Variable bandwidth fmt frequency division multiple access method based on single carrier transmission
A frequency division multiple access and access method technology, applied in the field of signal transmission, can solve the problems of reducing the implementation complexity of the transmitter, and achieve the effects of reducing complexity, reducing requirements, and improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
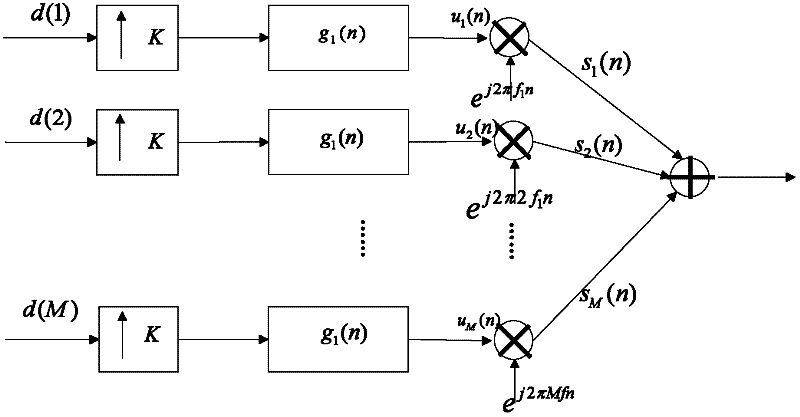
[0049] This embodiment is a sub-carrier (one-tone)-FMT scheme suitable for digital television return channels.
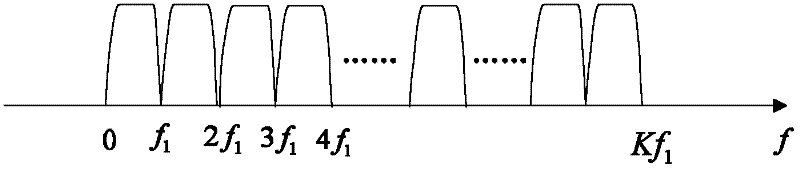
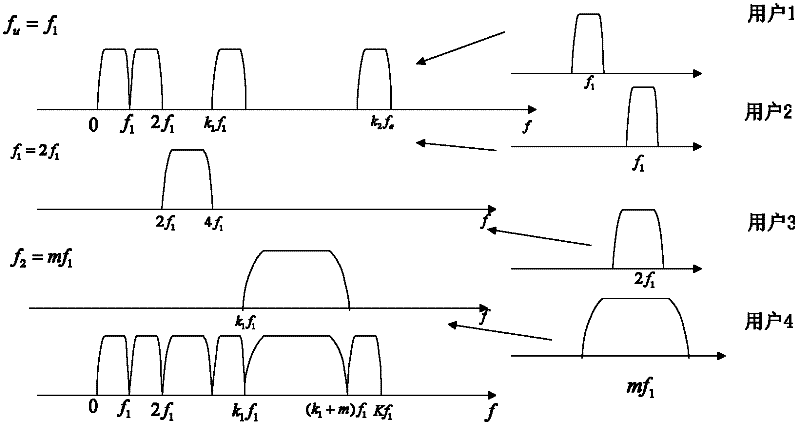
[0050] Assume that an uplink system has M sub-carrier bandwidth requirements. Then define {f 1 ,..., f M} Kinds of carrier bandwidth, where
[0051] f m =k m f 1 (1)
[0052] k m is a positive integer, and m refers to the carrier numbers from low-frequency sub-carriers to high-frequency sub-carriers.
[0053] A user uses the service with the lowest rate, and the minimum bandwidth of its transmitter is f 1 The subcarriers of , the shaping filter adopts the root raised cosine filter or other filters with better truncation effect in the frequency domain, the roll-off coefficient is α, and the passband bandwidth is The shaping filter used when recording the minimum bandwidth is g(n), where g(n) is called the original filter. Bandwidth is f 1 The subcarriers sent by the user are
[0054] s ( u ...
Embodiment 2
[0068] If the transmitted single-carrier signal cannot be regarded as flat fading, a CP header can be added to the OFDM block for protection, such as Figure 4 , the implementation method steps are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
[0069] As can be seen from the above embodiments, the present invention is variable through 1) the bandwidth of the subcarriers sent by each user (subcarriers with different bandwidths have different capabilities against time-selective and frequency-selective fading), and the bandwidth of the subcarriers needs to be Satisfy certain conditions; 2) The variable bandwidth sub-carrier is a filtered single-carrier signal; 3) The transmitter sends data synchronously and demodulates in parallel at the receiver, which reduces the complexity of the transmitter and implementation, and at the same time reduces the system's need for synchronization The peak-to-average ratio of requirements and systems improves the efficiency of resource allocation.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com