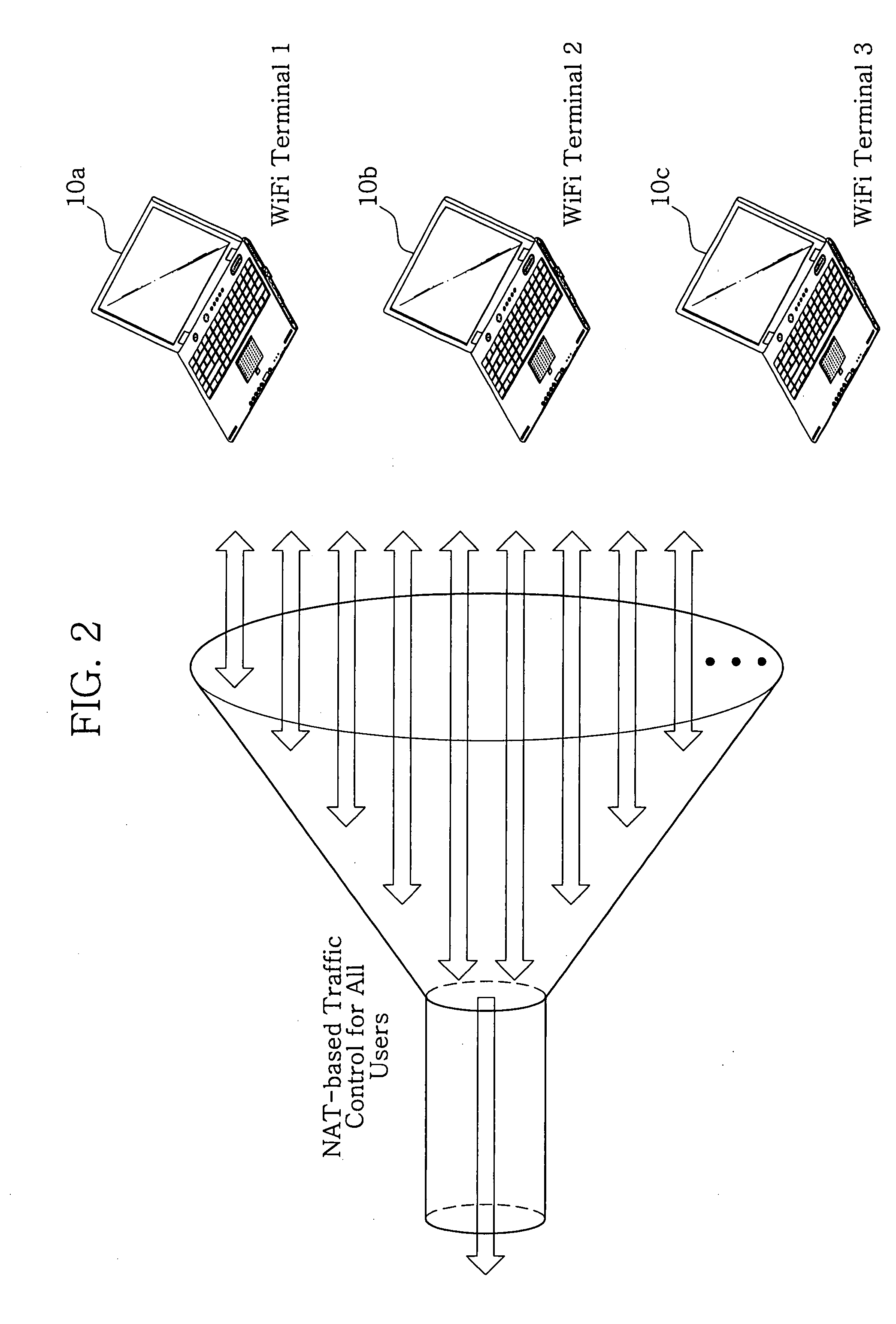
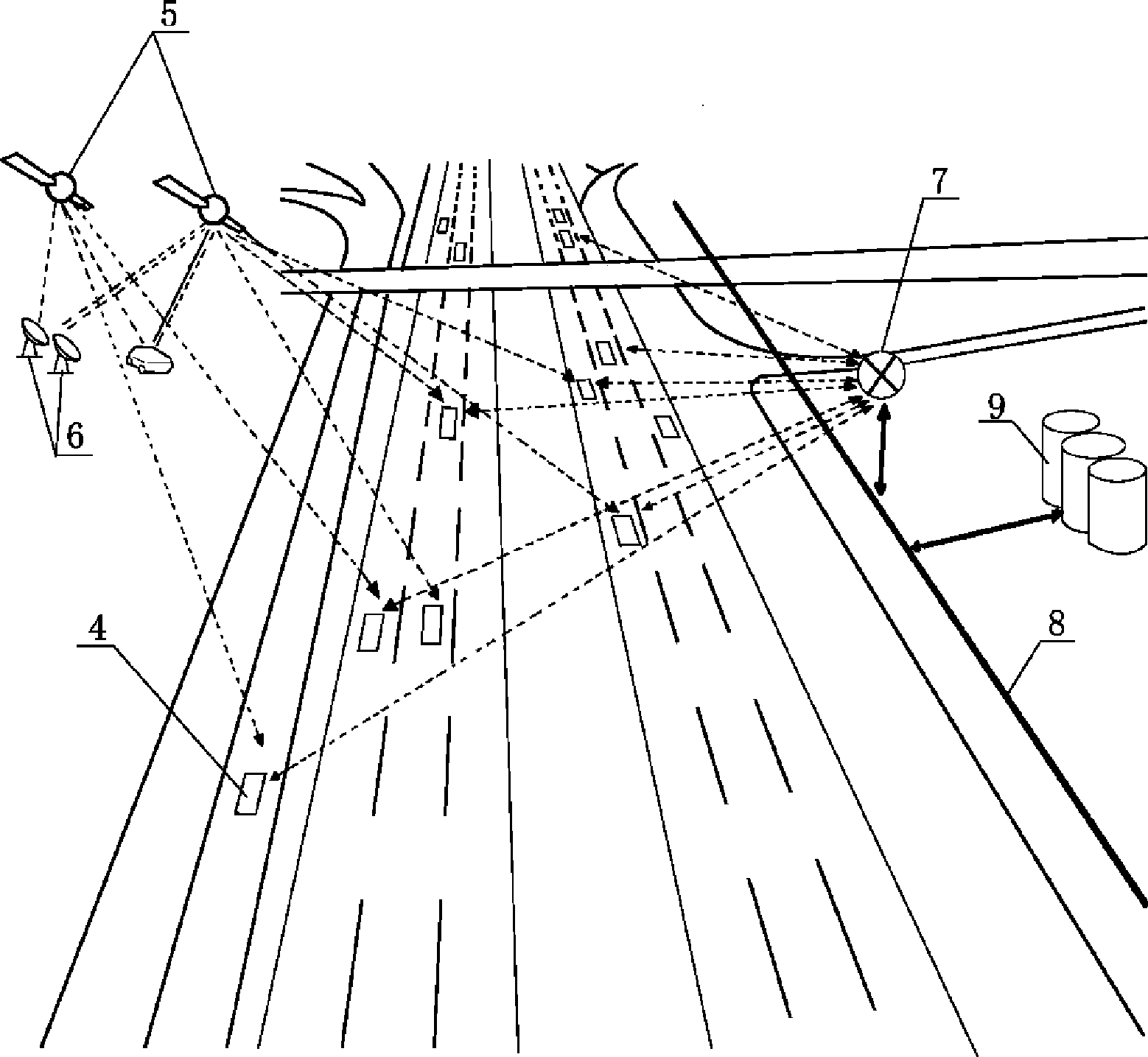
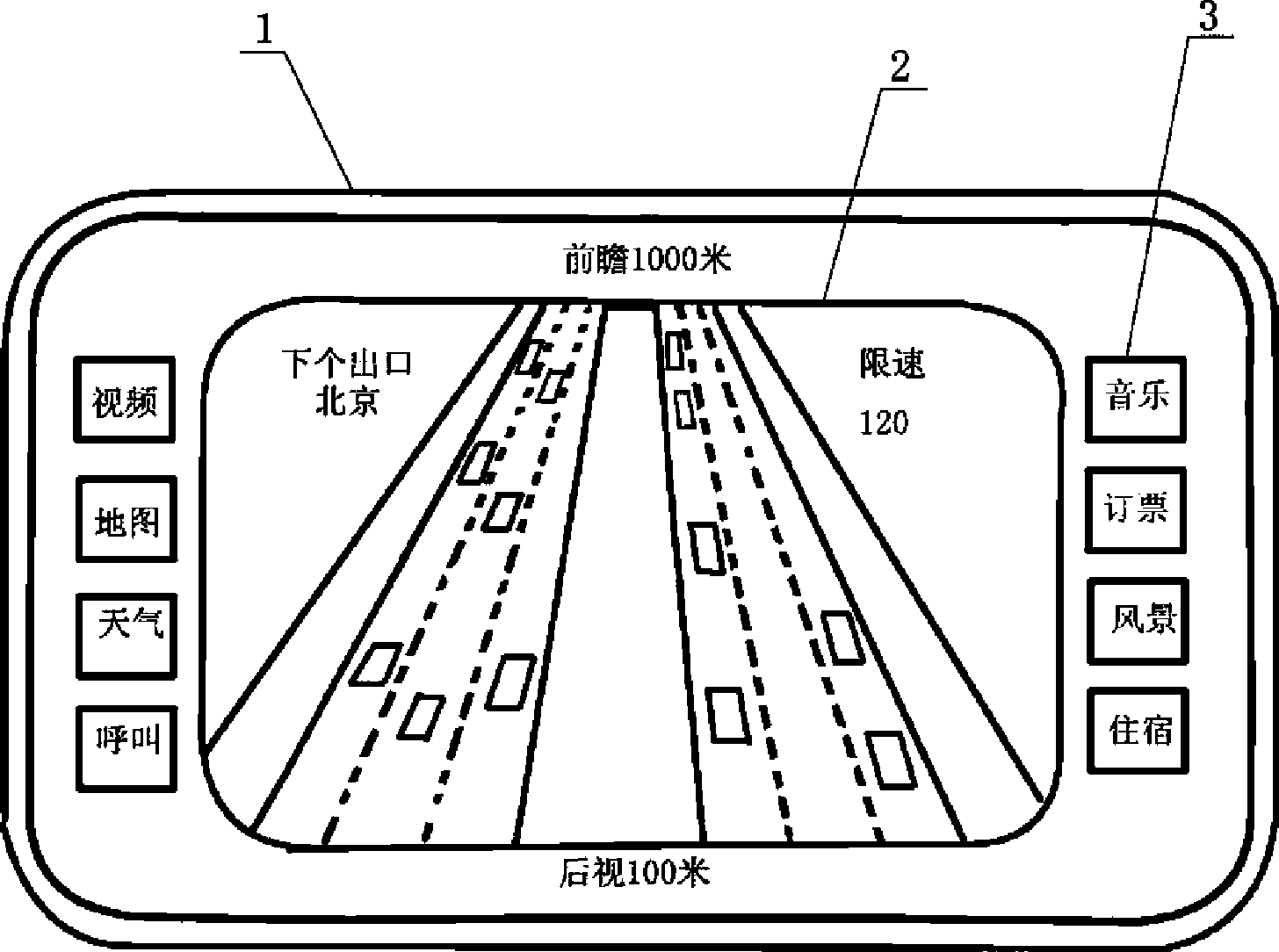
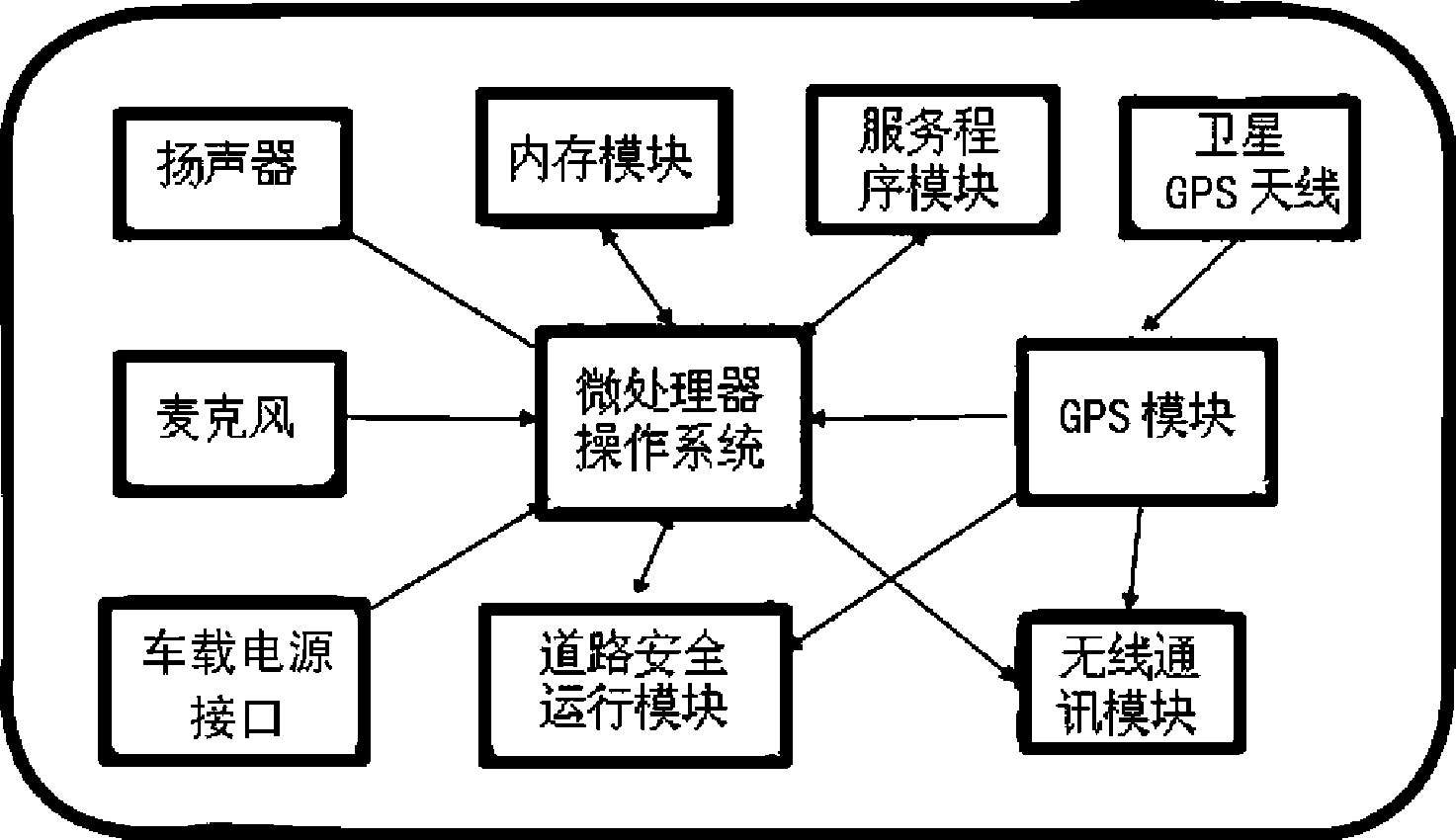
Patents
Literature
199 results about "WiBro" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
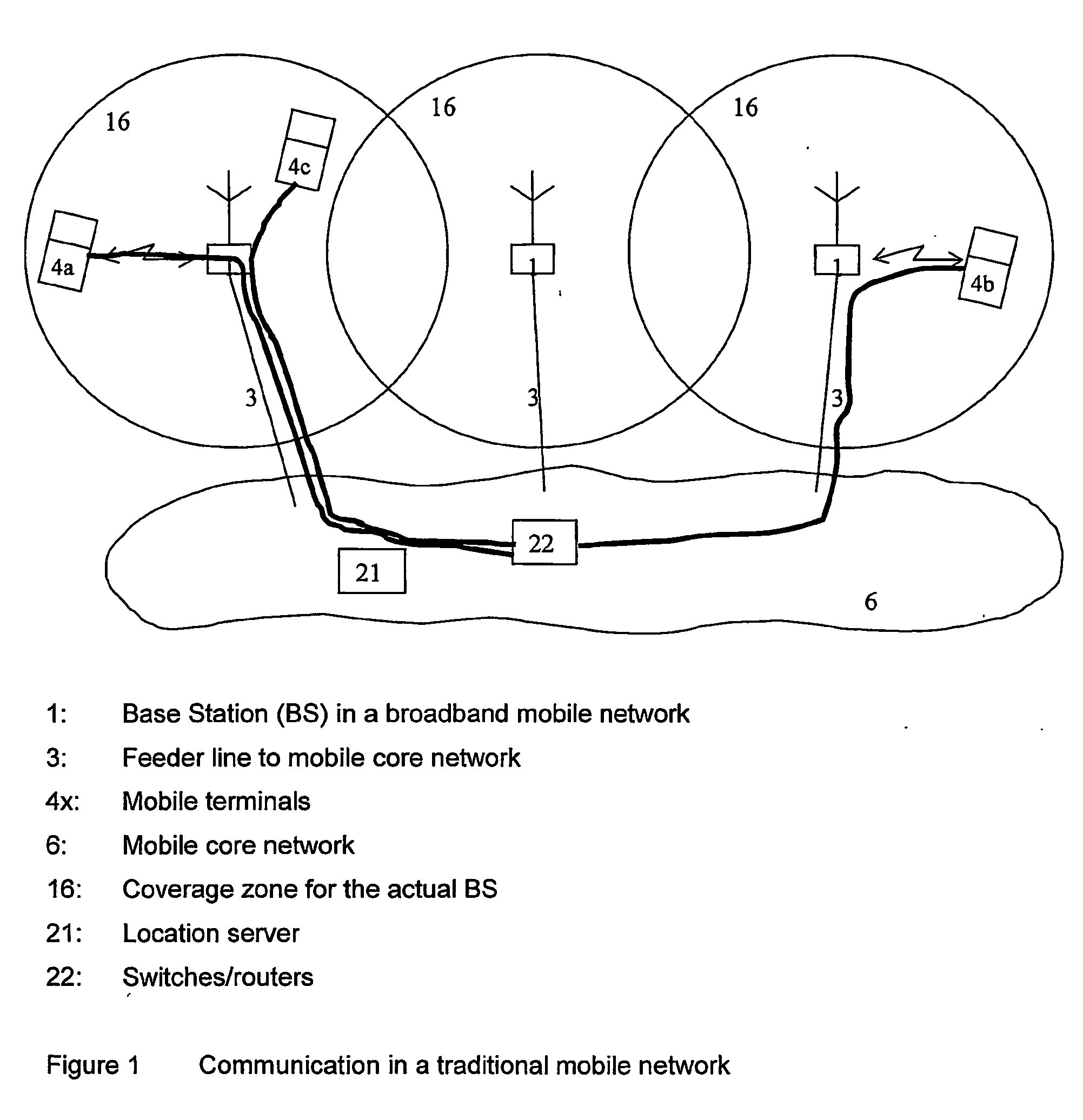
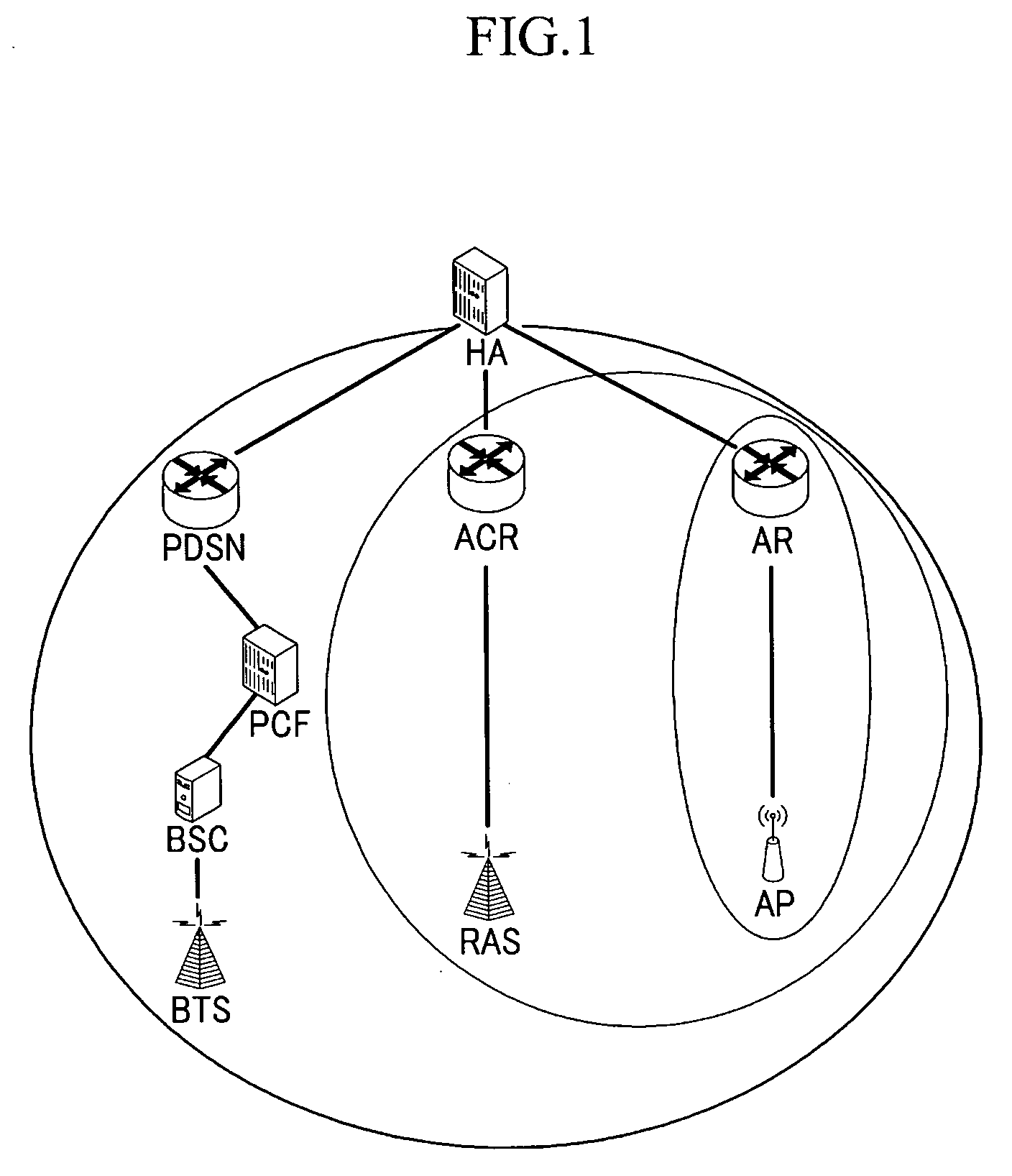
WiBro (wireless broadband) is a wireless broadband Internet technology developed by the South Korean telecoms industry. WiBro is the South Korean service name for IEEE 802.16e (mobile WiMAX) international standard. By the end of 2012, the Korean Communications Commission intends to increase WiBro broadband connection speeds to 10Mbit/s, around ten times the 2009 speed, which will complement their 1Gbit/sec fibre-optic network. The WiBro networks were shut down at the end of 2018.
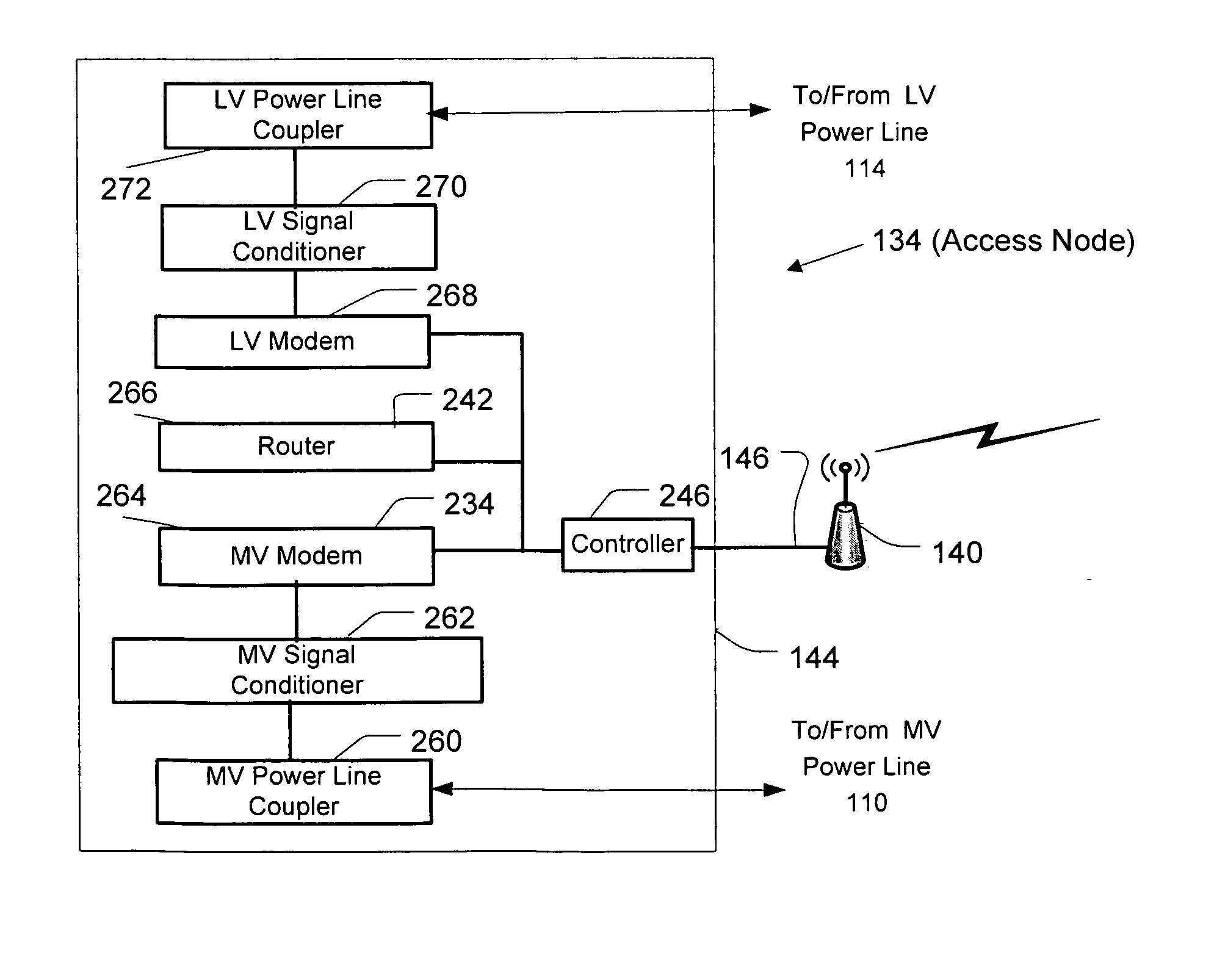
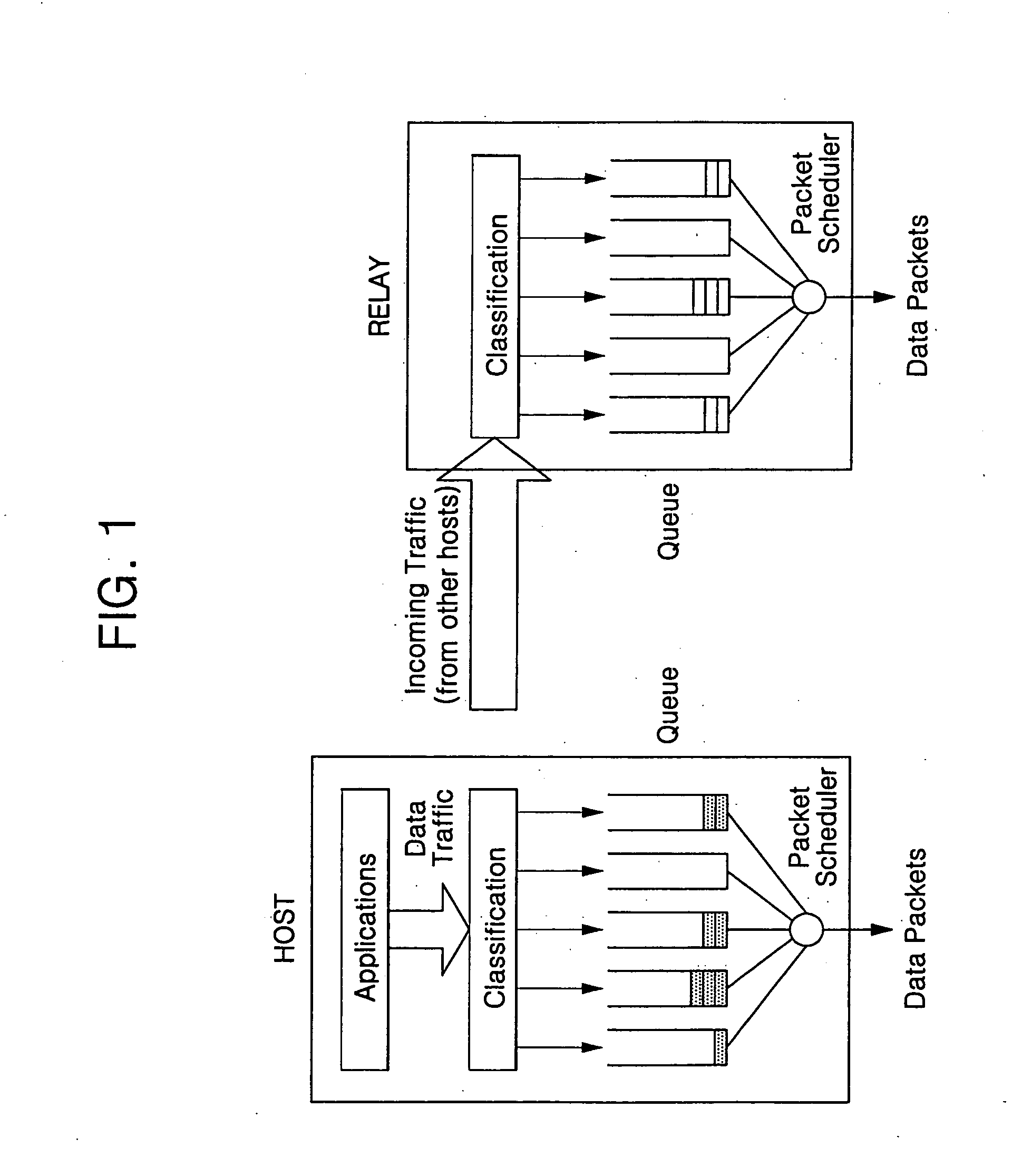
Hybrid power line wireless communication network
InactiveUS20070201540A1Wireless systems/telephoneLock network applicationsCommunications systemLow voltage
A hybrid power line wireless communication system may include an access controller and plurality of communication nodes that each may include a wireless access point coupled to a power line communication device. The wireless access points may provide wireless broadband communications to one or more user devices while the power line communication devices may provide low voltage power line broadband communications. The access controller remotely manages the wireless access points by sending control messages to the communication nodes. Control messages may traverse a power line, a non-power line medium, and / or a wireless medium. Control messages may include information relating to encryption parameters, transmission power levels, communication channels, access control, and other such parameters.
Owner:CURRENT TECH
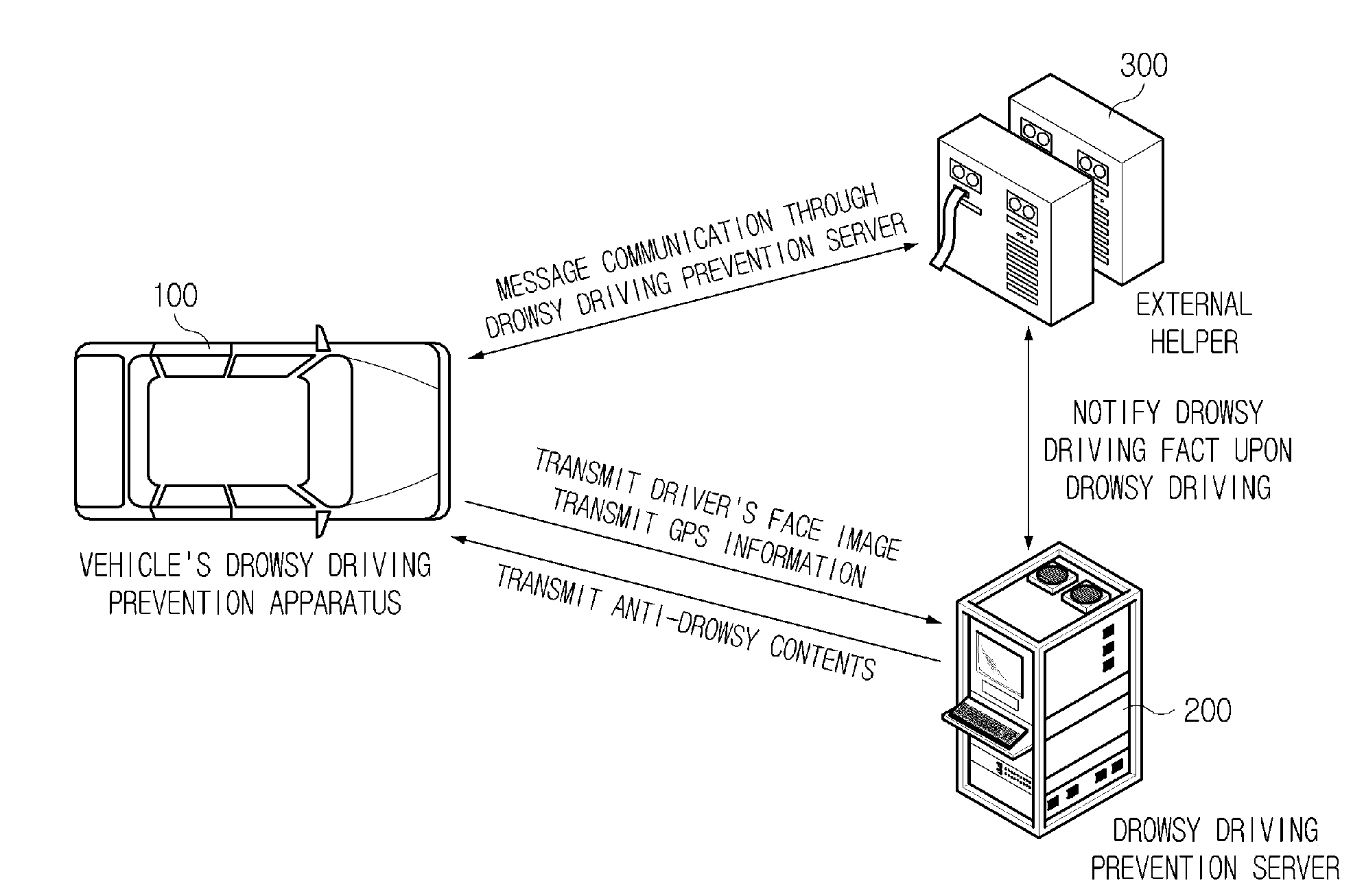
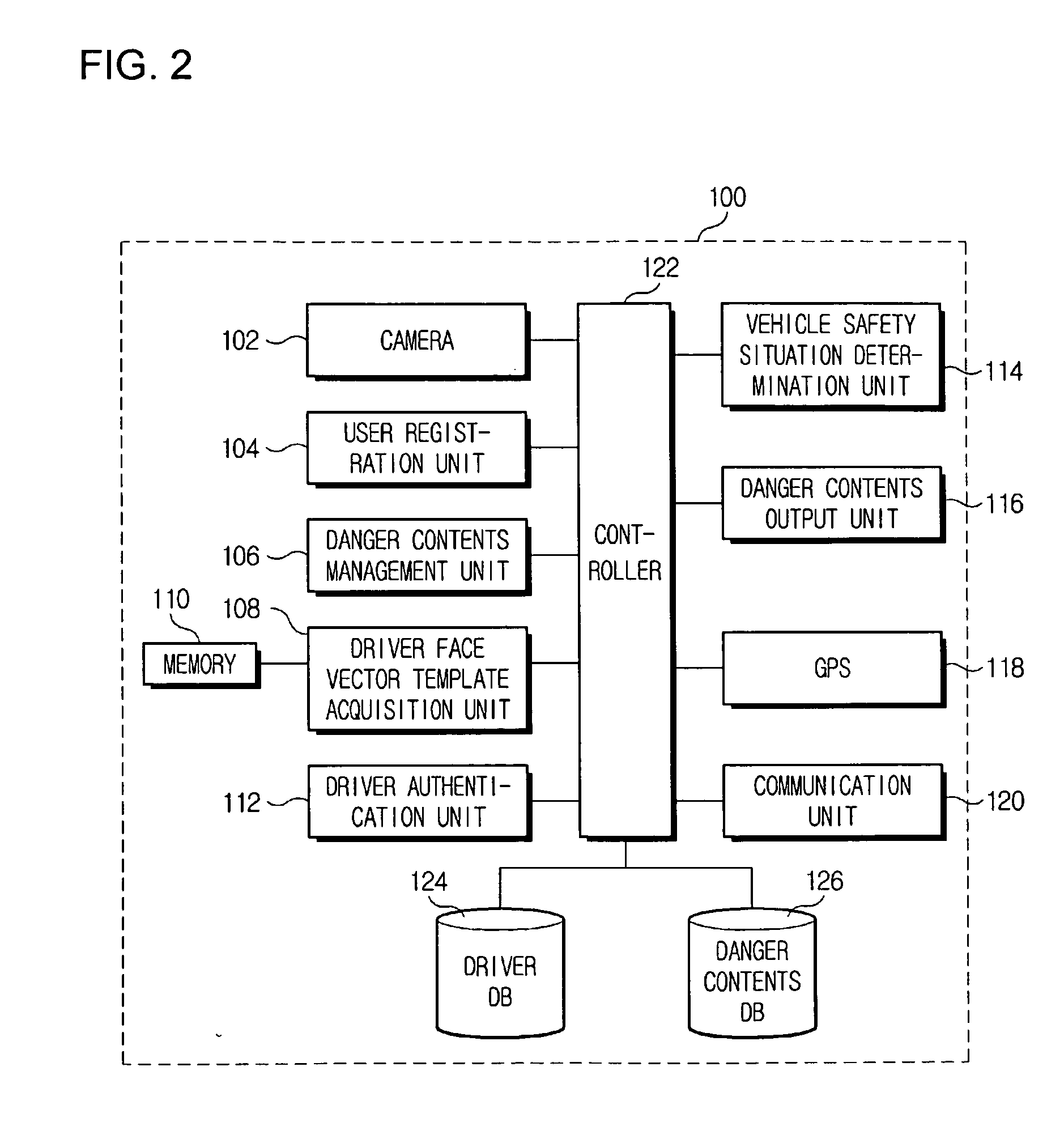
Preventive terminal device and internet system from drowsy and distracted driving on motorways using facial recognition technology
InactiveUS20080291008A1Avoid driving fatigueCharacter and pattern recognitionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsDriver/operatorTerminal equipment
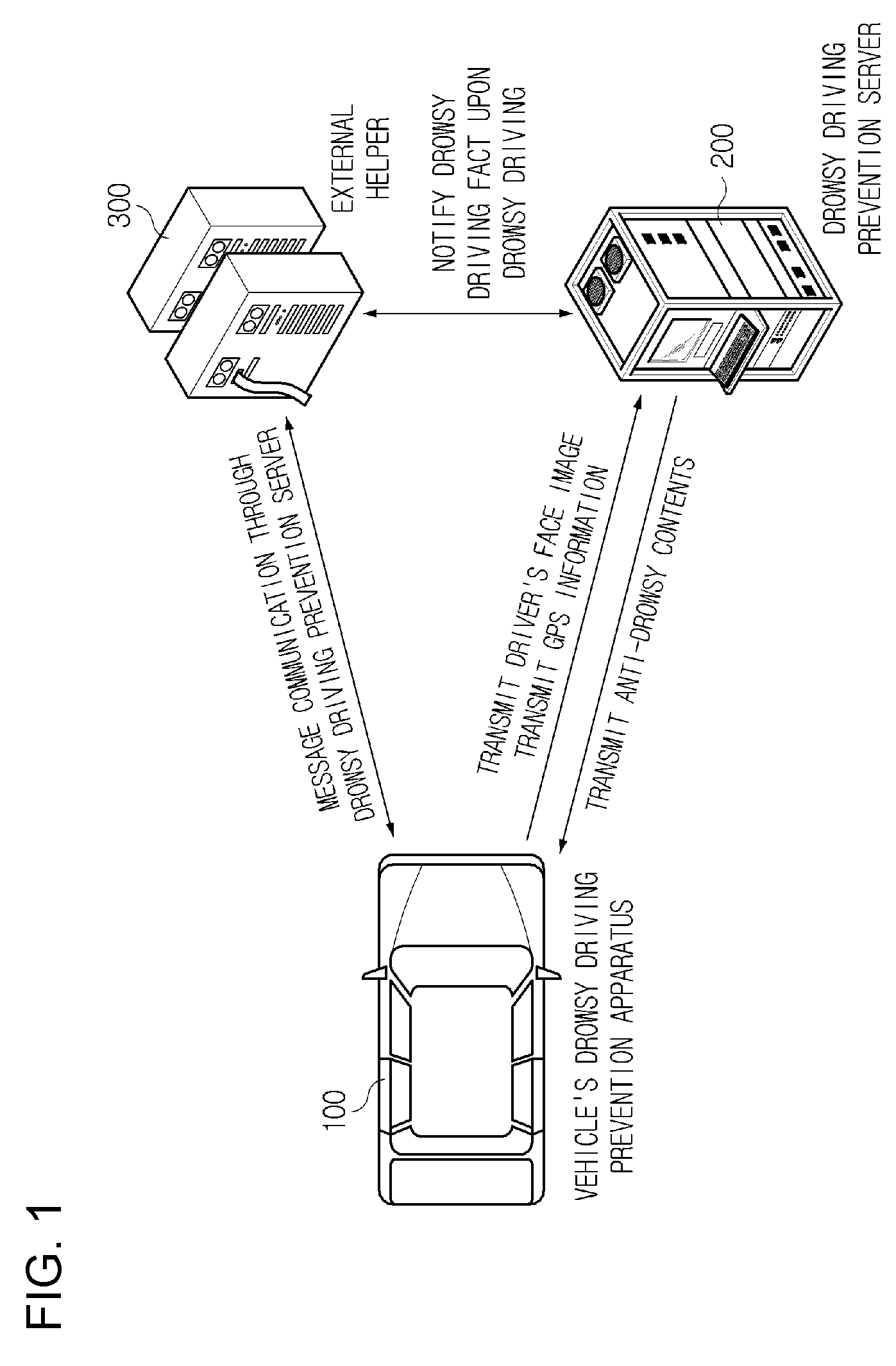
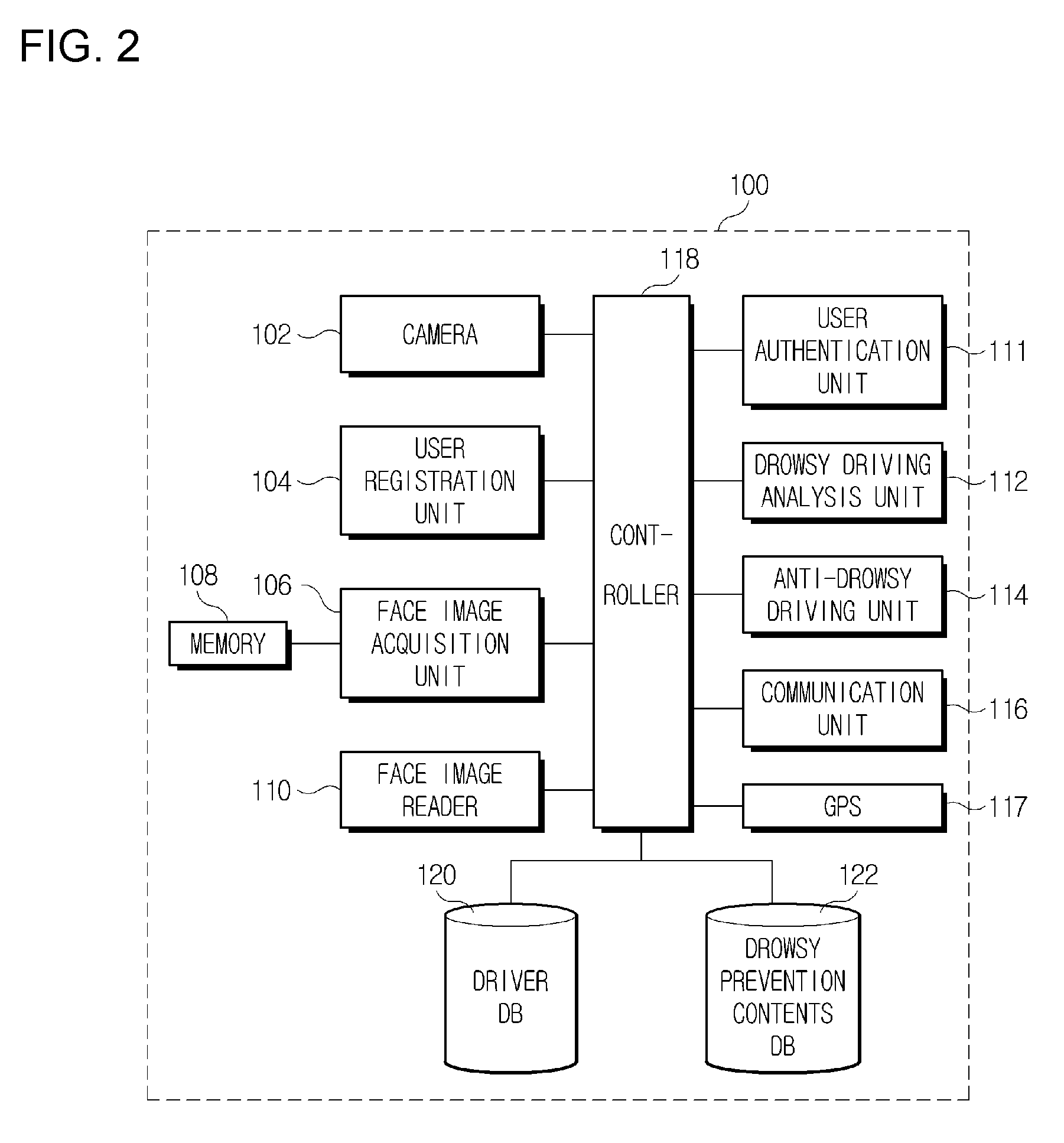
A drowsy driving prevention apparatus employing a facial recognition technology and a drowsy driving prevention system employing the same is provided. A GPS and a communication unit for informing a central control center or a traffic accident prevention management institute of information about a drowsy driving state and the position of a vehicle are mounted in the drowsy driving prevention apparatus. Thus, traffic accidents can be prevented. A management server is informed of a driver's drowsiness and a driver can access a portable telephone of an external helper over a network using wireless Internet communication technologies, such as Wibro (also called Mobile WiMAX), HSDPA & HSUPA, Long Term Evolution (LTE), Ultra Mobile Broadband (UMB), TD-SCDMA, TRS, GPRS GSM and CDMA. It is therefore possible to prevent traffic accidents caused by drowsy driving in synthetic and multidimensional ways.
Owner:TELICSTA
System and method for voice data handoff between cellular network and WiBro/WLAN network in heterogeneous network environment
InactiveUS20060246903A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsSubstation equipmentInternet networkWiBro
A system and method are provided for performing voice data handoff from a cellular network to a portable Internet / wireless local area network (WLAN) network by a mobile terminal in a heterogeneous network environment. The system and method are provided wherein whether to perform handoff is determined, and a location of a mobile terminal in the portable Internet / WLAN network is registered, a request for handoff is sent to the cellular network, and in response thereto, a request for voice-over-Internet protocol (VoIP) call setup through a specific upper node of the portable Internet / WLAN network is received, and the VoIP call to the upper node of the portable Internet / WLAN network is set-up, and resources of a circuit voice call to a specific upper node of the cellular network are released.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
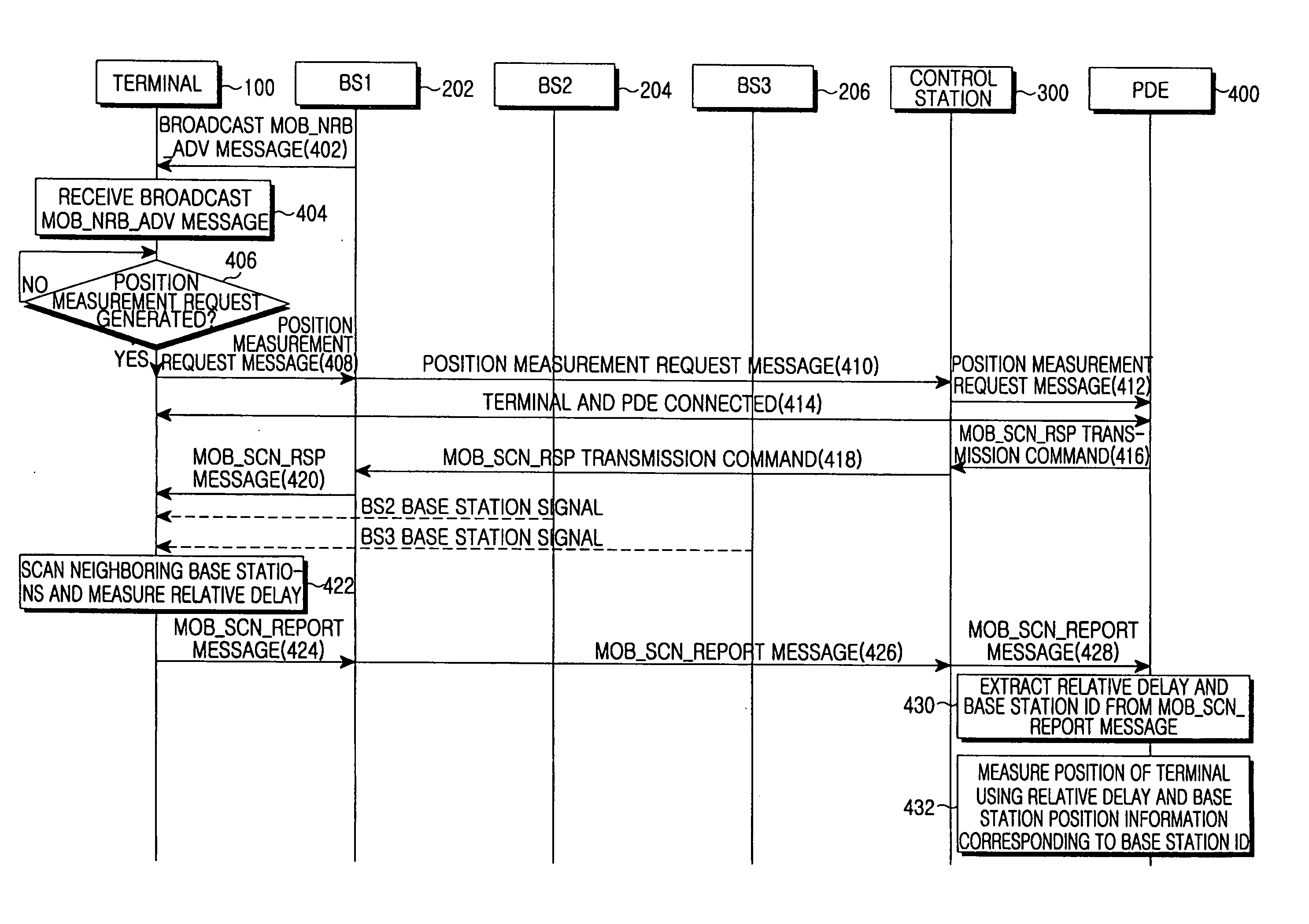
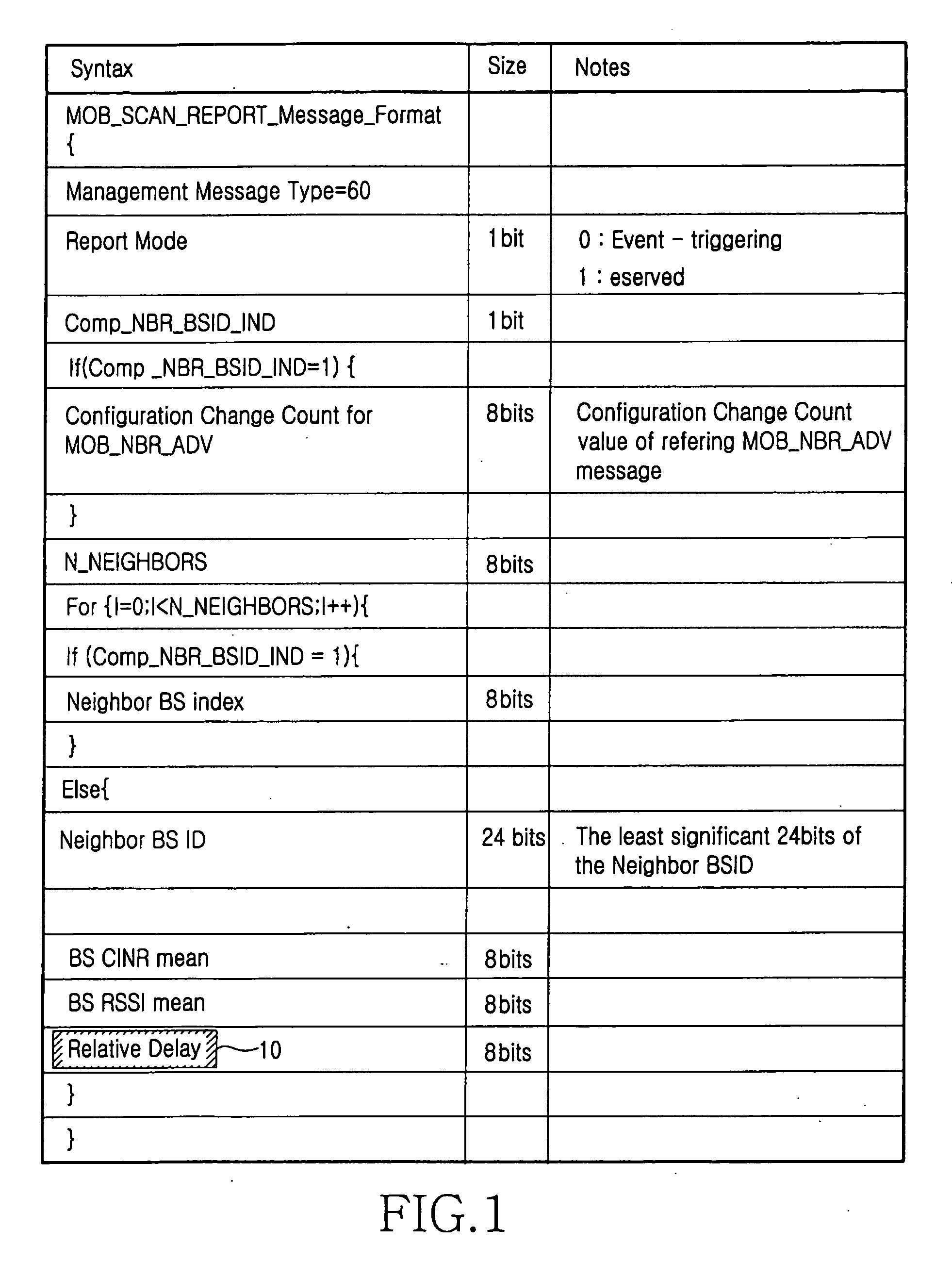
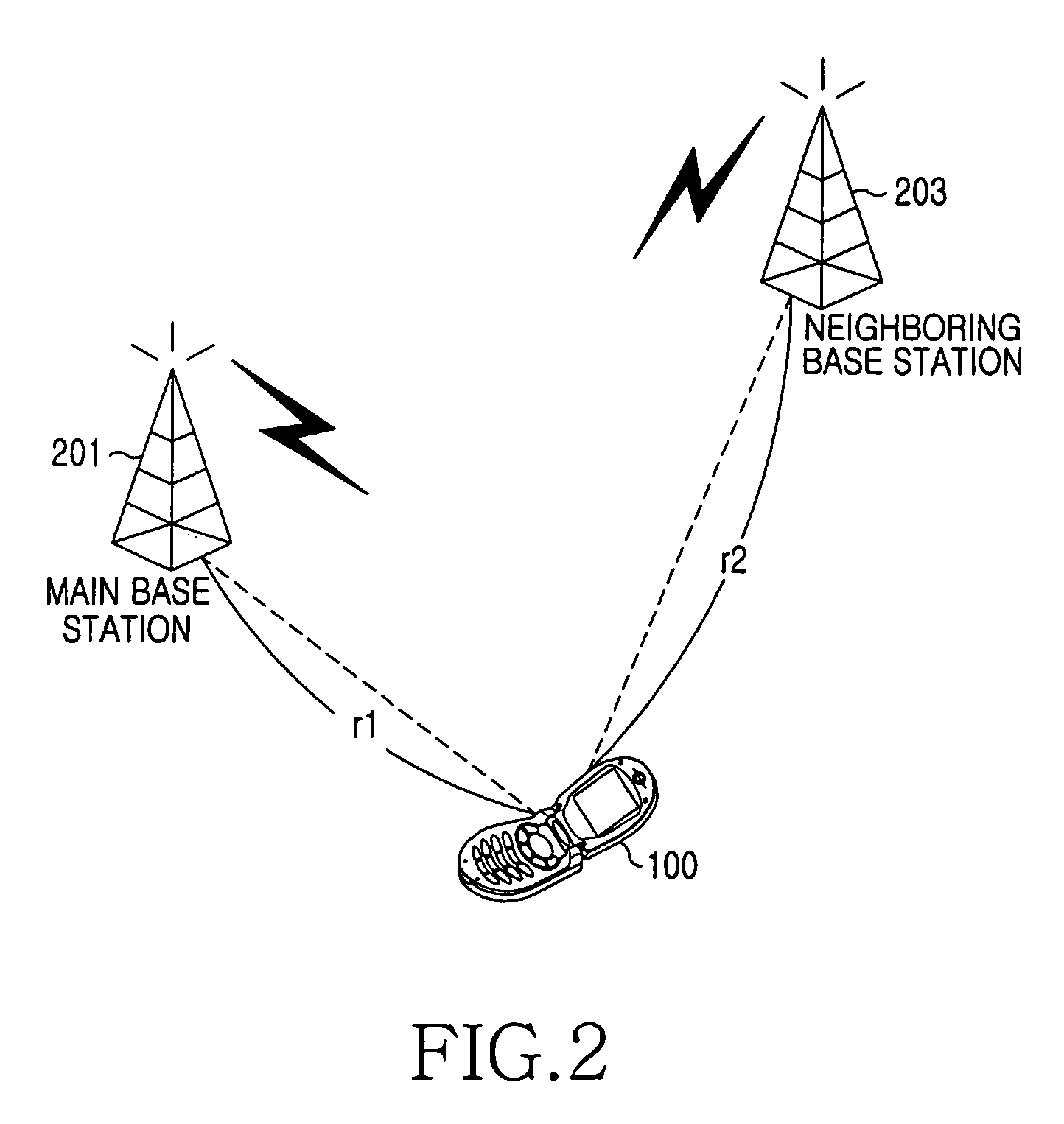
Position measuring system and method using wireless broadband (WIBRO) signal
InactiveUS20070004430A1Easy to measureSpecial service for subscribersPosition fixationWiBroComputer terminal
Provided is a position measuring system and method using a Wireless Broadband (WiBro) signal. The position measuring system measures the position of a terminal using relative delay information that is a parameter of the WiBro signal, used for a hand-over. Since the position of a terminal is measured using a parameter for a hand-over, additional data measurement is not required for the position measurement. Furthermore, efficiency in the use of a parameter of a WiBro system can be improved by using a parameter used only in the hand-over for position measurement.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
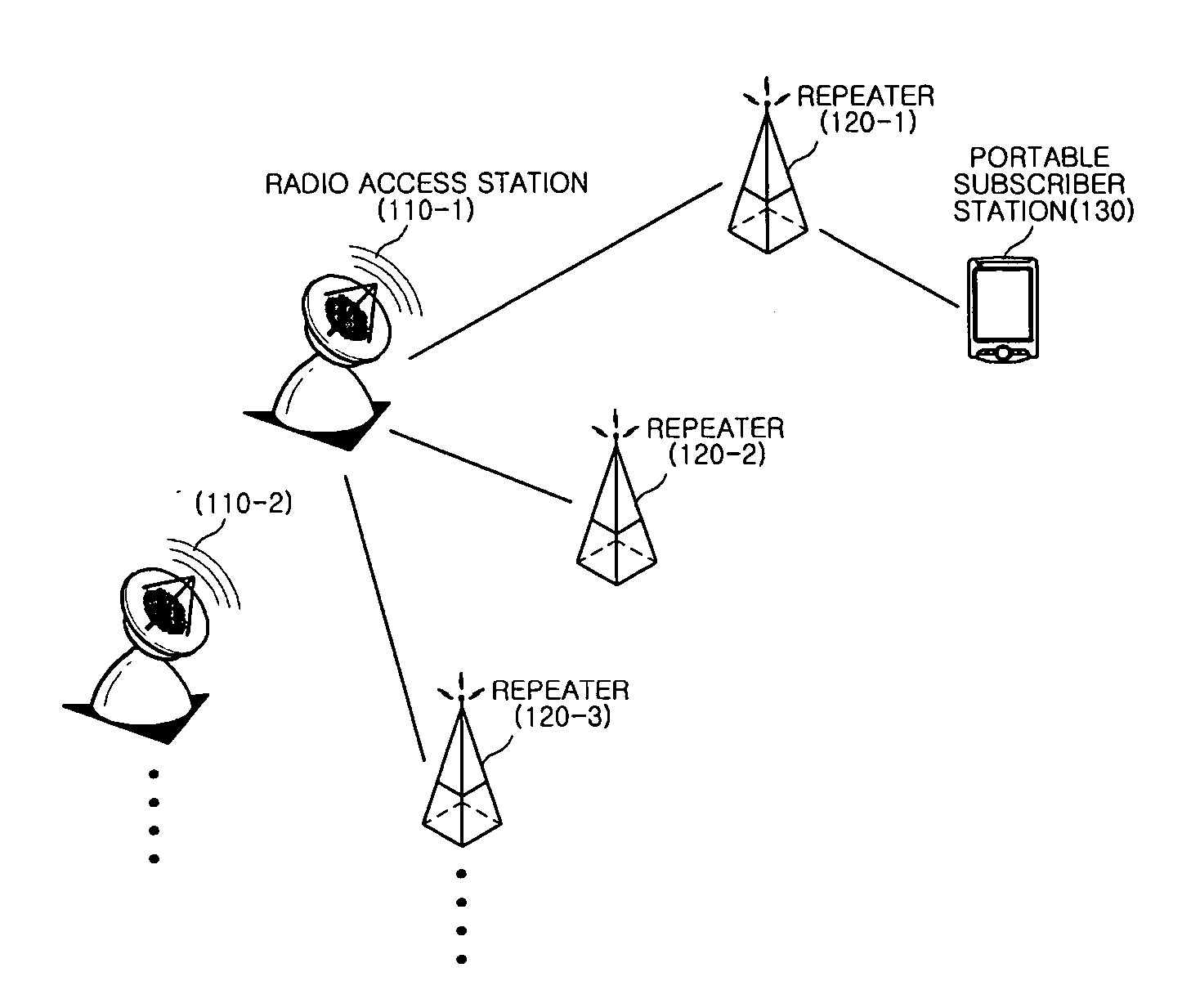
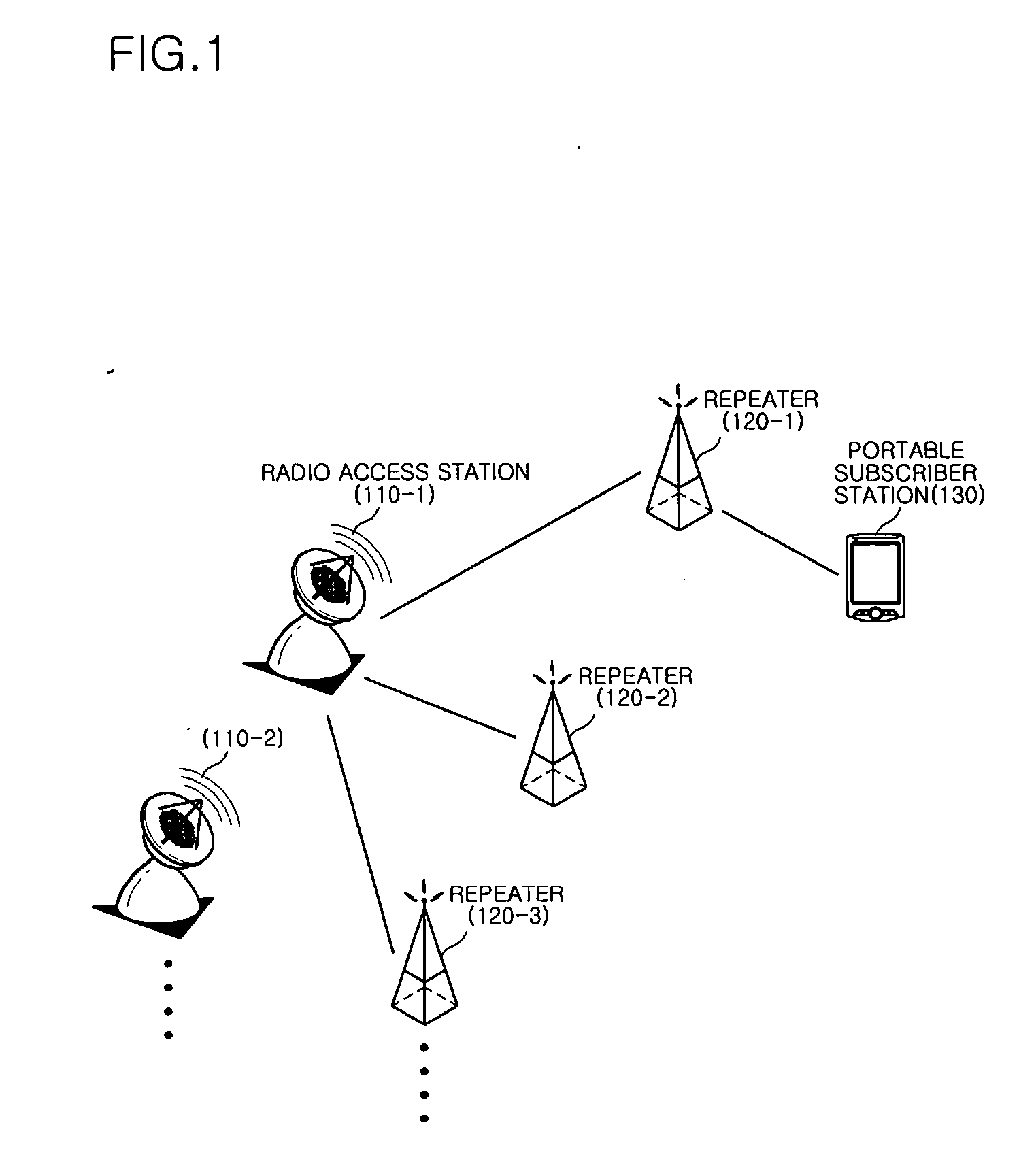
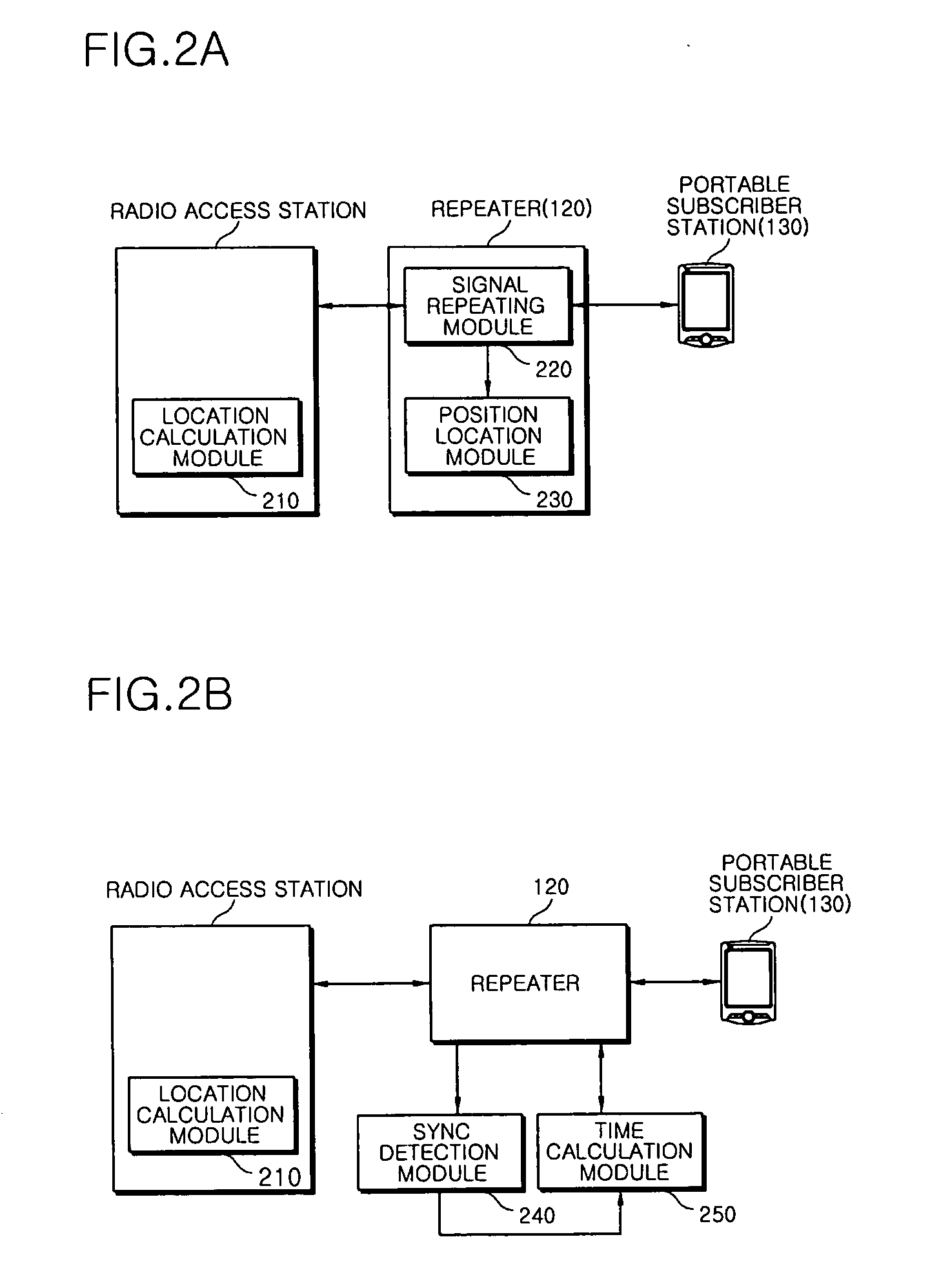
Method and apparatus for positioning portable subscriber station in WiBro network, and repeater having the same
Disclosed is a method and apparatus for positioning a portable subscriber station (PSS) using a WiBro repeater, and a repeater having the apparatus. The method of positioning the portable subscriber station in a network having a radio access station (RAS) and a repeater, including the operations of: detecting a preamble signal transmitted from the RAS; generating a reference time by measuring a receiving time of the preamble signal and by compensating the receiving time of the preamble signal by taking into consideration a signal delay time between the RAS and the repeater; measuring a receiving time of a ranging signal received from the PSS on the basis of the reference time; and calculating the receiving time of the ranging signal by using a time stamp generated on the basis of the receiving time of the preamble signal.
Owner:ALOGICS
Network protocol for wireless broadband-ISDN using ATM
InactiveUS6151312AInterference minimizationMinimum delaySynchronisation arrangementError preventionNetworking protocolIntegrated Services Digital Network
A network protocol for the delivery of wireless broadband integrated services digital network (ISDN) using asynchronous transfer mode (ATM).
Owner:ALCATEL USA SOURCING
Open access network architecture
InactiveUS20060098593A1Increase in sizeGreat advantageRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesAccess networkNetwork architecture
Owner:TELENOR AS
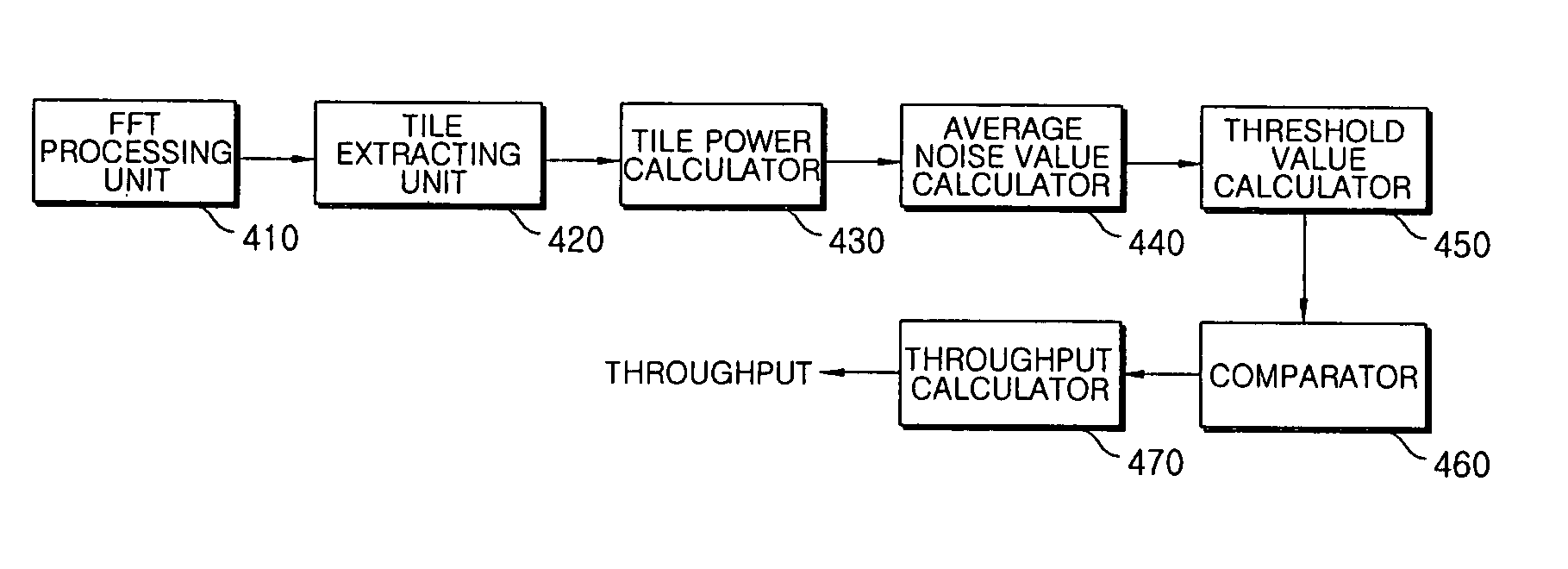
Method and apparatus for measuring uplink data throughput in WiBro repeater
Disclosed is a method of measuring the throughput of uplink data in a WiBro repeater, the method including the operations of: (a) extracting a plurality of tiles from a predetermined number of symbols that are collected over a plurality of times by performing frequency conversion on the uplink data; (b) calculating power values for the respective extracted tiles; (c) calculating an average noise value from the calculated power values; (d) calculating a threshold value, which is used to identify noise, from the average noise value, and calculating the number of tiles having power values more than the threshold value; and (e) calculating the throughput by estimating based on the number of the tiles the number of subchannels carrying data.
Owner:ALOGICS
Vehicle accuracy positioning method based on inertial navigation and satellite differential positioning
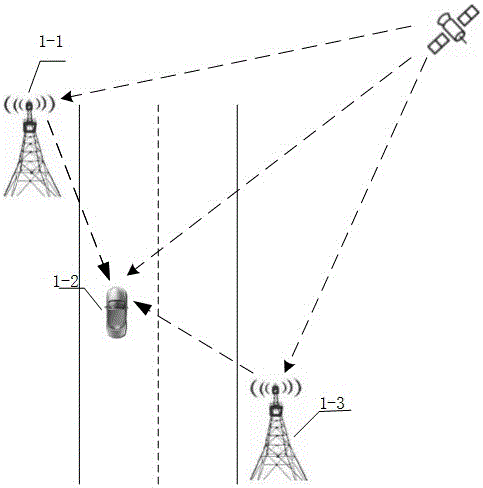
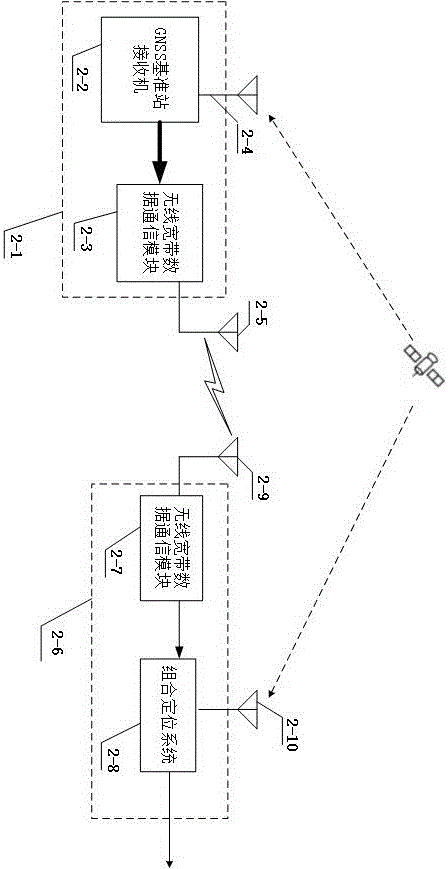
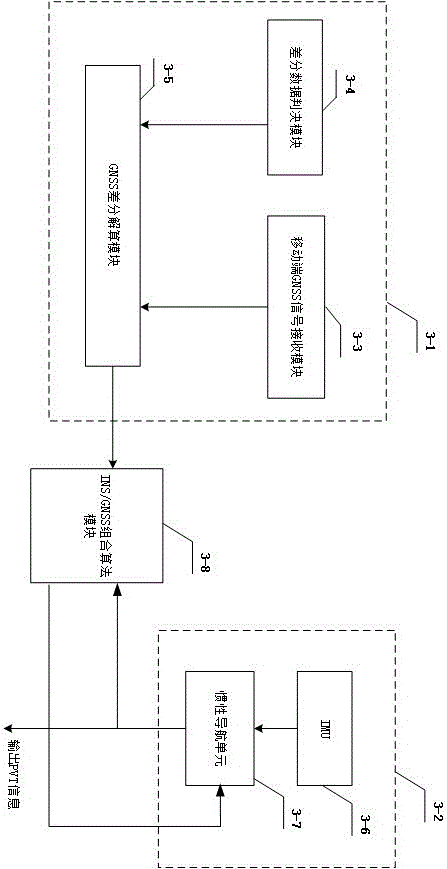
InactiveCN106324645AReal-time stable positioning serviceSolve the difficult problem of obtaining high-precision position dataSatellite radio beaconingMobile vehicleBroadband
The invention relates to the inertial-navigation-based technology and the satellite real time differential positioning technology. The vehicle accuracy positioning method of the invention utilizes wireless broadband data communication to provide accurate positioning to the vehicle. The vehicle accuracy positioning method combines the inertial navigation, the satellite real-time differential positioning technology and wireless broadband data communication together, provides a seamless positioning system applicable to intelligent transportation, provides real-time, stable and continuous position information from a sub-meter level to a centimeter level to a moving vehicle, and can realize a lane level positioning navigation. The technical scheme of the vehicle accuracy positioning method is that: the vehicle accuracy positioning method comprises a base station and a mobile terminal; a base station is installed near a road and consists of a base station satellite receiving machine and a wireless broadband communication module; and the mobile terminal is installed on the vehicle and consists of a wireless broadband communication module and a combination positioning system.
Owner:付寅飞
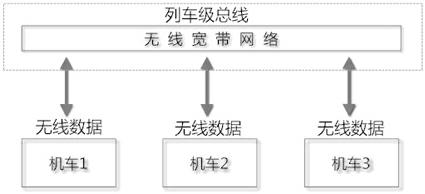
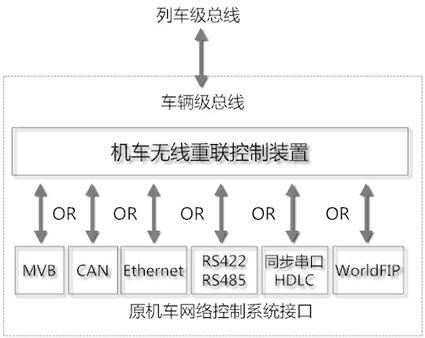
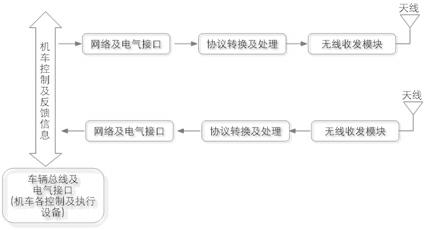
A locomotive wireless reconnection control method based on wireless broadband communication
ActiveCN102267480AEstablish interconnectionRealize interconnectionRailway traffic control systemsTransmissionControl systemWiBro
The invention provides a locomotive wireless reconnection control method based on wireless broadband communication. A wireless reconnection control device system is additionally arranged on the conventional locomotive network control system to replace the conventional locomotive and train level wired gateway, so that near wireless reconnection marshalling of locomotives can be realized and a plurality of locomotives can be controlled to run after being subjected to wireless reconnection; furthermore, interconnection among the locomotives can be established quickly, effectively and stably, so the interconnection and reconnection control of different types of locomotives can be realized.
Owner:CHANGSHA NANRUI RAIL TRANSPORT ELECTRIC EQUIP CO LTD
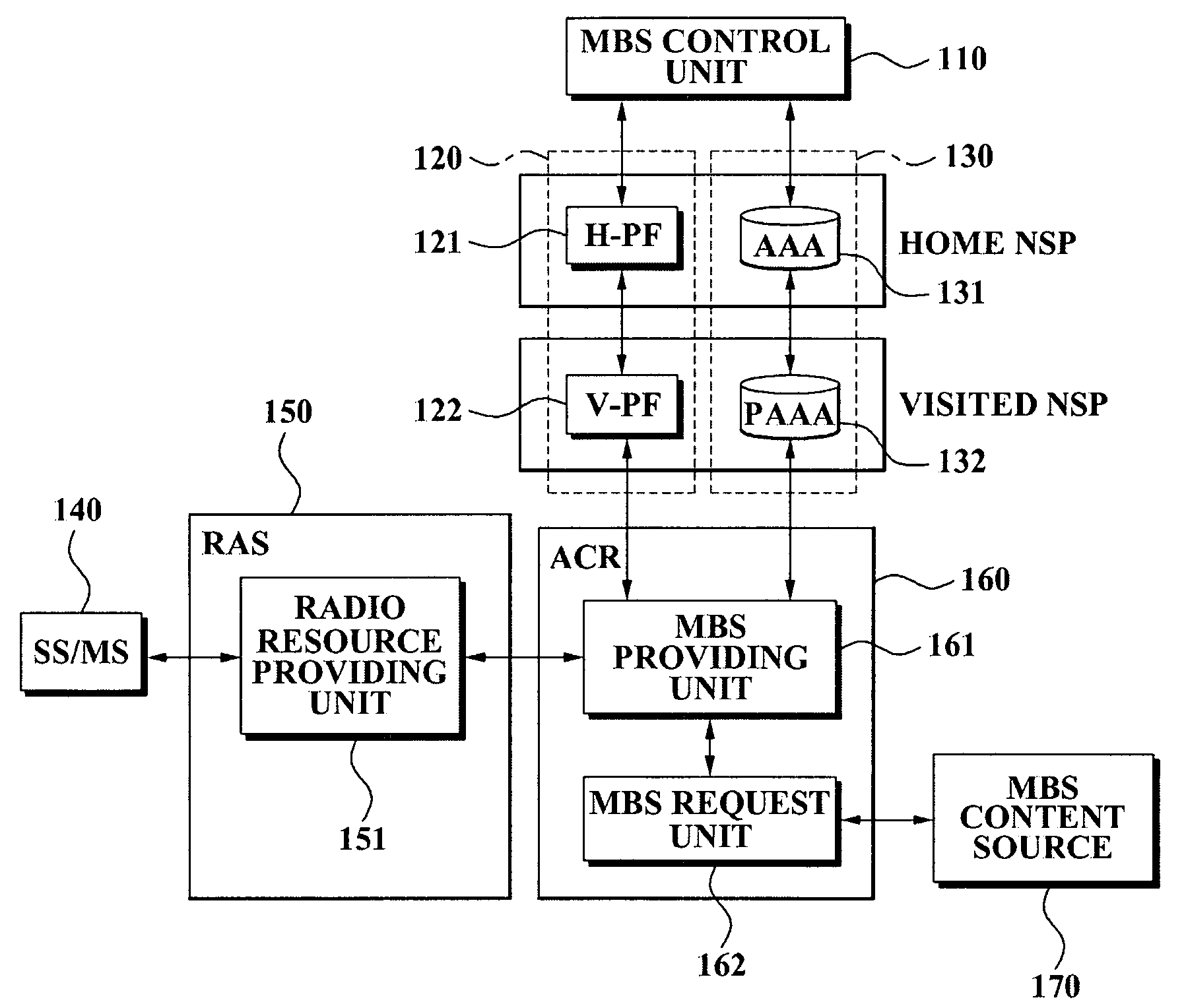
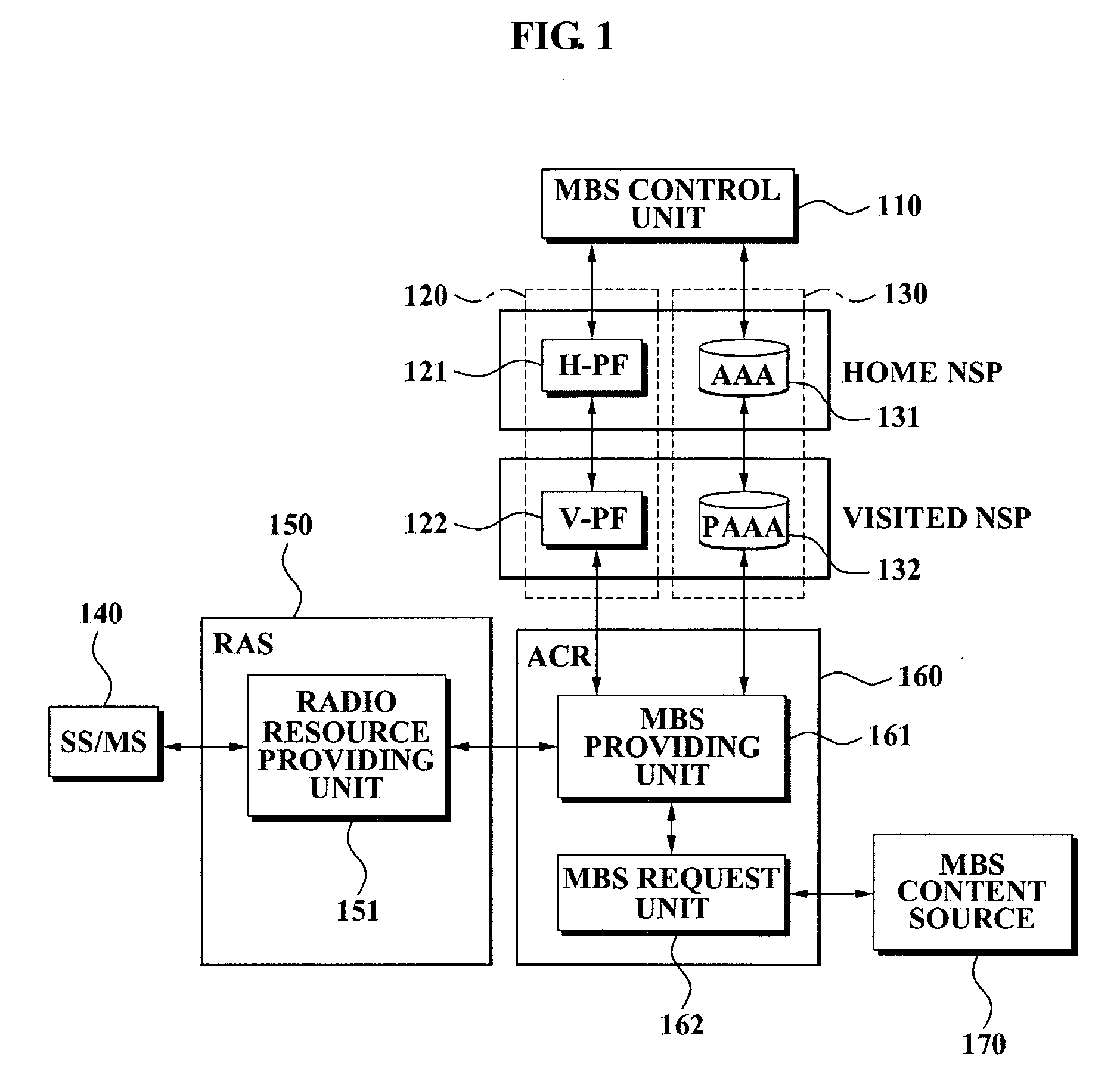
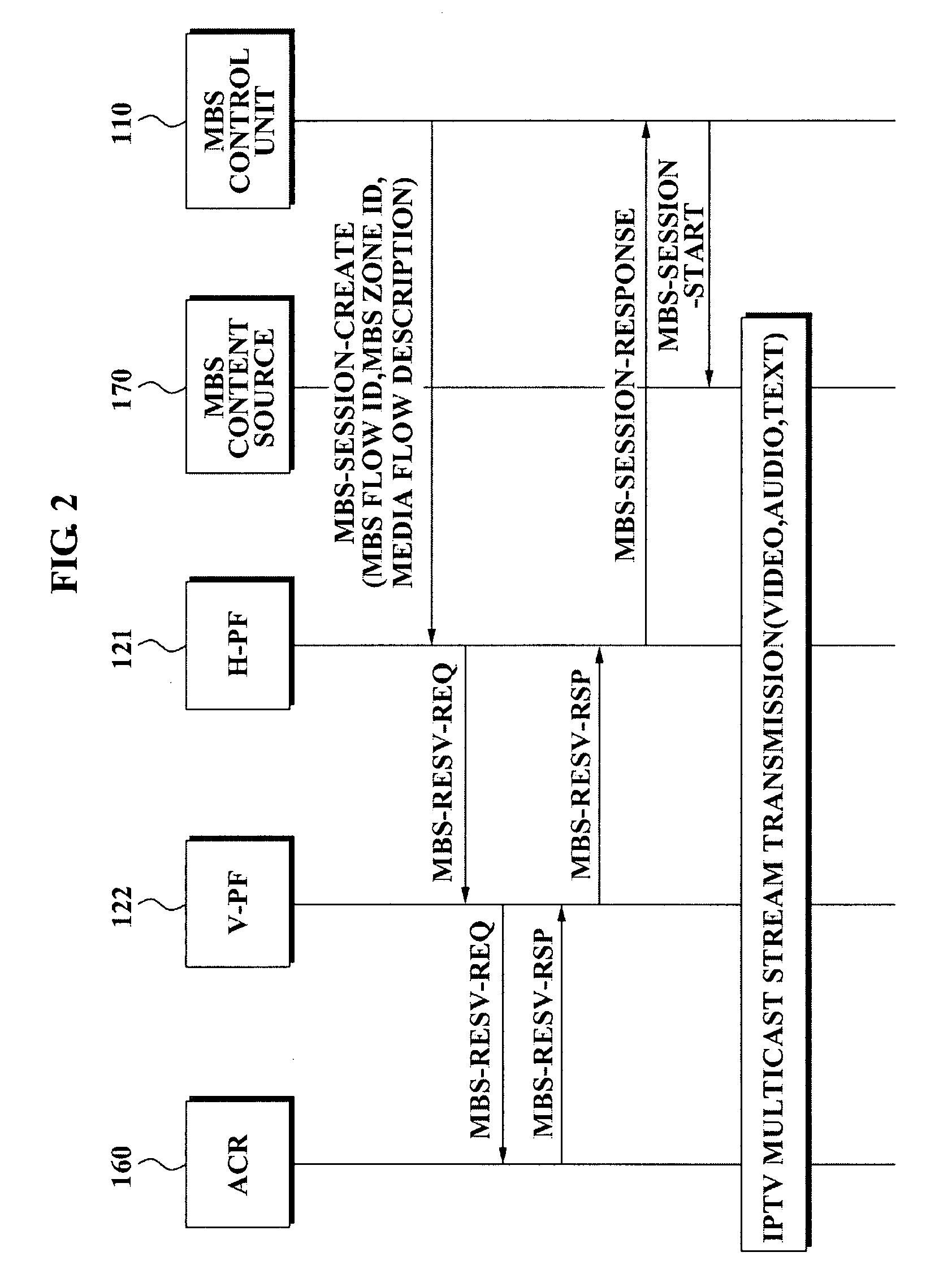
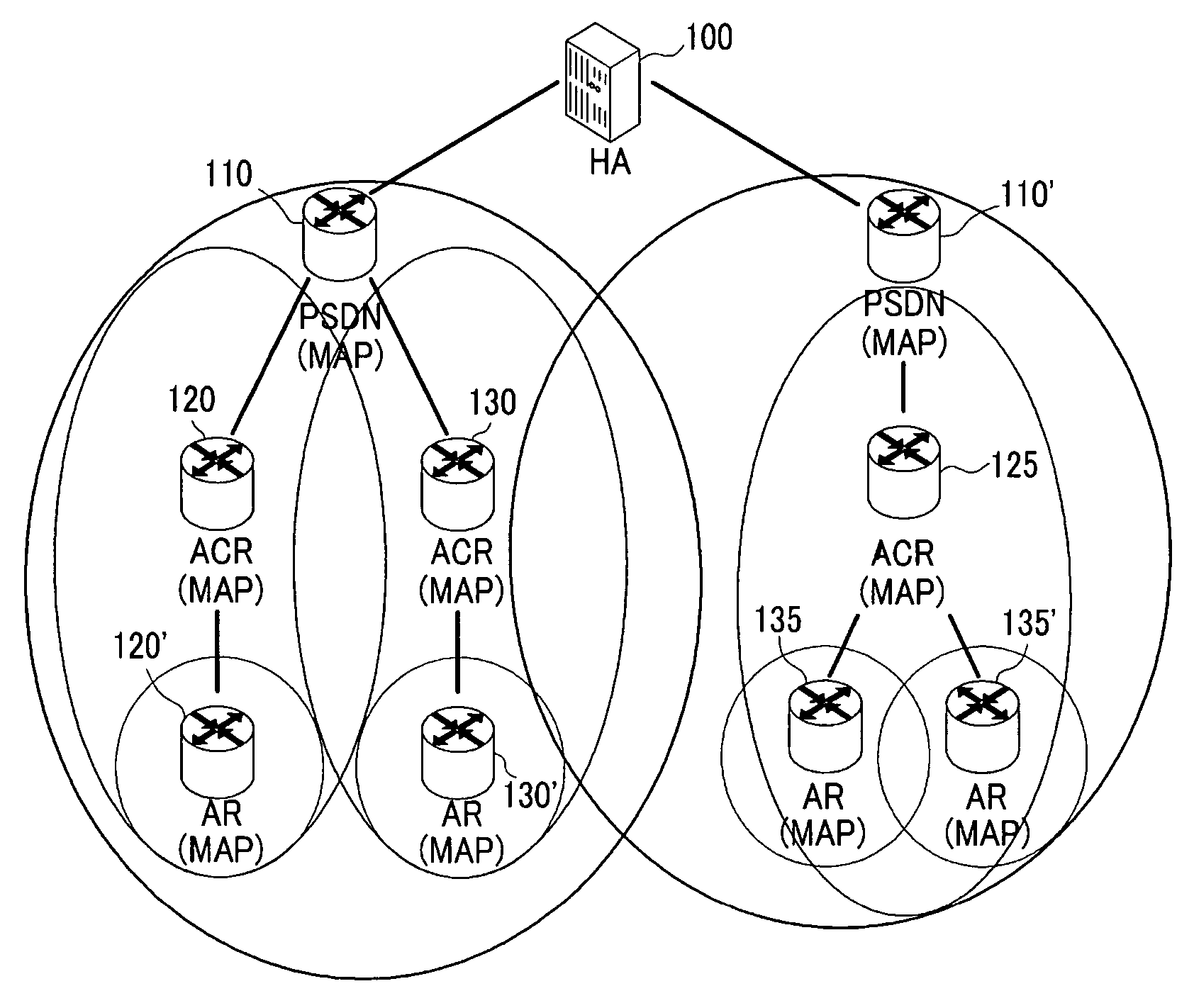
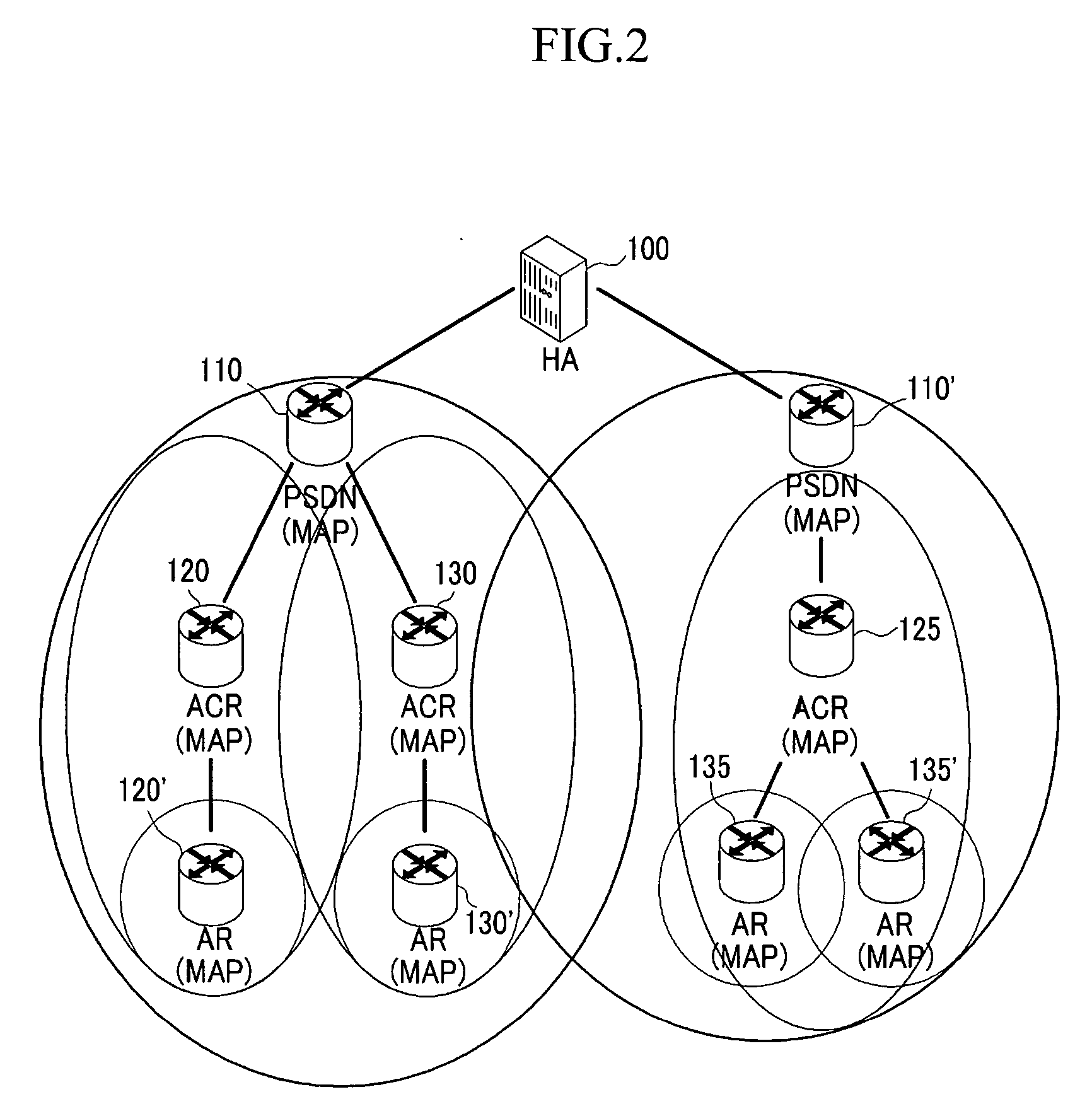
Method of providing multicast/broadcast service using wibro/wimax network and system using the method
InactiveUS20080101376A1Fast channel changeQuick changeSpecial service provision for substationConnection managementQuality of serviceService flow
A system and method for providing a multicast / broadcast service (MBS) using a Wireless Broadband Internet / World Interoperability for Microwave Access (WiBro / WiMAX) network are provided, which include an MBS control unit for generating a beginning and an end of an MBS bearer session, a quality of service (QoS) control unit for requesting an allocation and release of a QoS, an access control router (ACR) for allocating a multicast service flow identifier (SFID) with respect to the MBS bearer session in order to provide an MBS user terminal with MBS bearer traffic which is received from an MBS content source, and for releasing the allocated multicast SFID when the release of the QoS is requested, and a radio access station (RAS) for allocating a multicast connection identifier (CID) corresponding to the allocated multicast SFID according to whether an MBS user requests the MBS bearer traffic, and controlling a radio resource with the MBS user terminal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
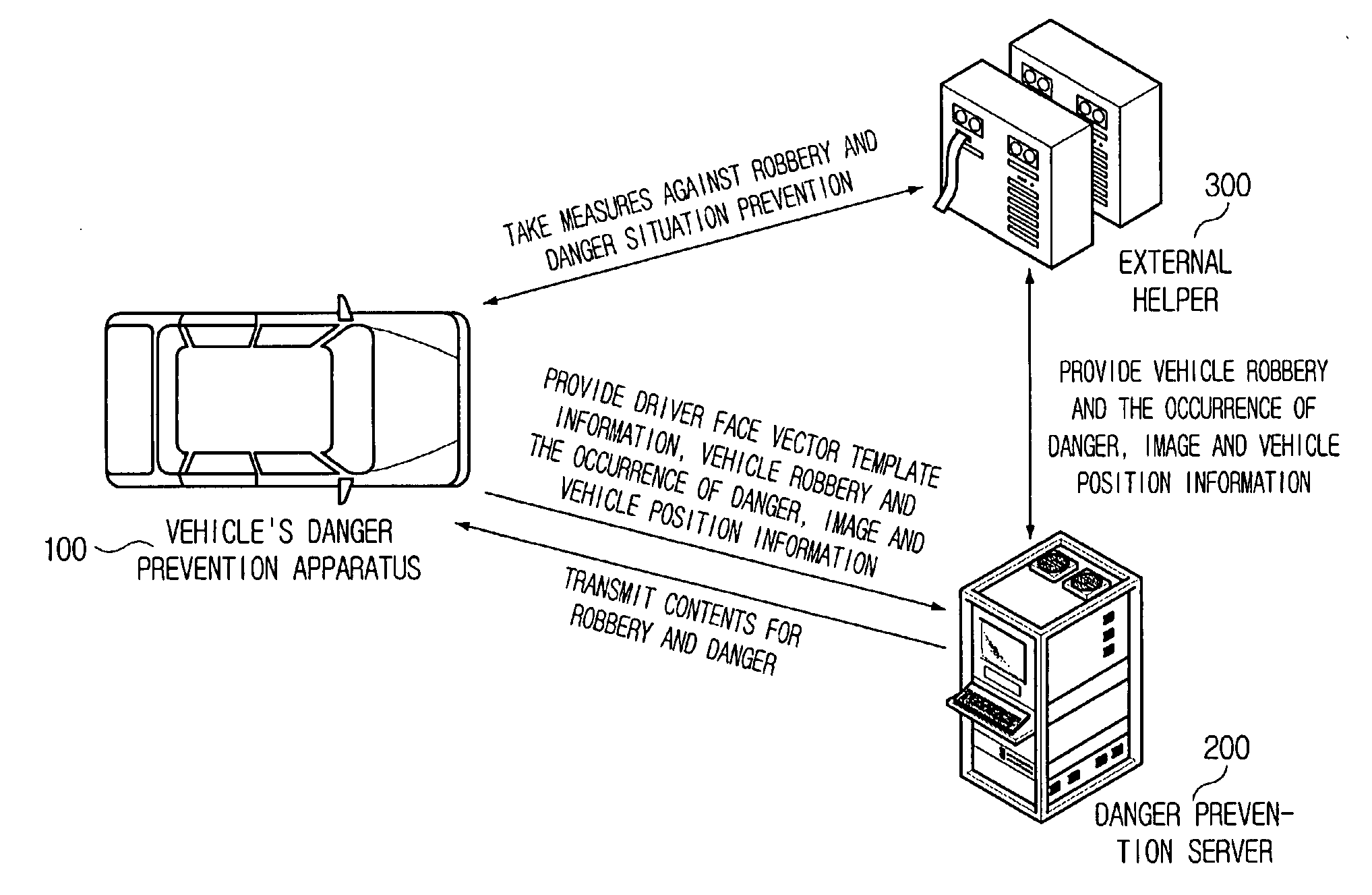
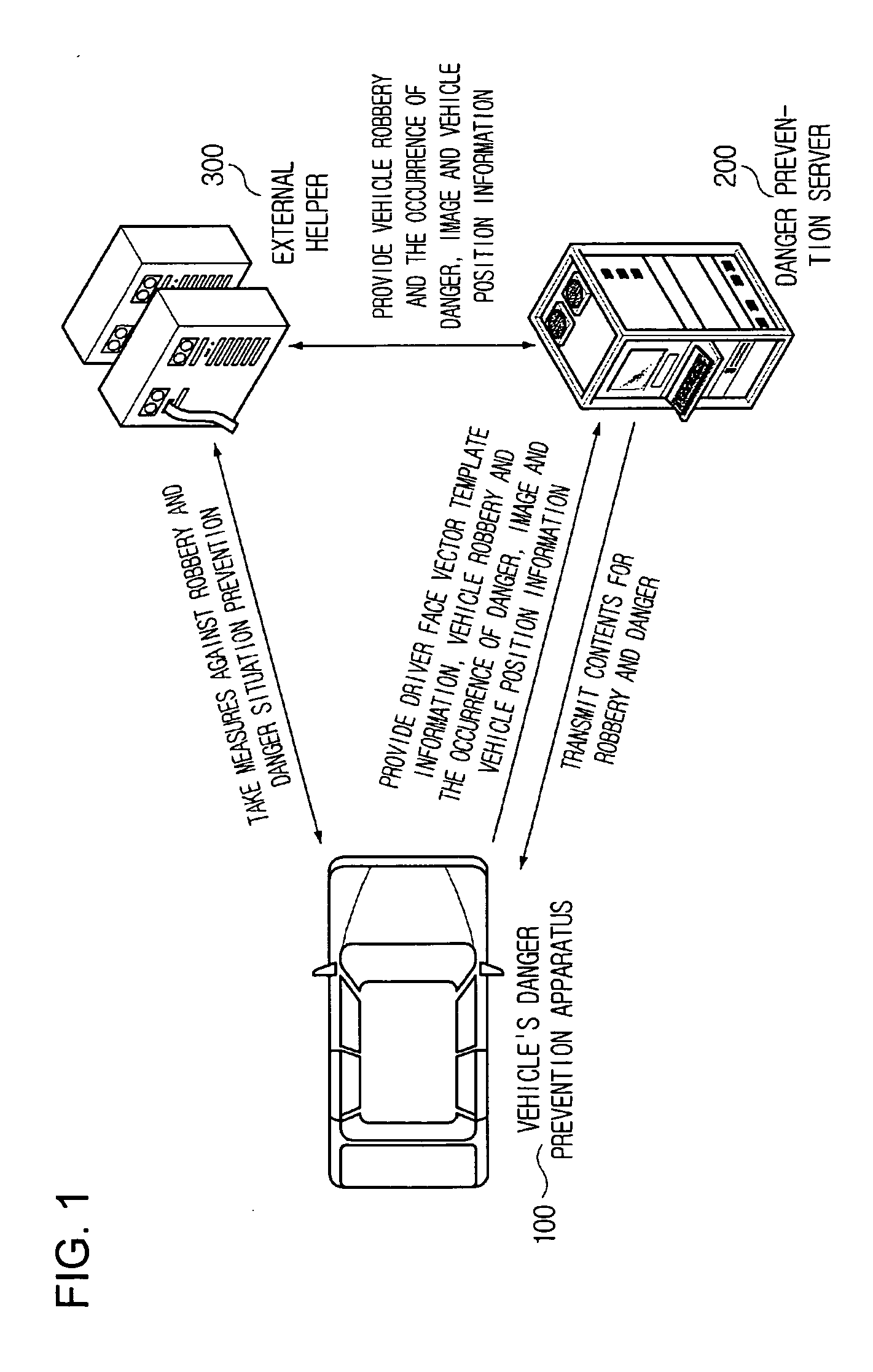
Vehicle emergency preventive terminal device and internet system using facial recognition technology
InactiveUS20080297330A1Quick fixAnti-theft devicesCharacter and pattern recognitionGSMReliability engineering
A danger preventive apparatus employing a facial recognition technology and a danger preventive system using the same is provided. According to the present invention, the robbery of a vehicle, and various crimes and unexpected dangers within a vehicle can be prevented and eliminated by employing a facial recognition algorithm. Further, dangerous situations can be solved rapidly by automatically transmitting a driver's position information and pertinent images from an external danger prevention server to external helpers, such as police and emergency help institutes, through wireless Internet communication technologies such as Wibro (also called Mobile WiMAX), HSDPA & HSUPA, Long Term Evolution (LTE), Ultra Mobile Broadband (UMB), TD-SCDMA, TRS, GPRS (GSM) and CDMA, when the robbery or danger of a vehicle is sensed in the danger preventive apparatus.
Owner:TELICSTA
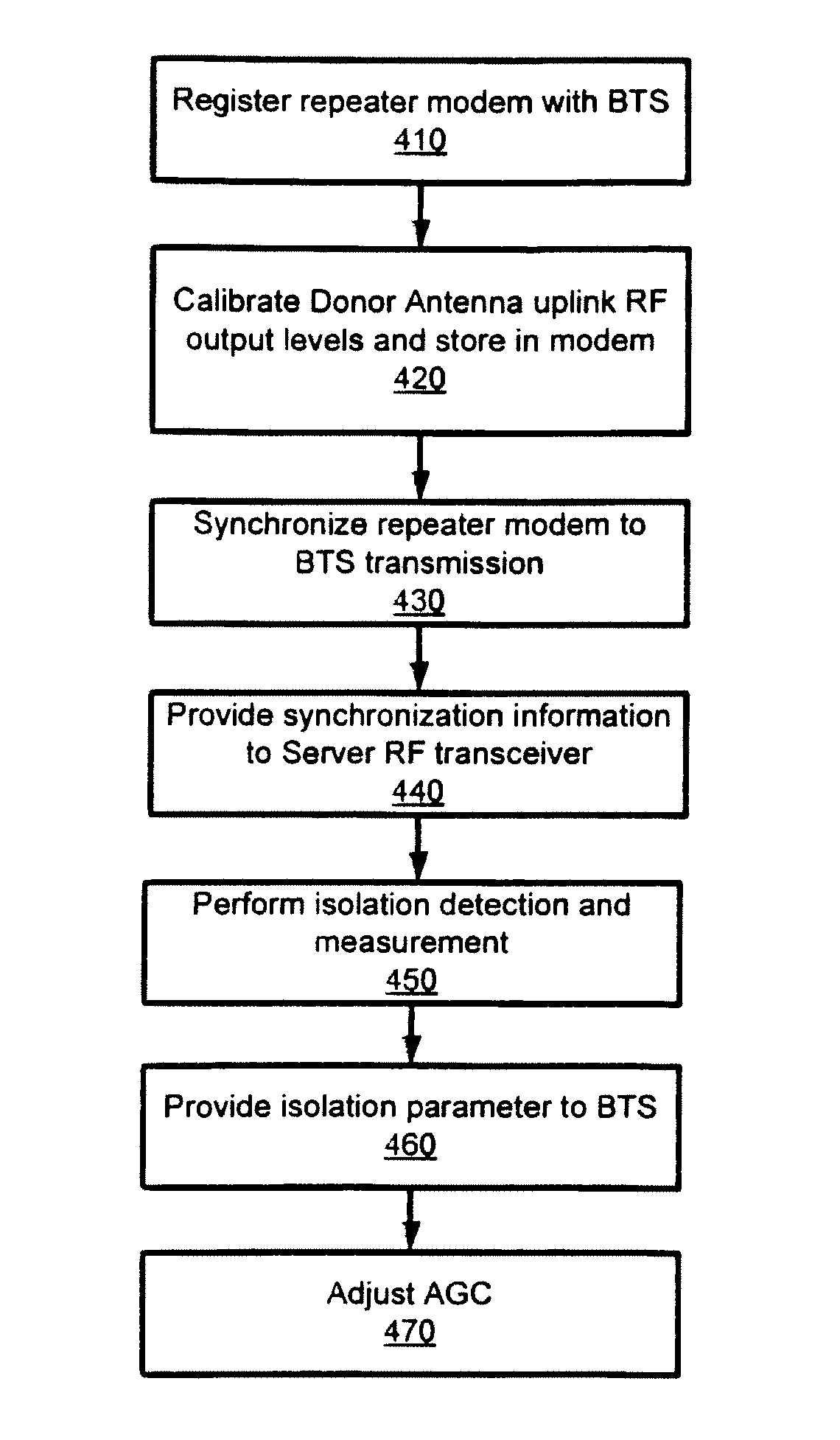
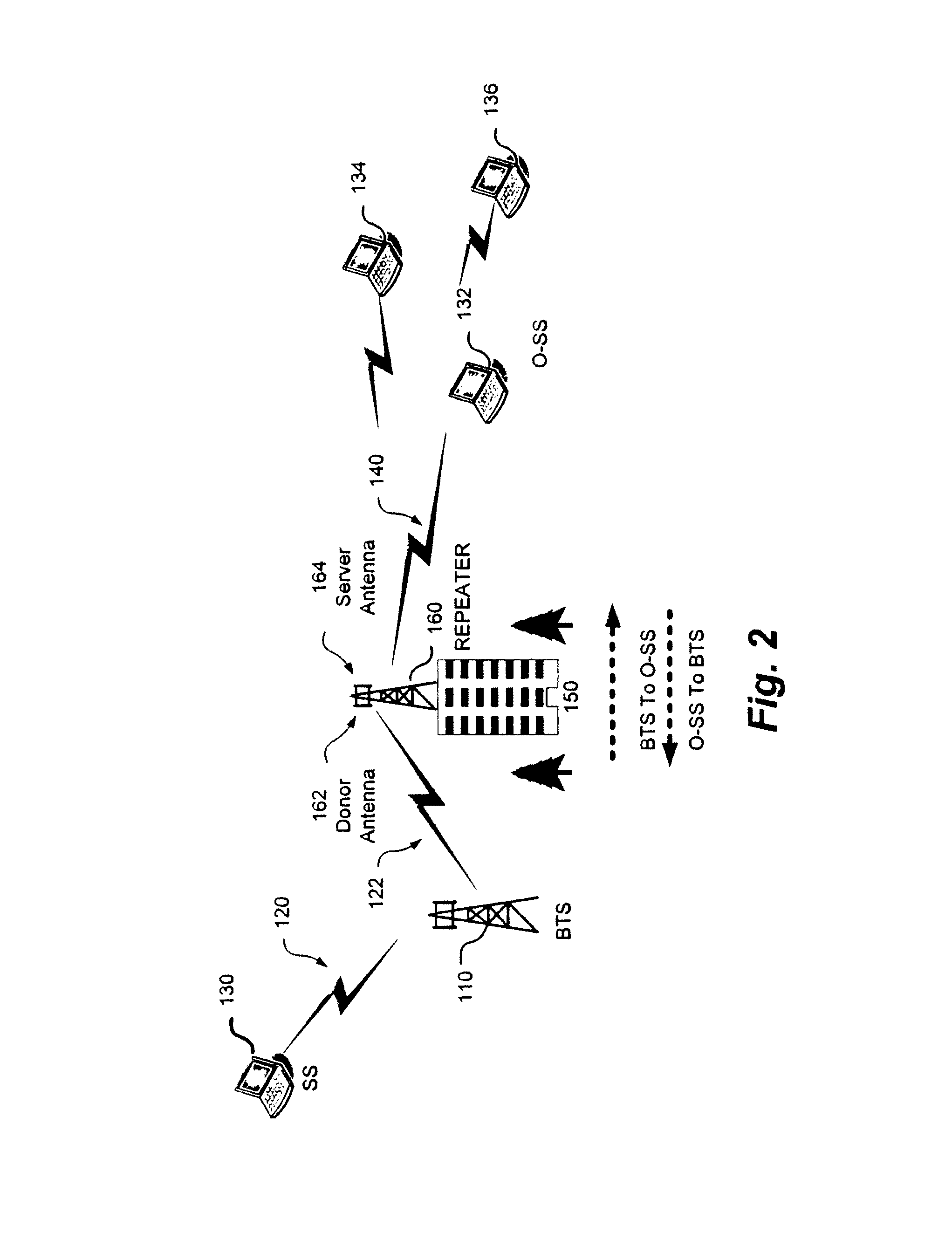
Isolation measurement and self oscillation prevention in TDD-OFDM repeater for wireless broadband distribution to shadowed areas
ActiveUS20120188919A1Synchronisation arrangementFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransceiverModem device
A method for determining isolation status of the RF repeater is provided. A modem in the repeater registers with a base transceiver station (BTS). Uplink output levels of a donor RF transceiver are calibrated and stored in the modem. The modem is synchronized to a BTS transmission received at the donor RF transceiver and the synchronization information is provided to a server RF transceiver of the repeater. Isolation detection and measurement can then be performed between donor transmit antenna and receive server antenna of the RF repeater and the automatic gain control parameter of donor RF transceiver and server RF transceiver are adjusted based upon the isolation detection and measurement value. The isolation and detection can be implemented in a co-processor coupled to the donor and server transceivers.
Owner:REDLINE COMM
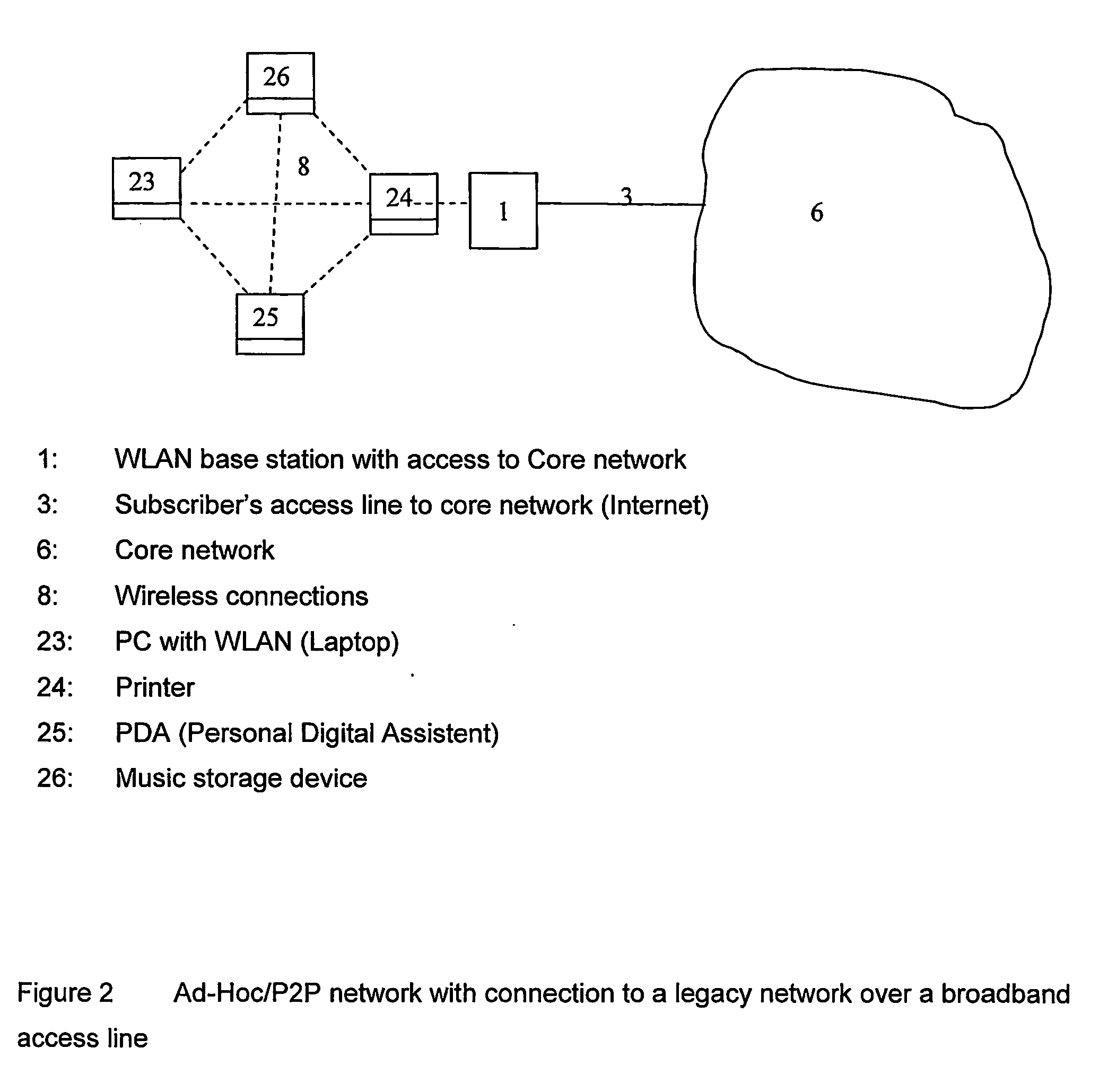
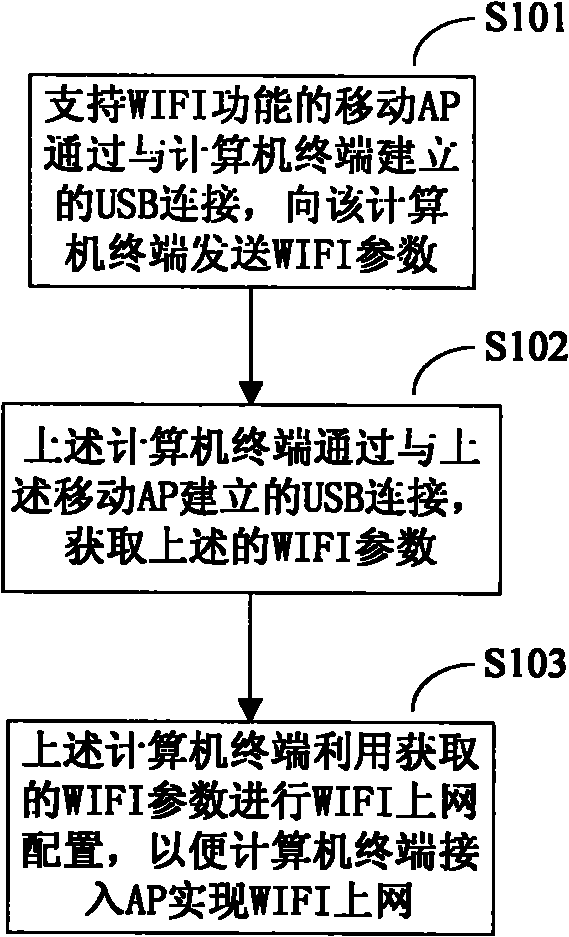
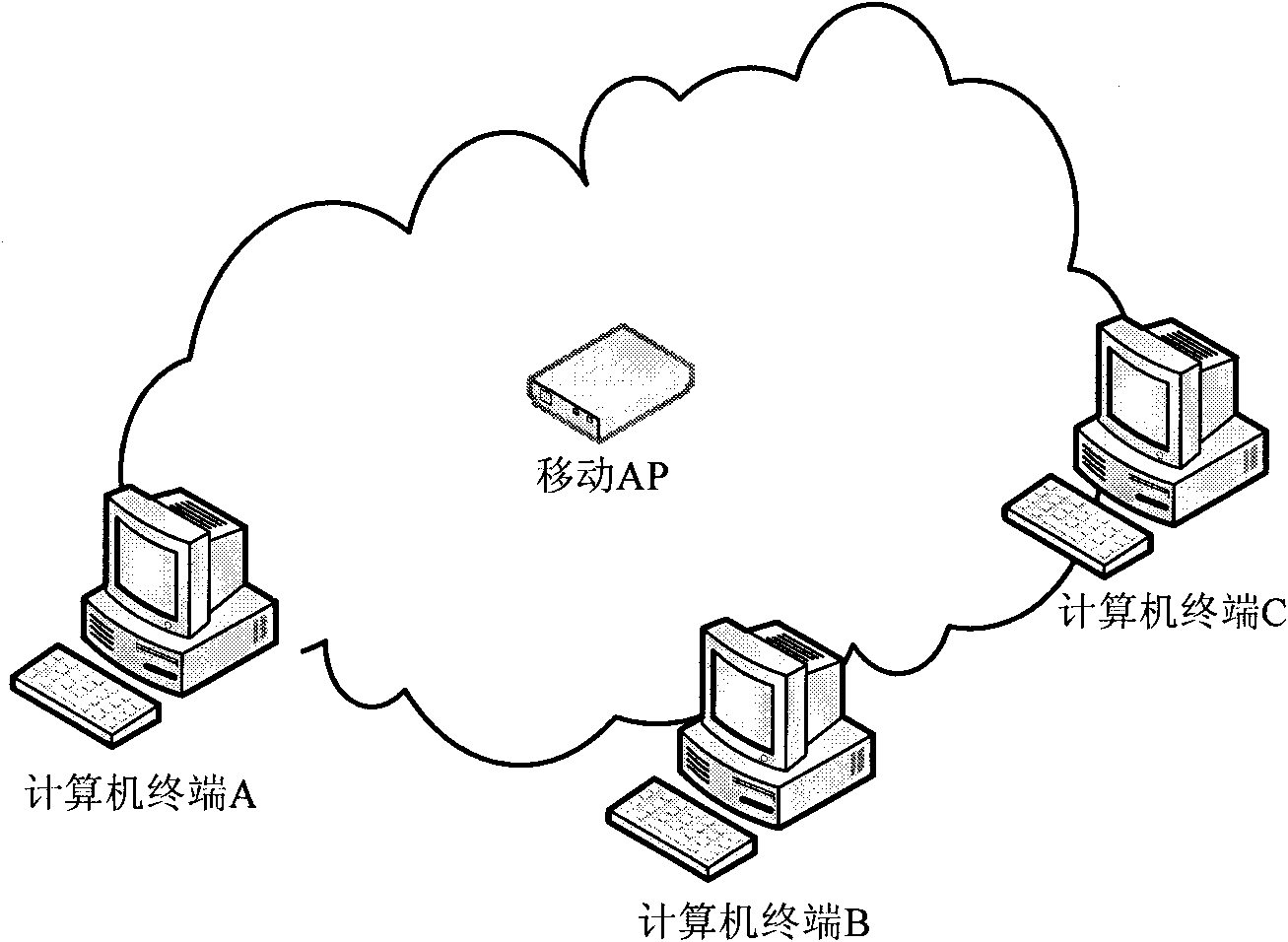
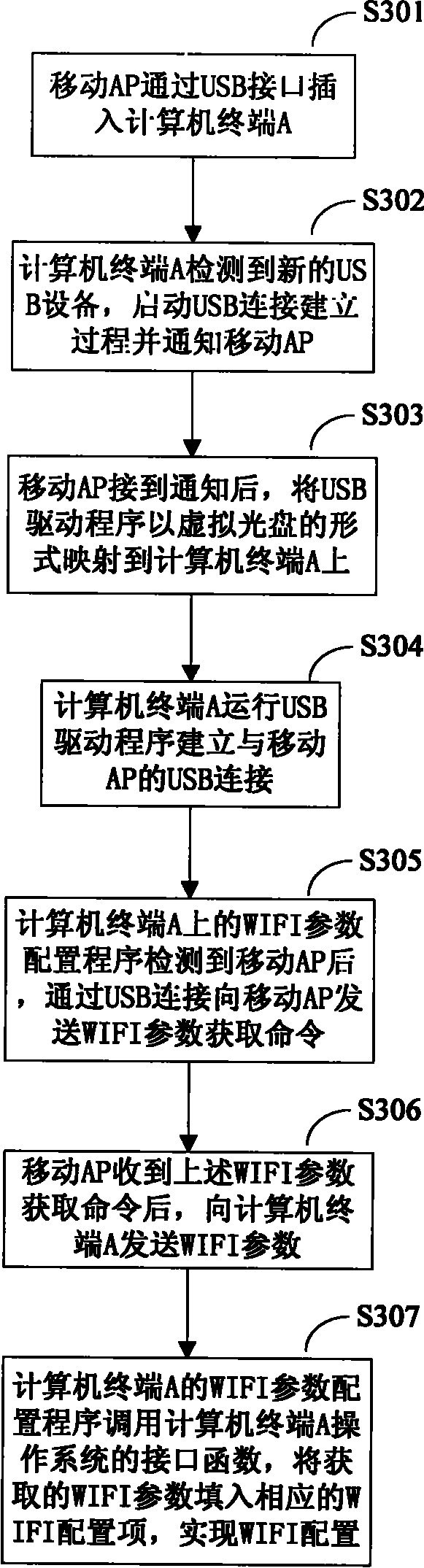
Method, device and system for configuring wireless fidelity (WIFI) parameter
InactiveCN101873719ASimplify the configuration processSave configuration timeNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesThe InternetComputer terminal
The invention relates to a method for configuring a wireless fidelity (WIFI) parameter. The method comprises the following steps that: when a universal serial bus (USB) connection is established between a computer terminal and a mobile access point (AP) which supports a wireless broadband WIFI function, the computer terminal acquires the WIFI parameter sent by the mobile AP through the USB connection; and the computer terminal performs WIFI Internet configuration by using the WIFI parameter. The embodiment of the invention also provides the computer terminal for configuring the WIFI parameter, the mobile AP which supports the WIFI function and a system. The WIFI parameter on the mobile AP is acquired automatically and the configuration of the WIFI parameter is performed automatically and a user does not need to manually input and configure the WIFI parameter, so that a WIFI parameter configuration process is simplified, WIFI parameter configuration time is saved and the accuracy of WIFI parameter configuration is improved.
Owner:HUAWEI DEVICE CO LTD
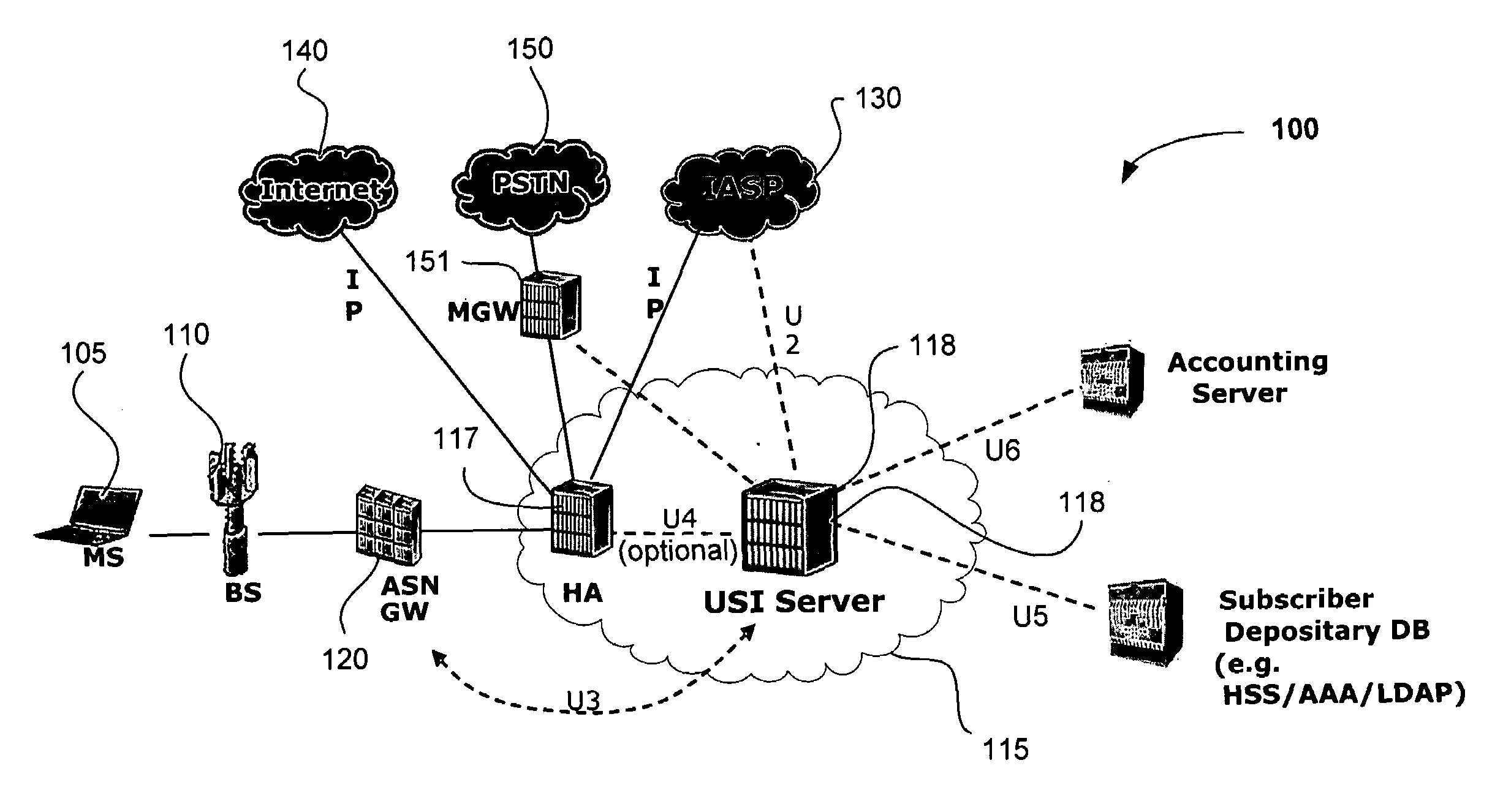
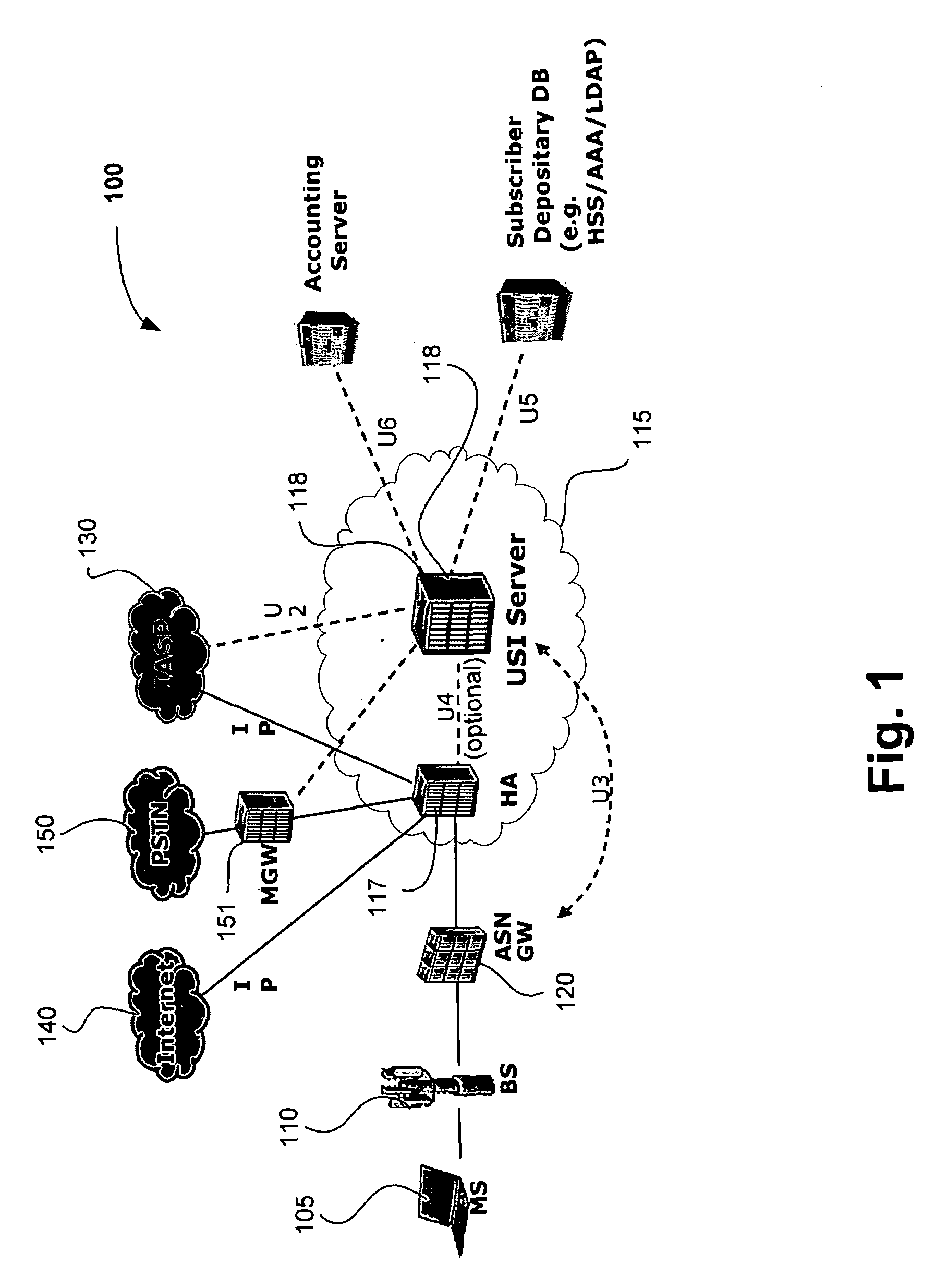
Universal services interface for wireless broadband networks
InactiveUS20080107092A1Convenient and smarter serviceRich varietyNetwork topologiesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsQuality of serviceInternet Protocol
Embodiment of the invention relate to a new type of service interface network node which enables a service provider of a broadband wireless access (BWA) network to provide relevant information to application service provider (ASPs) in a public Internet and in turn allows ASPs to provide value add services or enhanced experience to mobile users in the network. Value add services may include content involving quality-of-service (Qos) IP flows such as Internet Protocol (IP) television (IPTV) as well as location-based service content such as location relevant searches or directions. Additional embodiments and variations are also disclosed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
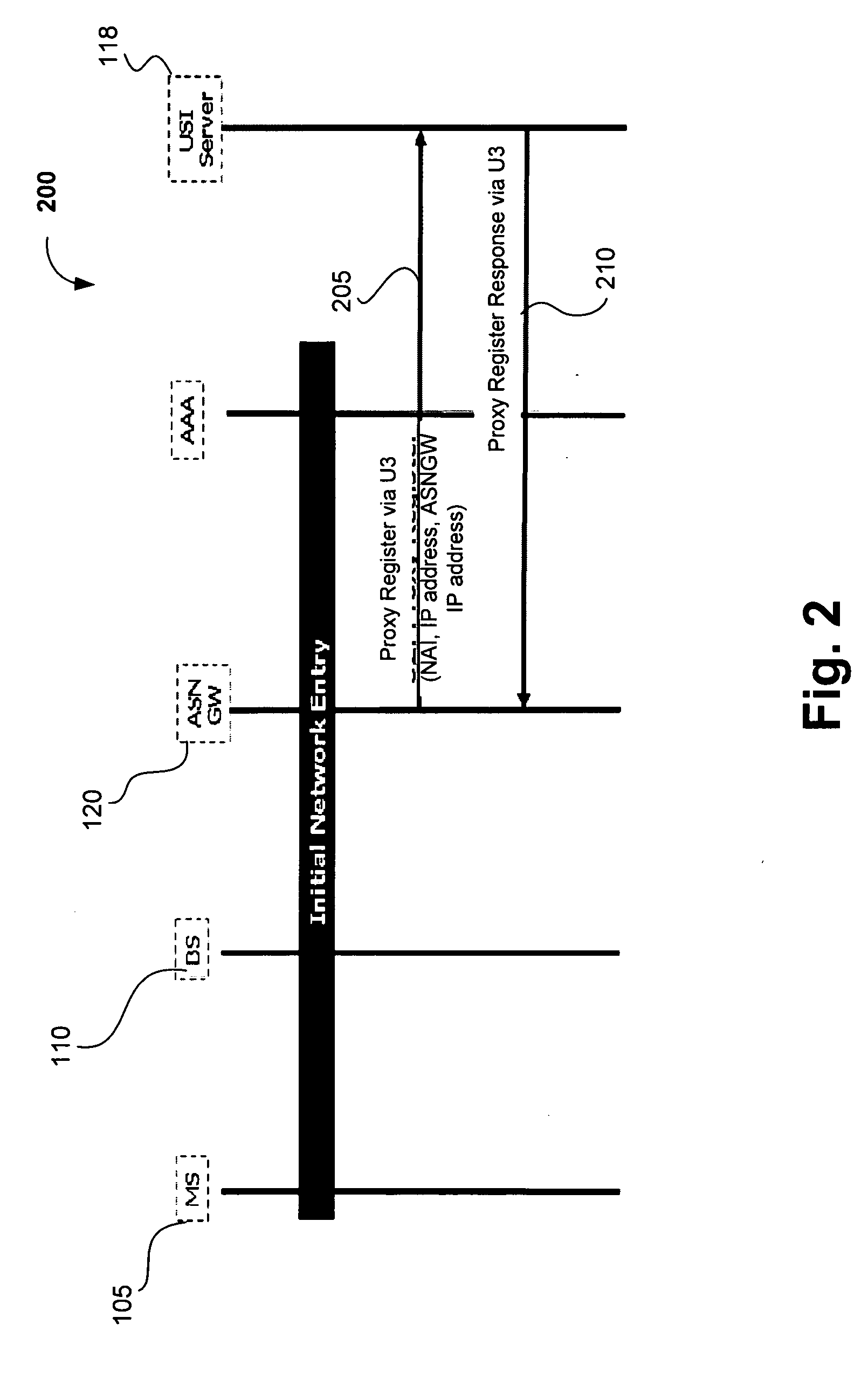
Method and system for WiBro network interworking in wireless terminal
ActiveUS20080117855A1Easy to useFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork traffic/resource managementTTEthernetIp address
A method and system for WiBro network interworking in a wireless terminal. The method includes: setting up, by a relay station for connecting the WLAN terminal with the WiBro network, a connection through an initial process with the WiBro network; performing, by an access router, Internet connection authentication on a user of the WLAN terminal in response to a request for Internet connection from the WLAN terminal; allocating, by the access router, an IP address in response to a request for IP address allocation from the WLAN terminal, and then allocating, by a WiBro radio access station, a unique Connection IDentification (CID) corresponding to a QoS level of the terminal user in response to a request from the relay station; and mapping, by the relay station, the allocated unique CID to the IP address of the WLAN terminal and providing Internet service.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Vehicle mounted electronic alarm system for road safety
InactiveCN101488287AAvoid tailgatingReduce property damageBeacon systems using radio wavesRoad vehicles traffic controlDriver/operatorPrivate network
The invention discloses an on-vehicle electronic warning system for road safety, comprising a wireless broadband special network established at the side of the road. The wireless broadband is composed of a road-side wireless signal transmitting tower, road-side optical cables and a database computing center and is used for receiving operational data of each vehicle on the road while uninterruptedly sending road feature data to each vehicle. An on-vehicle road safety electronic shield terminal arranged in the vehicle uninterruptedly transmits vehicle locations, time and speed data computed by a satellite and land station signals to the database computing center of the road-side wireless special network subsequent to the reception of a positioning signal from a global positioning system so that all the vehicles share the positioning data, meanwhile, the terminal uninterruptedly receives and reads the road feature data sent by the wireless broadband special network during the traveling, and sends, in case that the distance between vehicles are too close or the vehicle is about to deviate from own traffic lane, warning information to related drives in order to avoid traffic accidents such as vehicle rear-end collision, deviation from the roads, side collision, etc.
Owner:曲涛
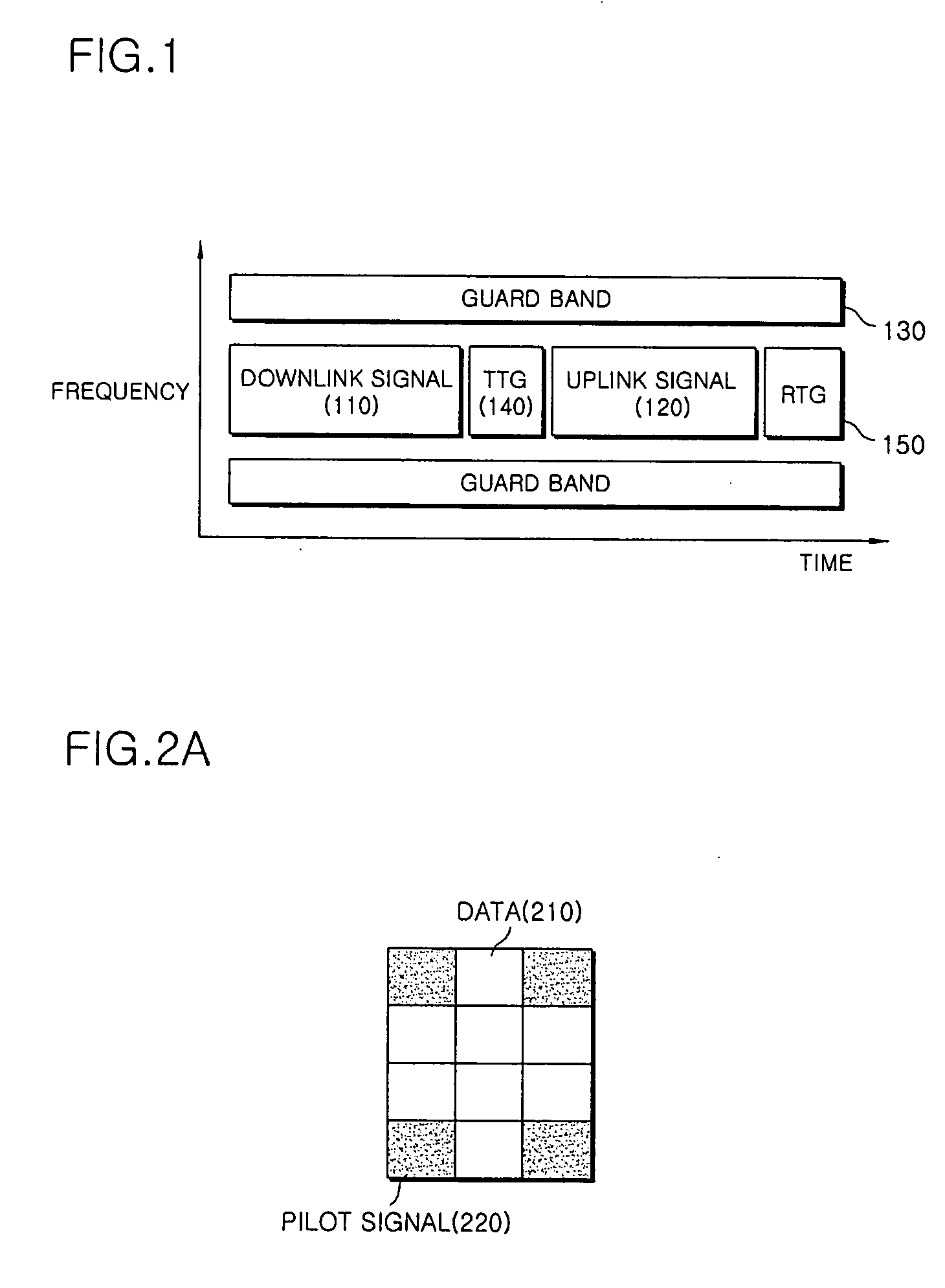
Novel physical layer header structure for decoding and synchronization
ActiveUS20100150037A1Synchronisation error correctionData switching by path configurationComputer hardwarePhysical layer
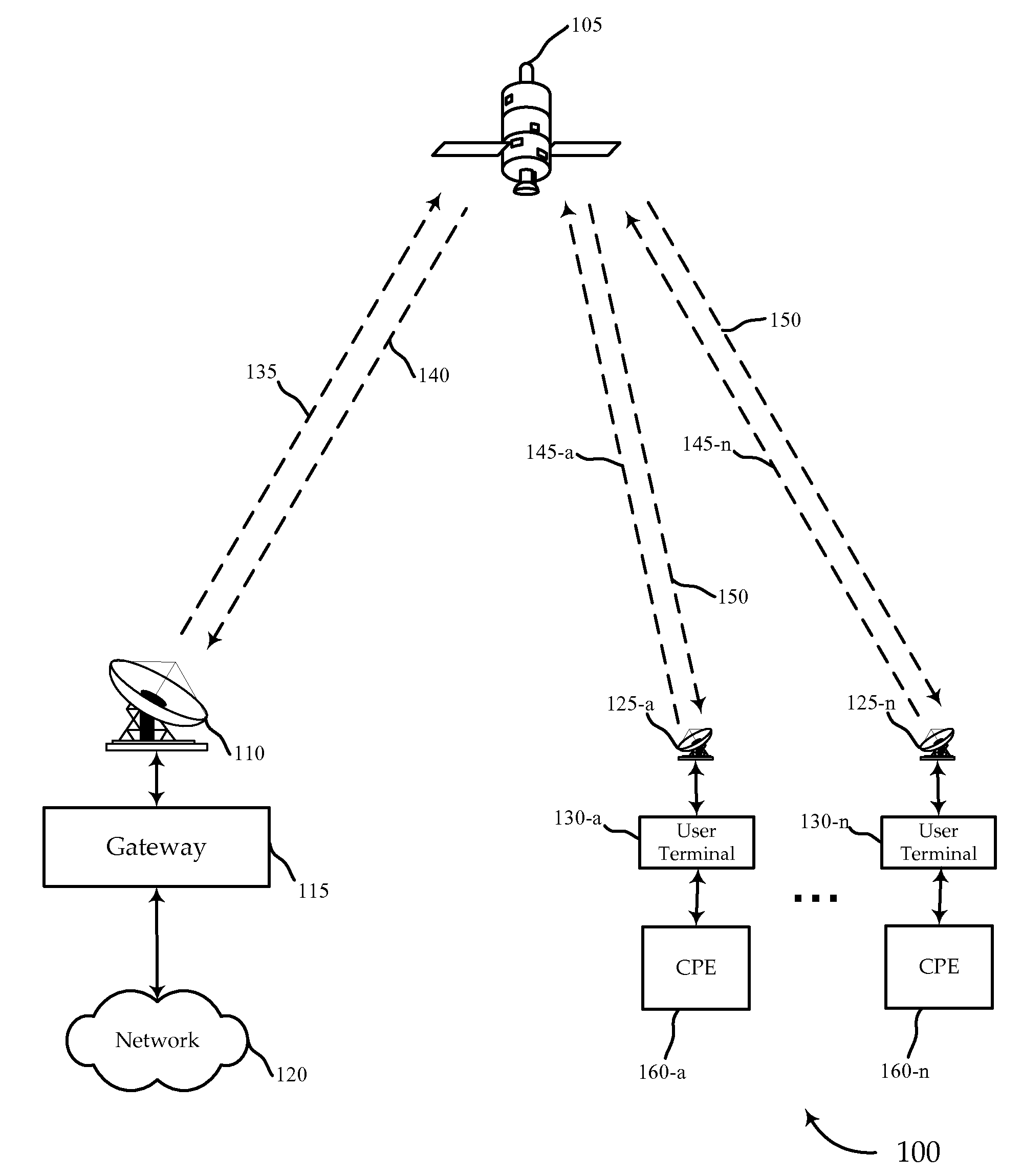
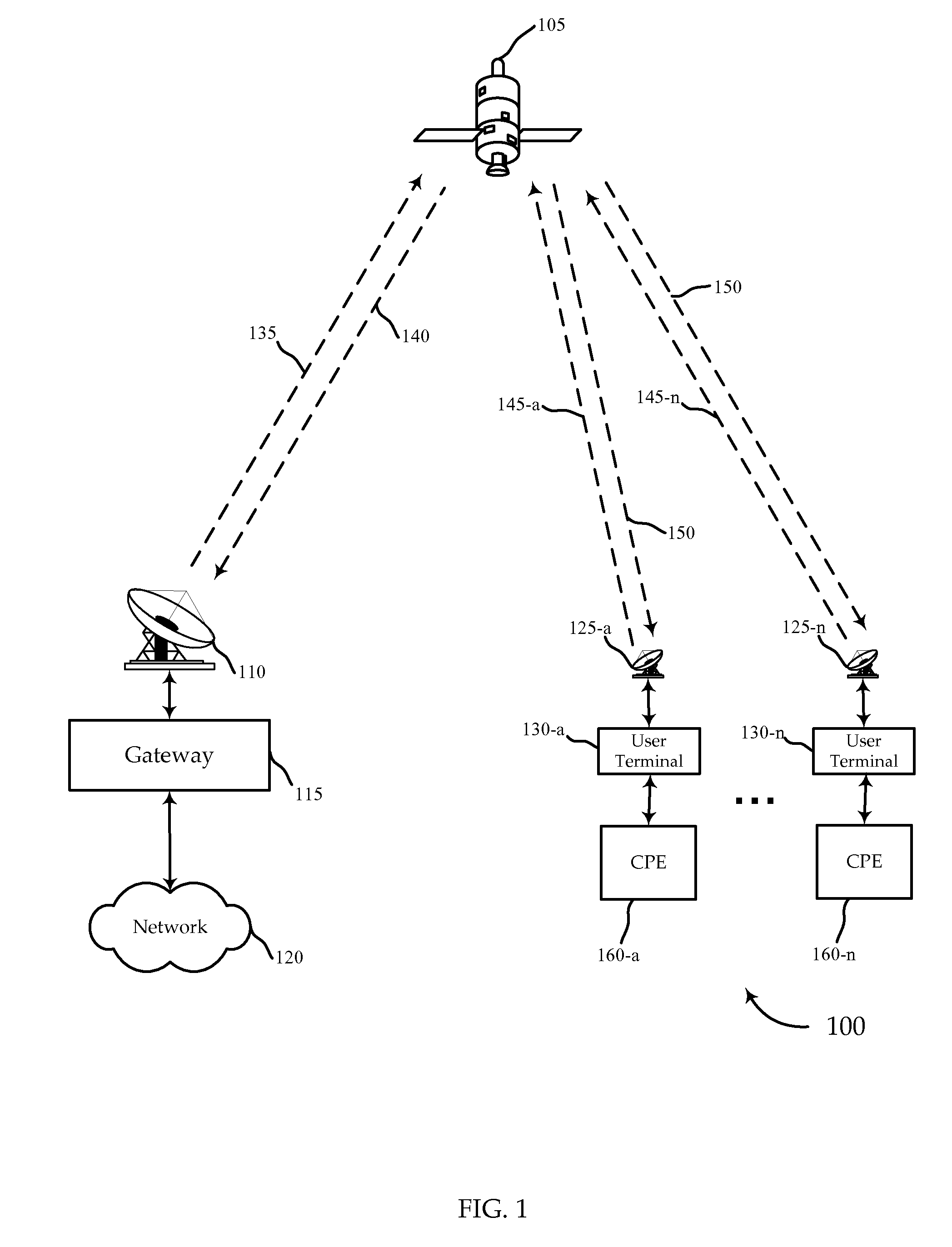
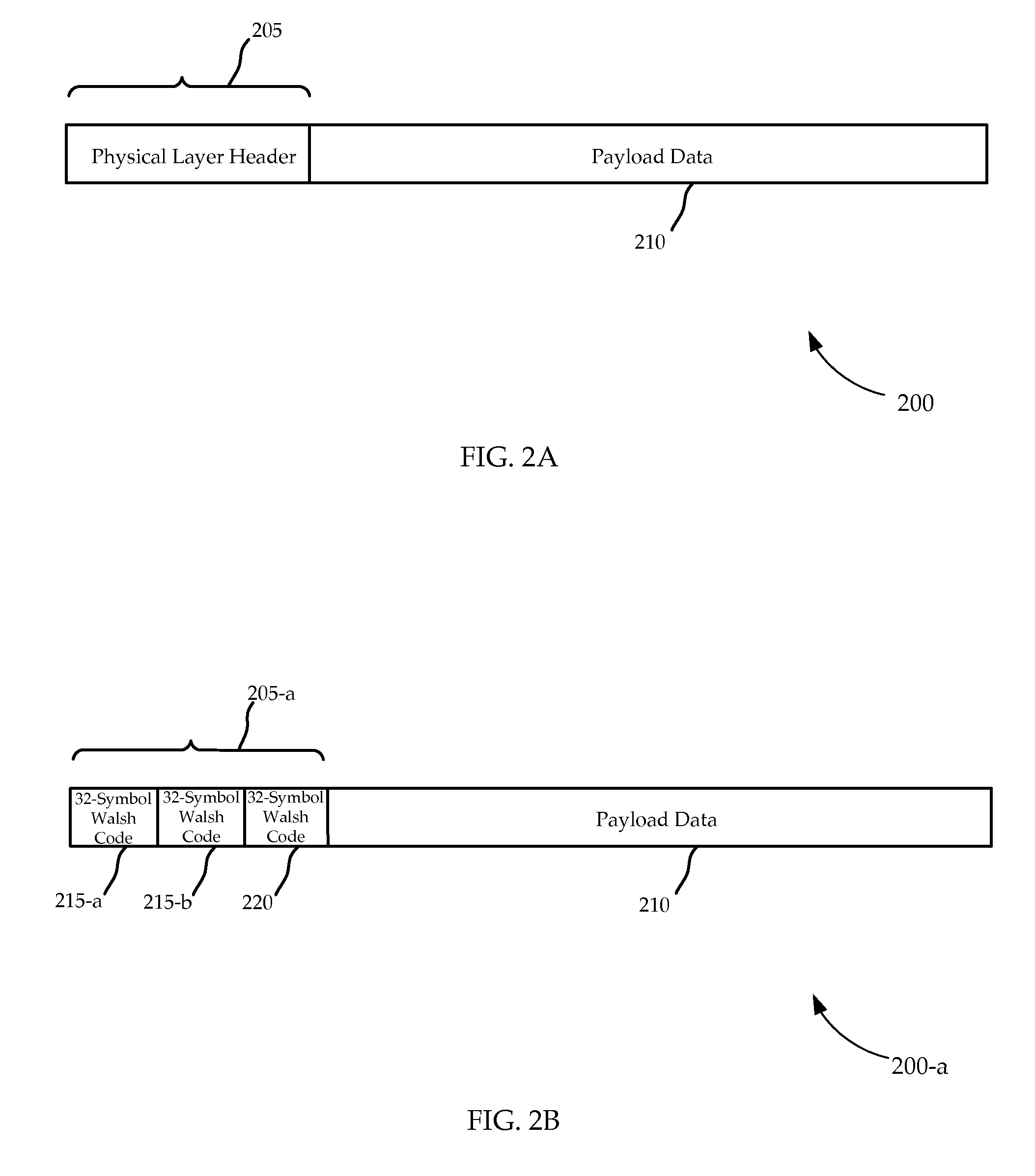
Systems, devices, processors, and methods are described which may be used for the reception of a wireless broadband signal at a user terminal from a gateway via a satellite. A wireless signal may include a series of physical layer frames, each frame including a physical layer header and payload. The received signal is digitized and processed using various novel physical layer headers and related techniques to synchronize the physical layer frames and recover data from physical layer headers for purposes of demodulation and decoding.
Owner:VIASAT INC
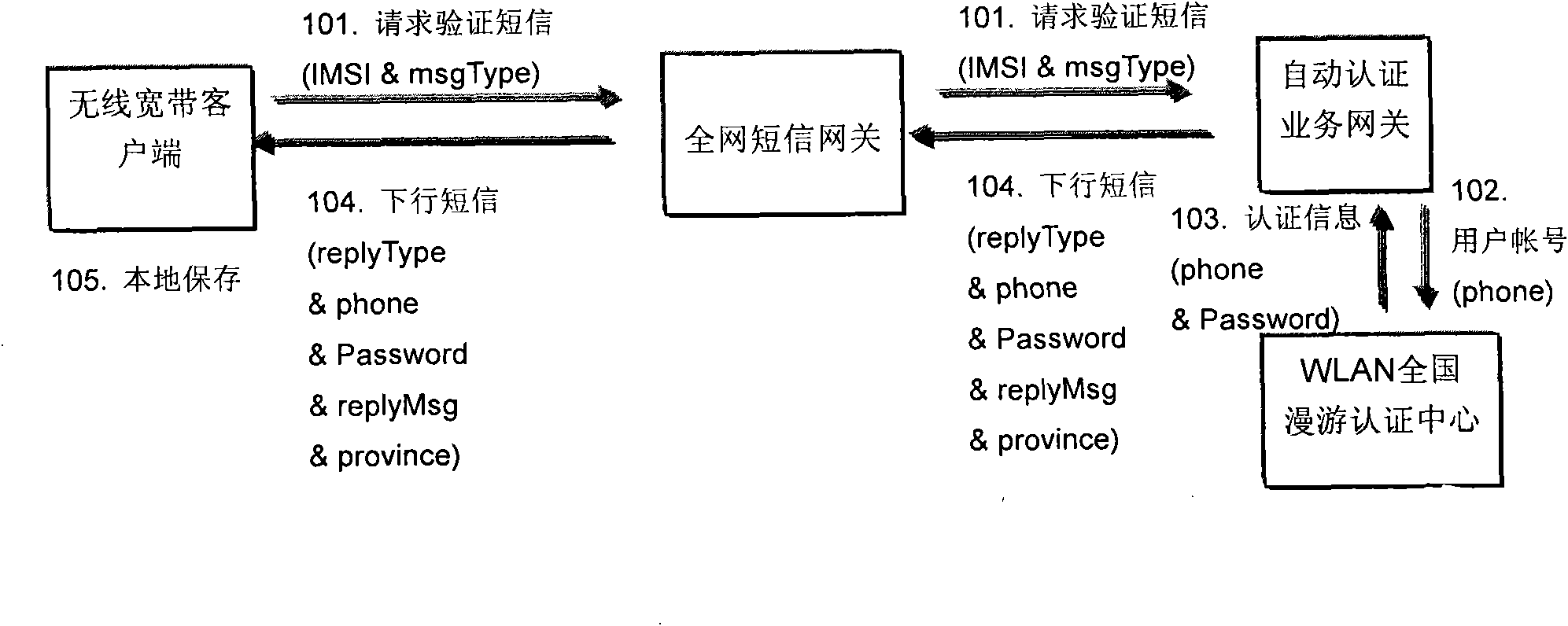
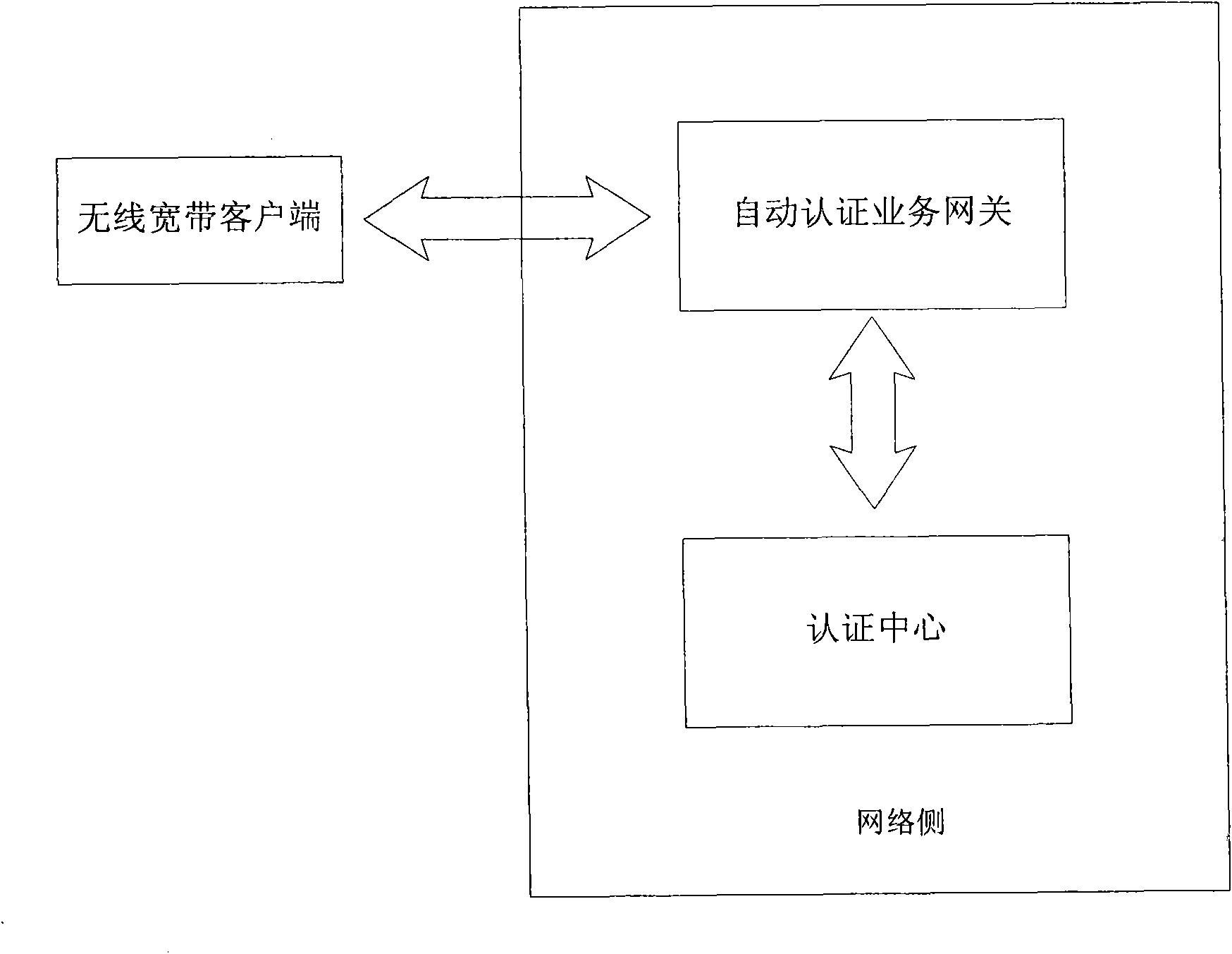
Method for realizing automatic certification of wireless access short message and system thereof
The invention discloses a method for realizing the automatic certification of a wireless access short message and a system thereof. The method comprises the steps: when firstly connecting with a wireless broadband (WiFi) after installing an user identification module (UIM), a wireless wideband user terminal backstage transmits a request certification short message with the international mobile subscriber identity (IMSI) of an UIM card to a network side; the network side returns the certification information of the WiFi to the wireless wideband user terminal by means of the short message, and the wireless wideband user terminal receives the certification information and memorizes the certification information at local; and when starting a wireless connection request, the wireless wideband user terminal directly extracts the certification information from the local and transmits to the network side to be certificated. The invention can automatically complete the certification of the wireless access without user manual intervention, thereby reducing the operation of the user and providing the convenience for the wireless wideband user.
Owner:CHINA TELECOM CORP LTD
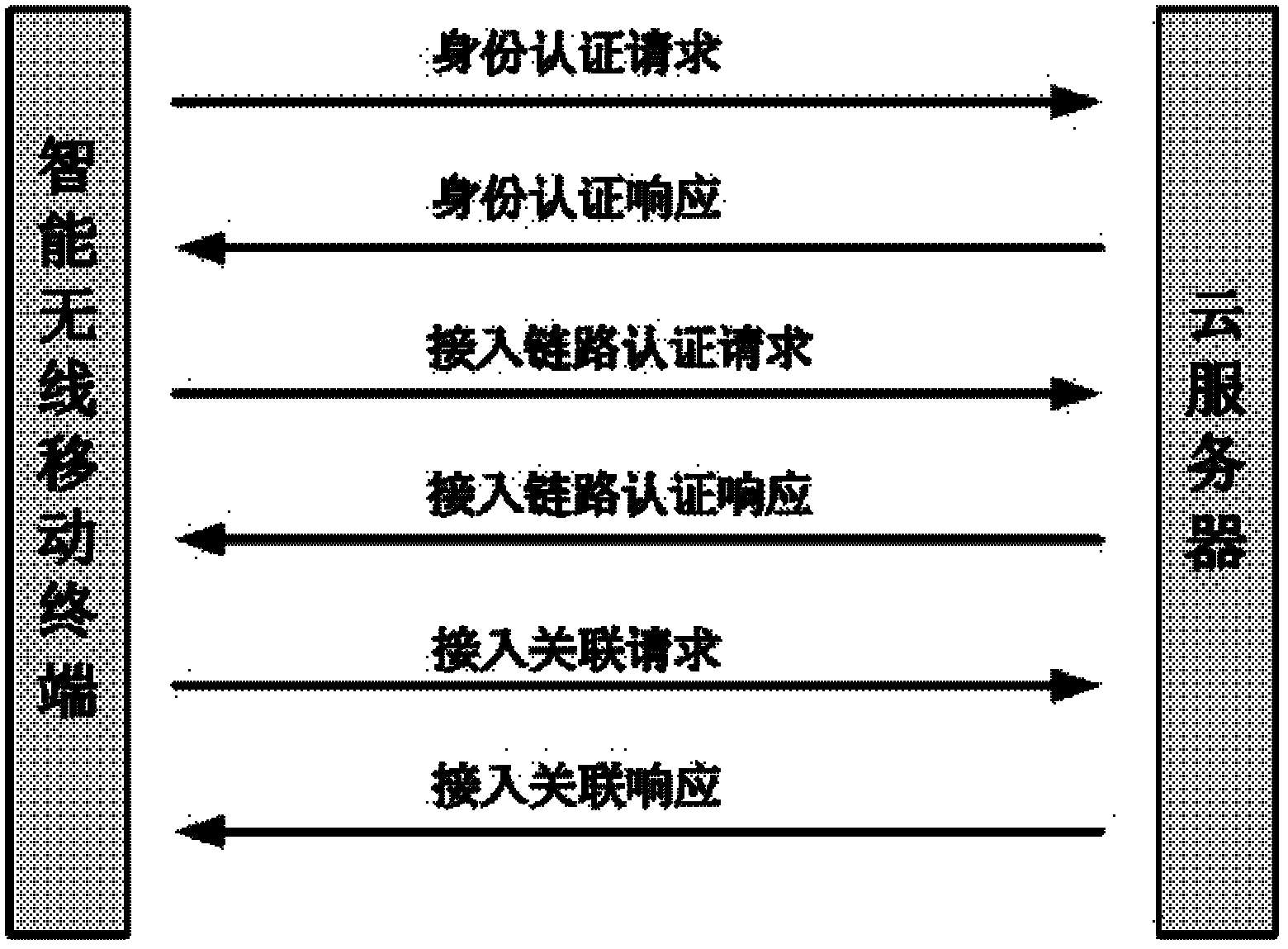
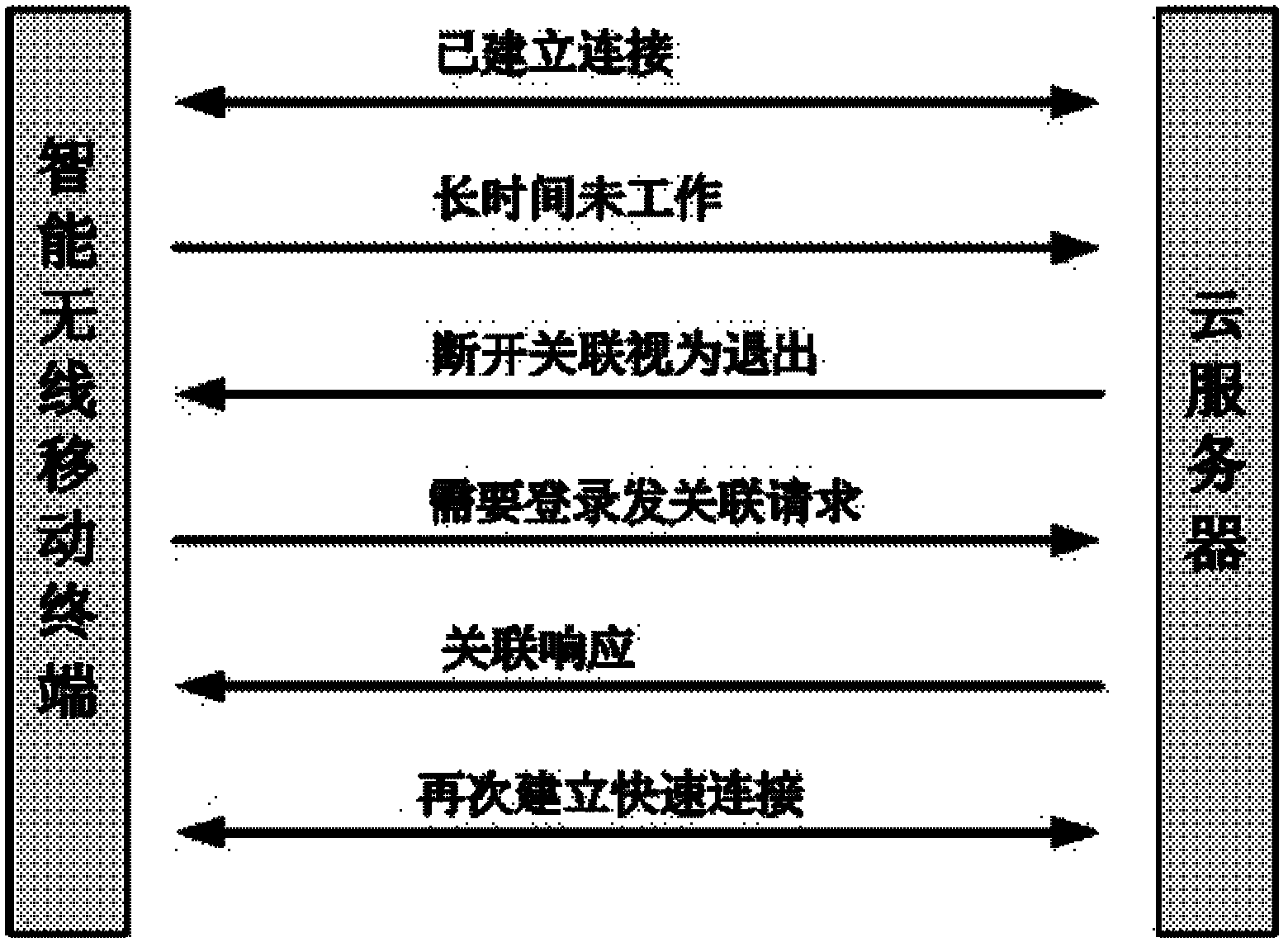
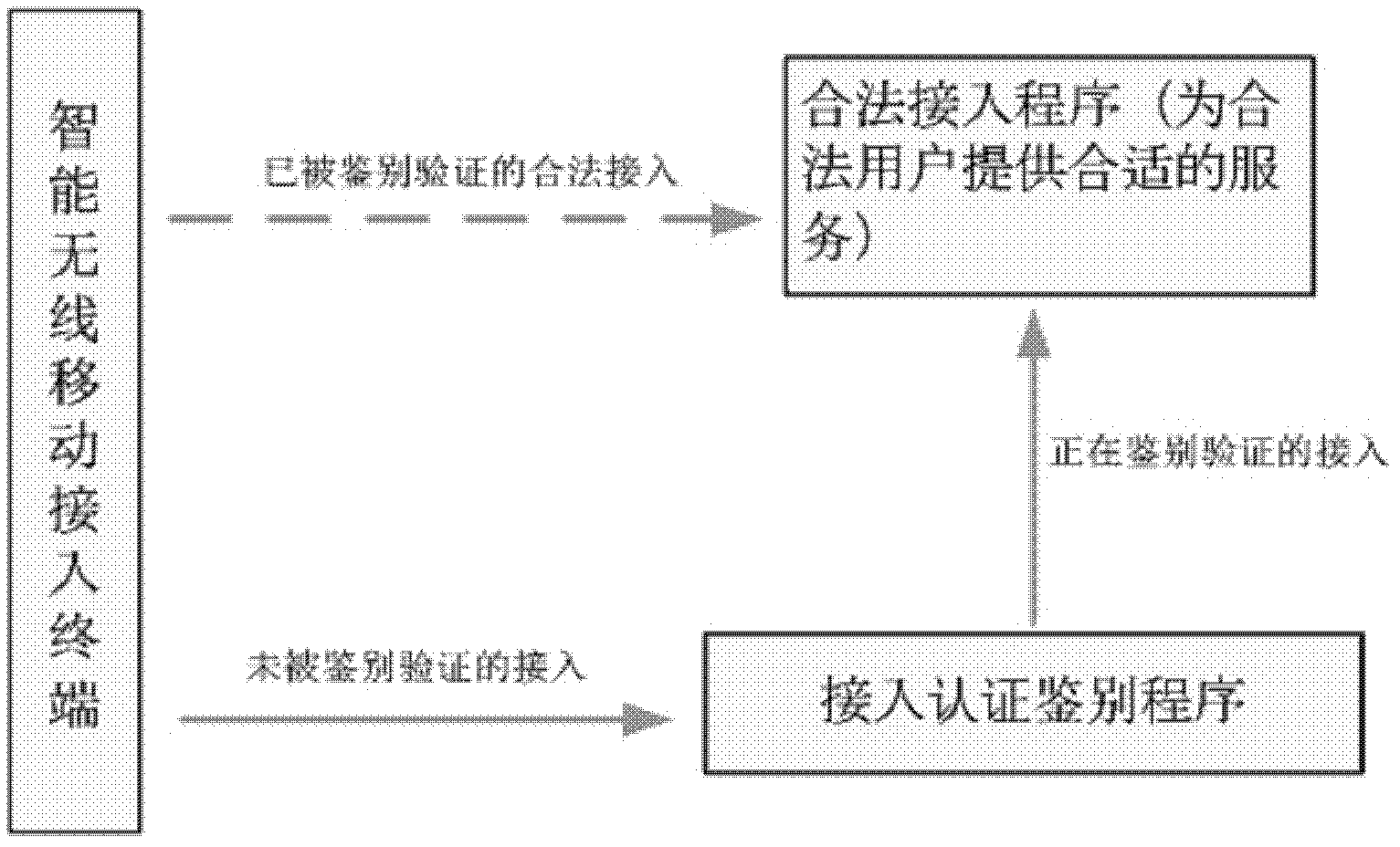
Identity authentication method allowing intelligent mobile wireless terminal to access cloud server
InactiveCN102571792AAvoid unreliableFix security issuesUser identity/authority verificationMobile WebBroadband
The invention discloses an identity authentication method allowing an intelligent mobile wireless terminal to access a cloud server, which comprises the following steps that 1, when the intelligent wireless mobile terminal privately accesses the cloud server through a wireless wideband mobile network, an identity authentication request is sent; 2, the cloud server sends an identity authentication response; 3, the intelligent wireless mobile terminal sends an access link authentication request to the cloud server; 4, the cloud server comprises the attributes of the intelligent wireless mobile terminal, such as identity, password and the like, in case of legitimate access, an access link authentication response is fed back; 5, the intelligent wireless mobile terminal sends an access link relevant request; 6, the cloud server responds to one access link relevant response, creating a bilateral link circuit connection; and 7, the reliable access process between the intelligent wireless mobile terminal and the cloud server is completed. Through the invention, the reliability and safety of the cloud server are ensured, thereby preventing the information at the cloud server end from leakage, and blocking dangerous access.
Owner:西安润基投资控股有限公司
System for interworking services of heterogeneous networks and method for vertical handoff
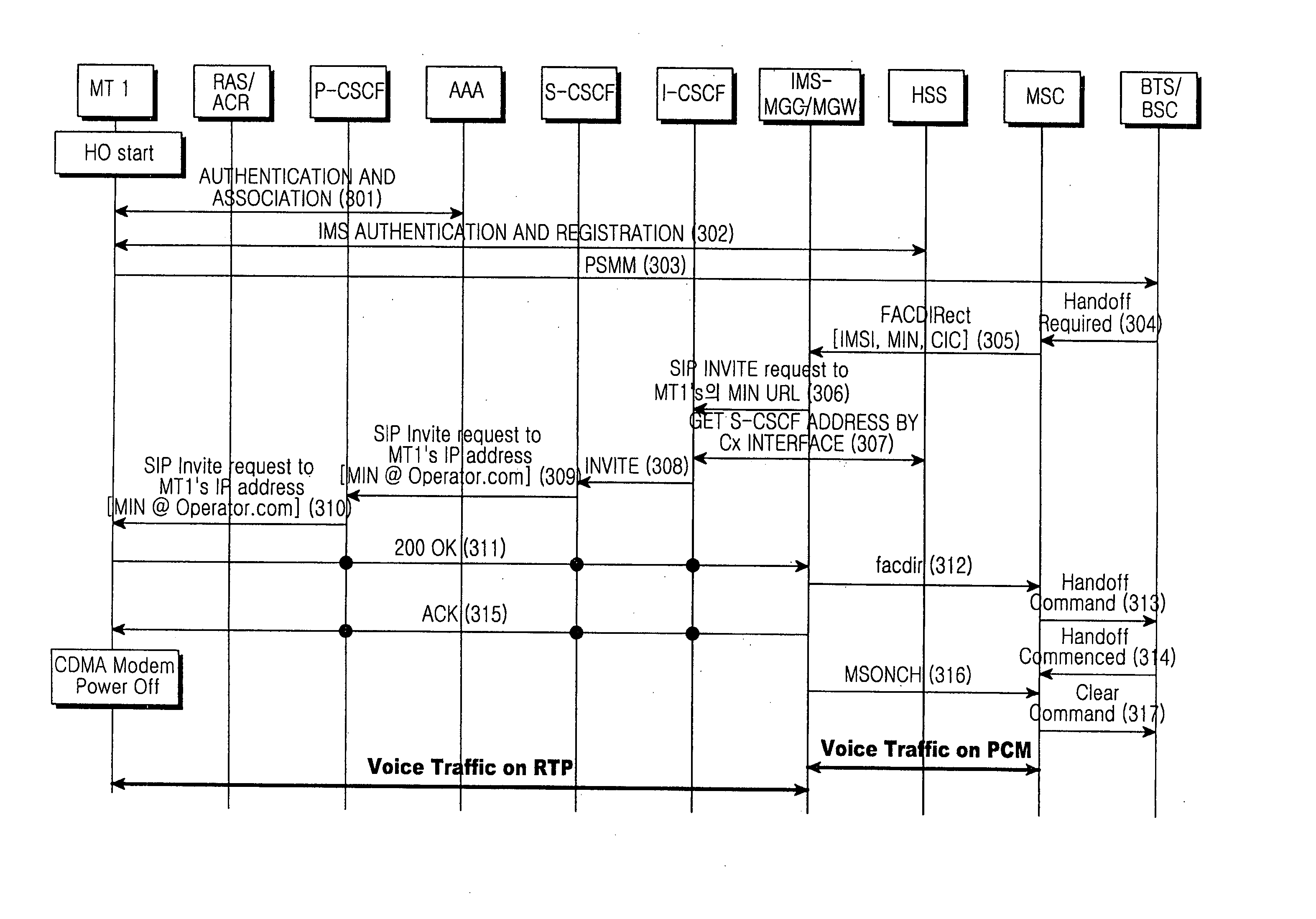
InactiveUS20070133471A1Packet lossReduce delaysData switching by path configurationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsPacket lossCode division multiple access
An interworking network system between heterogeneous networks and a vertical hand-off method for supporting QoS are provided. WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) and Wibro (Wireless Broadband) have a service range overlaid with that of the CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) 2000 that has been provided over the whole area, and routers of the respective networks are hierarchically connected by setting the CDMA 2000 as a higher network, the WiBro as a middle network, and the WLAN as a lower network according to service area and transmission speed of the respective networks. Accordingly, a hierarchical interworking method has been provided as an integrating network of the CDMA 2000, WiBro, and WLAN independently providing a service so that it may minimize packet loss and delay.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
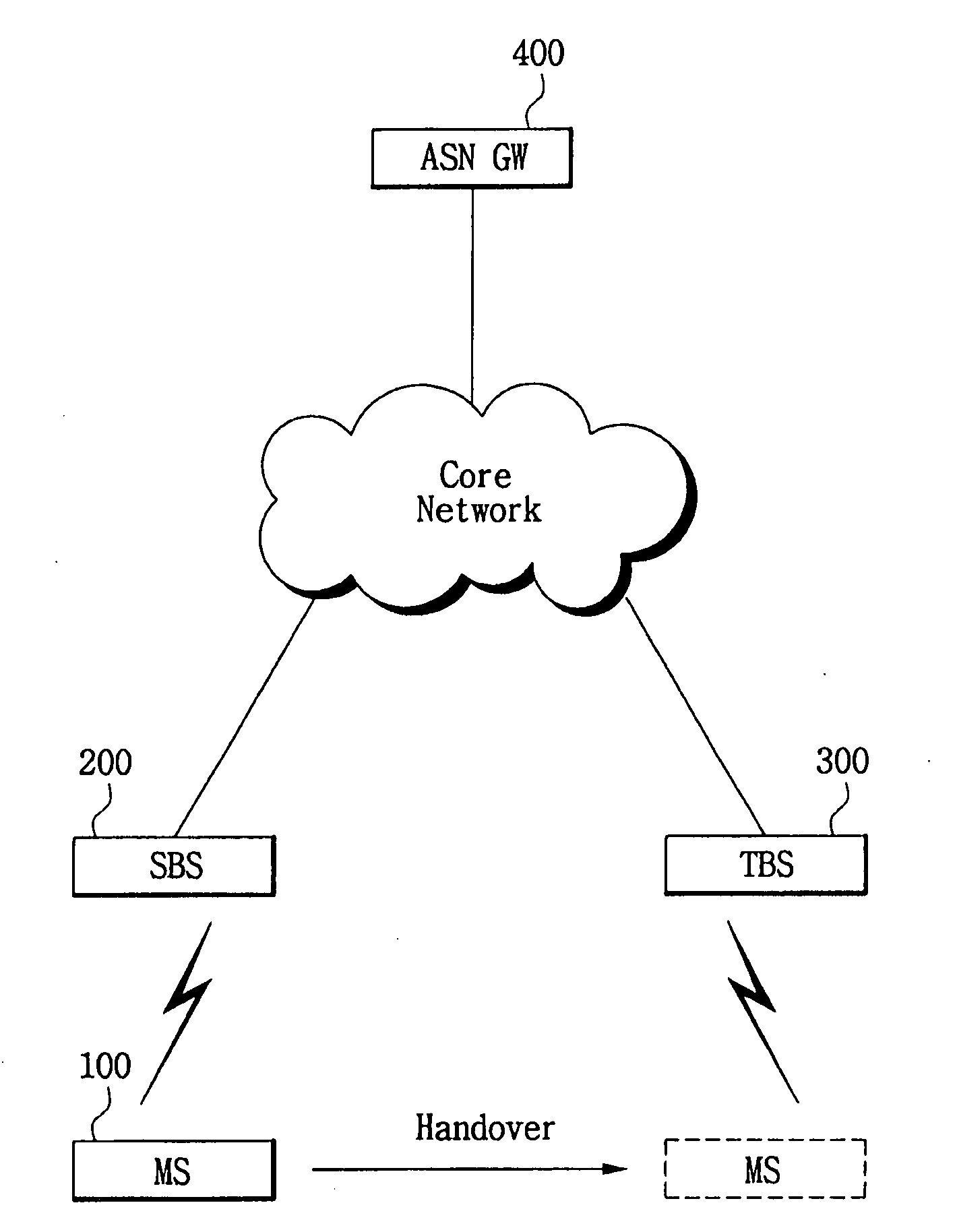
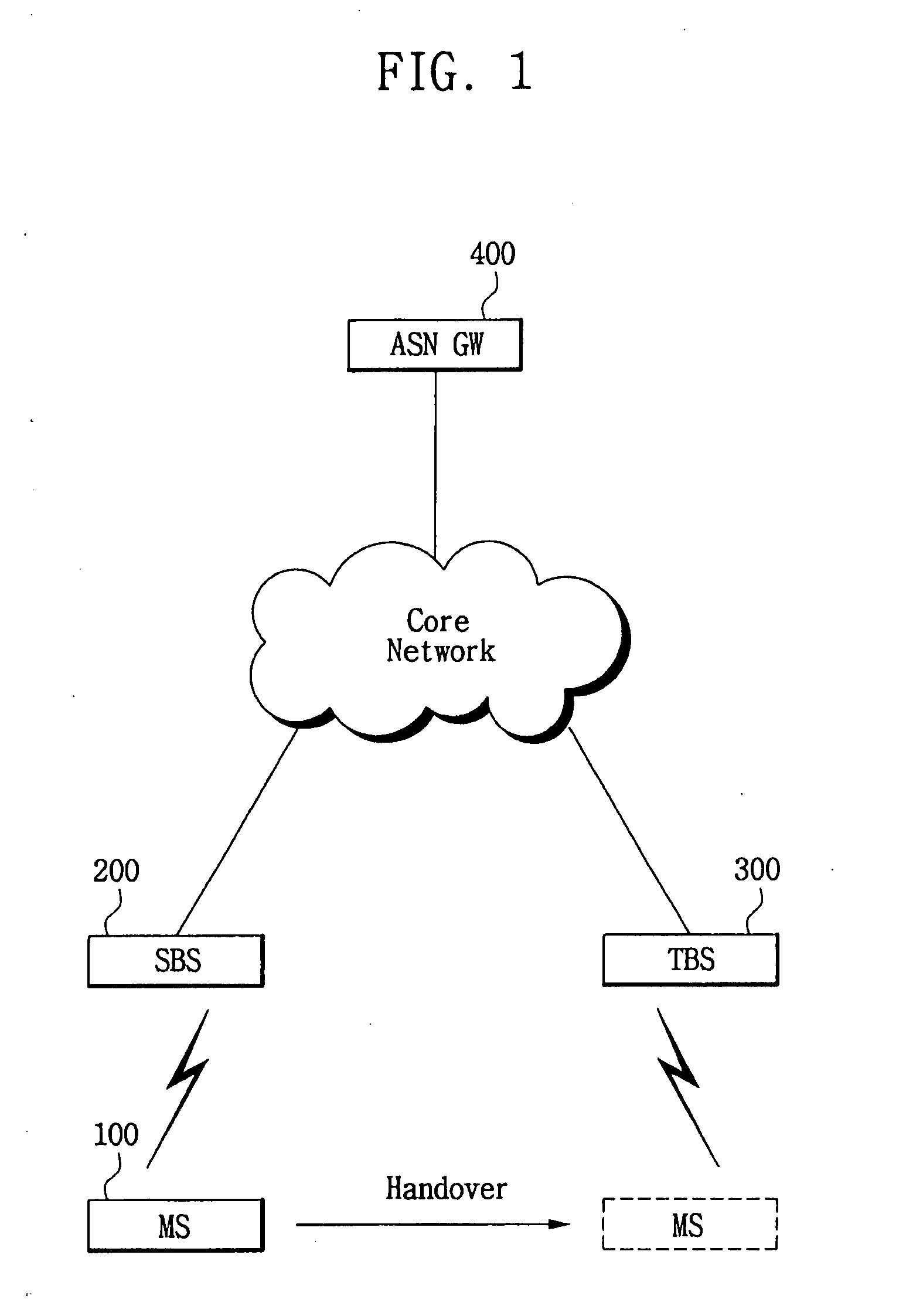
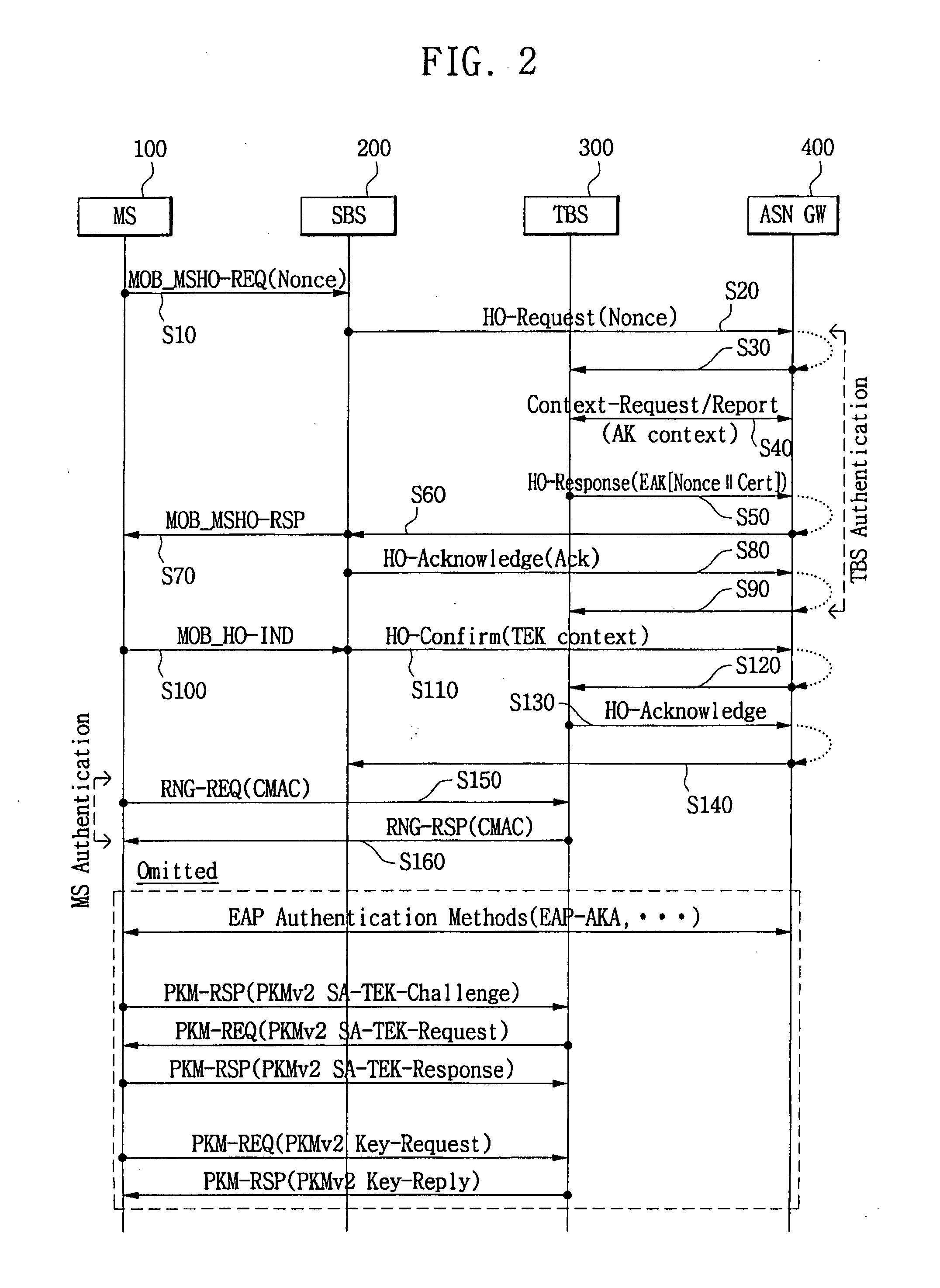
Performing handover using mutual authentication in wireless broadband (WiBro) network
InactiveUS20080089294A1Improve securityRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesUltrasound attenuationWiBro
A method and system to perform a handover using mutual authentication in a Wireless Broadband (WiBro) network includes: generating a temporary number of a mobile station needing handover from a first base station to a second base station and requesting a handover from the first base station; transferring a handover request message, including a field for storing the temporary number of the mobile station, from the first base station to the second base station according to the handover request of the mobile station; transferring a handover response message, including respective fields for storing the mobile station's temporary number and the second base station's certification encoded using an authentication key received from an authentication server, from the second base station to the first base station; verifying the encoded temporary number of the mobile station and the encoded certification of the second base station in the handover response message transferred from the second base station, and transferring a handover acknowledge (ACK) message including a field for storing an authentication result for the second base station, from the first base station to the second base station; transmitting an initial communication request message, including a Control Mobile Attenuation Code (CMAC) value to be authenticated by the second base station, from the mobile station to the second base station; and authenticating the mobile station and transmitting a response message to the initial communication request message, from the second base station to the mobile station in response to the CMAC value transmitted from the mobile station being the same as a CMAC value of the second base station.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
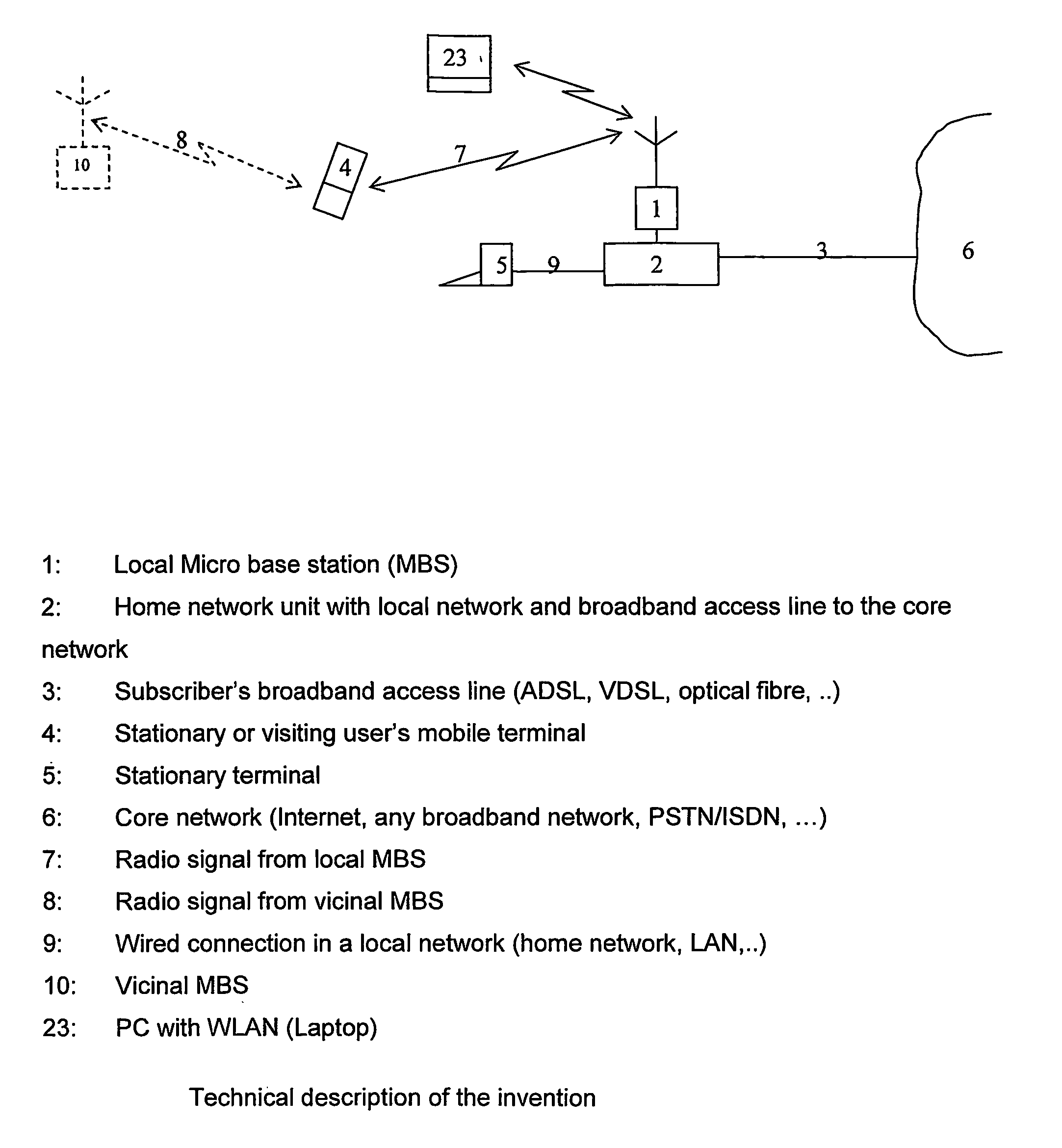
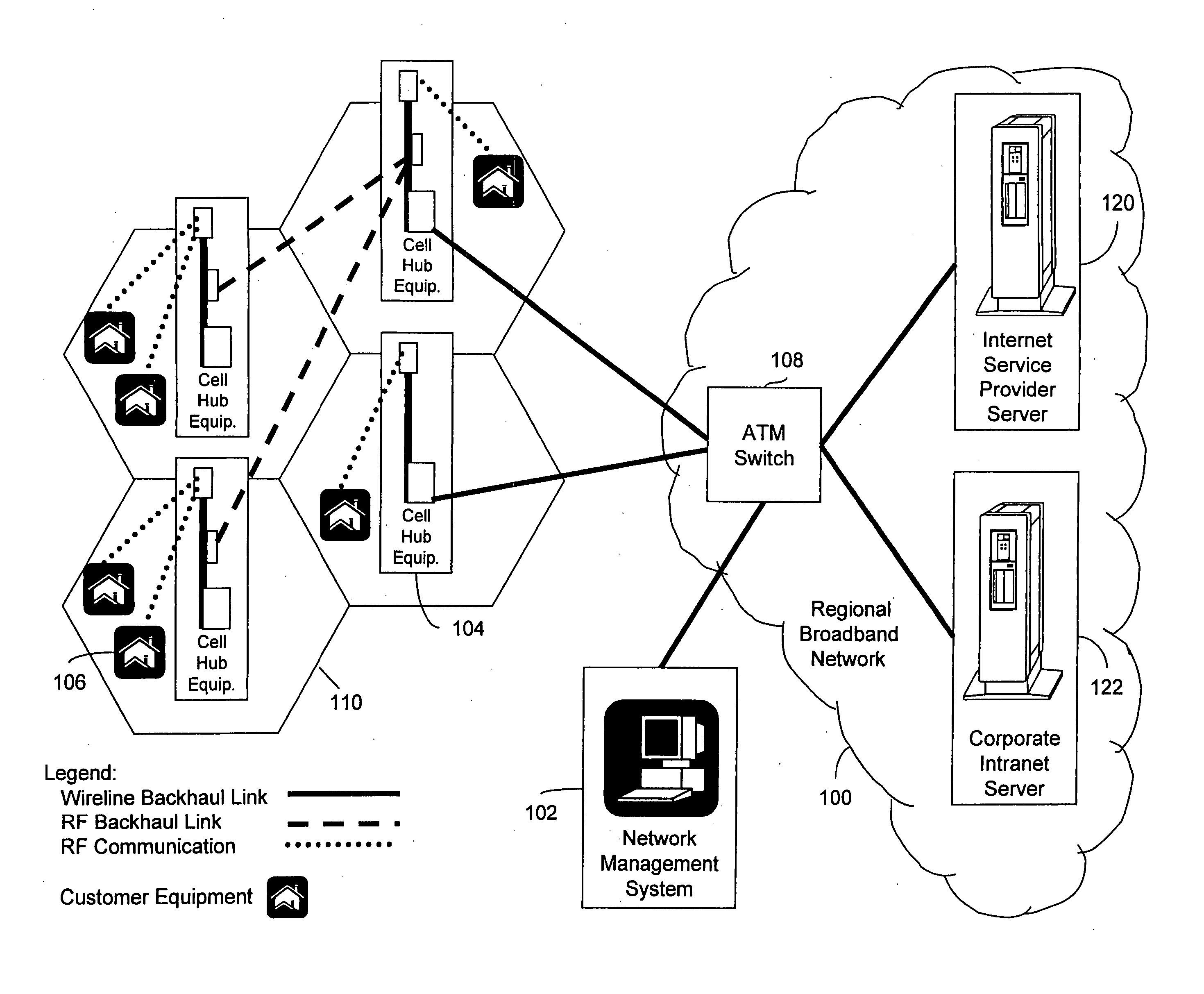
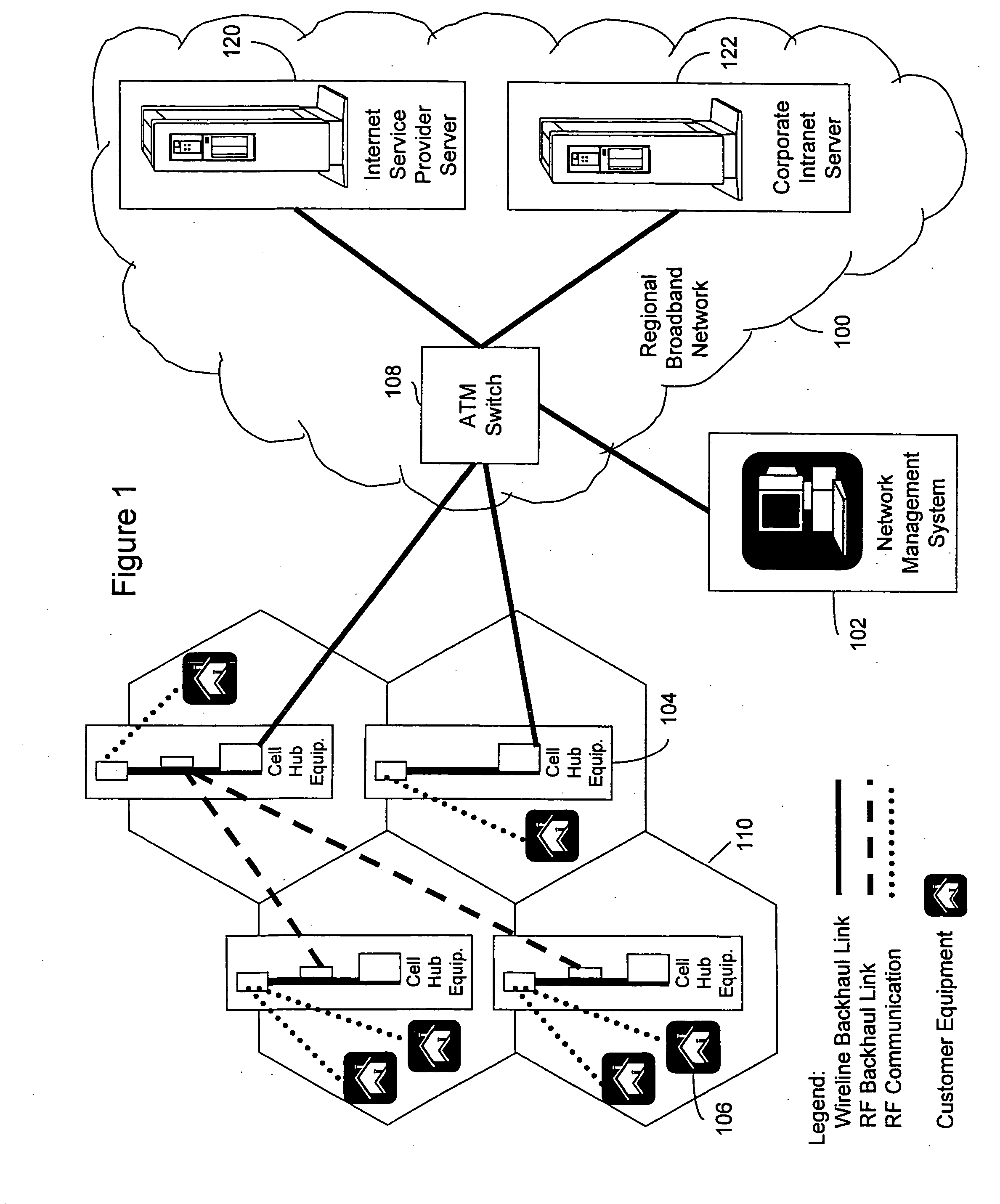
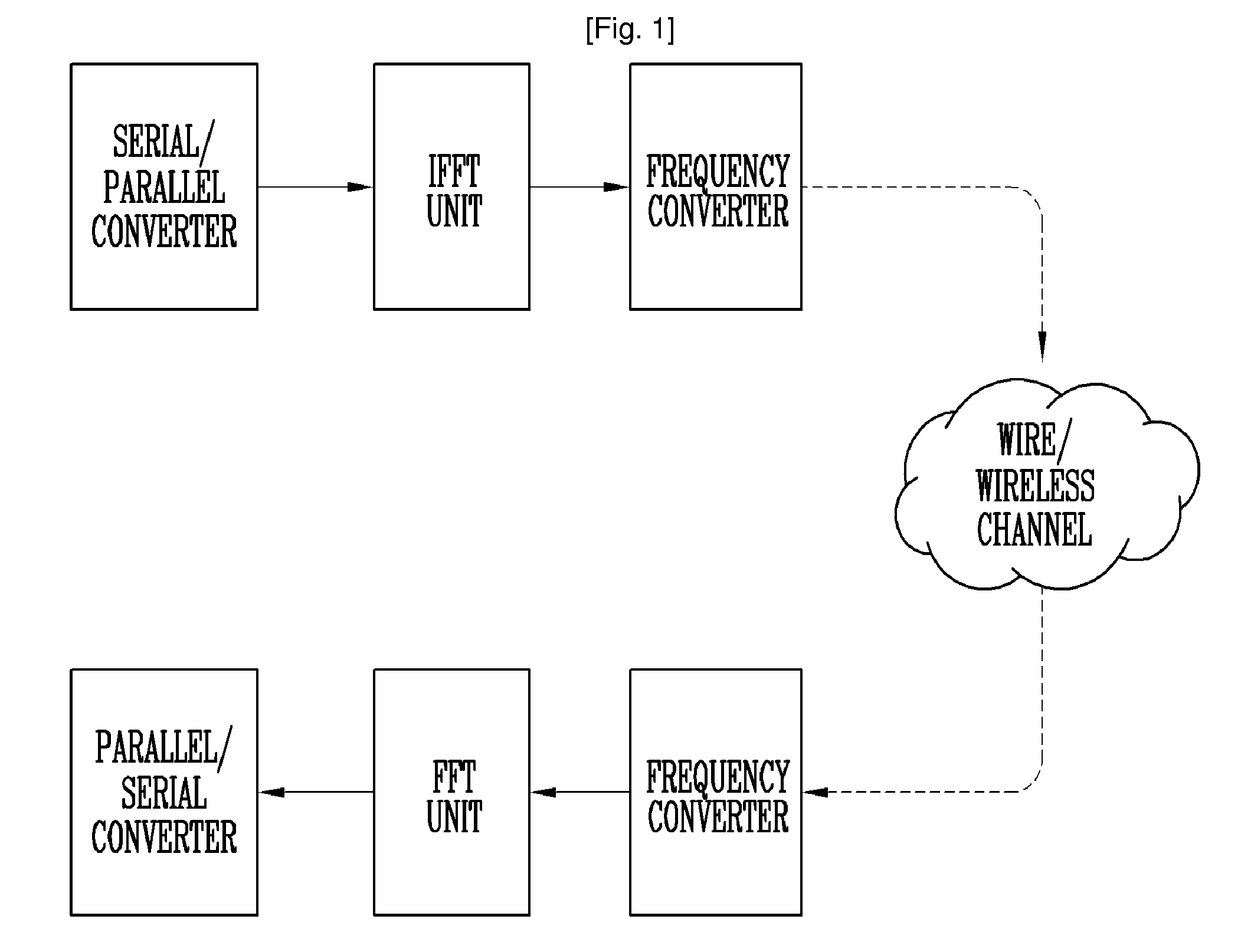
Wireless broadband service
InactiveUS20050030907A1Facilitate communicationBroadband local area networksNetwork topologiesIntegrated Services Digital NetworkData access
A fixed broadband wireless data access service providing shared wide-band packet-switched data transport for high speed data access in areas where conventional ADSL service and fiber optic service are unavailable. The wireless data access service is a point-to-multipoint cellular-type network that connects customers to data service providers through the ATM backbone of an existing network. Customers connect to the ATM backbone and data service provider through a cellular grid in which a wireless base station in each cell communicates with the individual customer wireless equipment within its cell site coverage area. The base stations are connected to an ATM backbone switch through wireless and wireline backhaul links. The upstream and downstream bandwidths of the wireless broadband network are engineered in various symmetric and asymmetric configurations to provide a shared packet-switched connection that emulates an uninterrupted, direct wireline ADSL connection. The wireless broadband network employs a data protocol of shared access bandwidth and adaptive asymmetric data rates to support multiuser service sessions by wireless transmission. The wireless broadband network is not network protocol specific and can be applied to wireless asymmetric digital subscriber line service, wireless integrated service digital network over digital subscriber line service, wireless very high bit rate digital subscriber line service, or wireless symmetric or single-line digital subscriber line service.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
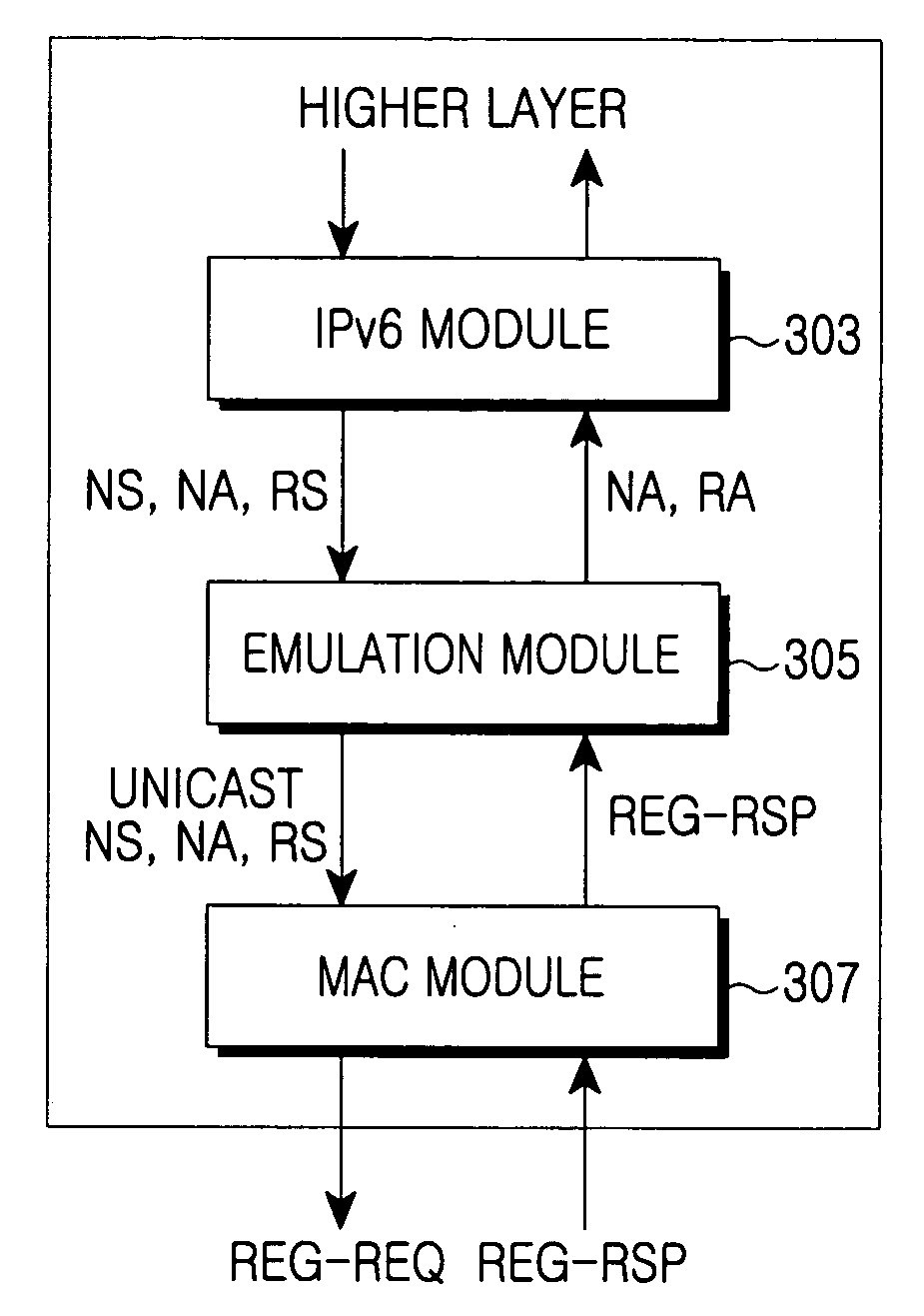
Emulation device and method for supporting IPv6 in WiBro terminal
InactiveUS20070153810A1Avoid collisionReduce resource consumptionAssess restrictionDispersed particle separationCommunications systemMessage type
A network emulation device and method in a terminal of an IEEE 802.16 communication system supporting IPv6 communications based on a Neighbor Discovery (ND) protocol are provided. The terminal includes an IPv6 module for performing an ND mechanism to search for a neighbor terminal or a router, a MAC module for communicating based on the IEE 802.16 standard, and a network emulation module provided between the IPv6 module and the MAC module for analyzing a ND message received from the IPv6 module and discarding the ND message or generating a response message for the ND message according to the message type. The network emulation module converts a broadcast ND message to a unicast message and provides the unicast message to a corresponding network device if network information needed to internally generate the response message is not collected.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for transmitting multicast data in wimax/wibro relay system
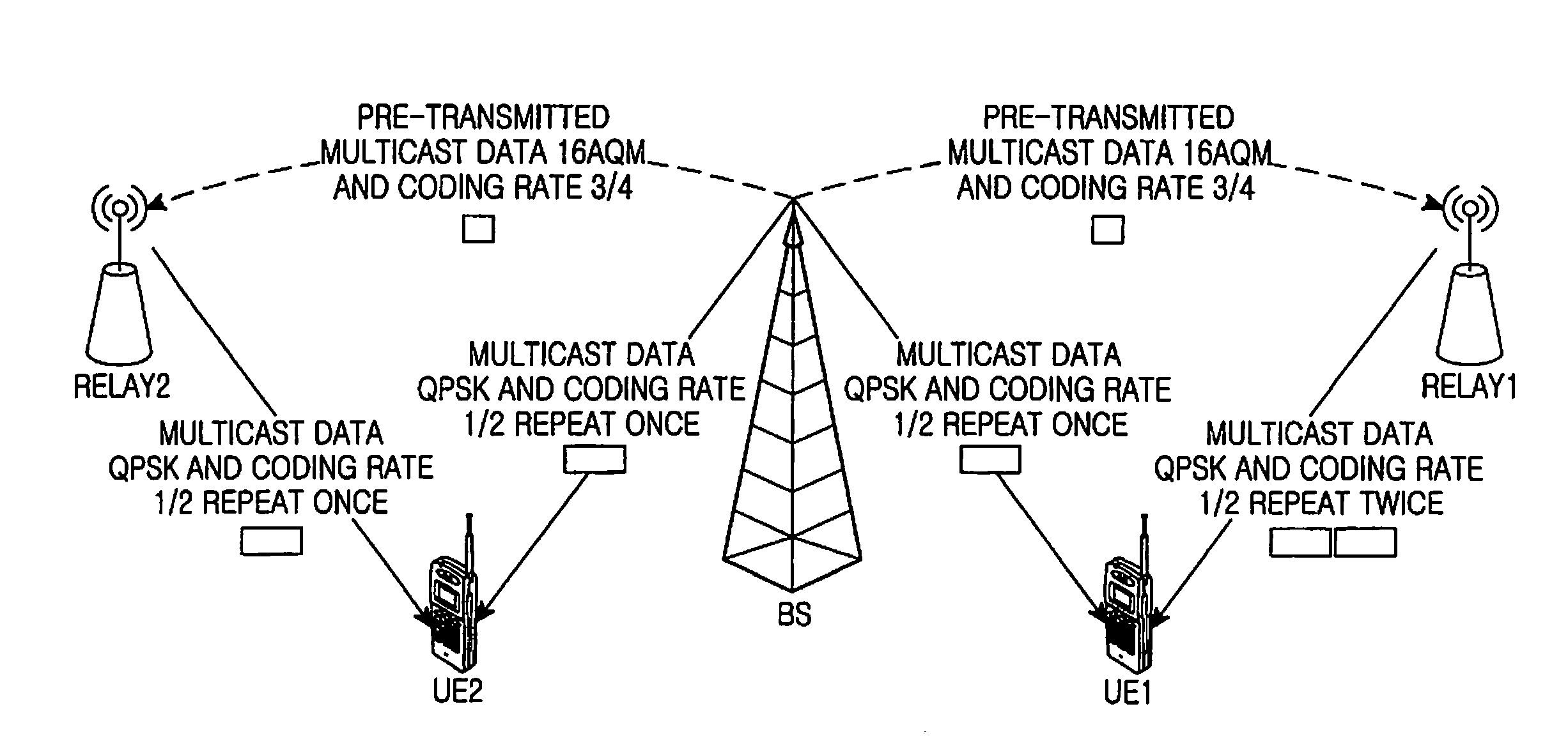
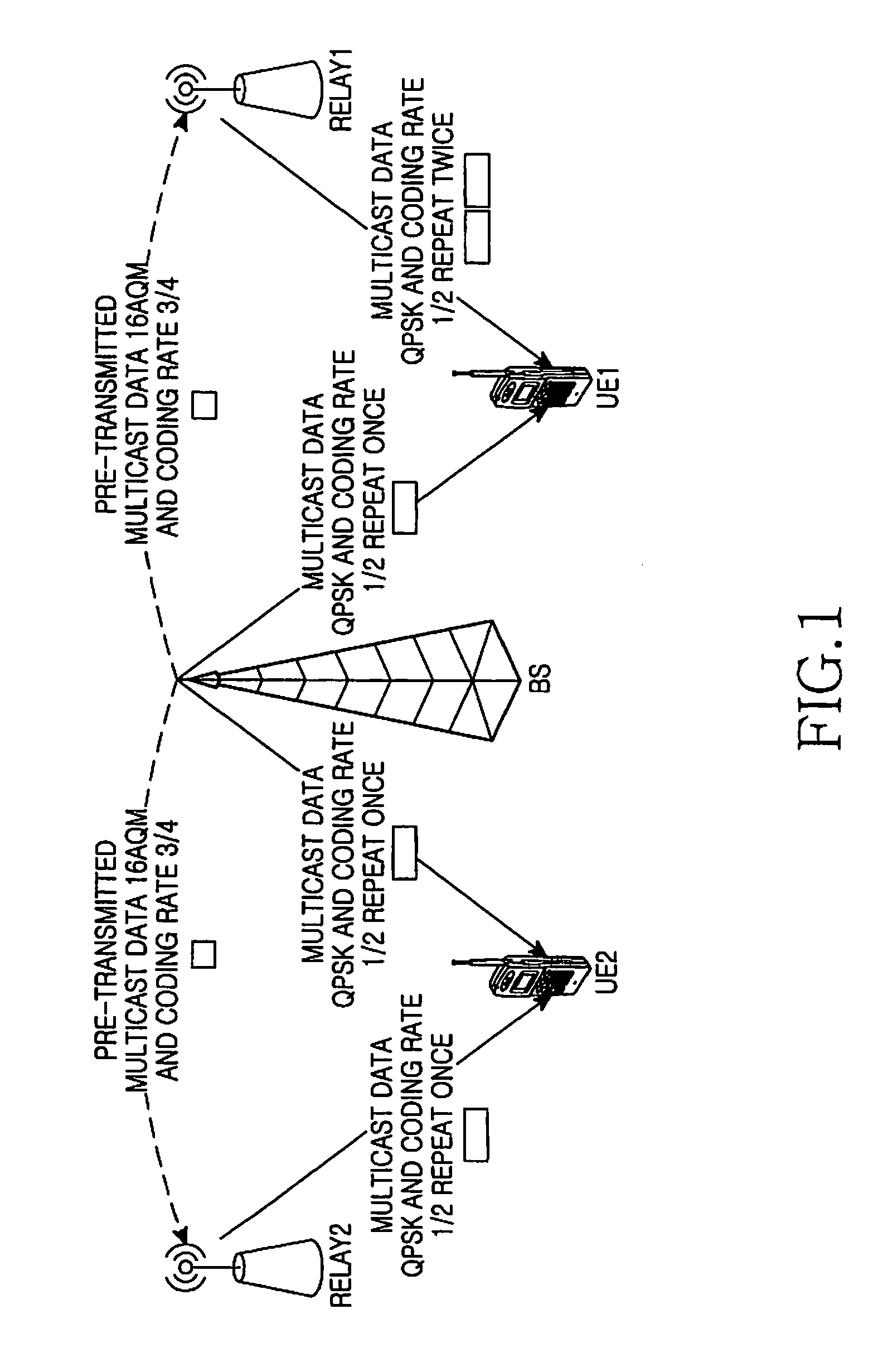
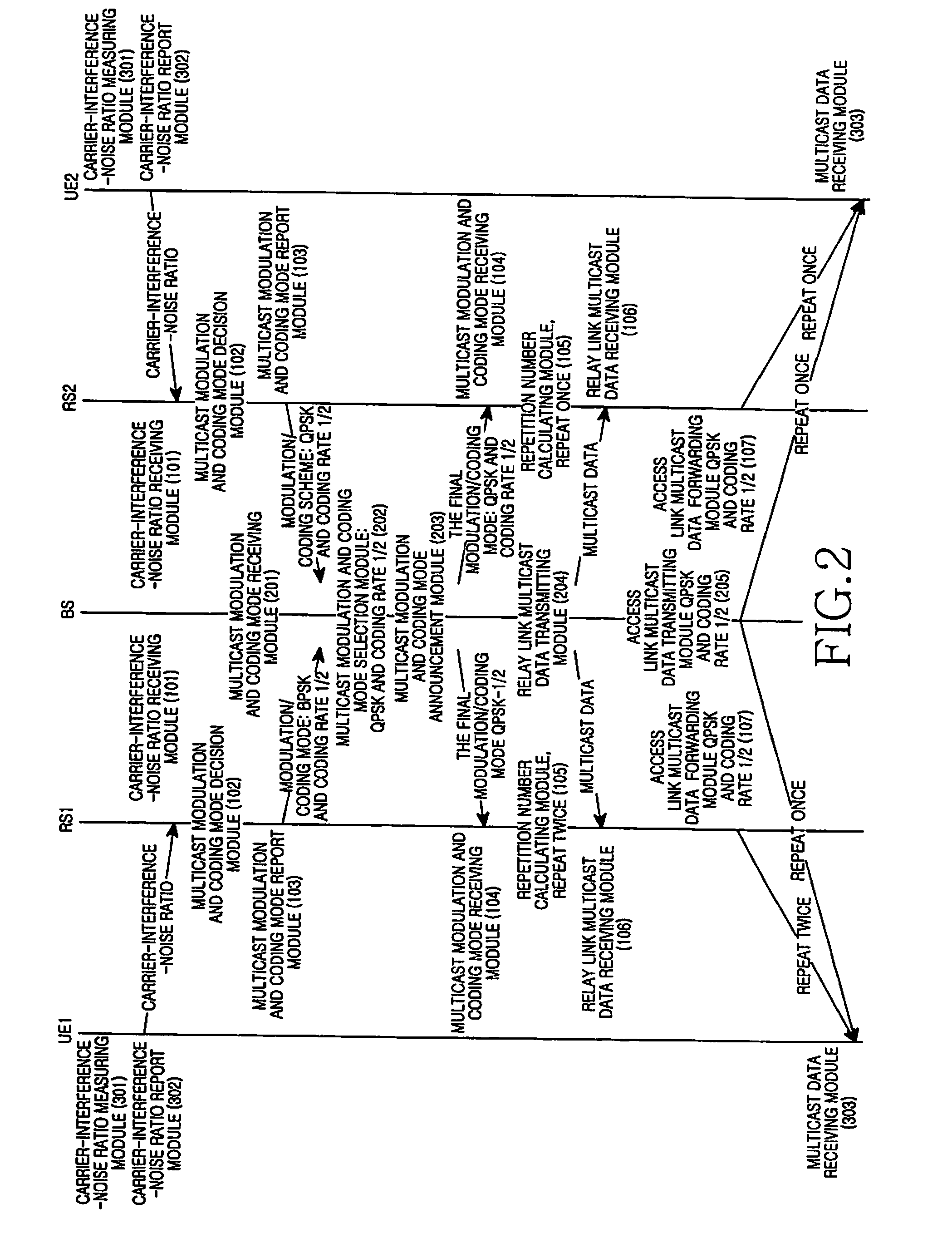
ActiveUS20080298296A1Guaranteed normal transmissionEffective resourcesError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsHigh rateWiBro
A method for transmitting multicast data in a WiMax / WiBro relay system, including transmitting carrier-interference-noise ratios from UEs to corresponding Relays; selecting the minimum value among the carrier-interference-noise ratios; determining the modulation and coding mode according to the selected minimum value; transmitting the modulation and coding mode to BS; selecting a modulation and coding mode with a highest rate for multicast data on an access link; transmitting the final modulation and coding mode to the Relays; and transmitting data via the access link with the modulation and coding mode determined by the BS.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Gallium nitride material transistors and methods for wideband applications
InactiveUS20070202360A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower applicationSignal quality
Gallium nitride material transistors and methods associated with the same are provided. The transistors may be used in power applications by amplifying an input signal to produce an output signal having increased power. The transistors may be designed to transmit the majority of the output signal within a specific transmission channel (defined in terms of frequency), while minimizing transmission in adjacent channels. This ability gives the transistors excellent linearity which results in high signal quality and limits errors in transmitted data. Such properties enable the transistors to be used in RF power applications including wideband power applications (e.g., WiMAX, WiBRO, and others) based on OFDM modulation.
Owner:INTERNATIONAL RECTIFIER COEP
Apparatus and Method for Estimating Carrier Frequency Offset in Communication Terminal, and Communication Terminal for Performing the Method
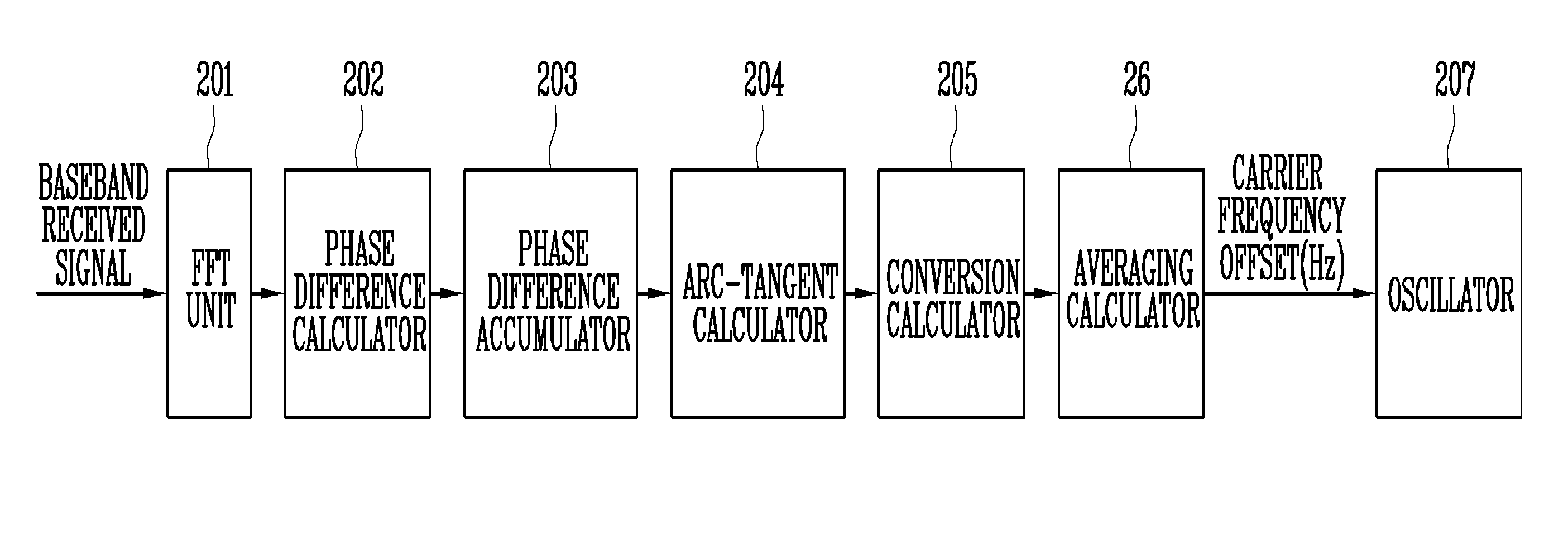
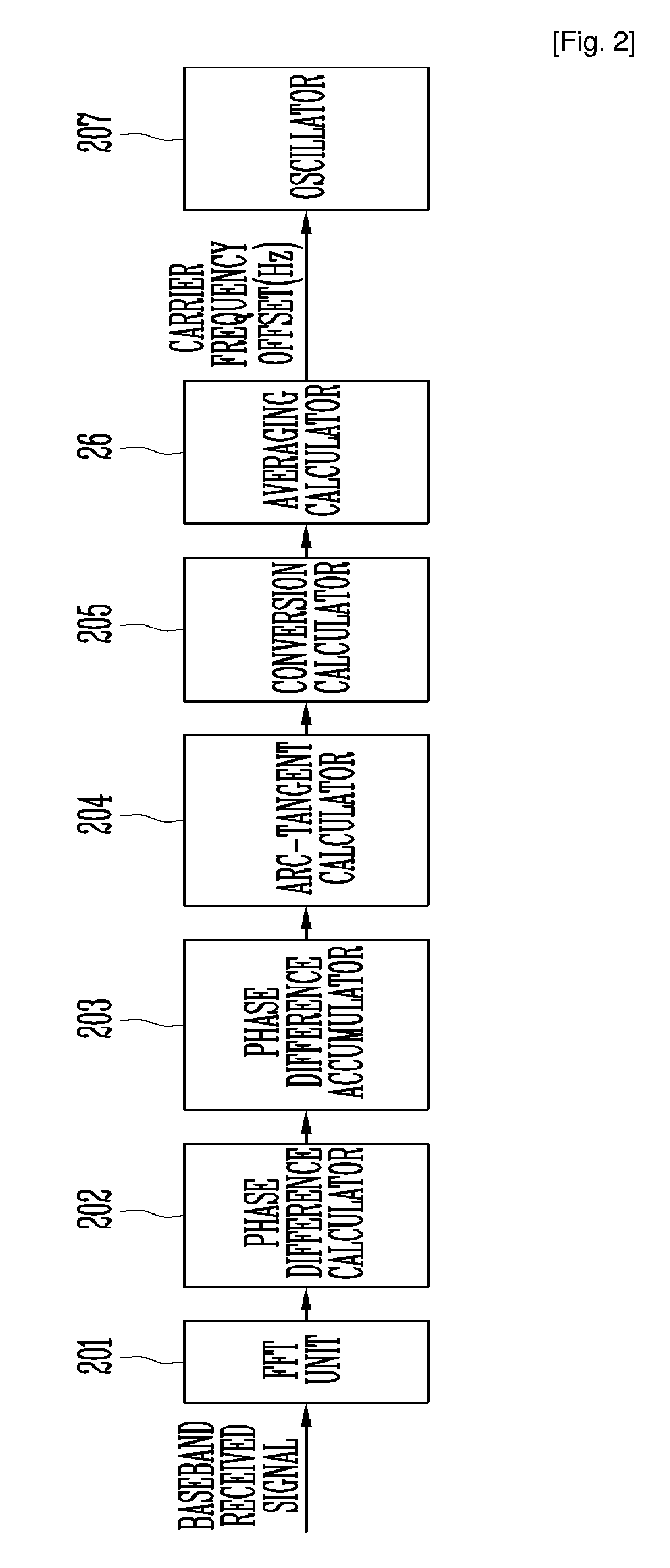
InactiveUS20080303508A1Avoid performanceStably estimatedDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionMulti-frequency code systemsPhase differenceCarrier frequency offset
Provided are an apparatus and method for estimating carrier frequency offset in a communication terminal operating in a communication system supporting Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) or Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing Access (OFDMA). More particularly, provided are a method of estimating carrier frequency offset in a communication terminal supporting DownLink (DL) Full Usage of SubChannel (FUSC) and DL Band-Adaptive Modulation and Coding (AMC) channel modes in a wireless communication system based on one of Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE) 802.16d / e, Wireless Broadband (WiBro), and Worldwide interoperability for Microwave Access (WiMAX) standards, and a communication terminal performing the method. The apparatus includes: a phase difference calculator for calculating a phase difference between pilot symbols having the same linear phase among the pilot symbols of a received signal; a phase difference accumulator for accumulating the phase difference and generating a phase difference accumulation value; and a calculator for converting the phase difference accumulation value into a carrier frequency offset estimation value.
Owner:POS DATA CO LTD
Wibro USB modem device having storage device
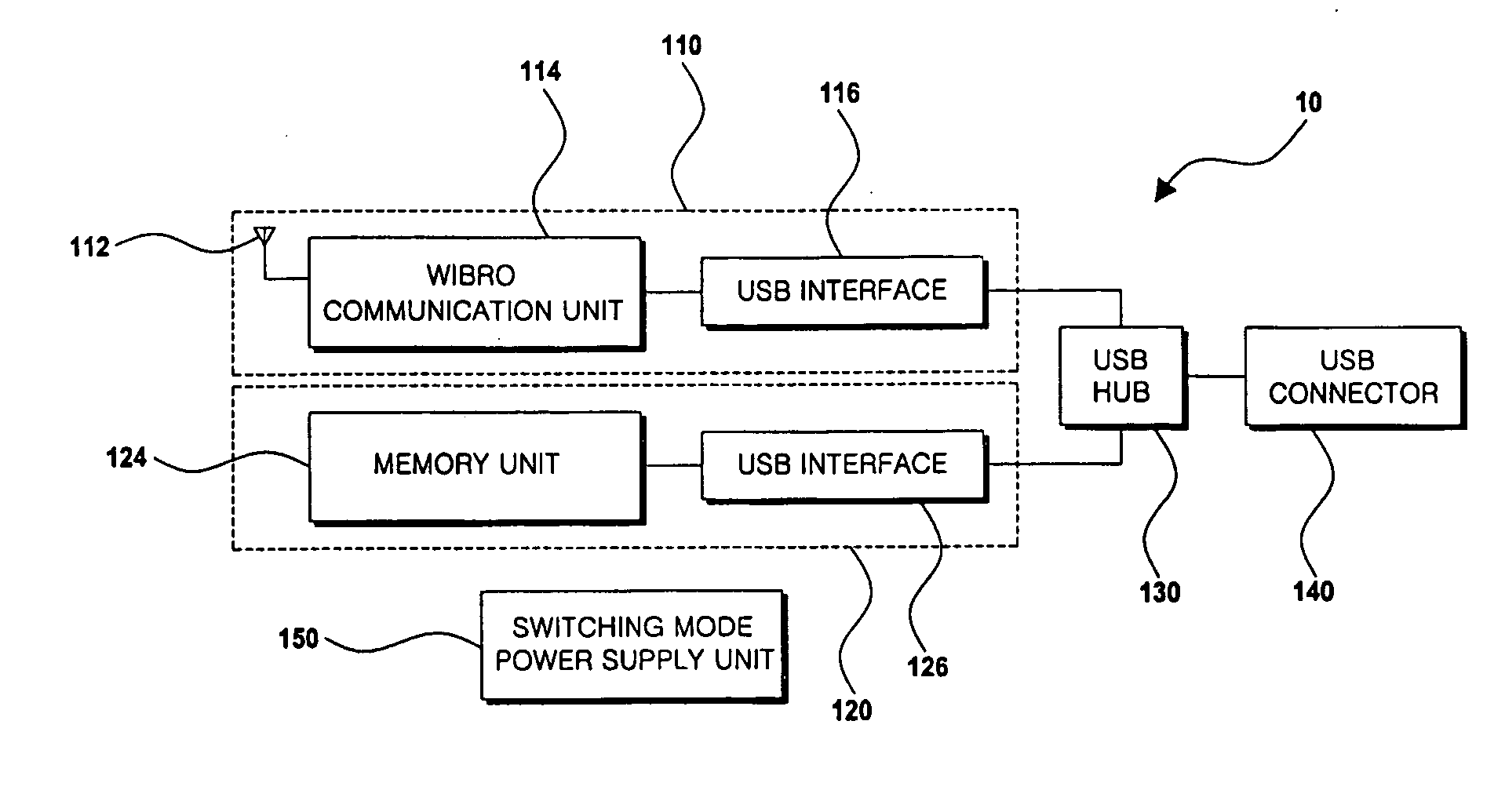
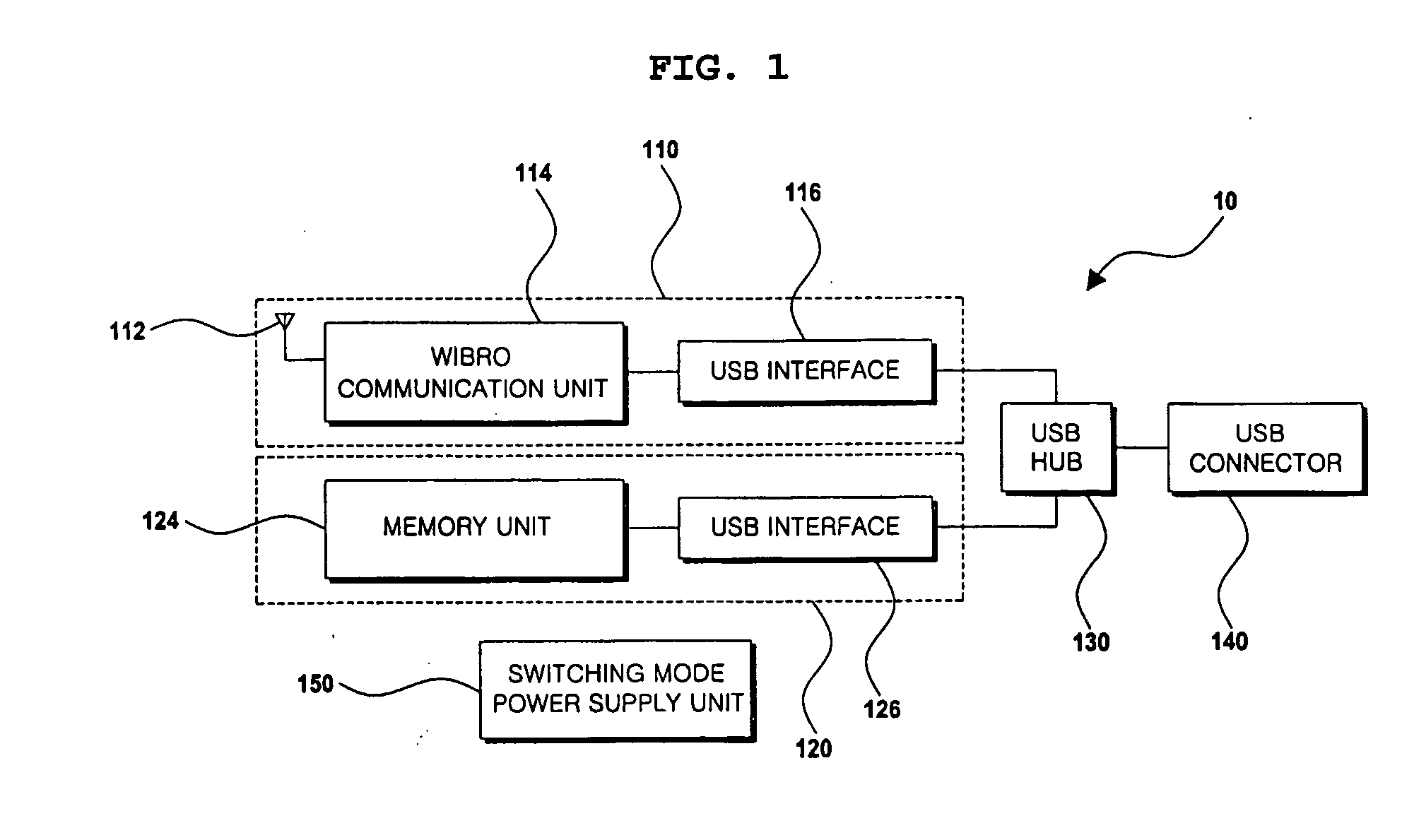
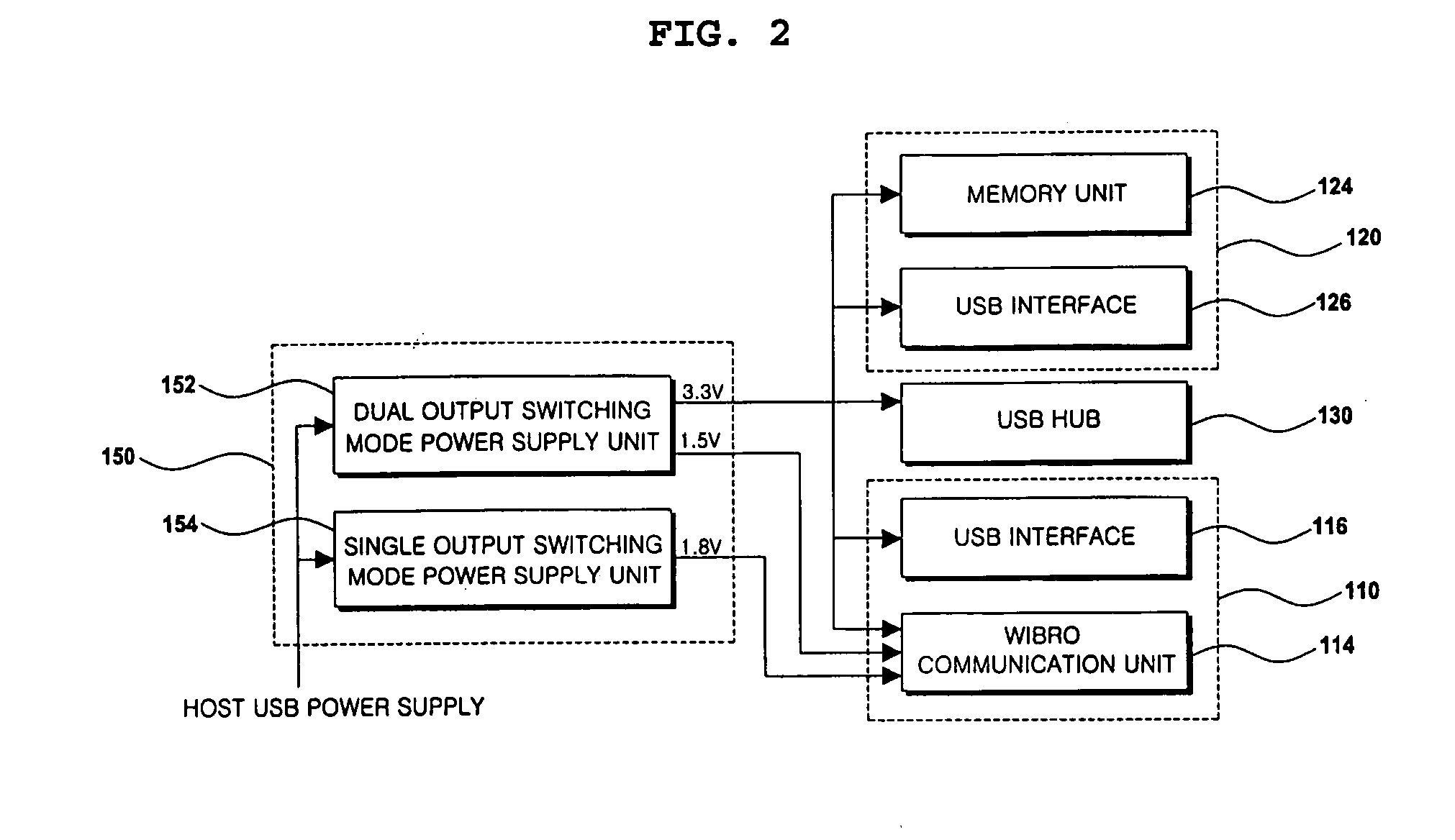
InactiveUS20090172208A1High-speed switchingSpecial service provision for substationDigital data processing detailsModem deviceUSB hub
Disclosed herein is a Wireless Broadband (WiBro) Universal Serial Bus (USB) modem device having a storage device and a WiBro communication device. A USB hub is connected to the USB interface of the WiBro communication device and the USB interface of the storage device, and configured to relay data to a user terminal through a USB connector. A switching mode power supply unit is configured to have a DC-DC switching mode, receive power from the user terminal, and apply the power by performing high-speed switching so that the WiBro communication device and the storage device are simultaneously driven. The switching mode power supply unit includes a dual output switching mode power supply unit and a single output switching mode power supply unit.
Owner:MODACOM
Communication apparatus and method for controlling the same
InactiveUS20080039154A1Reduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTPower managementCommunication unitThe Internet
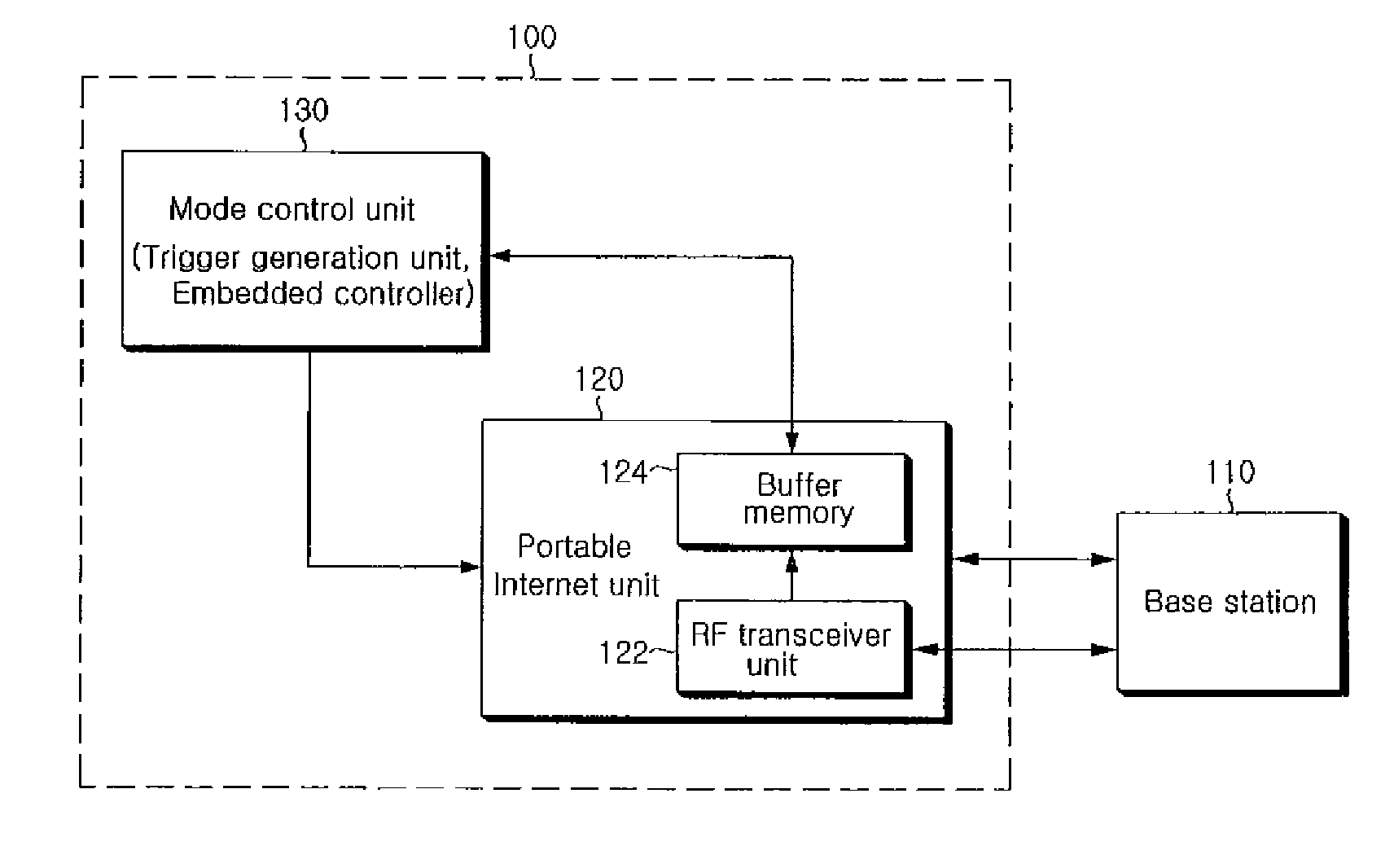
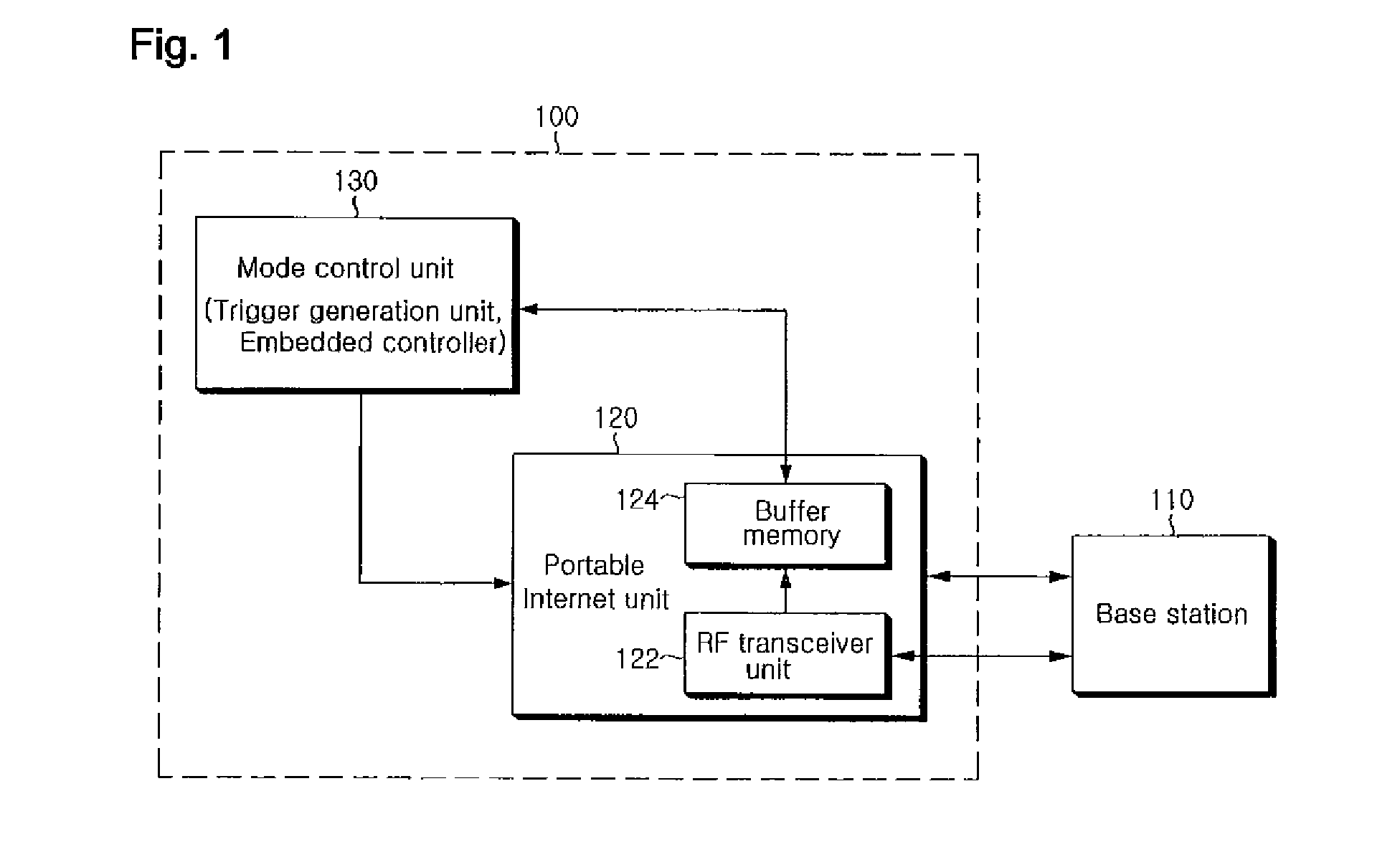
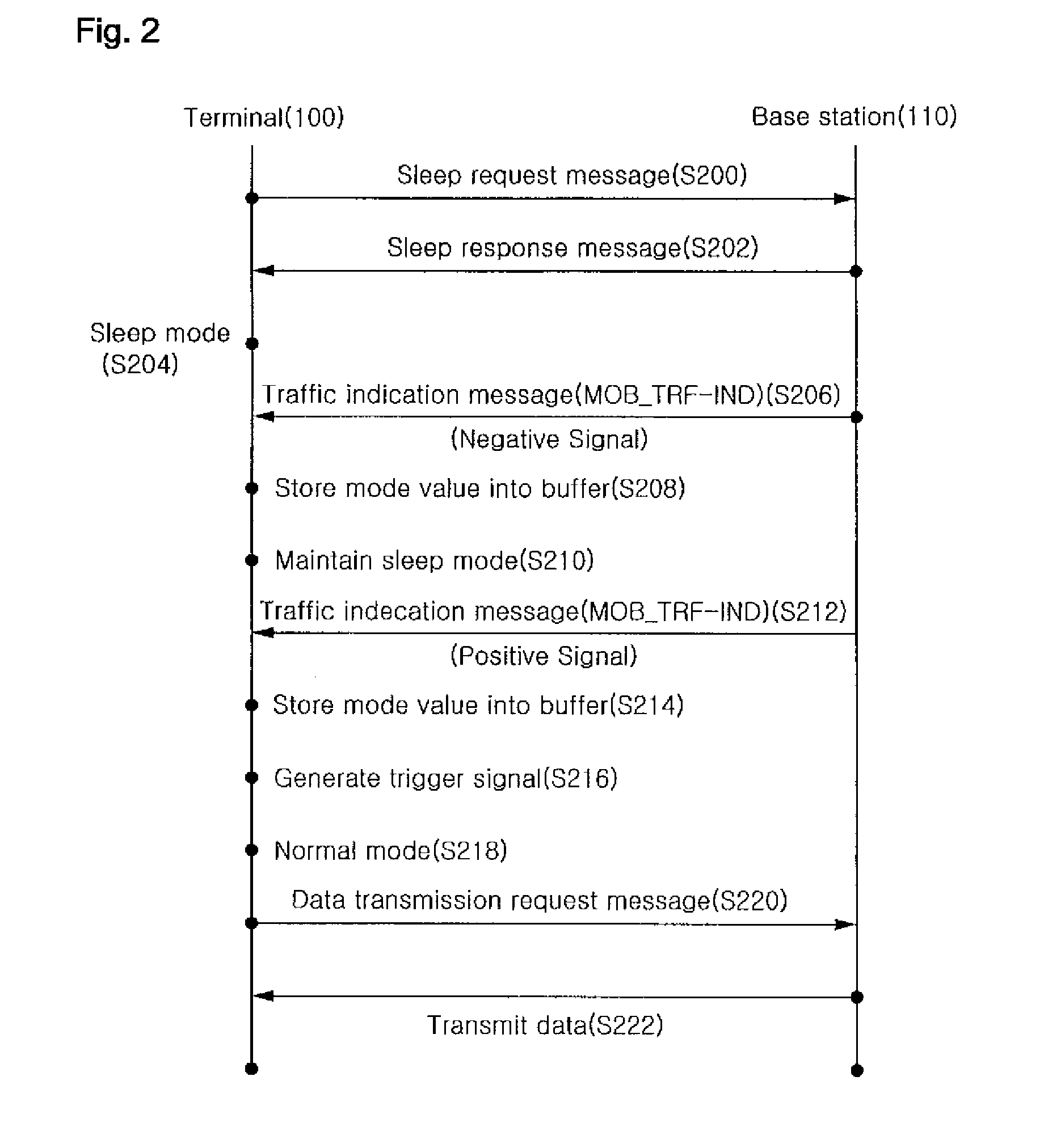
The present invention relates to a communication apparatus and a method for controlling the same, which controls an operation mode of a communication unit in a portable terminal capable of supporting the portable Internet (Wibro). In the present invention, when the communication unit of the portable terminal that provides the Wibro service is in a sleep mode, the communication unit is not periodically switched (waken up) to a normal mode but is switched to the normal mode only when a traffic indication message containing a mode-setting value for returning to the normal mode is received from a base station. Then, the portable terminal can receive a signal transmitted from the base station through the Wibro. Therefore, the present invention has an advantage in that power consumption of the portable terminal is reduced when the Wibro service is not used.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
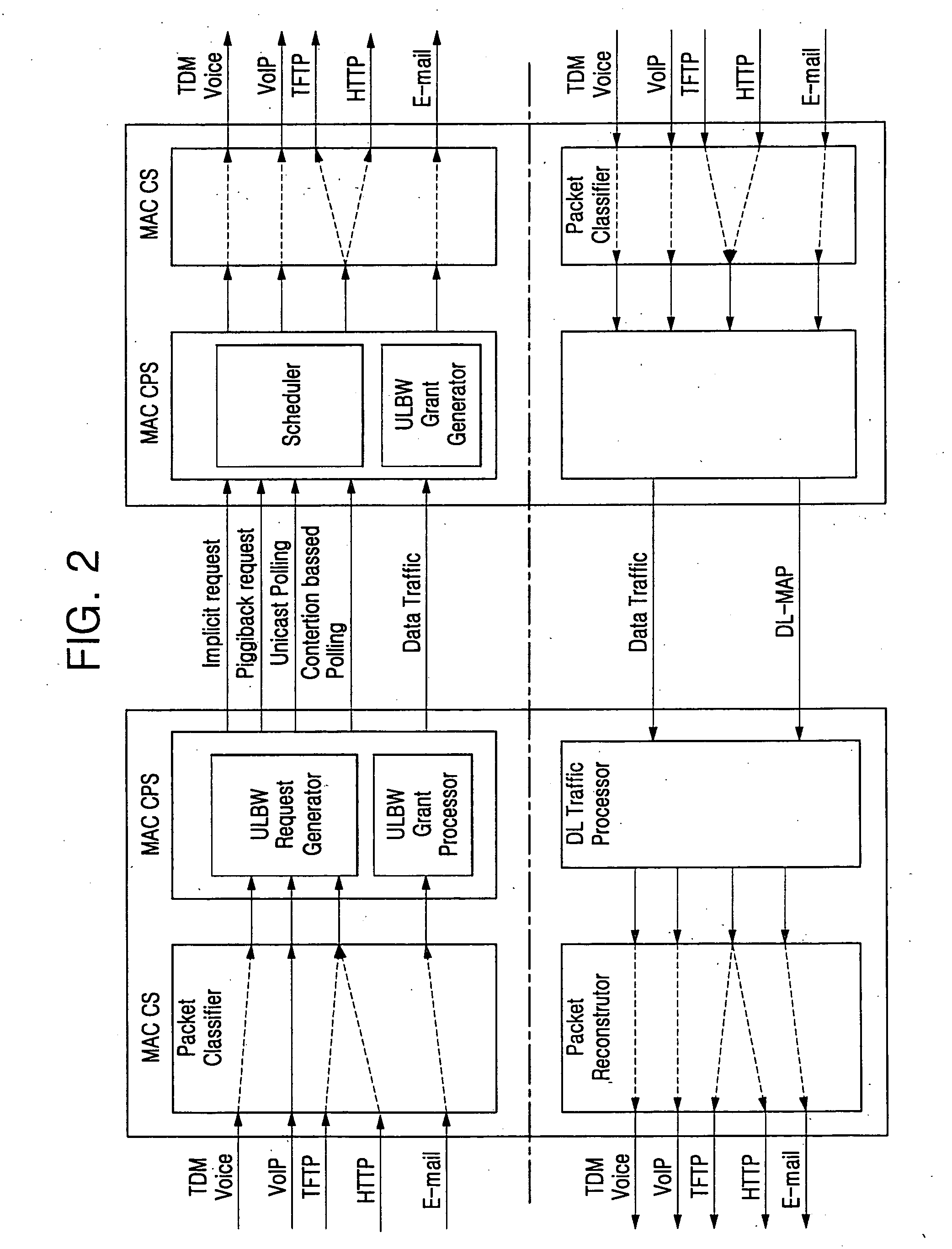
Wireless broadband (WiBro) station capable of supporting quality of service (QoS) and method for servicing QoS in WiBro network
InactiveUS20070165565A1Network traffic/resource managementDispersed particle filtrationQuality of serviceWiBro
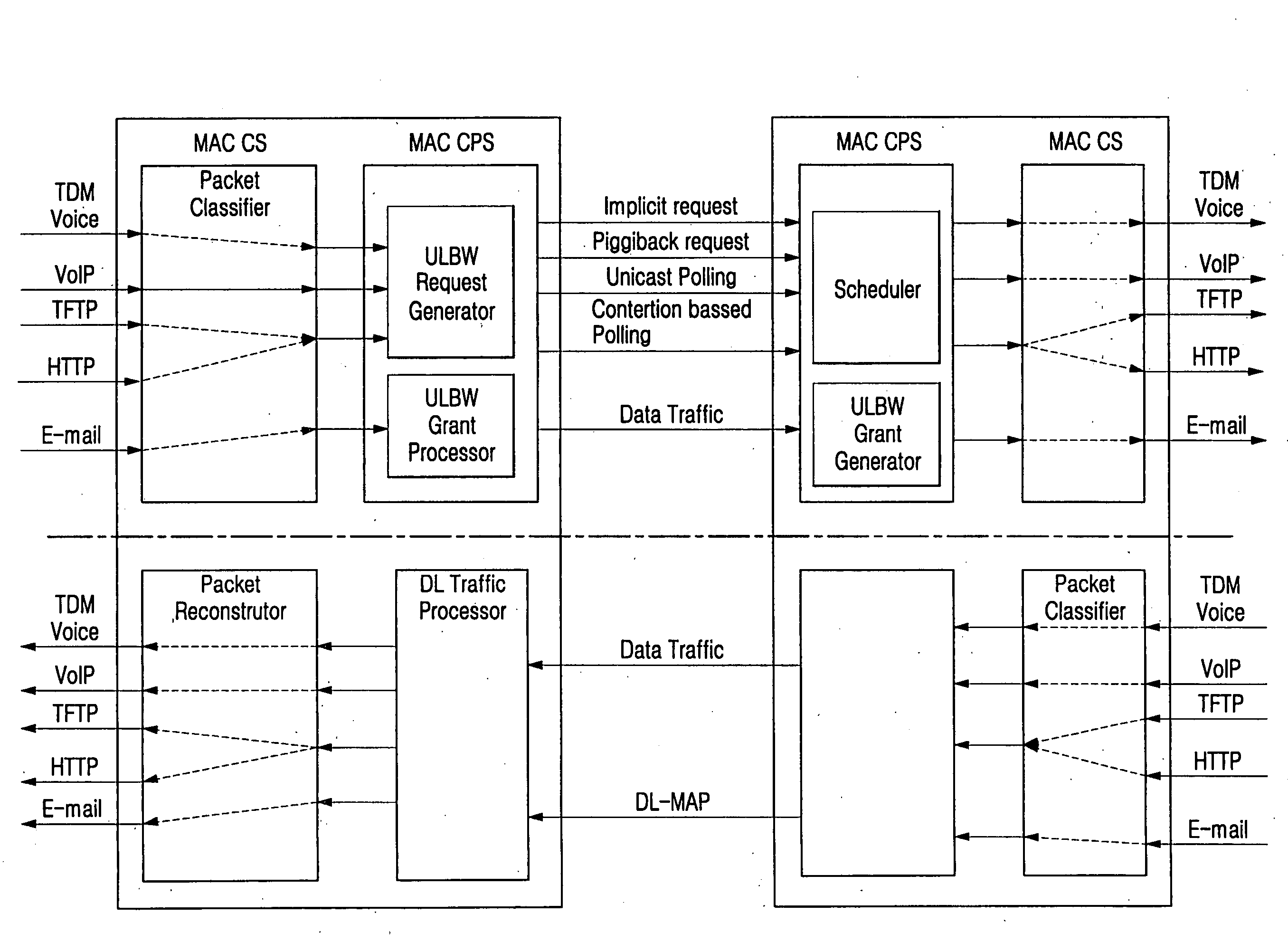
A wireless broadband (WiBro) station is capable of supporting Quality of Service (QoS), and a method provides the QoS service in a WiBro network. A High_MAC processor is additionally constructed to parse a packet inputted from an application layer, assigns a QoS class according to a feature of the parsed packet, and transmits the packet through a channel corresponding to the assigned QoS class, thereby performing a QoS service through a separate QoS processing module provided between the application layer and a Media Access Control (MAC) layer. Thus, a burden imposed on the MAC layer is reduced, and a faster QoS service is provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com