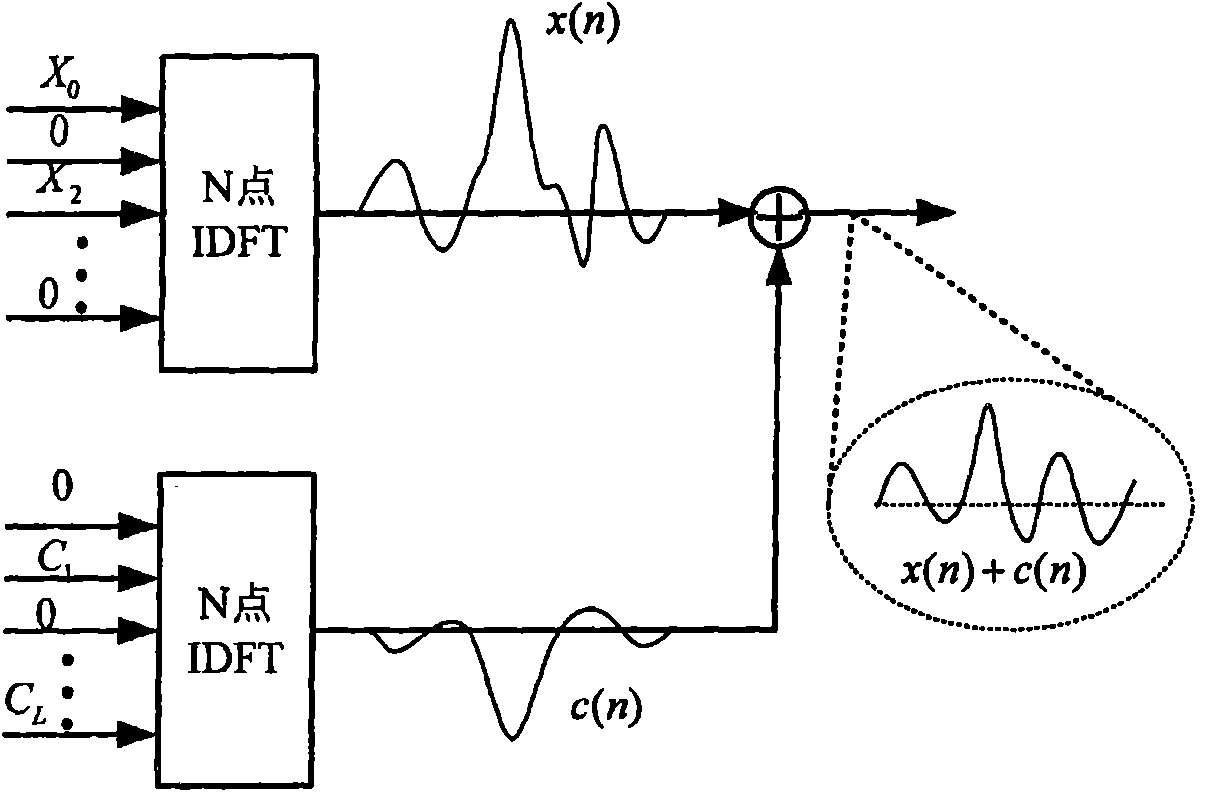
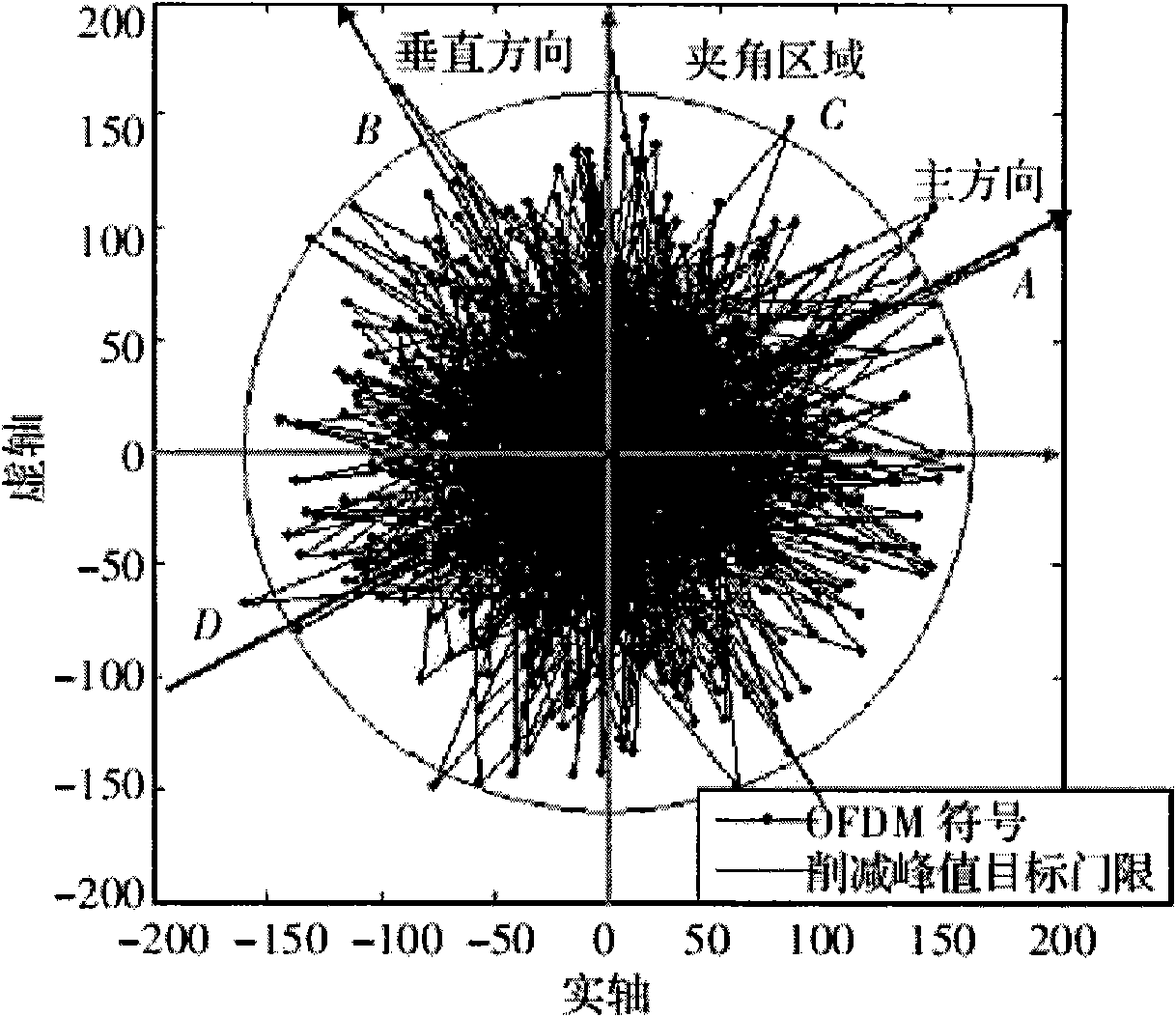
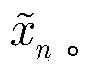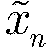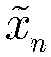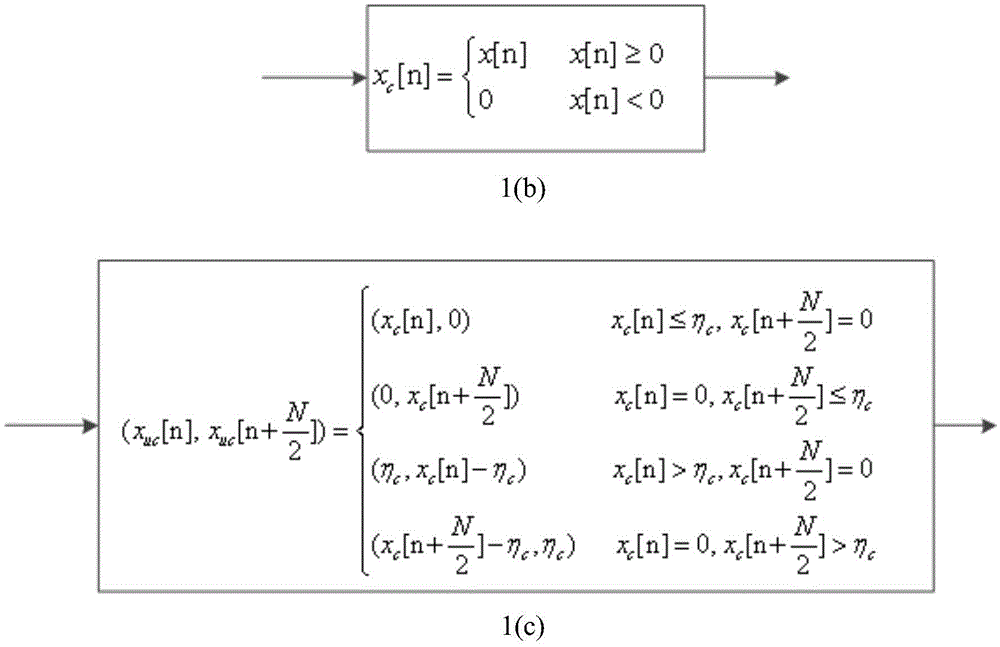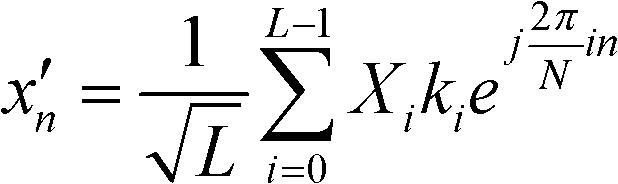Patents
Literature
250results about How to "Lower peak-to-average ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
High efficiency variable voltage supply
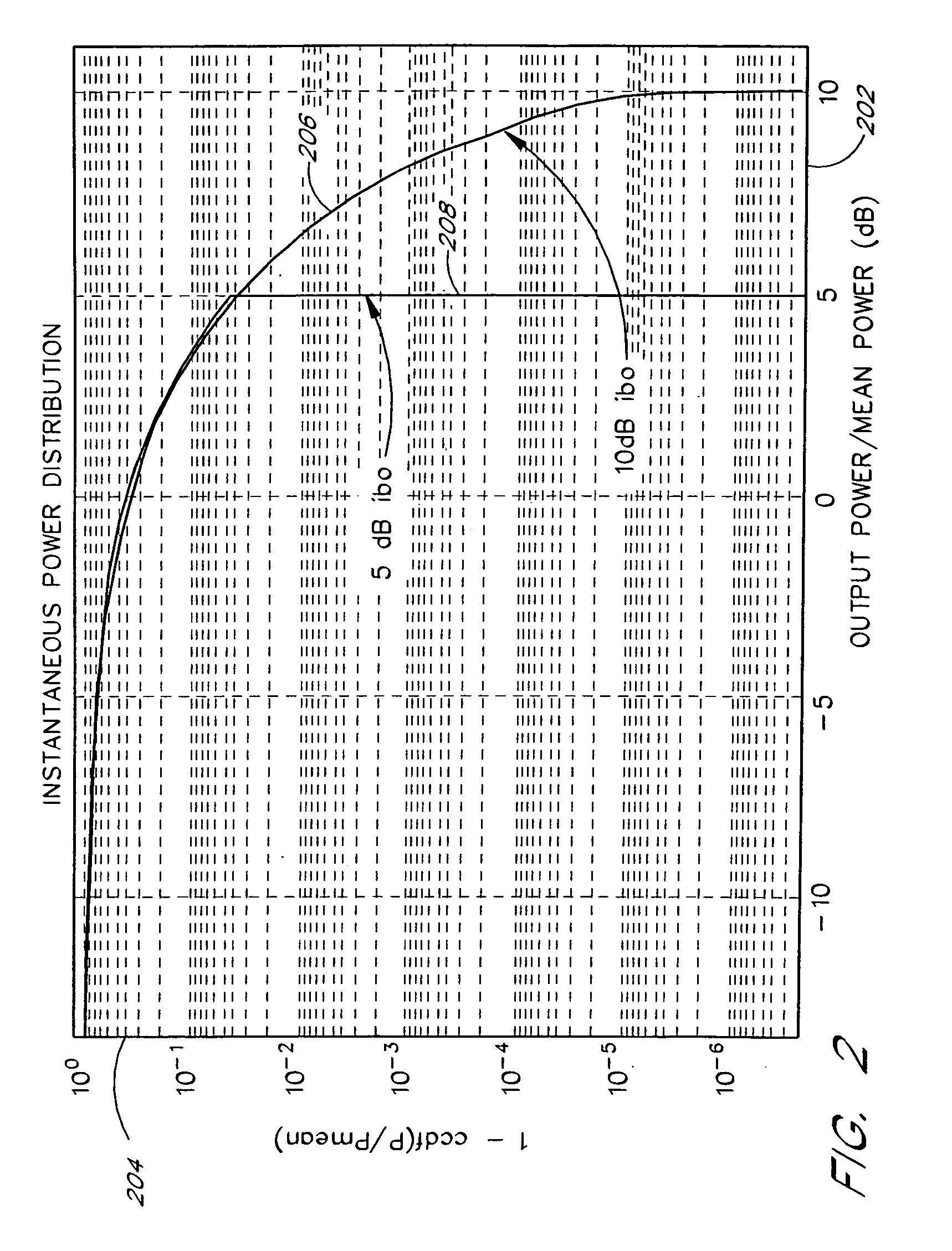
InactiveUS20070210771A1Minimising peak amplitudeMinimising slew rateHigh frequency amplifiersAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyEngineeringVariable-voltage power supply
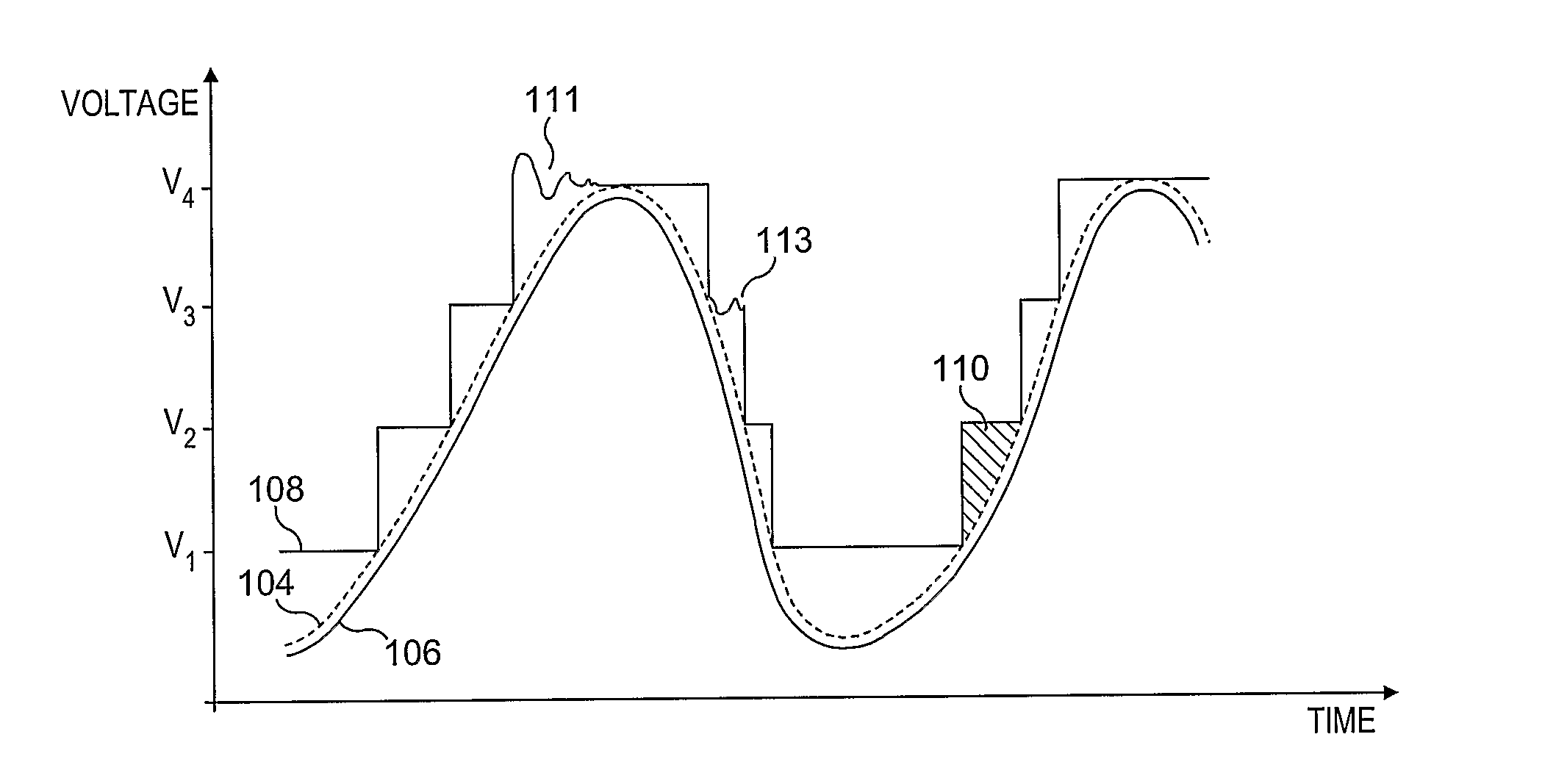
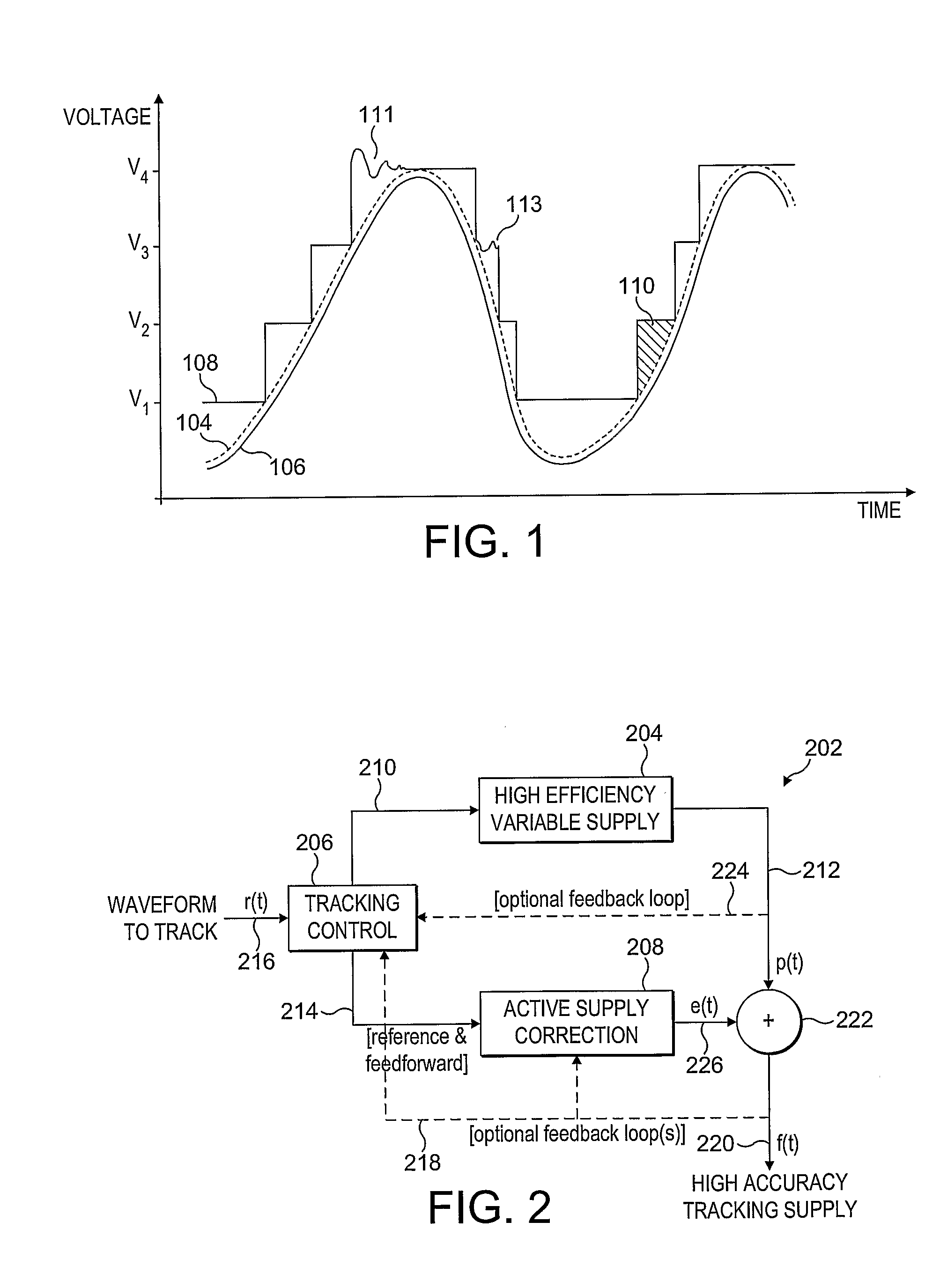
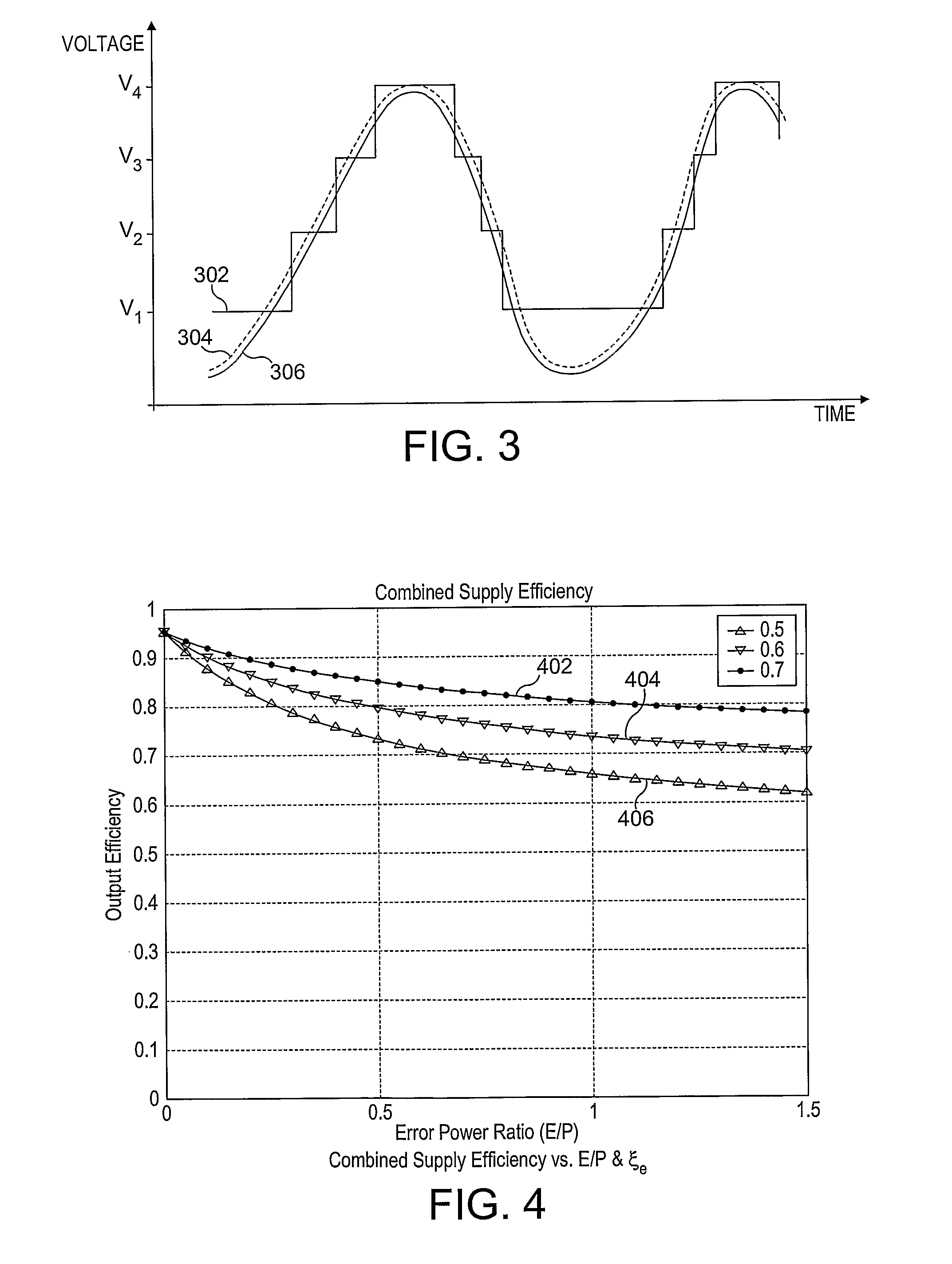
There is disclosed a power supply stage (202), comprising: generating means for generating a power supply voltage from a high efficiency variable voltage supply (204) in dependence on a reference signal; adjusting means for receiving the generated power supply voltage (220), and adapted to provide an adjusted selected power supply voltage tracking the reference signal (216) in dependence thereon.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
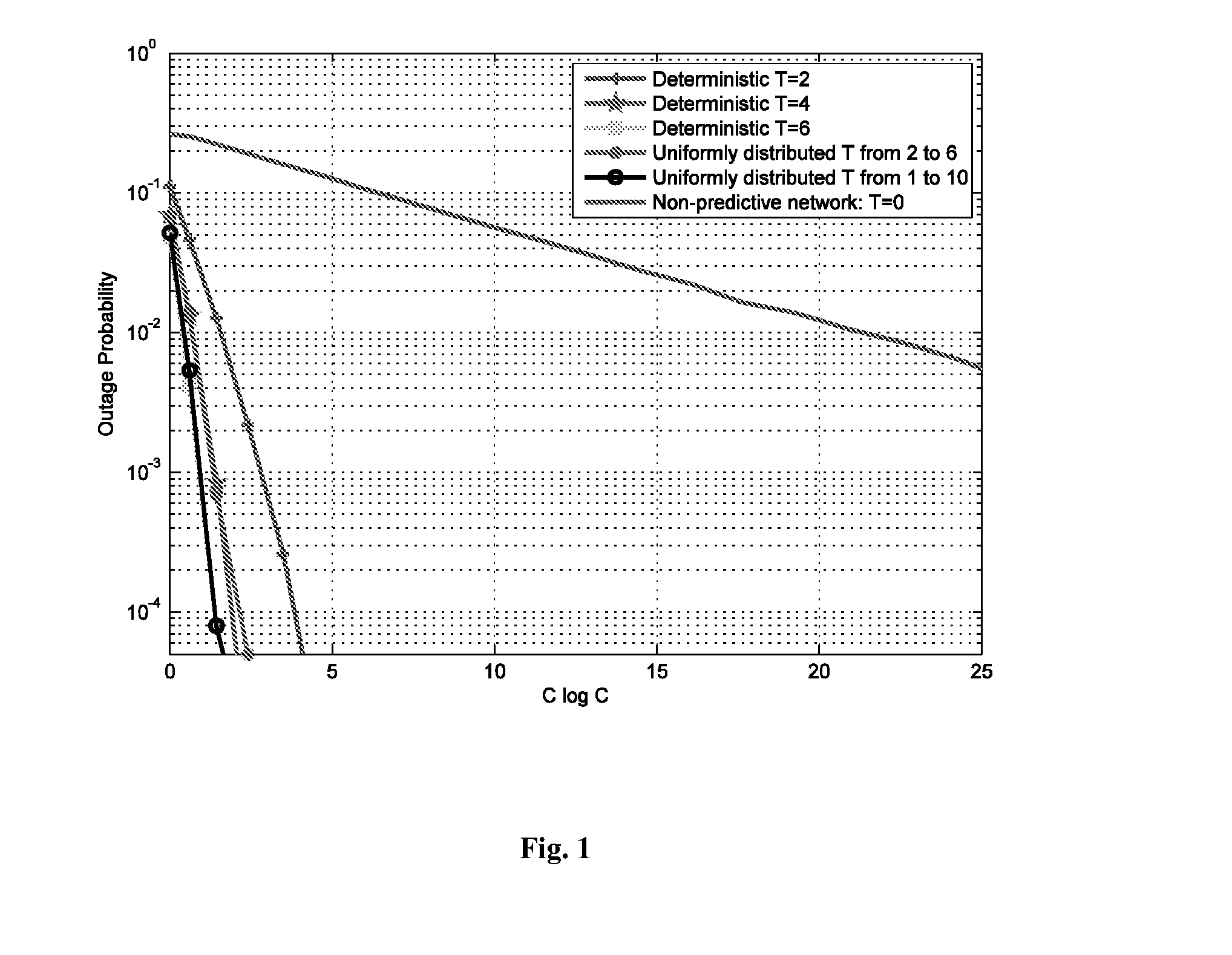
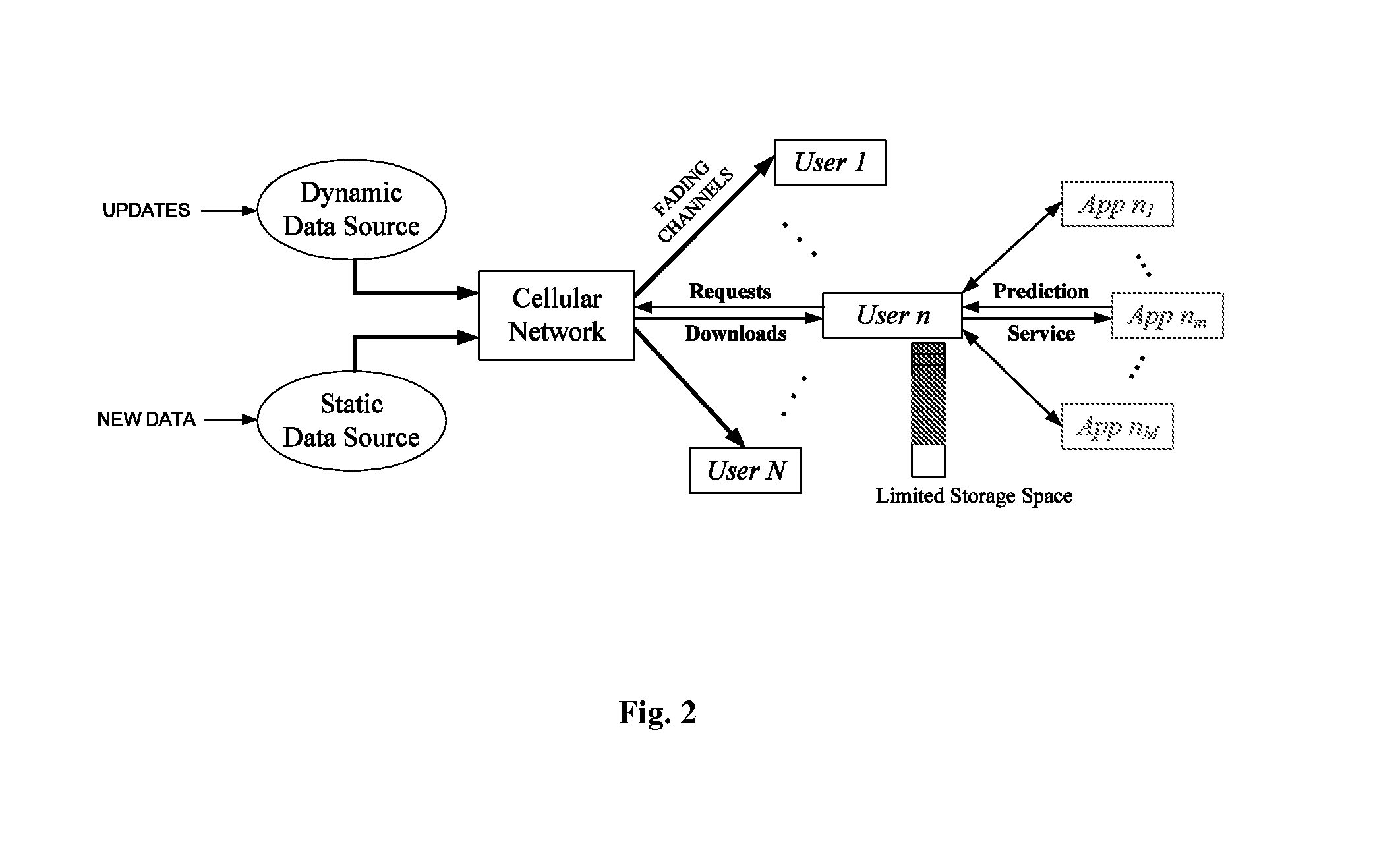
Predictive network system and method
ActiveUS20140113600A1Maximize Spectral EfficiencyReduction in peak to average demand ratioNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching networksCellular architectureQuality of service
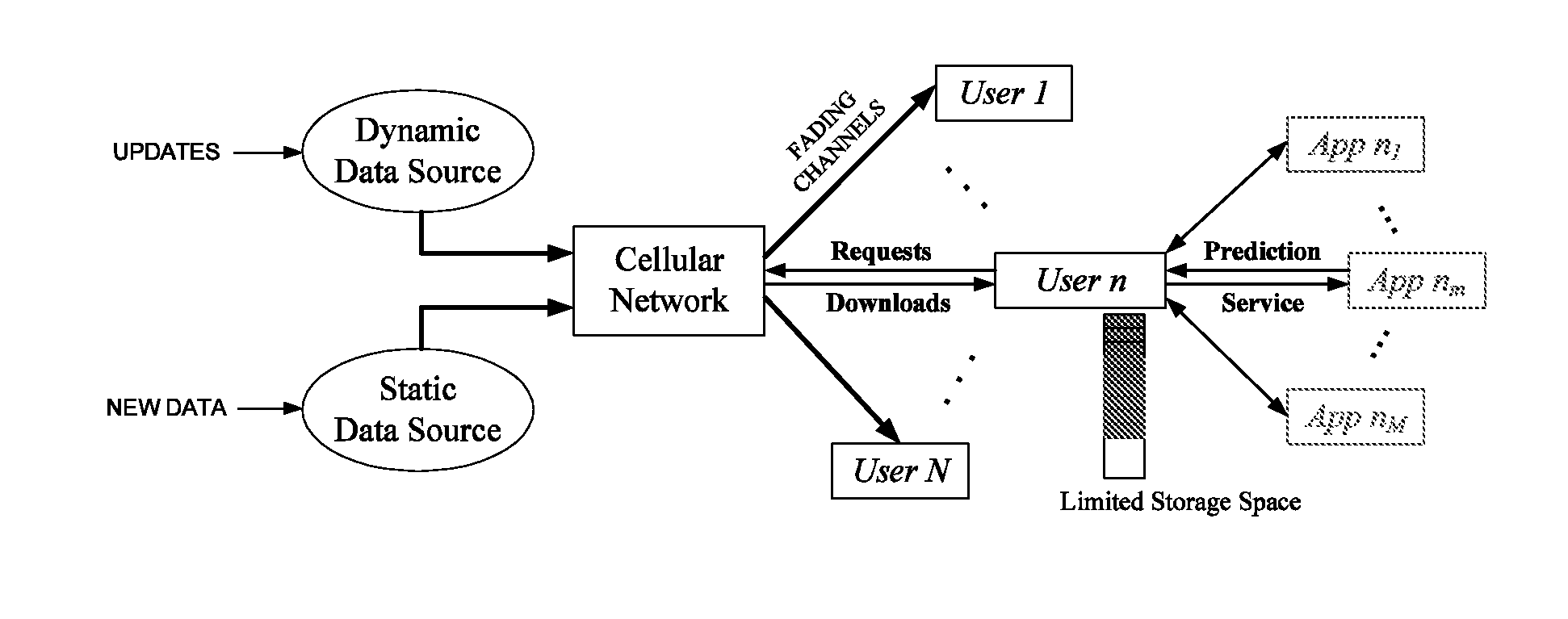
A proactive networking system and method is disclosed. The network anticipates the user demands in advance and utilizes this predictive ability to reduce the peak to average ratio of the wireless traffic and yield significant savings in the required resources to guarantee certain Quality of Service (QoS) metrics. The system and method focuses on the existing cellular architecture and involves the design and analysis of learning algorithms, predictive resource allocation strategies, and incentive techniques to maximize the efficiency of proactive cellular networks. The system and method further involve proactive peer-to-peer (P2P) overlaying, which leverages the spatial and social structure of the network. Machine learning techniques are applied to find the optimal tradeoff between predictions that result in content being retrieved that the user ultimately never requests, and requests that are not anticipated in a timely manner.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
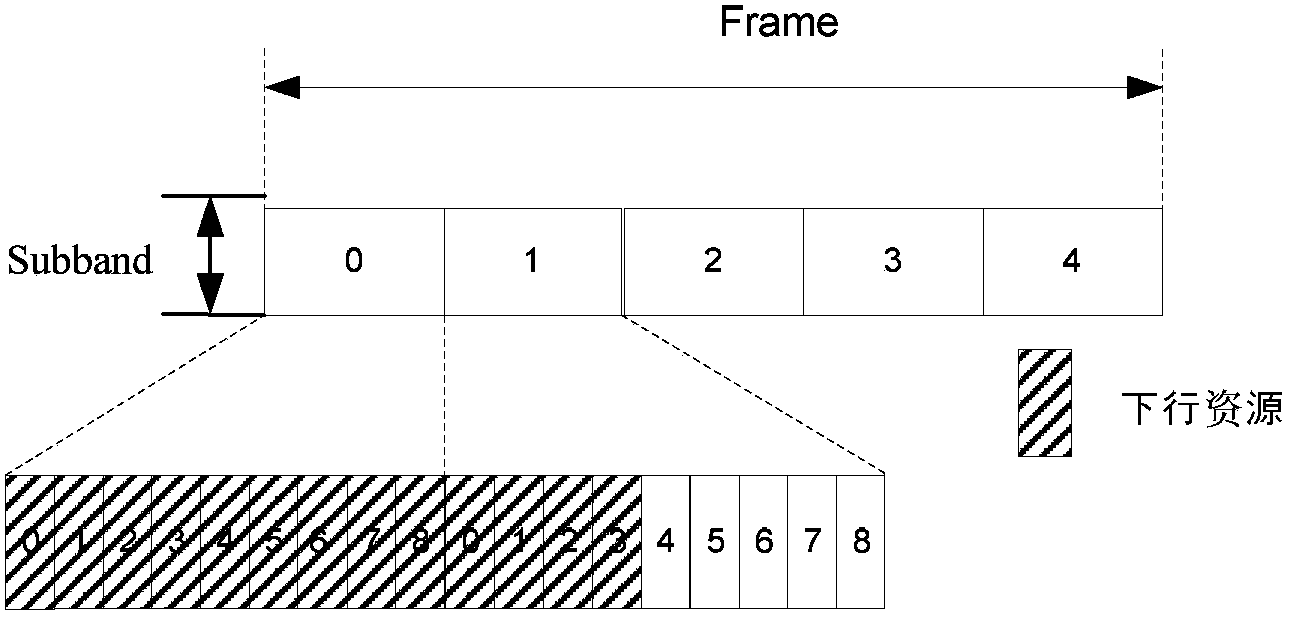
Method for sending synchronization signals
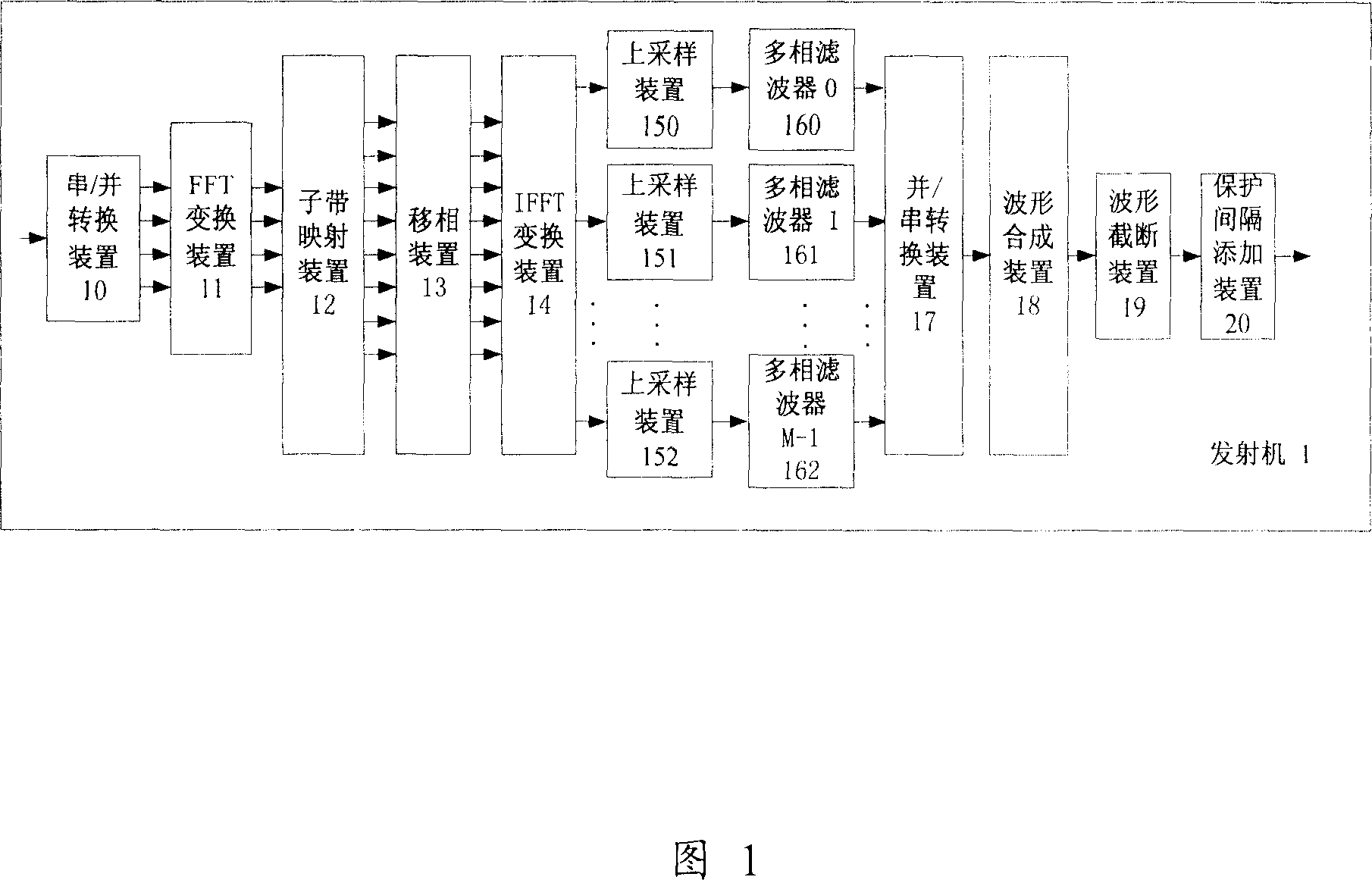
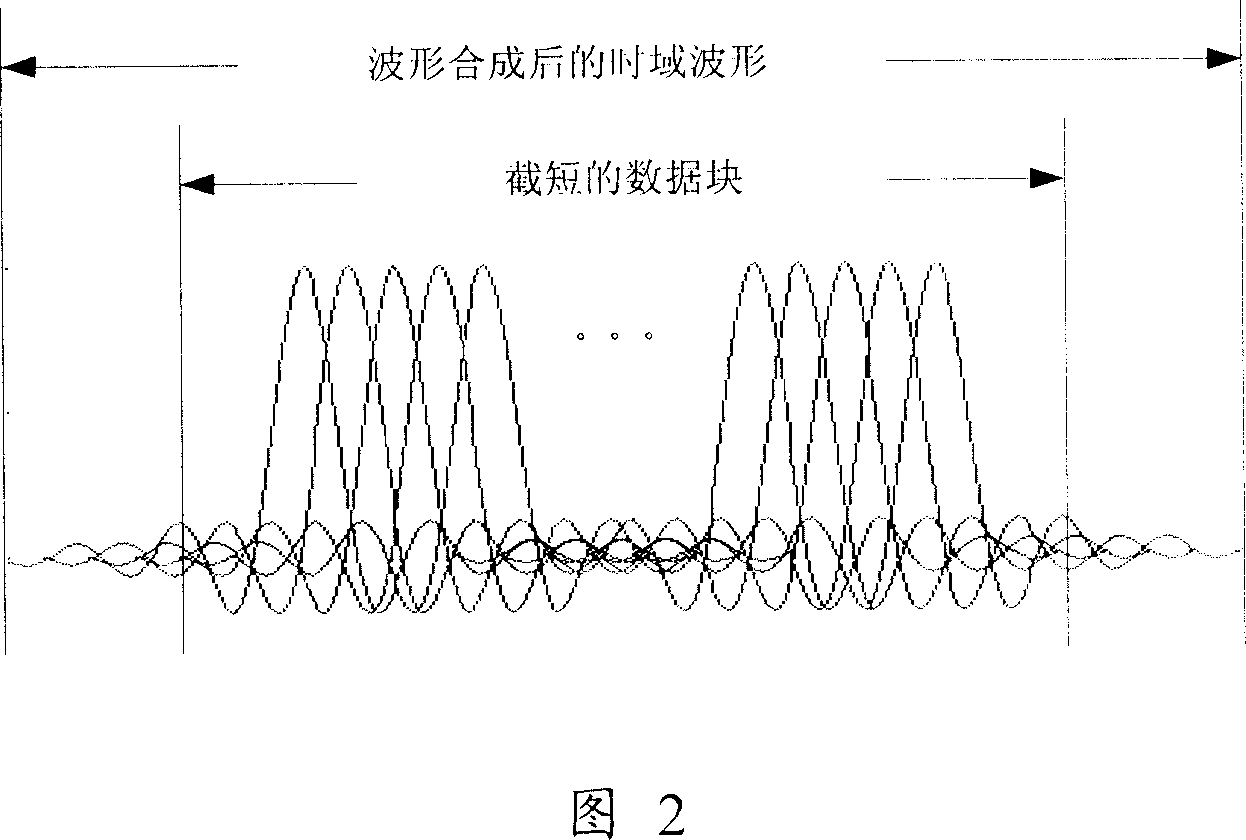
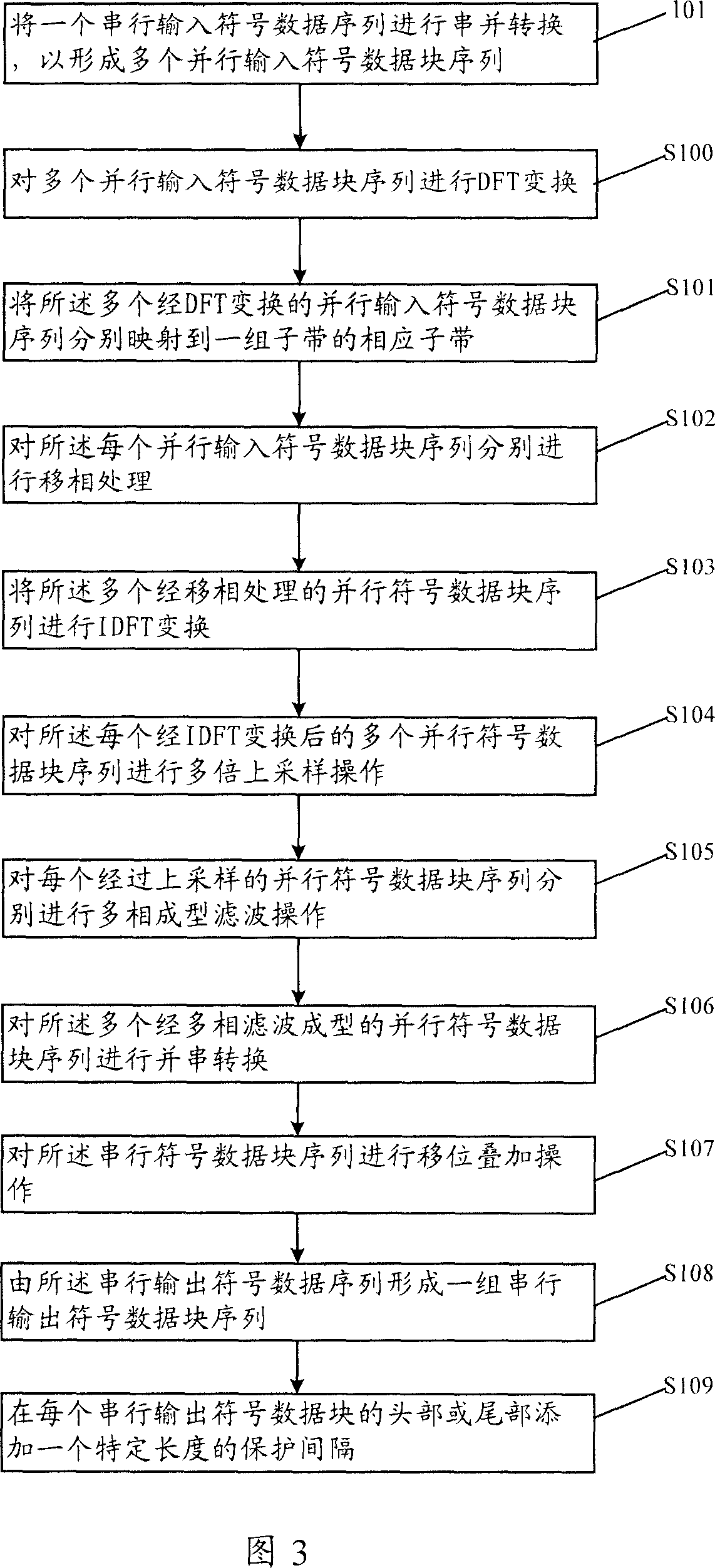
InactiveCN103428143ALower peak-to-average ratioMulti-frequency code systemsTransmission path multiple useTime domainResource location
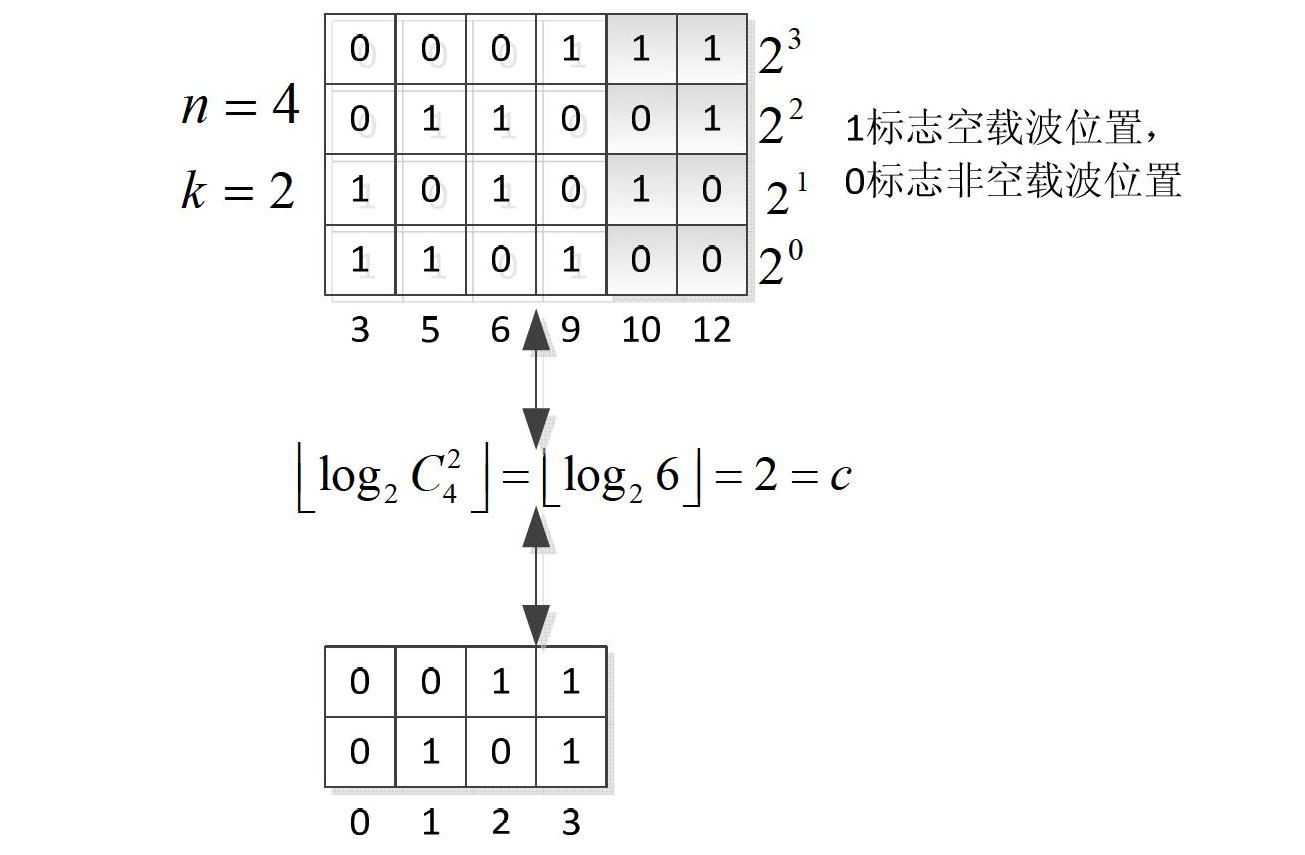
The invention provides a method for sending synchronization signals. The method includes the steps that the synchronization signals of each sub-band are generated corresponding to each sub-band according to the ID of a cell and the serial number of a corresponding absolute sub-band of each sub-band, wherein the synchronization signals generated by the different sub-bands are mutually different; all points of the synchronization signals of each sub-band are mapped to the time-frequency resource positions of the synchronization signals of each sub-band where the pointes are located for transmitting, wherein time-frequency resources of the synchronization signals comprise all downlink resources on the whole sub-bands in a synchronization frame. By the application of the method for sending the synchronization signals, the peak-to-average ratio of time-domain signals can be reduced.
Owner:POTEVIO INFORMATION TECH
Broadband power line carrier communication physical layer signal processing method based on OFDM
ActiveCN106603457ALower peak-to-average ratioImprove frequency band utilizationMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsPower distribution line transmissionIntersymbol interferenceSubcarrier
The invention discloses a broadband power line carrier communication physical layer emission signal processing method based on OFDM. The method includes: receiving data from a link layer, and dividing the data into frame control data and load data; performing channel coding on the frame control data and the load data, and modulating the frame control data and the load data after channel coding to subcarriers; performing inverse Fourier transform on the modulated frame control data and the load data, performing power control, and generating a time domain frame control symbol and a time domain load symbol; and adding a cyclic prefix to the time domain frame control symbol and the time domain load symbol, adding a time domain leading symbol, performing windowing processing, and generating physical layer emission signals. According to the method, the utilization rate of the frequency band is high, the transmission rate is high, and the intersymbol interference resistance and the channel fading resistance are excellent.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Multi-carrier transmission method and device based on selected carrier modulation
InactiveCN102638437AReduce input powerLower peak-to-average ratioMulti-frequency code systemsEnd-groupCarrier signal
The invention relates to a multi-carrier transmission method and a multi-carrier transmission device based on selected carrier modulation. The multi-carrier transmission method comprises the steps that a transmitting end groups sub-carriers in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) system and correspondingly groups bit data to be transmitted, after grouping, one part of bit data in each group of data selects n-k sub-carriers from n sub-carriers of each group as virtual carriers, the other part of bit data is modulated into k symbols which are mapped to the remaining k sub-carriers, and virtual carriers and the carriers which carry the data form OFDM symbols and then are transmitted; and a receiving end groups balanced receiving frequency domain symbols in a way as the same as the grouping way of the transmitting end, virtual carrier position identification is conducted in each group of symbols, virtual carrier positions are mapped to be bits to obtain the first part of data , virtual carrier position symbols in each group are removed and the remaining k symbols are demodulated to obtain the second part of data. The multi-carrier transmission method and the multi-carrier transmission device based on the selected carrier modulation solve the problem that the energy consumption of the traditional OFDM system is high in order to obtain more information under the situation that the bandwidth and the noise power of the system are determined.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method and device for reducing peak-to-average power ratio in filter-bank multi-carrier system
InactiveCN102904854ALower peak-to-average ratioReduce nonlinear distortionLine-faulsts/interference reductionMulti-frequency code systemsNonlinear distortionCarrier system
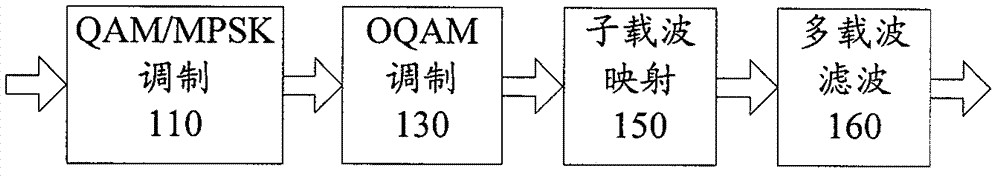
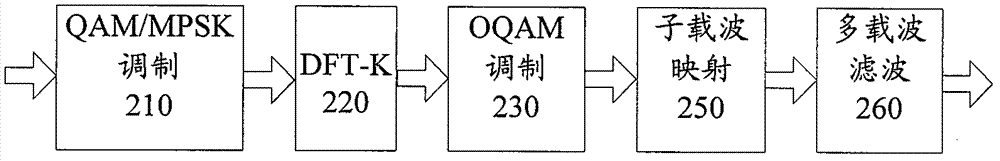
The invention relates to a method for reducing a peak-to-average power ratio in a filter-bank multi-carrier system. The method comprises the following steps of: 210, performing constellation modulation on data to be transmitted; 220, performing K-point discrete Fourier transformation on K vectors consisting of constellation symbols obtained by the constellation modulation; and 230, performing offset quadrature amplitude modulation on data vectors obtained through discrete Fourier transformation, wherein the parameter K represents the number of sub carriers distributed for transmission of the data to be transmitted. By the scheme, under the condition that the increase of operations is low, the peak-to-average power ratio of a signal can be obviously reduced, so that the efficiency of a power amplification circuit is improved, the effective emission power is increased, and the nonlinear distortion of the signal in a power amplification stage is reduced.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SHANGHAI BELL CO LTD
Signal crest trimming method and equipment
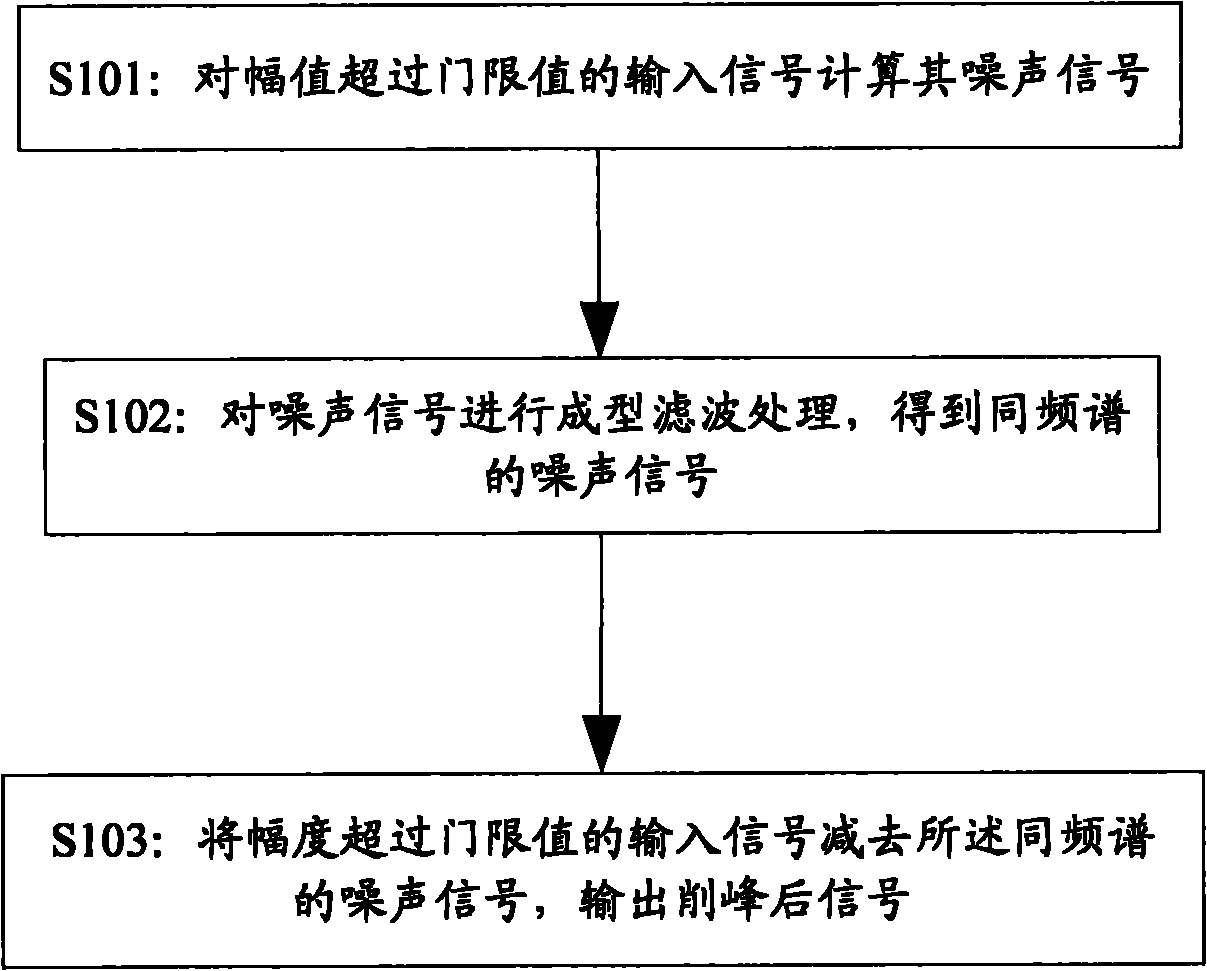
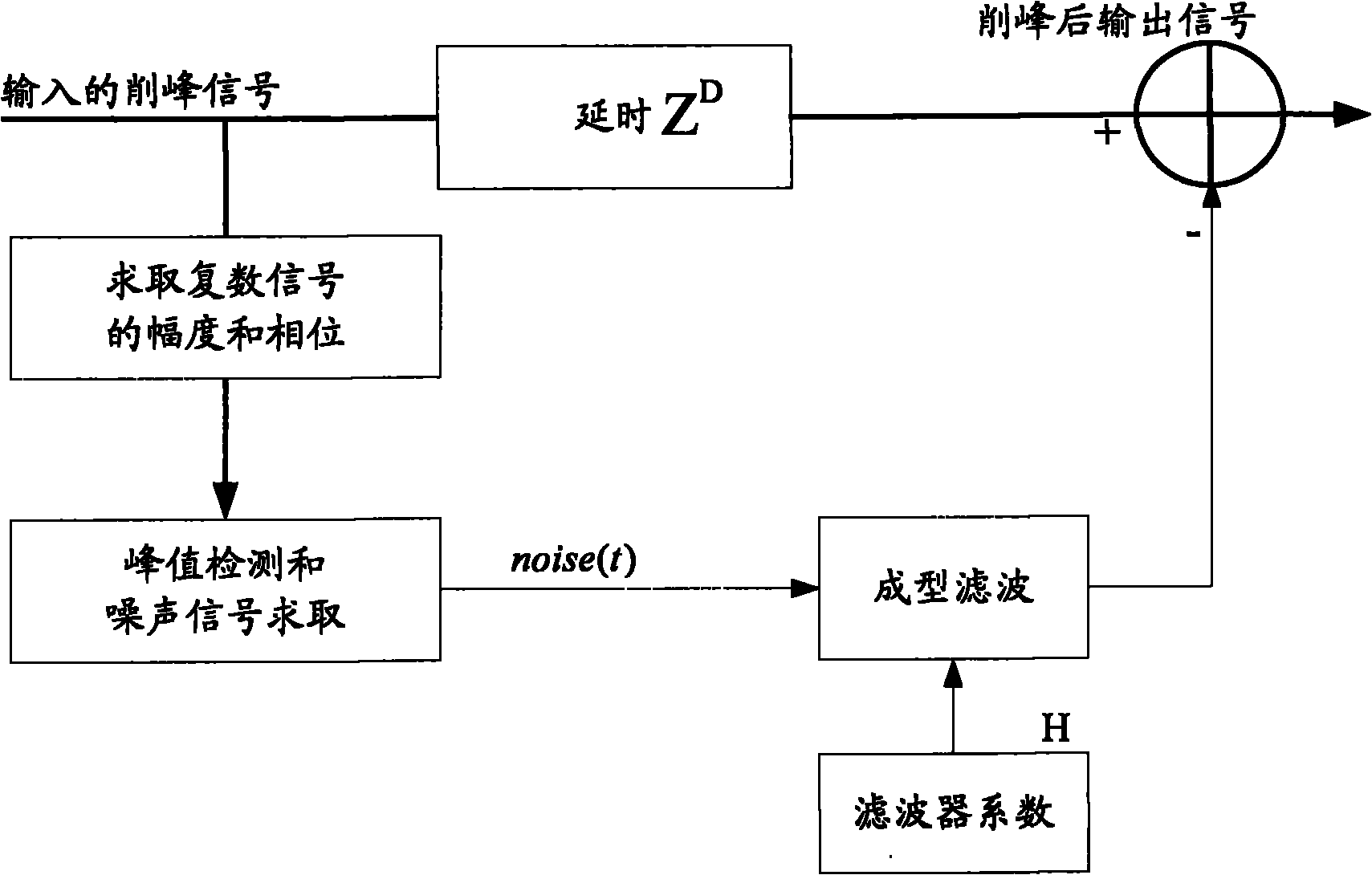
ActiveCN101867541ALower peak-to-average ratioEffective removalMulti-frequency code systemsFrequency spectrumFiltration
The invention discloses a signal crest trimming method, which comprises the following steps of: computing the amplitude and phase of an input signal x(t), and if the amplitude, which is represented as the absolute value of x(t), of the input signal x(t) exceeds a threshold, subtracting the threshold from the signal to obtain a noise signal; performing molding filtration on the noise signal to obtain a same-frequency spectrum noise signal; and subtracting the same-frequency spectrum noise signal from the input signal x(t) of which the amplitude exceeds the threshold, and outputting the crest-trimmed signal. The technical scheme of the invention has the advantages of simplicity, high efficiency, relatively lower hardware equipment resource consumption in particular realization, short processing time delay, and the capacity of effectively performing crest trimming on randomly appearing signal peaks exceeding the threshold so as to reduce the peak-to-average power ratio of the signal.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Multi-user block-transmission communication transmitting method and receiving method
InactiveCN1571414ALower peak-to-average ratioComplexity balanceEqualisersMultiple carrier systemsTime domainFrequency spectrum
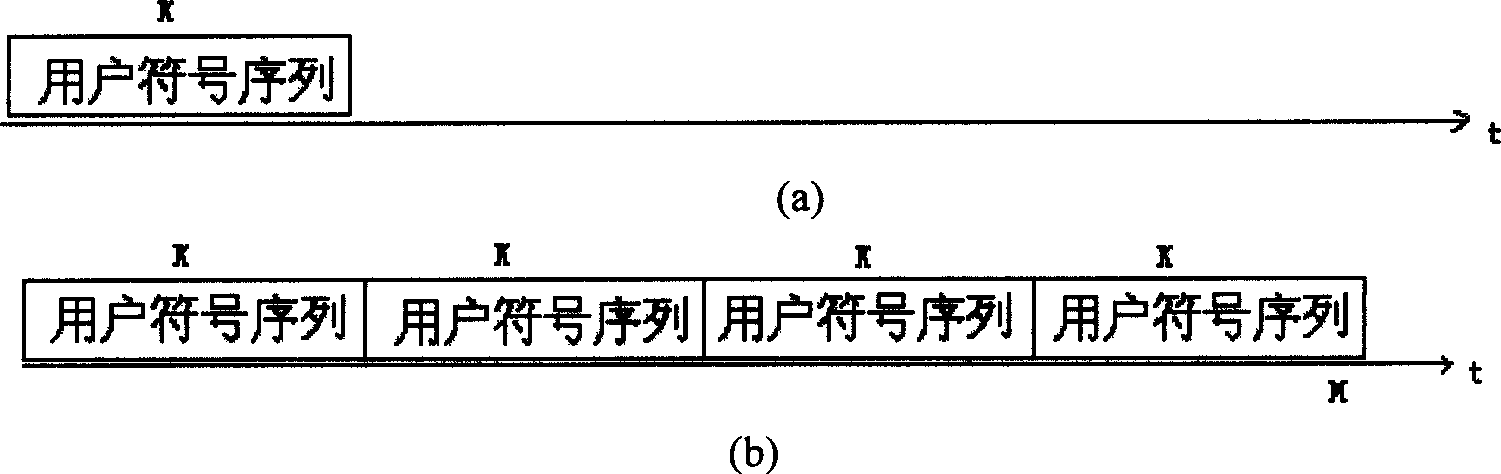
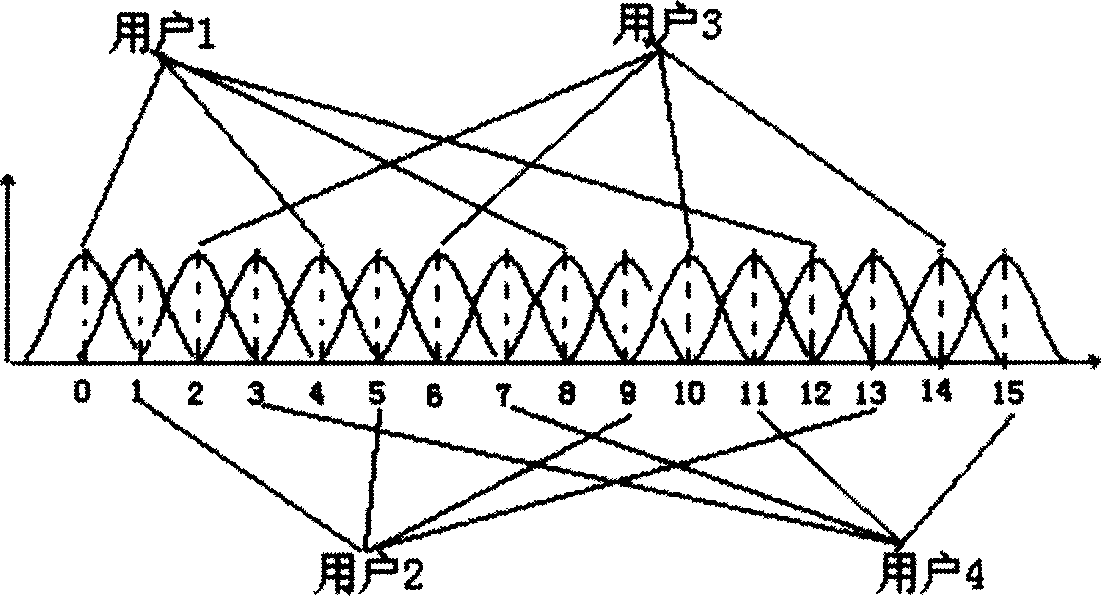
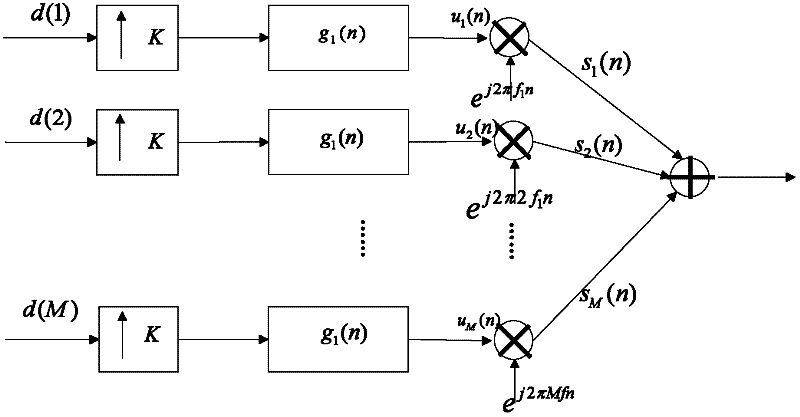
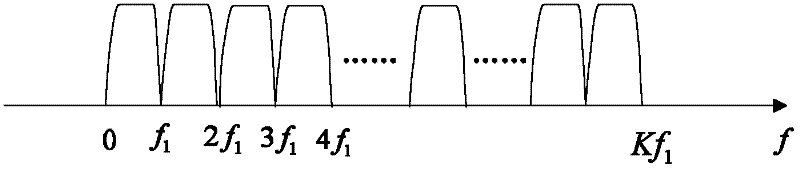
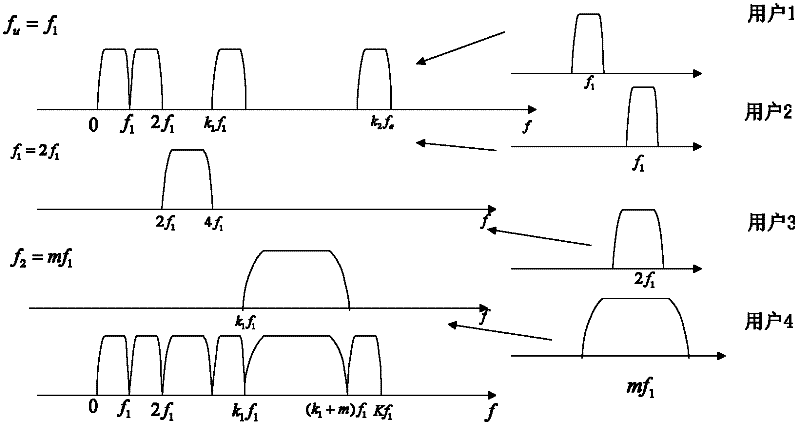
The invention discloses a new emission method and reception method of multi-user block transmission communication. The emission method is that the Nu userí»s data are divided as the unit with K symbols; the K symbols of each user are repeated N times at time domain; and each of them is formed to Nu pectination frequency spectrum symbol sequences whose length are M; the sequence are modulated as quadrature carrier to make the each userí»s symbol sequence frequency spectrum not be aliasing each other; the Nu symbol sequences are superposed to form data blocks whose length is M; thus, the steps of partitioning and multiple access are completed. Correspondingly, the reception method is that multiple access separation is did according to the frequency spectrum took up by the user who need to receive to gain K symbol sequences of the user needed. The technical proposal of the invention is adopts to utilize the quadrature carrier modulation to do multiple access at the emission end, and utilize the jump corresponding operation with low complexity to separate the user data at the reception end. Thus, the complexity of the post-treatment is reduced.
Owner:焦秉立
Variable bandwidth fmt frequency division multiple access method based on single carrier transmission
ActiveCN102263766AImprove distribution efficiencyReduce complexityMulti-frequency code systemsOriginal dataCarrier signal
The invention relates to the technical field of signal transmission, and discloses a frequency division multiple access method of a variable-bandwidth FMT (frequency modulated transmitter) based on single-carrier transmission. The frequency division multiple access method comprises the following steps: S1. different users transmit variable-bandwidth subcarrier signals synchronously at the transmitting end, wherein the subcarrier signals are obtained through filtering of original data to be transmitted by the users; and S2. the signals sent from different users are received in parallel at the receiving end. In the frequency division multiple access method disclosed by the invention, (1) the bandwidth of subcarriers transmitted by each user is variable (subcarriers of different bandwidth have different resistance to time selective fading and frequency selective fading), and the bandwidth of the subcarriers needs to meet a certain condition; (2) the variable-bandwidth subcarriers are filtered single-carrier signals; and (3) a transmitter transmits data synchronously, and the data is demodulated in parallel by a receiver, thus the realizing complexity of the transmitter and the receiver is reduced, the requirement of the system on synchronization and the peak-to-average power ratio of the system are reduced, and the resource allocation efficiency is improved simultaneously.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method and apparatus lowering peak average ratio
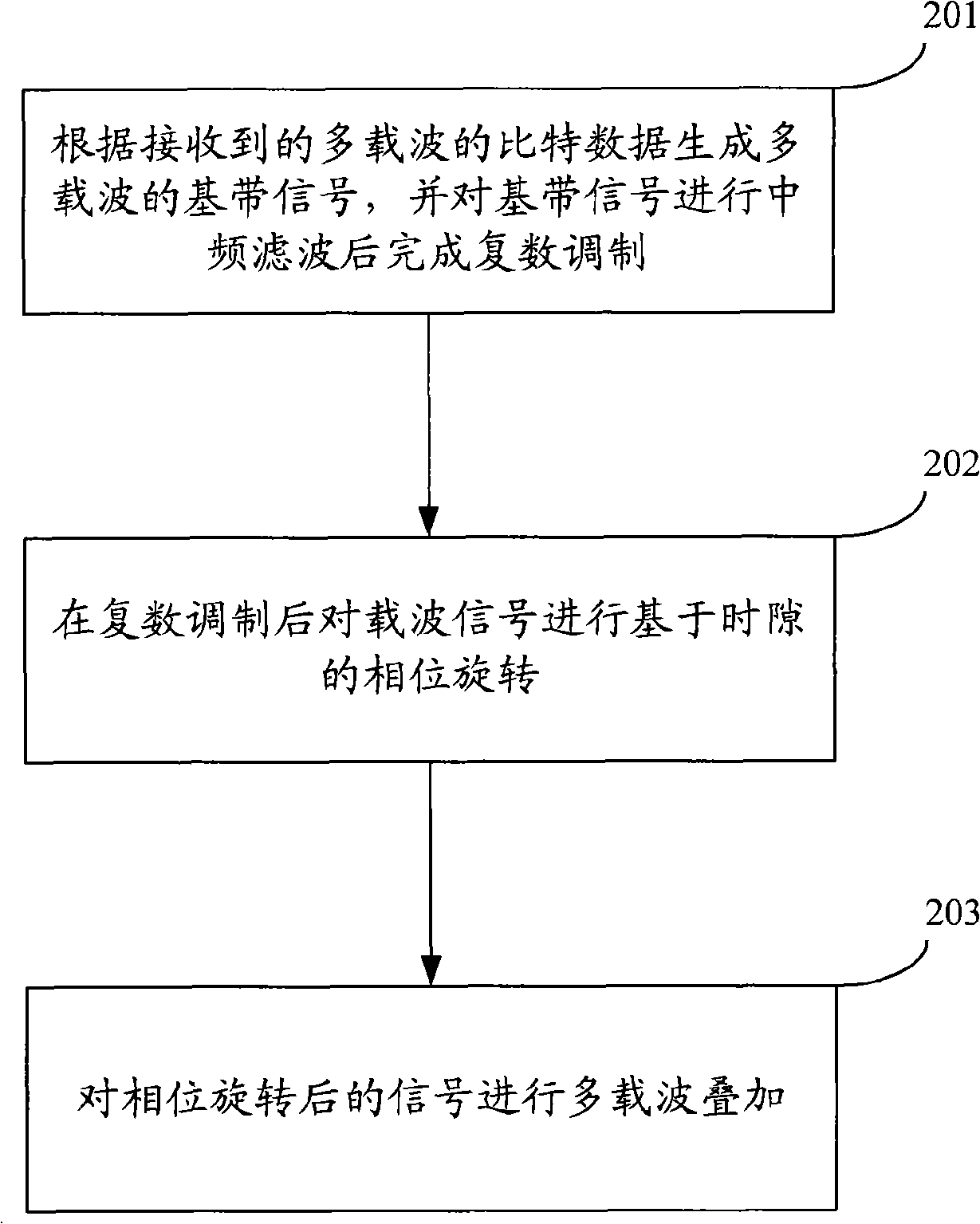
ActiveCN101359945AAvoid recurrenceEasy to implementSpatial transmit diversityMulti-frequency code systemsTD-SCDMAFpga implementations
The invention provides a method to reduce peak-to-average power ratio including: A. generating multi-carrier base band signals according to received multi-carrier bit data, and finishing IF filtering and plural modulations to base band signals; B. Processing phase rotation based on time slot to the carrier signals after the plural modulations. C. Processing multi-carrier superposition to the signals after phase rotation. The invention also provides a device for reducing peak-to-average power ratio. The method and the device can avoid the peak through processing the phase rotation after the IF interpolation filtering so that the peak-to-average power ratio is effectively reduced and the more the carrier increases, the more obvious the peak-to-average power ratio is reduced. The multiplex phase rotation can go on parallel processing with no convolution operation and less multiplication resources so that FPGA is easy to realize without any deterioration of EVM and of BER. TD-SCDMA uses correlation detection so as to avoid the transmission of the phase rotation information.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
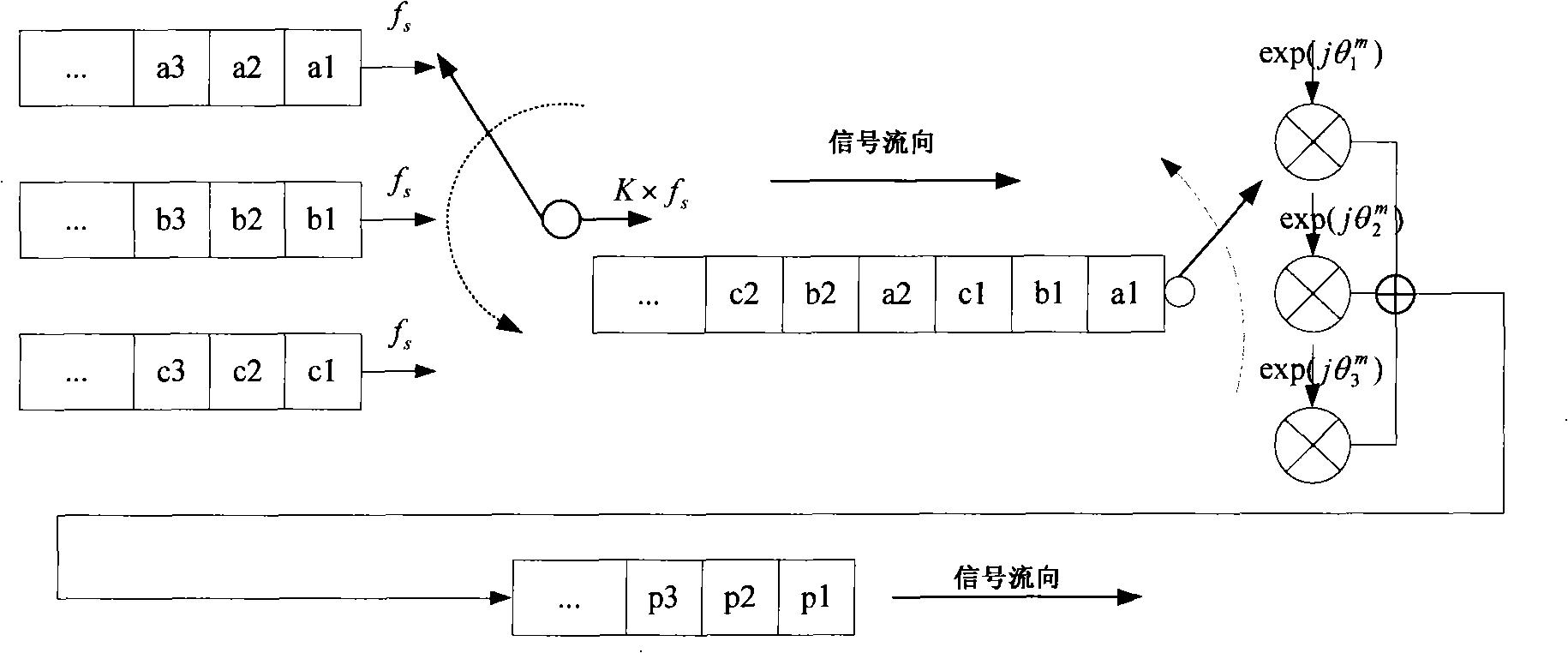
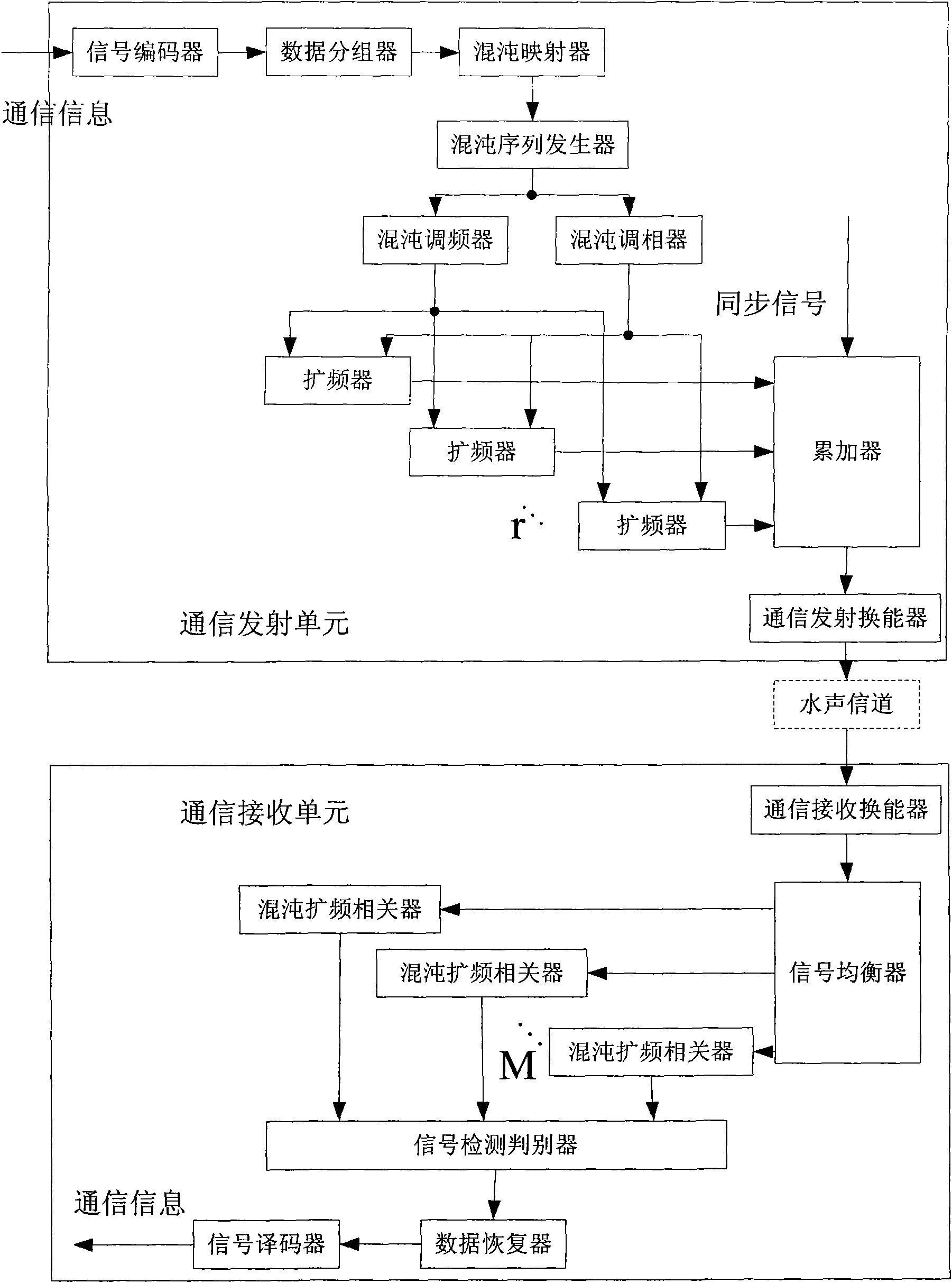
Chaotic sequence-based packet M element spread spectrum communication method and device
ActiveCN101645743ALower peak-to-average ratioLow level of mutual interferenceTransmissionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Coded element
The invention provides a chaotic sequence-based packet M element spread spectrum communication method and a device, and the method comprises the following steps: 1) dividing communication coded data to be sent into data blocks consisting of K code elements; 2) leading each data block to obtain and form a combination of a chaotic frequency regulation value sequence and a chaotic phase regulation value sequence according to a certain chaotic mapping relationship; 3) generating a chaotic frequency regulation, phase regulation and spread spectrum signal set through the combinations of the chaoticphase regulation value sequences and the chaotic phase regulation value sequences, overlapping various elements of the set into a group of concurrent chaotic frequency regulation, phase regulation and spread spectrum signals, further adding synchronous signals and then transmitting; and 4) carrying out signal channel equalization and synchronization on the received data, detecting and judging by copy correlation and recovering coded information according to the chaotic mapping relationship. The method can effectively reduce the peak-to-average ratio of communication transmitted signals, lead the mutual interference level among the various concurrent signals to be low, lead the number of the concurrent signals to be large and effectively improve the acoustic communication performance underlow signal noise ratio.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
LTE system OFDM signal peak-to-average ratio suppression method combining constellation expansion with tone reservation
ActiveCN104468455AIncrease powerLower peak-to-average ratioCriteria allocationMulti-frequency code systemsFrequency spectrumGradient mapping
The invention discloses an LTE system orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) signal peak-to-average ratio suppression method combining constellation expansion with tone reservation. According to the suppression method, an active constellation expansion intelligent gradient mapping algorithm principle and a tone reservation least square estimation algorithm are combined, and control over the signal peak-to-average ratio performance, the bit error rate performance of a system and the out-of-band frequency spectrum extension performance of transmitting signals is effectively achieved by correcting the position of constellation points. A high convergence speed can be obtained, and the system operation time is effectively optimized, so that it is ensured that under the condition of little influence on the bit error rate performance of the system, the OFDM signal peak-to-average ratio is reduced substantially, and the overall comprehensive performance of the LTE system is improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
New compression extension method for reducing OFDM signal peak to average ratio
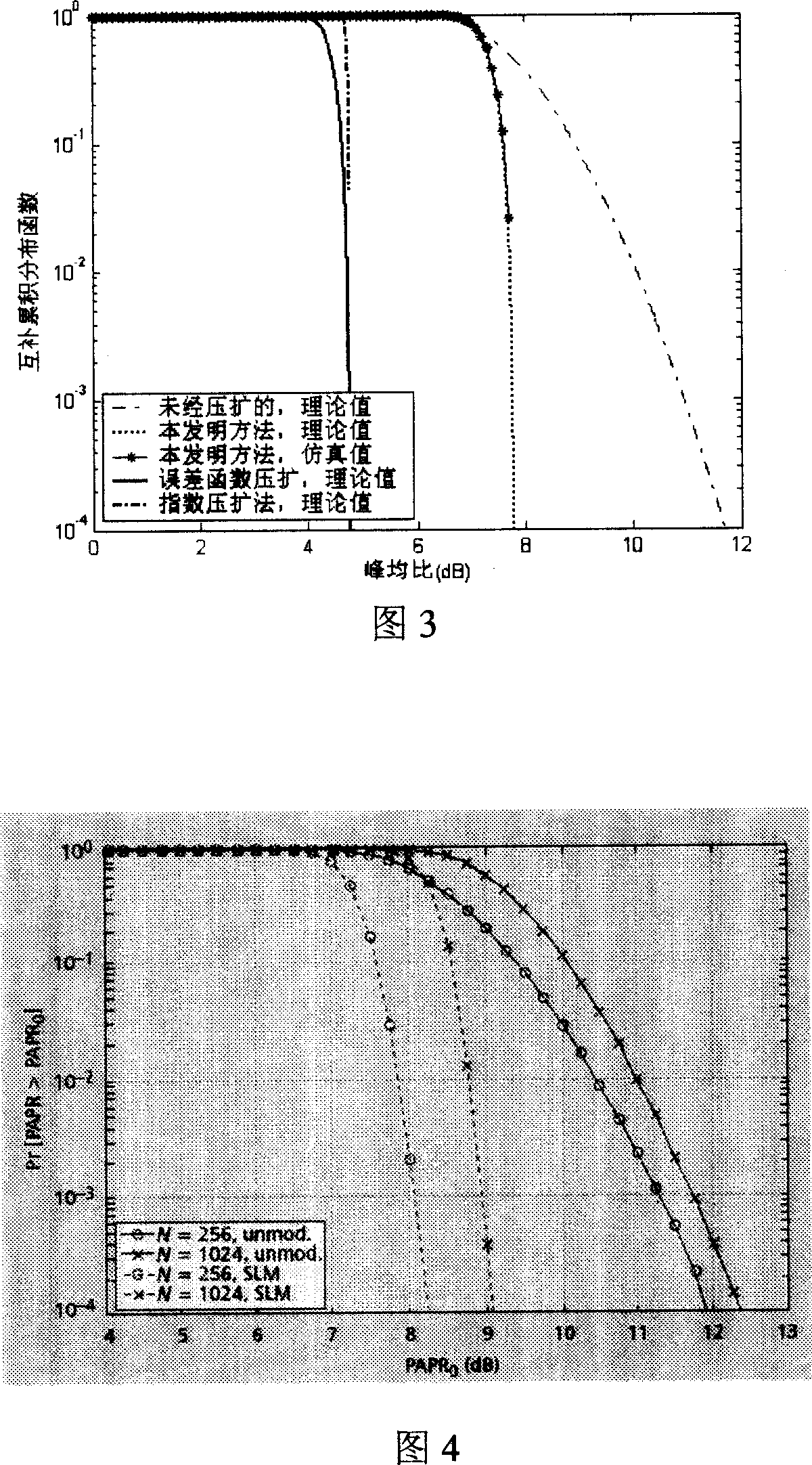
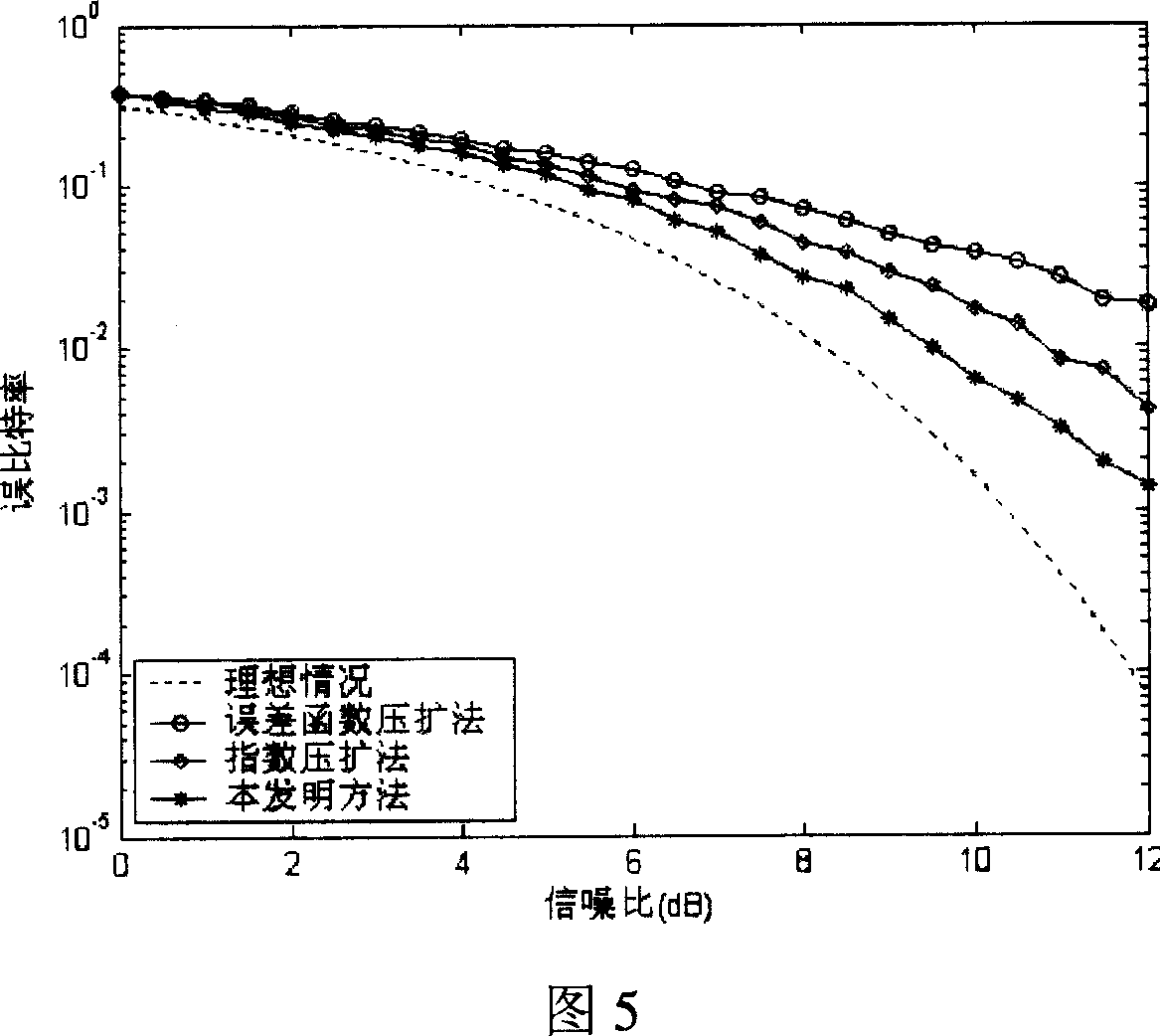
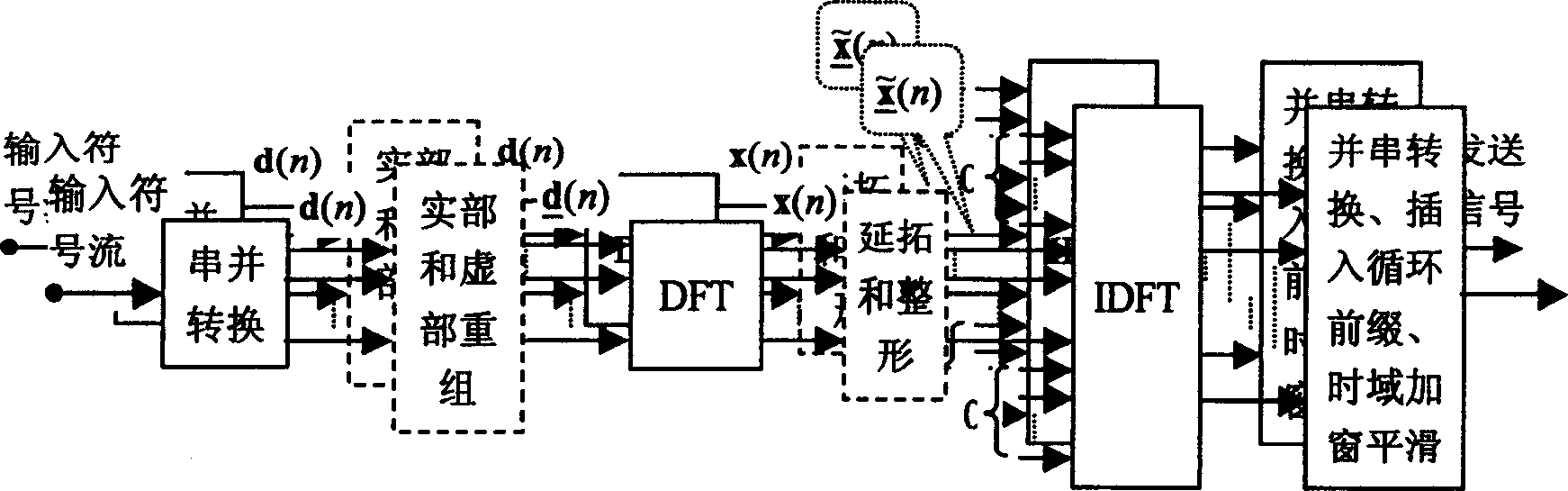
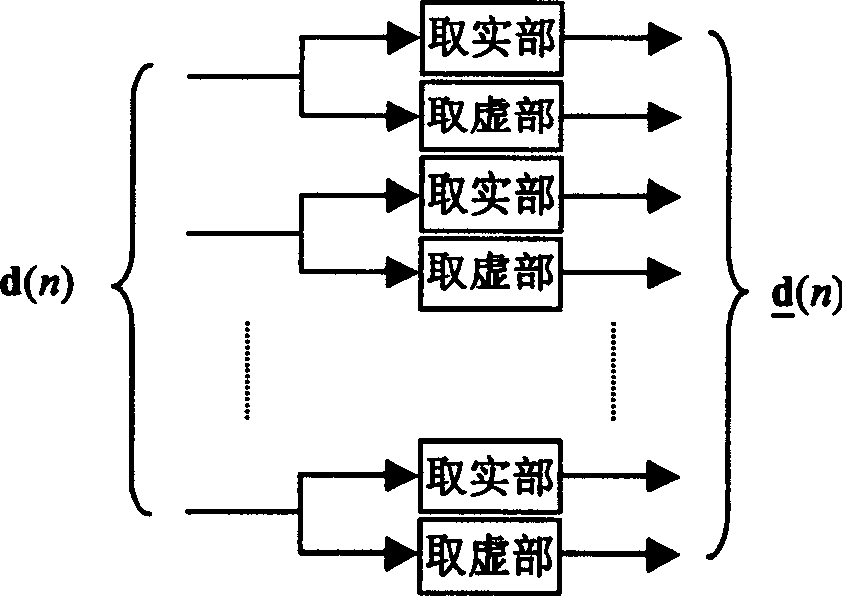
InactiveCN101005474AHigh utility valueLower peak-to-average ratioMulti-frequency code systemsInverse scattering transformExtension method
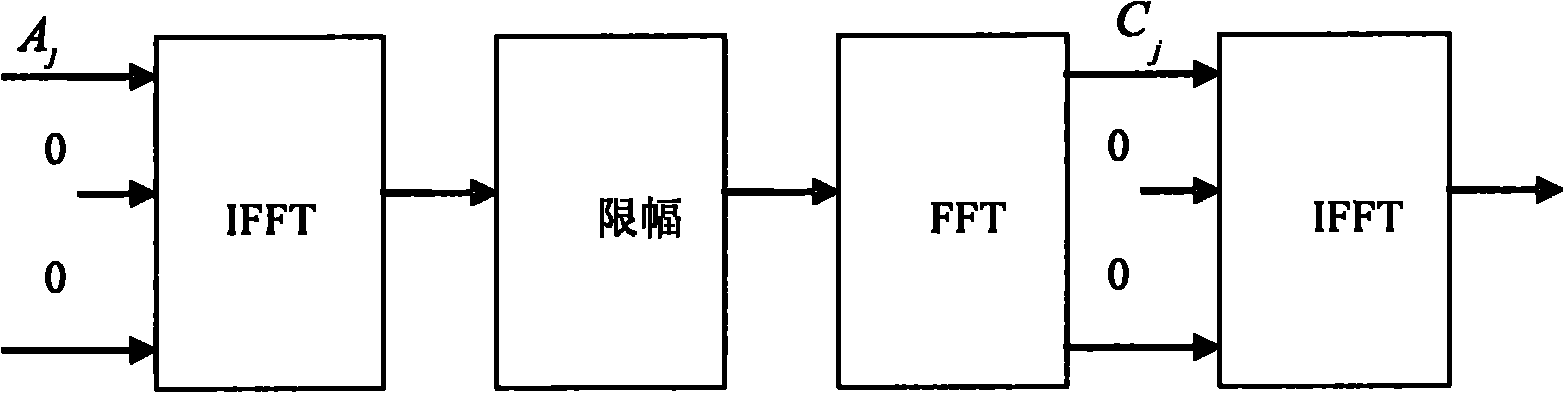
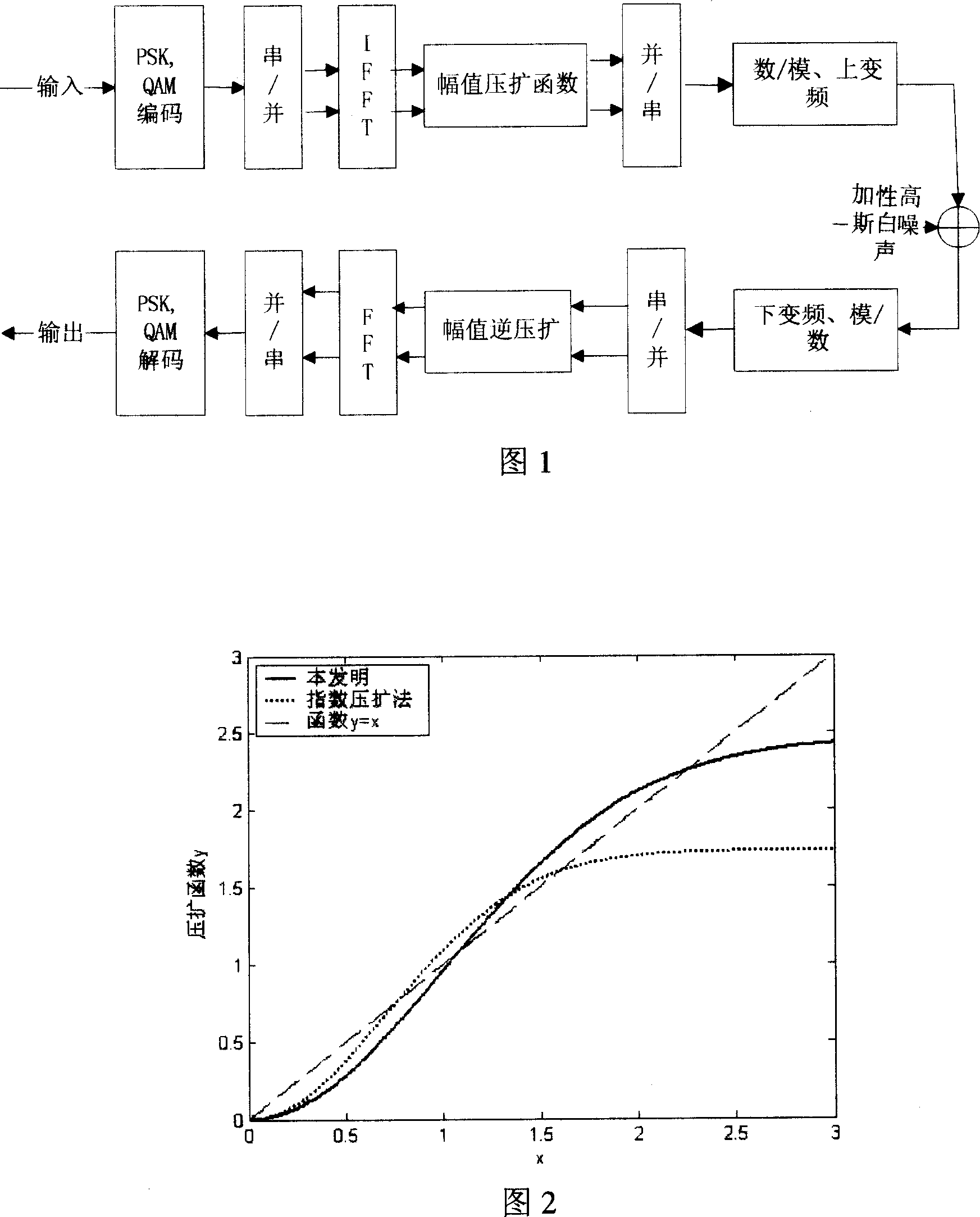
The method comprises: after sending end makes inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT), it determines the amplitude value of OFDM signals. The invention provides a companding function for making transform in order to make the transformed amplitude value submits to the linear function distribution and the phase of signal keep unchanged; the receiving end makes inverse companding transform for amplitude value of the received signals, and then makes fast Fourier transform (FFT) and decode for it.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Transmission tech. scheme for low peak equal ratio orthogonal frequency division multiplex
ActiveCN1787413ALower peak-to-average ratioOvercome the disadvantage of high peak-to-average ratioFrequency-division multiplexOrthogonal multiplexFrequency spectrumMean square
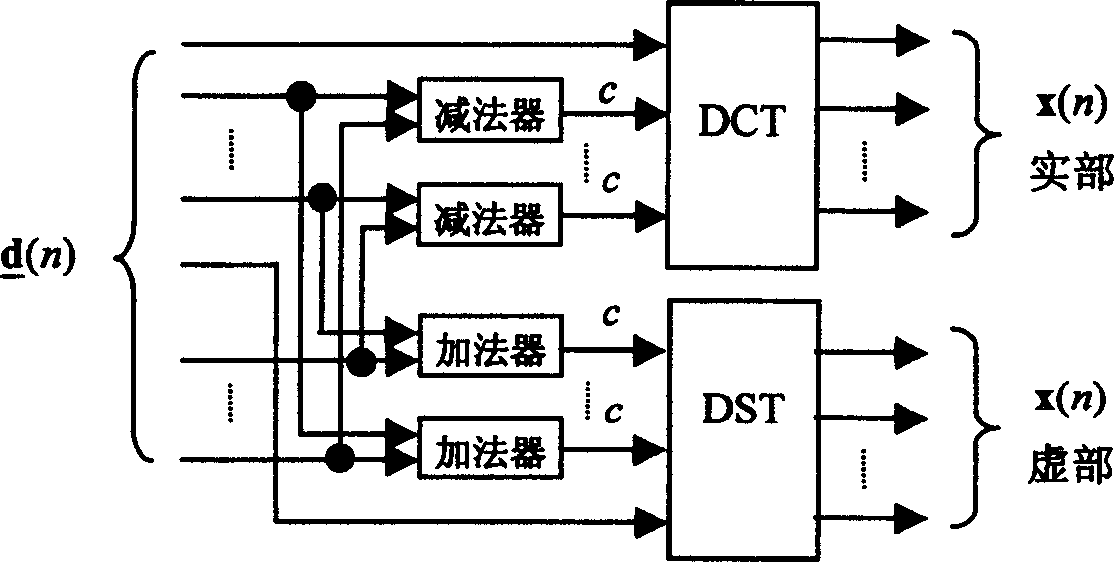
This invention relates to an OFDM transmission method of a low peak and equal ratio, which carries out reassembling of real part and a virtual part to the vector signal sequences got from the code regulation and serial-parallel transformation to get real vectors then carries out an extended dispersed Fourier transformation to the real vectors and a conjugate symmetric extension and a mean square root rising cosine shaping to be imaged onto a set of sub-carries of the OFDM to generate OFDM signals with fine spectrum performance and low peak and equal ratio.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
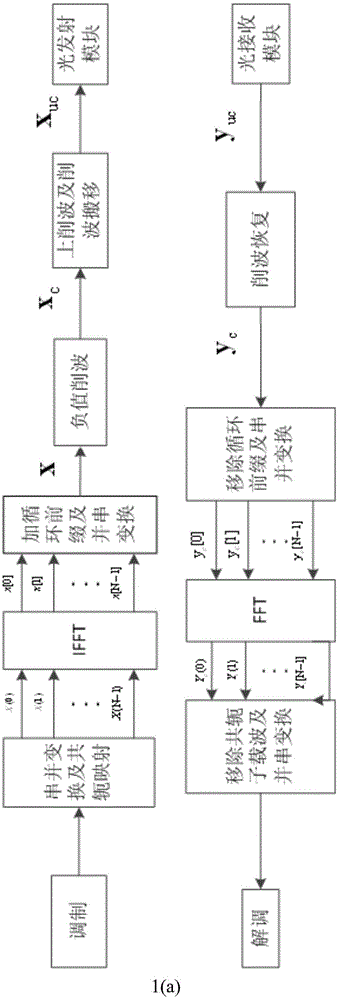
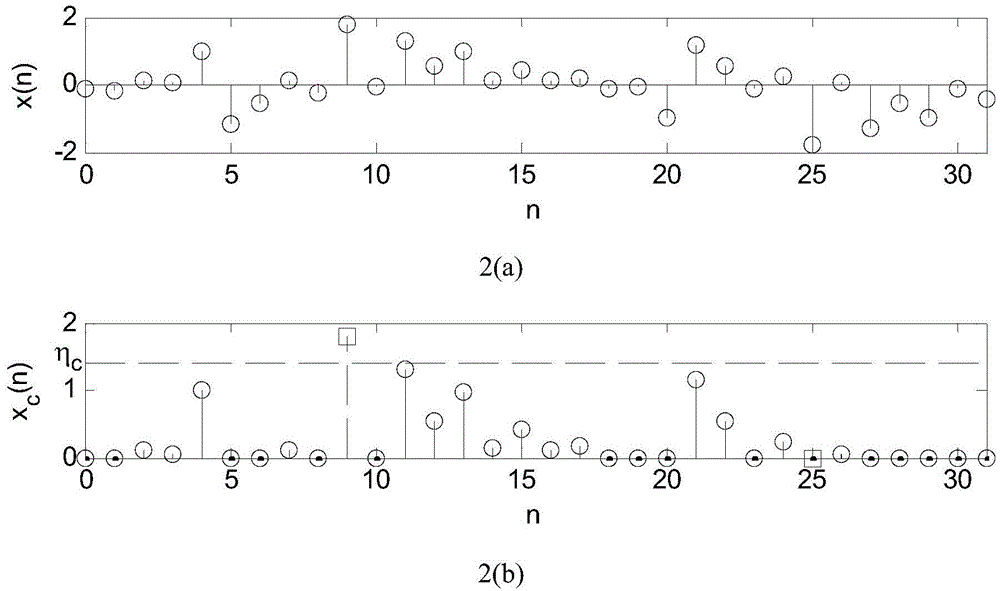
Low peak-to-average ratio wireless light transmission method with clipping moving
ActiveCN103986681ANo Communication Reliability CompromiseReduce power amplifierEnergy efficient ICTMulti-frequency code systemsVIT signalsElectricity
The invention discloses a low peak-to-average ratio wireless light transmission method with clipping moving. The feature that one of paring signals in ACO-OFDM time domain signals must be zero is utilized, if a positive signal in the pairing signals exceeds the set threshold value, clipping is conducted on the positive signal, and the clipped quantity is put at the zero position in the paring signals, and therefore the function of reducing the PAPR is achieved. The low peak-to-average ratio wireless light transmission method is easy to achieve, the PARP of an ACO-OFDM wireless optical communication system can be effectively reduced, system power consumption is reduced, the requirement for the linearity of a power amplifier and an LED lamp is lowered, nonlinear distortion of the signals in electricity and light domains is reduced, and therefore the receiving performance of the system is improved.
Owner:上海瀚芯实业发展合伙企业(有限合伙)
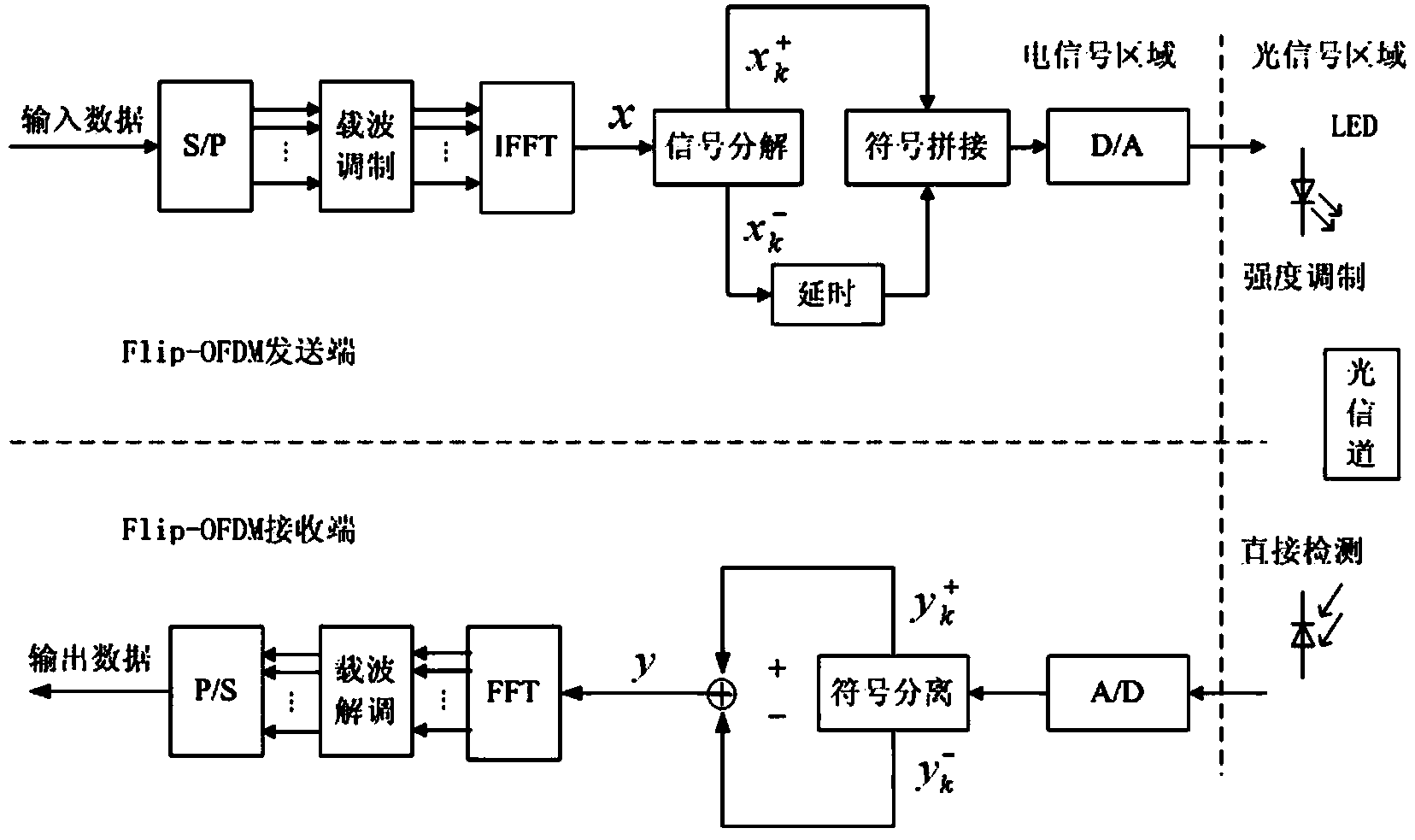
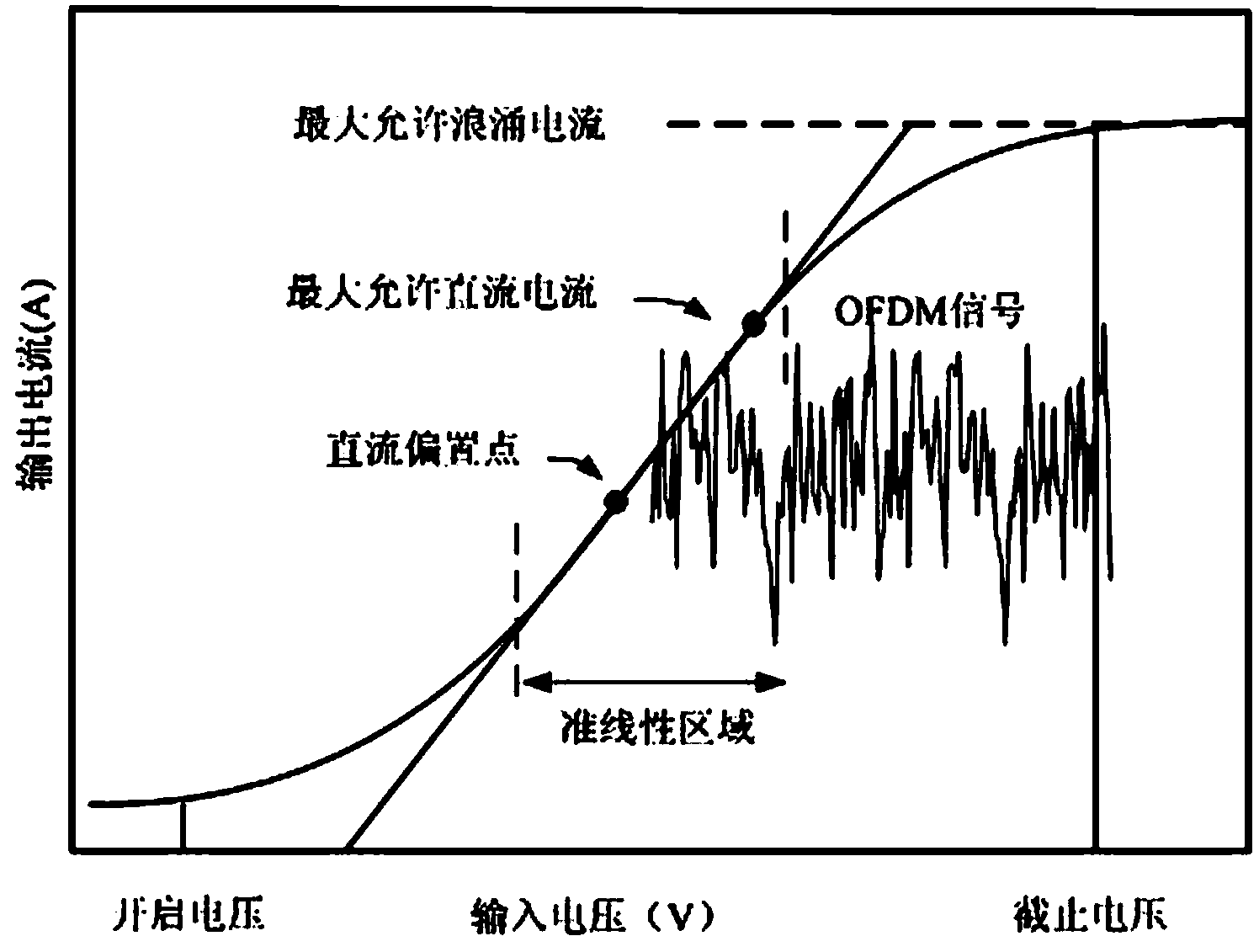
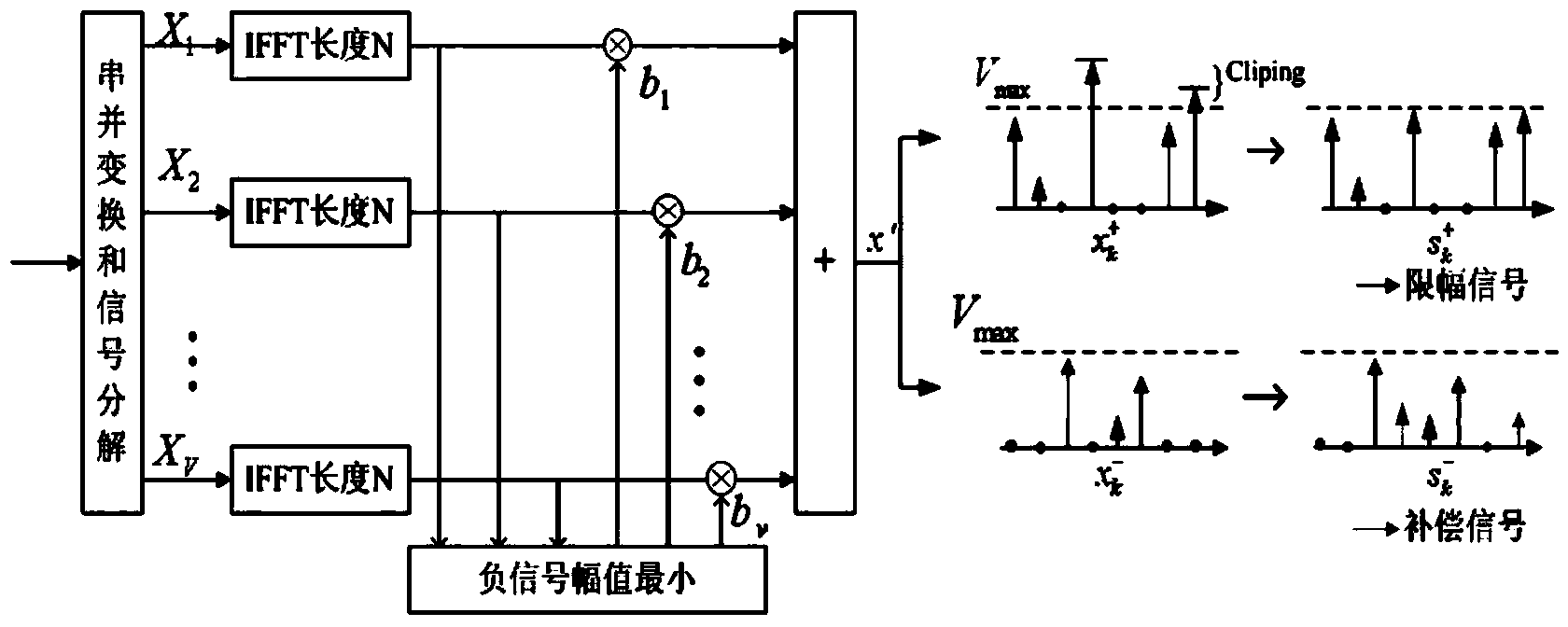
Dynamic compensation method for reducing LED (Light Emitting Diode) nonlinear distortion of visible light Flip-OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) communication system
InactiveCN103532900AReduce the amplitudeSmall clipping noiseError preventionClose-range type systemsData vectorA-weighting
The invention relates to a dynamic compensation method for reducing LED (Light Emitting Diode) nonlinear distortion of a visible light Flip-OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) communication system. The method comprises the following steps: segmenting a modulated subcarrier data vector into a plurality of non-overlapped subsequences; multiplying by a corresponding weighting coefficient, extending to be a hermitian symmetric sequence and then performing IFFT (Inverse Fast Fourier Transform); selecting a weighting coefficient for keeping the negative signal amplitude of a combined signal to be minimum; decomposing the polarity of the combined signal into a Flip-OFDM positive signal and a flip negative signal and limiting the amplitude; carrying an end cut signal of the positive signal at a zero signal position corresponding to the flip negative signal as a compensation signal; restoring the positive signal by a receiving end through the compensation signal. By using the method, PAPR (Peak to Average Power Ratio) in the Flip-OFDM system can be effectively suppressed, and the LED nonlinear distortion is reduced, so that the usability and the reliability of the system are greatly improved.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
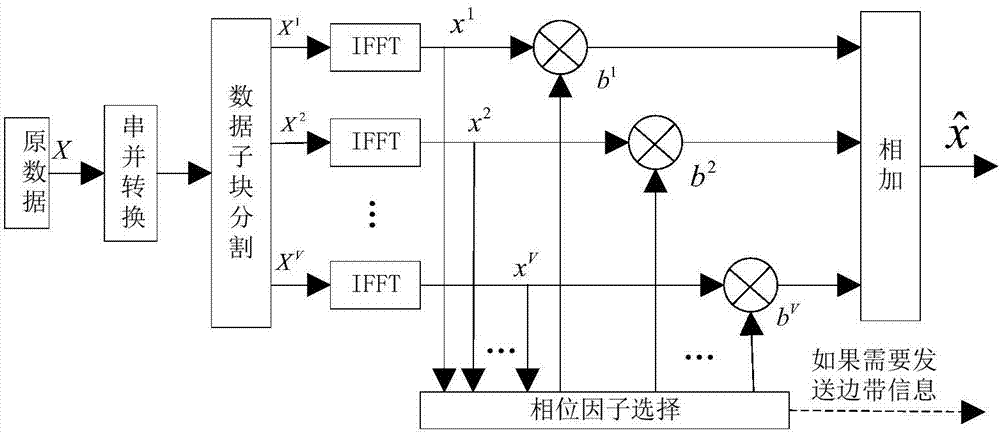
Method for reducing signal peak-to-average ratio in FBMC system
InactiveCN106941470ALower peak-to-average ratioReduce transmission efficiencyMultiple carrier systemsFrequency spectrumSideband
The present invention discloses a method for reducing the signal peak-to-average ratio in an FBMC system. According to the method, firstly, a signal is pre-processed at a signal transmission end and the data overlapping condition is avoided even after data are multiplied by a phase rotation factor after being subjected to constellation mapping. Secondly, in combination with the conventional PTS method, data are partitioned, and a set of data smallest in peak-to-average ratio among multiple sets of data is selected and transmitted. Therefore, the signal peak-to-average ratio is well reduced. Meanwhile, the signal demodulation is conducted at a receiving end according to the discriminant rule of signals. In this way, the transmission of the sideband information is avoided. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the peak-to-average power ratio of the FBMC system is reduced, while the information demodulation of the receiving end is enabled without the transmission of the phase rotation factor. Under the same condition, the utilization rate of spectrum resources is improved and the use efficiency of the entire system is increased.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
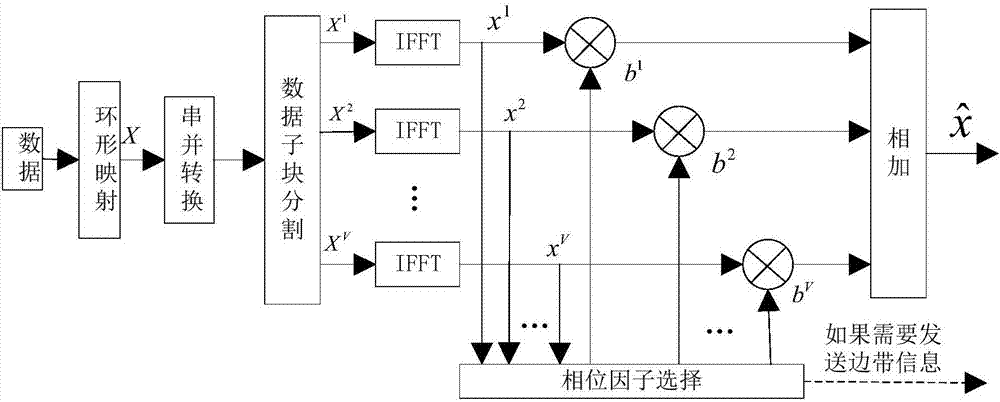
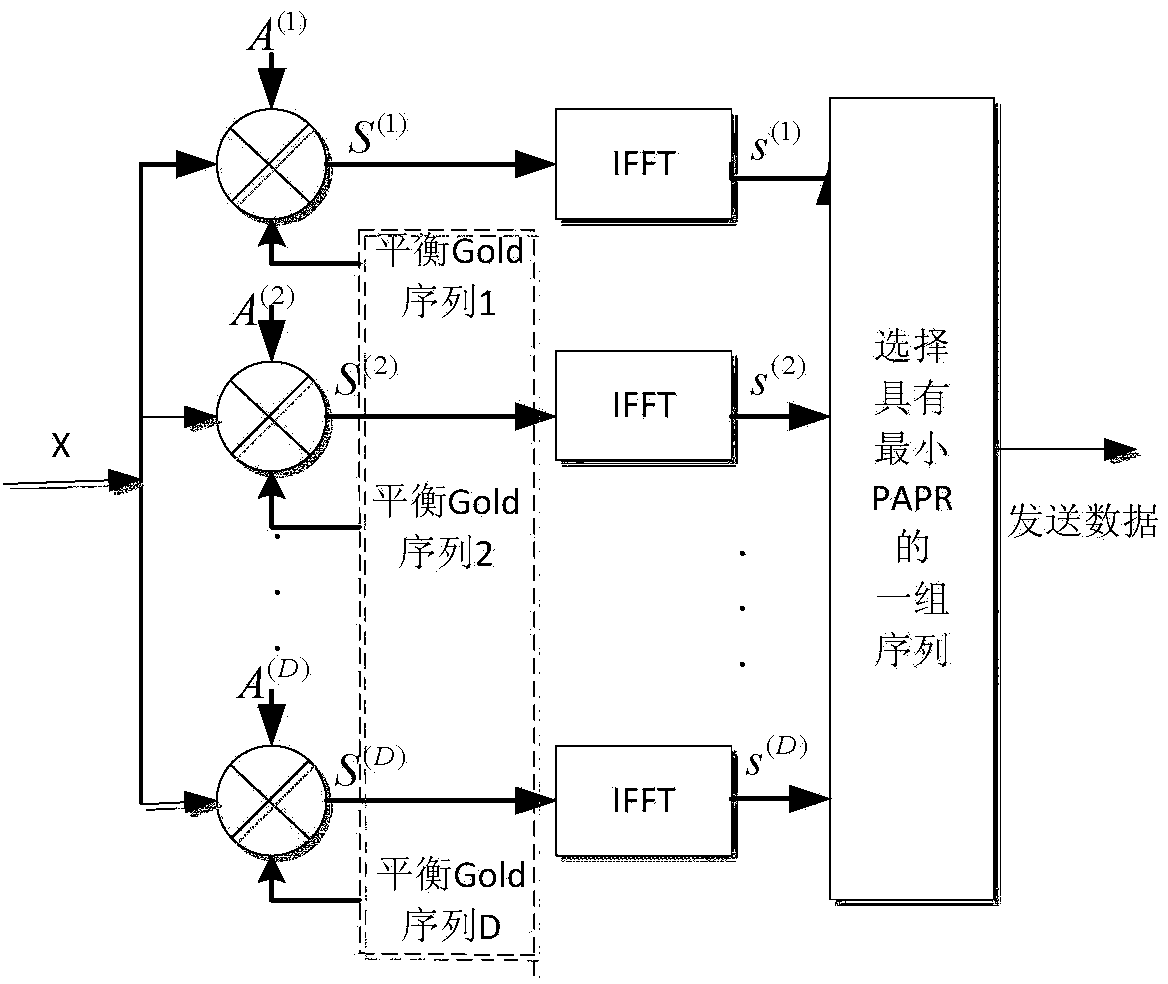
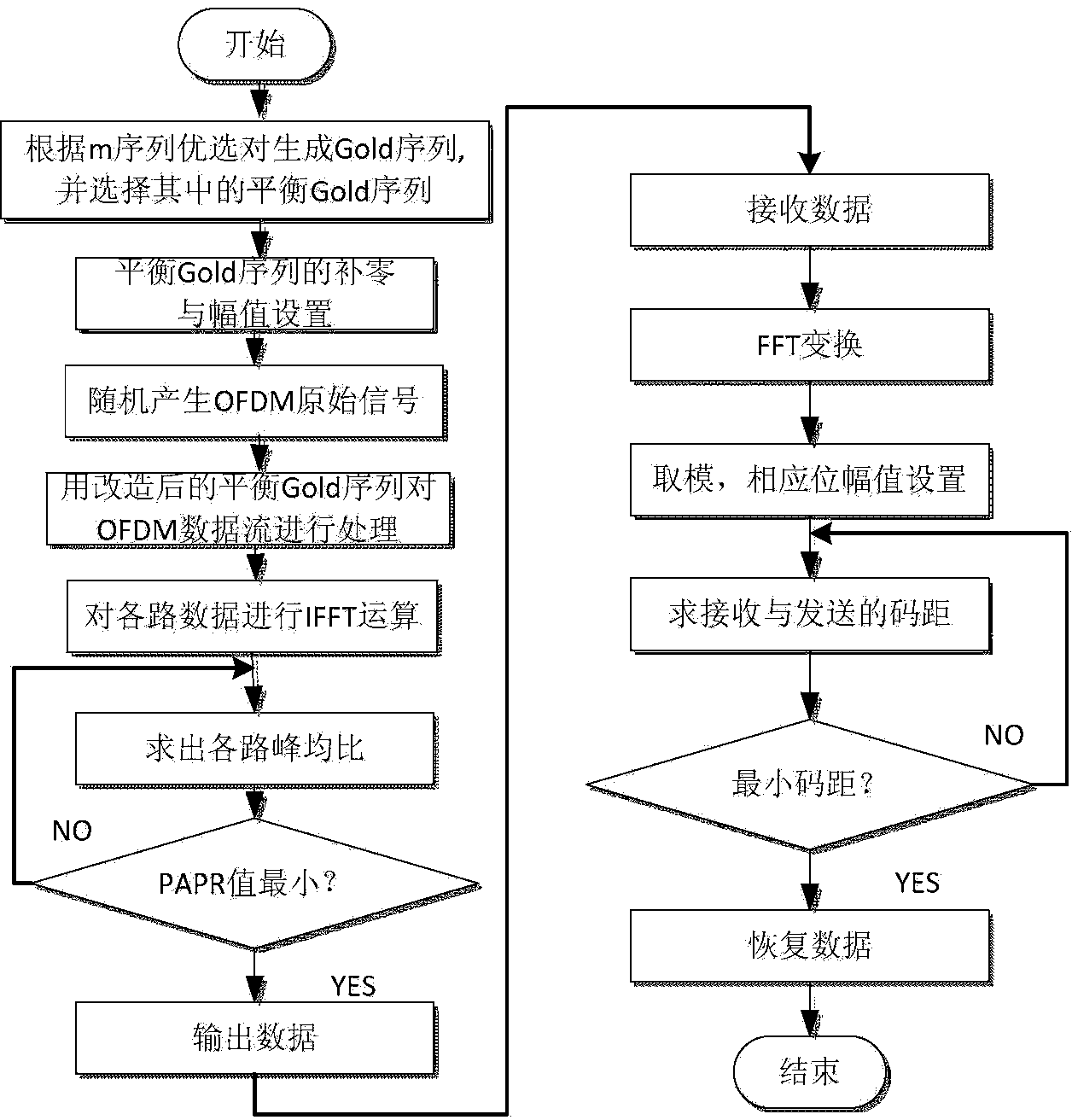
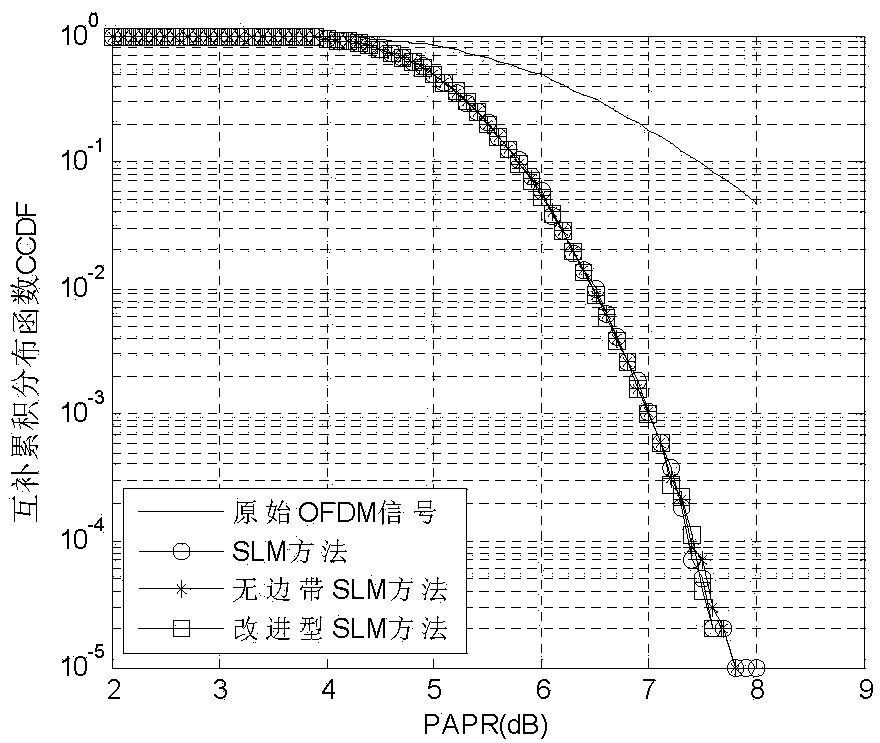
Method for reducing PAPR of OFDM system through improved SLM algorithm
InactiveCN104065610AReduce PAPR valueReduce bit error rateMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainSideband
The invention discloses a method for reducing the PAPR of an OFDM system through an improved SLM algorithm and relates to an OFDM technology. The method for reducing the PAPR of the OFDM system through the improved SLM algorithm aims to solve the problem that the system error rate of an existing non-sideband transmission SLM algorithm is high, and includes the first step of determining a frequency domain data vector of an OFDM signal, the second step of processing the input vector X through the improved SLM algorithm, the third step of carrying out IFFT on obtained D paths of independent output vectors S(d) to obtain D paths of time-domain signals, the fourth step of selecting and sending the path of signal with the minimum PAPR value, the fifth step of carrying out FFT on the received D paths of signals by a receiving end, the sixth step of carrying out module picking on the obtained D paths of signals after FFT, the seventh step of estimating out which path of signal is emitted by an emitting end and the eighth step of recovering original signal information. The method is applied to the field of wireless communications.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
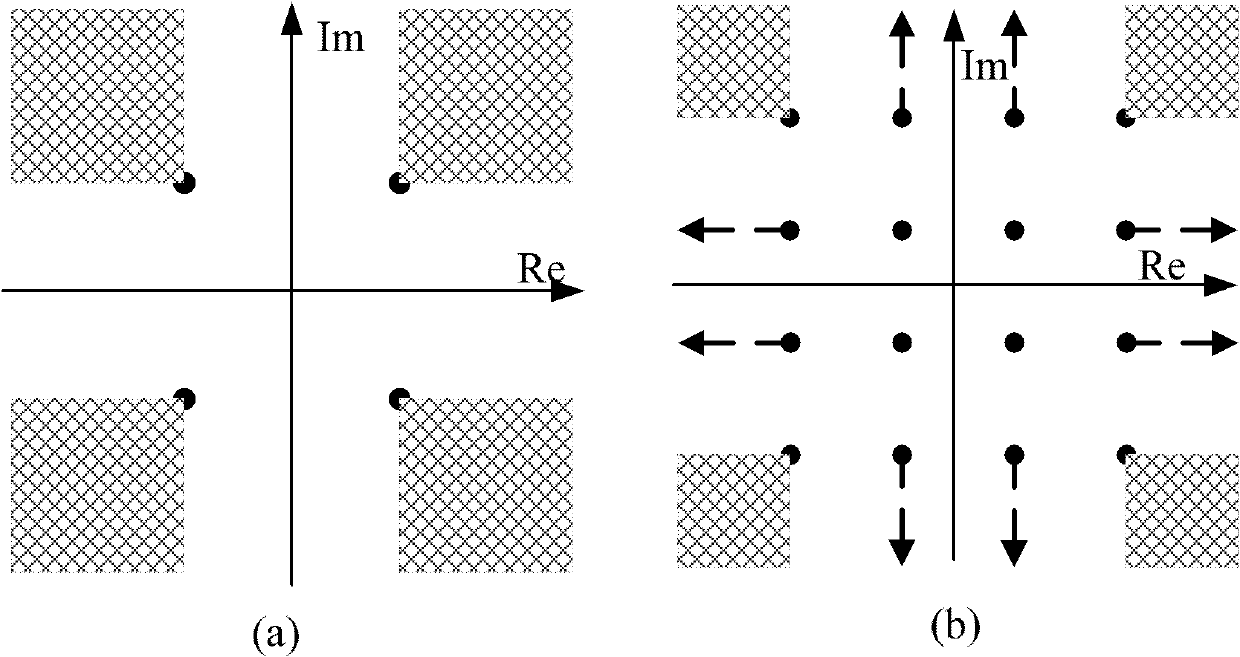
Signal peak-to-average ratio reduction method for orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) system
InactiveCN102255844ALower peak-to-average ratioReduce the number of iterationsMulti-frequency code systemsMultiple carrier systemsCarrier signalPeak value
The invention discloses a signal peak-to-average ratio reduction method for an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) system. A peak-to-average ratio is reduced by combining a constellation extension method and null sub-carriers. Regulation is performed on data sub-carriers according to constellation extension rules. Frequency domain filtering is performed on the null sub-carriers. In the method, amplitude-prelimited signal noises are processed to generate a peak cancellation vector in ways of regulating data on the data sub-carriers according to the constellation extension rules, performing a frequency domain filtering operation on the null sub-carriers, reserving noises of a null sub-carrier part and zero-setting the noises of a data sub-carrier part to completely transfer the noises to areas of the null sub-carriers and constellation extension without influencing judgment in a constellation diagram of a receiver to further reduce the peak-to-average ratio of a signal. By the method, the peak-to-average ratio of the OFDM signal can be effectively reduced, and iteration times can be reduced.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method and device for processing peak-to-mean ratio
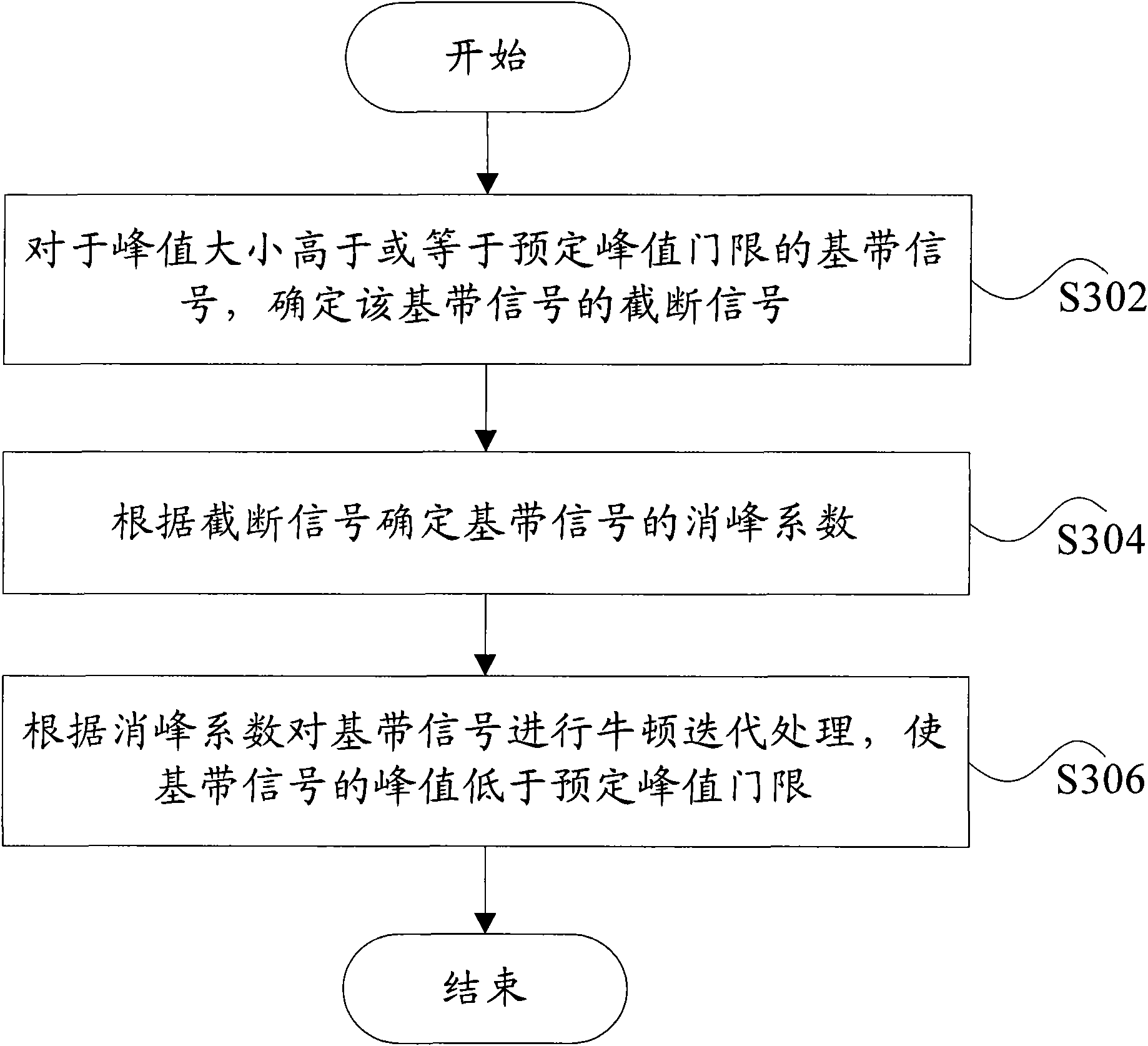
InactiveCN101888361ALower peak-to-average ratioQuality improvementBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsPeak valueWhole systems
The invention discloses a method and a device for processing peak-to-mean ratio. The method for processing peak-to-mean ratio comprises the following steps of: firstly, determining a truncation signal of a baseband signal, the peak value of which is higher than or equal to the preset peak value threshold; secondly, determining a peak extinction coefficient of the baseband signal according to the truncation signal; and thirdly, processing the baseband signal in the Newton iteration method according to the peak extinction coefficient and making the peak value of the baseband signal lower than the peak value threshold. By adopting the invention, the quality of the signal is improved, the complexity of the whole system is reduced and no negative effect occurs.
Owner:ZTE CORP
A device and method for reducing peak mean ratio
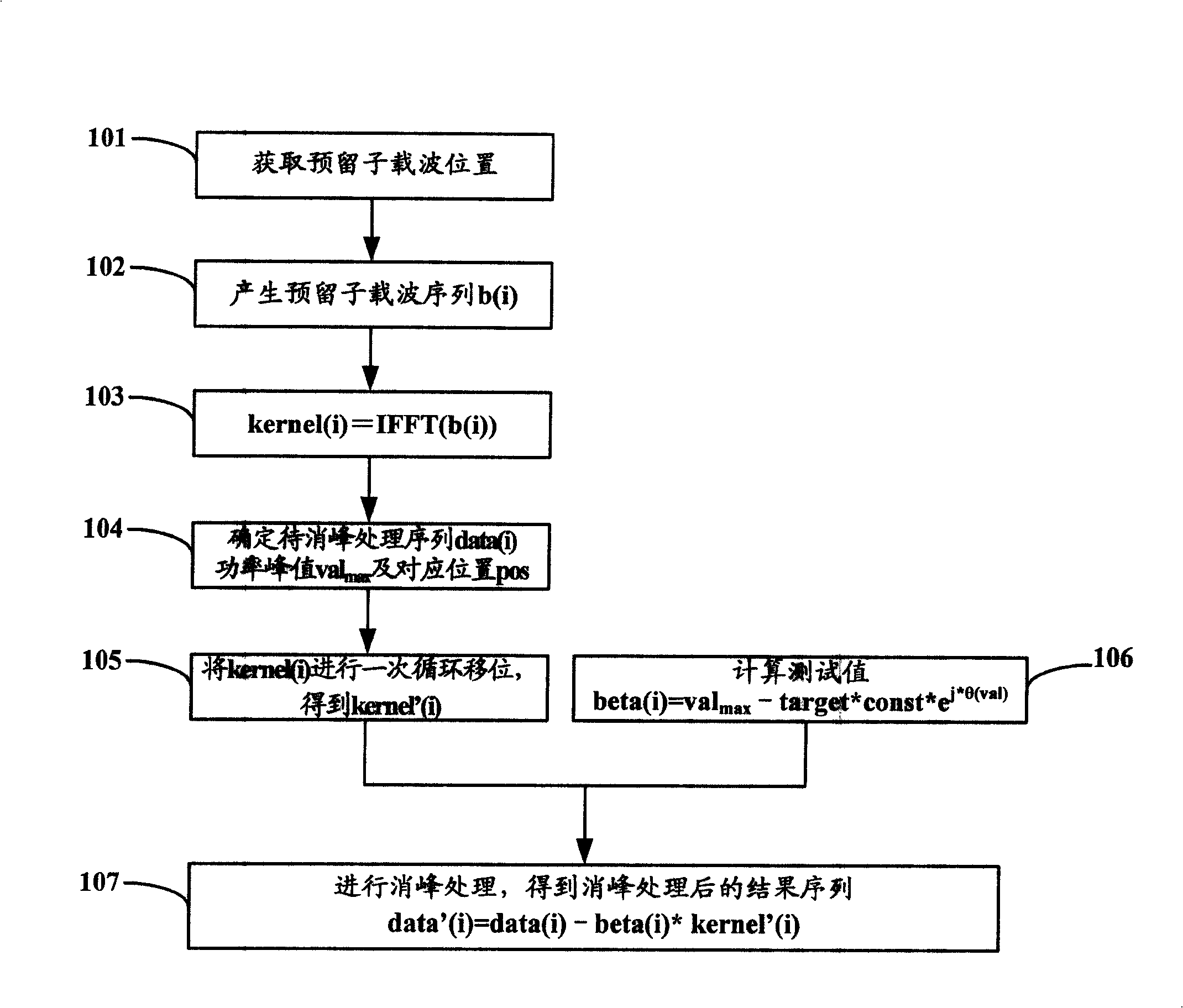
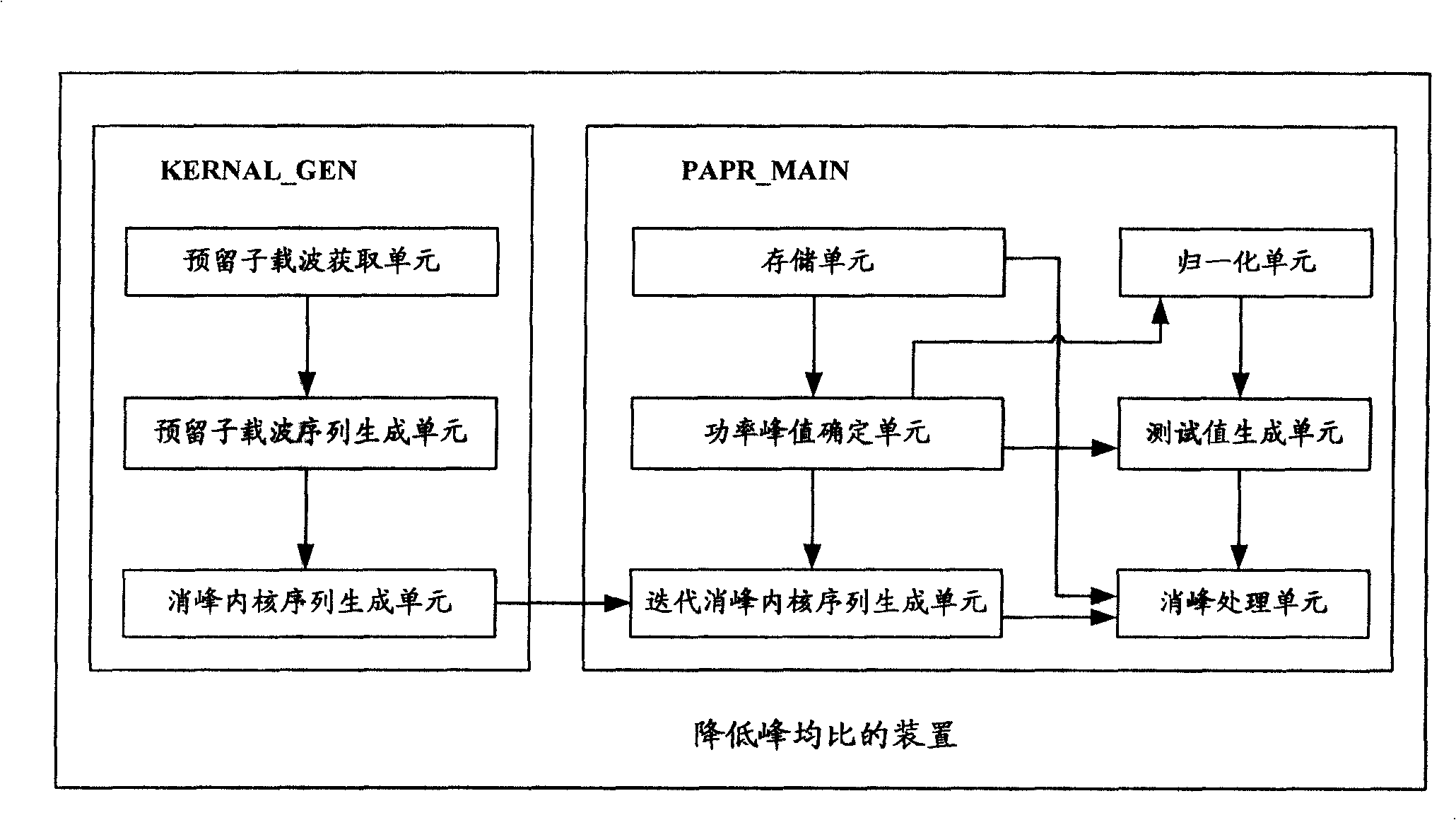
InactiveCN101262460AQuick responseLower peak-to-average ratioTransmission control/equalisingMulti-frequency code systemsPeak valueSubcarrier
The invention discloses a method for reducing peak-to-average ratio, which comprises the steps: (a) determining off-peak kernel sequence: kernel(i), i is an element of a set [1, N] by utilizing a tone preservation algorithm according to the position information of reserved subcarrier; (b) determining power peak value val in current off-peak sequence to be processed and determining the testing value beta(i) according to beta(i) = val- target*const*Theta< j*Theta(val) >, wherein, the target refers to target power value of off-peak, the constant refers to the step size of off-peak, Theta(val) refers to phase angle corresponding to the power peak value val; (c) carrying out cyclic shift to the off-peak kernel sequence: kernel(i) to obtain an iteration off-peak kernel sequence: kernel'(i); and (d) determining result sequence of off-peak process: data' (i). By adopting the method and the device disclosed by the invention, peak-to-average ratio in OFDM system can be effectively reduced.
Owner:ZTE CORP
OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) peak-to-average power ratio lowering method based on constellation linear expansion
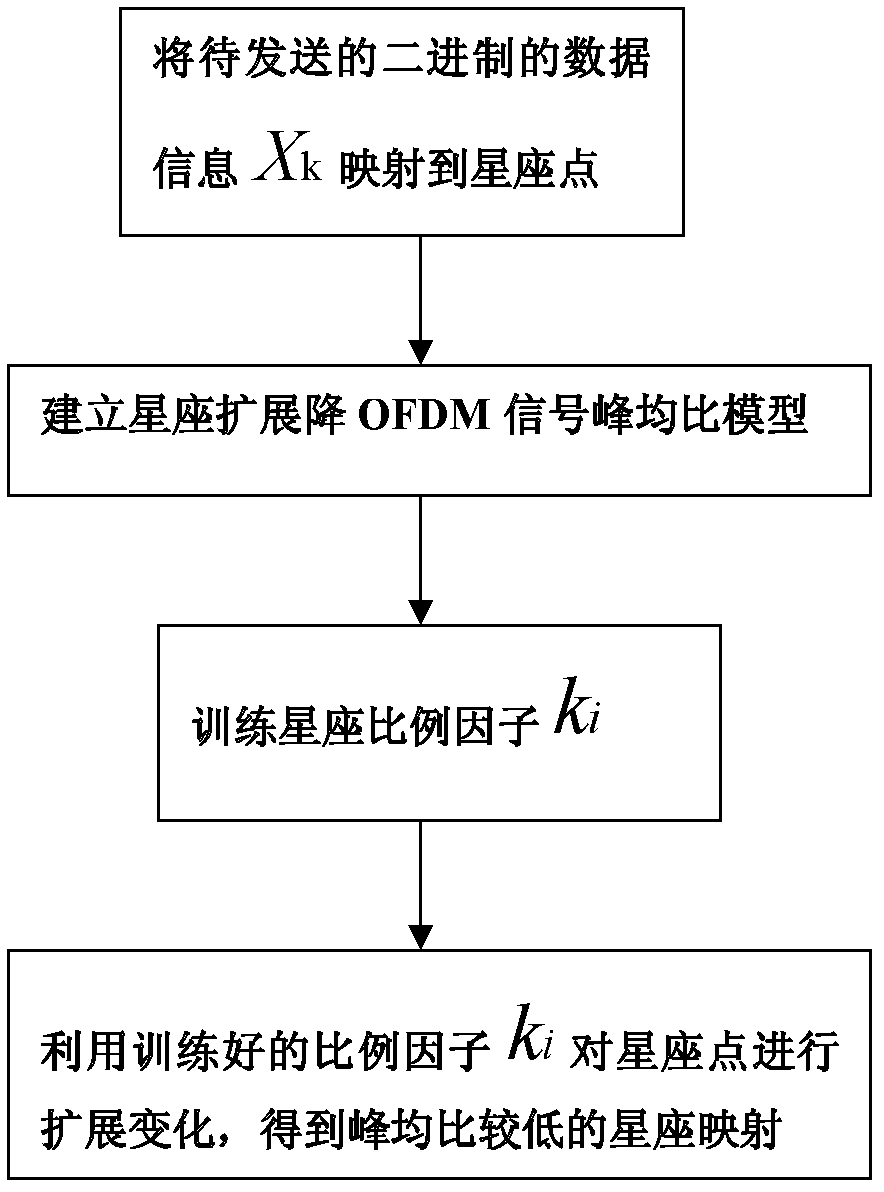
InactiveCN102497350ALow costLower peak-to-average ratioMulti-frequency code systemsFast Fourier transformTime domain
The invention discloses an OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) peak-to-average power ratio lowering method based on constellation linear expansion, which has the advantages of capability of greatly lowering a peak-to-average ratio, small influence on a system error rate, no need of transmitting sideband information, no need of changing a receiving end, low calculation amount and low hardware implementation cost. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) mapping binary data to be transmitted into a constellation point; (2) establishing a constellation expansion OFDM signal peak-to-average ratio lowering model; (3) training a constellation proportional factor ki; and (4) performing expansion changing on the constellation point by using the trained constellation proportional factor ki to obtain constellation mapping with a low peak-to-average ratio, i.e., multiplying a frequency domain complex signal of bearing information by the proportional factor for performing IFFT (Inverse Fast Fourier Transform) calculation to obtain an output time domain complex signal.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
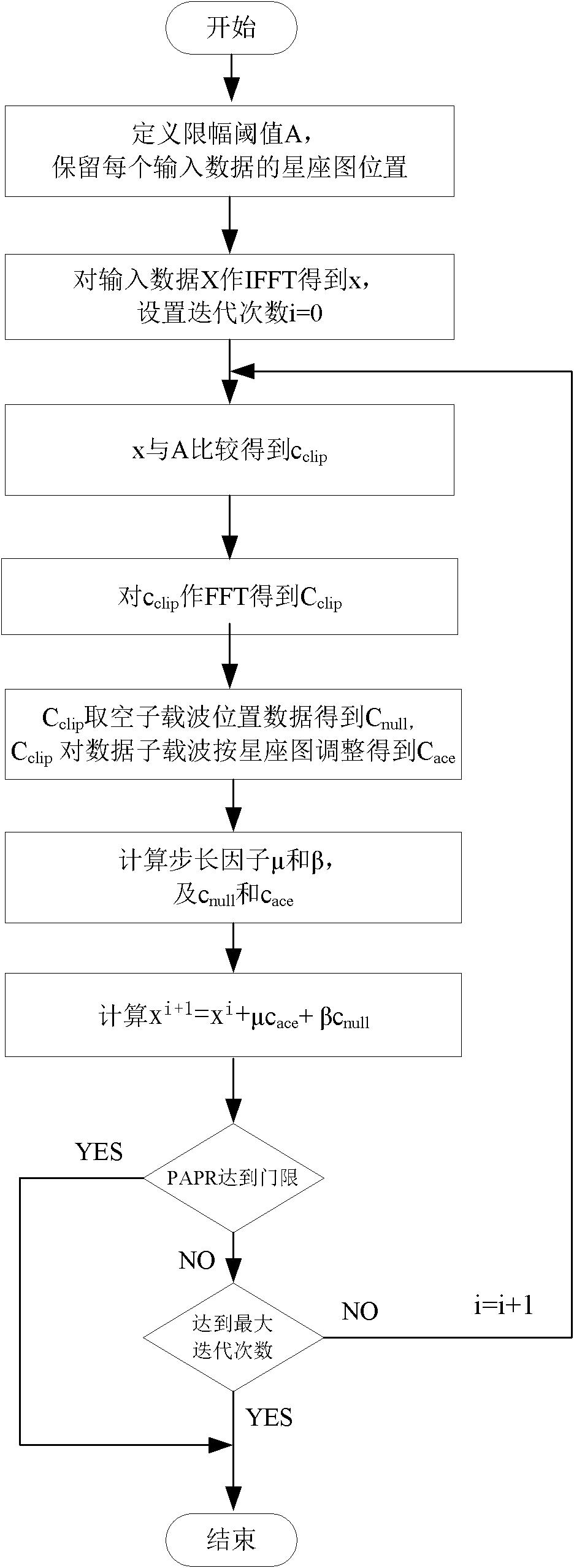
Method and system for suppressing ACE of peak-to-average ratio of high-order modulation OFDM signal
ActiveCN110336763AGuaranteed lossFast convergenceMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainExpansion factor
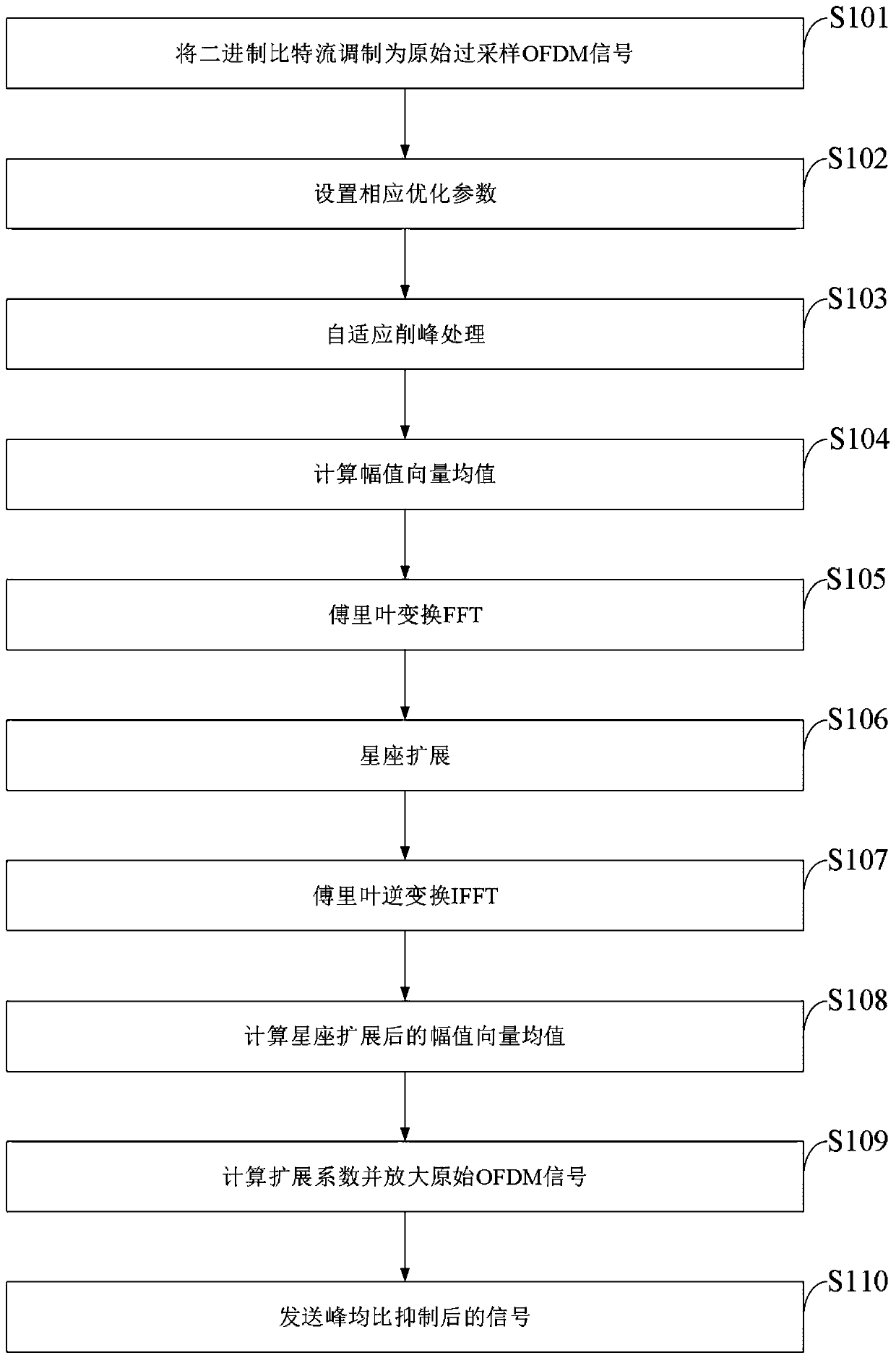
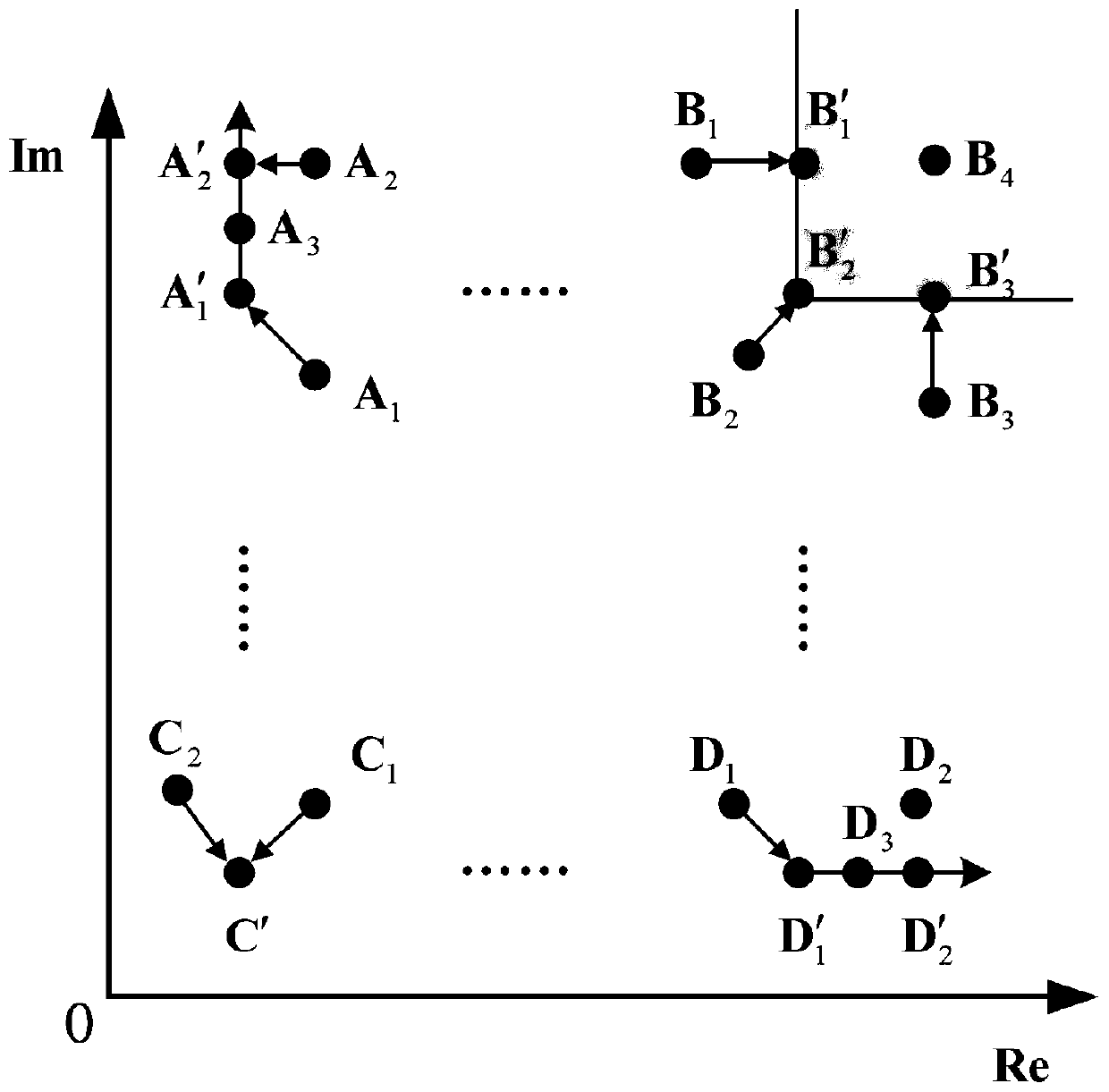
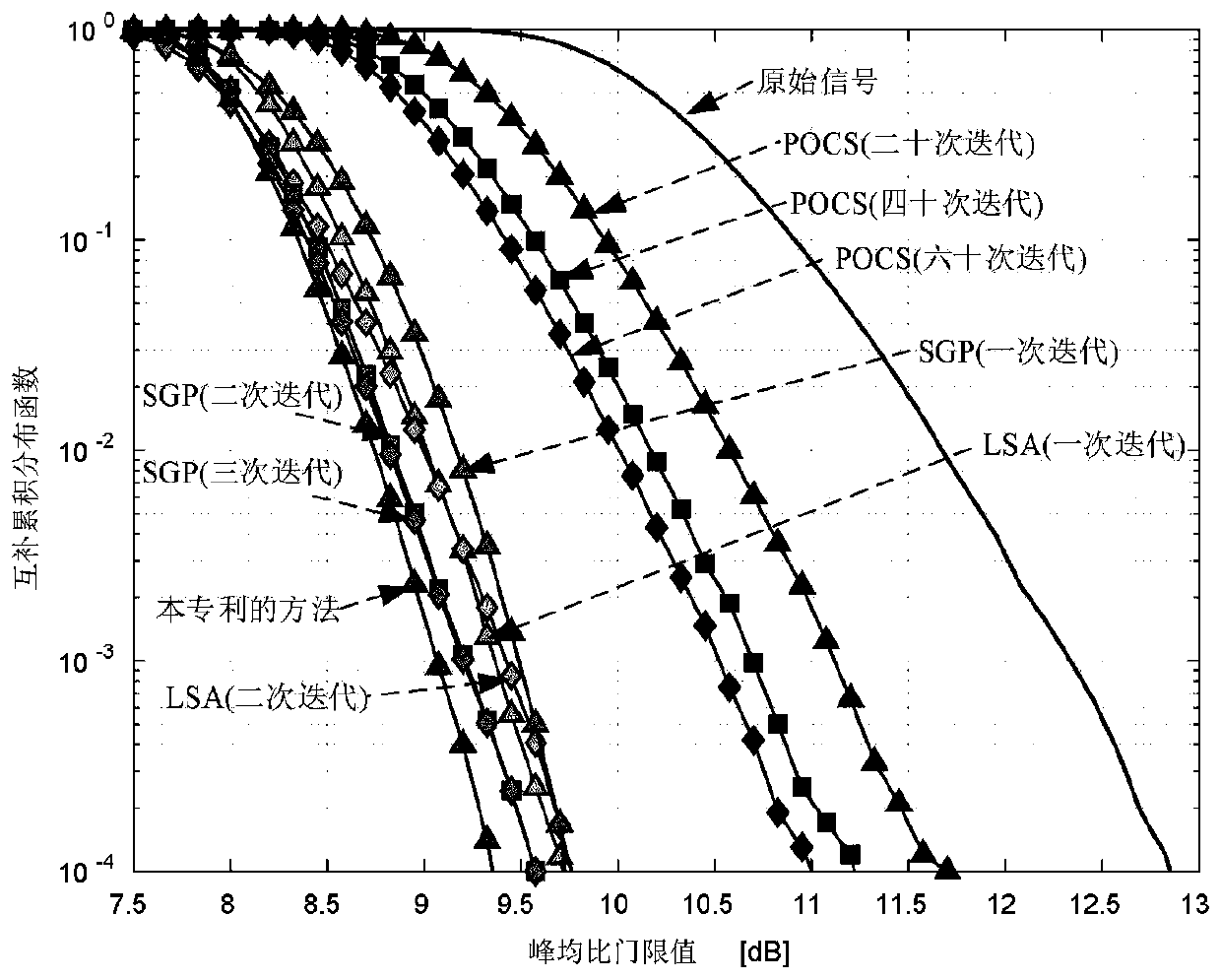
The invention belongs to the technical field of electronic communication, and discloses a method and a system for suppressing ACE of a peak-to-average ratio of a high-order modulation OFDM signal. Themethod comprises steps of redefining expansion rules of constellation in frequency domain; dynamically adjusting a peak clipping threshold according to the peak-to-average ratio of the current signalto obtain an effective peak-to-average ratio suppression gain, and enabling the bit error rate of the system not to be seriously deteriorated; after the effective peak-to-average ratio suppression gain is obtained, obtaining a proper expansion factor by correcting a least square approximation formula, amplifying an original time domain signal, and enhancing the signal peak-to-average ratio suppression effect. Based on the optimization strategy, the peak-to-average ratio of OFDM transmission signals is remarkably reduced under the condition that only one iteration is needed, the implementationcomplexity of the system is greatly reduced, meanwhile, it is guaranteed that the bit error rate and the loss of the out-of-band power spectrum performance are within an acceptable range, and the overall performance of the OFDM system is effectively improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method for reducing peak-to-average ratio in OFDM system and access device
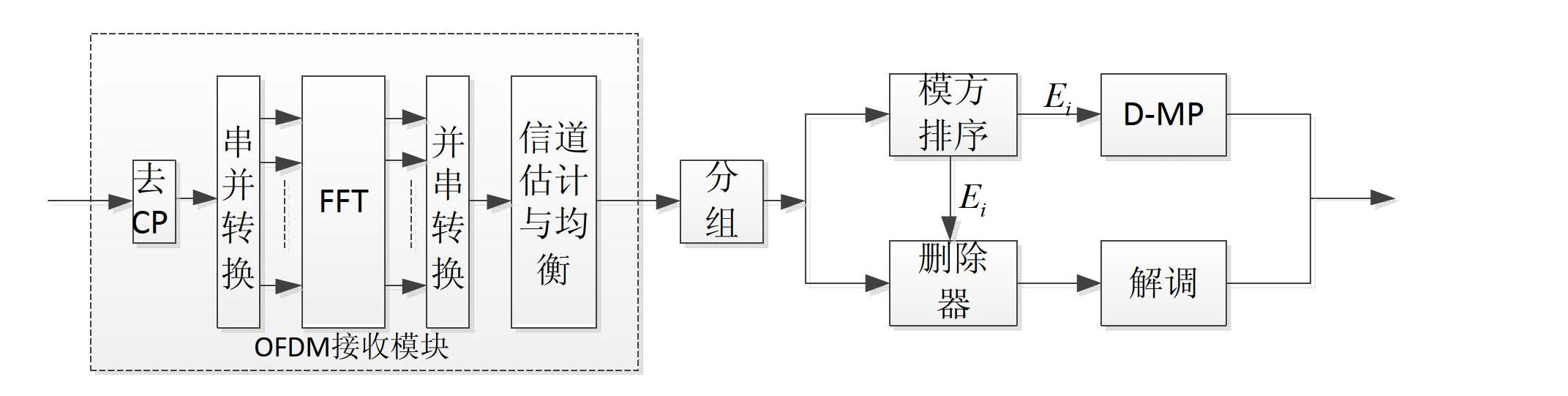
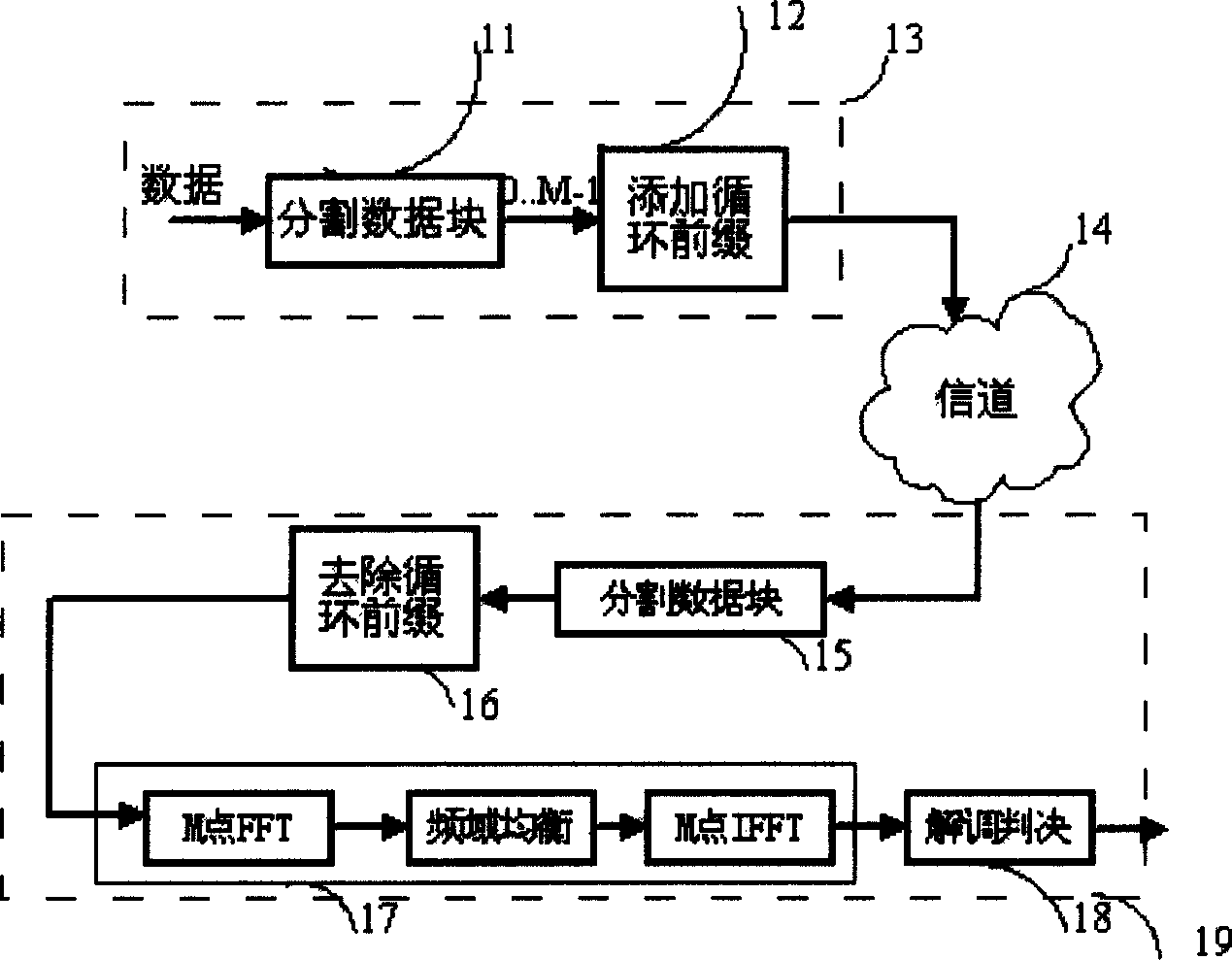
InactiveCN104144140AImprove processing efficiencyLower peak-to-average ratioTransmission control/equalisingMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainEngineering
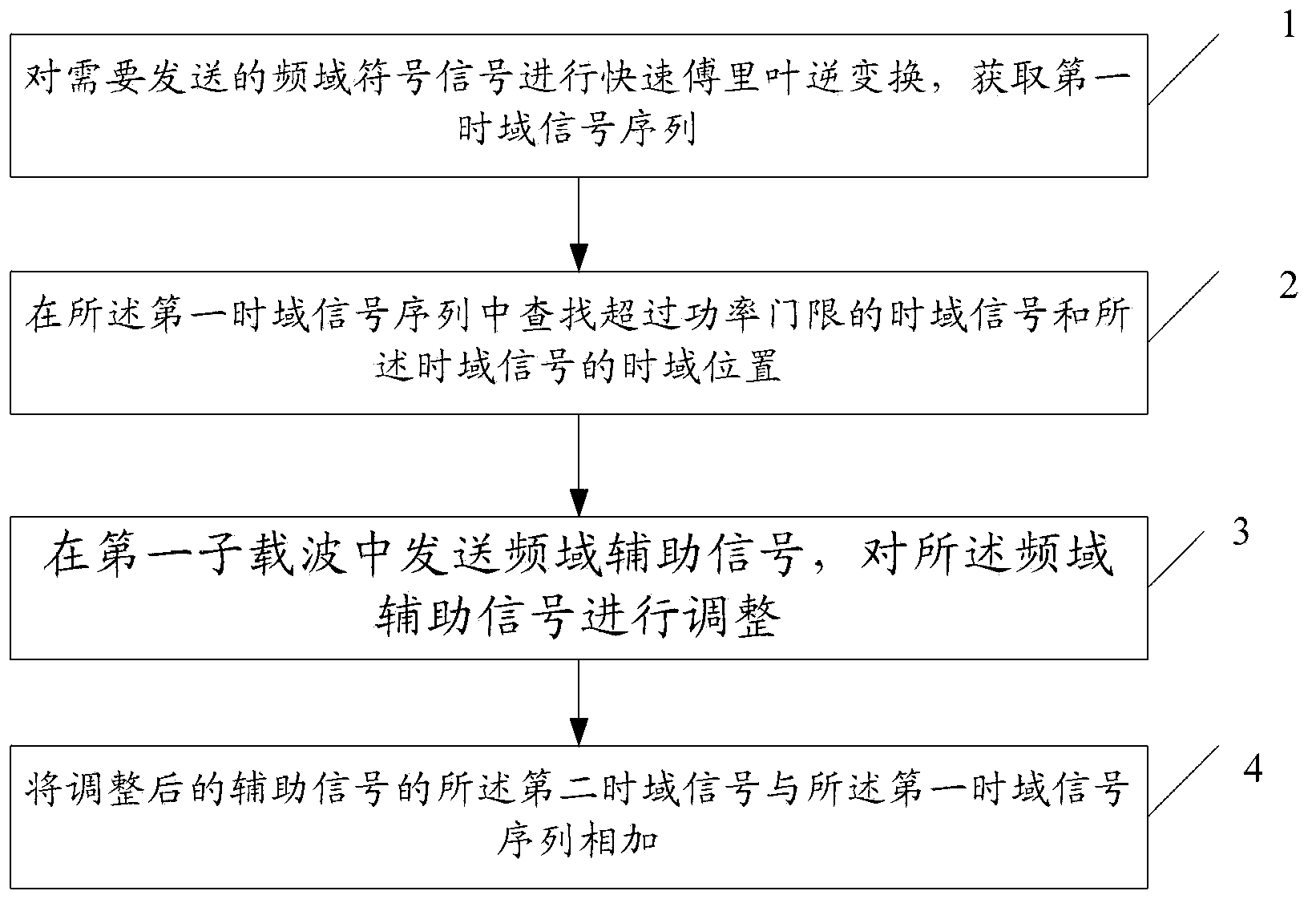
The present invention relates to a method for reducing the peak-to-average ratio in an OFDM system. The method comprises the steps of: step 1, rapid inverse Fourier transforming a modulation signal that needs to be transmitted, acquiring a first time-domain signal collection; step 2, searching in the first time-domain signal collection for multiple time-domain signals of powers that satisfy a threshold and time-domain positions of the time-domain signals when at maximum power; step 3, transmitting a frequency-domain auxiliary signal in a determined subcarrier, and reversely adjusting second time-domain signals of the auxiliary signal at the time-domain positions of first time-domain signals when at maximum power, where the first time-domain signals are the time-domain signals of the greatest power among the multiple time-domain signals; and, step 4, adding the adjusted second time-domain signals of the auxiliary signal to the multiple first time-domain signals to reduce the peak-to-average ratio of the modulation signal. The method allows for implementation of a reduction in the peak-to-average ratio of the modulation signal in the OFDM system insofar that power consumption and the amount of computations are reduced.
Owner:GLOBAL INNOVATION AGGREGATORS LLC
Signal modulation method, device and system
ActiveCN106027441AImprove experienceReduce demodulation timeMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksTime domainCarrier signal
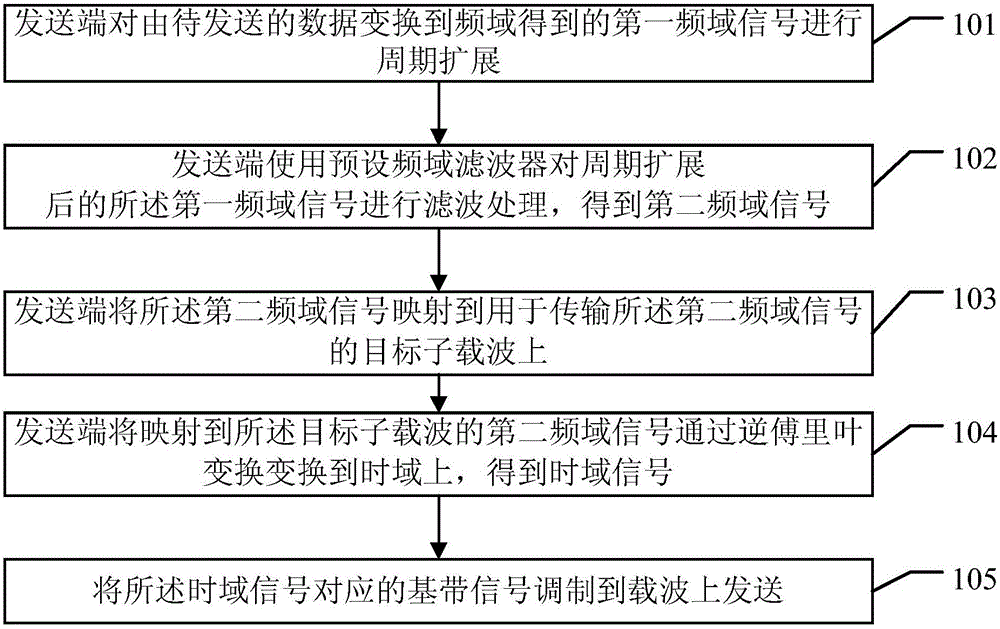
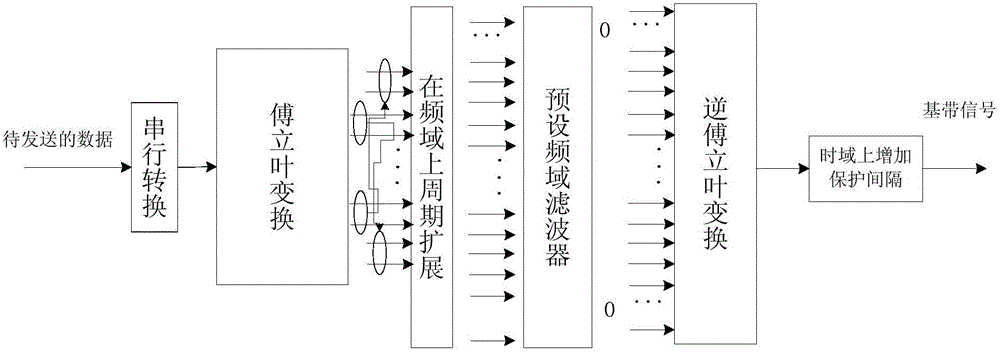
The invention provides a signal modulation method, device and system. The method comprises the steps that a sending end carries out periodic extension on a first frequency domain signal acquired by converting to-be-sent data into a frequency domain; the sending end uses a preset frequency domain filter to carry out filtering processing on the first frequency domain signal after the periodic extension to acquire a second frequency domain signal; the sending end maps the second frequency domain signal onto a target subcarrier used for transmitting the second frequency domain signal; and the sending end transforms the second frequency domain signal mapped onto the target subcarrier onto a time domain via inverse Fourier transform to acquire a time domain signal and modulates a baseband signal corresponding to the time domain signal onto the carrier to be sent. A peak-to-average ratio of the sending signal and the complexity of channel estimation of a receiving end can be reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Scrambling method of downlink channel
InactiveCN105024778ALower peak-to-average ratioError preventionTransmission path multiple useCommunications systemCarrier signal
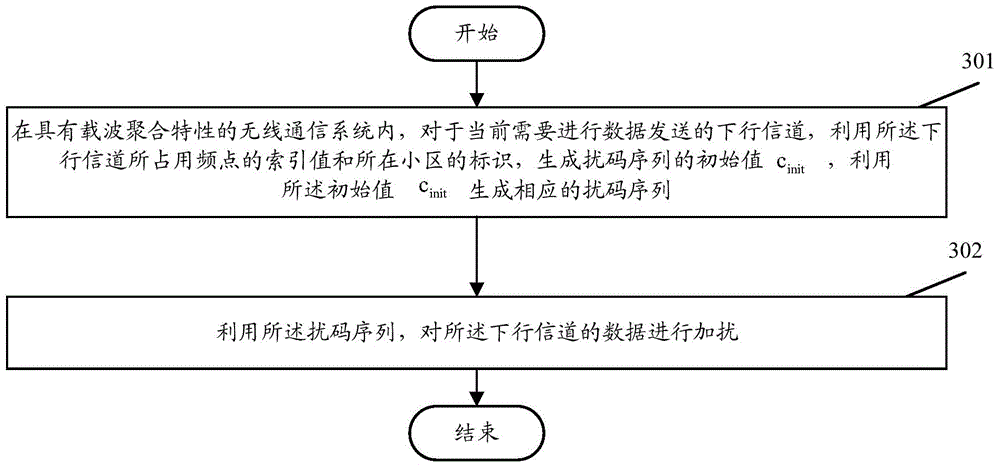
The invention discloses a scrambling method of a downlink channel. The method comprises the following steps of in a wireless communication system possessing a carrier wave aggregation characteristic, for the current downlink channel needing to carry out data sending, using an index value of a frequency point occupied by the downlink channel and an identification of a cell to generate an initial value cinit of a scrambling code sequence; using the initial value cinit to generate a corresponding scrambling code sequence; using the scrambling code sequence to carry out scrambling on data of the downlink channel. By using the method, a problem of a high peak-to-average ratio in the wireless communication system possessing the carrier wave aggregation characteristic can be effectively solved.
Owner:POTEVIO INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
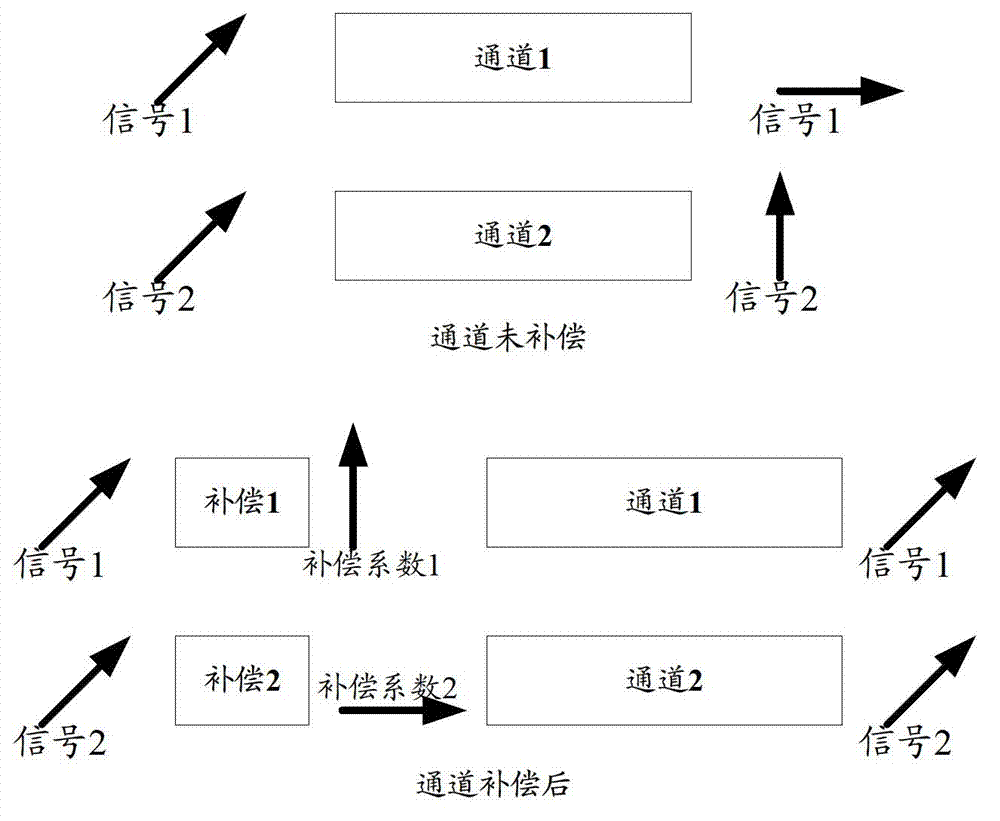
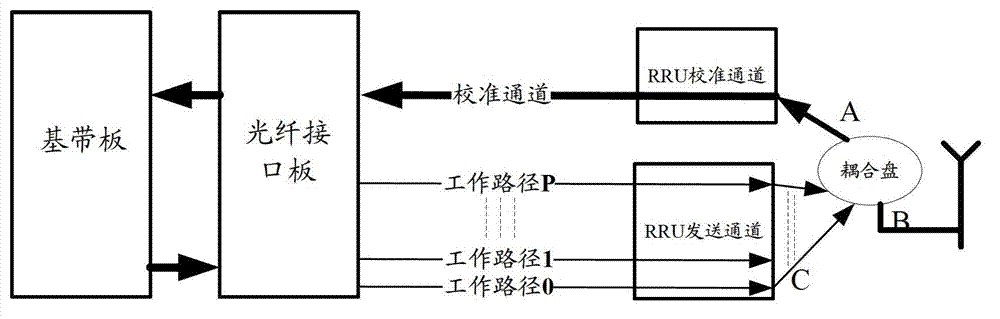
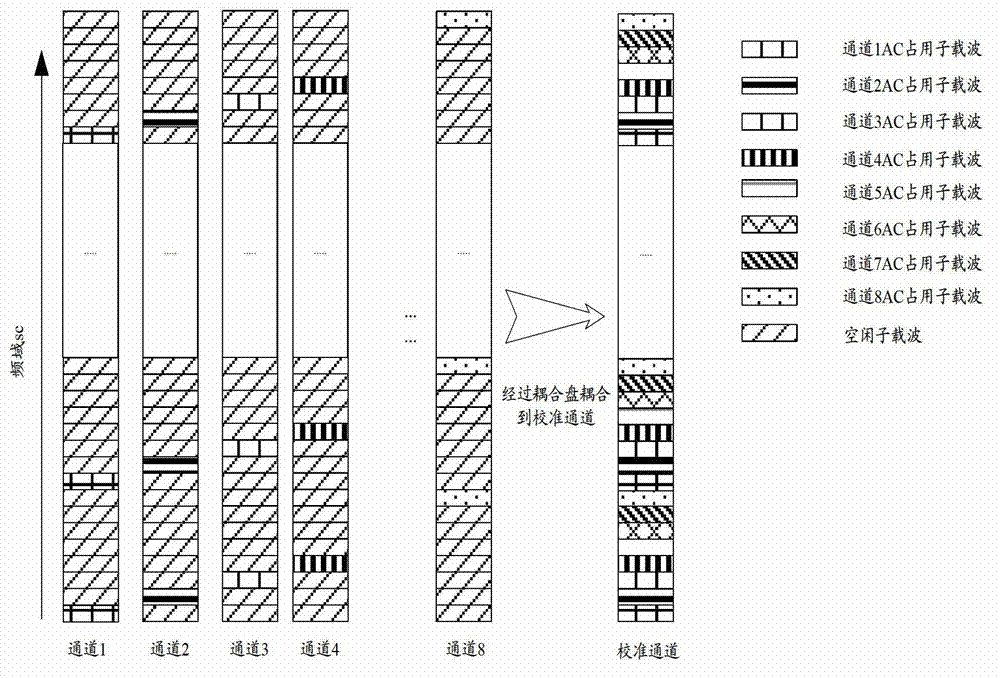
Antenna calibration method and base band unit
ActiveCN103209010AIncrease sending powerImprove accuracyTransmitters monitoringSpatial transmit diversityAntenna calibrationCalibration result
An embodiment of the invention discloses an antenna calibration method and a base band unit, belongs to the field of wireless communication and is used for improving the accuracy of antenna calibration. According to the scheme of the antenna calibration method and the base band unit, at least two times of calibration processes are performed in a current calibrating period after a calibrating signal to be sent is generated, and during every calibration process, the calibrating signal is firstly needed to be subjected to channel difference compensation according to a phase compensation coefficient and then sent by a sending channel. Therefore, the signal peak-to-average ratio is reduced and the accuracy of the final calibration result can be improved.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Quasi-lossless compression method based on corrected OFDM sub-carriers
ActiveCN103944853ALower peak-to-average ratioExcellent complexityMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainLossless compression
The invention discloses a quasi-lossless compression method based on corrected OFDM sub-carriers. The method comprises the steps that at a sending end, an information source sequence is subjected to constellation map mapping and then is modulated to the sub-carriers through conjugate antisymmetry for IFFT to a time domain; a sub sequence 1 is extracted out through a down sampling device, data of the rest of sampling points are used as a sub sequence 2 and subjected to the companding process; at a receiving end, each received OFDM symbol sequence is divided into two sub sequences, and the sub sequence 2 is subjected to de-companding; every two sub sequences are combined to form a complete OFDM time-domain signal which is transformed to a frequency domain through FFT and recovered on a constellation map; the signal is transformed to the time domain through IFFT, a sub sequence 3 is extracted out through the down sampling device, and the sub sequence 3 and the sub sequence 1 are subjected to subtraction to obtain a time-domain signal deviation value; the deviation value is subjected to FFT, and through judgment of magnitude of the deviation value and a preset threshold value, the sub-carriers with constellation point deviation are determined; the deviation values of constellation mapping points are compensated on corresponding sub-carriers and transformed to the time domain through the IFFT.
Owner:SYSU CMU SHUNDE INT JOINT RES INST +1
Systems and methods for the reduction of peak to average signal levels of multi-bearer single-carrier and multi-carrier waveforms
InactiveUS20060198466A1Lower peak-to-average ratioLow costSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsCommunications systemFrequency spectrum
The present invention is related to methods and apparatus that can advantageously reduce a peak to average signal level exhibited by single or by multicarrier multibearer waveforms. Embodiments of the invention further advantageously can manipulate the statistics of the waveform without expanding the spectral bandwidth of the allocated channels. Embodiments of the invention can be applied to either multiple carrier or single carrier systems to constrain an output signal within predetermined peak to average bounds. Advantageously, the techniques can be used to enhance the utilization of existing multicarrier RF transmitters, including those found in third generation cellular base stations. However, the peak to average power level managing techniques disclosed herein can apply to any band-limited communication system and any type of modulation. The techniques can apply to multiple signals and can apply to a wide variety of modulation schemes or combinations thereof.
Owner:MAXLINEAR ASIA SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Single carrier frequency-division multi-address transmitting, receiving device based on multiple subband wave filter set and method thereof
InactiveCN1925474AReduce distractionsExpand coverageMulti-frequency code systemsFrequency spectrumCarrier signal
This invention provides one single load wave and frequency address system emission device, receive device and its method based on multiple sub filter set, which comprises the following steps: through multiple sub filter set, the whole system wide band is divided into several crossing thin band signal channel by use of signal load transmission pattern; each user can align one or more sub signal channels according to transmission speed; each user adopts several sub channel with continuous lining or discrete sequence.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES CENT FOR WIRELESS COMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com