Non-data auxiliary frequency offset estimation method applicable to amplitude phase shift keying
An amplitude phase shift keying, non-data-assisted technology, which is applied in the field of digital communication, can solve the problems of difficult to obtain high-precision frequency offset estimation value, small frequency offset estimation range, and large estimation range, so as to expand the frequency offset estimation range , reduce the bit error rate, improve the effect of estimation accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] The technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention will be described clearly and in detail below in conjunction with the drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. The described embodiments are only a part of the embodiments of the present invention.
[0026] The technical scheme of the present invention is as follows:
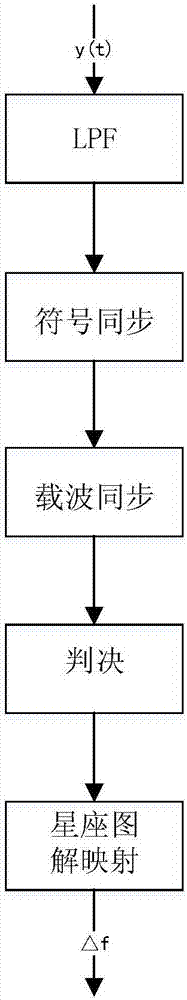
[0027] At the receiving end, APSK (AmplitudePhaseShiftKeying, amplitude phase shift keying) signal demodulation is sequentially processed by low-pass filter, synchronization processing, based on the decision threshold, constellation diagram mapping processing and output. The synchronization processing includes timing synchronization and carrier synchronization. And the signal demodulation at the receiving end mainly solves the synchronization problem.
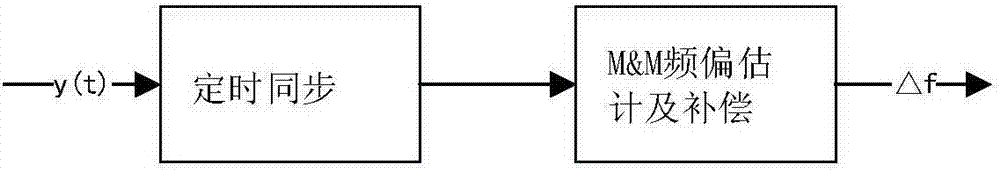
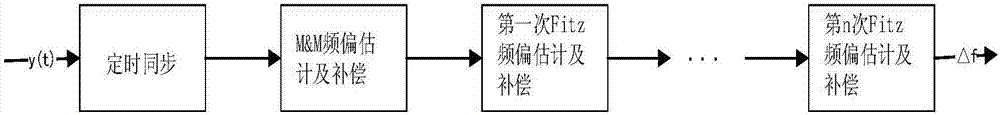
[0028] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the frequency synchronization processing steps at the APSK receiving end. The input data is processed by constellation map mapping, sha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com