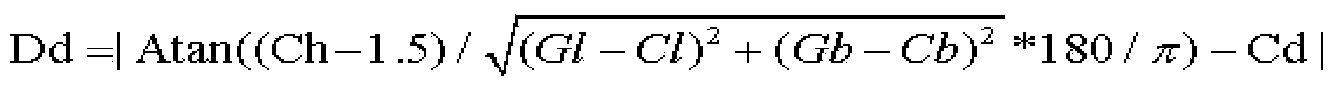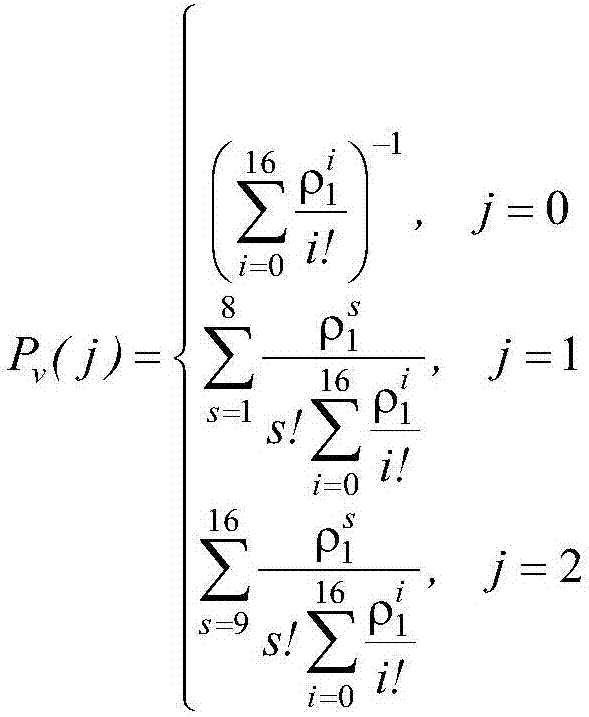Patents
Literature
1379 results about "TD-SCDMA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
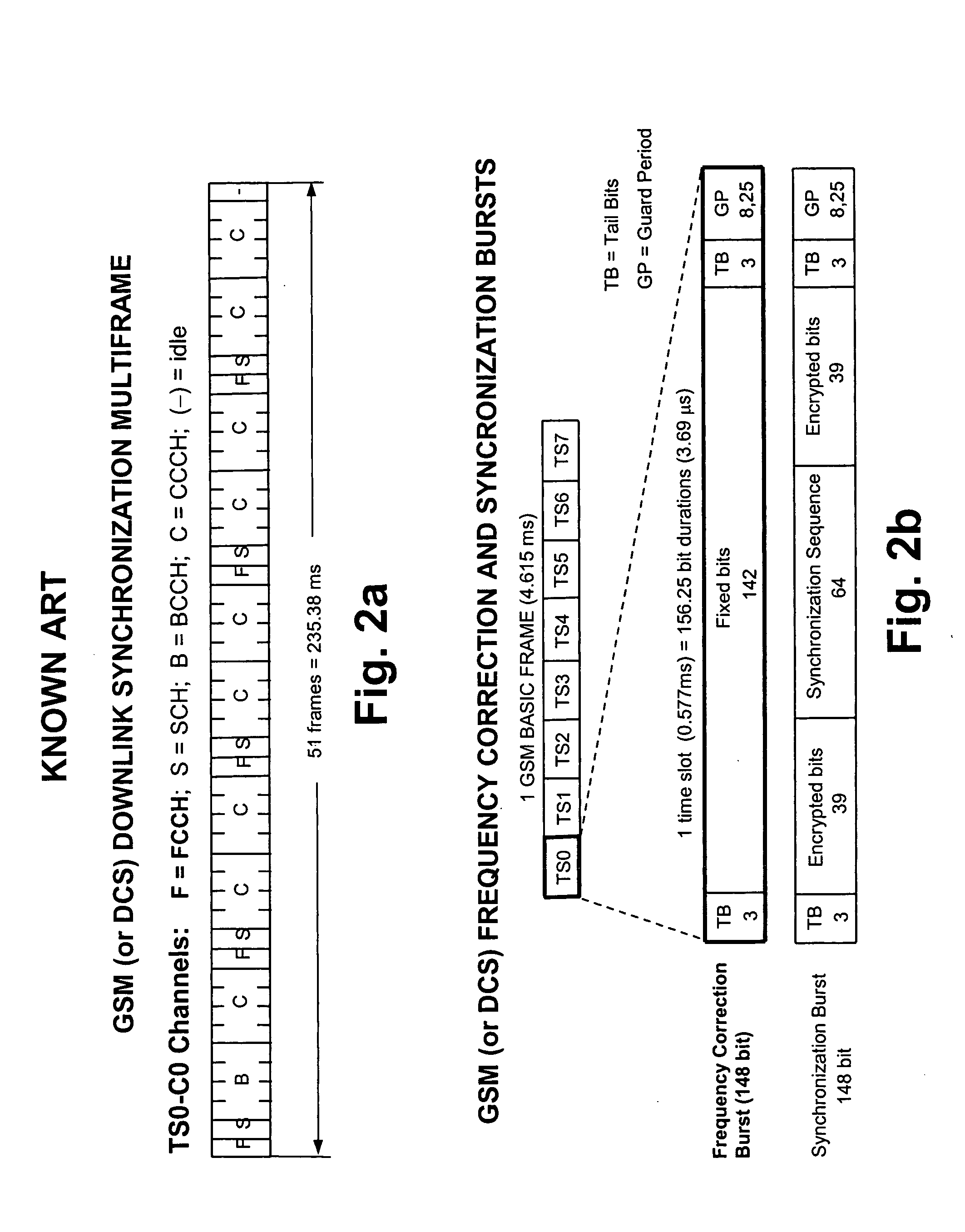
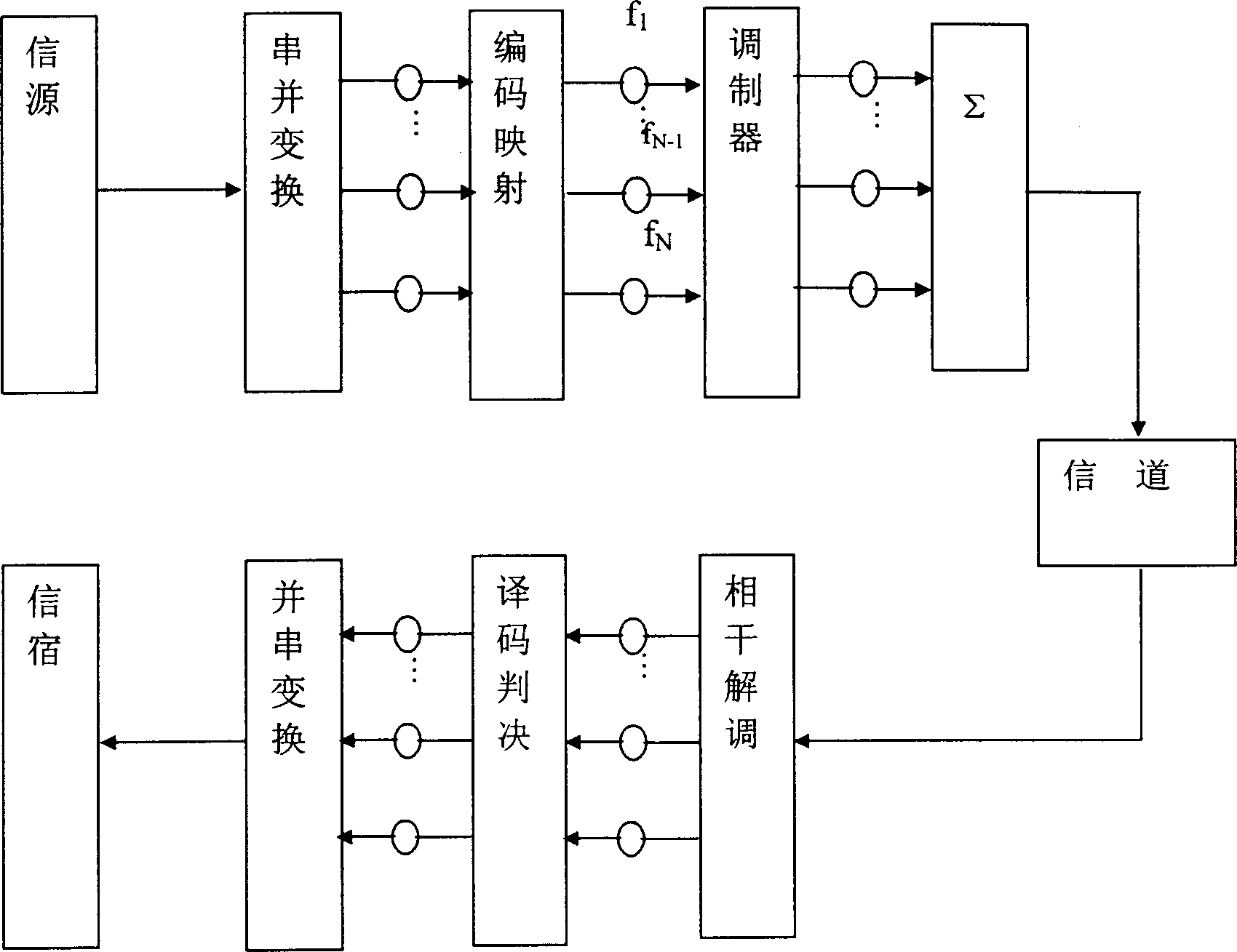
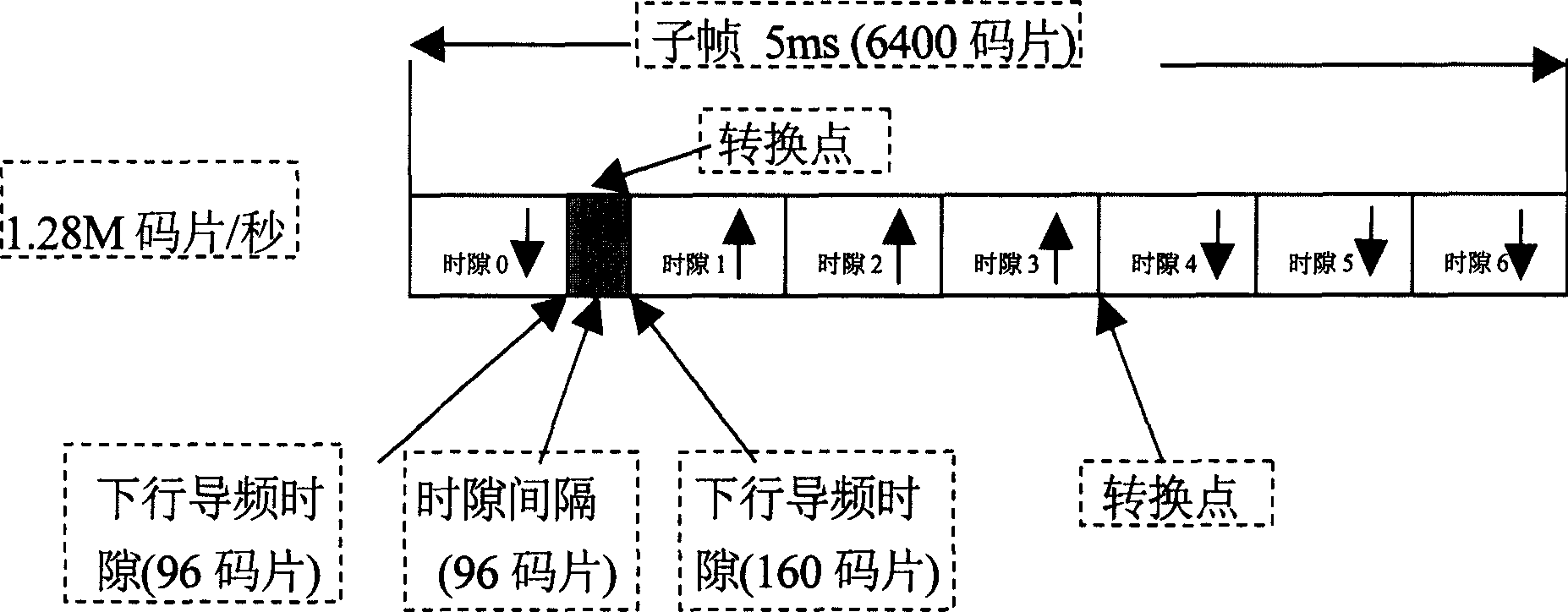
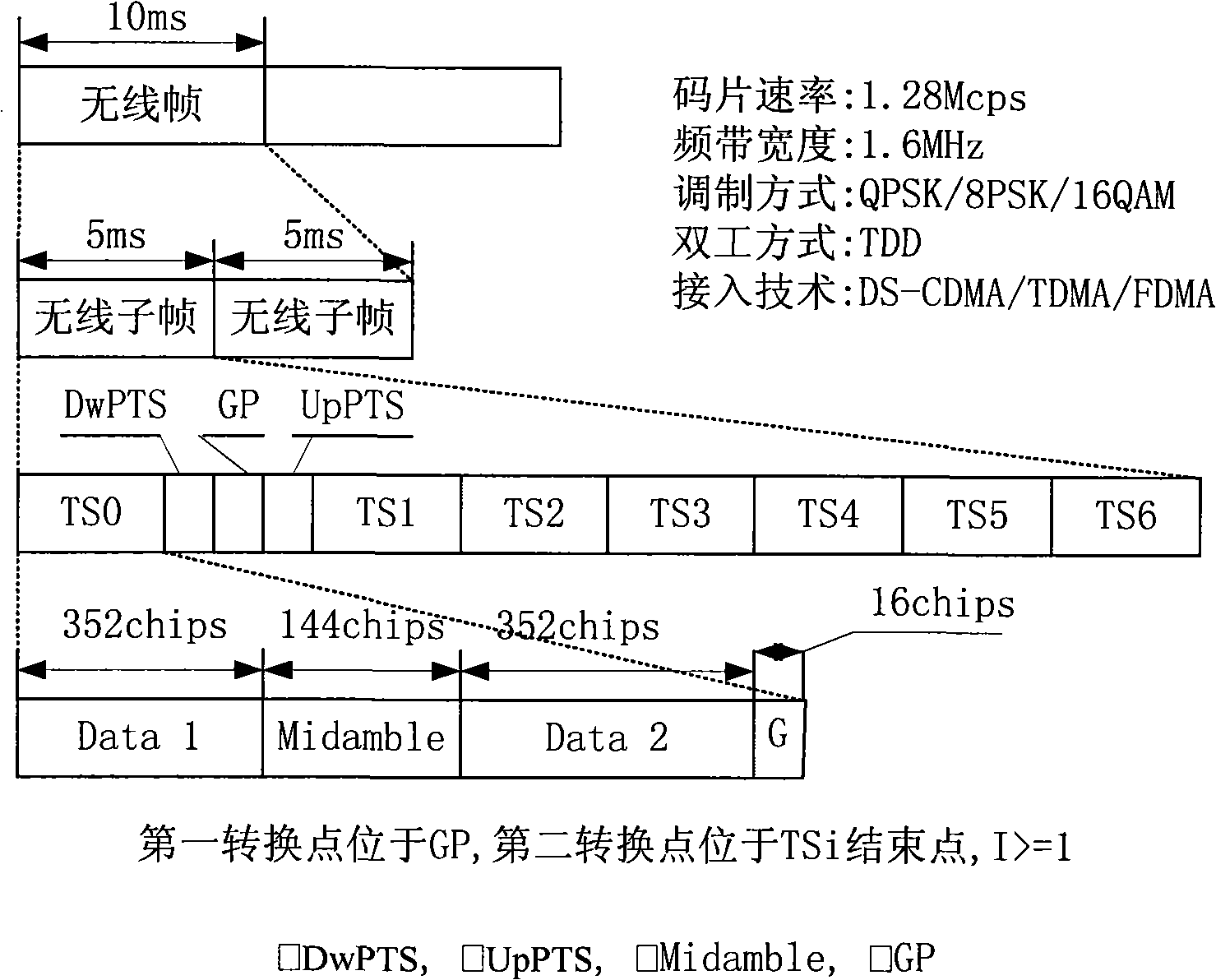
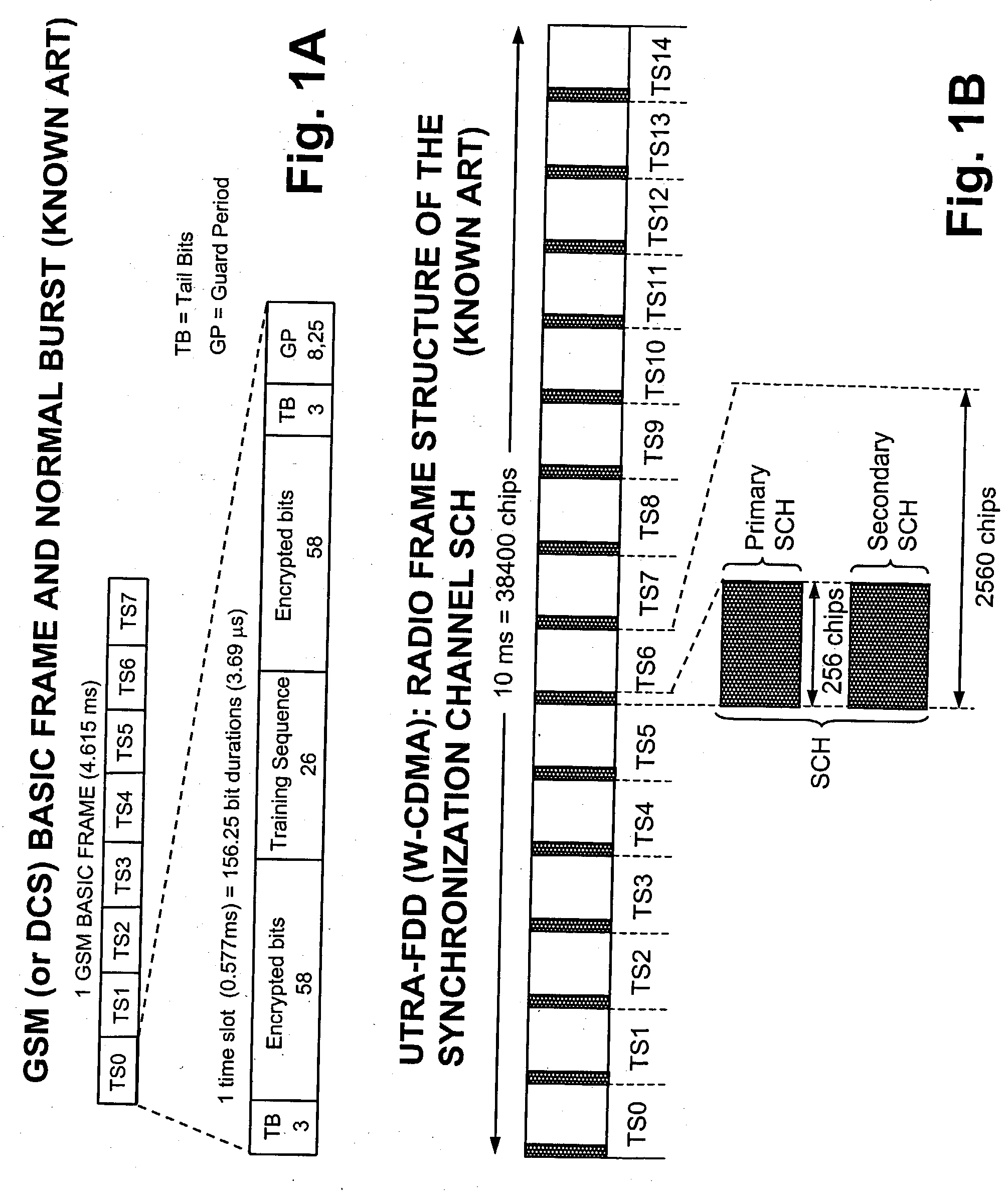
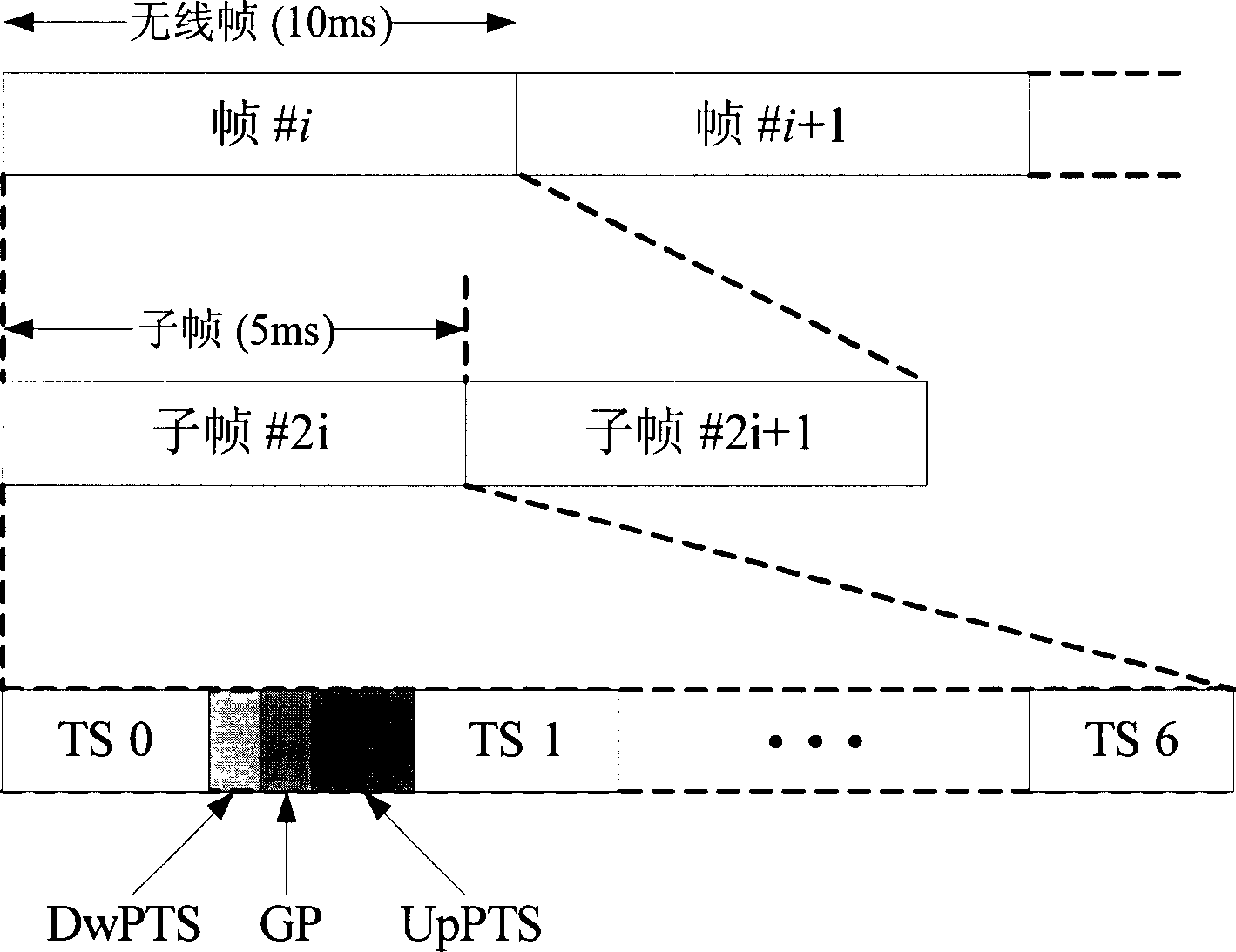
Time Division Synchronous Code Division Multiple Access or UTRA/UMTS-TDD 1.28 Mcps Low Chip Rate, is an air interface found in UMTS mobile telecommunications networks in China as an alternative to W-CDMA. Together with TD-CDMA, it is also known as UMTS-TDD or IMT 2000 Time-Division. The term "TD-SCDMA" is misleading. While it suggests covering only a channel access method based on CDMA, it is actually the common name for the whole air interface specification. TD-SCDMA uses the S-CDMA channel access method across multiple time slots.
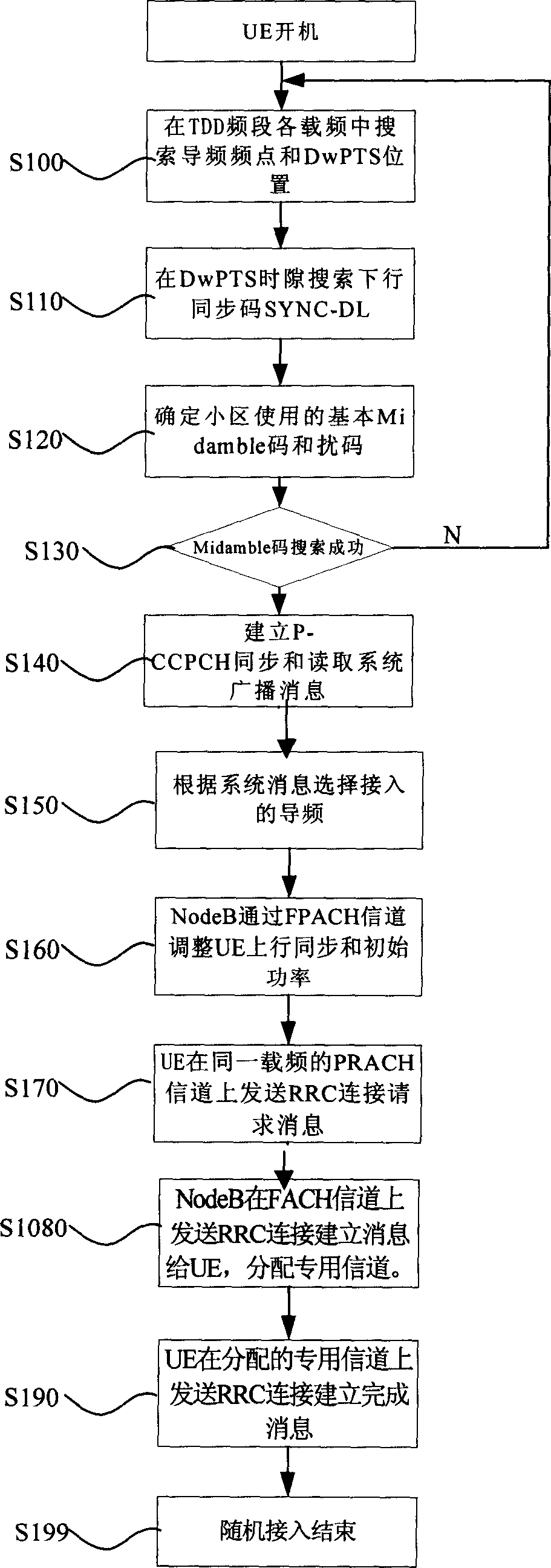
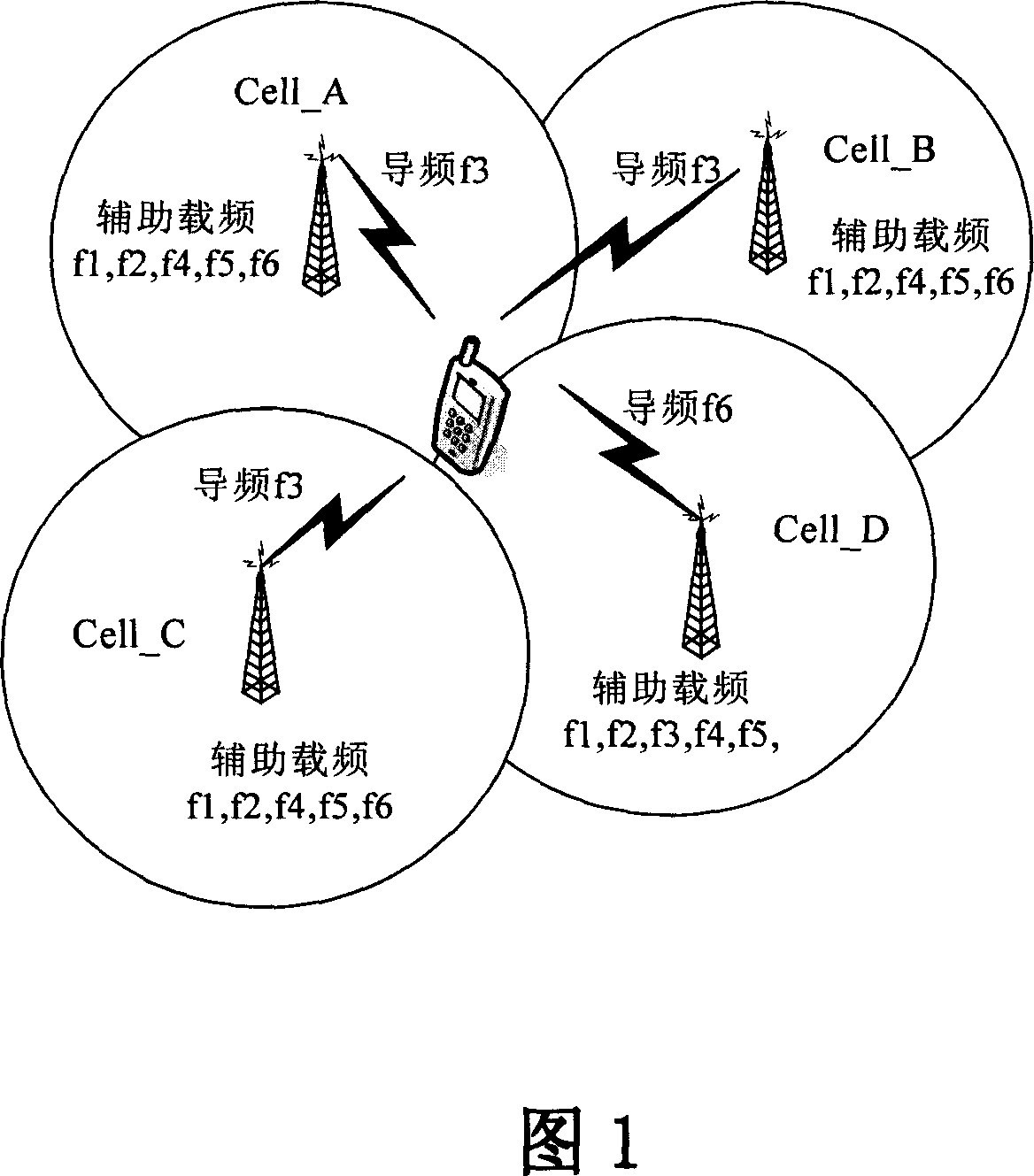
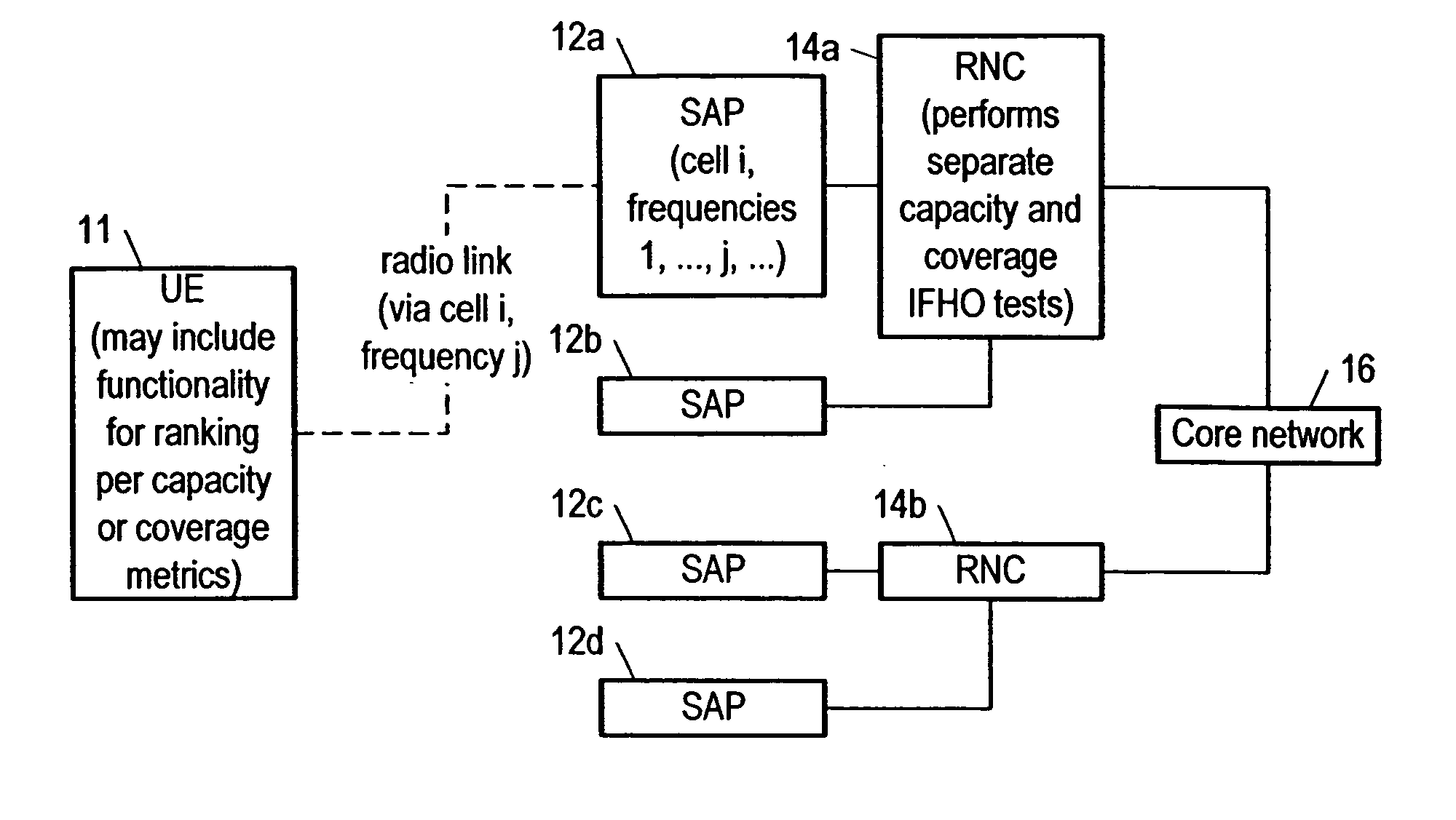
Method and mobile station to perform the initial cell search in time slotted systems
InactiveUS20050075125A1Speed up scan operationConvenient ArrangementSynchronisation arrangementAssess restrictionLow-pass filterCarrier signal
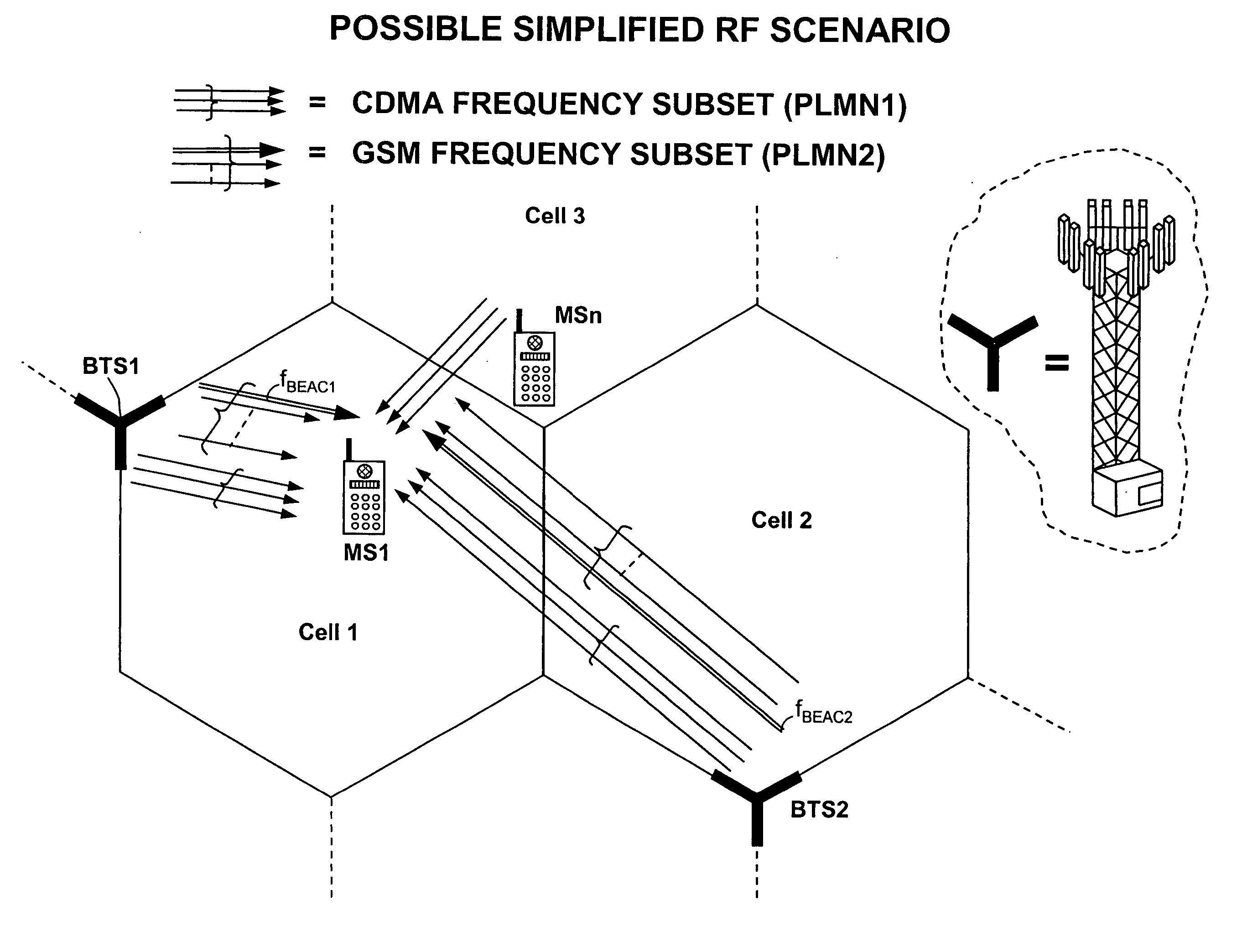
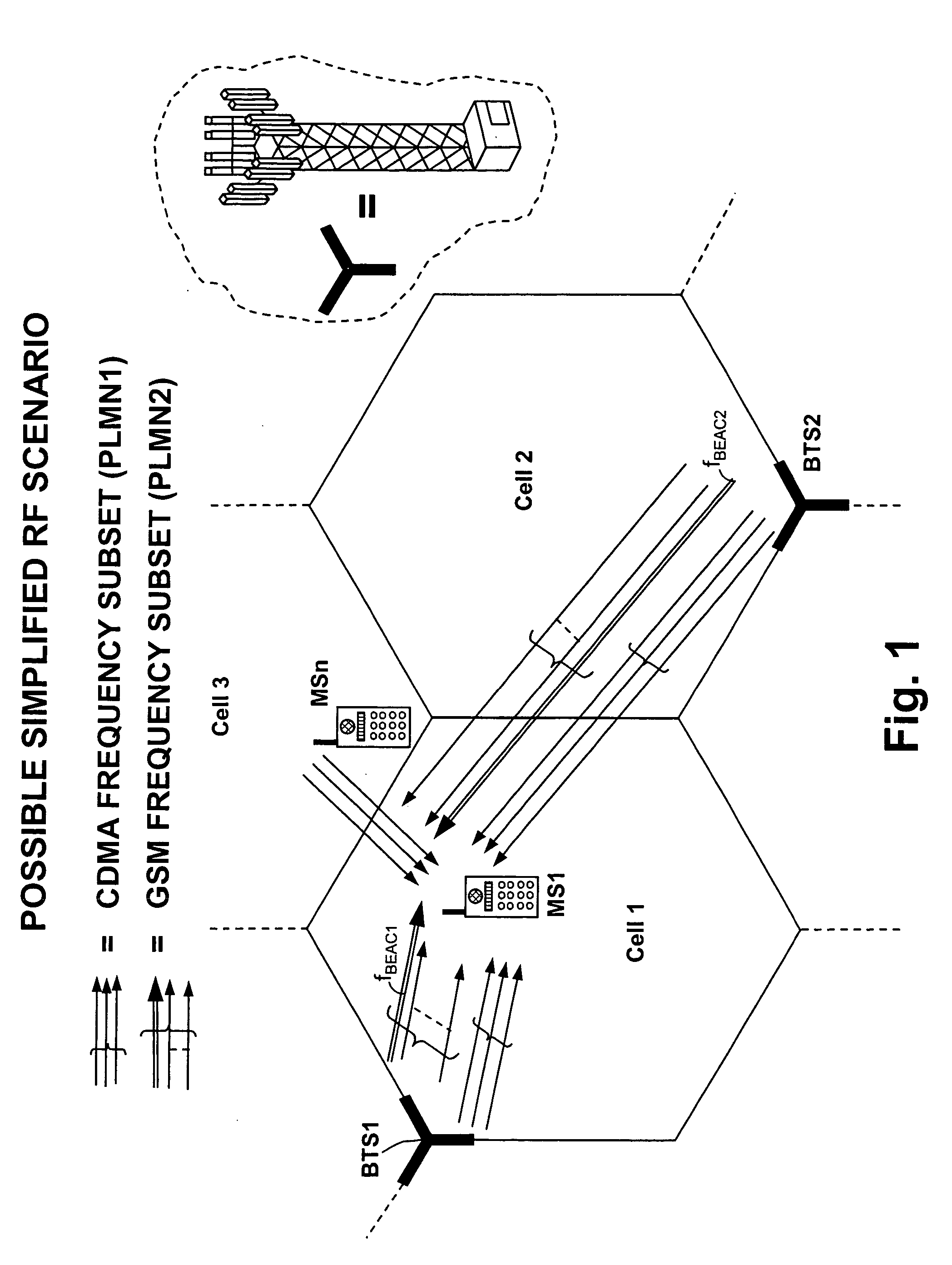
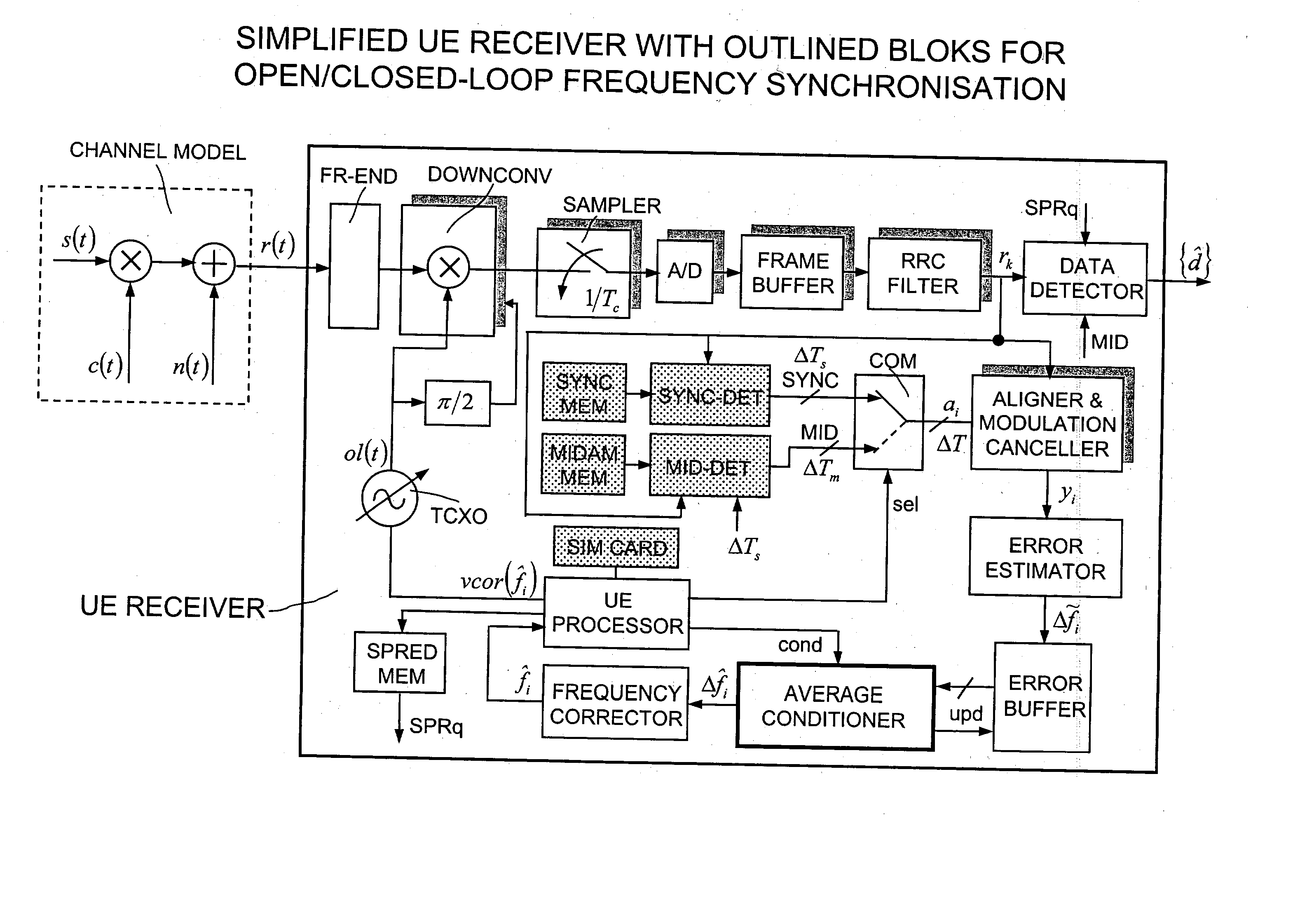
A method is disclosed that a Mobile Station MS performs at switch-on to search the most favorable target cell in UMTS systems like the 3GPP CDMA—LCR (Low Chip Rate) option at 1.28 Mcps—TDD (Time Division Duplex) mode and the equivalent TD-SCDMA (Time Division—Synchronous CDMA). Signal at the MS antenna is the sum of different RF downlink frames coming from different carriers in the assigned frequency ranges. A DL synchronization timeslot and a BCCH TS0 are both transmitted with full power in the frames, the first one includes one out of 32 SYNC codes assigned on cell basis. Following a conventional approach the absence of a common downlink pilot and without prior knowledge of the used frequencies would force the MS, for all the frequencies of the channel raster stored in the SIM card, the correlation of the received frame with all the 32 SYNCs stored in the MS, in order to detect the BSIC of a cell to which associate the power measures. Following the two-step method of the invention the power measures are performed in two-step scan of the PLMN band without interleaved correlation steps; once a final frequency is selected the respective frame is the only correlated one. At least one frame duration about 5 ms long of the whole 15 MHz bandwidth is acquired, IF converted, A / D converted and the digital set is stored. A rough scan is performed multiplying the digital set by a digital IF tuned in steps wide as the channel band (1.6 MHz) along the 15 MHz band, and filtering the baseband signal with a Root Raise Cosine low-pass filter. The 5 ms baseband signal is subdivided into 15 blocks of half timeslot (337.5 μs) and the power of each block is measured. The power of the strongest block indicates the priority of the respective frequency. The strongest power values are put in a Spectral Table together with respective frame load indicators. The load indicator is the percentage of timeslots in a frame almost equally loaded as the strongest block. The three strongest frequencies are selected for the successive scan. The second step search is performed like the first one but the IF steps are now 200 kHz wide and cover the only 1.6 MHz spectrum around a selected frequency. A final frequency is selected for the successive correlation step. Then the frequency error of the MS reference oscillator is corrected with data-aided techniques and a calibration value stored for successive connections (FIG. 9).
Owner:SIEMENS INFORMATION & COMM NEWTWORKS INC
Distribution method of multi-carrier reinforced uplink power resource
InactiveCN101340622ATransmission control/equalisingRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTD-SCDMATransmitted power
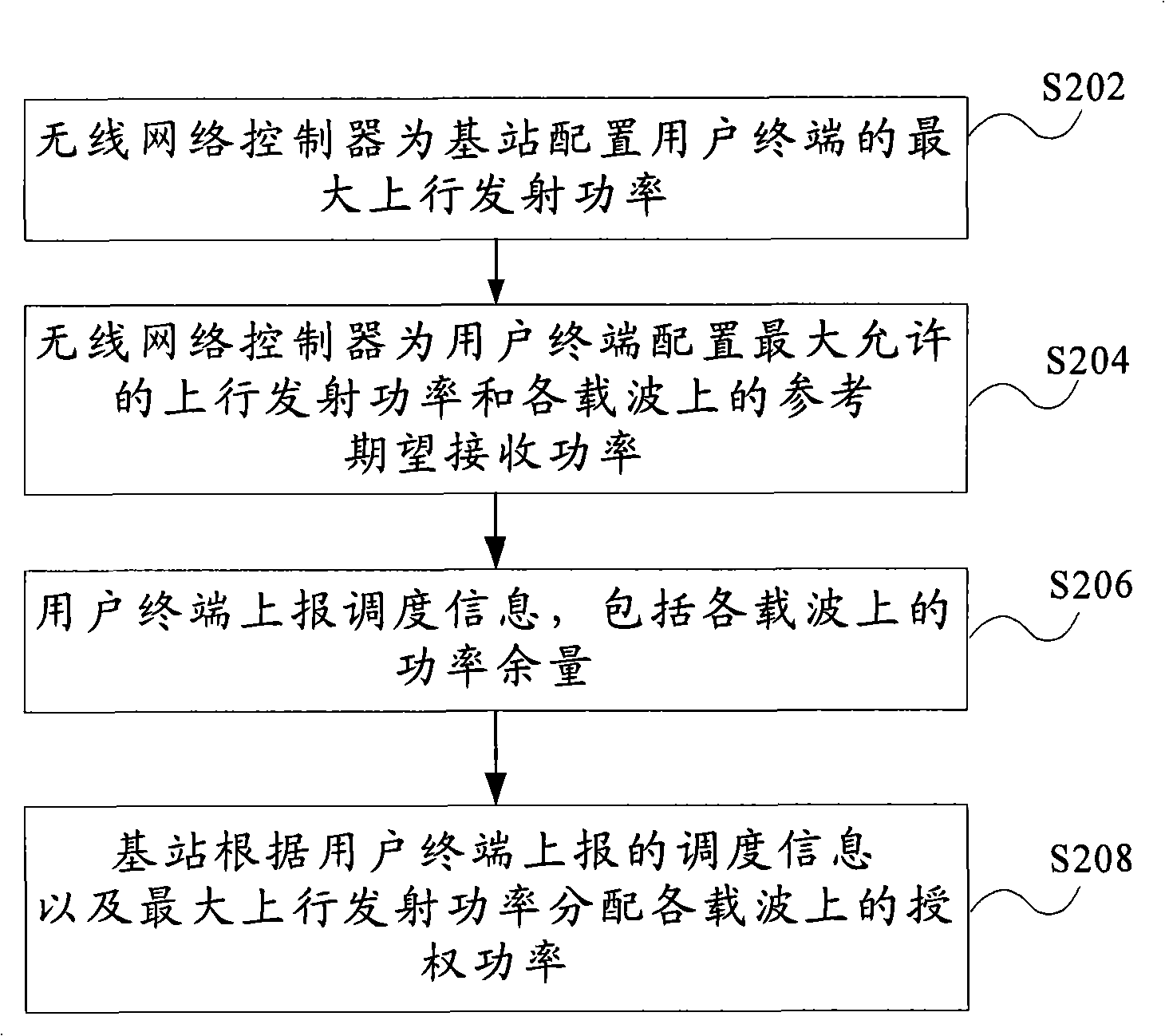
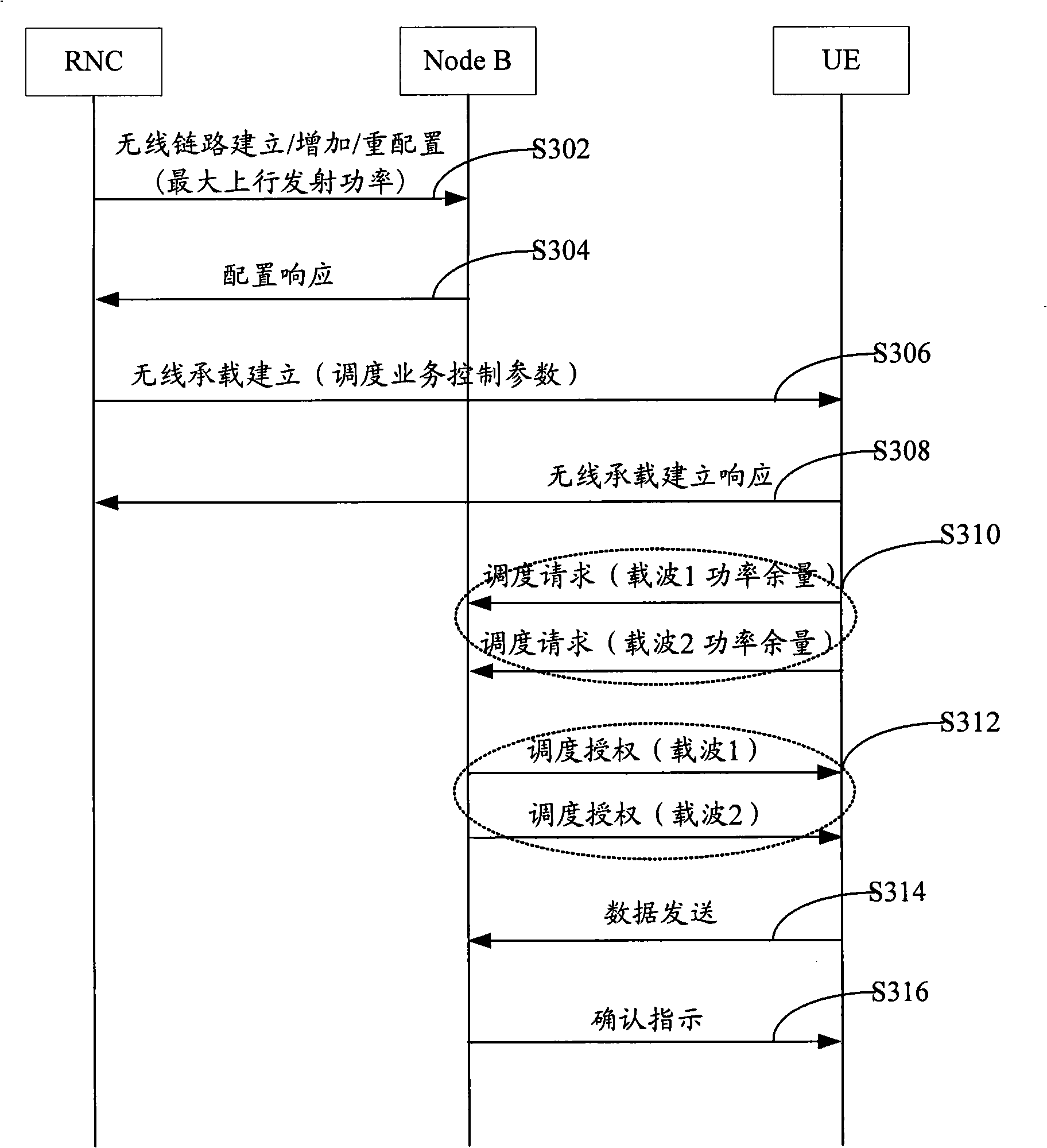
The invention provides a method for distributing power resource of a multi-carrier enhanced uplink, which includes the steps that: a wireless network controller configures maximum uplink transmitted power of a user terminal for a base station; the wireless network controller configures allowable maximum uplink transmitted power for the user terminal and expected reference received power of each carrier; the user terminal reports dispatching information including remained power of each carrier; the base station, after receiving the reported dispatching information from the user terminal, distributes power for each carrier according to the reported dispatching information and the maximum uplink transmitted power. Therefore, by adopting the method of the invention, the remained power of each carrier of UE can be concerned without transcending the capacity of the UE; furthermore, the method of the invention can be applied to a TD-SCDMA system.
Owner:ZTE CORP
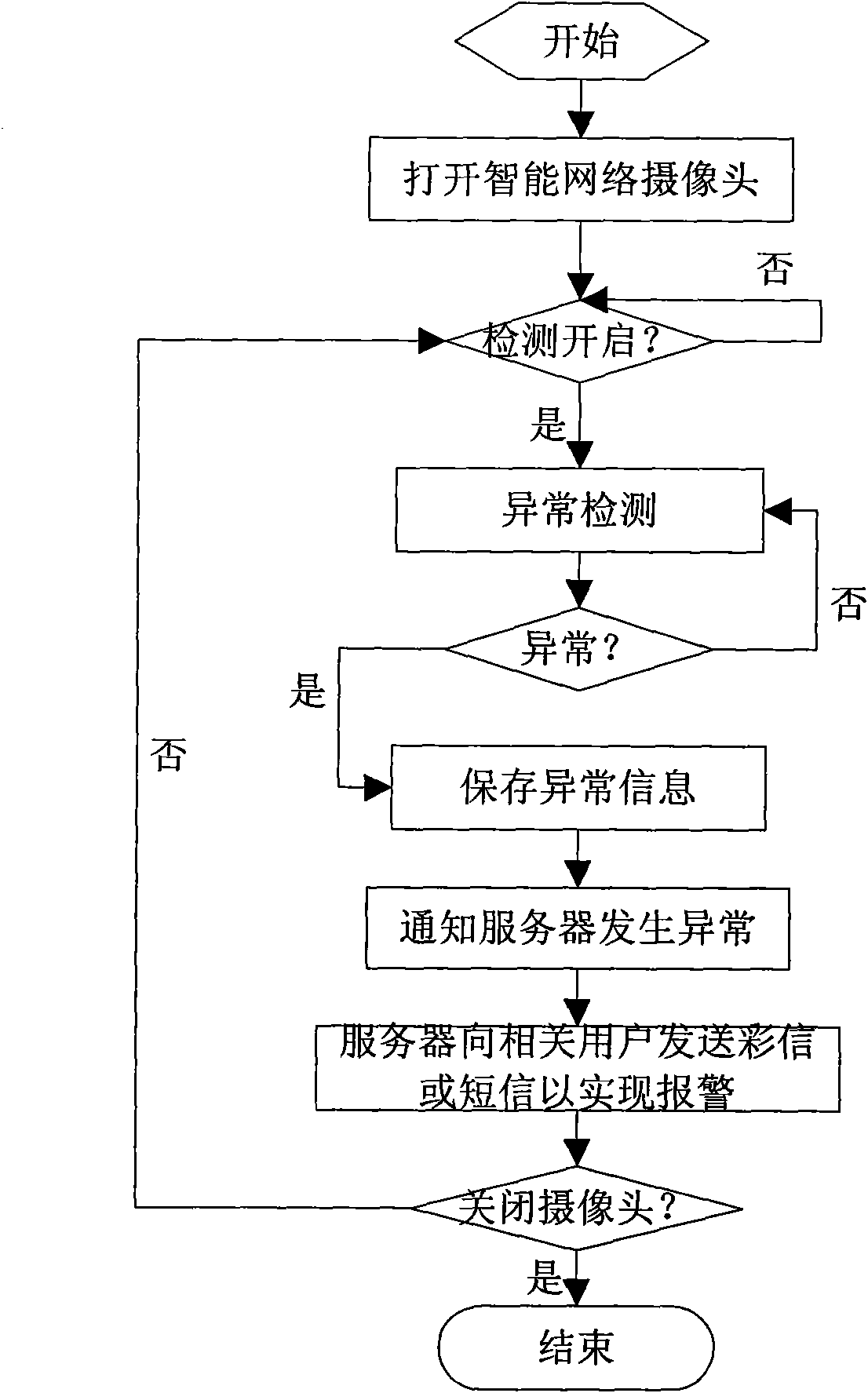
Remote video monitoring method
InactiveCN101656874AMeet quality requirementsAvoid false alarmsClosed circuit television systemsSubstation equipmentVideo monitoringThird generation
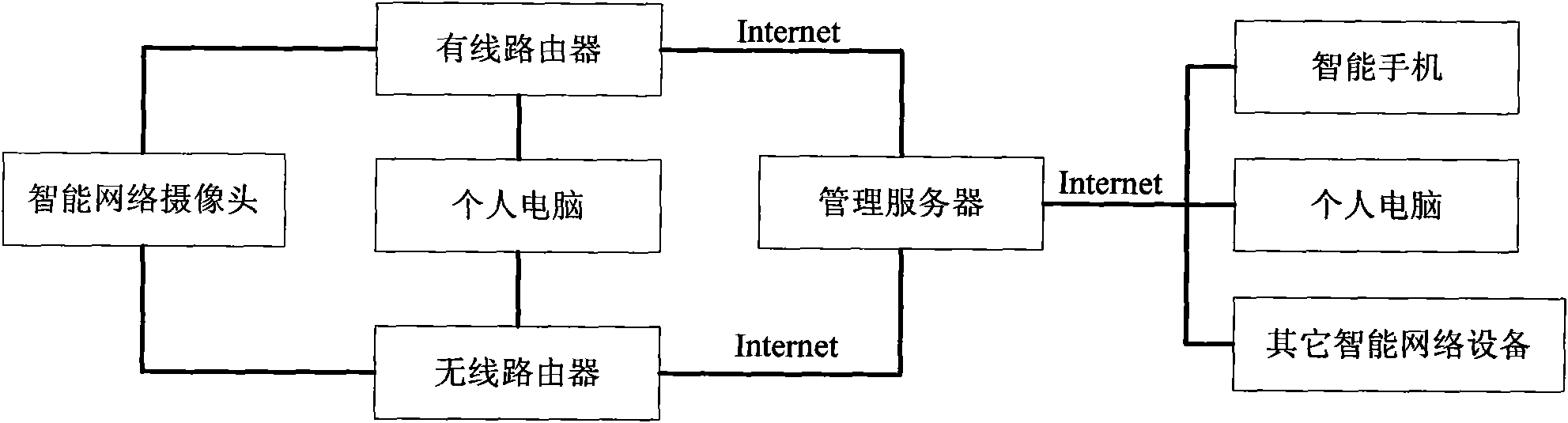
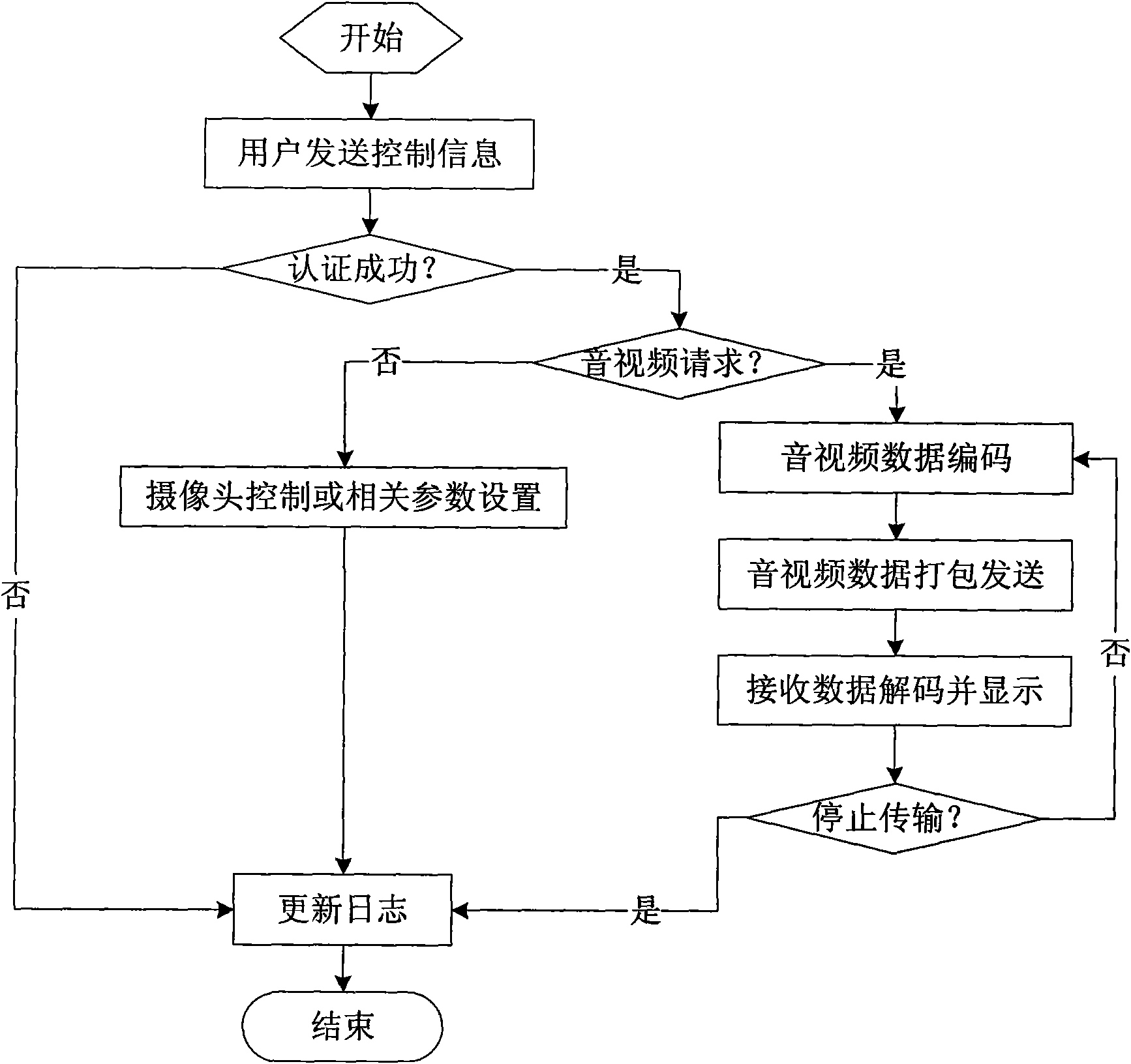
The invention discloses remote video monitoring system and method suitable for 3G mobile network communication, relating to the field of remote control and monitoring. The invention realizes the purpose of remotely controlling or viewing a target scene in real time by connecting a mobile phone or a personal computer to one or more intelligent network cameras, wherein the mobile phone can be any 3Gsmart mobile phone which supports WCDMA, TD-SCDMA or CDMA2000, which guarantees the universality of remote monitoring. The intelligent monitoring system of the invention has the characteristics of convenient use, easy deploy, easy popularization, and the like and brings a new bright spot to security causes.
Owner:HANGZHOU ZOOMTEC TECH
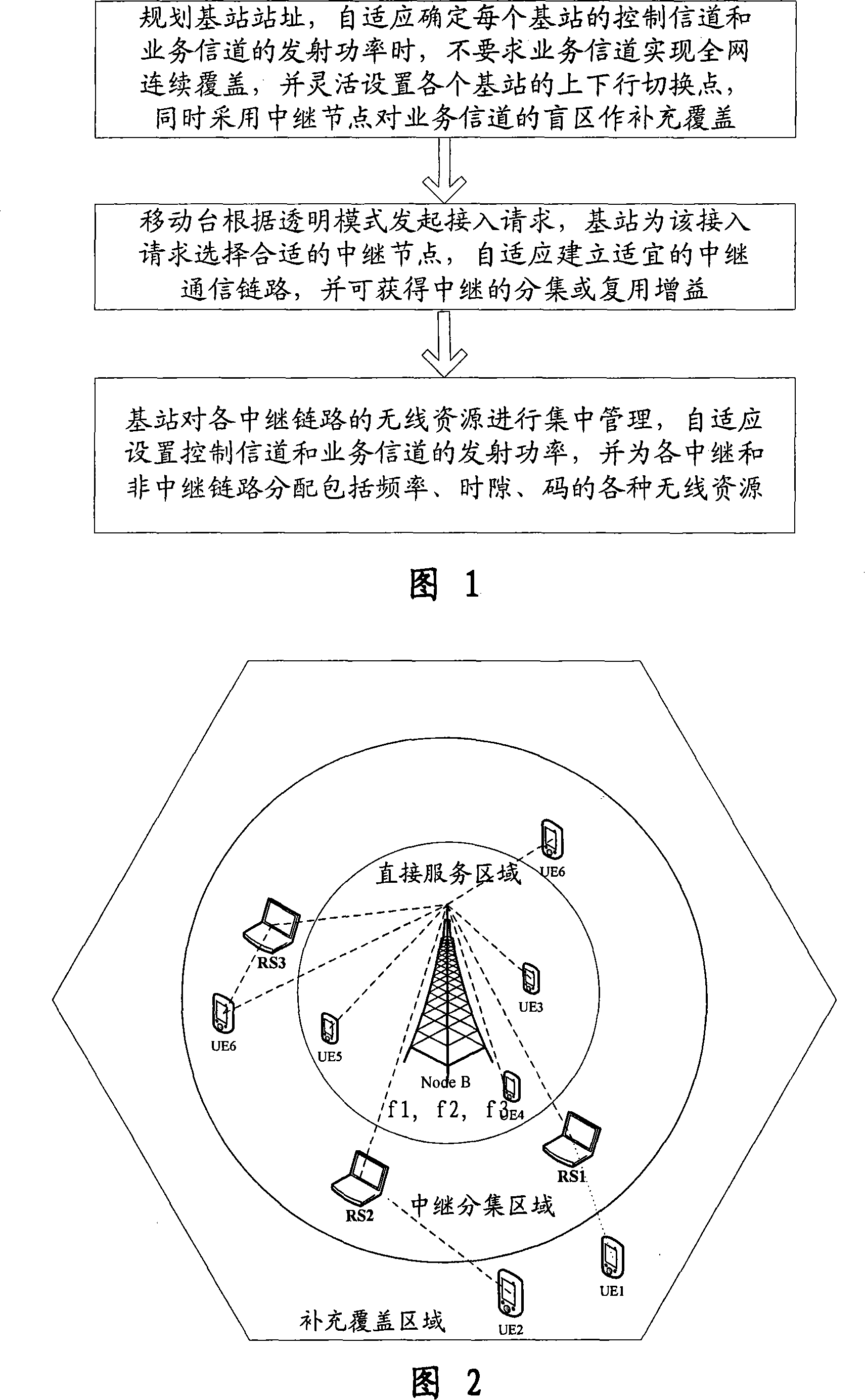
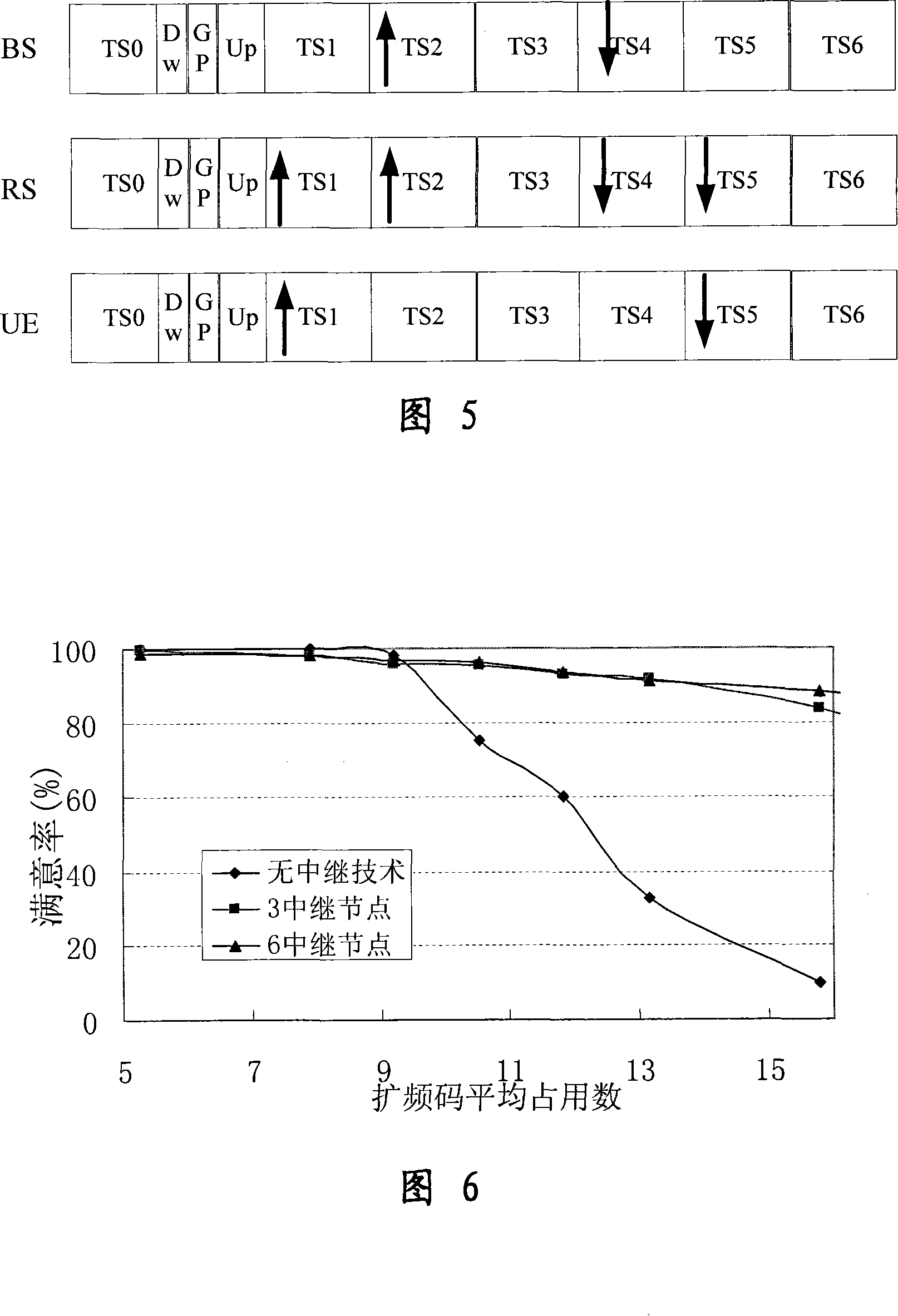
Multi-frequency point TD-SCDMA group network and communication implementing method based on relaying technology
InactiveCN101132601AReduce the difficulty of planning and layoutMinor changesPower managementTransmission control/equalisingSystem capacityTD-SCDMA
This invention relates to realizing method for multi-point TD-SCDMA netwroking and comunication including: 1, programming addresses of base stations, determining the emission power of control channel and service channel of each station adaptively and setting up-and down-line switch points flexibly and carrying out supplement cover to blind regions of service channels with relay nodes, 2, a mobile station initiates an access request according a transparent mode and the base station selects a suitable relay node for it to set up a communication link adaptively and get diversity and multiplex gain of the relay, 3, the base station manages radio resources of relay links in concentration to set emission power of the control channel and service channels and distribute radio resources of frequency, time slot and codes to relay and non-relay links.
Owner:COMBA TELECOM SYST CHINA LTD
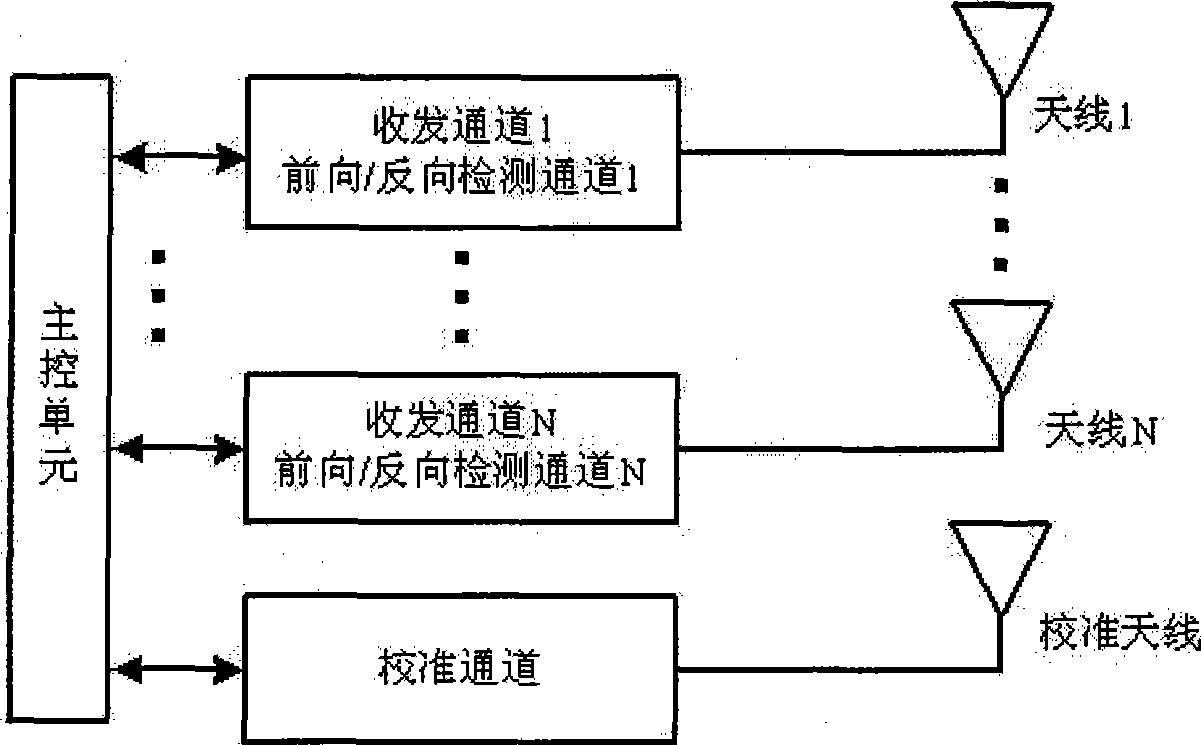
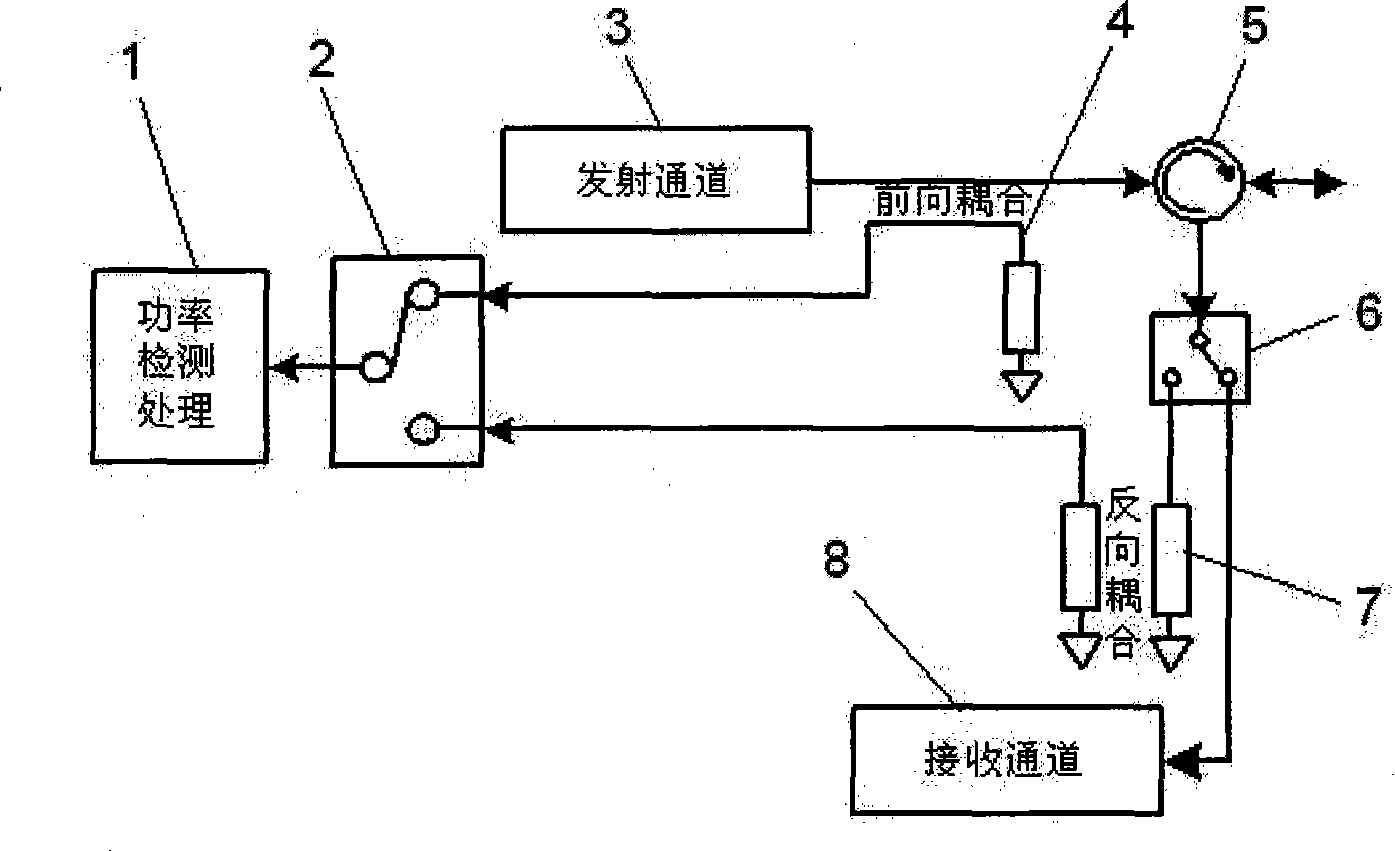
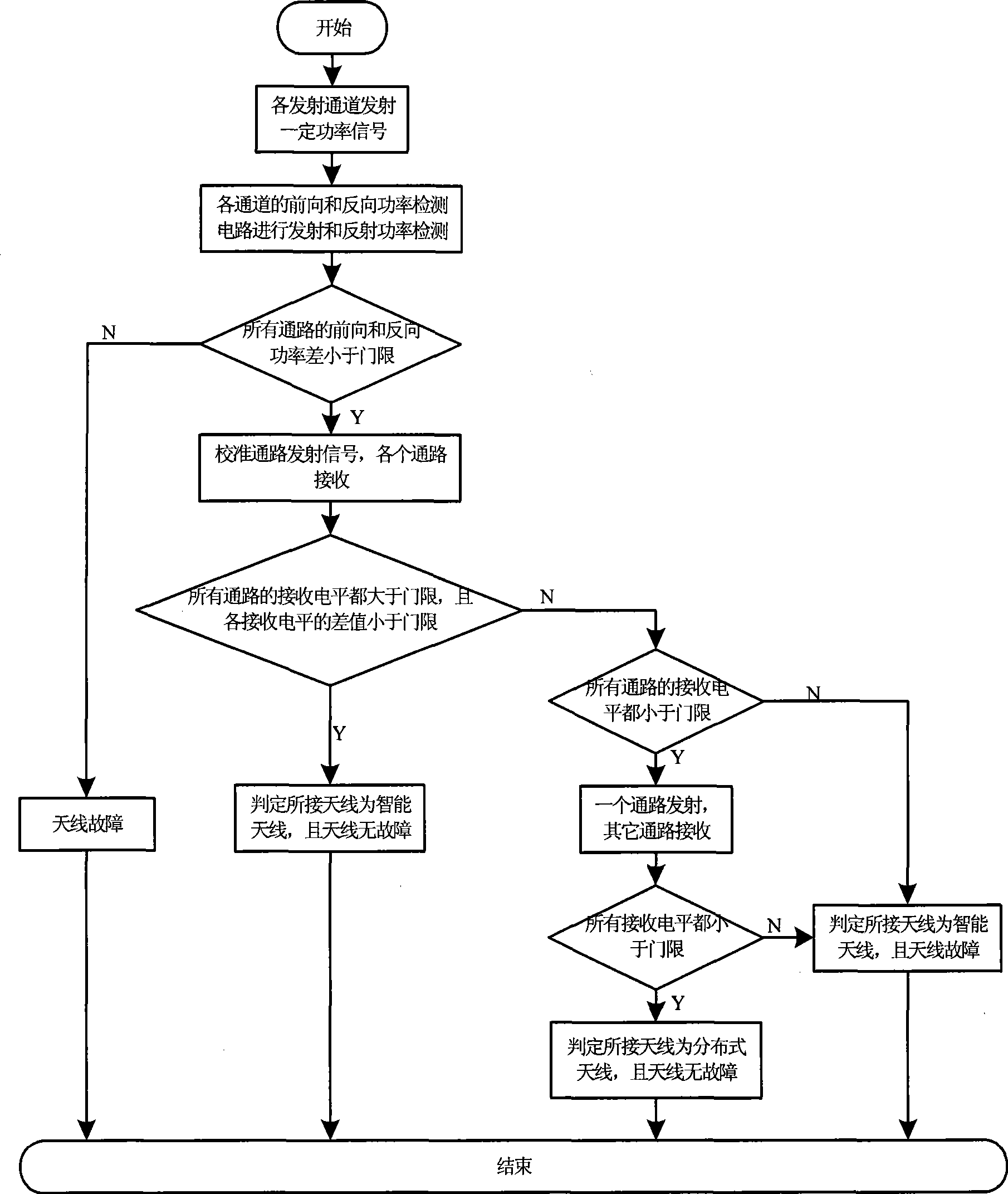
Detection method for TD-SCDMA multichannel radio frequency remote unit antenna system
The present invention provides a method for testing TD-SCDMA multi-channel radio remote unit antenna system. Each gateway of original radio remote signal receiving-transmitting channel system is respectively provided with a power detecting and processing unit and a detecting channel of frontward and backward power testing circuit connected with the power detecting and processing unit. The method according to the invention comprises the following steps: 1) transmitting a signal by a main control unit to each receiving-transmitting channel according to a certain power, detecting the transmitting and reflecting signal powers of each radio remote unit antenna opening by the frontward and backward power detecting circuit of each gateway, calculating the difference between the frontward detected power and the backward detected power and comparing the difference with a preset threshold, and detecting whether the antenna of each channel is failed; 2) transmitting a certain power signal by an adjusting channel for being received by other gateway, comparing the receiving level with the preset threshold for detecting whether the connected antenna is an intelligent antenna and whether the connected antenna is in fault; and 3) transmitting a certain power signal by a transmitting channel wherein for being received by the other channels, and comparing the receiving level of each channel with the preset threshold for determining whether the antenna connected with the transmitting channel is an intelligent antenna and / or whether the antenna is in fault.
Owner:成都芯通软件有限公司
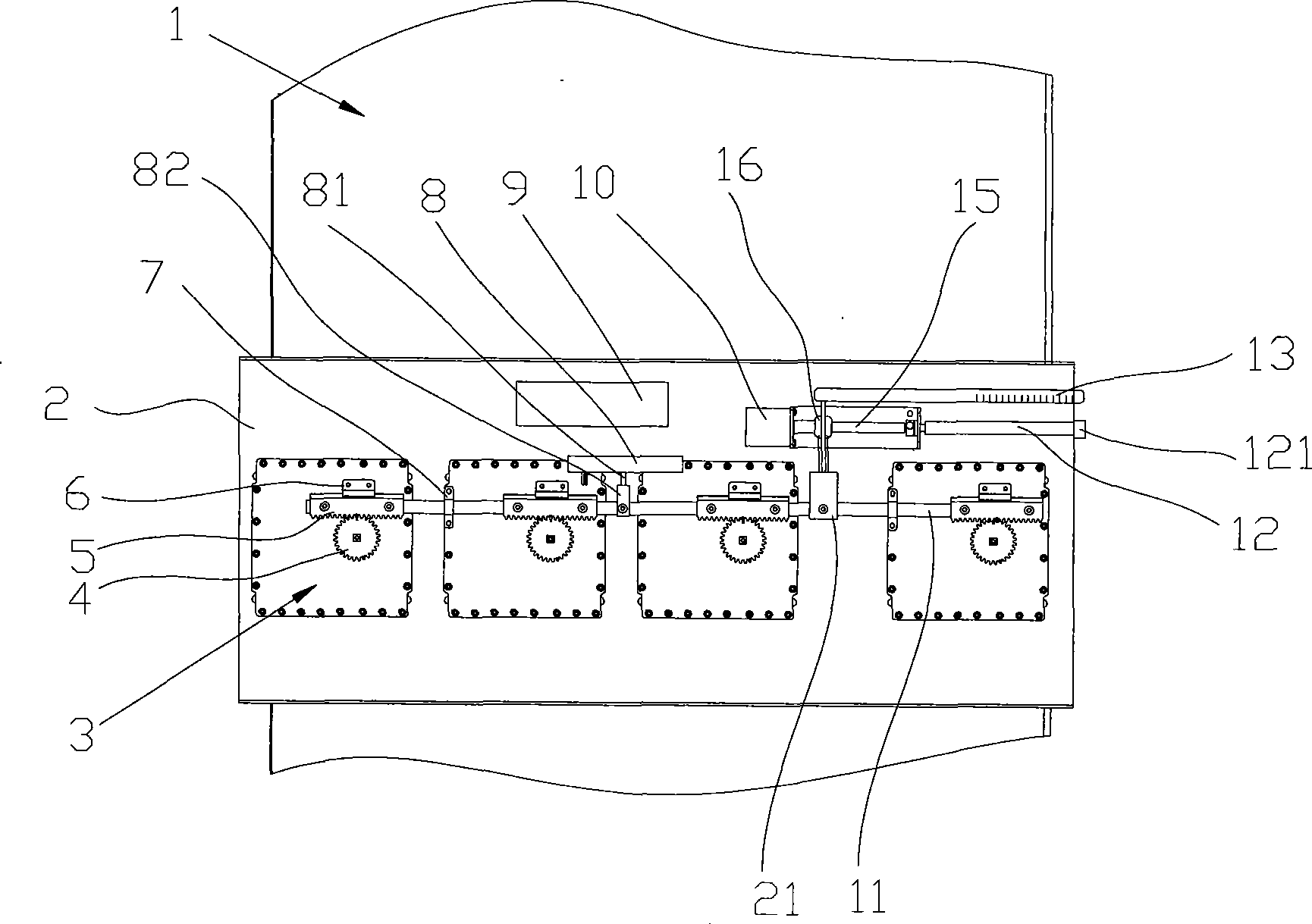
Antenna phase-shift system
ActiveCN101521312ACompact structureSynchronized movement is preciseWaveguide type devicesAntennasLinear motionPhase shifted
The invention relates to an antenna phase-shift system, in particular to a simultaneous transmission device which accurately adjusts a plurality of groups of beam-forming networks in a multi-array antenna, a beam-forming network which is suitable for the antenna phase-shift system, and a precise phase-adjusting measurement and control device. The simultaneous transmitting device is used in an antenna which is provided with at least two radiating element arrays, implements control and realizes simultaneous phase shift to a phase-shift part which is owned by the beam-forming network of each radiating element array, comprising a driving device, a connecting rod and a transmission device, wherein the driving device is under the control of a control system which is independent of the antenna and provides a circular motion arm, the connecting rod is flexibly connected with the phase-shift part of each beam-forming network and causes each beam-forming network to shift the phase in a linking way under the linear motion of the connecting rod, and the transmission device converts the circular motion arm of the driving device into the linear motion of the connecting rod. The whole antenna phase-shift system has compact structure and can realize simultaneous precise phase adjustment to the antenna, in particular to TD-SCDMA antenna.
Owner:COMBA TELECOM TECH (GUANGZHOU) CO LTD +1
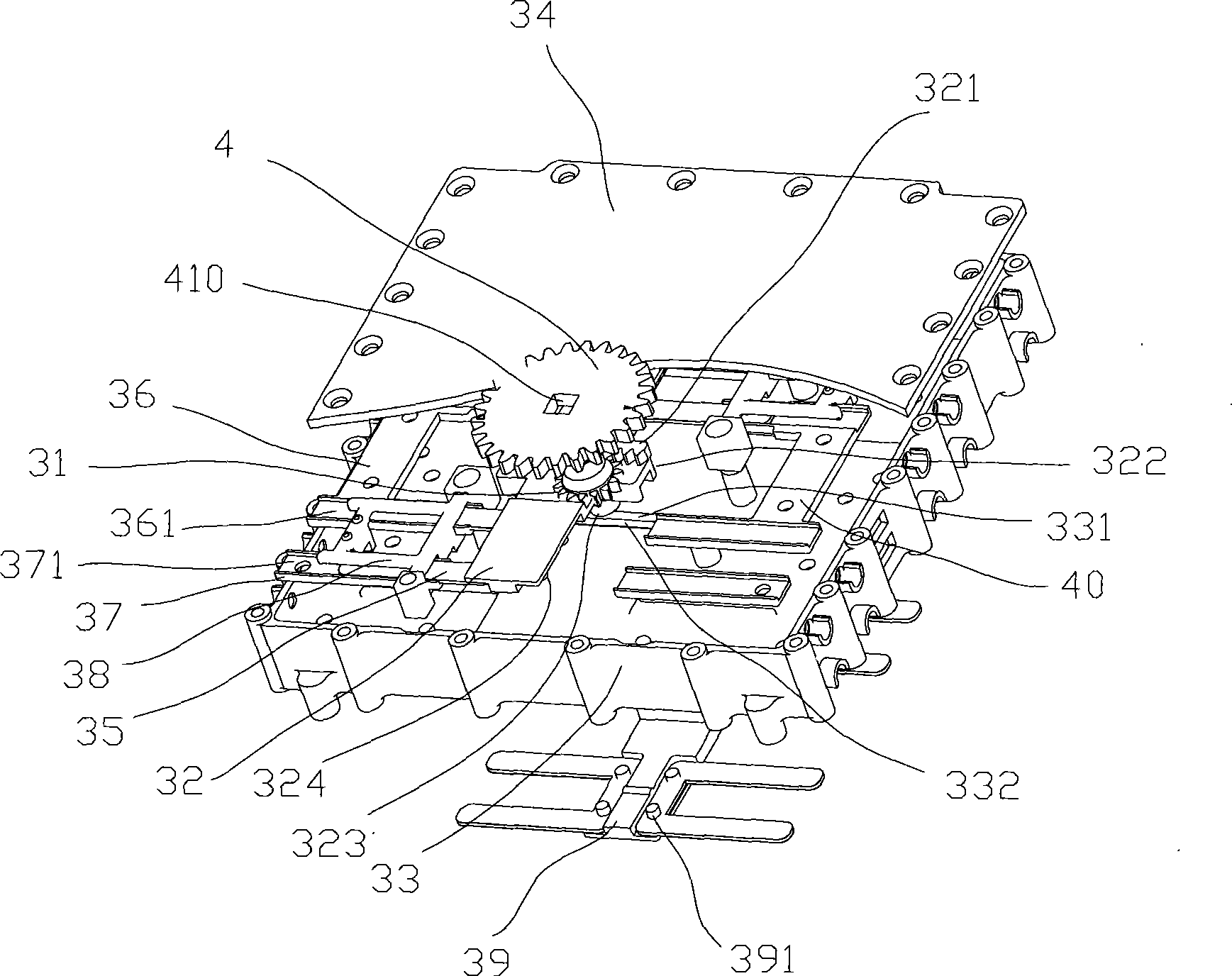
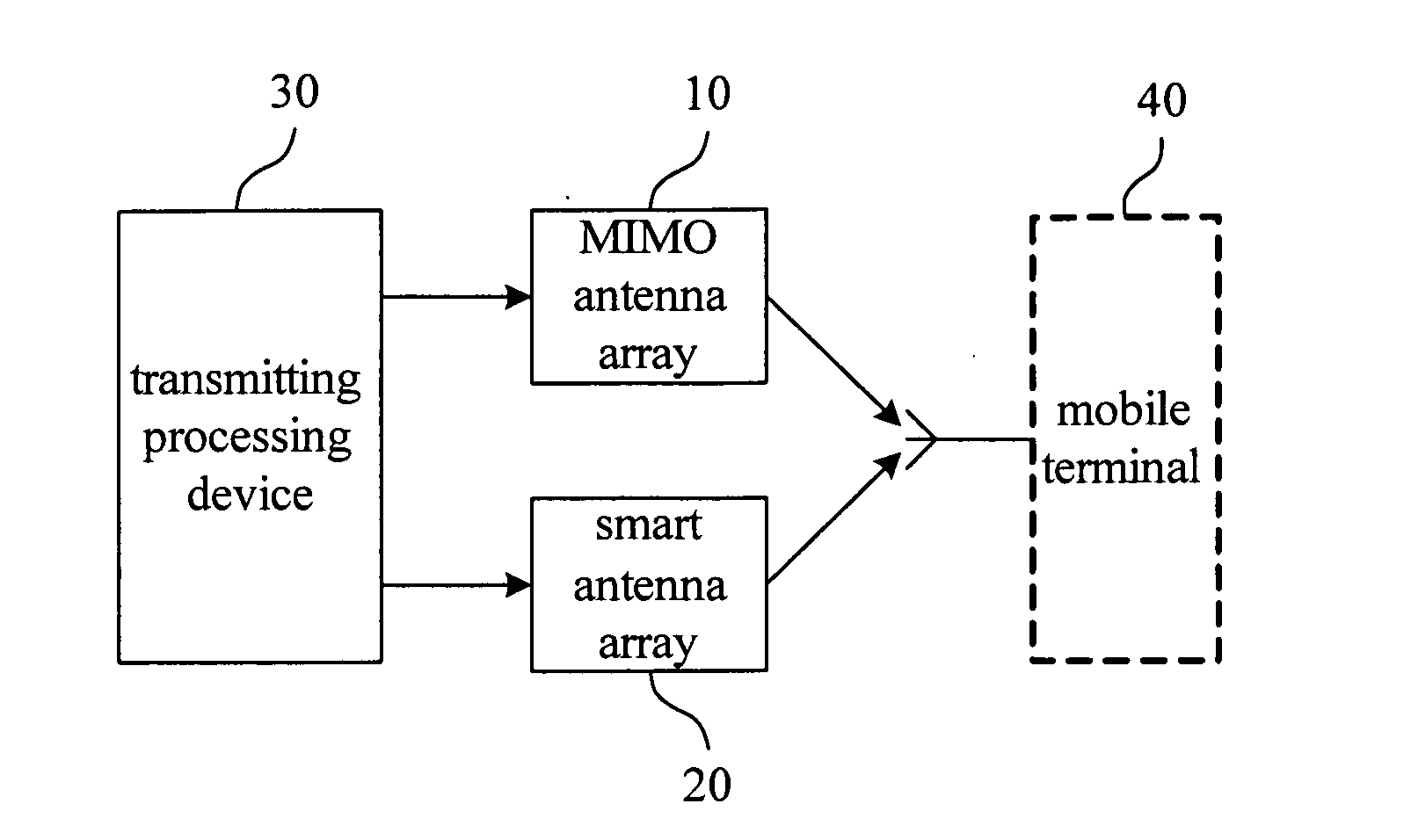
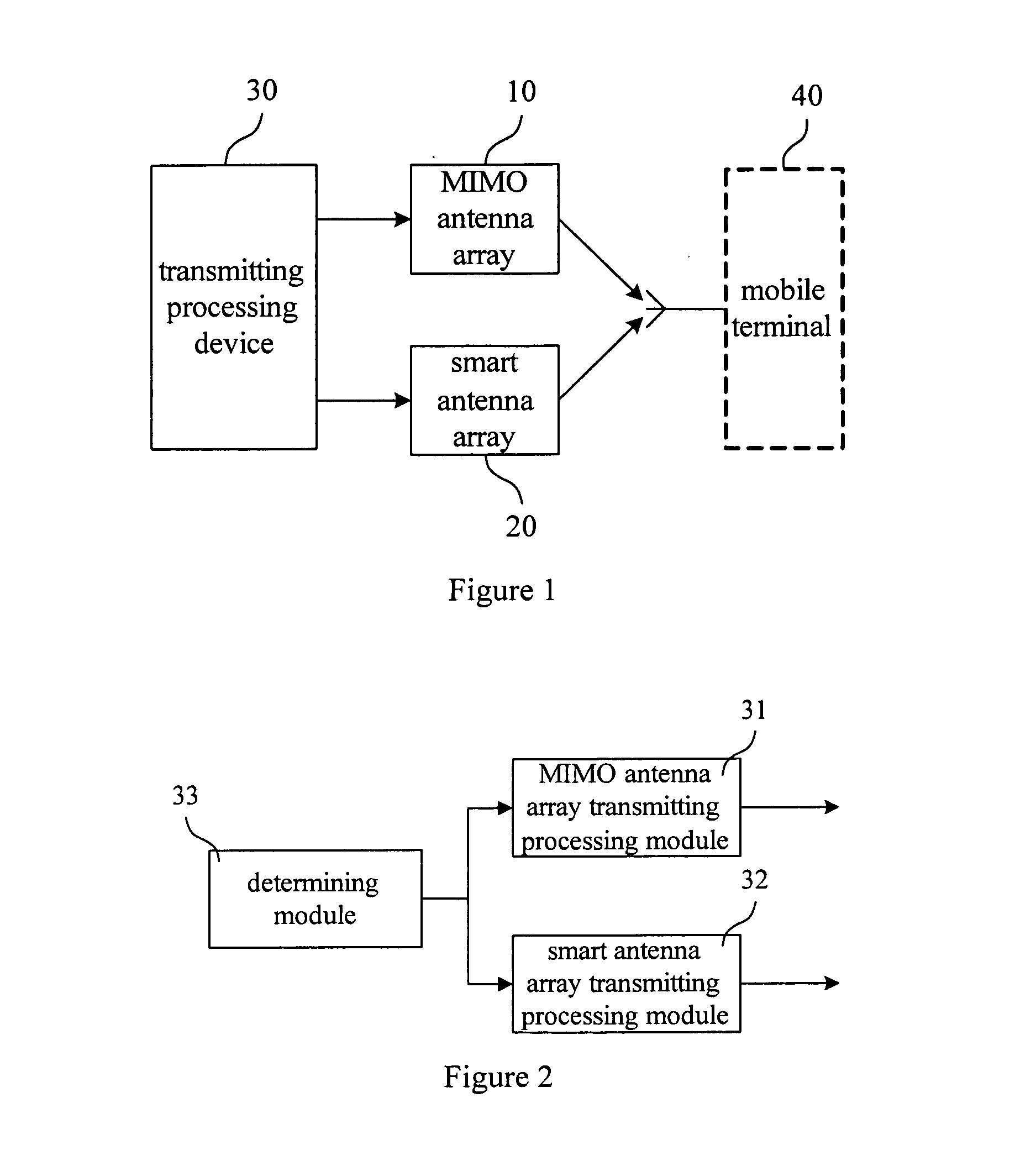
Antenna multiplexing system and method of smart antenna and multiple-input multiple-output antenna
ActiveUS20100135420A1Improve throughputCommonly usedDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationMultiplexingTD-SCDMA
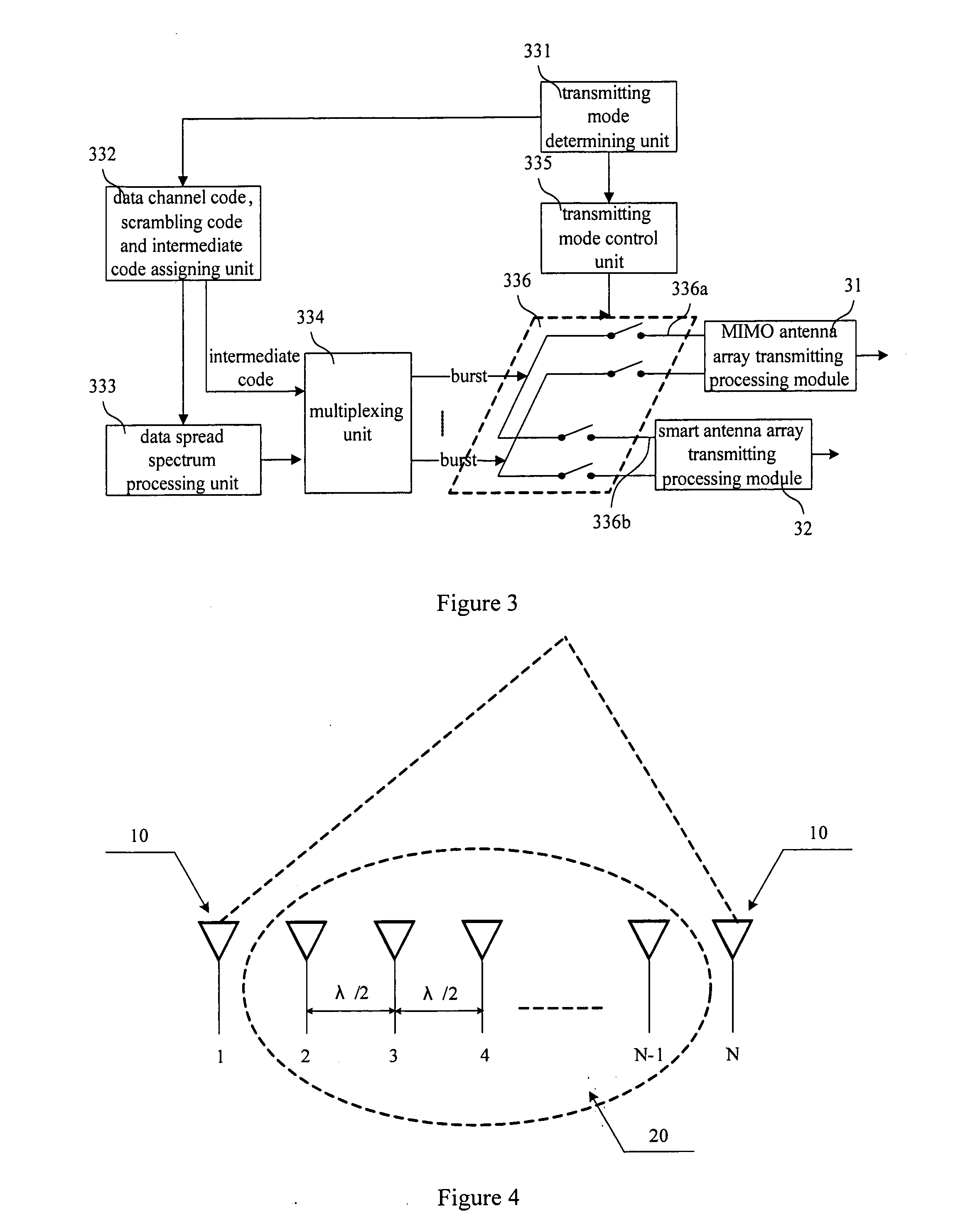
An antenna multiplexing system and a method of a smart antenna and a Multiple-Input Multiple-Output antenna are provided, wherein the system includes a MIMO antenna array and a smart antenna array, the smart antenna array includes several groups of antenna array elements in which the distance between neighbor antenna array elements is less than or equal to one half of wavelength, and the smart antenna array comprises at least two groups of antenna array elements with the coherence sufficient for the requirement of the MIMO applications. The method includes: in accordance with the type of the data to be transmitted, determining a transmitting mode and processing the data to be transmitted accordingly, and in accordance with the transmitting mode, controlling the MIMO antenna array or smart antenna array, so as to transmitting the data to the mobile terminal. With the premise that the actual coverage of TD-SCDMA system should be further improved, the requirement of higher user throughout could be met, and the MIMO antenna system could satisfy the requirement of the future system evolution. Both of the applications of the MIMO and the smart antenna could be met with the use of the same antenna feeding system, and the adaptive switching of the MIMO and the smart antenna with respect to the user could be achieved.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
Frequency offset and phase estimation method based on differential phase in TD-SCDMA communication system receiving synchronization
InactiveCN101553028ABest Estimated Mean Squared Error PerformanceImprove estimation performanceSynchronisation arrangementRadio transmission for post communicationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)TD-SCDMA
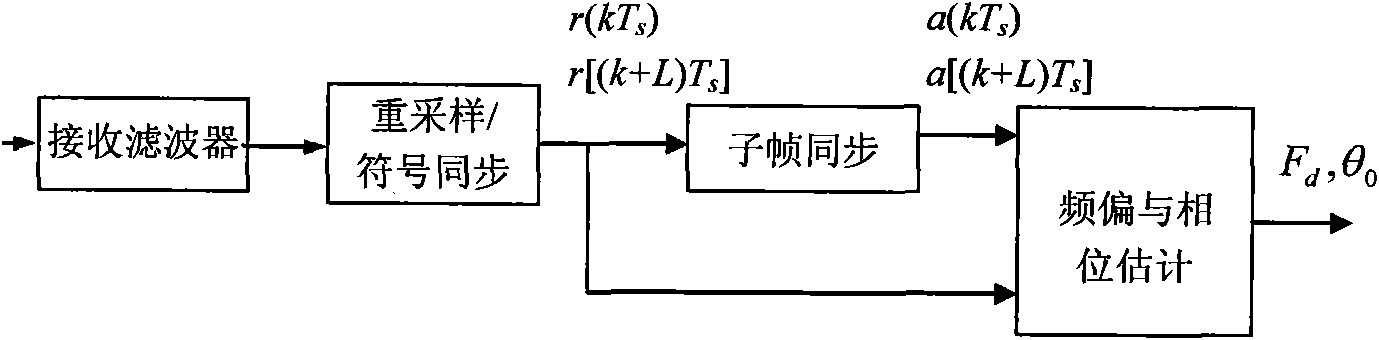
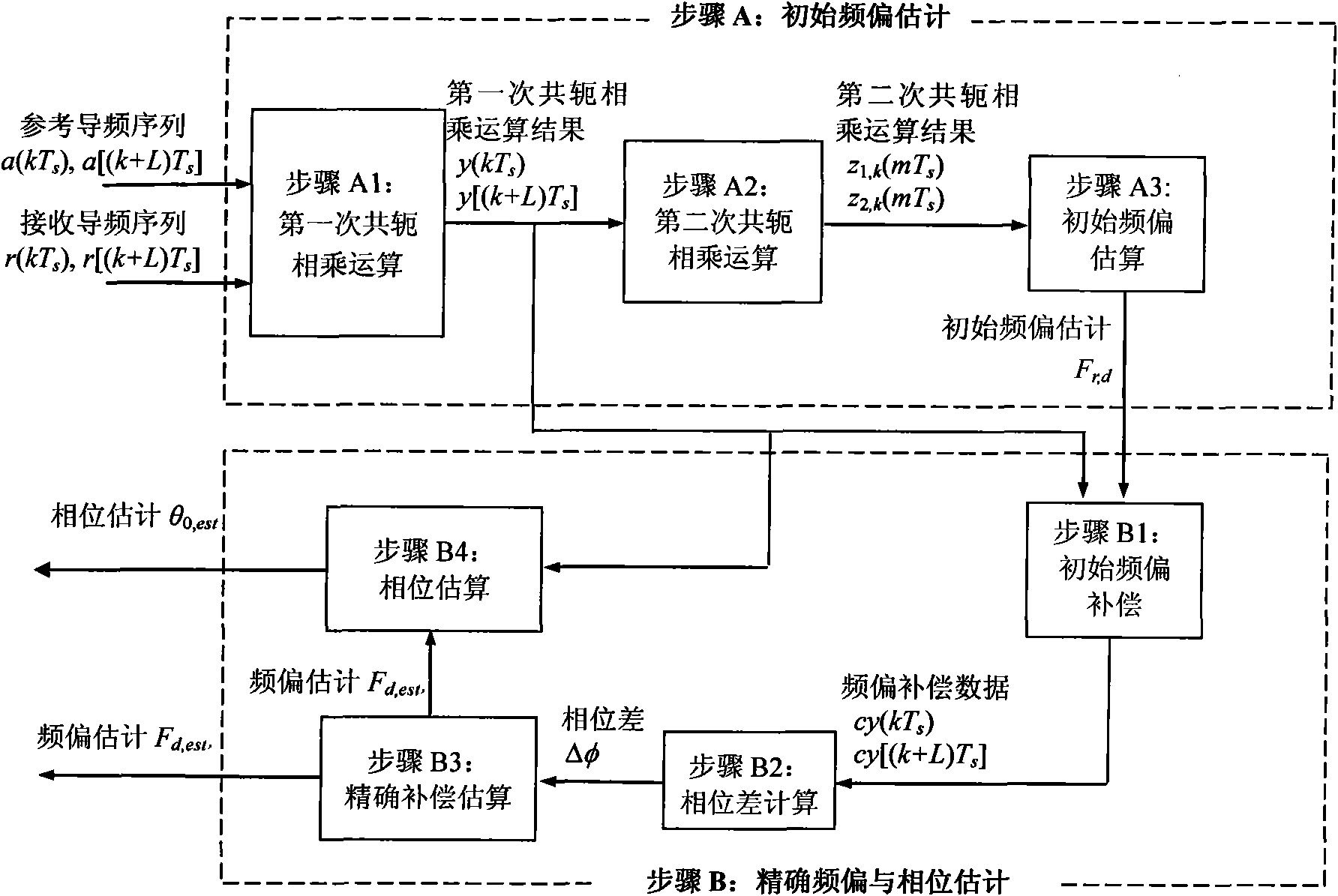
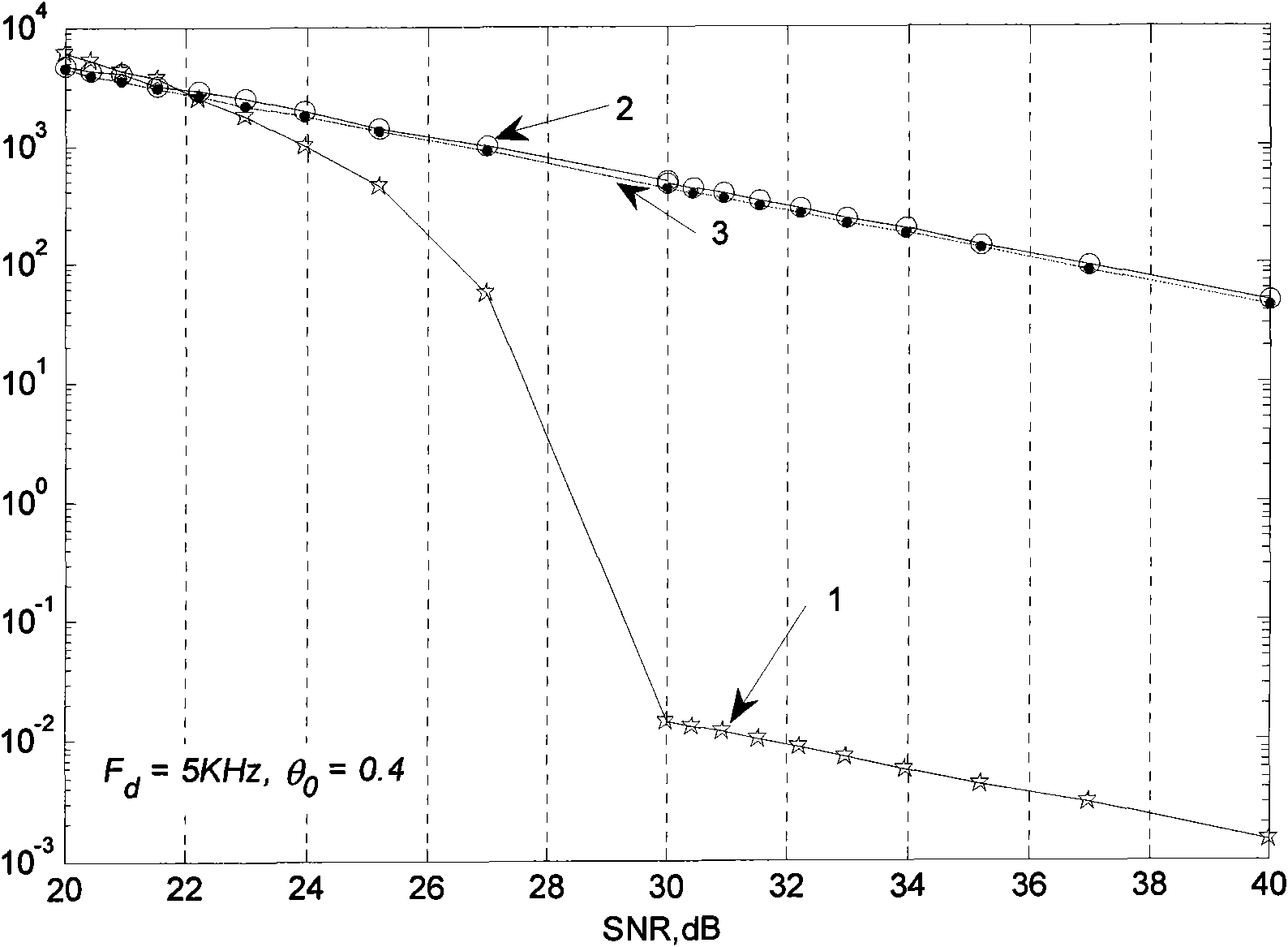
The invention discloses a frequency offset and phase estimation method based on differential phase in TD-SCDMA communication system receiving synchronization; the invention uses fractional step estimation strategy of two periods of initial frequency offset estimation and precise frequency offset and phase estimation, combines and uses two groups of pilot frequency identifier sequences in present adjacent two sub-frames having related frequency offset, implements TD-SCDMA communication system frequency offset and phase estimation through differential phase calculation. The method has precise frequency offset and phase estimation under middle and high signal-to-noise ratio; fluctuation range of estimated value is less.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
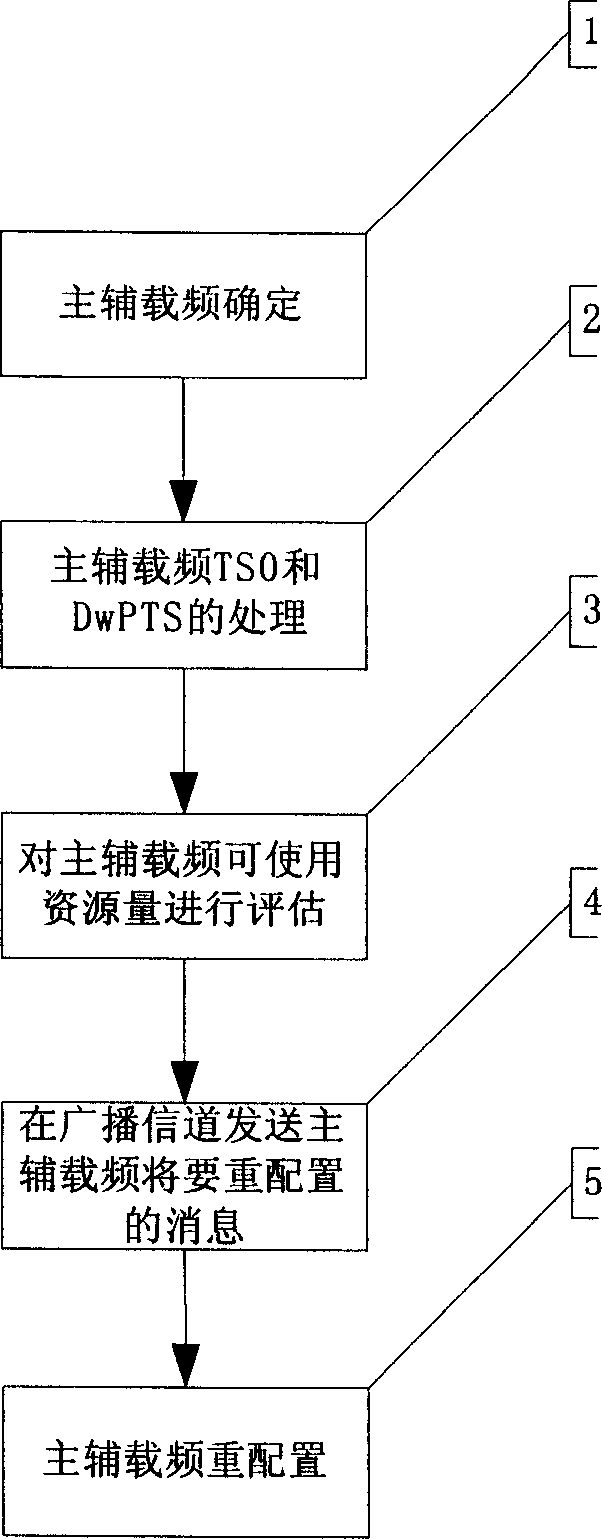
A method of primary carrier frequency reconfiguration in multi-carrier cell
InactiveCN1722895ARadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless communicationTD-SCDMACarrier signal
This invention discloses a method of reshuffling the master carrier frequency in multiply carrier wave area, which comprises the following steps: a) the node B find that the channel which charges the master frequency out of work, sending the notice to the radio network controller; b) the radio network controller will decide whether opening the master carrier frequency reshuffling procedure, if it is, go to the next step; c) opening the master carrier frequency reshuffling procedure, then the base station realize the master and stand-by carrier frequency reshuffling. By said method, the mobile terminal can get system information and other allocation information when the master carrier frequency out of work in the TD-SCDMA agreement standard.
Owner:ZTE CORP
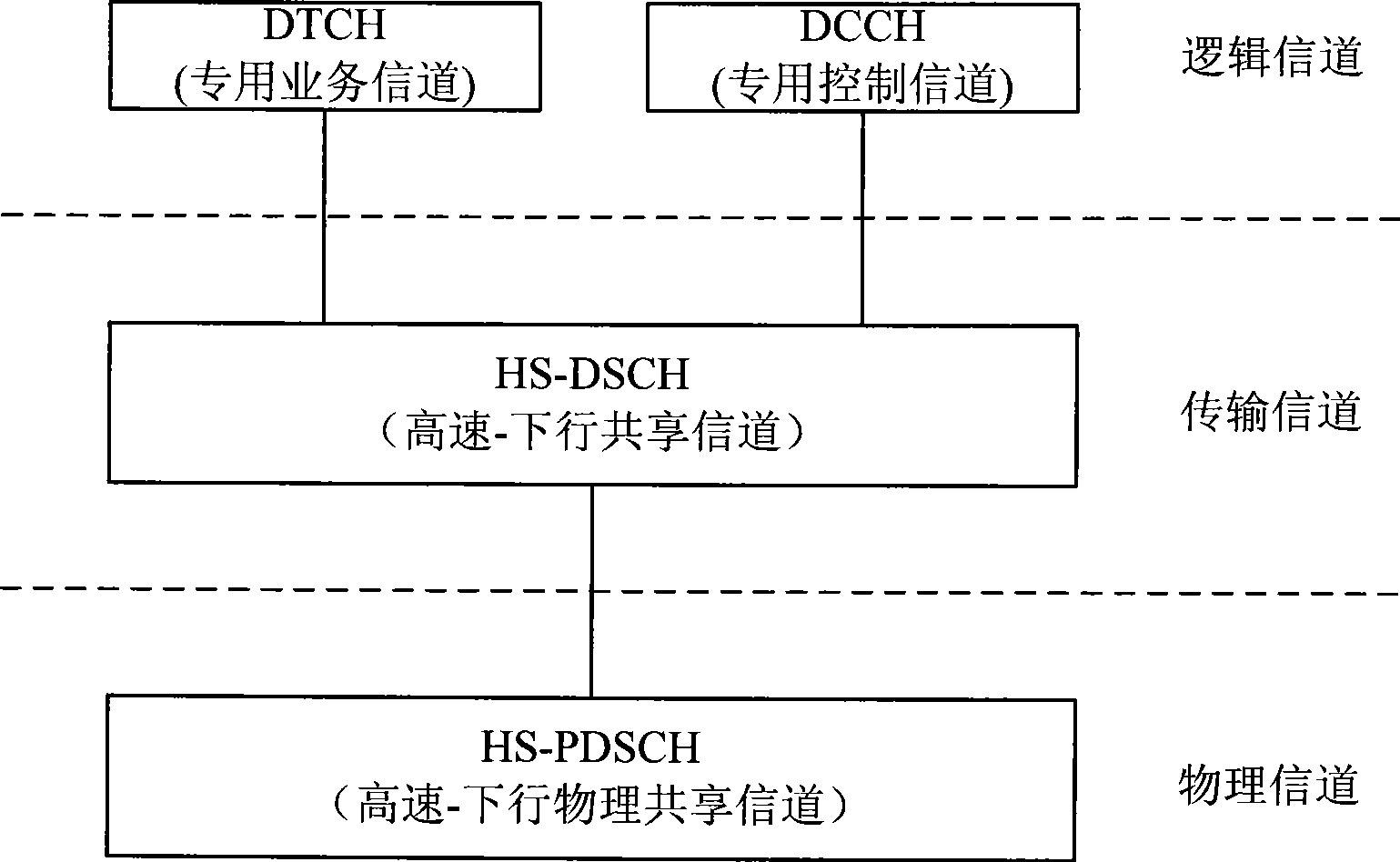
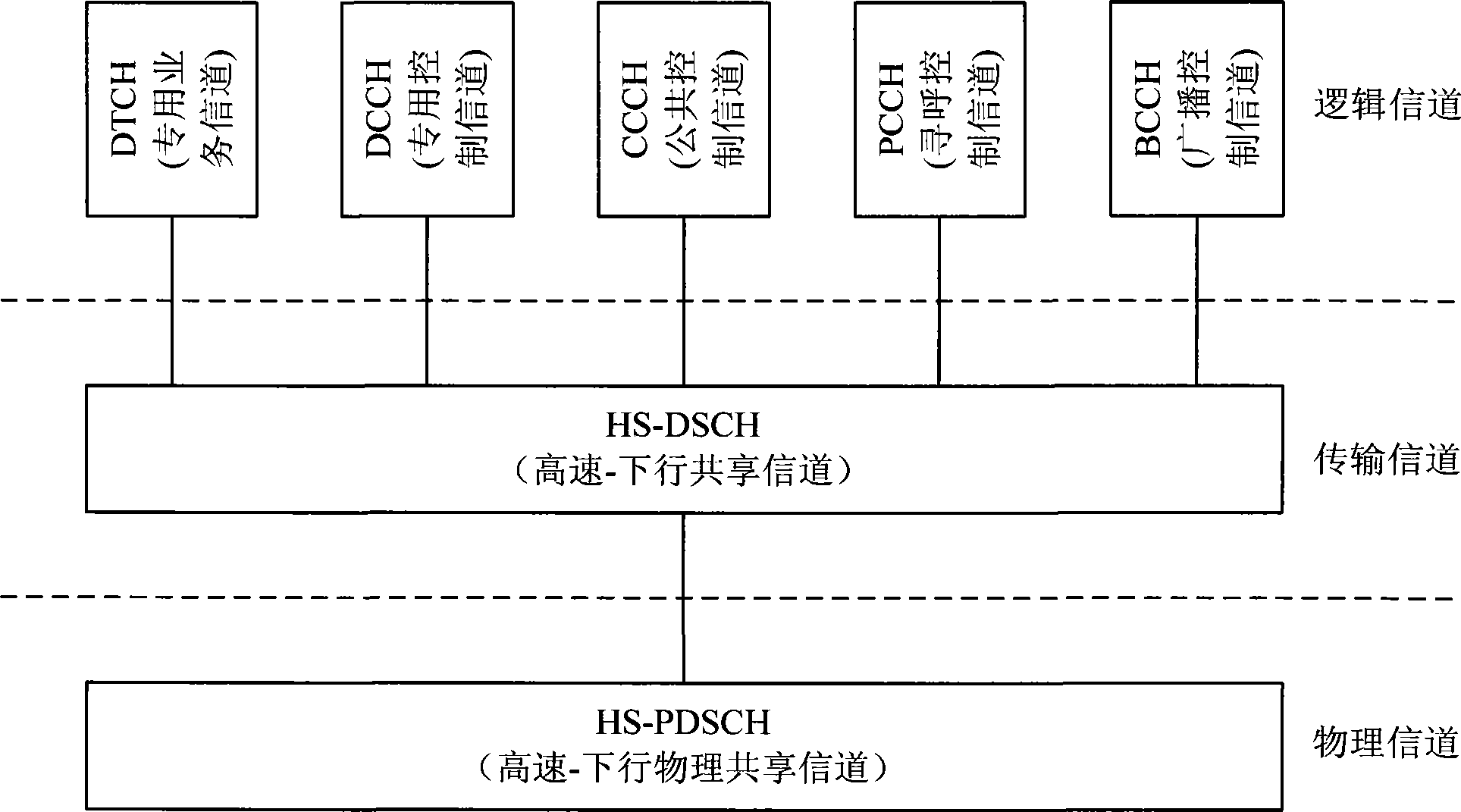
Transmission method for high-speed downlink shared channel under non-CELL_DCH state
ActiveCN101400188AComplies with receiver capabilitiesReceiver capability limitationsNetwork topologiesSystem capacityTD-SCDMA
The present invention discloses an HS-DSCH transmission method in a under non-CELL_DCH state, applied in a multi-carrier TD-SCDMA system. The method includes the following steps: Step A: establishing the HS-FACH relevant channels on the main carrier and / or secondary carrier, the network side notifying the HS-FACH relevant collocation information to user terminals through the district system information or dedicated signaling; Step B: the user terminal selecting a carrier with uplink random access resources to perform uplink accessing, and a base station Node B selecting a carrier with high speed forward access channel HS-FACH resources as a user terminal to schedule high speed downstream shared channel HS-DSCH resources. By the use of the method provided by the invention, it is defined that when HS-DSCH transfer is performed under non-CELL_DCH state in the multi-carrier HSDPA system, so that by changing the UE carrier presence mode under non-CELL_DCH state in the prior system, larger gain in the power system capacity aspect can be obtained; and this change conforms to the UE receiver gift in the prior system.
Owner:ZTE CORP
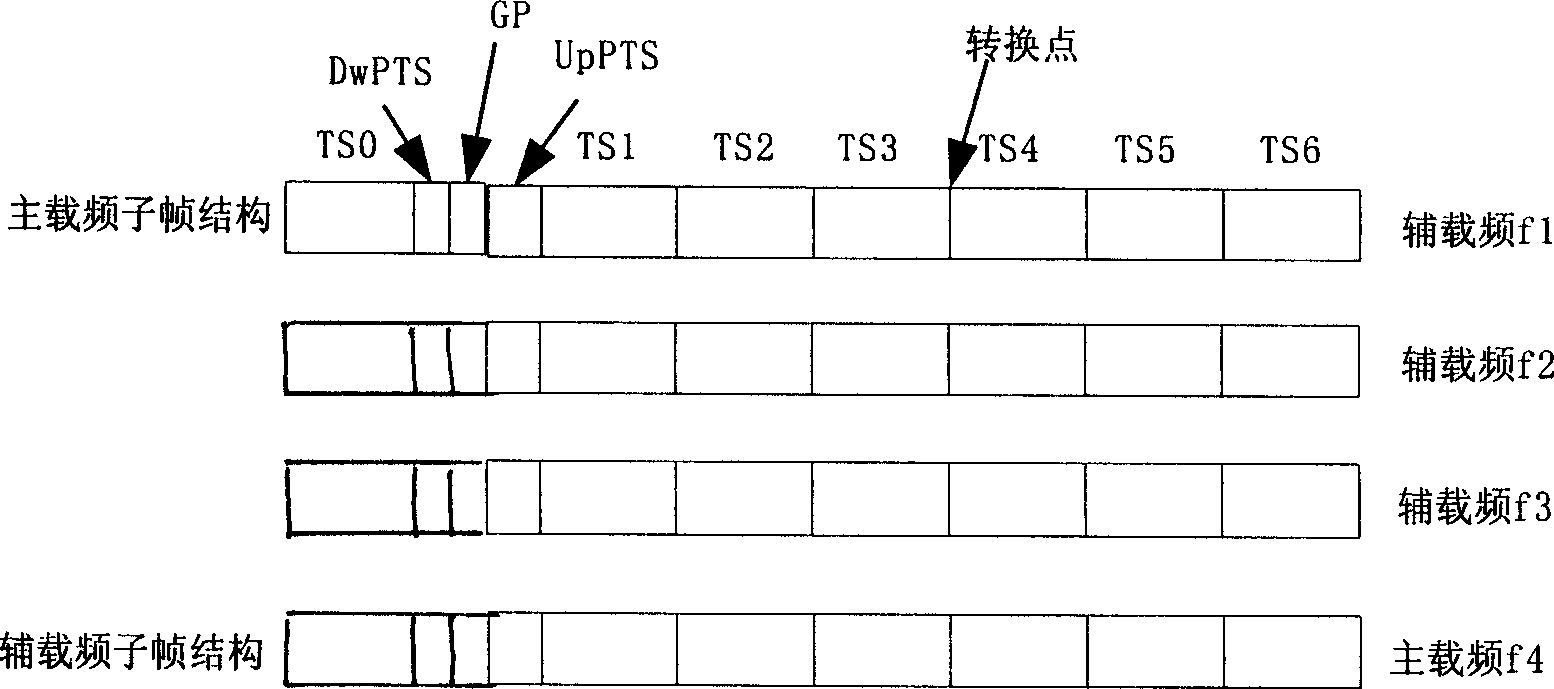
Multi-carrier frequency cell major and minor carrier frequency adjusting method in TD-SCDMA system
InactiveCN1735258AReduce the probability of collisionImprove acceptance rateBroadcast service distributionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTD-SCDMAEngineering
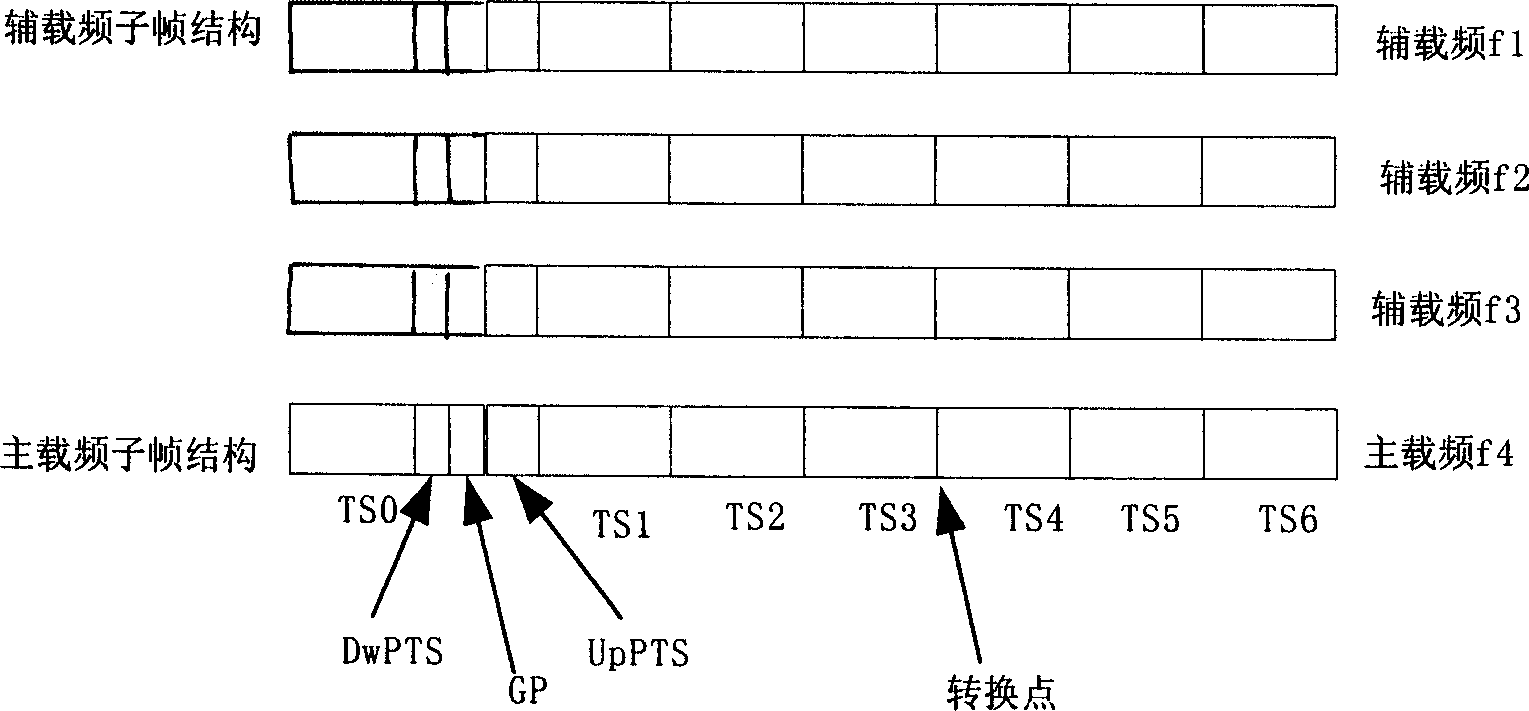
The adjust method for main and auxiliary carrier for multi carrier sub zone in TD-SCDMA system comprises: selecting a carrier as main carrier and the other as auxiliary carrier; creating sub zone, activating the TSO and DwPTS of main carrier to shield the auxiliary's and configure the public channel on main carrier; the P-CCPCH of main carrier uses full-direction coverage mode, all UE receives broadcast information from main carrier; detecting the power, disturbance and load of main carrier to evaluate the available resource of main carrier; when there is carrier has larger available resource, switching the main and auxiliary carrier. The invention can accommodate user both for main and auxiliary carrier with less collision possibility and high success rate.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Random access method of multi-carrier covering of TD-SCDMA system
ActiveCN1719932ACode division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTelecommunicationsTD-SCDMA
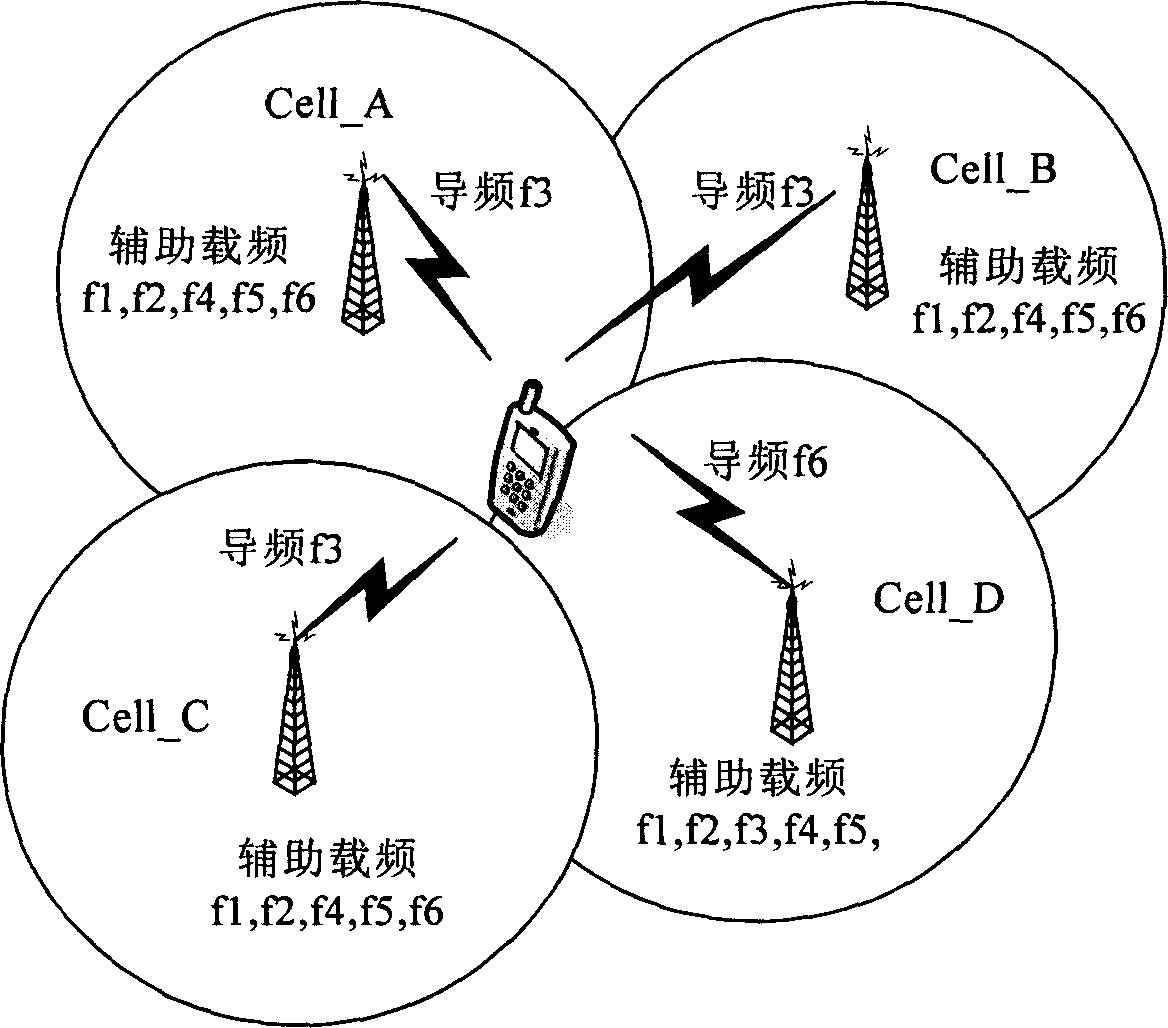
This invention relates to a random access method covered by multi-carrier frequency for realizing TD-SCDMA system, which designs every primary / sector a logic zone composed of multiple carrier frequencies with one as the pilot and those of other points as the assistant, said pilot carrier frequency sends down stream synchronous channel at the downstream synchronous time slot, and that of the assistant is at the blocking state, the two frequencies use the same intrusion code and basic training sequence code. A public control channel is set at TSO of the pilot to carry data from the transmission channel and provide system information broadcast covering the entire primary / sector. The assistant public control channel and bp instruction channel loading the access and bp channels are matched at the pilot, a forward physical access channel and random access channel are set on the pilot and assistant the UE is accessed at the up DCH channels of the pilot or that of the assistant.
Owner:ZTE CORP
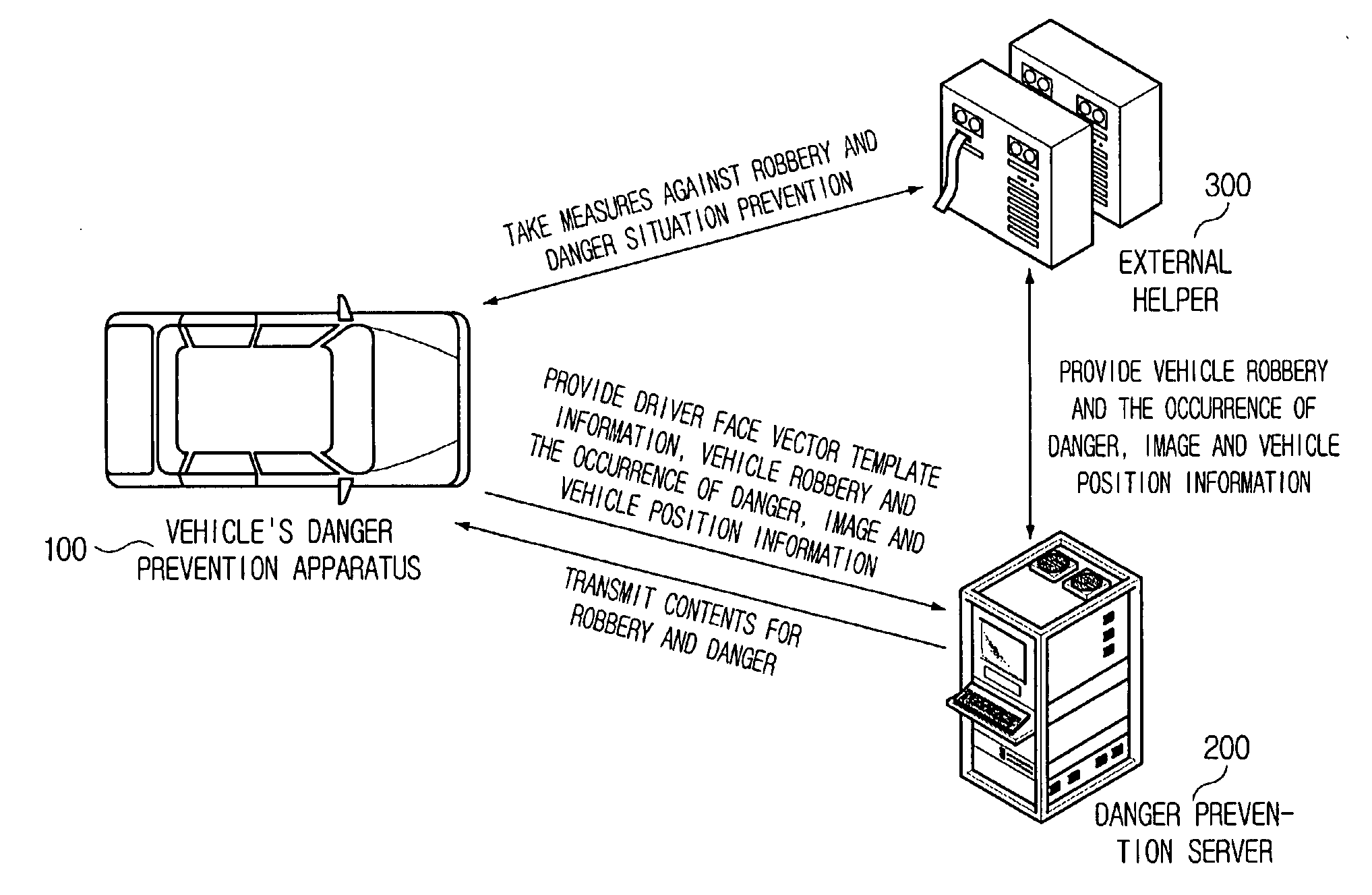
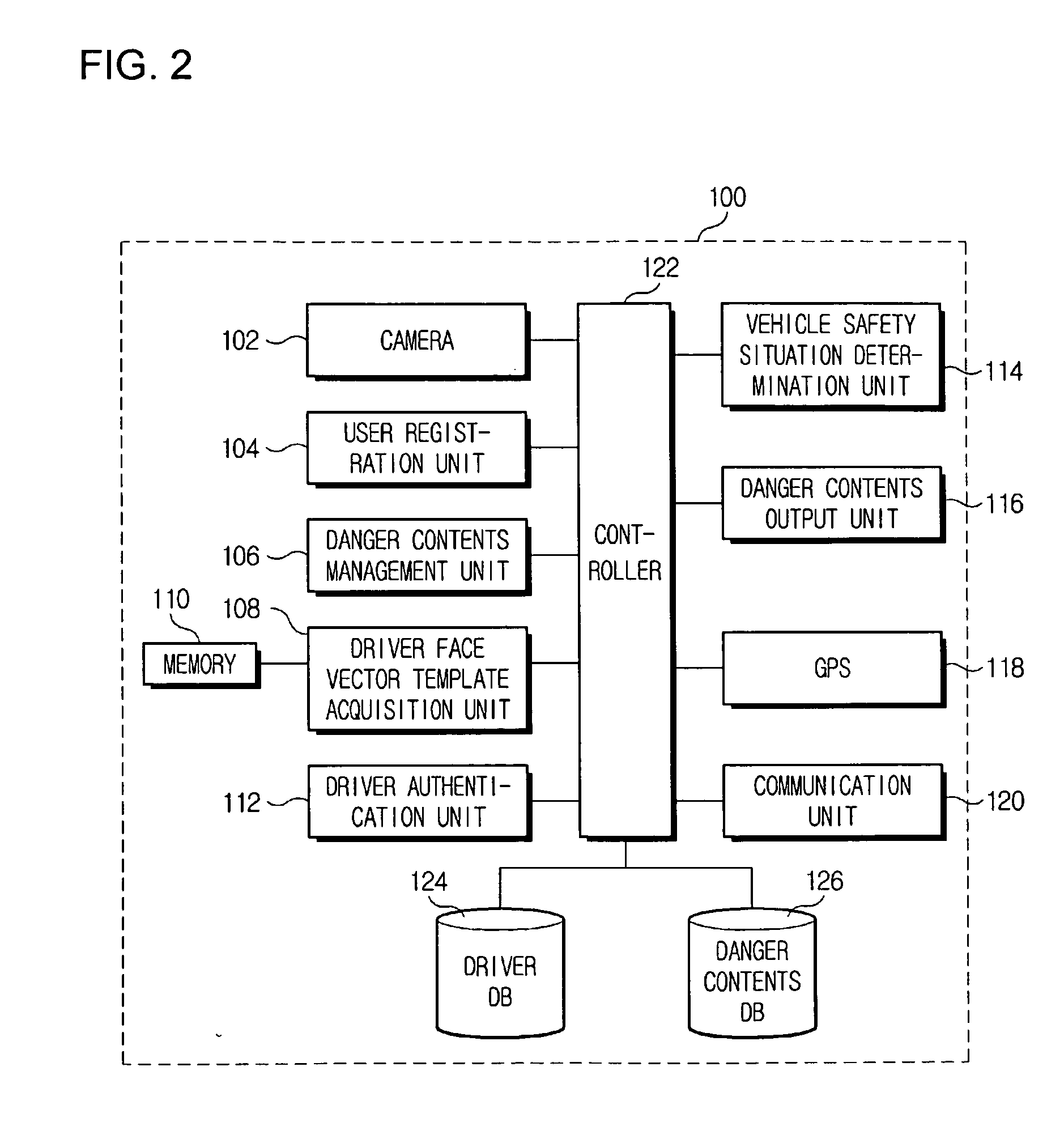
Vehicle emergency preventive terminal device and internet system using facial recognition technology
InactiveUS20080297330A1Quick fixAnti-theft devicesCharacter and pattern recognitionGSMReliability engineering
A danger preventive apparatus employing a facial recognition technology and a danger preventive system using the same is provided. According to the present invention, the robbery of a vehicle, and various crimes and unexpected dangers within a vehicle can be prevented and eliminated by employing a facial recognition algorithm. Further, dangerous situations can be solved rapidly by automatically transmitting a driver's position information and pertinent images from an external danger prevention server to external helpers, such as police and emergency help institutes, through wireless Internet communication technologies such as Wibro (also called Mobile WiMAX), HSDPA & HSUPA, Long Term Evolution (LTE), Ultra Mobile Broadband (UMB), TD-SCDMA, TRS, GPRS (GSM) and CDMA, when the robbery or danger of a vehicle is sensed in the danger preventive apparatus.
Owner:TELICSTA
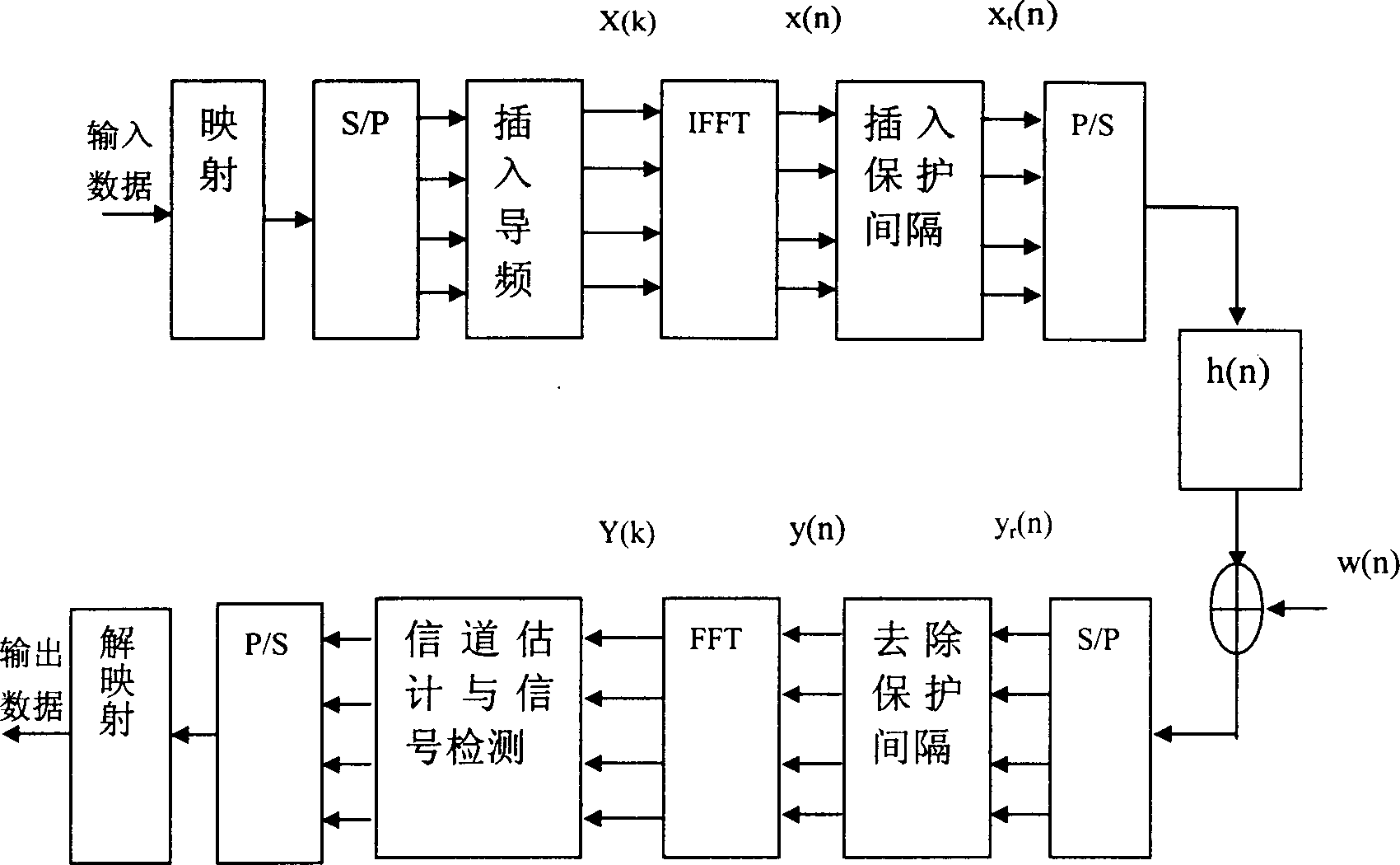
Method for compatible OFDM technology by TD-SCDMA system
InactiveCN1694441ACountering the effects of multipath interferenceEffect of Ideal Frequency DiversityBaseband system detailsCode division multiplexTD-SCDMAMultipath interference
This invention discloses a method for TD-SCDMA compatible with OFDM technology, which carries out serial parallel conversion to the due-out high speed serial code sheet sequence and generates multiple parallel sub-sequences to be modulated to multiple sub-carriers for parallel transmission to reduce the transmit rate of each channel so as to increase the symbol period and weaken the influence of multi-channel interference, at the same time, it uses the circular prefix as the protection interval, the interference among symbols are reduced greatly and the orthogonality among channels are ensured.
Owner:上海贝豪通讯电子有限公司
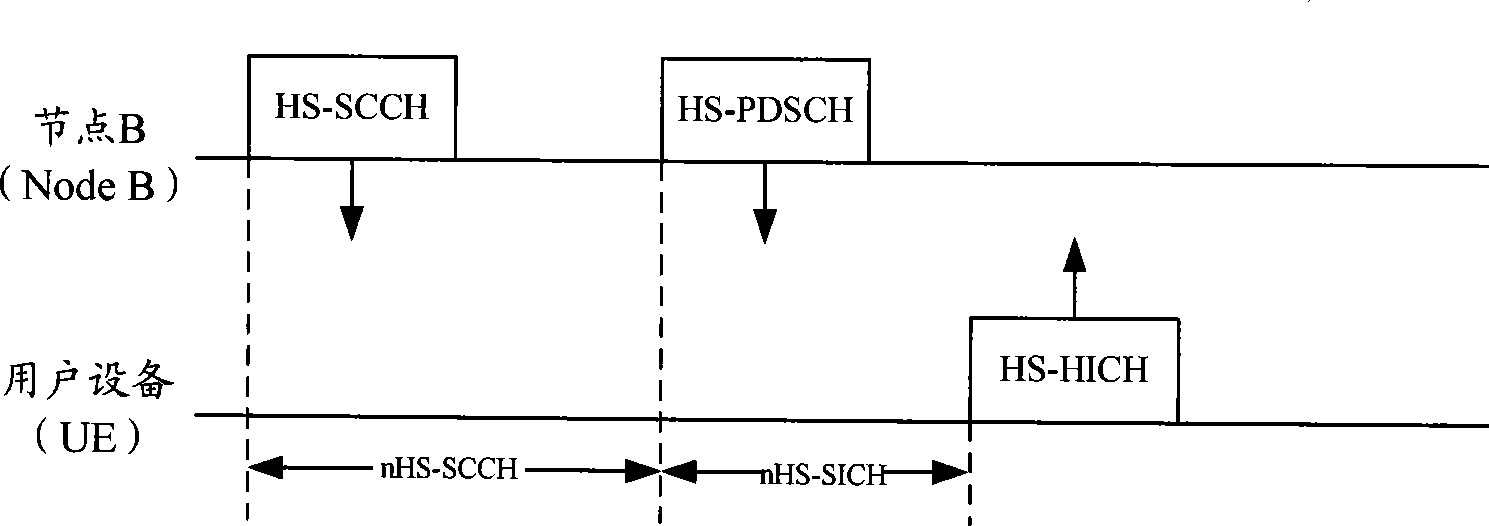
Method for implementing hsdpa for td-scdma
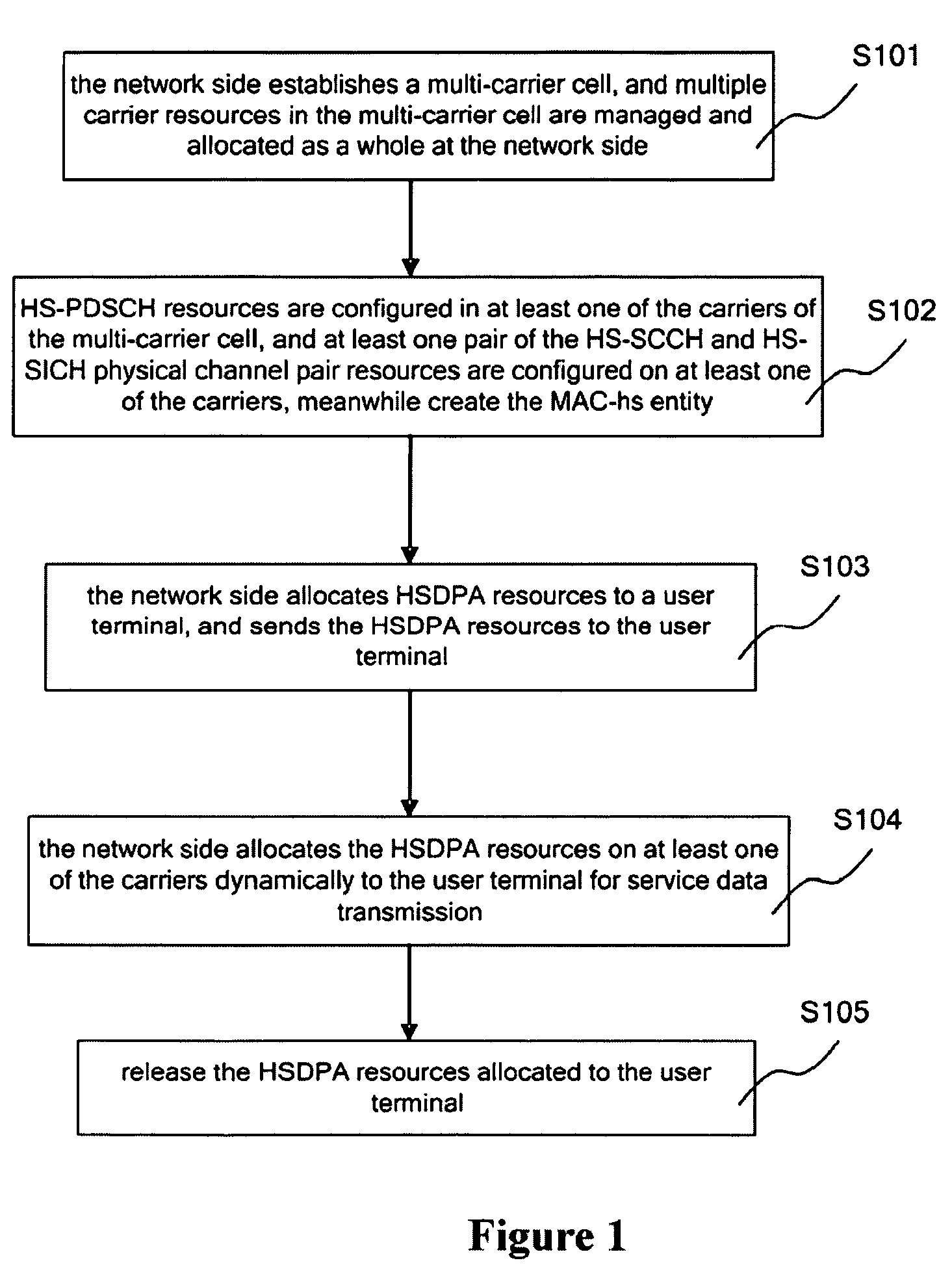
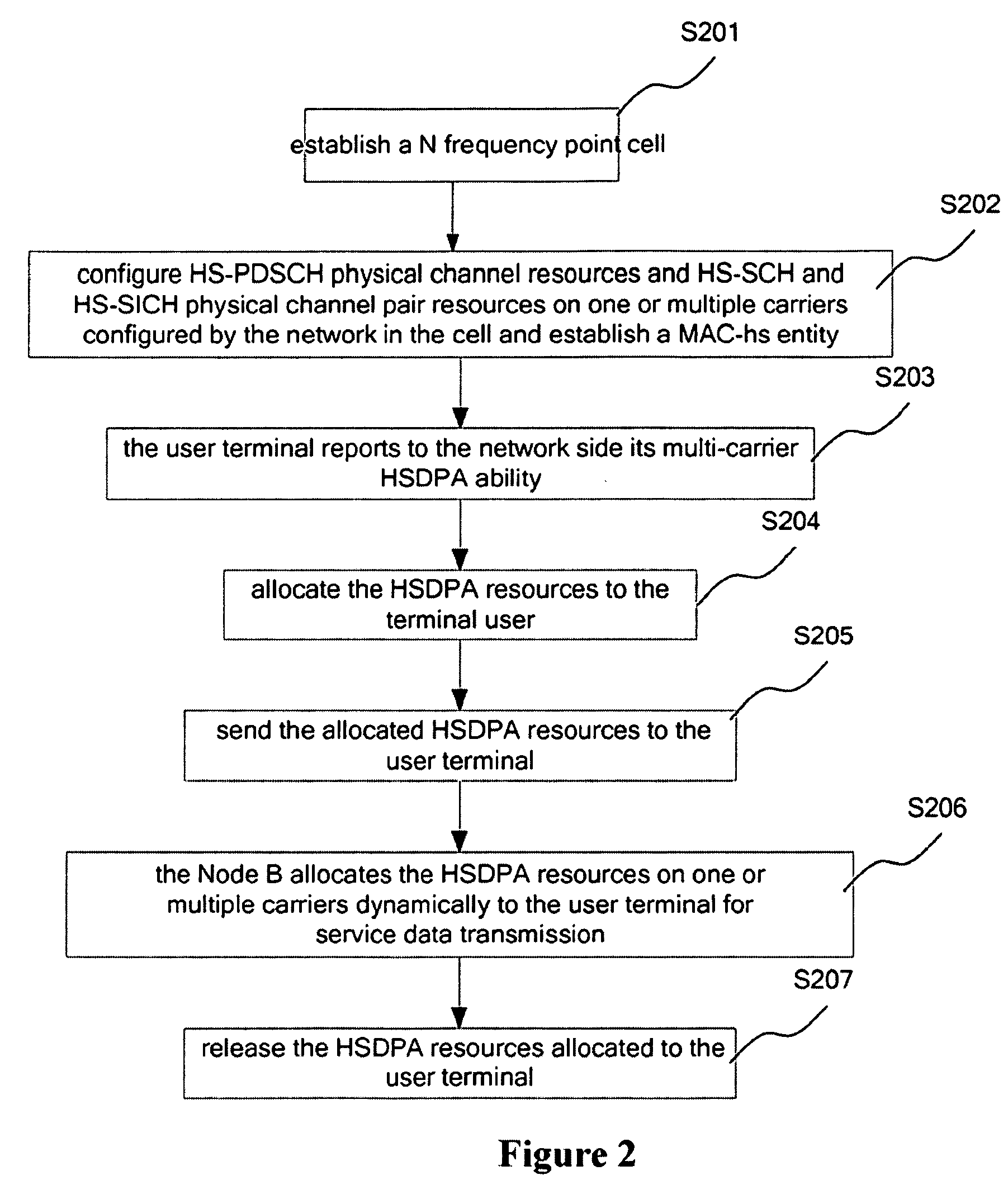
The present invention discloses a method for implementing multi-carrier HSDPA for TD-SCDMA system, comprises: establishing a multi-carrier cell at the network side, wherein multiple carrier resources in the multi-carrier cell being managed and allocated as a whole at the network side; configuring HS-PDSCH resources on at least one of the carriers of the multi-carrier cell, and at least one pair of HS-SCCH and HS-SICH physical channel resources on at least one of the carriers, at the same time, creating a MAC-hs to manage the channel resources on the carriers and the configuration of the MAC-hs entity itself; the network side allocating HSDPA resources to a user terminal, and sending the HSDPA resources to the user terminal; and the network side dynamically allocating the HSDPA resources on at least one carrier for the user terminal to transmit service data.
Owner:ZTE CORP
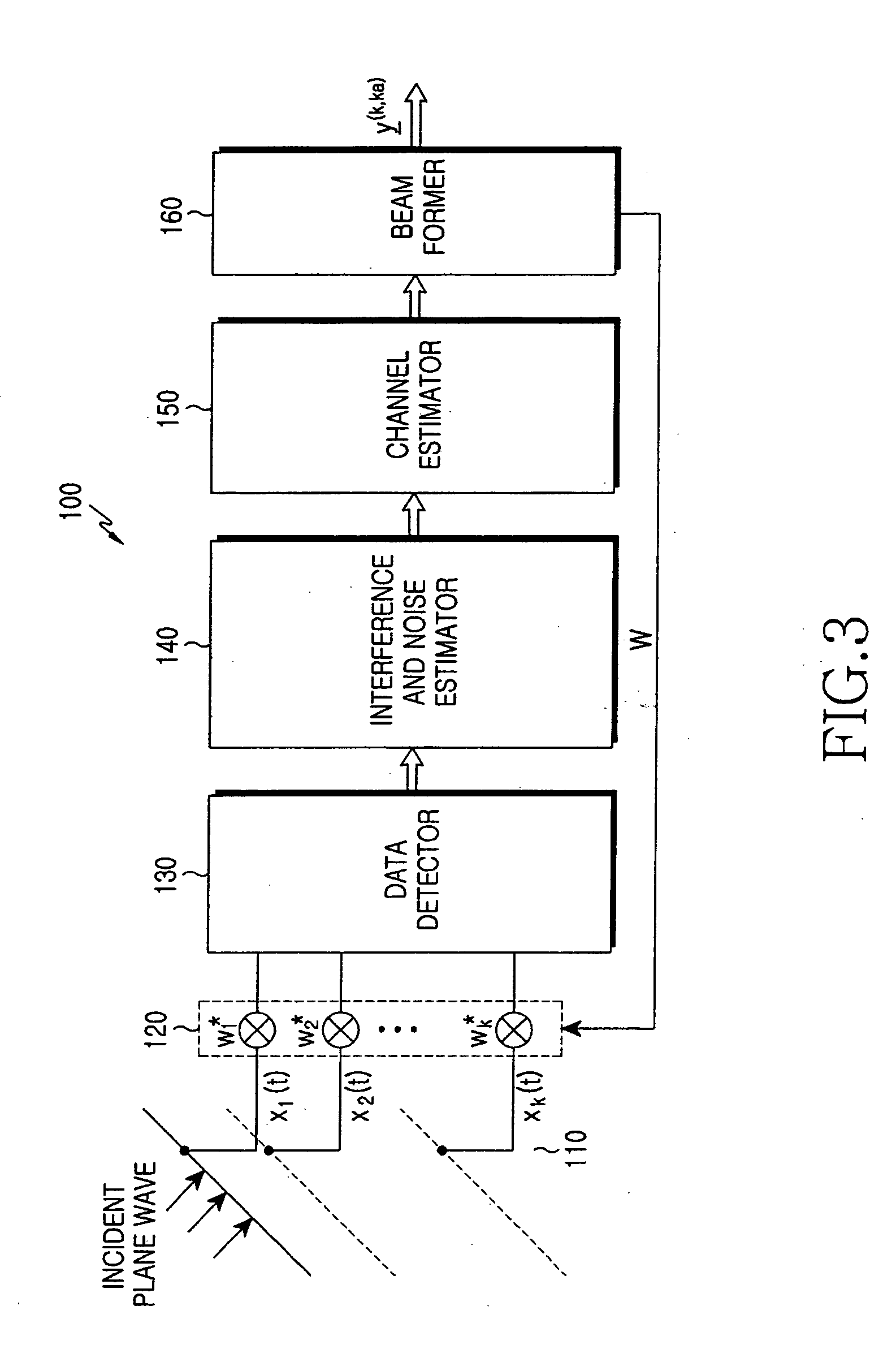
Beam forming apparatus and method using interference power estimation in an array antenna system
InactiveUS20050259006A1Reduce implementation complexityEasy to useElectroconductive/antistatic filament manufactureShielding materialsFrequency spectrumTD-SCDMA
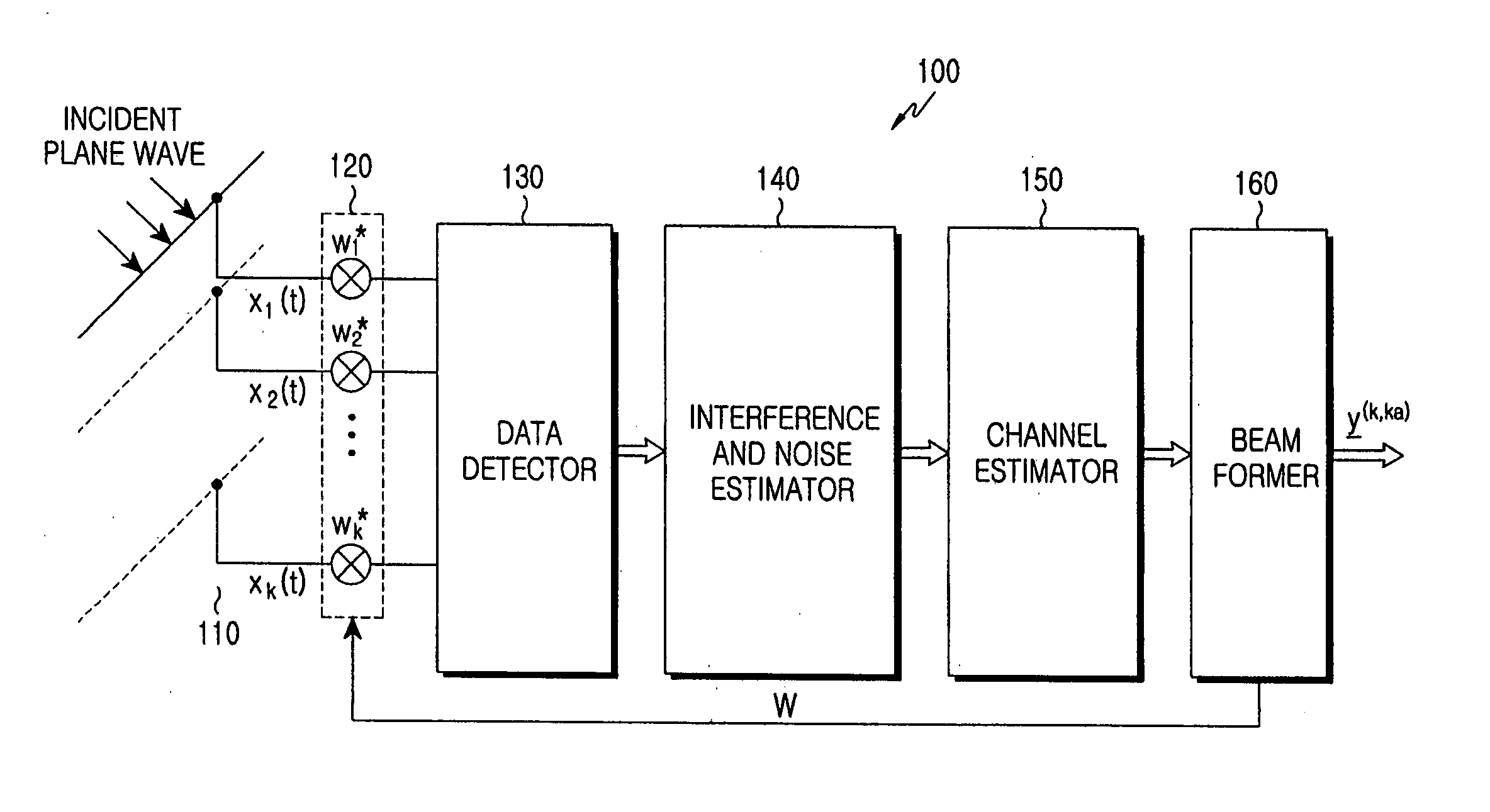
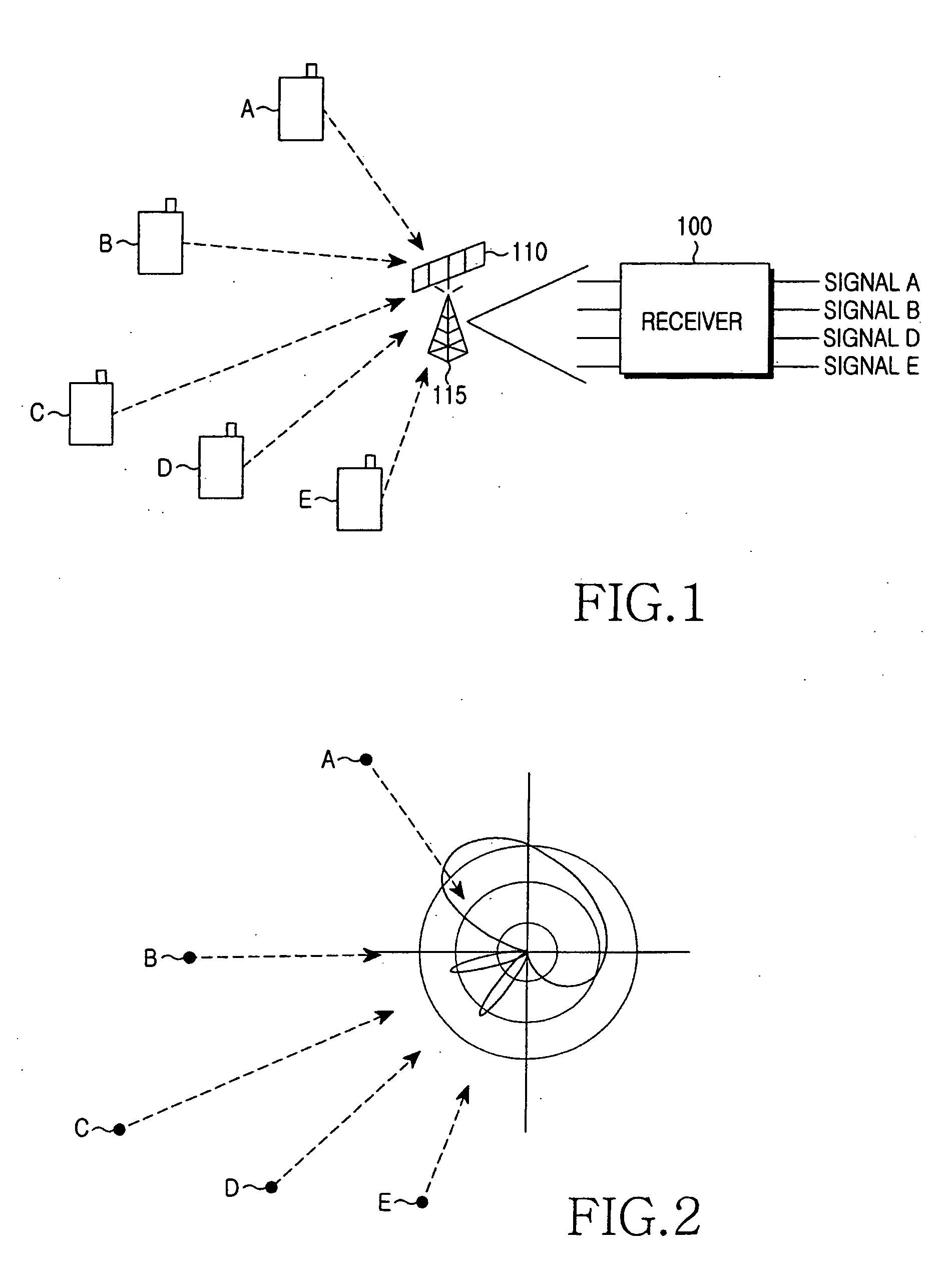
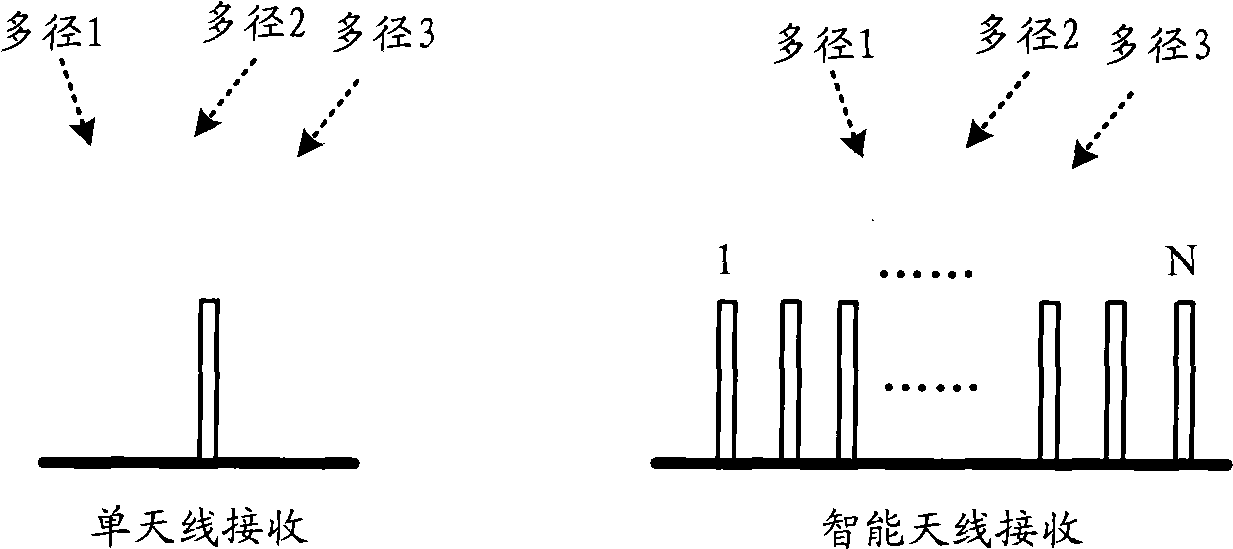
An apparatus and method are provided for simply estimating joint channel and Direction-of-Arrival (DOA) to efficiently estimate a channel impulse response associated with a spatially selective transmission channel occurring in a mobile radio channel, and performing efficient beam forming using the simplified joint channel and DOA estimation are provided. A receiver estimates the total interference power using power for each interference signal, estimates a spectral noise density, calculates steering vectors considering predetermined DOAs, and jointly calculates optimal weight vectors for each DOA of each user by applying the interference power and the spectral noise density to the steering vectors. The beam forming reduces implementation complexity of a TDD system such as a TD-SCDMA and increases beam forming efficiency in a mobile environment by efficiently using spatial diversity.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
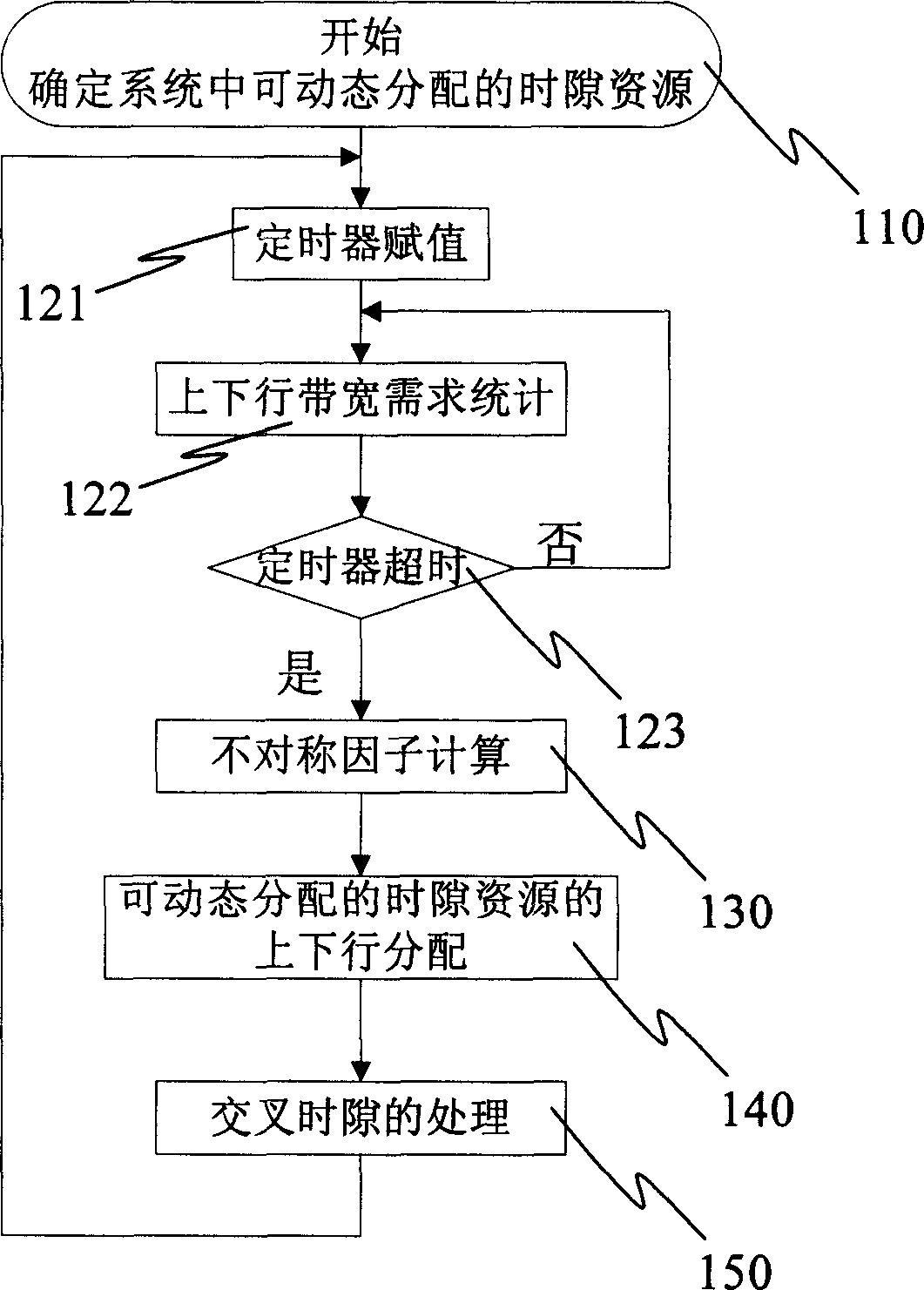
Dynamic channel distributing method of TD-SCDMA
InactiveCN1564483AReduce distractionsEasy to implementRadio transmission for post communicationTD-SCDMACommunications system
The method includes steps: determining assignable dynamic time slot resources and fixed time slot resources in frame structure of communication system; carrying out statistics for demanding of up going and down going bandwidths on small zone or cluster of small zone in a period of time preset; based on result of statistics, calculating parameters of reflecting demand relation between up going and down going bandwidths; based on the said parameters, allotting assignable dynamic time slot resources for up going and down going bandwidths. The invention realizes dynamic channel allocation at slow speed in TD_SCDMA.
Owner:ZTE CORP
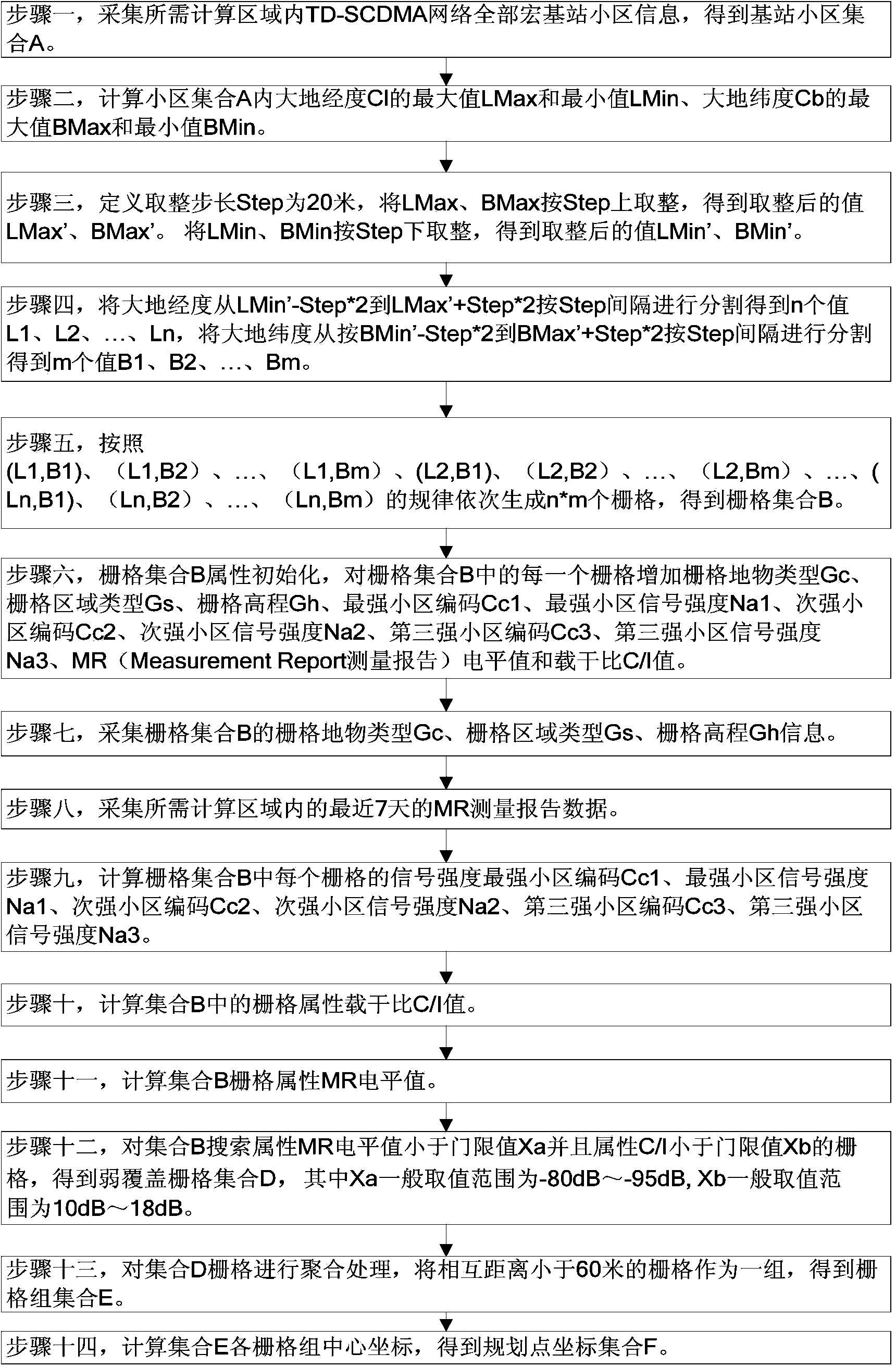
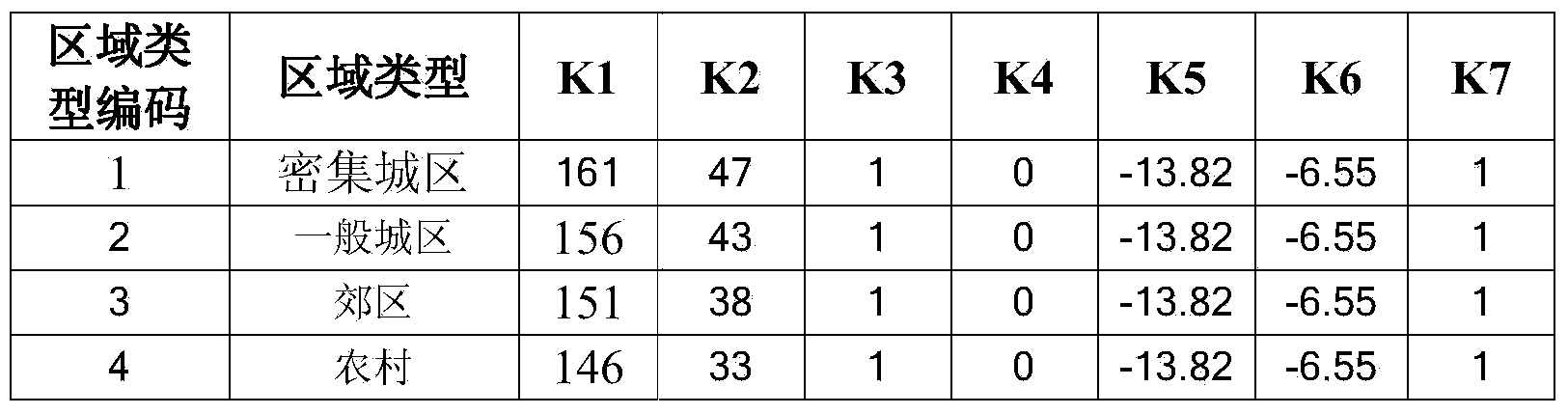
TD-SCDMA base station planning point automatic selection method based on coverage prediction
ActiveCN104378769AReduced precision requirementsImprove rationalityNetwork planningHigh signal intensityInterference ratio
The invention discloses a base station planning point automatic selection method. The method comprises the core steps that cell information of macro base stations is acquired, and a set A is obtained; the maximum value and the minimum value of cell longitudes and latitudes in the set A are calculated, and the maximum value and the minimum value are rounded according to the step length; the longitudes and the latitudes are segmented according to the step length from the minimum value to the maximum value; according to pairing of the longitudes and the latitudes, a set B is obtained; the attributes of the set B are initialized; grid ground feature information of the set B is acquired; an MR level value is acquired; the signal intensity of each grid in the set B is calculated, and the first three cells with the first three high signal intensities are obtained; the carrier-to-interference ratio of the grids in the set B are calculated; the attribute MR level values of the grids in the set B are calculated; the grids with the attribute MR level values smaller than a threshold value Xa and the carrier-to-interference ratios smaller than a threshold value Xb are searched for in the set B, and a poor coverage set D is obtained; aggregation processing is carried out on the grids of the set D, and the grids with the distances smaller than a threshold value are arranged in one set, so that a grid group set E is obtained; the center coordinates of the grid groups of the grid group set E are calculated, and a planning point coordinate set F is obtained.
Owner:CHINA INFOMRAITON CONSULTING & DESIGNING INST CO LTD
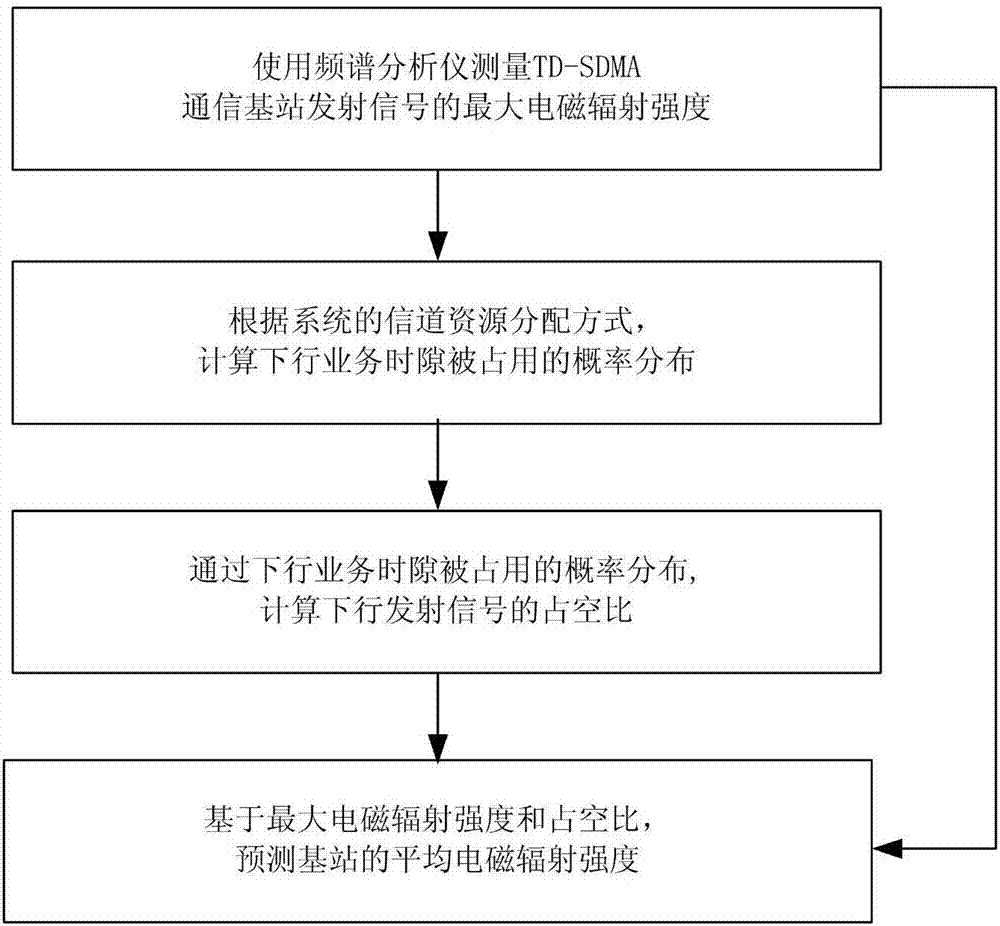
New electromagnetic radiation prediction method for TD-SCDMA communication base station
ActiveCN107124238AFast average electromagnetic radiation intensityFast prediction of average electromagnetic radiation intensityTransmission monitoringSocial benefitsTD-SCDMA
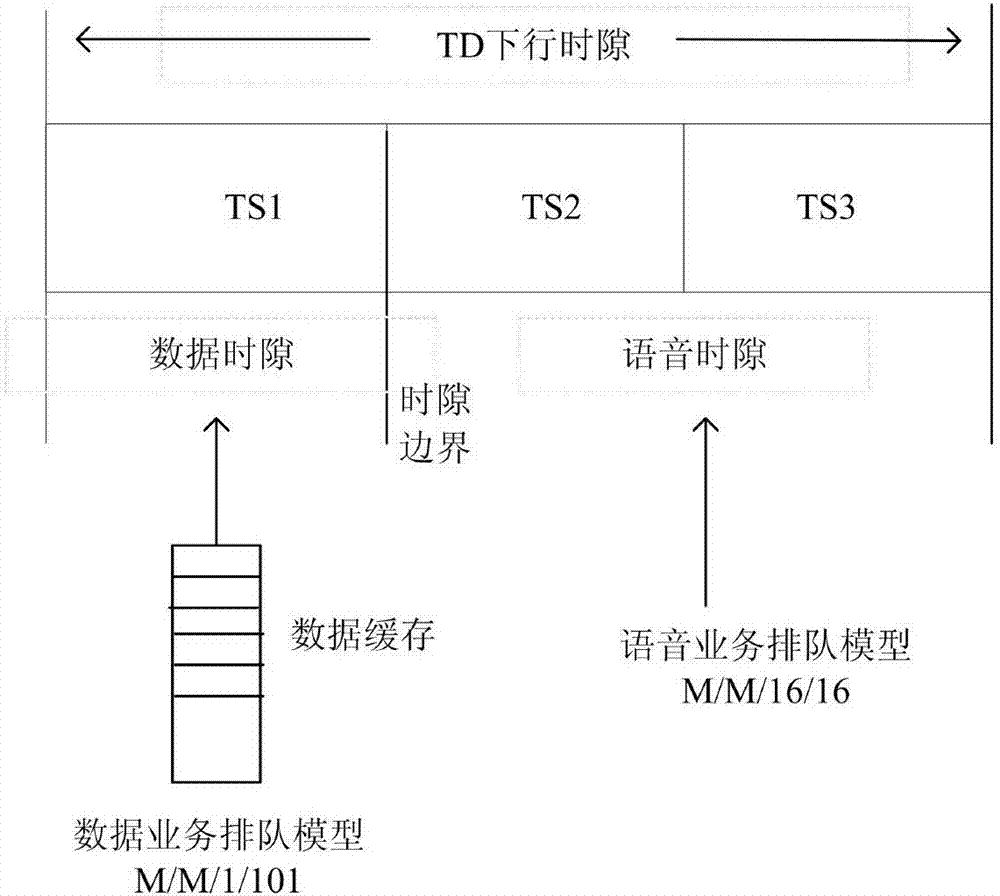
The invention discloses a new electromagnetic radiation prediction method for a TD-SCDMA communication base station. The method comprises the steps of using a spectrum analyzer to measure maximum electromagnetic radiation intensity of a TD-SCDMA signal; building a service queuing model according to a channel resource distribution mode of a TD-SCDMA system, and computing probability distribution of the occupied downlink service slot; computing a duty ratio of the TD-SCDMA signal via the probability distribution of the occupied downlink service slot; and predicting the average electromagnetic radiation intensity of the TD-SCDMA communication base station based on the maximum electromagnetic radiation intensity and the duty ratio. According to the method provided by the invention, the service queuing model by analyzing the channel resource distribution mode of the TD-SCDMA system, the duty ratio of the transmitt4d signal is computed, and the average electromagnetic radiation intensity is predicted by using the maximum electromagnetic radiation intensity and the duty ratio of the TD-SCDMA signal. The method provided by the invention has a great reference value to build a TD-SCDMA communication base station, assess influence of an electromagnetic radiation environment and protect environment, and has excellent social benefit.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Wireless network overlapping road detecting software supporting TD-SCDMA
InactiveCN101296470AEasy to detectEliminate Power Measurement ErrorsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless mesh networkGeolocation
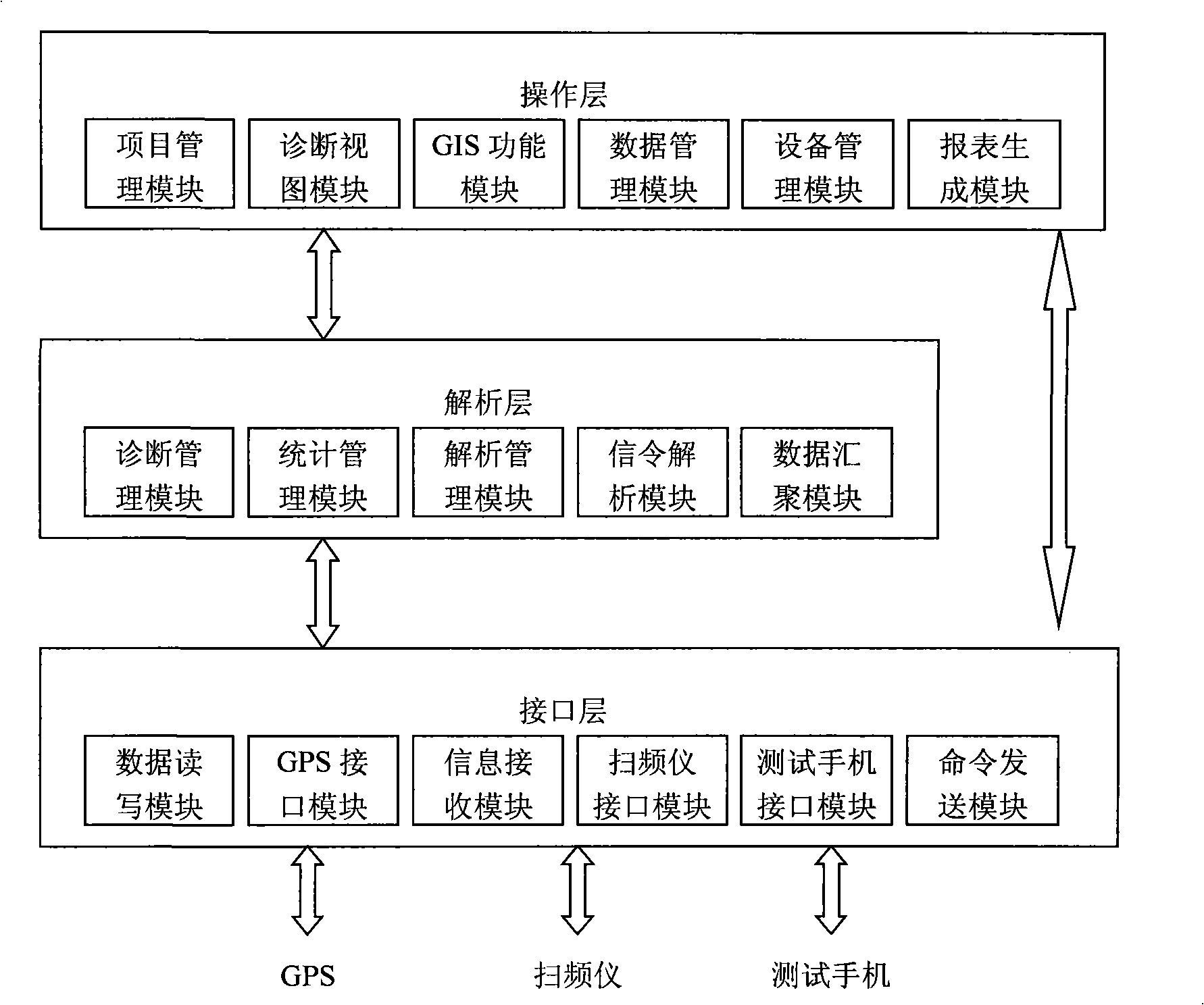
The invention provides road test software supporting a TD-SCDMA wireless access network, which can meet the requirements of the planning and optimization of the TD-SCDMA network in combination with a receiver and a GPS. The invention provides a method for calculating the performance parameter of the TD-SCDMA network and can intuitively and correctly reflect the quality of the network. The invention also provides a structuring thought of the TD-SCDMA road test software which comprises: an interface layer, which communicates with the receiver and the GPS, sends a network parameter value measured on the spot and geographical position information to an analytics layer; the analytics layer corresponds the geographical position information to the network parameter value one by one and classifies and reorganizes the TD-SCDMA network parameter value according to the standard set by users, thereby being capable of analyzing and diagnosing the state of the network measured in an intelligent manner; a presentation layer visually presents the classified and reorganized network parameter value and the analytic and diagnostic results of users in many ways, such as map, report form, and diagnostic listing presenting and so on. The invention also provides key technologies of propagation model correction, network coverage and test, data analysis and diagnosis, etc.
Owner:BEIJING PEOPLE ENJOY TECH
Data aided frequency synchronisation in cellular mobile equipments
InactiveUS20030181183A1Convergence can be speededOvercomes drawbackCarrier regulationRadio transmissionShift registerGreek letter sigma
Some improvements to the conventional algorithms for data aided frequency synchronisation in cellular systems are introduced in a new method executable by the user equipments of various standards, i.e. 3GPP CDMA-TDMA, FDD mode at 3.84 Mcps, TDD mode at 3.84 Mcps, TDD mode at 1.28 Mcps; CWTS TD-SCDMA; GSM / DCS / GPRS. The method begins to obtain the suboptimal frequency errors Deltafi using a well known formula which calculates the argument of the autocorrelation over a subset of the baseband samples of the detected training sequence. The errors Deltafi are stored into a shift register L-position long and averaged to obtain an estimated frequency error Deltafi used for recursively correcting the reference frequency of the local oscillator, as: fi=fi-1+KDeltafi where K (0<=K<=1) is a weighting factor. Contrarily to the simple averaged error of the prior art, a sign criterion is used by which the average is performed on the only terms having the most recurrent algebraic sign among the stored terms Deltafi. The content of the shift register is corrected after each non-null frequency correction by subtracting K.Deltafi to all the stored terms Deltafi. Besides the frequency is corrected upon the following optional conditions, each other independents: The number of terms Deltafi having equal algebraic sign is greater than a constant alpha lower than L. The standard deviation sigma of the averaged terms Deltafi is lower than beta.sigmaold, being sigmaold the sigma of the last non-null frequency correction, and beta a constant >=1. After a minimum number gamma of iterations between two non-null frequency corrections are spent, being gamma a constant comprised between 1 and L. According to another variant the iterations of the recursive update are subdivided into an initial group with a higher K value for achieving fast convergence and a subsequent group with a lower K for achieving the required accuracy (FIG. 13).
Owner:SIEMENS INFORMATION & COMM NEWTWORKS INC
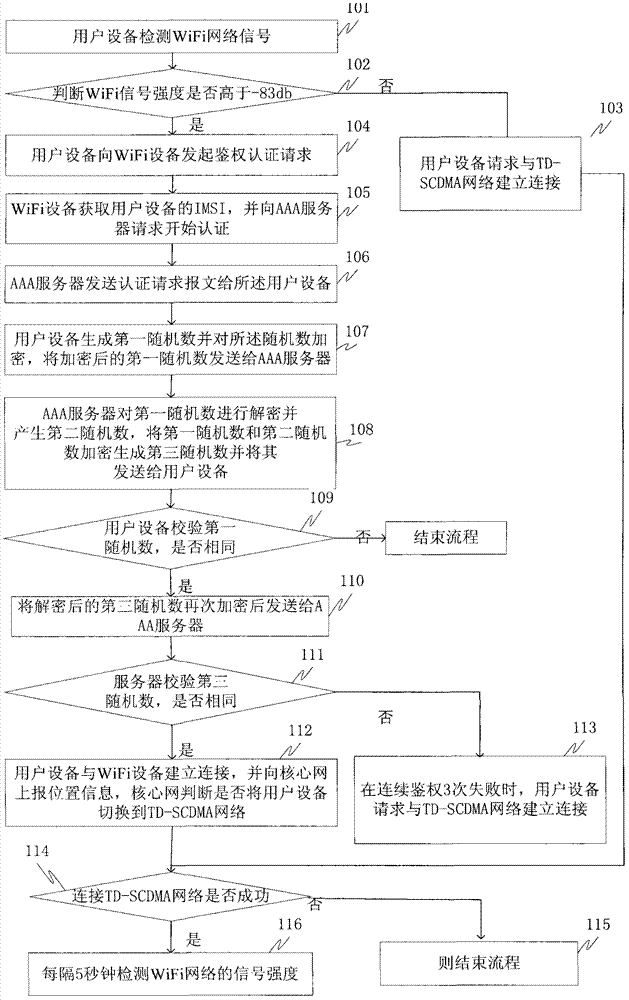
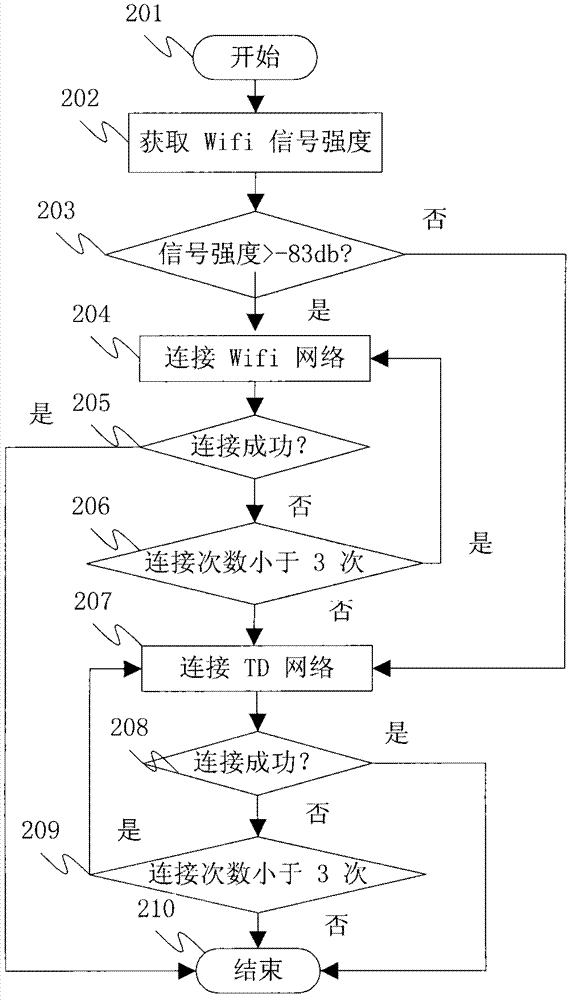
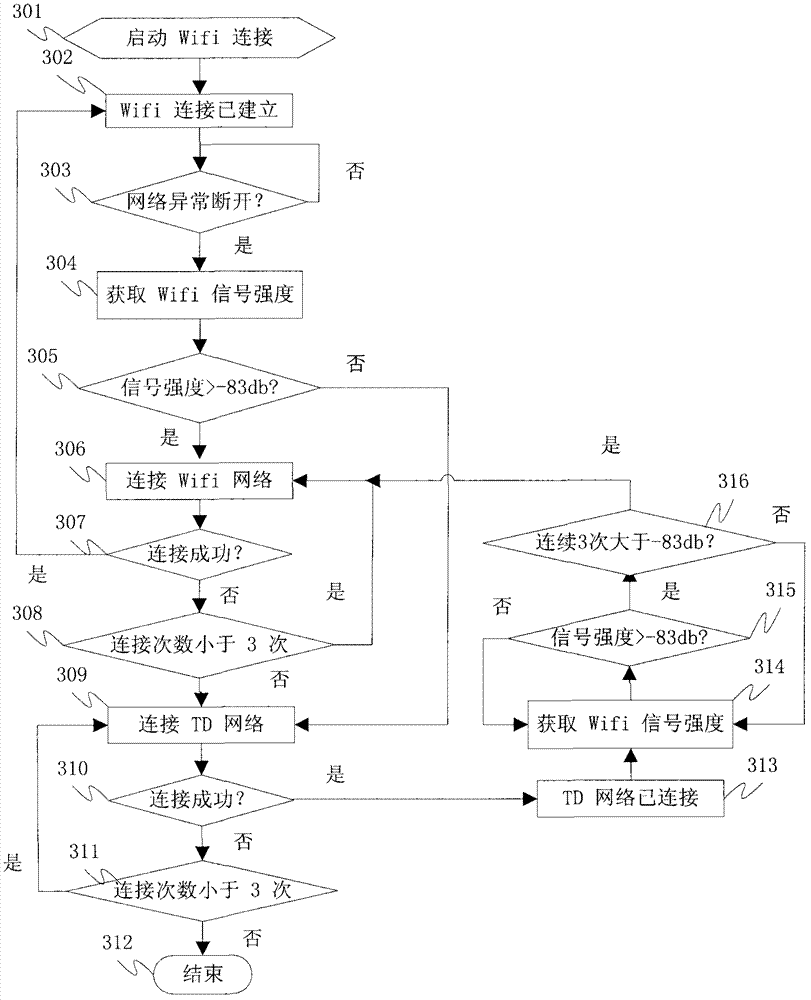
Method for optimal selection between WiFi (wireless fidelity) network and TD-SCDMA (time division-synchronous code division multiple access) network
InactiveCN102958048ARealize seamless switchingImprove experienceAssess restrictionSecurity arrangementTD-SCDMAWifi network
An embodiment of the invention discloses a method for optimal selection between a WiFi (wireless fidelity) network and a TD-SCDMA (time division-synchronous code division multiple access) network. The method includes that user equipment detects a signal of the WiFi network; the user equipment requests for establishing a connection with the TD-SCDMA network when the intensity of the signal of the WiFi network is lower than -83db; the user equipment requests for establishing a physical connection with WiFi equipment when the intensity of the signal of the WiFi network is higher than -83db, an authentication request is initiated to the WiFi equipment, the connection between the user equipment and the WiFi equipment is established if authentication is successful, and a core network judges whether the user equipment needs to be switched from the WiFi network to the TD-SCDMA network or not; and the intensity of signals of the WiFi network is detected in every five seconds if the user equipment is successfully connected with the TD-SCDMA network. The method has the advantage that the optimal selection between the WiFi network and the TD-SCDMA network is realized.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GROUP SHANDONG
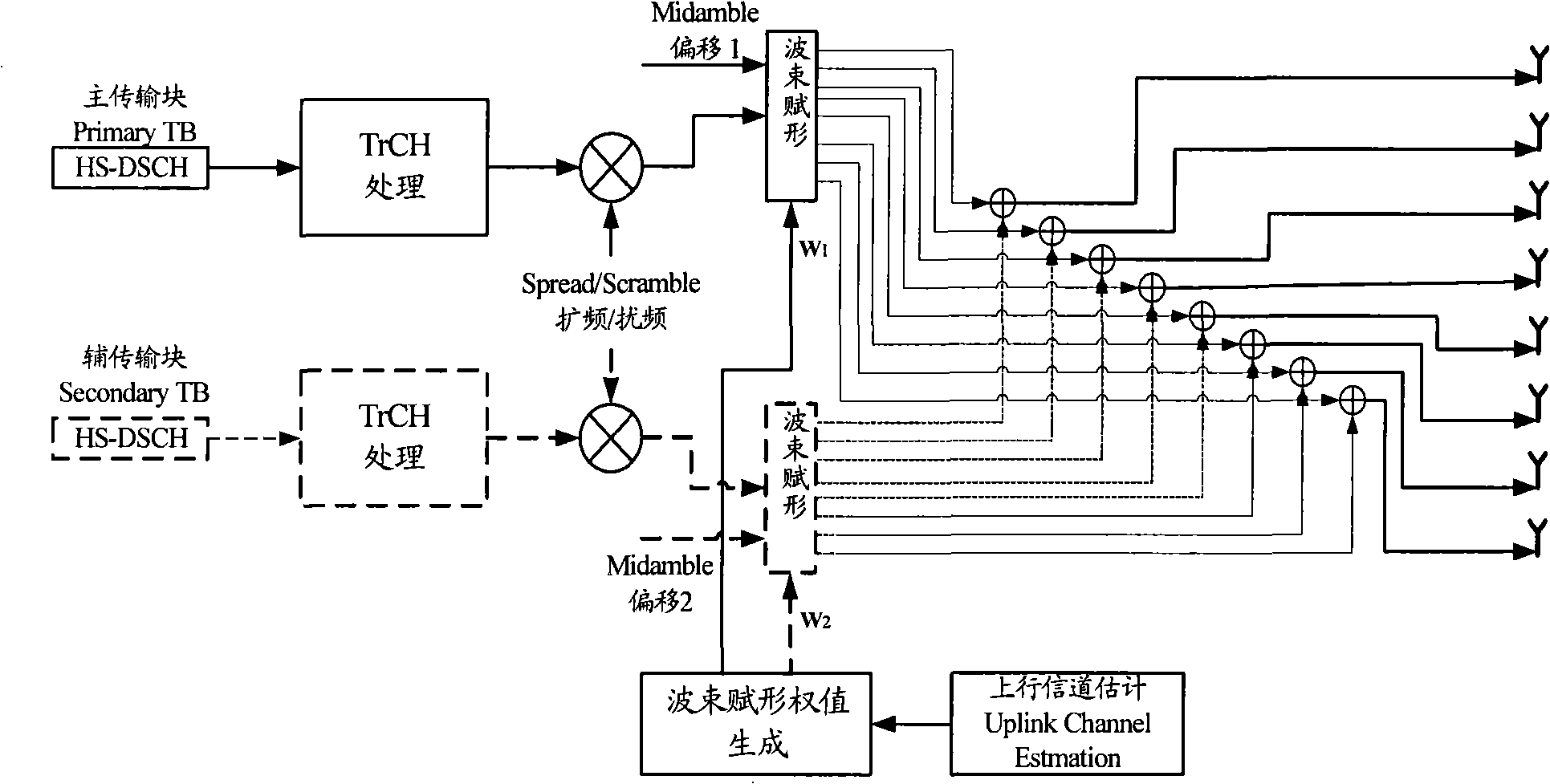
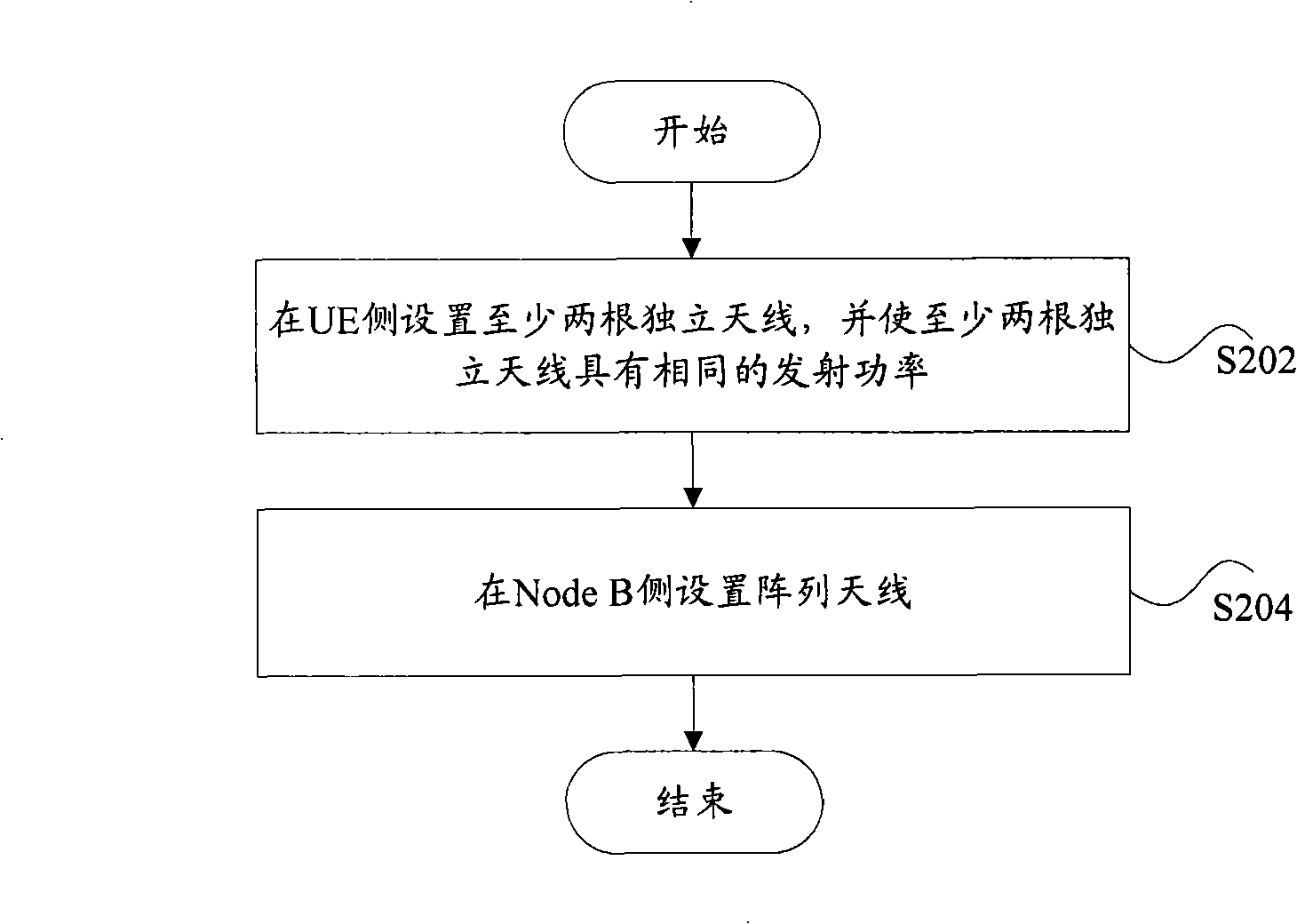
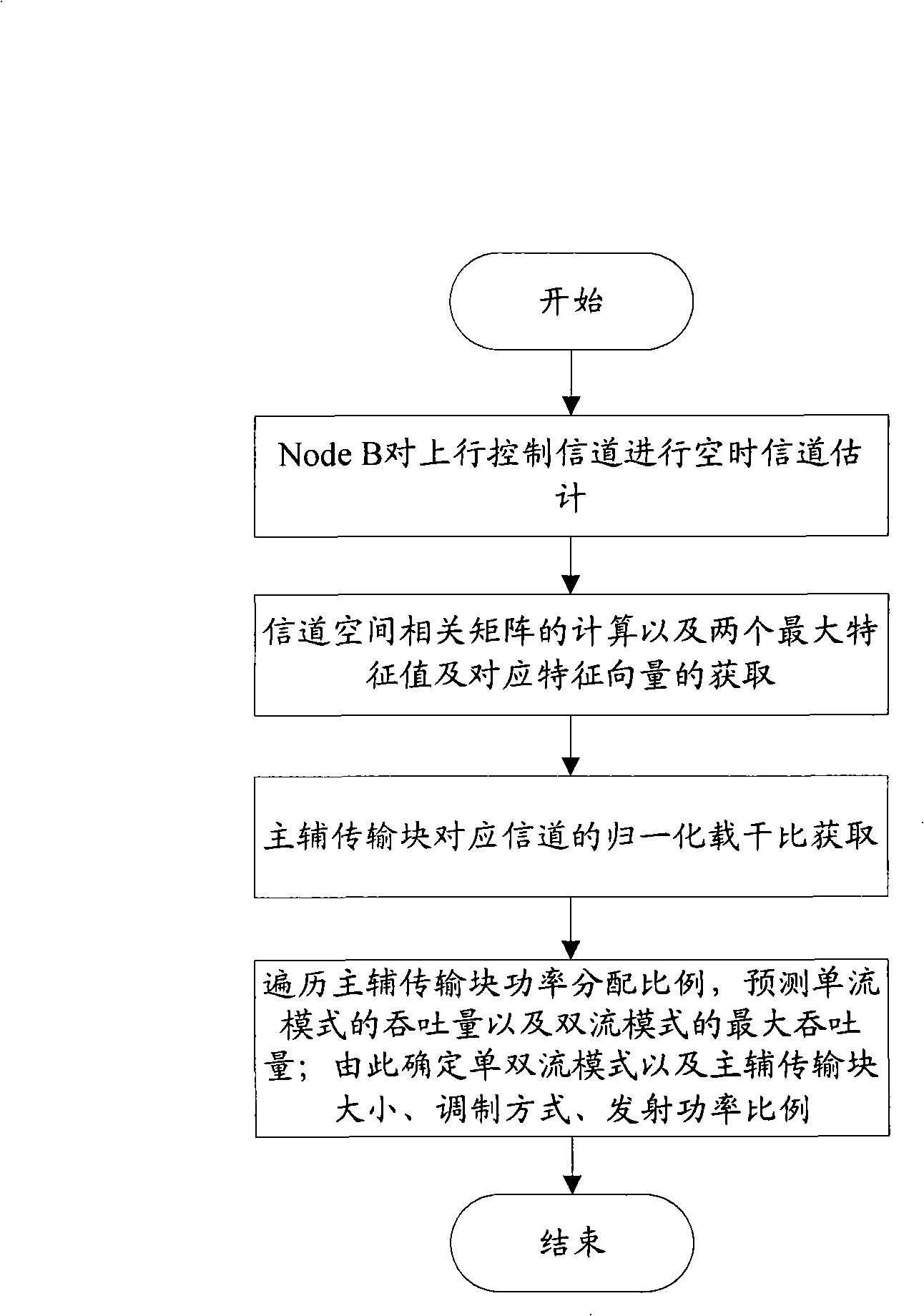
Method for applying MIMO technique in TD-SCDMA system outdoor macrocell
ActiveCN101359953AAvoid the disadvantages faced when applied aloneImprove throughputSpatial transmit diversityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionPrecodingTD-SCDMA
The invention provides a method which applies multiple input multiple output technology in an outdoor macrocell of a TD-SCDMA system, wherein, the user equipment side is provided with at least two independent antennas and at least two independent antennas have the same launching power; the node B side is provided with array antennas; wherein, downlink supports single-stream mode launch under beam-forming mode and double-stream mode launch under pre-encoding mode, and the node B can carry out switch of the single-stream mode and the double-stream mode to user equipment.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Descending synchronous calibrating method and apparatus for TD-SCDMA system
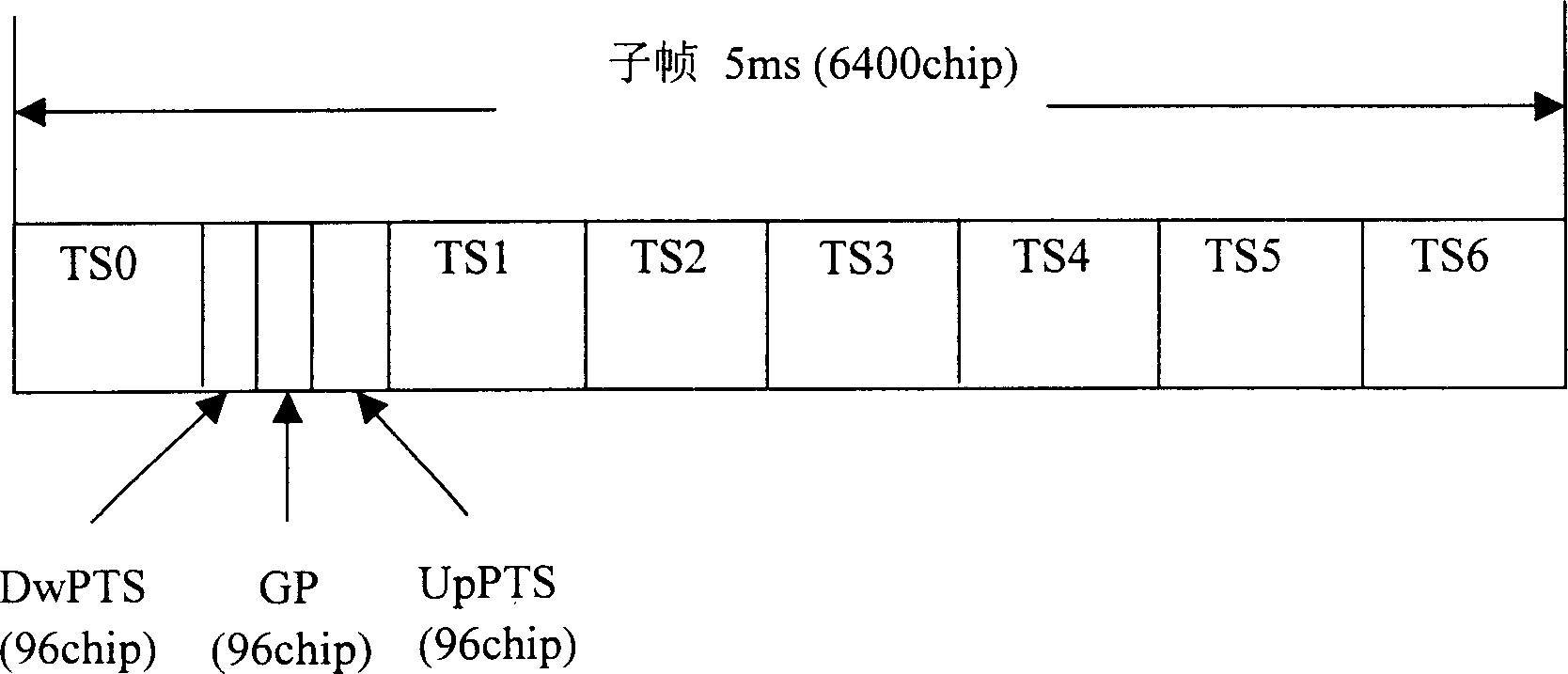
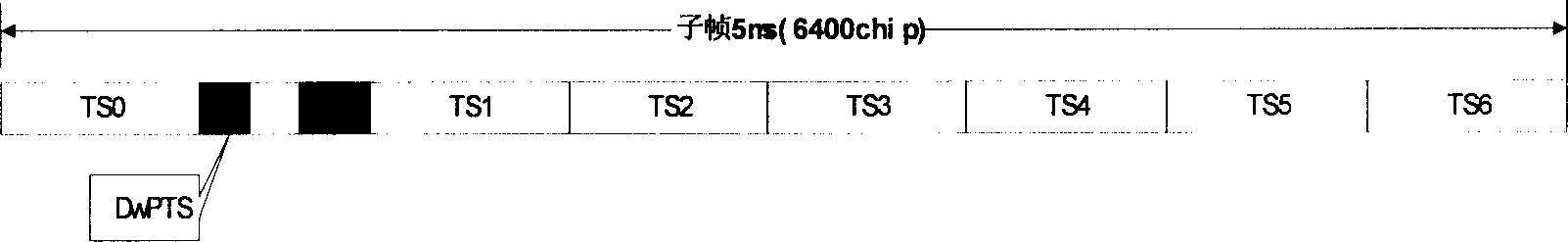
ActiveCN1553586AReduce the chance of getting out of syncImprove performanceCode division multiplexTransmissionTD-SCDMAChannel impulse response
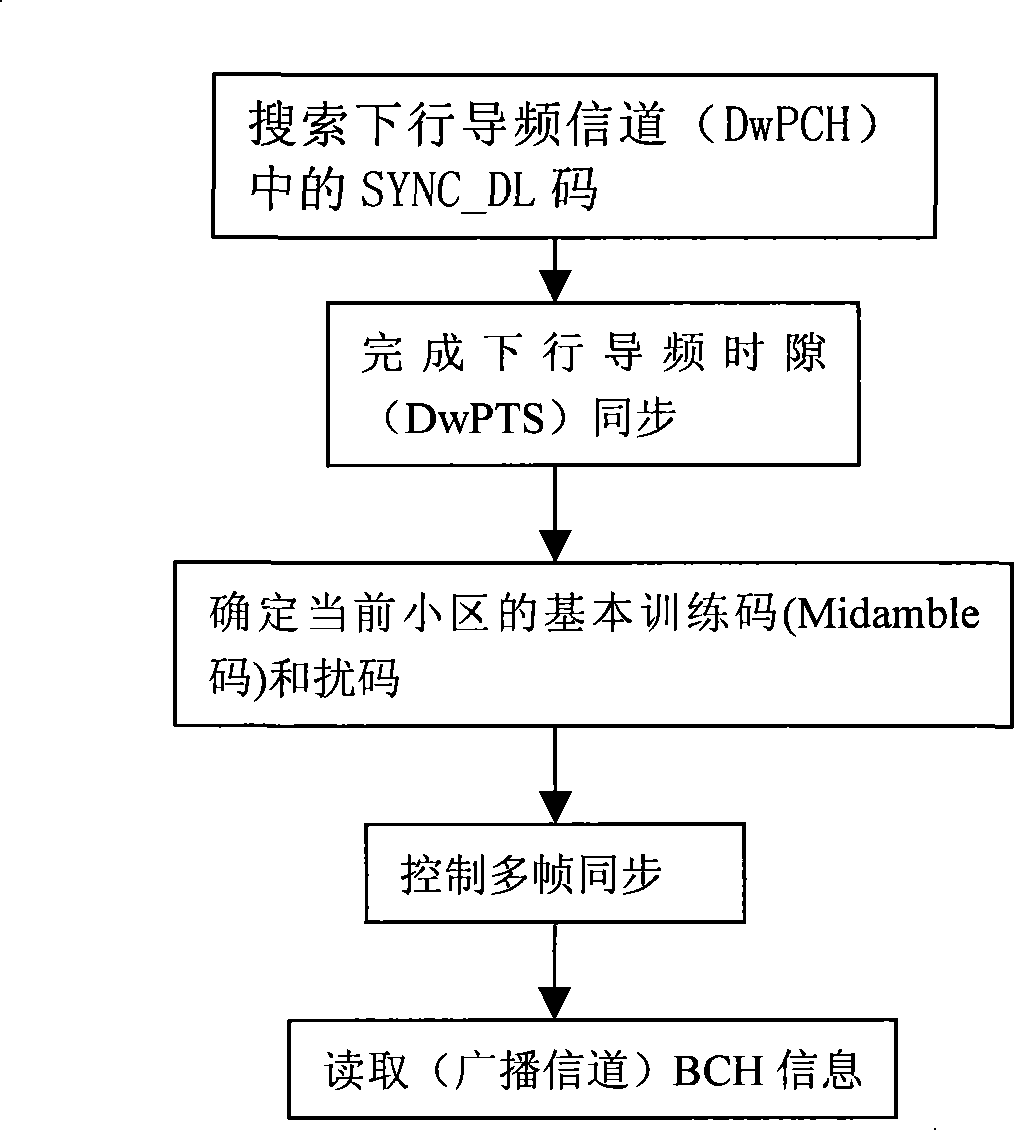
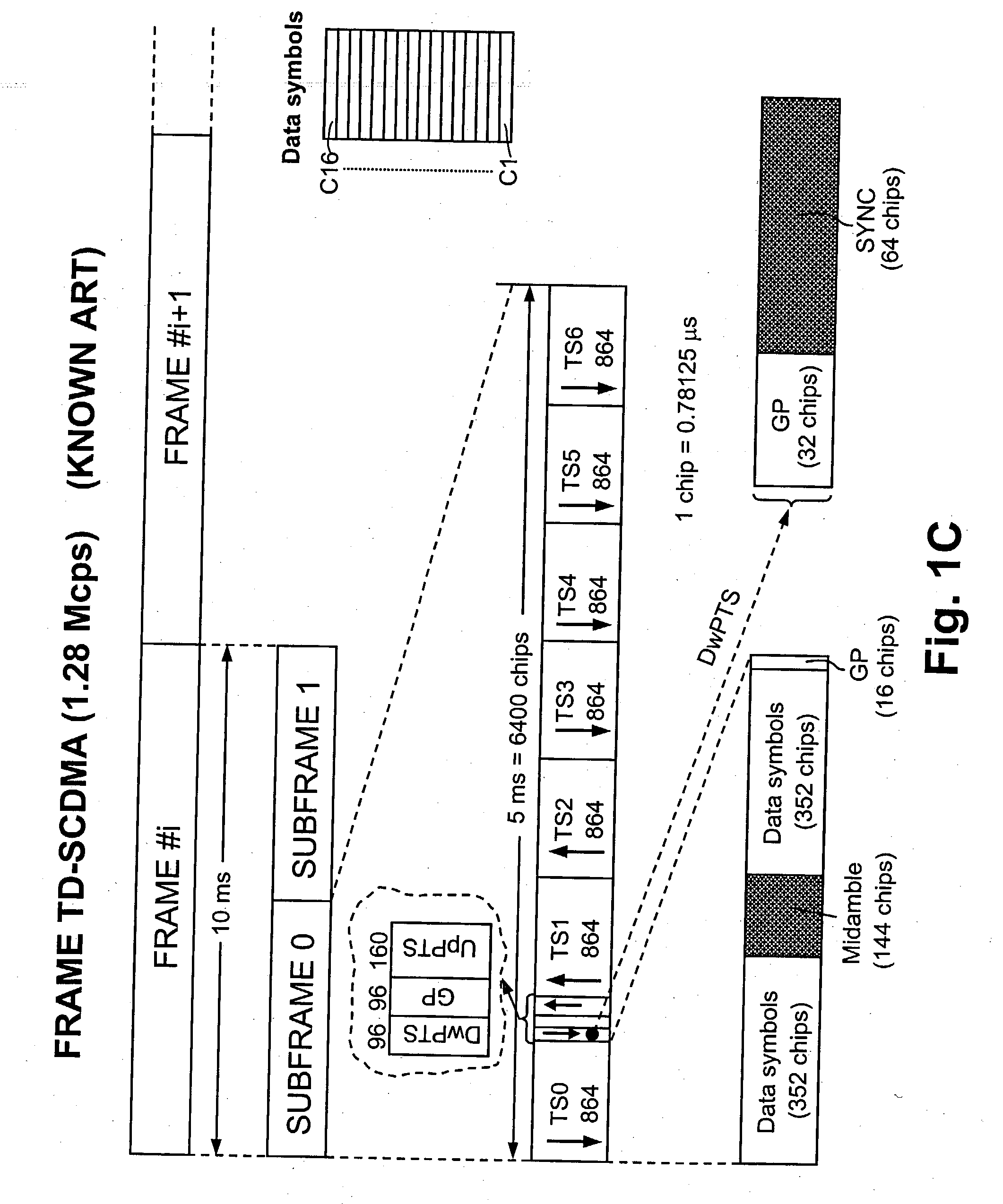
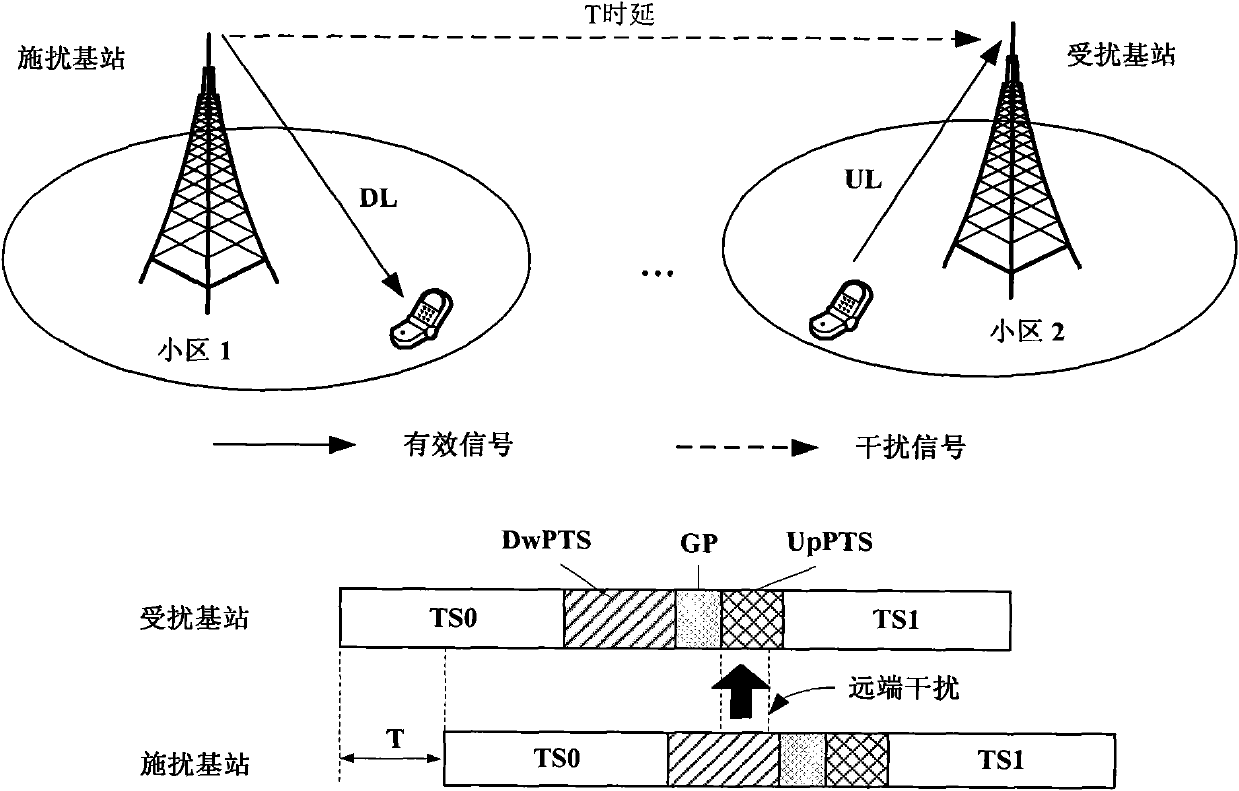
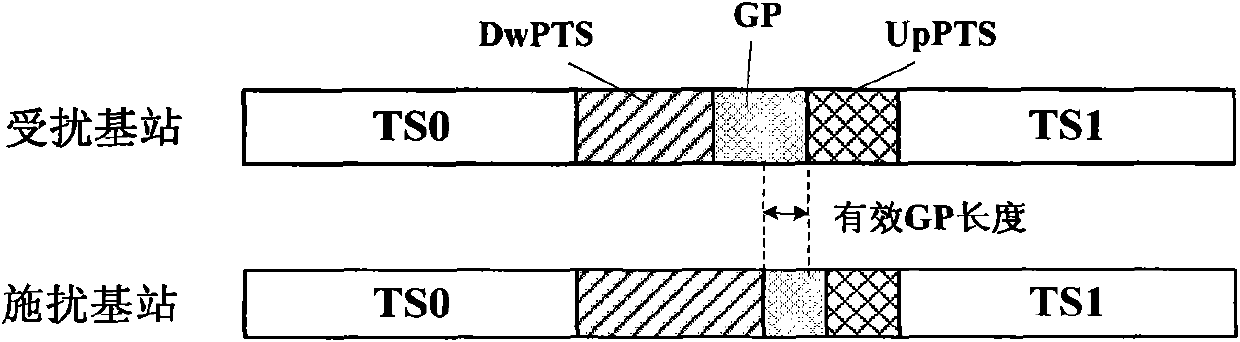
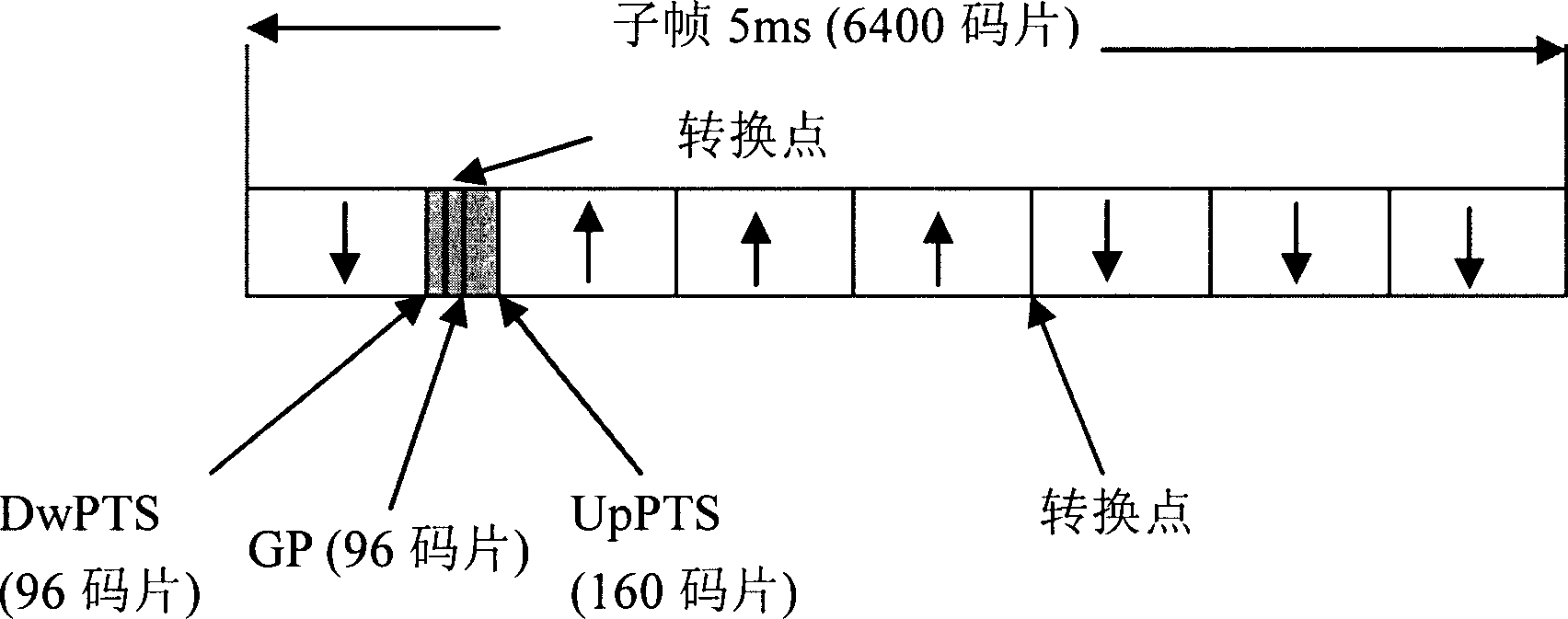
This invention provides a down stream synchronous calibration method in TD-SCDMA system and its device. It includes following steps: receiving down stream signal. Looking up the down stream SYNC_DL to control the synchronous timing; using the midamble code of the above received signal to calculate the channel impulse response to regulate the synchronous timing; getting the channel impulse response and multiple correlation corresponding to DwPTS channel; getting the left edge of the channel impulse response to get the amount for regulating the synchronous timing calibration; further regulating and calibrating the synchronous timing. The device comprises: receiving device ; looking up device; control and calculation device; regulating device.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Frequency quality criteria for inter-frequency handover in a TD-CDMA communication system
InactiveUS20060014538A1Code division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemTelecommunications network
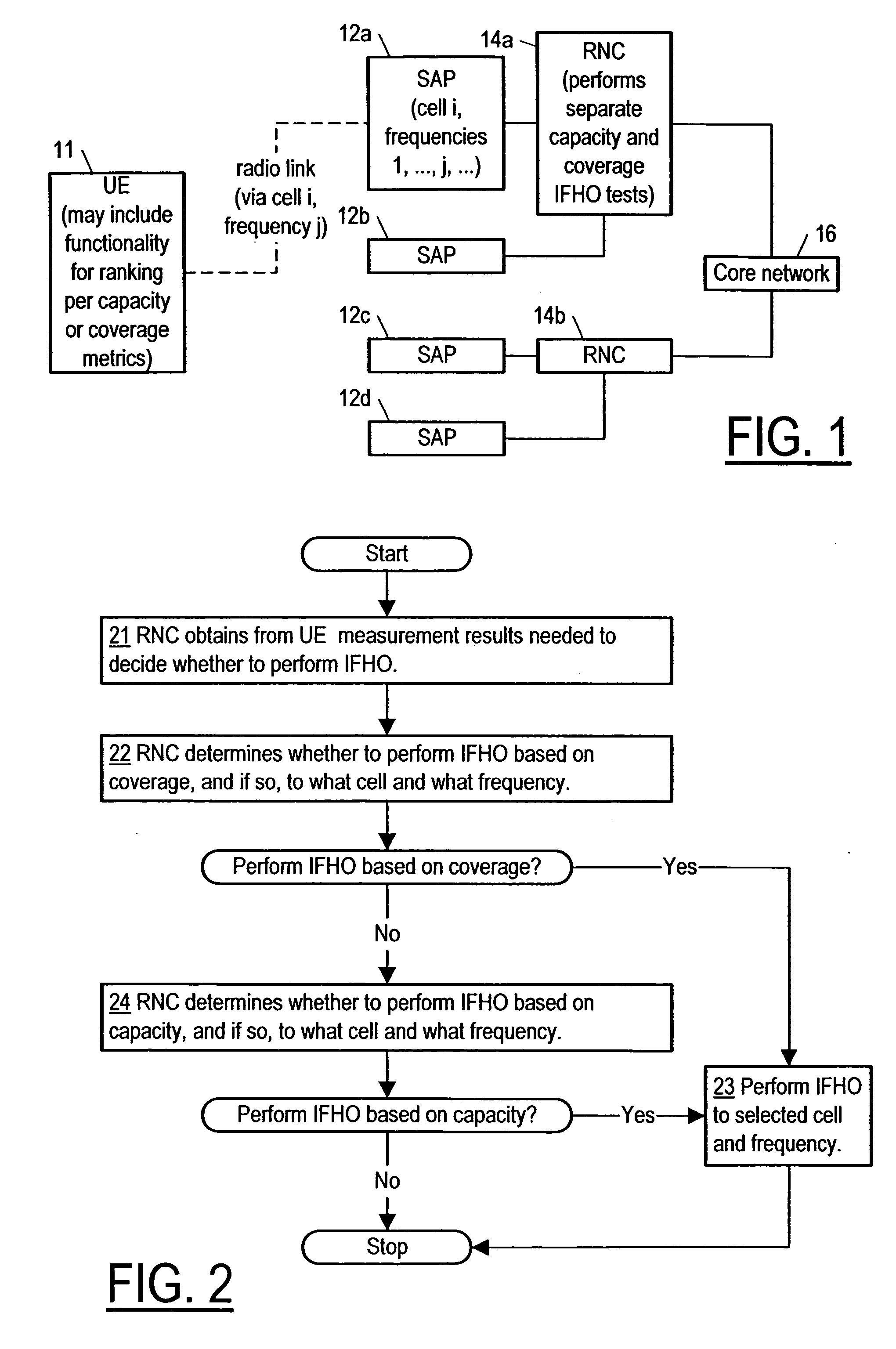
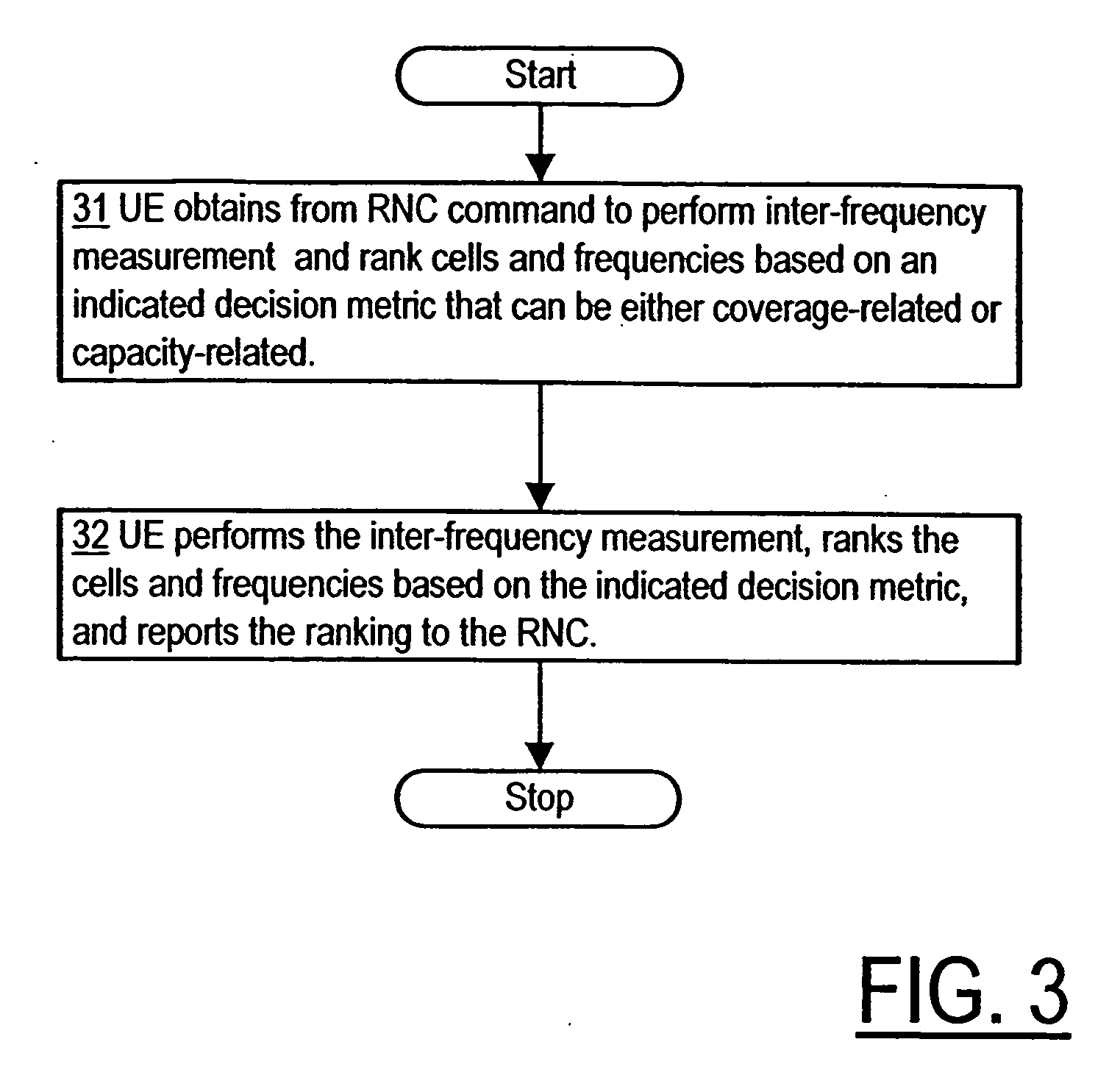
A method for determining whether to perform IFHO (inter-frequency handover) of a UF apparatus from one cell to another and from one carrier frequency to another in a TD-CDMA telecommunications network (including e.g. a TD-SCDMA network)—based separately on coverage and capacity, using one decision metric for coverage (e.g. based on received signal code power for each candidate cell and each candidate carrier frequency) and a different decision metric for capacity (e.g. based on a quantity proportional to the received signal code power and inversely proportional to the difference between a received signal strength indicator and the received signal code power). Corresponding equipment and a computer program product is also provided. In deciding whether IFHO is needed based on capacity, a threshold for received signal code power may be used in addition to the metric for capacity.
Owner:YUAN ZHU
Interference self-avoidance substation site selection method of TD-LTE (TD-SCDMA Long Term Evolution) system
ActiveCN101998415ASuppress interferenceImprove performanceNetwork planningQuality of serviceTD-SCDMA
The invention provides an interference self-avoidance substation site selection method of a TD-LTE (TD-SCDMA Long Term Evolution) system, which is used for optimizing the site of a new substation so as to avoid same frequency interference between the new substation and a potential interfered substation. The method comprises: when a new substation is required to build and configure, obtaining the system information and configuration situation of each deployed substation; according to a preset screening criteria, determining the potential interfered substation from the deployed substations; according to potential interfered substation information (such as coverage area, service user number, user QoS (quality of service) requirements and the like), determining the priority level of each potential interfered substation; according to the priority level of each potential interfered substation, generating a list of the priority levels of the potential interfered substations; according to the near-end interference and far-end interference to the potential interfered substation by the new substation, determining the low-interference space between the new substation and each potential interfered substation; according to the list of the priority levels of the potential interfered substations and the low-interference space between the new substation and each potential interfered substation, determining the site selection area of the new substation.
Owner:COMBA TELECOM TECH (GUANGZHOU) CO LTD +1
Smart antenna performance test method, apparatus and system
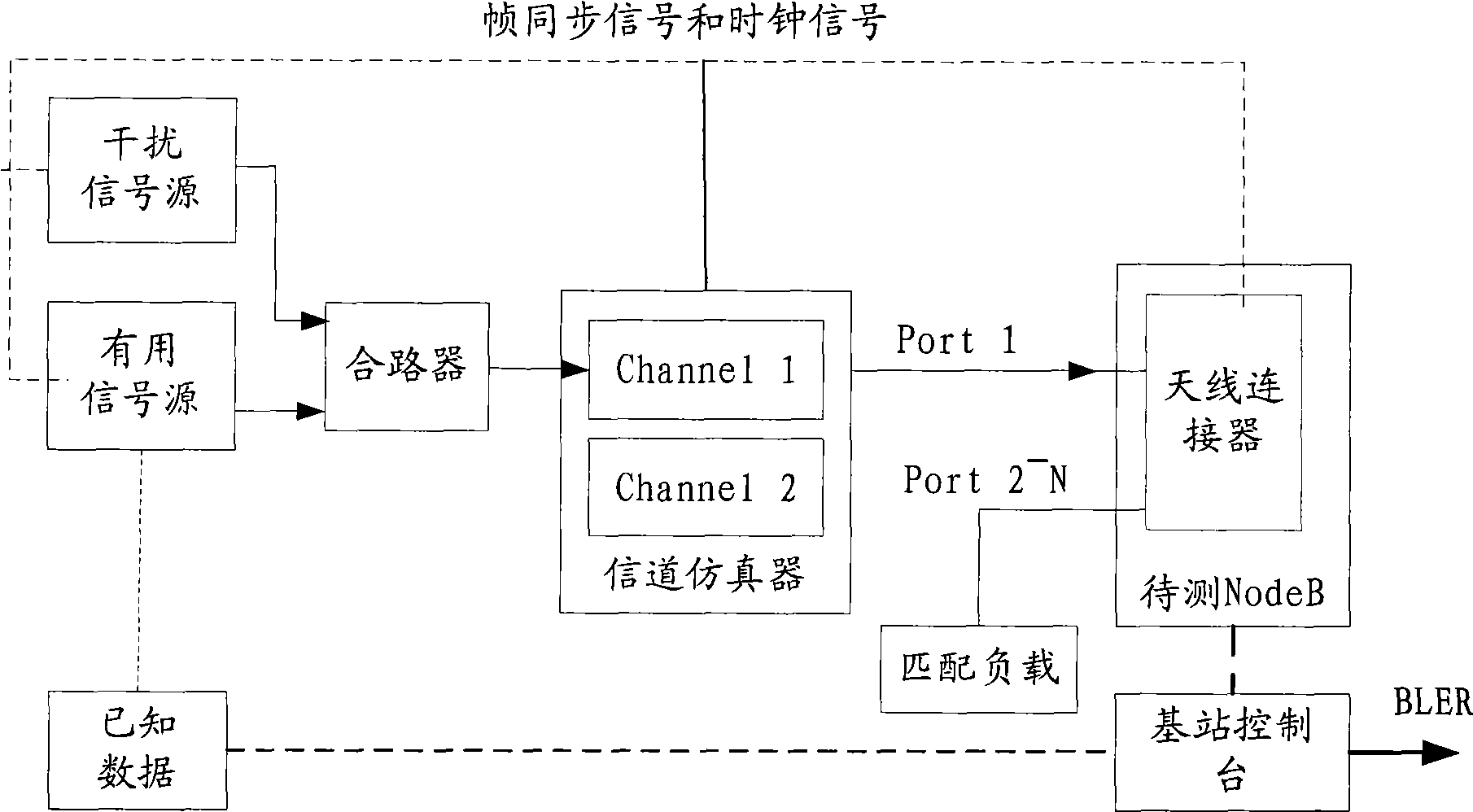
InactiveCN101500254AImplement joint testingRealize evaluationTransmission monitoringWireless communicationTD-SCDMASmart antenna
The invention discloses a test method for performances of an intelligent antenna, and a device and a system thereof, which are applied to a TD-SCDMA (time division synchronous code division multiple access) system. The method comprises the steps as follows: an up useful signal and an up interfering signal are generated according to preset data and the generated signals are merged and then input to a channel simulation device; the channel simulation device configures channel simulation parameters for a plurality of channels, generates simulation signals of the plurality of channels and inputs the generated simulation signals to all receive ports corresponding to array elements of the intelligent antenna; the intelligent antenna analyzes the simulation signals and obtains a data bit stream of the simulation signals; and an RNC simulator compares the data bit stream of the simulation signals with the corresponding bit stream of the preset data and then obtains a BLER (block error rate) or a BER (bit error rate). The method for carrying out united test to a plurality of array elements of the intelligent antenna can simulate complicated network situations sufficiently so as to lead the test to receiving and demodulating performances of the antenna to be more objective and accurate.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
A multi-carrier based public physical channel assignment method
InactiveCN1722640AImprove search speedImprove reliabilityRadio transmission for post communicationMulti-frequency code systemsCommunications systemTD-SCDMA
This invention relates to a common physics signal channel distributing method based on multicarrier, which comprises the following steps: a) for every small area or sector, making sure one carrier wave as the first main carrier wave from the distributed N carrier waves, making sure another carrier wave as the second main carrier wave, the rest are assistant carrier waves, wherein one can be the alternate assistant carrier wave of the first or second main carrier wave; b) in the same small area or sector, the first and second main carrier wave, combined with the assistant carrier wave use the same interference code and the base train sequence; c) allocating the common physics signal channel in the first or second main carrier wave. Said method can overcome the disadvantages of TD-SCDMA communication system.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method and apparatus for implementing TD-SCDMA base station synchronization
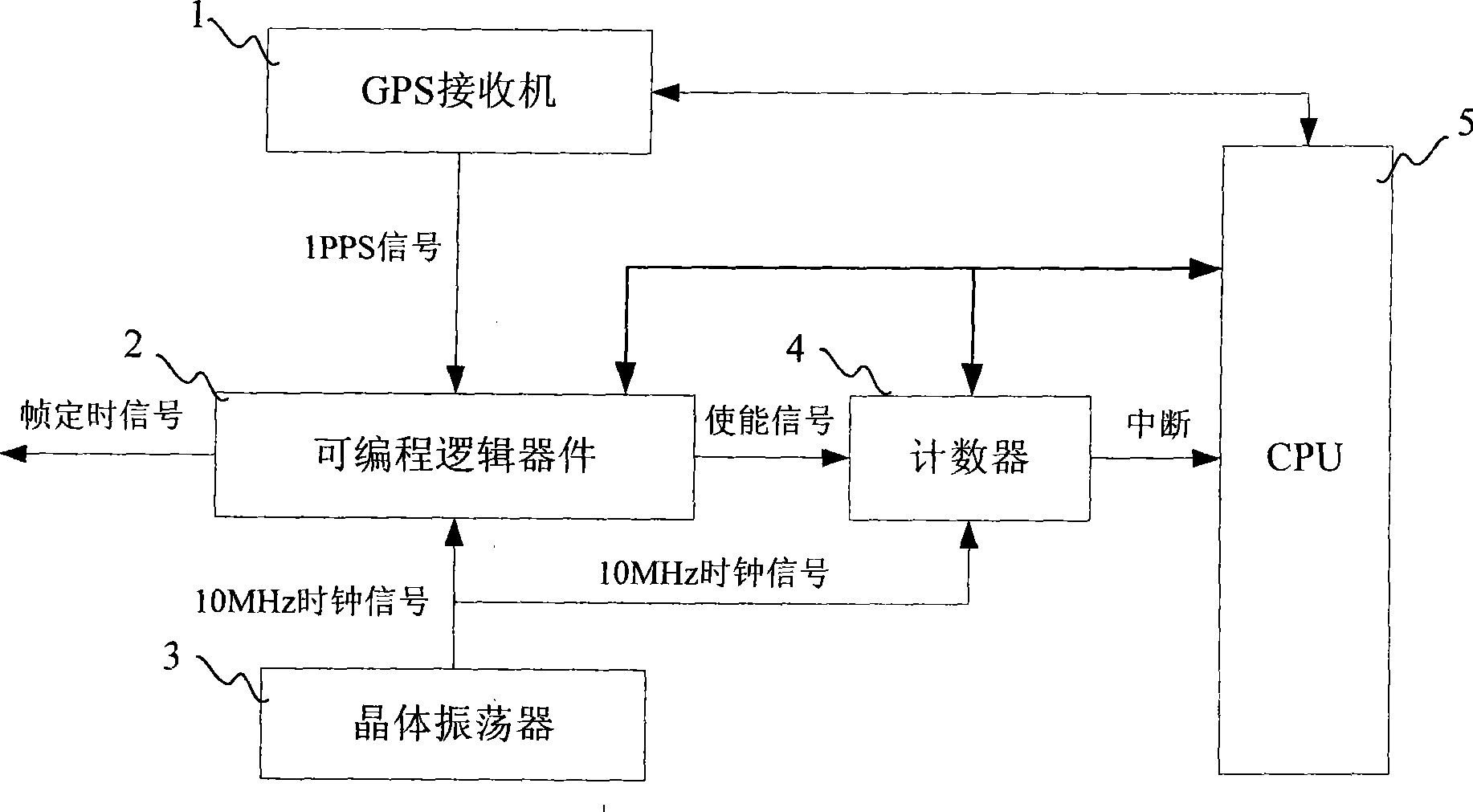
InactiveCN101465686AImprove sync reliabilityEliminate phase deviationRadio transmission for post communicationCrystal oscillator frequenciesPulse-per-second signal
The invention discloses a method for realizing TD-SCDMA base station synchronization, which is used for synchronizing a base station in the absence of GPS signal and includes that: step1, a GPS receiver receives a GPS satellite signal and transmits pulse per second signal to a synchronization module; the synchronization module adopts the pulse per second signal to measure the deviation value of work frequency and standard frequency of a crystal oscillator, and compute the frequency deviation compensation of the crystal oscillator; step 2, when the GPS receiver receives no GPS satellite signal, the GPS receiver informs the synchronization module; when the synchronization module is informed that the GPS receiver receives no GPS satellite signal, the synchronization module adopts frequency deviation compensation to compensate a frame timing signal generated by a clock signal of the crystal oscillator, and the frame timing signal is used for synchronizing the base station. The invention can eliminate phase deviation caused by the frequency deviation of the crystal oscillator and continuously accumulated with time, and enable the frame timing signal of the base station to be synchronous with frame timing signals of other base stations in longer time.
Owner:JIANGSU HUACAN TELECOMM
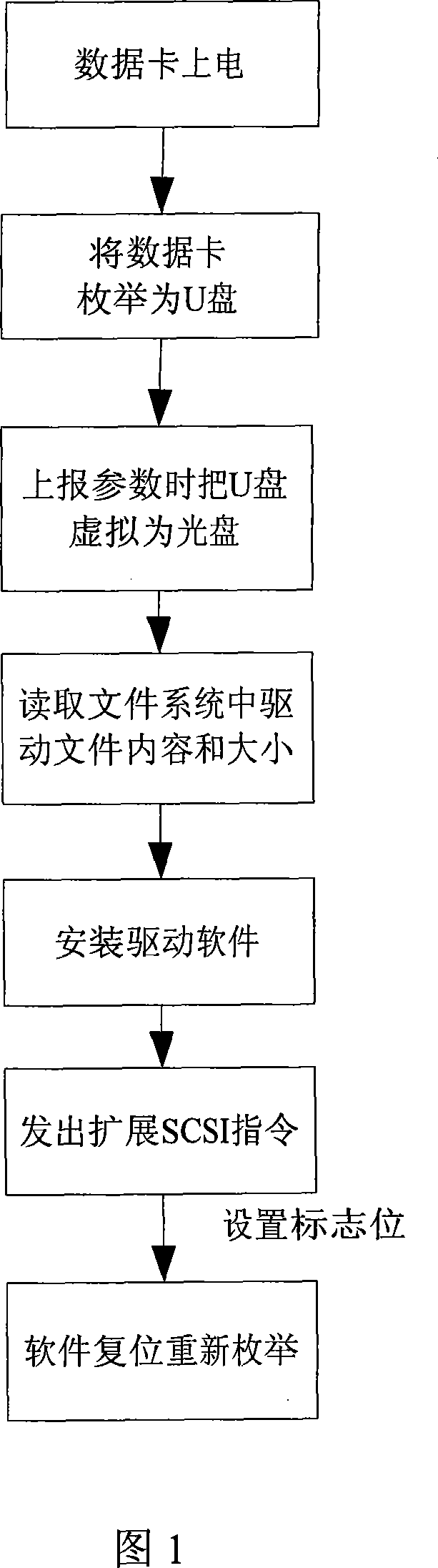
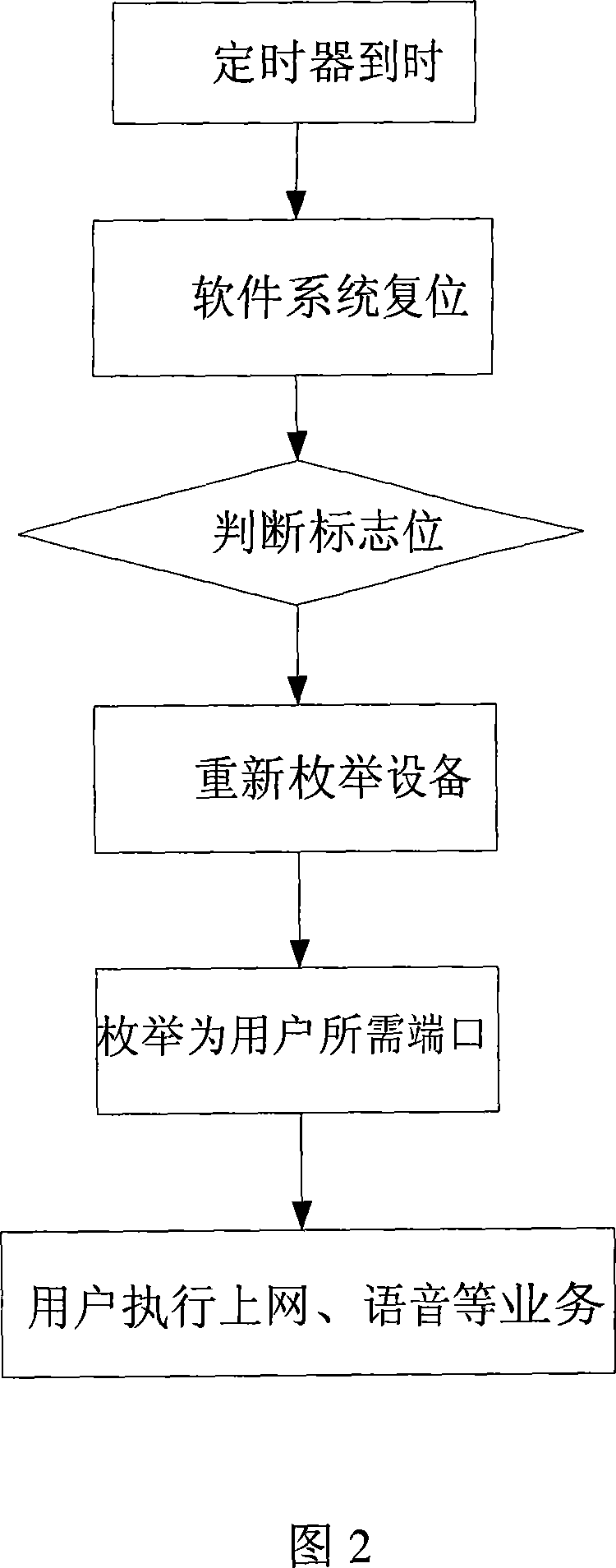
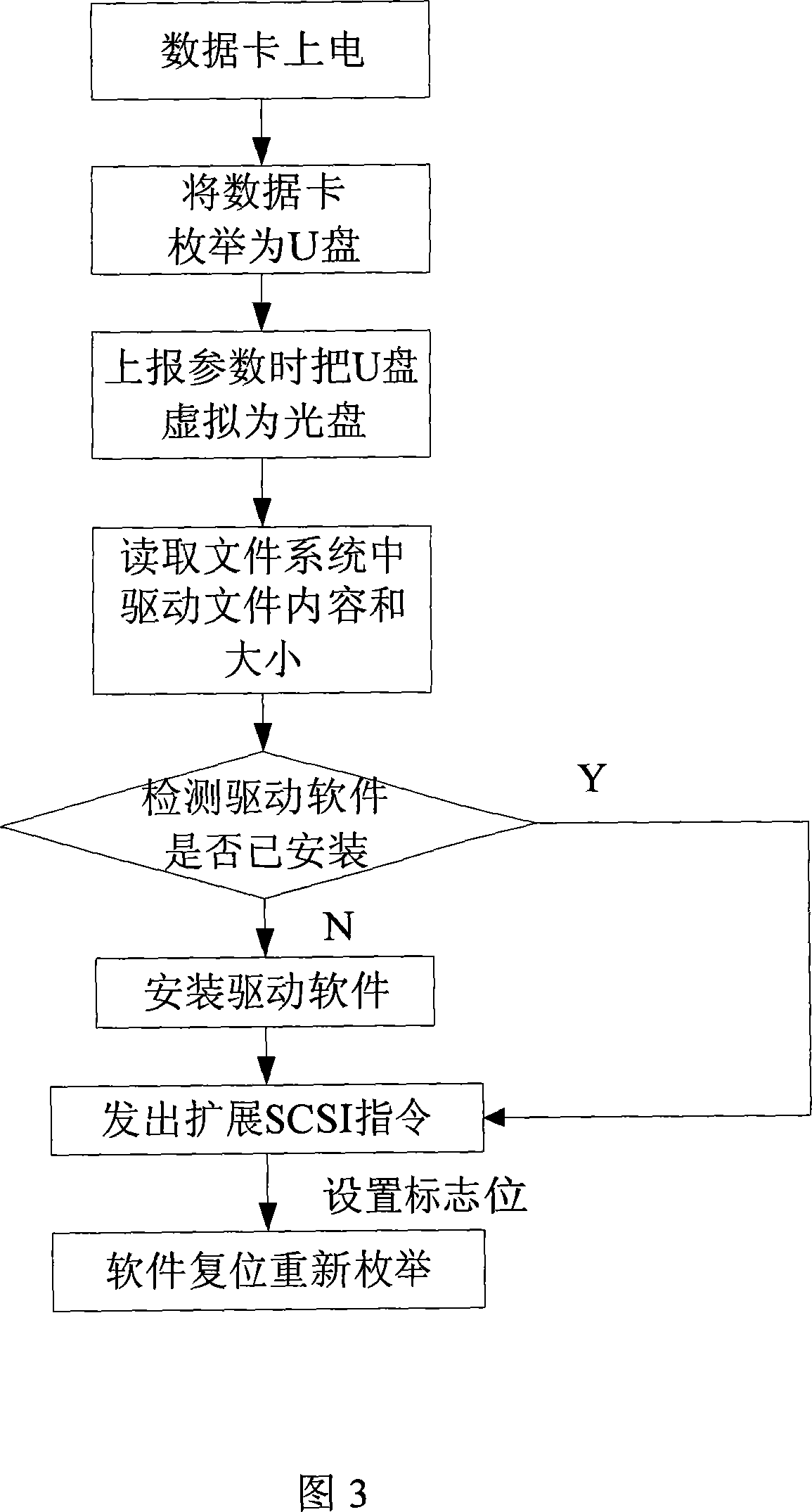
Method for automatically starting TD-SCDMA wireless data card
ActiveCN101075178AEasy to useAvoid the hassle of manually installing drivers and resettingInput/output to record carriersTD-SCDMASCSI
A method for starting up TD-SCDMA radio data card on PC terminal includes reporting U disc to be optical disc based on successful enumeration of U disc, realizing automatic erection by fetching driving program file in U disc then fetching optical disc based on standard SCSI command set. The method for automatic-resetting TD-SCDMA radio data card is also disclosed.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com