Patents
Literature
41 results about "Raised-cosine filter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The raised-cosine filter is a filter frequently used for pulse-shaping in digital modulation due to its ability to minimise intersymbol interference (ISI). Its name stems from the fact that the non-zero portion of the frequency spectrum of its simplest form (β=1) is a cosine function, 'raised' up to sit above the f (horizontal) axis.
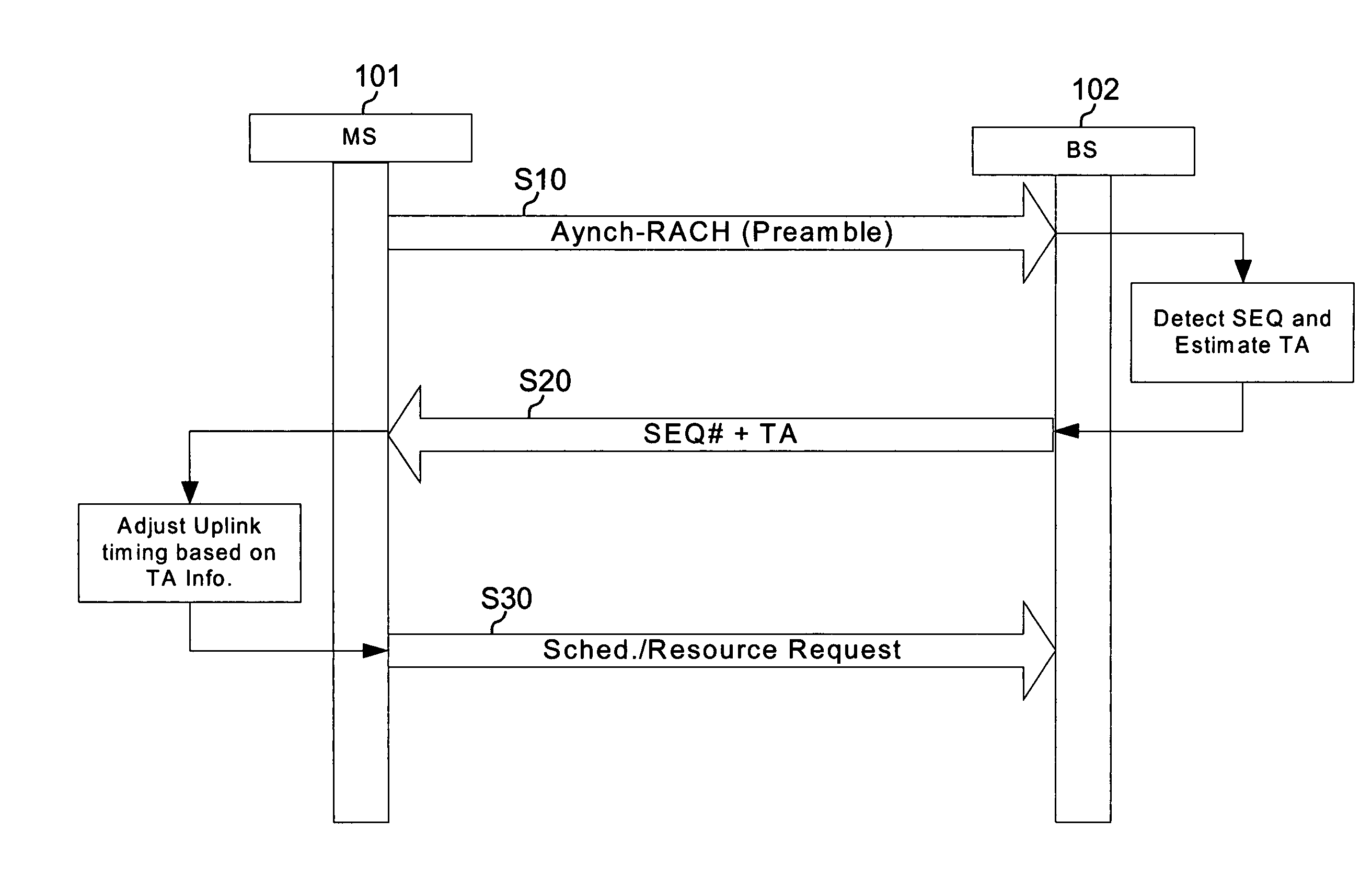
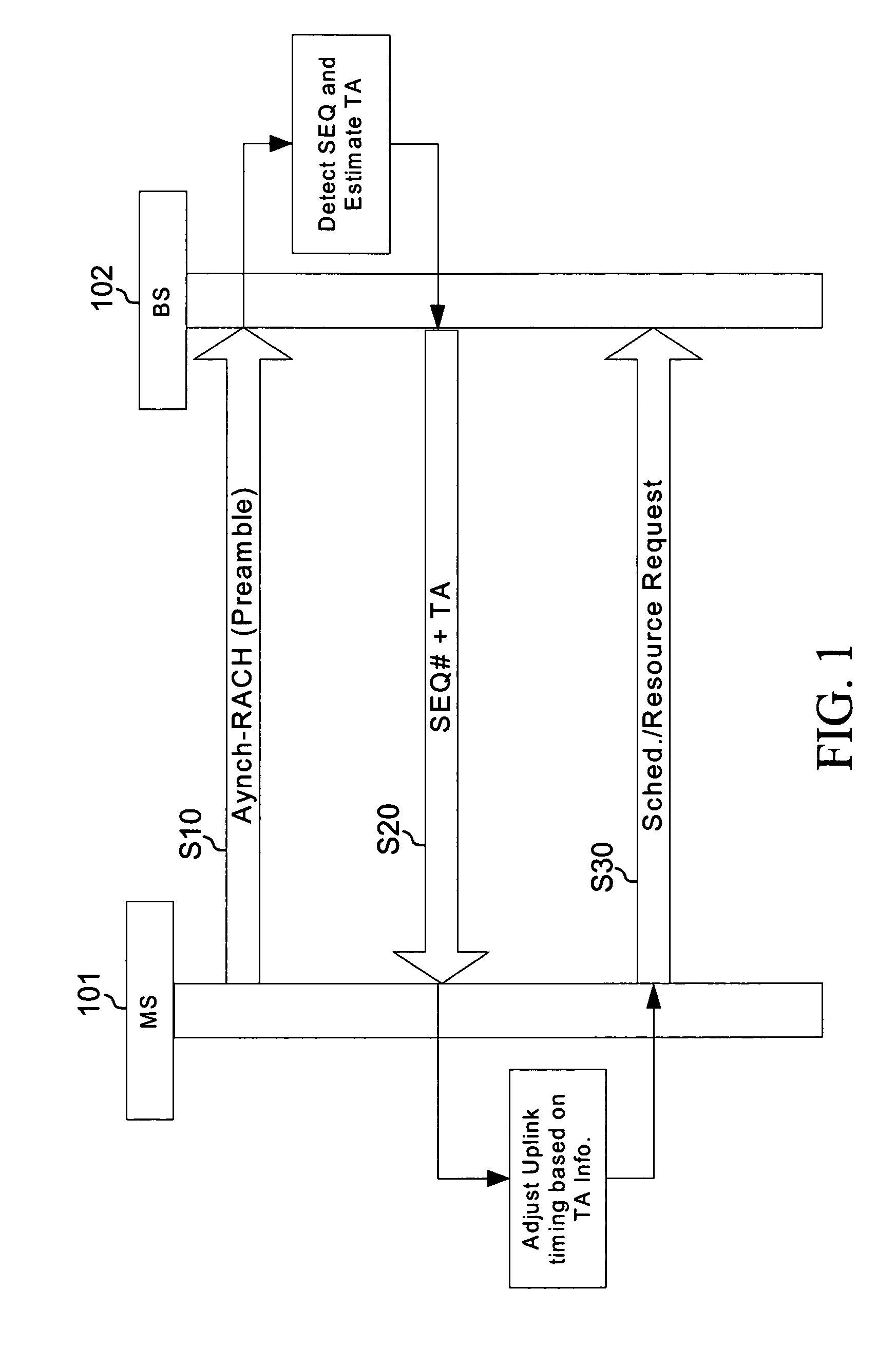
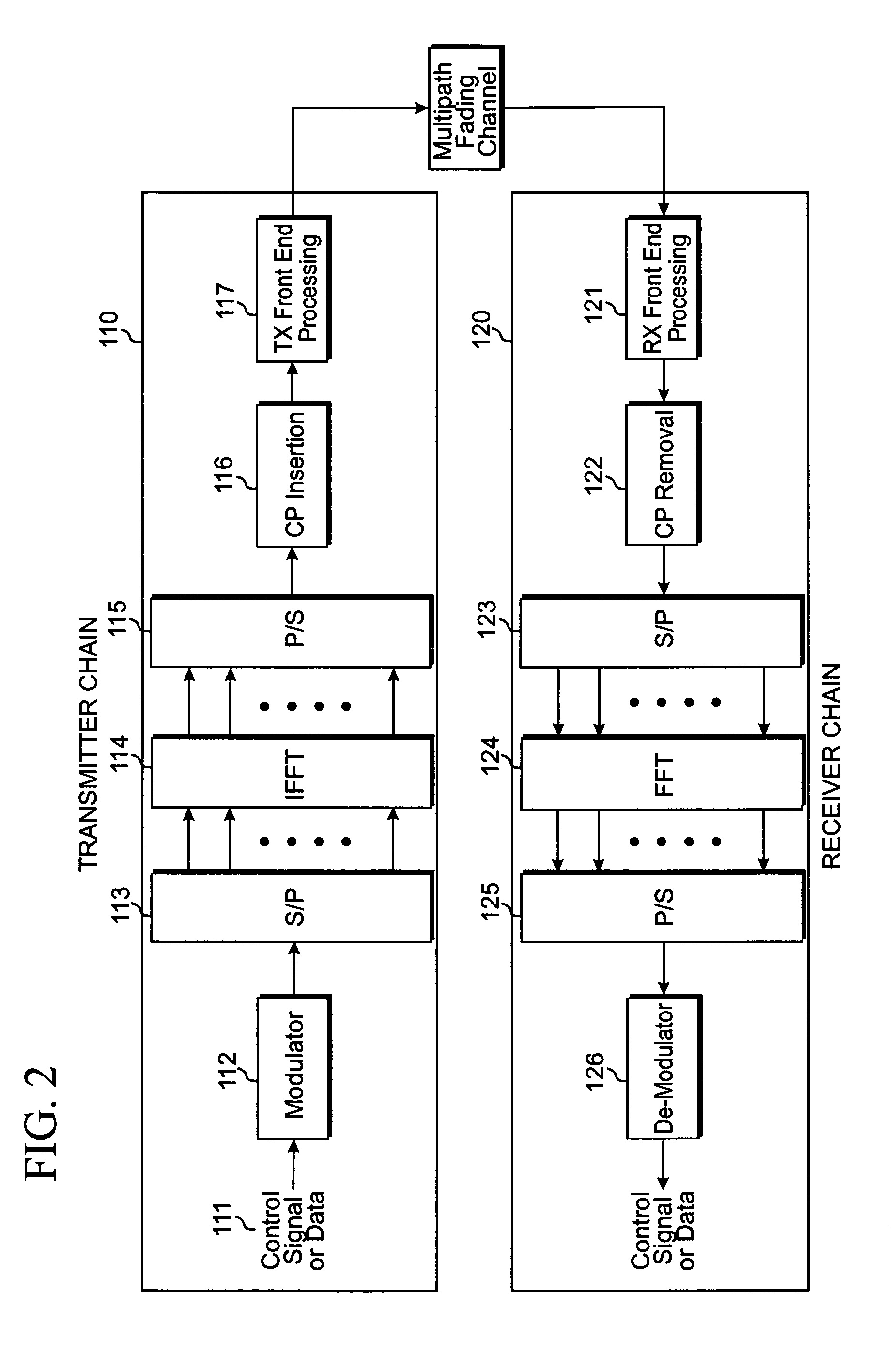
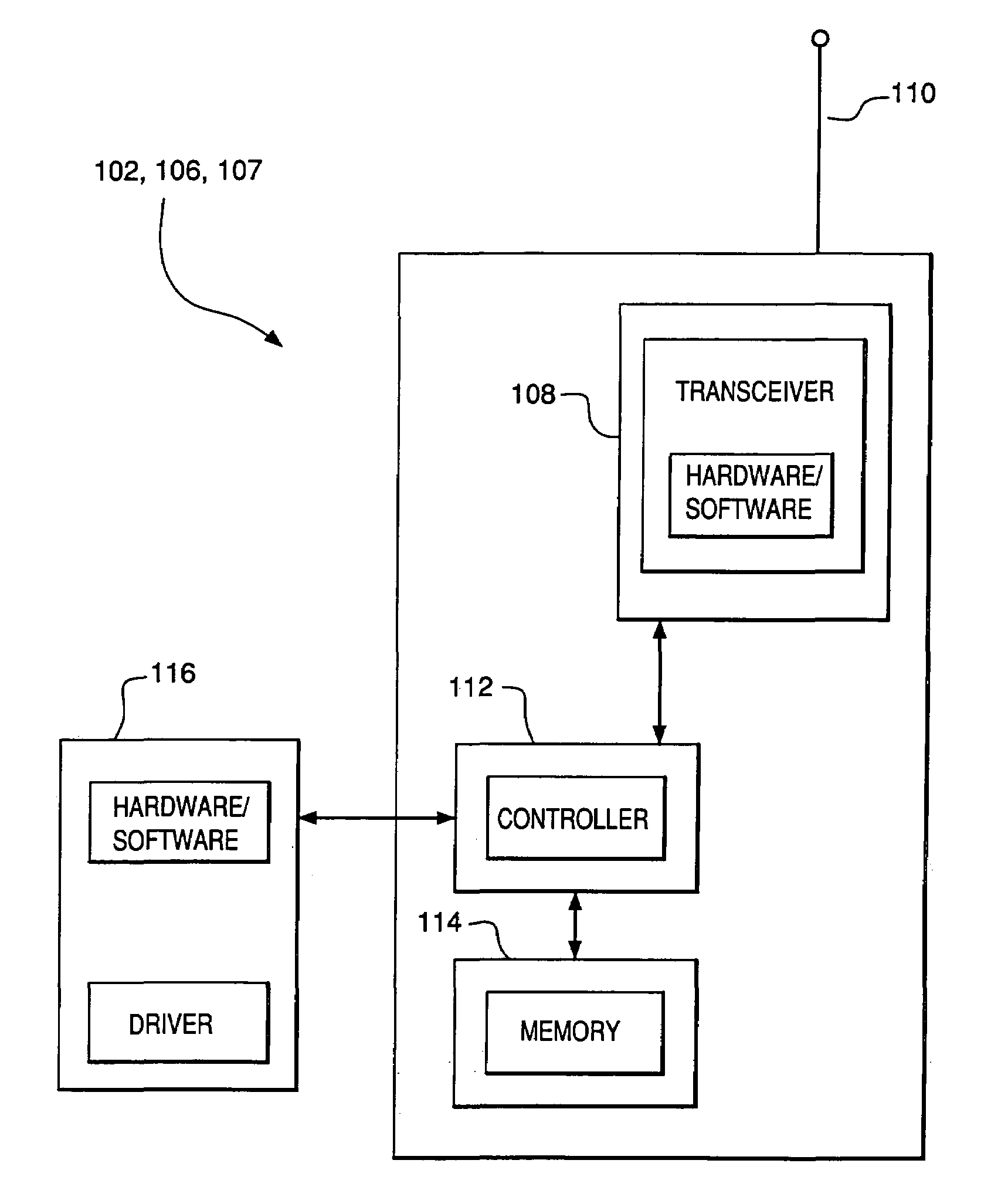
Filtering and guard band for non-synchronized transmission
InactiveUS20080240028A1Simple systemReduce distractionsTime-division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemCarrier signal
A wireless terminal capable of communicating with a wireless communication system comprised of a plurality of wireless terminals and a plurality of base stations. The wireless terminal selects a sequence from a group of certain sequences for random access. At least one sub-carriers on an uplink channel including at least one data channel is allocated for at least one random access channel. Each data channel includes a continuous set of data sub-carriers. The wireless terminal then filters the at least one random access channel by applying a Raised Cosine filter, maps the selected sequence to the at least one random access channel to generate a random access channel signal, and transmits the random access channel signal to a base station.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for improving the accuracy of time of arrival measurements in a wireless ad-hoc communications network
ActiveUS7054126B2Improve accuracySynchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesCorrelation functionPeak value
A system and method for improved Time Of Arrival (TOA) distance measurements between nodes of a wireless ad-hoc network. Specifically, the present invention is a system and method of distance estimation using square-root raised-cosine pulse shaping and chip matched filters on direct sequence spreading waveforms, the multiplication of which produces raised-cosine filtered pulse responses. The responses are used to identify a time when a function is at a maximum, corresponding to the actual signal reception time. The system and method produces a raised-cosine filtered pulse response and an auto-correlation function based on a received signal. A peak value of the auto-correlation function is calculated based on a quadratic approximation, which is corrected using a signal sampling phase offset detected between the raised-cosine filtered pulse response and the calculated peak value. The calculated peak value is then corrected to represent an actual reception time for received signals.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
Linearization of power amplifier
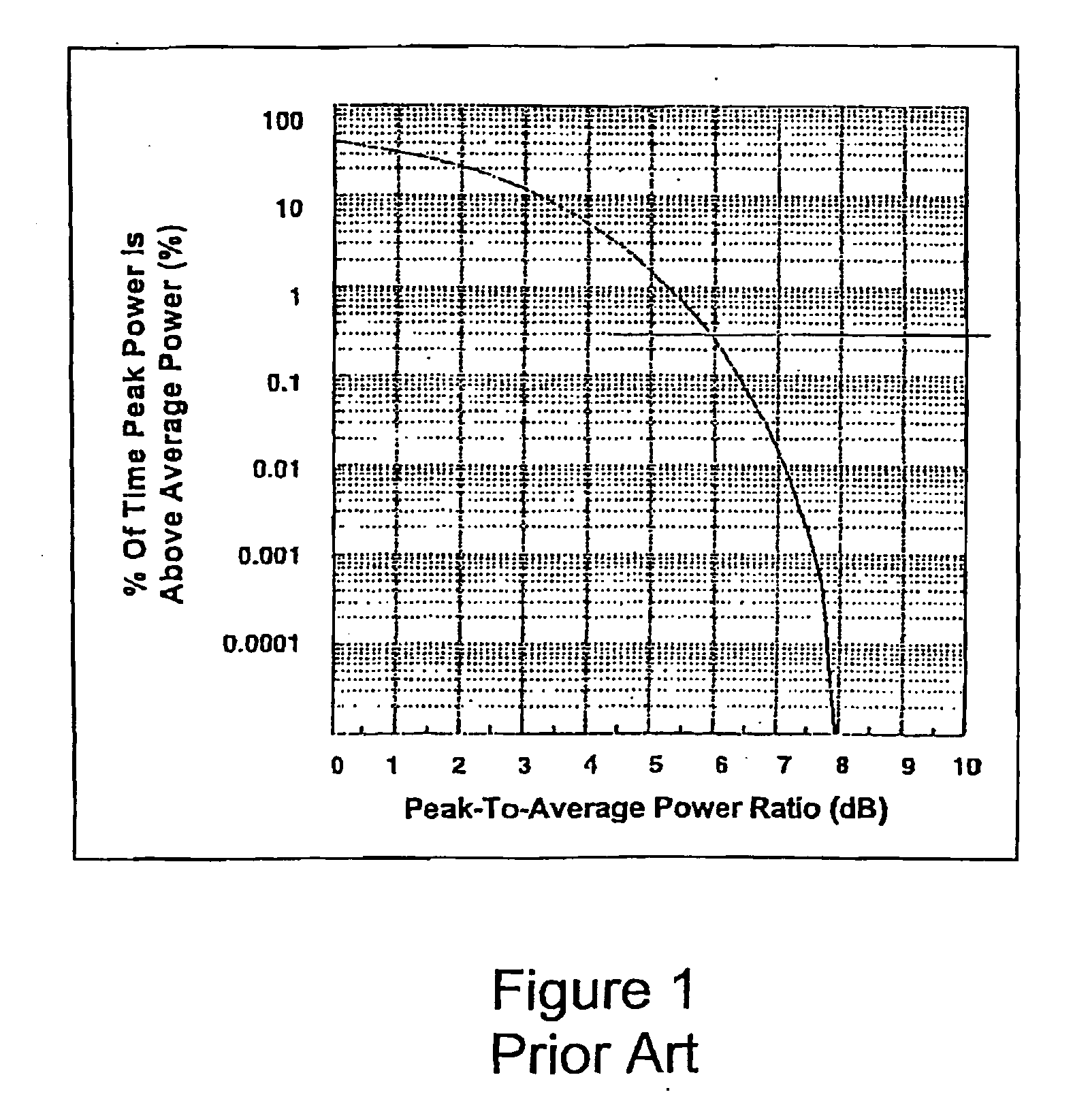
InactiveUS6546233B1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasFrequency spectrumLinear power amplifier
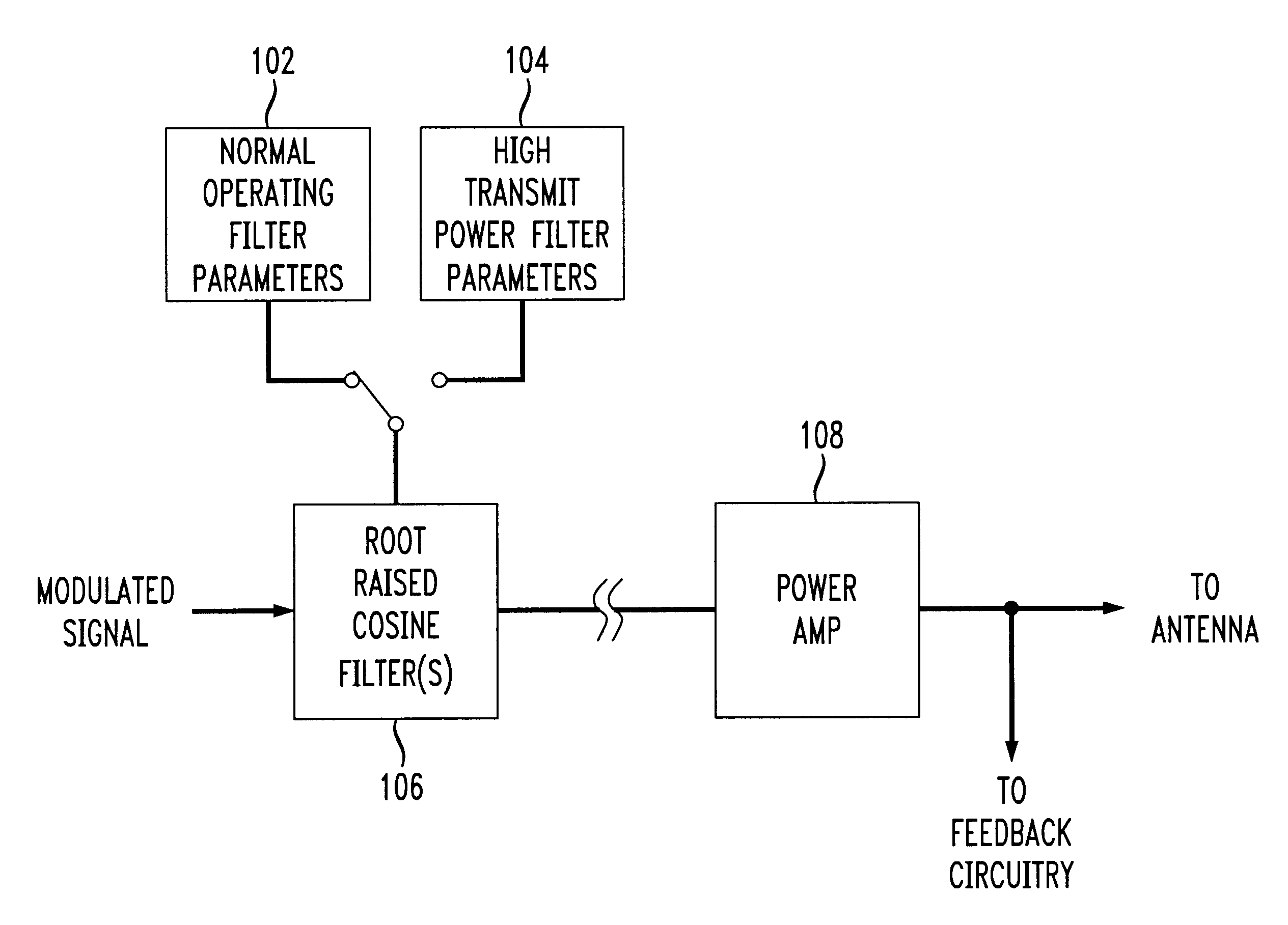
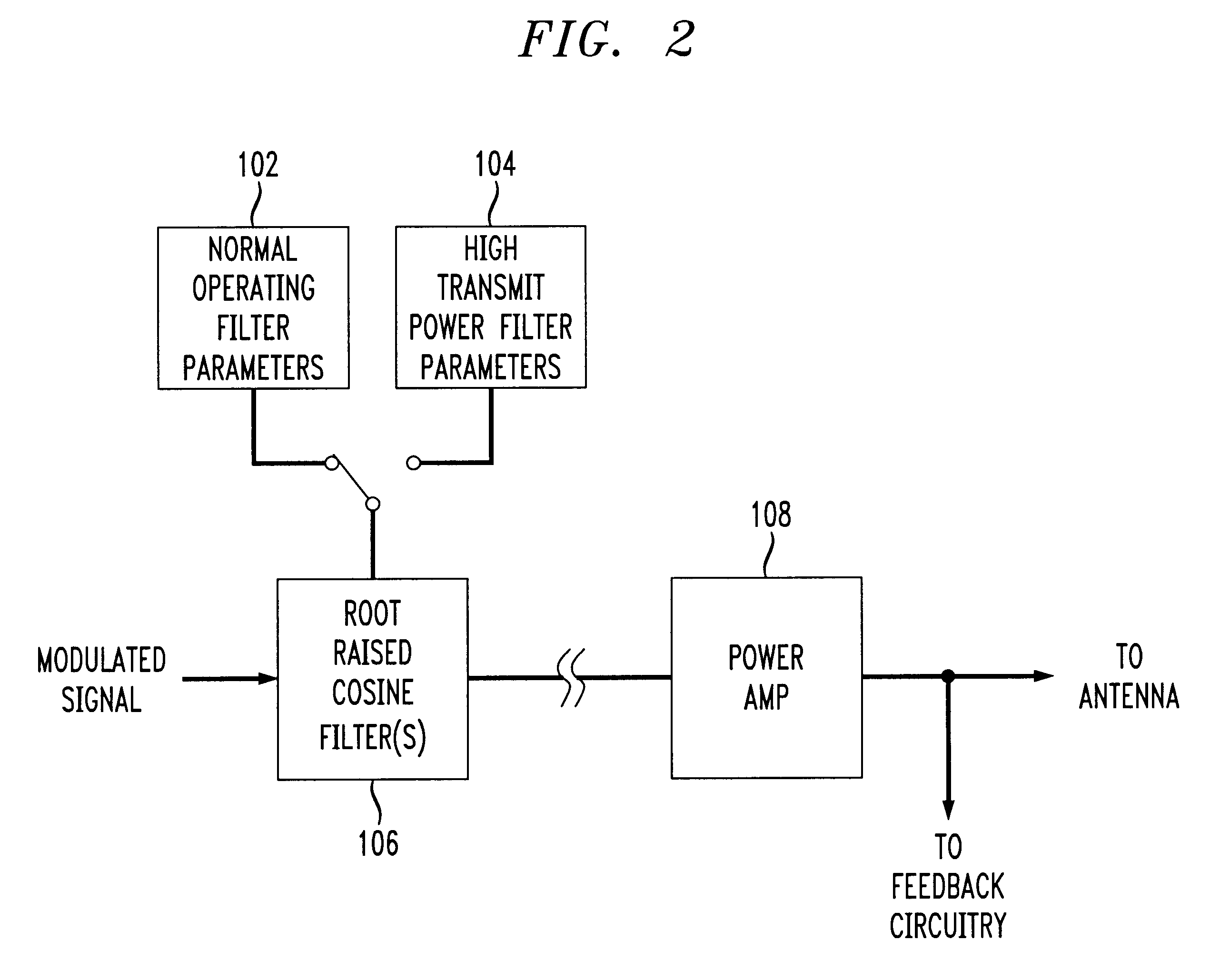
A apparatus linearizing and technique for linearizing a non-linear power amplifier used in a transmitter of, e.g., a TDMA mobile wireless telephone. Linearization of the non-linear amplifier by changing the shape of the input signal is performed when the input signal level is high, thus increasing efficiency or reducing power consumption at that time, albeit at the cost of increased inter-symbol interference (ISI). However, since the input signals at that time are at a high level, the increased ISI can be tolerated and adjacent symbols can still be distinguished from one another. The invention allows use of a non-linear power amplifier which typically enjoys a lower current consumption than that of a linear power amplifier, thus increasing the time between battery recharges and / or reducing the overall size of the wireless telephone device. The power amplifier is operated in a linear mode when transmitted power is low, thus allowing differentiation between adjacent symbols (i.e., improvement of ISI). At high input power, the power amplifier is used in its non-linear mode to reduce current consumption. The signal shape is changed by changing the parameters of the root raised cosine filters. When the input level is low, the existing, otherwise conventional filter's parameters are used. However, when the input power level is high, modified parameters are used. Switching between the two sets of filter parameters is preferably performed at baseband. Thus, a relationship between RRCF filter parameters and the amount of spectrum utilized by the transmitted signal is utilized, and RRCF filter parameters are adjusted based on a desired limitation to an output spectrum.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
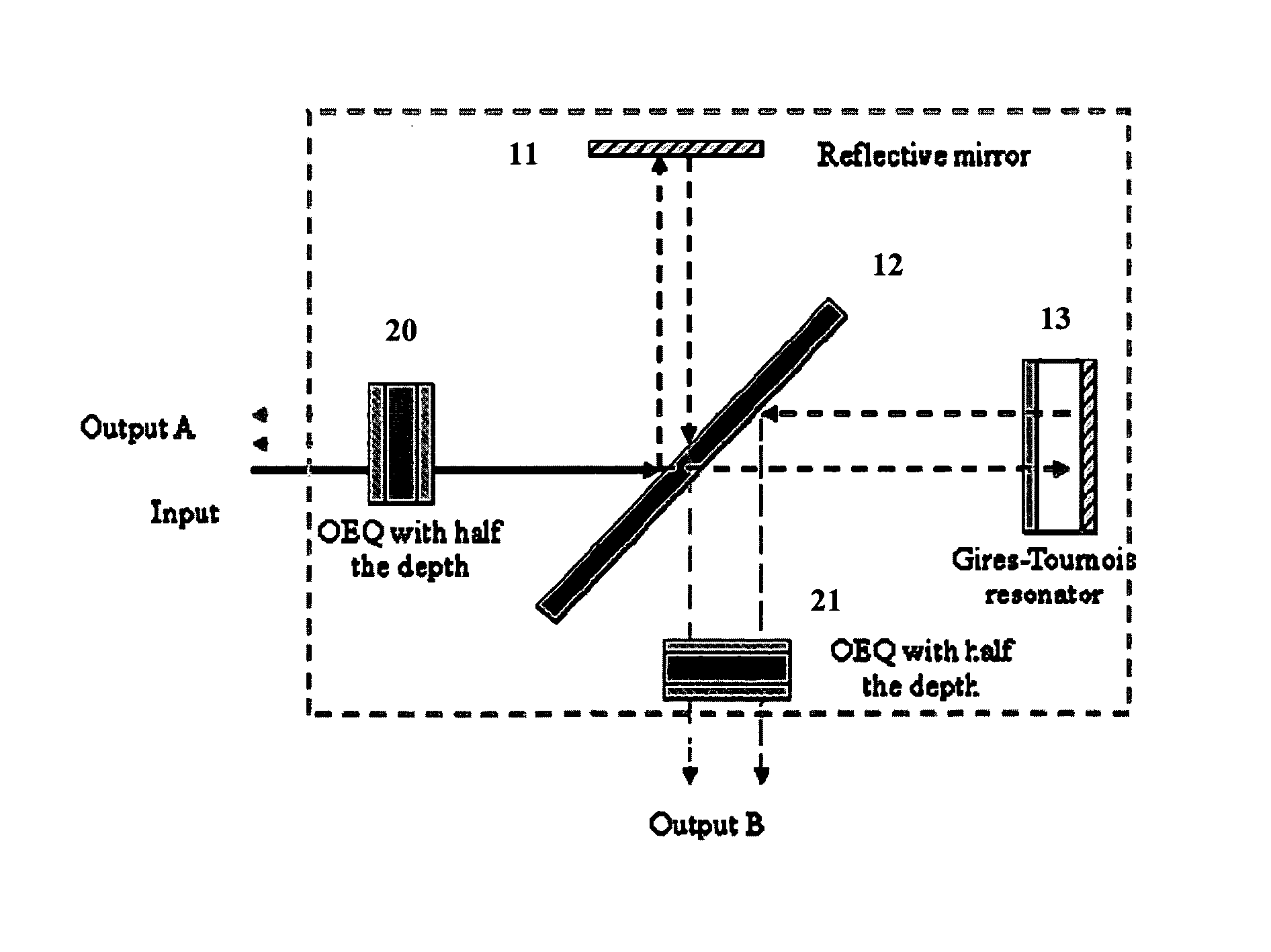
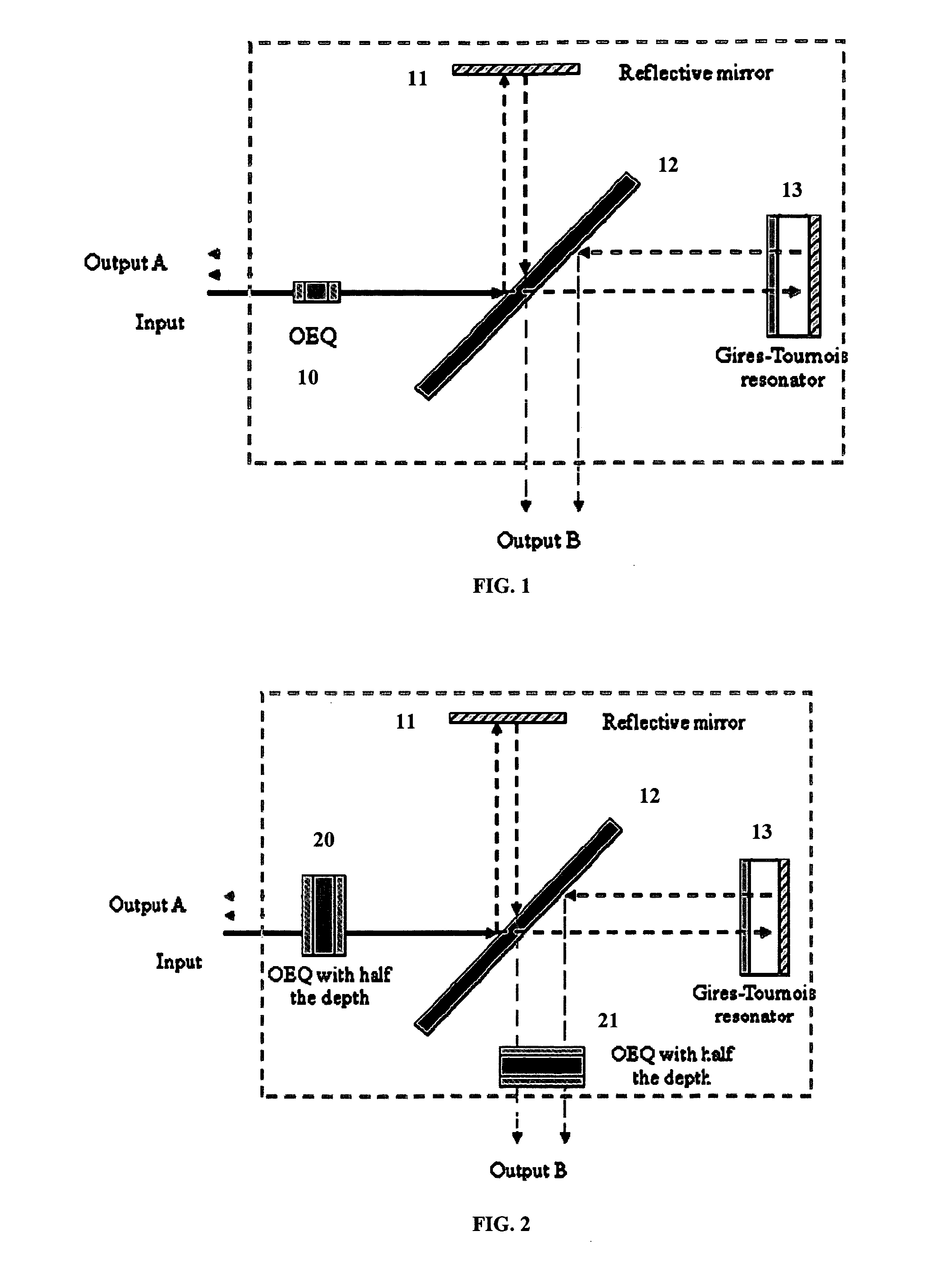
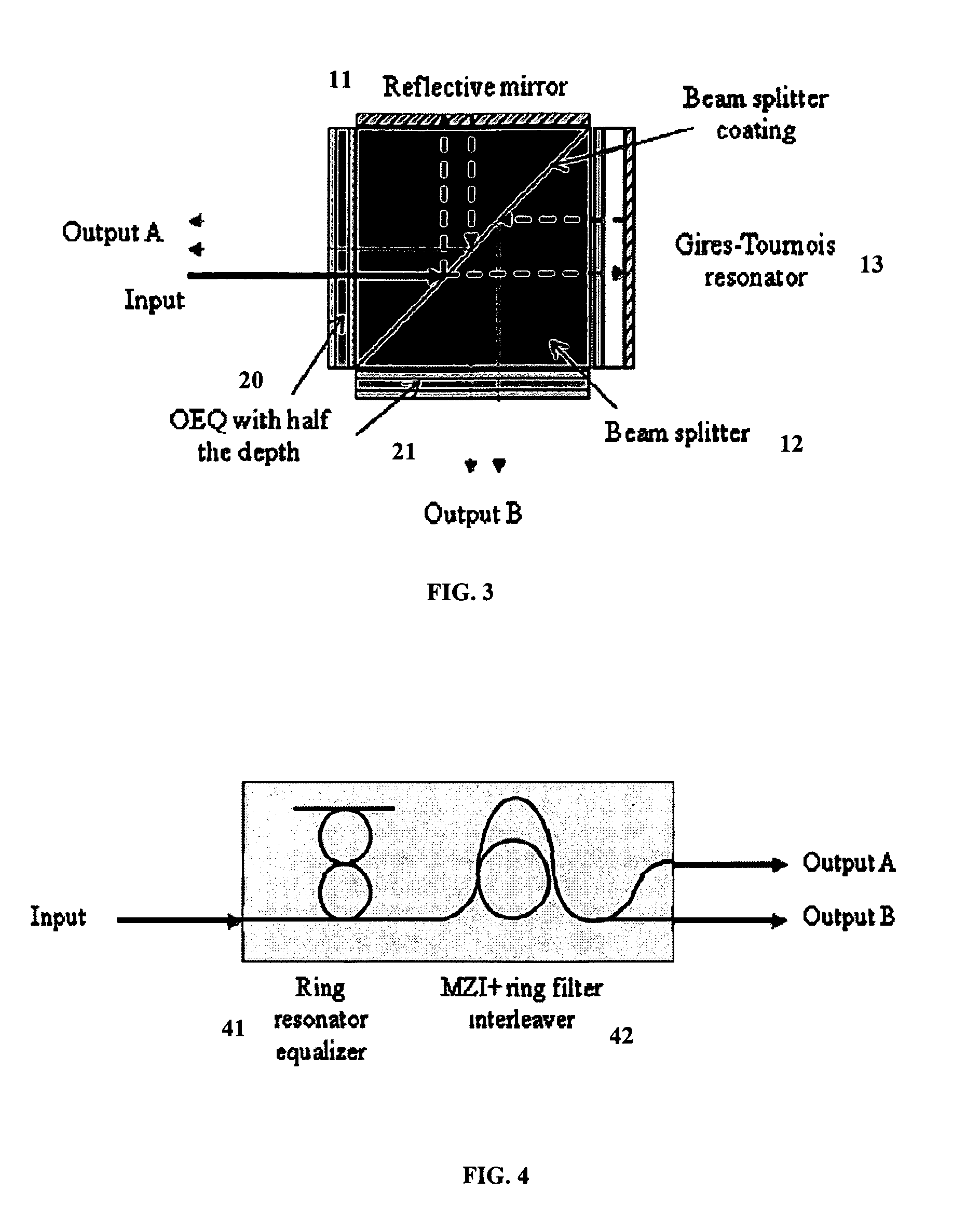
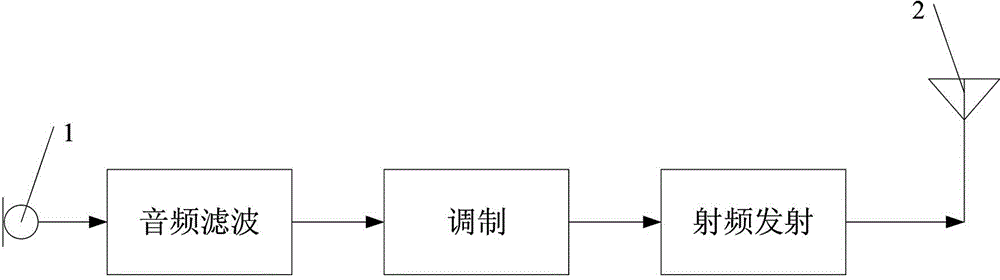
Intra-Channel Equalizing Optical Interleaver
ActiveUS20090162066A1Suppress Intersymbol InterferenceWavelength-division multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationChannel densityIntersymbol interference
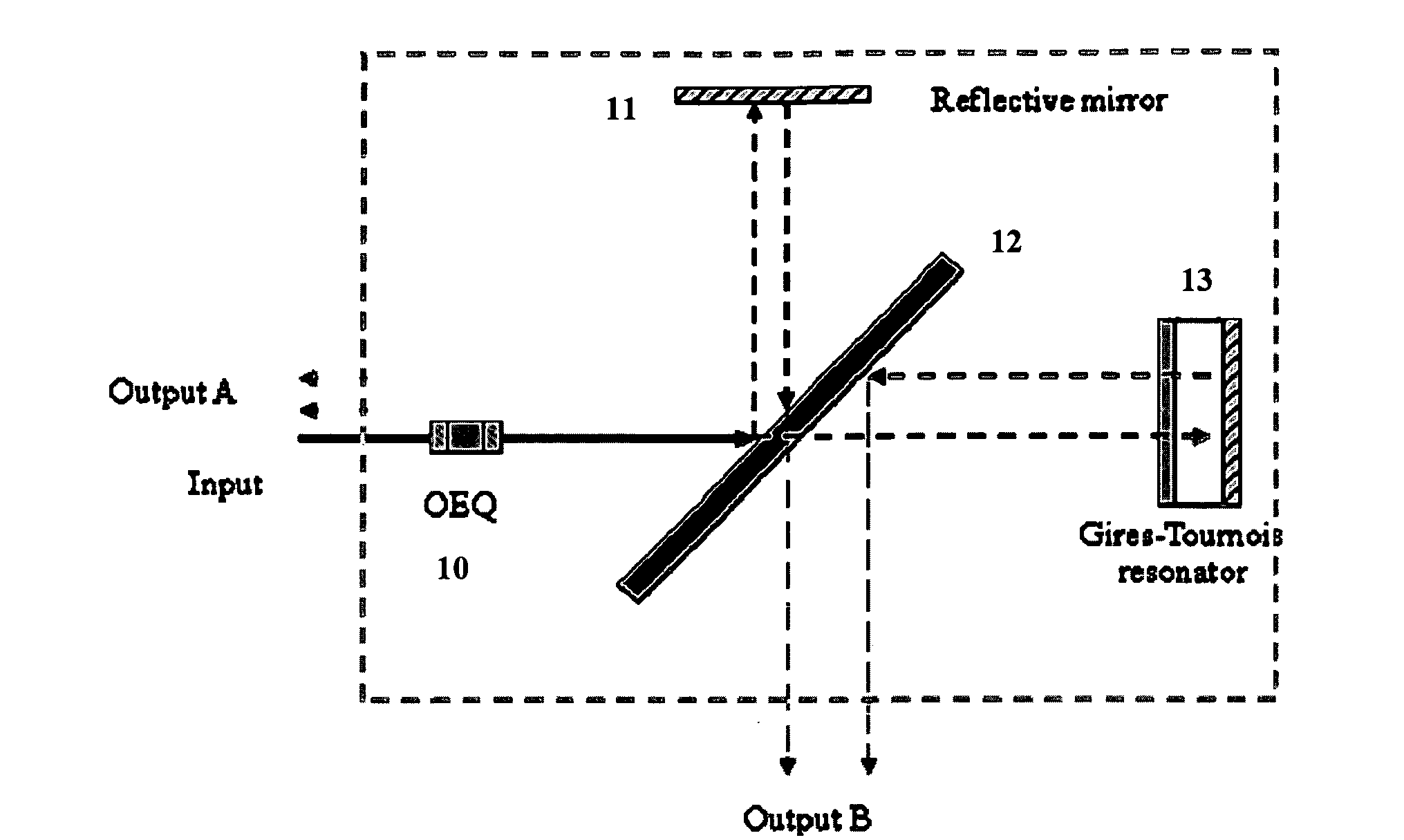
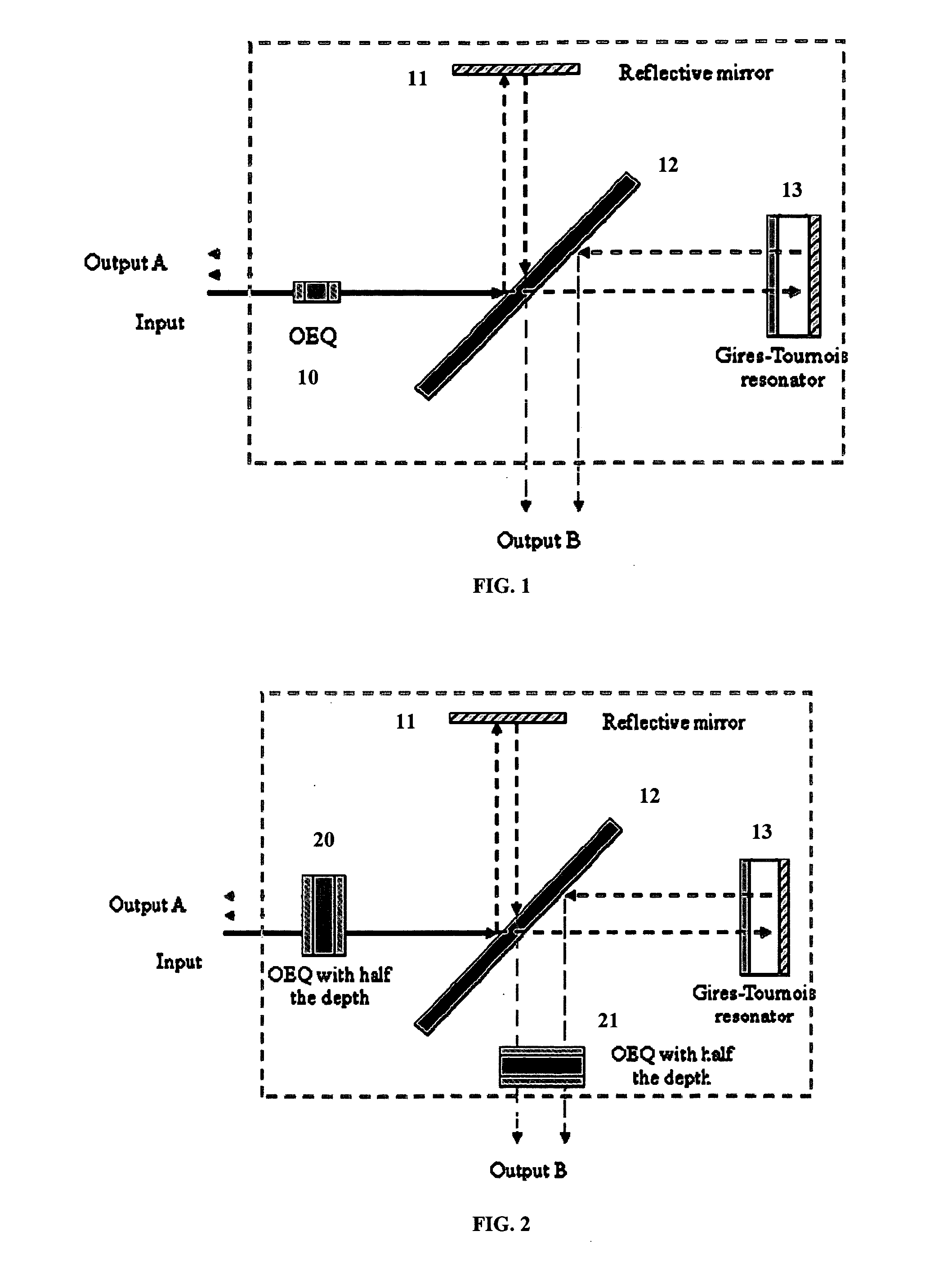
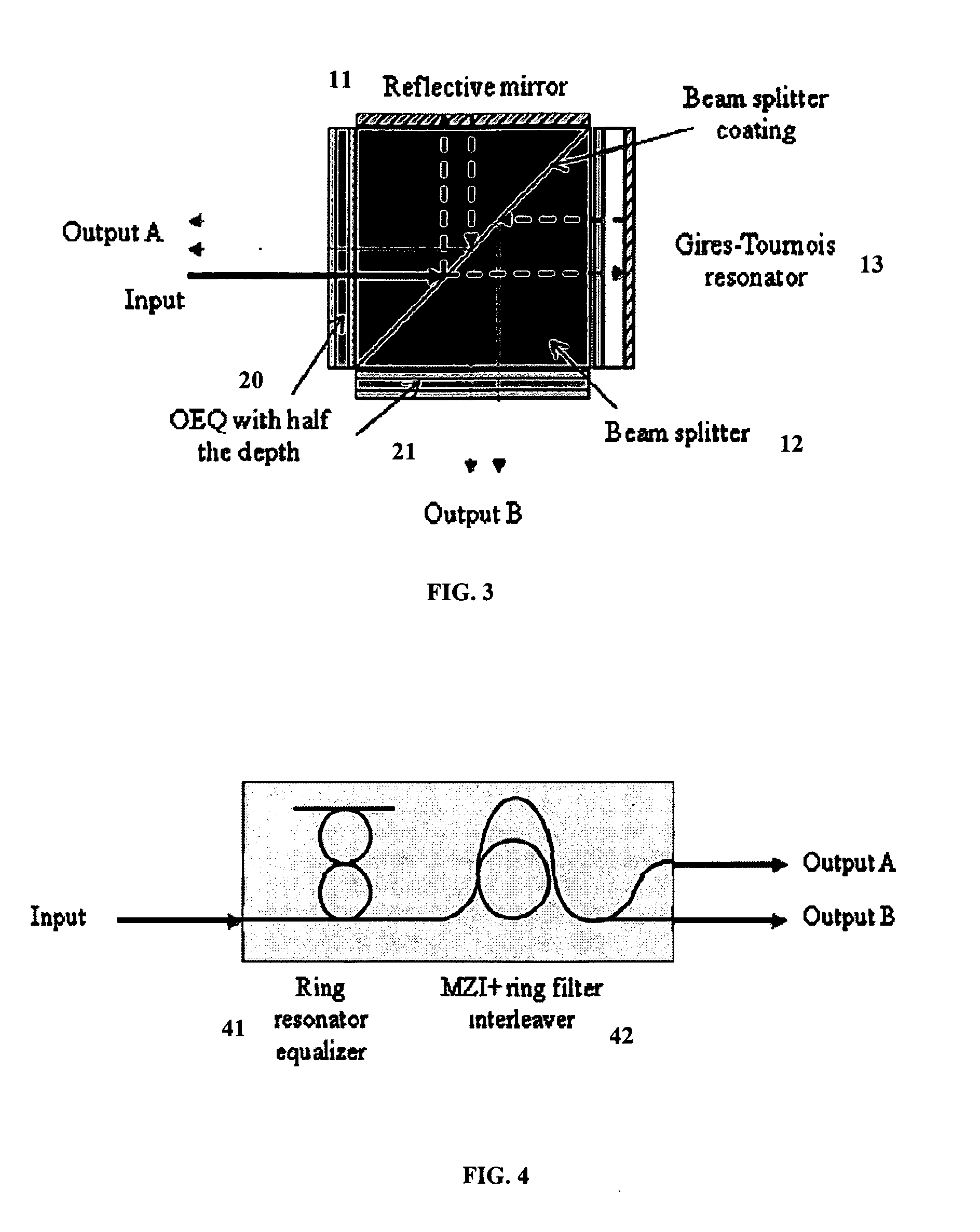
An apparatus includes an interleaver configuration for at least one of combining or separating odd and even channel groups to achieve channel density doubling; and an optical equalizer for suppressing inter symbol interference within the channels to provide intra-channel equalizing in the optical path, the equalizer being integrated into the interleaver. Preferably, optical equalizer and interleaver are integrated together as a single monolithic device, the optical equalizer includes a passband that has a dip in the channel center to achieve a raised-cosine filtering profile in the optical signal path to achieve inter-symbol interference ISI suppression, and the equalizer includes integration into the optical path of the interleaver to realize a monolithic device combining or separating odd and even channel groups to achieve channel density doubling. Preferably, also, the optical equalizer includes a first equalizer with half the depth of required ripple dips at both a first output port and an input port and a second equalizer with half the depth of required ripple dips at a second output port.
Owner:NEC CORP +1
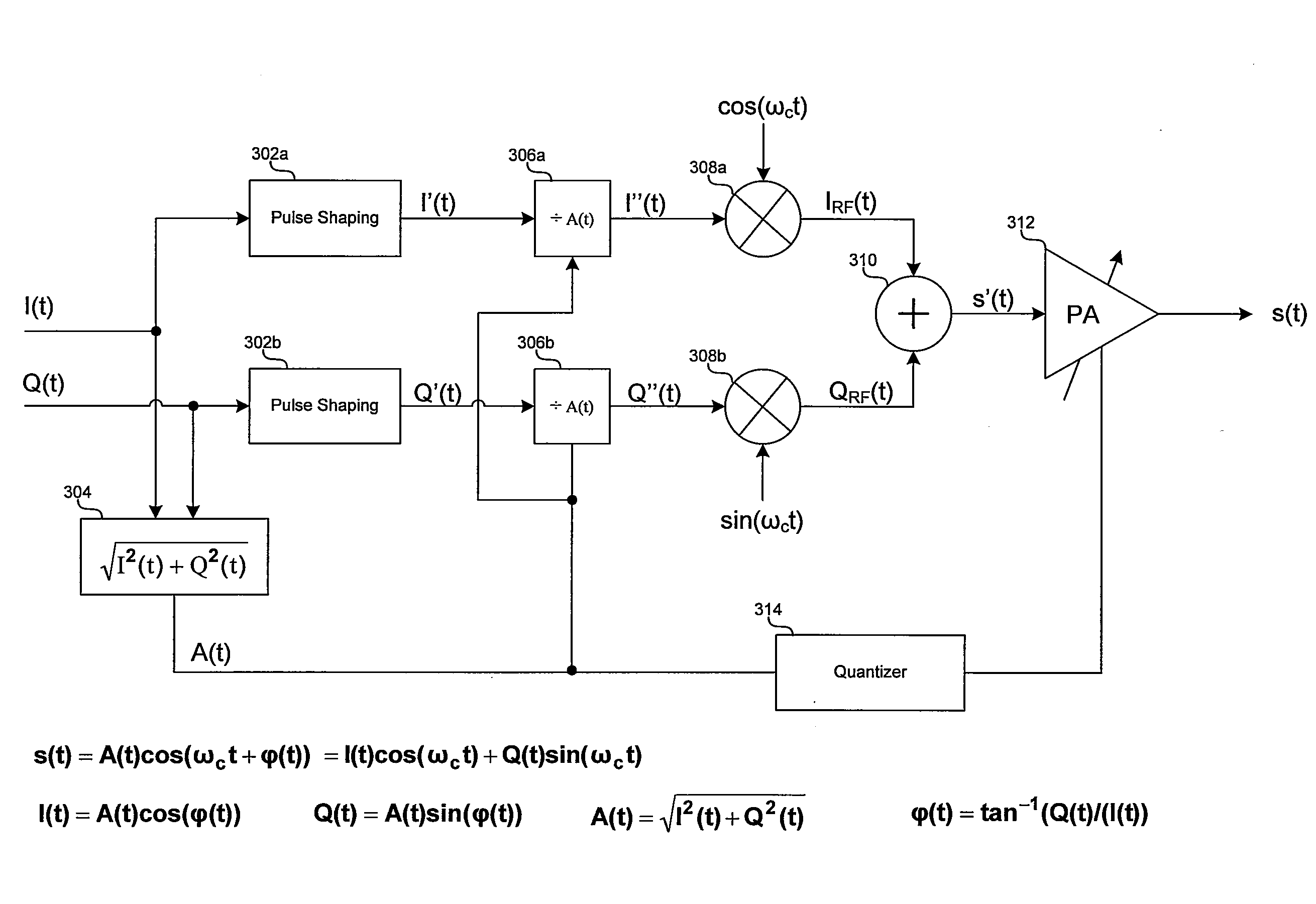
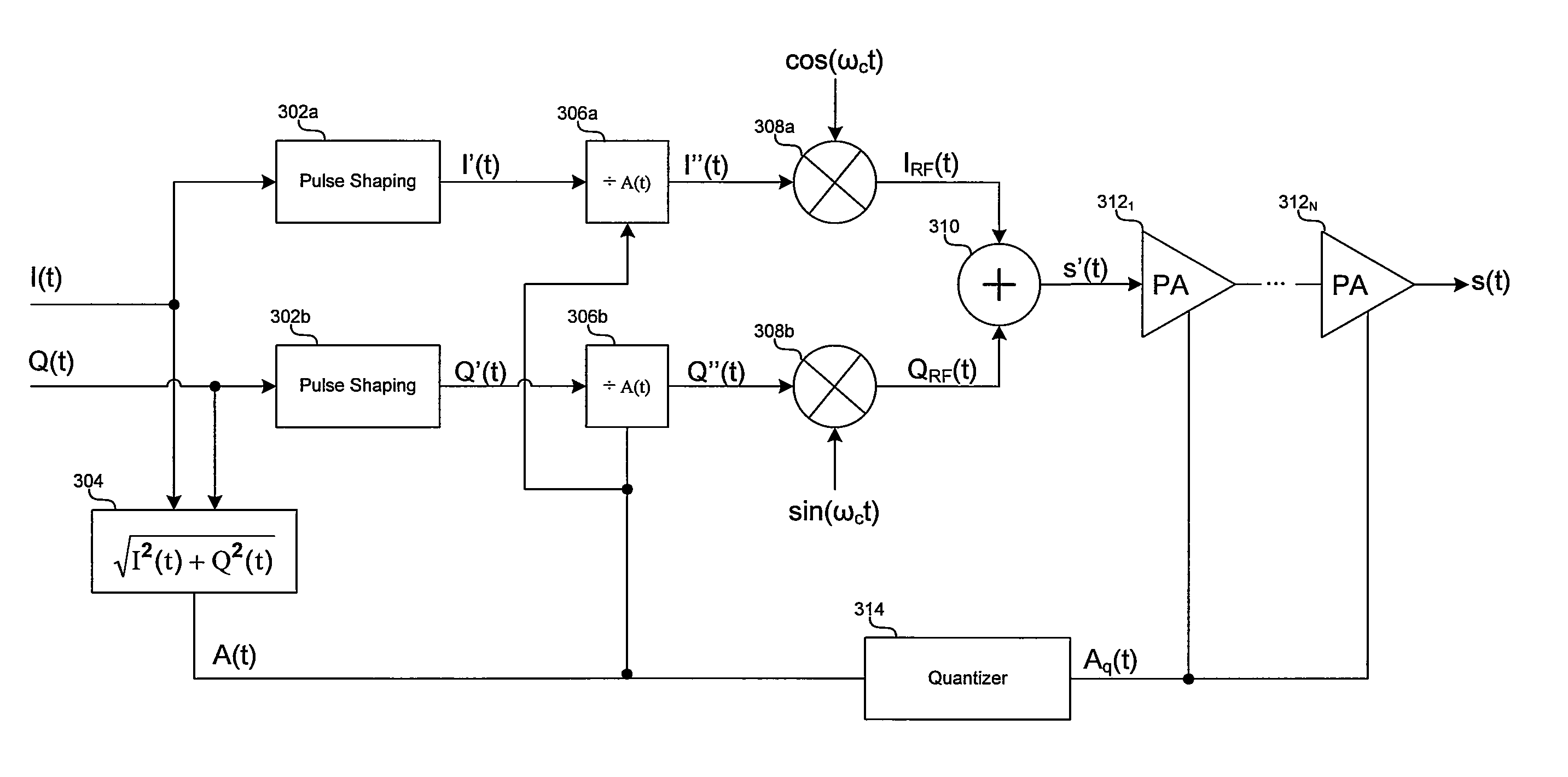
Method and system for polar modulation with discontinuous phase
InactiveUS20090034653A1High frequency amplifiersMultiple carrier systemsSoftware engineeringPulse shaping
Aspects of a method and system for polar modulation with discontinuous phase are provided. In this regard, in-phase and quadrature-phase components may be generated from a modulated baseband signal, and the signal components may be utilized to generate a signal representative of the amplitude of the baseband signal. Furthermore, the signal components may be pulse shaped and the pulse-shaped components may be divided by the signal representative of the amplitude of the baseband signal. The resulting signals may be up-converted to RF, summed, and amplified, where the amplification may be controlled via a quantized representation of the signal representative of the amplitude of the baseband signal. In this regard, one or more bias points, and / or one or more binary weighted current sources coupled to one or more power amplifiers may be controlled. The pulse-shaping may comprise passing the signal components through a raised cosine filter.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
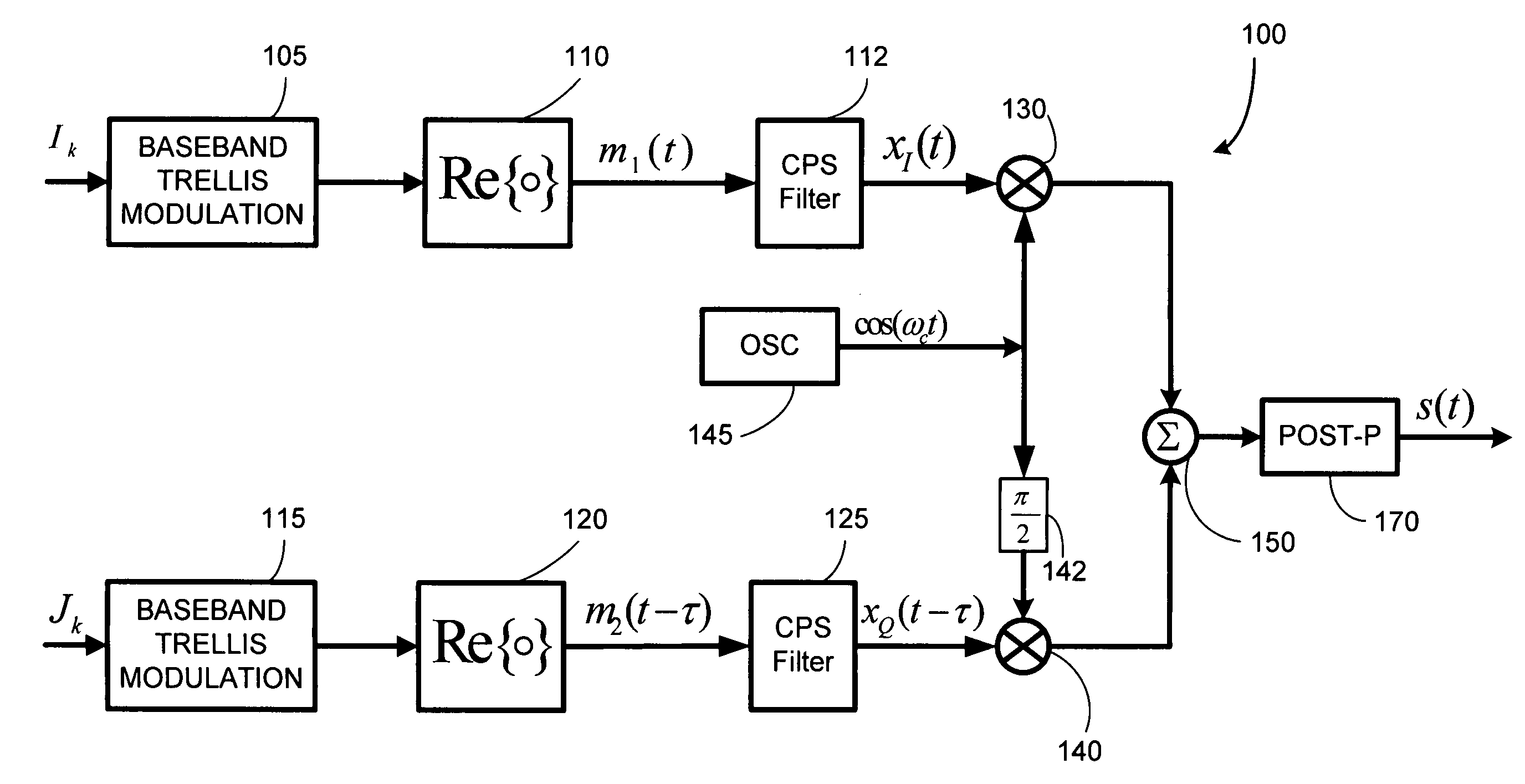
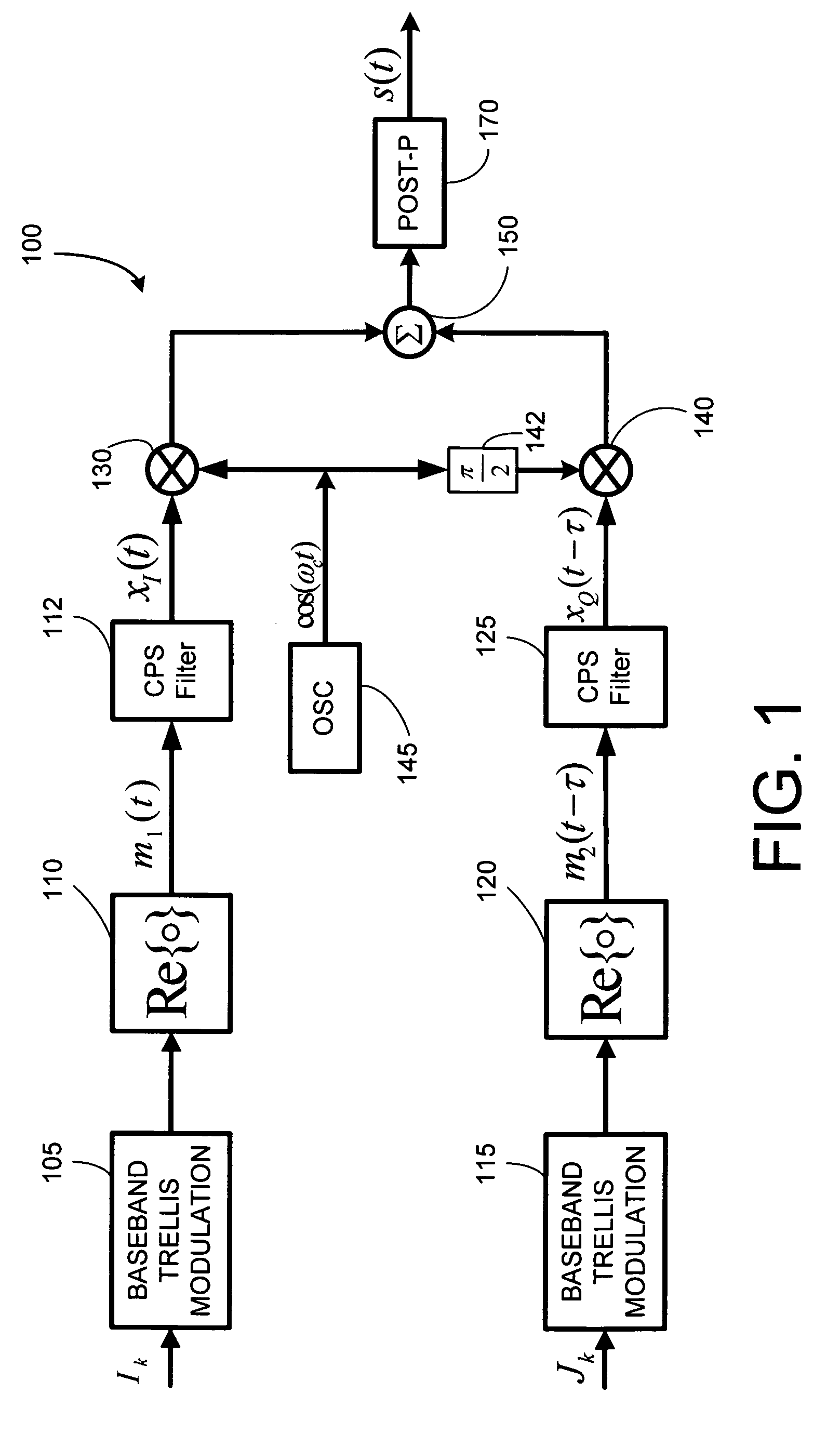
Compact pulse shaping for QM-MSK and PAM/QAM reception
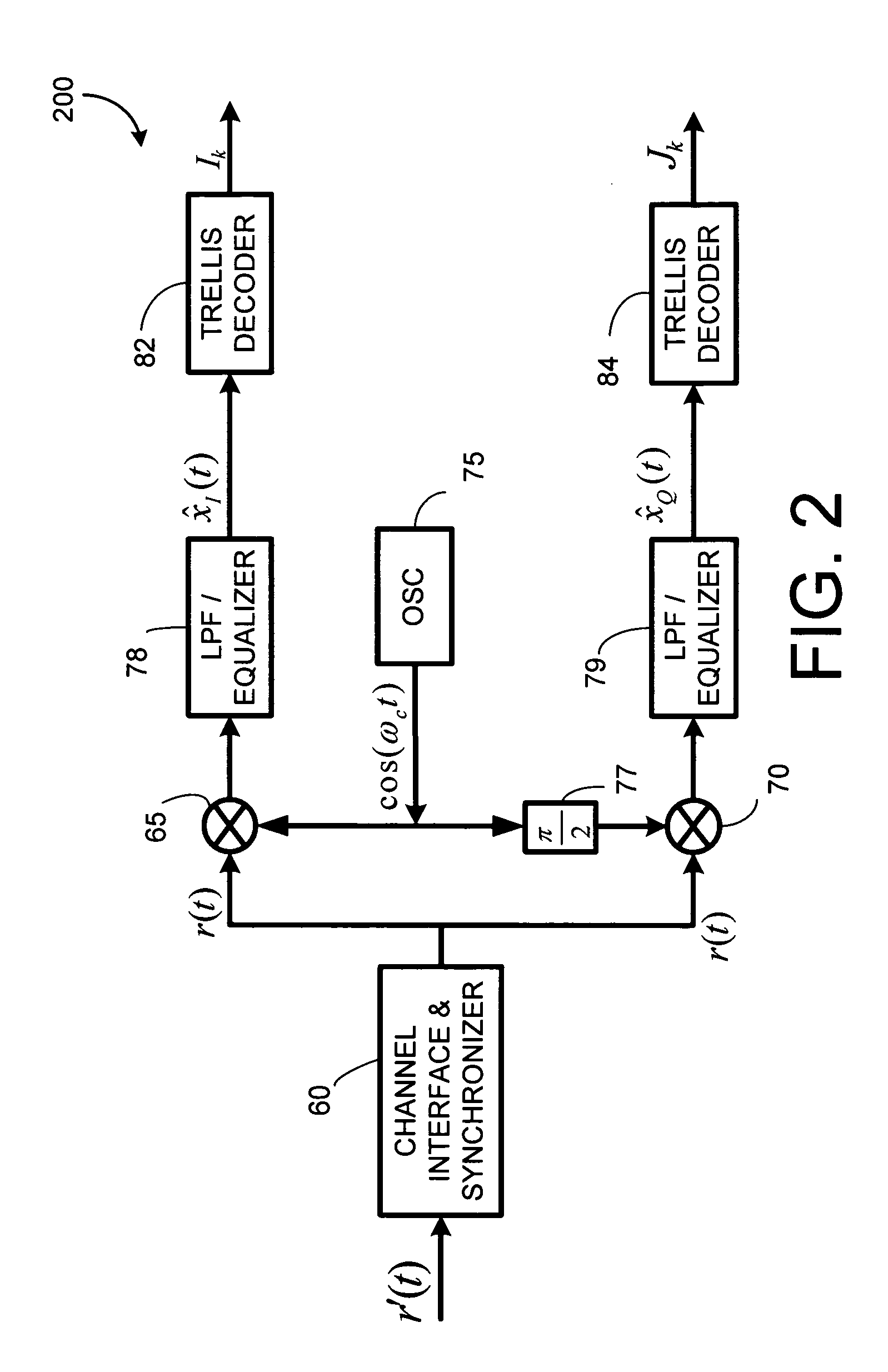
InactiveUS20110188613A1Error preventionAmplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsIntersymbol interferenceConstellation
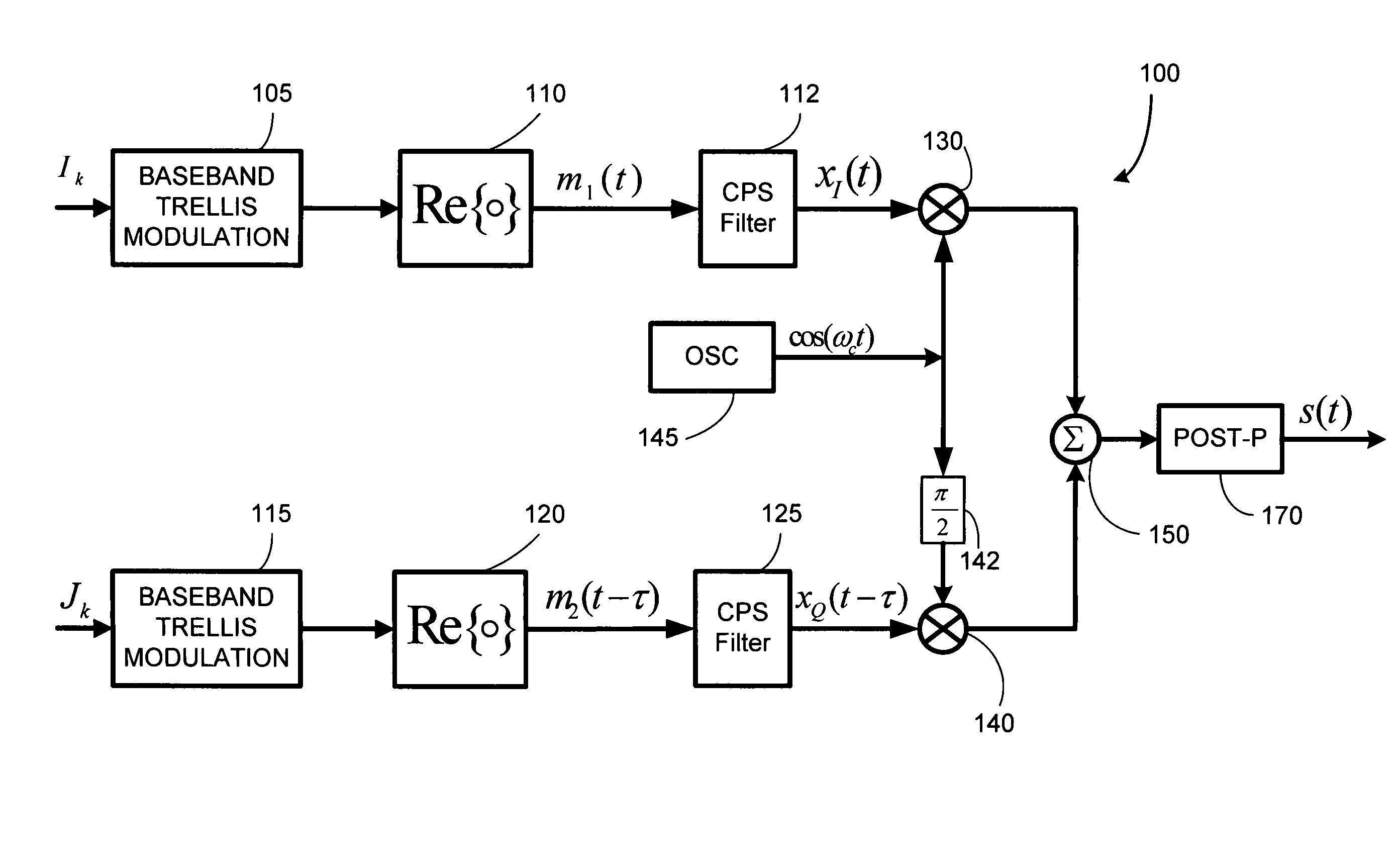
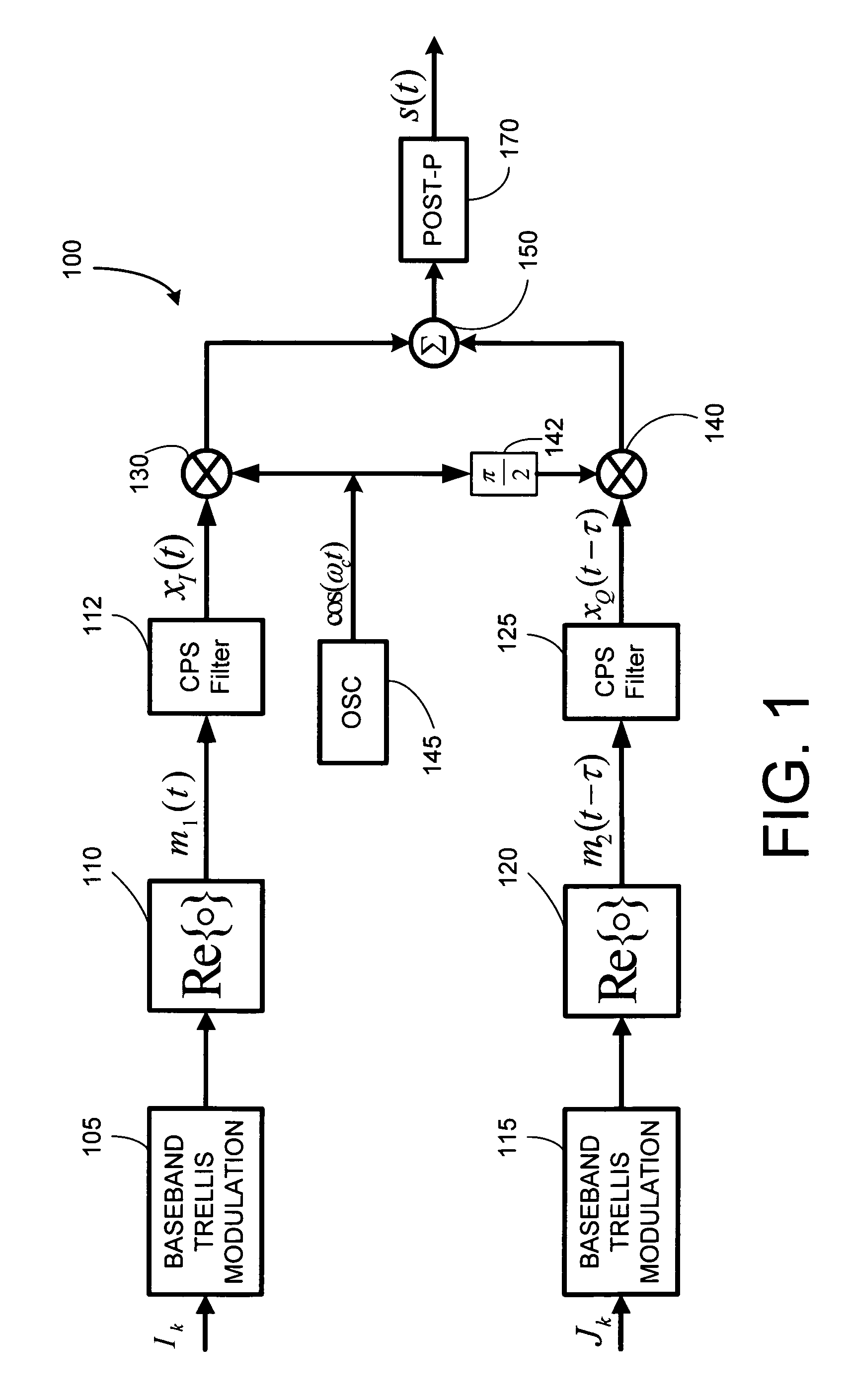
Compact pulse shape partial response (CPS PR) signaling is developed for trellis based signals like QM-MSK, and for PAM / QAM type signals to improve the performance to bandwidth tradeoff. Compact pulse shaped signals are partial response signals that employ a very short pulse shaping filter and use Viterbi decoding to optimally detect the CPS signal in presence of its inherent inter-symbol interference. The CPS filters considered herein have much shorter impulse response than the well-known raised cosine (RC) filter. There is no need to equalize the received signal to eliminate ISI or to allow a fixed amount of ISI between received signal samples as sampled at the symbol rate as is common in partial response maximum likelihood (PRML) systems. Numerical results indicate that CPS QM-MSK and CPS QAM provides between several dB of gain, depending on constellation size, over PR-CPM and RC QAM, when compared at a given value of bandwidth, i.e., B99Tb.
Owner:TRELLIS PHASE COMM LP
Non-data auxiliary frequency offset estimation method applicable to amplitude phase shift keying
ActiveCN107342960AExpand the range of frequency offset estimationTroubleshooting Carrier Synchronization Processing IssuesMulti-frequency code systemsEffective solutionCommunications system
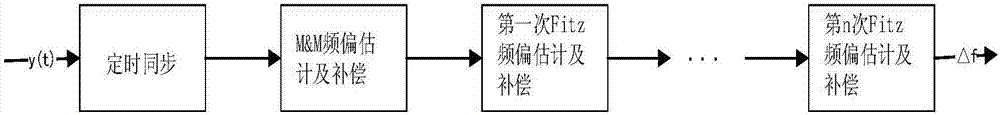
The invention discloses a non-data auxiliary frequency offset estimation method applicable to amplitude phase shift keying and relates to the technology of digital communication system receiving end processing. Frequency offset estimation and compensation are carried out on APSK signals by a receiving end. According to the method, the precision of carrying out the frequency offset estimation and compensation on the APSK signals by the receiving end is improved. The method comprises the steps of processing receiving signals by a rooted raised cosine filter and carrying out synchronization processing on the signals, wherein the synchronization processing comprises timing synchronization, frequency synchronization and phase synchronization processing. According to the method, for the frequency synchronization processing, frequency offset coarse estimation is carried out through utilization of an M&M algorithm according to a frequency range of the APSK signals, a frequency offset range is reduced, n times of frequency offset fine estimation is carried out through selective utilization of a Fitz algorithm according to a precision demand, and finally a precise frequency offset value is obtained. After the synchronization processing is carried out, judgment, constellation graph demapping and output are carried out. The invention provides an effective solution scheme for the APSK signal frequency offset estimation and compensation.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
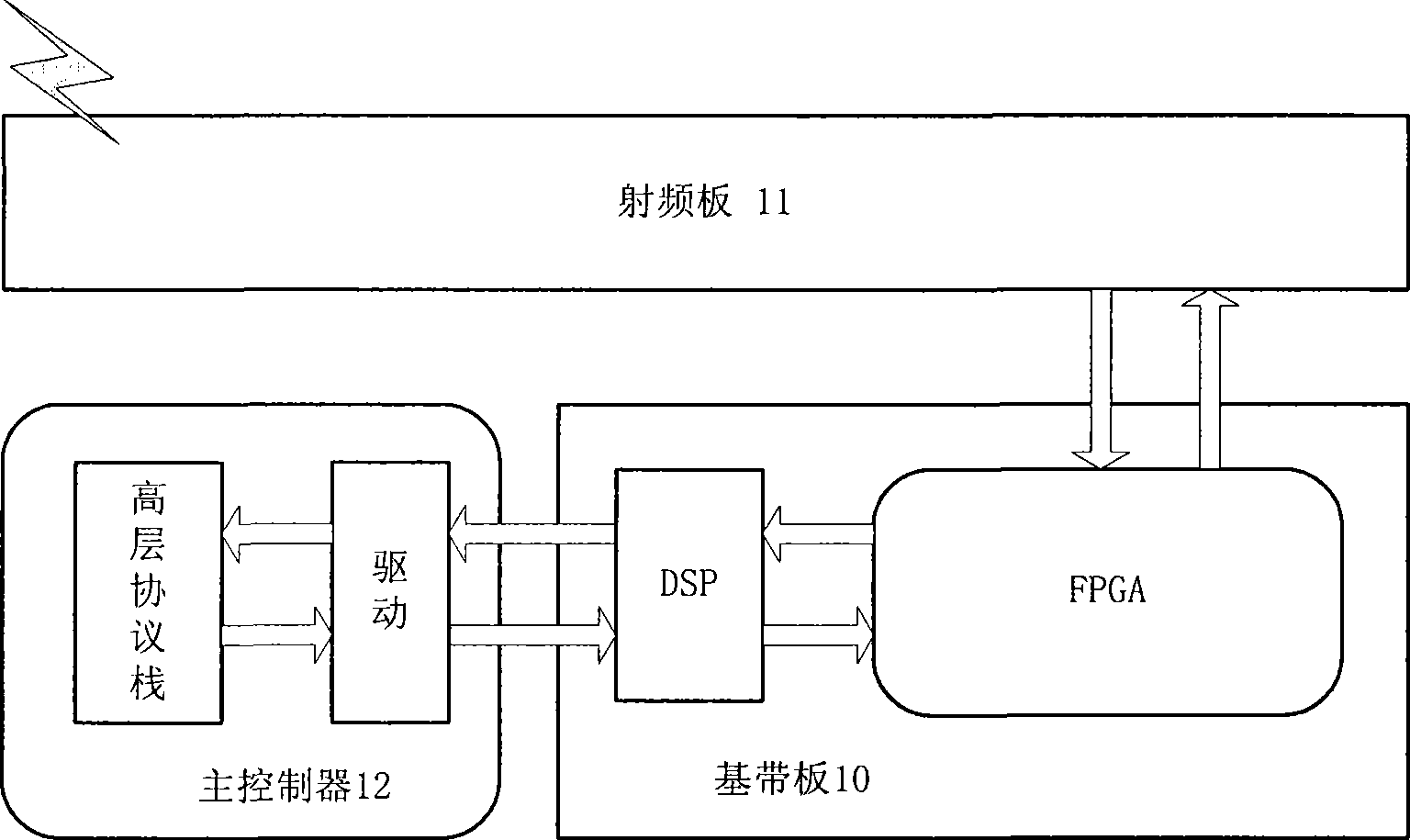
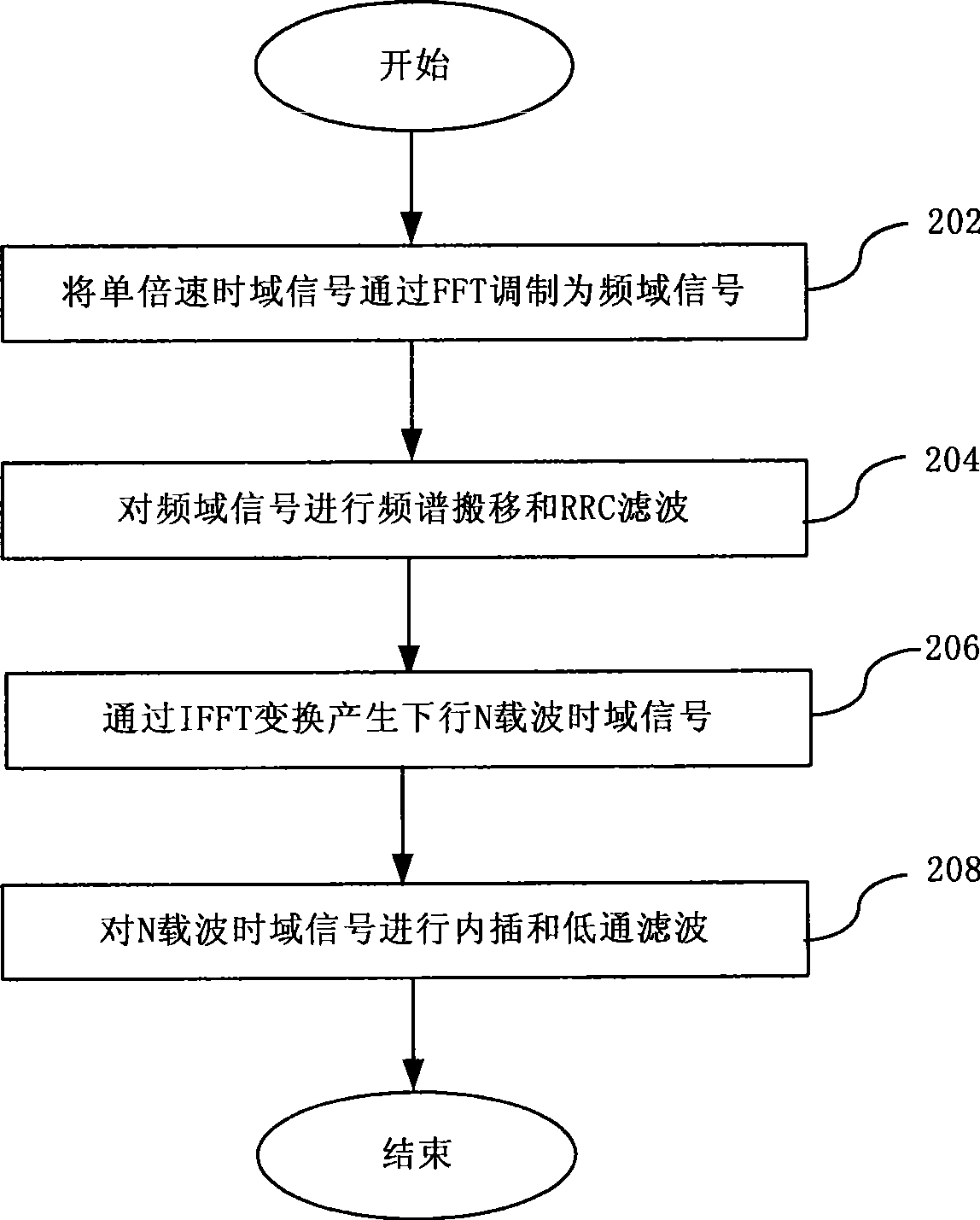
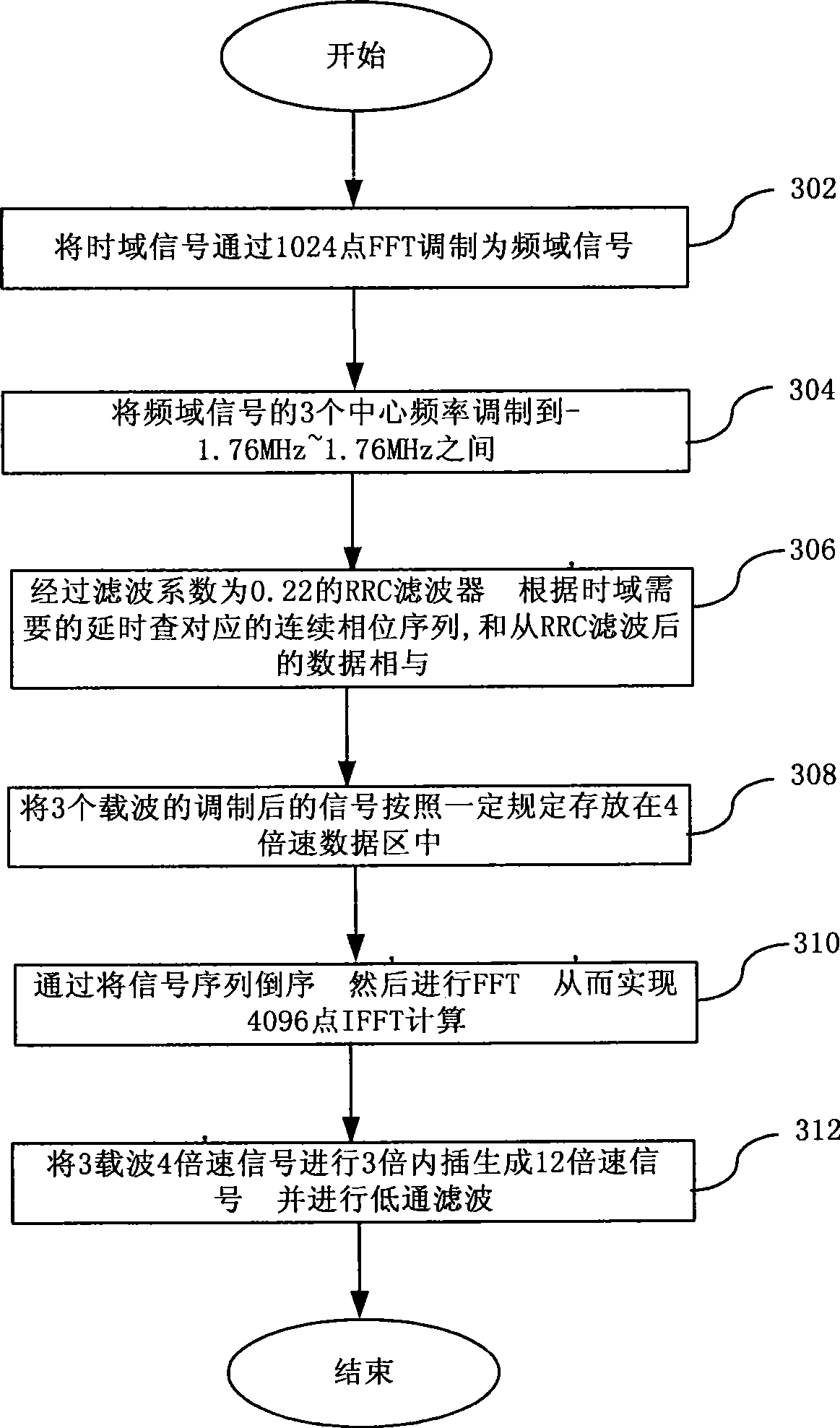
Multi-carrier implementing method and apparatus for TD-SCDMA system
ActiveCN101370000AReduce investmentCost controlCode division multiplexMulti-frequency code systemsFrequency spectrumFourier transform on finite groups
Owner:BEIJING STARPOINT TECH COMPANY +1
Receiver, transmitter and variable bandwidth transmission method
InactiveUS20070005352A1Simple interfaceUnwanted response can be avoidedSpeech analysisTransmissionTransmission bandwidthFilter bank
Solutions for receiving and transmitting variable transmission bandwidth signal are provided. A receiver comprises square-root raised cosine filter bank, each filter of the filter bank configured to filter a subband, and an adder configured to add up the output signals of one or more filters of the filter bank to obtain a sum signal, the sum of the subbands of the one or more filters being equal to the transmission bandwidth of the received signal. A transmitter comprises a transmission filter, the roll-off factor of the transmission filter being selected on the basis of the bandwidth of the signal to be transmitted.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
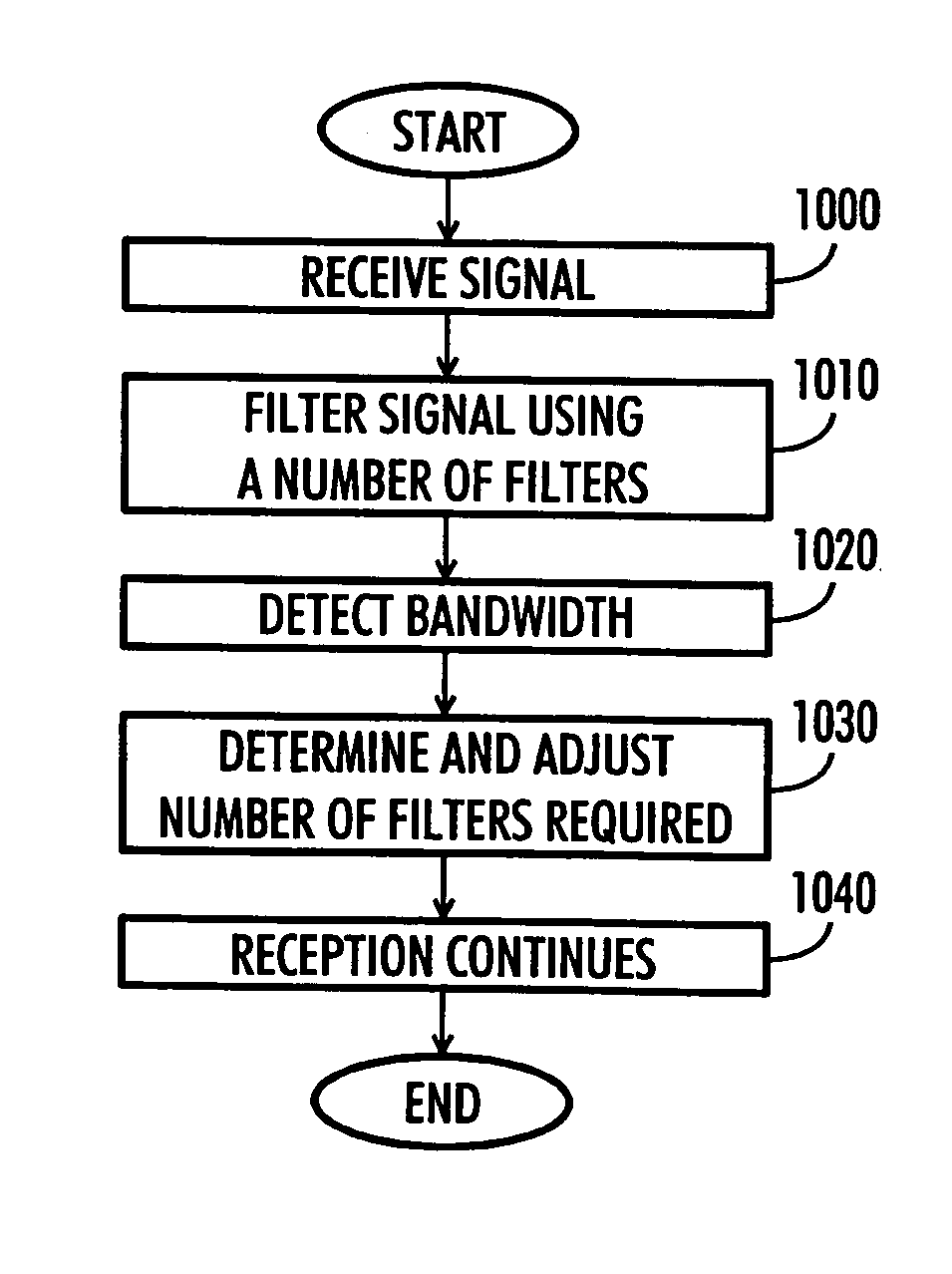
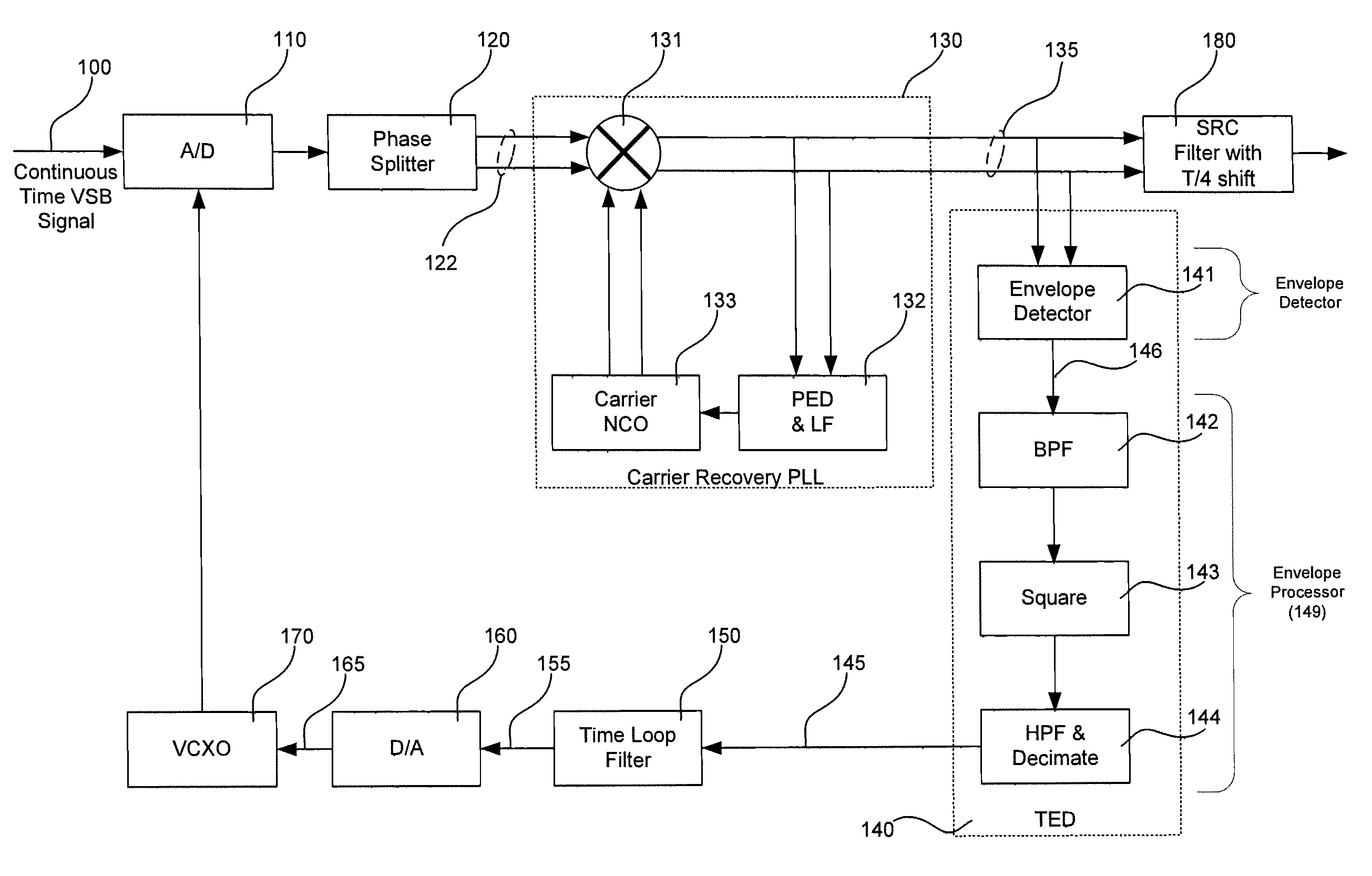
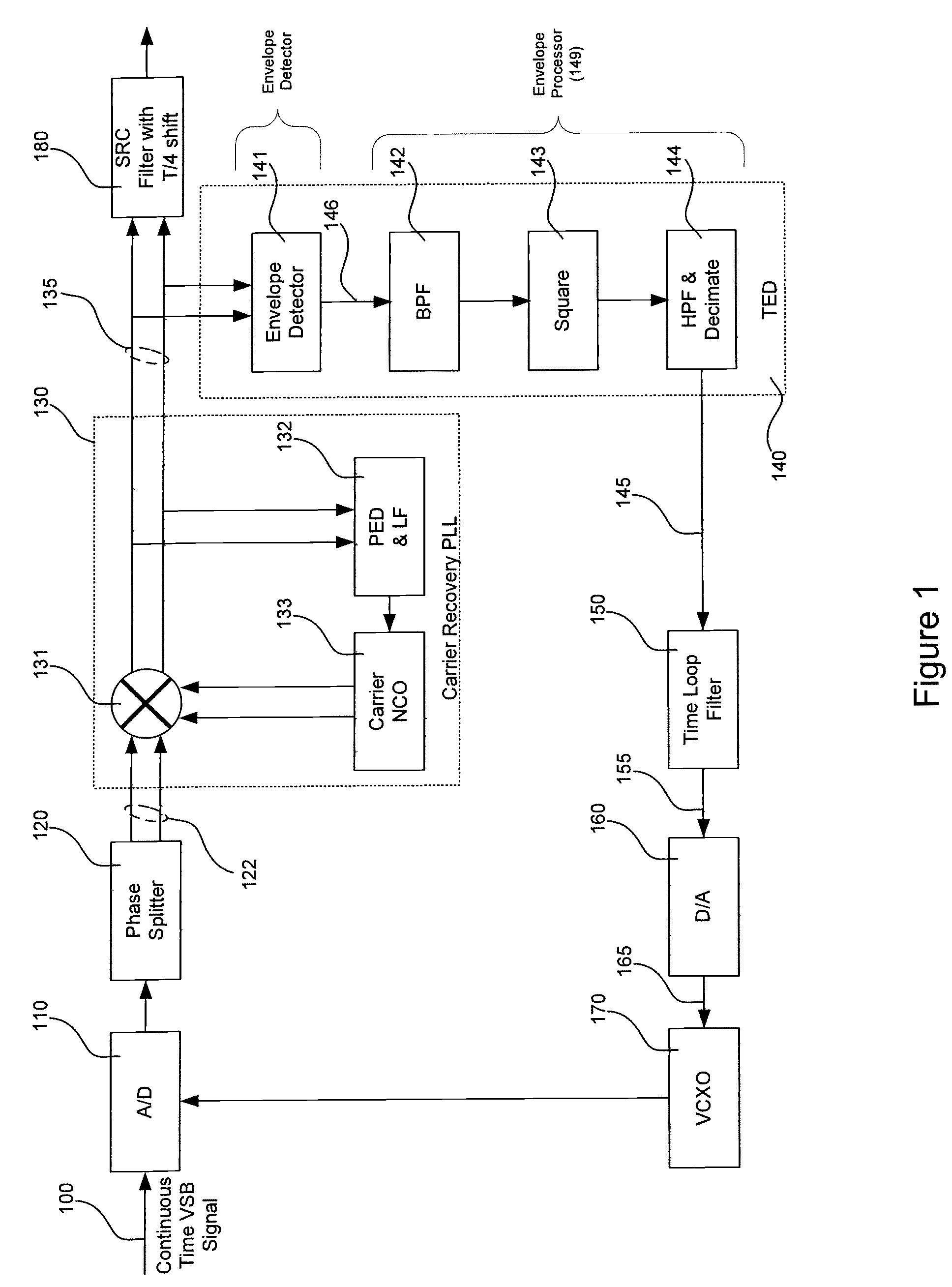
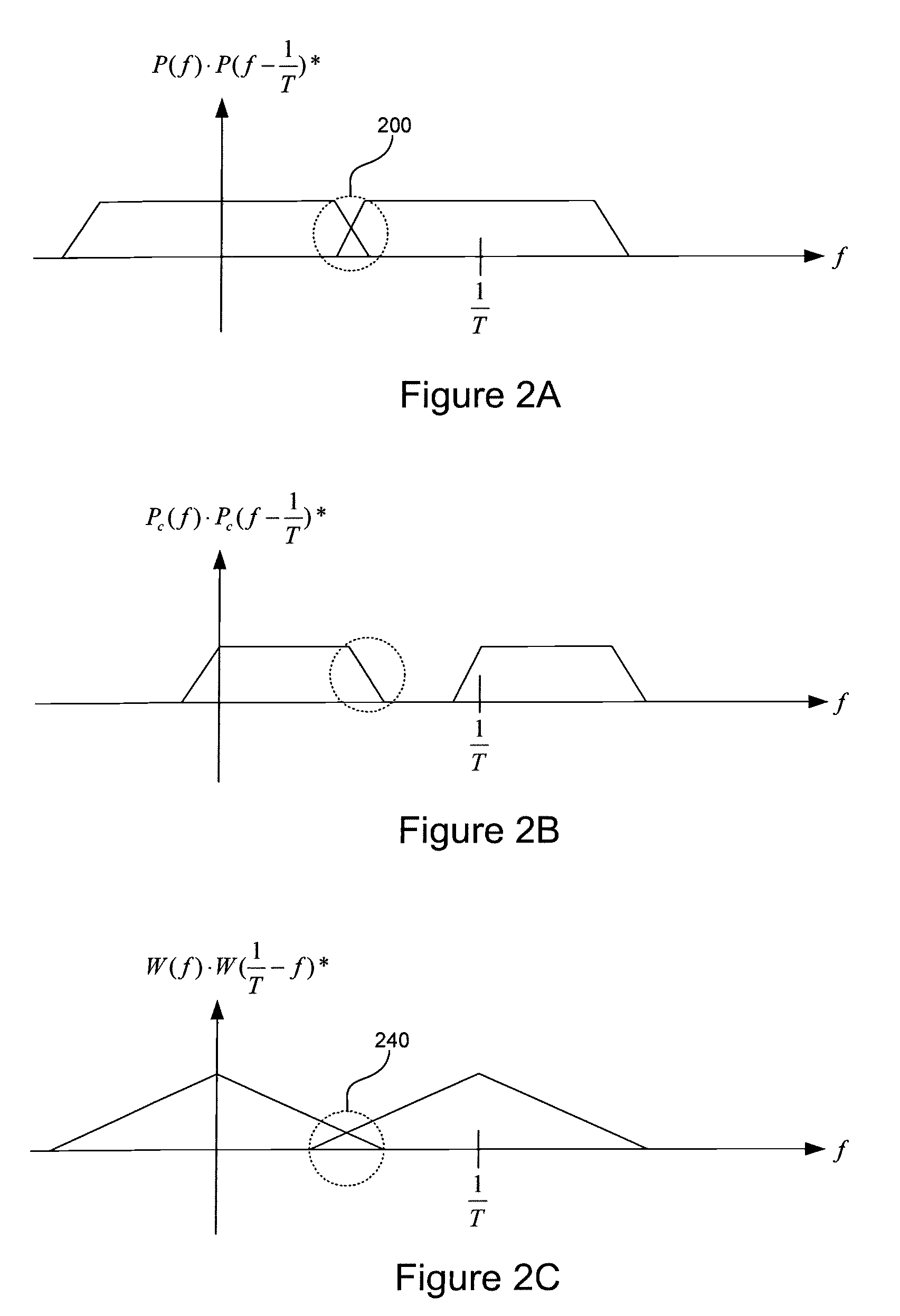
Timing error detector for vestigial side band (VSB)
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Filtering and guard band for non-synchronized transmission
InactiveUS8223700B2Reduce distractionsEasy to useTime-division multiplexRadio transmissionCommunications systemCarrier signal
A wireless terminal capable of communicating with a wireless communication system comprised of a plurality of wireless terminals and a plurality of base stations. The wireless terminal selects a sequence from a group of certain sequences for random access. At least one sub-carriers on an uplink channel including at least one data channel is allocated for at least one random access channel. Each data channel includes a continuous set of data sub-carriers. The wireless terminal then filters the at least one random access channel by applying a Raised Cosine filter, maps the selected sequence to the at least one random access channel to generate a random access channel signal, and transmits the random access channel signal to a base station.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optional-forward-link encoding method of ultra-high frequency reader
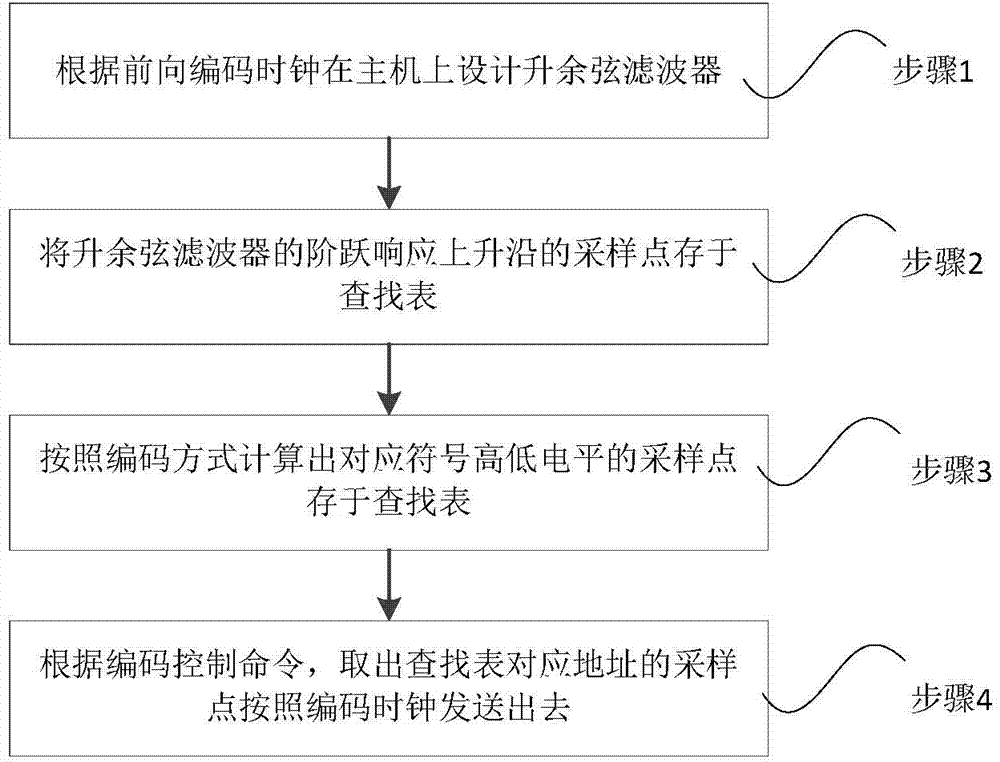
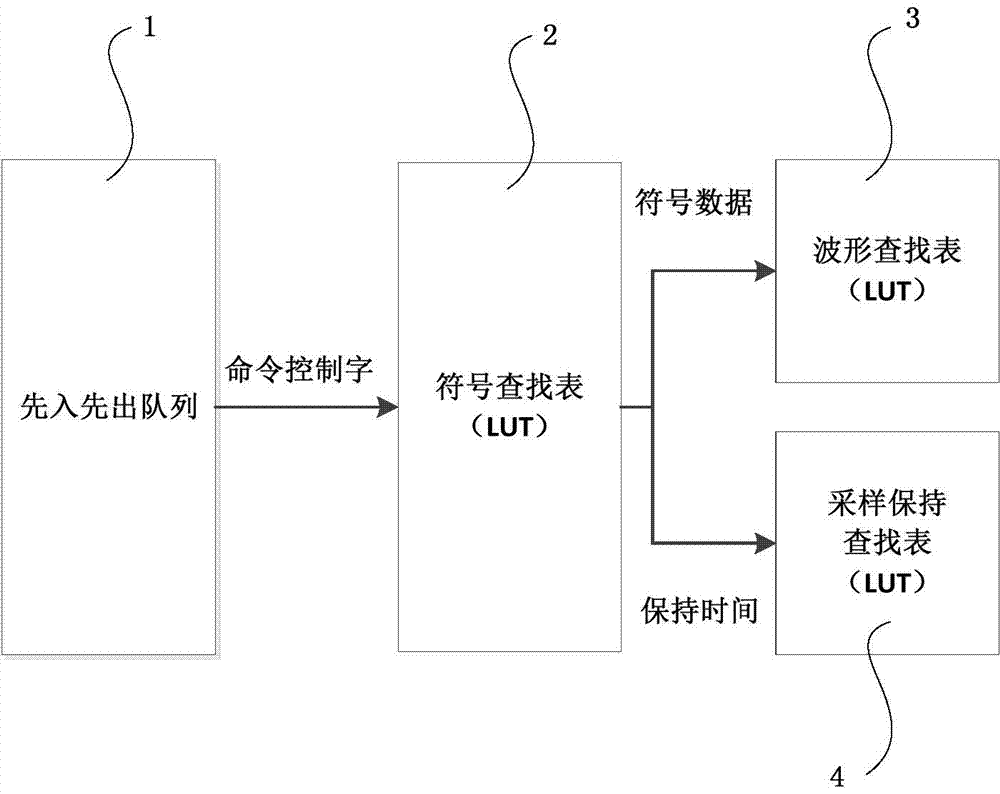
ActiveCN104751209AReduce distractionsSimple designCo-operative working arrangementsAir interfaceStep response
The invention discloses an optional-forward-link encoding method of an ultra-high frequency reader. The optional-forward-link encoding method includes the steps of 1), determining an encoding clock of a forward link of the ultra-high frequency reader, determining the sampling frequency according to the encoding clock and calculating out a raised cosine filter conforming to the ultra-high frequency air interference protocol standard; 2), according to waveforms of step response of the raised cosine filter, taking multiple discrete points at least including the highest point and the lowest point in the ascending portion of the waveforms of the step response as ascend-descend edges of modulating signals and storing in a waveform look-up table; 3), according to the encoding mode of the ultra-high frequency air interface protocol standard, calculating out sampling points of high-low electrical levels of symbols corresponding to the encoded waveforms and storing in a sampling sustaining look-up table; 4), according to encoding control instructions sent by a controlled and received by the ultra-high frequency reader, taking out the quantized sampling points from addresses corresponding to the waveform look-up table and the sampling sustaining look-up table, and sending the sampling points according to the encoding clock.
Owner:706 INST SECOND RES INST OF CHINAAEROSPACE SCI & IND
Blind estimation method for large frequency bias in ground digital television system and apparatus thereof
InactiveCN101378382AHigh speedLarge carrier frequency offset estimation rangeMulti-frequency code systemsIntermediate frequencyCarrier signal
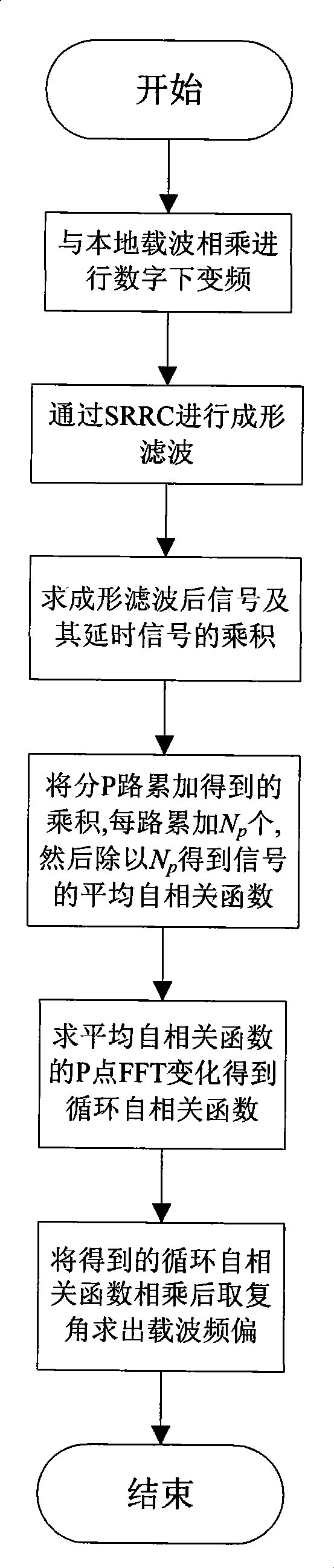
The invention discloses a large frequency hemiopia estimation method, which is carried out according to circular correlation property of receiving data without using auxiliary data, of a digital television terrestrial broadcasting transmission system receiver and a device thereof, belonging to the processing field of digital information. The invention adopts a digital intermediate signal which is subjected to A / D sampling to be multiplied by a local carrier signal so as to carry out digital down conversion and then forms filtering by a square root raising cosine (SRRC) filter. A complex signal output by the SRRC filter is delayed for Tau sampling points and subjected to conjugation-obtaining, and the delayed and conjugated complex signal is subjected to re-multiplication with the original signal before being delayed. The result of re-multiplication is divided into p branches for summarizing, the results of the p branches are subjected to FFT of p point, and then the estimation value of the frequency offset is obtained. The invention is applicable to the frame structures of two modes: single carrier and multi-carrier, can carry out blind estimation on the frequency offset under the state without any auxiliary information, and has the advantages of large scale of frequency offset estimation, good noise immunity, being suitable for hardware realization and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
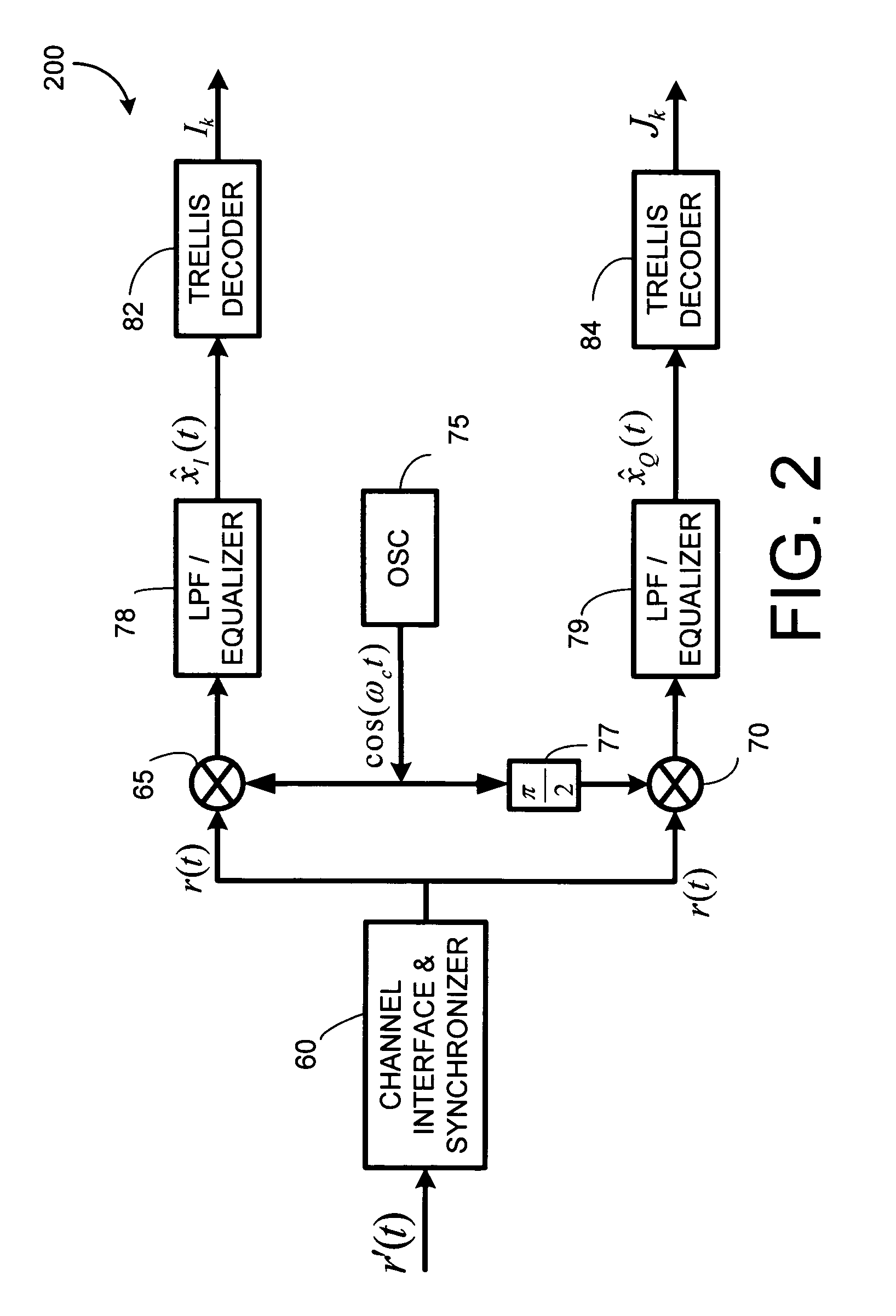
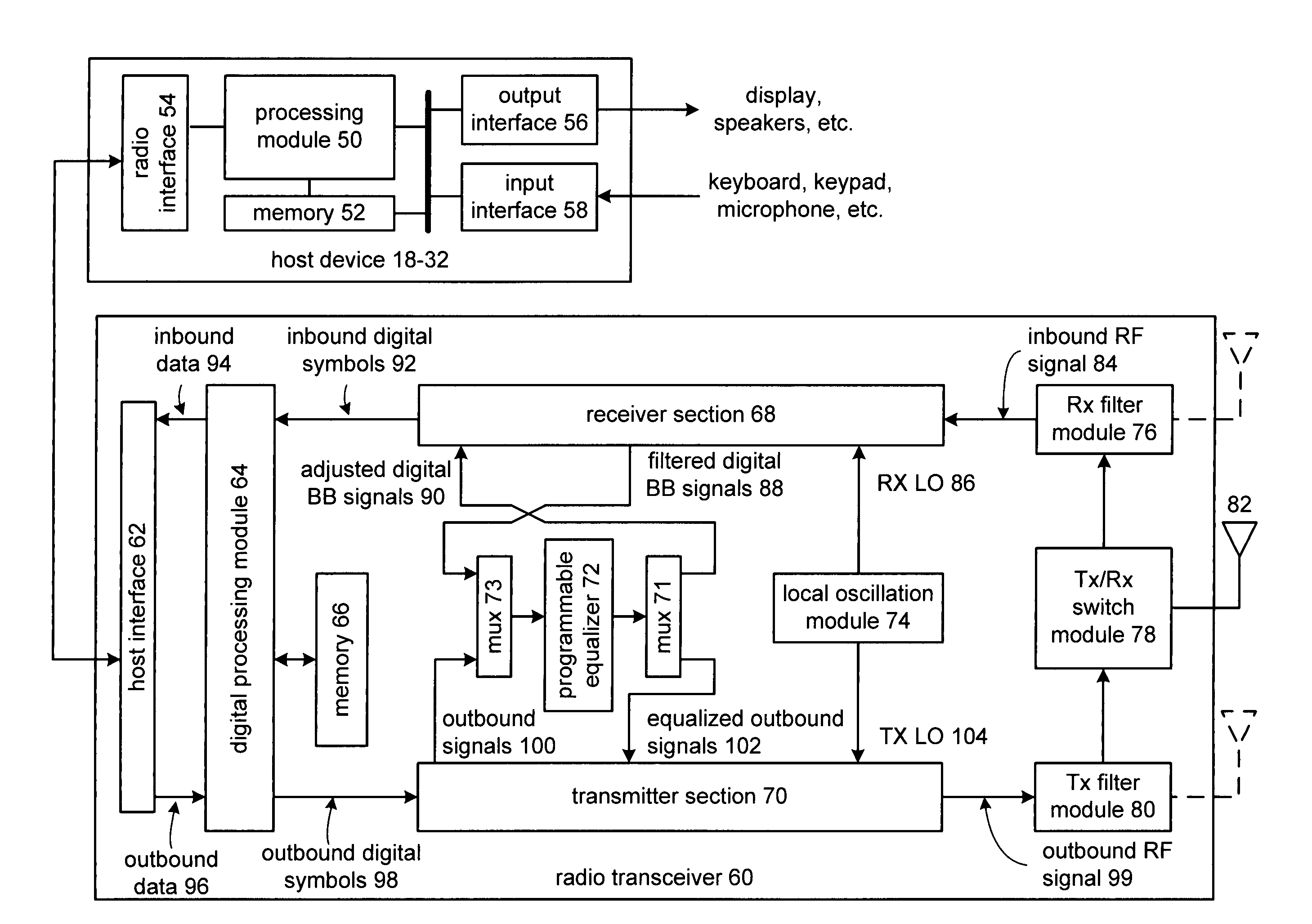
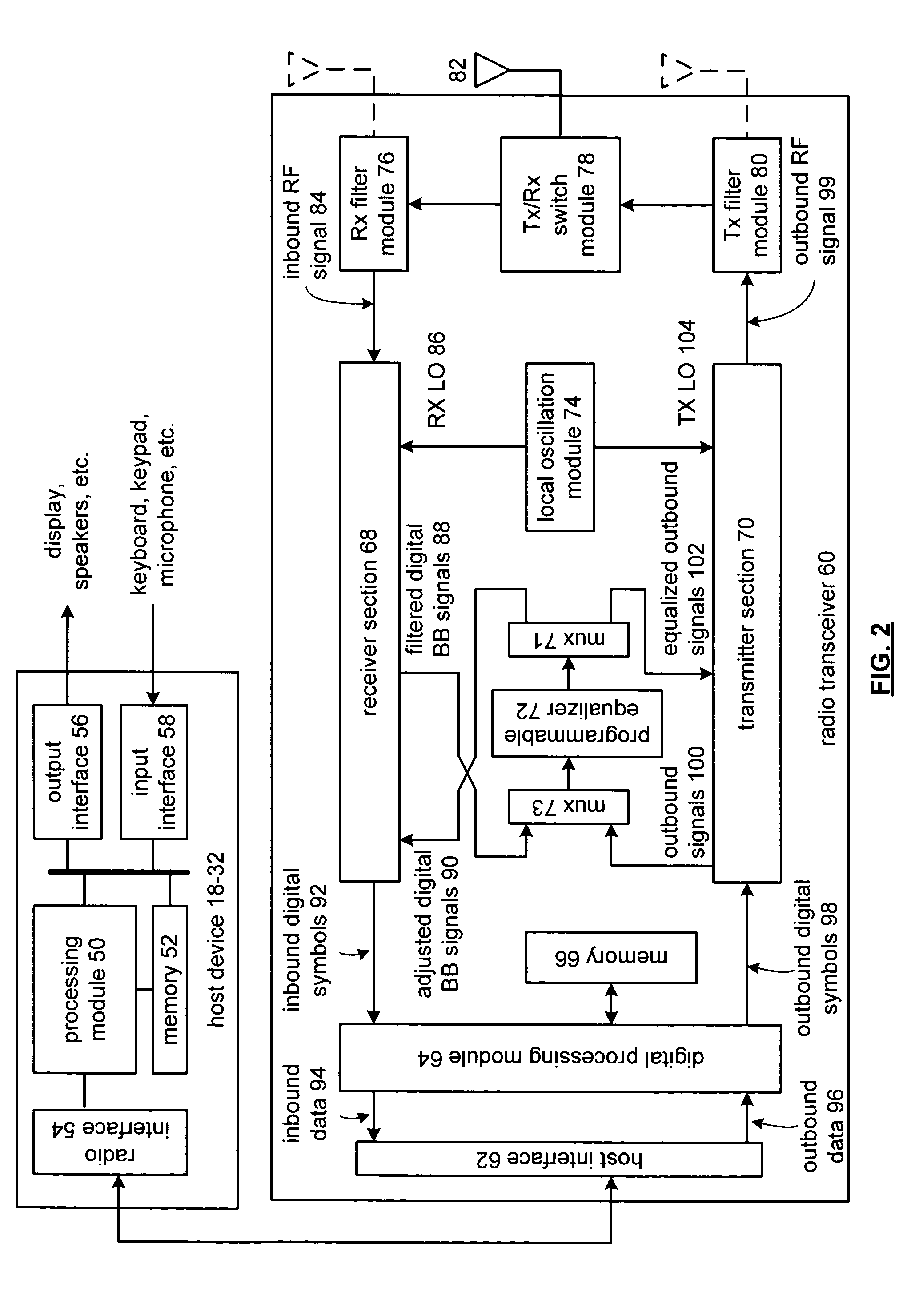
Radio receiver and/or transmitter including a programmable equalizer
A radio receiver includes a low noise amplifier, a down conversion module, an analog to digital converter, and a digital demodulator. The digital demodulator is operably coupled to convert the digital low IF signals into inbound digital symbols and includes a baseband conversion module, a filtering module, a programmable equalizer, a CORDIC module, and a demodulation module. The programmable equalizer is operably coupled to equalize phase and frequency response of filtered digital baseband signals from the filtering module such that the phase and frequency response of the filtered digital baseband signals approximates phase and frequency response of a square root raised cosine filter to produce adjusted digital baseband signals. The CORDIC module is operably coupled to produce phase and magnitude information from the adjusted digital baseband signals. The demodulation module is operably coupled to produce the inbound digital symbols from the phase and magnitude information.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
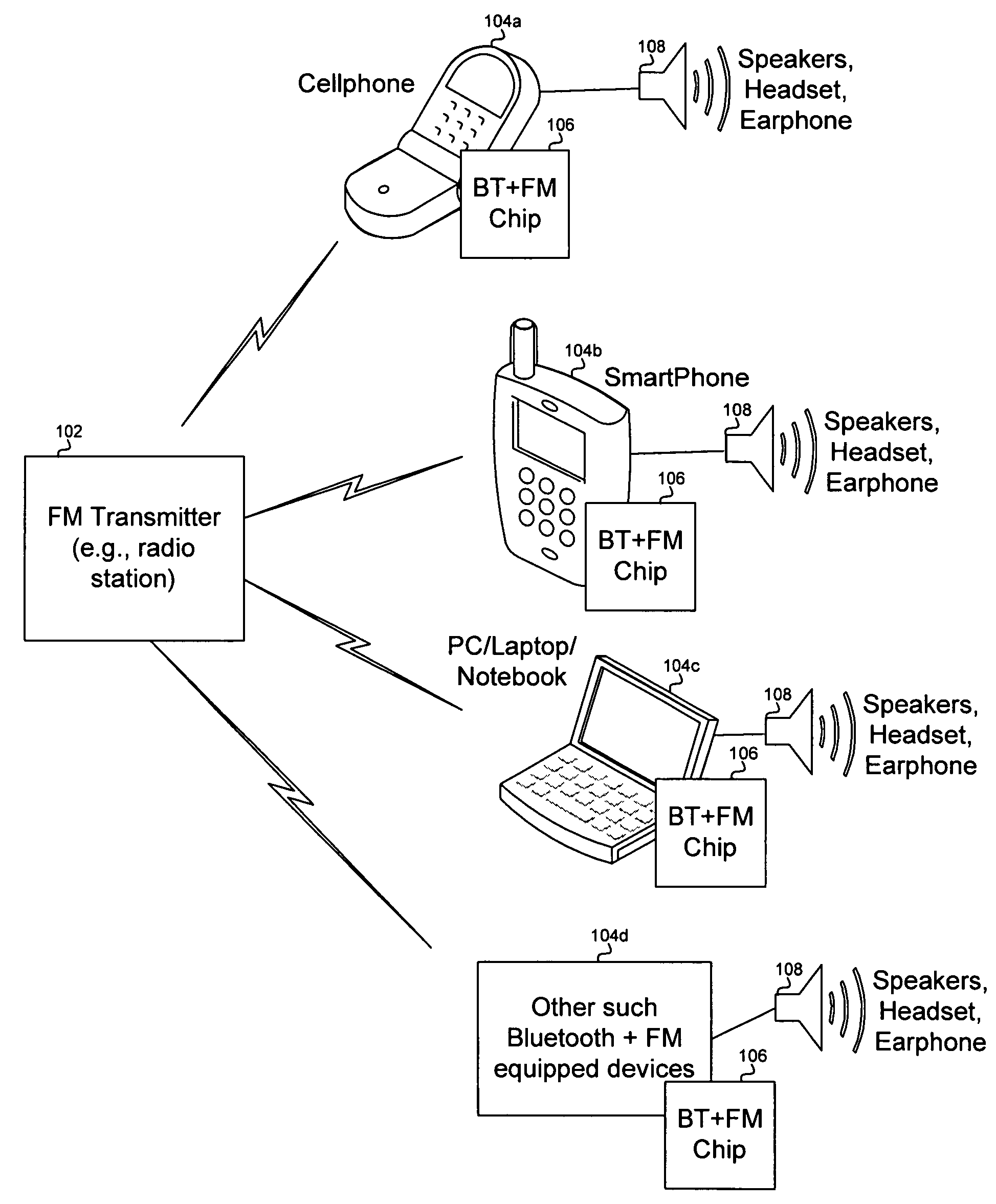
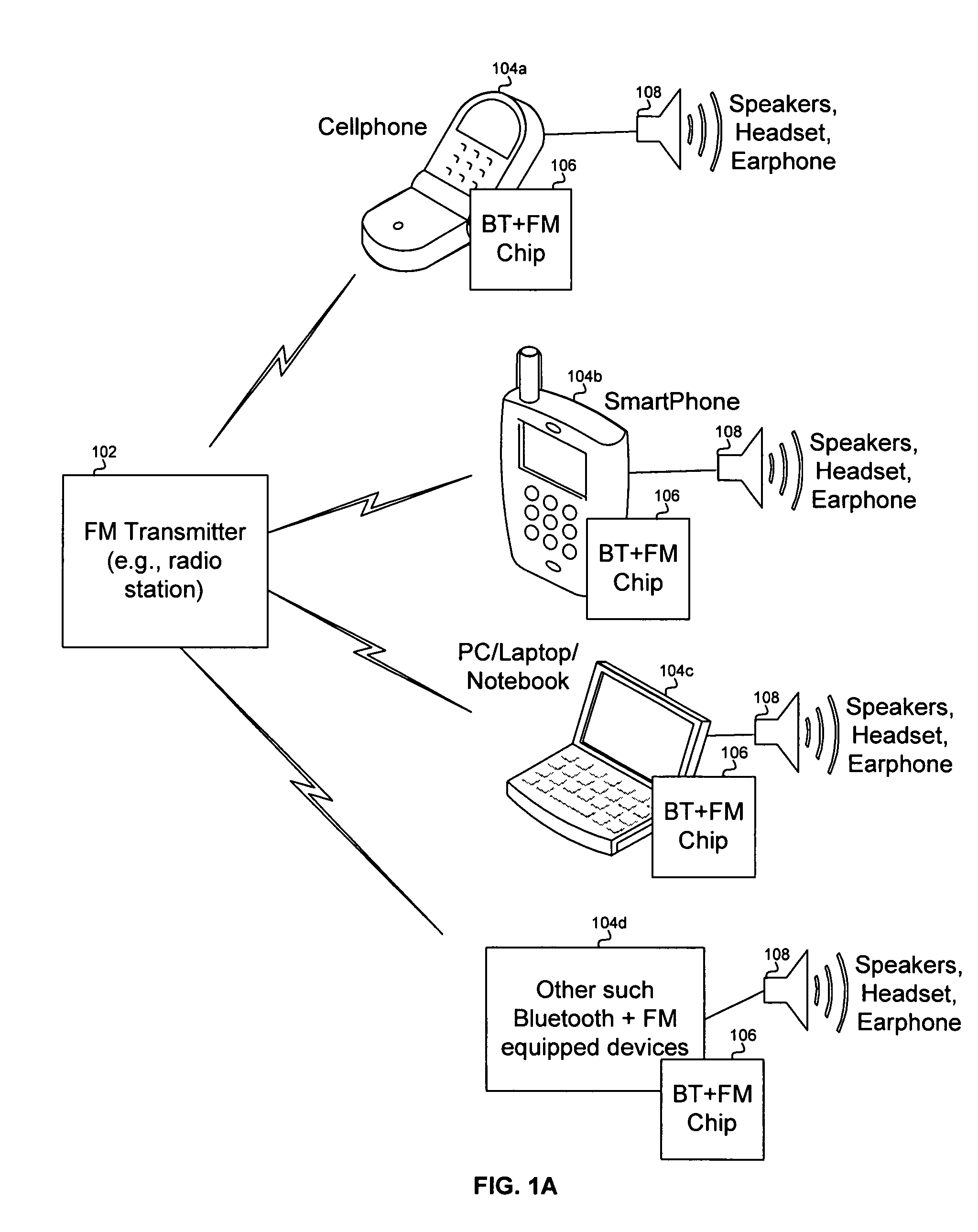
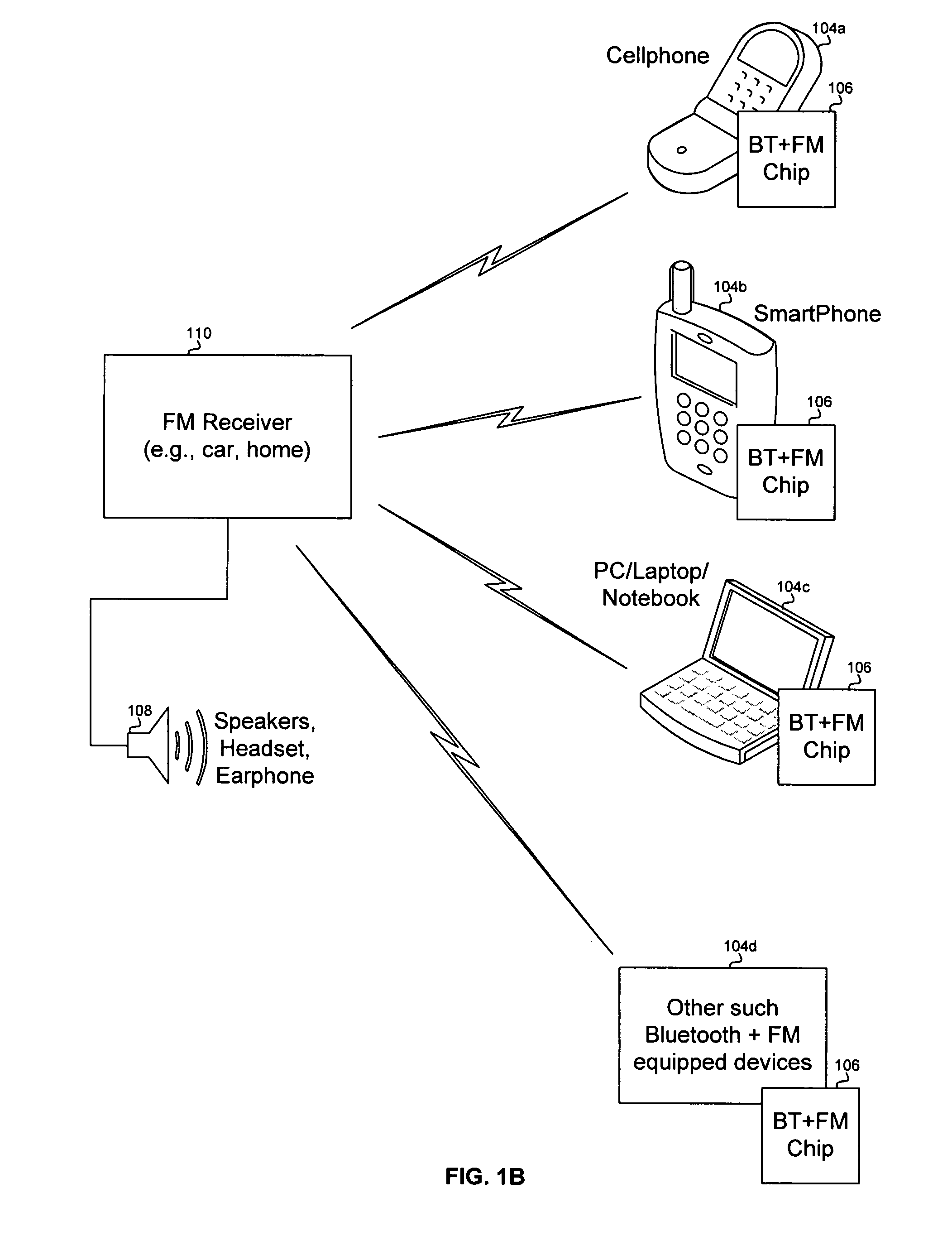
Method and system for a radio data system (RDS) demodulator for a single chip integrated bluetooth and frequency modulation (FM) transceiver and baseband processor
Aspects of a method and system for a radio data service (RDS) demodulator for a single chip integrated Bluetooth and frequency modulation (FM) transceiver and baseband processor are presented. Aspects of the system may include circuitry on a single chip that enables demodulation of an RDS signal, filtering of the RDS signal, and detection of binary bits in the filtered RDS signal. The filtered RDS signal may be generated by filtering the RDS signal based on a raised cosine filter, or a doublet filter. In general, the RDS signal may also be filtered by a filter that is a first, or greater derivative of a Gaussian filter in either the time or frequency domain. Aspects of the method may include demodulating the RDS signal, filtering the RDS signal, and detecting binary bits in the filtered RDS signal.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Intra-channel equalizing optical interleaver
ActiveUS8064768B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationChannel densityVIT signals
An apparatus includes an interleaver configuration for at least one of combining or separating odd and even channel groups to achieve channel density doubling; and an optical equalizer for suppressing inter symbol interference within the channels to provide intra-channel equalizing in the optical path, the equalizer being integrated into the interleaver. Preferably, optical equalizer and interleaver are integrated together as a single monolithic device, the optical equalizer includes a passband that has a dip in the channel center to achieve a raised-cosine filtering profile in the optical signal path to achieve inter-symbol interference ISI suppression, and the equalizer includes integration into the optical path of the interleaver to realize a monolithic device combining or separating odd and even channel groups to achieve channel density doubling. Preferably, also, the optical equalizer includes a first equalizer with half the depth of required ripple dips at both a first output port and an input port and a second equalizer with half the depth of required ripple dips at a second output port.
Owner:NEC CORP +1
General 4FSK modem and digital interphone capable of supporting multiple standards
ActiveCN104836762AReduce volumeLow costFrequency-modulated carrier systemsModem deviceComputer science
The invention discloses a general 4FSK modem and a digital interphone capable of supporting multiple standards. The general 4FSK modem comprises a 4FSK general modulator and a 4FSK general demodulator, the 4FSK general modulator comprises a first rooted raised cosine filter, a shaping filter, a first switch and a double up-sampling module, and the 4FSK general demodulator comprises a second rooted raised cosine filter, a bit synchronizer, a frame synchronizer, a double down-sampling module, an anti-shaping filter, a second switch and a synchronous code selection module. A plurality of communication standards are integrated, the aim that the digital interphone is low in cost and supports multiple standards is achieved, and the size of the present interphone is not increased.
Owner:无锡士康通讯技术有限公司
Multi-rate subcarrier modulation signal receiving and transmitting method and system
ActiveCN113726433AFlexible allocationHigh Dispersion ToleranceDistortion/dispersion eliminationElectromagnetic transmittersFiber chromatic dispersionFrequency spectrum
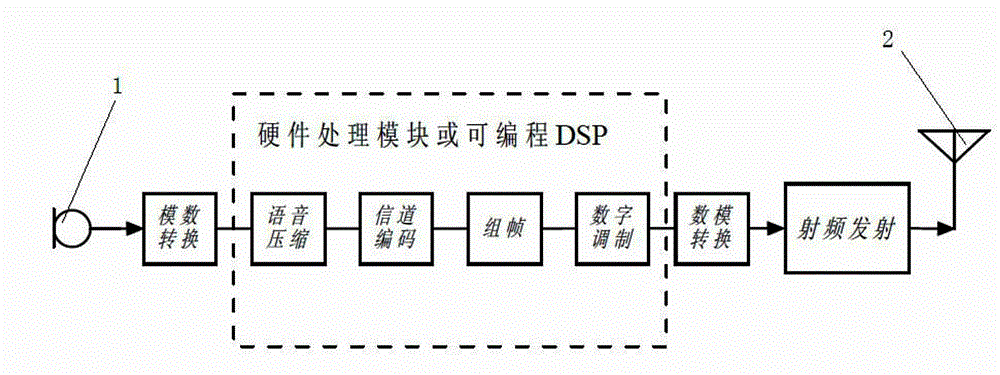
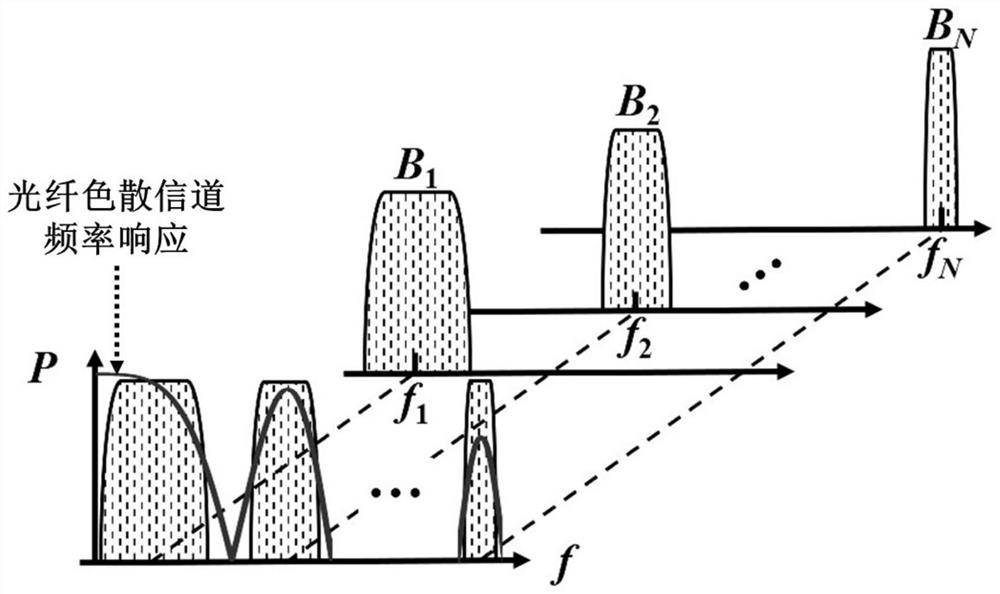
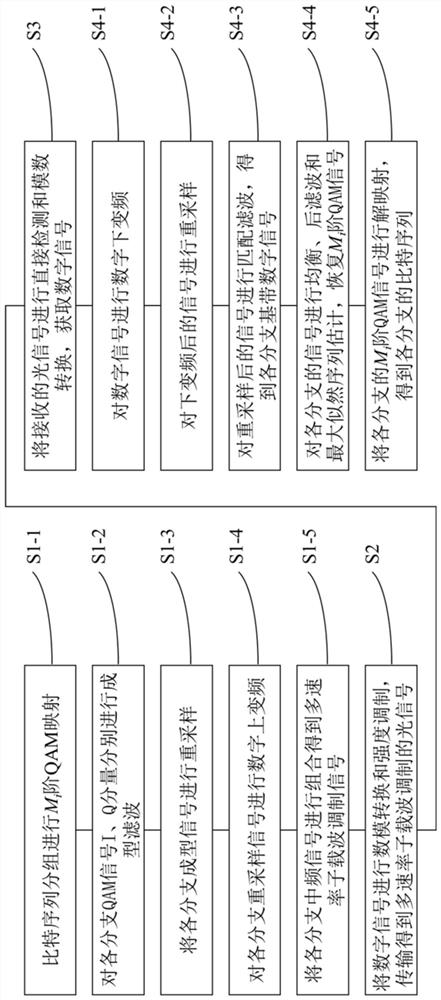
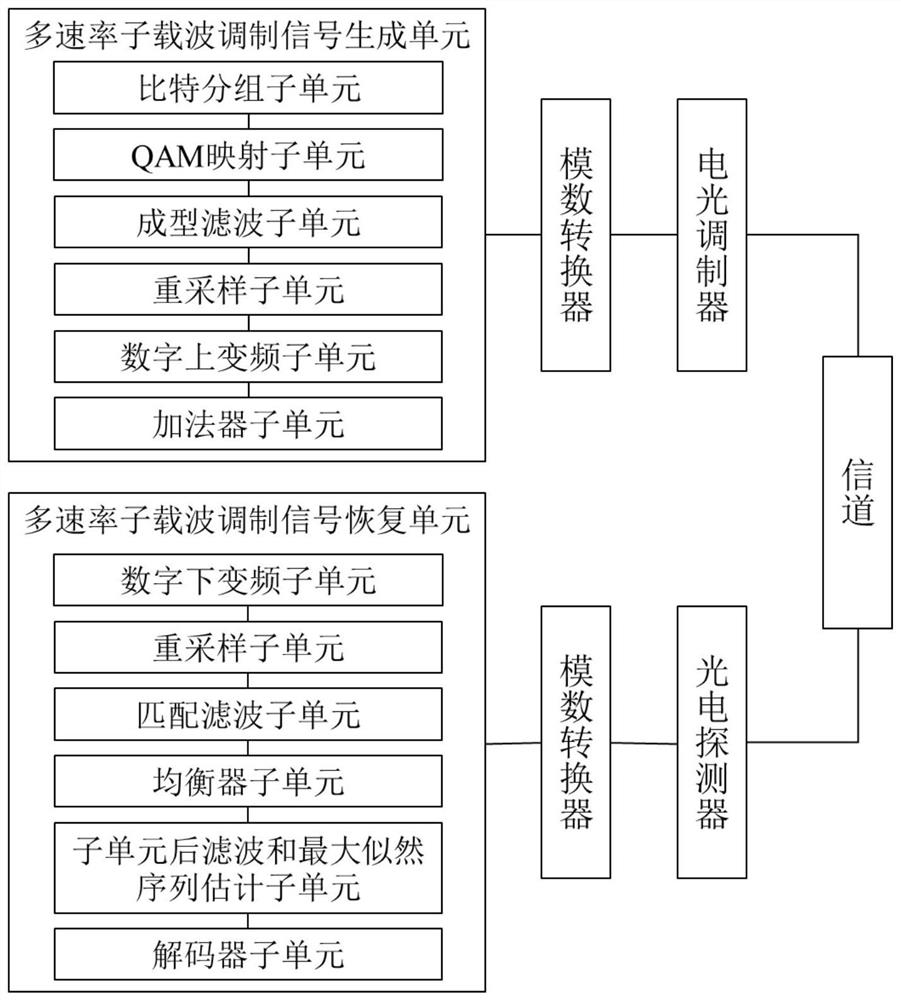
The invention relates to a multi-rate subcarrier modulation signal receiving and transmitting method and system, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the grouping and Mi-order mapping of a bit sequence according to the zero information of an optical fiber dispersion channel, so as to flexibly distribute the rate; carrying out the shaping filtering of each branch through a roll-off raised cosine filter, so as to eliminate a part of inter-symbol crosstalk; adjusting the bandwidth of each branch through resampling and rate adjustment of the formed filtering signal; realizing the frequency spectrum shifting through digital up-conversion of the resampled signal, and obtaining each subcarrier intermediate frequency signal with the center frequency being fi and the bandwidth being Bi and successfully avoiding the zero point position of each channel; and finally, adding the subcarrier signals to obtain a multi-rate subcarrier modulation signal. According to the sending method disclosed by the invention, the to-be-sent signal which can flexibly avoid the frequency spectrum zero point position of the optical fiber dispersion channel and has high dispersion tolerance can be generated while the rate is flexibly distributed.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY +1
Method and system for polar modulation with discontinuous phase
Aspects of a method and system for polar modulation with discontinuous phase are provided. In this regard, in-phase and quadrature-phase components may be generated from a modulated baseband signal, and the signal components may be utilized to generate a signal representative of the amplitude of the baseband signal. Furthermore, the signal components may be pulse shaped and the pulse-shaped components may be divided by the signal representative of the amplitude of the baseband signal. The resulting signals may be up-converted to RF, summed, and amplified, where the amplification may be controlled via a quantized representation of the signal representative of the amplitude of the baseband signal. In this regard, one or more bias points, and / or one or more binary weighted current sources coupled to one or more power amplifiers may be controlled. The pulse-shaping may comprise passing the signal components through a raised cosine filter.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
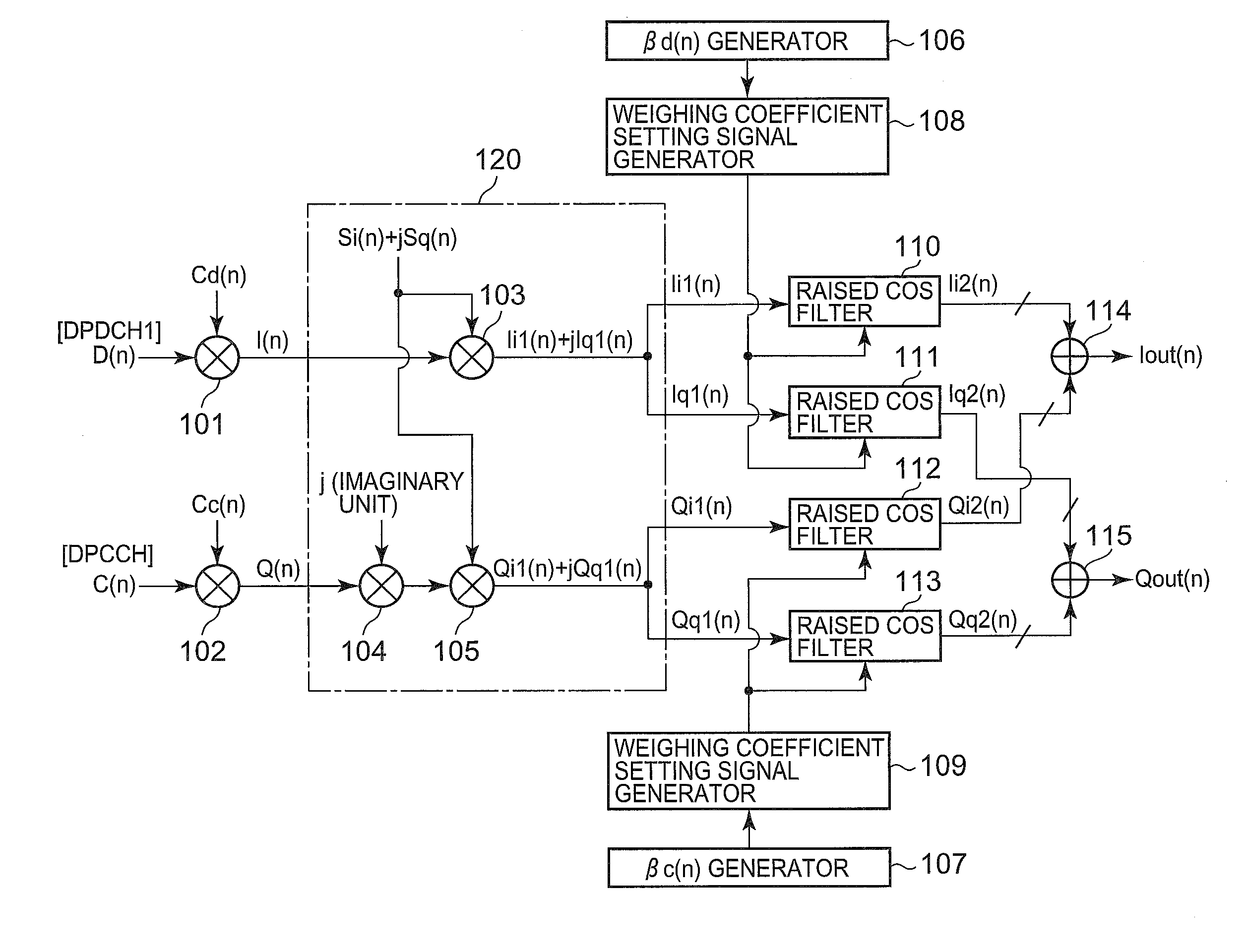
Modulator, filter, method of controlling gain of filter, and code modulating method
InactiveUS20120281771A1Small sizeLow costPhase-modulated carrier systemsBaseband systemsControl signalSoftware engineering
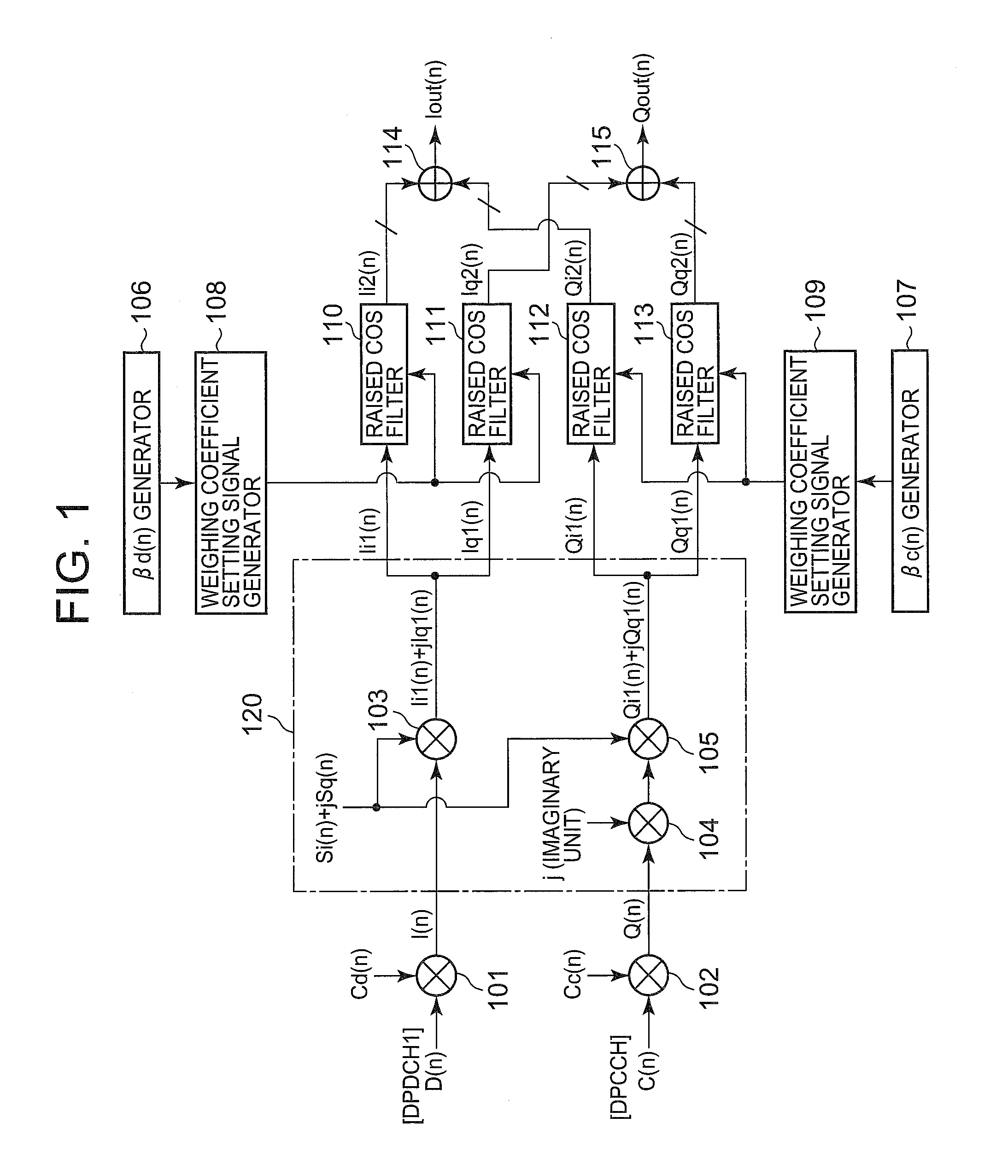
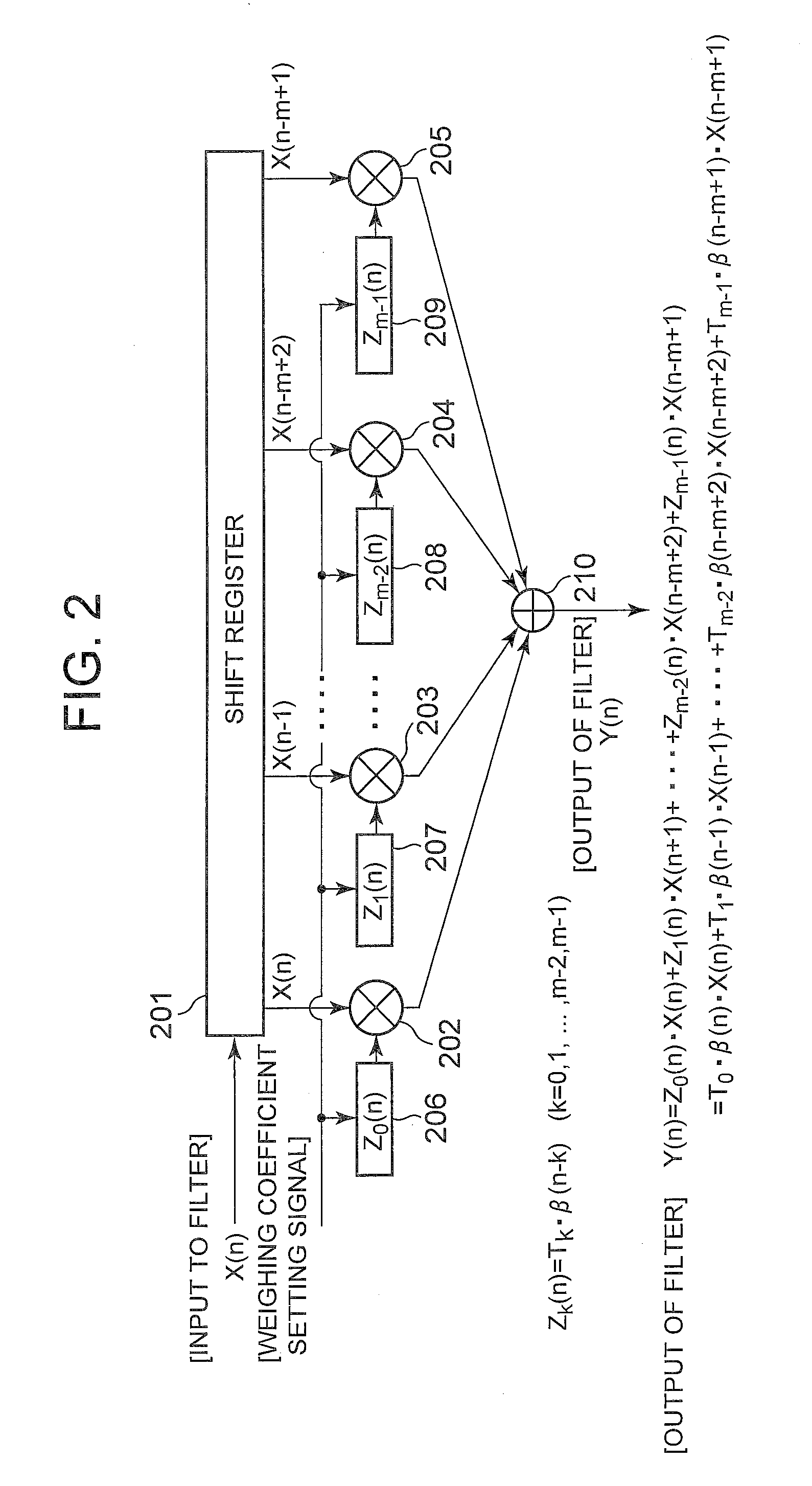
A modulator being made small in size, low in costs, low in power consumption, small in heat generation and spurious signals. The modulator includes multipliers (101, 102) for code-modulating received transmission data (D(n), C(n)), and outputting the modulated data, a control channel gain factor signal generator (106) for generating a gain control signal, a control channel gain factor signal generator (107), and weighting coefficient setting signal generators (108, 109) for receiving the output of the complex-number computing section (120) and controlling the gains of the raised cosine filters (110 to 113).
Owner:LENOVO INNOVATIONS LTD HONG KONG
Compact pulse shaping for QM-MSK and PAM/QAM transmission
InactiveUS20110188603A1Modulation with suppressed carrierAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsHigh bandwidthPulse shaping
Compact pulse shape partial response (CPS PR) signaling is developed for trellis based signals like QM-MSK, and for PAM / QAM type signals to improve the performance to bandwidth tradeoff. Compact pulse shaped signals are partial response signals that employ a very short pulse shaping filter and use Viterbi decoding to optimally detect the CPS signal in presence of its inherent inter-symbol interference. The CPS filters considered herein have much shorter impulse response than the well-known raised cosine (RC) filter. There is no need to equalize the received signal to eliminate ISI or to allow a fixed amount of ISI between received signal samples as sampled at the symbol rate as is common in partial response maximum likelihood (PRML) systems. Numerical results indicate that CPS QM-MSK and CPS QAM provides between several dB of gain, depending on constellation size, over PR-CPM and RC QAM, when compared at a given value of bandwidth, i.e., B99Tb.
Owner:TRELLIS PHASE COMM LP
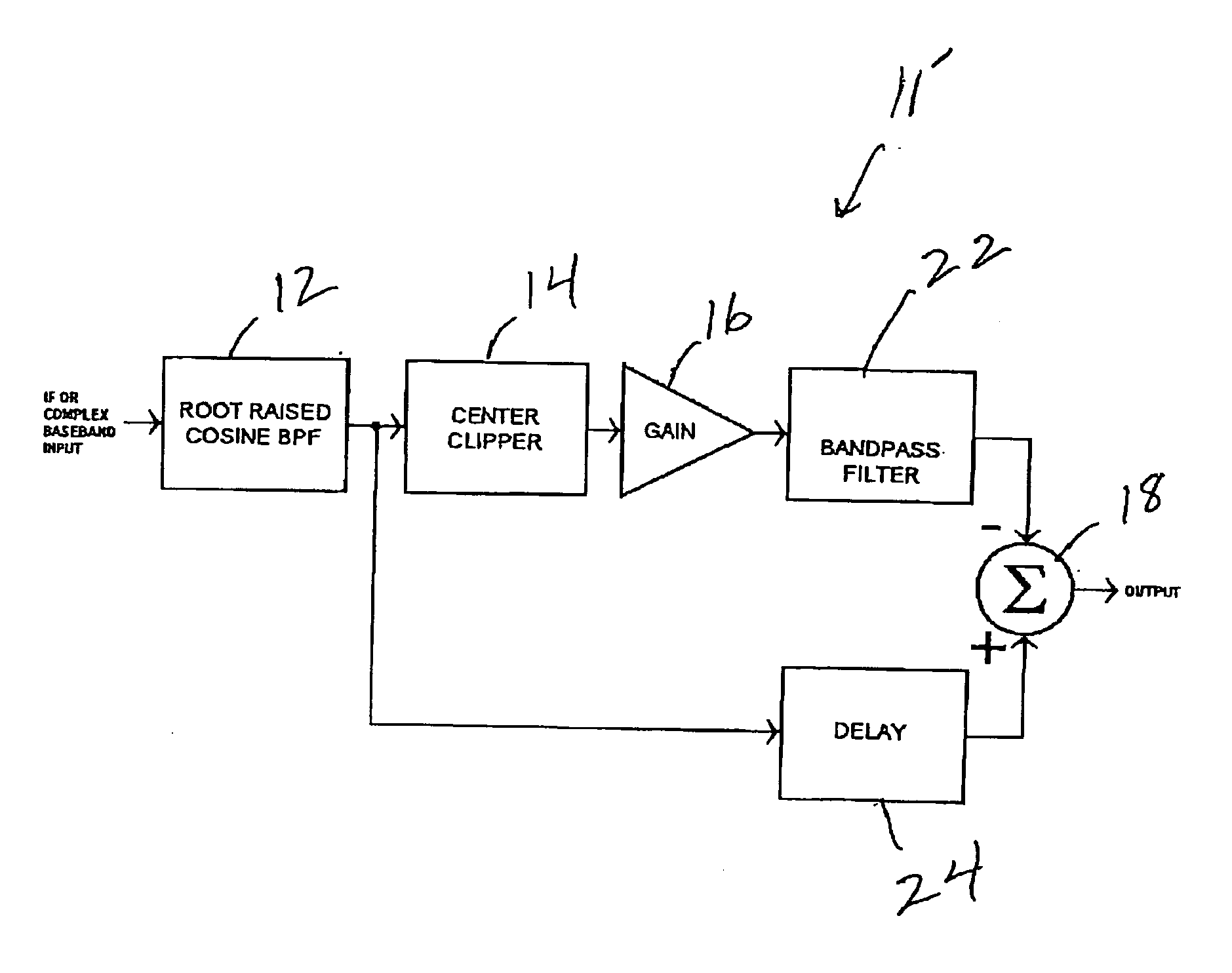
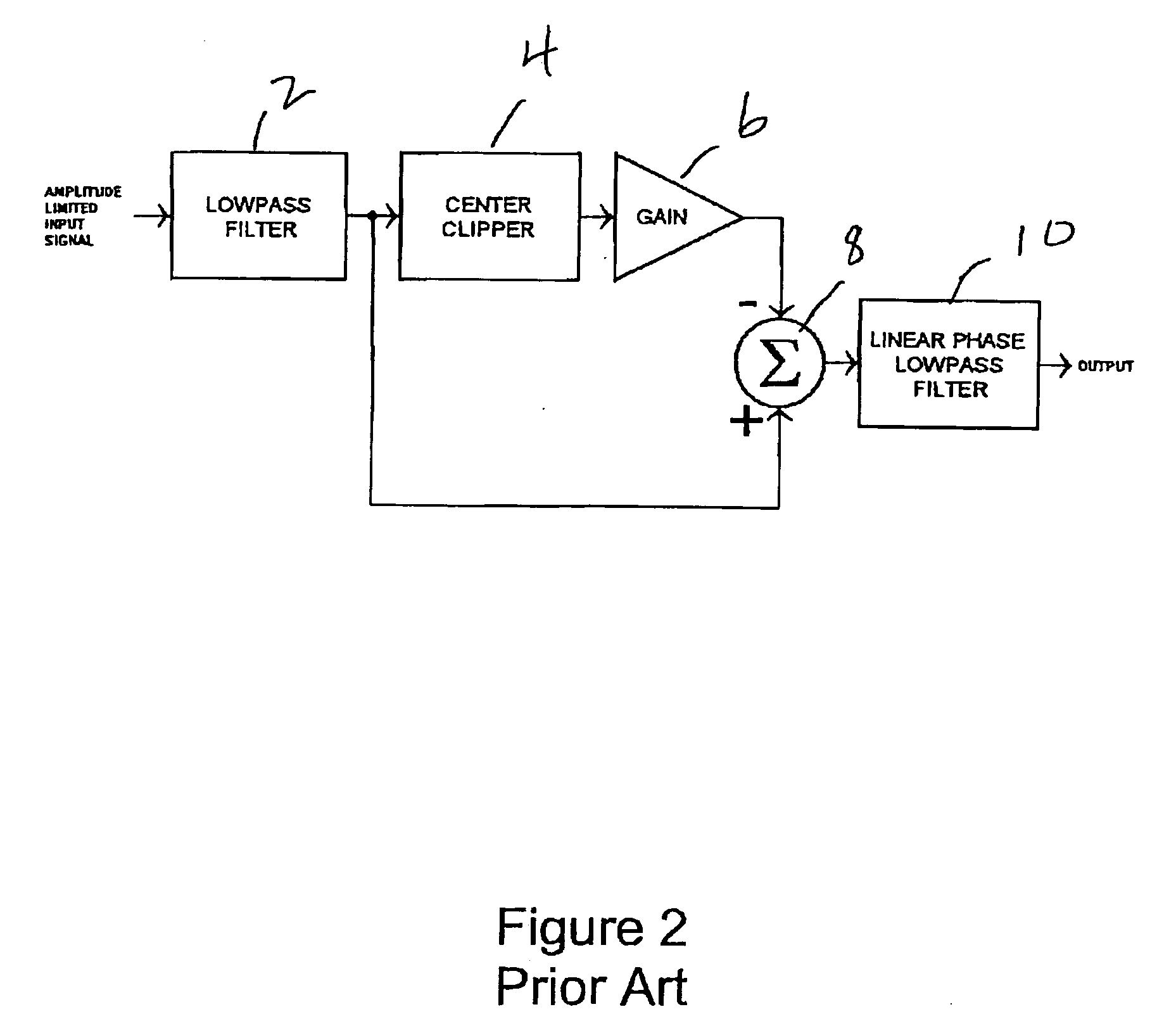
8VSB bandwidth-limited peak filter
InactiveUS20070076819A1Amplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsBandpass filteringSideband
In an 8-level vestigial sideband (8VSB) filter and method, a bandpass filter processes an input signal to produce a first bandpass filtered output signal. A center clipper circuit is responsive to first and second threshold values and the first bandpass filtered output signal to produce a center clipper output signal that has (1) zero amplitude when the bandpass filtered output signal has an amplitude that is between the first and second threshold values and (2) an amplitude equal to an amplitude of the bandpass filtered output signal minus a value of one of the threshold values otherwise. A summing circuit is responsive to the combination of the center clipper output signal and the first bandpass filtered output signal to produce a summing circuit output signal. The first bandpass filter output signal is a square root raised cosine filter output signal.
Owner:AXCERA
Universal 4fsk modem and multi-standard digital walkie-talkie
ActiveCN104836762BReduce volumeLow costFrequency-modulated carrier systemsModem deviceComputer science
The invention discloses a general 4FSK modem and a digital interphone capable of supporting multiple standards. The general 4FSK modem comprises a 4FSK general modulator and a 4FSK general demodulator, the 4FSK general modulator comprises a first rooted raised cosine filter, a shaping filter, a first switch and a double up-sampling module, and the 4FSK general demodulator comprises a second rooted raised cosine filter, a bit synchronizer, a frame synchronizer, a double down-sampling module, an anti-shaping filter, a second switch and a synchronous code selection module. A plurality of communication standards are integrated, the aim that the digital interphone is low in cost and supports multiple standards is achieved, and the size of the present interphone is not increased.
Owner:无锡士康通讯技术有限公司
RFID reader capable of increasing forward anti-interference function
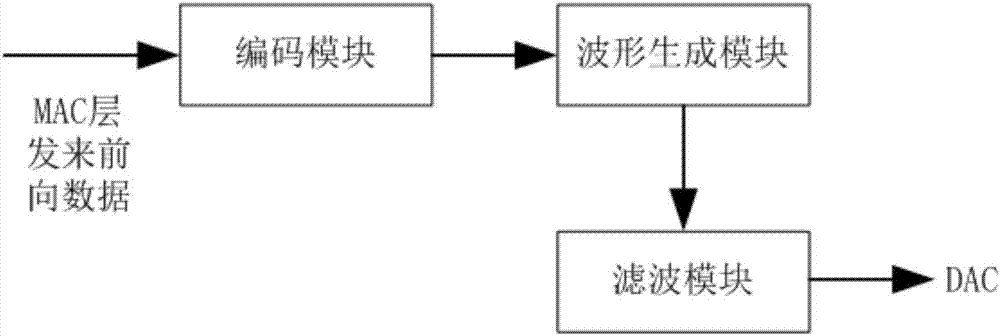
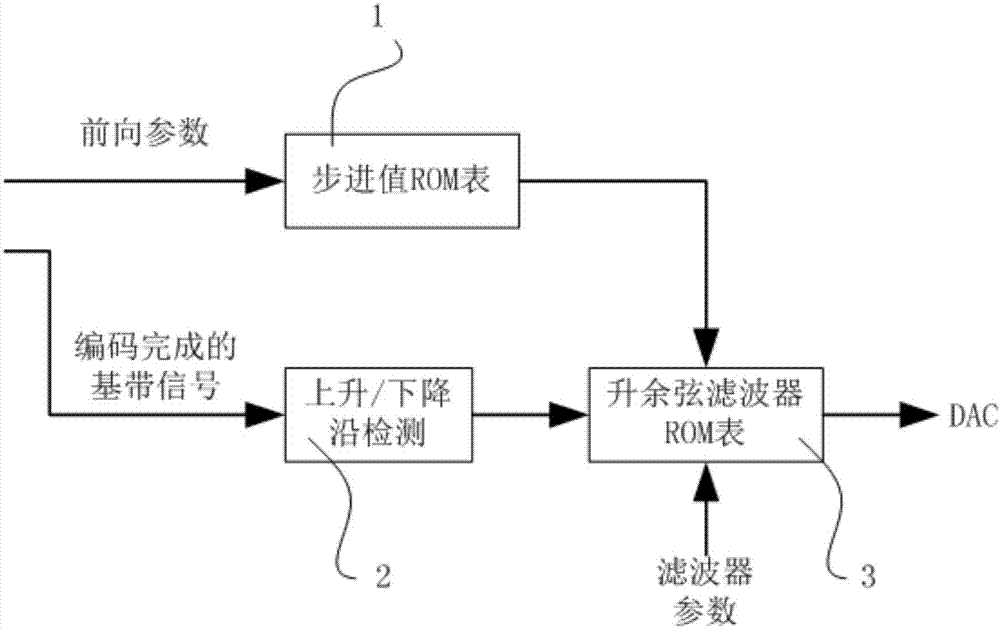
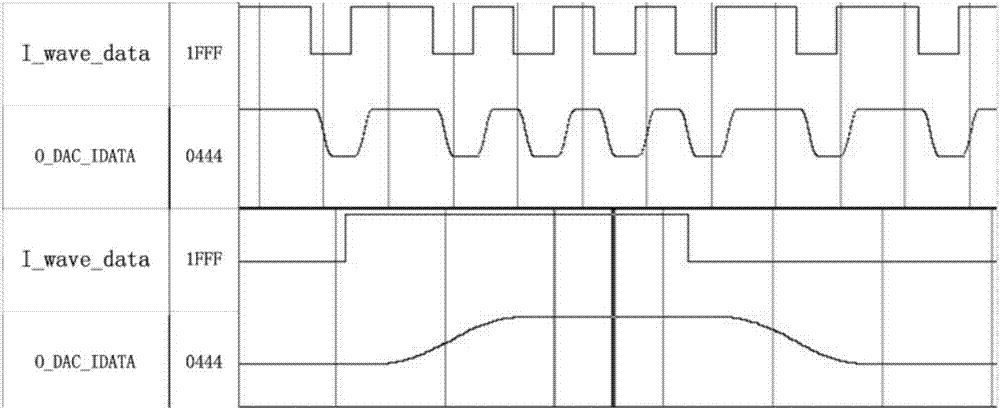
ActiveCN107423648ASave bandwidthReduce crosstalkCommunication jammingSensing by electromagnetic radiationComputer moduleComputer science
The invention provides a RFID reader capable of increasing forward anti-interference function. A forward link includes an encoding module, a waveform generation module, a filtering module and a DAC. The filtering module is a Raised Cosine Filter which is implemented by look-up table in a FPGA. The method for implementing the Raised Cosine Filter includes the following steps: 1. on the basis of the modulation method of a RFID reader and the rate of outputting a baseband signal by the encoding module, taking a corresponding a step value from a step value ROM table; 2. if the rising edge or falling edge of forward data which is output by the waveform generation module is detected, starting to look up a filtering parameter ROM table, acquiring a filtering parameter, wherein the step value is one look-up parameter in the filtering parameter ROM table; and 3. on the basis of filtering parameter, setting the Raised Cosine Filter. According to the invention, the RFID reader has the characteristics of reduced bandwidth of baseband signals, sufficient capability of channel transmission, and reduced intersymbol interference.
Owner:ZTE INTELLIGENT IOT TECH
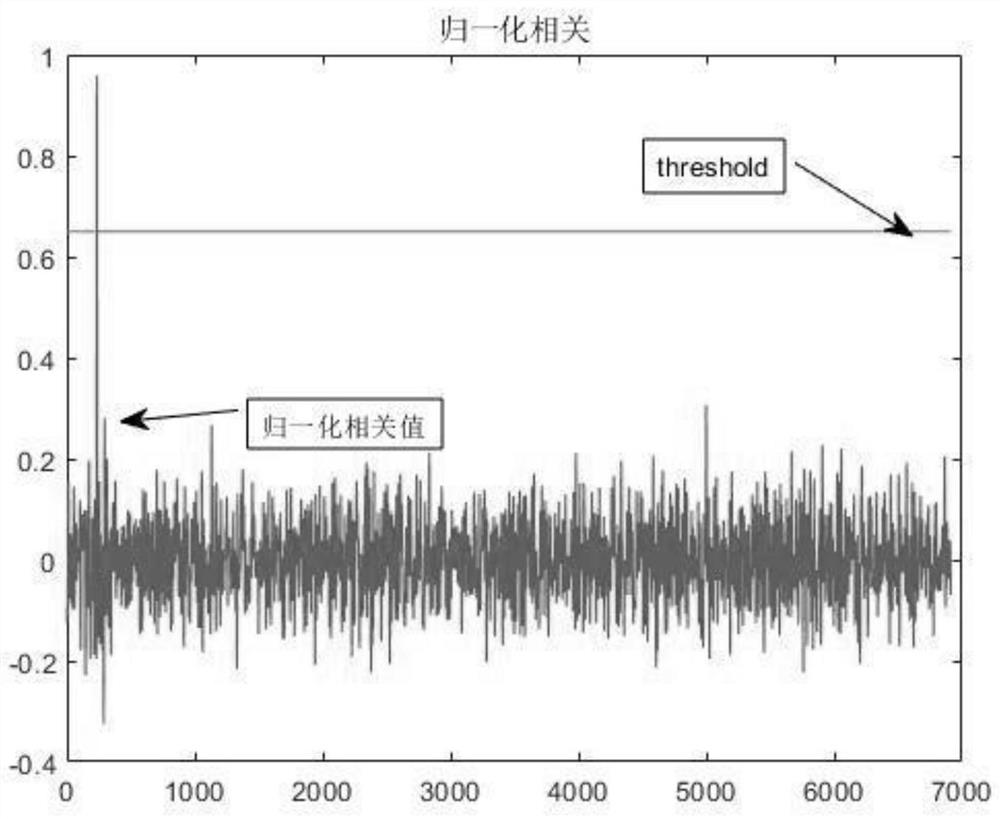
Anti-frequency-offset DMR interphone signal rapid identification method
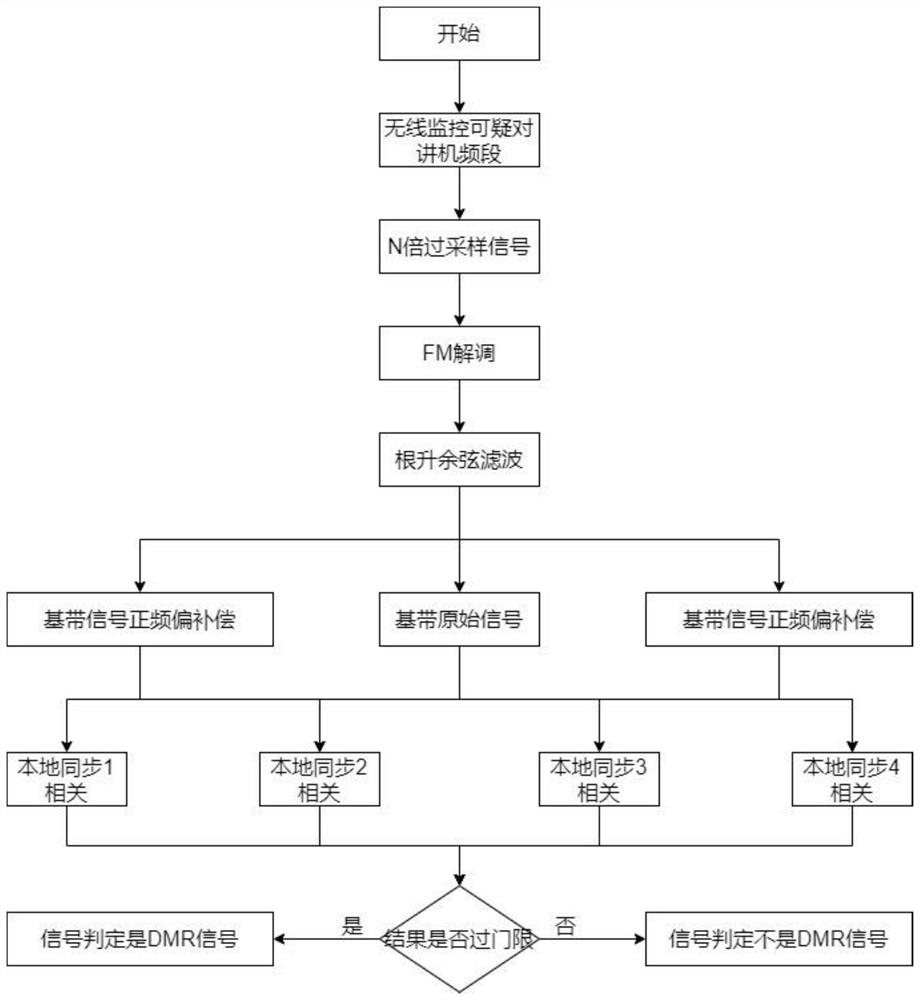
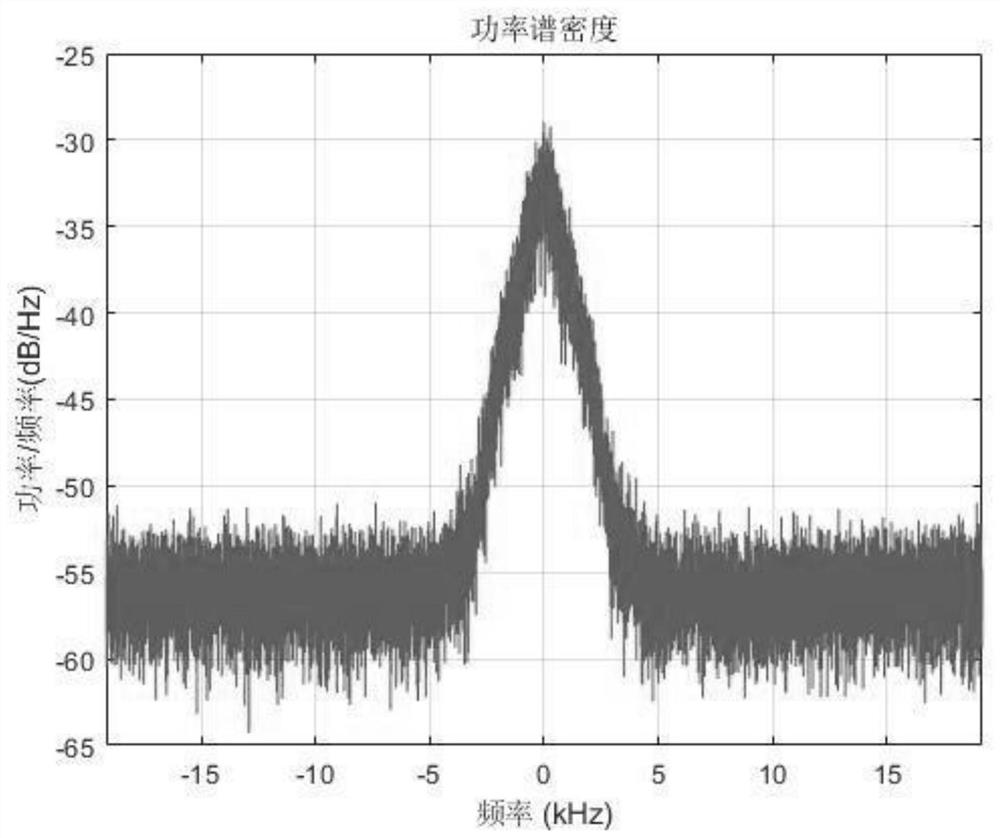
PendingCN112865882AReduce complexitySimplify hardware designTransmission monitoringComputer scienceSpeech sound
The invention discloses an anti-frequency offset DMR interphone signal rapid identification method, which comprises the following steps: after monitoring and finding out a suspected signal of a DMR interphone, carrying out integer multiple and decimal multiple extraction on baseband data, carrying out root raised cosine filter, FM demodulator and frequency offset component pre-compensation, and carrying out normalized correlation on a plurality of locally reserved voice synchronization signals; and finally, judging whether the signal is a DMR interphone signal or not through a threshold. According to the method, the receiving range of the equipment to the signal frequency offset is enhanced, and the identification probability of the DMR interphone is improved. The method solves the problem that the DMR detection probability is reduced when the frequency offset exists, and is suitable for the field of wireless communication.
Owner:南京中新赛克科技有限责任公司
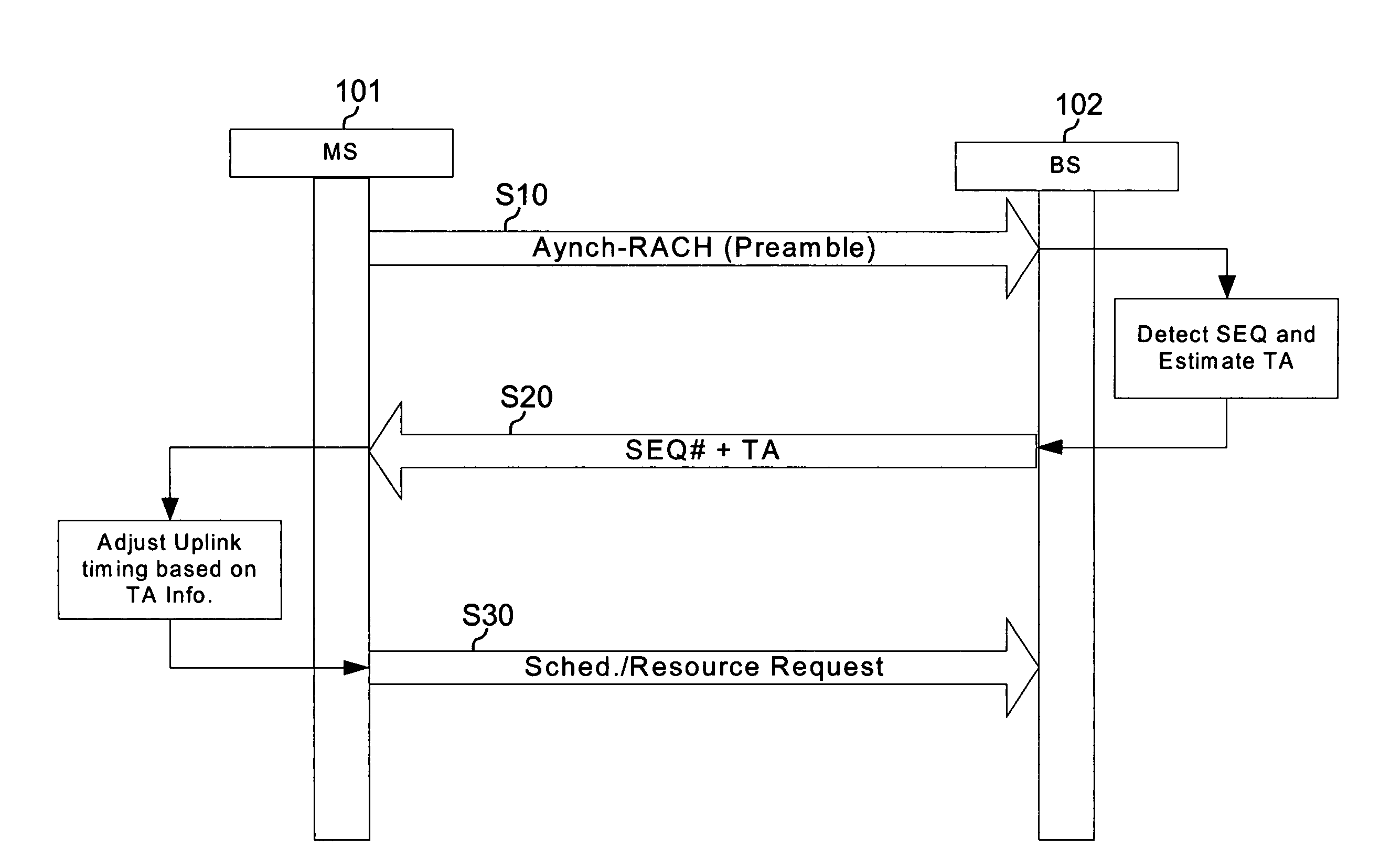
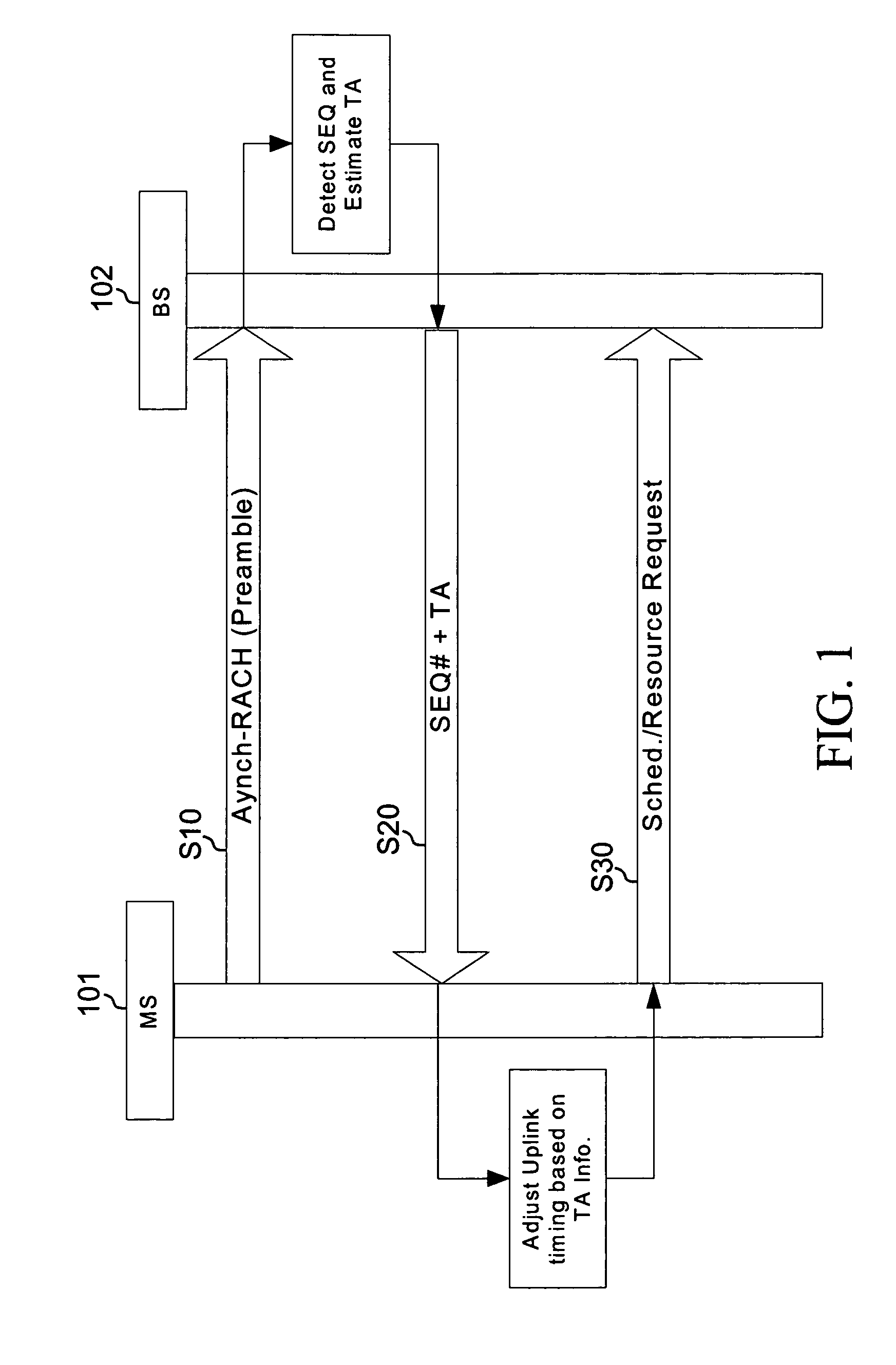
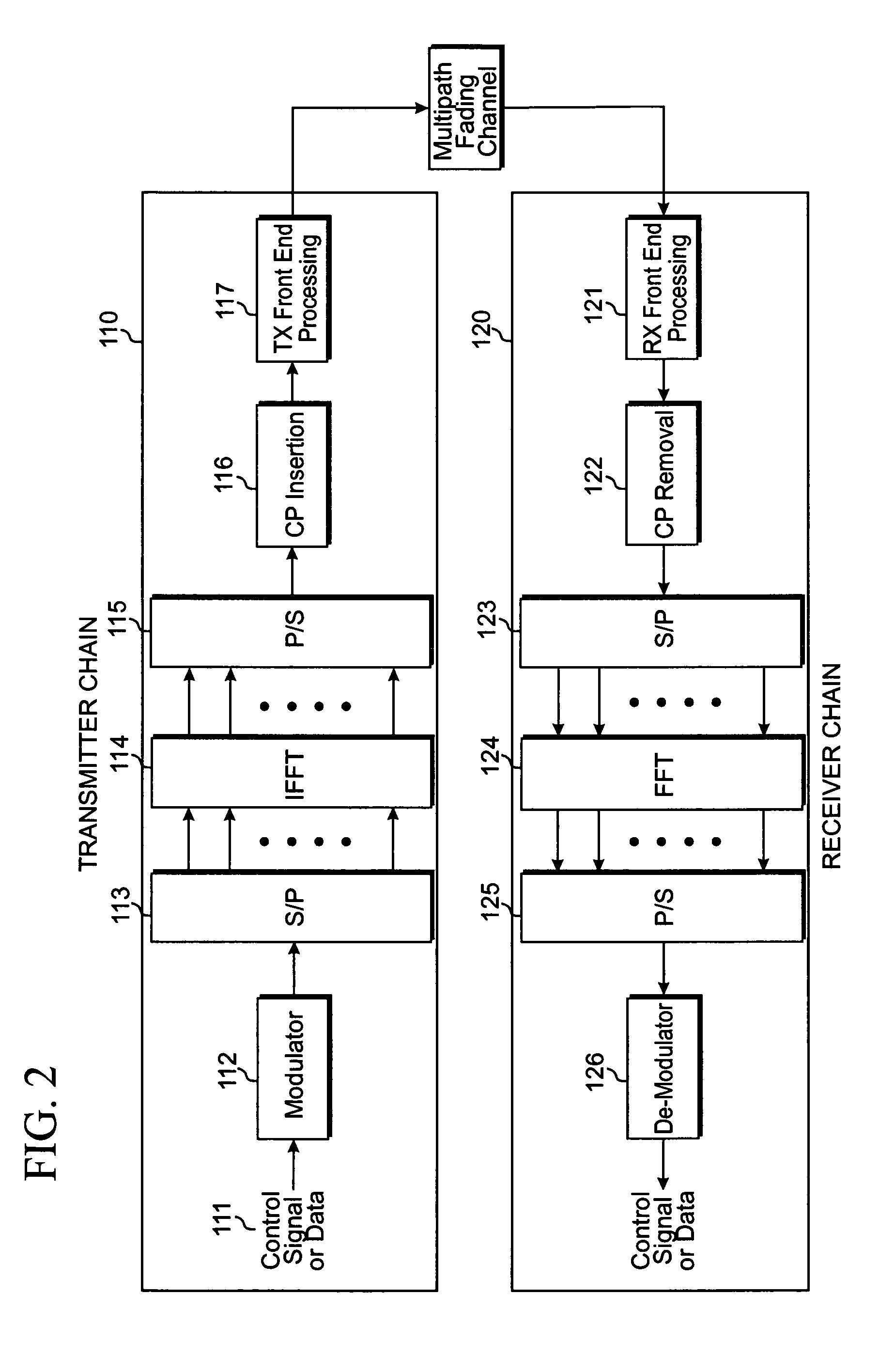
Joint timing recovery and equalization for an N-antenna system
InactiveCN1316774CTelevision system detailsSpatial transmit diversityFinite impulse responseControl signal
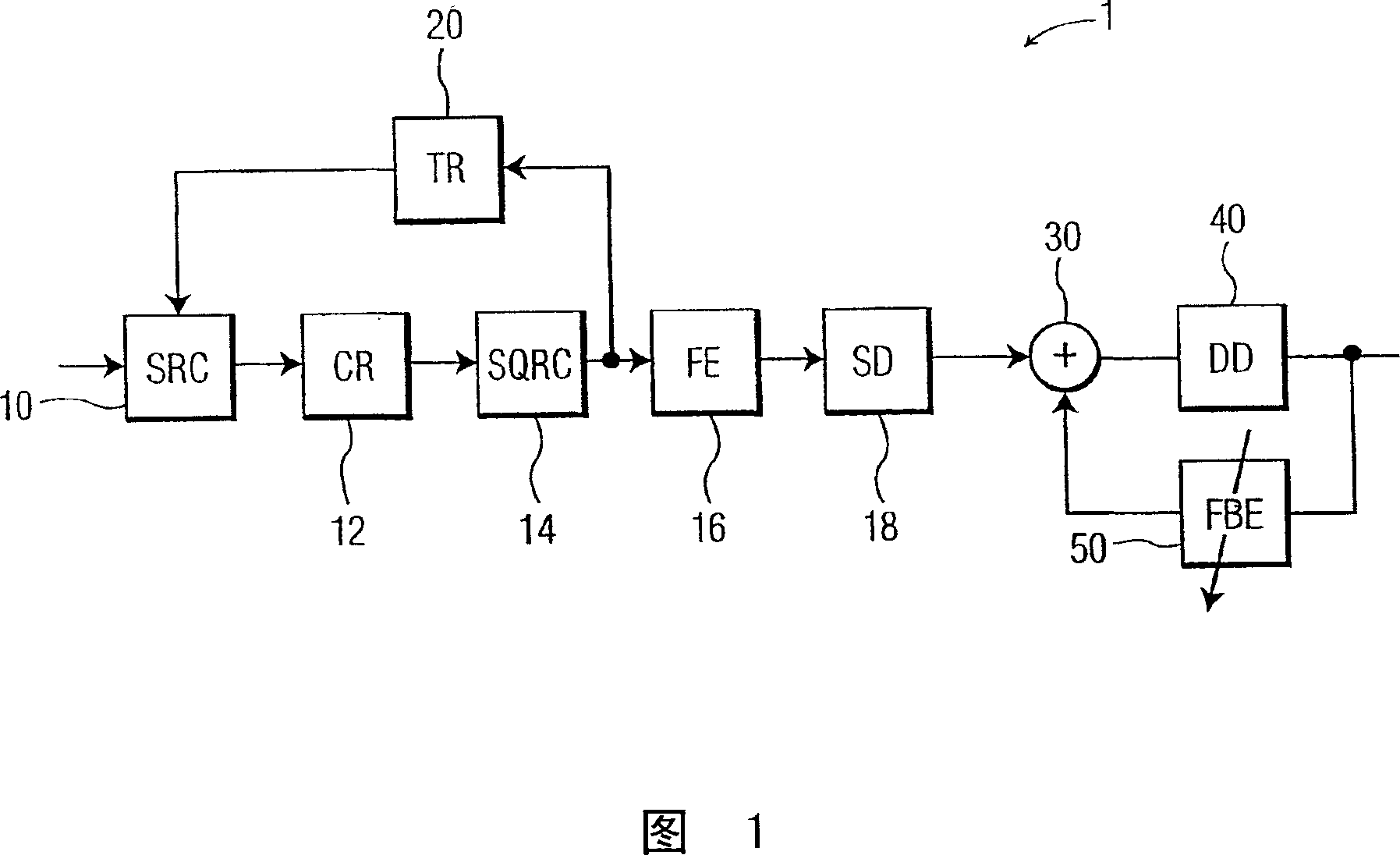
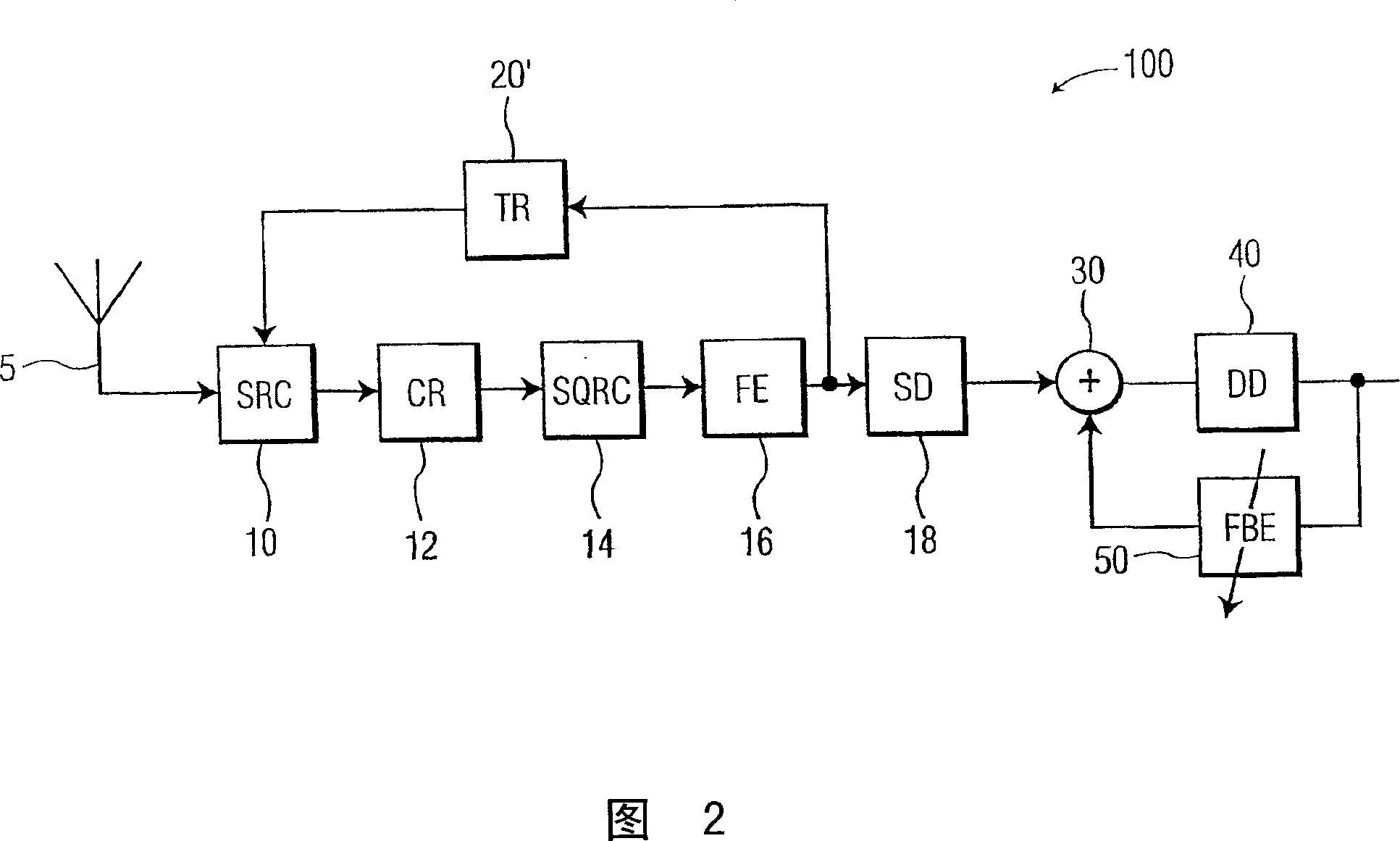
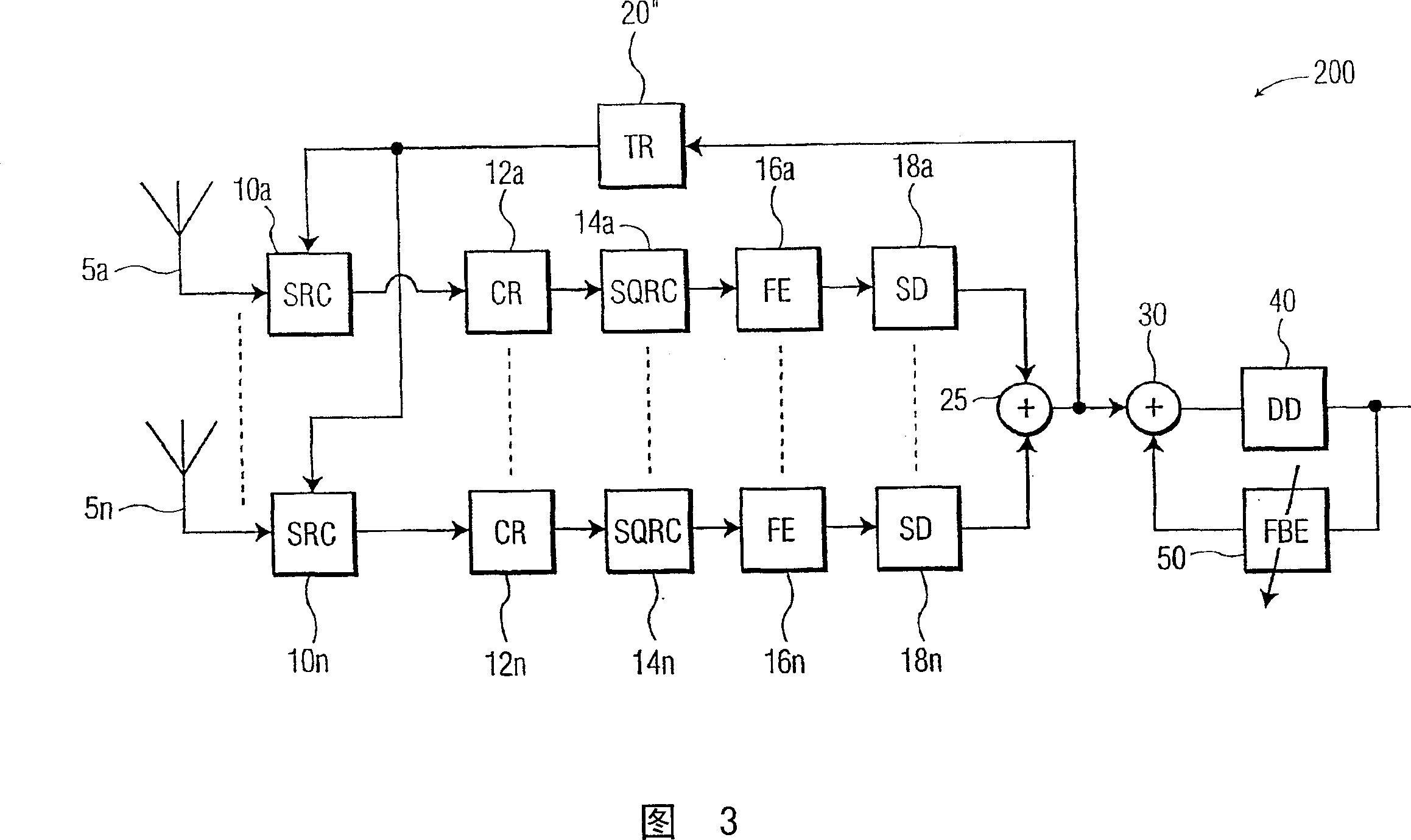
A timing recovery loop in the front end of a digital receiver includes a sample rate converter which receives a symbol stream at a first sampling rate and outputs the symbol stream at a second sampling rate responsive to a timing recovery (TR) control signal, a forward equalizer generating an equalized feedback signal based on the symbol stream at the second sampling rate, and a timing recovery circuit generating the TR control signal based upon the equalized feedback signal. If desired, the timing recovery loop may include a carrier recovery circuit electrically coupling the sample rate converter to the forward equalizer and a finite impulse response (FIR) filter electrically coupling the carrier recovery circuit to the forward equalizer. In an exemplary case, the FIR filter is a square-root raised cosine filter. A method for controlling the timing recovery loop based on the equalized feedback signal and a corresponding timing recovery control signal are also described.
Owner:PENDRAGON WIRELESS LLC
FPGA-based variable symbol sampling rate raised cosine filter
PendingCN110890874AFast samplingEasy to implementDigital technique networkBinary multiplierControl theory
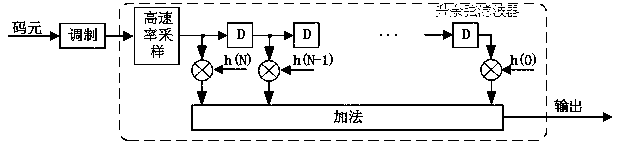
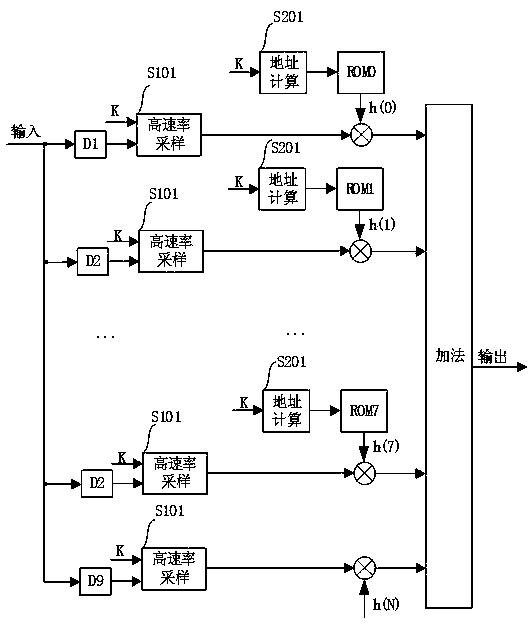
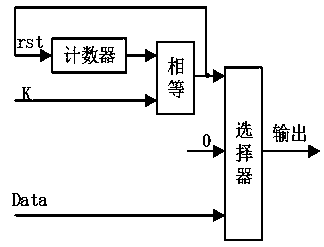
The invention relates to an FPGA-based variable symbol sampling rate raised cosine filter, which comprises L + 1 high-speed sampling modules and L address calculation modules, wherein N = KL, K is thenumber of sampling points of each symbol, L represents that the cut-off time length of the filter is L symbols, and the number of filter coefficients is N + 1; L+ 1 high-speed sampling modules sequentially delay one clock period for sampling, the output ends of the high-speed sampling modules are connected to multipliers respectively, the output ends of the multipliers are connected to an adder,and the adder performs addition operation on L + 1 paths of signals input in parallel and is used for outputting raised cosine filtering signals; the device further comprises L ROM memories, the ROM memories are used for storing raised cosine filter coefficients h (n), n is equal to 0, 1, 2-N-1, and each ROM memory is connected with an address calculation module and used for calculating the address of the subsequent ROM memory. The scheme can adapt to a variable symbol sampling rate, and consumed FPGA multiplier resources do not change along with the symbol sampling rate.
Owner:成都微泰科技有限公司
A signal processing method suitable for high-sensitivity spaceborne ads-b receiver
ActiveCN111884981BEfficient receptionImprove detection rateError preventionRadio transmissionRadio frequencyFalse alarm
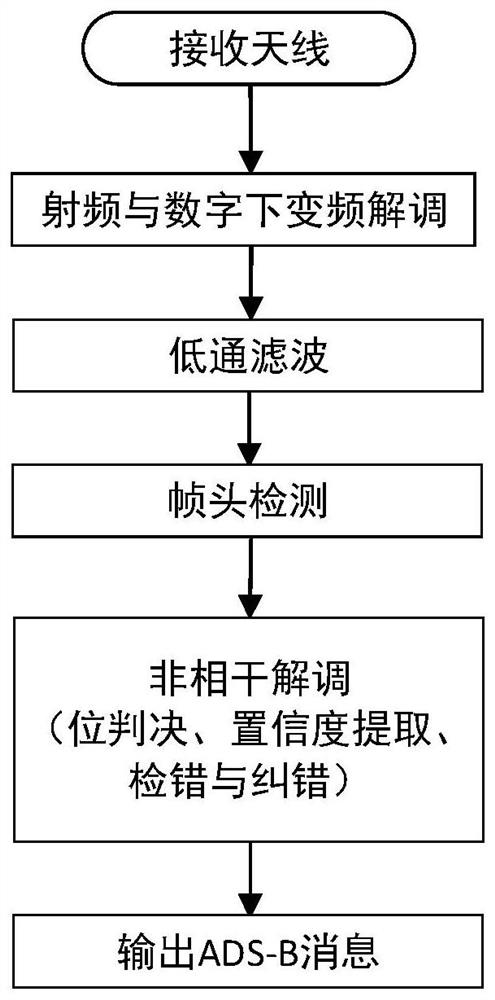
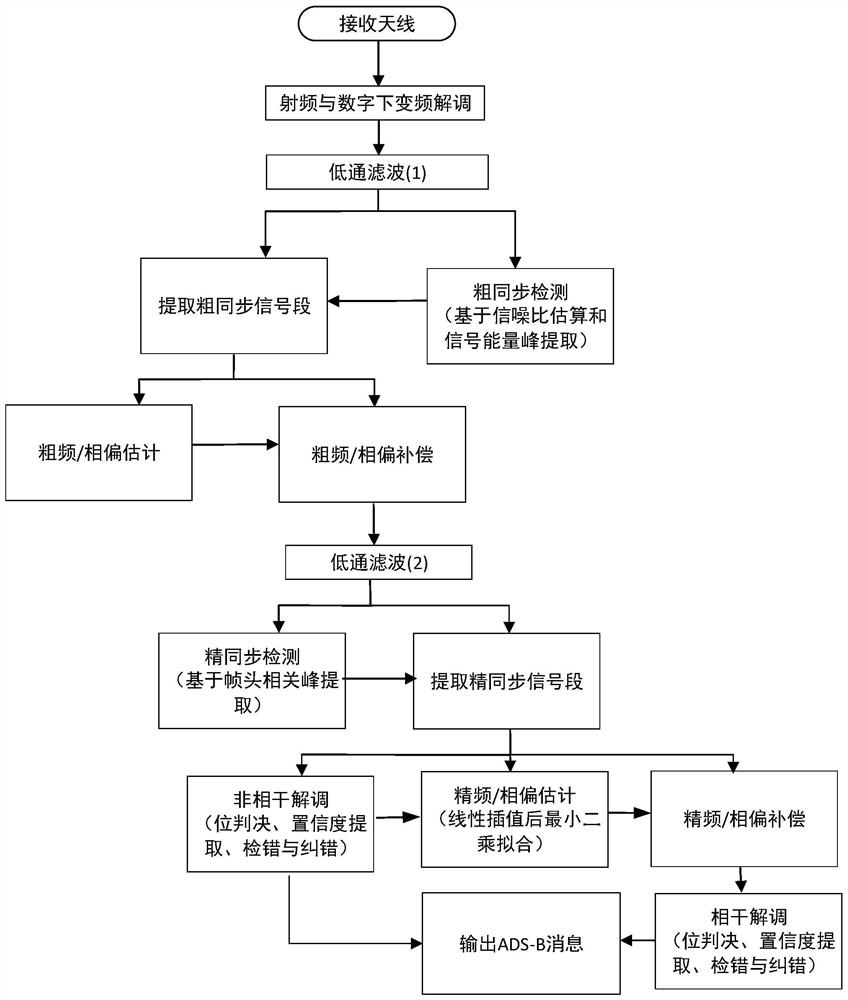
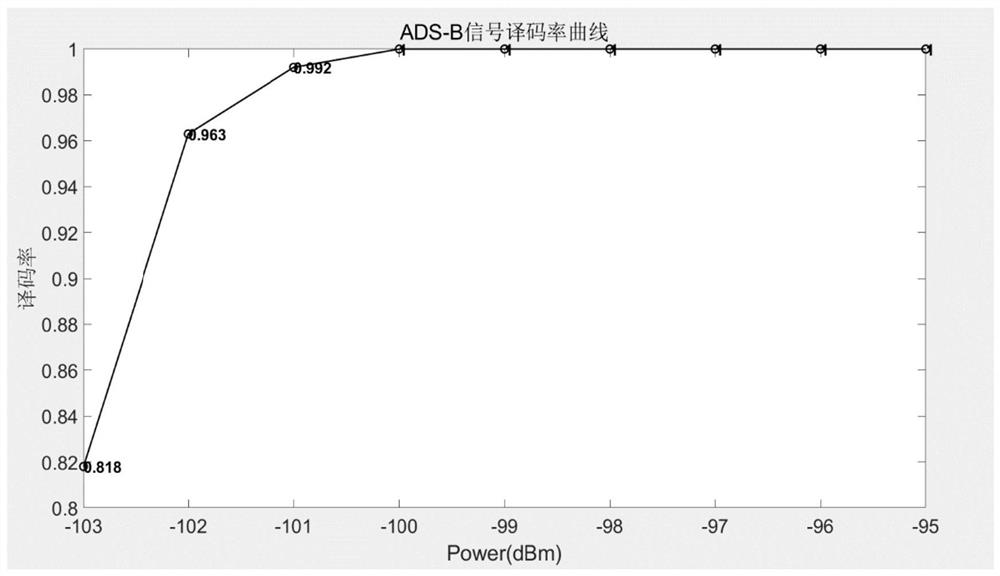
The invention relates to a signal processing method suitable for a high-sensitivity space-borne ADS-B receiver, belonging to the field of aviation surveillance technology, including S1: the ADS-B signal received by the antenna is demodulated by radio frequency to obtain an intermediate frequency signal, and the digital signal after digital-to-analog conversion Down-conversion demodulation to obtain digital baseband signals; S2: low-pass filtering: preliminary filtering of out-of-band noise; S3: coarse synchronization detection, extracting coarse synchronization signal segments; S4: coarse frequency / phase offset estimation and compensation; S5: raised cosine filtering Device: improve signal-to-noise ratio; S6: fine synchronization detection, extracting fine synchronization signal segment; S7: non-coherent demodulation, if it passes the verification, then output ADS-B message; if not, then implement step S8; S8: carry out Precise frequency / phase offset estimation and compensation, and coherent demodulation, if the verification is passed, an ADS‑B message will be output; if it fails, the data will be discarded. The method has high detection rate, low false alarm rate and high decoding success rate.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Communication parameter estimation method and system in blind signal detection
ActiveCN113542164ASolve the problem of inaccurate estimatesMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksTime domainFrequency spectrum
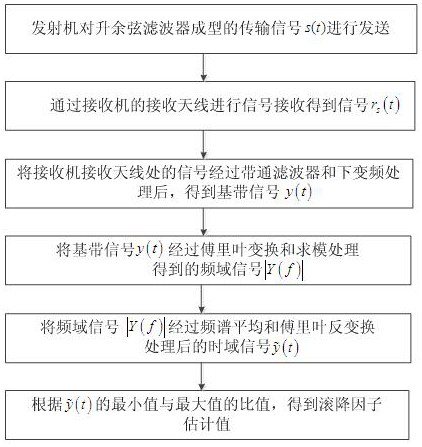
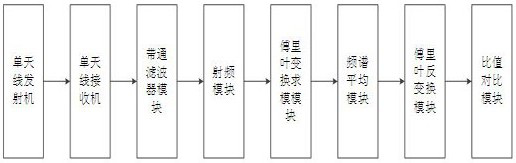
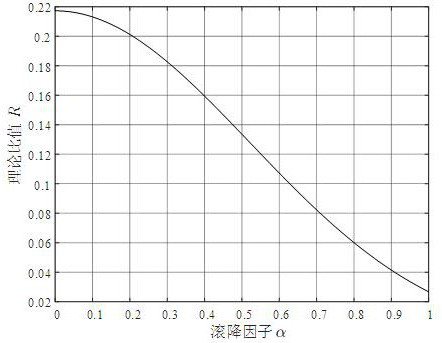
The invention discloses a communication parameter estimation method and system in blind signal detection. The method comprises the following steps: S1, sending, by a transmitter, a transmission signal s(t) formed by a raised cosine filter; S2, receiving a signal by a receiving antenna of a receiver to obtain a signal rs(t); S3, transmitting a signal at the receiving antenna of the receiver through a band-pass filter and performing down-conversion processing on the signal to obtain a baseband signal y(t); S4, performing Fourier transform and modulo processing on the baseband signal y(t) to obtain a frequency-domain signal |Y(f)|; S5, subjecting the frequency-domain signal |Y(f)| to frequency spectrum averaging and Fourier inverse transform to obtain a time-domain signal y<~>(t); and S6, according to the ratio of the minimum value to the maximum value of the y<~>(t), obtaining a roll-off factor estimation value. According to the invention, roll-off factor blind estimation is carried out on the raised cosine forming signal, and the problem that the estimation performance is not ideal when the signal-to-noise ratio condition is poor is effectively solved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Multi-carrier implementing method and apparatus for TD-SCDMA system
ActiveCN101370000BLow costMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksFrequency spectrumFourier transform on finite groups
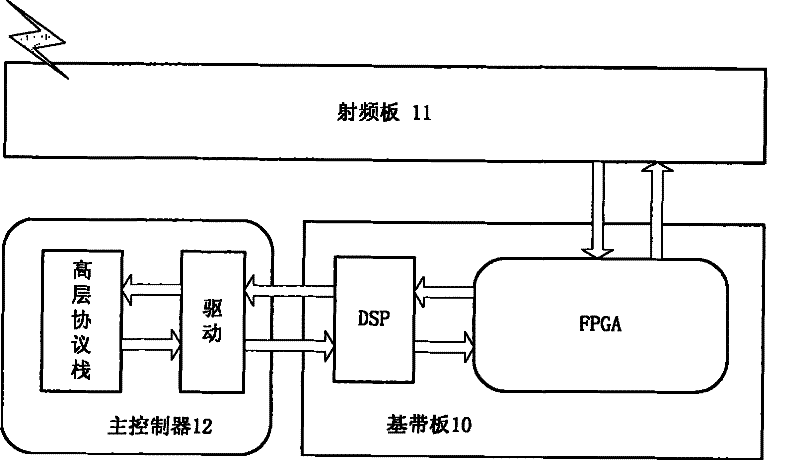
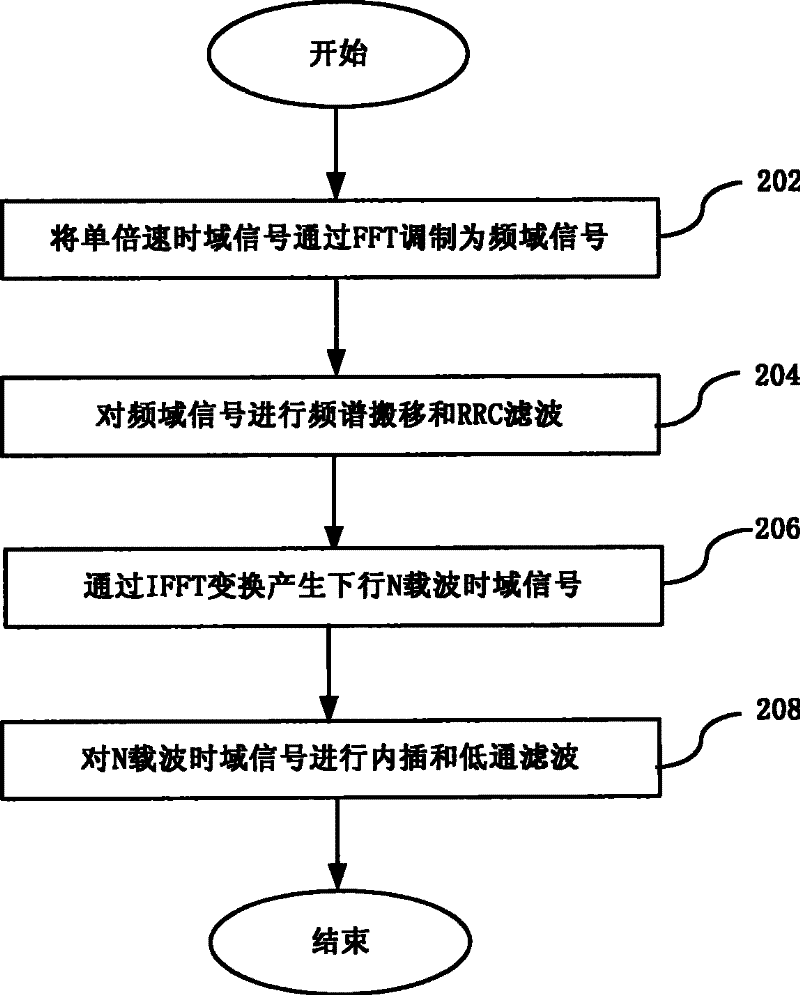
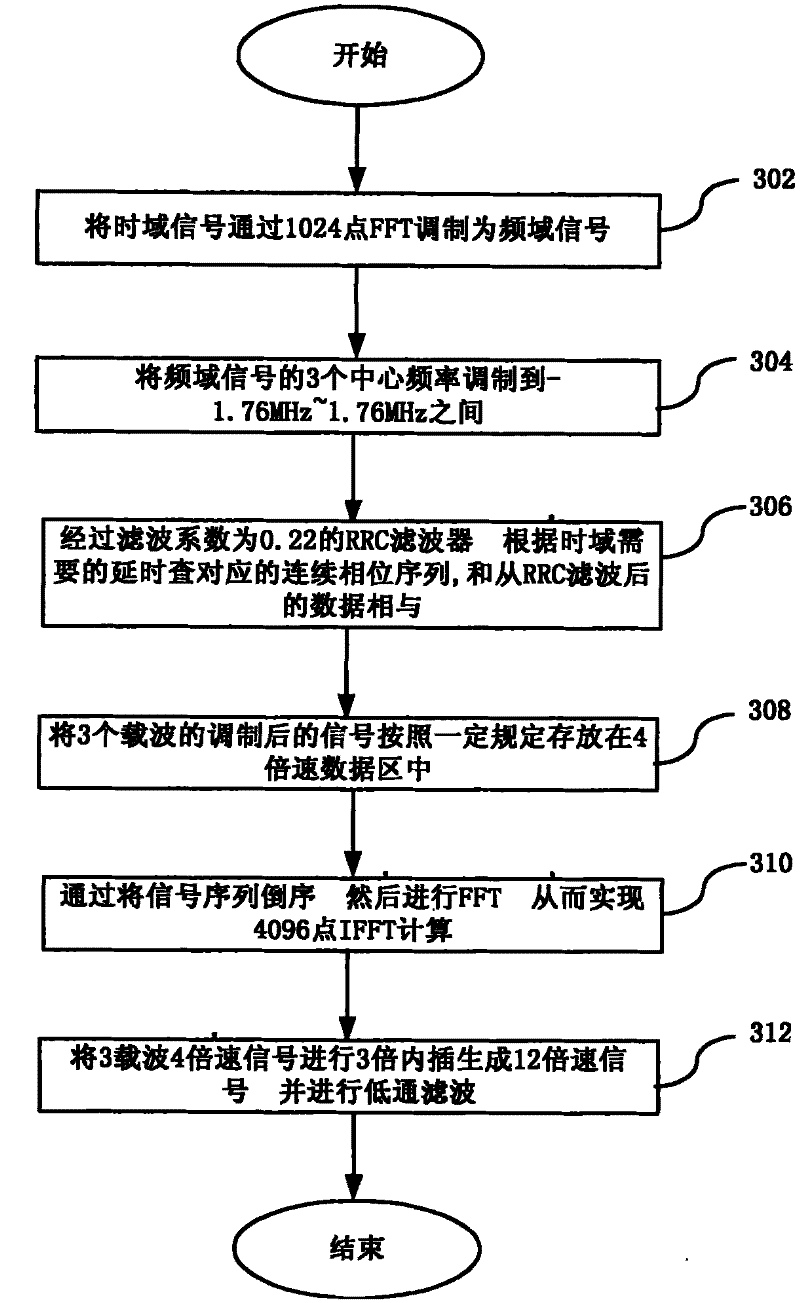
The invention discloses a multi-carrier accomplishing method and device of time-division synchronization code division multiple access system. The method comprises: modulating downlink single speed time domain signal to frequency domain signal through quick Fourier transform, performing spectrum shift and rooted raised cosine filter for frequency domain signal, then performing reverse quick Fourier transform to produce downlink N carrier time domain signal, interpolating the downlink N carrier time domain signal to produce K speed signal then low pass filtering. The inventive TD-SCDMA multi-carrier accomplishes combination on DSP, so a radio frequency can accomplish multi-carrier function. Multi-carrier filtering separately accomplish on DSP and FPGA, DSP can accomplish RRC filtering, FPGA can accomplish low pass filtering. Transmission time delay controls digital signal and continuous phase of frequency domain which enables high precision algorithm and low complexity.
Owner:BEIJING STARPOINT TECH COMPANY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com