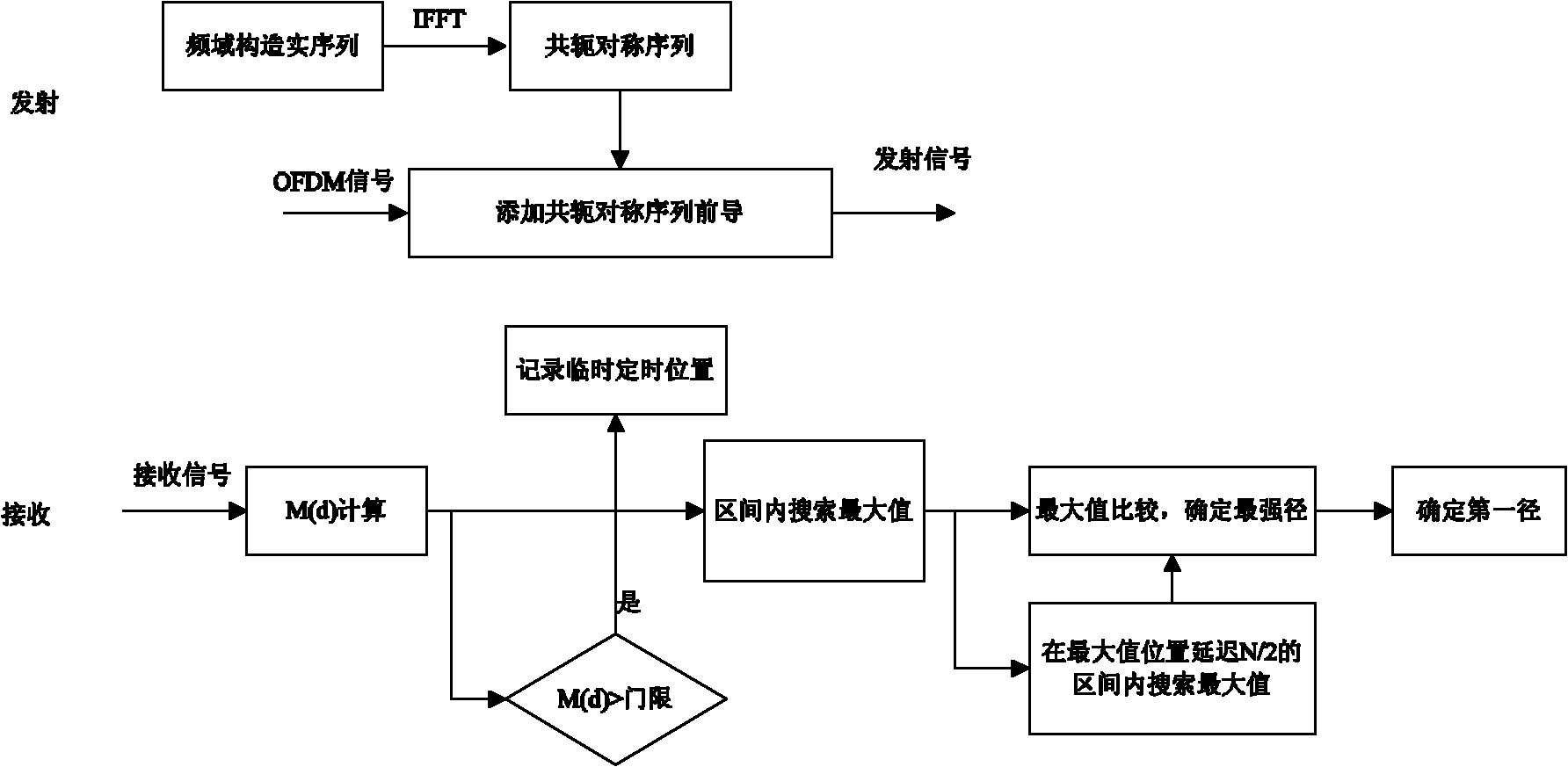
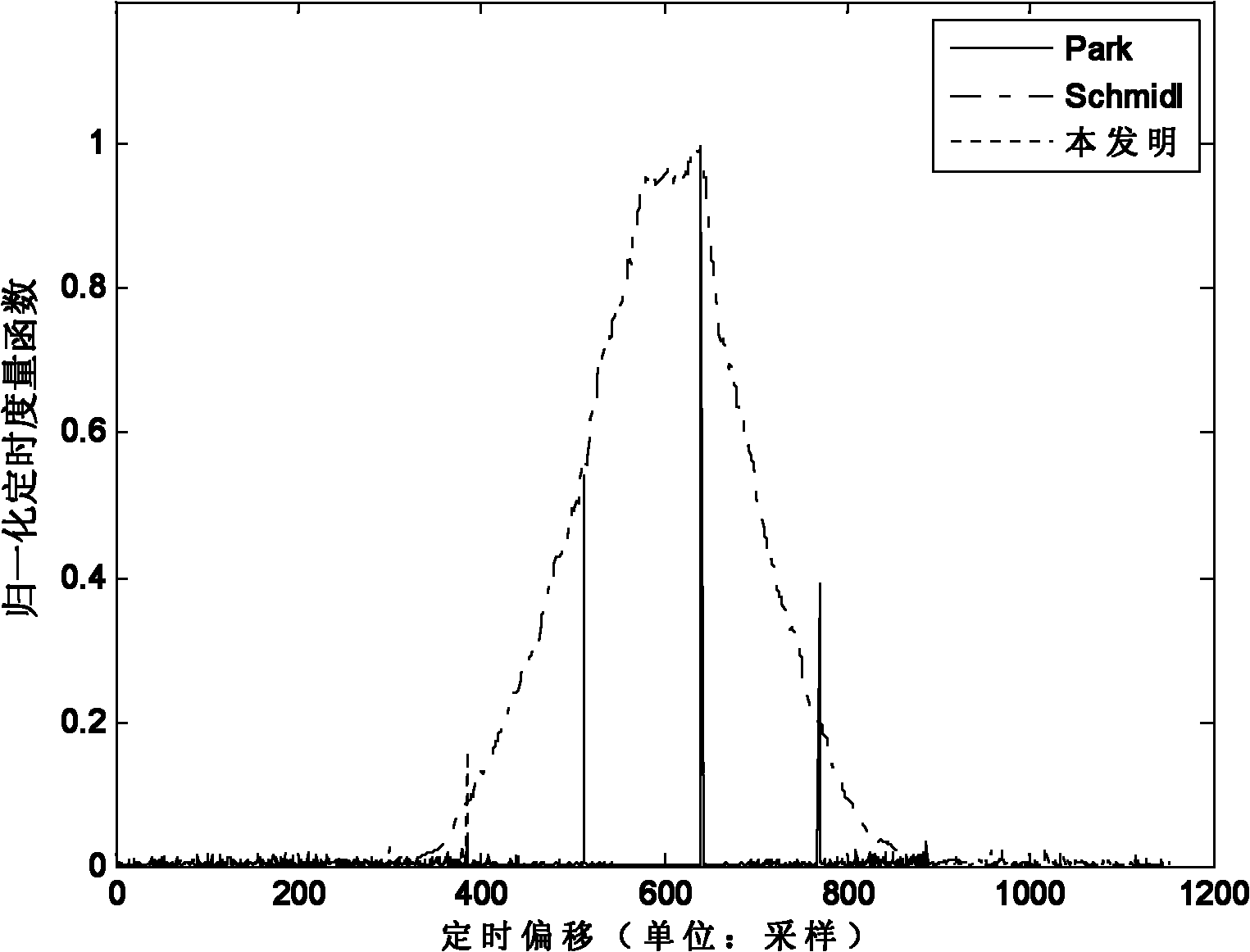
Timing frequency synchronization method based on improved Park frequency domain training sequence
InactiveCN109660478AEliminate side peaksAccurate timingMulti-frequency code systemsConjugate symmetryTime domain
The invention discloses a timing frequency synchronization method based on an improved Park frequency domain training sequence. The timing frequency synchronization method comprises the following steps: firstly sending a training sequence before an OFDM data symbol is sent, wherein all the sub carriers of the training sequence in the frequency domain respectively send a pseudorandom real number, and structure of a corresponding time domain training symbol is conjugate symmetric; performing timing synchronization by an FS-Park synchronization method firstly by using the time domain training symbol, then performing estimation on fractional part of frequency offset based on a cyclic prefix in the time domain and performing estimation on integral frequency offset by utilizing cross correlationof the training sequence in the frequency domain, obtaining the total frequency offset, namely the sum of the integral frequency offset and the fractional part of frequency offset, and completing synchronization. The timing frequency synchronization method disclosed by the invention designs a new training sequence, and then a more ideal time domain training symbol structure is obtained; and thenbased on the training sequence and the corresponding time domain training symbol thereof, the integral frequency offset and the fractional part of frequency offset are estimated respectively, and timing synchronization estimation is performed.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV +1
LED array visible light communication system and method
ActiveCN103457661AImprove performancePeak-to-average suppression ratioTransmission control/equalisingClose-range type systemsEngineeringVisible light communication
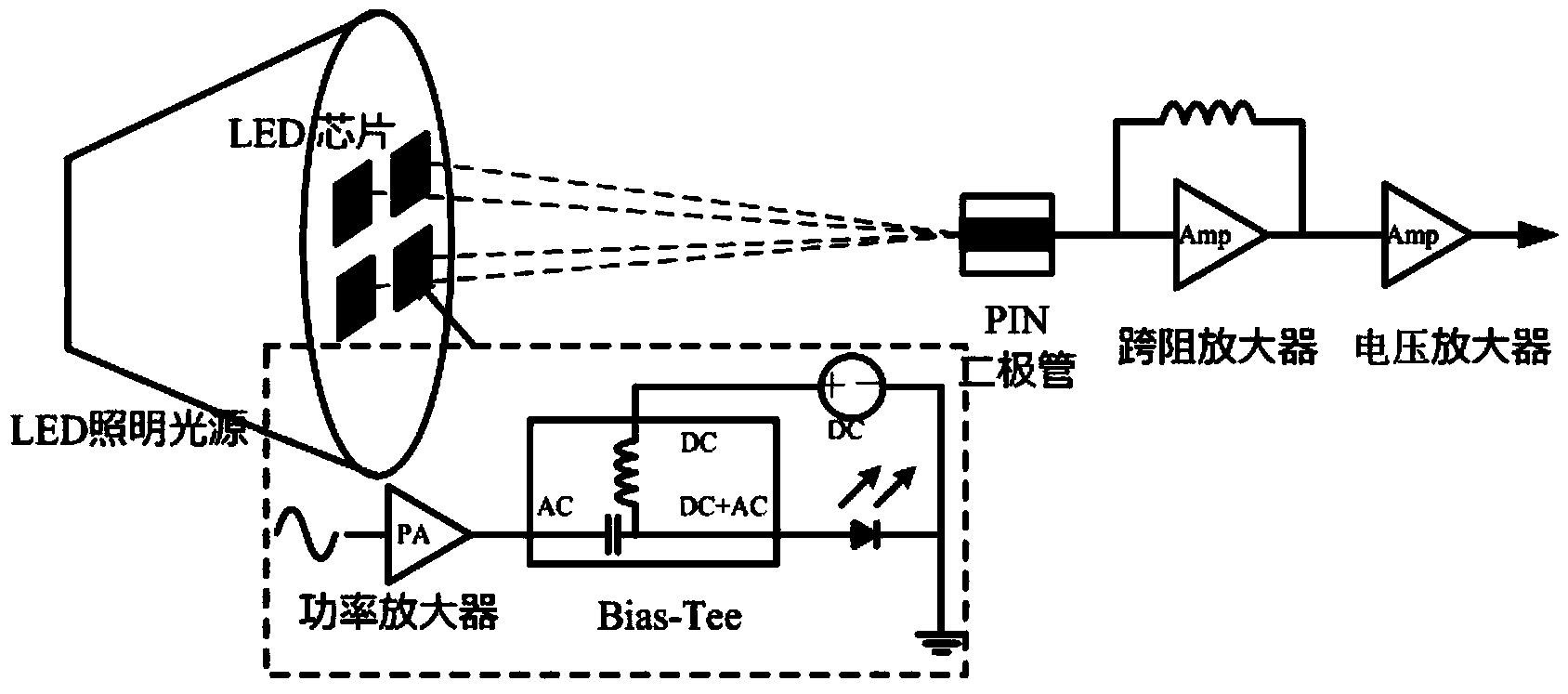
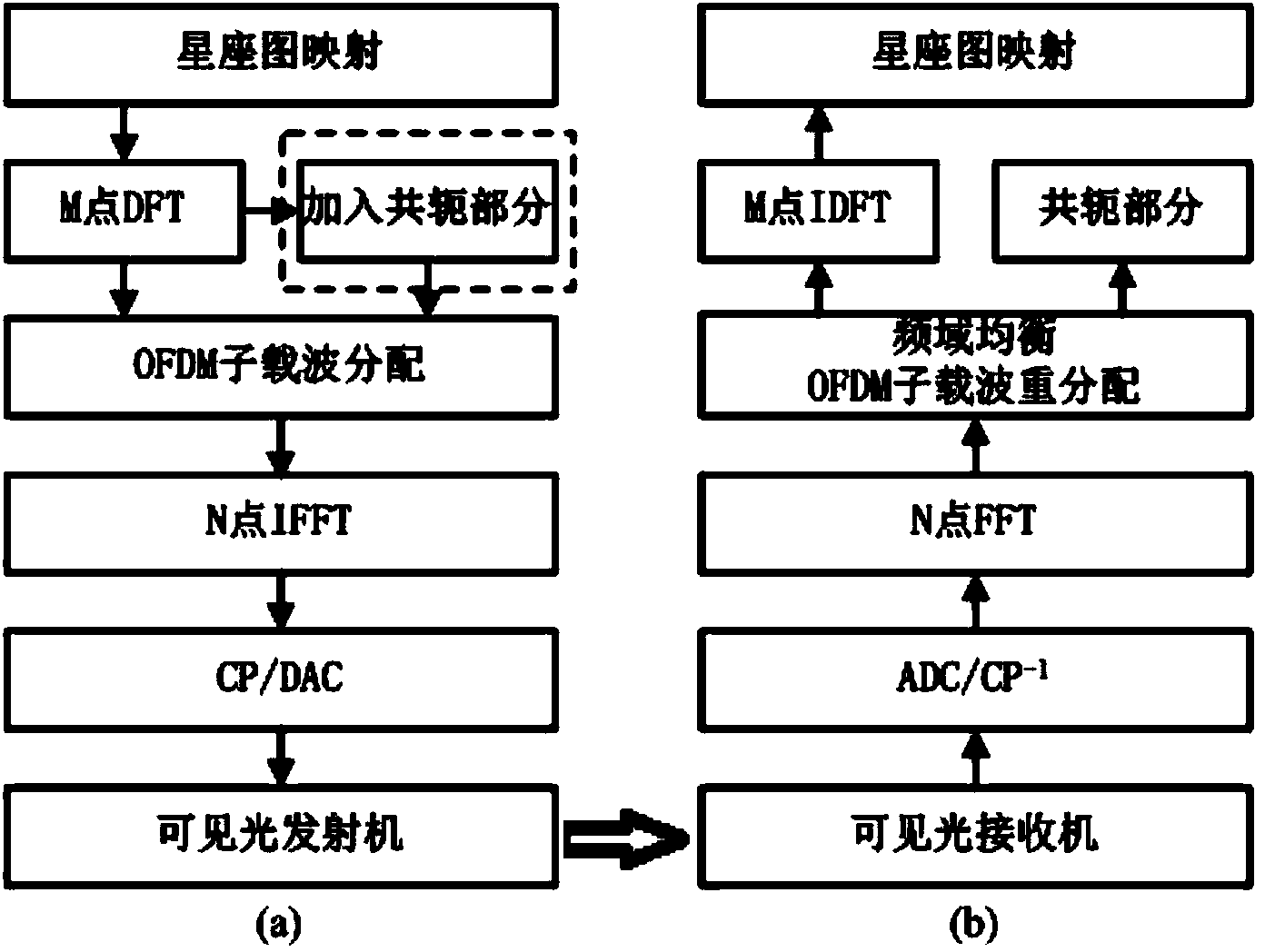
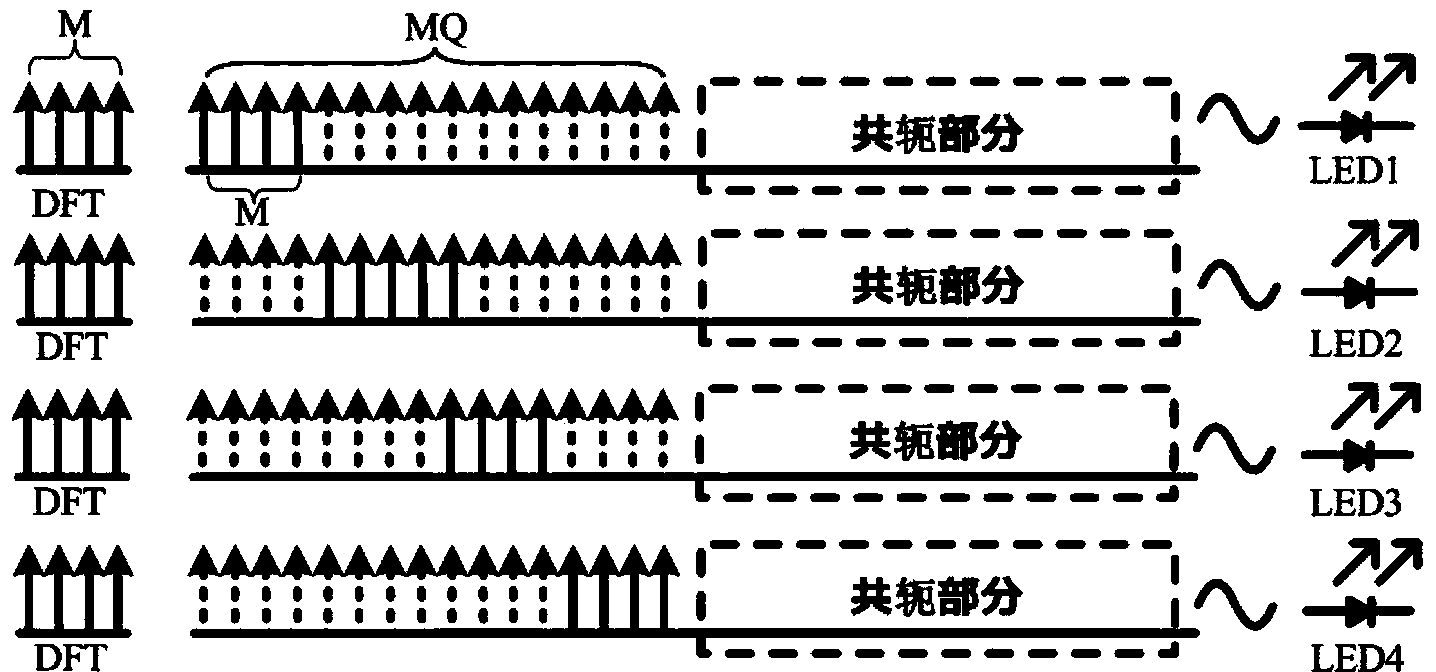
The invention discloses an LED array visible light communication system based on DFT-S OFDM and an LED array visible light communication method. An LED light source composed of a plurality of LED chips serves as the emitting end, and the LED chips are independently driven to form LED array emitting systems which do not disturb each other. The DFT-S OFDM modulation mode is adopted by each LED emitter, the LED emitters occupy different OFDM frequency band resources respectively, circumference conjugate symmetry is applied to OFDM frequency domain subcarriers to guarantee real number property of OFDM base band data, and a centralized DFT-S OFDM mode and a staggered DFT-S OFDM mode are applied to the visible light communication system. The DFT-S technology applied to the LED array visible light communication system based on DFT-S OFDM and the LED array visible light communication method can obviously restrain the peak-to-average power ratio of the visible light communication system, obvious frequency domain diversity gains are acquired in the aspect of bit error rate performance, and the LED array emitting structure protects system transmission ratio against effect.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
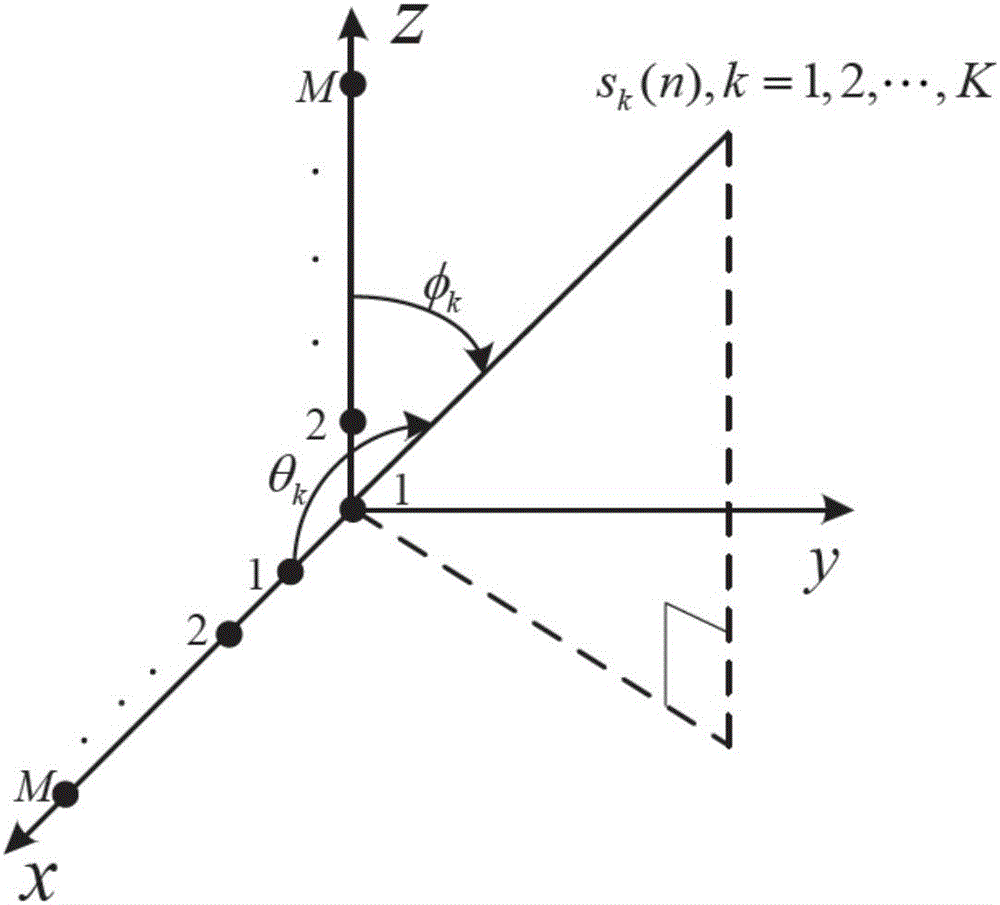
Estimation algorithm for two-dimensional direction of arrival (DOA) of L-shaped array by adopting time-frequency analysis
InactiveCN106772224AEliminate the effects ofImprove robustnessRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsFrequency spectrumCross correlation matrix
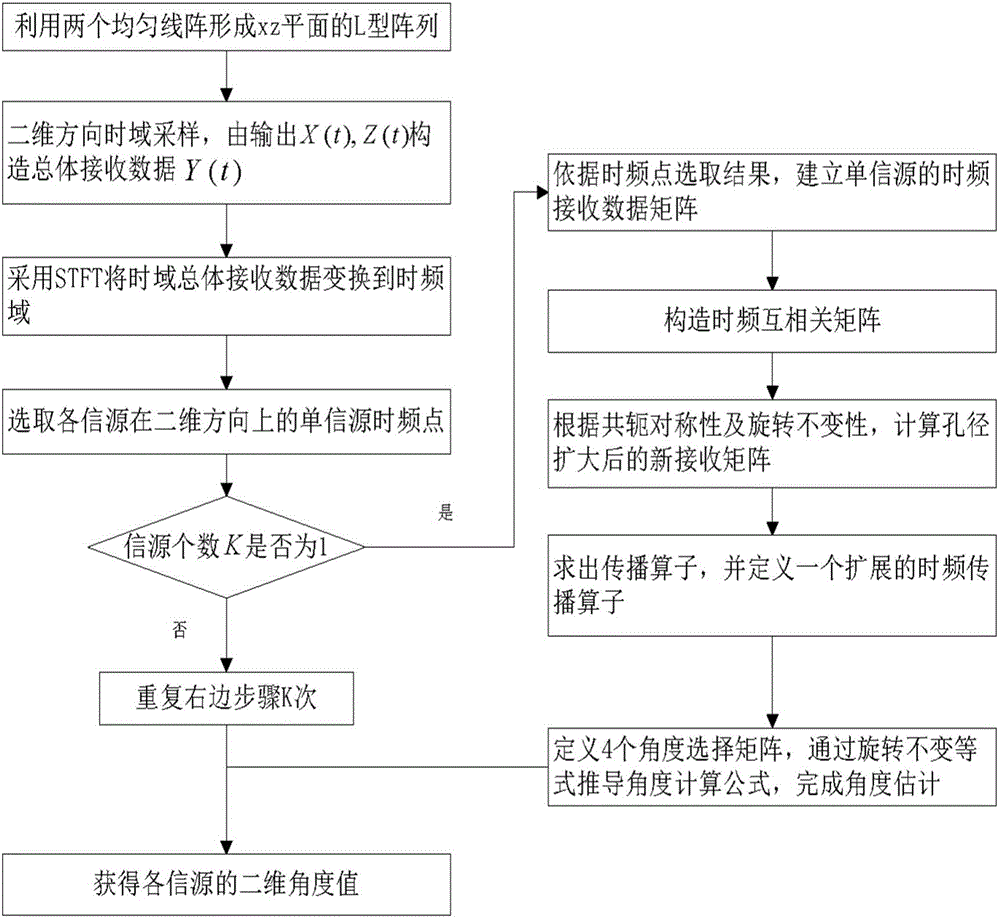
The invention discloses an estimation algorithm for two-dimensional direction of arrival (DOA) of an L-shaped array by adopting time-frequency analysis. The estimation algorithm disclosed by the invention mainly aims at solving the problem of two-dimensional DOA estimation of time-frequency spectrum aliasing and spatial neighborhood information sources and is suitable for low signal to noise ratio and underdetermined conditions. The estimation algorithm is realized by the following steps: firstly, forming the L-shaped array on an xz plane by using two uniform linear arrays to construct total receiving data; secondly, transforming the total receiving data into a time-frequency domain by adopting STFT (Short Time Fourier Transform); thirdly, selecting single information source time-frequency points of all the information sources in a two-dimensional direction, and establishing a time-frequency receiving data matrix of single information sources; fourthly, constructing a time-frequency cross correlation matrix; fifthly, calculating a novel receiving matrix subjected to aperture expansion; sixthly, based on a propagation operator principle, defining a propagation operator subjected to the aperture expansion; seventhly, constructing an angle selection matrix, and calculating the two-dimensional DOA according to rotational invariance among sub-matrixes. According to the estimation algorithm disclosed by the invention, estimation precision of the time-frequency spectrum aliasing and spatial neighborhood information sources and the success rate are improved, high robustness of noises is realized, and required number of array elements can be reduced.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
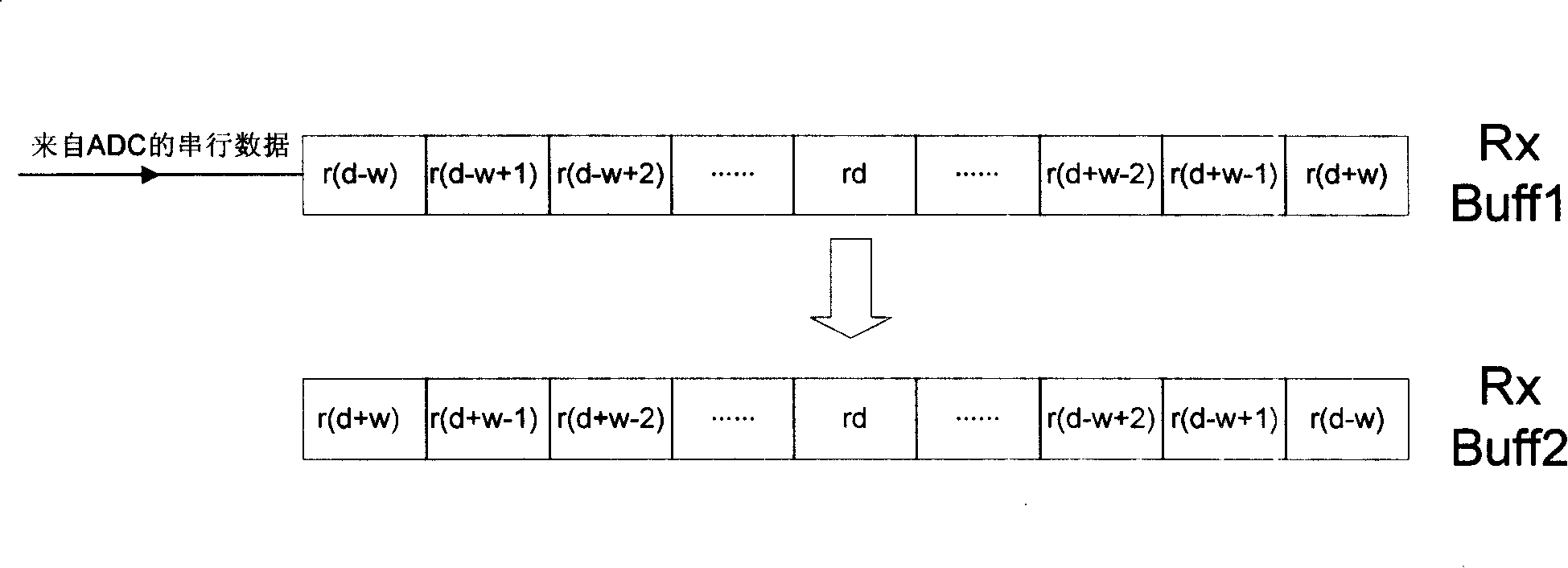
OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) time synchronization algorithm based on conjugate symmetric sequence
InactiveCN102185819AShield interferencePrecise time synchronizationMulti-frequency code systemsConjugate symmetryMultipath channels
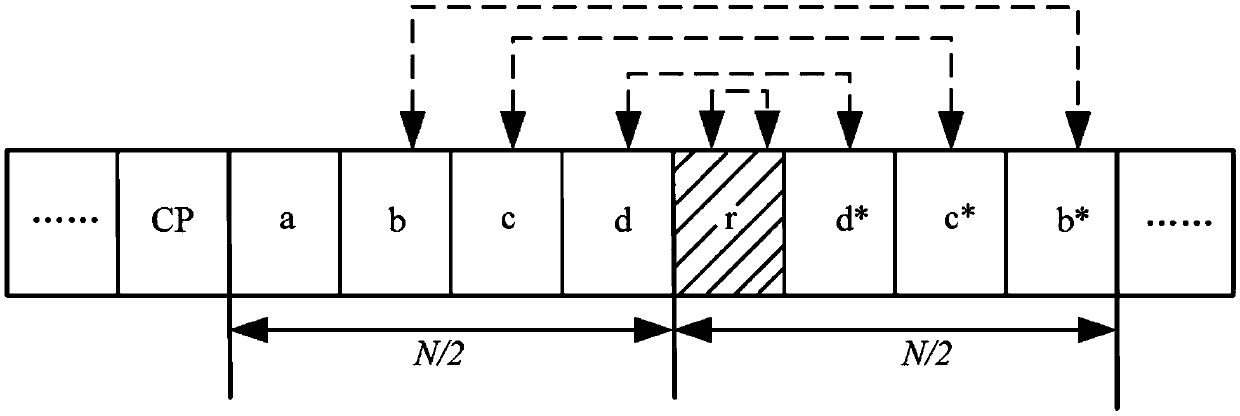
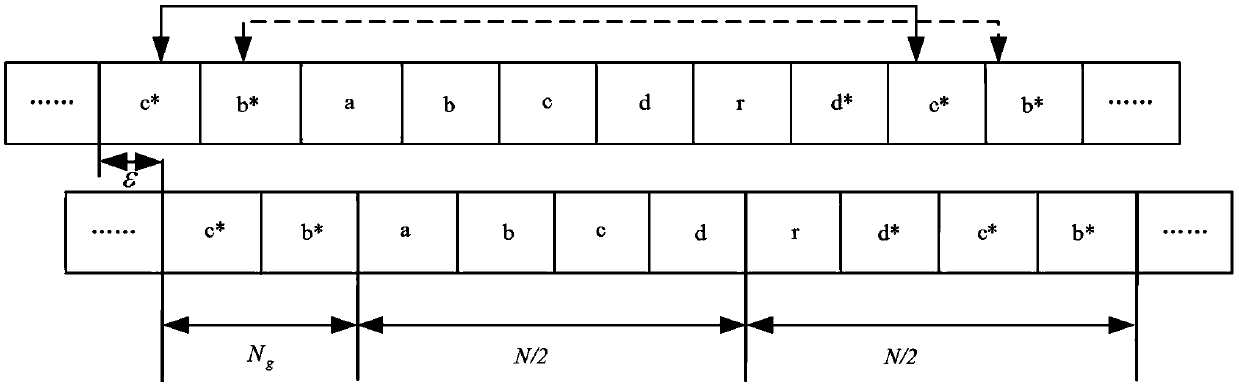
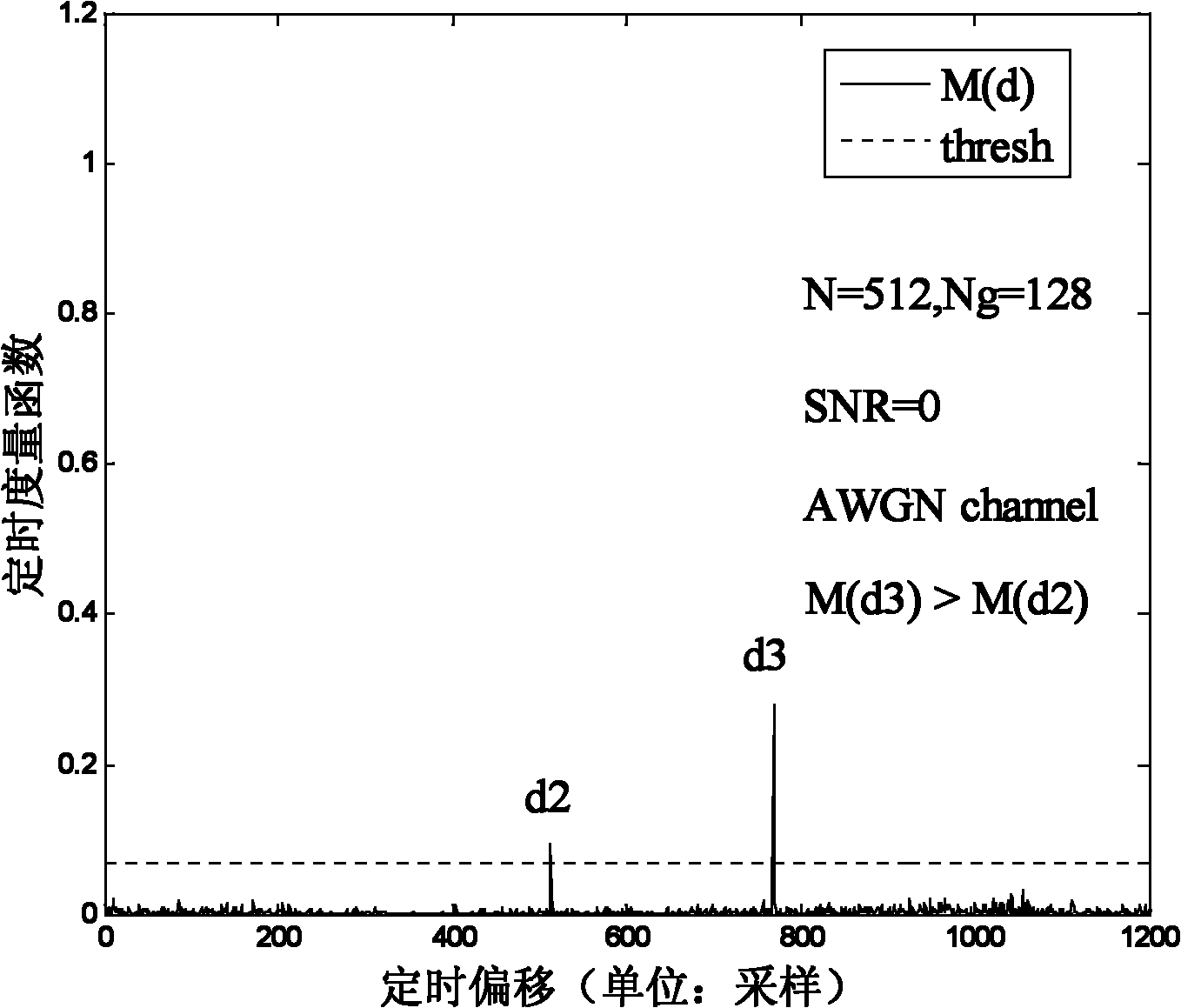
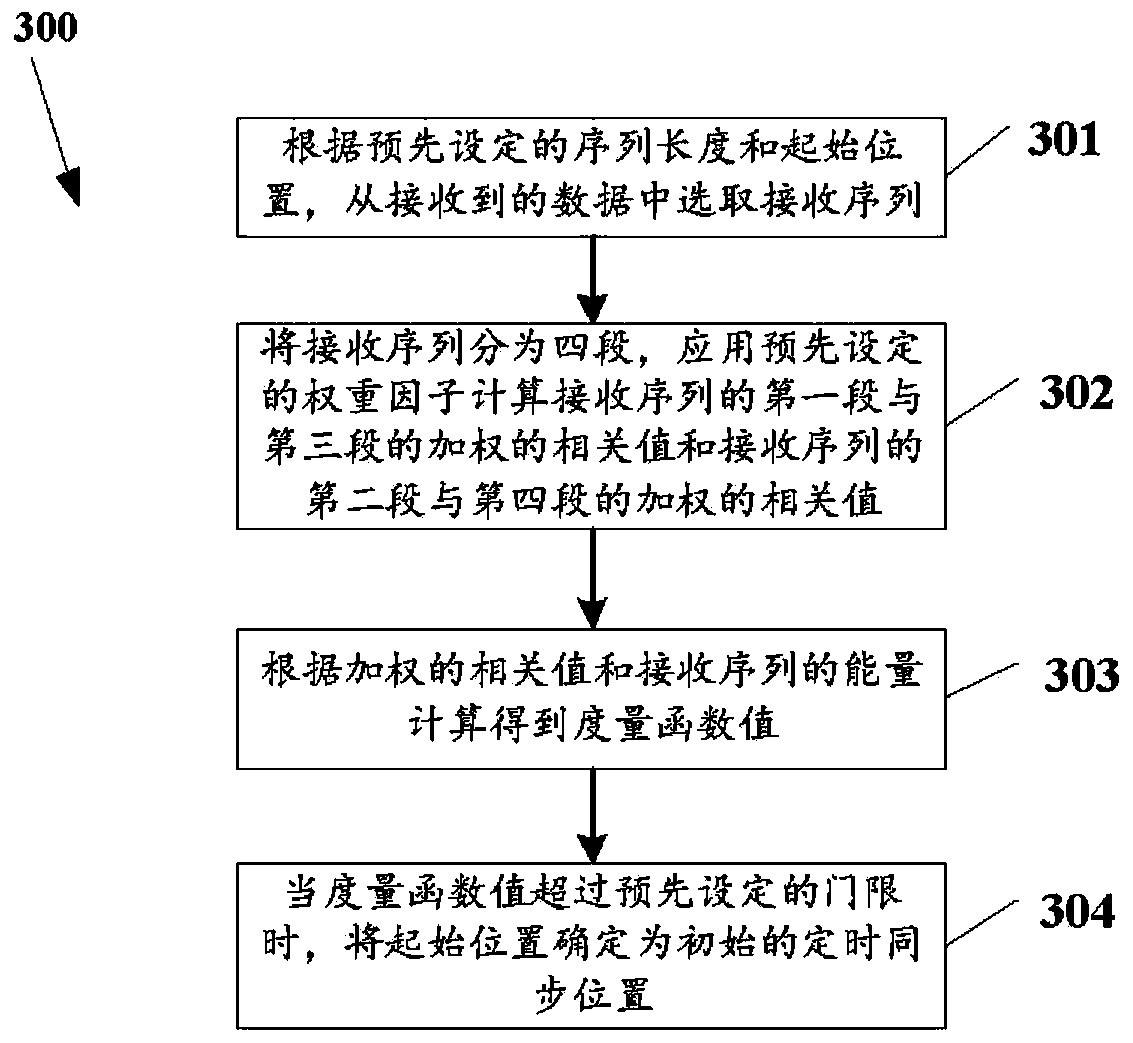
The invention relates to an OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) time synchronization algorithm based on a conjugate symmetric sequence. The OFDM time synchronization algorithm comprises the steps of constructing a sequence with conjugate symmetry; carrying out symmetric related calculation at a receiving end by using the conjugate symmetry of the sequence so as to obtain a related peak value of a timing measurement function; and determining a beginning position of an OFDM signal by using the position of the related peak value so as to finish time synchronization. By using the invention, the adverse effect on the time synchronization, caused by a cyclic prefix and the conjugate symmetry of the sequence, is overcome, and higher timing accuracy is obtained; and the OFDM time synchronization algorithm based on the conjugate symmetric sequence, provided by the invention, can be effectively used for the time synchronization of the OFDM system under a multipath channel.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for transmitting physical layer id information
InactiveUS20110098070A1Easy to identifyEasy searchSynchronisation arrangementRadio transmissionConjugate symmetryTelecommunications
A method for transmitting IDs of cells of a specific type as physical cell ID information in addition to existing cell ID information is disclosed. For transmission of the physical cell ID information, the number of cell IDs used in transmitting the existing cell ID information on a synchronization channel is increased or a part of existing cell IDs are reserved for transmitting the additional specific-cell ID information. If the number of cell IDs is to be increased, the number of cell ID groups related to a secondary synchronization channel is increased in a manner that removes ambiguity and collision, a cell ID related to a primary synchronization channel is added, which satisfies conjugate symmetry, information is transmitted based on a transmission timing relationship between a primary synchronization code and a secondary synchronization code, or a scrambling scheme is modified. When a part of the existing cell IDs are reserved, conjugate symmetry is also considered in relation to a primary synchronization channel and ambiguity and collision are also considered in relation to a secondary synchronization channel.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method for reduced field of view MRI in an inhomogeneous field with rapid outer volume suppression
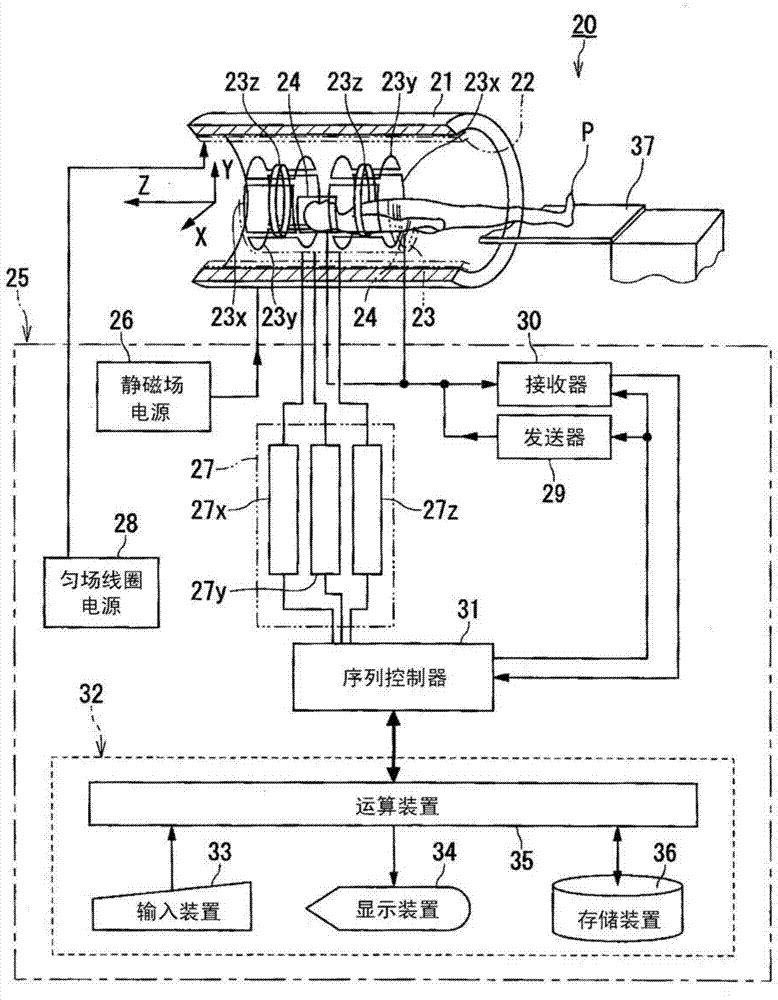
ActiveUS20130278258A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionConjugate symmetrySuperconducting Coils
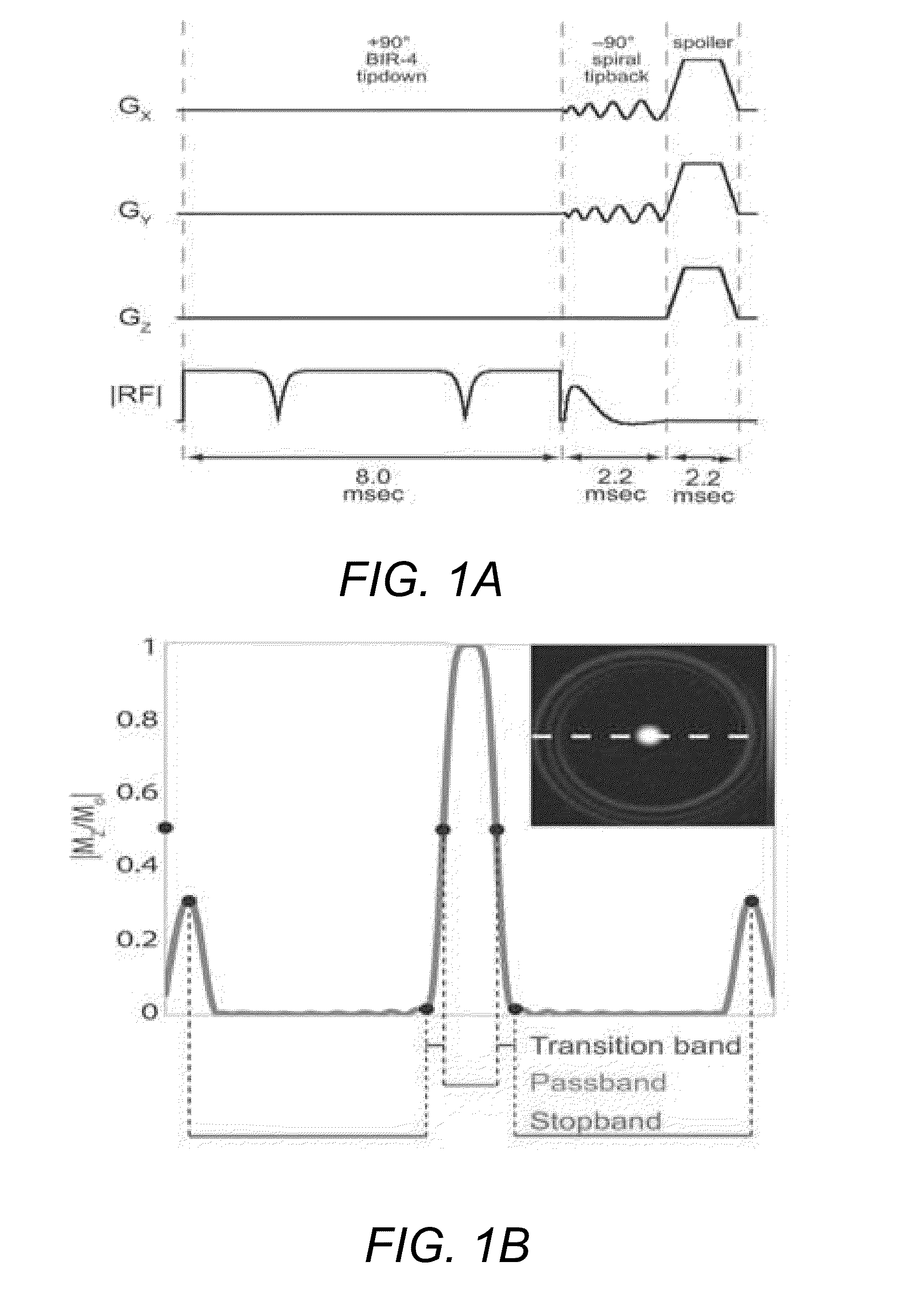
An MRI scanner may include one or more gradient waveform generators, gradient amplifiers, gradient coils, an RF waveform generator, an RF amplifier, an RF coil, a superconducting magnet, an RF detector; a digitizer, and a computer system that controls the one or more gradient waveform generators and the RF waveform generator so as to generate a magnetization saturation preparation pulse sequence that includes a tip-down pulse that is insensitive to RF field inhomogeneity followed by a tip-back pulse that employs a conjugate symmetry constraint in its energy spectrum.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Sequence generating method for efficient detection and method for transmitting and receiving signals using the same
ActiveUS20090310703A1Improve featuresEasily detect sequenceSynchronisation arrangementModulated-carrier systemsConjugate symmetryEngineering
A sequence generation method for allowing a reception end to effectively detect a sequence used for a specific channel of an OFDM communication system, and a signal transmission / reception method using the same are disclosed. During the sequence generation, an index is selected from among the index set having the conjugate symmetry property between indexes, and a specific part corresponding to the frequency “0” is omitted from a transmitted signal. In addition, a reception end can calculate a cross-correlation value between a received (Rx) signal and each sequence using only one cross-correlation calculation based on the conjugate symmetry property.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
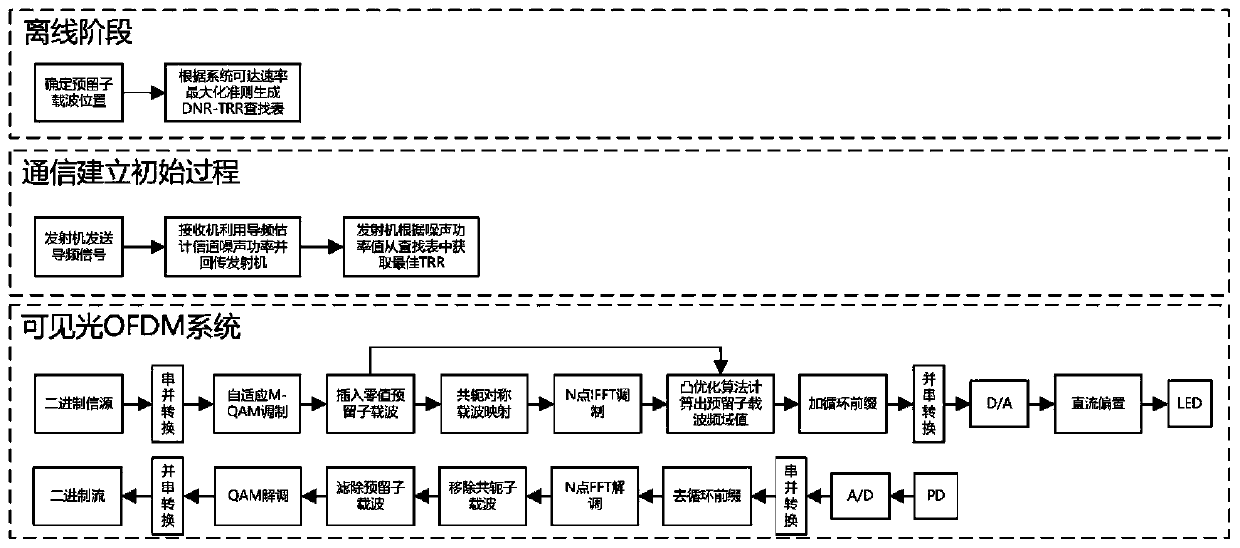
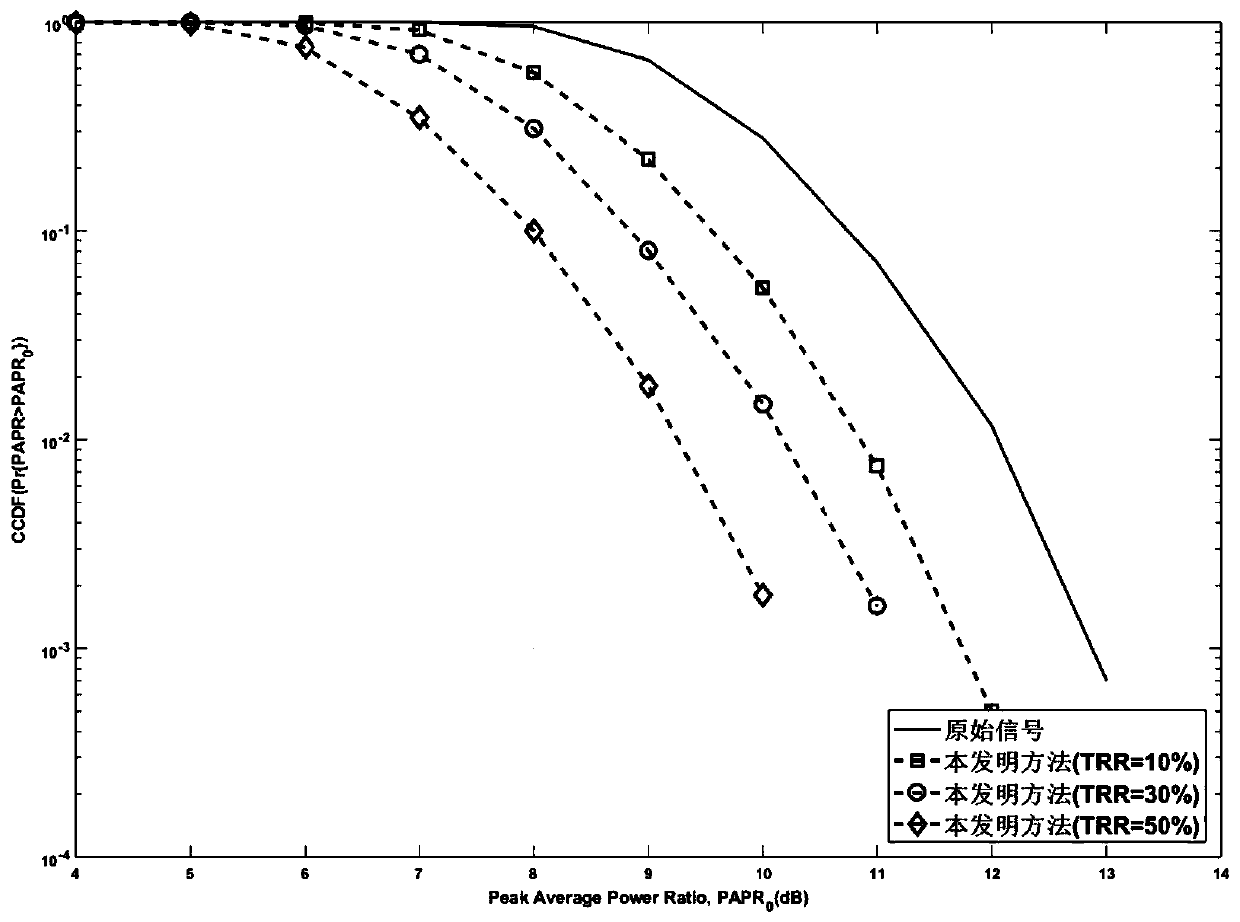
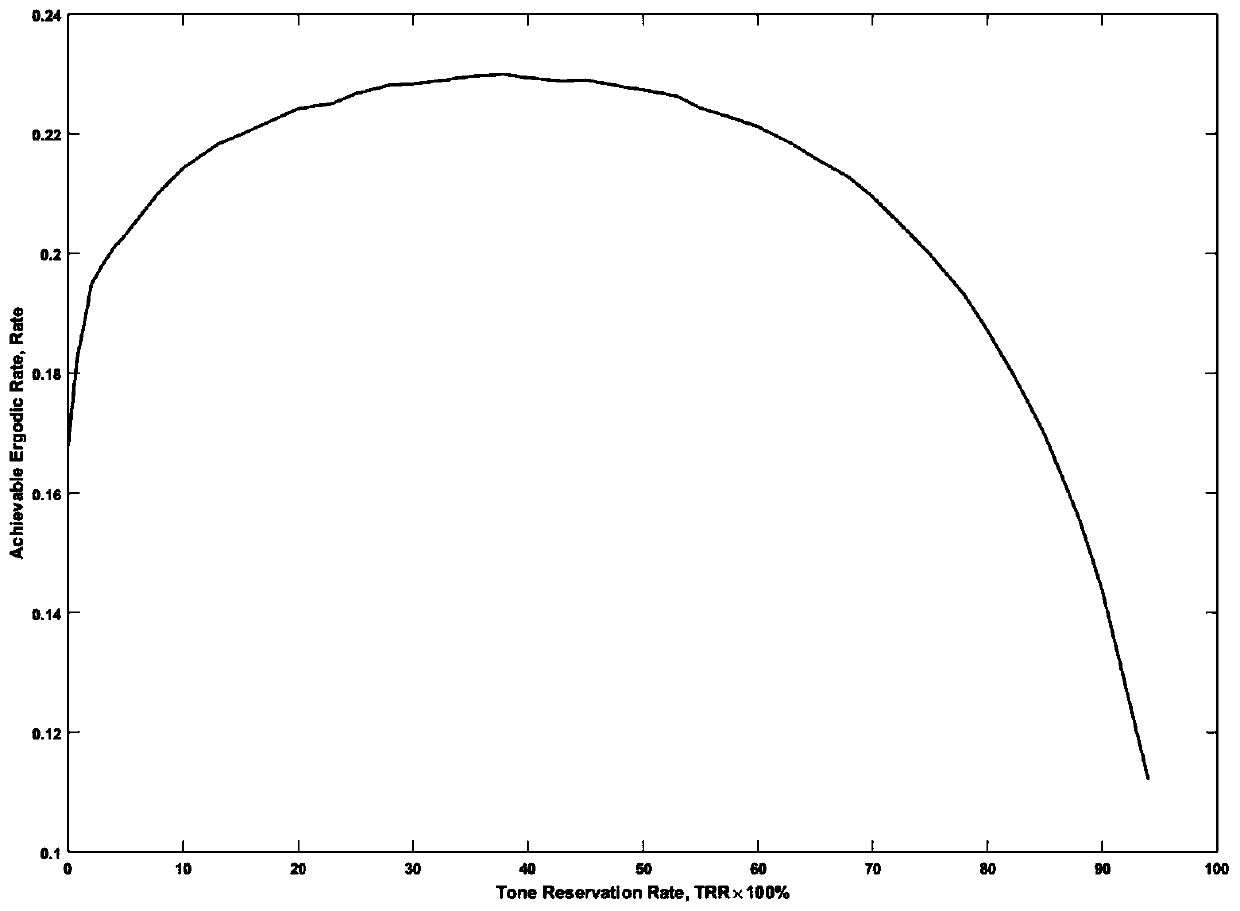
A visible light OFDM system self-adaptive low peak ratio method based on subcarrier reservation
ActiveCN109787685AImprove utilizationNo impact on system performanceClose-range type systemsMulti-frequency code systemsNonlinear distortionSignal on
The invention discloses a visible light OFDM system self-adaptive low peak ratio method based on subcarrier reservation. The method comprises the following steps: (1) at a transmitting end, allowing binary bit information flow generated by an information source to be subjected to adaptive orthogonal amplitude modulation to form a frequency domain data signal of the transmitting end; (2) determining the number of reserved subcarriers and corresponding positions in the visible light communication system; (3) performing conjugate symmetry processing on the frequency domain data signal on the OFDMsubcarrier; (4) calculating a reserved subcarrier frequency domain value; (5) performing IFFT operation on the OFDM frequency domain signal, and adding a cyclic prefix to obtain a time domain electric signal for driving the LED; (6) carrying out direct current bias or clipping on the electric signal, and then an LED is driven to emit an optical signal; (7) at a receiving end, converting the optical signal into an electric signal through a photodiode; (8) converting the obtained electric signal into a frequency domain signal; And (9) demodulating to obtain binary information flow. According to the invention, the requirement of the system on the linearity of the power amplifier and the LED lamp is reduced, and the nonlinear distortion is reduced.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
LED visible light orthogonal multicarrier communication method with low peak average power ratio
InactiveCN106453191AImprove transmission performanceNo lossDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionMulti-frequency code systemsConjugate symmetryTime domain
The invention discloses an LED visible light orthogonal multicarrier communication method with low peak average power ratio. The LED visible light orthogonal multicarrier communication method with low peak average power ratio comprises the steps of deducing and transforming a problem of optimizing a peak to average power ratio into a convex optimization problem based on a characteristic of OFDM subcarrier conjugate symmetry in visible light communication at a transmitting end; calculating a reserved subcarrier frequency threshold through a conventional convex optimization method; processing a signal in which the reserved subcarriers are inserted to obtain a time domain transmitting signal; and removing conjugate subcarriers from the signal at a receiving end, then filtering away the reserved subcarriers through a filtering module and finally demodulating to obtain a received signal. According to the LED visible light orthogonal multicarrier communication method with low peak average power ratio, a traditional subcarrier reservation method is applied to the visible light communication, the number and position of the reserved subcarriers are determined based on the channel characteristics in the visible light, deductive analysis is carried out based on the characteristic of the optical channel subcarrier conjugate symmetry, and the optimization problem of the peak average power ratio is accordingly solved. In addition, the LED visible light orthogonal multicarrier communication method with low peak average power ratio is applicable to a DCO-OFDM system and an ACO-OFDM system.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Frame synchronization detection method and device for OFDM system
InactiveCN101242259AResolve synchronizationConvenience to workData switching by path configurationSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlConjugate symmetryStart time
A frame synchronization detecting method in an orthogonal frequency division multiplex system comprises: conjugating correlation calculation to data signals in a fore and aft conjugate correlation window of data signal in a data signal sequence to obtain a correlation calculation accumulate result by accumulating; calculating an average energy of data signals in the fore and aft conjugate correlation window; taking a metric value of a data signal as a ratio between the correlation calculation accumulate result and the average energy, and in a detecting period, such as in a length of 1.5 frame, determining a frame starting time based on a data signal with a metric value maximal. The method, based on a character that predecessor using BPSK modulate conjugates symmetry, performs a frame synchronization detect, solves the synchronization problem in the orthogonal frequency division multiplex system.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES CENT FOR WIRELESS TECH
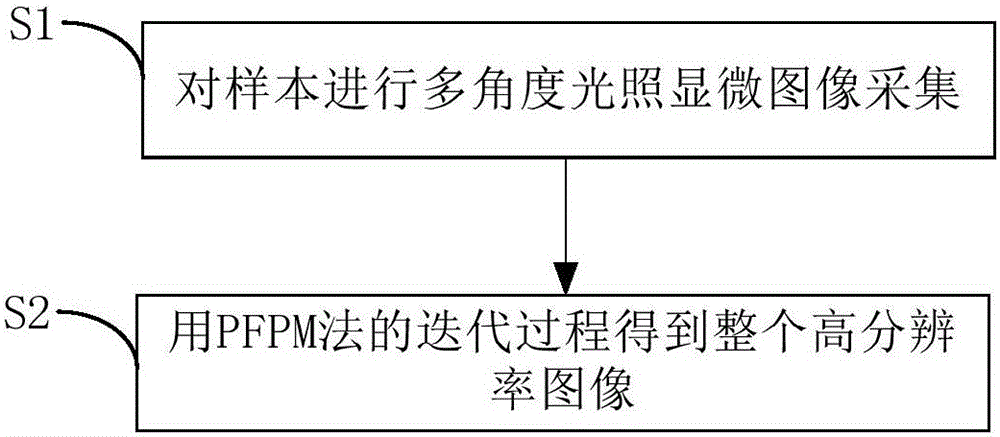
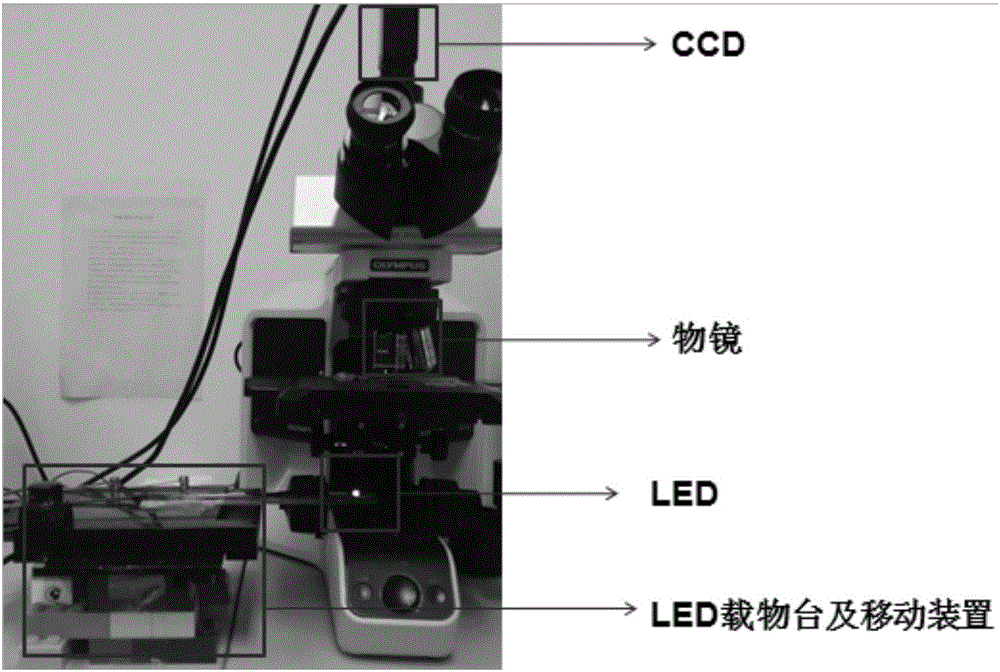
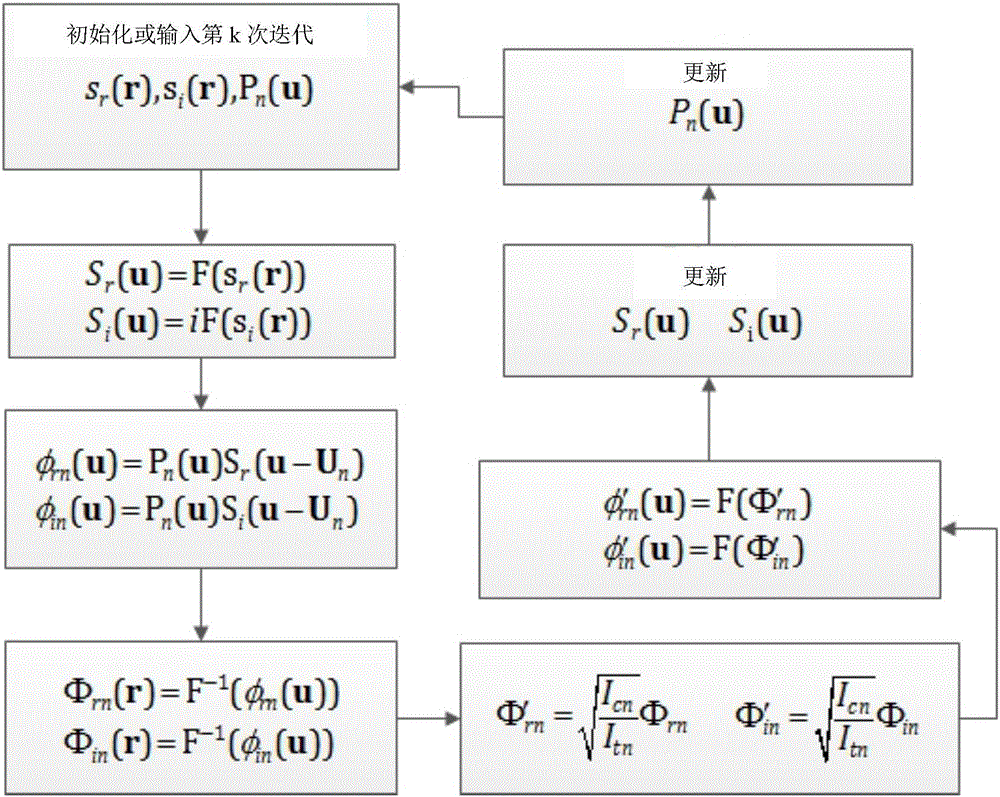
Microscopic imaging method based on partial Fourier space
The invention discloses a microscopic imaging method based on a partial Fourier space, comprising the following steps: S1, collecting microscopic images of a sample under multi-angle lighting; and S2, getting a whole high-resolution image through an iteration process of a PFPM method. Step S1 includes collecting a central image of the sample and multiple images obtained under lighting of a half light matrix in a set range. Step S2 includes the sub steps of processing the central image to get an iterative initial figure of Fourier space, iteratively updating the multiple images one by one according to the iterative initial figure to complete a round of iteration, performing a plurality of rounds of iteration to get the Fourier space of the high-resolution image, and filling in the missing data according to the Fourier space of the high-resolution image and based on the conjugate symmetry of Fourier transform to generate a whole high-resolution image. Through the microscopic imaging method based on a partial Fourier space, the iteration speed is increased. The application scope of the microscopic imaging method based on a partial Fourier space is expanded.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Low-complexity peak-to-average ratio restraining method for optical communication DCO-OFDM (direct current-biased optical-orthogonal frequency division multiplexing) system
InactiveCN104753848ALower peak-to-average ratioReduce correlationMultiplex system selection arrangementsFibre transmissionConjugate symmetryFast Fourier transform
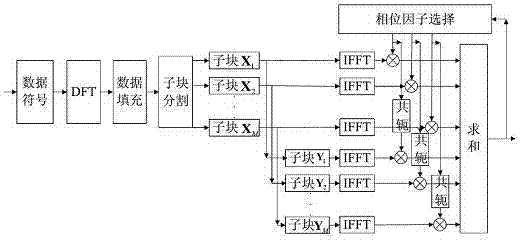
The invention discloses a low-complexity peak-to-average ratio restraining method for an optical communication DCO-OFDM (direct current-biased optical-orthogonal frequency division multiplexing) system. The low-complexity peak-to-average ratio restraining method comprises the following steps of firstly, performing precoding DFT (discrete Fourier transform) on inputted digital modulation signs so as to reduce correlation between the signs; secondly, performing subblock division and conjugate symmetry on a precoded data sequence; and finally, selecting a suboptimal phase twiddle factor for each subblock so as to reduce a peak-to-average ratio. Because IFFT (inverse fast Fourier transform) and suboptimal iterative loop phase factor selection are carried out sequentially, the implementing complexity of the system can be reduced while the peak-to-average ratio is restrained.
Owner:LINYI UNIVERSITY
Method for magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20150279065A1Minimize cost functionImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionConjugate symmetryComputer science
A method is presented for accelerating magnetic resonance imaging. In 3D MRI, the k-space in the phase encoding plane is divided into two symmetric parts and three asymmetric parts. Different sampling densities are applied in different parts. Images are reconstructed by iteratively minimizing a cost function when random sampling is applied in each part. A phase constraint term is added into the cost function to improve the quality of the reconstruction by exploiting the conjugate symmetry of k-space.
Owner:ALBERT LUDWIGS UNIV FREIBURG
Method for generating OFDM synchronization training sequence and OFDM synchronization method
InactiveCN104270333AHigh synchronization accuracyEnhance the ability to resist multipath interferenceMulti-frequency code systemsConjugate symmetryComputer science
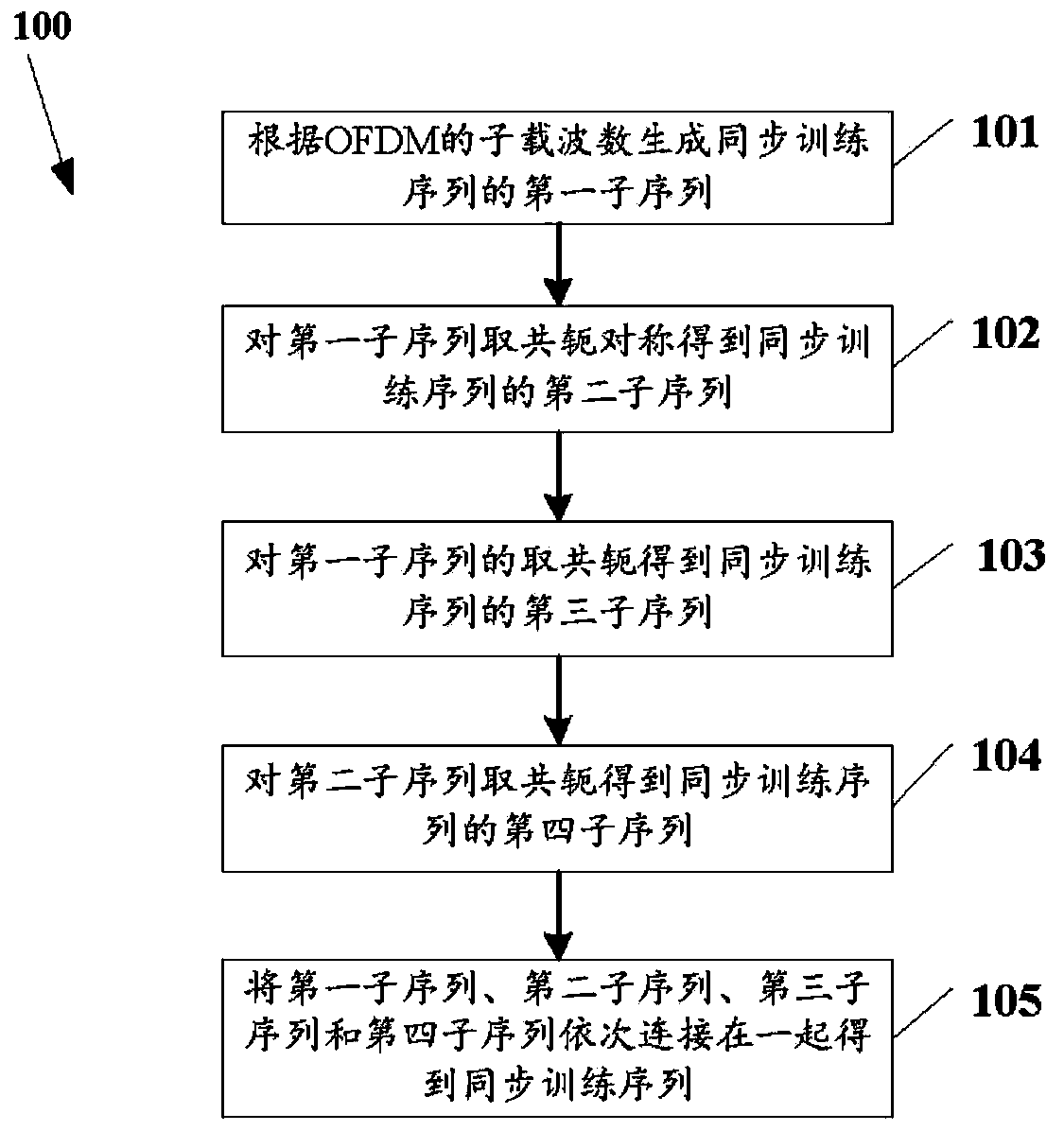
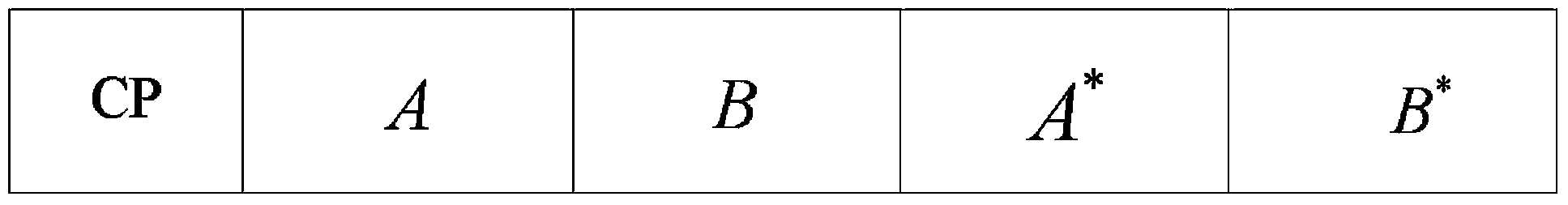
The invention relates to a method for generating an OFDM synchronization training sequence and an OFDM synchronization method. The method for generating the OFDM synchronization training sequence includes the steps that a first subsequence of the synchronization training sequence is generated according to the number of OFDM subcarriers; conjugate symmetry is carried out on the first subsequence to obtain a second subsequence of the synchronization training sequence; conjugation is carried out on the first subsequence to obtain a third subsequence of the synchronization training sequence; conjugation is carried out on the second subsequence to obtain a fourth subsequence of the synchronization training sequence; the first subsequence, the second subsequence, the third subsequence and the fourth subsequence are sequentially connected to obtain the synchronization training sequence.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for searching physical cell identifier, computer readable storage medium and small base station
ActiveCN110519196AReduce the probability of error detectionReduce error rateSynchronisation arrangementMulti-frequency code systemsCurrent cellTime domain
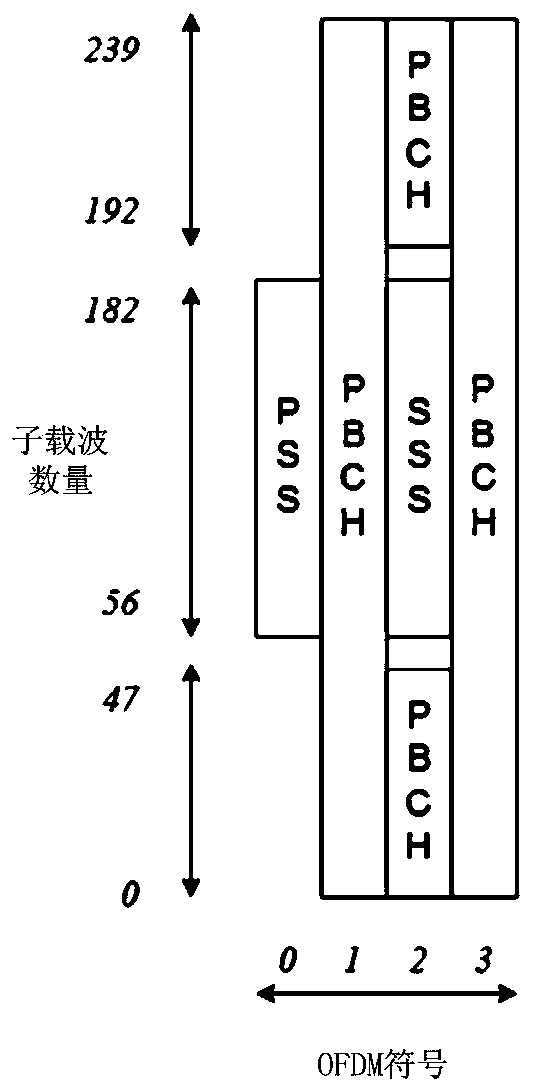
The invention is applicable to the field of communication, and provides a method for searching a physical cell identifier, a computer readable storage medium and a small base station. The method comprises the following steps: determining a strongest PSS signal position by adopting a sliding autocorrelation method by adopting a PSS sequence time domain mirror image conjugate symmetry characteristic, and finally determining a strongest SSB beam position of a current cell according to the strongest PSS signal position; and adopting different PSS sequences for cyclic shift in a frequency domain. According to the invention, the error probability of searching the strongest SSB wave beam when the carrier frequency offset exists in the received signal is reduced, and the operand caused by directlyadopting three PSS local sequences and receiving wireless frame sliding correlation calculation in the time domain is reduced.
Owner:深圳磊诺科技有限公司
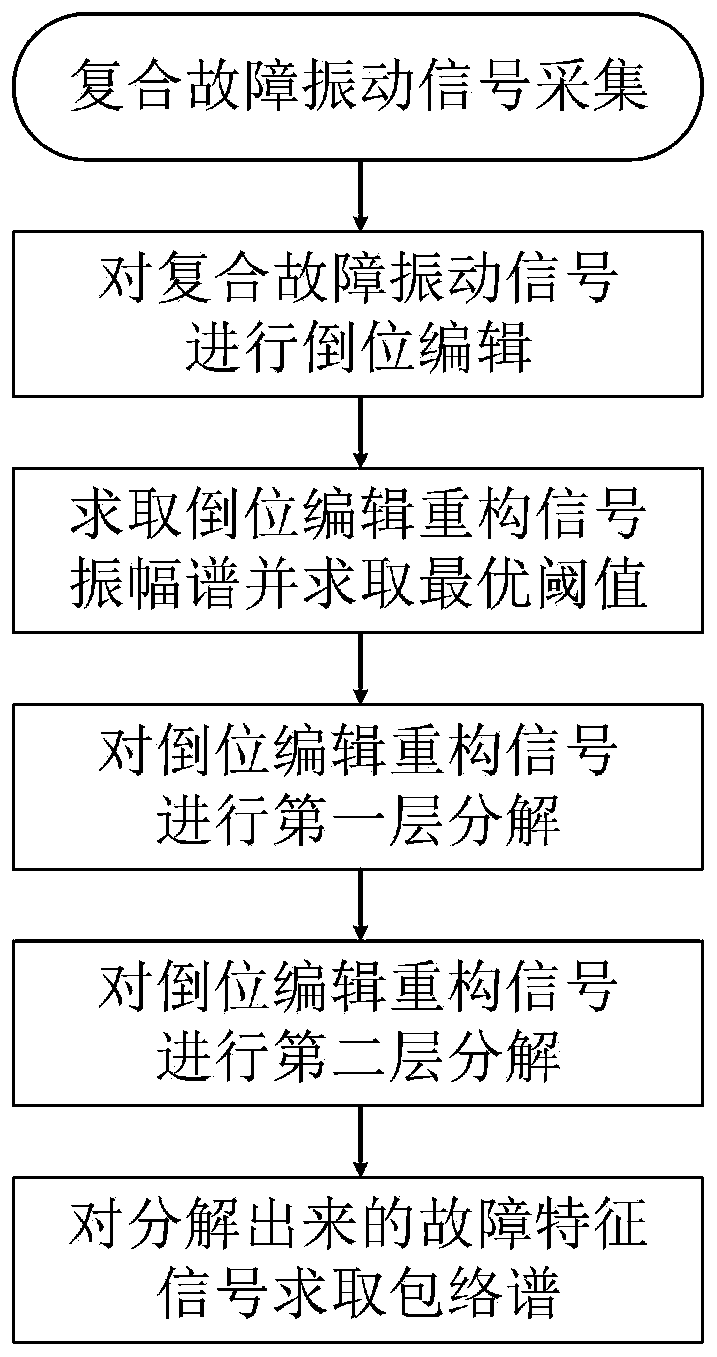
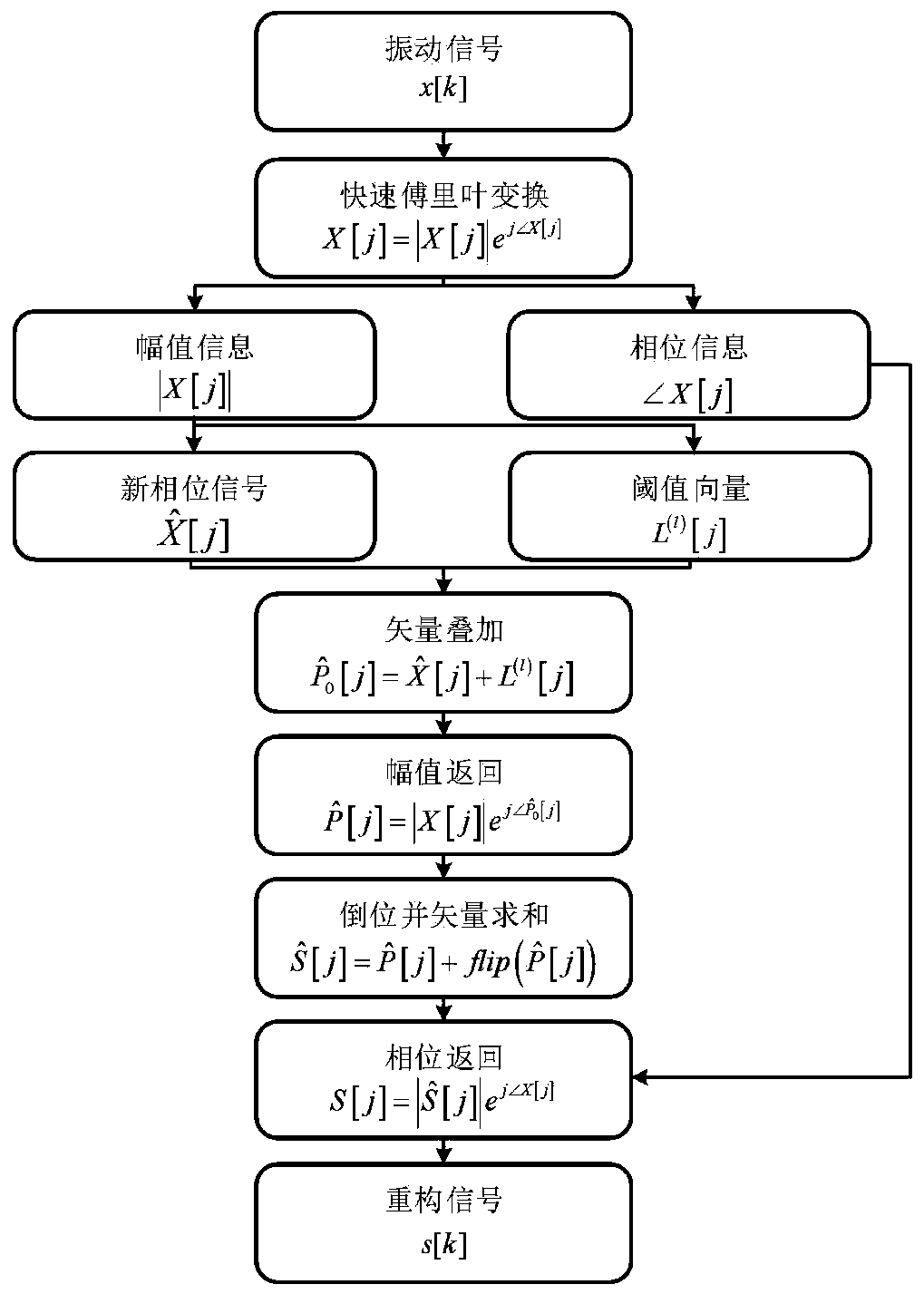
Gear box composite fault diagnosis method based on reverse editing
ActiveCN110806315APreserve integrityAchieve preliminary divisionGeometric CADMachine part testingConjugate symmetryFeature extraction
The invention discloses a gear box composite fault diagnosis method based on reverse editing. The method comprises the steps of: performing initial phase identification, editing, inversion and vectorsuperposition on an original vibration signal according to energy differences of a gear fault signal, a bearing fault signal and noise and conjugate symmetry of Fourier transform, so that effective noise reduction of the signal and division of different energy components in the signal are achieved; applying an amplitude level decomposition method based on the maximum between-cluster variance to automatically decompose energy difference features in the signal to achieve effective separation of composite faults; and performing Hilbert envelope demodulation analysis on the separated fault signalsagain, and finally achieving fault feature extraction and diagnosis. Through simulation analysis of the composite fault signal, effectiveness of the method is verified. Experimental data analysis results also show that the method can effectively separate and diagnose the bearing and gear composite fault in the gear box.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Wave beam-doppler unitary ESPRIT multi-target angle estimation method
InactiveCN107783078AReduce operational complexityImprove estimation accuracyDirection findersConjugate symmetryTime domain
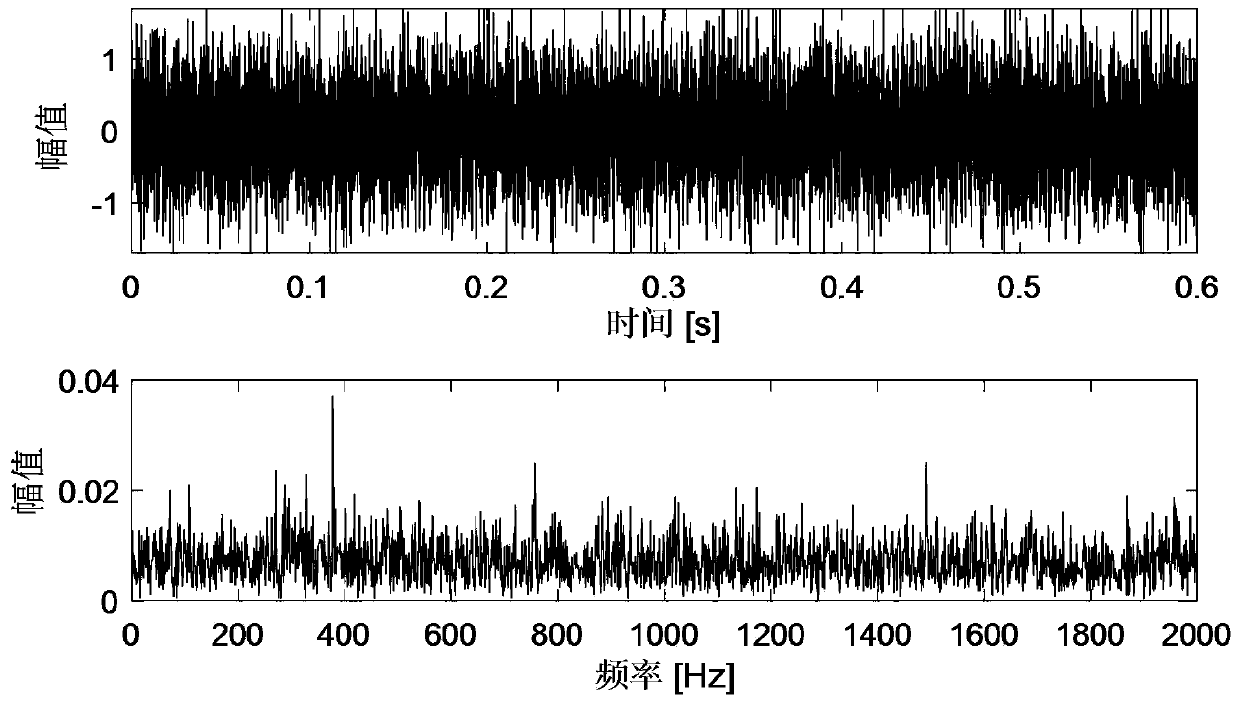
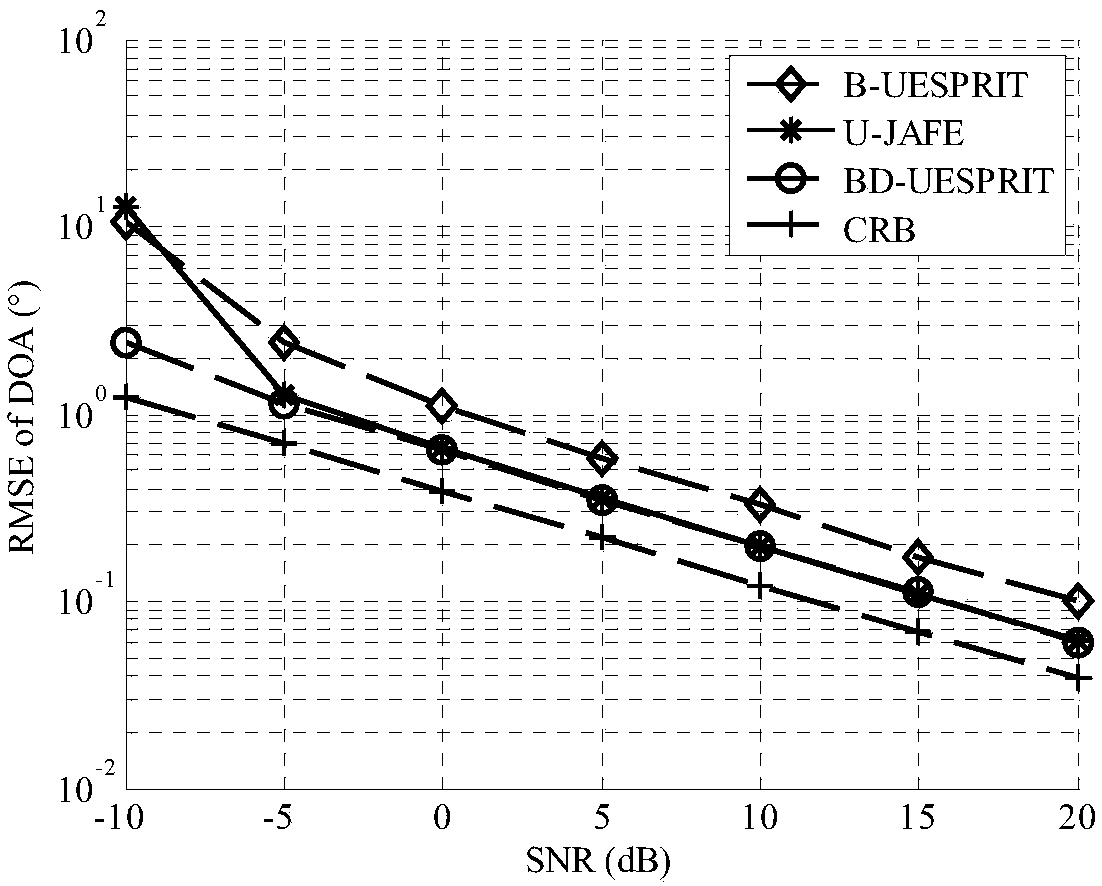
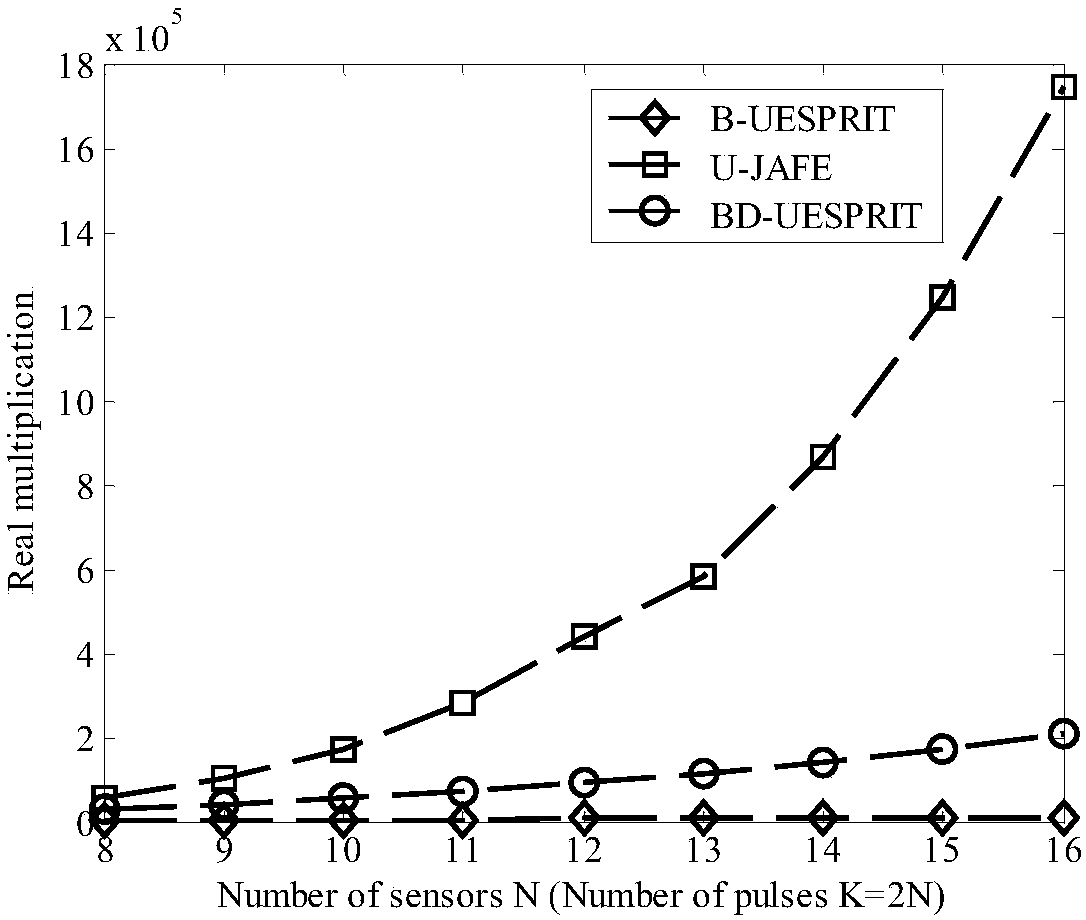
The invention relates to a wave beam-doppler unitary ESPRIT multi-target angle estimation method, and mainly solves the multi-target direction of arrival (DOA) estimation problem. One specific embodiment of the method comprises the following steps: smoothing the time domain of the distance unit data to which the target is located, thus obtaining L smoothed time domain snapshot data pieces; using acenter conjugate symmetry Fourier transform matrix to transform the time domain snapshot data into the wave beam-doppler domain, and keeping a rotation unchanged structure in the same time; finally using an actual value unitary ESPRIT algorithm to estimate the target DOA. The method fully uses the signal time domain information to improve spatial domain parameter estimation performance, is high in precision, and low in computing complexity.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
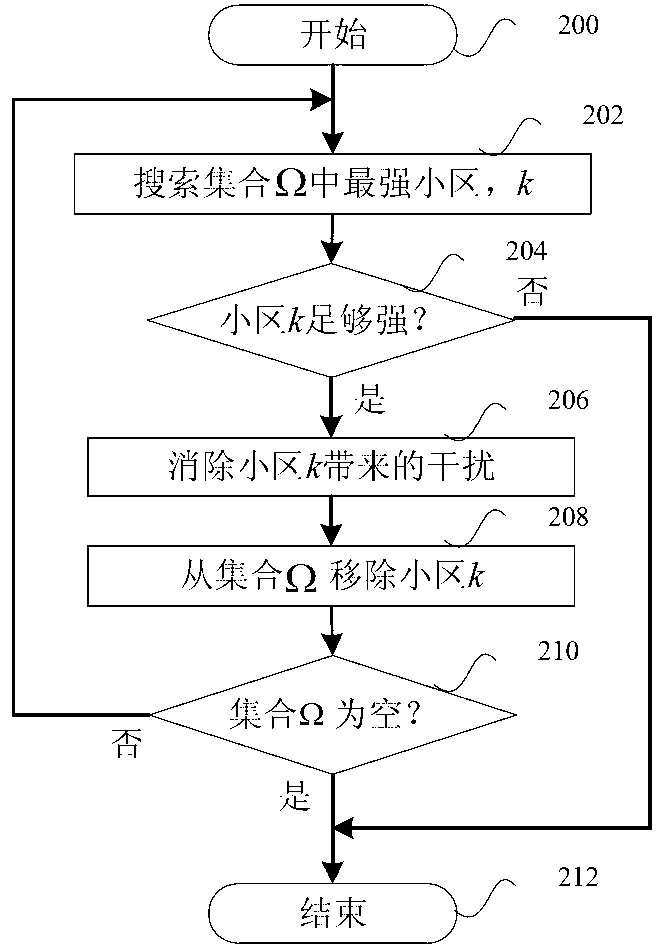
Cell detecting method and device for interference cancellation
ActiveCN102710285AEliminate distractionsReduce complexityTransmissionConjugate symmetryInterference cancelation
The embodiment of the invention discloses a cell detecting method and a cell detecting device for interference cancellation. The method comprises the following steps of: performing full system multipath scanning based on secondary synchronization signal center conjugate symmetry; picking a strongest path with highest power, and identifying the time delay position of the strongest path; comparing the power of the strongest path with a first power threshold, and if the power of the strongest path is greater than the first power threshold, cancelling interference caused by signals of the path from the received mixed signals; identifying a cell of the strongest path, and accumulating the channel measurement of the cell; repeating the interference cancellation process till the detected power of the strongest path is smaller than or equal to the first power threshold; and performing valid cell screening based on a second power threshold to acquire a valid cell set and an intensity measurement sequence thereof. According to the embodiment, a valid interference cancellation effect can be achieved, and complexity can be reduced.
Owner:HONOR DEVICE CO LTD
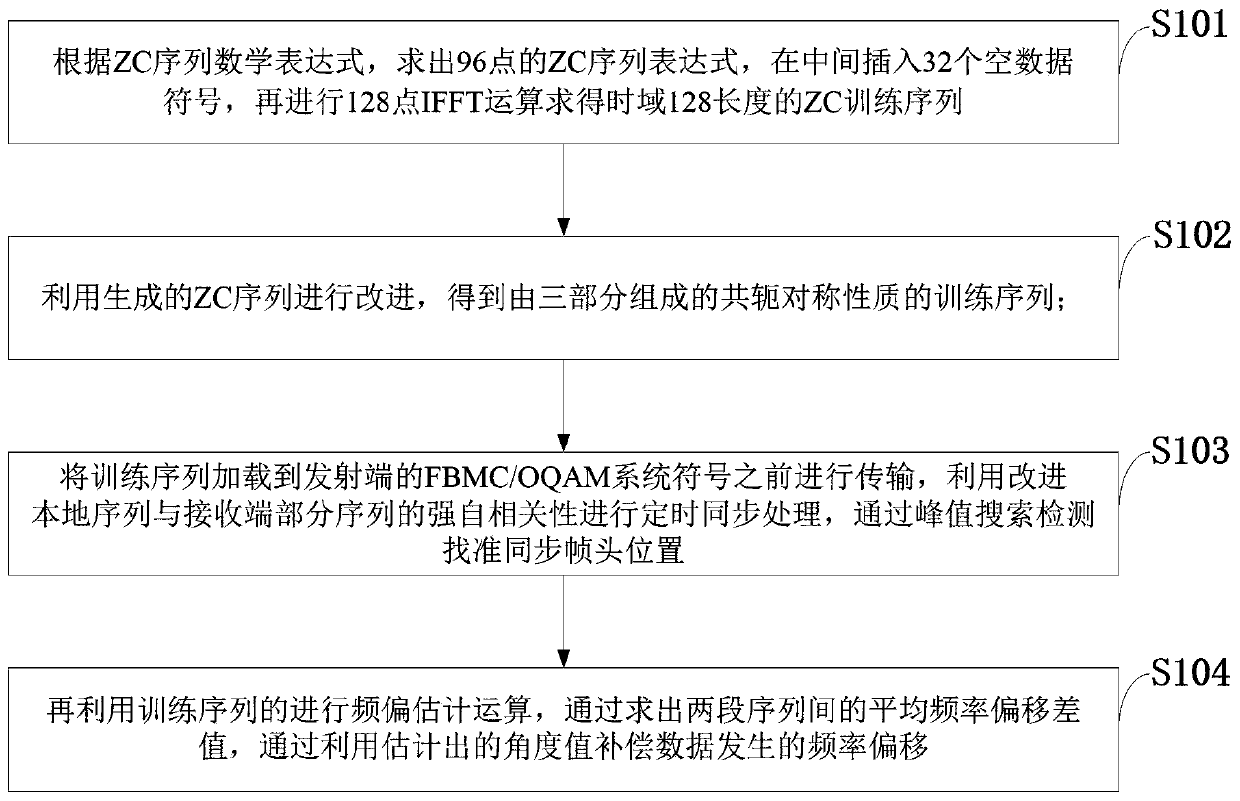
Transmission signal synchronization processing method, system, storage medium, program, and terminal
ActiveCN111585740AAccurate extractionHigh precisionTime-division multiplexSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlConjugate symmetryWireless transmission
The invention belongs to the technical field of signal processing, and discloses a sending signal synchronous processing method and system, a storage medium, a program and a terminal. The method comprises the steps: obtaining a conjugate symmetry training sequence composed of three parts through a generated ZC sequence; loading the training sequence to the front of an FBMC / OQAM system symbol of atransmitting end for transmission, performing timing synchronization processing by utilizing the strong autocorrelation of an improved local sequence and a part of sequences of a receiving end, and detecting and finding the position of a synchronization frame header through peak search; and performing frequency offset estimation operation by utilizing the training sequence, and compensating frequency offset of data by utilizing the estimated angle value through solving an average frequency offset difference value between the two sections of sequences. According to the method, the precision ofsynchronous operation is improved, the receiver can accurately extract effective signals from the received signals under the condition that the communication channel environment is severe, and phase and frequency deflection generated by data symbols, reaching the receiver through wireless transmission, of the transmitted signals is successfully compensated.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
High-resolution minimum variance ultrasonic imaging method based on frequency domain segmentation
ActiveCN110501423AReduce strong correlationMeet narrowband requirementsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSonificationArray element
The invention relates to a high-resolution minimum variance ultrasonic imaging method based on frequency domain segmentation and belongs to the acoustic imaging field. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, carrying out delay processing on a sampling signal received by an array element to obtain echo data required by ultrasonic focusing; secondly, selecting a frequency domain segmentation optimal window function according to a maximum concentration measurement criterion of an adaptive window function in STFT; converting an ultrasonic echo signal into a narrow-band sub-signal by using STFT; carrying out conjugate symmetry processing on a first half of narrow-band sub-signal to generate the other half of narrow-band signal by using conjugate symmetry; successively dividing a receiving array into sub-arrays with overlapped array elements, and carrying out forward and backward smoothing and diagonal loading processing on a frequency domain signal to obtain a sample covariancematrix; and finally, processing a frequency domain segmented minimum variance beam forming weight by using inverse fast Fourier transform to obtain a final time domain adaptive beam forming signal. By using the method, an ultrasonic imaging resolution can be remarkably improved, a contrast ratio is increased, and ultrasonic imaging quality can be integrally improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV +3
Array antenna optimization method for effectively controlling dynamic range of excitation amplitude
ActiveCN107766631AImprove Radiation Performance ParametersComputing results with high performanceDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsPerformance indexArray element
The invention discloses an array antenna optimization method for effectively controlling a dynamic range of excitation amplitude. Wave beams of different radiation requirements are realized in a relatively small excitation dynamic range; unit excitation corresponding to a directional graph meeting radiation performance requirements is obtained by using an improved iterative Fourier algorithm; units of a maximum part and a minimum part of the excitation amplitude are determined; an excitation complex value of the unit of the minimum part of the excitation amplitude is subjected to phase preservation and amplitude direct assignment processing; the obtained excitation complex value serves as a part of a final complex excitation vector of an antenna; and a complex excitation value of the unitof the residual part is searched for by utilizing an improved convex optimization algorithm to meet the radiation performance index requirements of the directional graph. The relatively small dynamicchange range of the complex excitation amplitude of the antenna can effectively simplify a feed network to reduce the feeder line cost, and the mutual coupling between the units can be well controlled; and the application range of the method is not limited to special preconditions such as excitation complex value conjugate symmetry, array element central symmetry layout, array element equal interval or the like.
Owner:JINLING INST OF TECH
Efficient transmission method of wireless light based on optimal amplitude modulation
ActiveCN104158783AEasy to implementImprove performanceFree-space transmissionMulti-frequency code systemsSignal onFiltration
The invention discloses an efficient transmission method of wireless light based on optimal amplitude modulation. The efficient transmission method is carried out according to the following steps that: a system generates a frequency domain symbol, which needs to be transmitted, on a transmitting end; a frequency domain signal generates a base band time domain transmitting signal in an actual value; optimal amplitude modulation coefficients are figured up, zoom amplitude modulation is carried out on the frequency domain signal on each sub-carrier and DC bias is added into an amplitude limiting time domain transmitting signal to drive a light emitting diode to transmit; a received optical signal is converted to an electric signal by a photoelectric diode, and a time domain receiving signal is obtained after processing, such as filtration and amplification, at a receiving end; fast Fourier transform is carried out on the time domain receiving signal, so that a frequency domain receiving signal is obtained and a conjugate symmetry part is removed; and lastly, a final receiving symbol is obtained through constellation demodulation. The efficient transmission method has the advantages of simple implementation and capabilities of reducing a peak-to-average power ratio of a wireless light communication OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) system, reducing requirements of the transmitting end on linearity of a power amplifier and an LED (Light Emitting Diode) lamp and improving an error rate of an AC signal transmitting power reducing system.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and magnetic resonance imaging method
ActiveCN103813749AGood qualityMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringWavenumberImaging data
The magnetic resonance imaging apparatus of an embodiment is provided with a data-collecting unit and an image-generating unit. From the subject, the data-collecting unit collects multiple magnetic resonance signals corresponding to a sampling region that is asymmetric in the wavenumber direction in the k-space with a data collection sequence having a first regularity and a data collection sequence having a second regularity that differs from the first regularity. The image-generating unit generates magnetic resonance image data by data-processing that comprises signal filling into the non-sampling region using k-space phase conjugate symmetry and image reconstruction processing based on the multiple magnetic resonance signals.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com