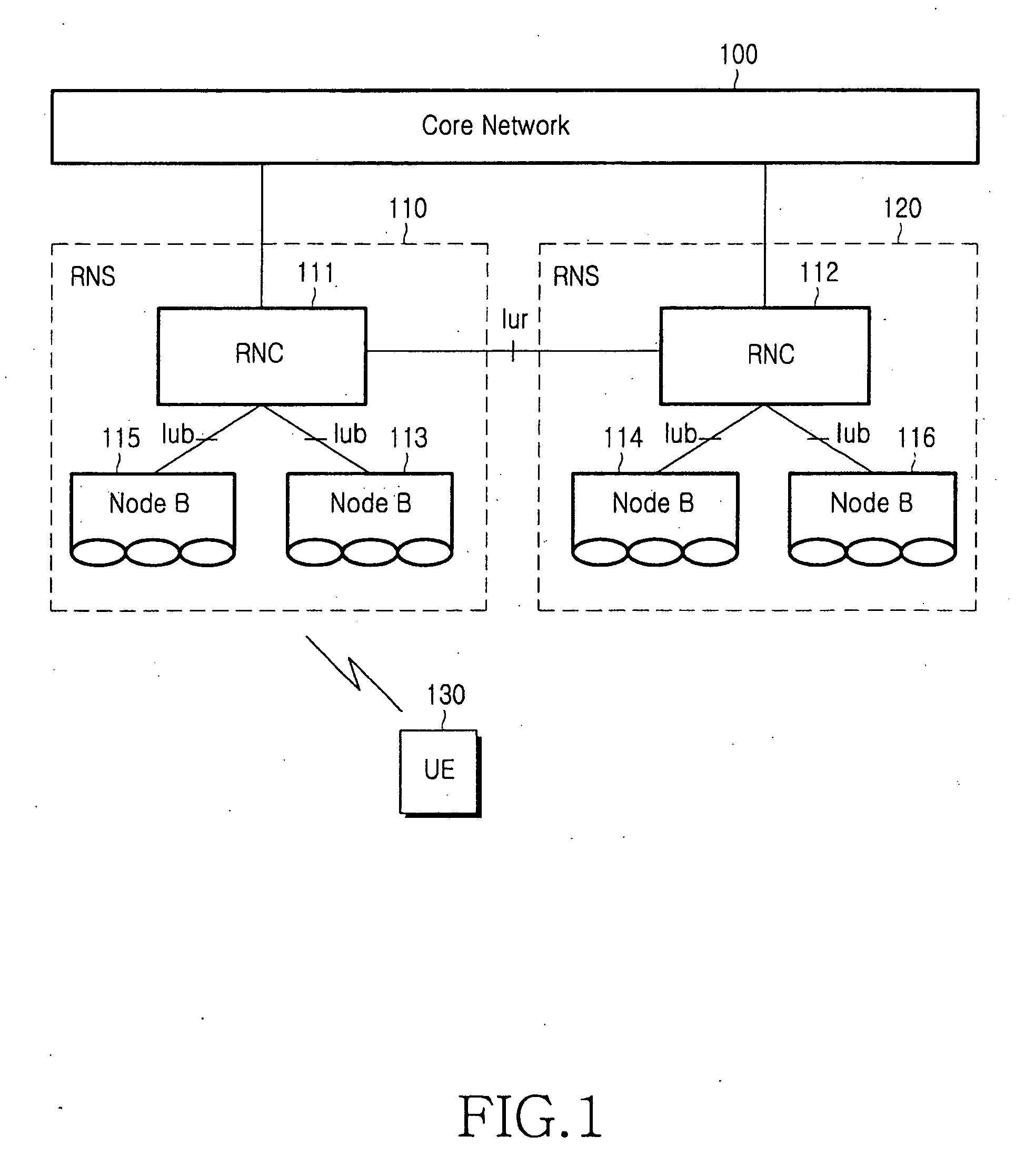
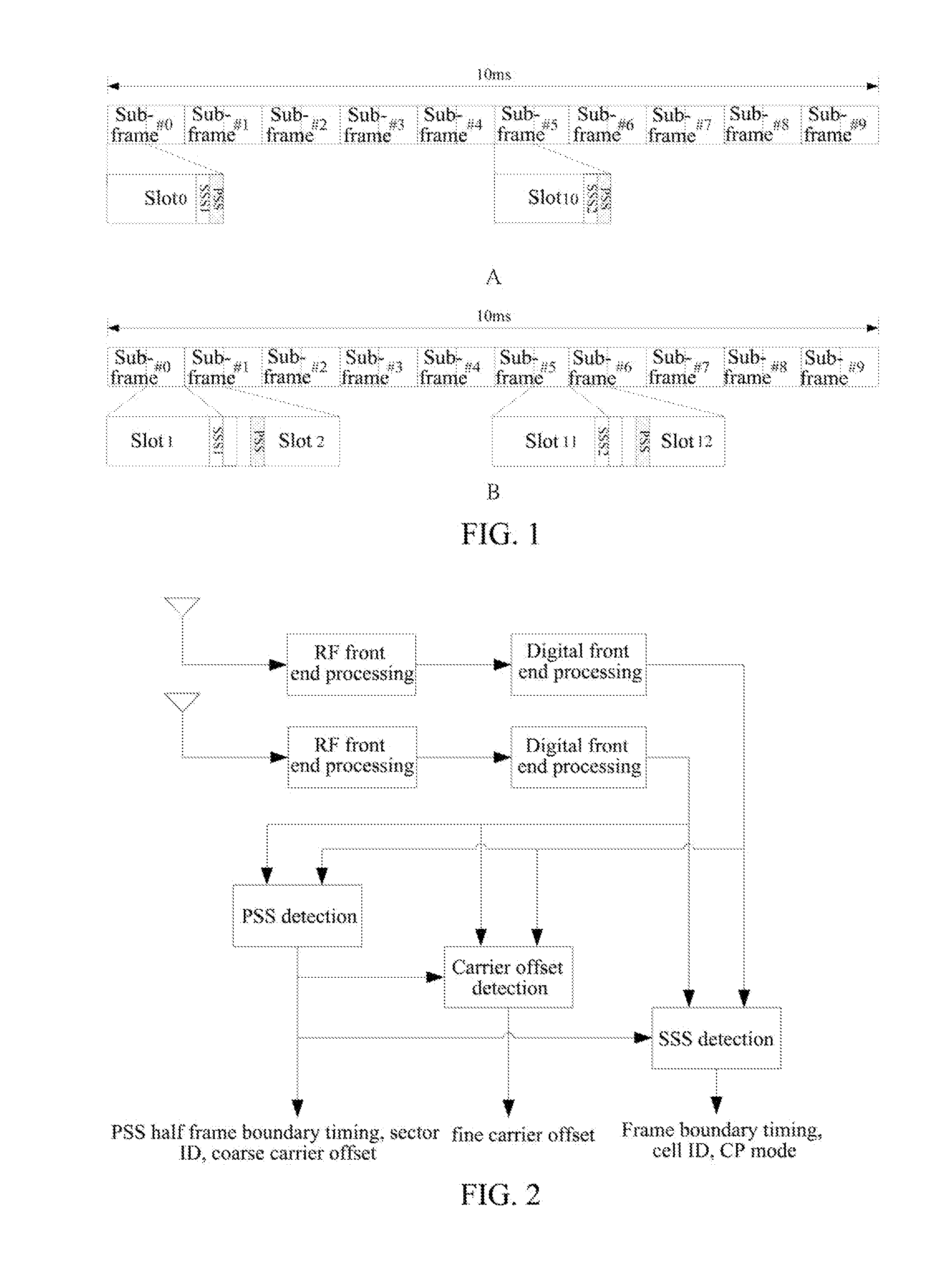
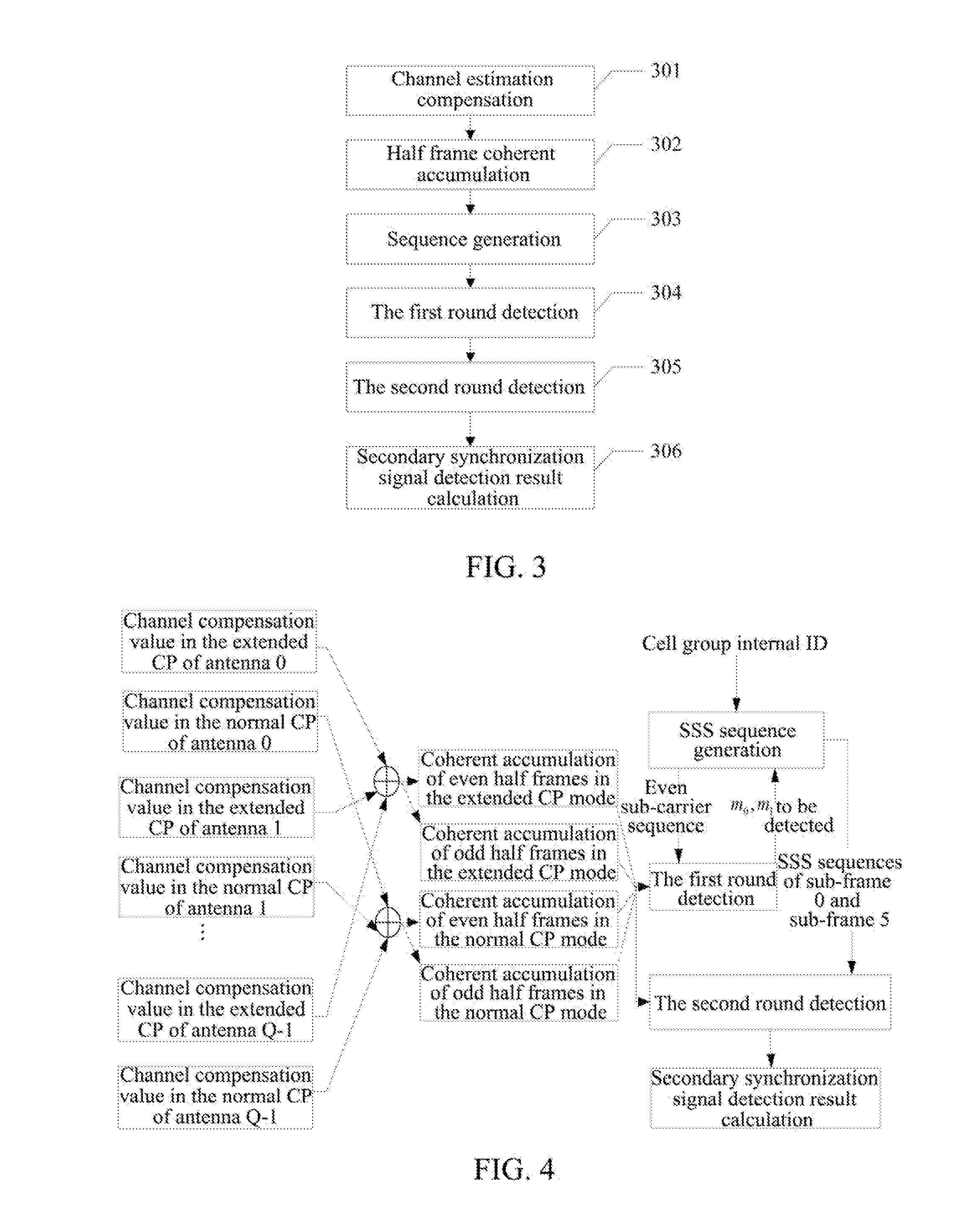
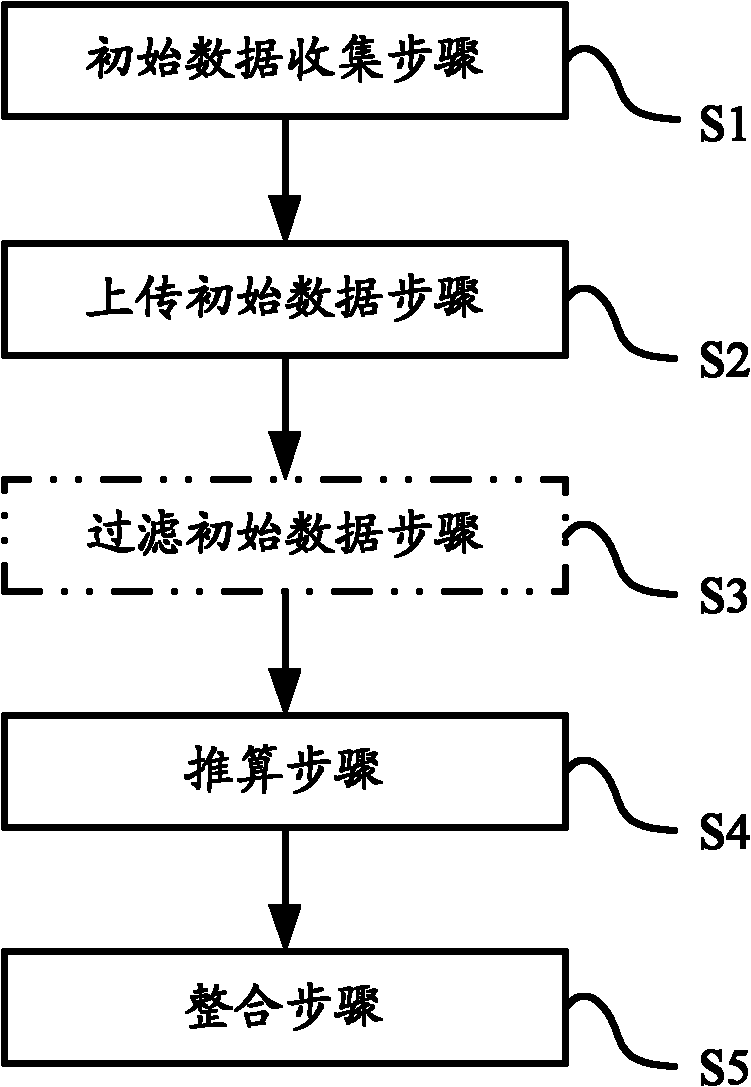
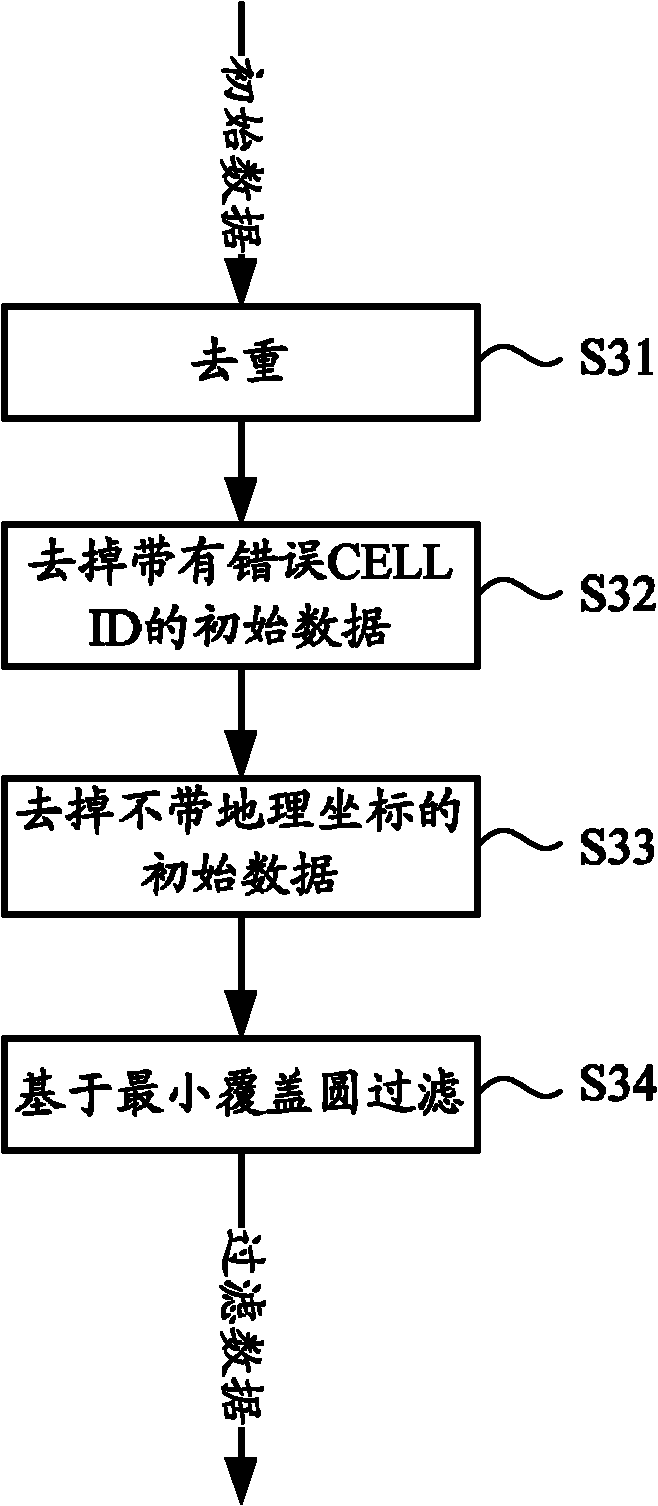
Patents
Literature
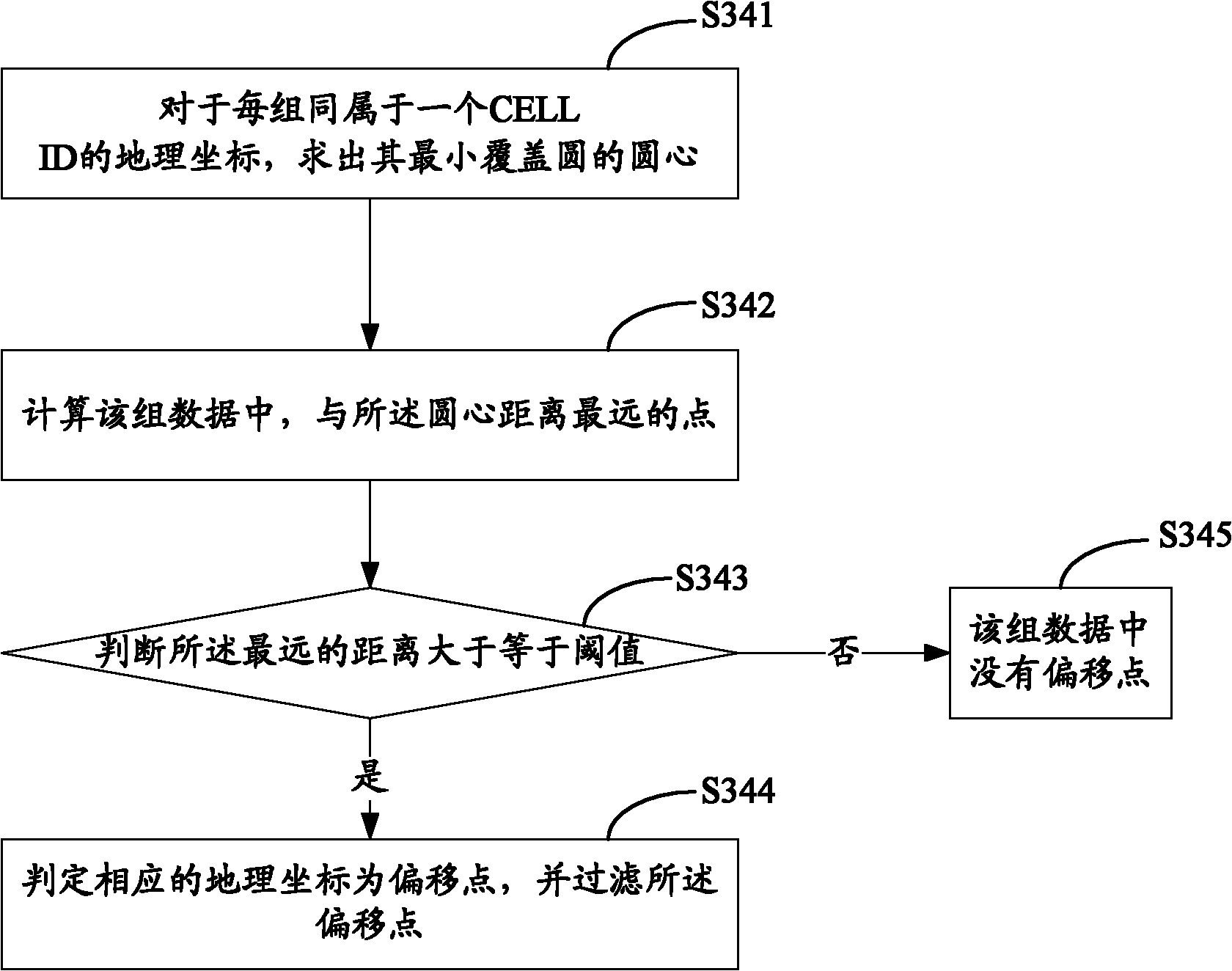
713 results about "Cell ID" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
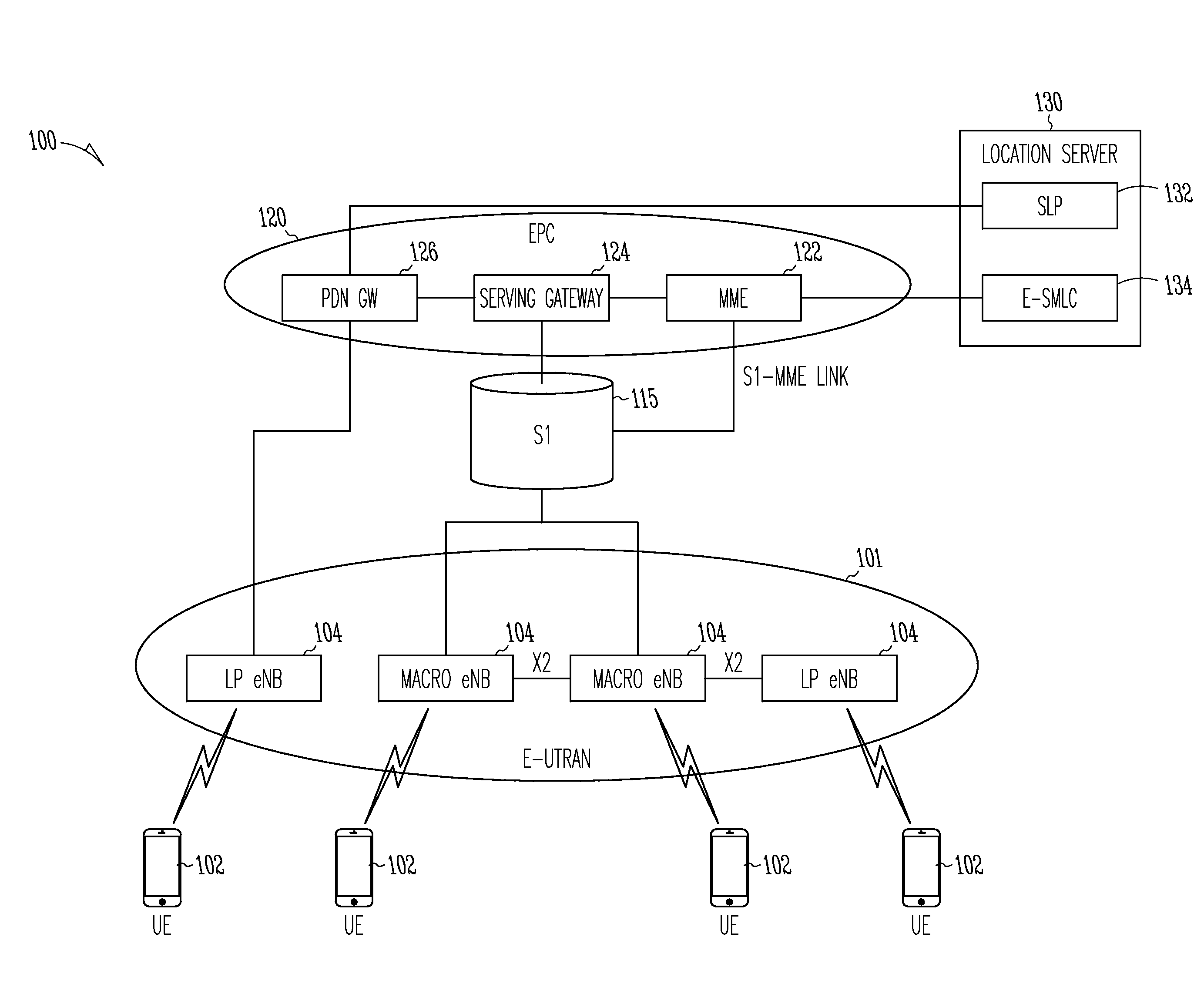
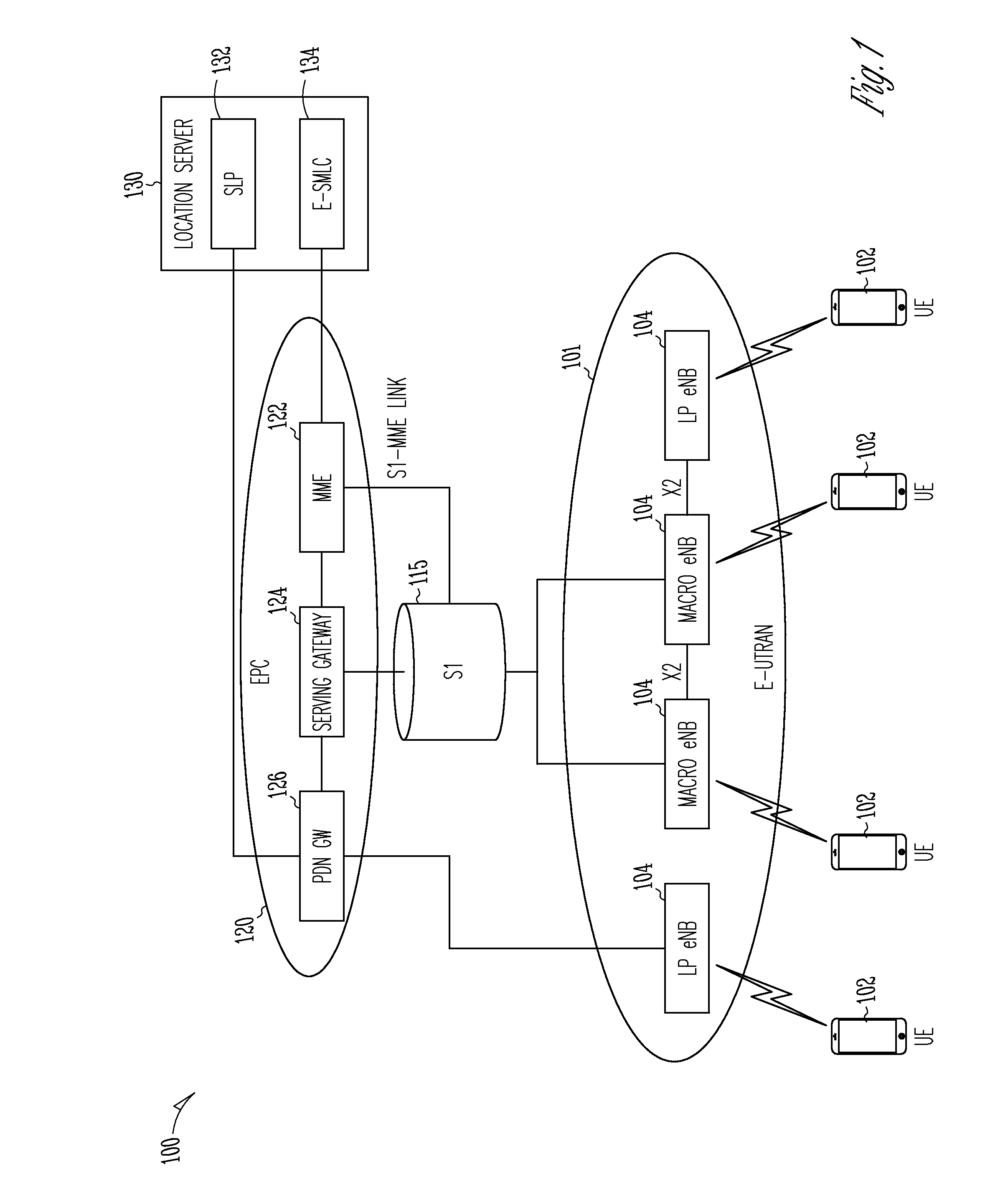
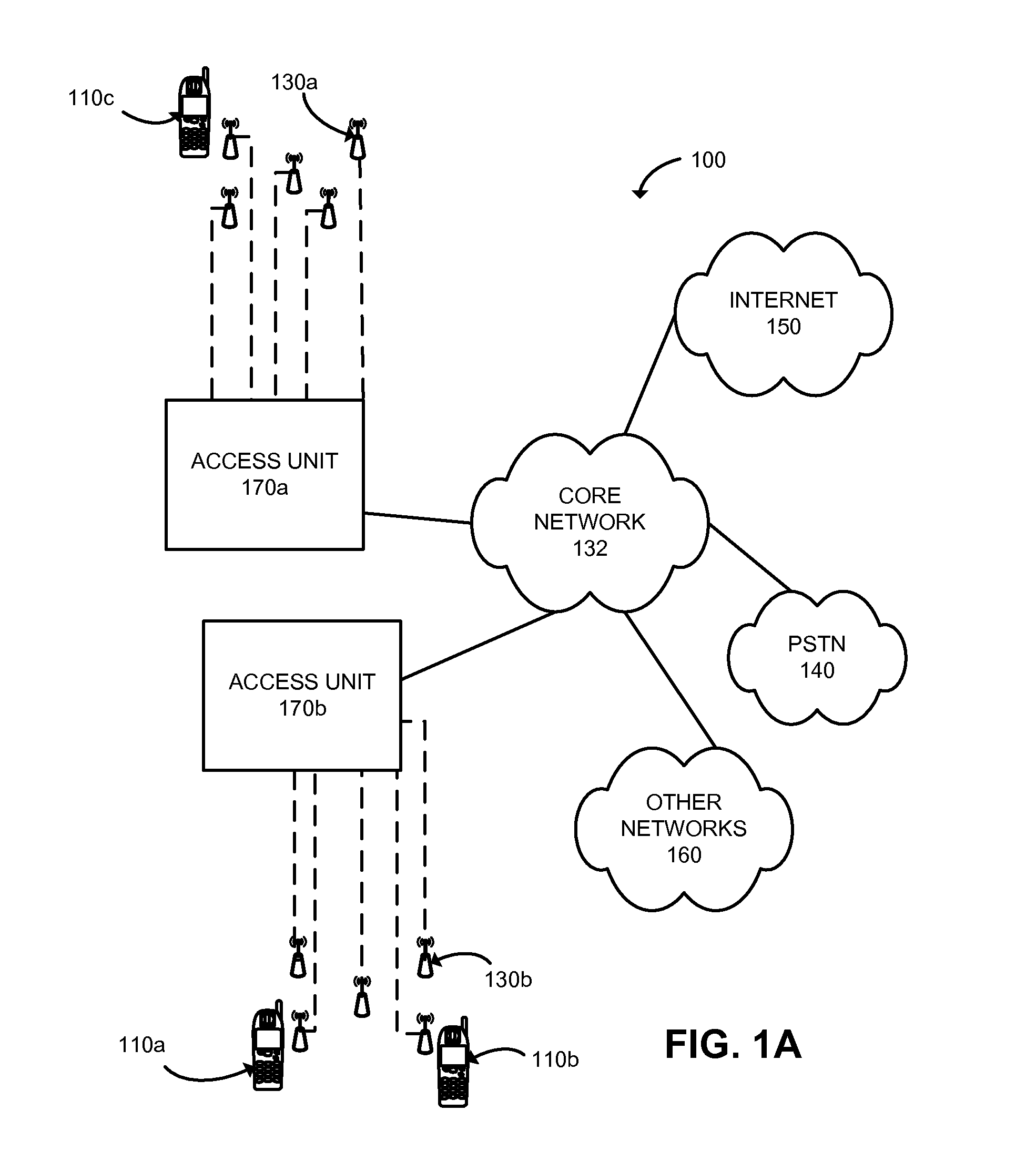
A GSM Cell ID (CID) is a generally unique number used to identify each base transceiver station (BTS) or sector of a BTS within a location area code (LAC) if not within a GSM network.
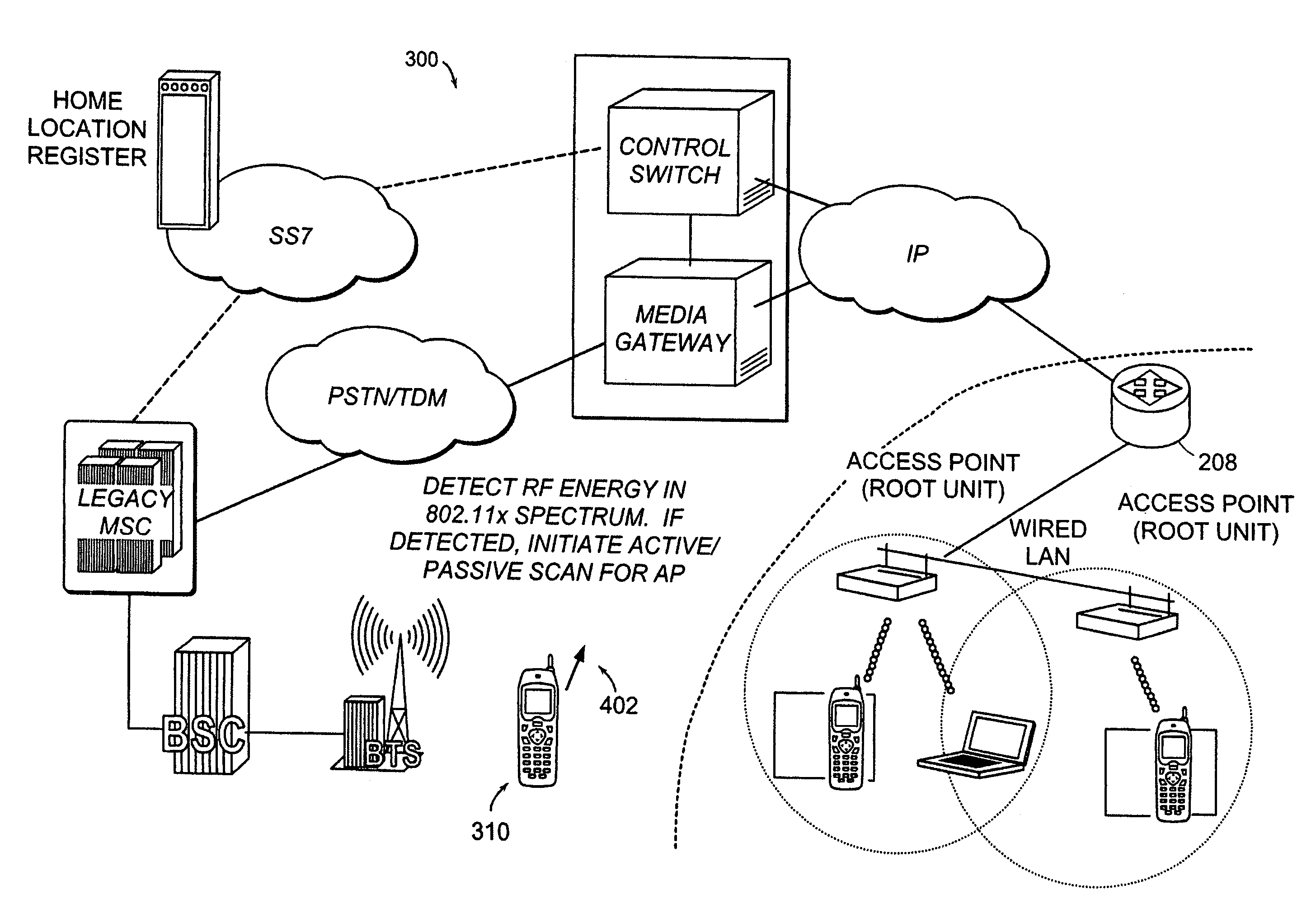
Method, system, and apparatus for a mobile station to sense and select a wireless local area network (WLAN) or a wide area mobile wireless network (WWAN)
ActiveUS7200112B2Improve connectivityEasy to useError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsWide areaFrequency spectrum
A method, system and apparatus for internetworking WWAN and WLAN are disclosed. More specifically, a method, system, and apparatus for a mobile station to sense and select a WLAN or a WWAN are disclosed. A mobile station may communicate according to an 802.xx wireless local area network air interface protocol via WLAN logic or according to a wireless wide area network air interface protocol via WWAN logic. The mobile station detects RF energy in the 802.xx spectrum and, in response to the energy detection, determines whether there is an 802.xx WLAN capable of servicing the mobile station by performing a scanning operation. If there is an 802.xx WLAN capable of servicing the mobile station, the mobile station selects the WLAN logic so that it may communicate via an air interface. Under some embodiments, WWAN has information identifying the areas in which capable WLANs operate and the WWAN provisions the mobile station with at least a subset of such information. The mobile station uses such area-identifying information to determine whether to perform the RF energy detection operation. The information may be cell ids, or GPS information.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Cell id based positioning from cell intersections
ActiveUS20080039114A1Improve accuracyDirection finders using radio wavesTelephonic communicationCell IDEngineering
Systems and methods are described for determining location of wireless devices using signal strength of signals detected by the wireless devices. The strength of signals received from identifiable sources is typically compared to reference signal strength measurements collected or estimated at known locations. Information identifying the source of the signals is typically obtained from data provided in the signals. Mappers associate combinations of reference signal strengths with geometrically shaped geographical regions such that signal strength measurements can be used as indices to locate a region in which a wireless device can be found. Systems and methods are described for receiving signal strength information from known locations where the information can be used to update and improve mapping system databases.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
Terminal apparatus and received data display method
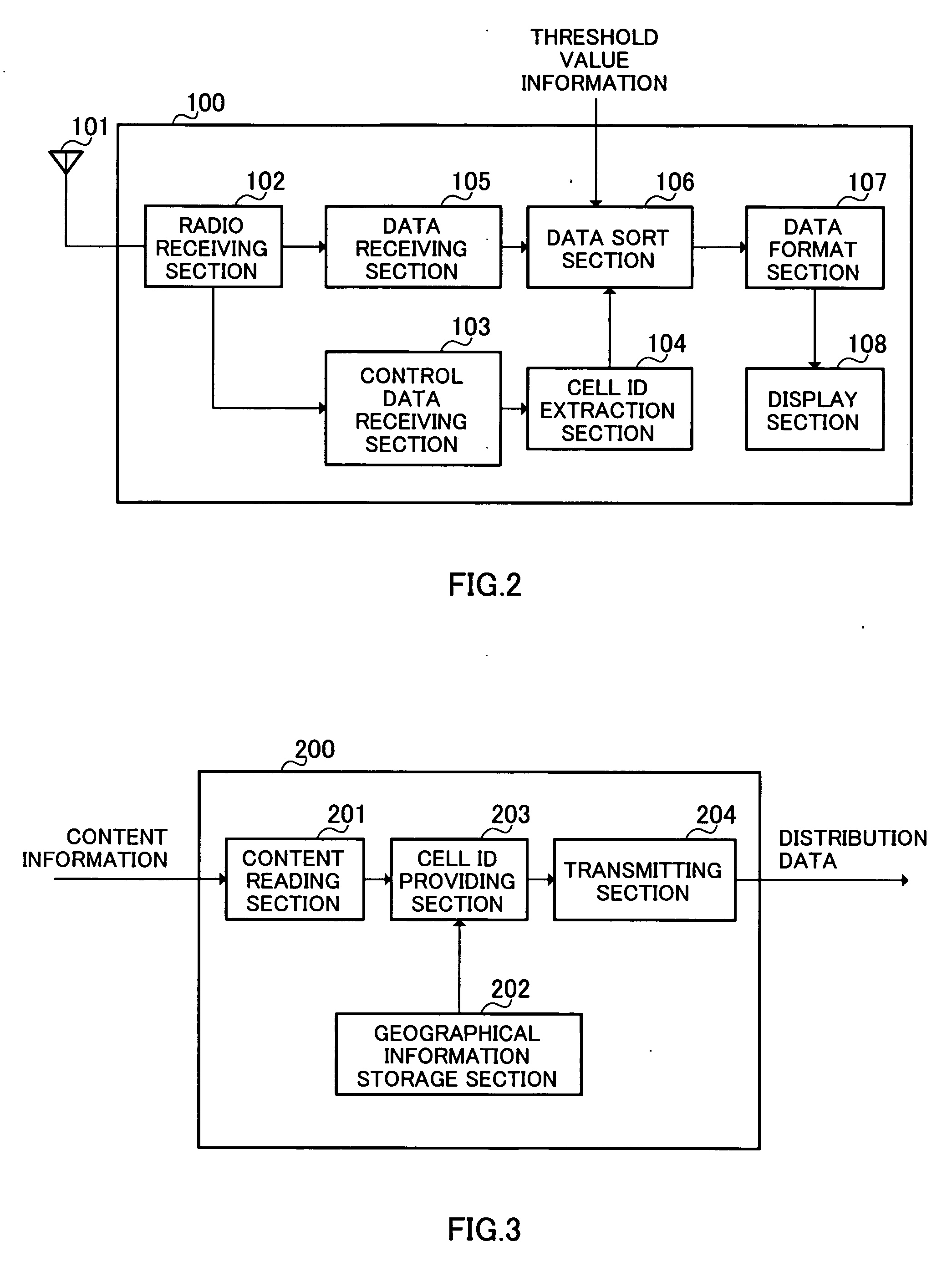
Distributed data is not edited at a distributing end but is edited in a terminal apparatus, thereby reducing the cost. The terminal apparatus can quickly retrieve necessary information. In the apparatus, a cell ID extracting part (104) extracts all the cell IDs that can be currently received. A data receiving part (105) extracts distributed data. A data sorting part (106) compares the cell ID related to the distributed data with the cell IDs that can be currently received, and adds priorities to the distributed data in such a manner that a “high” priority is given to the distributed data related to the same cell ID as the local cell, while the lower priorities being given to the distributed data related to the cell IDs of other cells that are farther from the local cell. A display part (108) sequentially displays the distributed data in decreasing order of the priority.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Selective Location Determination
ActiveUS20110250903A1Maximize accuracyStability of the locationPosition fixationWireless commuication servicesCell IDMedia access control
Methods, program products, and systems for selective location determination are described. A mobile device can determine a location of the mobile device using various techniques. When there is a conflict between the locations determined using different techniques, the mobile device can select a most trustworthy location from the locations, and designate the most trustworthy location as a current location of the mobile device. The mobile device can determine a first location of the mobile device (e.g., a coarse location) using a cell identifier (cell ID) of a cellular network. The mobile device can determine a second location of the mobile device (e.g., a fine location) using one or more media access control (MAC) addresses of a WLAN. The first location and second location can be associated with confidence values that can indicate trustworthiness of the first location and second location.
Owner:APPLE INC
Position-tracking system
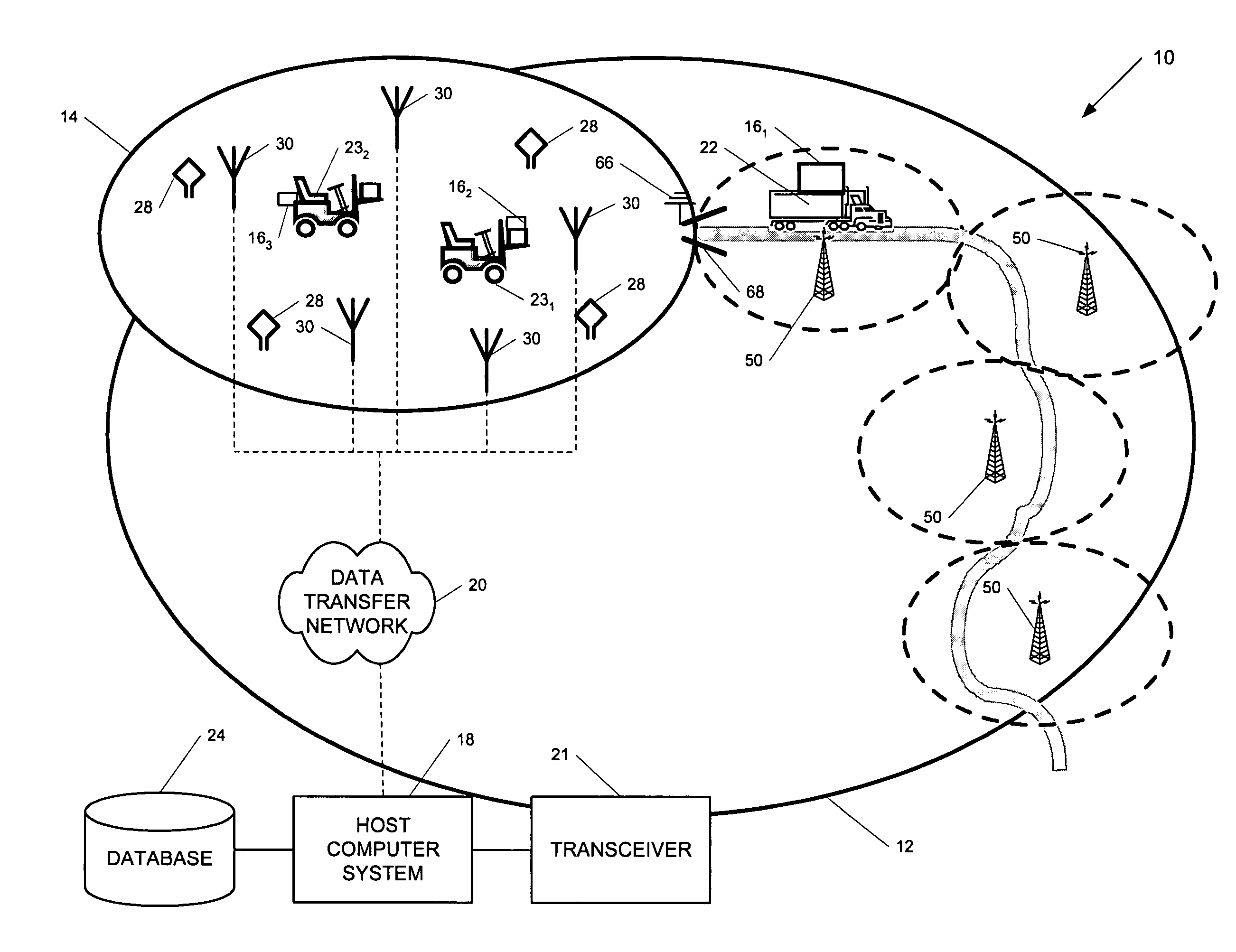
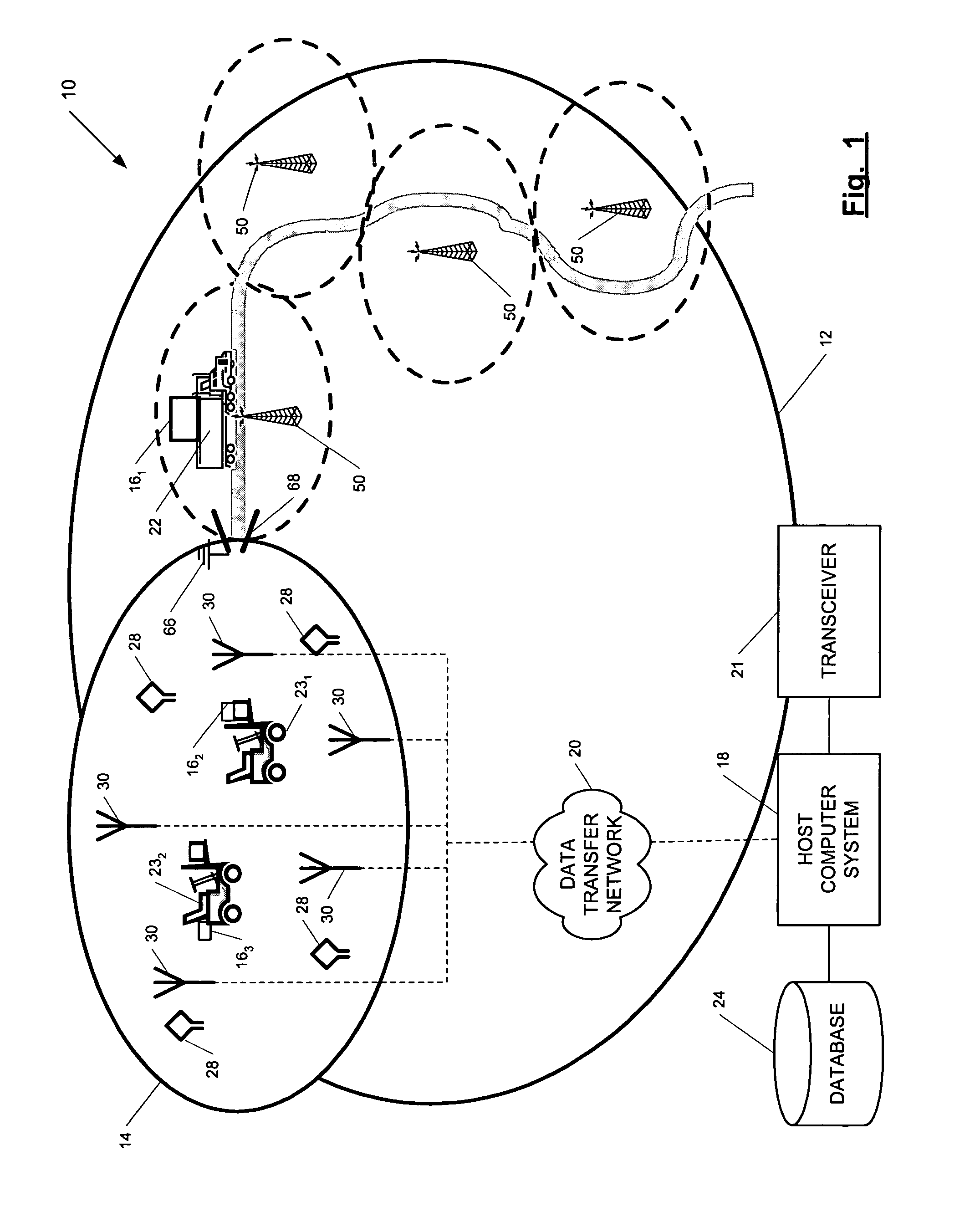
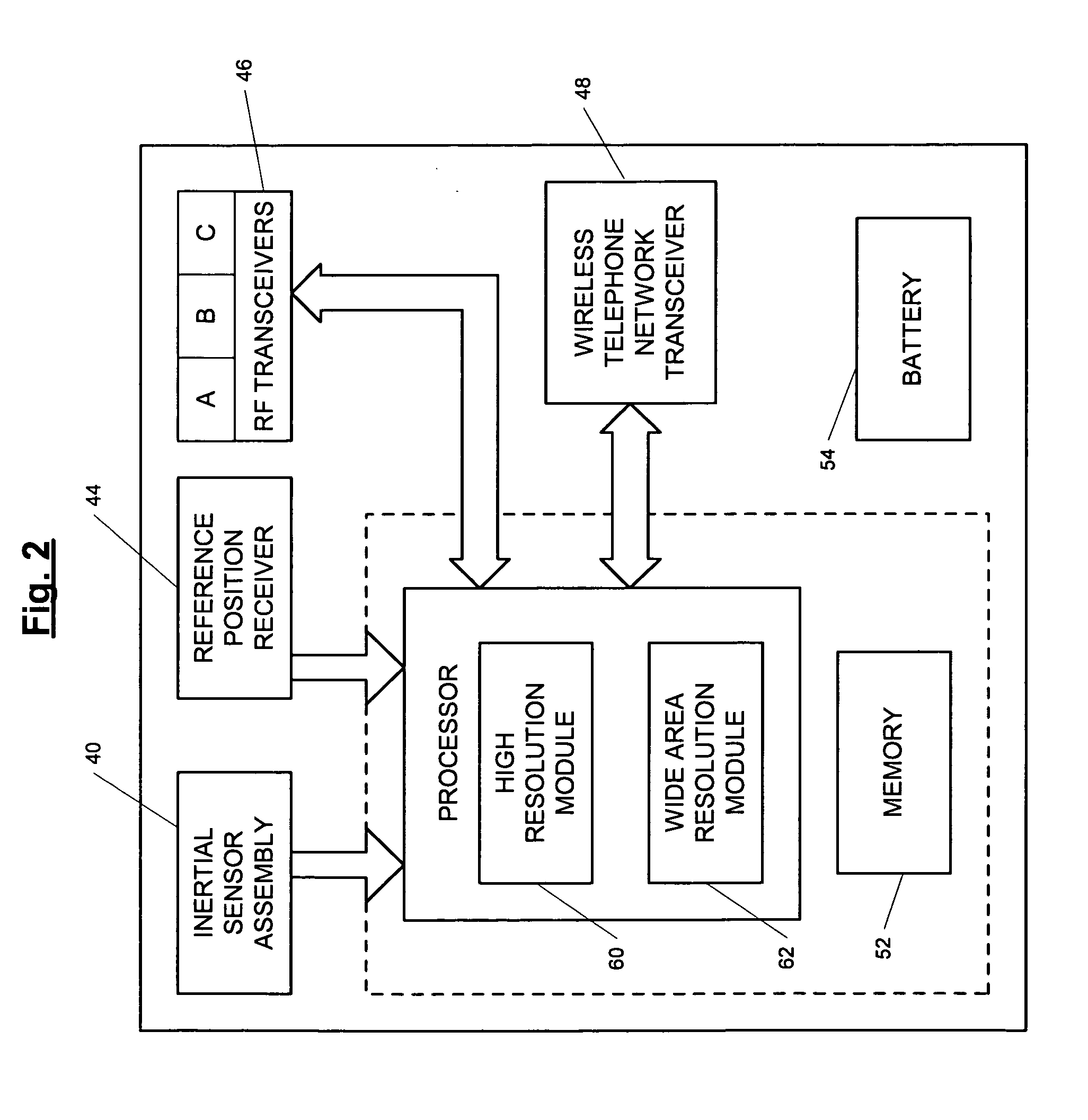
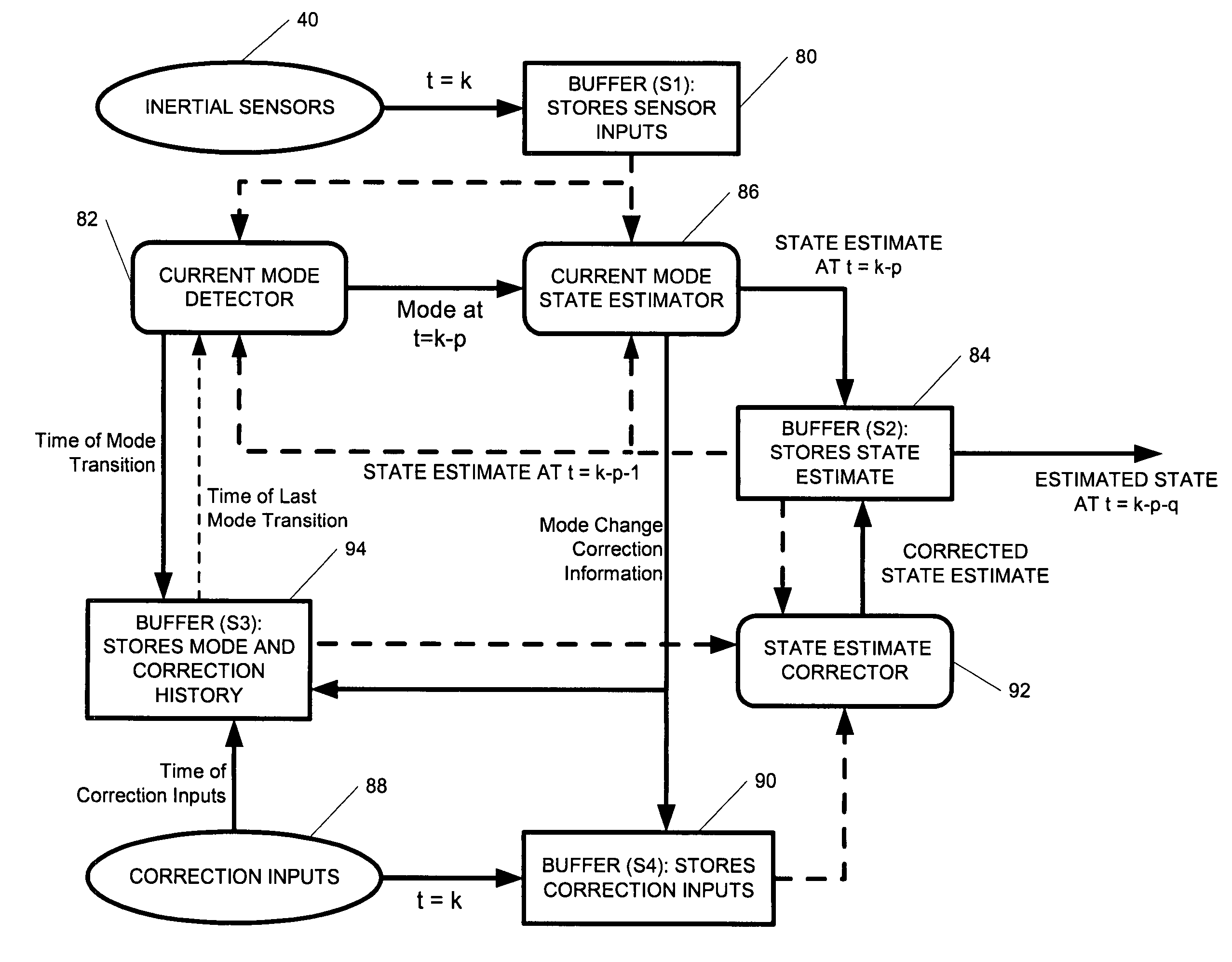
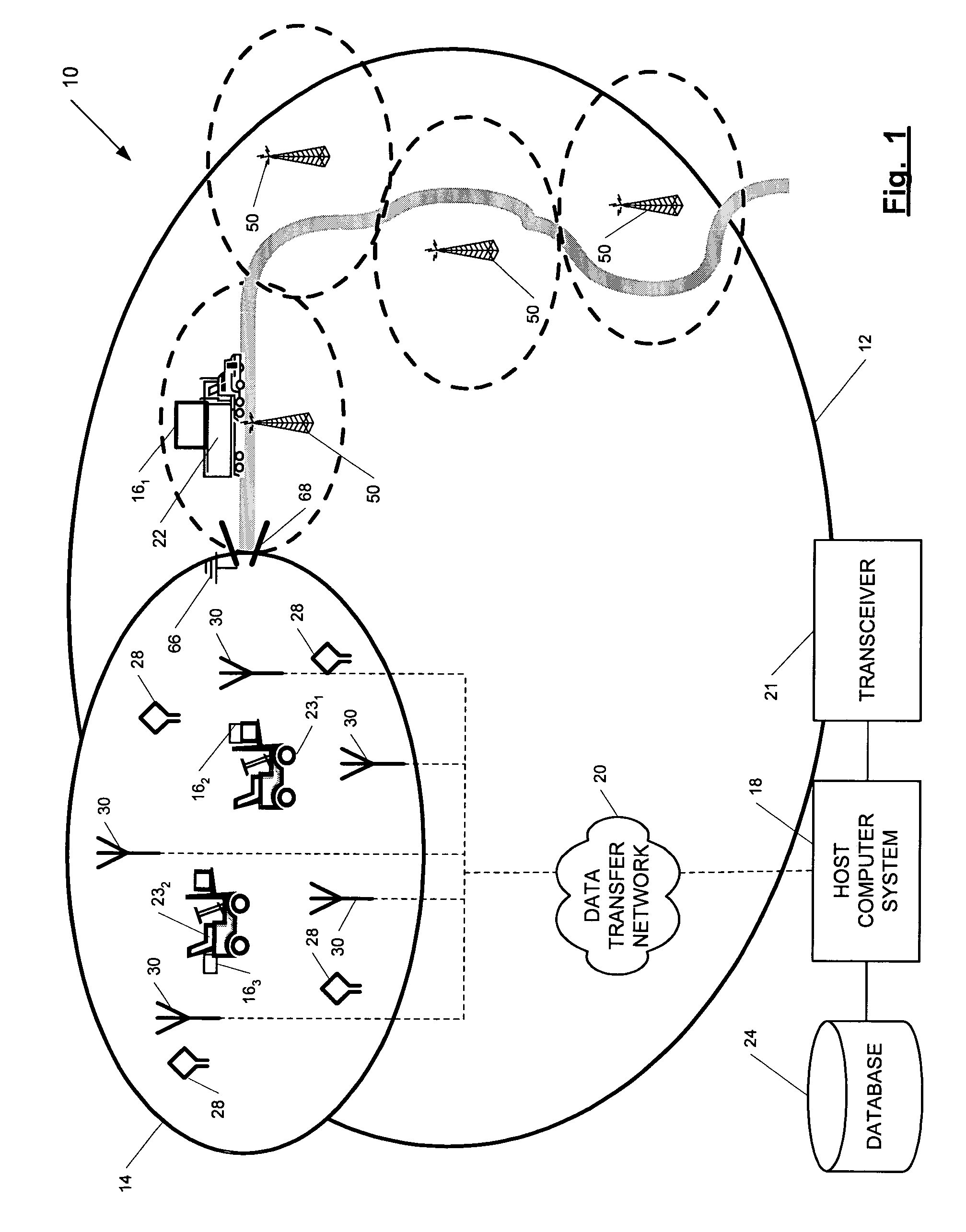
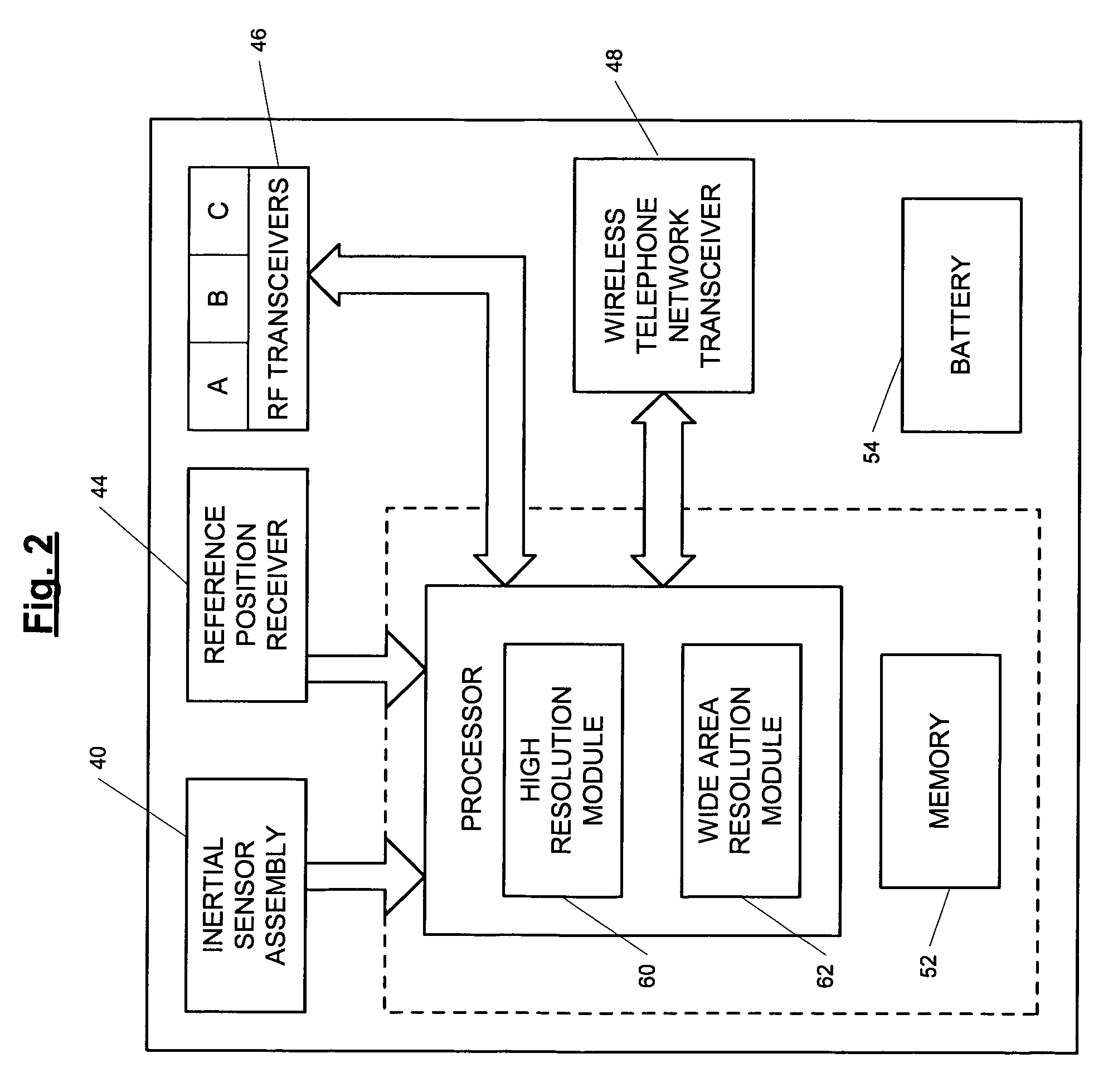
ActiveUS7236091B2High position resolutionImprove accuracyRoad vehicles traffic controlElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingObject basedTransceiver
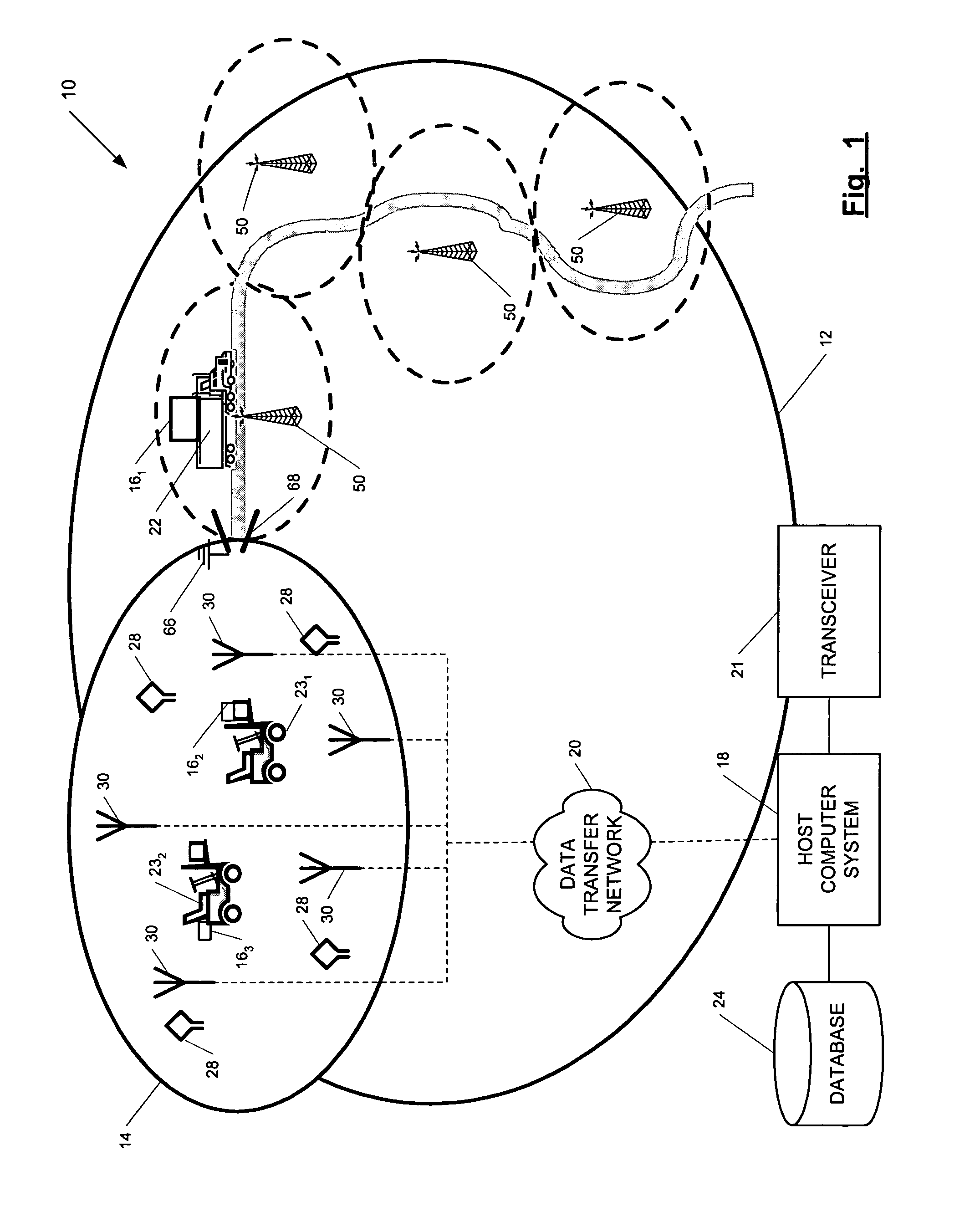
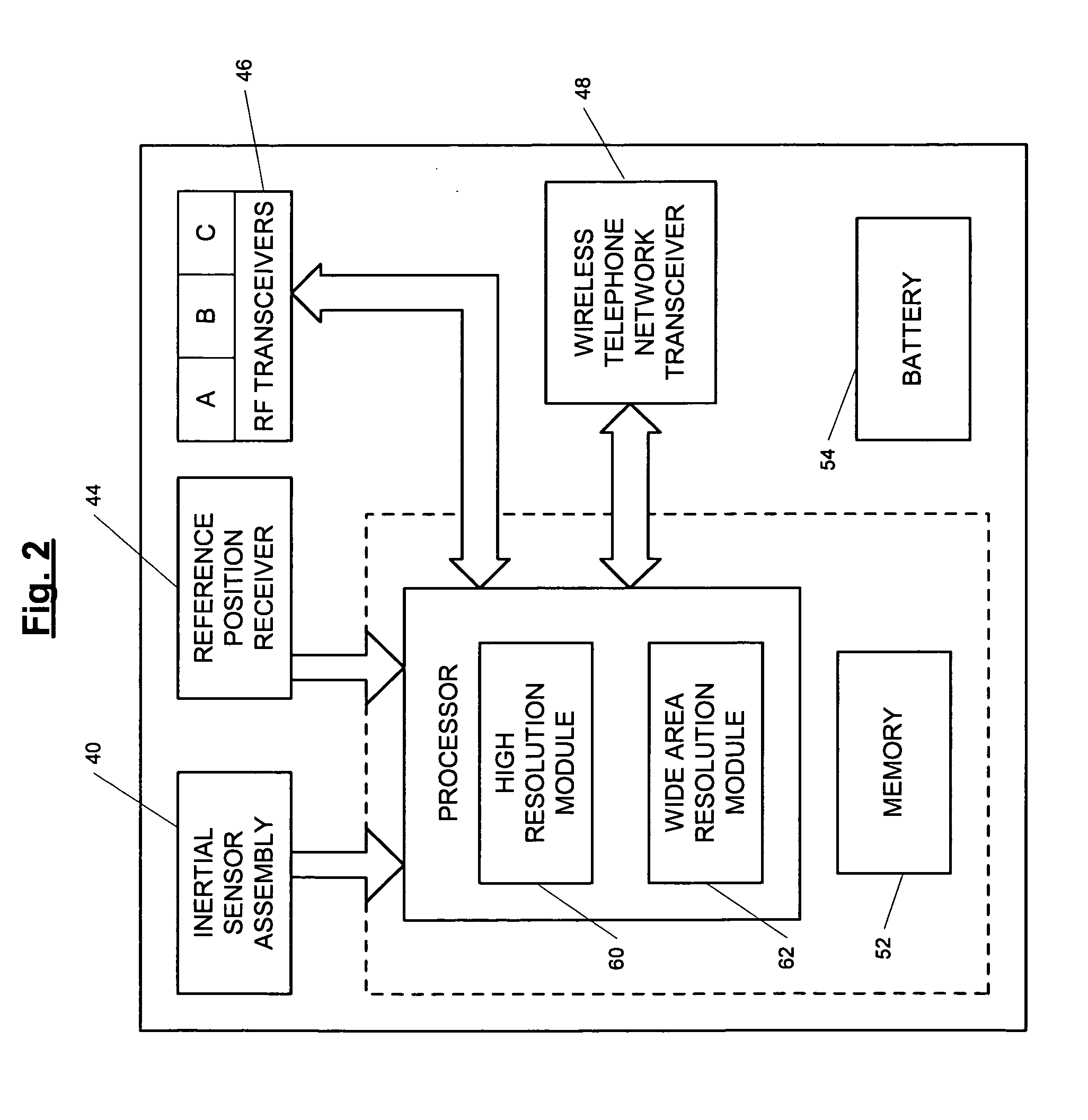
A position-tracking system for tracking the position of an object is disclosed. According to various embodiments, the tracking system includes a tracking device that is connected to or otherwise affixed to the object to be tracked. The tracking device may include, among other things, an inertial sensor assembly, radio transceivers and a processor. The position tracking system may also include a host processing system that is in communication with the tracking device. The position tracking system may provide variable-resolution position information based on the environment in which the object is moving. In a “wide resolution” area, the system may compute a general position for the object based on a wireless telephone network Cell-ID / map correlation architecture. In a high-resolution area, greater position resolution may be realized from the combination of a wireless aiding system and inputs from the inertial sensors. In the high-resolution mode, the system may exploit distinct patterns of motion that can be identified as motion “signatures” that are characteristic of certain types of motion. Kinematic (or object movement) models may be constructed based on these motion signatures and the position tracking system may estimate the state of the object based on the kinematic model for the current mode of the object. Adaptive and cascaded Kalman filtering may be employed in the analysis to more accurately estimate the position and velocity of the object based on the motion pattern identified.
Owner:PINC SOLUTIONS
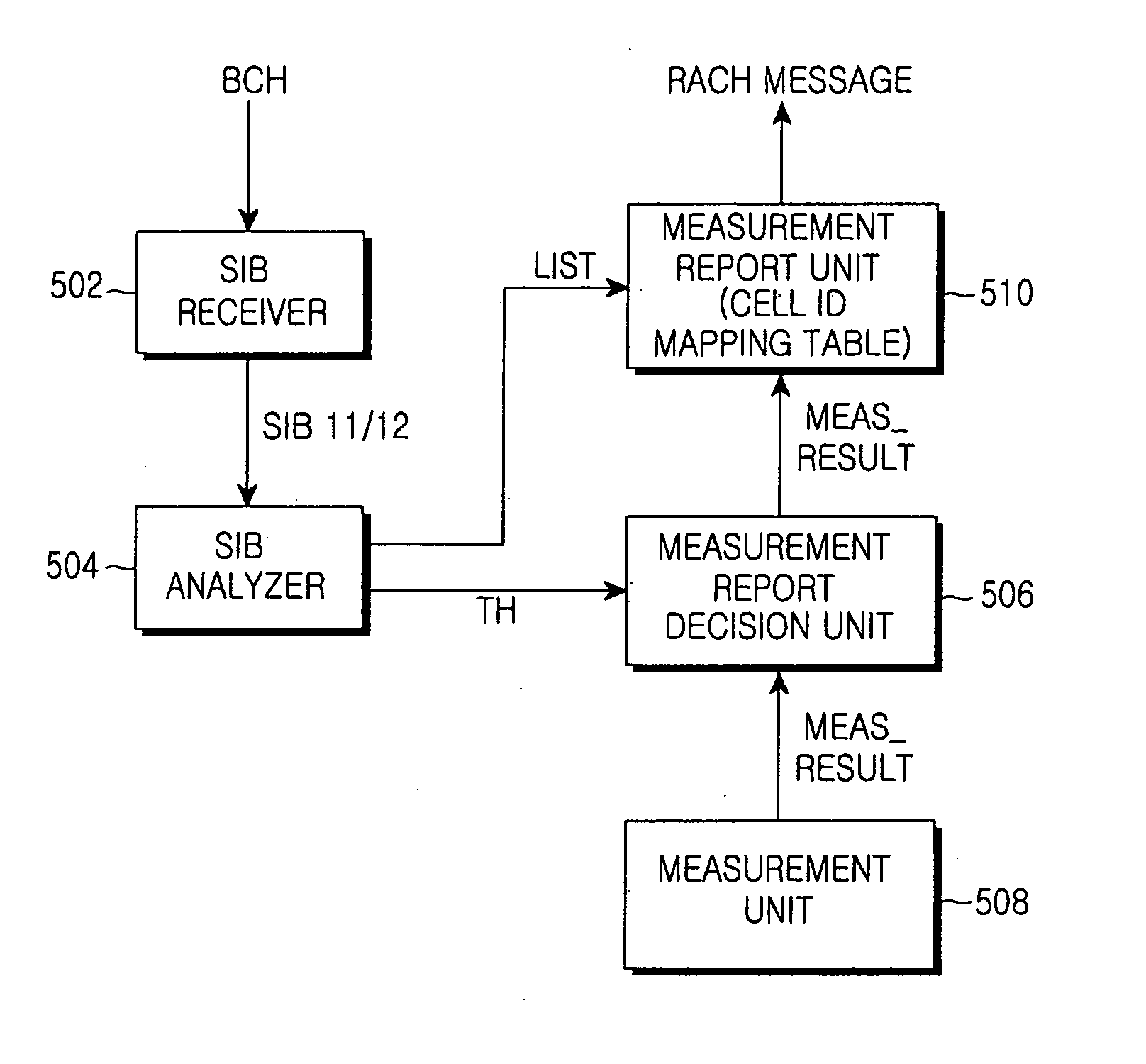
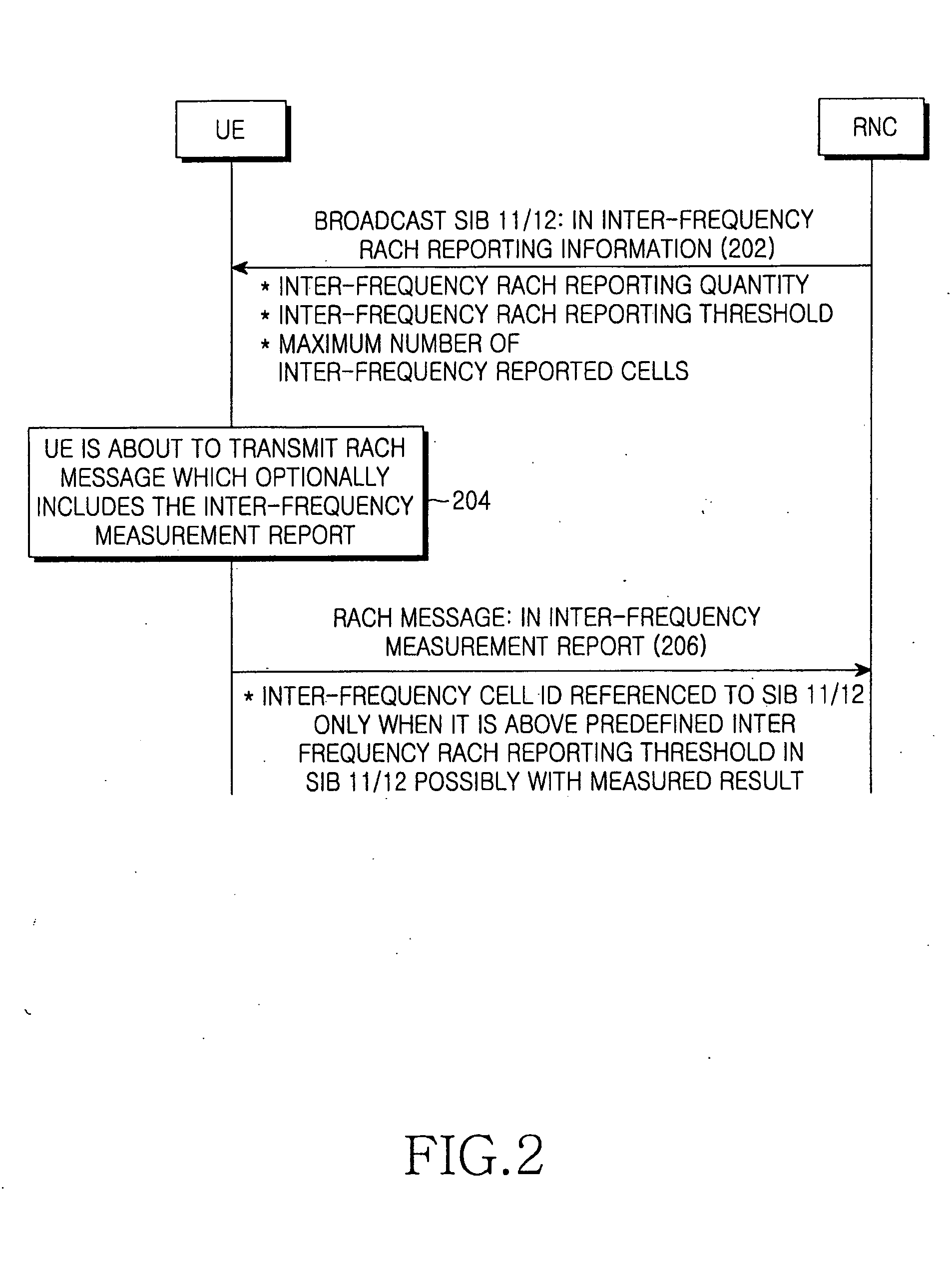
Method and apparatus for reporting inter-frequency measurement using RACH message in a mobile communication system
ActiveUS20060252377A1Reduce signaling overheadError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelecommunicationsFrequency measurements
A user equipment (UE) is provide which reduces uplink signaling overhead in the process of reporting inter-frequency measurement results over a RACH. For measurement reporting, the UE receives an SIB including a cell information list for non-used frequency cells and a threshold from an RNC, compares signal strengths of signals received from the non-used frequency cells with the threshold, and acquires at least one inter-frequency cell ID indicating at least one non-used frequency cell having signal strength exceeding the threshold from the cell information list. The at least one inter-frequency cell ID is included in a RACH message as measurement result information for the at least one non-used frequency cell, and transmitted to the RNC. The RNC determines that the cell corresponding to the inter-frequency cell ID has signal strength exceeding the threshold.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
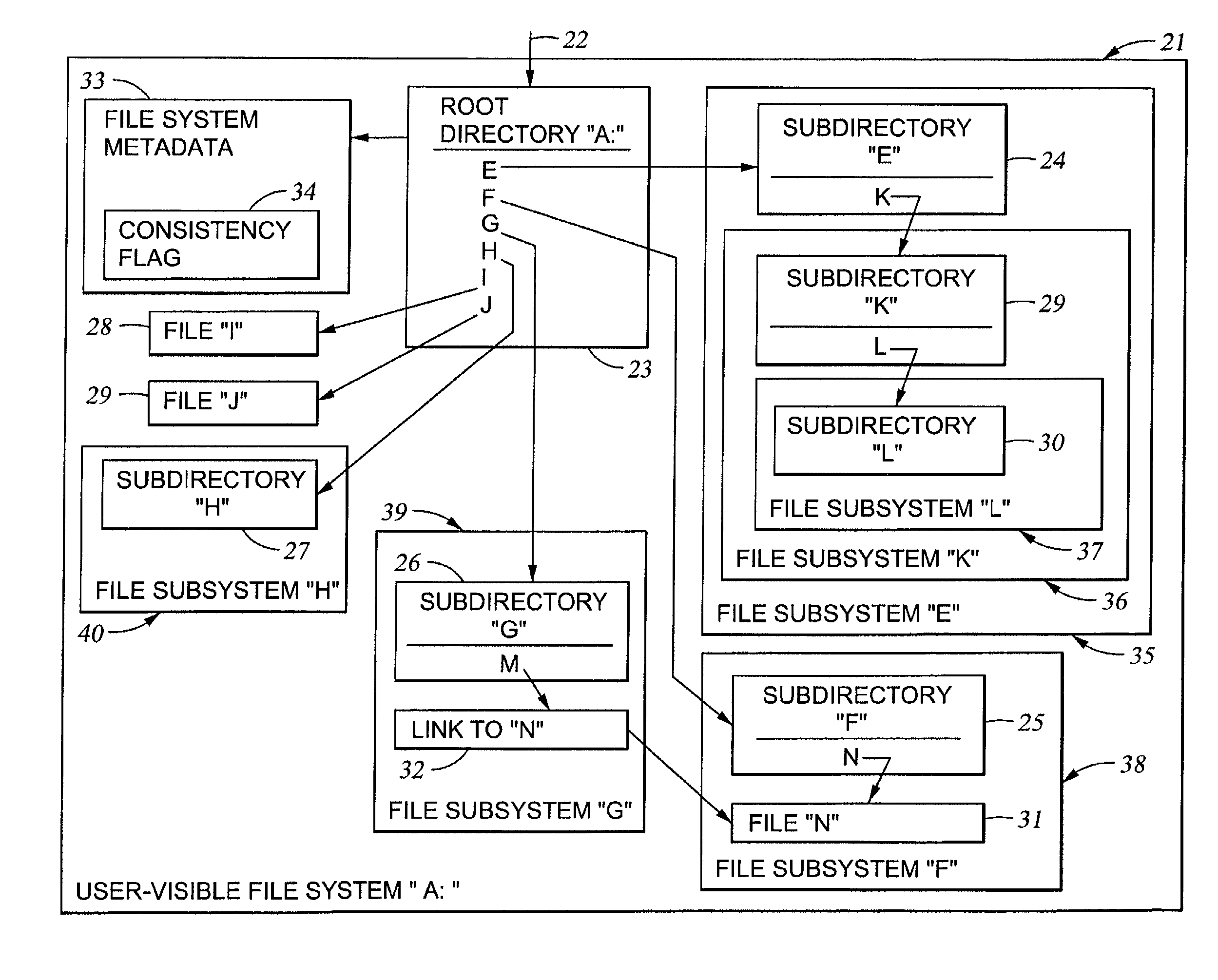
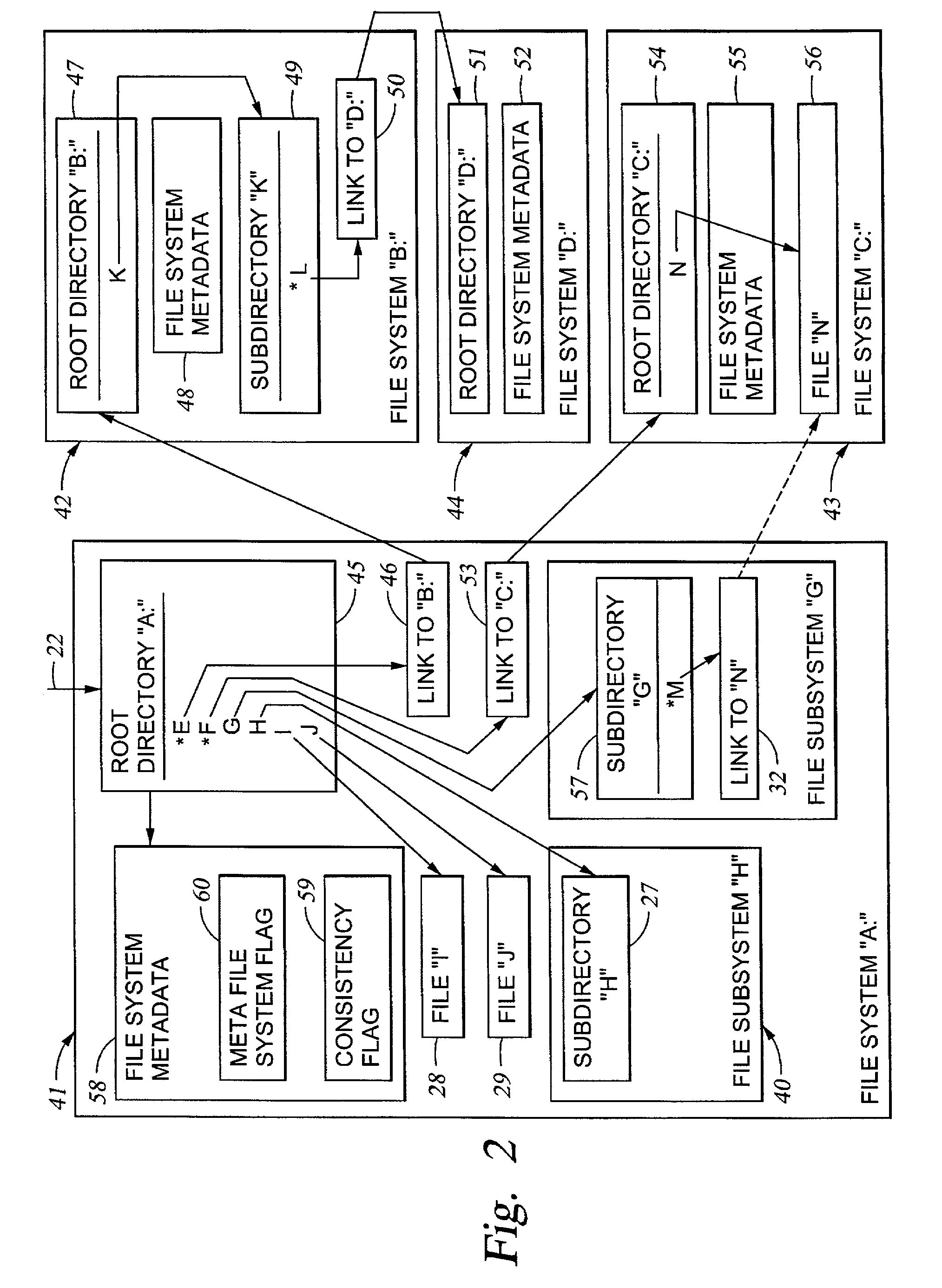
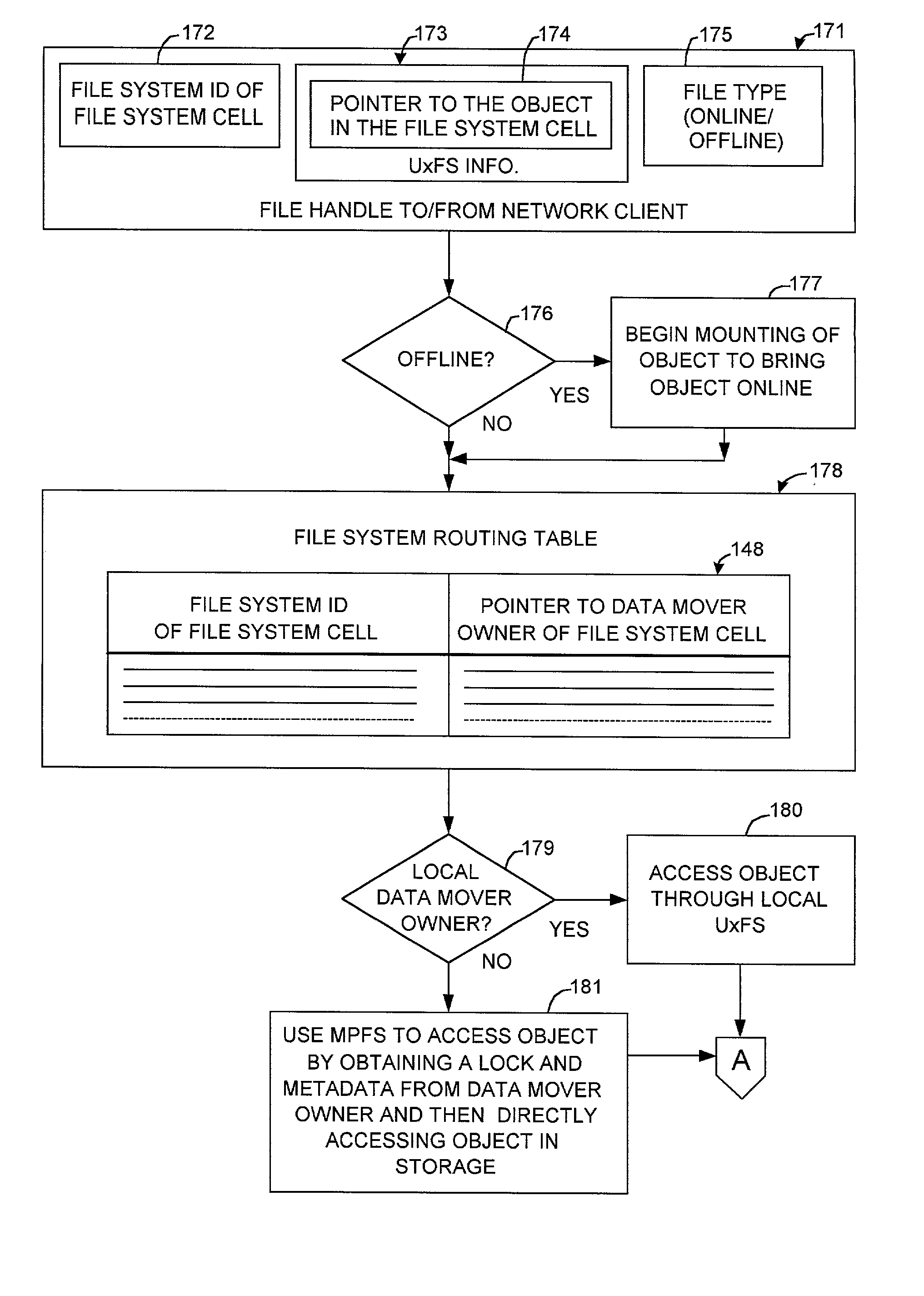
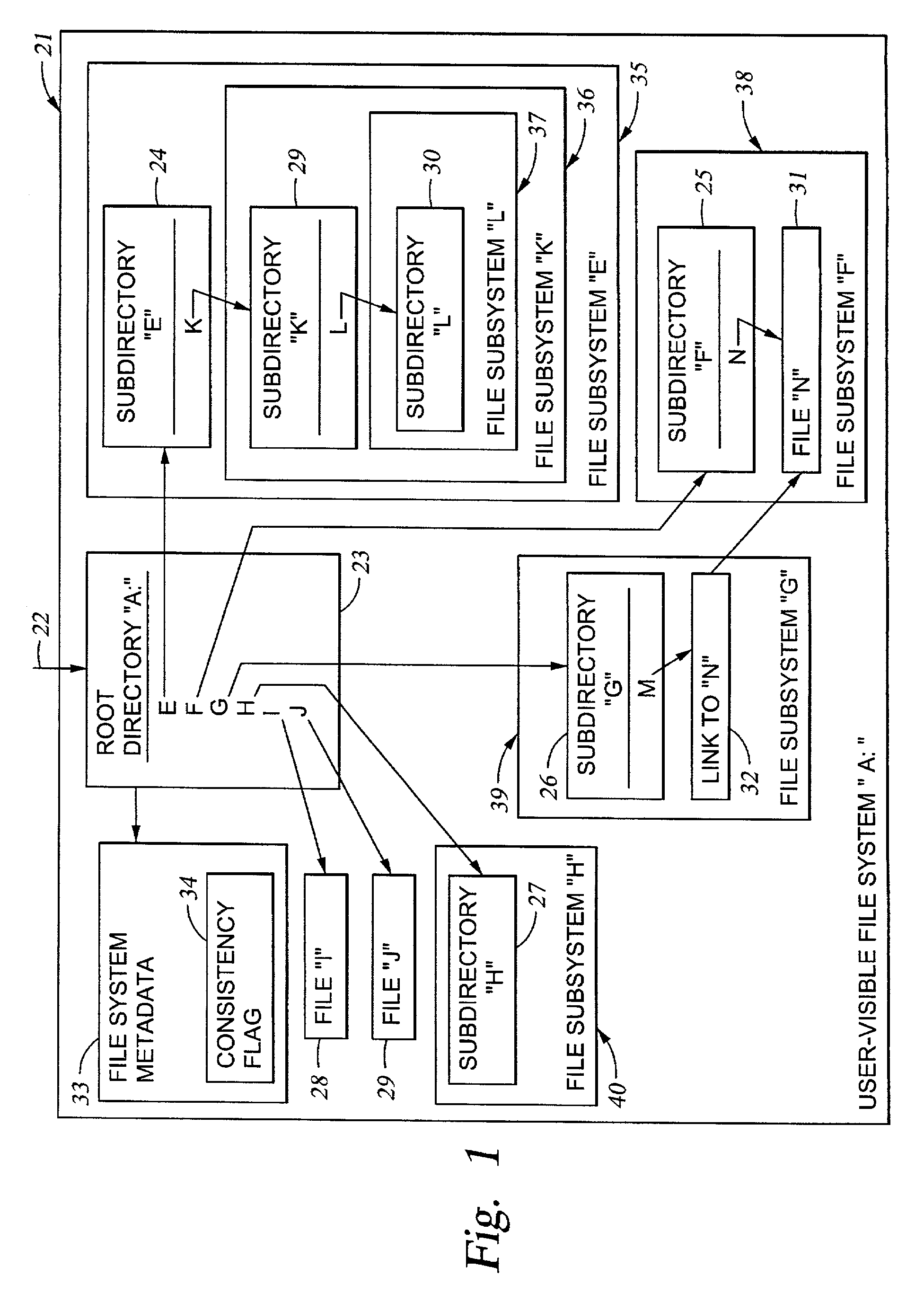
Cluster meta file system of file system cells managed by respective data movers of a network file server
InactiveUS20030158836A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsRouting tableFile system
File system cells are linked together to form a meta file system that appears to a user or application program to be a single file system. The meta file system permits concurrent access by multiple processors in a file server wherein each file system cell is managed by a respective one of the processors. The file server responds to a directory access request by returning a file handle containing a file system cell ID and a pointer to a file in the file system cell. The file server responds to a subsequent file access request including the file handle by extracting the file system cell ID and the pointer to the file, searching a routing table for an entry having a file system cell ID matching the file system cell ID extracted from the file handle, and routing the request to the processor managing the file system cell.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Position-tracking device for position-tracking system
ActiveUS7245215B2High position resolutionImprove accuracyInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlTransceiverObject based
A position-tracking system for tracking the position of an object is disclosed. According to various embodiments, the tracking system includes a tracking device that is connected to or otherwise affixed to the object to be tracked. The tracking device may include, among other things, an inertial sensor assembly, radio transceivers and a processor. The position tracking system may also include a host processing system that is in communication with the tracking device. The position tracking system may provide variable-resolution position information based on the environment in which the object is moving. In a “wide resolution” area, the system may compute a general position for the object based on a wireless telephone network Cell-ID / map correlation architecture. In a high-resolution area, greater position resolution may be realized from the combination of a wireless aiding system and inputs from the inertial sensors. In the high-resolution mode, the system may exploit distinct patterns of motion that can be identified as motion “signatures” that are characteristic of certain types of motion. Kinematic (or object movement) models may be constructed based on these motion signatures and the position tracking system may estimate the state of the object based on the kinematic model for the current mode of the object. Adaptive and cascaded Kalman filtering may be employed in the analysis to more accurately estimate the position and velocity of the object based on the motion pattern identified.
Owner:PINC SOLUTIONS
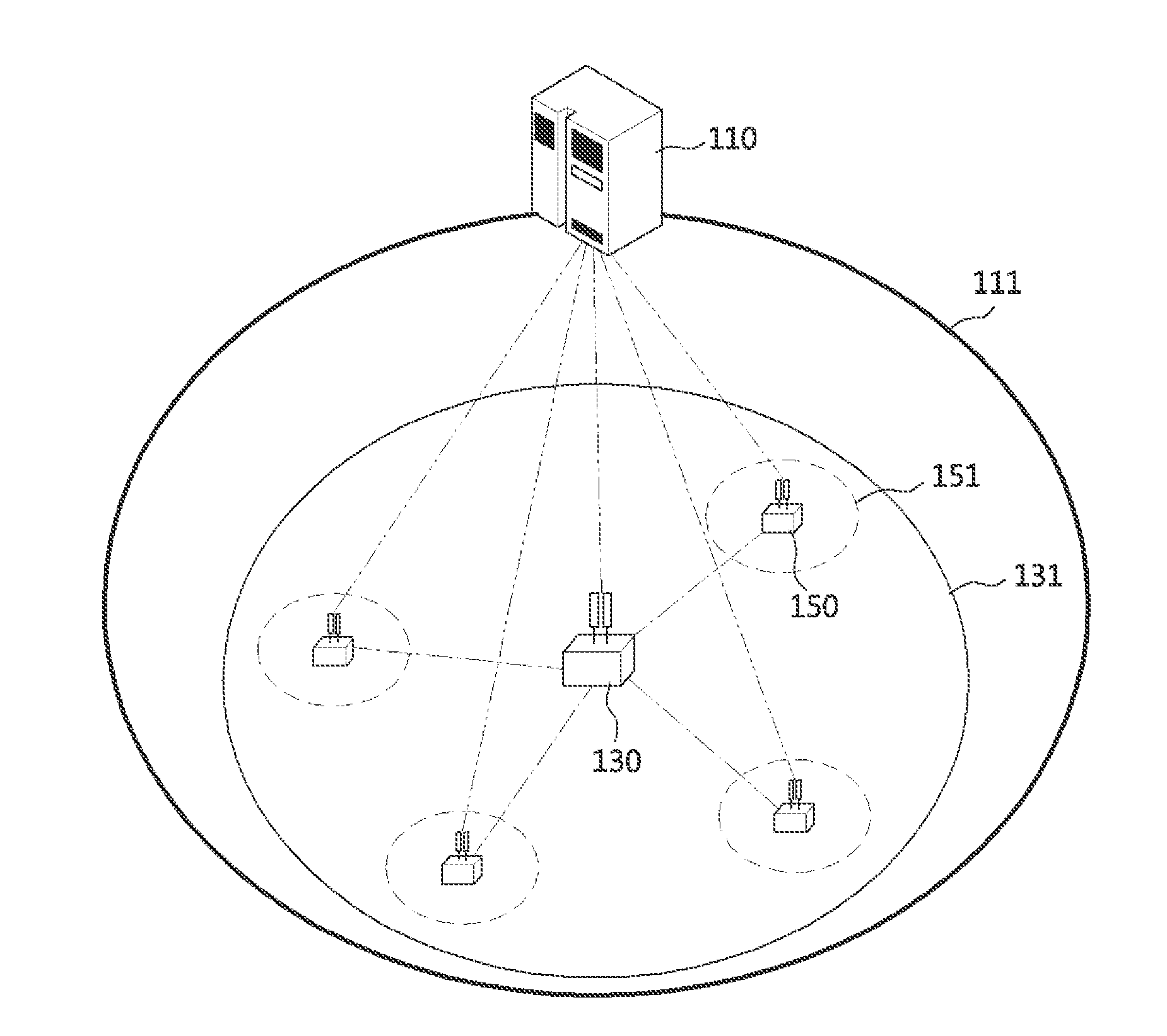
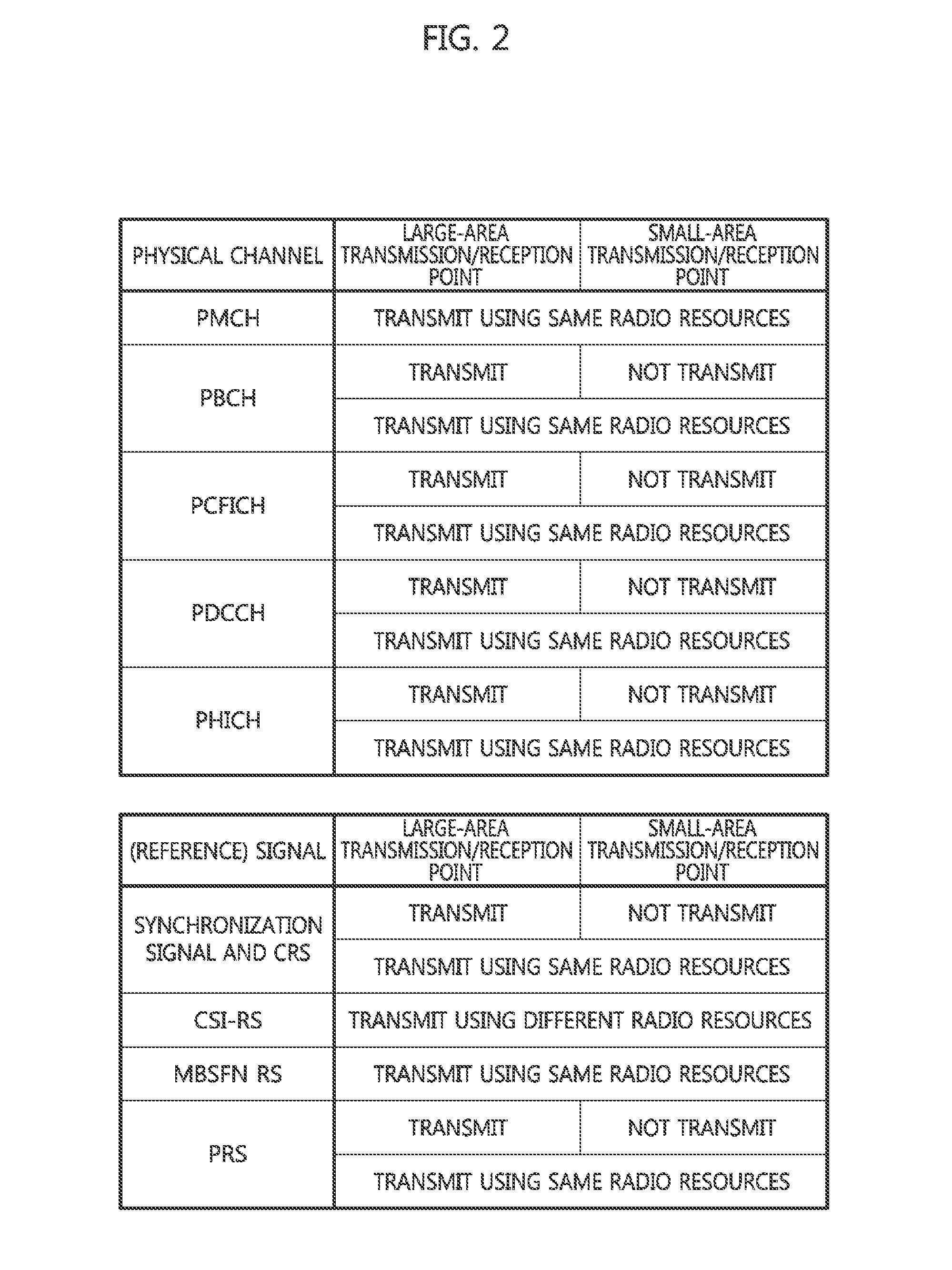
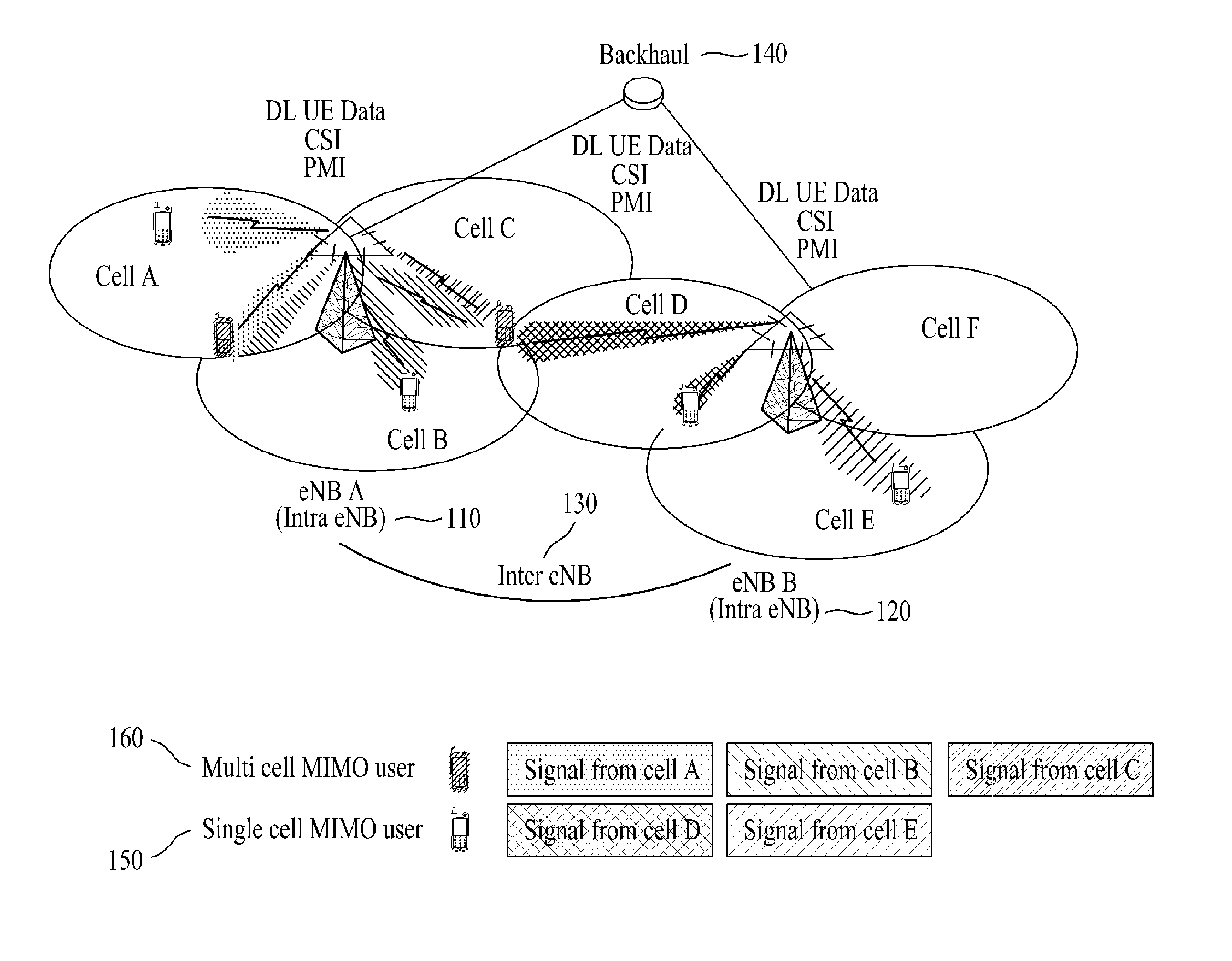
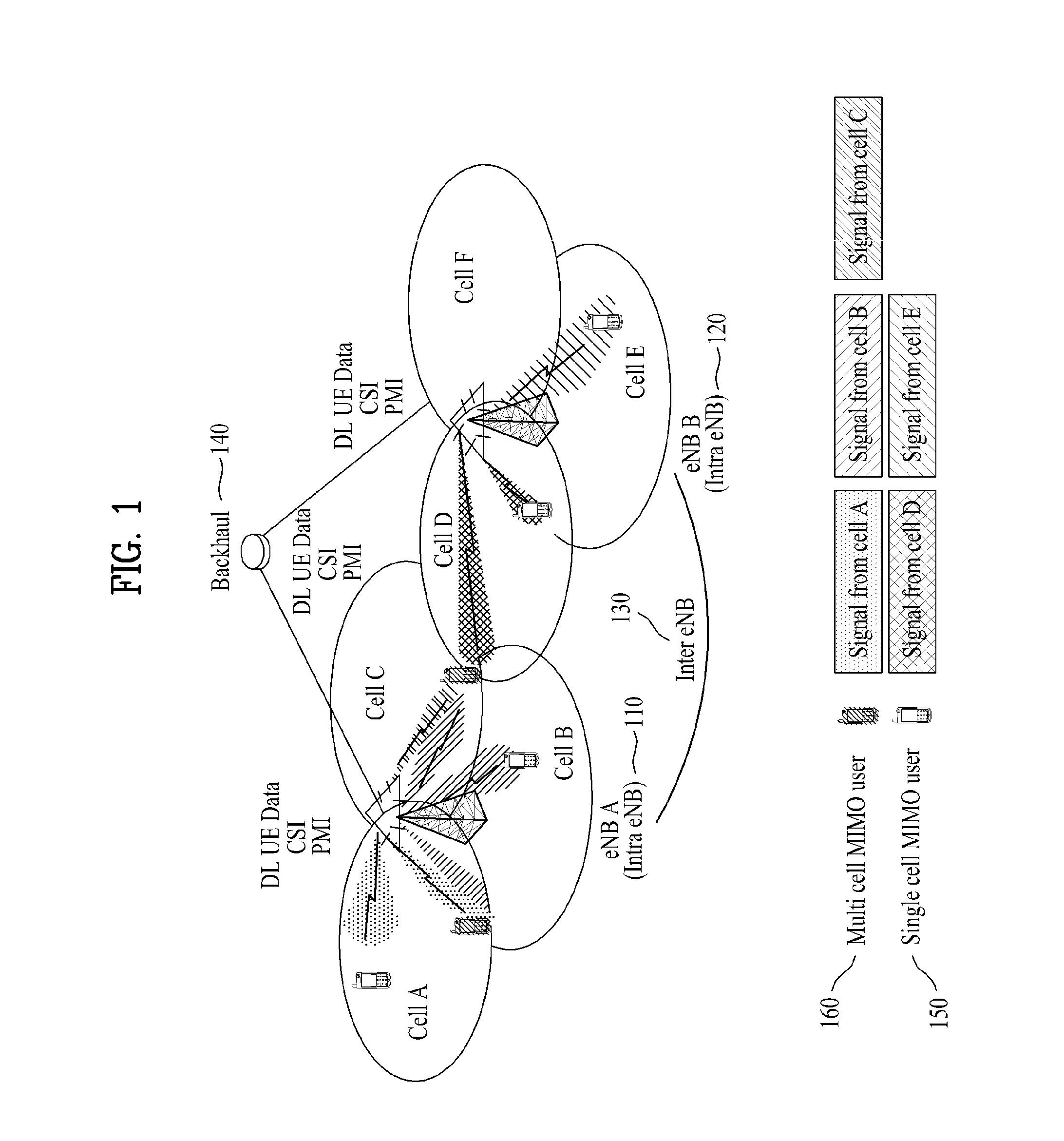
Wireless communication system using multiple transmission and reception points
ActiveUS20130315195A1Guaranteed normal transmissionMinimize changesSite diversityReceivers monitoringVirtual terminalVirtual cell
Disclosed is a wireless communication system using multiple transmission and reception points. In a wireless communication system having a first transmission and reception point and at least one second transmission and reception point belonging to the same cell, the first transmission and reception point has a wider transmission area than the at least one second transmission and reception point, and the first transmission and reception point and the at least one second transmission and reception point generate downlink transmission signals by using the same physical layer cell ID or virtual cell IDs allocated to each terminal, and then the terminals generate uplink transmission signals by using the allocated virtual cell IDs.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
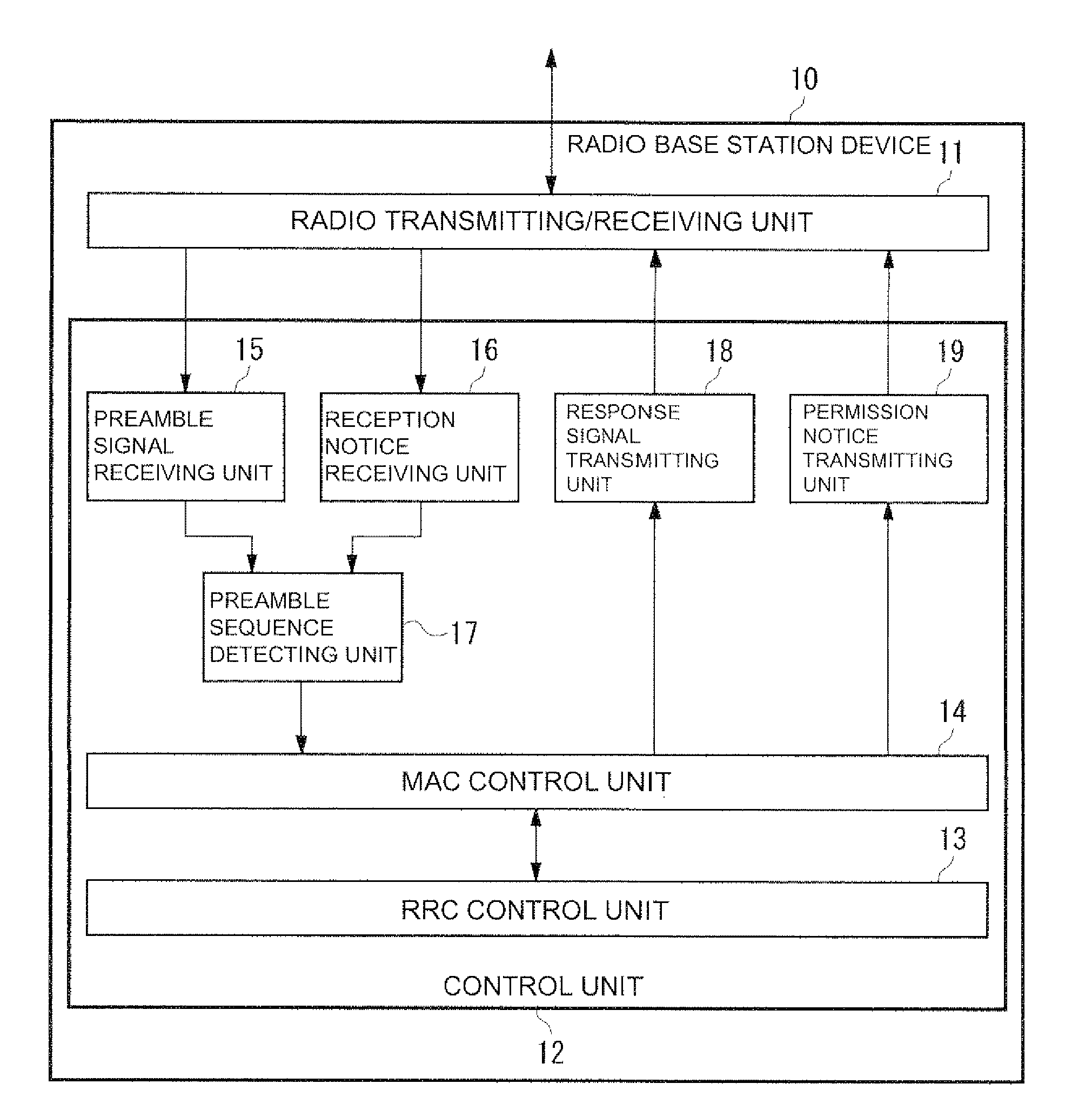
Radio base station device, radio relay station device, and radio terminal device
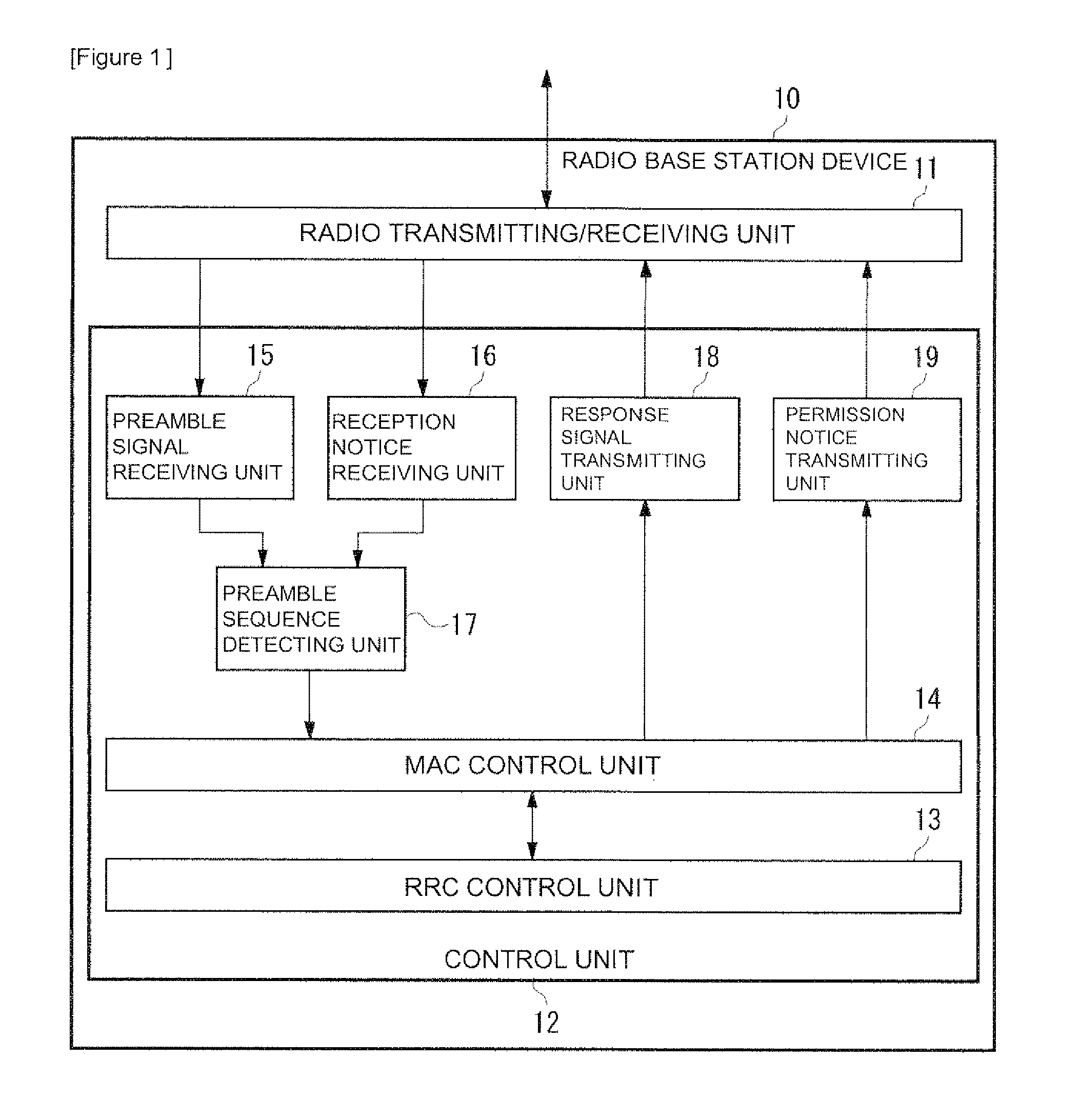
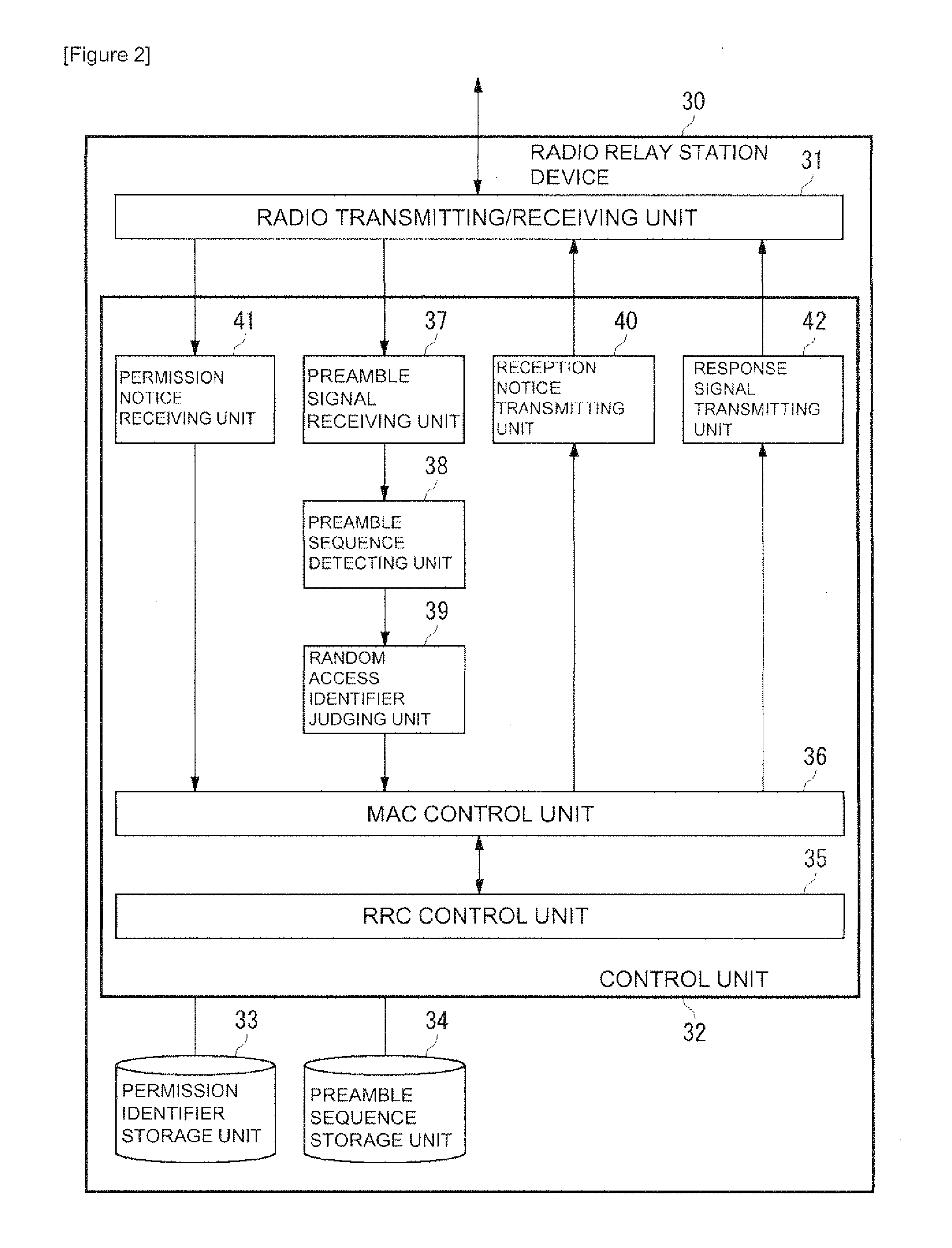
InactiveUS20110110258A1High frequencyExacerbate latencyError preventionTransmission systemsCell IDTerminal equipment
A radio base station device comprises: a preamble signal receiving unit (15) that receives a RACH preamble signal transmitted from a radio terminal device; a reception notice receiving unit (16) that receives, from a radio relay station device, a reception notice indicating that the radio relay station device has received the RACH preamble signal; and a response signal transmitting unit (18) which, when an identifier (RA-ID) of the RACH preamble signal transmitted from the radio terminal device matches an identifier comprised in the preamble reception notice transmitted from the radio relay station device, permits the use of an identifier by the radio relay station device and transmits, to the radio terminal device, a RACH response signal (RACH Response) comprising a cell identifier (Cell ID) of a cell managed by the radio relay station device permitted to use the identifier. Accordingly, the latency when establishing a connection can be reduced.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
Communication control apparatus, communication control method, program, terminal equipment and wireless communication system
InactiveUS20110244859A1Optimize switching orderEasy to switchWireless communicationCommunications systemTerminal equipment
There is provided a communication control apparatus to control handover with terminal equipment including a position information acquisition unit to acquire position information containing a cell ID specifying a cell to which the terminal equipment is connected, a storage unit to store a series of the position information acquired by the position information acquisition unit as position information history, a determination unit to determine whether the terminal equipment should have been connected to each cell specified by each cell ID contained in the position information history on a movement route of the terminal equipment, and a data generation unit to generate recommended handover order data indicating connection order of cells to be recommended for the terminal equipment by removing a cell ID specifying a cell determined to which the terminal equipment should not have been connected by the determination unit from the position information history.
Owner:SONY CORP
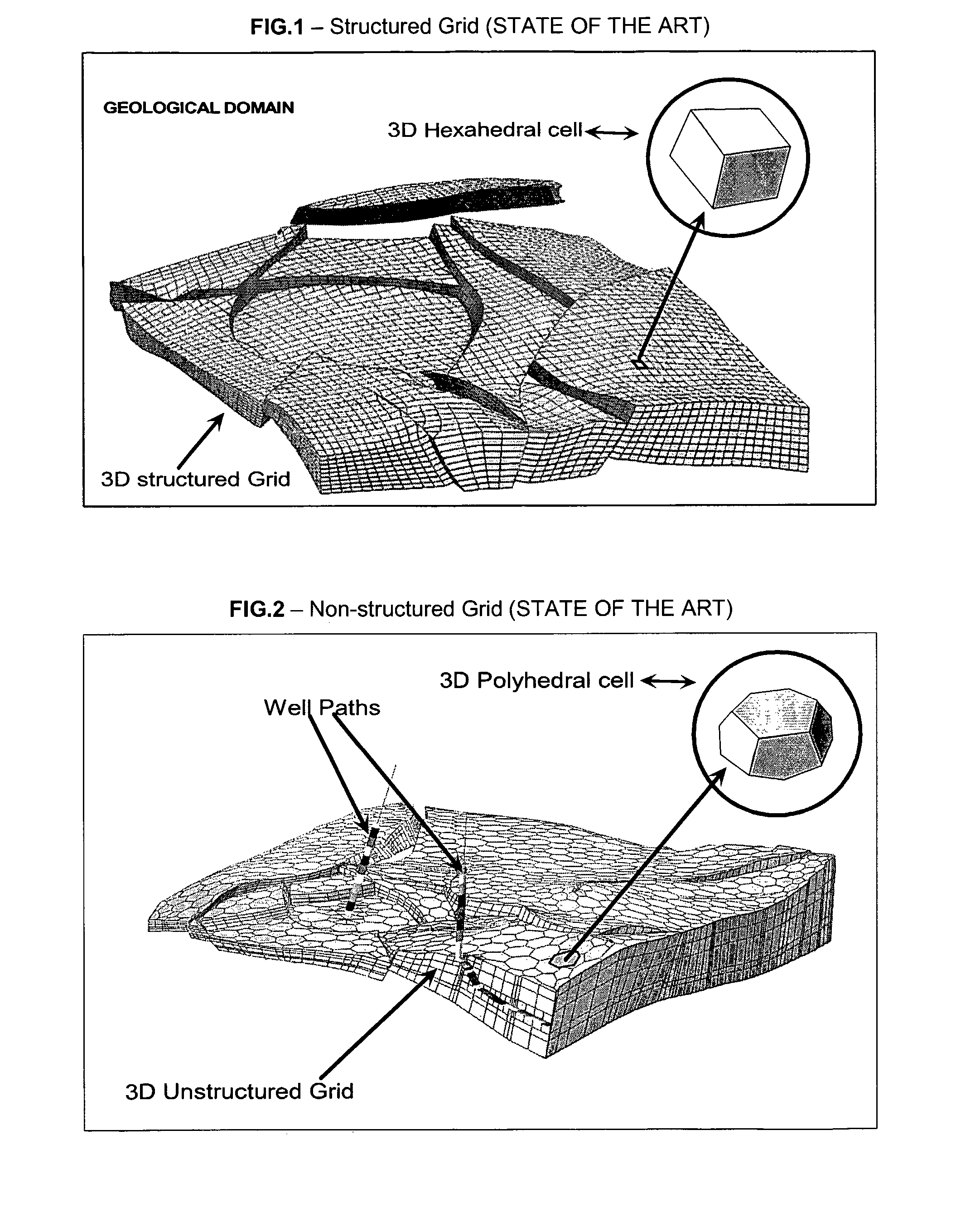
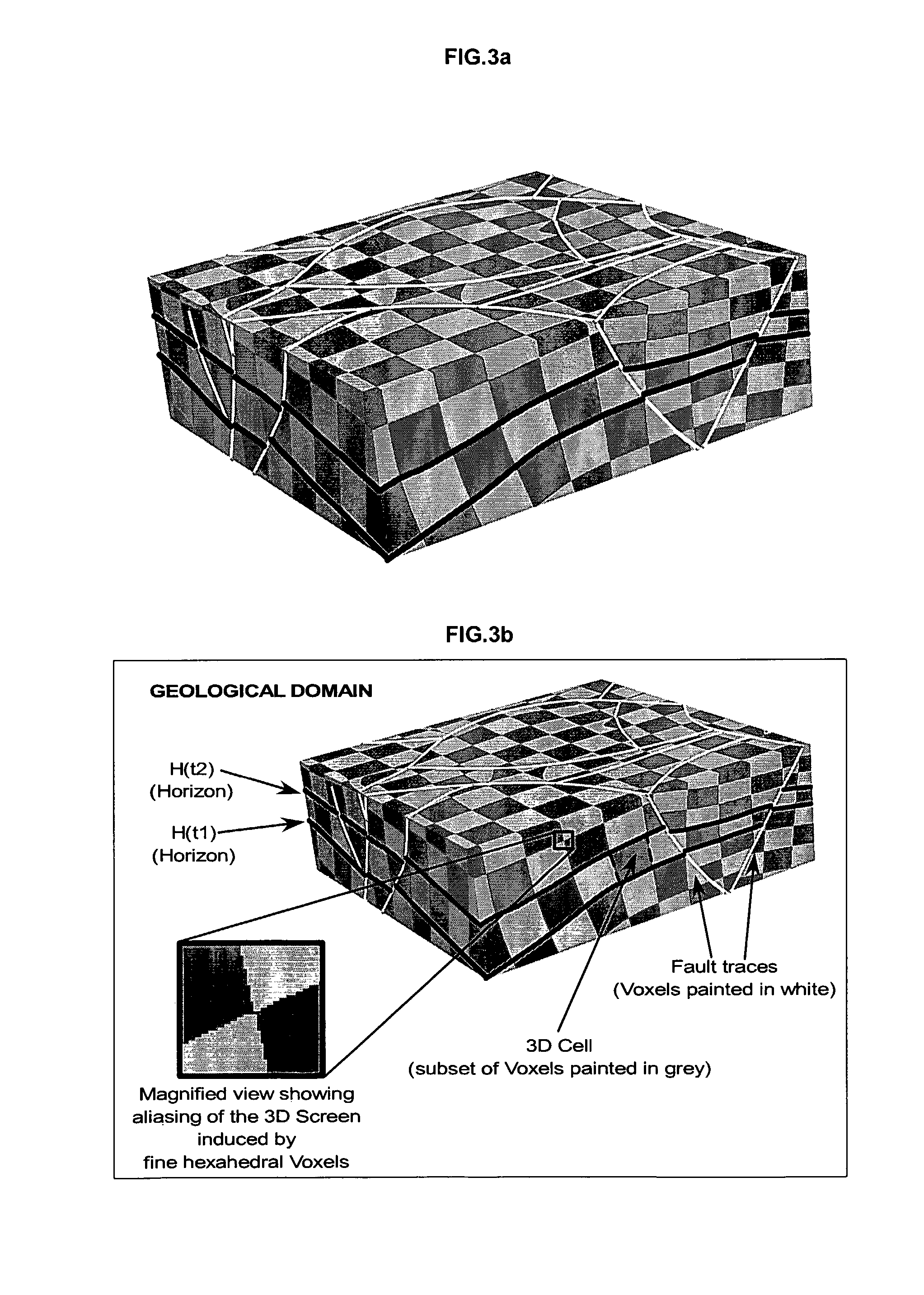
Method For Building A Three Dimensional Cellular Partition Of A Geological Domain
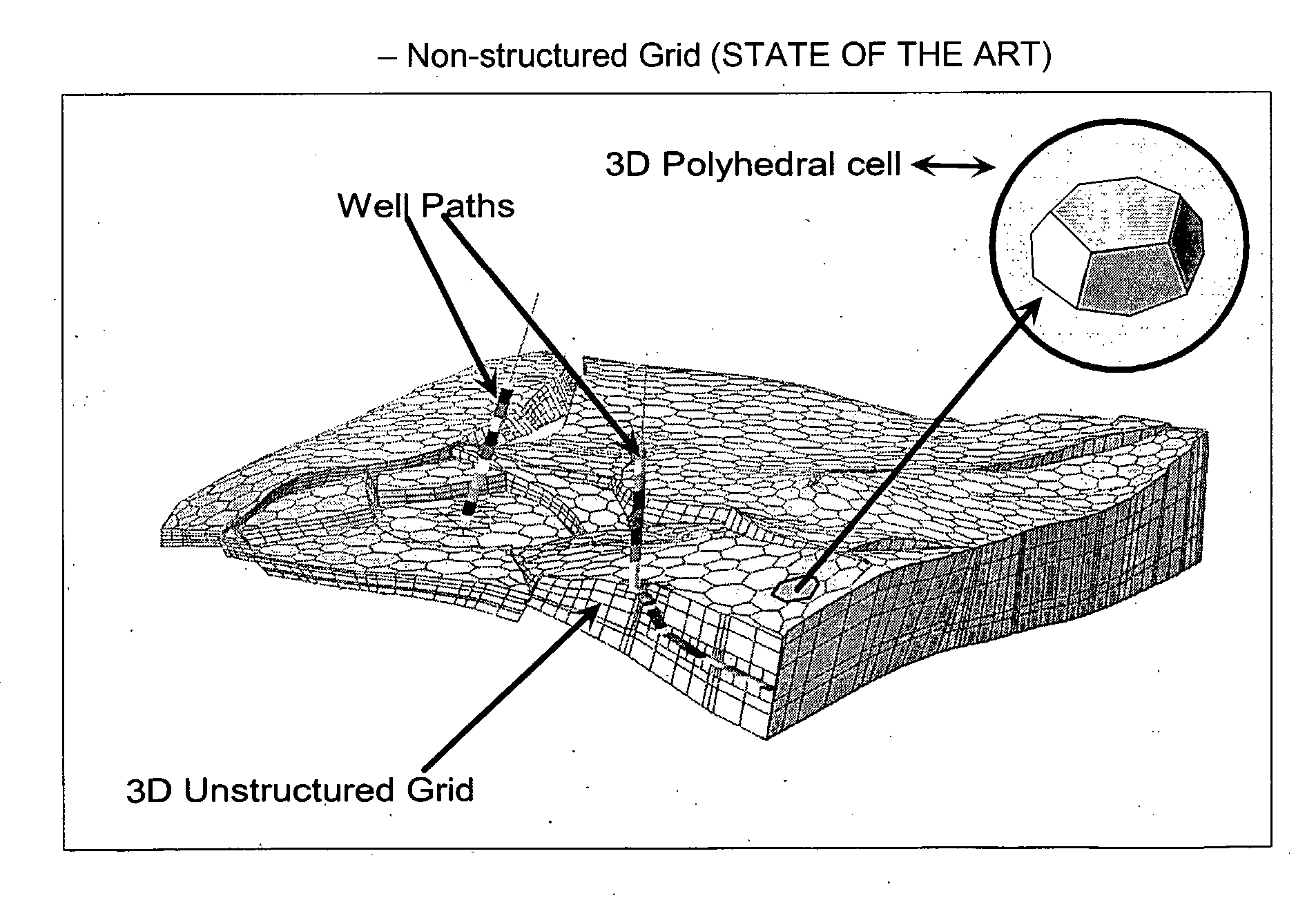
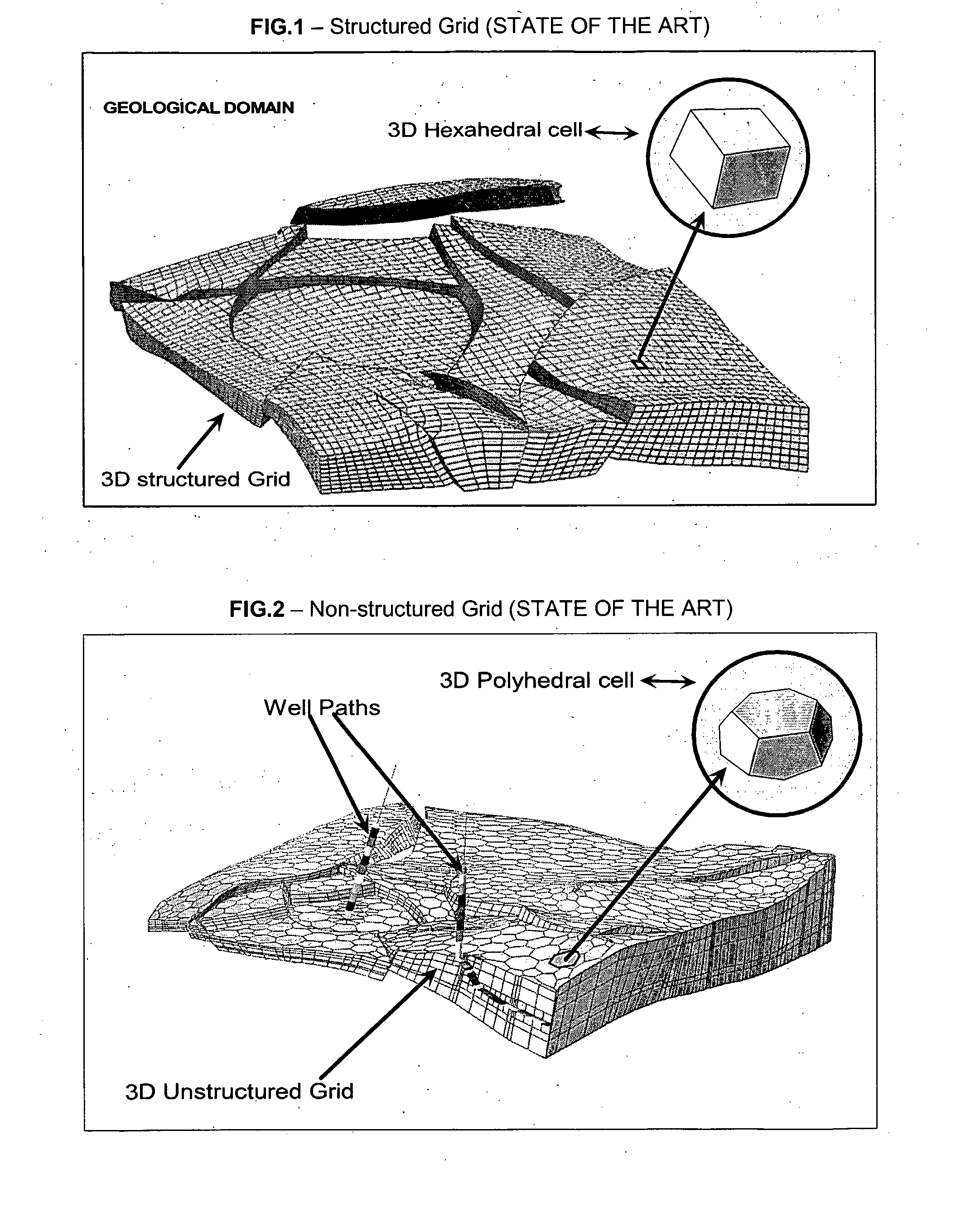
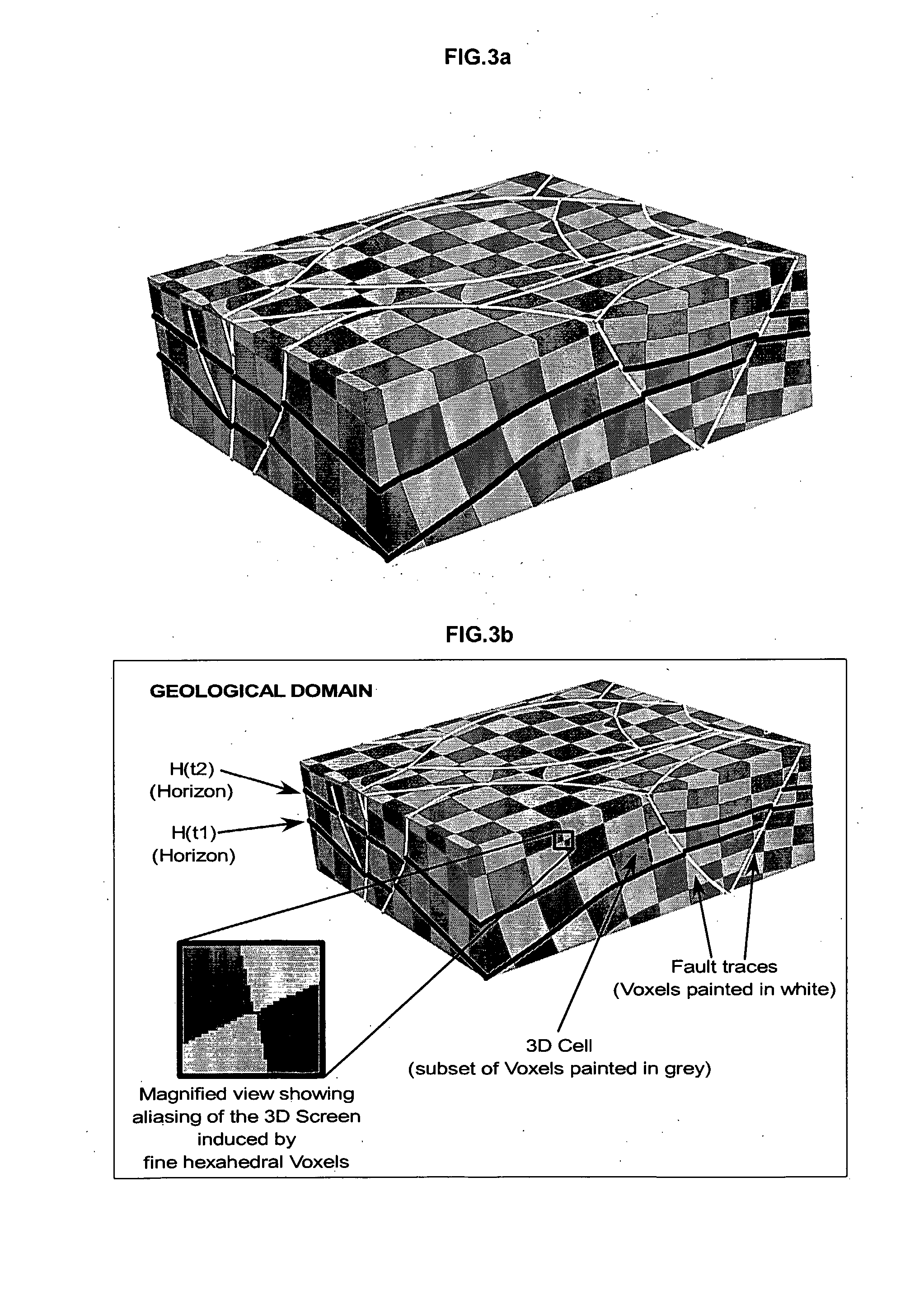
The invention concerns a method for building a three-dimensional (3D) cellular partition covering a 3D geological domain by defining the cells of the partition, characterized in that said method comprises the following steps A “3D screen construction step” for constructing a 3D screen which is a 3D elementary partition covering the geological domain, said 3D screen being composed of a plurality of voxels (Vi) which are elementary volume elements, A “voxel painting step” for associating a cell identifier (Cell-id) to each voxel, A “cell definition step” for defining the cells of the geological domain, each cell of the geological domain being defined as the subset of voxels of the 3D screen associated to the same cell identifier, thereby allowing the definition of the cells of the geological domain without having to code the geometry and / or topology of said cells in said geological volume. The invention further provides a “parametric” method and a “cookiecutter” method using such method for building a 3D cellular partition.
Owner:PARADIGM FRANCE
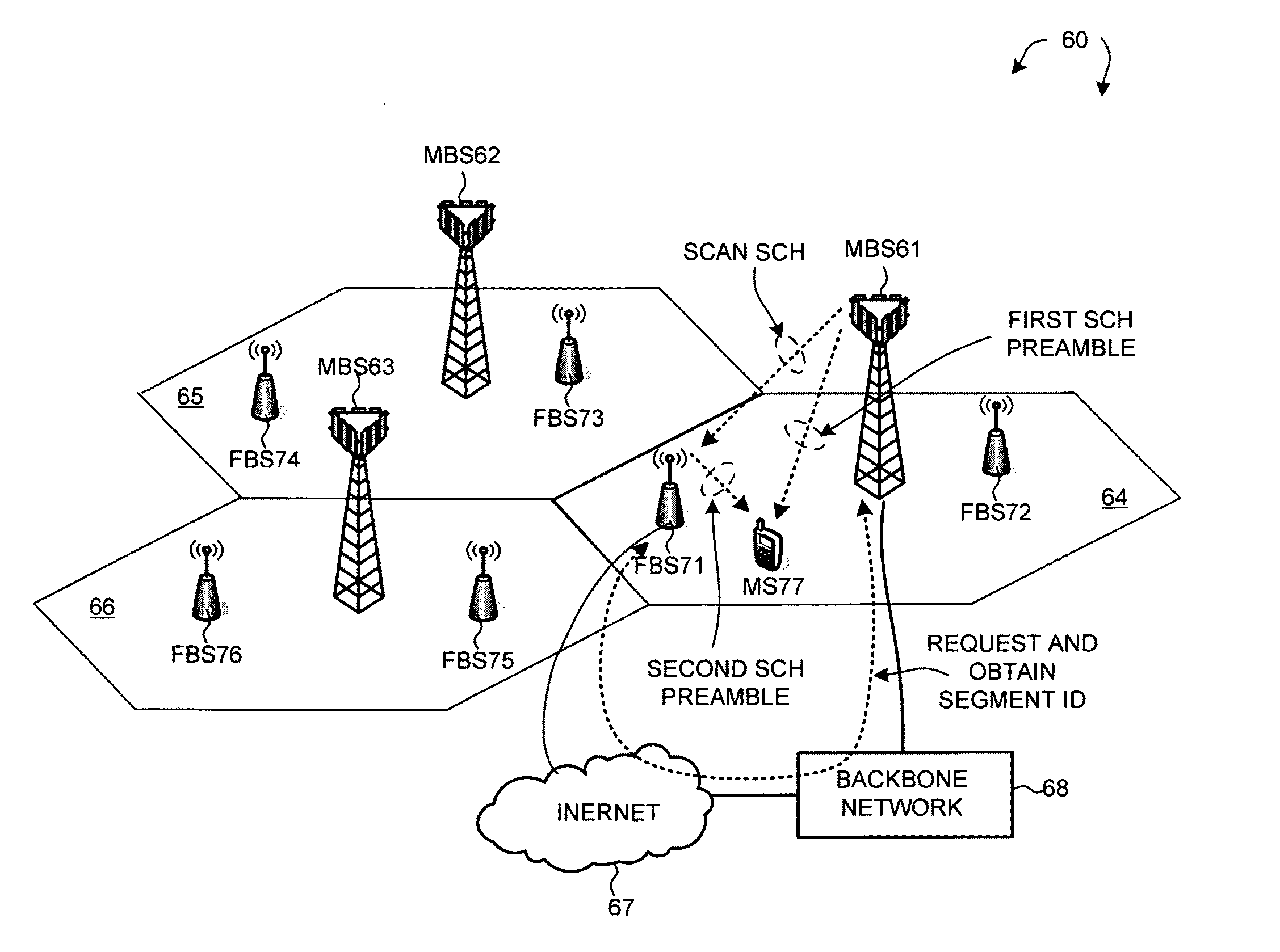
Synchronization channel for advanced wireless OFDM/OFDMA systems
ActiveUS20100165942A1Improve accuracyReduce distractionsSynchronisation arrangementData switching by path configurationTime domainTelecommunications
A hierarchical downlink (DL) synchronization channel (SCH) is provided for wireless OFDM / OFDMA systems. The SCH includes a Primary SCH (P-SCH) for carrying PA-Preambles used for coarse timing and frequency synchronization, and a Secondary SCH (S-SCH) for carrying SA-Preambles used for cell ID detection. The total time length occupied by P-SCH and S-SCH is equal to one OFDM symbol time length of a data channel, and S-SCH is located in front of P-SCH in each DL frame. A perfect multi-period time-domain structure is created and maintained in P-SCH to increase preciseness of frame boundary estimation. With overlapping deployment of macrocells and femtocells, a predefined SCH configuration scheme is provided to separate frequency subbands used for macrocells and femtocells such that interferences in S-SCH can be mitigated. In addition, a self-organized SCH configuration scheme is provided to allow more flexibility for femtocells to avoid or introduce interference in S-SCH.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
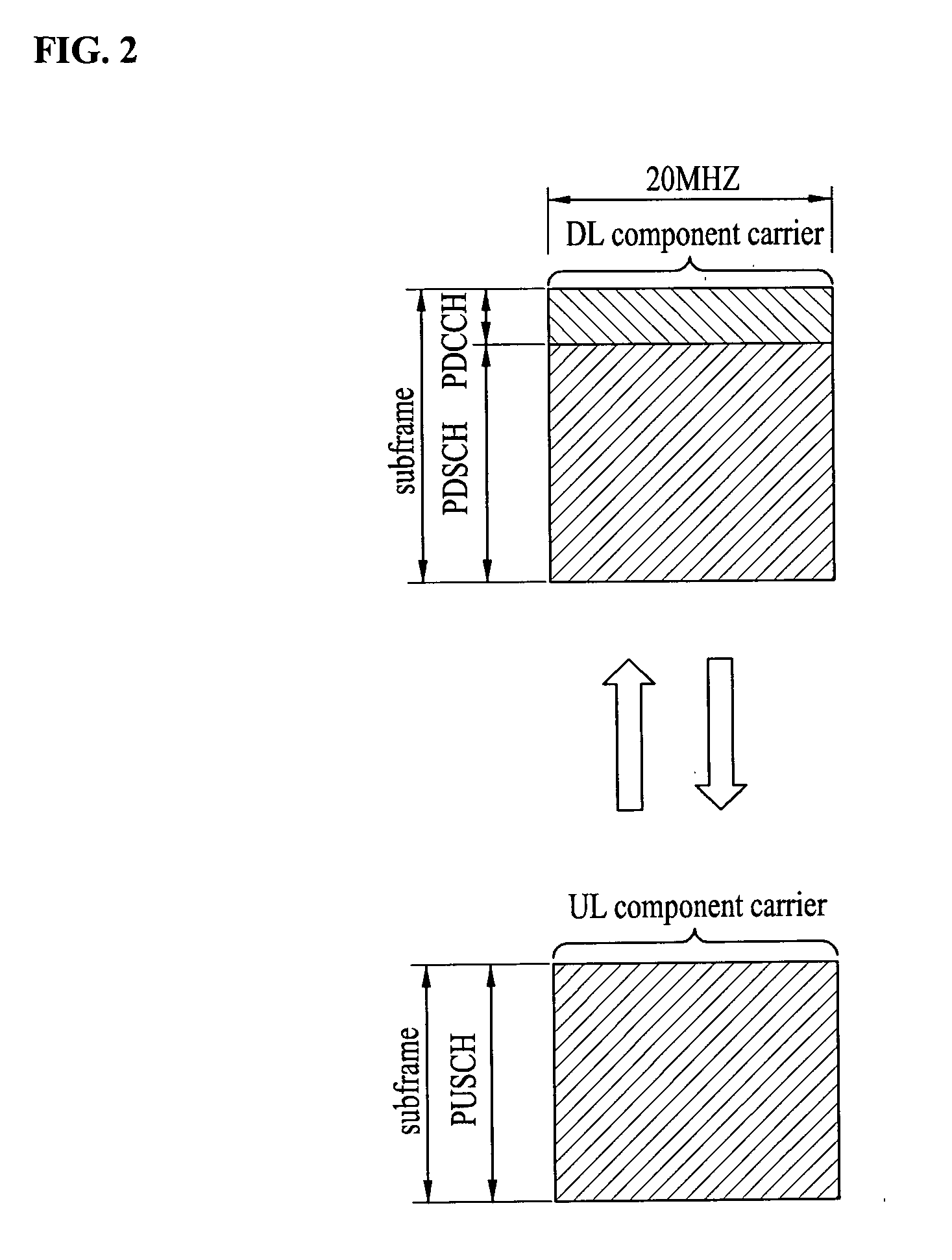
Method for wireless communication between user equipment and base station in wireless communication system supporting first user equipment that uses single frequency band and second user equipment that uses plurality of frequency bands
InactiveUS20110098074A1Increase valueTransmission path divisionRadio transmissionCommunications systemCarrier signal
A method for wireless communication between user equipments (UEs) and a base station in a wireless communication system that supports a first UE using a single band and a second UE using multiple bands is provided. In the method, UE receives, from the base station, resource allocation information including information regarding a downlink component carrier (CC) and an uplink CC allocated to the UE, receives the allocated downlink CC, and transmits the allocated uplink CC by applying a cell ID thereto. The allocated downlink CC is one of downlink CCs to which different cell IDs are applied, pairs of CCs are predefined by associating uplink CCs respectively with downlink CCs in order to support the first UE. When the allocated downlink and uplink CCs do not belong to the pairs of CCs, the applied cell ID is a cell ID of a downlink CC that is paired with the allocated uplink CC in the predefined pairs of CCs.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method for building a three dimensional cellular partition of a geological domain
ActiveUS7711532B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingComputation using non-contact making devicesVoxelCell ID
Owner:PARADIGM FRANCE
Method for Estimating Channel State in a Wireless Communication System Using Fractional Frequency Reuse and Mobile Station Using the Same
InactiveUS20100311349A1Eliminate the problemSite diversityAssess restrictionCommunications systemFrequency reuse
A method for estimating channel state in a wireless communication system and a mobile station using the same are disclosed. The method includes acquiring cell Identifiers (IDs) of a serving cell and one or more neighbor cells, acquiring information about preset power level patterns for one or more frequency partitions to which FFR is applied according to the cell IDs, and estimating a channel state of the serving cell based on the power level pattern information.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Positioning method for the user plane to observe the reached time difference
InactiveCN101035379ALow investment costPosition fixationCode division multiplexOperational maintenanceCell ID
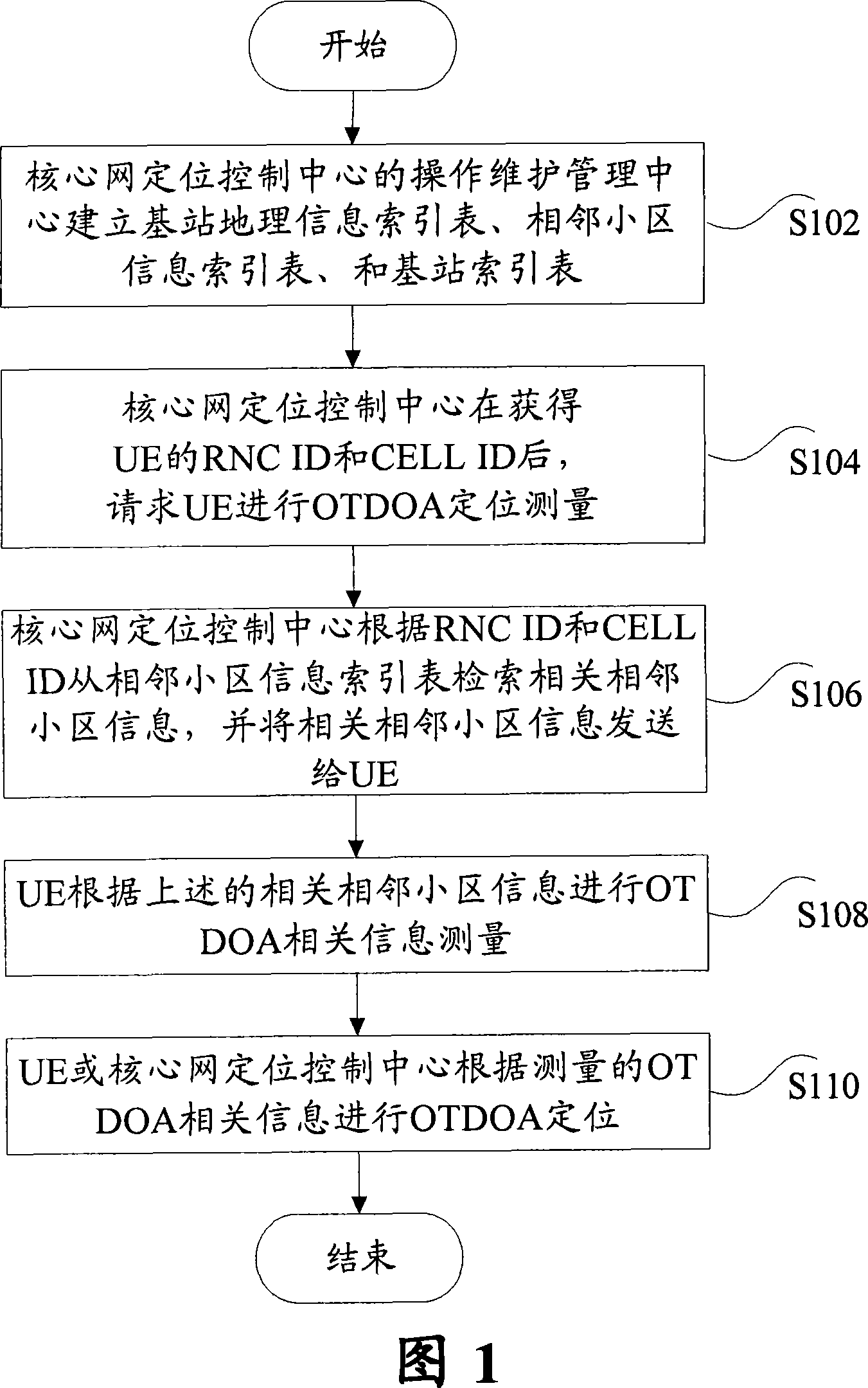
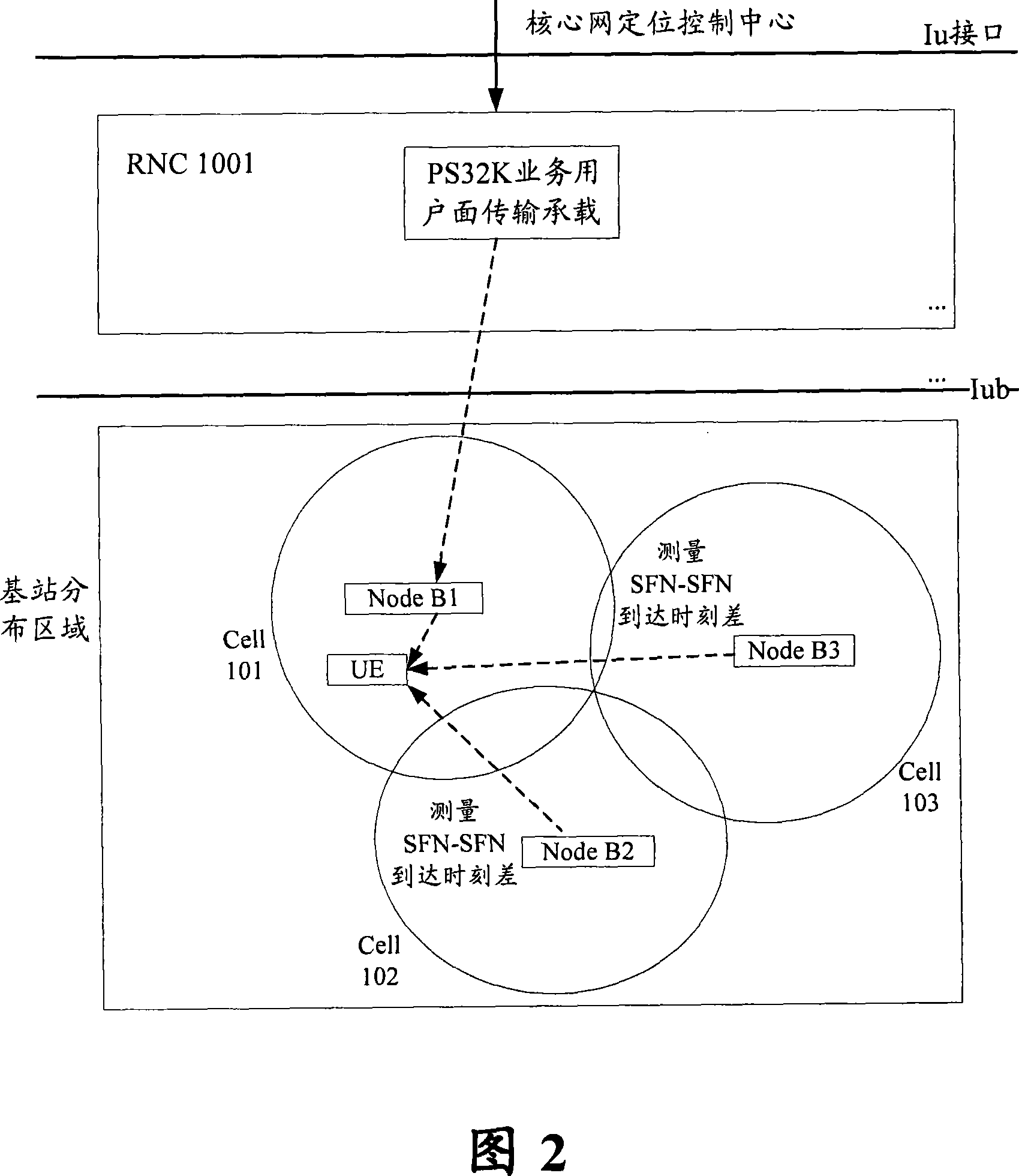
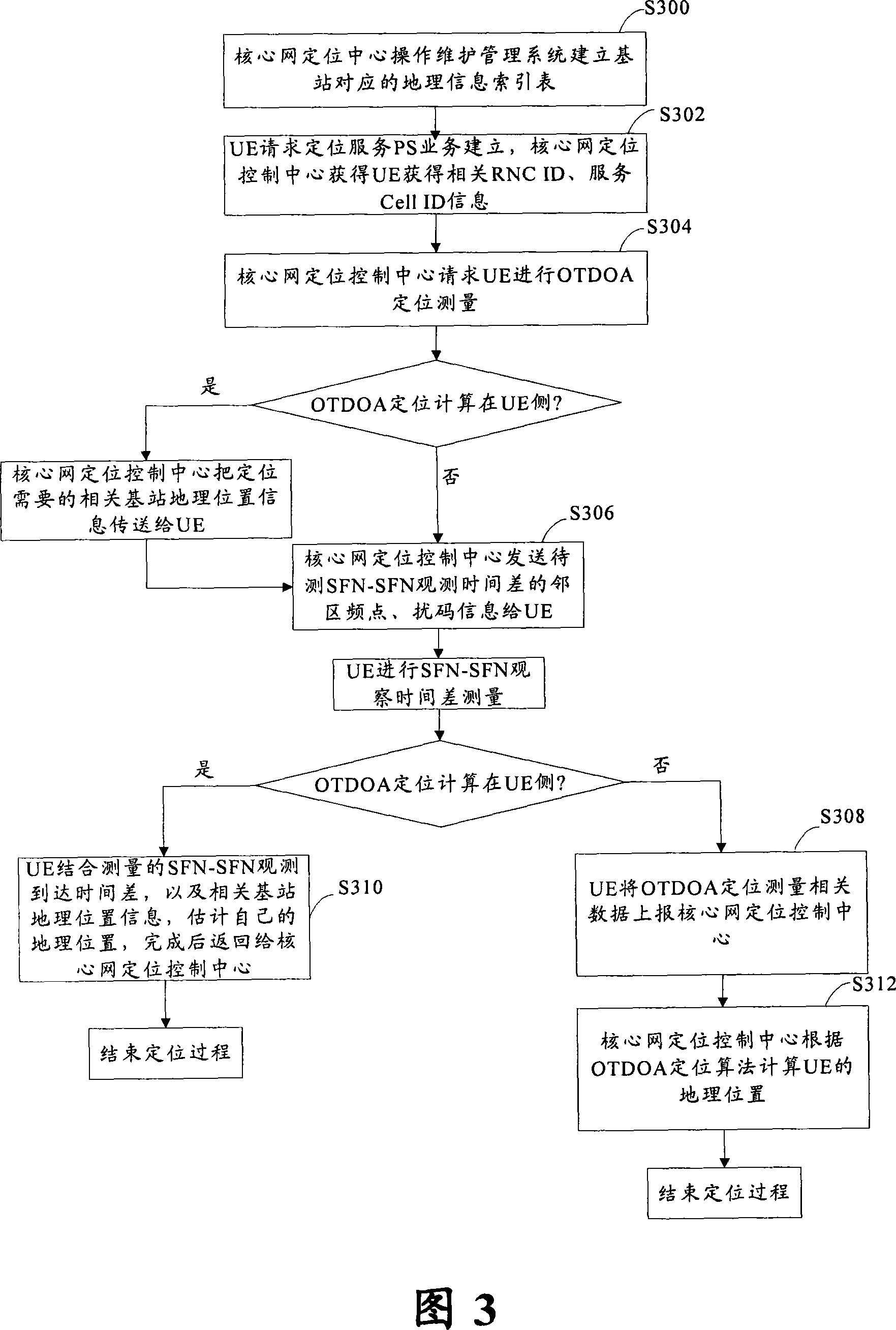
The invention discloses a user-interface OTDOA locating method, comprising the steps of: S102. the operation and maintenance system of a kernel network locating control center establishes a base station's geographic information index table, an adjacent cell information index table and a base station index table; S104. the kernel network locating control center obtains RNC ID and CELL IN of UE and then requests the UE to make OTDOA locating measurement; S106. the kernel network locating control center searches the related adjacent cell information in the adjacent cell information index table according to the RNC ID and CELL ID of the UE and sends the related adjacent cell information to the UE; S108. the UE makes OTDOA-related information measurement according to the related adjacent cell information; and S110. the UE or kernel network locating control center makes OTDOA locating according to the measured OTDOA-related information.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Position-tracing system
ActiveUS20060187028A1Improve accuracyHigh position resolutionInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlTransceiverObject based
A position-tracking system for tracking the position of an object is disclosed. According to various embodiments, the tracking system includes a tracking device that is connected to or otherwise affixed to the object to be tracked. The tracking device may include, among other things, an inertial sensor assembly, radio transceivers and a processor. The position tracking system may also include a host processing system that is in communication with the tracking device. The position tracking system may provide variable-resolution position information based on the environment in which the object is moving. In a “wide resolution” area, the system may compute a general position for the object based on a wireless telephone network Cell-ID / map correlation architecture. In a high-resolution area, greater position resolution may be realized from the combination of a wireless aiding system and inputs from the inertial sensors. In the high-resolution mode, the system may exploit distinct patterns of motion that can be identified as motion “signatures” that are characteristic of certain types of motion. Kinematic (or object movement) models may be constructed based on these motion signatures and the position tracking system may estimate the state of the object based on the kinematic model for the current mode of the object. Adaptive and cascaded Kalman filtering may be employed in the analysis to more accurately estimate the position and velocity of the object based on the motion pattern identified.
Owner:PINC SOLUTIONS
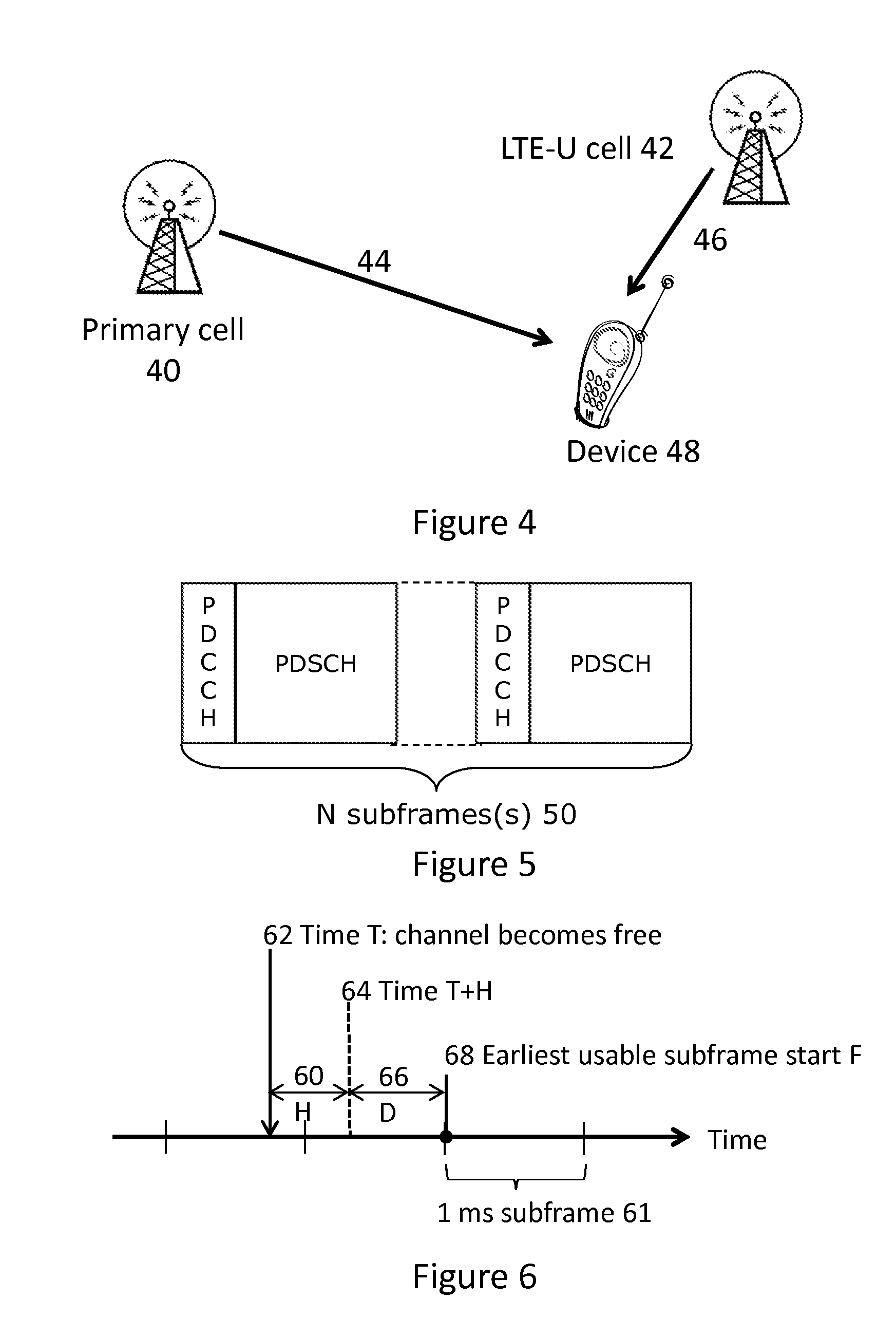
LTE Transmission in Unlicensed Bands
ActiveUS20160007378A1Synchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementTelecommunicationsCell ID
A method of receiving LTE data by a user device, the data being transmitted on a channel of an unlicensed band comprising the steps of receiving a cell ID from a primary LTE cell, receiving system information from the primary LTE cell for access to an unlicensed channel, receiving LTE data on the channel of an unlicensed band.
Owner:SEQUANS COMMUNICATIONS
Method for measuring road traffic load based on analyzing cellular communications
InactiveUS20050227696A1Detection of traffic movementVehicle position indicationCell IDControl channel
A system and method that continuously extracts traffic load and speed on roads within the coverage area of a cellular network. The data is extracted directly from communications in a cellular network without using any external sensors. The method enables correlating a car to a road it travels on and determining its speed by using only the partial data that arrives to the cellular switch. The method consists of the following stages: A learn phase, which can include a vehicle(s) with a location device (say GPS system) travels across the covered routes within a designated area and collects the cellular data (cell handover sequences and signal strength reports) and location data in parallel. The accumulated data is then analyzed and processed to create the reference database. An operational stage in which communications on the cellular network control channel are monitored continuously, and matched against the reference database in order to locate their route and speed. The route and speed data is used in order to create a traffic status map within the designated area and alarm in real time on traffic incidents. The data analysis and data base structure are done in a manner that will enable the following: Very fast, high reliability initial identification of the vehicle's route in the operational stage, based on handovers' cell ID only. Very fast, high reliability follow up forward and backwards of the vehicle's route in the operational stage. Real time, high reliability Incident detection.
Owner:CELLINT TRAFFIC SOLUTIONS LTD
Lte-a systems and method of drs based positioning
A Long Term Evolution Advanced (LTE-A) location server, user equipment (UE) and evolved Node-B (eNB) are generally described. Information may be transmitted to the UE from the location server. The transmission may be triggered by the location server or another entity requesting the UE location. The information may permit the UE to receive a discovery reference signal (DRS) from at least one eNB. The information may contain an indication of measurements to be performed using the DRS. The UE may measure Reference Signal Received Power (RSRP) or Reference Signal Time Difference (RSTD) of the DRS. The UE may send the measurement information to the location server where the UE location is estimated. The UE location may be based on measurements of the DRS and a positioning reference signal (PRS) from one or more eNBs to obtain the Observed Time Difference of Arrival (OTDOA) or Enhanced Cell ID (ECID).
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and Apparatus for Detecting Secondary Synchronization Signal
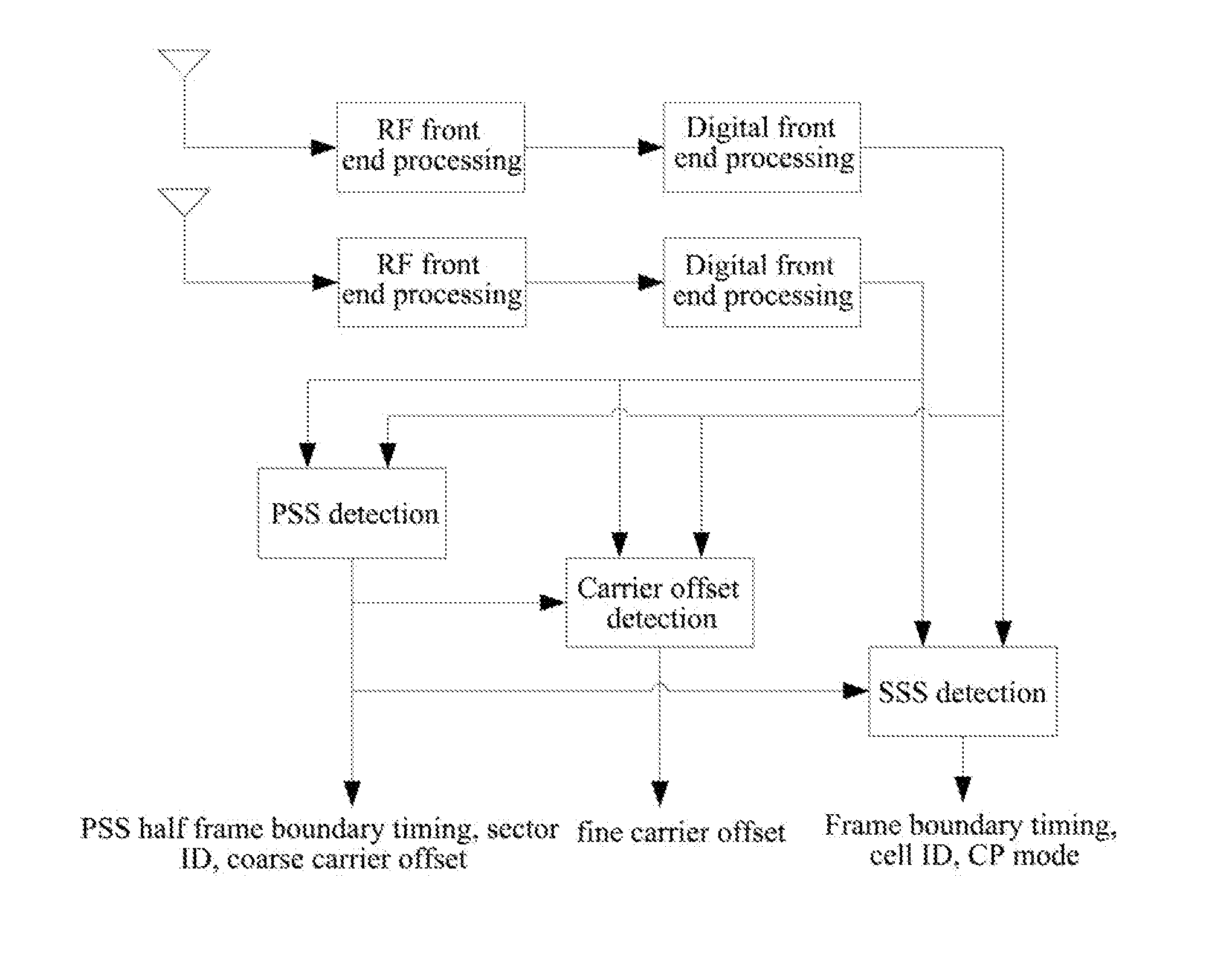
ActiveUS20130176991A1Reduce the amount of calculationIncrease resource consumptionSynchronisation arrangementModulated-carrier systemsTelecommunicationsCell ID
a method and apparatus for detecting a secondary synchronization signal, the method including: calculating a channel estimation compensation value of each sub-carrier of a Secondary Synchronization Signal (SSS) symbol in different Cyclic Prefix (CP) modes; obtaining coherent accumulative results of even half frames and odd half frames of each sub-carrier according to the channel estimation compensation value of each sub-carrier of said SSS symbol; generating a SSS sequence; obtaining an index of the SSS sequence corresponding to an over-threshold value of a first round detection, determining indexes composed of the SSS sequence used in a second round detection according to said index, using coherent accumulative results of all the sub-carriers in the even and odd half frames and SSS sequences of all the sub-carriers to obtain an over-threshold value of the second round detection; and obtaining a CP mode, and calculating a cell ID and a radio frame boundary.
Owner:SANECHIPS TECH CO LTD
Method and system for constructing electronic map locating database
InactiveCN102063499AImprove collection efficiencyShort data acquisition cycleTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsCell IDComputer terminal
The invention discloses a method for constructing an electronic map locating database, comprising the following steps of: simultaneously collecting ID information of a plurality of wireless equipment on a plurality of different geographic coordinates; uploading the collected ID information of the plurality of wireless equipment and the geographic coordinates to a server; solving a position coordinate corresponding to each ID according to the ID information of the plurality of wireless equipment and the geographic coordinates; and integrating each ID and the position coordinate corresponding to the ID to form a locating database. With the method, a plurality of CELL IDs of a plurality of base states and / or a plurality of MAC (Multi-Access-Computer) addresses of a plurality of WIFIs (Wireless Fidelity) on a same location can be simultaneously collected through a mobile communication terminal, the plurality of CELL IDs and / or the plurality of MAC addresses can be uploaded to a back-end server for operation and the plurality of CELL IDs and / or the plurality of MAC addresses with a plurality of corresponding position coordinates are bound to form the electronic map locating database, thereby higher collection efficiency and shorter collection data period are realized and the electronic map locating database can be established to conveniently provide location service to a user in a plurality of modes and satisfy the location needs under various conditions.
Owner:BAIDU ONLINE NETWORK TECH (BEIJIBG) CO LTD
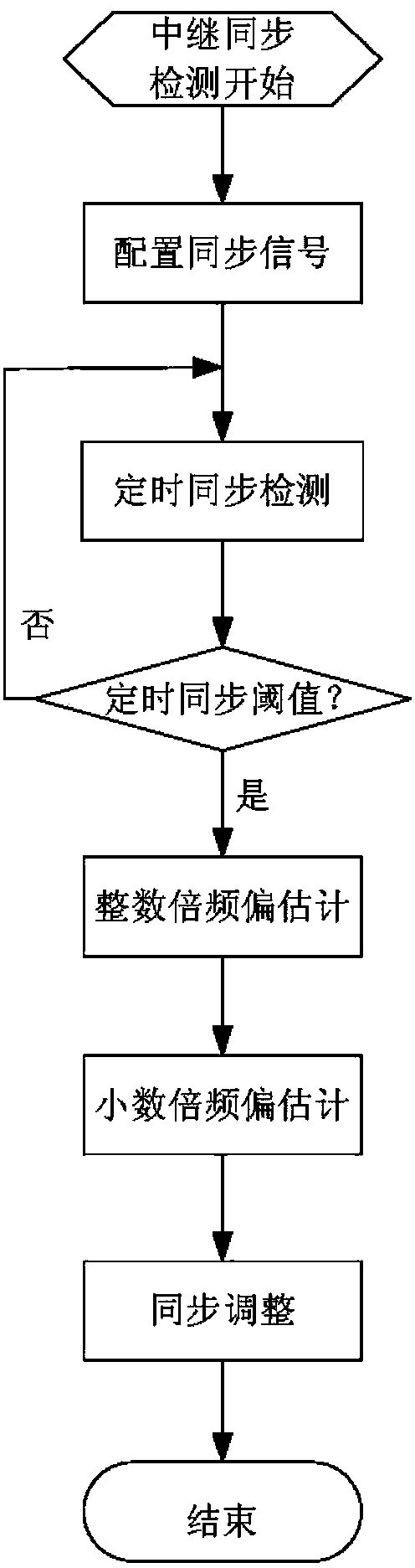
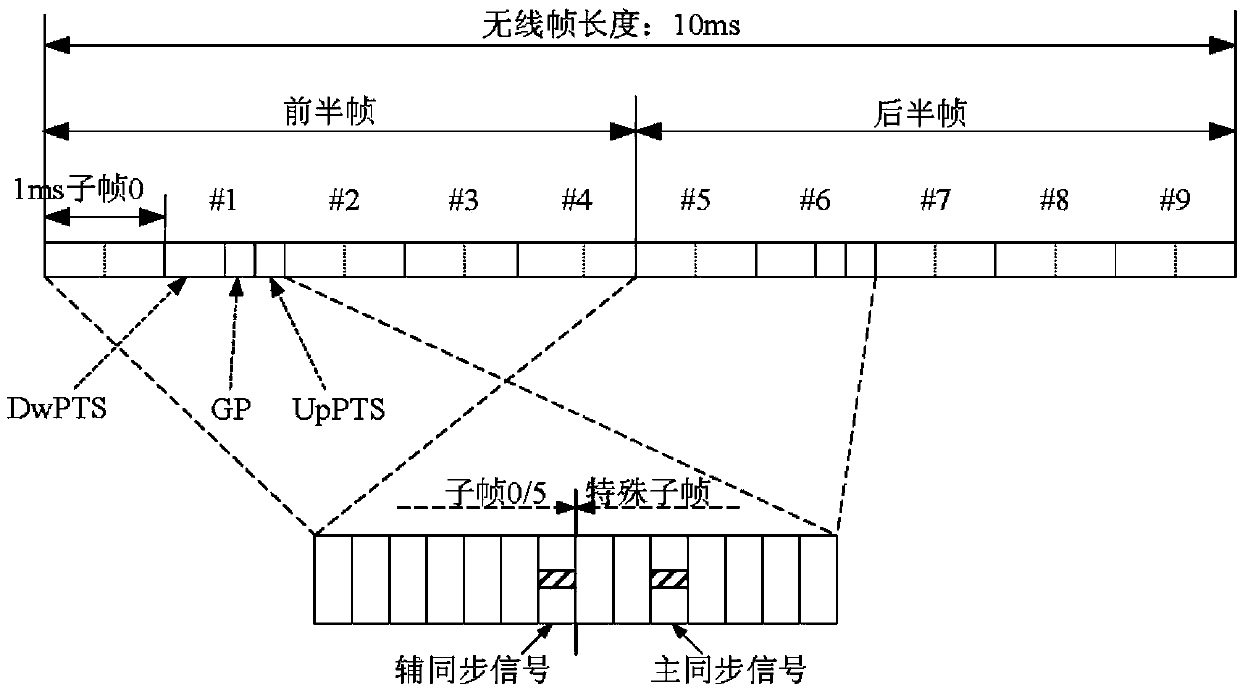
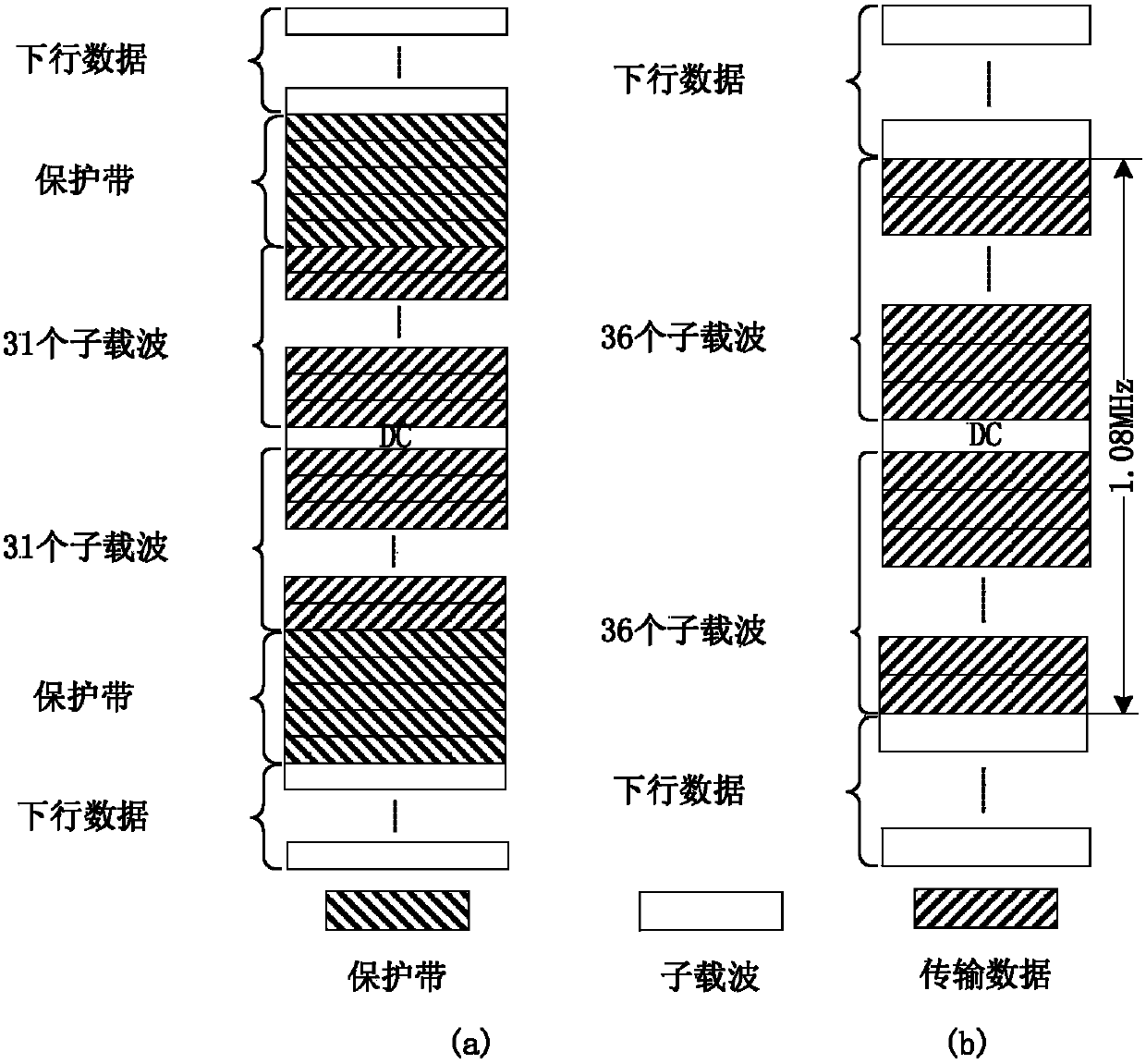
TD-LTE (Time Division-Long Term Evolution) frequency offset estimation method for relay system
InactiveCN103701733AMake up for the disadvantage of unknown bandwidthSynchronous sending signal frequencyTransmitter/receiver shaping networksTime-Division Long-Term EvolutionEstimation methods
The invention provides a TD-LTE (Time Division-Long Term Evolution) frequency offset estimation method for a relay system and relates to services or facilities suitable for a wireless communication network. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining positions of synchronizing signals and information about cell ID (Identity) number and cell group ID number inside a cell identification group from receiving signals at a relay end, so as to obtain a synchronizing signal sequence received by a relay; secondly, generating a local PSS (Primary Synchronization Signal) and an SSS (Secondary Synchronization Signal) according to the obtained relay-end cell ID number and cell group ID number relay end; thirdly, carrying out an integer-frequency-offset estimation process by using the PPS received at the relay end and the obtained relay locally-generated PSS; and finally, carrying out integer-frequency-offset adjustment on the receiving signals of the PSS / SSS at the relay end by using the obtained result epsilon I of the integer-frequency-offset estimation, and carrying out fine-frequency-offset estimation process by using a corresponding algorithm. Therefore, the problem of the frequency offset estimation at the relay end can be solved, and the sending frequencies of the signals received at the relay end and the signals at a base station end are synchronous.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH +1
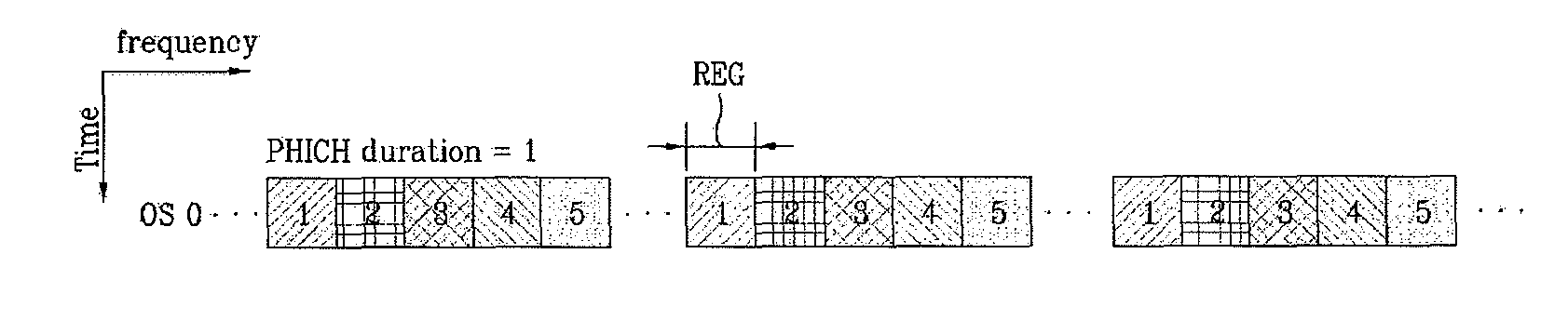
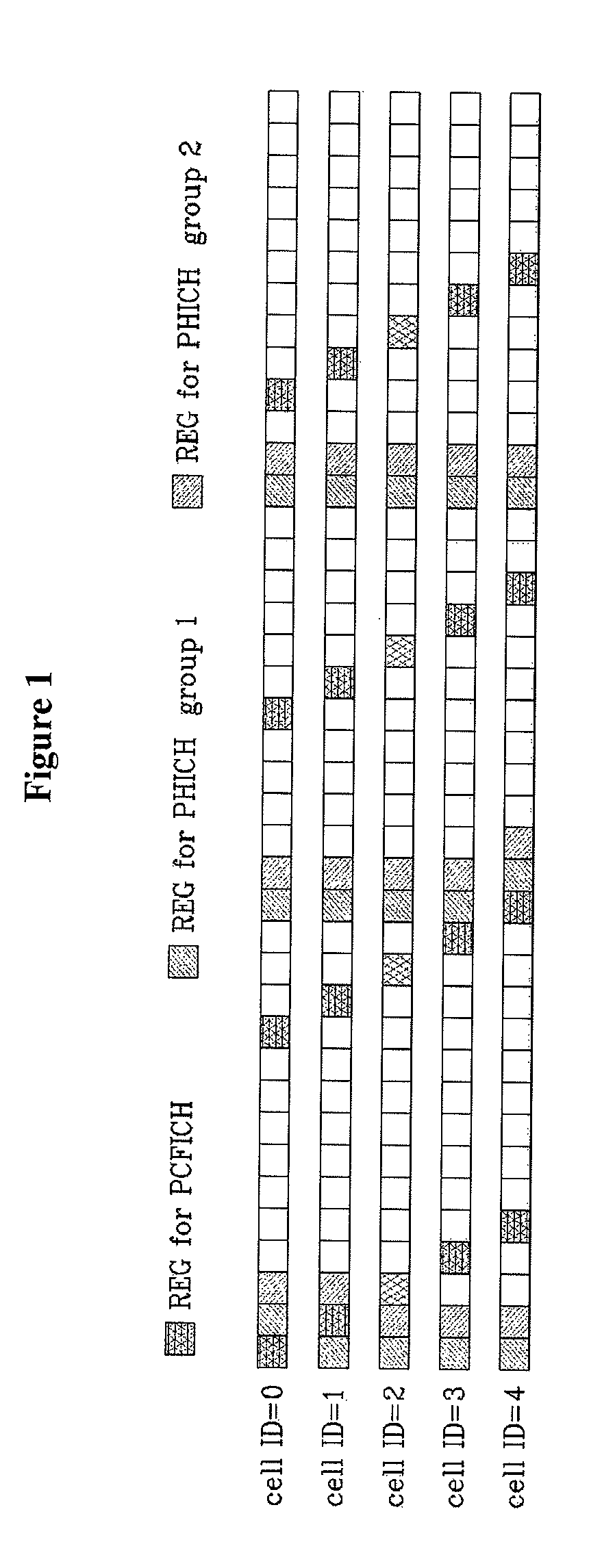
Method for mapping physical hybrid automatic repeat request indicator channel
ActiveUS7894330B2Improve performanceError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission path divisionAutomatic repeat requestResource element
A method for mapping a physical hybrid automatic repeat request indicator channel (PHICH) is described. The method for mapping a PHICH includes determining an index of a resource element group transmitting a repetitive pattern of the PHICH, according to a ratio of the number of available resource element groups in a symbol in which the PHICH is transmitted and the number of available resource element groups in a first or second OFDM symbol, and mapping the PHICH to the symbol according to the determined index. In transmitting the PHICH, since efficient mapping is performed considering available resource elements varying with OFDM symbols, repetition of the PHICH does not generate interference between neighbor cell IDs and performance is improved.
Owner:PANTECH CORP
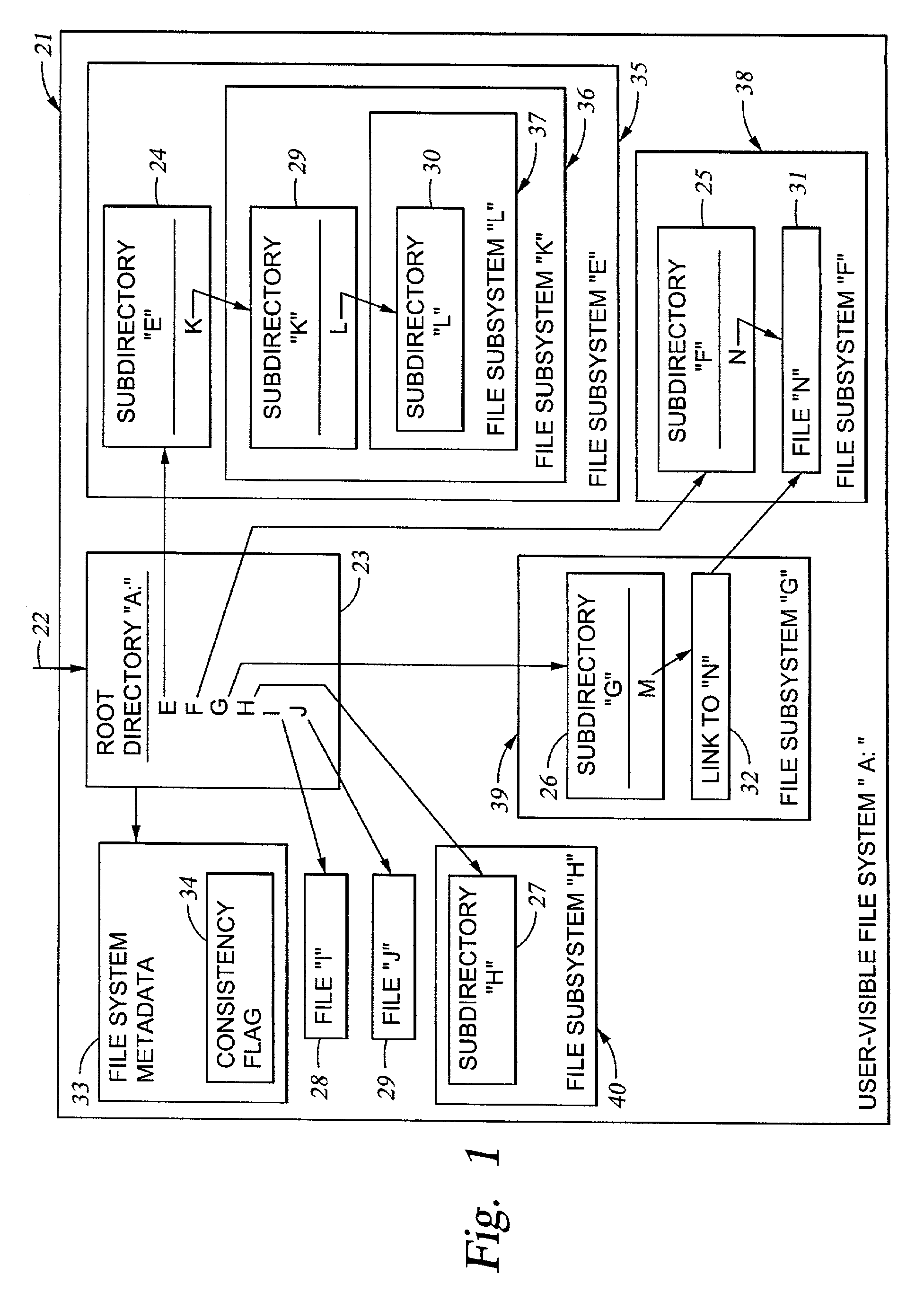
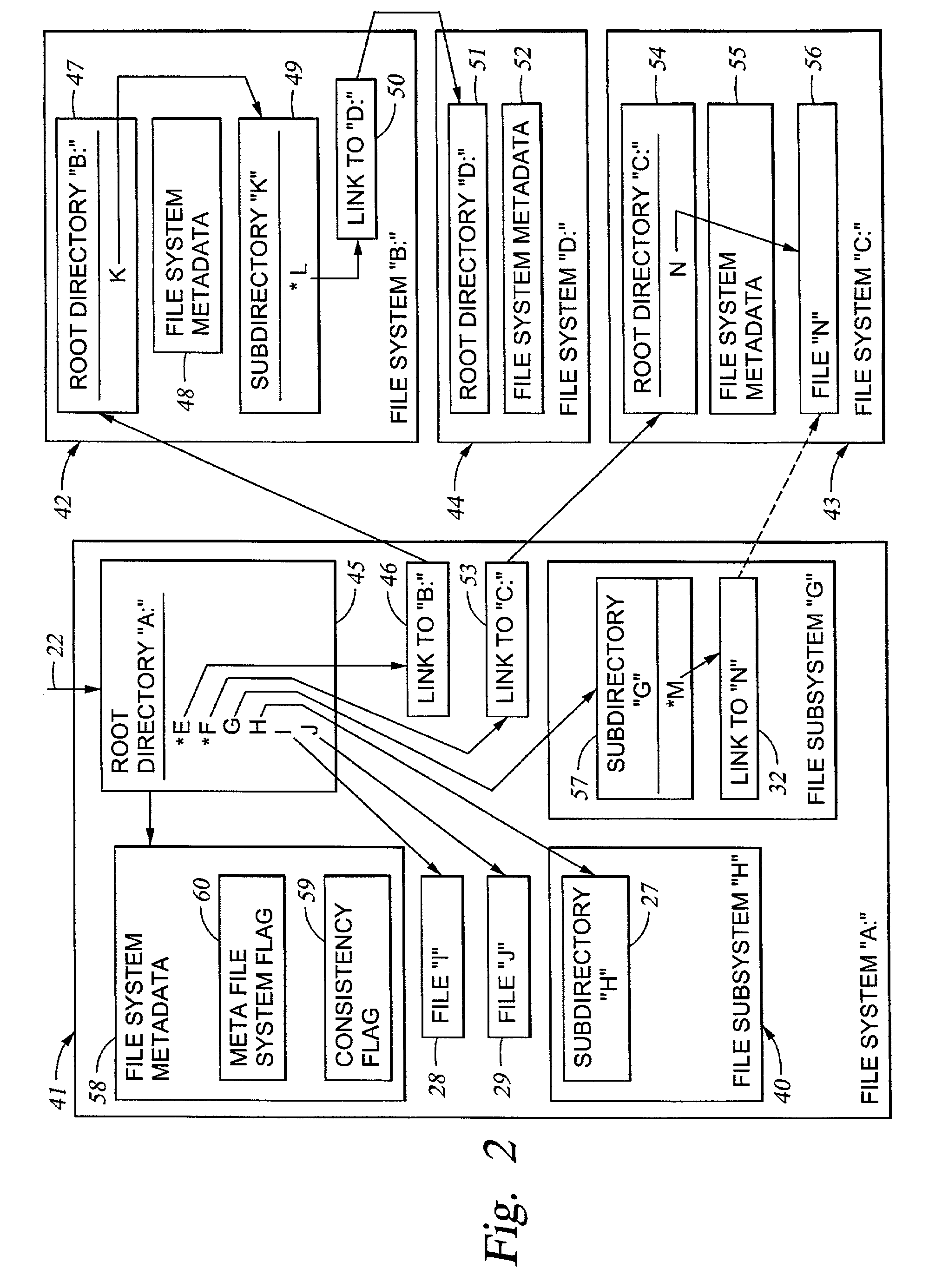
Cluster meta file system of file system cells managed by respective data movers of a network file server
InactiveUS6985914B2Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsRouting tableFile system
File system cells are linked together to form a meta file system that appears to a user or application program to be a single file system. The meta file system permits concurrent access by multiple processors in a file server wherein each file system cell is managed by a respective one of the processors. The file server responds to a directory access request by returning a file handle containing a file system cell ID and a pointer to a file in the file system cell. The file server responds to a subsequent file access request including the file handle by extracting the file system cell ID and the pointer to the file, searching a routing table for an entry having a file system cell ID matching the file system cell ID extracted from the file handle, and routing the request to the processor managing the file system cell.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Method and apparatus for performing coordinated multi-point transmission and reception in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20110124345A1Improve system efficiencyAssess restrictionNetwork planningCommunications systemCell ID
A method and an apparatus for performing a Coordinated Multi-Point (CoMP) transmission in a wireless communication system are provided. An operating method of a base station for the CoMP transmission in a wireless communication system includes performing a cell clustering for CoMP transmission of a terminal, receiving a reference signal from the terminal, determining cell IDentifier (ID) information of the terminal, when the terminal uses a cell ID for the CoMP transmission, comparing a Channel Quality Indicator (CQI) value of the reference signal with a threshold, and when the CQI value of the reference signal is greater than or equal to the threshold, participating in the CoMP transmission of the terminal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Mobile communication system, terminal device, and base station
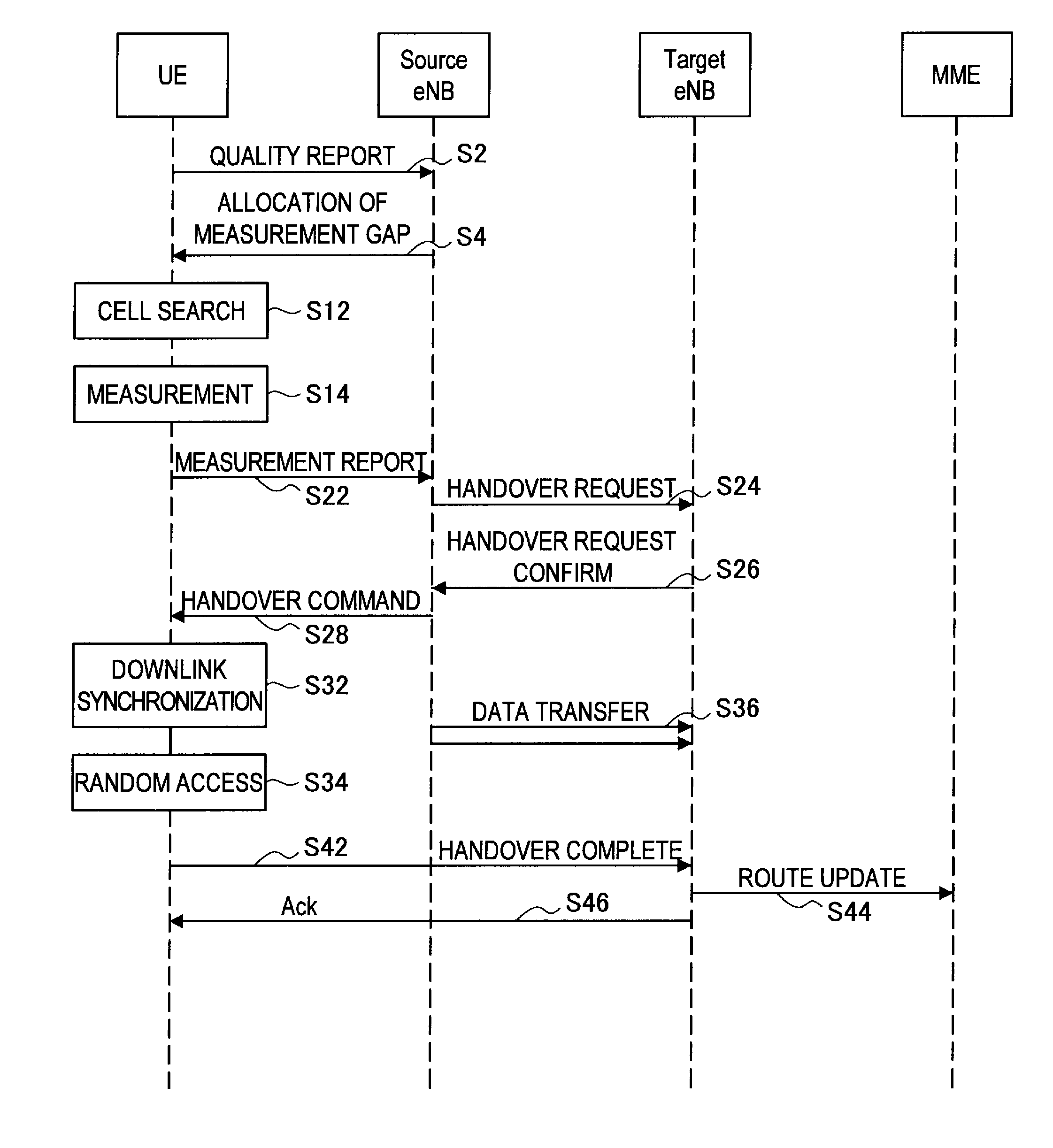
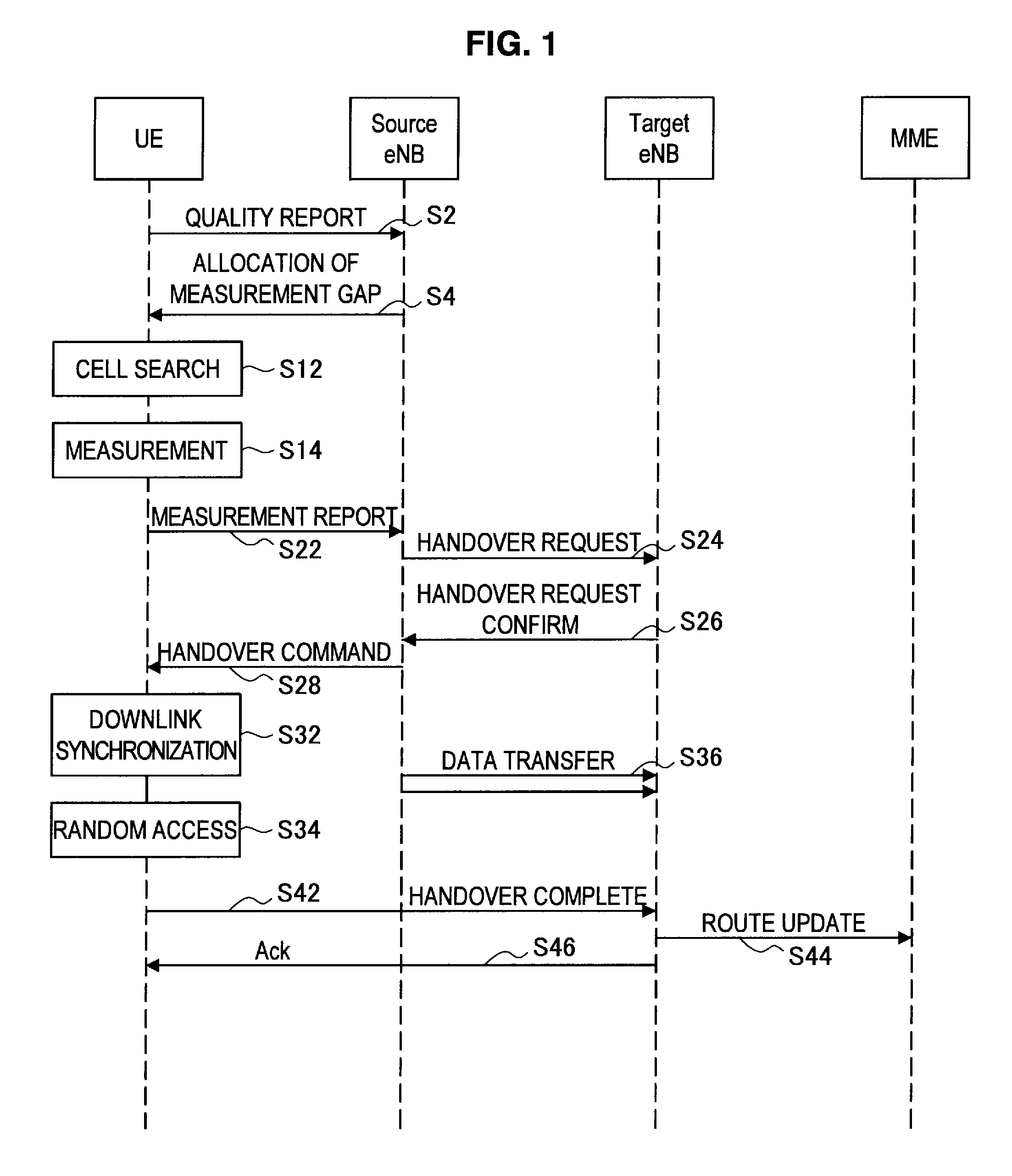
InactiveUS20120100856A1Reduce waiting timeAvoid it happening againWireless communicationHandoff controlCell ID
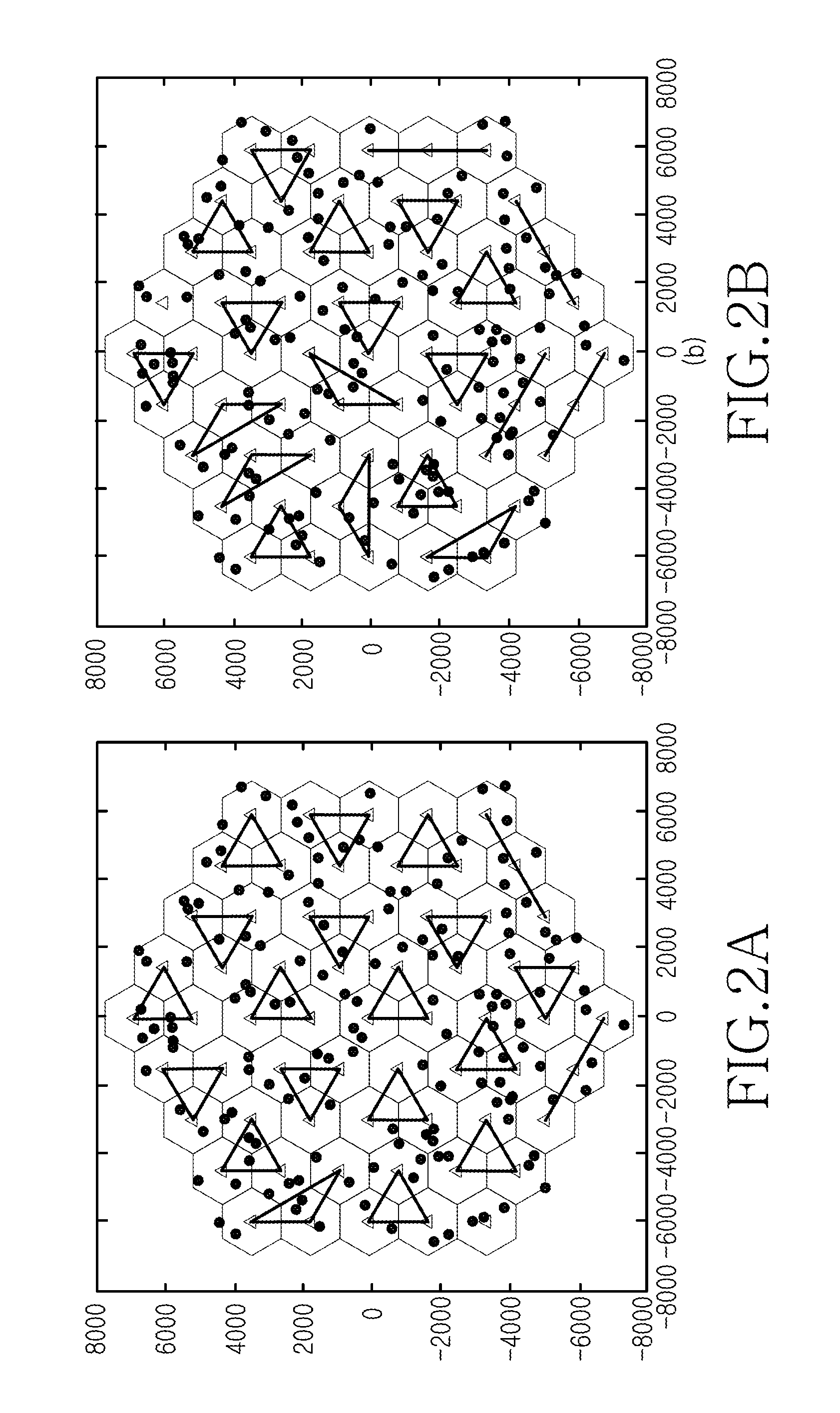
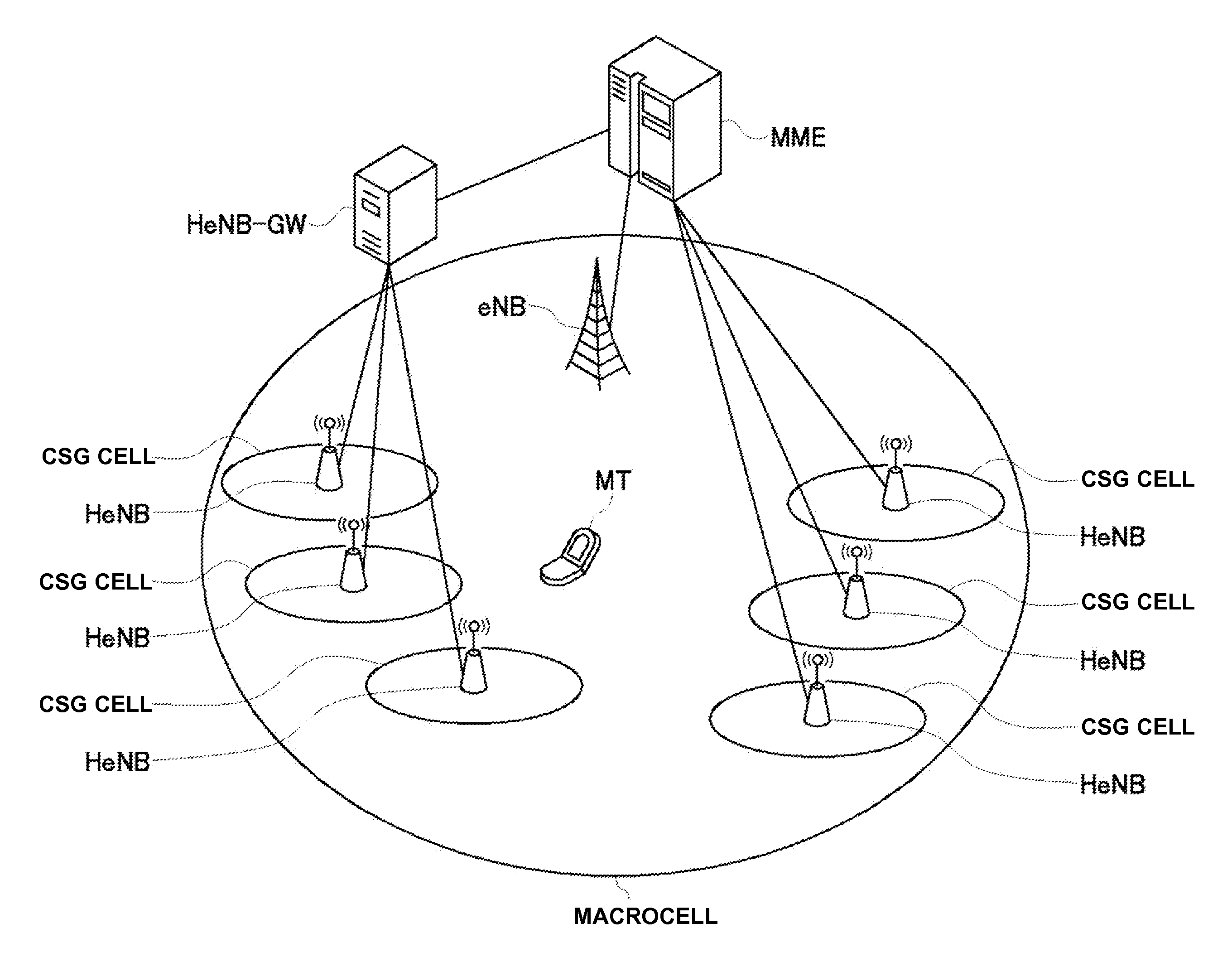
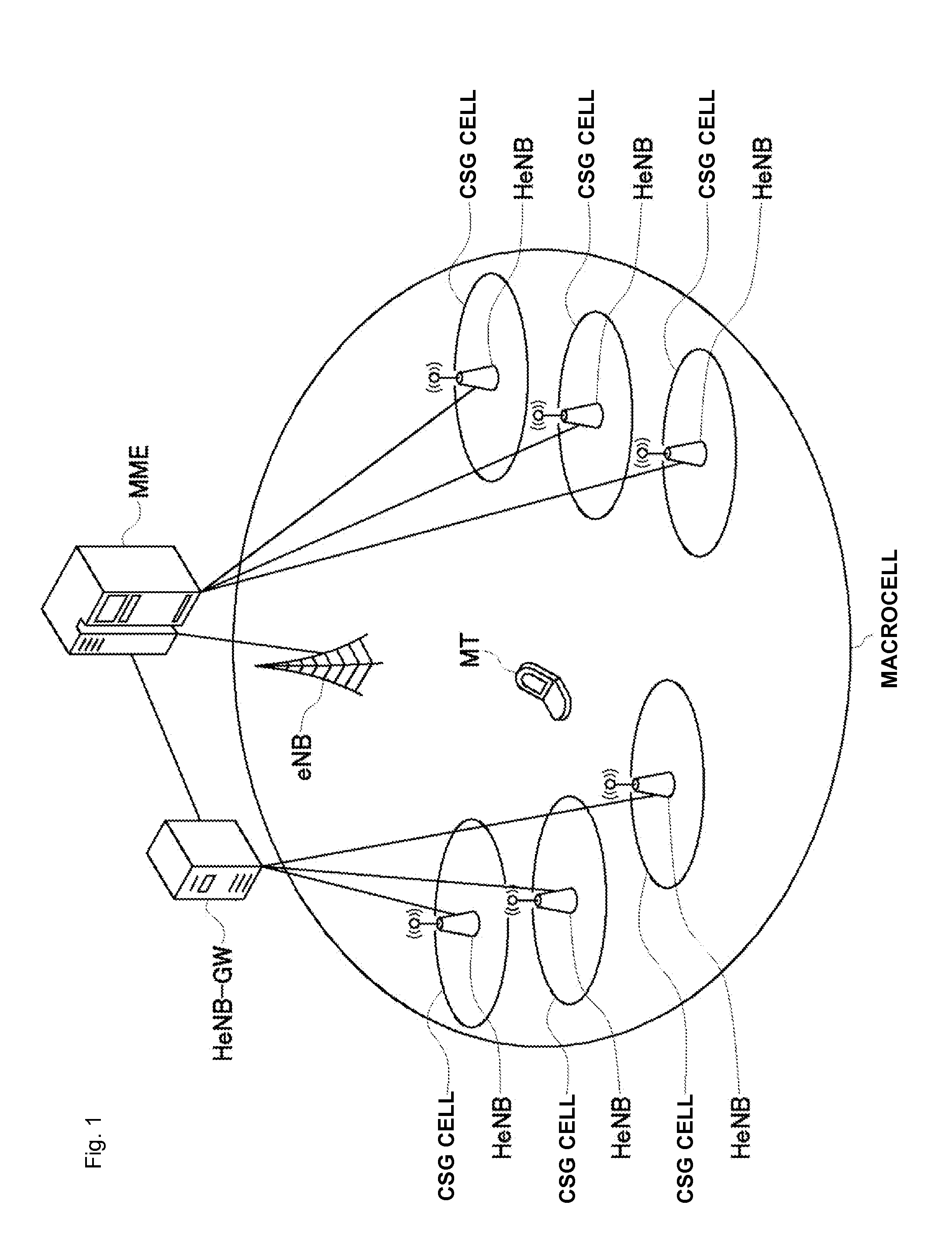
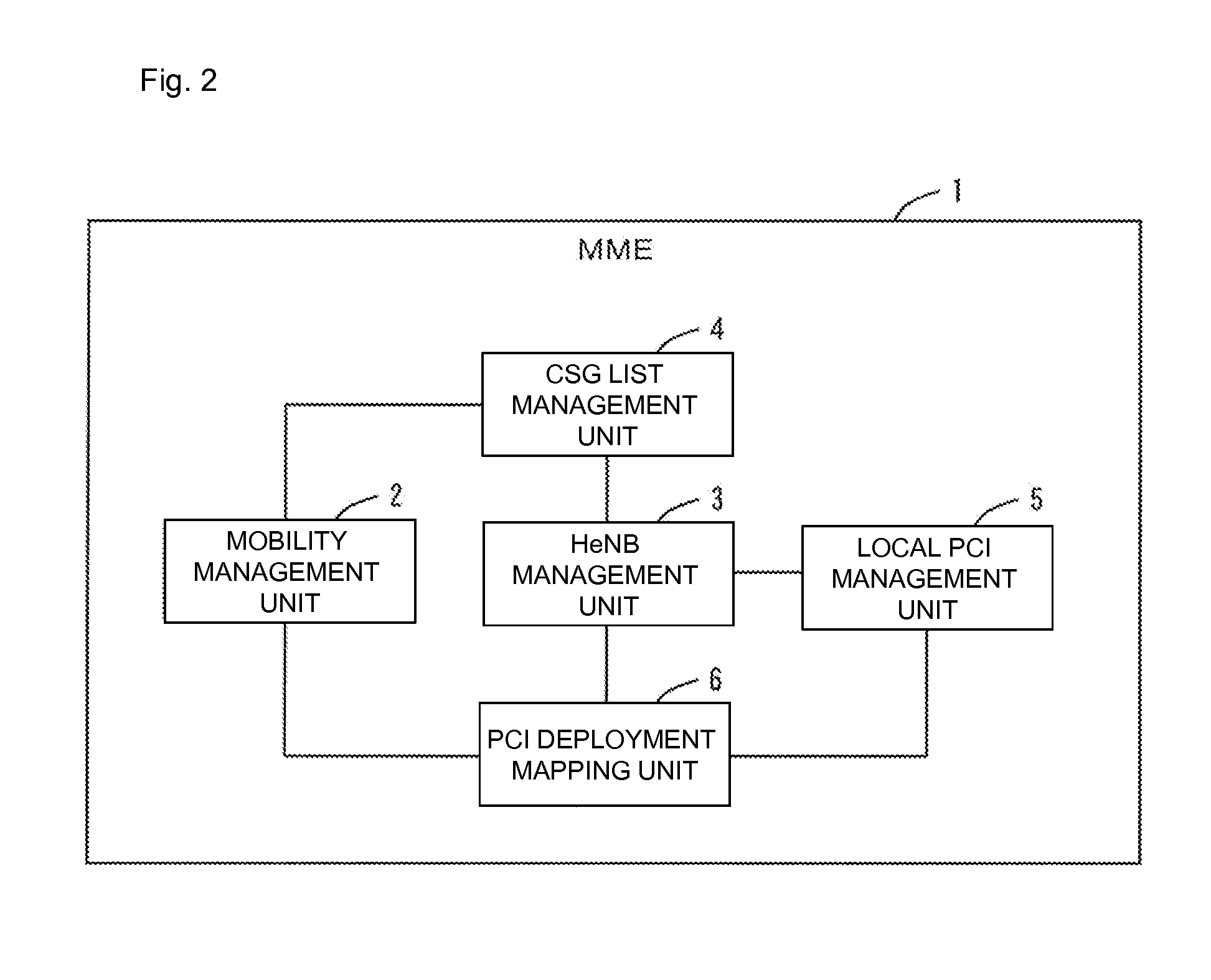
In a mobile communication system, a handover of a terminal device (MT) from a macrocell base station (eNB) to a small cell base station (HeNB) is controlled via a host device (MME or HeNB-GW). Physical cell ID deployment map information (PCI deployment map information), which includes at least information (PCI / CGI map information) indicating the correspondences between physical cell IDs and unique cell IDs of CSG cells for which access is granted, is generated in the host device (MME or HeNB-GW). When the terminal device measures the reception quality for surrounding CSG cells for handover control to any of the CSG cells, the terminal device uses the PCI deployment map information to generate a measurement result report. Thus, a service interruption caused by handover control to an inaccessible small cell can be avoided, and the wait time for handover control can be reduced.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
System and Methods for Observed Time Difference of Arrival Measurements for Location Services in Cellular Devices
InactiveUS20110275385A1Save powerShorten the timeAssess restrictionWireless commuication servicesCommunications systemCell ID
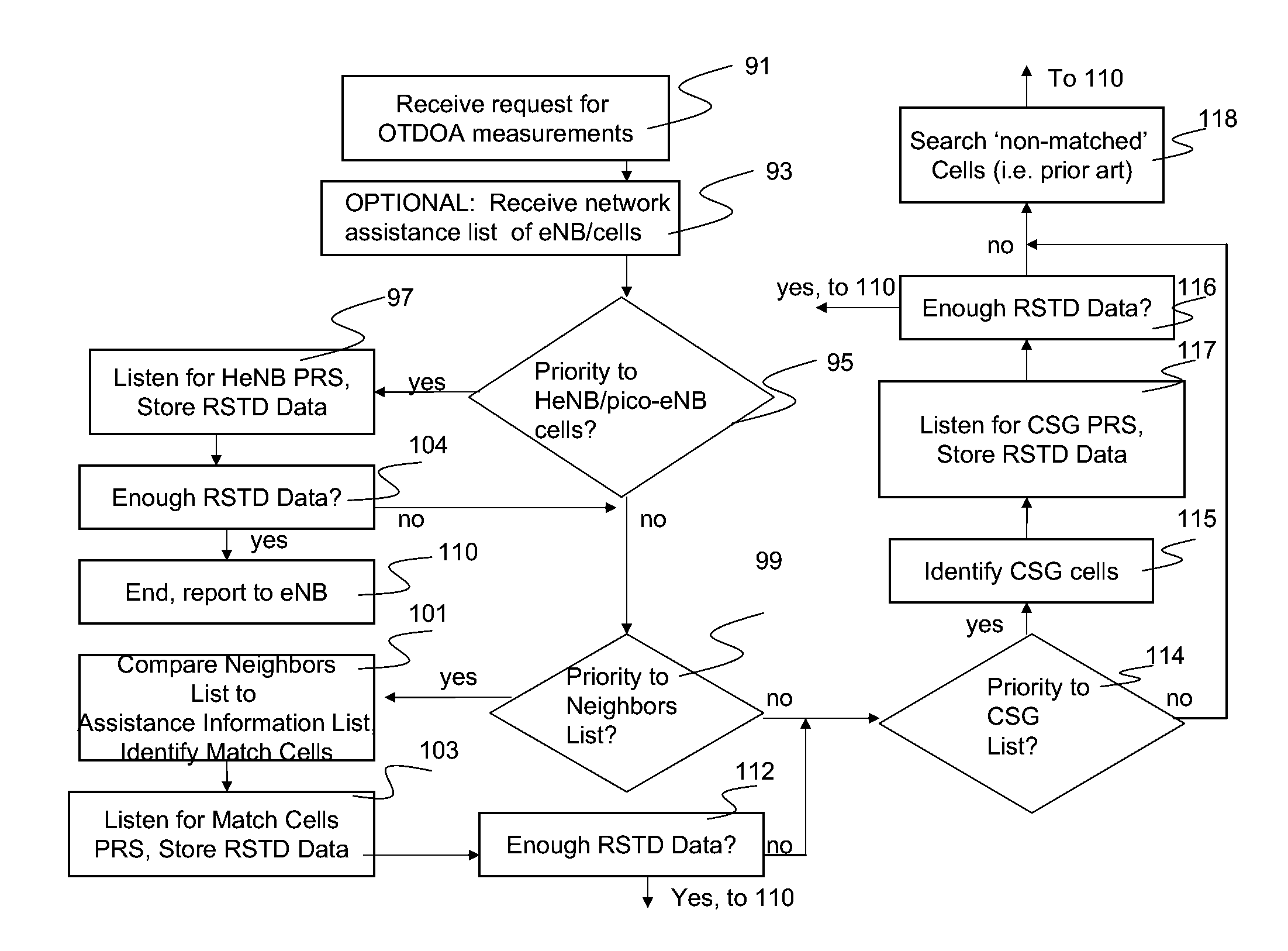
Systems and methods for providing improved location such as emergency services location of mobile devices in an over the air communications system are disclosed. On receiving a request, a user equipment (UE) mobile device makes observed time difference of arrival (OTDOA) measurements on signals received from certain cell communication elements. The UE selects or prioritizes the cells based on one of several schemes, including comparing internally stored cell ID information to cell ID information provided by the network, and using lists of cells that are recently used, recently received, previously used, or on a closed subscriber group (CSG) list are alternative embodiments. The UE may prioritize home eNB cells that it is a member of for the measurements. By prioritizing the cells used for the measurements, the OTDOA measurements may be limited to a few cells and the time needed to make the measurements may be reduced.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Method and system for dynamic cell configuration
An apparatus for adapting hyper cells in response to changing conditions of a cellular network is disclosed. During operation, the apparatus collects data regarding network conditions of the cellular network. In accordance with the collected network condition data, the apparatus changes an association of a transmit point from a second cell ID of a second hyper cell to a first cell ID of a first hyper cell. Virtual data channels, broadcast common control channel and virtual dedicated control channel, transmit point optimization, UE-centric channel sounding and measurement, and single frequency network synchronization are also disclosed.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com