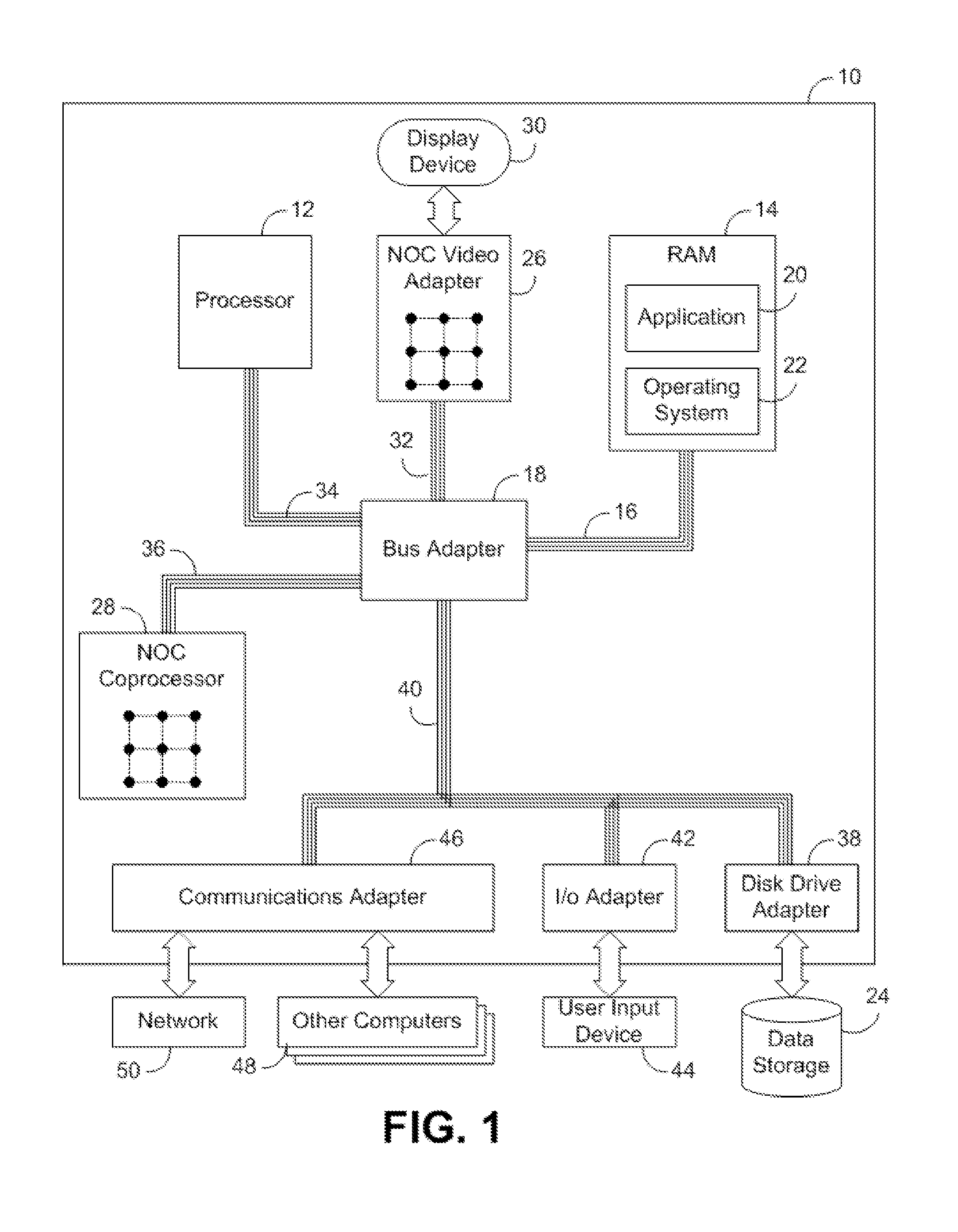
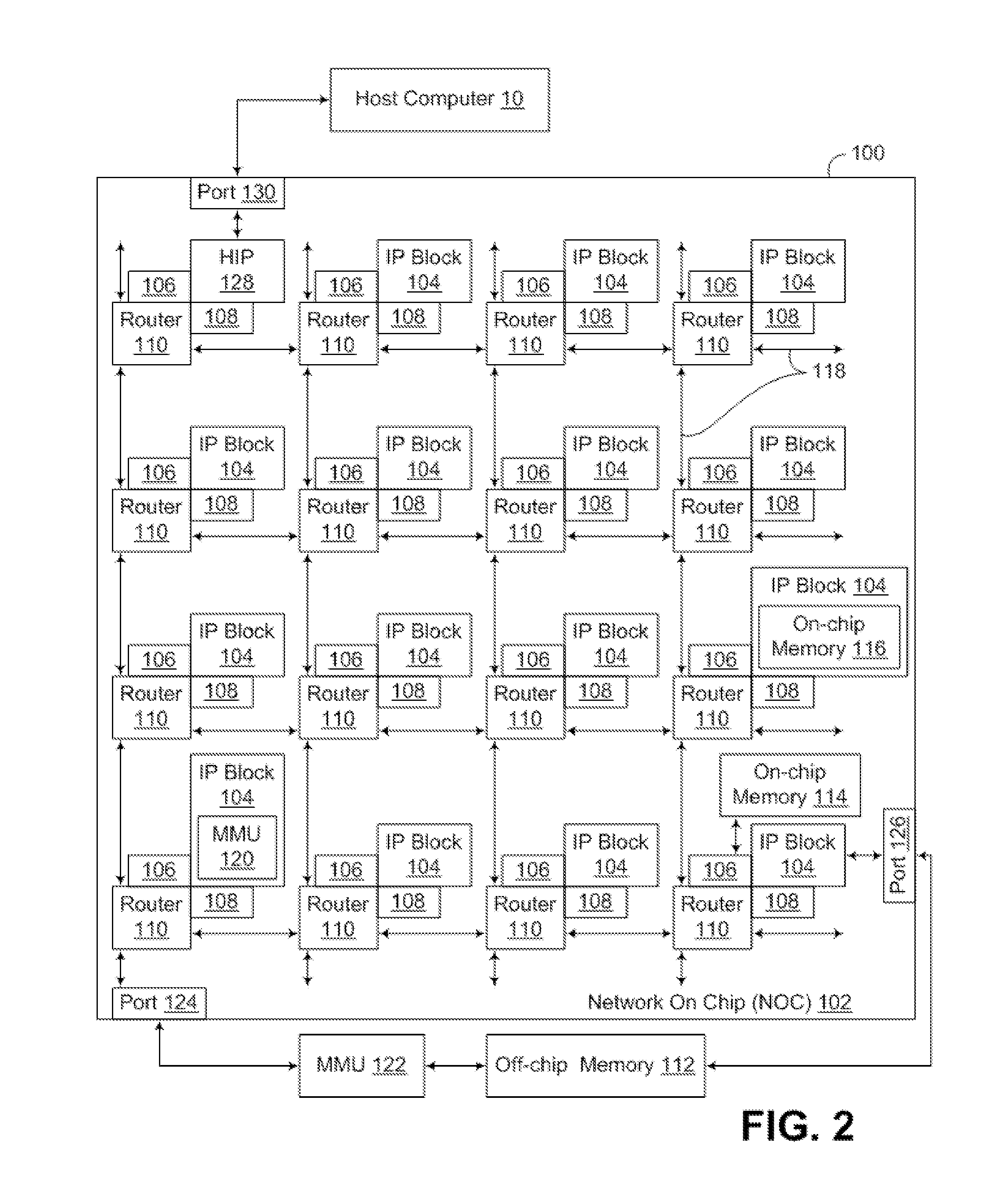
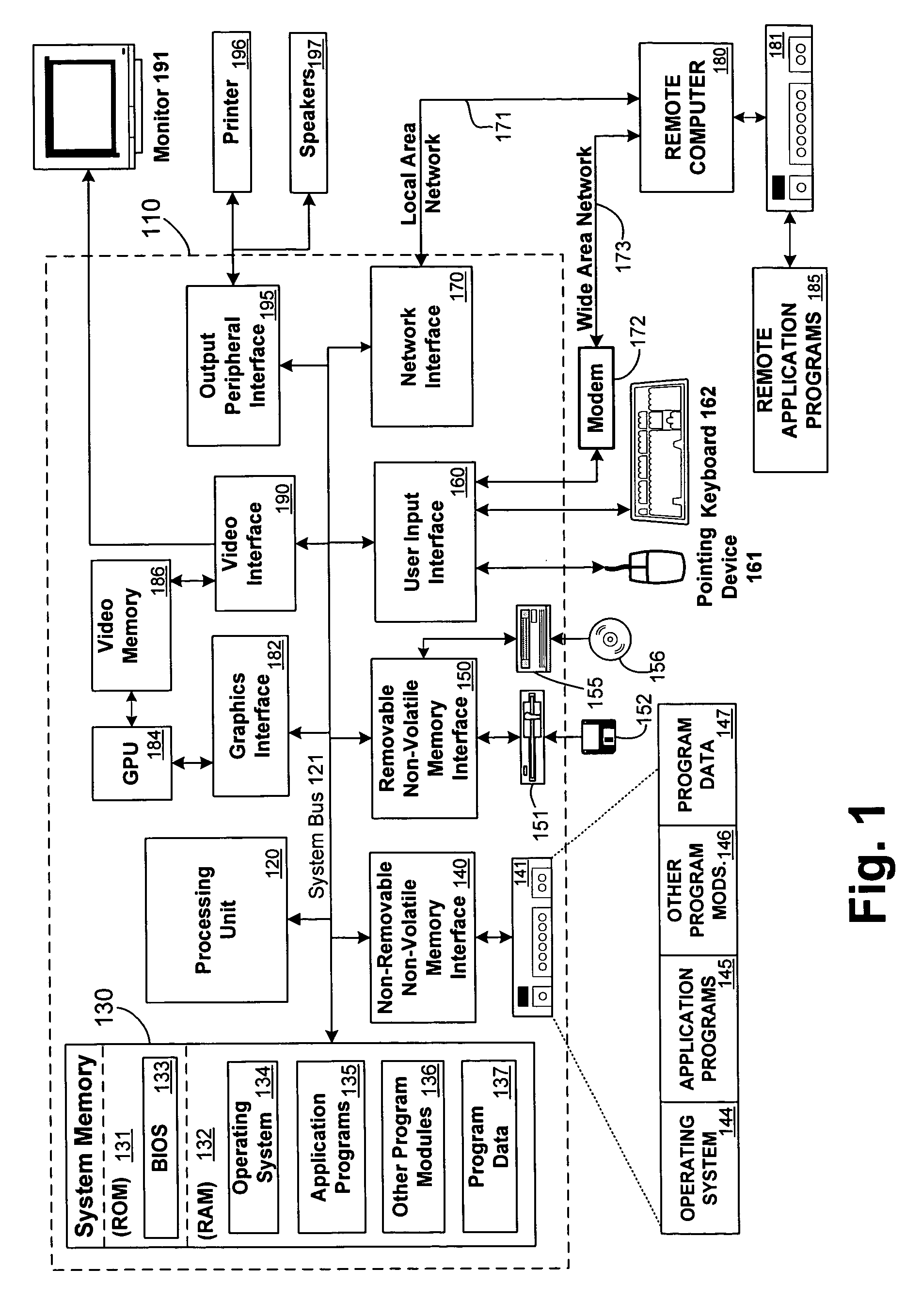
Patents
Literature
404 results about "Translation lookaside buffer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
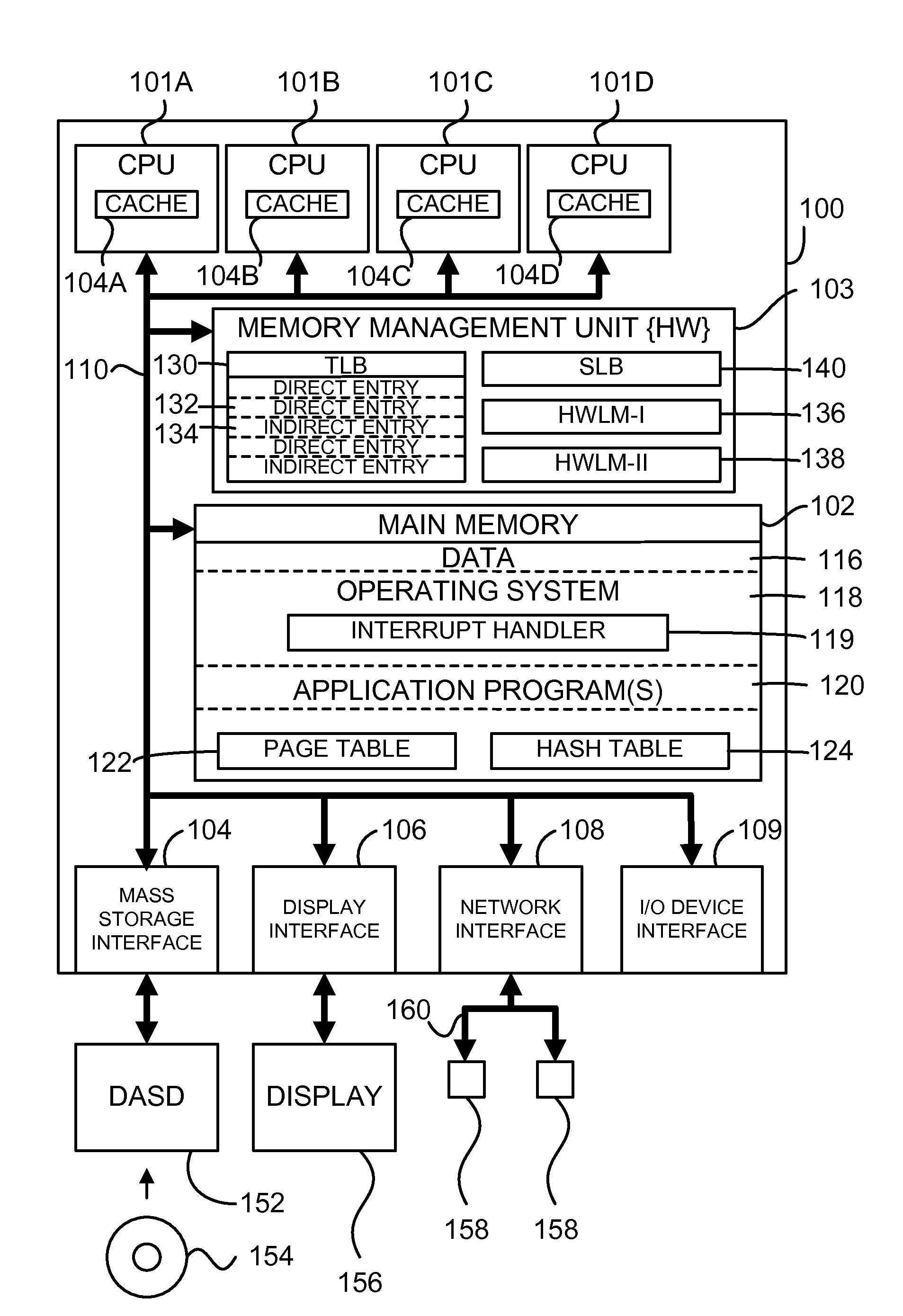
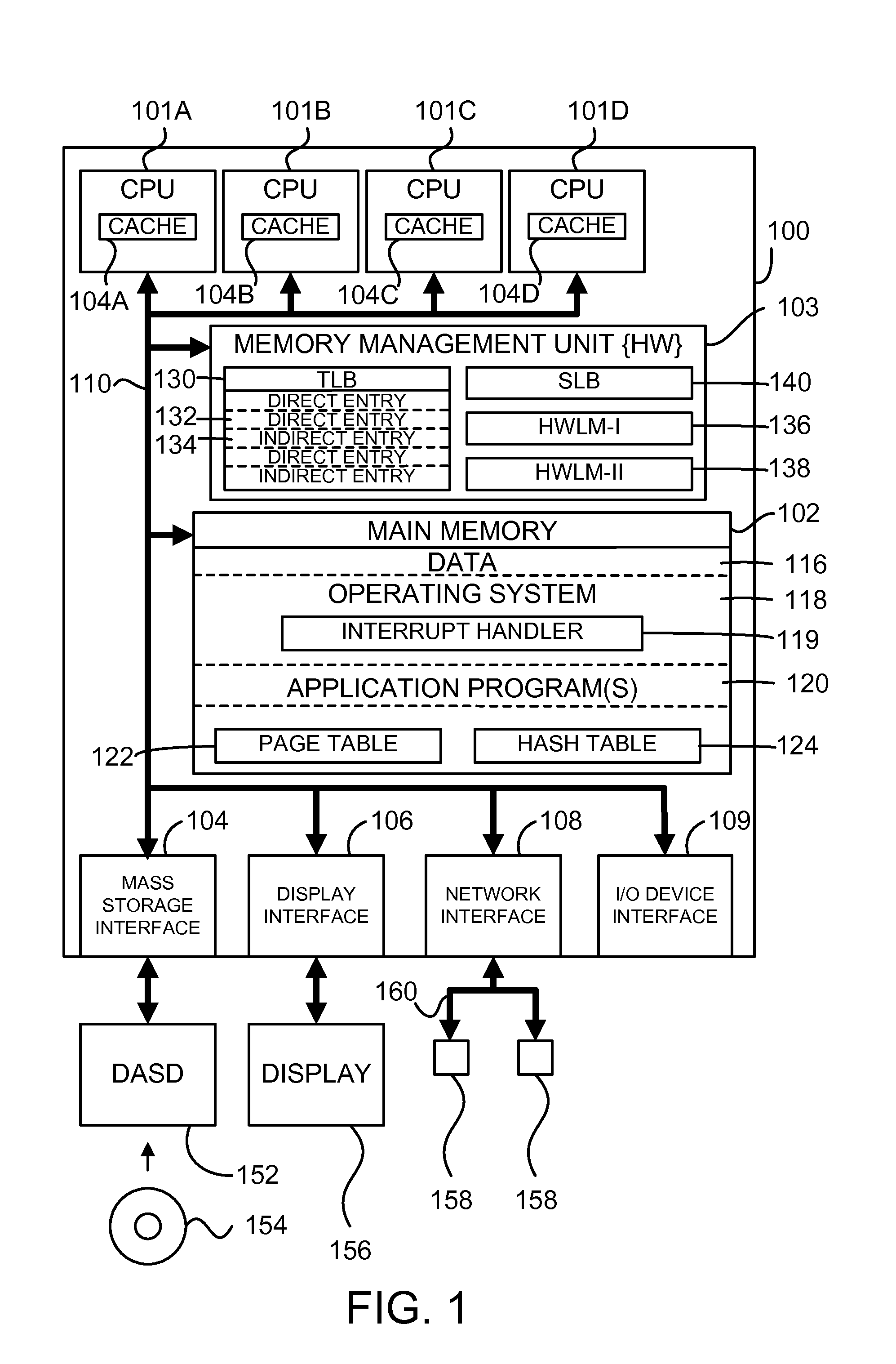
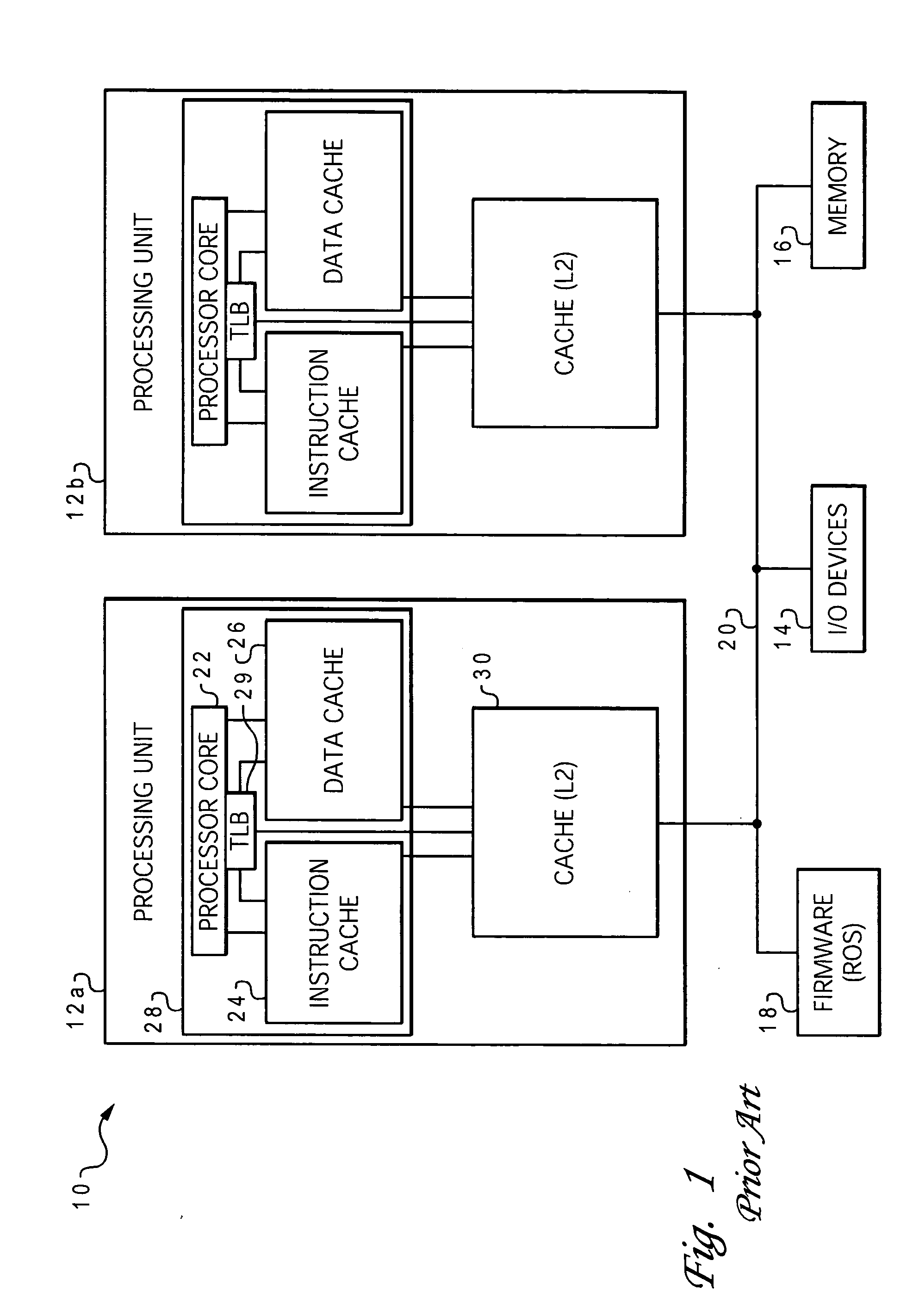
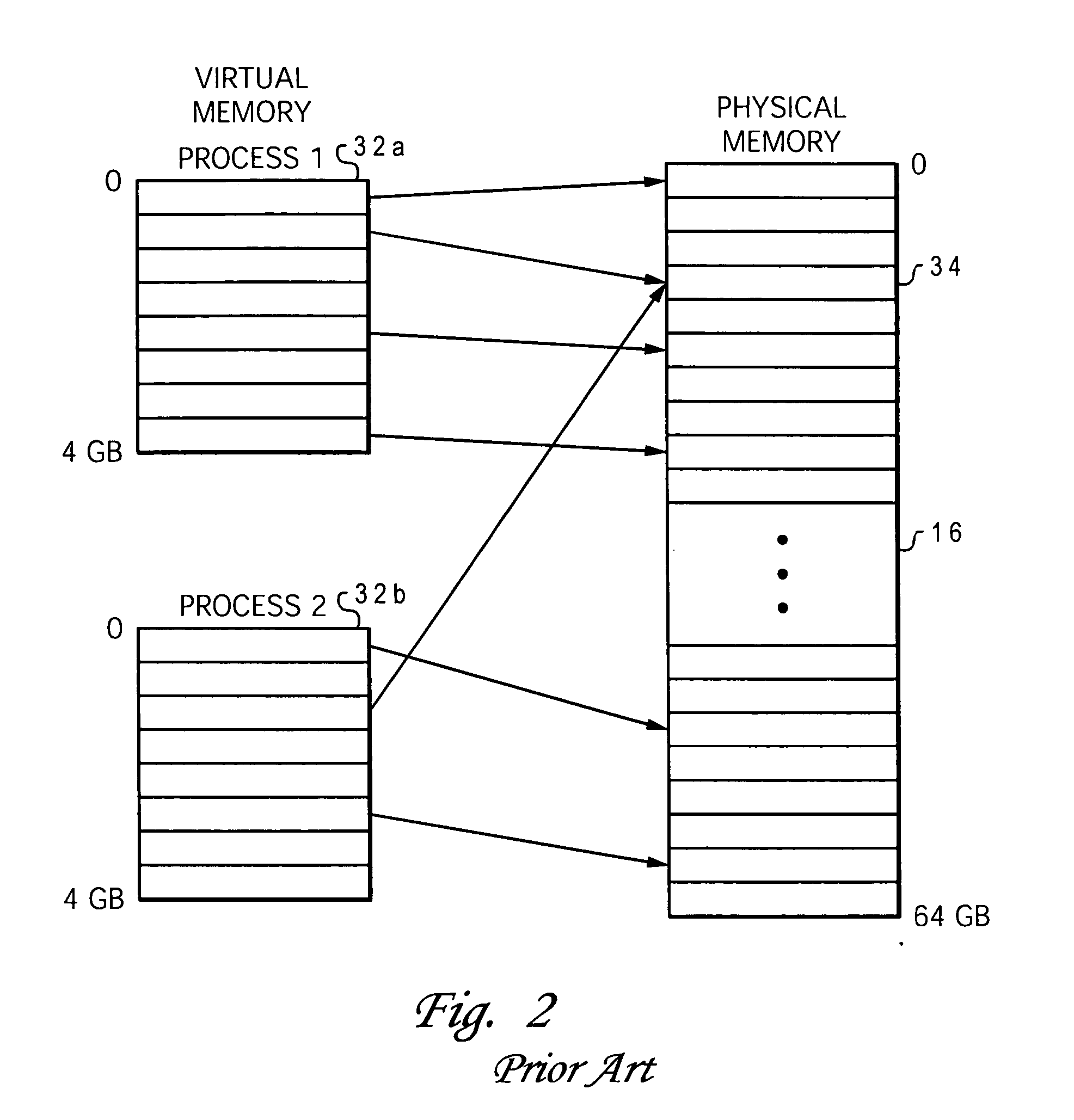
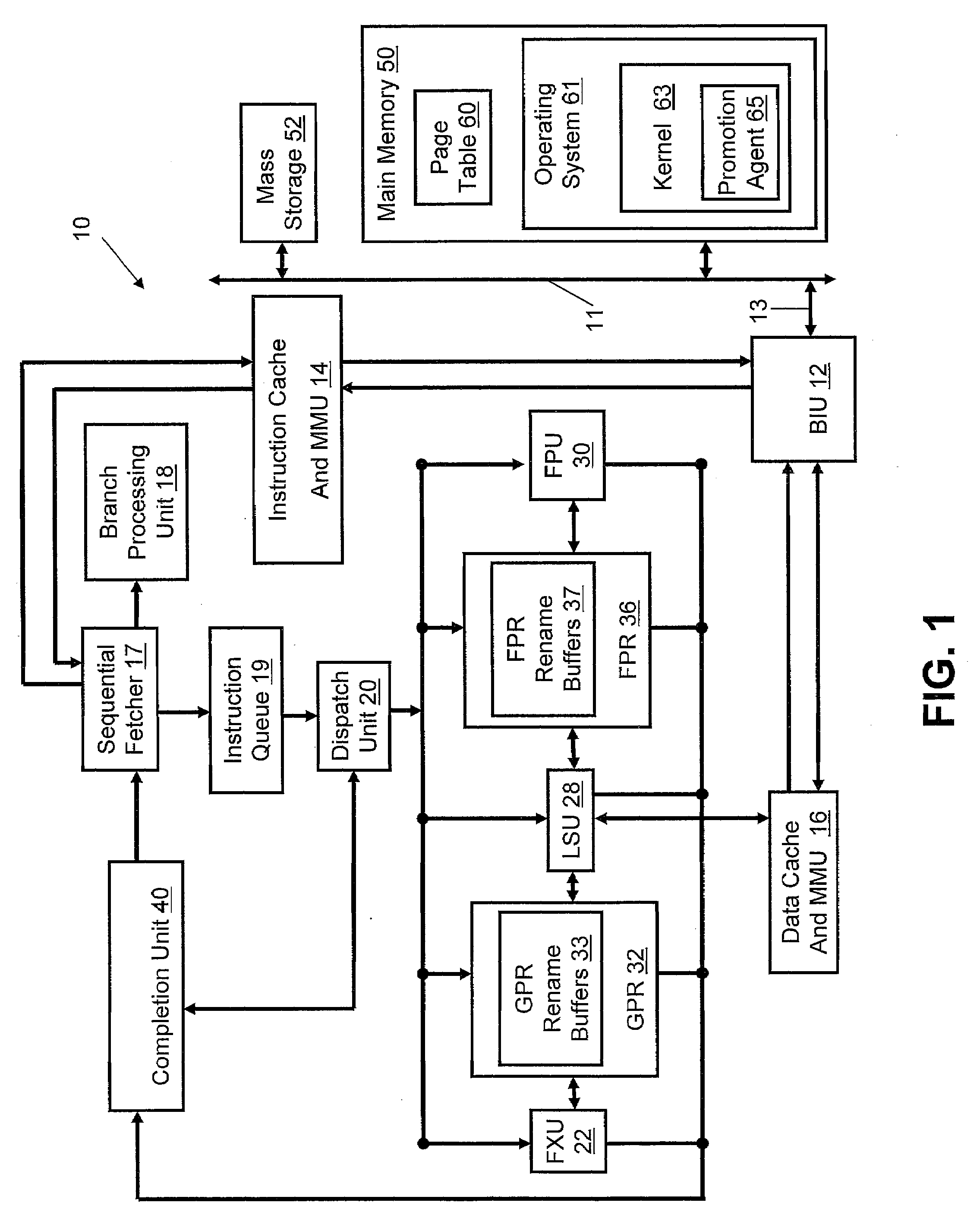
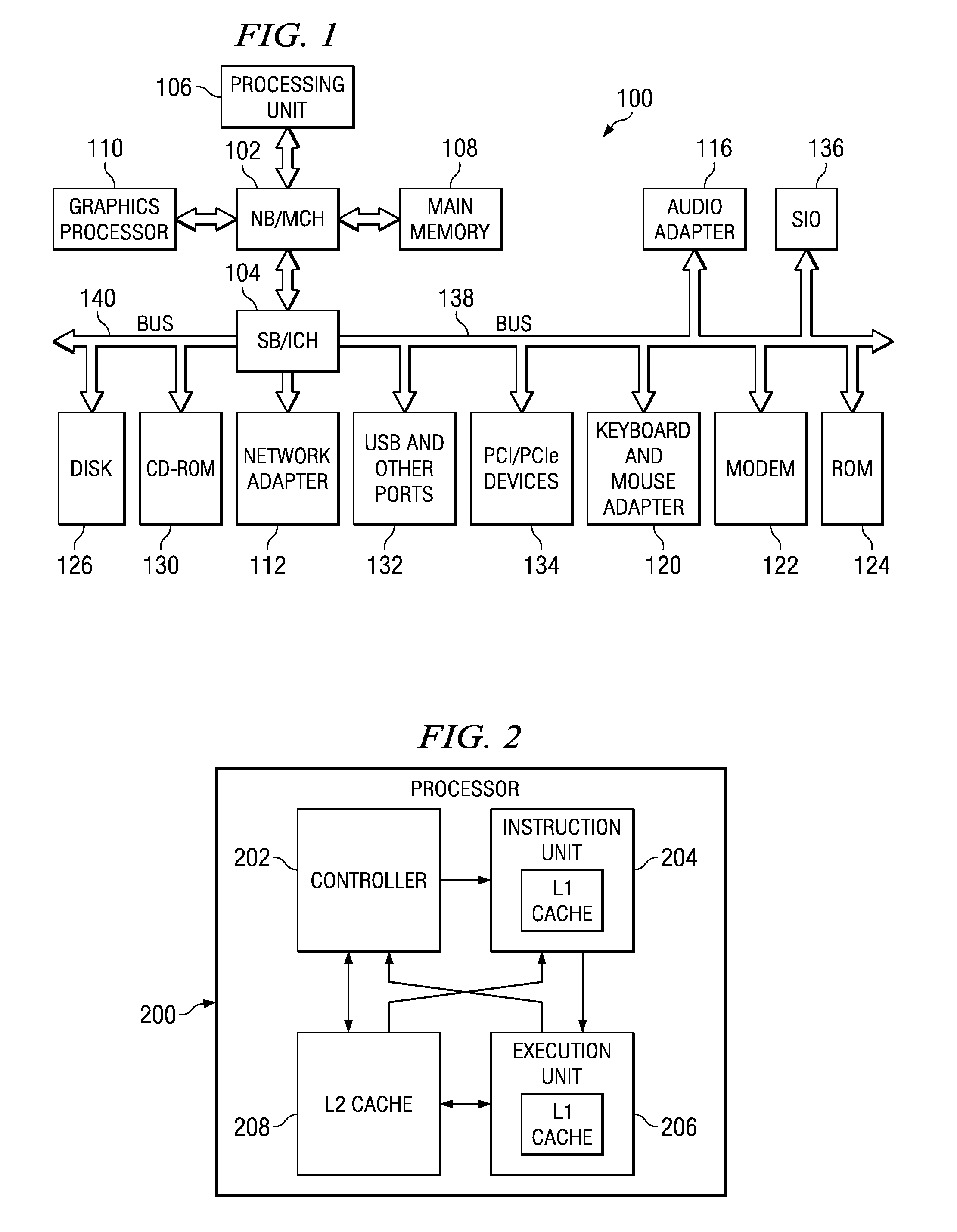
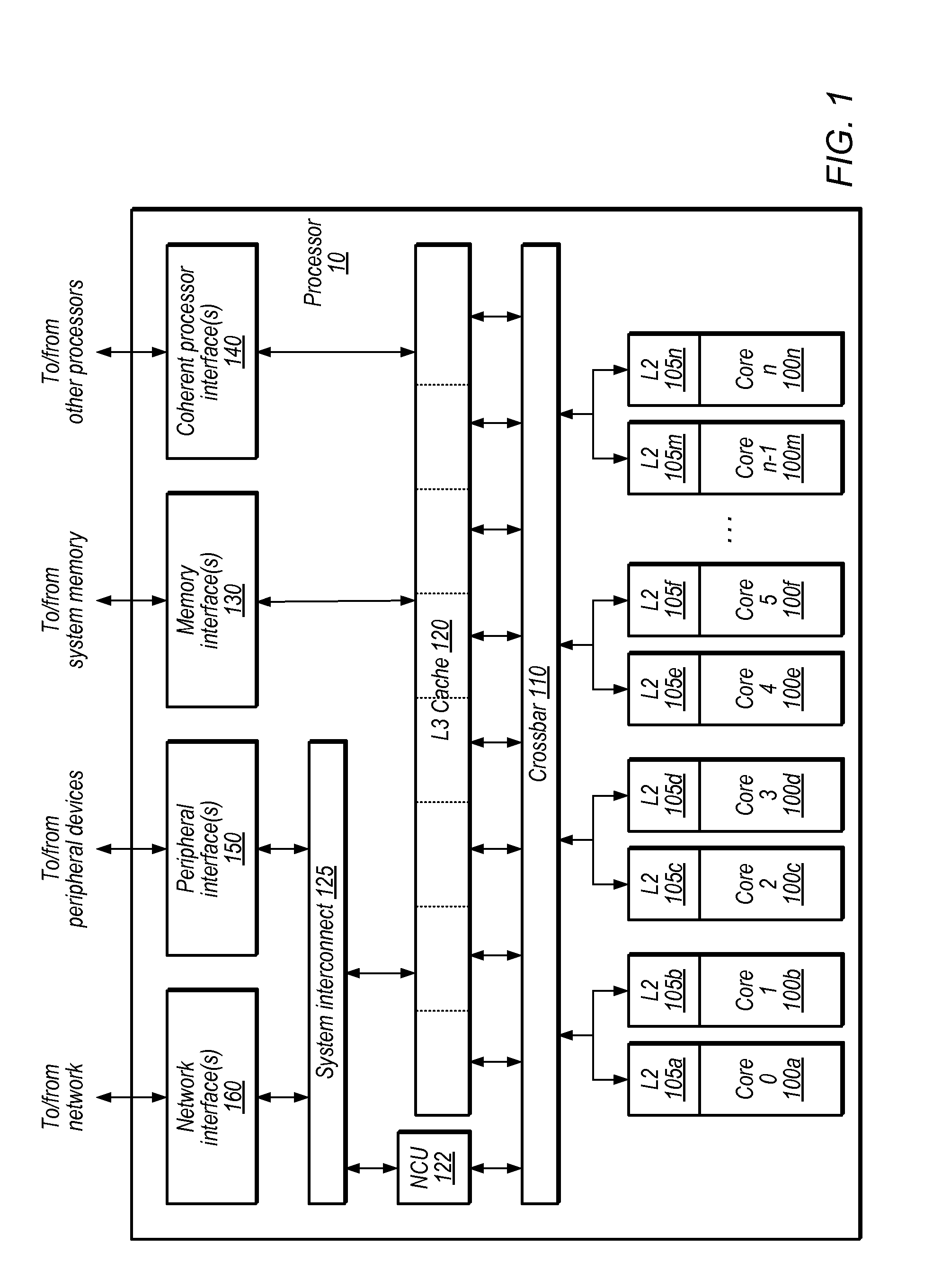
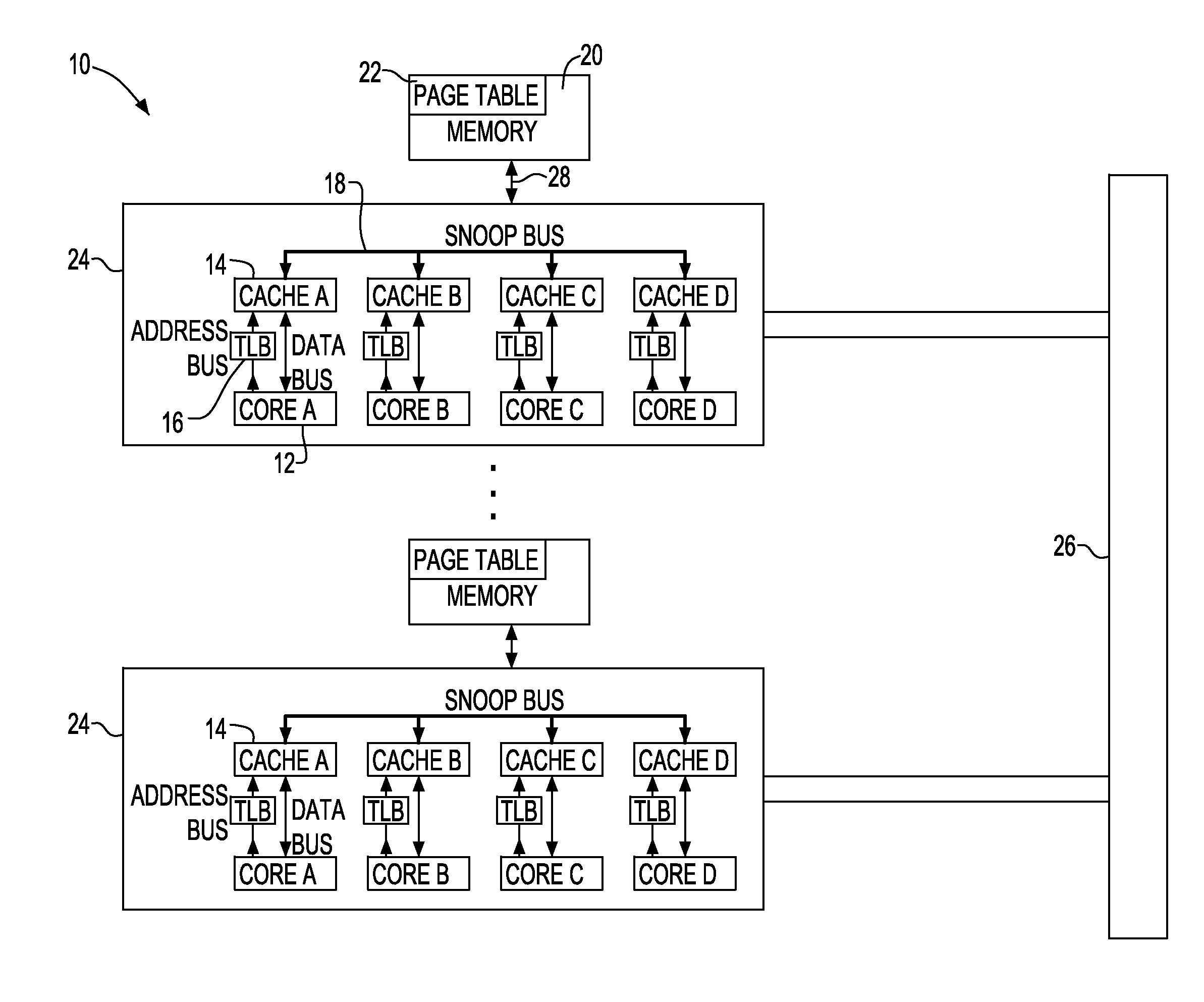
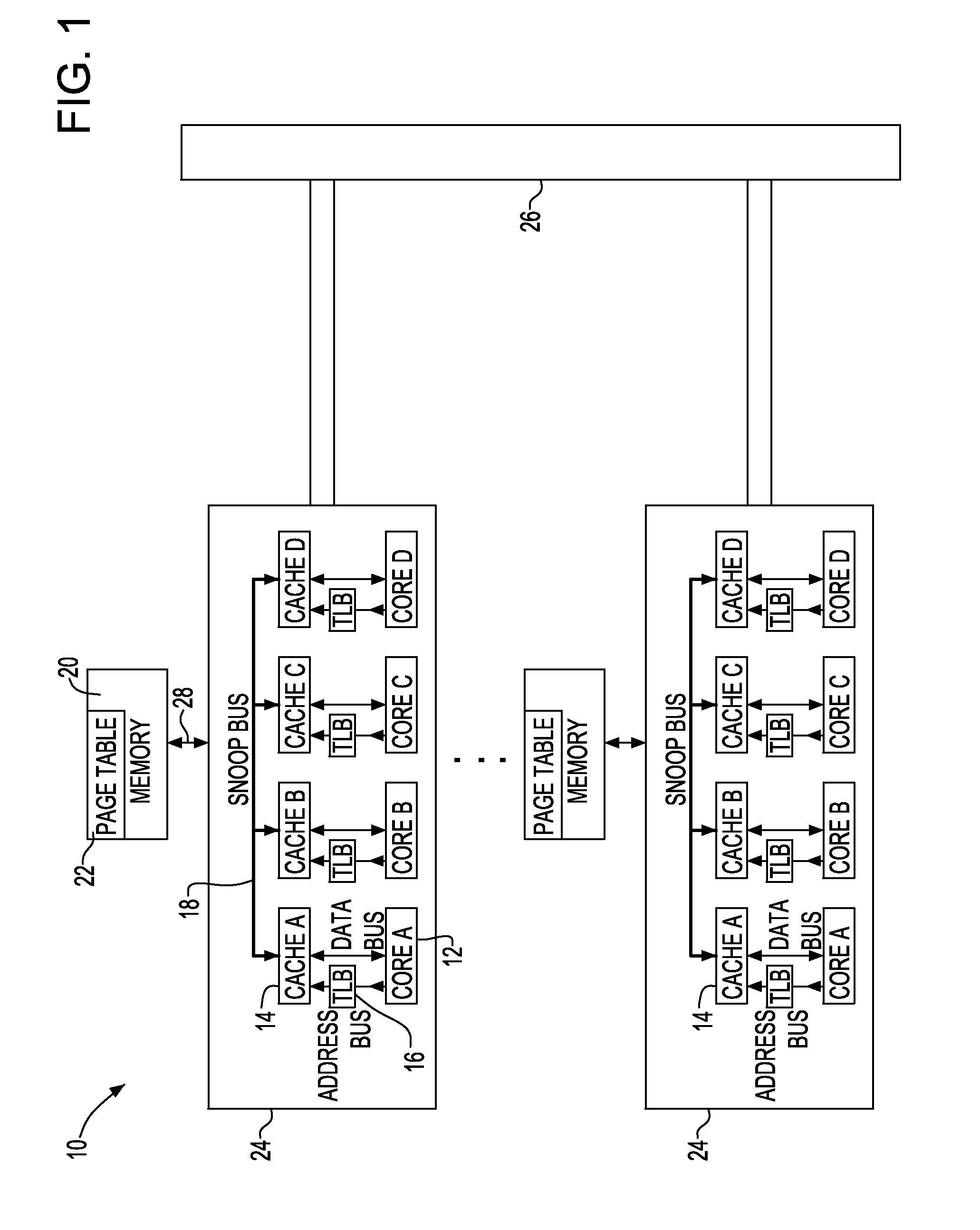
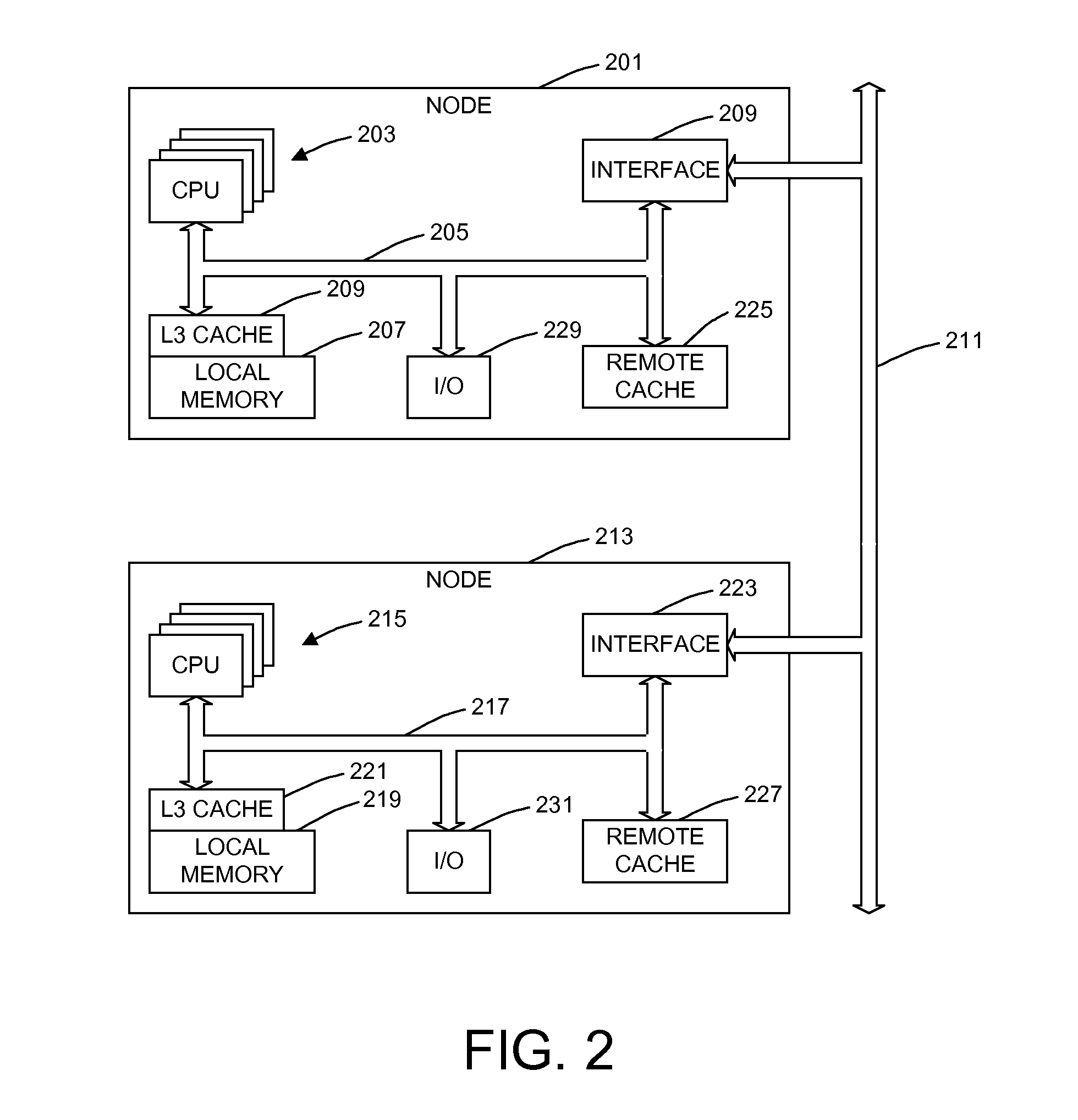
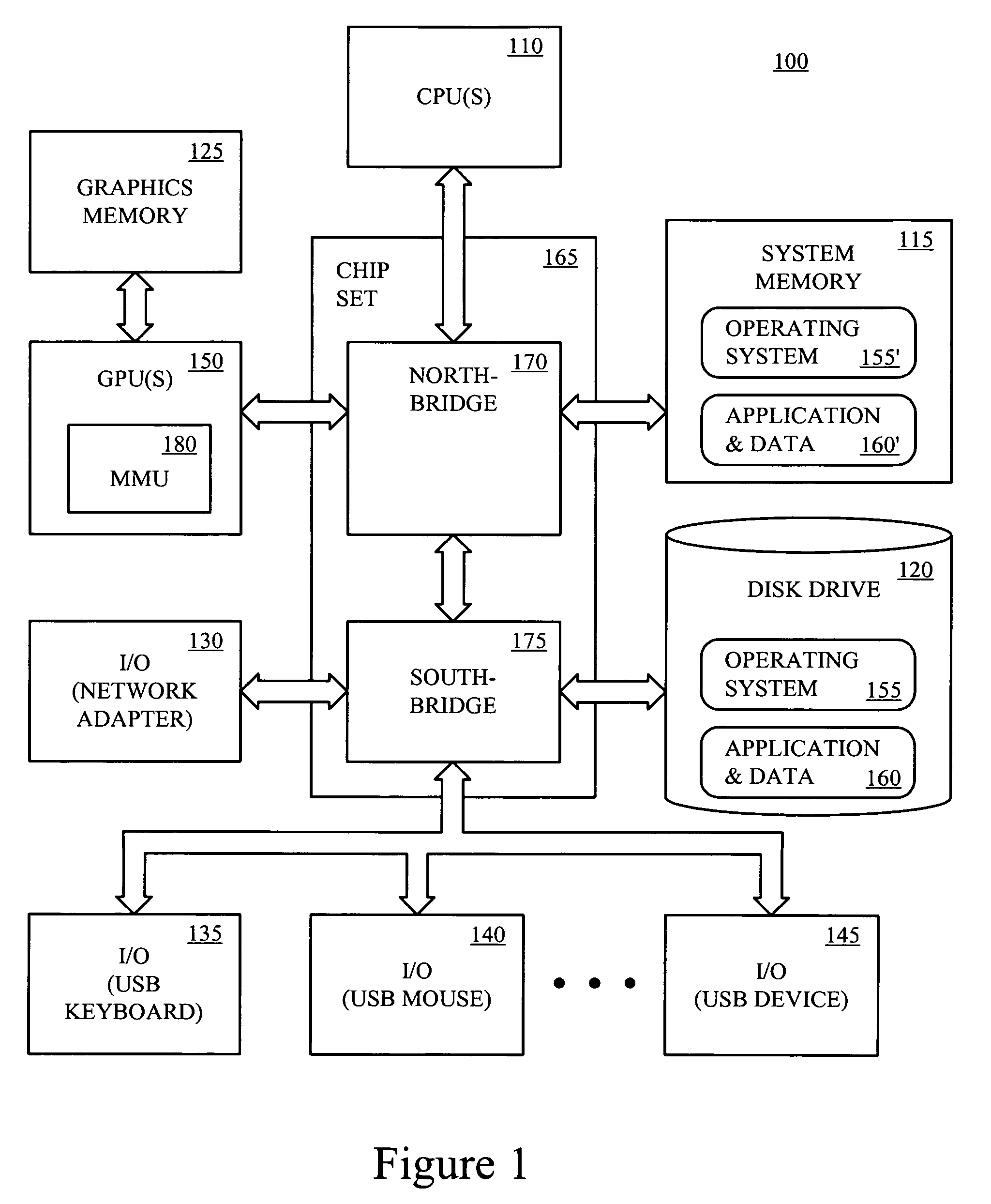
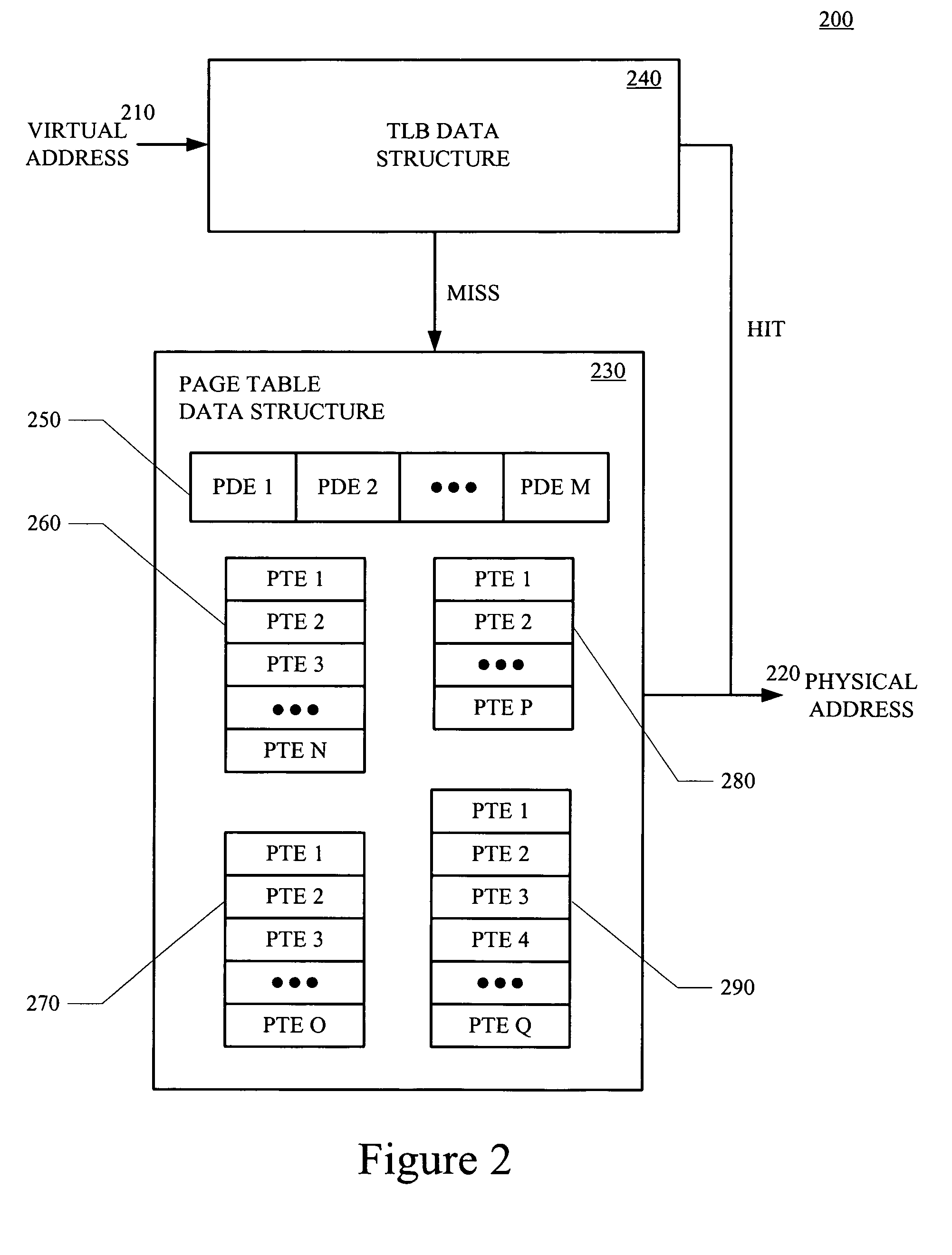
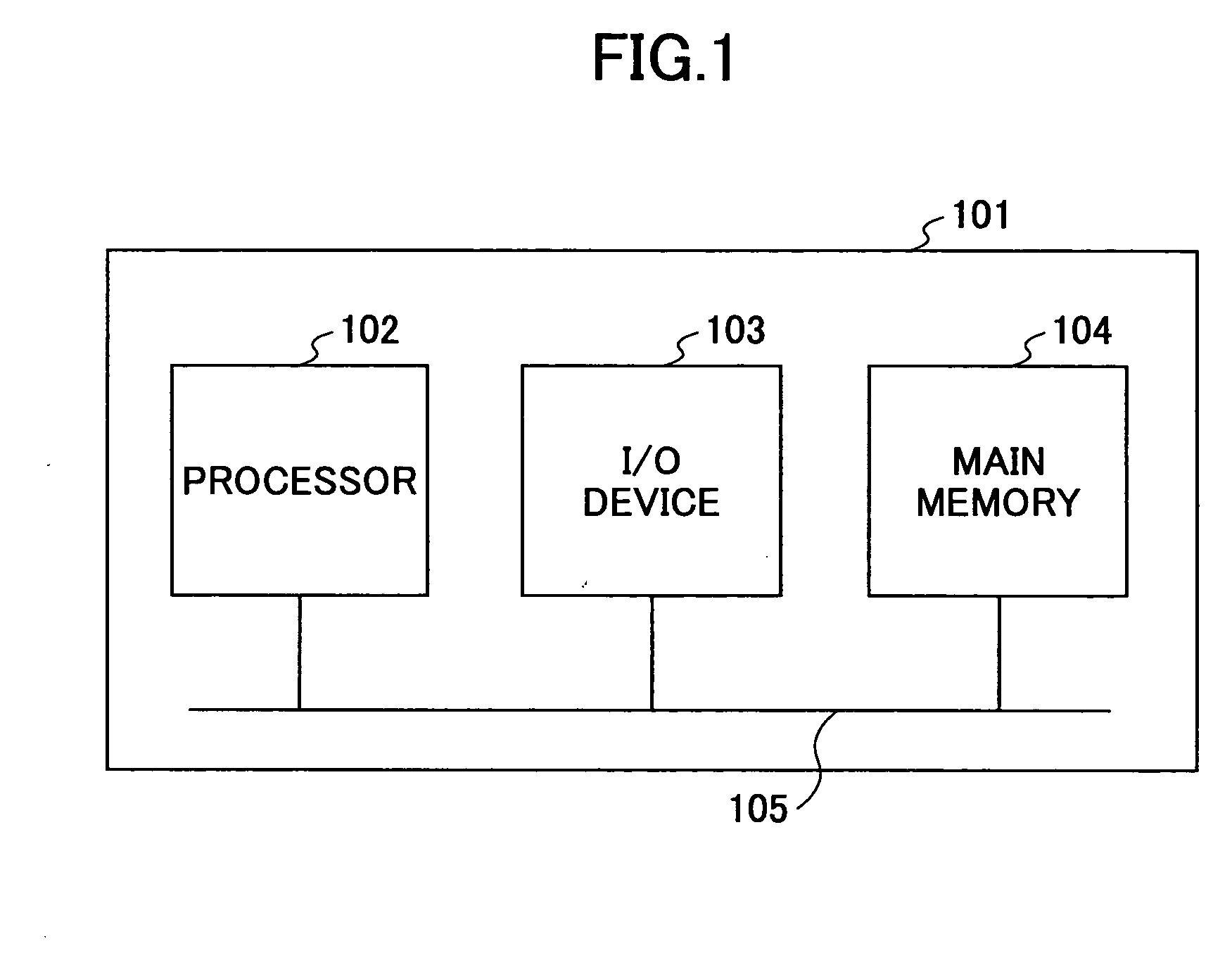
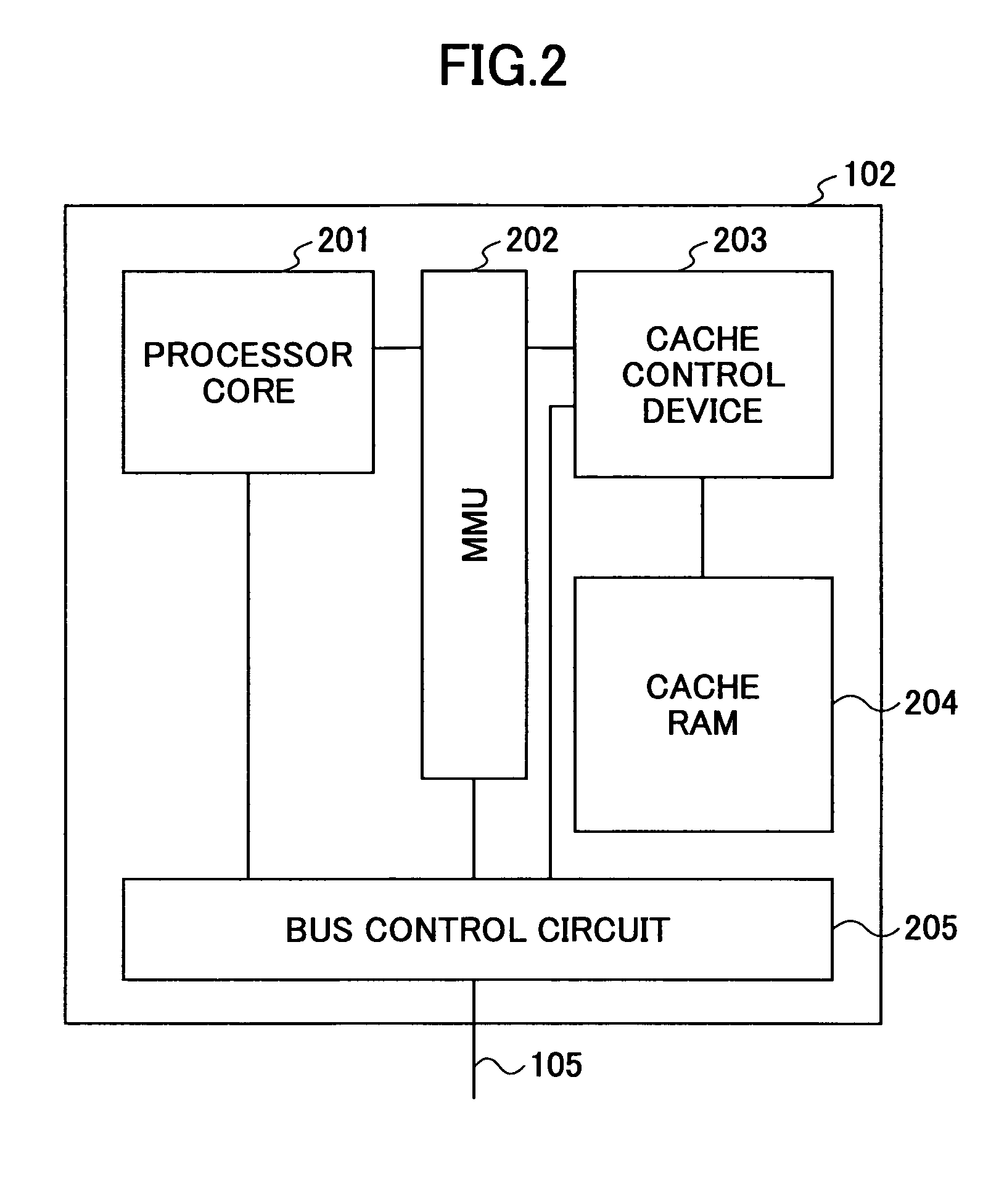
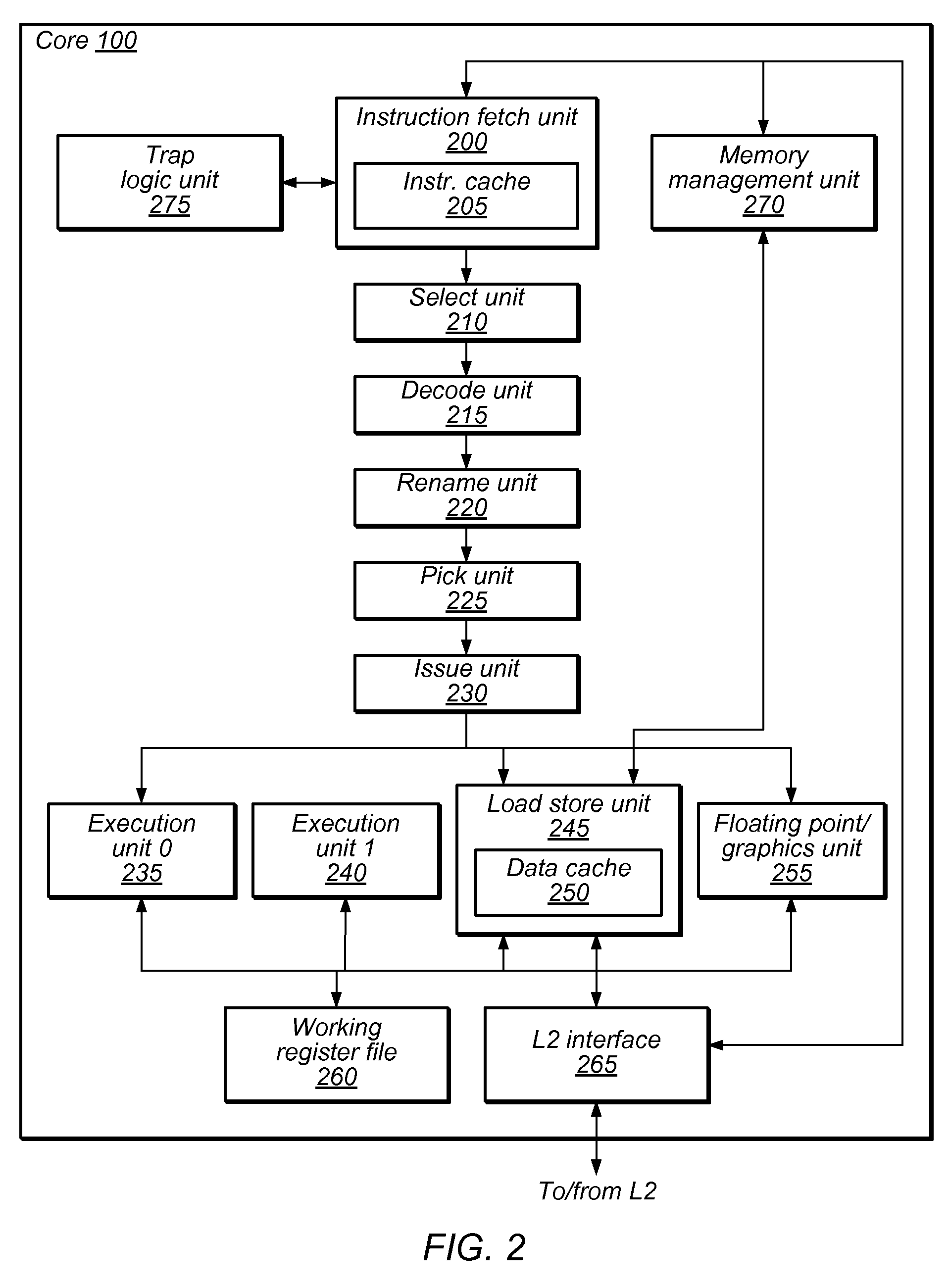
A translation lookaside buffer (TLB) is a memory cache that is used to reduce the time taken to access a user memory location. It is a part of the chip's memory-management unit (MMU). The TLB stores the recent translations of virtual memory to physical memory and can be called an address-translation cache. A TLB may reside between the CPU and the CPU cache, between CPU cache and the main memory or between the different levels of the multi-level cache. The majority of desktop, laptop, and server processors include one or more TLBs in the memory-management hardware, and it is nearly always present in any processor that utilizes paged or segmented virtual memory.
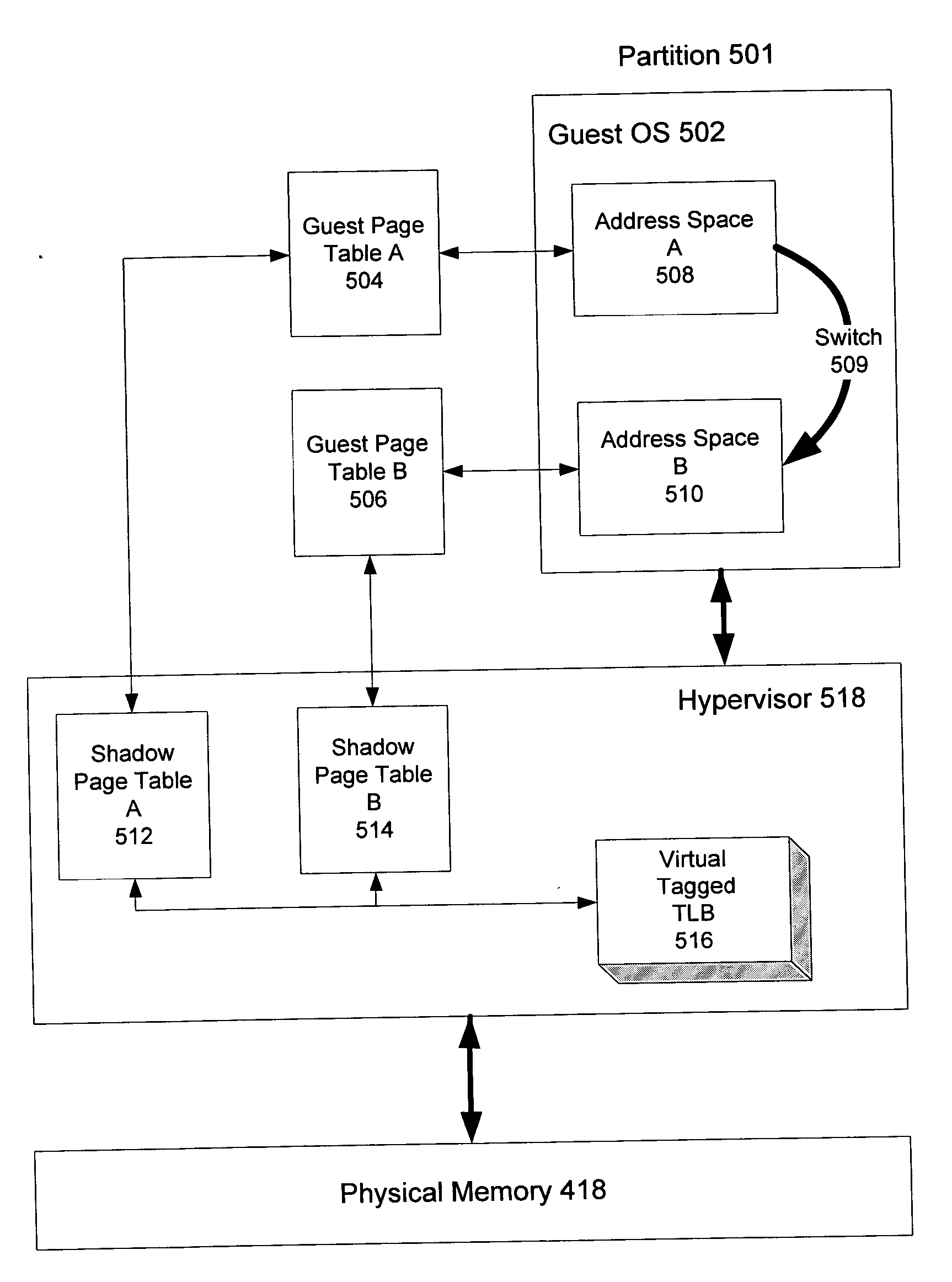
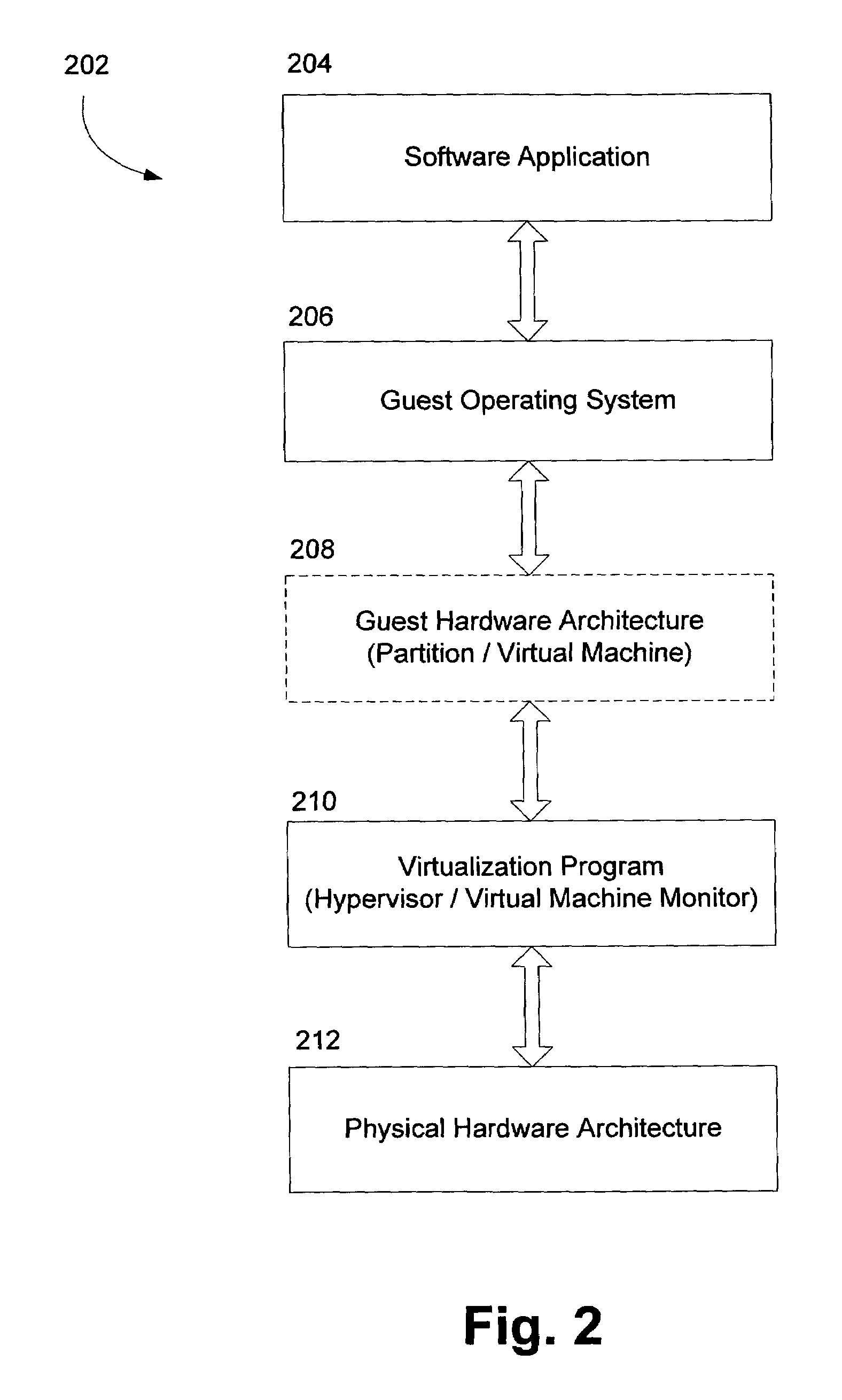
Method and system for caching address translations from multiple address spaces in virtual machines
InactiveUS20060259734A1Reduce memory overheadLow costMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsVirtualizationPage table
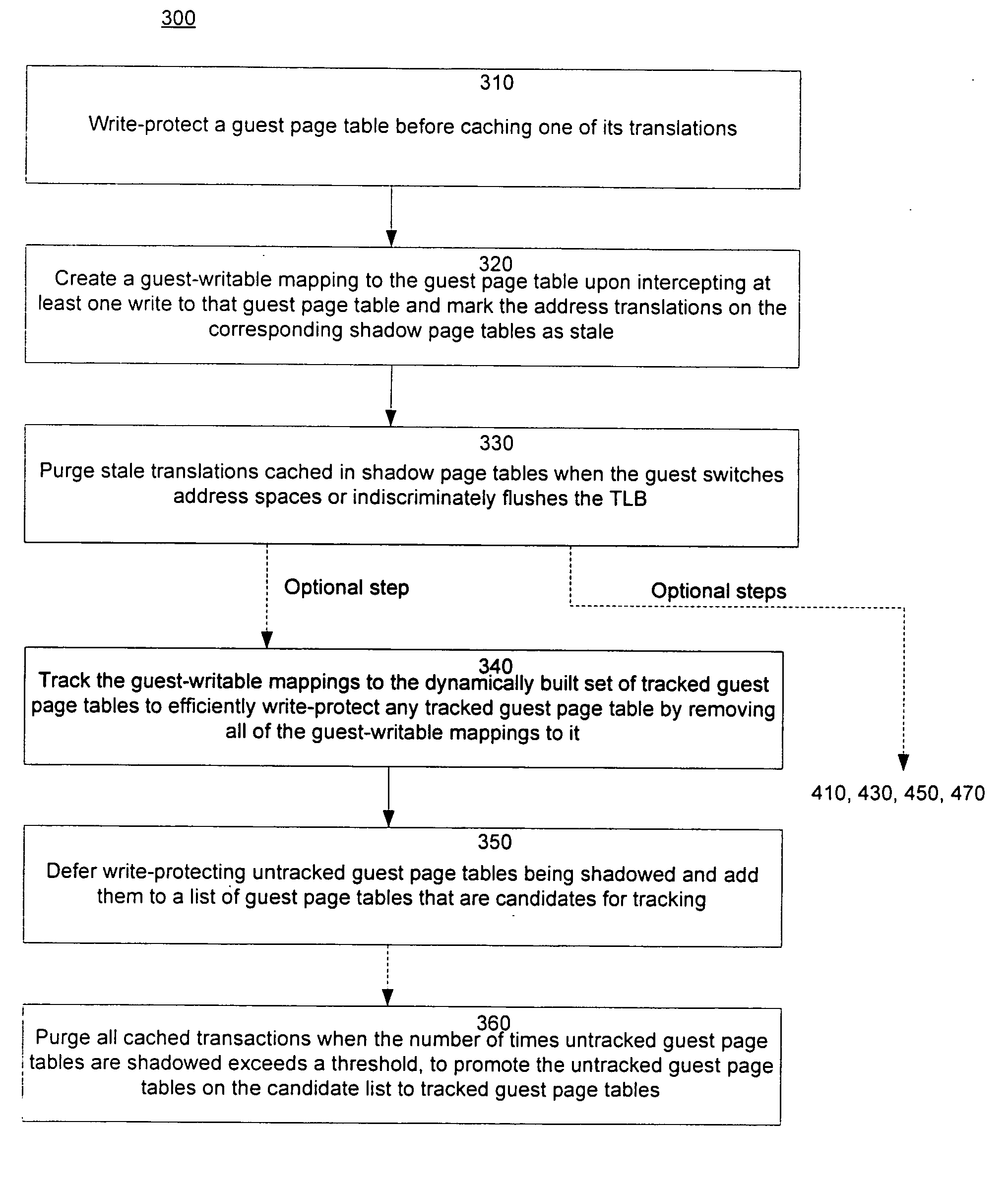
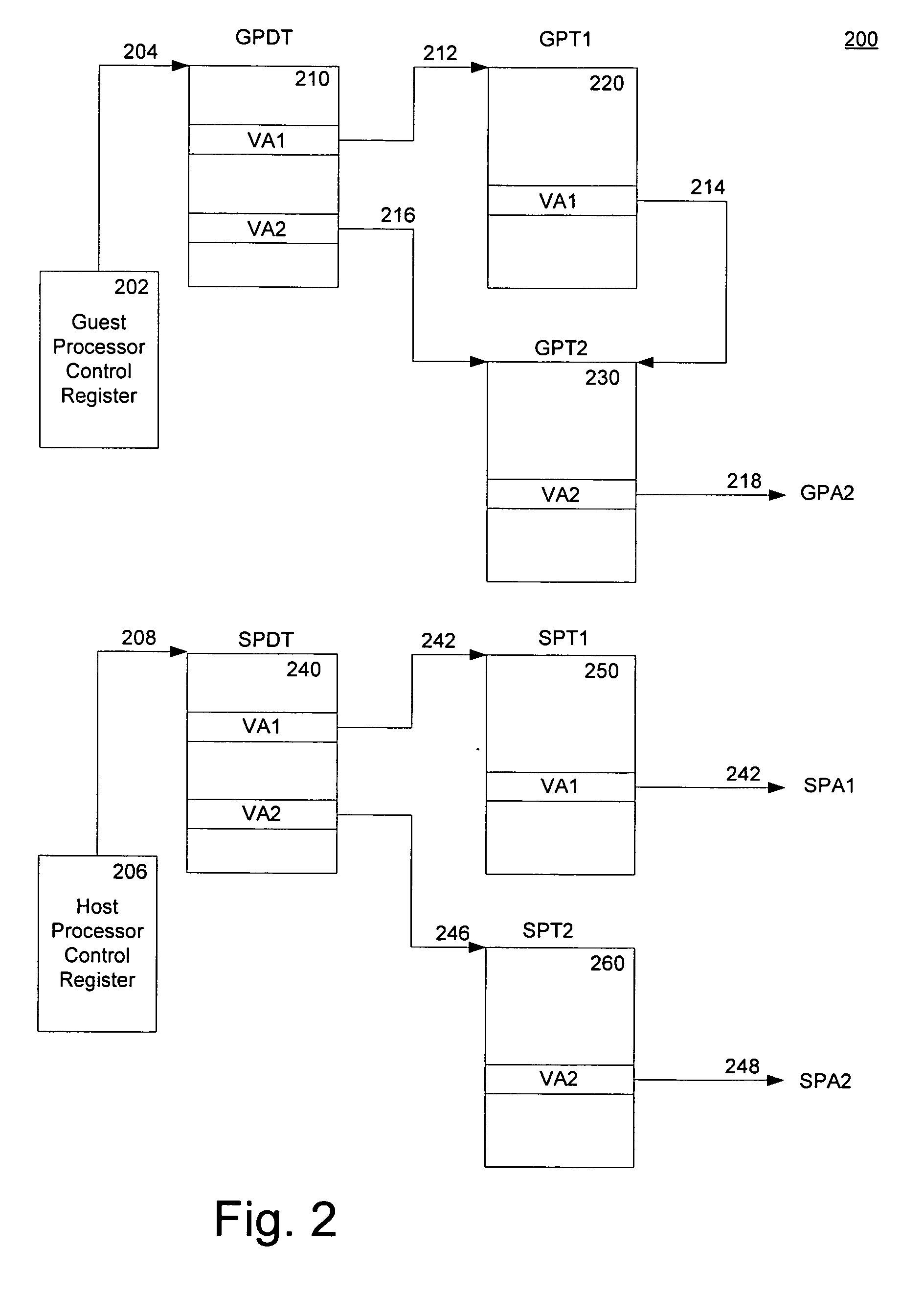
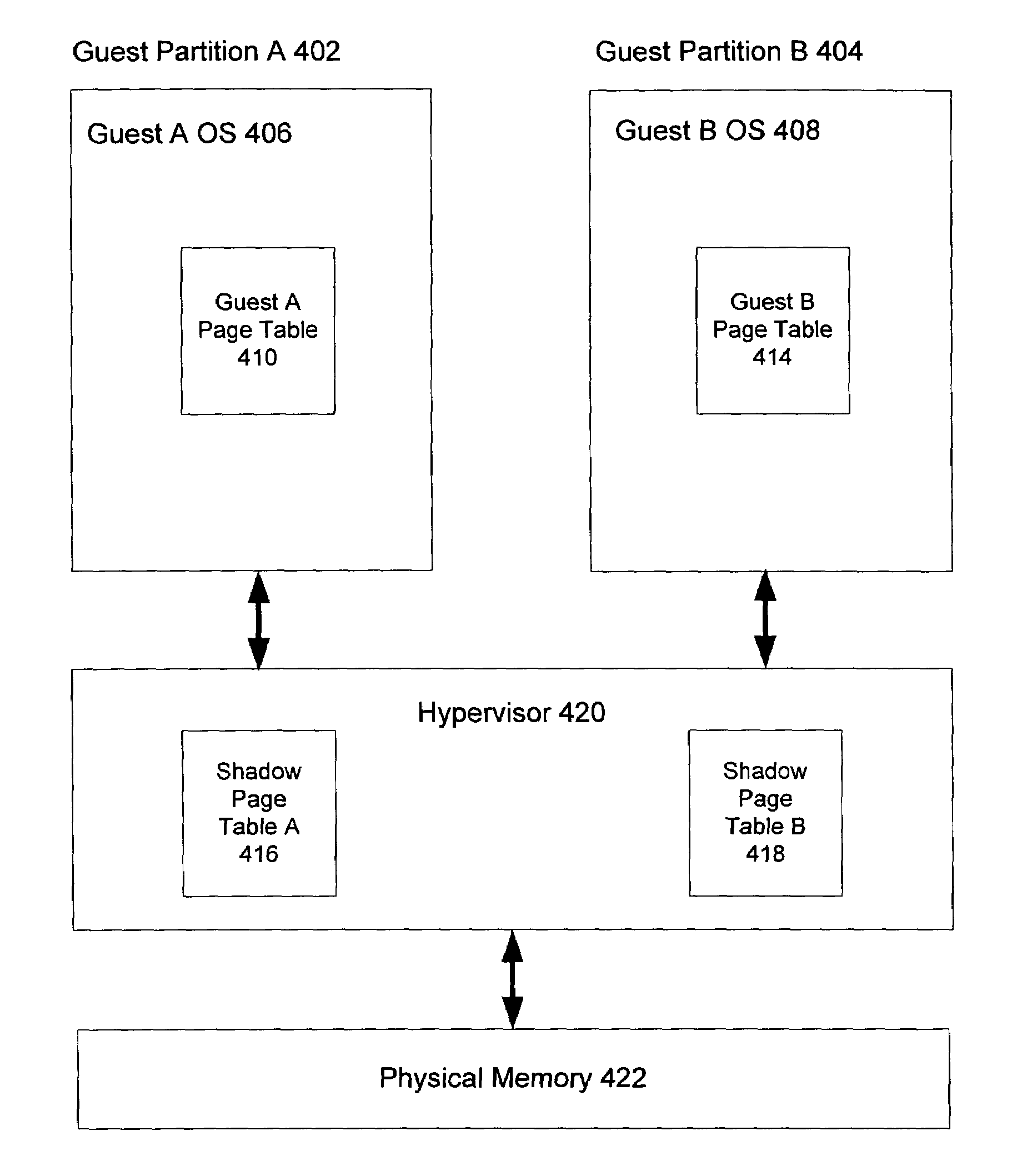
A method of virtualizing memory through shadow page tables that cache translations from multiple guest address spaces in a virtual machine includes a software version of a hardware tagged translation look-aside buffer. Edits to guest page tables are detected by intercepting the creation of guest-writable mappings to guest page tables with translations cached in shadow page tables. The affected cached translations are marked as stale and purged upon an address space switch or an indiscriminate flush of translations by the guest. Thereby, non-stale translations remain cached but stale translations are discarded. The method includes tracking the guest-writable mappings to guest page tables, deferring discovery of such mappings to a guest page table for the first time until a purge of all cached translations when the number of untracked guest page tables exceeds a threshold, and sharing shadow page tables between shadow address spaces and between virtual processors.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
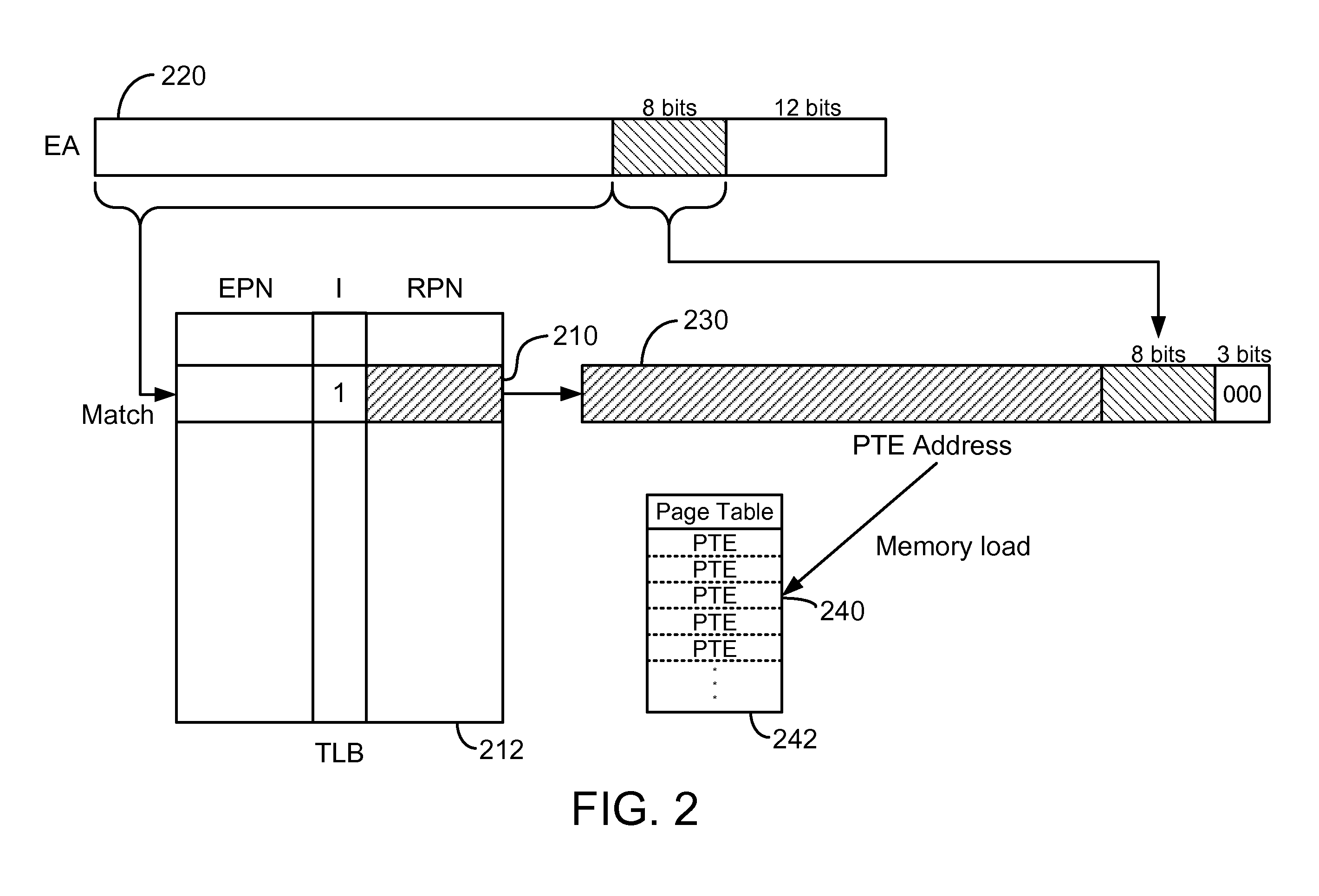
Loading entries into a tlb in hardware via indirect tlb entries
ActiveUS20100058026A1Eliminate areaEliminates powerMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMicro-instruction address formationPage tableTranslation lookaside buffer
An enhanced mechanism for loading entries into a translation lookaside buffer (TLB) in hardware via indirect TLB entries. In one embodiment, if no direct TLB entry associated with the given virtual address is found in the TLB, the TLB is checked for an indirect TLB entry associated with the given virtual address. Each indirect TLB entry provides the real address of a page table associated with a specified range of virtual addresses and comprises an array of page table entries. If an indirect TLB entry associated with the given virtual address is found in the TLB, a computed address is generated by combining a real address field from the indirect TLB entry and bits from the given virtual address, a page table entry (PTE) is obtained by reading a word from a memory at the computed address, and the PTE is loaded into the TLB as a direct TLB entry.
Owner:IBM CORP
Data processing system and method for maintaining translation lookaside buffer TLB coherency without enforcing complete instruction serialization
InactiveUS6119204AMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData processing systemProcessing Instruction
A data processing system includes at least a first processor and a second processor that each have a respective translation lookaside buffer (TLB). In response to detection by the second processor of a TLB entry invalidation request, the second processor marks at least one memory referent instruction that is being processed by the second processor and invalidates a TLB entry in the TLB of the second processor. In response to receipt of a synchronization request at the second processor, the second processor indicates to the first processor that the second processor has invalidated the TLB entry if the second processor has completed processing the marked instruction. During the interval between receipt of the synchronization request and indicating to the first processor that the second processor has invalidated the TLB entry, the second processor continues to process instructions, including fetching instructions for processing. In this manner, the second processor is able to continue normal instruction processing during the process of TLB synchronization.
Owner:NXP USA INC +1
System and method for maintaining translation look-aside buffer (TLB) consistency
InactiveUS6105113AMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationVirtual memoryMemory address
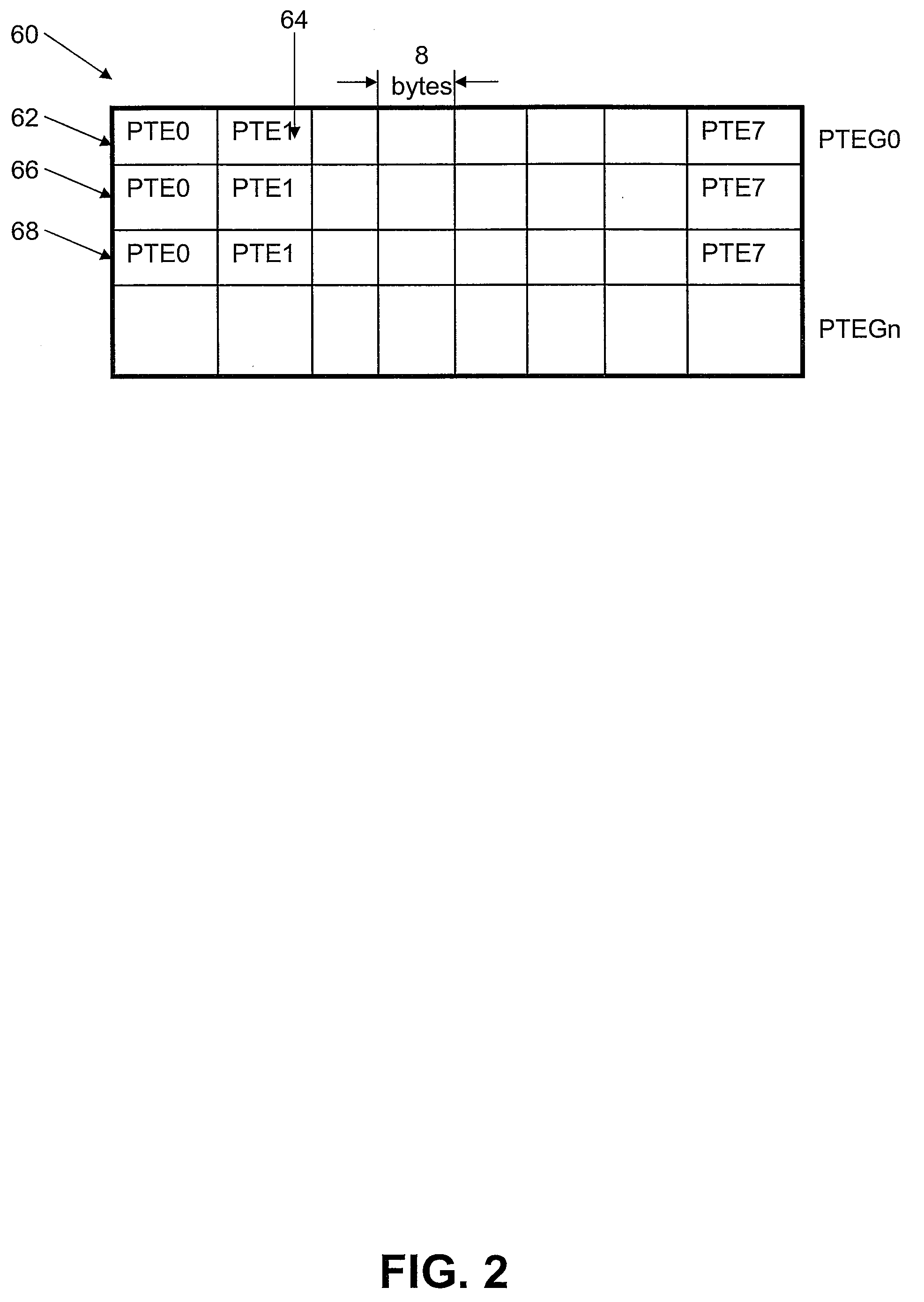
A system and method for maintaining consistency between translational look-aside buffers (TLB) and page tables. A TLB has a TLB table for storing a list of virtual memory address-to-physical memory address translations, or page table entries (PTES) and a hardware-based controller for invalidating a translation that is stored in the TLB table when a corresponding page table entry changes. The TLB table includes a virtual memory (VM) page tag and a page table entry address tag for indexing the list of translations The VM page tag can be searched for VM pages that are referenced by a process. If a referenced VM page is found, an associated physical address is retrieved for use by the processor. The TLB controller includes a snooping controller for snooping a cache-memory interconnect for activity that affects PTEs. The page table entry address tag can be searched by a search engine in the TLB controller for snooped page table entry addresses. The TLB controller includes an updating module for invalidating or updating translations associated with snooped page table entry addresses. Translations in TLBs are thus updated or invalidated through hardware when an operating system changes a PTE, without intervention by an operating system or other software.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
Enhanced shadow page table algorithms
InactiveUS20060259732A1Reduce processImprove efficiencyMemory systemsMicro-instruction address formationOperational systemPage table
Enhanced shadow page table algorithms are presented for enhancing typical page table algorithms. In a virtual machine environment, where an operating system may be running within a partition, the operating system maintains it's own guest page tables. These page tables are not the real page tables that map to the real physical memory. Instead, the memory is mapped by shadow page tables maintained by a virtualing program, such as a hypervisor, that virtualizes the partition containing the operating system. Enhanced shadow page table algorithms provide efficient ways to harmonize the shadow page tables and the guest page tables. Specifically, by using tagged translation lookaside buffers, batched shadow page table population, lazy flags, and cross-processor shoot downs, the algorithms make sure that changes in the guest pages tables are reflected in the shadow page tables.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
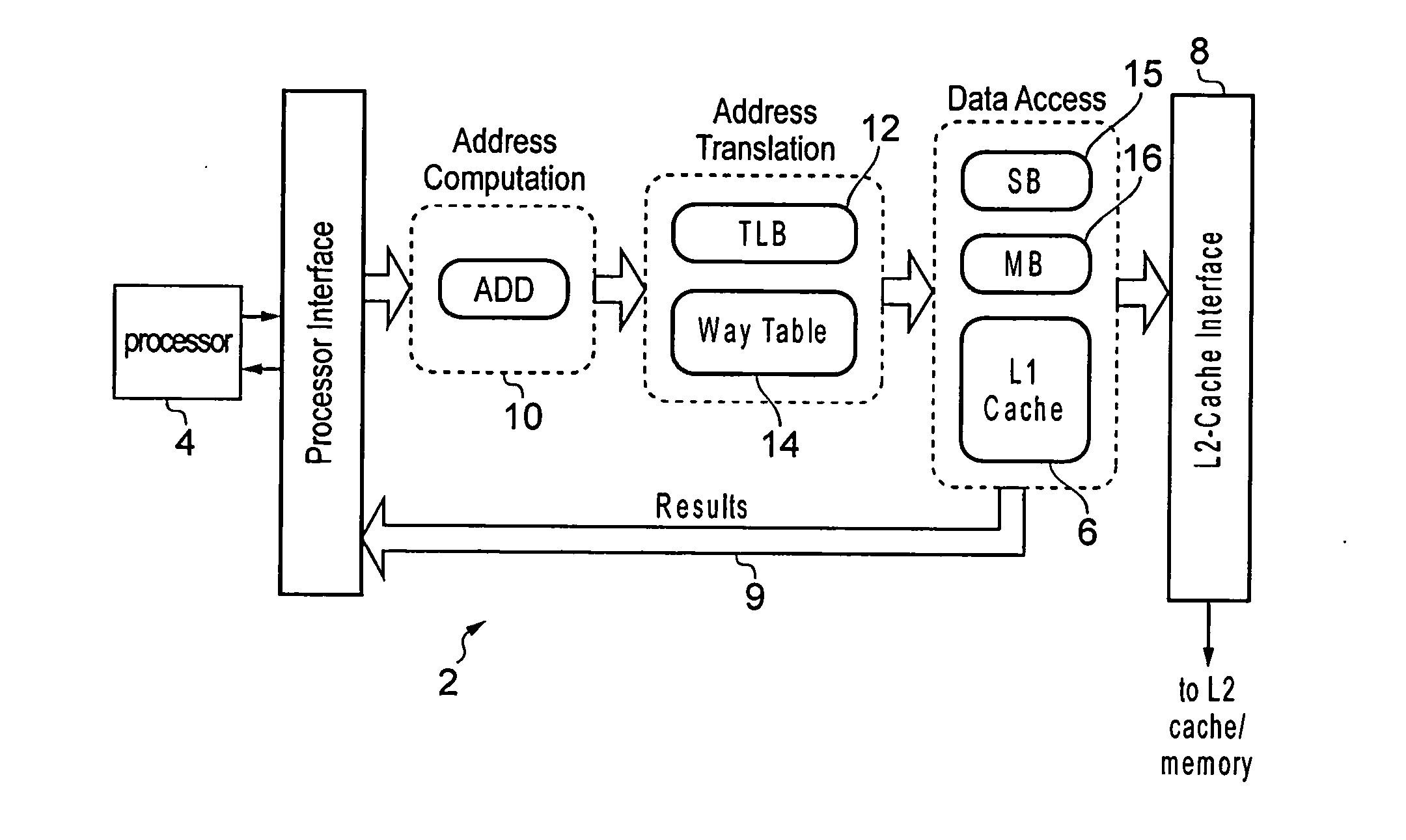
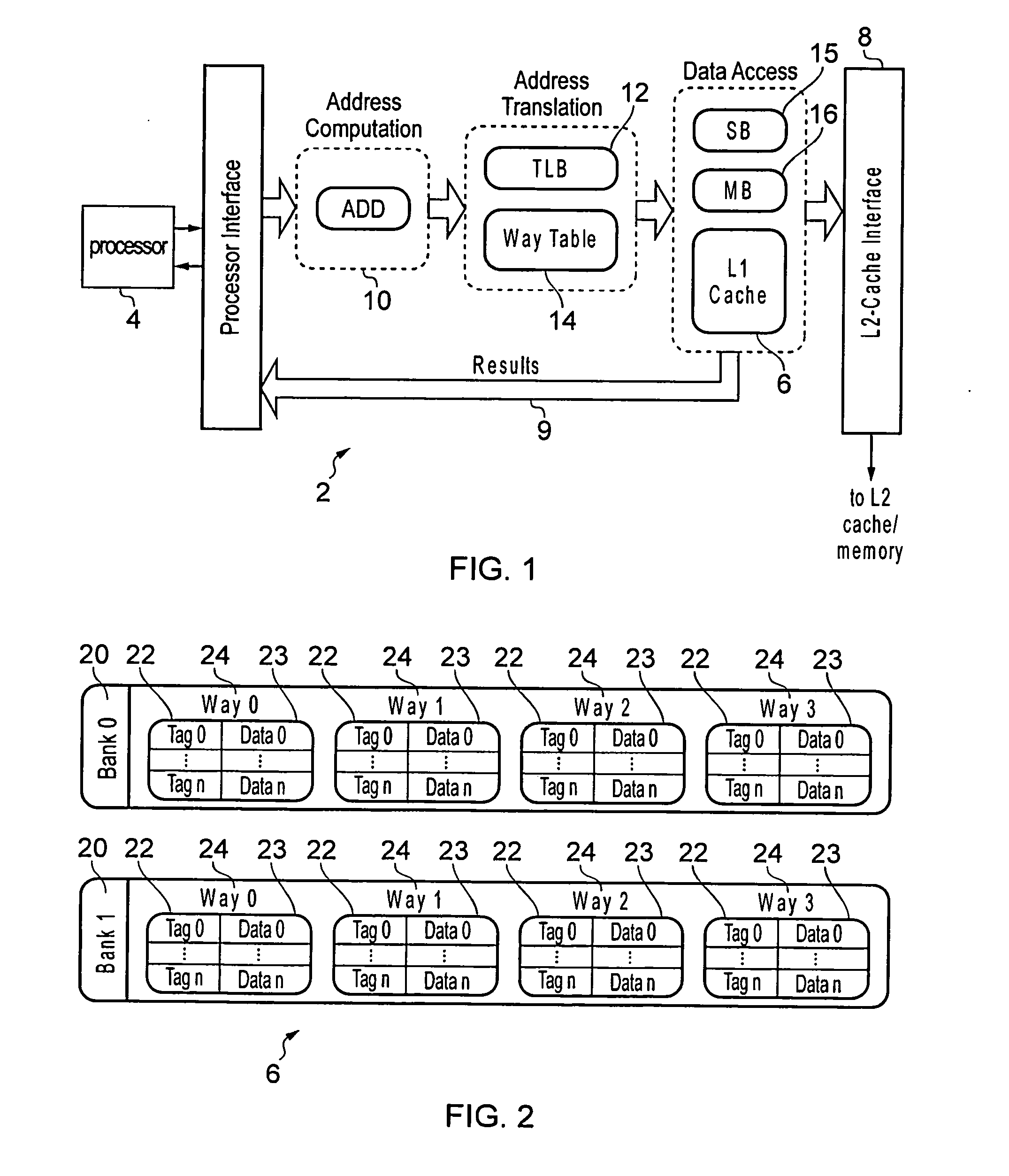
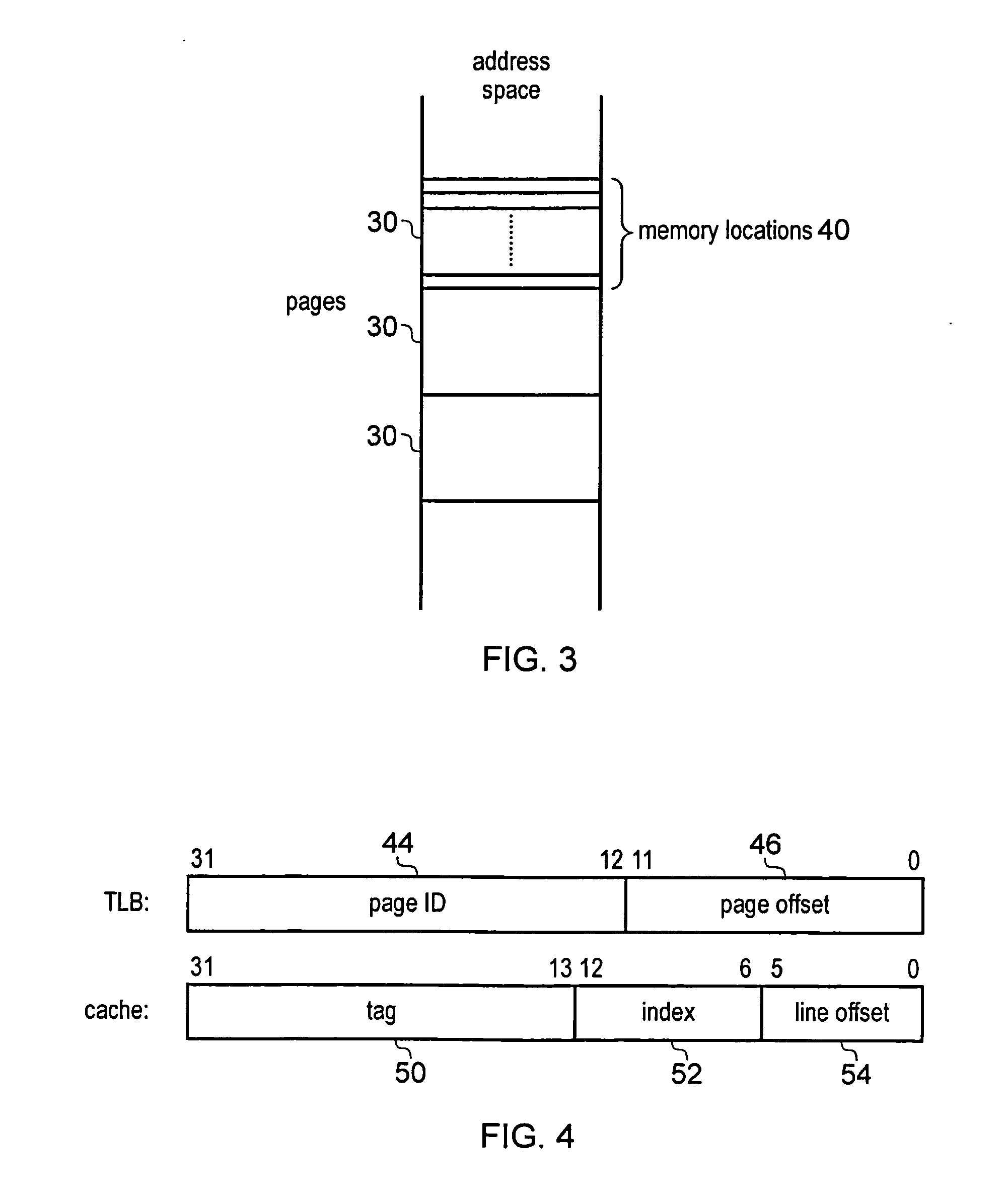
Data processing apparatus having cache and translation lookaside buffer
ActiveUS20130304991A1Efficient executionEasy to operateMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingTranslation lookaside buffer
A data processing apparatus has a cache and a translation look aside buffer (TLB). A way table is provided for identifying which of a plurality of cache ways stores require data. Each way table entry corresponds to one of the TLB entries of the TLB and identifies, for each memory location of the page associated with the corresponding TLB entry, which cache way stores the data associated with that memory location. Also, the cache may be capable of servicing M access requests in the same processing cycle. An arbiter may select pending access requests for servicing by the cache in a way that ensures that the selected pending access requests specify a maximum of N different virtual page addresses, where N<M.
Owner:ARM LTD
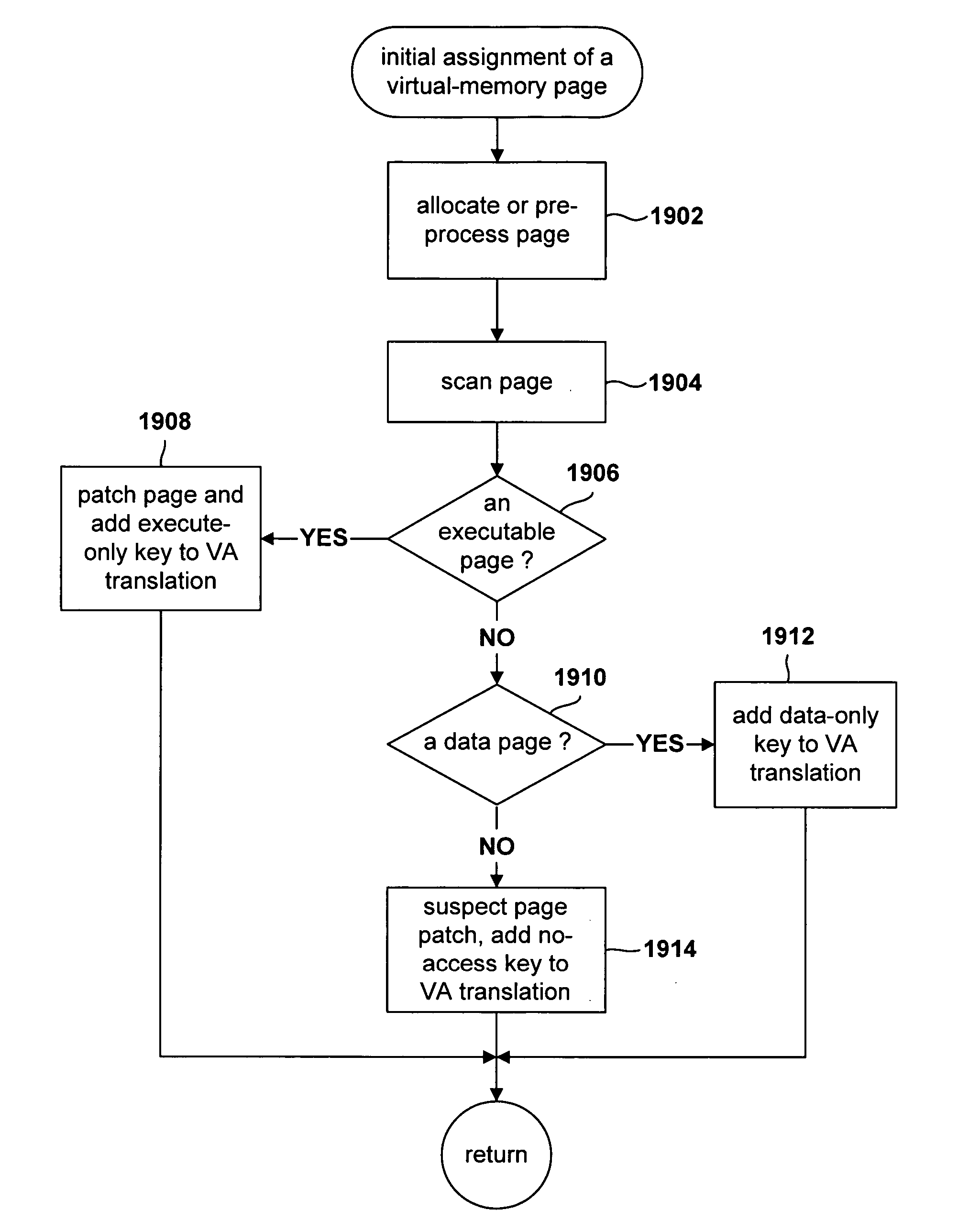
Method for monitoring access to virtual memory pages
InactiveUS20060036830A1Internal/peripheral component protectionMemory systemsVirtual memoryOperational system
Various embodiments of the present invention are directed to efficient methods for virtual-machine monitors to detect, at run time, initial attempts by guest operating systems and other higher-level software to access or execute particular instructions or values corresponding to the particular instructions, that, when accessed for execution, need to be emulated by a virtual-machine monitor, rather than directly accessed by guest operating systems. In certain embodiments of the present invention, the virtual-machine monitor assigns various guest-operating-system-code-containing memory pages to one of a small number of protection-key domains. By doing so, the virtual-machine monitor can arrange for any initial access to the memory pages assigned to the protection-key domains to generate a key-permission fault, after which the key-permission-fault handler of the virtual-machine monitor is invoked to arrange for subsequent, efficient access or emulation of access to the protected pages. In alternative embodiments, protection domains can be implemented by using page-level access rights or translation-lookaside-buffer entry fields.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
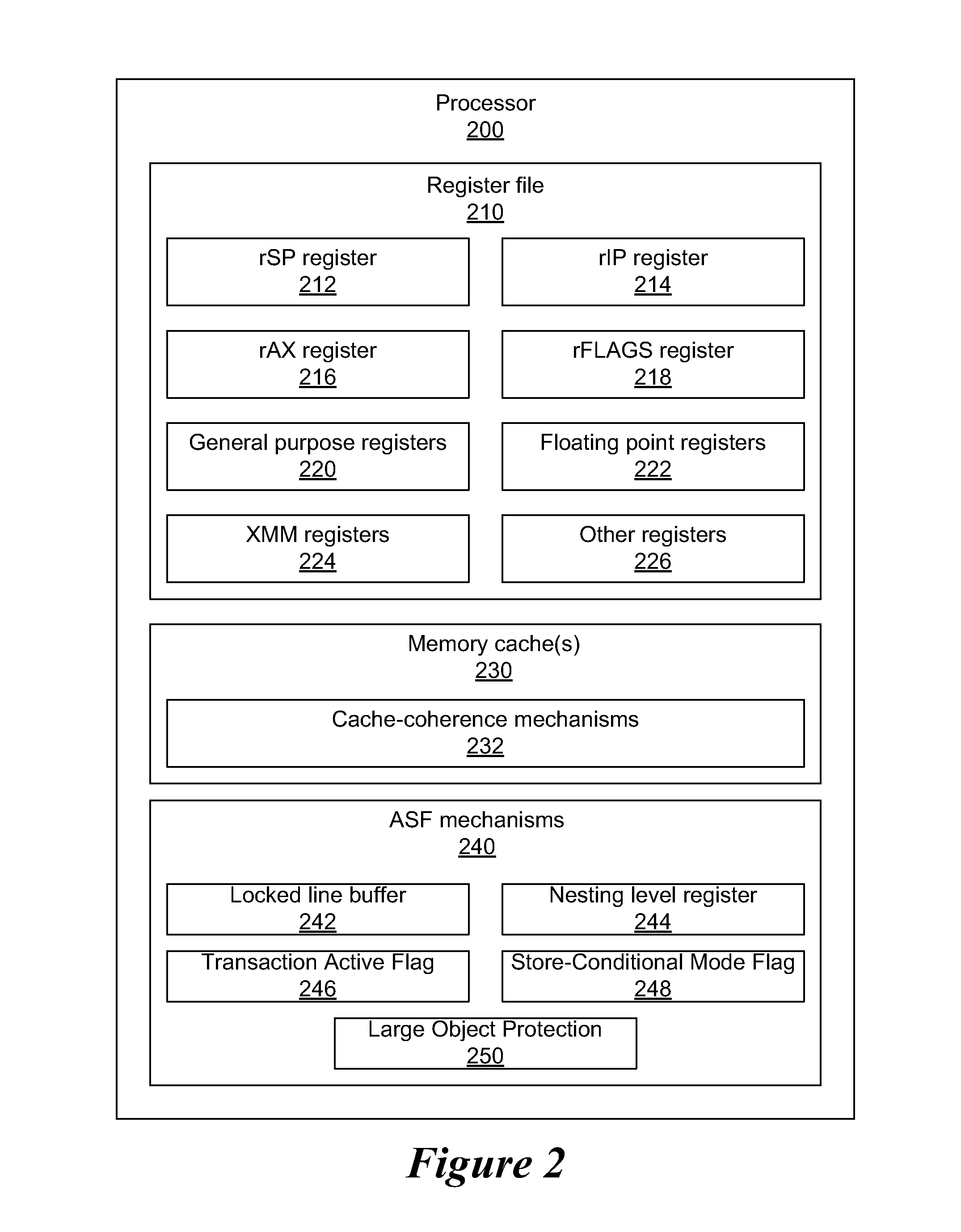
Protecting Large Objects Within an Advanced Synchronization Facility
A system and method are disclosed for allowing protection of larger areas than memory lines by monitoring accessed and dirty bits in page tables. More specifically, in some embodiments, a second associative structure with a different granularity is provided to filter out a large percentage of false positives. By providing the associative structure with sufficient size, the structure exactly specifies a region in which conflicting cache lines lie. If entries within this region are evicted from the structure, enabling the tracking for the entire index filters out a substantial number of false positives (depending on a granularity and a number of indices present). In some embodiments, this associative structure is similar to a translation look aside buffer (TLB) with 4 k, 2M entries.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
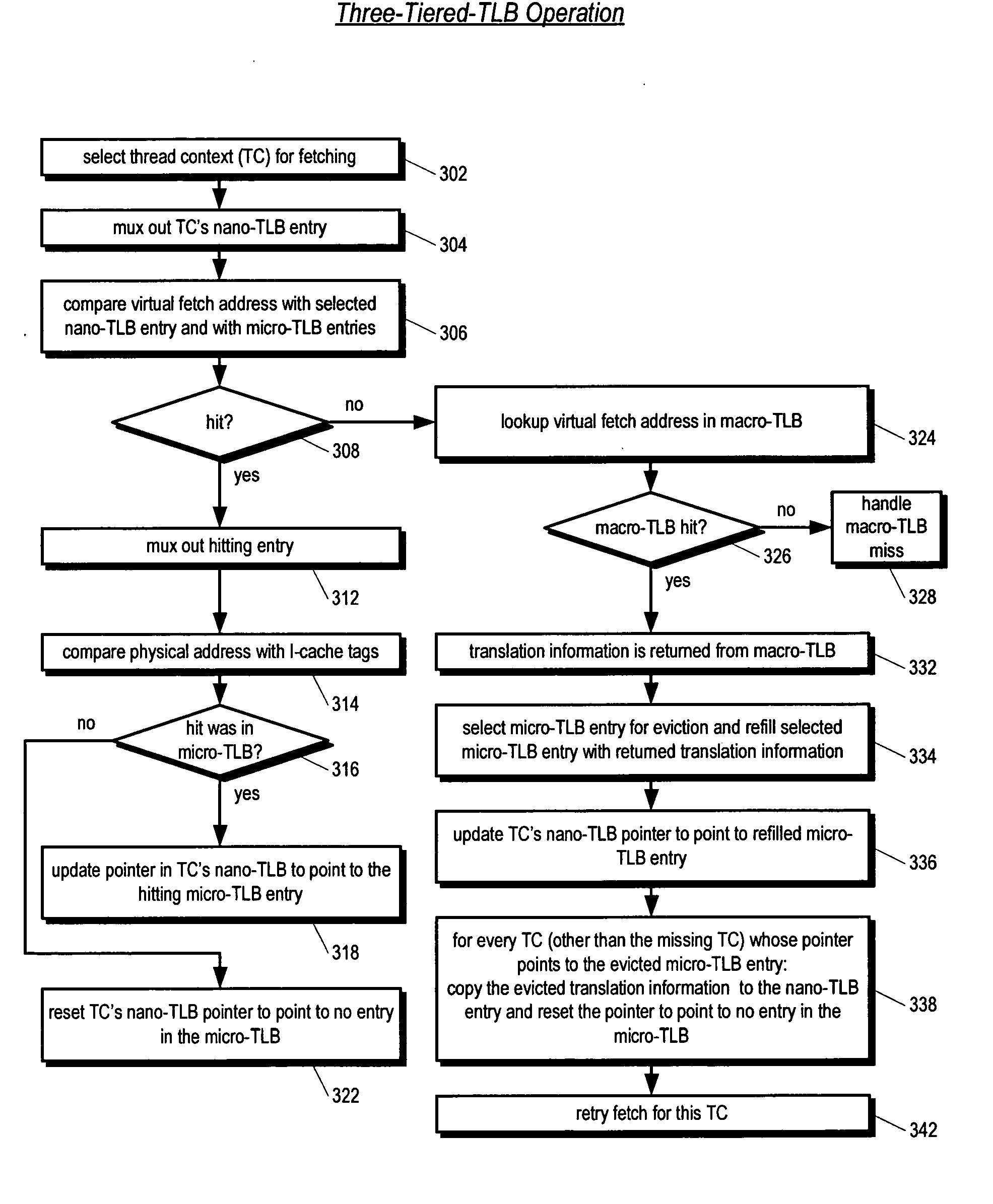
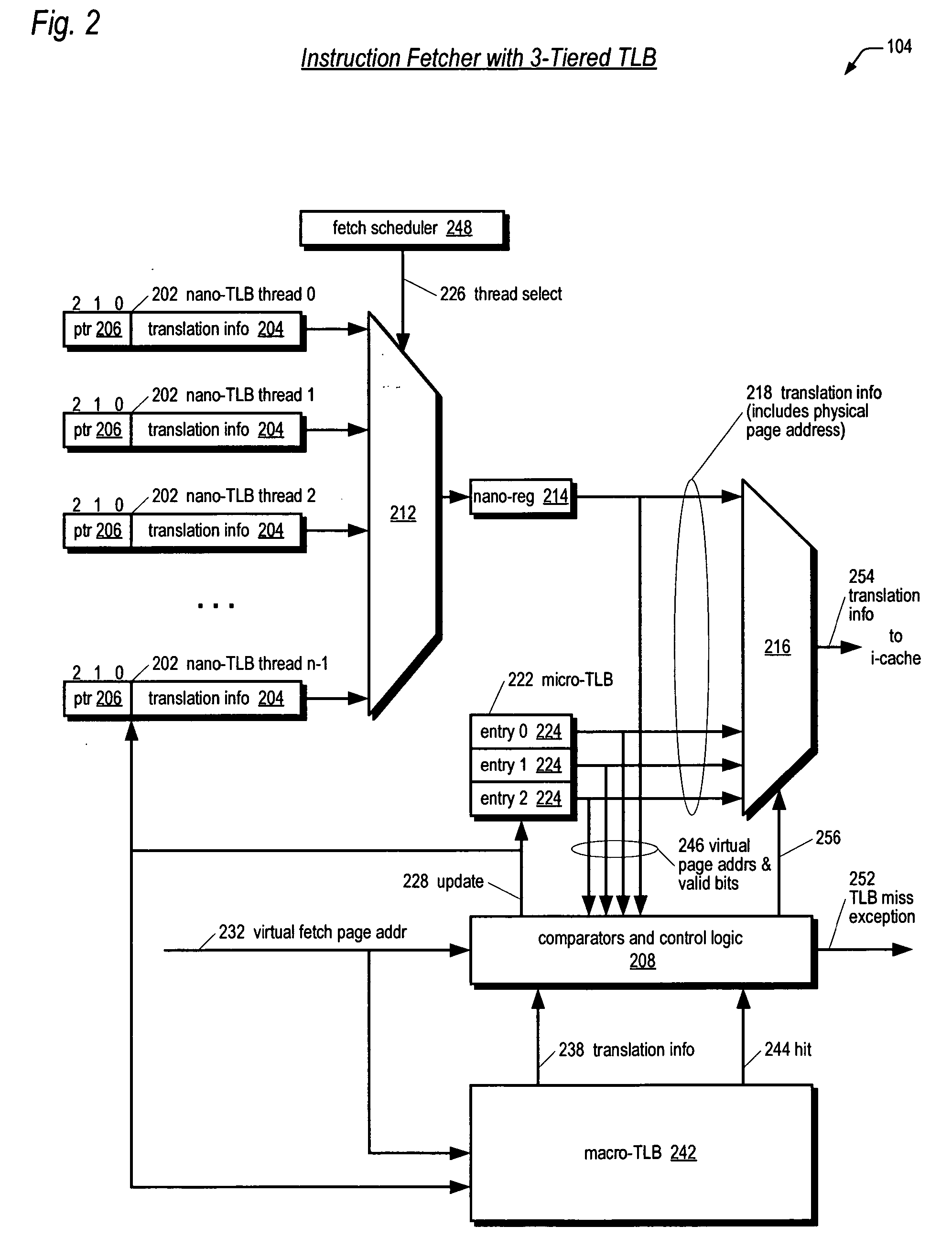
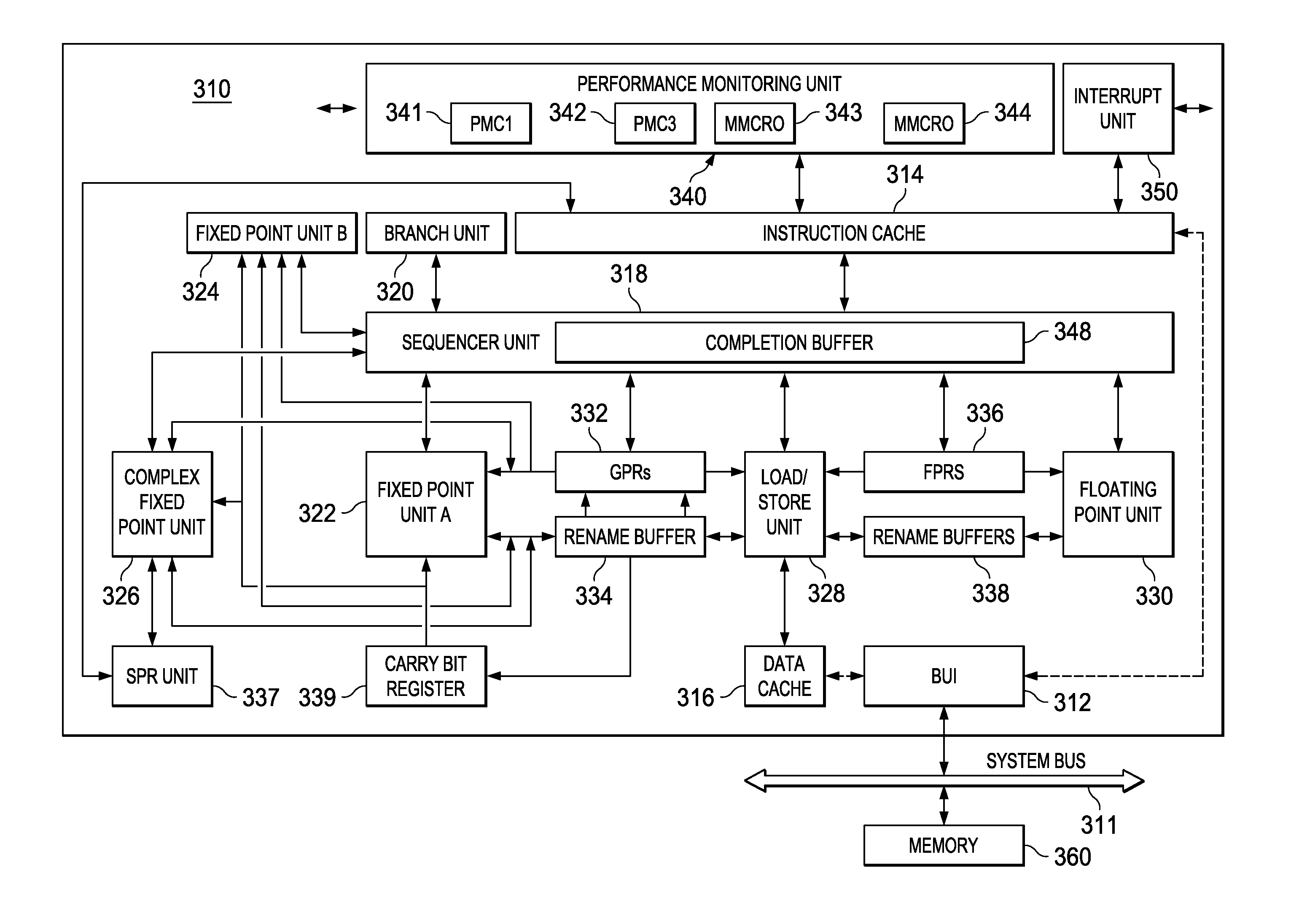
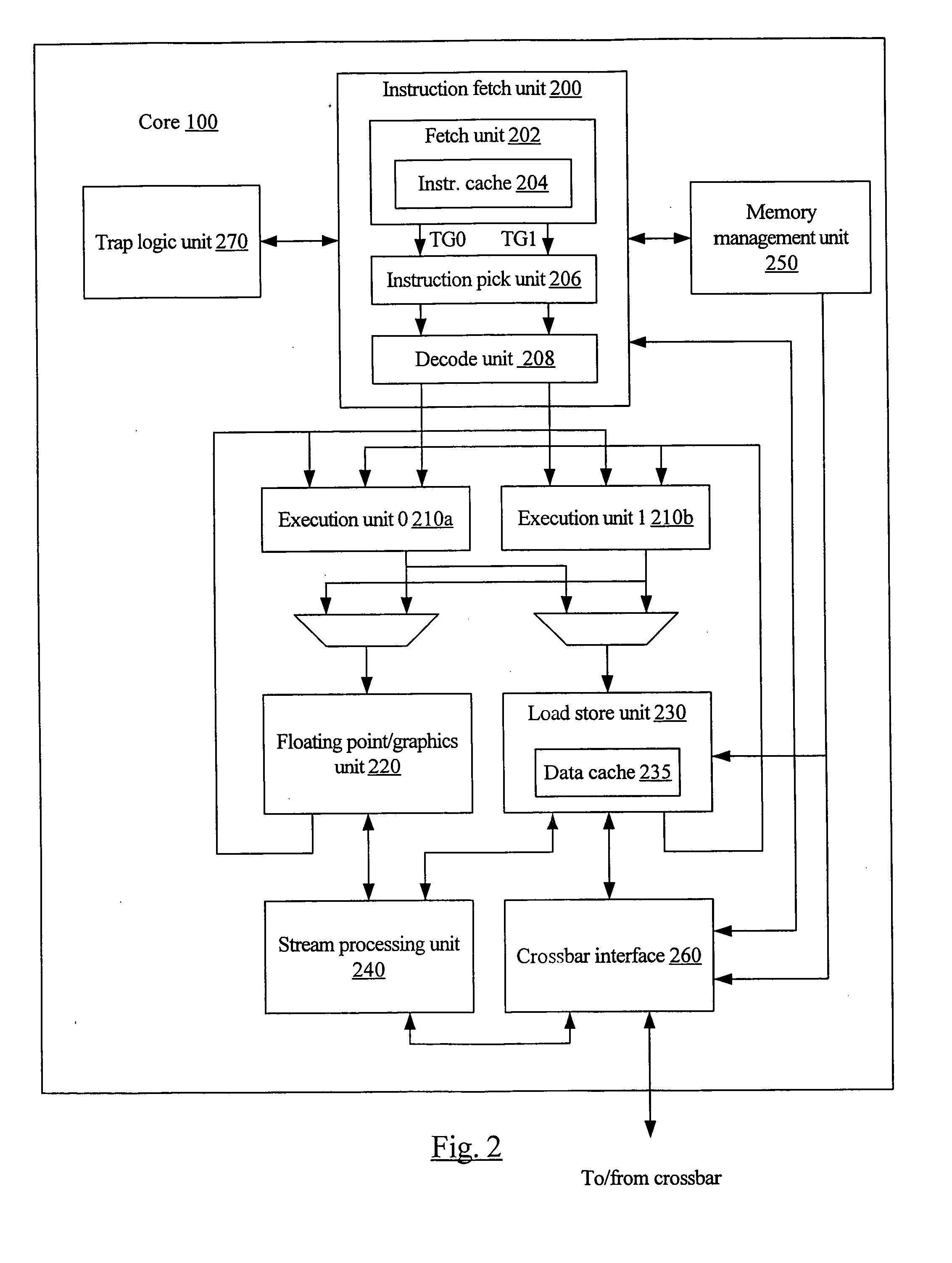
Three-tiered translation lookaside buffer hierarchy in a multithreading microprocessor
ActiveUS20060206686A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingTranslation lookaside buffer
A three-tiered TLB architecture in a multithreading processor that concurrently executes multiple instruction threads is provided. A macro-TLB caches address translation information for memory pages for all the threads. A micro-TLB caches the translation information for a subset of the memory pages cached in the macro-TLB. A respective nano-TLB for each of the threads caches translation information only for the respective thread. The nano-TLBs also include replacement information to indicate which entries in the nano-TLB / micro-TLB hold recently used translation information for the respective thread. Based on the replacement information, recently used information is copied to the nano-TLB if evicted from the micro-TLB.
Owner:MIPS TECH INC
Memory address translation-based data encryption/compression
InactiveUS20130191649A1Digital data processing detailsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory addressStreaming data
A method and circuit arrangement selectively stream data to an encryption or compression engine based upon encryption and / or compression-related page attributes stored in a memory address translation data structure such as an Effective To Real Translation (ERAT) or Translation Lookaside Buffer (TLB). A memory address translation data structure may be accessed, for example, in connection with a memory access request for data in a memory page, such that attributes associated with the memory page in the data structure may be used to control whether data is encrypted / decrypted and / or compressed / decompressed in association with handling the memory access request.
Owner:IBM CORP
Enhanced shadow page table algorithms
InactiveUS7299337B2Improve efficiencyReduce processMemory systemsMicro-instruction address formationOperational systemPage table
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
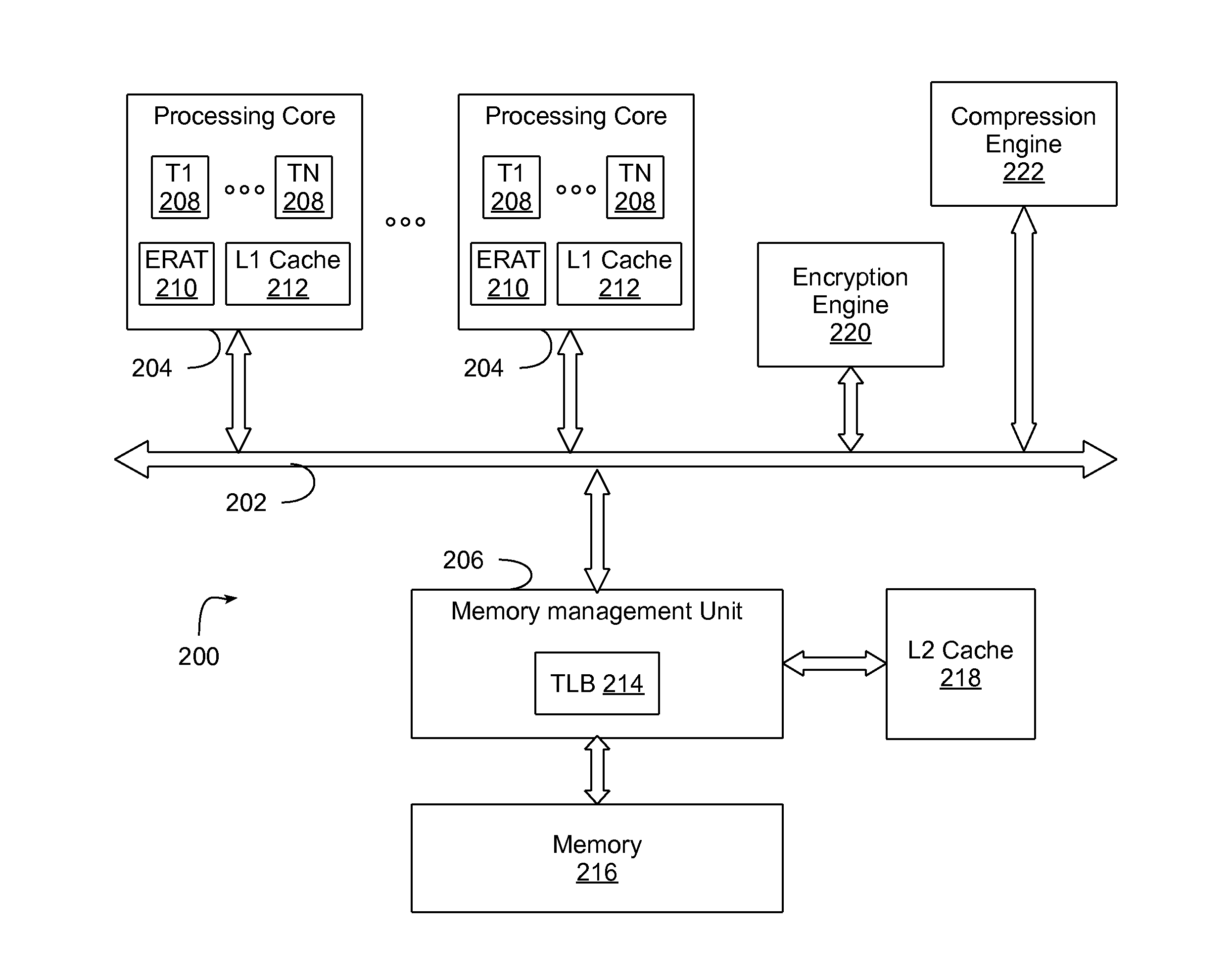
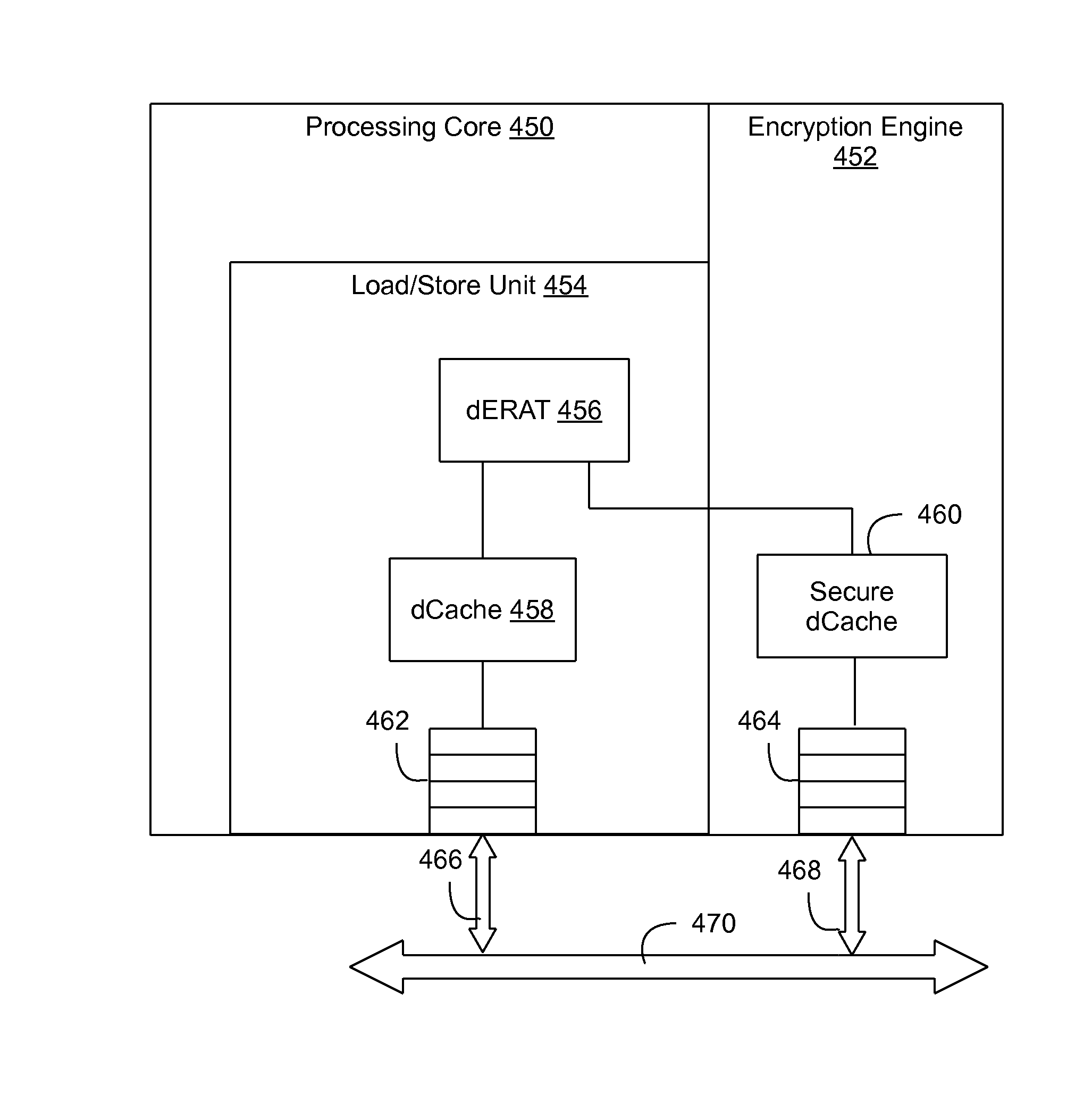
Memory address translation-based data encryption with integrated encryption engine
ActiveUS20130191651A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationUnauthorized memory use protectionMemory addressProcessing core
A method and circuit arrangement utilize an integrated encryption engine within a processing core of a multi-core processor to perform encryption operations, i.e., encryption and decryption of secure data, in connection with memory access requests that access such data. The integrated encryption engine is utilized in combination with a memory address translation data structure such as an Effective To Real Translation (ERAT) or Translation Lookaside Buffer (TLB) that is augmented with encryption-related page attributes to indicate whether pages of memory identified in the data structure are encrypted such that secure data associated with a memory access request in the processing core may be selectively streamed to the integrated encryption engine based upon the encryption-related page attribute for the memory page associated with the memory access request.
Owner:IBM CORP
Hardware support for superpage coalescing
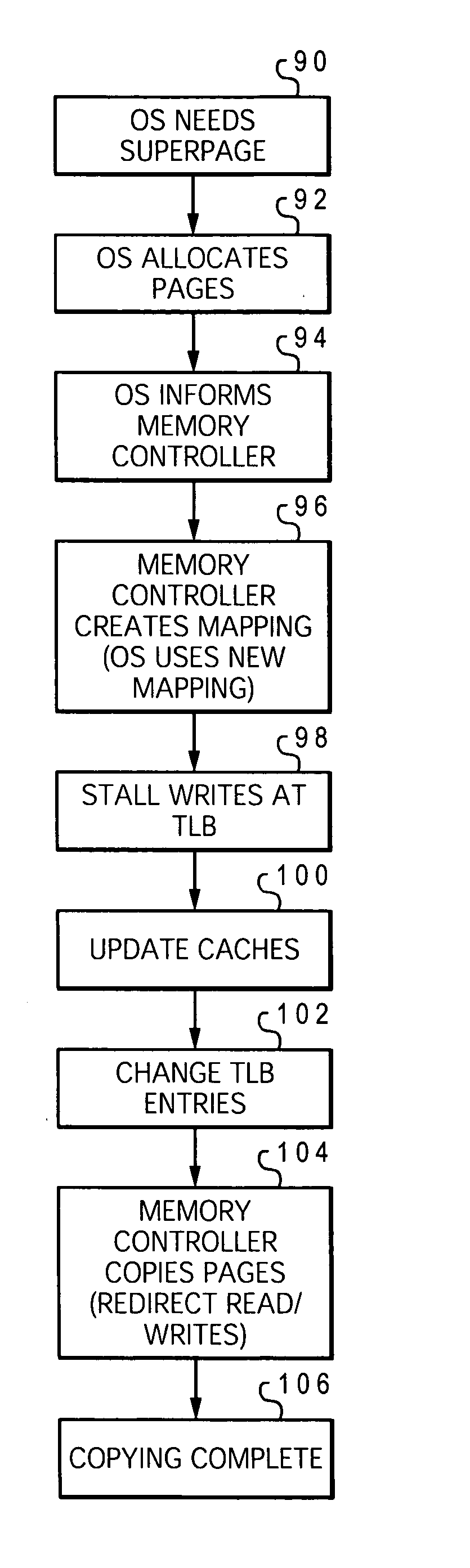
InactiveUS20050108496A1Facilitates efficient superpage coalescingReducing latentcies associated with page copyingMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMicro-instruction address formationVirtual memoryData processing system
A method of assigning virtual memory to physical memory in a data processing system allocates a set of contiguous physical memory pages for a new page mapping, instructs the memory controller to move the virtual memory pages according to the new page mapping, and then allows access to the virtual memory pages using the new page mapping while the memory controller is still copying the virtual memory pages to the set of physical memory pages. The memory controller can use a mapping table which temporarily stores entries of the old and new page addresses, and releases the entries as copying for each entry is completed. The translation lookaside buffer (TLB) entries in the processor cores are updated for the new page addresses prior to completion of copying of the memory pages by the memory controller. The invention can be extended to non-uniform memory array (NUMA) systems. For systems with cache memory, any cache entry which is affected by the page move can be updated by modifying its address tag according to the new page mapping. This tag modification may be limited to cache entries in a dirty coherency state. The cache can further relocate a cache entry based on a changed congruence class for any modified address tag.
Owner:IBM CORP
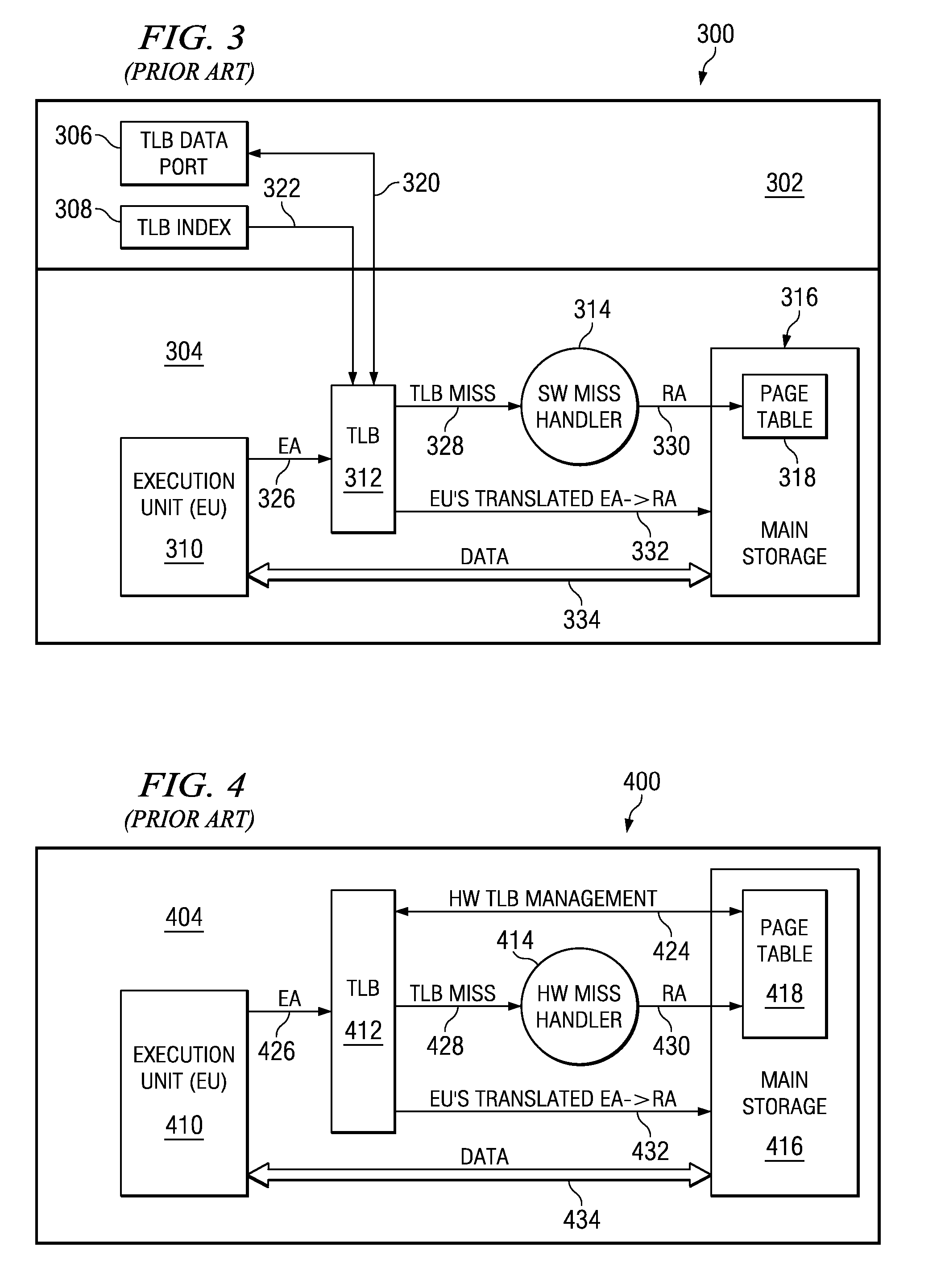
Software assisted translation lookaside buffer search mechanism
InactiveUS20110153955A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationProcessor registerTranslation lookaside buffer
A computer implemented method searches a unified translation lookaside buffer. Responsive to a request to access the unified translation lookaside buffer, a first order code within a first entry of a search priority configuration register is identified. A unified translation lookaside buffer is then searched according to the first order code for a hashed page entry. If the hashed page entry is not found when searching a unified translation lookaside buffer according to the first order code, a second order code is identified within a second entry of the search priority configuration register. The unified translation lookaside buffer is then searched according to the second order code for the hashed page entry.
Owner:IBM CORP
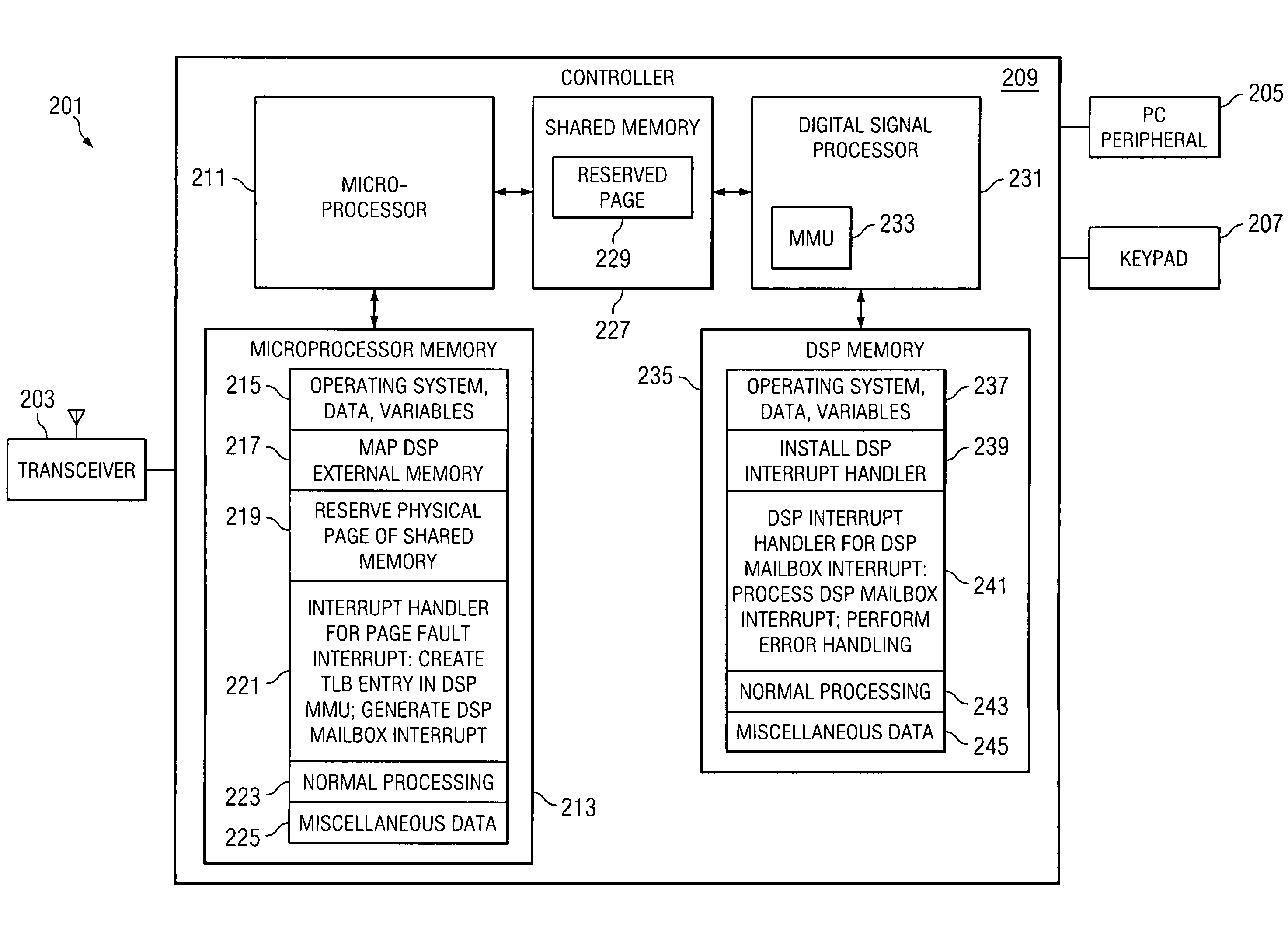
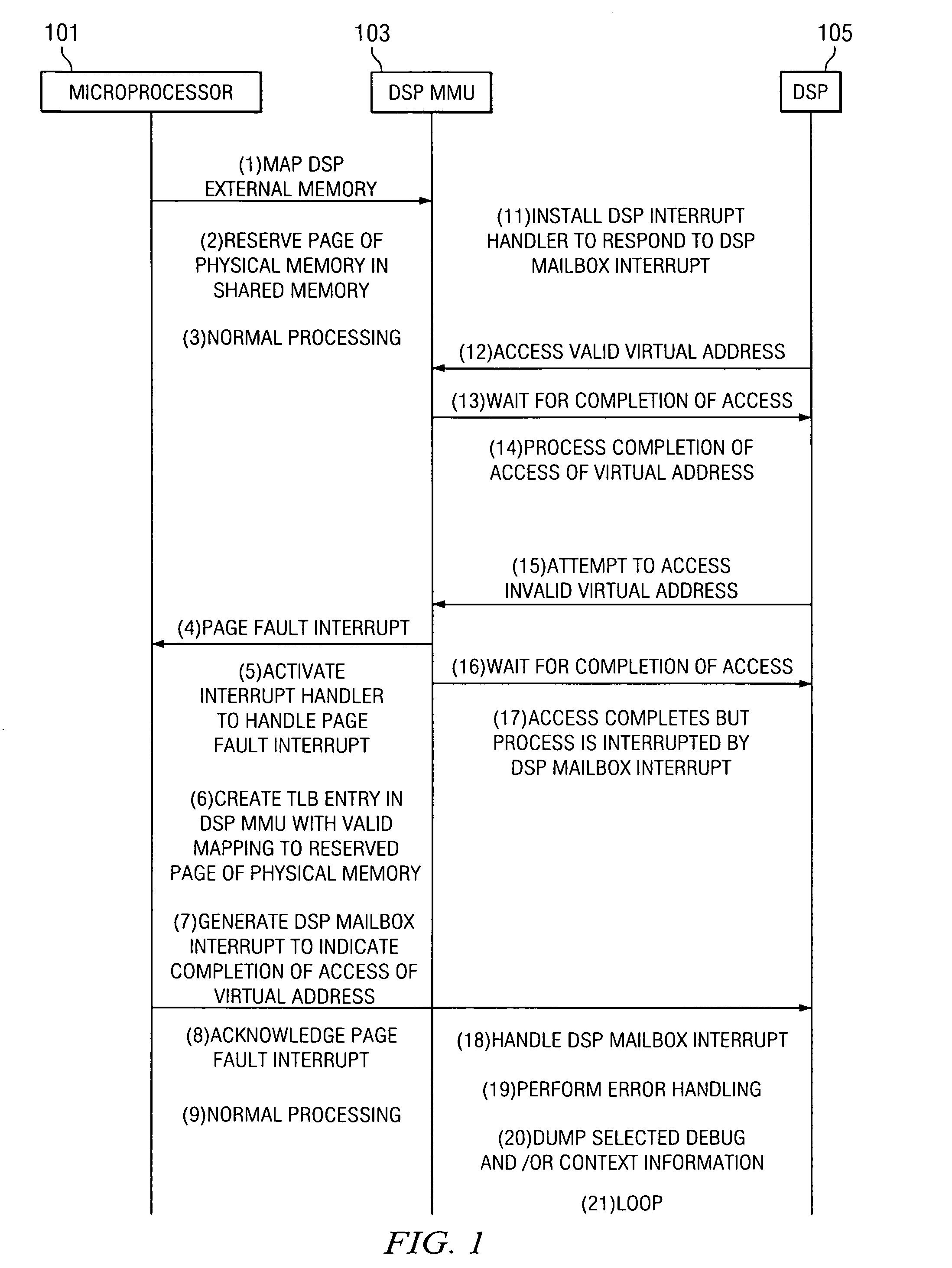
Method, system and device for handling a memory management fault in a multiple processor device
ActiveUS20080183931A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationFault responseComputer architectureMulti processor
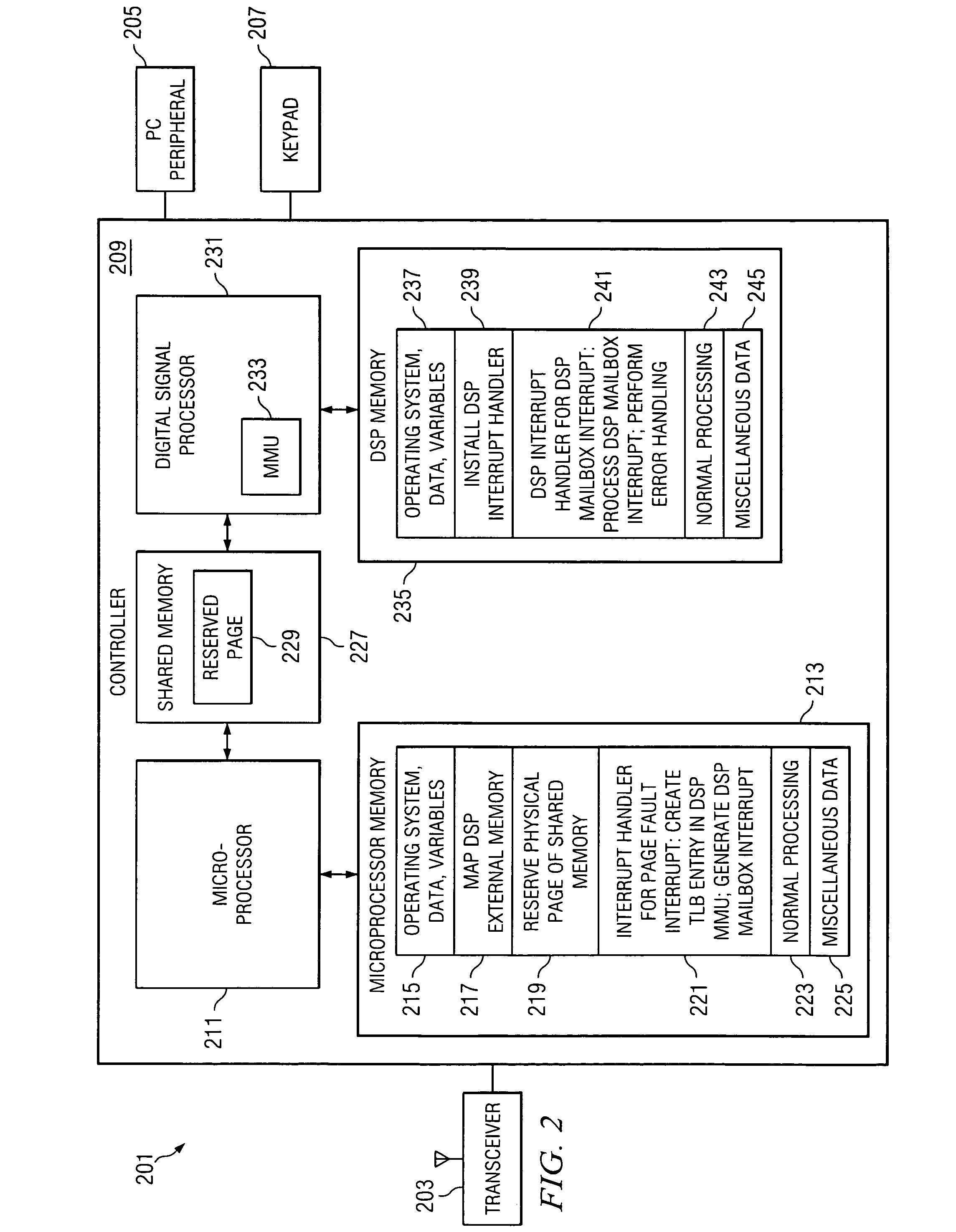
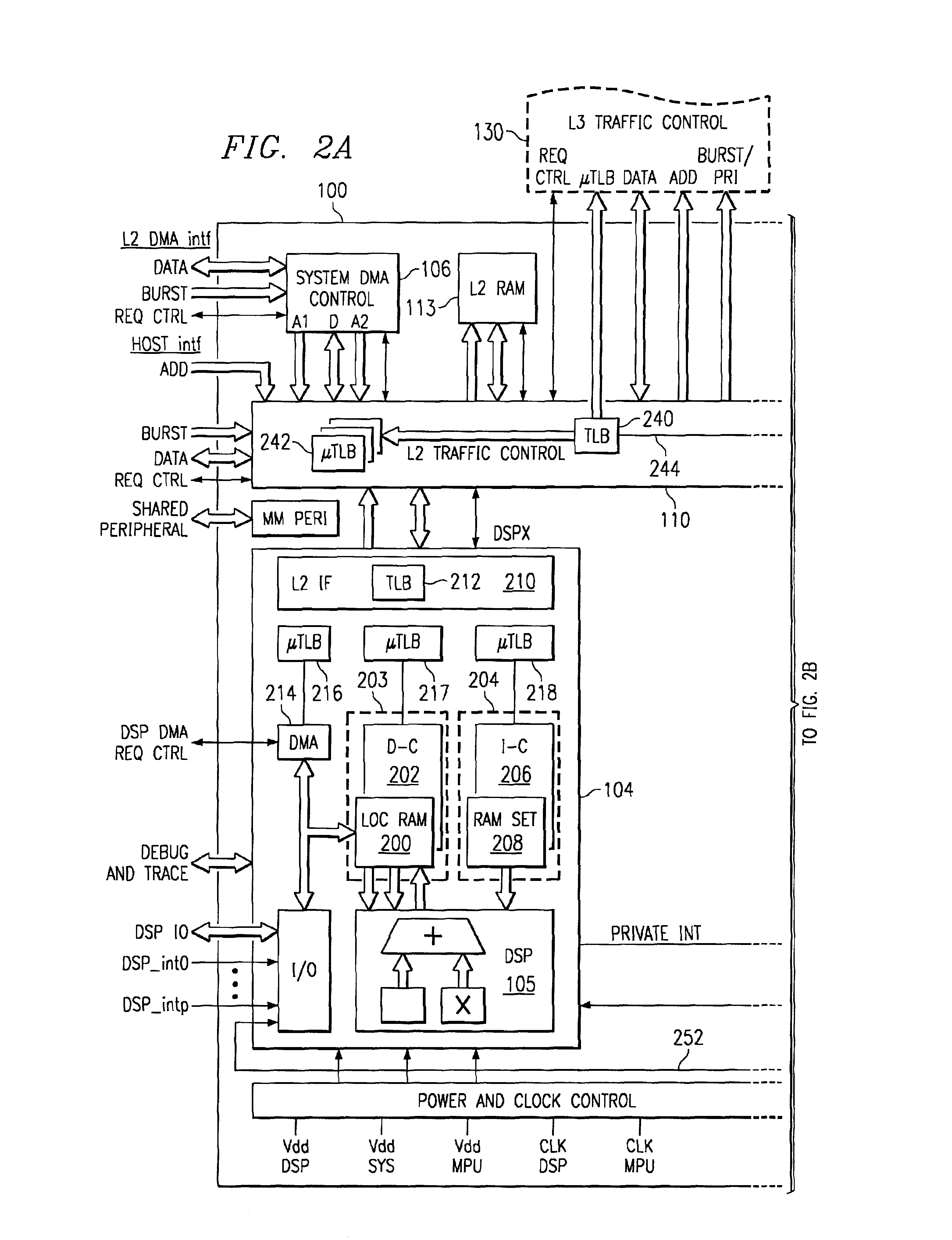
A method or device handles memory management faults in a device having a digital signal processor (“DSP”) and a microprocessor. The DSP includes a memory management unit (“DSP MMU”) to manage memory access by the DSP, and the DSP and the microprocessor access shared physical memory. Upon the DSP executing an instruction attempting to access a virtual address wherein the virtual address is invalid, a page fault interrupt is generated by the DSP MMU. A microprocessor interrupt handler in the microprocessor is activated in direct response to the page fault interrupt. Thereafter in the microprocessor, a translation lookaside buffer (“TLB”) entry is created in the DSP MMU, which includes a valid mapping between the virtual address and a page of physical memory. After creating the TLB entry, the microprocessor indicates to the DSP that the access by the DSP of the virtual address is completed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
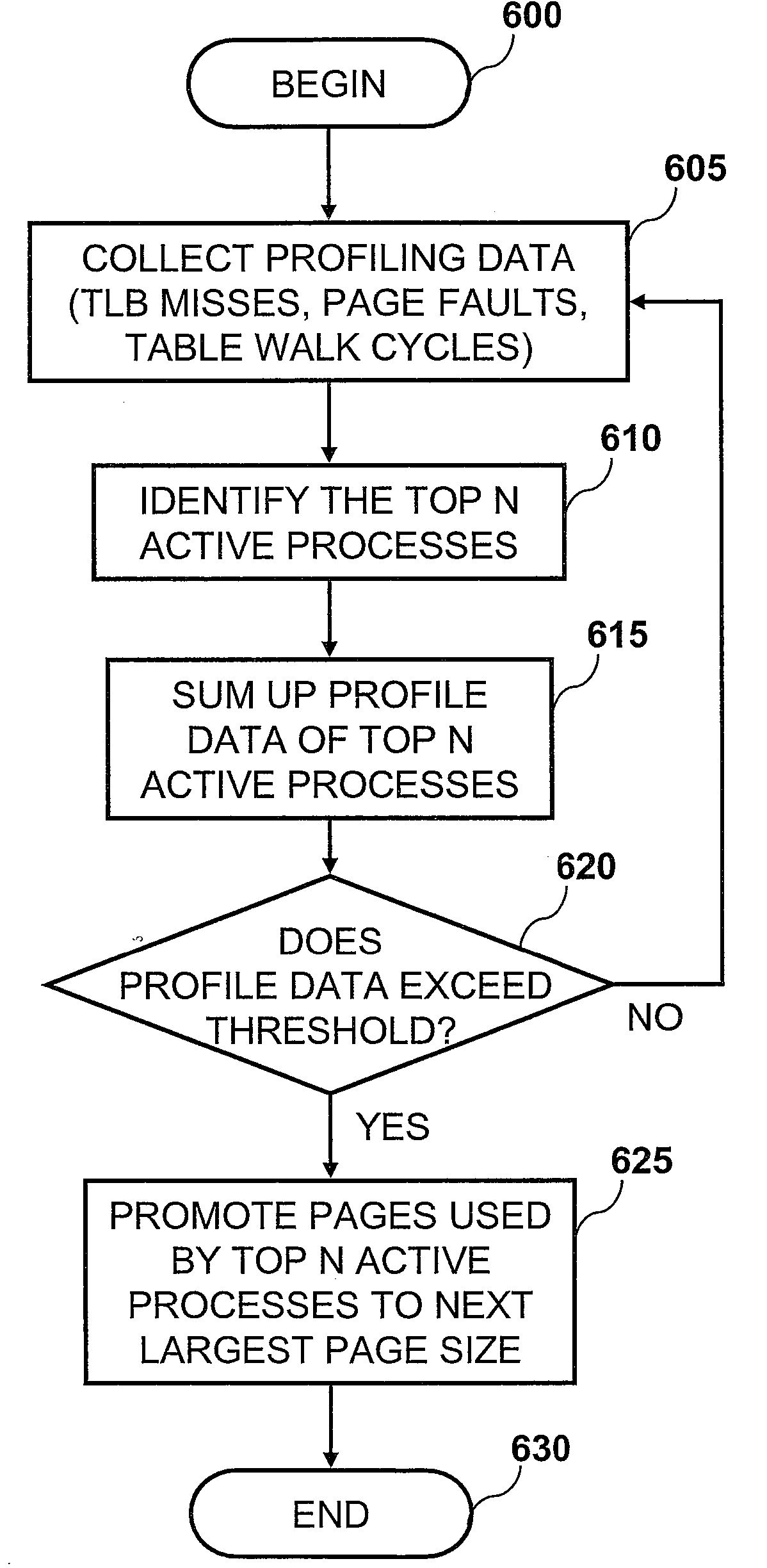
Method and System for Performance-Driven Memory Page Size Promotion
A method, system, and computer program product enable the selective adjustment in the size of memory pages allocated from system memory. In one embodiment, the method includes, but is not limited to, the steps of: collecting profile data (e.g., the number of Translation Lookaside Buffer (TLB) misses, the number of page faults, and the time spent by the Memory Management Unit (MMU) performing page table walks); identifying the top N active processes, where N is an integer that may be user-defined; evaluating the profile data of the top N active processes within a given time period; and in response to a determination that the profile data indicates that a threshold has been exceeded, promoting the pages used by the top N active processes to a larger page size and updating the Page Table Entries (PTEs) accordingly.
Owner:IBM CORP
TLB operations based on shared bit
InactiveUS6839813B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTCoprocessorCourse of action
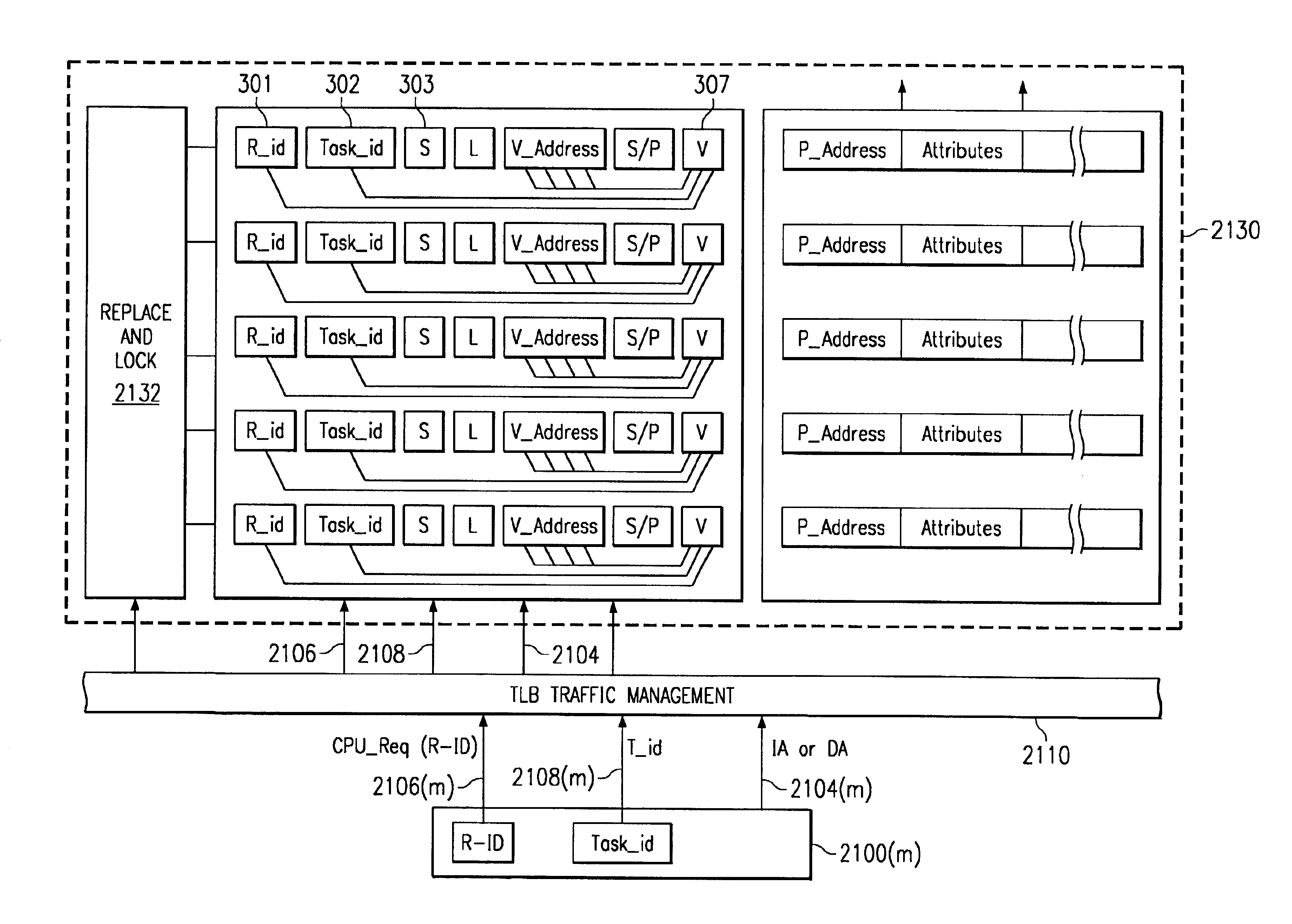
A digital system and method of operation is provided in which several processing resources (340) and processors (350) are connected to a shared translation lookaside buffer (TLB) (300, 310(n)) of a memory management unit (MMU) and thereby access memory and devices. These resources can be instruction processors, coprocessors, DMA devices, etc. Each entry location in the TLB is filled a during the normal course of action by a set of translated address entries (308, 309) along with qualifier fields (301, 302, 303) that are incorporated with each entry. Operations can be performed on the TLB that are qualified by the various qualifier fields. A command (360) is sent by an MMU manager to the control circuitry of the TLB (320) during the course of operation. Commands are sent as needed to flush (invalidate), lock or unlock selected entries within the TLB. Each entry in the TLB is accessed (362, 368) and the qualifier field specified by the operation command is evaluated (364). This can be task ID field 302, resource ID field 301, shared indicator 303, or combinations of these. Operation commands can also specify a selected virtual address entry (305). Each TLB entry is modified in response to the command (366) only if its qualifier field(s) match the qualifier(s) specified by the operation command.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and Apparatus for Preloading Translation Buffers
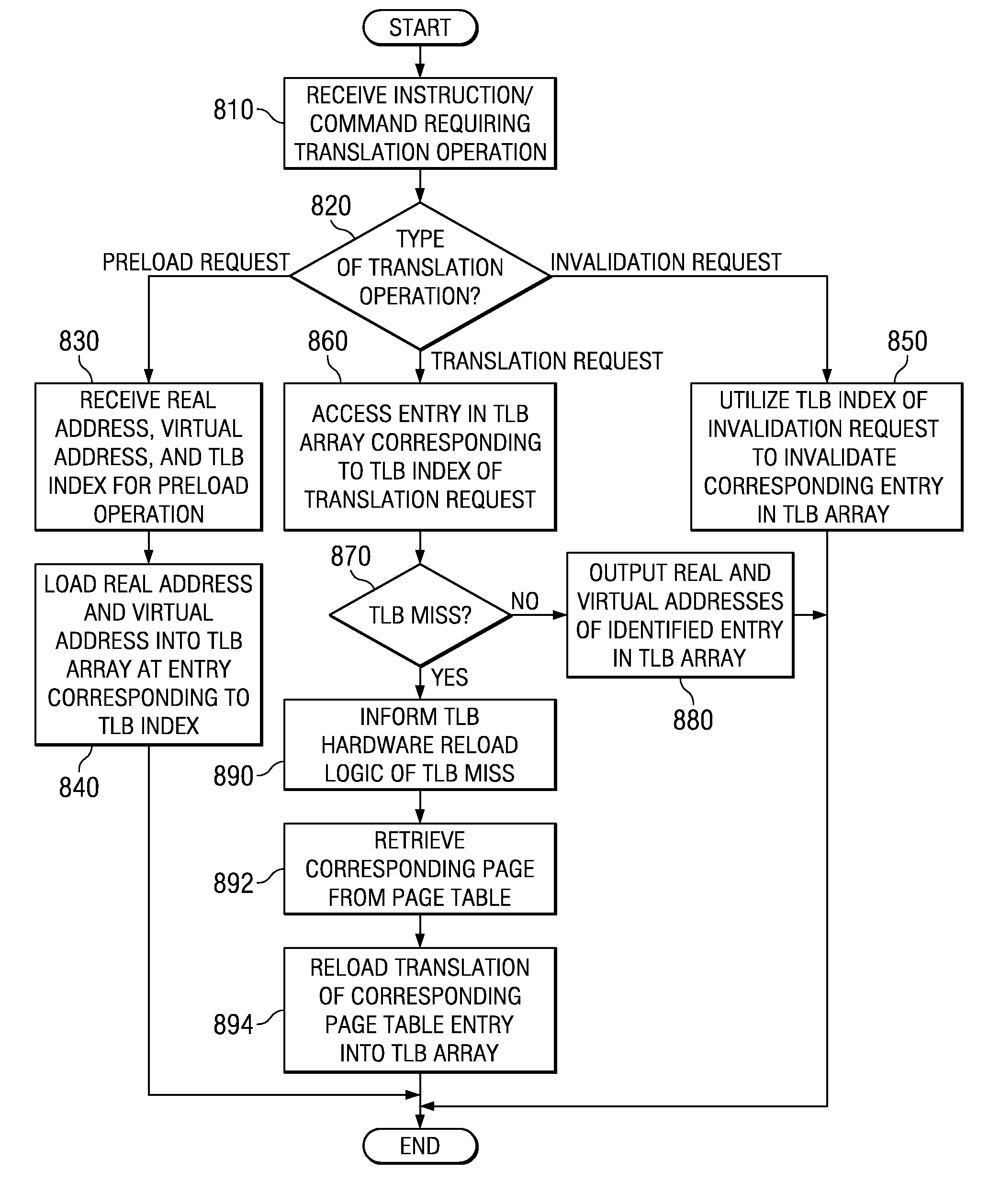
InactiveUS20070113044A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationHardware implementationsTranslation lookaside buffer
A method and an apparatus are provided for efficiently managing the operation of a translation buffer. A software and hardware apparatus and method are utilized to pre-load a translation buffer to prevent poor operation as a result of slow warming of a cache. A software pre-load mechanism may be provided for preloading a translation lookaside buffer (TLB) via a hardware implemented controller. Following preloading of the TLB, control of accessing the TLB may be handed over to the hardware implemented controller. Upon an application context switch operation, the software preload mechanism may be utilized again to preload the TLB with new translation information for the newly active application instance.
Owner:IBM CORP
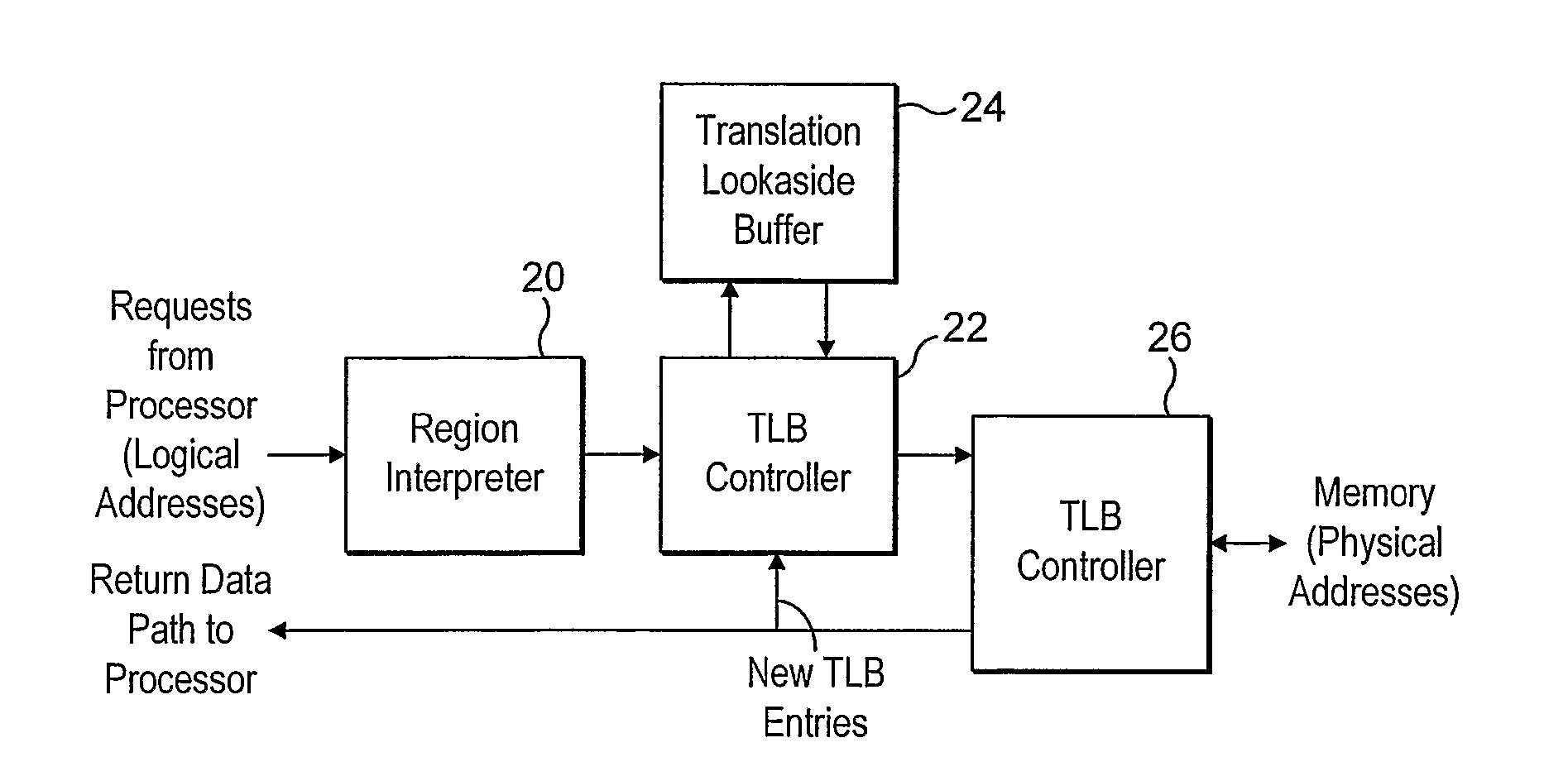
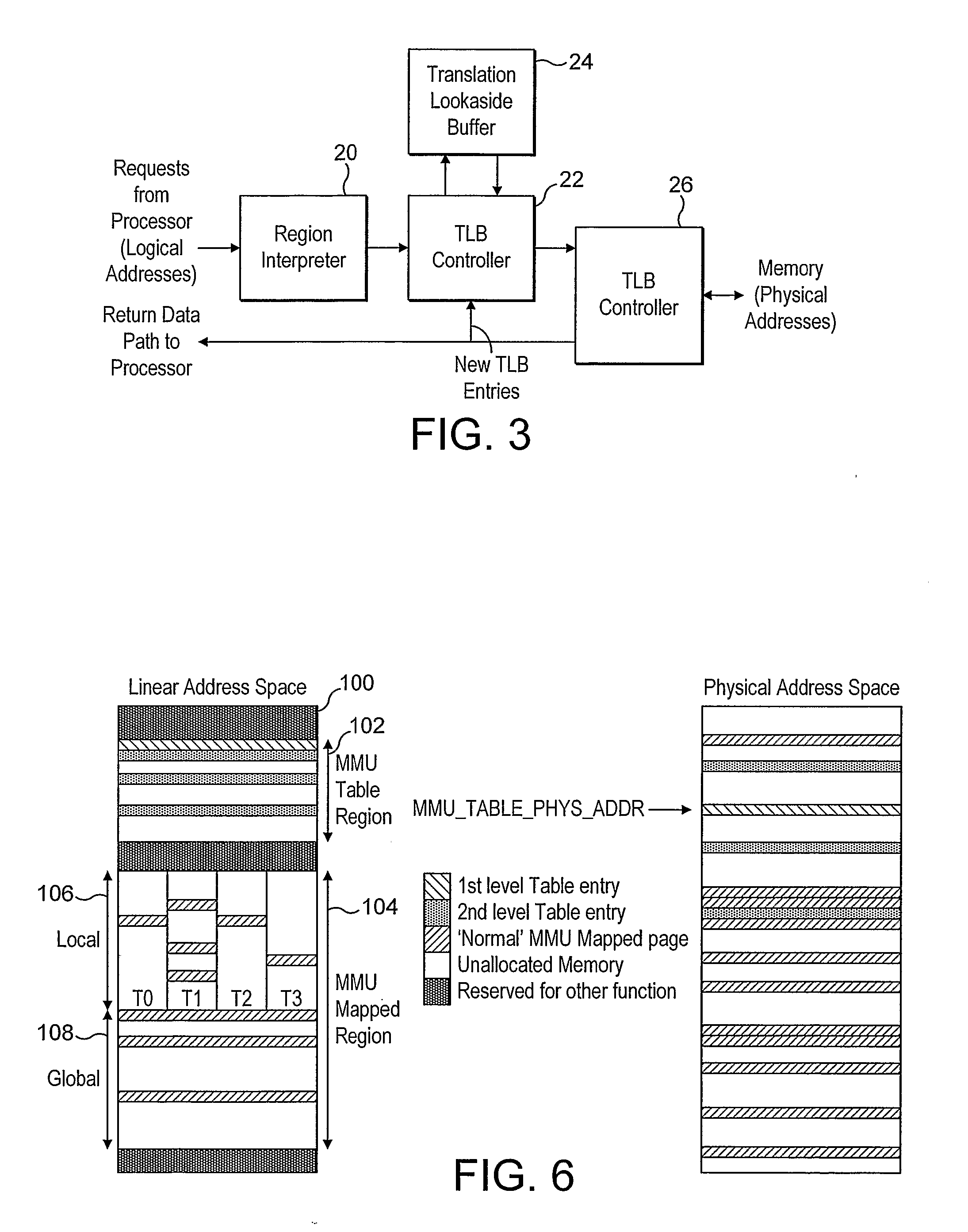
Memory Management System
InactiveUS20070283108A1Perform updateMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingMemory management unit
A system and method for managing accesses to a memory are provided. A memory management unit (MMU) and a translation lookaside buffer (TLB) are used. The TLB stores addresses of pages which have been recently accessed. The MMU includes a virtual map of an MMU table which stores physical addresses of memory pages linked to logical addresses. A virtual map is stored in a linear address space and the MMU can update the addresses stored in the TLB in response to memory accesses made in the MMU table. The MMU table comprises at least first and second level table entries. The first level table entries store data for map logical addresses to the second level table entries. The second level table entries store data for map logical addresses to physical addresses in memory.
Owner:IMAGINATION TECH LTD
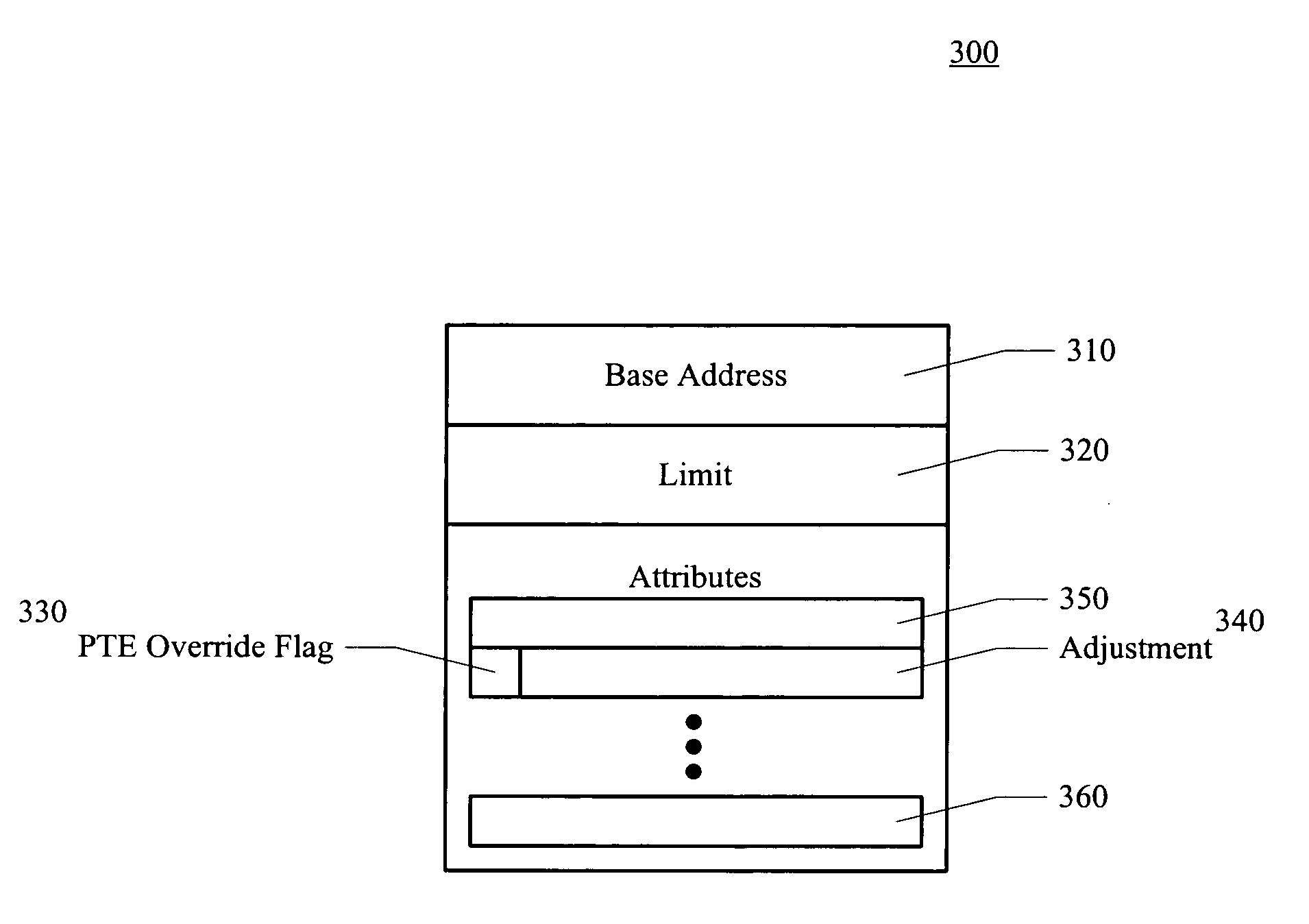
Memory access techniques providing for override of page table attributes
A memory access technique, in accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, includes selectively overriding attributes contained in a translation lookaside buffer or page table data structure with attributes contained in a context specifier.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Remote address translation in a multiprocessor system
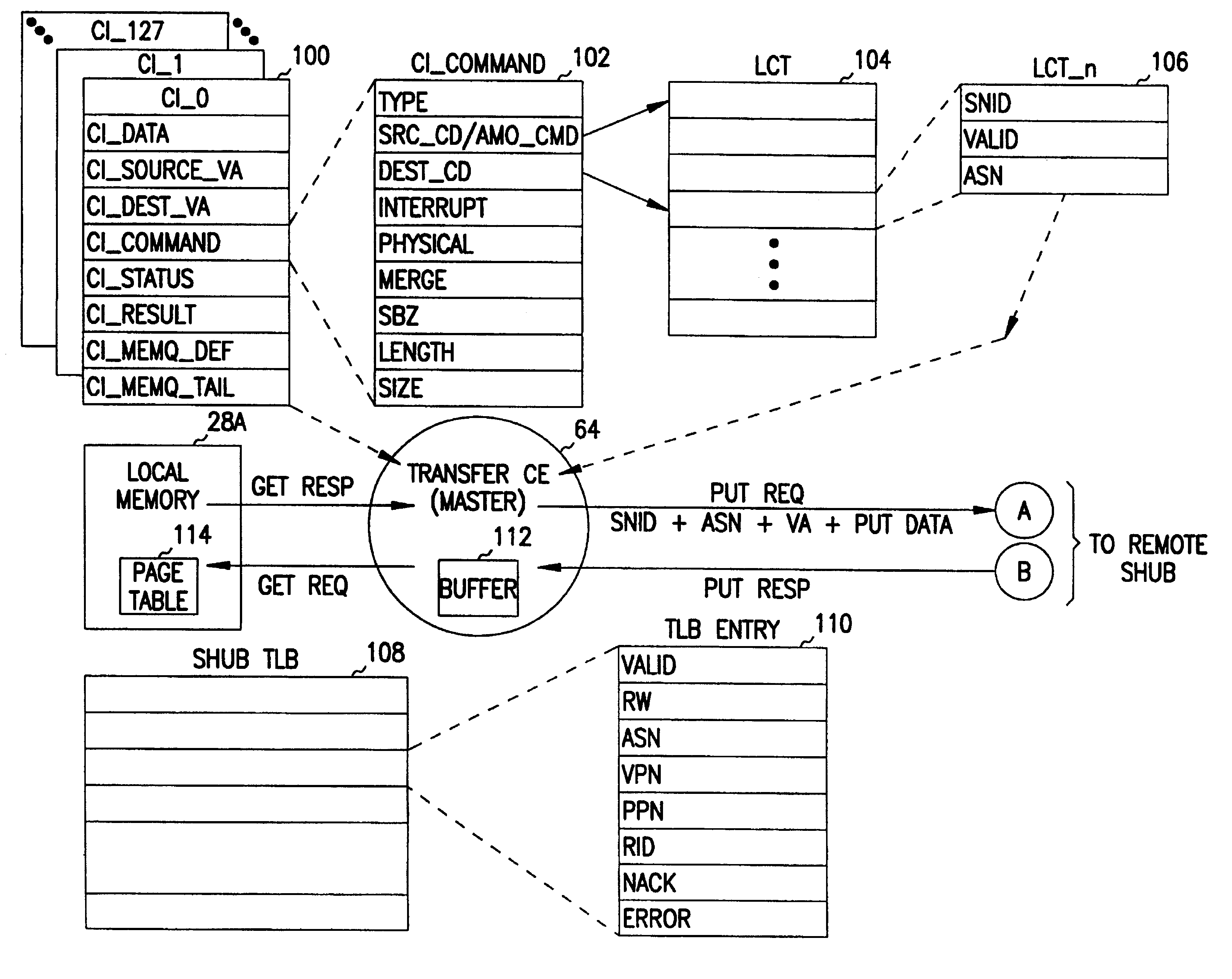
InactiveUS6925547B2Memory adressing/allocation/relocationData switching by path configurationRemote memory accessConnection table
A method of performing remote address translation in a multiprocessor system includes determining a connection descriptor and a virtual address at a local node, accessing a local connection table at the local node using the connection descriptor to produce a system node identifier for a remote node and a remote address space number, communicating the virtual address and remote address space number to the remote node, and translating the virtual address to a physical address at the remote node (qualified by the remote address space number). A user process running at the local node provides the connection descriptor and virtual address. The translation is performed by matching the virtual address and remote address space number with an entry of a translation-lookaside buffer (TLB) at the remote node. Performing the translation at the remote node reduces the amount of translation information needed at the local node for remote memory accesses. The method supports communication within a scalable multiprocessor, and across the machine boundaries in a cluster.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
System and Method to Manage Address Translation Requests
ActiveUS20100332787A1Efficient managementEfficient recyclingMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationManagement unitTranslation table
A system and method for servicing translation lookaside buffer (TLB) misses may manage separate input and output pipelines within a memory management unit. A pending request queue (PRQ) in the input pipeline may include an instruction-related portion storing entries for instruction TLB (ITLB) misses and a data-related portion storing entries for potential or actual data TLB (DTLB) misses. A DTLB PRQ entry may be allocated to each load / store instruction selected from the pick queue. The system may select an ITLB- or DTLB-related entry for servicing dependent on prior PRQ entry selection(s). A corresponding entry may be held in a translation table entry return queue (TTERQ) in the output pipeline until a matching address translation is received from system memory. PRQ and / or TTERQ entries may be deallocated when a corresponding TLB miss is serviced. PRQ and / or TTERQ entries associated with a thread may be deallocated in response to a thread flush.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
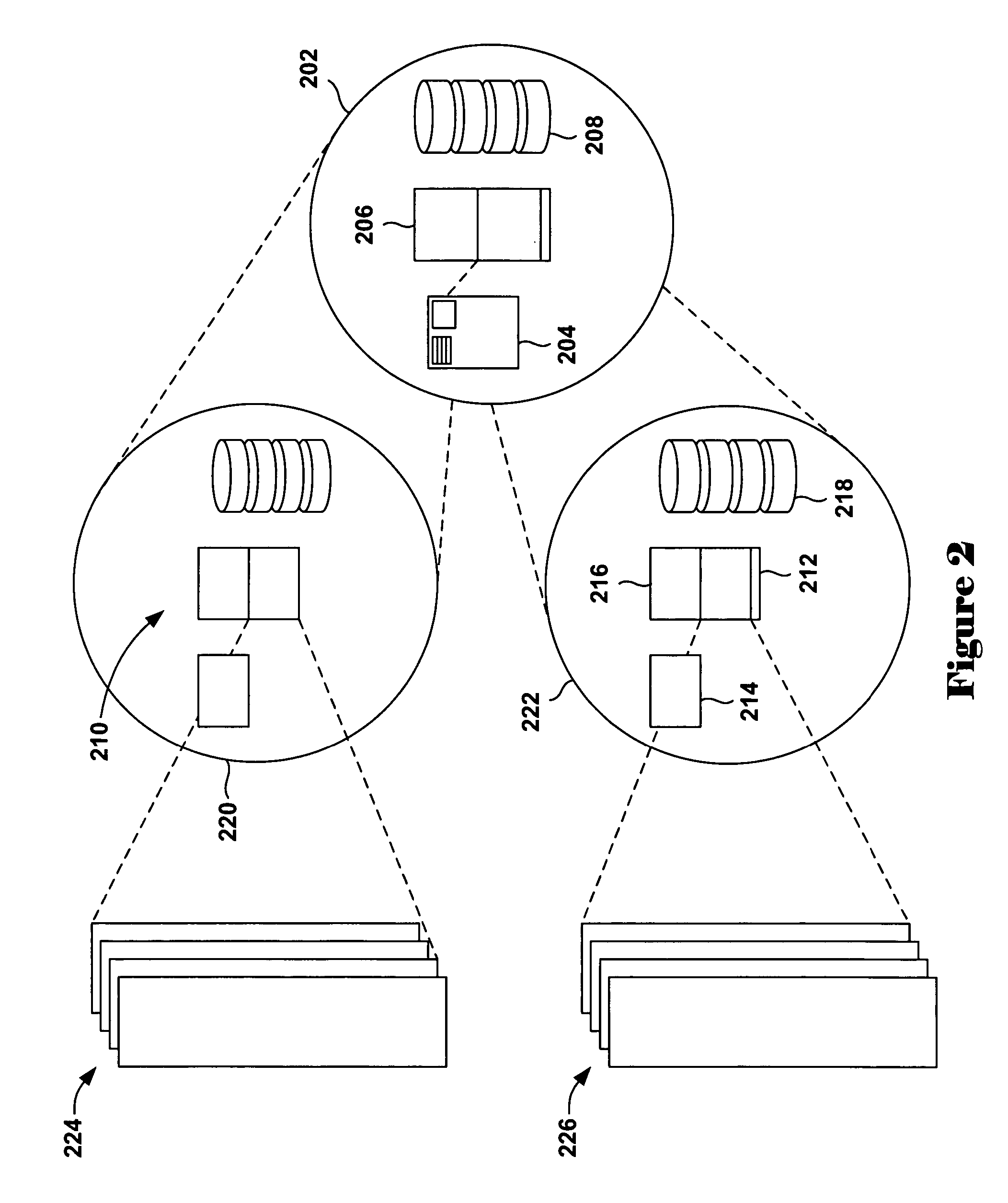
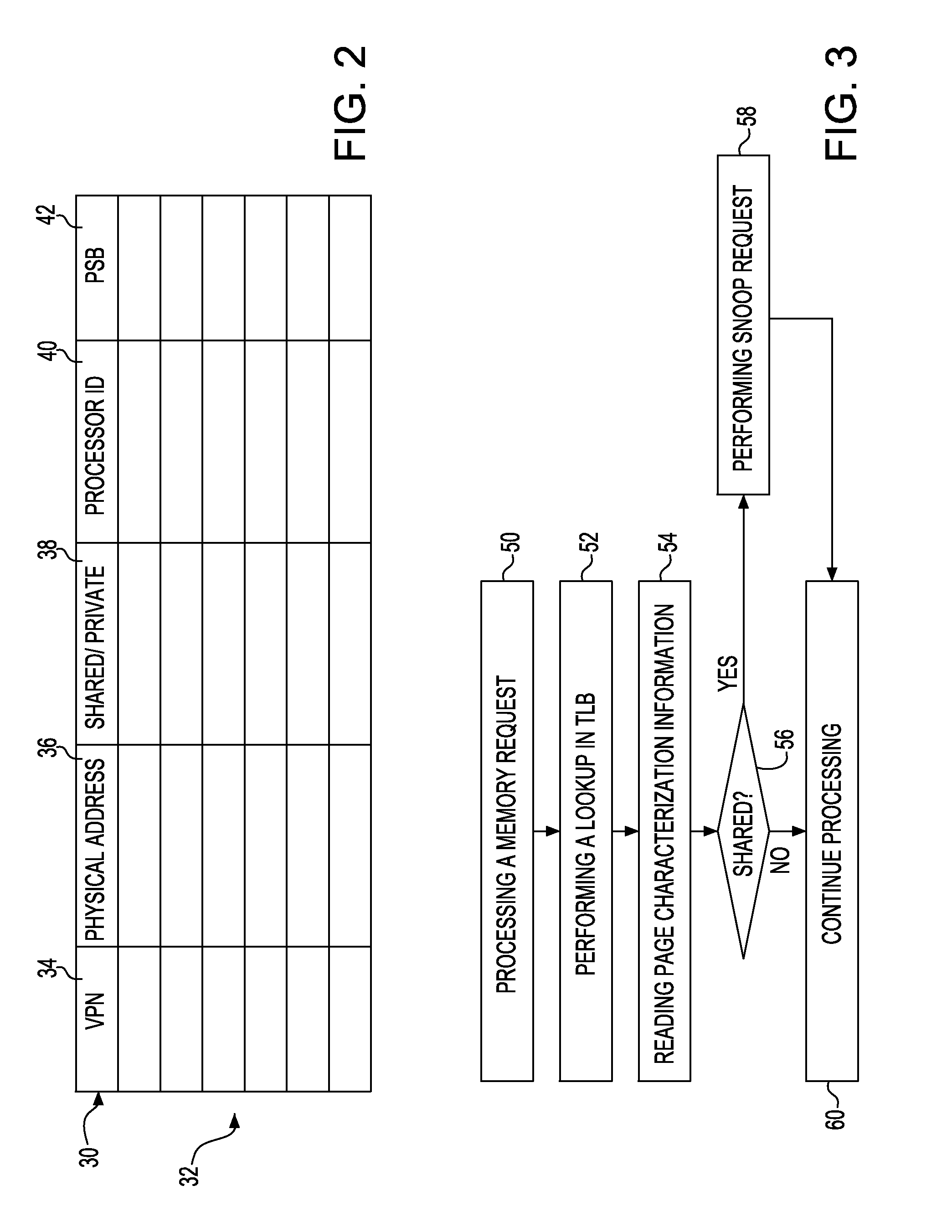
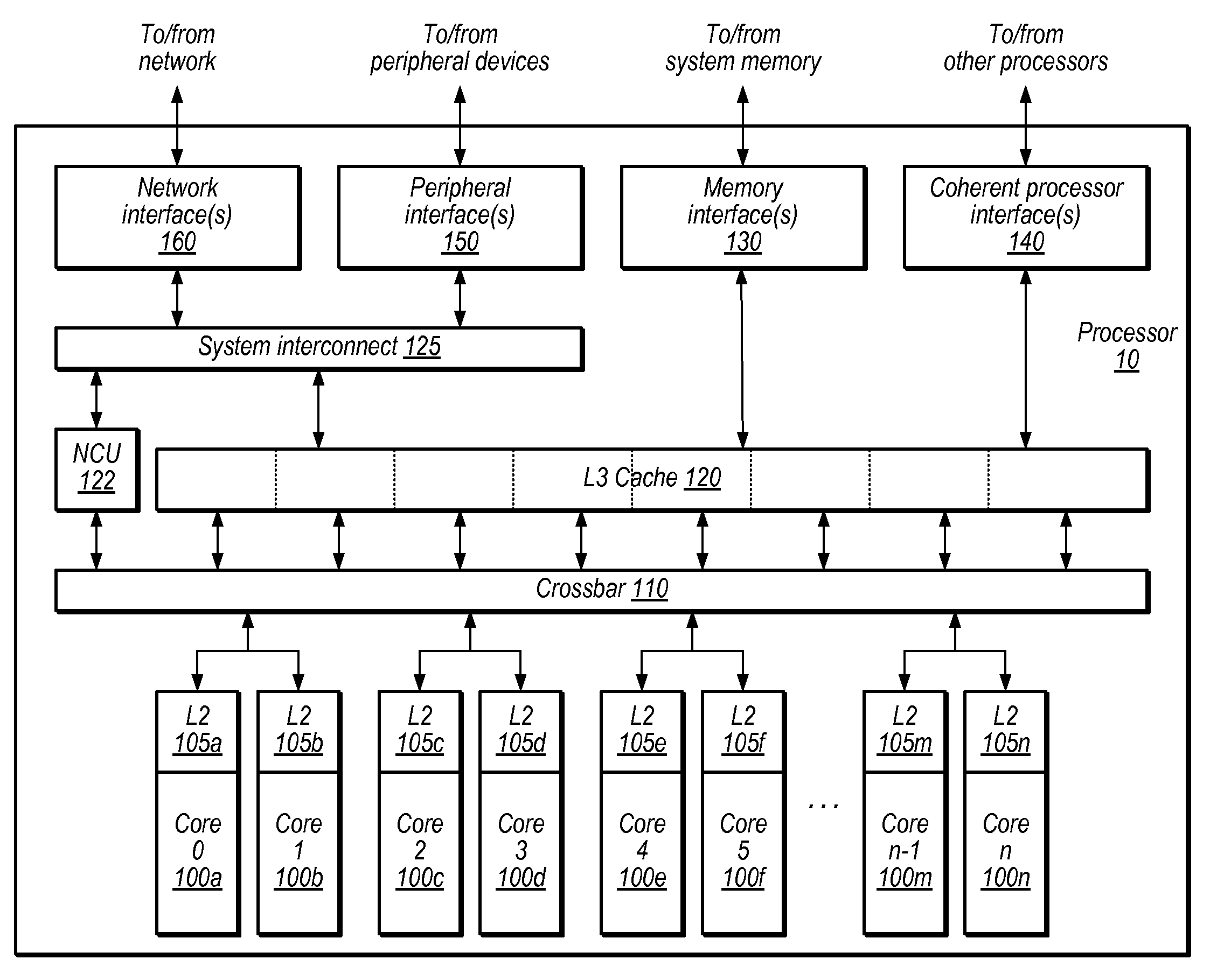
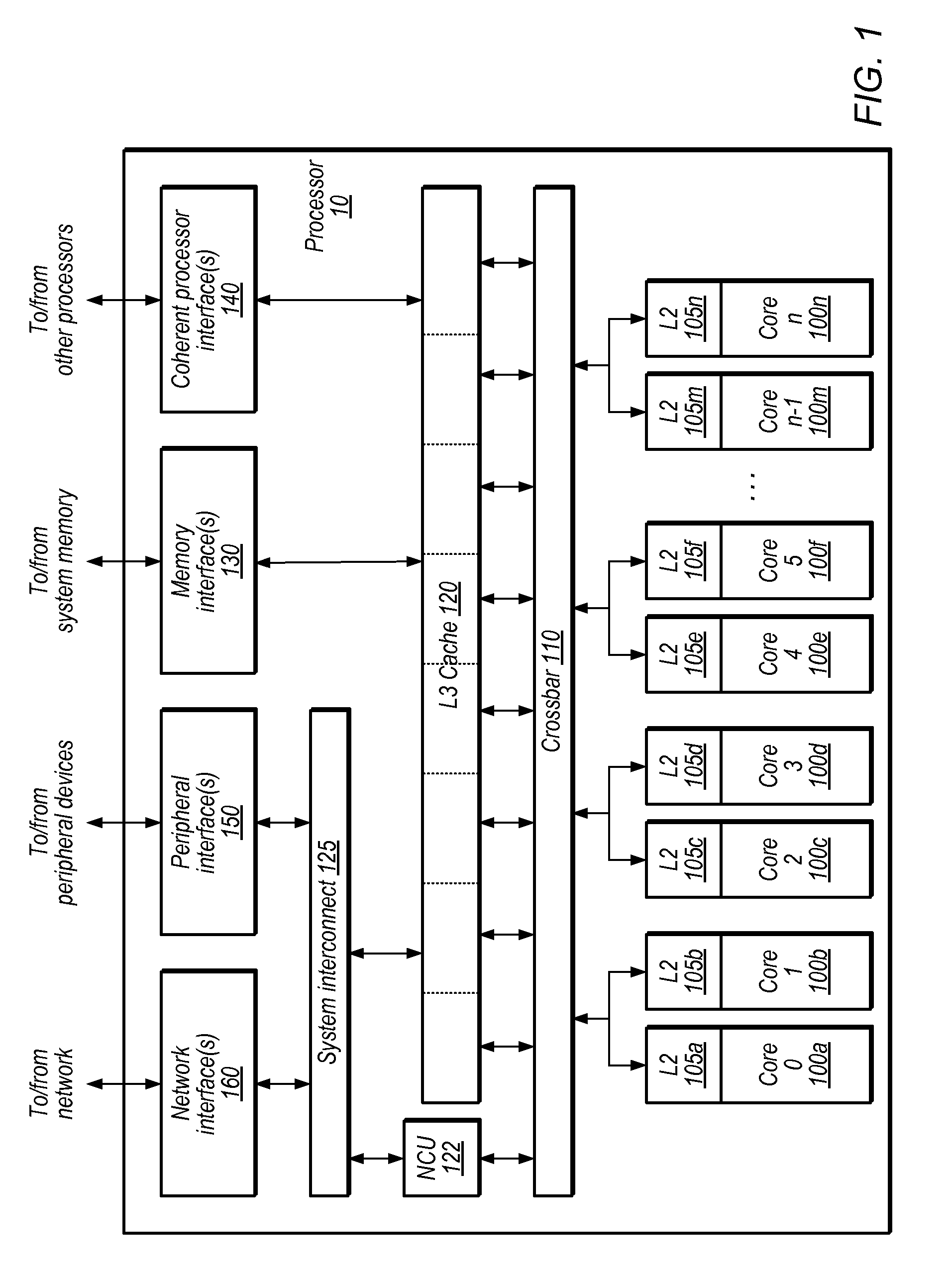
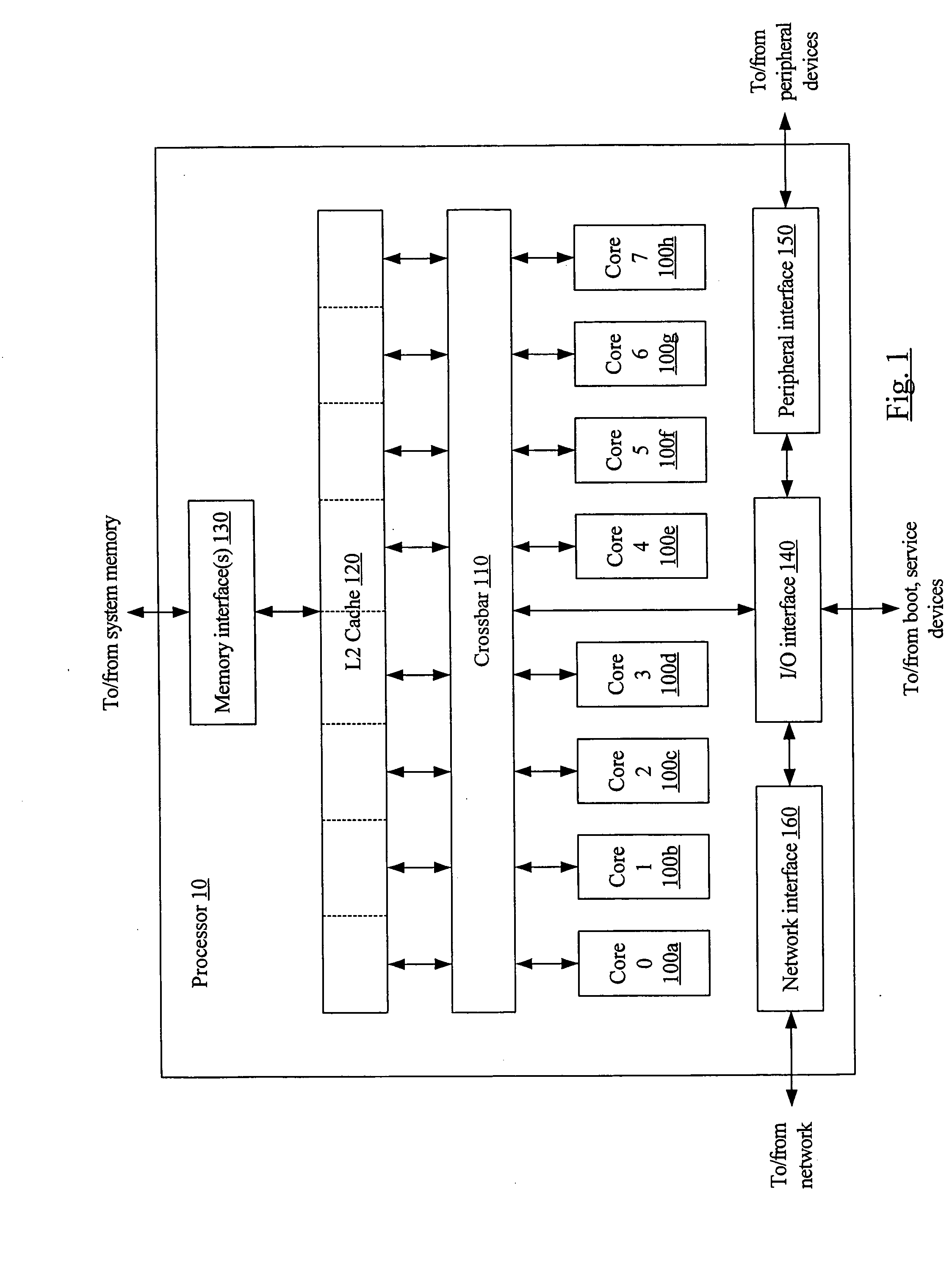
Reducing broadcasts in multiprocessors
ActiveUS20110055515A1Reduce broadcastRelatively large bandwidthEnergy efficient ICTMemory adressing/allocation/relocationVirtual memoryMulti processor
Disclosed is an apparatus to reduce broadcasts in multiprocessors including a plurality of processors; a plurality of memory caches associated with the processors; a plurality of translation lookaside buffers (TLBs) associated with the processors; and a physical memory shared with the processors memory caches and TLBs; wherein each TLB includes a plurality of entries for translation of a page of addresses from virtual memory to physical memory, each TLB entry having page characterization information indicating whether the page is private to one processor or shared with more than one processor. Also disclosed is a computer program product and method to reduce broadcasts in multiprocessors.
Owner:IBM CORP
Software table walk during test verification of a simulated densely threaded network on a chip
ActiveUS20100223505A1Error detection/correctionAnalogue computers for electric apparatusParallel computingNetwork on
A computer-implemented method, system and computer program product are presented for managing an Effective-to-Real Address Table (ERAT) and a Translation Lookaside Buffer (TLB) during test verification in a simulated densely threaded Network On a Chip (NOC). The ERAT and TLB are stripped out of the computer simulation before executing a test program. When the test program experiences an inevitable ERAT-miss and / or TLB-miss, an interrupt handler walks a page table until the requisite page for re-populating the ERAT and TLB is located.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
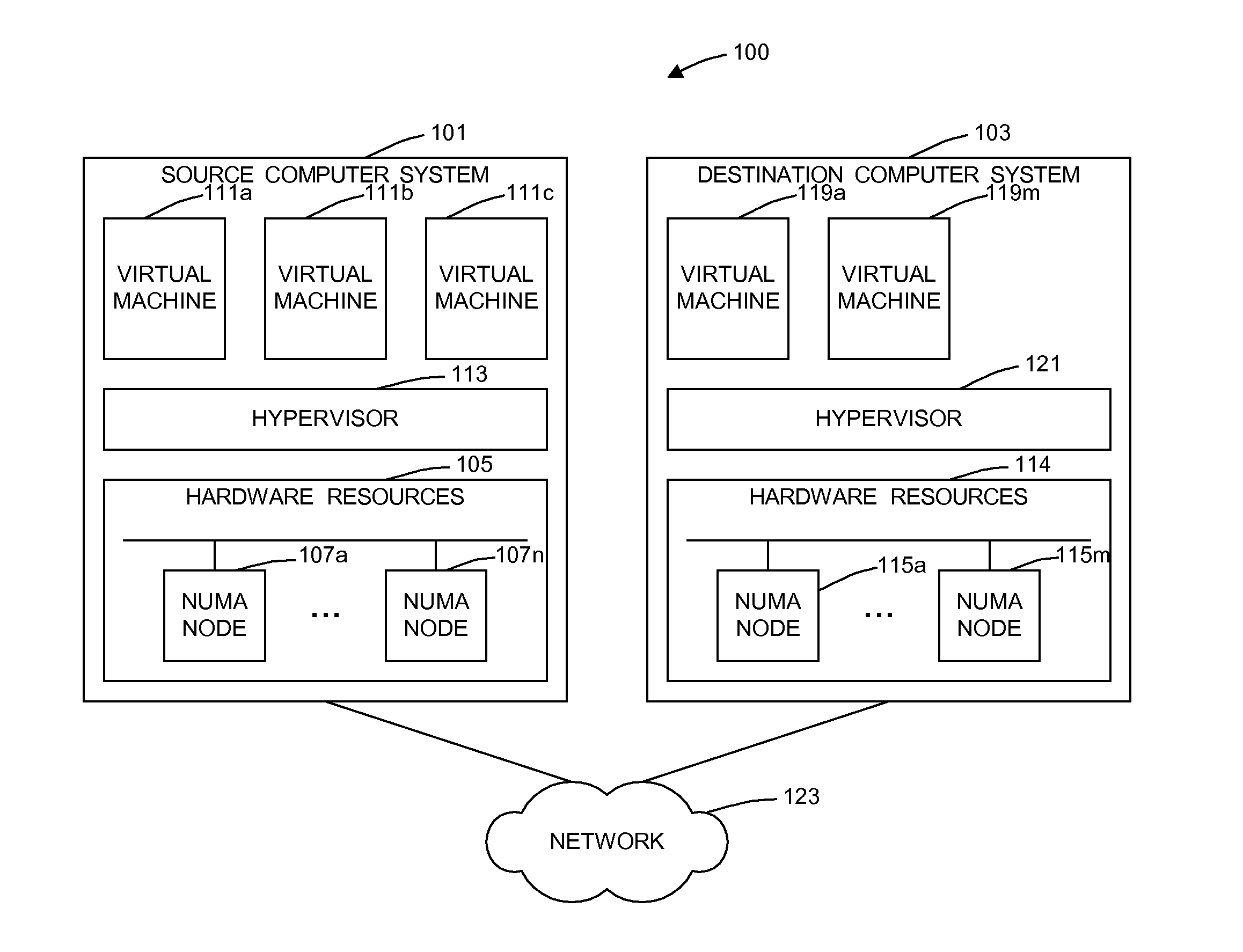
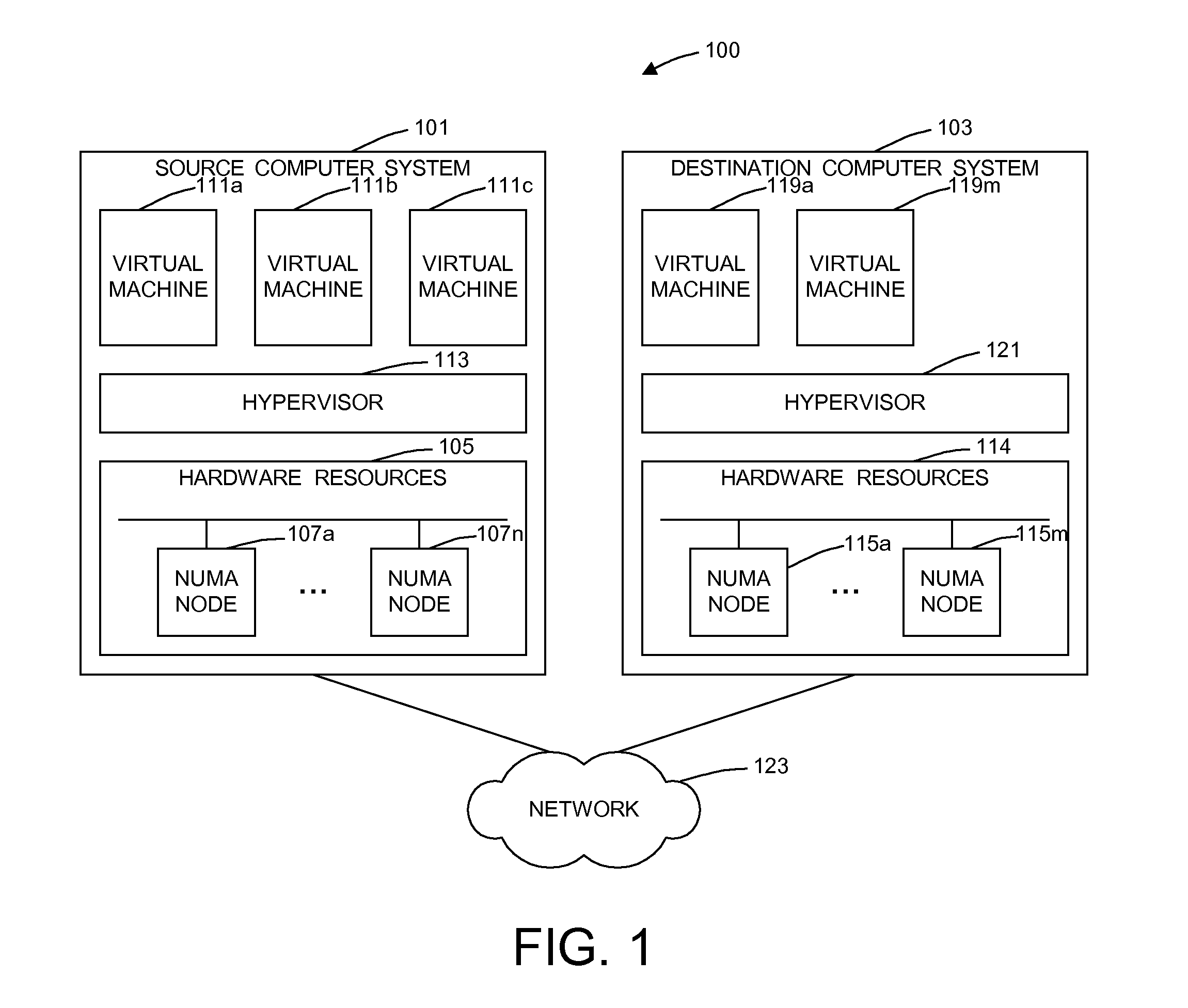
Dynamic memory affinity reallocation after partition migration
ActiveUS20120102258A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer security arrangementsProcessor nodeComputerized system
A method of dynamically reallocating memory affinity in a virtual machine after migrating the virtual machine from a source computer system to a destination computer system migrates processor states and resources used by the virtual machine from the source computer system to the destination computer system. The method maps memory of the virtual machine to processor nodes of the destination computer system. The method deletes memory mappings in processor hardware, such as translation lookaside buffers and effective-to-real address tables, for the virtual machine on the destination computer system. The method starts the virtual machine on the destination computer system in virtual real memory mode. A hypervisor running on the destination computer system receives a page fault and virtual address of a page for said virtual machine from a processor of the destination computer system and determines if the page is in local memory of the processor. If the hypervisor determines the page to be in the local memory of the processor, the hypervisor returning a physical address mapping for the page to the processor. If the hypervisor determines the page not to be in the local memory of the processor, the hypervisor moves the page to local memory of the processor and returns a physical address mapping for said page to the processor.
Owner:IBM CORP
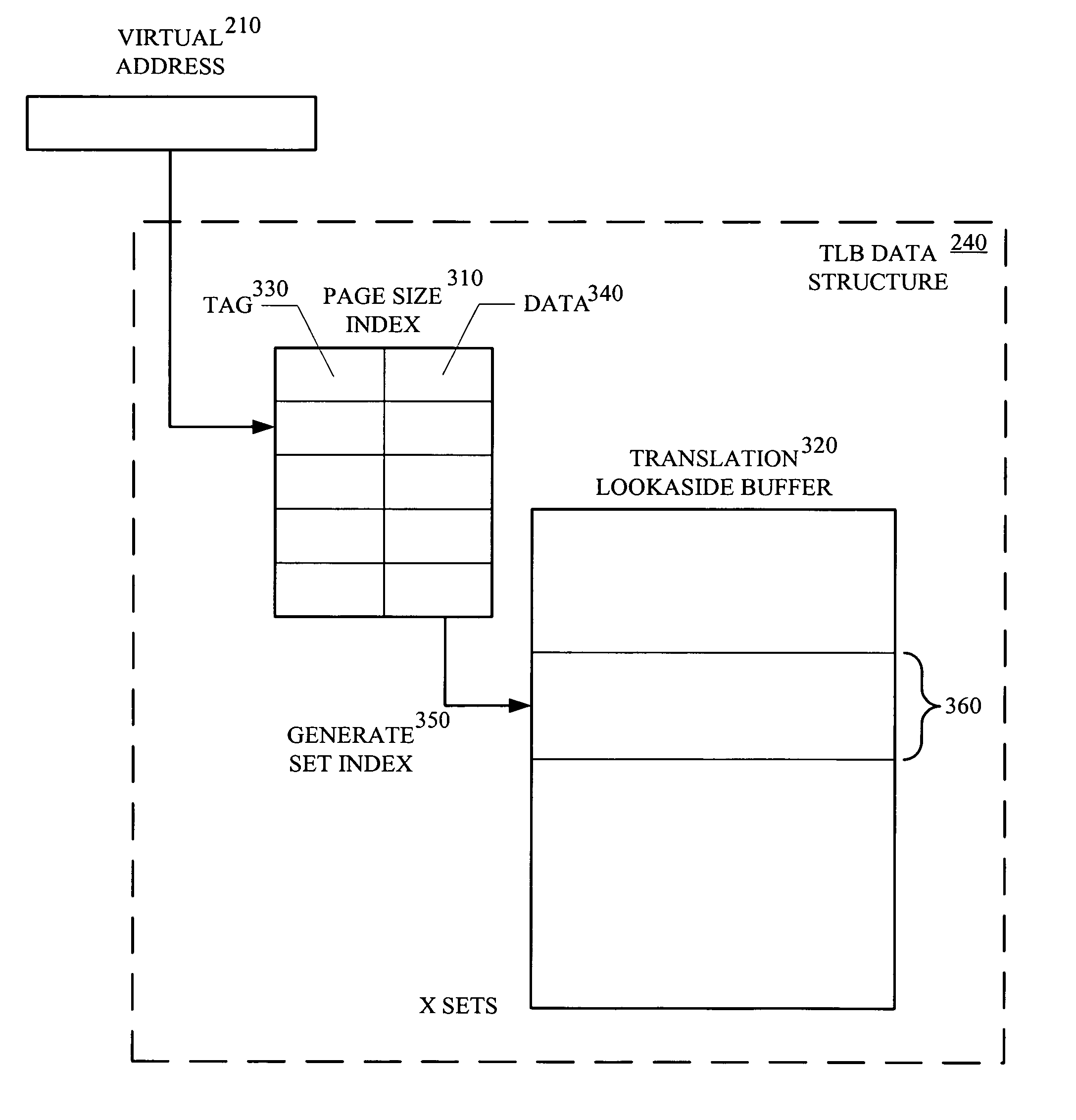
Memory access techniques utilizing a set-associative translation lookaside buffer
ActiveUS8707011B1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsCache pageTranslation lookaside buffer
A memory access technique, in accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, includes caching page size data for use in accessing a set-associative translation lookaside buffer (TLB). The technique utilizes a translation lookaside buffer data structure that includes a page size table and a translation lookaside buffer. Upon receipt of a memory access request a page size is looked-up in the page size table utilizing the page directory index in the virtual address. A set index is calculated utilizing the page size. A given set of entries is then looked-up in the translation lookaside buffer utilizing the set index. The virtual address is compared to each TLB entry in the given set. If the comparison results in a TLB hit, the physical address is received from the matching TLB entry.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Method and apparatus of controlling electric power for translation lookaside buffer
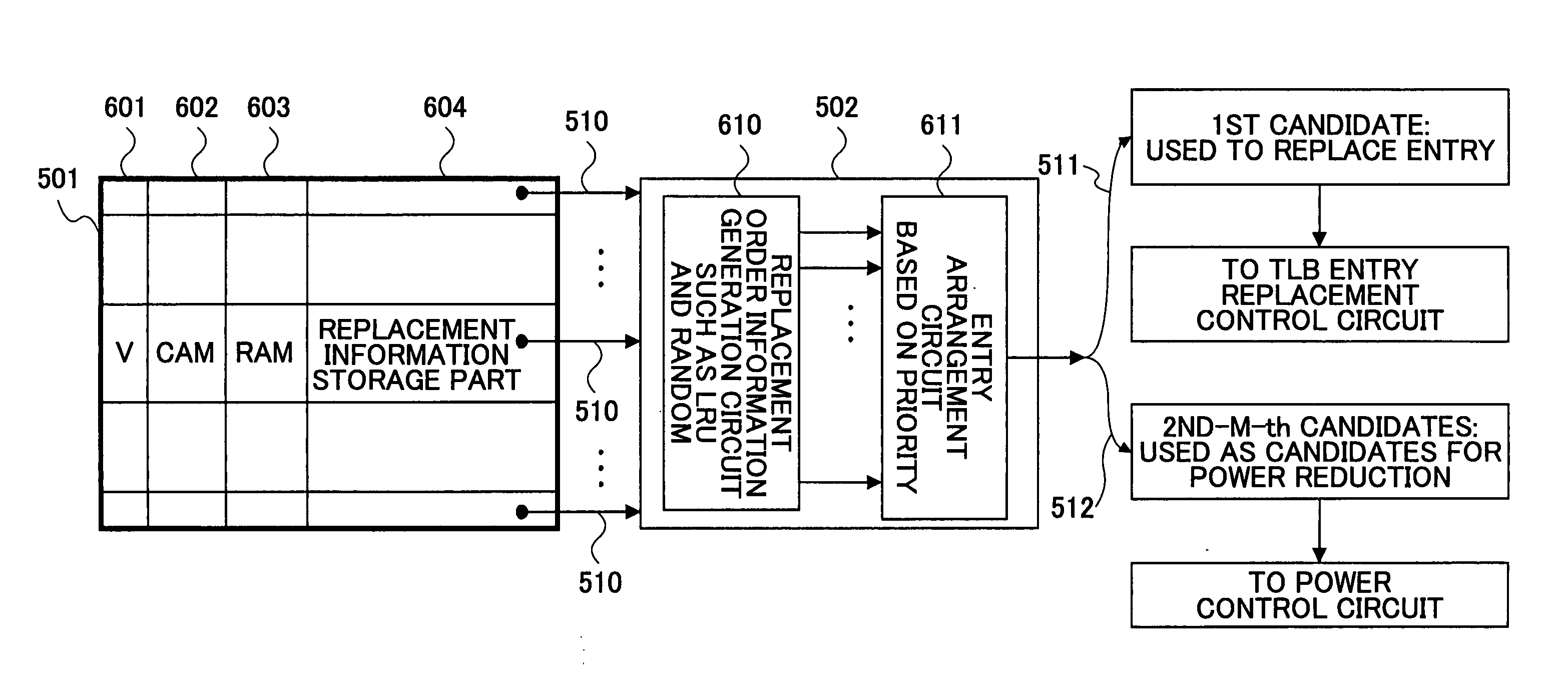
InactiveUS20050160250A1Reduce unnecessary power consumptionReduce power consumptionMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTOperating systemTranslation lookaside buffer
The present invention is intended to reduce unnecessary power consumption by controlling disconnection of entries unused in a translation lookaside buffer (TLB) for a long time. In an aspect of the present invention, there is provided a method of controlling electric power consumed for a translation lookaside buffer (TLB) within a central processing device having the TLB and an entry replacement mechanism wherein the TLB includes a plurality of entries and performs translation from a logical address to a physical address and the entry replacement mechanism replaces the entries of the TLB, the method including the steps of: selecting one or more entries among the plurality of entries of the TLB in accordance with one or more predefined criteria based on an output from the entry replacement mechanism, and controlling electric power supplied to the selected entries.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
System and Method to Invalidate Obsolete Address Translations
ActiveUS20100332786A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationVirtual memoryMulti processor
A system and method for invalidating obsolete virtual / real address to physical address translations may employ translation lookaside buffers to cache translations. TLB entries may be invalidated in response to changes in the virtual memory space, and thus may need to be demapped. A non-cacheable unit (NCU) residing on a processor may be configured to receive and manage a global TLB demap request from a thread executing on a core residing on the processor. The NCU may send the request to local cores and / or to NCUs of external processors in a multiprocessor system using a hardware instruction to broadcast to all cores and / or processors or to multicast to designated cores and / or processors. The NCU may track completion of the demap operation across the cores and / or processors using one or more counters, and may send an acknowledgement to the initiator of the demap request when the global demap request has been satisfied.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
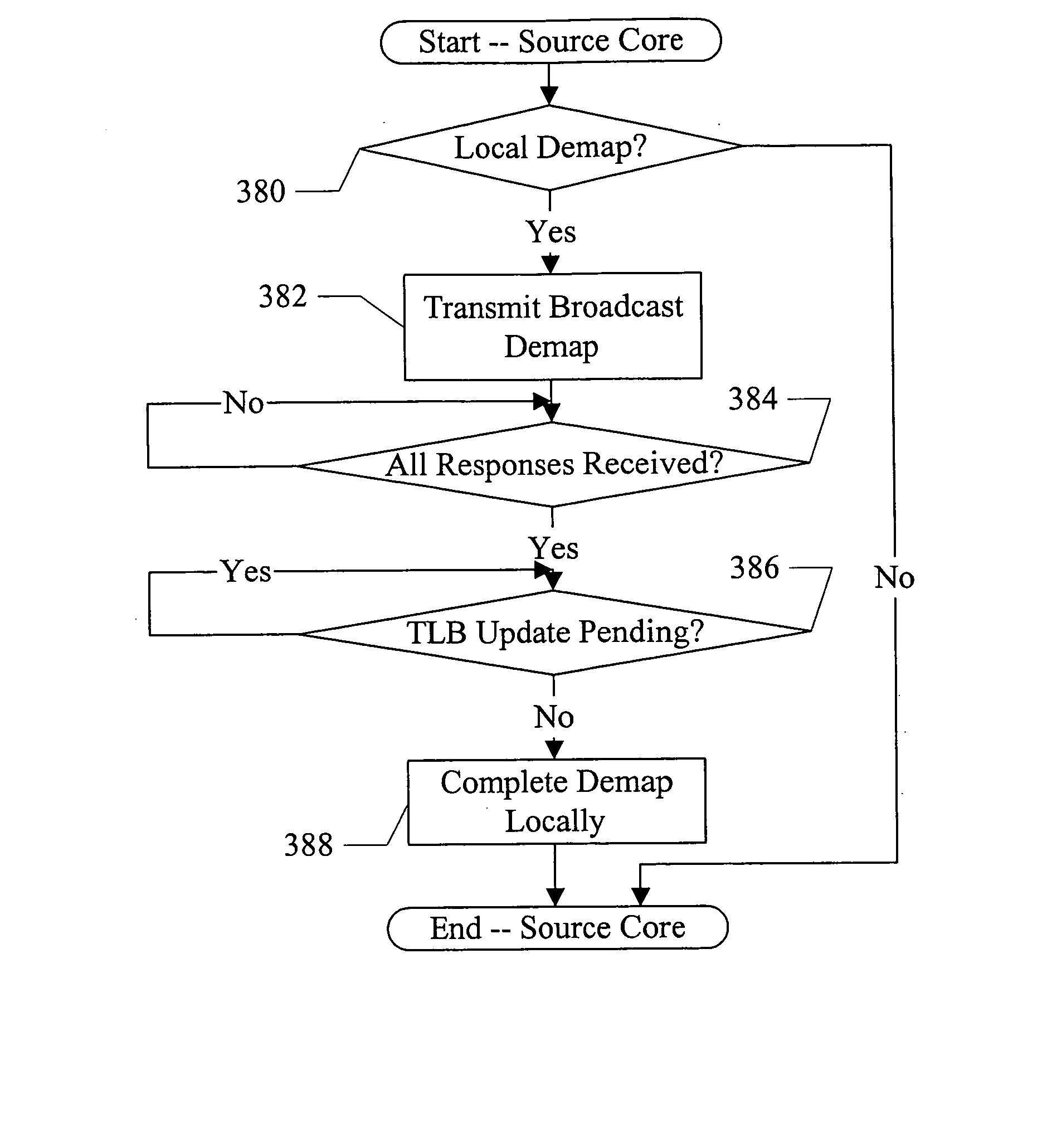
Demapping TLBs across physical cores of a chip
ActiveUS20070061548A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsParallel computingBroadcasting
In one embodiment, a processor comprises a plurality of processor cores and an interconnect to which the plurality of processor cores are coupled. Each of the plurality of processor cores comprises at least one translation lookaside buffer (TLB). A first processor core is configured to broadcast a demap command on the interconnect responsive to executing a demap operation. The demap command identifies one or more translations to be invalidated in the TLBs, and remaining processor cores are configured to invalidate the translations in the respective TLBs. The remaining processor cores transmit a response to the first processor core, and the first processor core is configured to delay continued processing subsequent to the demap operation until the responses are received from each of the remaining processor cores.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method for efficient virtualization of physical memory in a virtual-machine monitor
ActiveUS7330942B2Without introducing excessive overhead and inefficiencyEfficient supplyComputer security arrangementsMemory systemsVirtual memoryVirtualization
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com