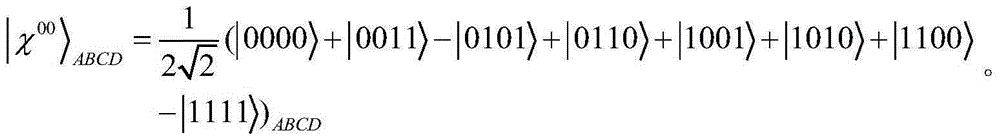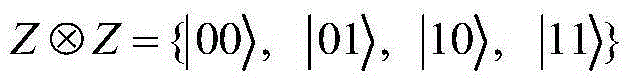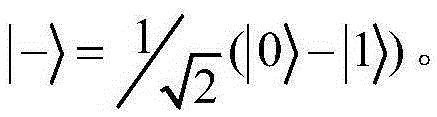Four-particle x state-based two-party quantum key agreement protocol
A quantum key agreement, four-particle technology, applied in the field of two-party quantum key agreement protocol, can solve the problems of low qubit efficiency, inability to resist Trojan horse attack and delayed photon Trojan attack, etc., and achieve the effect of high qubit efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] 1. Preliminary knowledge
[0024] As we all know, {|0>,|1>} forms the Z basis, and {|+>,|->} forms the X basis, where | - > 1 / 2 ( | 0 > - | 1 > ) . The four Bell states are defined as follows:
[0025] | φ + > = 1 / 2 ( | 00 > + | 11 > ) , | φ - > = 1 / 2 ( | 00 > + | 11 > ) , ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com