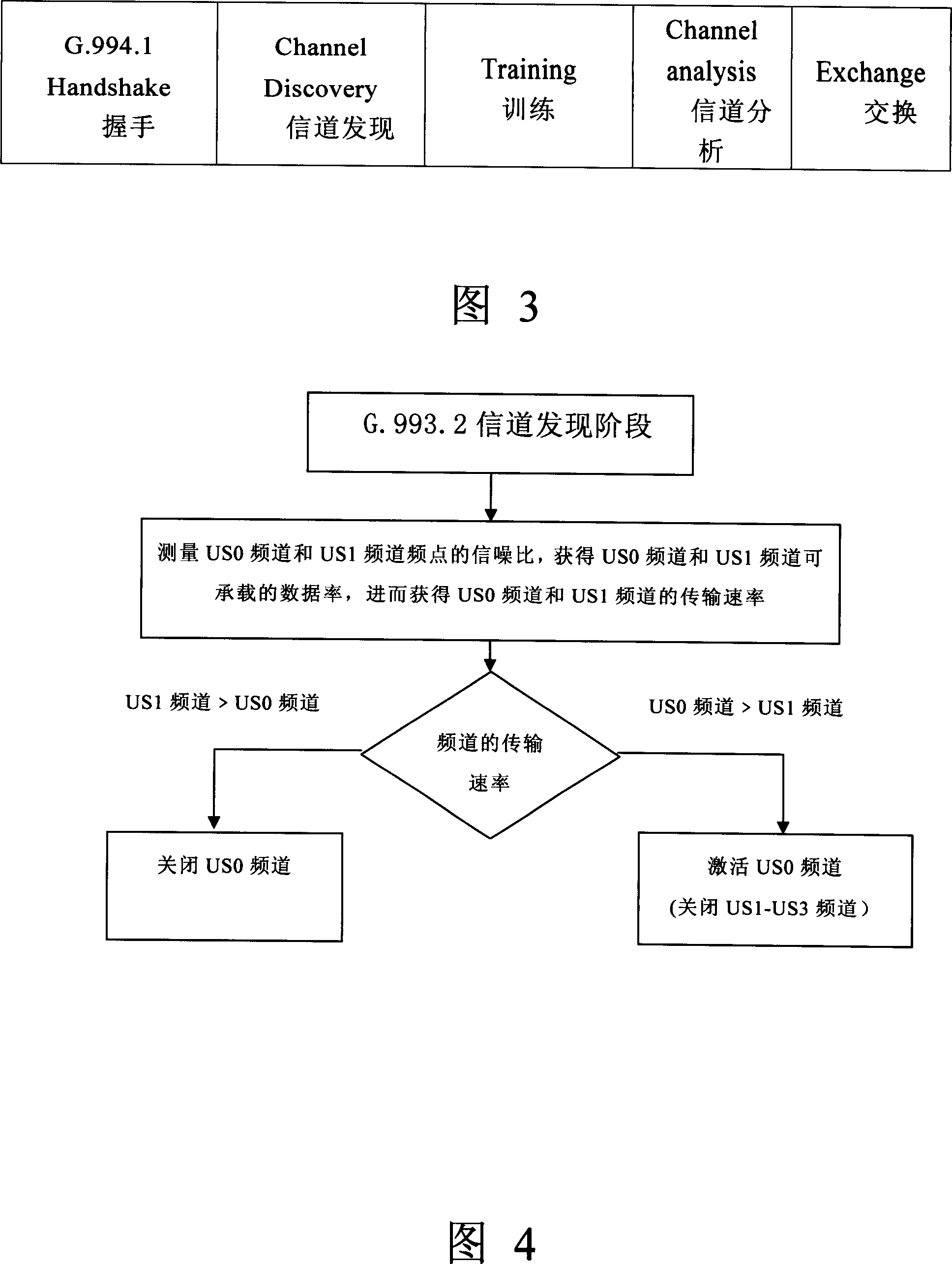
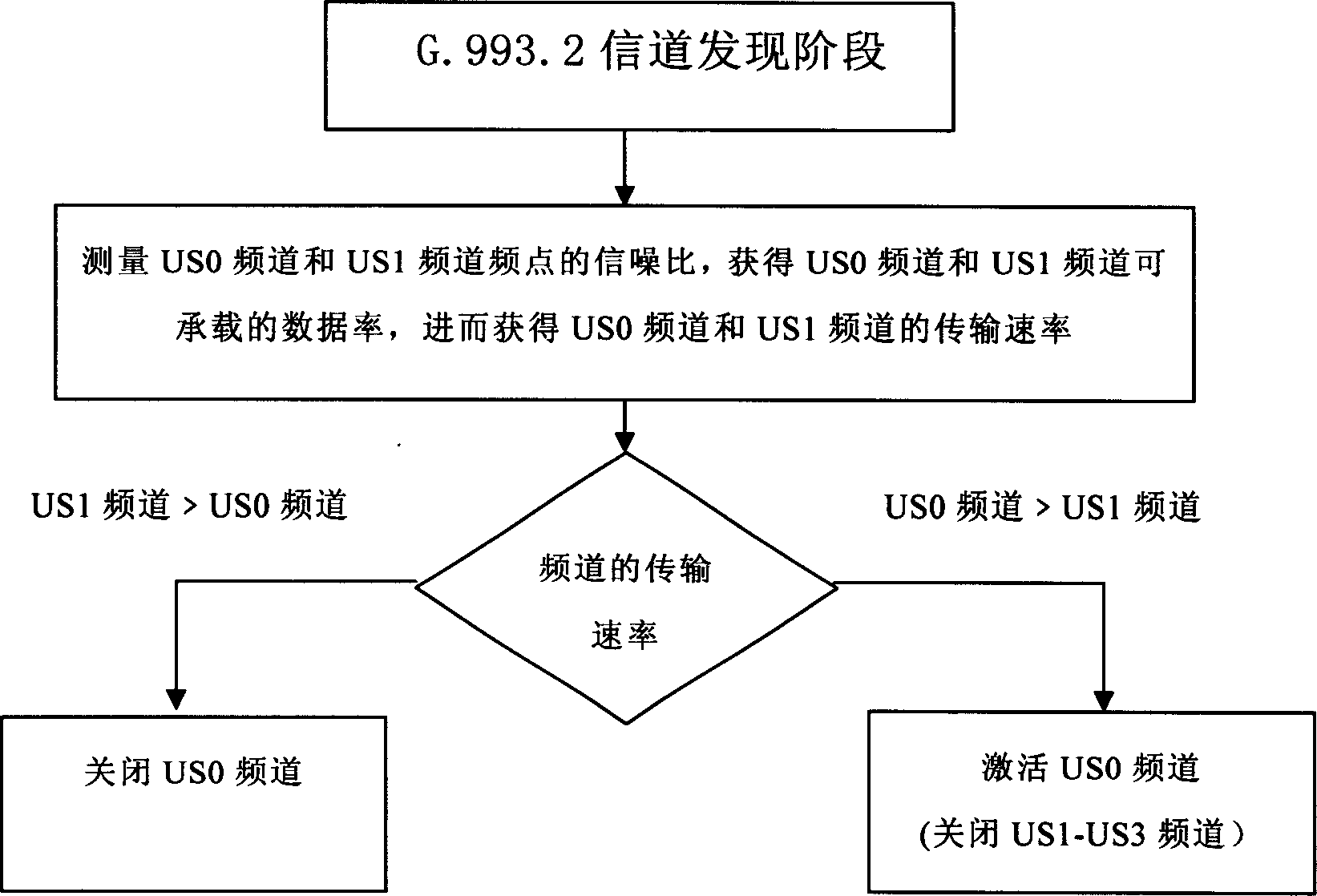
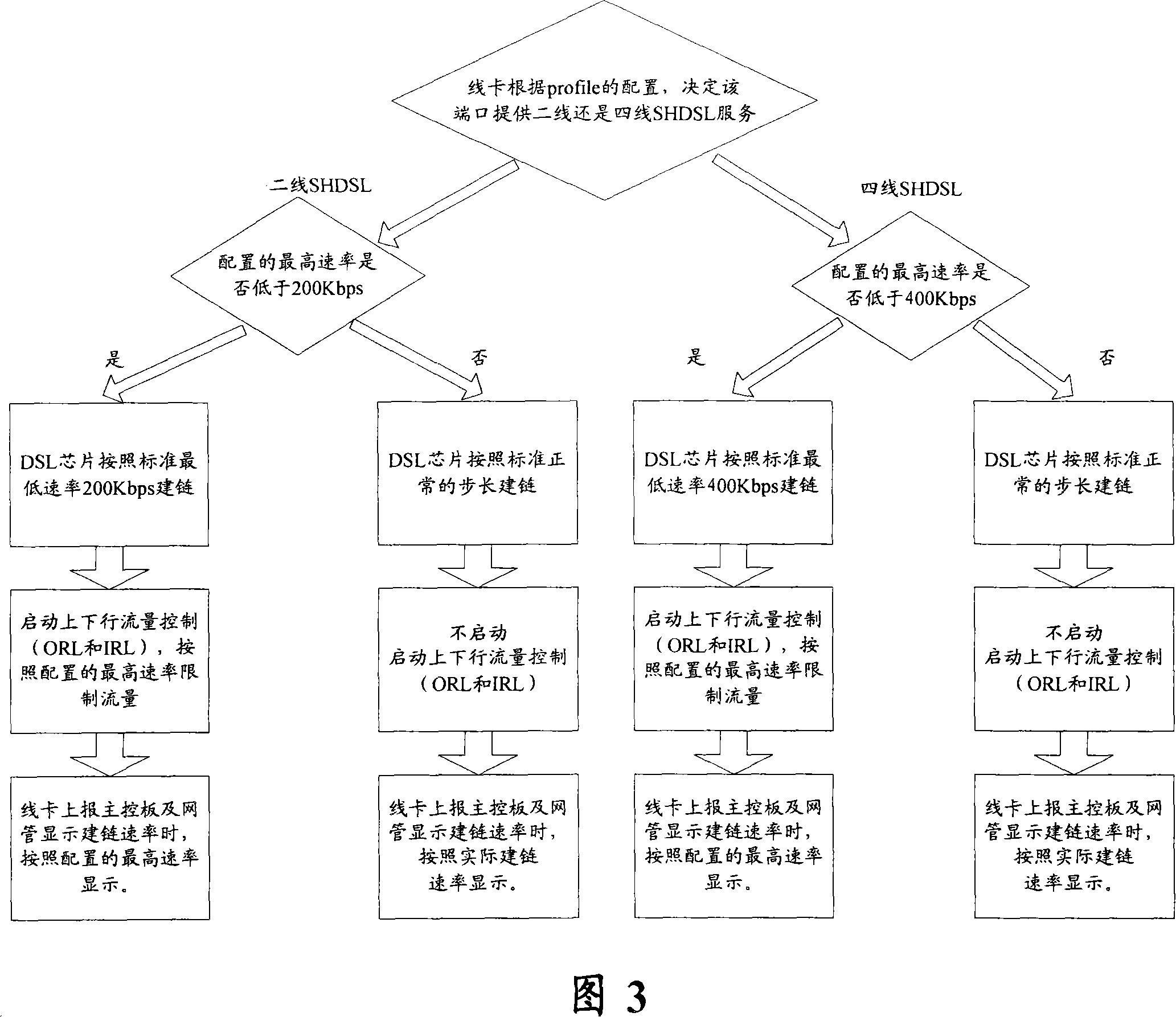
Patents
Literature
37 results about "High-bit-rate digital subscriber line" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
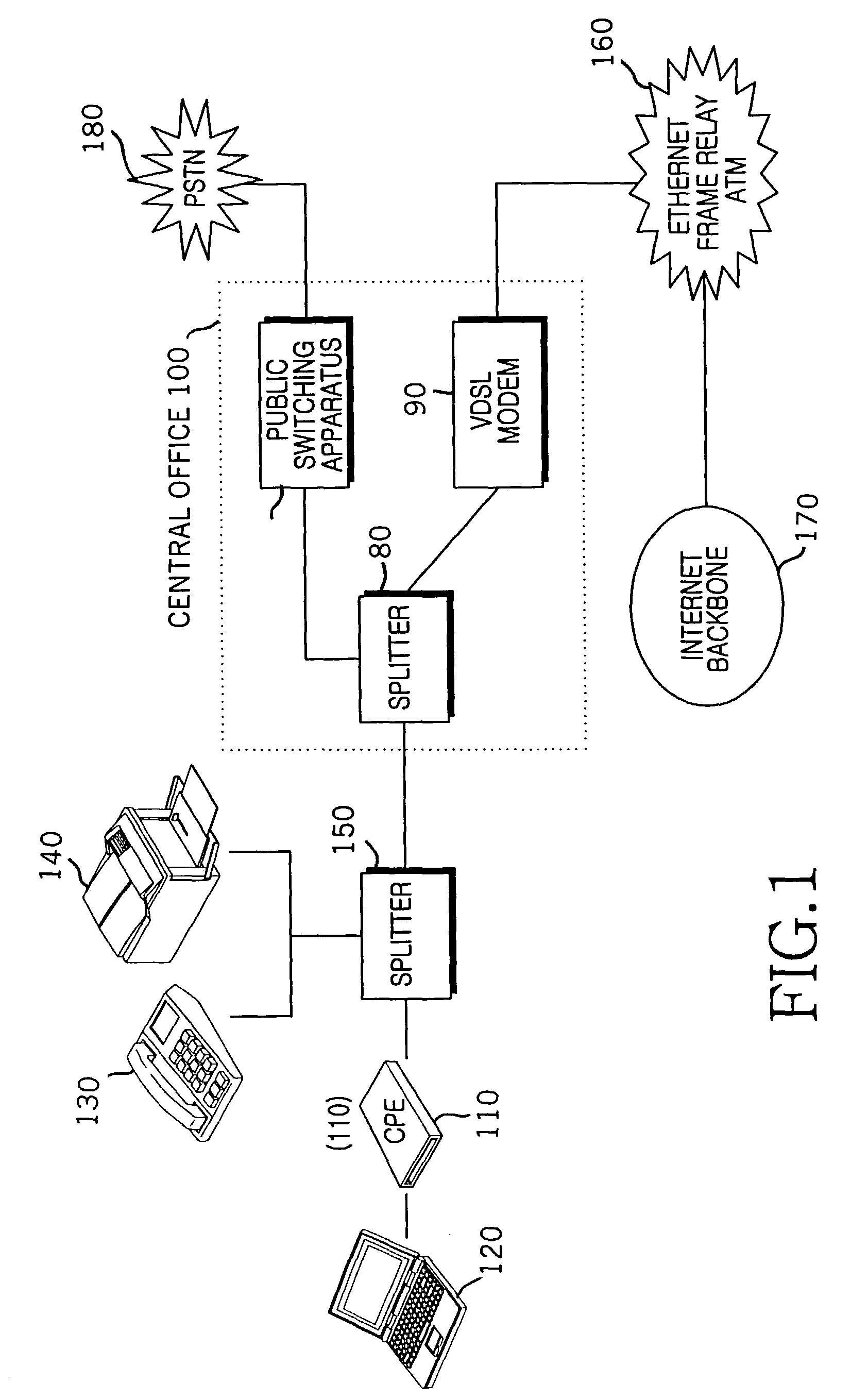
High-bit-rate digital subscriber line (HDSL) is a telecommunications protocol standardized in 1994. It was the first digital subscriber line (DSL) technology to use a higher frequency spectrum over copper, twisted pair cables. HDSL was developed to transport DS1 services at 1.544 Mbit/s and 2.048 Mbit/s over telephone local loops without a need for repeaters. Successor technology to HDSL includes HDSL2 and HDSL4, proprietary SDSL, and G.SHDSL.
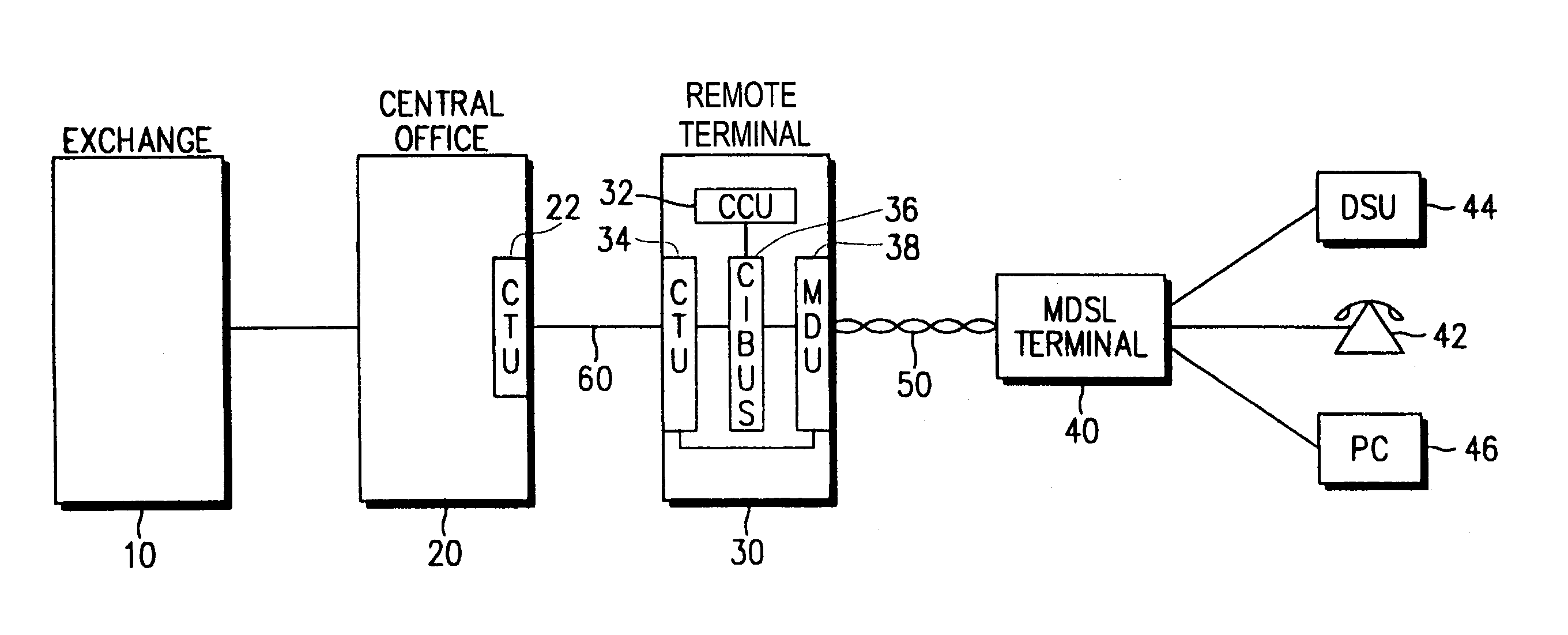
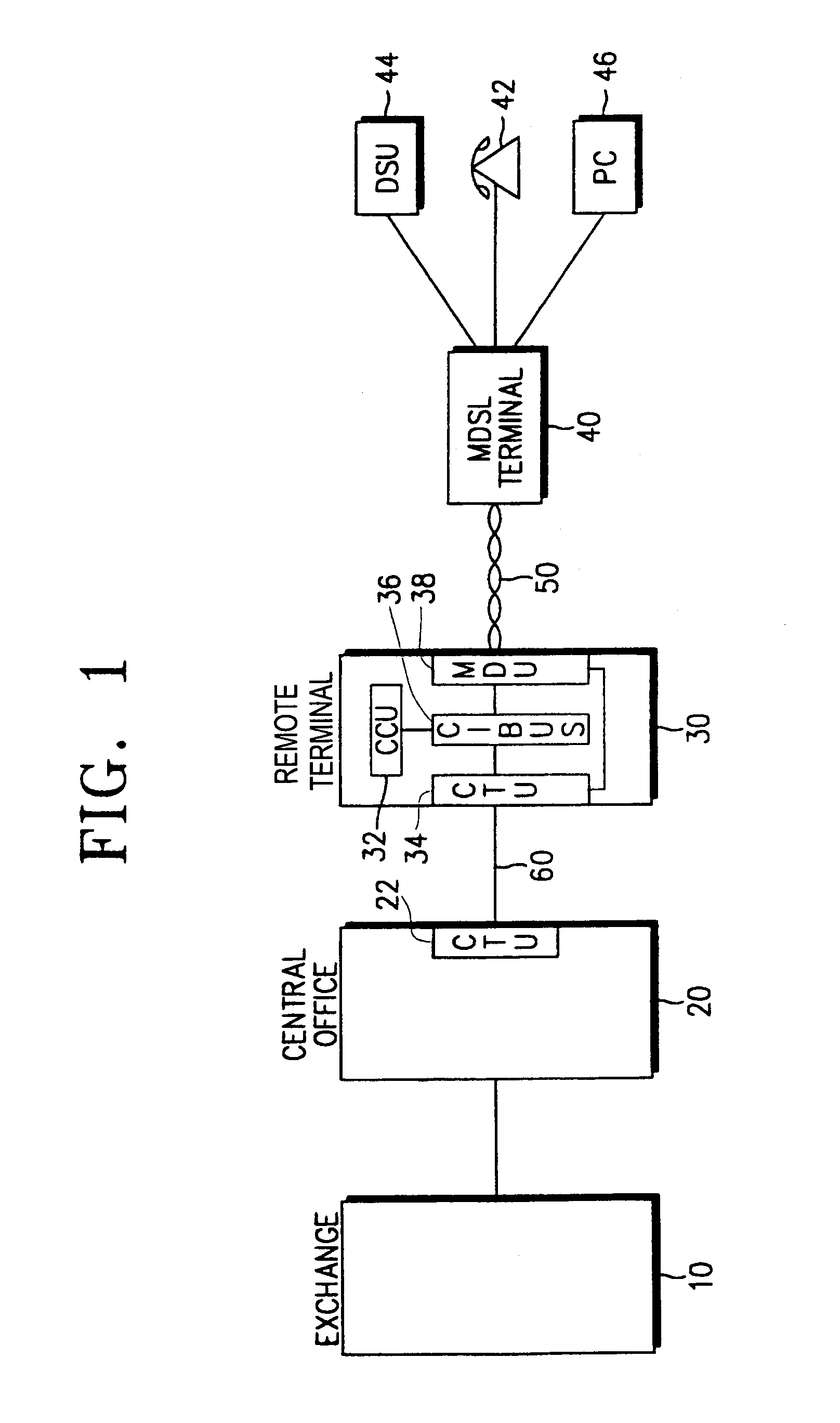
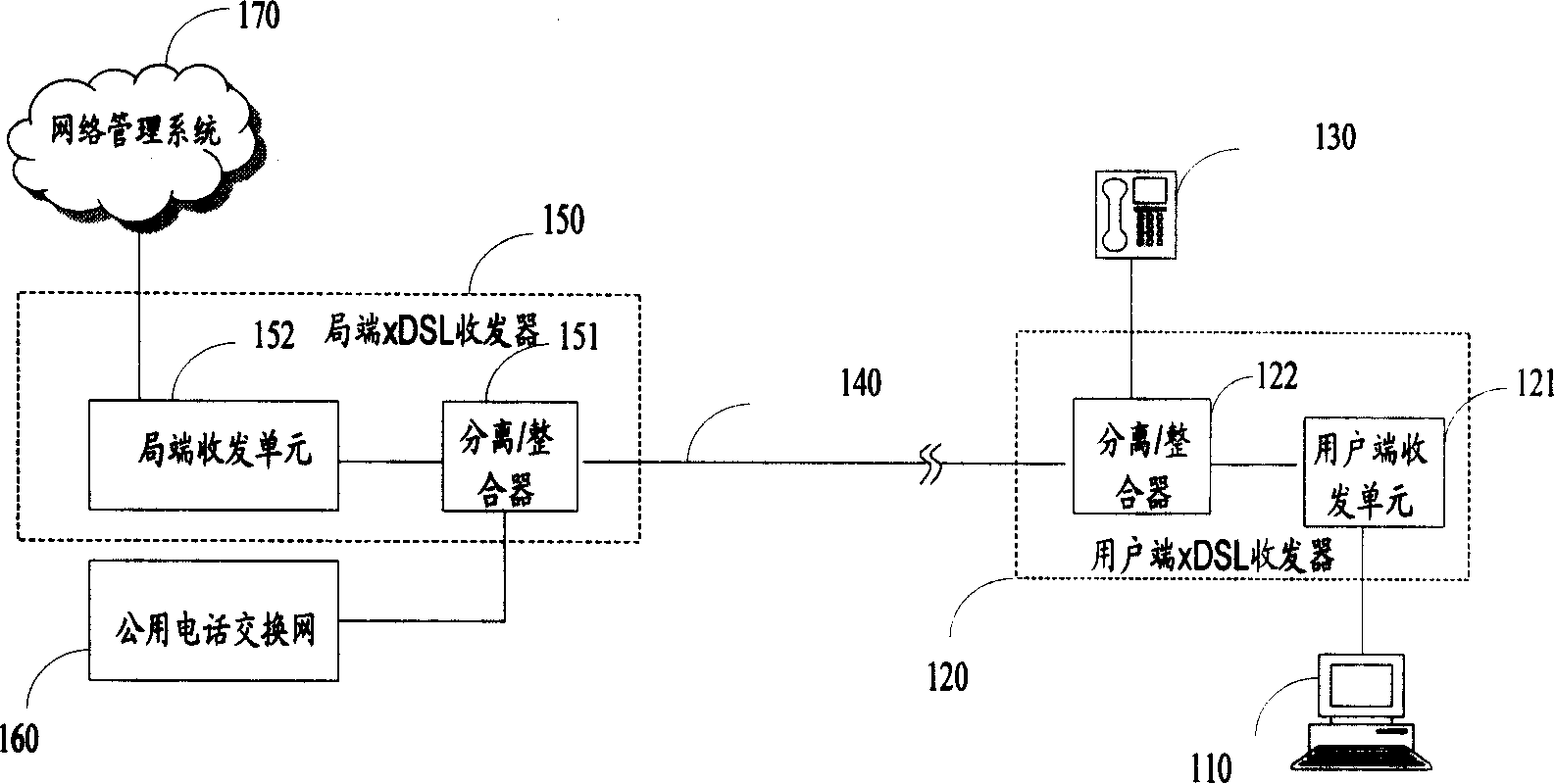
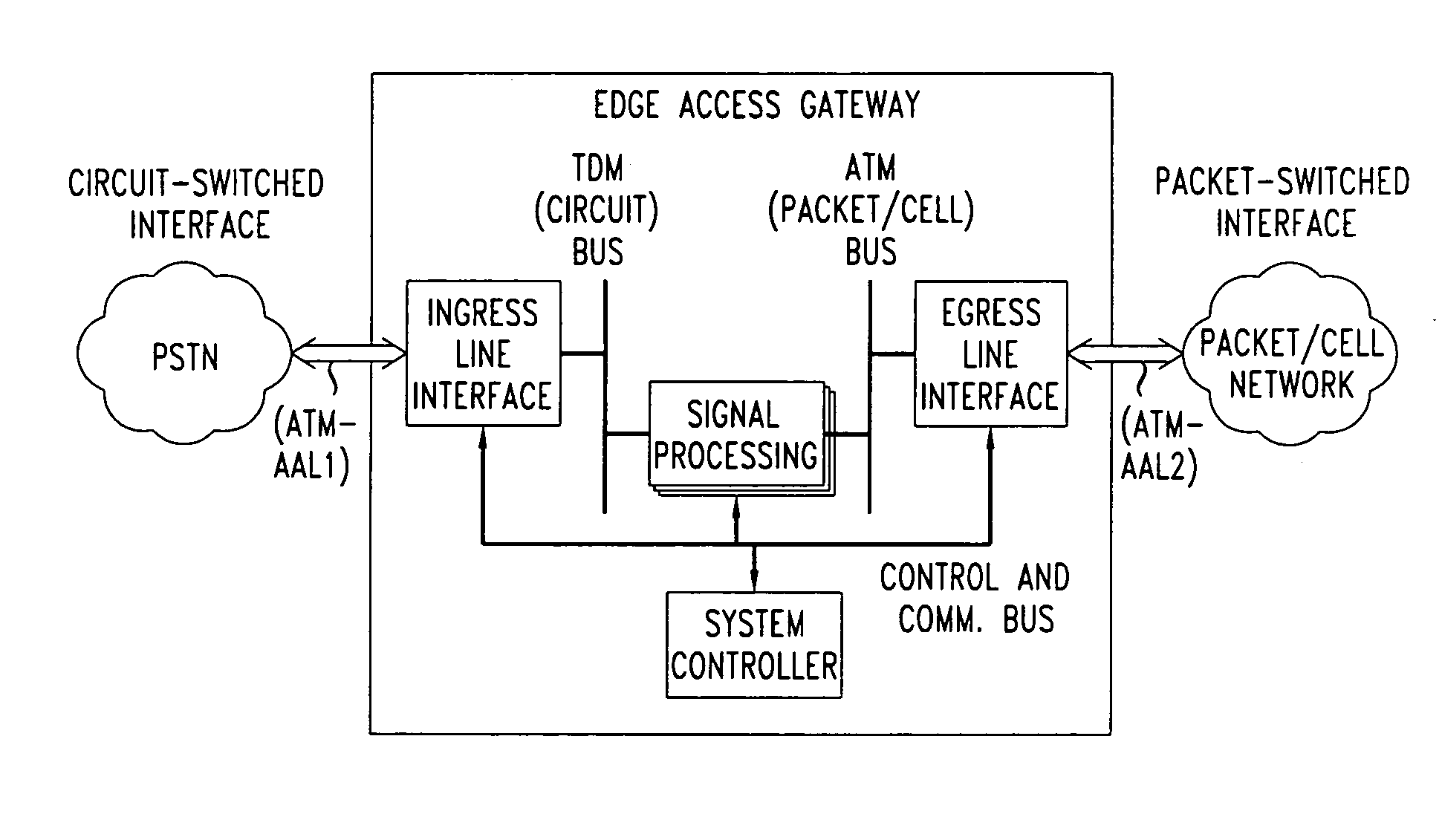
Method for providing high-speed data service and voice service
InactiveUS6970502B2Increase speedInterconnection arrangementsFrequency-division multiplexDigital subscriber lineTransport system
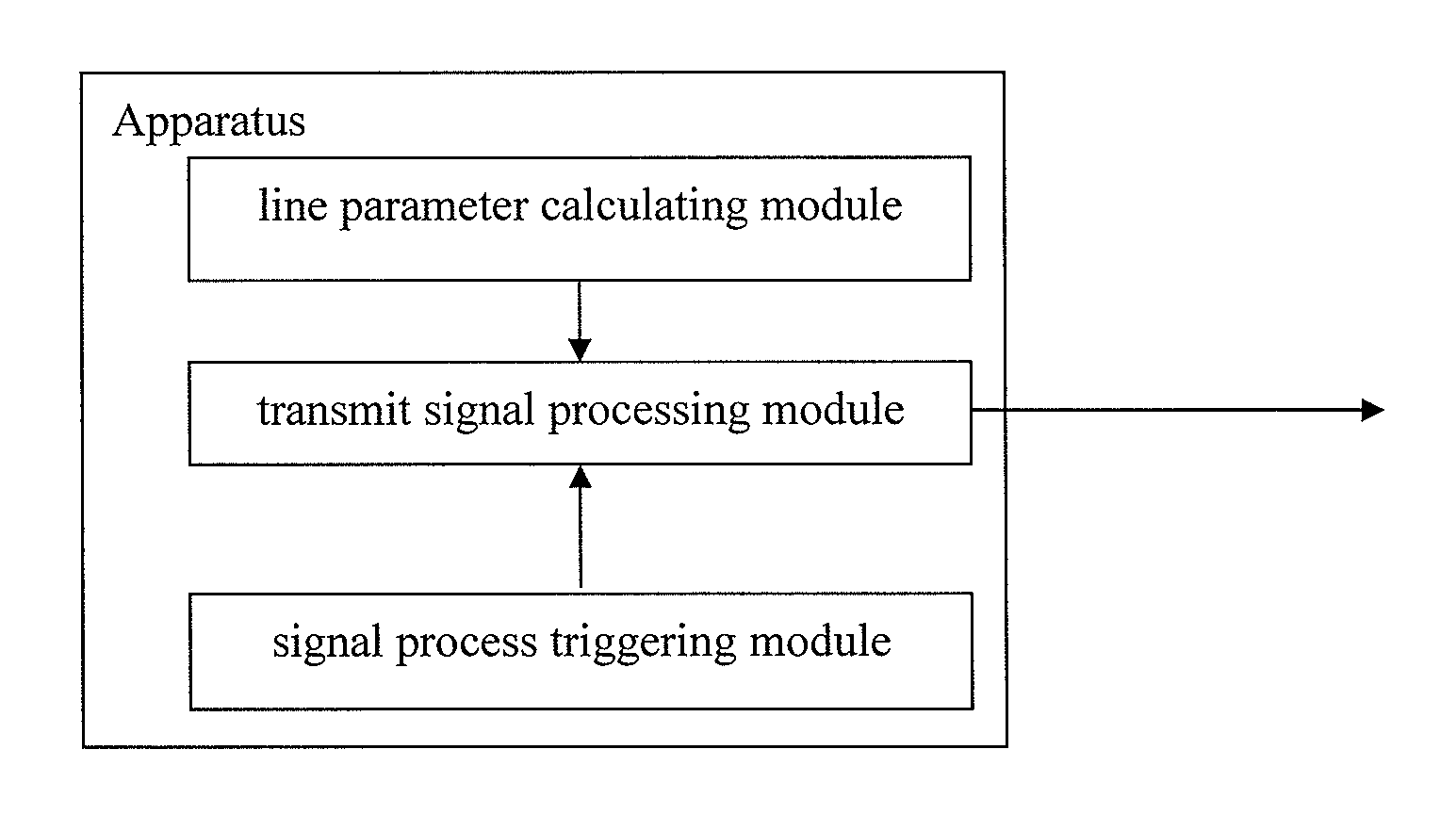
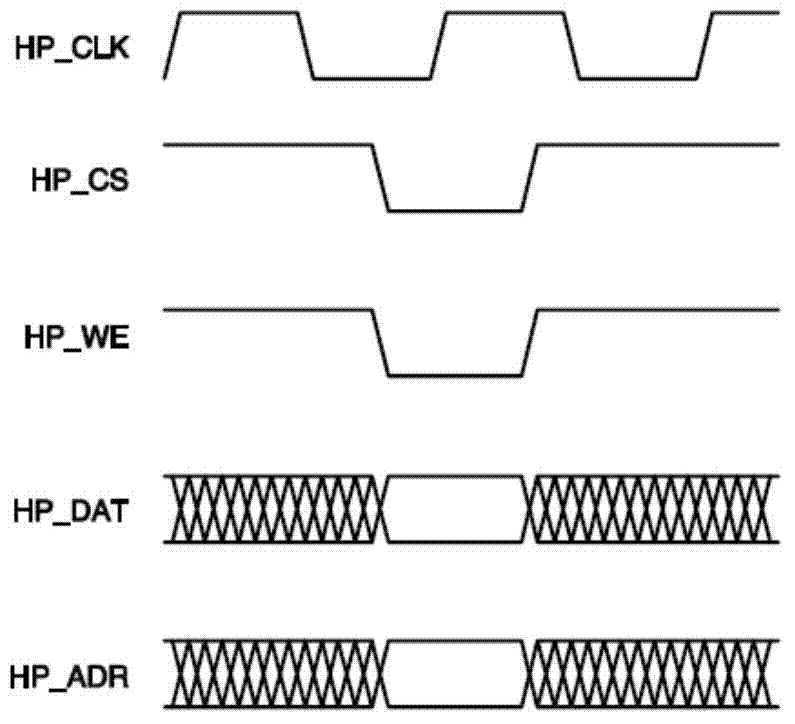
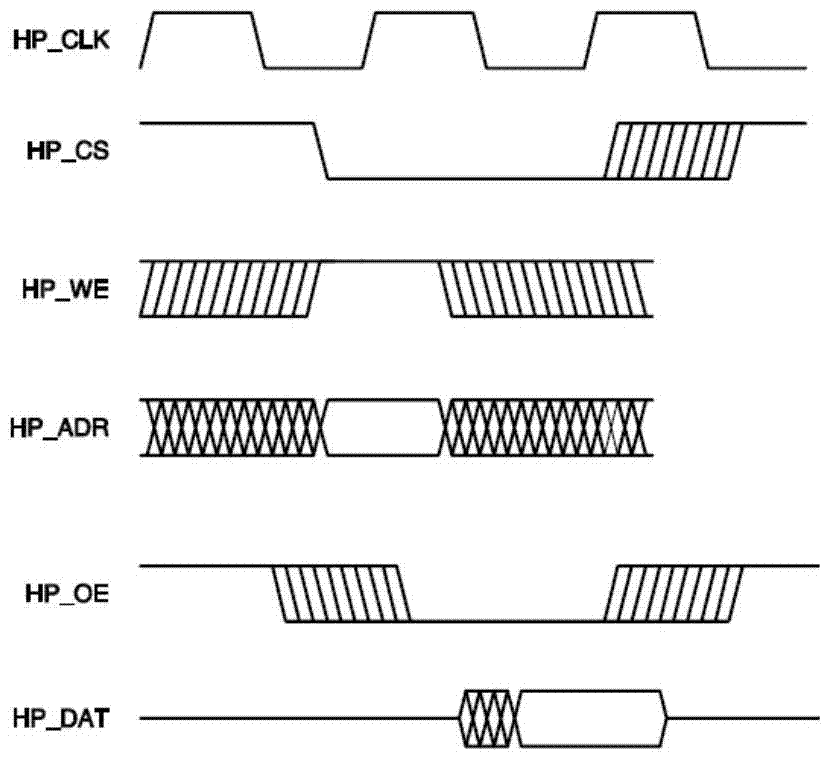
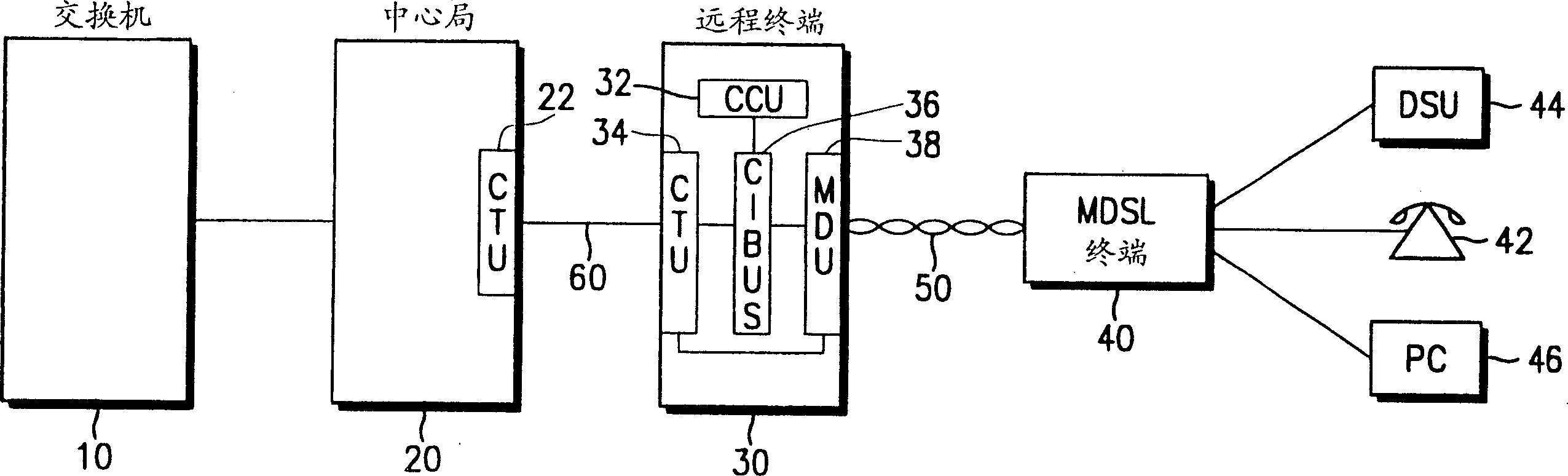
Providing a high-speed data service and voice service in a transmission system employing two binary, one quarternary (2B1Q) modulation / demodulation, using a high-speed data service remote terminal, a plurality of user data service and voice service terminals, and a multi-rate digital subscriber line (MDSL) terminal connected to the remote terminal through a twisted pair line, and to the user terminals. During downstream voice service, the remote terminal assembles and transmits an high bit rate digital subscriber line (HDSL) frame by including signaling signals for the voice service and signal processing mode information in a user-defined interval of the high bit rate digital subscriber line frame, to the multi-rate digital subscriber line terminal through the twisted pair line. During upstream voice service, the remote terminal receives the high bit rate digital subscriber line frame and transmits the signaling signals received to an exchange.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
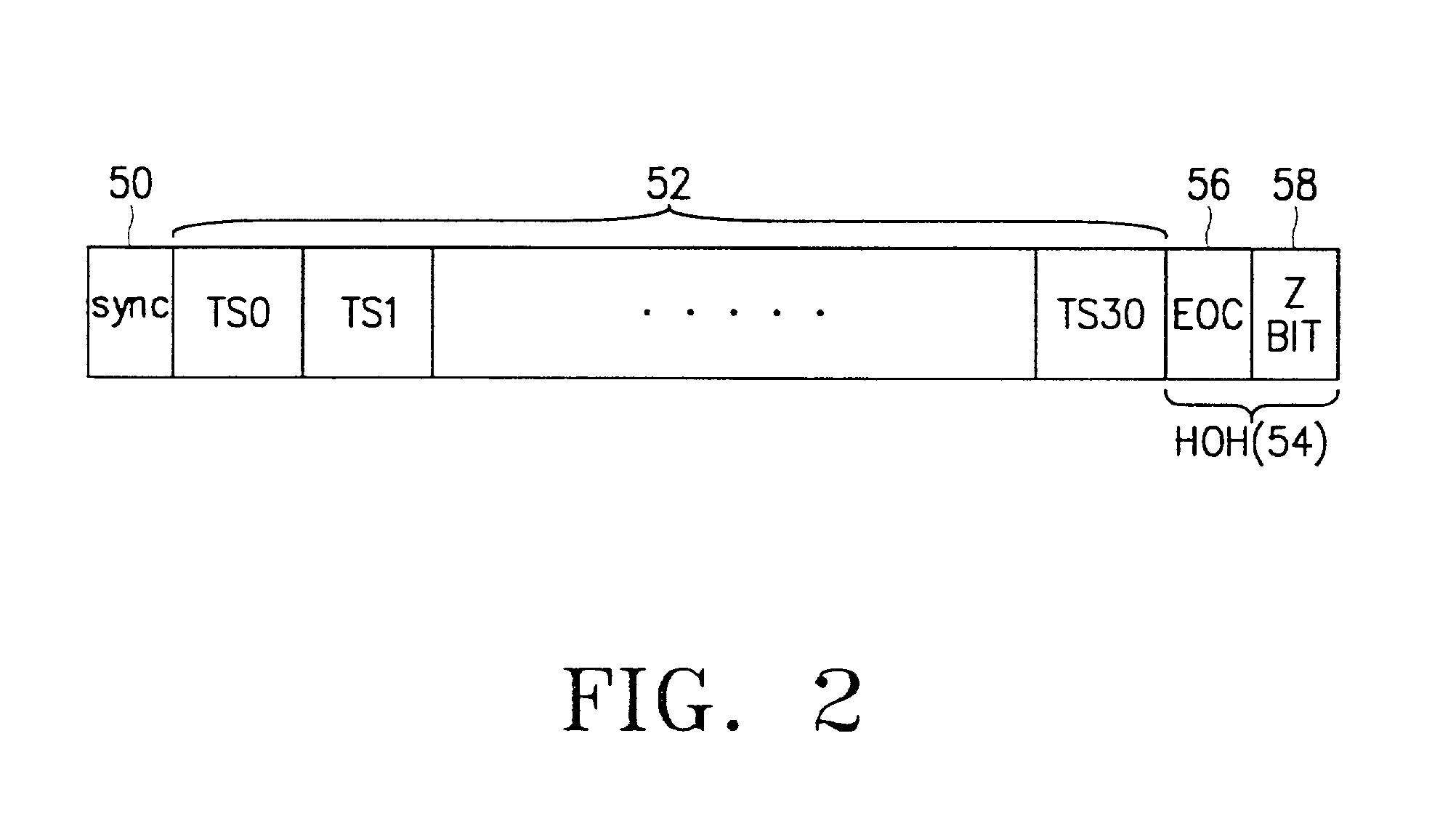
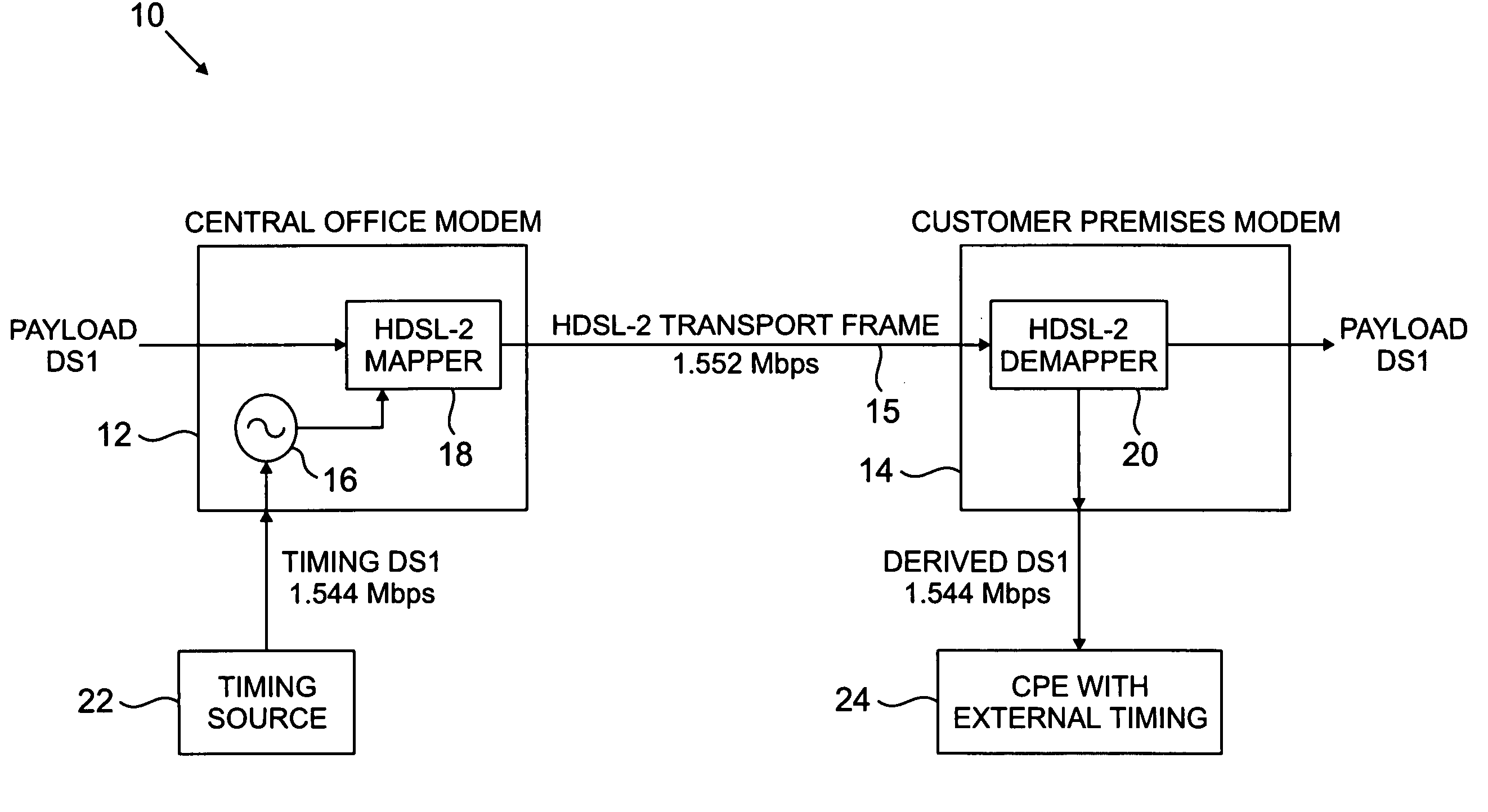
Method and apparatus for synchronization of high-bit-rate digital subscriber line signals
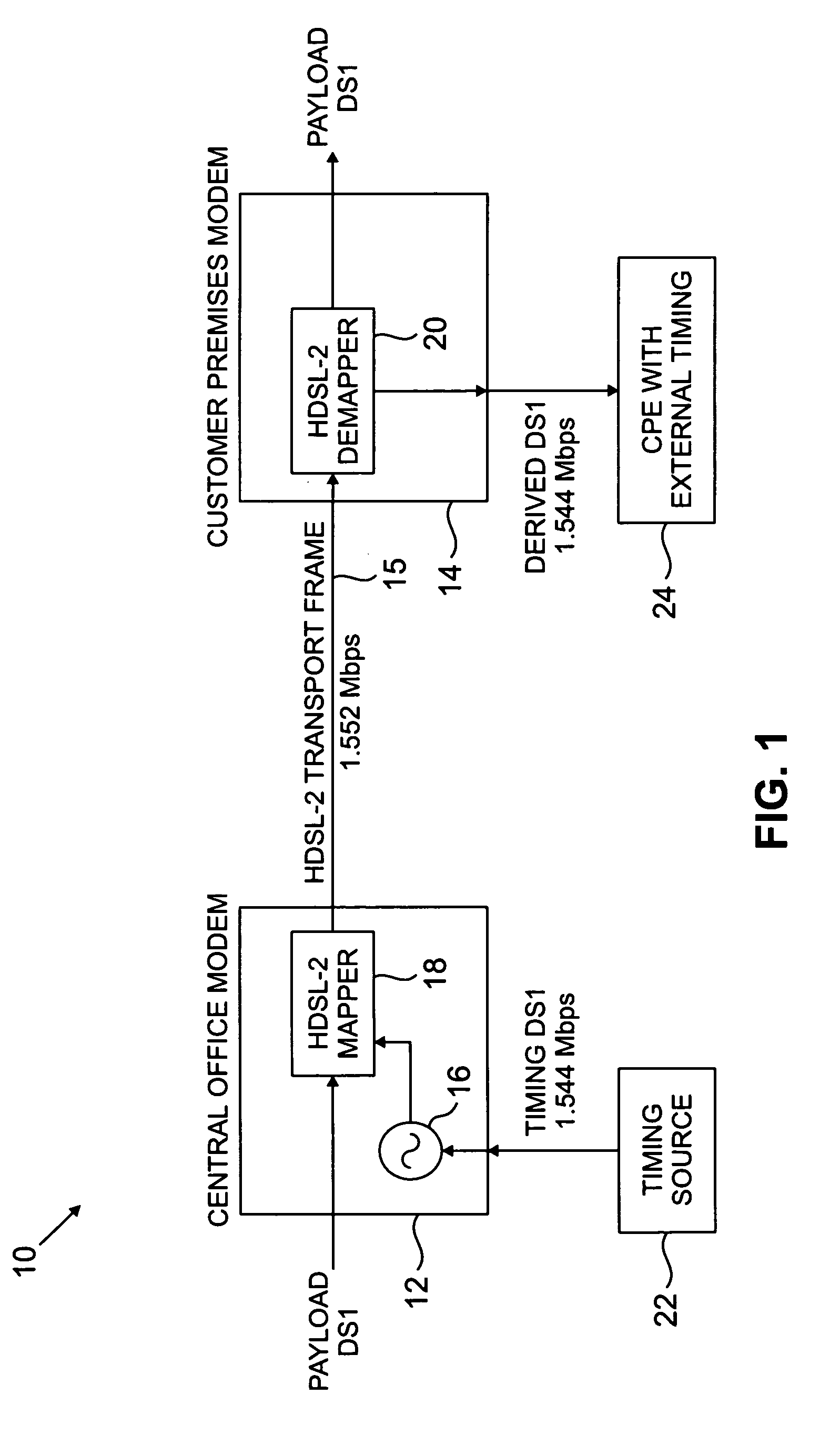
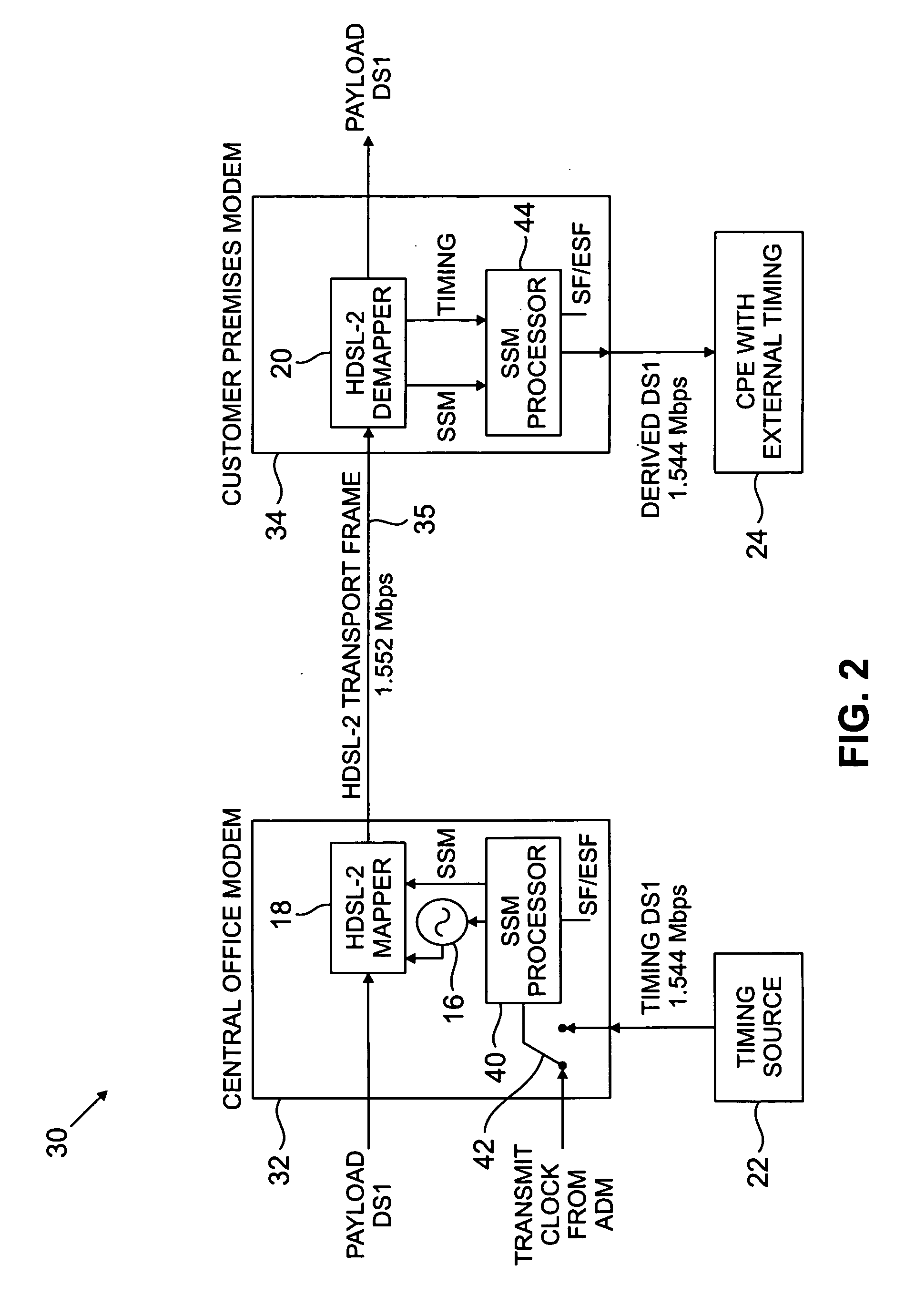
Timing information, such as stratum 1 traceable synchronization information, is transmitted in a high-bit-rate digital subscriber line (HDSL) transport frame by timing the transport frame using a corresponding timing reference signal. In an illustrative embodiment, a central office modem maps a DS1 payload at 1.544 Mbps into HDSL transport frames at 1.552 Mbps, using a DS1 timing reference signal generated by, e.g., a building integrated timing supply (BITS) having global positioning system (GPS) capability. The transport frame is transmitted by the central office modem to a customer premises modem which demaps the transport frames to recover the DS1 payload and the DS1 timing reference signal. The recovered timing reference signal is then delivered to an external timing input of a computer, set-top box or other customer premises equipment (CPE). Synchronization status messages (SSMs) may be included in the timing information transmitted between the central office and customer premises modems. The invention is applicable to DSL signals other than HDSL2, including, e.g., single-pair HDSL signals, multiple-pair HDSL signals, as well as other types of signals used in conjunction with the transport of information over existing wired connections.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
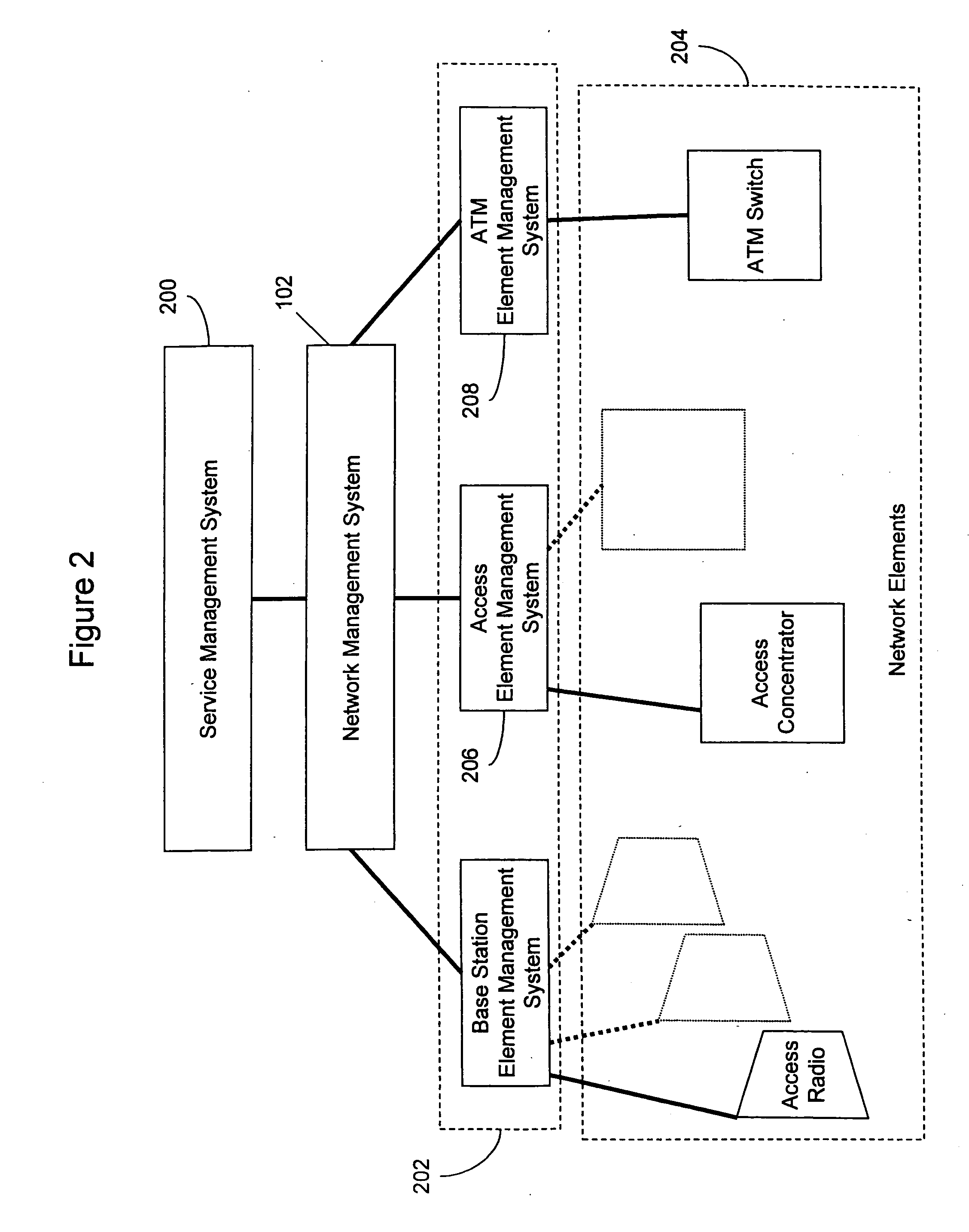
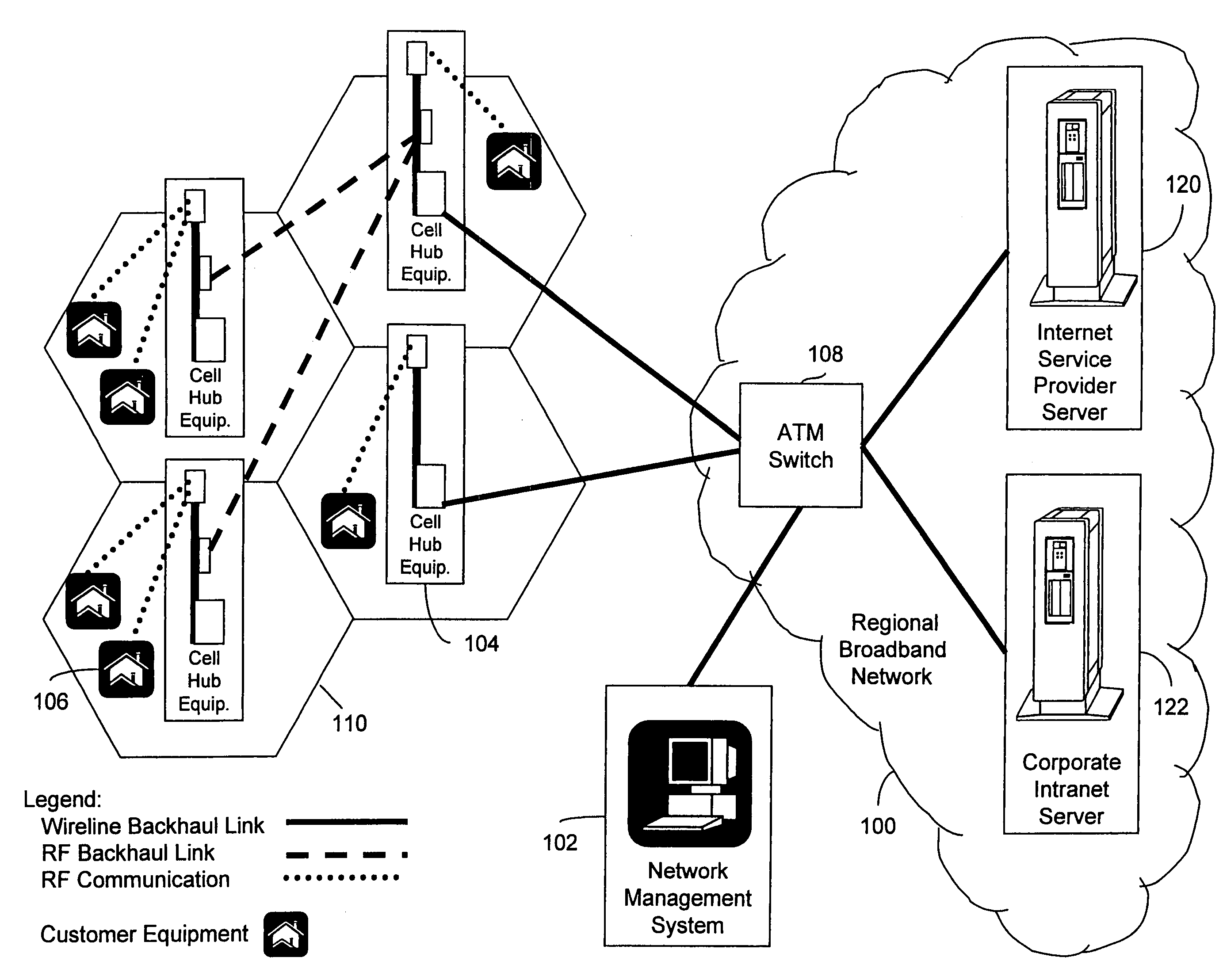
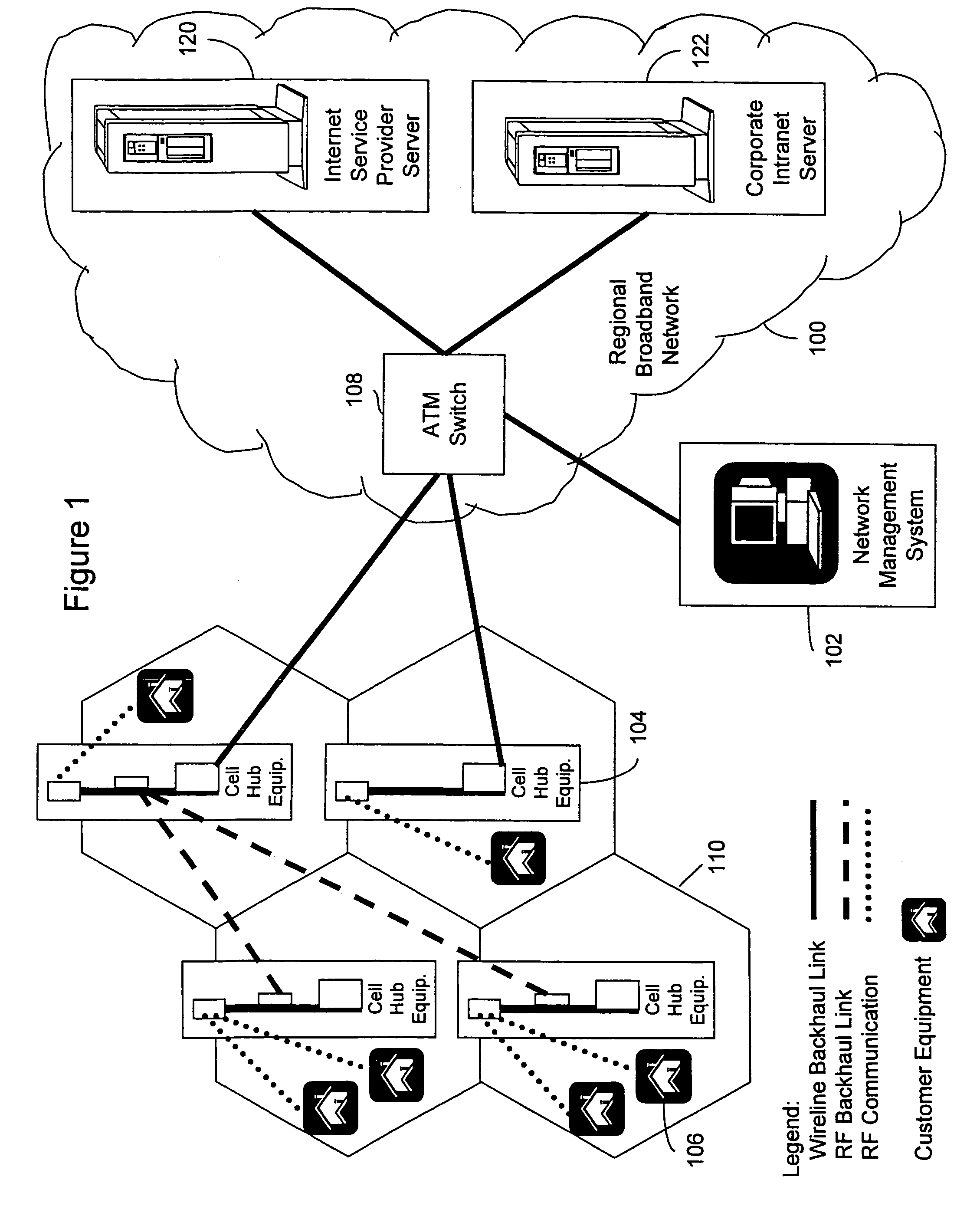
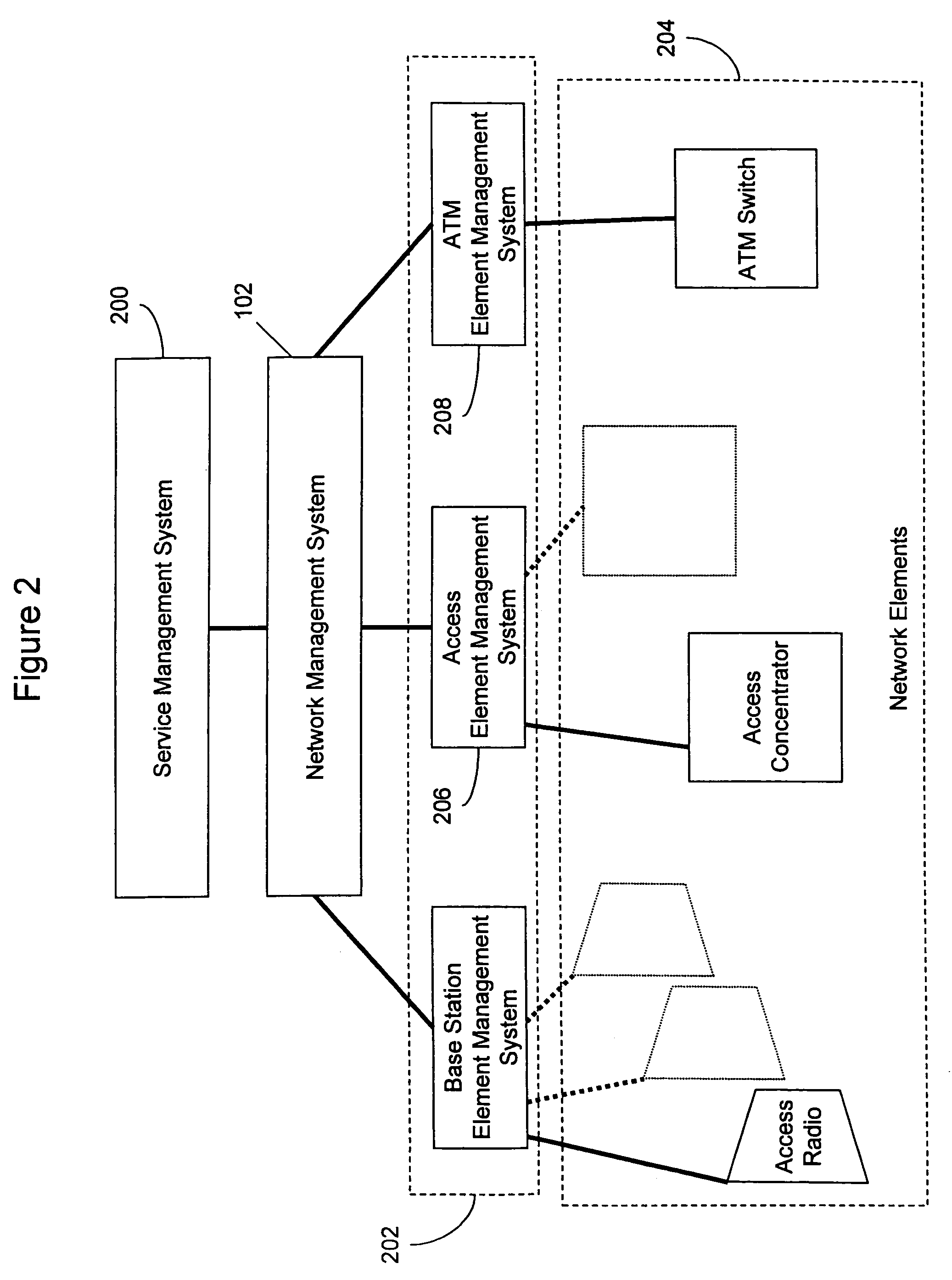
Wireless broadband service
InactiveUS20050030907A1Facilitate communicationBroadband local area networksNetwork topologiesIntegrated Services Digital NetworkData access
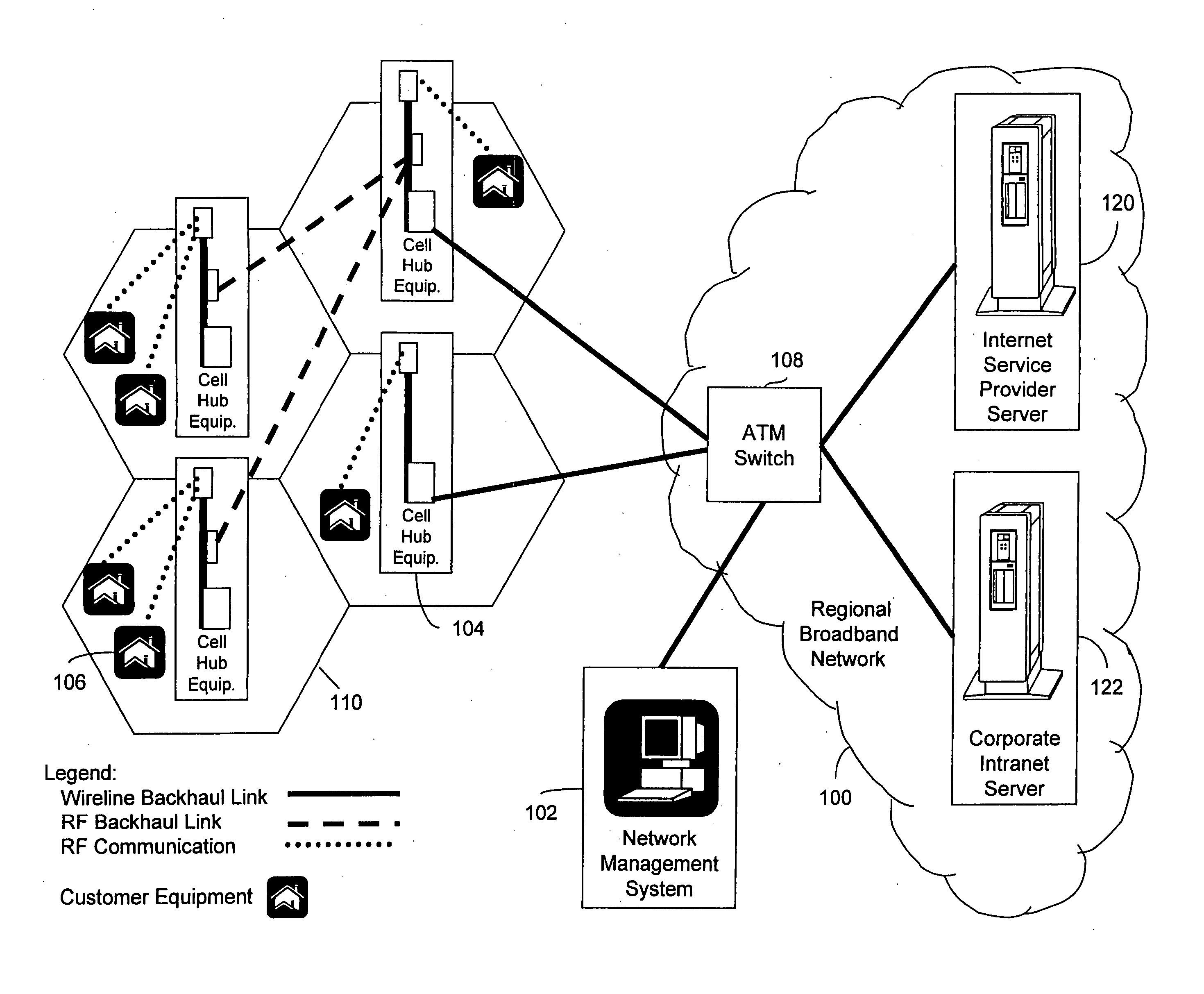
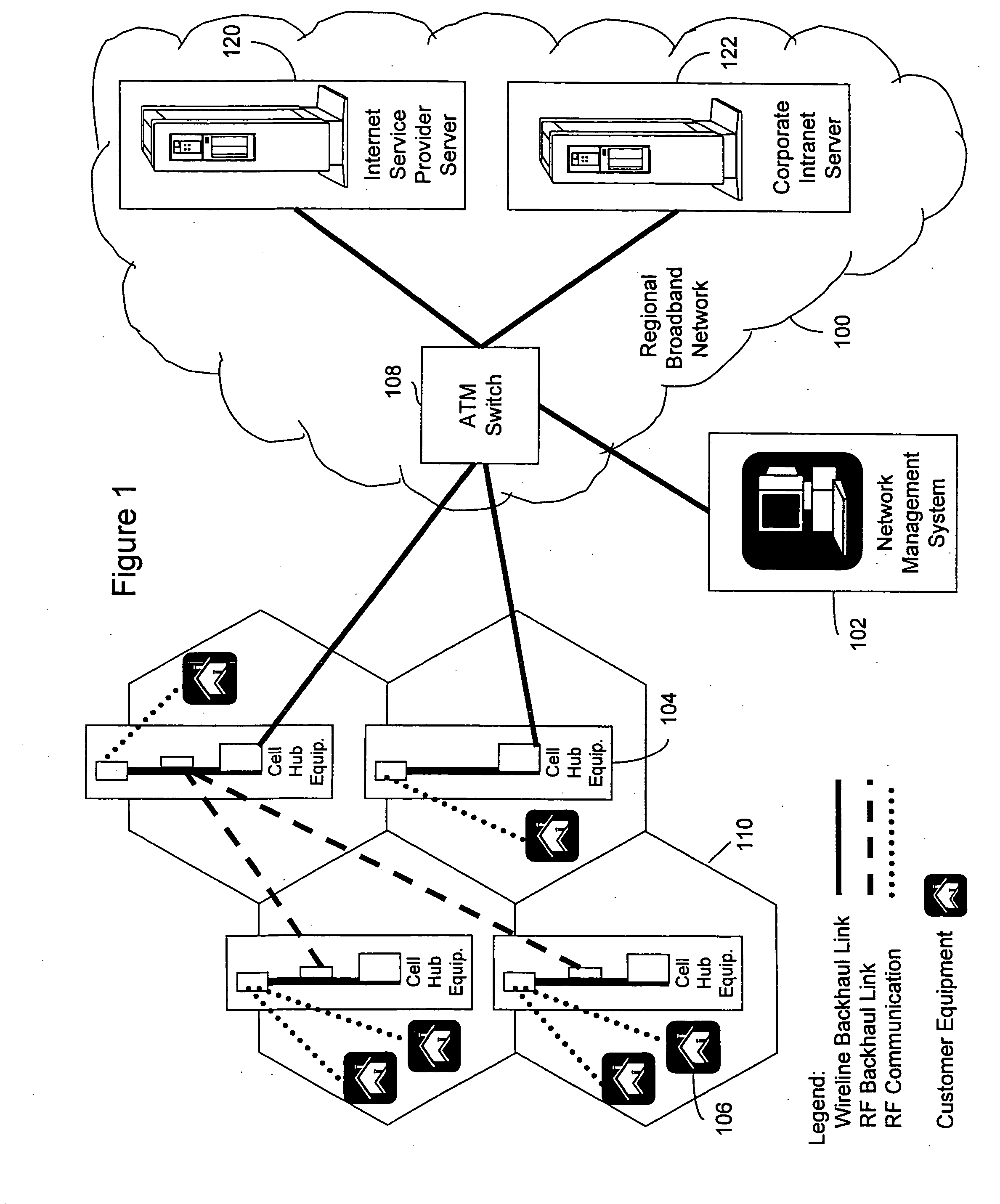
A fixed broadband wireless data access service providing shared wide-band packet-switched data transport for high speed data access in areas where conventional ADSL service and fiber optic service are unavailable. The wireless data access service is a point-to-multipoint cellular-type network that connects customers to data service providers through the ATM backbone of an existing network. Customers connect to the ATM backbone and data service provider through a cellular grid in which a wireless base station in each cell communicates with the individual customer wireless equipment within its cell site coverage area. The base stations are connected to an ATM backbone switch through wireless and wireline backhaul links. The upstream and downstream bandwidths of the wireless broadband network are engineered in various symmetric and asymmetric configurations to provide a shared packet-switched connection that emulates an uninterrupted, direct wireline ADSL connection. The wireless broadband network employs a data protocol of shared access bandwidth and adaptive asymmetric data rates to support multiuser service sessions by wireless transmission. The wireless broadband network is not network protocol specific and can be applied to wireless asymmetric digital subscriber line service, wireless integrated service digital network over digital subscriber line service, wireless very high bit rate digital subscriber line service, or wireless symmetric or single-line digital subscriber line service.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Method and system for improving VDSL stability
InactiveCN101237398AFix stability issuesTelephonic communicationData switching by path configurationComputer hardwareData transmission
The present invention discloses a method and a system for VDSL data transmission, the method comprises the following steps: a. the physical medium specific transmission coverage layer PMS-TC of very high bit-rate digital subscriber line VDSL divides the sent data into a first portion and a second portion; b. the PMS-TC transmits the first portion data to a receiving end via a basic physical channel, and transmits the second portion data to the receiving end via an extended physical channel.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
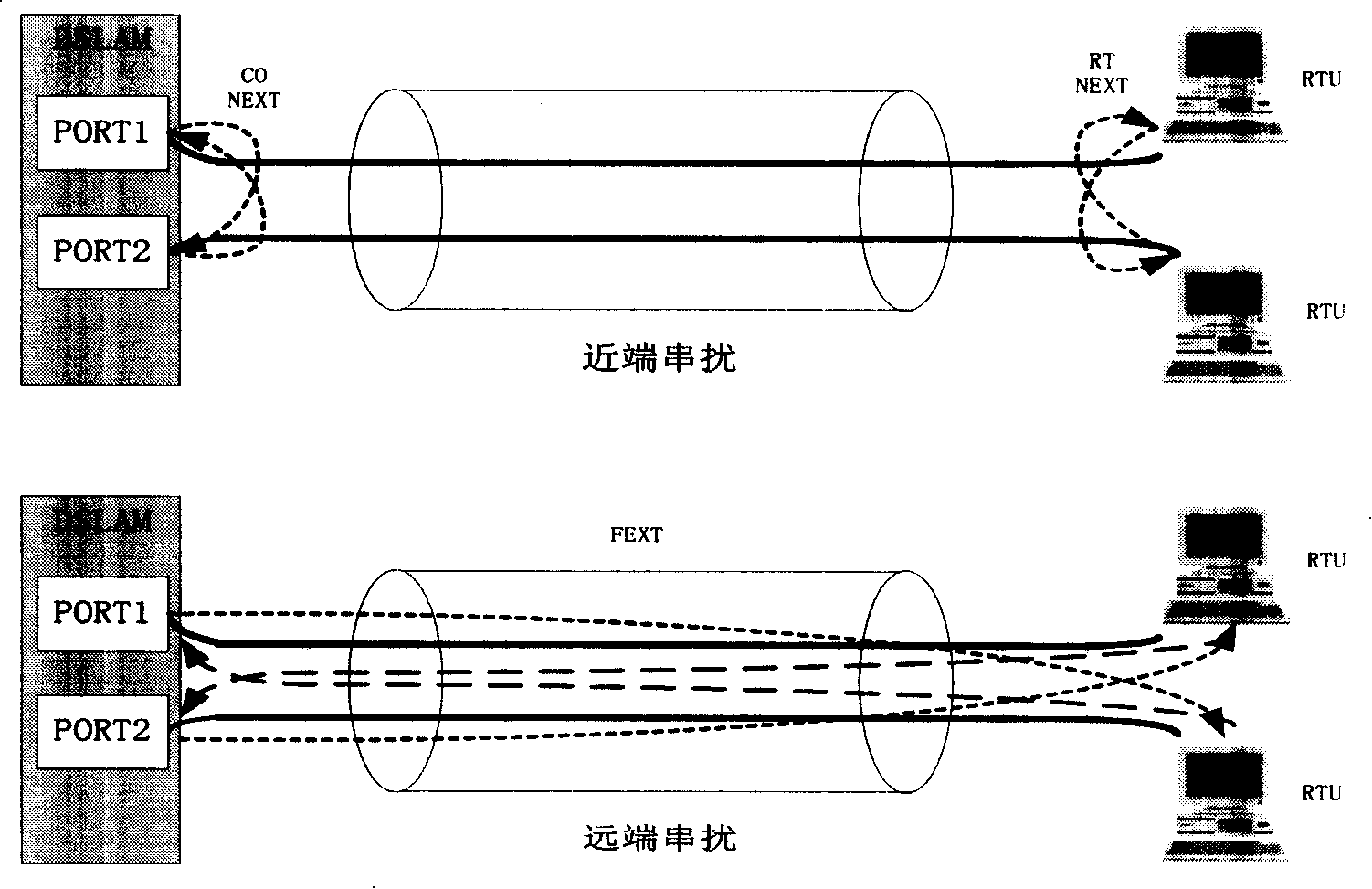
Method and device for reducing VDSL high-frequency crosstalk
ActiveCN101222242AGuaranteed transmission performanceAvoid crosstalkSubstation equipmentLine-transmissionData transmissionTransmission performance
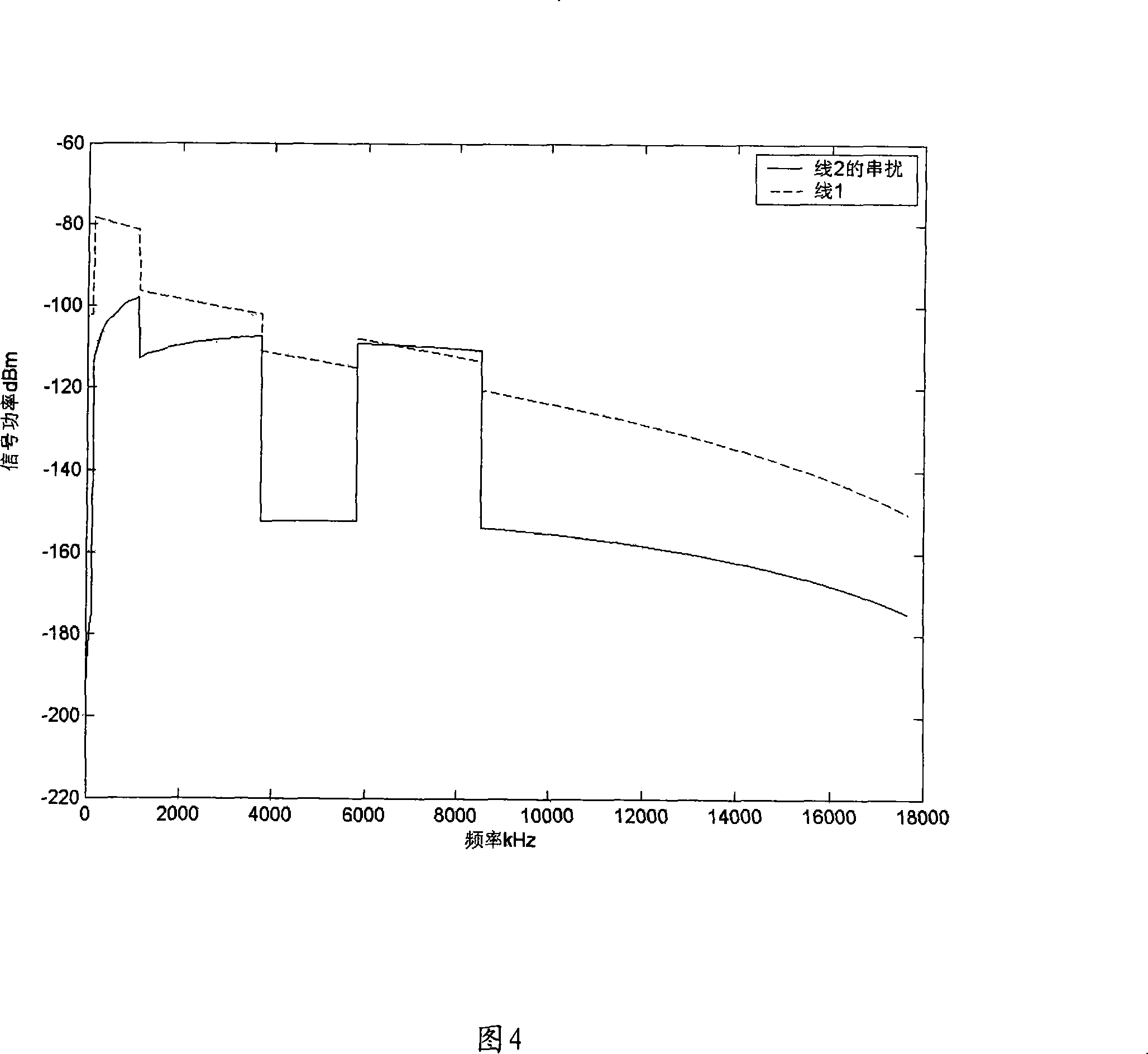
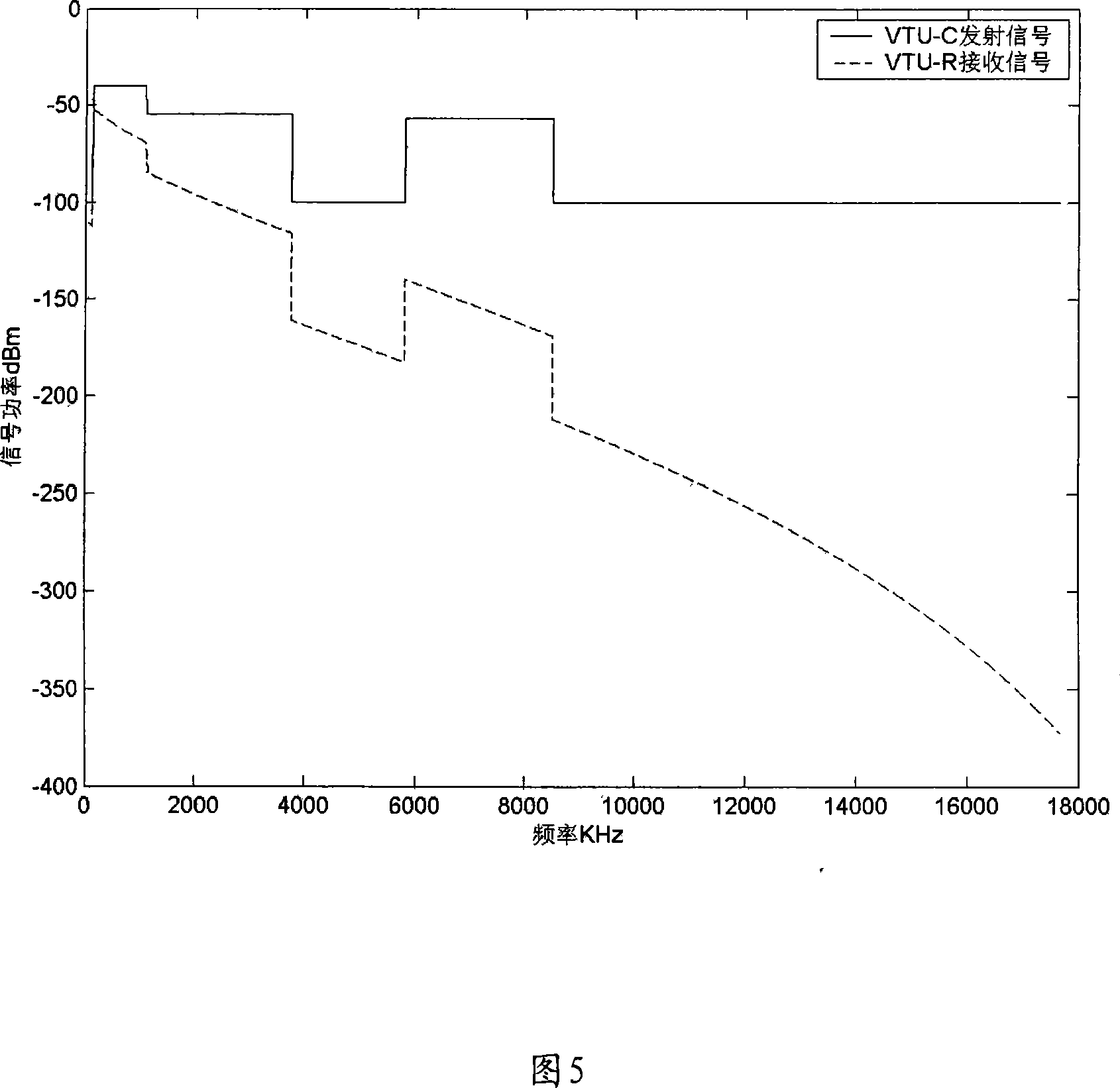
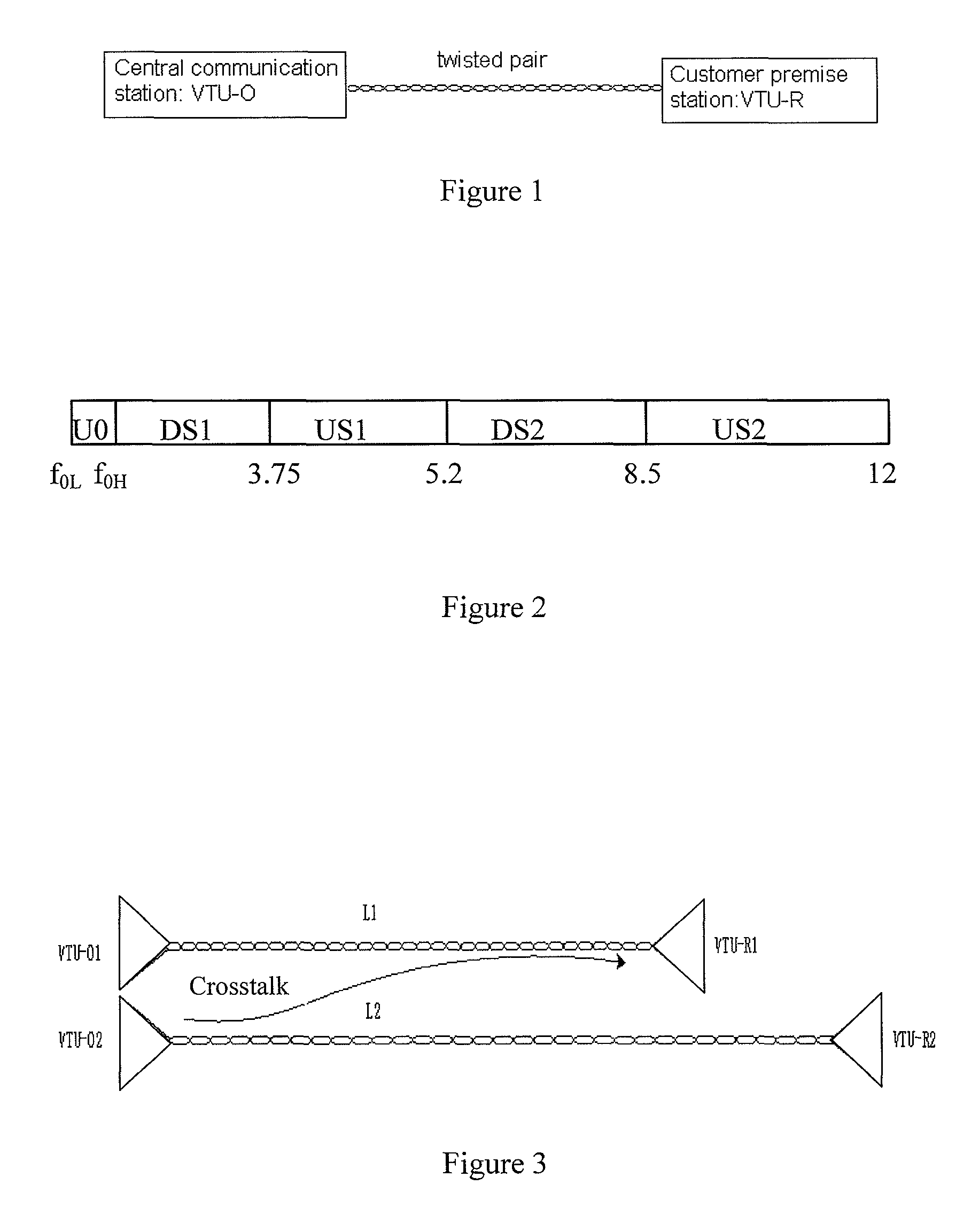
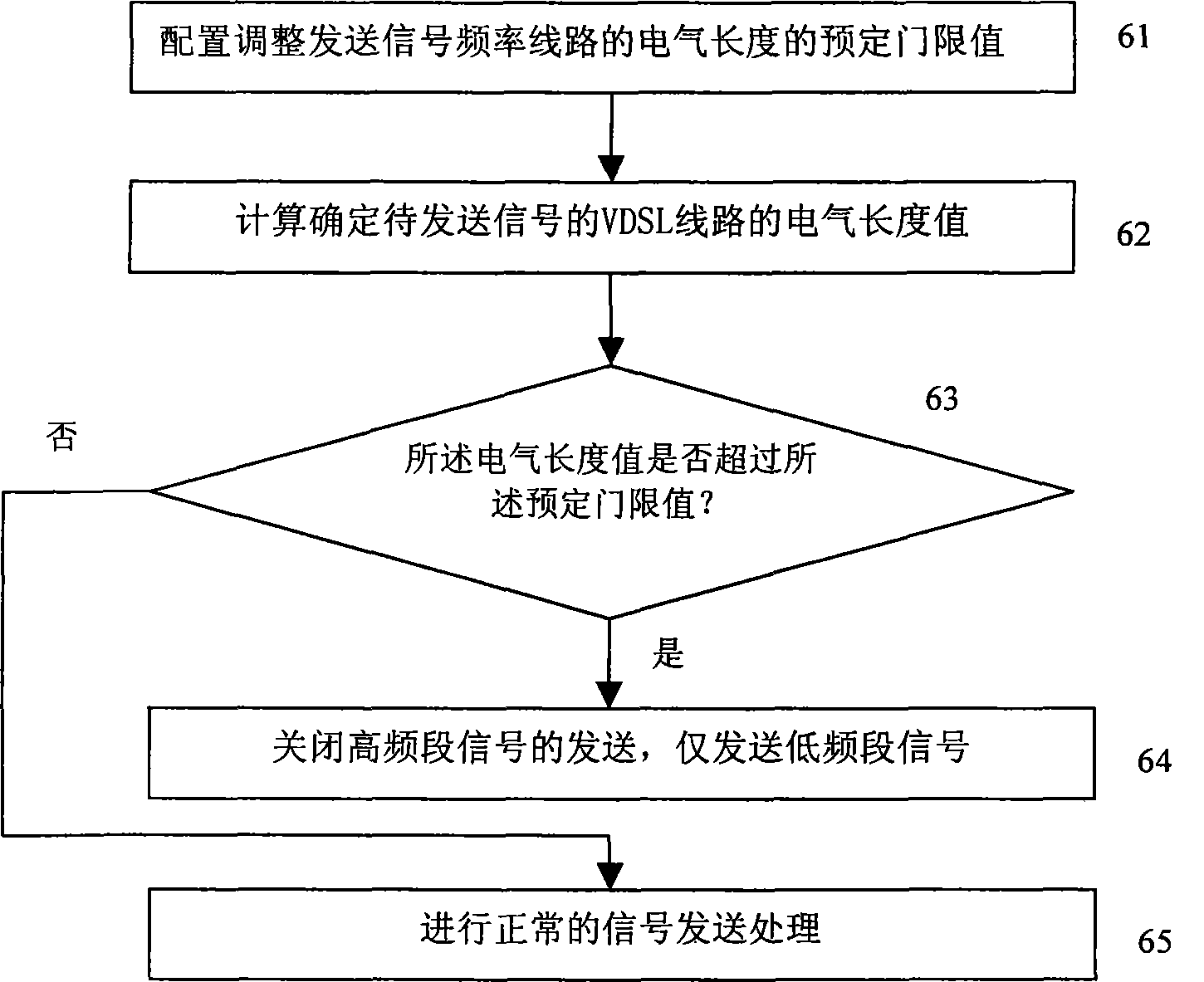
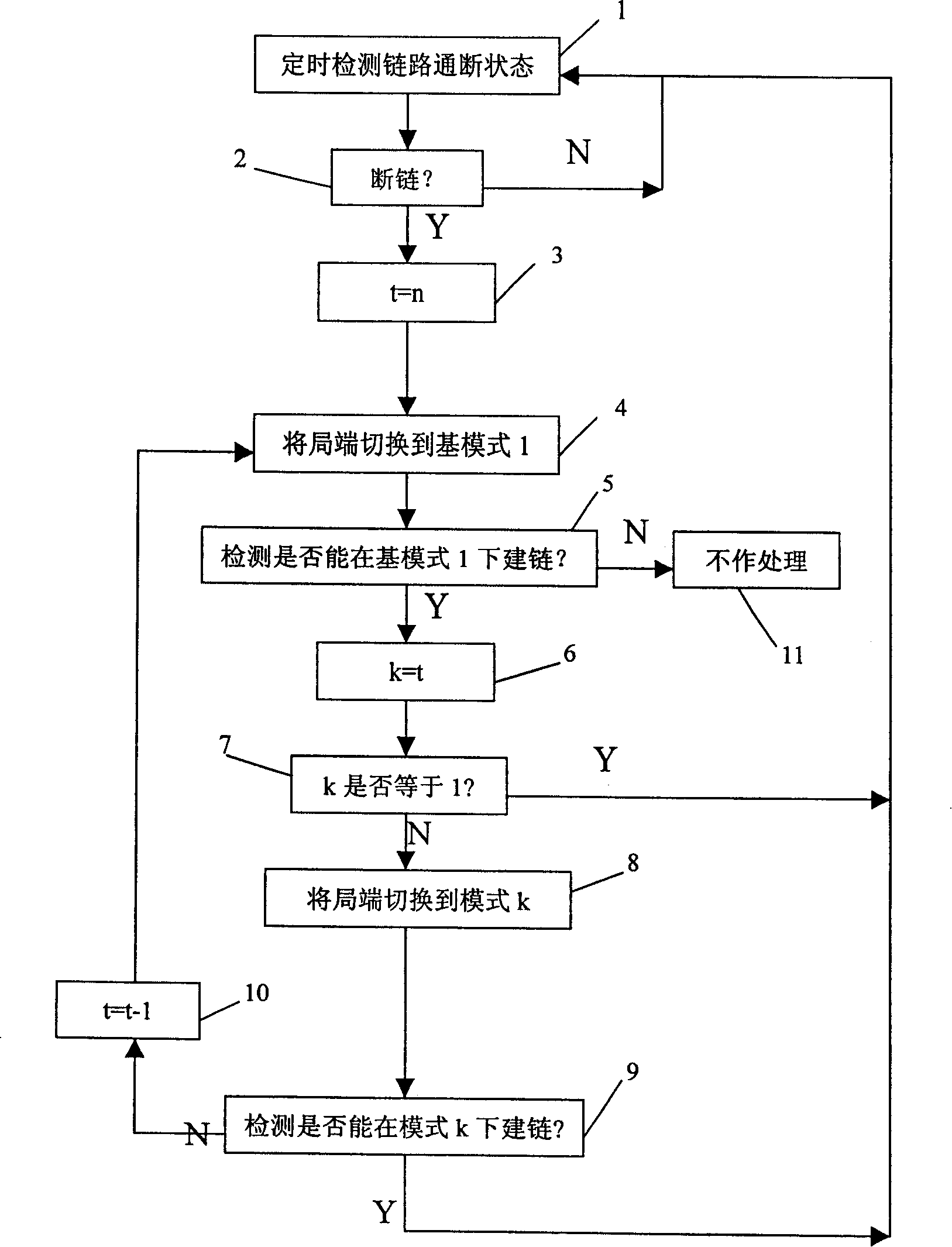
The invention relates to a method and a device for reducing VDSL high frequency crosstalk; the method mainly comprises the following steps: firstly, the electric length value of a VDSL (very high bit rate digital subscriber line) is determined; secondly, according to the electric length value, the frequency range of the signal transmitted through a corresponding line is determined; moreover, signal is transmitted through a corresponding line according to the determined frequency range. The invention is mainly used to switch off the transmission of high frequency signal and only transmits low frequency signal when the electric length value of a line exceeds a preset value, thereby reducing the crosstalk in the line. The implementation of the invention can effectively overcome the crosstalk on an adjacent line during the channel finding stage of the VDSL, thereby ensuring the transmission performance of the VDSL transmitting data; meanwhile, the implementation of the invention is based on the prior standard; therefore, the invention has the advantages of simplicity and easy implementation.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Universal interface
InactiveUS20050025177A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationFrame RelayIntegrated Services Digital Network
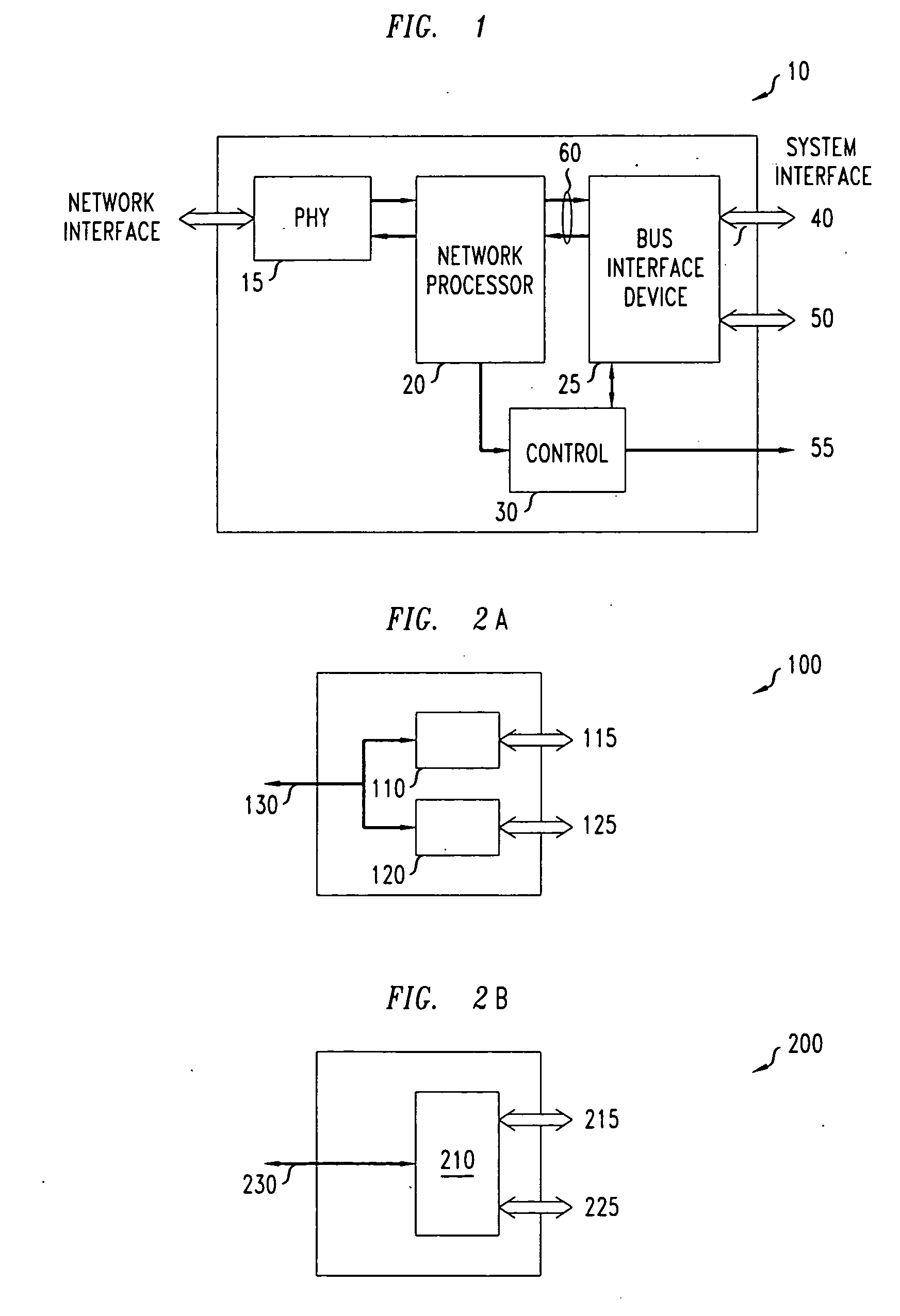
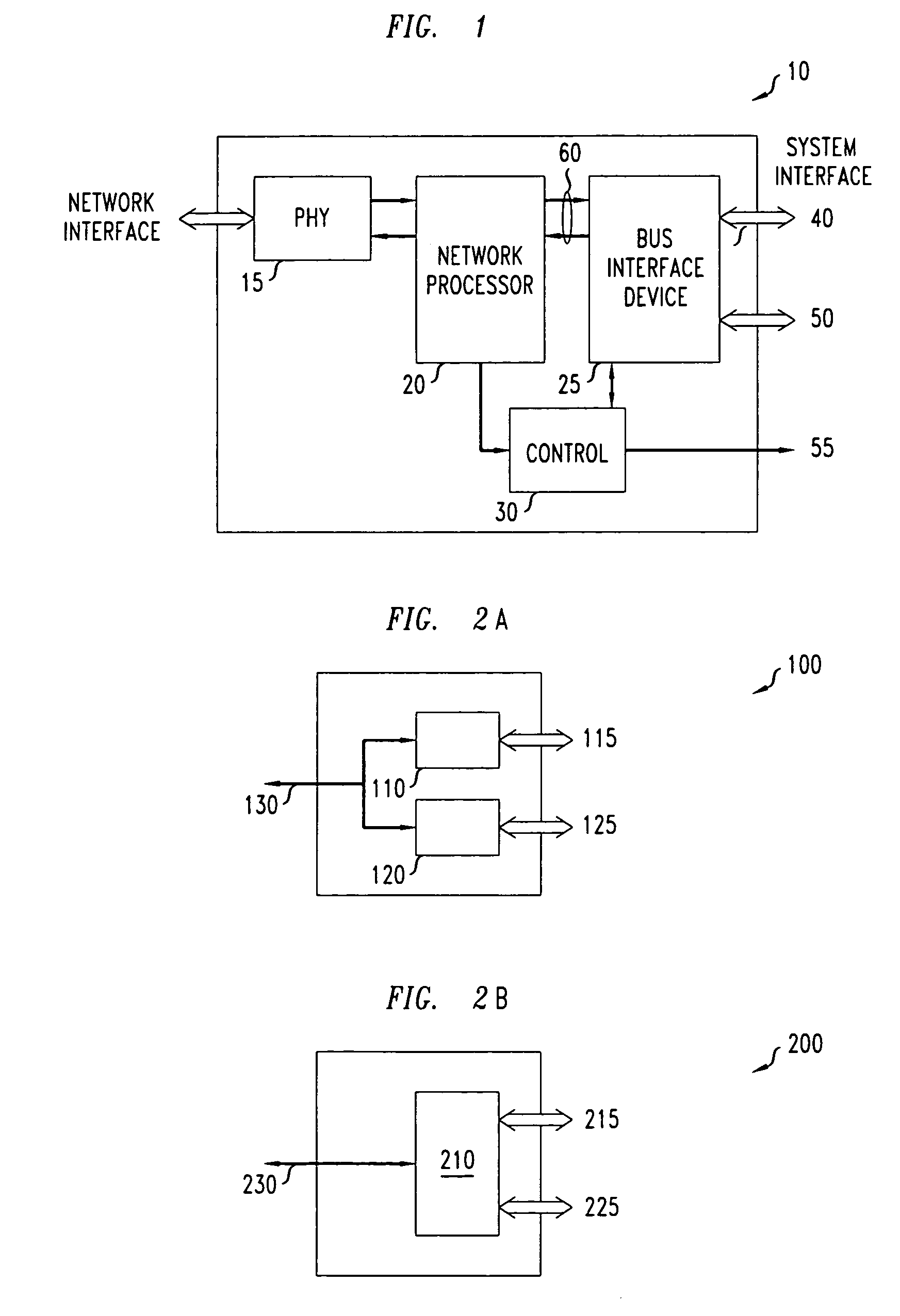
A universal interface apparatus having a processor for receiving one or more Network Interface signals having a transport mechanism associated therewith. The transport mechanism may include Asynchronous Transfer Mode, Internet Protocol, Frame Relay, Integrated Services Digital Network, High bit-rate Digital Subscriber Line, Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line, Very High Data Rate Digital Subscriber Line, Symmetric Digital Subscriber Line, 10 base T, 100 Base T, Gigabit Ethernet and E1 / T1. The processor may recognize the transport mechanism associated with each Network Interface signal. In the event Asynchronous Transfer Mode is recognized as the transport mechanism, the processor may also segment perform ATM adaptation layer processing on each Network Interface signal. Further, the universal interface apparatus includes a bus interface device for generating a System Interface signal from the ATM adaptation layer processed Network Interface signal in response to the recognized transport mechanism.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Method and system for sending data using a very high bit rate digital subscriber line
ActiveUS20080080595A1Repeater/relay circuitsActive radio relay systemsElectricityAudio power amplifier
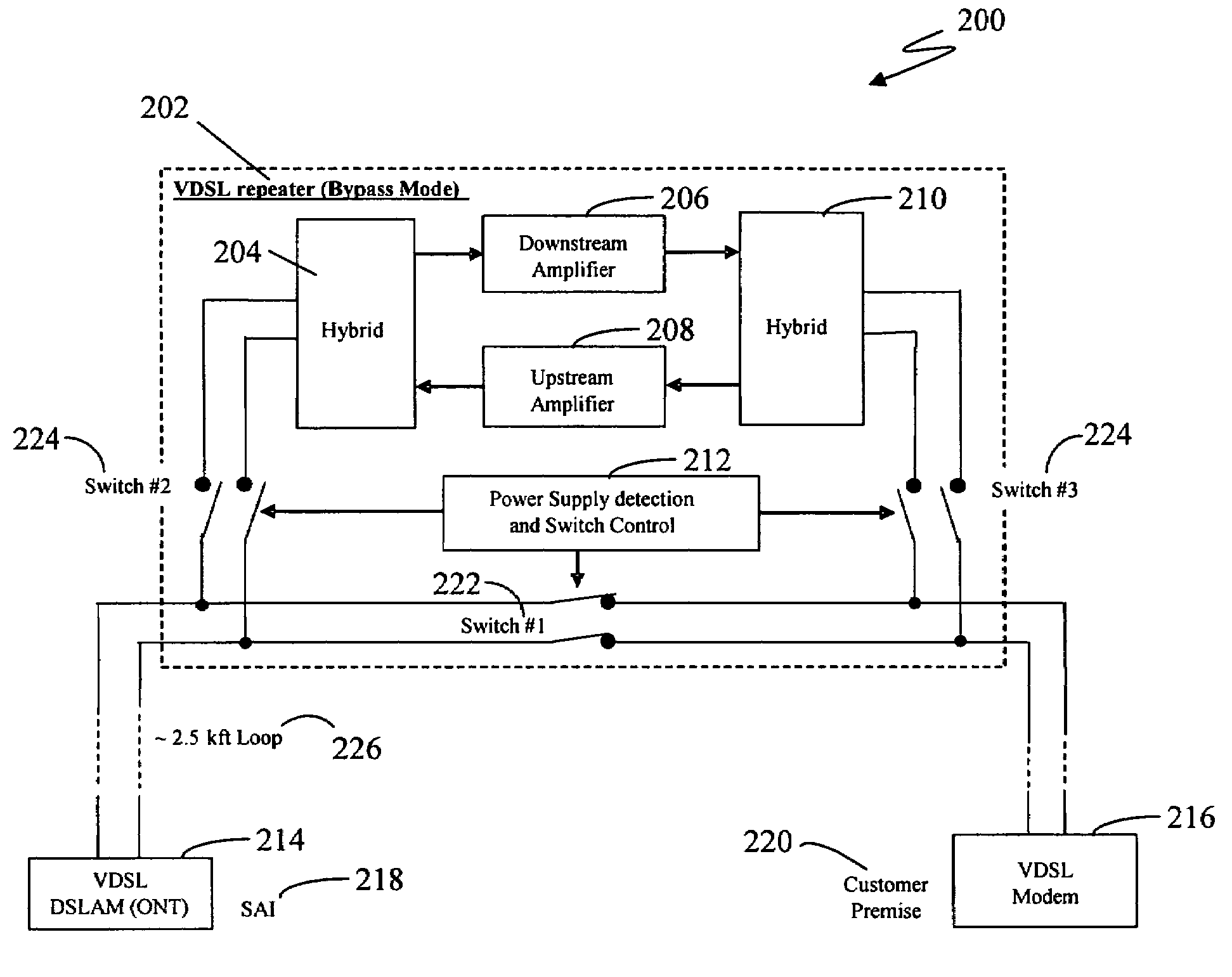
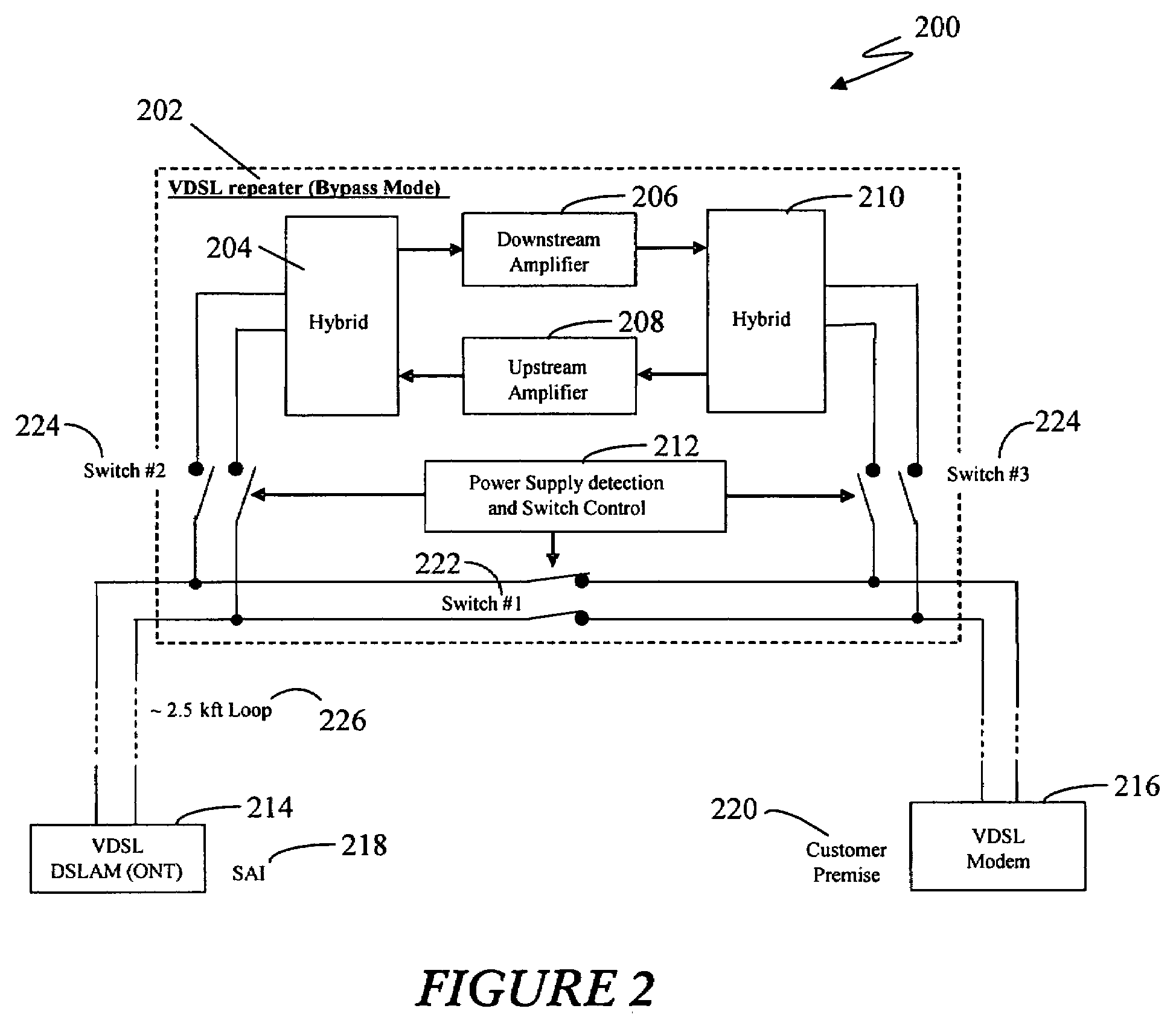
In a particular embodiment a VDSL repeater is disclosed. The VDSL repeater includes a first interface for receiving data from an IPTV network node; a second interface for sending data to an end user client device; and an amplifier in electrical communication with the first interface for amplifying data received on the first interface from the IPTV network node when a power supply voltage is present on the first interface, wherein the amplifier sends the amplified data received on the first interface to the second interface. In another aspect of a particular embodiment the VDSL repeater further includes a circuit that bypasses the amplifier when the power supply voltage is not present on the first interface. In another particular embodiment a method for amplifying a VDSL signal when a power supply voltage is present on the twisted pair using the power supply voltage is disclosed.
Owner:SBC KNOWLEDGE VENTURES LP
Network interface
InactiveUS20090060168A1Durable and flexibleAccess is deniedInterconnection arrangementsSubstation equipmentTamper resistanceNetwork interface device
A network interface device (NID) and associated printed circuit board is provided that includes metallic die cast housing and doors configured so that one of the doors, when closed, physically separates service provider circuitry from the customer premise equipment (CPE) side connections on a circuit card within the NID so that an end-customer may access the CPE side connections while the service provider circuitry remains secured from end-customer access. Moreover, the metallic housing provides increased physical strength and tamper resistance, including improved heat dissipation properties to radiate internal heat build-up more efficiently. The NID may be configured to provide insertable interface cards to permit flexibility in service provisioning and includes options for a type-200 T1 module, a type-400 T1 module, a type-200 high bit rate Digital Subscriber Line (HDSL) module, a type-400 HDSL module or an ISDN module.
Owner:SK COMMUNICATIONS
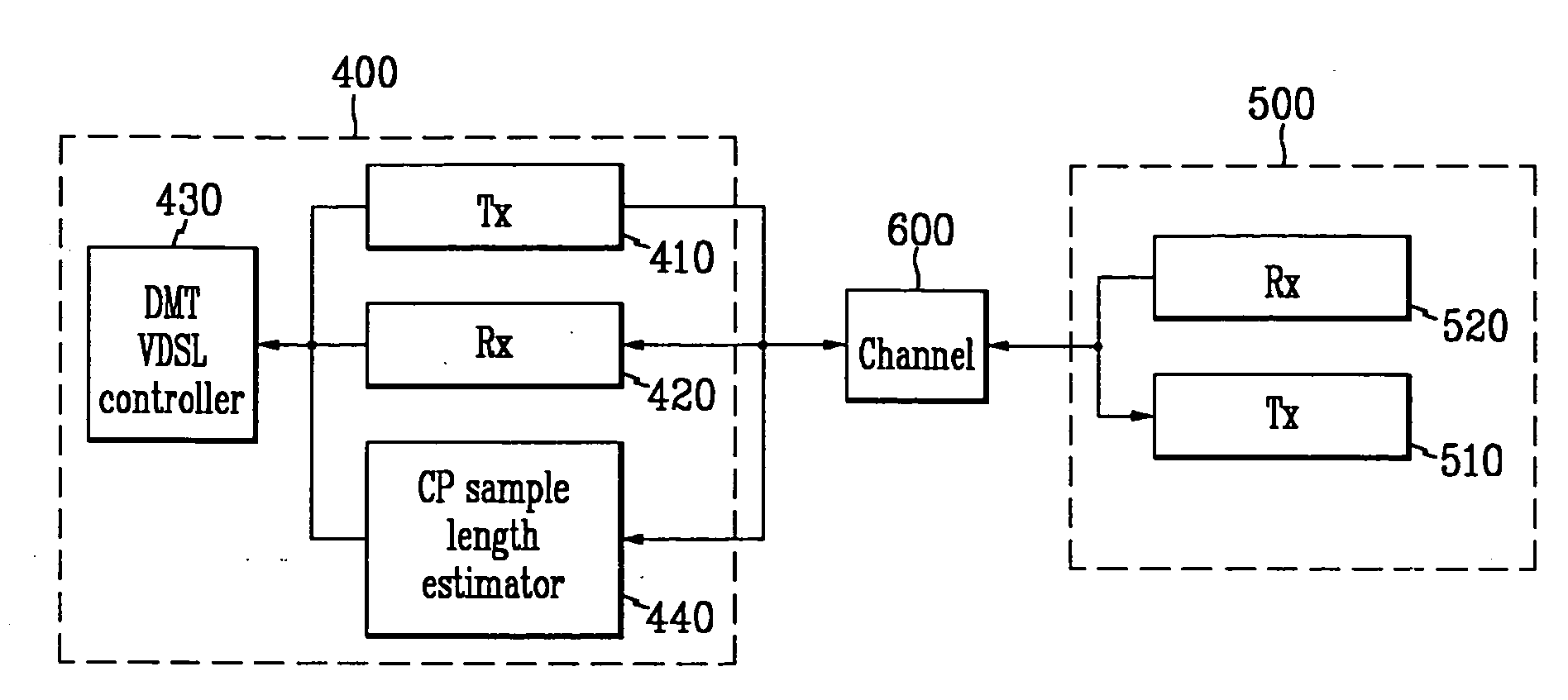
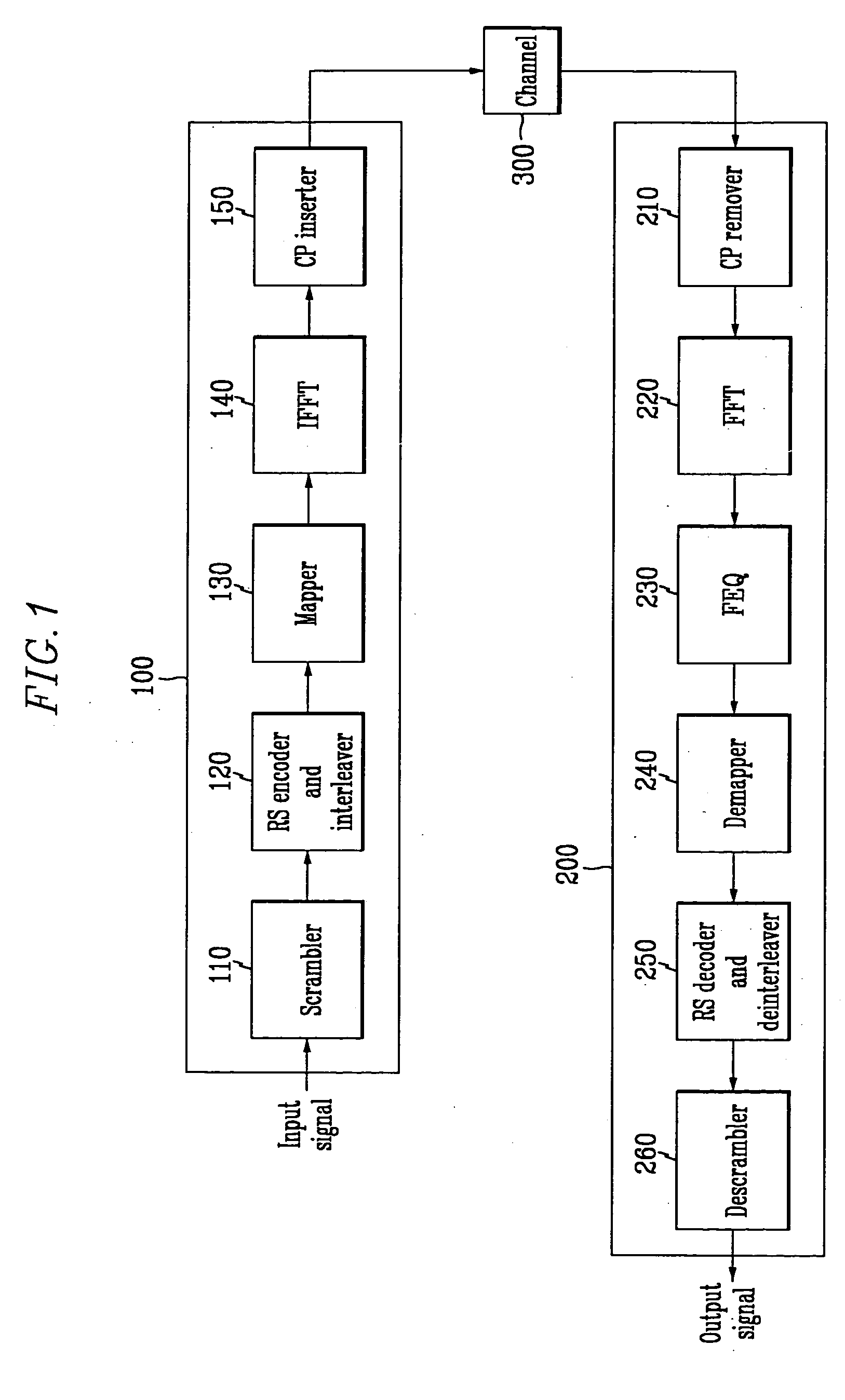
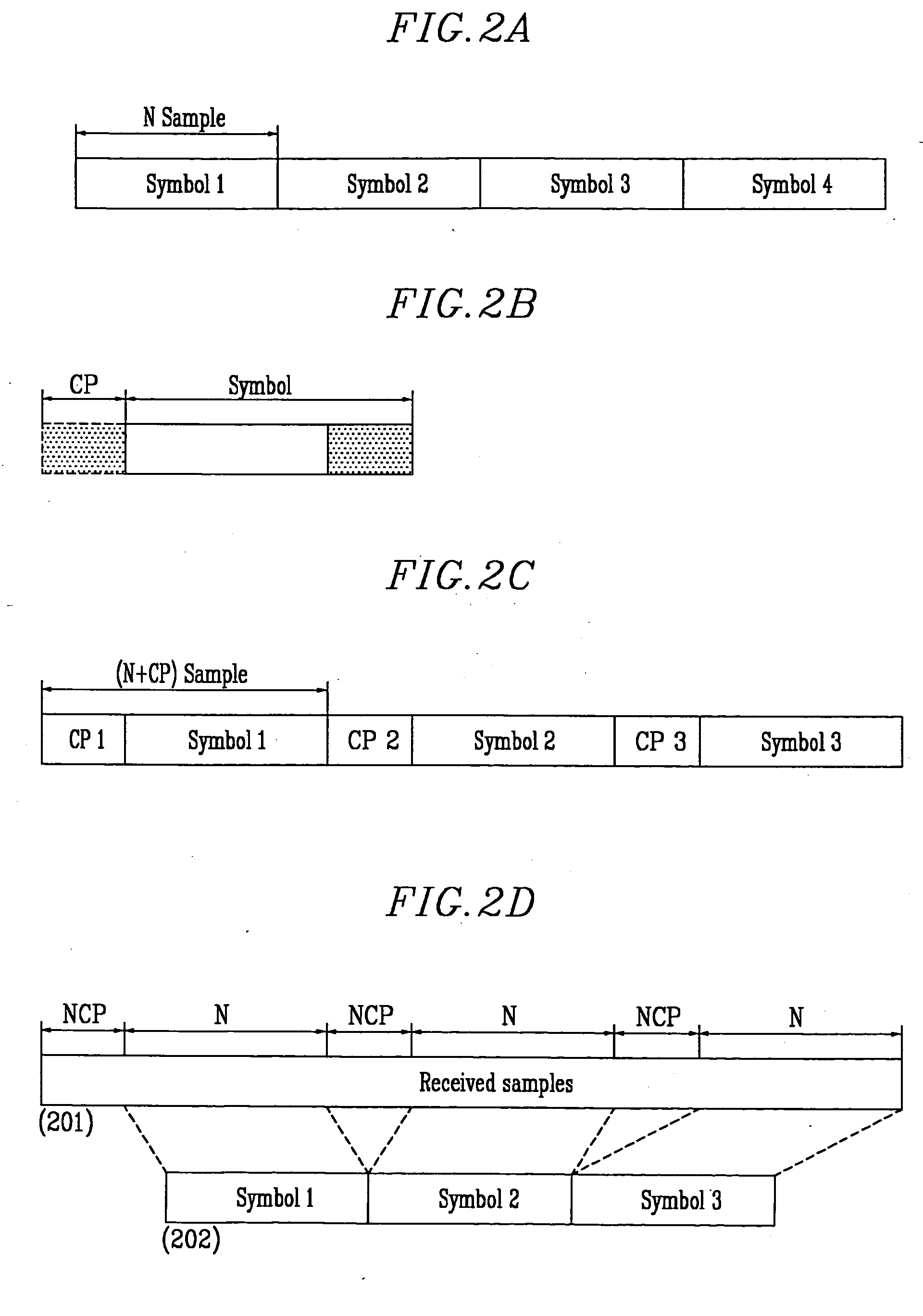
Vdsl system based on dmt line coding, and method for determining length of cyclic prefix samples using the system
InactiveUS20060050776A1Convenient lengthSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlMulti-frequency code systemsAlgorithmCyclic prefix
Disclosed is a VDSL (very high bit-rate digital subscriber line) system on the DMT line coding method basis and a method for determining a length of cyclic prefix samples using the system. The VDSL system comprises a transmitter data including cyclic prefix samples through a channel; a receiver for receiving the data including the cyclic prefix samples; a controller for controlling the transmitter and the receiver to control an initialization operation including handshake, training, channel analysis, and exchange, and a data transmission operation after the initialization operation; and a cyclic prefix sample length estimator for estimating an optimized length of the cyclic prefix sample on the basis of the correlation between the cyclic prefix sample and other data. According to the present invention, since no complex TEQ configuration required when fixing and using the length of the cyclic prefix sample is used, its configuration becomes simpler, and the optiized length of the cyclic prefix sample can be accurately determined.
Owner:NAT RES FOUND OF KOREA NRF +2
Wireless broadband service
InactiveUS7292560B2Facilitate communicationBroadband local area networksNetwork topologiesWireless dataData access
A fixed broadband wireless data access service providing shared wide-band packet-switched data transport for high speed data access in areas where conventional ADSL service and fiber optic service are unavailable. The wireless data access service is a point-to-multipoint cellular-type network that connects customers to data service providers through the ATM backbone of an existing network. Customers connect to the ATM backbone and data service provider through a cellular grid in which a wireless base station in each cell communicates with the individual customer wireless equipment within its cell site coverage area. The base stations are connected to an ATM backbone switch through wireless and wireline backhaul links. The upstream and downstream bandwidths of the wireless broadband network are engineered in various symmetric and asymmetric configurations to provide a shared packet-switched connection that emulates an uninterrupted, direct wireline ADSL connection. The wireless broadband network employs a data protocol of shared access bandwidth and adaptive asymmetric data rates to support multiuser service sessions by wireless transmission. The wireless broadband network is not network protocol specific and can be applied to wireless asymmetric digital subscriber line service, wireless integrated service digital network over digital subscriber line service, wireless very high bit rate digital subscriber line service, or wireless symmetric or single-line digital subscriber line service.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
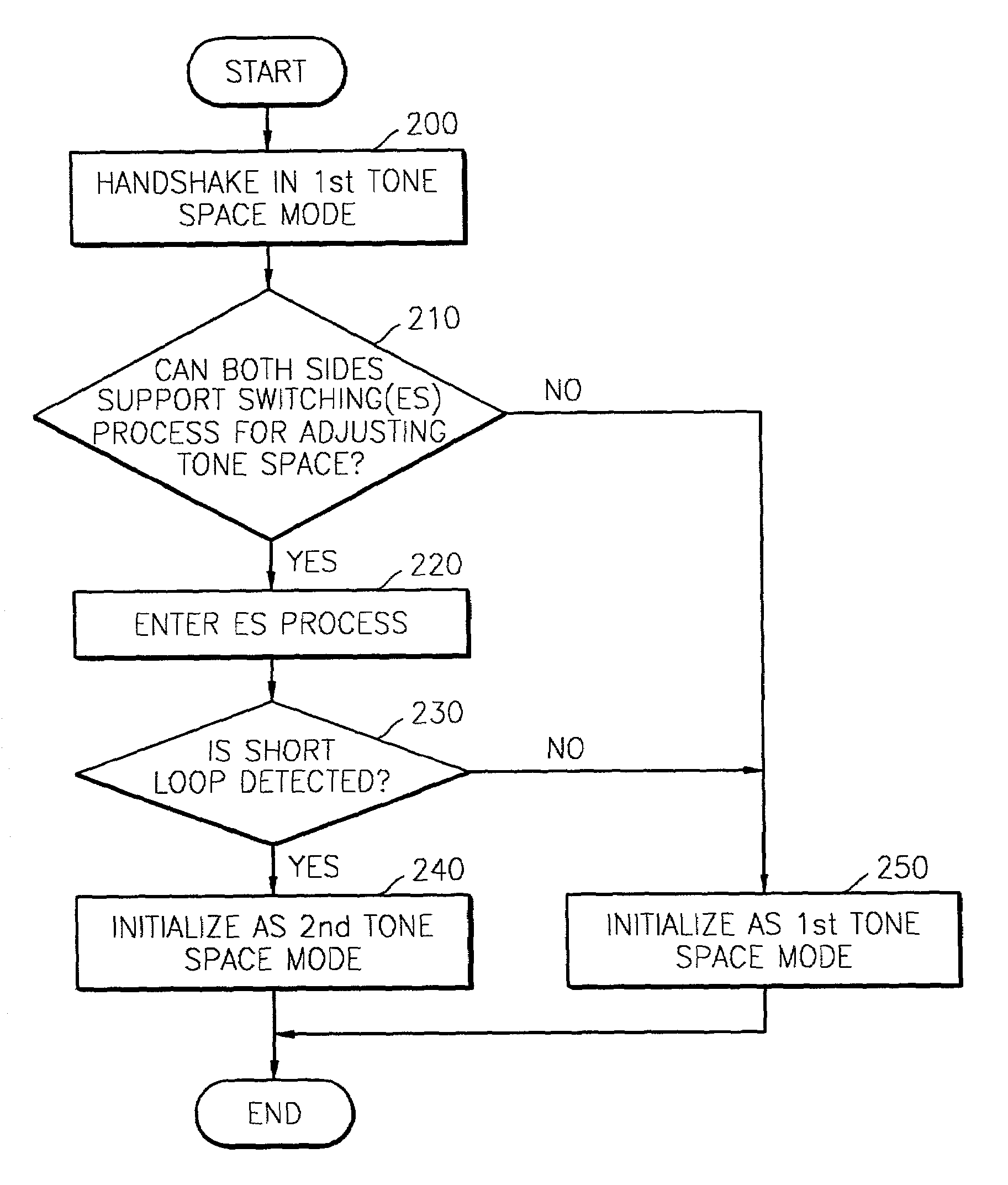
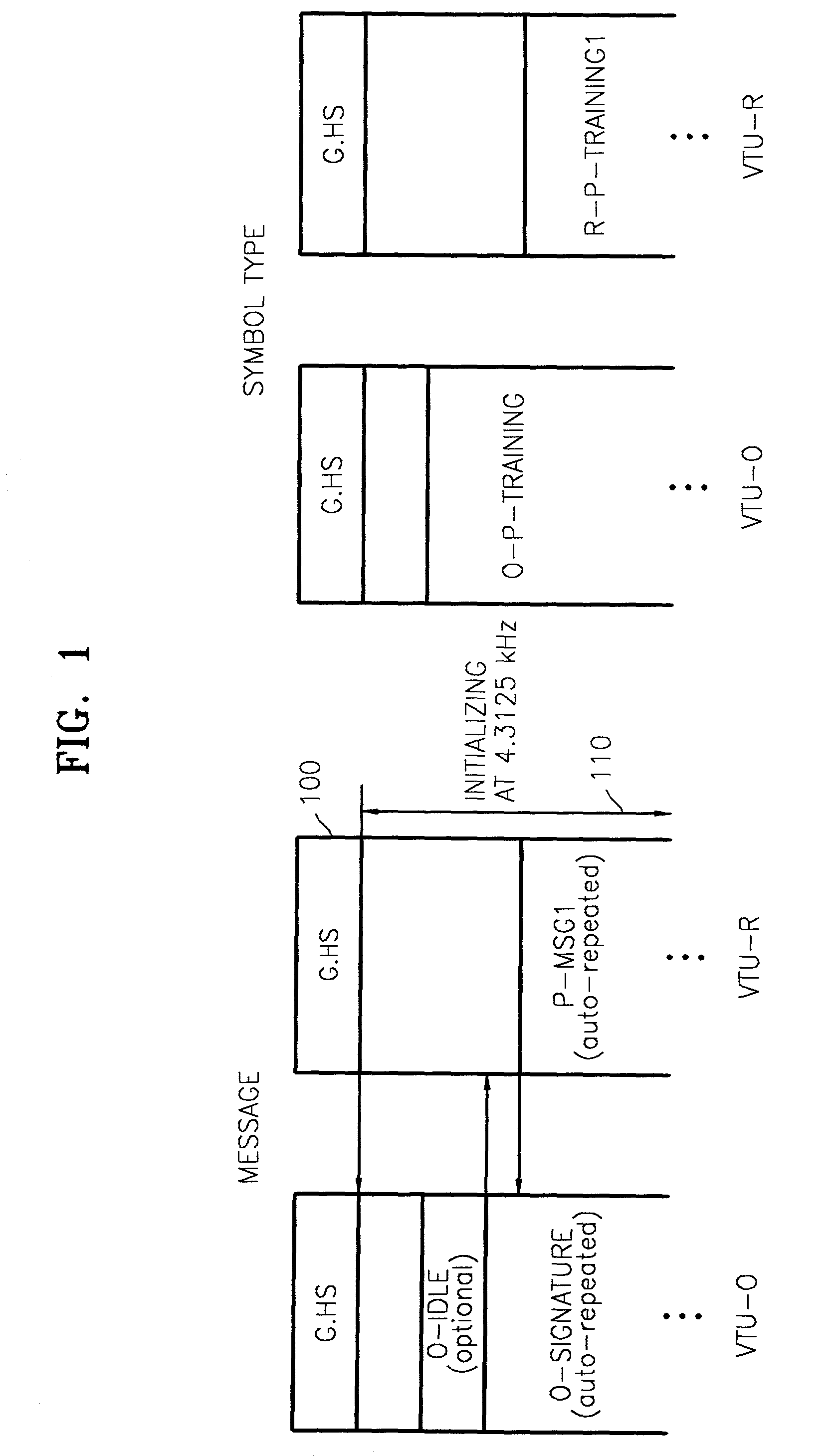
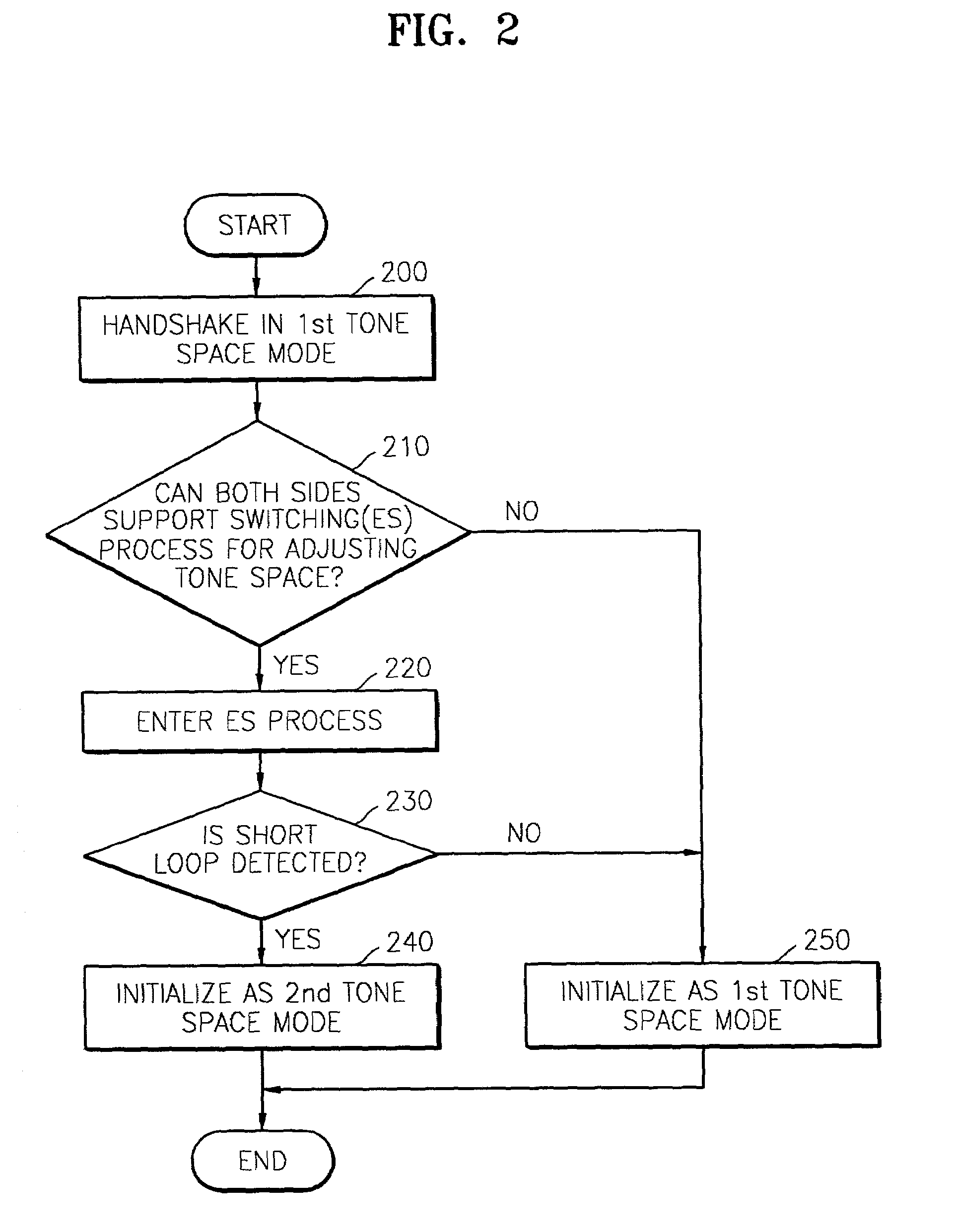
Initialization method for VDSL including tone space adjustment
An initializing method for Very high bit rate Digital Subscriber Line (VDSL), including adjusting tone spaces, and a system supporting the method are provided. The method includes: (a) handshaking for exchanging basically needed information between the two stations in a first one space mode, and for determining whether or not each of the two stations supports a second tone space; (b) switching the first tone space mode to the second tone space mode by detecting a short loop in each of the two stations for adjusting a tone space when it is determined in step (a) that each of the two stations supports the second tone space; and (c) exchanging information actually needed in data communications between the two stations in the second tone space mode for an actual initialization. When a 8.625 kHz tone space is used, a data communications link can be established with only one initialization process through the ES process according to the method and accordingly time for initialization is greatly reduced. In addition, since some identical signals used in the prior art actual initialization process are also used in the ES process, which is an intermediate process, additional hardware is not needed and in software aspect, it is easy to implement the system.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
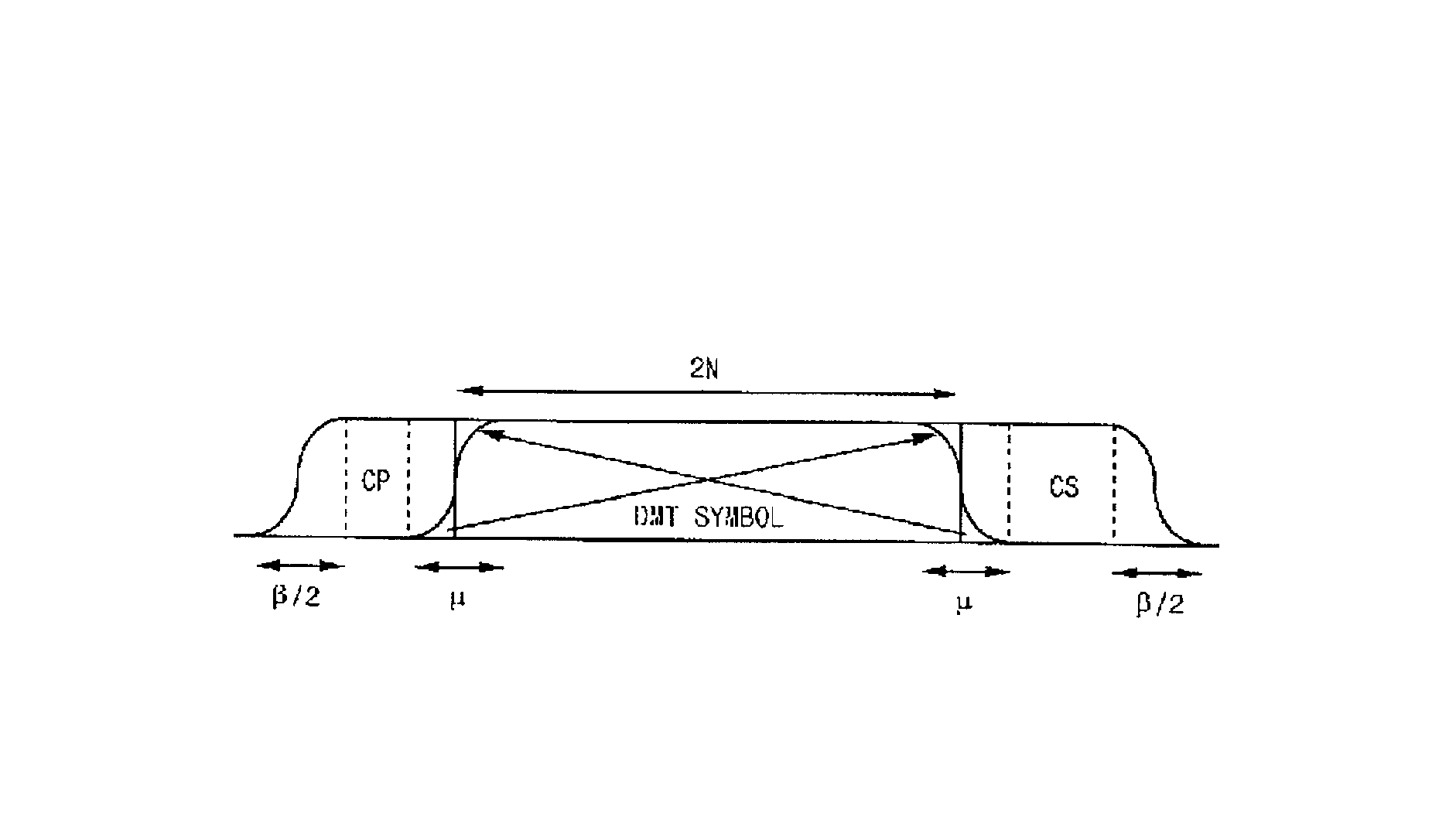
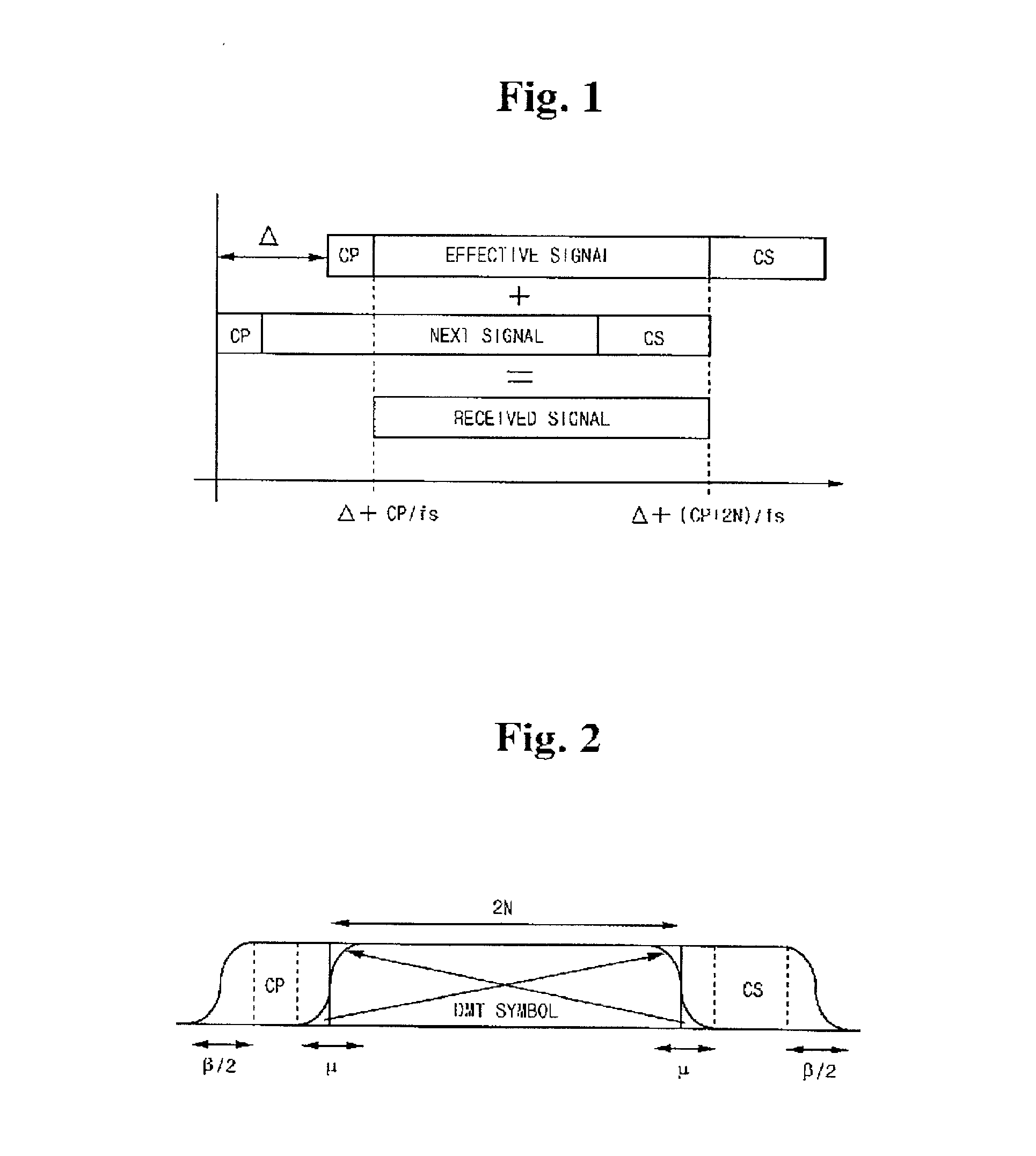
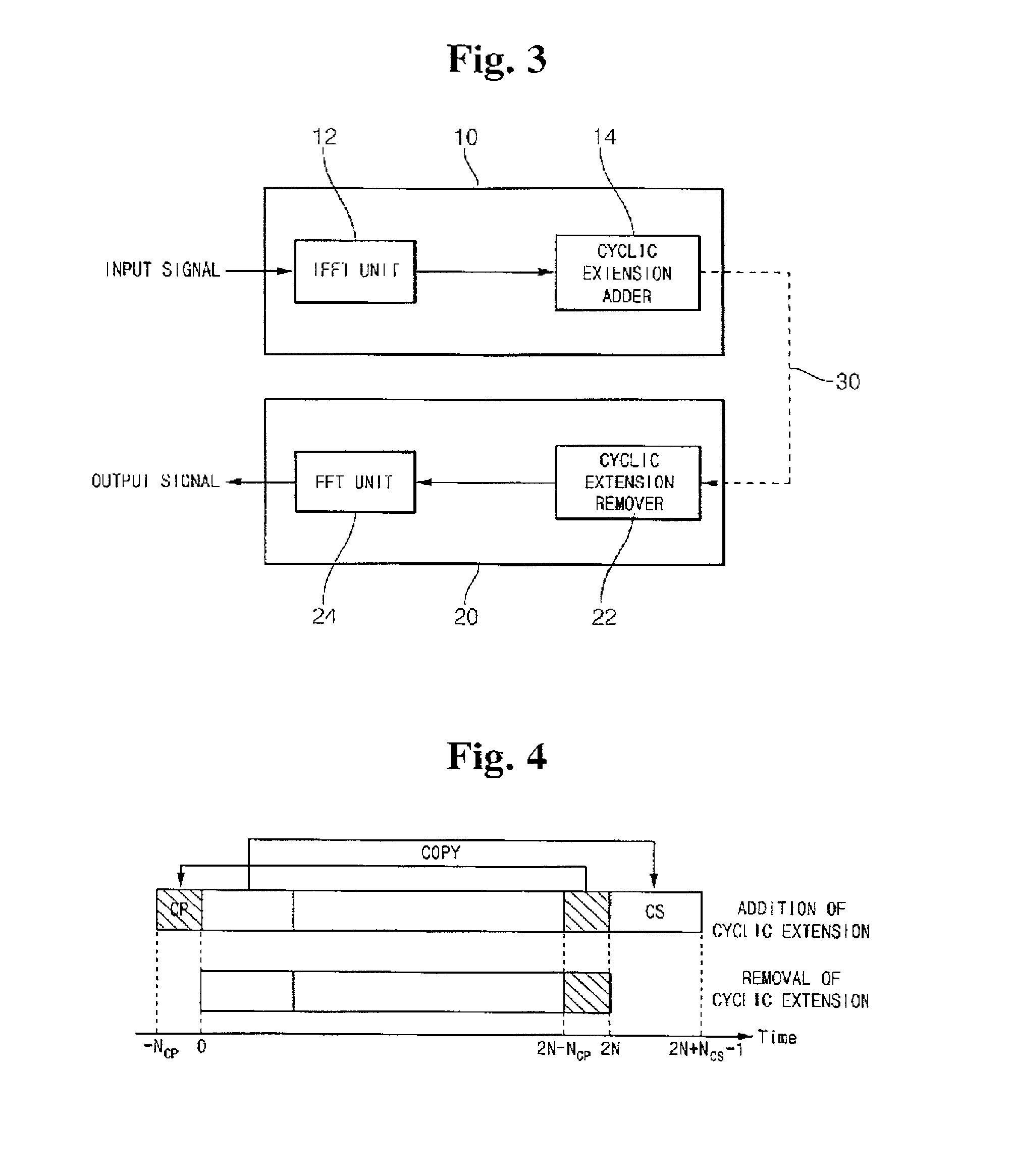
Zipper type VDSL system
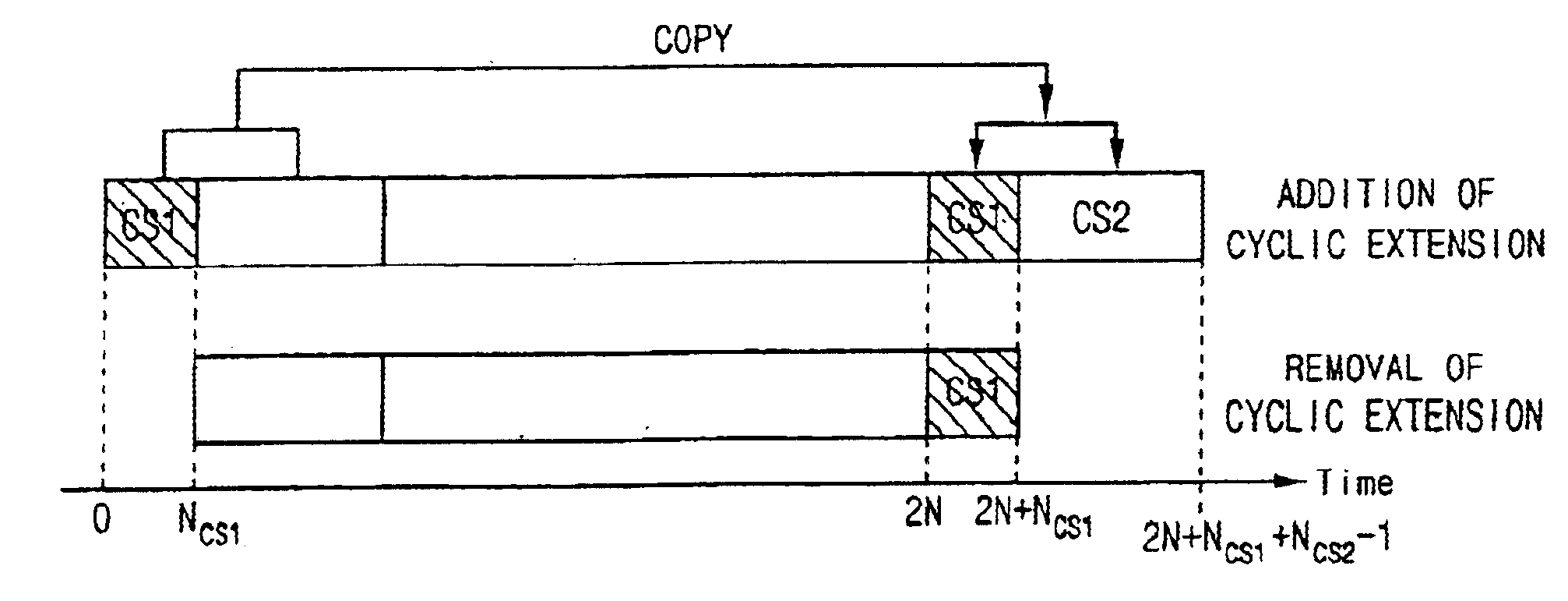
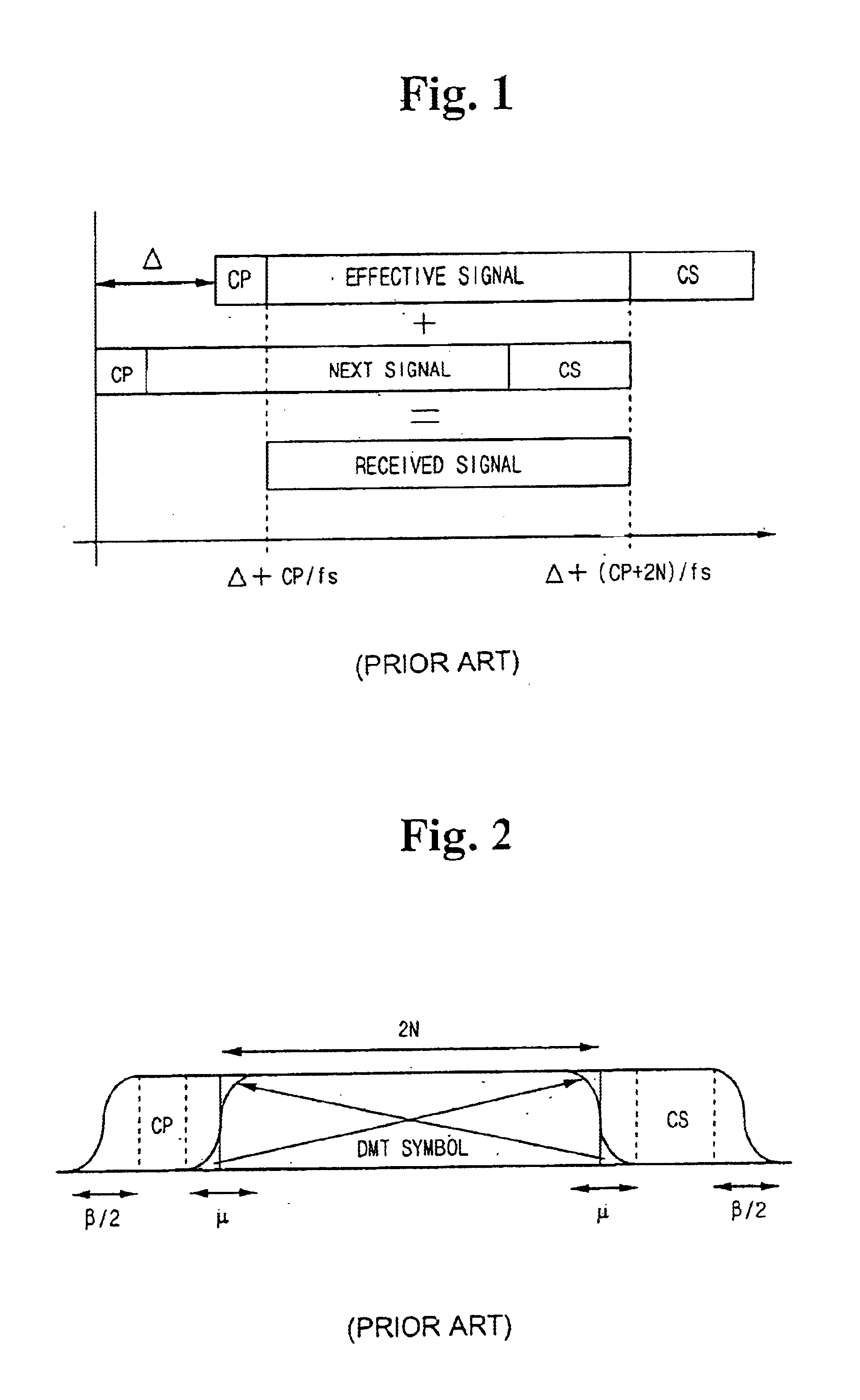
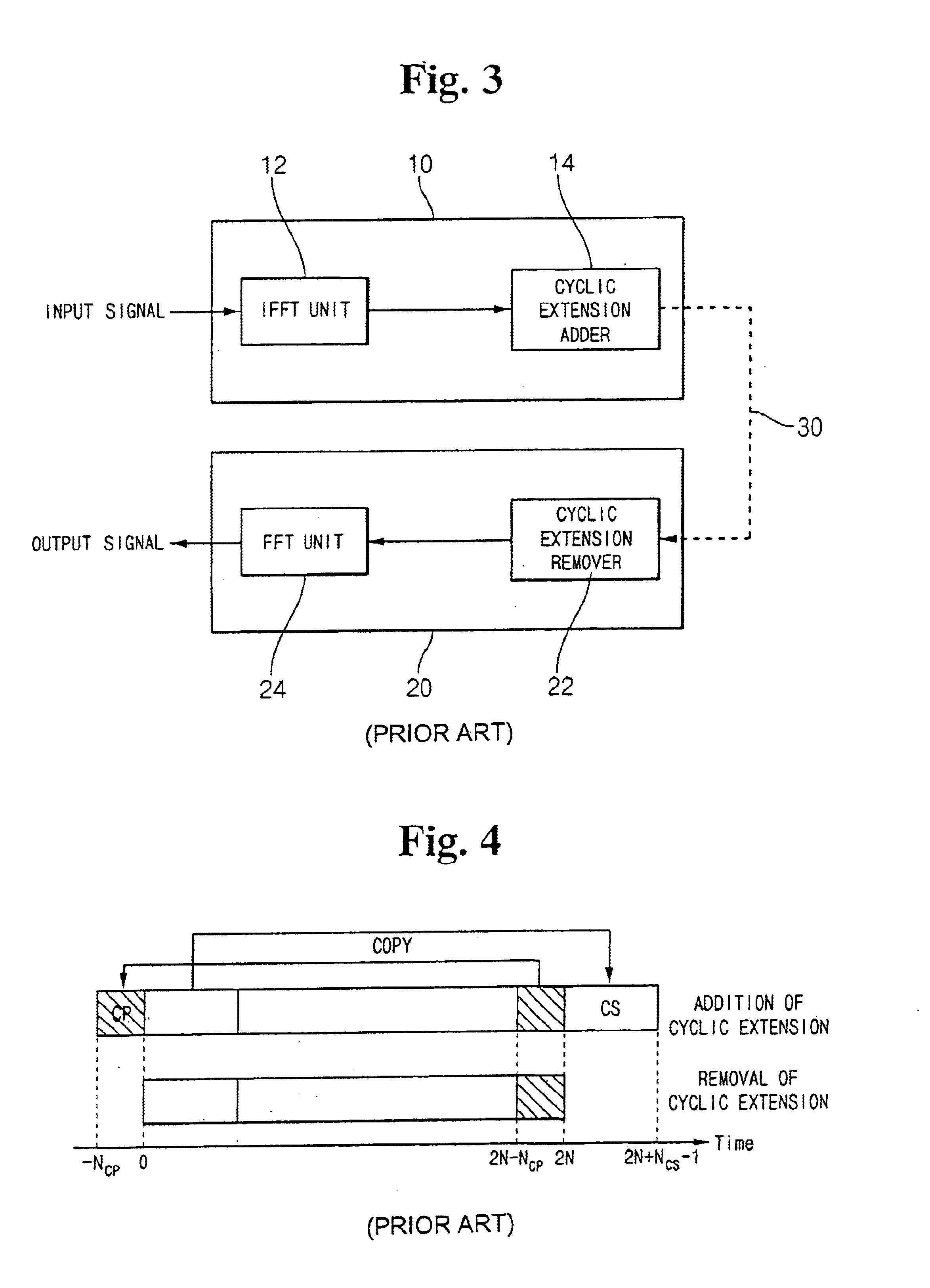
InactiveUS6862261B2Reduce hardware complexityModulated-carrier systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransformerInverse discrete fourier transform
Disclosed is a zipper type Very high bit-rate Digital Subscriber Line (VDSL) system which comprises a transmitter including an inverse fast Fourier transformer for performing an inverse fast Fourier transform on input data, and a cyclic extension adder for adding a cyclic extension for each symbol to the data output from the inverse fast Fourier transformer and outputting the data to a transmission channel; and a receiver including a cyclic extension remover for removing the cyclic extension from the data received through the transmission channel, and a fast Fourier transformer for performing a fast Fourier transform on the data output from the cyclic extension remover. The cyclic extension adder copies a first predetermined number of data starting from the leading part of the input symbol data received from the inverse fast Fourier transformer into a first cyclic suffix for removing interference between symbols and maintaining orthogonality between sub-carriers; adds the first cyclic suffix to the end of the symbol data; copies a second predetermined number of data subsequent to the first predetermined number of data into a second cyclic suffix for maintaining orthogonality between upstream and downstream; and adds the second cyclic suffix to the end of the first cyclic suffix.
Owner:KOREA ELECTRONICS TECH INST
Zipper type VDSL system
InactiveUS20020064219A1Frequency-division multiplex detailsModulated-carrier systemsFast Fourier transformInverse discrete fourier transform
Disclosed is a zipper type Very high bit-rate Digital Subscriber Line (VDSL) system which comprises a transmitter including an inverse fast Fourier transformer for performing an inverse fast Fourier transform on input data, and a cyclic extension adder for adding a cyclic extension for each symbol to the data output from the inverse fast Fourier transformer and outputting the data to a transmission channel; and a receiver including a cyclic extension remover for removing the cyclic extension from the data received through the transmission channel, and a fast Fourier transformer for performing a fast Fourier transform on the data output from the cyclic extension remover. The cyclic extension adder copies a first predetermined number of data starting from the leading part of the input symbol data received from the inverse fast Fourier transformer into a first cyclic suffix for removing interference between symbols and maintaining orthogonality between sub-carriers; adds the first cyclic suffix to the end of the symbol data; copies a second predetermined number of data subsequent to the first predetermined number of data into a second cyclic suffix for maintaining orthogonality between upstream and downstream; and adds the second cyclic suffix to the end of the first cyclic suffix. According to the present invention, the cyclic extension system uses the CS alone to greatly reduce hardware size and delay, but it has the same transmission performance as the conventional system under normal channel environments. Furthermore, the present invention system in the asynchronous mode employs pulse shaping and windowing functions so as to enhance the performance as in the synchronous mode.
Owner:KOREA ELECTRONICS TECH INST
Universal interface
InactiveUS7289516B2Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationFrame RelayIntegrated Services Digital Network
A universal interface apparatus having a processor for receiving one or more Network Interface signals having a transport mechanism associated therewith. The transport mechanism may include Asynchronous Transfer Mode, Internet Protocol, Frame Relay, Integrated Services Digital Network, High bit-rate Digital Subscriber Line, Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line, Very High Data Rate Digital Subscriber Line, Symmetric Digital Subscriber Line, 10 base T, 100 Base T, Gigabit Ethernet and E1 / T1. The processor may recognize the transport mechanism associated with each Network Interface signal. In the event Asynchronous Transfer Mode is recognized as the transport mechanism, the processor may also segment perform Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) adaptation layer processing on each Network Interface signal. Further, the universal interface apparatus includes a bus interface device for generating a System Interface signal from the Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) adaptation layer processed Network Interface signal in response to the recognized transport mechanism.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Method and apparatus for reducing crosstalk between digital subscriber lines
ActiveUS8081752B2Reduce crosstalkData efficientTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSubstations coupling interface circuitsLow frequency bandData transmission
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method of operating, administrating and maintaining very high bit rate digital subscriber line
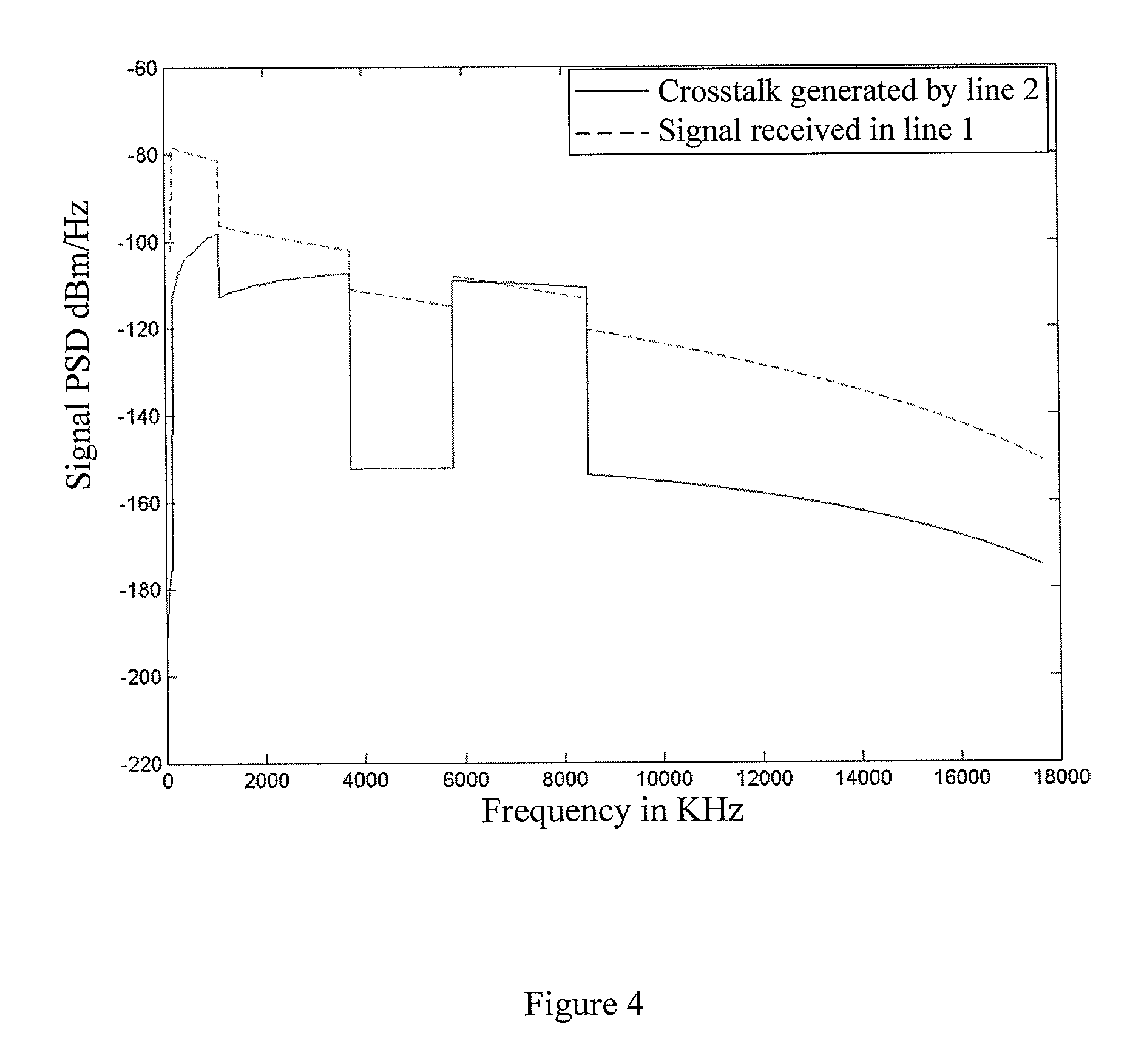
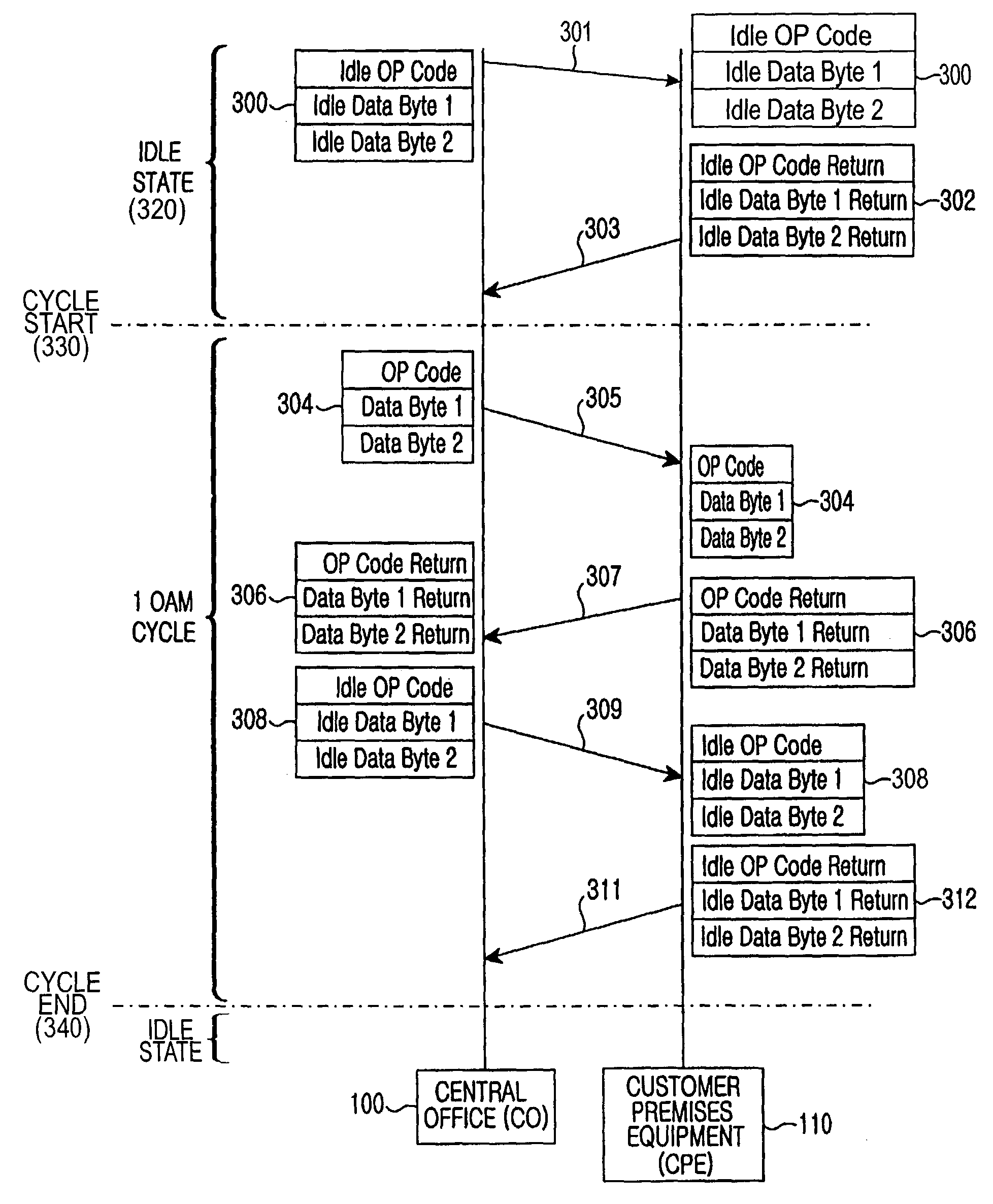
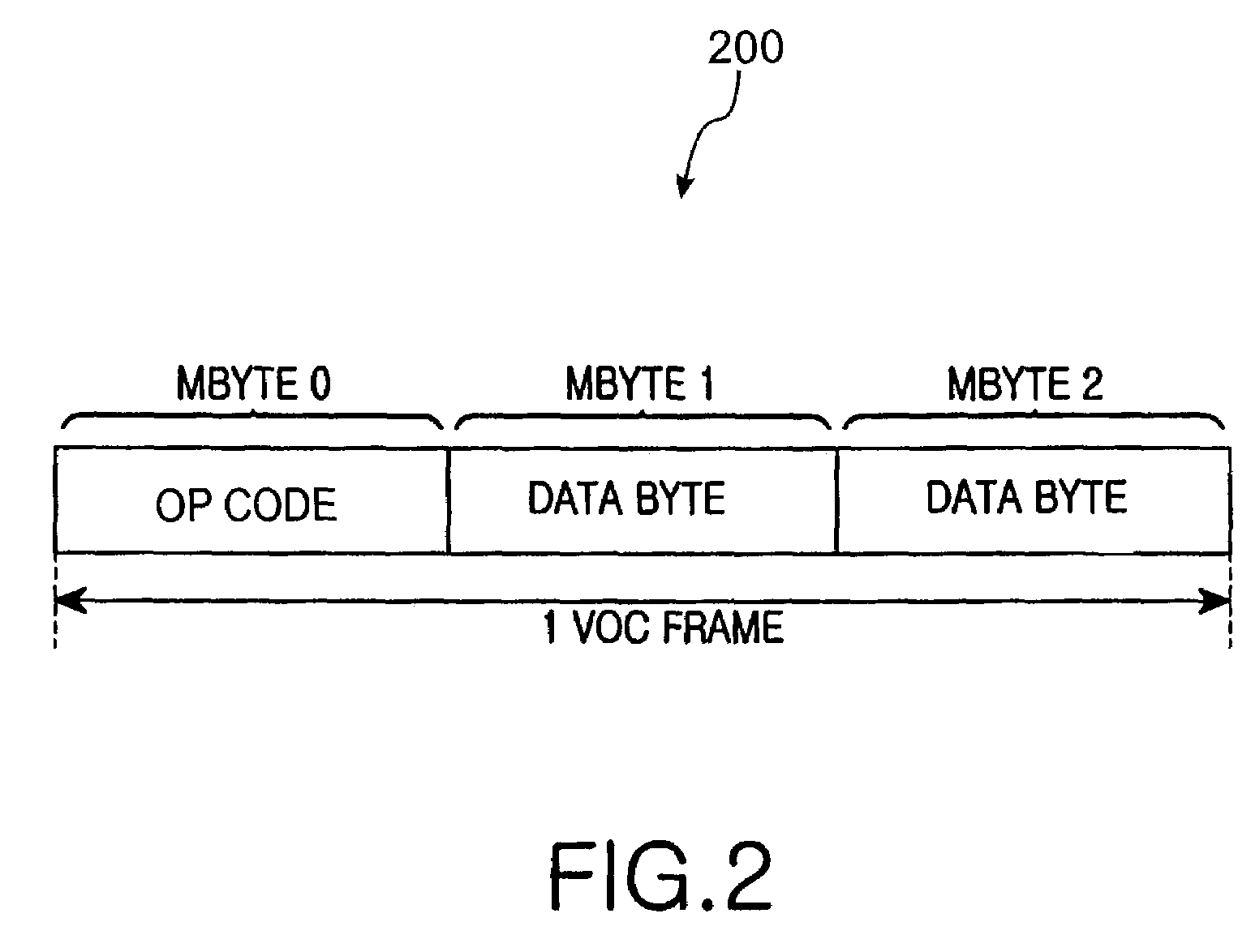
InactiveUS7327684B2Increase bitrateSimple frame structureError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDigital subscriber lineAction Code
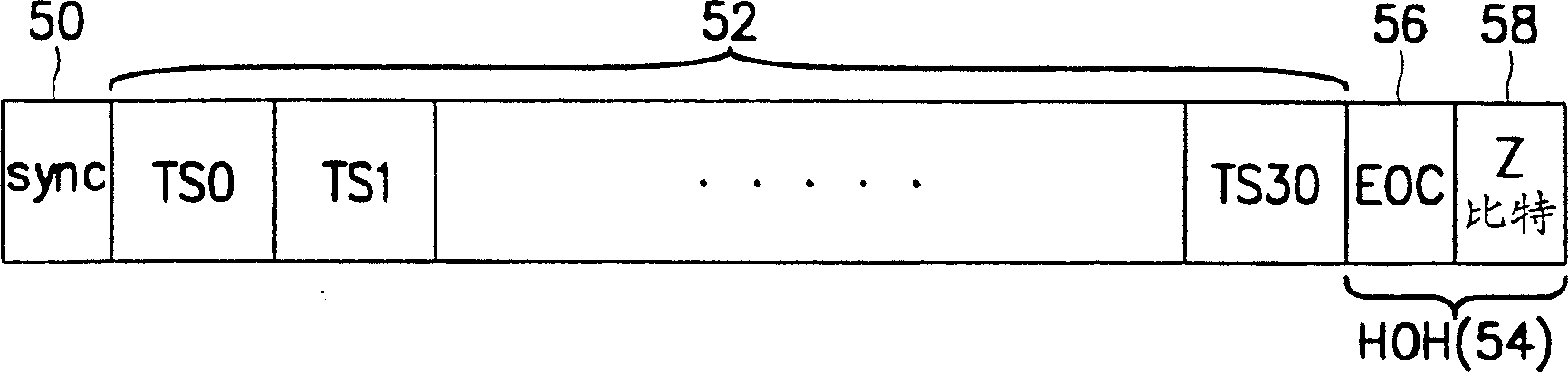
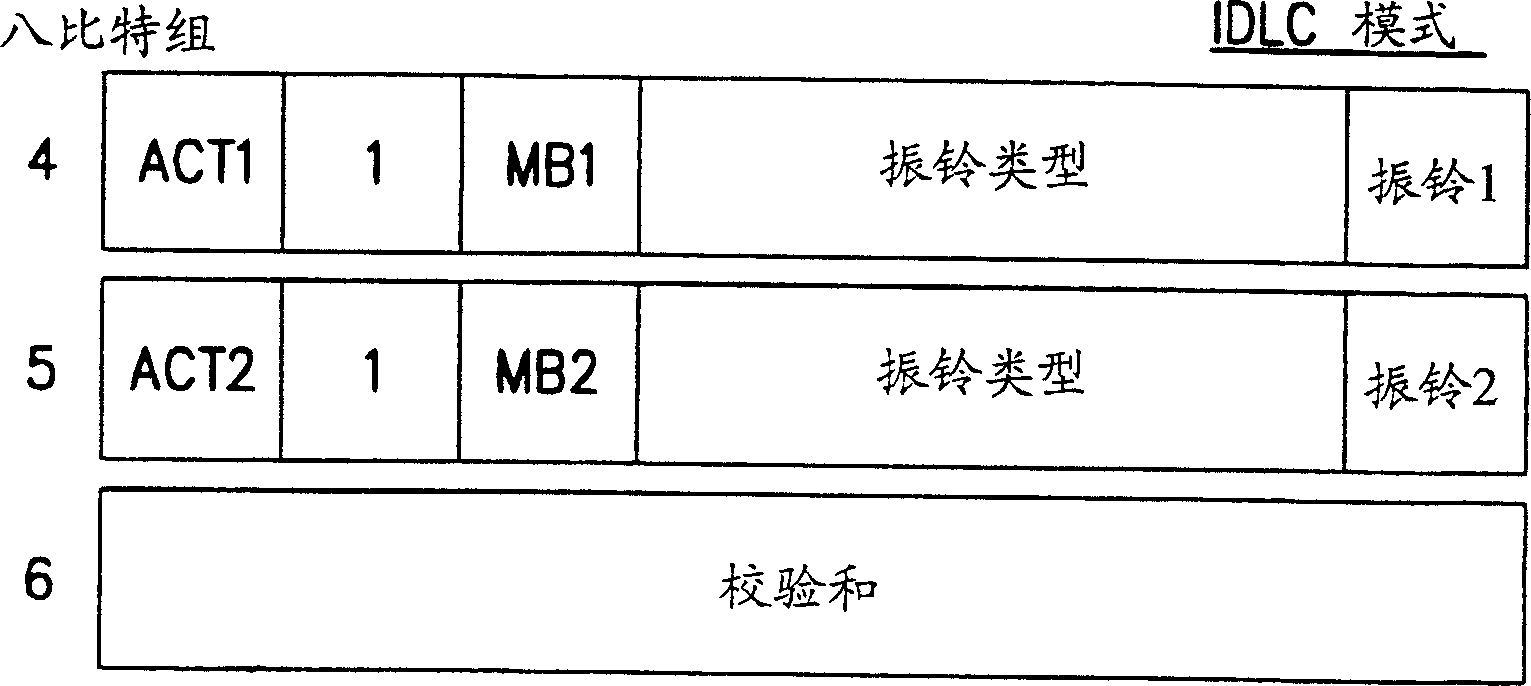
Disclosed is an operation, administration, and maintenance method for very high bit rate digital subscriber line, which has a simplified frame structure, can be easily modified, and can provide various information. In very high bit rate digital subscriber line system which performs a link set between central office and customer premises equipment connected to each other by a very high bit rate digital subscriber line by transmitting / receiving very high bit rate digital subscriber line overhead control frame having operation code, unique operation codes are identically set at the central office and the customer premises equipment. Unique operation codes prescribe all kinds of messages to be transmitted between central office and customer premises equipment. Operation, administration, and maintenance for customer premises equipment is performed by exchanging messages by central office and customer premises equipment in very high bit rate digital subscriber line overhead control frames. Very high bit rate digital subscriber line overhead control frames each has operation code which prescribes corresponding message among set operation codes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for distributing signals
ActiveUS8209727B2Closed circuit television systemsSelective content distributionCommunication interfaceTransceiver
Owner:SBC KNOWLEDGE VENTURES LP
Method and device for reducing VDSL high-frequency crosstalk
ActiveCN101222242BGuaranteed transmission performanceAvoid crosstalkLine-faulsts/interference reductionSubstation equipmentEngineeringData transmission
The invention relates to a method and a device for reducing VDSL high frequency crosstalk; the method mainly comprises the following steps: firstly, the electric length value of a VDSL (very high bit rate digital subscriber line) is determined; secondly, according to the electric length value, the frequency range of the signal transmitted through a corresponding line is determined; moreover, signal is transmitted through a corresponding line according to the determined frequency range. The invention is mainly used to switch off the transmission of high frequency signal and only transmits low frequency signal when the electric length value of a line exceeds a preset value, thereby reducing the crosstalk in the line. The implementation of the invention can effectively overcome the crosstalkon an adjacent line during the channel finding stage of the VDSL, thereby ensuring the transmission performance of the VDSL transmitting data; meanwhile, the implementation of the invention is based on the prior standard; therefore, the invention has the advantages of simplicity and easy implementation.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Very high bit rate digital user line link rate switching method
InactiveCN100407717CIncrease flexibilityImprove reliabilityMultiple carrier systemsHigh rateBasic mode
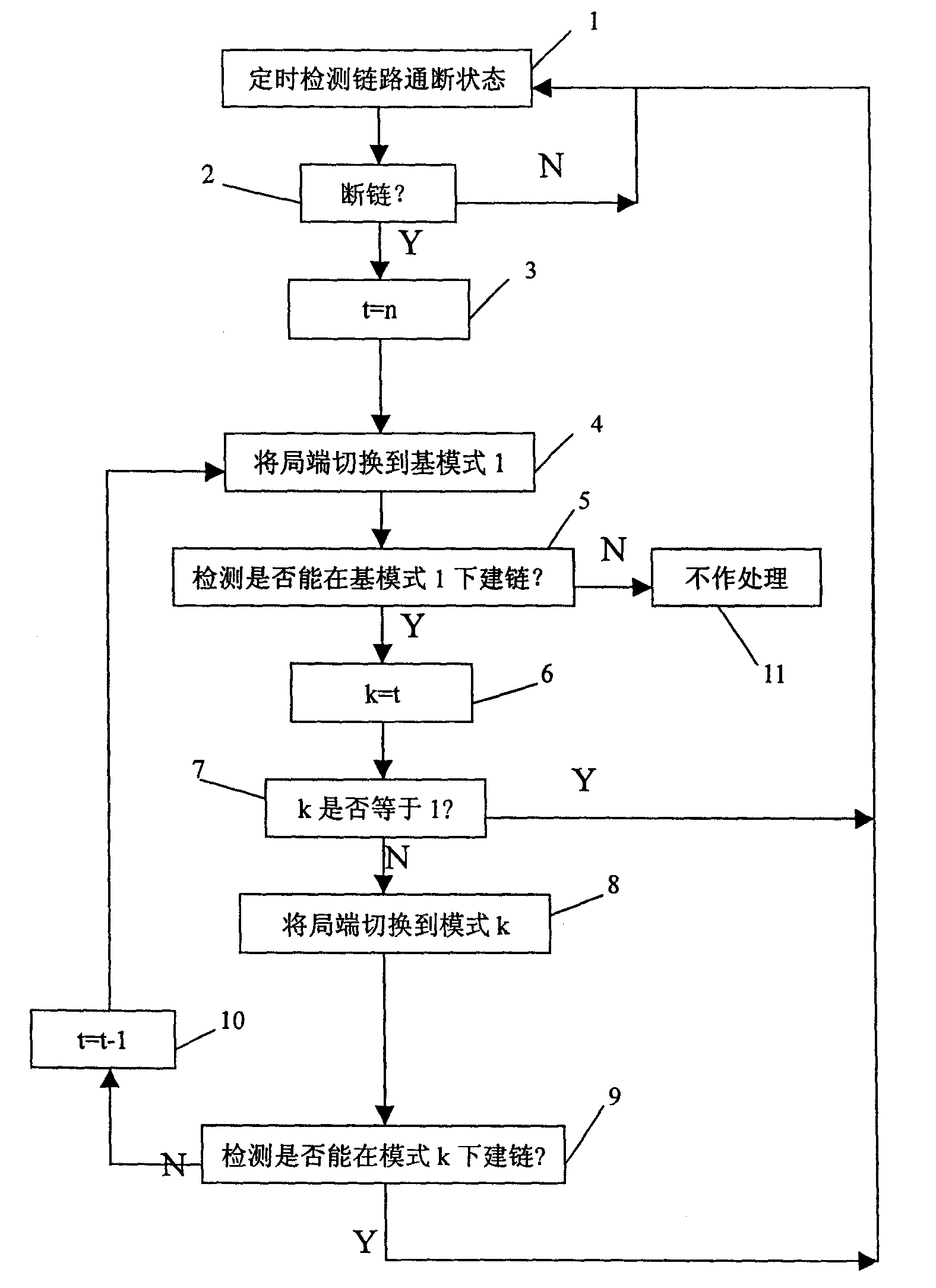
Based on range, VDSL link rate is divided into multi-steps form high to low. In each step, one combination of an upward rate and a downward rate in easiest to build link is selected as a mode. In run time, the link state is detected timely. If broken link state is detected, then the configuration at local end is changed to basic mode. If the link can be built at basic mode, then the highest rate mode is setup for both local and remote end. If the link cannot be built at the highest rate, then building link is returned back to the basic mode, and the mode with lower one step than highest rate is setup for both local and remote end. Descending in turn, till link is built at a mode. The invention detects and switches VDSL link rate automatically so as to raise adaptability and reliability of system, reduce maintenance work and lower maintenance cost.
Owner:ZTE CORP
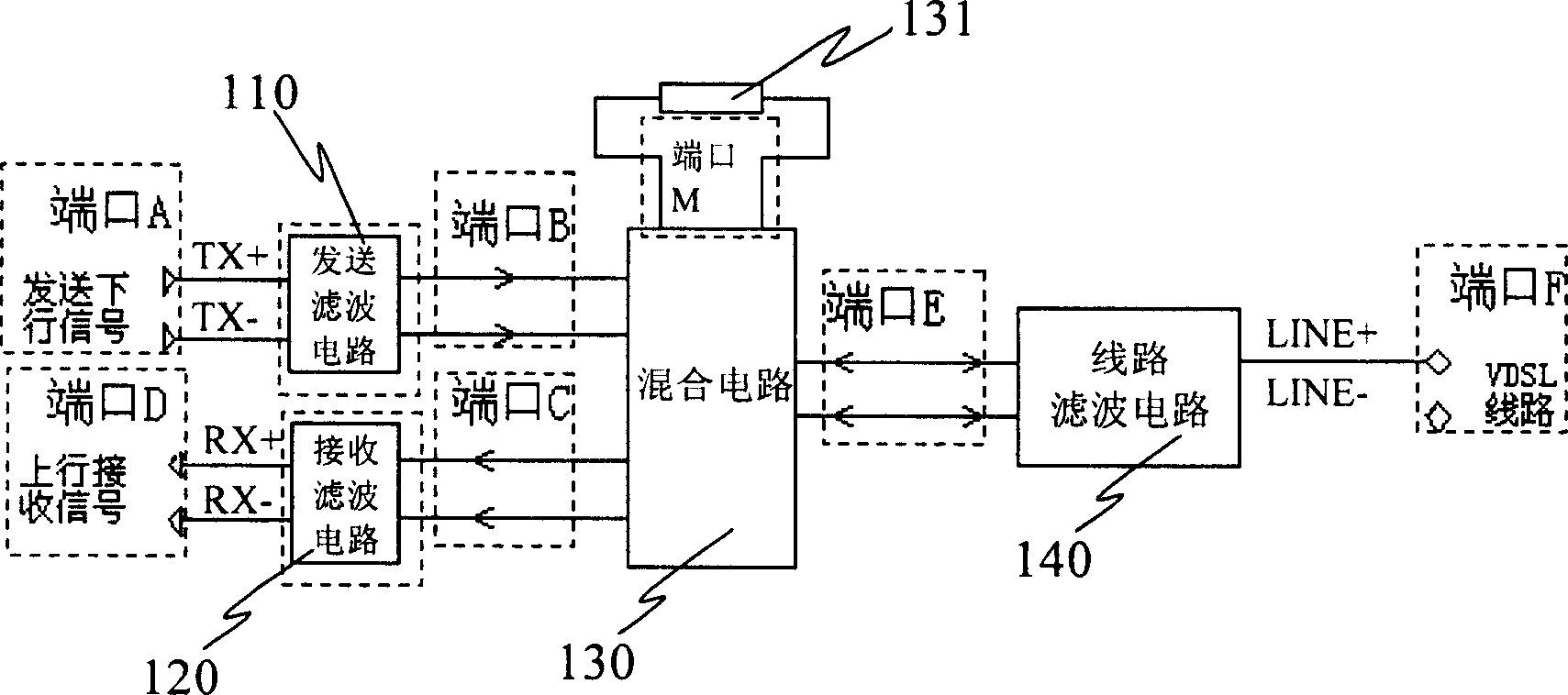
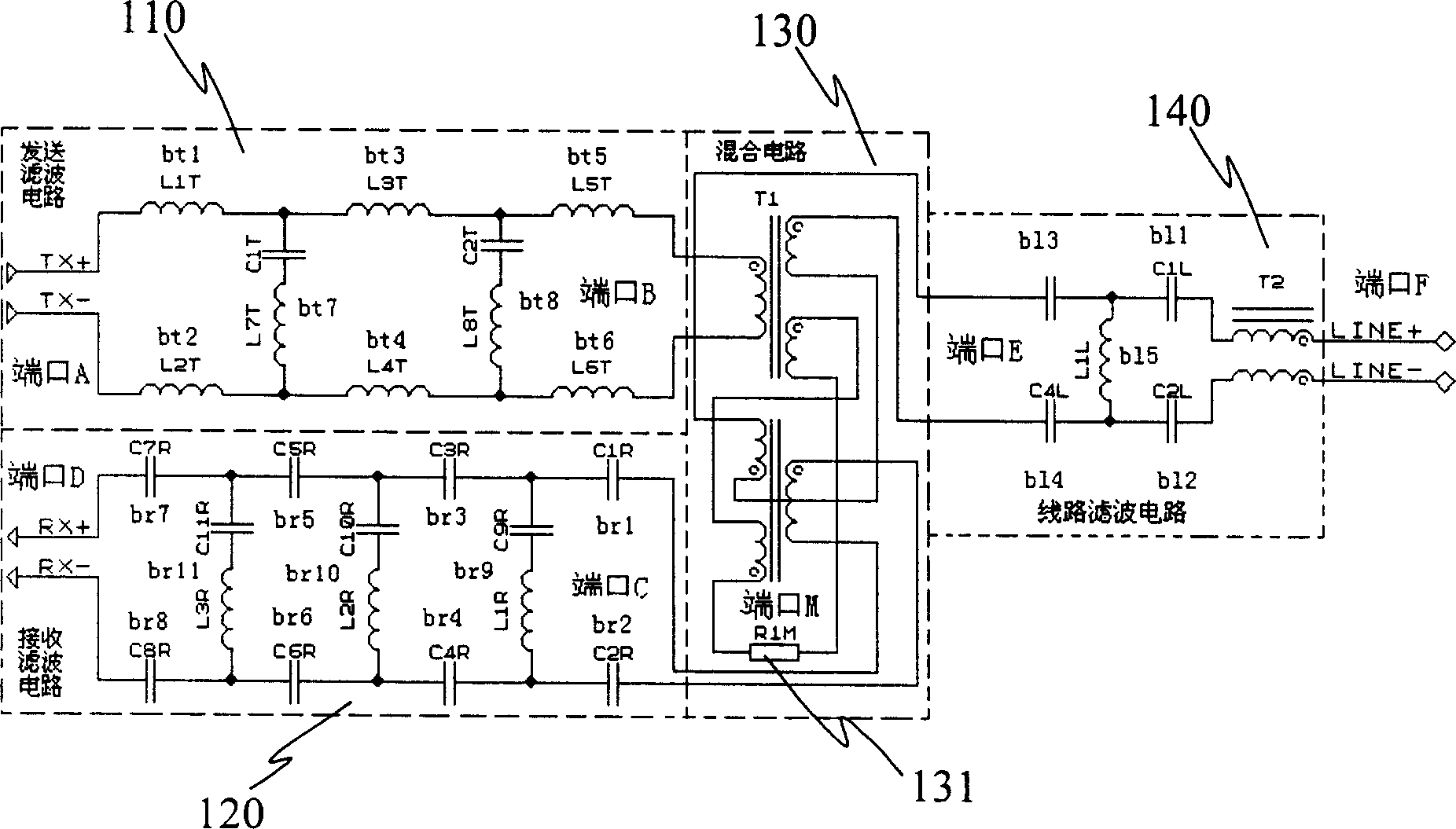
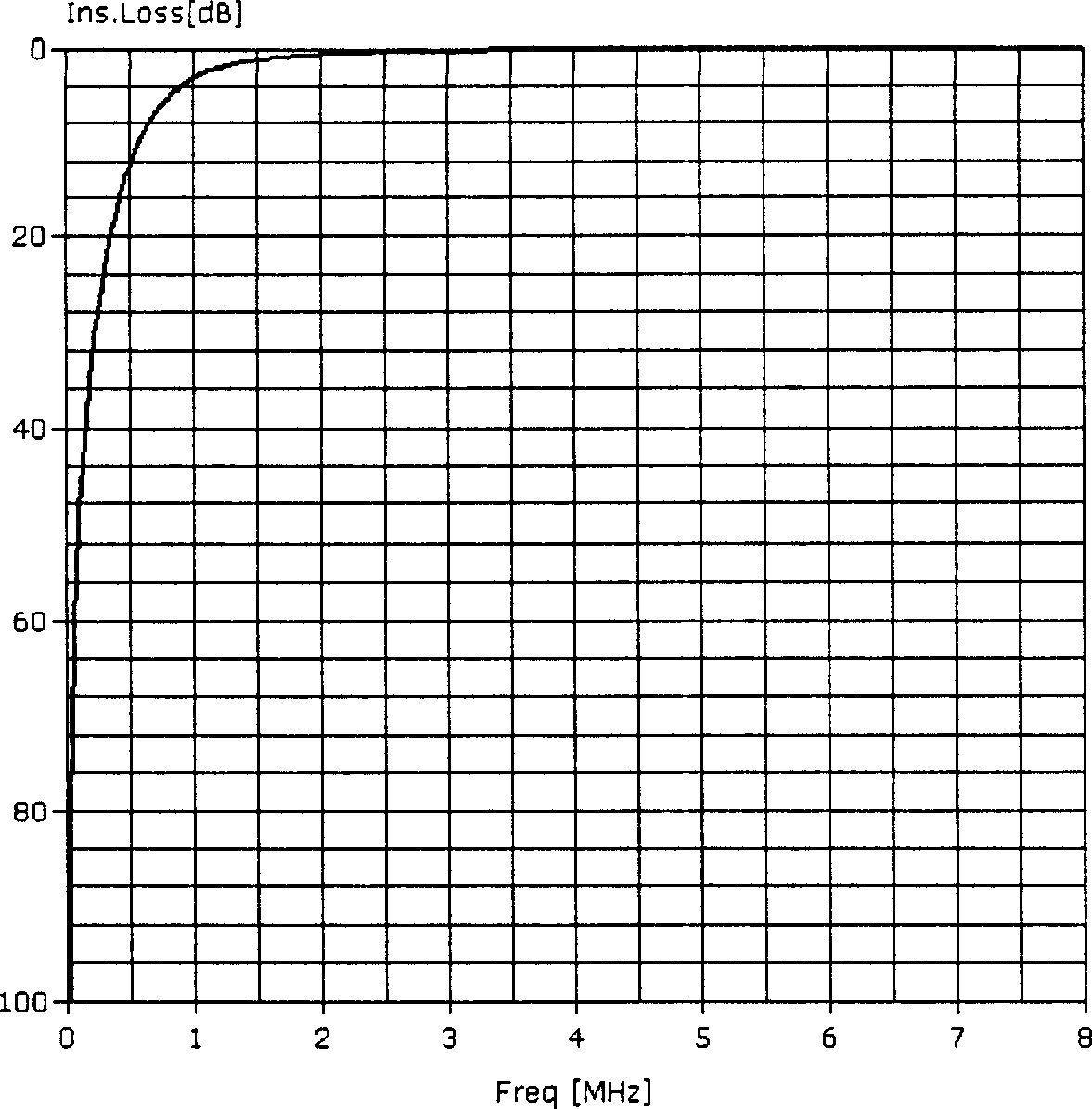
Filtering circuit for very high bit-rate digital subscriber line
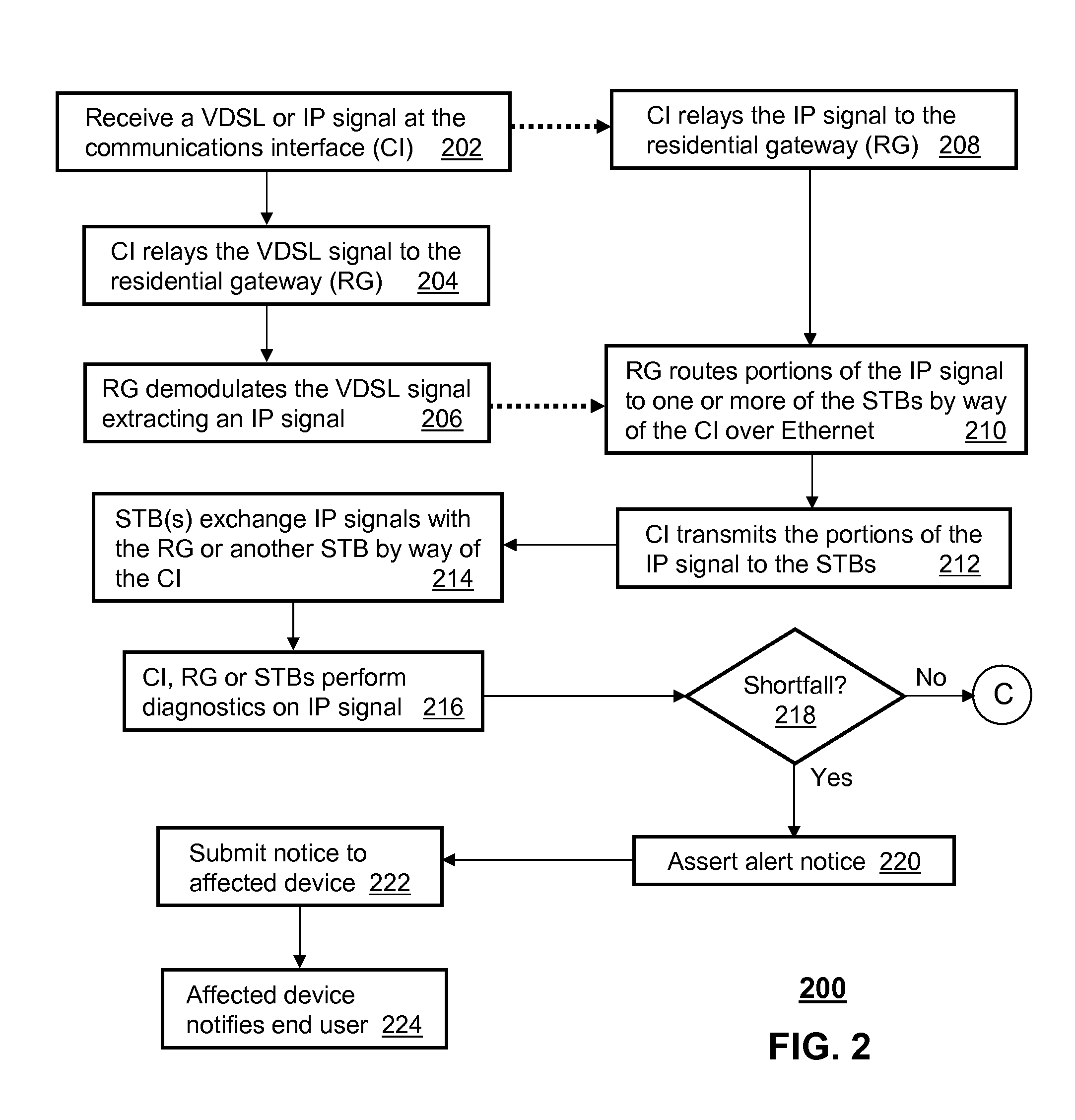
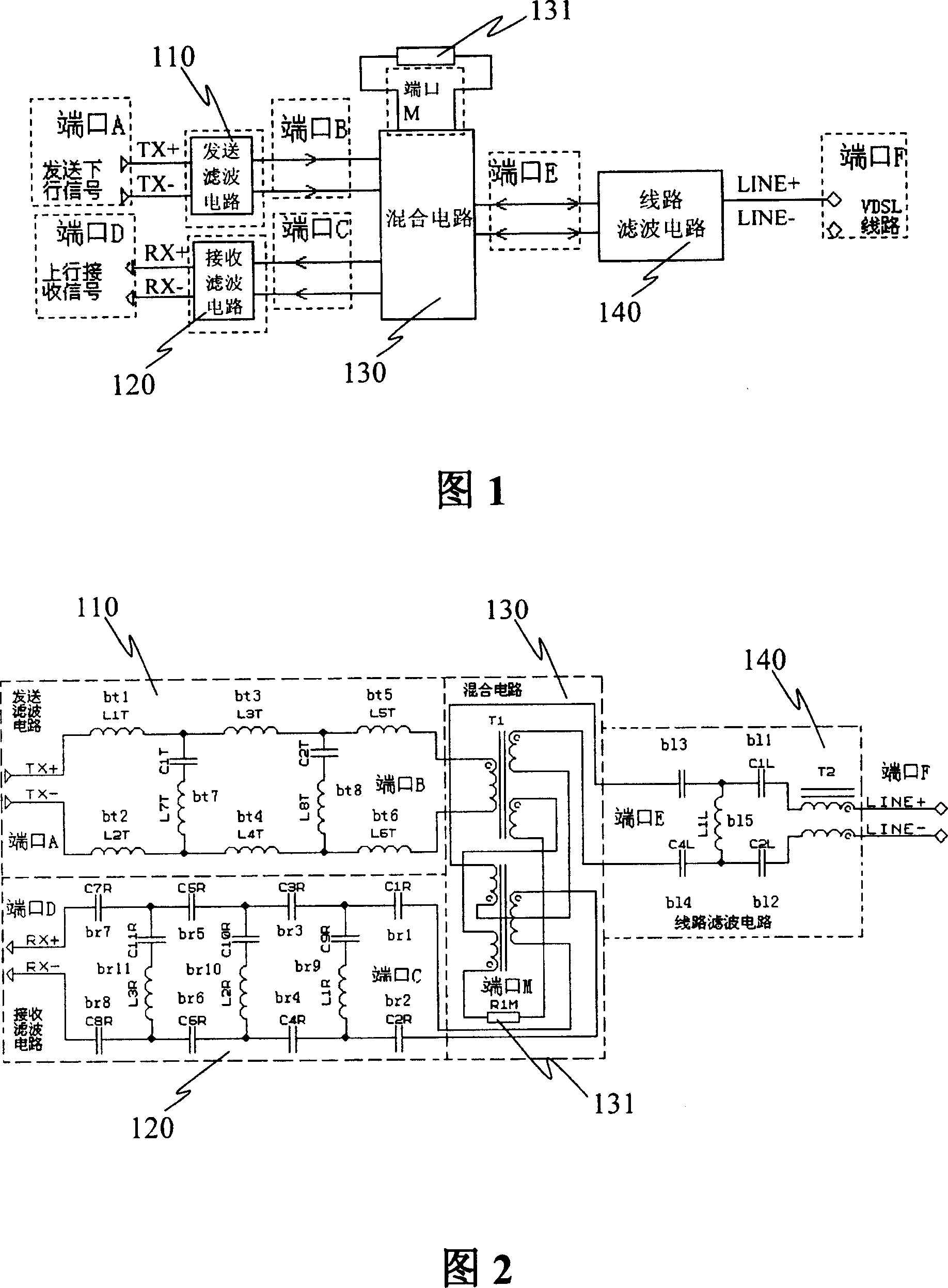
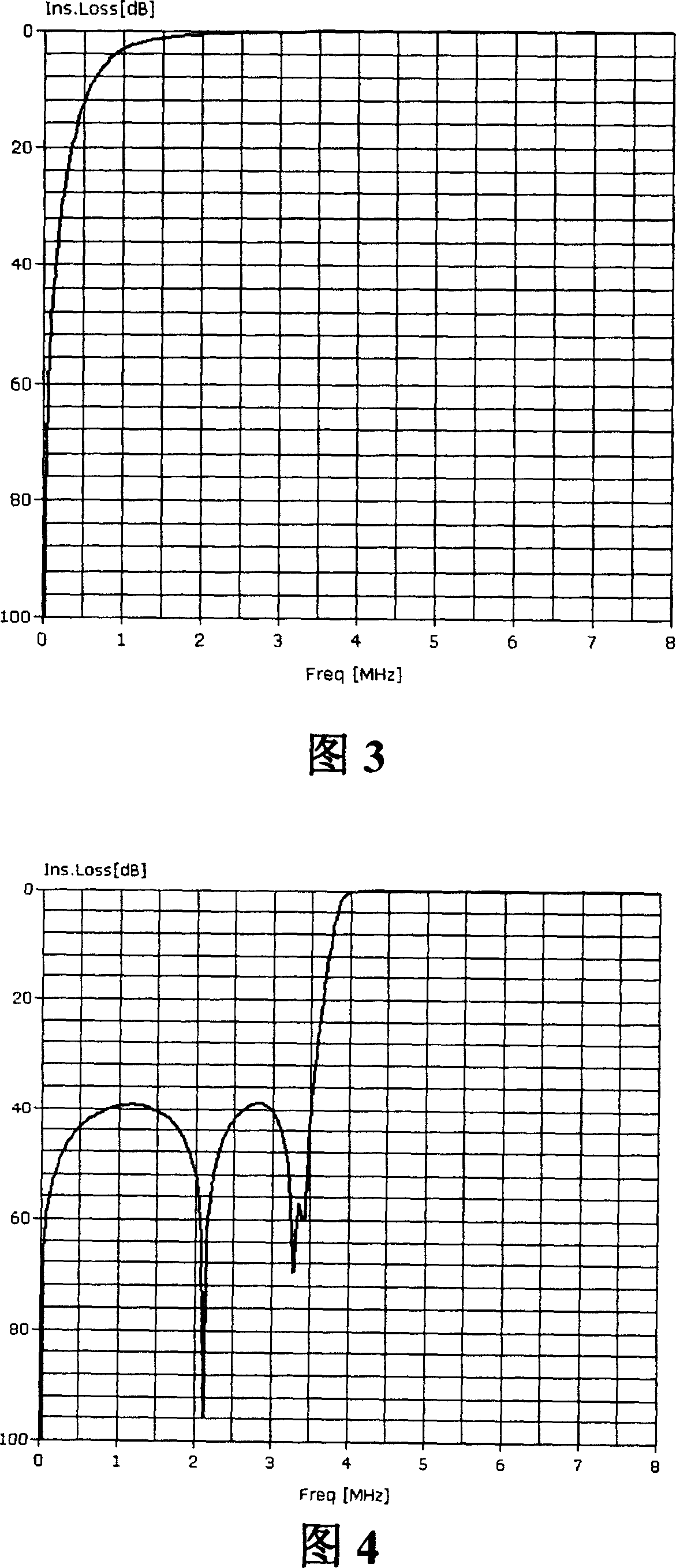
InactiveCN1655469AImprove performanceImprove design densityUnbalanced current interference reductionTelephonic communicationDigital subscriber lineImpedance matching
The present invention discloses a sort of wave filter circuit used for the very high bit-rate digital subscriber loop, used to fulfill the filtering, frequency mixing and severing of the upgoing signal and the downward signal of very high bite-rate digital subscriber loop VDSL, which includes: a transmitting wave filter circuit unit, a receiving wave filter circuit unit, a line wave filter circuit unit, a mixer circuit unit; the mixer circuit unit is respectively connected to the transmitting wave filter circuit unit, the receiving wave filter circuit unit and the line wave filter circuit unit, the sequence of the downward signal passes through the transmitting wave filter circuit unit, the mixer circuit unit and the line wave filter circuit unit; the sequence of the upgoing signal passes through the line wave filter circuit unit, the mixer circuit unit and the receiving wave filter circuit unit. Using this filter circuit the layout density of the VDSL equipment can be enhanced, the required expense of the replaced device in facility maintenance can be reduced, the circuit can well satisfy the requirement of matching the various characteristic impedance by replacing the build-out resistor.
Owner:晋江市高新技术开发办公室
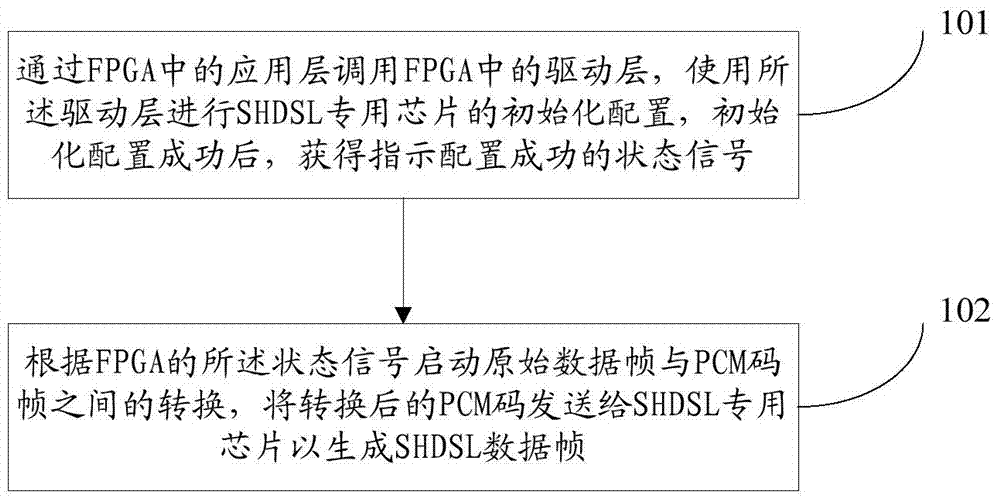
An SHDSL (Single-pair High bit rate Digital Subscriber Line) data frame processing method and device
ActiveCN104506273AIncrease conversion rateMeet transmission needsError preventionOriginal dataPulse-code modulation
The present application provides an SHDSL (Single-pair High bit rate Digital Subscriber Line) data frame processing method and device. The method comprises: calling a drive layer in an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) through an application layer in the FPGA, using the drive layer to execute initialization configuration of an SHDSL dedicated chip, and obtaining, after the configuration is successful, a status signal that indicates the configuration is successful; and starting conversion between an original data frame and a PCM (Pulse Code Modulation) code frame according to the status signal of the FPGA, and sending the converted PCM code to the SHDSL dedicated chip to generate a SHDSL data frame. Therefore, the SHDSL (Single-pair High bit rate Digital Subscriber Line) data frame processing method and device solve the problems in the prior art that the rate of the conversion between the original data frame and the PCM code frame is low, and that an SHDSL-related module is large in size and causes high difficulty in management and maintenance of software and hardware.
Owner:北京航天晨信科技有限责任公司
Method for supplying phonetic service of high speed data business
InactiveCN1251420CFixed station two-conductor transmission systemsTelephonic communicationDigital subscriber line2B1Q
Disclosed is a method for providing a high-speed data service and a voice service in a transmission system employing two binary, one quarternary (2B1Q) modulation / demodulation, the transmission system including a remote terminal providing a high-speed data service, a plurality of user terminals including data service terminals and voice service terminals, and a multi-rate digital subscriber line (MDSL) terminal connected to the remote terminal through a twisted pair line, the multi-rate digital subscriber line terminal being also connected to the user terminals. During a downstream voice service, the remote terminal assembles an high bit rate digital subscriber line (HDSL) frame by including signaling signals for the voice service and signal processing mode information in a user-defined interval of the high bit rate digital subscriber line frame, and transmits the assembled high bit rate digital subscriber line frame to the multi-rate digital subscriber line terminal through the twisted pair line. During an upstream voice service, the remote terminal receives the high bit rate digital subscriber line frame and transmits the signaling signals in the received high bit rate digital subscriber line frame to an exchange.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
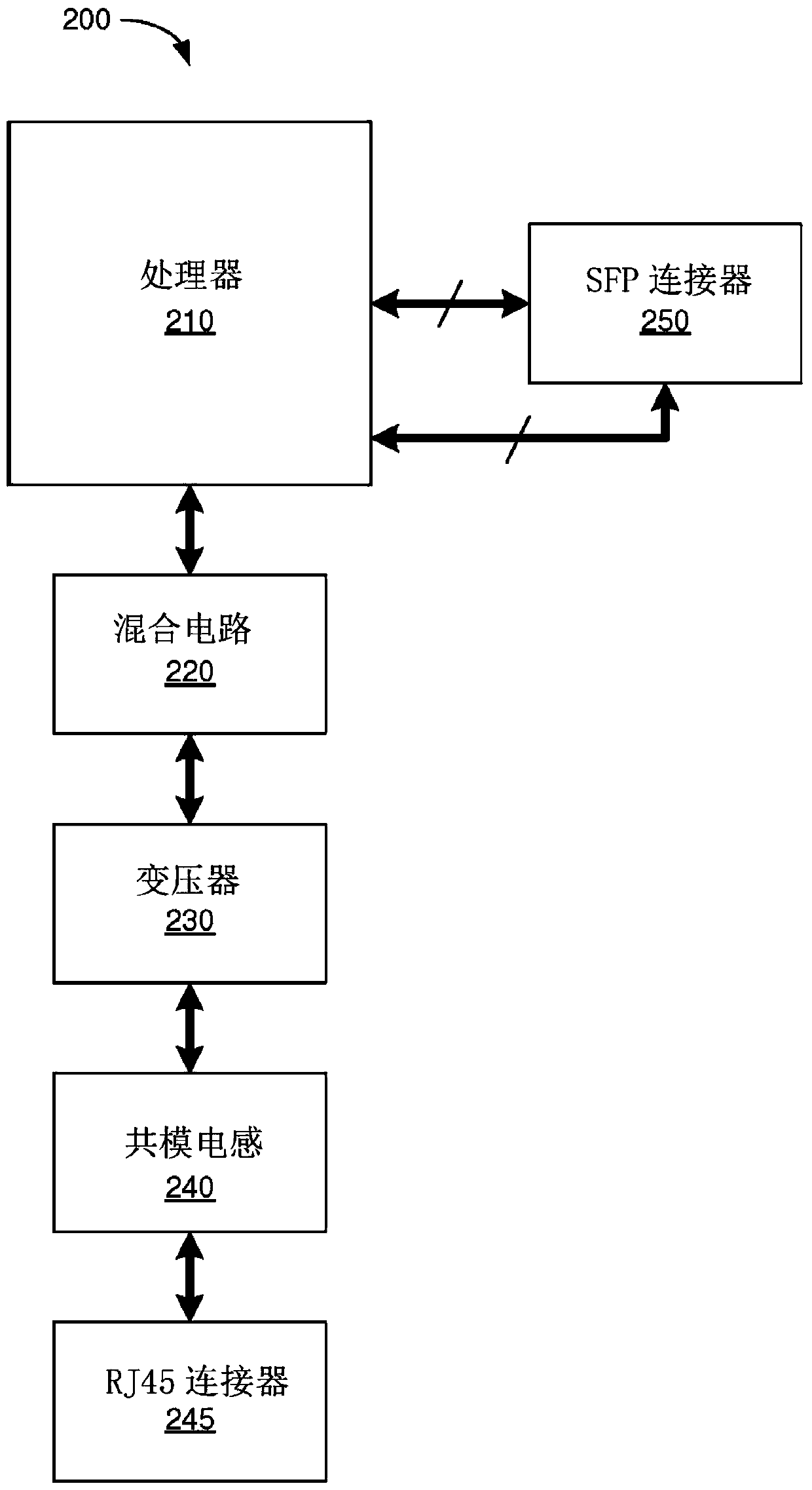
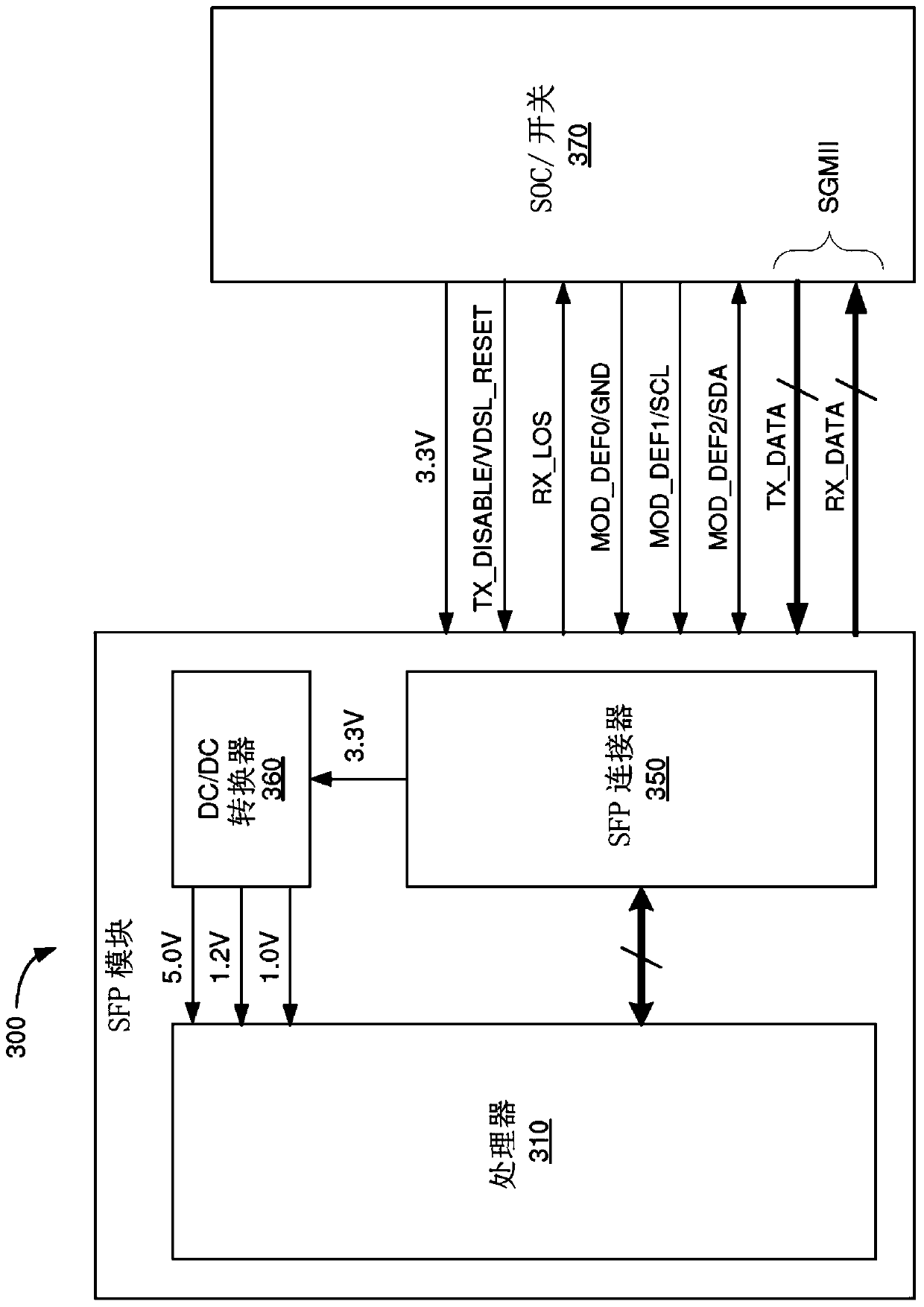
vdsl2 and gfast small pluggable modules for any physical layer platform
A transceiver in the form of an integrated small form-factor pluggable (SFP) module is described. The SFP module may include a processor, a hybrid circuit, a transformer, a RJ45 connector and a SFP connector. The processor may be configured to perform functions as a serializer / deserializer (SerDes), a digital signal processor (DSP), an analog front-end and a line driver. The hybrid circuit may be configured to neutralize signals reflected from a transmit direction to a receive direction. The DSP may be configured to support communication according to a Very-high-bit-rate Digital Subscriber Line (VDSL) technology such as the G.Fast standard.
Owner:METANOIA COMM
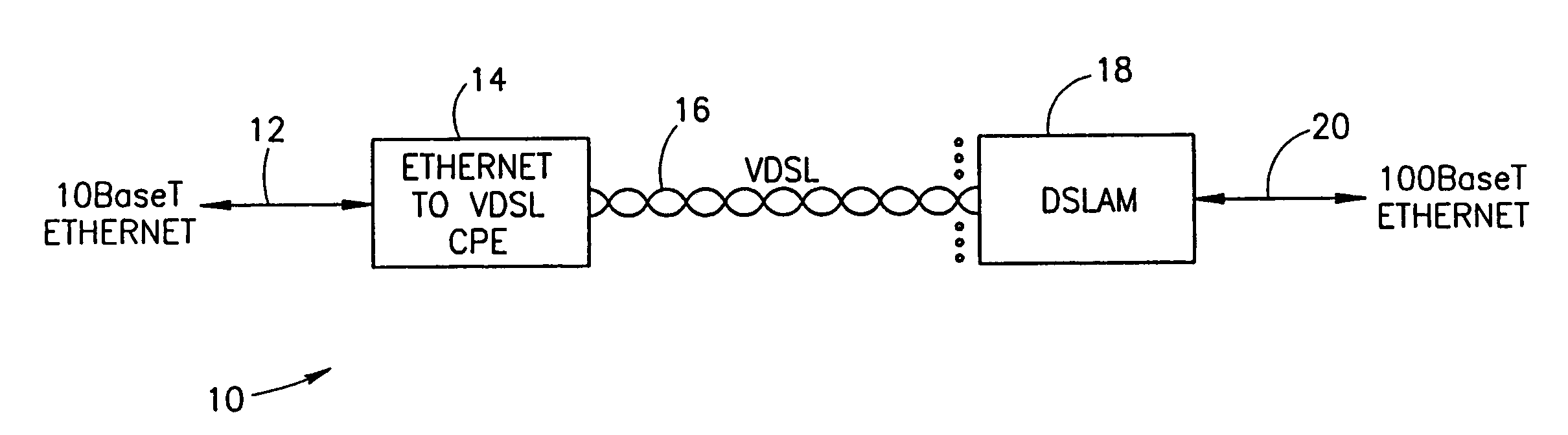
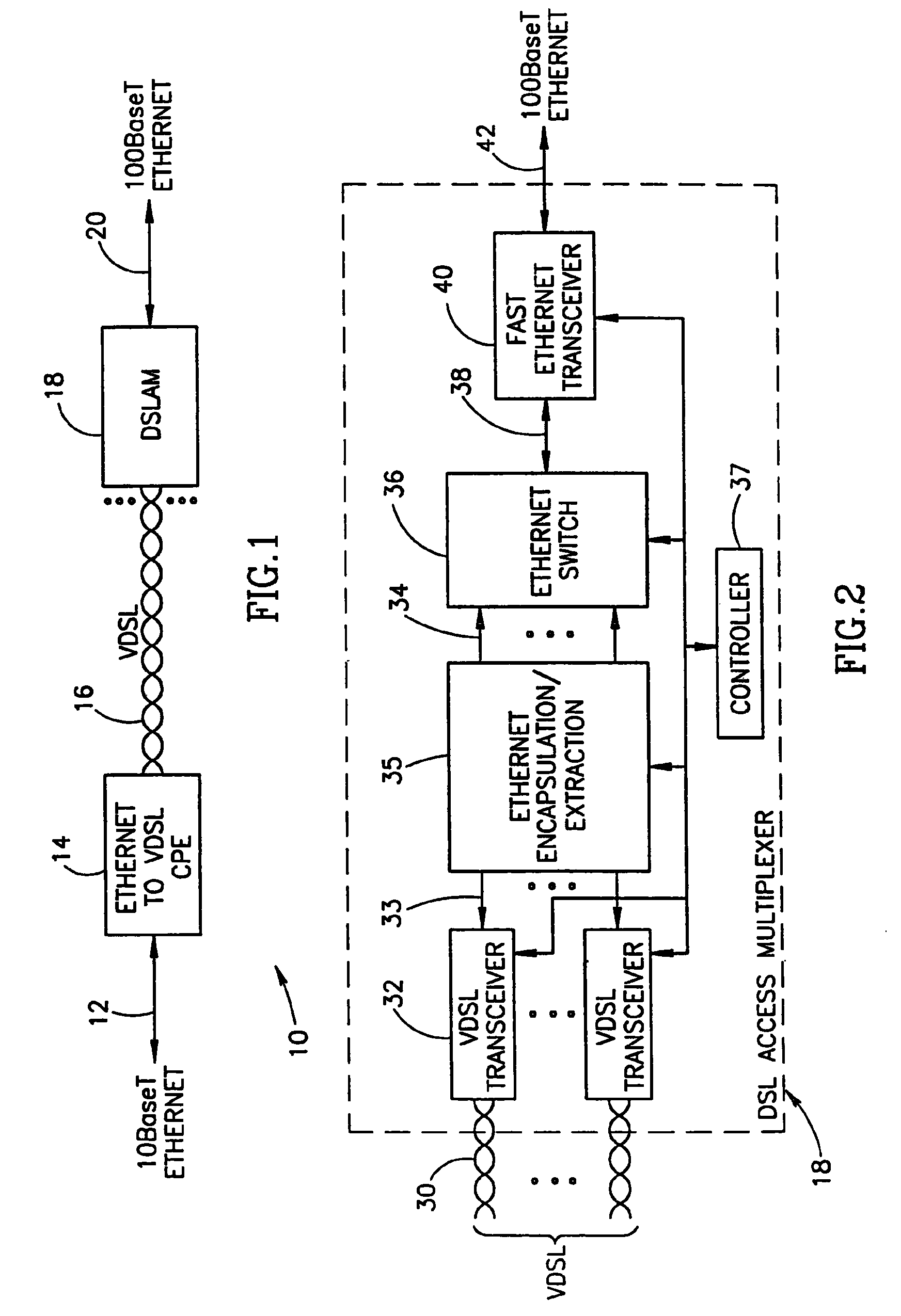
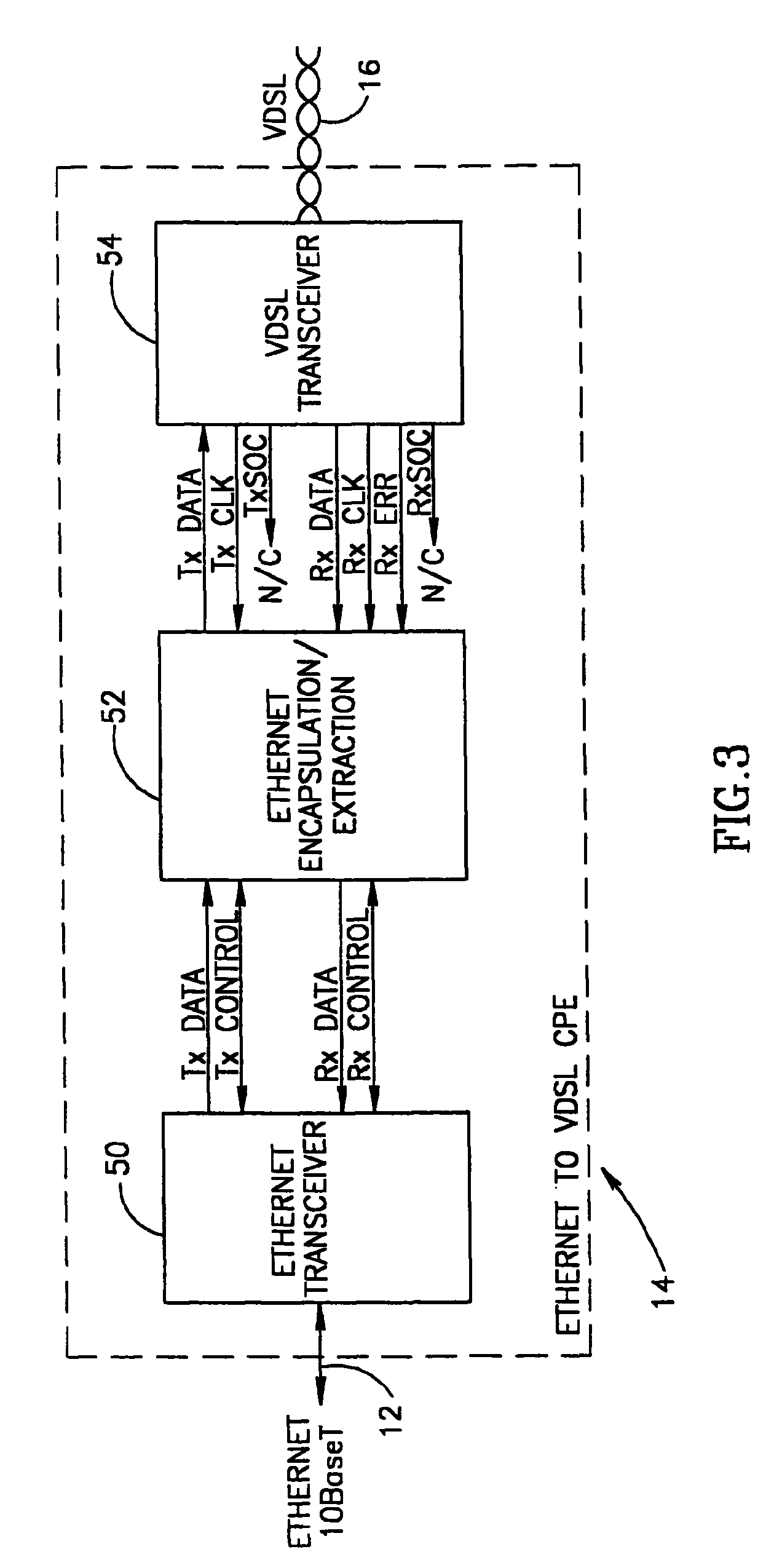
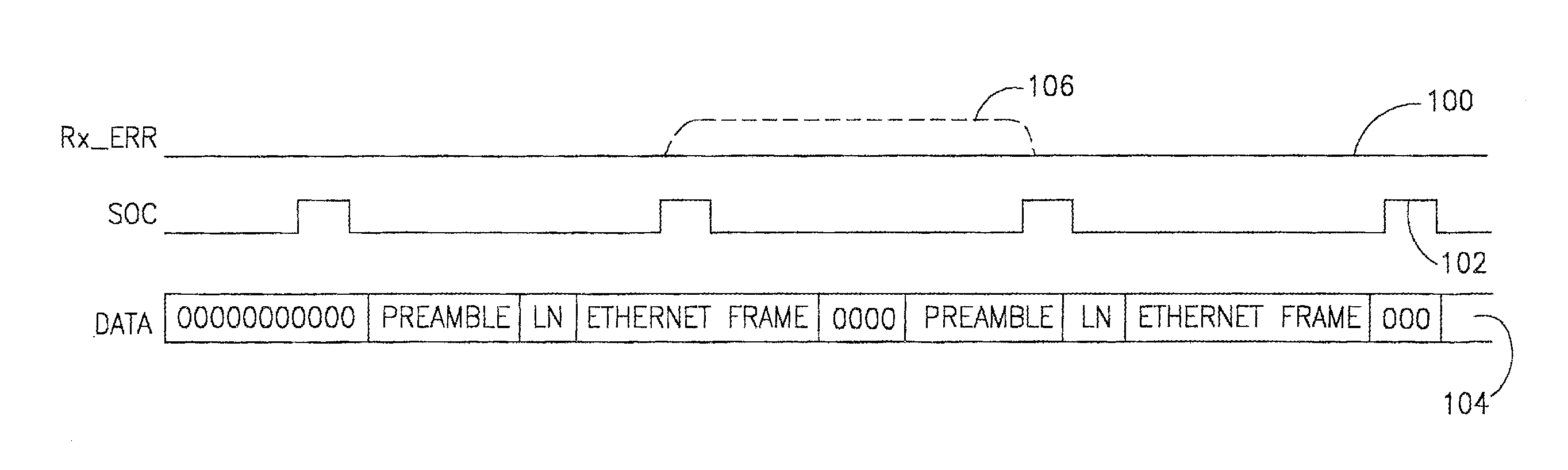
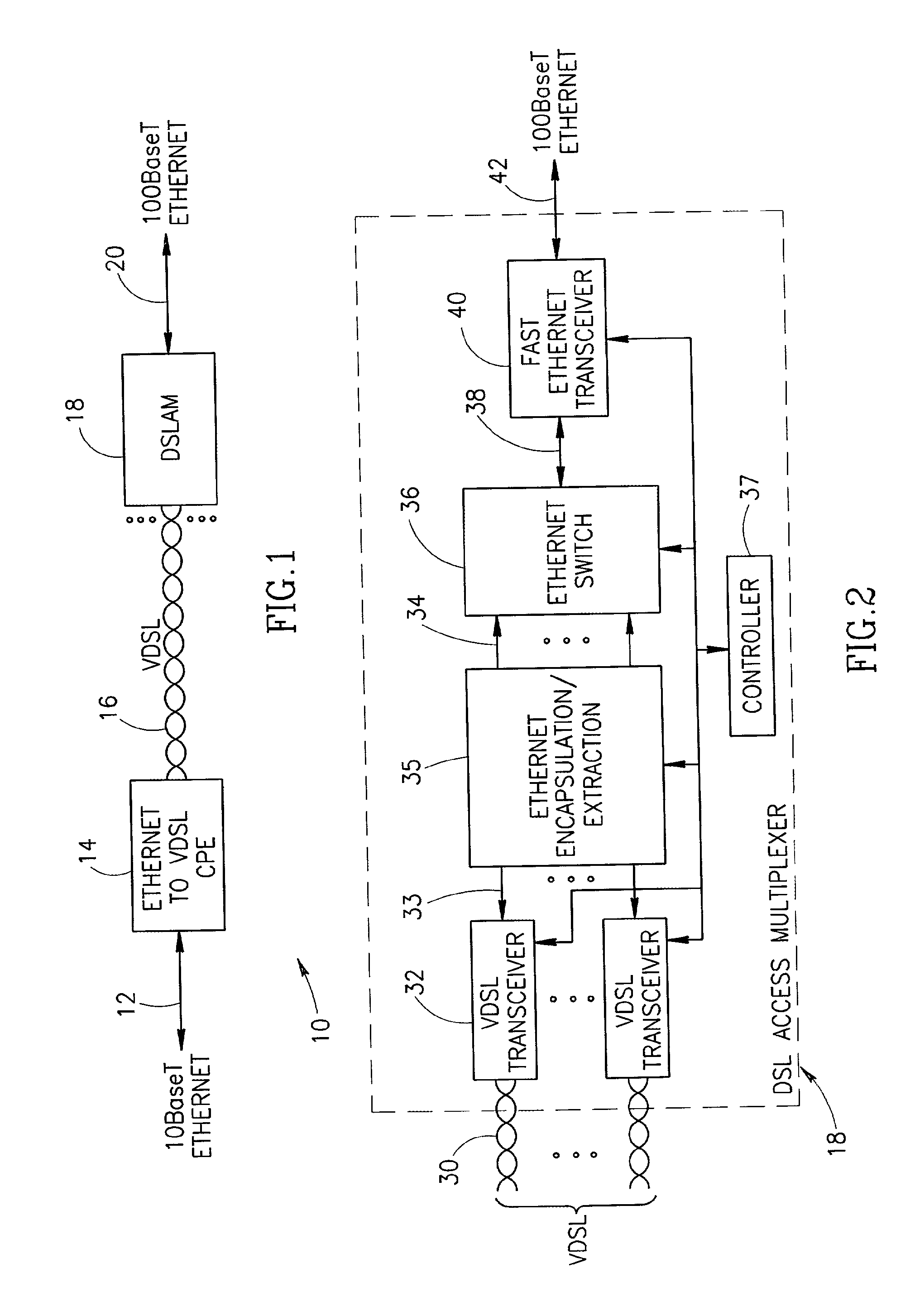
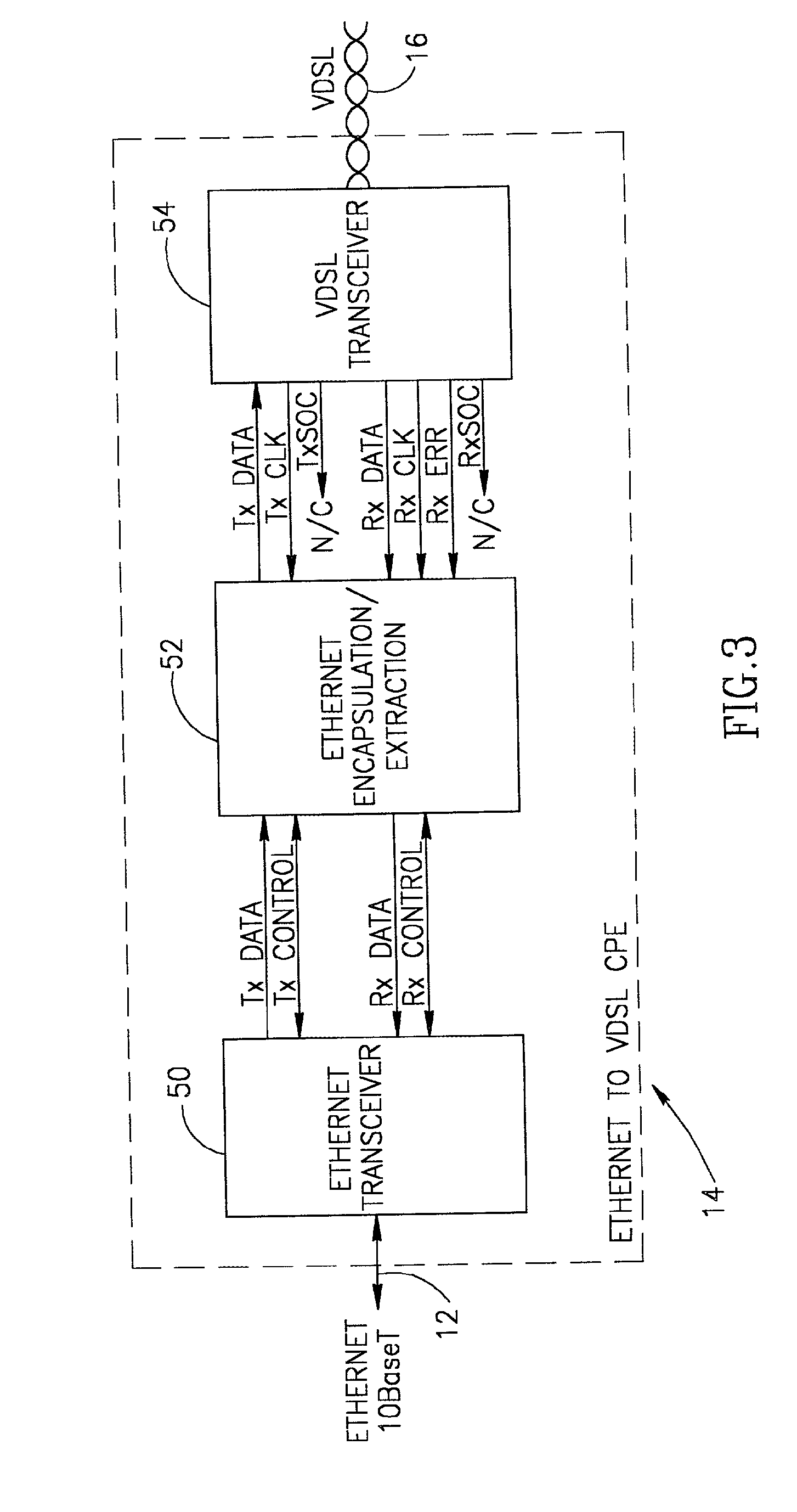
System for encapsulating Ethernet frames over very high speed digital subscriber lines
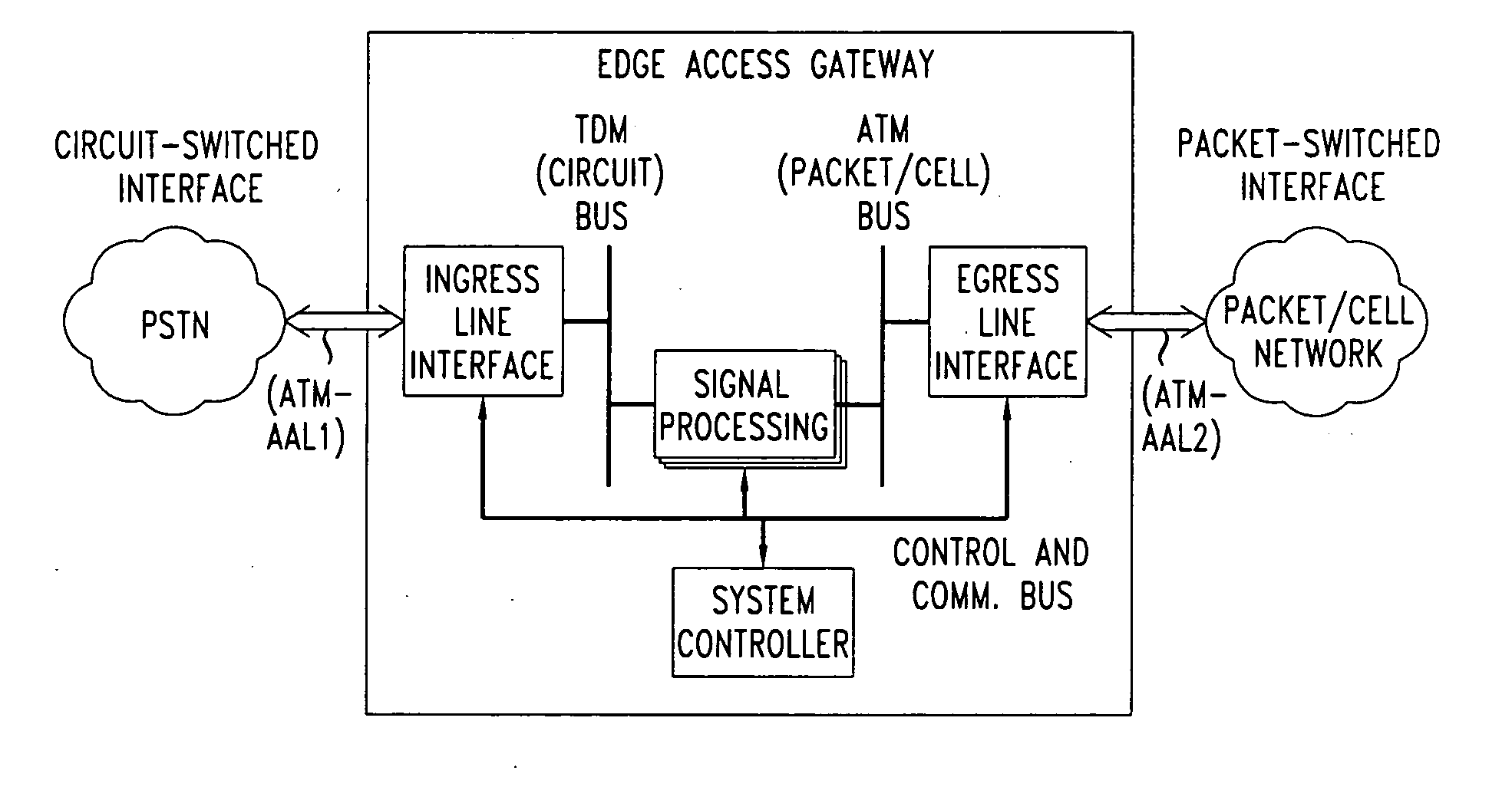
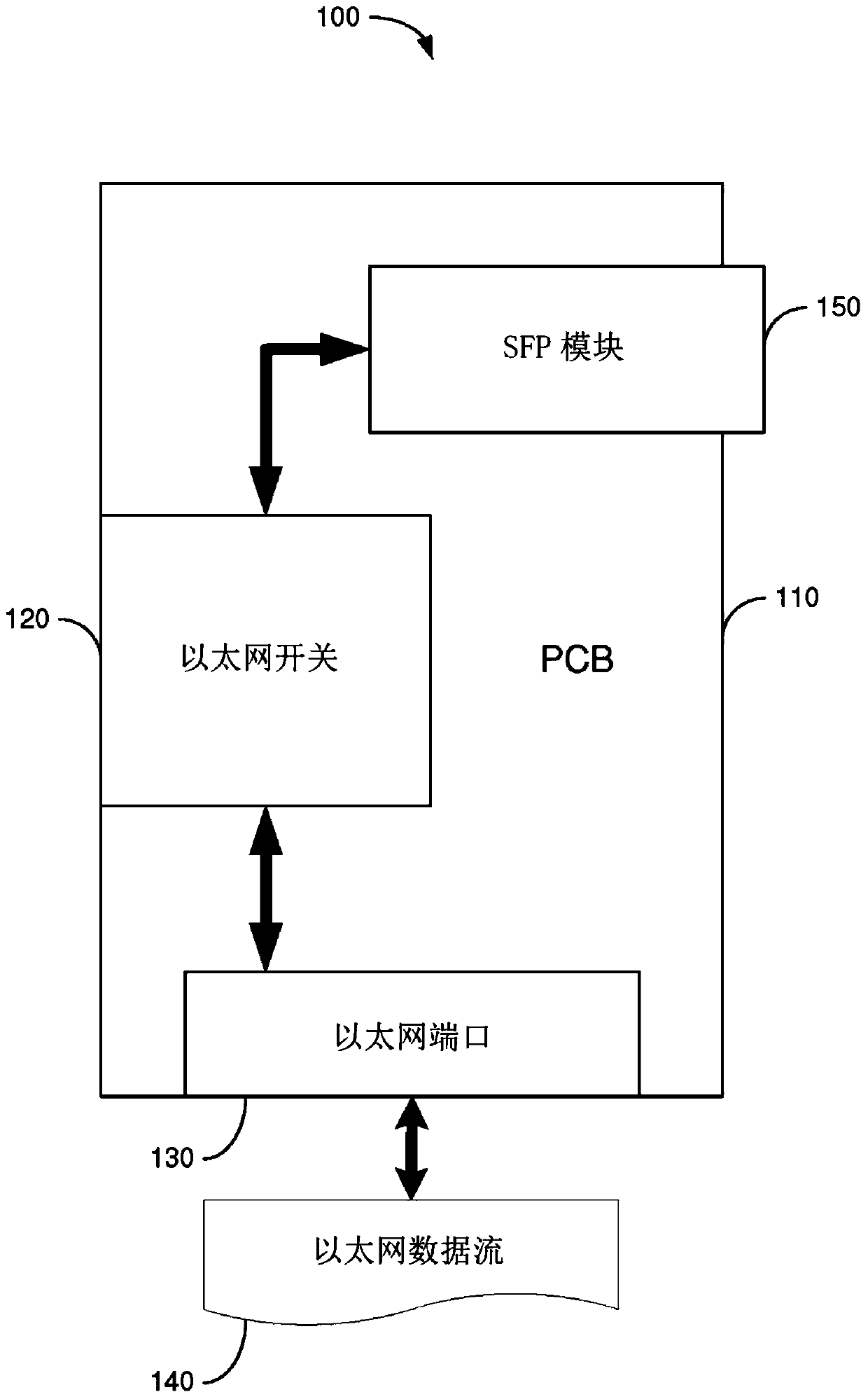
InactiveUS7903634B2Increase speedMulti-frequency code systemsNetworks interconnectionTransport systemISDN digital subscriber line
An apparatus for and method of encapsulating Ethernet frame data in Very high speed Digital Subscriber Line (VDSL) frames. The VDSL frames are transmitted over a point to point VDSL link where they are subsequently extracted and forwarded as standard Ethernet frames. The VDSL facility transport system comprises an Ethernet to VDSL Consumer Premises Equipment (CPE) coupled to a DSL Access Multiplexor (DSLAM) over a VDSL transport facility. The Ethernet to VDSL CPE functions to receive a 10BaseT Ethernet signal and encapsulate the Ethernet frame into a VDSL frame for transmission over the VDSL facility. The DSLAM is adapted to receive VDSL frames, extract Ethernet frames therefrom and generate and output a standard Ethernet signal. Ethernet frames are encapsulated within VDSL frames and transmitted on the wire pair without regard to the state of the SOC signals. This overcomes the problems associated with syncing the transmission of the Ethernet data with the SOC signals. The present invention also provides a method of providing the receiving station an indication of the start of a VDSL frame. A preamble having certain desirable characteristics such as good autocorrelation properties, is used by the receiving station to identify the start of a VDSL frame. To further ensure that a detected start of frame is valid, the length field of the VDSL frame is examined for a legal length value.
Owner:FAR NORTH PATENTS LLC
Method for activating VDSL/VDSL2 USO channel
InactiveCN1852379BAccurately determine the activation timeTelephonic communicationTransmissionCommunications systemSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method for implementing non-standard low-speed chain building on serial high bit rate digital subscriber line
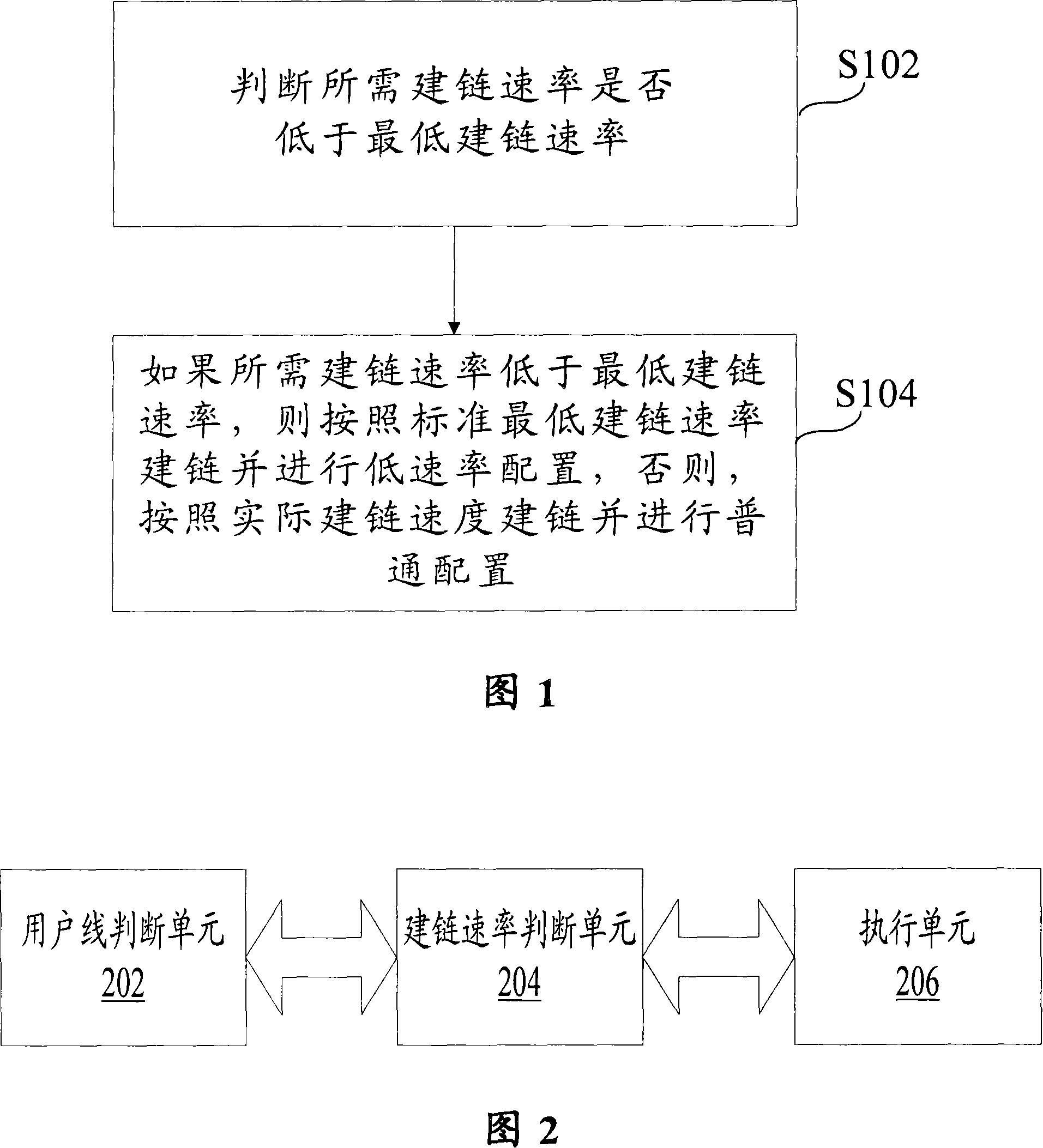
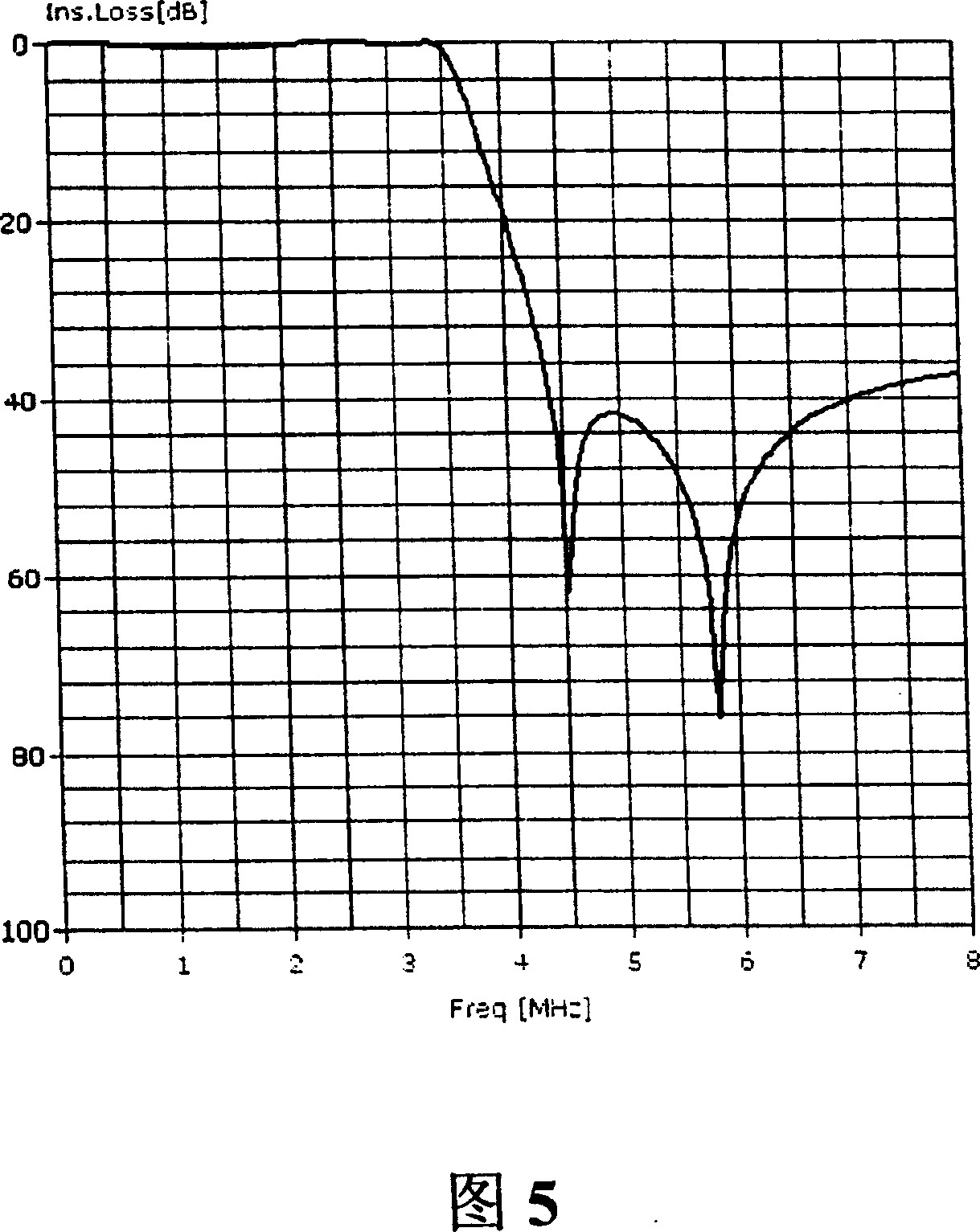
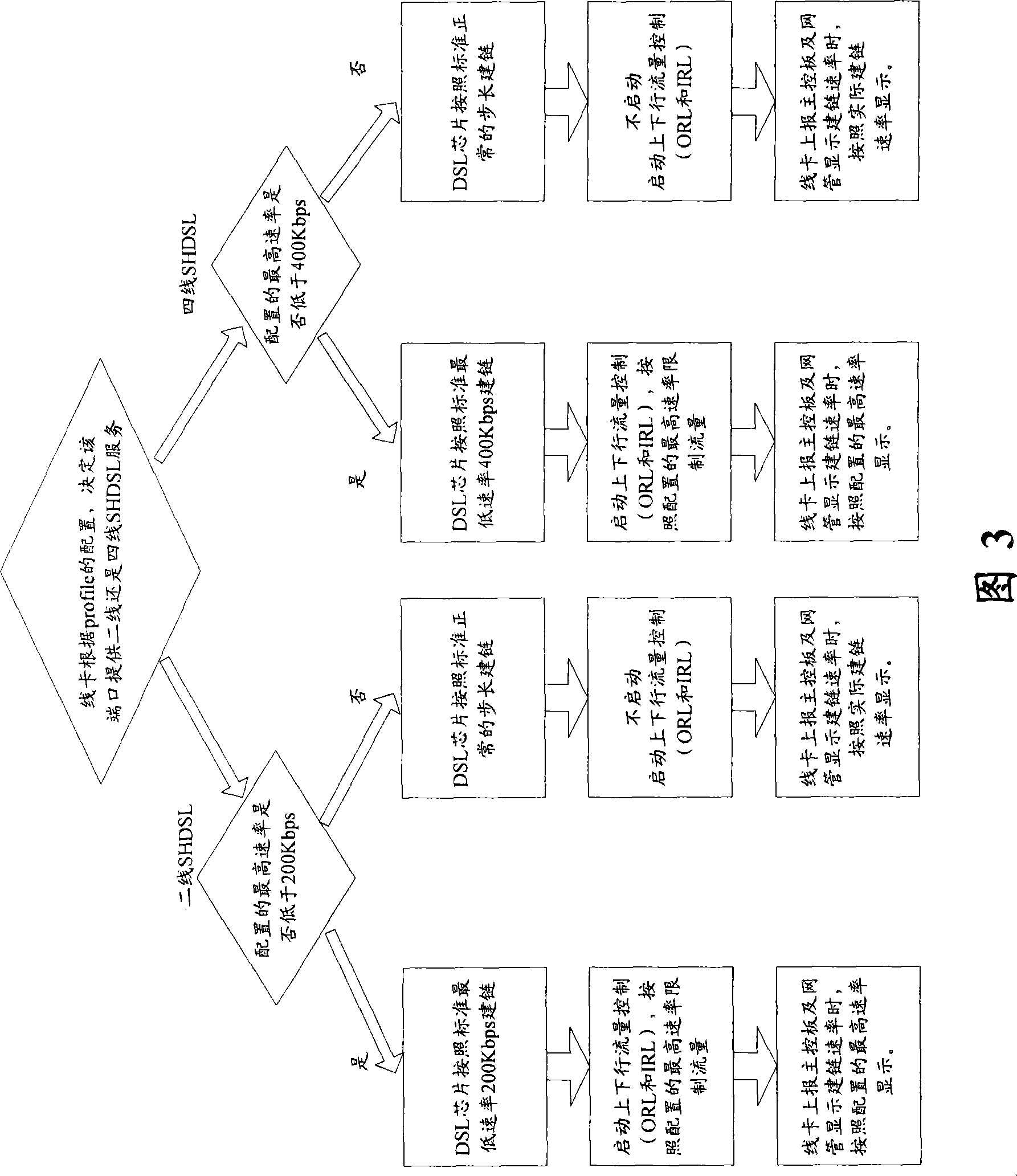
ActiveCN101110739AMeet operational needsSmooth upgradeEnergy efficient ICTData switching by path configurationTelecommunicationsLow speed
The present invention comprises the following steps: the required link building rate is judged whether the rate is lower than the lowest link building rate; if the required link building rate is lower than the lowest link building rate, the low rate configuration of the link building is performed according to the standard lowest link building rate, and otherwise, the common configuration of the link building is performed according to the actual link building rate. The present invention also discloses a device for realizing a non-standard low rate link building on the single line pair high bit rate digital user line. Through the present invention, under the precondition that the network cost is not added, the application mode of the current perfect SHDSL technology is adopted to solve the special demand of the operator, and to provide powerful guarantee to the product leading in the market, and the present invention has very practical application prospect.
Owner:ZTE CORP
System for transporting ethernet frames over very high speed digital subscriber lines
An apparatus for and method of encapsulating Ethernet frames over a Very high speed Digital Subscriber Line (VDSL) transport facility. The VDSL frames are transmitted over a point to point VDSL link where they are subsequently extracted and forwarded as standard Ethernet frames. The VDSL facility transport system comprises an Ethernet to VDSL Customer Premises Equipment (CPE) coupled to a DSL Access Multiplexor (DSLAM) over a VDSL transport facility. The Ethernet to VDSL CPE functions to receive a 10BaseT Ethernet signal and encapsulate the Ethernet frame into a VDSL frame for transmission over the VDSL facility. The DSLAM is adapted to receive VDSL frames, extract Ethernet frames therefrom and generate and output a standard Ethernet signal. Ethernet frames are encapsulated within VDSL frames and transmitted on the wire pair without regard to the state of the SOC signals.
Owner:FAR NORTH PATENTS LLC
Method and apparatus for distributing signals
ActiveUS20070250869A1Closed circuit television systemsSelective content distributionCommunication interfaceTransceiver
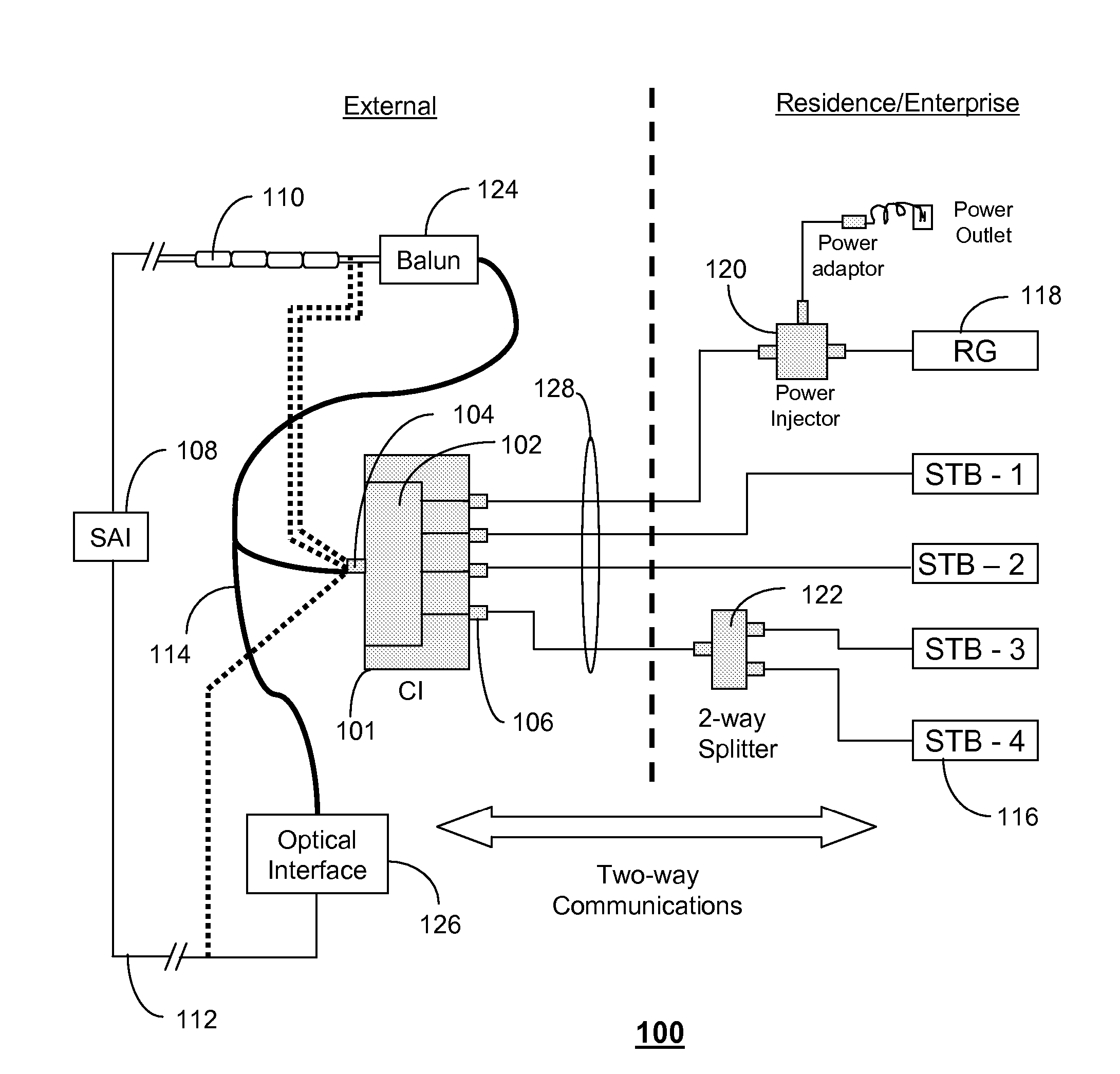
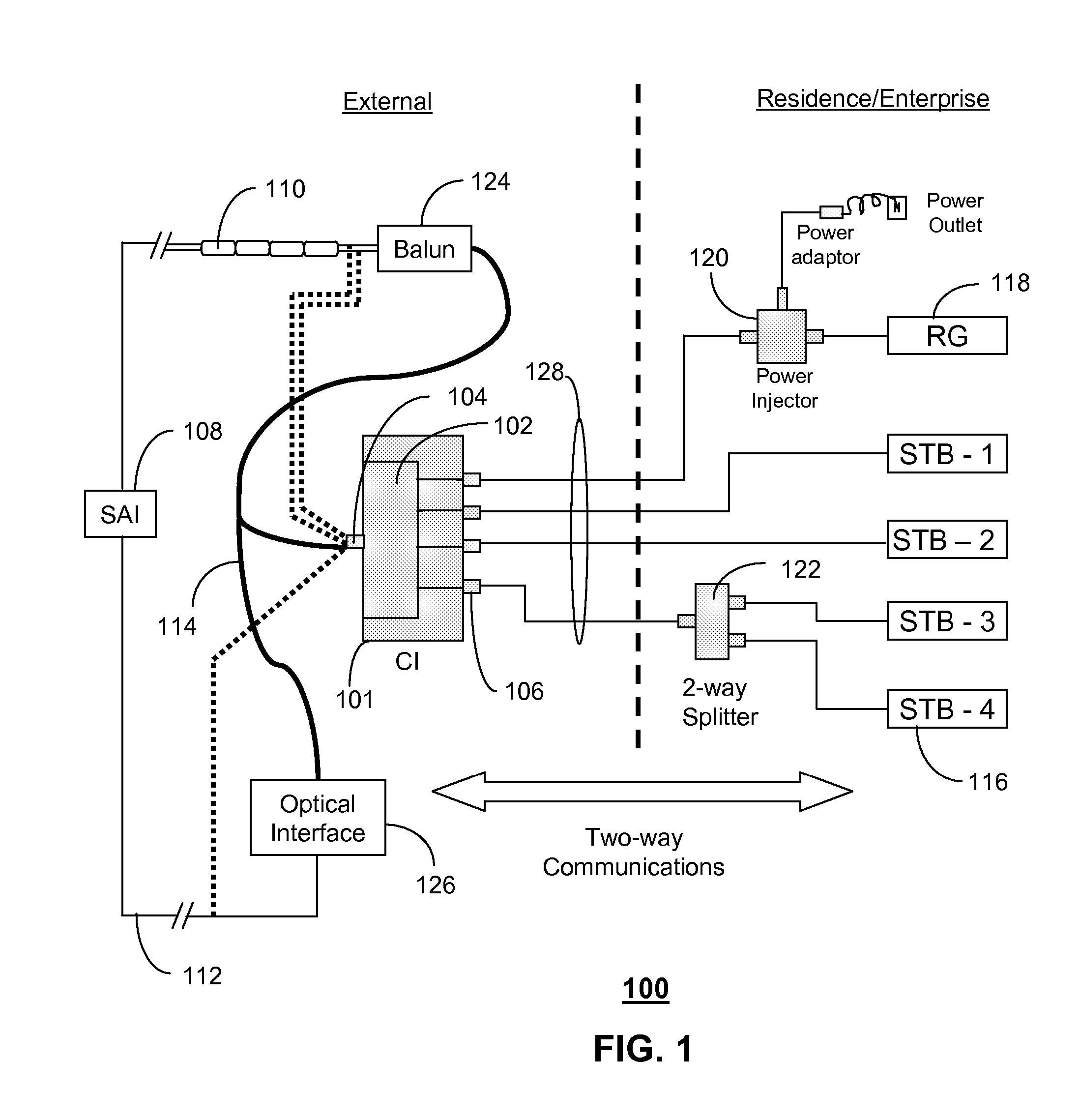
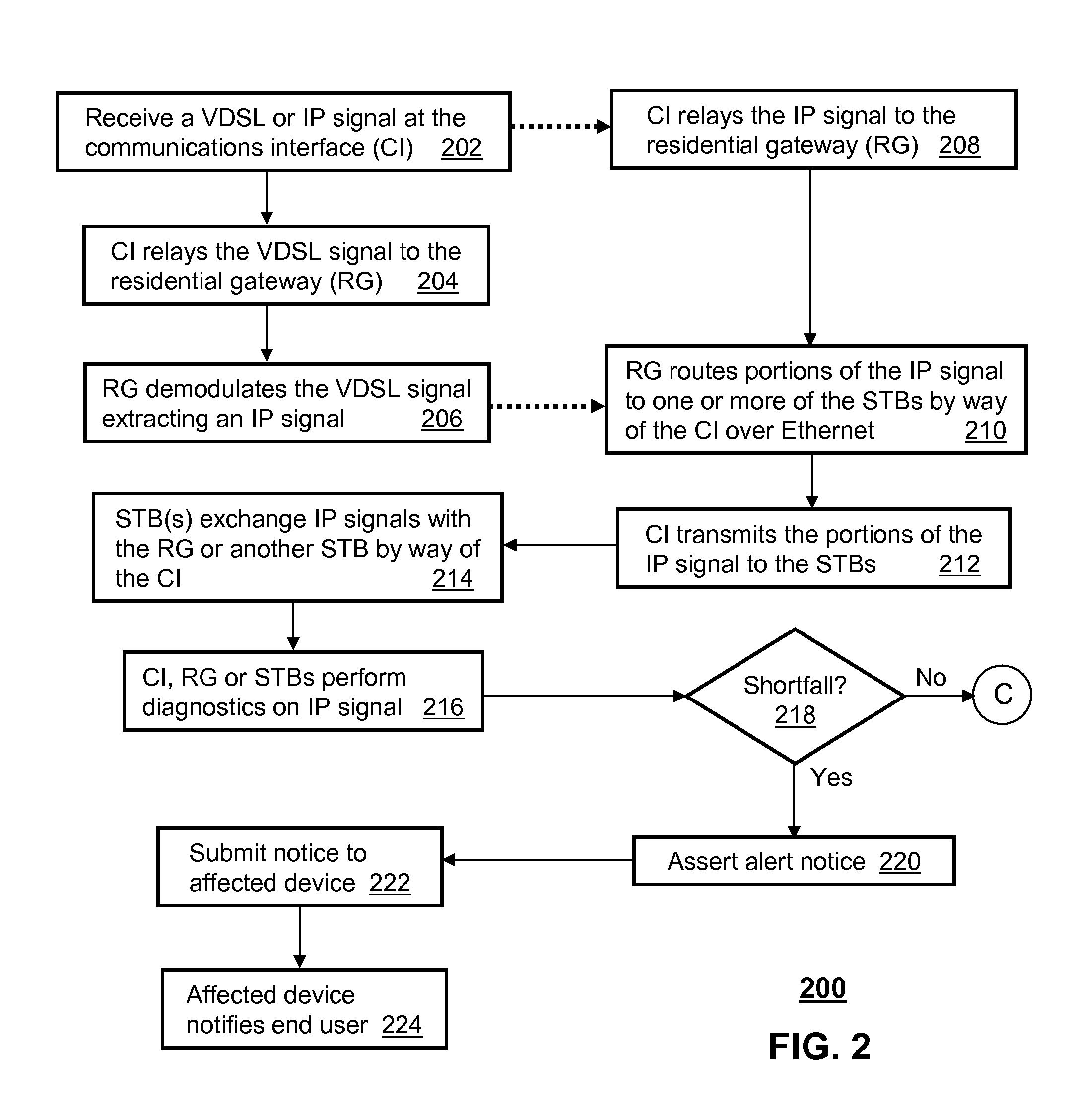
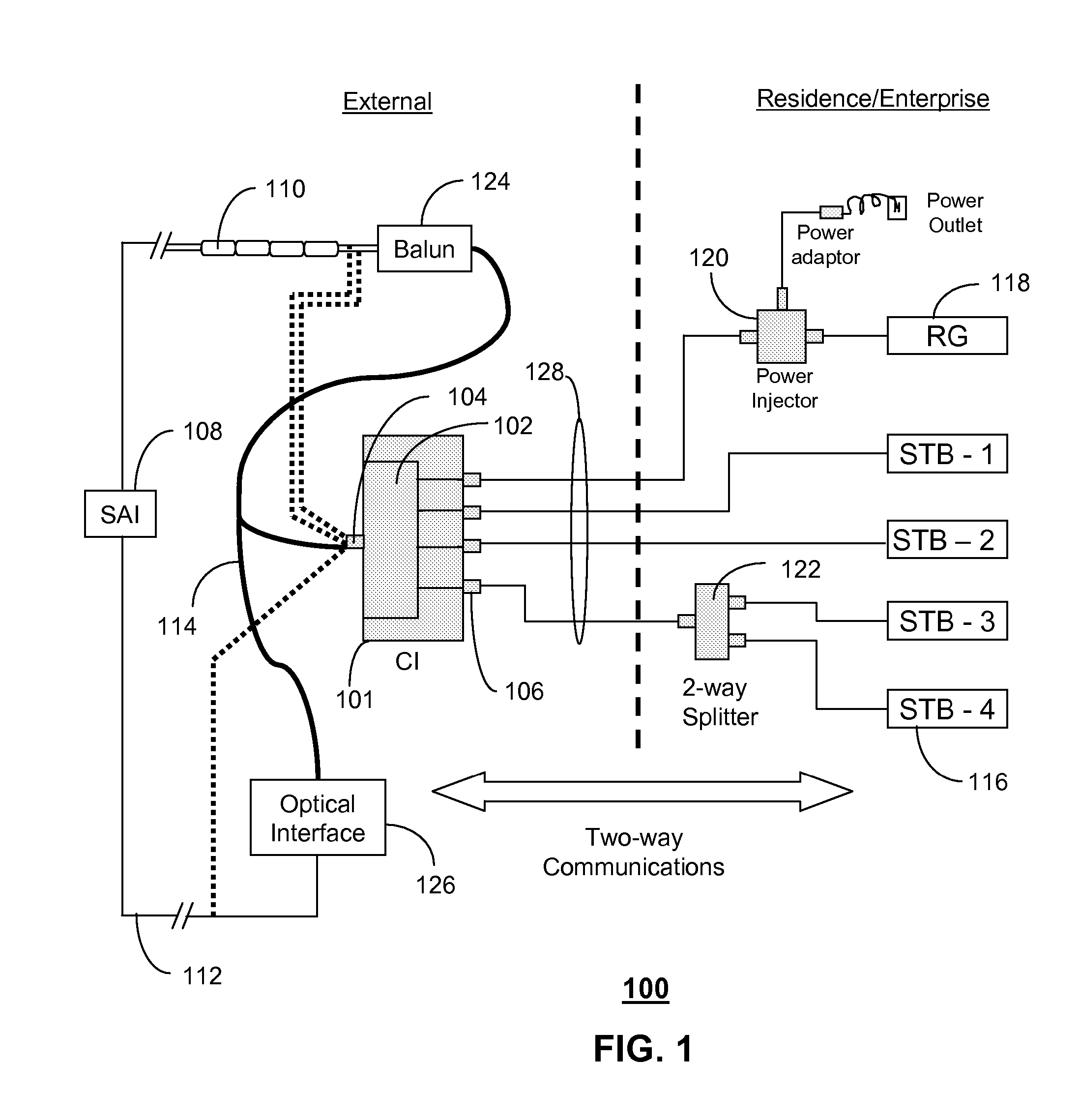
A system and method are disclosed for method and apparatus for distributing signals. A system that incorporates teachings of the present disclosure may include, for example, a communications interface (CI) (101 having a controller that manages a transceiver (102) coupled to a residential gateway (RG) (118) and one or more set top boxes (STBs) (116). The controller can be programmed to receive (202) a very high bit rate digital subscriber line (VDSL) signal, transmit (204, 208) the VDSL signal to the RG over a select one of a plurality of coaxial interfaces, and receive (210) an IP signal from the RG for distribution to the one or more STBs. Additional embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:SBC KNOWLEDGE VENTURES LP
Filtering circuit for very high bit-rate digital subscriber line
InactiveCN1328854CImprove performanceImprove design densityUnbalanced current interference reductionTelephonic communicationDigital subscriber lineImpedance matching
The present invention discloses a sort of wave filter circuit used for the very high bit-rate digital subscriber loop, used to fulfill the filtering, frequency mixing and severing of the upgoing signal and the downward signal of very high bite-rate digital subscriber loop VDSL, which includes: a transmitting wave filter circuit unit, a receiving wave filter circuit unit, a line wave filter circuit unit, a mixer circuit unit; the mixer circuit unit is respectively connected to the transmitting wave filter circuit unit, the receiving wave filter circuit unit and the line wave filter circuit unit, the sequence of the downward signal passes through the transmitting wave filter circuit unit, the mixer circuit unit and the line wave filter circuit unit; the sequence of the upgoing signal passes through the line wave filter circuit unit, the mixer circuit unit and the receiving wave filter circuit unit. Using this filter circuit the layout density of the VDSL equipment can be enhanced, the required expense of the replaced device in facility maintenance can be reduced, the circuit can well satisfy the requirement of matching the various characteristic impedance by replacing the build-out resistor.
Owner:晋江市高新技术开发办公室
Method for implementing non-standard low-speed chain building on serial high bit rate digital subscriber line
ActiveCN101110739BMeet operational needsSmooth upgradeEnergy efficient ICTData switching by path configurationLow speedMarket place
The present invention comprises the following steps: the required link building rate is judged whether the rate is lower than the lowest link building rate; if the required link building rate is lower than the lowest link building rate, the low rate configuration of the link building is performed according to the standard lowest link building rate, and otherwise, the common configuration of the link building is performed according to the actual link building rate. The present invention also discloses a device for realizing a non-standard low rate link building on the single line pair high bitrate digital user line. Through the present invention, under the precondition that the network cost is not added, the application mode of the current perfect SHDSL technology is adopted to solve the special demand of the operator, and to provide powerful guarantee to the product leading in the market, and the present invention has very practical application prospect.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com