Patents
Literature
1716results about How to "Avoid performance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
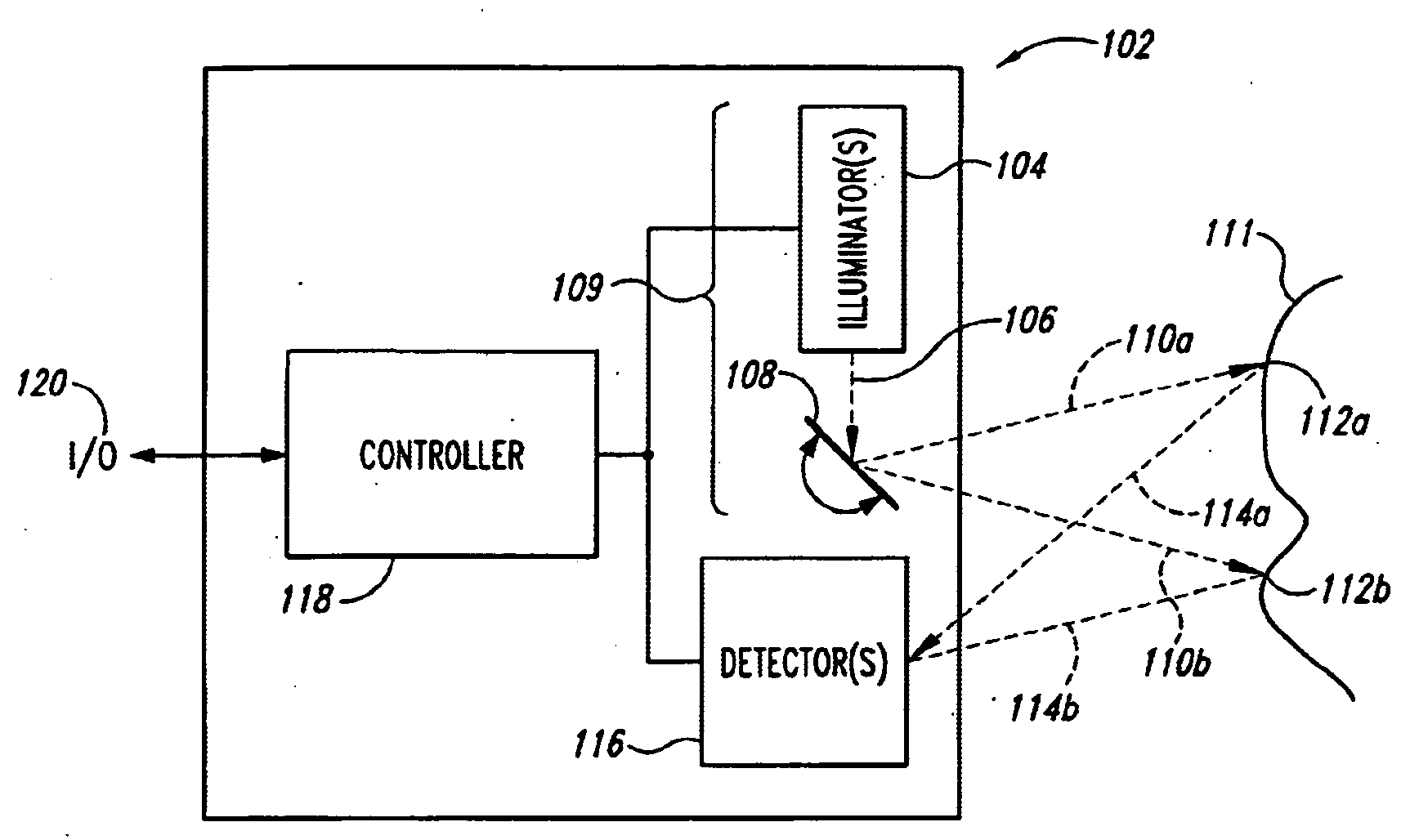
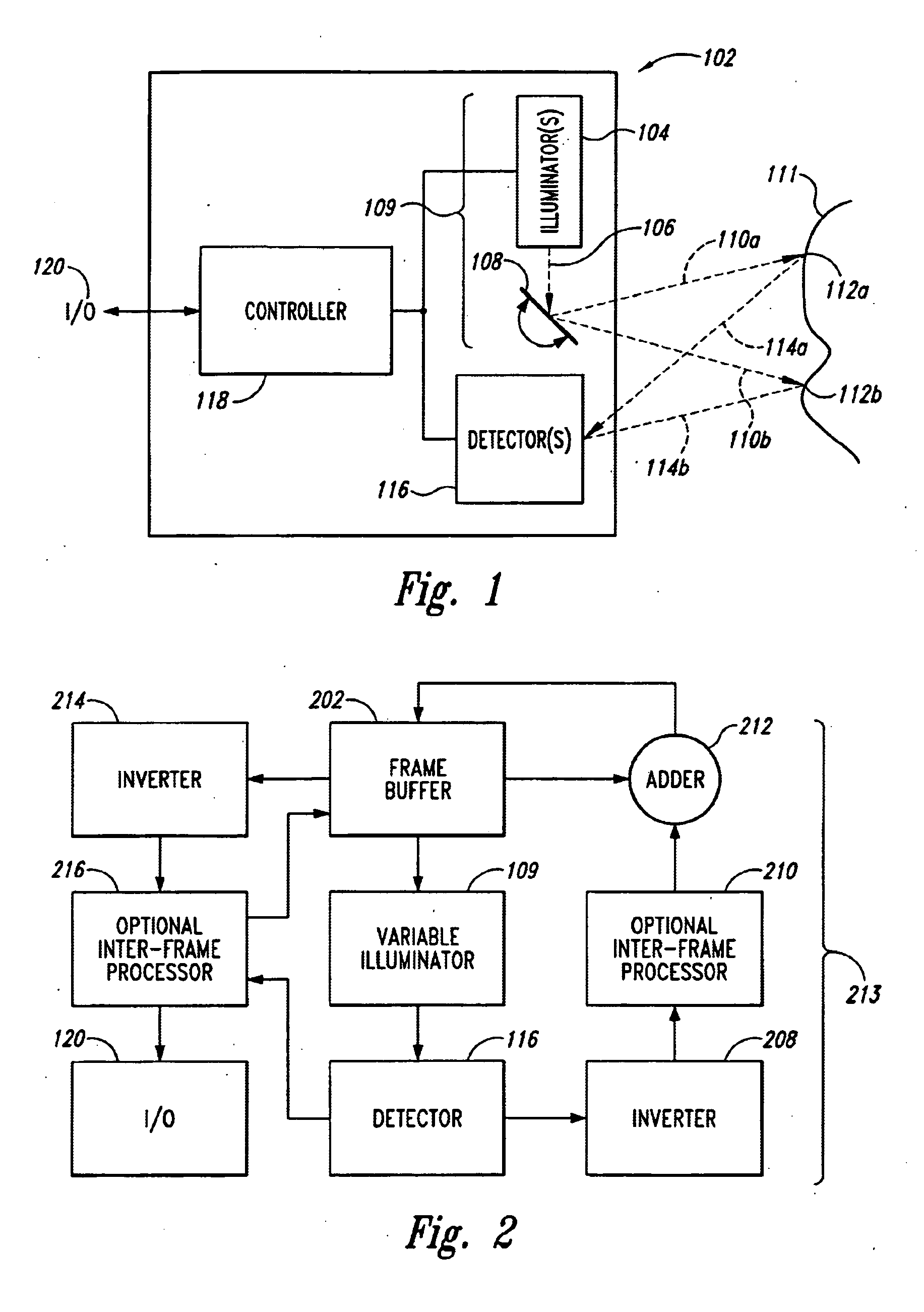
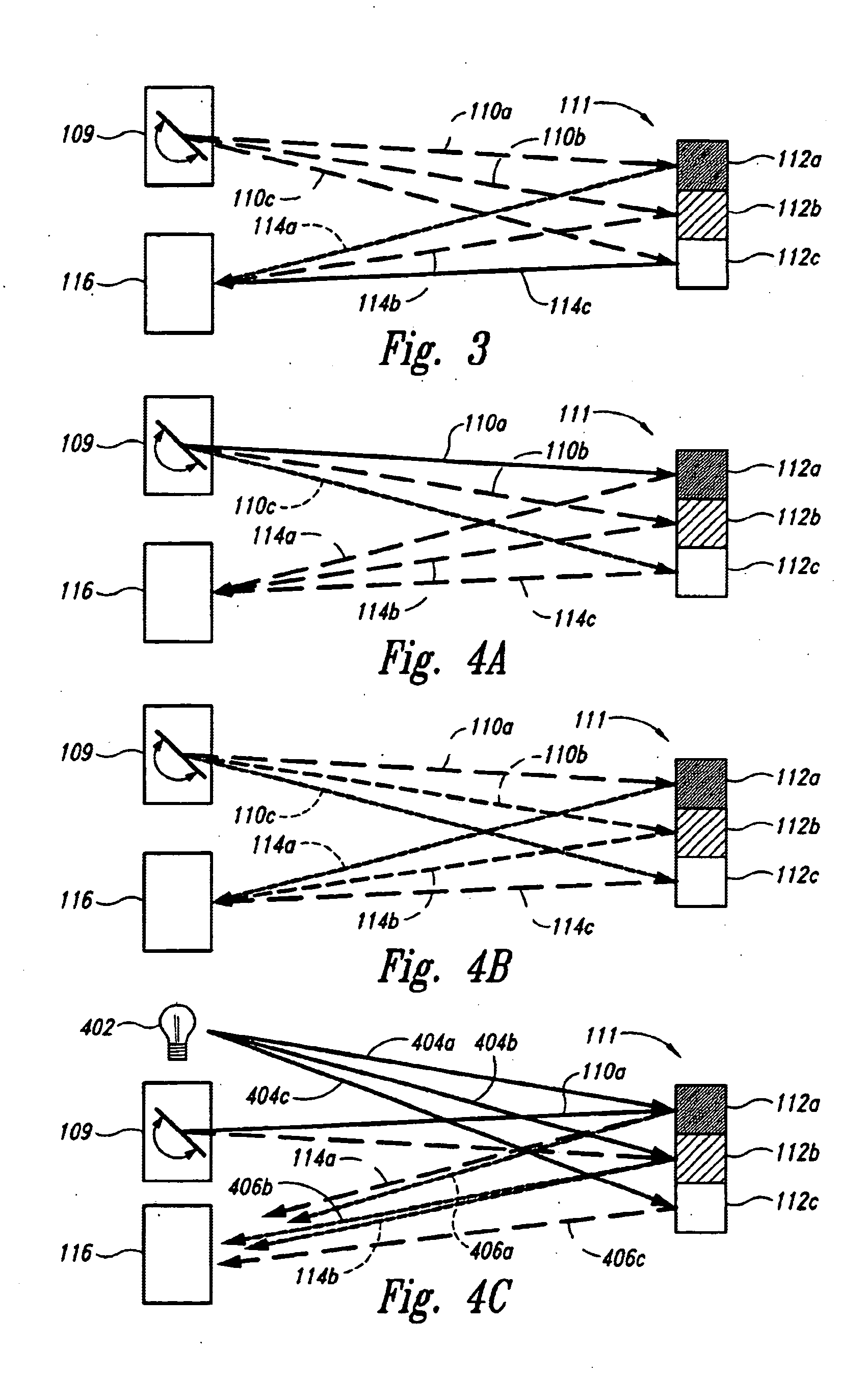
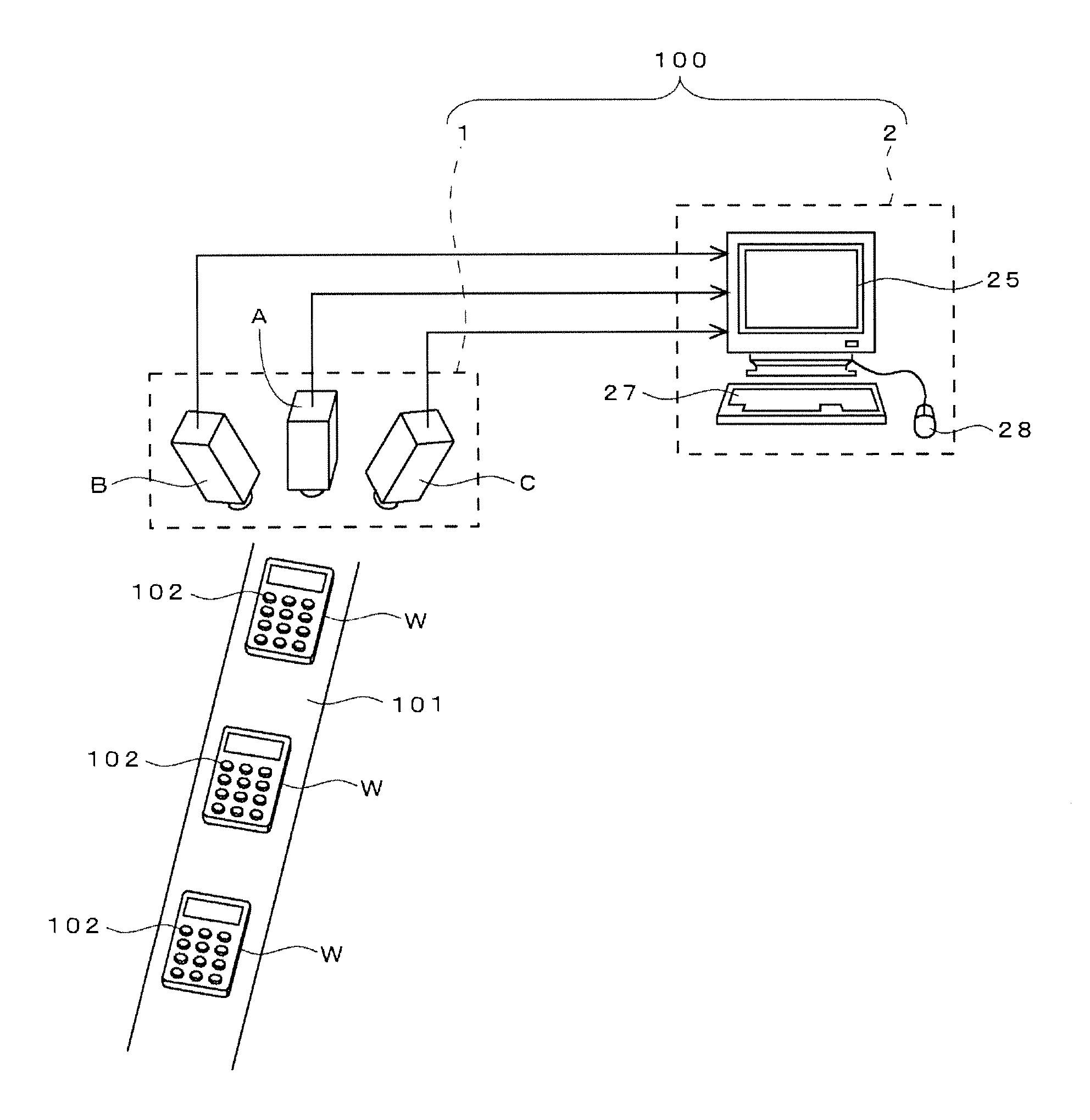
Method and apparatus for illuminating a field-of-view and capturing an image
ActiveUS20050023356A1Improve dynamic rangeImproved determinationCharacter and pattern recognitionRecord carriers used with machinesPhysicsLight beam
A variable illuminator, for instance a device for scanning a beam of light, emits a selected amount of power to a plurality of spots across a field of view. The amount of power is determined as inversely proportional to the apparent brightness of each spot. In the case where the spot size is equal to pixel size, the device may operate with a non-imaging detector. In the case where pixel size substantially equals spot size, the output of the variable illuminator may be converged to produce a substantially uniform detector response and the image information is determined as the inverse of a frame buffer used to drive the variable illuminator. The illuminator and detector may be driven synchronously. In the case where an imaging detector is used, the variable illumination may be used to compress the dynamic range of the field of view to substantially within the dynamic range of the imaging detector.
Owner:MICROVISION
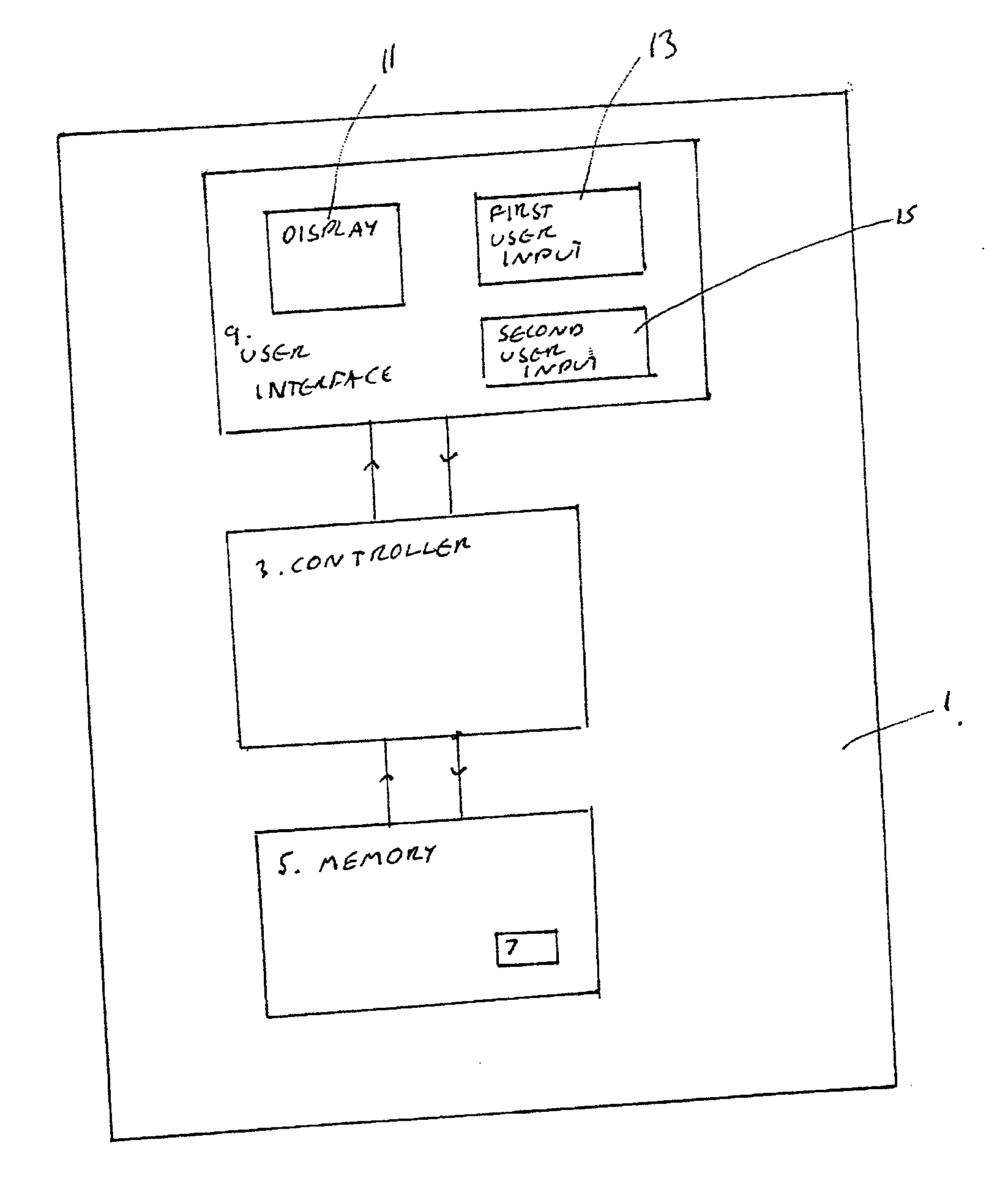
Electronic device having a plurality of modes of operation
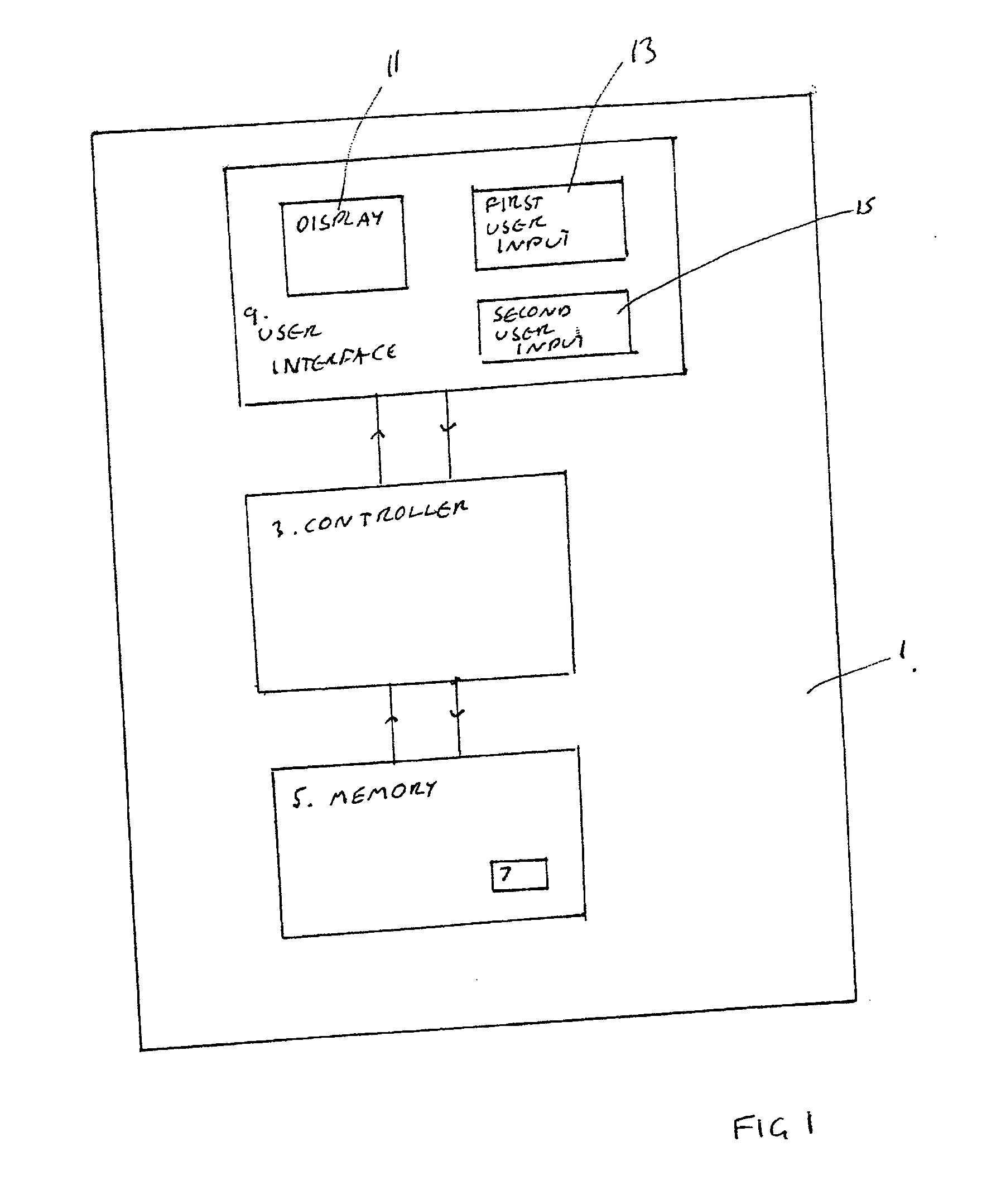
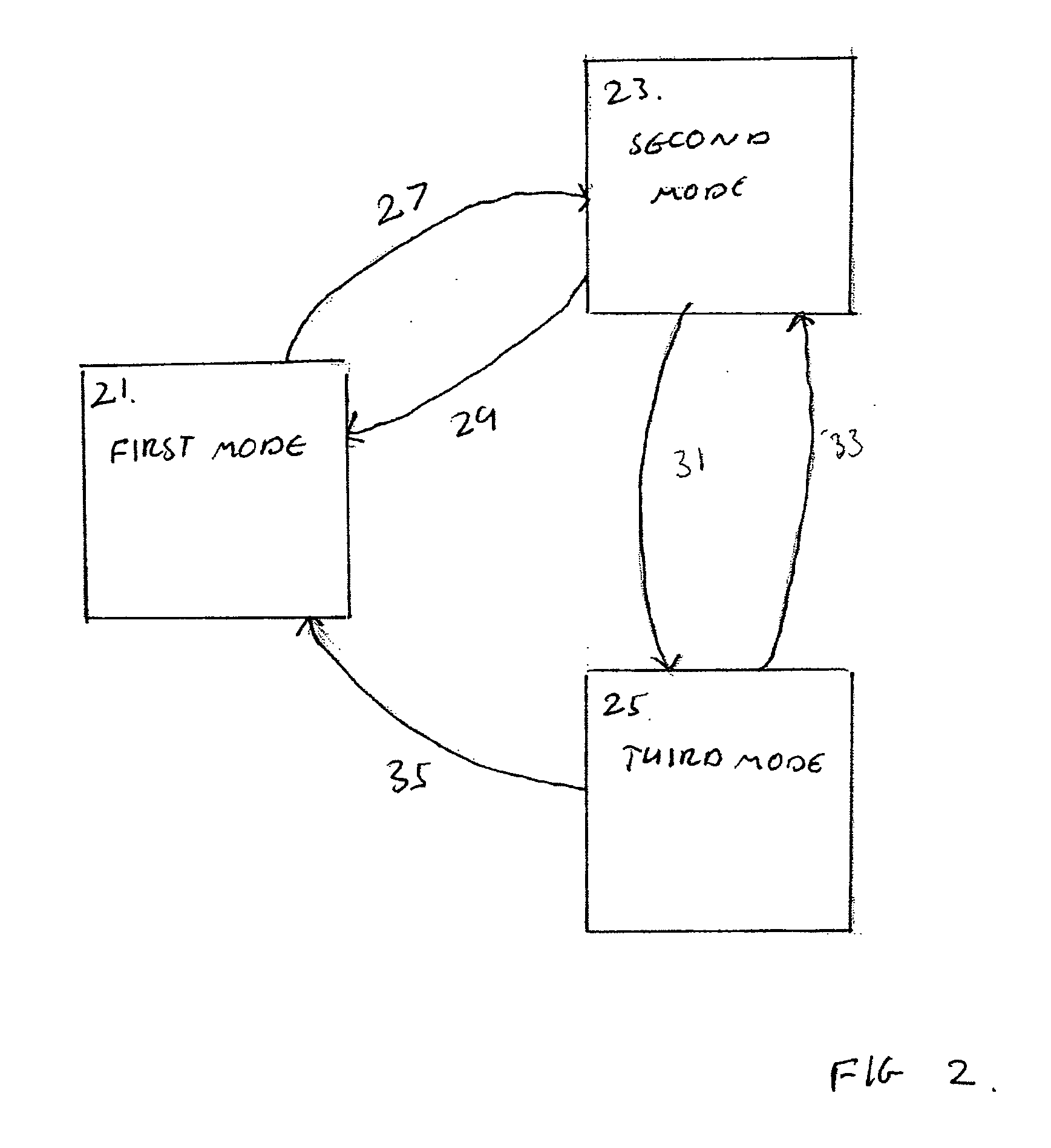
InactiveUS20070300140A1Easy accessAvoid performanceError preventionTransmission systemsUser inputDisplay device
An electronic device including a display, a first user input, for enabling access to a plurality of functions, a second user input, and a controller, operable, in response to an input, to change the mode of operation of the device from a first, active mode of operation, in which the controller is operable to enable a user access to a plurality of functions, to a second, restricted mode of operation in which the controller is operable to disable user access to the plurality of functions, and operable, in response to an input via the second user input, to change the mode of operation of the device from the second, restricted mode of operation to a third, restricted mode of operation in which the controller is operable to disable user access to the plurality of functions and is operable to present information not presentable in the second restricted mode of operation.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Multimodal phone data session management enhancement that alleviates dual transmission problems
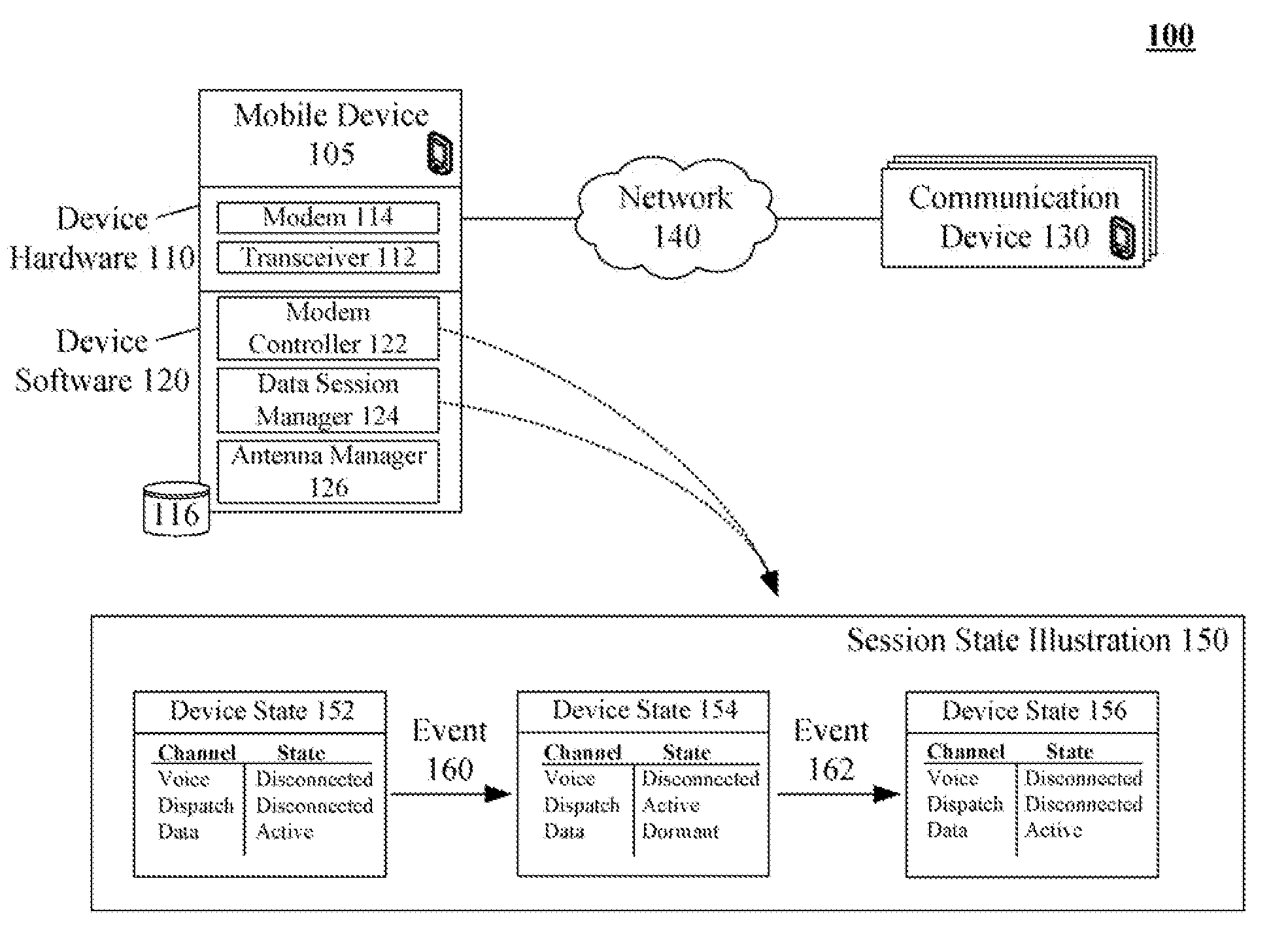
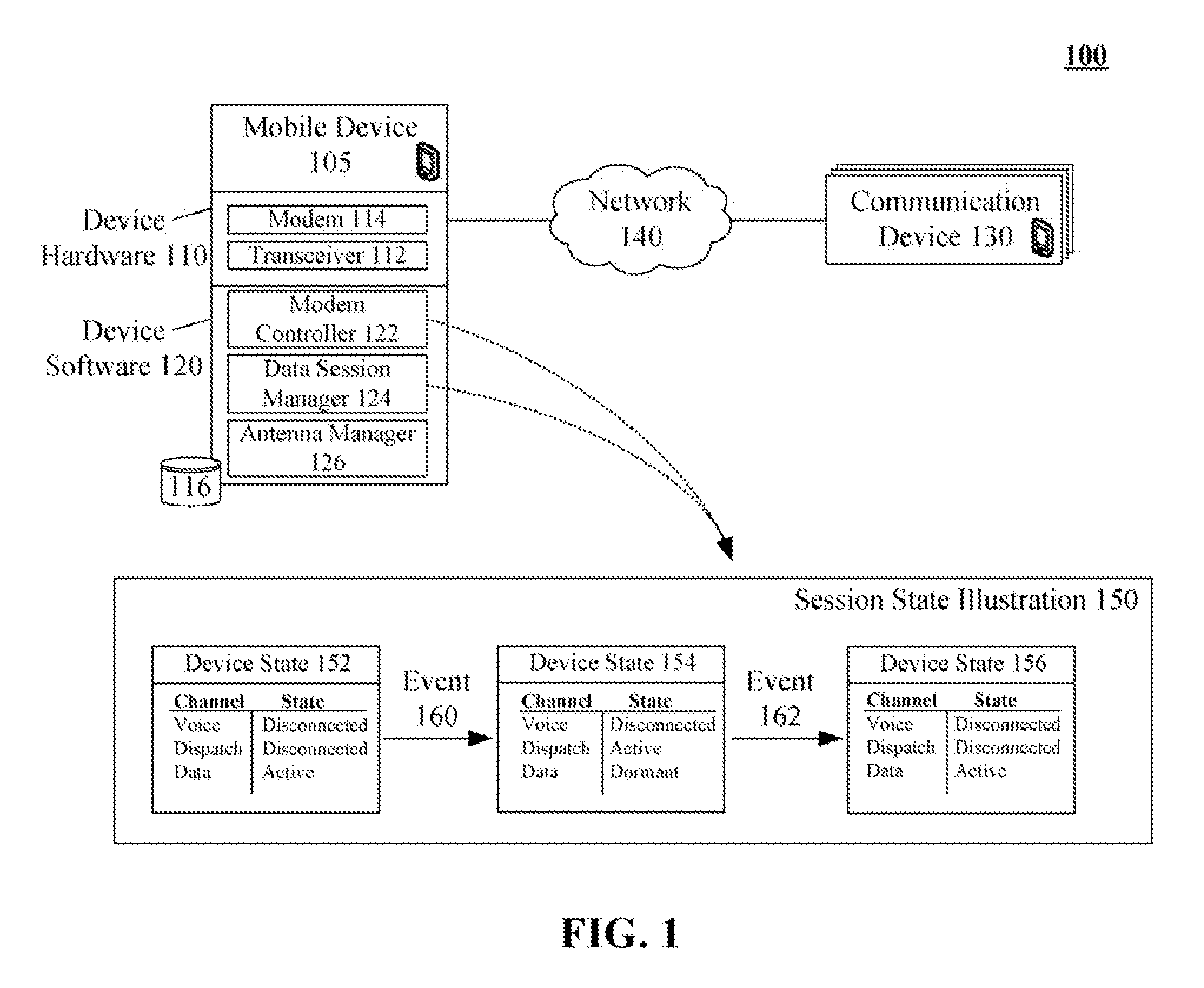
InactiveUS20080146268A1Avoid spreadingTransmission becomes disabledSubstation equipmentProgram controlSession managementModem device
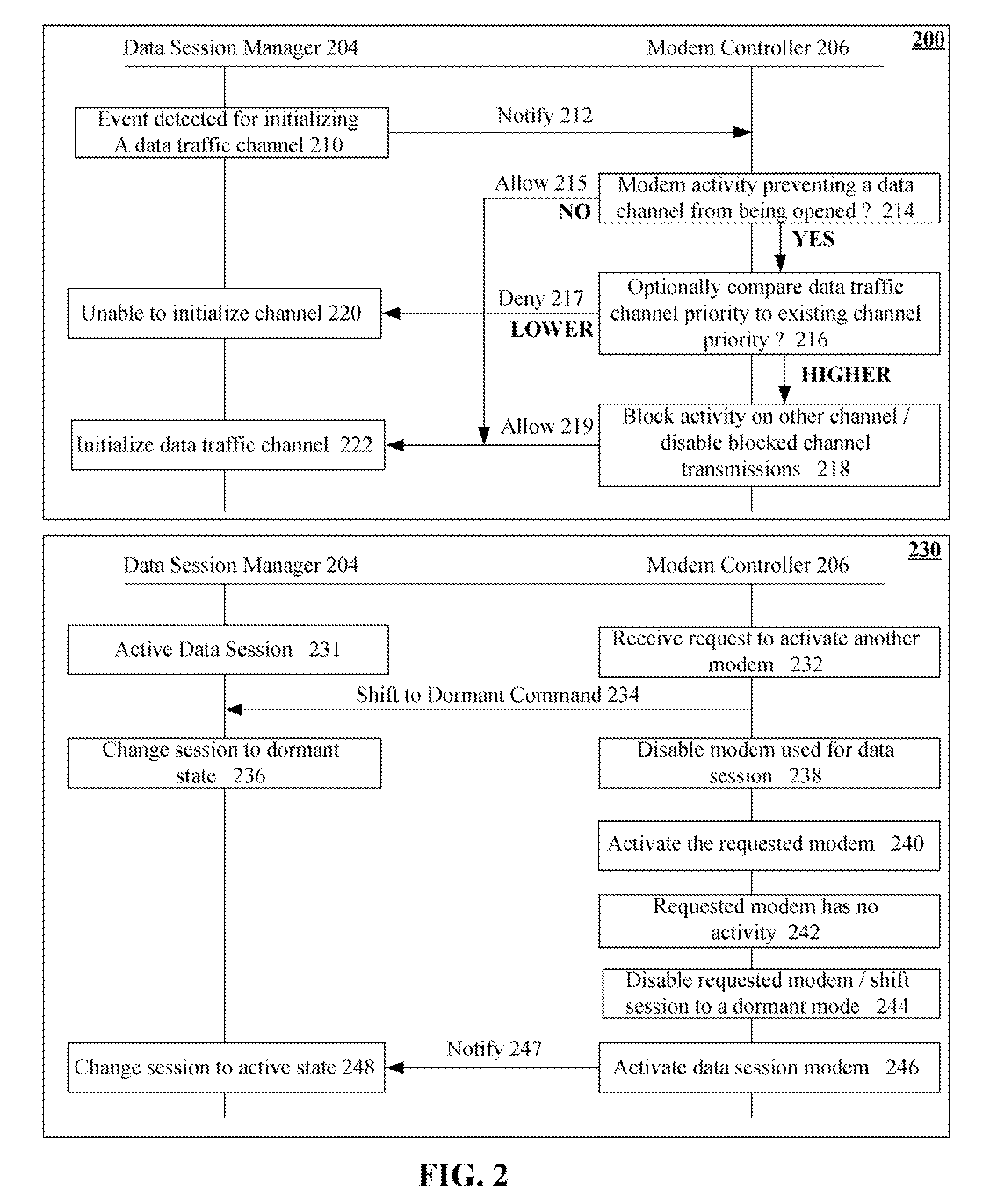
One aspect of the present invention can include a dual transmit mobile communication device that includes multiple modems, a modem controller, and a data session manager. The modem controller can programmatically control the modems. The data session manager can manage data sessions of the mobile communication device. The data session manager can programmatically interact with the software modem controller to ensure that only one of the modems is transmitting at any one time. States of data communication sessions can be automatically adjusted as necessary. For example, the modem controller can block transmissions over a data traffic channel in order to use a modem other than one associated with the data traffic channel, such as using a modem to handle a dispatch session. The data session manager can preserve state information of blocked data sessions, so that the sessions can be resumed when a modem is available.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Systems and methods for detecting and mitigating threats to a structured data storage system
ActiveUS20140201838A1Avoid performanceMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionInternet trafficScoring algorithm
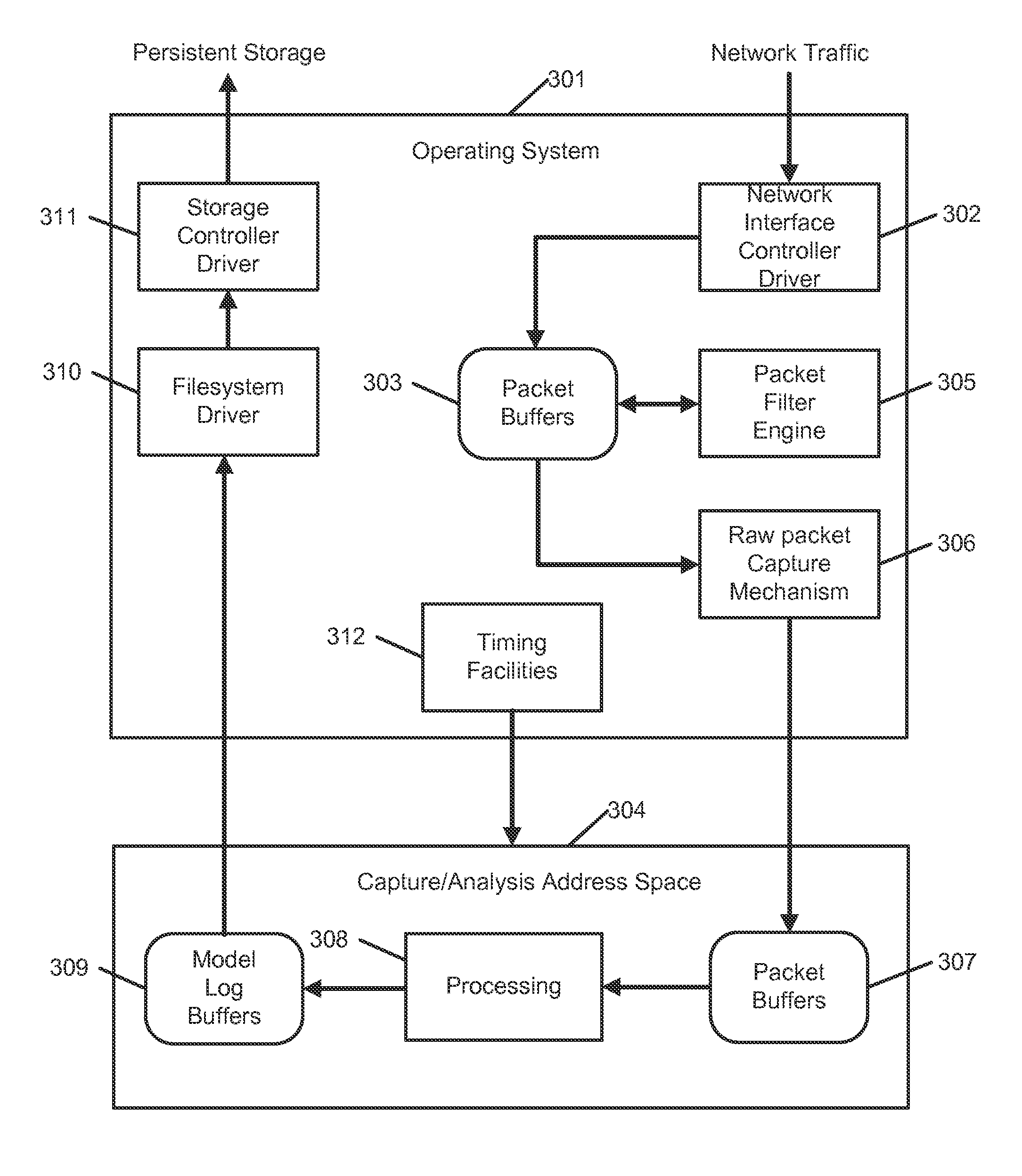
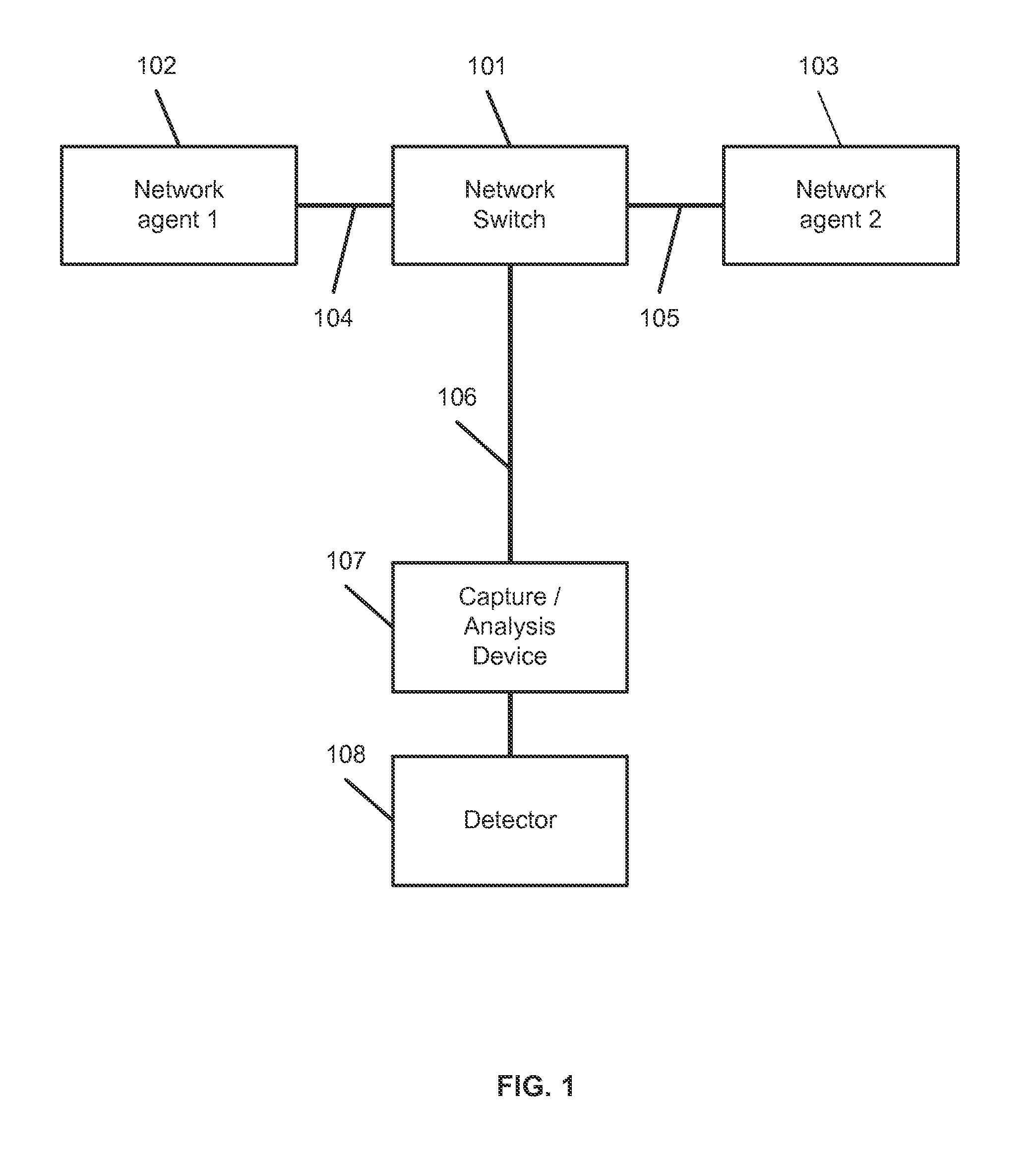
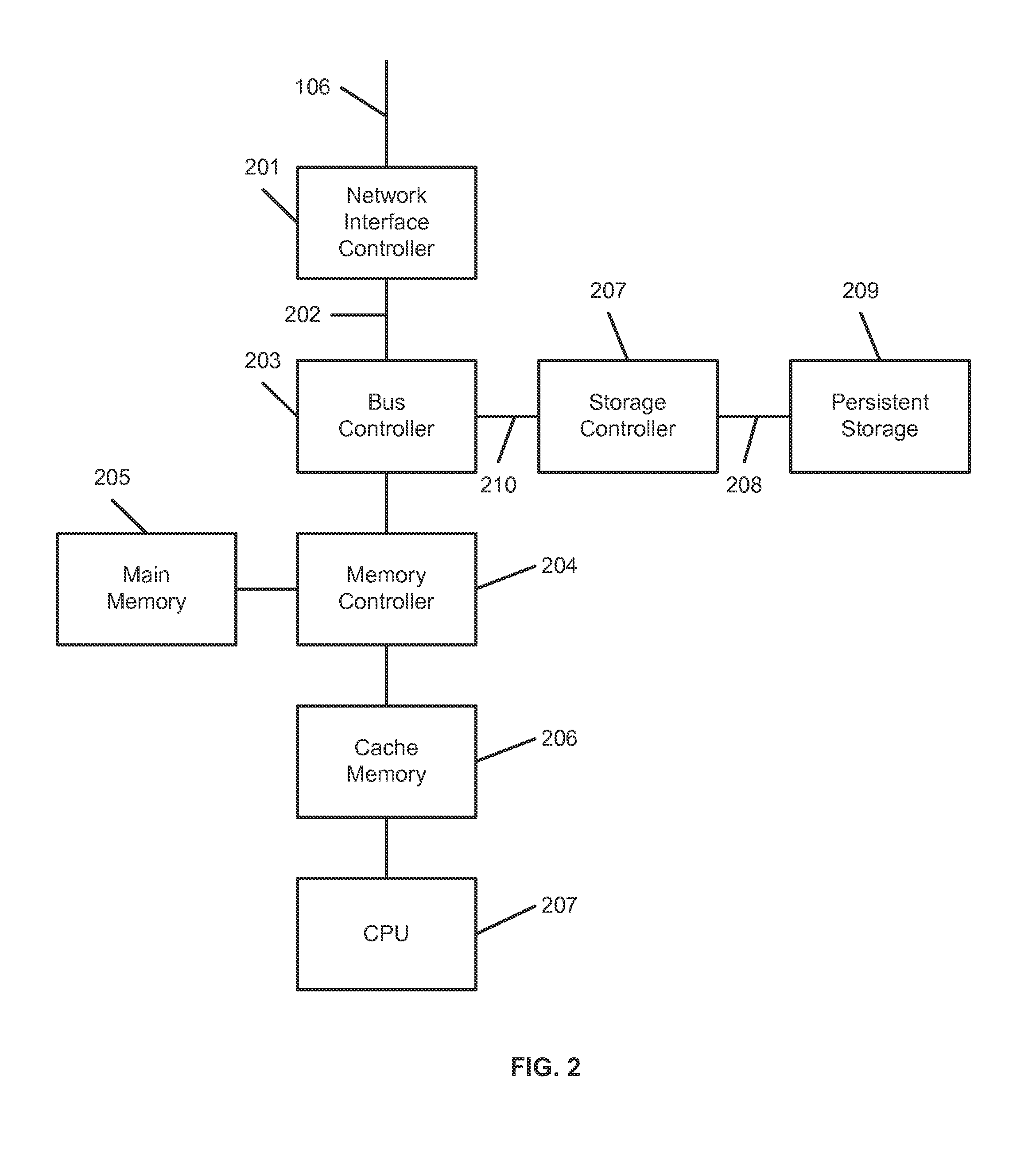
Systems, methods, and computer-readable media for detecting threats on a network. In an embodiment, target network traffic being transmitted between two or more hosts is captured. The target network traffic comprises a plurality of packets, which are assembled into one or more messages. The assembled message(s) may be parsed to generate a semantic model of the target network traffic. The semantic model may comprise representation(s) of operation(s) or event(s) represented by the message(s). Score(s) for the operation(s) or event(s) may be generated using a plurality of scoring algorithms, and potential threats among the operation(s) or event(s) may be identified using the score(s).
Owner:IPIVOT CORP
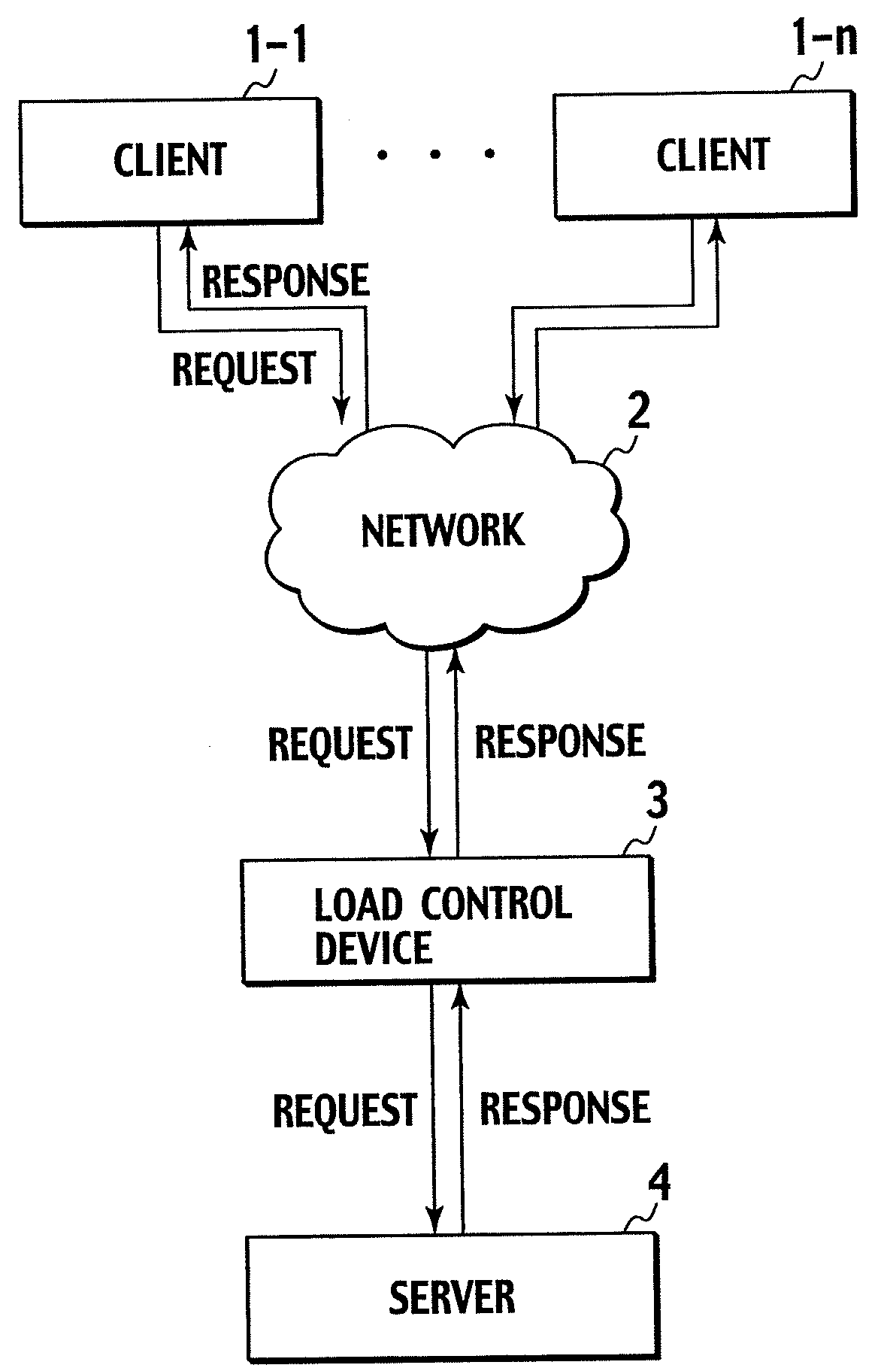
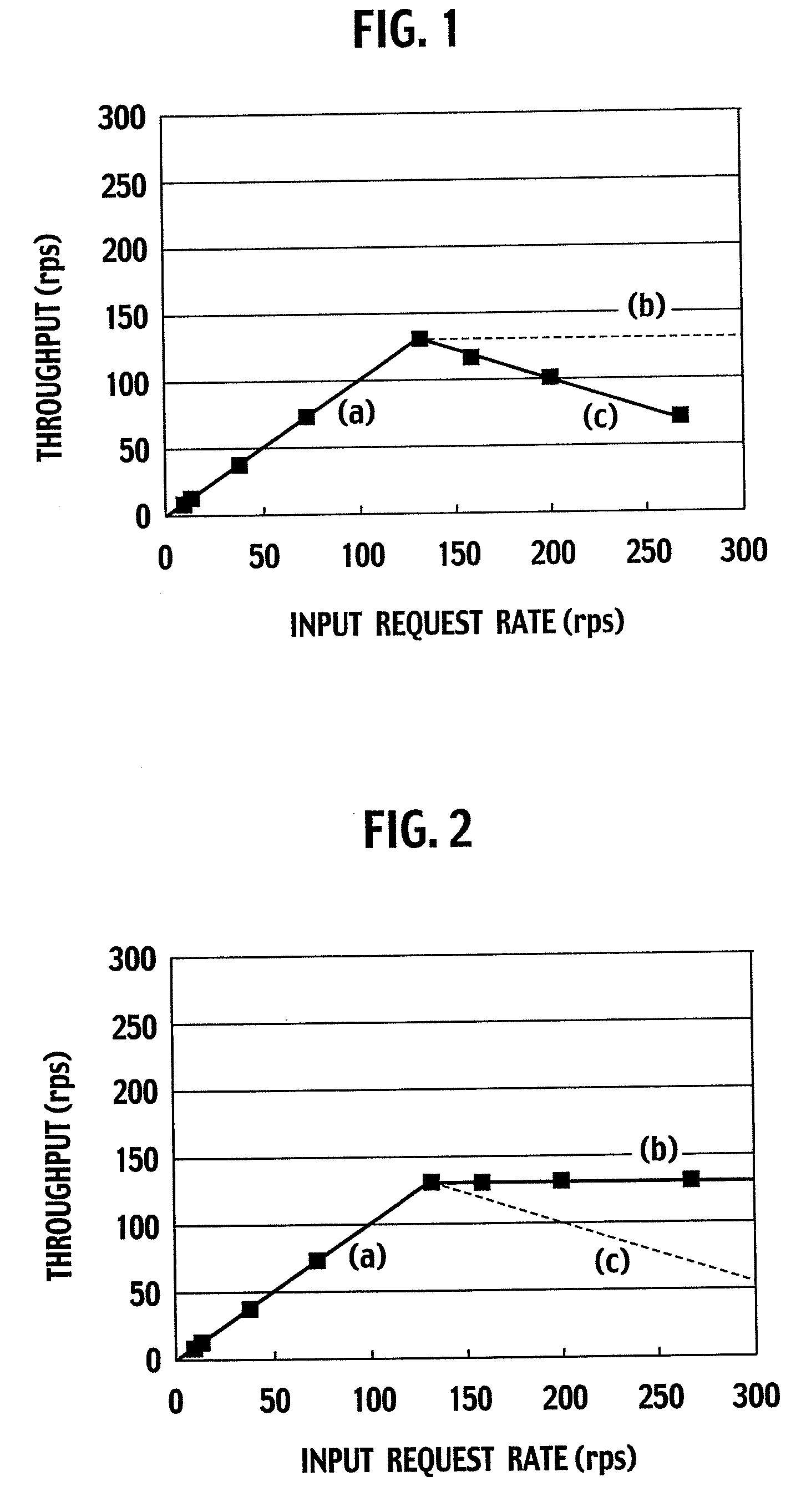
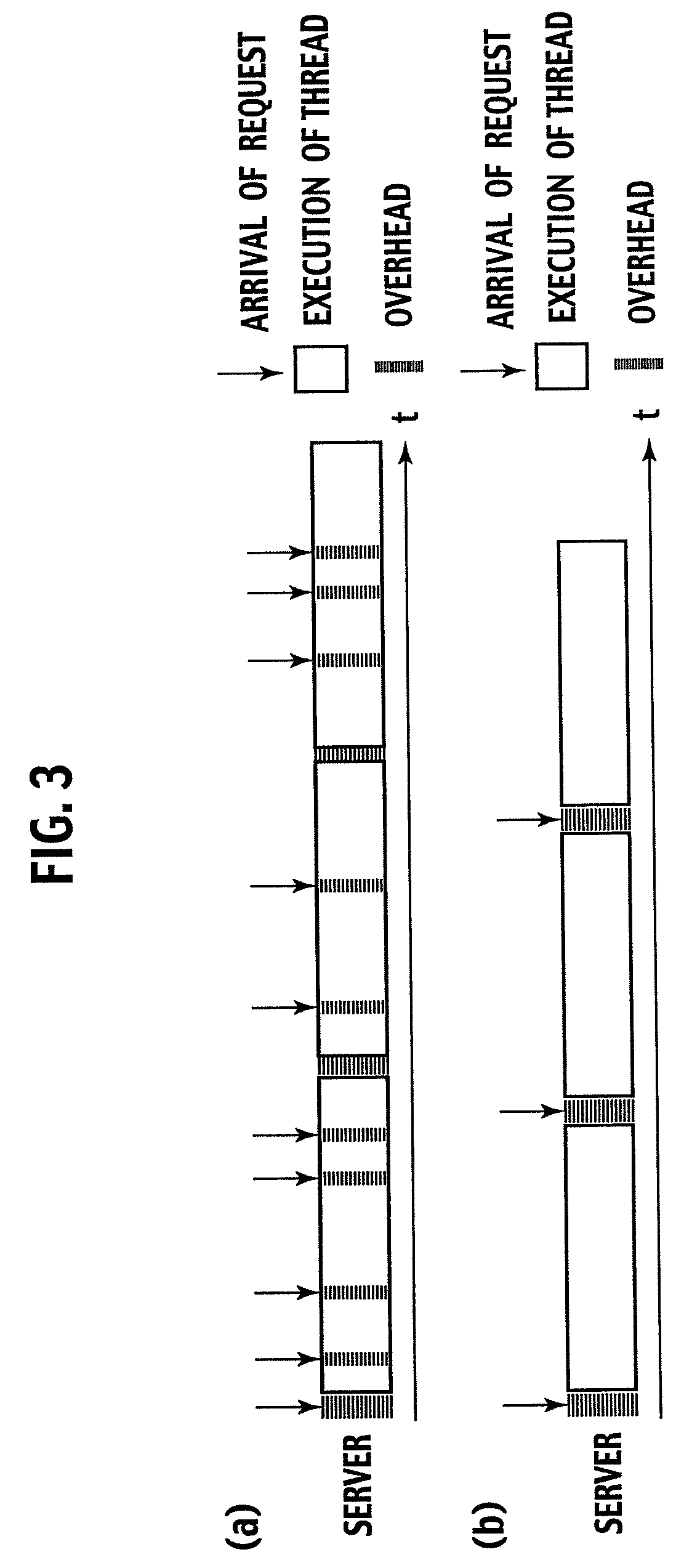
Load Control Device and Method Thereof
ActiveUS20090077233A1Avoid performance degradationReduce loadDigital computer detailsProgram controlControl equipmentReal-time computing
The number of response-waiting requests which are already sent to a server (4) but to which a response is not yet returned from the server (4) is limited. To limit this number, received requests are temporarily accumulated in a buffer if the number of response-waiting requests has reached a threshold and, until the number of response-waiting requests falls below the threshold, requests are not sent from the buffer. The execution status of the server (4) is monitored, and the threshold is increased when the response time from the server (4) to a request is within an allowable range, and the threshold is decreased when the response time exceeds the allowable range. In addition, TCP connections between a load control device (3) and clients (1-1, 1-n) are aggregated so that the number of simultaneous connections of TCP connections between the server (4) and the load control device (3) becomes equal to or smaller than the threshold of the number of response-waiting requests.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
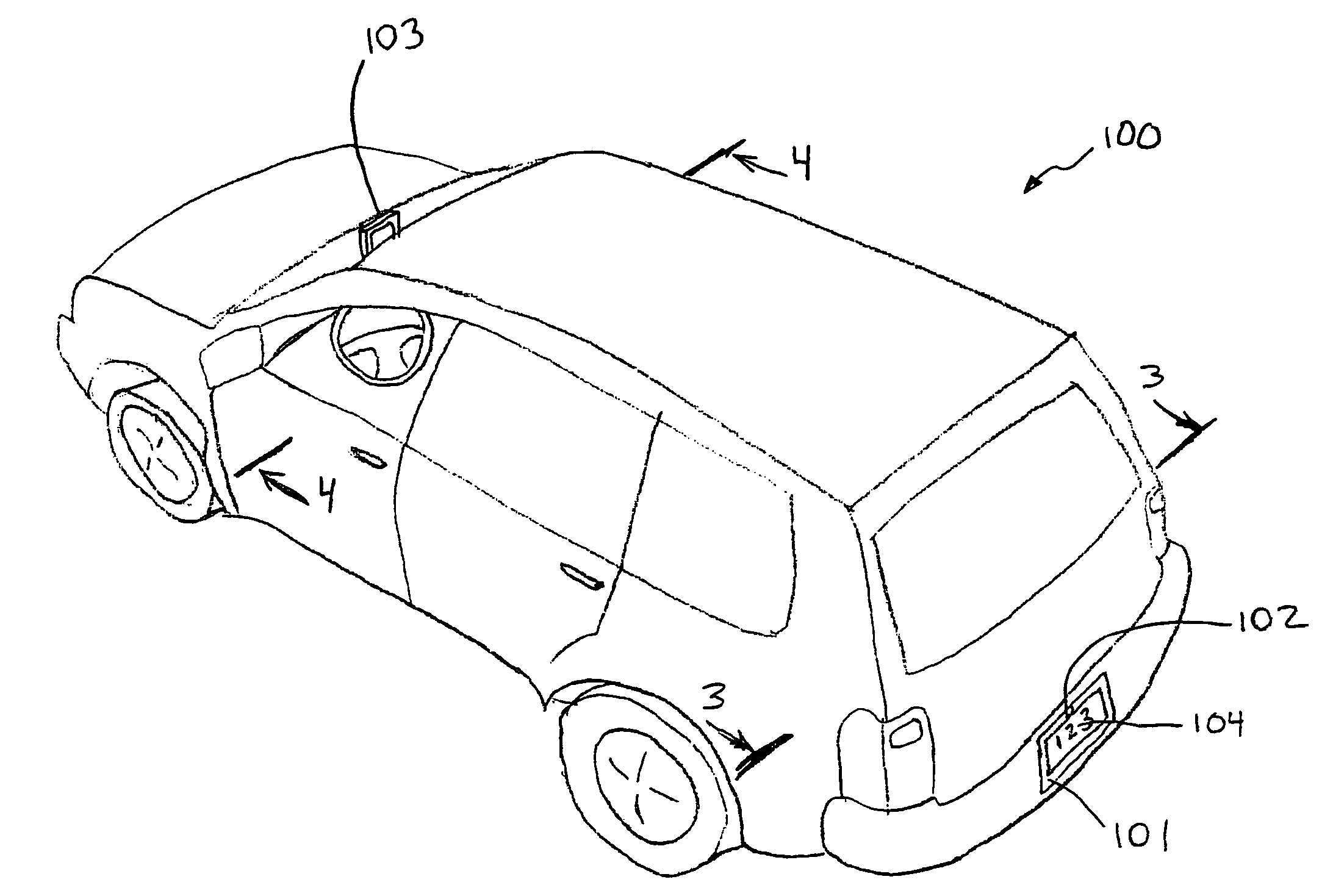
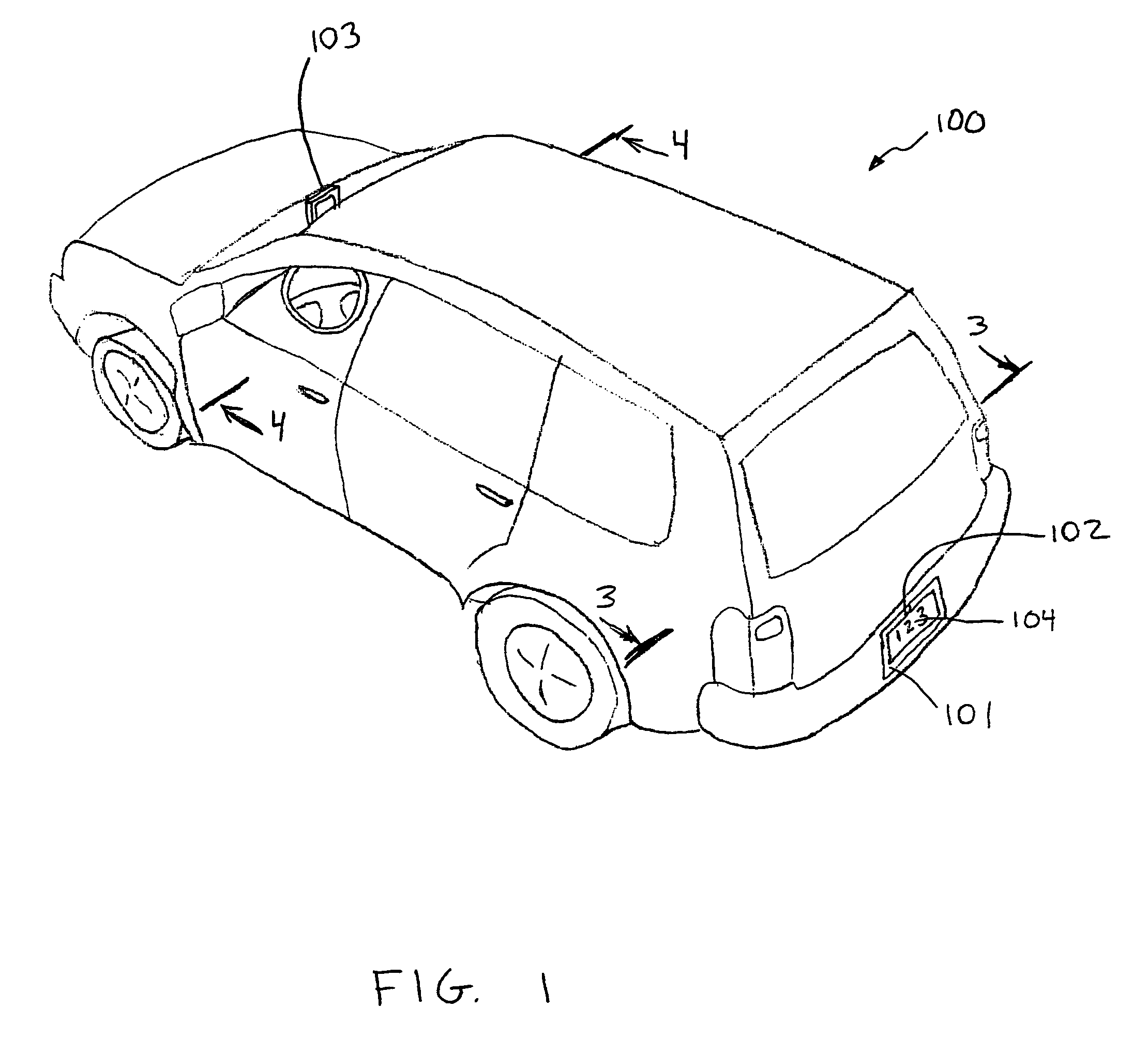
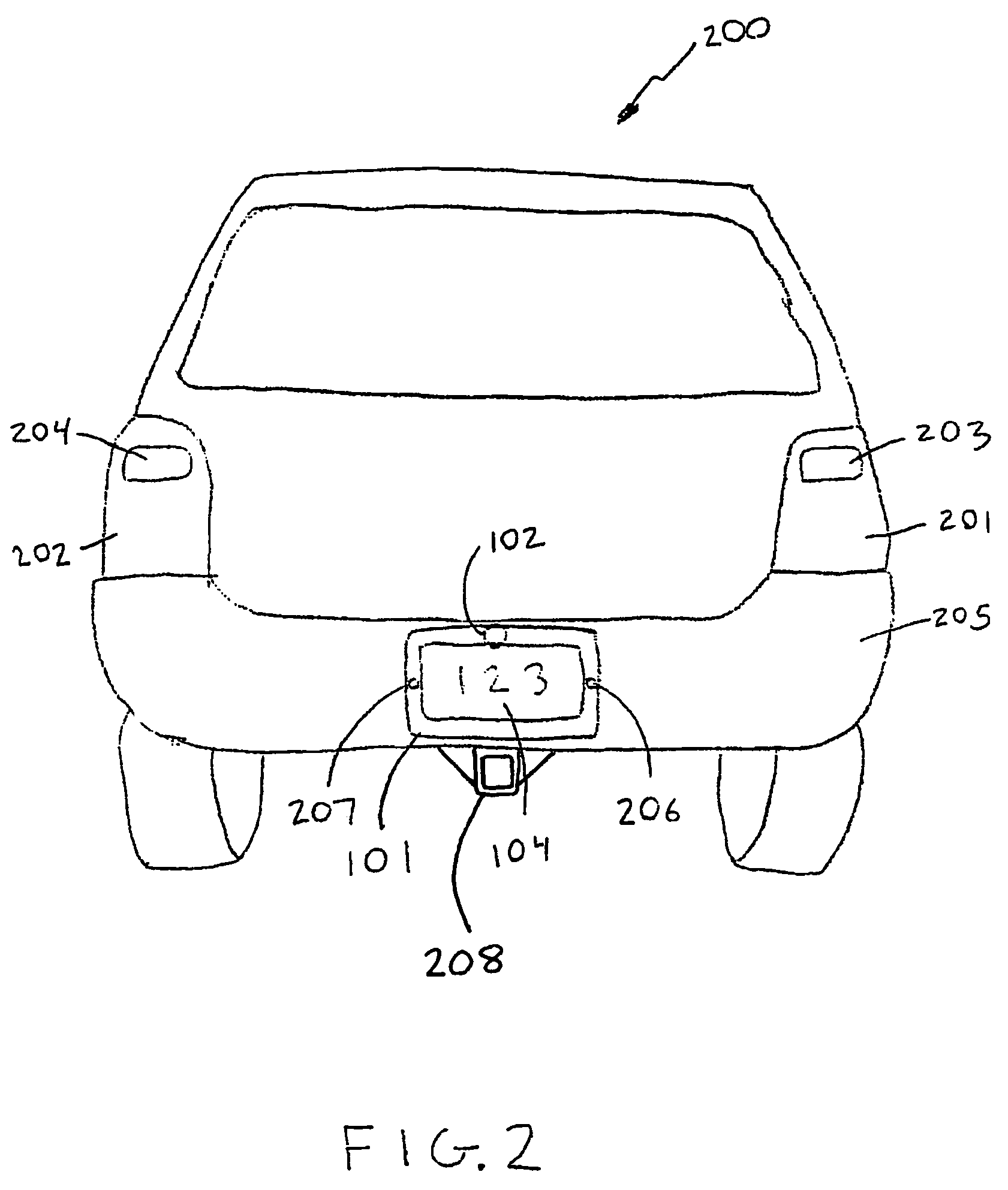
Vehicle back-up viewing system
ActiveUS7511607B2Easy to installSimple to useTelevision system detailsFrequency-division multiplex detailsElectricityDashboard
A system for displaying an external view of a vehicle is provided. The system may comprise a video camera for capturing images external to the vehicle and a display for displaying the images for the vehicle operator. The camera is powered by electrically connecting it to the reverse lamp power line and is operable to continuously capture images when powered. The camera may be mounted in a license plate frame to further simplify installation. The camera may communicate with the display through a wireless connection. The receiver and display may be mounted in the field of view of the vehicle operator, such as on the dashboard of the vehicle.
Owner:D LARRY HUBBARD +1
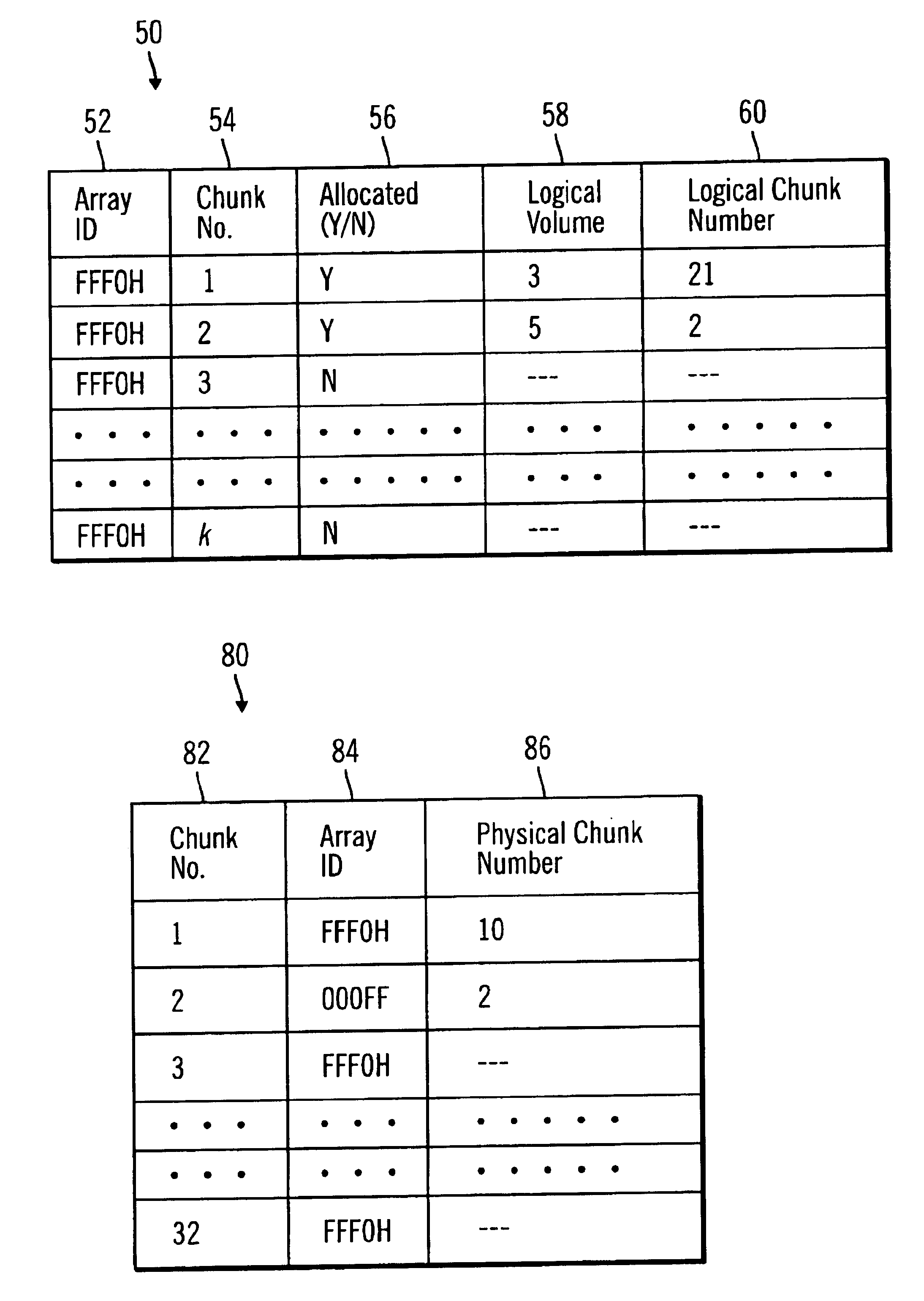
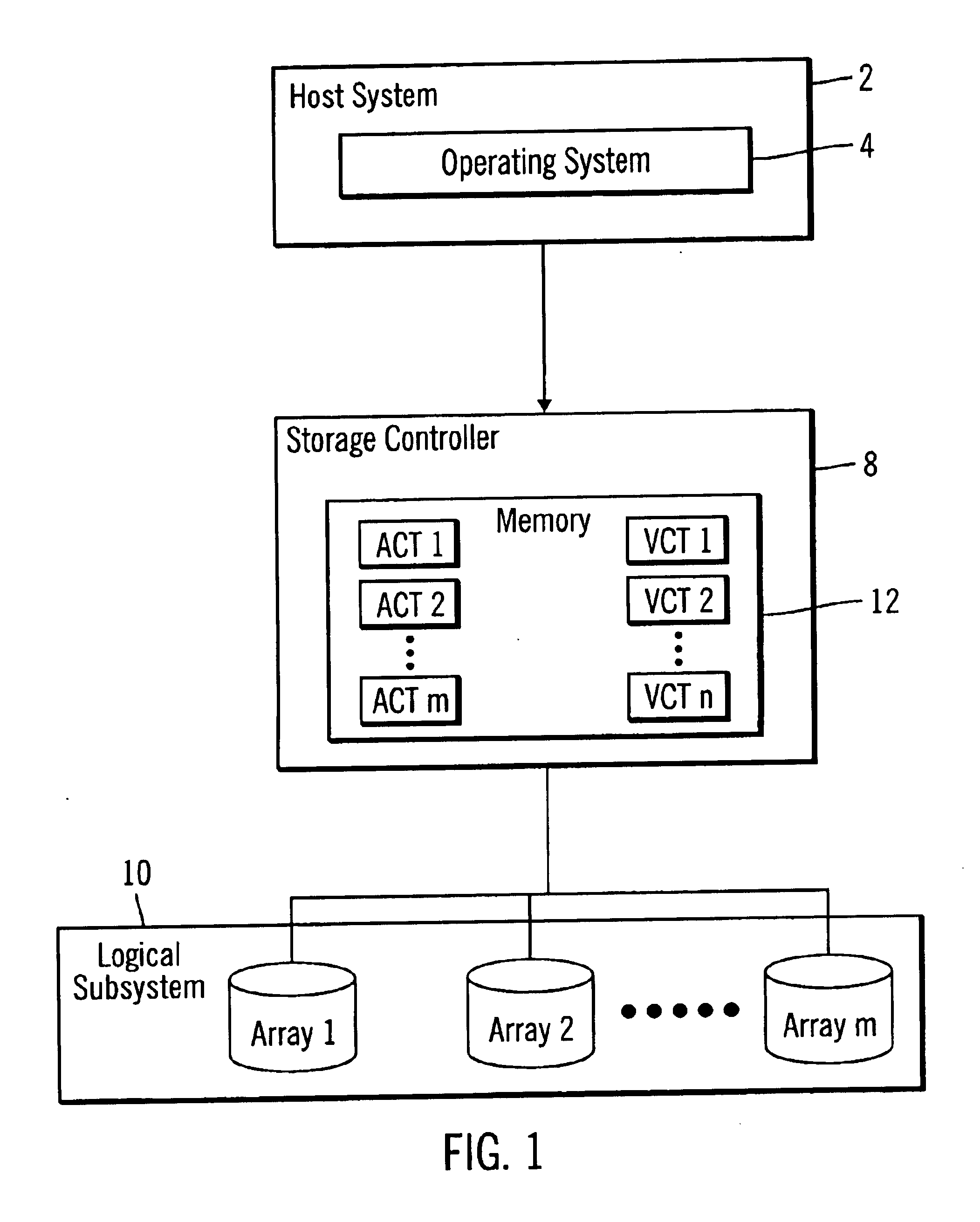
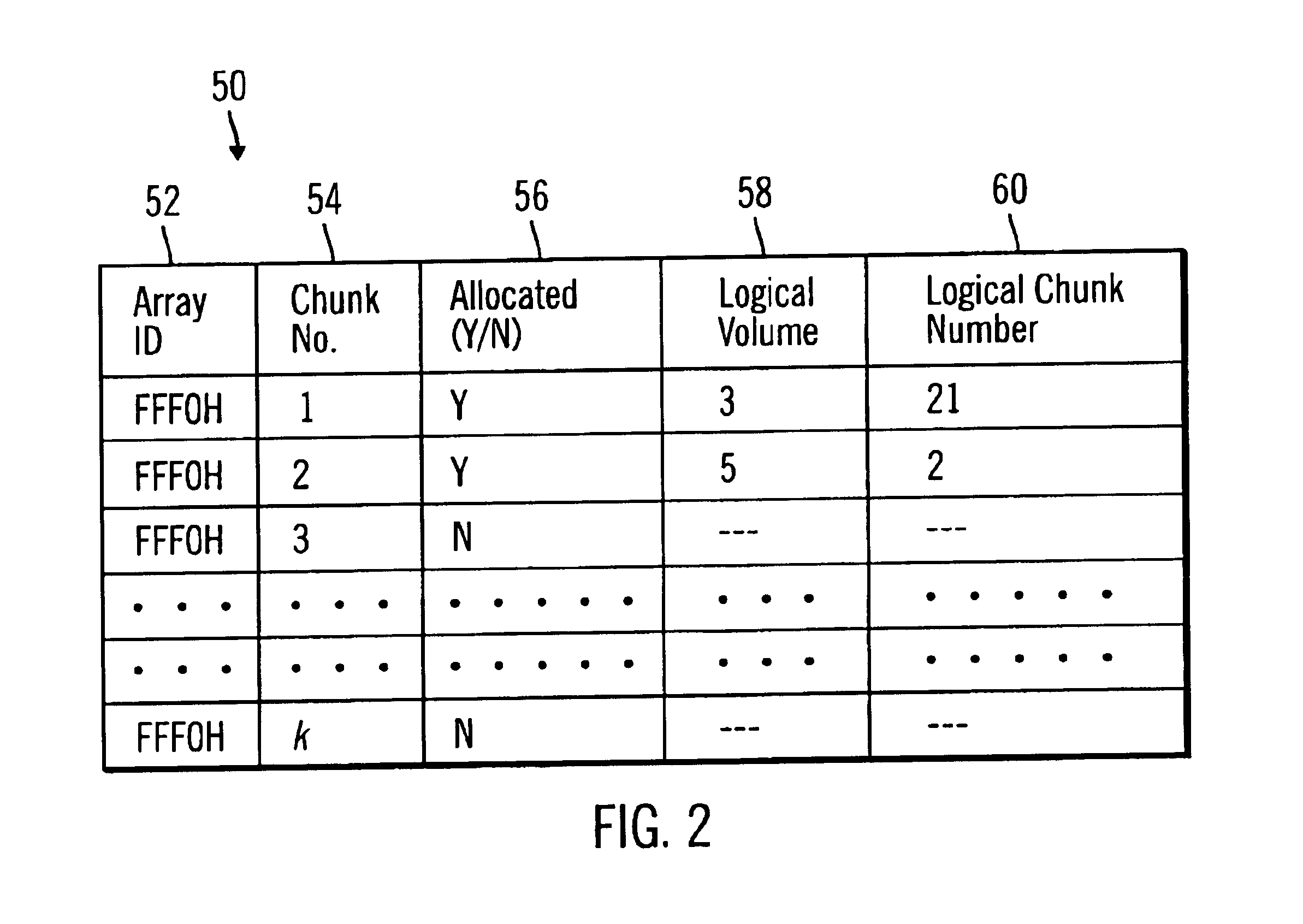
Method, system, program, and data structures for mapping logical blocks to physical blocks
InactiveUS6839827B1Increase in sizeAvoid performanceInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationArray data structureControl store
Disclosed is a method, system, program, and data structure for a storage controller to map logical blocks to physical storage blocks. The storage controller is in communication with at least one host system that views a logical storage space. The storage controller defines the logical storage space as a sequence of logical chunks, wherein each logical chunk comprises a plurality of logical blocks in the logical storage space. The storage controller further defines a physical storage space as a sequence of physical chunks, wherein each physical chunk comprises a plurality of physical blocks in the physical storage system. The storage controller associates each logical chunk in the sequence of logical chunks defining the logical storage space with one physical chunk in the physical storage system. Further, the contiguous logical chunks are capable of being associated with non-contiguous physical chunks.
Owner:IBM CORP
Cycle segmented prefix circuits
InactiveUS6609189B1Improve performanceAvoid performanceComputation using non-contact making devicesGeneral purpose stored program computerExtensibilityScalar processor
The poor scalability of existing superscalar processors has been of great concern to the computer engineering community. In particular, the critical-path delays of many components in existing implementations grow quadratically with the issue width and the window size. This patent presents a novel way to reimplement these components and reduce their critical-path delay growth. It then describes an entire processor microarchitecture, called the Ultrascalar processor, that has better critical-path delay growth than existing superscalars. Most of our scalable designs are based on a single circuit, a cyclic segmented parallel prefix (cspp). We observe that processor components typically operate on a wrap-around sequence of instructions, computing some associative property of that sequence. For example, to assign an ALU to the oldest requesting instruction, each instruction in the instruction sequence must be told whether any preceding instructions are requesting an ALU. Similarly, to read an argument register, an instruction must somehow communicate with the most recent preceding instruction that wrote that register. A cspp circuit can implement such functions by computing for each instruction within a wrap-around instruction sequence the accumulative result of applying some associative operator to all the preceding instructions. A cspp circuit has a critical path gate delay logarithmic in the length of the instruction sequence. Depending on its associative operation and its layout, a cspp circuit can have a critical path wire delay sublinear in the length of the instruction sequence.
Owner:YALE UNIV
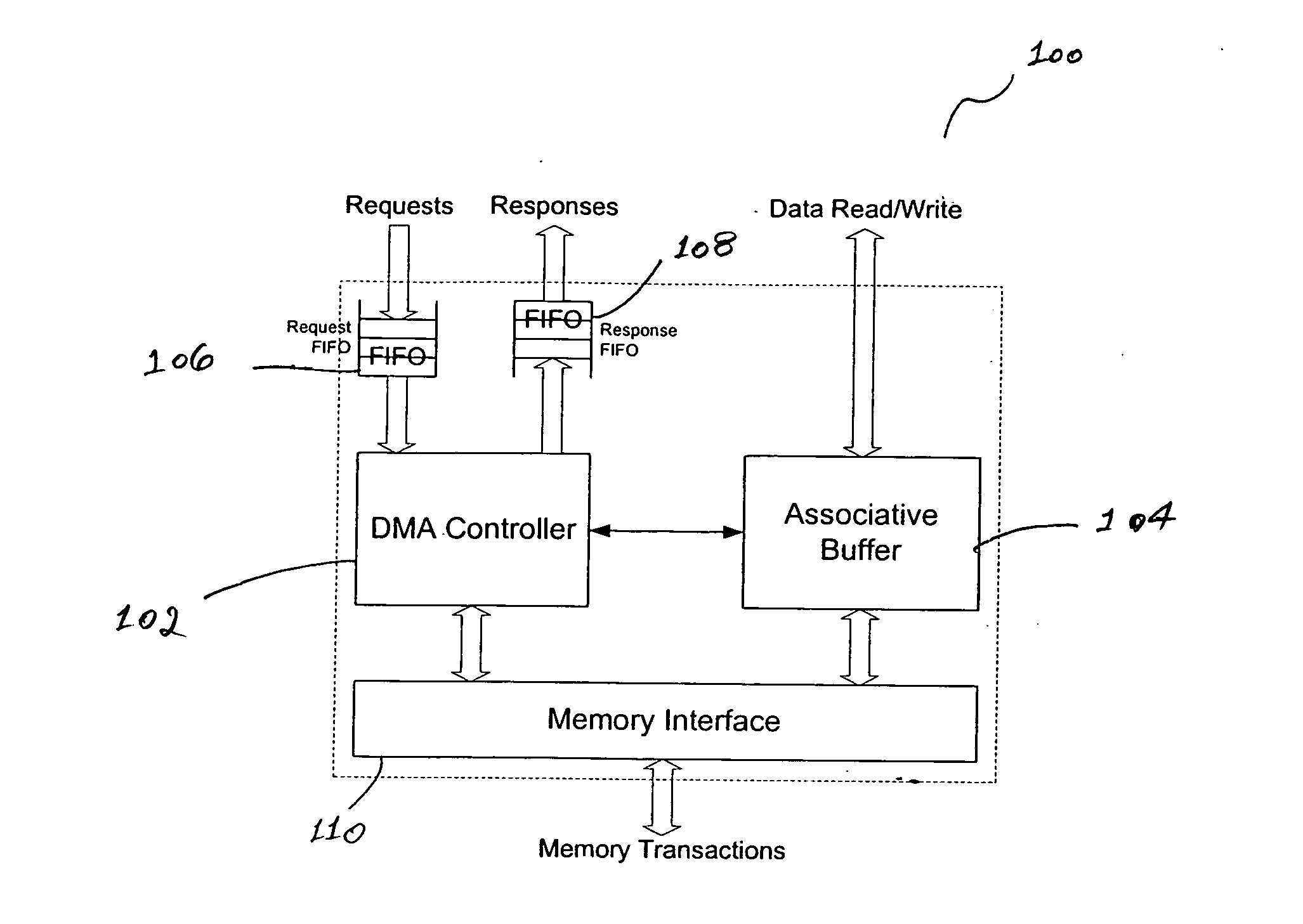
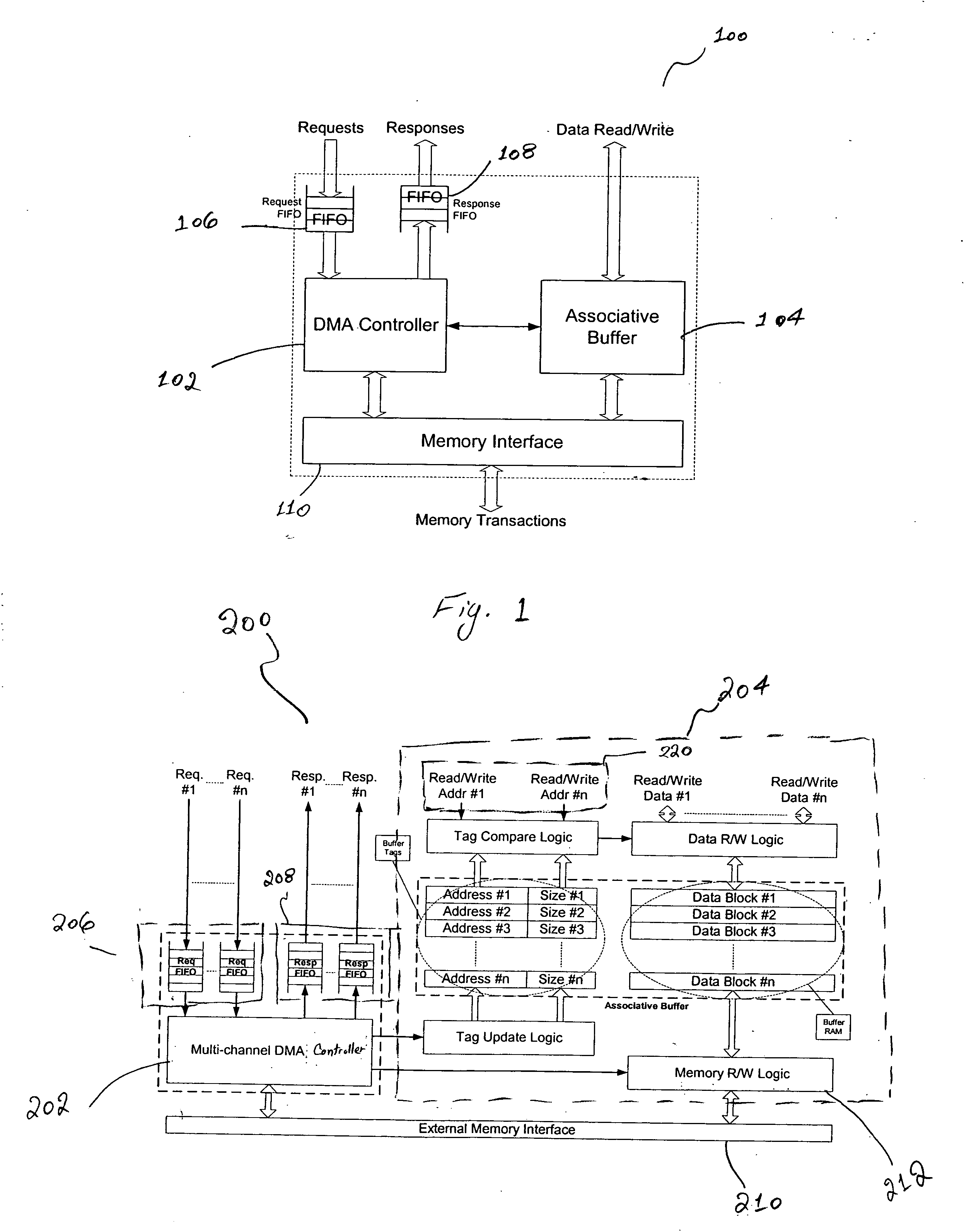
DMA engine for protocol processing
InactiveUS20060206635A1Determinism and uniformity in operationPredictable performance gainElectric digital data processingData transmissionProtocol processing
A DMA engine, includes, in part, a DMA controller, an associative memory buffer, a request FIFO accepting data transfer requests from a programmable engine, such as a CPU, and a response FIFO that returns the completion status of the transfer requests to the CPU. Each request includes, in part, a target external memory address from which data is to be loaded or to which data is to be stored; a block size, specifying the amount of data to be transferred; and context information. The associative buffer holds data fetched from the external memory; and provides the data to the CPUs for processing. Loading into and storing from the associative buffer is done under the control of the DMA controller. When a request to fetch data from the external memory is processed, the DMA controller allocates a block within the associative buffer and loads the data into the allocated block.
Owner:PMC-SIERRA
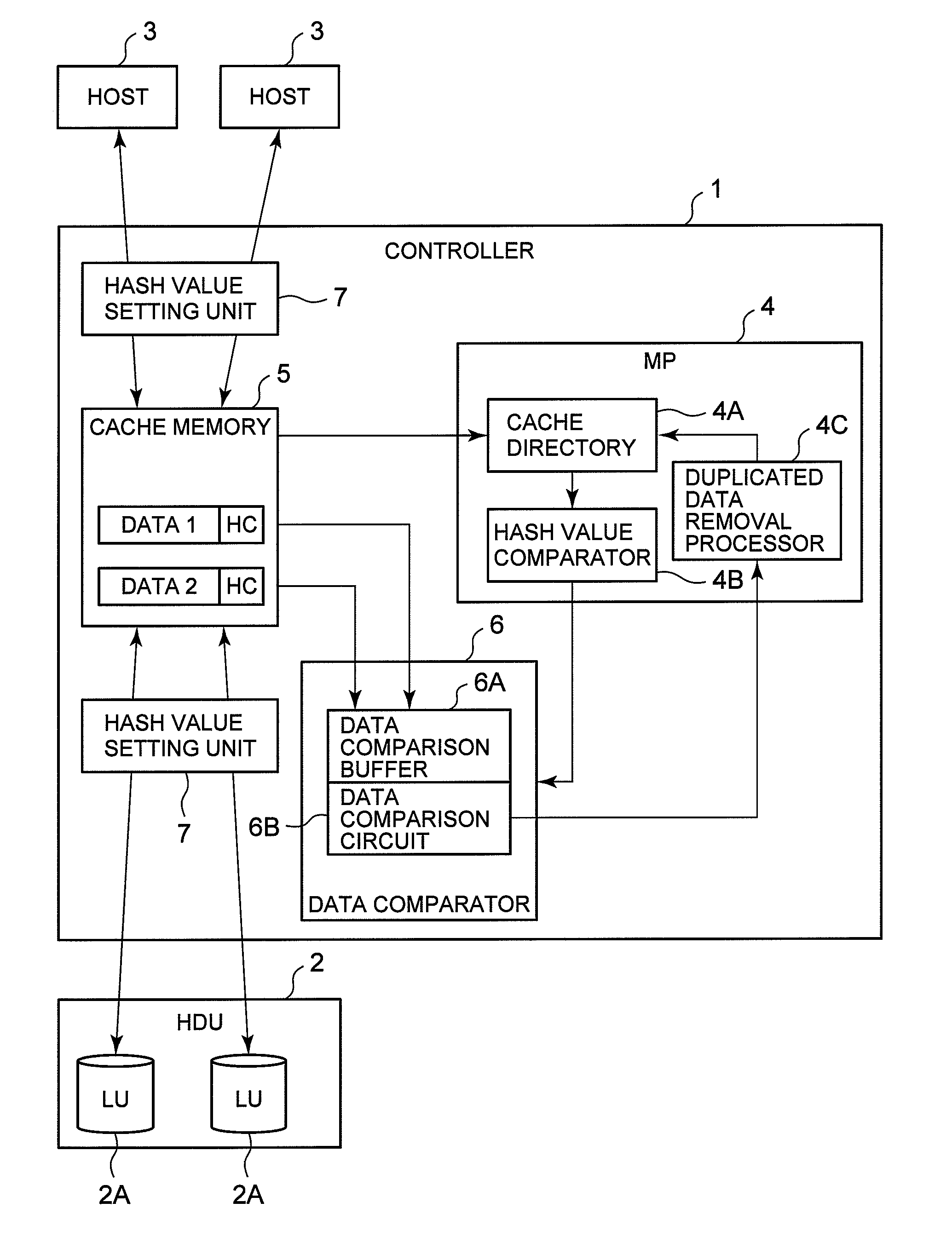
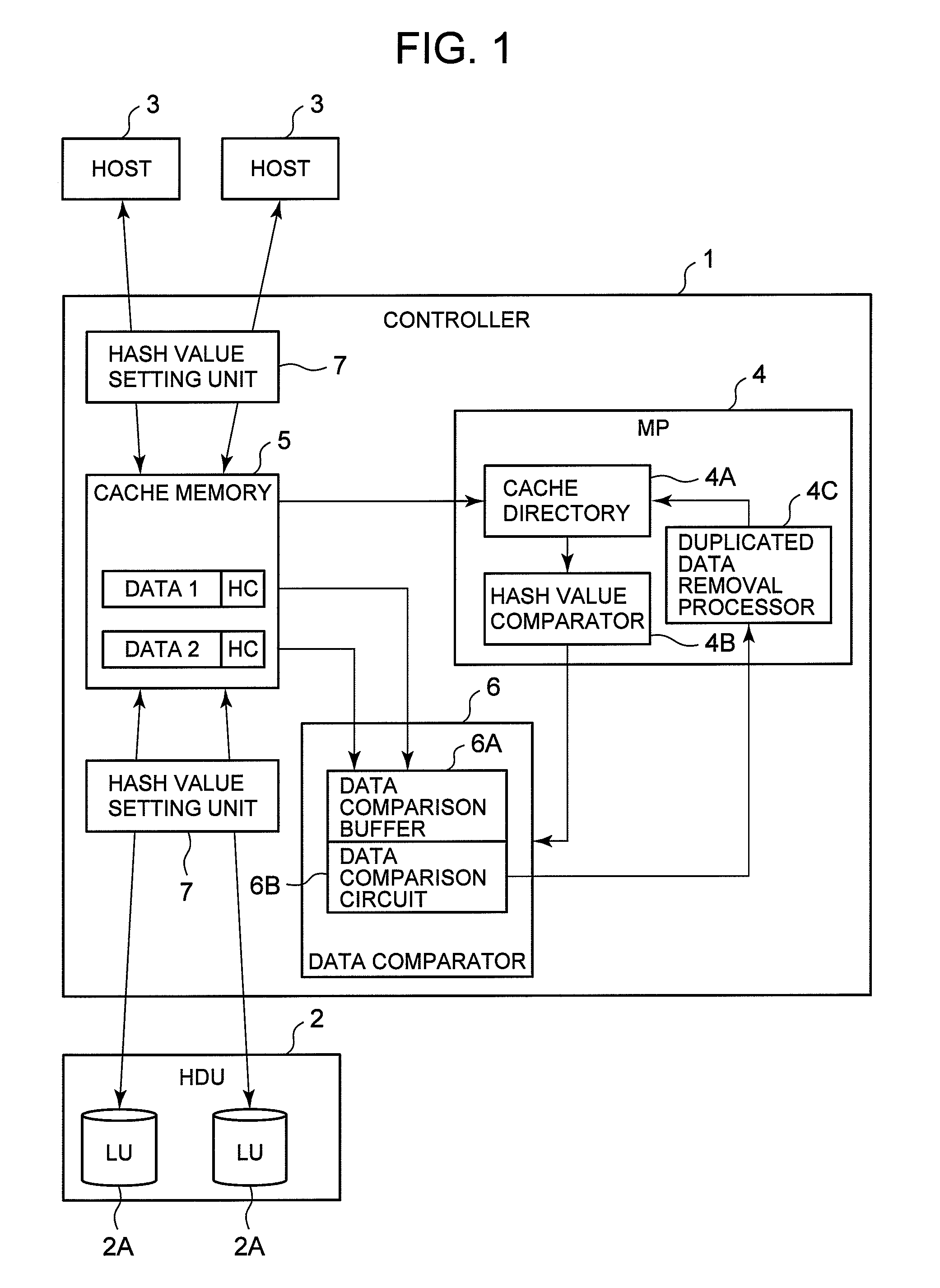
Storage Controller and Duplicated Data Detection Method Using Storage Controller
InactiveUS20090254507A1Remove dataDetect removeError detection/correctionDigital data processing detailsValue setFile comparison
A storage controller of the present invention narrows down the target for data comparison by comparing hash codes beforehand and rapidly detects duplicated data. A hash value setting unit sets a hash code in data received from a host. Hash code-attached data is stored in a logical volume. A microprocessor unit compares the hash codes for each comparison-targeted data. When hash codes match with one another, a data comparator compares the target data, and determines whether or not the data is duplicated data. When duplicated data is detected, the microprocessor unit removes the duplicated data.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Multi-source gaseous fuel blending manifold
InactiveUS9964052B2Maintain continuityMaintain performanceInternal combustion piston enginesEngine controllersAutomotive engineeringMixed fuel
A device, system, and method are provided for blending multiple fuels in multiple states and optimizing the blended fuel for parameters including cost, energy content, pressure, etc. In a primary fuel / supplemental fuel system, the present invention allows a user to consume as much primary fuel as possible even if the primary fuel is hampered by inconsistent pressure or quality issue, thus ensuring a downstream engine runs continuously.
Owner:BM GRP
Storage control device and method for detecting write errors to storage media
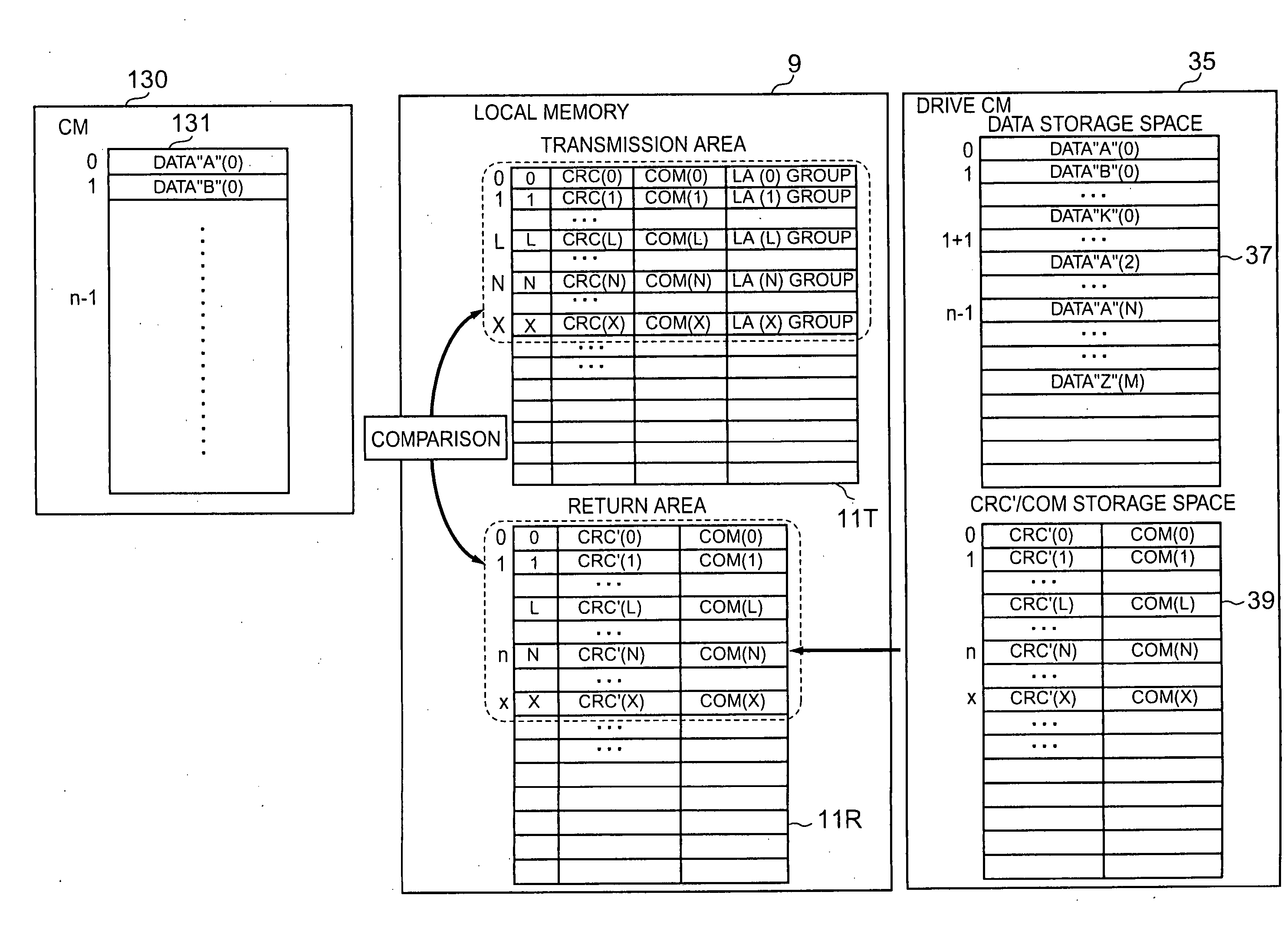
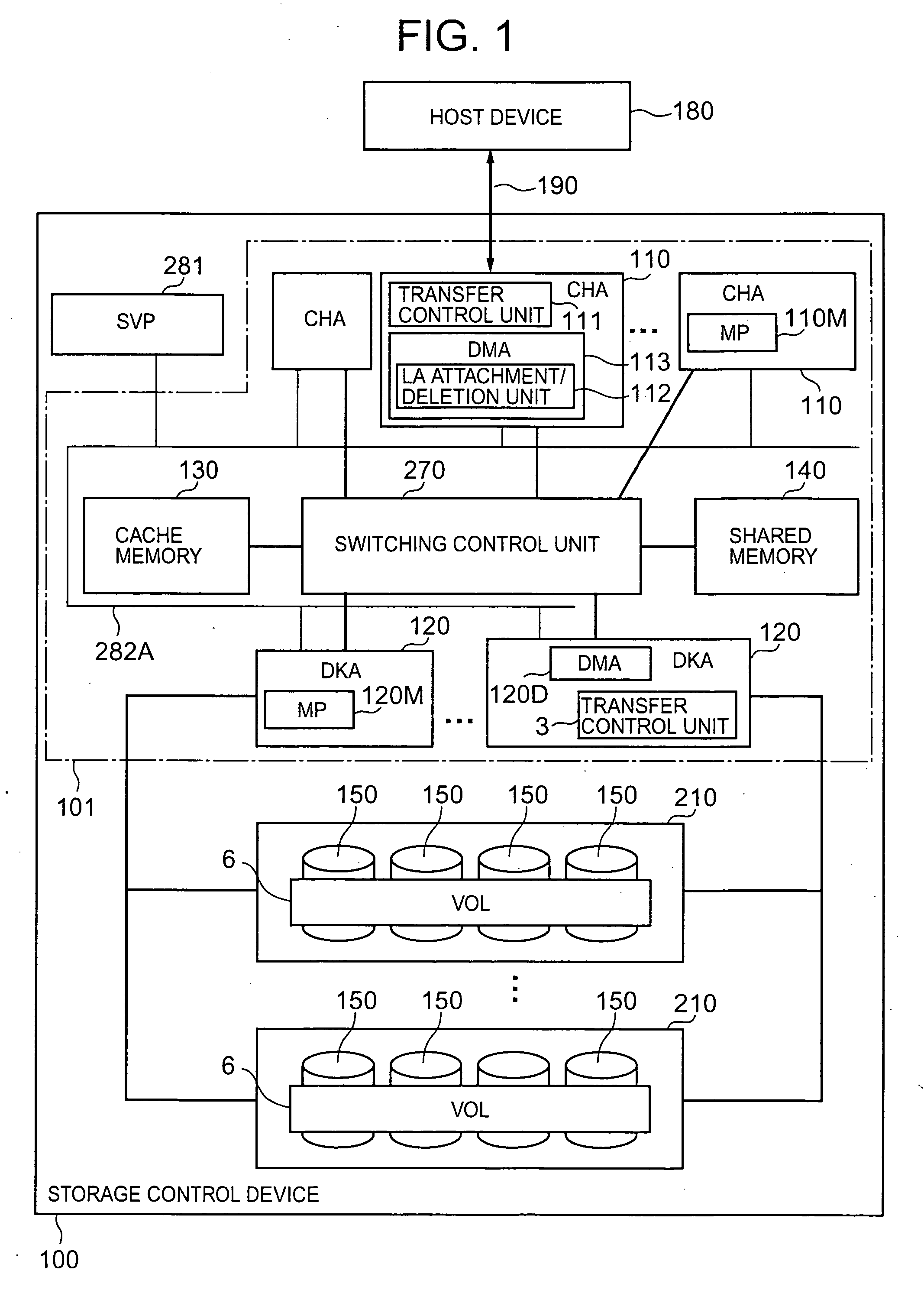
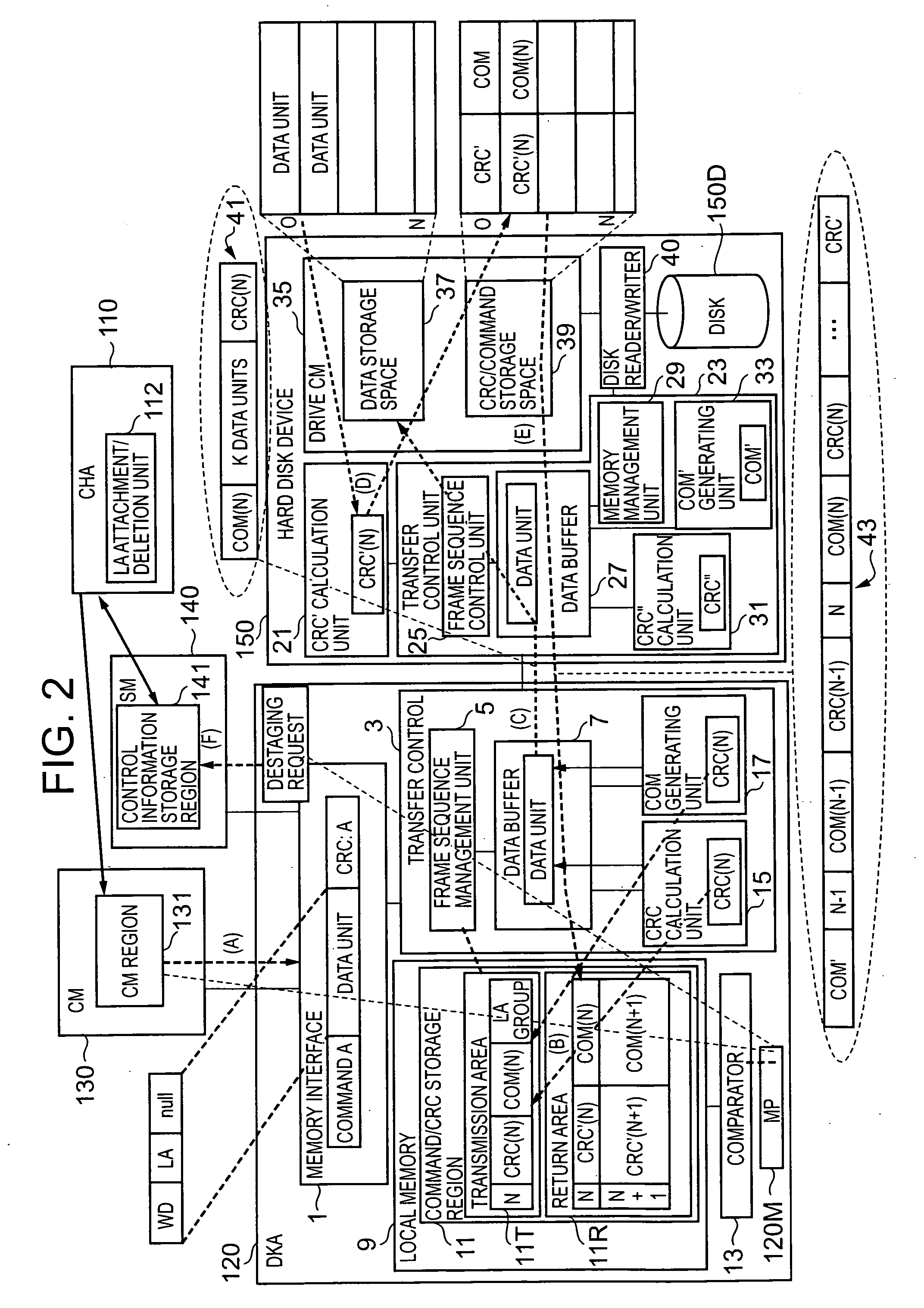
InactiveUS20060098320A1Avoid in performance of storageAvoid performanceCode conversionRecord information storageData shippingControl equipment
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Relay system and method for cellular communication
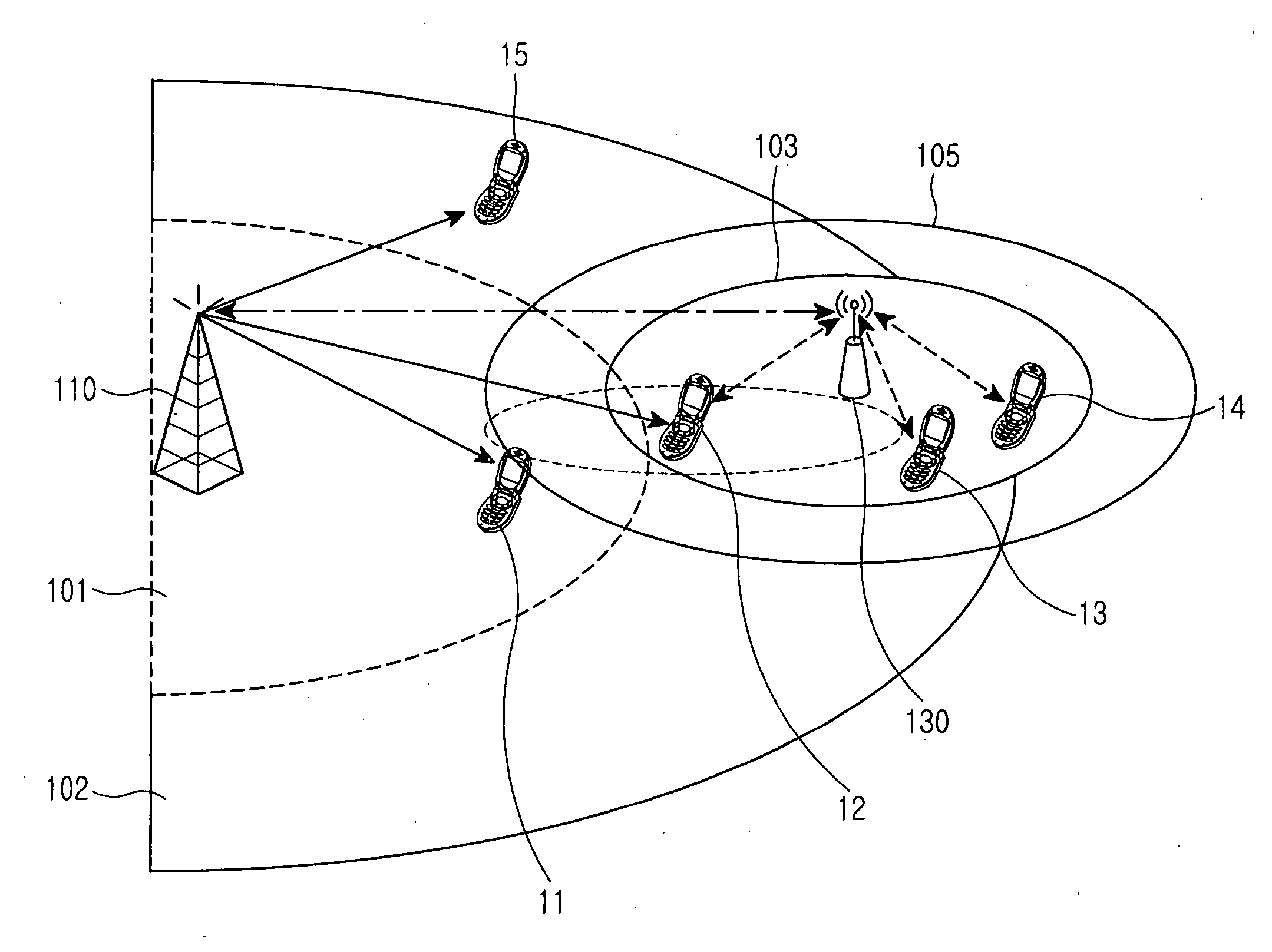
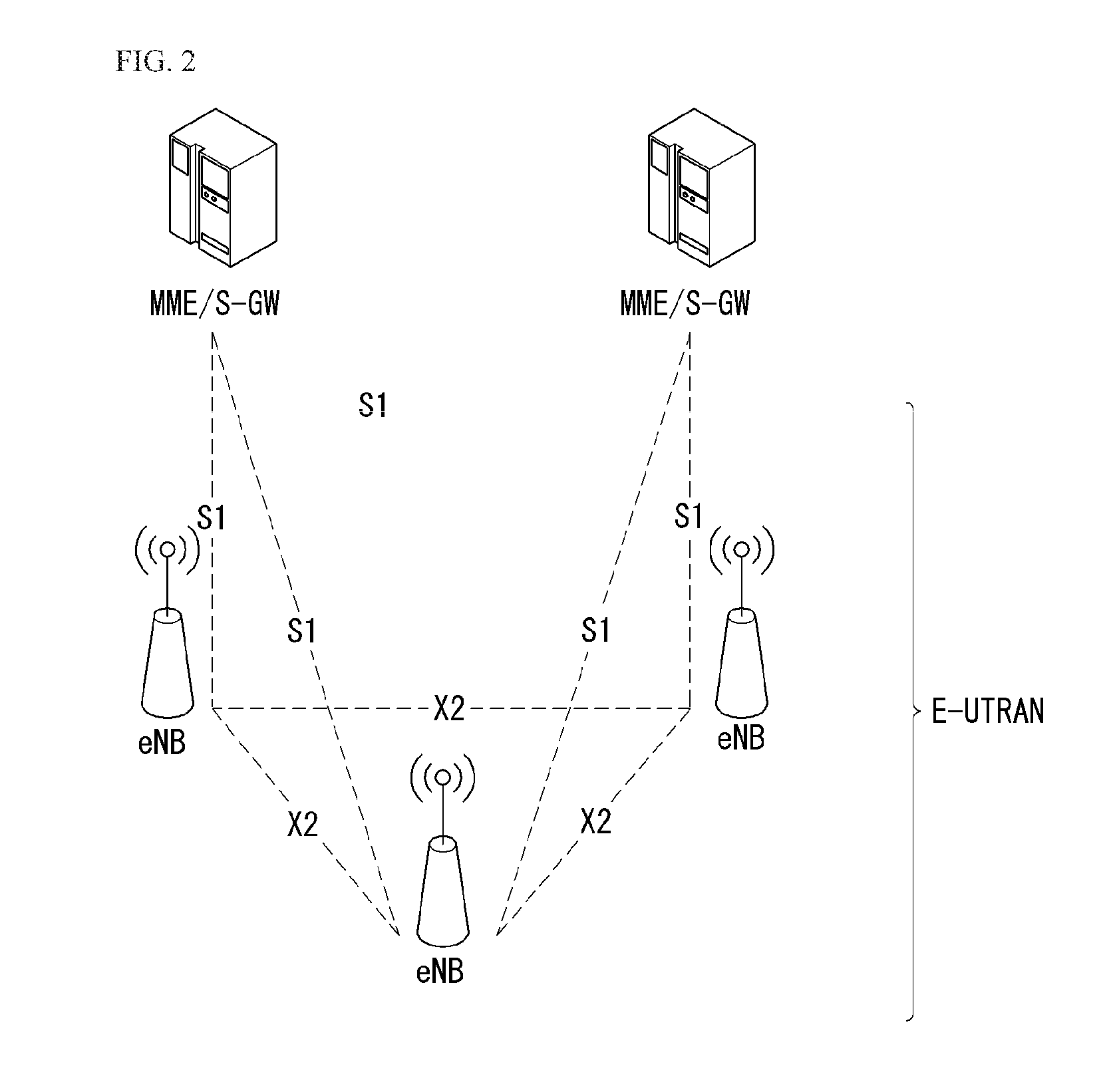
ActiveUS20060281404A1Extend service areaRemove shadow areaFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork topologiesCellular communication systemsUnlicensed band
A relay method is disclosed in a cellular communication system including an access node for providing an access service using resources of a licensed band to a particular terminal among a plurality of terminals with a partial licensed band of the full frequency spectrum, and a relay station for relaying communication between the terminal and an access node. The relay method includes performing base station-led resource allocation on a licensed band for a terminal and a relay station located in a service area of the base station, and performing relay station-led resource allocation on the licensed band and an unlicensed band for a terminal located in a service area of the relay station.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
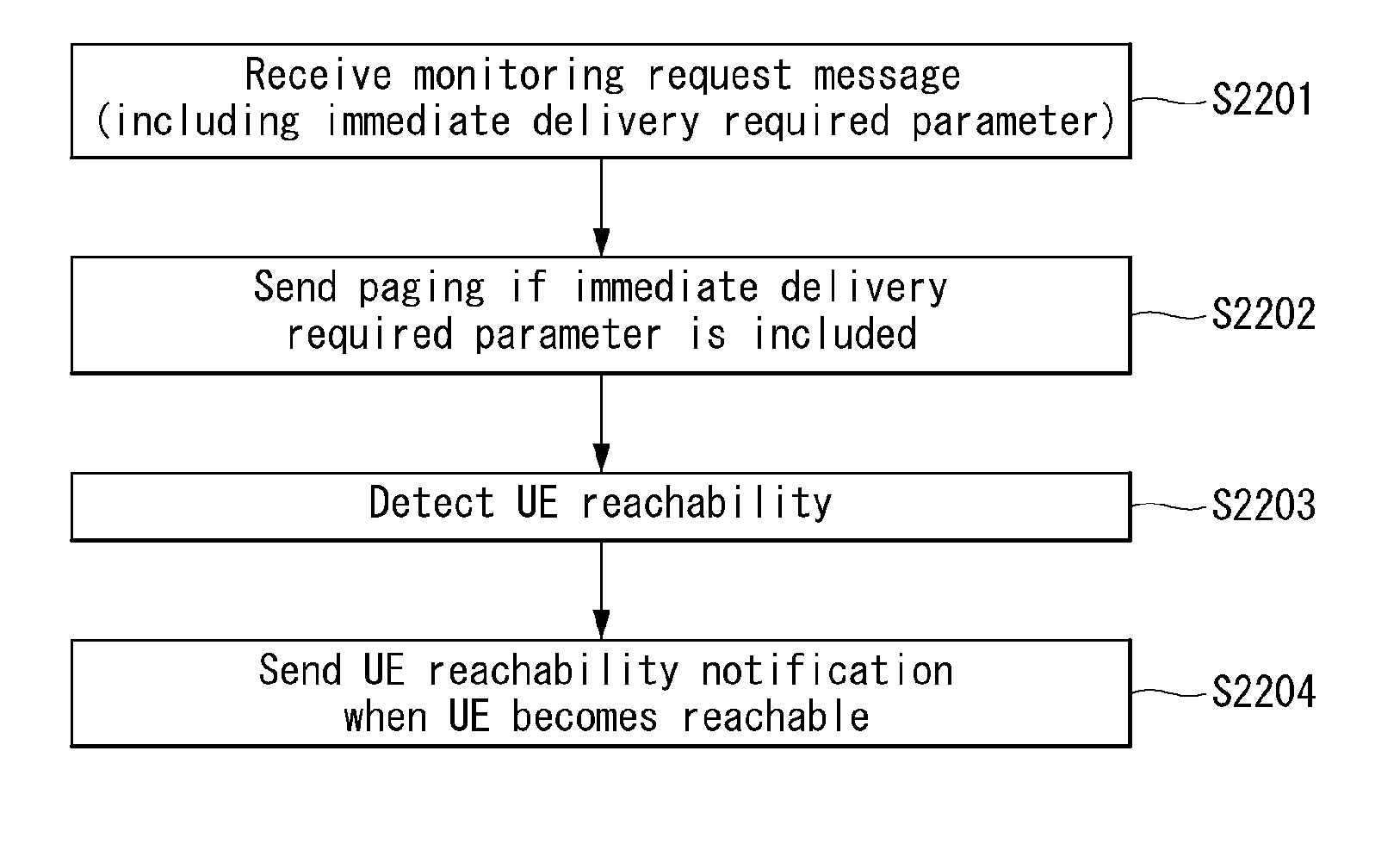
Method and apparatus for monitoring user equipment reachability in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20160286385A1Effective serviceExtended Discontinuous ReceptionConnection managementNetwork data managementCommunications systemReachability
Disclosed herein are a method and apparatus for monitoring UE reachability in a wireless communication system. A method for monitoring UE reachability may include receiving, by a Mobility Management Entity, a monitoring request message for UE reachability including a maximum response time from a Home Subscriber Server, detecting, by the MME, the UE reachability if it is expected that paging is able to be transmitted to UE when extended Discontinuous Reception is applied to the UE, and sending, by the MME, a UE reachability notification to a Service Capability Exposure Function before a next paging occasion of the UE, wherein the maximum response time may indicate a time during which the UE maintains a reachable state so that downlink data is reliably delivered to the UE, and wherein an occasion when the UE reachability notification is transmitted may be determined by taking into consideration the maximum response time.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Forward Collision Avoidance Assistance System
InactiveUS20090143951A1Reduce driver 's uncomfortable feelingImprove drivabilityAnalogue computers for trafficPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementEngineeringActuator
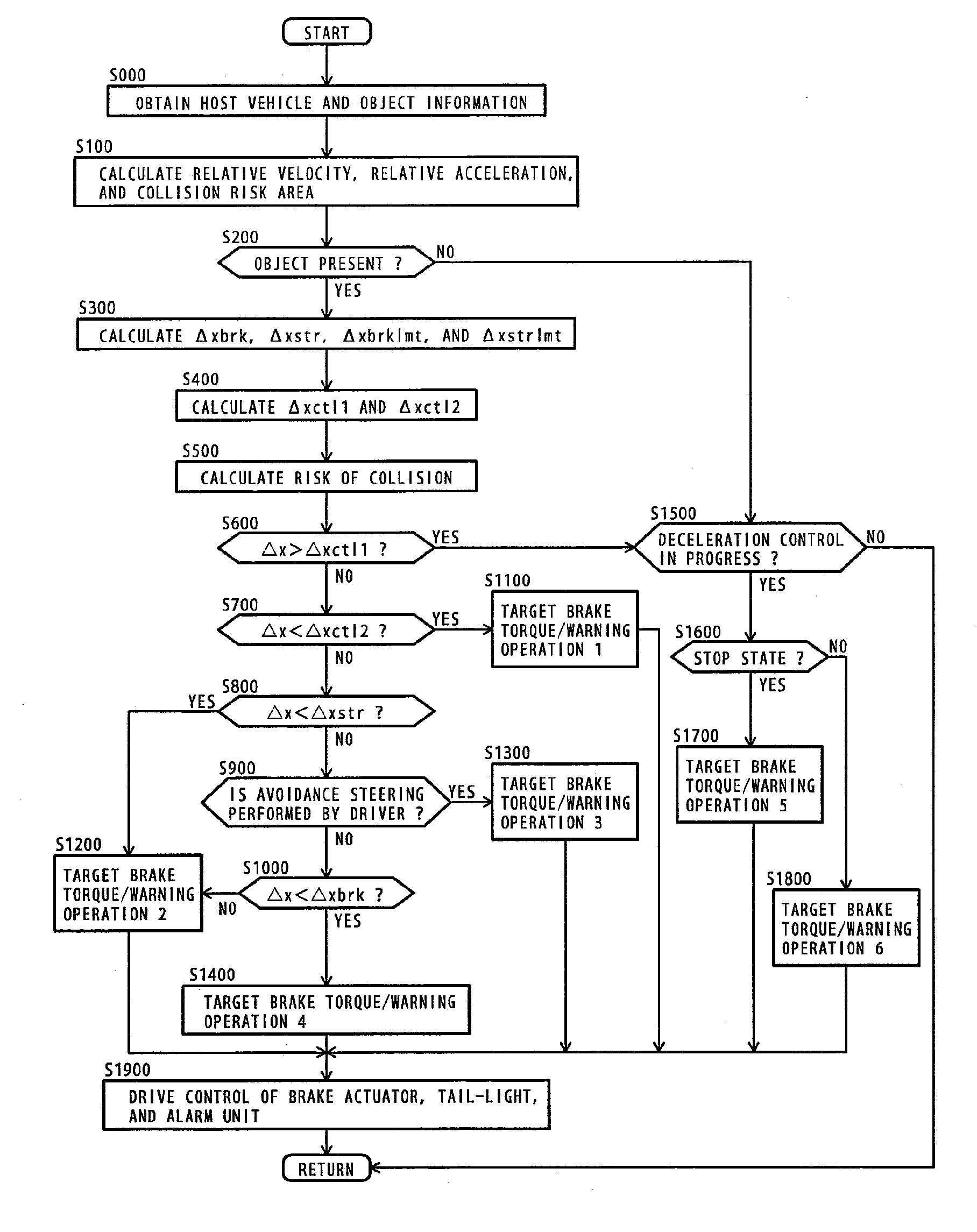
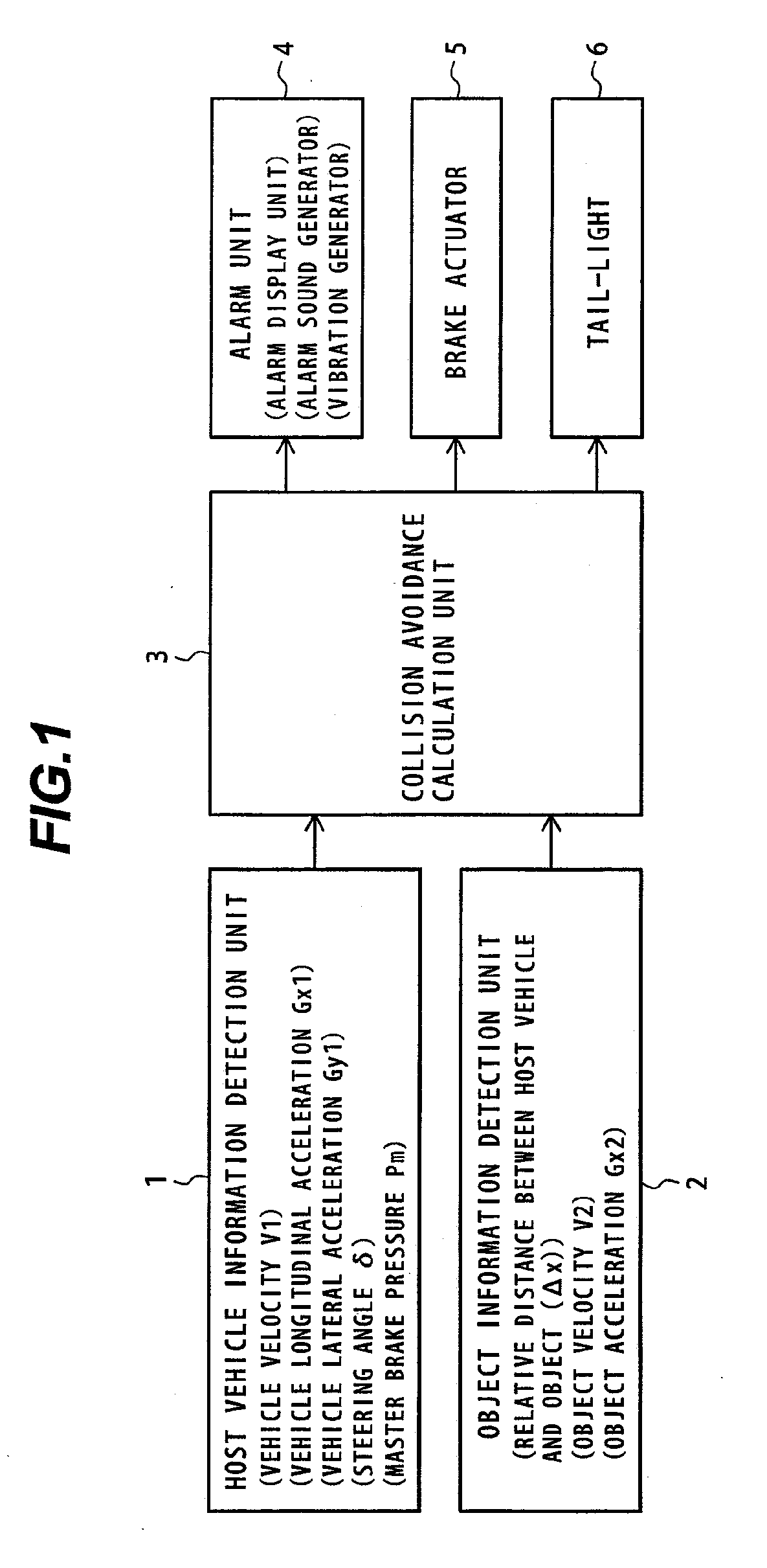
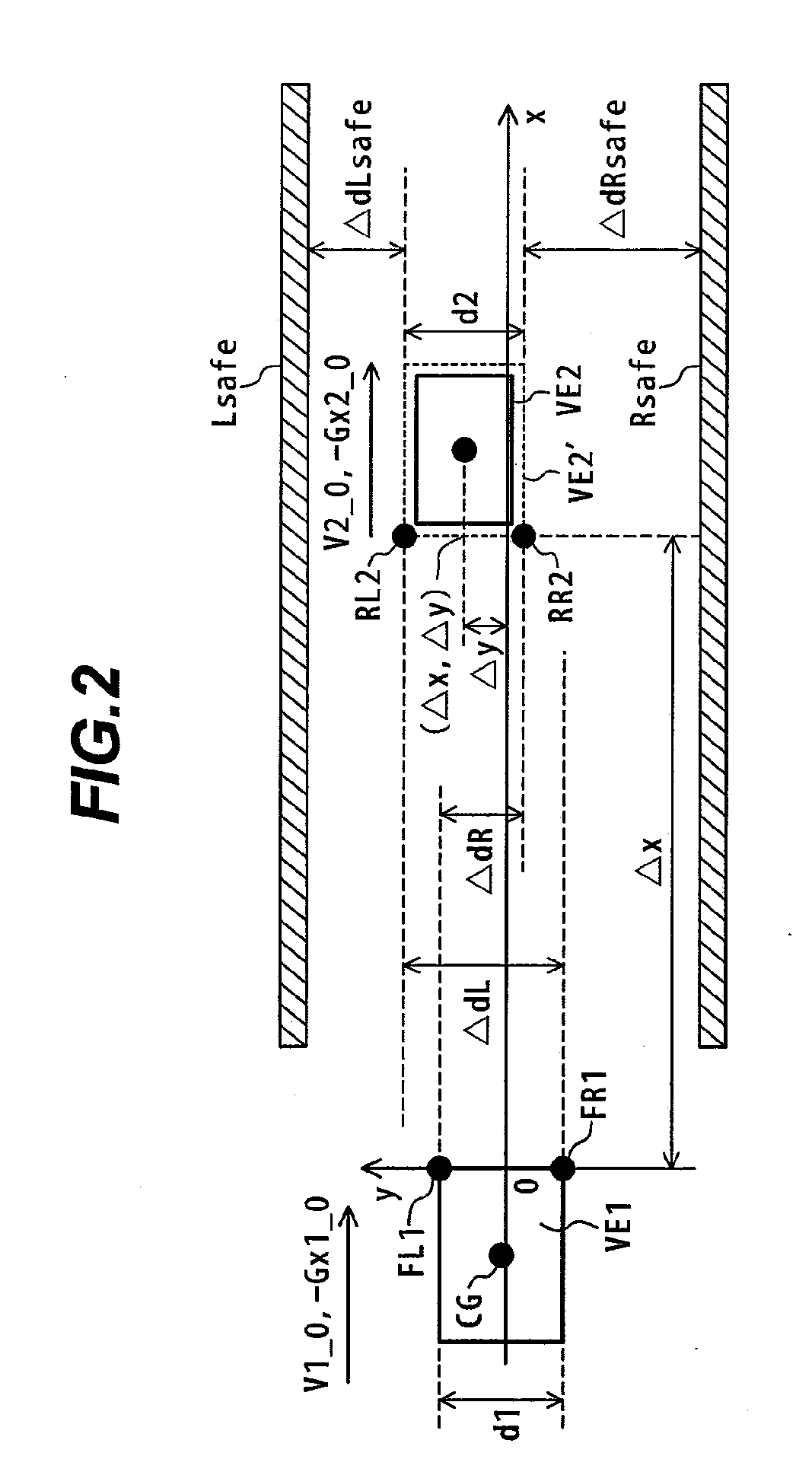
An object of the present invention is to provide a forward collision avoidance assistance system that attains the reduction of driver's uncomfortable feeling and the improvement in drivability while ensuring the collision avoidance performance during operation for avoiding contact with an object.A collision avoidance calculation unit 3 determines a risk of collision between a host vehicle and an object detected in the host vehicle traveling direction based on information about the host vehicle detected by a host vehicle information detection unit 1 and information about the object detected by an object information detection unit 2, and calculates control information for object avoidance to be output to an actuator 5 based on a result of collision risk judgment. The collision avoidance calculation unit 3 uses a collision-avoidable limit distance Δxctl2 determined based on a physical limit that can avoid collision with the object, and a jerk-limited collision avoidable distance Δxctl1 determined based on the acceleration and jerk generated on the host vehicle by object avoidance movement, to control the brake force generated on the host vehicle by a brake actuator 5.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Wireless transmitter and precoding method
InactiveUS20110286502A1Decrease of data ratePrevent error rate performanceMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsError ratioDecomposition
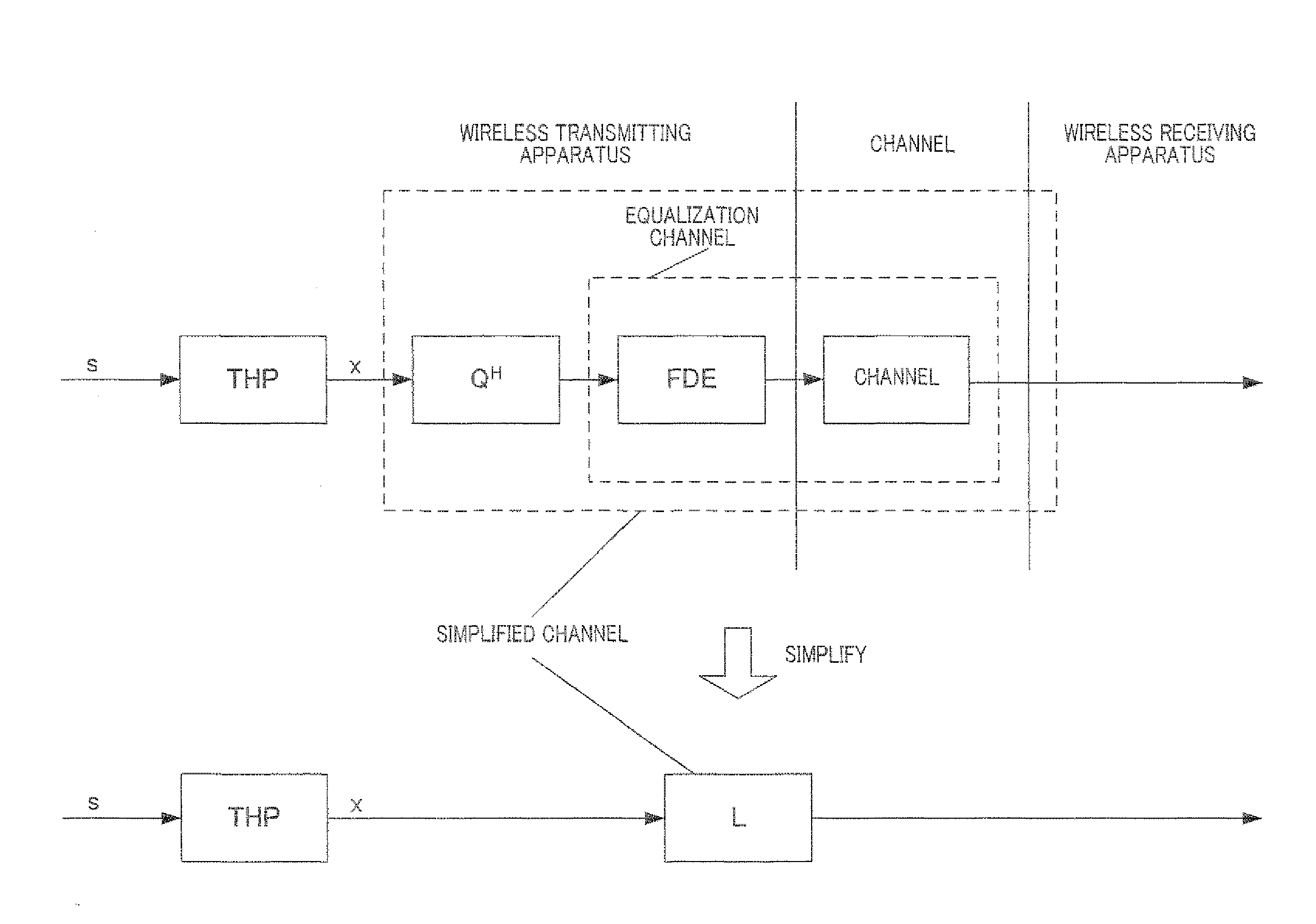
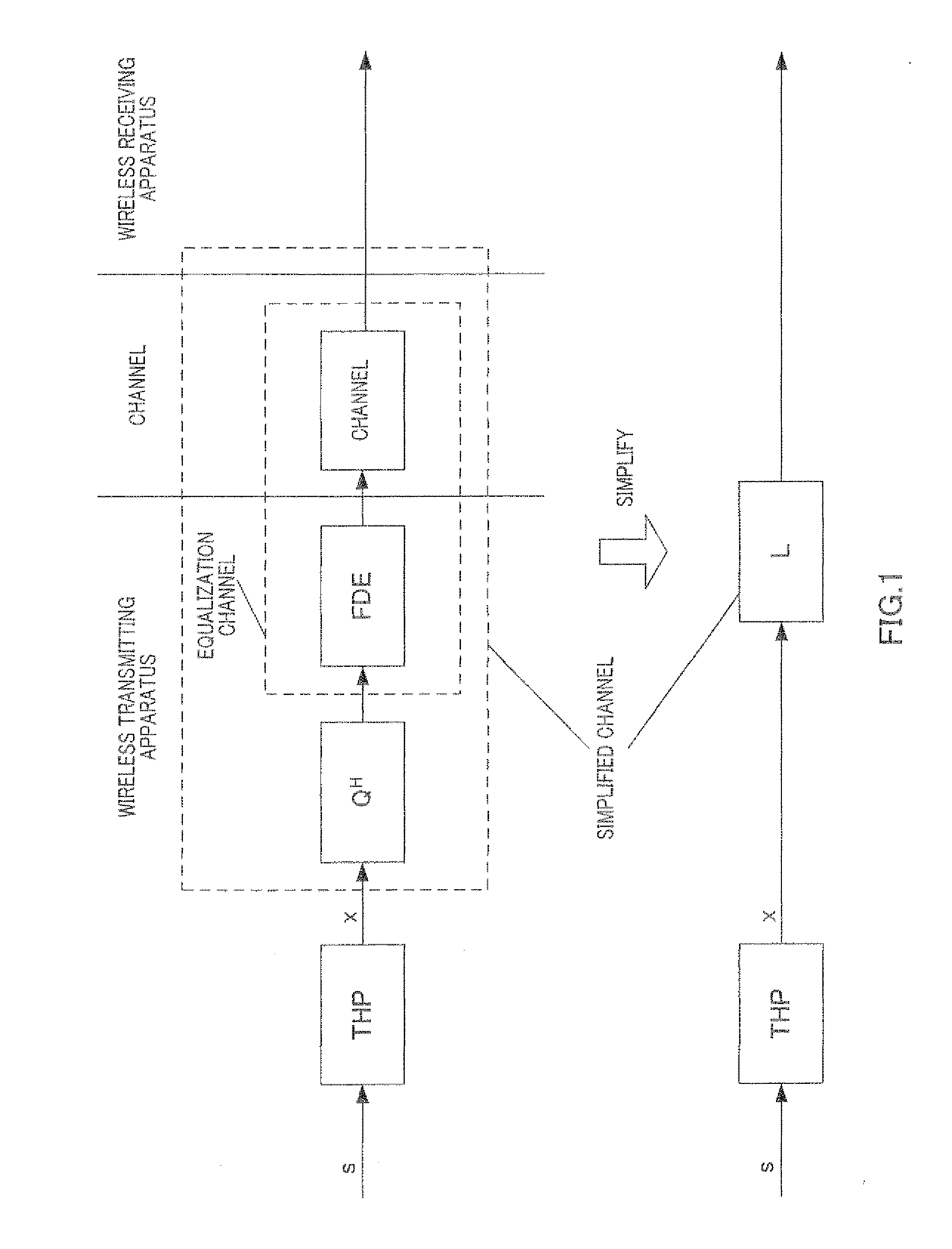
Disclosed is a wireless transmitter that can prevent deterioration of the error rate characteristic without reducing the data rate during mobile communications also utilizing THP for FDE. In the device, an equivalent channel matrix computation unit (118) computes weights to be used for FDE of a transmission block and an equivalent channel matrix indicating equivalent channels that are generated from channel impulse responses, and a decomposition unit (119) obtains a lower triangular matrix (L), that consists of a diagonal element that includes a high channel quality at the front of the transmitting block and a low channel quality at the rear, so as to indicate the channel quality of the transmission block, and an element indicating interference with the transmission block, and a unitary matrix (Q) by means of LQ decomposition of the equivalent channel matrix. A computation unit (120) uses the lower triangular matrix (L) and the average channel quality to compute a matrix (B) that minimizes the mean square error of all symbols between the transmission block before precoding and a block received by a wireless receiver. A preceding unit (103) performs THP of the transmission block using the matrix (B).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Power and optical frequency monitoring system and transmission system of frequency-modulated optical signal
InactiveUS20020154372A1Realized easily and economicallyAvoid performanceWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmittersTransport systemMonitoring system
The present invention relates to a monitoring system that observes the power and optical frequency of a frequency-modulated optical signal, which is utilized in the communication network employing the WDM (wavelength division multiplexing) method. The monitoring system comprises demultiplex means for demultiplexing the frequency-modulated optical signal outputted from a transmitter including frequency-modulation means, photo-detection means for converting the output of demultiplex means into an electrical signal, and extraction means for extracting the power and optical frequency of an optical signal by measuring the magnitude of an amplitude-modulated tone.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
System and method of adaptive frequency hopping with look ahead interference prediction
ActiveUS20090257396A1Maximize capacityImprove performanceRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesSelf adaptiveEngineering
A novel and useful adaptive frequency hopping scheme for wireless devices and networks operating in a congested environment of similar devices, where capacity maximization is desired. The hopping sequence of each wireless link is dynamically adapted such that the impact of the surrounding interference is minimized and the interference induced onto the coexisting systems is also minimized. The scheme detects the repetitive presence of interference on a particular channel and comprises a replacement mechanism for swapping the interfered frequency-channel with one that would be clear for that particular time-slot. The mechanism detects interference during a redundant portion of the transmission (i.e. header or trailer) without having to experience packet failures (i.e. data loss). If the interference impact (e.g. corrupted header bits) exceeds a predefined threshold, that frequency channel is declared temporarily unusable for that time slot and is replaced with another in accordance with a frequency replacement policy. Periodic interference at a particular frequency, originating from a coexisting system of similar operating parameters, may also be detected at instances that are distant from the timeslots for which that particular frequency is to be used, such that frequency replacement in the hopping sequence can be scheduled ahead of time and collisions would be avoided altogether.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
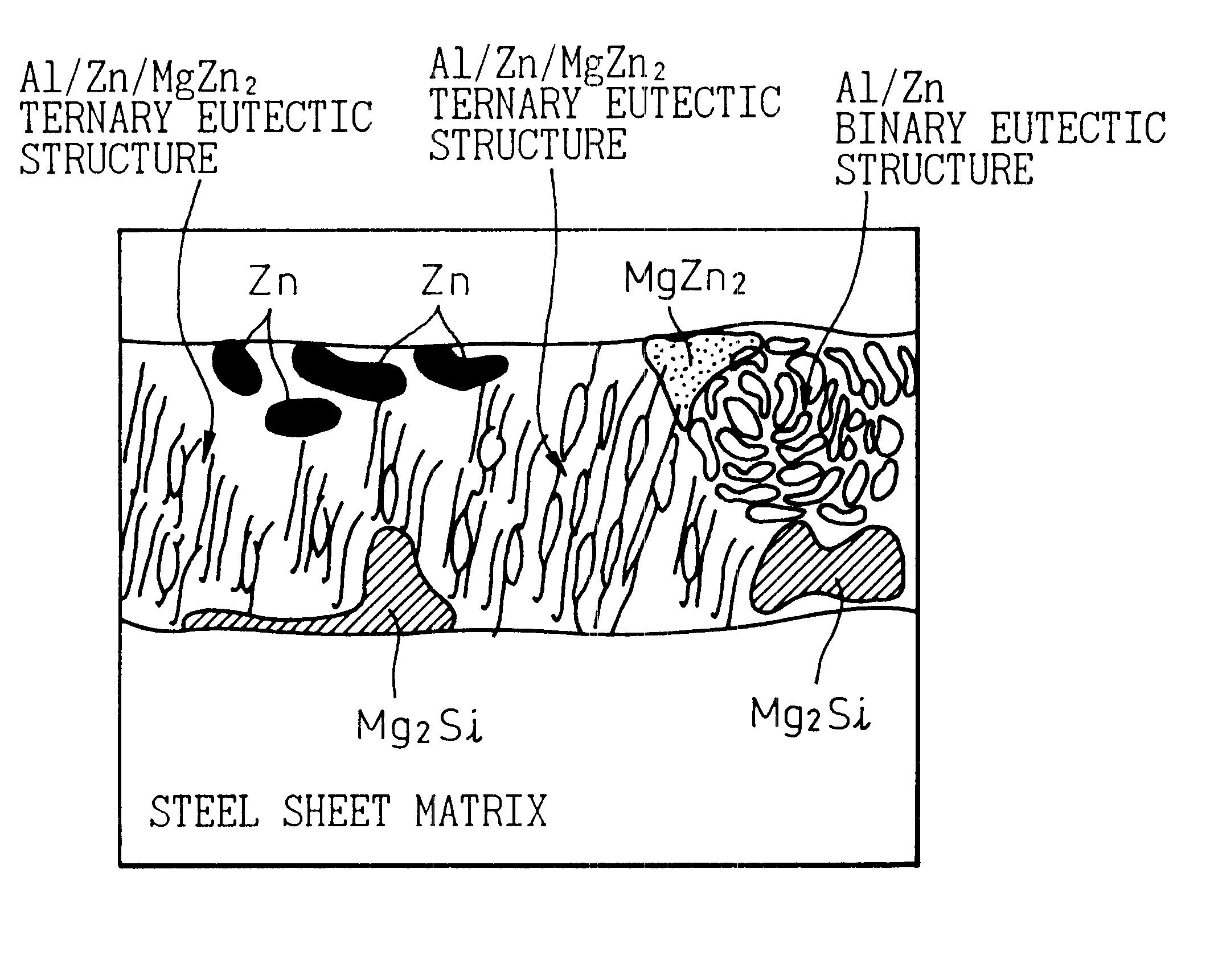
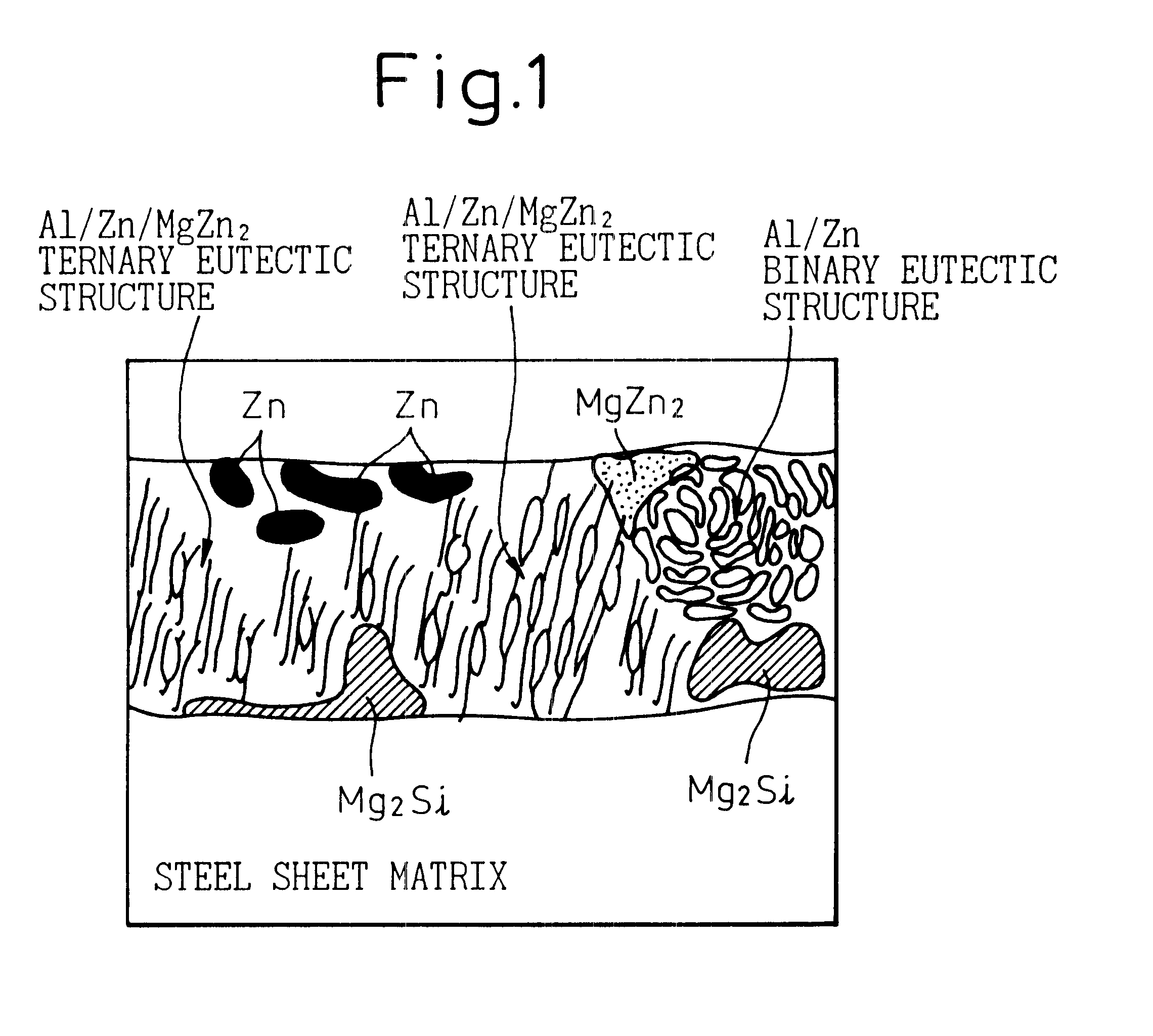
-Zn coated steel material, ZN coated steel sheet and painted steel sheet excellent in corrosion resistance, and method of producing the same
InactiveUS6465114B1Improve corrosion resistanceResistance to red rustHot-dipping/immersion processesLiquid surface applicatorsSheet steelAlloy coating
A coated steel material excellent in corrosion resistance and a method of producing the same, wherein a coated steel material has on the surface of the steel sheet a Zn-alloy coating layer containing 1-10 wt % of Mg, 2-19 wt % of Al and 0.01-2 wt % of Si, where Mg and Al satisfy Mg (%)+Al (%)<=20%, the balance being Zn and unavoidable impurities, and has a coating layer structure of a Mg intermetallic compound or the like. As a base metal treatment, it is preferably provided with a Ni coating layer. The coated Zn-alloy coated steel sheet may have provided on the coating layer, as an intermediate layer, a chromate film layer, and, as an upper layer, an organic coating layer. The Zn-alloy coating layer may further contain one or more of 0.01-1 wt % of In, 0.01-1 wt % of Bi and 1-10 wt % of Sn. The coated steel material may be painted.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
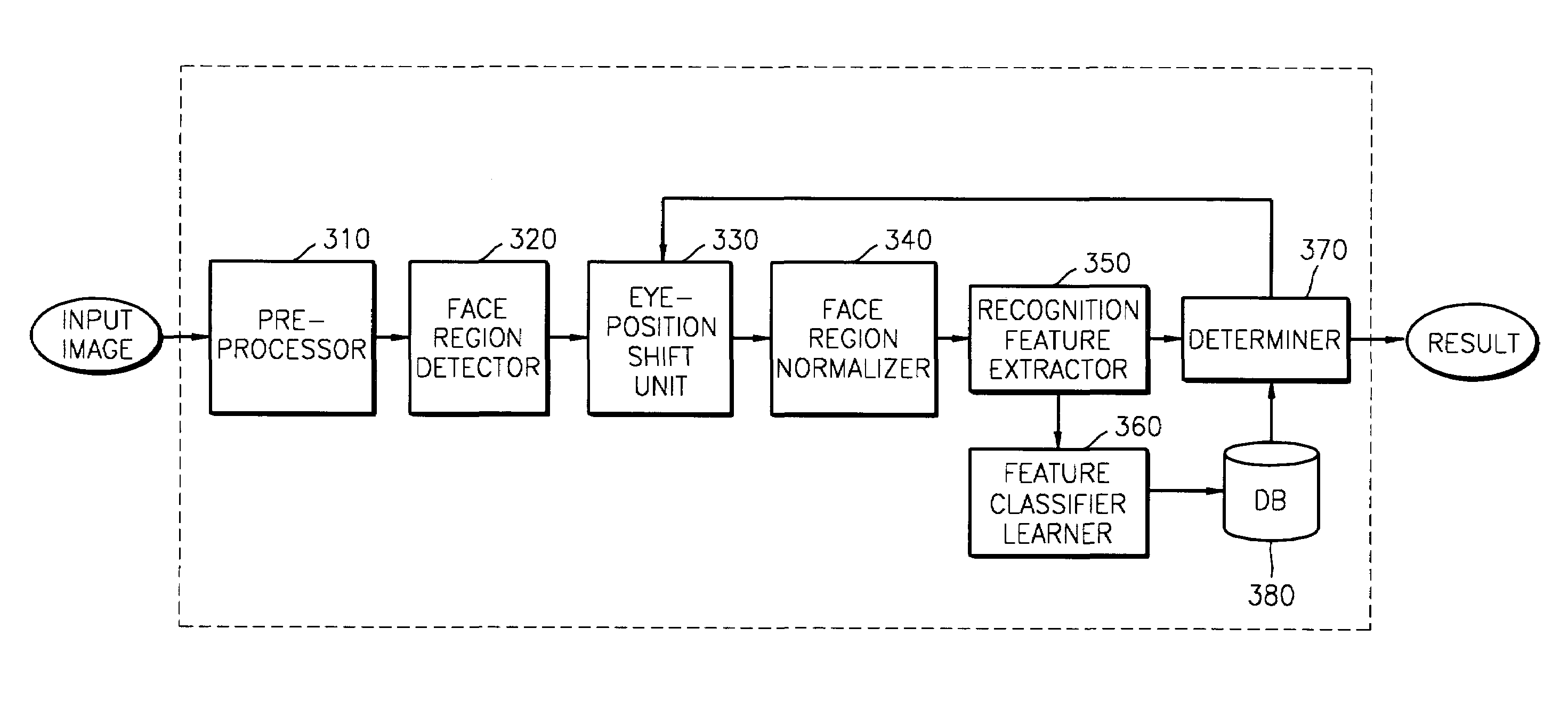
Method for verifying users and updating database, and face verification system using the same
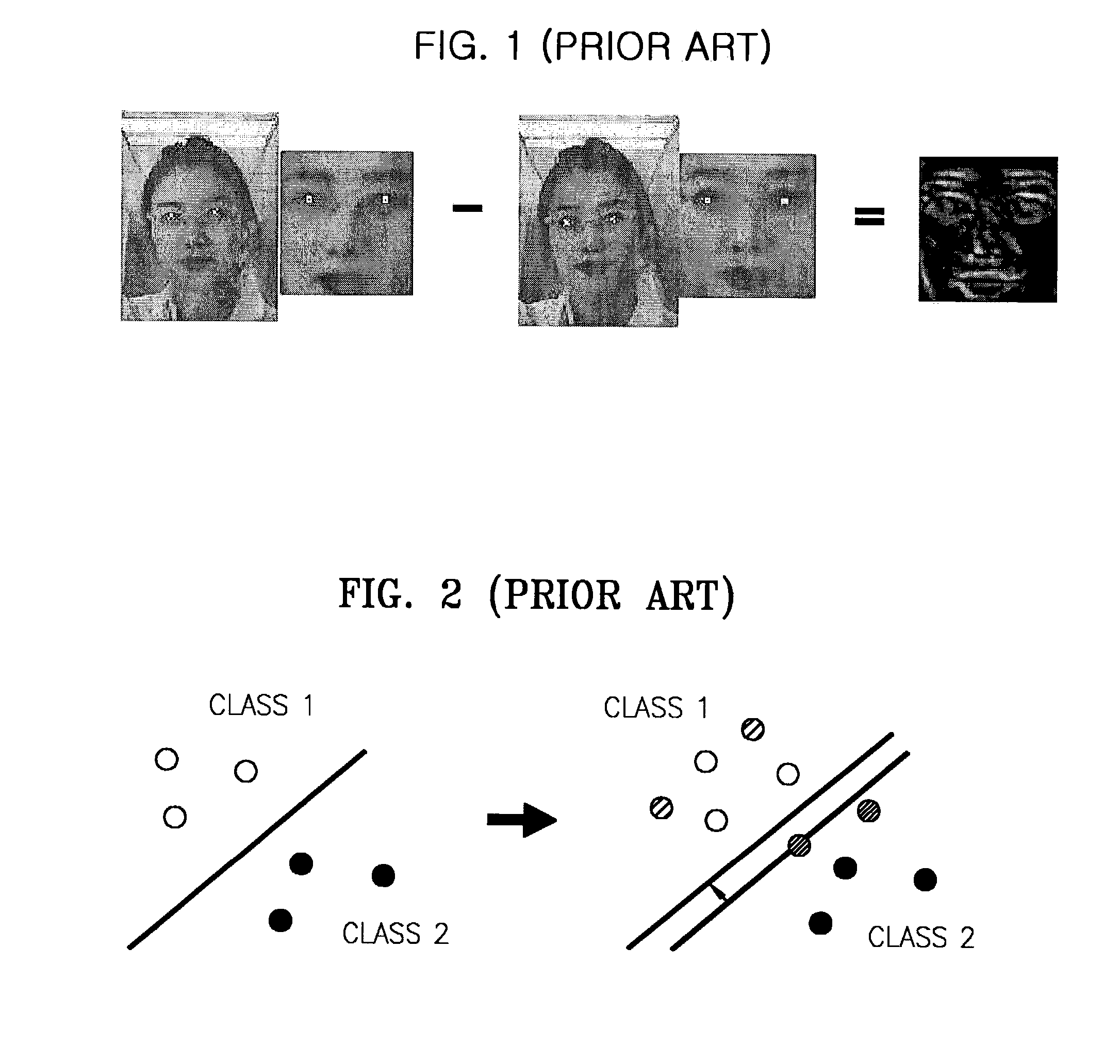
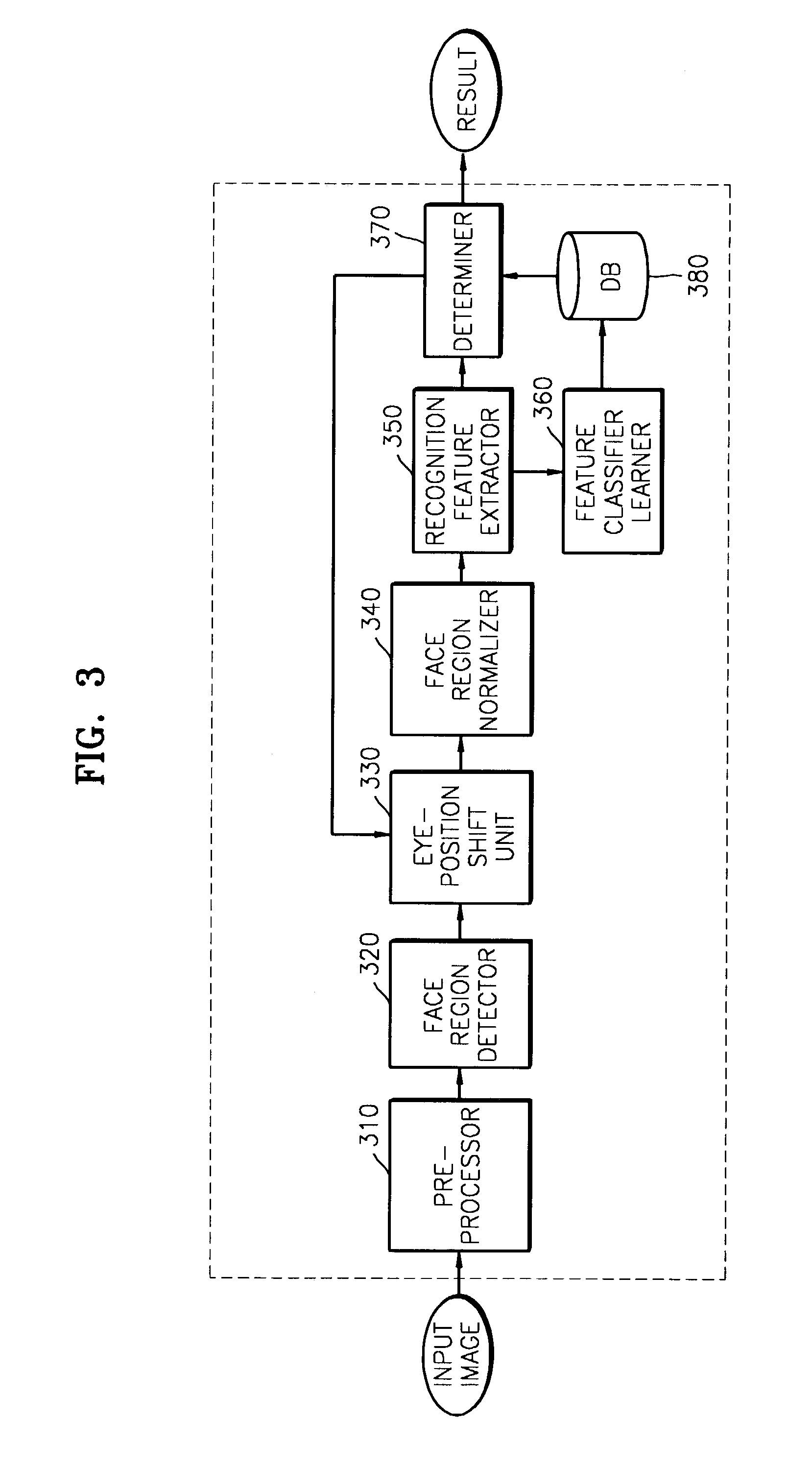
ActiveUS7187786B2Preventing recognition performanceAvoid performanceImage analysisDigital computer detailsPattern recognitionFace verification
To reduce degradation of recognition performance due to eye detection errors during face verification and to overcome a problem in that sufficient data to design an optimum feature classifier cannot be obtained during face registration, a method includes shifting the positions of eyes detected during face registration in predetermined directions by a predetermined distance to generate pairs of new coordinate points of the eyes; normalizing a face image on the basis of each pair of new coordinate points of the eyes; using the results of normalization in teaching a feature classifier, thereby coping with eye detection errors. In addition, two threshold values are used to prevent a database from being updated with a face of an unregistered person and to update the database with a normal client's face image that has been used during the latest face verification.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Data delivery in conjunction with a hybrid automatic retransmission mechanism in CDMA communication systems
InactiveUS20050022098A1Reduce the impactImprove stall avoidance performanceError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementData packCommunications system
Techniques for delivering data recovered by a HARQ entity in proper order to higher layers in a CDMA system. In a method, packets are received from the HARQ entity by the re-ordering entity and missing packets among the received packets are detected. Packets may be transmitted in a sequential order based on transmission sequence numbers (TSNs) assigned to the packets, and missing packets may be detected based on the TSNs of the received packets. Delivery of received packets later than the missing packets are stalled because higher layers expect data in-order. A determination is thereafter made whether each missing packet is (1) subsequently received from the HARQ entity or (2) lost, by successively eliminating HARQ channels that may be used to send the missing packet. Received packets previously stalled by each missing packet are delivered after the missing packet is determined to be lost or received.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
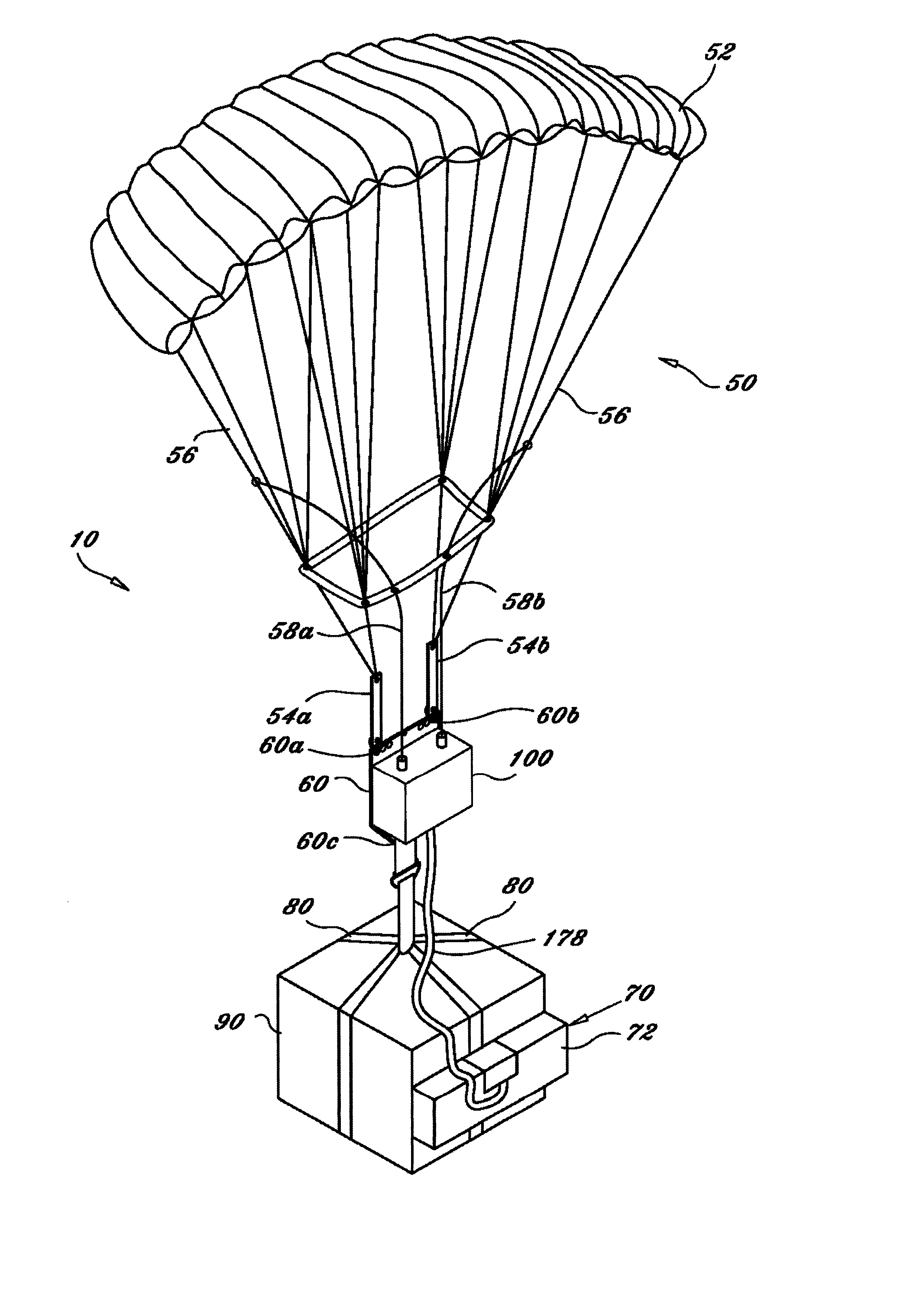
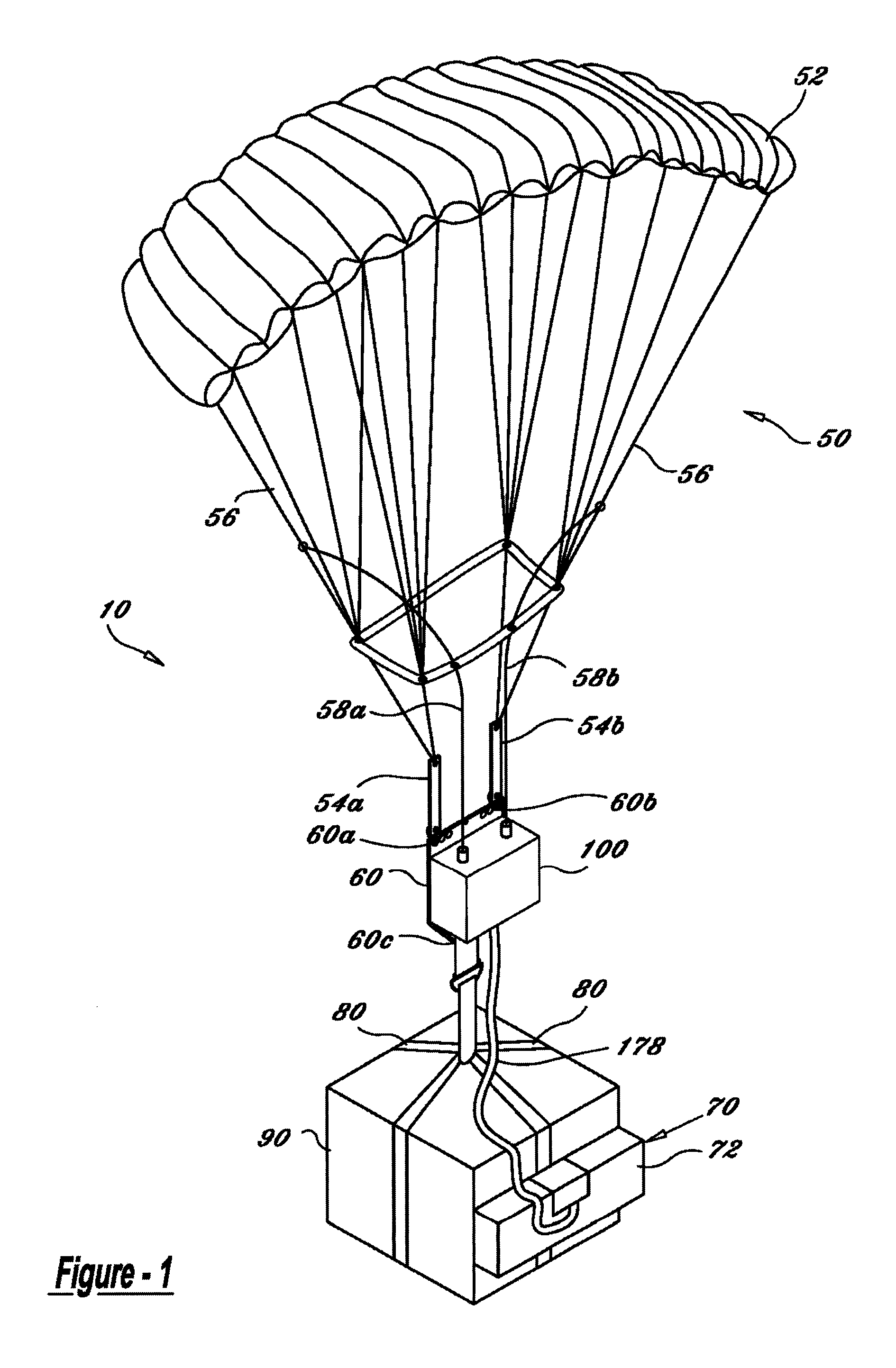
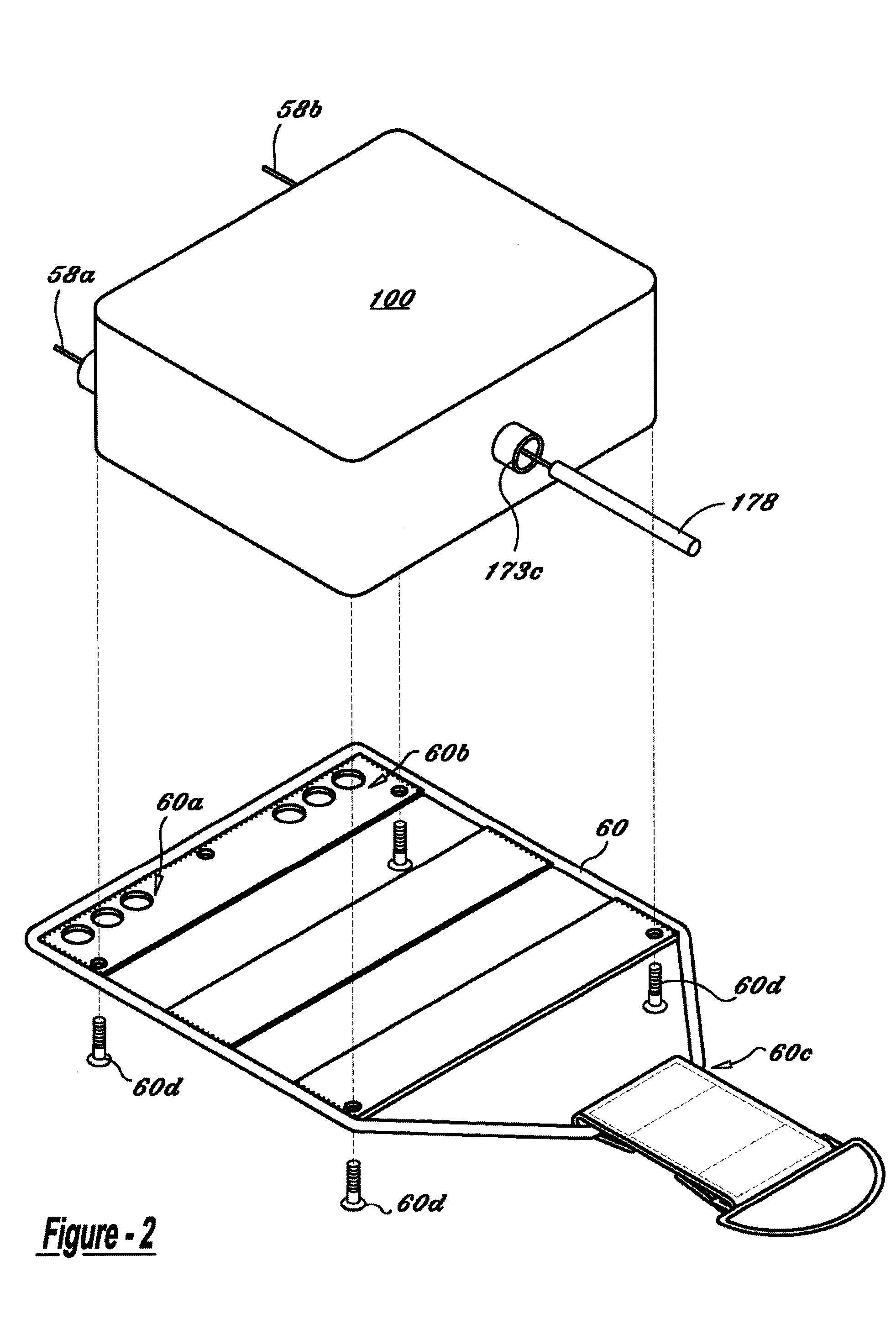
Aerial delivery device
InactiveUS20050230555A1Reduce dragPerformance be not hinderParachutesLaunching weaponsGuidance systemDrogue parachute
A guided aerial delivery device which can be used to safely and accurately deliver a payload and supplies from an aircraft in flight to a specific target location in a reduced time. The aerial delivery device uses an overloaded ram-air drogue parachute controlled by a guidance system to steer the payload towards the intended target. When a selected altitude is reached, a recovery parachute is activated and the payload descends the remaining distance under the recovery parachute.
Owner:STRONG EDWARD
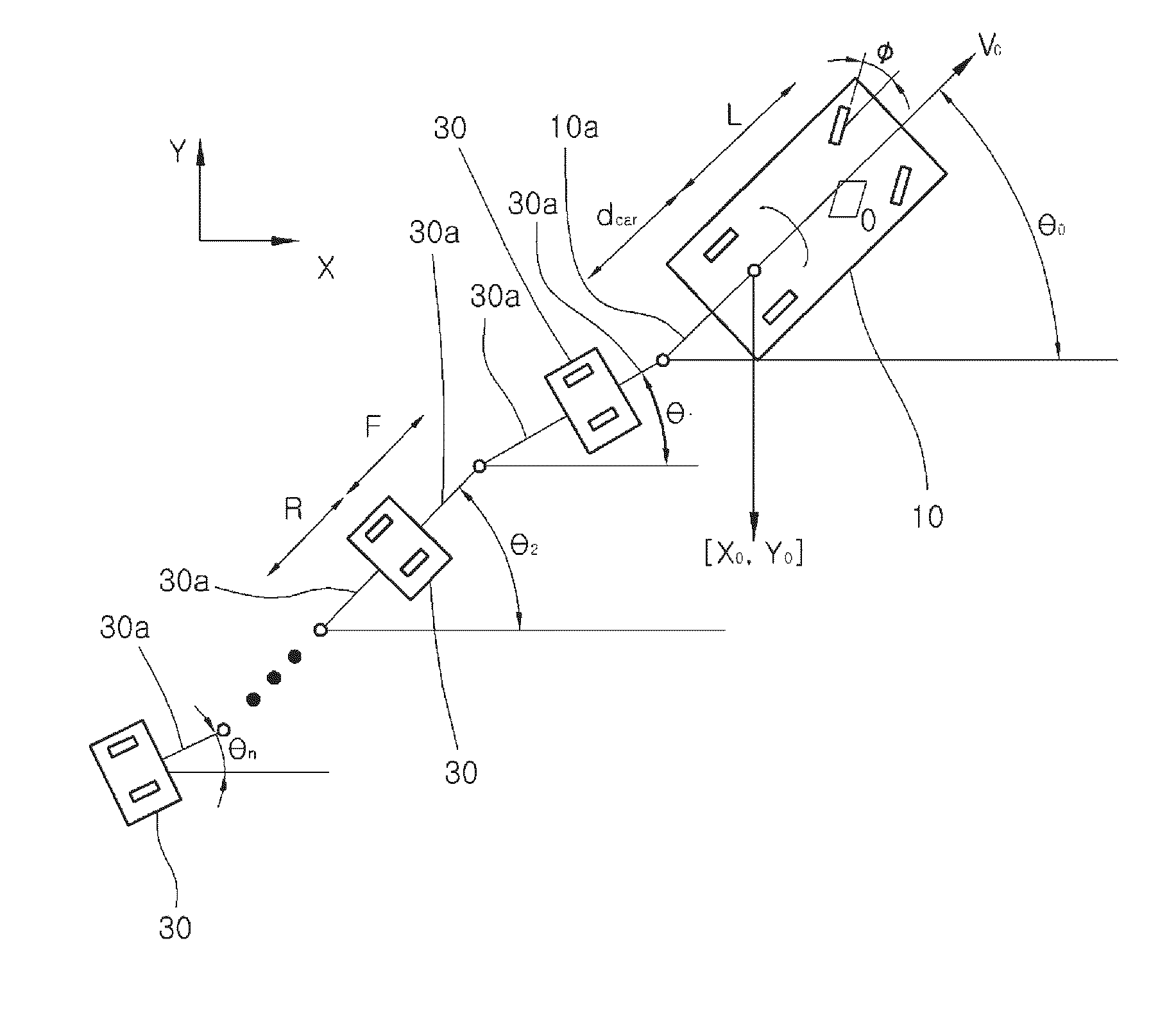
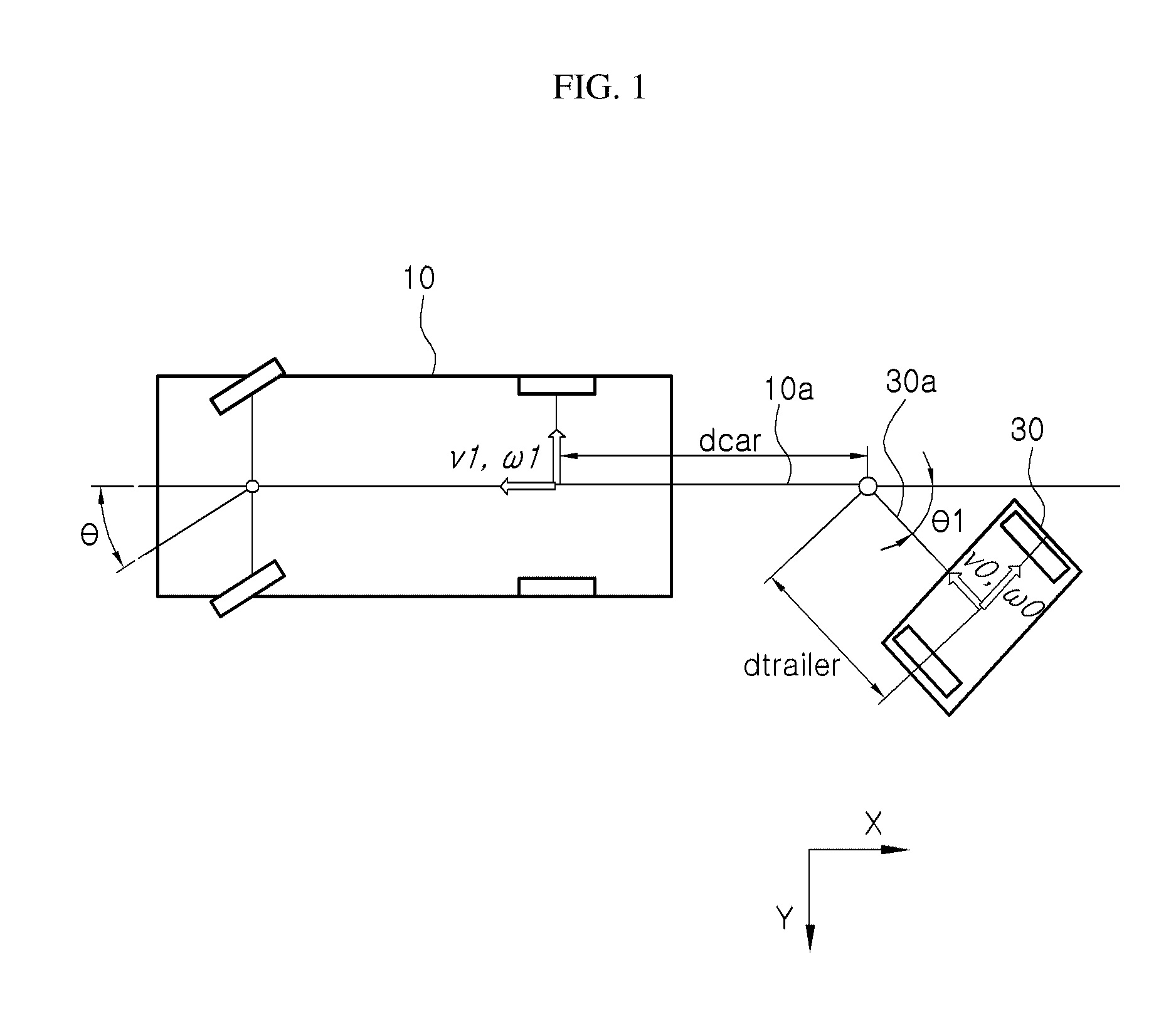
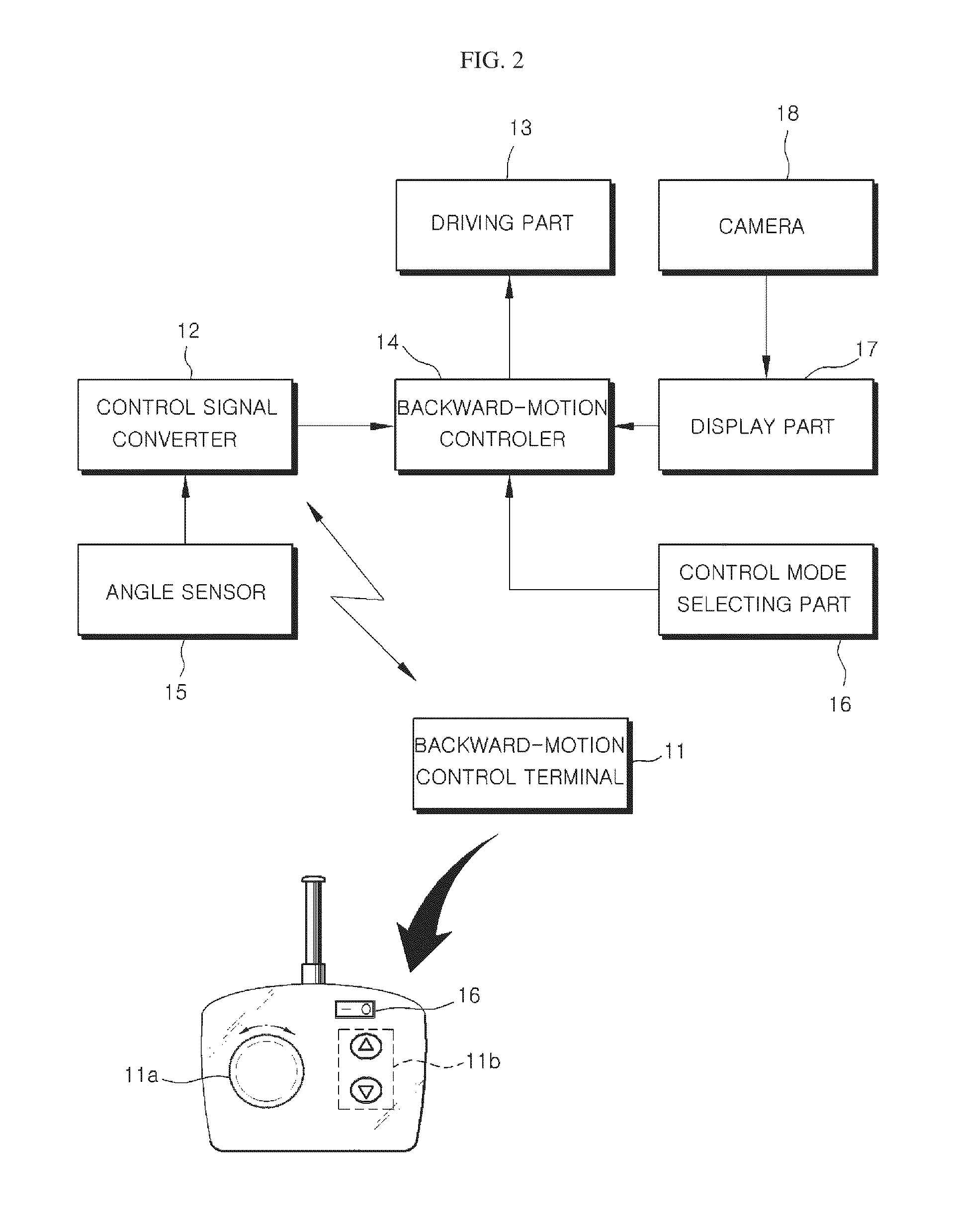
Car connected to at least one trailer and backward motion control method
ActiveUS20110160956A1Easy to controlReduce processing stepsSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsEngineeringMotion controller
A car connected to at least one trailer and backward motion control method are provided. The car includes a driving part controlling a velocity and a direction of the car, a backward-motion control terminal outputting a first backward-motion control signal corresponding to a backward velocity and a backward direction of the last trailer according to a user's operation, a control signal converter converting the first backward-motion control signal to a second backward-motion control signal which corresponds to a backward velocity and a backward direction of the car and makes the last trailer move backward as the backward velocity and the backward direction corresponding to the first backward-motion control signal, and a backward-motion controller controlling the driving part on the basis of the second backward-motion control signal so that the last trailer moves backward by the backward velocity and the backward direction corresponding to the first backward-motion controlling signal.
Owner:KOREA UNIV RES & BUSINESS FOUND
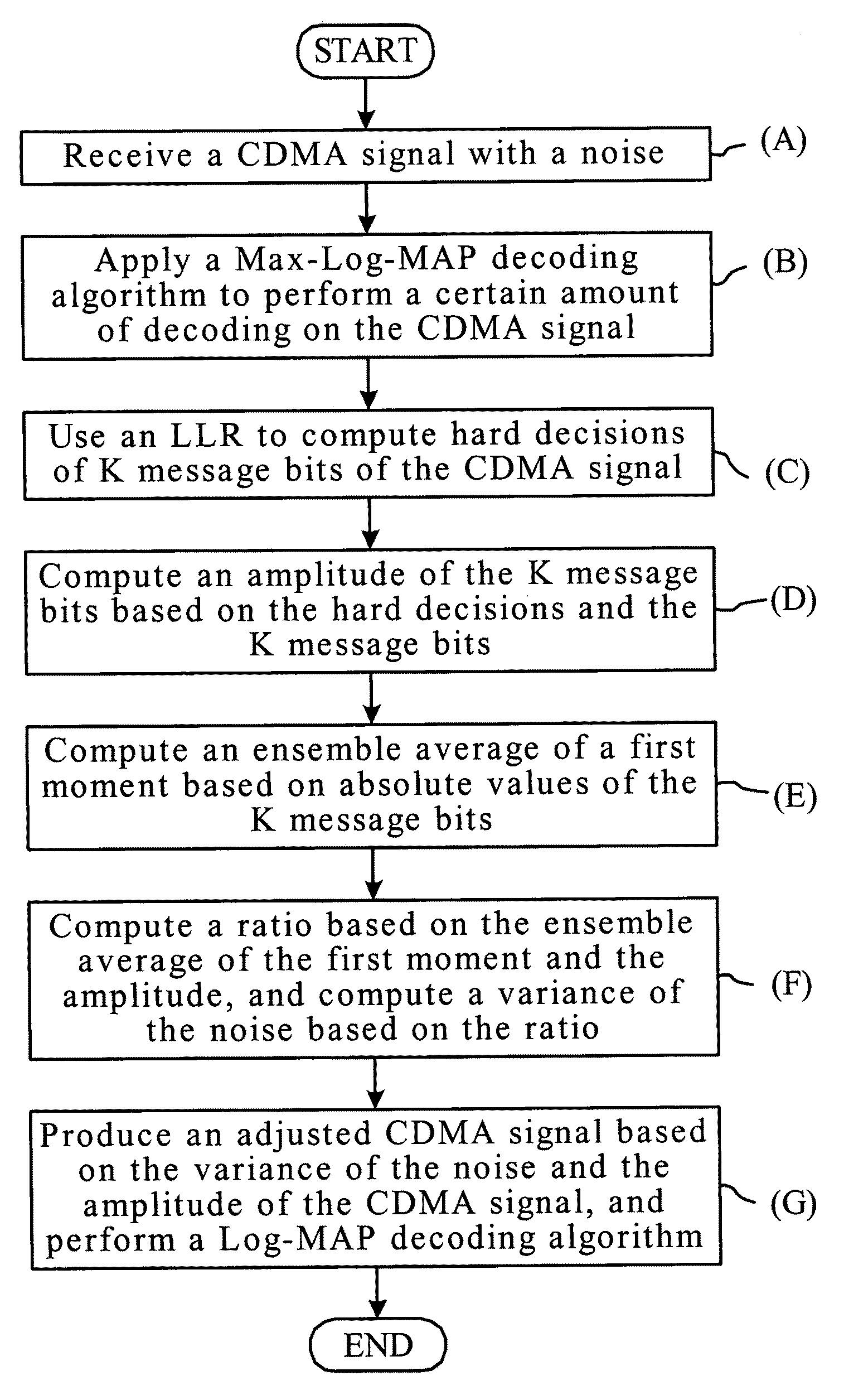
Decoding method and system for real-time wireless channel estimation
InactiveUS7974368B2Avoid performanceAvoid problemsCode conversionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsDecoding methodsComputer science
Owner:SUNPLUS TECH CO LTD
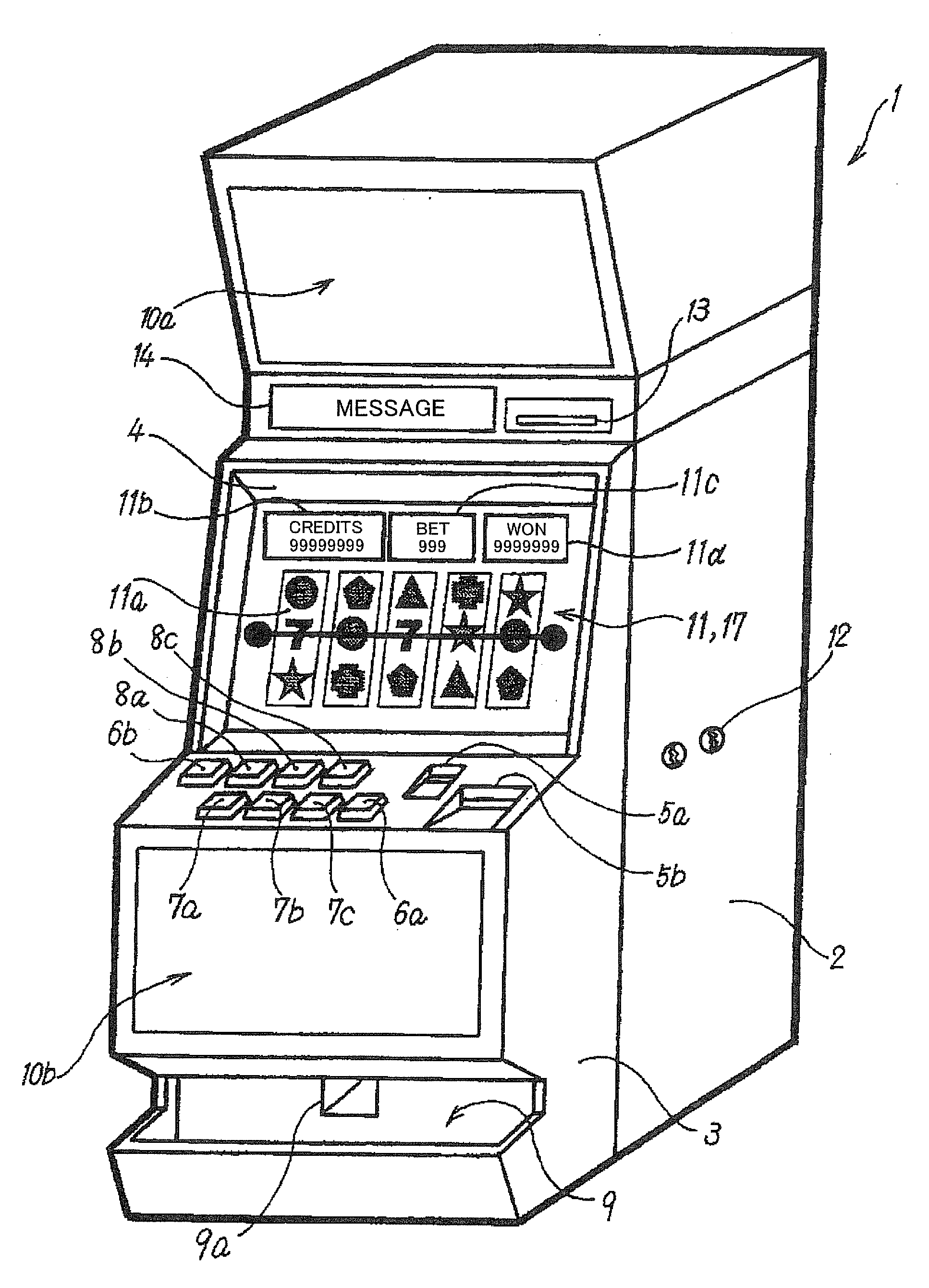
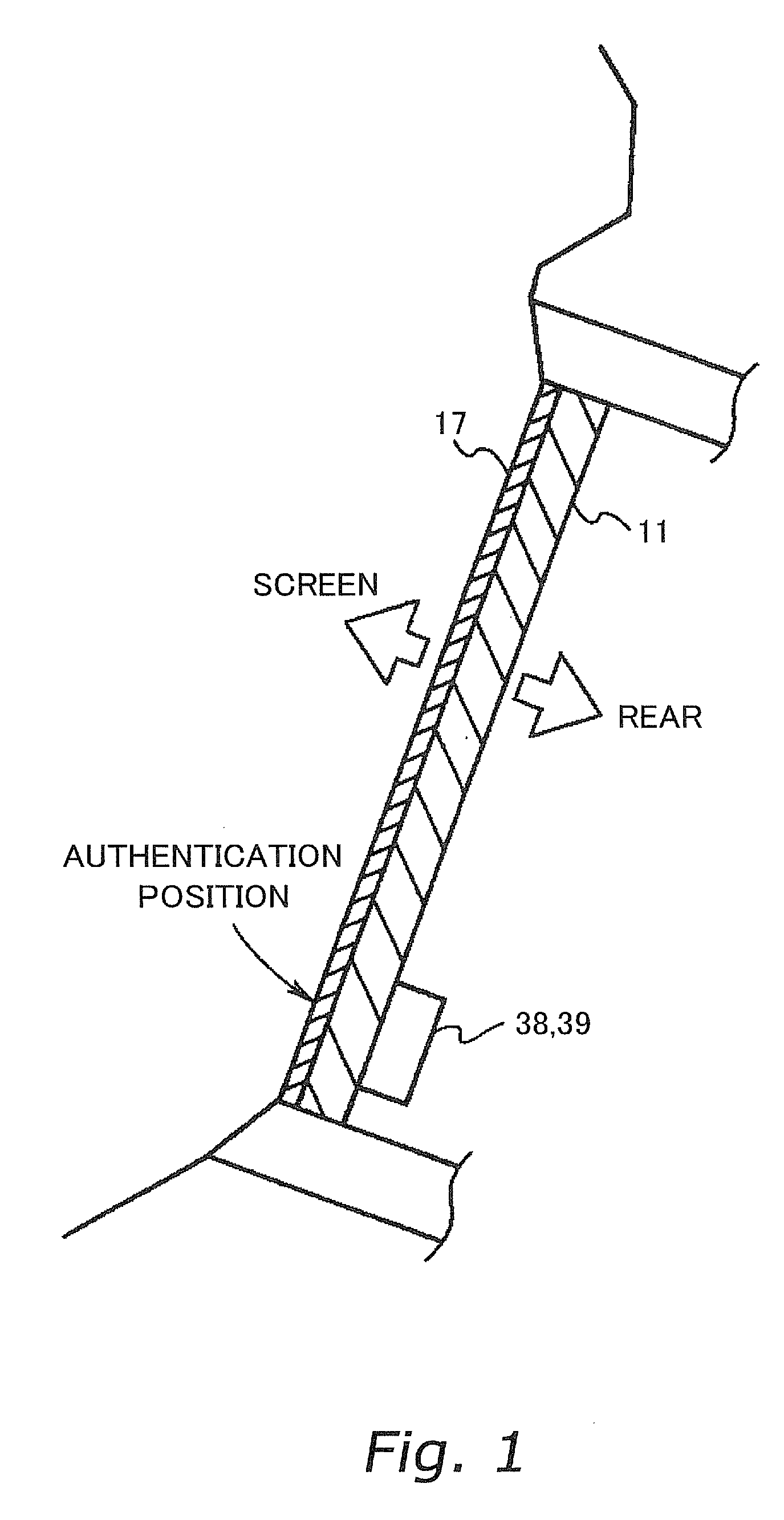
Authentication device and gaming machine equipped with the same
InactiveUS20070021194A1Save energyPrecise positioningImage analysisDigital data processing detailsAuthenticationFingerprint
An authentication device according to the present invention is preferably installed in a gaming machine. In this authentication device, in particular, an authentication data input unit is located on the rear side of a display unit. Furthermore, the screen of the display unit includes an authentication position where an authentication object (for example, a player's finger) is to approach or touch the screen. The authentication data input unit reads the authentication data (for example, fingerprint pattern data) through the screen from the authentication object approaching or touching the screen of the display unit.
Owner:KONAMI GAMING
Translation lookaside buffer for virtual memory systems
InactiveUS6418522B1Avoid loss of performanceLarge access timeMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData bufferVirtual memory
The basic idea comprised of the present invention is to provide a translation lookaside buffer (TLB) arrangement which advantageously uses two buffers, a small first level TLB1 and a larger second level TLB2. The second level TLB feeds address information to the first level TLB when the desired virtual address is not contained in the first level TLB. According to the invention the second level TLB is structured advantageously comprising two n-way set-associative sub-units of which one, a higher level unit covers some higher level address translation levels and the other one, a lower level unit, covers some lower level translation level. According to the present invention, some address information holds some number of middle level virtual address (MLVA) bits, i.e., 8 bits, for example, being able to serve as an index address covering the address range of the higher level sub-unit. Thus, the same information is used as a tag information in the lower-level sub-unit and is used herein as a quick reference in any look-up operation in order to find the absolute address of the concerned virtual address. Further, the commonly used status bits, like; e.g., valid bits, are used in both TLB structures, too.
Owner:IBM CORP
Three-dimensional vision sensor
InactiveUS20100232681A1Avoid performanceCancel noiseImage enhancementImage analysisTransformation parameterThree dimensional measurement
An object of the present invention is to enable performing height recognition processing by setting a height of an arbitrary plane to zero for convenience of the recognition processing. A parameter for three-dimensional measurement is calculated and registered through calibration and, thereafter, an image pickup with a stereo camera is performed on a plane desired to be recognized as having a height of zero in actual recognition processing. Further, three-dimensional measurement using the registered parameter is performed on characteristic patterns (marks m1, m2 and m3) included in this plane. Three or more three-dimensional coordinates are obtained through this measurement and, then, a calculation equation expressing a plane including these coordinates is derived. Further, based on a positional relationship between a plane defined as having a height of zero through the calibration and the plane expressed by the calculation equation, a transformation parameter (a homogeneous transformation matrix) for displacing points in the former plane into the latter plane is determined, and the registered parameter is changed using the transformation parameter.
Owner:ORMON CORP
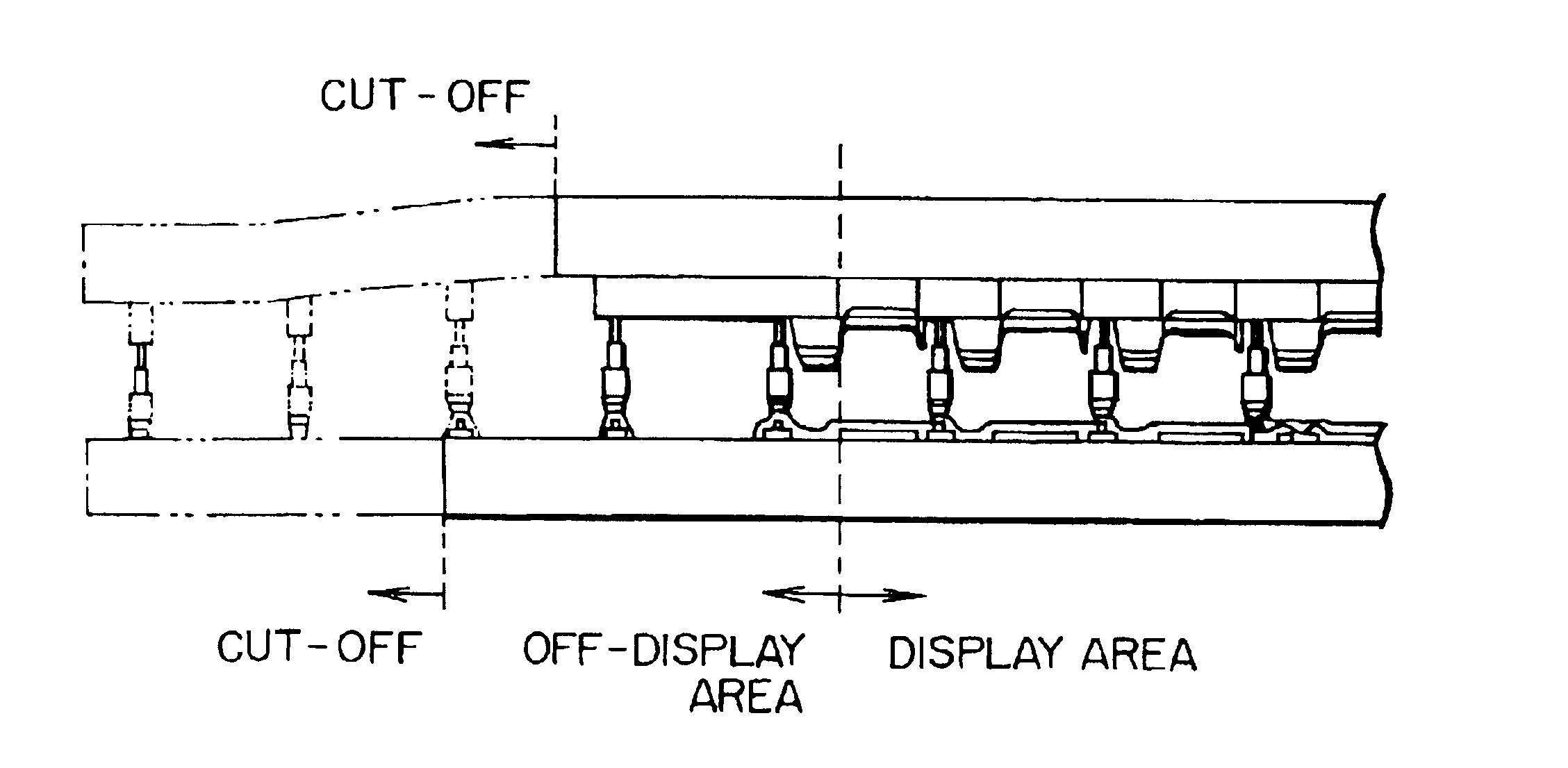
Liquid crystal display device
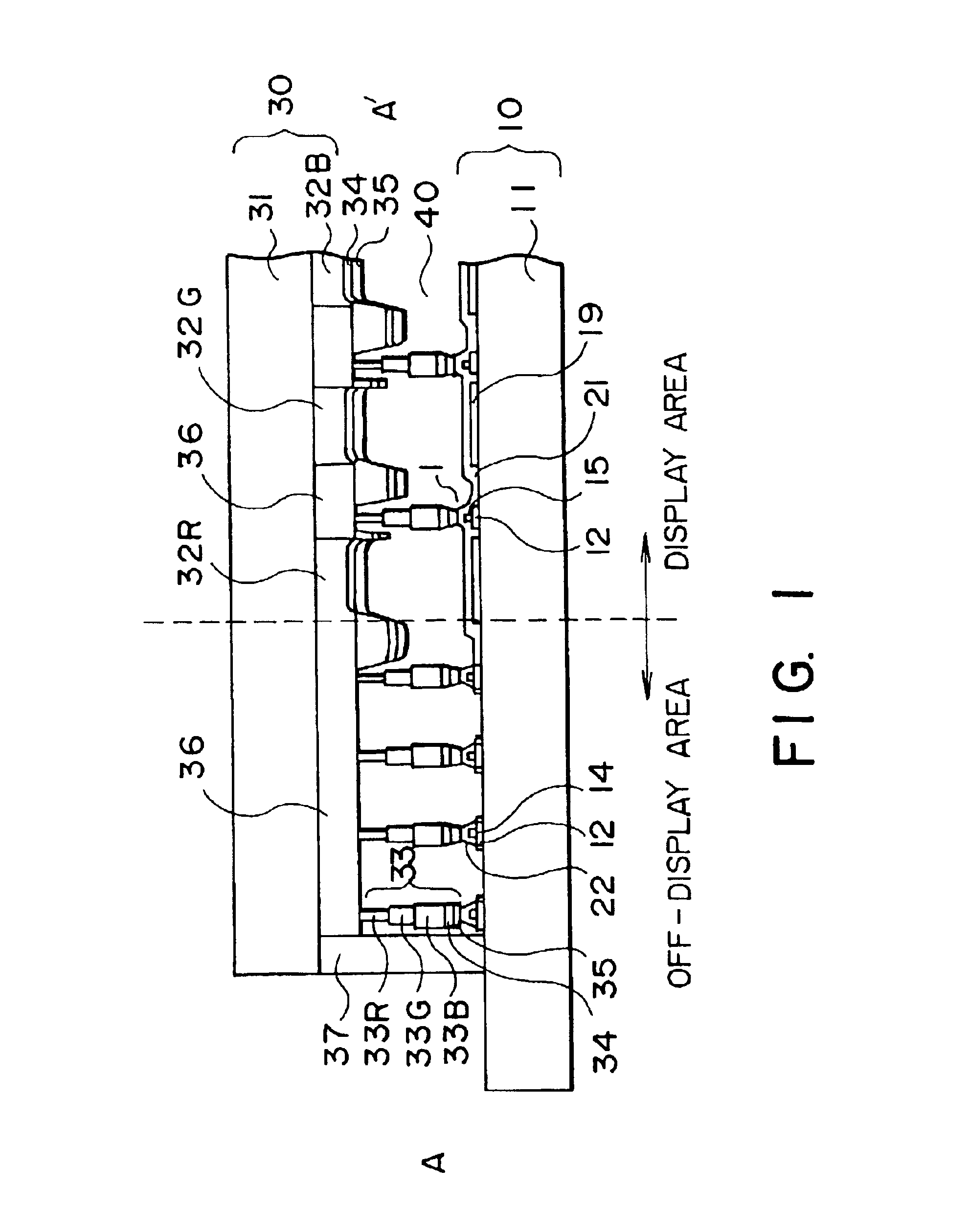
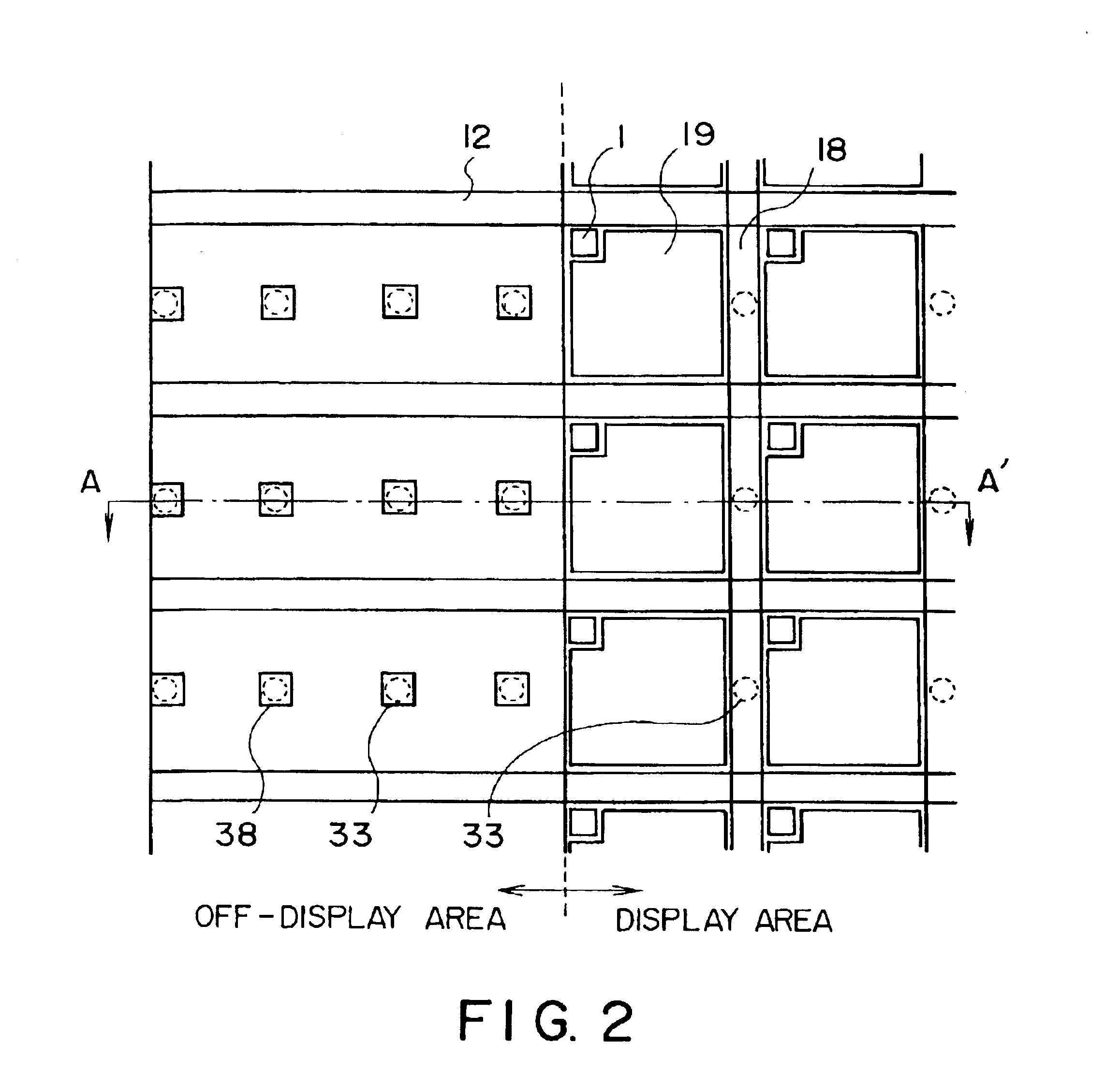
InactiveUS6888608B2Reduce the number of stepsReduce in quantityNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
A improved liquid crystal display device including two substrates each having transparent electrode thereon disposed in parallel while keeping a predetermined gap by means of pillar-shaped spacers and a liquid crystal held between said first and second substrates is proposed. In the liquid crystal display device, density or volume of the number of the pillar-shaped spacers provided in the off-display area is higher than those of a density of the number of said pillar-shaped spacers provided in the display area. This change is made continuously or stepwise along areas. The spacers are preferably disposed so that a contact area between the spacer and a rubbing cloth during the rubbing process is minimized, or so that an orientation defective area caused starting from the spacer does not extend into the pixel area, or so that a plurality of spacers are disposed along a flow of liquid crystal from filling port into the gap between the first and second substrate.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Memory system, host system, and method of performing write operation in memory system
ActiveUS20150149789A1Performance degradation can be preventedReduce power consumptionUnauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringOriginal dataOperating system
A write operation is performed in a memory system by encoding, in the memory system, original data transmitted from a host system, according to a first type of host command, to produce an encoding result, transmitting information about the encoding result to the host system after the encoding, and writing the encoding result or the original data into a nonvolatile memory device, according to a second host command, wherein the second host command is transmitted from the host system based on the information about the encoding result.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
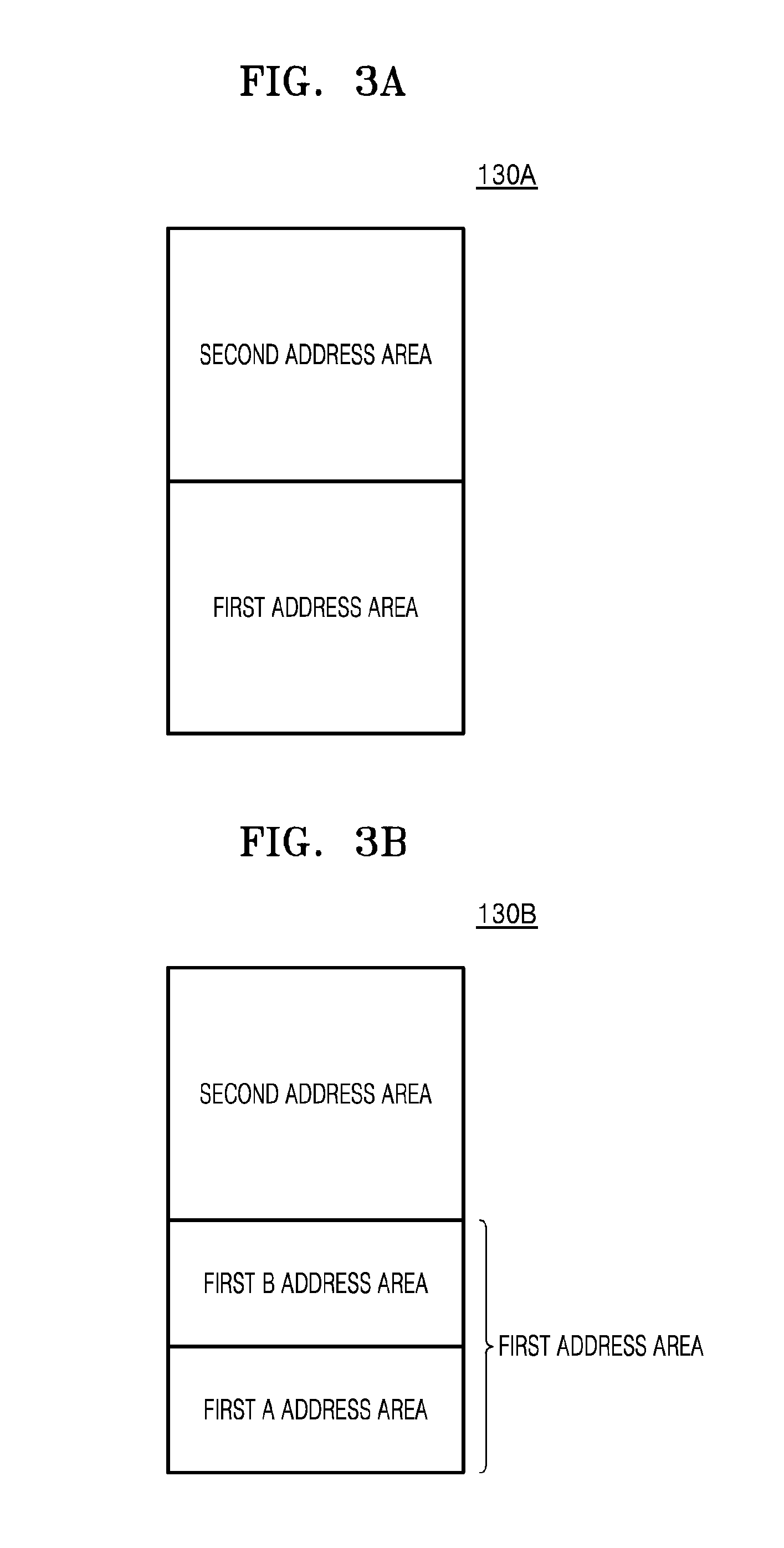
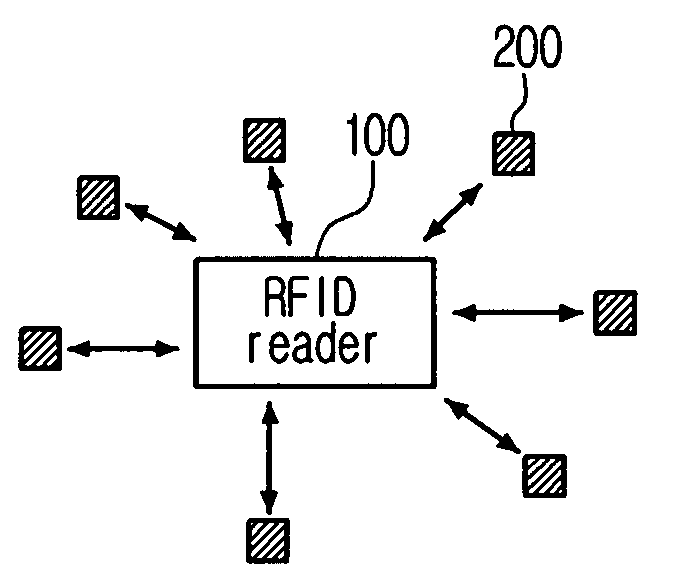
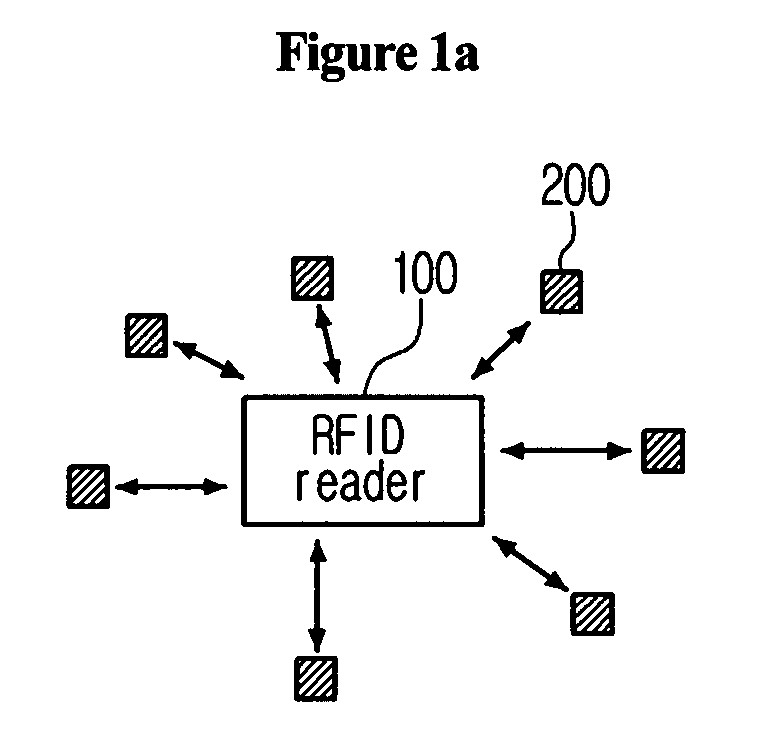
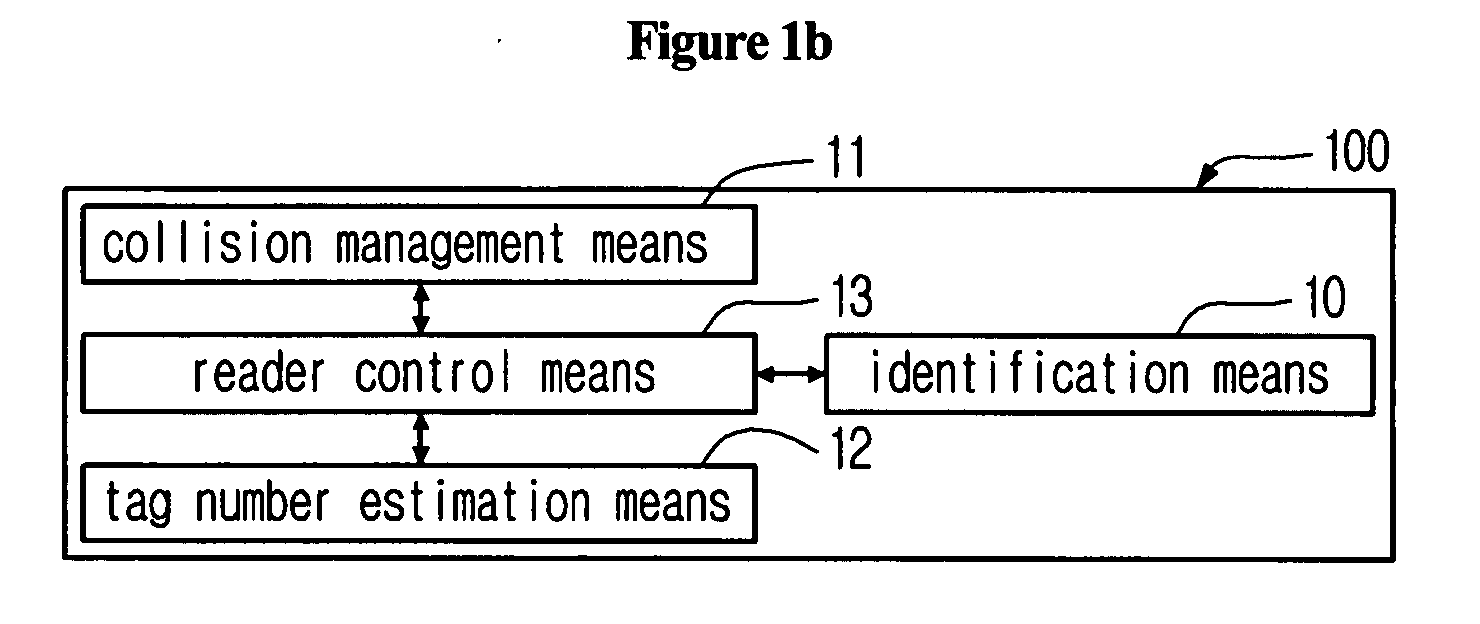
System for tag estimation and anti-collision and method thereof
ActiveUS20080150674A1Overcomes shortcomingQuick identificationNetwork traffic/resource managementElectric testing/monitoringIdle timeIdentification device
The present application discloses a system and a method for tag estimation and anti-collision in an RFID system, which can estimate an exact number of tags within an RF area and can rapidly identify tags by using the estimated number of tags in an RFID system. The system includes an RFID reader and RFID tags. The RFID reader includes an identification means, a collision management means, a tag number estimation means, and a reader control means. The RFID tag includes a tag communication means, a message reading means, a counter management means, an information storage means, and a tag control means. The disclosed system and method can prevent occurrence of too many idle times slots in the DFSA and too many initial collisions in the binary tree scheme, and thus can identify a large number of tags at a high speed with a small number of time slots.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL DISCOVERY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com