Patents
Literature
638 results about "Probability of error" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In statistics,the term "error" arises in two ways. Firstly, it arises in the context of decision making, where the probability of error may be considered as being the probability of making a wrong decision and which would have a different value for each type of error. Secondly, it arises in the context of statistical modelling (for example regression) where the model's predicted value may be in error regarding the observed outcome and where the term probability of error may refer to the probabilities of various amounts of error occurring.
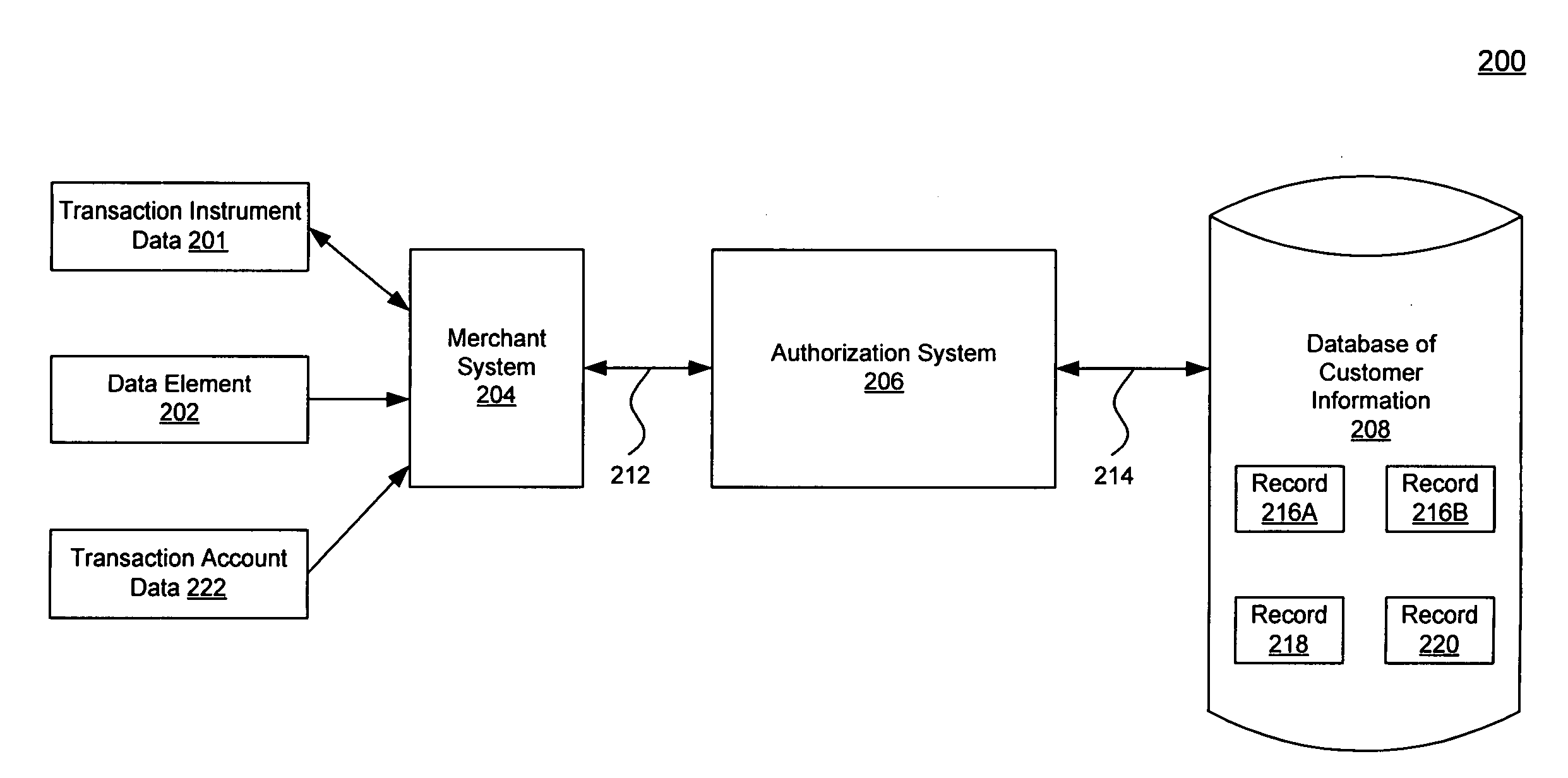
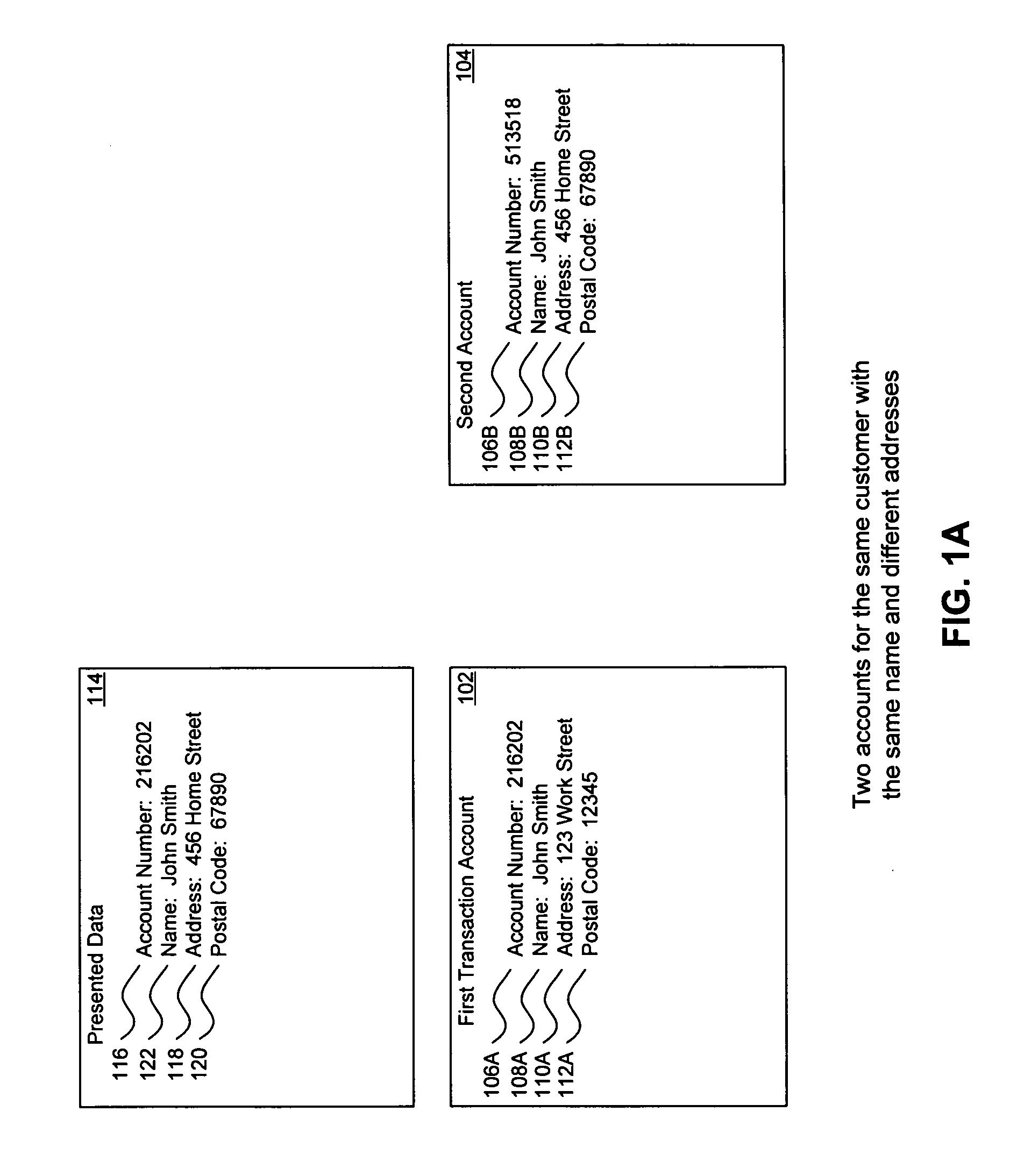
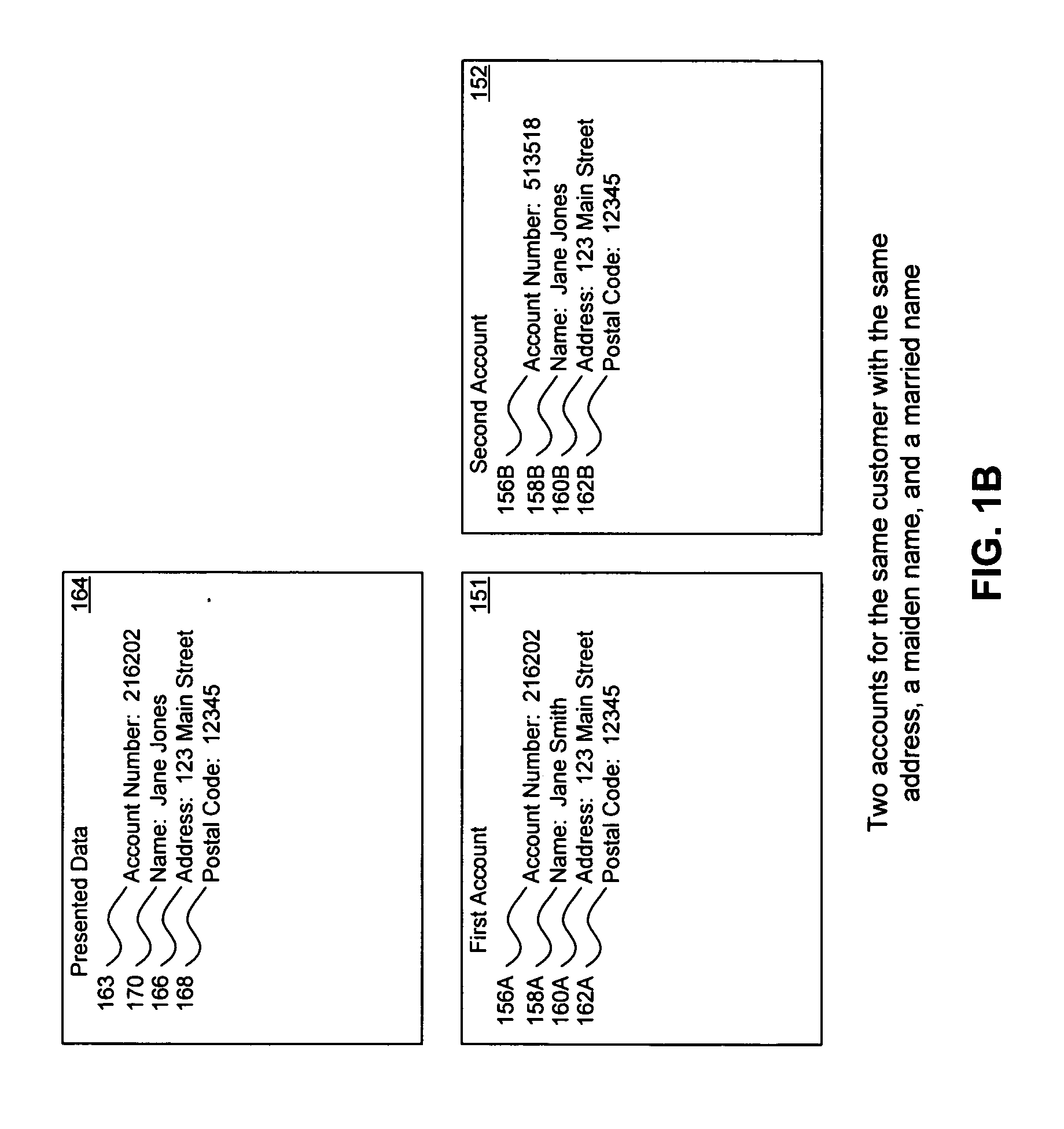
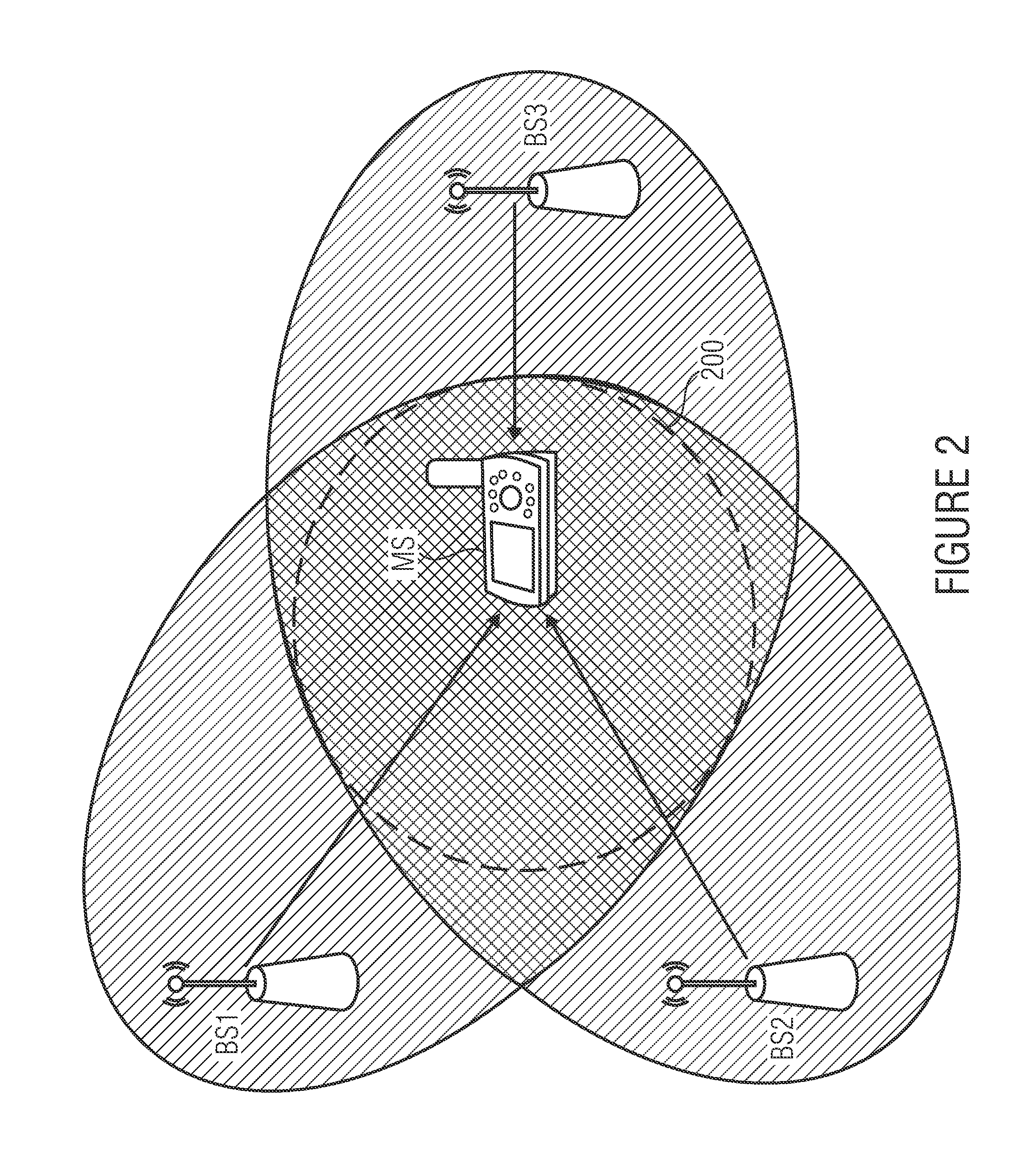
Method, system, and computer program product for customer-level data verification
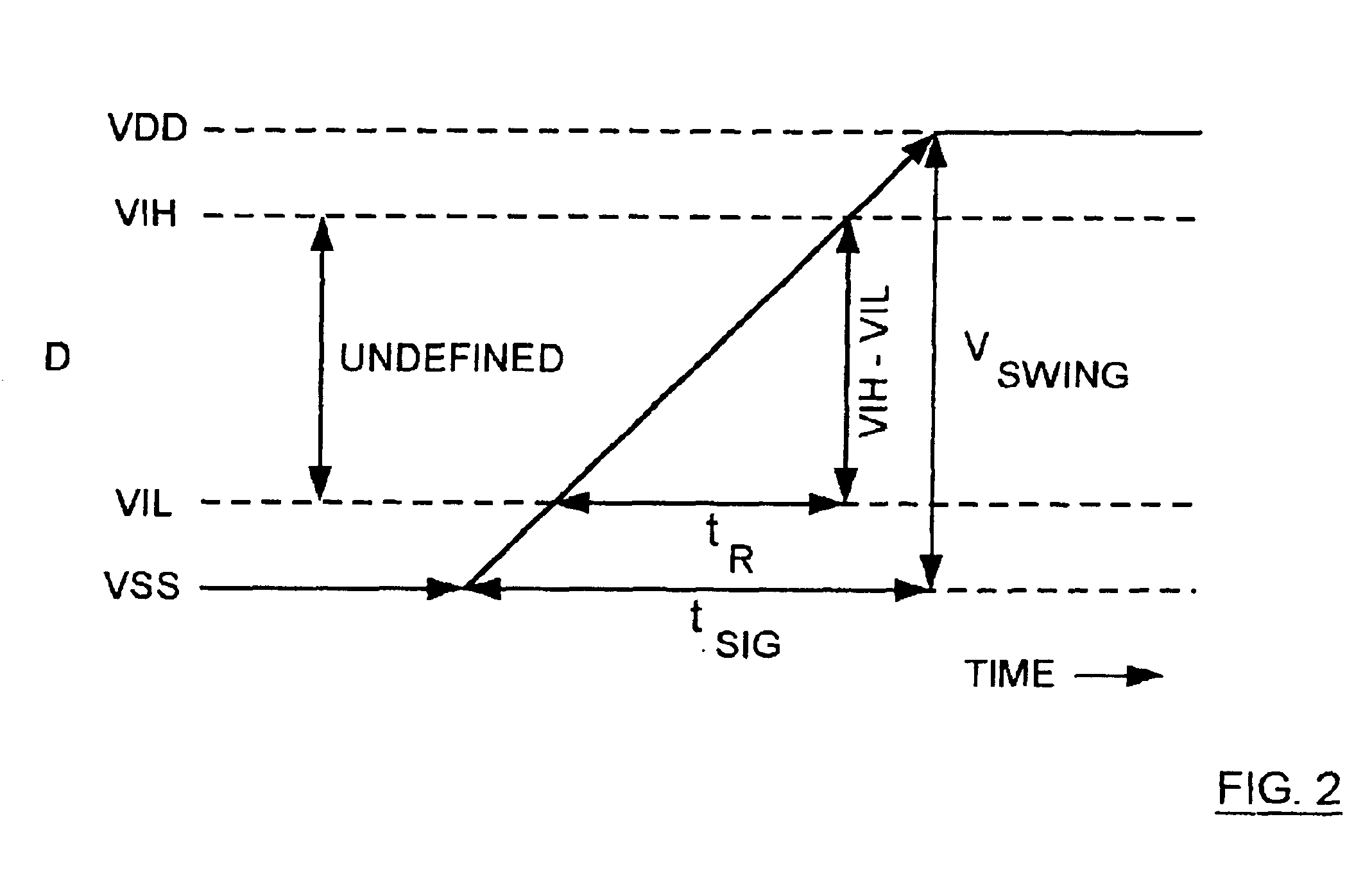
ActiveUS20070284433A1Improve accuracyReduce error rateComplete banking machinesFinanceData validationSource Data Verification
A system, method, and computer program to reduce incorrectly declined transactions and improve risk calculation accuracy by reducing error probability during fraud detection. The tool first receives at least one data element as well as transaction account data and / or financial transaction instrument data. Then a customer is determined from a first record associated with the transaction account data and / or financial transaction instrument data. A record search is performed to identify at least one additional record associated with the customer. Finally, the data element is compared to the information contained in the additional record to create a comparison result that verifies a customer address. The comparison result may be used as an input to transaction risk calculations. The comparison result may also be provided to a merchant system and / or merchant for use in a decision-making process, for example, to verify customer identity.
Owner:LIBERTY PEAK VENTURES LLC
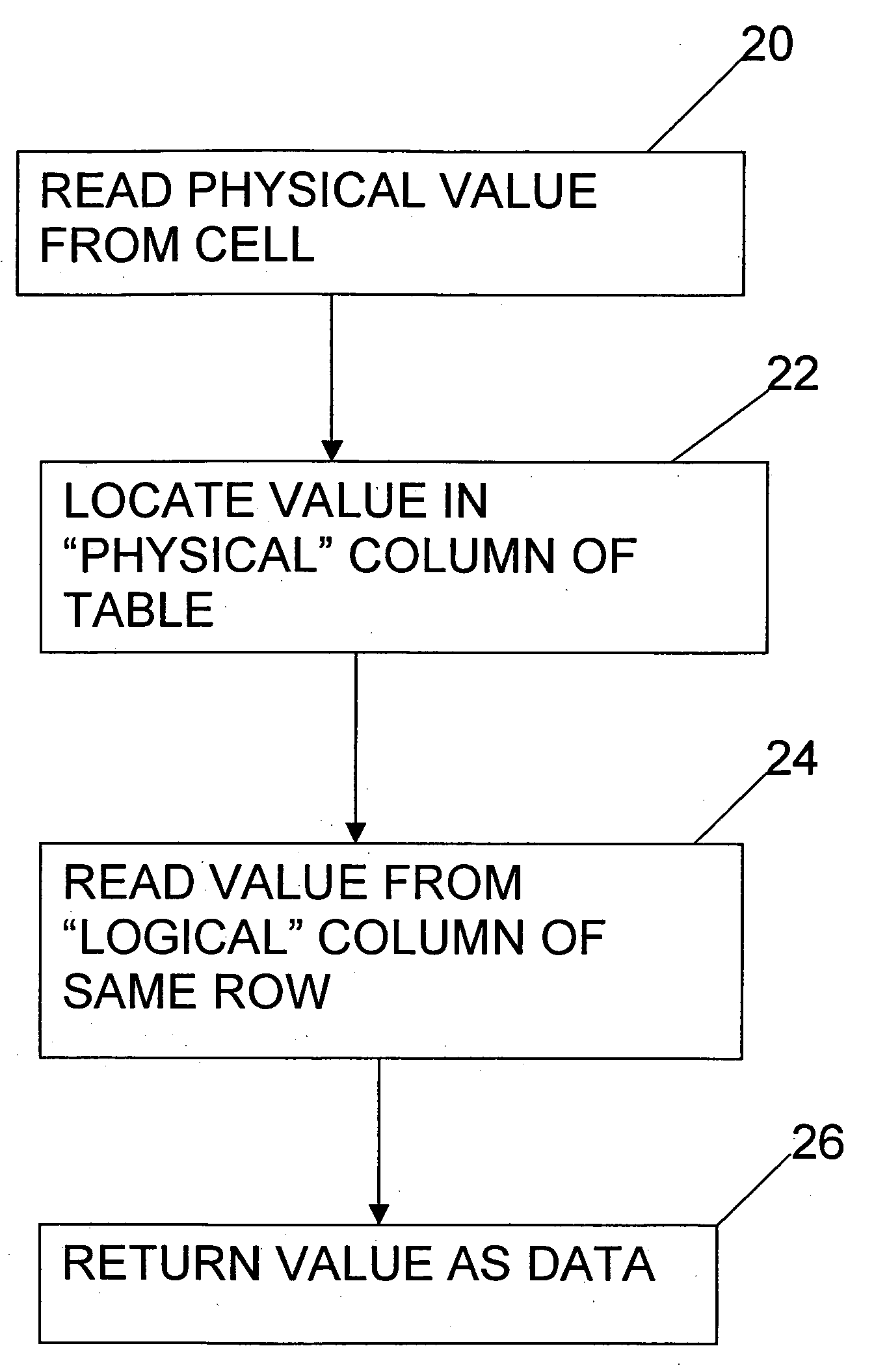
States encoding in multi-bit flash cells for optimizing error rate
InactiveUS20050213393A1Equally distributedRead-only memoriesDigital storageTest error rateData error
Owner:SANDISK IL
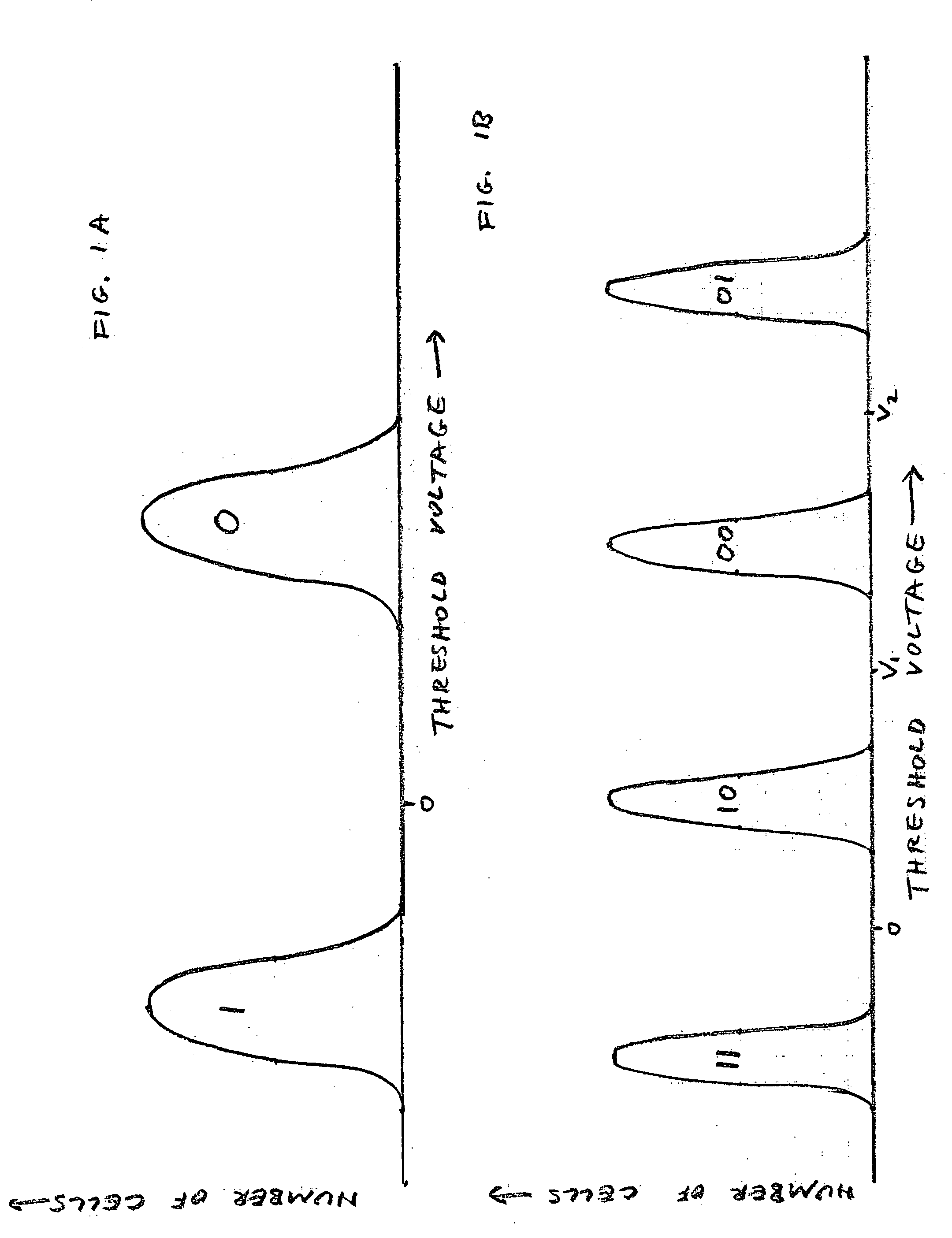
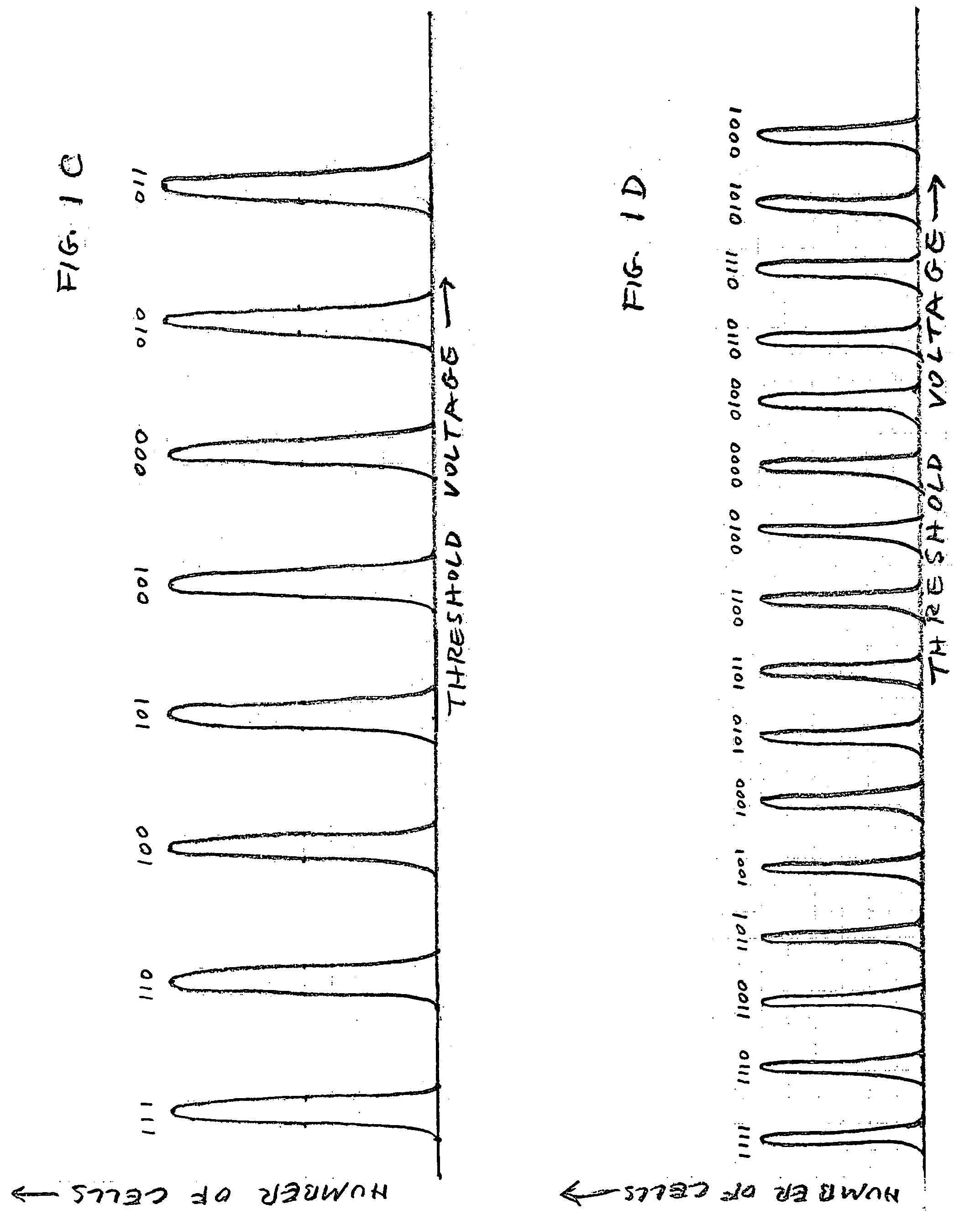
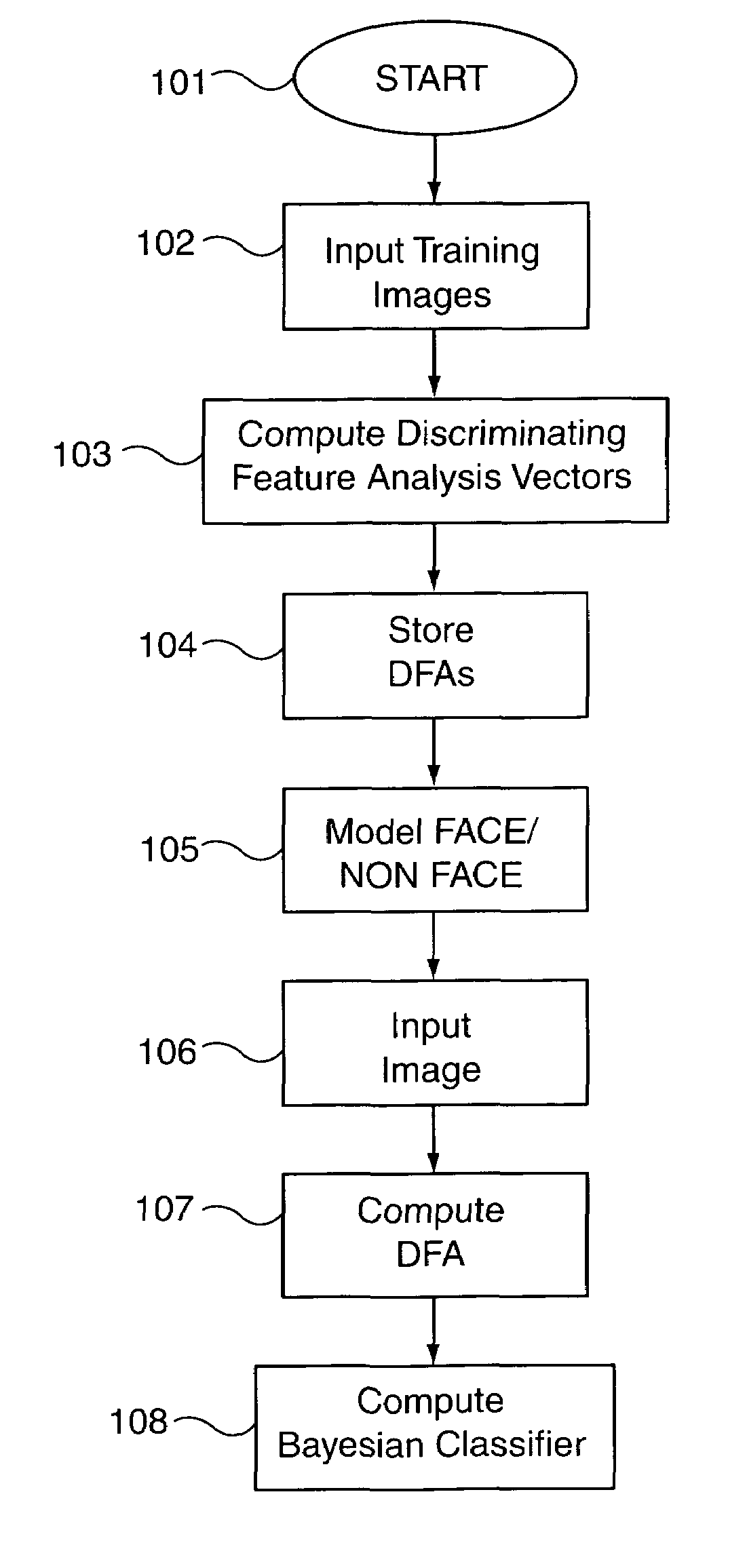
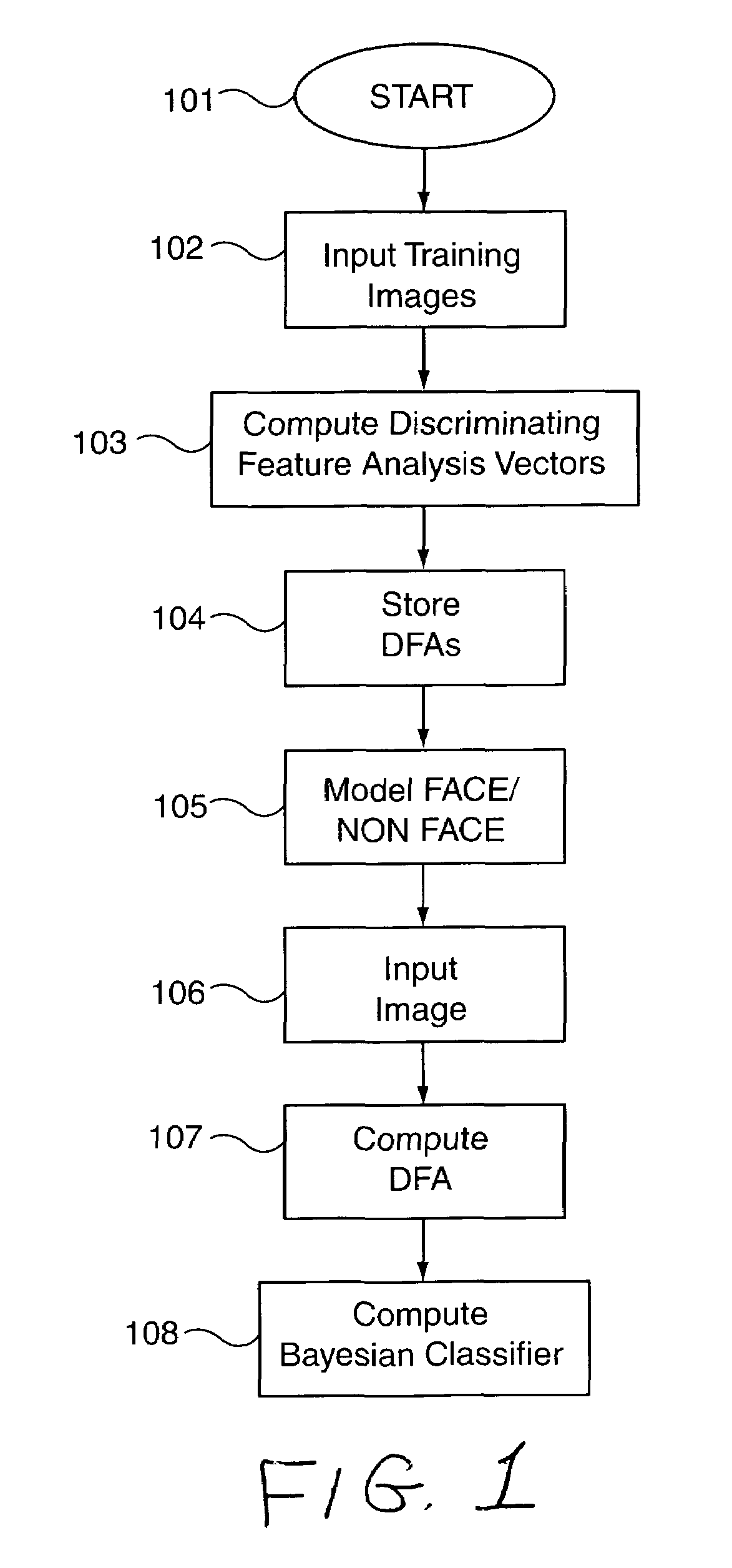
Face detection method and apparatus
InactiveUS7162076B2Improve accuracyHigh precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionFace detection
A method and apparatus as disclosed for face detection within images. A new vector, the discriminating feature analysis vector, is introduced to represent an image to be analyzed, from the DFA vector as processed using a Bayesian Classifier technique. The methodology provides a computationally efficient manner in which to detect faces with relatively low probability of error and false detection rate.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
States encoding in multi-bit flash cells for optimizing error rate
ActiveUS20080104312A1Equally distributedMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRead-only memoriesData errorCell state
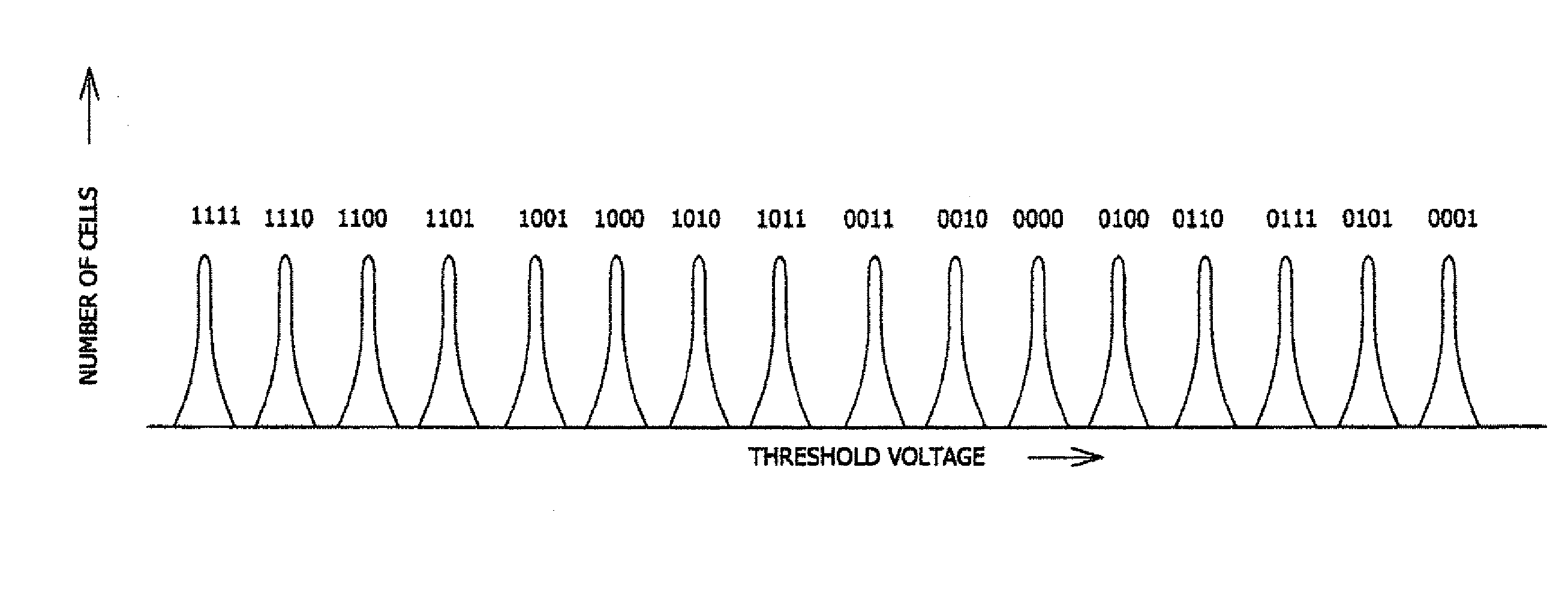
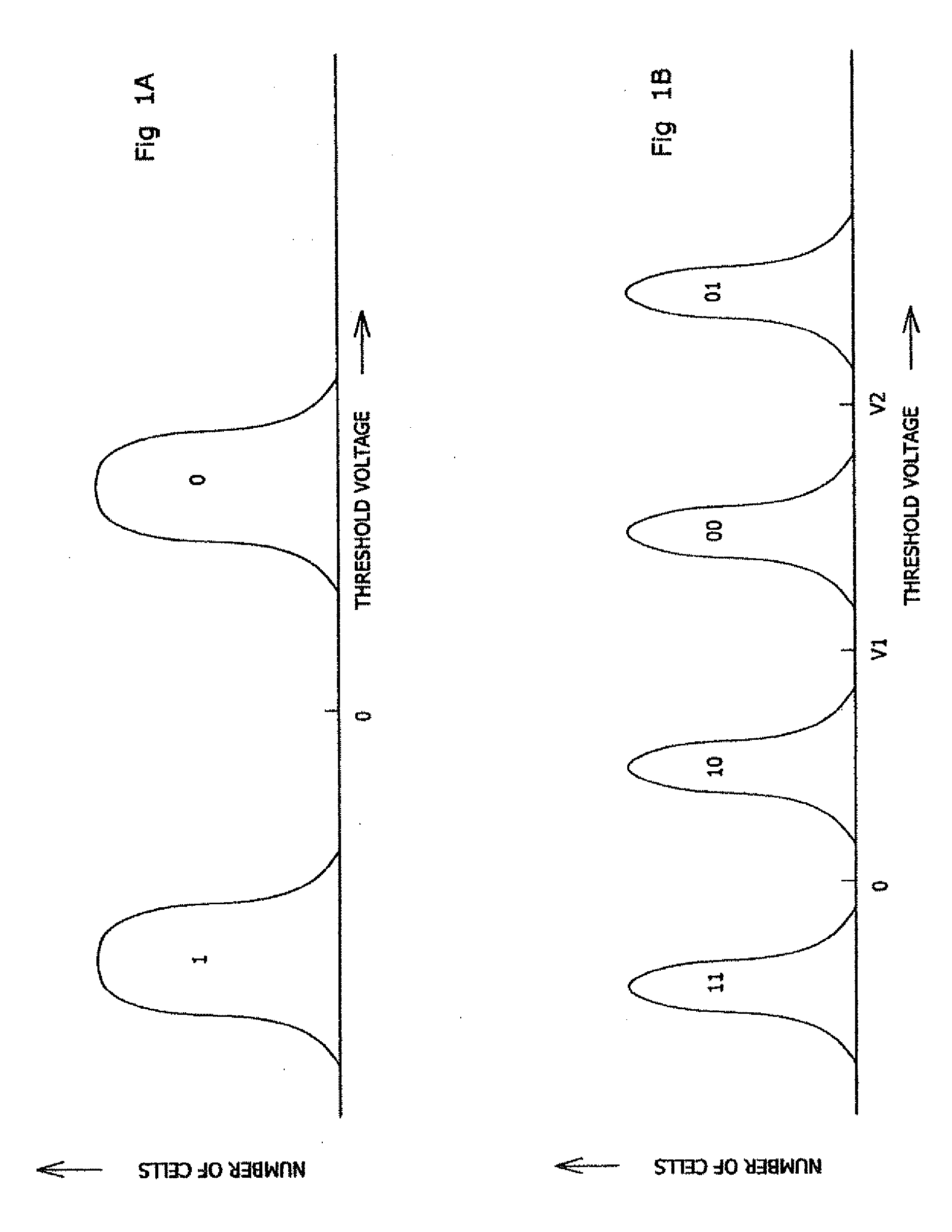
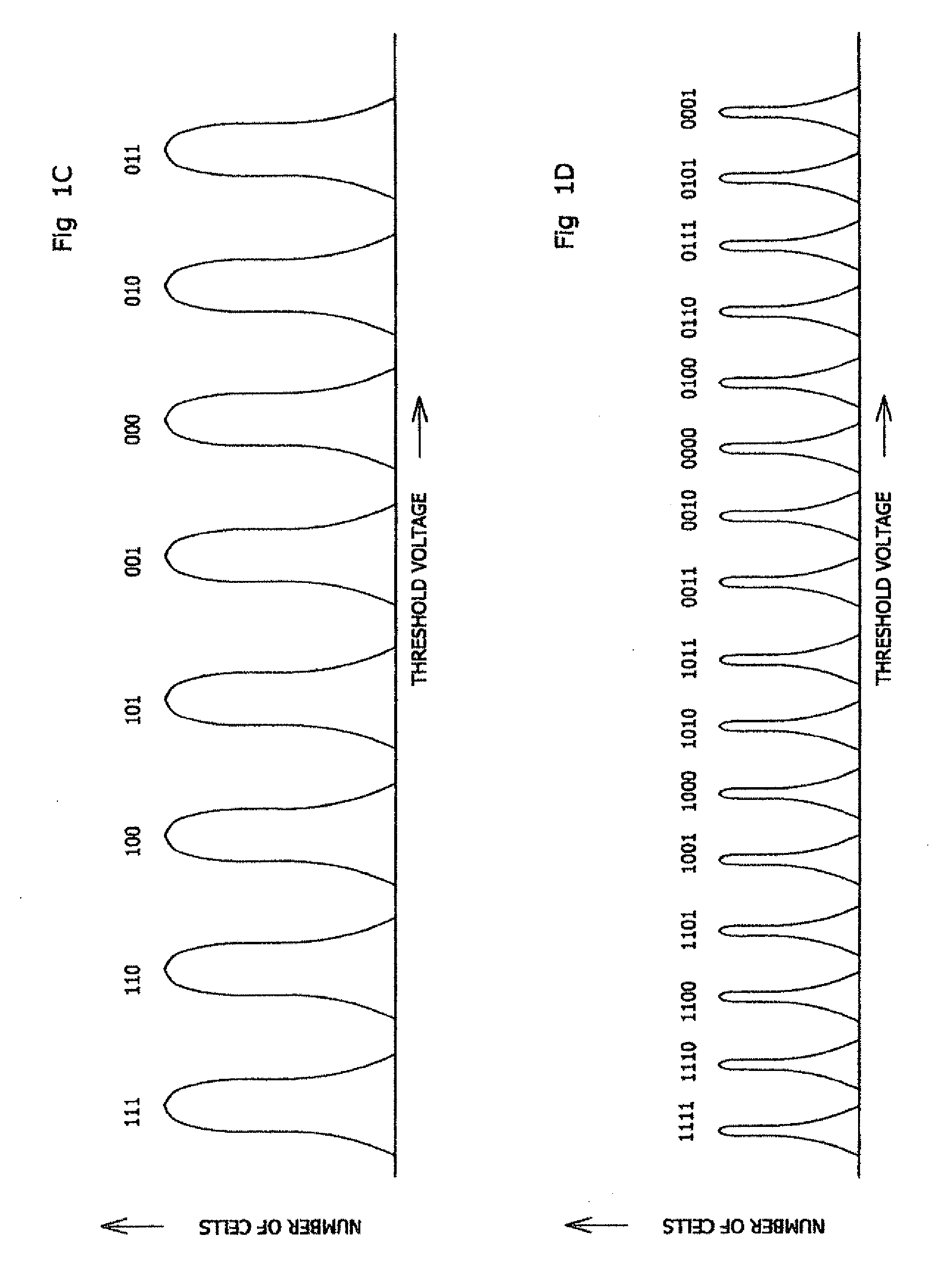
Memory cells are programmed and read, at least M=3 data bits per cell, according to a valid nonserial physical bit ordering with reference to a logical bit ordering. The logical bit ordering is chosen to give a more even distribution of error probabilities of the bits, relative to the probability distributions of the data error and the cell state transition error, than would be provided by the physical bit ordering alone. Preferably, both bit orderings have 2M−1 transitions. Preferably, the logical bit ordering is evenly distributed. The translation between the bit orderings is done by software or hardware.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL ISRAEL LTD
Data storage apparatus, read data processor, and read data processing method
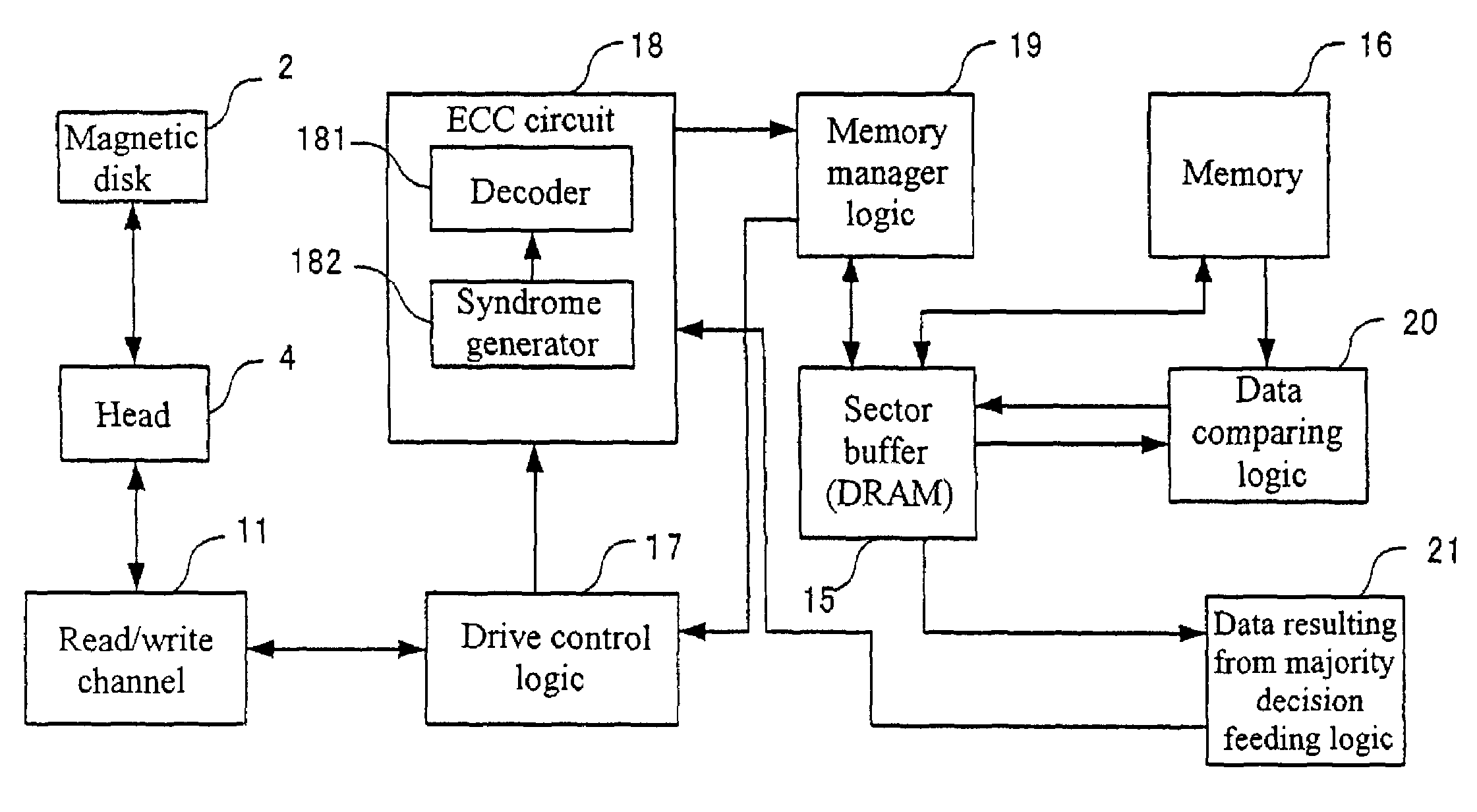
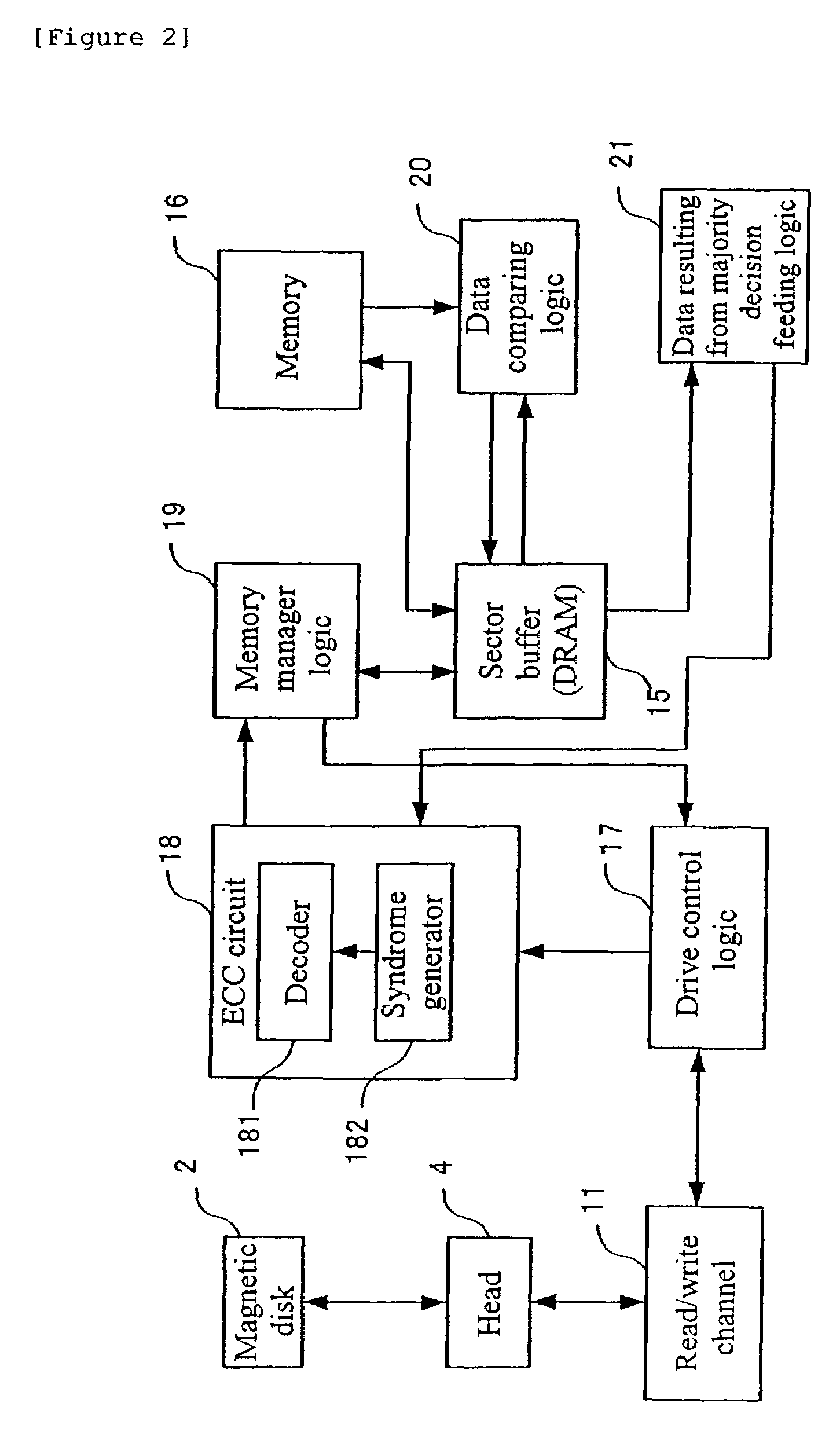
ActiveUS6981205B2Improving error correcting probabilityIncrease probabilityInput/output to record carriersOther decoding techniquesComputer architectureData value
To improve the probability of error correction, thereby generating correct read data. Data is read from the same sector by a number of times and a majority decision is done in the same address, thereby the most frequently read value is regarded as the true data value in the address. For example, for an address 00, “00” is handled as a true data value.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
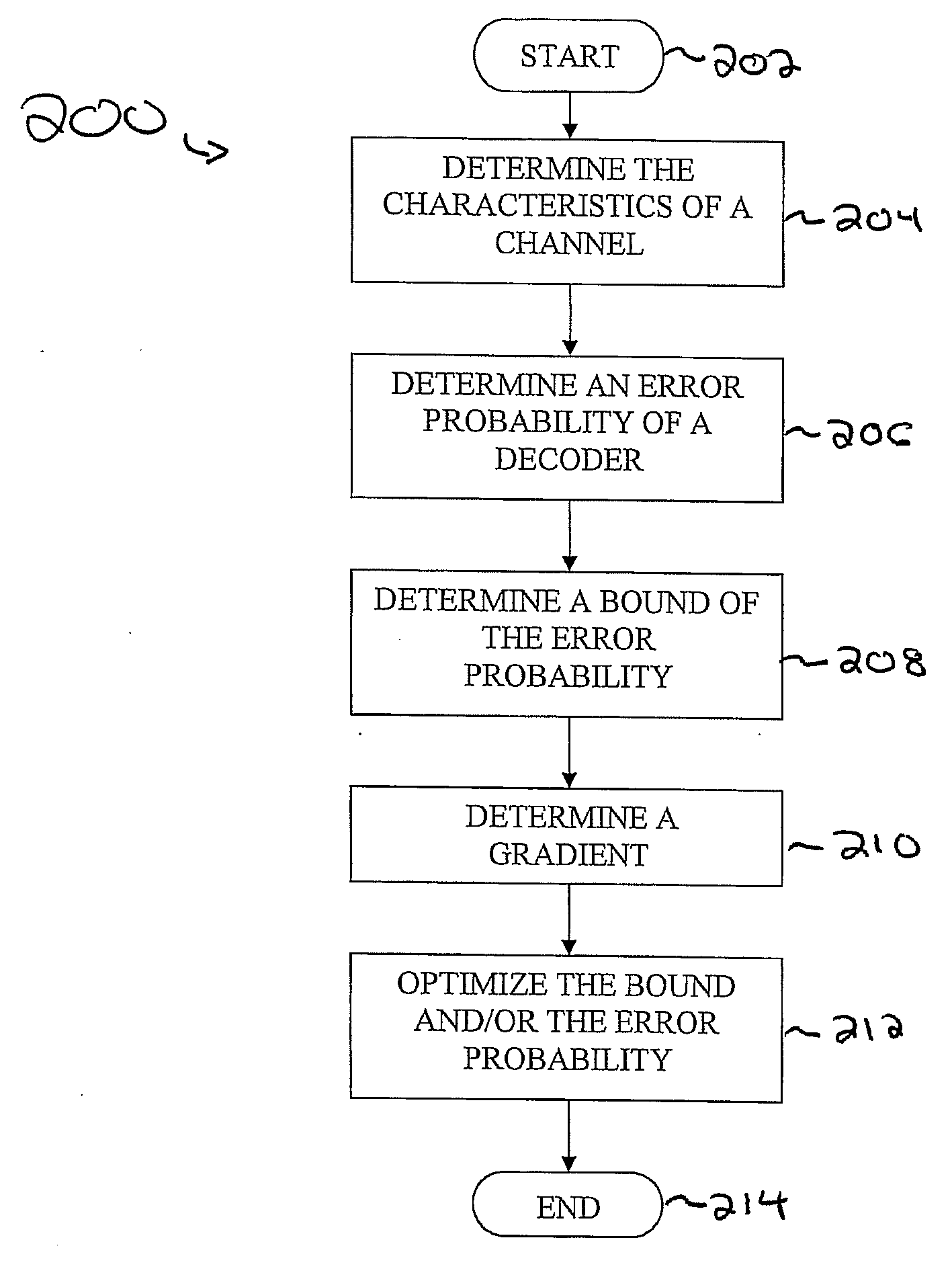
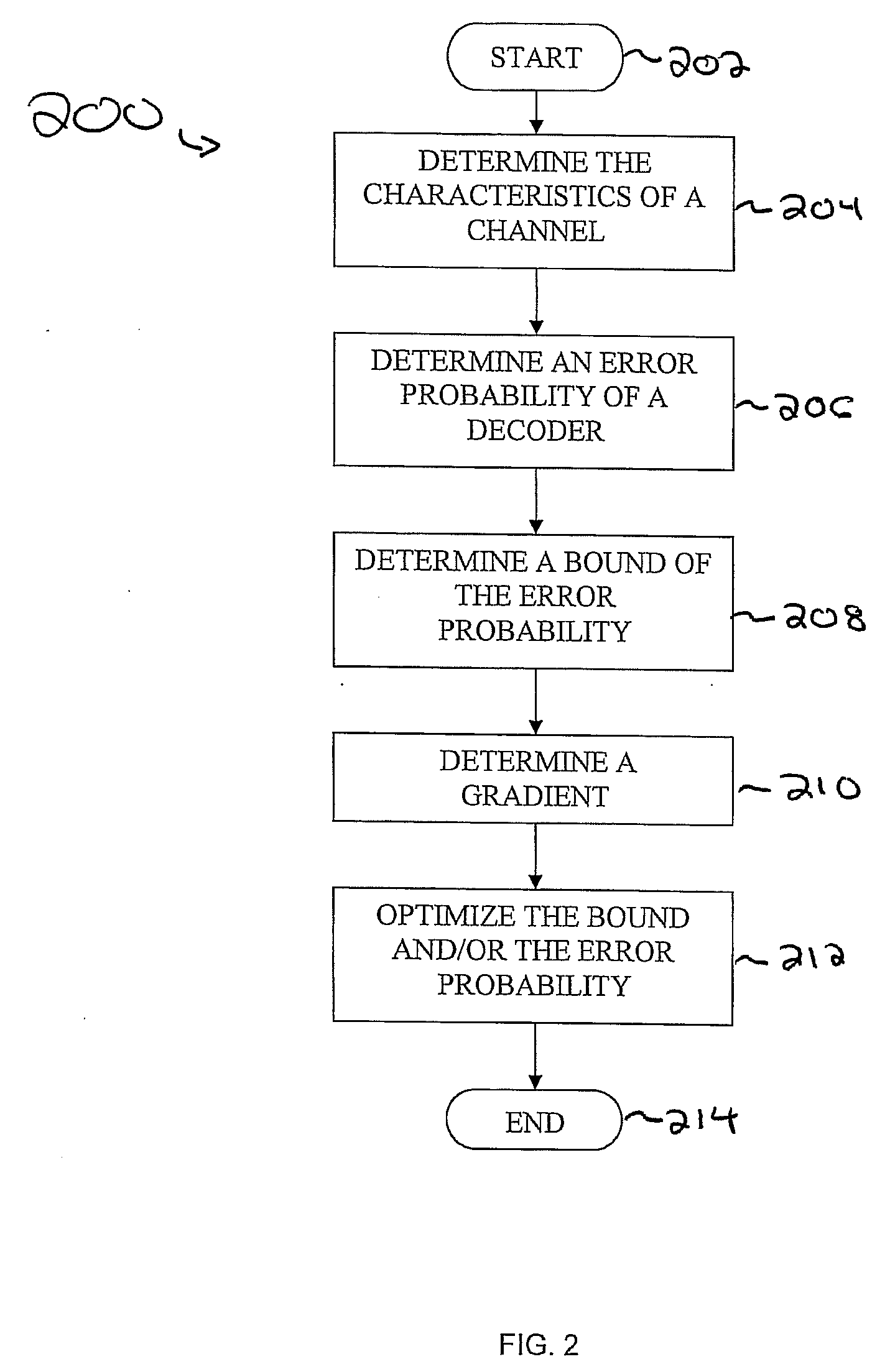
Spherical lattice codes for lattice and lattice-reduction-aided decoders
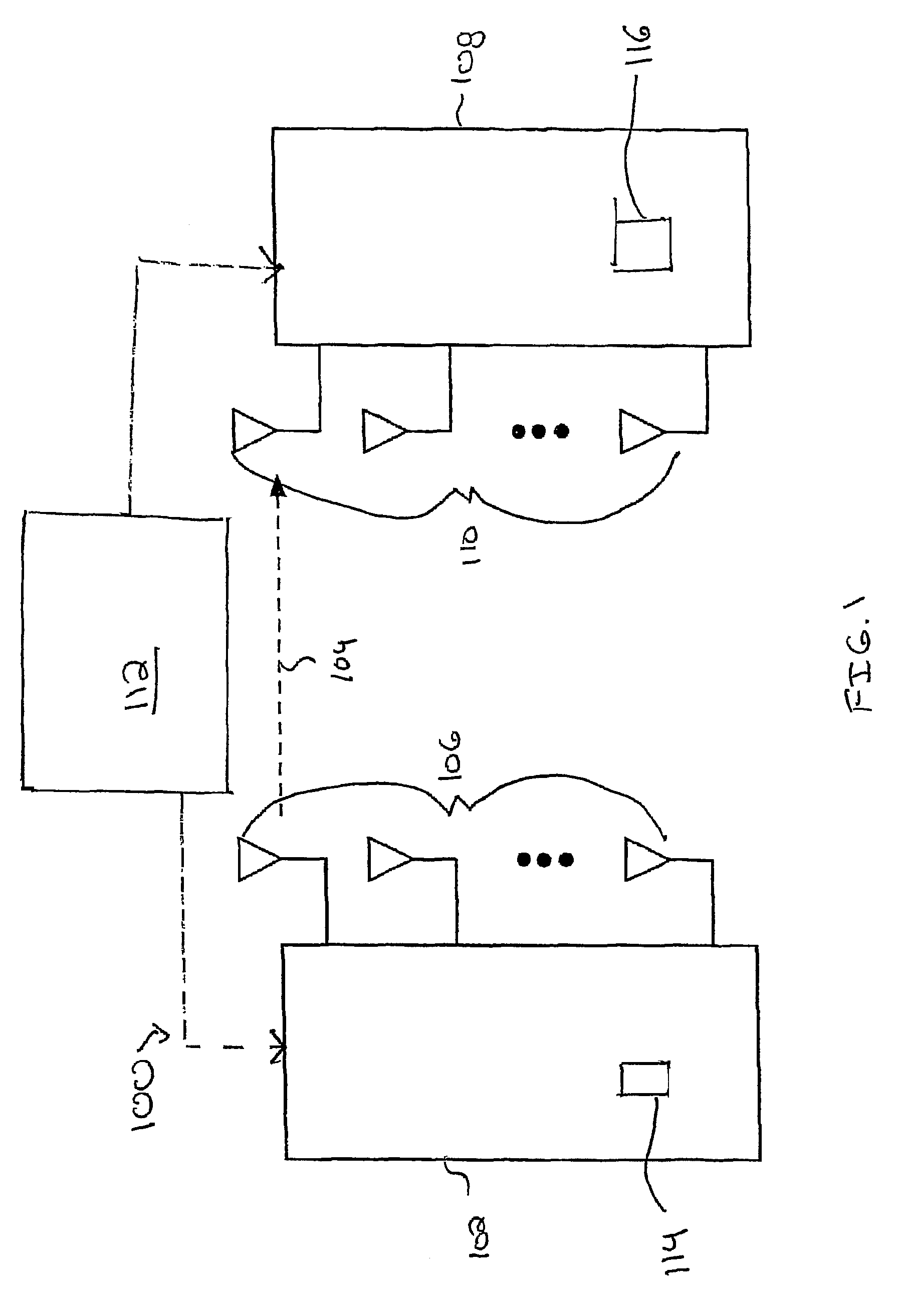
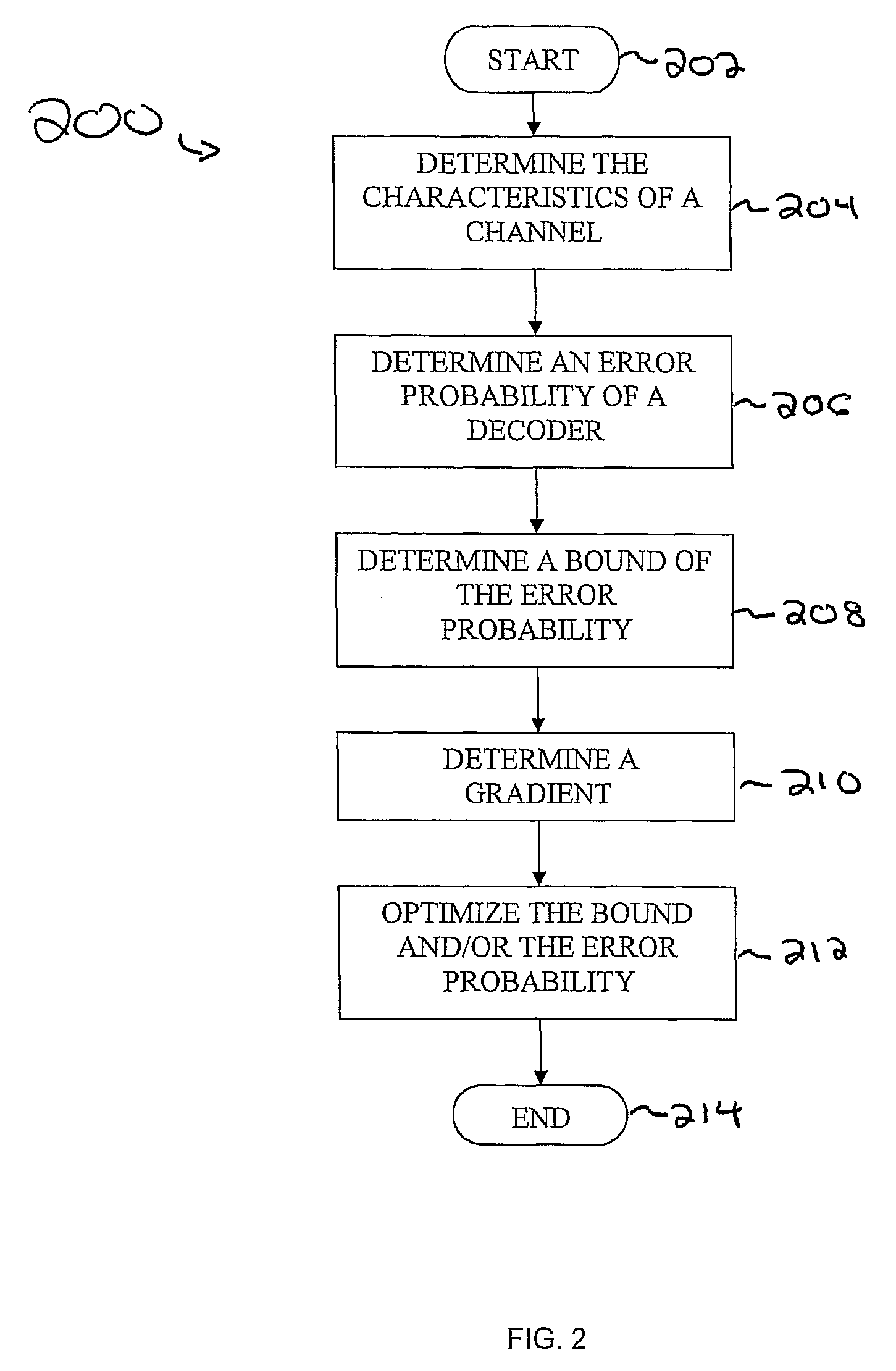
Methods and apparatus for designing spherical lattice codebooks for use in data transmission systems are provided. A spherical lattice codebook is constructed by determining the channel statistics of one or more channels, which can be accomplished by observing a sufficiently large set of channel realizations. After determining the channel statistics, an expression for the error probability of the decoder or expressions for bounds on the error probability and expressions for the corresponding gradients are determined. The gradient is then used in an optimization technique to produce a spherical lattice codebook which is subsequently used for transmission.
Owner:NEC CORP
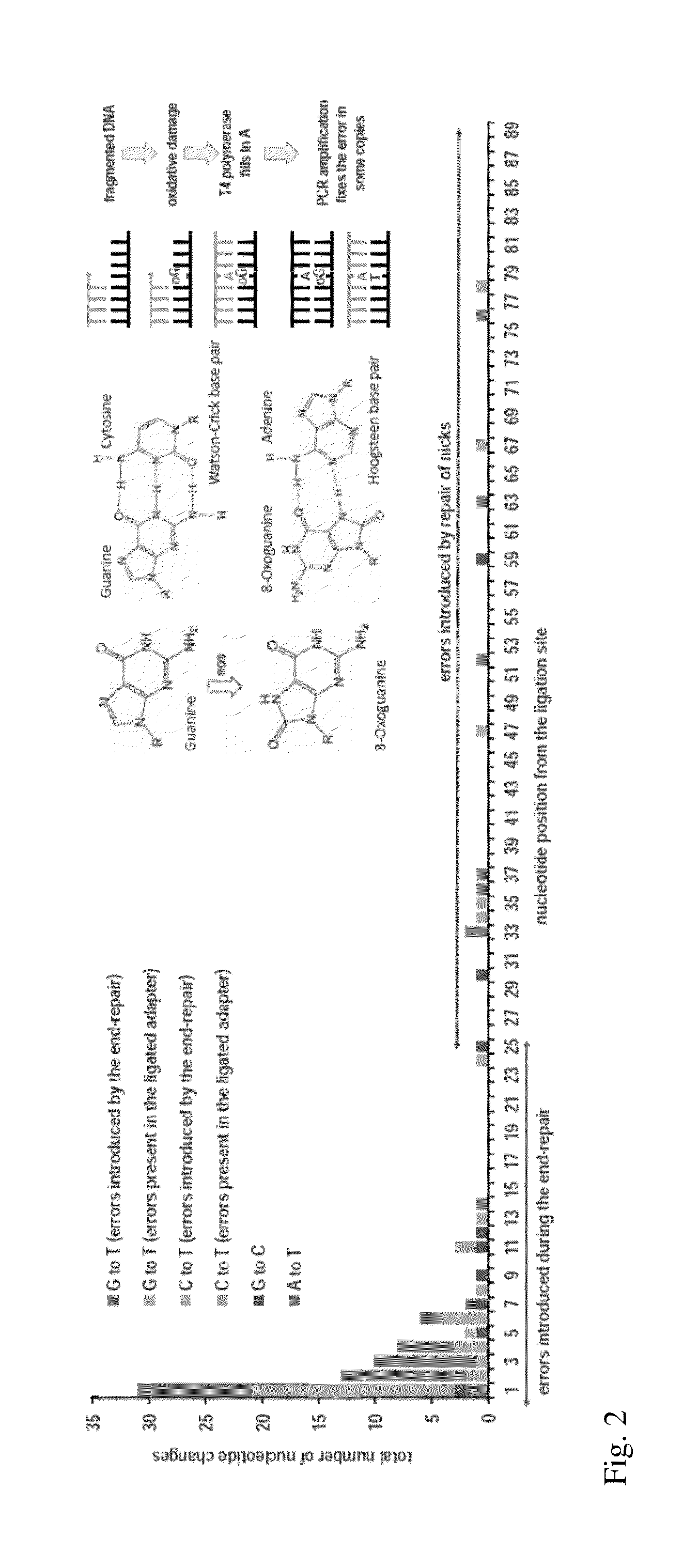
Method for Accurate Sequencing of DNA
ActiveUS20150275289A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationDNA formationComputational biology
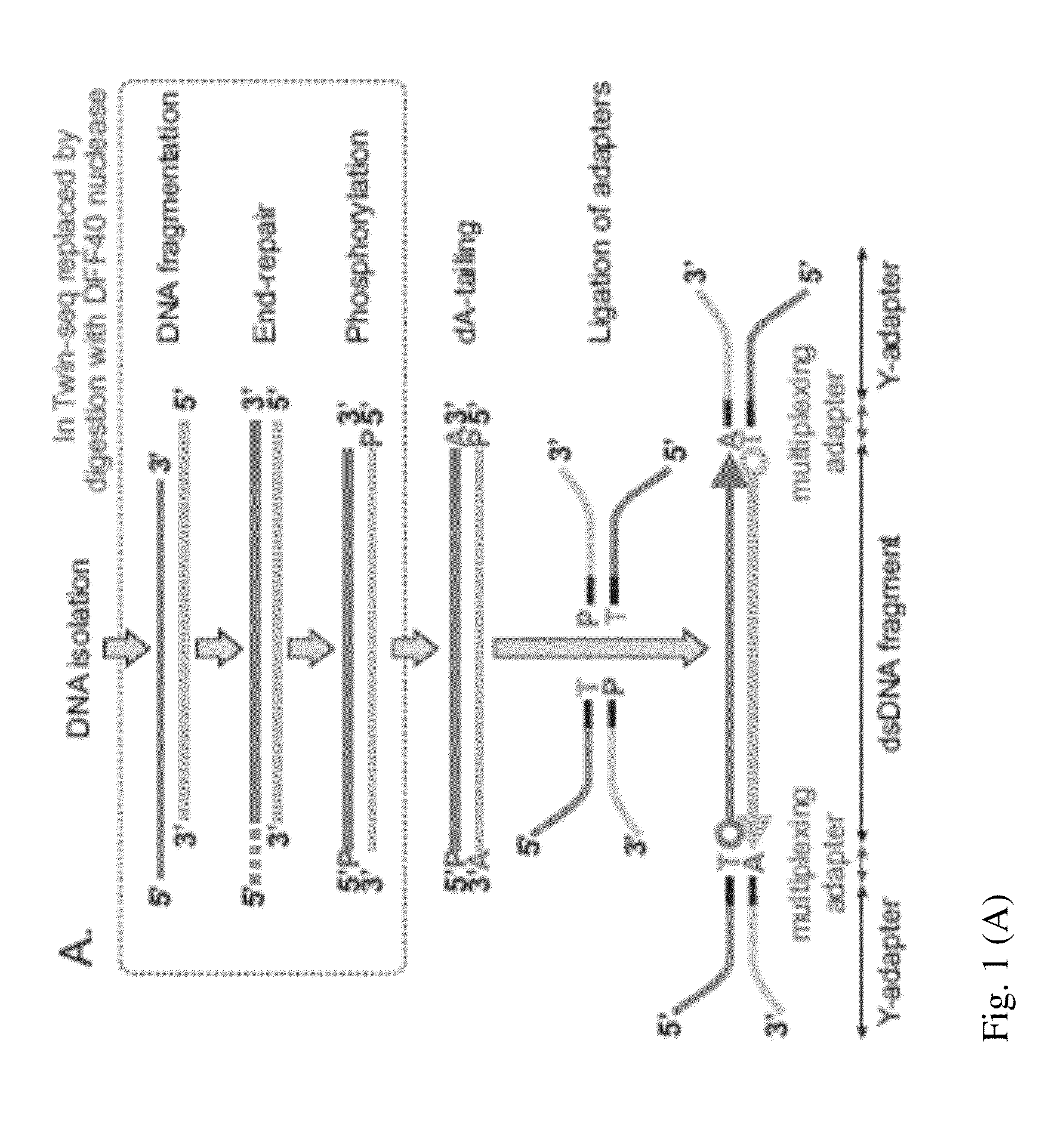
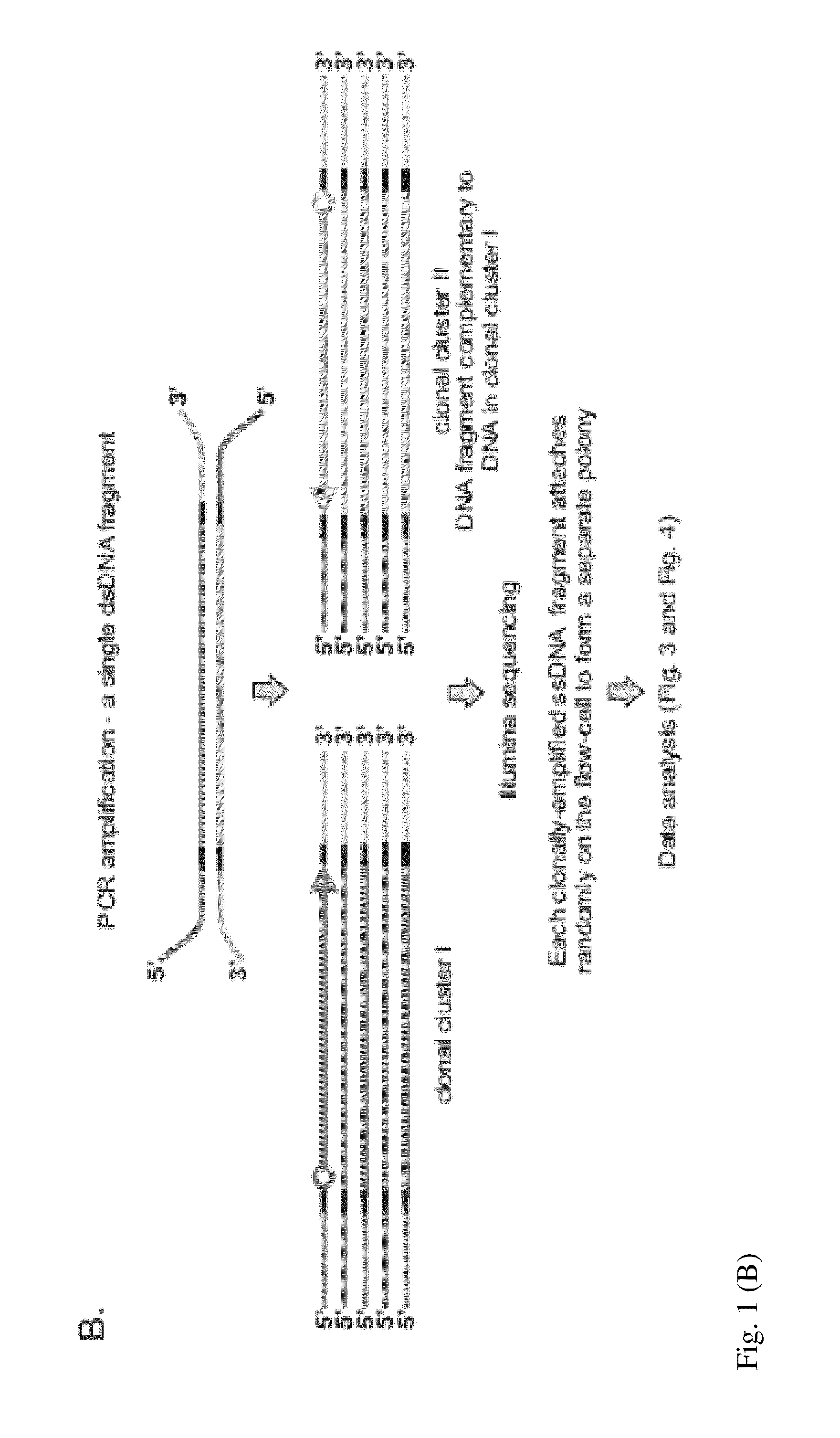
DNA is sequenced by (a) independently sequencing first and second strands of a dsDNA to obtain corresponding first and second sequences; and (b) combining the first and second sequences to generate a consensus sequence of the dsDNA. By independently sequencing first and second strands the error probability of the consensus sequence approximates a multiplication of those of the first and second sequences.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Design of Spherical Lattice Codes for Lattice and Lattice-Reduction-Aided Decoders
ActiveUS20070283210A1Reduce transmit energyCode conversionDiversity/multi-antenna systemsChannel statisticsLattice reduction
Methods and apparatus for designing spherical lattice codebooks for use in data transmission systems are provided. A spherical lattice codebook is constructed by determining the channel statistics of one or more channels, which can be accomplished by observing a sufficiently large set of channel realizations. After determining the channel statistics, an expression for the error probability of the decoder or expressions for bounds on the error probability and expressions for the corresponding gradients are determined. The gradient is then used in an optimization technique to produce a spherical lattice codebook which is subsequently used for transmission.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method and apparatus for processing an image
InactiveUS20090232358A1Reduce error rateFast processingCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingMaximally stable extremal regions
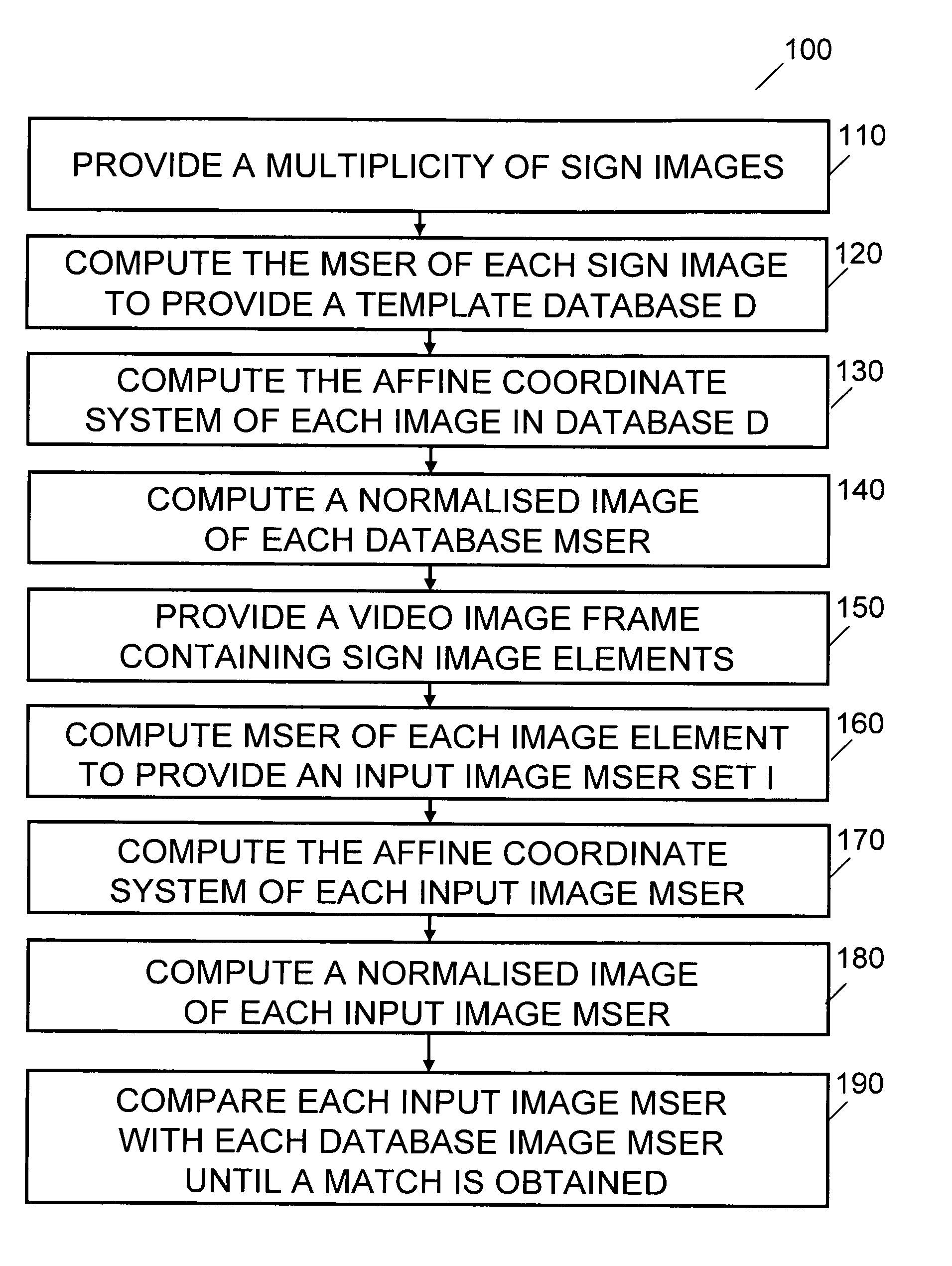
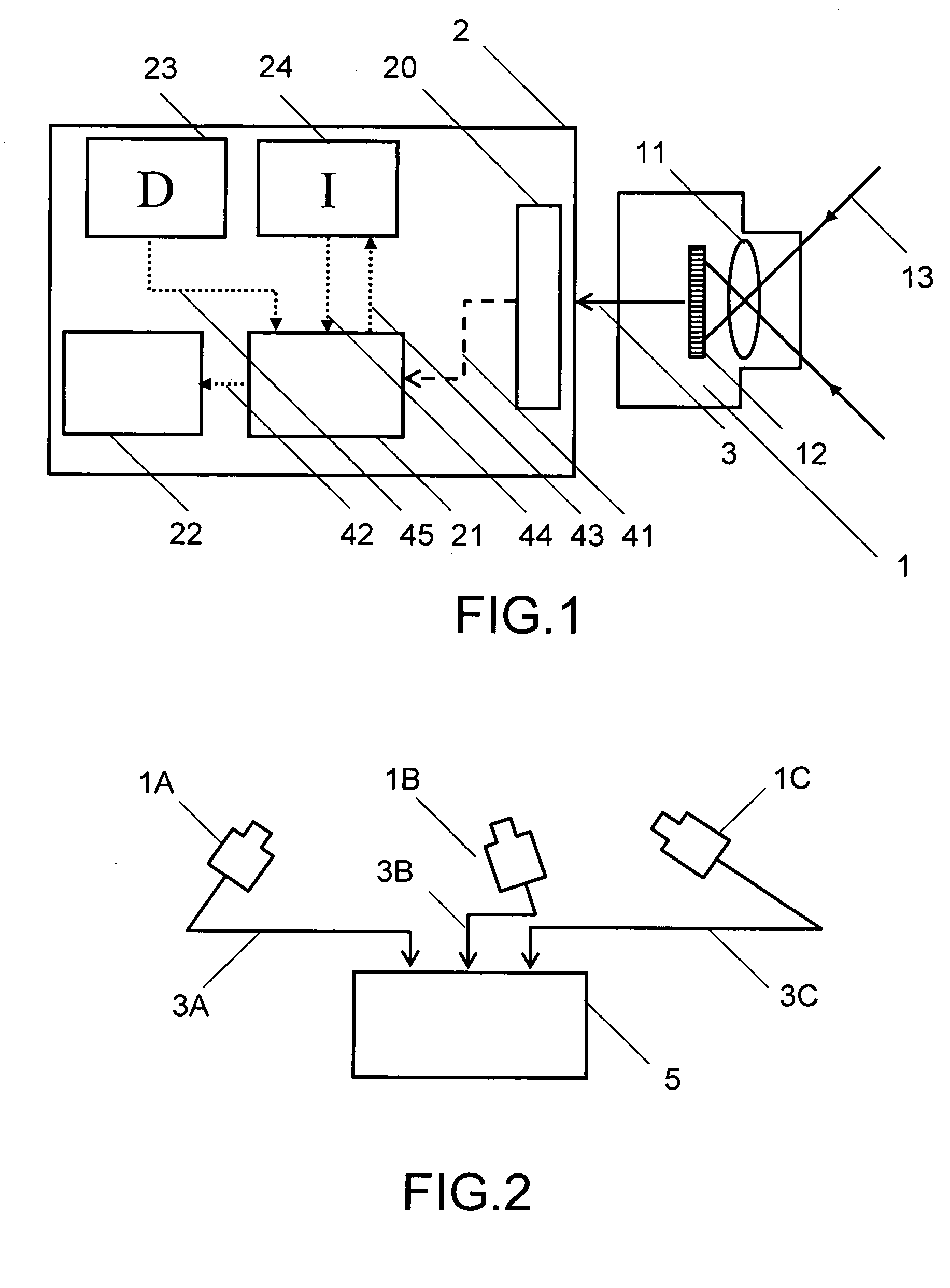
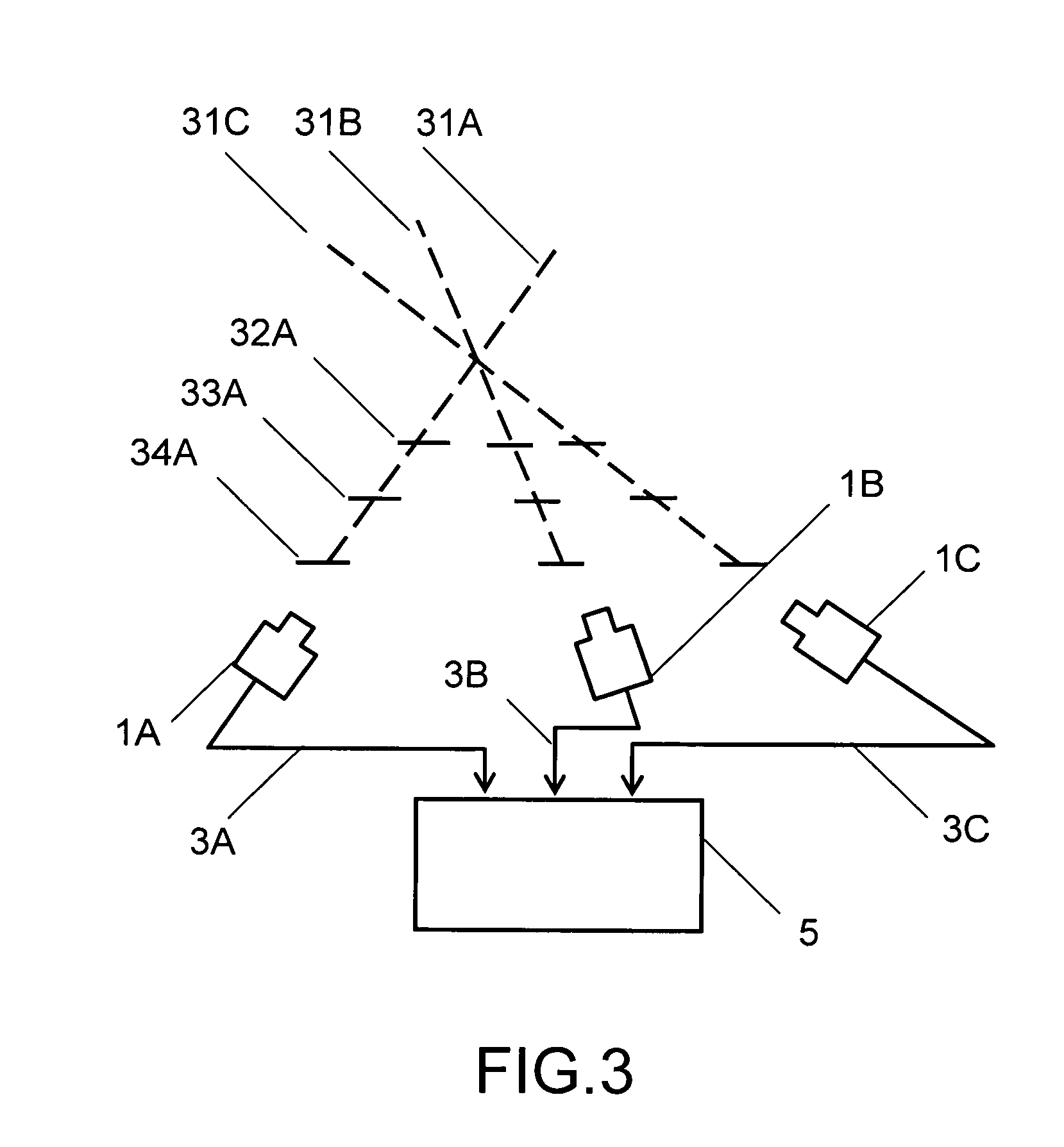
There is provided an efficient, fast image processing apparatus with low error probability for rapidly scrutinizing a digitized video image frame and processing said image frame to detect and characterize features of interest while ignoring other features of said image frame. There is further provided an efficient fast image processing method with low error probability for rapidly scrutinizing a digitized video image frame and processing said image frame to detect and characterize features of interest while ignoring other features of said image frame. In a first embodiment of the invention an image processing apparatus comprises an imaging device coupled to a digital electronic image processor. Video data from the imaging device is linked to a location data source. Objects of interest in a scene are identified by comparing computed Maximally Stable Extremal Regions (MSERs) of captured images with MSERs of images of objects contained in a object template database.
Owner:CROSS GEOFFREY MARK TIMOTHY
Method and system for deploying cloud host computer
ActiveCN101840346ARapid deploymentReduce error rateSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationProduction rateData file
The invention discloses a method and a system for deploying a cloud host computer. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a virtual machine object according to a virtual machine establishing request of a user; modifying the attribute of the virtual machine object; converting the virtual machine object into a template data file; copying the template data file and creating a preset amount of pre-manufactured virtual machines; and receiving addresses and public key setting of the pre-manufactured virtual machines and enabling one of the pre-manufactured virtual machines. The method and the system for deploying the cloud host computer have the advantages of overcoming the disadvantages that the current cloud host deployment entirely depends on manual operation, production rate is low and maintenance cost is high, solving the problem of high error probability of the manual deployment of the cloud machine, and meeting the requirements of quickly deploying the cloud host machine and acquiring enough computing power.
Owner:上海蓝云网络科技有限公司
MIMO decoding
ActiveUS20050265465A1Improve performancePolarisation/directional diversityDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionCommunications systemInterference (communication)
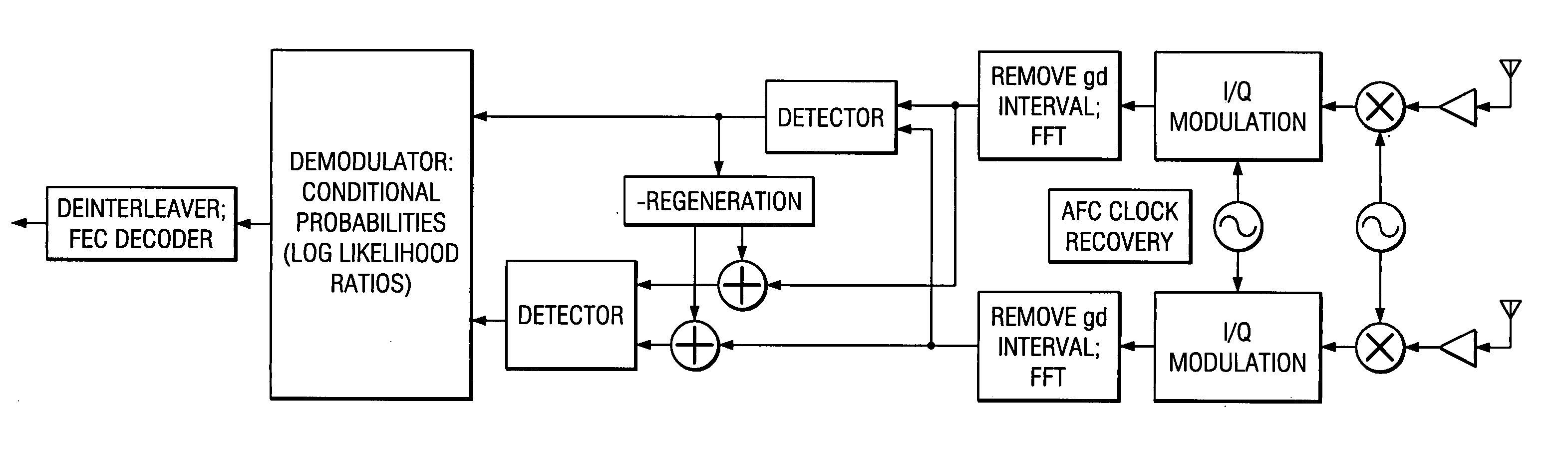
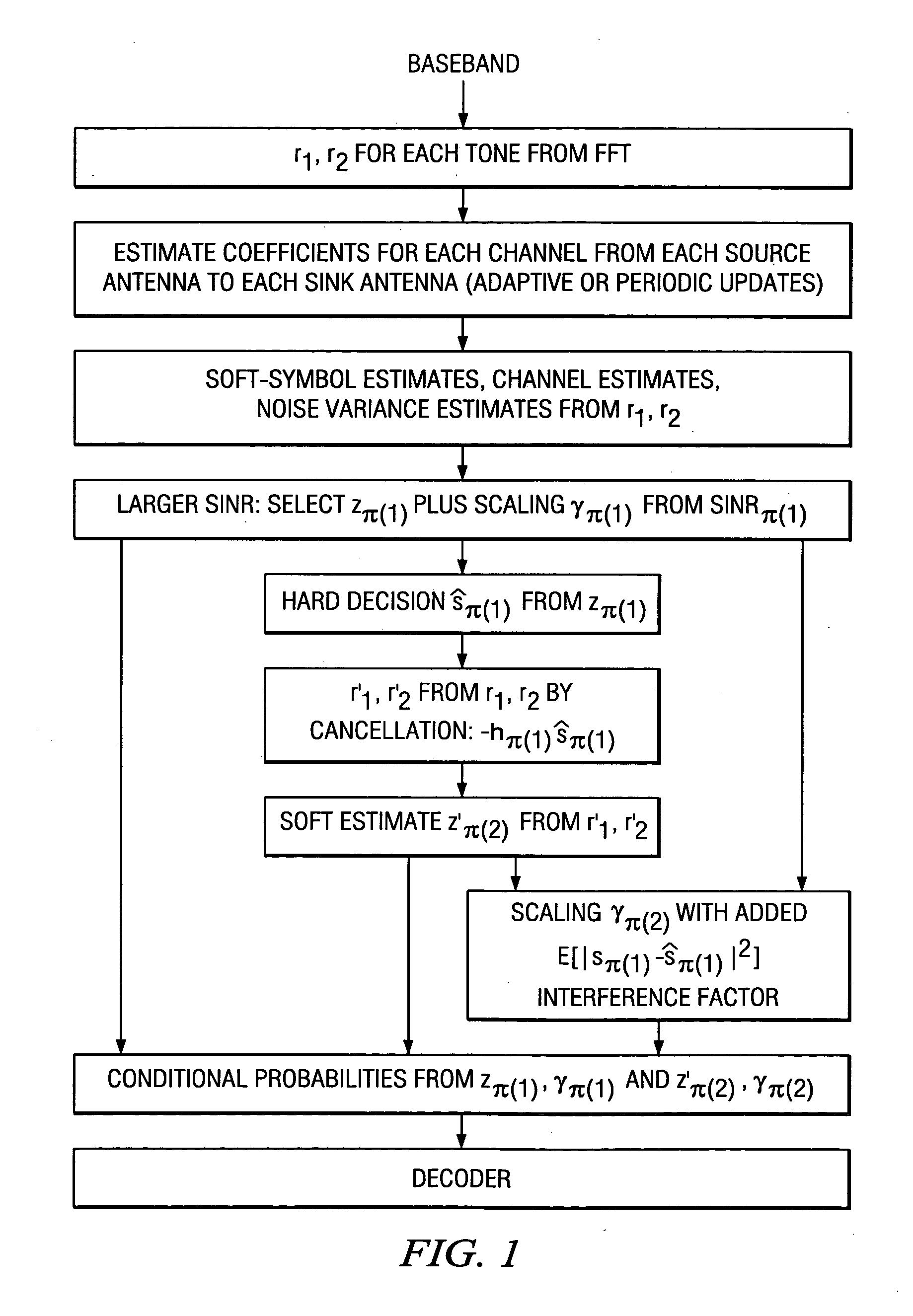
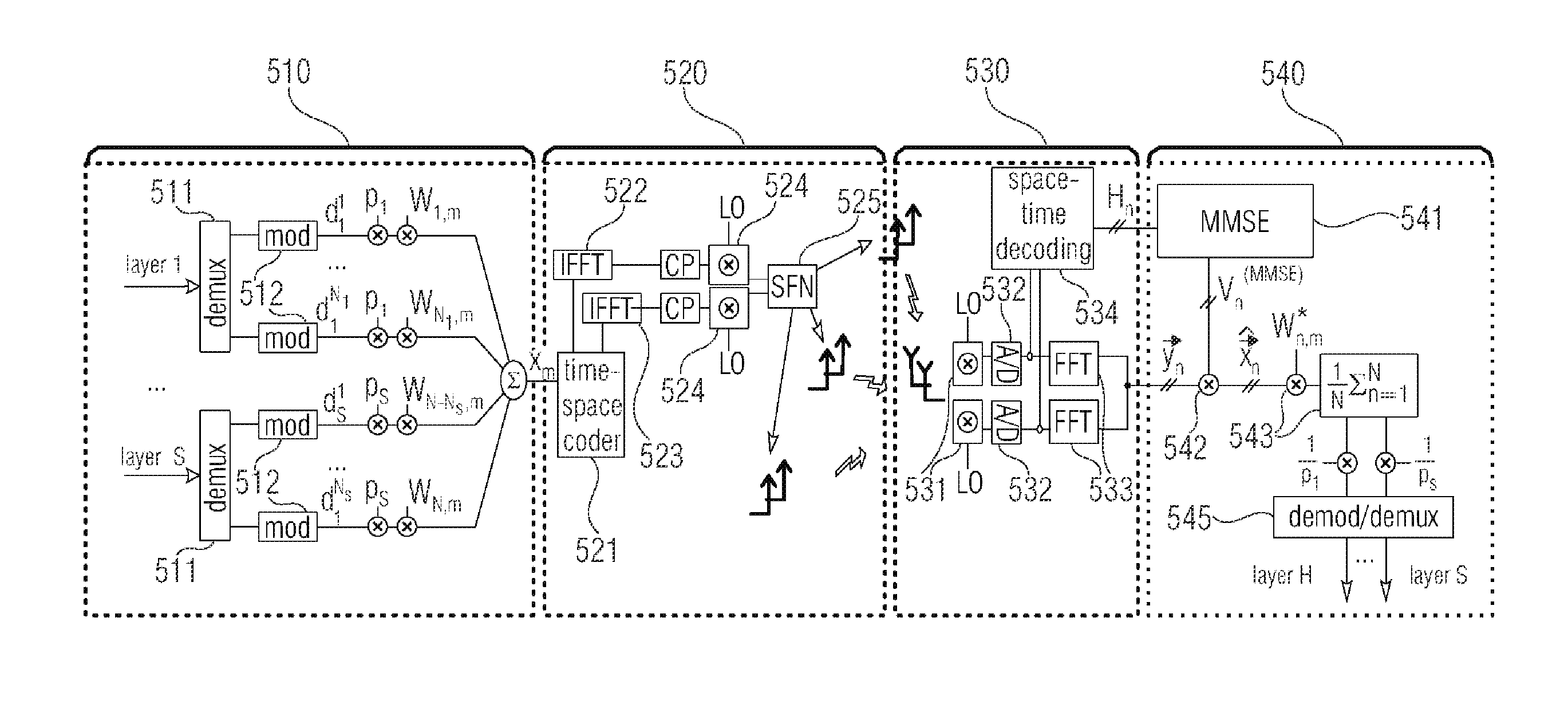
In MIMO wireless communications employing LMMSE receiver, the symbols transmitted through a transmit antenna are estimated at the receiver in the presence of interference consisting of two main components: one due to the additive noise and the other due to (interfering) symbols transmitted via the remaining antennas. This has been shown to hamper the performance of a communication system resulting in incorrect symbol decisions, particularly at low SNR. IMMSE has been devised as a solution to cope with this problem; In IMMSE processing, the symbols sent via each transmit antenna are decoded iteratively. In each stage of processing, the received signal is updated by removing the contribution of symbols detected in the previous iterations. In principle, this reduces the additive interference in which the desired symbols are embedded in. Therefore, the interference level should reduce monotonically as one goes down in processing order. In a noisy environment, however, any incorrect decision made on a symbol in an iteration leaves its contribution in the updated received signal available for processing in the following iterations. Fortunately, if the level of interference is estimated and the soft bits are scaled appropriately by the estimated interference power, the performance of IMMSE receiver can be greatly improved. Preferred embodiments estimate the interference by computing the probability of error in decoding the symbols of the previous stage(s). The computation of decision error probability depends on the constellation size of transmitted symbols and introduces very little processing overhead.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
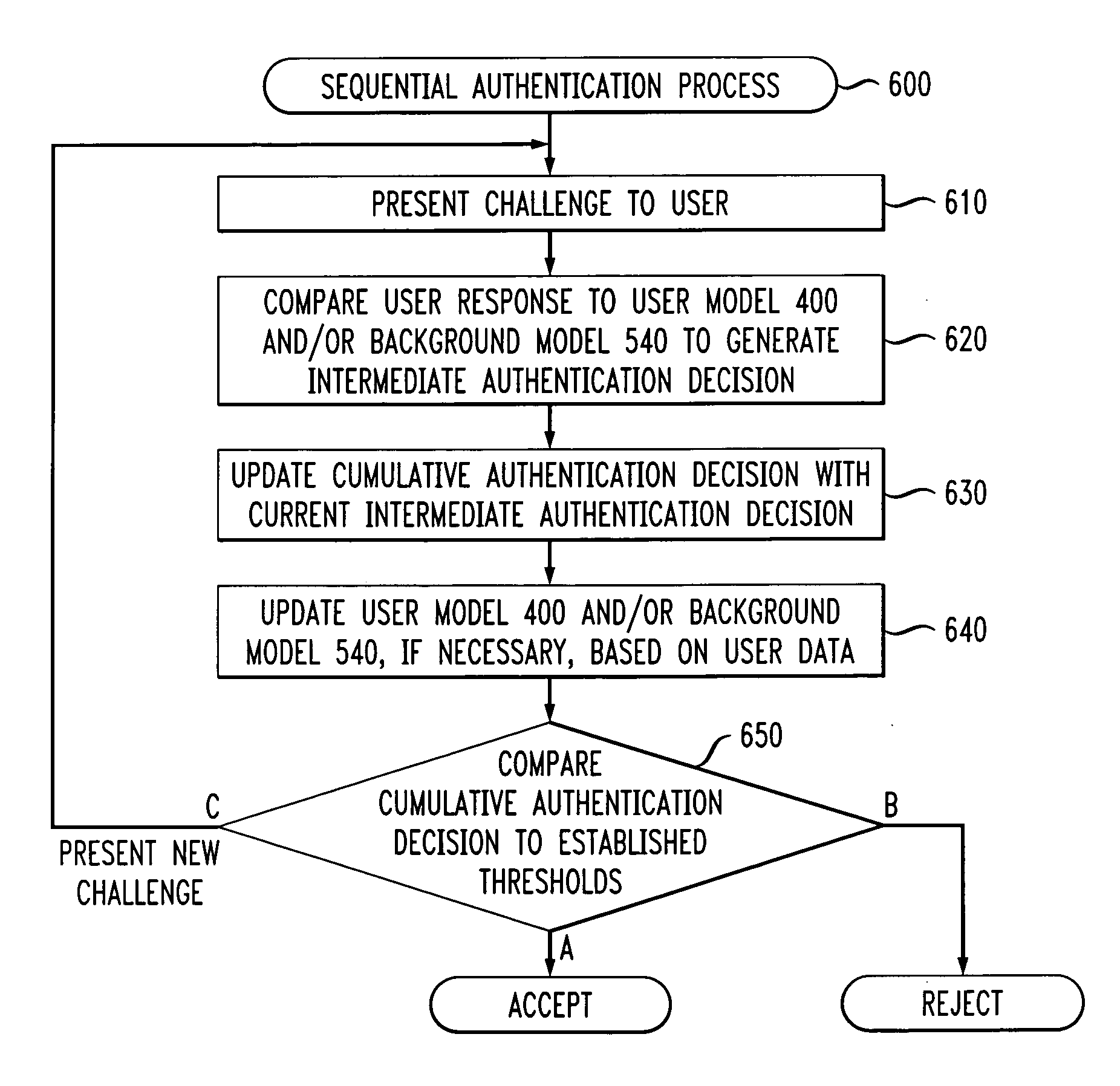
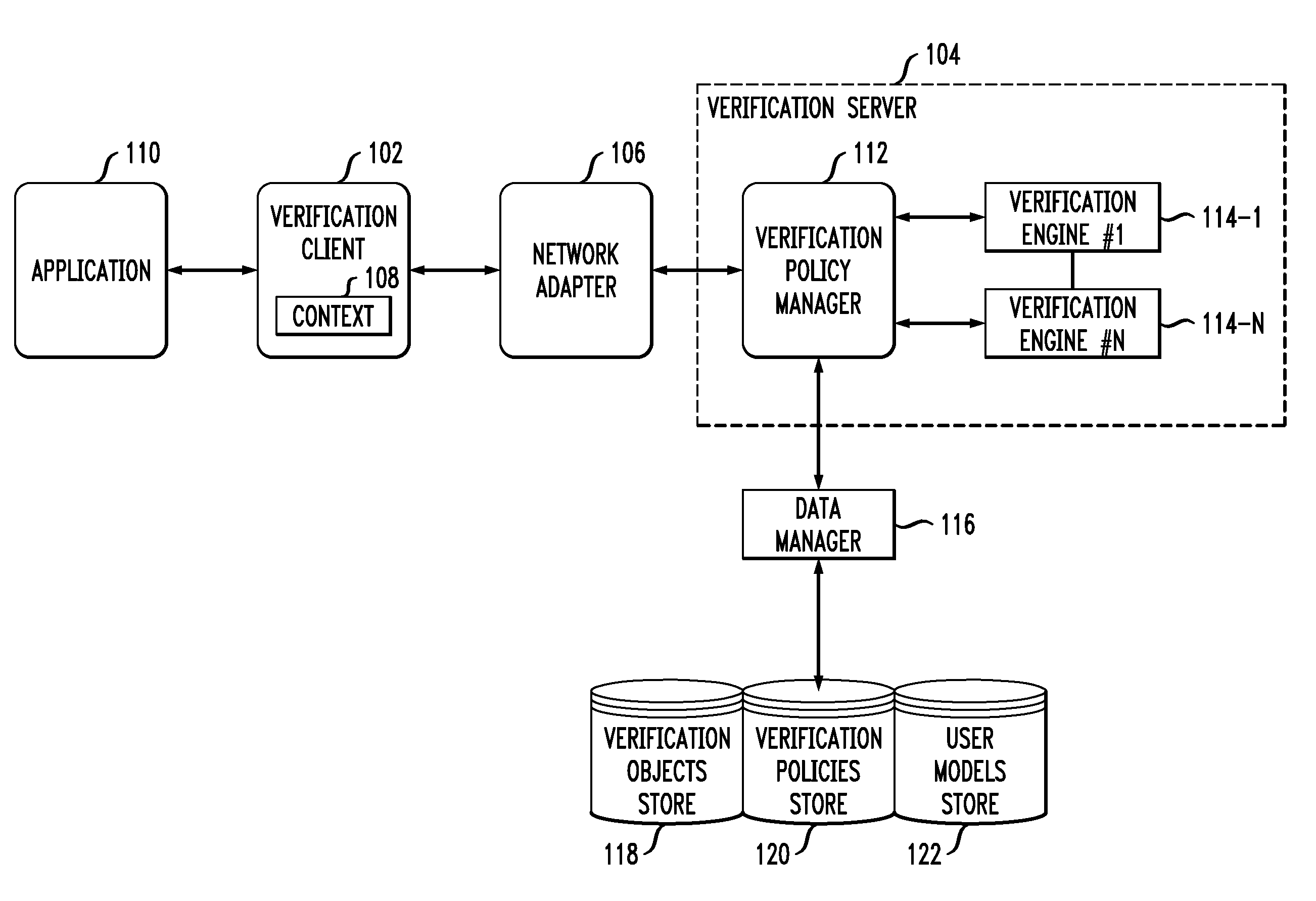
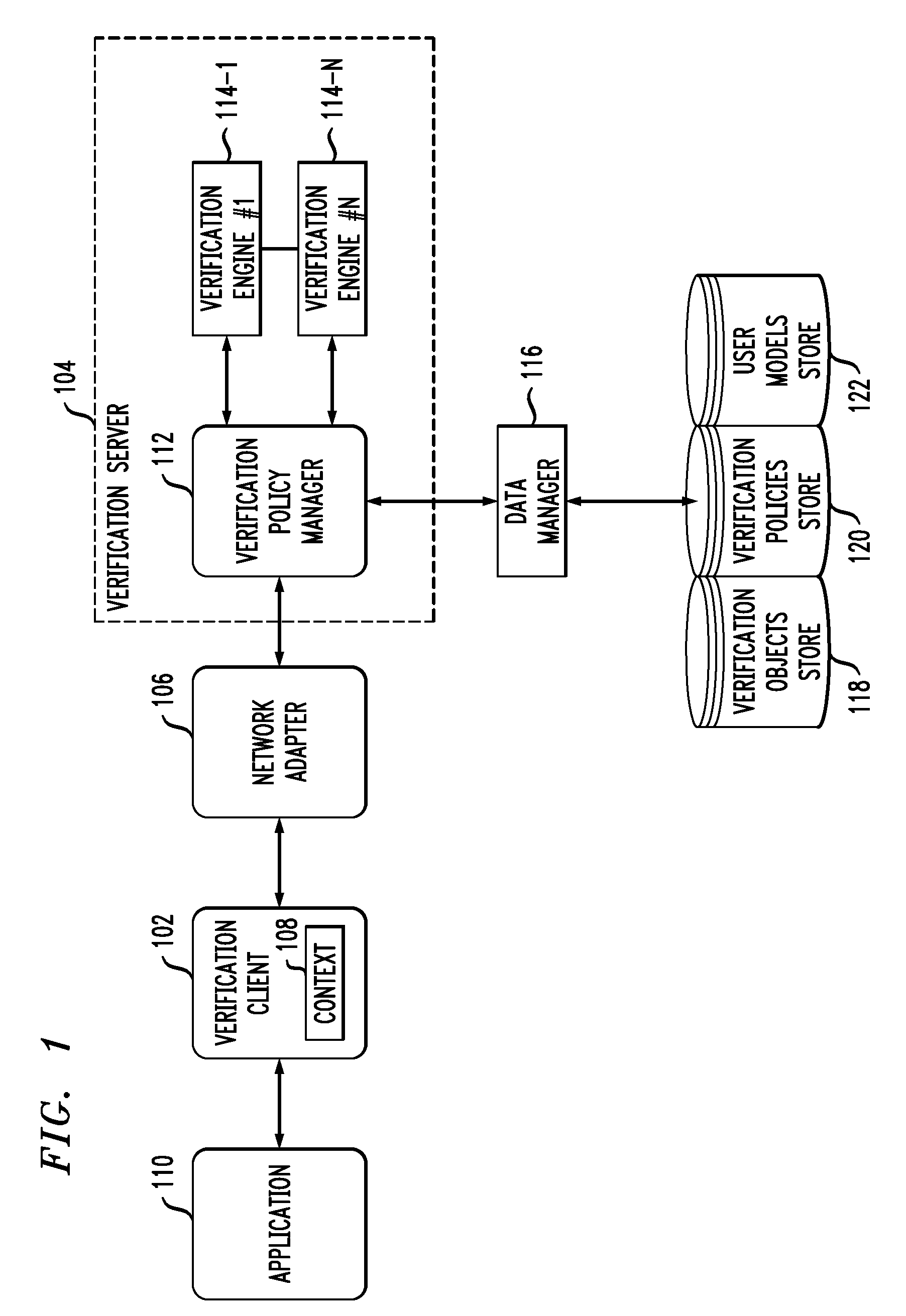
Method and apparatus for sequential authentication using one or more error rates characterizing each security challenge
InactiveUS20060294390A1Easy to adaptDigital data authenticationSecuring communicationProbabilistic descriptionField data
Methods and apparatus are provided for sequential authentication of a user that employ one or more error rates characterizing each security challenge. According to one aspect of the invention, a user is challenged with at least one knowledge challenge to obtain an intermediate authentication result; and the user challenges continue until a cumulative authentication result satisfies one or more criteria. The intermediate authentication result is based, for example, on one or more of false accept and false reject error probabilities for each knowledge challenge. A false accept error probability describes a probability of a different user answering the knowledge challenge correctly. A false reject error probability describes a probability of a genuine user not answering the knowledge challenge correctly. The false accept and false reject error probabilities can be adapted based on field data or known information about a given challenge.
Owner:IBM CORP
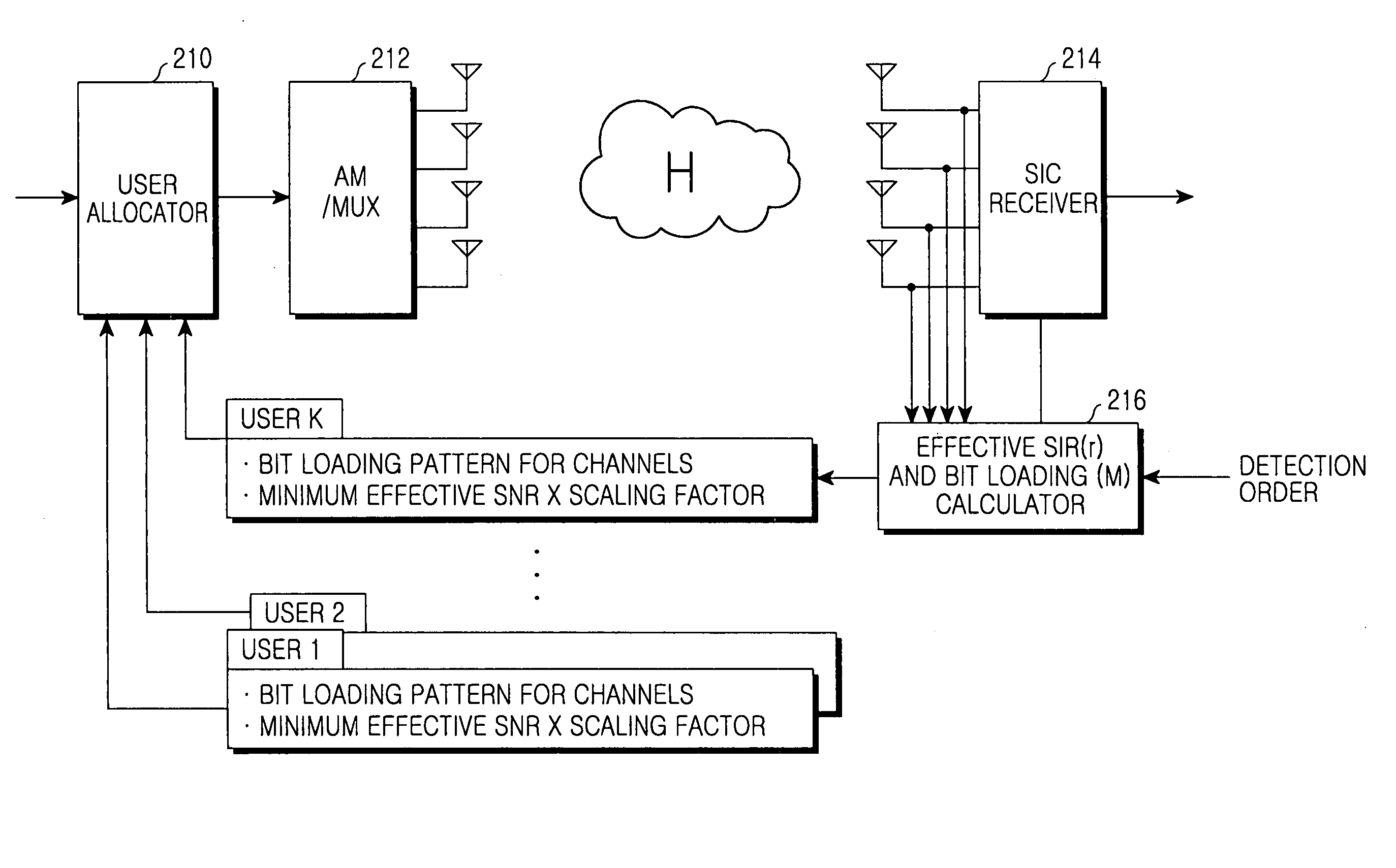
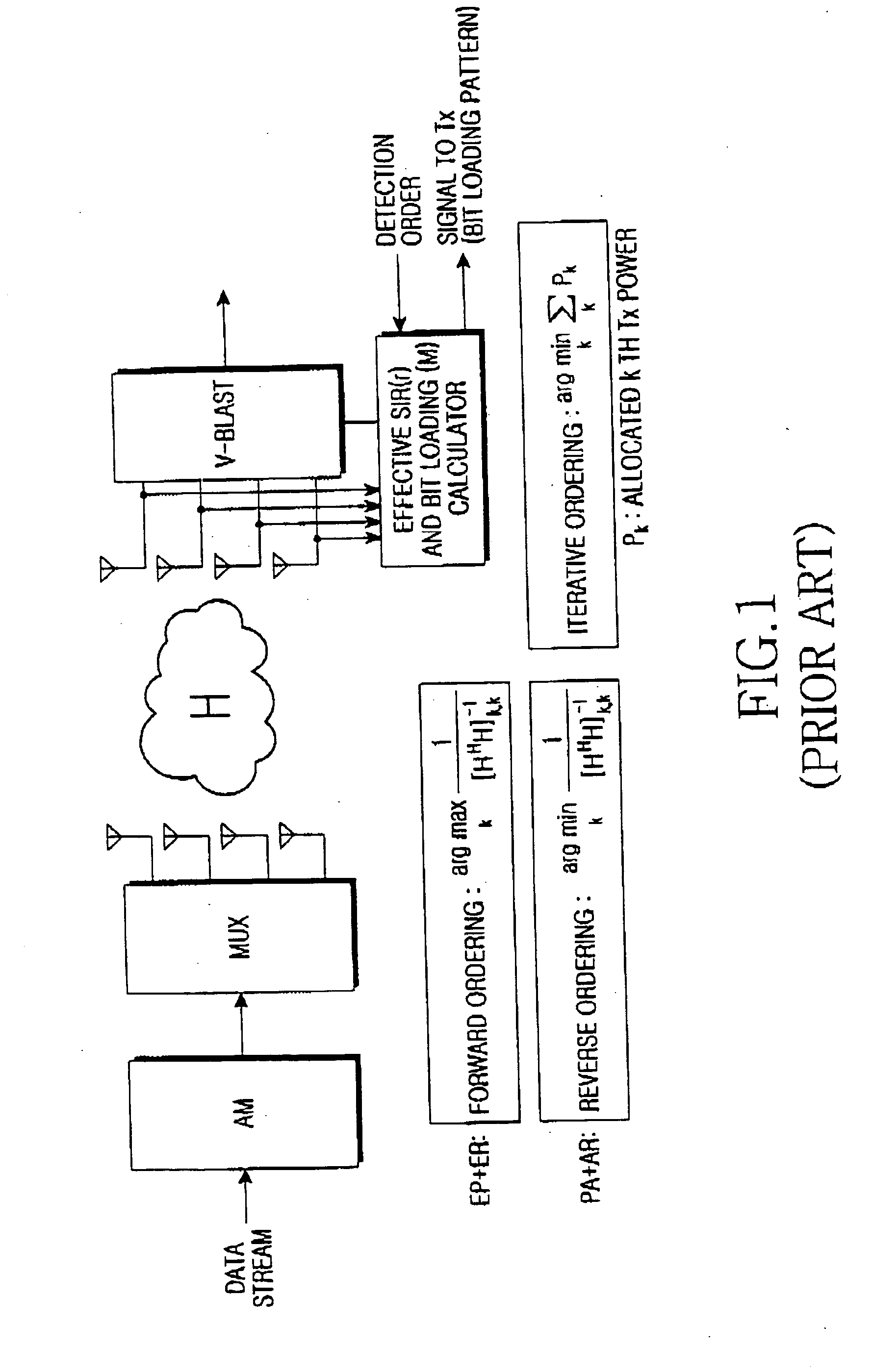
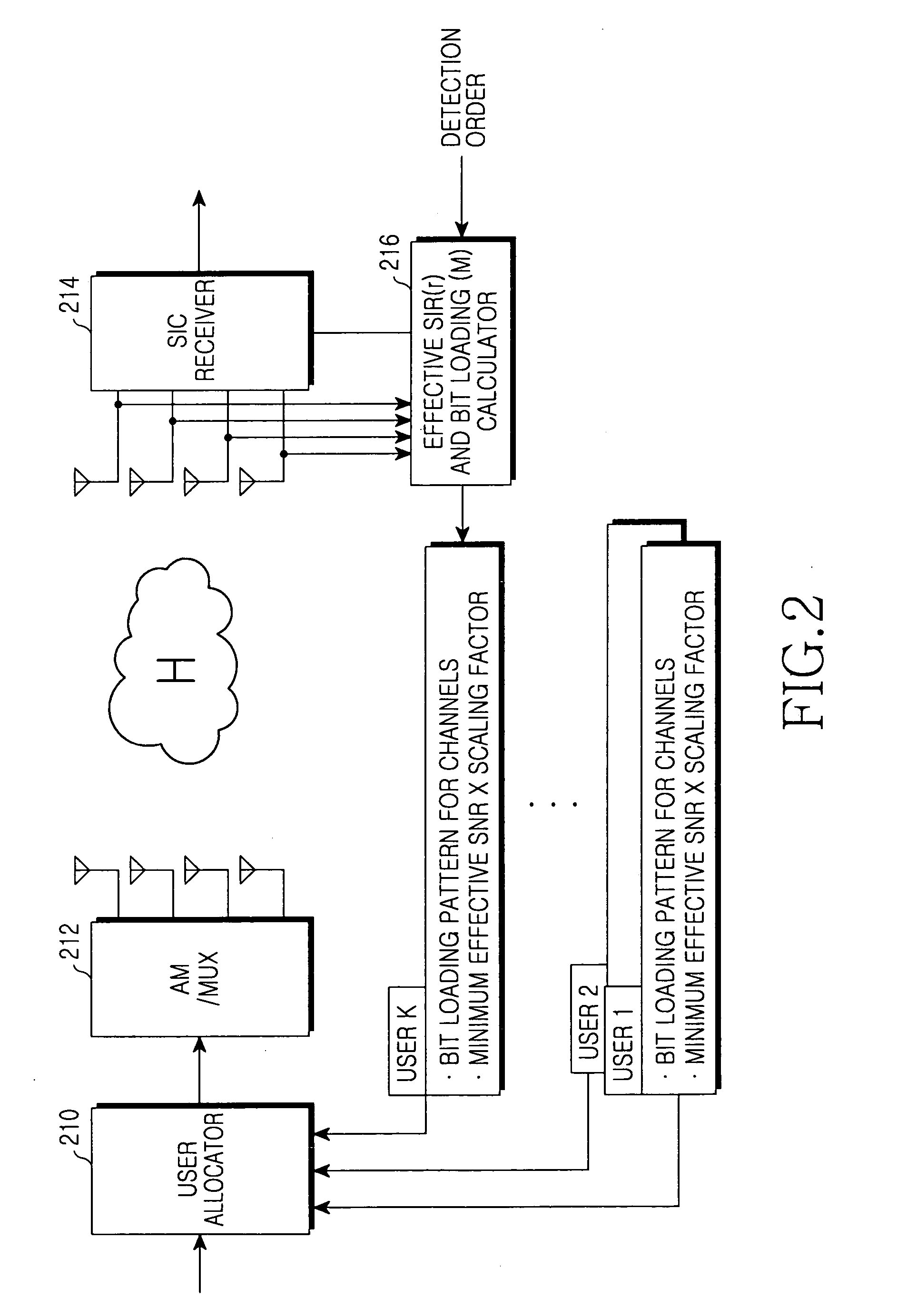
Apparatus and method for allocating user in a multiple antenna mobile communication system supporting multi-user diversity
InactiveUS20060203777A1Minimizes average error probabilityMaximizing numberPolarisation/directional diversityFire rescueCommunications systemMobile communication systems
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
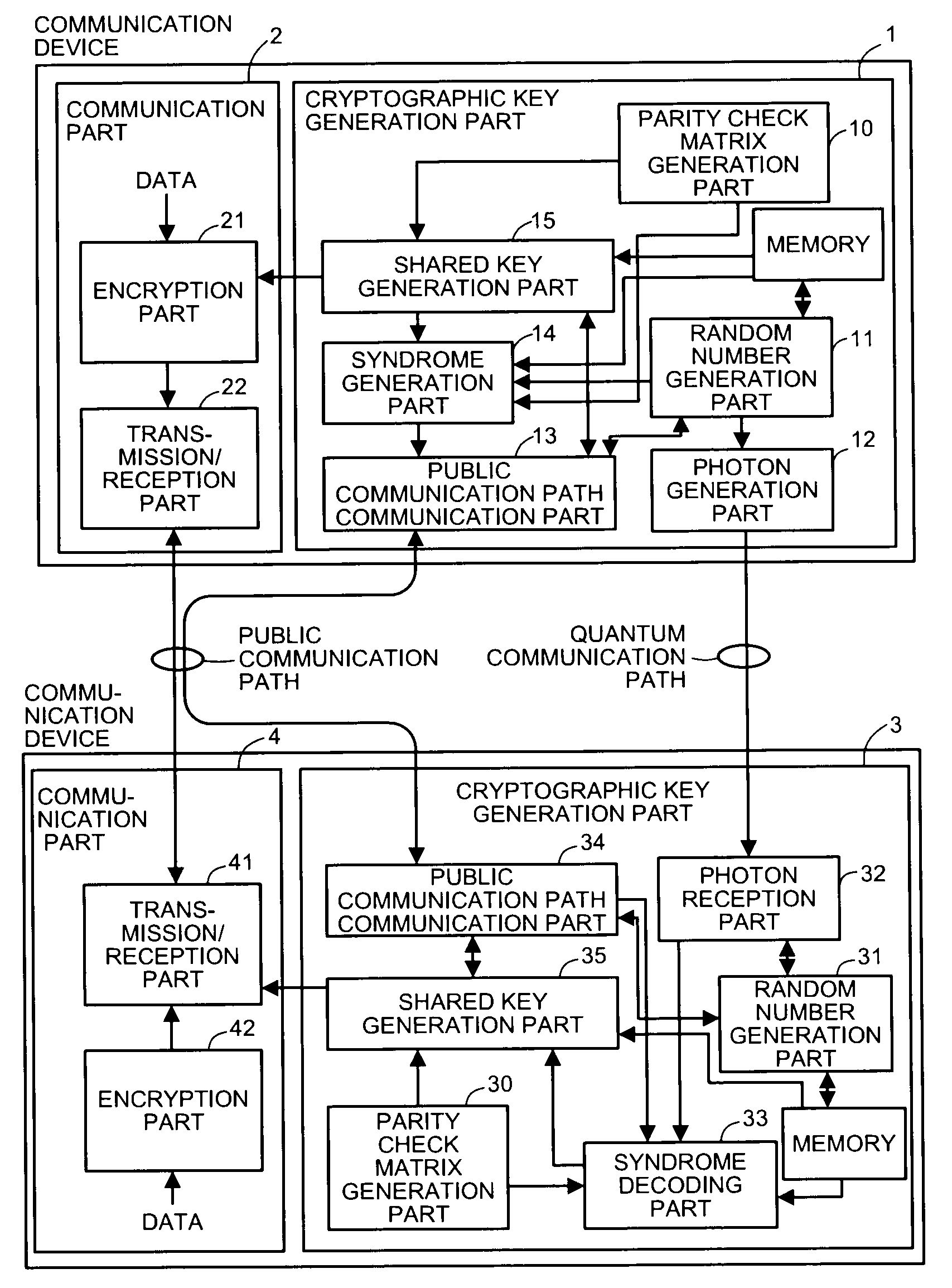
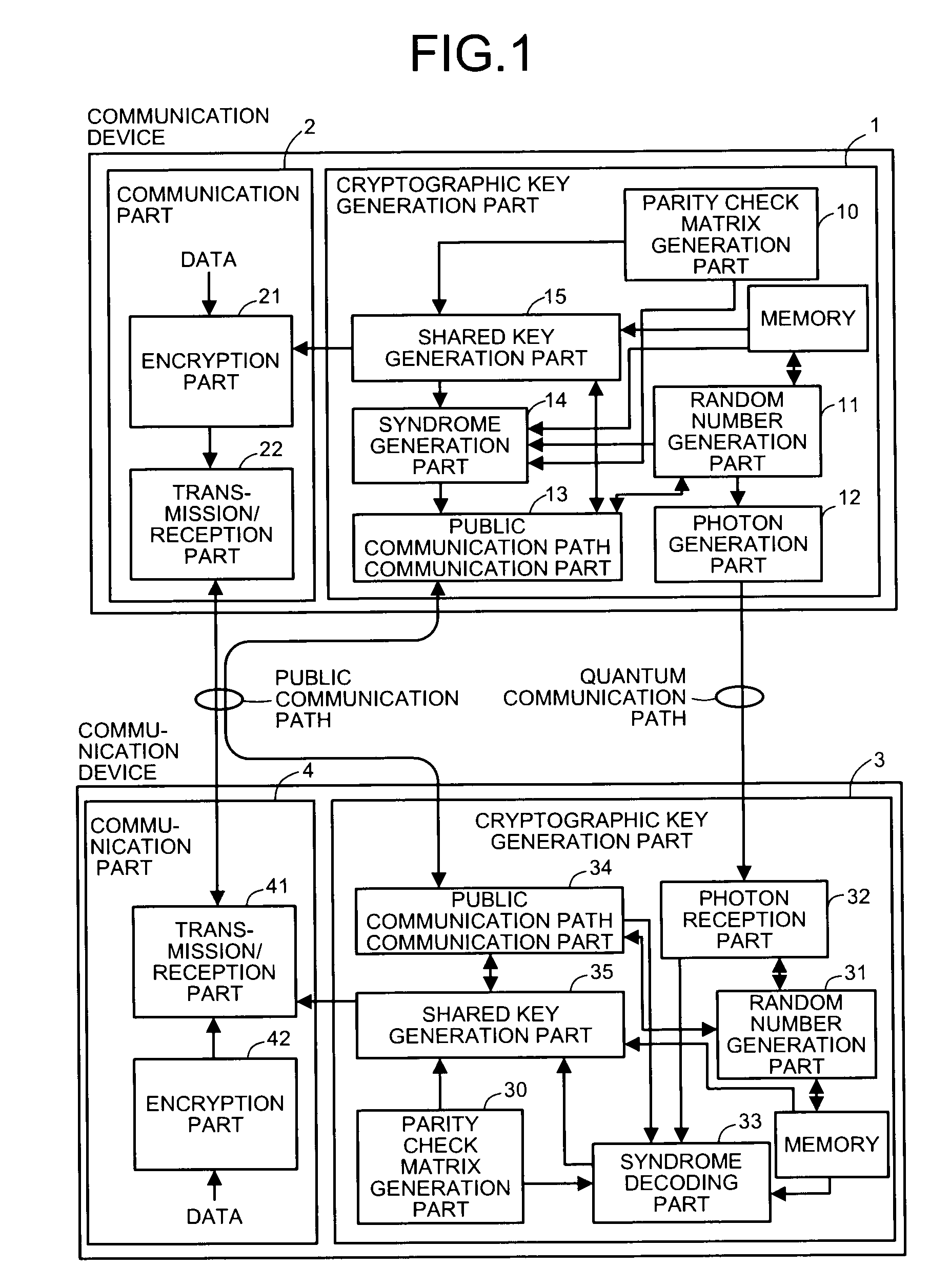
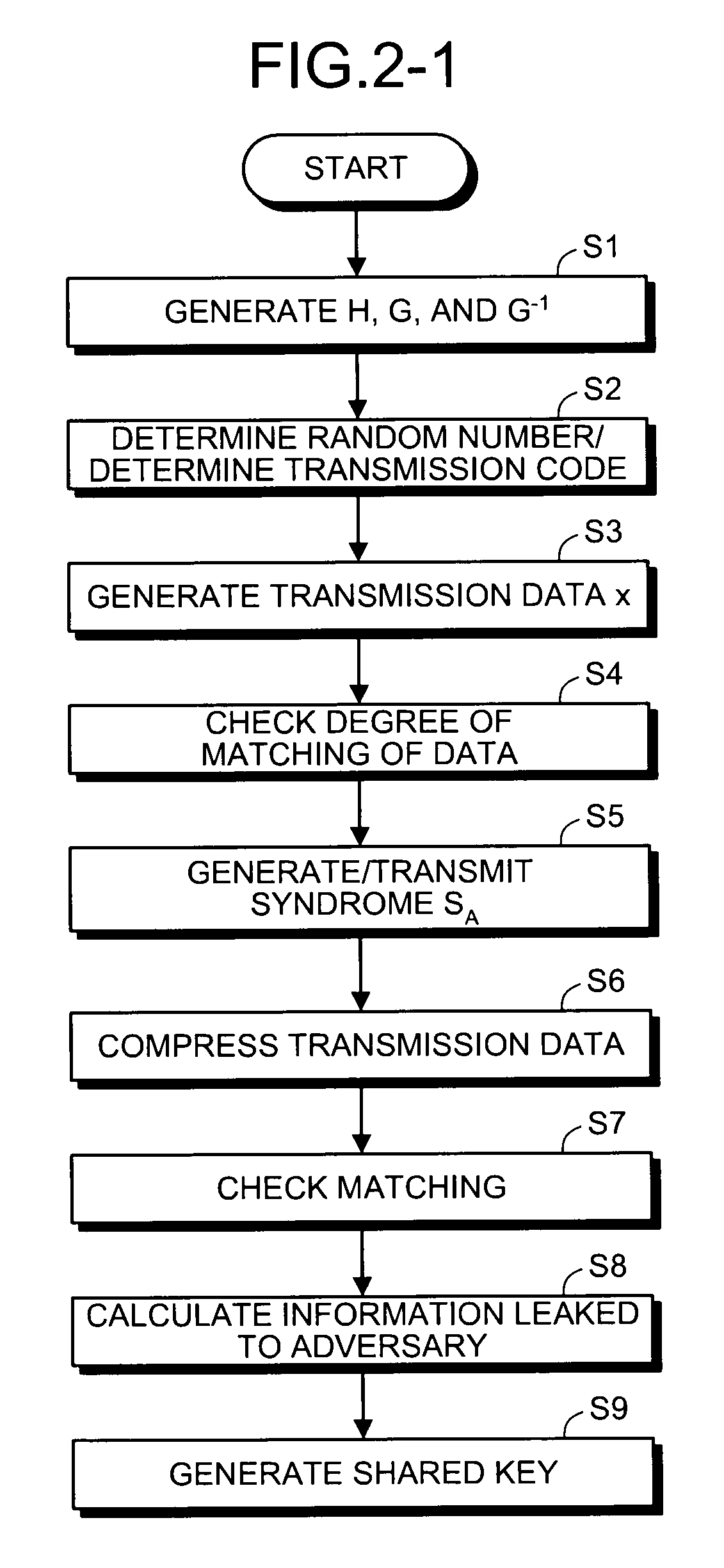
Quantum key distribution method, communication system, and communication device
InactiveUS20090169015A1Generate efficientlyImprove securityKey distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationComputer hardwareCommunications system
A quantum key distribution method according to the present invention includes an error probability estimation step of estimating error probabilities of transmission data and the received data, an error correcting step of correcting errors in the received data based on error correcting information, a matching determination step of determining whether the transmission data and the received data after correcting errors match, and an information amount estimating step of estimating an amount of information leaked to an adversary through a quantum communication path, and further compresses data based on the amount of information made public in a process of processing via a public communication path and an estimated value of the amount of information leaked to the adversary through the quantum communication path to make the data after compression a cryptographic key shaped by devices.
Owner:INTER UNIV RES INST RES ORG OF INFORMATION & SYST
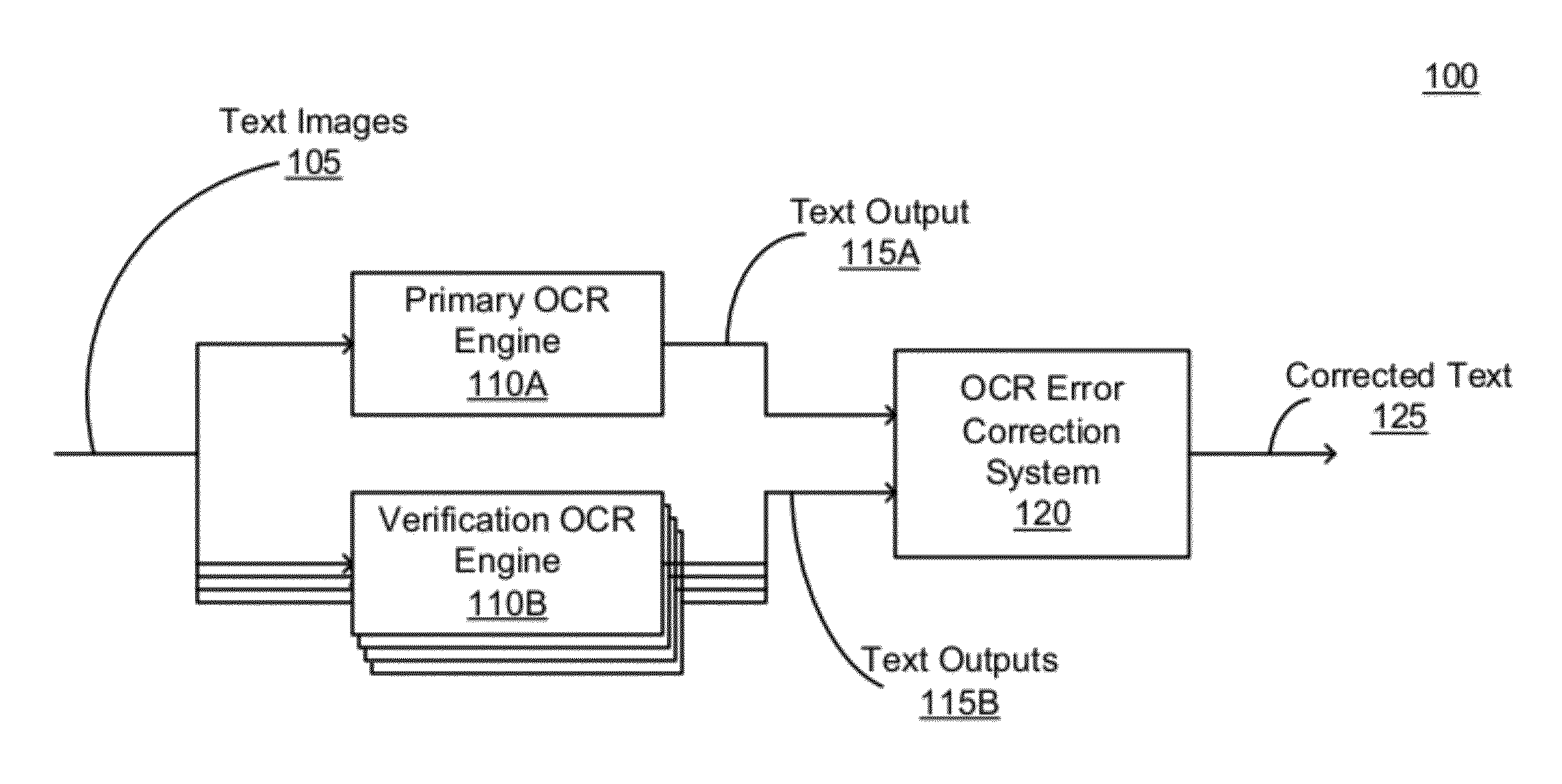
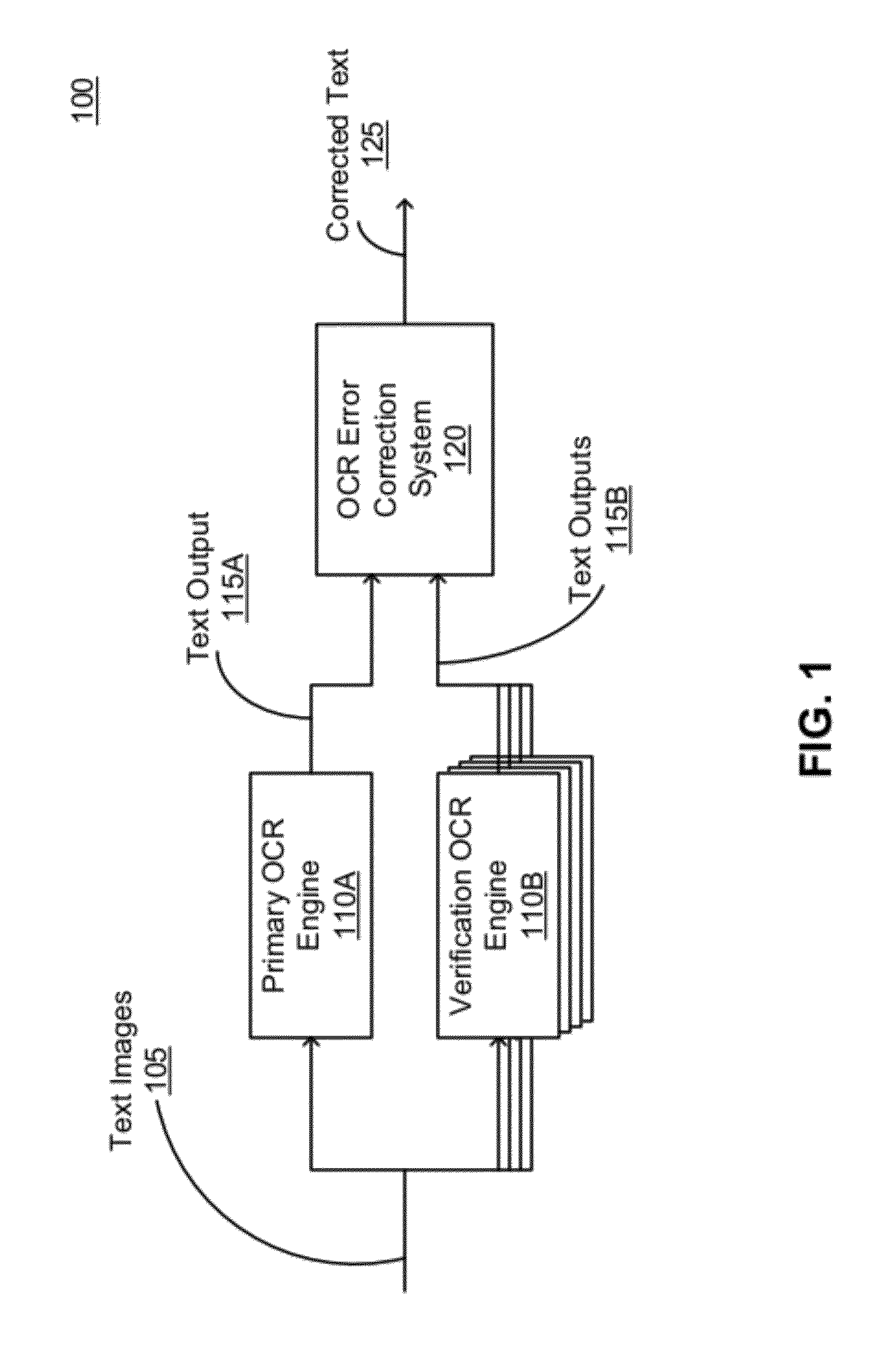
Efficient identification and correction of optical character recognition errors through learning in a multi-engine environment
InactiveUS8331739B1Adapt quicklyLow costDigitally marking record carriersDigital data processing detailsGround truthProbability estimation
OCR errors are identified and corrected through learning. An error probability estimator is trained using ground truths to learn error probability estimation. Multiple OCR engines process a text image, and convert it into texts. The error probability estimator compares the outcomes of the multiple OCR engines for mismatches, and determines an error probability for each of the mismatches. If the error probability of a mismatch exceeds an error probability threshold, a suspect is generated and grouped together with similar suspects in a cluster. A question for the cluster is generated and rendered to a human operator for answering. The answer from the human operator is then applied to all suspects in the cluster to correct OCR errors in the resulting text. The answer is also used to further train the error probability estimator.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
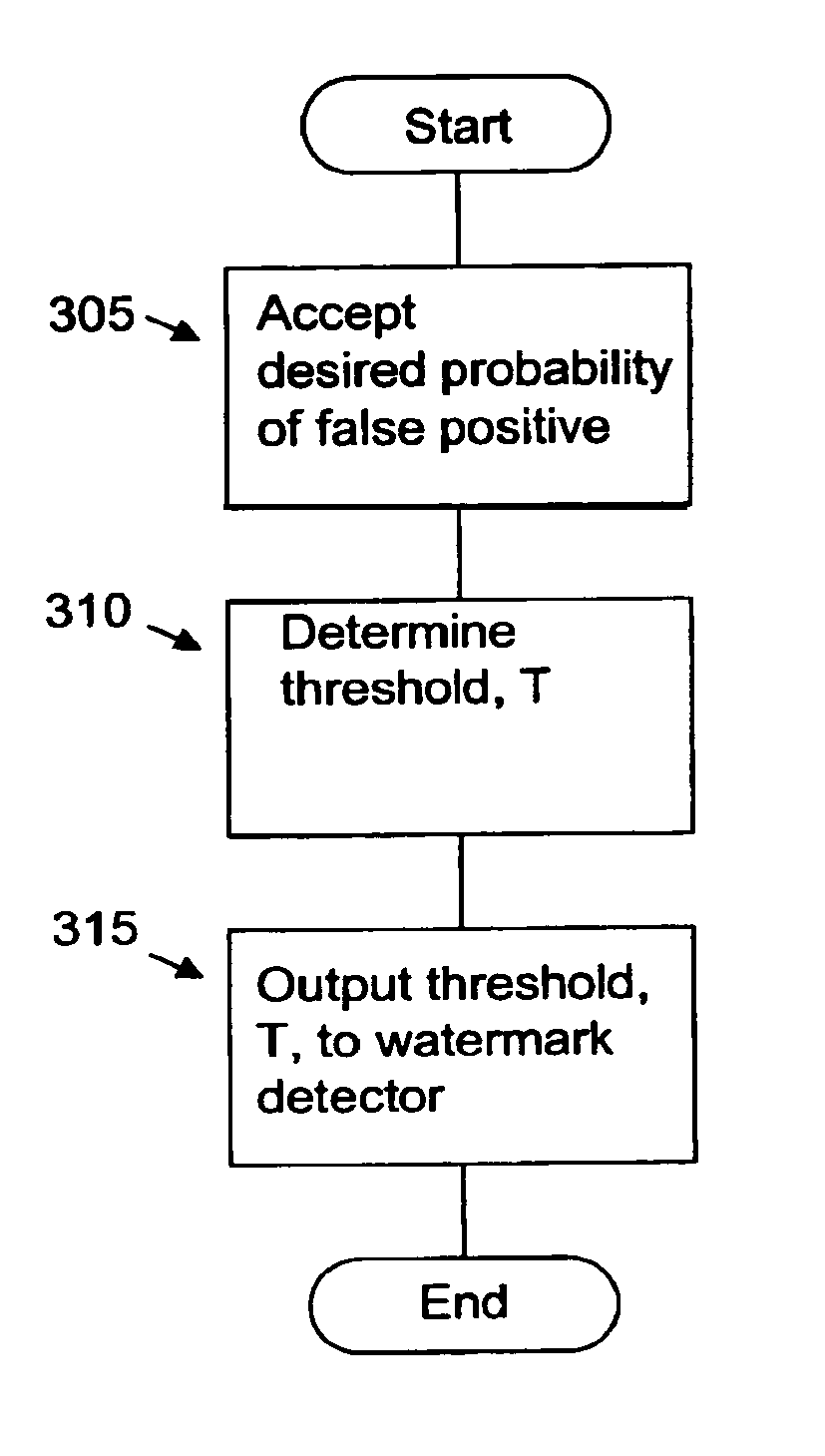
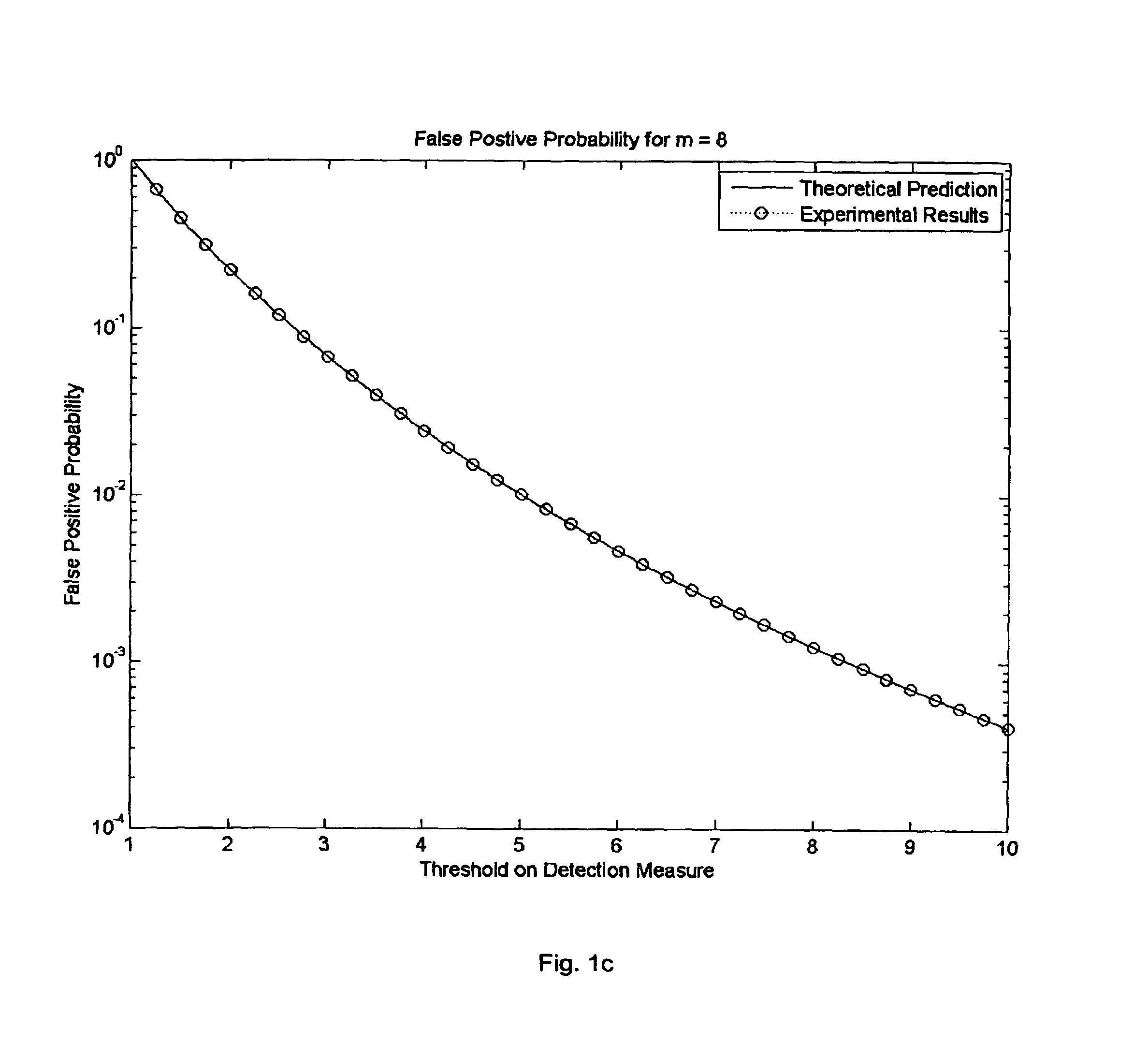
Method and apparatus for setting a detection threshold given a desired false probability
Owner:MAGNOLIA LICENSING LLC
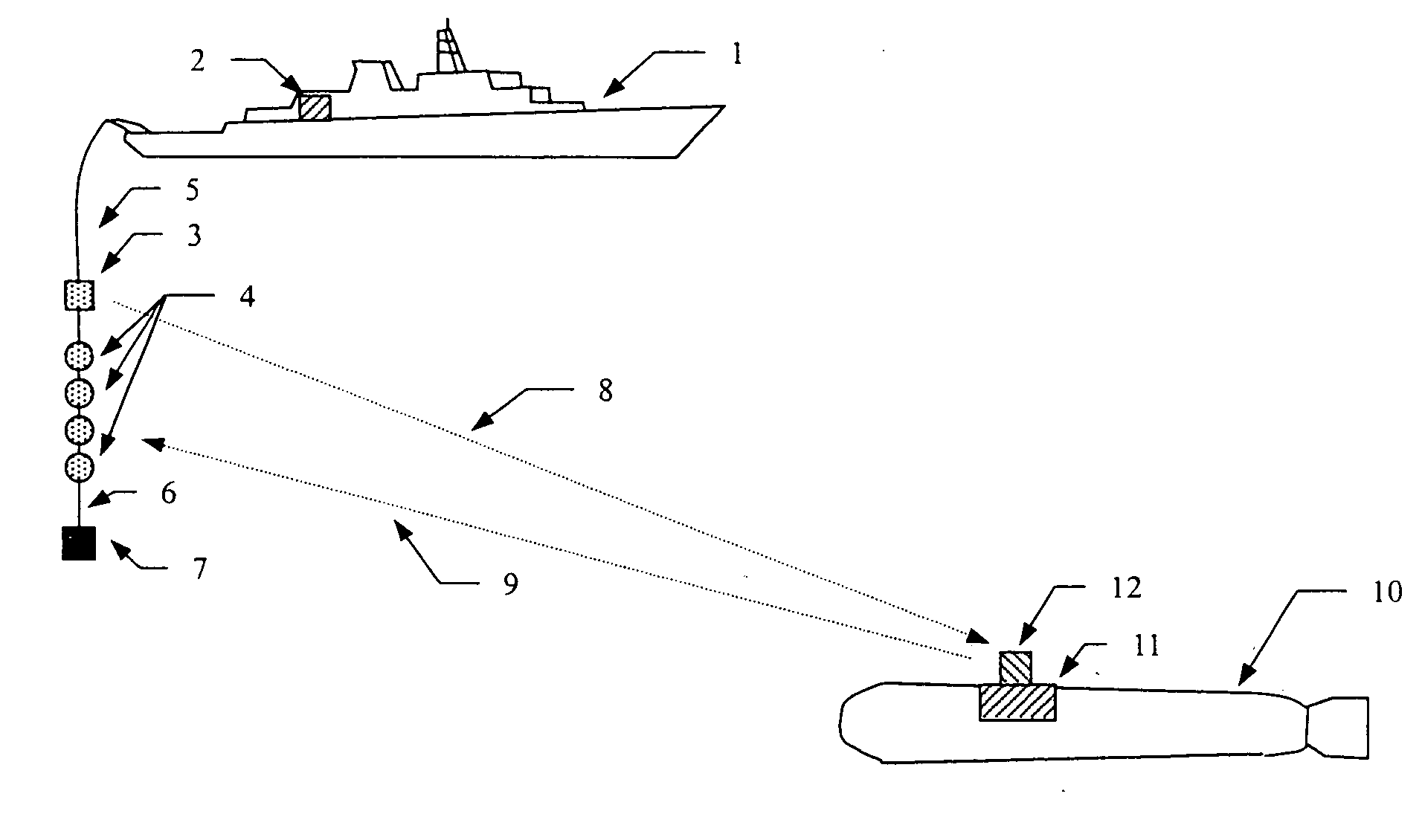
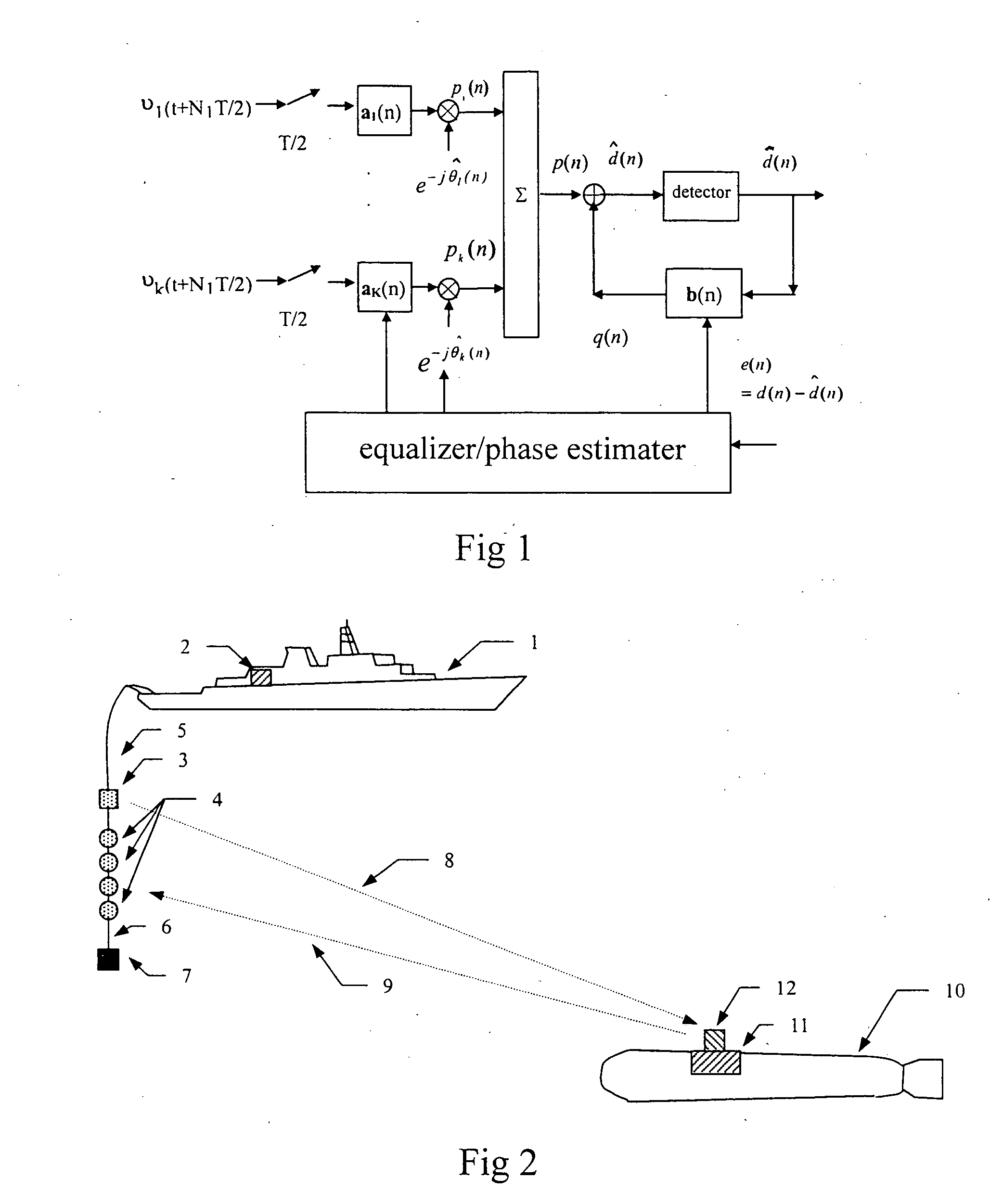
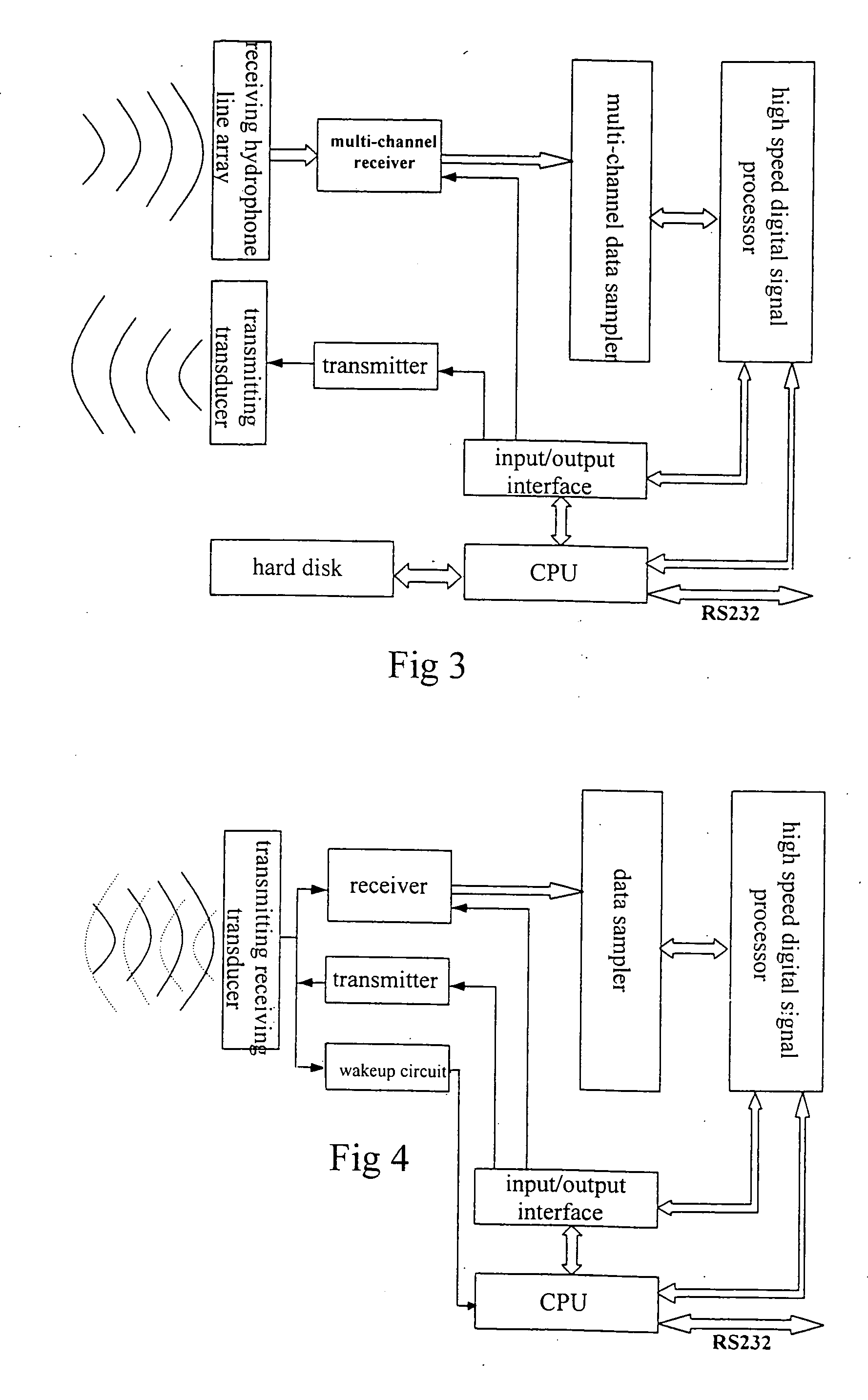
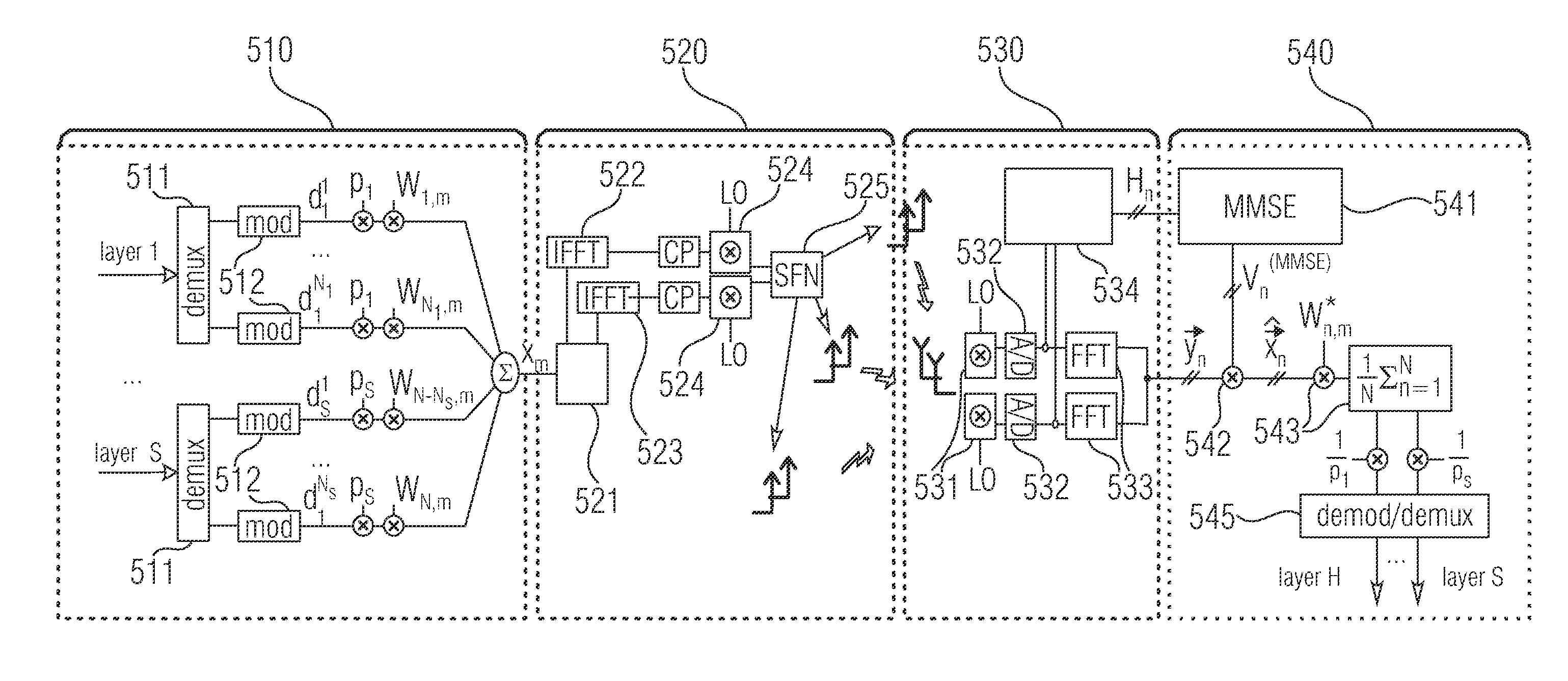
Water acoustic coherently communication system and signal processing method having high code rate, low probability of error
Owner:ZHU WEIQING +3
Apparatus for assigning and estimating transmission symbols
ActiveUS20110129025A1Reduce error rateRelatively large bandwidthCode conversionSecret communicationData streamTransmission channel
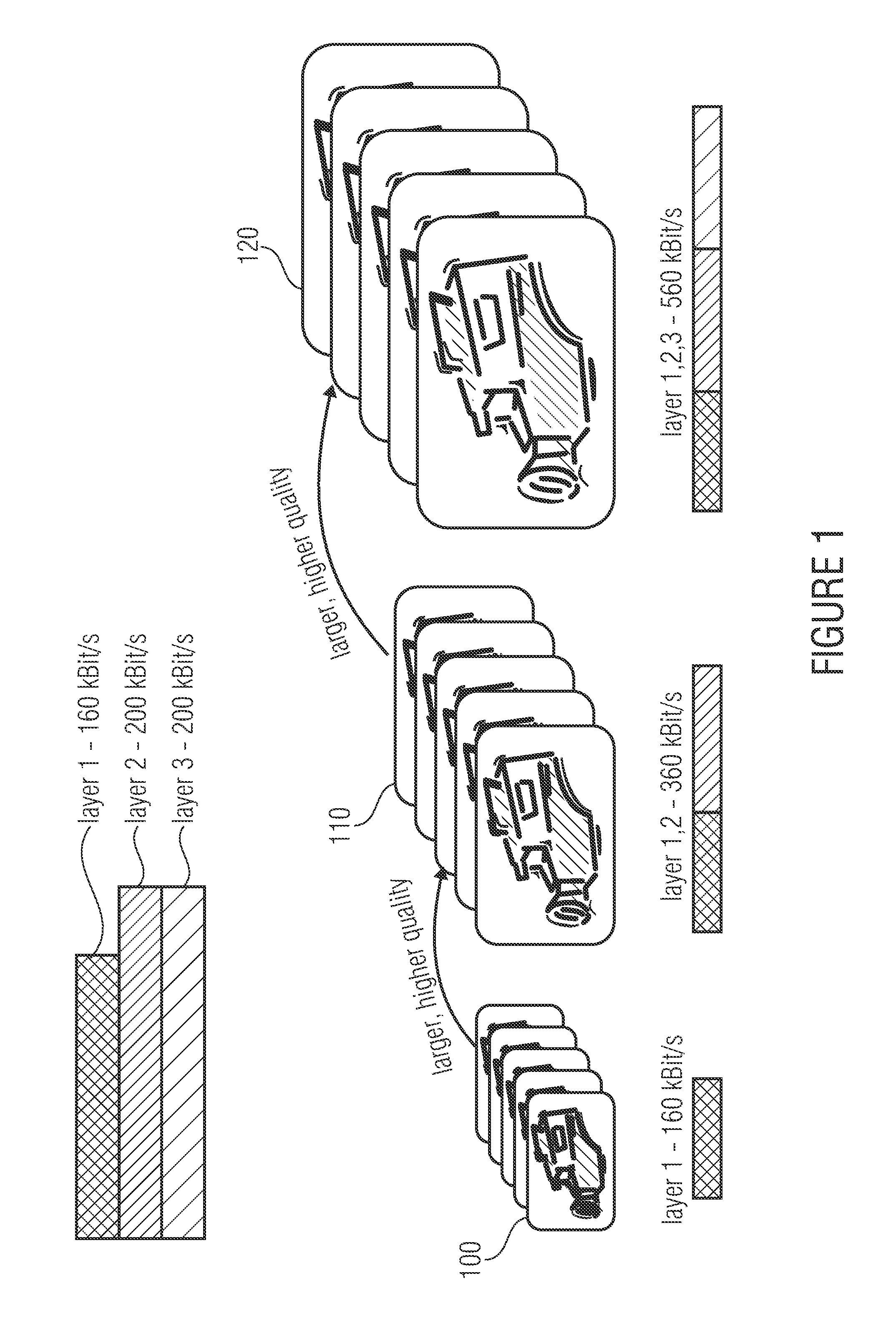
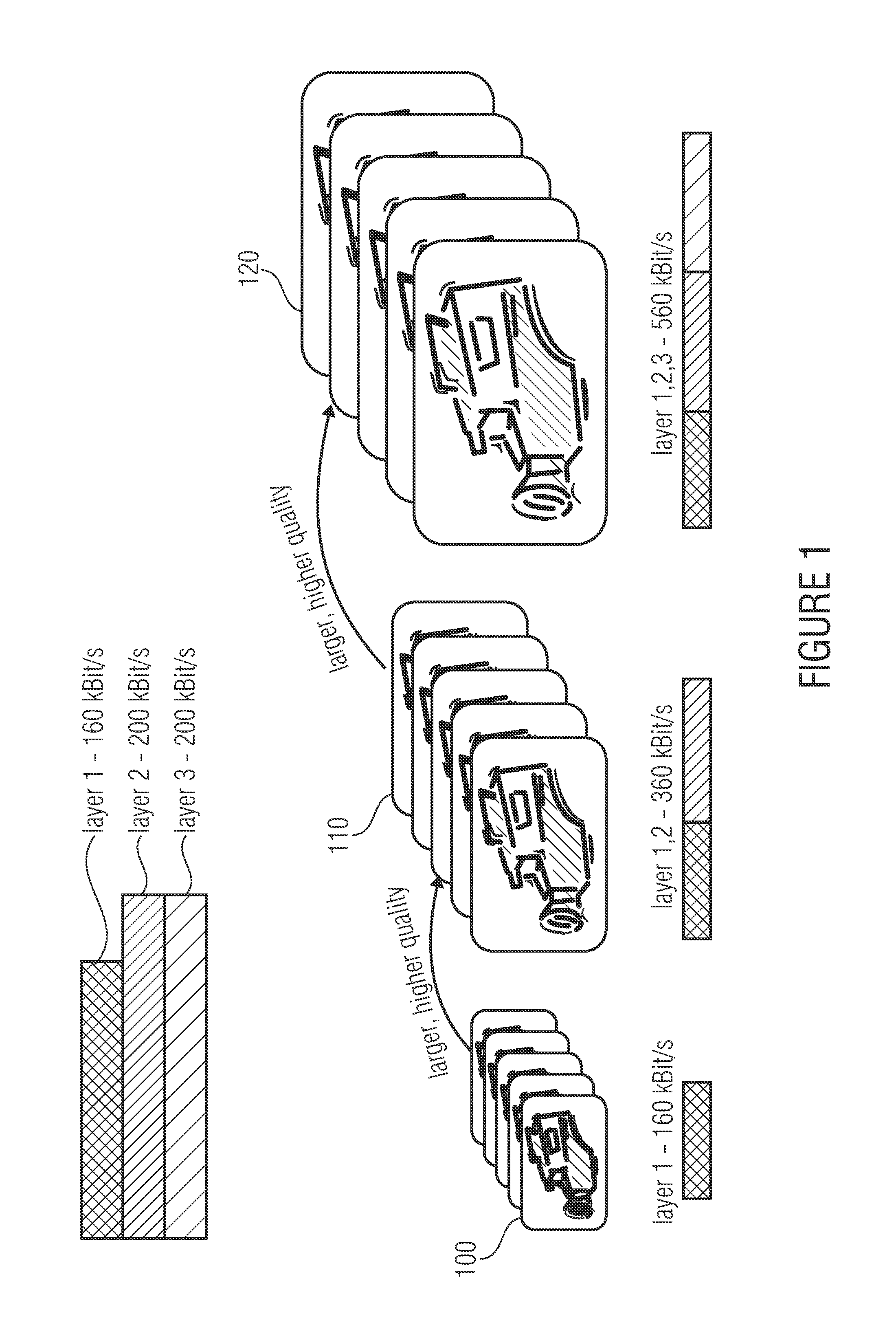
An apparatus for assigning transmission symbols to a media data stream of information symbols is described, the media data stream including a first substream for representing a media content in a basic quality and a second substream including additional data for representing the media content, along with the first substream, in an improved quality. The apparatus includes a first means for assigning first transmission symbols to the information symbols of the first substream and a second means for assigning second transmission symbols to the information symbols of the second substream, the first transmission symbols being transmissible, via a transmission channel, with reduced error probability as compared to the second transmission symbols.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Apparatus for assigning and estimating transmission symbols
ActiveUS8976838B2Reduce error rateRelatively large bandwidthUnequal/adaptive error protectionCode conversionData streamTransmission channel
An apparatus for assigning transmission symbols to a media data stream of information symbols is described, the media data stream including a first substream for representing media content in a basic quality and a second substream including additional data for representing the media content, along with the first substream, in an improved quality. The apparatus includes a first assigner for assigning first transmission symbols to the information symbols of the first substream and a second assigner for assigning second transmission symbols to the information symbols of the second substream, the first transmission symbols being transmissible, via a transmission channel, with reduced error probability as compared to the second transmission symbols.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
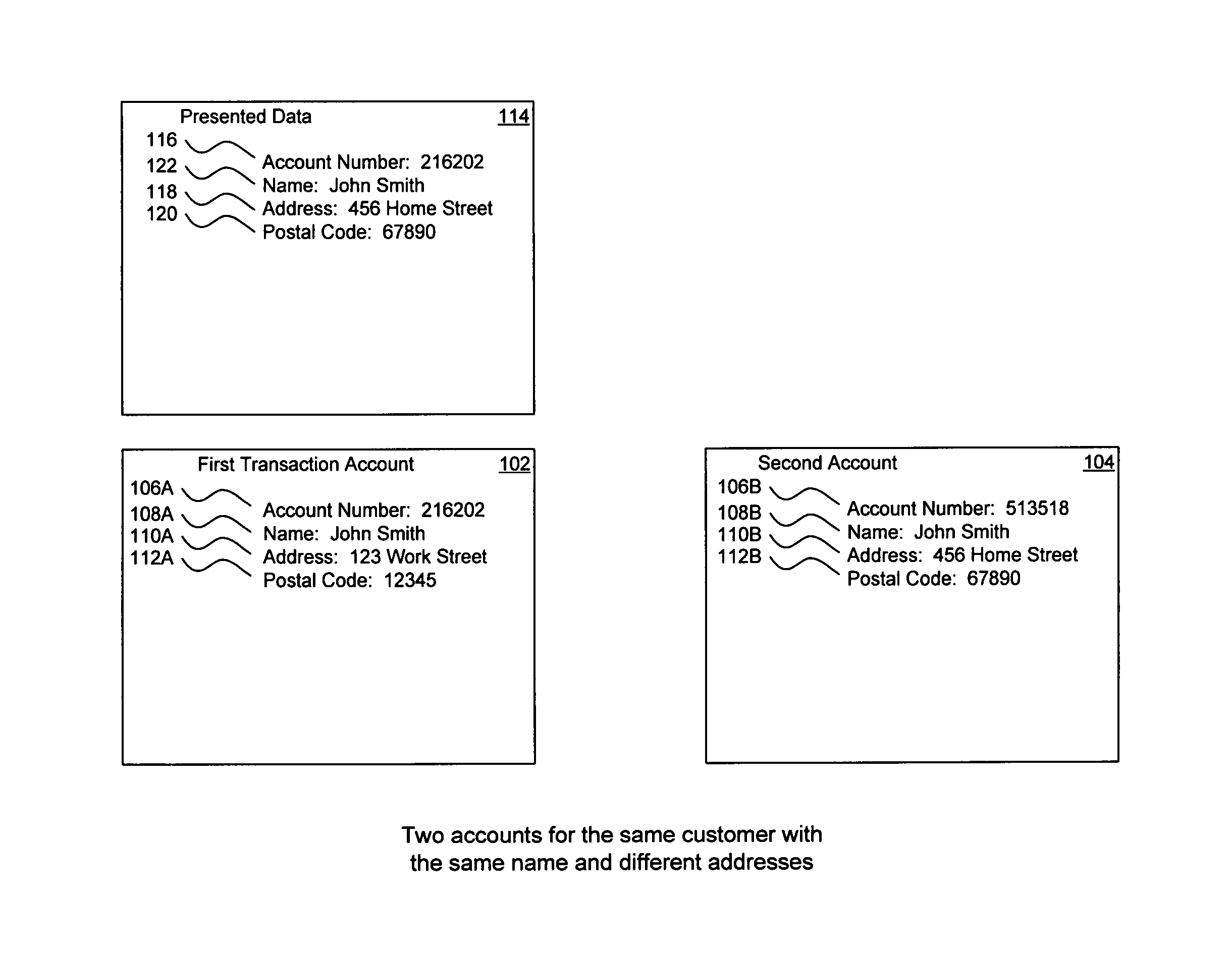
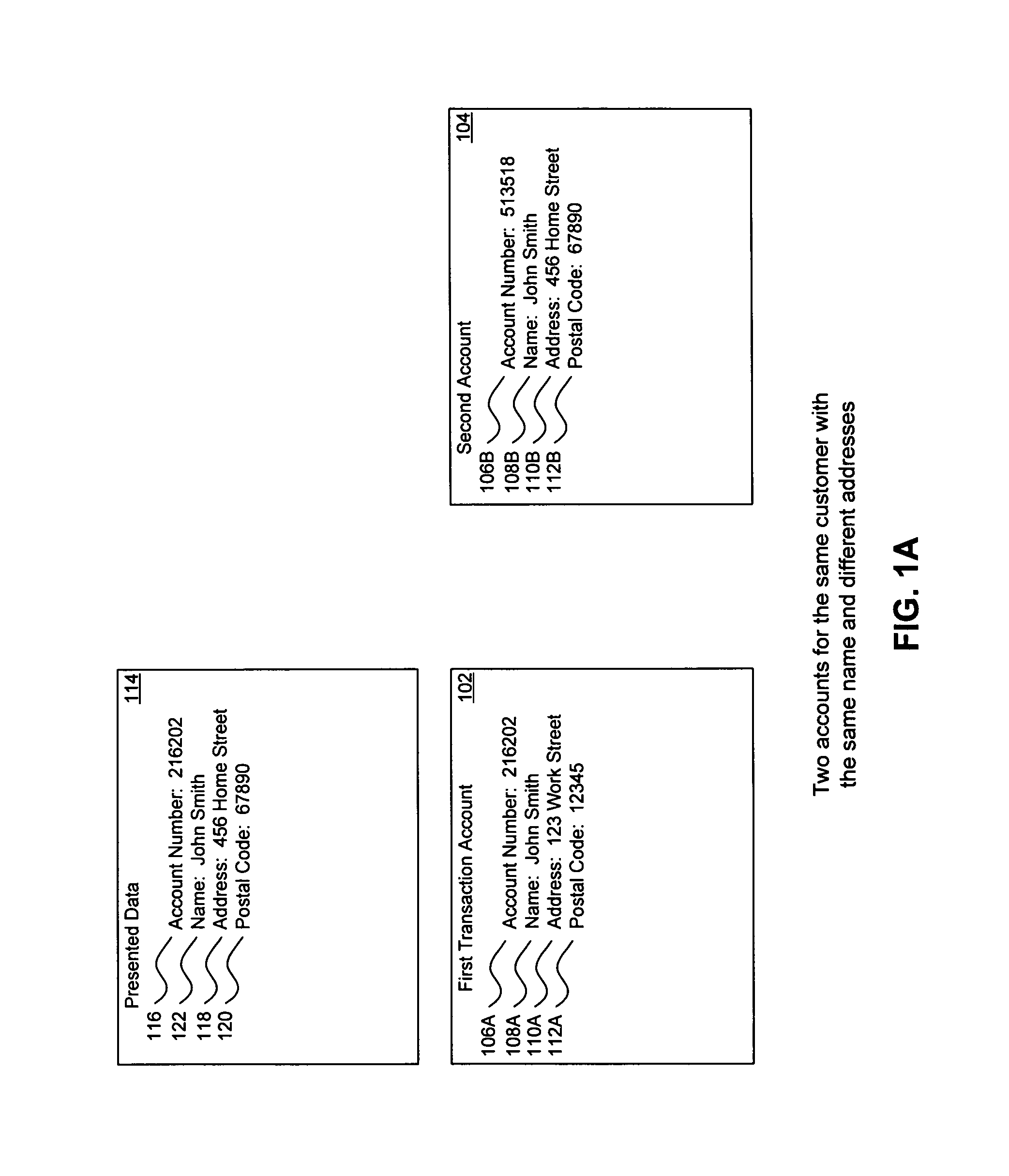
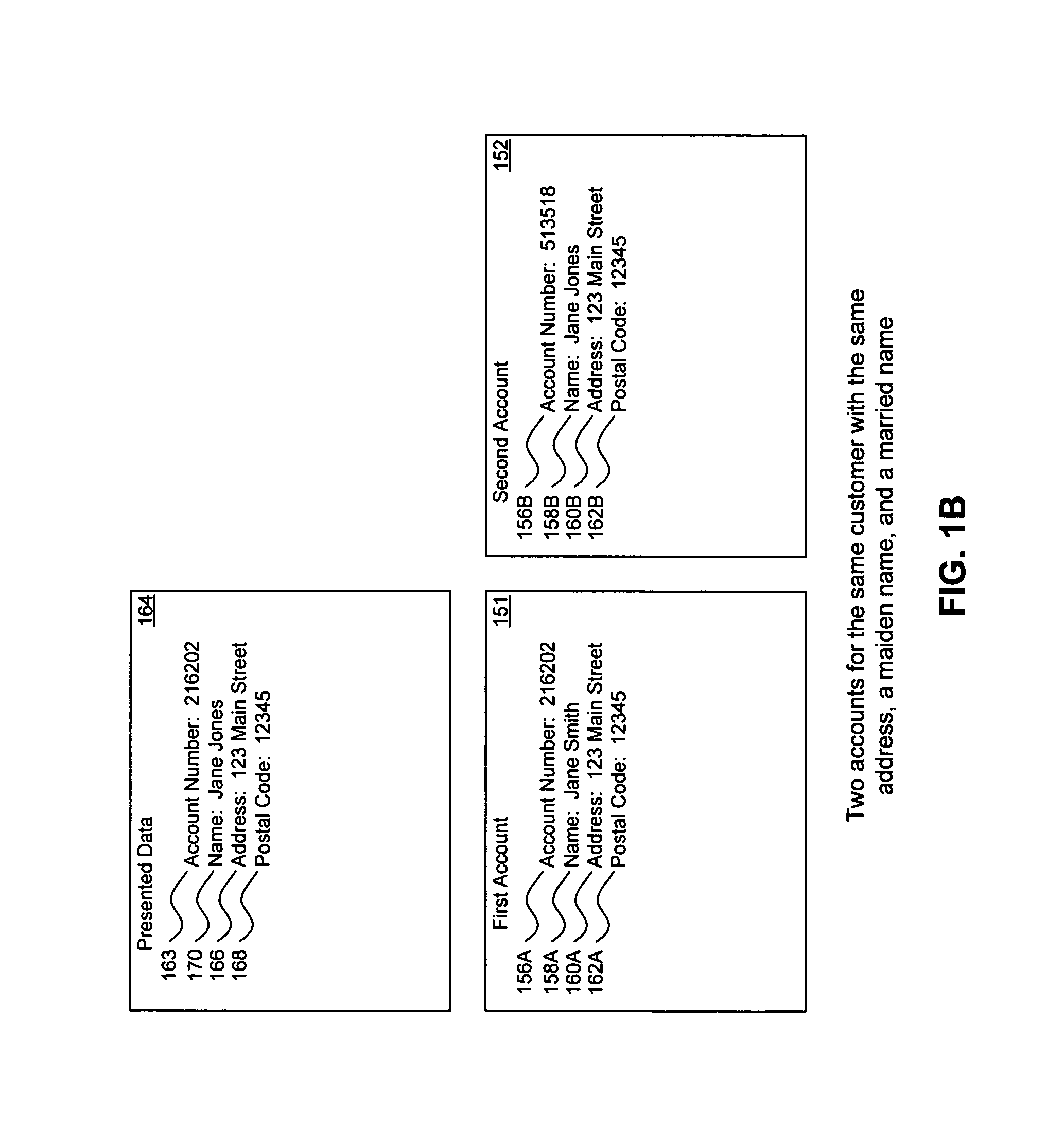
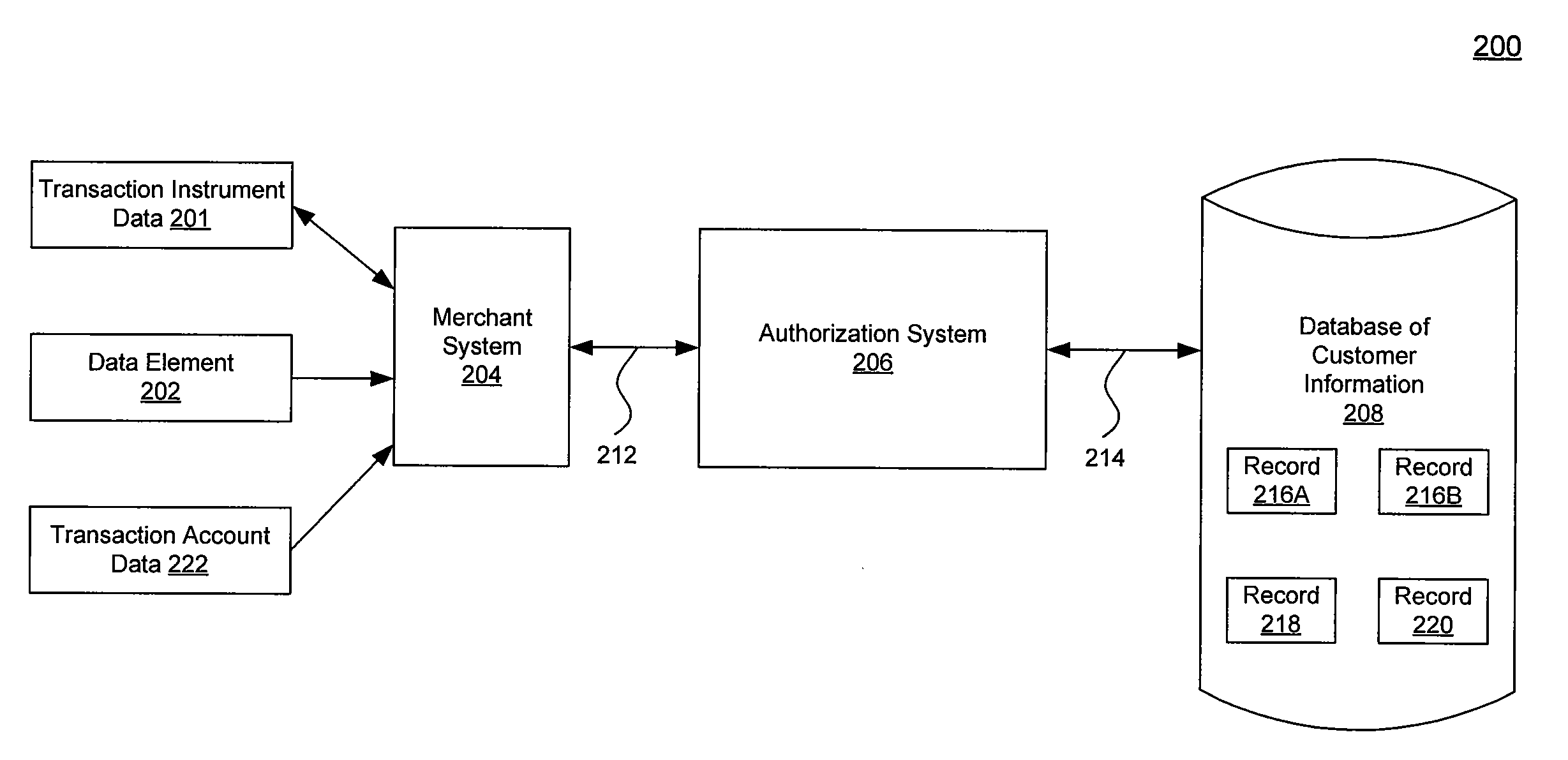
Method, system, and computer program product for customer-level data verification
ActiveUS9195985B2Improve accuracyReduce error rateComplete banking machinesFinanceFinancial transactionData element
A system, method, and computer program to reduce incorrectly declined transactions and improve risk calculation accuracy by reducing error probability during fraud detection. The tool first receives at least one data element as well as transaction account data and / or financial transaction instrument data. Then a customer is determined from a first record associated with the transaction account data and / or financial transaction instrument data. A record search is performed to identify at least one additional record associated with the customer. Finally, the data element is compared to the information contained in the additional record to create a comparison result that verifies a customer address. The comparison result may be used as an input to transaction risk calculations. The comparison result may also be provided to a merchant system and / or merchant for use in a decision-making process, for example, to verify customer identity.
Owner:LIBERTY PEAK VENTURES LLC
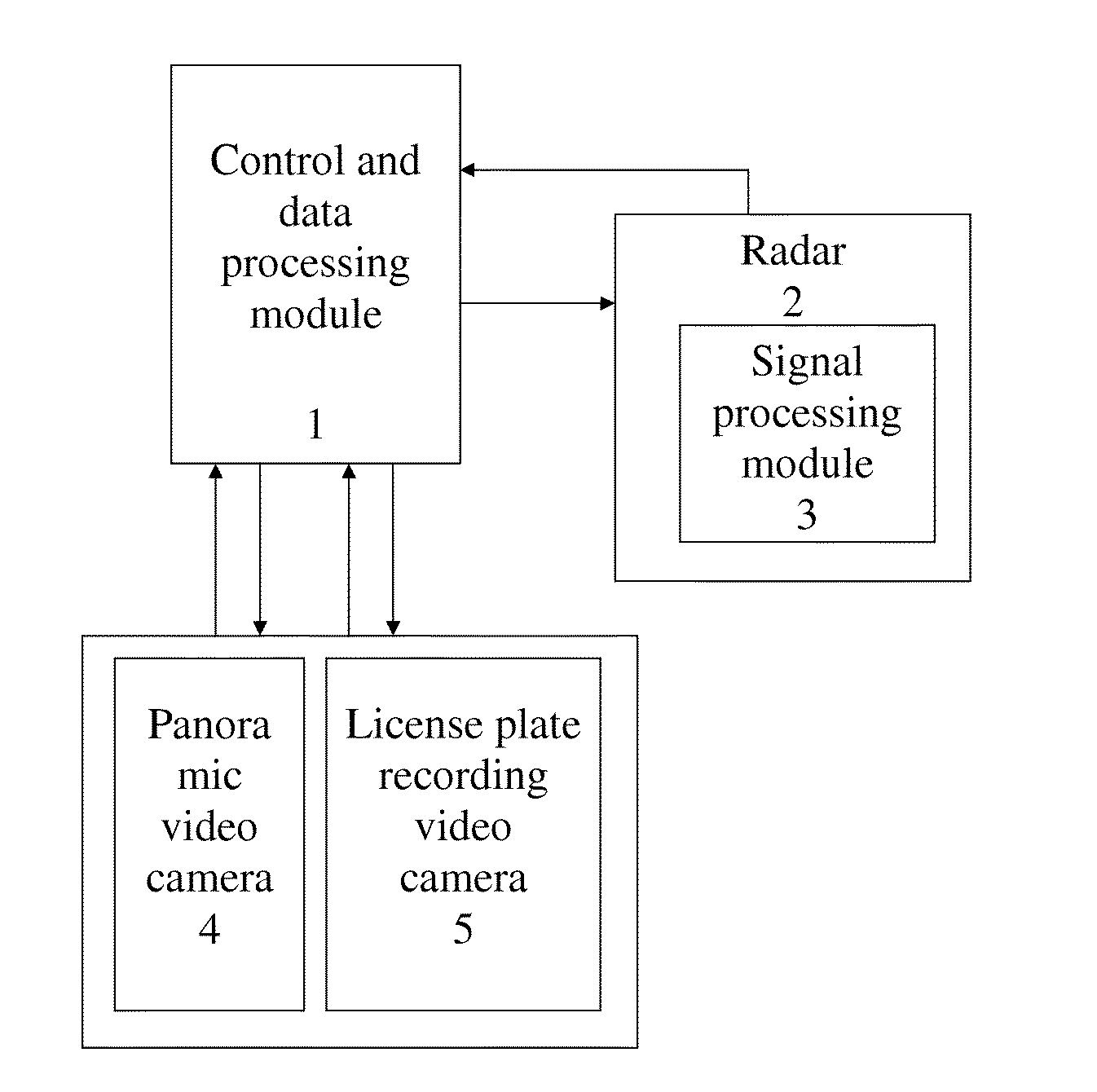
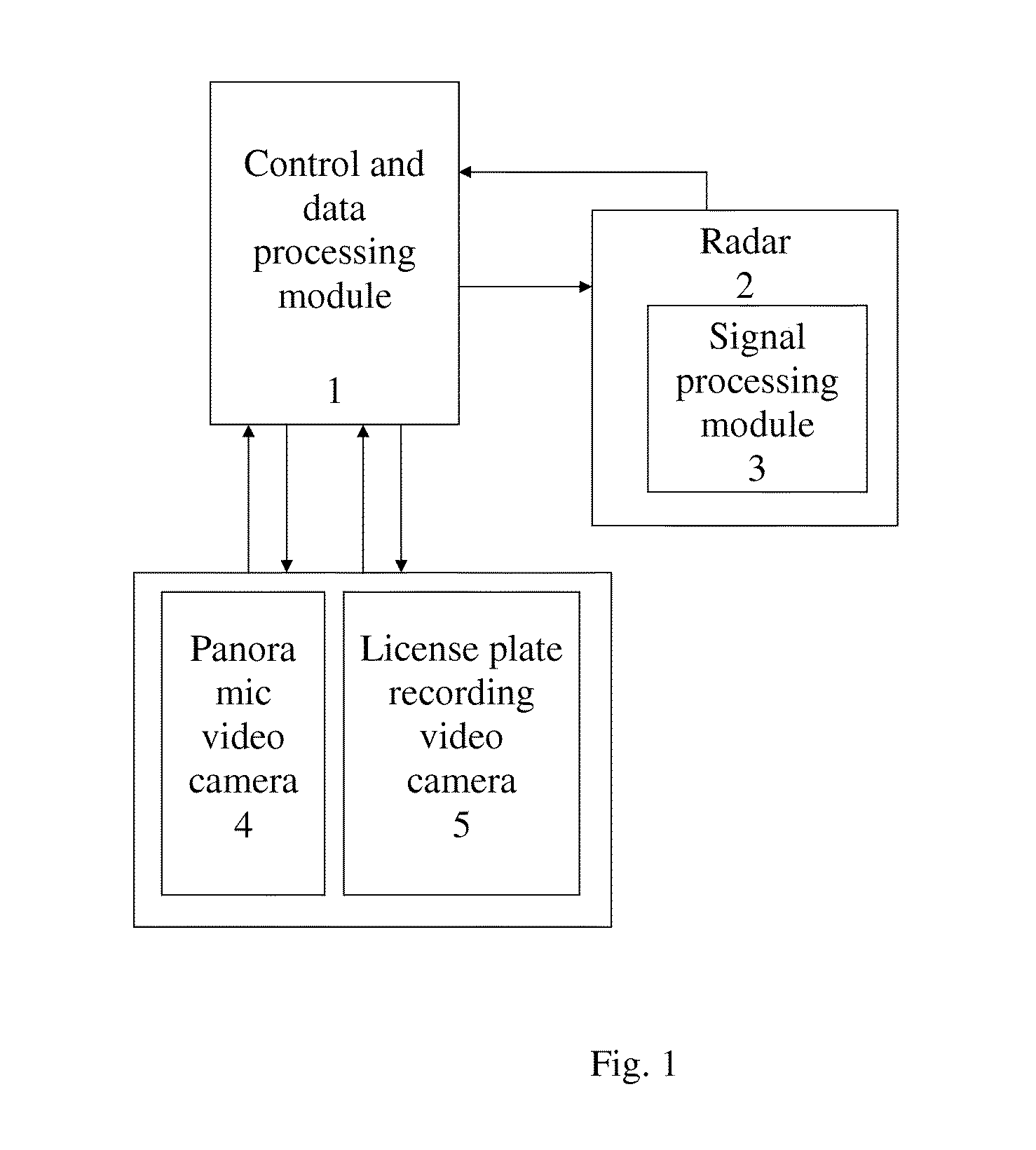
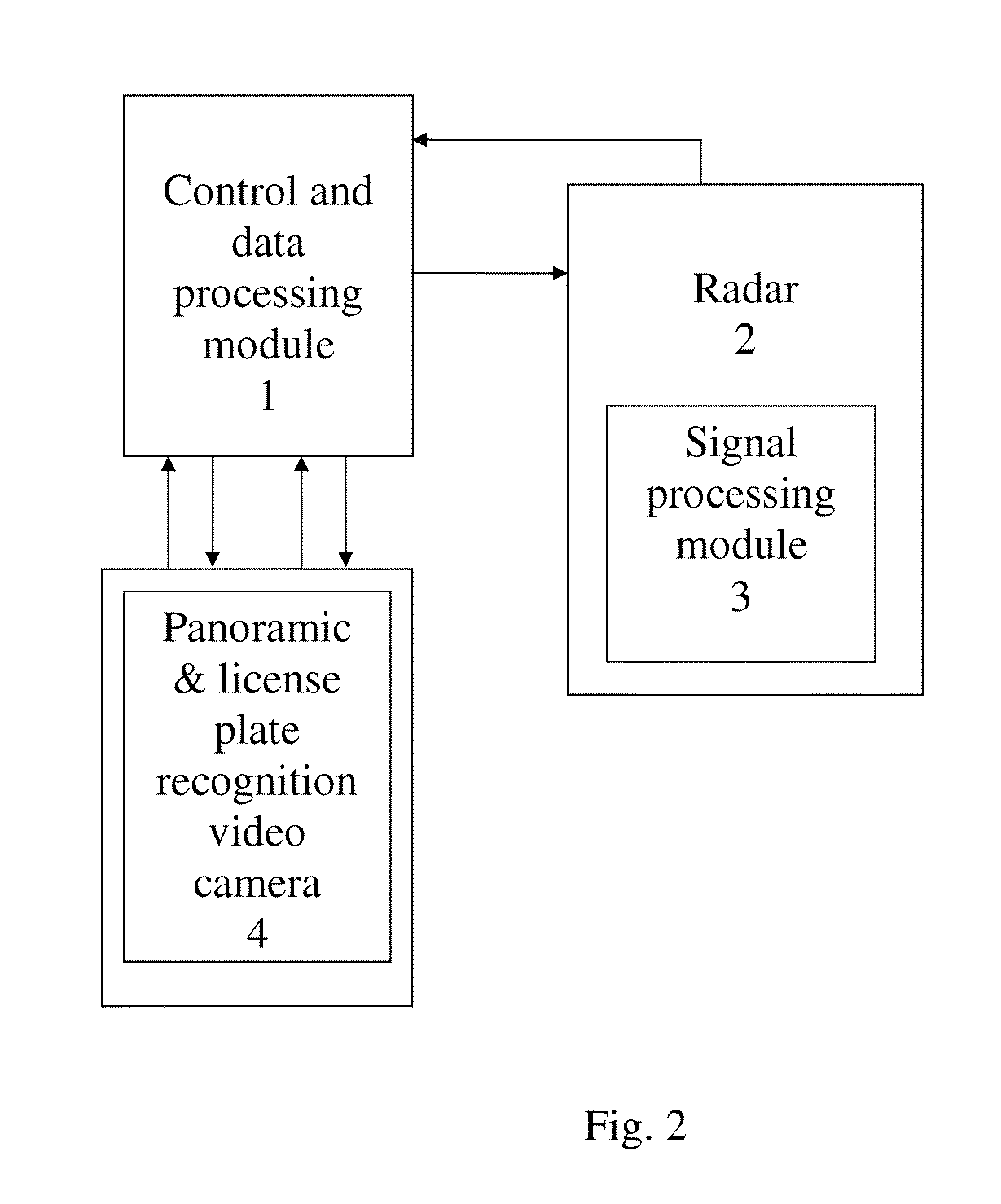
Method and Device for Determining the Speed of Travel and Coordinates of Vehicles and Subsequently Identifying Same and Automatically Recording Road Traffic Offences
ActiveUS20130038681A1Reduce probabilityLow costRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesRoad vehicles traffic controlRadarMonitor equipment
The automatic system makes it possible to reduce the probability of error when identifying the vehicle of an offender, increases the length of a speed limit monitoring zone to several hundreds / thousands of meters, and makes it possible to cut expenditure on the construction and maintenance of gantries for the installation of speed limit monitoring devices. A method for the combined processing of signals from a radar and a panoramic video camera is proposed, in which data flows from the video camera and the radar are independently obtained, after which they are compared and data about the speed and coordinates are obtained with little probability of error in identifying the vehicle of an offender. The device for realizing the method comprises a radar with a signal processing module to calculate the speed and distance of all vehicles on a chosen section of road, and a panoramic video camera.
Owner:OBSHCHESTVO S OGRANICHENNOJ OTVETSTVENNOSTJU KORPORATSIJA STROJ INVEST PROEKT M
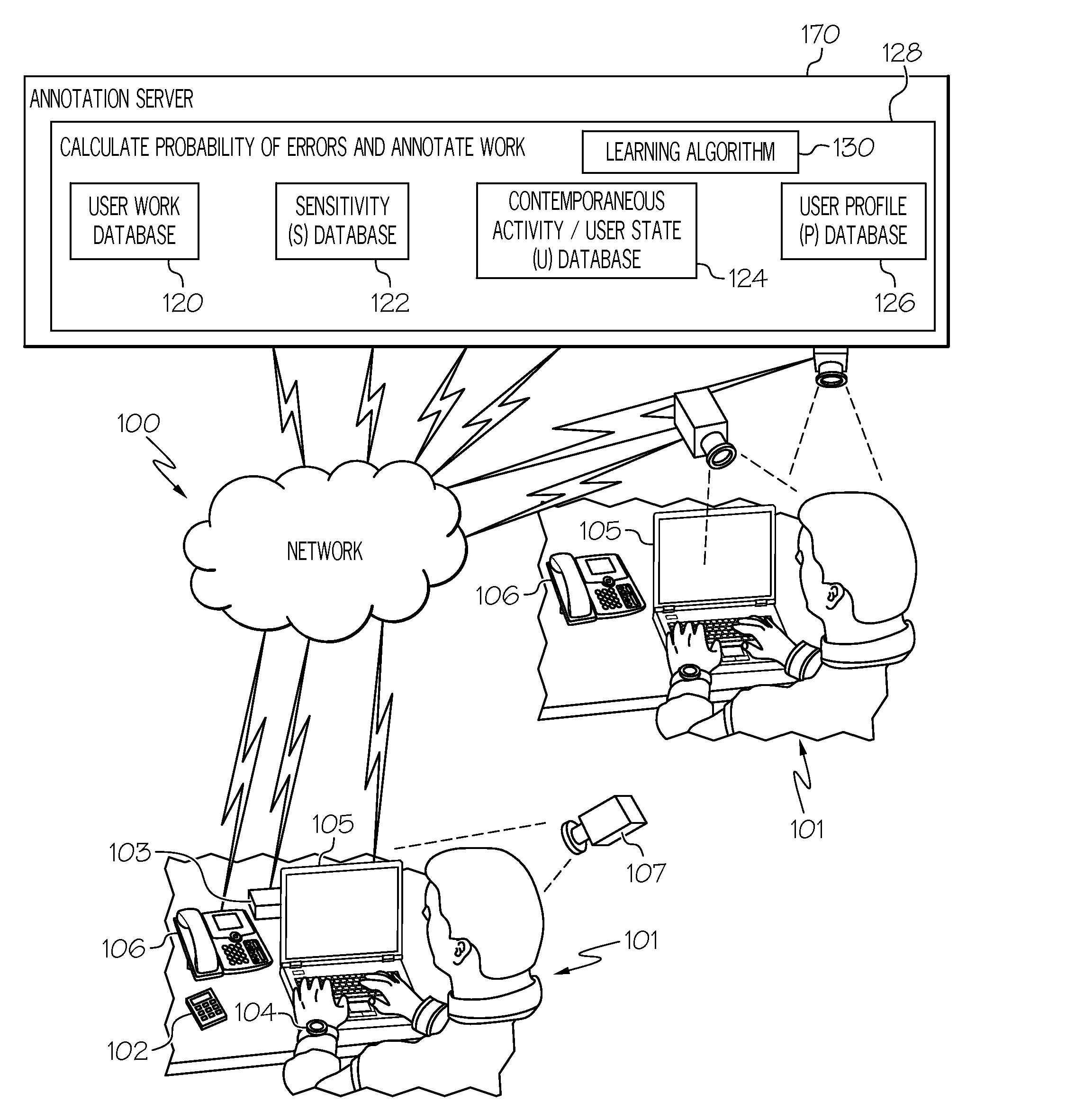
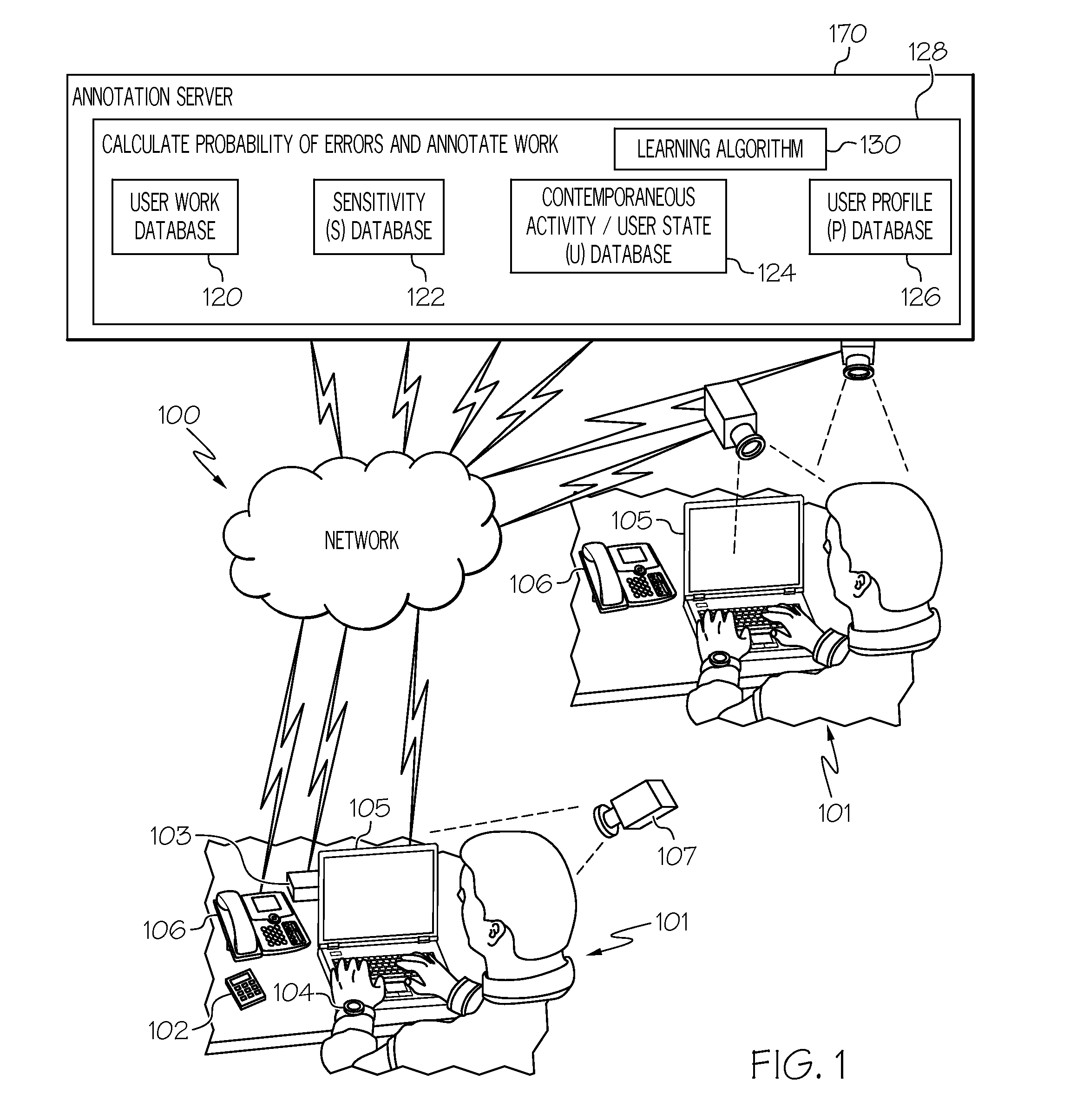
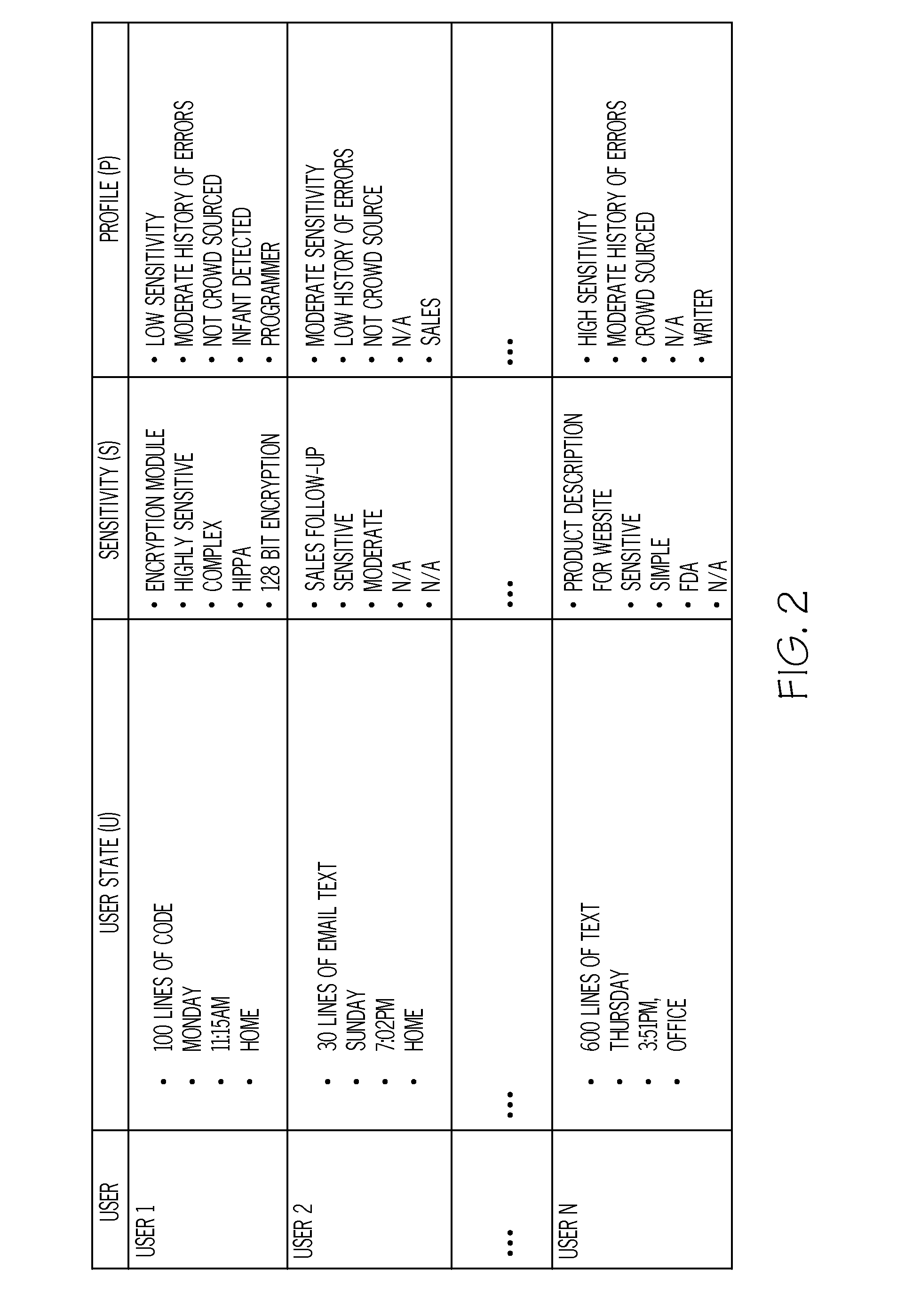
Indentifying locations of potential user errors during manipulation of multimedia content
Disclosed is a novel system and method for indicating a probability of errors in multimedia content. The system determines a user state or possible user distraction level. The user distraction level is indicated in the multimedia content. In one example, work is monitored being performed on the multimedia content. Distractions are identified while the work is being monitored. A probability of errors is calculated in at least one location of the multimedia content by on the distractions that have been identified. Annotations are used to indicate of the probability of errors. In another example, the calculating of probability includes using a function F(U,S,P) based on a combination of: i) a determination of user state (U), ii) a determination of sensitivity (S) of user input, and iii) a determination of user characteristics stored in a profile (P).
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and Apparatus for Sequential Authentication Using One or More Error Rates Characterizing Each Security Challenge
ActiveUS20080222722A1Easy to adaptDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationProbabilistic descriptionField data
Methods and apparatus are provided for sequential authentication of a user that employ one or mole error rates characterizing each security challenge. According to one aspect of the invention, a user is challenged with at least one knowledge challenge to obtain an intermediate authentication result; and the user challenges continue until a cumulative authentication result satisfies one or more criteria. The intermediate authentication result is based, for example, on one or more of false accept and false reject error probabilities for each knowledge challenge. A false accept error probability describes a probability of a different user answering the knowledge challenge correctly. A false reject error probability describes a probability of a genuine user not answering the knowledge challenge correctly. The false accept and false reject error probabilities can be adapted based on field data or known information about a given challenge.
Owner:IBM CORP
Long window scaling factor-based playback voice attack detection algorithm
ActiveCN105913855AIncrease aggressivenessImprove securitySpeech analysisSpeaker recognition systemSpeech sound
The invention discloses a long window scaling factor-based playback voice attack detection algorithm which is developed for solving a problem that rights and interests of a legitimate are damaged when conventional attackers use playback voice to enter a speaker identification system. The detection algorithm can be used for effectively identifying playback voice from different sources and is high in detection accuracy; after a module of the detection algorithm is loaded to a GMM-UBM system, playback voice attack resistant capability is improved, error probability of the identification system and the like is lowered by 32%, and a safety problem of the identification system is greatly alleviated.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Steering engine tester and testing method thereof
ActiveCN103076195AEasy to observe test resultsAvoid lossStructural/machines measurementKey pressingEngine testing
The invention relates to a steering engine tester and a testing method thereof, which belong to the technical field of guided bombs. The tester comprises a control cabinet and a simulation load table, wherein the control cabinet comprises a steering engine controller, a regulated power supply, an industrial control computer, a display, a keyboard and a main power supply switch; the simulation load table comprises a photoelectric encoder, a torque sensor and a magnetic powder brake; a steering engine shaft of a steering engine to be tested is mechanically connected with a rotating shaft of the photoelectric encoder through a shaft coupling; the steering engine to be tested is in digital signal communication with the steering engine controller through a data line; and steering engine testing software is installed in the industrial control computer. The tester provided by the invention has the advantages of more plentiful testing contents, more complete testing equipment, more intelligent testing software, prompting of operating information on a software interface, shielding of keys which are required to be operated, change of parameter input items according to selected testing items, information prompt for improper operation, and great reduction in the probability of error operation.
Owner:CHINA AEROSPACE TIMES ELECTRONICS CORP
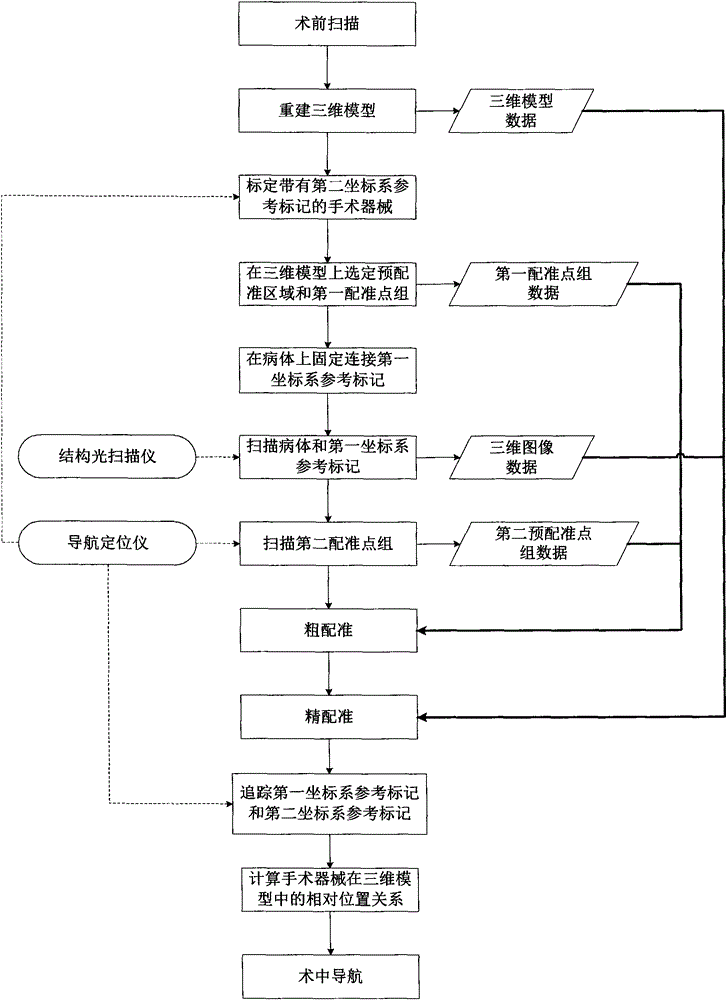
Intraoperative navigation method and system for assisting in surgery
InactiveCN104146767AQuality improvementIncrease success rateDiagnosticsSurgeryThree-dimensional spaceDisplay device
The invention discloses an intraoperative navigation method and system for assisting in surgery. The method comprises the steps of preoperative scanning, establishment of a three-dimensional model, fixation of a first coordinate system reference mark and a second coordinate system reference mark, scanning through a structured light scanner, rough registration, refined registration and completion of the navigation process through a controller and a displayer. Due to the rough registration process, the process of refined registration between a three-dimensional image and a pre-registered region is very short, and registration preparation time before start of surgical navigation can be greatly shortened. Moreover, since two three-dimensional spaces are utilized for refined registration, the probability of errors is extremely low, and the accuracy and reliability of registration between a sick body and the three-dimensional model can be improved apparently; accordingly, the quality of the surgery is improved, and the success rate of the surgery is increased.
Owner:李书纲
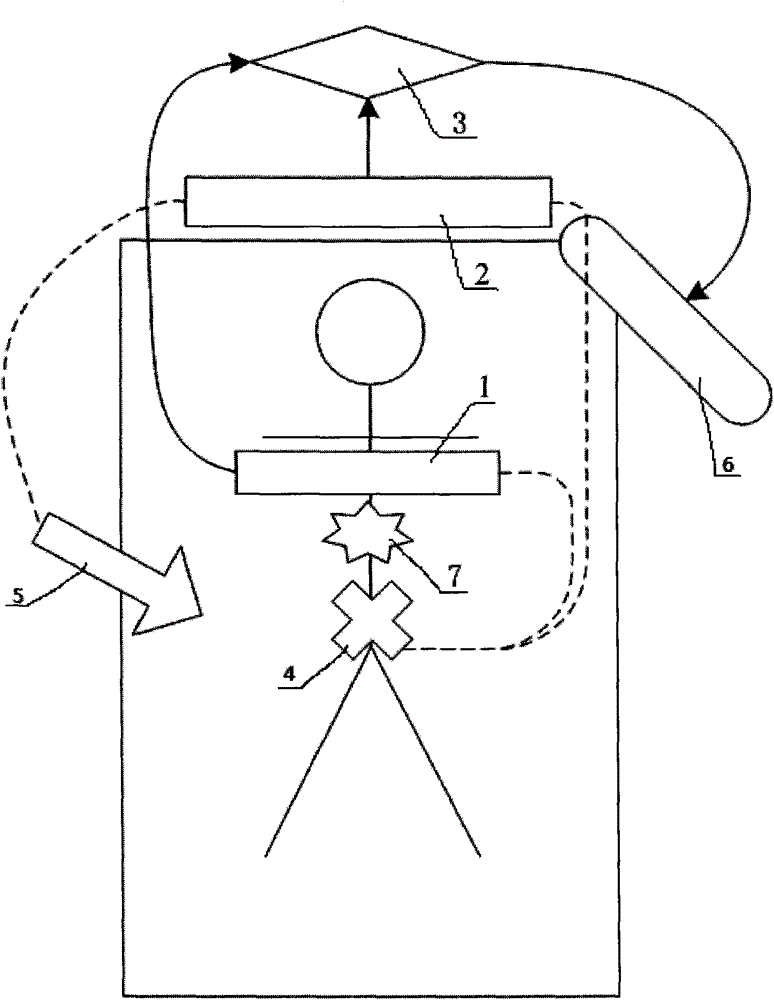
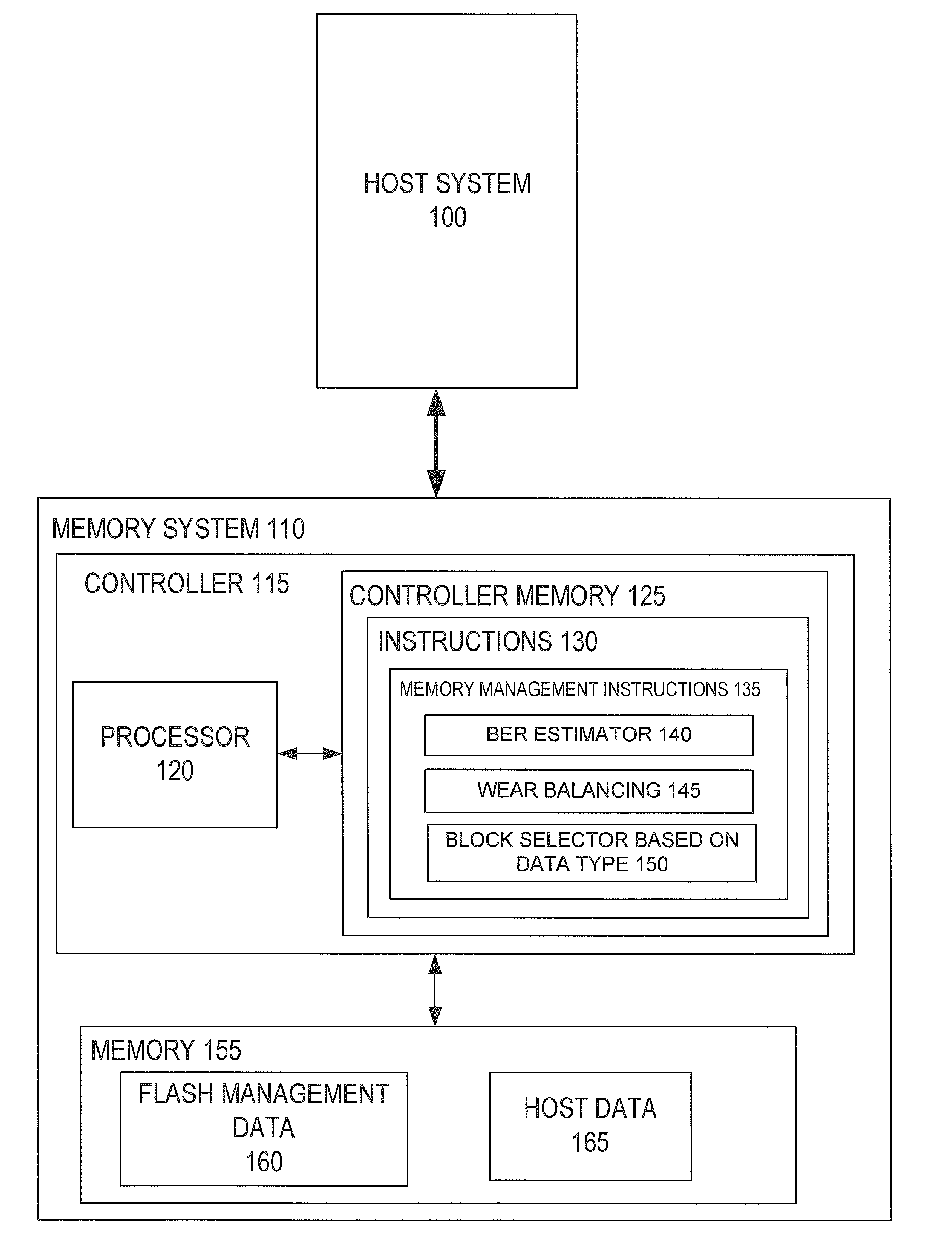
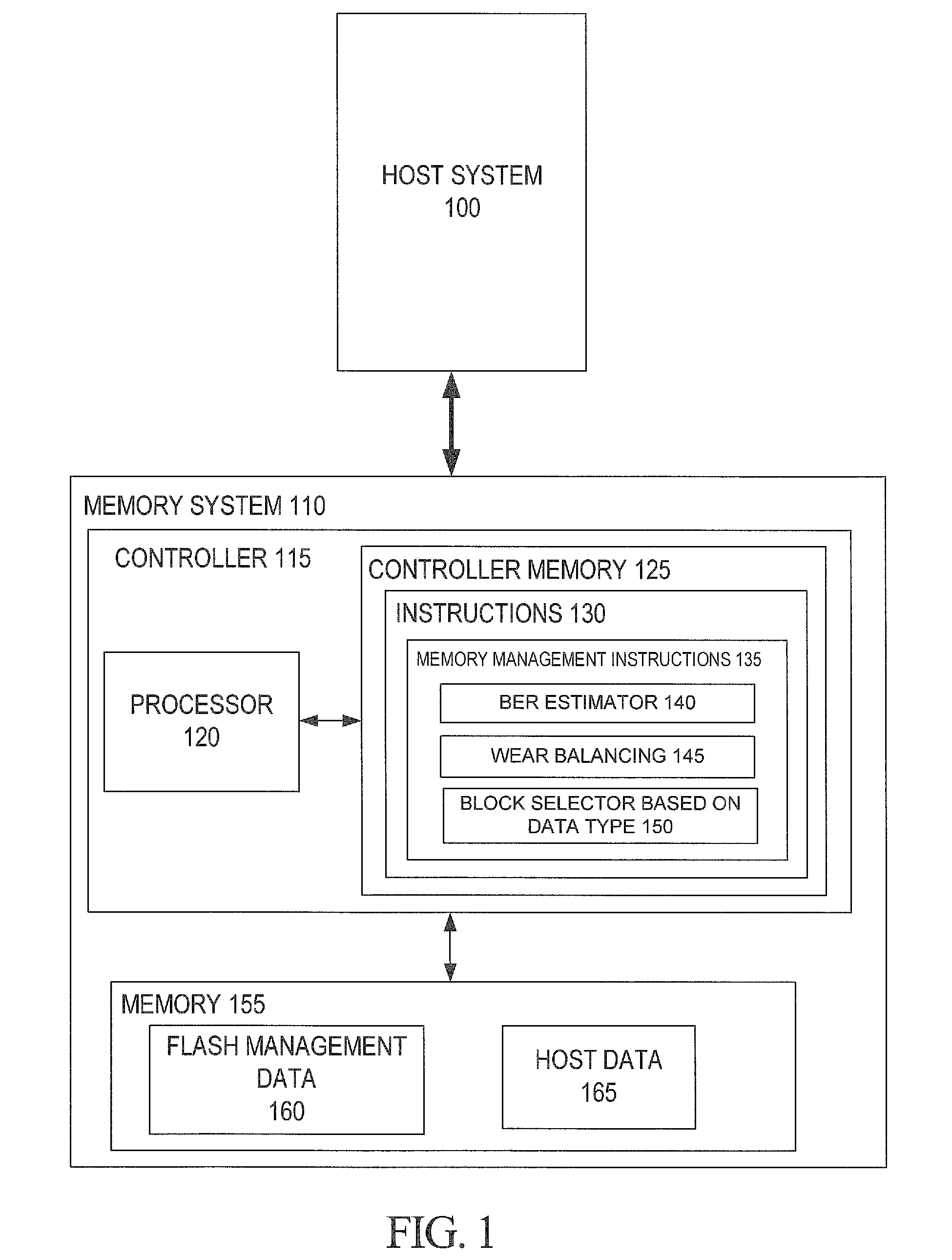
Bit Error Rate Estimation for Wear Leveling and for Block Selection Based on Data Type
A method and system for wear balancing in a flash memory device using bit error probability is disclosed. The flash memory device includes blocks with different life spans, leading potentially to one block wearing out before the other. In order to avoid this, a controller is configured to determine a bit error probability of a block and determine, based on the bit error probability, whether to select the block for storage of data. A method and system for selecting a block in a flash memory device based on the type of data is disclosed. The type of data may comprise flash management data (which may be used to manage the flash memory device) and host data. An indication of age associated with the block (such as bit error probability) is analyzed in order to determine whether to store the data in the block based on the type of data.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Near-optimal multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) channel detection via sequential Monte Carlo
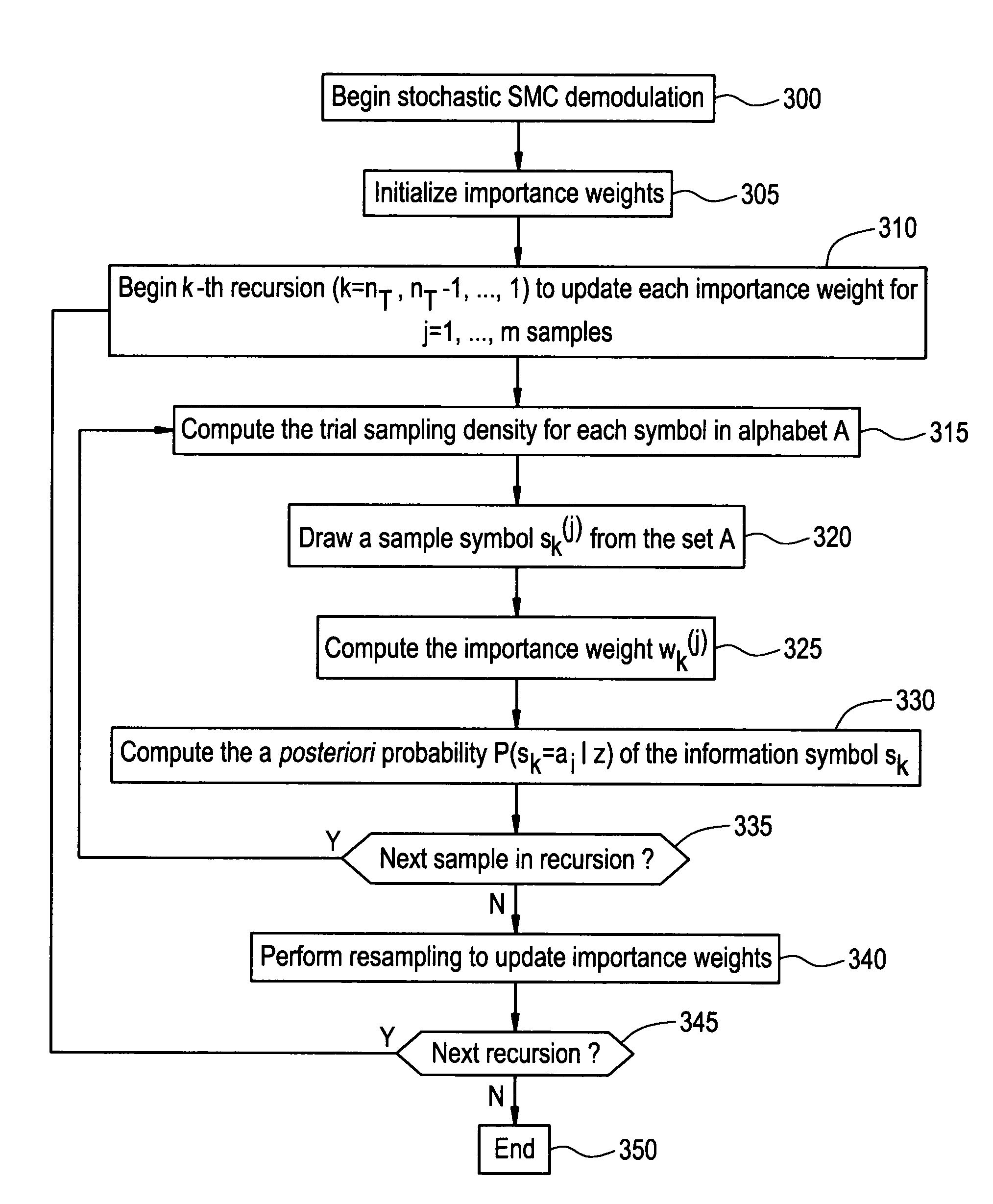
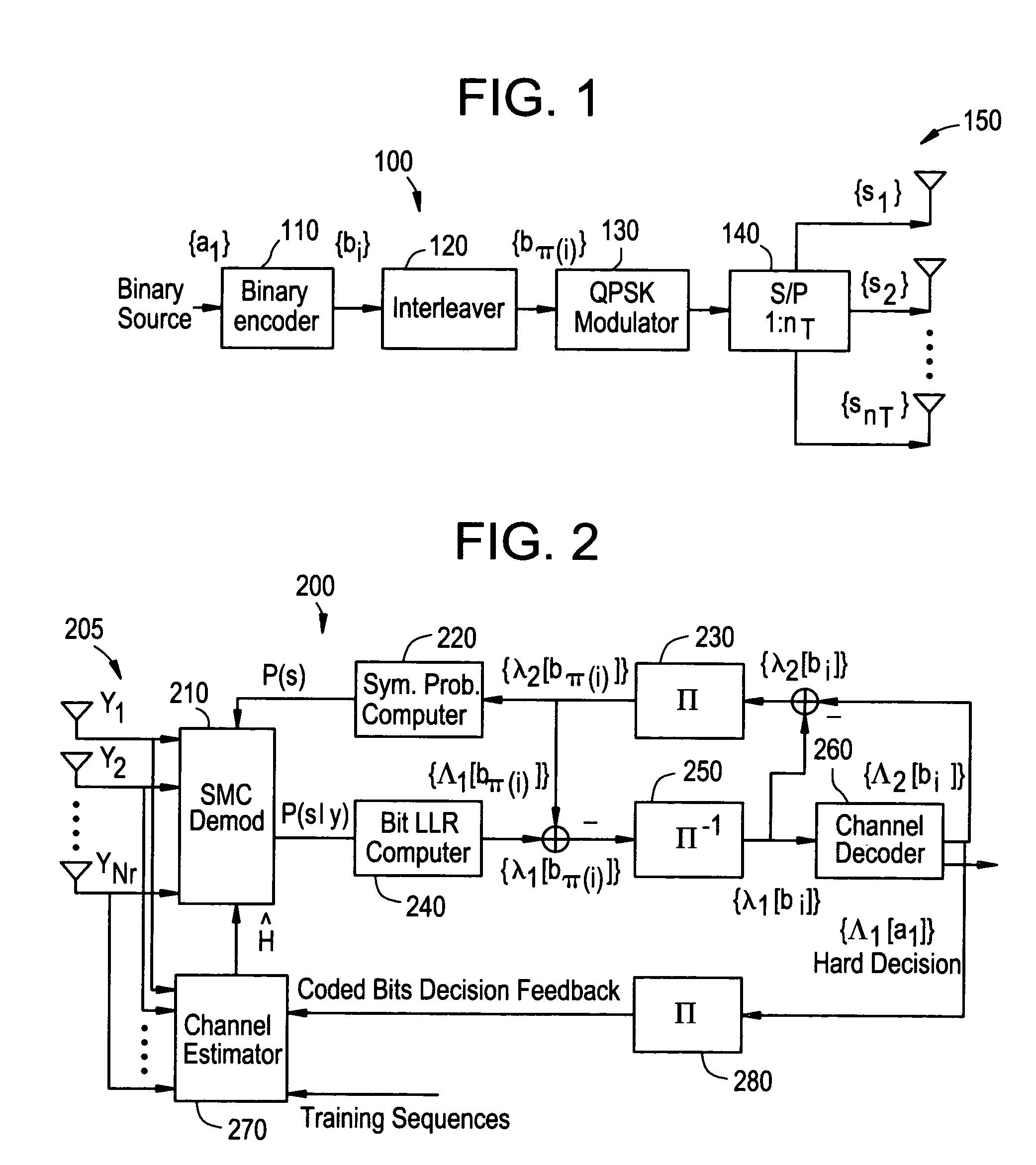
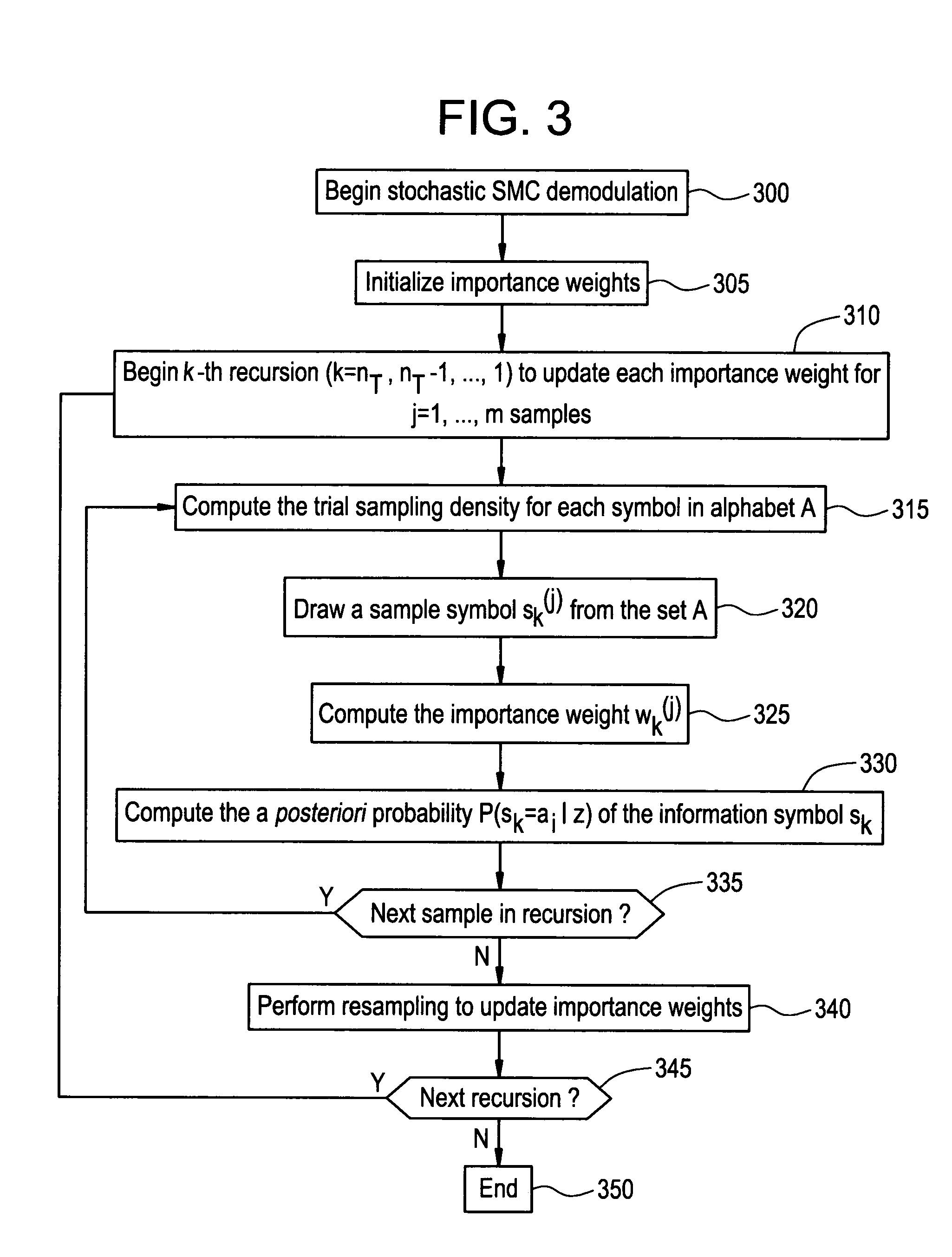
InactiveUS7317770B2Improve performanceImprove reliabilityThermometer detailsSpatial transmit diversityRound complexitySymbol of a differential operator
A class of soft-input soft-output demodulation schemes for multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) channels, based on the sequential Monte Carlo (SMC) framework under both stochastic and deterministic settings. The stochastic SMC sampler generates MIMO symbol samples based on importance sampling and resampling techniques, while the deterministic SMC approach recursively performs exploration and selection steps in a greedy manner. By exploiting the artificial sequential structure of the existing simple Bell Labs Layered Space Time (BLAST) detection method based on nulling and cancellation, the proposed algorithms achieve an error probability performance that is orders of magnitude better than the traditional BLAST detection schemes while maintaining a low computational complexity. Performance is comparable with that of the sphere decoding algorithm, with a much lower complexity. Both the stochastic and deterministic SMC detectors can be employed as the first-stage demodulator in an iterative or turbo receiver in coded MIMO systems.
Owner:NEC CORP
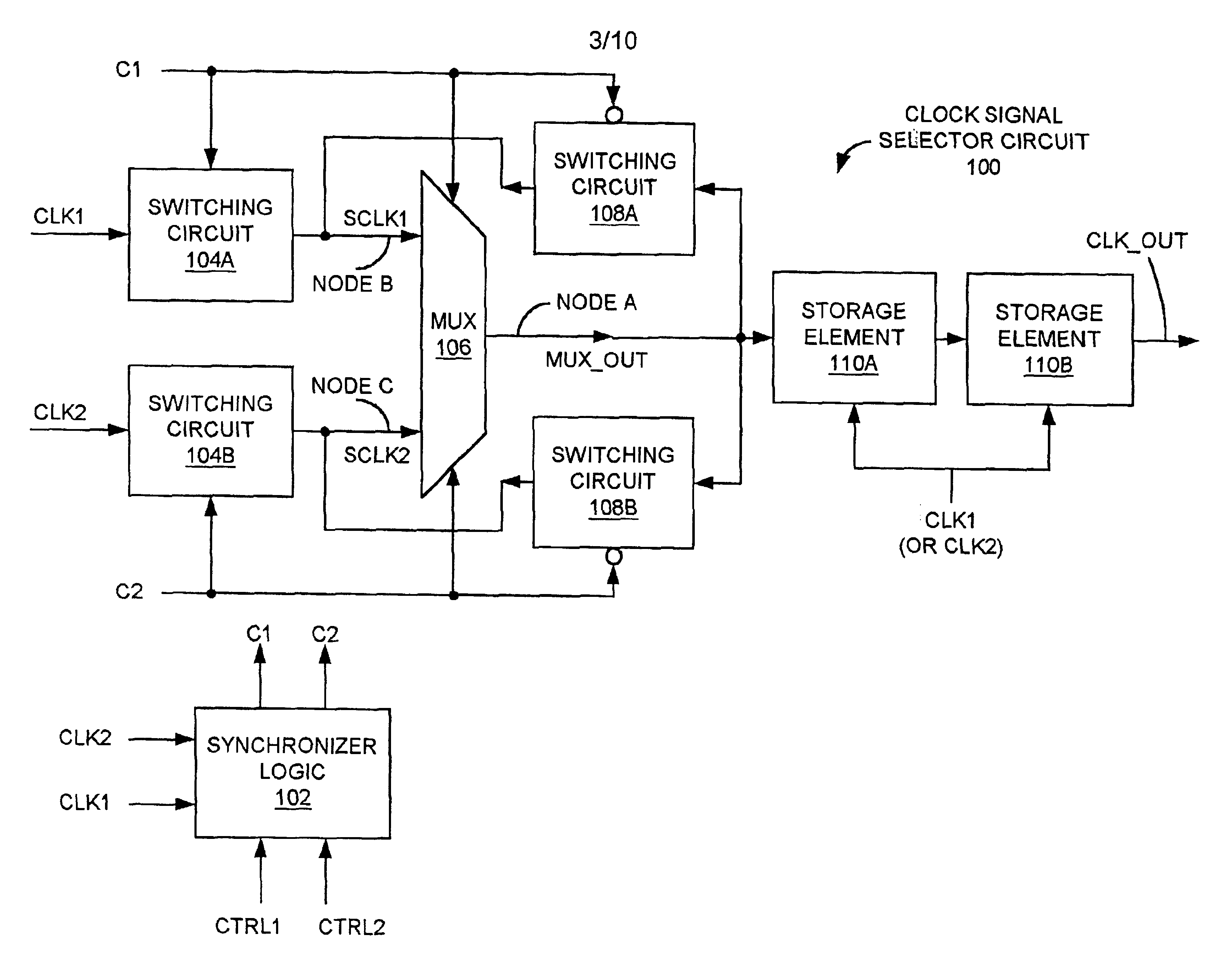
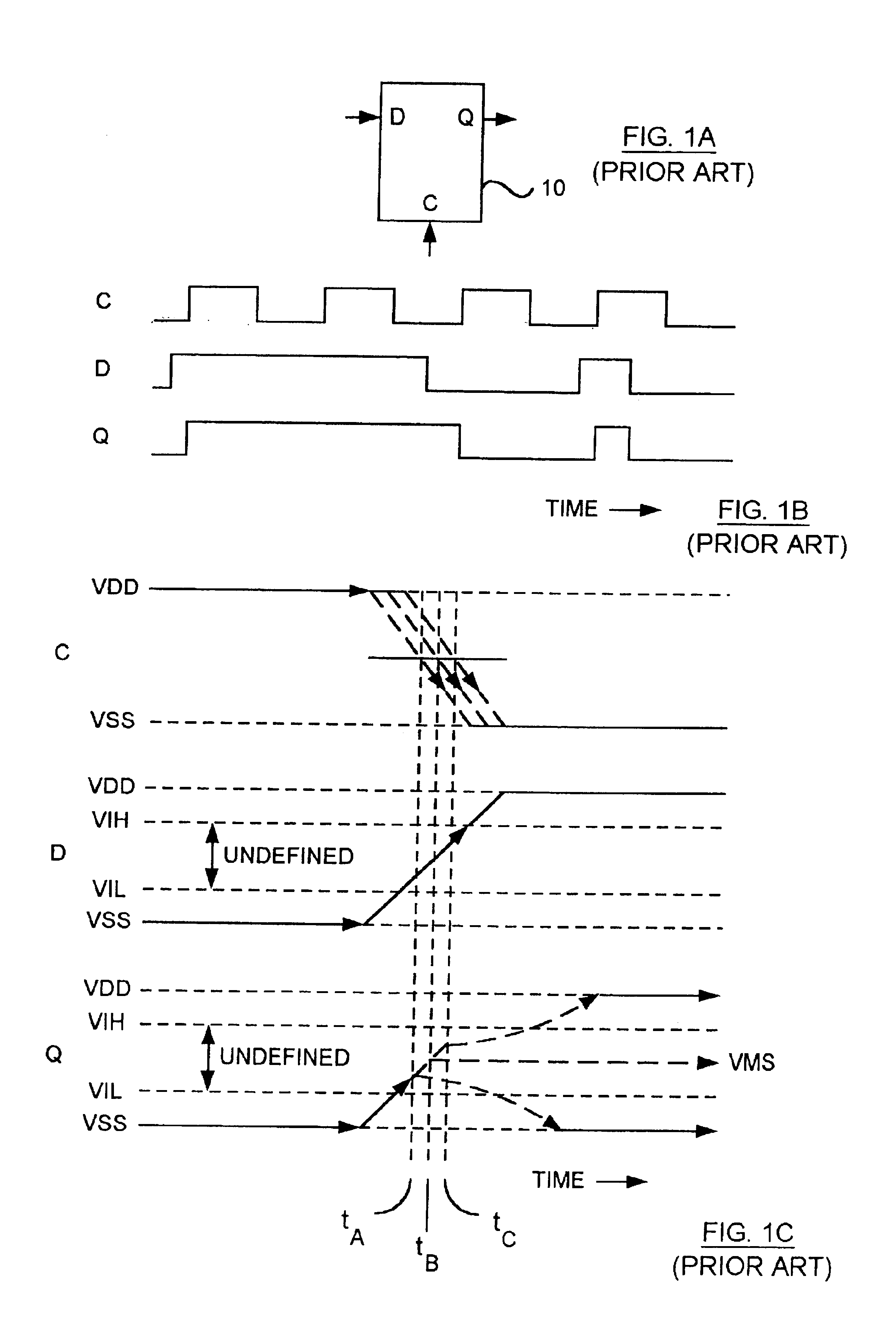
Clock signal selector circuit with reduced probability of erroneous output due to metastability
InactiveUS6927604B2Reduce error rateElectronic switchingElectric pulse generatorMultiplexerControl signal
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
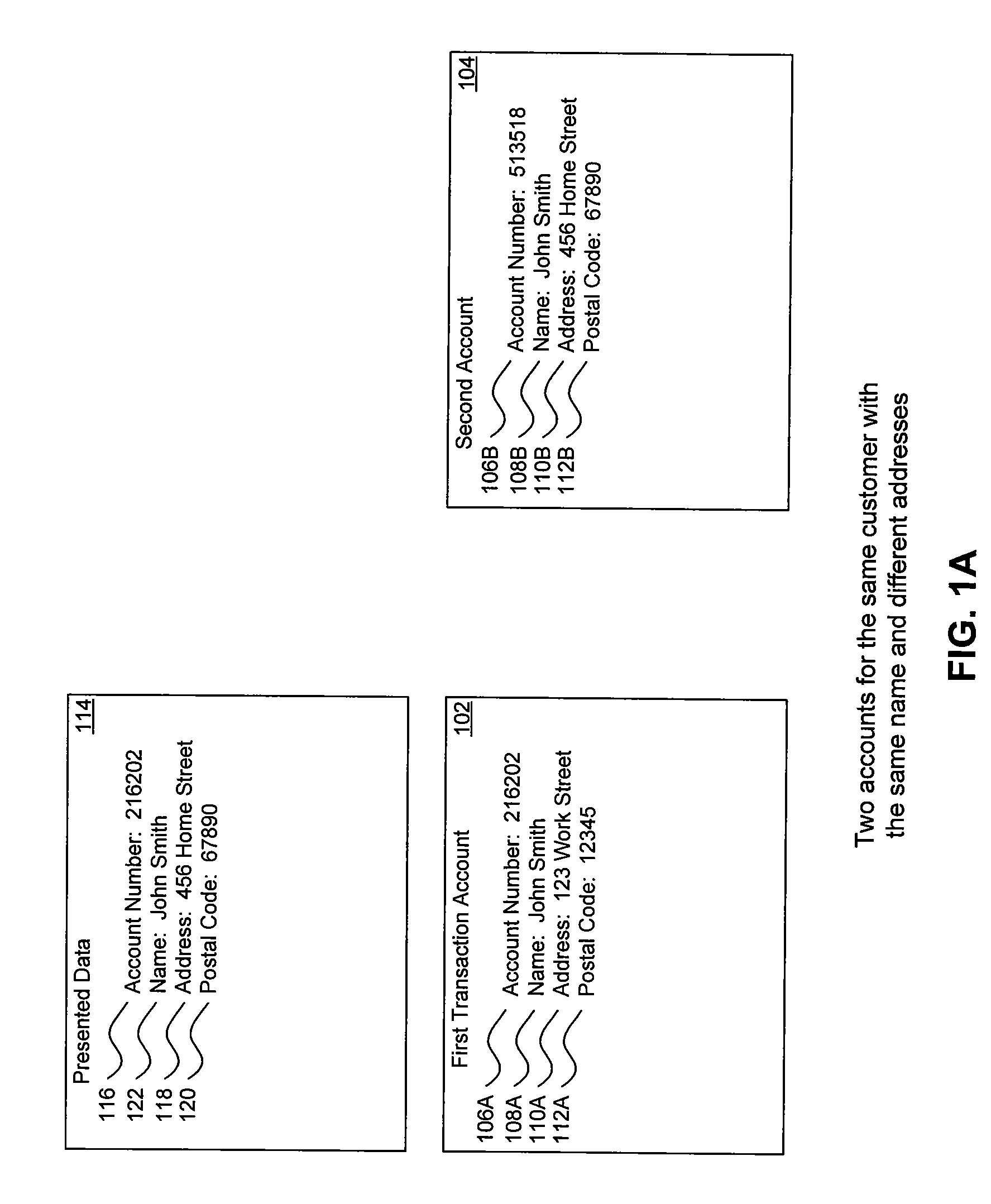
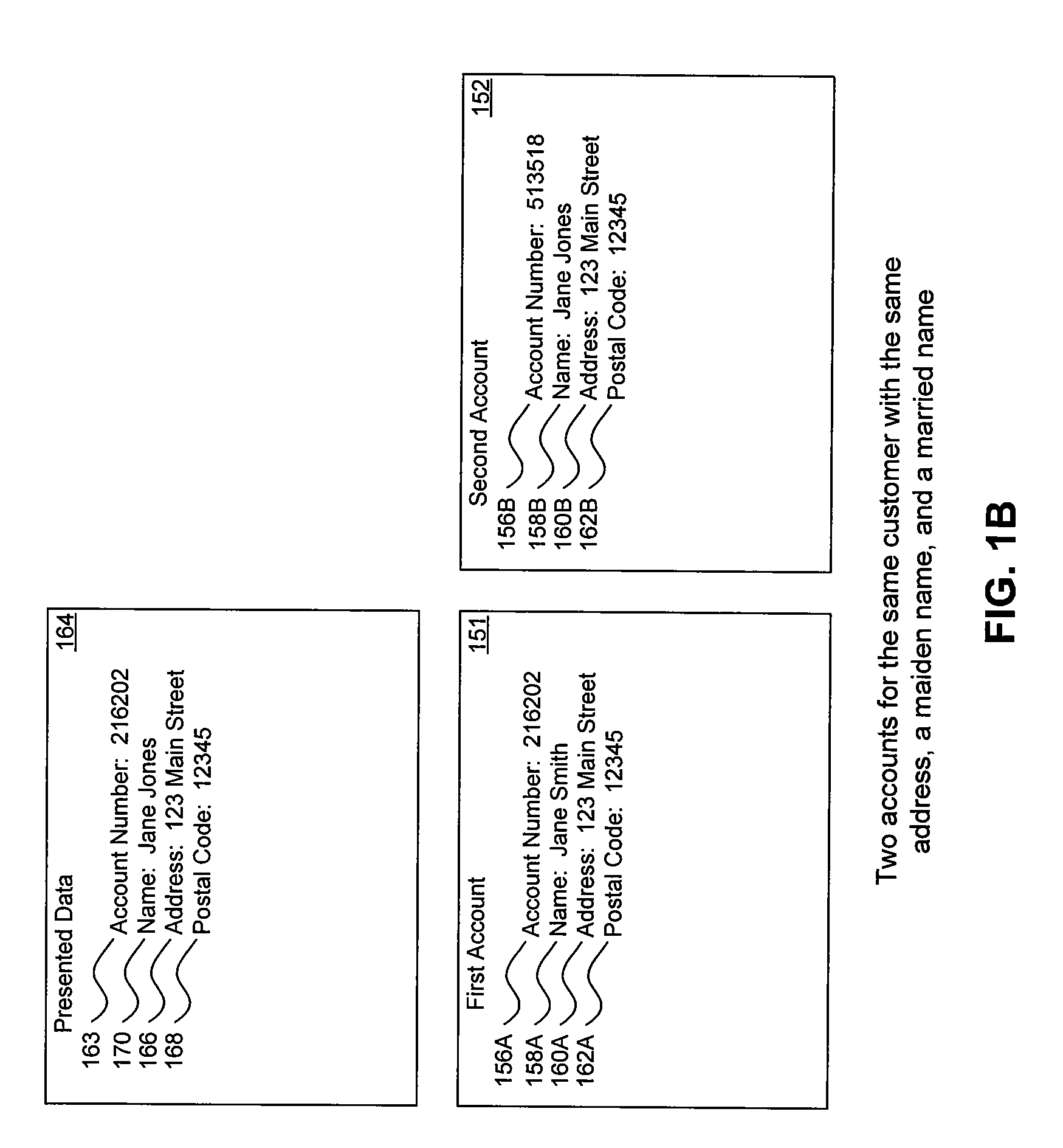
Method, System, and Computer Program Product for Customer-Level Data Verification
InactiveUS20080314977A1Improve accuracyReduce error rateIndividual entry/exit registersBuying/selling/leasing transactionsData validationSource Data Verification
A system, method, and computer program to reduce incorrectly declined transactions and improve risk calculation accuracy by reducing error probability during fraud detection. The tool first receives at least one postal address as well as transaction account data and / or financial transaction instrument data. Then a customer is determined from a first customer record associated with the transaction account data and / or financial transaction instrument data. A record search is performed to identify at least one additional customer record associated with the customer. Finally, the postal address is compared to the information contained in the additional record to create a comparison result that verifies the submitted postal address. The comparison result may be used as an input to transaction risk calculations. The comparison result may also be provided to a merchant system and / or merchant for use in a decision-making process, for example, to verify customer identity.
Owner:LIBERTY PEAK VENTURES LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com