Patents
Literature
79results about How to "Avoid unreliable" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
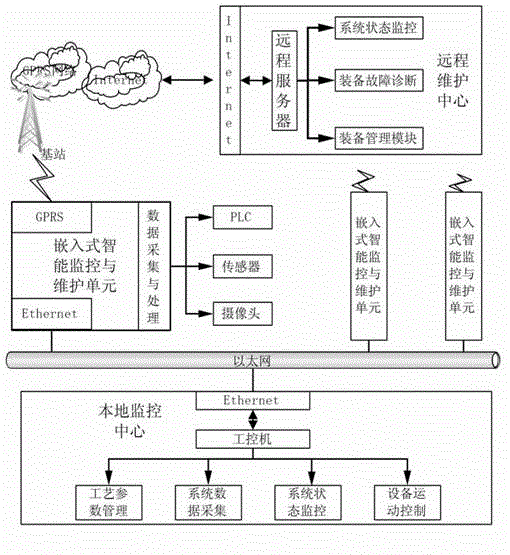
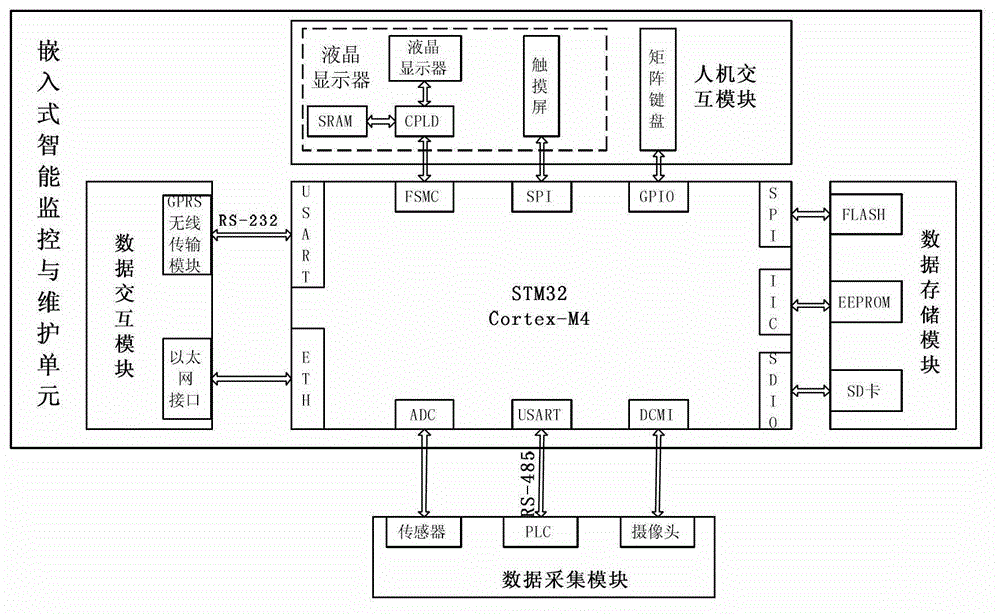
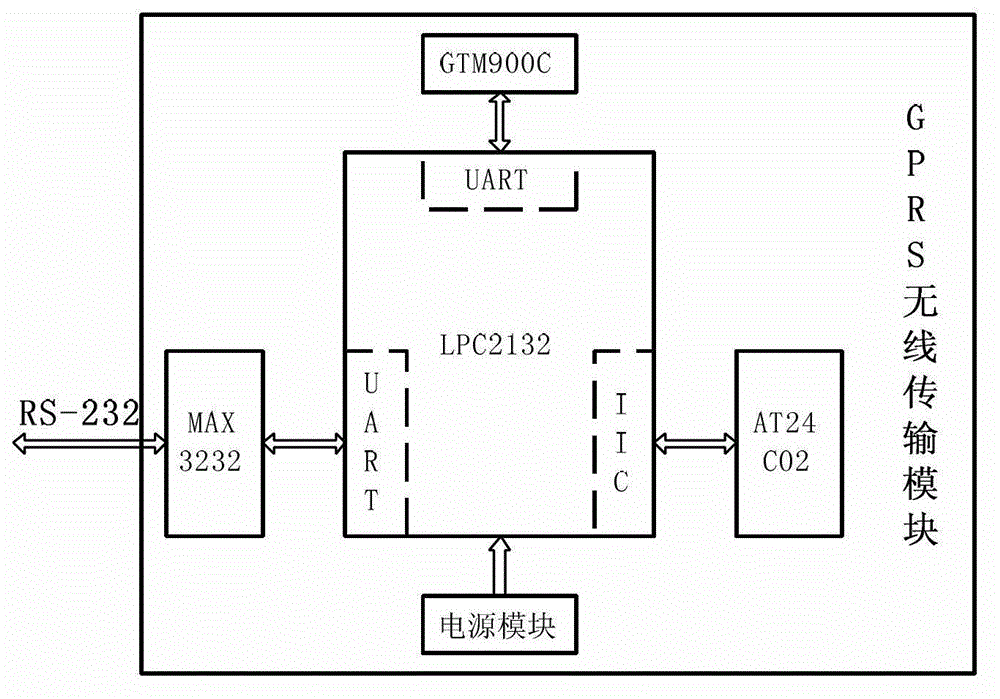
Embedded intelligent monitoring and remote maintaining system of manufacturing equipment
ActiveCN103149901AReduce power consumptionMeet real-time processing needsTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlReal-time dataData acquisition
The invention discloses an embedded intelligent monitoring and remote maintaining system of manufacturing equipment. A remote maintaining center and an embedded intelligent monitoring and maintaining unit which is installed at a different place constitute a star network, wherein the embedded intelligent monitoring and maintaining unit comprises a micro controller, a data acquisition module, a data interaction module, a man-machine interaction module and a data memory module, and the remote maintaining center comprises a system state monitor, an equipment fault diagnosis module and an equipment management module. The embedded intelligent monitoring and remote maintaining system has a man-machine interaction function, is wide in application occasion, and can well conduct real-time data processing.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
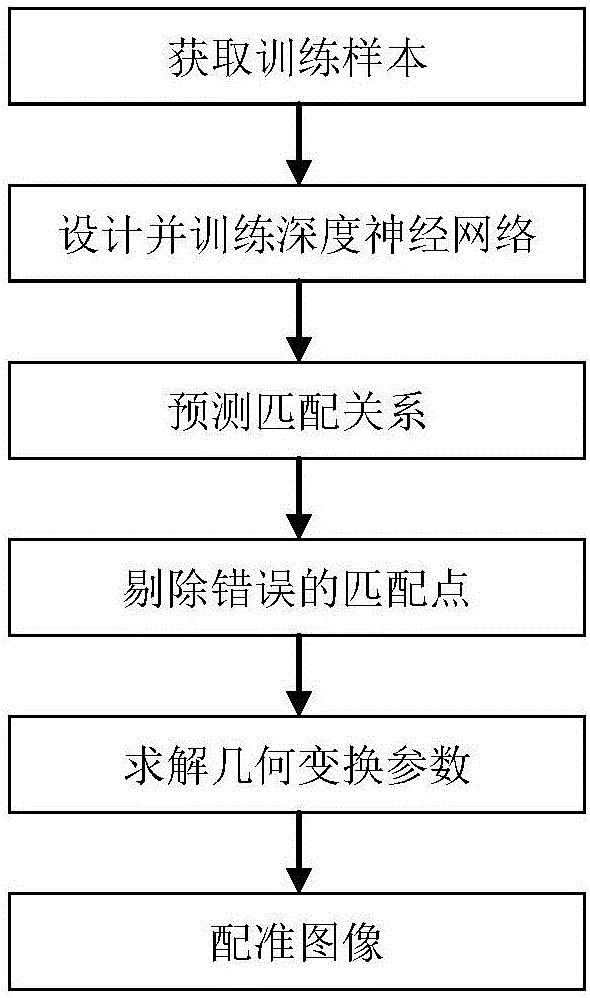
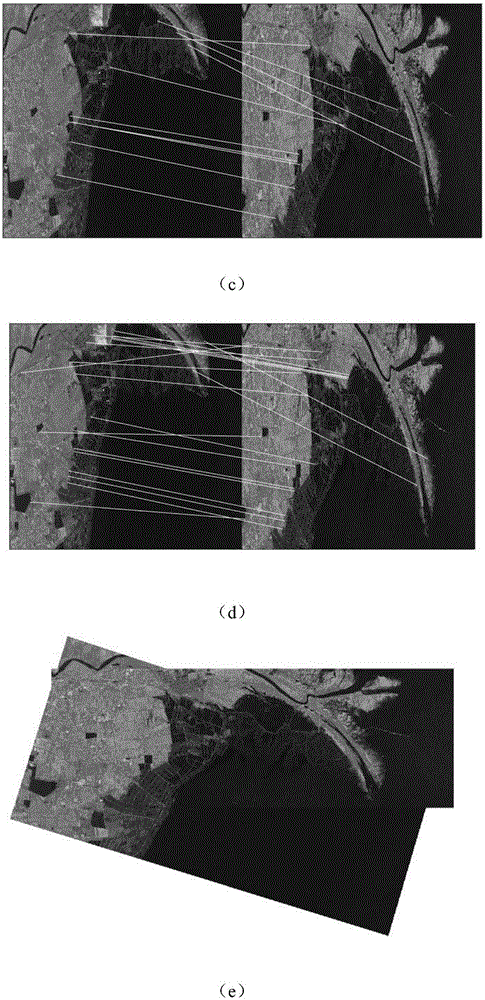
SAR image registration method based on deep neural networks
ActiveCN105809693AOvercome problems limited by specialized domain knowledgeReduce the amount of calculationImage enhancementImage analysisFeature extractionComputer science
The invention provides a SAR image registration method based on deep neural networks, and the method comprises the realization steps: (1) a training sample is acquired; (2) the deep neural networks are designed and trained; (3) matching relations are predicted; (4) wrong matching points are removed; (5) a geometric transformation parameter is calculated; and (6) the image is registrated. According to the invention, the SAR image registration method based on deep neural networks is adopted, the artificial design feature extraction operator defects including high complexity, large amount of computation, poor robustness in a process and the like in prior art can be effectively overcome, the amount of computation can be effectively reduced, the deep neural networks can extract substantive characteristics of the image, the robustness is better than before, and the precision of the registration is higher than before.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
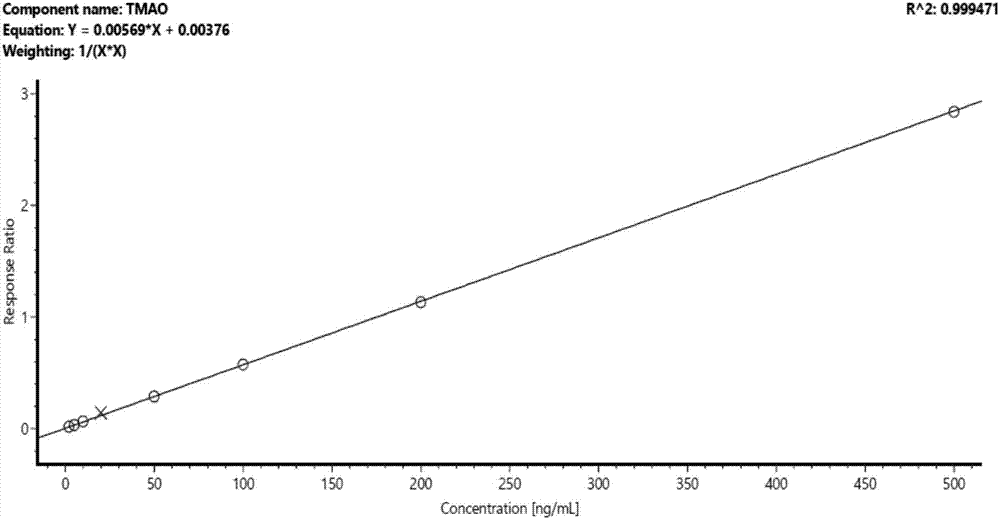
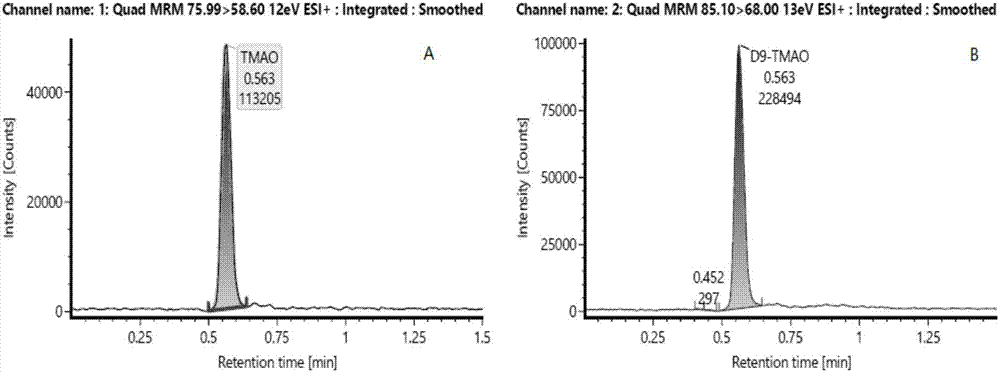
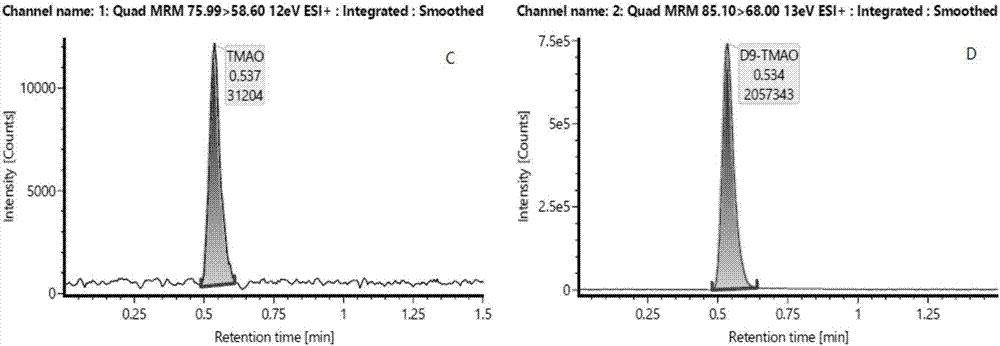
Kit and method for quantitatively detecting trimethylamine N-oxide
PendingCN107340341AImprove reliabilityAvoid unreliableComponent separationBovine serum albuminConcentration gradient
Provided are a kit and method for quantitatively detecting trimethylamine N-oxide. The method for quantitatively detecting trimethylamine N-oxide comprise the following steps of adding trimethylamine N-oxide in an aqueous solution of human serum albumin to prepare a series of trimethylamine N-oxide standard solutions with a concentration gradient, adding an internal standard substance and a precipitating agent to each standard solution respectively, centrifuging the obtained standard solutions, obtaining a series of supernatant, analyzing the supernatant by using liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry respectively, and obtaining the ratio of the chromatographic peak area of trimethylamine N-oxide to that of the internal standard substance in each trimethylamine N-oxide standard solution and a relationship between the ratios and concentrations of trimethylamine N-oxide; adding the internal standard substance and the precipitating agent to a to-be-tested blood serum sample, conducting centrifugation, analyzing obtained supernatant by using liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry, obtaining the ratio of the chromatographic peak area of trimethylamine N-oxide to that of the internal standard substance in the to-be-tested blood serum sample, and obtaining the concentration of trimethylamine N-oxide in the to-be-tested blood serum sample according to the relationship between the ratios and the concentrations of trimethylamine N-oxide. According to the kit and method for quantitatively detecting trimethylamine N-oxide, the problem that unreliable detection results can be caused by application of water, a bovine serum albumin solution or a phosphate buffer solution and other blank biological matrix which are far from plasma components of the human body can be avoided, and the reliability of the detection results is improved.
Owner:CHANGSHA DUXACT BIOTECH CO LTD
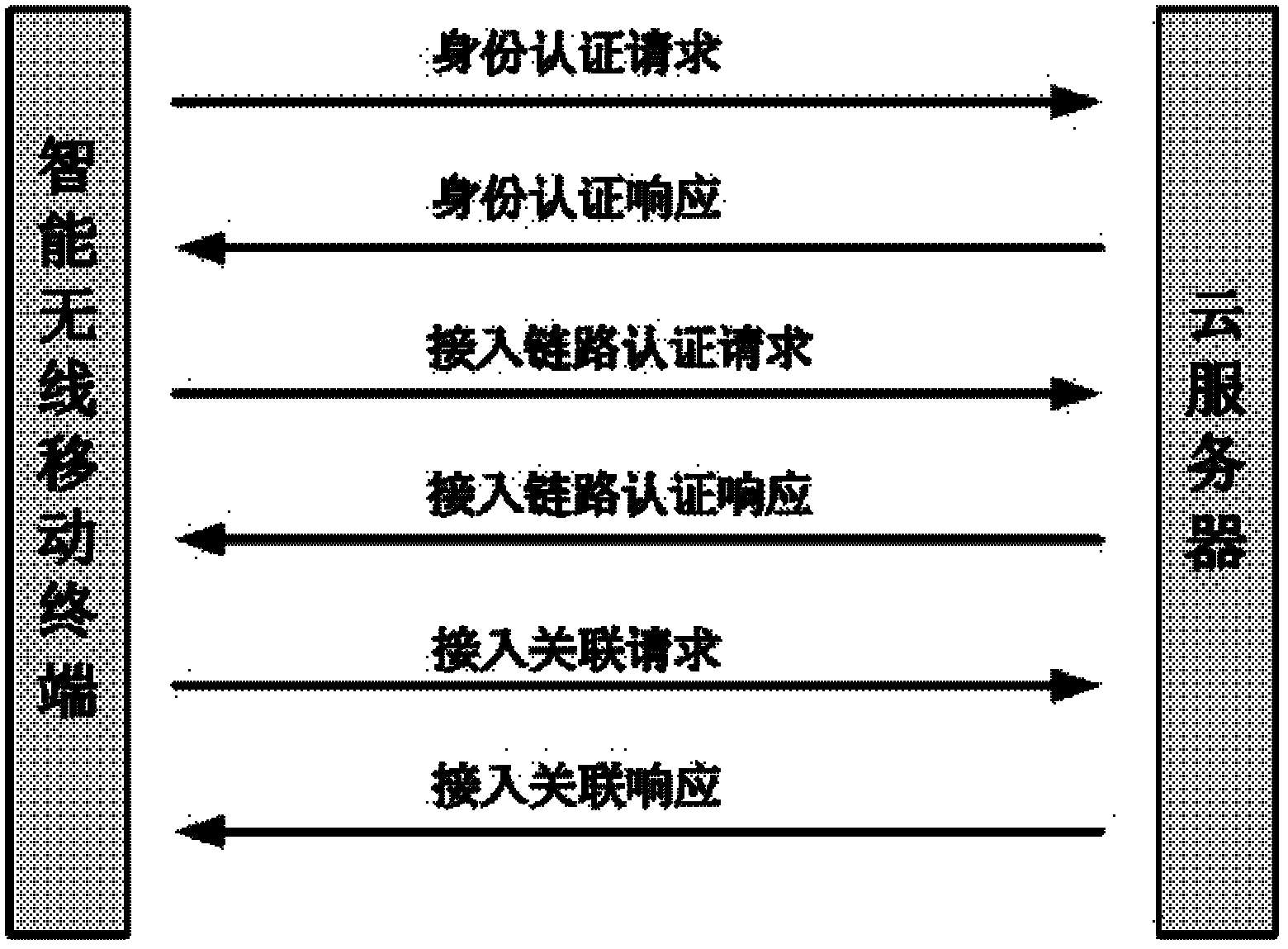
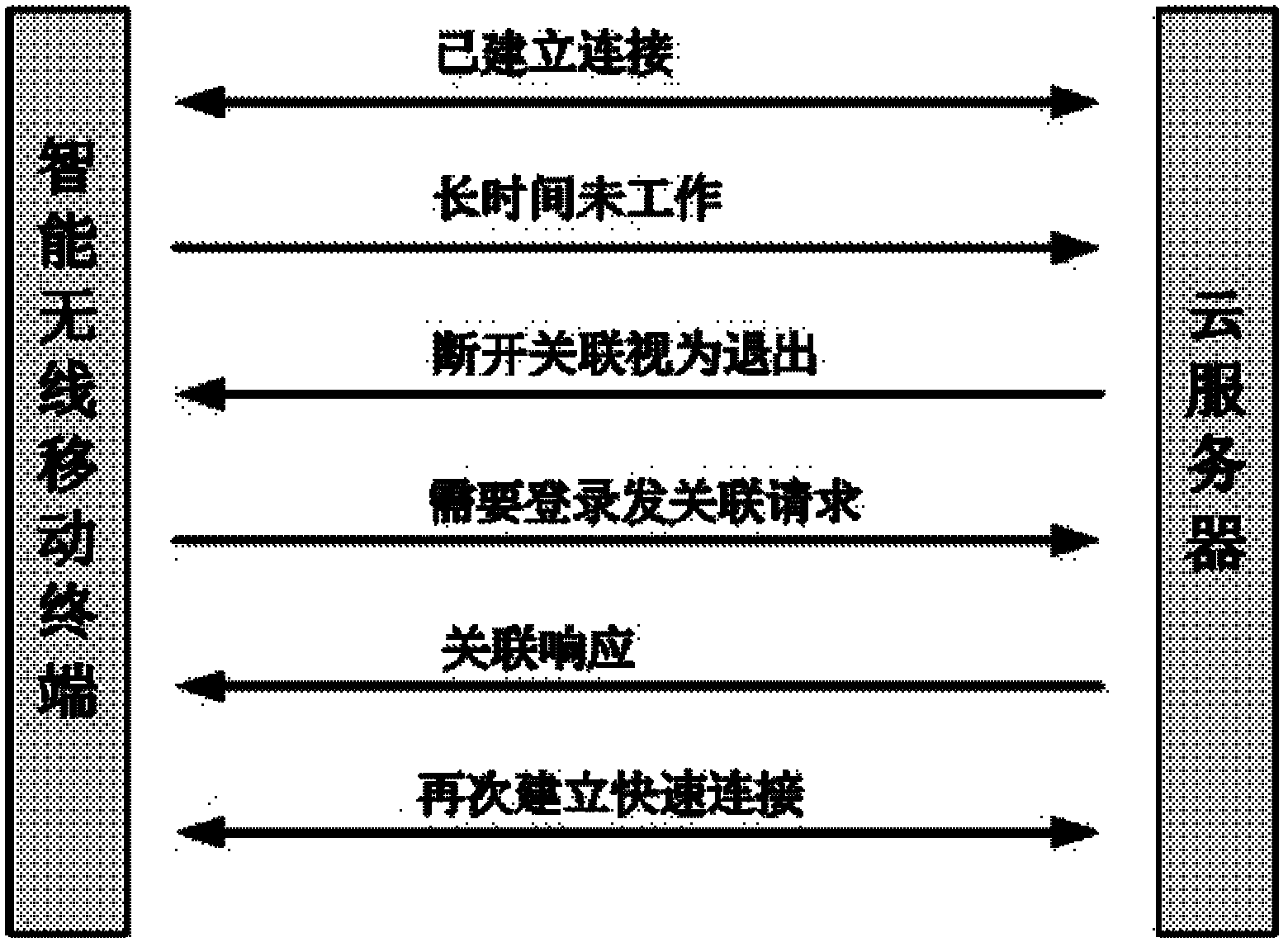
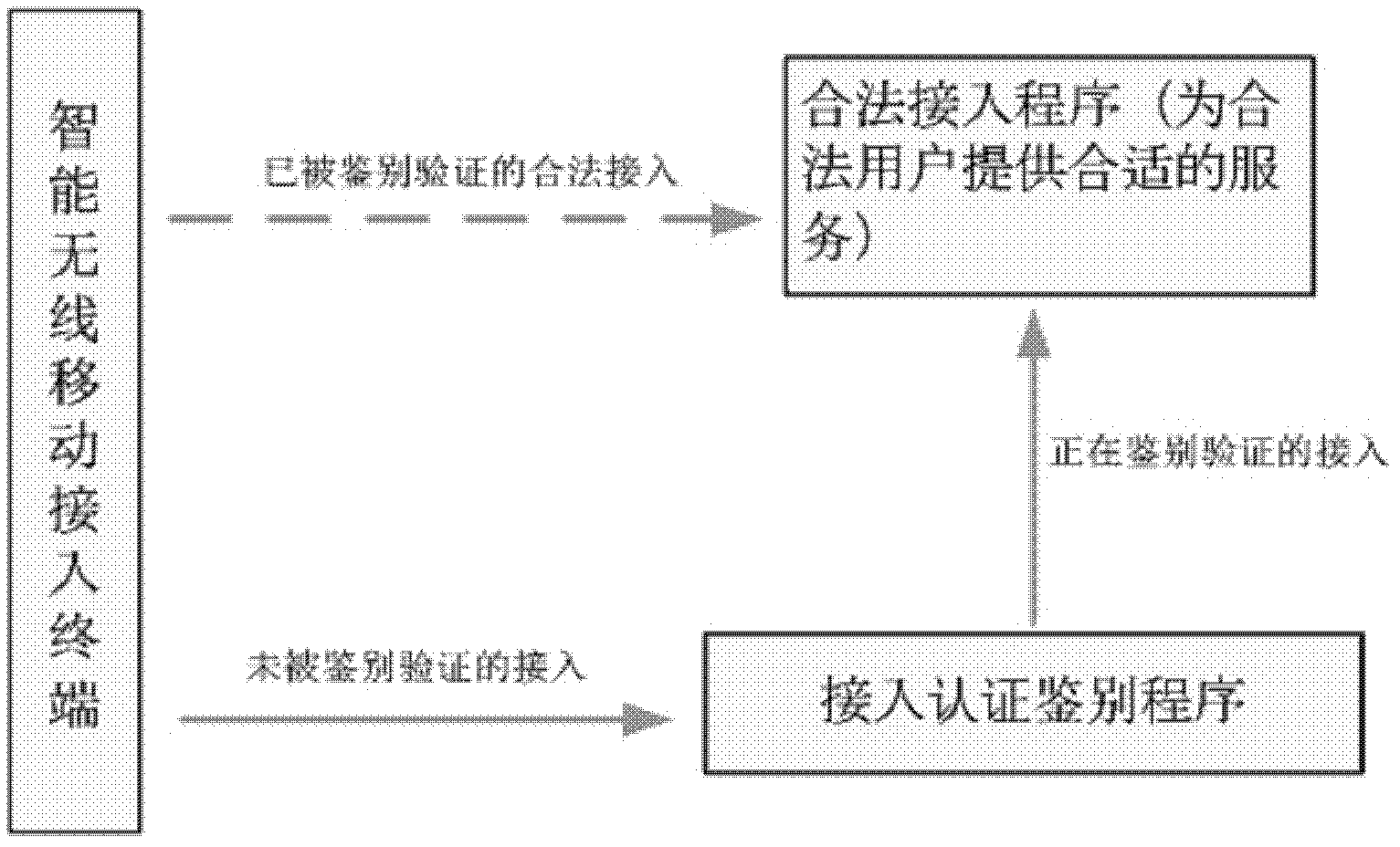
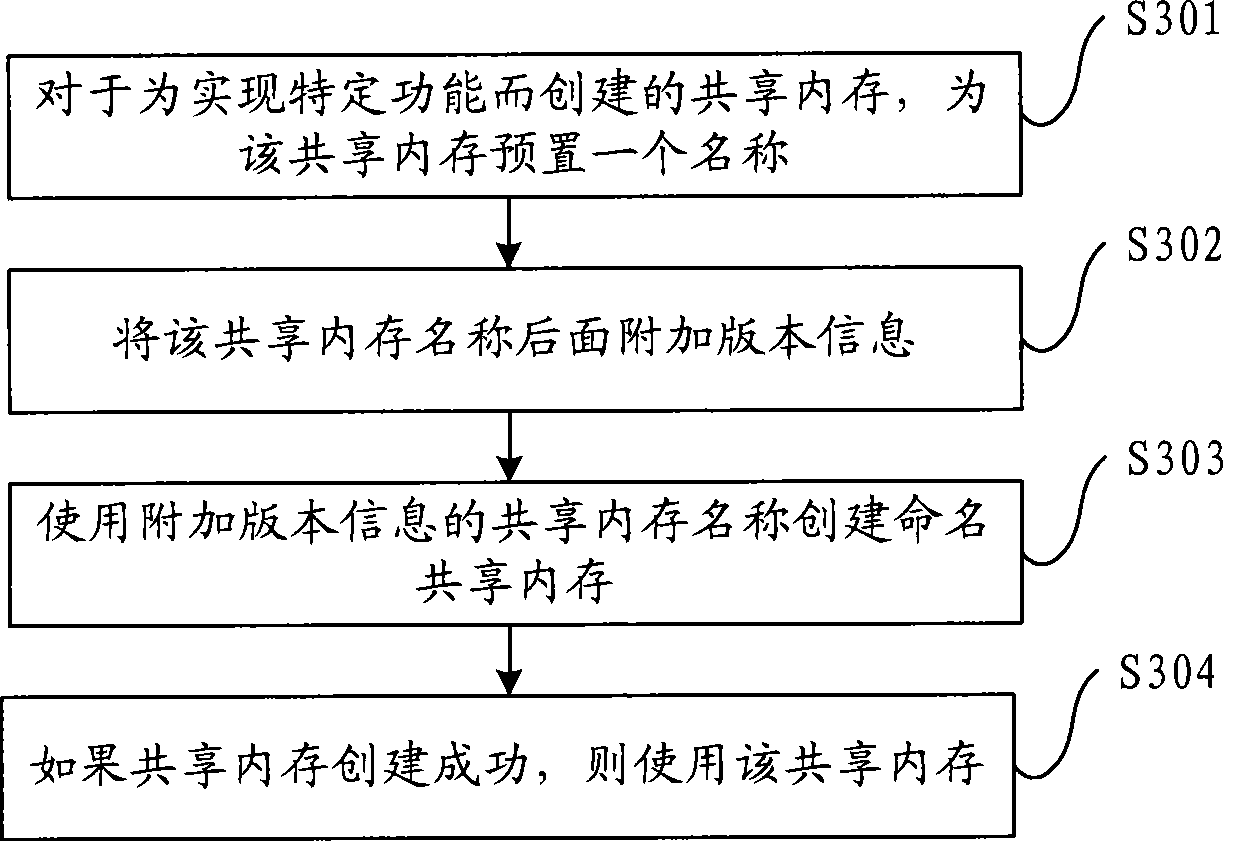
Identity authentication method allowing intelligent mobile wireless terminal to access cloud server
InactiveCN102571792AAvoid unreliableFix security issuesUser identity/authority verificationMobile WebBroadband
The invention discloses an identity authentication method allowing an intelligent mobile wireless terminal to access a cloud server, which comprises the following steps that 1, when the intelligent wireless mobile terminal privately accesses the cloud server through a wireless wideband mobile network, an identity authentication request is sent; 2, the cloud server sends an identity authentication response; 3, the intelligent wireless mobile terminal sends an access link authentication request to the cloud server; 4, the cloud server comprises the attributes of the intelligent wireless mobile terminal, such as identity, password and the like, in case of legitimate access, an access link authentication response is fed back; 5, the intelligent wireless mobile terminal sends an access link relevant request; 6, the cloud server responds to one access link relevant response, creating a bilateral link circuit connection; and 7, the reliable access process between the intelligent wireless mobile terminal and the cloud server is completed. Through the invention, the reliability and safety of the cloud server are ensured, thereby preventing the information at the cloud server end from leakage, and blocking dangerous access.
Owner:西安润基投资控股有限公司
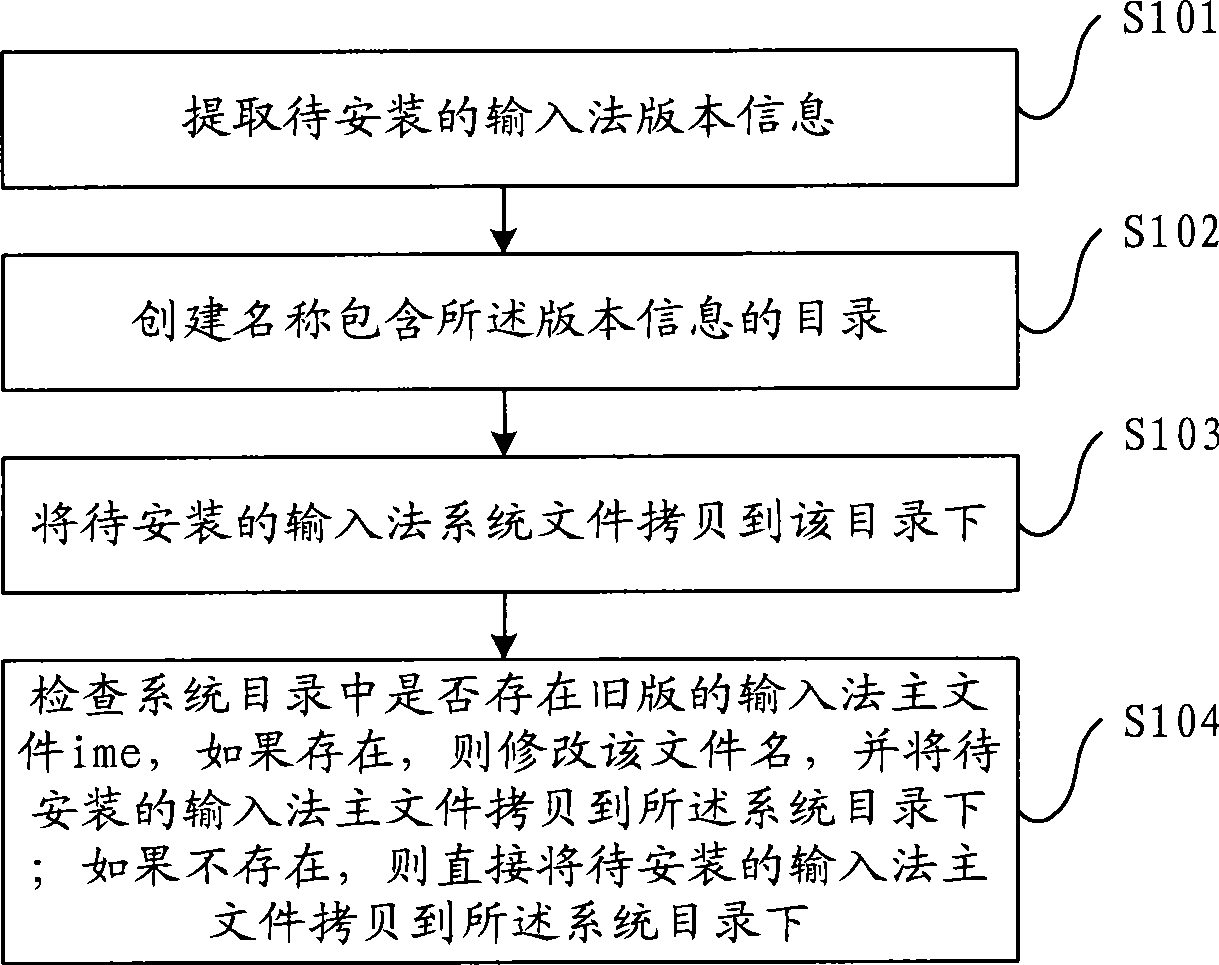
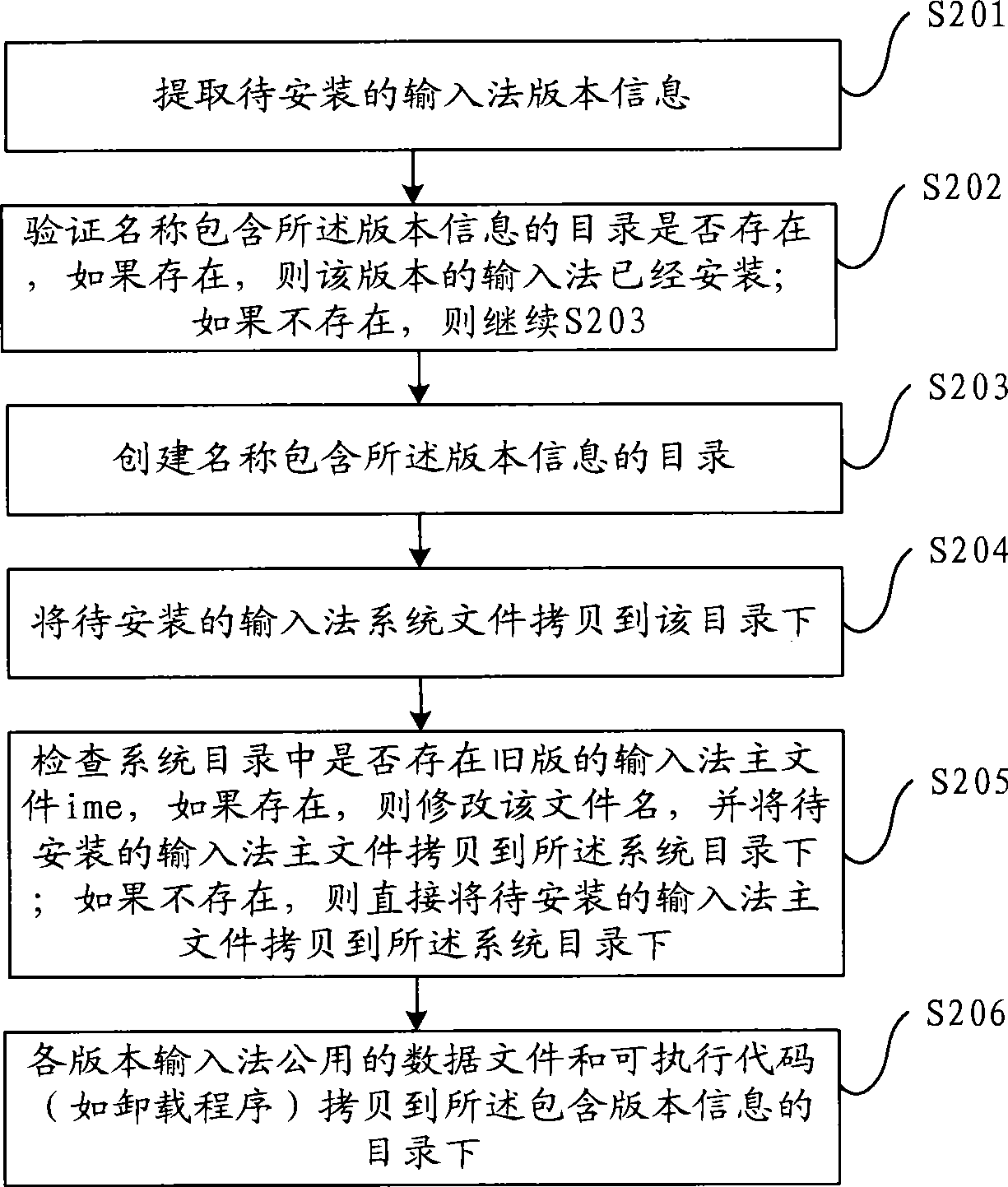
Input method installation method and device
ActiveCN101510157AWill not interfere with each otherInterfere with normal workProgram loading/initiatingSoftware engineeringInput method
The invention discloses an input method installation method and device, aiming at solving the problem of the existing installation method that the newly installed input method can be used after being restarted in most cases. The method comprises the steps of extracting version information of the input method to be installed; creating a catalog with the name containing the version information and copying the system file of the input method to be installed to the catalog; checking whether the main file of the input method of the old version exists in the system catalog or not, if so, amending the file name and copying the main file of the input method to be installed to the system catalog; and if not, directly copying the main file of the input method to be installed to the system catalog. The method leads the newly installed input method to be capable of being used immediately without restart; moreover, when the input methods of new version and old version run at the same time, the new and old input methods cannot generate interference.
Owner:BEIJING SOGOU TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT CO LTD
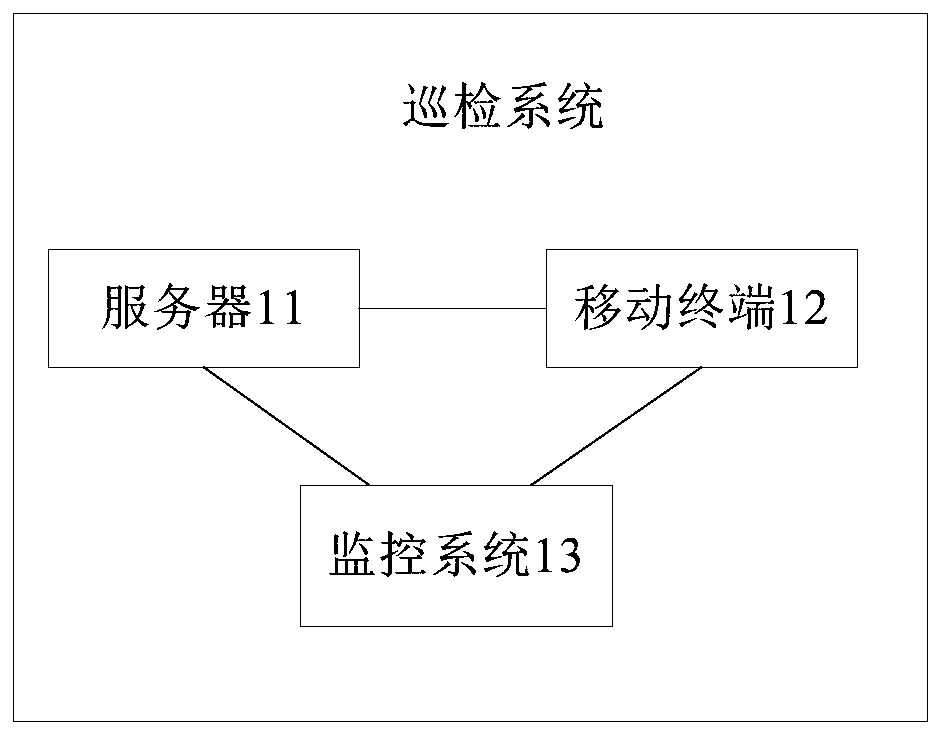
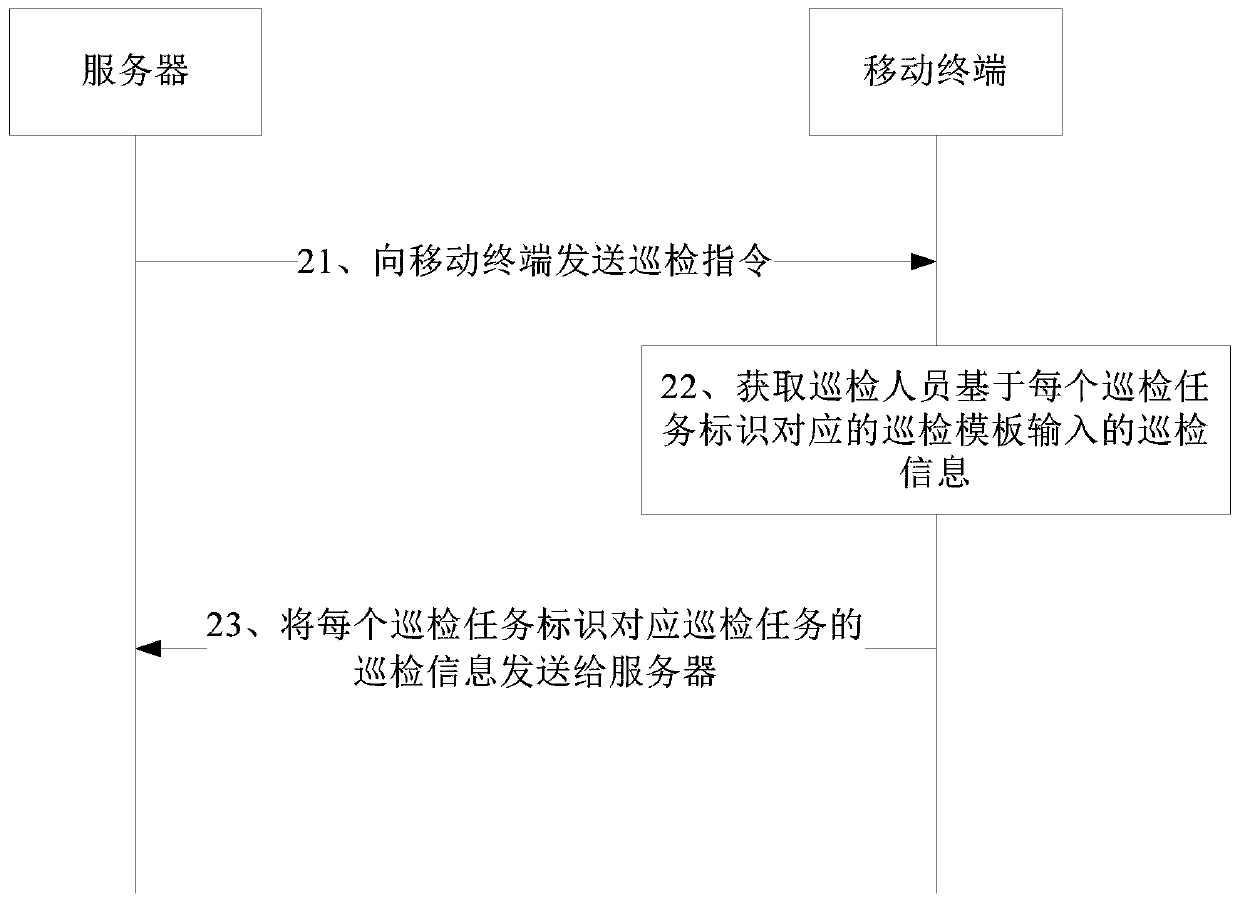
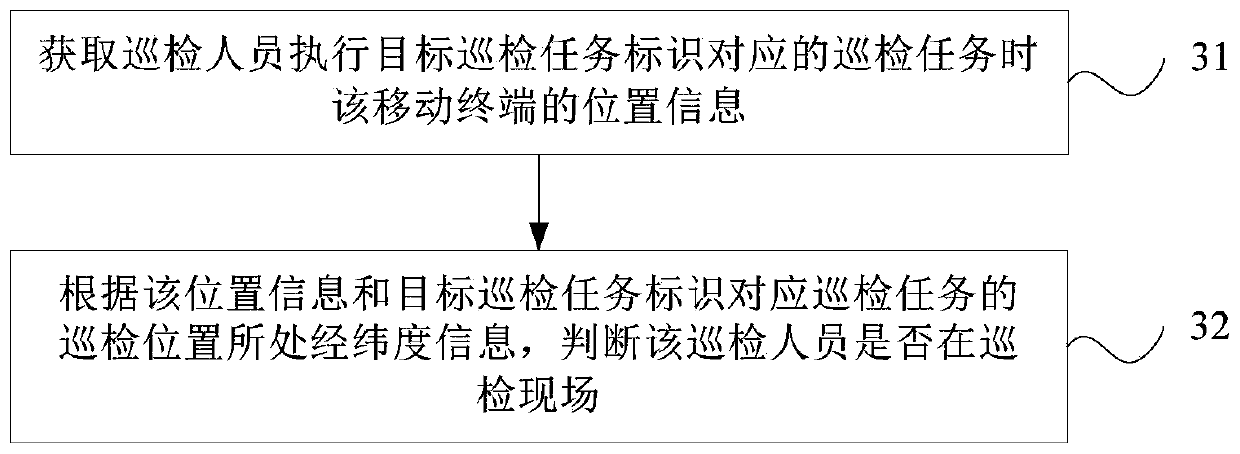
Inspection method and device and storage medium
InactiveCN109728940AReduce workloadImprove work efficiencyChecking time patrolsData switching networksComputer terminalWorkload
The invention provides an inspection method and device and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps that a server sends an inspection instruction to a mobile terminal, and after the mobile terminal receives the inspection instruction issued by the server, inspection information input by inspection personnel based on an inspection template corresponding to each inspection task identifier isobtained, and the inspection information of the inspection task corresponding to each inspection task identifier is sent to the server. According to the technical scheme, the inspection information of each inspection task is directly uploaded to the server and does not need to be collected by material personnel in a unified manner, so that the workload is reduced, the working efficiency is improved, the inspection personnel fill the inspection information based on the inspection template, and the problem that the inspection result is unreliable is avoided.
Owner:CHINA UNITED NETWORK COMM GRP CO LTD
Mechanical sliding sheet translation type precise seeding mechanism
ActiveCN110291872ATake advantage ofAvoid shortageDibble seedersSeed depositing seeder partsGear wheelReciprocating motion
The invention relates to a mechanical sliding sheet translation type precise seeding mechanism which comprises a seed selecting mechanism, a seed filling mechanism and a seed filling-discharging mechanism. The seed filling mechanism comprises a mechanical translation driving mechanism fixedly connected with the side wall of a seed filling box, a translation sliding sheet structure is arranged on one side opposite to the mechanical translation driving mechanism and comprises a U-shaped sliding groove in fixed arrangement and a supporting sliding sheet, and one horizontal end of the supporting sliding sheet is fixed on the side wall of the seed filling box while the other end of the same can slide in the U-shaped sliding groove; a power output shaft of a small motor of the seed filling-discharging mechanism is horizontal, an upper linkage gear is meshed with an upper rack frame, a lower linkage gear is meshed with a lower rack frame, the upper rack frame is fixedly connected with an upper cover plate, and the lower rack frame is fixedly connected with a lower bottom plate; each of the upper linkage gear and the lower linkage gear is a non-full-tooth gear, and only one of the upper linkage gear and the lower linkage gear is in a meshed state; the small gear respectively drives the upper cover plate and the lower bottom plate to be in reciprocating motion through the two rack frames to realize seed filling and seed discharging.
Owner:NANJING AGRI MECHANIZATION INST MIN OF AGRI
Pre-sorting method for service life of insulated gate bipolar transistor
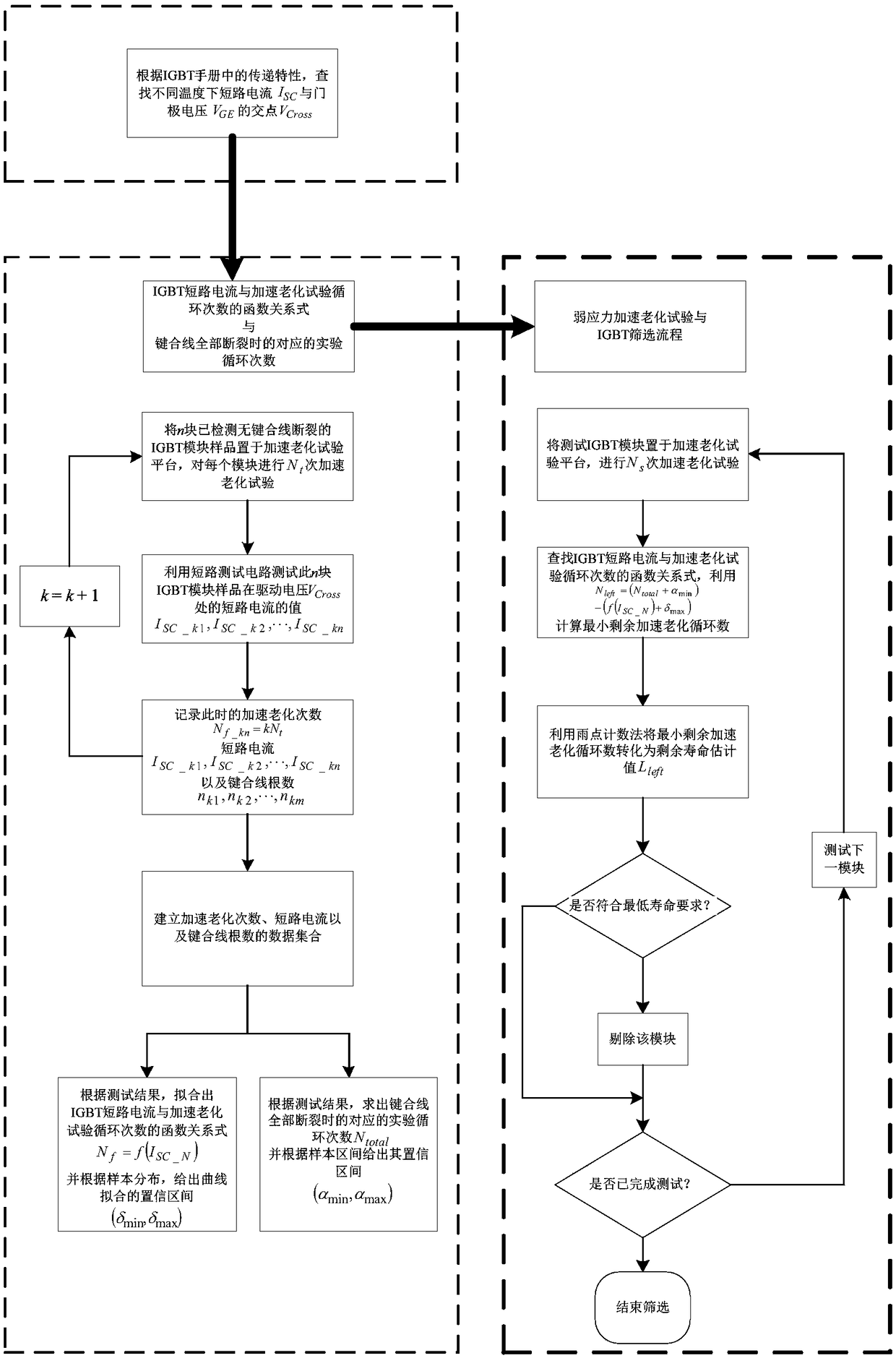
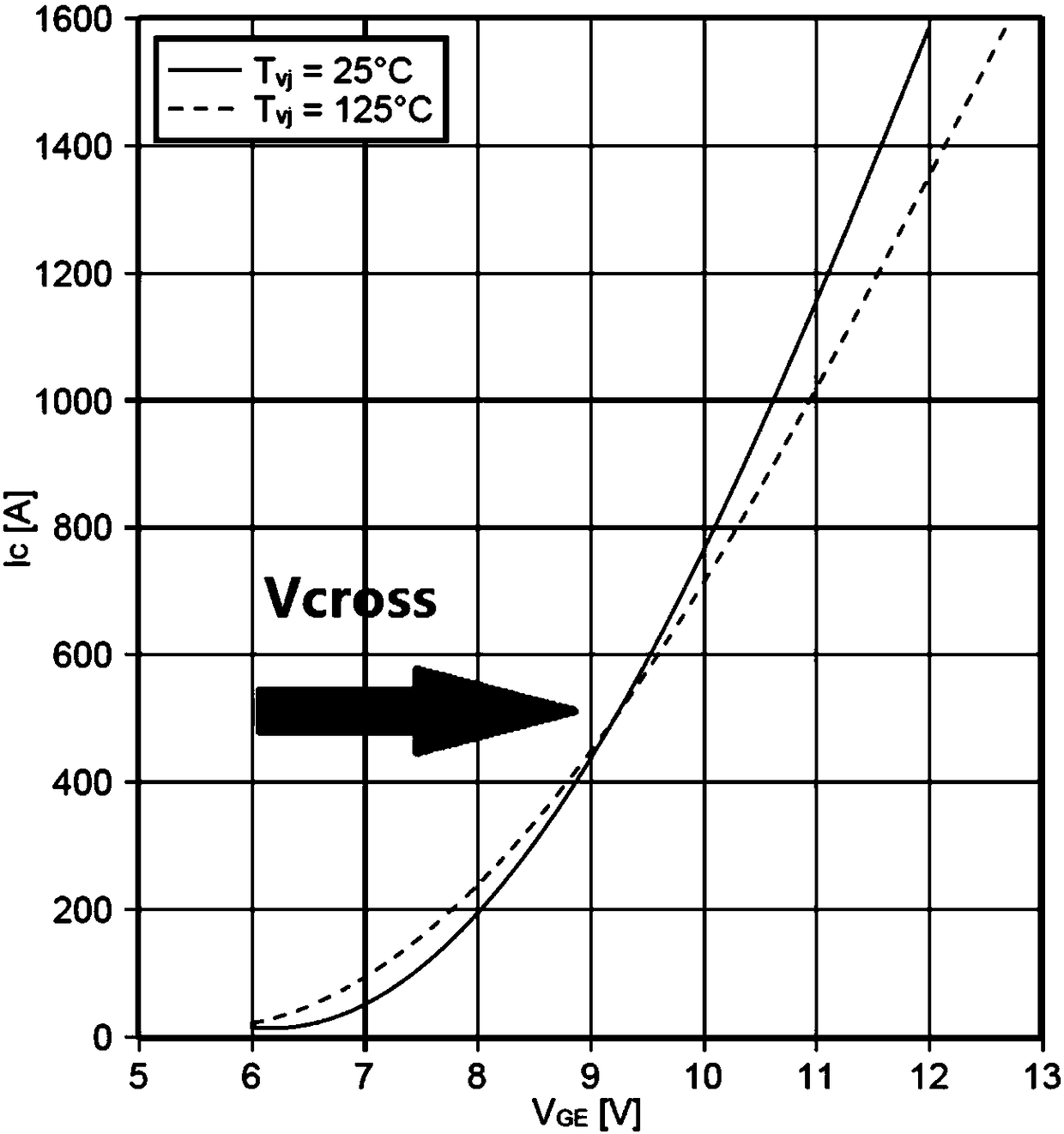
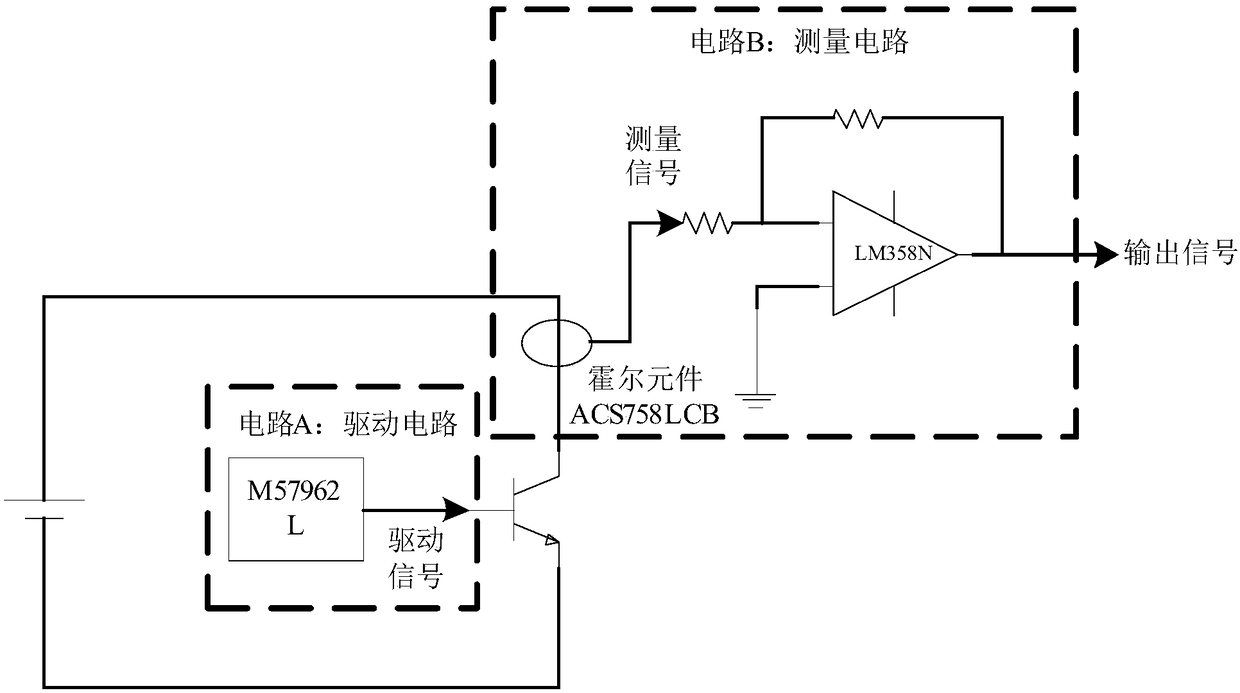
ActiveCN108445371AAvoid unreliableAvoid measurement errorsBipolar transistor testingSemiconductor operation lifetime testingShort-circuit testPower flow
The invention relates to a pre-sorting method for the service life of an insulated gate bipolar transistor, and relates to a detection method for a transistor. The method comprises the steps: A, searching an intersection point of crossing characteristic curves under different temperatures according to the crossing characteristics of an IGBT, and defining a drive voltage corresponding to the intersection point as a crossing point gate electrode voltage VCross; B, selecting a sample according to IGBT products of the selected batch, taking VCross as a drive voltage, carrying out the accelerated aging testing of the IGBTs, recording a short-circuit current in a module testing process through a short-circuit testing circuit, determining a function relation between the short-circuit current of the IGBT and the number of accelerated circulation times according to a testing result, and recording the number of accelerated circulation times when all bonding wires are broken; C: carrying out theaccelerated aging testing of a to-be-tested IGBT module for Ns times, calculating the remaining service life of the module through the built function relation between the short-circuit current of theIGBT and the number of accelerated circulation times after testing, and completing the screening of the module according to the specific requirements of the remaining service life. The method achievesthe purpose of deducing the remaining service life of the IGBT through a few of samples.
Owner:ZHOUSHAN ELECTRIC POWER SUPPLY COMPANY OF STATE GRID ZHEJIANG ELECTRIC POWER +2
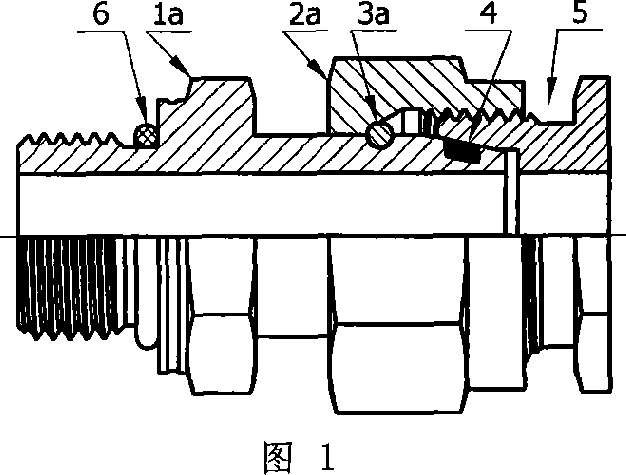
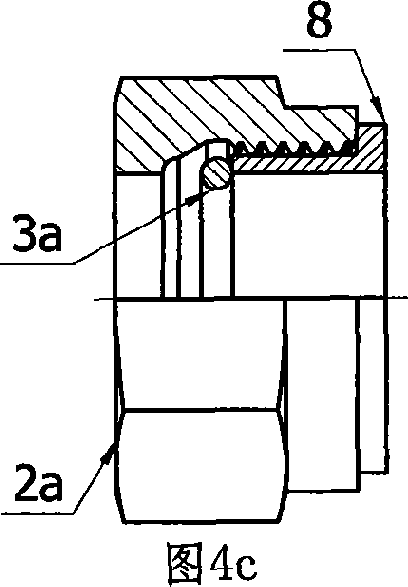
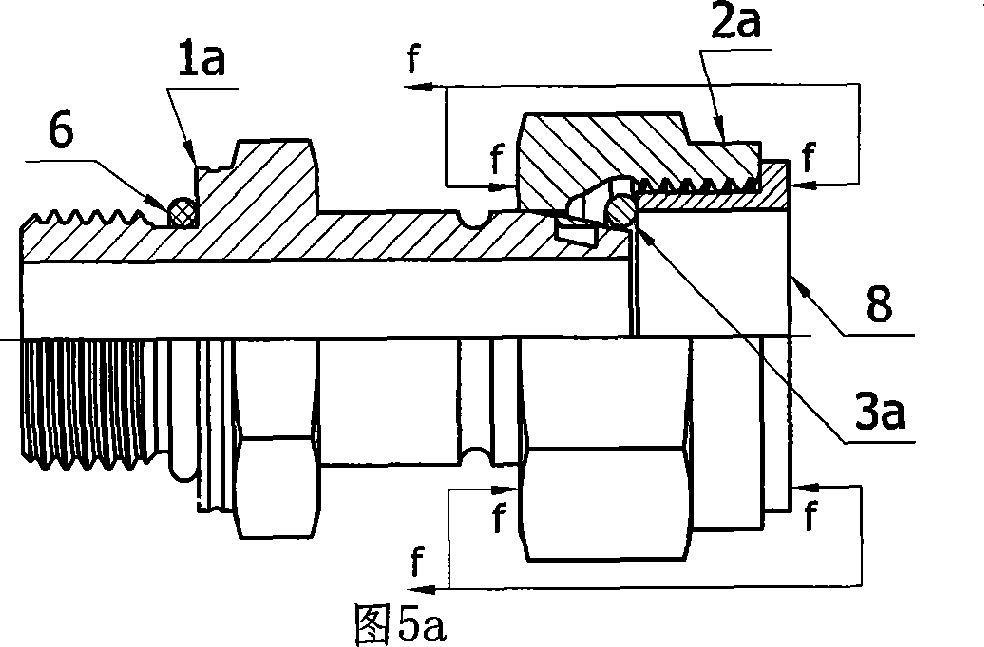
Pipe union fastening structure and its assembling process
InactiveCN101046267AAvoid unreliableOvercome installation difficultiesJoints with sealing surfacesForce structureSteel ball
The pipe union fastening structure consists of one screw nut capable of rotating on the pipe union and one screw nut meshed and operated thrust force structure. The thrust force structure is used to push the conic mouth, conic head or spherical head of the union to the pipe end with corresponding structure to realize the pipeline connection. The thrust force structure has prefabricated step in the screw nut as the pushing step and the prefabricated open-mouthed steel wire or steel ball embedded in the slot on the connected pipe as the pushed step.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUAXIA VALVE
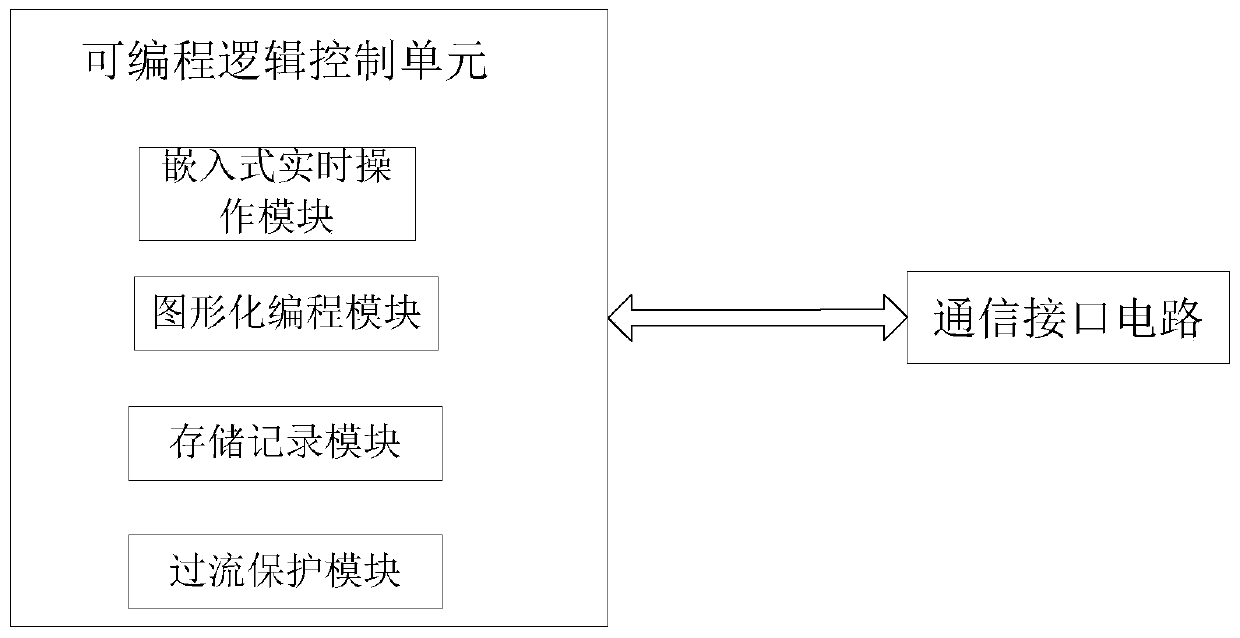
Programmable logic control system applied to subway train
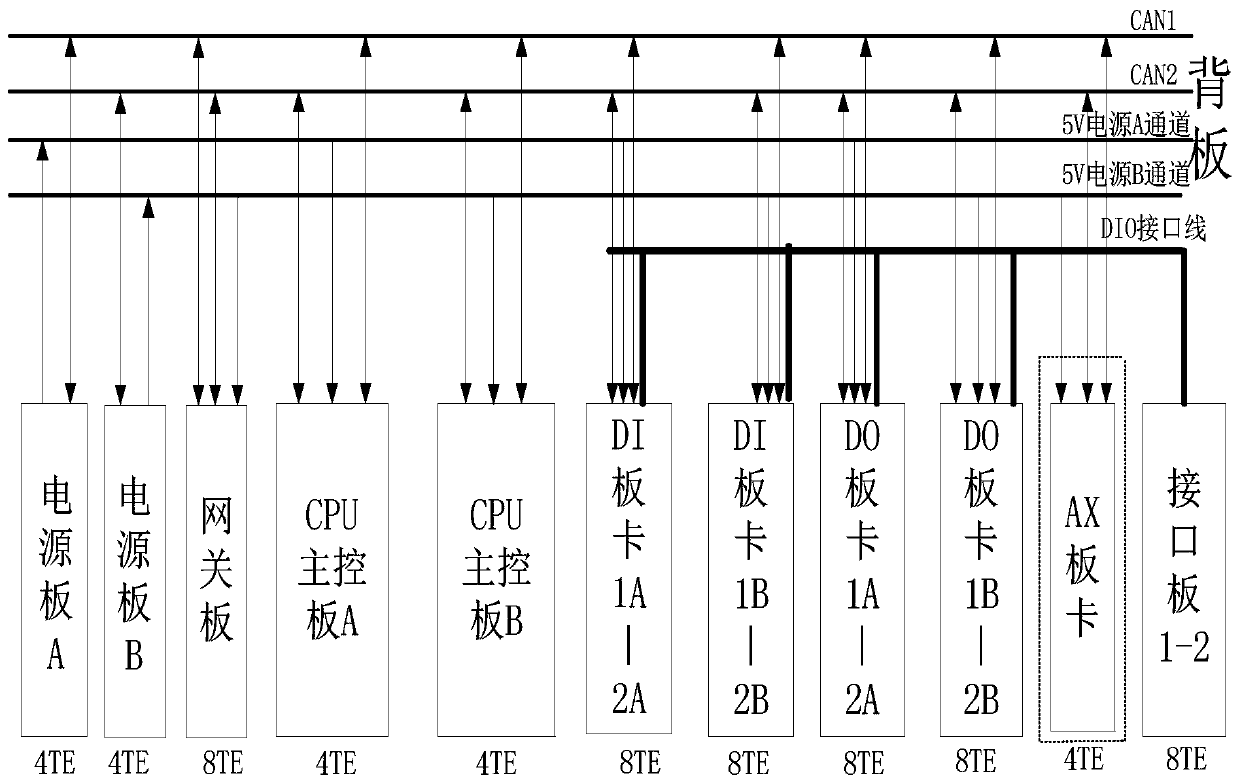
PendingCN110979393AAvoid unreliableEasy programmingSignalling indicators on vehicleCommunication interfaceControl system
The invention discloses a programmable logic control system applied to a subway train. The system comprises a programmable logic control unit, an embedded real-time operation module, a graphical programming module and a storage recording module are operated on the programmable logic control unit, and the periphery of a main control chip is connected with a communication interface circuit; and theprogrammable logic control unit at least comprises a power supply board card, a gateway board card with a recording function and various communication interfaces, two redundant main control board cards, a large bypass board card with four independent CAN communications, a plurality of groups of redundant digital quantity input and output board cards, an interface board card for external wiring anda back board, the main control board card is used for controlling input and output of digital quantity signals and controlling redundancy switching of fault board cards, the gateway board card is indata communication with external equipment, and the digital quantity input and output board cards are used for collecting and driving data signals.
Owner:CRRC DALIAN R & D CO LTD
Vehicle information sharing method and device, computer readable medium and electronic equipment
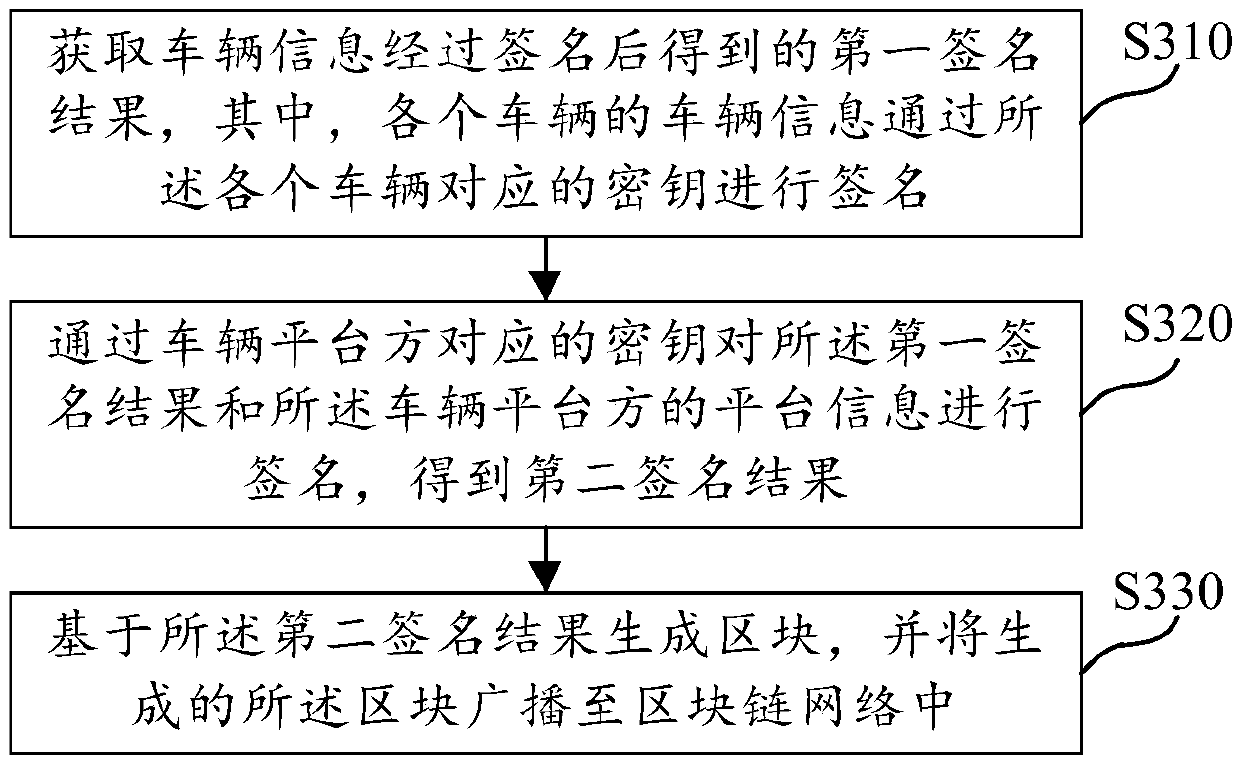
ActiveCN110266635AAvoid unreliablePrevent tamperingUser identity/authority verificationInformation sharingCentralized management
The embodiment of the invention provides a vehicle information sharing method and device based on a block chain, a computer readable medium and electronic equipment. The vehicle information sharing method based on the block chain comprises: obtaining a first signature result obtained after vehicle information is signed, whereinthe vehicle information of all vehicles is signed through secret keys corresponding to all the vehicles; signing the first signature result and the platform information of the vehicle platform party through a secret key corresponding to the vehicle platform party to obtain a second signature result; and generating a block based on the second signature result, and broadcasting the generated block to a block chain network. According to the technical scheme provided by the embodiment of the invention, the vehicle information is shared through the decentralized block chain network, so that the problem of unreliability caused by centralized management of the vehicle information by a vehicle platform side in the prior art is solved.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
Counting apparatus of photosensitive gray scale
InactiveCN102426028AAvoid mechanical errorsAvoid errorsConverting sensor output opticallyMicrocomputerMicrocontroller
The invention relates to a counting apparatus of a photosensitive gray scale. The counting apparatus comprises a plurality of counting print wheels corresponded to different unit amounts and all the counting print wheels are connected with a drive unit. Different gray scale segments that are different from shallow to deep are arranged at an arc surface or a side surface of each of the counting print wheel, and all the gray scale segments are in end-to-end connection. Meanwhile, at least one support is arranged at a position that is corresponded to the arc surface or the side surface of each of the counting print wheel as well as is provided with a photosensitive sensor and a luminescent device; each of the photosensitive sensor is configured with at least two luminescent devices; and the photosensitive sensors and the luminescent devices are connected with a one-chip microcomputer. According to the invention, defects of other sensing modes can be overcome, wherein the defects include a requirement on complex determination, easiness to make errors of carrying critical points and easiness of wearing and corrosion of resistor sensing contacts and the like; photosensitive sensors are used to carry out non-contact detection on different gray scales, so that purposes of print wheel numerical code determination and print wheel data reading are achieved.
Owner:SHANDONG WEIWEI TECH
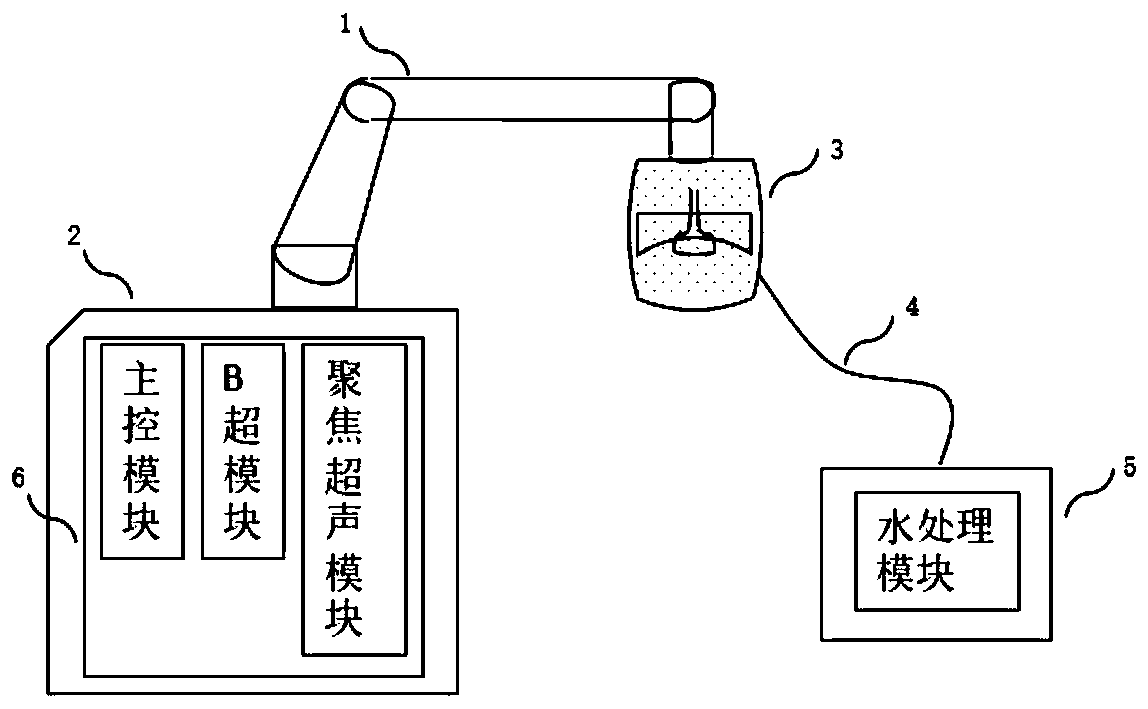
High-intensity focused ultrasound diagnosis and treatment system with temperature measurement function, and control method thereof
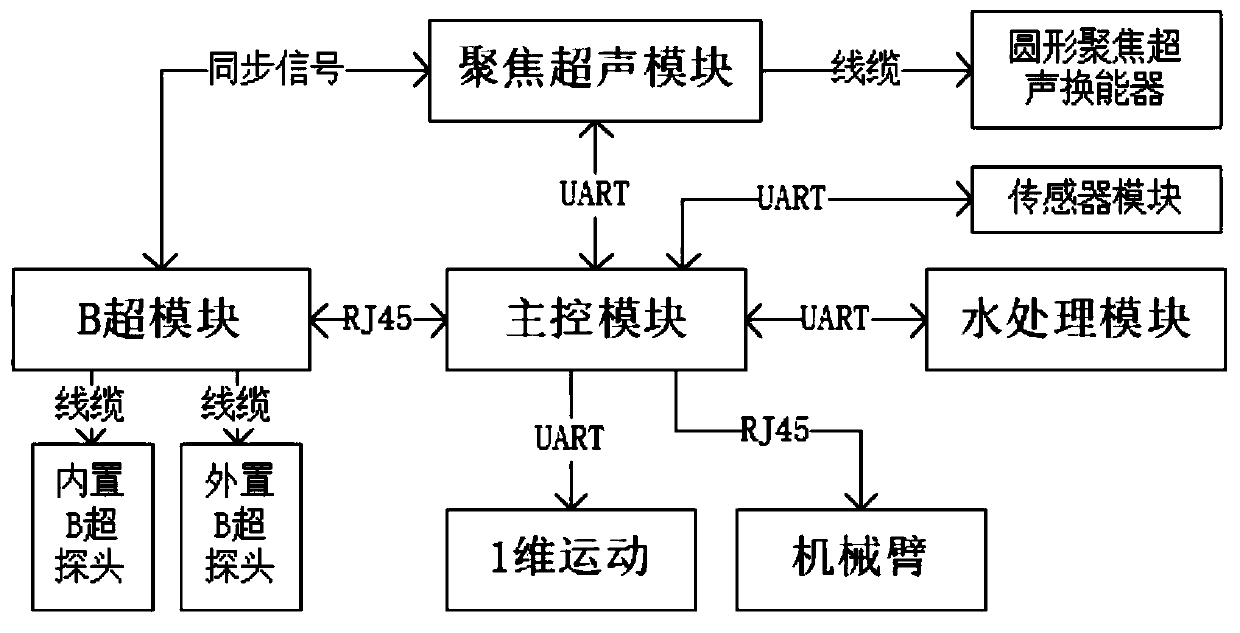
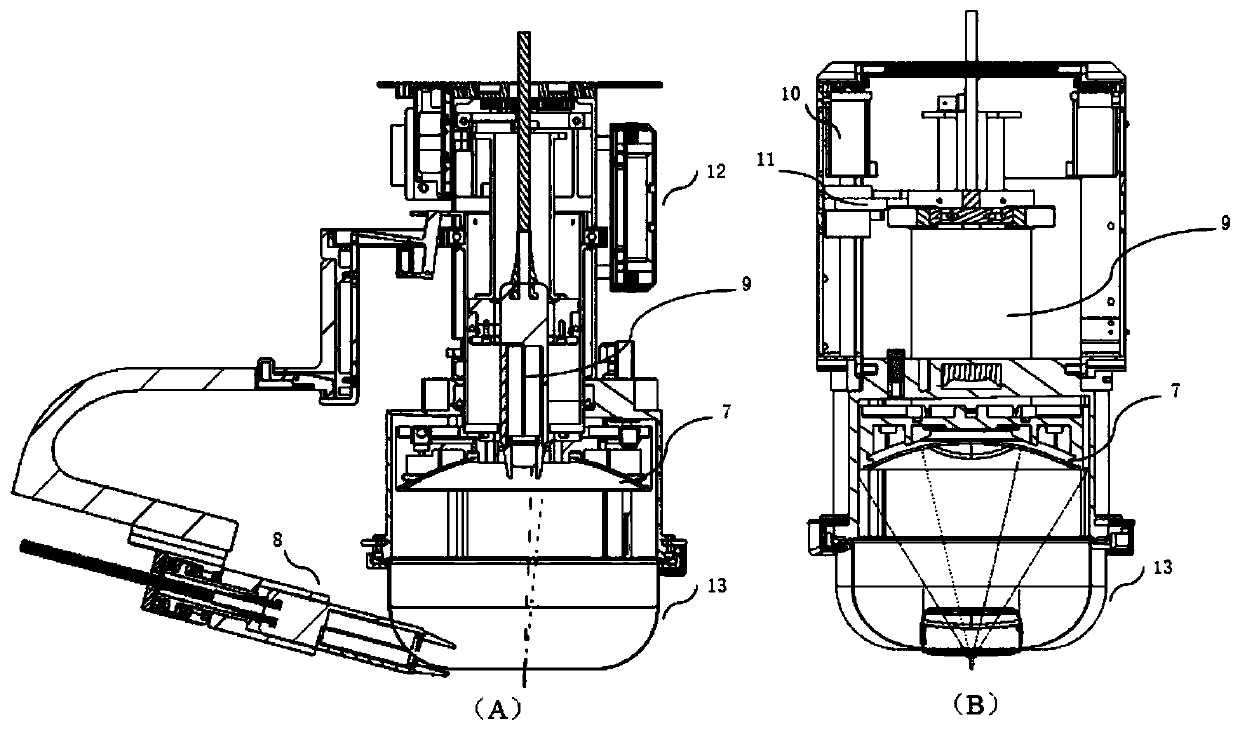
ActiveCN111408075AReduce usage and installation requirementsAvoid unreliableUltrasound therapyElectric machineryHigh-intensity focused ultrasound
The invention discloses a high-intensity focused ultrasound diagnosis and treatment system with the temperature measurement function, and a control method thereof. The system comprises a main controlmodule, a B-ultrasound module, a focused ultrasound module, a motion module, a combined probe and a water treatment module, wherein the main control module, the B-ultrasound module and the focused ultrasound module constitute a host of the system, the motion module comprises a six-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm, and a one-dimensional motor motion module inside the combined probe, the six-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm is installed on a machine frame of the system host, the combined probe is installed at the terminal end of the six-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm, the water treatment module is used as a part of a water tank, and the water tank is connected with the combined probe by a water pipe. A novel integrated diagnosis and treatment system is formed by integrating a B-ultrasoundsystem and a focused ultrasound control system, and the timing management is performed on the two parts at the bottom layer of the system to realize configurable real-time B-ultrasound image monitoring of a visual area.
Owner:NANJING GUANGCI MEDICAL TECH
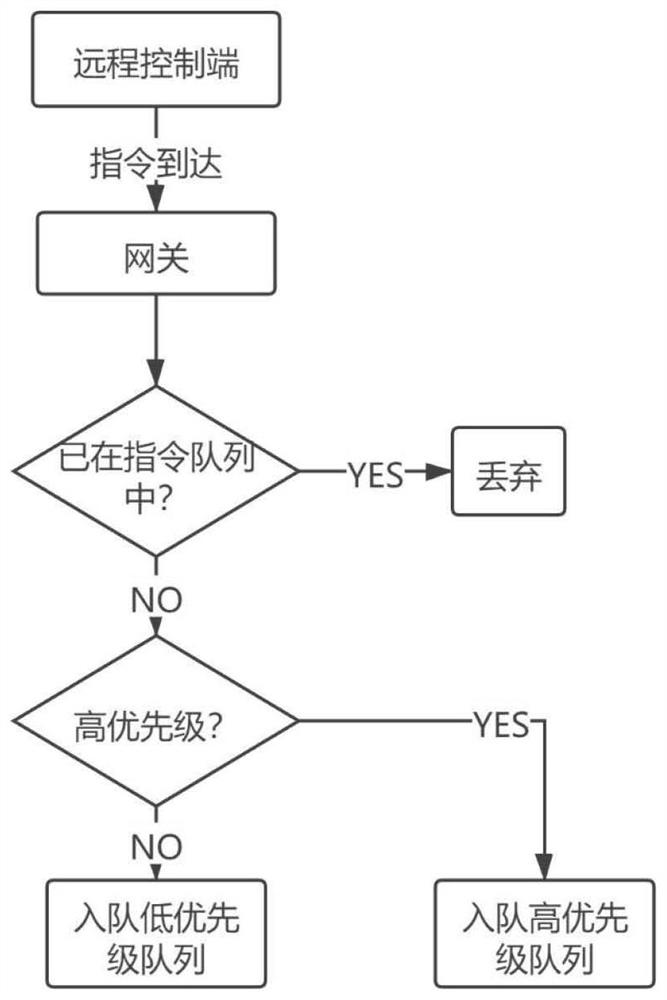
Optimization method for Bluetooth Mesh remote control system
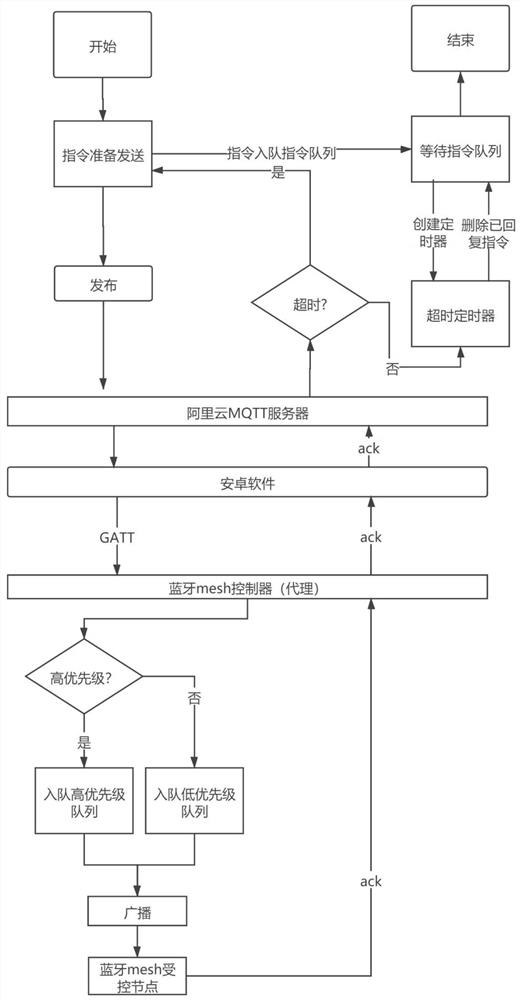
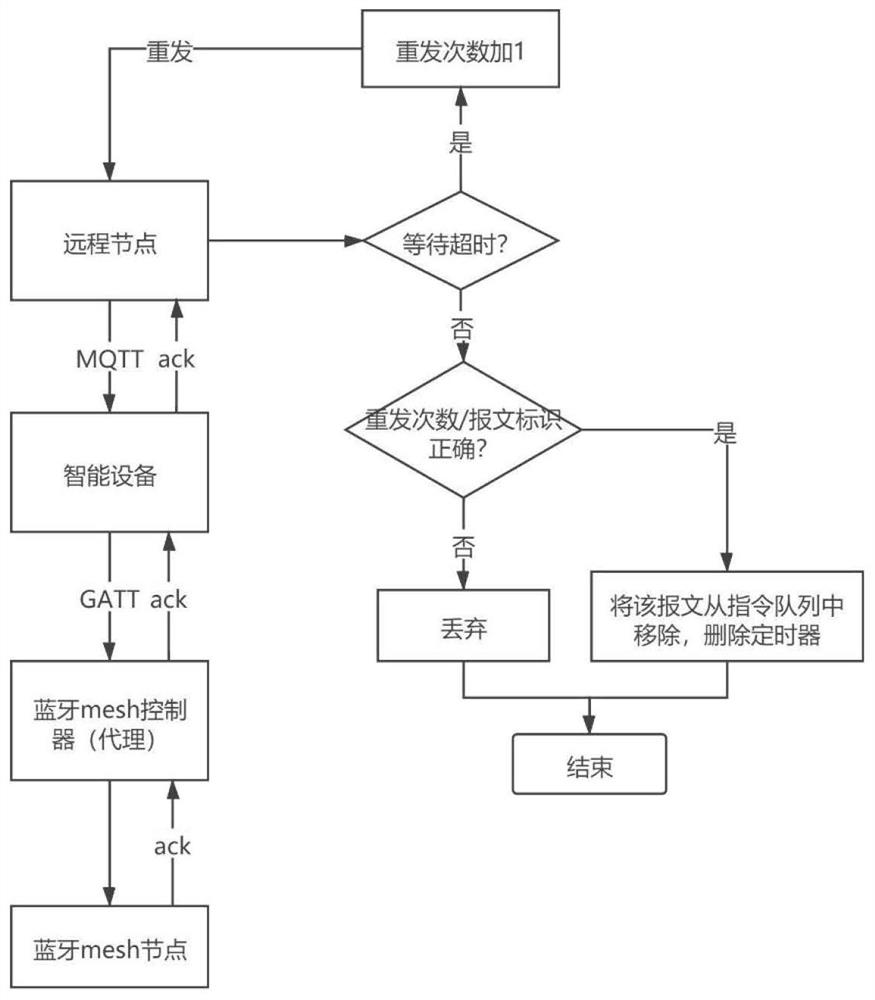
InactiveCN112017413ASolution system is unreliableLower overall latencyError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsControl systemPacket loss
The invention discloses an optimization method for a Bluetooth Mesh remote control system. The limited retransmission of a data package which does not receive an ack message in a set time is carried out through an ack and a timeout retransmission mechanism, and the reliability of the system can be improved to a certain degree; for the problem that a packet loss retransmission mechanism may cause time delay increase, the queuing time delay of high-priority instructions is reduced through a priority queue algorithm such that the overall time delay of the instructions is reduced. On the premise of ensuring the reliability of remote data transmission, the end-to-end time delay of the high-priority instructions in remote control is effectively reduced such that the method is suitable for widerapplication scenarios, and the value of Bluetooth Mesh in remote control of the Internet of Things is further improved.
Owner:苏州博联科技有限公司
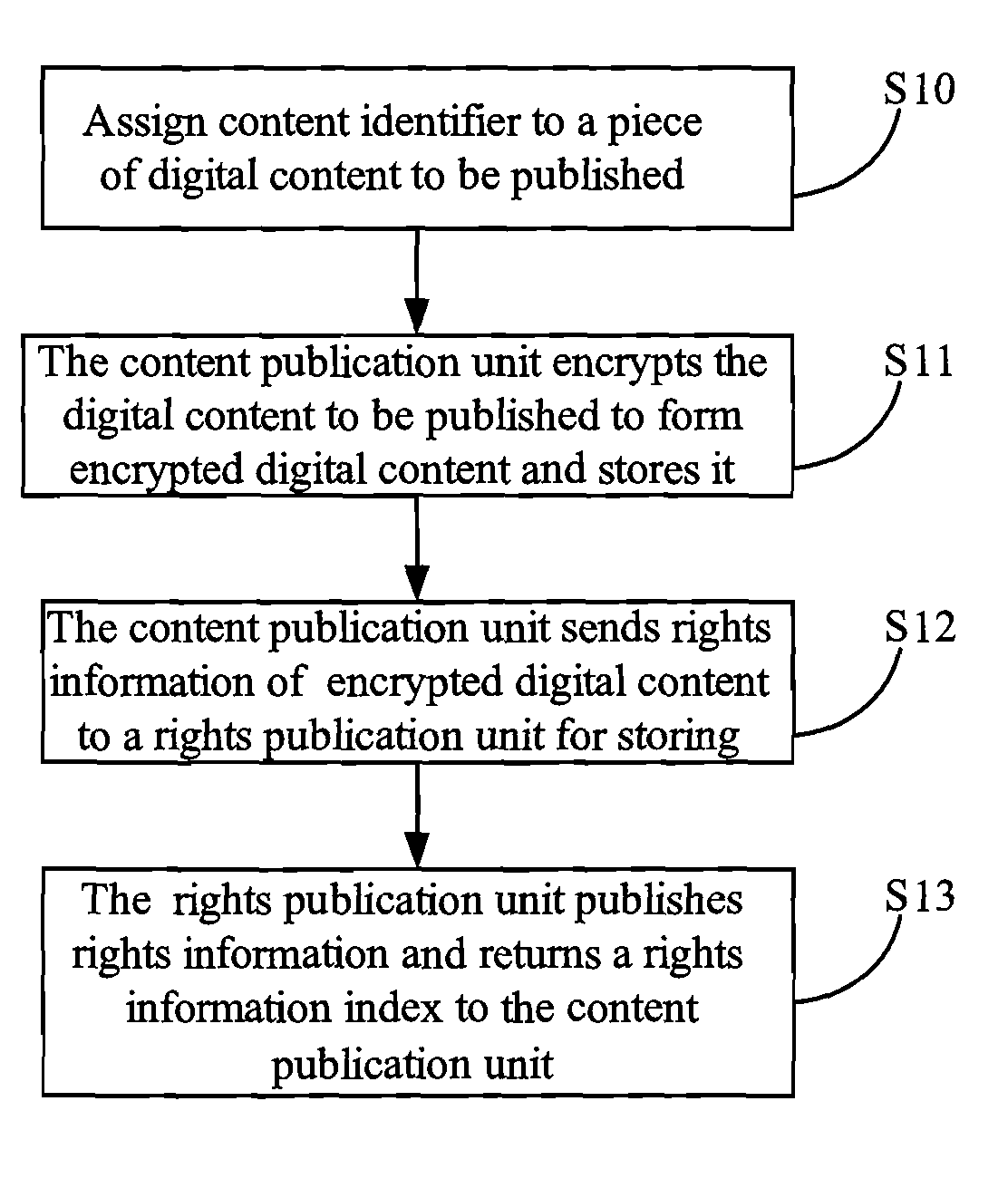
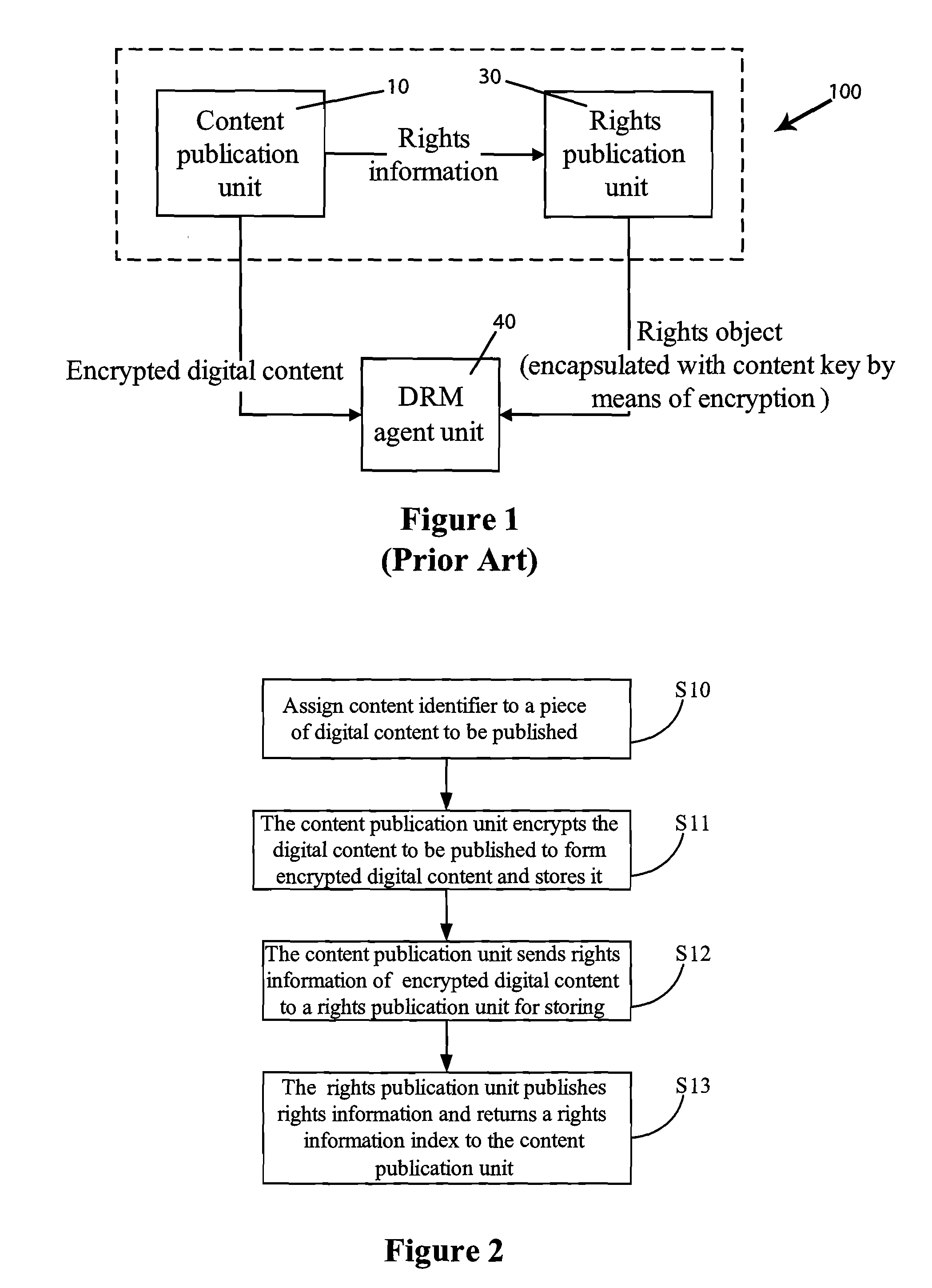
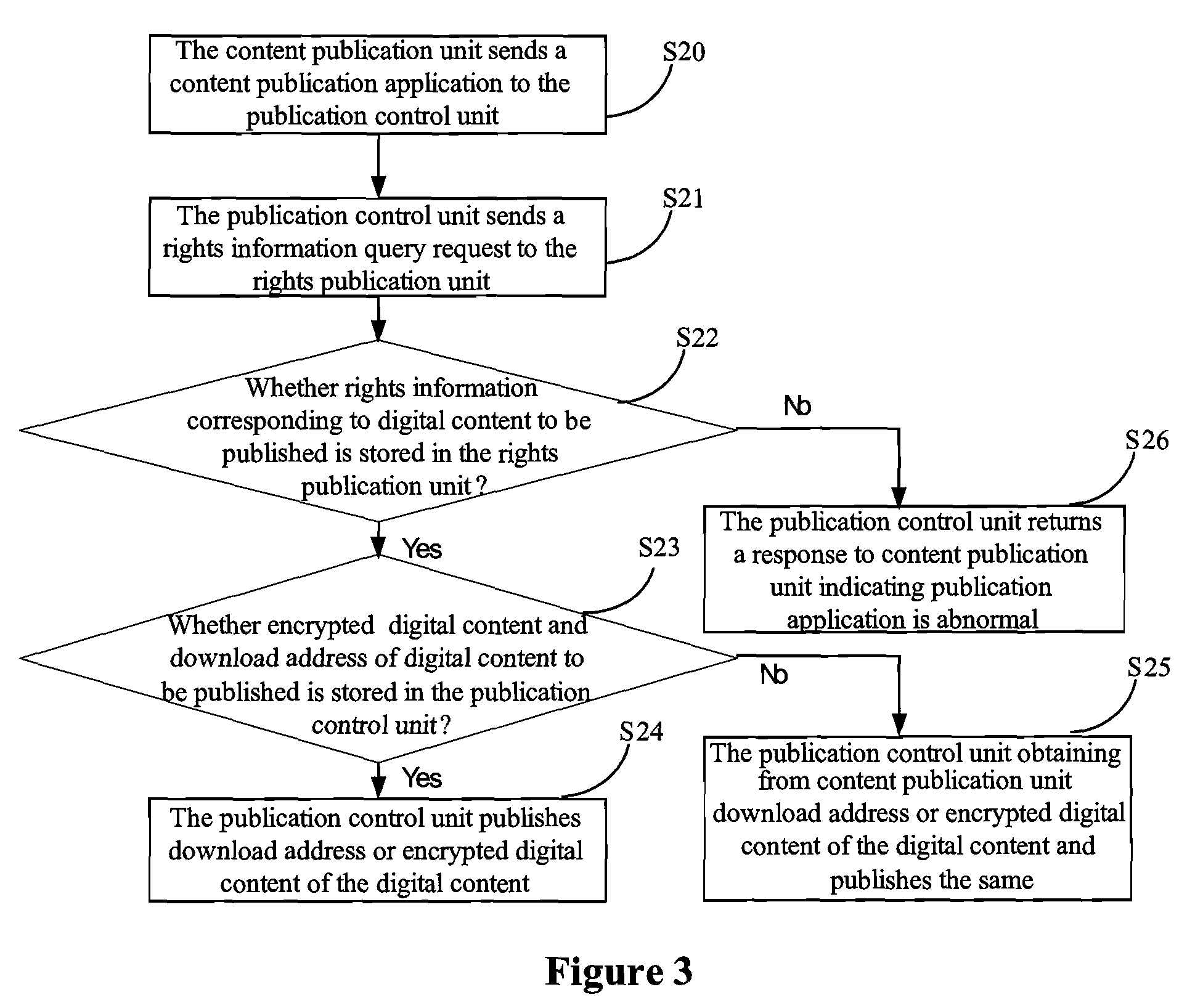
Method and system for publication control of digital content
InactiveUS20080271160A1Capability be avoidedAvoid limitationsDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsDigital contentApplication software
A method and system for publication control of digital content for validating the rights information registered by a plurality of separate content providers. When receiving a digital content publication application from a content publication unit, a publication control unit queries whether rights information corresponding to the digital content to be published is stored in a rights publication unit, and if stored, allows the publication of the digital content and of a download address thereof. By messaging rights information in this centralized manner, it may be ensured that a content buyer can efficiently obtain the rights object distributed after the digital content is published.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Network quality estimation and detection method and device
InactiveCN104320296AAccurate and effective assessmentAvoid unreliableData switching networksTime delaysDependability
The invention provides a network quality estimation and detection method, and belongs to the application field of network technology. According to the estimation and detection method, the problem that the prior art only relies on one factor selected from package loss, time delay and jitter for network quality estimation and thus the detection result is not reliable can be solved, and three factors of package loss, time delay and jitter are combined at the same time for estimating the network quality, unreliability when one factor is used for estimation can be avoided, and the network quality can be accurately and effectively estimated. In addition, the time delay and jitter calculation method also has specific beneficial effects, and reliability of network quality estimation is greatly improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN YUNZHIXUN NETWORK TECH
Zoom tracking method and device, equipment, and storage medium
ActiveCN112135055AThe image is clear throughoutAvoid unreliableTelevision system detailsColor television detailsControl theoryTrack algorithm
The invention provides a zoom tracking method and device, equipment and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: adjusting the step length of a focusing motor according to the proportional quantity of a current period; obtaining n+1 frames of images when the focusing motor steps according to the step length in the current period, wherein n is an integer greater than or equal to 1; inthe n + 1 frames of images, taking the sum of difference values of detail information of each pair of two adjacent frames of images as an integral quantity of a current period; calculating the feedback quantity of the current period at least according to the detail information of the image of the current period; and calculating the proportional quantity of the next period according to the proportional quantity of the current period, the integral quantity of the current period and the feedback quantity of the current period. According to the method and device provided by the invention, the calibration cost is reduced, and the stability and robustness of the zoom tracking algorithm are improved.
Owner:SUZHOU KEDA TECH
Mechanical sliding piece translational motion type precise sowing device with air channel seed selecting function
InactiveCN110402647AAvoid shortagePrevent fallingDibble seedersSeed depositing seeder partsCharge dischargeMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a mechanical sliding piece translational motion type precise sowing device with an air channel seed selecting function. The precise sowing device comprises a seed selecting mechanism, a seed charging mechanism and a seed charging-discharging mechanism. The seed selecting mechanism comprises a seed cleaning part and a sorting part; a funnel of the seed cleaning part is installed on a seed cleaning rack, the bottom of the funnel is provided with a guide groove, a poking amount adjusting plate is installed in the guide groove, a fan is arranged below the poking amount adjusting plate, one end of a conveying pipe is connected with an air outlet of the fan, and the other end of the conveying pipe extends to a position above the sorting part; the sorting part comprises aplurality of stacked sorting boxes, and the bottommost sorting box is arranged above the seed charging mechanism. The seed charging mechanism comprises a mechanical translational motion driving mechanism fixedly connected with the side wall of a seed charging box, a translational motion sliding piece mechanism is arranged on the opposite side of the mechanical translational motion driving mechanism, the translational motion sliding piece mechanism comprises a U-shaped sliding groove and a supporting sliding piece which are fixedly arranged, the supporting sliding piece is horizontal, one endof the supporting sliding piece is horizontally fixed on the side wall of the seed charging box, and the other end of the supporting sliding piece can slide in the U-shaped sliding groove.
Owner:NANJING AGRI MECHANIZATION INST MIN OF AGRI
Interlocking device used for high-voltage switch equipment
ActiveCN102646543ASimple structureDoes not affect the effectAir-break switch detailsEngineeringHigh pressure
The invention discloses an interlocking device used for high-voltage switch equipment. The interlocking device comprises an isolation switch operation mechanism and a circuit breaker on-off mechanism and also comprises a transmission mechanism, wherein one end of the transmission mechanism is connected with a shifting fork of the isolation switch operation mechanism, the other end of the transmission mechanism is arranged at the bottom of a circuit breaker and is connected with the circuit breaker on-off mechanism, and the transmission mechanism comprises a link mechanism arranged at the outer side of the circuit breaker and a lever mechanism arranged at the inner side of a circuit breaker. The interlocking device used for the high-voltage switch equipment is arranged at the bottom of the circuit breaker, and therefore, compared with the existing interlocking device, the interlocking device used for the high-voltage switch equipment is simple in structure, flexible in transmission, safety in use, reliable in interlocking and convenient in manufacturing, installation and debugging.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LINGAO ELECTRICAL IND
Obstacle detection method and device, computer readable storage medium and processor
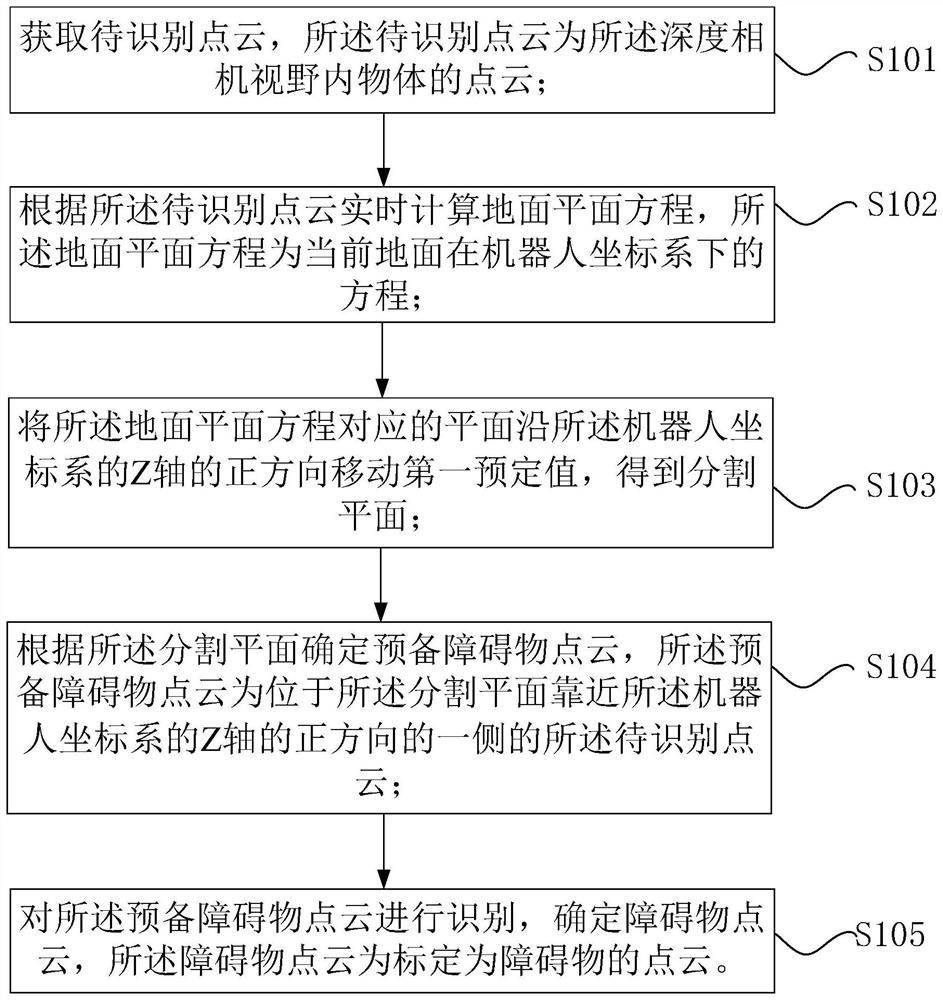
PendingCN114764885ASolve missing detectionSolve the problem of false detectionImage enhancementImage analysisPoint cloudComputer graphics (images)
The invention provides an obstacle detection method and device, a computer readable storage medium and a processor, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a to-be-recognized point cloud which is the point cloud of an object in the visual field of a depth camera; calculating a ground plane equation in real time according to the to-be-identified point cloud, wherein the ground plane equation is an equation of the current ground under a robot coordinate system; a plane corresponding to the ground plane equation is moved by a first preset value in the positive direction of the Z axis of the robot coordinate system, and a segmented plane is obtained; determining a preparation obstacle point cloud according to the segmentation plane, wherein the preparation obstacle point cloud is a to-be-recognized point cloud located on one side, close to the positive direction of the Z axis of the robot coordinate system, of the segmentation plane; and the prepared obstacle point cloud is identified, the obstacle point cloud is determined, and the obstacle point cloud is the point cloud calibrated as an obstacle. The method solves the problem that in the prior art, due to the low reliability of a ground plane equation, missing detection and false detection of obstacles are caused.
Owner:HANGZHOU LANXIN TECH CO LTD
Measuring system and method of low-speed non-linear seepage parameters
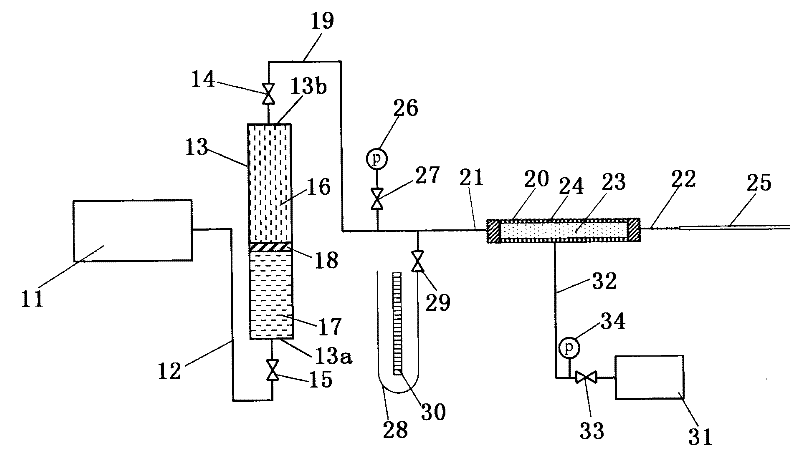
InactiveCN101852714BNot easy to damageWill not be damagedPermeability/surface area analysisLow speedHeight difference
The embodiment of the invention provides measuring system and method of low-speed non-linear seepage parameters. The system comprises a power output device, a pressure measuring device and a flow measuring device, wherein the power output device is connected with a first opening of an intermediate container through a pipeline and is used for outputting different drive pressures so as to displace a displacing fluid in the intermediate container to be transmitted to a core of a core holder by the pipeline; the pressure measuring device comprises a pressure gage and a U-shaped pipe pressure gagewhich are respectively connected with a third opening of the core holder through pipelines and is used for measuring the pressure of the third opening of the core holder under different drive pressures; the U-shaped pipe pressure gage can display the level height difference so as to acquire the starting pressure of the core when the drive pressure is reduced to the minimum value, a switching partis in a closed state and the self level is stable; and the flow measuring device is connected with a fourth opening of the core holder through a pipeline and is used for measuring the volume of the displacing fluid seeped from the core under the different pressures of the third opening. The system can accurately measure the pressure, the starting pressure and the fluid volume under the low-speed non-linear seepage conditions.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
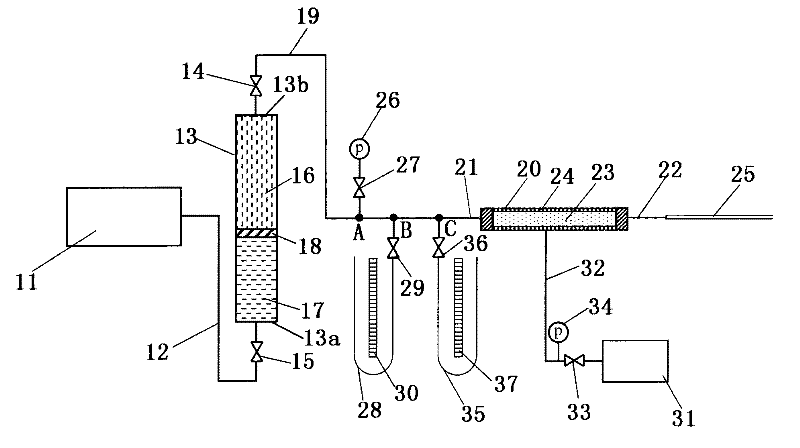
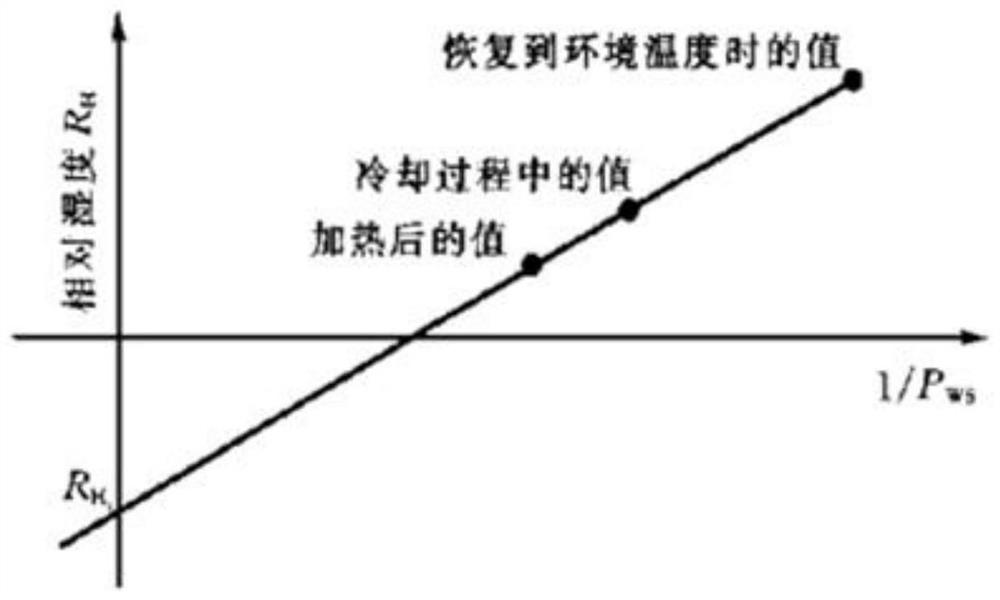
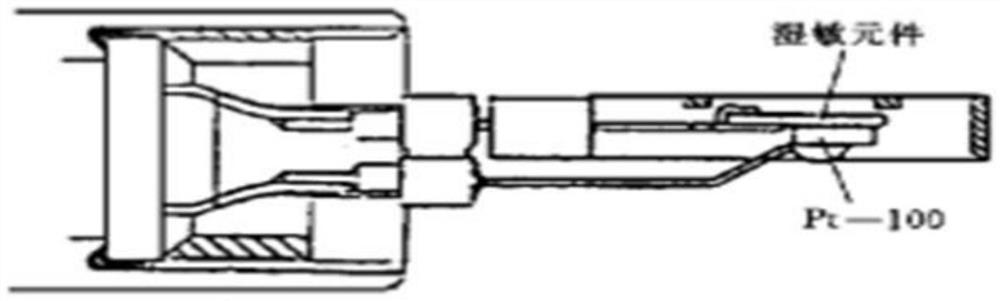
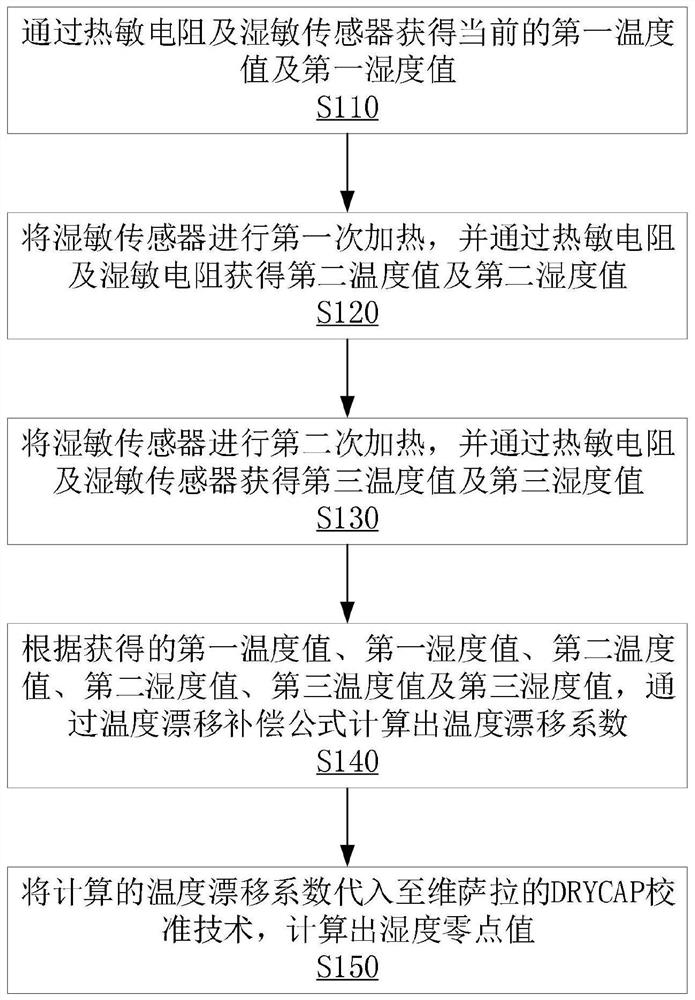
High-precision micro-water sensor zero drift correction method and storage device
PendingCN113484376AAvoid unreliableReliable humidity zero point valueMaterial capacitanceEngineeringAtmospheric sciences
The invention relates to a high-precision micro-water sensor zero drift correction method and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a current first temperature value and a current first humidity value through a thermistor and a humidity-dependent sensor; heating the humidity-sensitive sensor for the first time, and obtaining a second temperature value and a second humidity value through the thermistor and the humidity-sensitive resistor; heating the humidity-dependent sensor for the second time, and obtaining a third temperature value and a third humidity value through the thermistor and the humidity-dependent sensor; according to the obtained first temperature value, the first humidity value, the second temperature value, the second humidity value, the third temperature value and the third humidity value, calculating a temperature drift coefficient through a temperature drift compensation formula; and substituting the calculated temperature drift coefficient into a DRYCAP calibration technology of Vaisala, and calculating a humidity zero point value. The problem of unreliability of measurement data is avoided, expensive sensors are not needed, and the purchase cycle and cost are reduced.
Owner:福州亿得隆电气技术有限公司
Disaster monitoring method and device, and electronic equipment
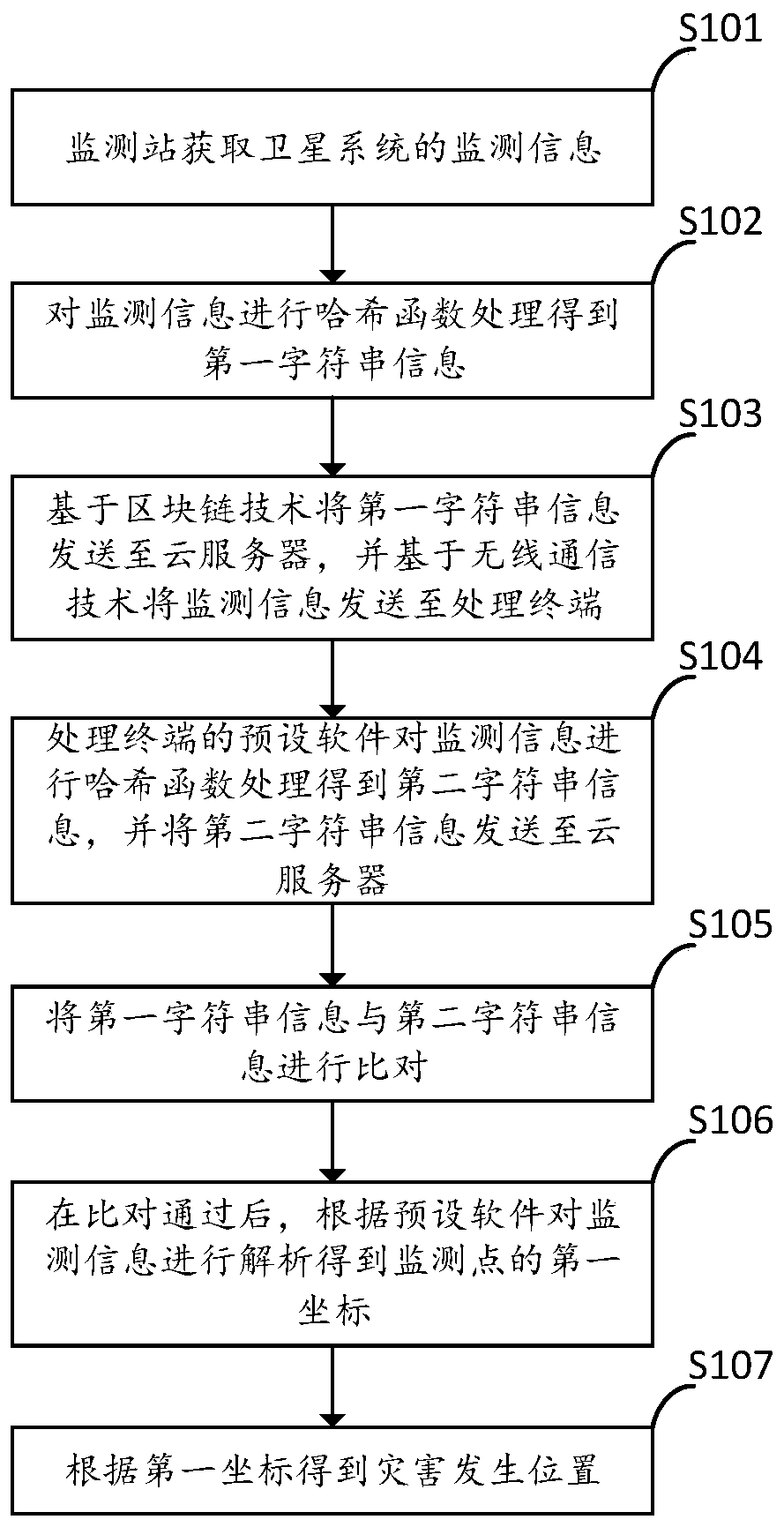
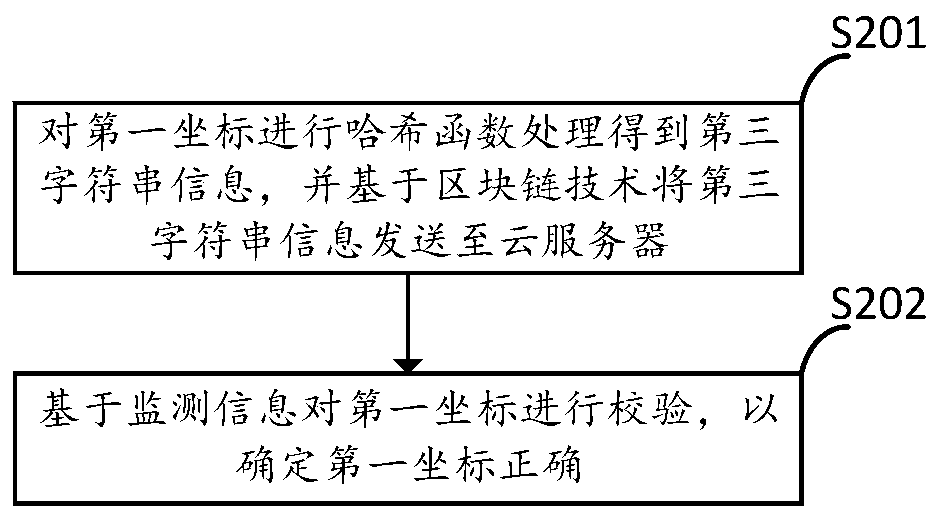
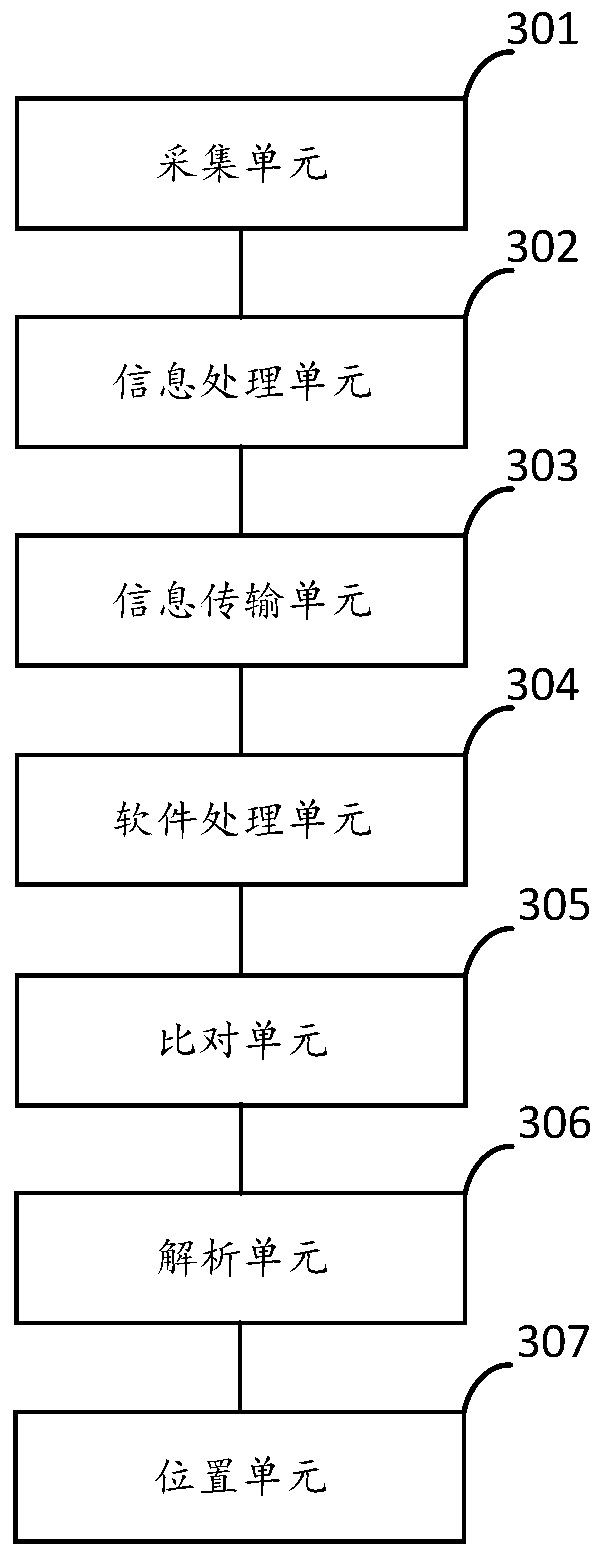
InactiveCN111063182AGuaranteed accuracyAvoid unreliableTransmission systemsHash functionDisaster monitoring
The invention provides a disaster monitoring method and device, and electronic equipment, and relates to the technical field of disaster monitoring. The method, the device and the equipment are applied to a monitoring station, a processing terminal and a cloud server which are connected. The method comprises the steps that the monitoring station acquires monitoring information of a satellite system; hash function processing is performed on the monitoring information to obtain first character string information; the first character string information is sent to a cloud server based on a block chain technology, and the monitoring information is sent to a processing terminal based on a wireless communication technology; preset software of the processing terminal carries out hash function processing on the monitoring information to obtain second character string information, and the second character string information is sent to the cloud server; the first character string information is compared with the second character string information; after the comparison is passed, the monitoring information is analyzed according to the preset software to obtain a first coordinate of a monitoring point; and obtaining a disaster occurrence position according to the first coordinate. Reliability of monitoring data can be effectively improved.
Owner:北京华力创通科技股份有限公司
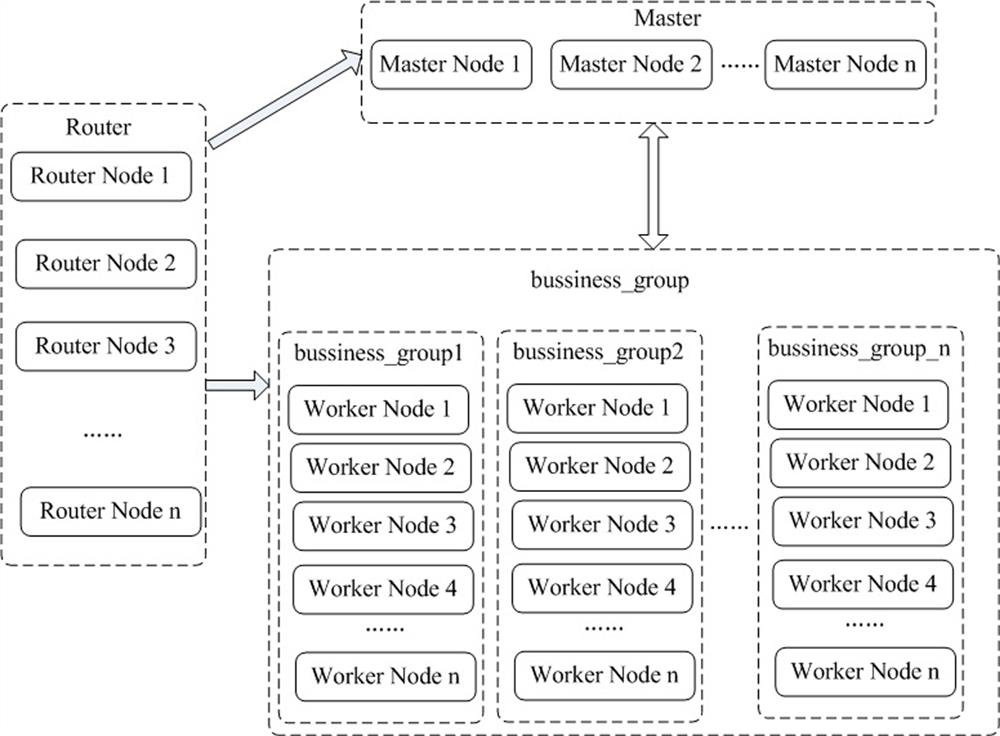
Multi-vehicle linkage system and method based on 5G virtual private communication
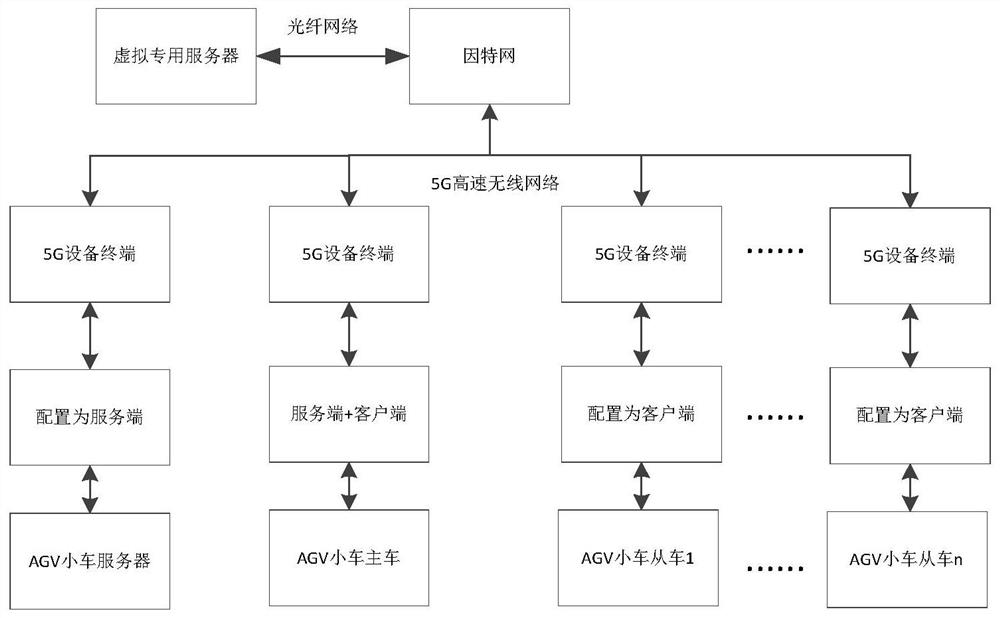
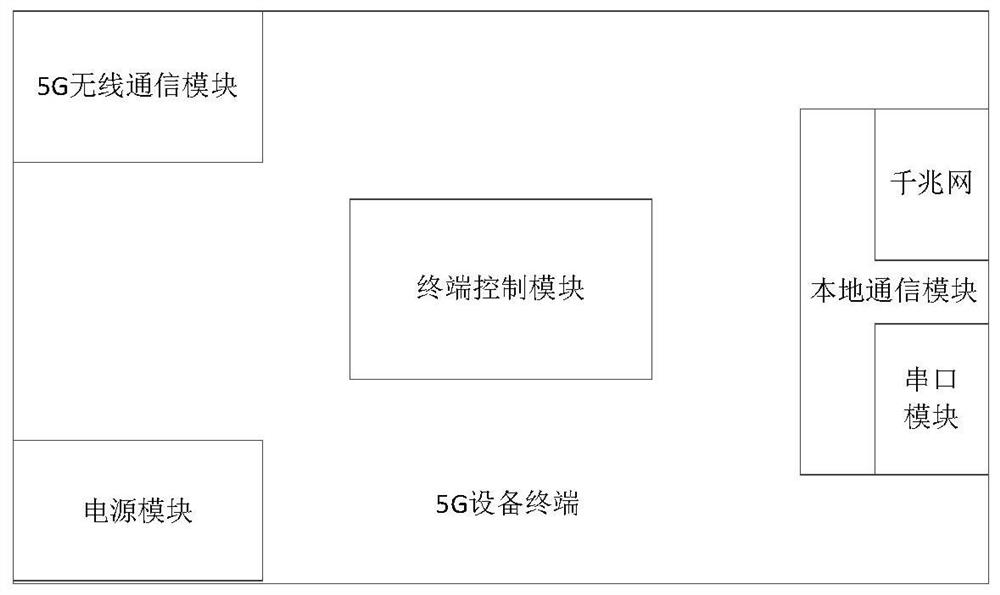
ActiveCN112512012ARealize multi-vehicle linkageRealize monitoringParticular environment based servicesVehicle-to-vehicle communicationPrivate communicationCommunications system
The invention discloses a multi-vehicle linkage system and method based on 5G virtual private communication, and belongs to the technical field of AGV linkage. The multi-vehicle linkage system comprises a 5G virtual communication system and an AGV system; the 5G virtual communication system comprises a virtual private server and a 5G equipment terminal, and the 5G equipment terminal comprises a 5Gwireless communication module, a terminal control module and a local communication module; the 5G communication module is used for being connected with a virtual private server, the local communication module is used for being connected with an AGV system, and the terminal control module is used for configuring the operation mode of the terminal so as to communicate with the AGV system. Accordingto the invention, the 5G technology, the AGV technology, the multi-vehicle interconnection technology and the like are fully combined, so that multi-vehicle linkage of the AGV can be realized, and the stability and safety of equipment operation are improved.
Owner:KEDA INTELLIGENT ELECTRICAL TECH +1
User remote meter reading data intelligent processing method based on cloud computing
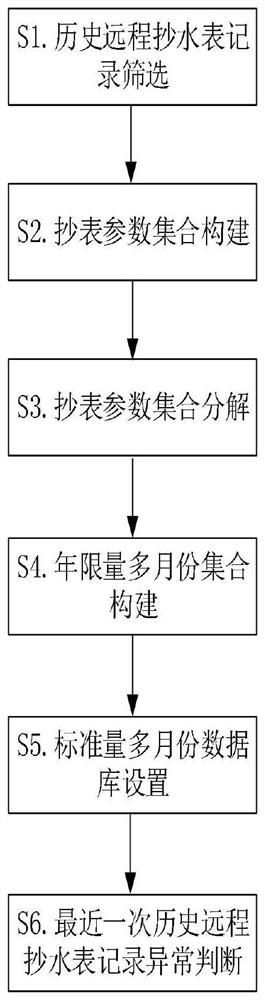
InactiveCN112489414ARealize the function of water consumption monitoringMeet the needs of water consumption monitoringTransmission systemsUtility meters data arrangementsEnvironmental resource managementEngineering
The invention discloses a user remote meter reading data intelligent processing method based on cloud computing. The method comprises six steps of historical remote meter reading record screening, meter reading parameter set construction, meter reading parameter set decomposition, annual limit quantity multi-month set construction, standard quantity multi-month database setting and latest historical remote meter reading record abnormity judgment. The historical remote water meter reading records in the preset screening time period are obtained through the personal login information of the user, and the meter reading parameter set is constructed, so that the multi-month database is set, whether the latest historical remote water meter reading record is abnormal or not is analyzed, and if so, early warning prompt is given to the user, and the function of monitoring the water consumption of the user is realized. The method has the characteristics of strong operability and high intelligentlevel, overcomes the defect of single function of the existing automatic remote water meter reading system, and meets the requirement of monitoring the water consumption of the user.
Owner:南京贺宇网络科技有限公司
Storage method for improving reliability of real-time image recording system
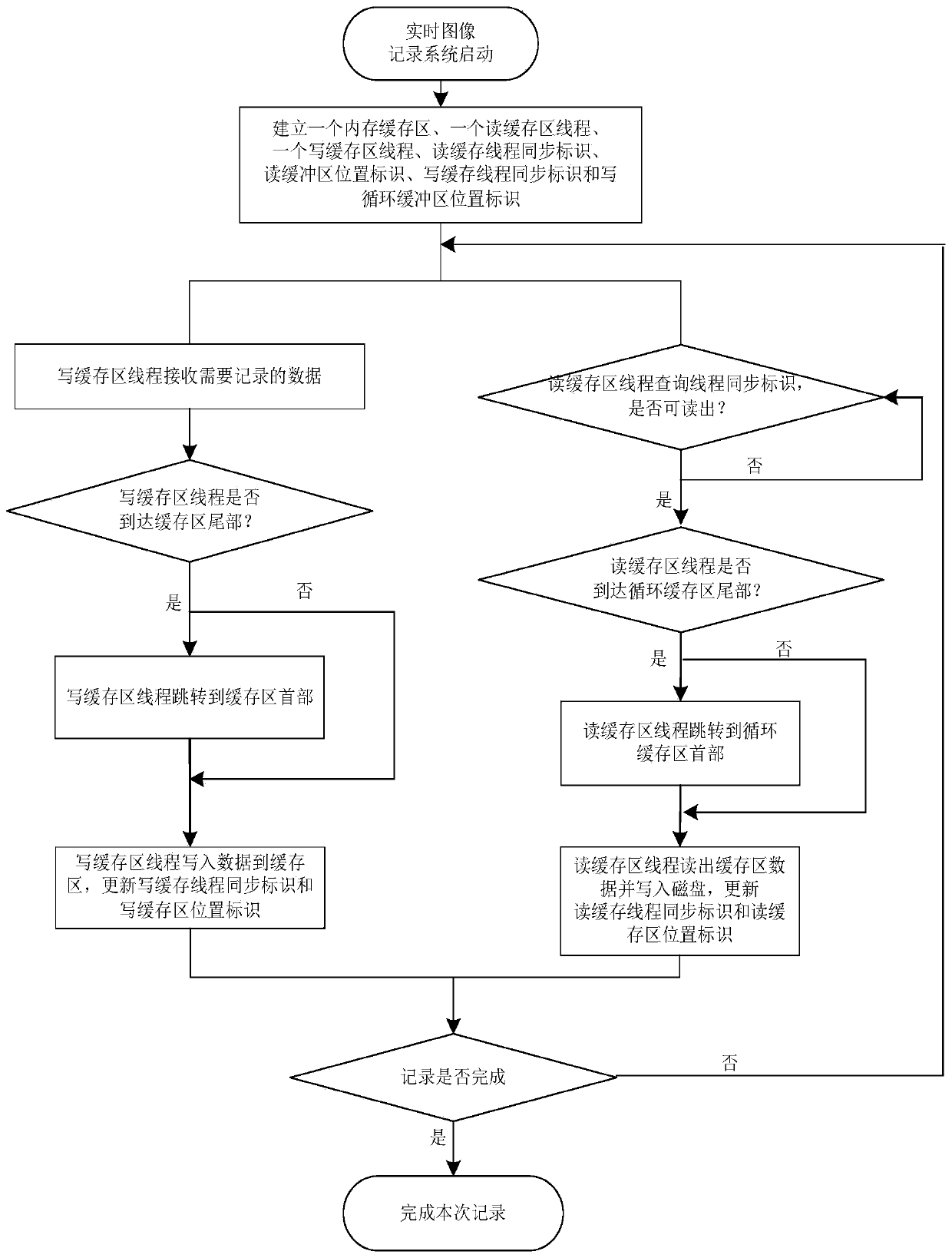
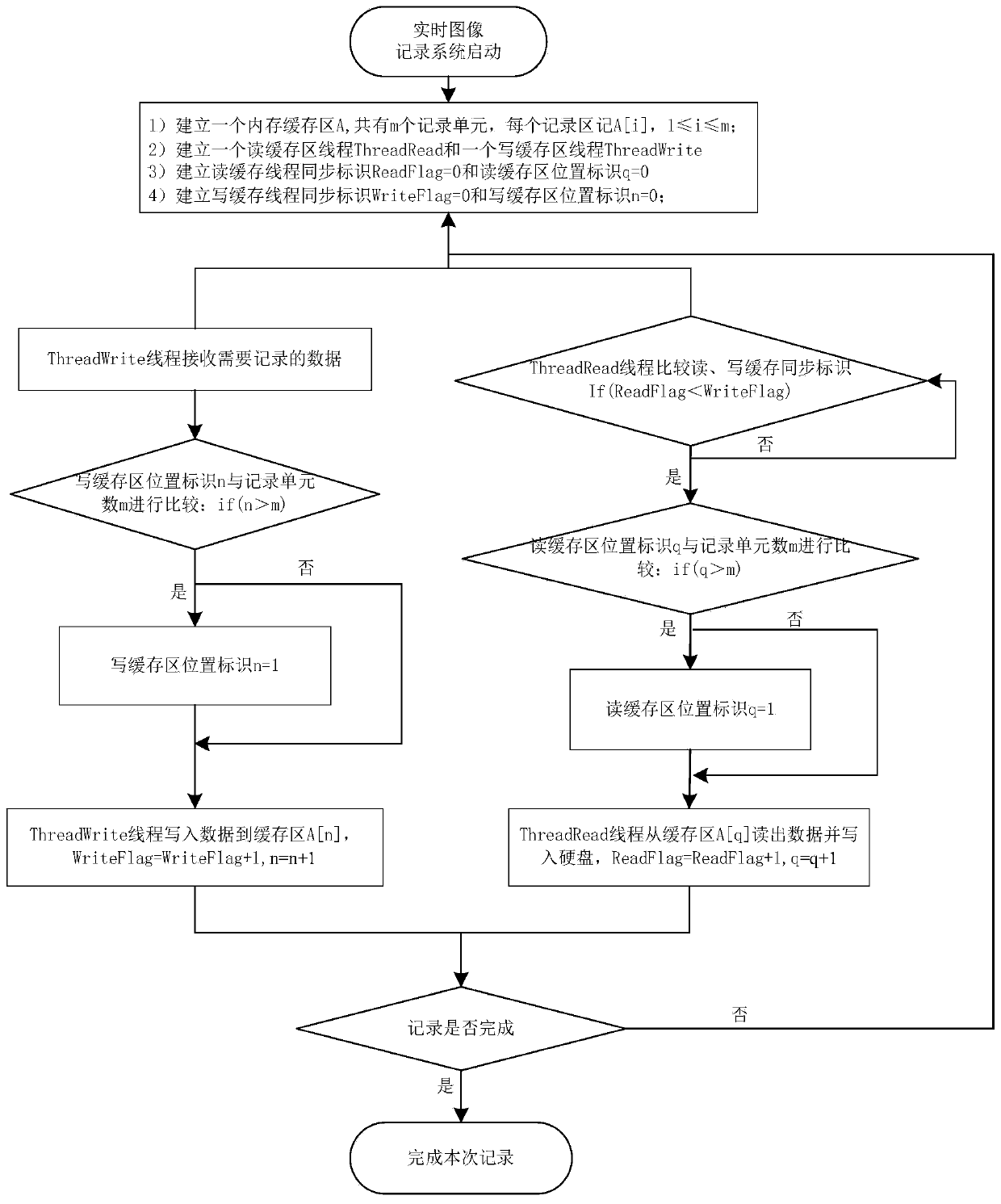
ActiveCN111399781AImprove reliabilityAvoid unreliableTelevision system detailsInput/output to record carriersComputer hardwareImage recording
The invention provides a storage method for improving the reliability of a real-time image recording system. The storage method comprises the following steps: establishing a memory cache region, a read cache region thread, a write cache region thread, a read cache thread synchronization identifier and a write cache thread synchronization identifier when the real-time image recording system is started; receiving data required to be recorded by the cache region writing thread; writing the data into the cache region by the cache region writing thread, and updating the cache region writing threadsynchronization identifier; after recording is started, enabling the cache region reading thread to query the thread synchronization identifier to judge whether the thread synchronization identifier can be read or not; judging the position of the read data in the cache region; enabling the cache region reading thread to read out the data in the cache region and write the data into a disk; and simultaneously running the cache region reading thread and the cache region writing thread in the recording process until the recording is finished. According to the method, the problem of unreliability caused by switching of a plurality of threads in a plurality of cache intervals is avoided by adopting a method of establishing a circular cache region and synchronizing read-write caches; and the problem of unreliability caused when multiple threads are written into the disk at the same time is avoided.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Well lid
InactiveCN113356274AEasy to fixGuaranteed stabilityArtificial islandsUnderwater structuresEngineeringStructural engineering
The invention provides a well lid, and relates to the technical field of well lids. The well lid is characterized in that a round well is formed in the top of a base, a stop block is arranged on the side wall of the top of the round well, a well lid body is placed on the stop block in a supported mode, a limiting block is arranged on the side wall of the round well, a limiting groove matched with the limiting block is formed in the side wall of the well lid body, the limiting groove comprises a matching groove which is used for accommodating the limiting block and is opened towards the side wall of the round well and a leading-in groove which is used for leading in the limiting block, and the leading-in groove is in communication with one end of the matching groove. The well lid can be quickly disassembled, assembled and fixed, is convenient to operate, safer, more stable and convenient to maintain, has the function of jacking up the well lid after being disassembled, saves time and labor, and is flexible and practical.
Owner:CHINA FIRST METALLURGICAL GROUP
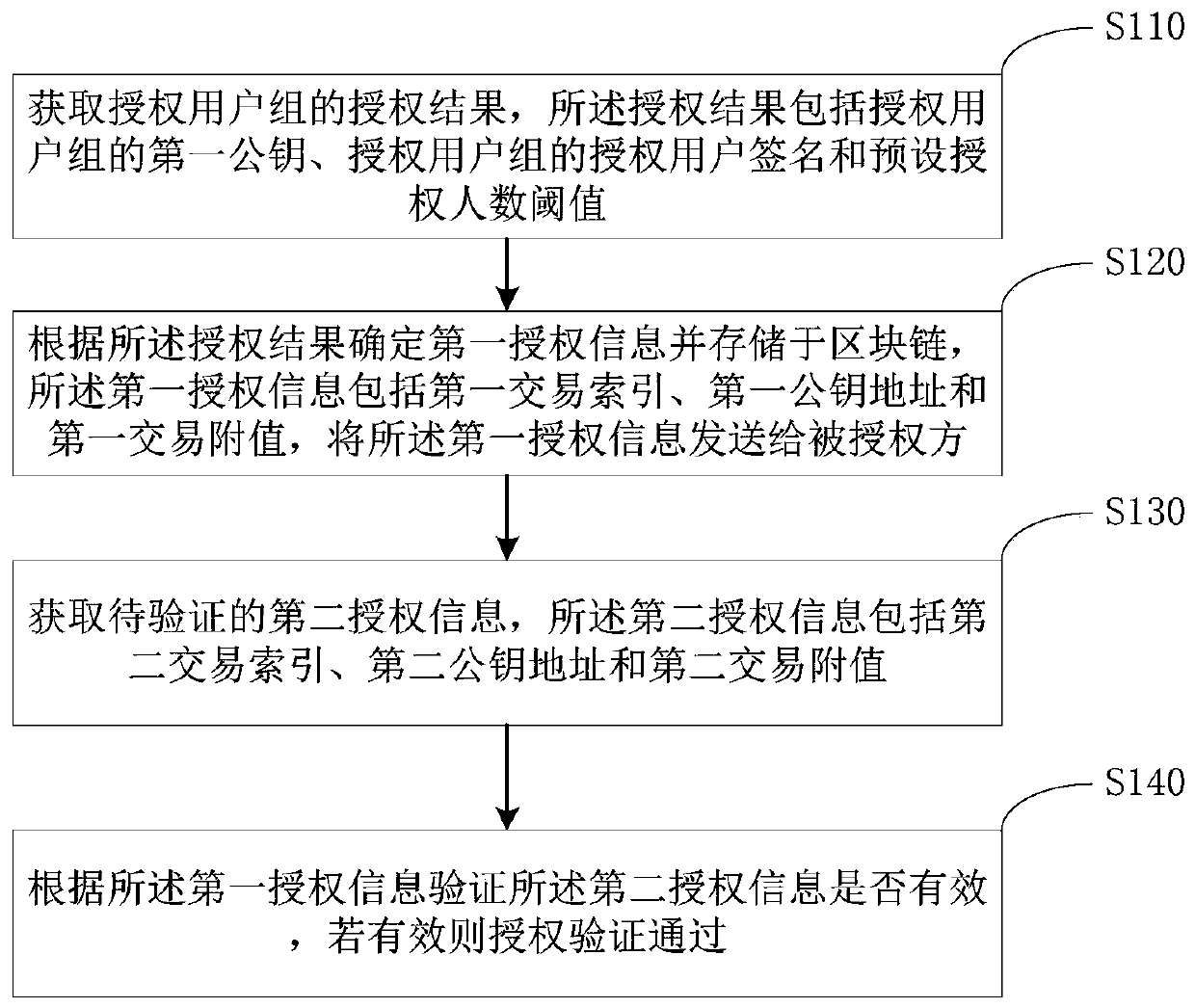
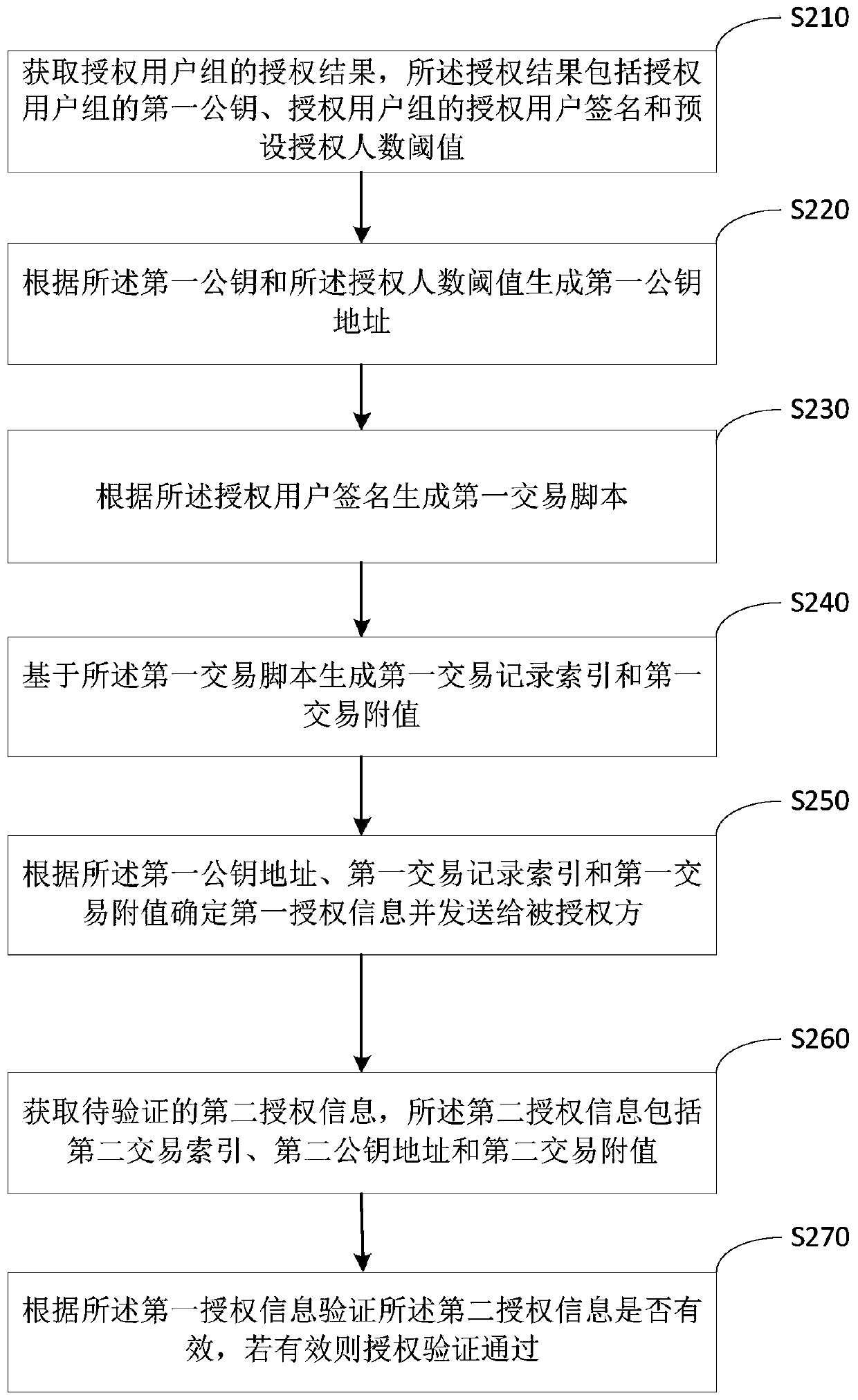
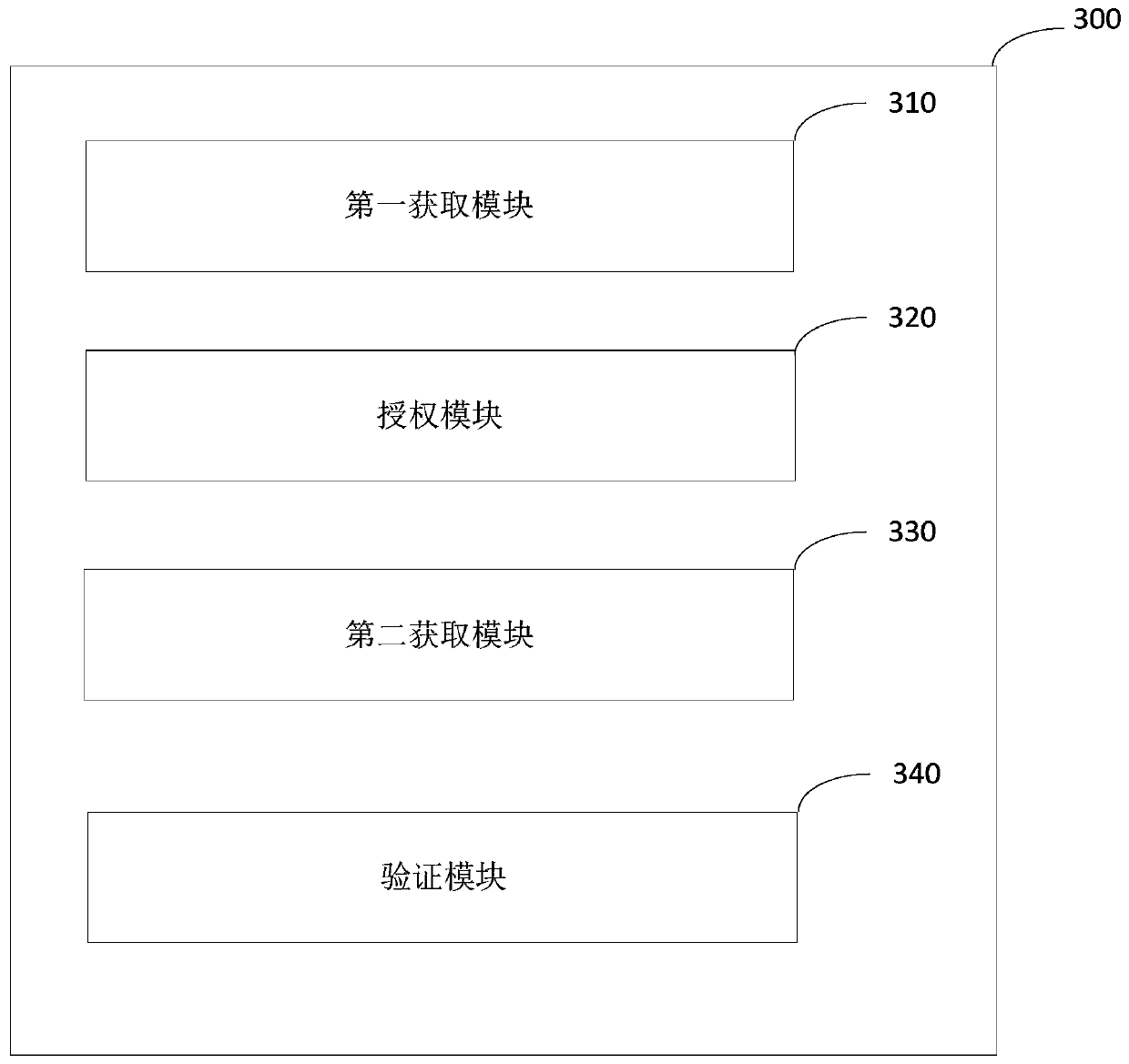
Authorization verification method and device and storage medium
PendingCN111353780AAvoid unreliableReduce the risk of authorization floodingProtocol authorisationAttackInternet privacy
The embodiment of the invention discloses an authorization verification method, device and equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring an authorization result of an authorized user group, wherein the authorization result comprises a first public key of the authorized user group, an authorized user signature of the authorized user group and a preset authorized people number threshold; determining first authorization information according to the authorization result, storing the first authorization information in the blockchain, and sending the first authorization information to the authorized party; acquiring second authorization information to be verified, wherein the second authorization information comprises a second transaction index, a second public key address and a second transaction attached value; verifying whether the second authorization information is valid according to the first authorization information, and if so, passing the authorization verification. According to the authorization verification method provided by the embodiment of the invention, the first authorization information is stored through the decentralized blockchain, so the unreliability caused by the attack of the central server is avoided, and the preset authorization number threshold is set for reducing the risk of authorization flooding caused by leakage ofprivate keys of a few users in the authorized user group.
Owner:SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY OF CHINA
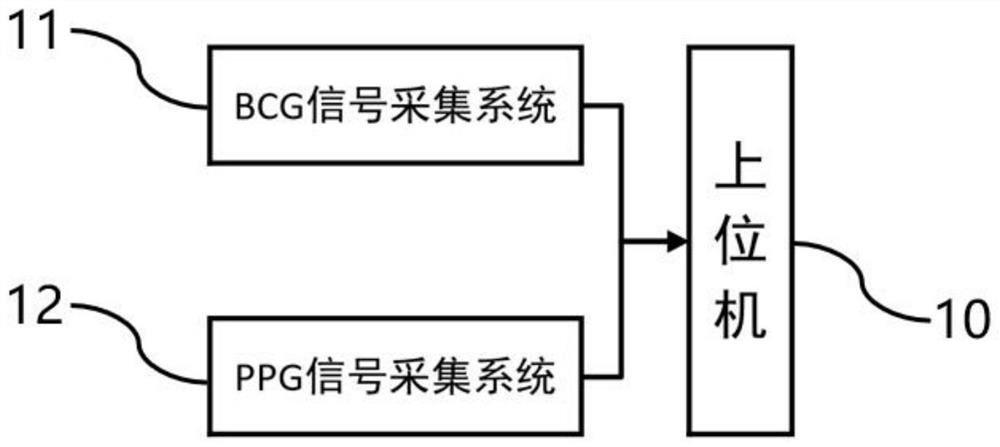
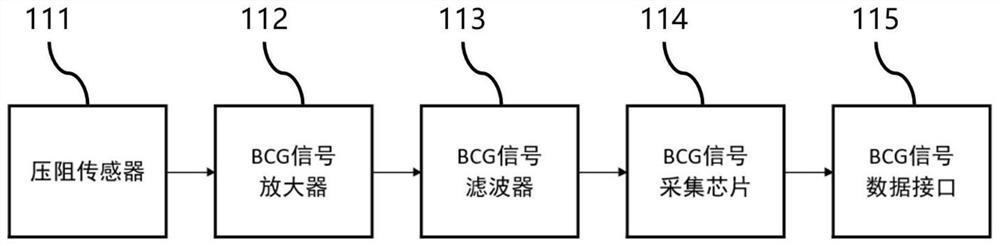
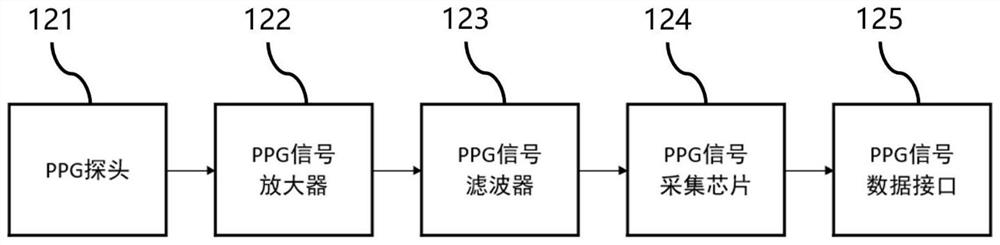
Physiological monitoring system based on BCG signal and PPG signal fusion
The invention relates to a physiological monitoring system based on fusion of a BCG signal and a PPG signal, and the system comprises a BCG signal collection system which is used for collecting the BCG signal of a human body; the PPG signal acquisition system is used for acquiring PPG signals of a human body; the upper computer is used for receiving the BCG signals collected by the BCG signal collection system and the PPG signal data collected by the PPG signal collection system, analyzing the two kinds of signal data and fusing analysis results in a nonlinear fitting mode to obtain final physiological parameter information. According to the invention, the monitoring accuracy can be improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LAB +1
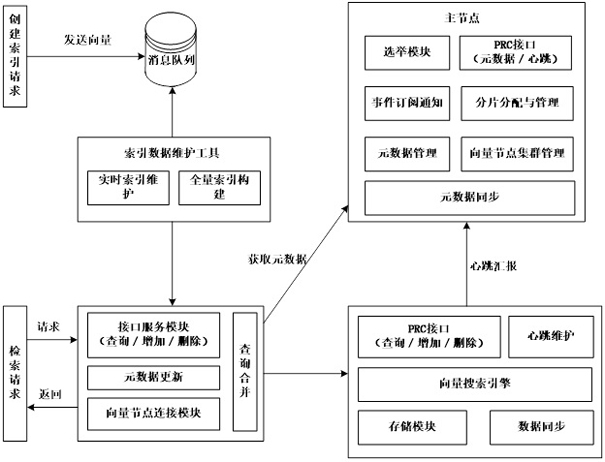
Distributed vector retrieval system and method
ActiveCN113254511AEnsure consistent updatesAchieve data isolationDatabase updatingSpecial data processing applicationsData synchronizationMessage queue
The embodiment of the invention discloses a distributed vector retrieval system, which comprises a main node group, which comprises a plurality of main nodes, one is a leader node, the leader node distributes an index table fragment to a specified vector node group, and the leader node synchronizes data of the index table to other main nodes; a plurality of vector node groups, each vector node group comprising a plurality of vector nodes, each vector node storing vector data and index table fragments, each vector node responding to a request from the routing node and retrieving data or synchronizing data; a routing node group which comprises a plurality of routing nodes, wherein each routing node sends the request to the corresponding vector node group and merges and returns retrieval results; and an index data maintenance tool which writes the index vector data into the index message queue according to the request and calls the routing node according to the message type. The embodiment of the invention further discloses a distributed vector retrieval method. Under the condition of high concurrent access, consistent updating of the offline index data and the online index data can be ensured.
Owner:北京华品博睿网络技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com