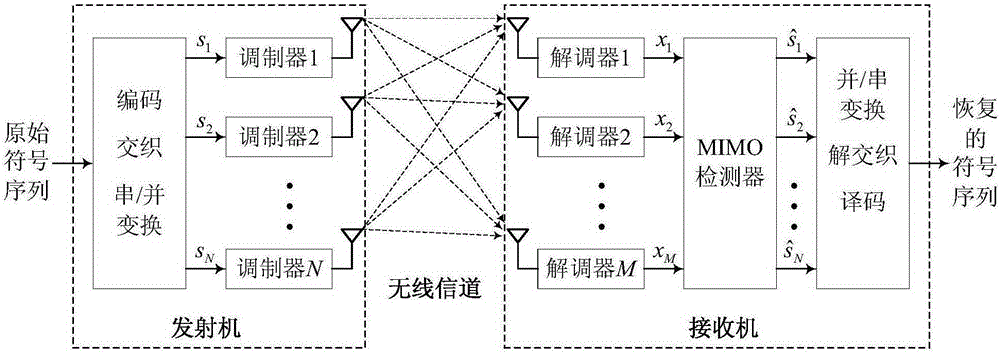
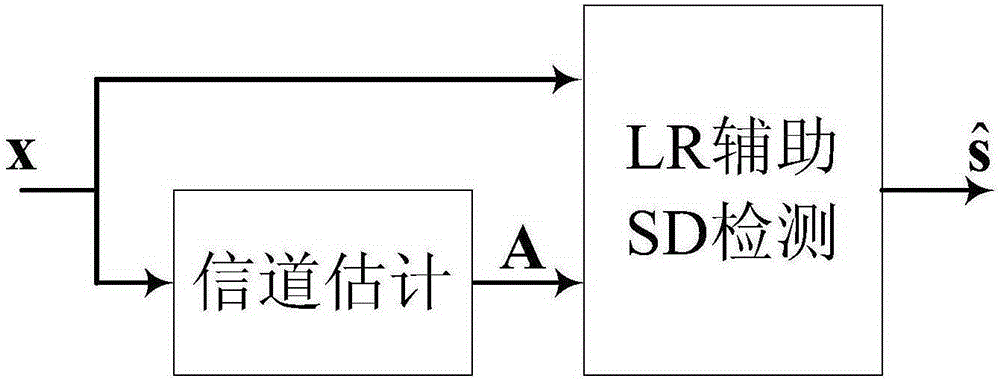
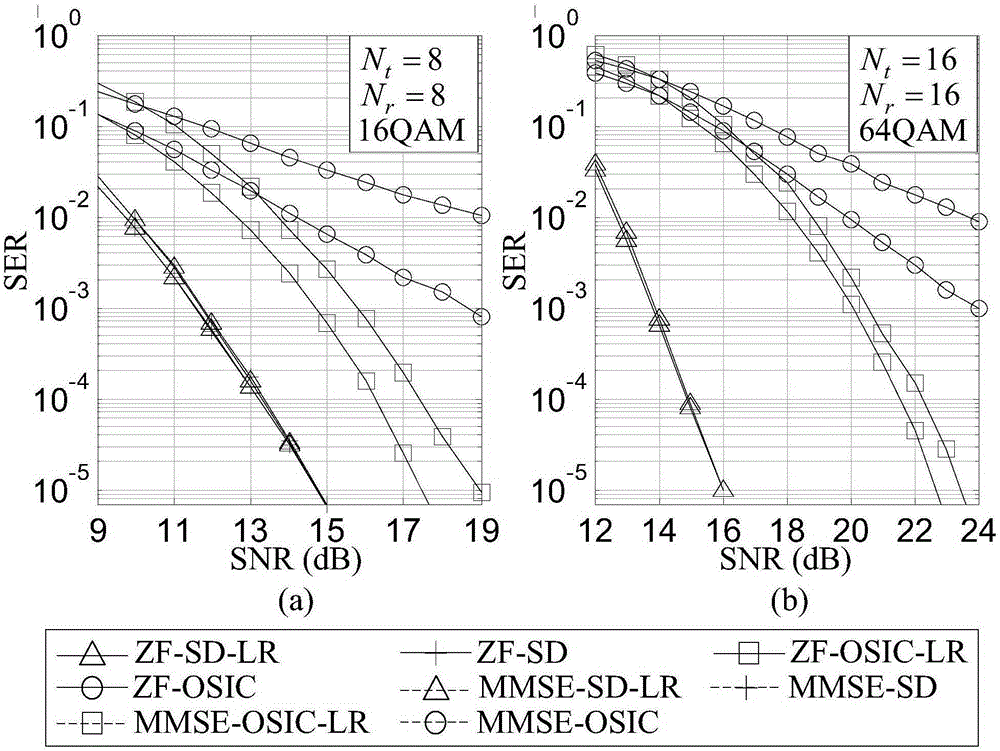
Patents
Literature
83 results about "Lattice reduction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
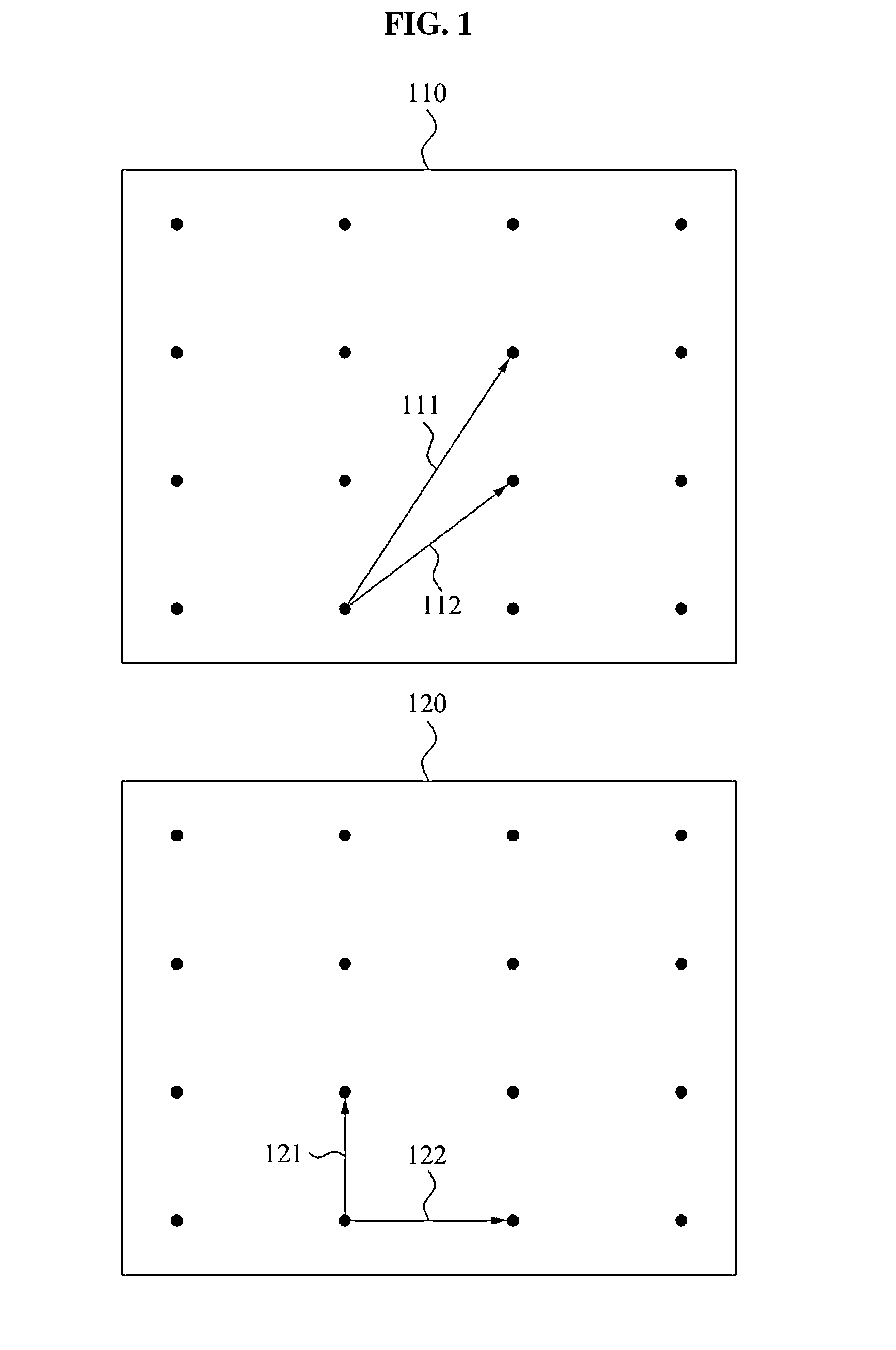
In mathematics, the goal of lattice basis reduction is given an integer lattice basis as input, to find a basis with short, nearly orthogonal vectors. This is realized using different algorithms, whose running time is usually at least exponential in the dimension of the lattice.
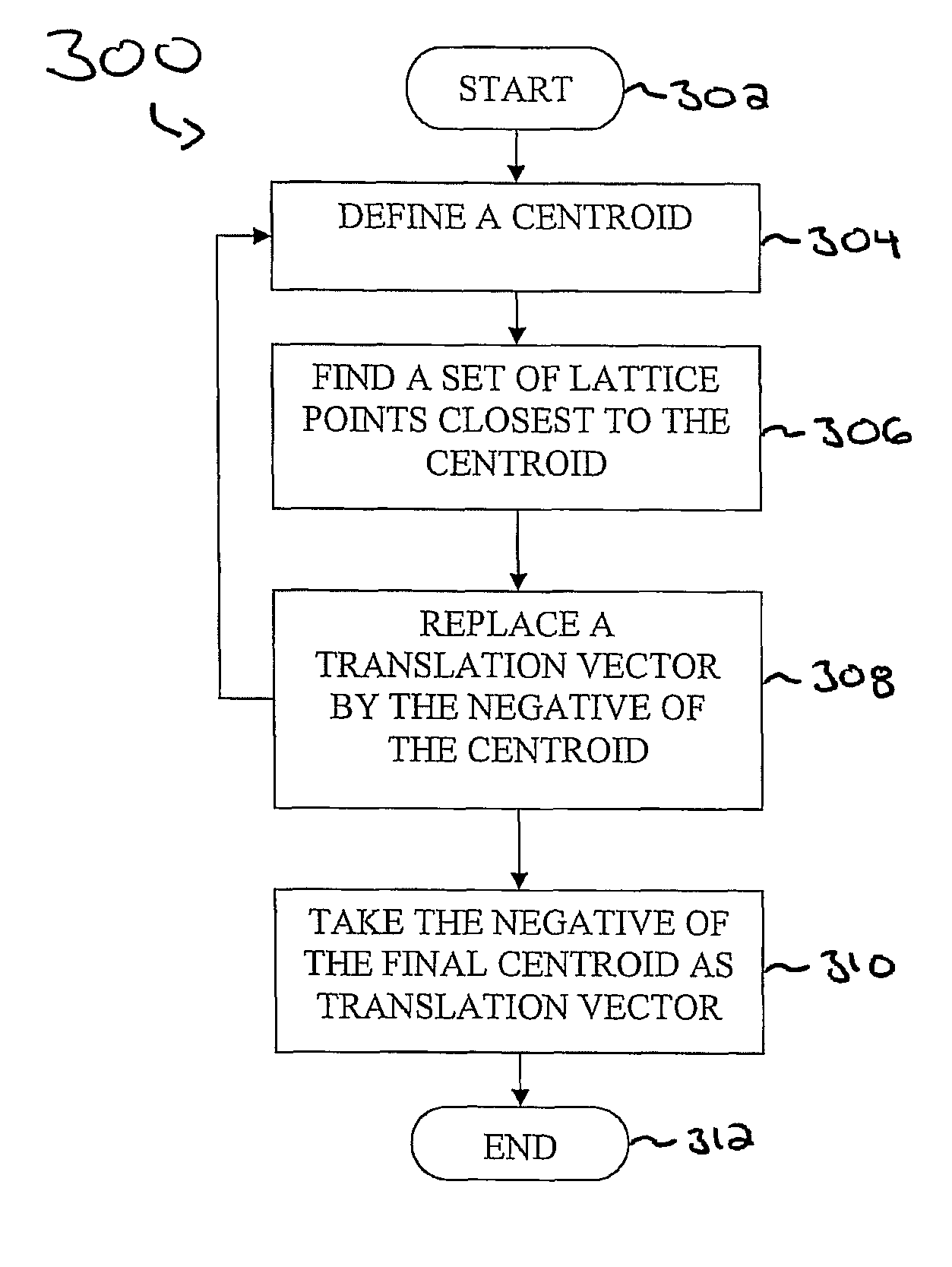
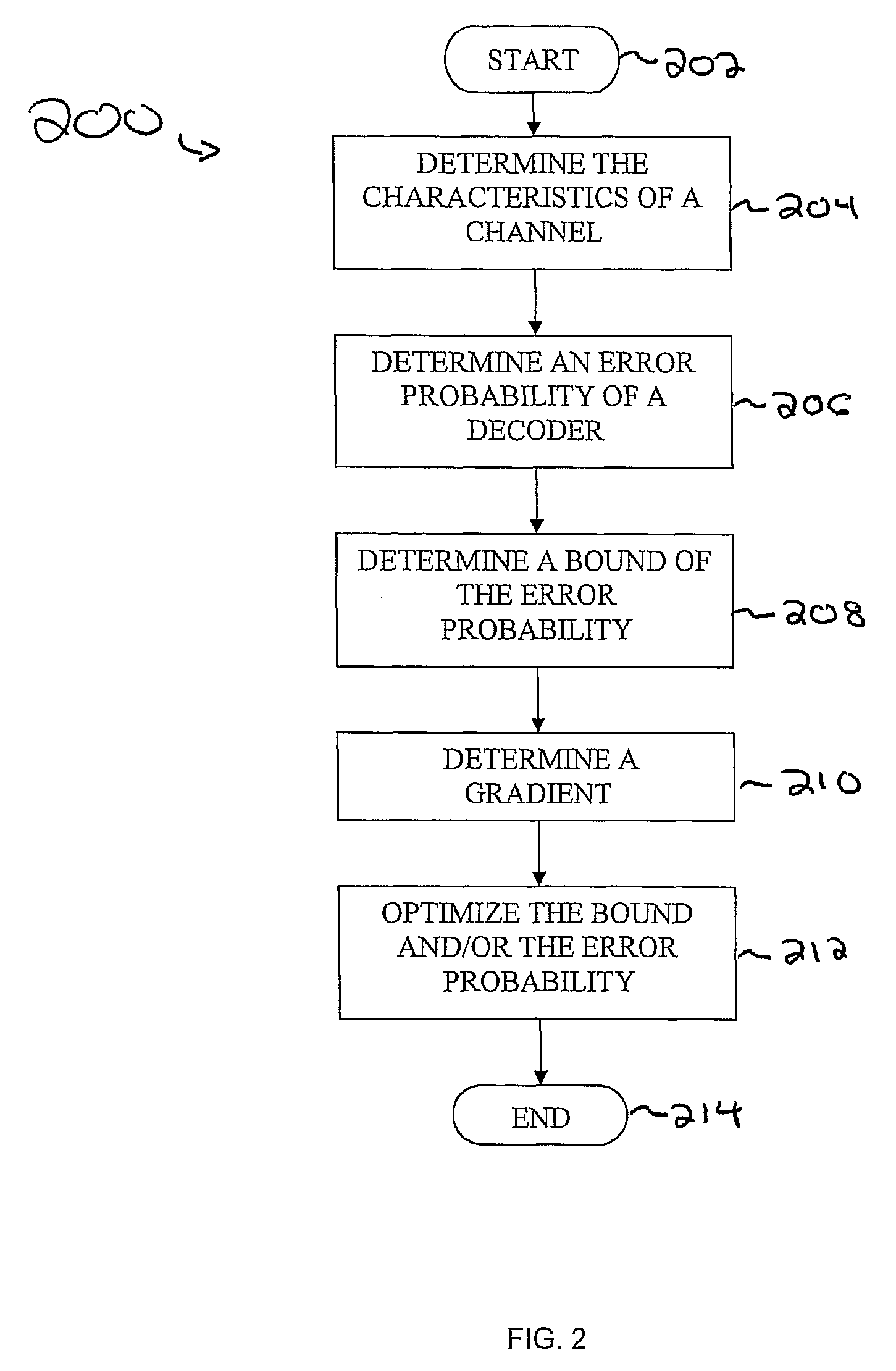
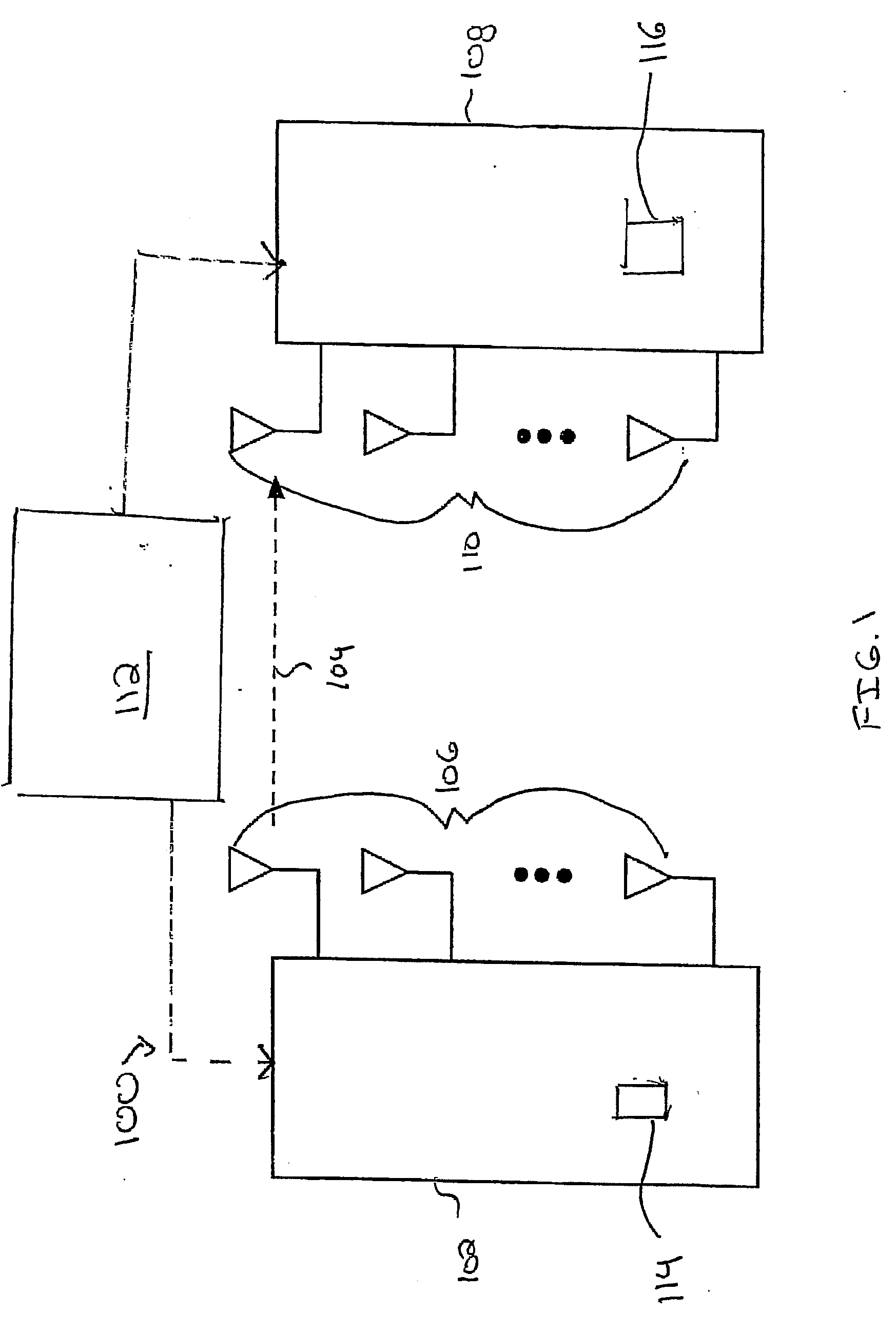
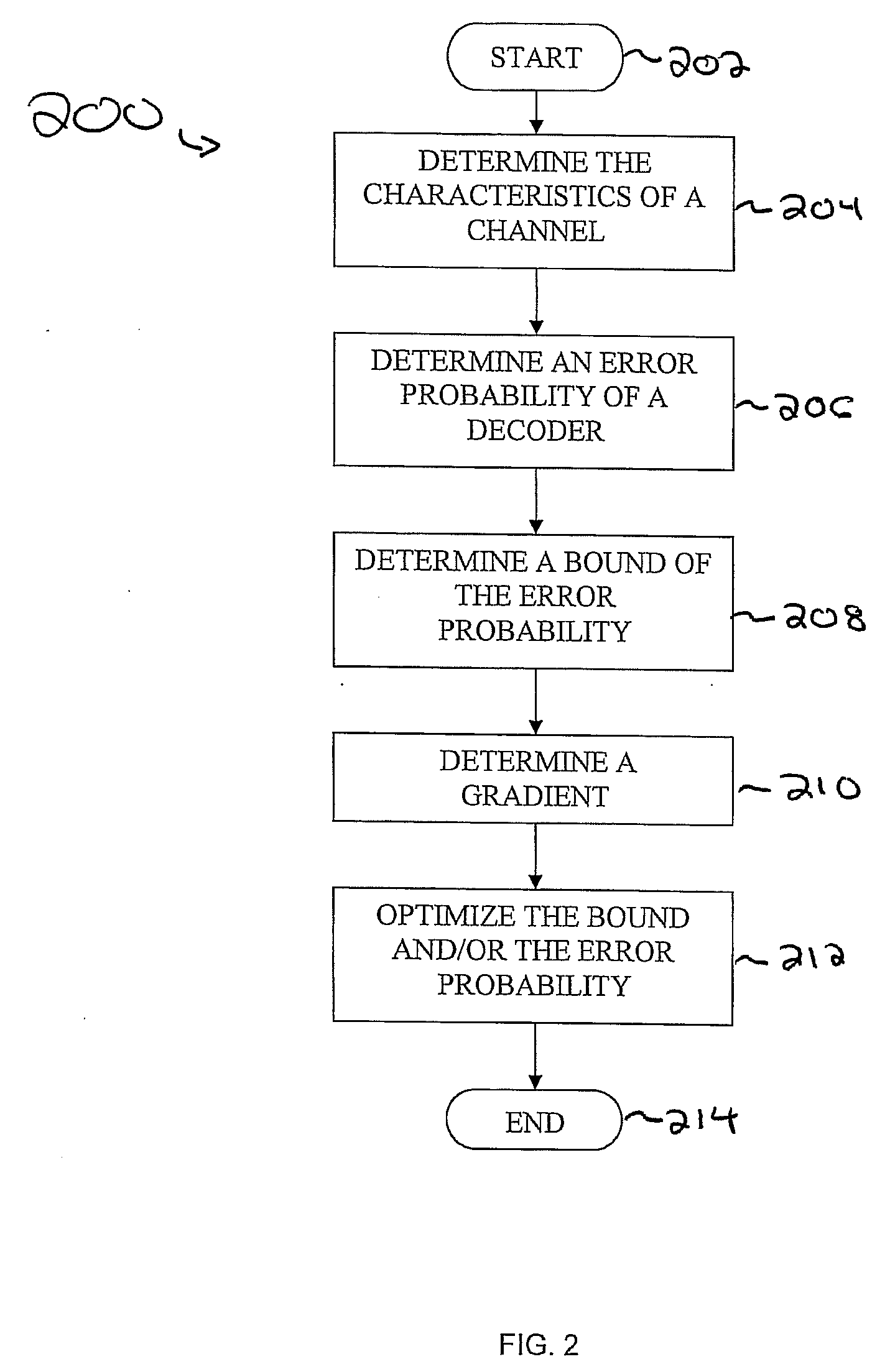
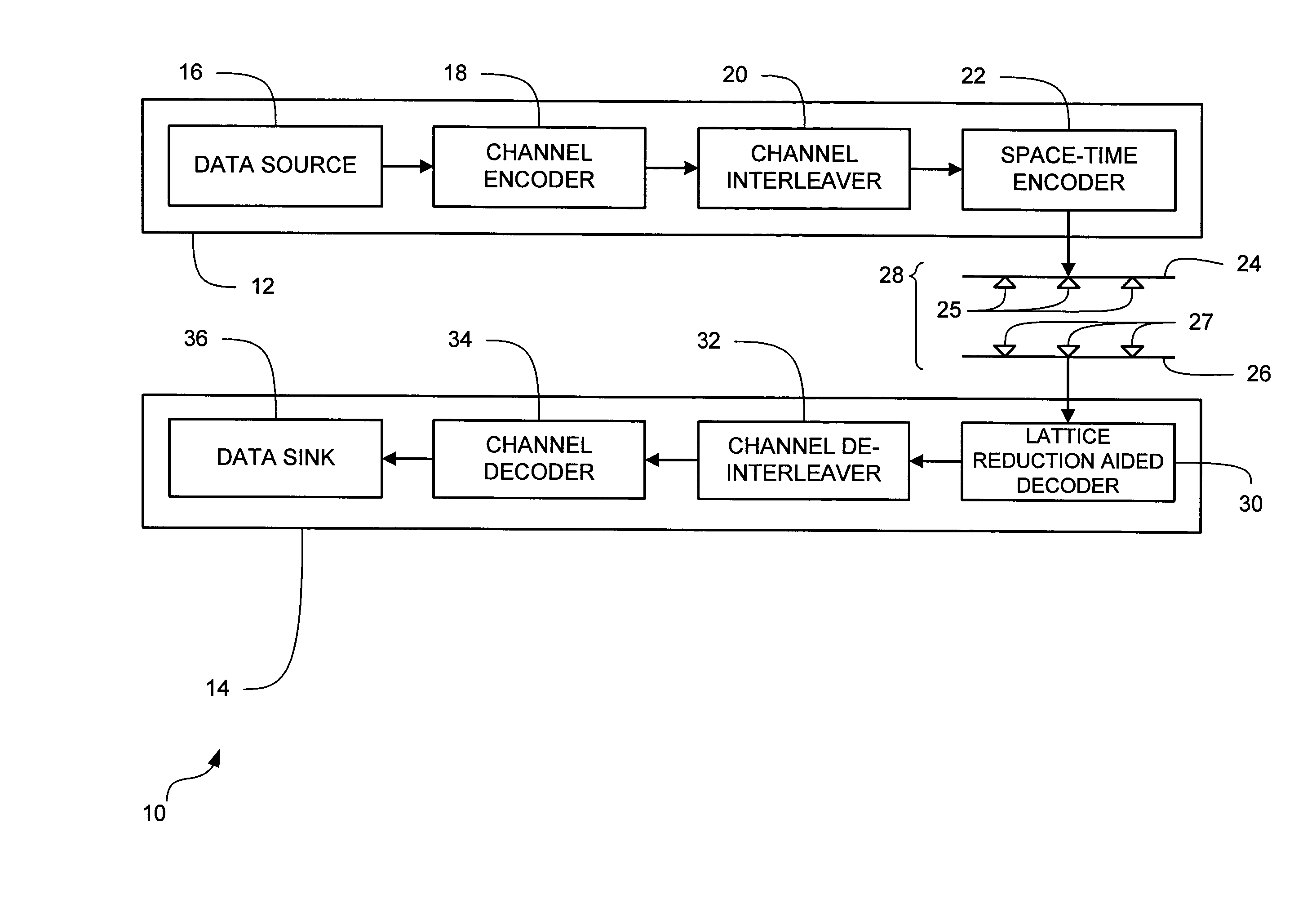
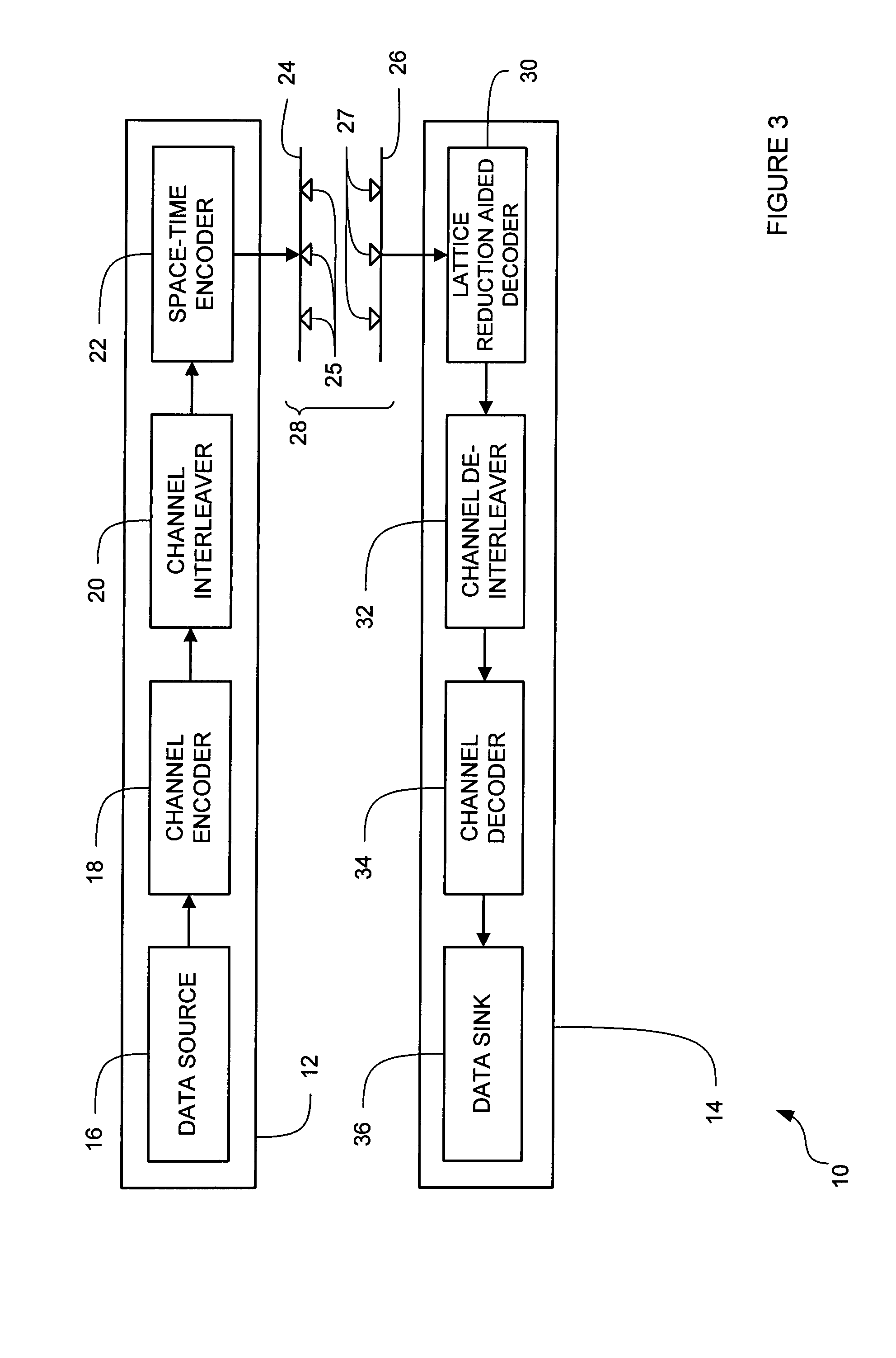
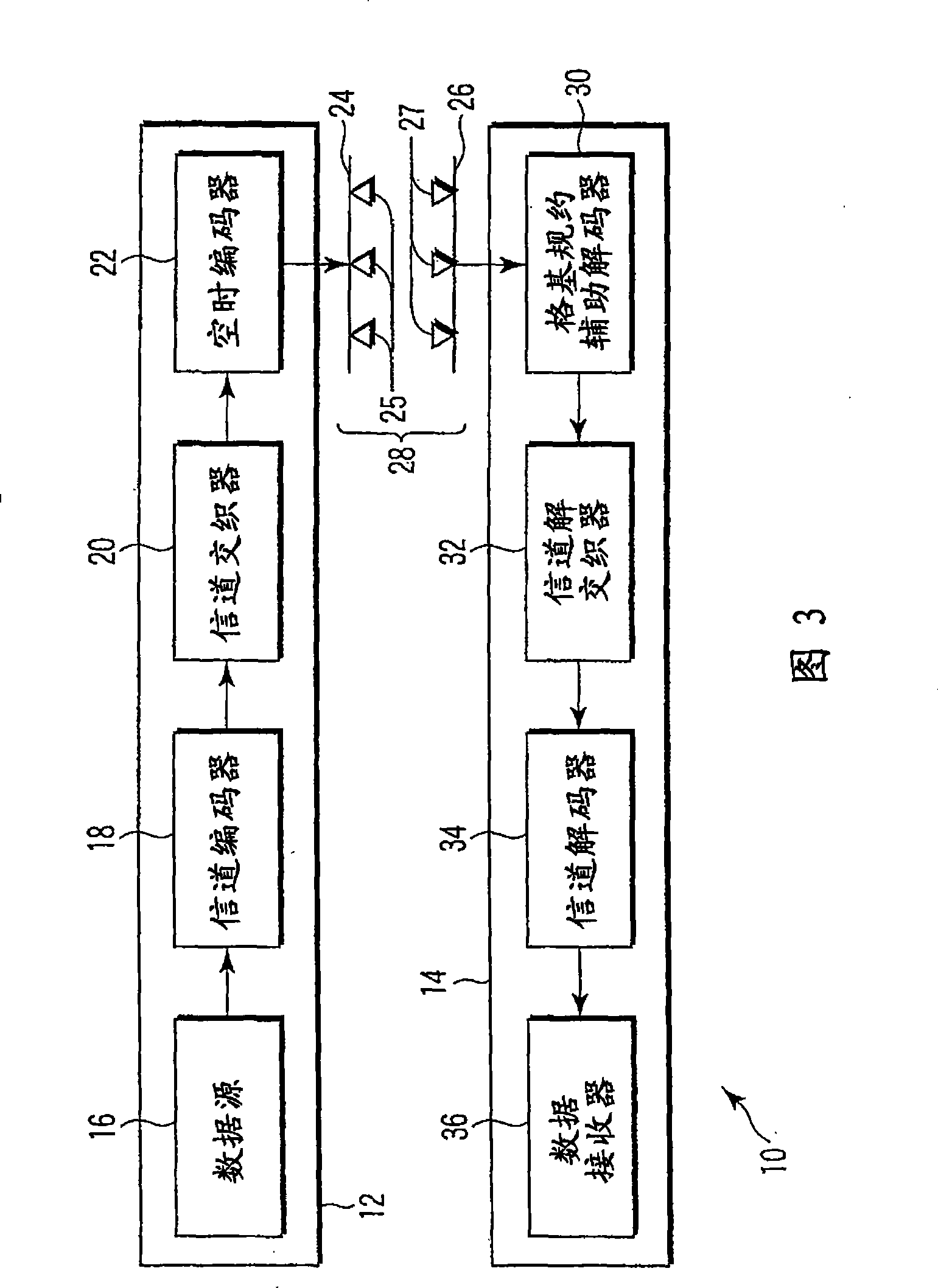
Spherical lattice codes for lattice and lattice-reduction-aided decoders
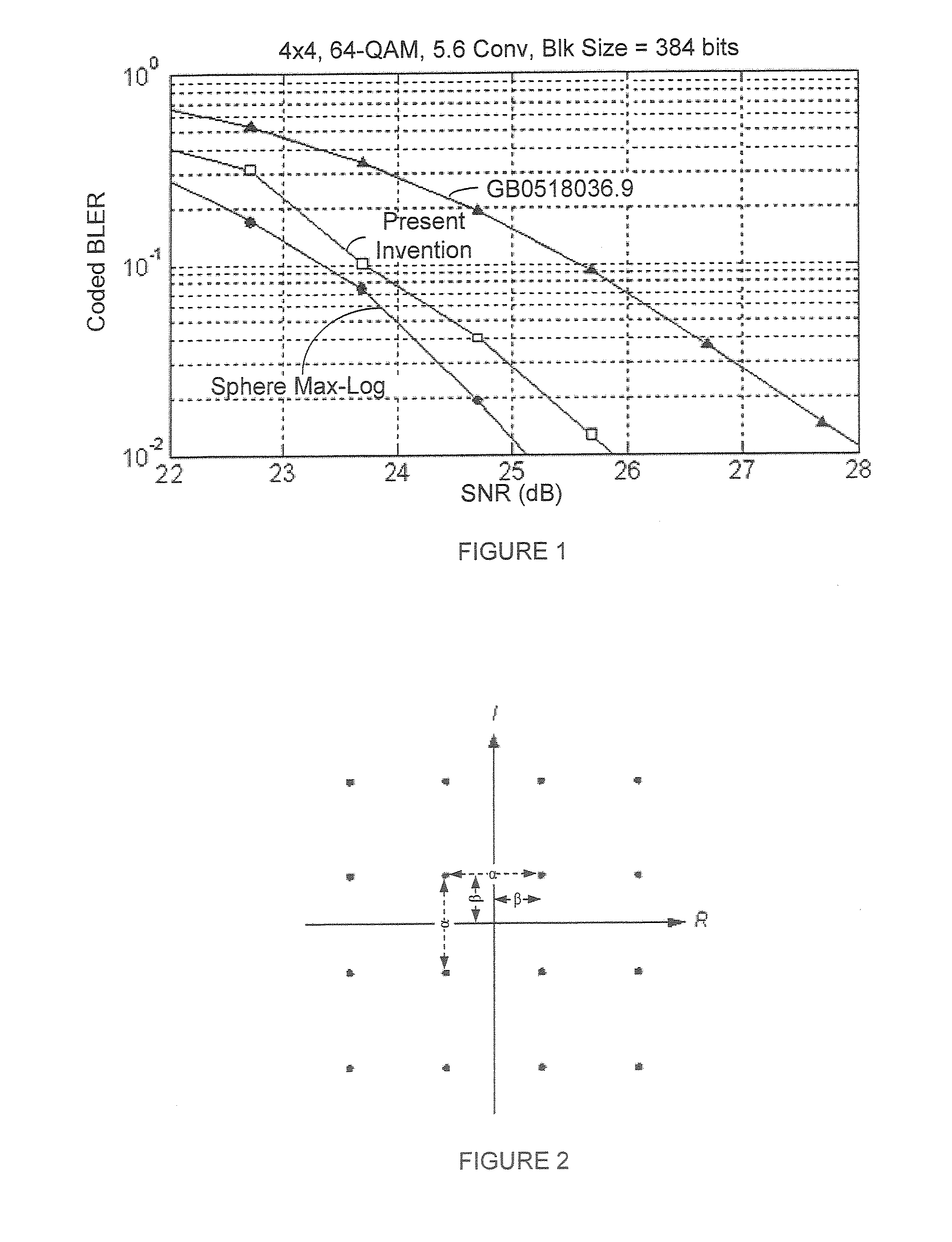
Methods and apparatus for designing spherical lattice codebooks for use in data transmission systems are provided. A spherical lattice codebook is constructed by determining the channel statistics of one or more channels, which can be accomplished by observing a sufficiently large set of channel realizations. After determining the channel statistics, an expression for the error probability of the decoder or expressions for bounds on the error probability and expressions for the corresponding gradients are determined. The gradient is then used in an optimization technique to produce a spherical lattice codebook which is subsequently used for transmission.
Owner:NEC CORP
Design of Spherical Lattice Codes for Lattice and Lattice-Reduction-Aided Decoders
ActiveUS20070283210A1Reduce transmit energyCode conversionDiversity/multi-antenna systemsChannel statisticsLattice reduction
Methods and apparatus for designing spherical lattice codebooks for use in data transmission systems are provided. A spherical lattice codebook is constructed by determining the channel statistics of one or more channels, which can be accomplished by observing a sufficiently large set of channel realizations. After determining the channel statistics, an expression for the error probability of the decoder or expressions for bounds on the error probability and expressions for the corresponding gradients are determined. The gradient is then used in an optimization technique to produce a spherical lattice codebook which is subsequently used for transmission.
Owner:NEC CORP
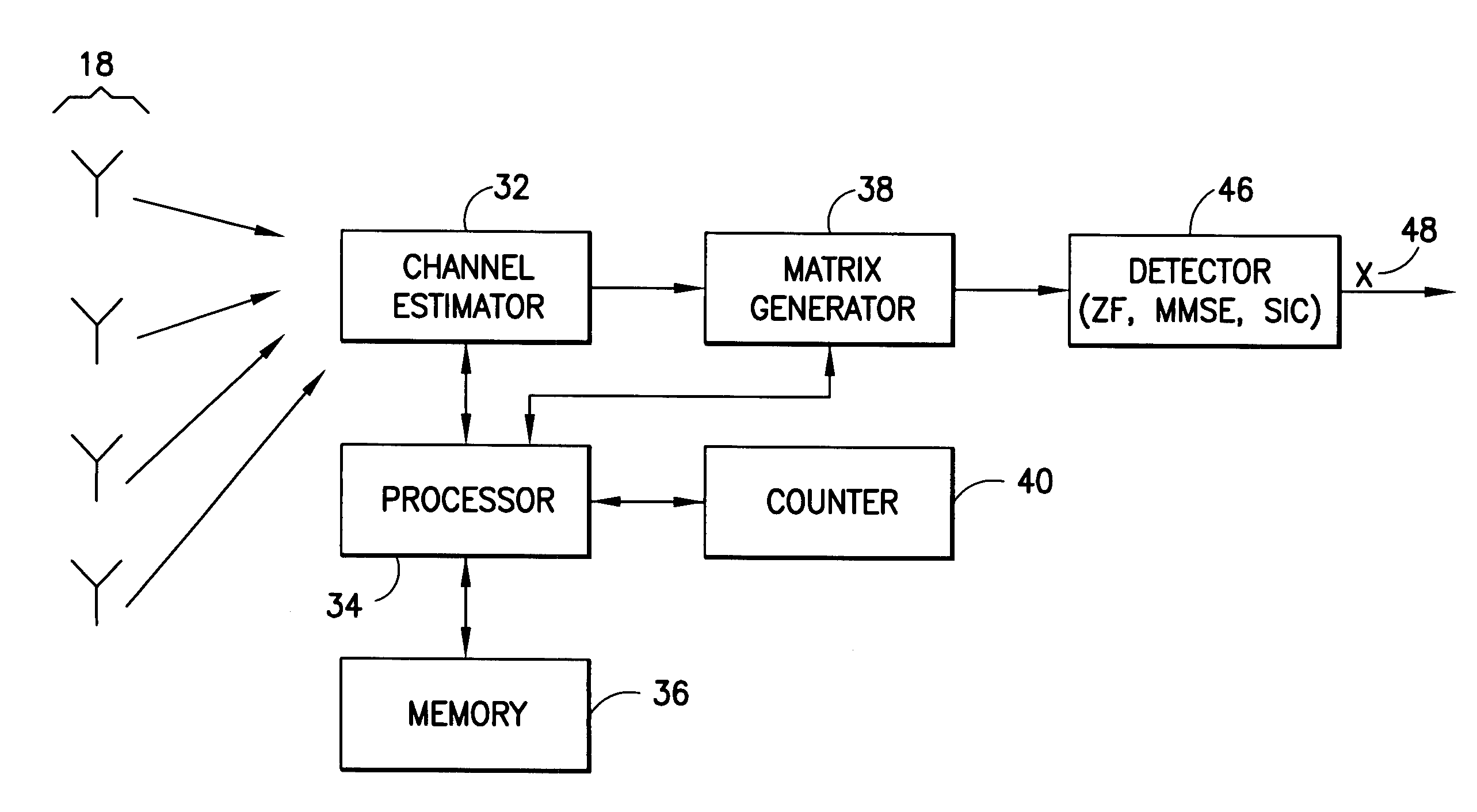
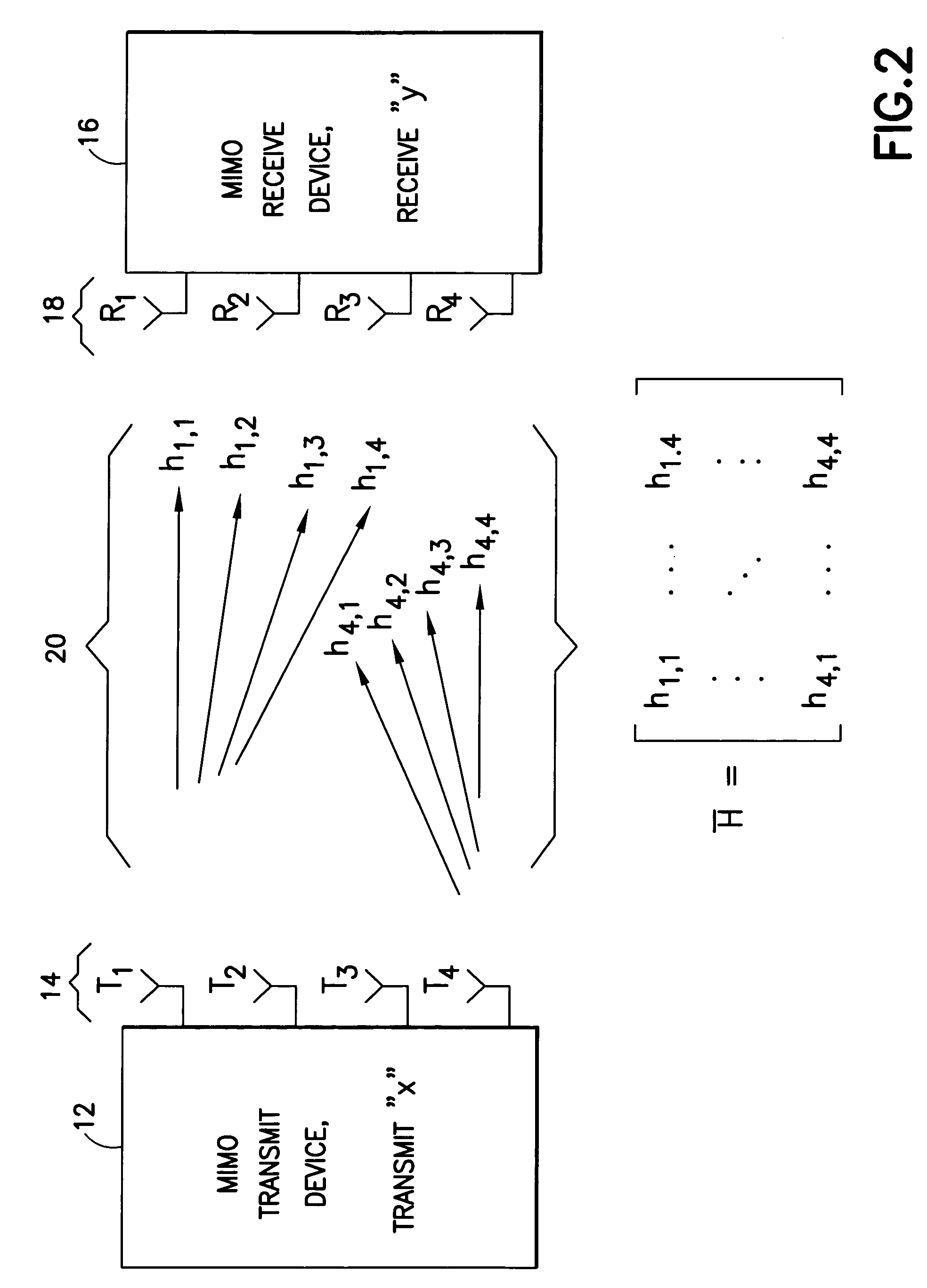
Lower complexity computation of lattice reduction
InactiveUS20070268981A1Easy to detectLine-faulsts/interference reductionAmplitude demodulation detailsChange of basisRound complexity
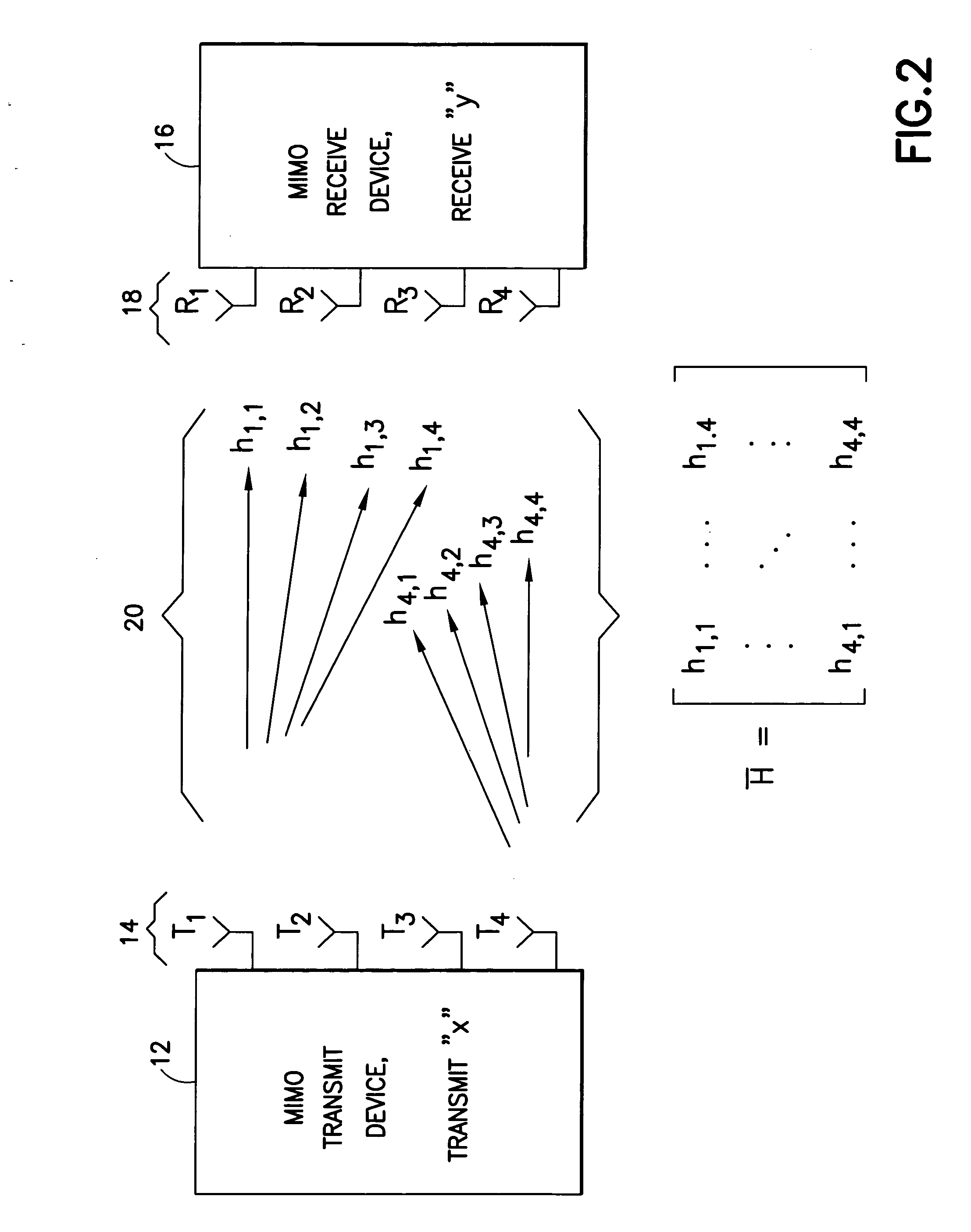
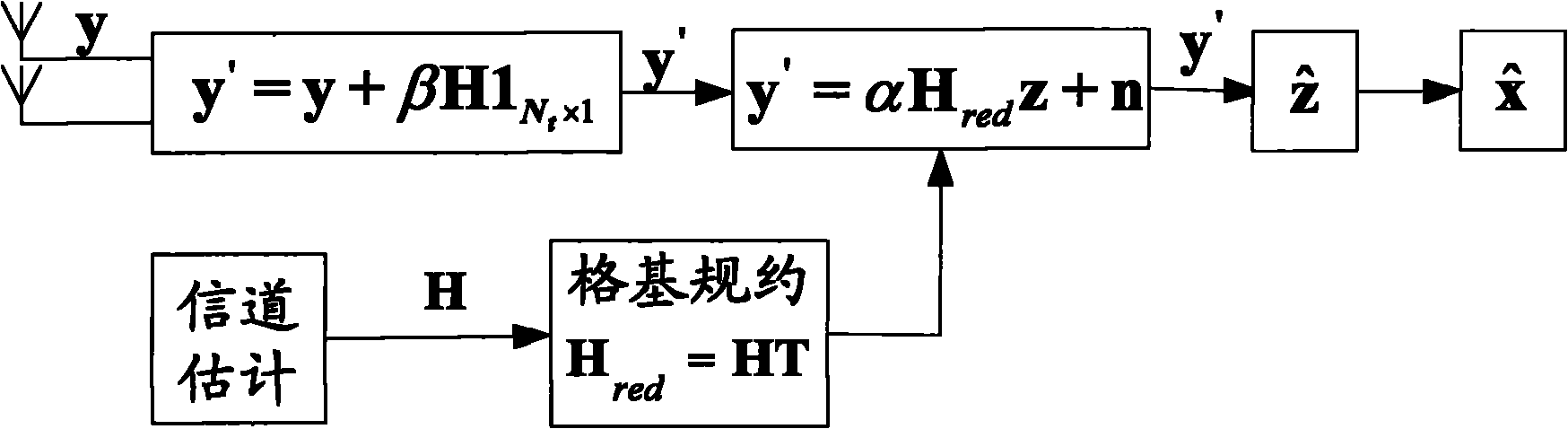
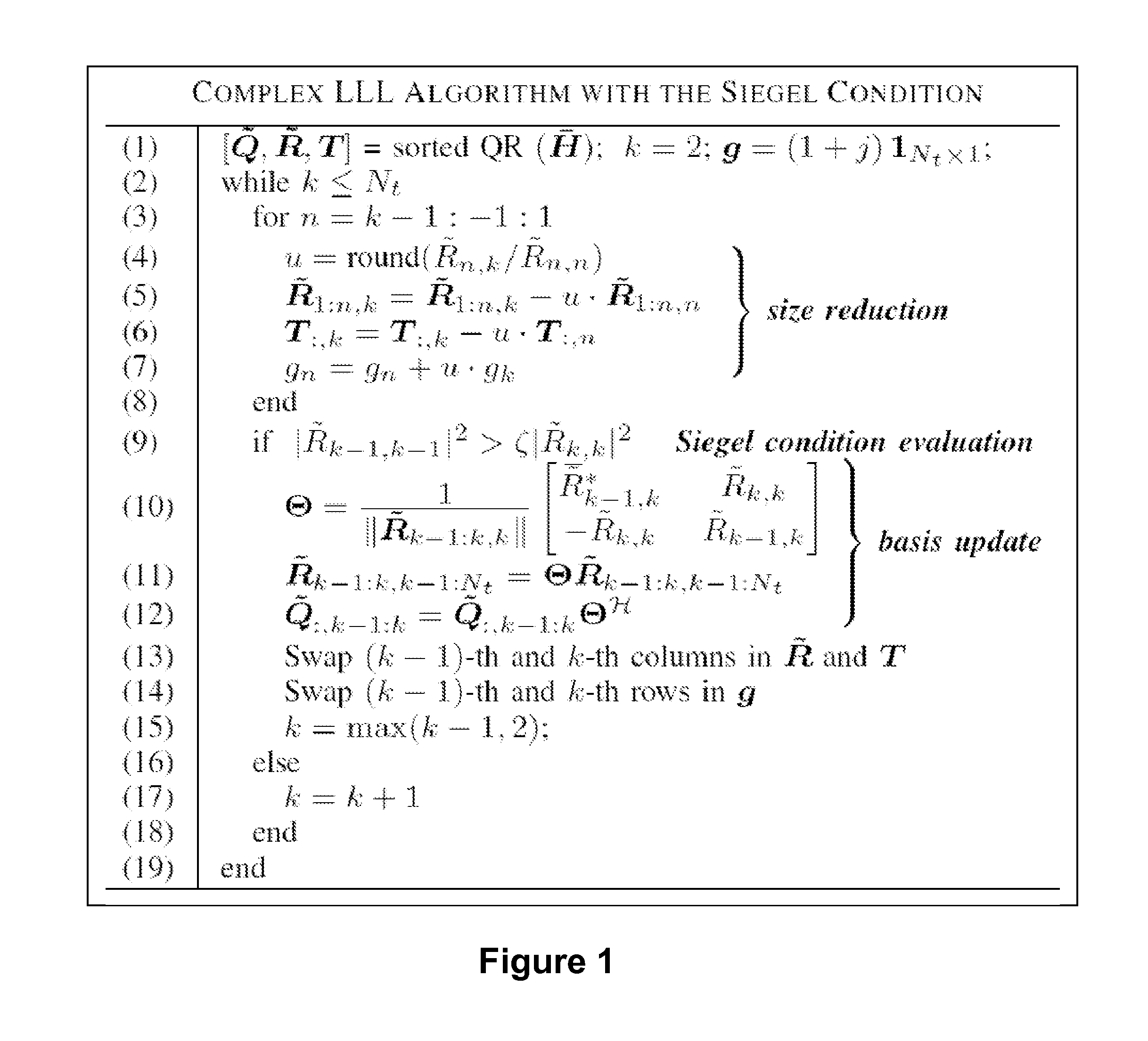
A signal vector is received over a plurality of channels. A channel matrix H is determined that represents at least one of the plurality of channels. An iterative algorithm such as Lenstra-Lenstra-Lovasz is used to determining a change of basis matrix T that when multiplied with the channel matrix H converges to a matrix H*T that is more orthogonal than the channel matrix H. In one aspect the iterative algorithm is upwardly bounded in the number of iterations (e.g., 20 or 30 iterations) that it may perform for any specific channel realization to determine the change of basis matrix T. In another aspect the algorithm is initiated with a matrix derived from a previously determined change of basis matrix. Both aspects may be combined in a single method or device, or either employed separately.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
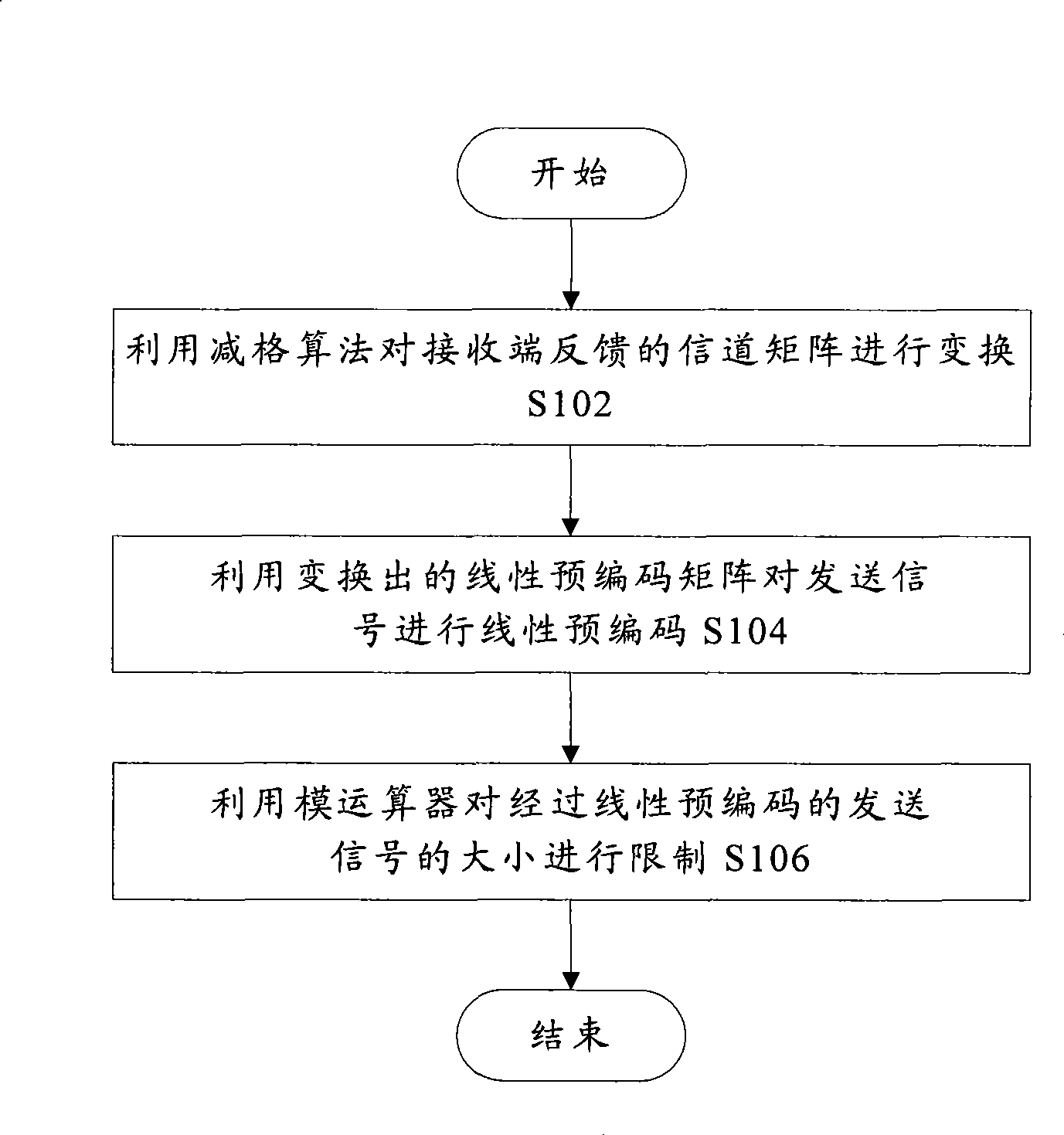
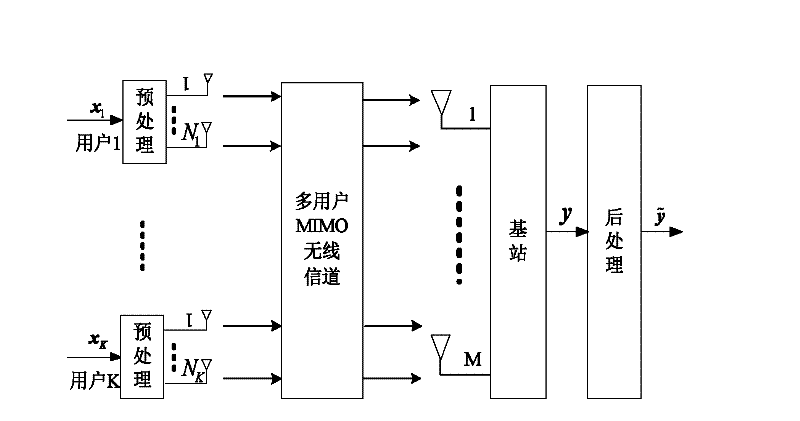
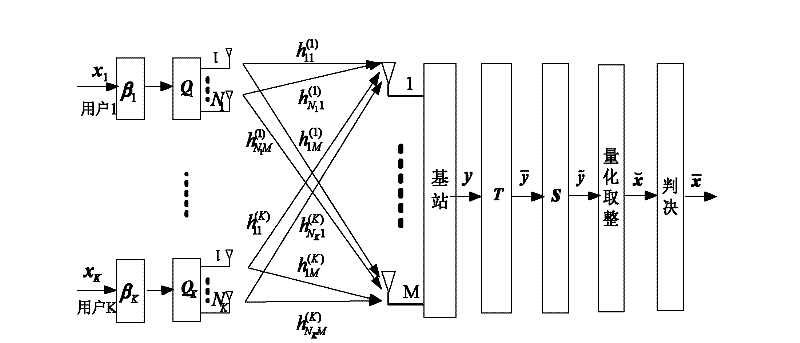
Achieving method for MU-MIMO precoding
InactiveCN103957086AEliminate distractionsImprove performanceSpatial transmit diversityTransmitter/receiver shaping networksQR decompositionMulti user interference
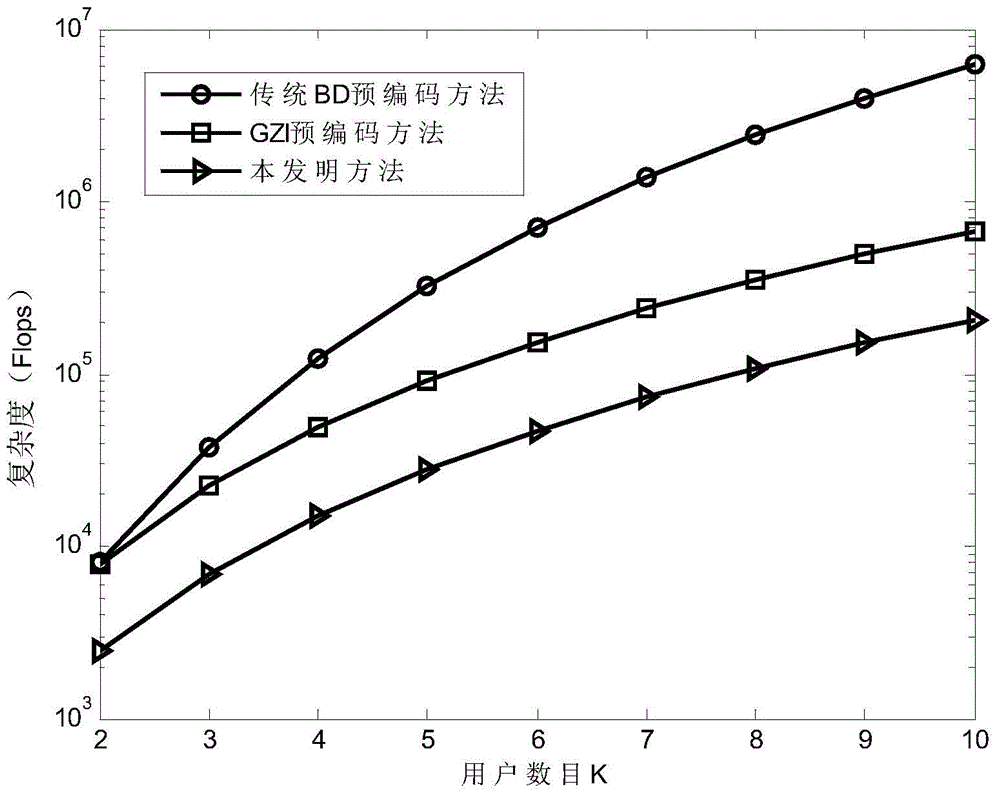
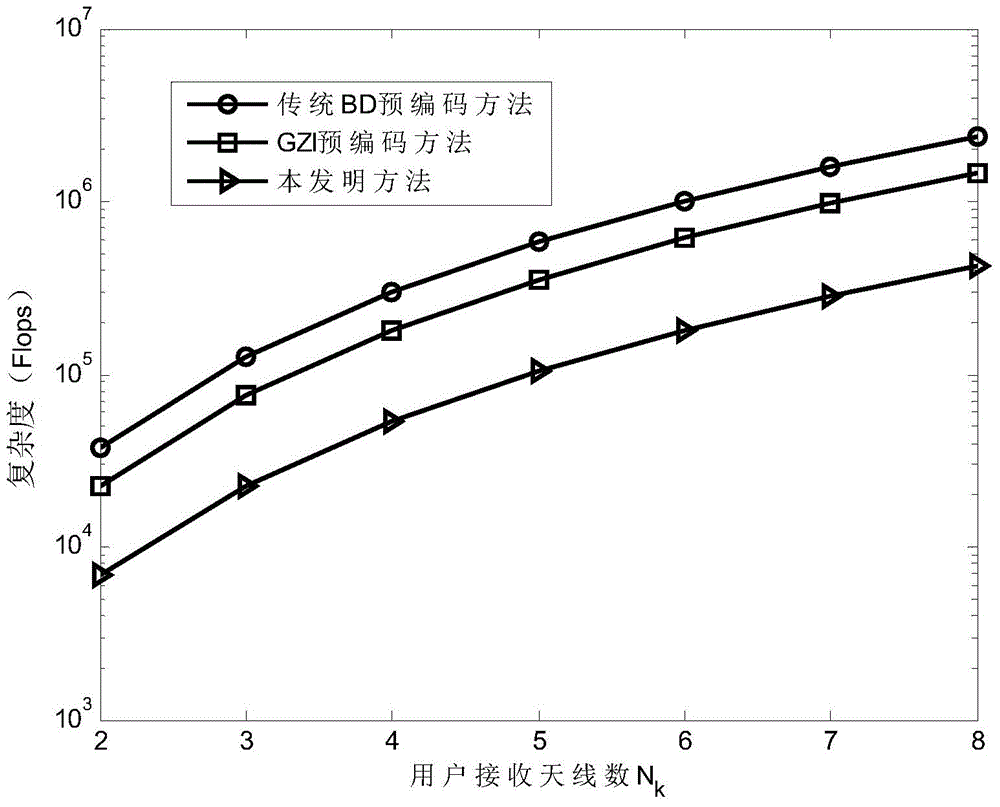
The invention discloses an achieving method for MU-MIMO precoding. The method includes the detailed steps that a first precoding matrix is obtained through performing improved QR decomposition on expanding matrixes H of joint channel matrixes HS of all users to eliminate multi-user interference, precoding matrixes of all the users are determined according to a QR decomposition result, and therefore calculation complexity is reduced; then a lattice reduction method is used for obtaining a second precoding matrix better in performance. Compared with a traditional MU-MIMO precoding method, the method is lower in complexity, and meanwhile system performance is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Lattice reduction-based multiple input multiple output (MIMO) detection soft output method
InactiveCN101917368AAvoid Weight CalculationReduce the numberDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionTransmitter/receiver shaping networksQR decompositionComputation complexity
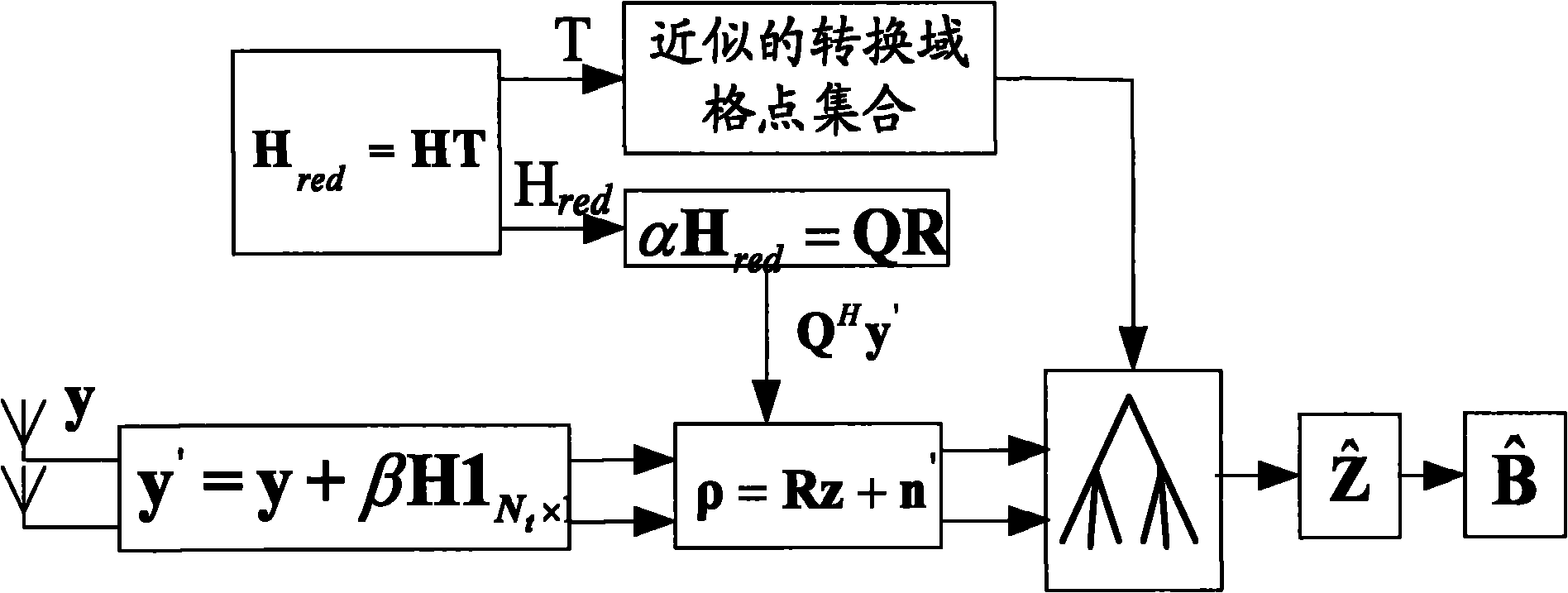
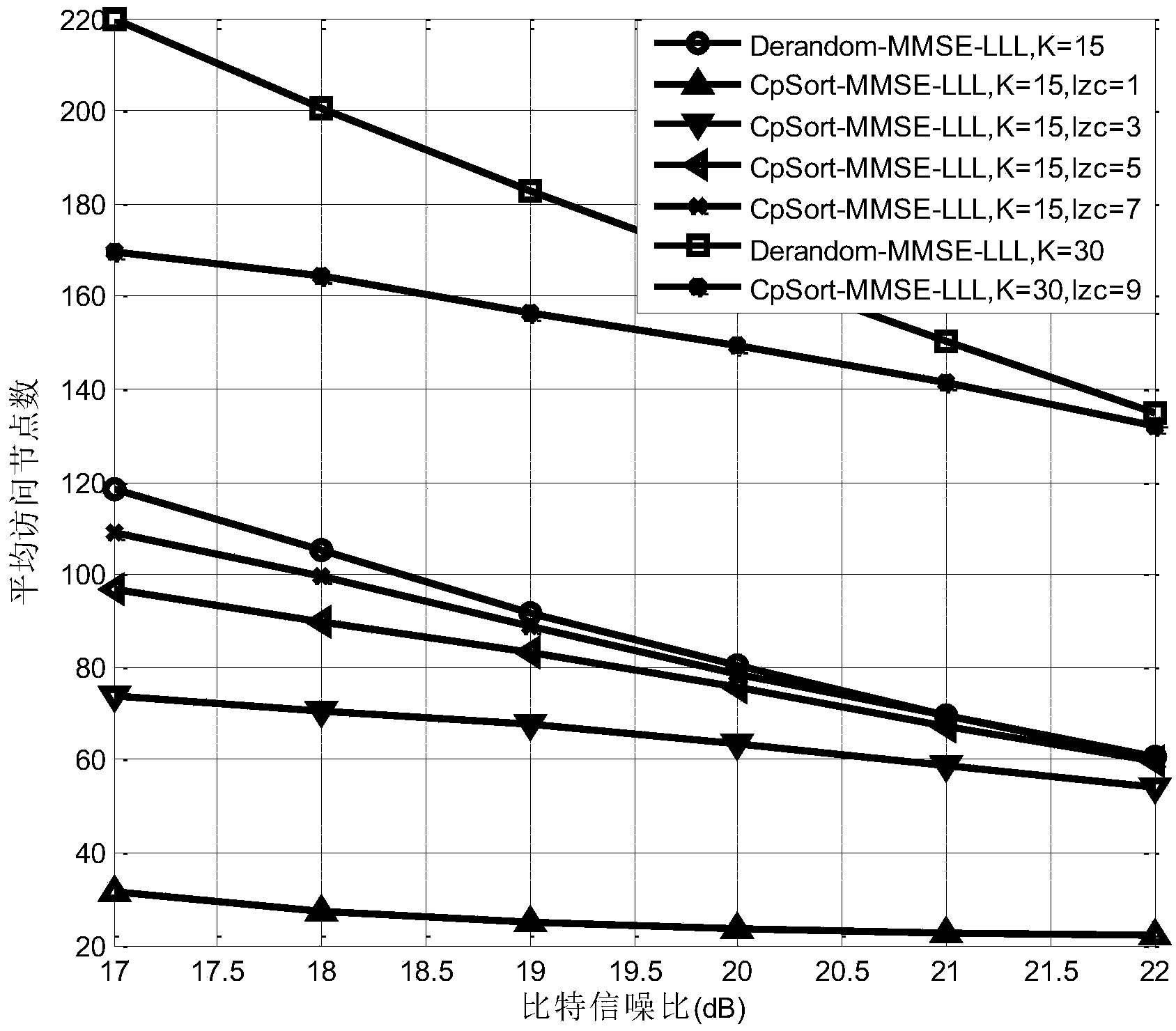
The invention relates to a lattice reduction-based multiple input multiple output (MIMO) detection soft output method. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, acquiring an ordered list of transform domain signals aiming at different transformation matrixes and storing the ordered list for inquiring during detection; secondly, when executing the lattice reduction-based MIMO detection at each time, applying the lattice reduction to a channel response matrix to obtain a lattice reduction base and the transformation matrixes and acquiring the corresponding ordered list of the transform domain signals by using the transformation matrixes; thirdly, executing QR Decomposition and M algorithm (QRM) detection by using the lattice reduction base and the ordered list of the transform domain signals to acquire survival vectors and the corresponding weight value of each survival vector; and finally, determining the soft information of each bit by using the survival vectors and the weight value of each survival vector. The method has the advantages of effectively reducing the number of nodes which need to calculate the weight values during the QRM detection by using the ordered list stored in advance, greatly reducing the complexity of the calculation, along with no need of model extension and easy implementation; and compared with a method for acquiring the set of the survival vectors through the disturbance of the optimum survival vector, the method has higher accuracy.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM +1
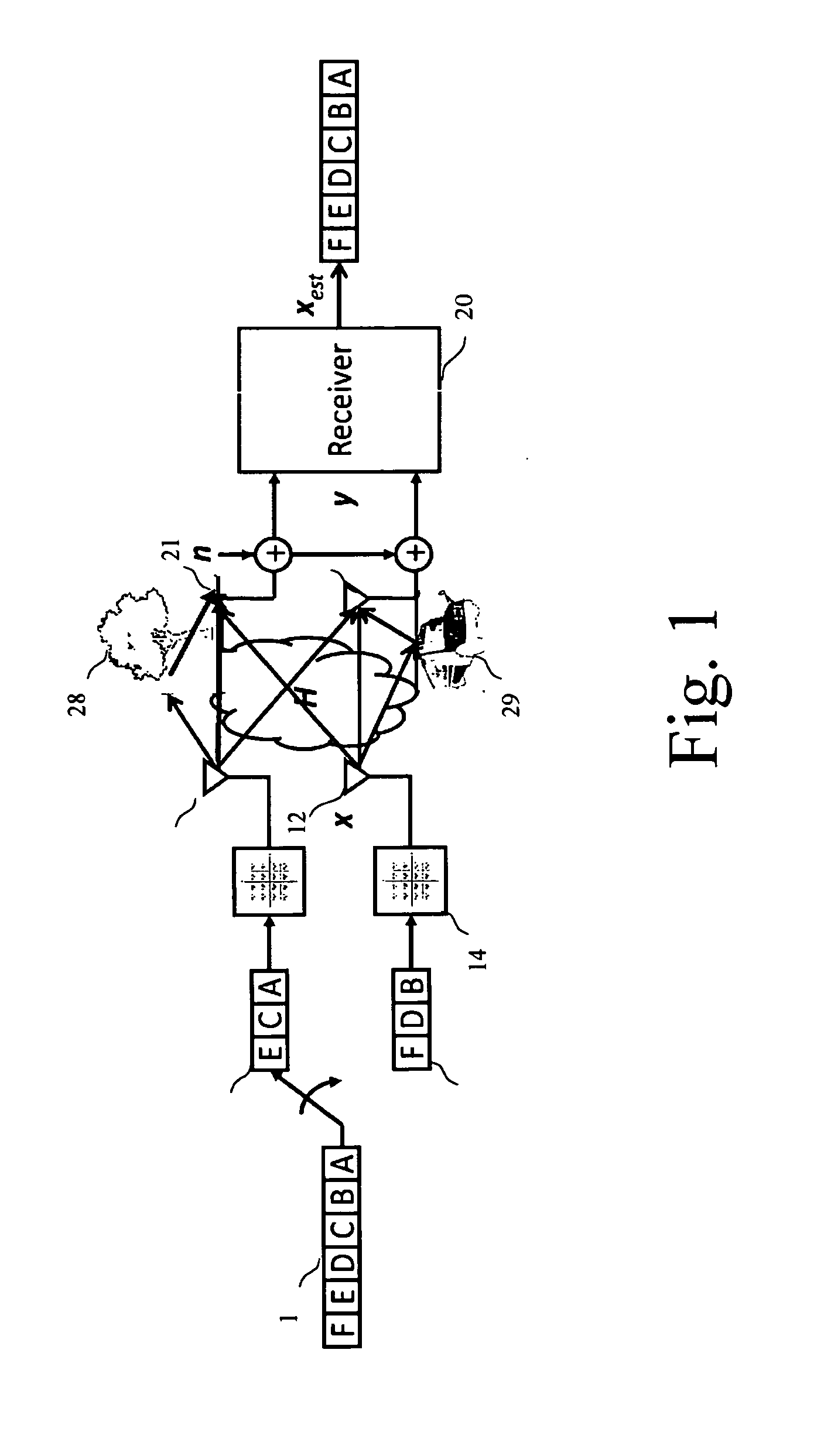
Mimo Receiver Using Lattic Reduction and K-Best Detection
InactiveUS20140185716A1Powerful near-ML detectionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsRadio transmissionStage iibCommunications system
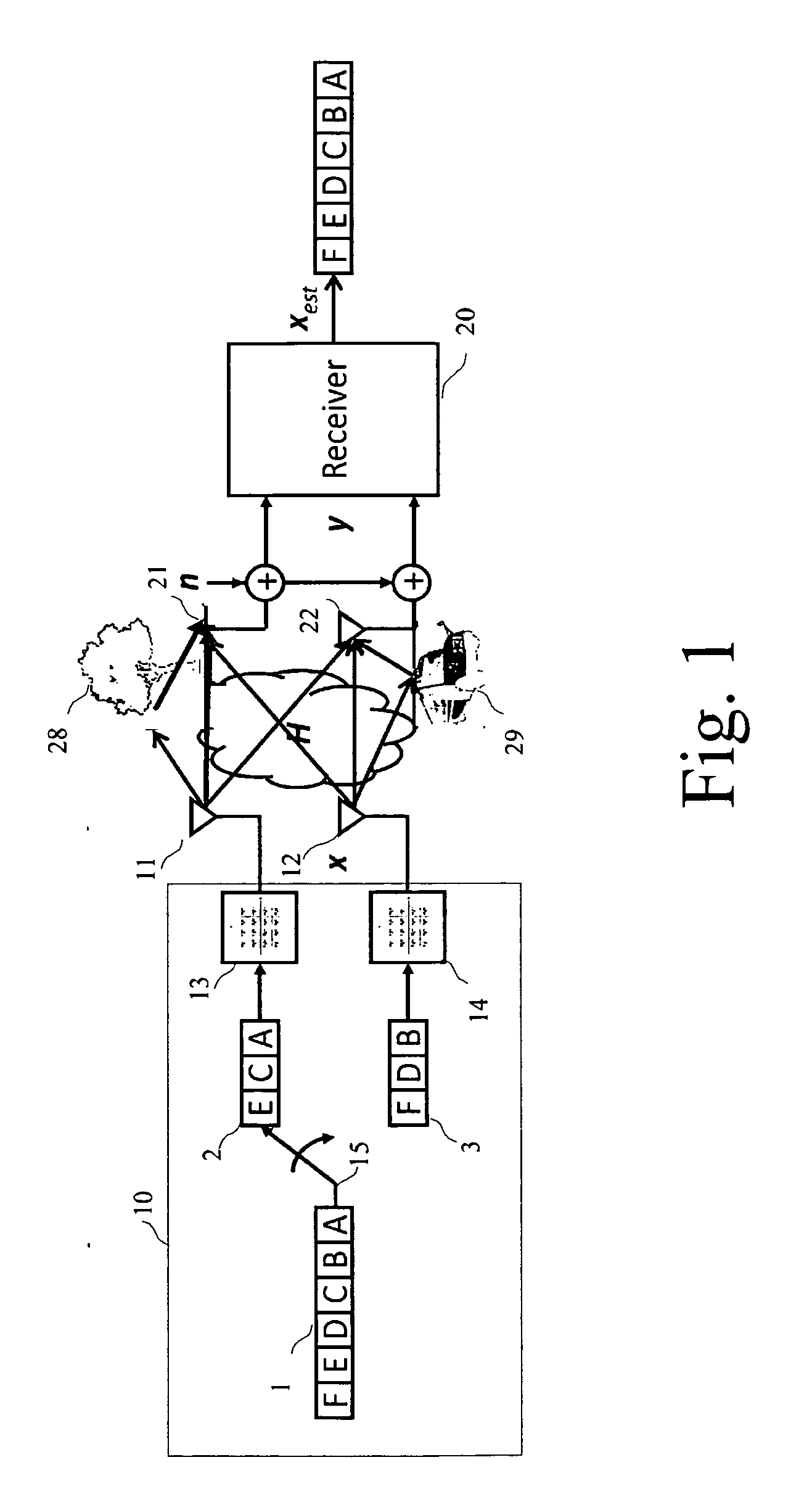
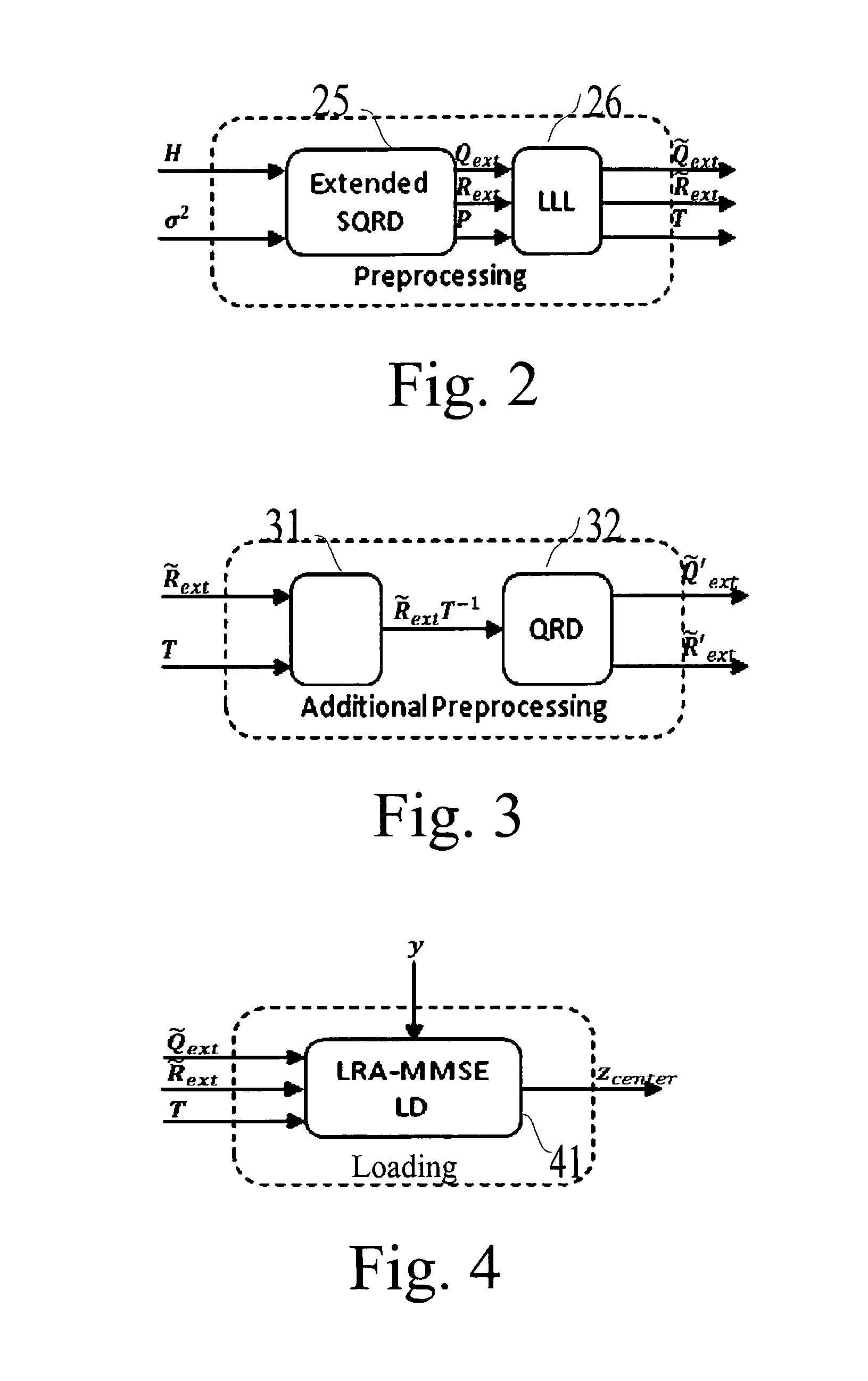
A detection process for a receiver of a wireless communication system based on Multiple-Input Multiple-Output antennas (nT, nR), said receiver processing observations symbols y derived from symbols x transmitted by an emitter through a channel H; characterized in that it involves: —a preprocessing which only depends on the channel H, said preprocessing involving: —a first QRD decomposition (61) for the purpose of decomposing said channel H into two Qext and Rext matrices, with QextHQext= / and Rext being upper triangular; —a lattice reduction (62) for the purpose of generating Qext, Rext and a transformation matrix T; —a second QRD decomposition (63) applied on the matrix Rext T−1 for the purpose of generating two matrixes Q′ext and R′ext, —a loading phase (64, 65, 66) comprising a linear detection process of the observations y for the purpose of generating a value xcenter; —a neighborhood search (67-70) performed in the Original Domain Neighborhood (ODN) with a search center being equal to the result xcenter of said loading phase, said neighborhood search determining a limited number of symbols (K-best).
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
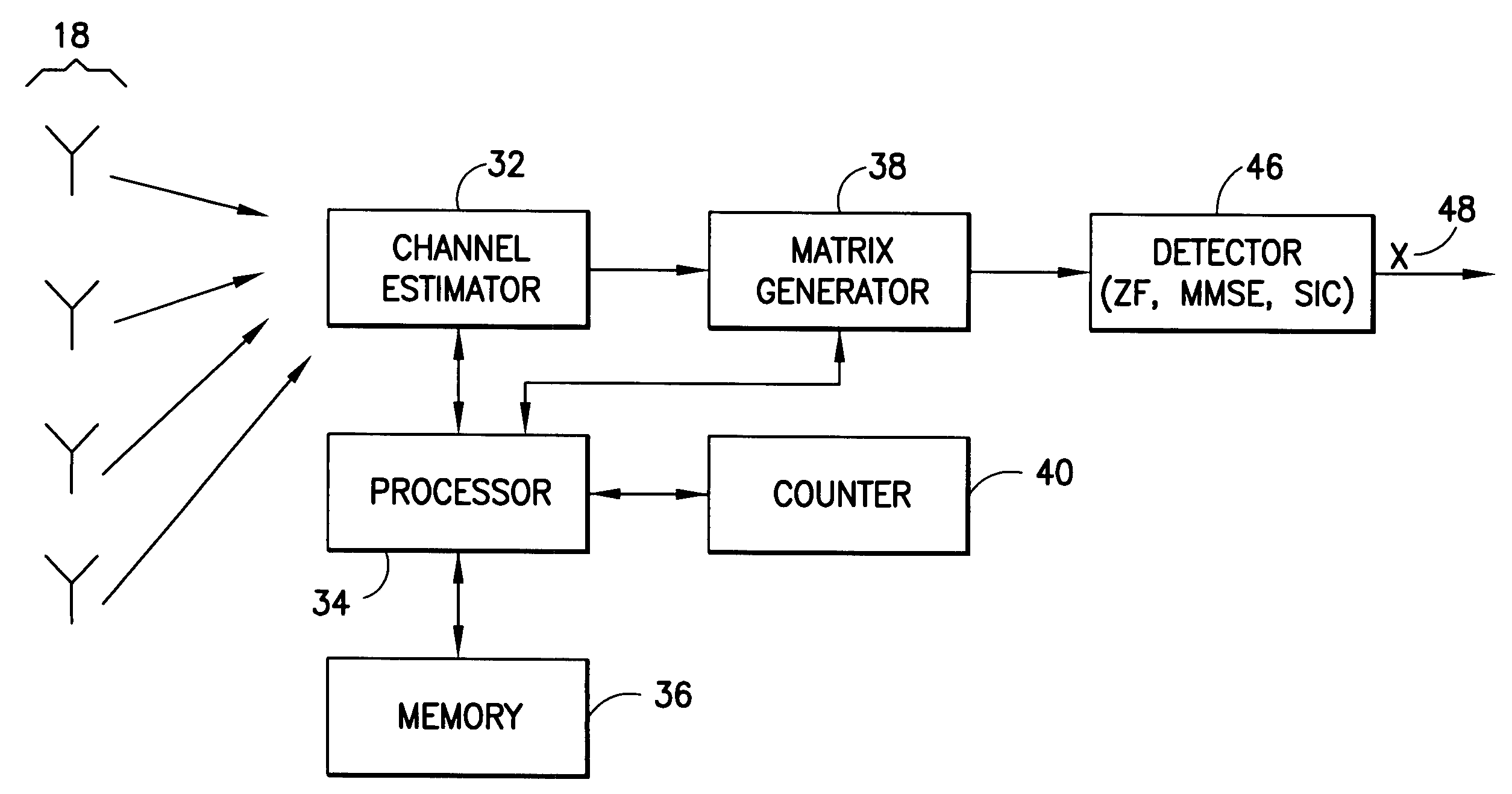
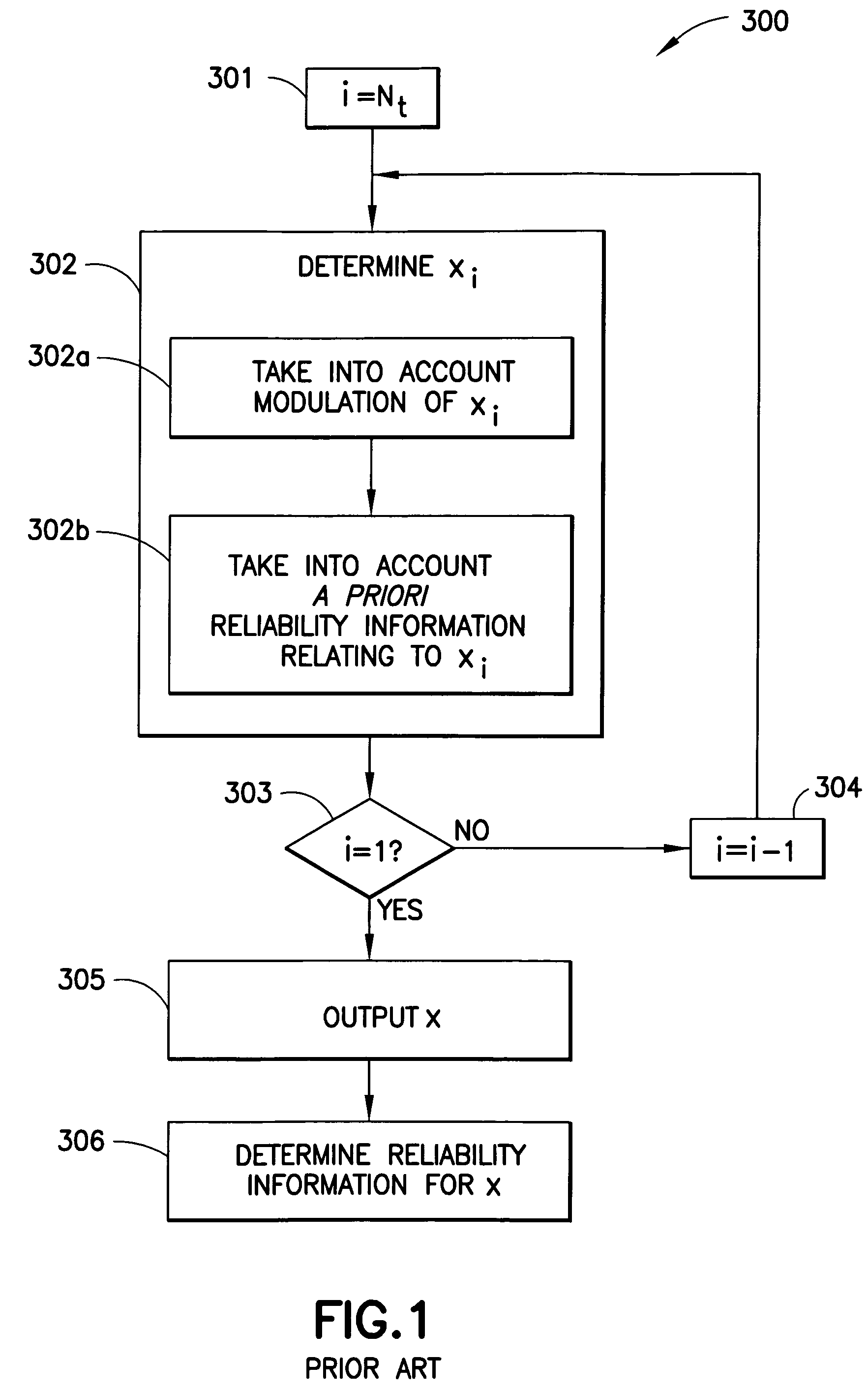
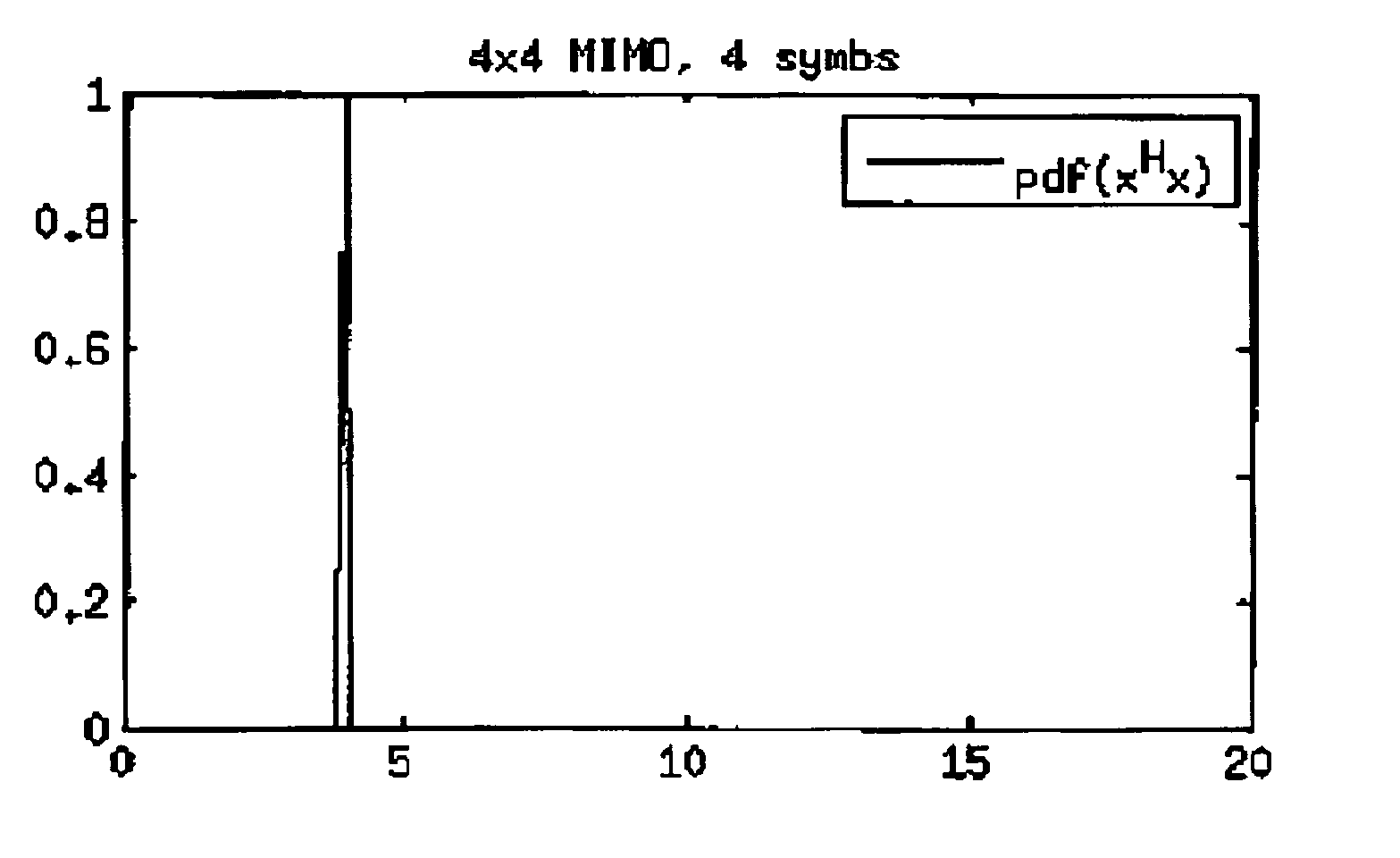
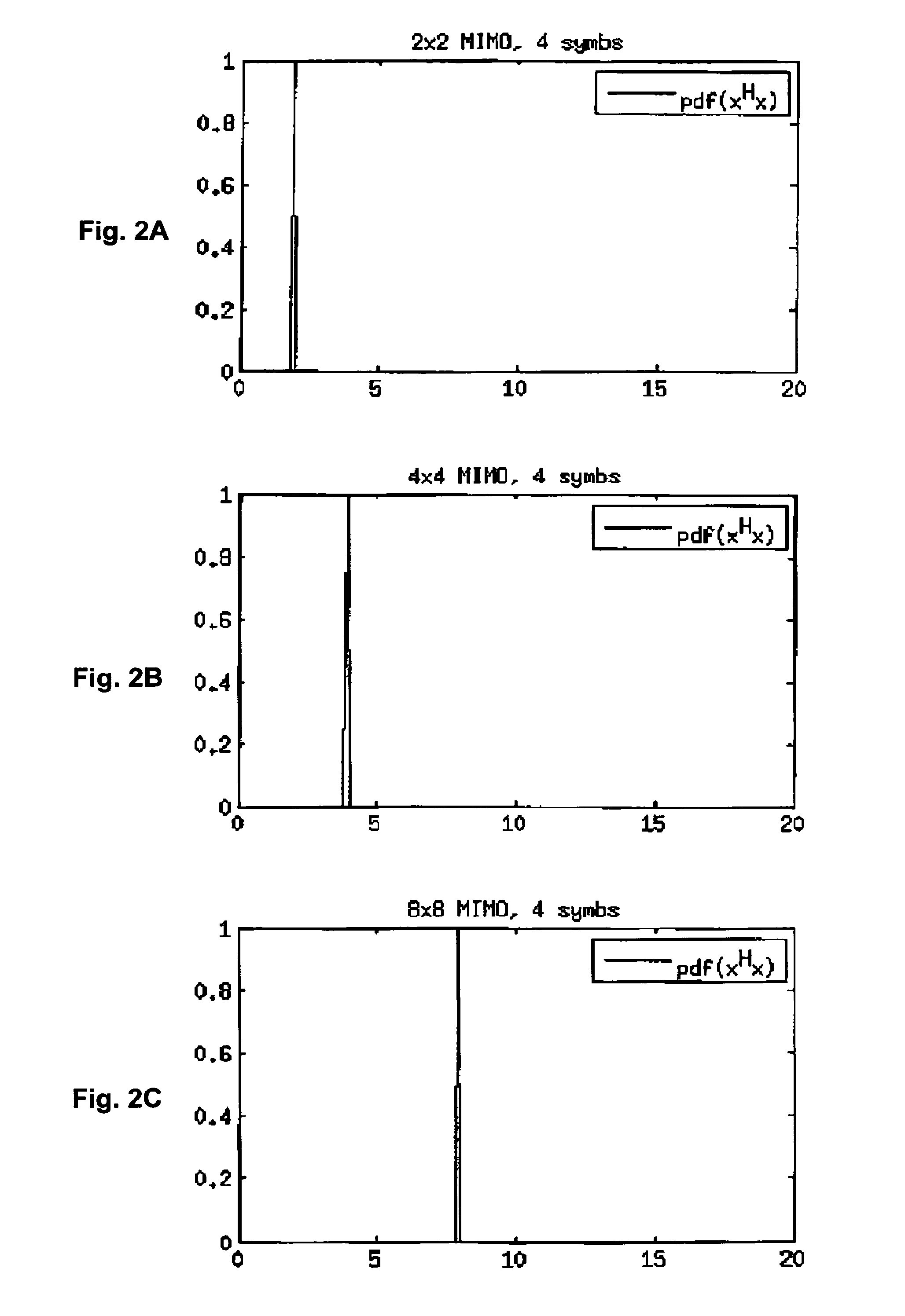
Incremental lattice reduction systems and methods
ActiveUS20120263261A1Early terminationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationAlgorithmLattice reduction
An exemplary embodiment of the present invention provides an incremental lattice reduction method comprising: receiving an input signal at a plurality of input terminals; evaluating a reliability assessment condition using a primary symbol vector estimate of at least a portion of the input signal; terminating the incremental lattice reduction method if the reliability assessment condition is satisfied; and if the reliability assessment condition is not satisfied, performing at least one iteration of a lattice reduction detection sub-method to obtain a secondary symbol vector estimate.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Lower complexity computation of lattice reduction
InactiveUS7668268B2Easy to detectLine-faulsts/interference reductionAmplitude demodulation detailsChange of basisRound complexity
A signal vector is received over a plurality of channels. A channel matrix H is determined that represents at least one of the plurality of channels. An iterative algorithm such as Lenstra-Lenstra-Lovasz is used to determining a change of basis matrix T that when multiplied with the channel matrix H converges to a matrix H*T that is more orthogonal than the channel matrix H. In one aspect the iterative algorithm is upwardly bounded in the number of iterations (e.g., 20 or 30 iterations) that it may perform for any specific channel realization to determine the change of basis matrix T. In another aspect the algorithm is initiated with a matrix derived from a previously determined change of basis matrix. Both aspects may be combined in a single method or device, or either employed separately.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Signal processing method and system for multi-user MIMO
InactiveCN101459488AImprove bit error rate performanceTransmit signal power reductionError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsMulti inputSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
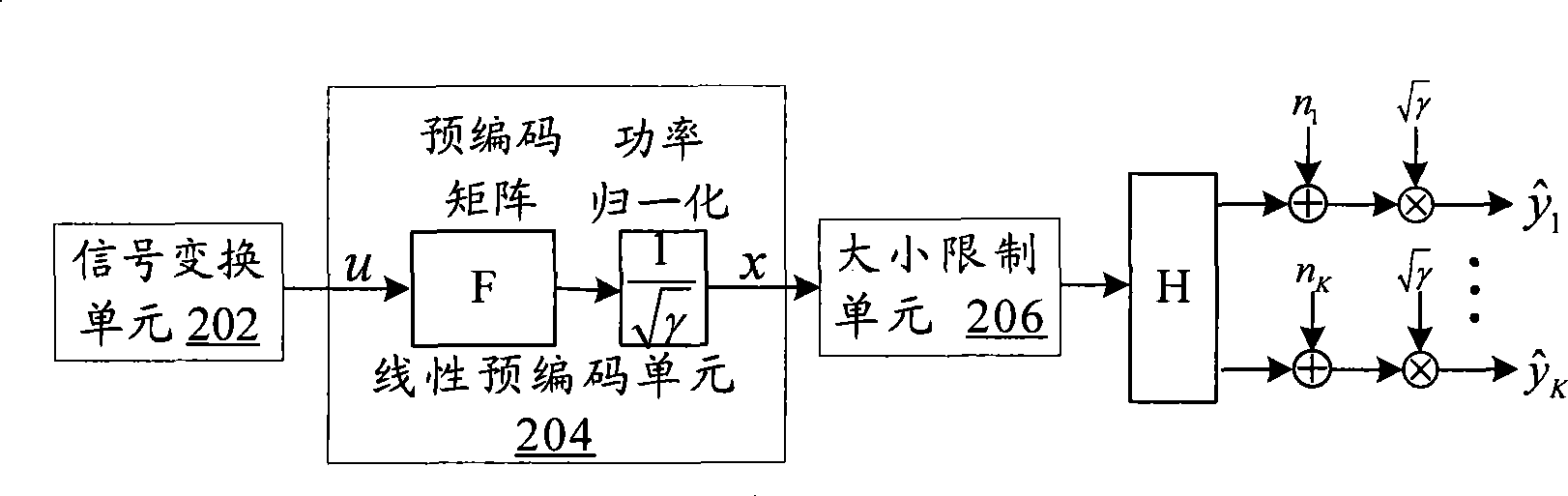
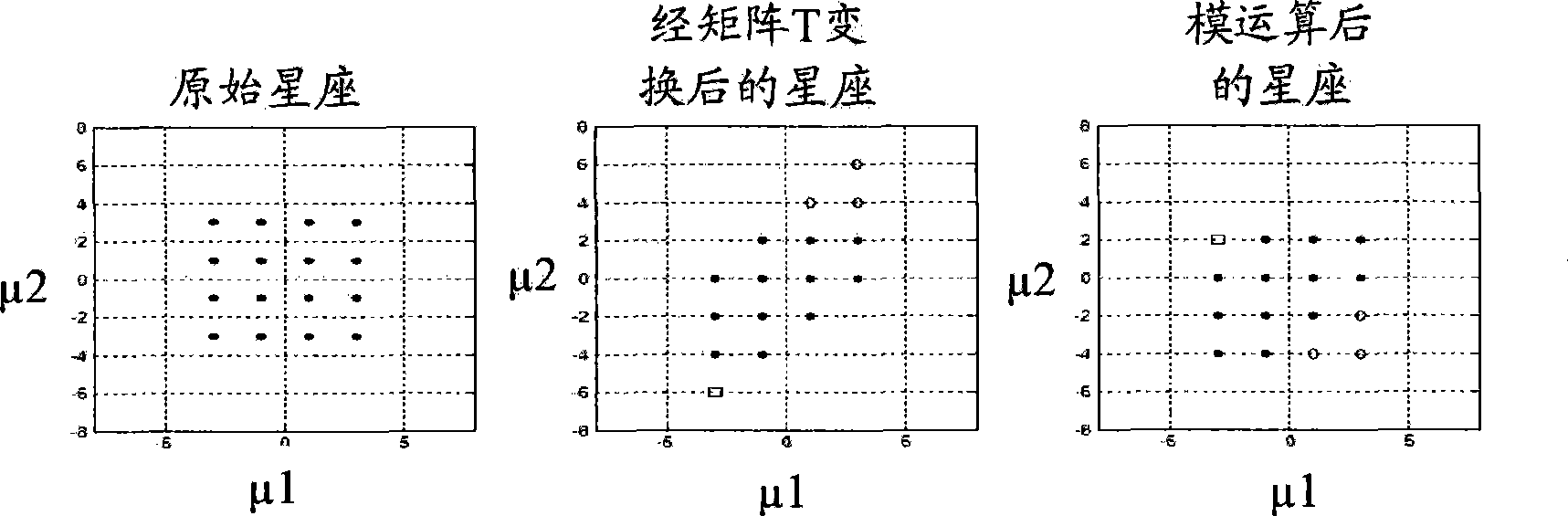
The invention discloses a signal processing method for a multi-user multi-input multi-output downlink and a system thereof, wherein the system comprises the following steps: an S102 step that transforming a channel matrix fed back by a receiving end through the lattice-reduction algorithm, an S104 step that conducting the linear precode for a sending signal through a transformed linear precode matrix, and an S106 step that restricting the size of the sending signal passing through the linear precode through a modular arithmetic unit. The invention effectively reduces the emitting power of thelinear precode algorithm, inhibits the noise enhancement, increases the receiving signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and improves the error code percentage performance of the system.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Singular value decomposition-based method for uplink transmission of multi-user MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) system
InactiveCN102647259AEliminate noise power enhancement effectsImprove transmission performanceSpatial transmit diversityHigh level techniquesSingular value decompositionUplink transmission
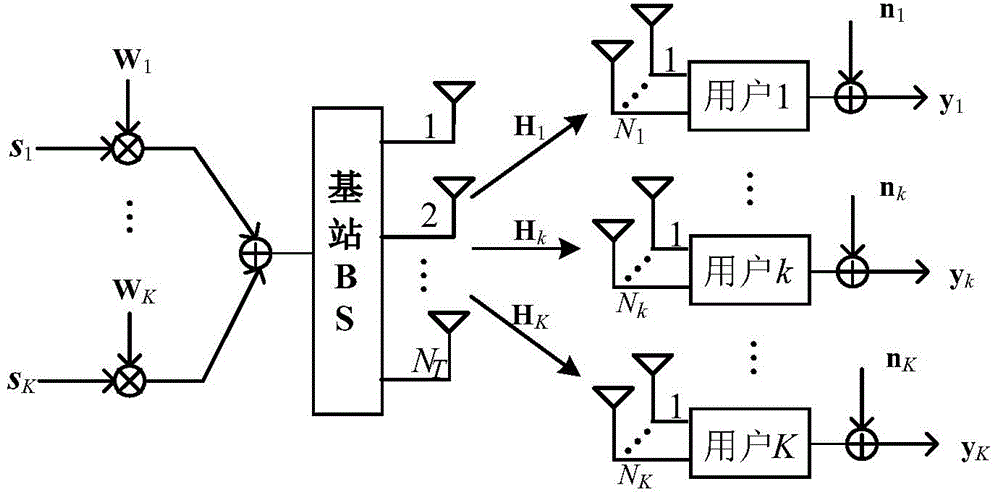
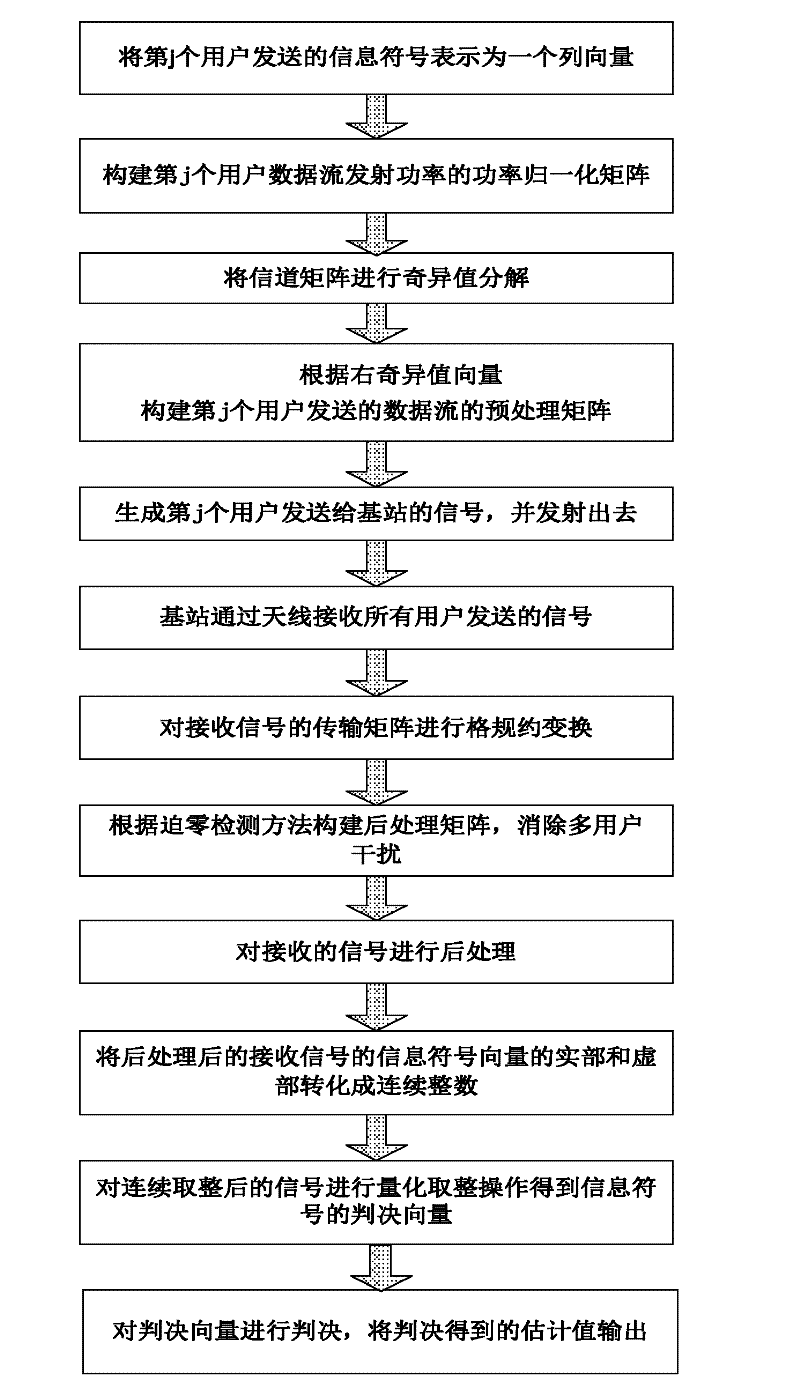
The invention discloses a singular value decomposition-based method for uplink transmission of a multi-user MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) system. According to the method, the noise power reinforcement caused by zero forcing postprocessing in the prior art is mainly solved, and the realization process is as follows: expressing information symbols sent by a user to be a column vector to construct a power adjustment matrix; conducting singular value decomposition on a channel matrix to construct a preprocessing matrix; conducting power normalization and preprocessing on vectors of the information symbols; sending signals to a base station by the user, conducting lattice reduction conversion on a transmission matrix for receiving signals by the base station to obtain an approximate orthogonal matrix; constructing a postprocessing matrix by utilizing the approximate orthogonal matrix according to a zero forcing detection method so as to conduct postprocesing on the received signals; and converting a real part and an imaginary part of the information symbols of the postprocessed signals into continuous integers, conducting quantization integer operation on the signals to obtain judgment vectors of the information symbols, judging and then outputting the obtained estimated value. The singular value decomposition-based method has the advantages that the noise power reinforcement effect can be eliminated effectively.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Wireless communication apparatus
InactiveUS20080075183A1Error preventionOther decoding techniquesCommunications systemLattice reduction
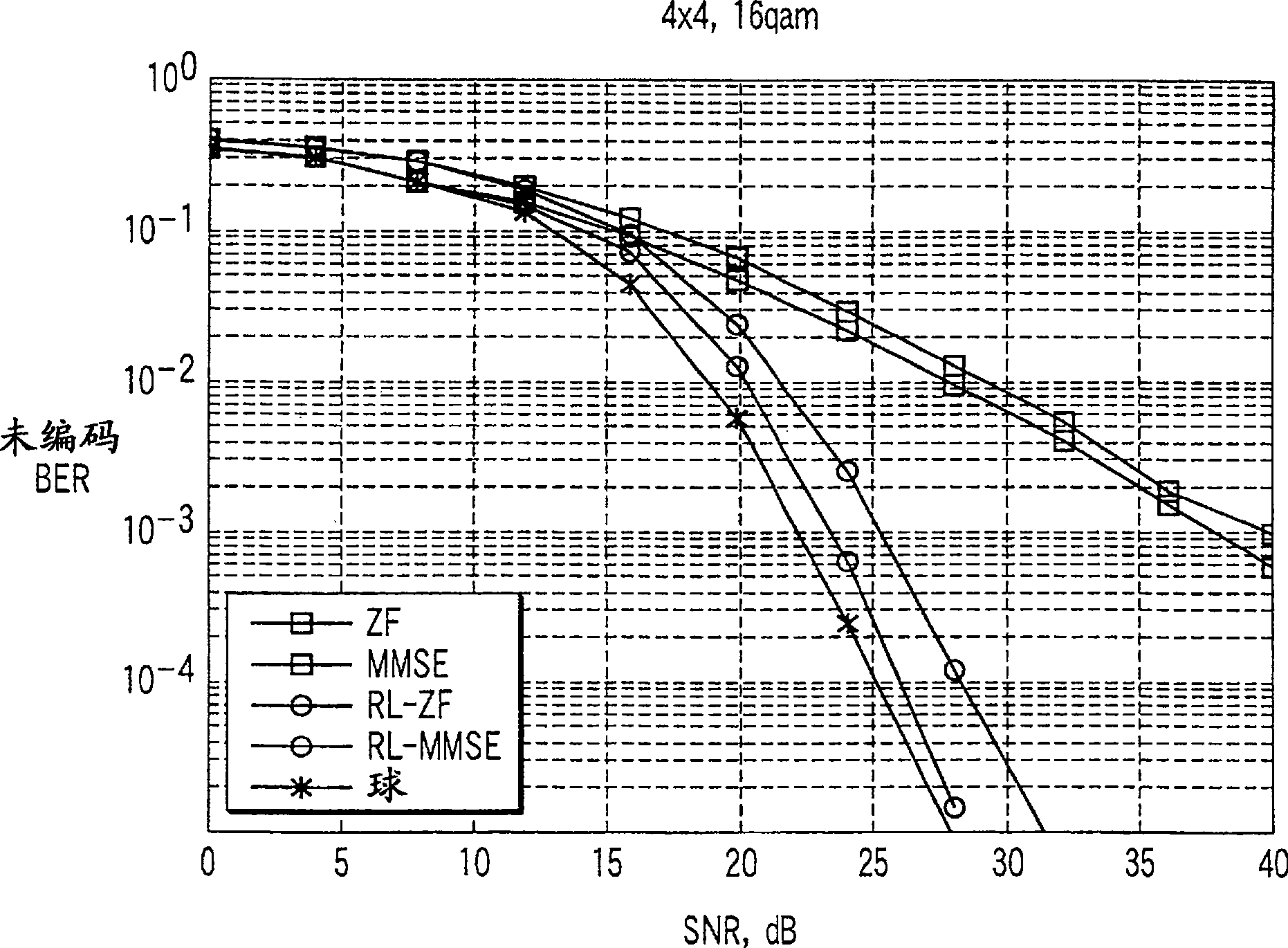
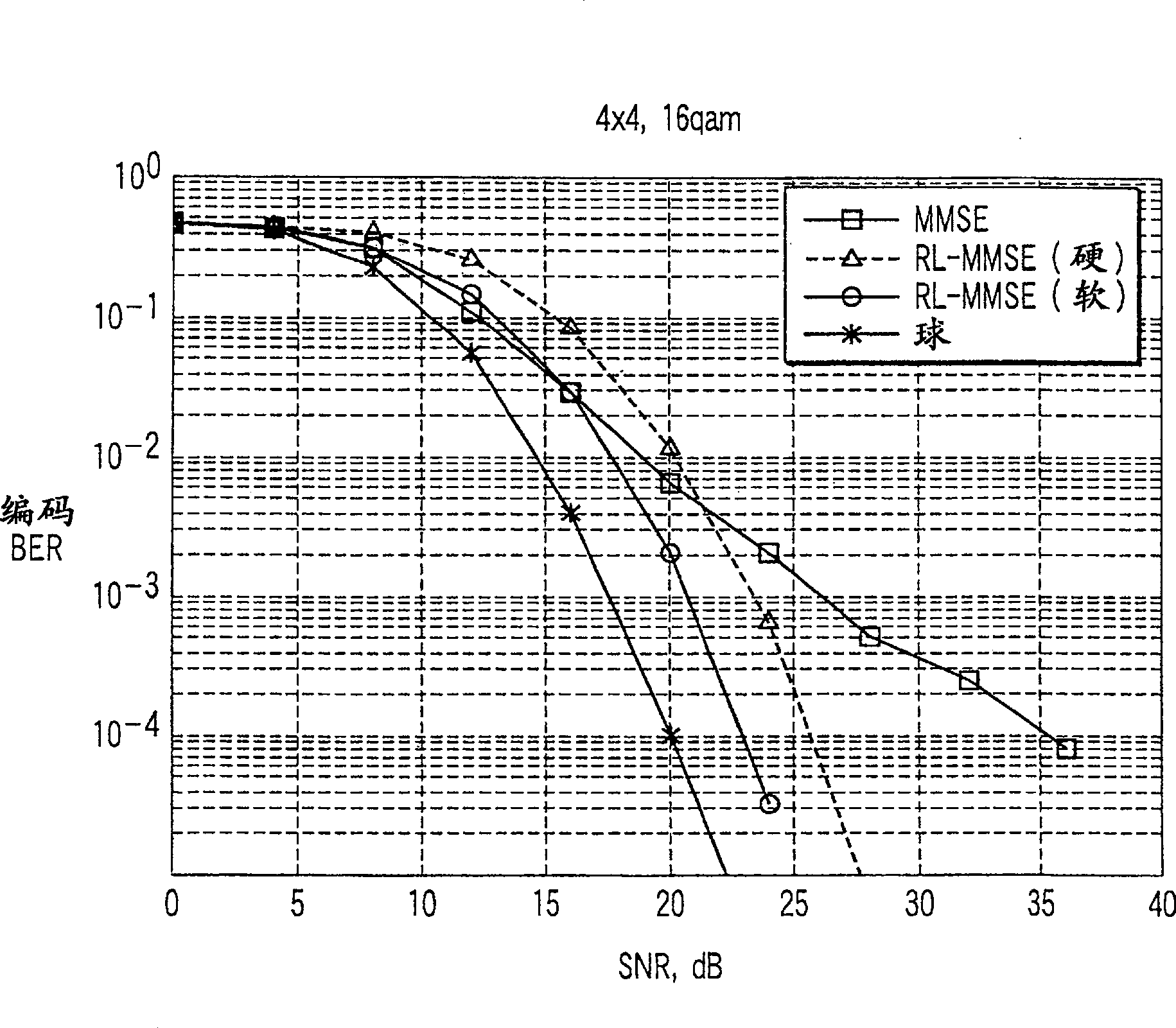
In a lattice-reduction-aided receiver based wireless communications system, soft estimates of transmitted bit values are determined from a received signal by applying lattice reduction to the channel estimate and equalising the received signal in accordance with the reduced basis channel, and determining probabilities of transmitted bits having particular values by generating a set of candidate vectors in the reduced basis based on nearest candidate vectors, determining a corresponding transmitted symbol vector for each candidate vector and, on the basis of the received signal determining the probability of each transmitted bit value having been transmitted.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Dual lattice reduction auxiliary detection method of multiple input multiple output (MIMO) signal
InactiveCN103166742AReduce computational complexityEasy to detectBaseband system detailsError prevention/detection by diversity receptionComputation complexitySign vector
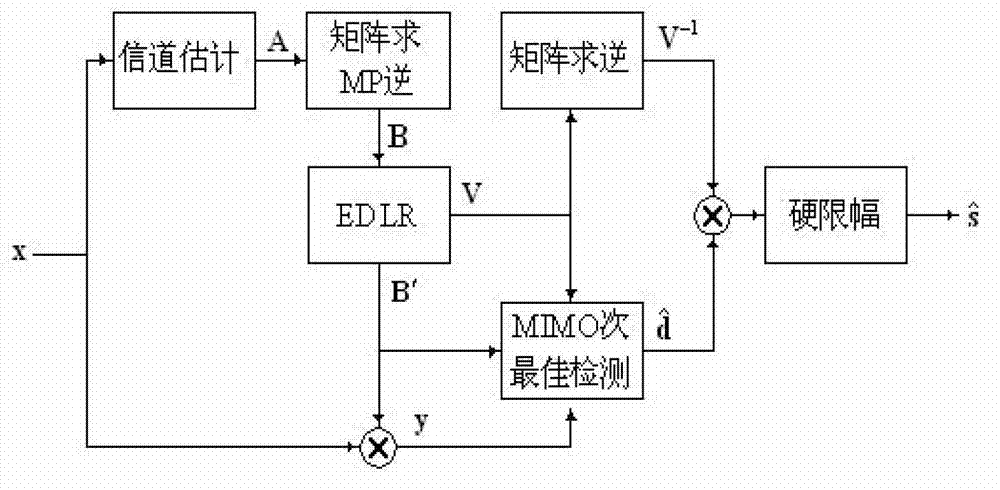
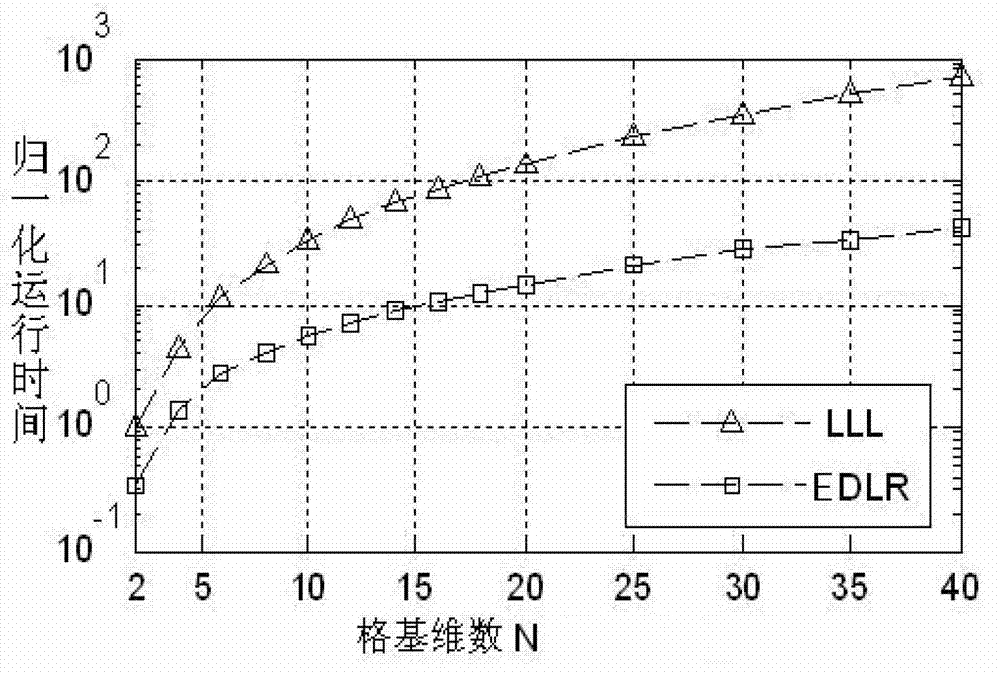
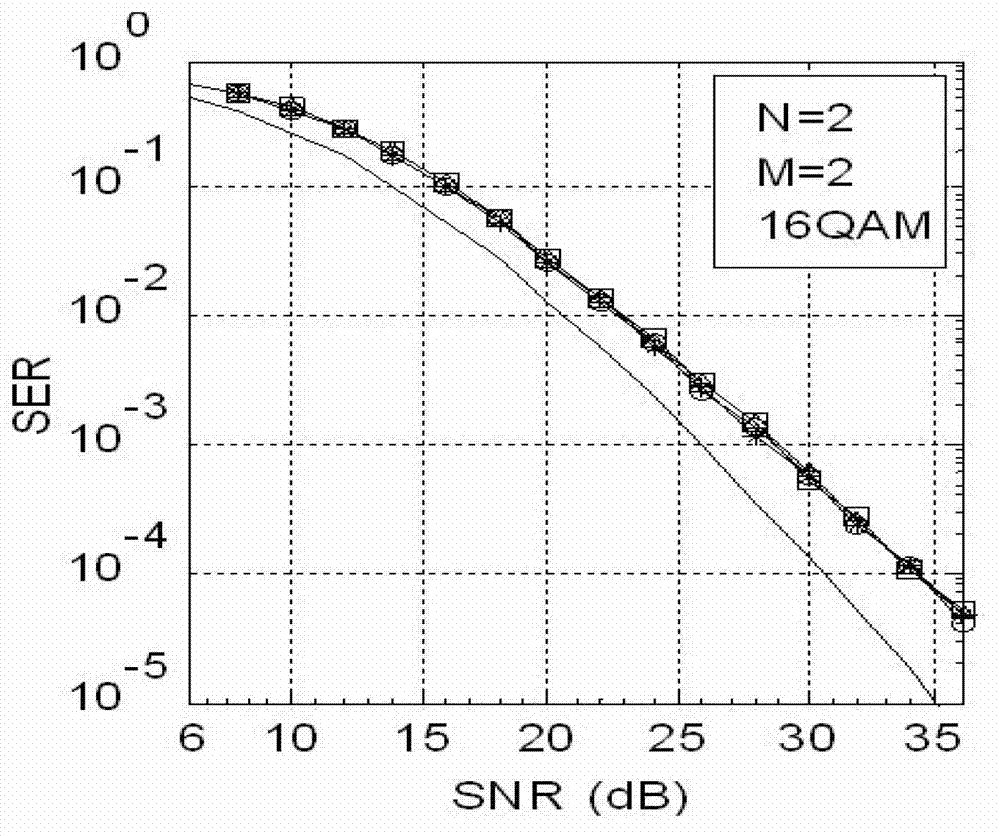
The invention provides a dual lattice reduction auxiliary detection method of a multiple input multiple output (MIMO) signal. According to the method, MP of a channel gain matrix is calculated so that a dual lattice matrix is obtained in a reversed mode; an efficient dual lattice reduction base matrix of the dual lattice matrix is obtained by means of efficient dual lattice reduction expected default loss ratio (EDLR); the dual lattice reduction auxiliary detection method based on an efficient reduction base is adopted; and sign vector inverse transformation is conducted to a detection result so that a sent sign vector estimated value is obtained. Compared with complexity of an existing LR algorithm, calculation complexity of the method is obviously reduced. The calculation complexity is reduced more and testing performance is superior along with increase of the number of transmitting antennas. The dual lattice reduction auxiliary detection method of the MIMO signal is specifically suitable for an MIMO system in a large scale and main obstacles of actual application of the MIMO system in the large scale are removed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Precoding method and precoding system for eliminating interference
ActiveCN104158573AHigh speedReduce complexitySpatial transmit diversityQR decompositionInterference elimination
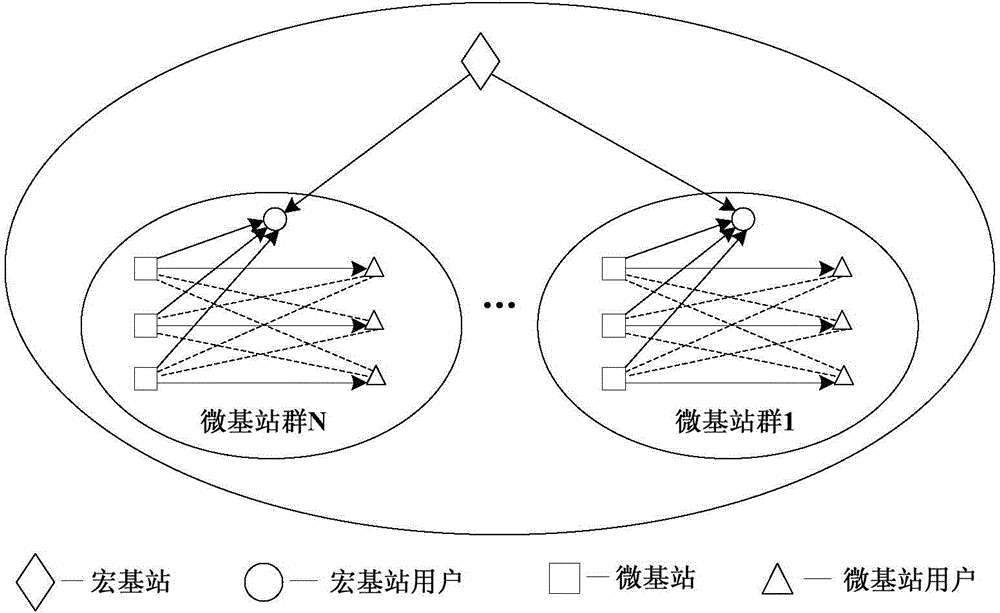
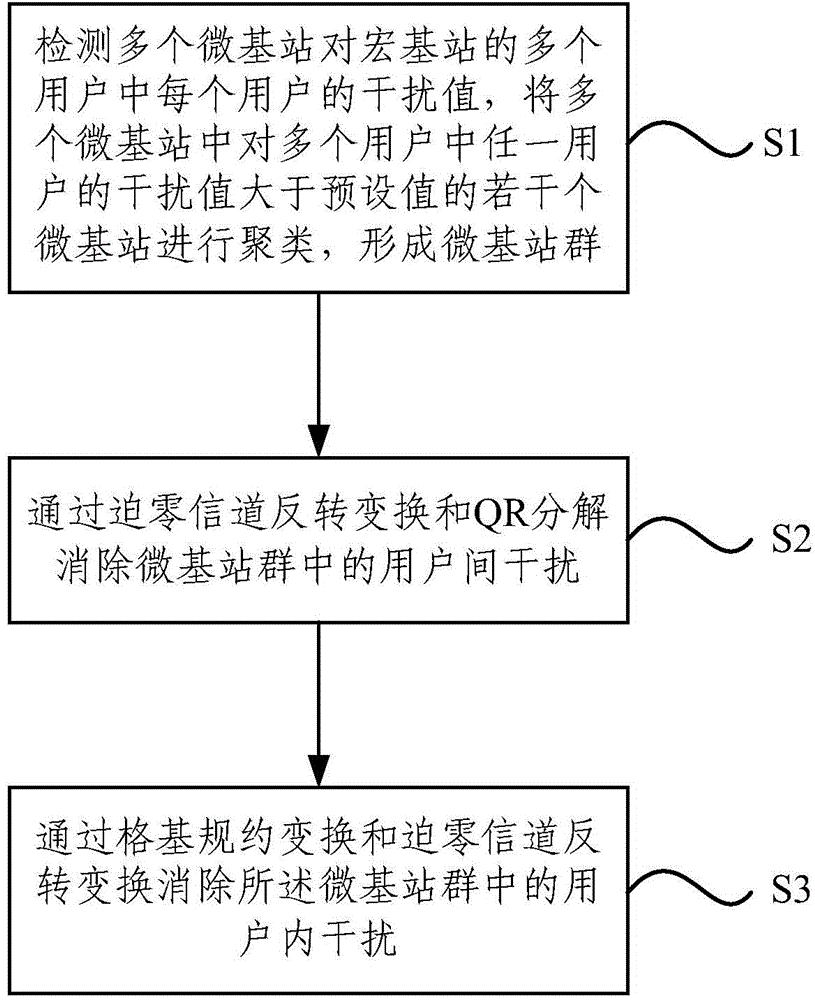
The invention relates to a precoding method and a precoding system for eliminating interference. The precoding method comprises a step S1 of detecting values of interference of multiple micro base stations on each user among multiple users of a macro base station, and clustering the multiple micro base stations with values of interference on any user of the multiple users larger than a preset value, in order to form a micro base station group, a step S2 of eliminating inter-user interference through zero-forcing channel inversion conversion and QR decomposition, and a step S3 of eliminating inter-user interference in the micro base station group through lattice reduction conversion and zero-forcing channel inversion conversion. With the technical scheme provided by the invention, the speed of precoding operation is accelerated, the precoding effect is improved, the overall complexity of precoding operation is reduced, and an interference elimination effect is improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
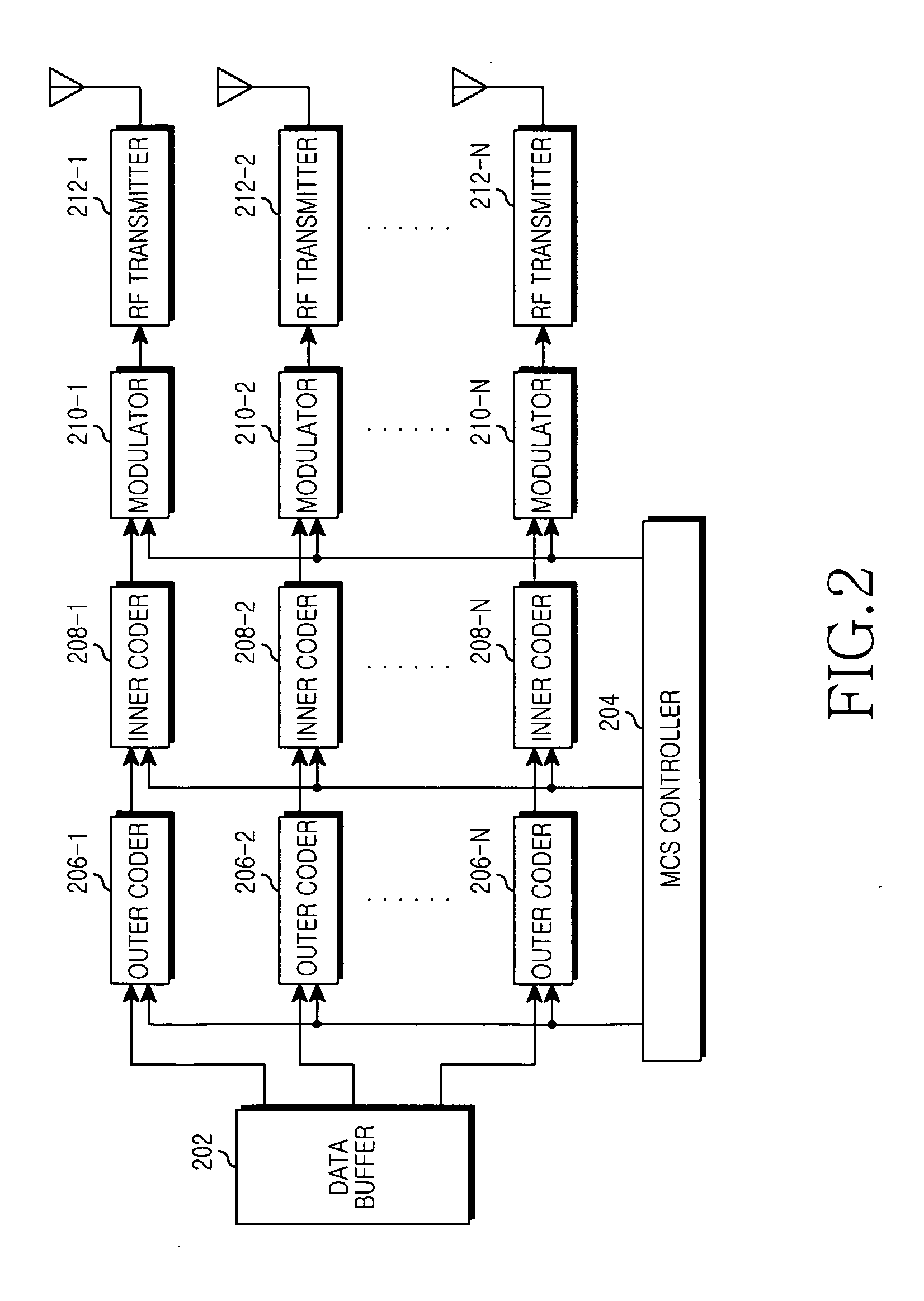
Apparatus and method for detecting signal based on lattice reduction to support different coding scheme for each stream in multiple input multiple output wireless communication system
ActiveUS20090252242A1Spatial transmit diversityCode conversionCommunications systemLattice reduction
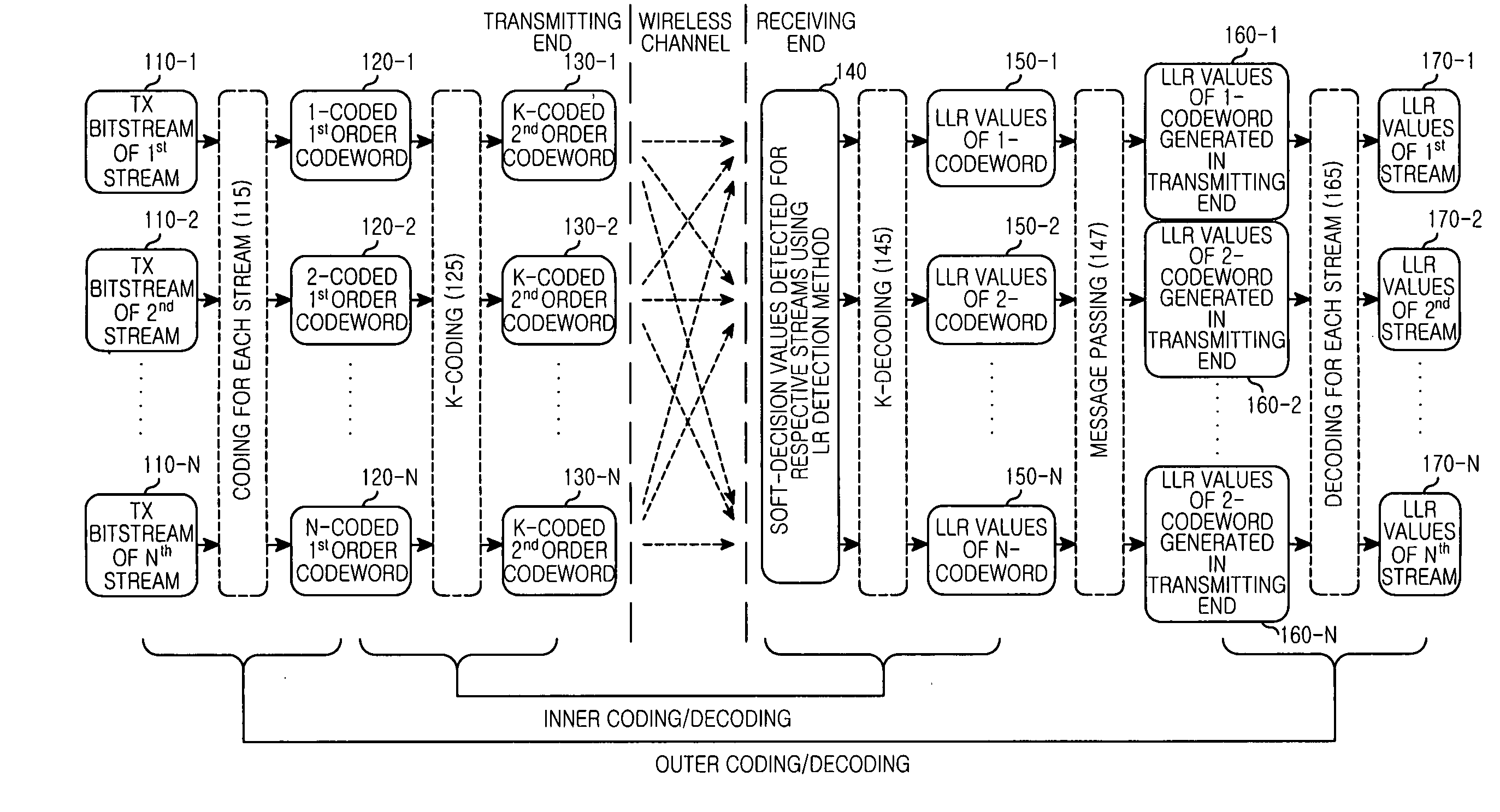
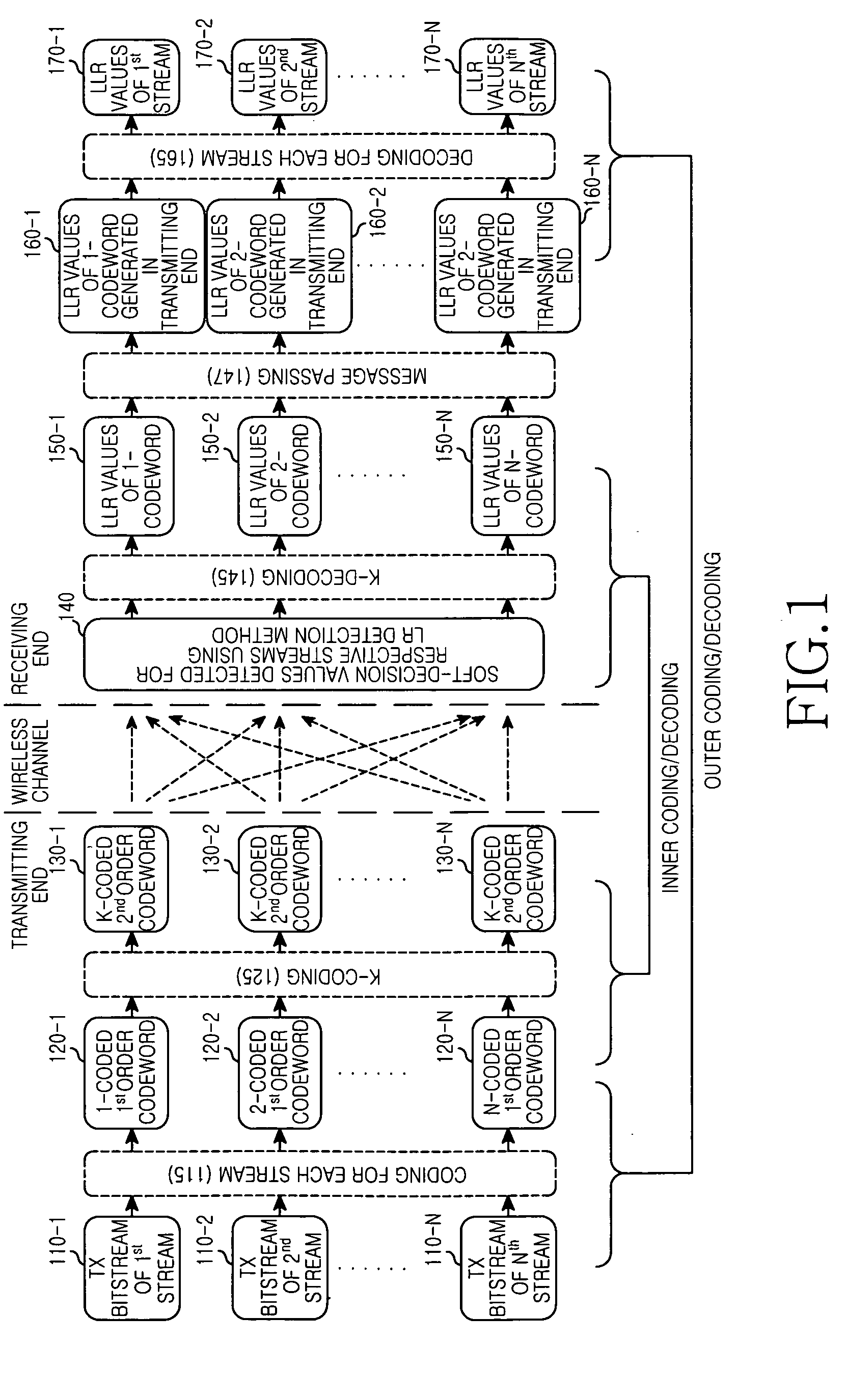
An apparatus and method for detecting signals based on a Lattice Reduction (LR) algorithm in a Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) wireless communication system are provided. The apparatus includes a plurality of operators for determining soft-decision values for respective streams by performing a soft modulo operation on respective symbol values included in a Receive (Rx) signal block multiplied by a lattice transformation matrix T, a plurality of inner decoders for determining Log Likelihood Ratio (LLR) values of codewords according to coding schemes for the respective streams by decoding the soft-decision values for the respective streams according to identical decoding scheme, a passer for restoring the LLR values representing the codewords generated in a transmitting end using the LLR values, and a plurality of outer decoders for determining LLR values of Transmit (Tx) bitstreams for the respective streams by decoding the LLR values representing the codewords generated in the transmitting end for the respective streams according to decoding schemes for the respective streams.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
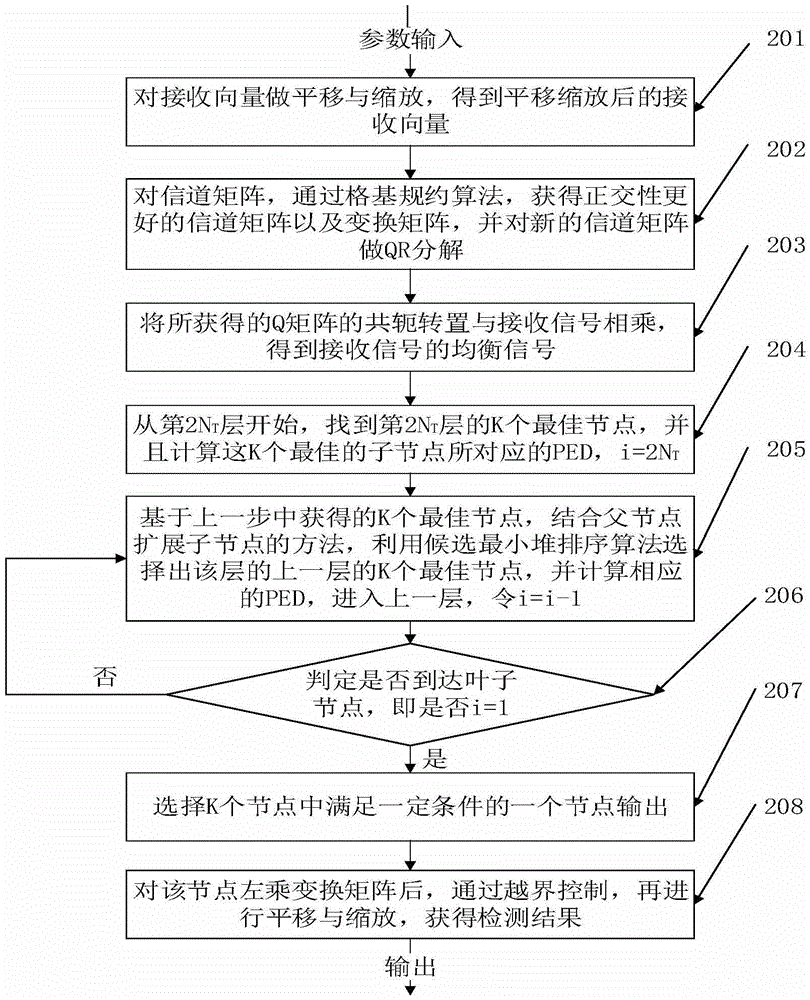
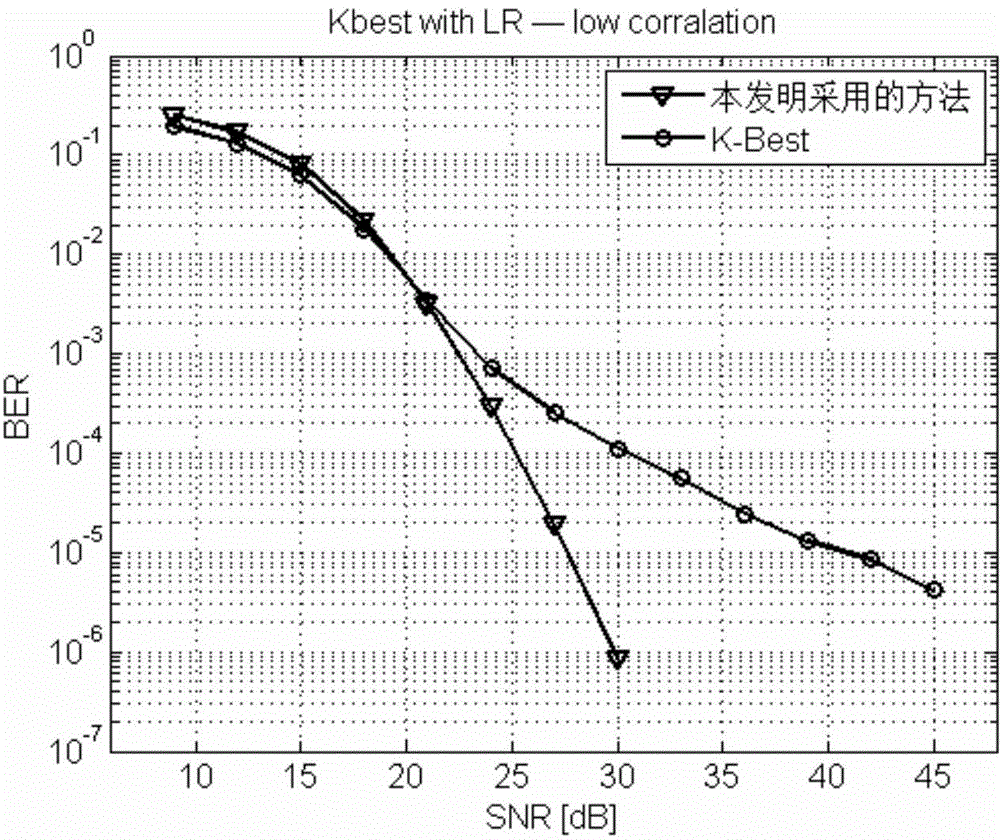
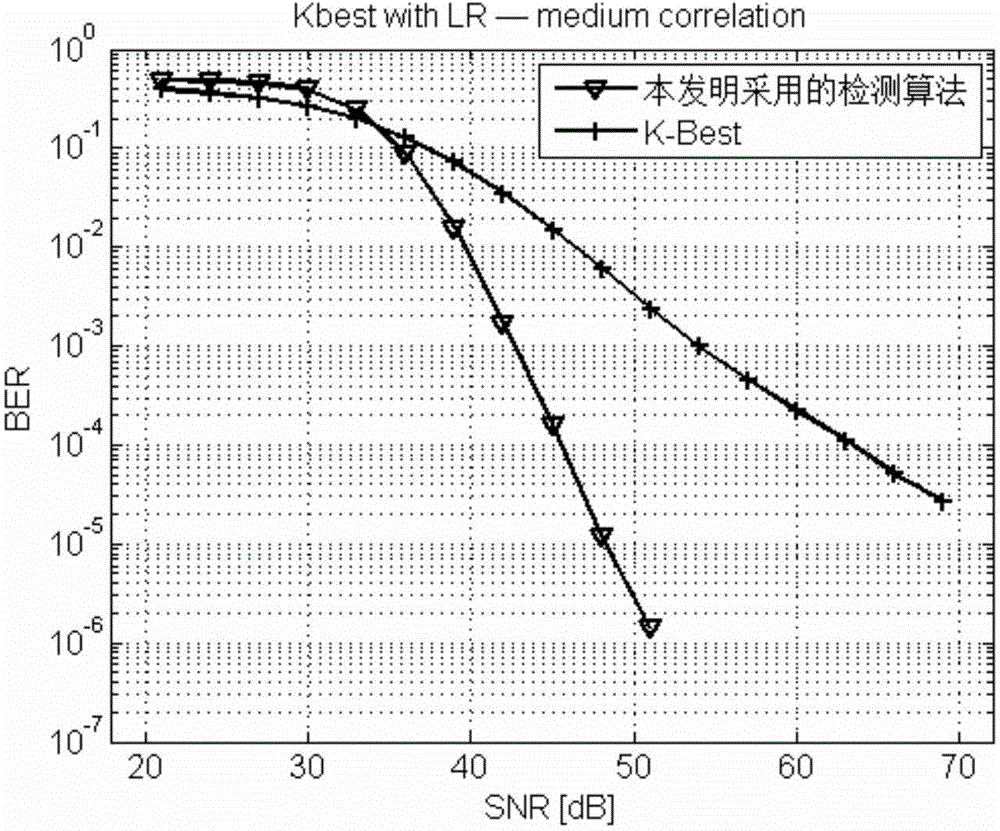
Receiver detection method assisted by lattice reduction algorithm and applied to wireless MIMO system
InactiveCN104580039AEasy to detectBaseband system detailsError prevention/detection by diversity receptionSorting algorithmAlgorithm
The invention provides a receiver detection method assisted by the lattice reduction algorithm and applied to a wireless MIMO system. The receiver detection method assisted by the lattice reduction algorithm and applied to the wireless MIMO system comprises the steps that horizontal moving and zooming are conducted on a receiving vector; a new channel matrix is obtained through the lattice reduction algorithm; in the layer where detection is started, integers within a certain value range are selected to serve as K optimum nodes of the layer; in the other layers, K optimum nodes of each layer are selected according to the method for expanding child nodes by means of father nodes and the candidate least heap sorting algorithm; for the K optimum nodes of the first layer, proper nodes are selected according to specific judgment conditions, and an original sending symbol is obtained by means of a left multiplication transformation matrix through horizontal moving and zooming. According to the receiver detection method assisted by the lattice reduction algorithm and applied to the wireless MIMO system, during multiple-input-multiple-output detection, the lattice reduction assisting algorithm is adopted, the influence of channel correlation on a multiple-input-multiple-output detector is reduced, and the detection performance is improved compared with a detector not based on the lattice reduction assisting algorithm.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
Lattice reduction assisted sphere decoding MIMO signal detection method
InactiveCN105356920AReduce complexityIncrease transfer rateSpatial transmit diversityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionRound complexityComputation complexity
The invention discloses a lattice reduction assisted sphere decoding MIMO signal detection method. The method includes the following steps that: an SD-LR detector executes a lattice reduction algorithm for a channel matrix, so that a reduction base matrix can be obtained; input signals of a receiving end are expressed by the reduction base matrix and transformation symbol vectors, so that SD detection can be executed; a detection result can be obtained through preliminary SD search, and then, whether the detection result is an ML detection result is judged; if the detection result is an ML detection result, detection is terminated; and if the detection result is not an ML detection result, a final ML detection result is obtained through further SD search. Compared with a traditional detection method, the lattice reduction assisted sphere decoding MIMO signal detection method of the invention can maintain optimal detection performance and can greatly reduce the computational complexity of a detector, and can improve the transmission rate of an MIMO system and reduce the implementation complexity of communication equipment; as for an MIMO system with a large number of antennas and large-scale QAM constellations, the lattice reduction assisted sphere decoding MIMO signal detection method can realize low computational complexity and reach or approximate optimal detection performance.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
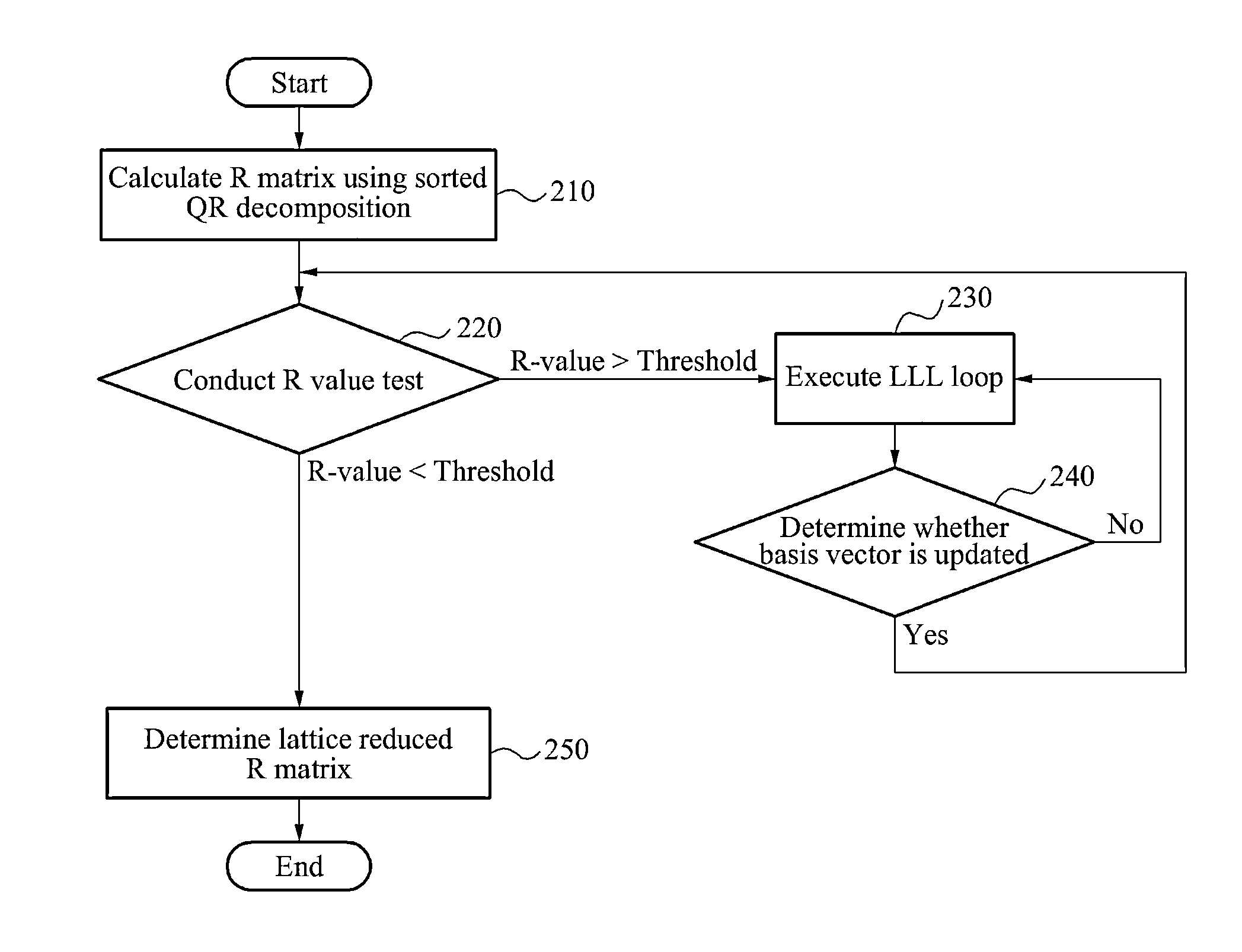
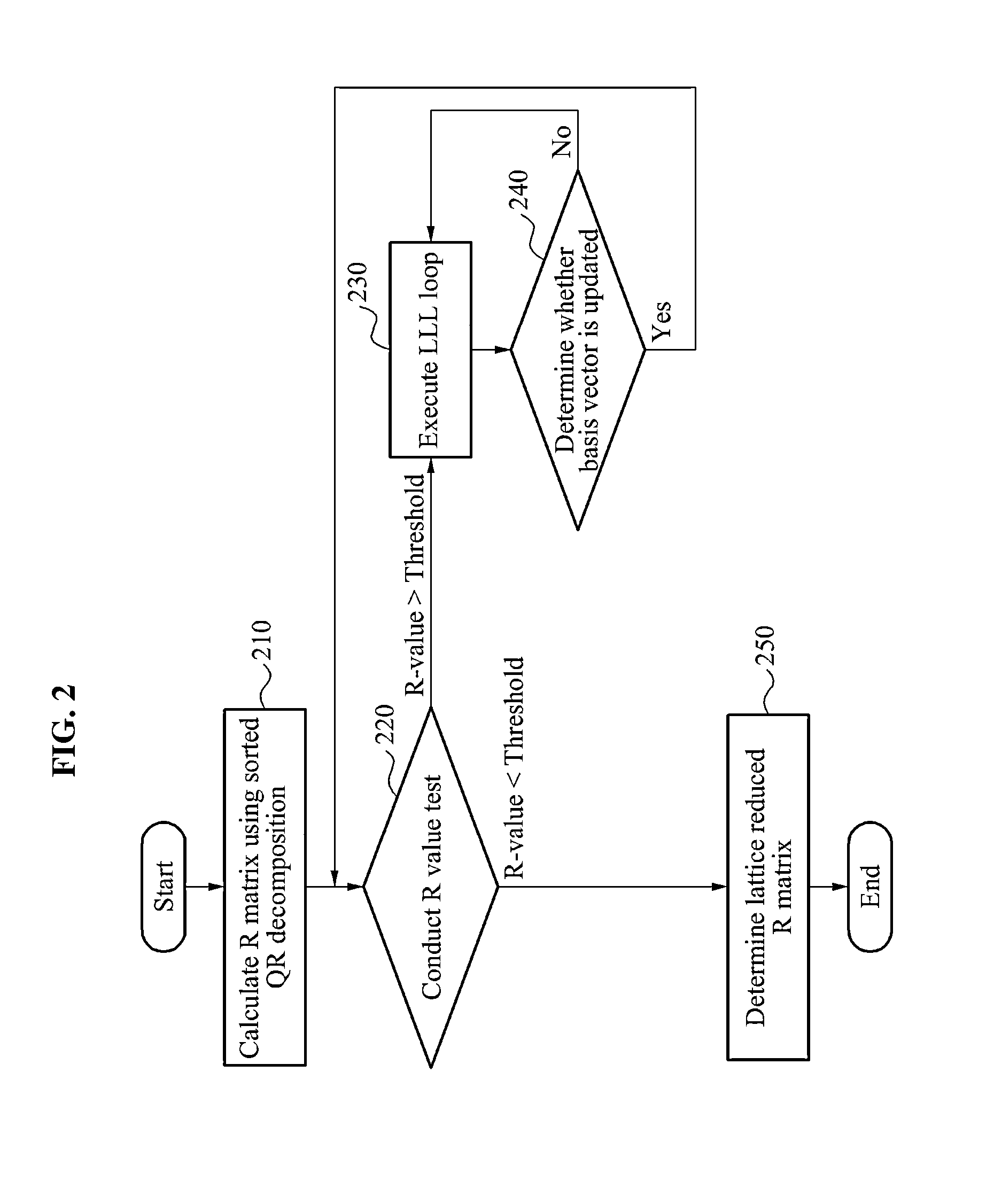
Method and apparatus for lattice reduction with reduced computational complexity
InactiveUS20140254727A1Well formedSpatial transmit diversityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsQR decompositionComputation complexity
Provided is a method and apparatus for lattice reduction with reduced computational complexity. The apparatus and method include calculating an R matrix using sorted QR decomposition, and conducting an R-value test using an R-value based on diagonal elements of the R matrix and a threshold value. The R matrix is an upper triangular matrix. The apparatus and method further execute a loop comprising a size reduction and a conditional update of a basis vector corresponding to a column element of the R matrix in response to the R-value being greater than or equal to the threshold value. The apparatus and method conduct another R-value test based on the R matrix comprising the updated basis vector in response to the basis vector being updated.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
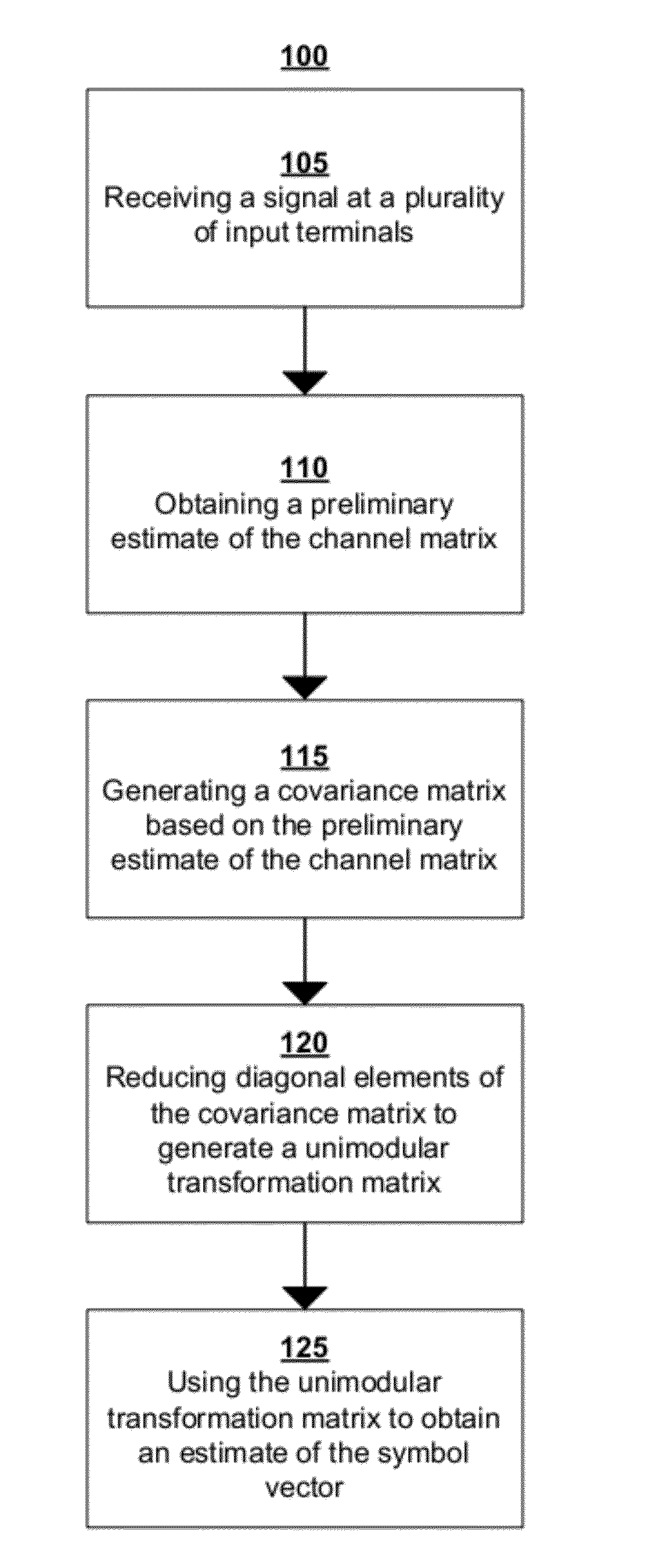
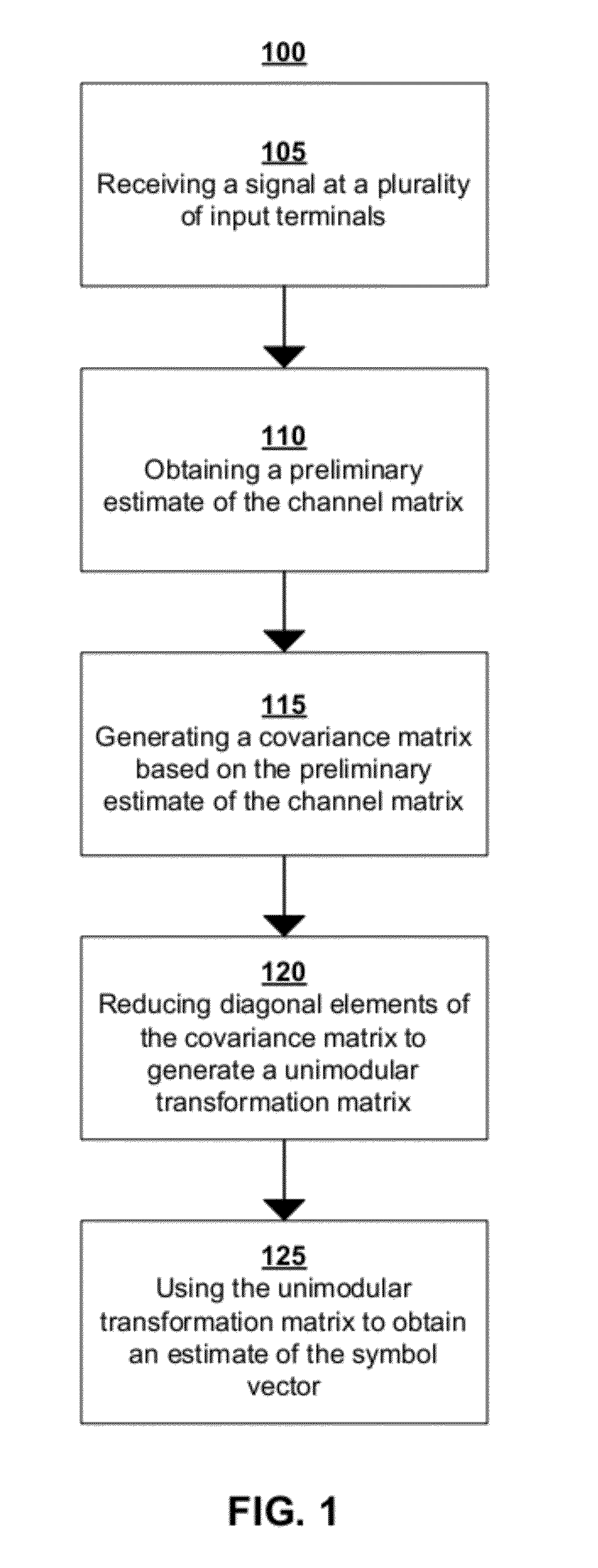
Enhanced lattice reduction systems and methods
ActiveUS20120236968A1Reduce decreaseLow costModulated-carrier systemsRadio transmissionUnimodular transformationLattice reduction
An exemplary embodiment of the present invention provides a lattice reduction method comprising obtaining a preliminary estimate of a transformation matrix, generating a covariance matrix based on the preliminary estimate of the transformation matrix, reducing diagonal elements of the covariance matrix to generate a unimodular transformation matrix, and using the unimodular transformation matrix to obtain an estimate of an input.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
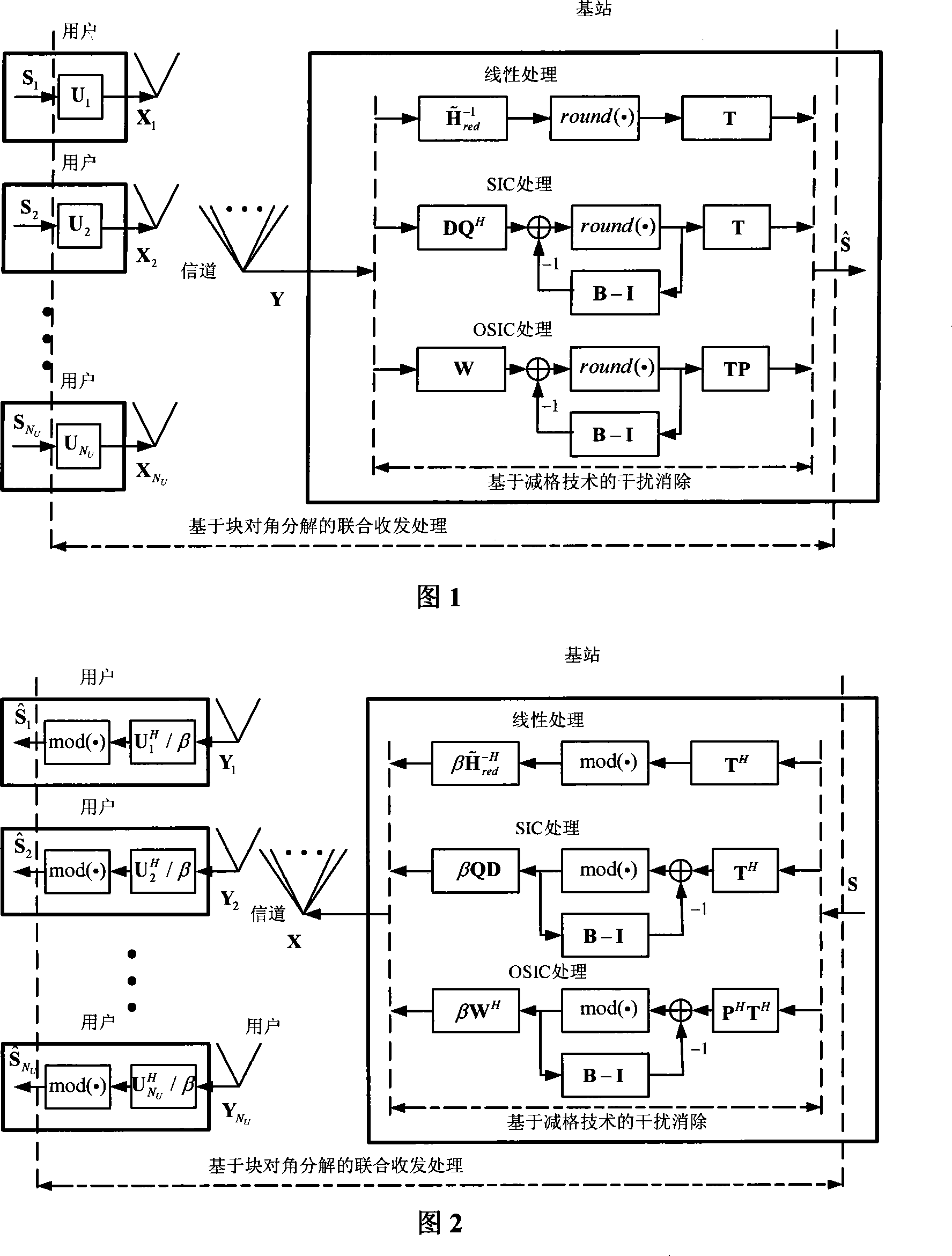
Signal processing method of multi-user multi-aerial communication system transmit-receive combination
InactiveCN101227219AReduce complexityImprove performanceSpatial transmit diversityCapacitanceInterference elimination
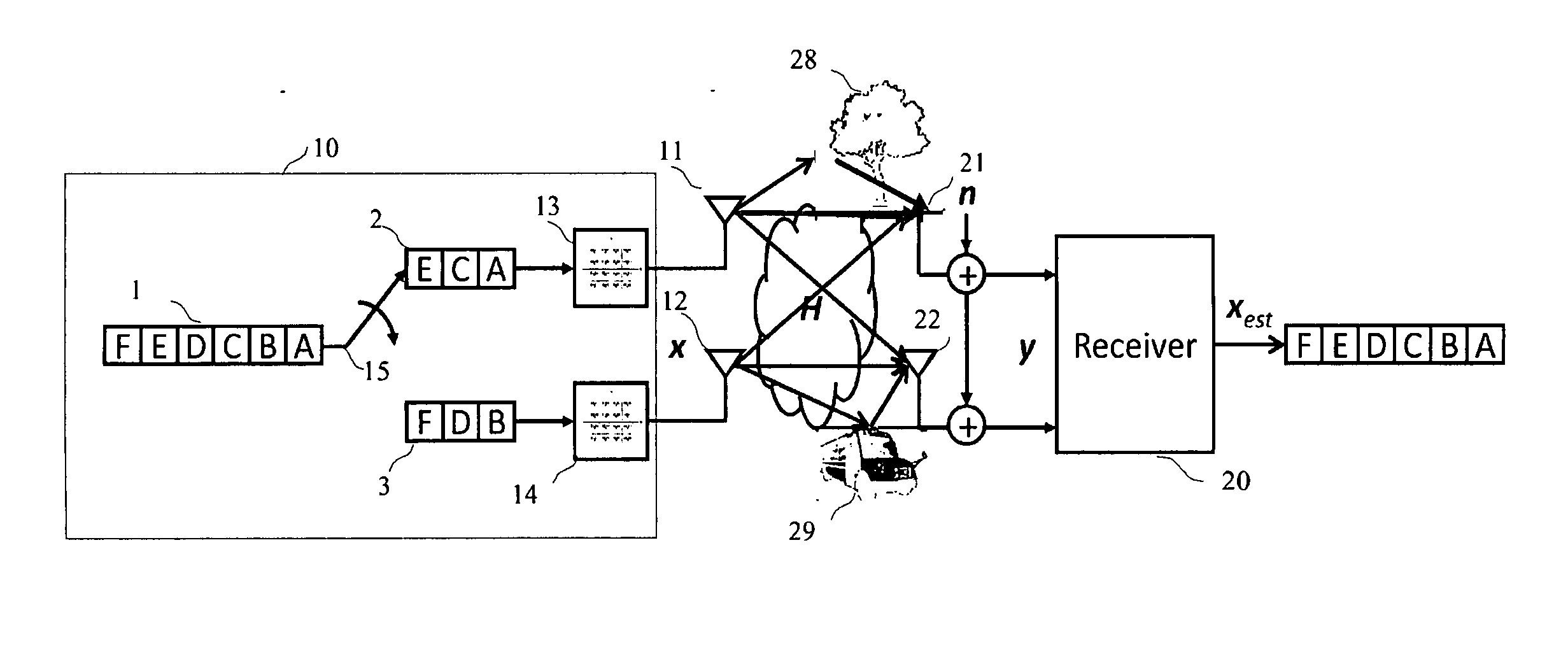
The invention relates to a method for treating received and transmitted joint signals in a multi-user multi-aerial system, a key station obtains the estimated value of present communication channel information and noise variance, the method comprises: firstly, breaking up a communication channel matrix in block diagonal, obtaining a unitary matrix with block diagonal characteristics and an expanded communication channel matrix after transformation, respectively acting each block of the unitary matrix on each corresponding user side to balance the communication channel partly, balancing the expanded communication channel matrix after the transformation on a key station end, wherein the key station end utilizes a lattice-reduction technique to obtain reduction bases with better performance, and then utilizing the reduction base to process by interference elimination to achieve the purpose for jointing a receiving end and a transmitting end to eliminate interference between multi-users and between multi-aerials. The invention increases the performance of an existing simple base on the basis of a scheme of a block diagonal decomposition method, increases diversity gain, simultaneously, keeps the increased lattice-reduction treatments with polynomial complexity still, and thereby achieves the purpose for increasing the system performance and the capacitance significantly with lower complexity.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
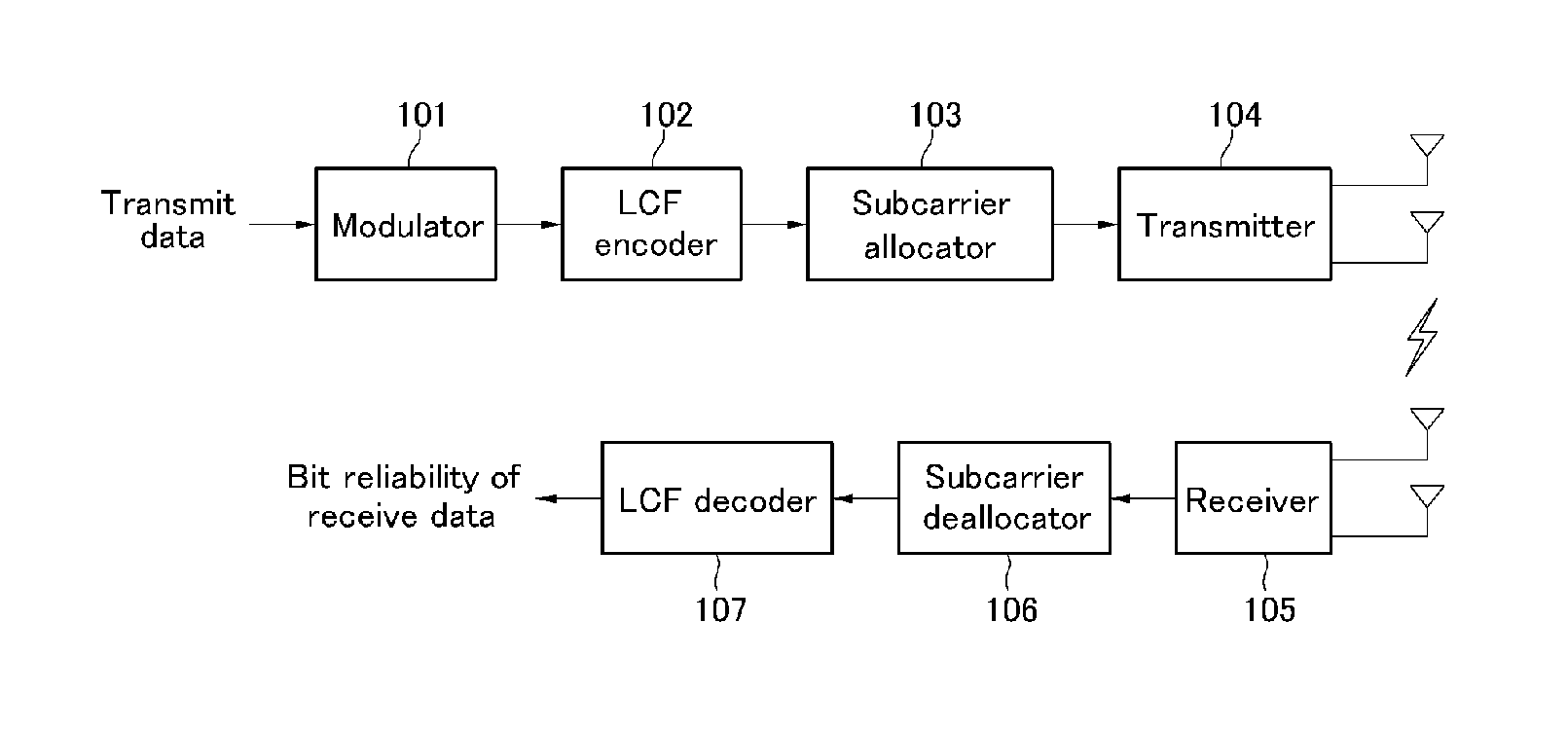
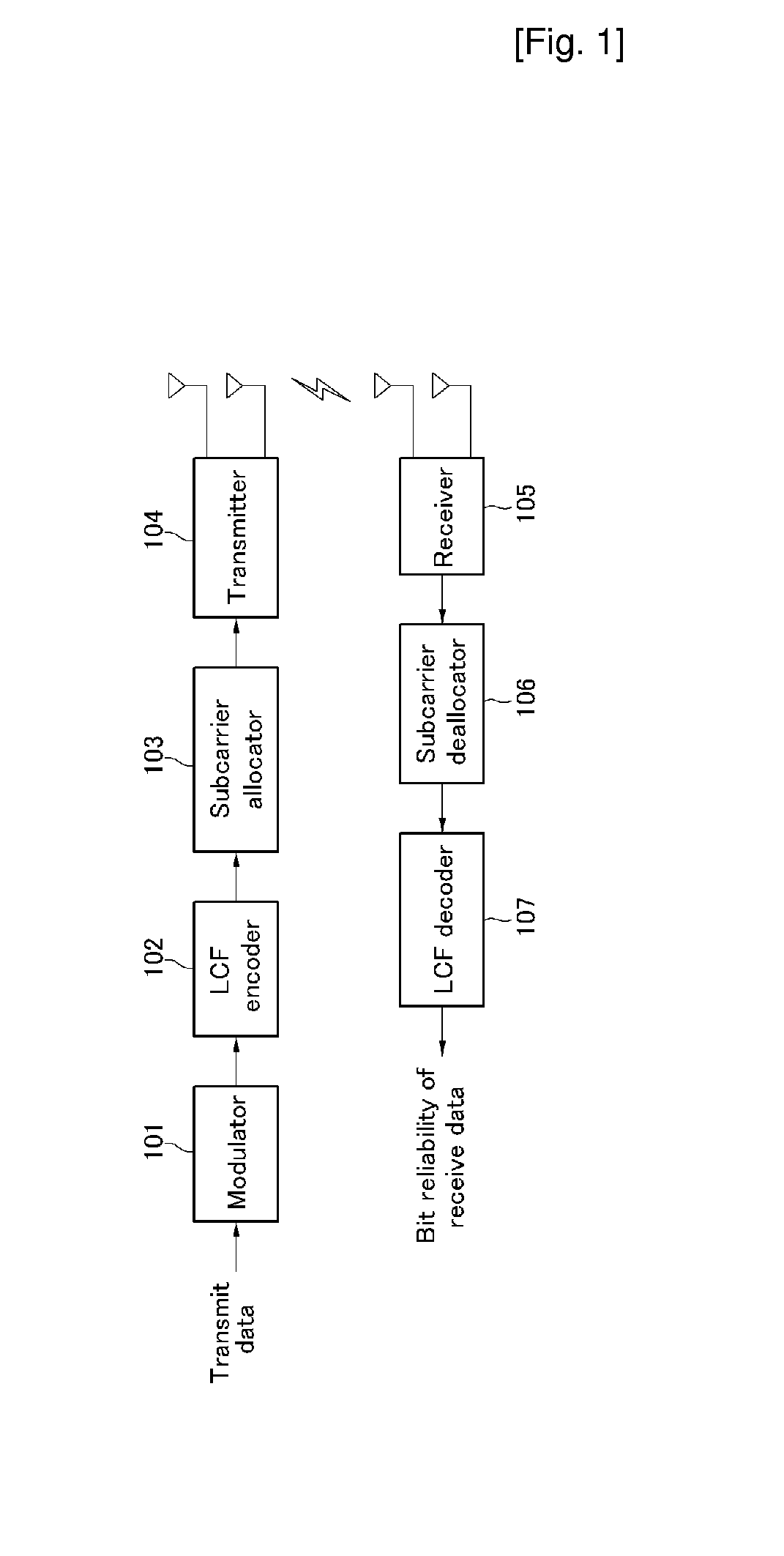
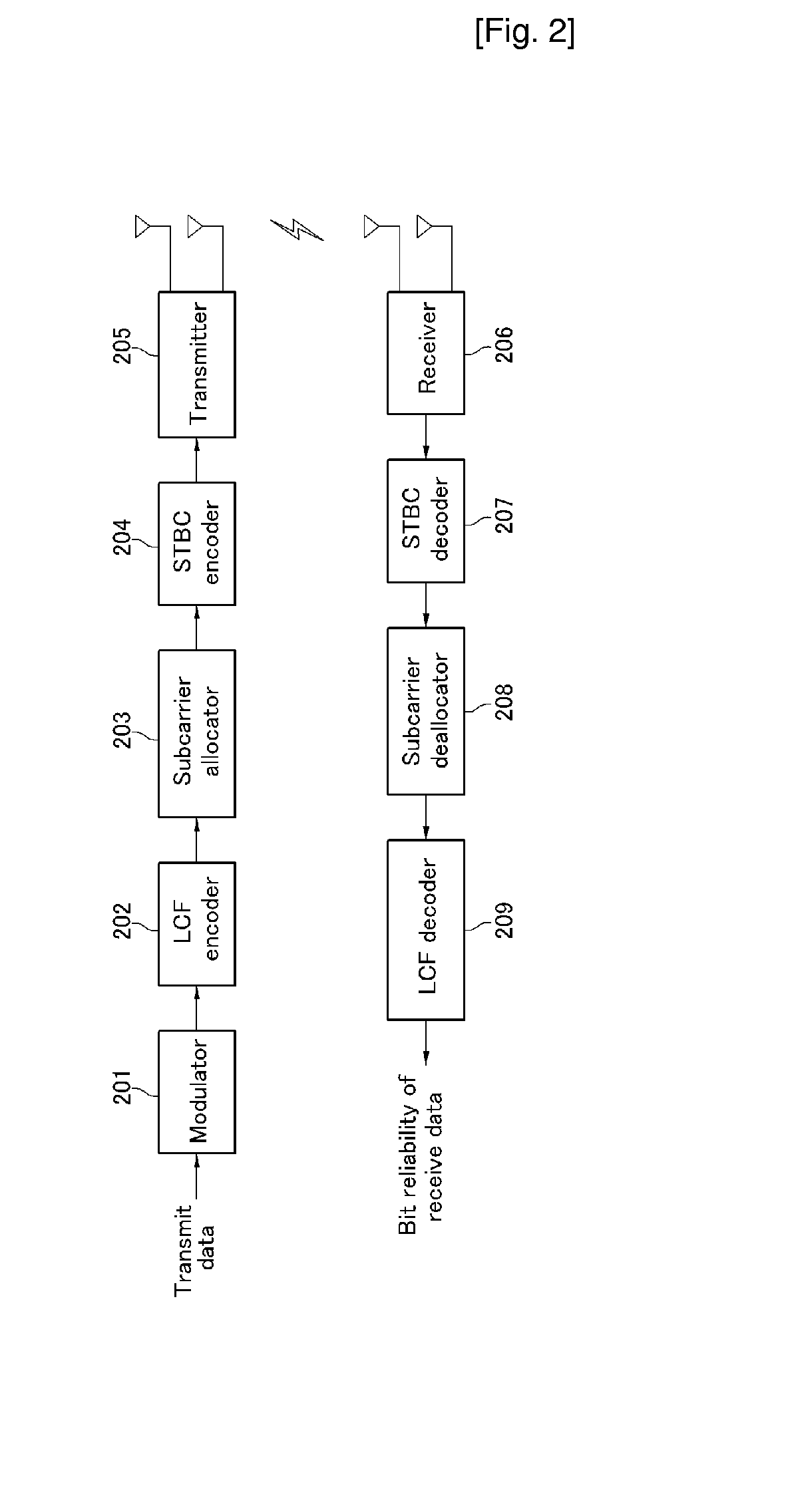
Transmitting Apparatus for Transmitting in a Multi-Carrier System Using Multiple Antennas and Receiving Apparatus in the Same System
ActiveUS20080298225A1Lower performance requirementsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationLattice reductionMaximum likelihood detection
A transmitting apparatus and receiving apparatus of a multi-carrier system using multiple antennas is proposed. An LCF encoder of the transmitting apparatus performs a liner precoding to input signals to be transmitted to a receiving apparatus using a liner complex matrix considering the number of multiple antennas and the number of subcarriers, and a subcarrier allocator respectively allocates a subcarrier to the signals liner-precoded by the LCF encoder. A transmitter respectively transmits the signals having a subcarrier allocated by the subcarrier allocator through the multiple antennas externally. A subcarrier de-allocator of a receiving apparatus extracts a liner-precoded signal by de-allocating a subcarrier allocated to the received signal. An LCF decoder outputs a bit reliability of the received signal to the liner-precoded signal extracted from the subcarrier de-allocator considering the number m of multiple antennas and the number n of subcarriers. A performance may be improved by using space diversity due to multiple antennas and a frequency diversity due to the OFDMA system, and a complexity may be reduced and a hard decision value of a performance similar to the maximum likelihood detection may be obtained by using a lattice reduction and a 2-branch Chase decoder.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Lattice reduction aided decoding in wireless MIMO receivers
In a lattice-reduction-aided receiver based wireless communications system, soft estimates of transmitted bit values are determined from a received signal by applying lattice reduction to the channel estimate and equalising the received signal in accordance with the reduced basis channel, and determining probabilities of transmitted bits having particular values by generating a set of candidate vectors in the reduced basis based on nearest candidate vectors, determining a corresponding transmitted symbol vector for each candidate vector and, on the basis of the received signal determining the probability of each transmitted bit value having been transmitted.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Detection Process for a Receiver of a Wireless MIMO Communication System
InactiveUS20130243068A1Limiting complexity of algorithmNear-ML performanceMultiple-port networksSpatial transmit diversityNeighborhood searchDecomposition
A detection process for a receiver of a wireless communication system based on Multiple-In-Multiple-Out antennas, the process involving: —a preprocessing which only depends on the channel H, said preprocessing involving: —A QRD decomposition (61) for the purpose of decomposing said channel H into two Q and R matrices, with QHQ=I and R being upper triangular; —a lattice reduction (62) for the purpose of generating (formula AA, formula BB) and a permutation matrix T; —a loading phase (63, 64, 65) comprising a linear LRA-Minimum-Mean-Square-Error equalization applied on said symbols y in accordance with the result of said lattice reduction for the purpose of generating a value (formula CC). The process is characterized by the fact that it further involves the steps of: —Performing a neighborhood search with a search center being equal to the result (formula CC) of said lattice reduction; —Determining the -BKest symbols in accordance with a Partial Euclidean Distance (PED) defined in accordance with the following formula (formula DD)—detecting each layer and with the result of said detection performing an update of the search center so as to perform detection of the next layer; —multiplying the estimated value (formula EE) by said matrix T plus quantizing it onto the original constellation so as to generate the estimated value (formula FF).
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
MIMO (multiple input and multiple output) detection method based on lattice reduction
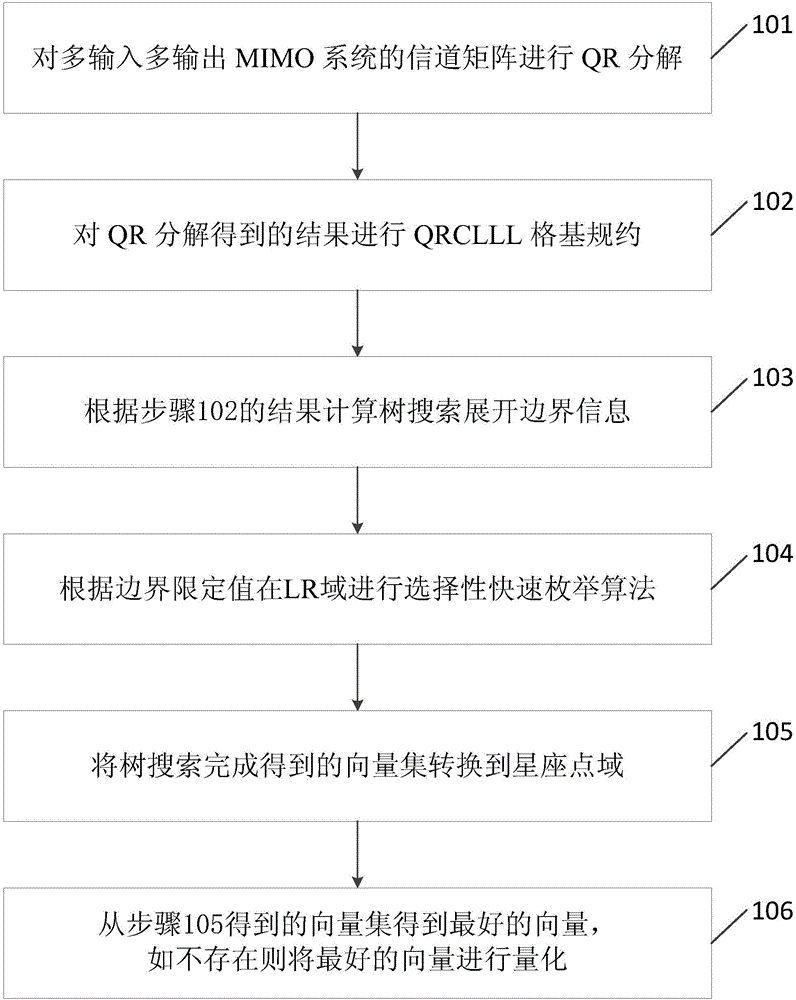
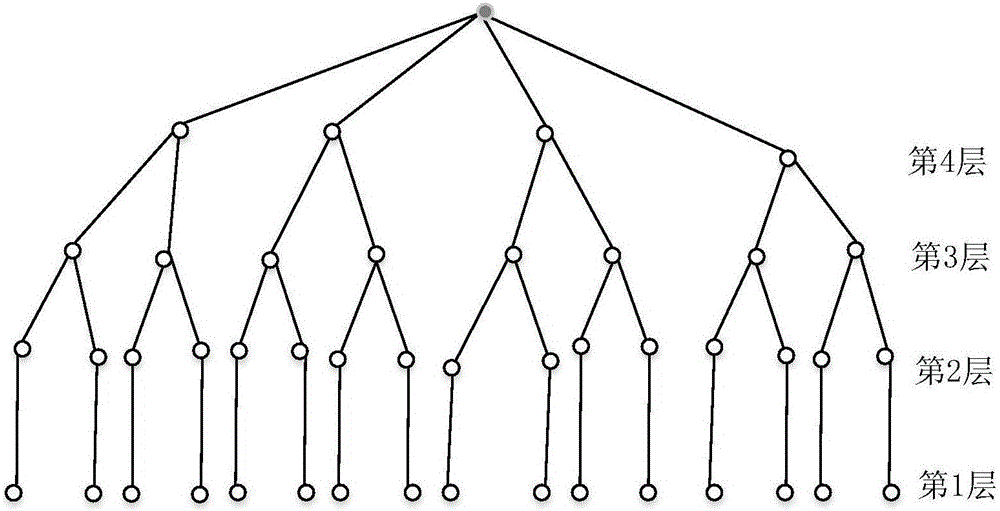
ActiveCN105119665AReduce complexityIncreased complexitySpatial transmit diversityPropogation channels monitoringQR decompositionAlgorithm
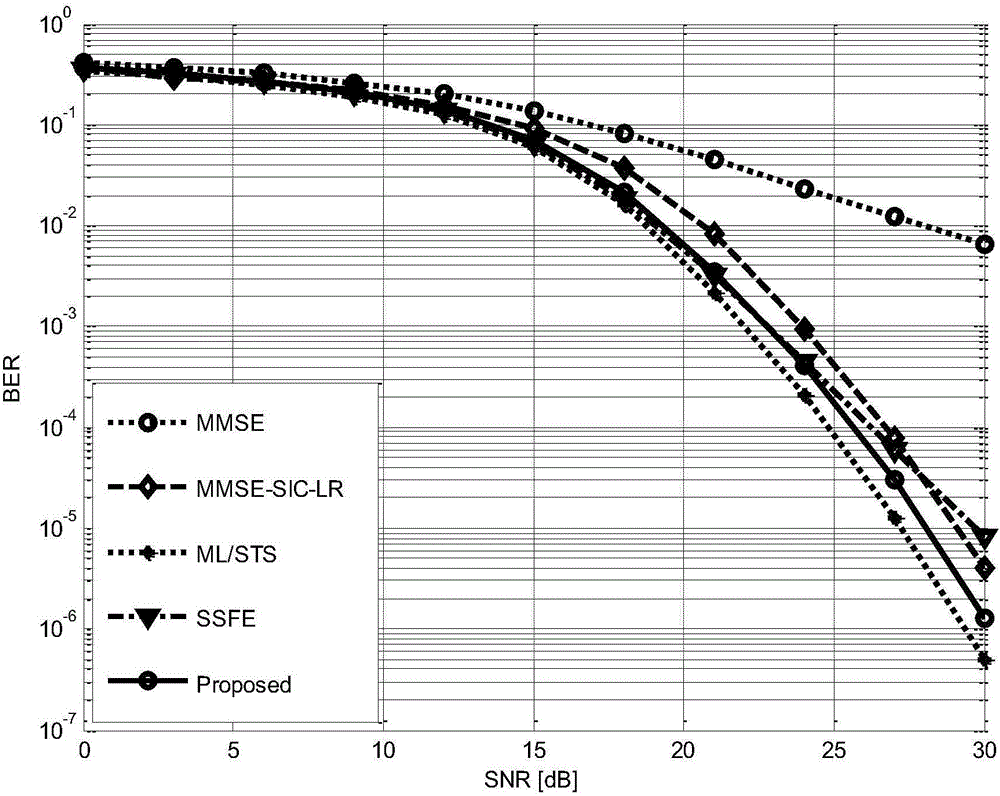
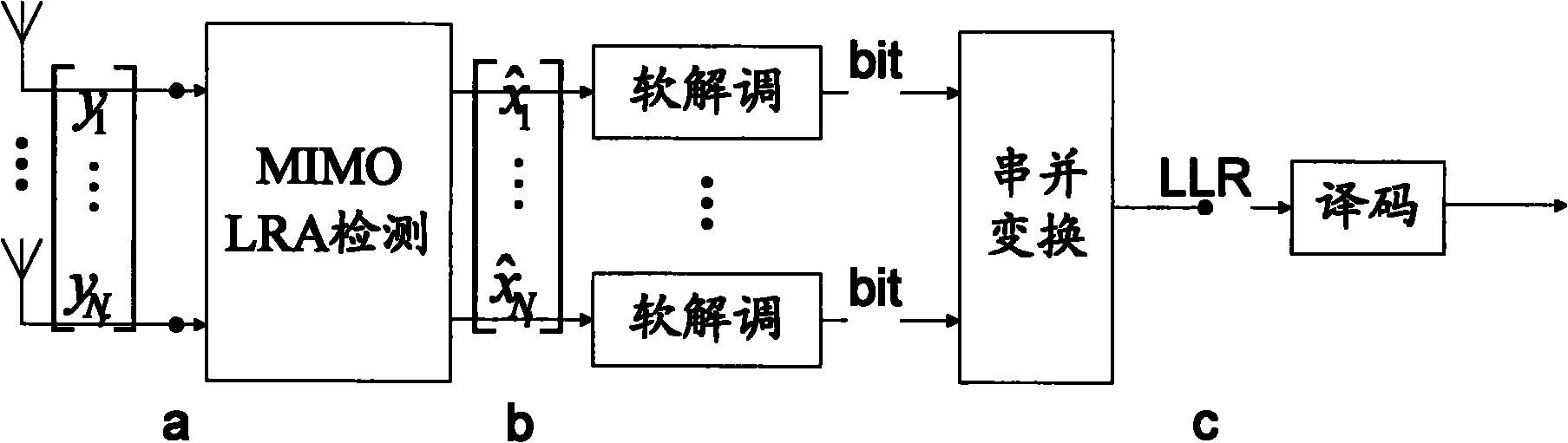
The invention discloses a MIMO (multiple input and multiple output) detection method based on lattice reduction, which comprises the steps of 1, carrying out QR decomposition on a channel matrix of a MIMO system; 2, carrying out a QRCLLL lattice reduction operation on a result acquired by QR decomposition; 3, calculating boundary information expanded by tree search according to a result of the step 2; 4, carrying out selective fast enumeration expansion in an LR region according to boundary restriction; 5, converting a vector set acquired by completion of tree search into a constellation point region; and 6, acquiring an optimal vector from the acquired vectors. According to the invention, the performance difference between an LR based detection algorithm and the optimal MIMO detection is enabled to be further reduced under the condition that the number of expanded nodes of tree search is very small relative to that of traditional tree search, and the operation complexity of a detector is reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
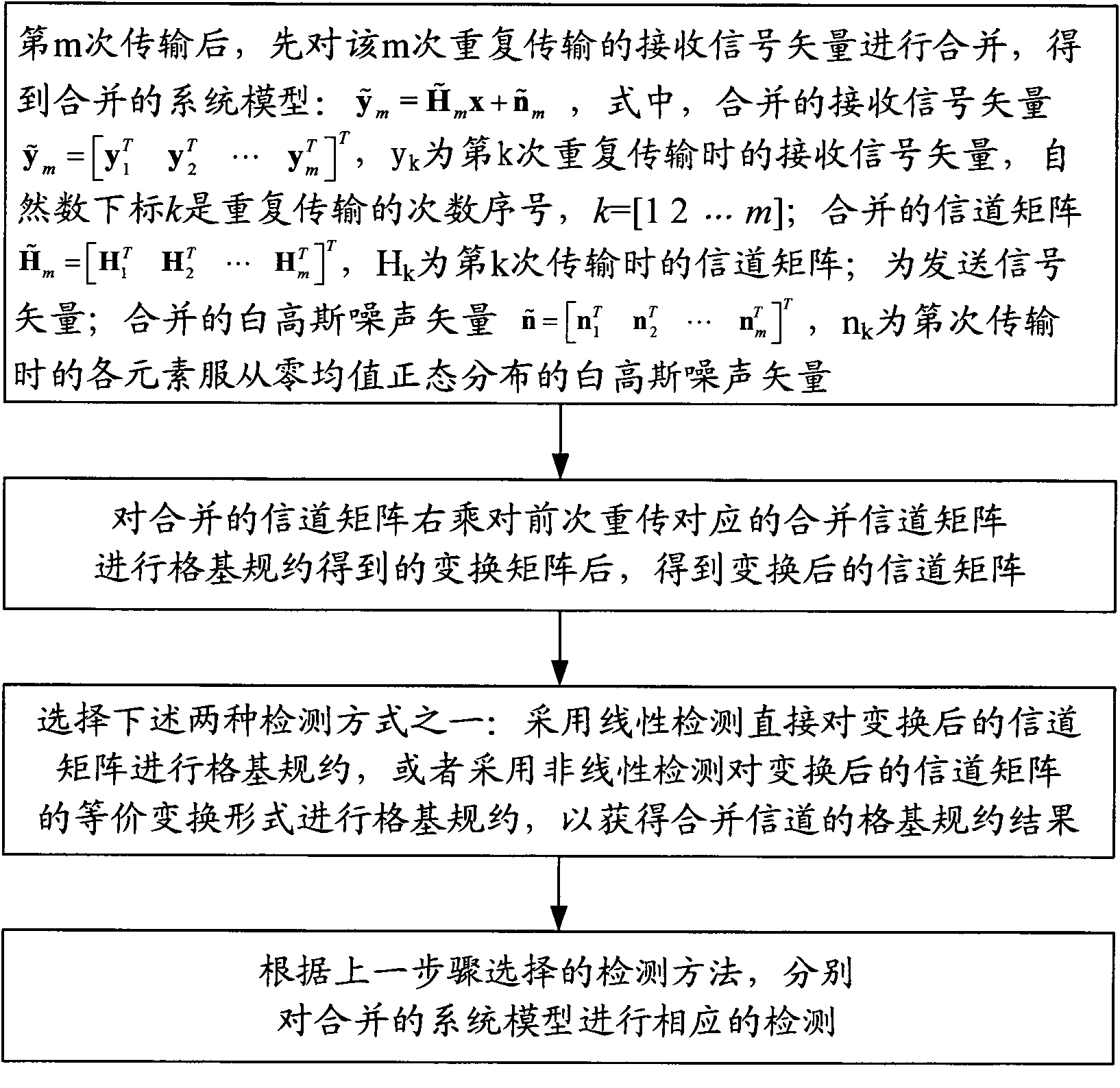
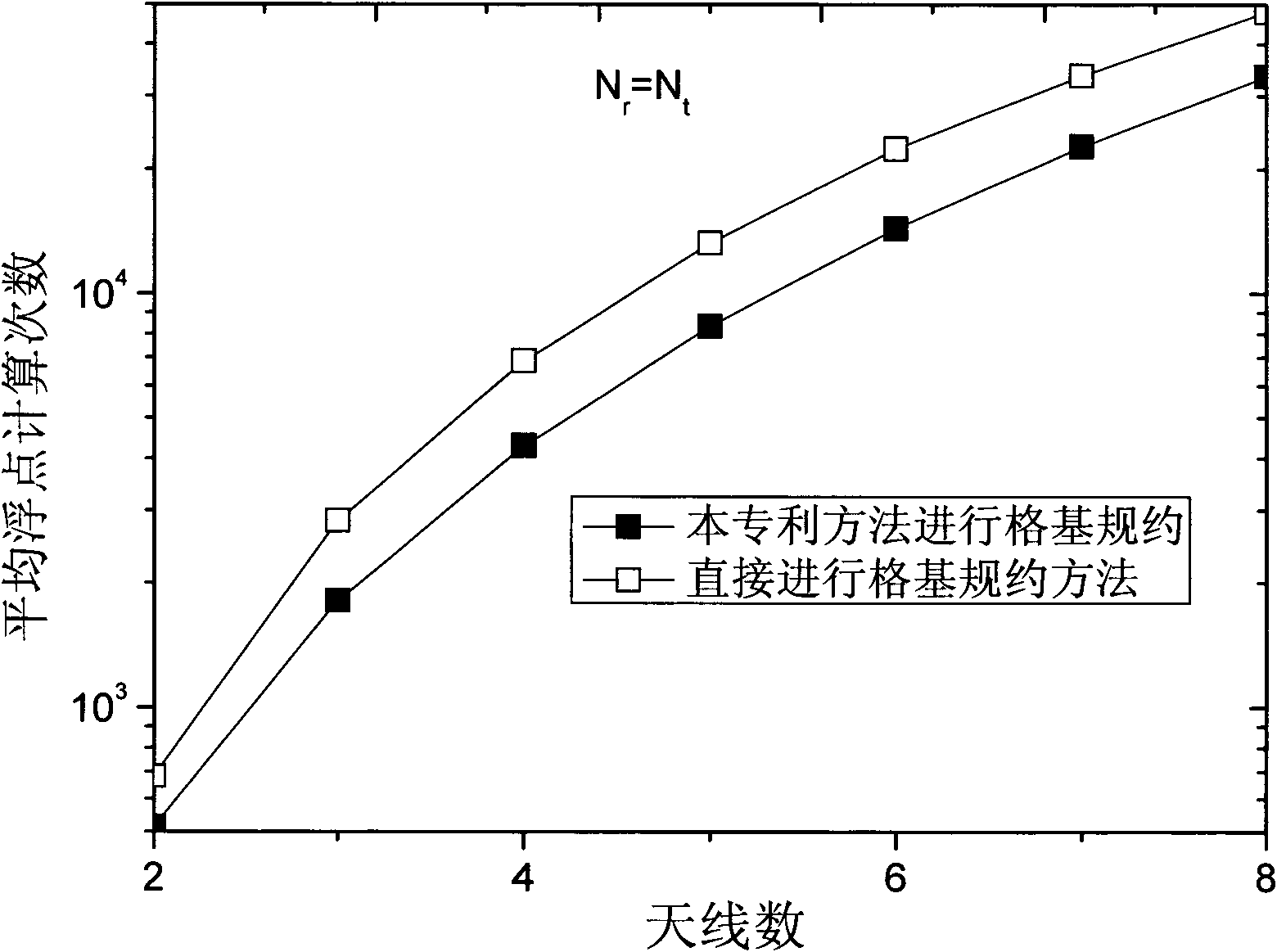
Lattice reduction based retransmission merging method for MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) system
InactiveCN102142947AAvoid lostReduce complexityError prevention/detection by using return channelError prevention/detection by diversity receptionLattice reductionMultiple input
The invention provides a lattice reduction based retransmission merging method for an MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) system, which comprises the steps of: after each retransmission, merging all received signal vectors to obtain a merged system model; postmultiplying a merged channel matrix by a transformation matrix obtained by carrying out lattice reduction on the merged channel matrix corresponding to the former retransmission to obtain a transformed channel matrix; subsequently, directly carrying out lattice reduction on the transformed channel matrix by selecting linear detection to obtain a lattice reduction result of the merged channel matrix; and finally, correspondingly detecting the merged system model according to the selected detection method. By fully utilizing all retransmitted receiving information, the invention avoids information loss caused by soft symbol or soft bit merging after each transmission is singly detected, and can obtain better detection performance. Meanwhile, algorithm complexity is effectively reduced by utilizing coherence among the channel matrixes during each retransmission.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
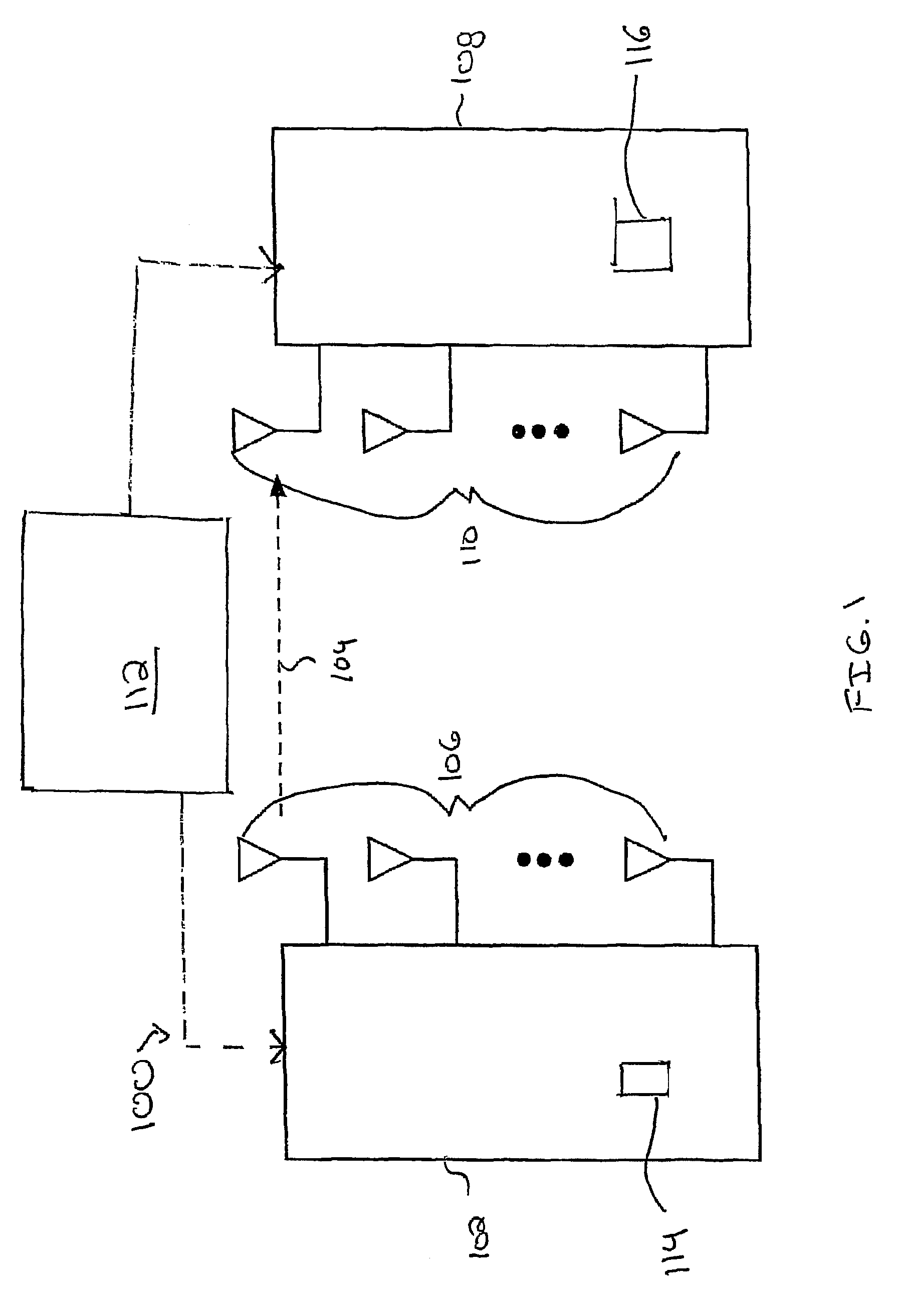
Wireless communication apparatus
InactiveCN101213804ASpatial transmit diversityBaseband system detailsCommunications systemLattice reduction
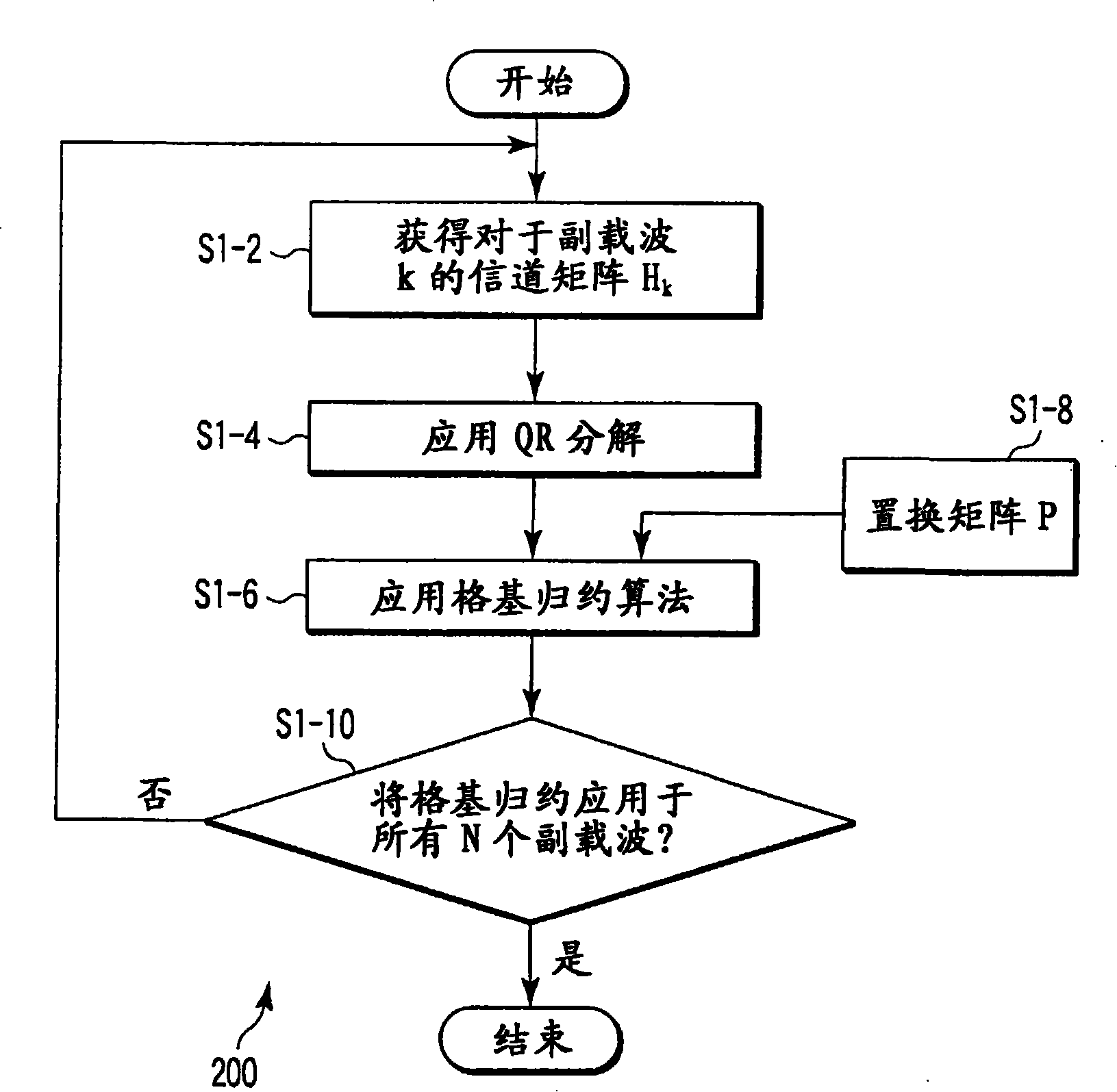
This invention relates to methods, apparatus, and processor control code for signal detection in Multiple Input Multiple Output Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexed (MIMO-OFDM) communications systems. A method for determining outputs from a received signal in a lattice-reduction-aided receiver based multi-carrier wireless communications system having a plurality of sub-carriers divided into a plurality of sets of sub-carriers, the method comprising performing a detection method for each of said sets, the detection method comprising the step of applying lattice reduction to said set of sub-carriers thereby generating a reduced basis channel response.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Signal detection method applied to MIMO system and based on generalized spatial modulation
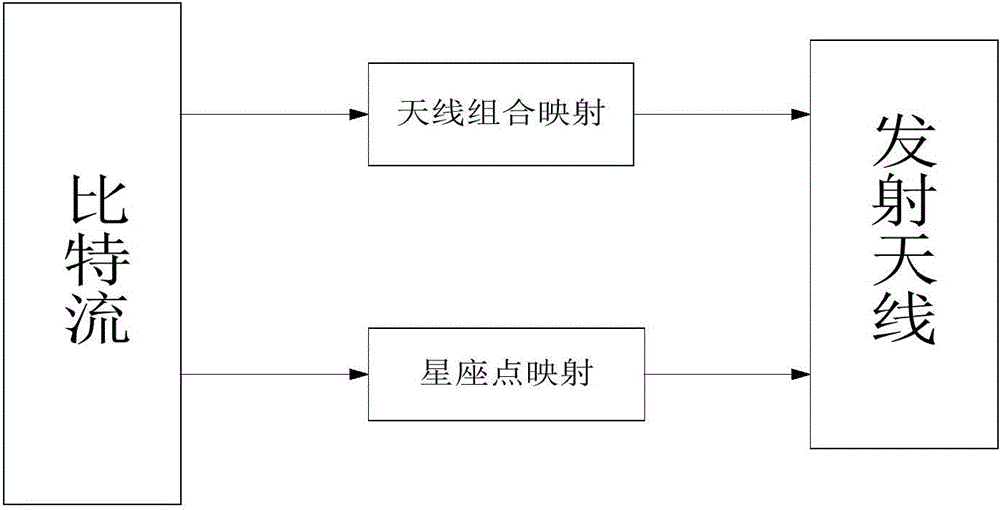
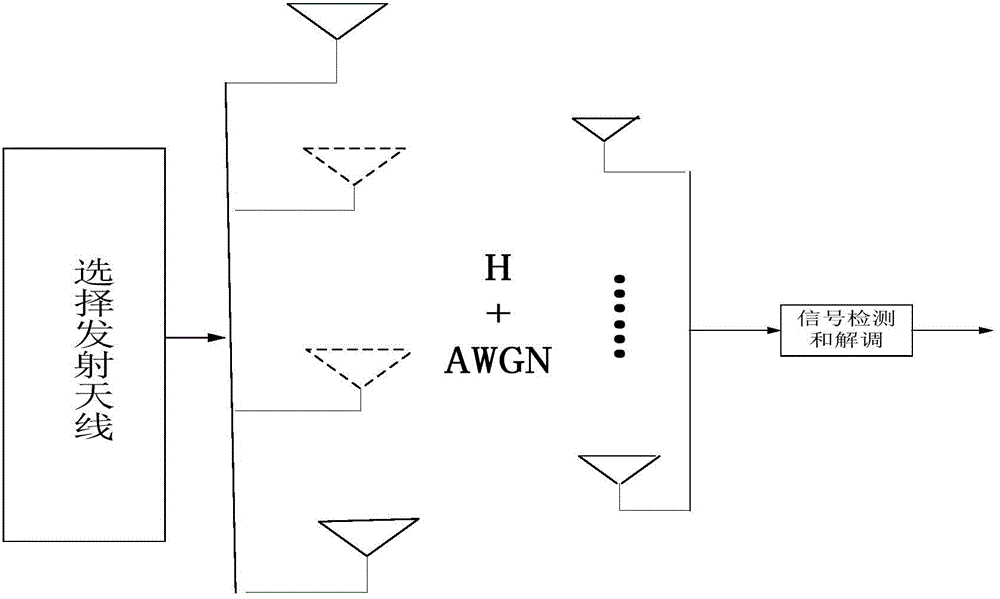
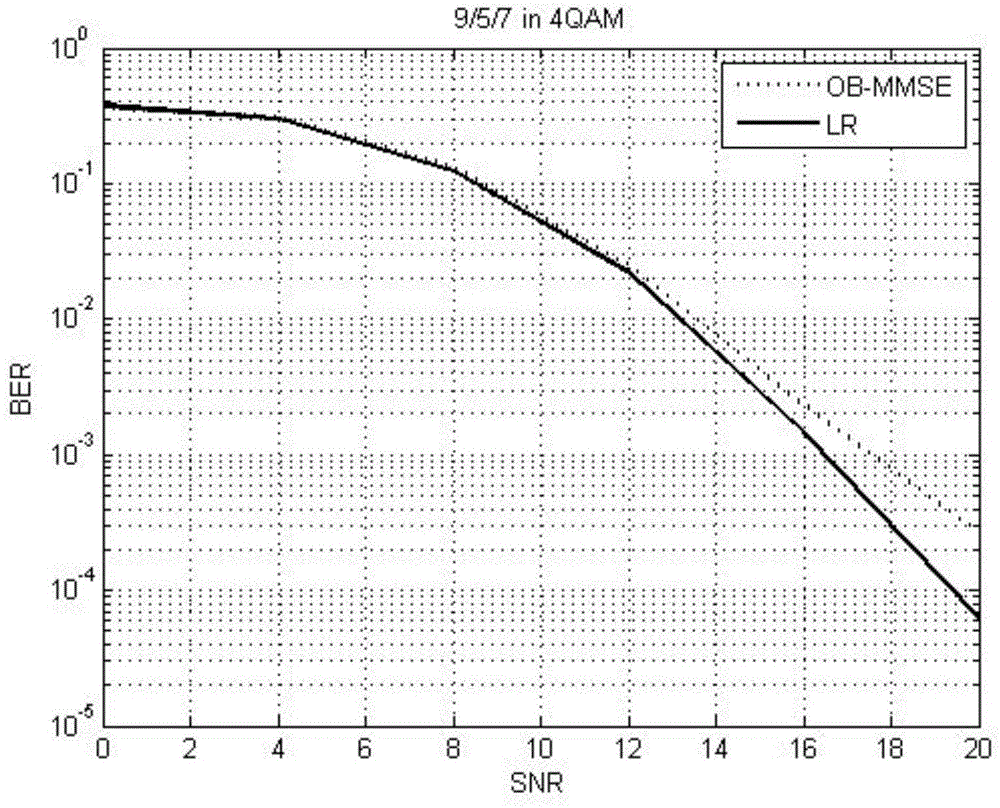
InactiveCN104168049ASolve problems with high computational complexityImprove performanceSpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemRound complexity
The invention belongs to the technical field of communication, and particularly relates to a Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) communication system and a Generalized Spatial Modulation (GSM) and Lattice Reduction (LR) technology. According to a signal detection method applied to the MIMO system and based on GSM, bit encoding is conducted at the transmitting end according to a transmitting antenna combination and a transmitting constellation symbol, and a channel matrix is processed by means of the LR algorithm to obtain a demodulated bit. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that the problem of high algorithm complexity is effectively solved, and OB-MMSE performance is improved under the condition of a high-dimensional transmitting antenna.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Lattice reduction assisted breadth-first tree searching MIMO detecting method
ActiveCN106357312ABest reduction performanceSpatial transmit diversityError preventionRound complexityAlgorithm
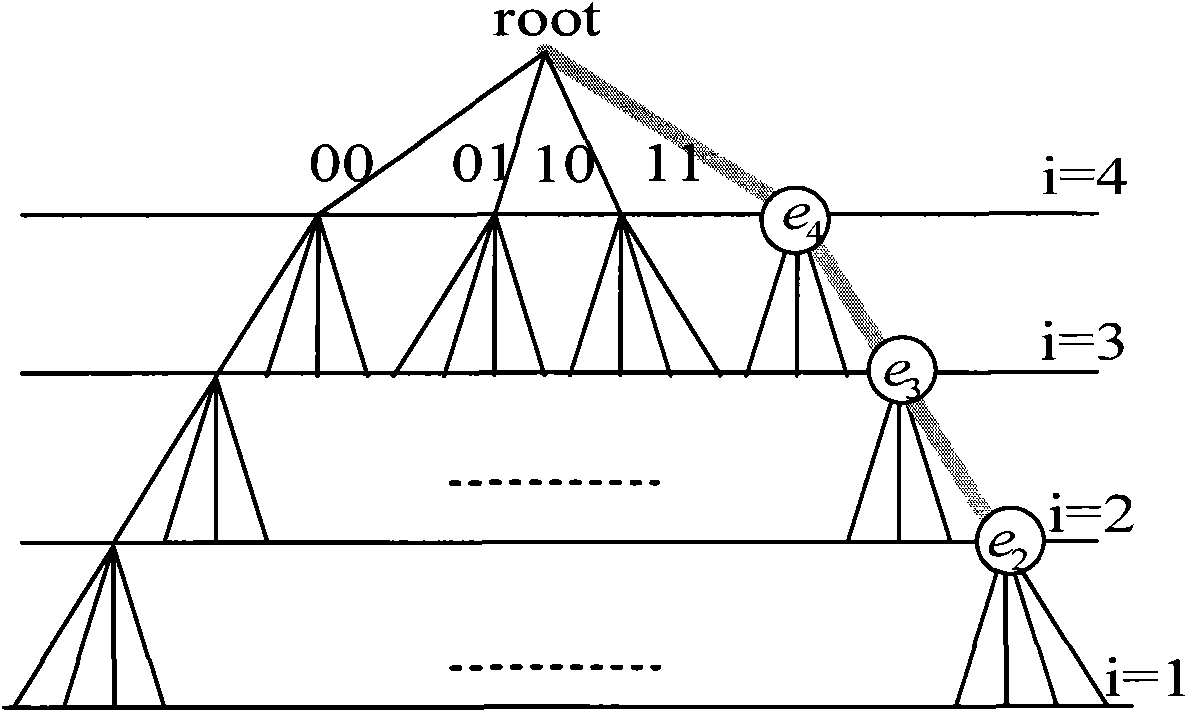
The invention discloses a lattice reduction assisted breadth-first tree searching MIMO detecting method. The lattice reduction assisted breadth-first tree searching MIMO detecting method comprises the following steps: changing a receiving complex vector as shown in the specification and a complex communication channel matrix as shown in the specification into minimum mean square error modes; carrying out lattice reduction on the complex communication channel matrix to obtain a reduction basis matrix as shown in the specification, and carrying out QR disintegration on the reduction basis matrix, wherein a V-BLAST sequence is adopted during QR disintegration; after received signals are expressed by the reduction basis matrix and a figure shift vector, carrying out breadth-first tree searching on the received signals, and determining Kk retaining paths of a kth layer; repeating the steps until retaining paths of which the number is as shown in the specification of a k=2Nt layer are obtained; and selecting a symbolic vector of which the measurement is minimum and the element does not exceed a used QAM symbol value range in symbolic vectors as a detection result as shown in the specification, and if all the symbolic vectors exceed the QAM symbol value range, randomly selecting one of the symbolic vectors as a final detection result as shown in the specification. By the method, the maximum complexity is limited, the average complexity is minimum, and requirements of large-scale MIMO systems are met.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Lattice reduction assisted linear detection method in generalized spatial modulation
InactiveCN107147606ASolve the problem that the linear detection process cannot be directly used in GSMSolve the problem that the modulation does not meet the LR requirementsSpatial transmit diversityMultiple carrier systemsQam modulationLattice reduction
The invention discloses a lattice reduction assisted linear detection method in generalized spatial modulation. The invention relates to a lattice reduction assisted linear detection method in generalized spatial modulation. The invention aims to solve the problems that the linear detection process of existing V-BLAST (Vertical Bell Labs Layered Space-Time) cannot be directly used for GSM (Generalized Spatial Modulation) and conventional QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation) does not meet the LR (Lattice Reduction) requirement. The lattice reduction assisted linear detection method has the specific process of 1, setting a LR assisted linear detection 8-QAM constellation diagram in the GSM; 2, obtaining a new channel matrix HLR and a unimodular matrix T; 3, obtaining an intermediate estimated value (with reference to the specification); 4, according to the unimodular matrix T obtained in the step 2 and the intermediate estimated value obtained in the step 3, calculating out an estimated value (with reference to the specification) of a transmission symbol X; 5, obtaining a spatial symbol estimated value (with reference to the specification); and 6, detecting out a modulation signal symbol (with reference to the specification) from the estimated value (with reference to the specification) of the transmission symbol X, and according to the spacial symbol estimated value (with reference to the specification) and the modulation signal symbol (with reference to the specification), completing lattice reduction assisted linear detection in the generalized spatial modulation. The lattice reduction assisted linear detection method disclosed by the invention is used for the field of wireless communication signal detection.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
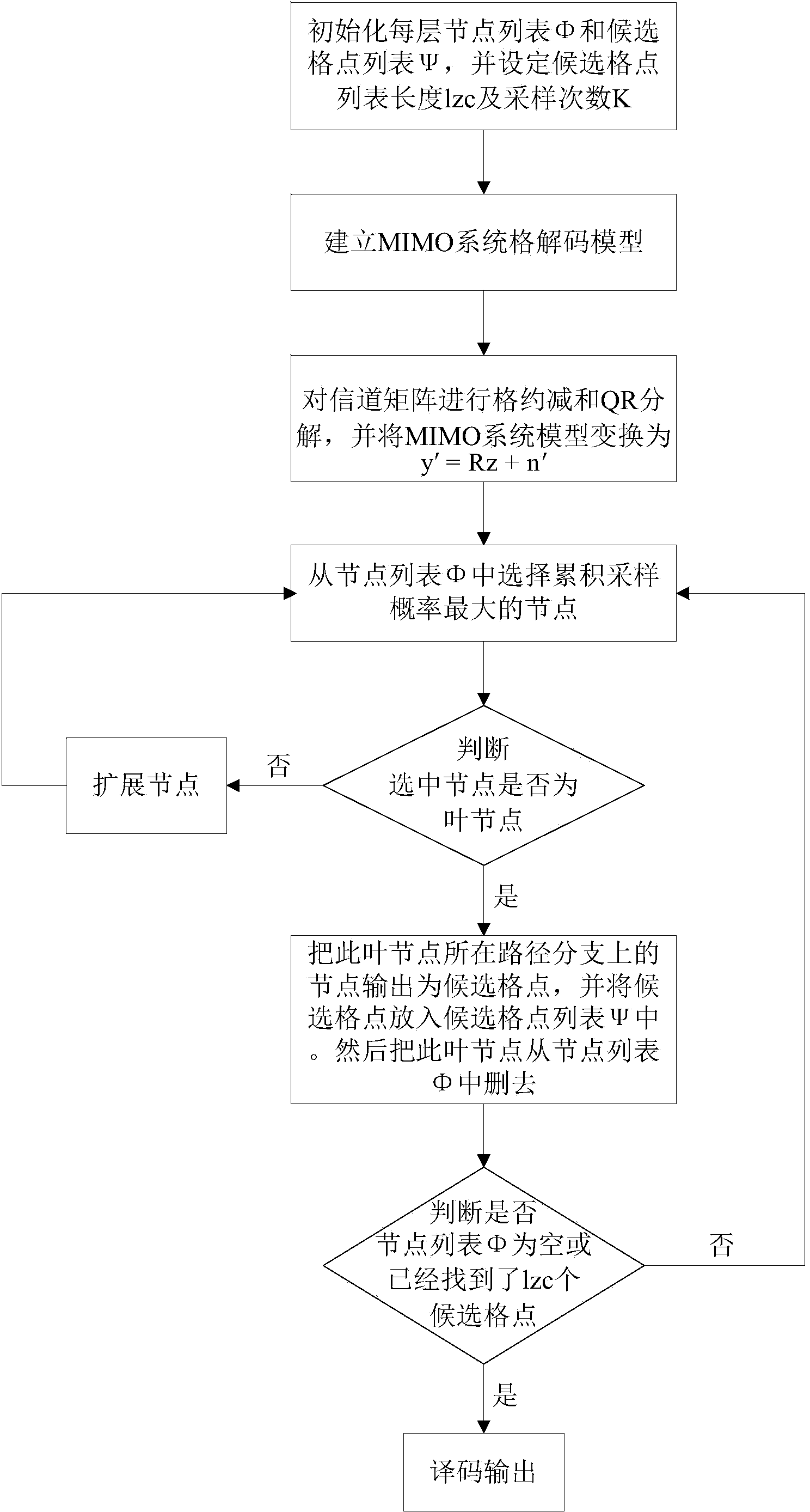
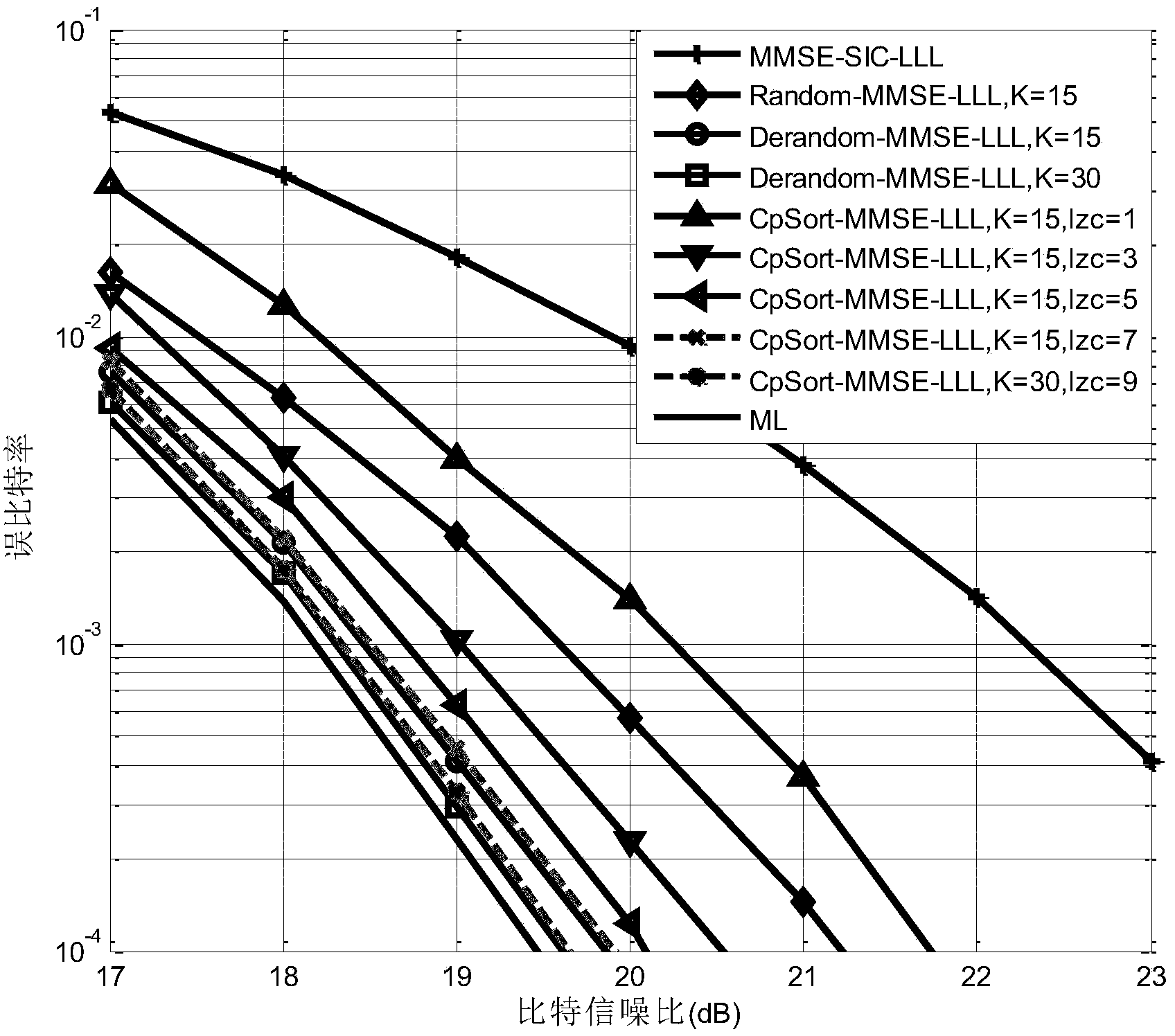
Randomization sampling lattice decoding method based on limited distance decoding
InactiveCN103780349AReduce complexityImprove decoding efficiencySpatial transmit diversityError preventionDecoding methodsQR decomposition
The invention relates to a randomization sampling lattice decoding method based on limited distance decoding. The method comprises the steps of initializing settings, establishing an MIMO system lattice decoding model, conducting lattice reduction and QR decomposition on a channel matrix sequentially, conducting sampling decoding on received signals according to the depth-first search strategy to obtain candidate lattice points in a lattice reduction region, and decoded output. According to the decoding method, under the situation that the sampling frequency set initially is fixed, the decoding performance approaches the decoding performance of a randomization sampling decoding algorithm with the increasing of the length of a candidate lattice point list set initially and the increasing the of the number of nodes in a tree, and the performance the same as that of the randomization sampling decoding algorithm can be finally obtained with an access node number and a candidate lattice point number smaller than those of the randomization sampling decoding algorithm; the common breadth-first search strategy is replaced with the depth-first search strategy, the performance close to the optimum performance is obtained with a smaller search node number, complexity is reduced, and decoding efficiency is improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Wireless communication apparatus
InactiveCN101379787AOther decoding techniquesDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionCommunications systemLattice reduction
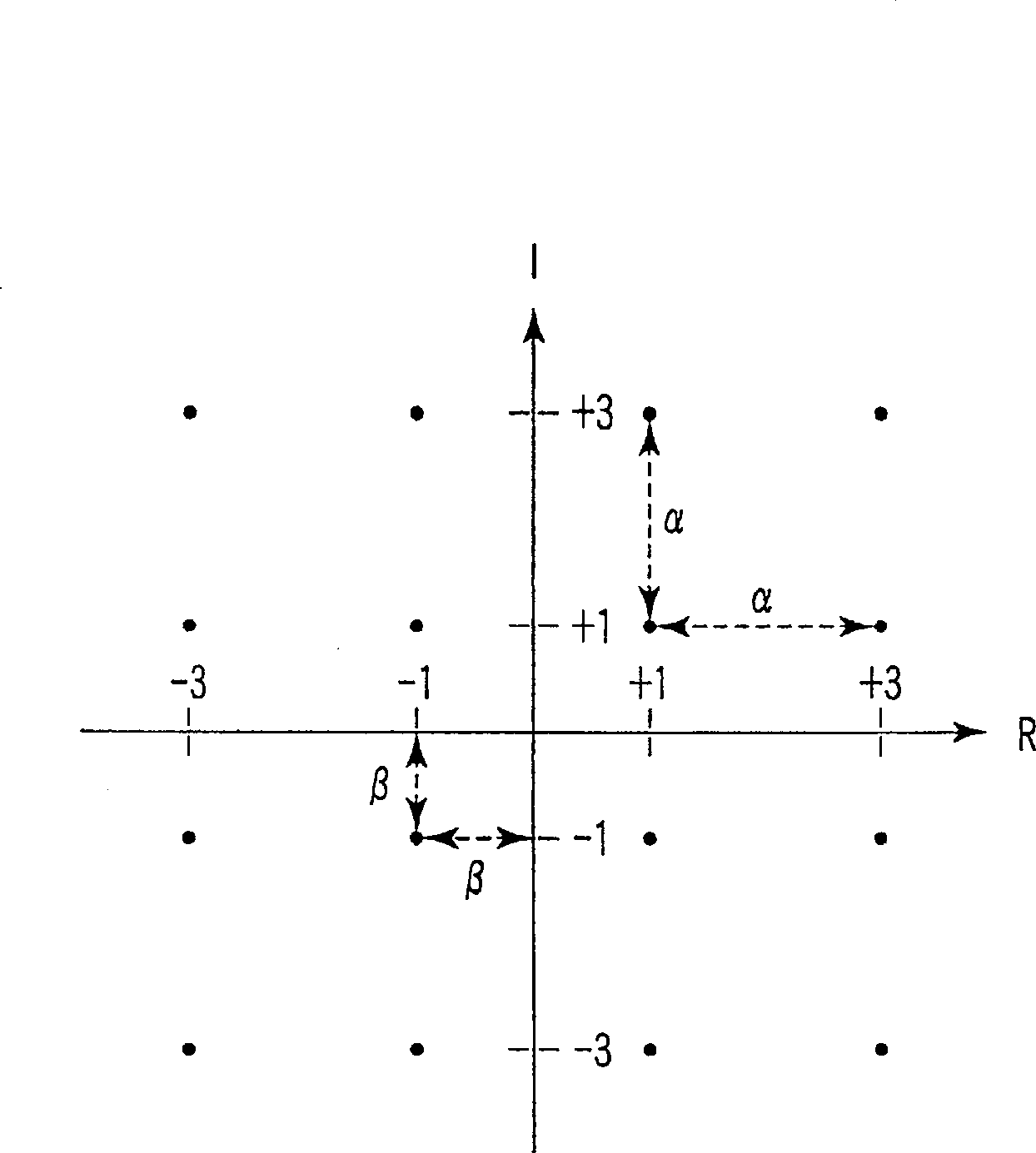
In a lattice-reduction-aided receiver based wireless communications system, soft estimates of transmitted bit values are determined from a received signal by applying lattice reduction to the channel estimate and equalising the received signal in accordance with the reduced basis channel, and determining probabilities of transmitted bits having particular values by selecting a core candidate vector in the reduced basis, determining a set of mapping functions between the core vector in the reduced basis and transmitted symbol vectors from which a set of candidate transmitted symbol vectors can be generated, generating a set of transmitted symbol vectors based on the mapping functions and, on the basis of the received signal determining the probability of each transmitted bit value having been transmitted.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com