Patents
Literature
83 results about "Shift vector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
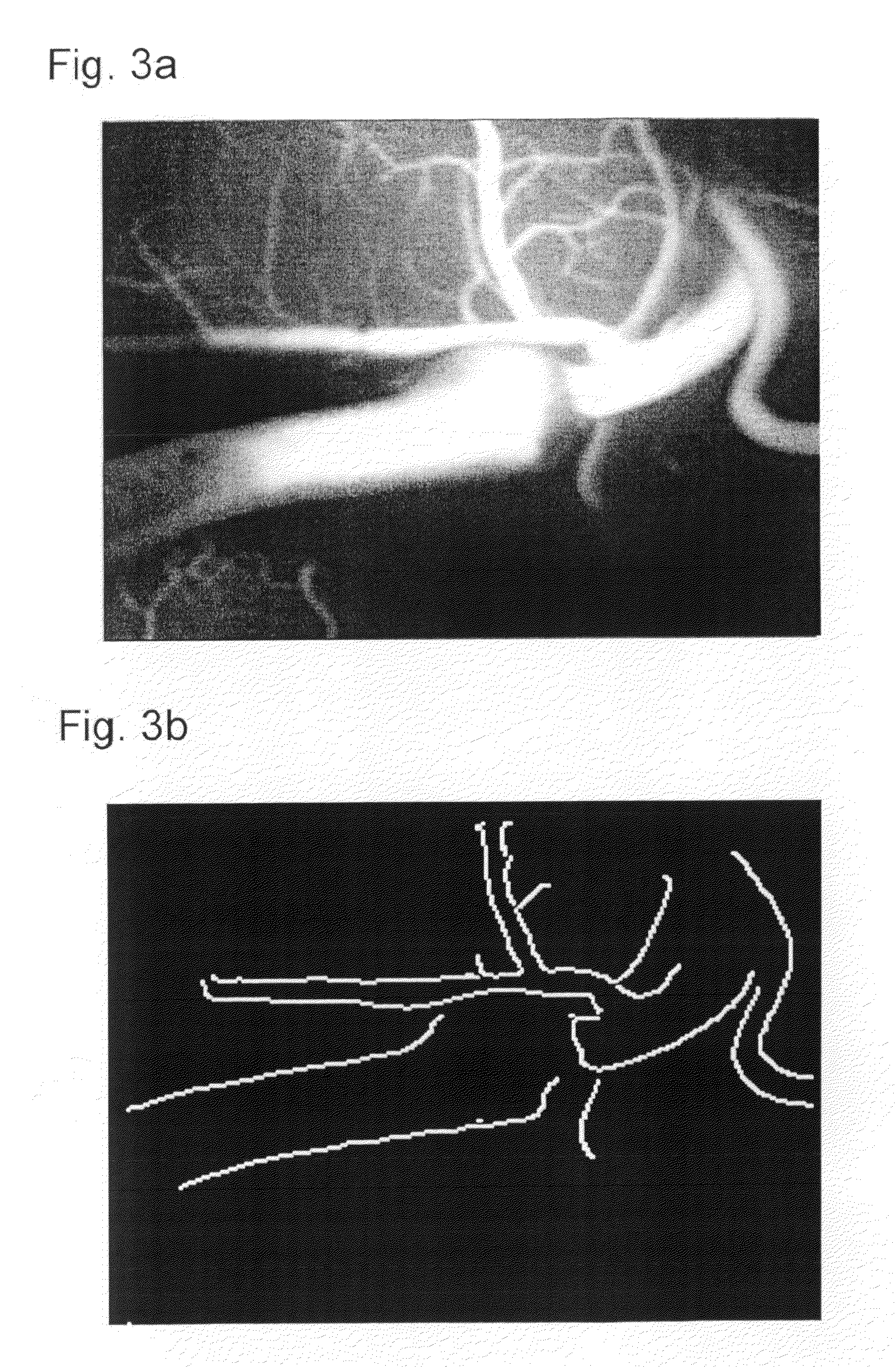
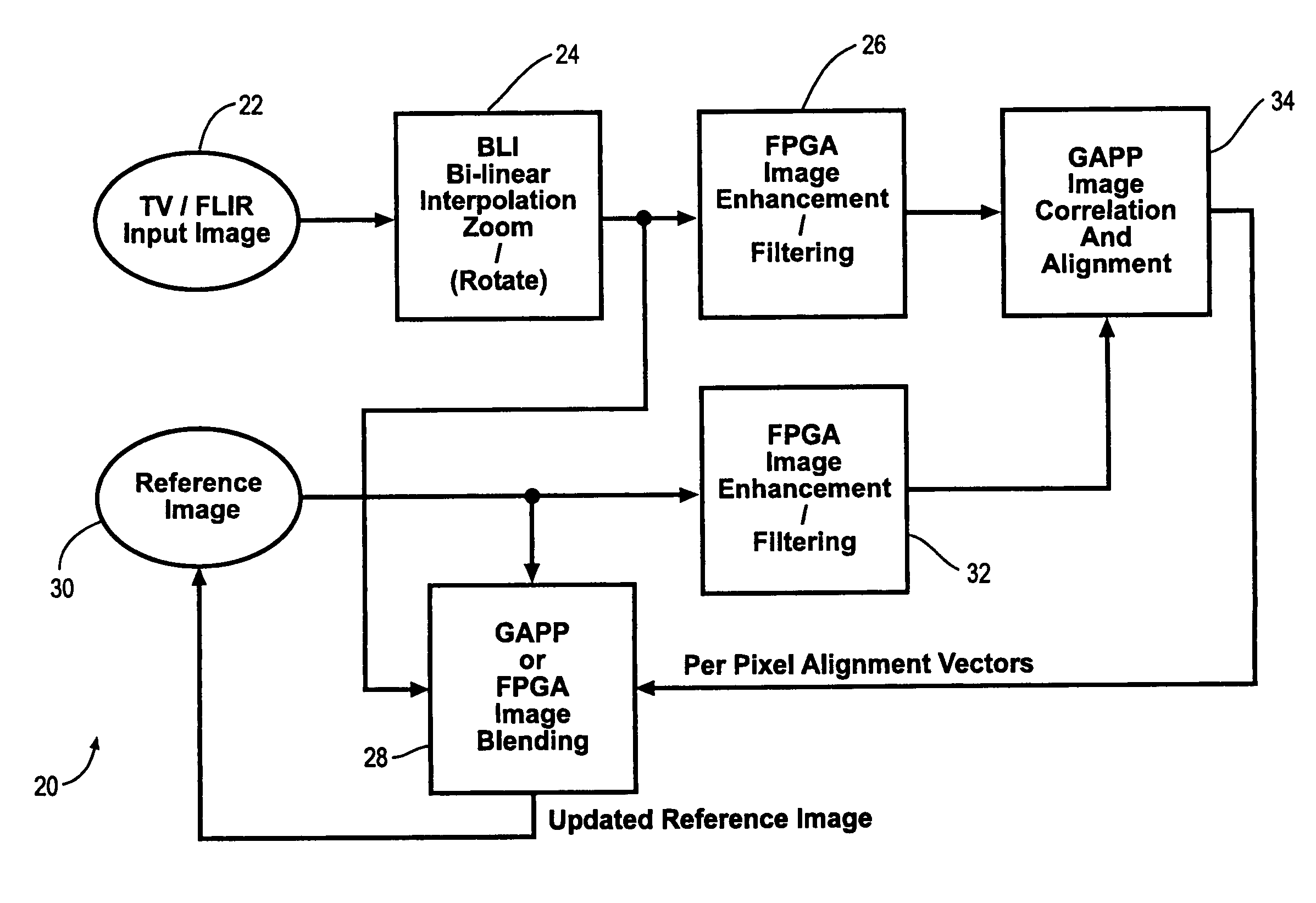
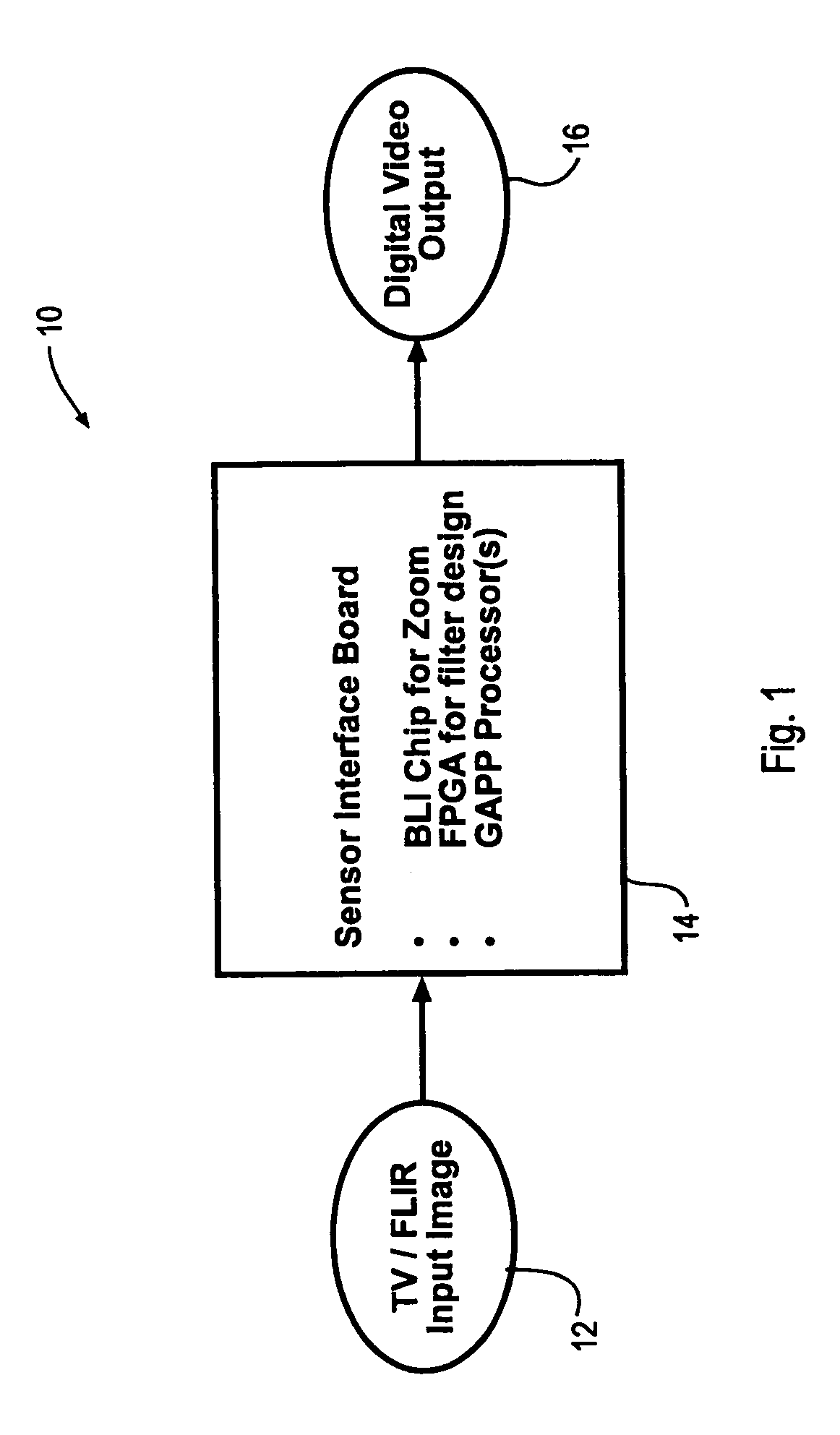
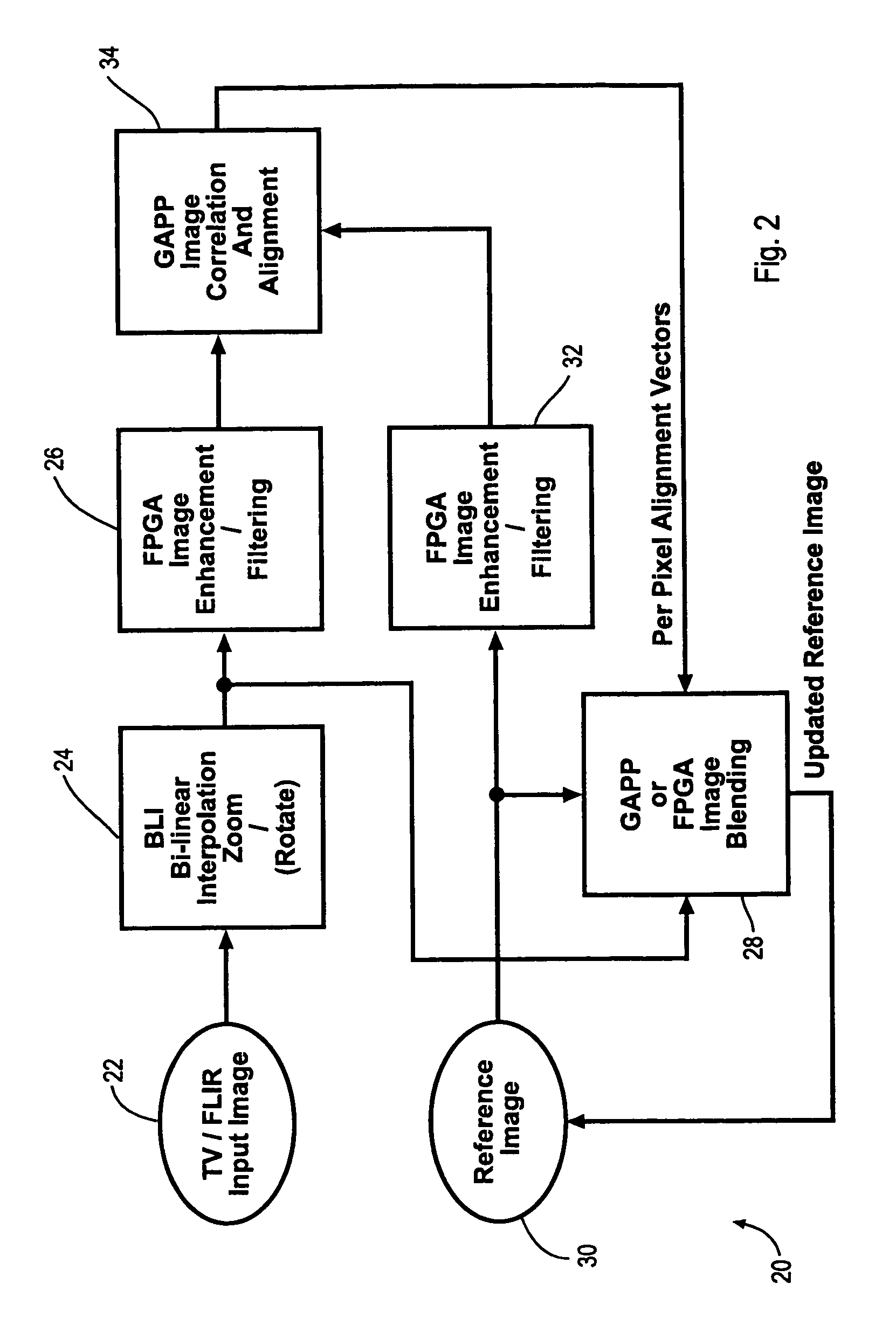
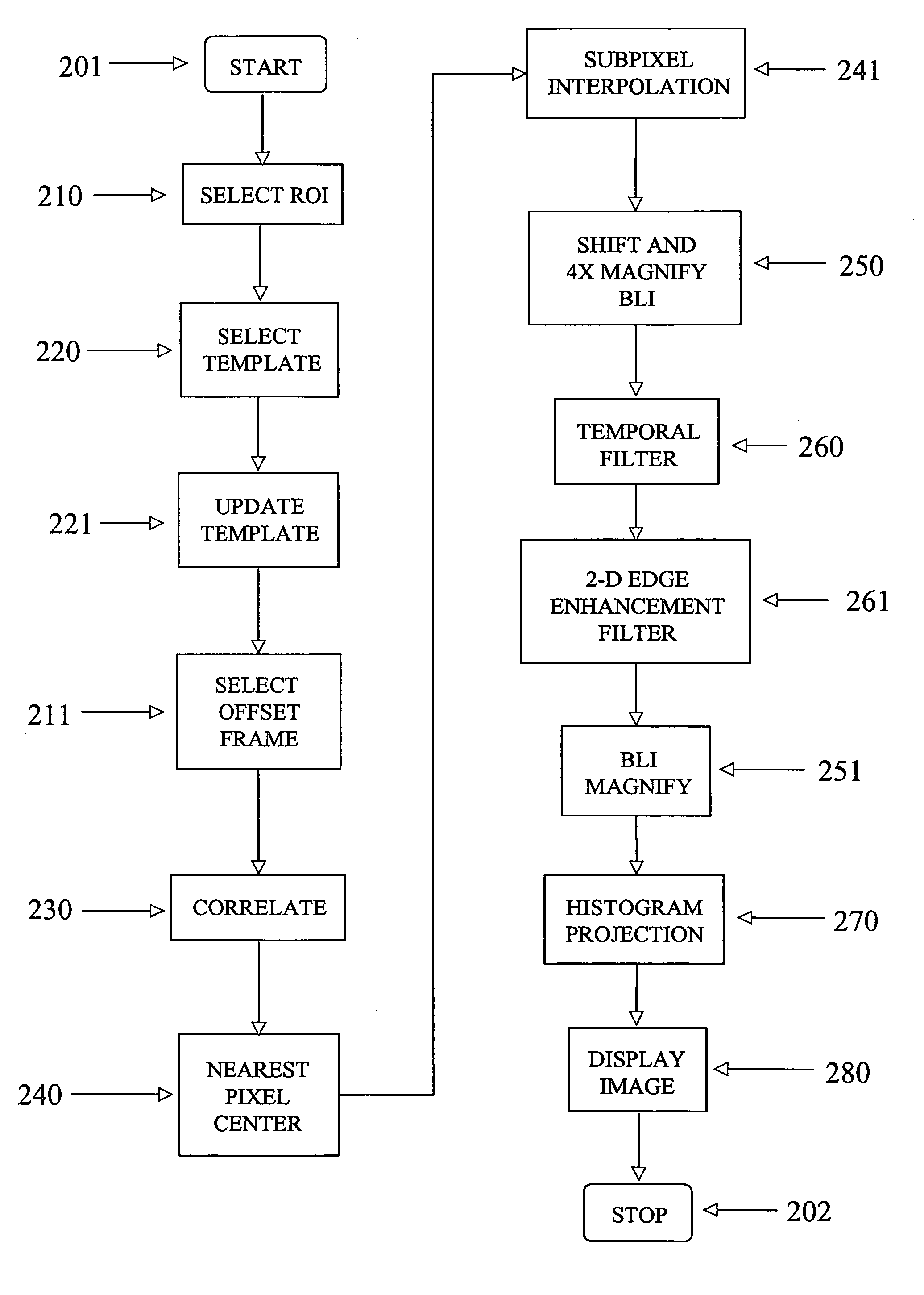
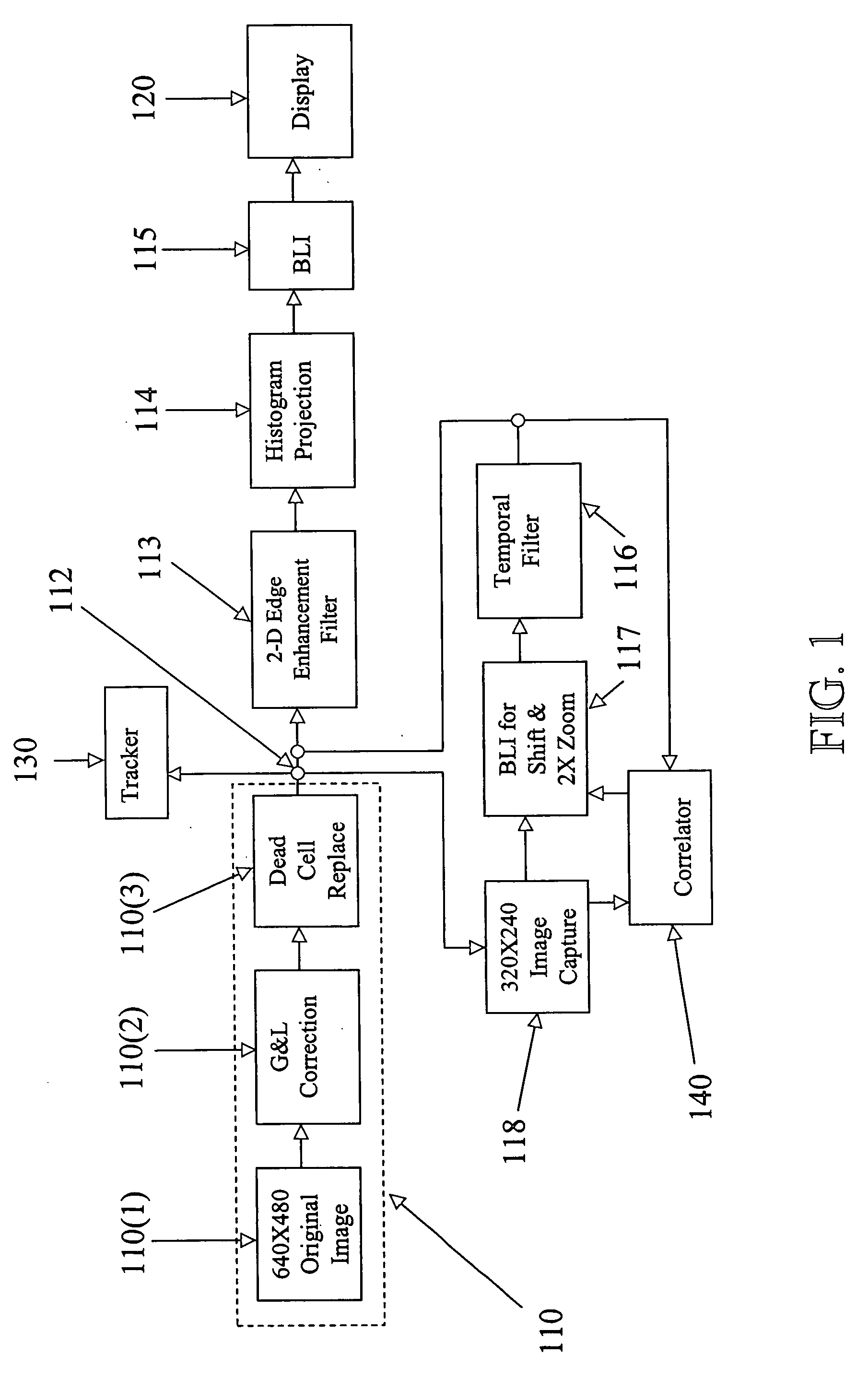
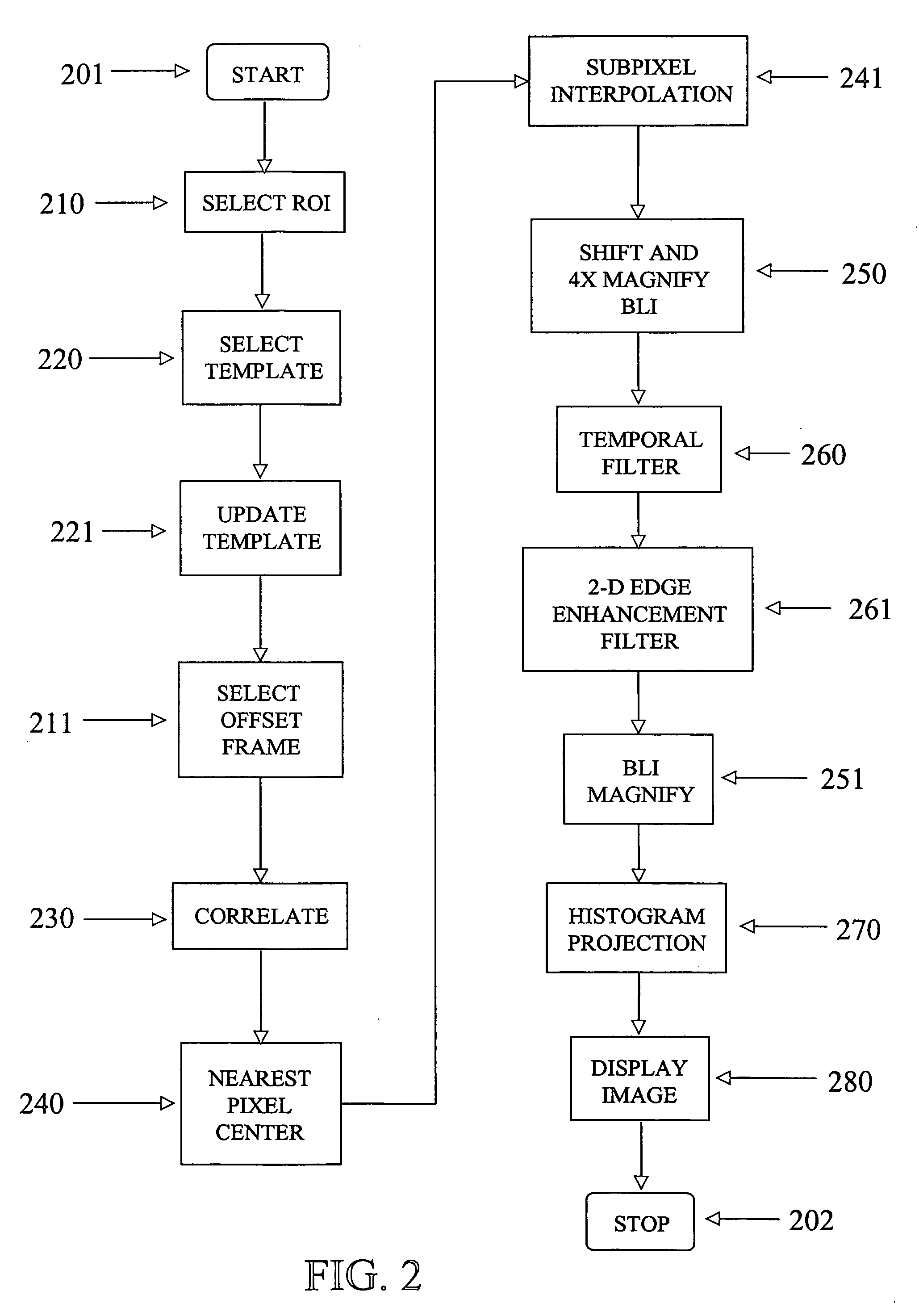
Digital image enhancement using successive zoom images
InactiveUS7346217B1Television system detailsImage enhancementRadiographic Image EnhancementDigital image
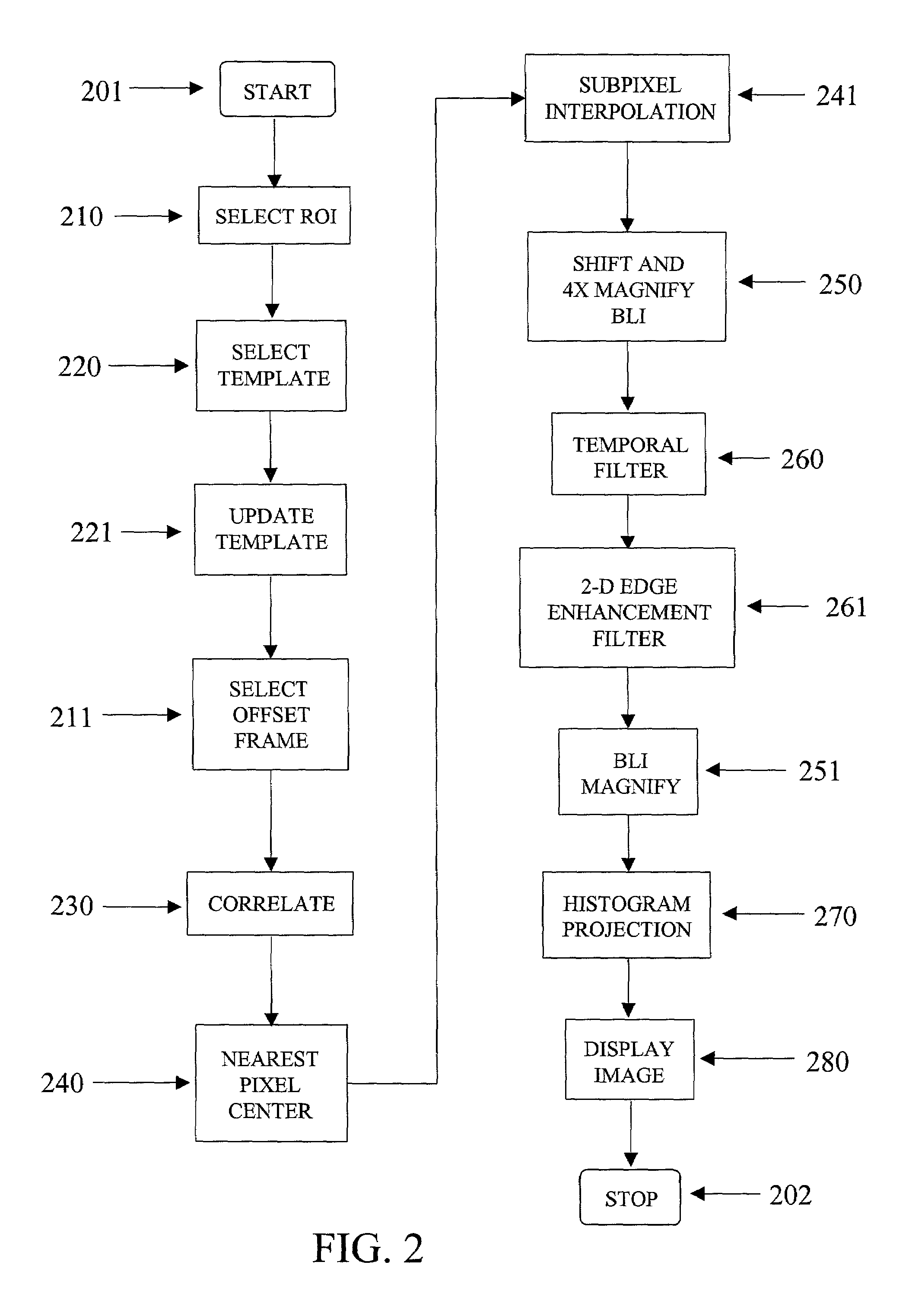
A method and Electro-Optical (EO) system for processing imagery comprising selecting a first frame of data as a template frame; capturing a second frame of data using the EO system, for a plurality of pixels of the second frame, correlating the plurality of pixels of the second frame with pixels of the template frame to generate a plurality of shift vectors, one for each pixel of the plurality of pixels of the second frame, registering the second frame with the template frame by interpolating the second frame using the plurality of shift vectors and re-sampling at least a portion of the second frame to produce a registered frame, re-sampling the template frame, and combining the re-sampled template frame and the registered frame to generate an averaged frame.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Extended range image processing for electro-optical systems
A method and apparatus for processing imagery using images acquired via any known Electro-Optical (EO) system. In accordance with exemplary embodiments of the present invention, a first frame of data is selected as a template frame (e.g., a given frame). A second frame of data can be captured using the EO system. At least a portion of the second frame can be correlated with the template frame to generate a shift vector. The second frame can then be registered with the template frame by interpolating the second frame using the shift vector and re-sampling at least a portion of the second frame to produce a registered frame. The template frame can also be re-sampled. The registered frame and the re-sampled template frame can then be combined to generate an averaged frame. The averaged frame can be spatially filtered to enhance edges within the averaged frame.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
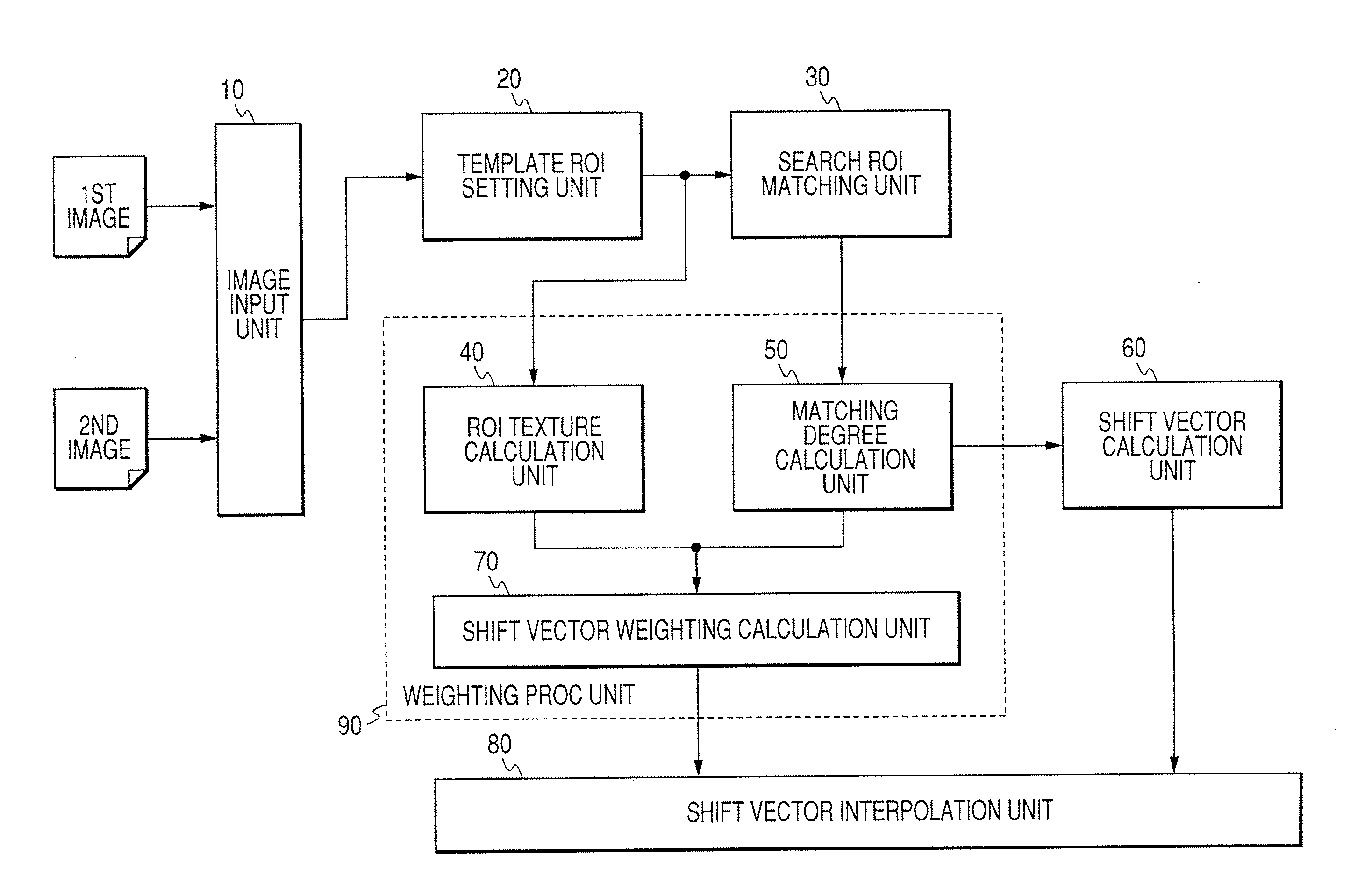
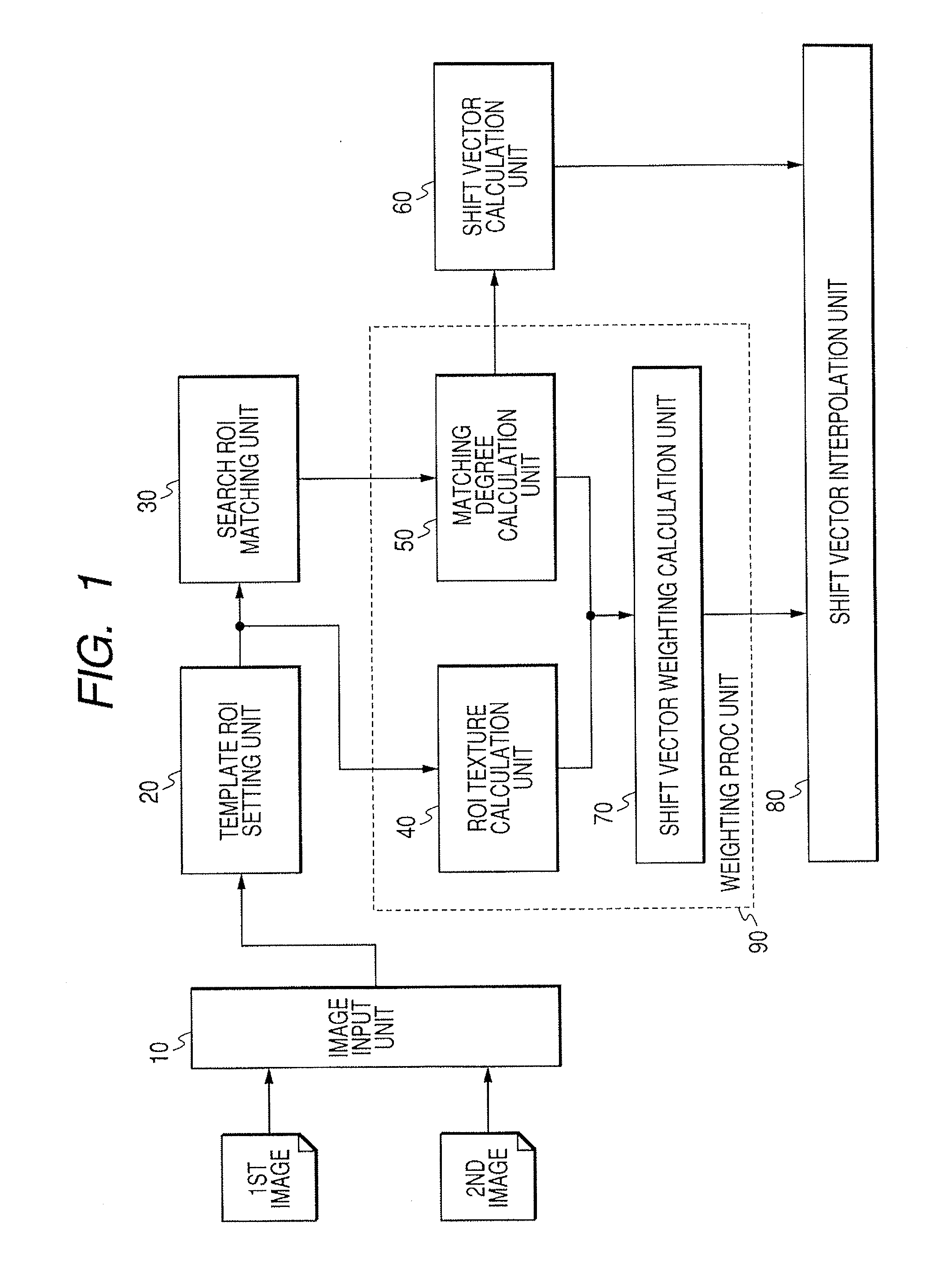
Image Processing Device And Method Which Use Two Images
ActiveUS20070260137A1Increase speedReduce misregistrationImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImaging processingShift vector
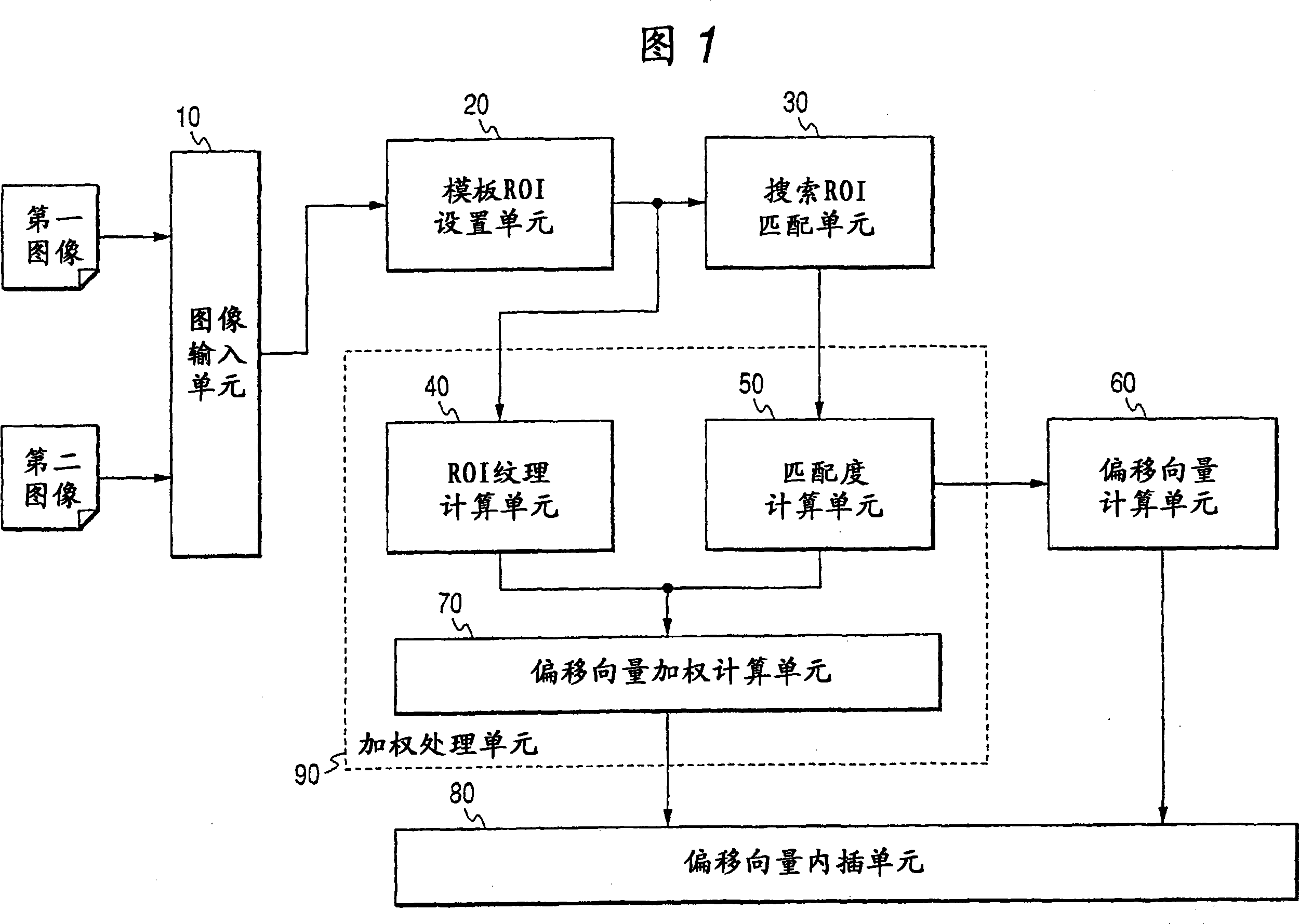
The present invention aims to provide image processing device and method capable of generating a difference image at high speed without occurring misregistration. To achieve this, in the image processing device and method, plural regions of interest are set respectively to input first and second images, a shift vector indicating a misregistration amount between the first and second images is calculated with respect to each of the regions of interest, a filter process is executed to the shift vector, the filter-processed shift vector is interpolated, the first and second images are registered based on the interpolated shift vector, and a subtraction operation is executed between corresponding pixels on the respective registered images to acquire the difference image.
Owner:CANON KK
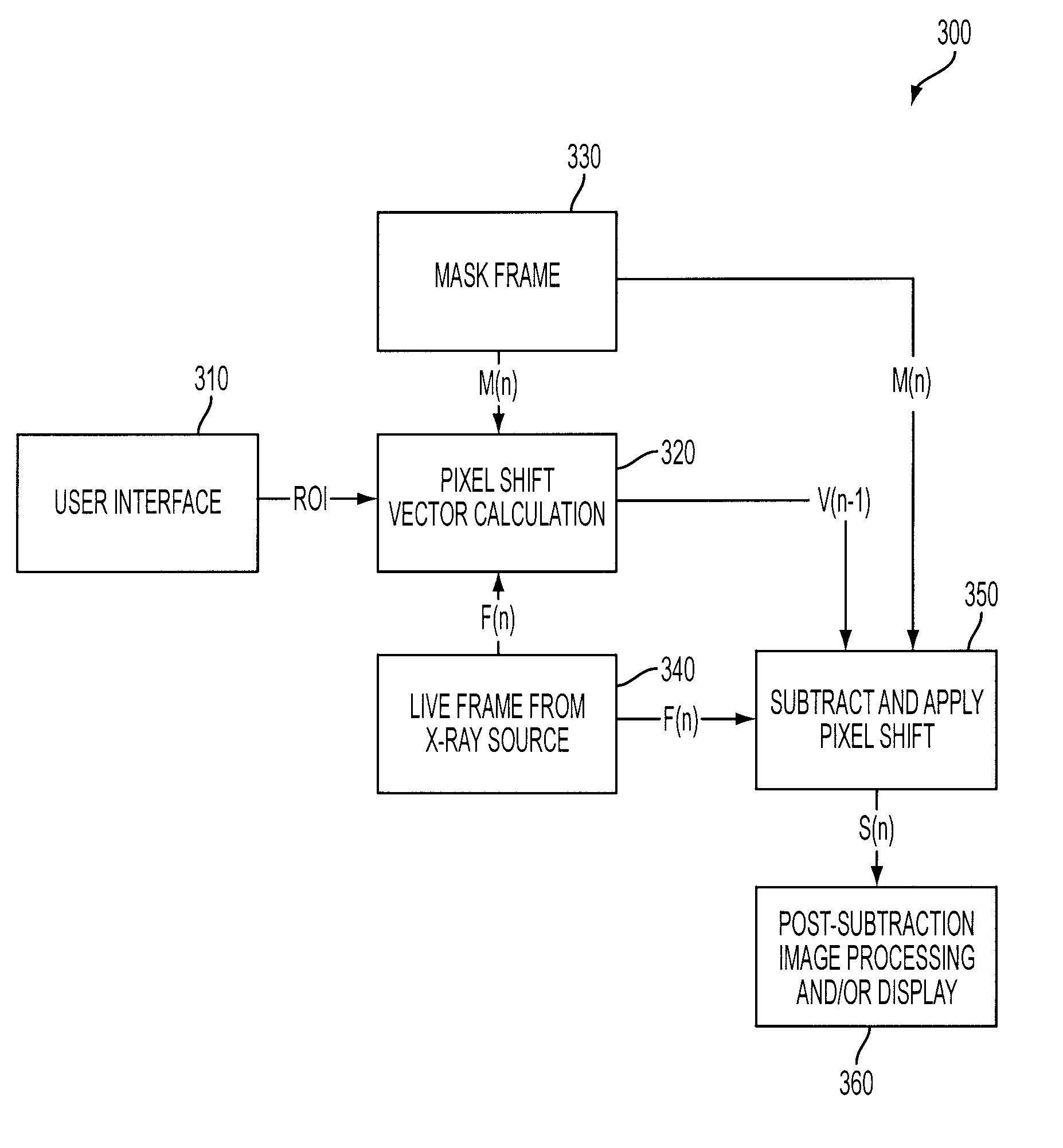
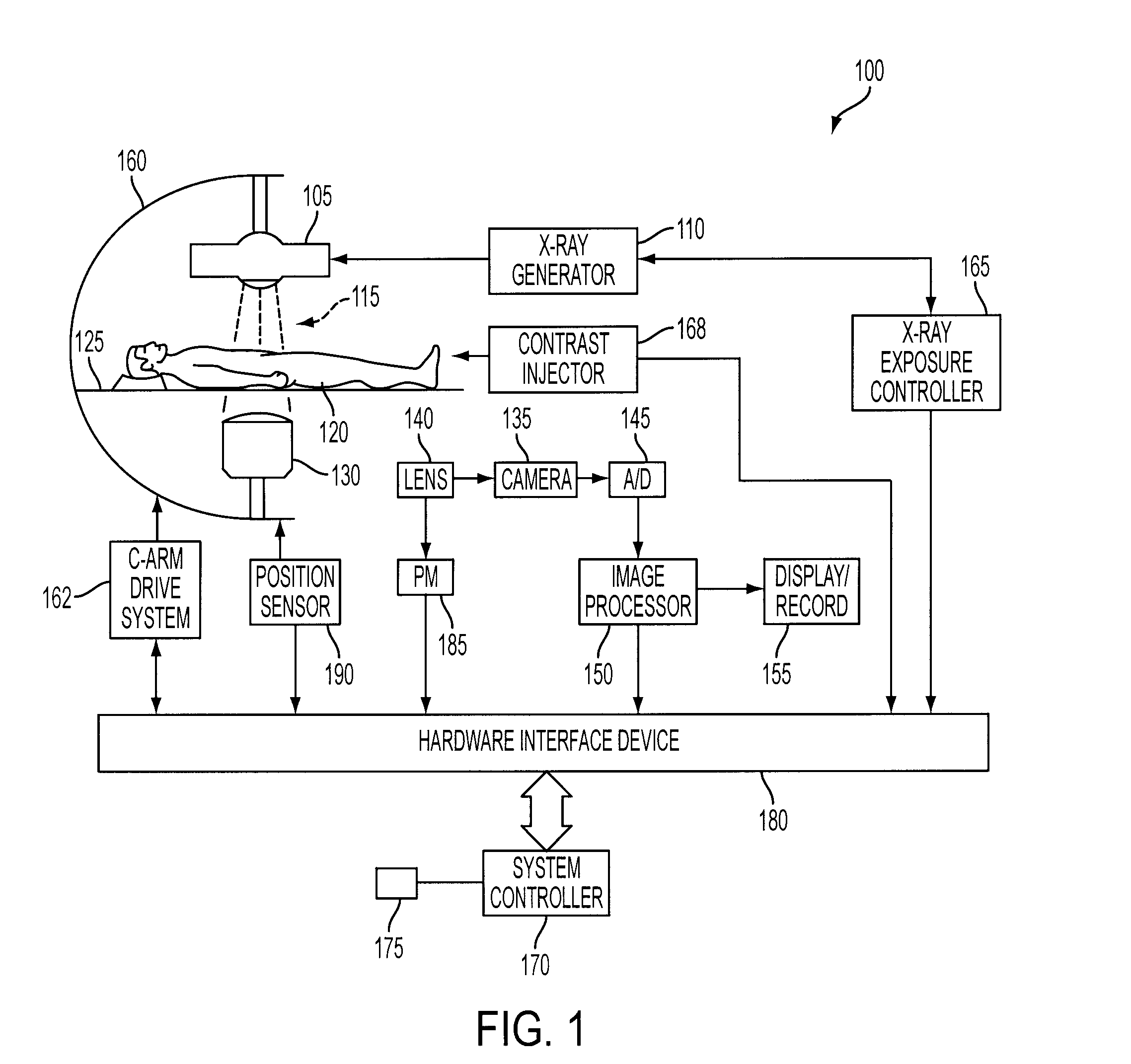
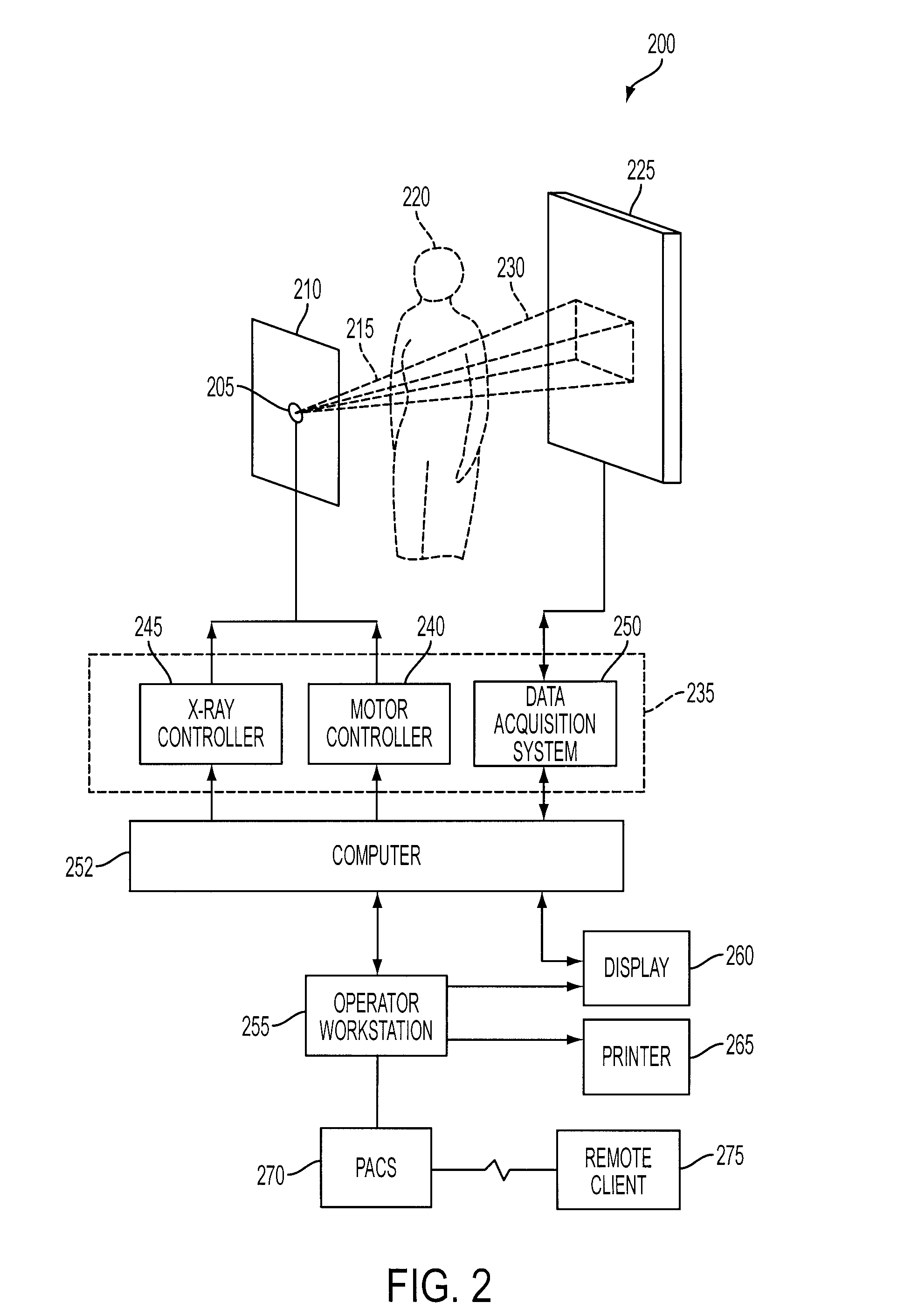
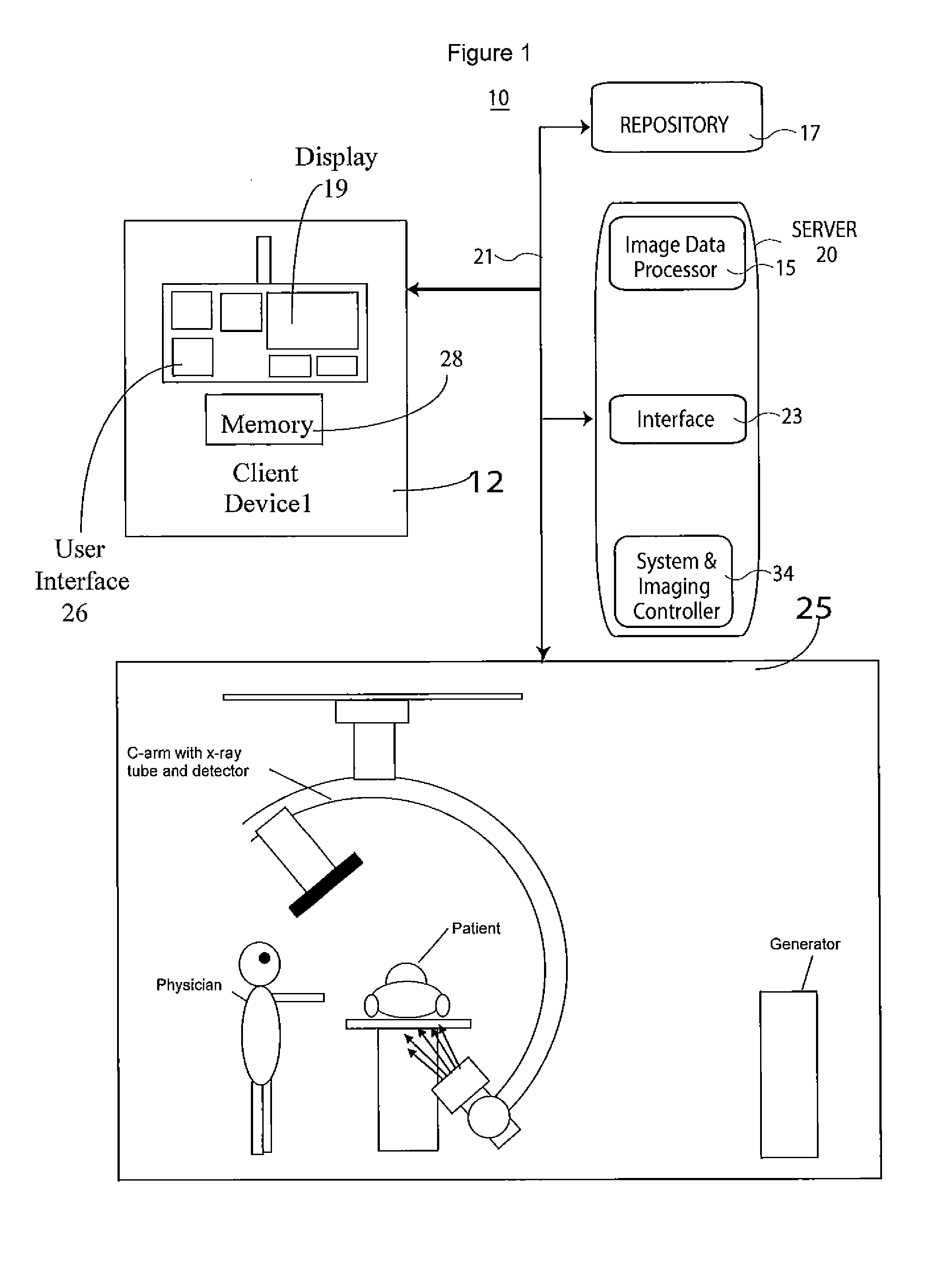
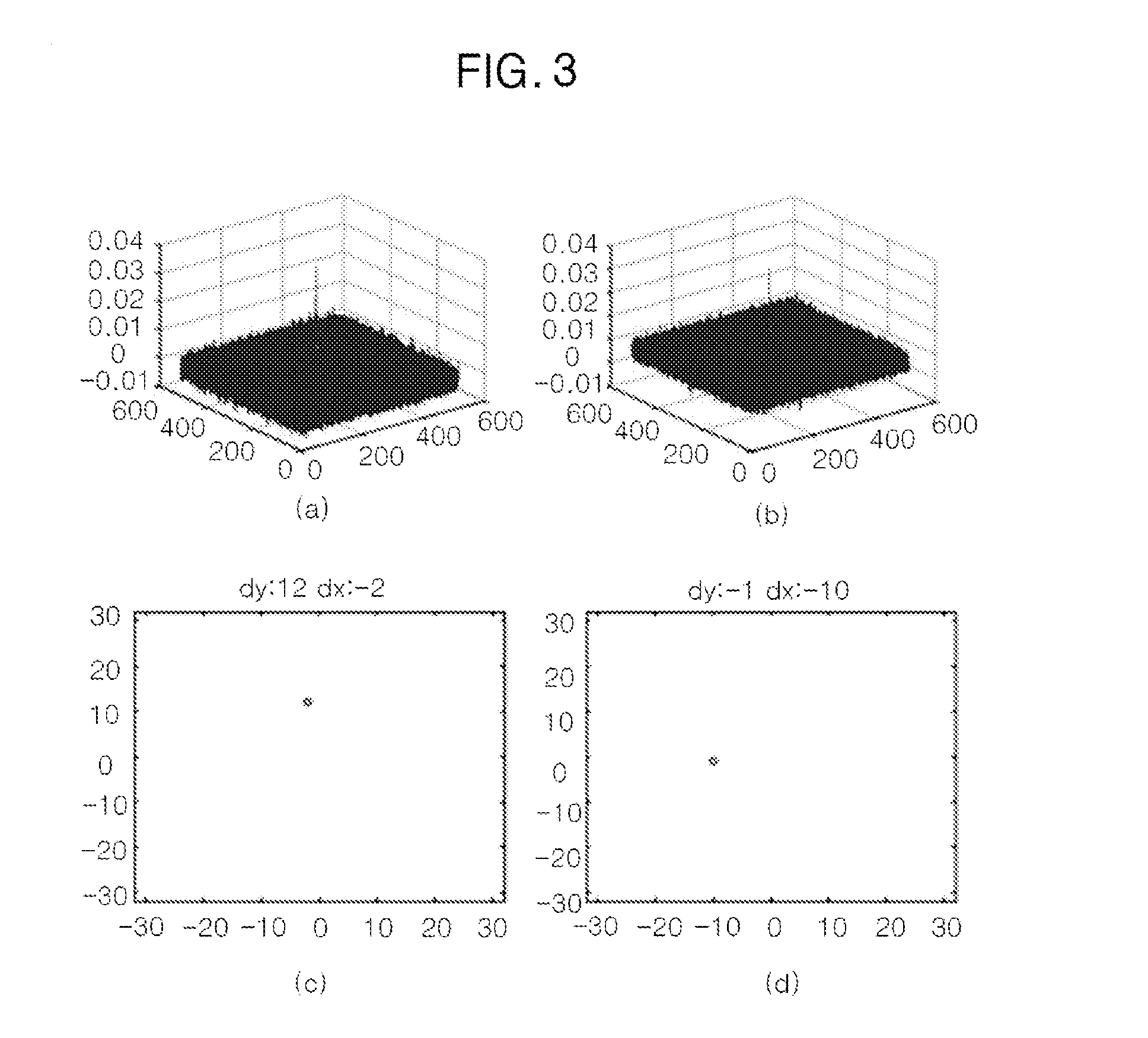
Live Fluoroscopic Roadmapping Including Targeted Automatic Pixel Shift for Misregistration Correction
ActiveUS20080027316A1Overcomes shortcomingCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringDisplay deviceX-ray
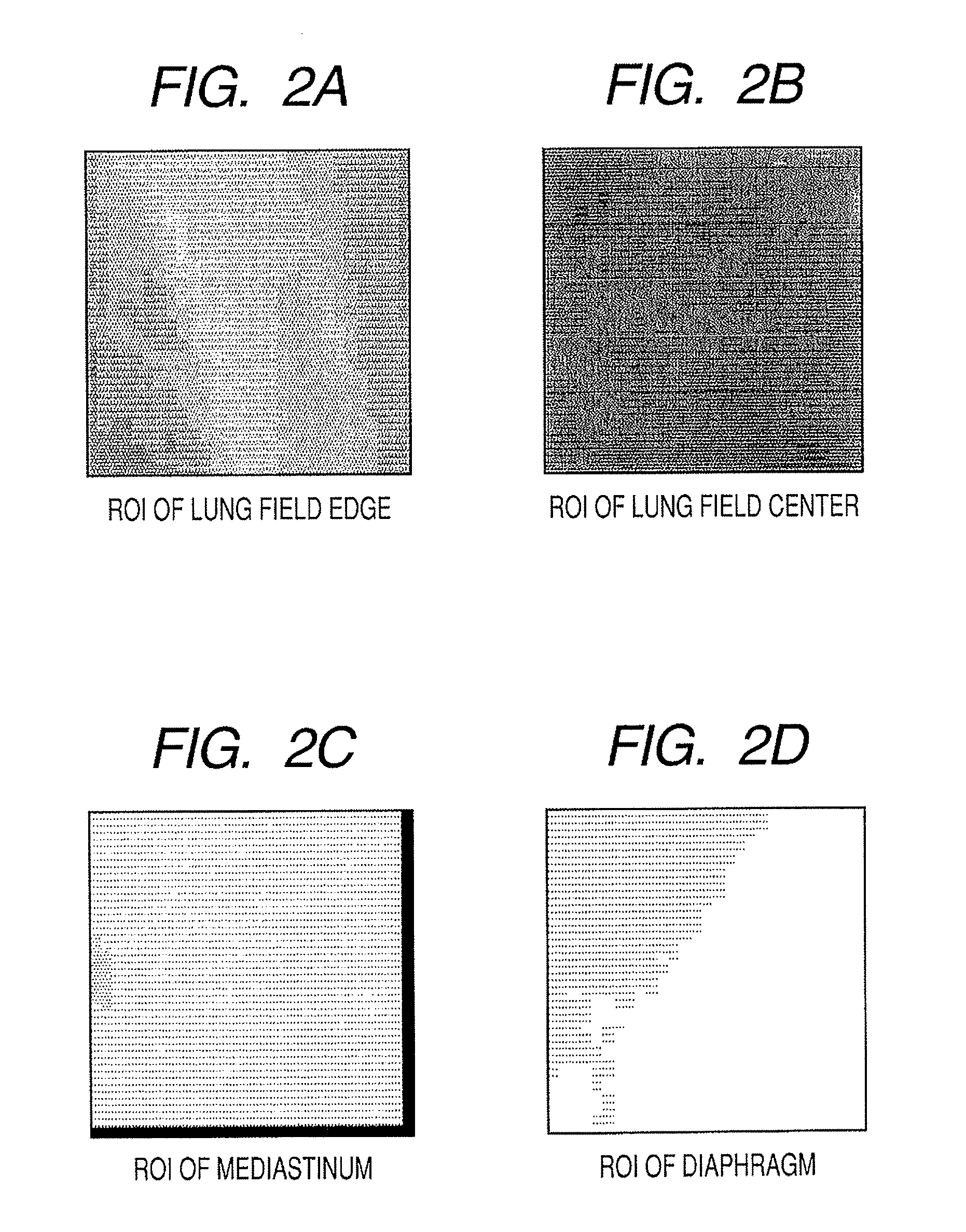
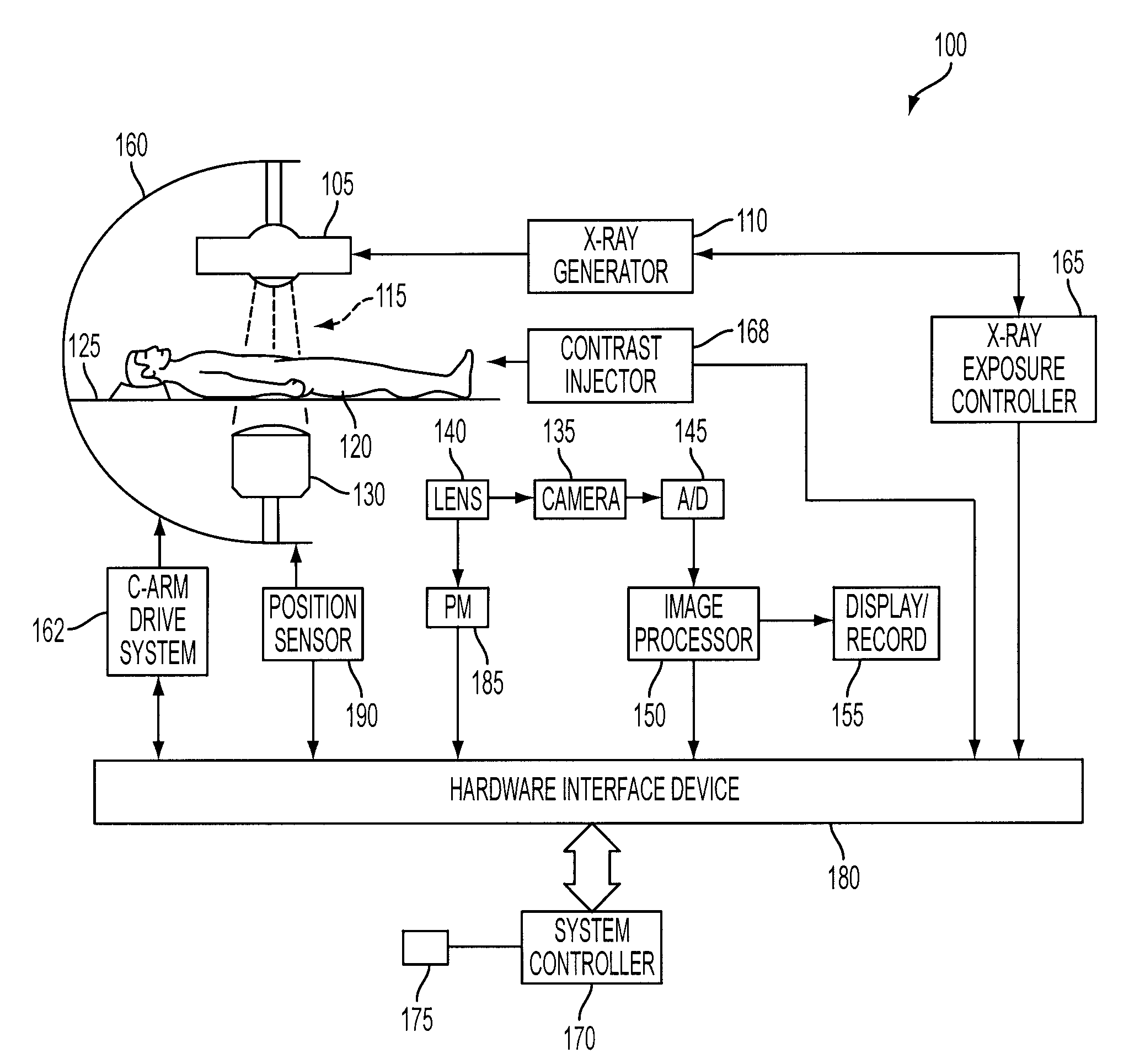
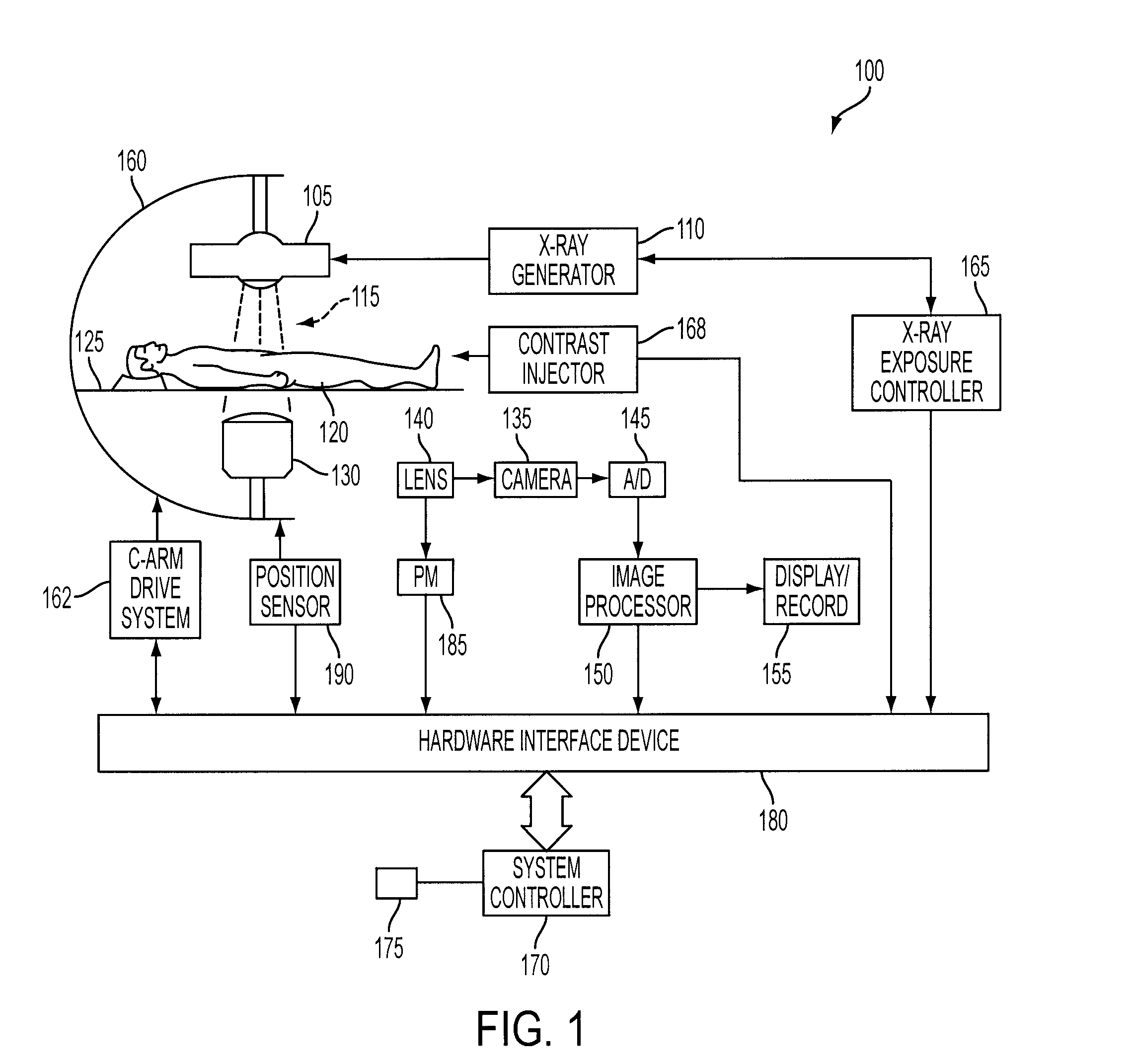
An X-ray diagnostic imaging system for conducting live fluoroscopic subtraction imaging is described as including an X-ray source for directing X-ray radiation to a patient being examined, an x-ray imaging device positioned for receiving the X-ray radiation and acquiring images in response thereto and a processor arranged in communication with the x-ray source and x-ray imaging device to control acquisition of a contrast-enhanced mask image frame and a live image frame without contrast enhancement, to conduct a pixel shift calculation operation based on a small, user-defined region of interest (ROI), for example, 1 / 16 of a full frame, to realize a pixel shift vector to correct for motion between live image frames, to shift pixels comprising the mask image frame by pixel shift directions defined by the pixel shift vector, and to subtract the shifted mask image frame from the live image frame to realize a live roadmapping image frame. The system includes a display for displaying the live roadmapping image frame, and a user interface that allows a user to define and capture the small ROI in the displayed image frame for use by the processor conducting the pixel shift calculation.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
Scene depth restoring and three dimension re-setting method for stereo visual system
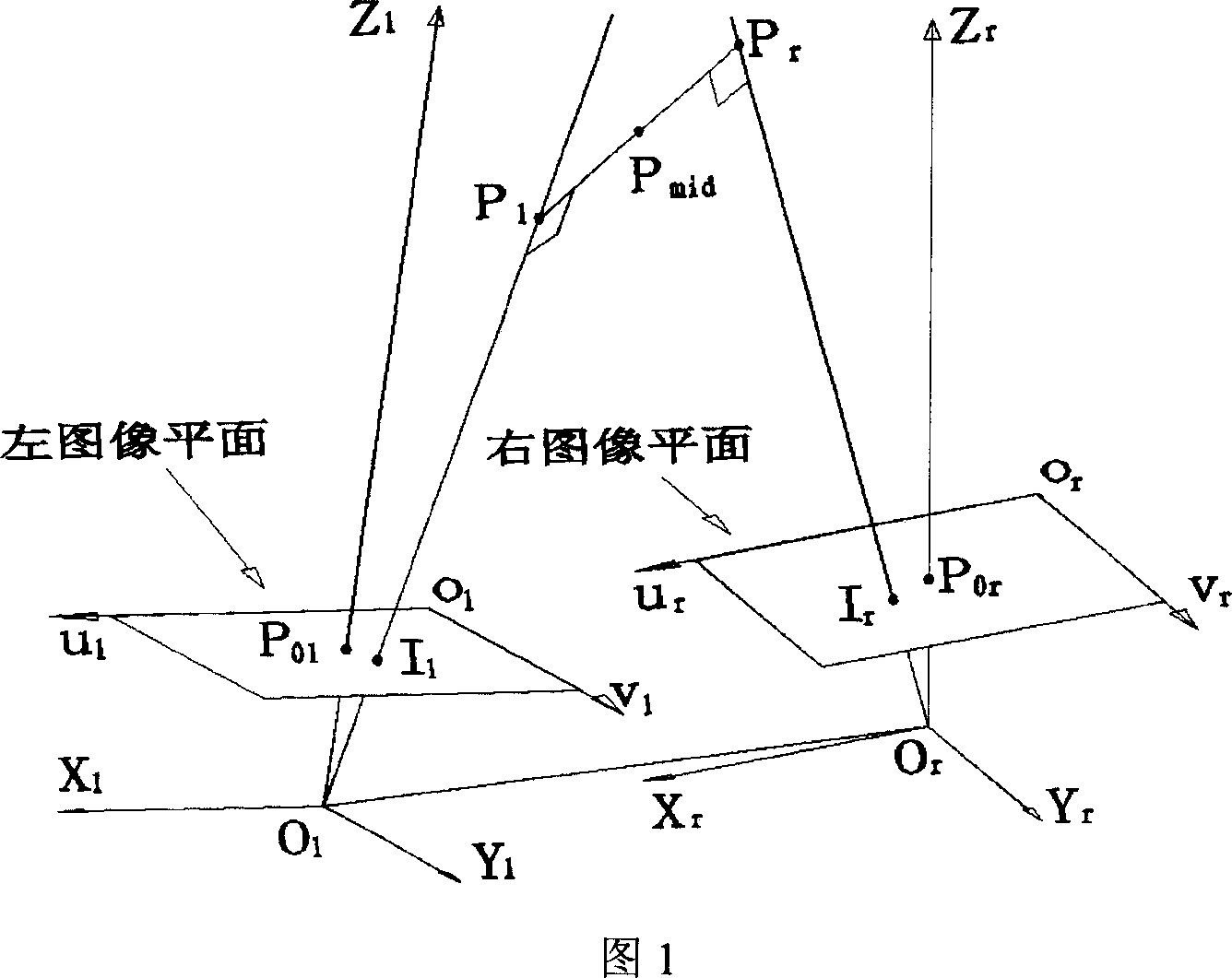
This invention relates to a method for recovering scene depth and re-building three-dimension of a stereoscopic vision system, which gets the inner parameters of right and left cameras, relative rotation matrix and shift vector by calibration, matching the corresponding points of the right and left images, evaluating the right and left normalization vectors of each pair of matched points from their image coordinates and relative inner parameters of the cameras, evaluating an equation of two projection lines from the center of the left camera to the left image point and from the center of the right camera to the right image point based on the coordinates and taking the depth value of the scene point in the coordinate systems of the two cameras as the parameter, evaluating the depth value and three-dimension coordinate of the common plumb end points of the two projection lines in the two camera coordinate systems by the normalized vector, the relative rotation matrix and the shift vector and evaluating the coordinate of the midpoint of the common plumb line from the coordinate of the two points of the line and takes the midpoint coordinate as the three-dimension one of the scene points to finish depth recovery and three-dimension restructuring.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
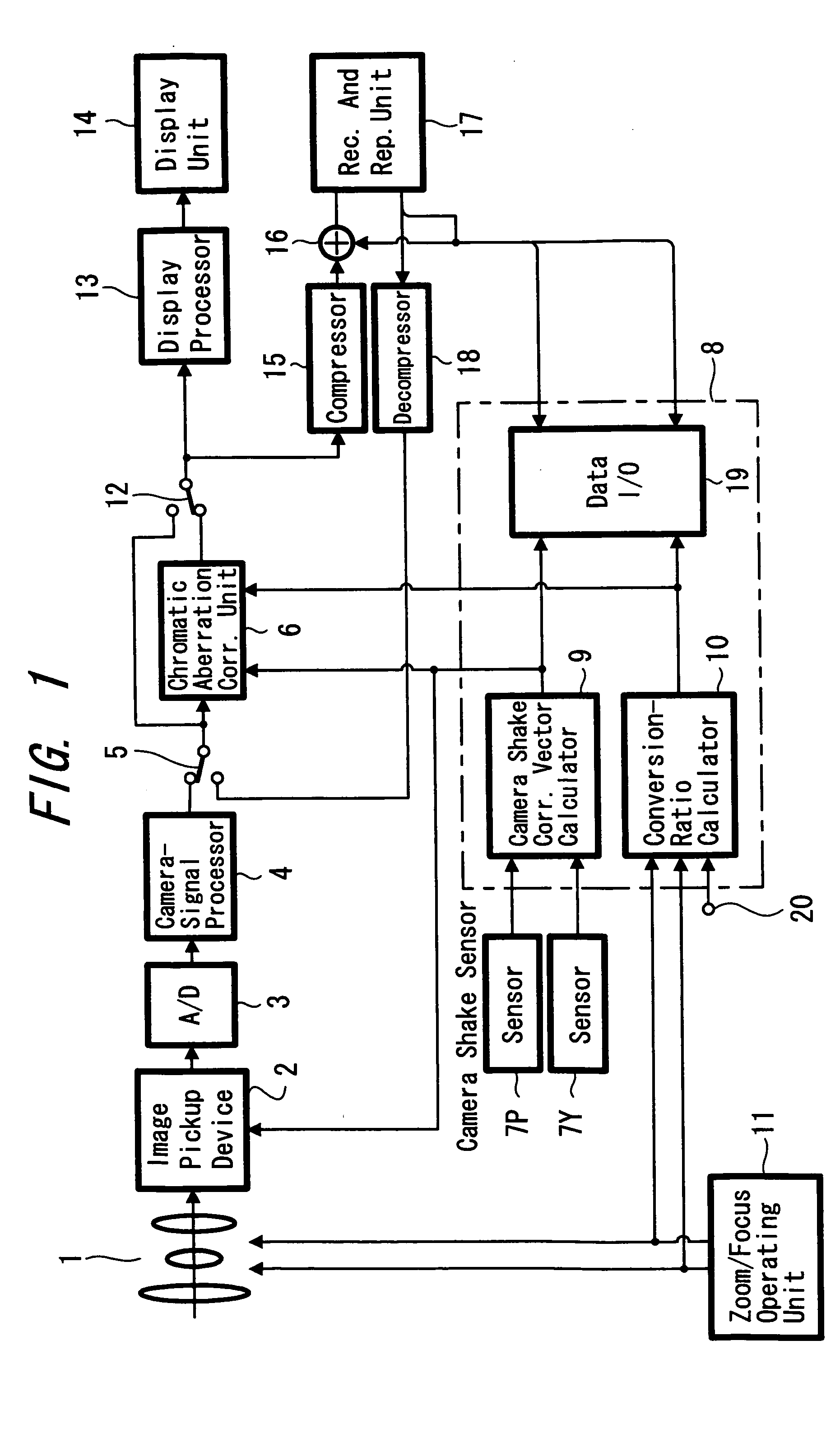
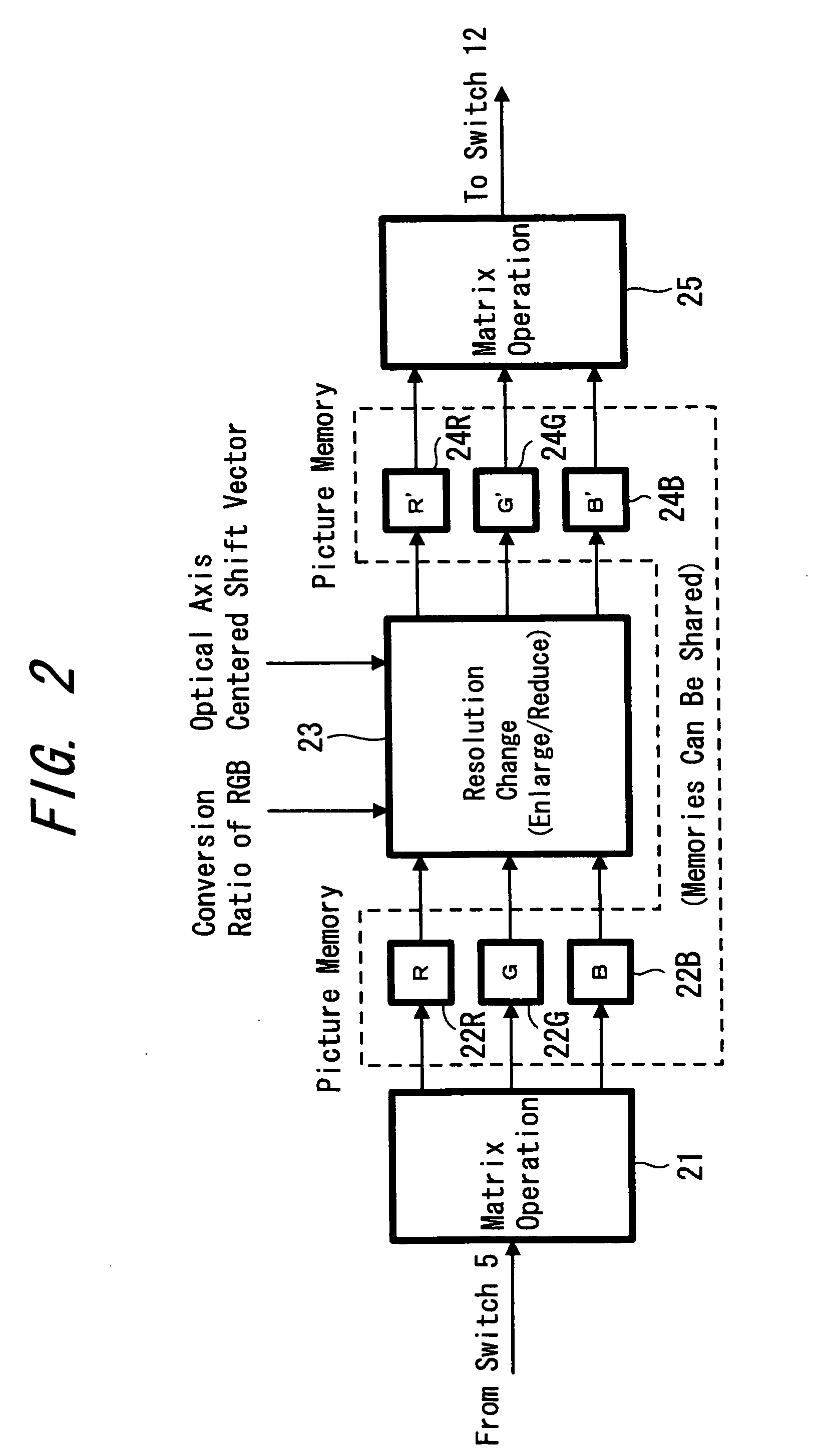
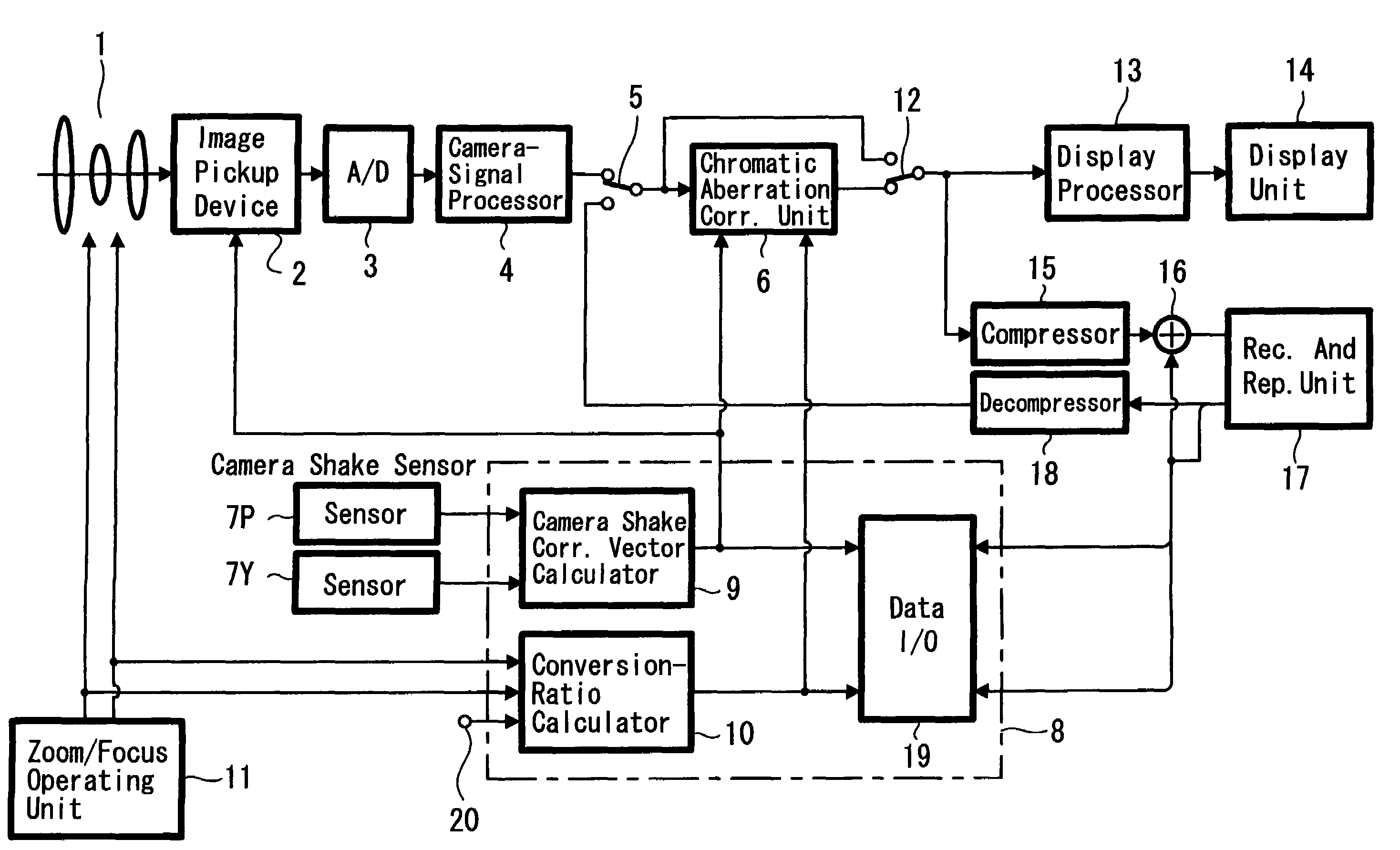
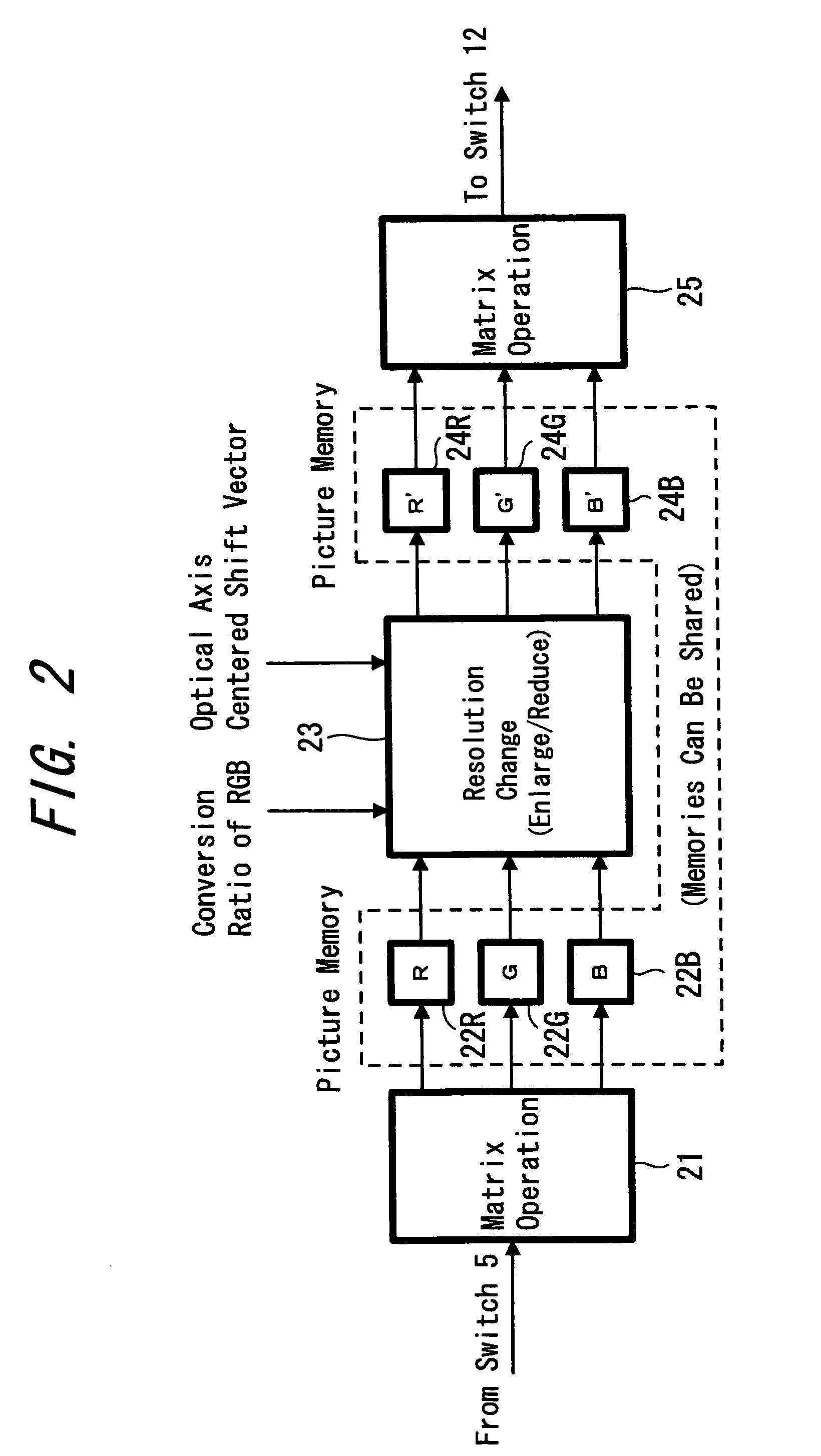
Image pickup device and chromatic aberration correction method
InactiveUS20050168614A1Satisfactory recordingPrecise processingTelevision system detailsPrintersData compressionCamera lens
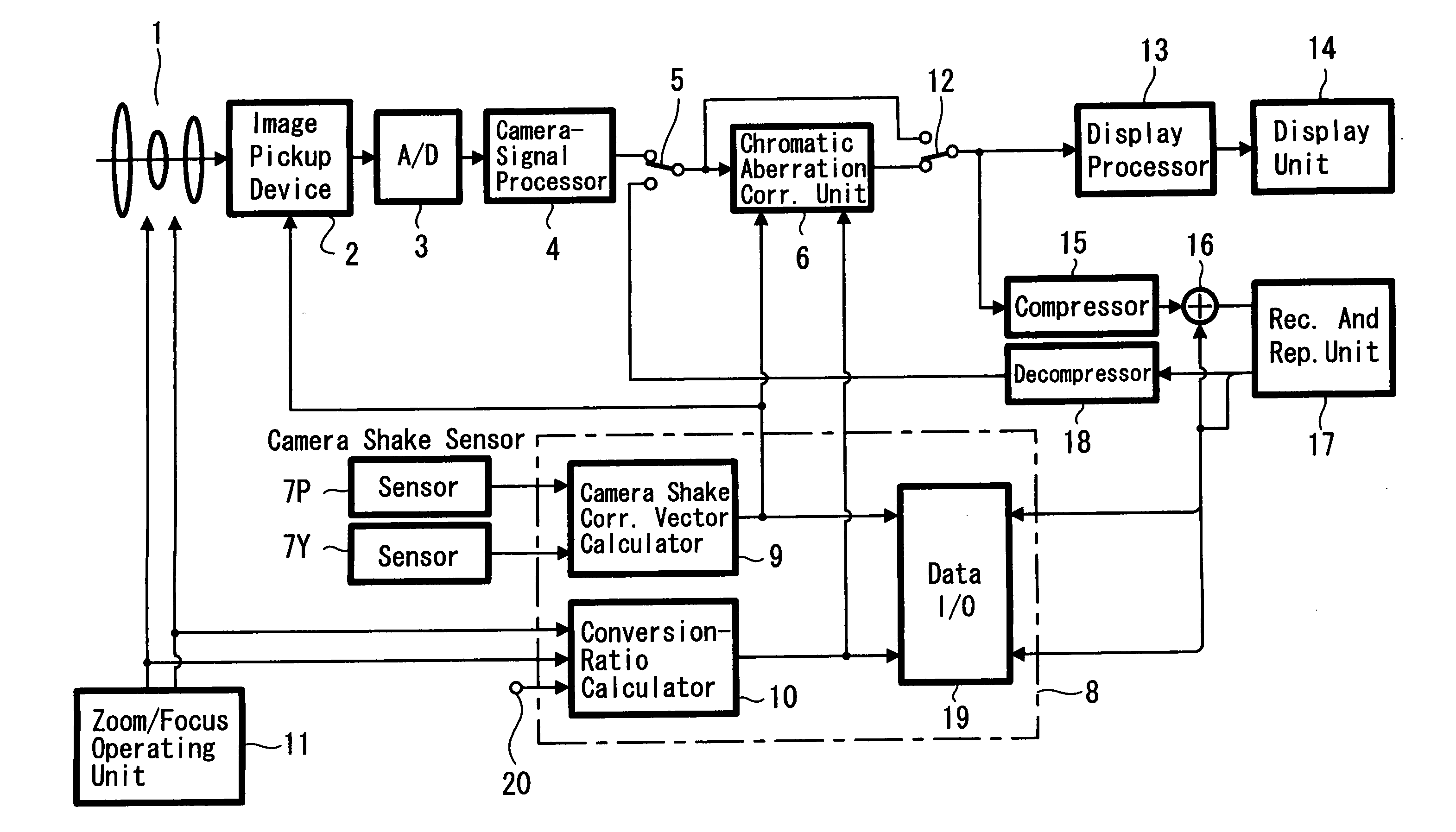
A picture taking apparatus and a chromatic aberration correcting method are provided in which a satisfactory correction processing can be performed even when the camera shake correction is simultaneously performed. An output signal from a camera-signal processing circuit 4 is selected by a selector switch 5 and is supplied to a chromatic aberration correcting unit 6. On the other hand, an angular velocity due to the camera shake is detected using sensors 7P, 7Y and the detected signal is supplied to a camera shake correcting vector calculating unit 9 in control microcomputer 8. A driving state of a camera lens 1 such as a zoom focal length and focal position is supplied to a conversion-ratio calculating unit 10. An optical axis centered shift vector of camera lens 1 is obtained from the camera shake correcting vector and is supplied to the above unit 6. A conversion ratio of each color is supplied to the above unit 6. A signal corrected by the above 6 is compressed by data compression circuit 15 and supplied to a recording medium of a recording and reproducing unit 17 for recording. A signal reproduced therefrom is decompressed by a data expansion circuit 18 and supplied to the selector switch 5. Accordingly the picture-quality deterioration caused in the miniaturized camera lens can be compensated by processing the captured image signal, and also a satisfactory correction processing can be performed even when the camera shake correction is performed simultaneously.
Owner:SONY CORP
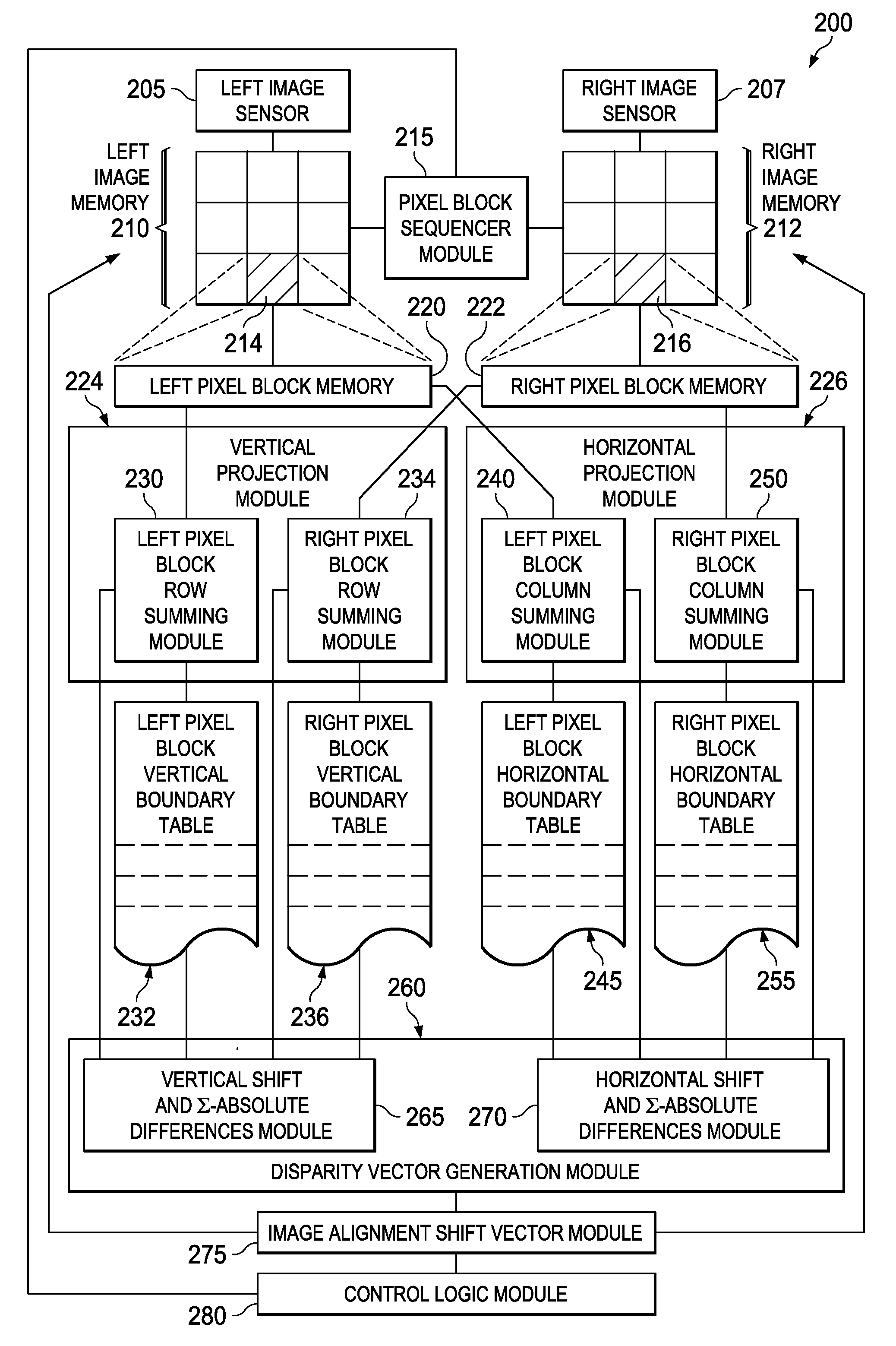
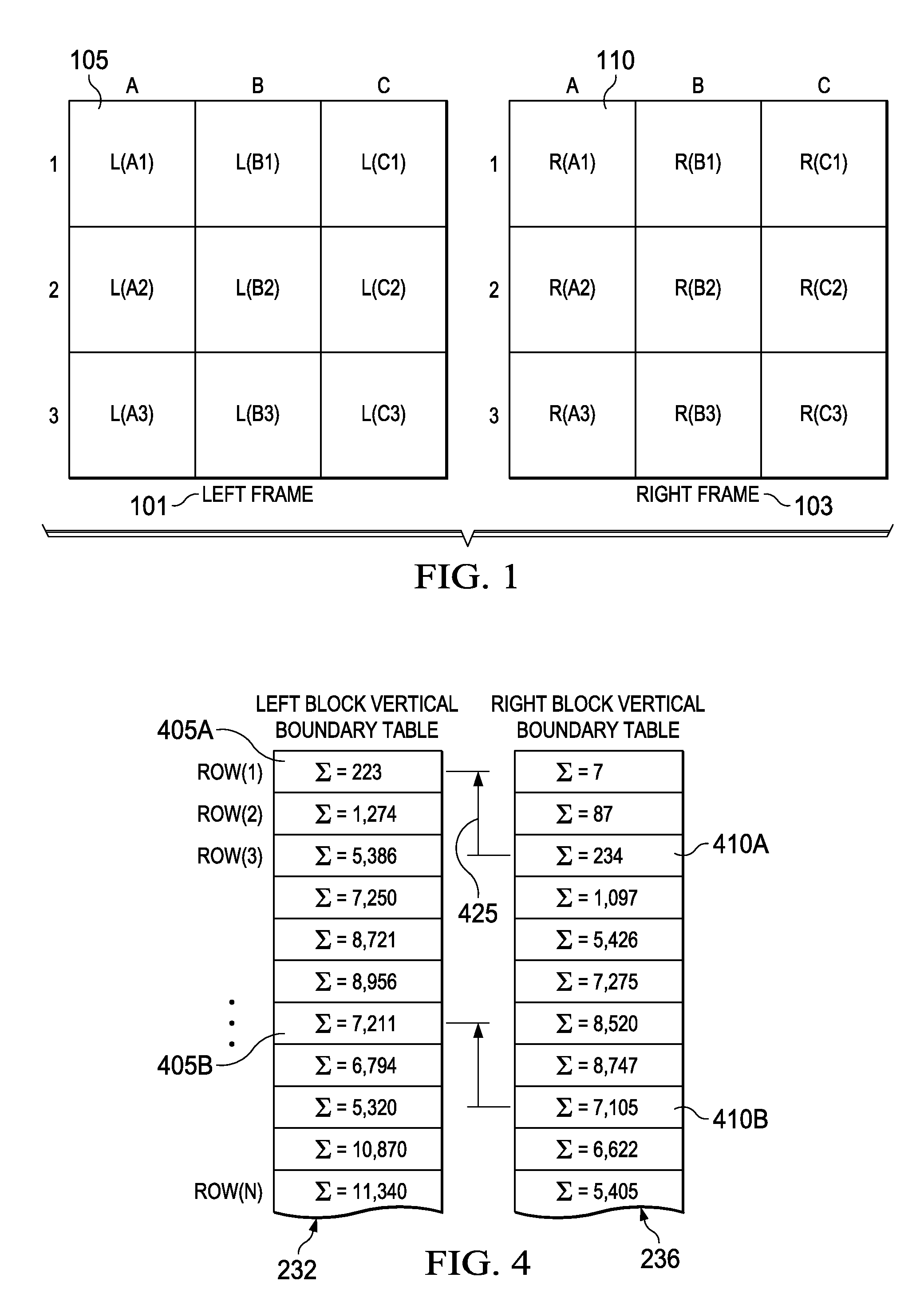
Stereoscopic image pair alignment apparatus, systems and methods
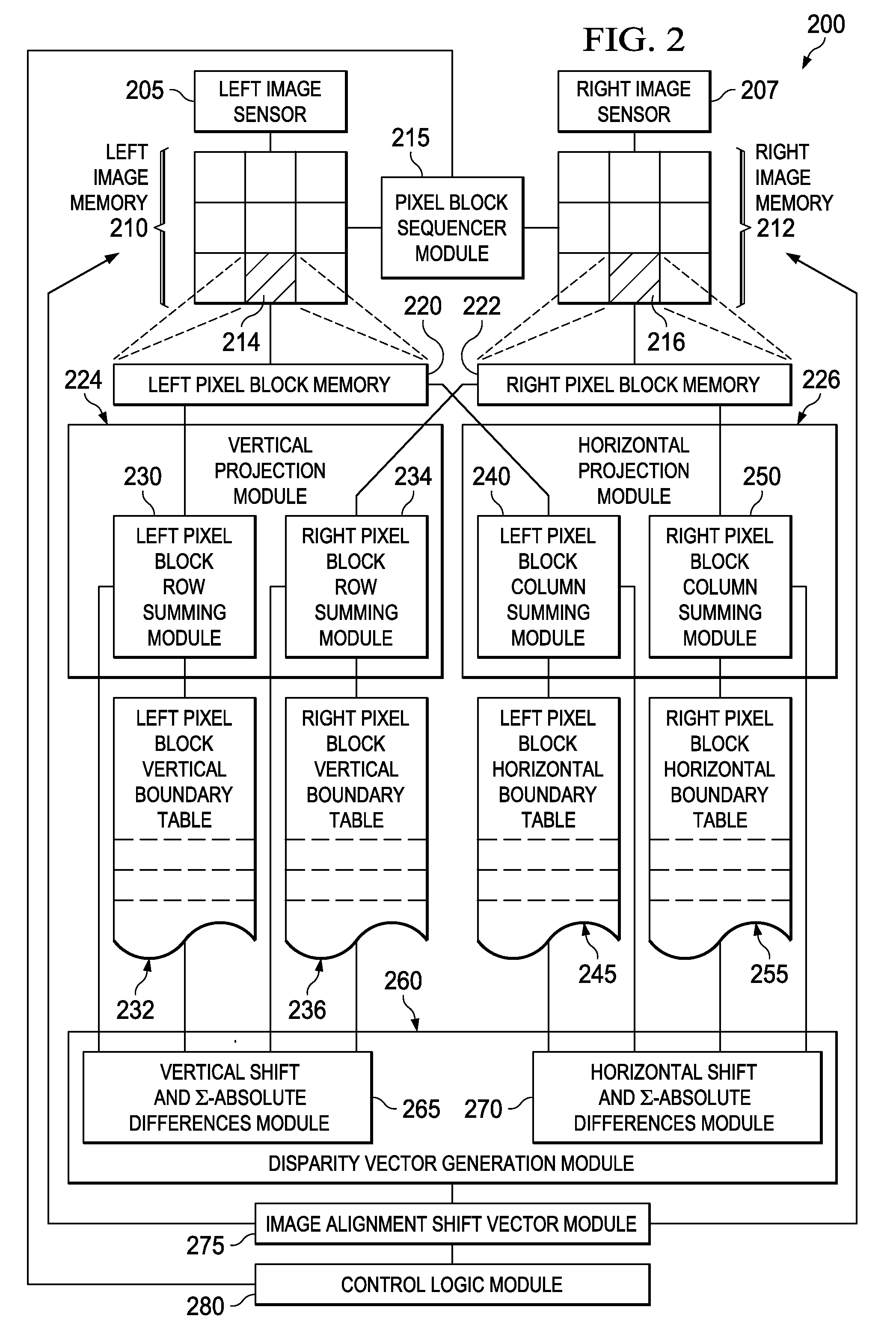
InactiveUS20110249889A1Reduce and eliminate and componentSave processing powerImage enhancementImage analysisParallaxImage alignment
Apparatus, systems, and methods disclosed herein operate to produce an image alignment shift vector used to shift left and right image portions of a stereoscopic image with respect to each other in order to reduce or eliminate undesirable horizontal and vertical disparity components. Vertical and horizontal projections of luminance value aggregations from selected left and right image pixel blocks are correlated to derive vertical and horizontal components of a disparity vector corresponding to each left / right pixel block pair. Disparity vectors corresponding to multiple image blocks are algebraically combined to yield the image alignment shift vector. The left and / or right images are then shifted in proportion to the magnitude of the image alignment shift vector at an angle corresponding to that of the image alignment shift vector.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Live fluoroscopic roadmapping including targeted automatic pixel shift for misregistration correction
ActiveUS7826884B2Overcomes shortcomingCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringDisplay deviceX-ray
An X-ray diagnostic imaging system for conducting live fluoroscopic subtraction imaging is described as including an X-ray source for directing X-ray radiation to a patient being examined, an x-ray imaging device positioned for receiving the X-ray radiation and acquiring images in response thereto and a processor arranged in communication with the x-ray source and x-ray imaging device to control acquisition of a contrast-enhanced mask image frame and a live image frame without contrast enhancement, to conduct a pixel shift calculation operation based on a small, user-defined region of interest (ROI), for example, 1 / 16 of a full frame, to realize a pixel shift vector to correct for motion between live image frames, to shift pixels comprising the mask image frame by pixel shift directions defined by the pixel shift vector, and to subtract the shifted mask image frame from the live image frame to realize a live roadmapping image frame. The system includes a display for displaying the live roadmapping image frame, and a user interface that allows a user to define and capture the small ROI in the displayed image frame for use by the processor conducting the pixel shift calculation.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Image registration method
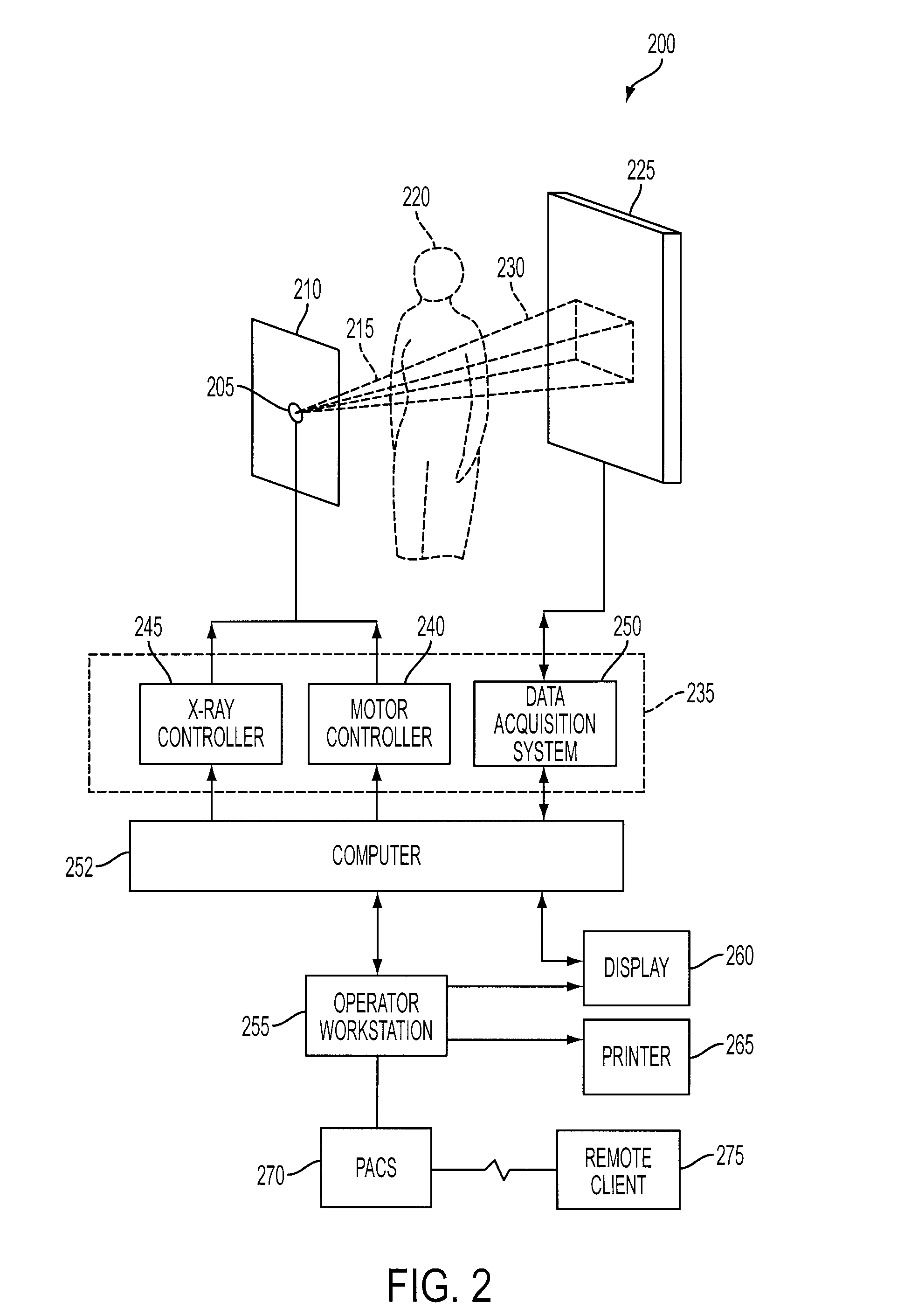
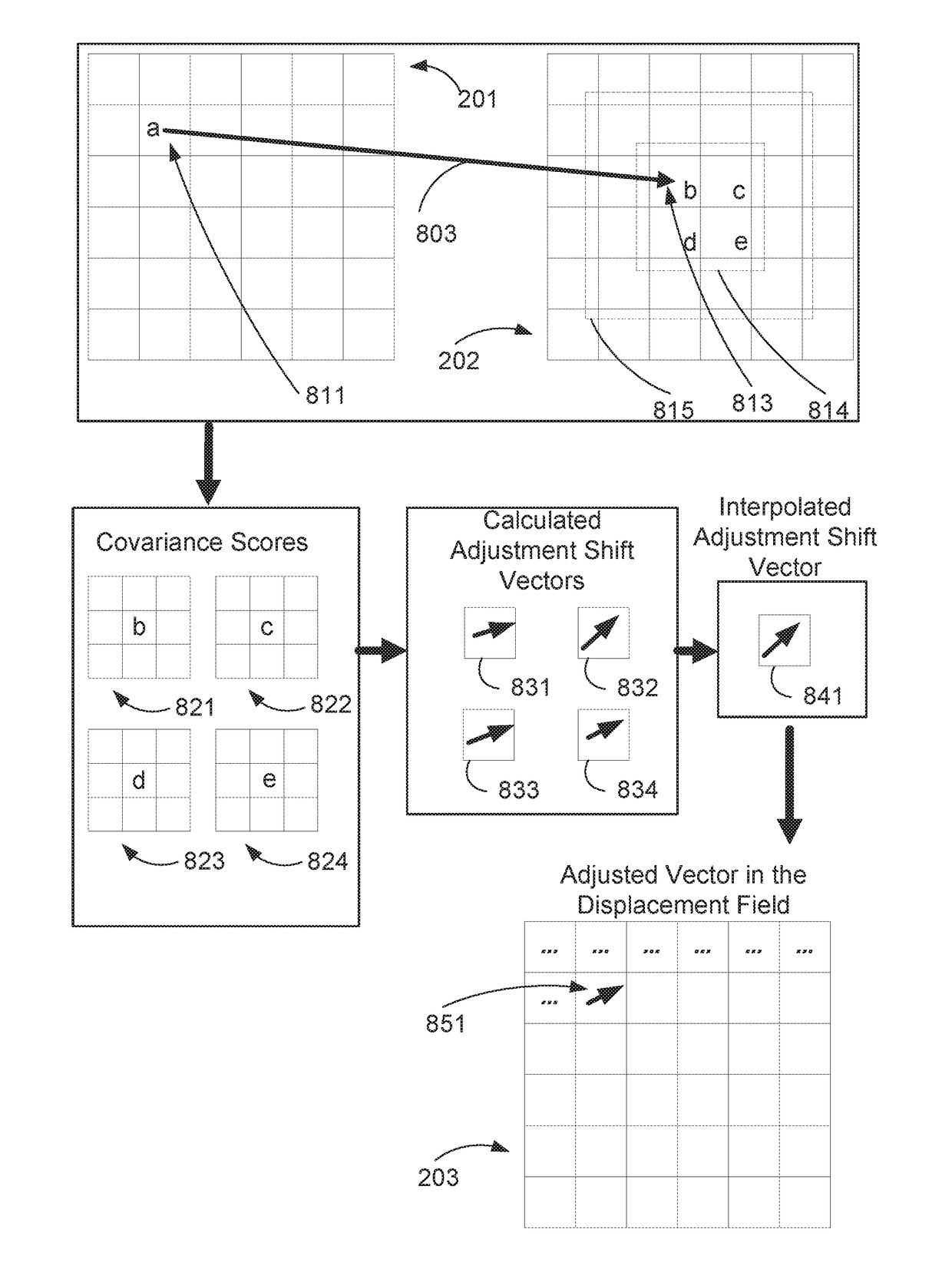
A displacement field relating positions of pixels between at least two images having an initial displacement field is adjusted. Each pixel of the first image and the second image is associated with a label. A first pixel in the first image maps to a second pixel in the second image based on a vector of the initial displacement field. A set of third pixels includes the second pixel and a plurality of adjacent pixels to the second pixel, the third pixels being associated with labels and a candidate shift vector with respect to the second pixel. A covariance score is determined for each of the third pixels, the covariance score defining a statistical dependence between the first label of the first pixel and each of the third labels. An adjustment shift vector is then determined based on the covariance scores and the candidate shift vectors of the third pixels.
Owner:CANON KK
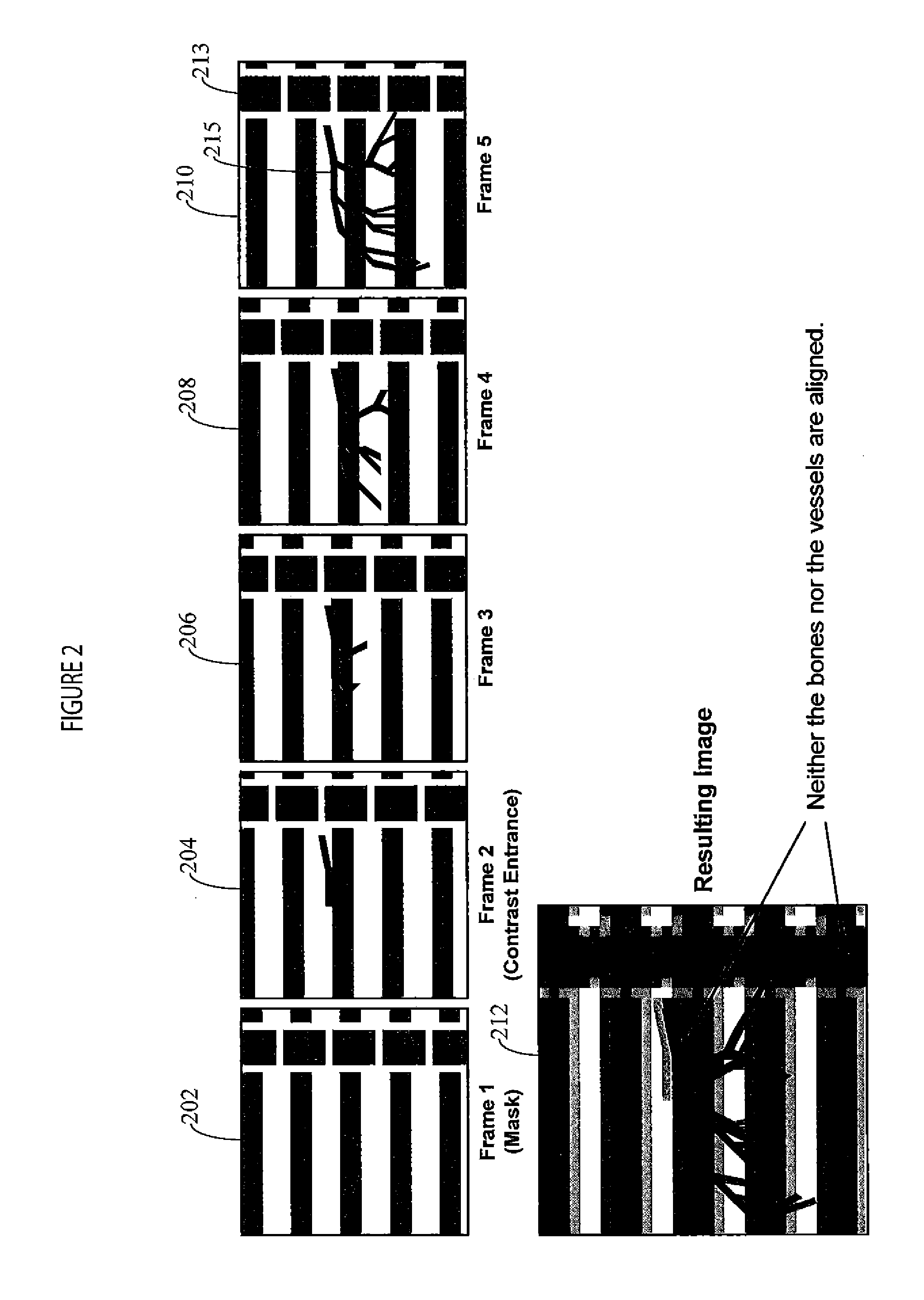
Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) Motion Compensated Imaging System
ActiveUS20120201439A1Improves pixel-shift motion correctionReduce relative motionImage enhancementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationReference imageShift vector
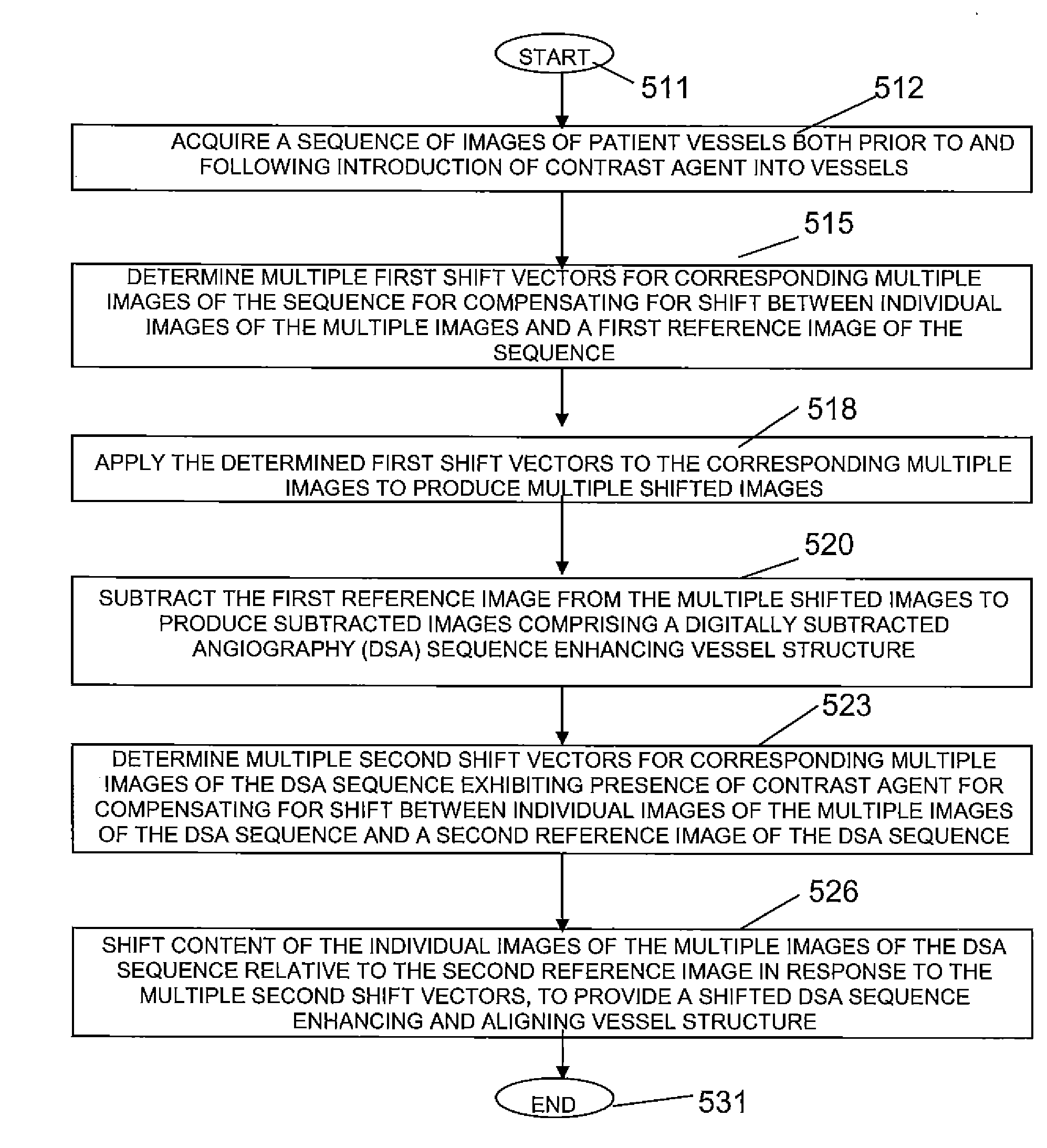
A motion compensated digitally subtracted Angiography (DSA) image processing system includes an interface for acquiring a sequence of images of patient vessels both prior to and following introduction of contrast agent into the vessels. An image data processor automatically, (a) determines a first shift vector for a first image of the sequence for compensating for shift between the first image and a first reference image of the sequence, (b) applies the determined first shift vector to the first image of the sequence to produce a shifted image, (c) subtracts the first reference image from the shifted image to produce a subtracted image enhancing vessel structure, (d) determines a second shift vector for compensating for shift between the subtracted image and a second reference image and (e) shifts content of the subtracted image relative to the second reference image in response to the second shift vector, to provide a shifted subtracted image enhancing and aligning vessel structure.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
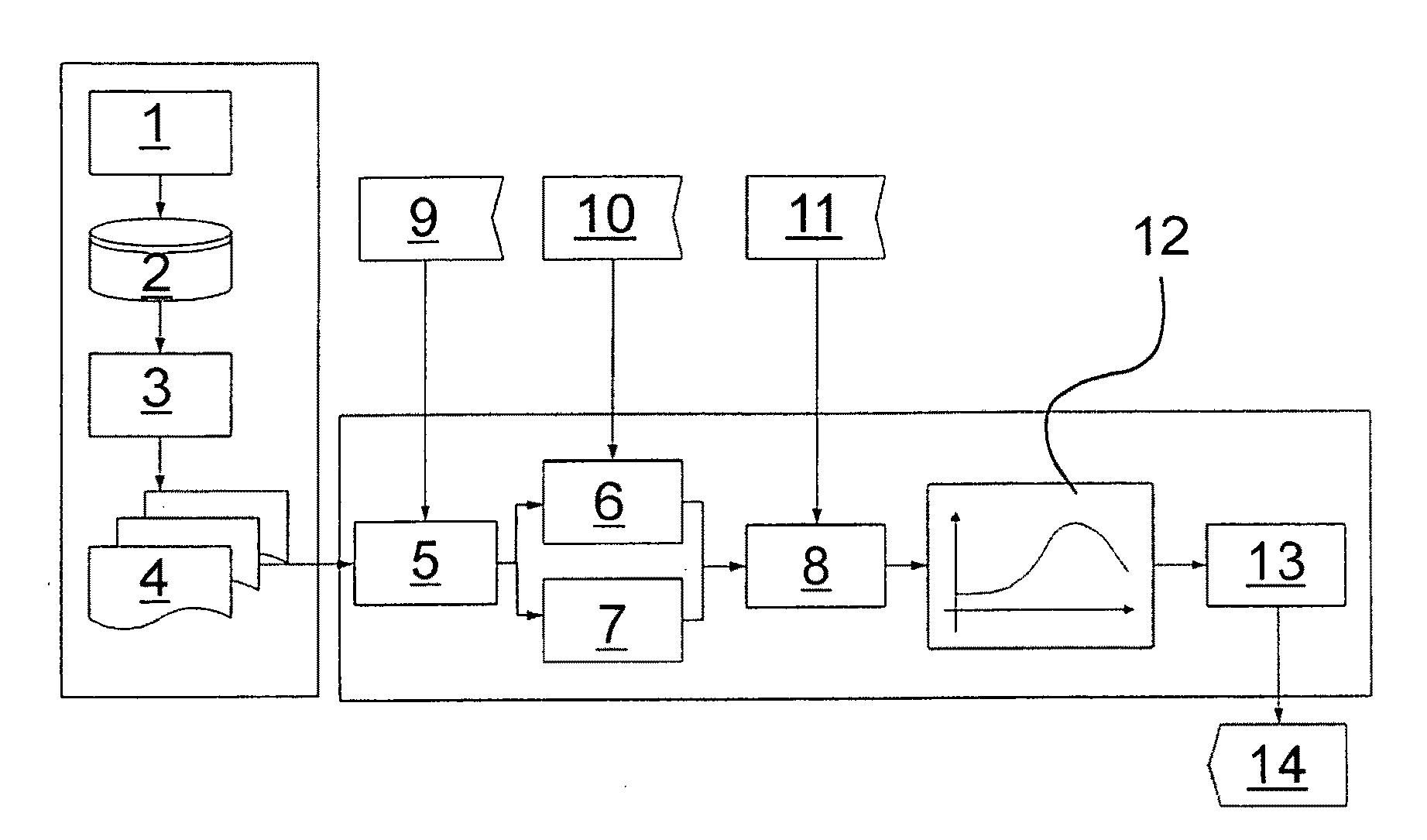
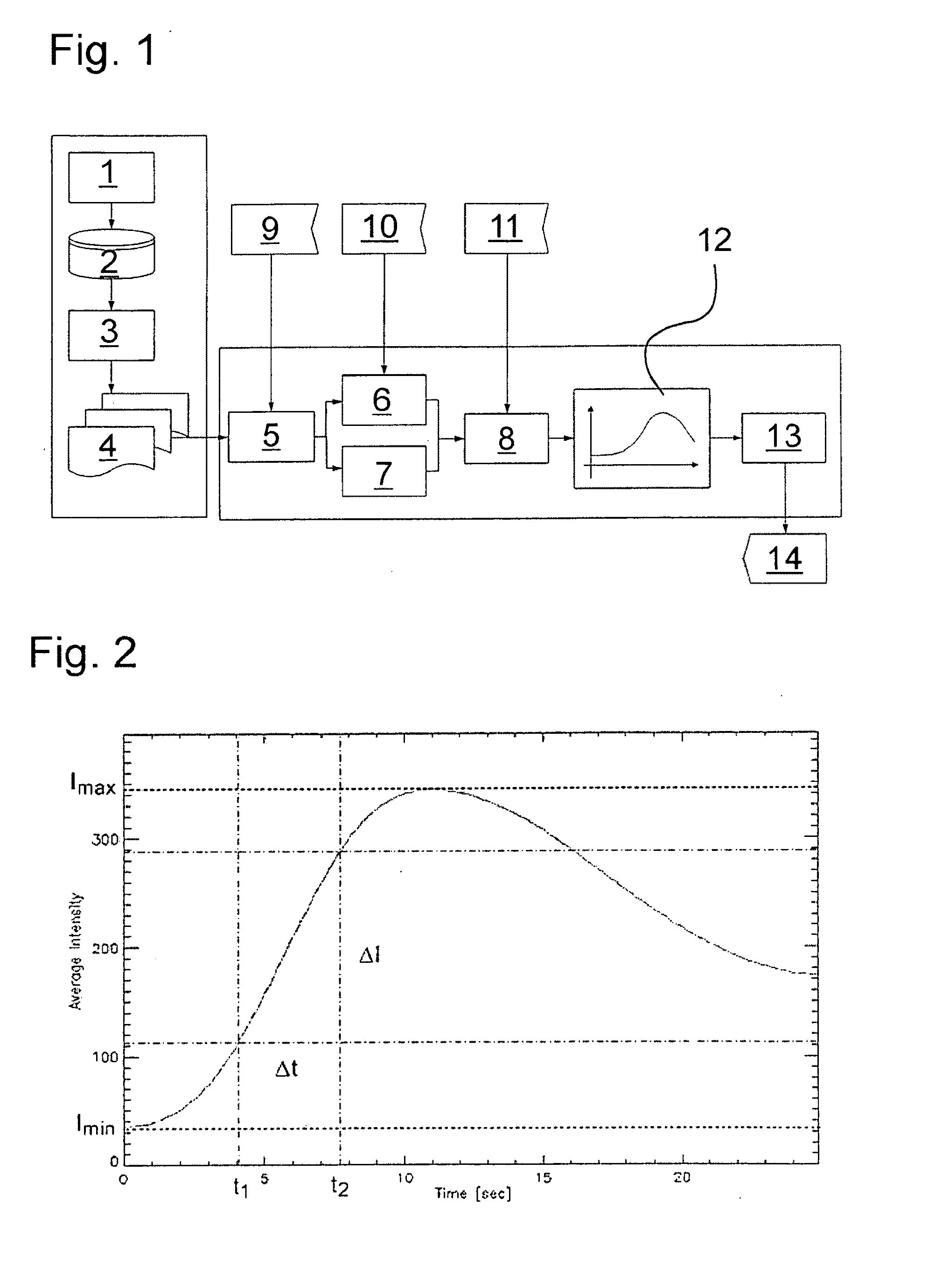
Method for correcting the image data that represent the blood flow
InactiveUS20100042000A1Robust methodBetter overviewImage enhancementImage analysisShift vectorComputer science
A method for correcting the image data representing the blood flow for the evaluation and quantitative representation of the blood flow in a tissue or vascular region is based on the signal of a contrast agent injected into the blood. Several individual images of the signal emitted by the tissue or vascular region are recorded and stored at successive points in time. At least two individual images are correlated and a shift vector is generated based on the correlation. Thereafter, the image data of the individual images are shifted in relation to each other according to the shift vector.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SURGICAL
Fusion method of different-accuracy three-dimension point cloud data based on mean shift
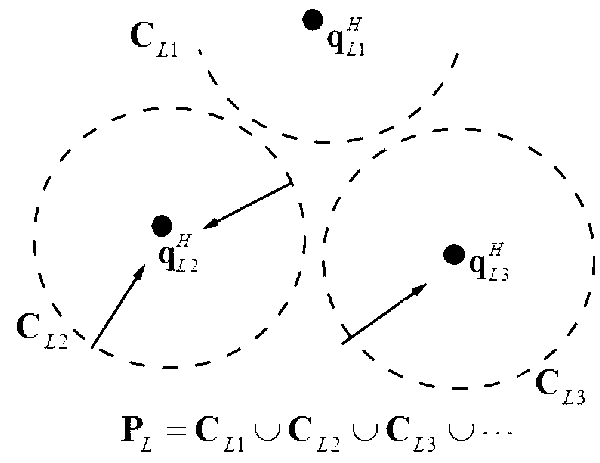
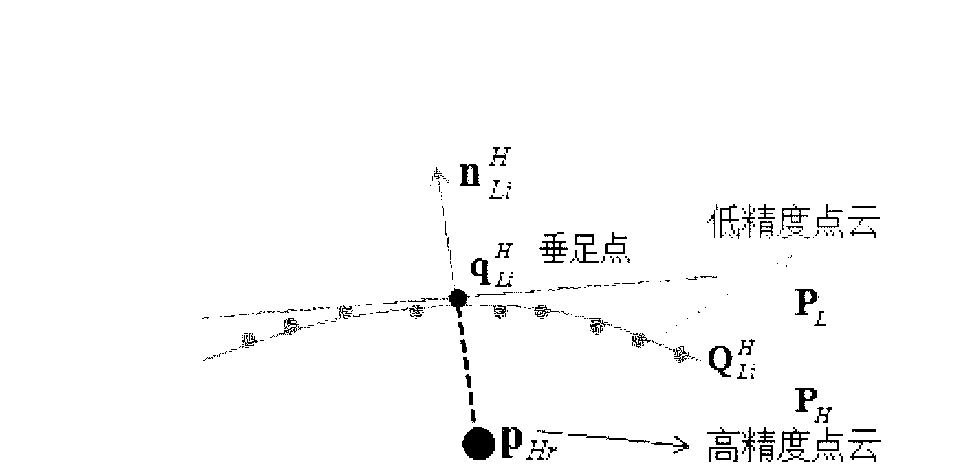
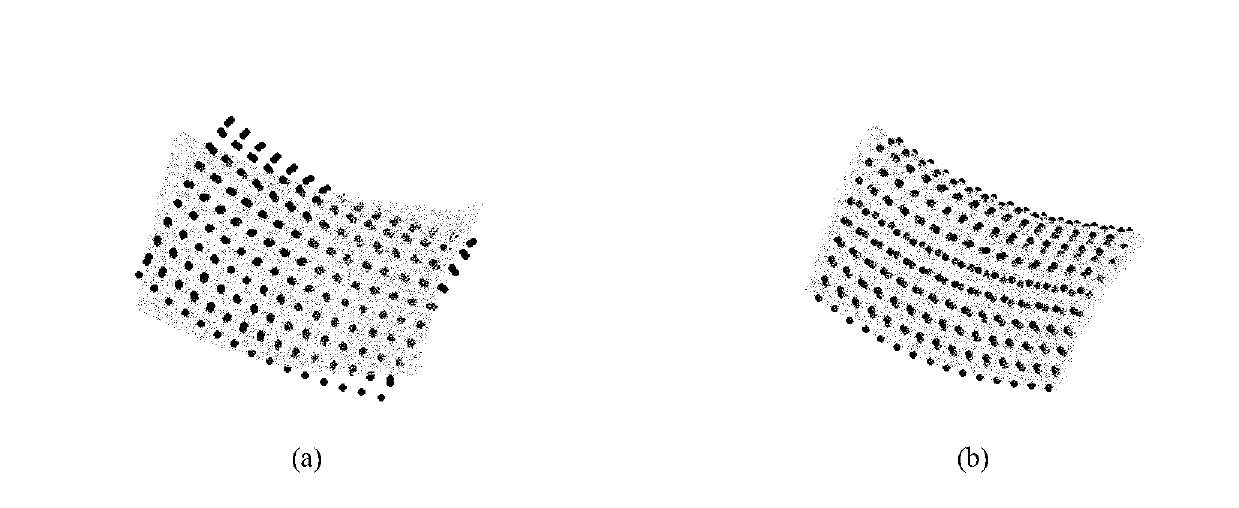
ActiveCN103106632AAccurate descriptionAccurately reflectImage enhancementUsing optical meansSmall amplitudePoint cloud
The invention discloses a fusion method of different-accuracy three-dimension point cloud data based on mean shift. Aiming at two groups of three-dimension point cloud data in different accuracy levels, through utilizing of high-accurate point cloud, error distribution of low-accuracy point cloud is set up, and the mean shift is carried out on the low-accuracy point cloud to eliminate shift errors of the low-accuracy point cloud, and therefore fusion of two groups of data information is realized. The method includes steps: (1) setting up topological structure information of the low-accuracy point cloud, and the topological structure information comprises neighborhood point sets and unit normal vector of every sample point; (2) utilizing the high-accurate point cloud to carry out density clustering on the low-accuracy point cloud, and ensuring shift errors of every sample point of the low-accuracy point cloud according to a clustering result; and (3) utilizing the topological structure information of the low-accuracy point cloud and shift errors to ensure the shift vector of every sample point of the low-accuracy point cloud, and then carrying out shift on every sample point of the low-accuracy point cloud according to the shift vector to realize fusion. According to the fusion method, shift errors of the low-accuracy point cloud are eliminated, and fairing of small-amplitude noises can be realized at the same time.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
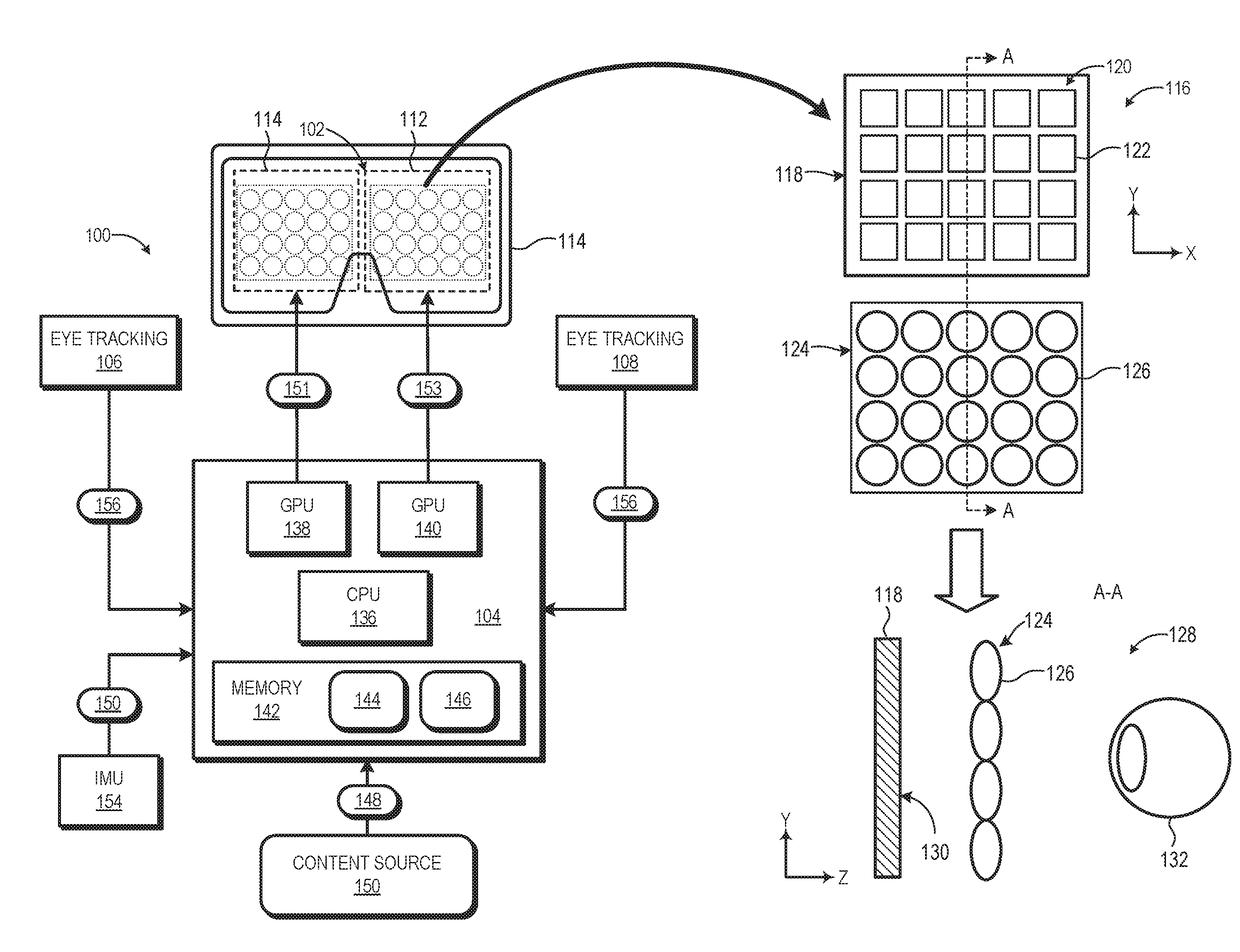
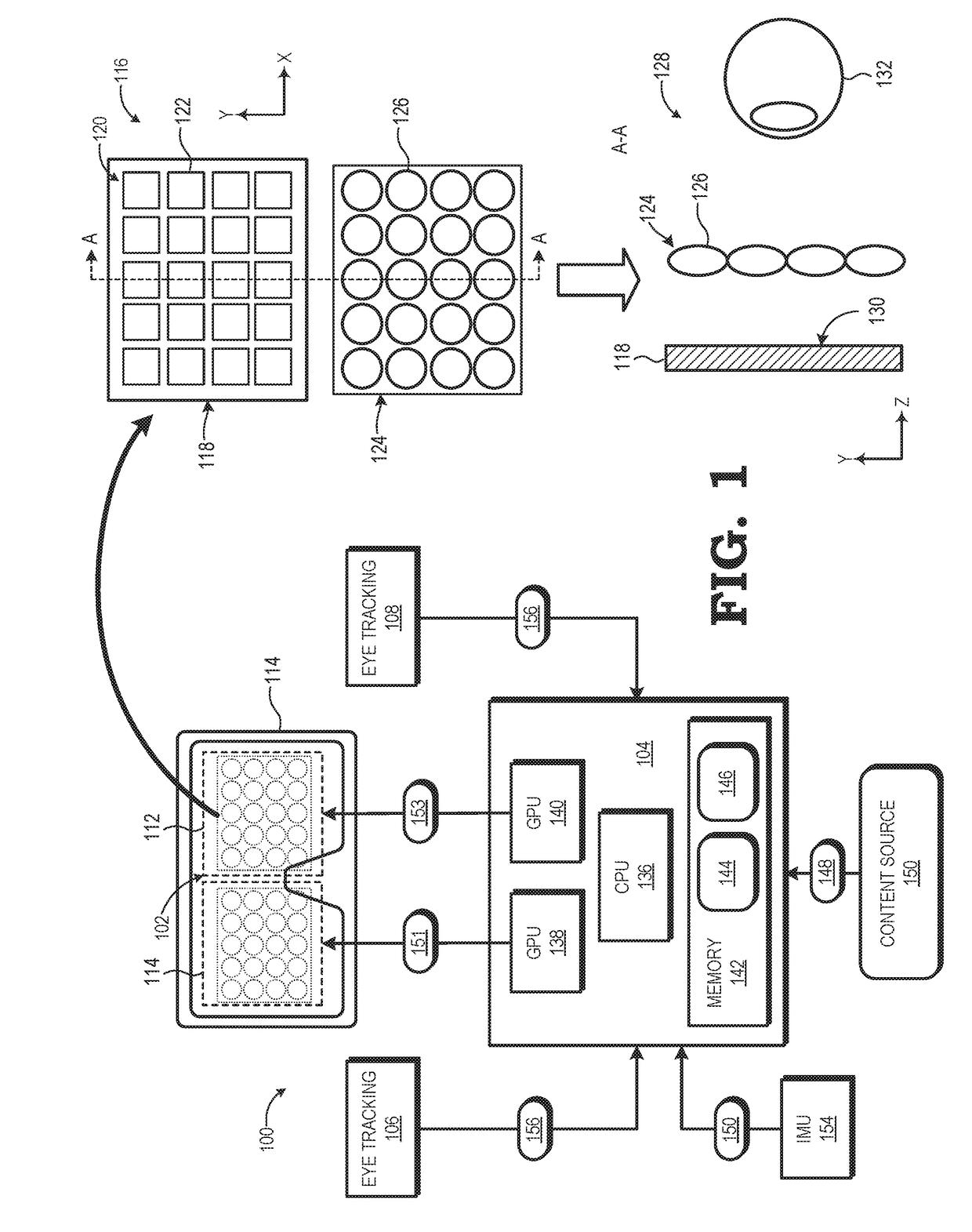
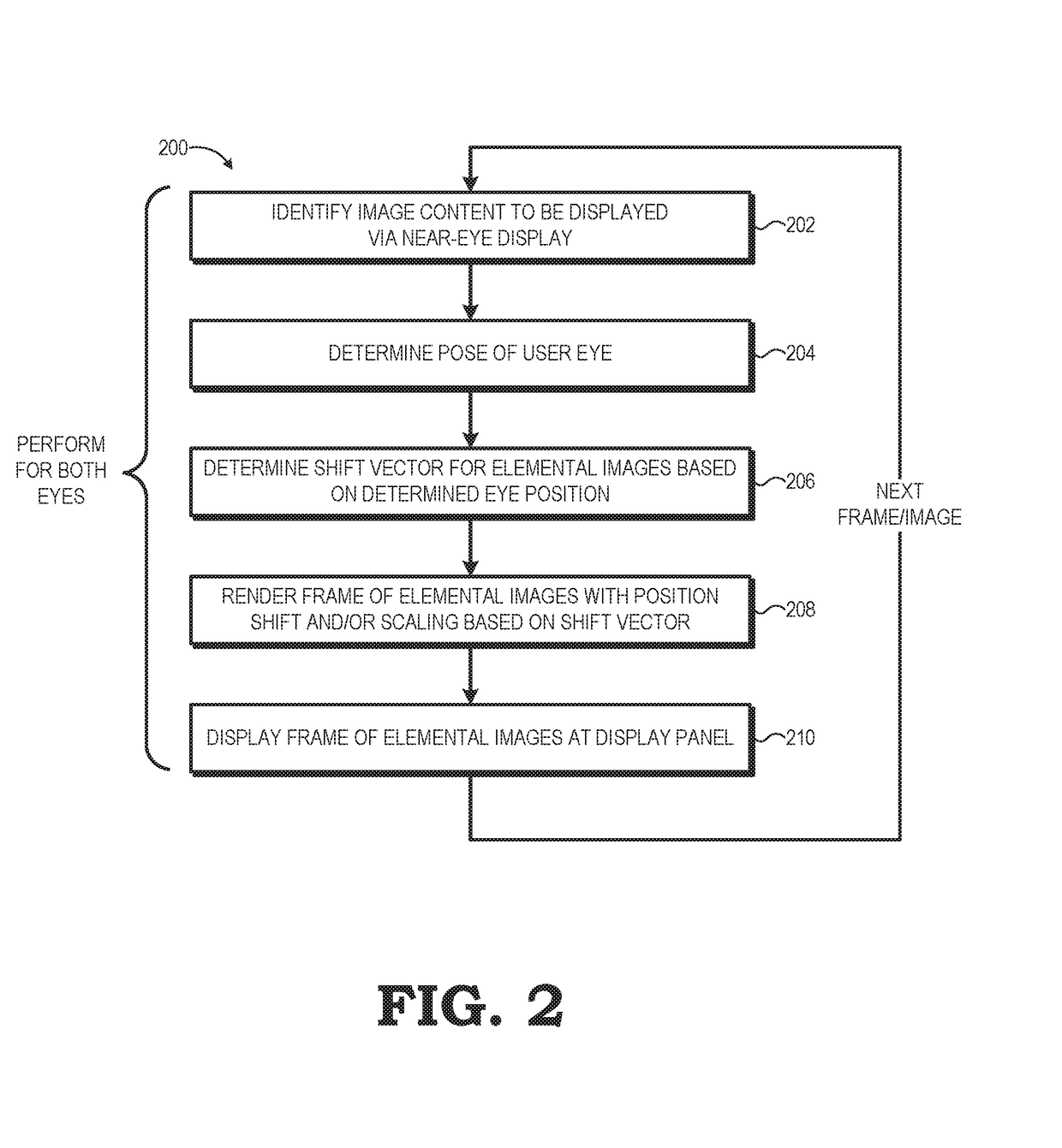
Near-eye display with extended effective eyebox via eye tracking
A near-eye display system includes a display panel to display a near-eye lightfield frame comprising an array of elemental images and an eye tracking component to track a pose of a user's eye. The system further includes a rendering component to position the array of elemental images within the near-eye lightfield frame based on the pose of the user's eye. A method of operation of the near-eye display system includes determining, using the eye tracking component, a first pose of the user's eye and determining a shift vector for an array of elemental images forming a near-eye lightfield frame based on the first pose of the user's eye. The method further includes rendering the array of elemental images at a position within the near-eye lightfield frame that is based on the shift vector.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
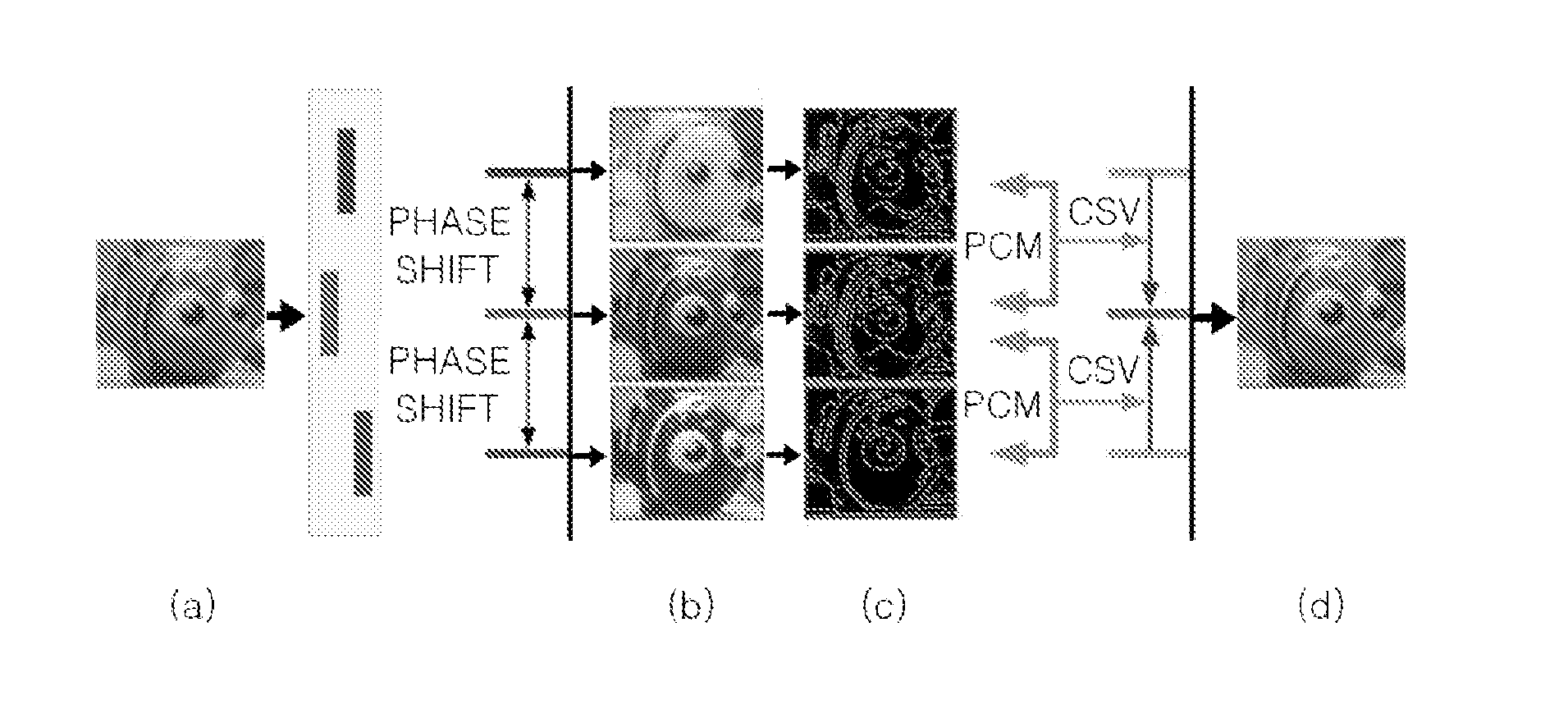
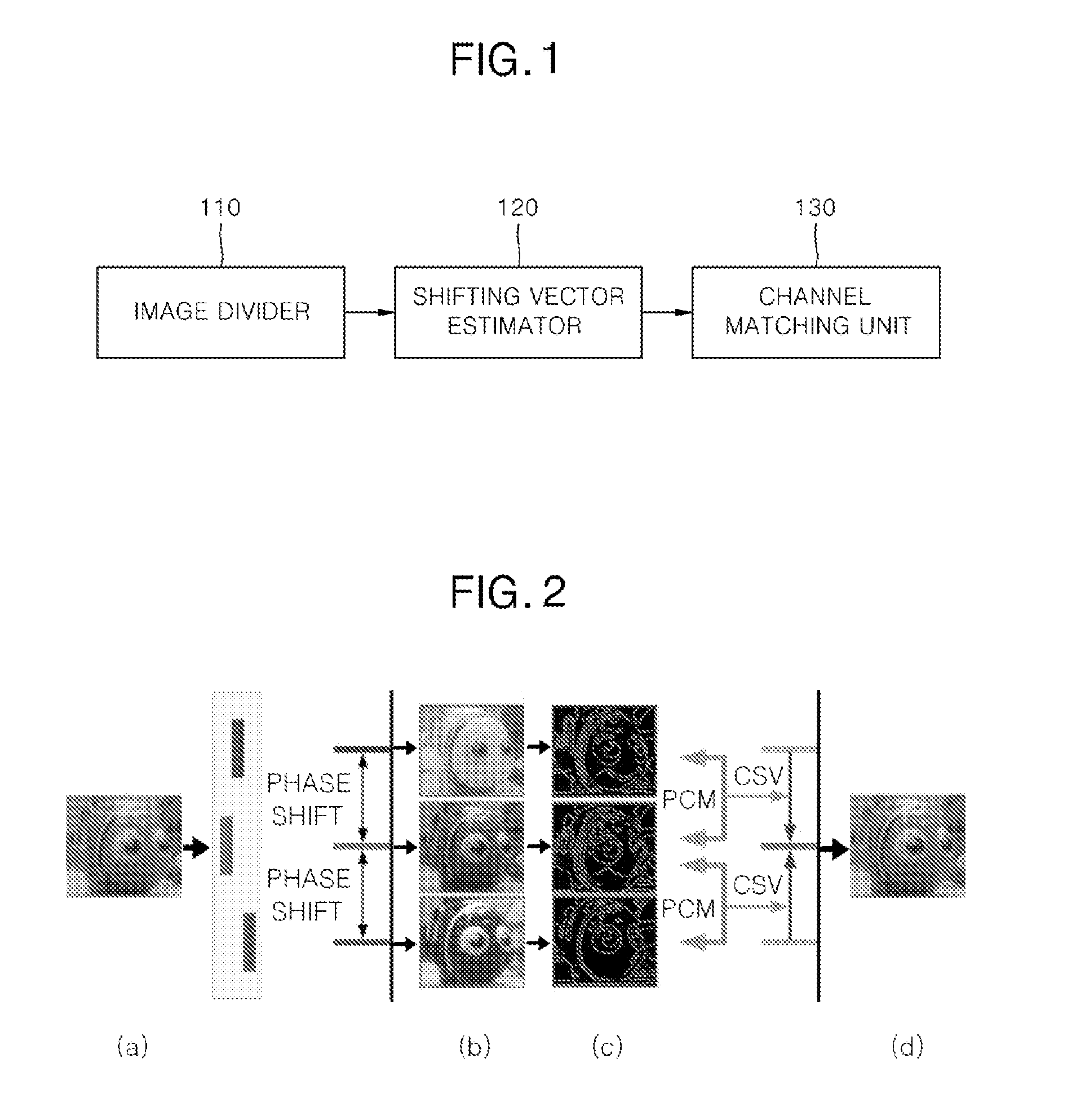
Apparatus and method for aligning color channels
Provided are an apparatus and method for aligning color channels on the basis of depth information on an image taken by an imaging device equipped with a multiple color-filter aperture (MCA). An image divider generates a binary image including edge information on an original image, and generates a label map including a plurality of regions of interest (ROIs) respectively corresponding to a plurality of objects included in the original image. A shifting vector estimator estimates color shifting vectors (CSVs) indicating shift directions and distances of color channels of the original image according to the respective ROIs. A channel matching unit obtains a plurality of matched images corresponding to the respective ROIs included in the label map by shifting the color channels according to the respective CSVs, and generates a multi-focus image by combining the matched images.
Owner:CHUNG ANG UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Method for pixel shift calculation in digital subtraction angiography and X-ray diagnostic imaging system for generating images in digital subtraction angiography
InactiveUS8299413B2Improve display image qualityFlickering is reduced or even completely avoidedImage enhancementImage analysisX-rayContrast enhancement
An X-ray diagnostic imaging system for generating images in digital subtraction angiography is proposed. A mask image frame of a patient and a series of live image frames of the patient acquired in the same imaging position of the mask frame acquisition are accessed. One of the mask and the live image frames is contrast-enhanced. Possible shift vectors in a region of interest are assumed being a difference vector between the mask and a respective live image frame and a scoring is calculated. Possible shift vector with the highest scoring is chosen as an elected shift vector. A likelihood representing a quality value of the elected shift vector is calculated. The mask image frame is shifted with respect to the respective live image frame by a modified shift vector depending on the likelihood. The shifted mask image frame is subtracted from the respective live image frame and is displayed.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
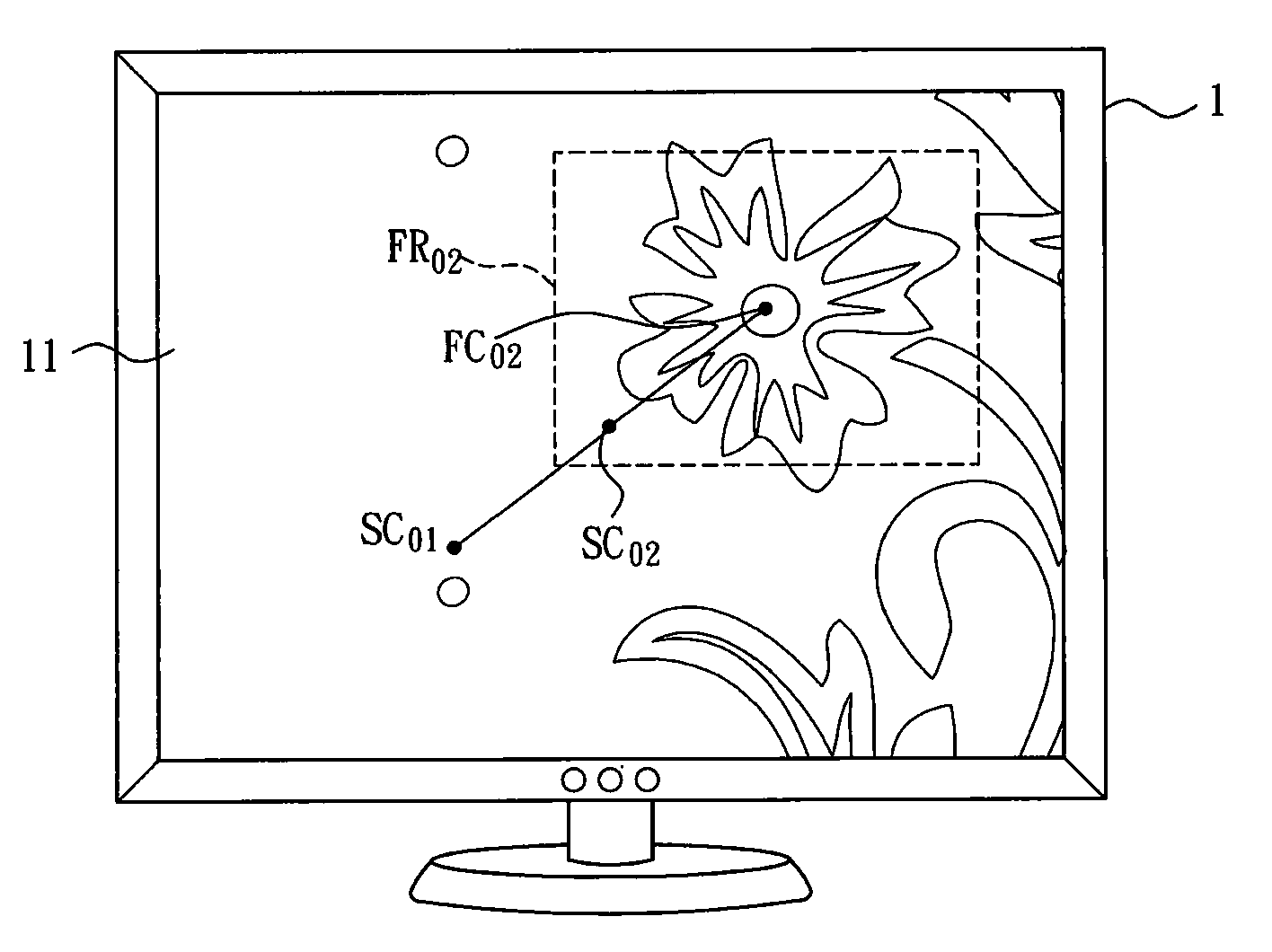
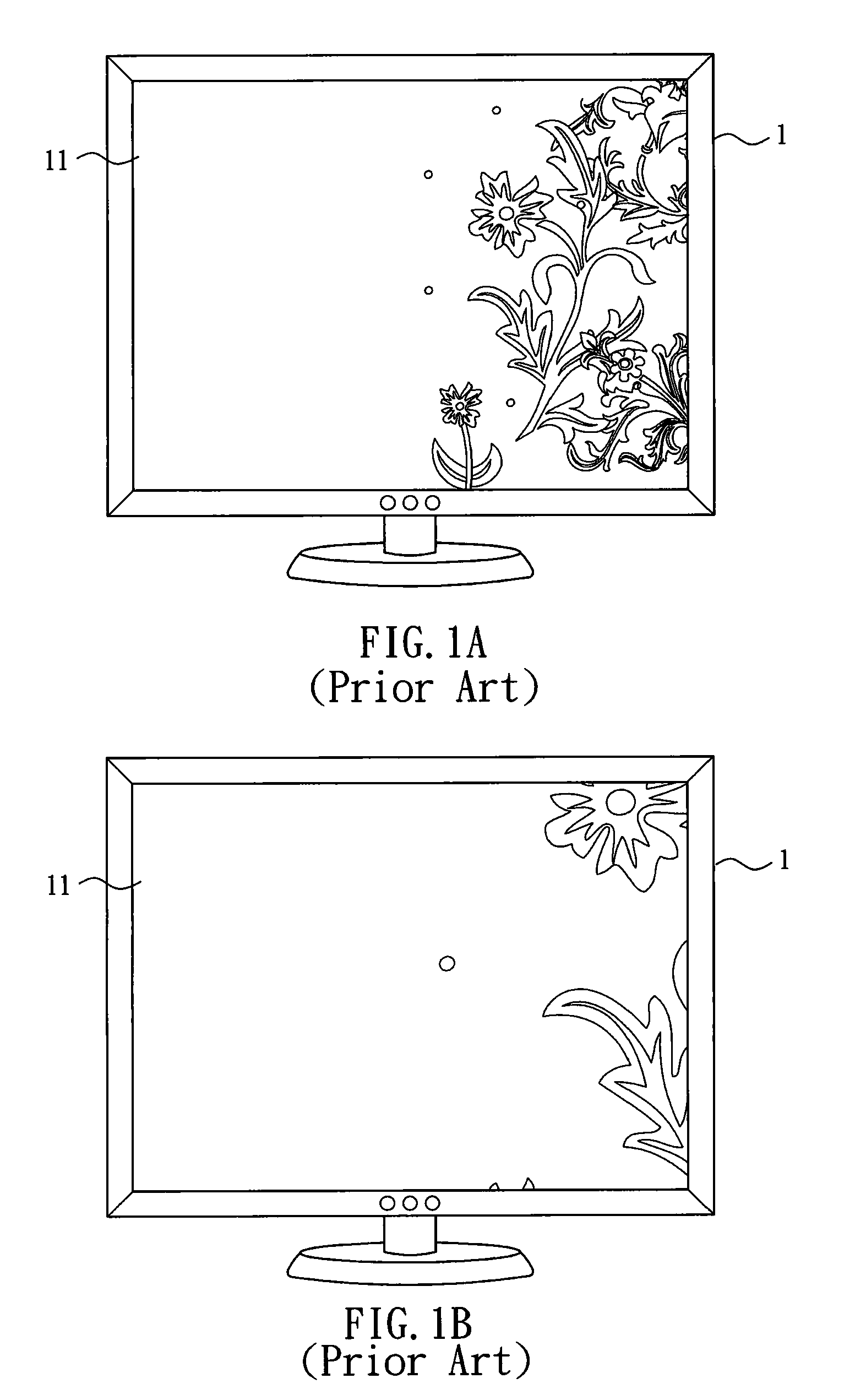
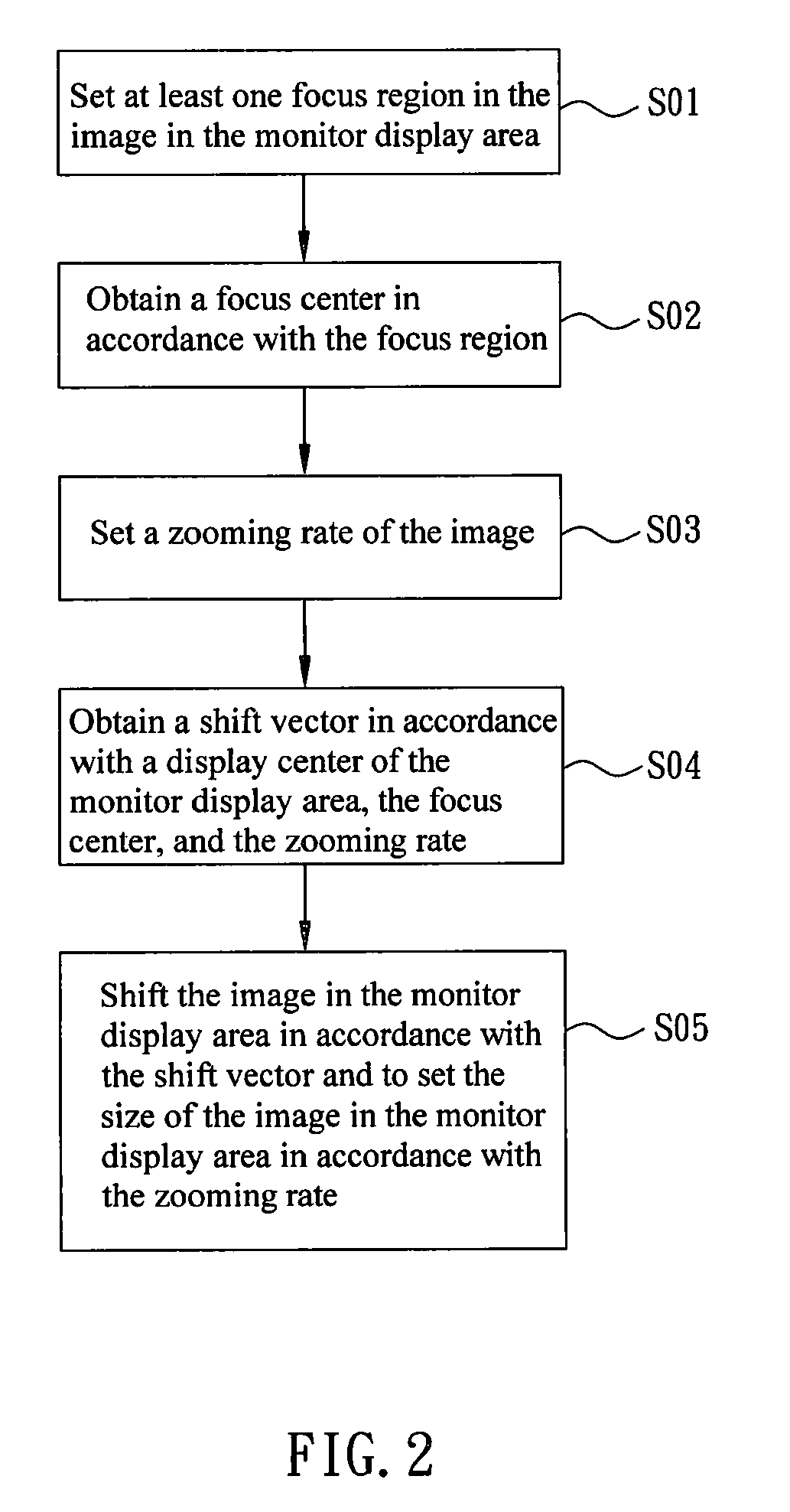
Image zooming device and image zooming method
ActiveUS20100171764A1Easy to viewAvoid draggingGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionShift vector
An image zooming method for adjusting an image in a monitor display area includes the steps of setting at least one focus region in the image in the monitor displaying area; obtaining a focus center in accordance with the focus region; setting a zooming rate of the image; obtaining a shift vector in accordance with a display center of the monitor display area, the focus center and the zooming rate; and shifting the image in the monitor display area in accordance with the shift vector, and setting the size of the image in the monitor display area in accordance with the zooming rate.
Owner:ARCSOFT CORP LTD
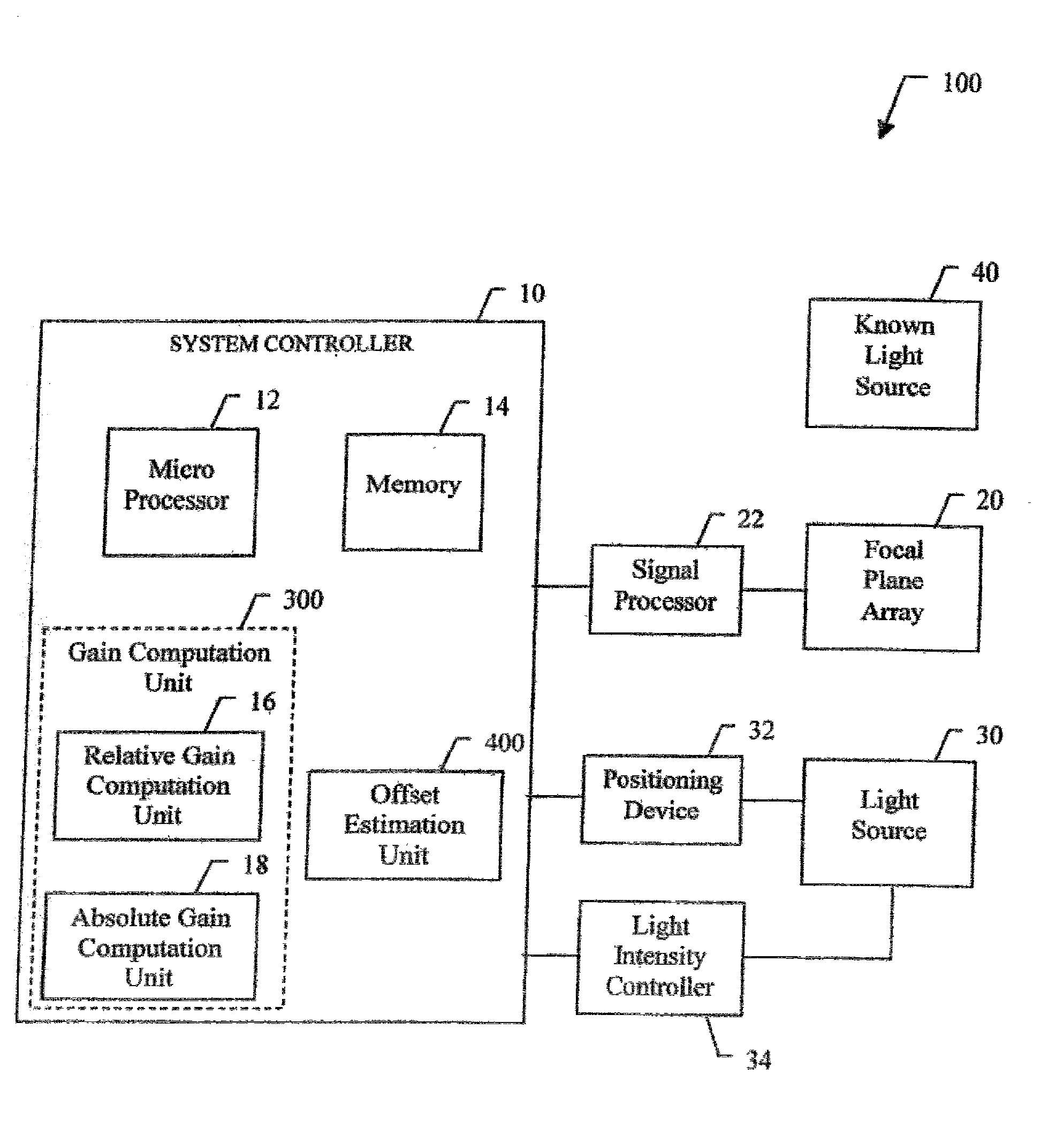
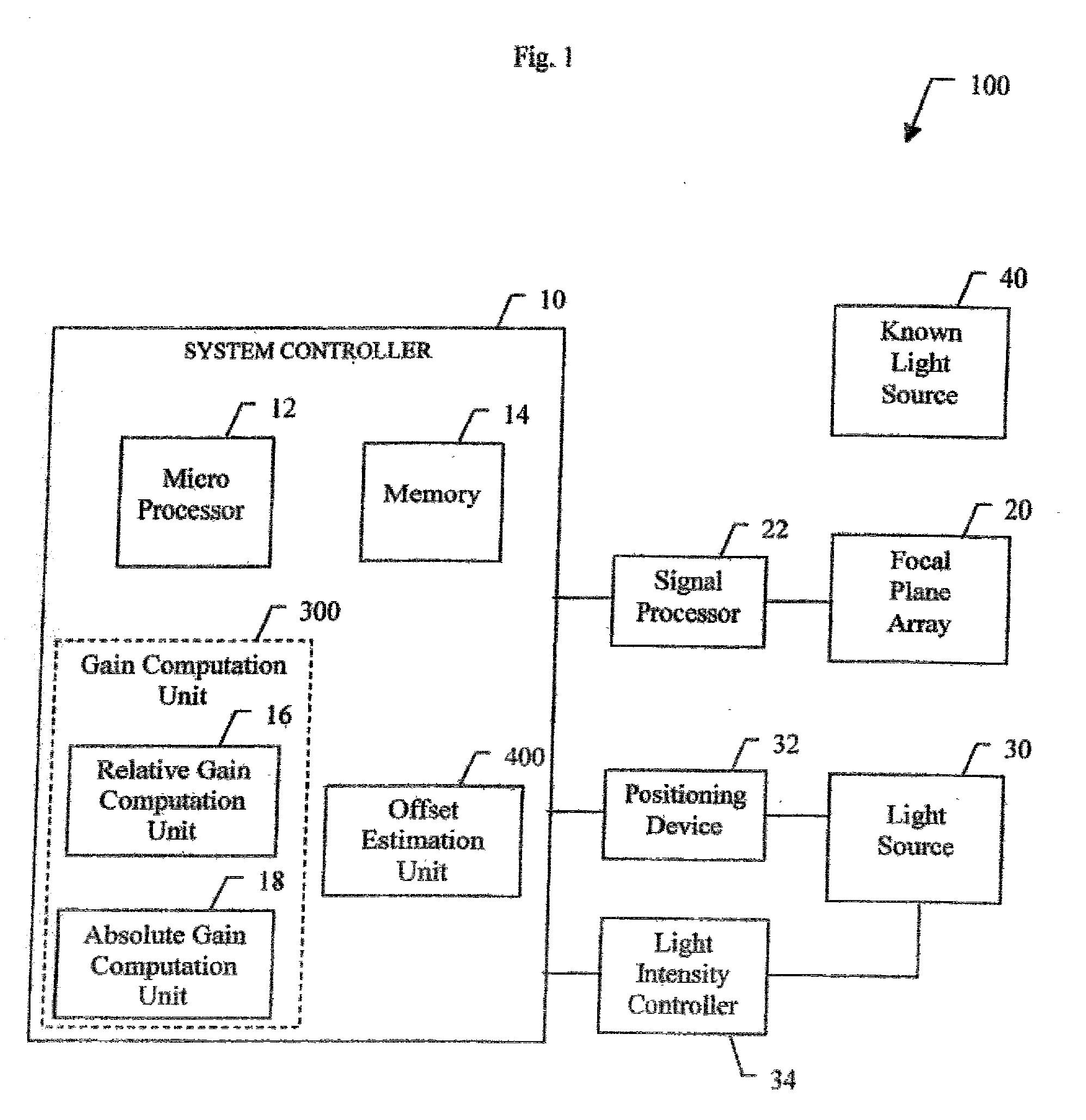
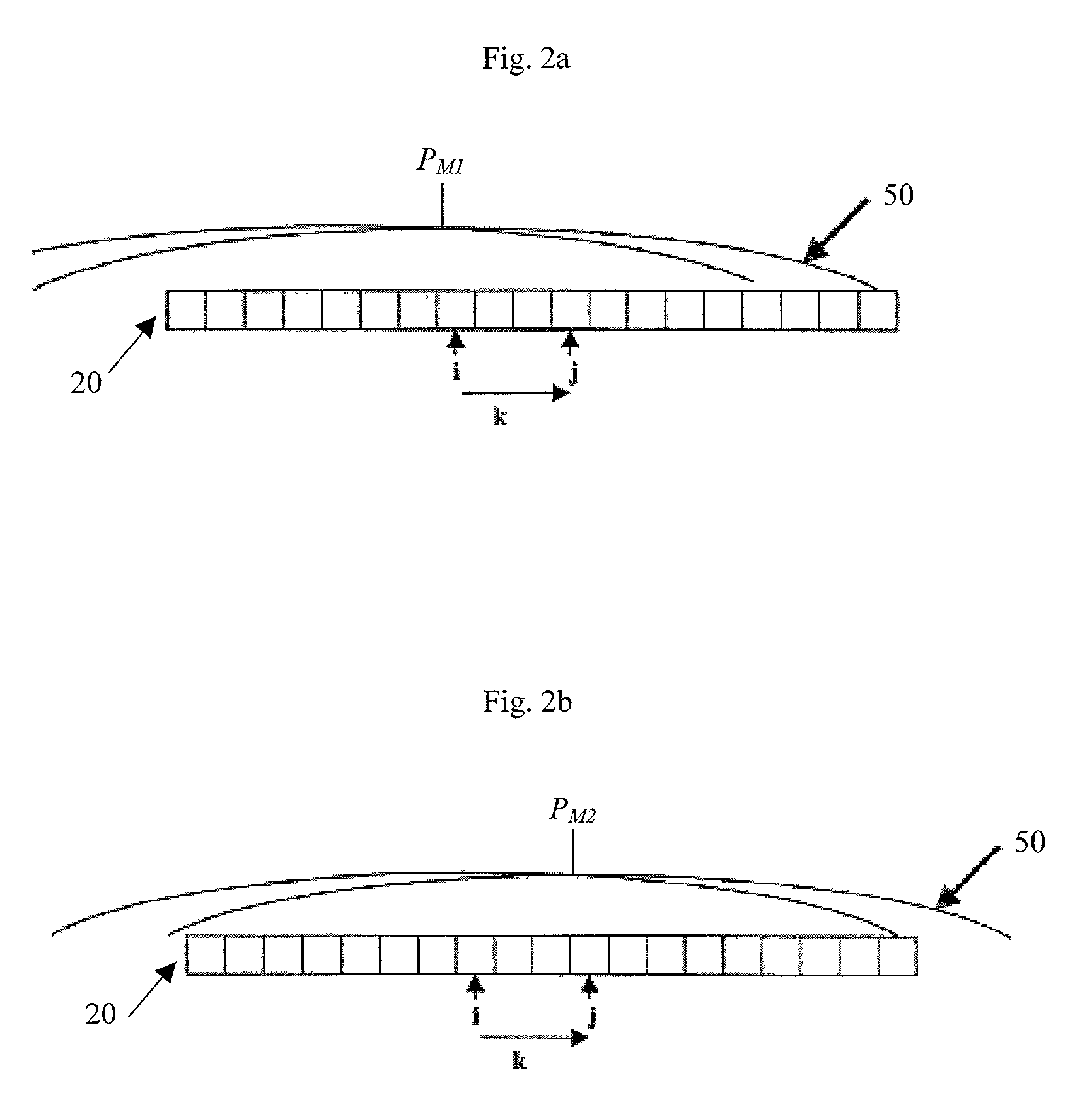
Radiometry calibration system and method for electro-optical sensors
InactiveUS20030025067A1Television system detailsRadiation pyrometryElectro-optical sensorShift vector
A system (100) and method for focal plane array calibration using an internal non-uniform calibration source (30). In the illustrative embodiment, the system (100) includes a first mechanism (16) for calculating a relative gain of each detector element in the focal plane array (20) relative to at least one reference element, a second mechanism (17) for obtaining the absolute gain of the reference element, and a third mechanism (18) for calculating the absolute gains for all other detector elements using the relative gains in conjunction with the absolute gain of the reference element. The relative response of each pixel is calculated from measurements of the response of each pixel using an internal calibration source (30) at two or more different source positions, and two illumination intensities at each position. Measurements using a pair of source positions separated by k pixels establishes the relative response of the ith pixel with respect to the (i+k)th pixel. Through this recursive relationship and other pairs of source position with a different shift vector k, the relative response of every pixel in the FPA can be established. Then, the absolute radiometric calibration of at least one reference pixel is accomplished using a known external source (40), such as a star. The absolute response calibration of each pixel can then be obtained using the recursive relationship in combination with the reference pixels.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
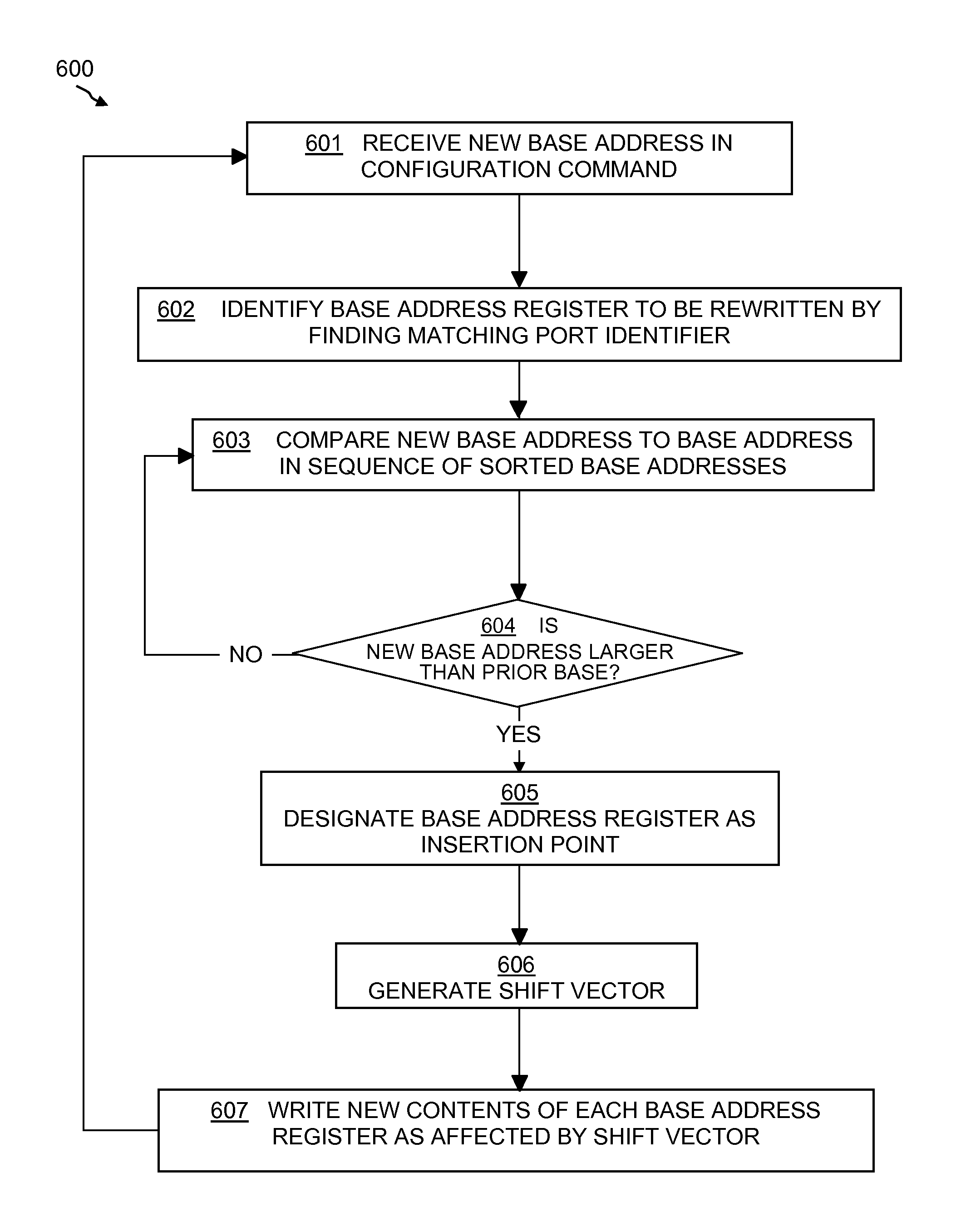
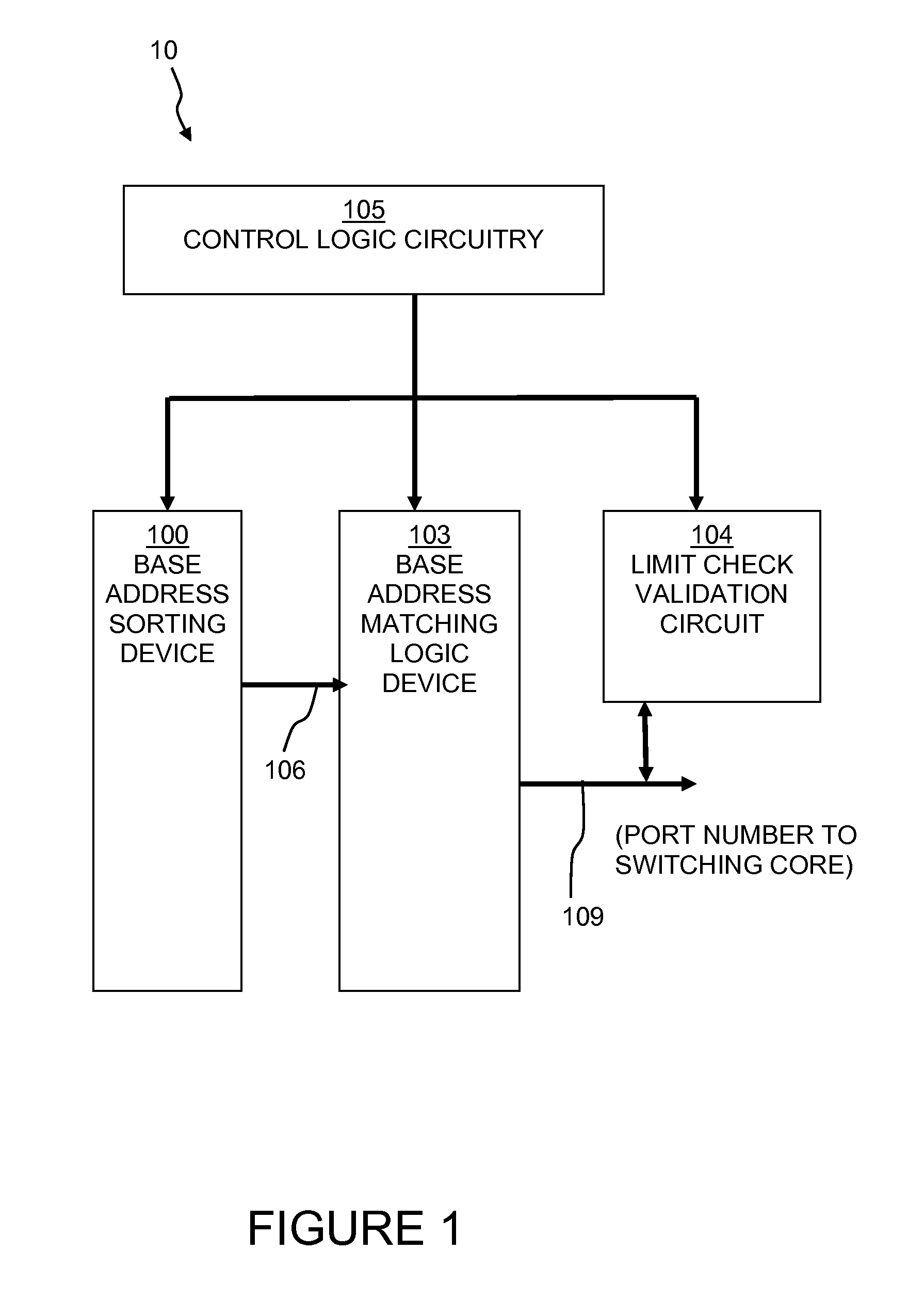
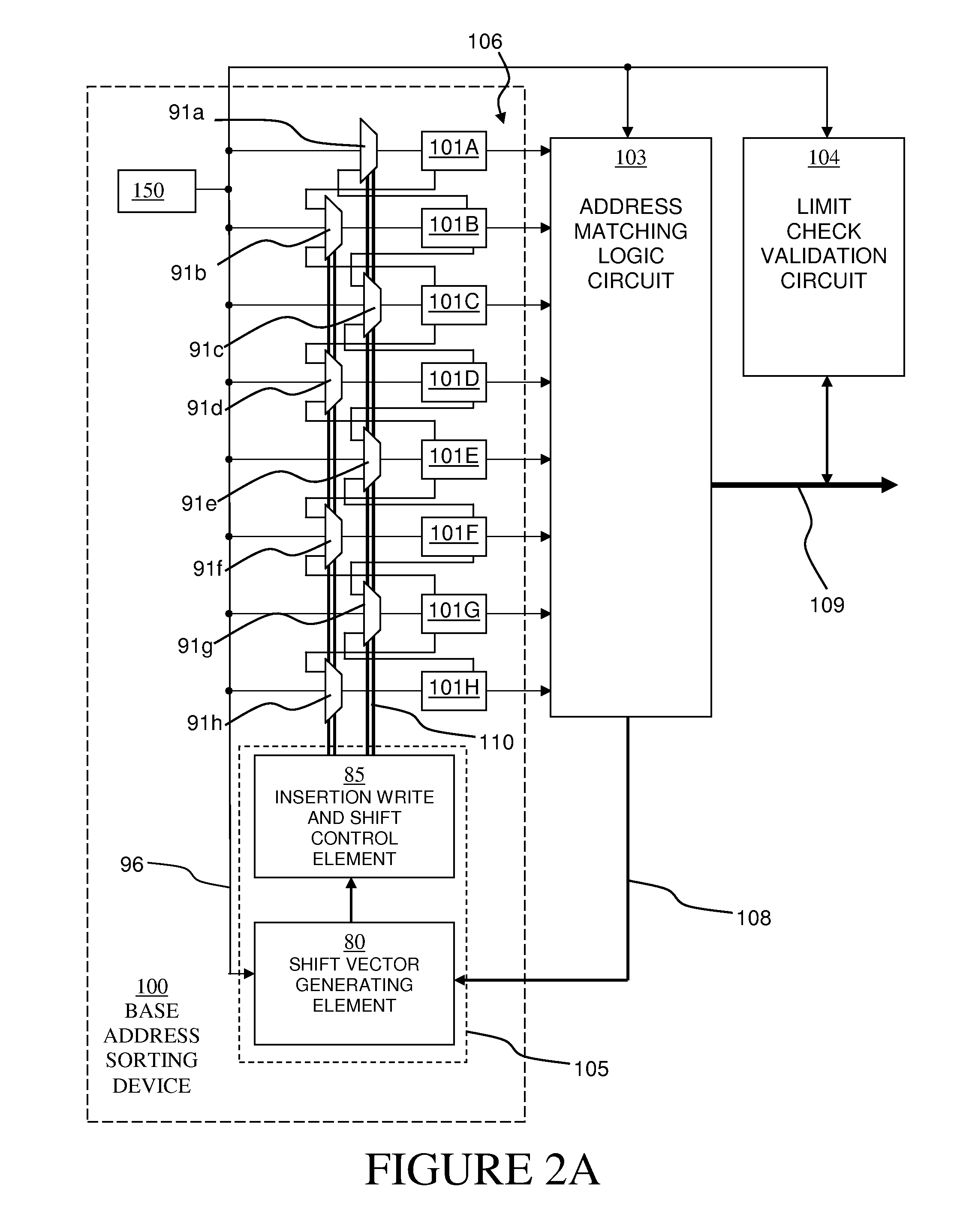
Binary base address sorting method and device with shift vector
ActiveUS7647438B1Without interrupting rapid switching operationQuickly and accurately insertingMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData switching by path configurationProcessor registerShift vector
A base address sorting device in a switching device is disclosed that includes an array of base address registers in which each base address register contains a base address, an address shifting device; and a control logic element electrically coupled to the array of base address registers and operable, upon receiving a configuration command comprising a new base address, to implement a method for reconfiguring the contents of the array of base address registers. The method includes determining an insertion point base address register in the array of base address registers into which to write the new base address, shifting the contents of one or more base address registers array to other base address registers to preserve the sorted order, and shifting the contents of the configuration command into the insertion point base address register. The inserting results in preserving the pre-determined order of the register array content.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS US INC
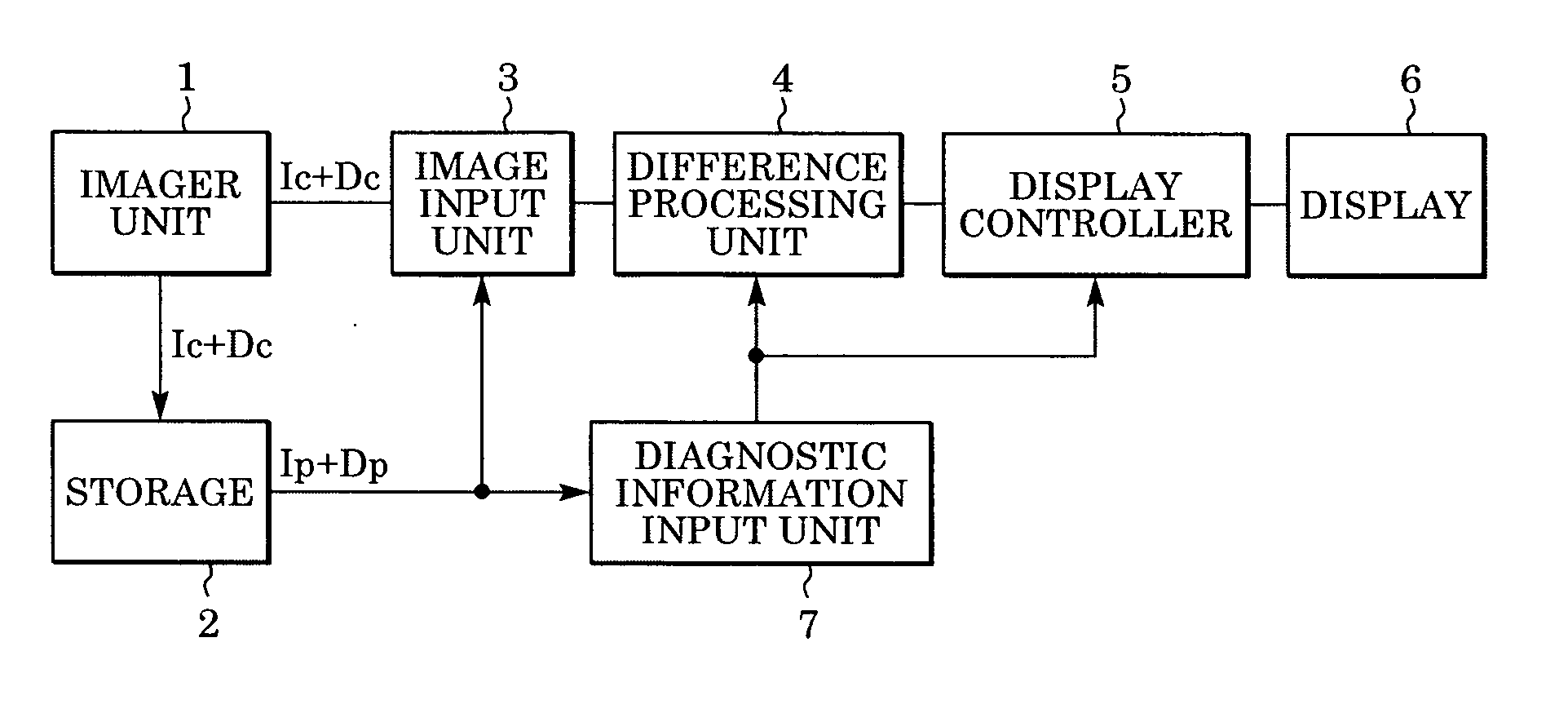
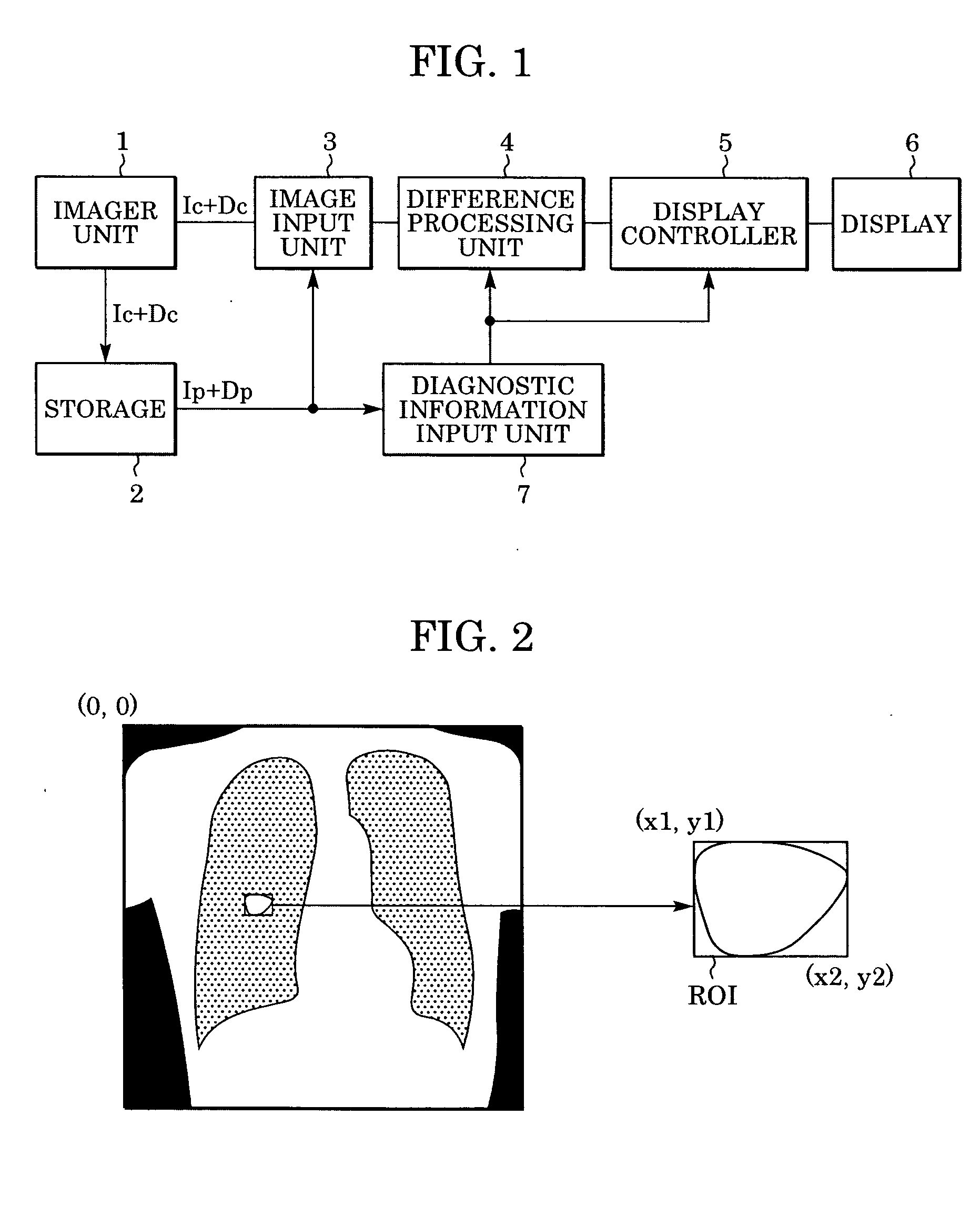
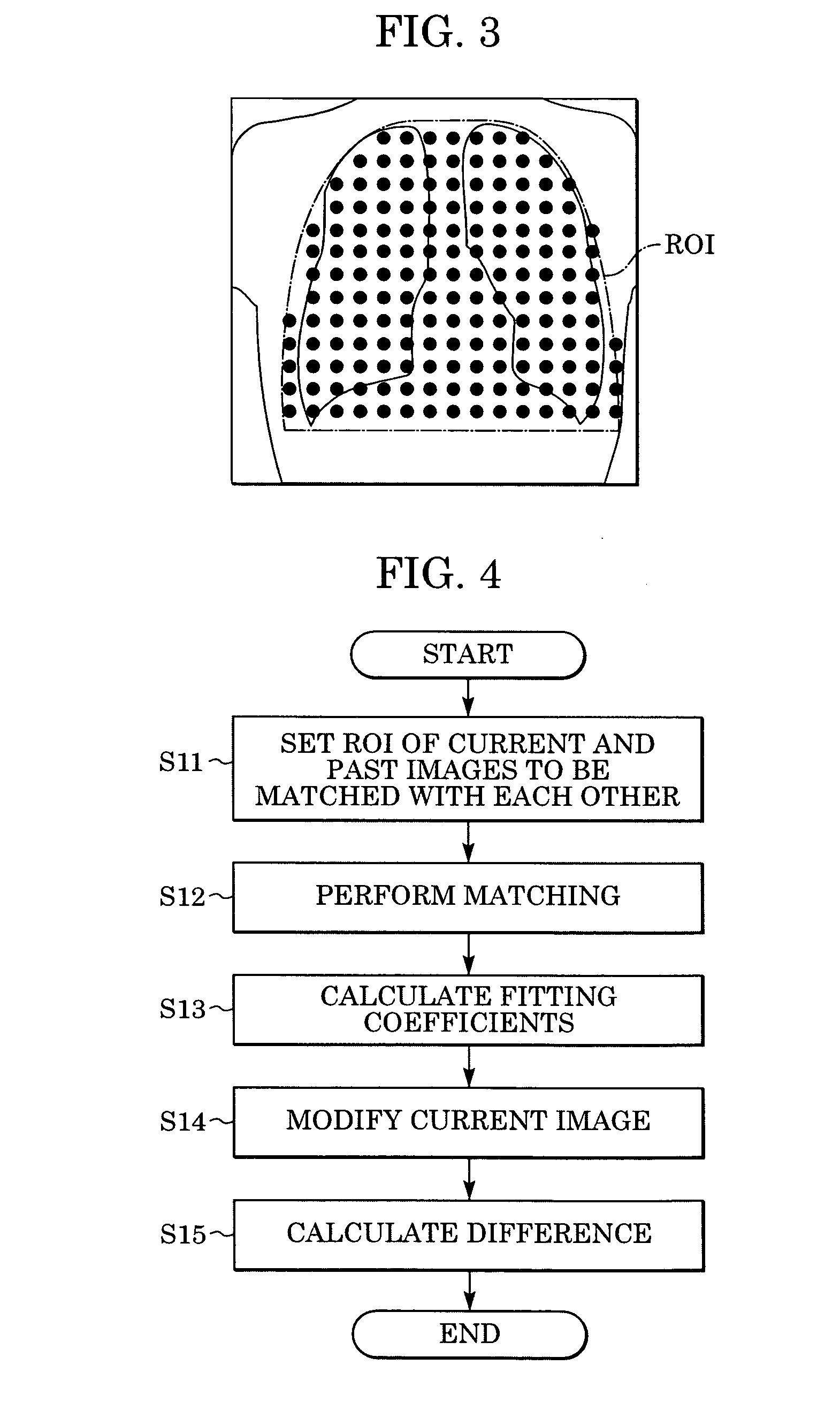
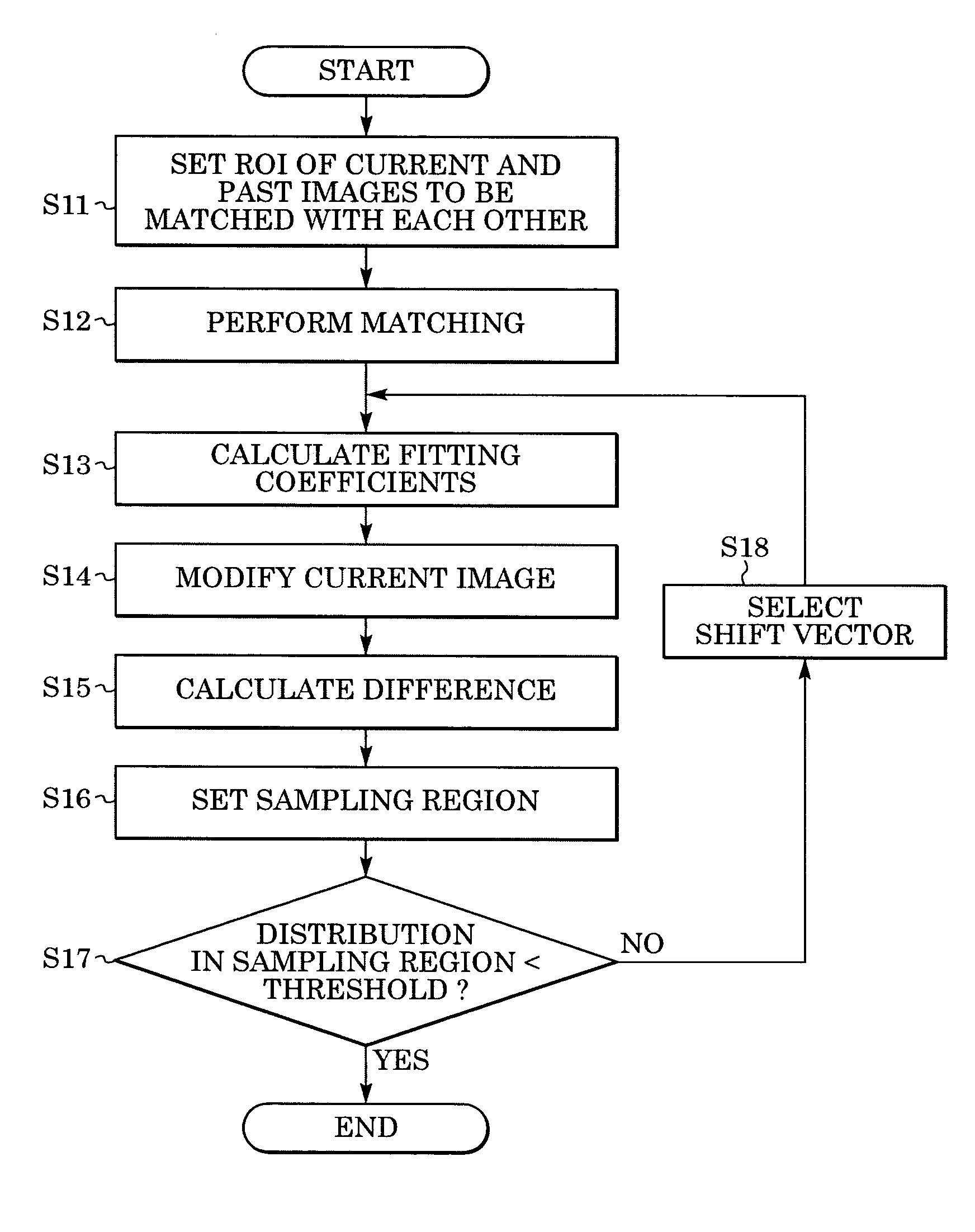
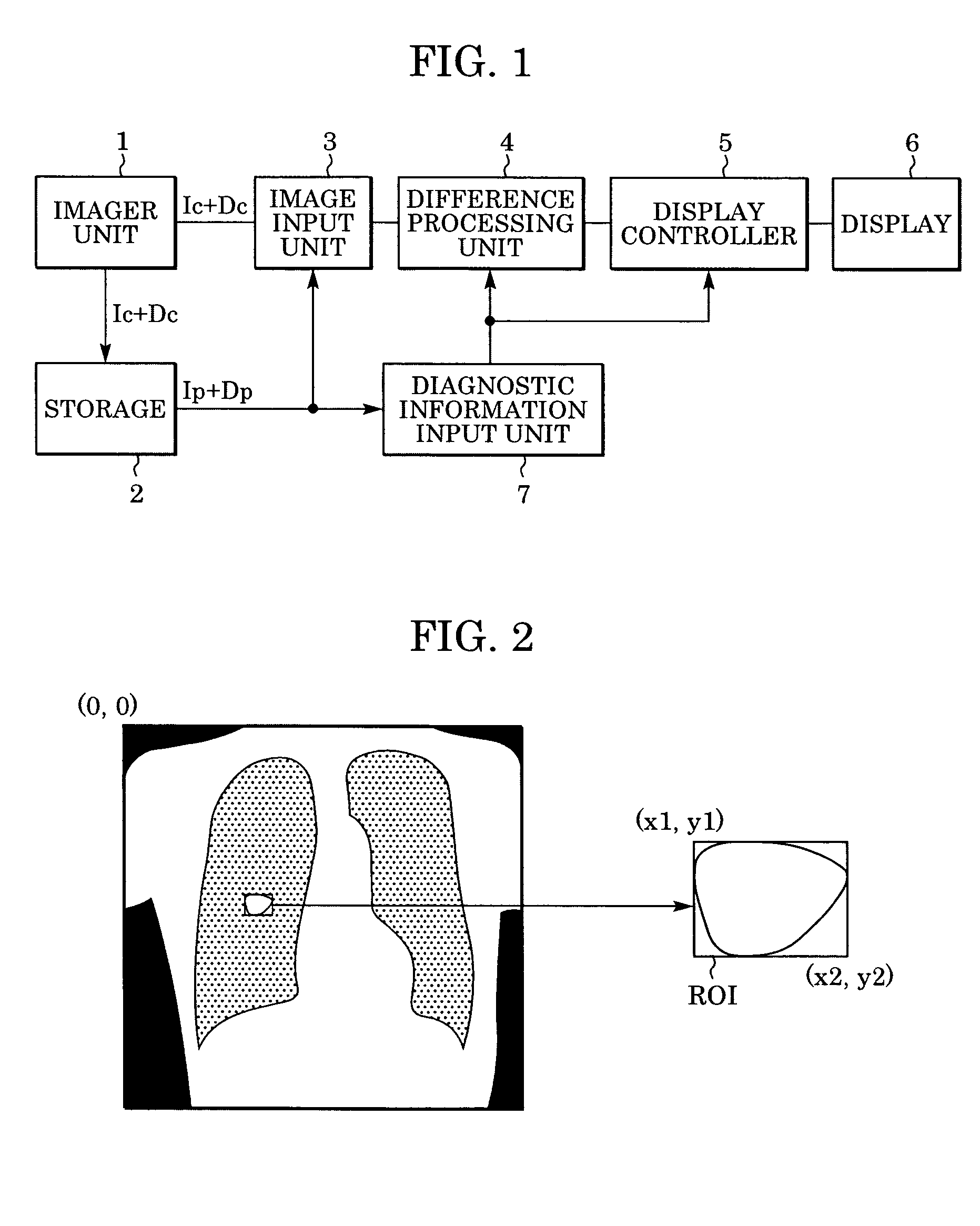
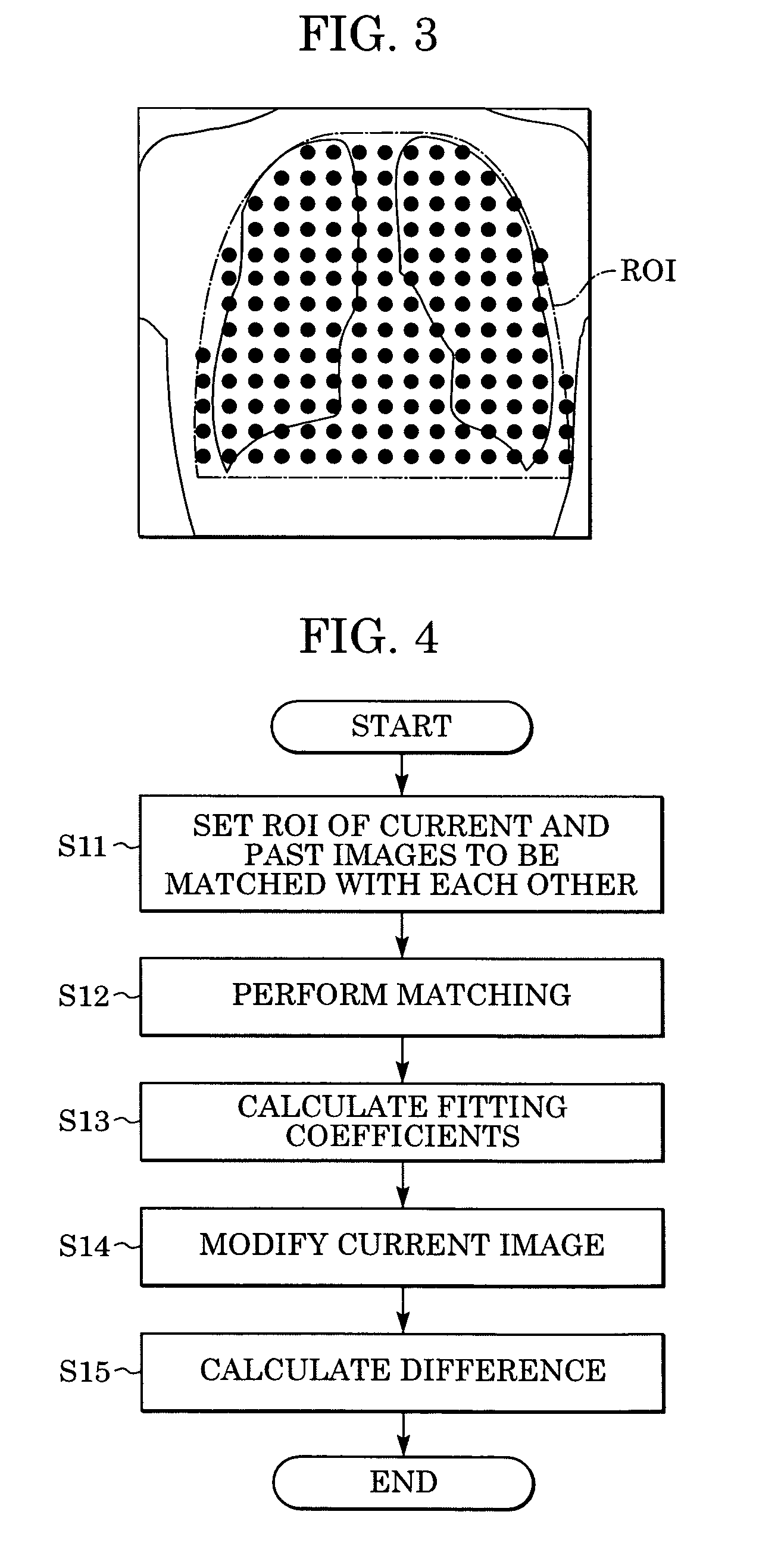
Method and system for processing an image
InactiveUS20050201607A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementShift vectorRegion of interest
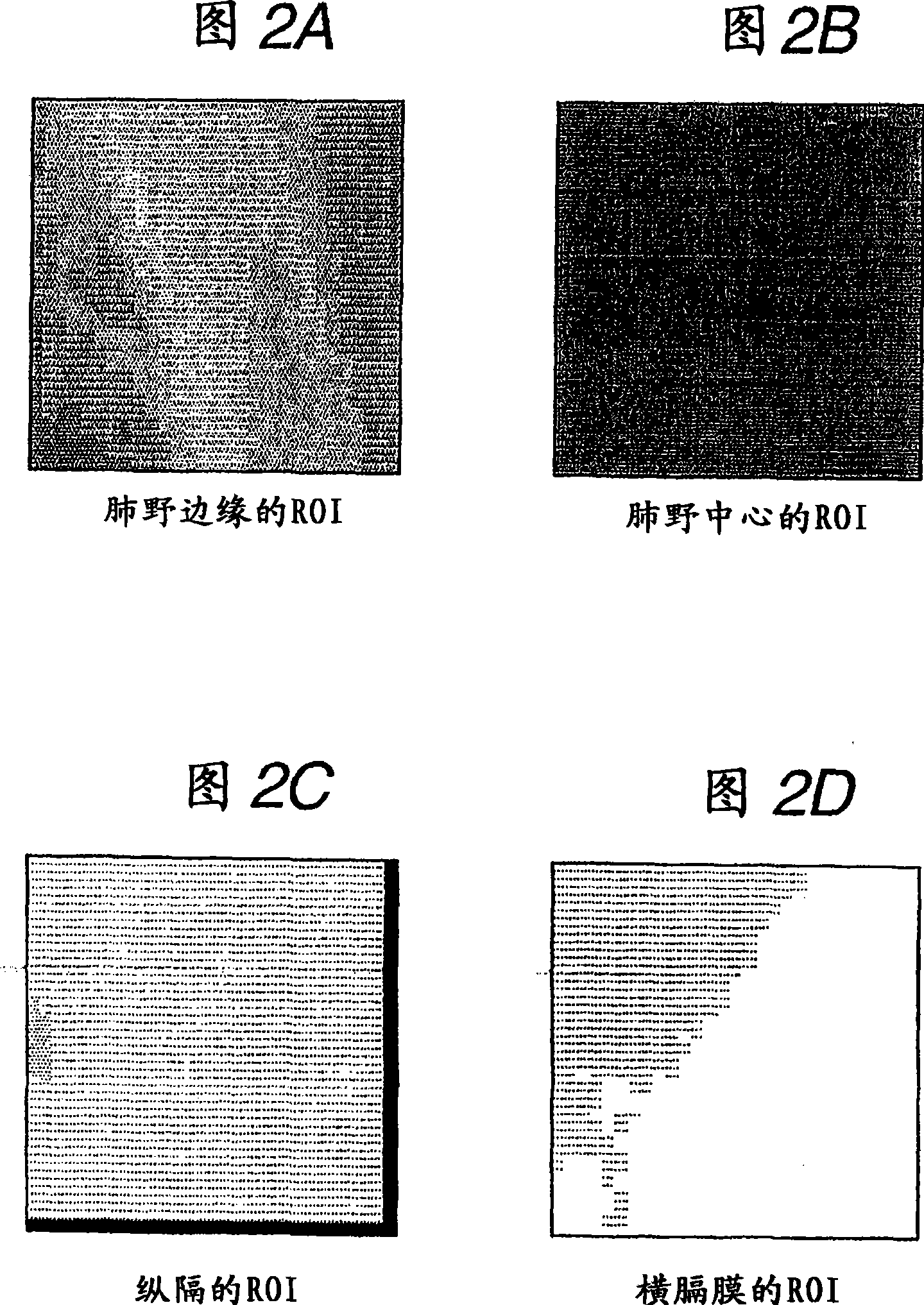
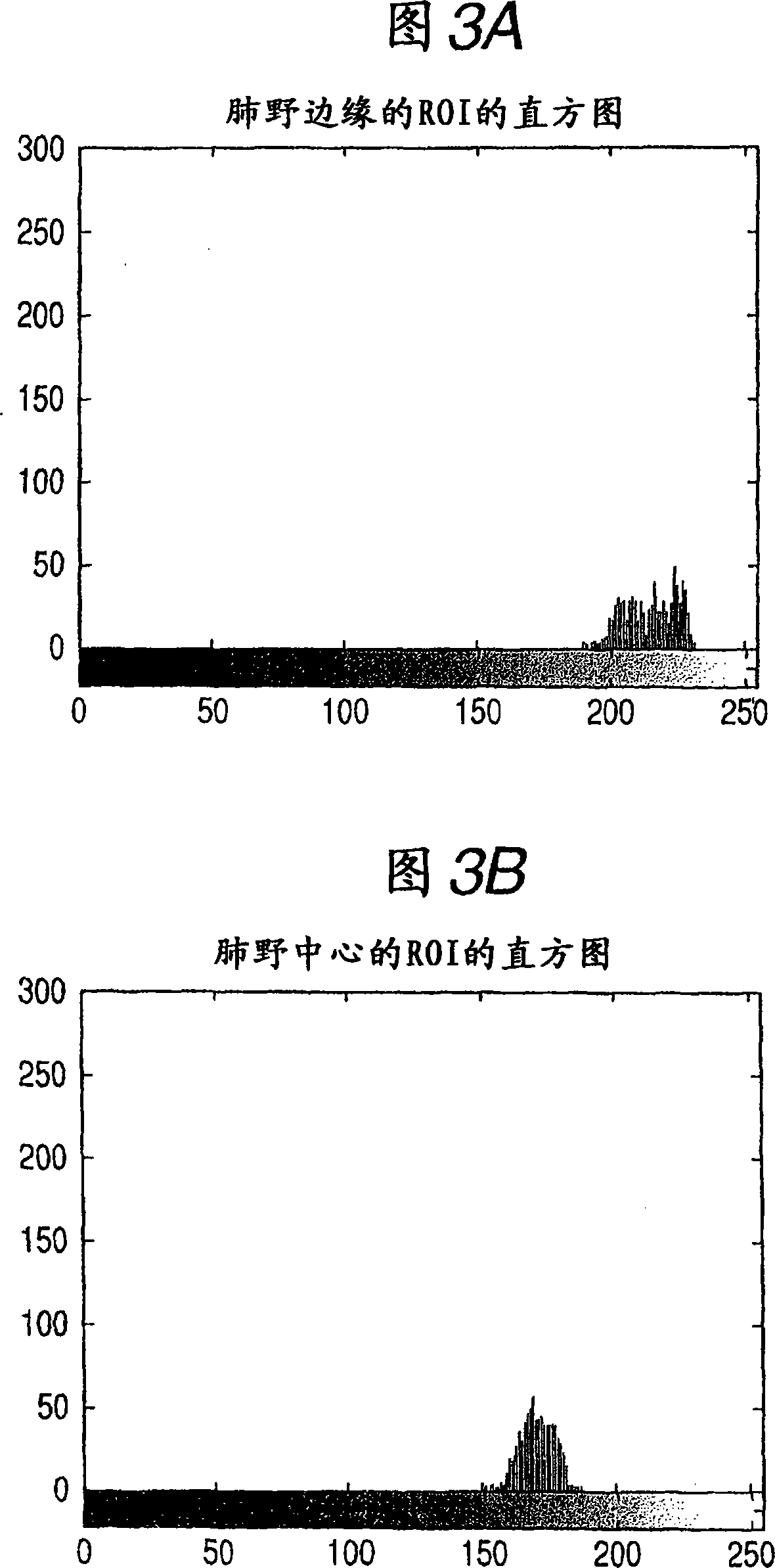
In computer aided diagnosis, a high-accuracy image indicating a temporal difference of a diseased part of a patient is produced from a current image and a past image as follows. First, a plurality of matching ROIs (Regions of Interest) are defined on the current image and the past image. A matching processing is performed on corresponding ROIs of the two images to determine points on the past image corresponding to the respective points on the current image. Obtained shift vectors are fitted to a two-dimensional polynomial. In the fitting, when a matching ROI of the current image is included in or overlapped with a previously-defined region of interest, shift vectors are weighted by a small factor. The current image is then modified according to obtained fitting coefficients. Finally, an image indicating the difference between the modified current image and the past image is produced.
Owner:CANON KK
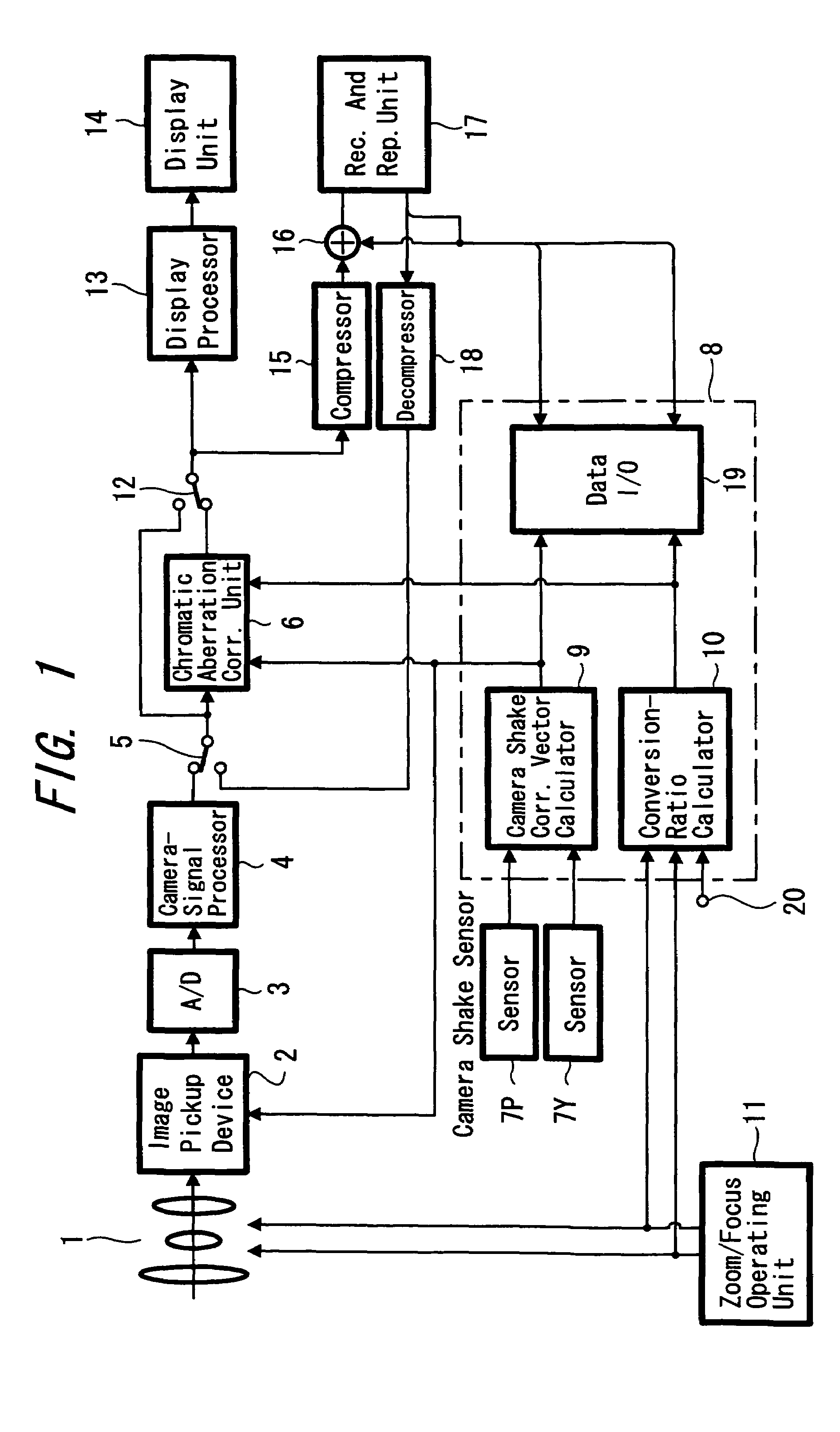
Image pickup device and chromatic aberration correction method
InactiveUS7397499B2Precise processingTelevision system detailsPrintersCamera lensSignal processing circuits
An image pick-up device and a chromatic aberration correcting method are provided in which a satisfactory correction processing can be performed even when the image pickup device, such as a camera, simultaneously performs shake correction. An output signal from a camera-signal processing circuit is selected by a selector switch and is supplied to a chromatic aberration correcting unit. An angular velocity due to the camera shake is detected using sensors and the detected signal is supplied to a camera shake correcting vector calculating unit. A driving state of a camera lens is supplied to a conversion-ratio calculating unit. An optical axis centered shift vector of camera lens is obtained from the camera shake correcting vector and is supplied to the correcting unit. Accordingly the picture-quality deterioration caused in the miniaturized camera lens can be compensated by processing the captured image signal, and also a satisfactory correction processing can be performed even when the camera shake correction is performed simultaneously.
Owner:SONY CORP
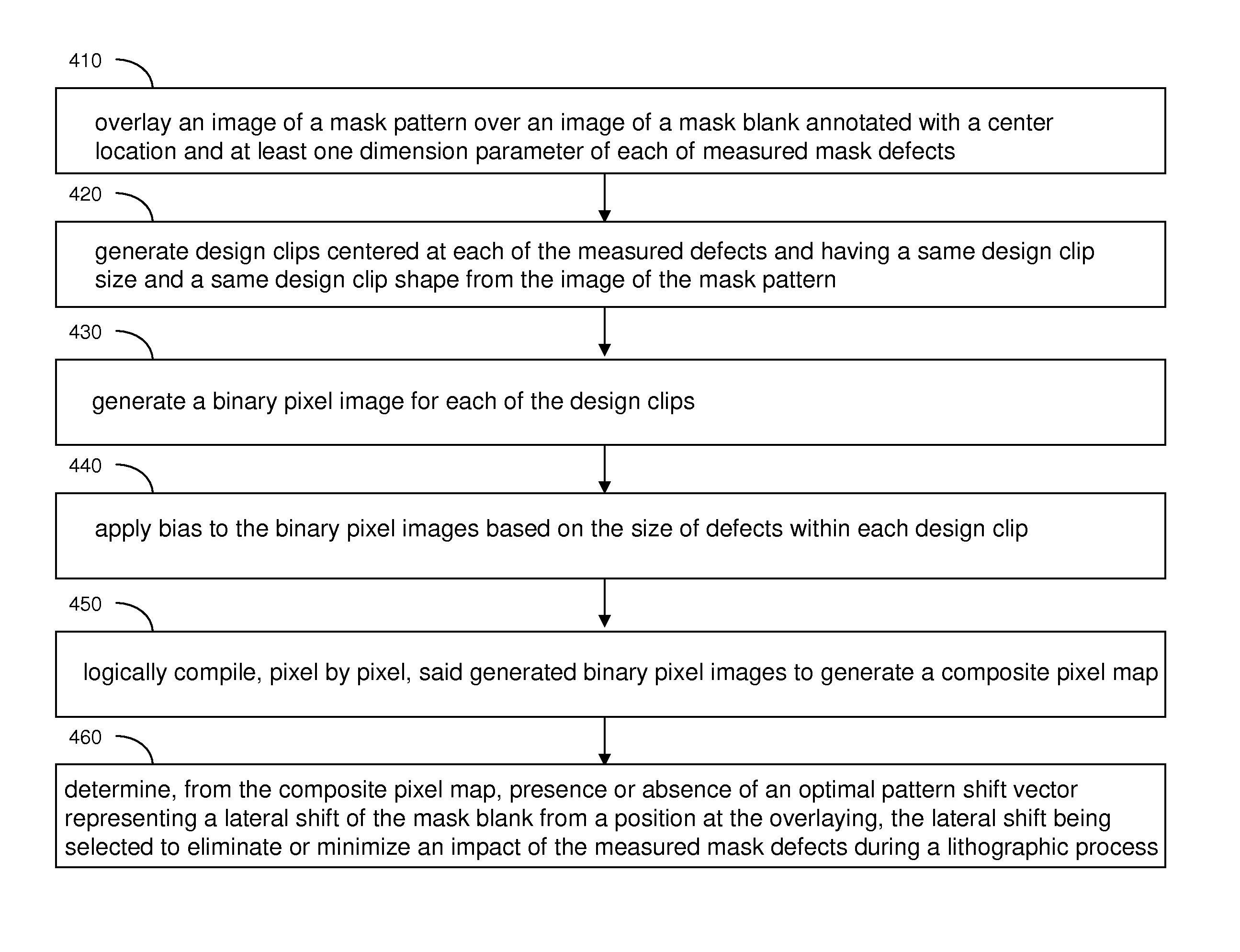
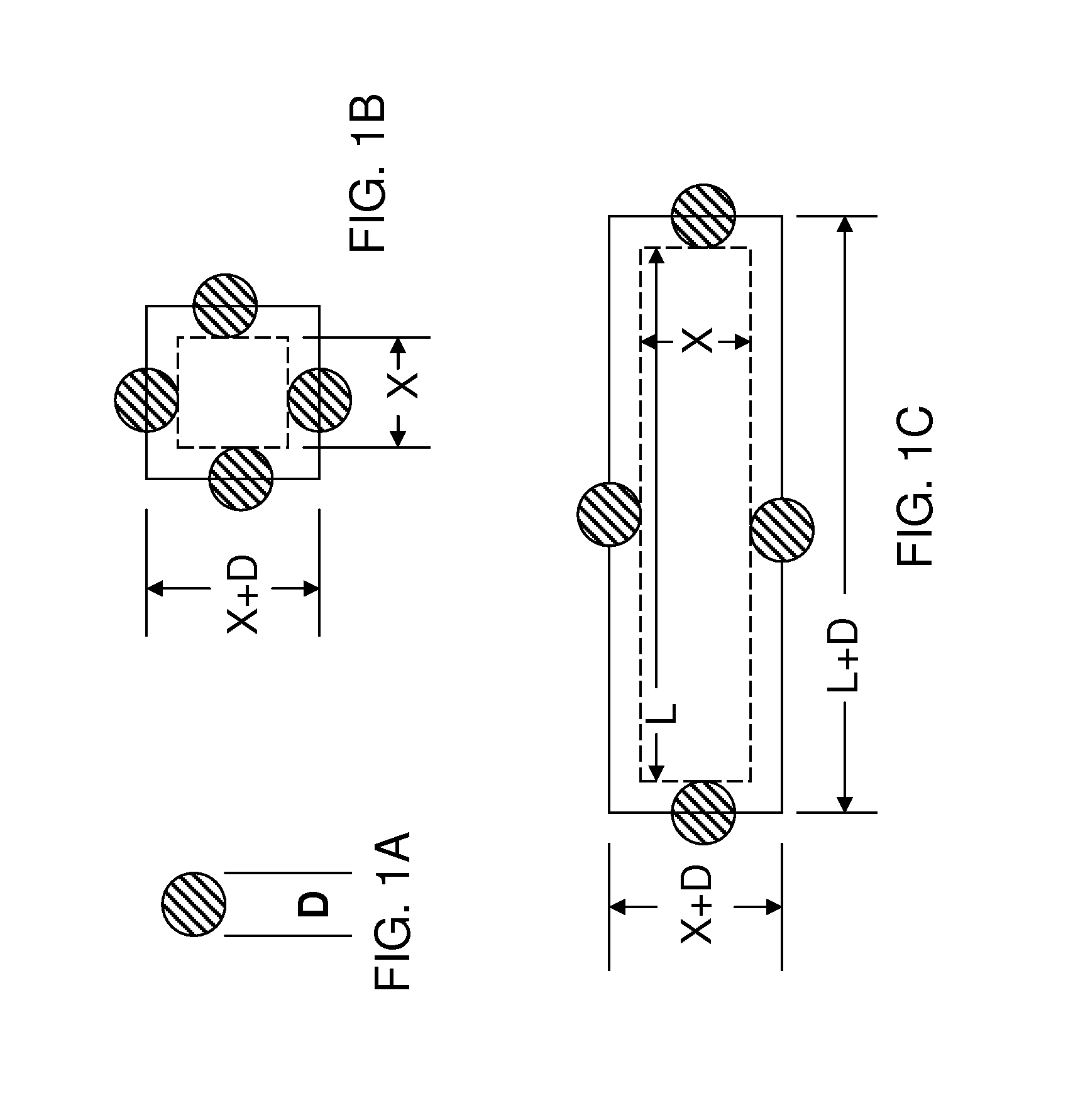
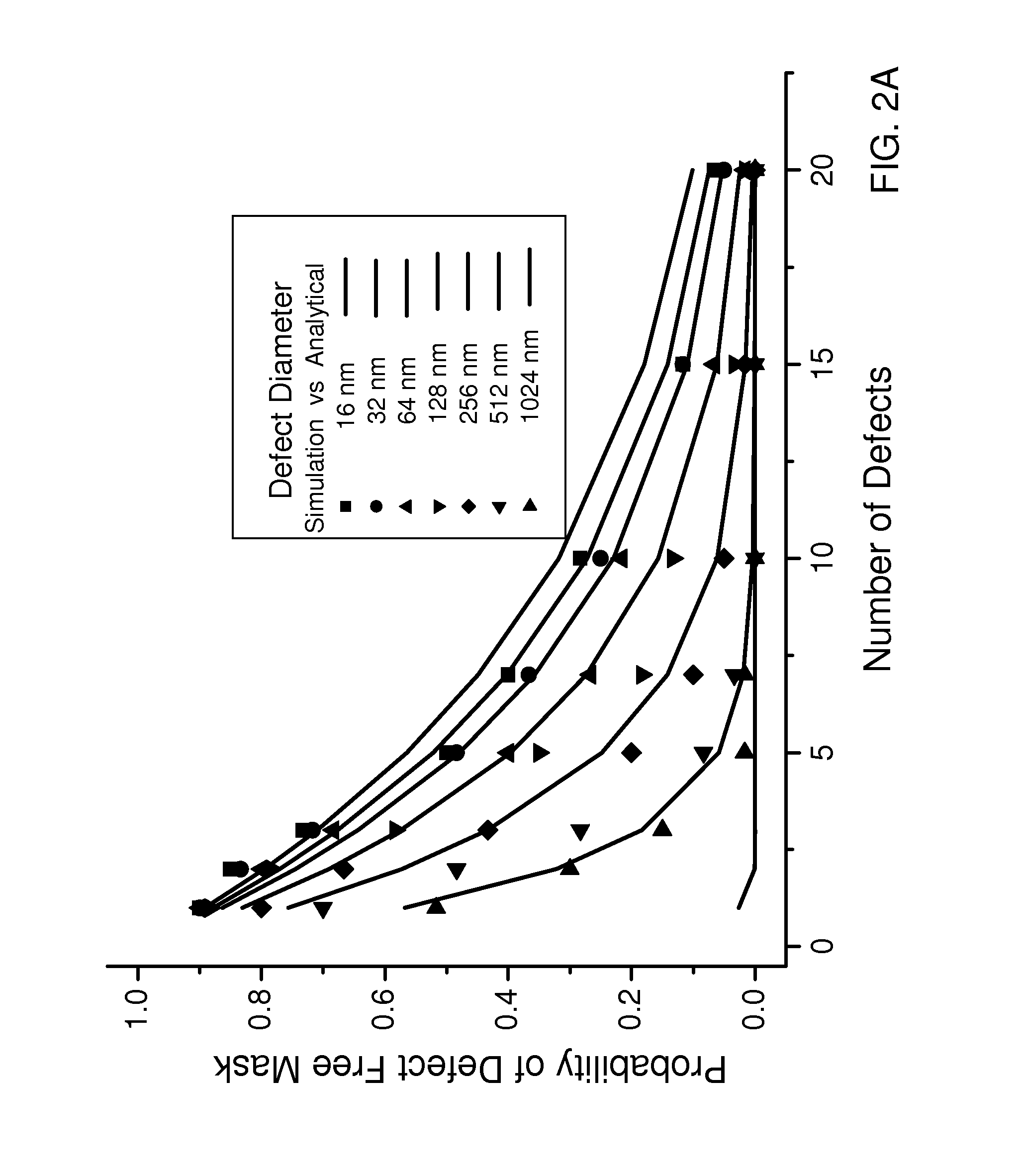
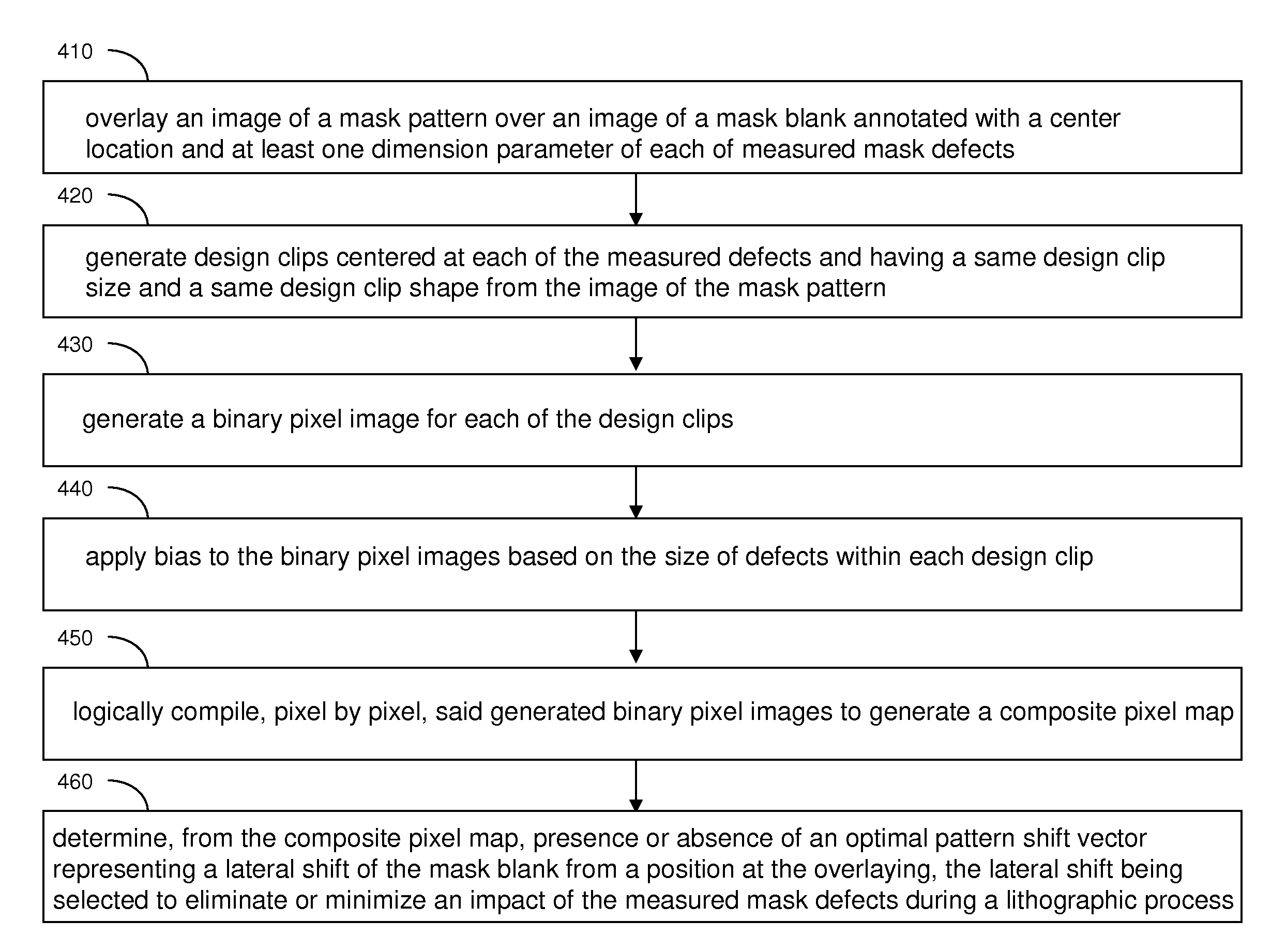
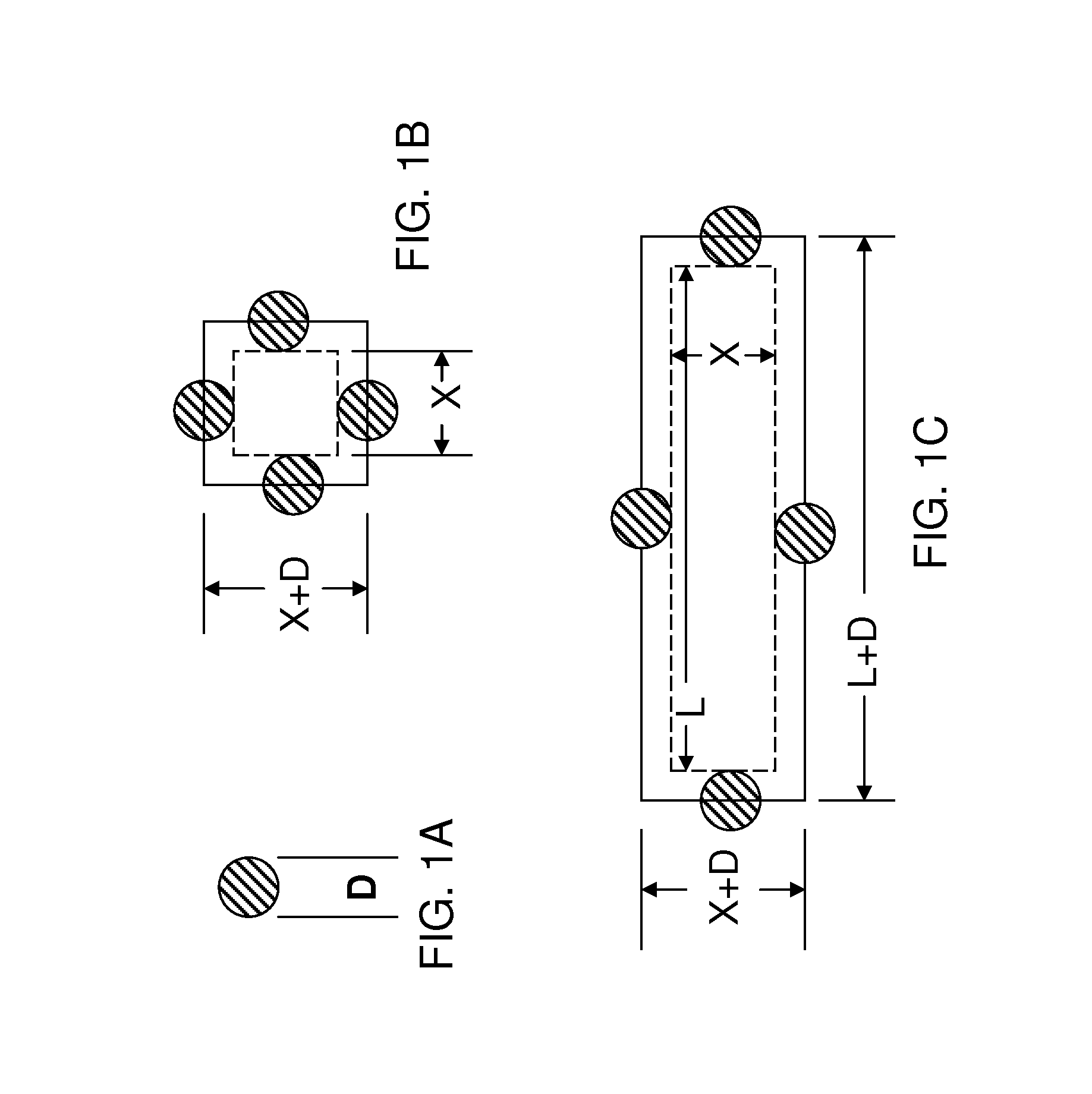
Mitigation of mask defects by pattern shifting
InactiveUS8458623B1Minimize the numberEliminating and minimizing impactNanoinformaticsPhotomechanical apparatusPattern recognitionShift vector
An image of a mask pattern is overlaid on an image of a mask blank annotated with the center location and dimensions of each measured mask defect. Design clips centered at the measured defects are generated with lateral dimensions less than allowable movement of the mask pattern over the mask blank. Each design clip is converted into a binary image including pixels corresponding to defect-activating regions and pixels corresponding to defect-hiding regions. Each pixel region representing the defect-activating region is expanded by laterally biasing peripheries by one half of the lateral extent of the defect located within the corresponding design clip. Biased design clips are logically compiled pixel by pixel to determine an optimal pattern shift vector representing the amount of pattern shift.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Extended range image processing for electro-optical systems
A method and apparatus for processing imagery using images acquired via any known Electro-Optical (EO) system. In accordance with exemplary embodiments of the present invention, a first frame of data is selected as a template frame (e.g., a given frame). A second frame of data can be captured using the EO system. At least a portion of the second frame can be correlated with the template frame to generate a shift vector. The second frame can then be registered with the template frame by interpolating the second frame using the shift vector and re-sampling at least a portion of the second frame to produce a registered frame. The template frame can also be re-sampled. The registered frame and the re-sampled template frame can then be combined to generate an averaged frame. The averaged frame can be spatially filtered to enhance edges within the averaged frame.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Image processing device and method which use two images
InactiveCN1964668AReduce mismatchTelevision system detailsImage analysisImaging processingShift vector
The present invention aims to provide image processing device and method capable of generating a difference image at high speed without occurring misregistration. To achieve this, in the image processing device and method, plural regions of interest are set respectively to input first and second images, a shift vector indicating a misregistration amount between the first and second images is calculated with respect to each of the regions of interest, a filter process is executed to the shift vector, the filter-processed shift vector is interpolated, the first and second images are registered based on the interpolated shift vector, and a subtraction operation is executed between corresponding pixels on the respective registered images to acquire the difference image.
Owner:CANON KK
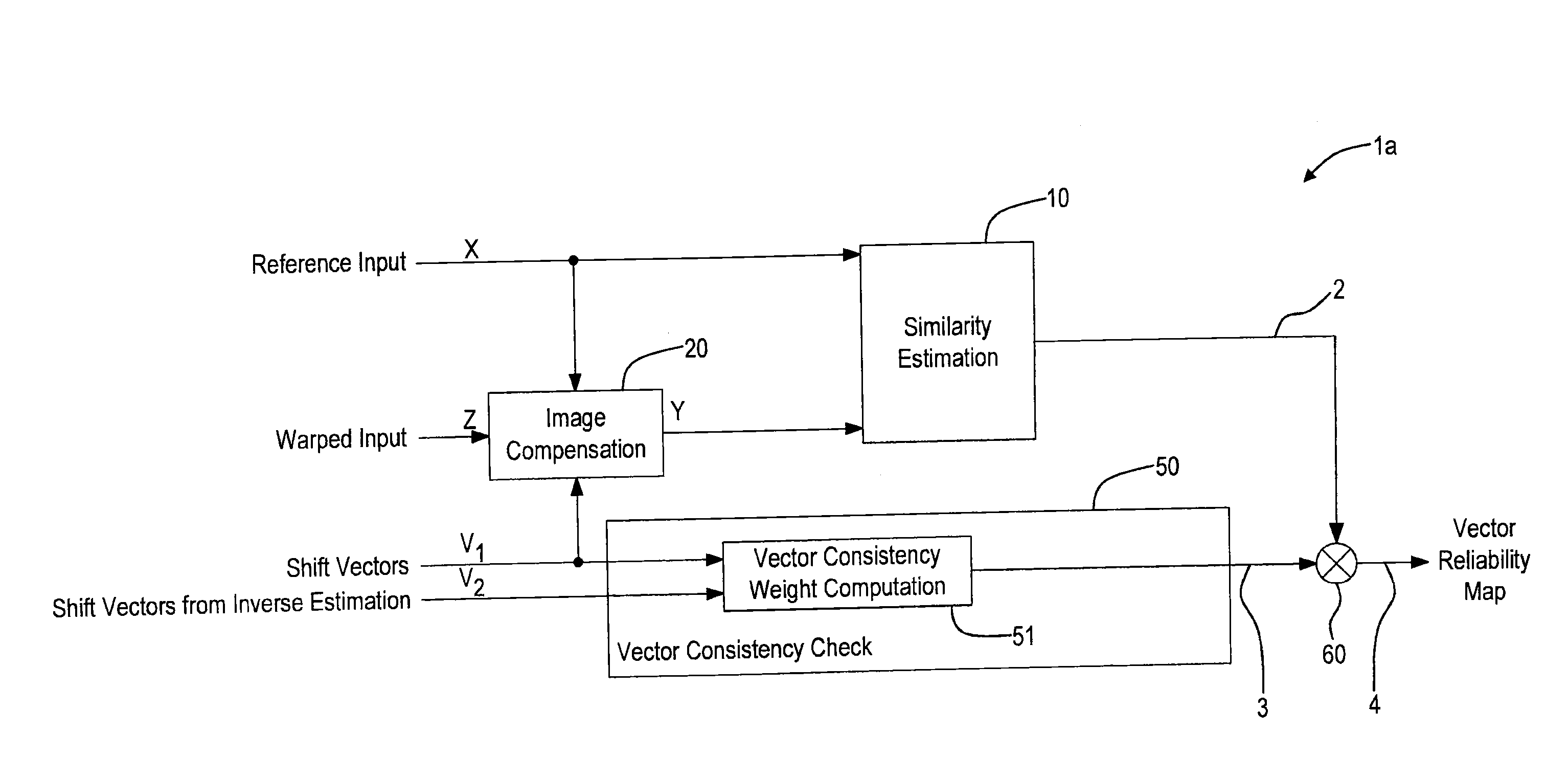
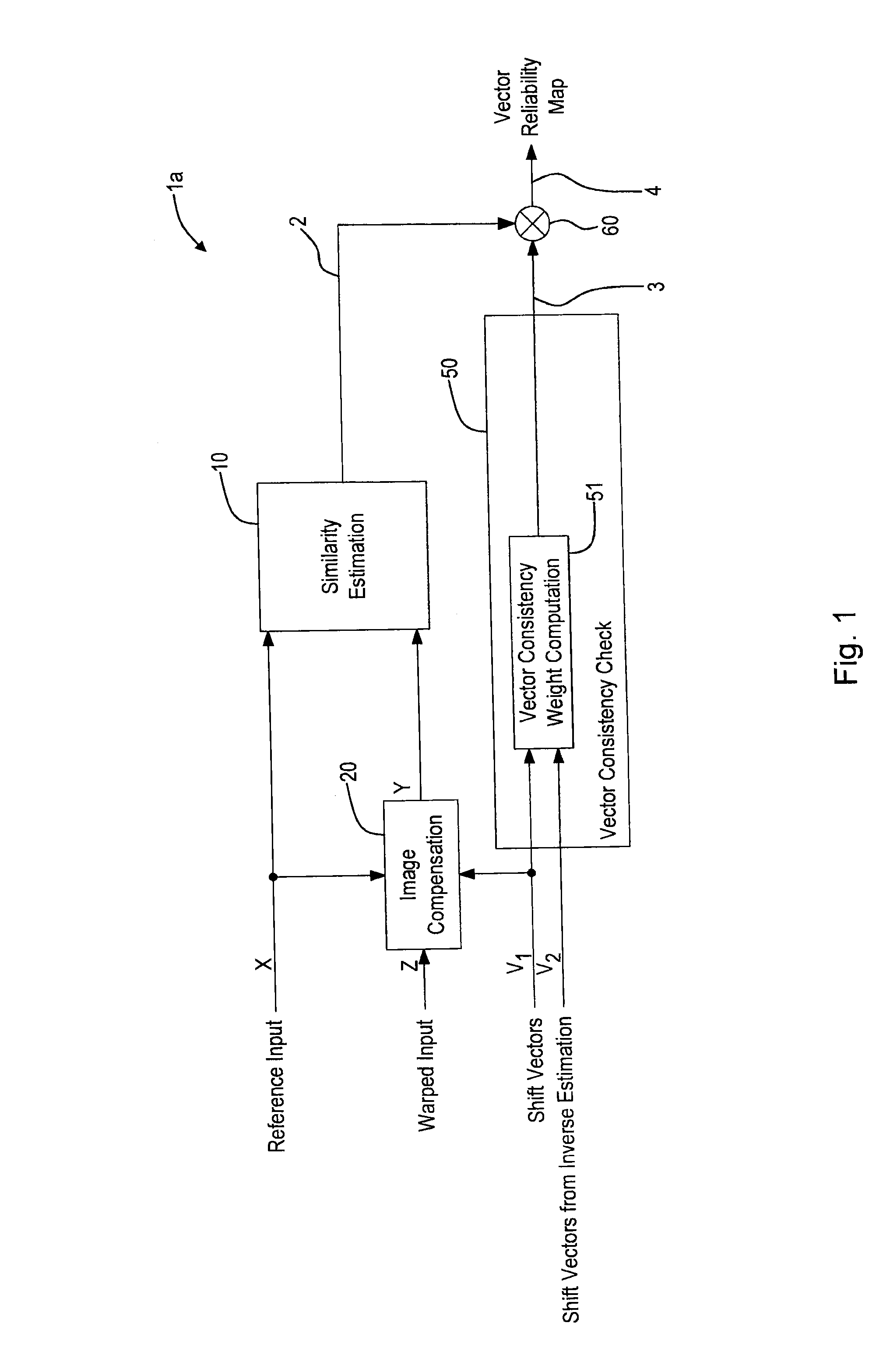
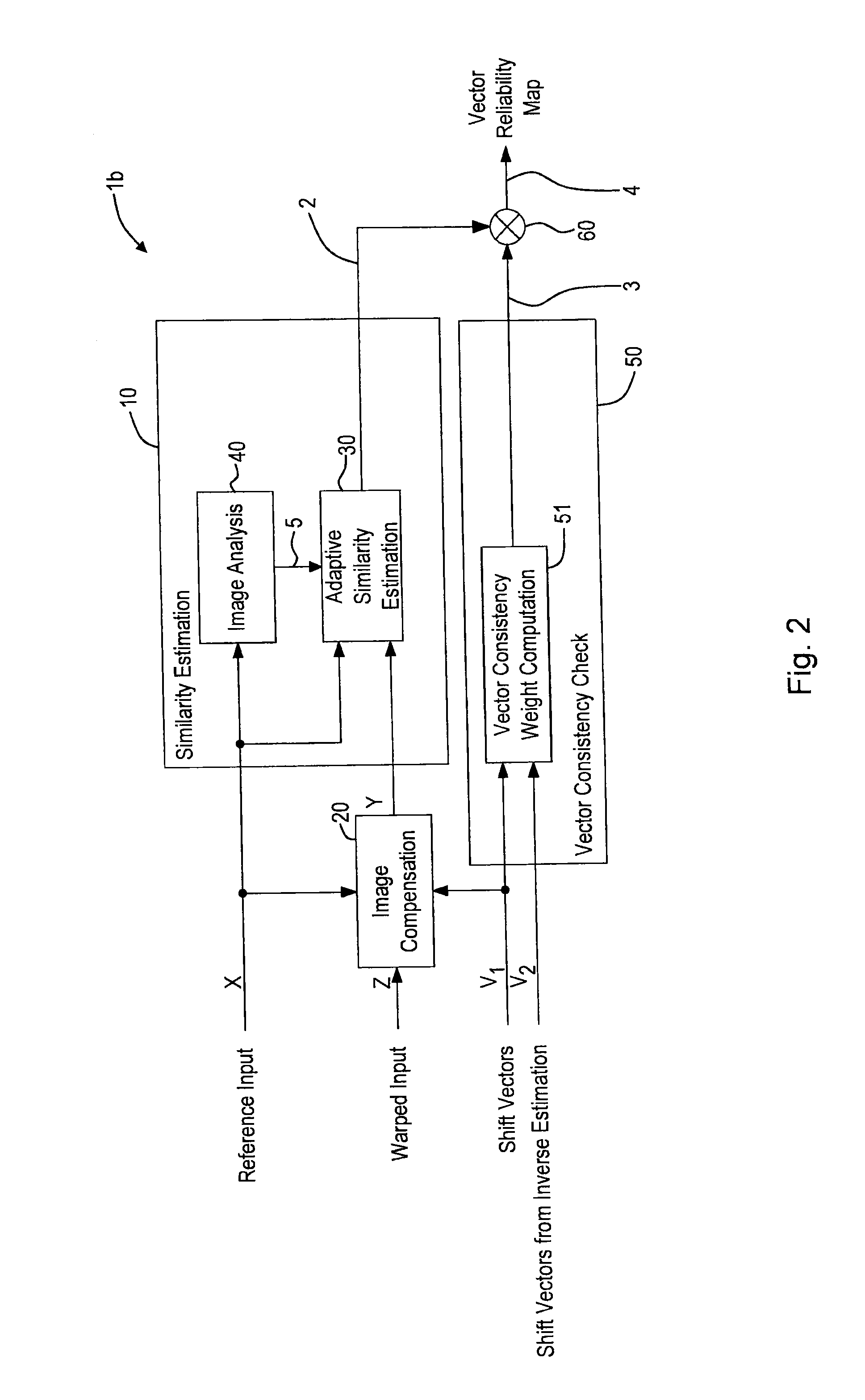
Shift vector reliability determining apparatus and method
An apparatus for determining the reliability of shift vectors between two images comprises an image compensation unit for compensating local shifts between a first image and a second image and to obtain a compensated second image. A similarity estimation unit is provided for determining a similarity information by determining one or more similarity measures between said first image and said compensated second image. A vector consistency check device for comparing shift vectors describing the shift between said first image and said second image from different shift estimation directions to obtain a consistency weight information, and a combination unit for combining said similarity information and said consistency weight information to obtain a reliability information describing the reliability of said shift vectors are provided.
Owner:SONY CORP
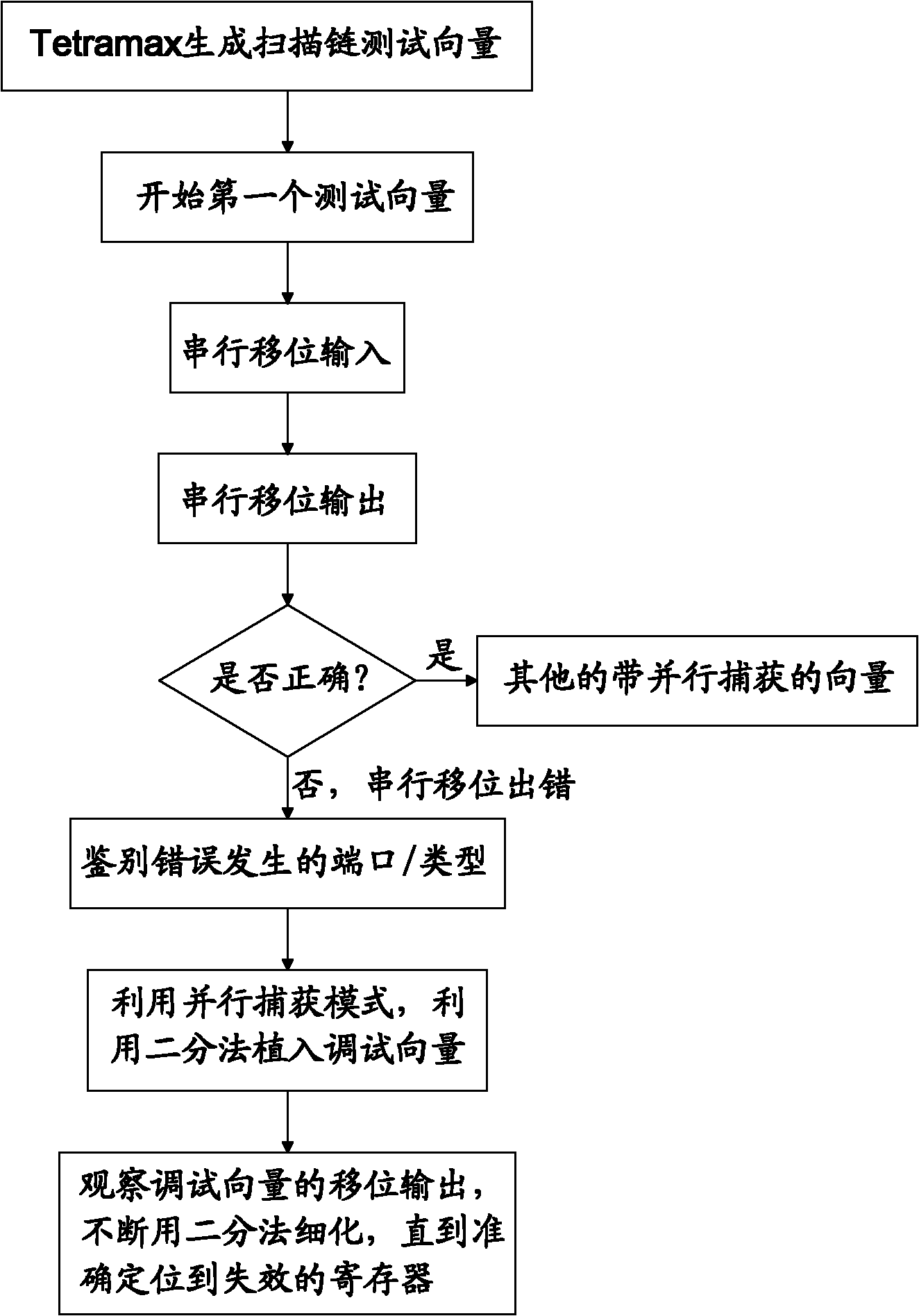
Scan chain-based method for testing memory
ActiveCN102034556AEffective positioningIncrease coverageStatic storageProcessor registerParallel computing
The invention provides a scan chain-based method for testing memory. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, a first test vector of Tetramax generally carries serial shift, if the test vector is passed, the test can be turned to a vector carrying a parallel capture mode; if the port of the scan chain has an error, the port or the type which has error is necessary to be identified; by the parallel capture mode, a test vector is implanted by adopting a dichotomy method; and the test output of a shift vector is observed, and the dichotomy method is used for thining constantly, until an invalid register is accurately positioned. By the function of parallel capture, the test vector can be implanted in the scan chain according to requirement, so that the position of serial shift error can be quickly and effectively positioned, and the coverage rate of test can be greatly improved.
Owner:FUZHOU ROCKCHIP SEMICON
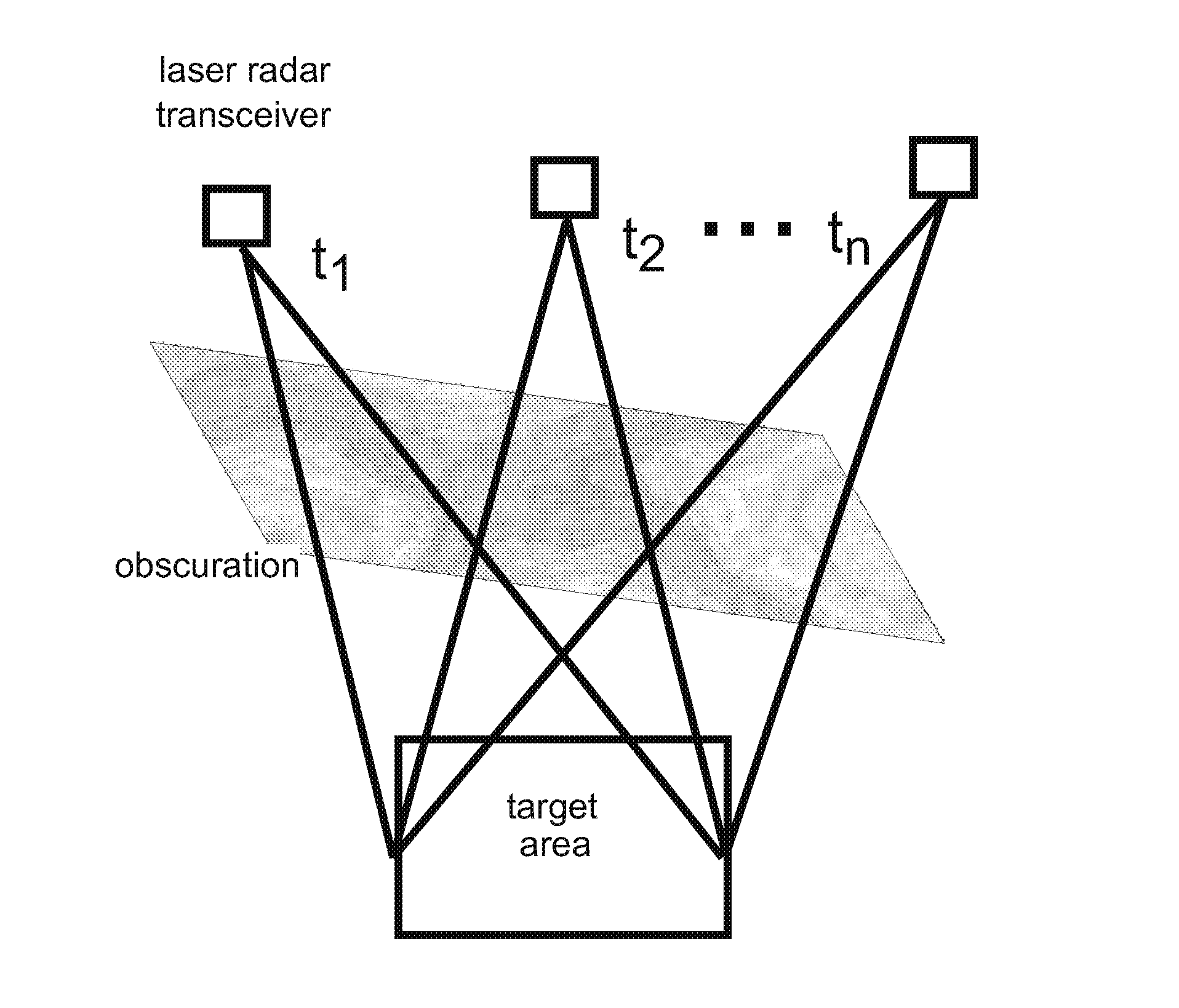
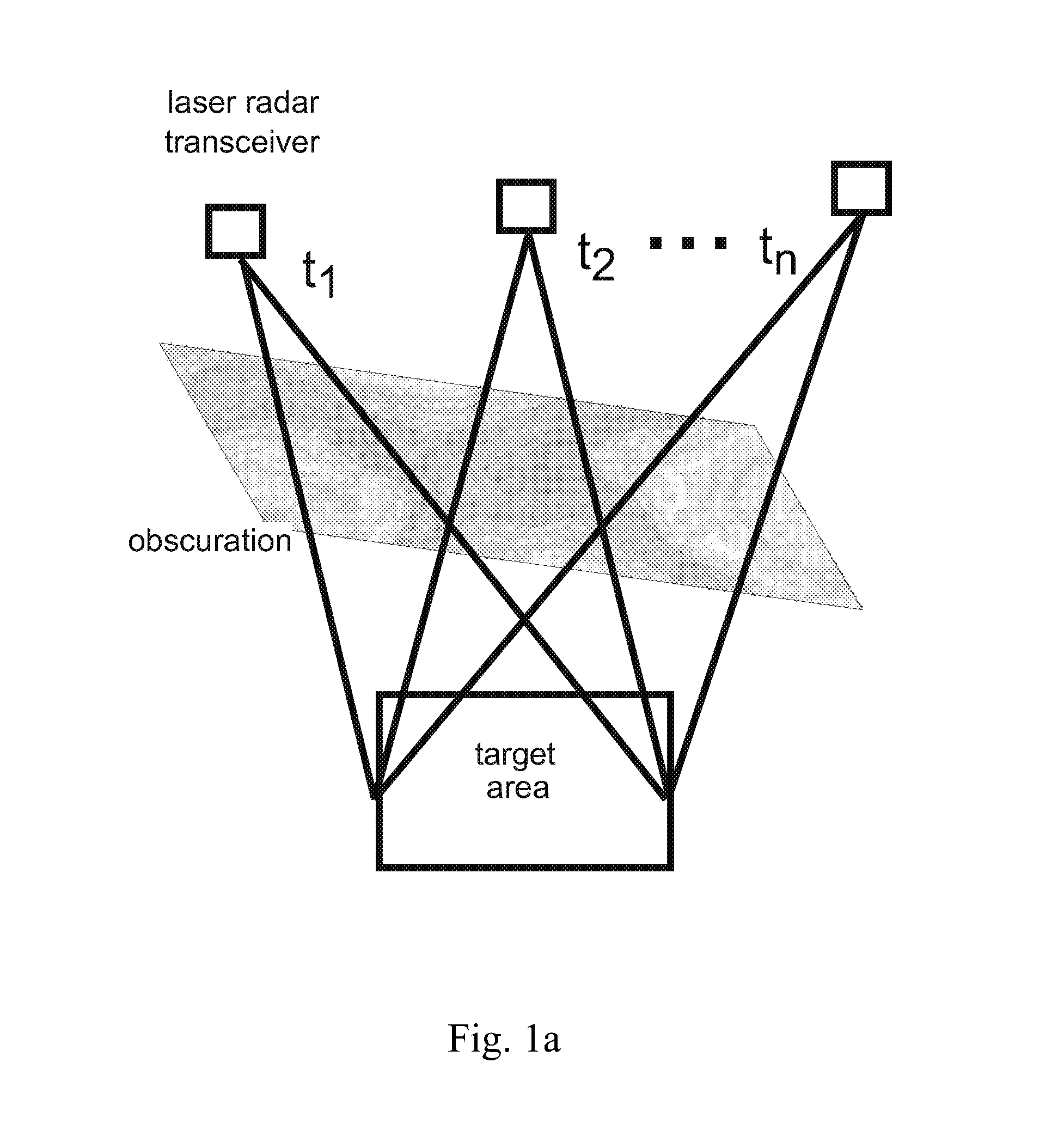
Digital registration of 3D laser radar data based on manually selected fiducials
InactiveUS20120001789A1Technique is tediousImprove of targetOptical rangefindersHeight/levelling measurementVoxelData set
A system and method for registering 3D data sets is disclosed based on manual fiducial selection. The technique is useful in imaging obscured targets with 3-D imaging laser radars. For such an exemplary method, which defines a three-dimensional linear shift vector for each data voxel, four fiducials are required to completely define the mapping for a 3D space. An exemplary registration algorithm as disclosed provides an approach to automatically make fine adjustments to the 3D data registration. The tedious technique of shifting data sets relative to each other, in many degrees of freedom, is eliminated. Instead, a fine adjust is applied to the digital mapping function, through fiducial perturbation.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Mitigation of mask defects by pattern shifting
InactiveUS20130273463A1Avoid harmful effectsEliminating and minimizing impactNanoinformaticsPhotomechanical apparatusPattern recognitionShift vector
An image of a mask pattern is overlaid on an image of a mask blank annotated with the center location and dimensions of each measured mask defect. Design clips centered at the measured defects are generated with lateral dimensions less than allowable movement of the mask pattern over the mask blank. Each design clip is converted into a binary image including pixels corresponding to defect-activating regions and pixels corresponding to defect-hiding regions. Each pixel region representing the defect-activating region is expanded by laterally biasing peripheries by one half of the lateral extent of the defect located within the corresponding design clip. Biased design clips are logically compiled pixel by pixel to determine an optimal pattern shift vector representing the amount of pattern shift.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
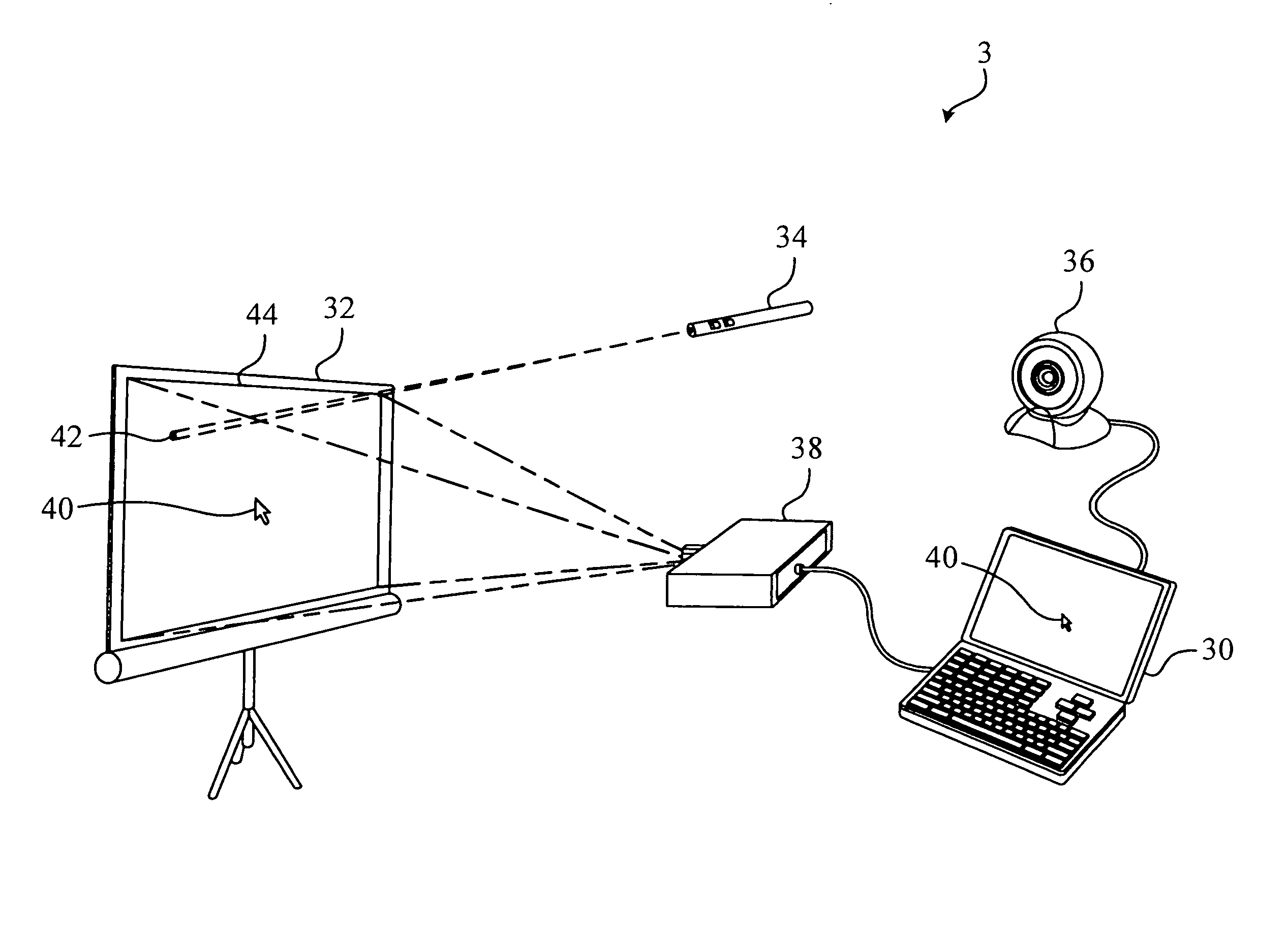
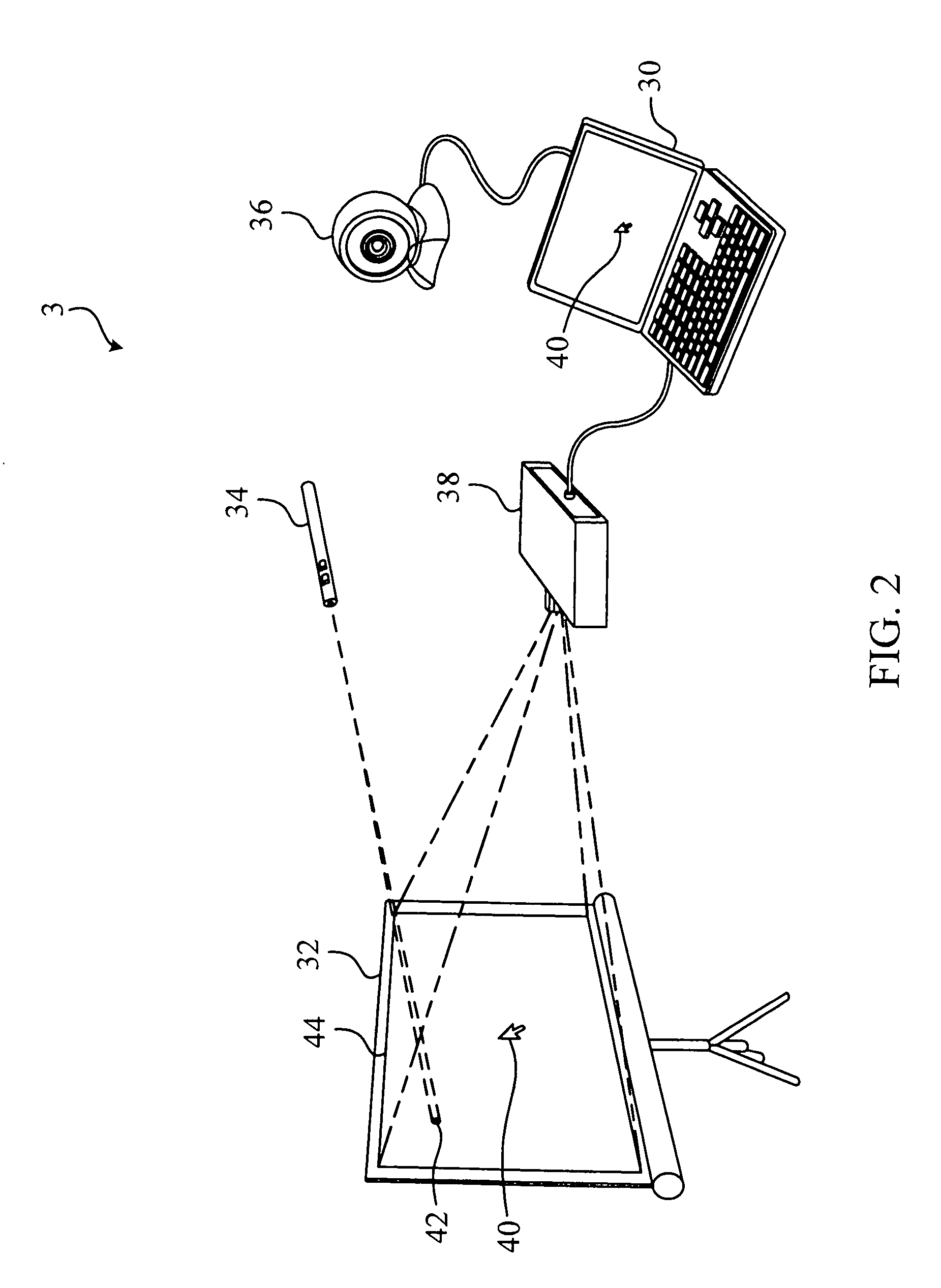
Cursor control method applied to presentation system and computer readable storage medium
ActiveUS8149215B2Good compensationEasy to controlCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingShift vectorProjector
Owner:QUANTA COMPUTER INC
Method and system for processing an image
InactiveUS7406187B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementShift vectorTime difference
In computer aided diagnosis, a high-accuracy image indicating a temporal difference of a diseased part of a patient is produced from a current image and a past image as follows. First, a plurality of matching ROIs (Regions of Interest) are defined on the current image and the past image. A matching processing is performed on corresponding ROIs of the two images to determine points on the past image corresponding to the respective points on the current image. Obtained shift vectors are fitted to a two-dimensional polynomial. In the fitting, when a matching ROI of the current image is included in or overlapped with a previously-defined region of interest, shift vectors are weighted by a small factor. The current image is then modified according to obtained fitting coefficients. Finally, an image indicating the difference between the modified current image and the past image is produced.
Owner:CANON KK
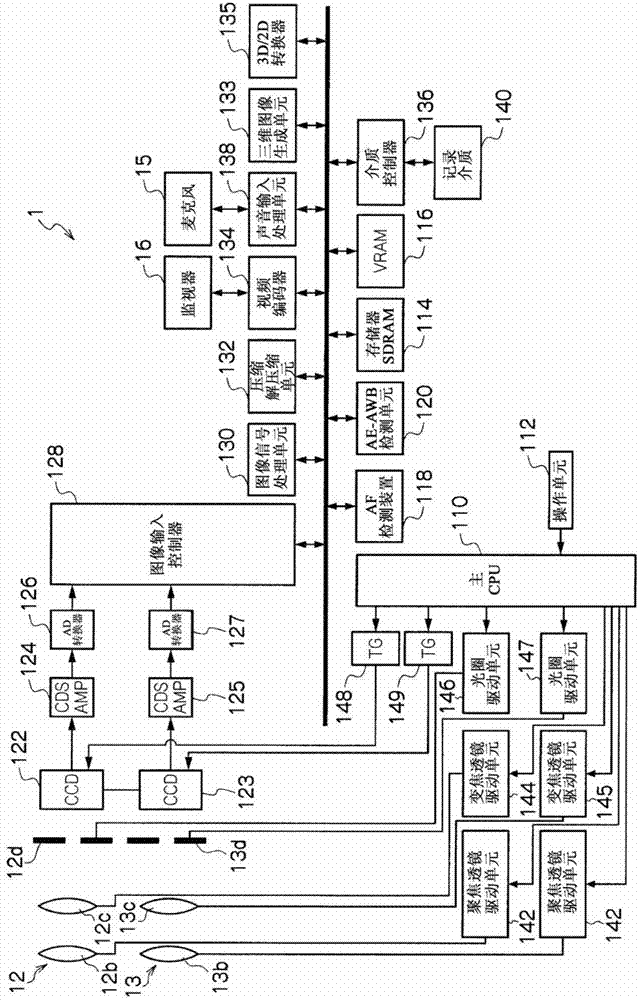
Three-dimensional image display device, three-dimensional image display method, three-dimensional image display program, and recording medium
InactiveCN102972032AAvoid excessive esotropiaAvoid fatigueTelevision system detailsColor television detailsBackground imageShift vector
Among objects in front of a main subject, an object having a shift vector having a magnitude of a predetermined threshold value or more is determined as a target subject. The background image of a right-eye image is extracted from a left-eye image and is combined with the right-eye image, thereby removing the target subject from the right-eye image. Further, the target subject is combined at the position in the left-eye image corresponding to the position of the target subject in the right-eye image, thereby doubly displaying the target subject in the left-eye image. The right-eye image from which the target subject is removed and the left-eye image in which the target subject is doubly displayed are three-dimensionally displayed on a monitor (16). This enables the target subject not to be seen as a three-dimensional image. Furthermore, this enables a three-dimensional image to be displayed in consideration of the fatigue of user's eyes.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com