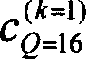A multi-carrier based public physical channel assignment method
A technology of physical channels and allocation methods, applied in the field of multi-carrier-based public physical channel allocation, can solve problems such as difficult access, complicated UE measurement, and access conflicts in dense user areas.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0089] Embodiment 1, for the case where Node B / UE only has the ability to process one carrier:
[0090] Since the Node B / UE can only process one carrier at the same time, the common physical channels are configured on the first primary carrier.
[0091] For P-CCPCH, its configuration method is as follows:
[0092] 1) P-CCPCH is configured on the first two code channels of TS0 of the first main carrier;
[0093] 2) The channelization codes of P-CCPCH1 and P-CCPCH2 are c Q=16 (k=1) and c Q=16 (k=2) ;
[0094] 3) Training sequence m in TS0 (1) and m (2) Allocated to P-CCPCH to support transmit diversity and beacon functions;
[0095] 4) adopt the fixed spread spectrum method of spreading factor SF=16;
[0096] 5) Full cell coverage mode, without beamforming.
[0097] For S-CCPCH, its configuration method is as follows:
[0098] 1) S-CCPCH is configured on TS0 of the first primary carrier;
[0099] 2) Adopting a fixed spread spectrum method with a spreading factor SF=1...
Embodiment 2
[0130] Embodiment 2, for the situation that Node B / UE has the ability to process two carriers simultaneously:
[0131] Because the Node B / UE can handle two carriers at the same time, there is a certain flexibility in the configuration of the common physical channel.
[0132] For P-CCPCH, its configuration method is as follows:
[0133] 1) P-CCPCH is configured on the first two code channels of TS0 of the first main carrier;
[0134] 2) The channelization codes of P-CCPCH1 and P-CCPCH2 are c Q=16 (k=1) and c Q=16 (k=2) ;
[0135] 3) Training sequence m in TS0 (1) and m (2) Allocated to P-CCPCH to support transmit diversity and beacon functions;
[0136] 4) adopt the fixed spread spectrum method of spreading factor SF=16;
[0137] 5) Full cell coverage mode, without beamforming.
[0138] For S-CCPCH, its configuration method is as follows:
[0139] 1) The S-CCPCH is configured on the TS0 of the first main carrier or the second main carrier;
[0140] 2) Adopting a fix...
Embodiment 3
[0176] Embodiment 3, for the situation that the Node B / UE has the ability to simultaneously process multiple (three or more) carriers:
[0177] Although the Node B / UE can process three or more carriers at the same time, the common physical channel configuration is still the same as that of the Node B / UE having the ability to process two carriers at the same time.
[0178] For P-CCPCH, its configuration method is as follows:
[0179] 1) P-CCPCH is configured on the first two code channels of TS0 of the first main carrier;
[0180] 2) The channelization codes of P-CCPCH1 and P-CCPCH2 are c Q=16 (k=1) and c Q=16 (k=2) ;
[0181] 3) Training sequence m in TS0 (1) and m (2) Allocated to P-CCPCH to support transmit diversity and beacon functions;
[0182] 4) adopt the fixed spread spectrum method of spreading factor SF=16;
[0183] 5) Full cell coverage mode, without beamforming.
[0184] For S-CCPCH, its configuration method is as follows:
[0185] 1) The S-CCPCH is config...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com