Patents
Literature
49 results about "Dirty bit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
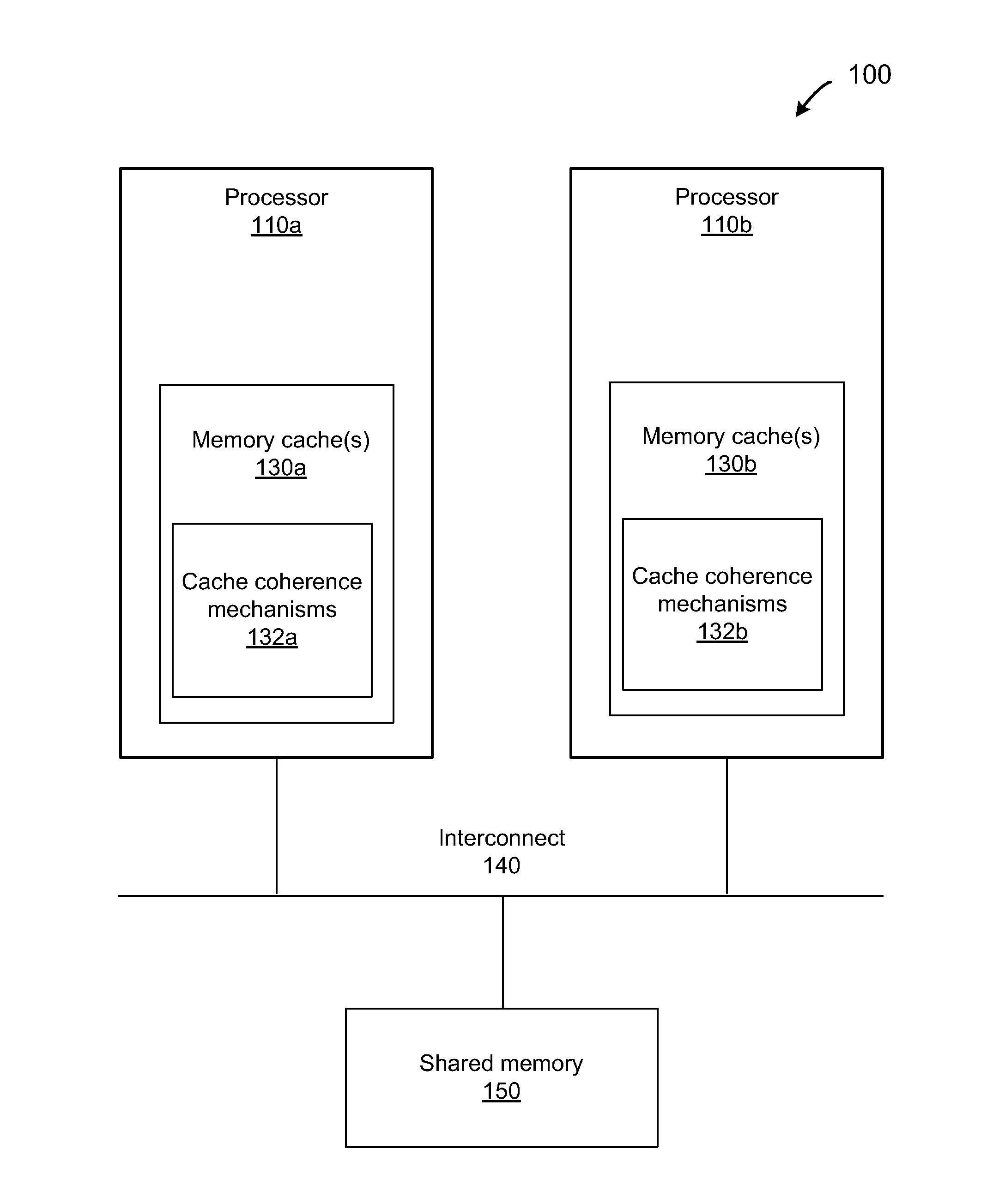
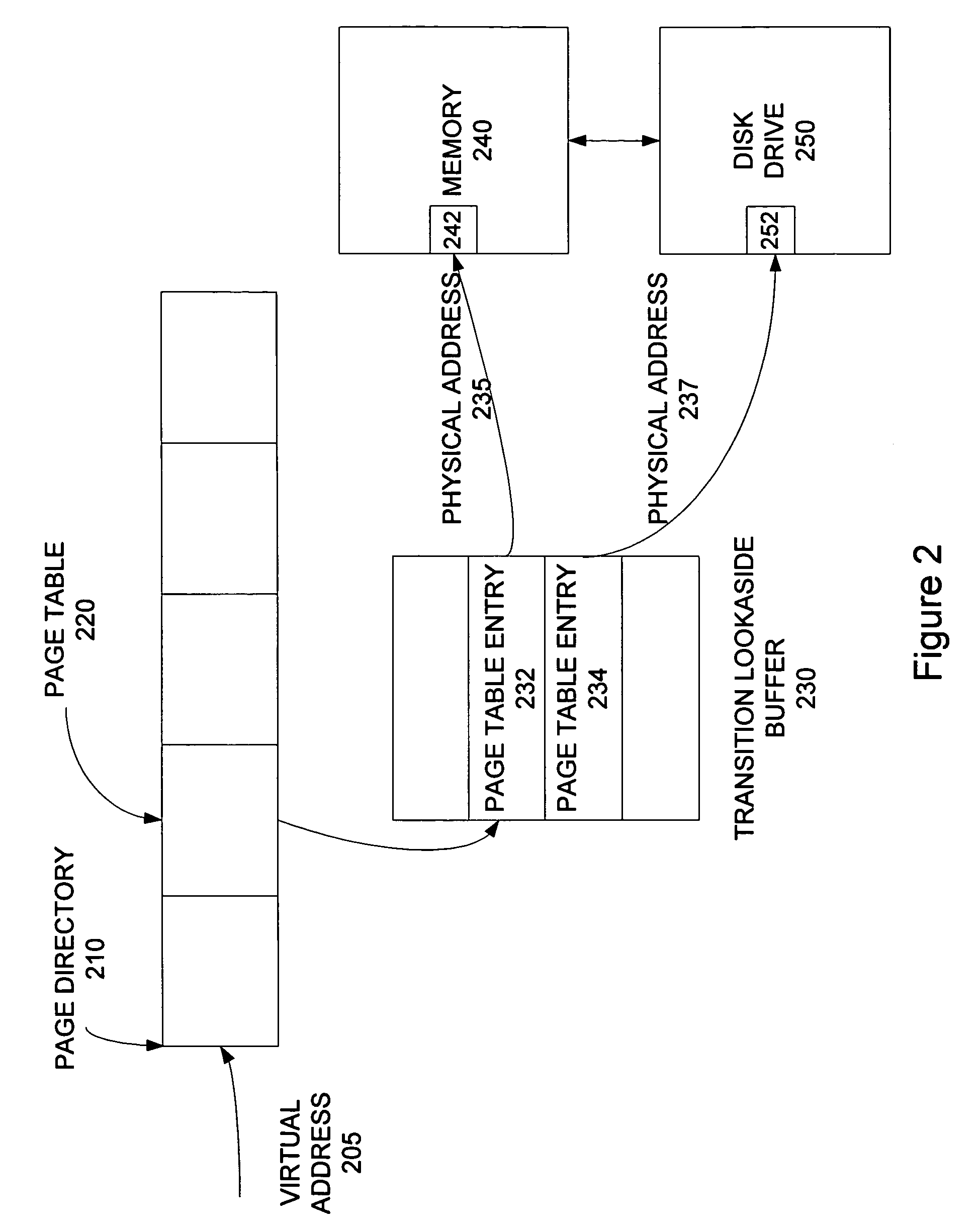
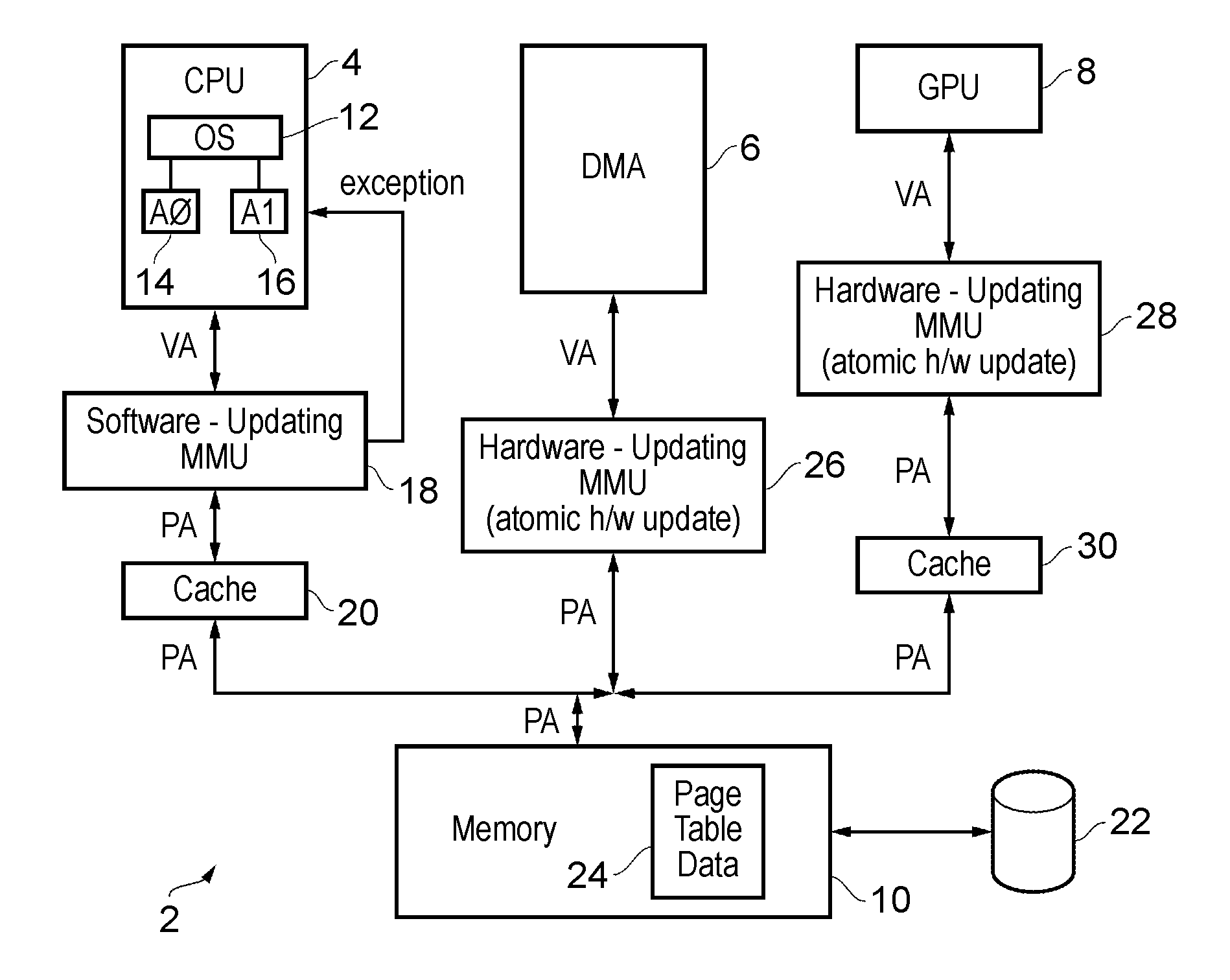
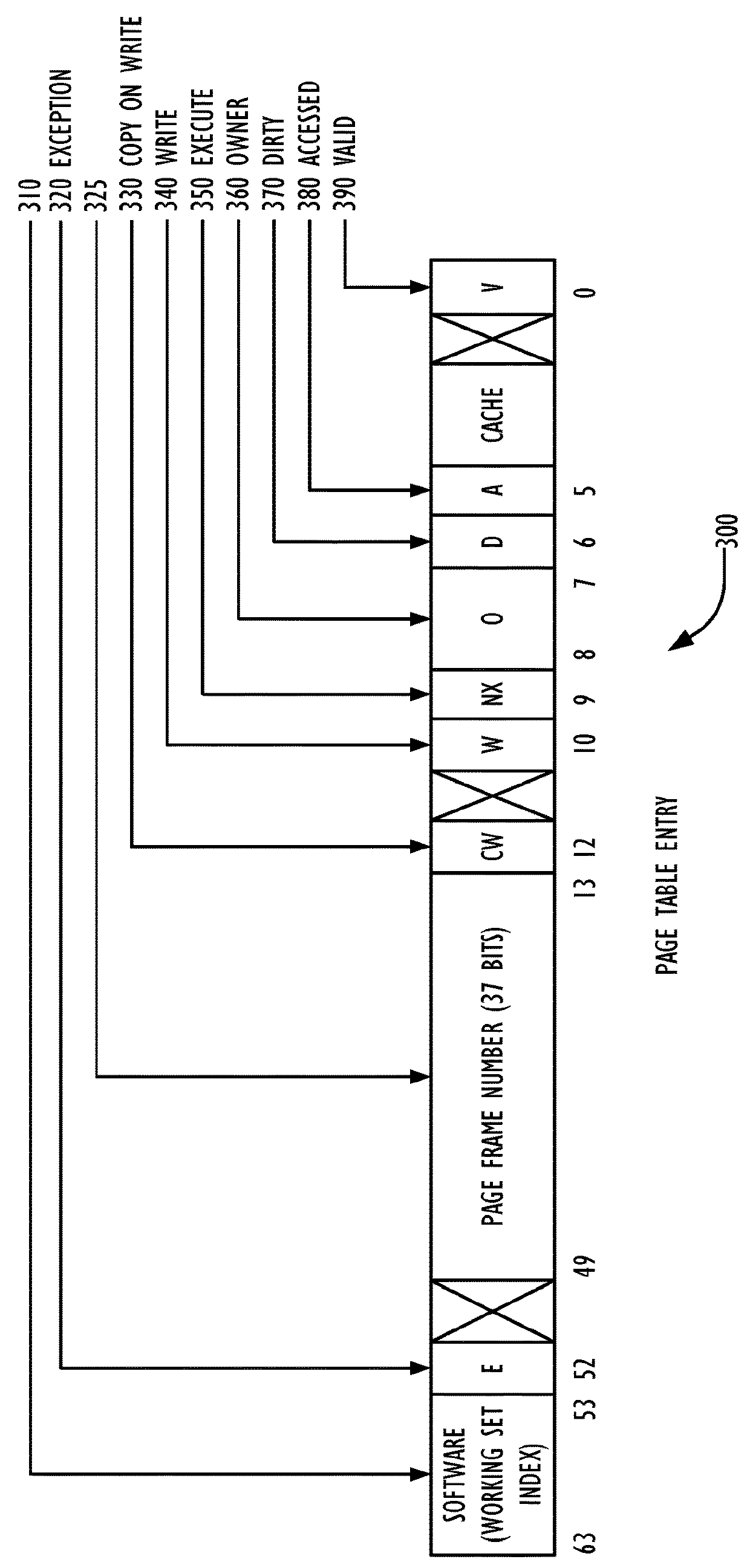
A dirty bit or modified bit is a bit that is associated with a block of computer memory and indicates whether or not the corresponding block of memory has been modified. The dirty bit is set when the processor writes to (modifies) this memory. The bit indicates that its associated block of memory has been modified and has not been saved to storage yet. When a block of memory is to be replaced, its corresponding dirty bit is checked to see if the block needs to be written back to secondary memory before being replaced or if it can simply be removed. Dirty bits are used by the CPU cache and in the page replacement algorithms of an operating system.
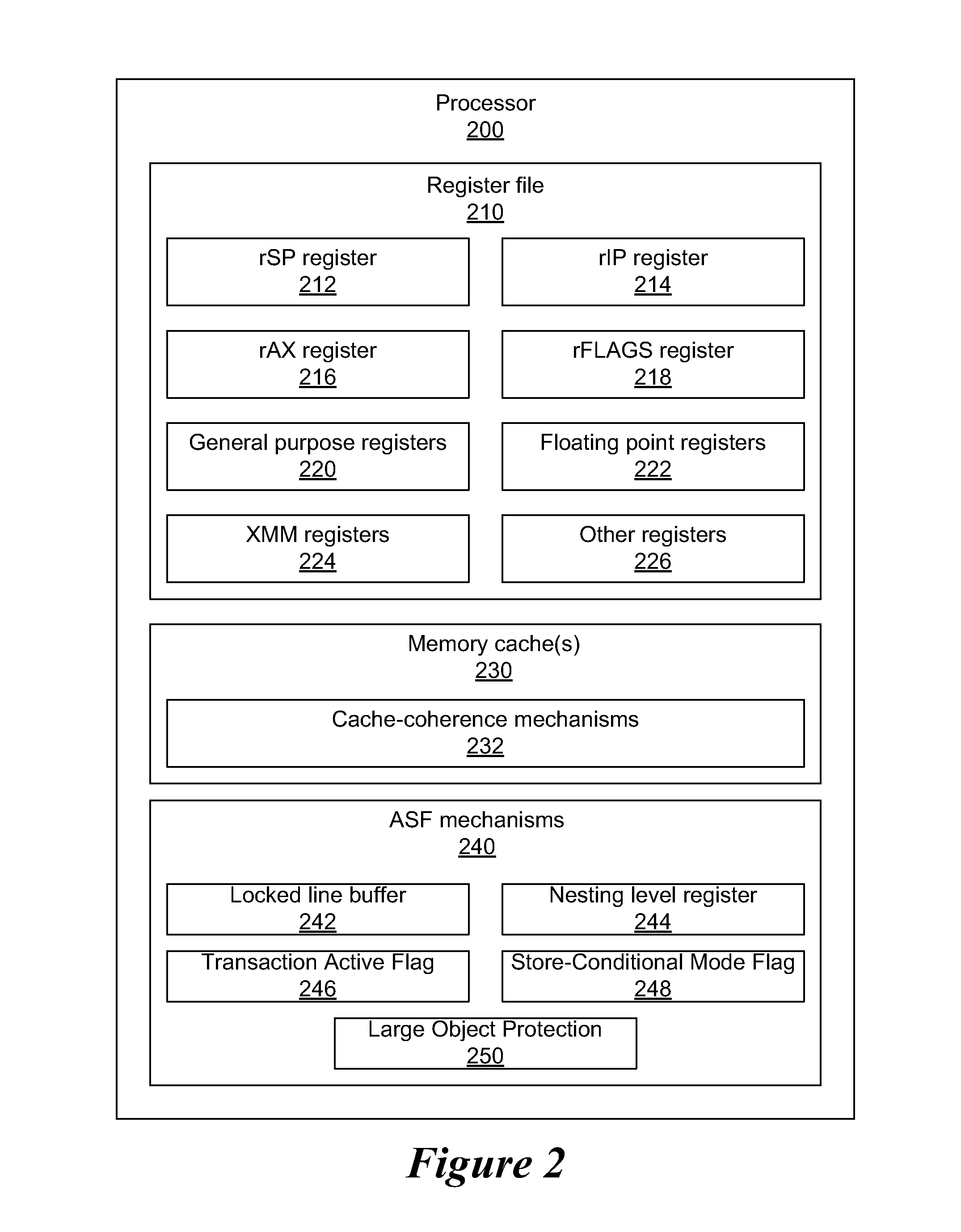
Protecting Large Objects Within an Advanced Synchronization Facility
A system and method are disclosed for allowing protection of larger areas than memory lines by monitoring accessed and dirty bits in page tables. More specifically, in some embodiments, a second associative structure with a different granularity is provided to filter out a large percentage of false positives. By providing the associative structure with sufficient size, the structure exactly specifies a region in which conflicting cache lines lie. If entries within this region are evicted from the structure, enabling the tracking for the entire index filters out a substantial number of false positives (depending on a granularity and a number of indices present). In some embodiments, this associative structure is similar to a translation look aside buffer (TLB) with 4 k, 2M entries.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
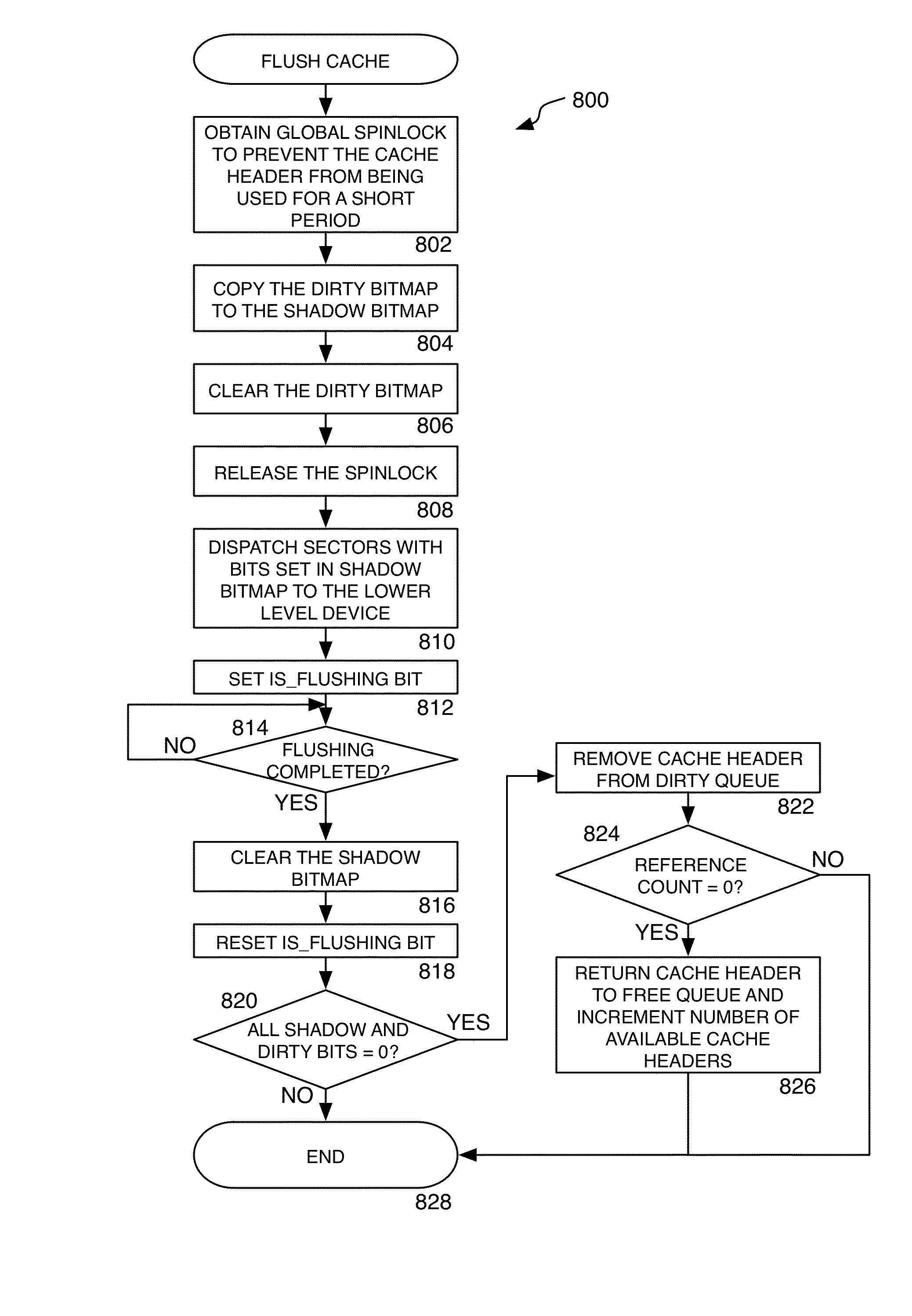
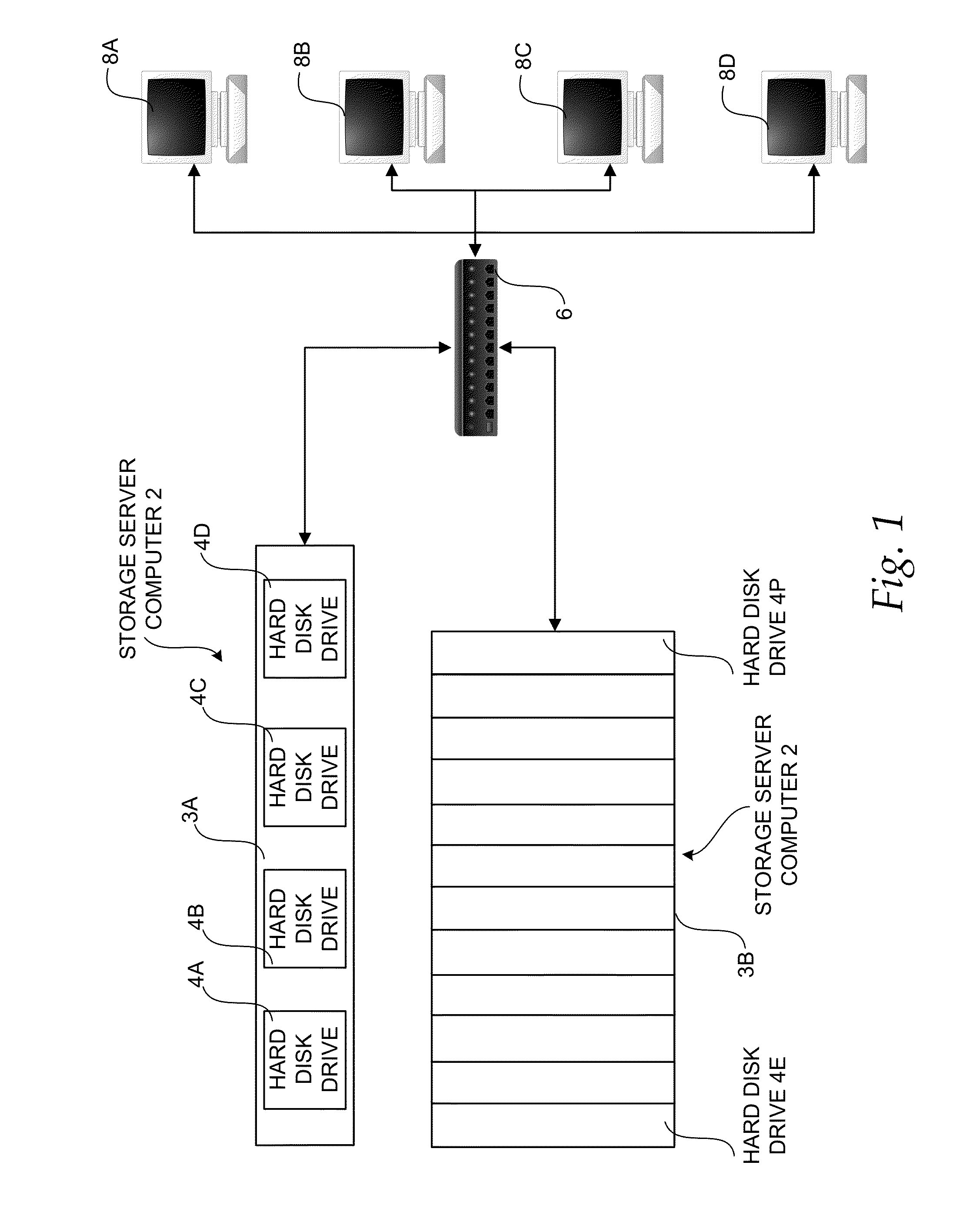
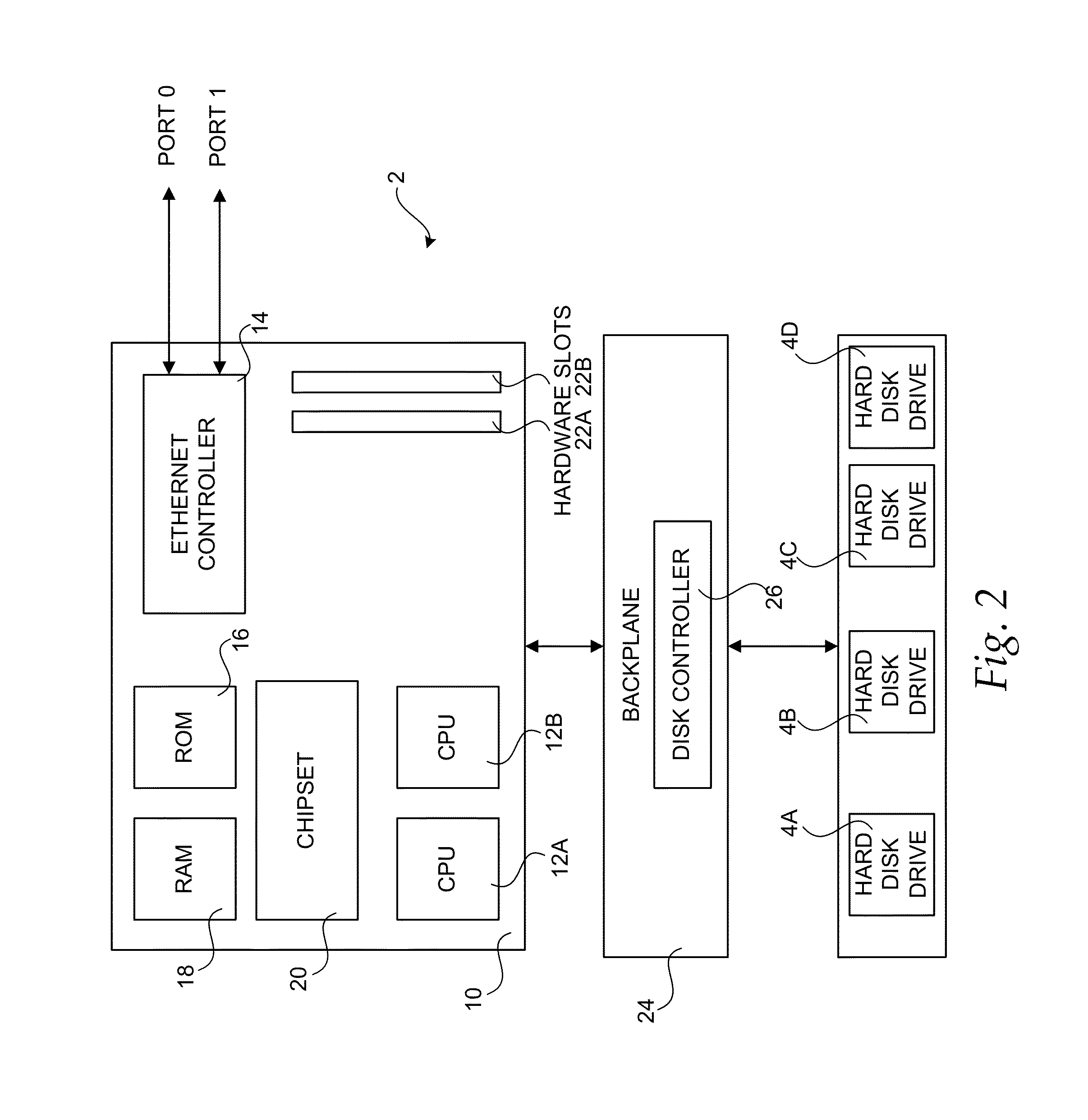
Method, system, apparatus, and computer-readable medium for implementing caching in a storage system
ActiveUS8549230B1Eliminate needUnnecessary operationMemory architecture accessing/allocationProgram controlUnit sizeDirty bit
A method, system, apparatus, and computer-readable medium are provided for implementing caching in a data storage system. According to aspects of the invention, a cache module is provided that utilizes cache lines sized according to a snapshot chunk size or an allocation unit size. The cache module utilizes cache header data structures corresponding to cache lines, each of which is assigned a device and logical block access range when active. The active headers are arranged in a set of hash queues. A free queue corresponds to the list of unused cache headers and a dirty queue corresponding to a list of unflushed cache headers. The cache header contains sector-level bitmaps of the cache line, specifying on a per sector granularity the bits that are dirty and valid. Flushing is performed by copying the dirty bitmap into a temporary memory location and flushing the bits set in it, while resetting the dirty bitmap and allowing writes to it. A read-ahead algorithm is used to perform read-ahead operations only in the event of a sequential read.
Owner:AMZETTA TECH LLC
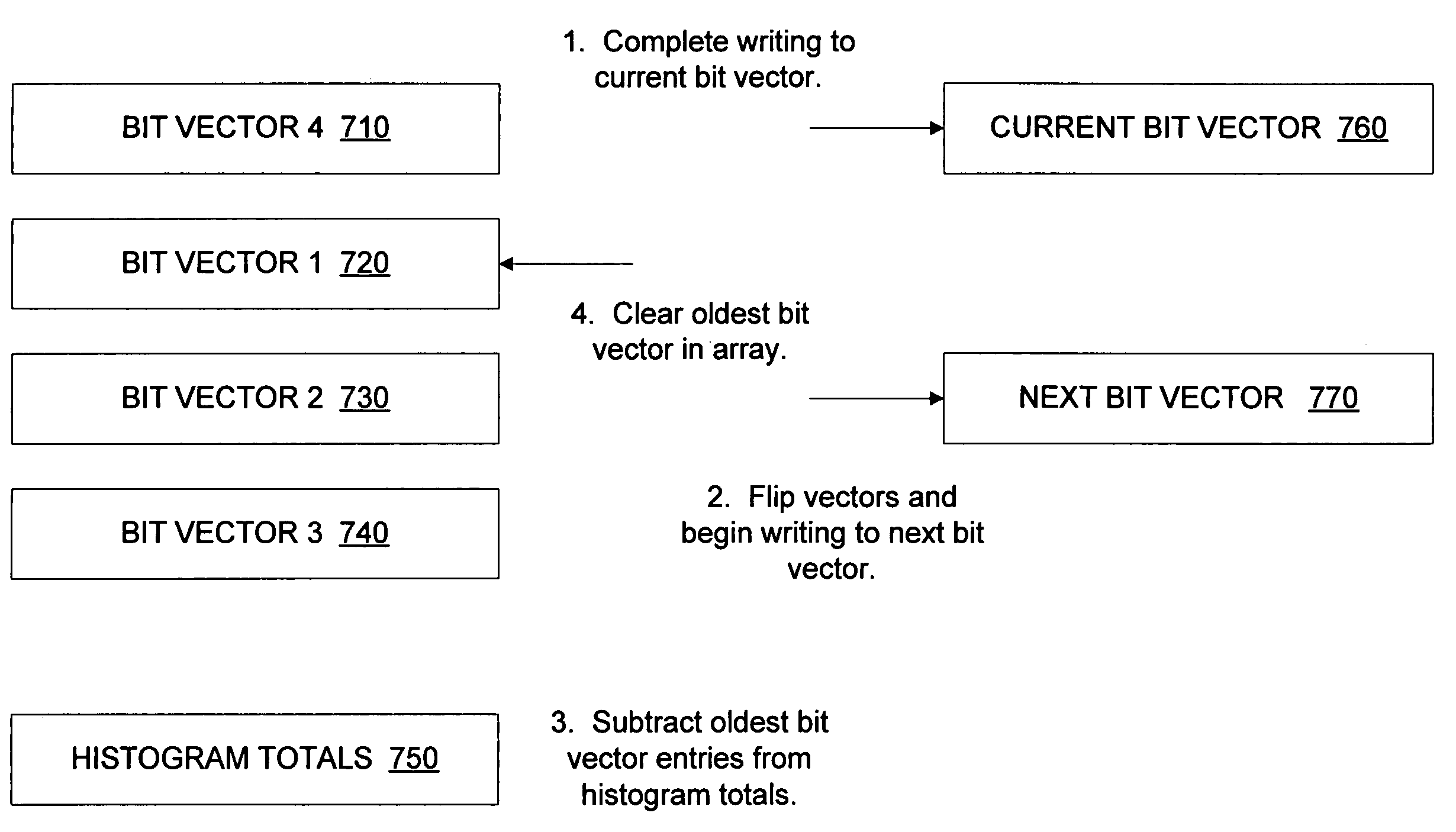
Physically-based page characterization data
ActiveUS7519781B1Efficient storageMemory adressing/allocation/relocationCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer hardwareDirty bit
Circuits, methods, and apparatus for efficiently storing page characteristics. Page characteristics for memory pages are stored post address translation using addresses for physical locations in memory, for example, in a bit vector. The characteristics may include access or dirty bits, as well as other types of information. These bit vectors can also be stored and accumulated to generate histogram data. Two bit vectors may be included, while a first bit vector is written to, another is used. After data has been written to the first, the bit vectors are flipped, and data is written to the second while the first is used.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Graphics processing systems
In a tile-based graphics processing system, when an overlay image is to be rendered onto an existing image, the existing tile data for the existing image from the frame buffer in the main memory is pre-loaded into the local colour buffer of the graphics processor (step 41). The overlay content is then rendered and used to modify the tile data stored in the colour buffer (step 44). When the data for a given sampling position stored in the tile buffer is modified as a result of the overlay image, a corresponding dirty bit for the tile region that the sampling position falls within is set (step 45). Then, when all the rendering for the tile has been completed, the dirty bits are examined to determine which regions of the tile have been modified (step 46). The modified tile regions are written back to the output image in the frame buffer in the main memory (step 47), but any regions whose dirty bits have not been set are not written back to the frame buffer in the main memory.
Owner:ARM LTD
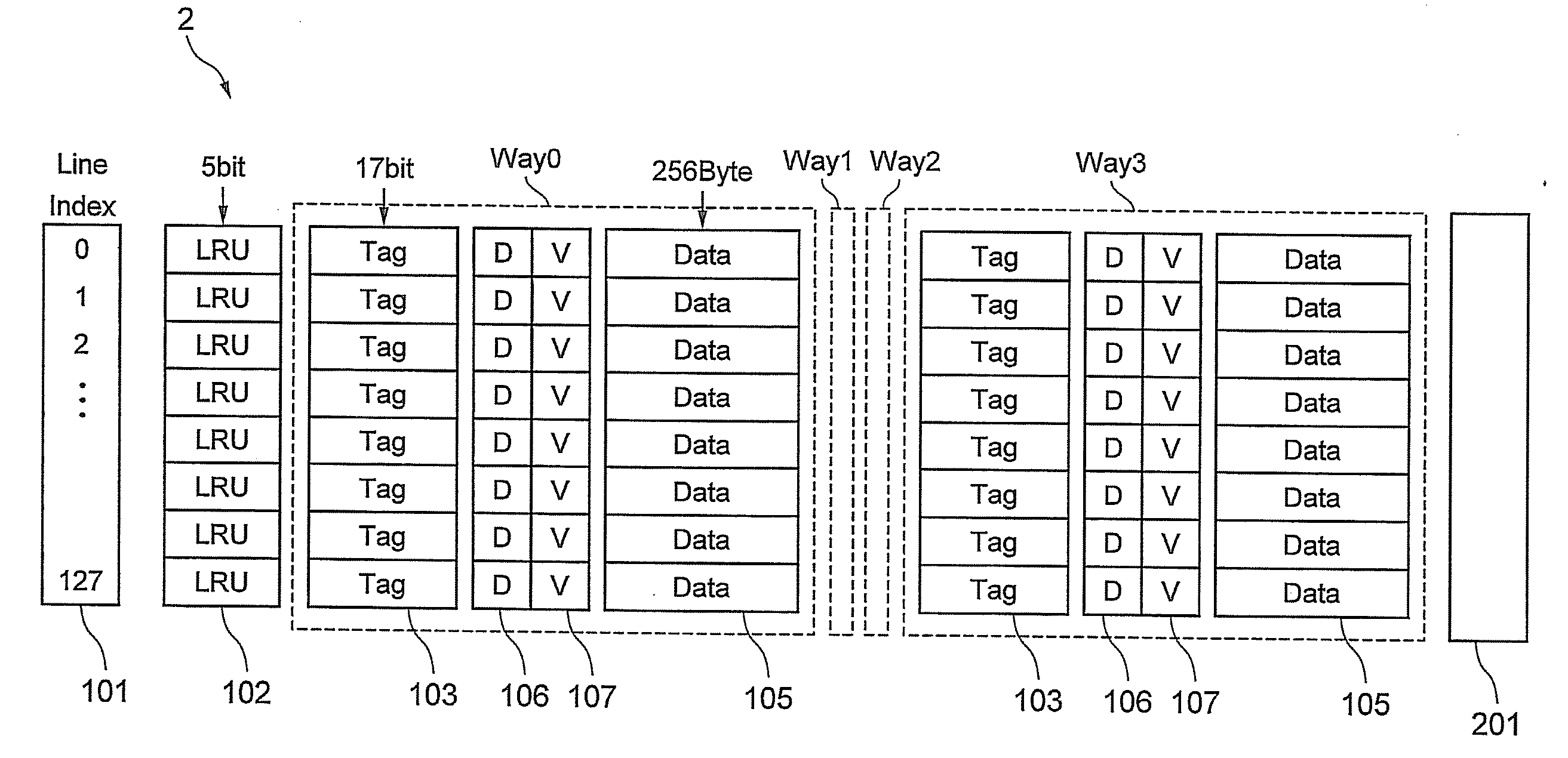
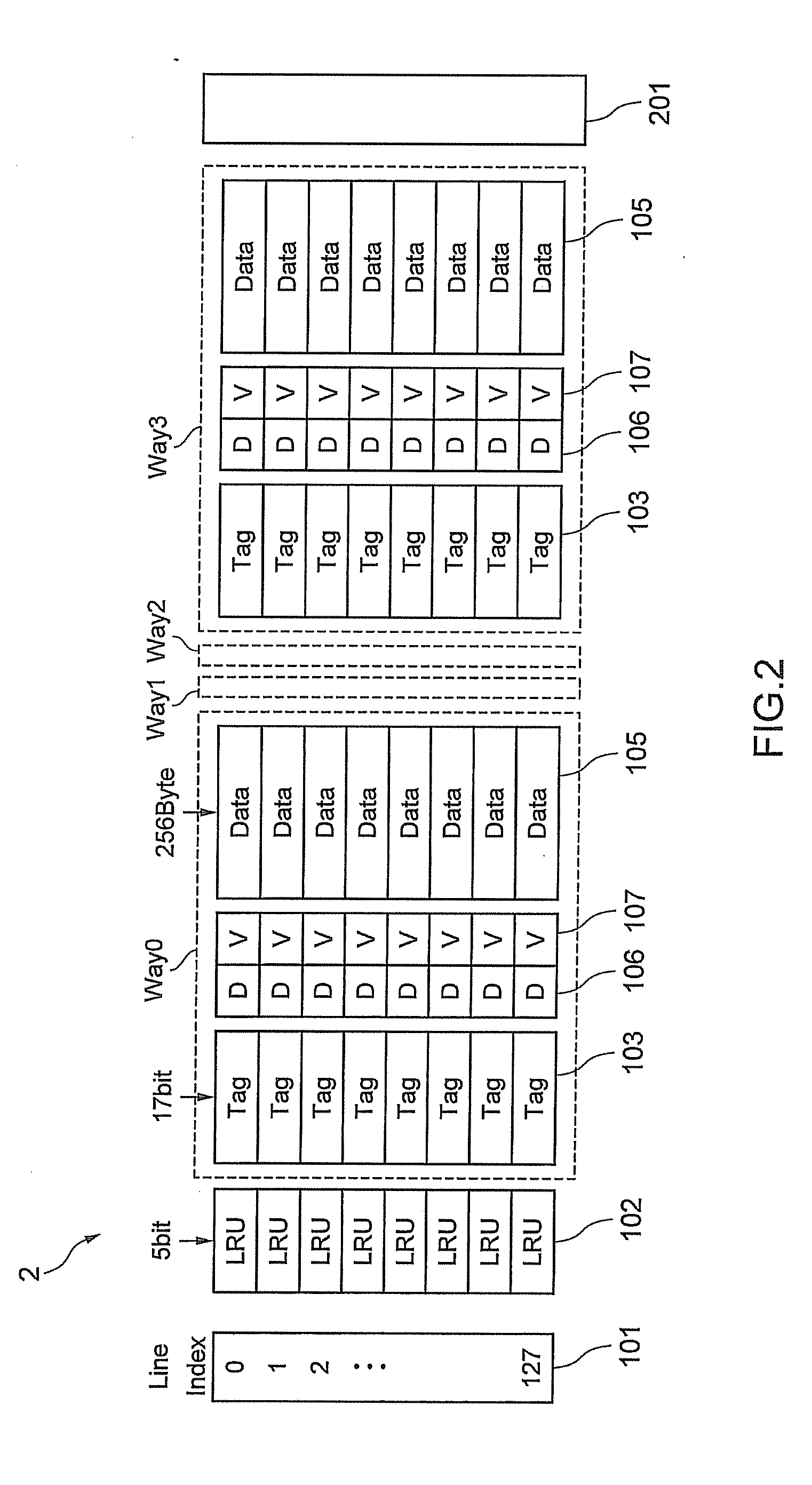
Cache memory and cache system
A cache memory has one or a plurality of ways having a plurality of cache lines including a tag memory which stores a tag address, a first dirty bit memory which stores a first dirty bit, a valid bit memory which stores a valid bit, and a data memory which stores data. The cache memory has a line index memory which stores a line index for identifying the cache line. The cache memory has a DBLB management unit having a plurality of lines including a row memory which stores first bit data identifying the way and second bit data identifying the line index, a second dirty bit memory which stores a second dirty bit of bit unit corresponding to writing of a predetermined unit into the data memory, and a FIFO memory which stores FIFO information prescribing a registered order. Data in a cache line of a corresponding way is written back on the basis of the second dirty bit.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Parallel read with source-clear operation
InactiveUS20030142101A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationCathode-ray tube indicatorsDirty bitMemory interface
A memory interface controls read and write accesses to a memory device. The memory device includes a level-one cache, level-two cache and storage cell array. The memory interface includes a data request processor (DRP), a memory control processor (MCP) and a block cleansing unit (BCU). The MCP controls transfers between the storage cell array, the level-two cache and the level-one cache. In response to a read request with associated read clear indication, the DRP controls a read from a level-one cache block, updates bits in a corresponding dirty tag, and sets a mode indicator of the dirty tag to a the read clear mode. The modified dirty tag bits and mode indicator are signals to the BCU that the level-one cache block requires a source clear operation. The BCU commands the transfer of data from a color fill block in the level-one cache to the level-two cache.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Page table management
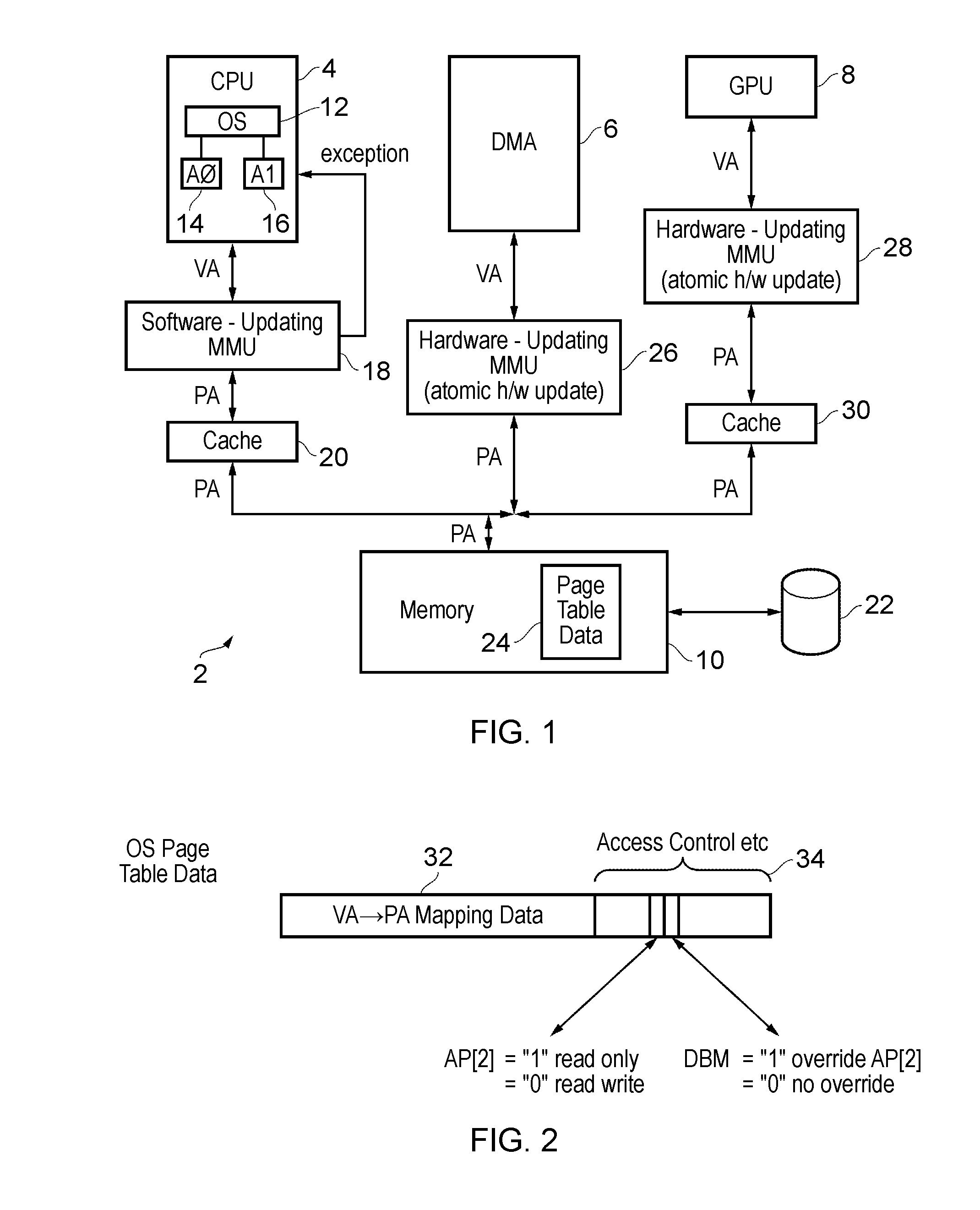
ActiveUS20140337585A1Improve software compatibilityMemory architecture accessing/allocationUnauthorized memory use protectionDirty bitMemory address
Page table data for each page within a memory address space includes a write permission flag and a dirty-bit-modifier flag. The write permission flag is initialised to a value indicating that write access is not permitted. When a write access occurs, then the dirty-bit-modifier flag indicates whether or not the action of the write permission flag may be overridden. If the action of the write permission flag may be overridden, then the write access is permitted and the write permission flag is changed to indicate that write access is thereafter permitted. A page for which the write permission flag indicates that writes are permitted is a dirty page.
Owner:ARM LTD
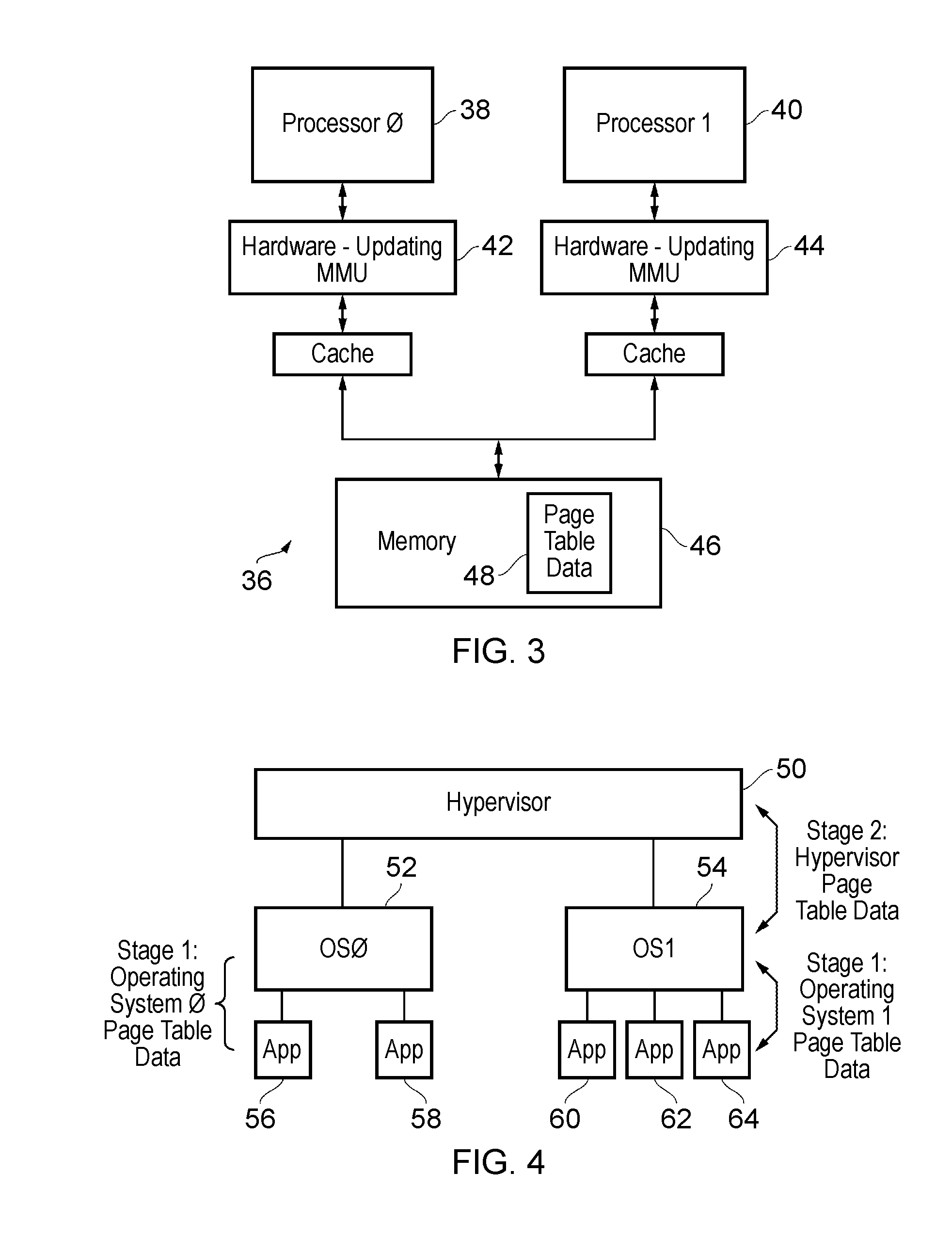
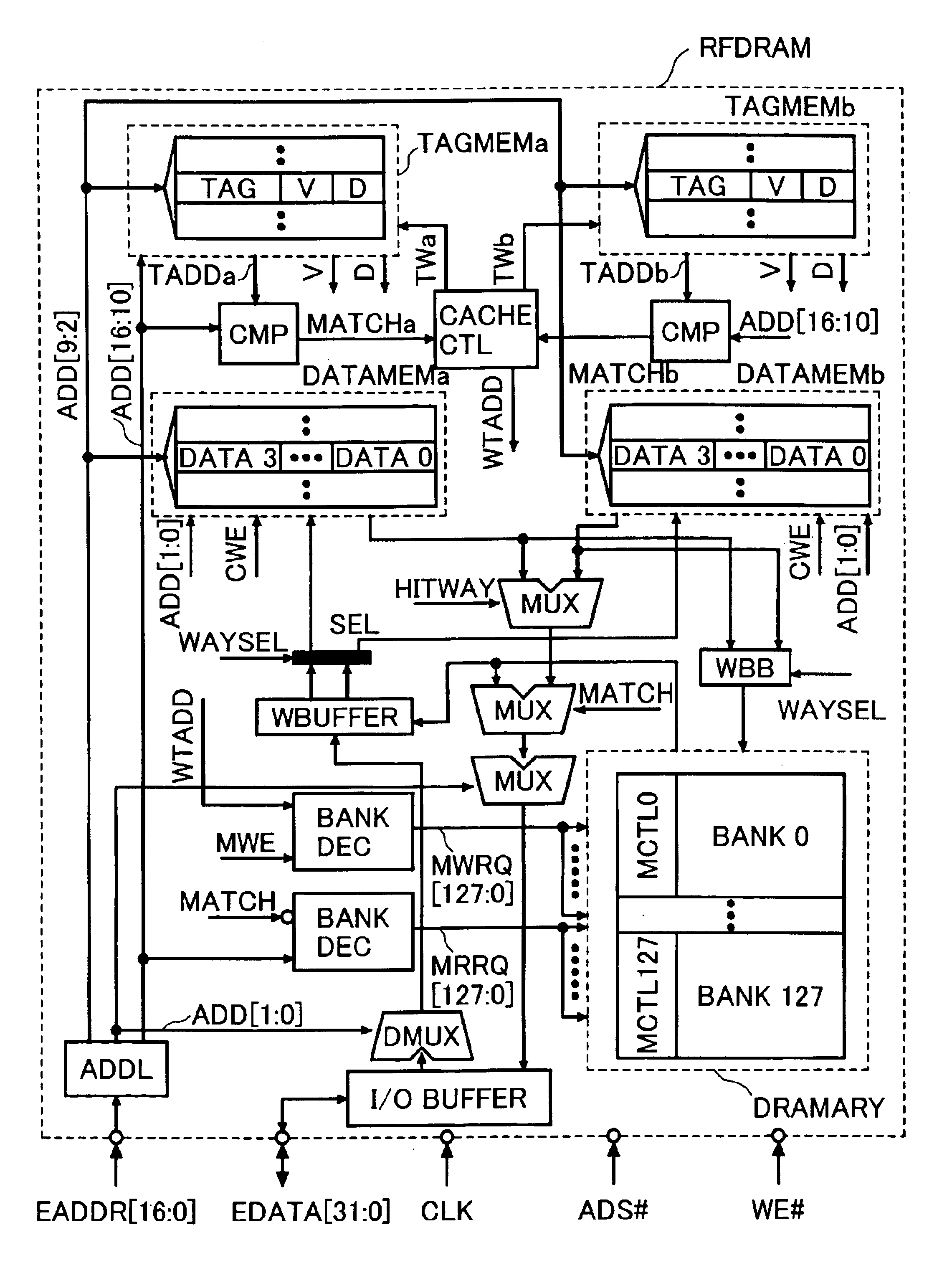
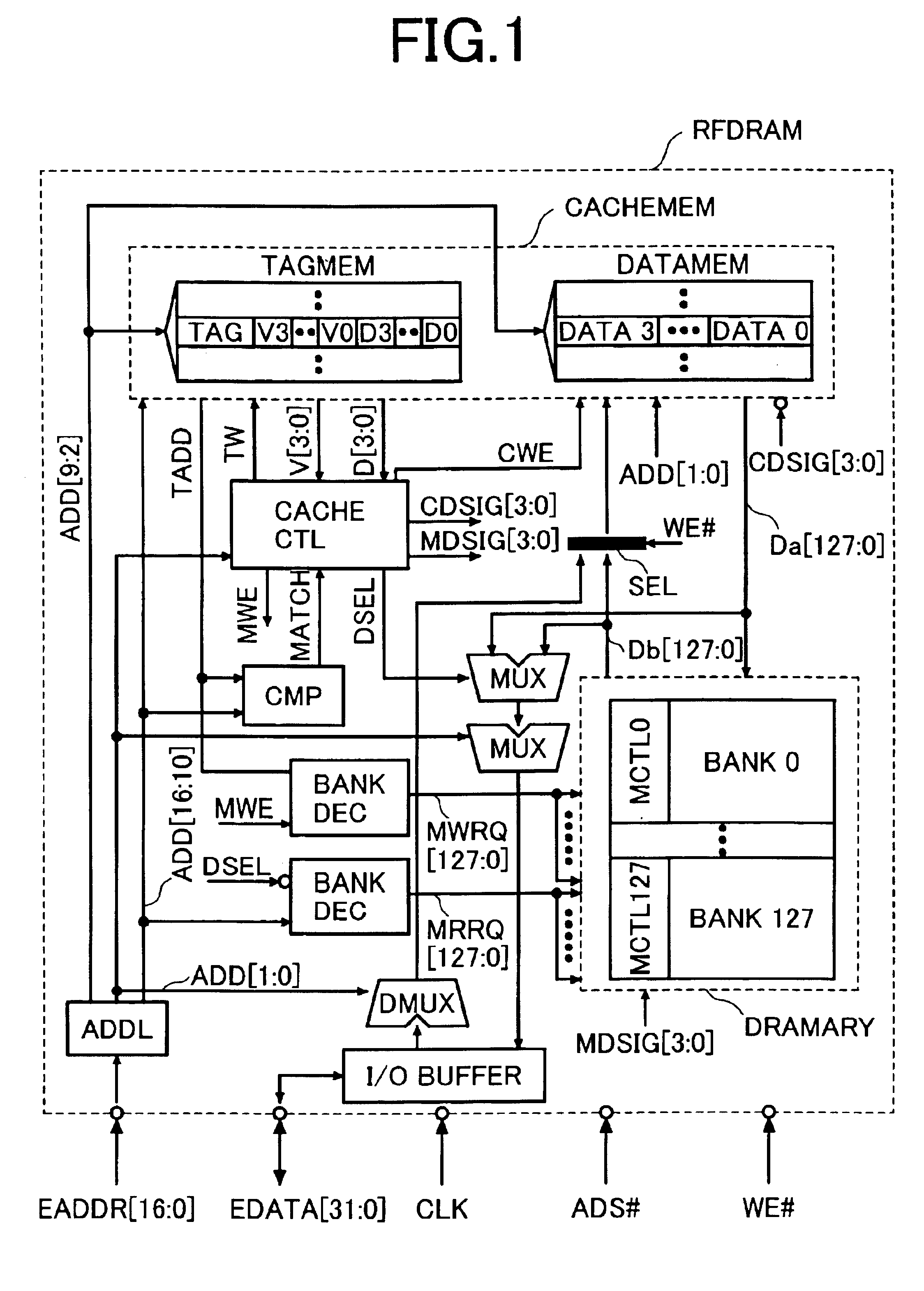
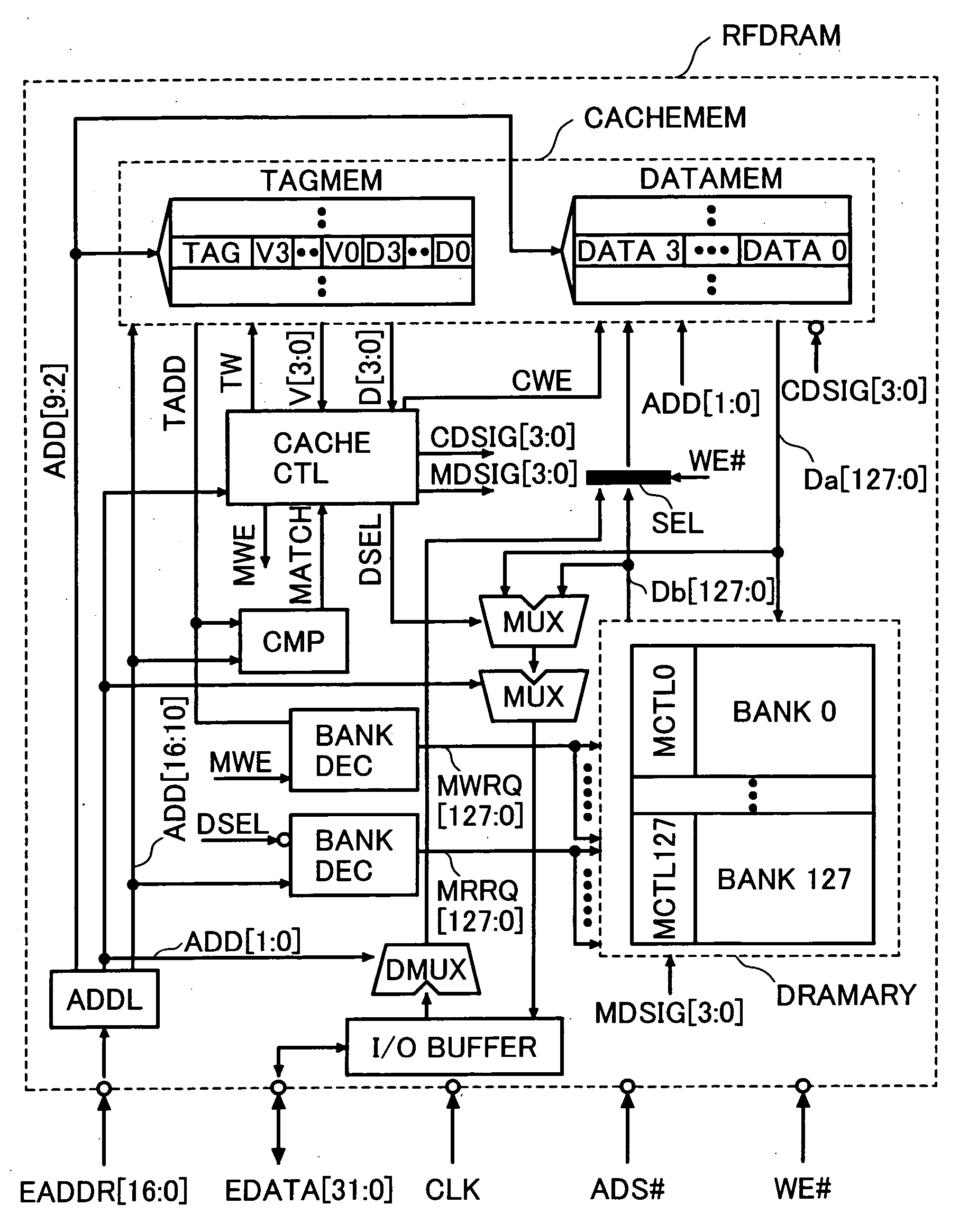
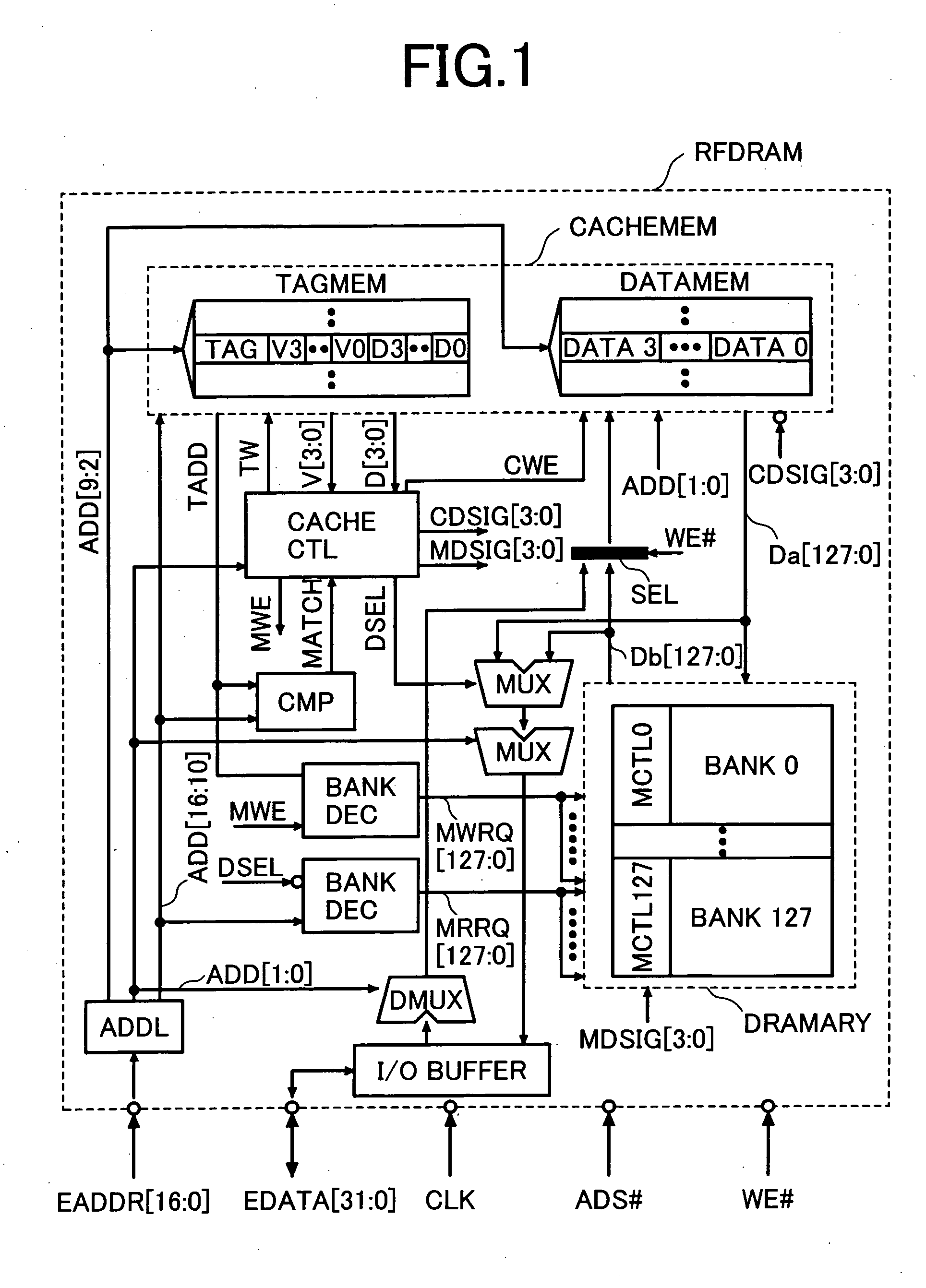
Semiconductor device with multi-bank DRAM and cache memory
InactiveUS6848035B2Easy to operateEliminate operationMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDirty bitExternal data
A semiconductor device is designed to hide refresh operations even when the data width of a cache line differs from that of the external data bus in a memory that uses a cache memory and a DRAM with a plurality of banks. The semiconductor device includes a plurality of memory banks BANK0 to BANK127, each having a plurality of memory cells, as well as a cache memory CACHEMEM used to retain information read from the plurality of memory banks. The cache memory CACHEMEM includes a plurality of entries, each having a data memory DATAMEM and a tag memory TAGMEM. The data memory DATAMEM has a plurality of sub lines DATA0 to DATA3 and the tag memory TAGMEM has a plurality of valid bits V0 to V3 and a plurality of dirty bits D0 to D3.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
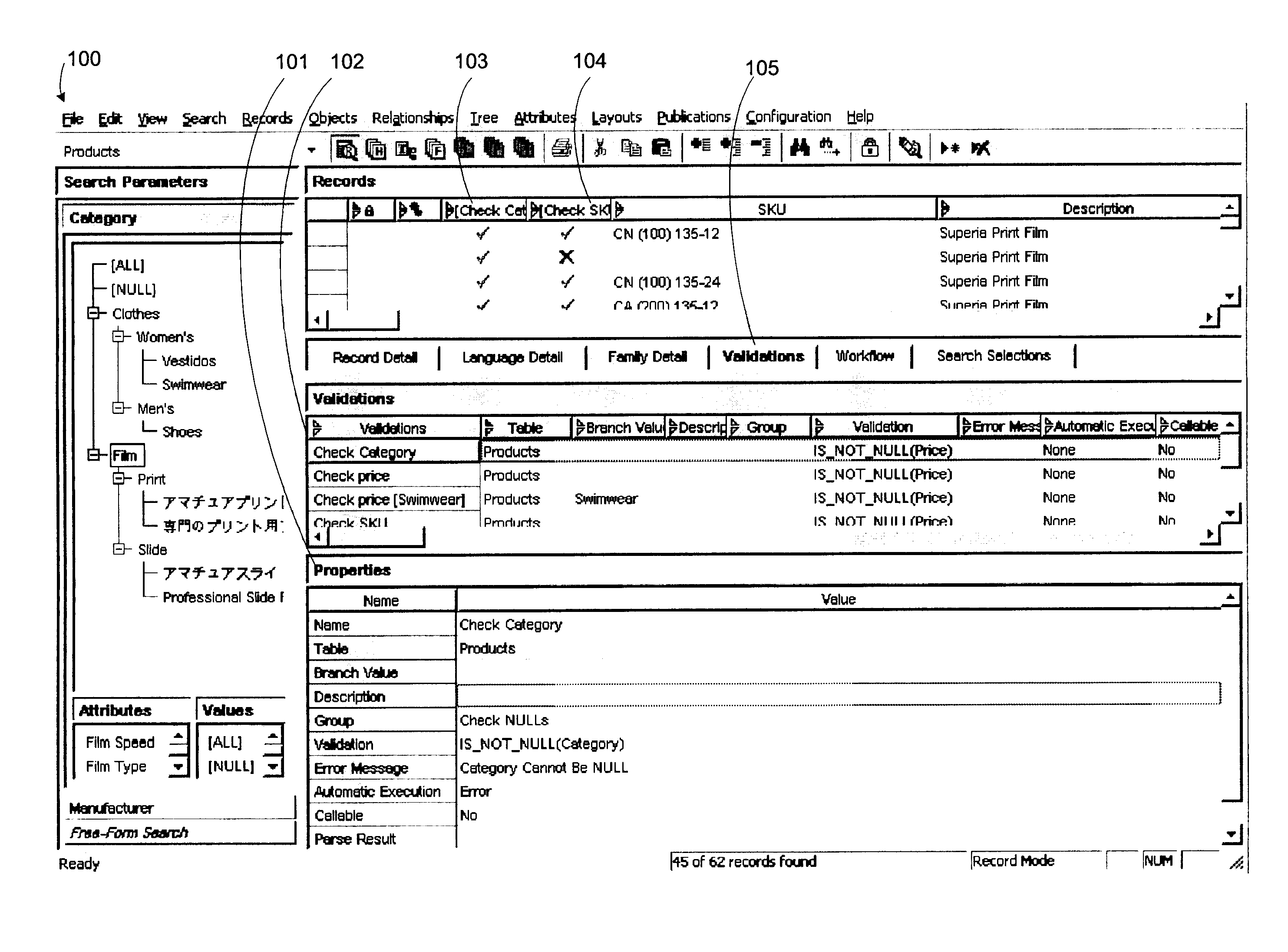
Method for improved processing of expression-based data
ActiveUS7725483B2Improve data integritySave a lot of spaceDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsDirty bitData recording
Expression-based data may comprise data that is processed by a validation expression for example. After a validation expression is created it may then be performed with respect to one or more data values or data records. A validation expression returns a Boolean result that signifies a success or failure result. A validation expression can define complex intra-record tests and inter-record tests with unlimited complexity. In order to improve processing of validations, the system uses virtual data known as calculation fields. Calculation fields are stored in memory at runtime and not in a database thereby eliminating the necessity of selecting and updating records in the database. A dirty bit identifying fields and attributes that need to be calculated based on a dependent data may be used to defer calculation to a later time when the calculation field is displayed or a sort operation occurs for example.
Owner:SAP AG
Parallel read with source-clear operation
InactiveUS6795078B2Memory adressing/allocation/relocationCathode-ray tube indicatorsDirty bitMemory interface
A memory interface controls read and write accesses to a memory device. The memory device includes a level-one cache, level-two cache and storage cell array. The memory interface includes a data request processor (DRP), a memory control processor (MCP) and a block cleansing unit (BCU). The MCP controls transfers between the storage cell array, the level-two cache and the level-one cache. In response to a read request with associated read clear indication, the DRP controls a read from a level-one cache block, updates bits in a corresponding dirty tag, and sets a mode indicator of the dirty tag to a the read clear mode. The modified dirty tag bits and mode indicator are signals to the BCU that the level-one cache block requires a source clear operation. The BCU commands the transfer of data from a color fill block in the level-one cache to the level-two cache.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20130297874A1Reduce power consumptionDecreased cache performanceDigital data processing detailsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationPower semiconductor deviceDirty bit
To provide a semiconductor device with less power consumption. In a semiconductor device including a CPU, the frequency of access to a cache memory is monitored. In the case where the access frequency is uniform, supply of a power supply voltage to the CPU is stopped. In the case where the access frequency is not uniform, stop of supplying the power supply voltage is performed on memories with a time interval, and eventually, supply of the power supply voltage to the CPU is stopped. Further, write back processing is efficiently performed in accordance with determination of a dirty bit, so that power consumption of the semiconductor device can be further achieved.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Non-blocking data transfer via memory cache manipulation
InactiveUS20110119451A1Improve system performanceImprove performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDirty bitComputer architecture
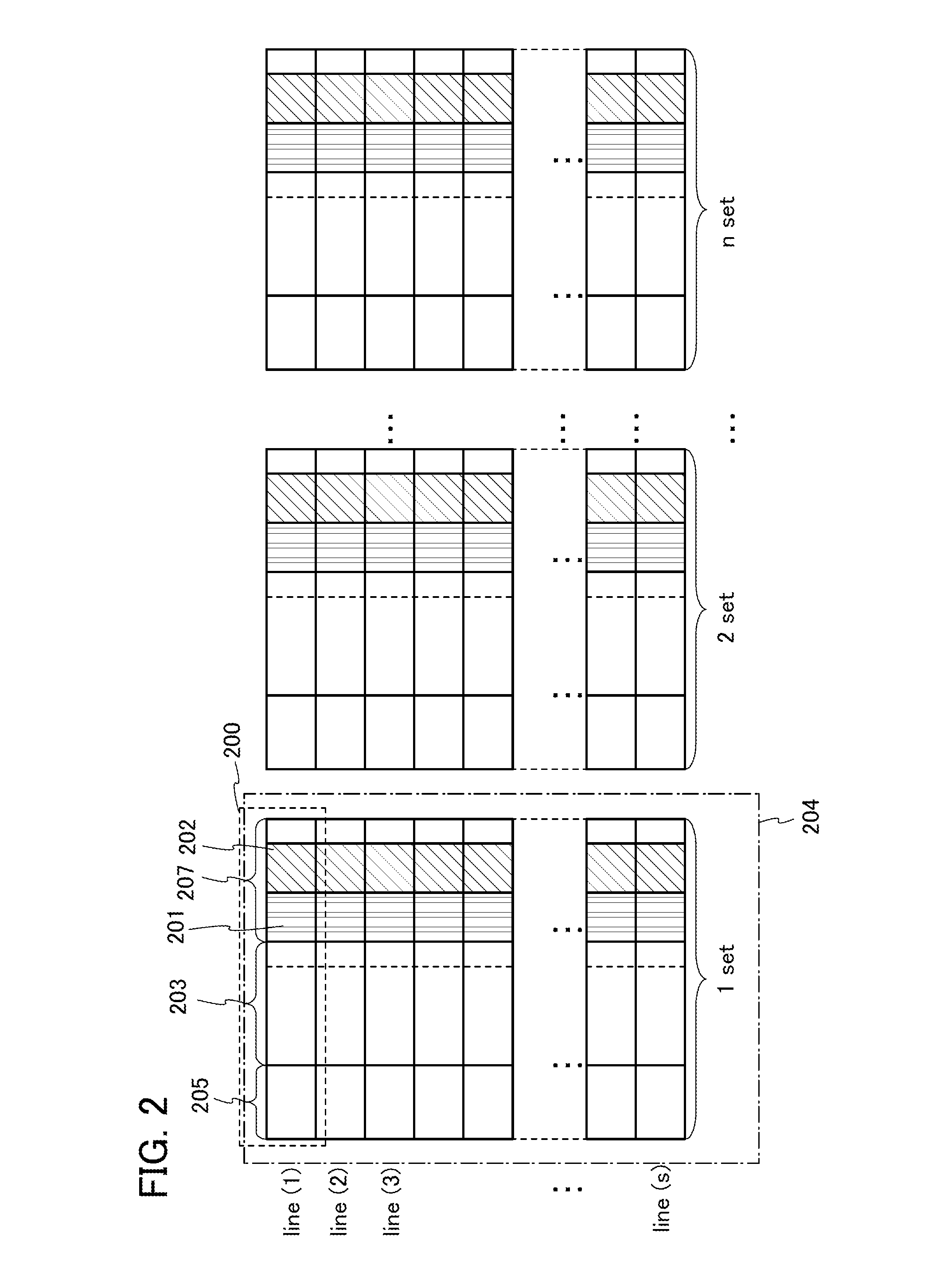
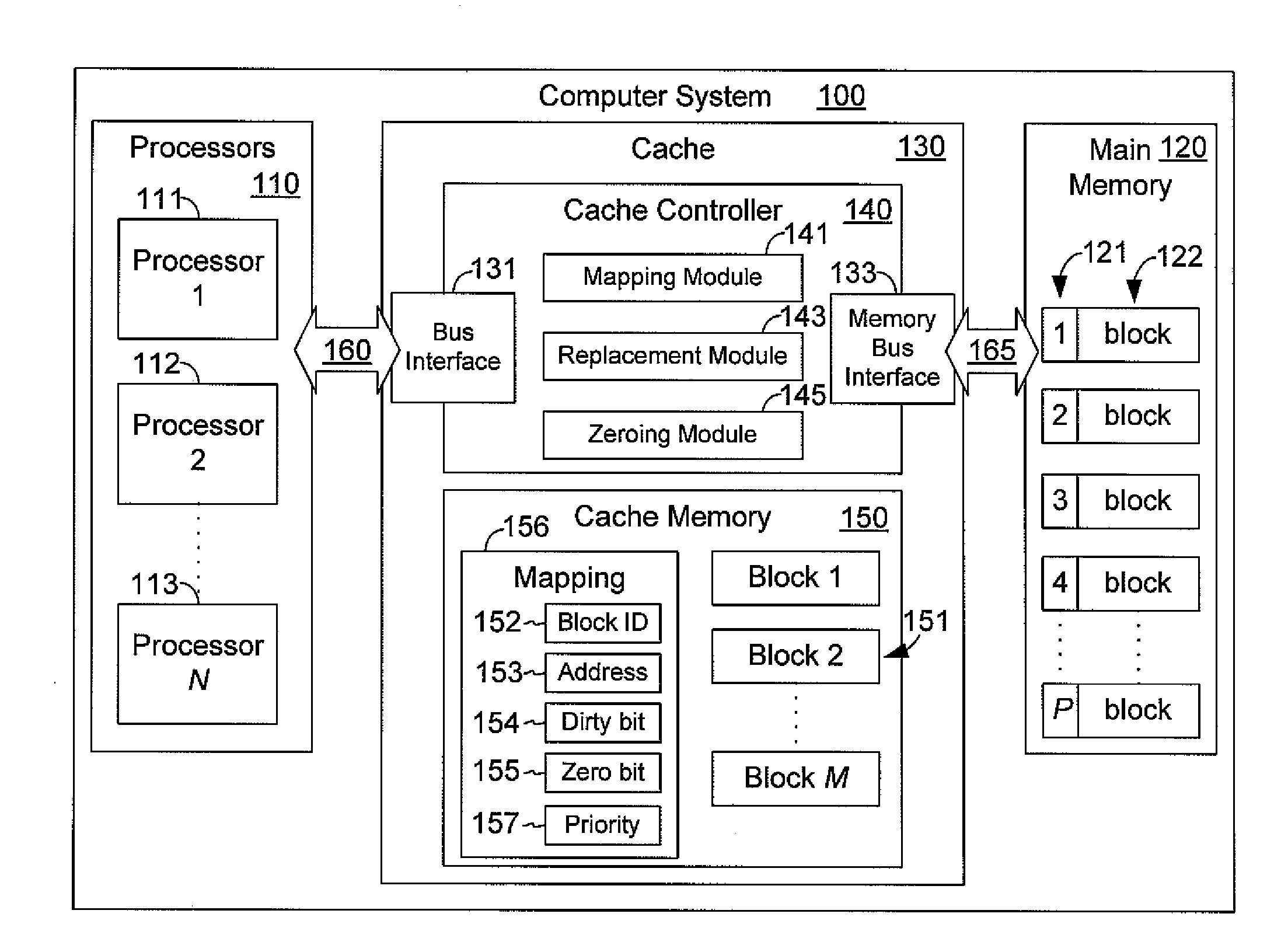
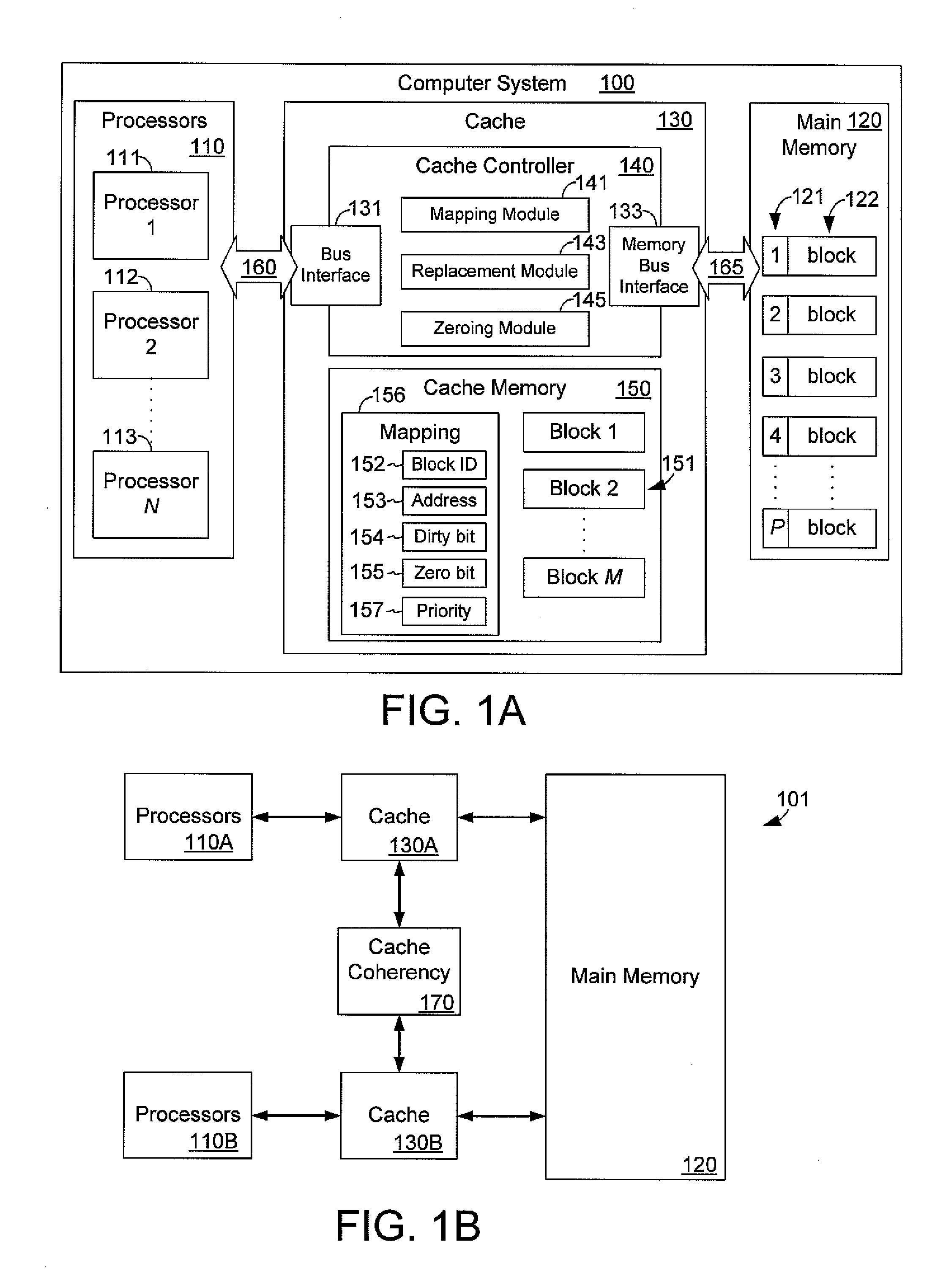
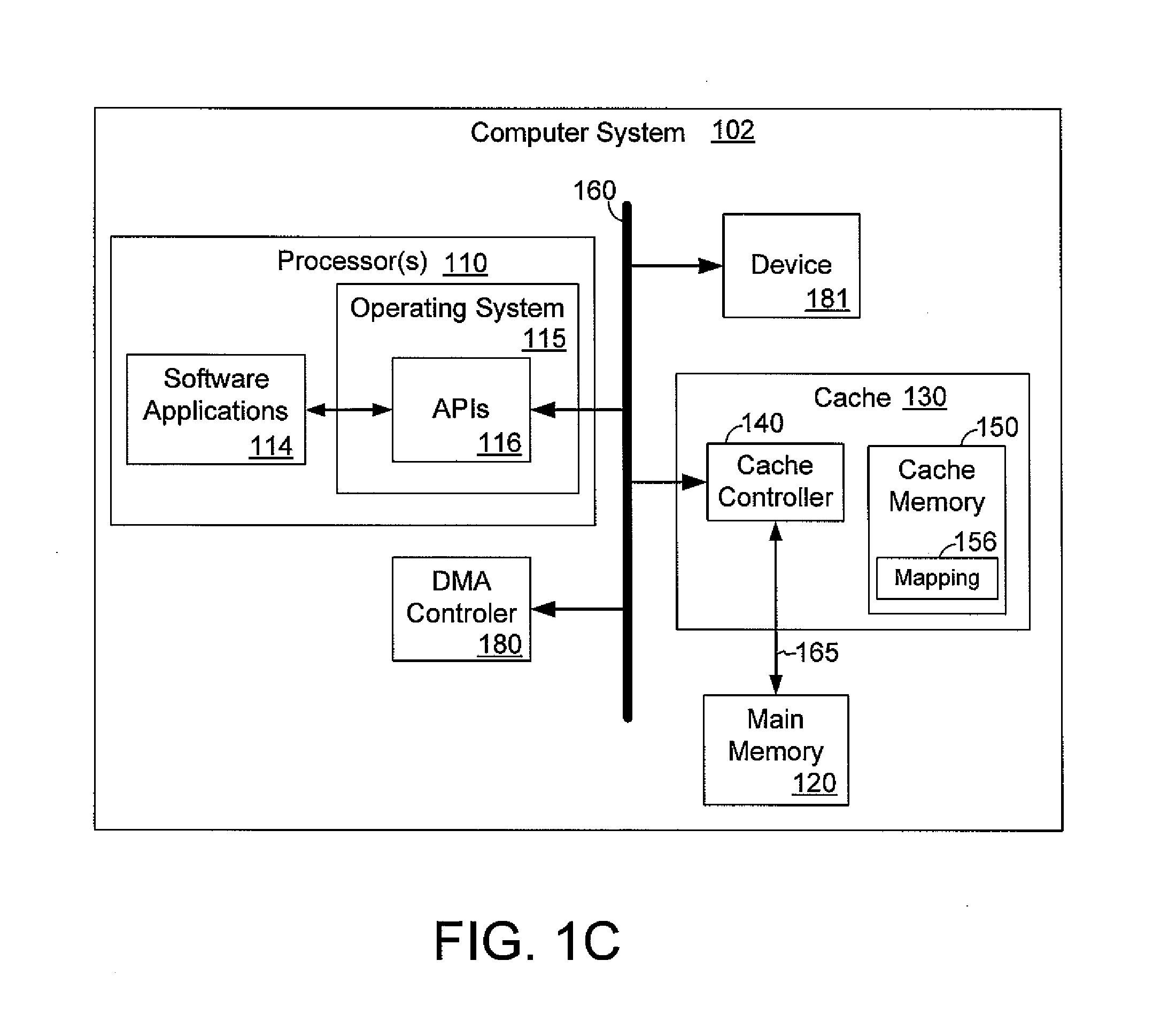
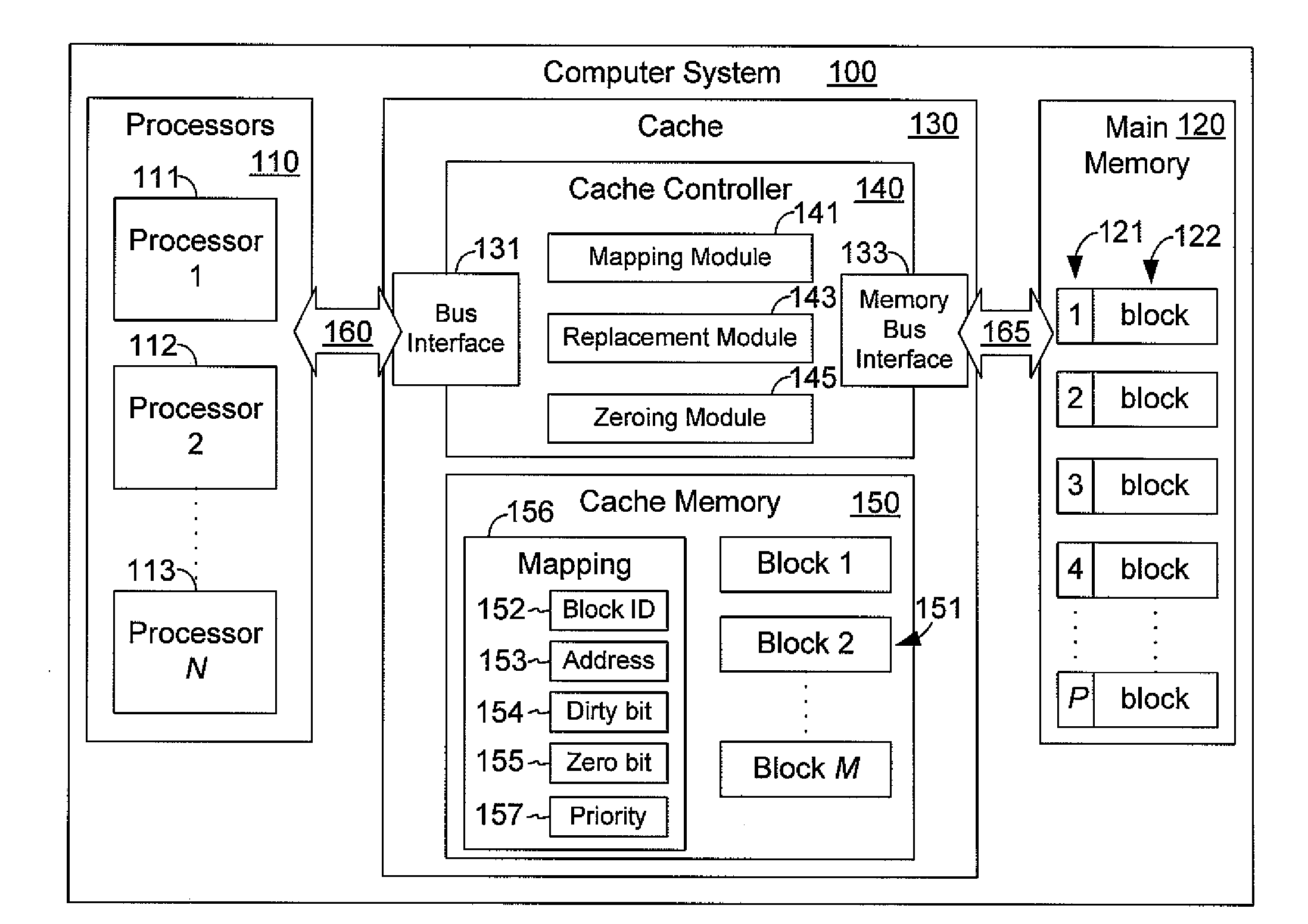
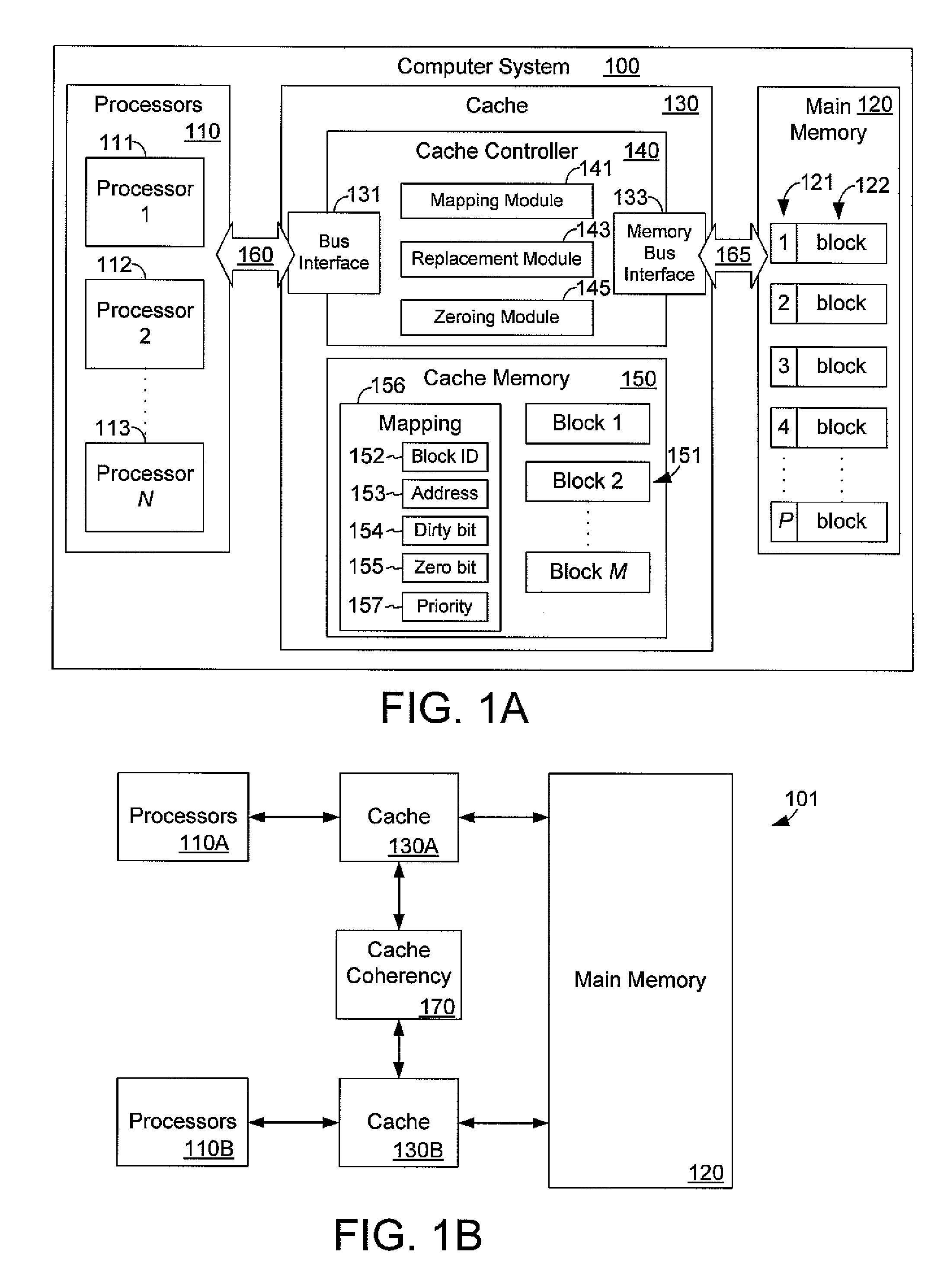
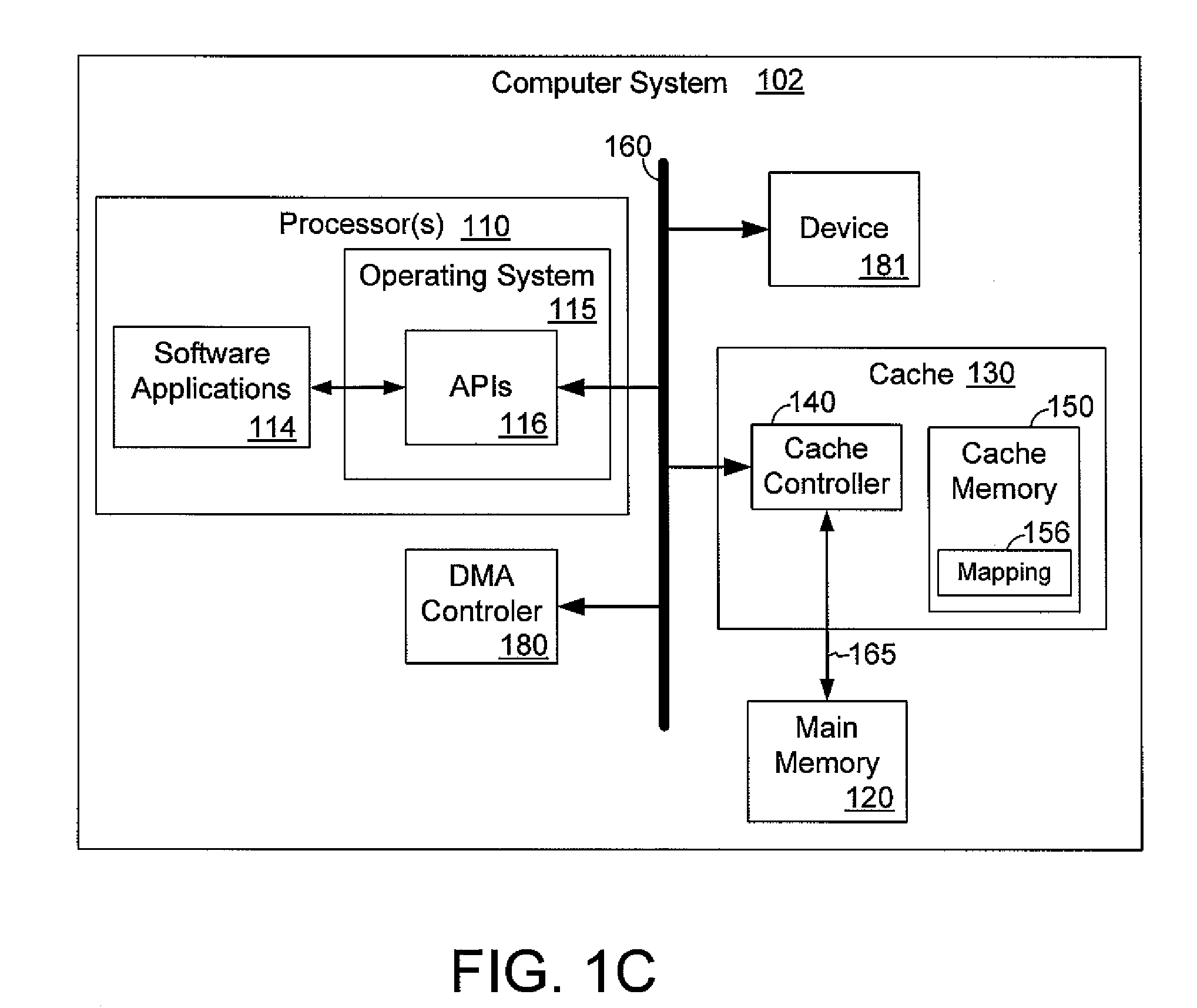
A cache controller in a computer system is configured to manage a cache such that the use of bus bandwidth is reduced. The cache controller receives commands from a processor. In response, a cache mapping maintaining information for each block in the cache is modified. The cache mapping may include an address, a dirty bit, a zero bit, and a priority for each cache block. The address indicates an address in main memory for which the cache block caches data. The dirty bit indicates whether the data in the cache block is consistent with data in main memory at the address. The zero bit indicates whether data at the address should be read as a default value, and the priority specifies a priority for evicting the cache block. By manipulating this mapping information, commands such as move, copy swap, zero, deprioritize and deactivate may be implemented.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Cache with DMA and dirty bits
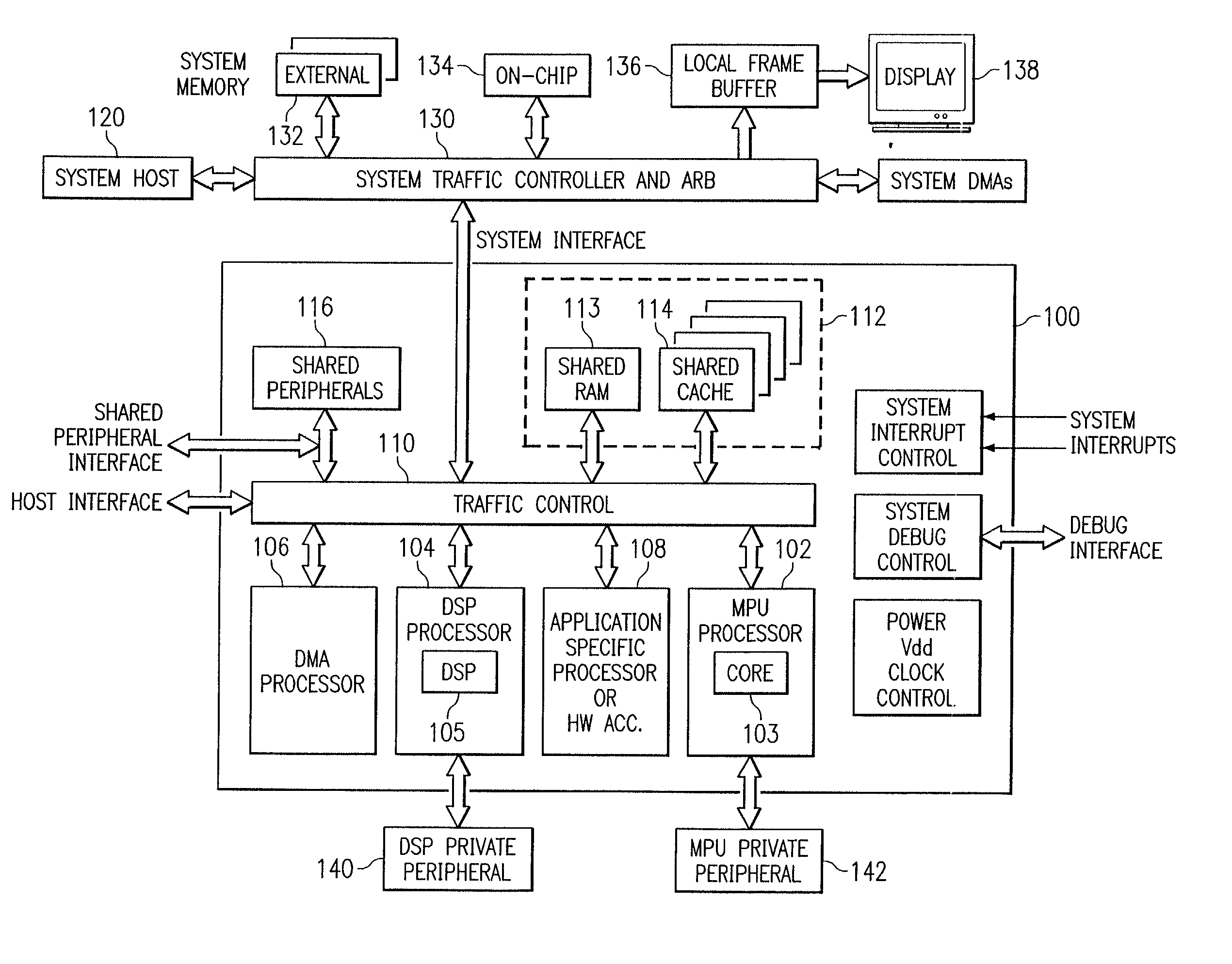
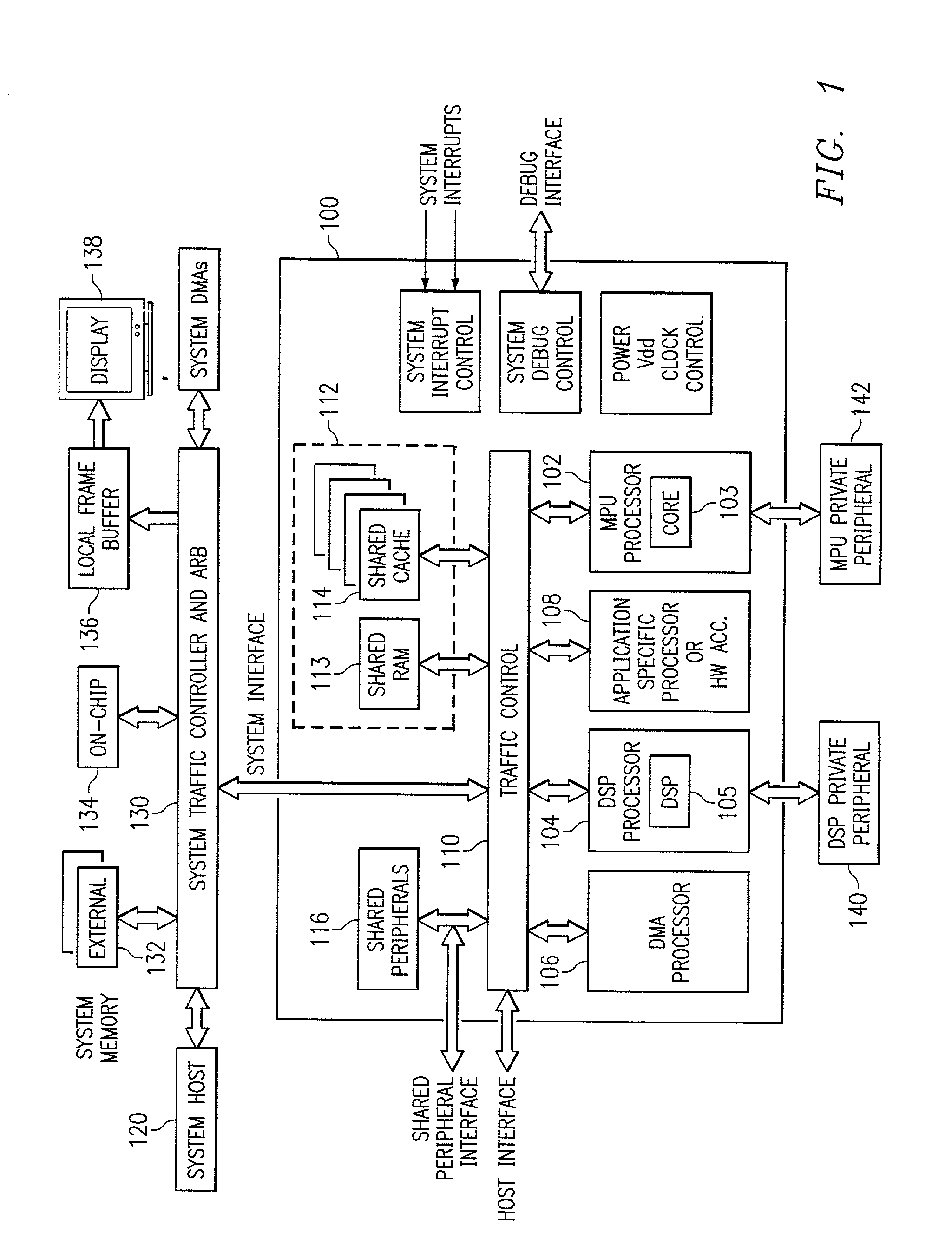
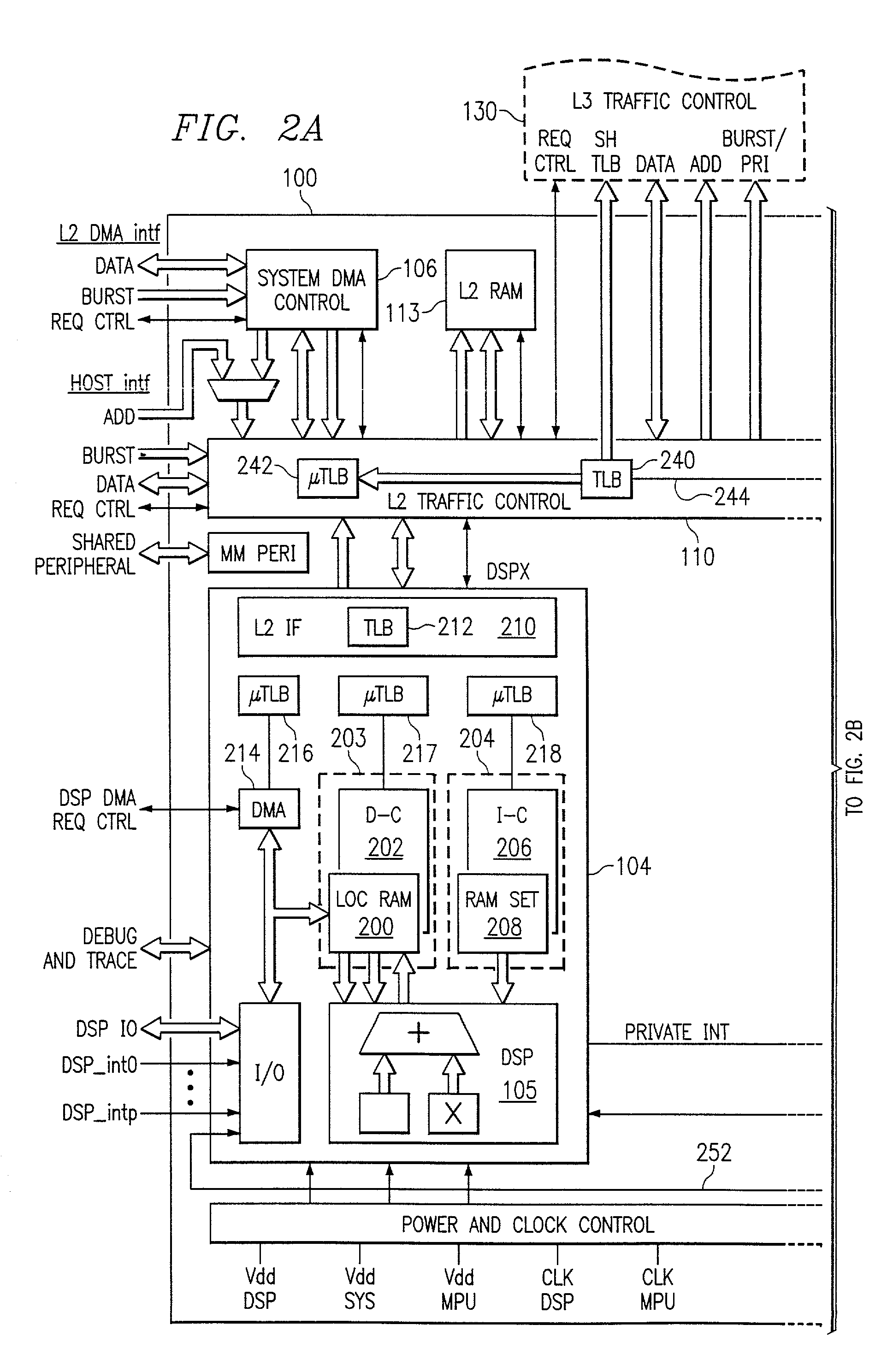
InactiveUS20020069330A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTDirty bitParallel computing
A digital system and method of operation is provided in which the digital system has at least one processor, with an associated multi-segment cache memory circuit (506(n). Validity circuitry (VI) is connected to the memory circuit and is operable to indicate if each segment of the plurality of segments holds valid data. Dirty bit circuitry (DI) is connected to the memory circuit for indicating if data within the cache is incoherent with a secondary back-up memory. DMA circuitry can transfer (1652) blocks of data / instructions (1660) between the cache and a secondary memory (1602). A transfer mode circuit (1681) controls how DMA operations are affected by the dirty bits. If the transfer mode circuit is in a first mode, a DMA operation transfers only segments (1661) indicated as dirty (1685). If the transfer mode circuit is in a second mode, a DMA operation transfers and entire block of data (1660) without regard to dirty indicators (1686). DMA transfers from the cache to secondary memory are thereby configured to be responsive to the dirty bits. A dirty bit mode circuit (1680) controls how DMA transfers affect the dirty bits. When the mode circuit is in a first mode, DMA transfers set the affected dirty bits to a clean state. When the dirty bit mode circuitry is in an alternate mode, DMA transfers set the affected dirty bits to a dirty state. A cache clean operation will thus copy data provided by a DMA transfer and indicated as dirty into backup secondary memory.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
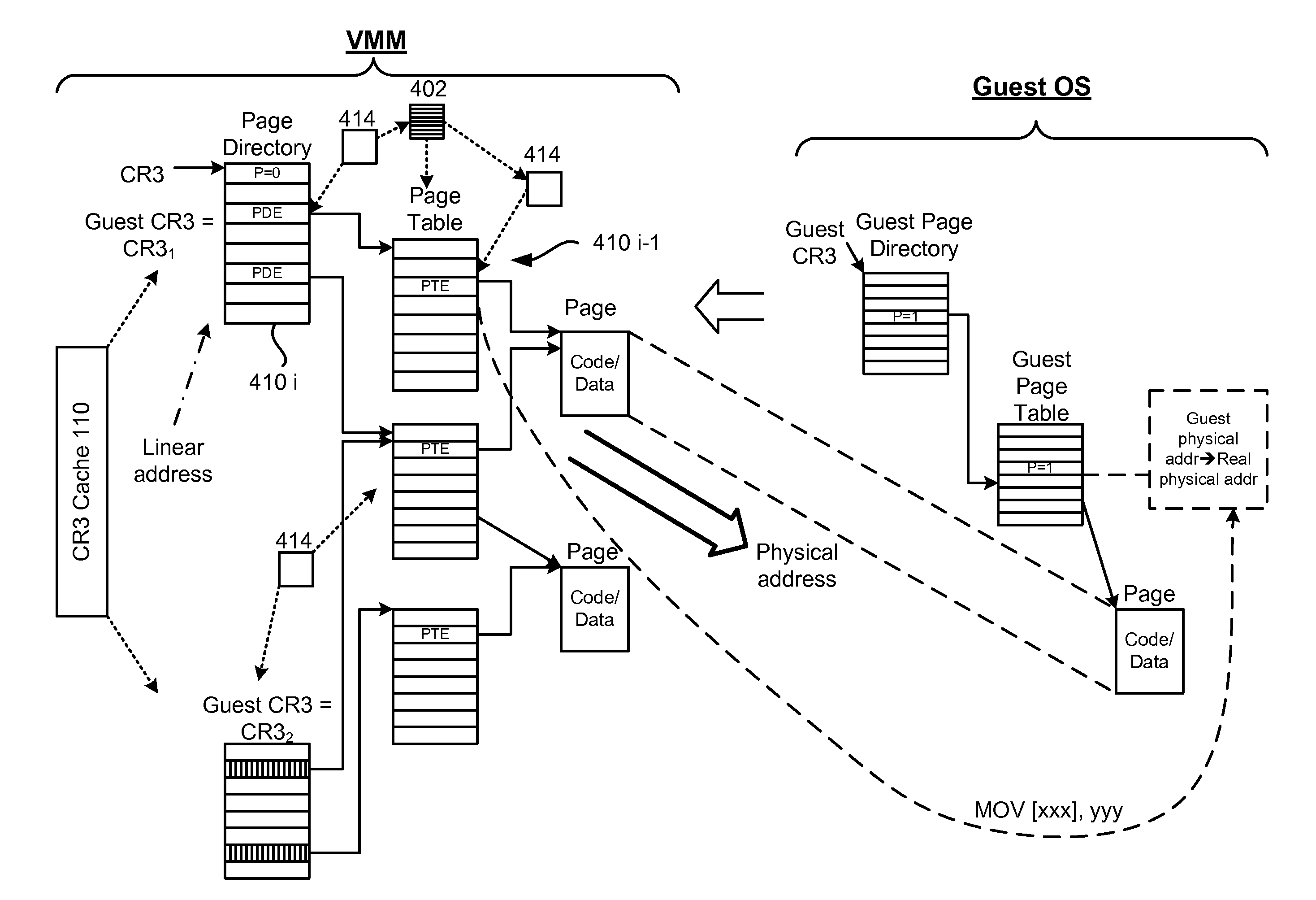
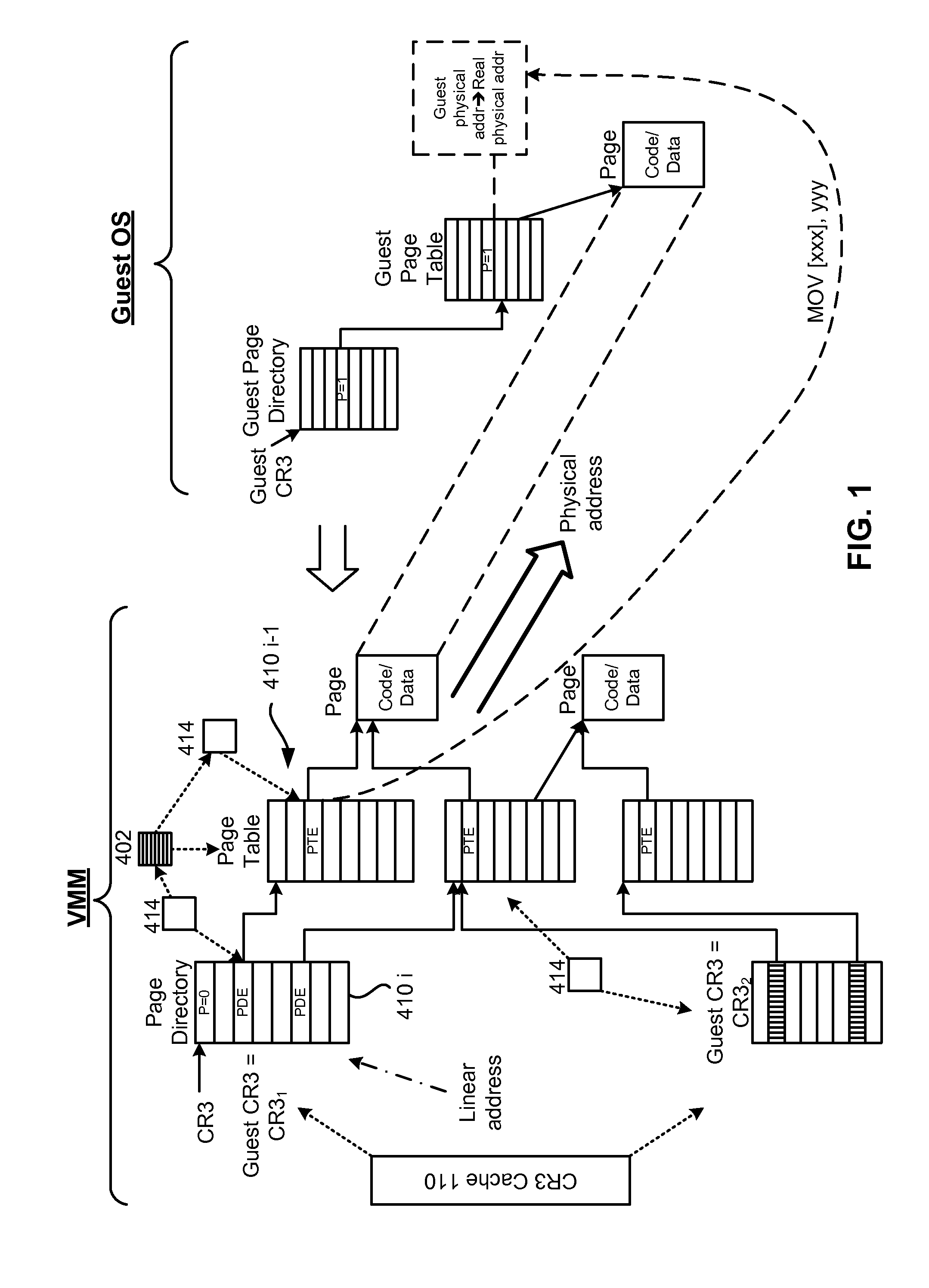
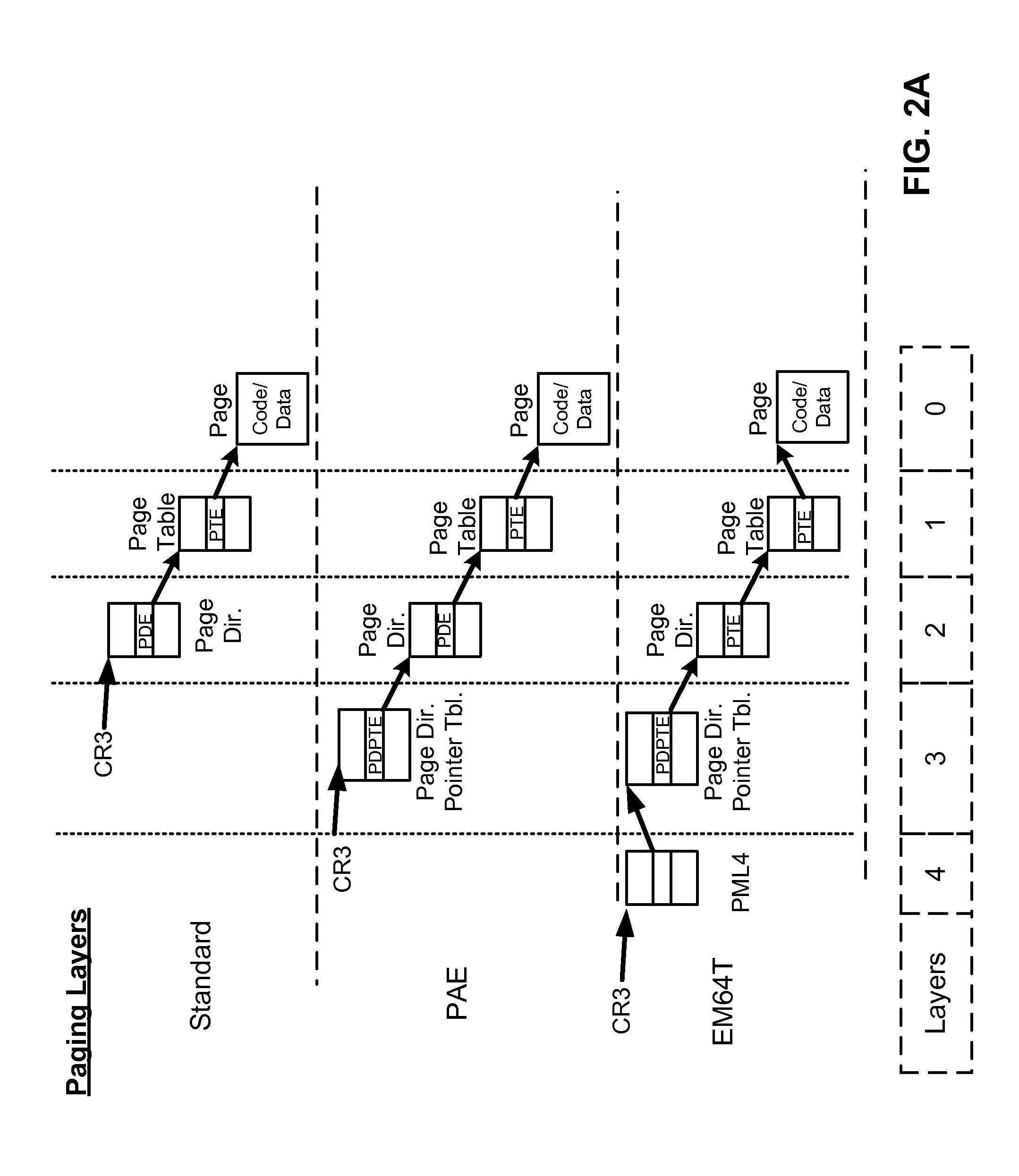
Optimization of paging cache protection in virtual environment
ActiveUS8171255B1Software simulation/interpretation/emulationMemory systemsVirtualizationParallel computing
A system, method and computer program product for virtualizing a processor include a virtualization system running on a computer system and controlling memory paging through hardware support for maintaining real paging structures. A Virtual Machine (VM) is running guest code and has at least one set of guest paging structures that correspond to guest physical pages in guest virtualized linear address space. At least some of the guest paging structures are mapped to the real paging structures. A cache of connection structures represents cached paths to the real paging structures. The mapped paging tables are protected using RW-bit. A paging cache is validated according to TLB resets. Non-active paging tree tables can be also protected at the time when they are activated. Tracking of access (A) bits and of dirty (D) bits is implemented along with synchronization of A and D bits in guest physical pages.
Owner:PARALLELS HLDG
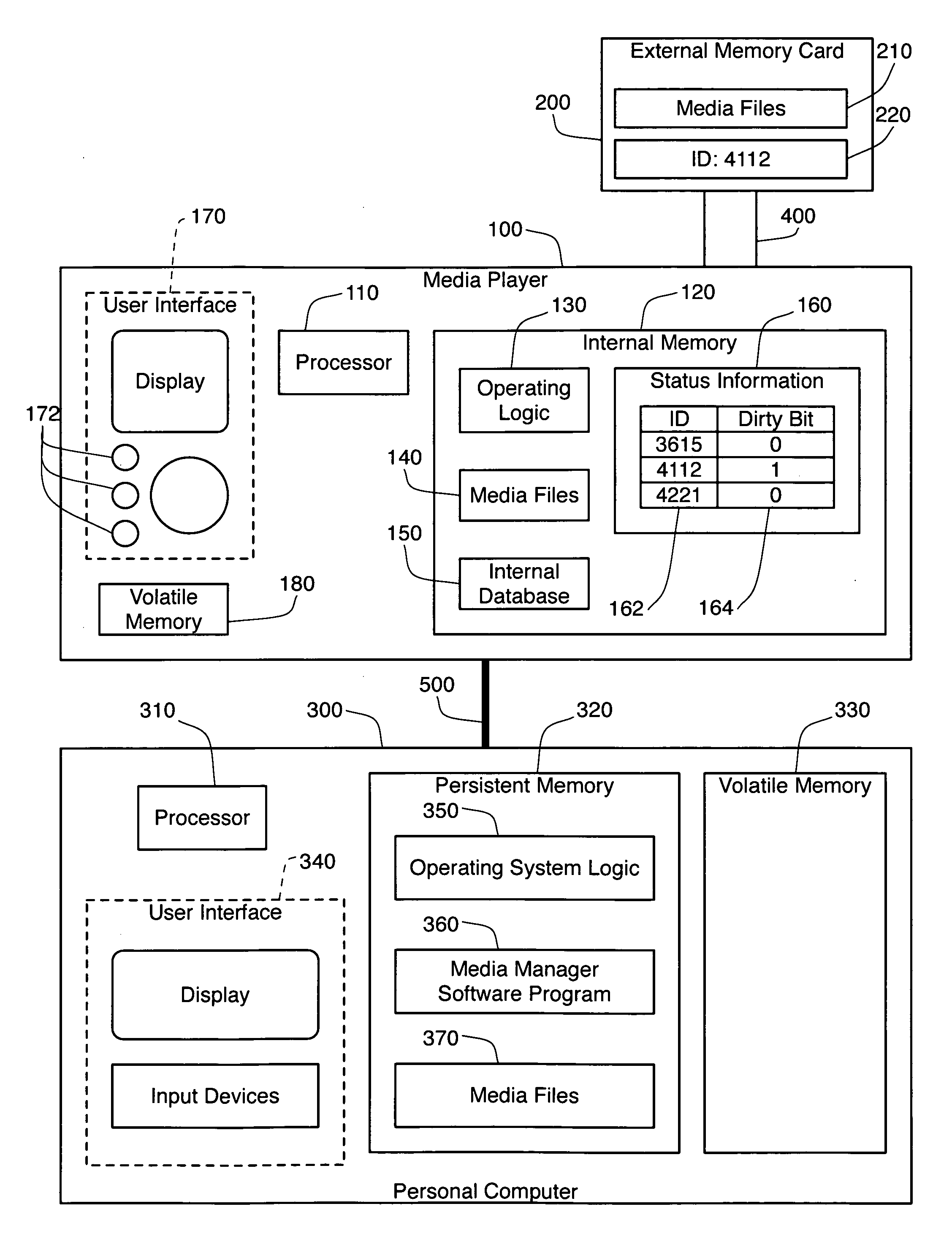
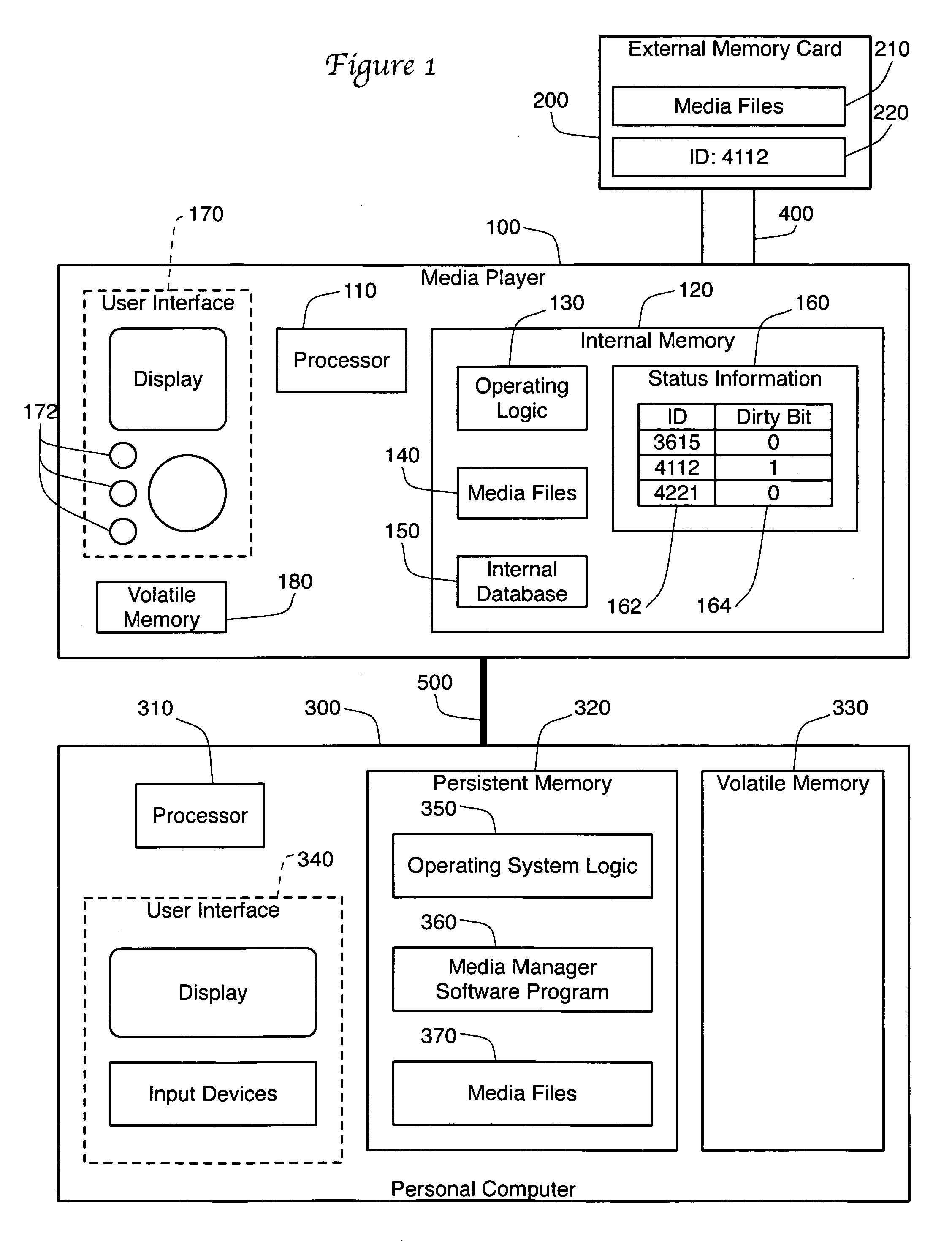
Boot in a media player with external memory
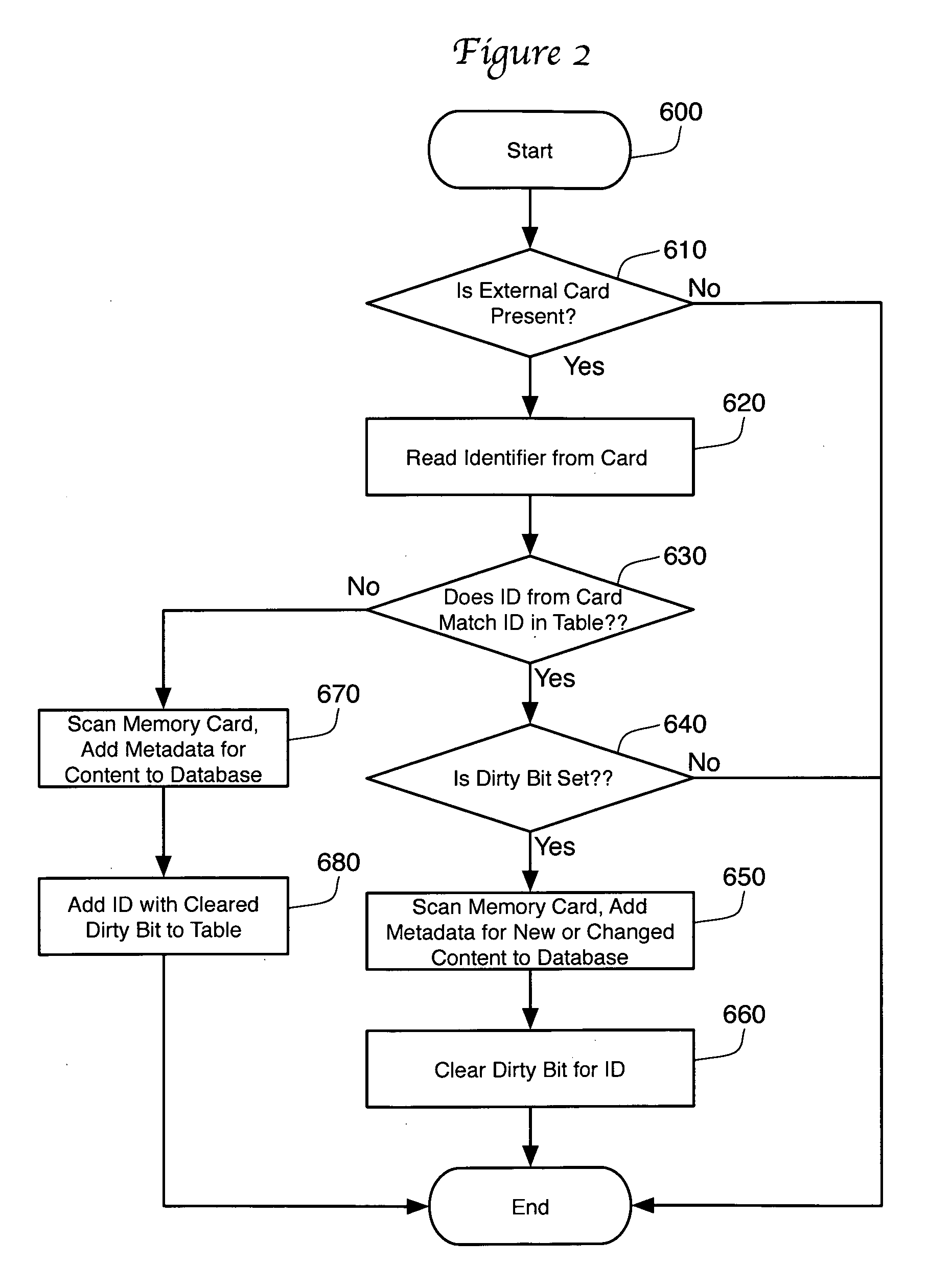
ActiveUS20080229016A1Using non-detectable carrier informationMetadata multimedia retrievalDirty bitInternal memory
A media player is presented that scans the media files stored on an external memory card in order to update the internal database of the player. Media manager software on a personal computer sets a dirty bit in the internal memory of the media player whenever the media files on the external memory card are altered. The media player checks the dirty bit on start up or when the memory card is inserted. If the dirty bit is set, the media player scans the media files on the memory card, updates its database, then clears the dirty bit. If the dirty bit is not set, the media player does not scan the memory card. The dirty bit is associated in the internal memory with an identifier for the memory card, allowing the use of multiple memory cards.
Owner:BBY SOLUTIONS
NOR-FLASH data storage method, computer device and storage medium
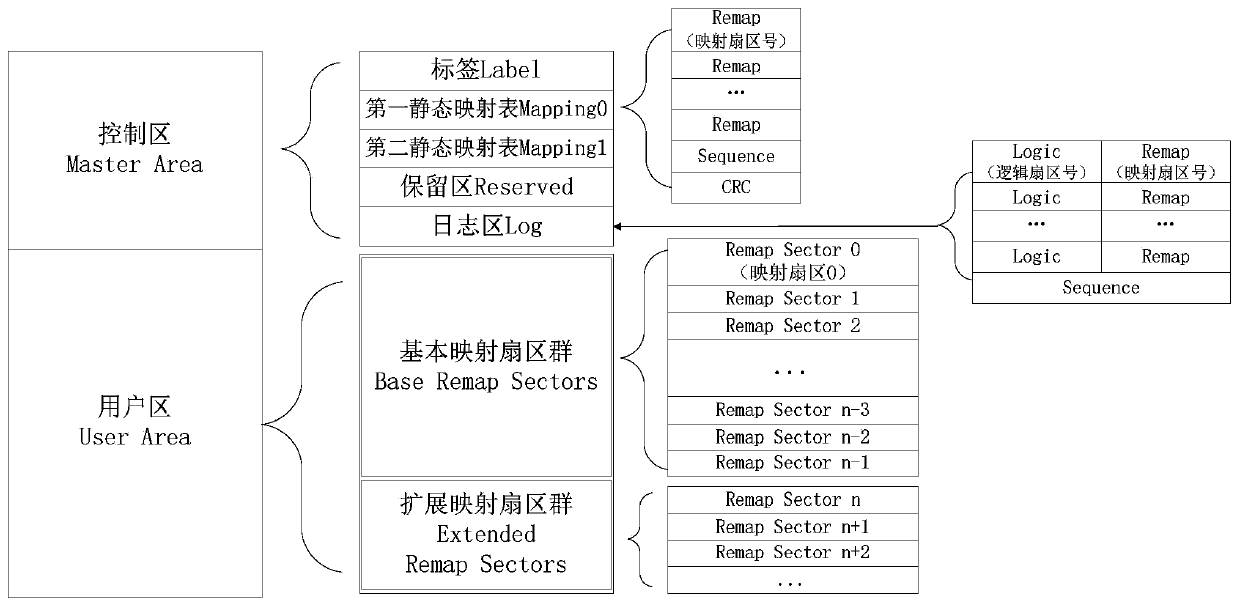
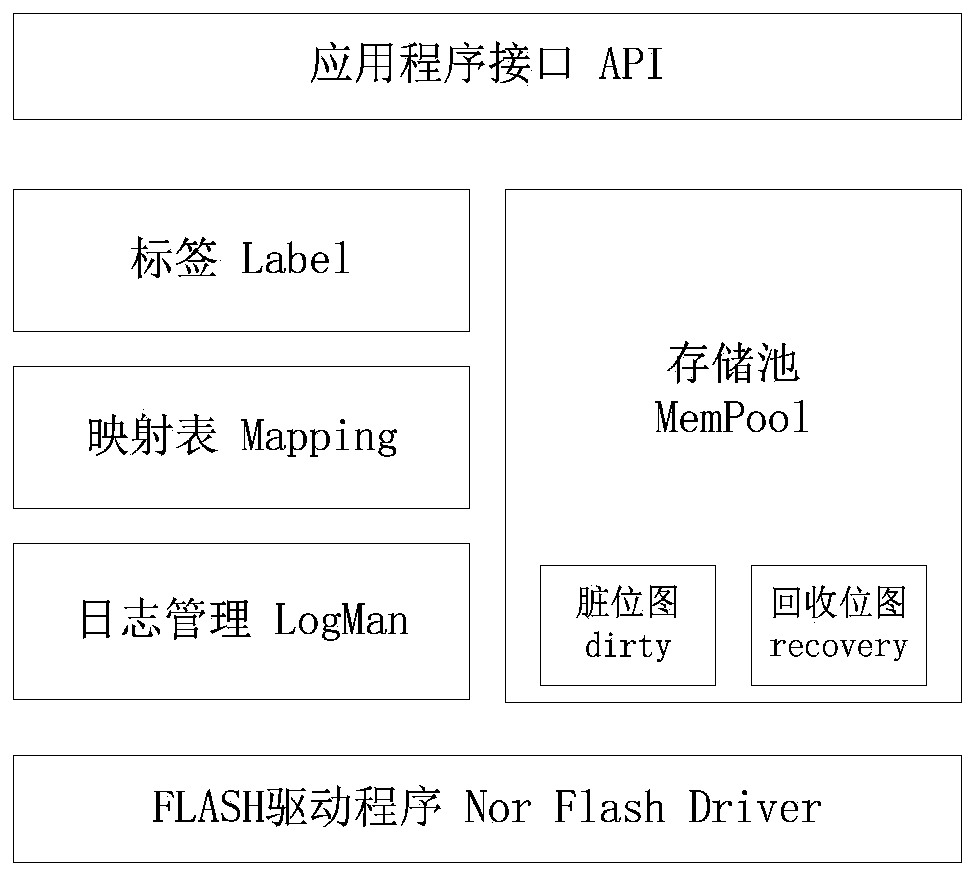
ActiveCN110175001AExtended service lifeNot lostInput/output to record carriersRedundant operation error correctionDirty bitElectricity
The invention discloses an NOR-FLASH data storage method, a computer device and a storage medium. The NOR-FLASH is divided into a control region and a user region, and the method comprises the following steps of applying for writing the sector data into an idle mapping sector from the user region according to a dirty bitmap; updating the dirty bitmap, a recovery bitmap and a dynamic mapping table;writing the mapping relation between a logical sector number and a mapping sector number into a log area, wherein if the log area is full before writing, the dynamic mapping table is backed up to thestatic mapping table, and the log area is erased. According to the NOR-FLASH data storage method, the computer device and the storage medium provided by the invention, by setting the dirty bitmap, the recovery bitmap and the dynamic mapping table, the sector of the NOR-FLASH is planned and managed, the limited abrasion uniformity of the sector in the NOR-FLASH is realized, and the service life ofthe NOR-FLASH can be prolonged; by setting the log records to record the data writing process and utilizing the static mapping table to back up the data of the dynamic mapping table, the data cannotbe lost when power failure occurs during data writing.
Owner:牧星机器人(江苏)有限公司
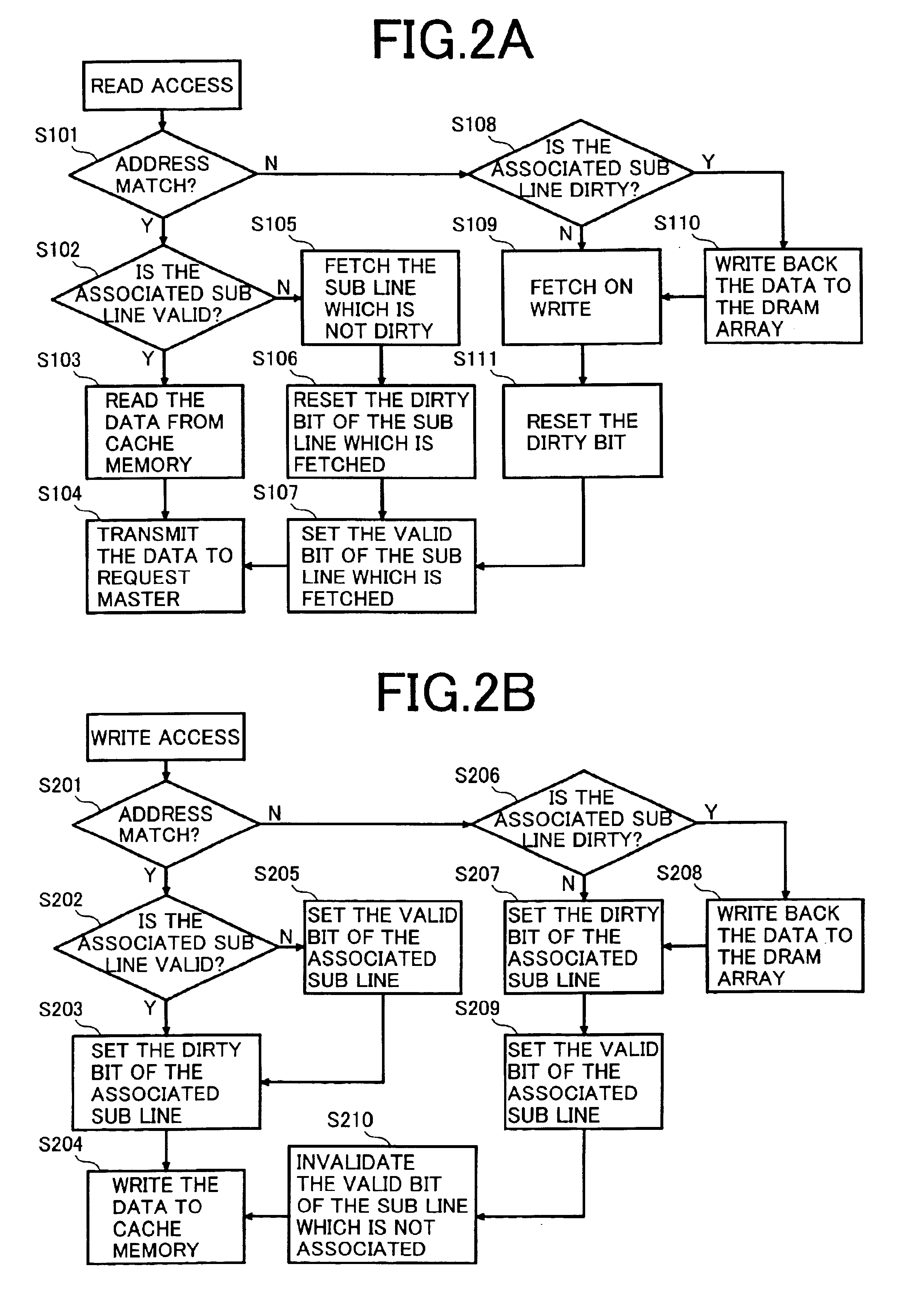
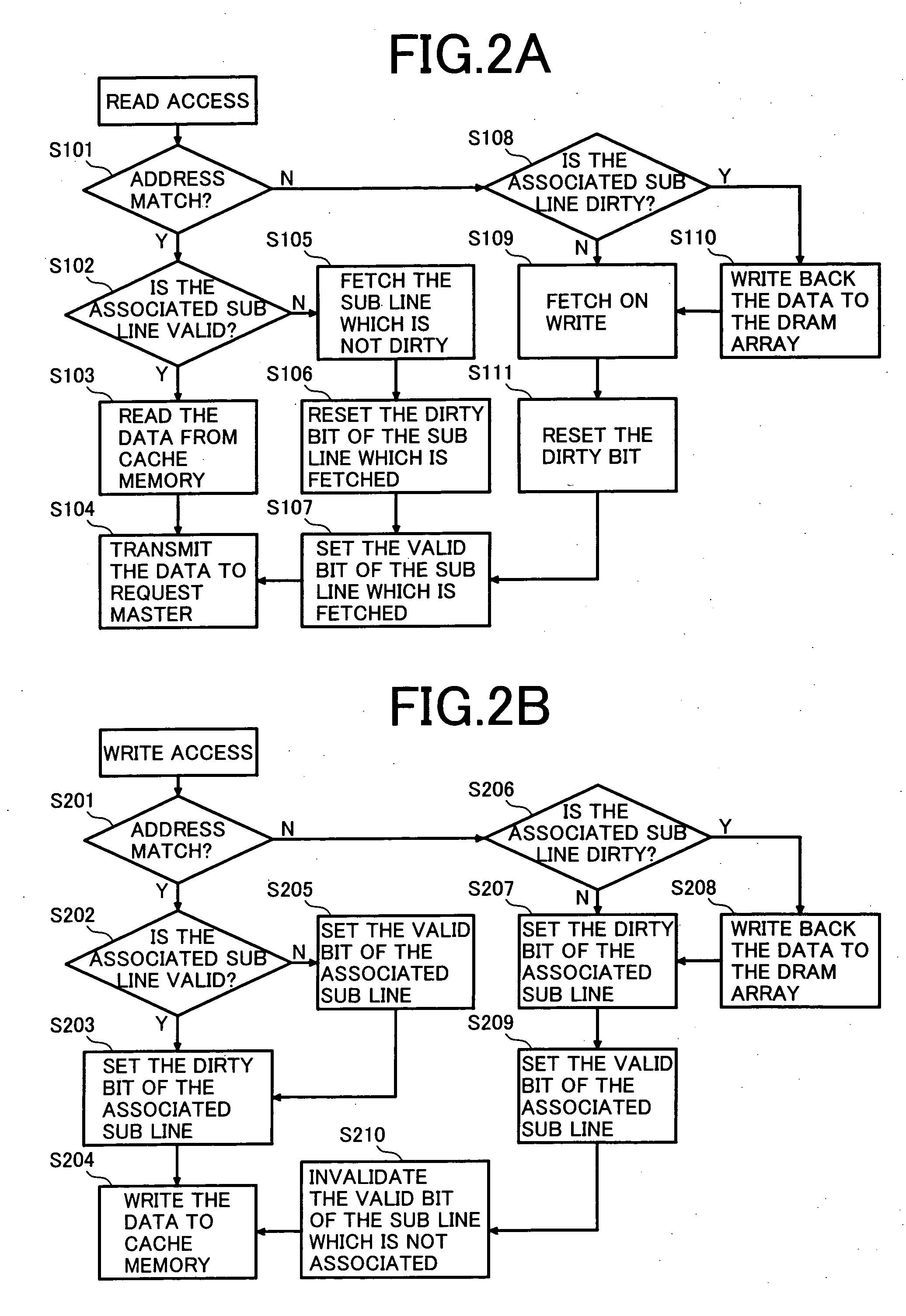
Cache memory control in electronic device
InactiveUS20150261683A1Increase write service efficiencyLower latencyMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDirty bitBiological activation
Disclosed are a method and apparatus for controlling a cache memory in an electronic device. The apparatus includes a cache memory having cache lines, each of which includes tag information and at least two sub-lines. Each of the at least two sub-lines including a valid bit and a dirty bit. A control unit may analyze a valid bit of a sub-line corresponding to an address tag of data when a request for writing the data is sensed, determine based on activation or deactivation of the valid bit whether a cache hit or a cache miss occurs, and perform a control operation for allocating a sub-line according to a size of the requested data and write the data when the cache hit occurs.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
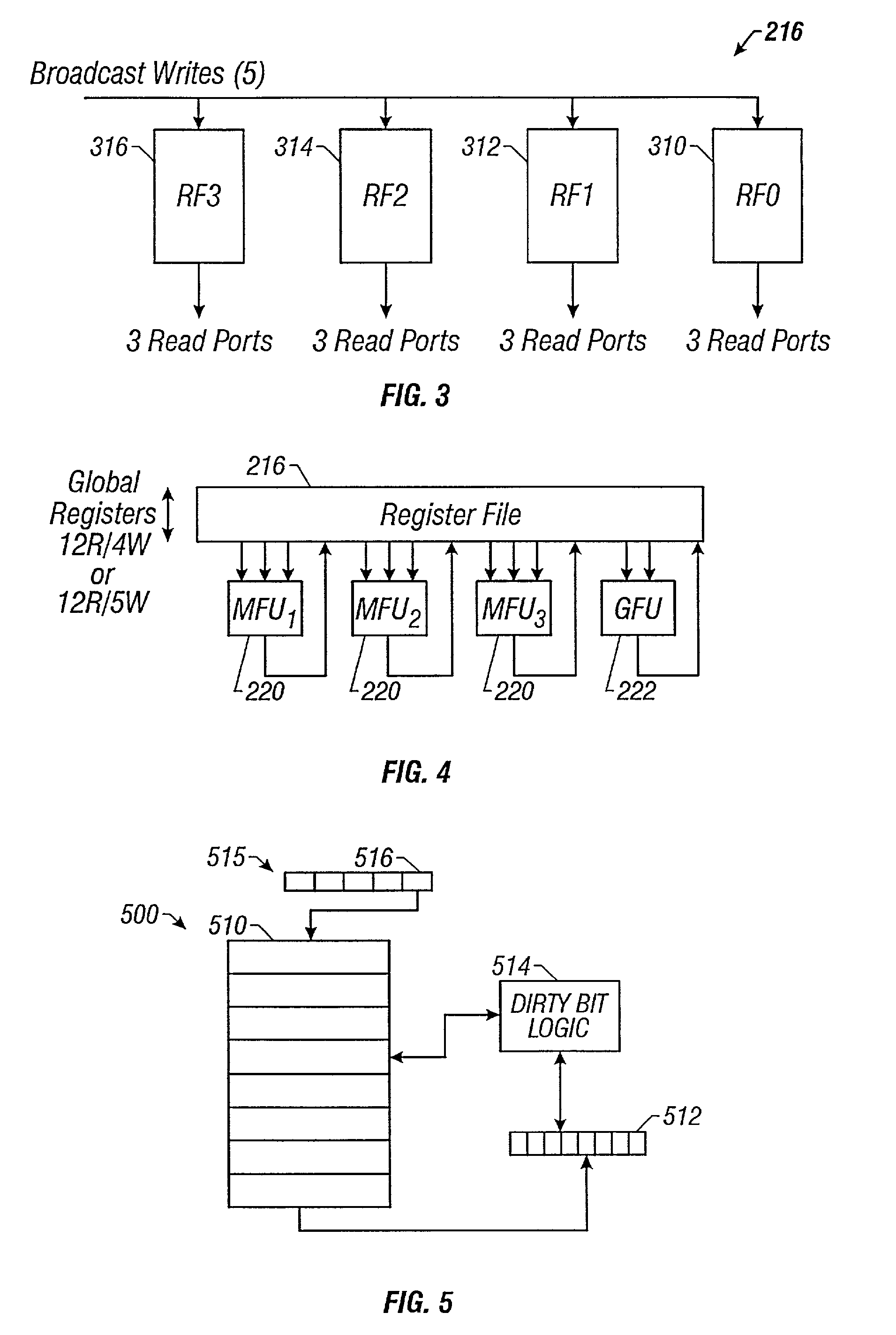
Efficient handling of a large register file for context switching and function calls and returns
A processor including a large register file utilizes a dirty bit storage coupled to the register file and a dirty bit logic that controls resetting of the dirty bit storage. The dirty bit logic determines whether a register or group of registers in the register file has been written since the process was loaded or the context was last restored and, if written generates a value in the dirty bit storage that designates the written condition of the register or group of registers. When the context is next saved, the dirty bit logic saves a particular register or group of registers when the dirty bit storage indicates that a register or group of registers was written. If the register or group of registers was not written, the context is switched without saving the register or group of registers. The dirty bit storage is initialized when a process is loaded or the context changes.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Detecting execution of modified executable code
A technique for detecting malware uses hardware capabilities of the processing element of a programmable device to detect modification of executable code during execution. By monitoring a dirty bit in page tables, pages that have been modified can be detected, allowing analysis of those pages during execution. An indication may then be passed to an anti-malware software to analyze the executable further.
Owner:MCAFEE LLC
Non-blocking data transfer via memory cache manipulation
InactiveUS8495299B2Improve efficiencyMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsDirty bitParallel computing
A cache controller in a computer system is configured to manage a cache. The cache controller receives commands from a processor. In response, a cache mapping maintaining information for each block in the cache is modified. The cache mapping may include an address, a dirty bit, a zero bit, and a priority for each cache block. The address indicates an address in main memory for which the cache block caches data. The dirty bit indicates whether the data in the cache block is consistent with data in main memory at the address. The zero bit indicates whether data at the address should be read as a default value, and the priority specifies a priority for evicting the cache block. By manipulating this mapping information, commands such as move, copy swap, zero, deprioritize and deactivate may be implemented.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and Method for Managing Memory
InactiveUS20090006505A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDirty bitDatabase
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Cache memory, computer system and memory access method
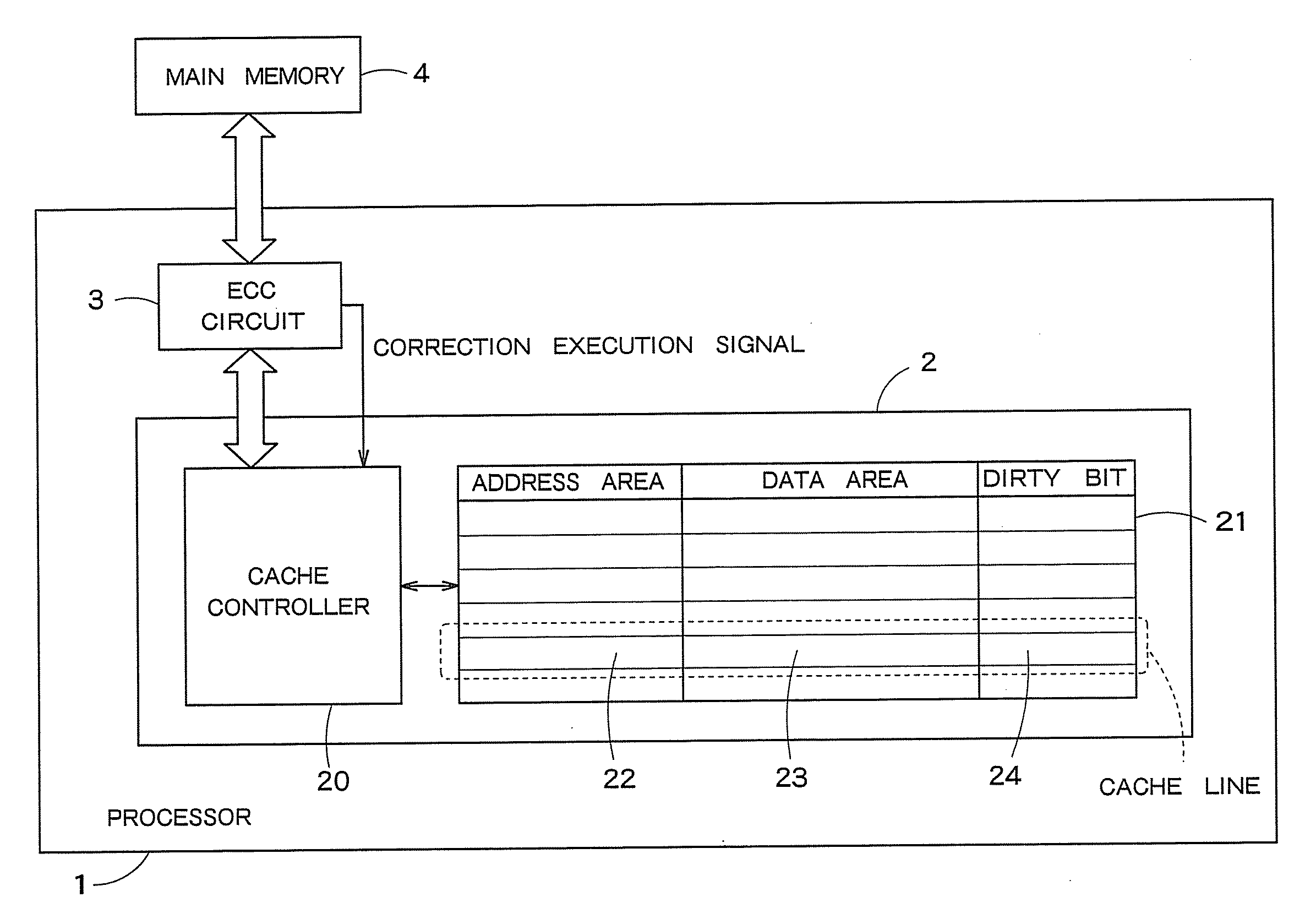
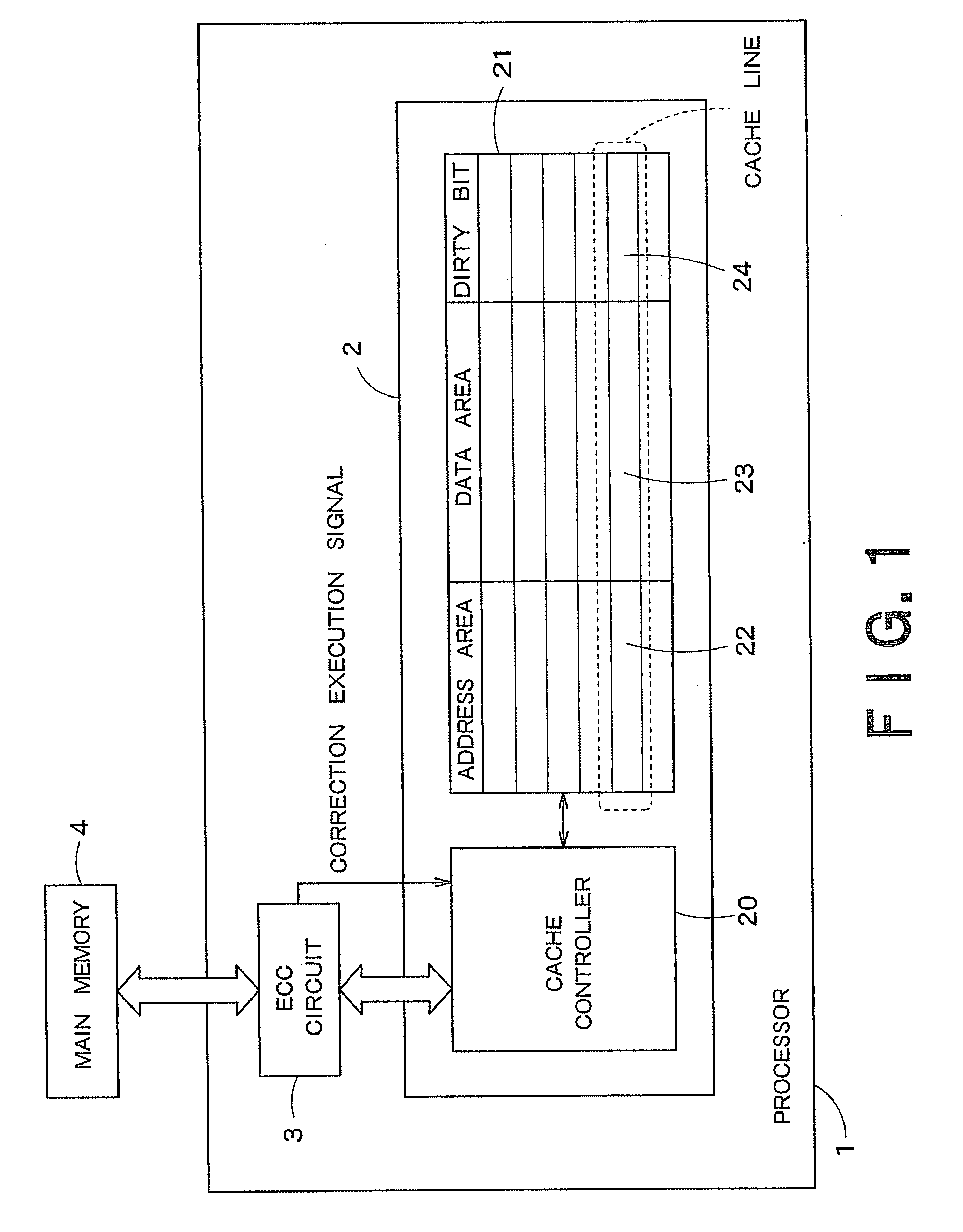
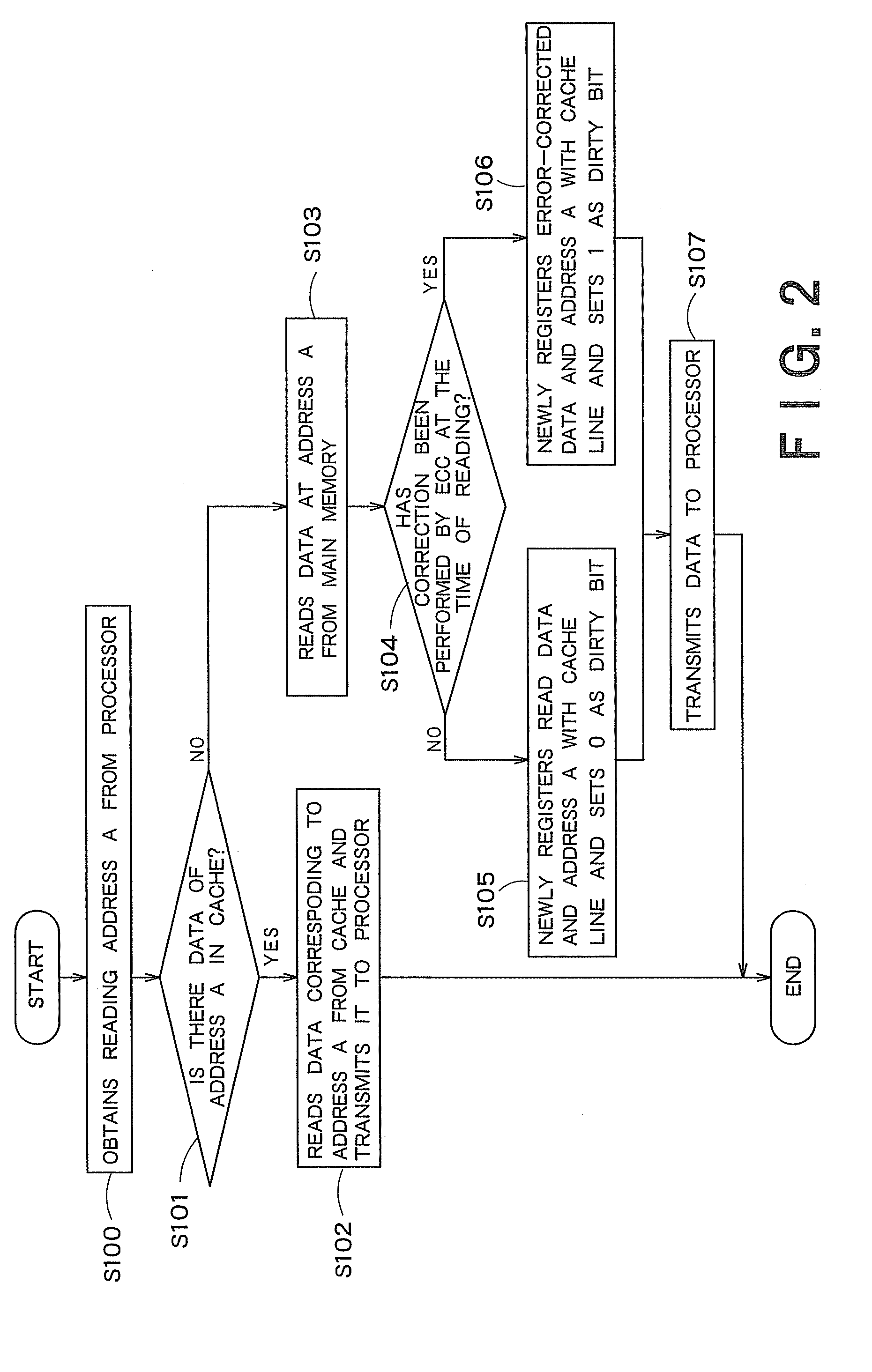
A cache memory has a data holding unit having multiple cache lines each of which includes an address area, a data area and a dirty bit, and a controller which is given read data and a correction execution signal indicating whether or not error correction has been performed for the read data, the read data has been read from a memory storing error-correction-coded data, which also stores address information corresponding to the read data into the address area of any one of the multiple cache lines, stores the read data into the data area, and sets a predetermine value as the dirty bit on the basis of the correction execution signal.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method and system for recording access situation of hybrid memory
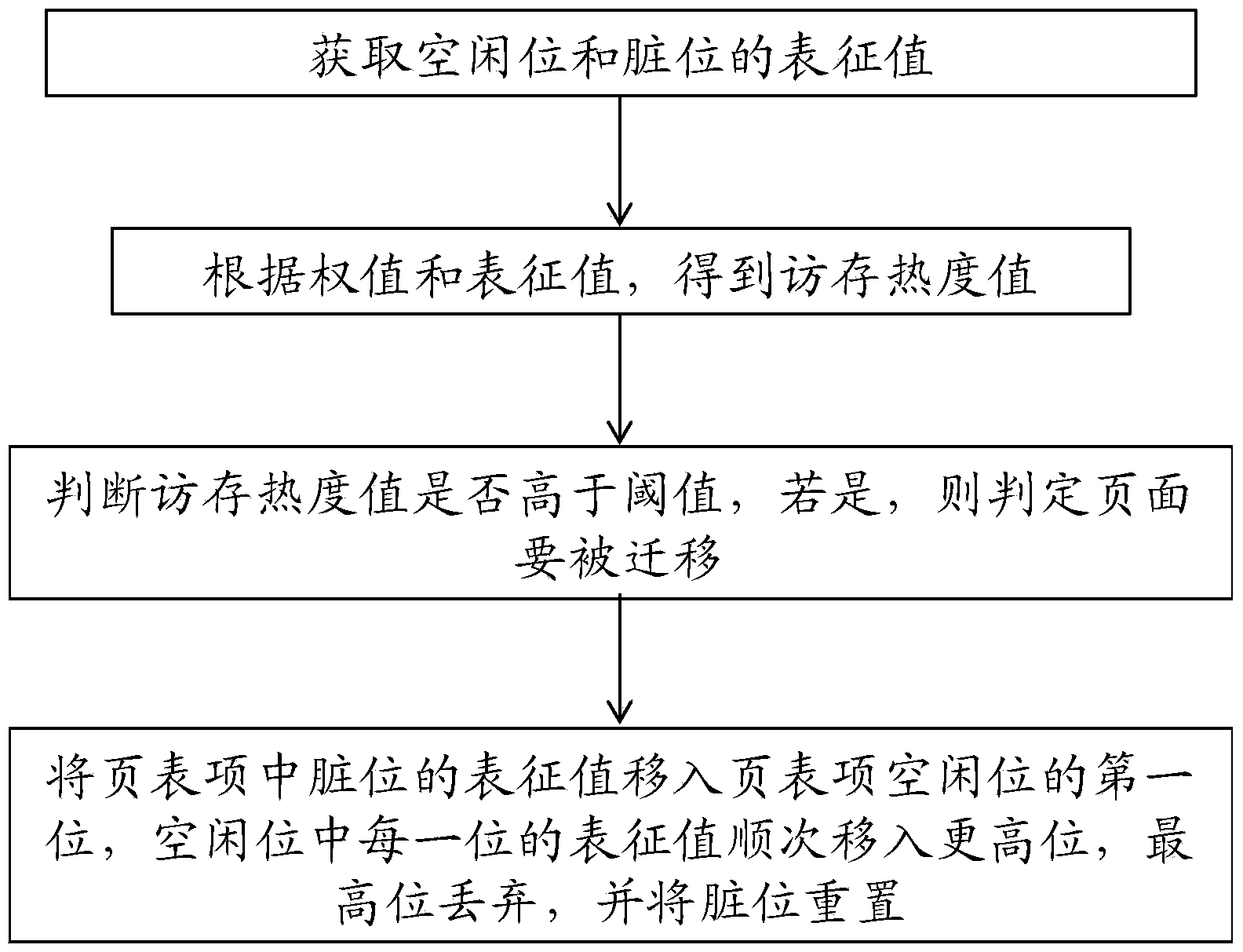
The invention provides a method for recording the access situation of a hybrid memory. The method includes the steps that the representation value of a vacancy bit in a page table entry and the representation value of the dirty bit in a page table entry are acquired; the write-back step is executed, wherein the representation value of the dirty bit in the page table entry is moved to a first bit of the vacancy bit of the page table entry, the representation values of all bits in the vacancy bit are sequentially moved to higher bits, and the dirty bit is reset. The use situation of a page is recorded through the vacancy bit and the dirty bit in the page table entry together, by the utilization of the characteristics that when the page is written in, the dirty bit is placed on the first bit and the vacancy bit is originally not used, additional special memory access statistical work is not needed, storage space does not need to be additionally developed for storing statistical results, historical access information of the page table entry can be acquired when the page table entry is traversed, and cost of system time and space is lowered.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Semiconductor device with multi-bank DRAM and cache memory
InactiveUS20050111284A1Eliminate operationAvoid accessMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDirty bitMemory bank
To provide means that can hide refresh operations even when the data width of a cache line differs from that of the external data bus in a memory that uses a cache memory and a DRAM consisting of a plurality of banks. A semiconductor device consisting of a plurality of memory banks BANK0 to BANK127, each consisting of a plurality of memory cells, as well as a cache memory CACHEMEM used to retain information read from the plurality of memory banks. The cache memory CACHEMEM consists of a plurality of entries, each having a data memory DATAMEM and a tag memory TAGMEM. The data memory DATAMEM consists of a plurality of sub lines DATA0 to DATA3 and the tag memory TAGMEM Consists of a plurality of valid bits V0 to V3 and a plurality of dirty bits D0 to D3. It is possible to realize a memory with excellent operability, causing no refresh operation to delay external accesses. In other words, it is possible to realize a memory compatible with an SRAM in which refresh operations are hidden from external.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Method for improved processing of expression-based data
ActiveUS20070027890A1Improve data integritySave a lot of spaceDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsDirty bitTerm memory
Expression-based data may comprise data that is processed by a validation expression for example. After a validation expression is created it may then be performed with respect to one or more data values or data records. A validation expression returns a Boolean result that signifies a success or failure result. A validation expression can define complex intra-record tests and inter-record tests with unlimited complexity. In order to improve processing of validations, the system uses virtual data known as calculation fields. Calculation fields are stored in memory at runtime and not in a database thereby eliminating the necessity of selecting and updating records in the database. A dirty bit identifying fields and attributes that need to be calculated based on a dependent data may be used to defer calculation to a later time when the calculation field is displayed or a sort operation occurs for example.
Owner:SAP AG
Cache system
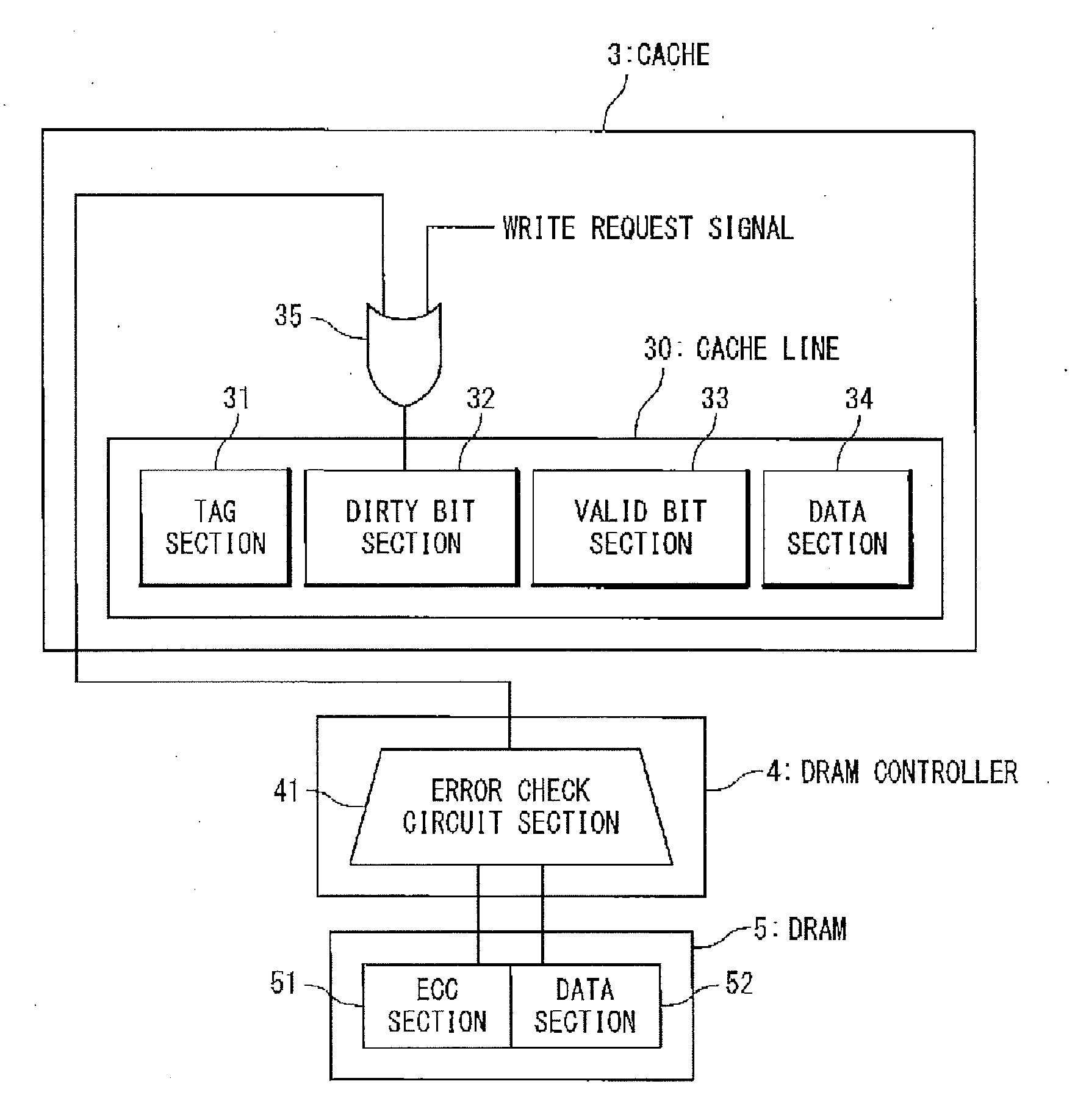
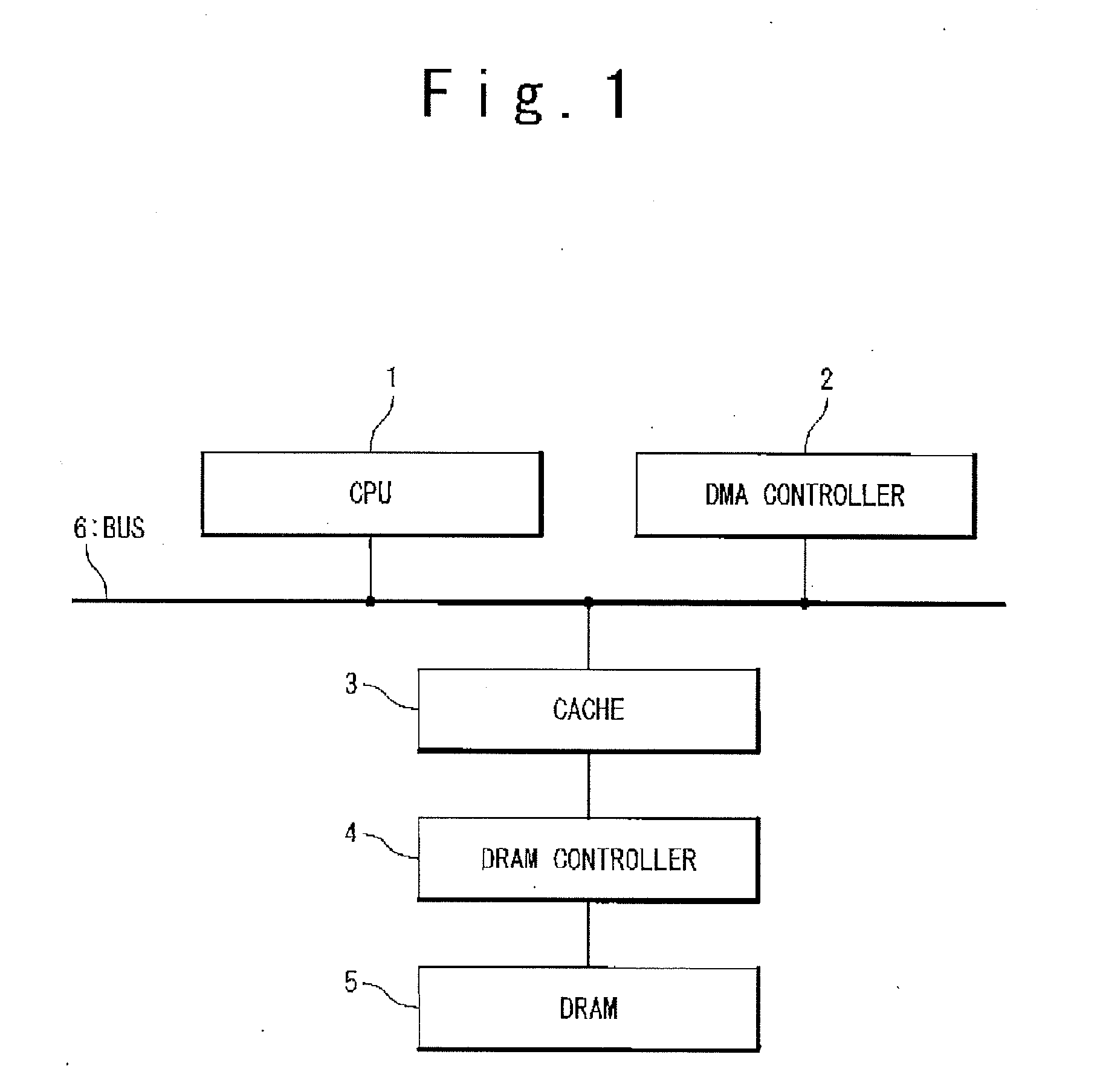
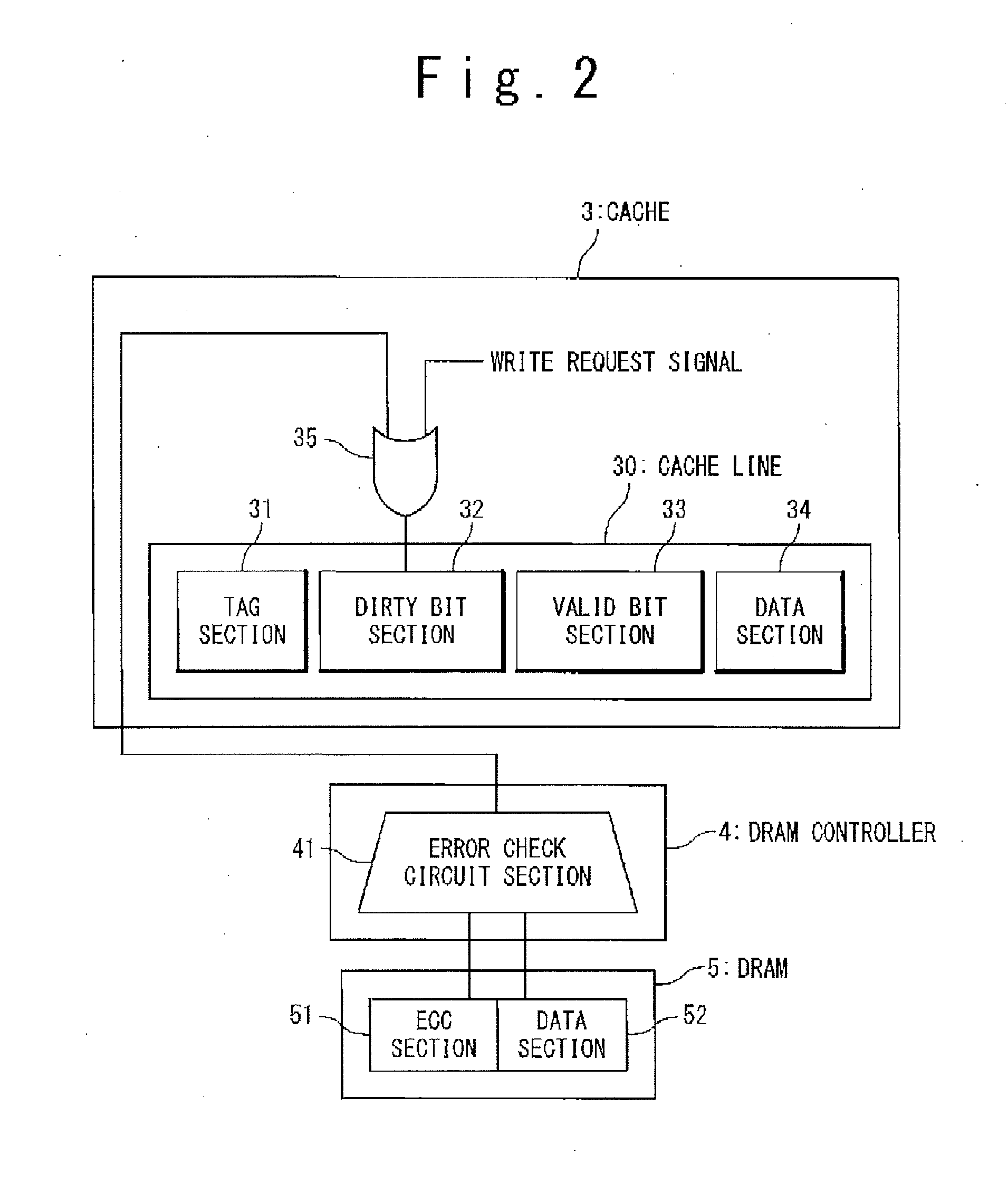
A write-back cache system includes: a dirty bit section configured to store a dirty indication data indicating that cache data is in a dirty state; and an OR calculation circuit connected with a front-stage to the dirty bit section. The OR calculation circuit includes: a first input node configured to receive a write request signal indicating a write request of a cache data; a second input node configured to receive a correctable error determination signal of the cache data indicating that a correctable error is present in the cache data; and an output node configured to output a signal such that the dirty indication data is stored in the dirty bit section, when receiving at least, one of the write request signal and the correctable error determination signal.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
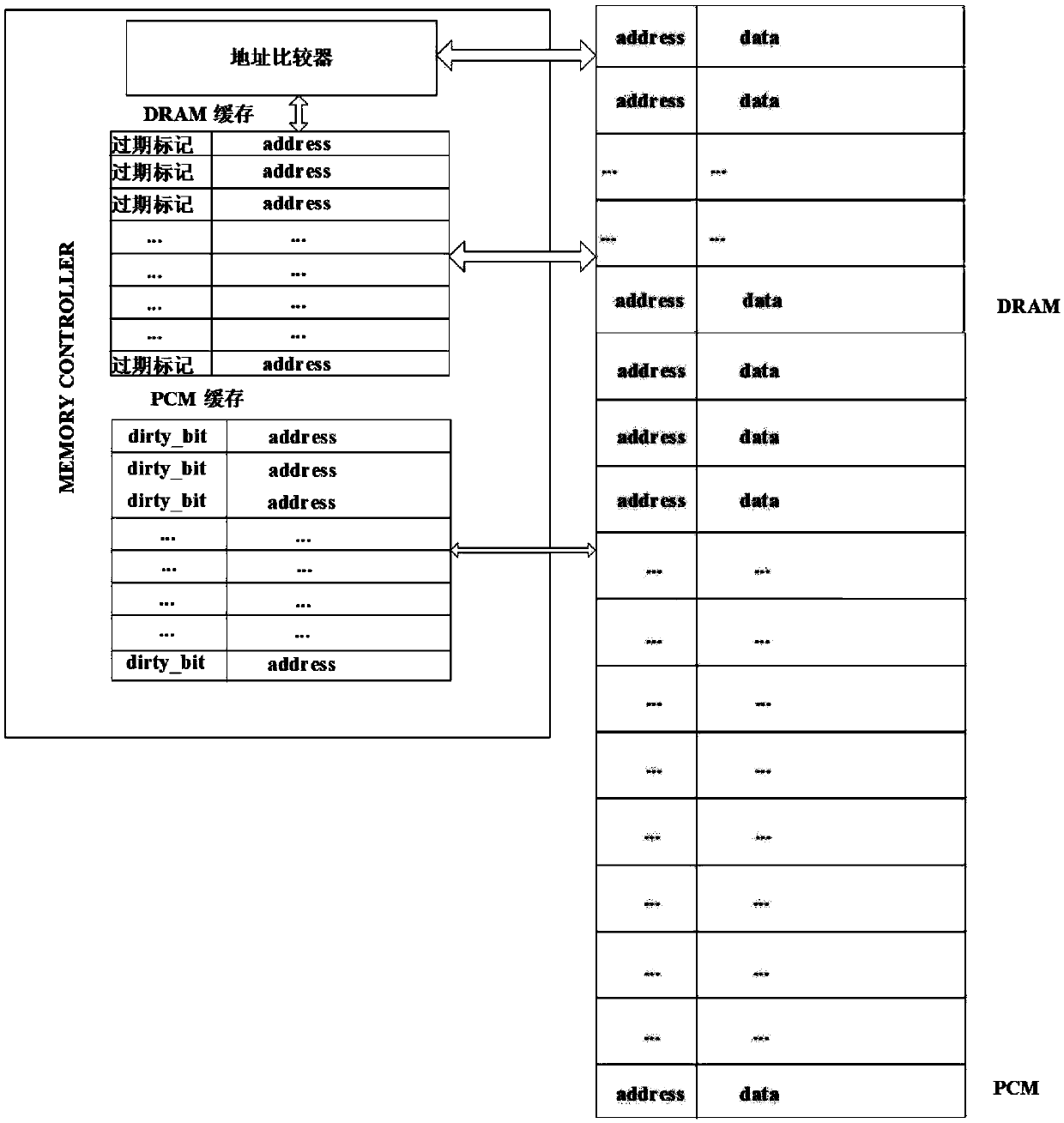
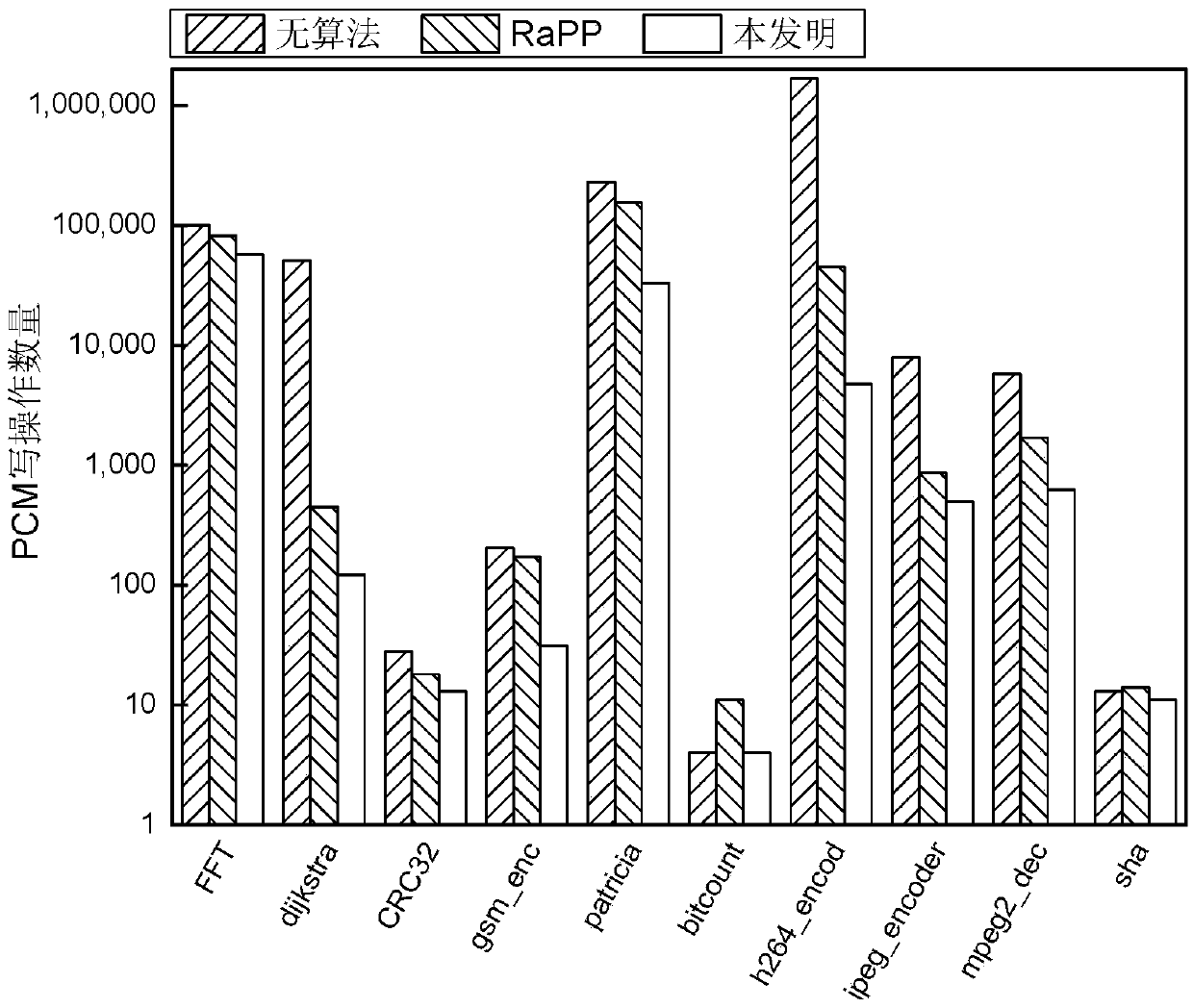
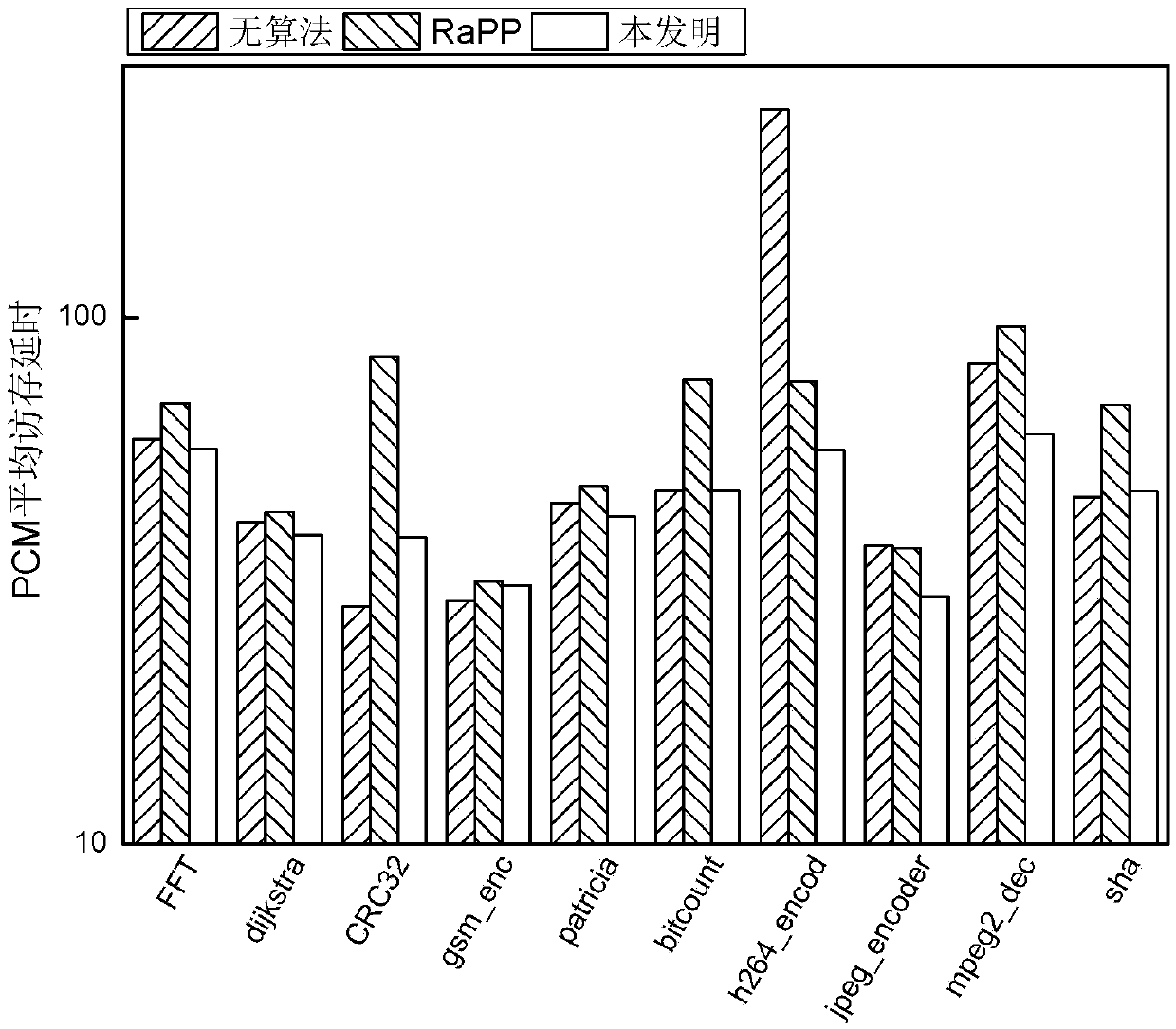
A hybrid memory page migration method for an image processing type load
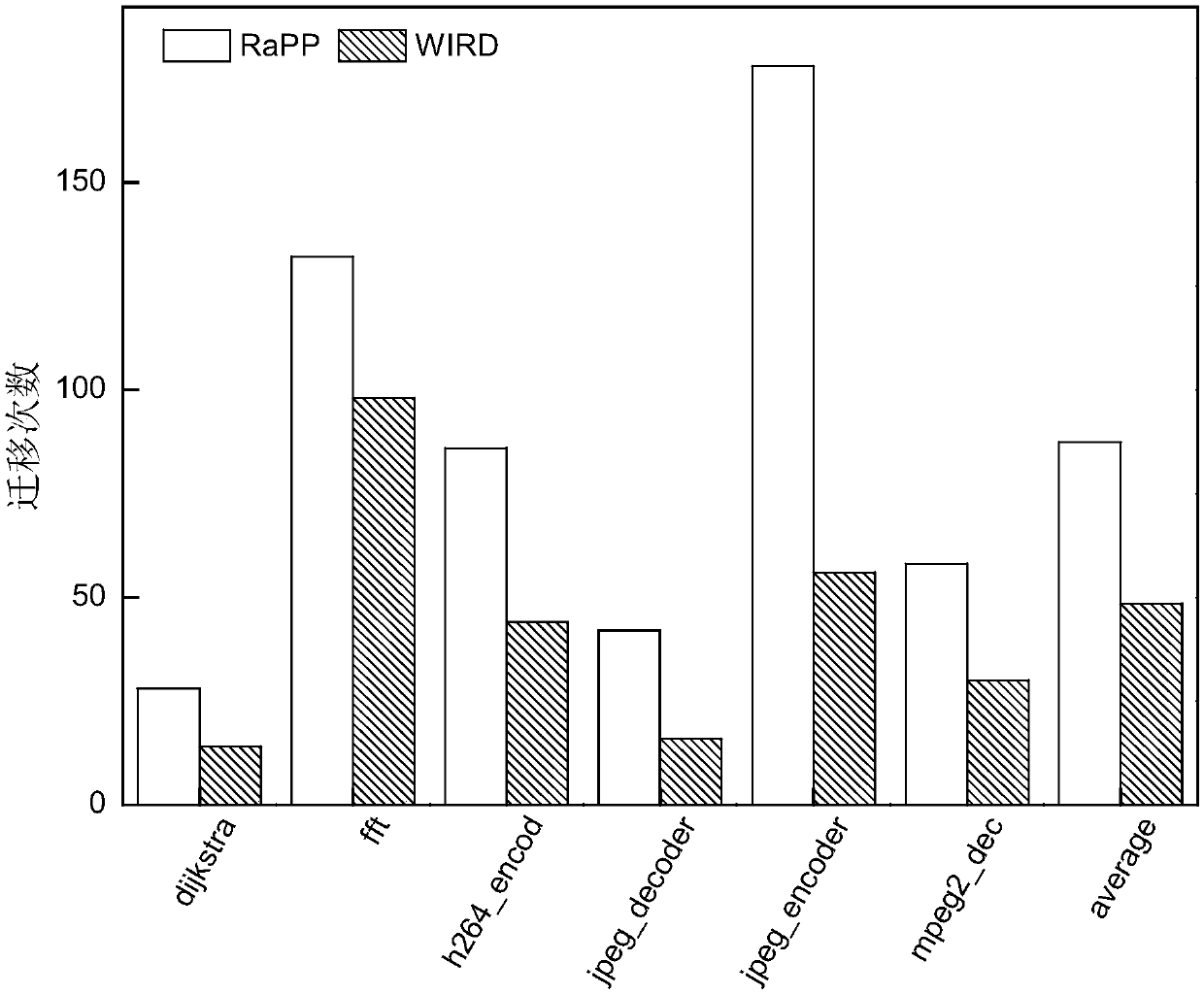
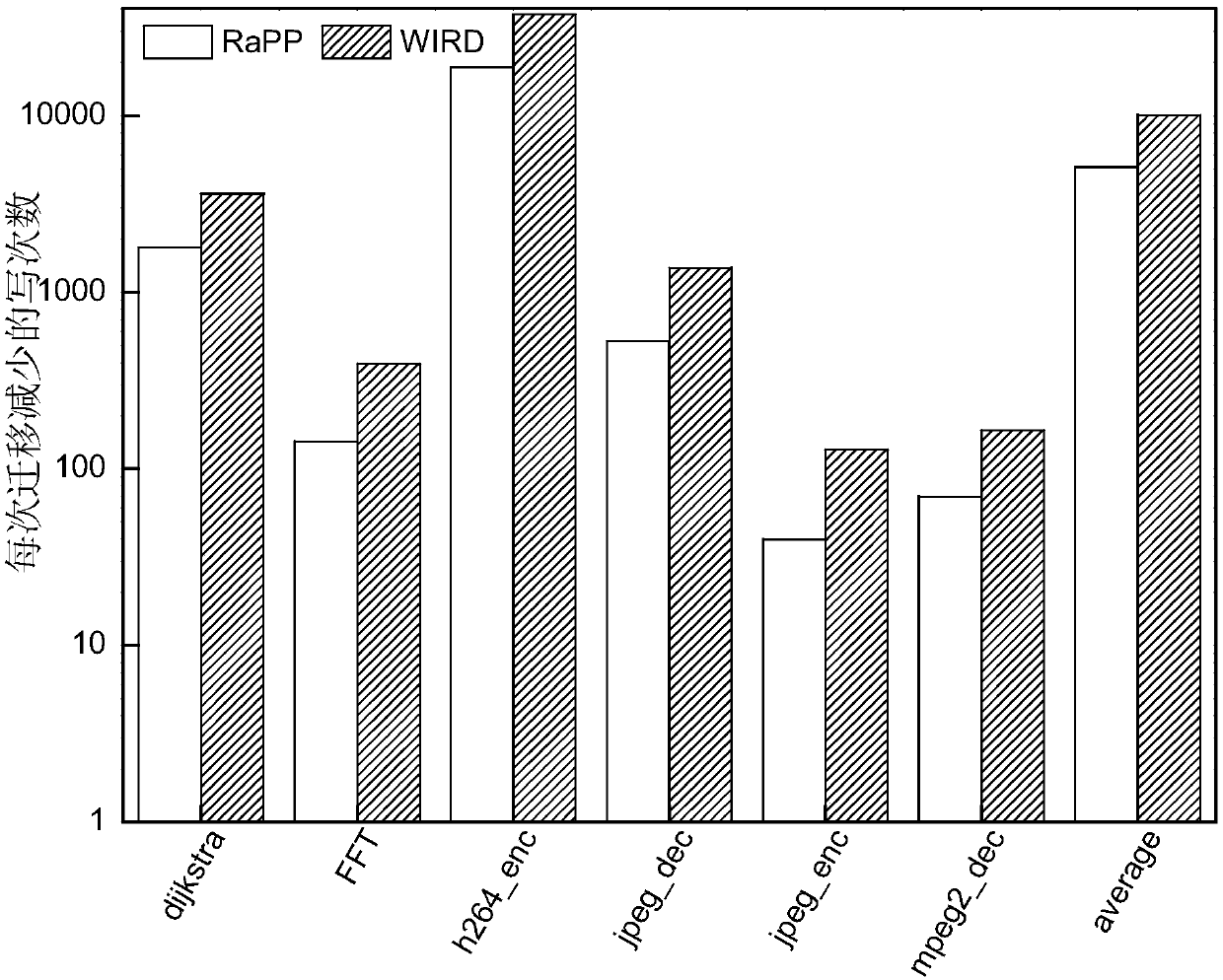
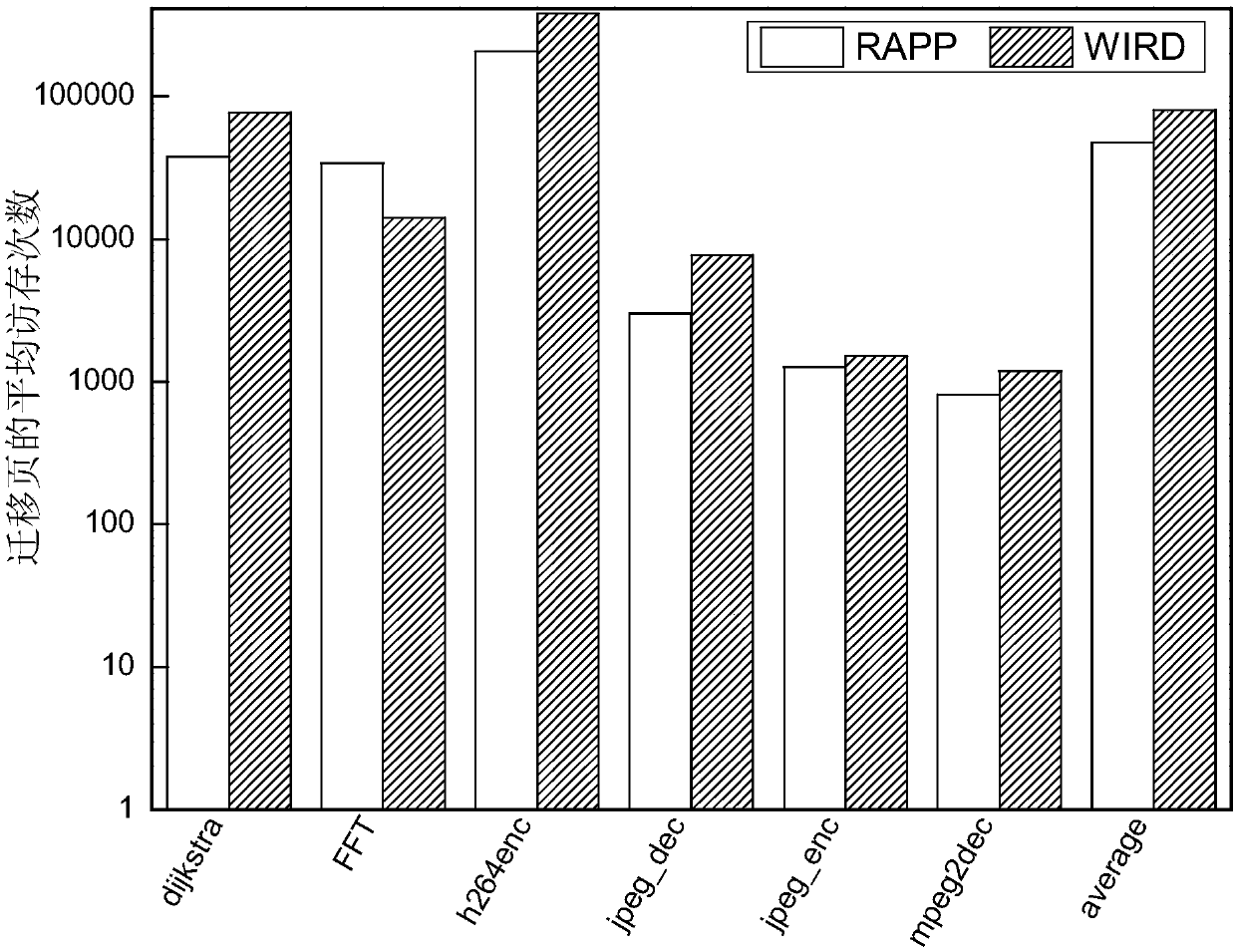
ActiveCN109558093AReduce the number of write operationsExtended service lifeInput/output to record carriersDirty bitImaging processing
The invention discloses a hybrid memory page migration method for an image processing type load, and relates to a hybrid memory page migration method. The invention aims to solve the problems of shortservice life and damaged performance of the existing hybrid memory. And at the moment t, when a write operation occurs in the PCM page and the number of times of the write operation of the page is greater than or equal to n and the dirty bit of the page is 1, searching for a replacement page in a DRAM or a DRAM cache, starting migration, and requesting a counter to add 1. Requesting the counter to restart counting every integer multiple of the memory reference distance, and setting all dirty bits of the page in the PCM cache to be zero. And then enabling t to be equal to t + 1, and executingthe above steps again. The method is applied to the field of hybrid memory page migration of image processing type loads.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Hot writing page prediction method based on memory access
ActiveCN109656482AReduce the number of write operationsExtended service lifeInput/output to record carriersDirty bitDram cache
The invention relates to a hot writing page prediction method based on memory access, in particular to a hot writing page prediction method based on memory access. The invention aims to solve the problems of short service life and damaged performance of the existing hybrid memory. According to the invention, the PCM cache and the DRAM cache are set; wherein the PCM access memory is used for storing a written PCM page; wherein the DRAM cache is used for storing an accessed DRAM page and time t, and when a write operation occurs in the PCM page, the page is in the PCM cache and the dirty position of the page is 1, a replacement page is searched in the DRAM or the DRAM cache, migration is started, and a counter is requested to add 1. Requesting the counter to restart counting every integer multiple of the memory reference distance, and setting all dirty bits of the page in the PCM cache to be zero. Then, t is made to be equal to t + 1, and the steps are executed again; The method is applied to the field of page write heat prediction.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
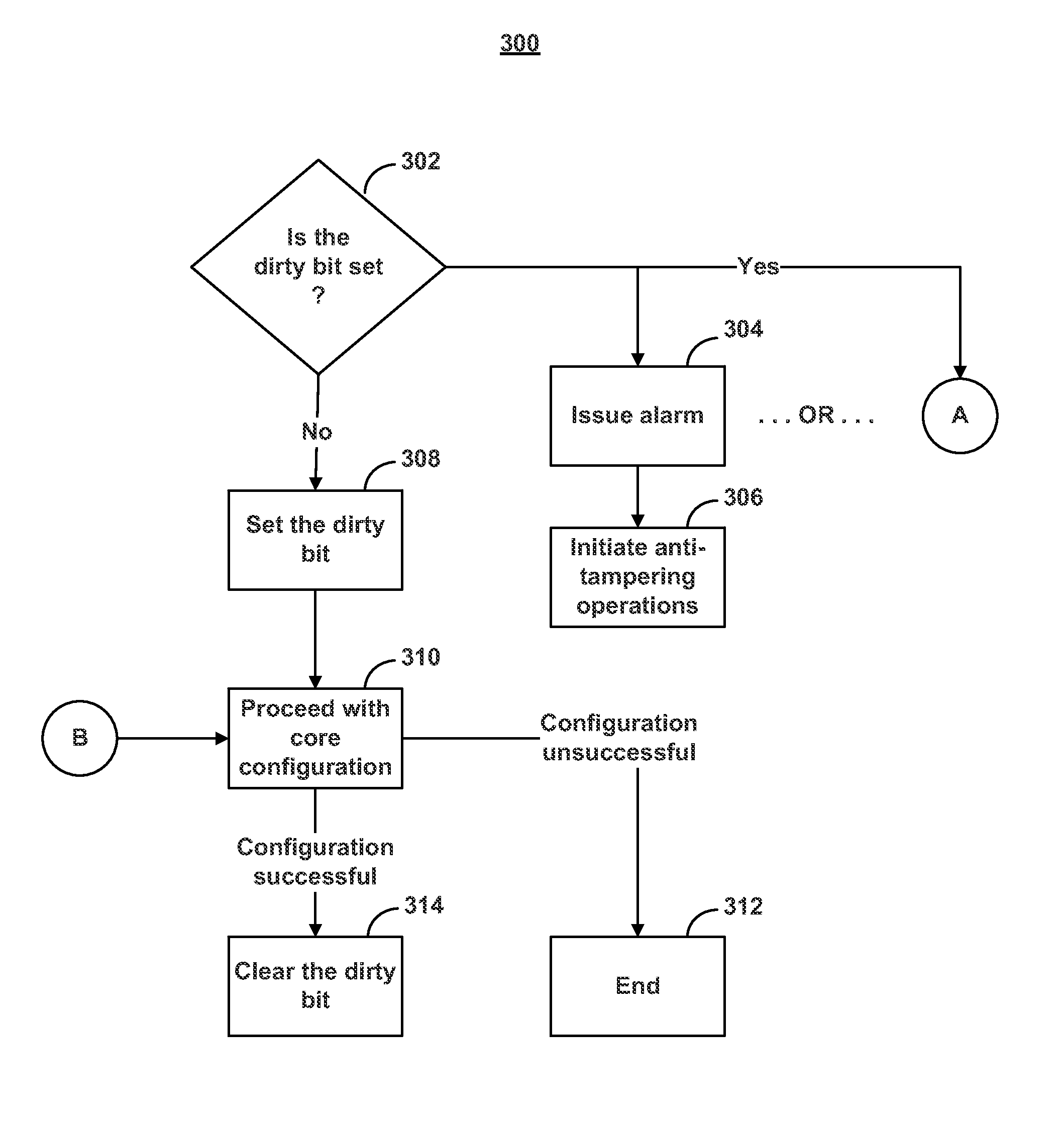
Systems and methods for detecting and mitigating programmable logic device tampering
ActiveUS8719957B2Volume/mass flow measurementUser identity/authority verificationDirty bitProgrammable logic device
Systems and methods are disclosed for preventing tampering of a programmable integrated circuit device. Generally, programmable devices, such as FPGAs, have two stages of operation; a configuration stage and a user mode stage. To prevent tampering and / or reverse engineering of a programmable device, various anti-tampering techniques may be employed during either stage of operation to disable the device and / or erase sensitive information stored on the device once tampering is suspected. One type of tampering involves bombarding the device with a number of false configuration attempts in order to decipher encrypted data. By utilizing a dirty bit and a sticky error counter, the device can keep track of the number of failed configuration attempts that have occurred and initiate anti-tampering operations when tampering is suspected while the device is still in the configuration stage of operation.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
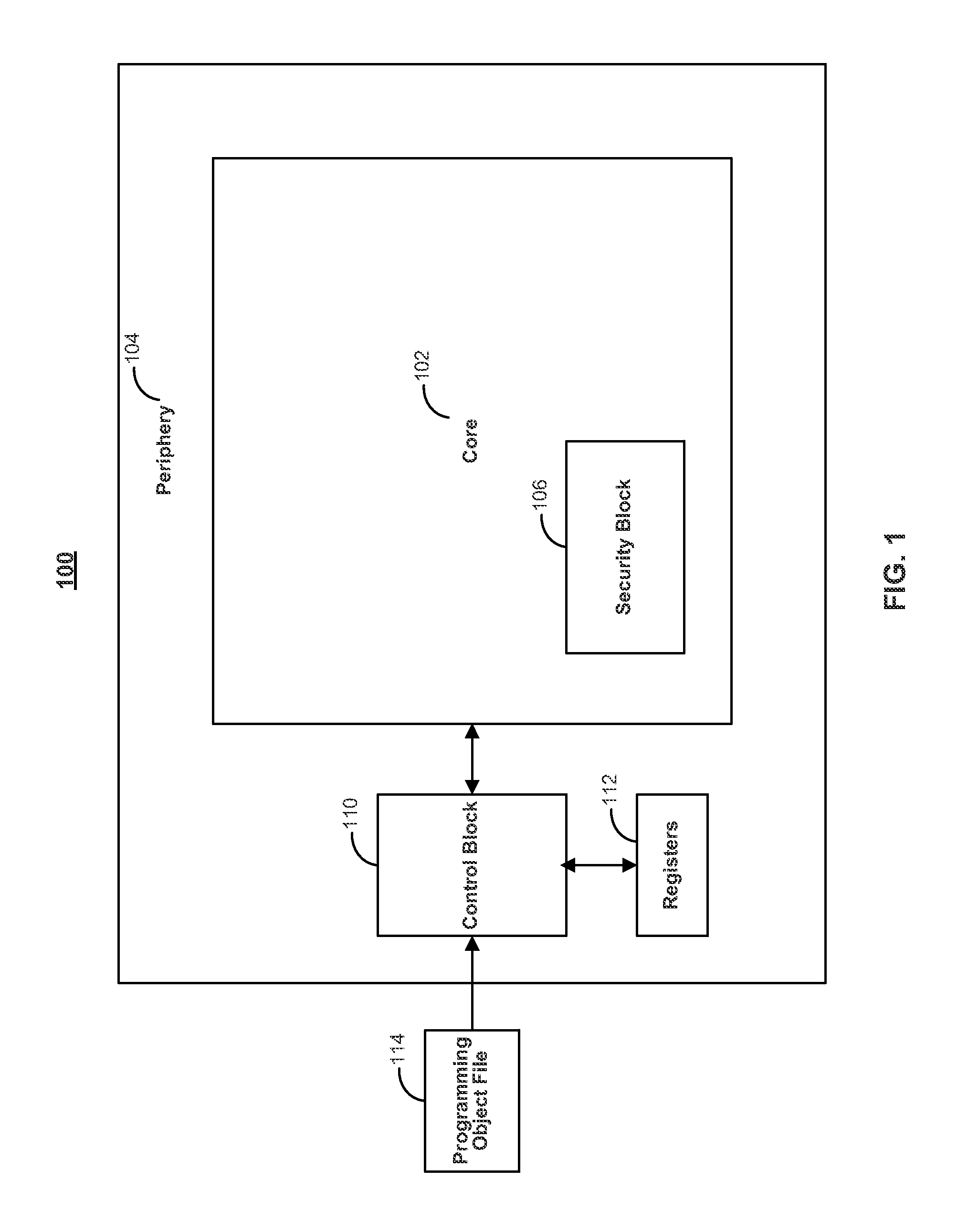
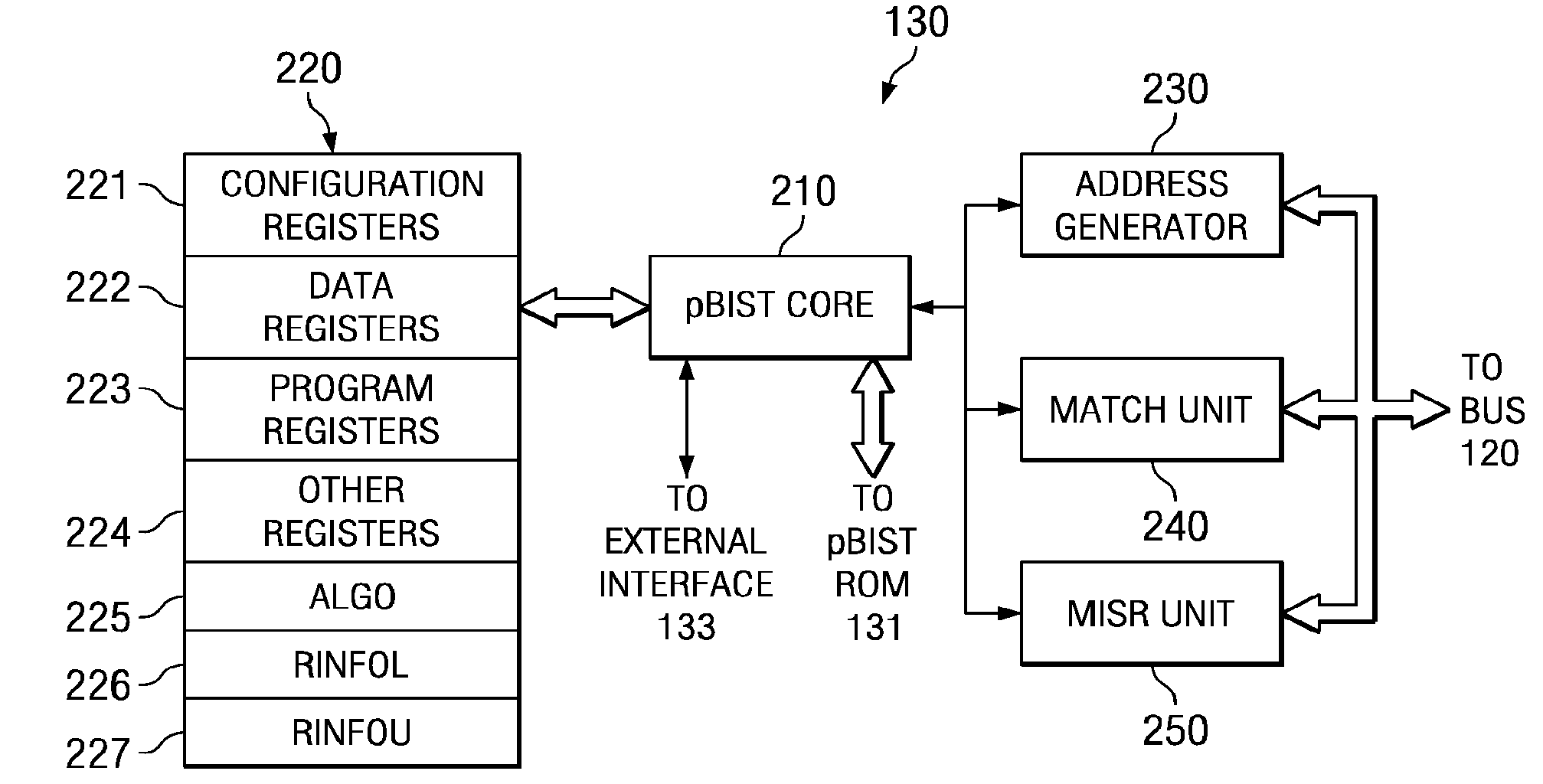
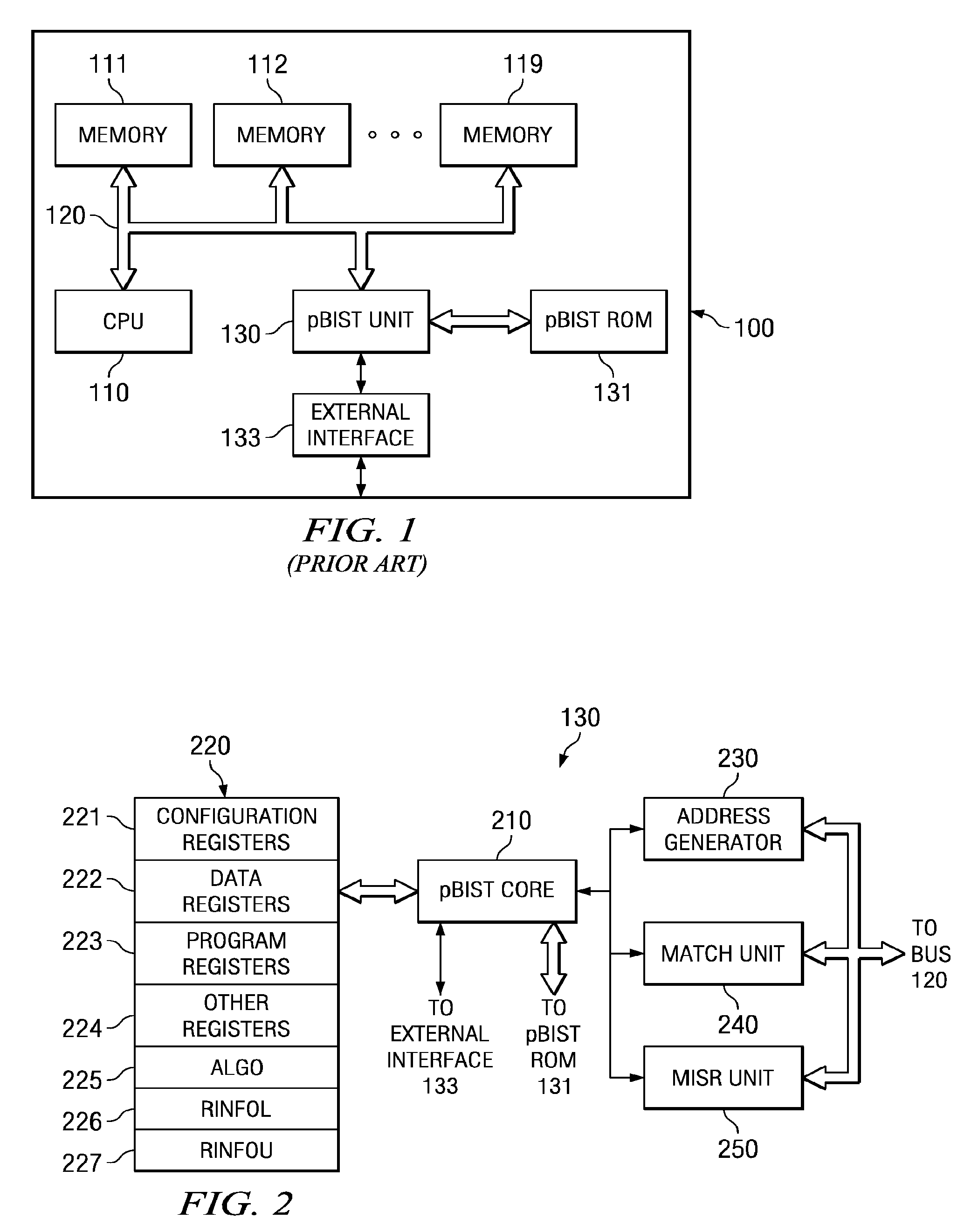
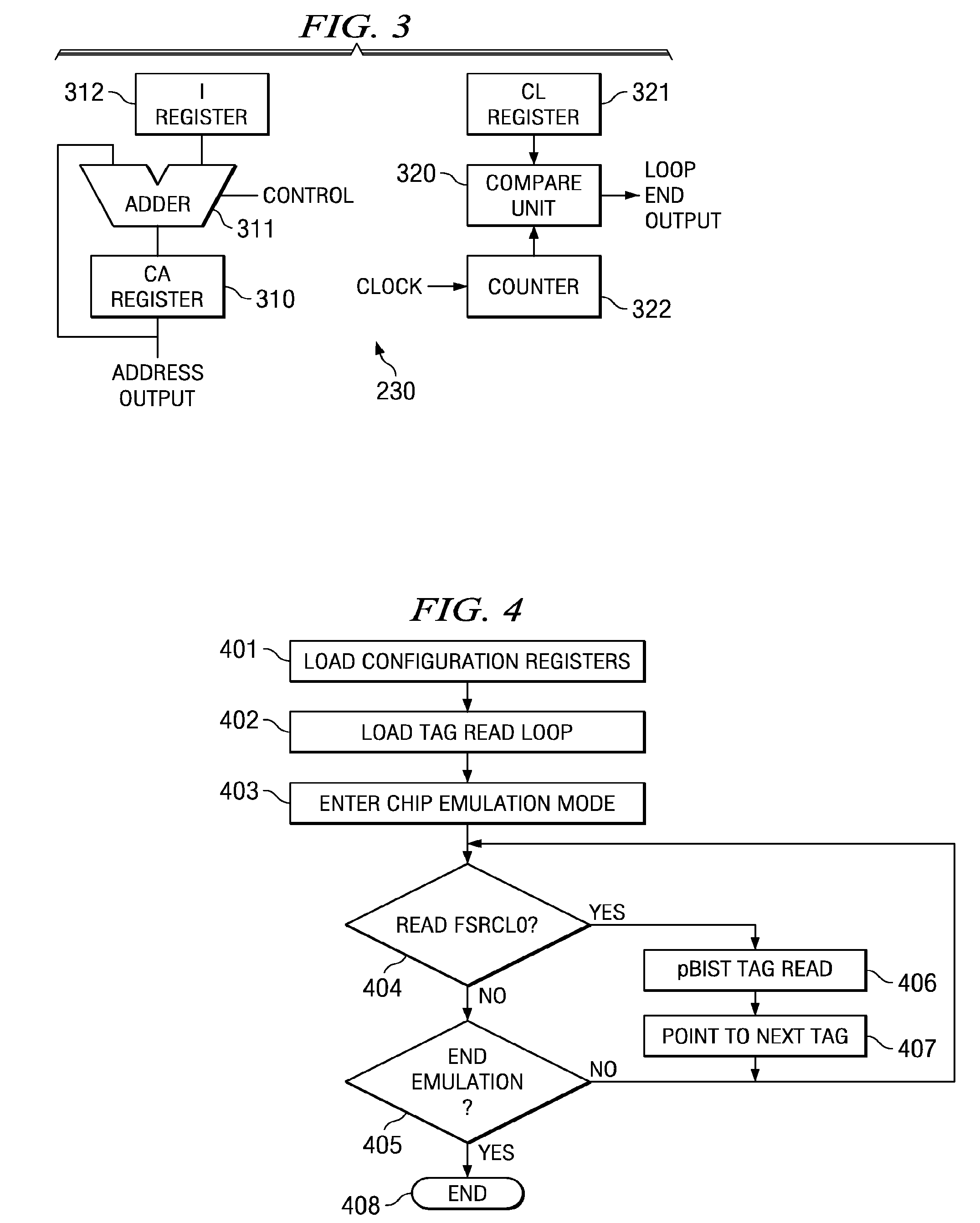
Emulation cache access for tag view reads
A built-in self test unit reads tag bits of a predetermined cache entry and outputs these tag bits via an external interface. The built-in self test unit enters an emulation mode upon receipt of an emulation signal via the external interface when a first configuration register has a predetermined state. The built-in self test unit then reads tag bits upon each memory mapped read of a second configuration register. The read operation advances to next sequential tag bits upon each memory mapped read of the second configuration register. The tag bits include at least one valid bit and at least one dirty bit. The tag bits also include the most significant bits of the cached address.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com