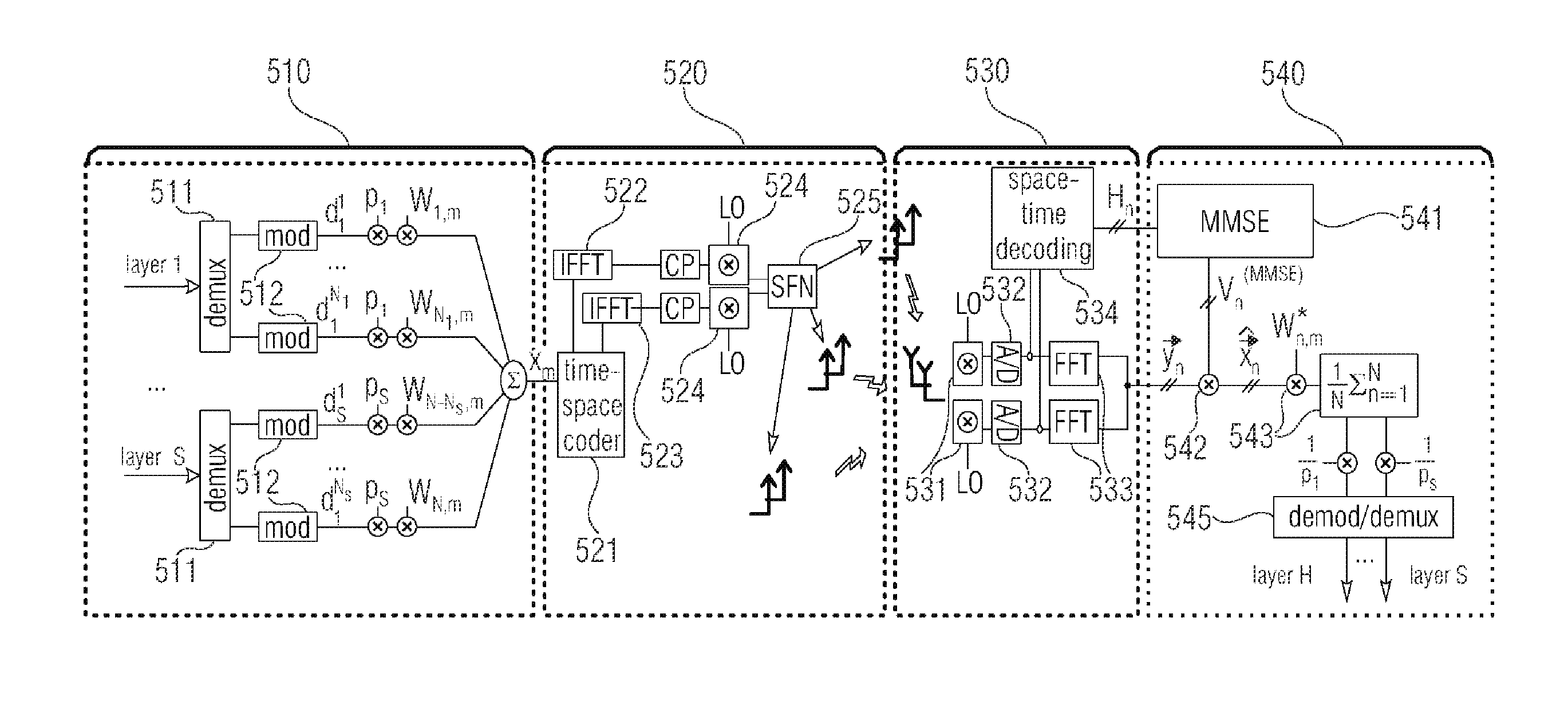
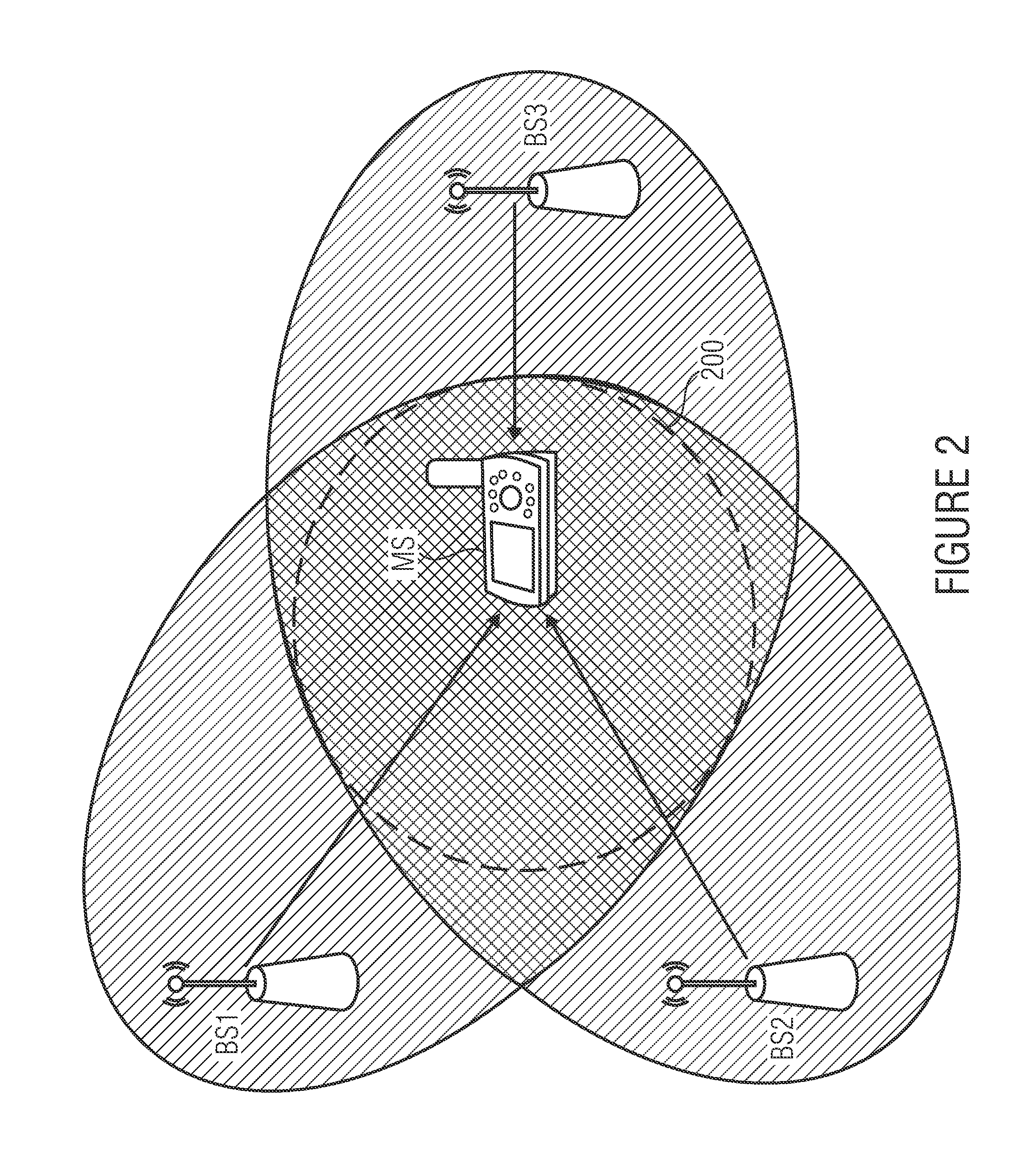
Apparatus for assigning and estimating transmission symbols
a technology of transmission symbols and symbols, applied in the field of apparatus for assigning and estimating transmission symbols, can solve the problems of not being able to obtain individual feedback on a transmission quality from each user, video transmission in mobile radio networks constitutes a problem, and transmission errors typically depend on the quality of reception, etc., to achieve a large video bandwidth and large transmission range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
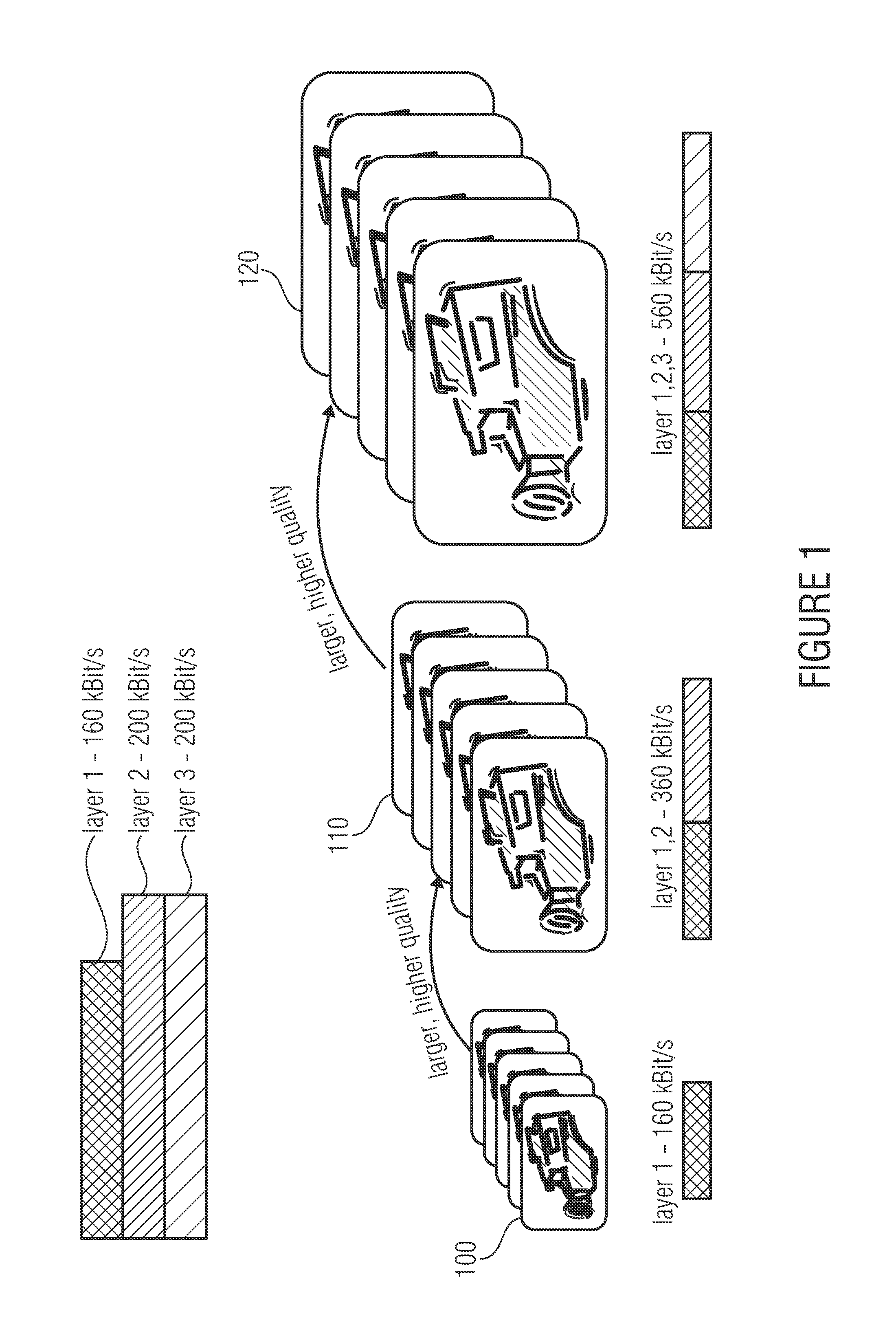
[0032]SVC is an upgrade of the H.264 / AVC video compression standard, cf. ITU-T Recommendation H.264 and ISO / IEC 14496-10 (MPEG-4 AVC), Advanced video coding for generic audiovisual services—version 8 (including SVC extension), ITU-T and ISO / IEC JTC 1, 07 2007). SVC allows efficient scaling of temporal, spatial and quality resolutions in a video signal. Scalability is achieved when parts of the data stream may be lost, the residual signal nevertheless allowing the video signal to be decoded. This is shown, by way of example, in the embodiment of scalable video coding, said embodiment being shown in FIG. 1. The embodiment of FIG. 1 is based on the assumption of scalable video coding that takes place in three layers. The individual layers correspond to data substreams of media data; layer 1 of said layers allows decoding of a video signal in a basic quality.
[0033]If the data of layer 2 is also available in addition to the data of layer 1, a video signal can be decoded whose resolution ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com