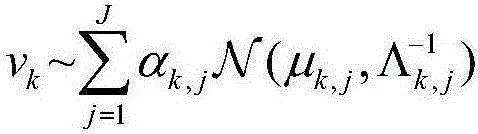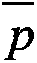Patents
Literature
668 results about "Re sampling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Resampling is the method that consists of drawing repeated samples from the original data samples.
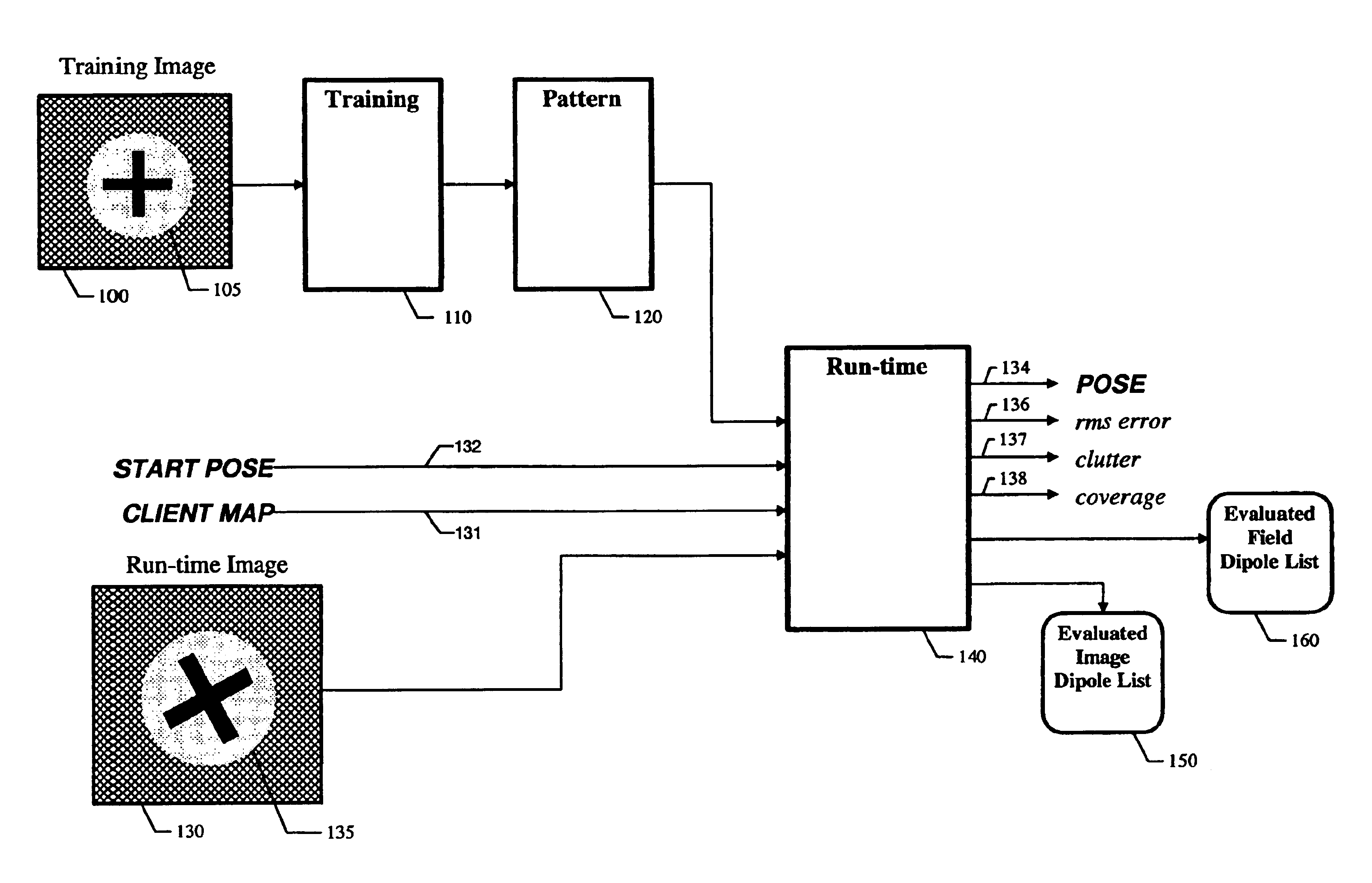
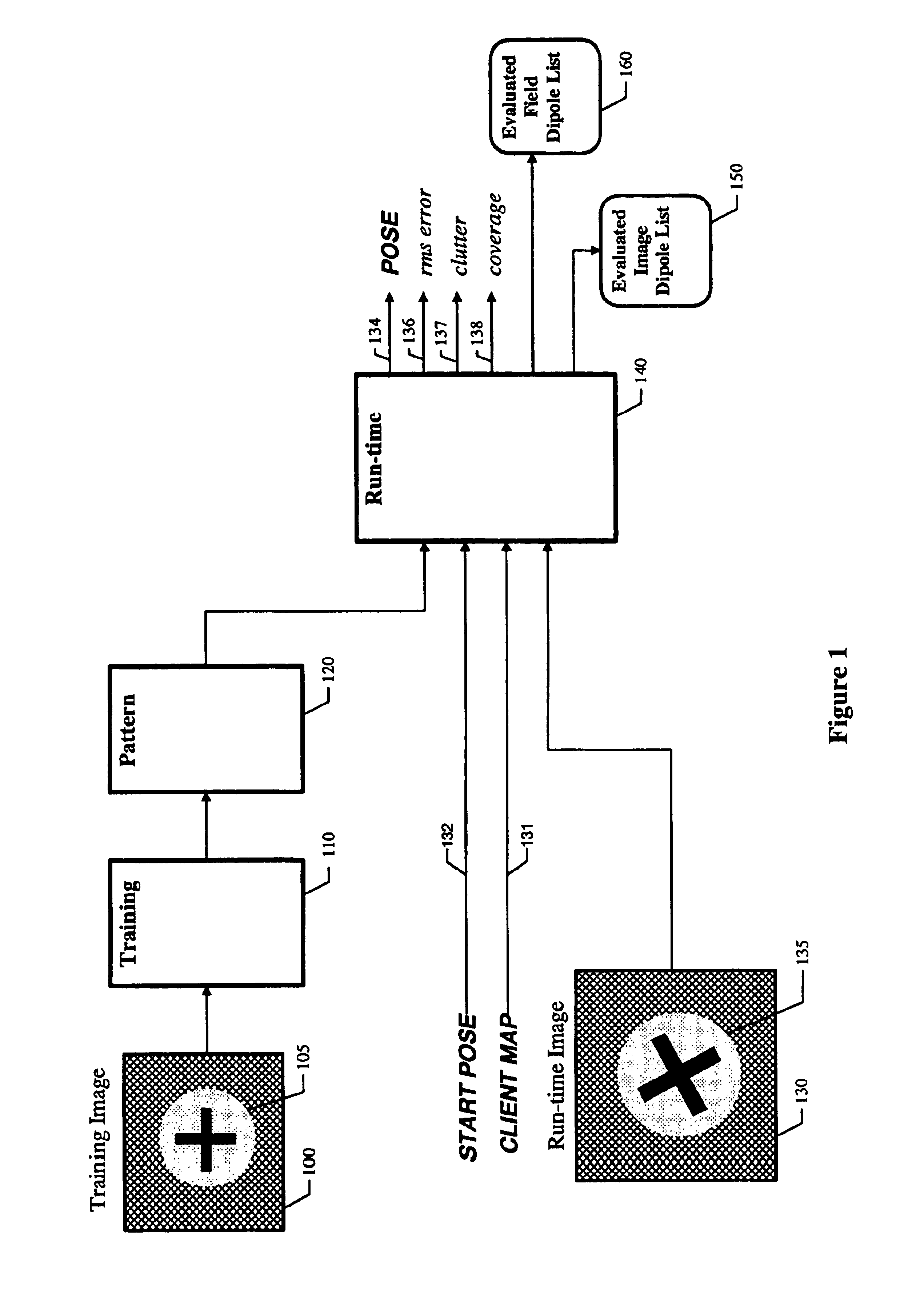
Digital image enhancement using successive zoom images
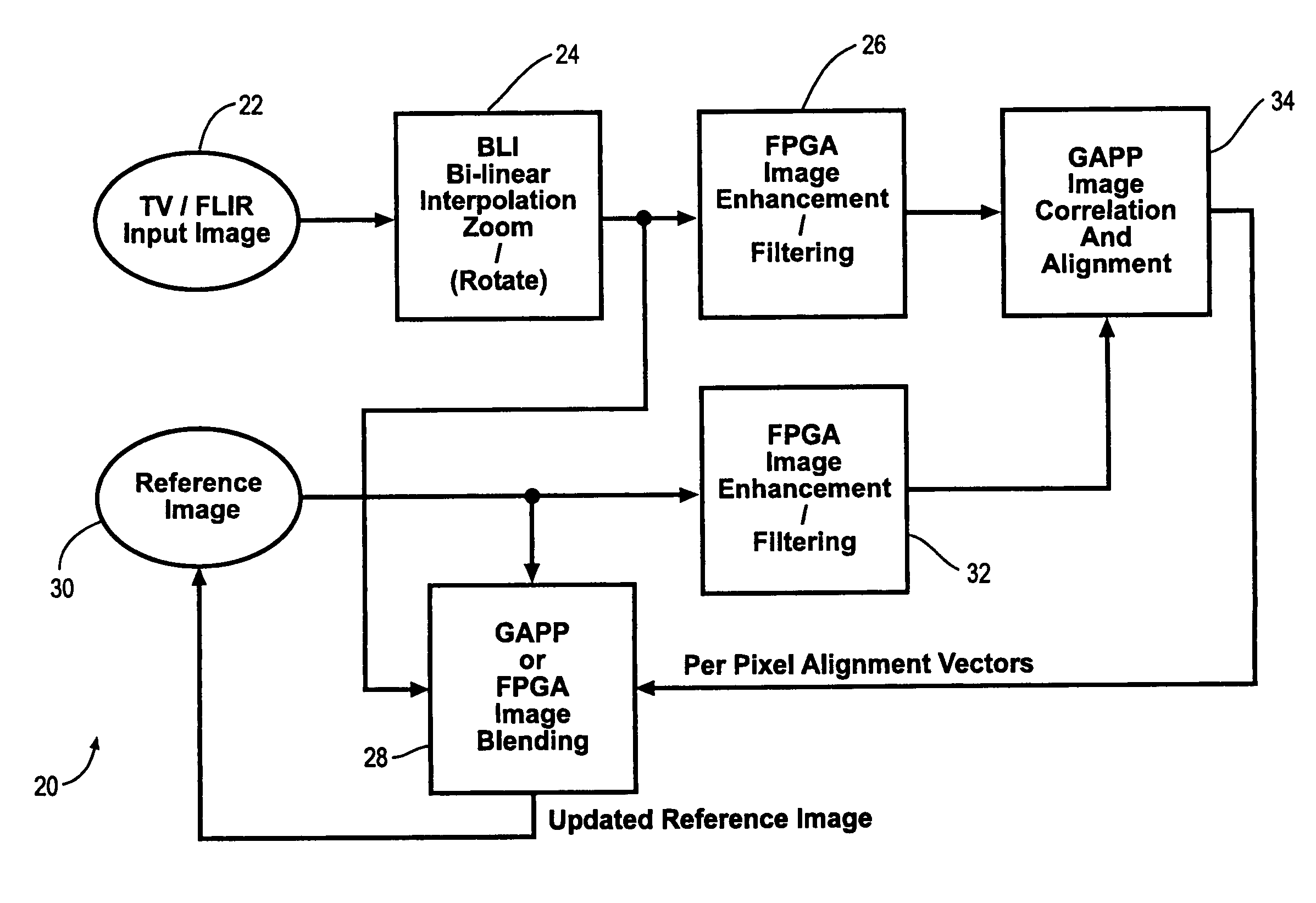
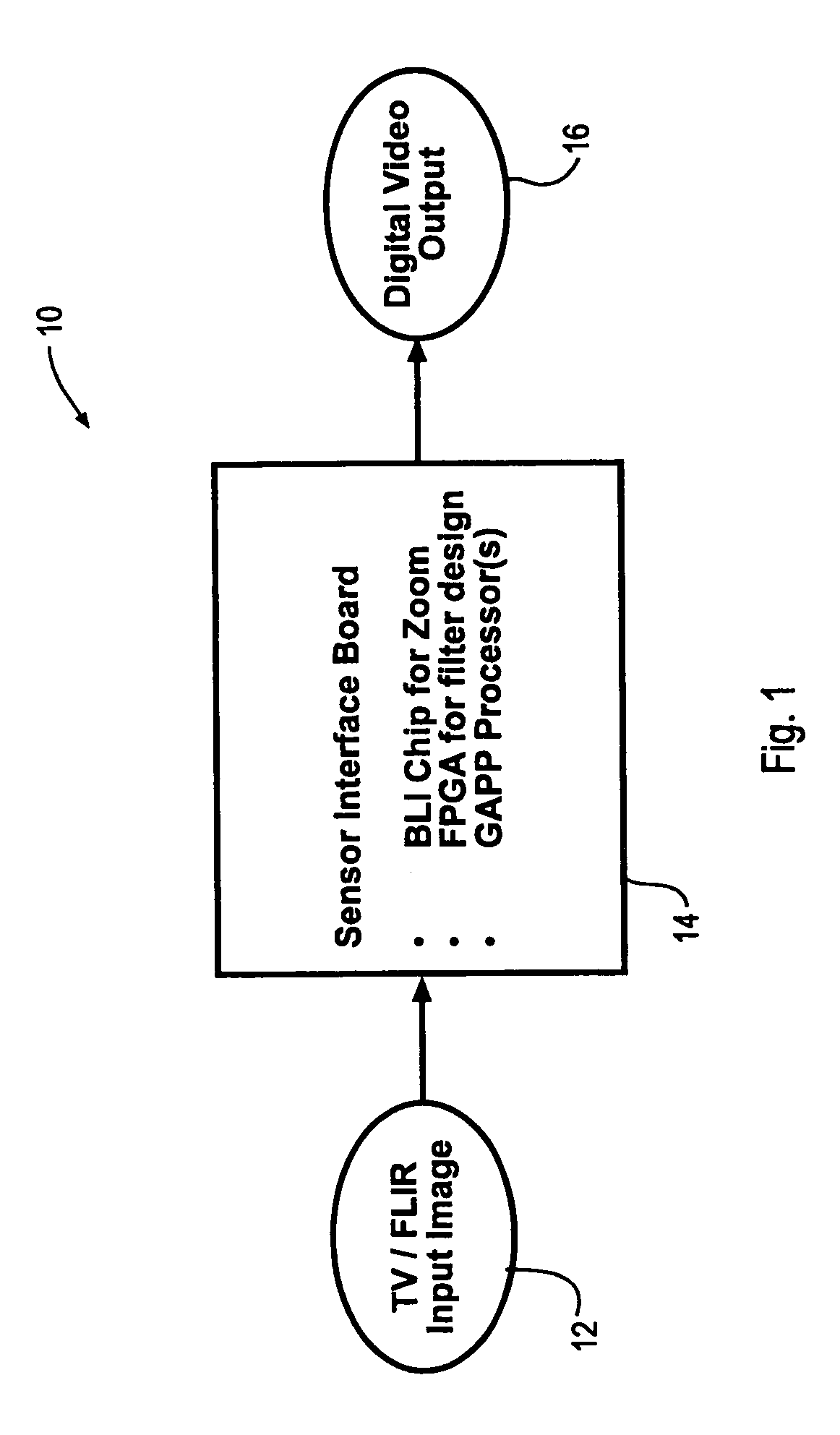
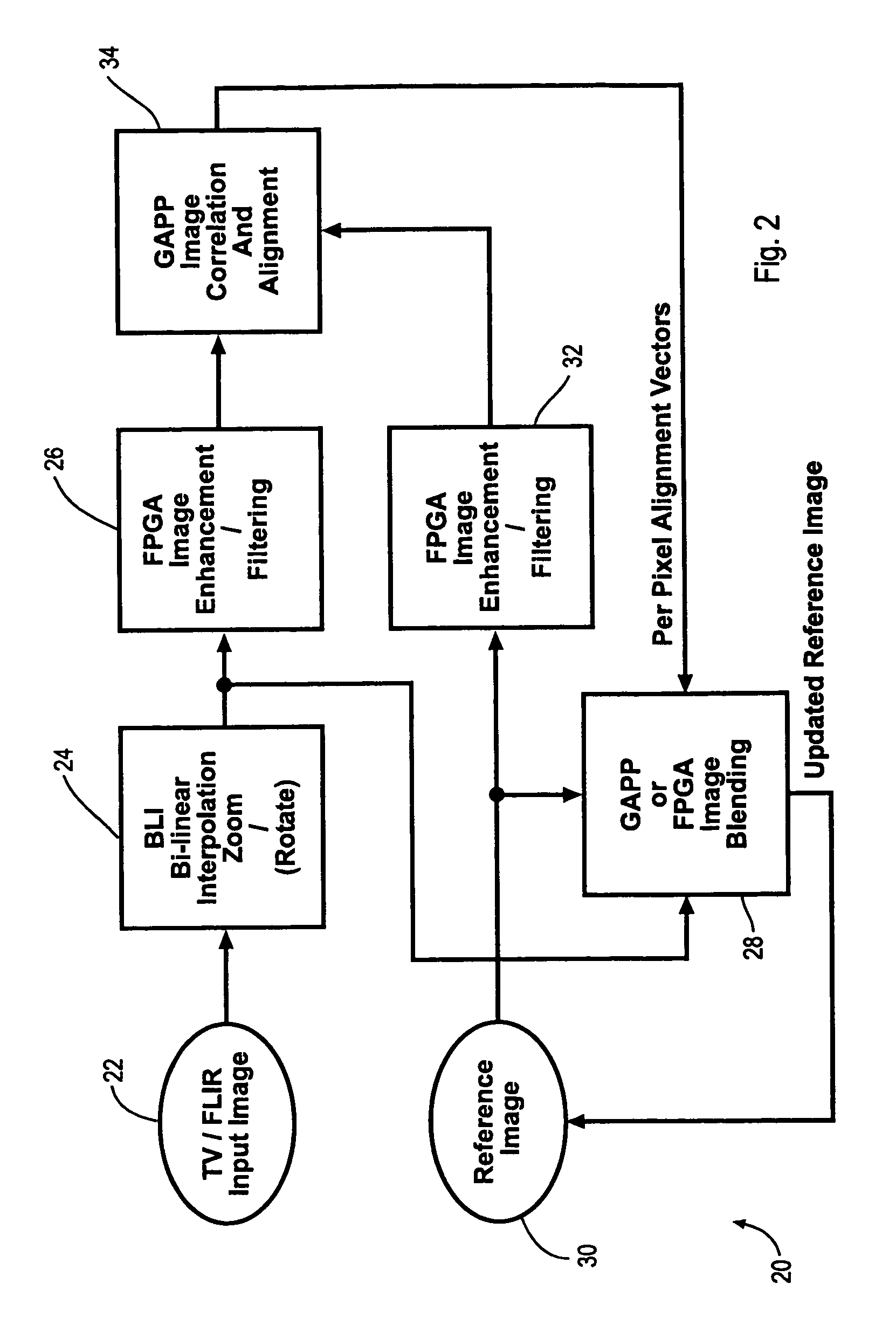
InactiveUS7346217B1Television system detailsImage enhancementRadiographic Image EnhancementDigital image
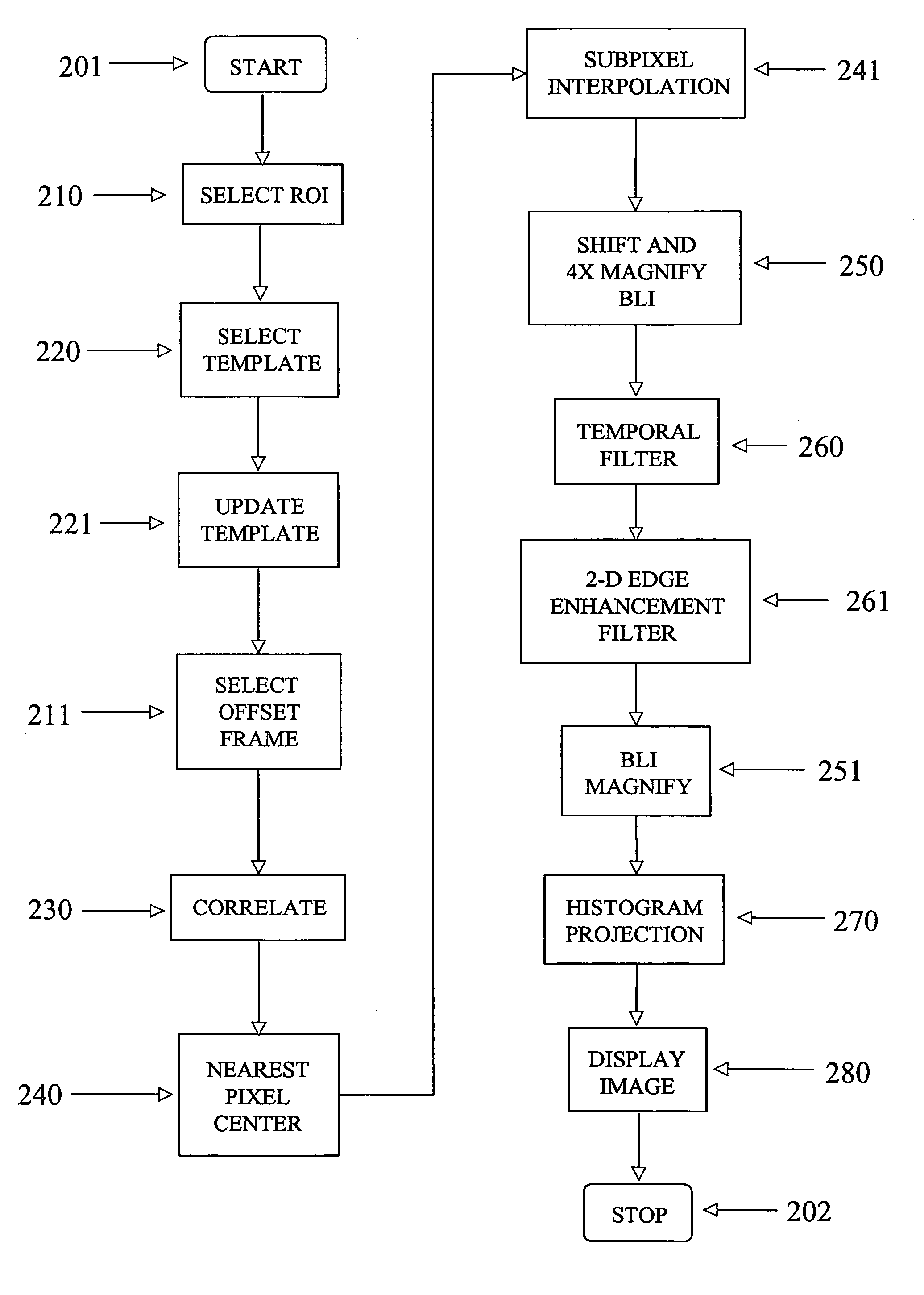
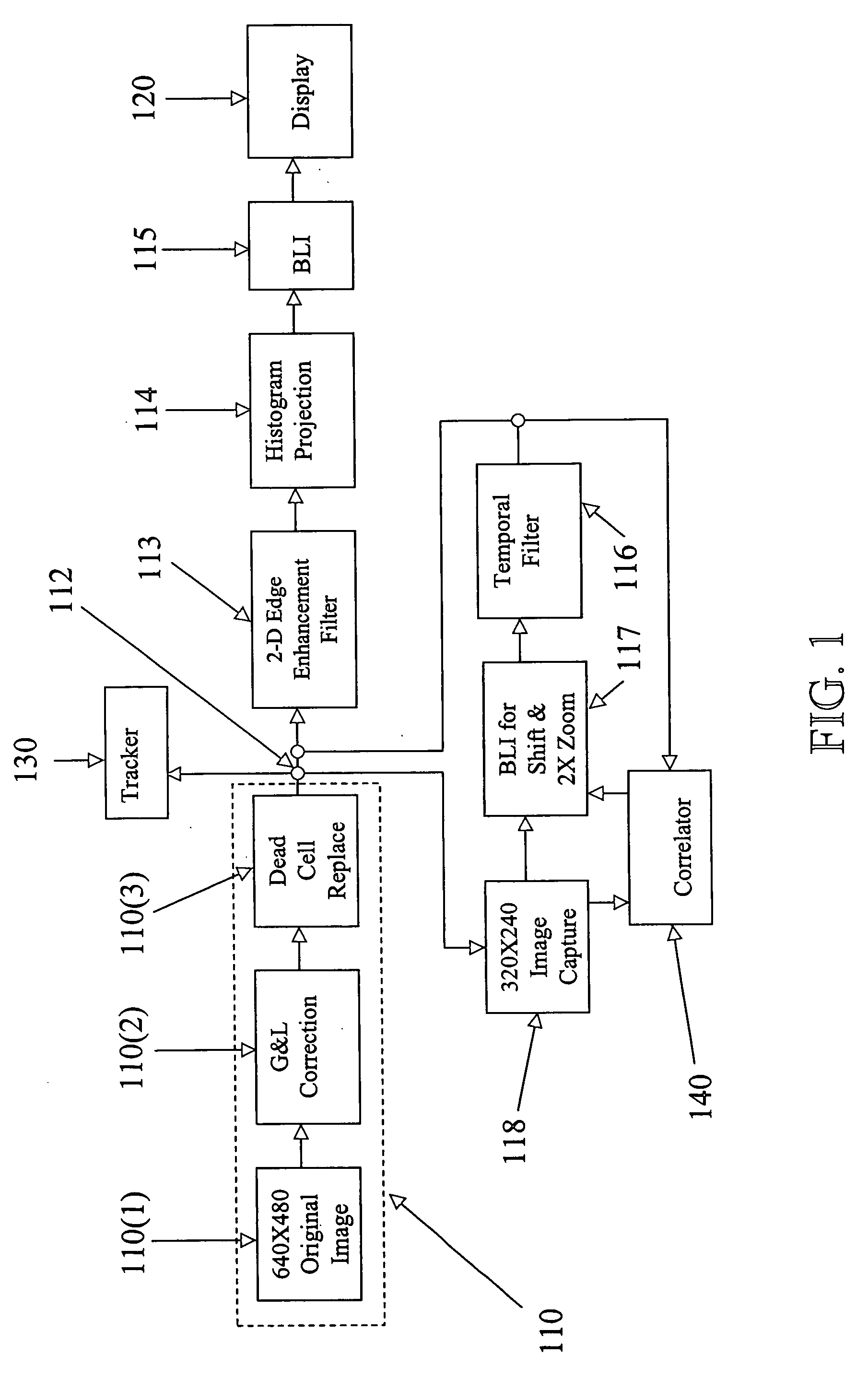
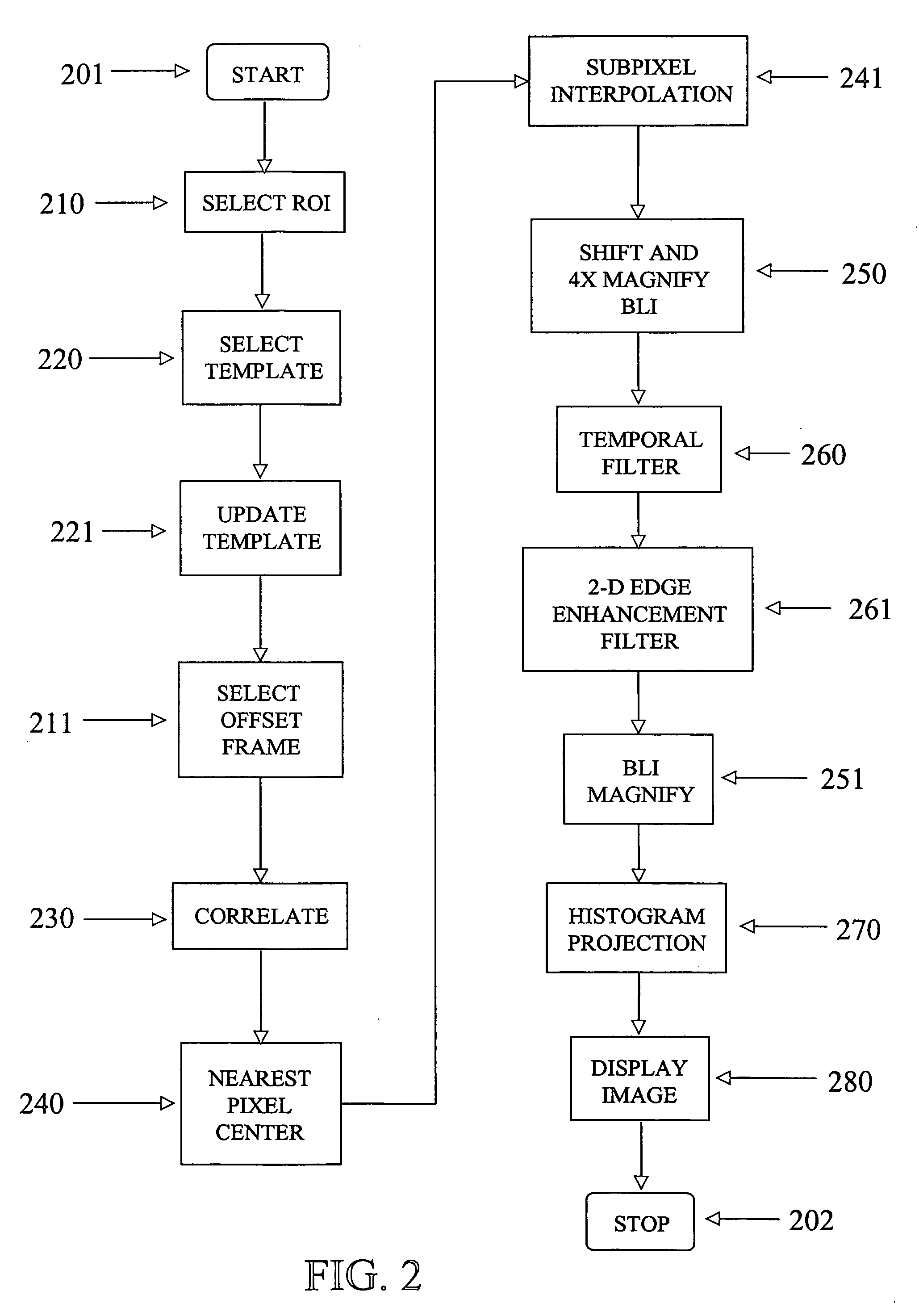
A method and Electro-Optical (EO) system for processing imagery comprising selecting a first frame of data as a template frame; capturing a second frame of data using the EO system, for a plurality of pixels of the second frame, correlating the plurality of pixels of the second frame with pixels of the template frame to generate a plurality of shift vectors, one for each pixel of the plurality of pixels of the second frame, registering the second frame with the template frame by interpolating the second frame using the plurality of shift vectors and re-sampling at least a portion of the second frame to produce a registered frame, re-sampling the template frame, and combining the re-sampled template frame and the registered frame to generate an averaged frame.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
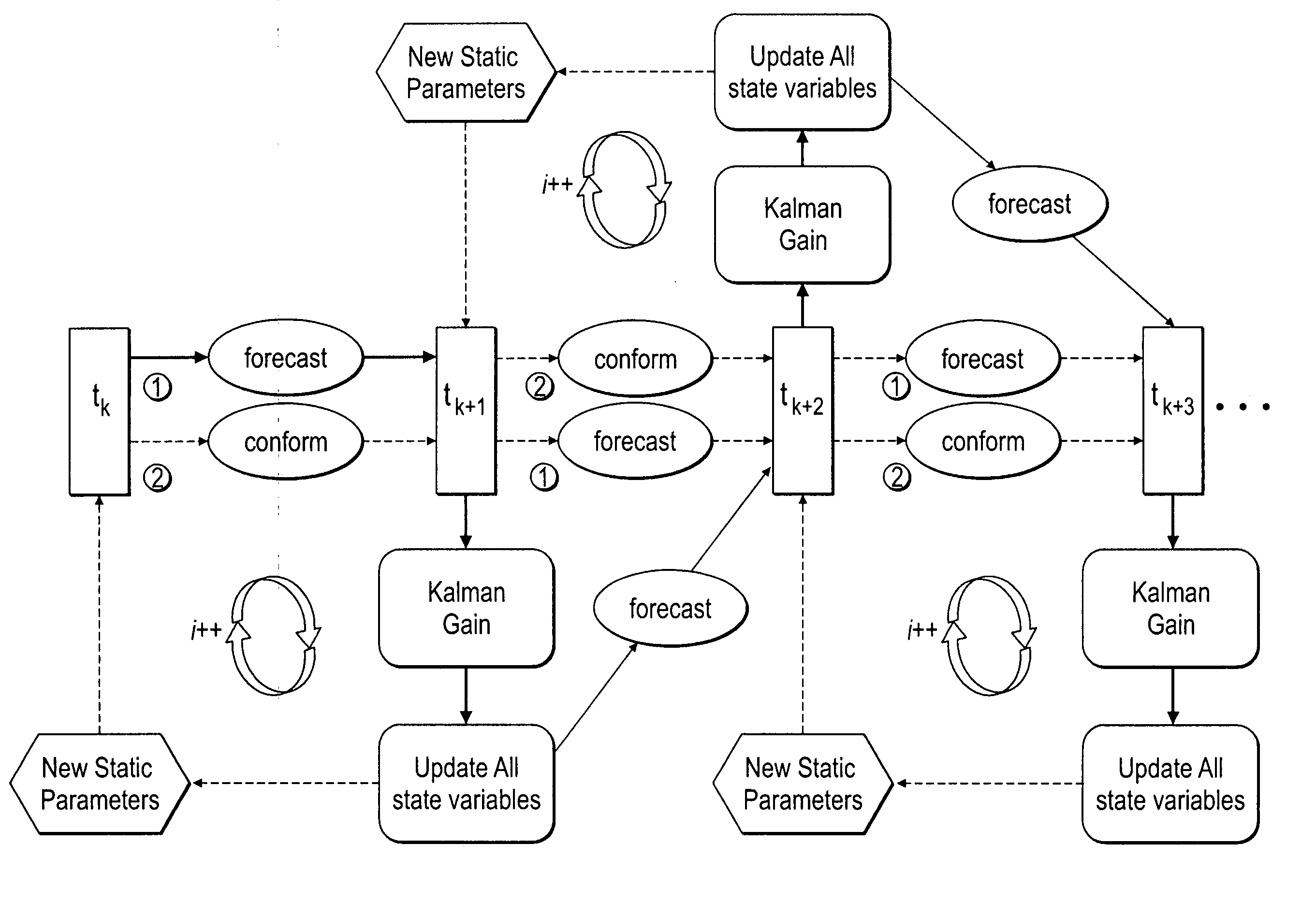
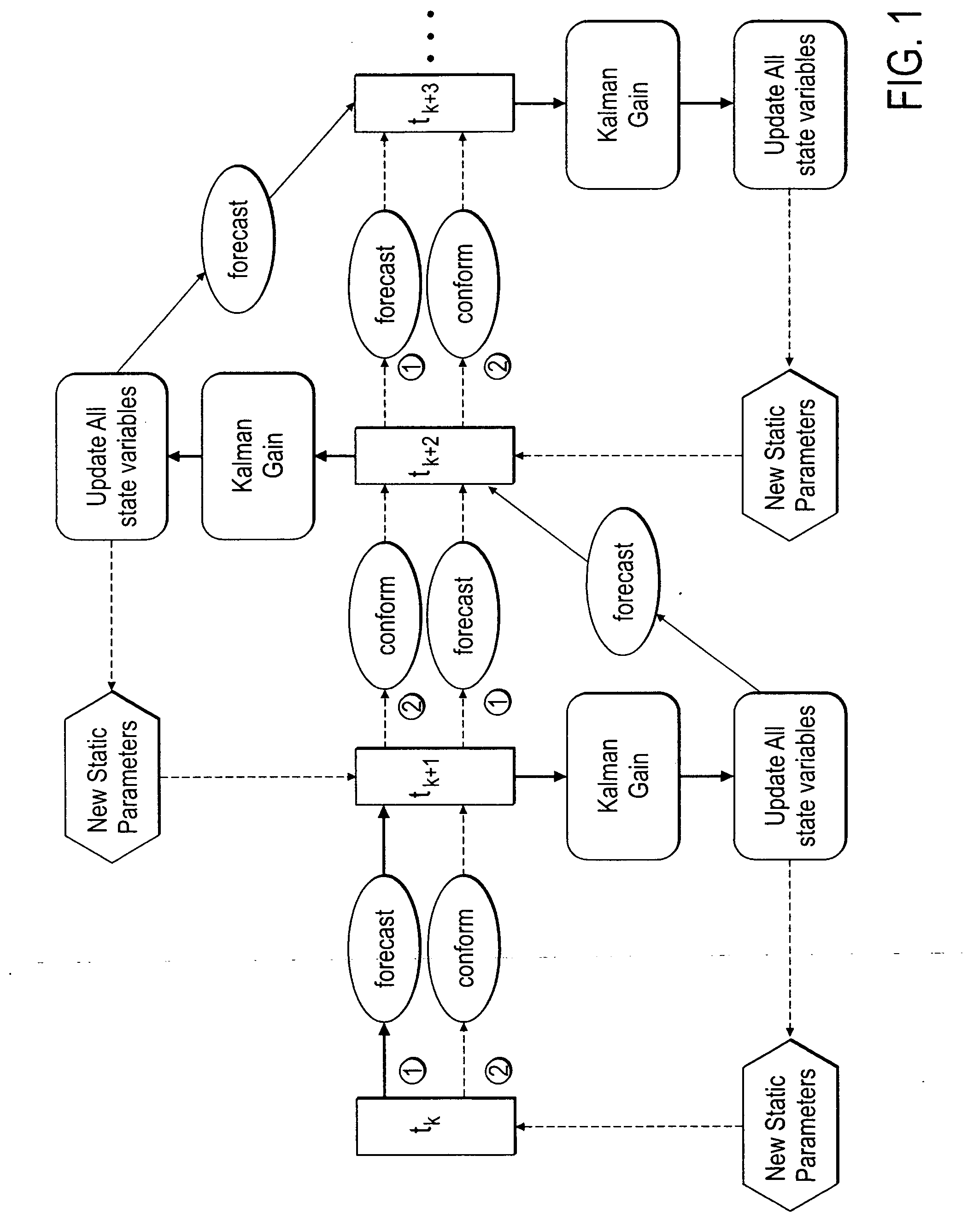
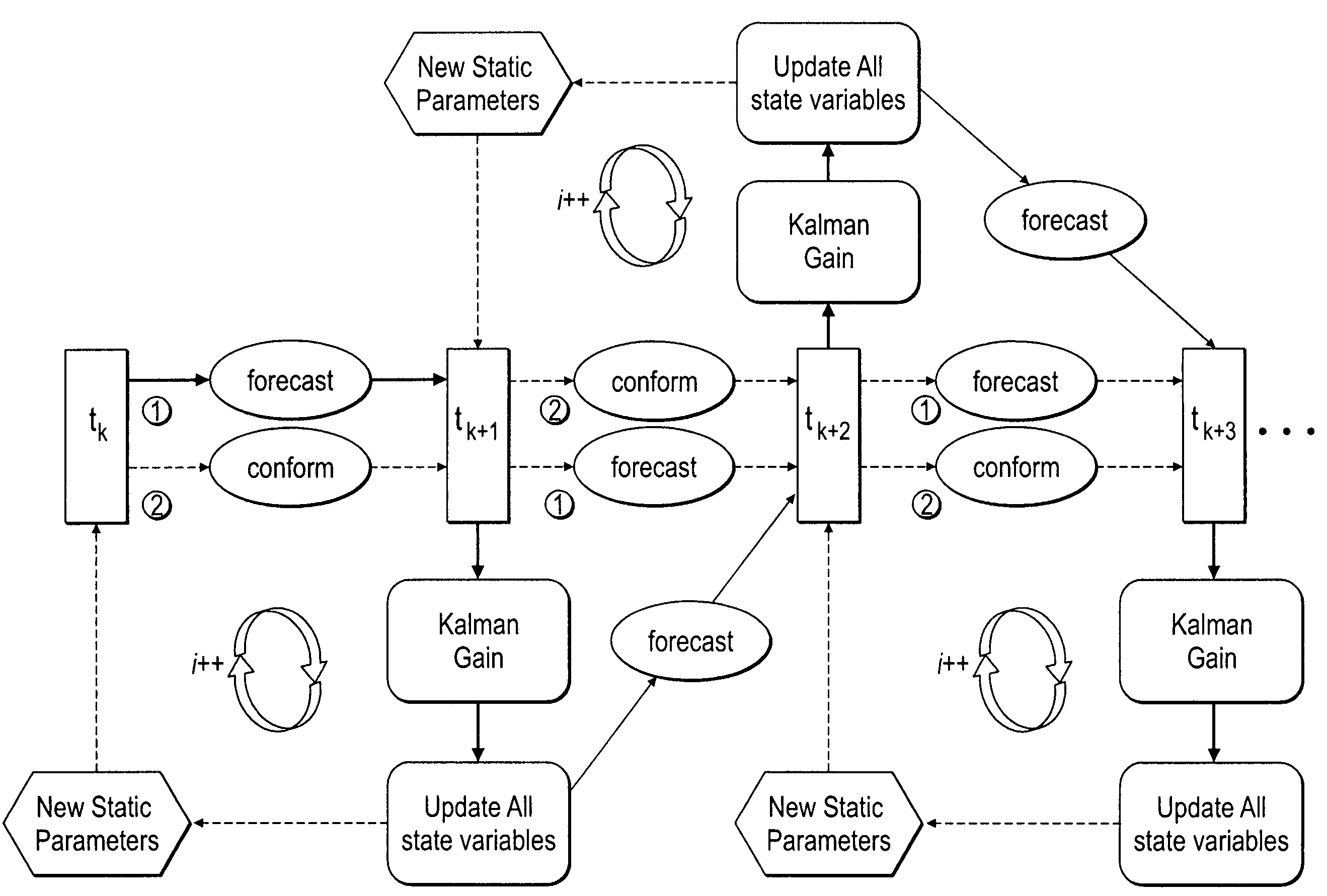
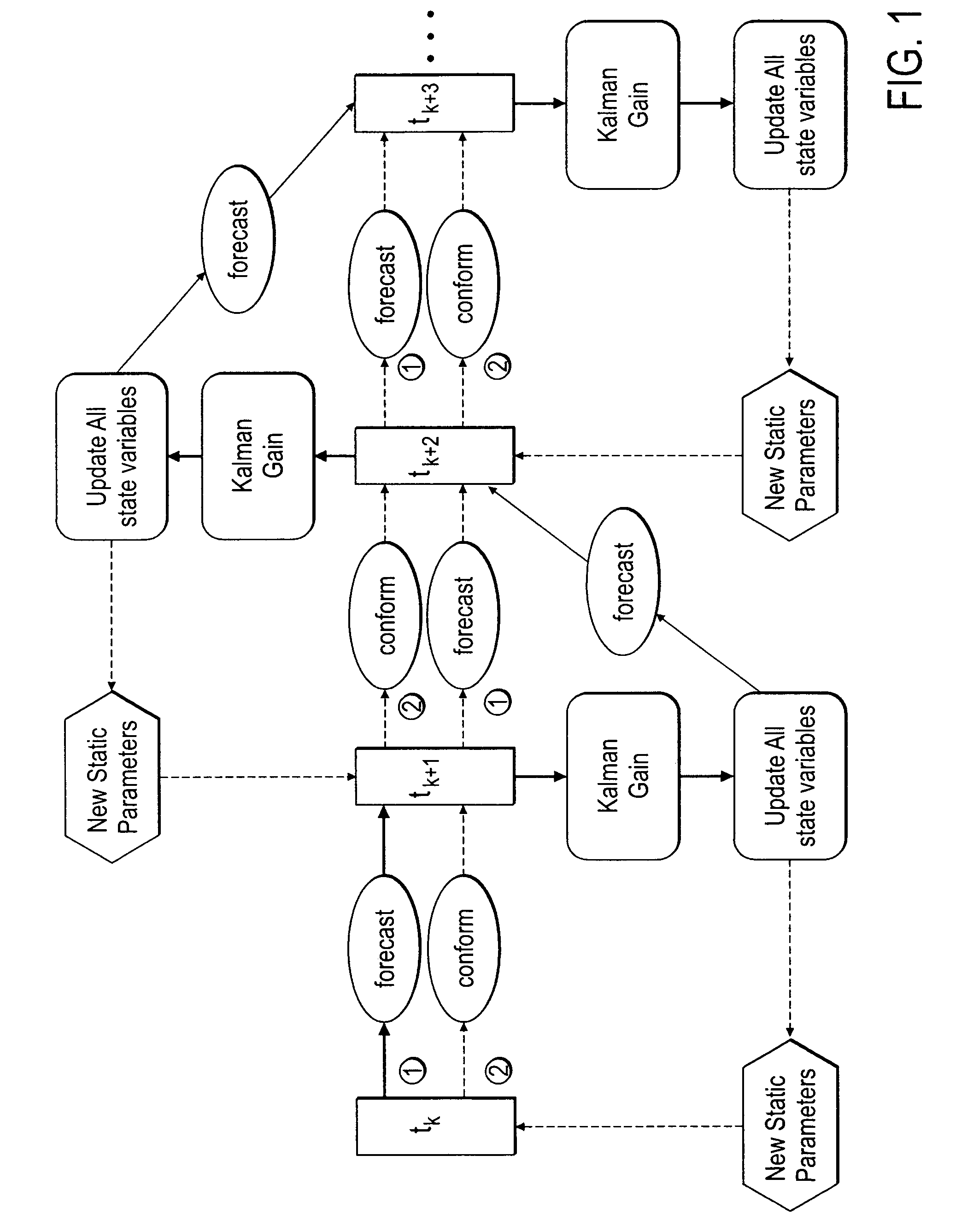
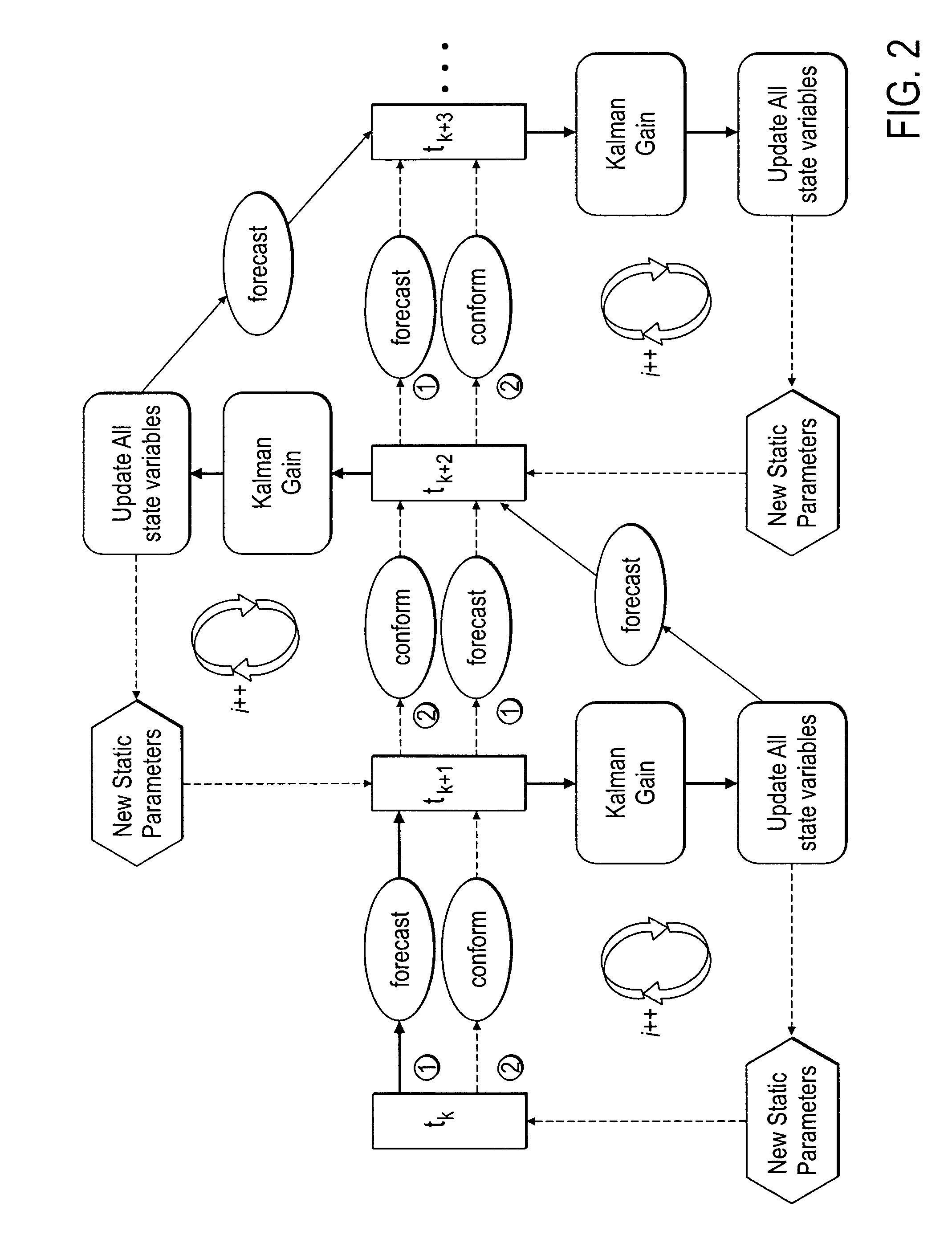
Method, system and apparatus for real-time reservoir model updating using ensemble Kalman filter
ActiveUS20070118346A1Reduce in quantityEnsure correct executionFluid removalComputation using non-denominational number representationKaiman filterState variable
A method, system and apparatus for real-time reservoir model updating using ensemble Kalman filters is described. The method includes a conforming step for bring bringing static and dynamic state variables into conformance with one another during a time step of the updating. Also, an iterative damping method is used in conjunction with the conformance step to account for nonGaussian and nonlinear features in a system. Also, a re-sampling method is described which reduces the ensemble size of reservoir models which are to be updated.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Fast high-accuracy multi-dimensional pattern inspection
InactiveUS6850646B1Improve matchImprove accuracyImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging FeatureRelevant feature
A method and apparatus are provided for identifying diffe rences between a stored pattern and a matching image subset, where variations in pattern position, orientation, and size do not give rise to false differences. The invention is also a system for analyzing an object image with respect to a model pattern so as to detect flaws in the object image. The system includes extracting pattern features from the model pattern; generating a vector-valued function using the pattern features to provide a pattern field; extracting image features from the object image; evaluating each image feature, using the pattern field and an n-dimensional transformation that associates image features with pattern features, so as to determine at least one associated feature characteristic; and using at least one feature characteristic to identify at least one flaw in the object image. The invention can find at least two distinct kinds of flaws: missing features, and extra features. The invention provides pattern inspection that is faster and more accurate than any known prior art method by using a stored pattern that represents an ideal example of the object to be found and inspected, and that can be translated, rotated, and scaled to arbitrary precision much faster than digital image re-sampling, and without pixel grid quantization errors. Furthermore, since the invention does not use digital image re-sampling, there are no pixel quantization errors to cause false differences between the pattern and image that can limit inspection performance.
Owner:COGNEX CORP
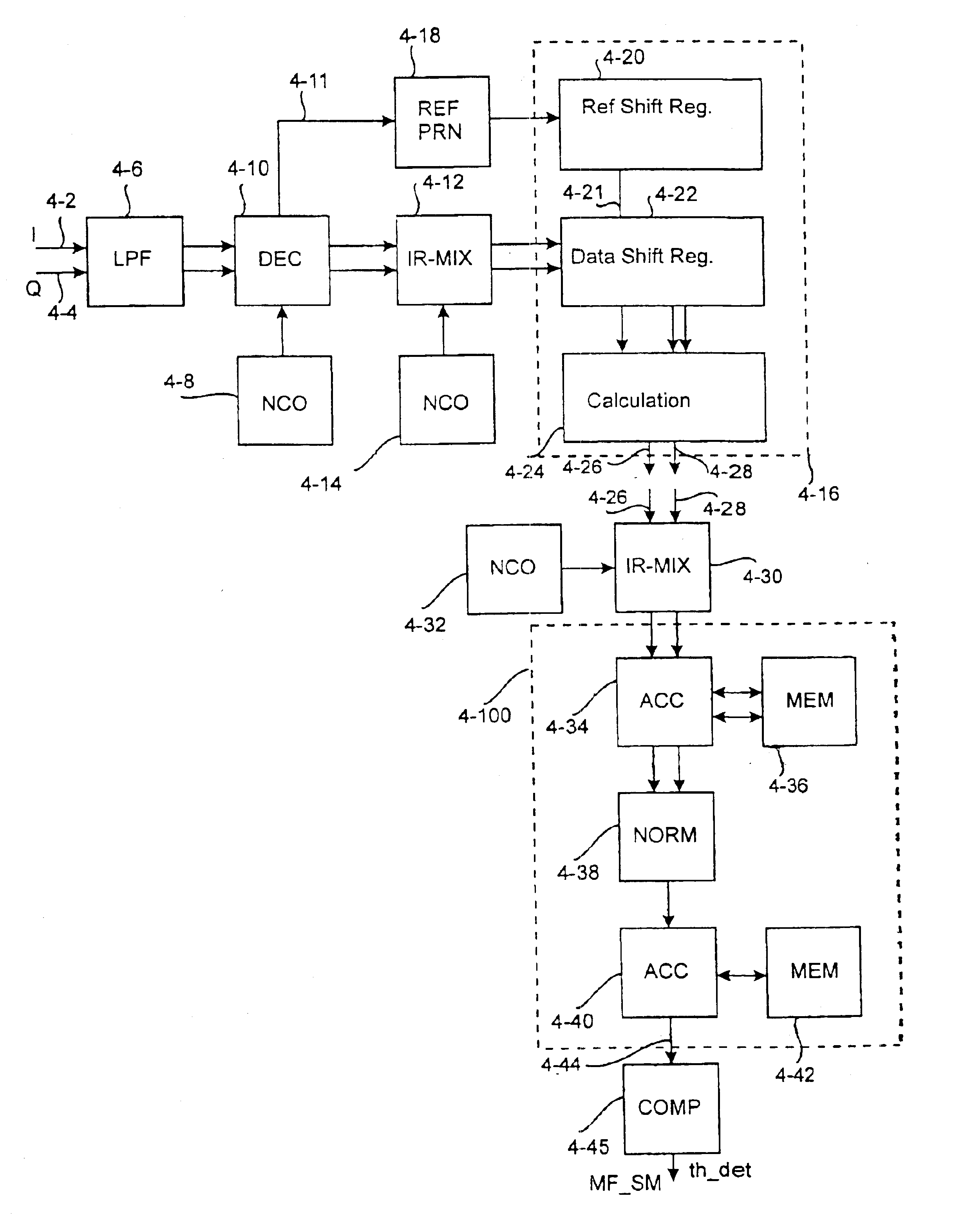
Signal acquisition system for spread spectrum receiver
InactiveUS6909739B1Extend integration timeLonger coherent integrationTransmissionSpread spectrum radarCarrier signal
A device for detecting a demodulated signal received by a spread spectrum receiver and converted into digital samples. The device is characterized by a matched filter for calculating the correlation between an incoming signal and at least one reference signal, an oscillator for generating a sampling frequency, and a sampling circuit for re-sampling the demodulated digital sample signal at the sampling frequency, which is such that the timing of samples of the references signals of the matched filter corresponds to the timing of a sample signal going from the sampling circuit to the matched filter. The device also includes a multiplier in which the sample signal is multiplied by a carrier replica generated locally before the sampling circuit or thereafter, to remove the carrier from the sample signal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
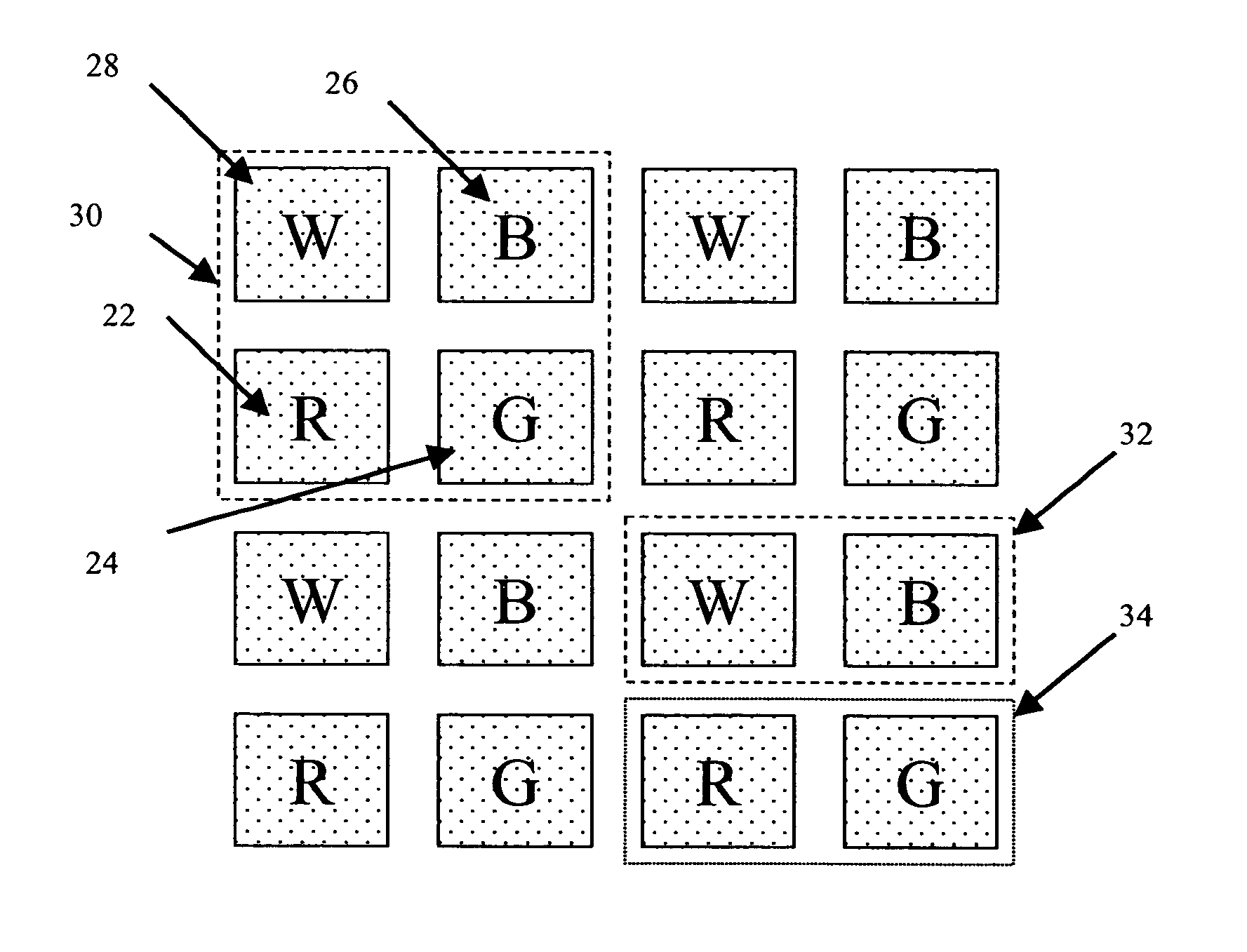
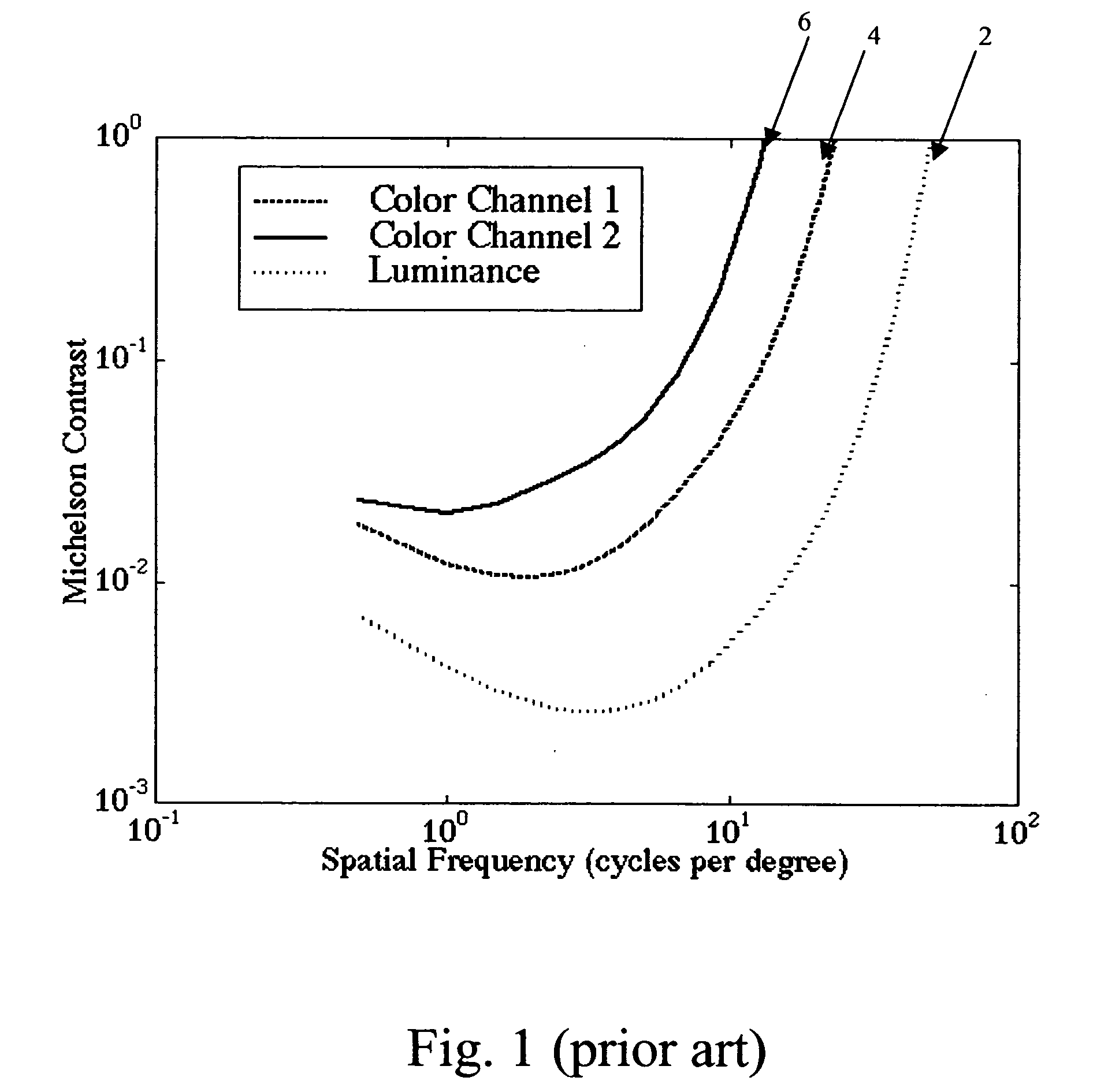
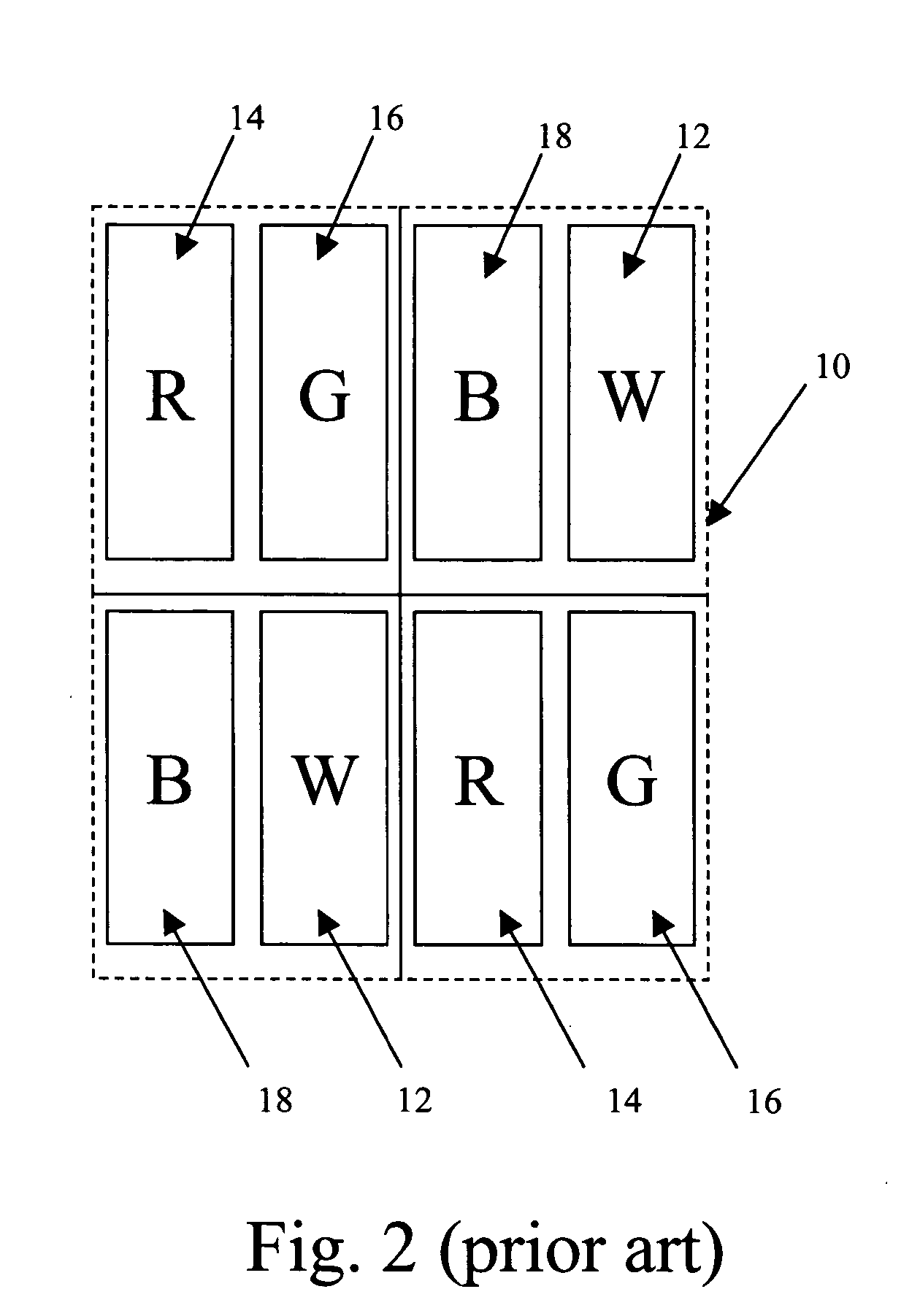
Color display system with improved apparent resolution
ActiveUS20070257944A1Improved apparent resolutionReduced image processing complexityCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingColor imageDisplay device
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
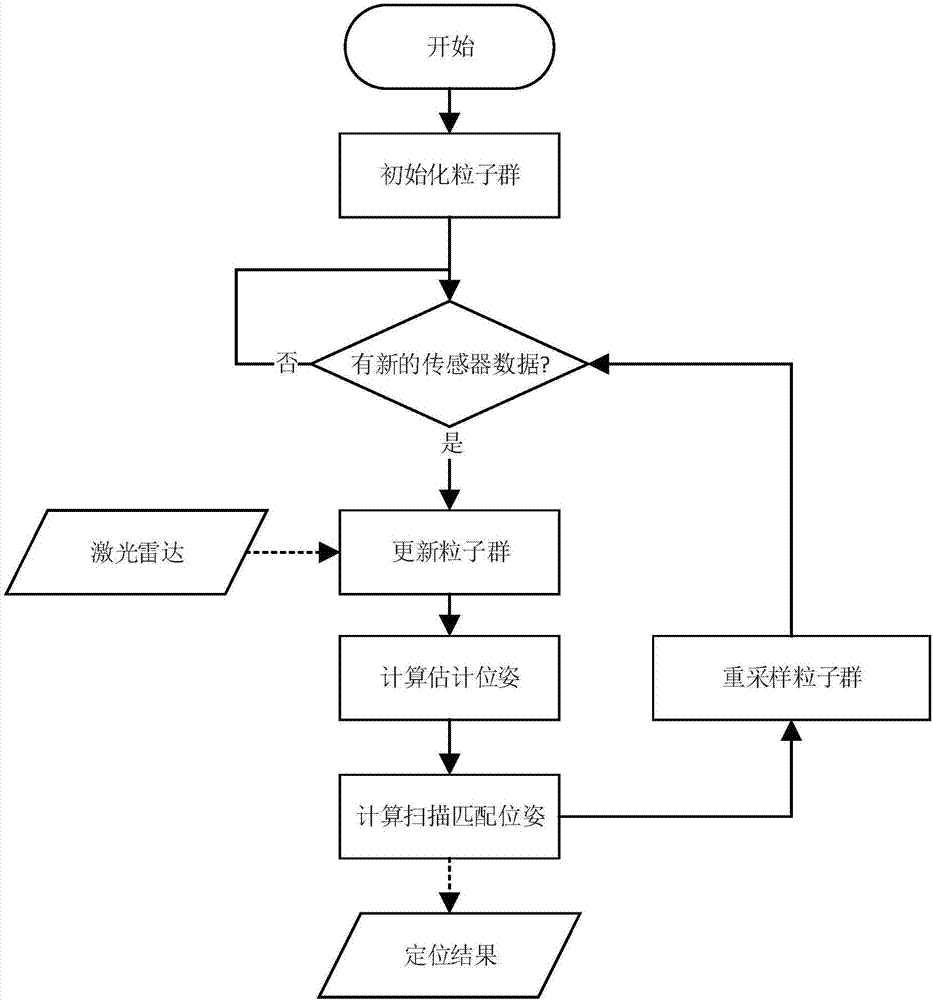
Method for autonomously localizing robots on basis of laser radar
ActiveCN107991683AAdd iterative optimizationEasy alignmentNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsElectromagnetic wave reradiationPoint cloudRadar
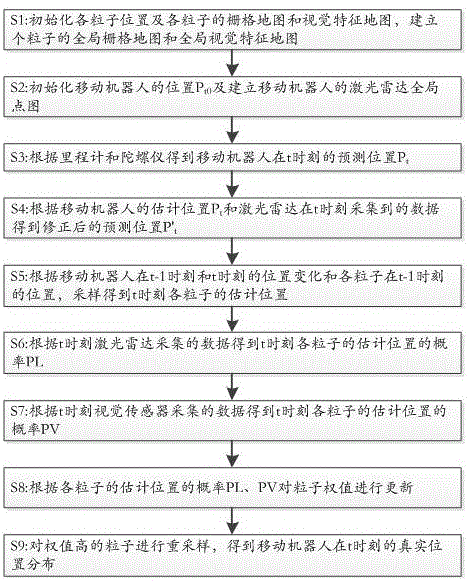
The invention discloses a method for autonomously localizing robots on the basis of laser radar. The method includes randomly generating N particles to form particle swarms around initial locations ofthe robots, and updating the particle swarms according to robot real-time movement distances and real-time rotation angles measured by sensors of the robots at current operation moments of the robots; computing the superposition quantity of point cloud of the laser radar and obstacles of maps for each particle to use the superposition quantity as a score of the particle, computing weighted position and posture average values of the particle swarms by the aid of the score, which is used as a weight, of each particle and utilizing the weighted position and posture average values as AMCL (adaptive Monte Carlo localization) estimation positions and posture; utilizing the AMCL estimation positions and posture as initial values, acquiring scanned and matched positions and posture by the aid ofscanning and matching algorithms on the basis of Gauss-Newton iterative processes and utilizing the scanned and matched positions and posture as the optimal positions and posture of the robots at thecurrent operation moments; re-sampling the particle swarms by the aid of AMCL algorithms to ultimately obtain the global optimal positions and posture of the robots during operation. The global optimal positions and posture of the robots are used as localization results. The method has the advantage that the localization convergence rate can be greatly increased, and the localization precision andthe localization stability can be greatly enhanced.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Fast high-accuracy multi-dimensional pattern localization
InactiveUS6856698B1Improve matchImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionDegrees of freedomDigital image
A method and apparatus are provided for rapidly refining a given approximate location of a pattern to produce a more accurate location. The invention employs a multi-dimensional space that includes translation, orientation, and scale. The invention can serve as a replacement for the fine resolution phase of any coarse-fine system for pattern location. Patterns and images are represented by a feature-based description that can be translated, rotated, and scaled to arbitrary precision much faster than digital image re-sampling, and without pixel grid quantization errors. Thus, accuracy is not limited by the ability of a grid to represent small changes in position, orientation, or size (or other degrees of freedom). The invention determines an accurate object pose from an approximate starting pose in a small, fixed number of increments that is independent of the number of dimensions of the space, and independent of the distance between the starting and final poses, provided that the starting pose is within the “capture range” of the true pose. Thus, accuracy need not be sacrificed to keep execution time acceptable for practical applications. Specifying locations in four or more dimensions will often result in better matches between the pattern and image than two-dimensional location systems, thereby improving accuracy. Accuracy is not degraded if some portion of the object is missing or occluded, or if unexpected extra features are present.
Owner:COGNEX CORP
System and Method for Real-Time Super-Resolution
InactiveUS20100272184A1Efficient and economical power requirementReduce image dataColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionFrame sequenceMotion vector
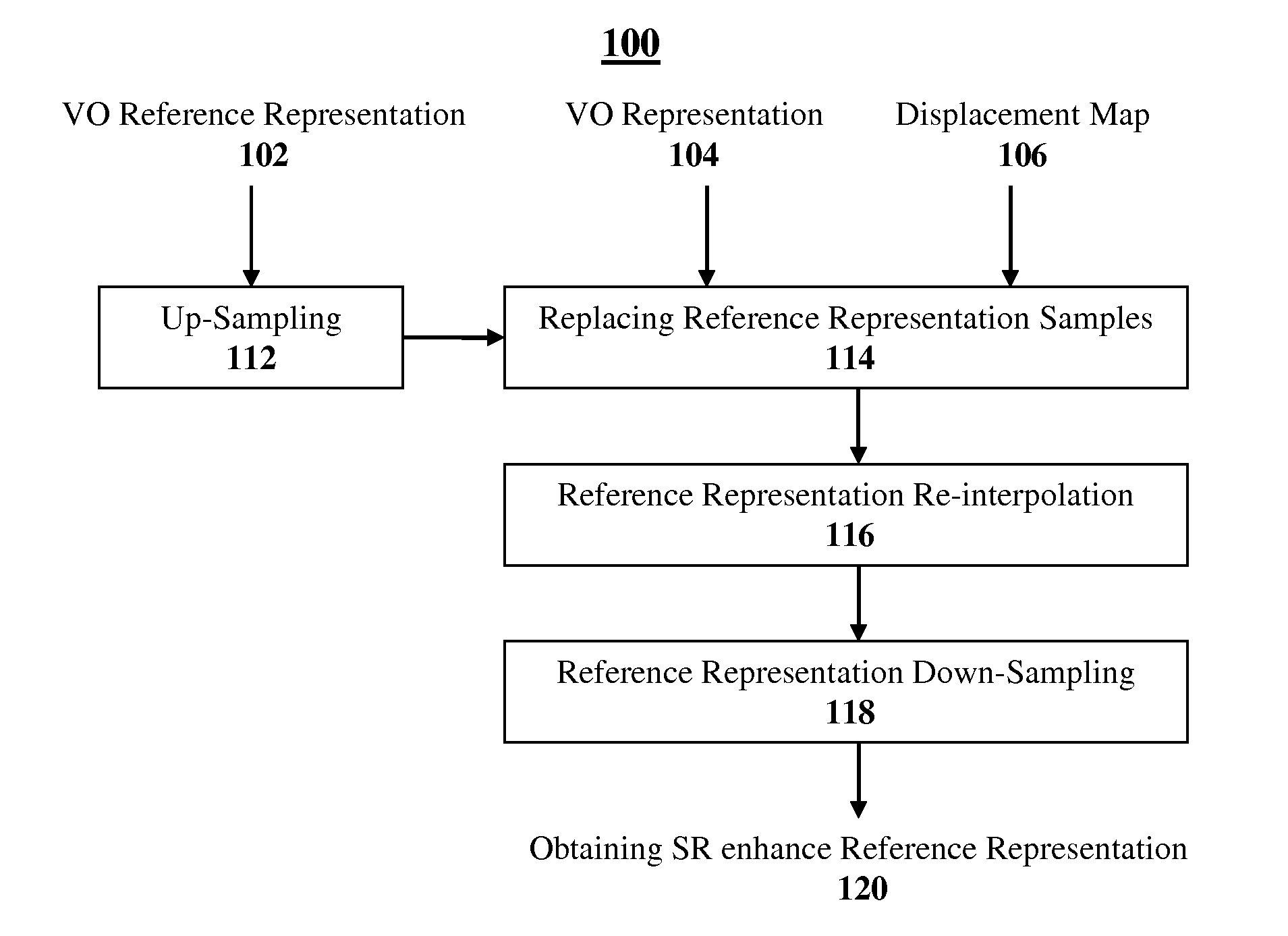
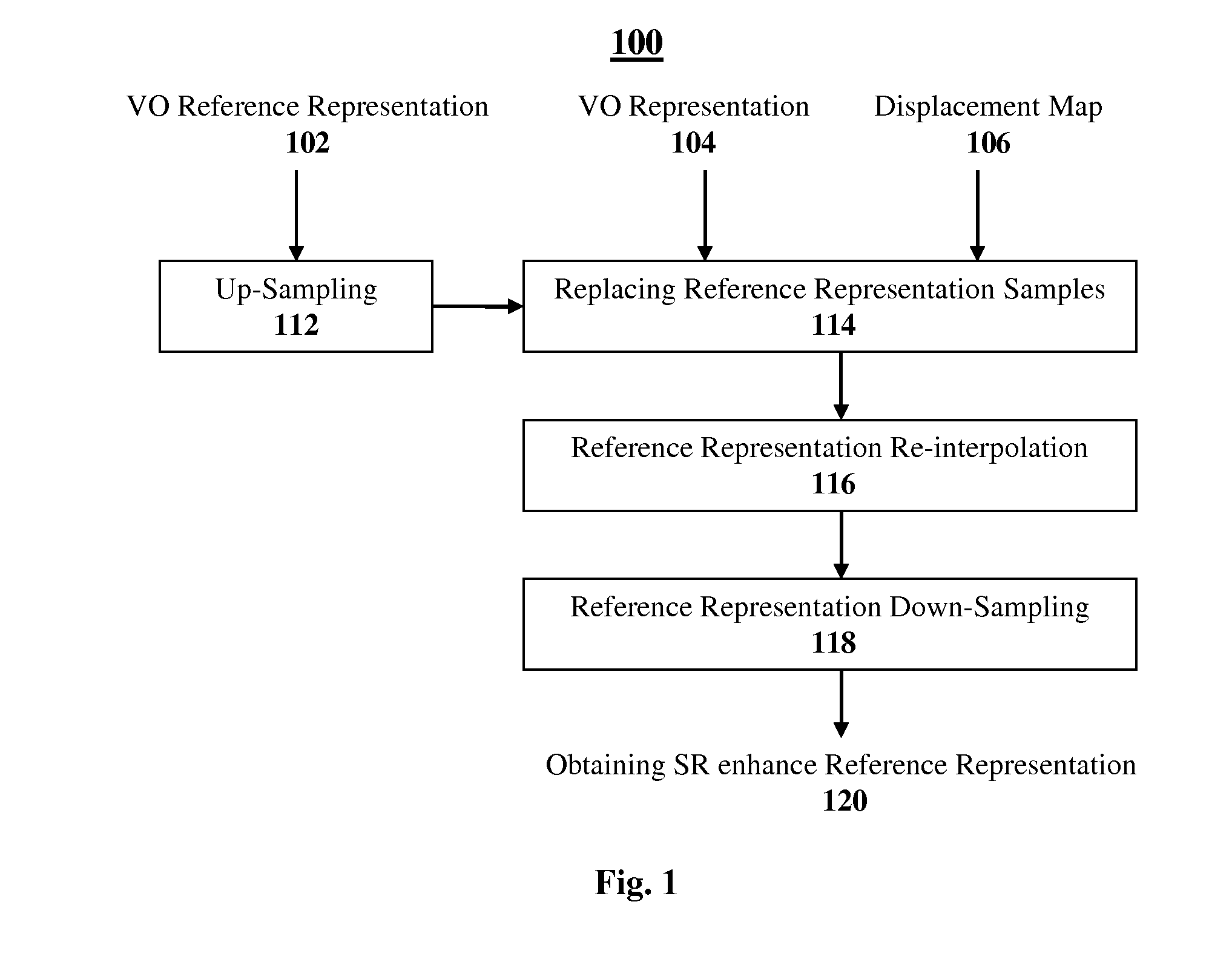
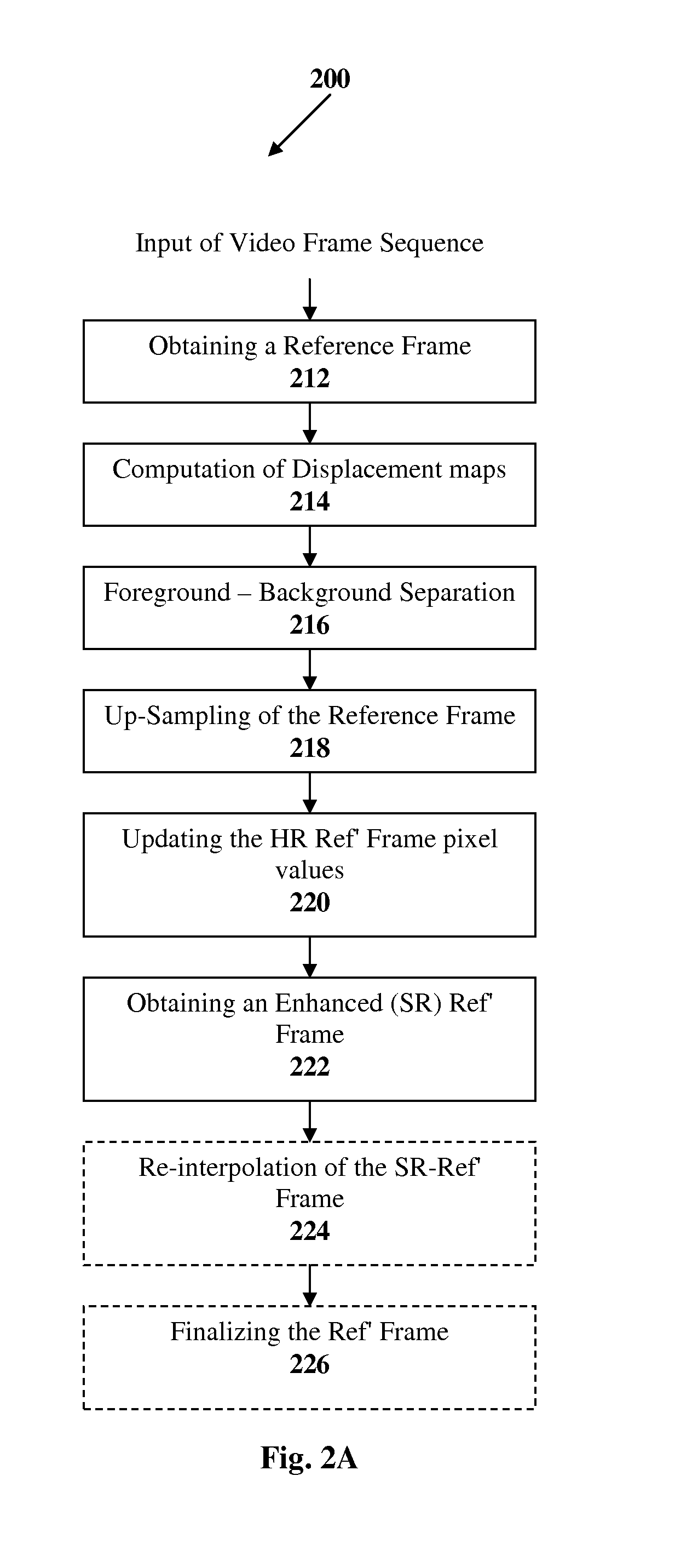
A method and system are presented for real time Super-Resolution image reconstruction. According to this technique, data indicative of a video frame sequence compressed by motion compensated compression technique is processed, and representations of one or more video objects (VOs) appearing in one or more frames of said video frame sequence are obtained. At least one of these representations is utilized as a reference representation and motion vectors, associating said representations with said at least one reference representation, are obtained from said data indicative of the video frame sequence. The representations and the motion vectors are processed, and pixel displacement maps are generated, each associating at least some pixels of one of the representations with locations on said at least one reference representation. The reference representation is re-sampled according to the sub-pixel accuracy of the displacement maps, and a re-sampled reference representation is obtained. Pixels of said representations are registered against the re-sampled reference representation according to the displacement maps, thereby providing super-resolved image of the reference representation of said one or more VOs.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Extended range image processing for electro-optical systems
A method and apparatus for processing imagery using images acquired via any known Electro-Optical (EO) system. In accordance with exemplary embodiments of the present invention, a first frame of data is selected as a template frame (e.g., a given frame). A second frame of data can be captured using the EO system. At least a portion of the second frame can be correlated with the template frame to generate a shift vector. The second frame can then be registered with the template frame by interpolating the second frame using the shift vector and re-sampling at least a portion of the second frame to produce a registered frame. The template frame can also be re-sampled. The registered frame and the re-sampled template frame can then be combined to generate an averaged frame. The averaged frame can be spatially filtered to enhance edges within the averaged frame.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
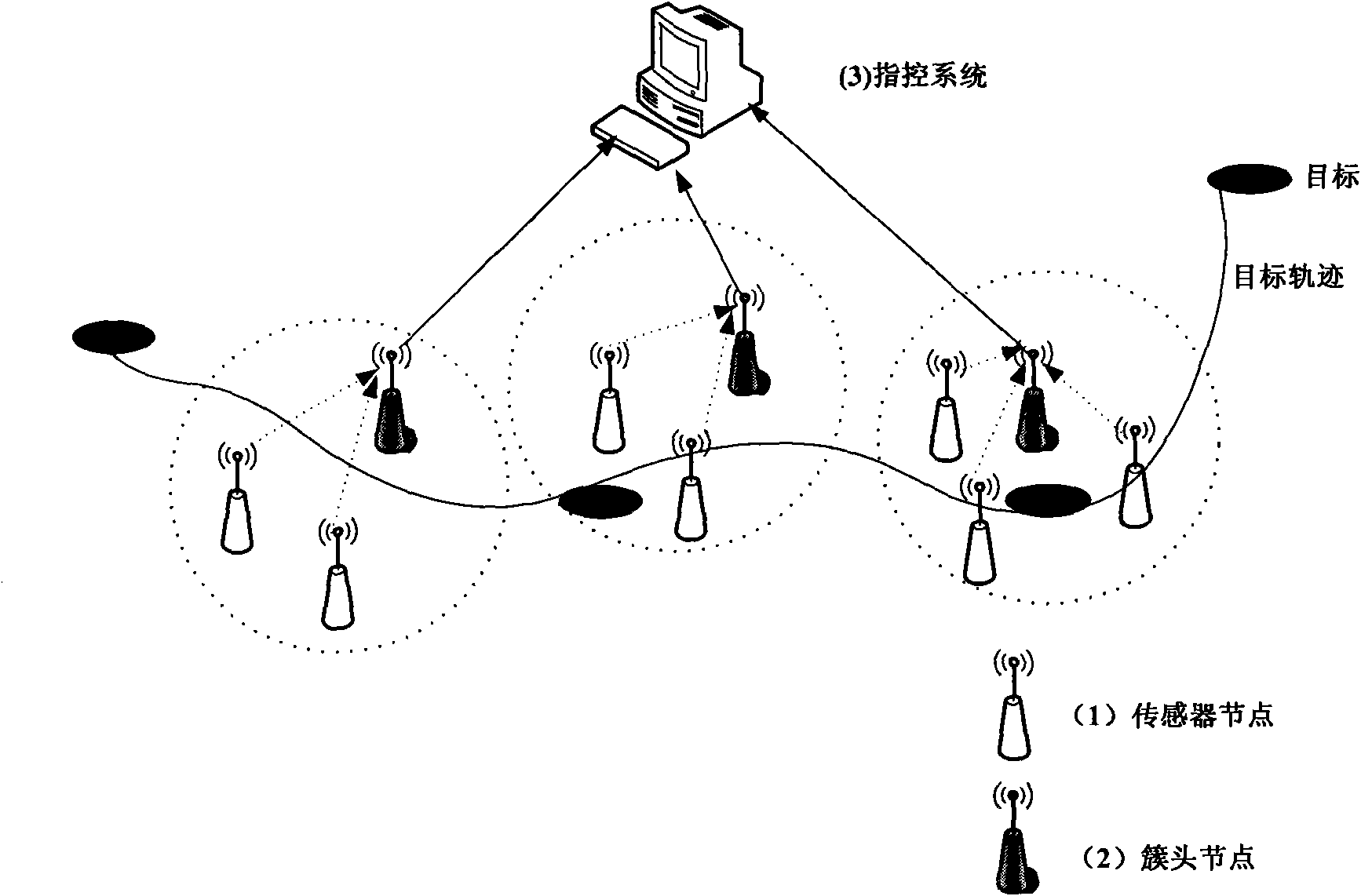
Target localization and tracking system and method
The invention relates to a target localization and tracking system and a method. The system comprises a plurality of cluster localization modules and command control modules, each cluster localizationmodule comprises a plurality of sensor nodes and cluster head nodes, and each cluster head node comprises an initialization module, a particle filtration module, a particle weight calculation module,a re-sampling determination module and an estimation target state module. The method which combines Kalman and particle filtration is adopted for realizing the passive localization of a target, and the computation speed is far lower than the particle filtration method on the basis of realizing high-precision localization; the localization and the track of the target is finally realized by adopting multiple sensors and being based on the observation of the direction of the target, thereby being capable of overcoming the constraint that the traditional machine-mounted or ship-mounted single station system must carry out motorization during the observation period, having no need of observing the motorization of a platform, improving the flexibility of target localization, greatly increasingthe area of a region of target monitoring localization, avoiding the shortcoming of existence of localization blind regions and having very high effectiveness, accuracy and feasibility.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
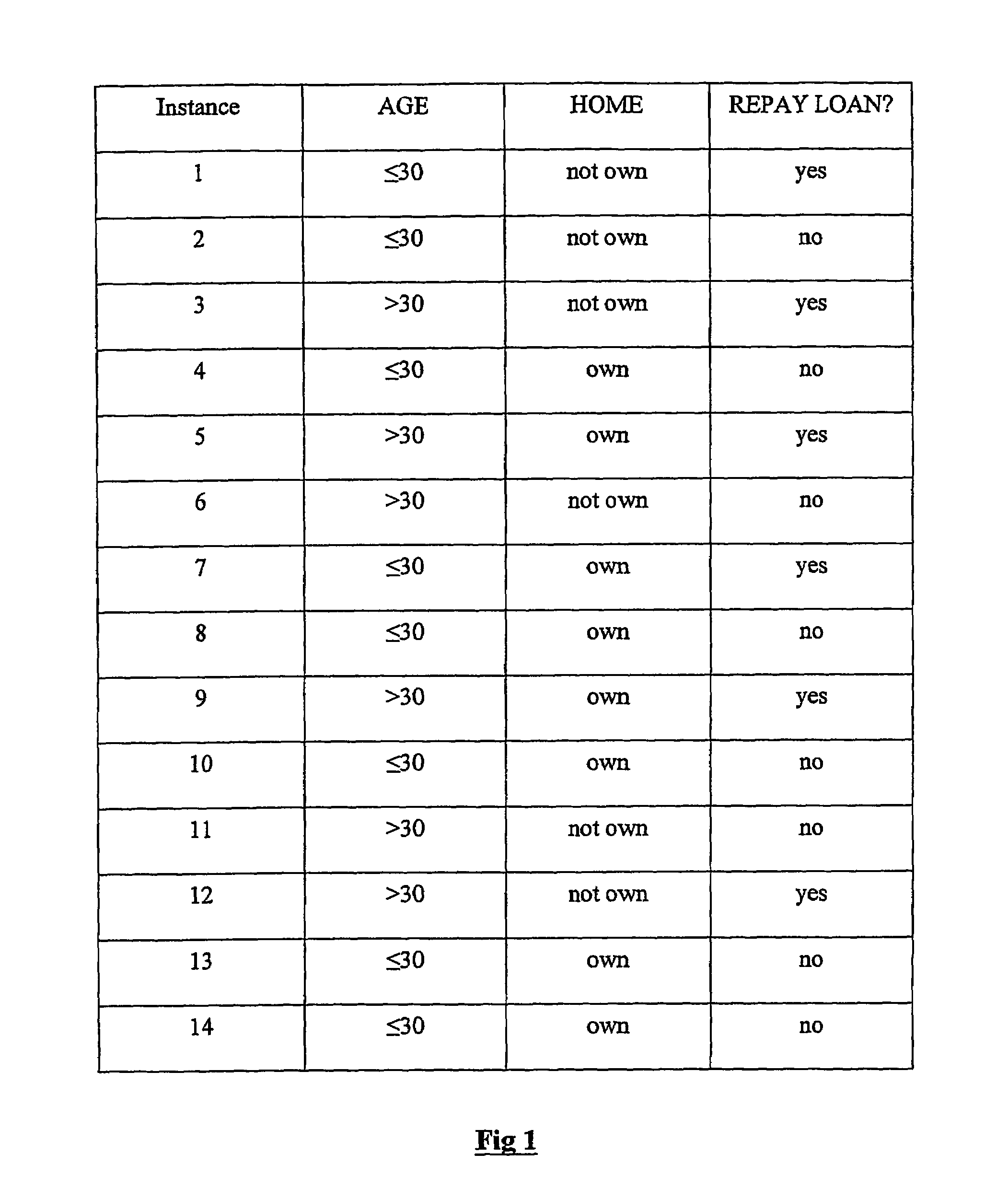
Classification using probability estimate re-sampling
ActiveUS7194380B2Improve fitEffective calculationMathematical modelsFinanceAlgorithmClass membership
Embodiments of a computer-implemented method of calculating estimates of a joint posterior probability of class membership given combinations of attribute values of a pair of attributes are disclosed. The calculating is performed on the basis of data representing a training set of a plurality of instances defined by attribute values for a plurality of attributes together with a class membership outcome. Embodiments of the method comprise calculating first and second estimates of a posterior probability of class membership given attribute values of a first and second attribute of the pair, respectively, and binning the first and second estimates into a respective plurality of first and second probability range bins. Instances of the training set are mapped to combinations of one of each of the first and second pluralities of probability range bins, and on the basis of the mapping, calculating estimates of a joint posterior probability of class membership.
Owner:CHORDIANT SOFTWARE INT
Apparatus and method for improving image resolution using fuzzy motion estimation
InactiveUS20090110285A1Improve imaging resolutionGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionImage resolutionSubject matter
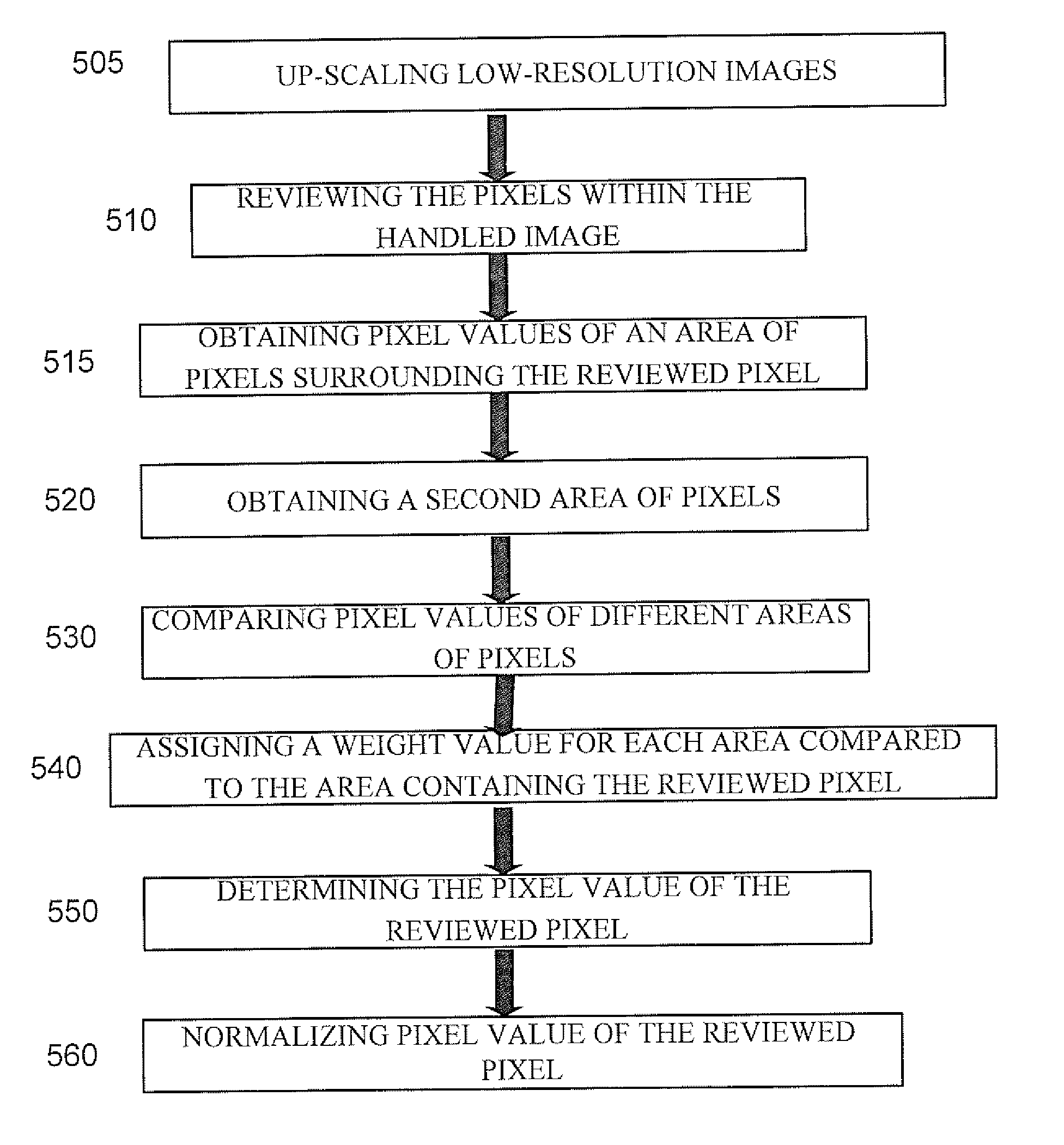
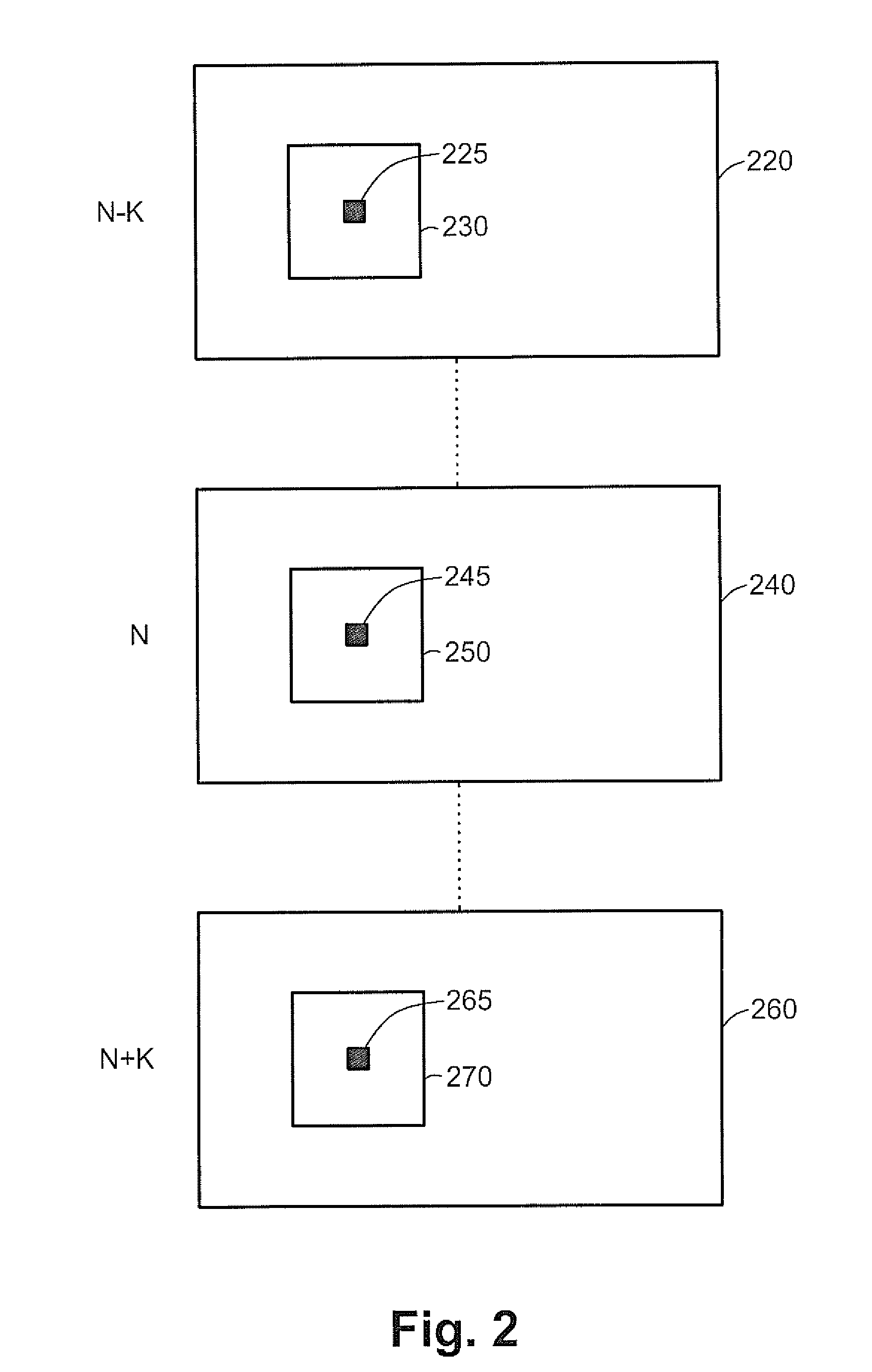
The subject matter discloses a method and apparatus for re-sampling a sequence of images in order to improve its resolution, fill-in missing pixels, or de-interlace it. The method operates locally in the images to be processed, comparing pixel values of pixels surrounding the target pixel to pixel values of substantially the same locations in neighboring images. The comparison results in assigning a weight value for each area compared with the area containing the reviewed pixel. The pixel value of the reviewed pixel is updated as a function of multiplying pixel values of the areas by the weight assigned to each area. In another embodiment, areas within the same image are compared to areas containing the reviewed pixel. The subject matter also discloses two possible penalty functions for improving the resolution of images.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Laser and vision-based hybrid location method for mobile robot
ActiveCN105865449AWide range of applicationsMake up for the shortcomings of unstable visual positioningNavigational calculation instrumentsRadarVision based
The present invention discloses a laser and vision-based hybrid location method for a mobile robot. The mobile robot comprises a laser radar and a vision sensor. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the weight of each particle at a predicted position is updated based on the collected data of the laser radar and the collected data of the vision sensor. After that, particles of higher weights are re-sampled, so that the real location distribution of the mobile robot at the moment t can be obtained. Compared with the prior art, the above technical scheme integrates the high accuracy of the laser radar with the information integrity of the vision sensor, thus being wider in application range. Meanwhile, the defect that the visual location is unstable is overcome. In addition, in one embodiment of the present invention, a conventional particle filtering sampling model is improved, so that the diversity of particles is ensured.
Owner:SHEN ZHEN 3IROBOTICS CO LTD
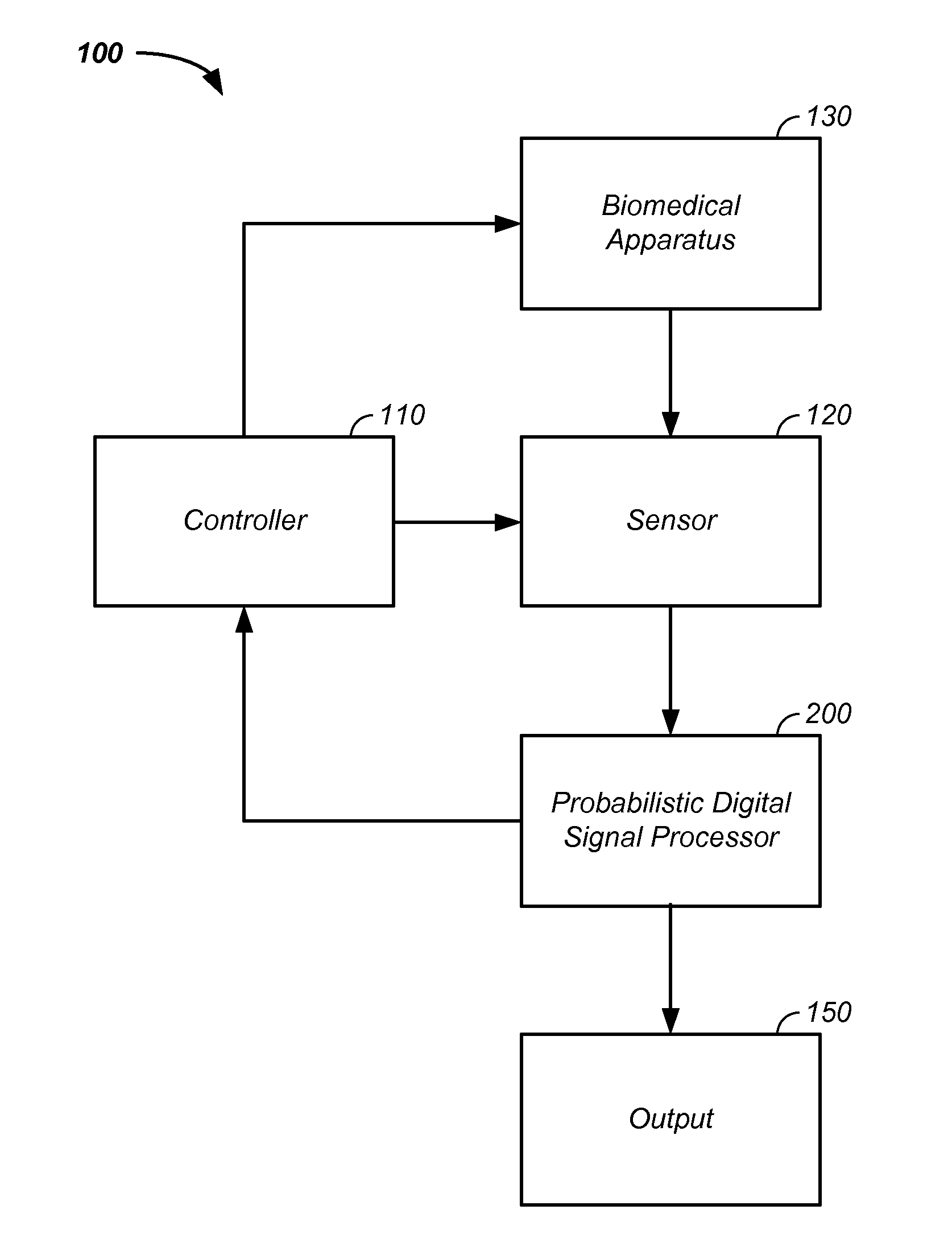
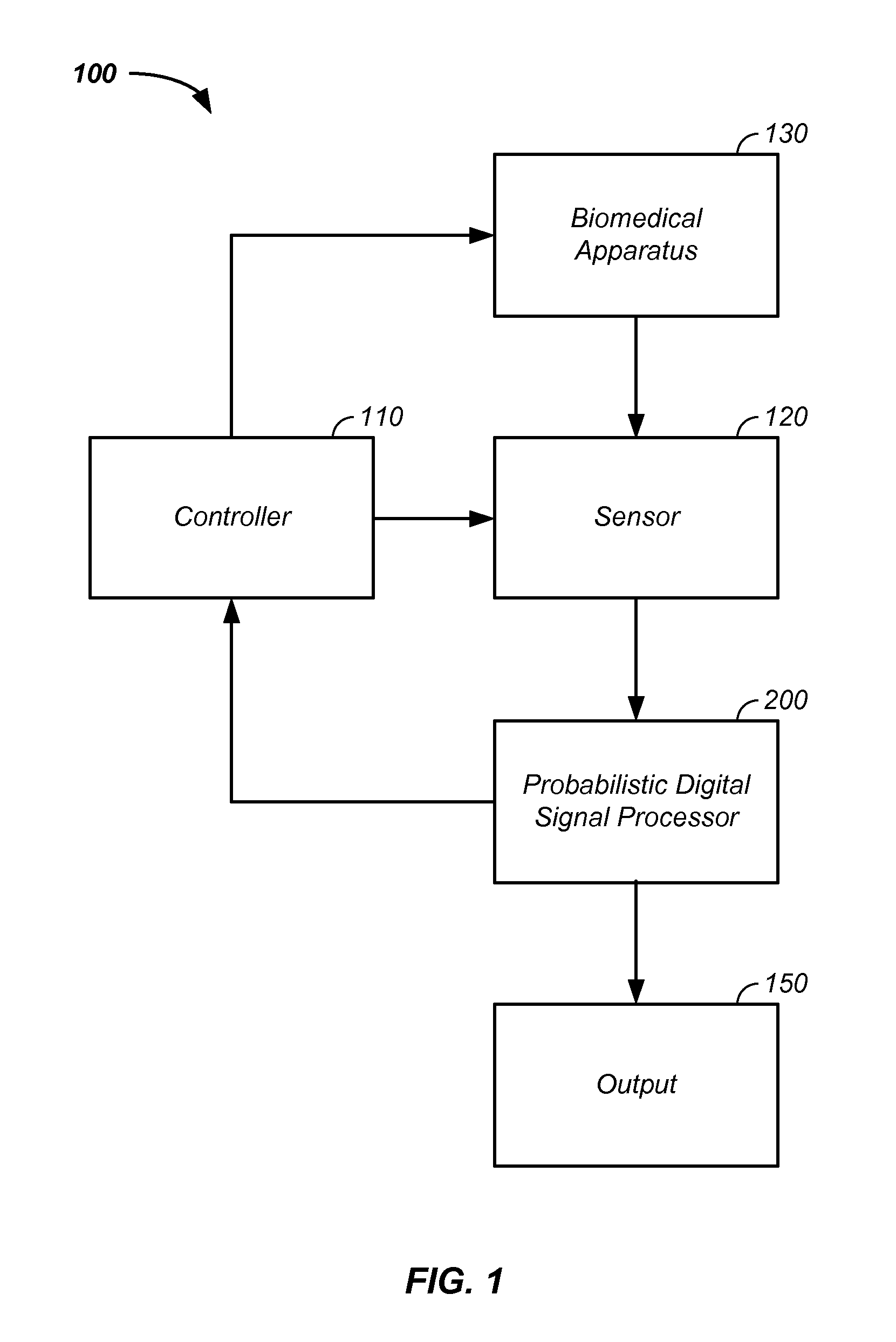
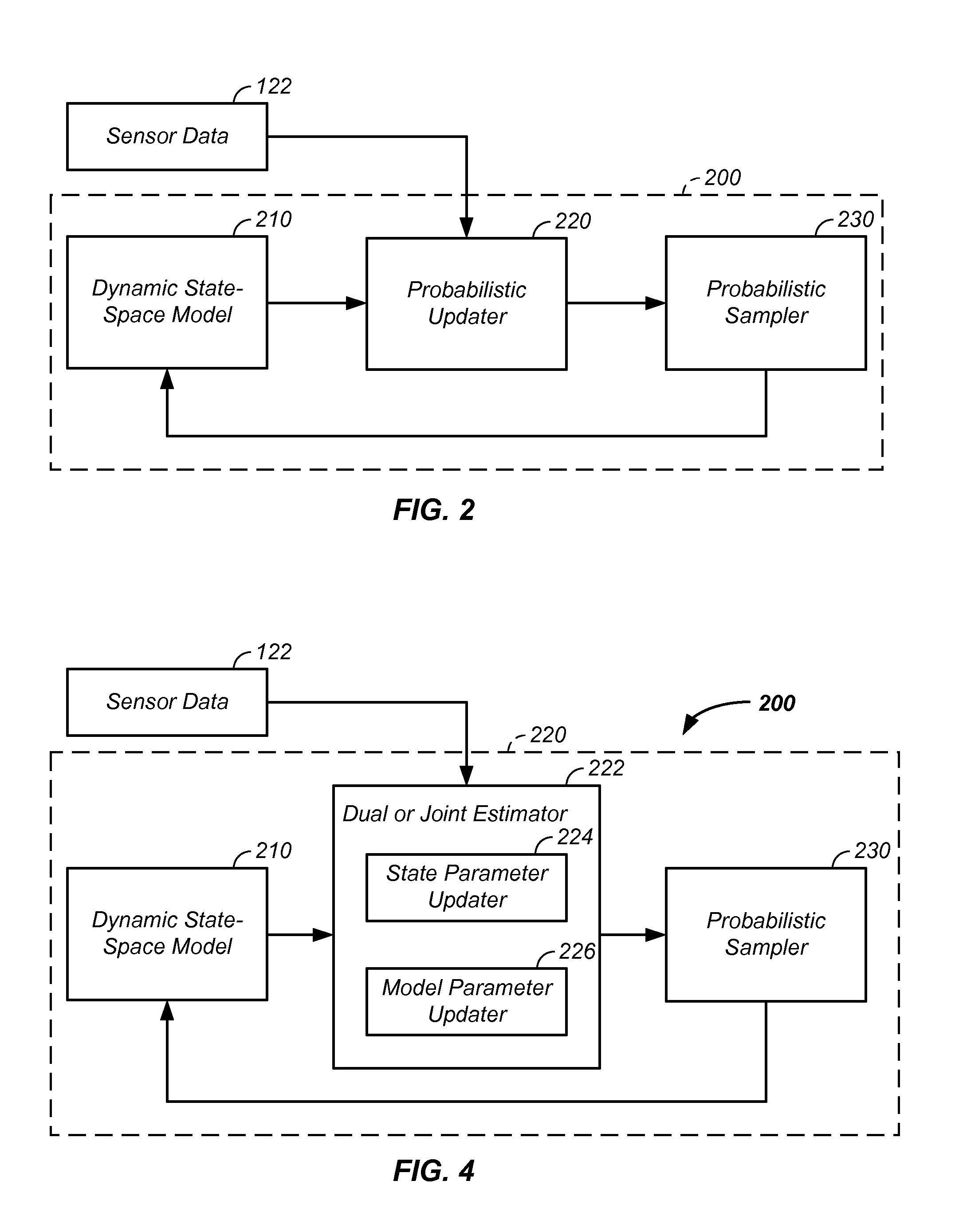
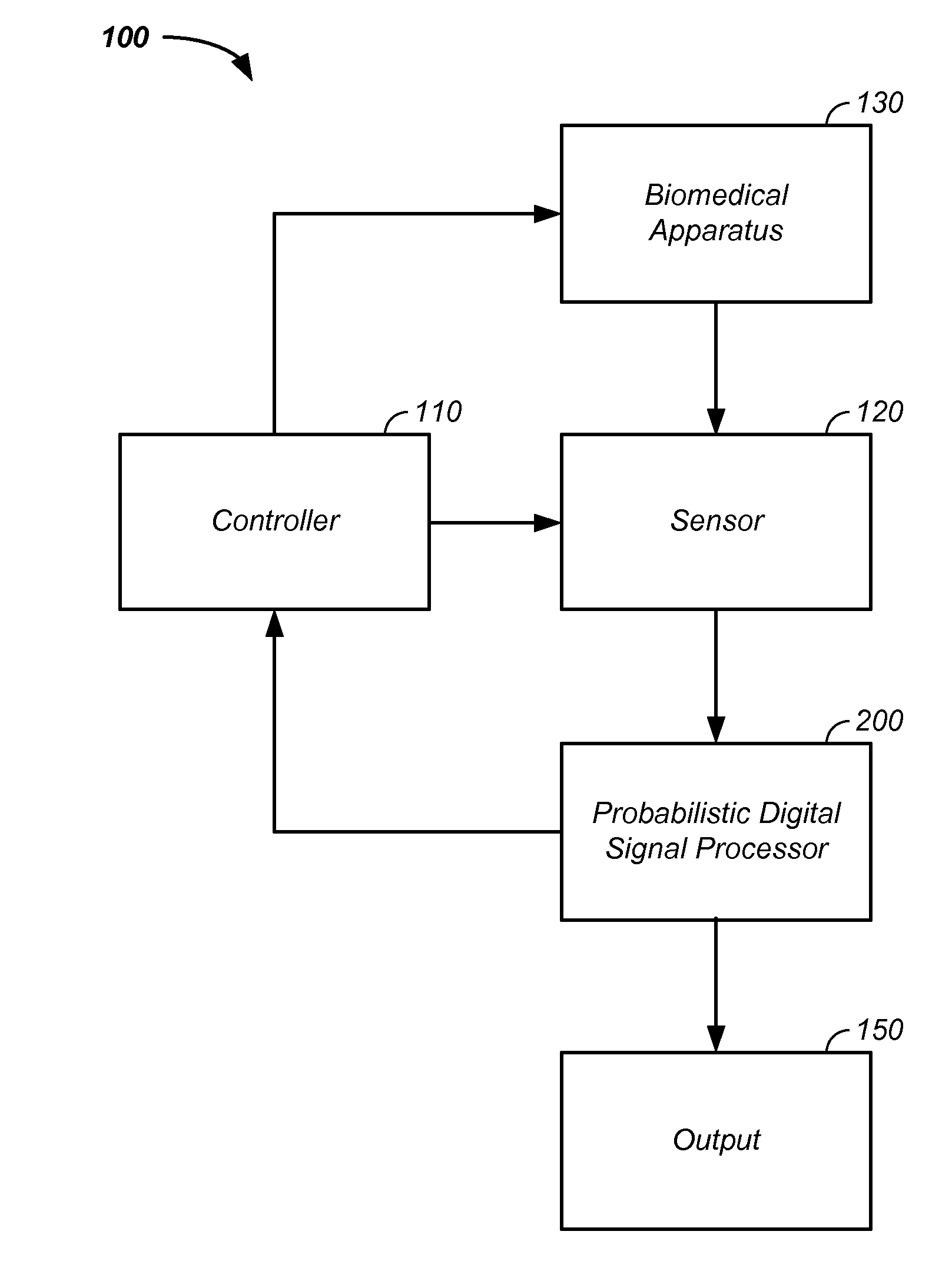
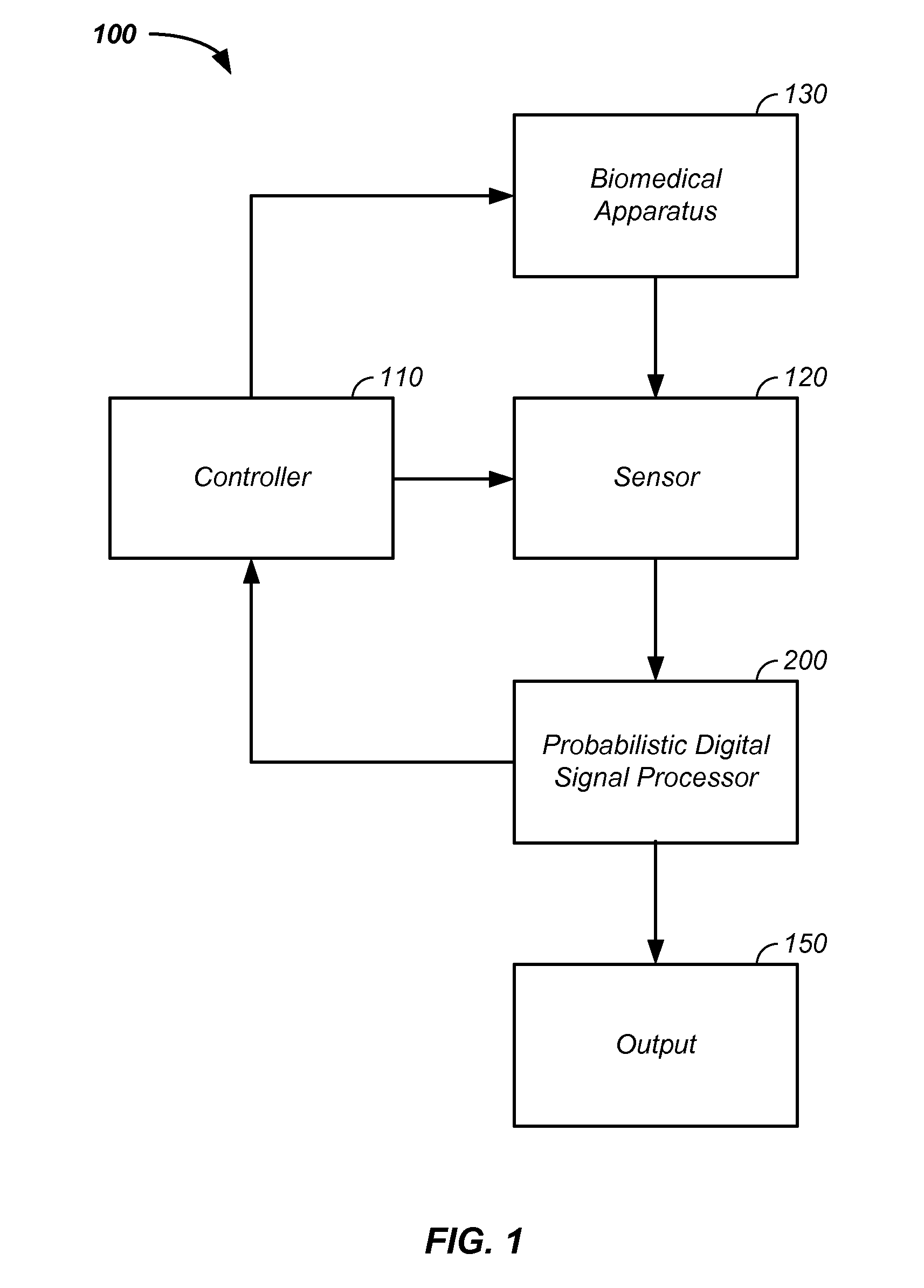
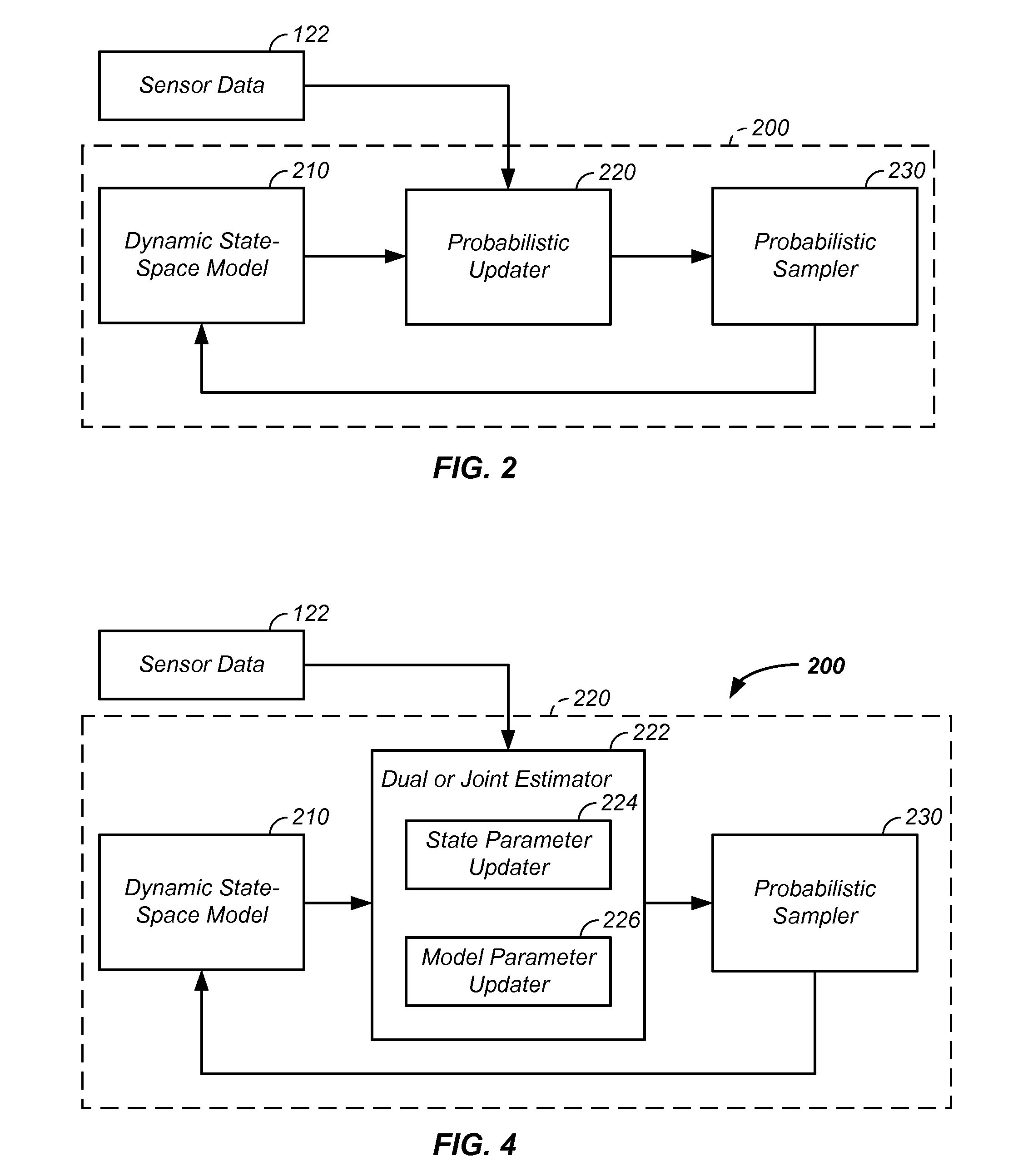
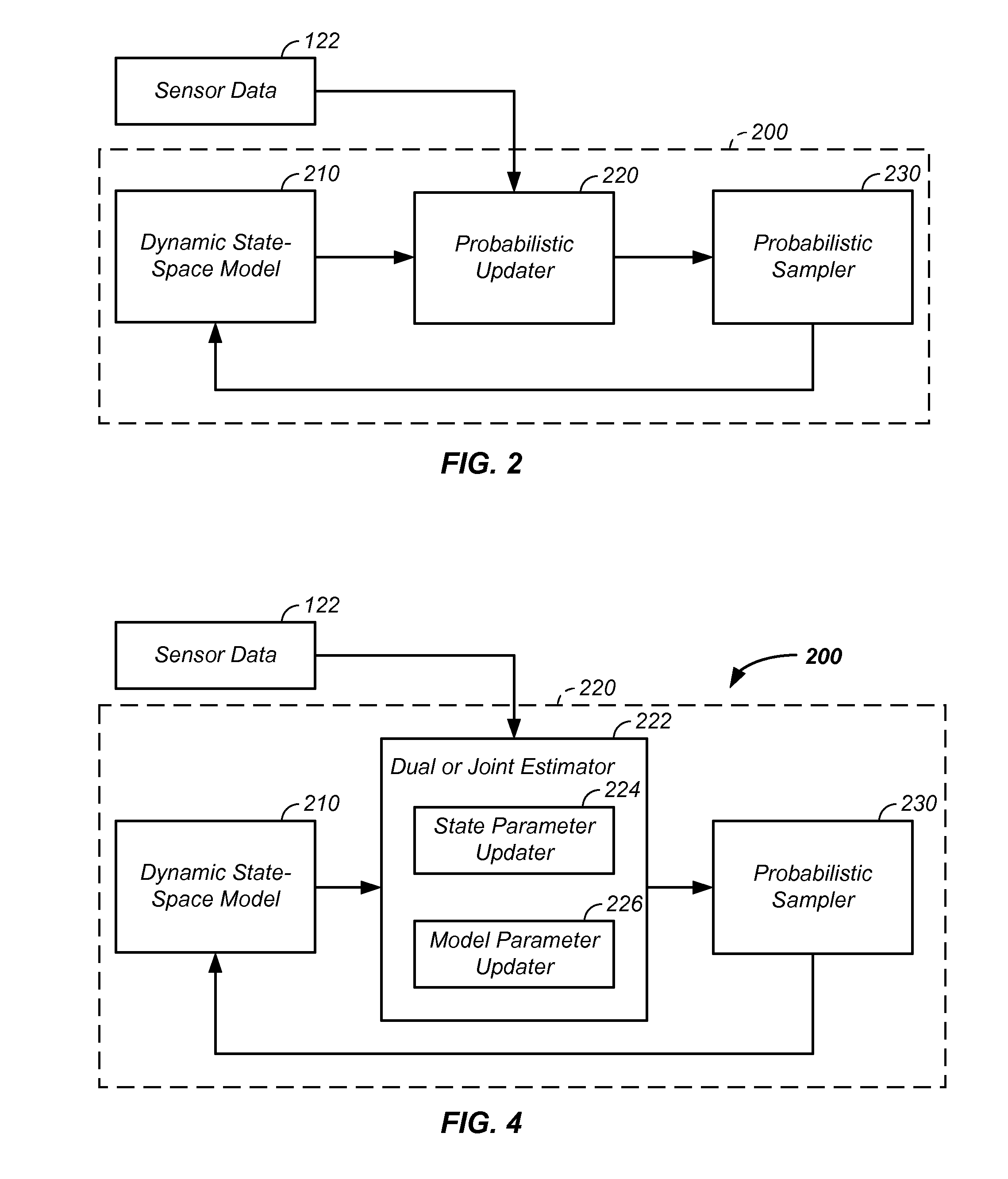
Sensor fusion and probabilistic parameter estimation method and apparatus
A probabilistic digital signal processor using data from multiple instruments is described. Initial probability distribution functions are input to a dynamic state-space model, which operates on state and / or model probability distribution functions to generate a prior probability distribution function, which is input to a probabilistic updater. The probabilistic updater integrates sensor data from multiple instruments with the prior to generate a posterior probability distribution function passed (1) to a probabilistic sampler, which estimates one or more parameters using the posterior, which is output or re-sampled in an iterative algorithm or (2) iteratively to the dynamic state-space model. For example, the probabilistic processor operates on fused data using a physical model, where the data originates from a mechanical system or a medical meter or instrument, such as an electrocardiogram or pulse oximeter to generate new parameter information and / or enhanced parameter information.
Owner:VITAL METRIX INC
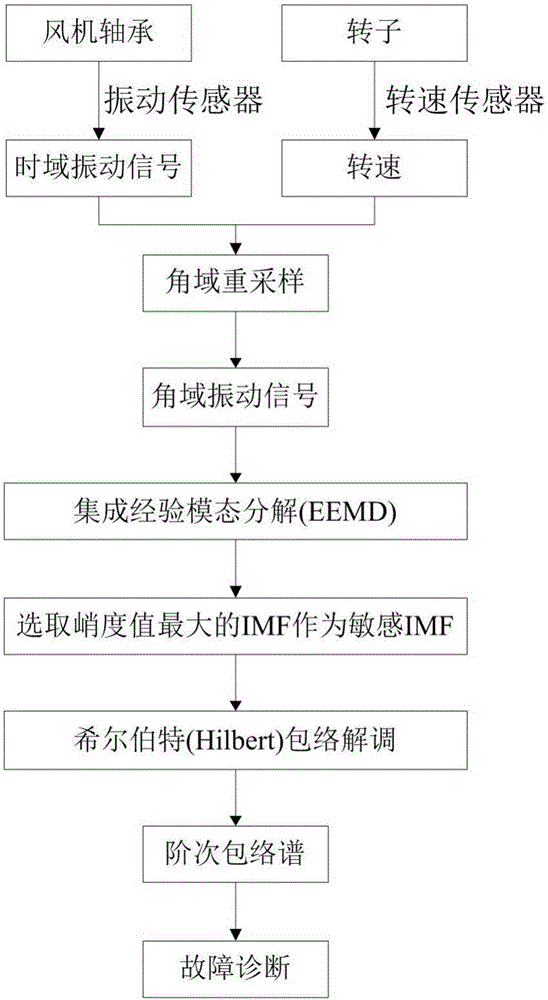
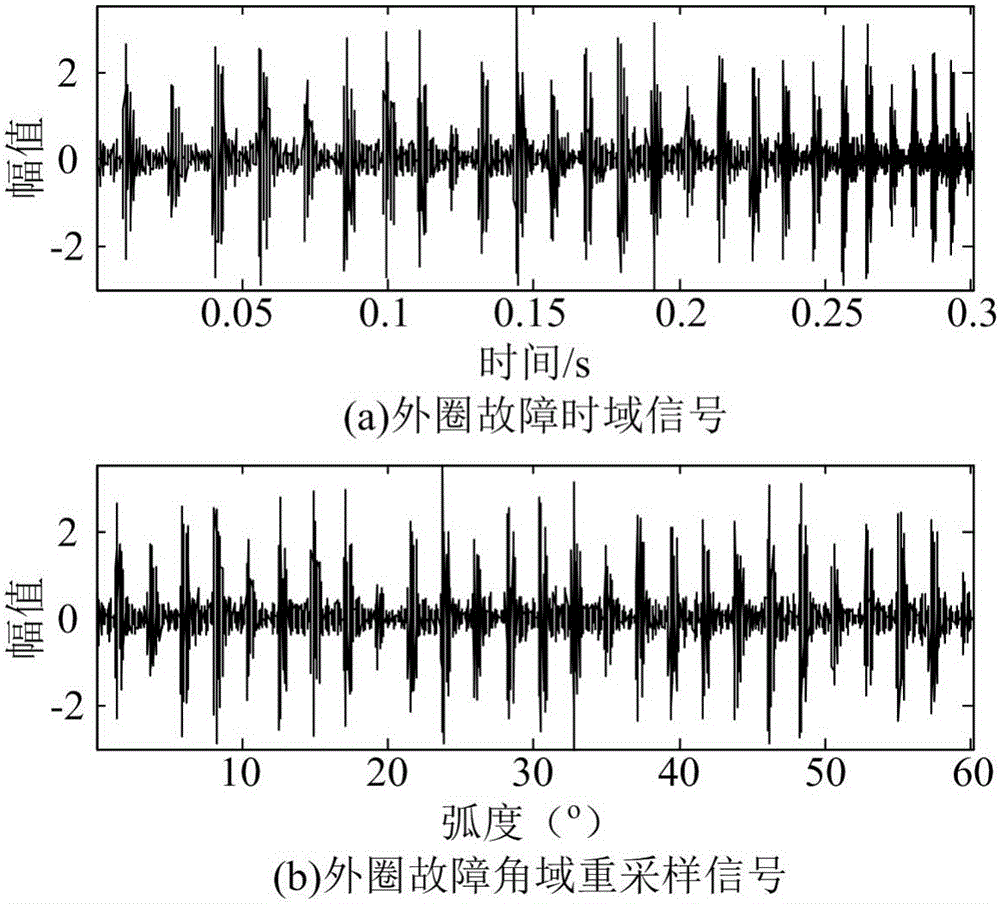
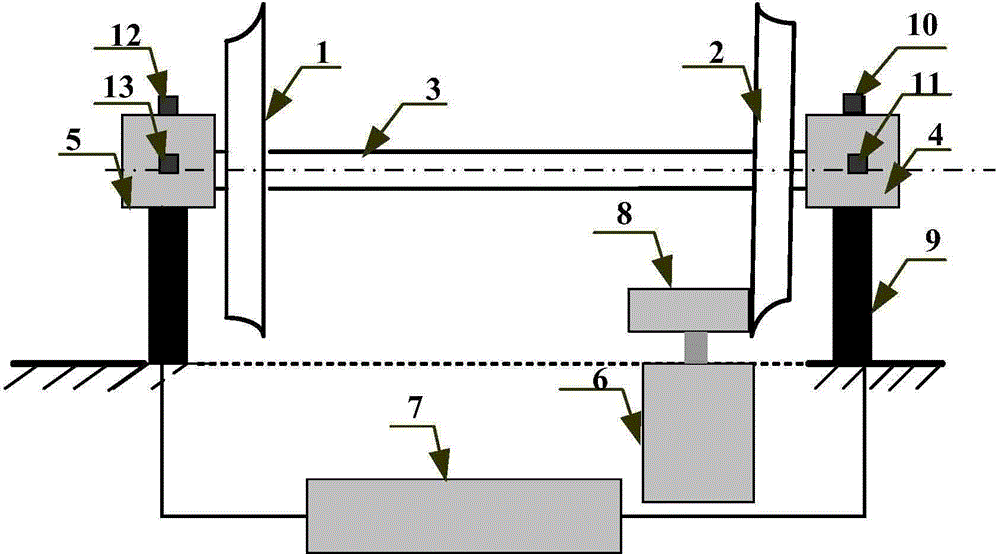
Wind turbine generator bearing fault diagnosis method under variable speed
InactiveCN105784366AEliminate the effects of analysisImprove accuracyMachine bearings testingElectricityBearing vibration
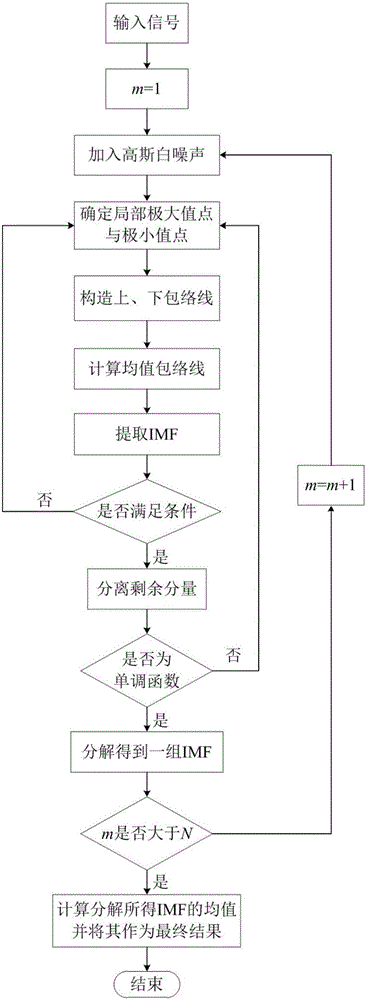
The invention discloses a wind turbine generator bearing fault diagnosis method under the variable speed. According to the method, a rotation angle change curve is drafted according to the bearing rotation speed; equal angle division for the rotation angle change curve is carried out, and an equal angle re-sampling time sequence is determined; interpolation for a bearing vibration signal is carried out according to the time sequence, a random Gauss white noise sequence is added to an angle domain vibration signal, and the signal added with the white noise is processed by utilizing an empirical mode decomposition (EMD) algorithm to acquire multiple sets of IMF; a kurtosis value of each IMF component is calculated; the IMF with the largest kurtosis value is selected and taken as a sensitive IMF; Hilbert envelope demodulation for the sensitive IMF is carried out to obtain an envelope signal, the envelope signal is processed by utilizing Fourier transform to obtain order envelope spectrum of the sensitive IMF, the fault characteristic frequency is extracted, and fault diagnosis on the wind turbine generator bearing is realized. The method is advantaged in that influence of rotation speed change on vibration signal analysis can be eliminated, and accuracy and validity of fault diagnosis can be improved.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
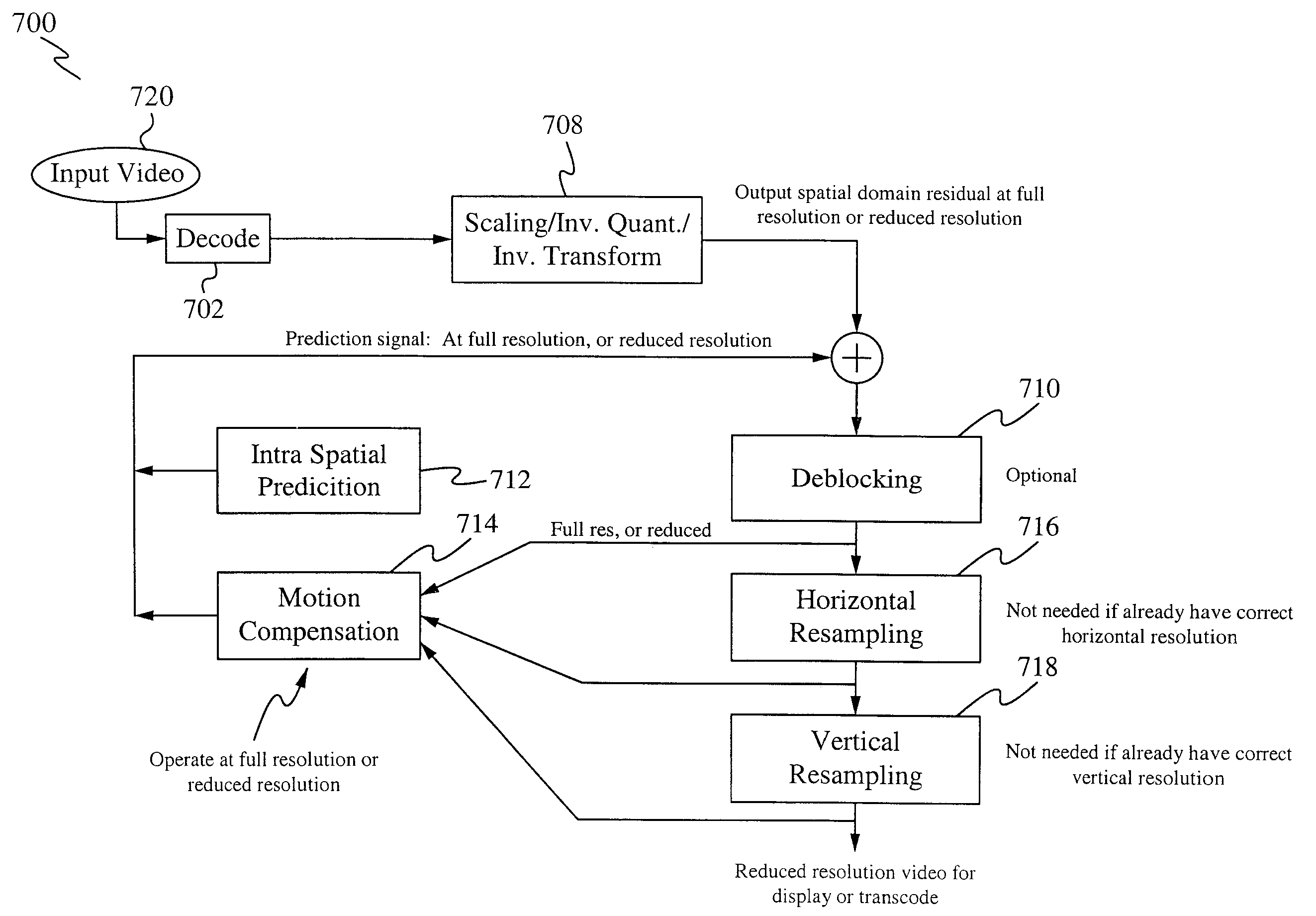
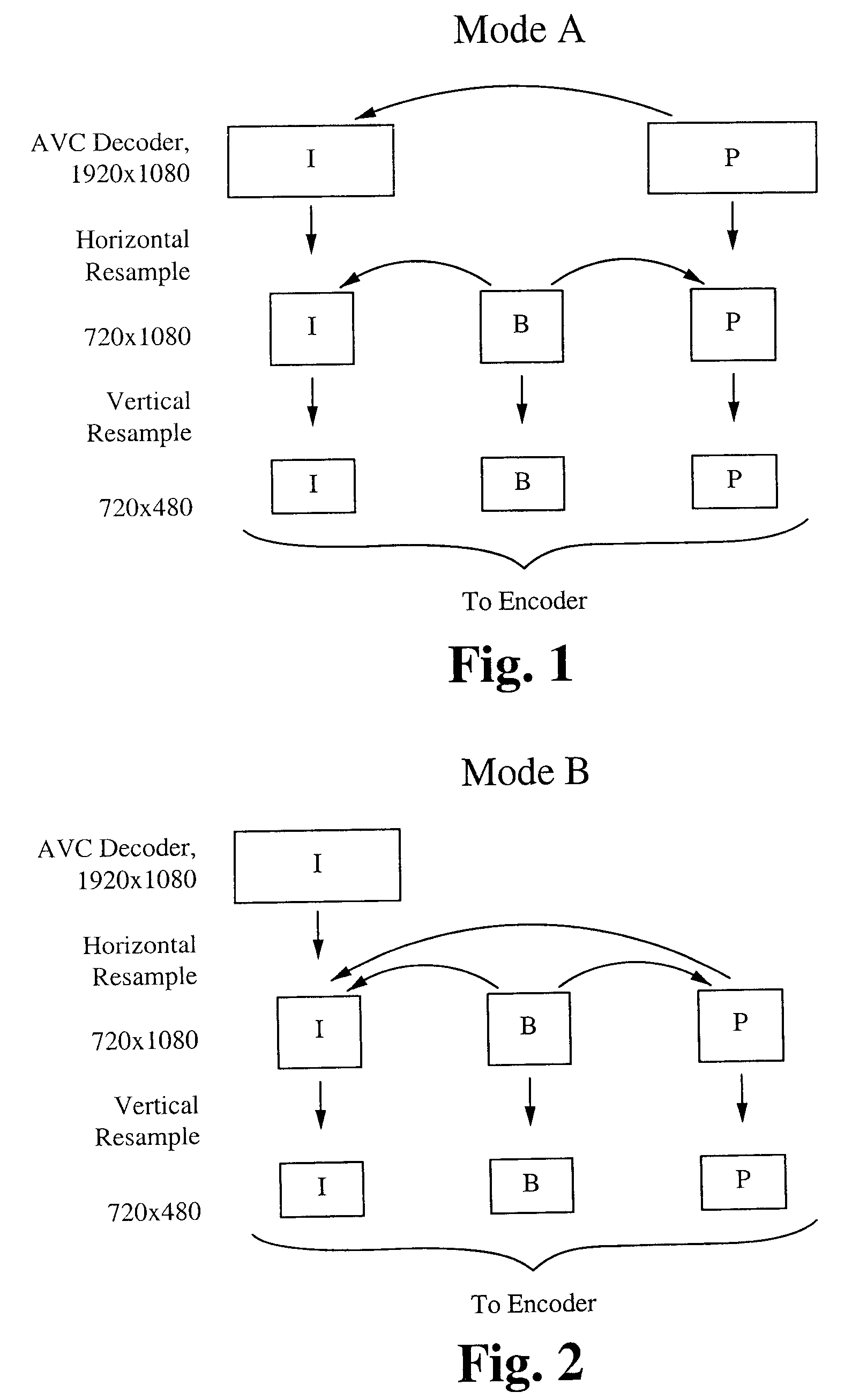
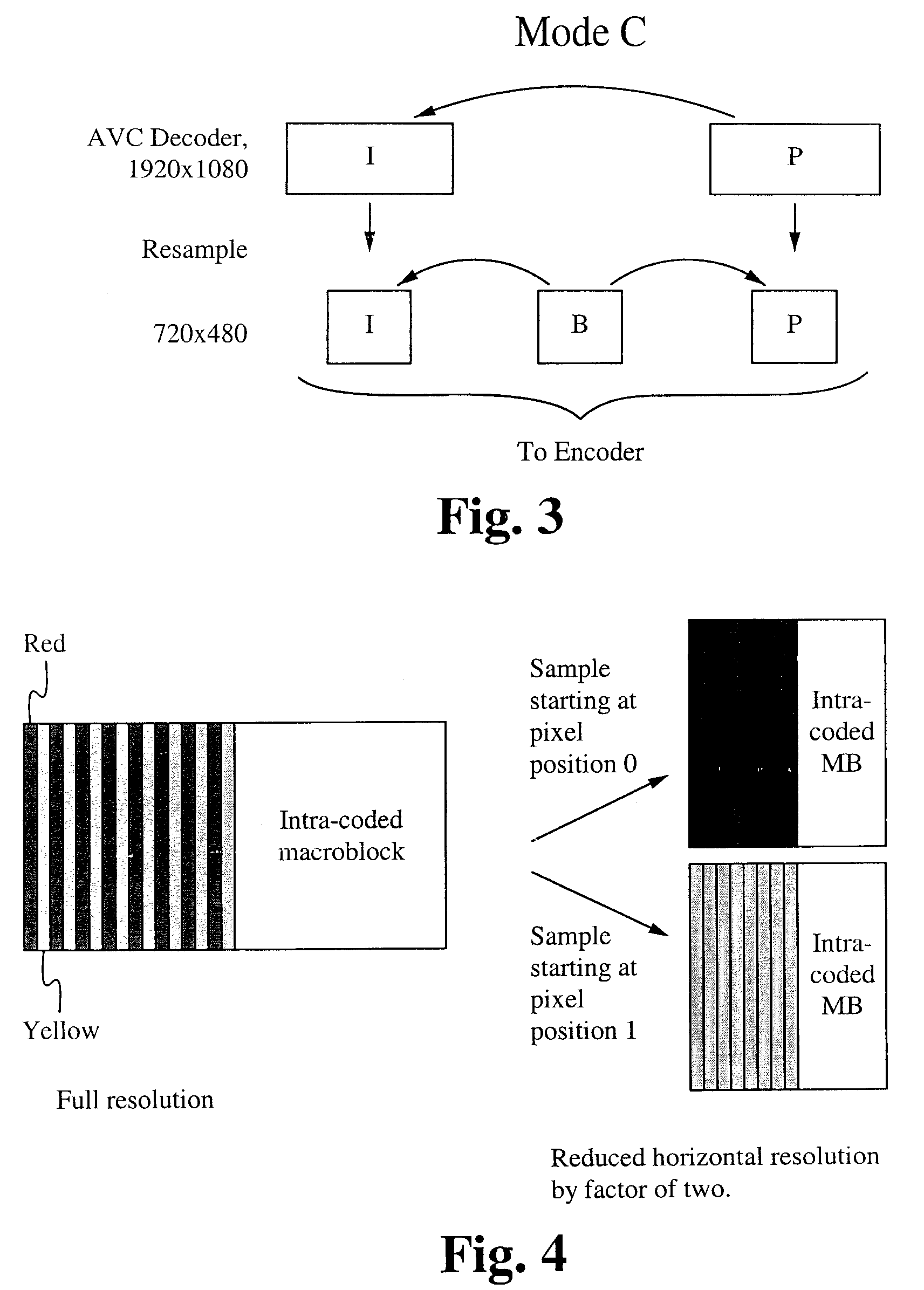
Reduced-resolution decoding of avc bit streams for transcoding or display at lower resolution
InactiveUS20100226437A1Reduce complexityReduce computing costColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer graphics (images)Image resolution
A method of and system for reducing complexity for transcoding Advanced Video Coding (AVC) videos is described herein. Transcoding from higher resolution signals to lower resolution signals or to signals for a lower resolution display is implemented. The complexity is reduced by decoding the AVC video at reduced horizontal and / or vertical resolution. This results in the reduction of computation cost for decoding and re-sampling the AVC video to lower resolution.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
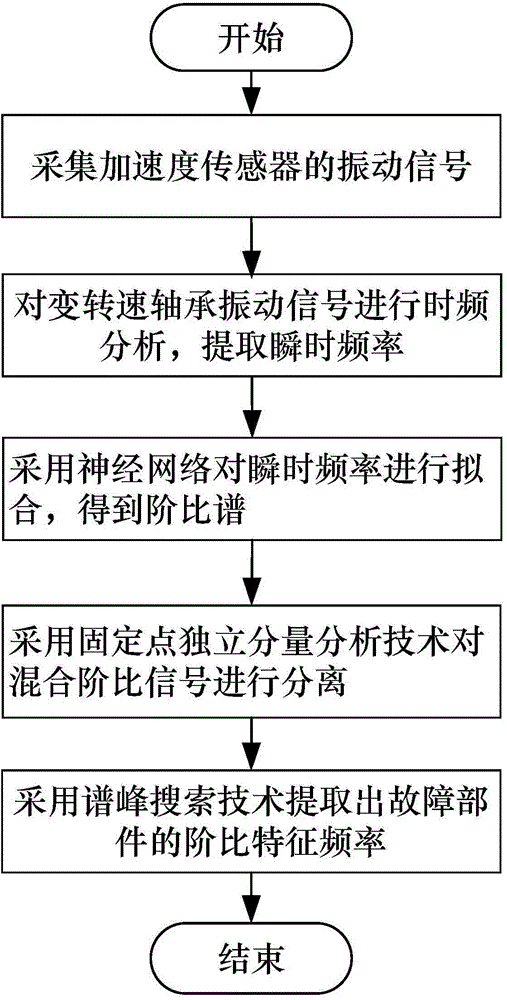
Method for extracting fault characteristic frequencies of train rolling bearings with variable rotational speeds
ActiveCN104568444AIncrease flexibilityCancel noiseMachine bearings testingRolling-element bearingSignal on
The invention discloses a method for extracting fault characteristic frequencies of train rolling bearings with variable rotational speeds, and belongs to the field of technologies for diagnosing faults and processing signals. The method includes steps of analyzing vibration signals of the bearings with the variable rotational speeds in time and frequency domains, searching local peak values of the vibration signals and extracting instantaneous frequency values corresponding to the rotational speeds at different moments; fitting instantaneous frequencies by the aid of neural networks, acquiring rotational speed curves of reference spindles, re-sampling original signals at uniform angles on the basis of the rotational speed curves and analyzing order ratios of the original signals on the basis of the rotational speed curves; separating signals with mixed order ratio signals by the aid of fixed-point independent component analysis and spectrum peak search technologies to acquire order ratio component characteristics of fault components of the bearings. The method has the advantages that the method is used for estimating the rotational speeds of the train bearings without tachometers in real time, the instable fault bearing signals can be converted into the stable signals in uniform-angle domains, independent order ratio components can be effectively separated from the signals, and the method is favorable for extracting the fault characteristic frequencies of the train bearings and detecting the fault characteristic frequencies of the train bearings in an online manner.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
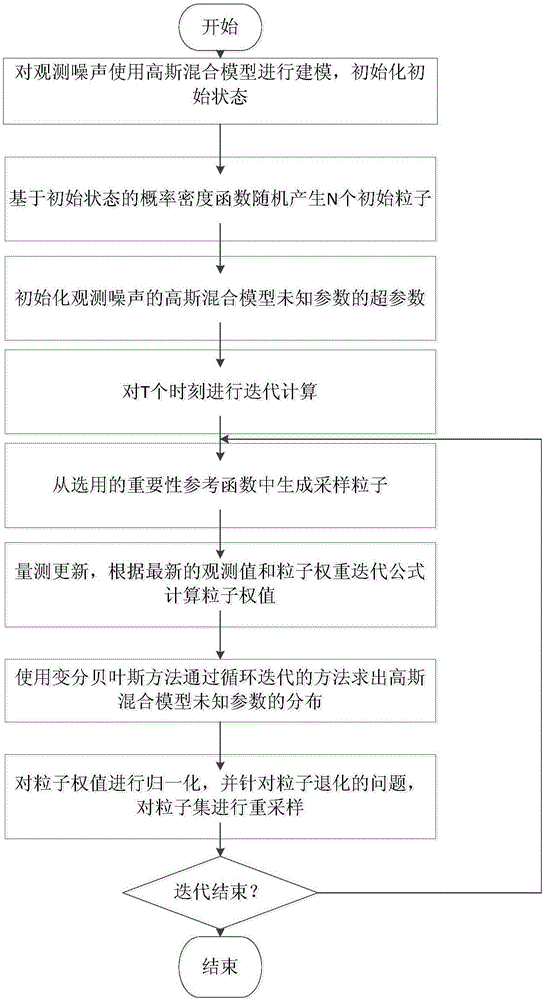
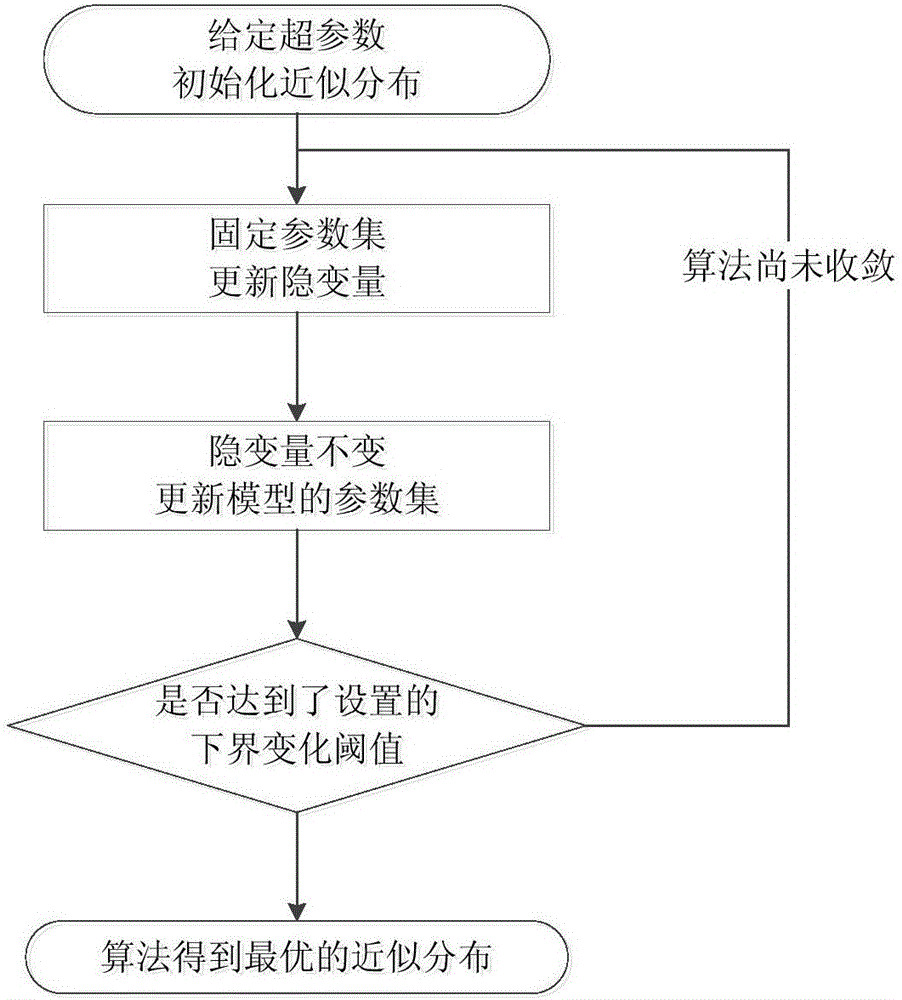
Particle filtering method based on Gaussian mixture model and variational Bayes
The invention discloses a particle filtering method based on a Gaussian mixture model and variational Bayes, comprising the following steps: (1) modeling observation noise using a Gaussian mixture model, and initializing the initial state; (2) randomly generating N initial particles based on the probability density function of the initial state; (3) initializing the super parameters of the unknown parameters in the Gaussian mixture model of observation noise; (4) generating sampling particles from a chosen importance reference function; (5) updating measurement, and calculating the particle weights according to the latest observation value and a particle weight iteration formula; (7) using a variational Bayesian method to get the distribution of the unknown parameters in the Gaussian mixture model by means of loop iteration; and (7) normalizing the particle weights, and re-sampling a particle set in view of particle degradation. Through the scheme, the filtering precision and the target state estimation performance are improved effectively.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
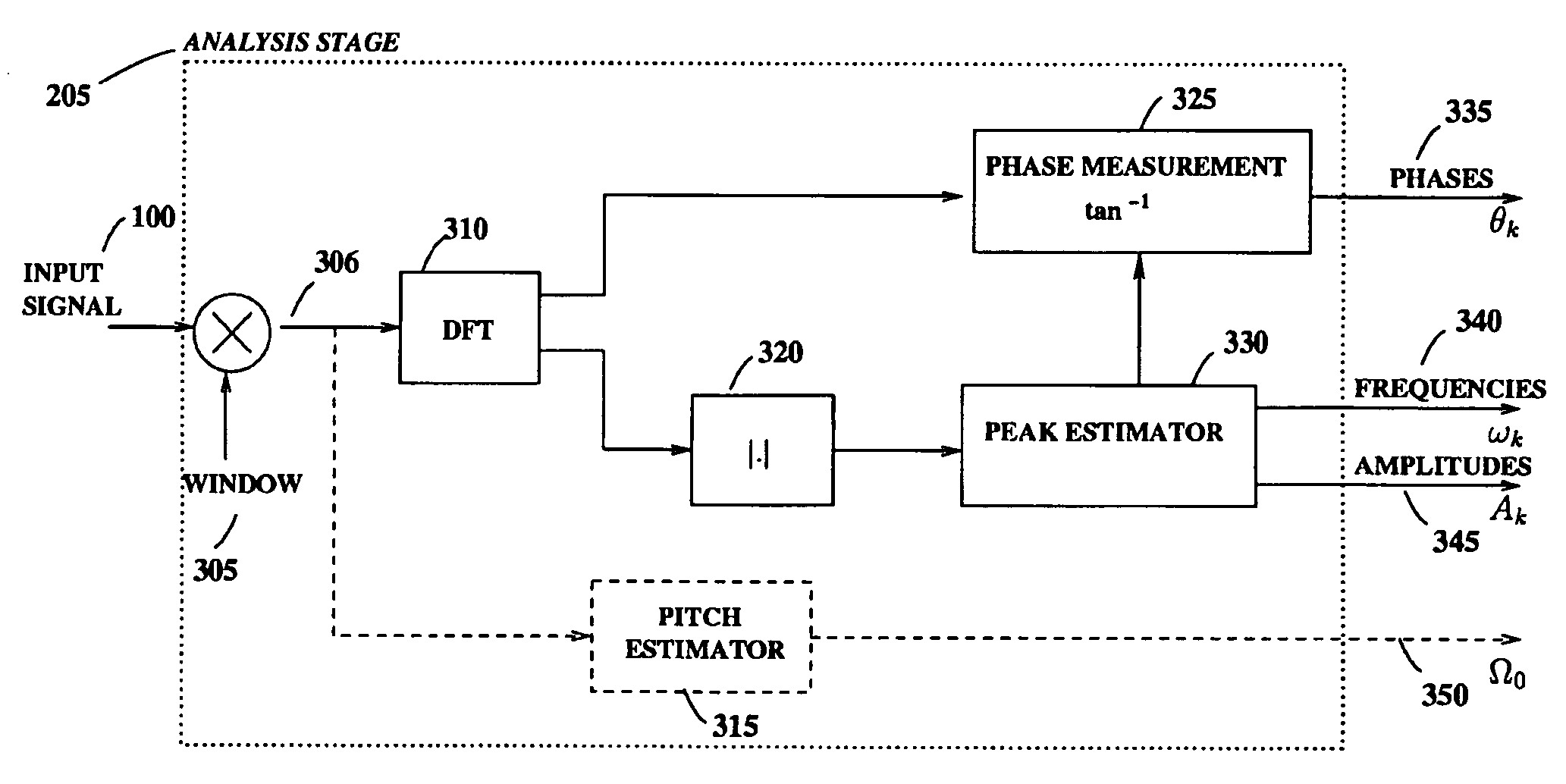
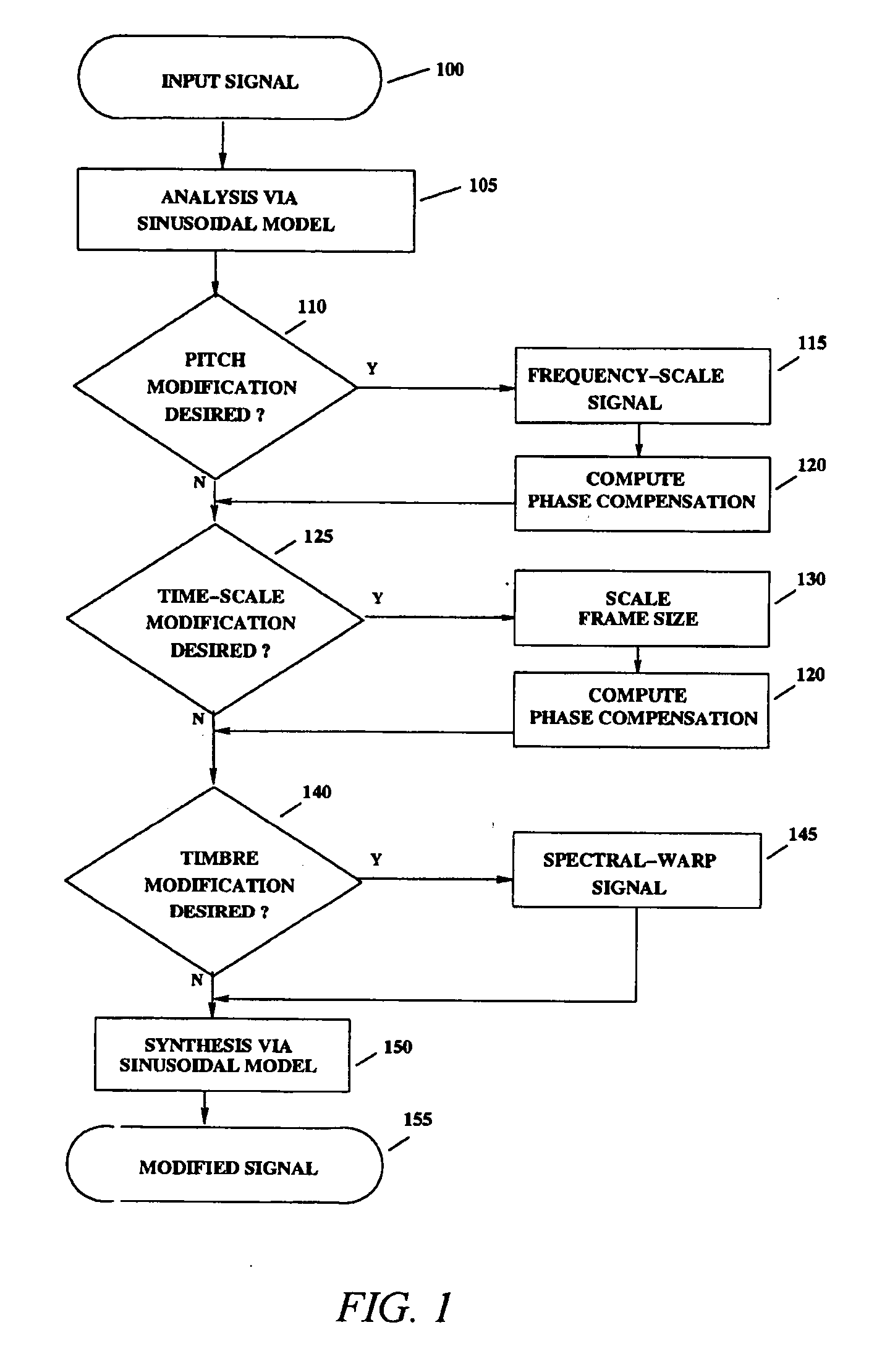
Modification of acoustic signals using sinusoidal analysis and synthesis
InactiveUS20050065784A1More realistic modified speechChange shapeSpeech synthesisVocal tractAudio frequency
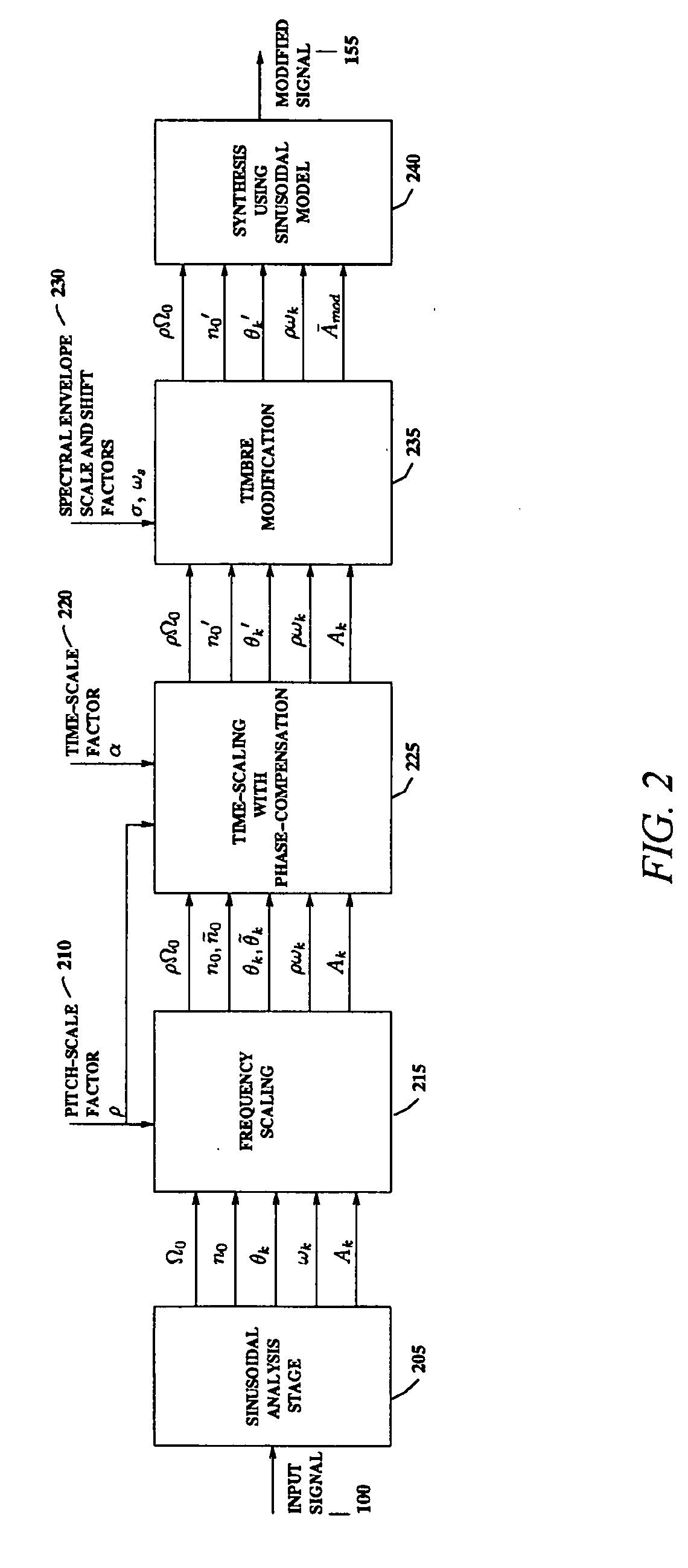
An analysis and synthesis system for sound is provided that can independently modify characteristics of audio signals such as pitch, duration, and timbre. High-quality pitch-scaling and time-scaling are achieved by using a technique for sinusoidal phase compensation adapted to a sinusoidal representation. Such signal modification systems can avoid the usual problems associated with interpolation-based re-sampling so that the pitch-scaling factor and the time-scaling factor can be varied independently, arbitrarily, and continuously. In the context of voice modification, the sinusoidal representation provides a means with which to separate the acoustic contributions of the vocal excitation and the vocal tract, which can enable independent timbre modification of the voice by altering only the vocal tract contributions. The system can be applied to efficiently encode the pitch in sinusoidal models by compensating for pitch quantization errors. The system can also be applied to non-speech signals such as music.
Owner:NELLYMOSER A MASSACHUSETTS CORP
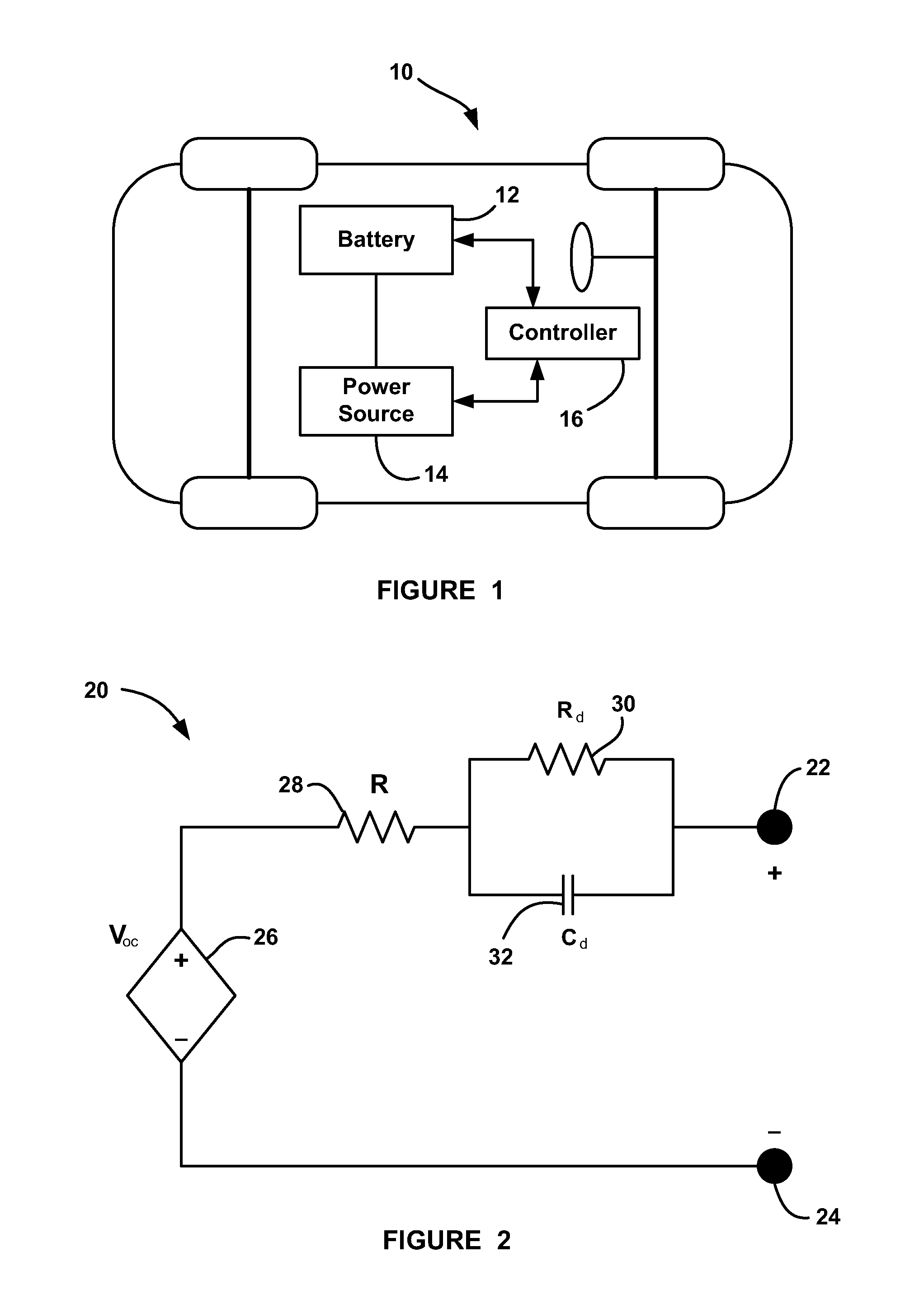
Battery state estimator using multiple sampling rates
ActiveUS20110224928A1Reduced sampling rate requirementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrical testingBattery state of chargeTerminal voltage
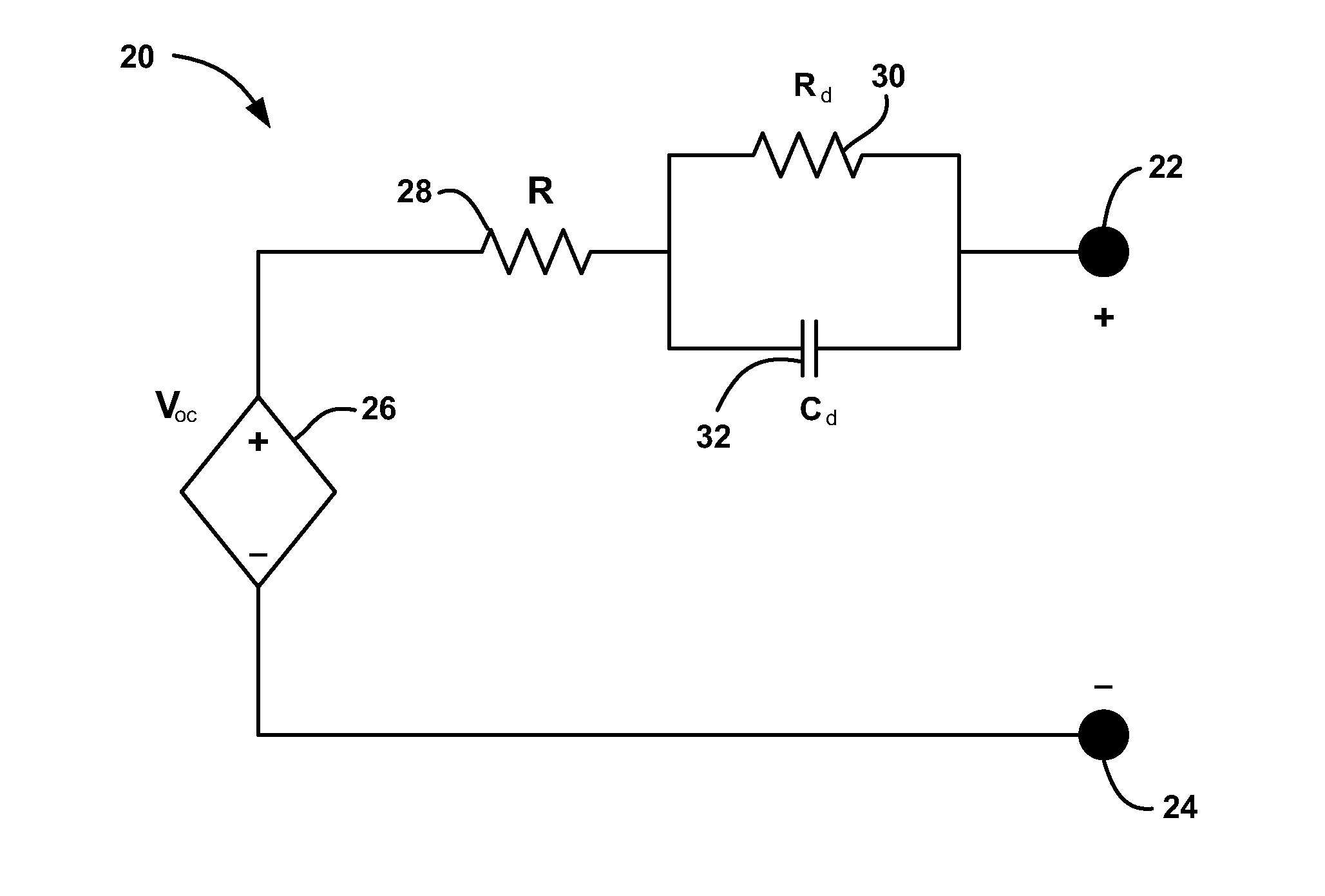
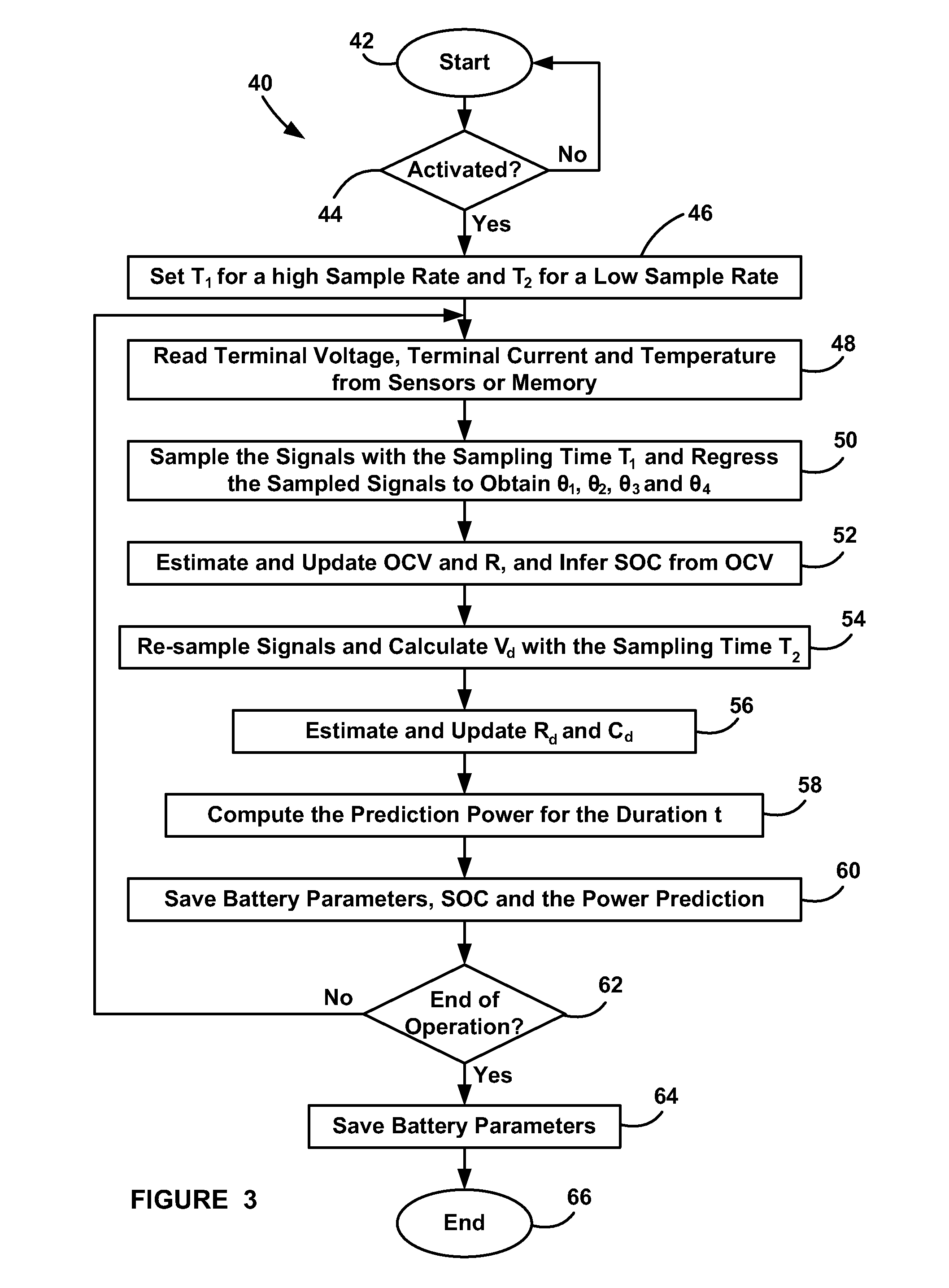
A method for estimating vehicle battery parameters that uses two different sampling rates. The method samples a battery terminal voltage and current at a high sampling rate to estimate the battery open circuit voltage and high frequency resistance. The battery state of charge (SOC) is derived from the open circuit voltage. Next, the battery terminal voltage and current are re-sampled at a low sampling rate. Other battery parameters can be extracted from the low-rate sampled signals. Next, all of the battery parameters that were obtained from the two sampling rates are used together to predict battery power.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Network advertisement effect estimating method and network advertisement effect estimating system
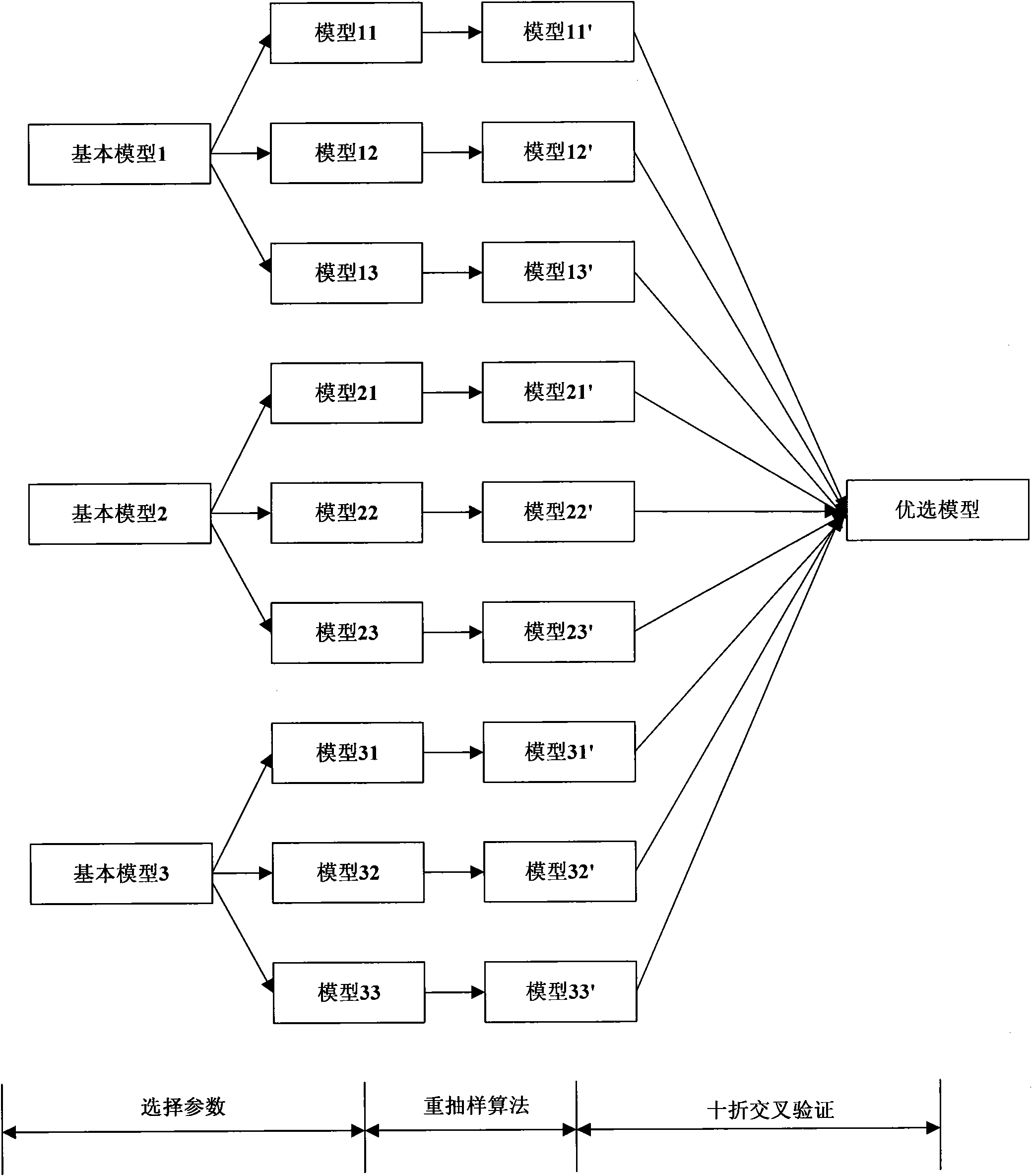
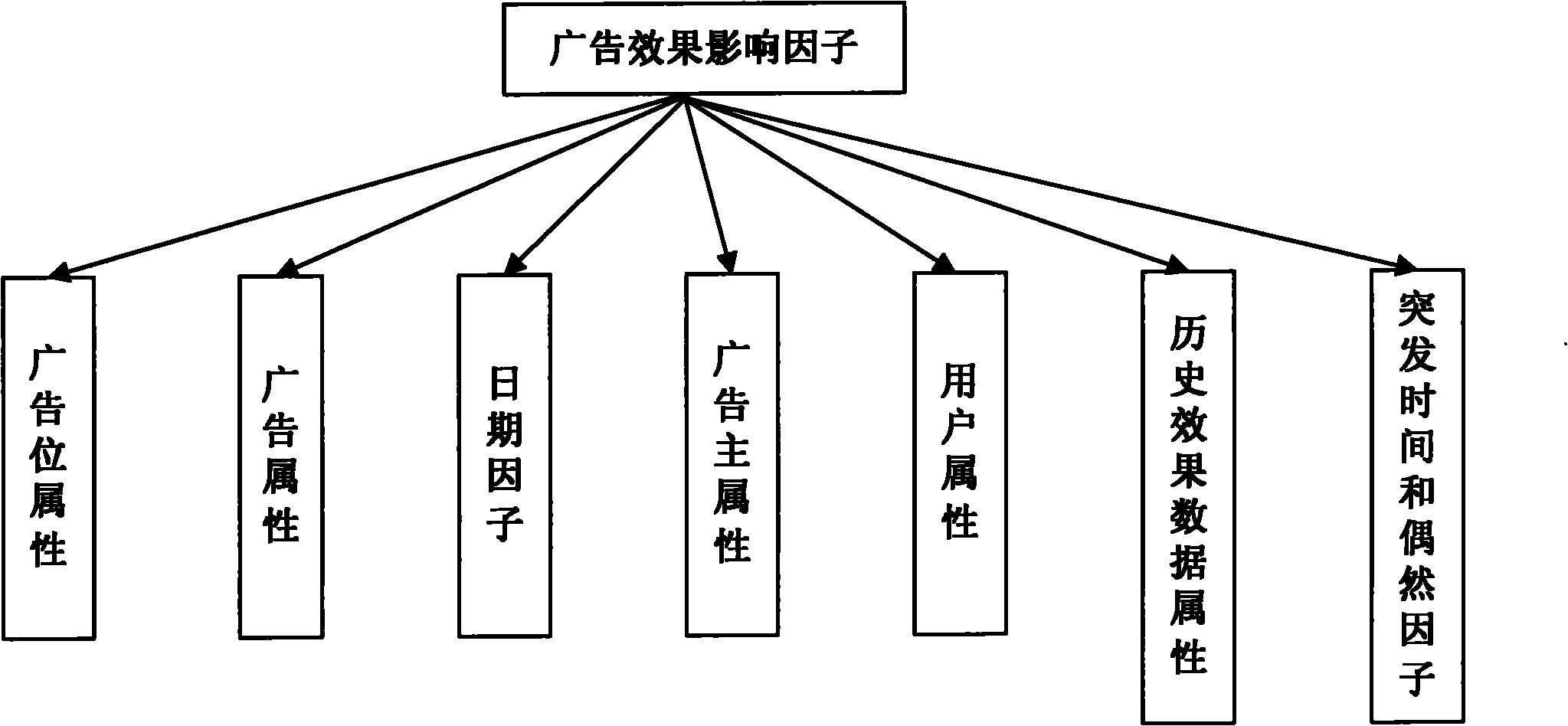
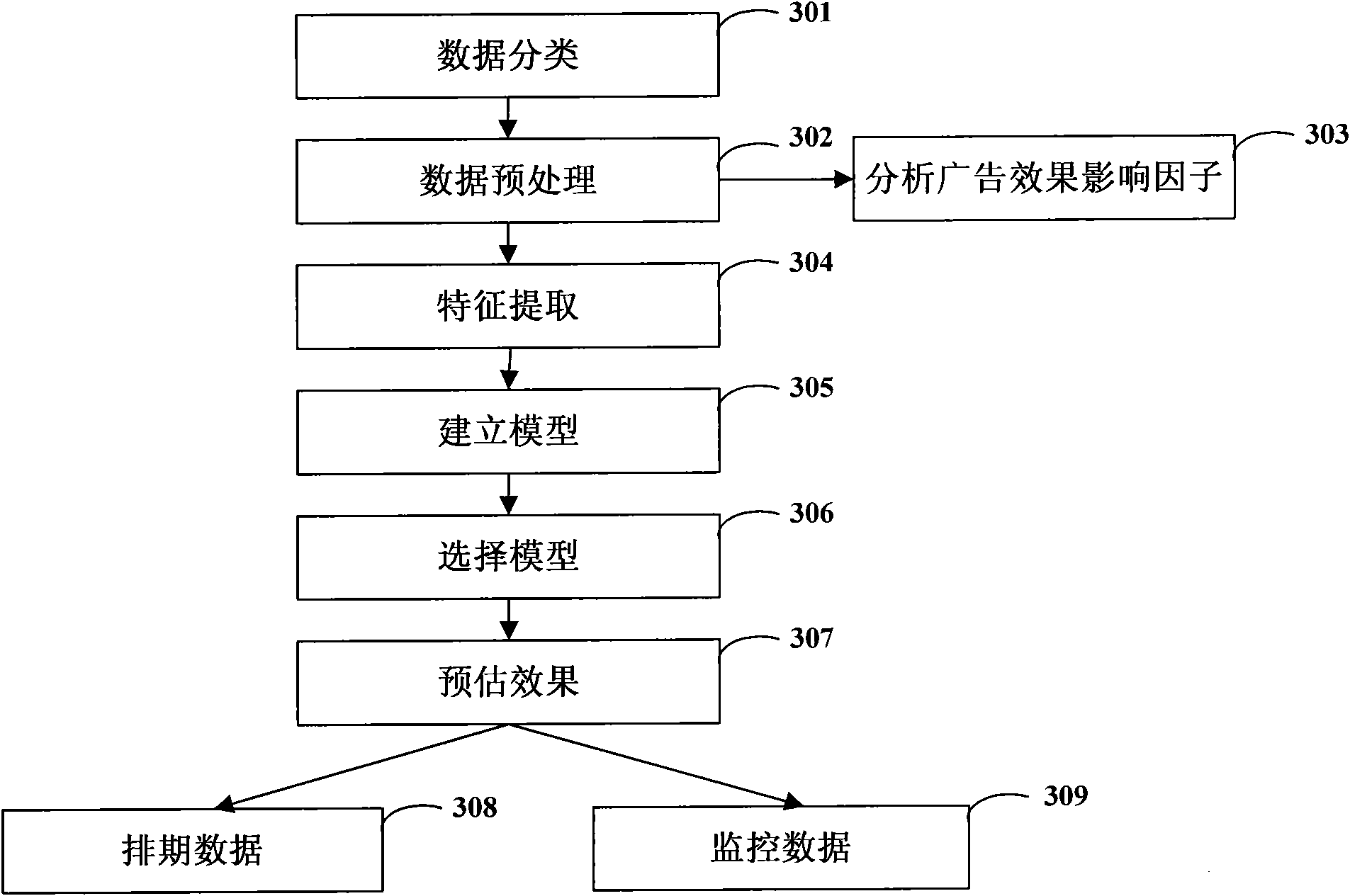
The invention discloses a network advertisement effect estimating method, which comprises the following steps of: classifying original data according to an impact factor of an advertisement effect; extracting an impact sub-factor of the advertisement effect from the impact factor of the advertisement effect, and establishing at least one estimating model by adopting regression analysis and a re-sampling algorithm (Bagging); selecting an optimal estimating model from the estimating models by a tenfold crossed validation method; and estimating the advertisement effect within a next prediction period by utilizing the optimal estimating model so as to obtain an advertisement estimated effect. By the application of an embodiment of the invention, the high-precision prediction of an advertisement delivery effect can be performed, and the estimated effect is diversified.
Owner:SHENZHEN TENCENT COMP SYST CO LTD
Multi-level-point-set characteristic extraction method applicable to ground laser radar point cloud classification
InactiveCN104091321AEfficient acquisitionImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPoint cloudRadar
The invention relates to a multi-level-point-set characteristic extraction method applicable to ground laser radar point cloud classification. Based on point set characteristics, high-precision classification of four kinds of common ground features including pedestrians, trees, buildings and automobiles and the like in a scene is realized. Firstly, point sets are constructed and a point cloud is re-sampled into a point cloud of different scales and thus point sets which are different in size and provided with layered structures are formed through clustering and characteristics of each point in the point sets are obtained; next, an LDA (Latent Dirichlet Allocation ) method is adopted to synthesizing point-based characteristics of all points in each point set into shape characteristics of the point sets; and at last, based on the shape characteristics of the point set, an Adaboost classifier is adopted to train the point sets of different levels so as to obtain a classification result of the whole point cloud. The multi-level-point-set characteristic extraction method has a higher classification precision and has a classification precision, which is far higher than that of point-based characteristics, Bag-of-Word-based characteristics and characteristics based on probabilistic latent semantic analysis (PLSA), in aspect of pedestrians and vehicles.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Sensor fusion and probabilistic parameter estimation method and apparatus
A probabilistic digital signal processor using data from multiple instruments is described. Initial probability distribution functions are input to a dynamic state-space model, which operates on state and / or model probability distribution functions to generate a prior probability distribution function, which is input to a probabilistic updater. The probabilistic updater integrates sensor data from multiple instruments with the prior to generate a posterior probability distribution function passed (1) to a probabilistic sampler, which estimates one or more parameters using the posterior, which is output or re-sampled in an iterative algorithm or (2) iteratively to the dynamic state-space model. For example, the probabilistic processor operates on fused data using a physical model, where the data originates from a mechanical system or a medical meter or instrument, such as an electrocardiogram or pulse oximeter to generate new parameter information and / or enhanced parameter information.
Owner:VITAL METRIX INC
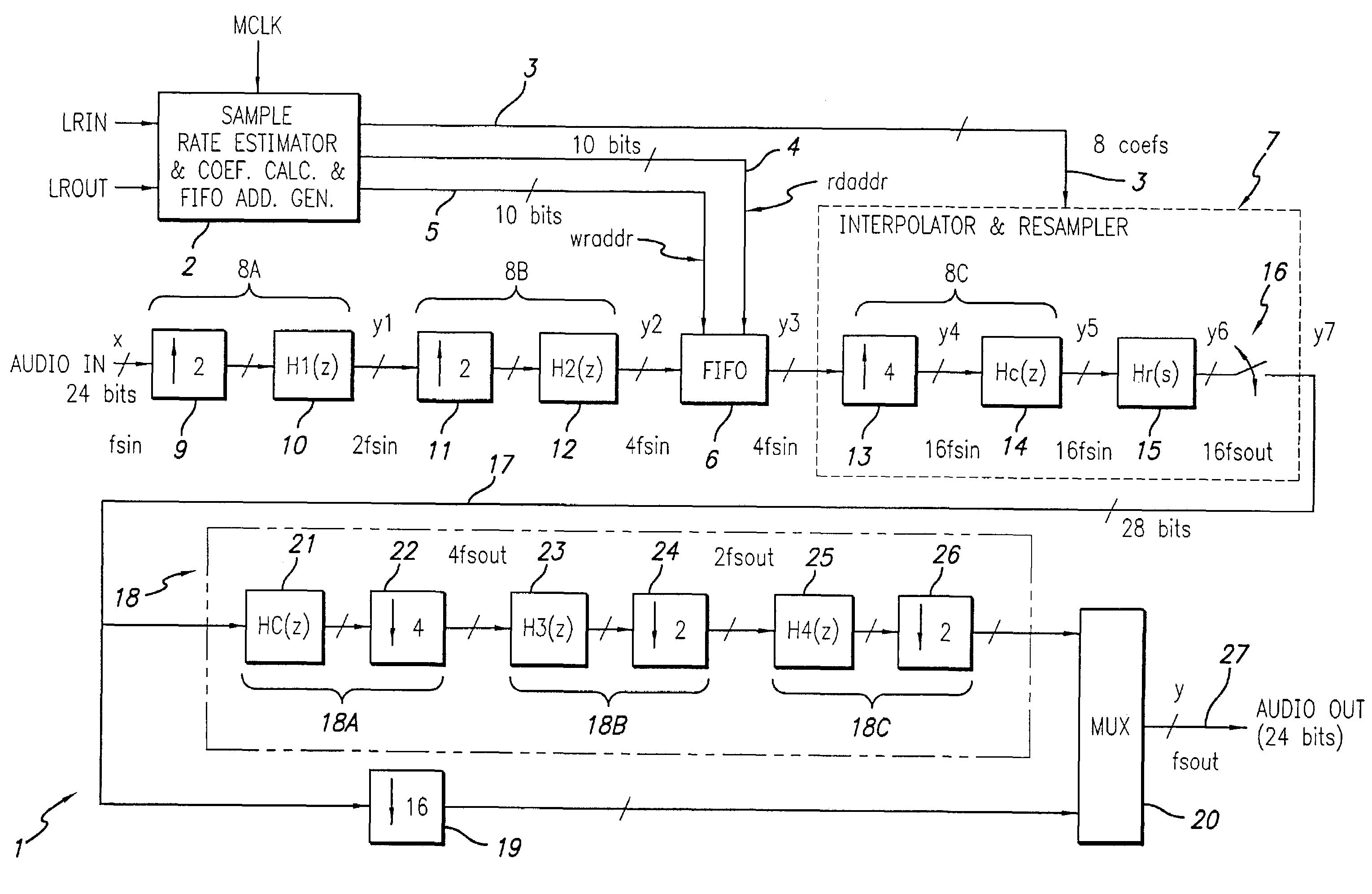
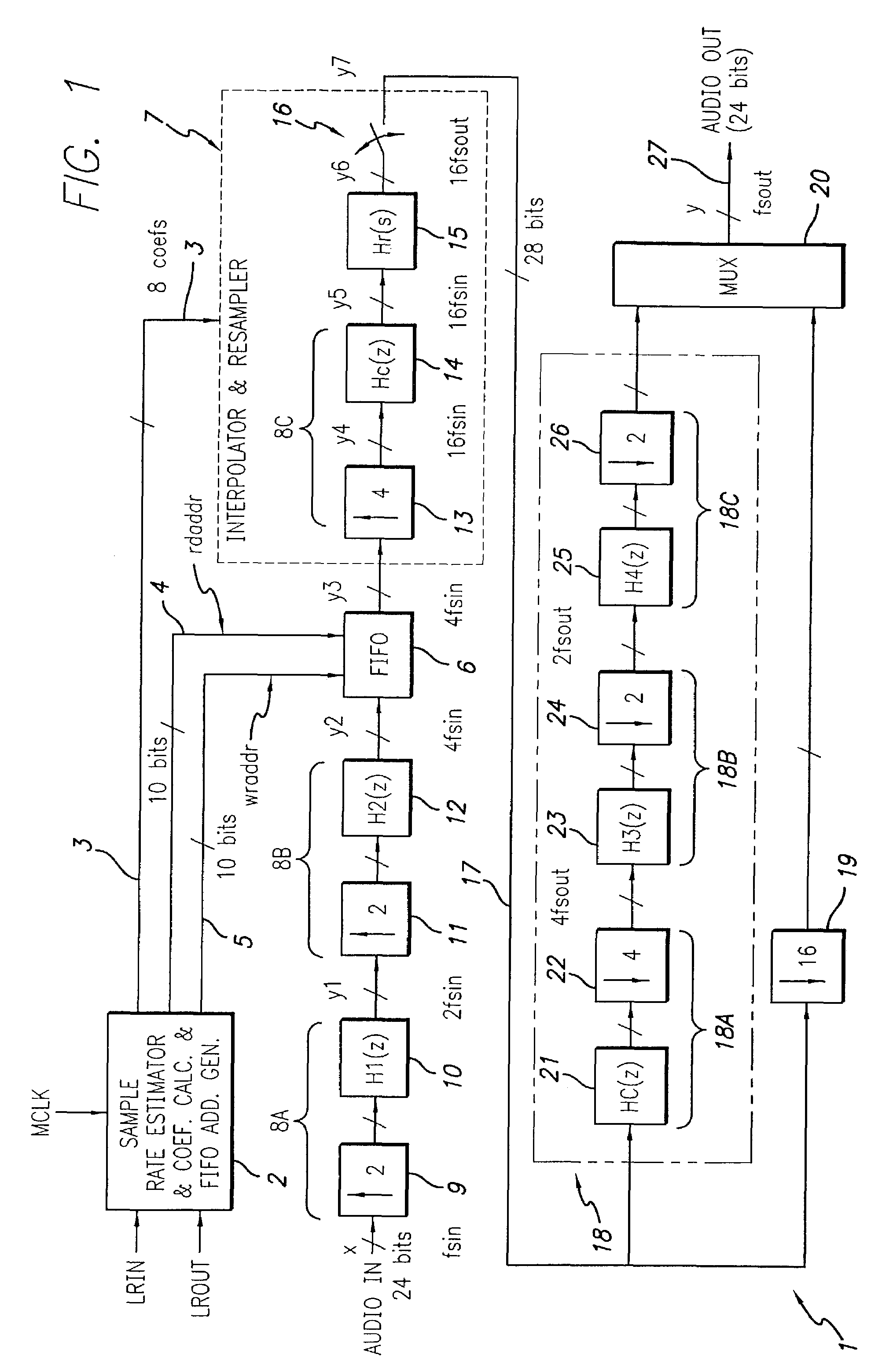
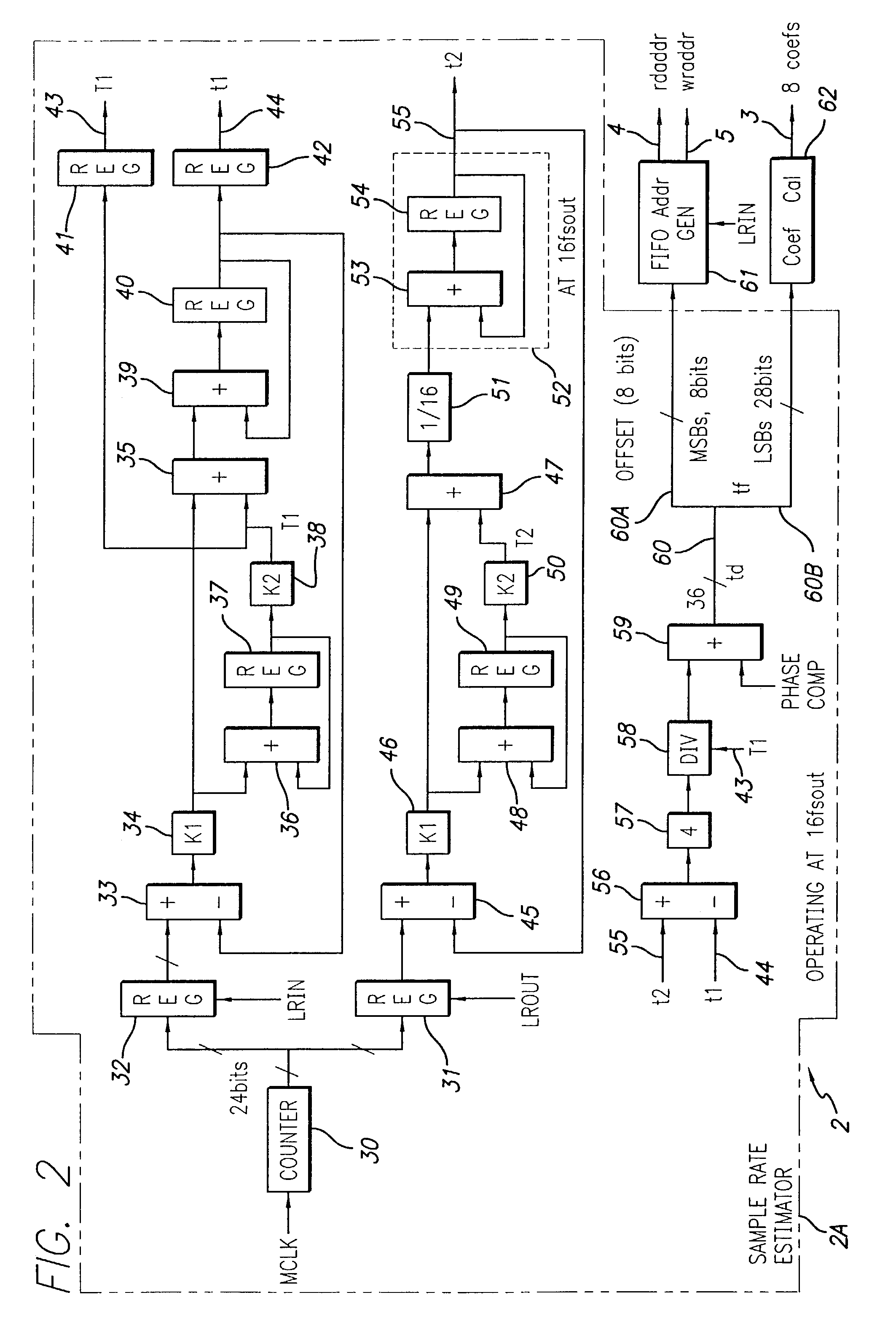
Asynchronous sample rate converter and method
ActiveUS7262716B2Exact matchReduce usageDigital technique networkCode conversionFifo memoryTime signal
An asynchronous sample rate converter interpolates and filters a digital audio input signal to produce a filtered, up-sampled first signal. A FIFO memory receives the first signal and stores samples thereof at locations determined by a write address and presents stored samples from locations determined by a read address. The presented samples are passed through an interpolation and resampling circuit to produce a continuous-time signal which is re-sampled to produce a signal that is up-sampled relative to a desired output. That signal then is filtered and down-sampled to produce the output signal. Sample rate estimating circuitry computes a difference signal representative of a time at which a data sample of the audio input signal is received and a time at which a corresponding audio output sample is required, and address generation circuitry generates the read and write addresses. A coefficient calculation circuit calculates filter coefficients for the interpolation and resampling circuit in response to the difference signal.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method for generating garment body prototype model based on personalized three-dimensional virtual dress form
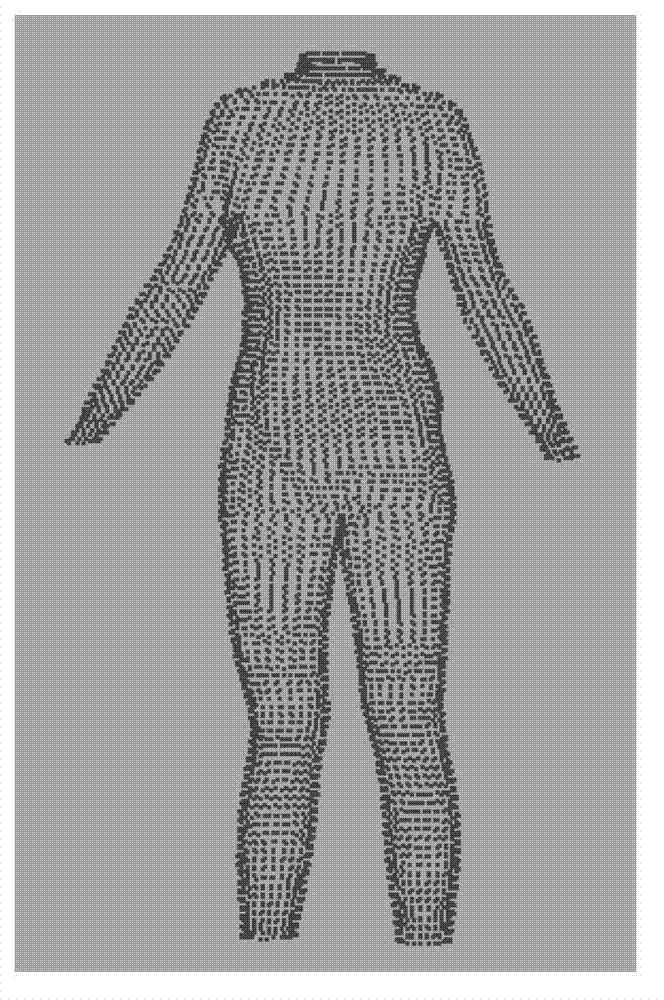
InactiveCN102880741AEvenly distributedAvoid phenomena such as reversed orderSpecial data processing applicationsPersonalizationHuman body
The invention relates to a method for generating a garment body prototype model based on a personalized three-dimensional virtual dress form. The method comprises the steps as follows: firstly, carrying out treatments such as section curve fitting, re-sampling, symmetrization, convex hull calculation, translation and curve fitting of inwardly recessed zone points and the like on three-dimensional data of a human body trunk to obtain the symmetric virtual dress form with a similar effect of wearing a body fitting garment; secondly, defining characteristic points and lines on the three-dimensional dress form of a half body, and further subdividing zone curves; and lastly, carrying out two-dimensional expansion on the three-dimensional curves to generate the personalized garment prototype model. The three-dimensional virtual dress form obtained by utilizing the method can be applied to personalized customization of industrial dress forms, the generated prototype model inherits the accuracy of the conventional three-dimensional curve expansion technology and can guarantee the structural characteristics of the conventional prototype, and the mature two-dimensional CAD (Computer Aid Design) technology can be made full use of in results for further model customization of garments with specific styles.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
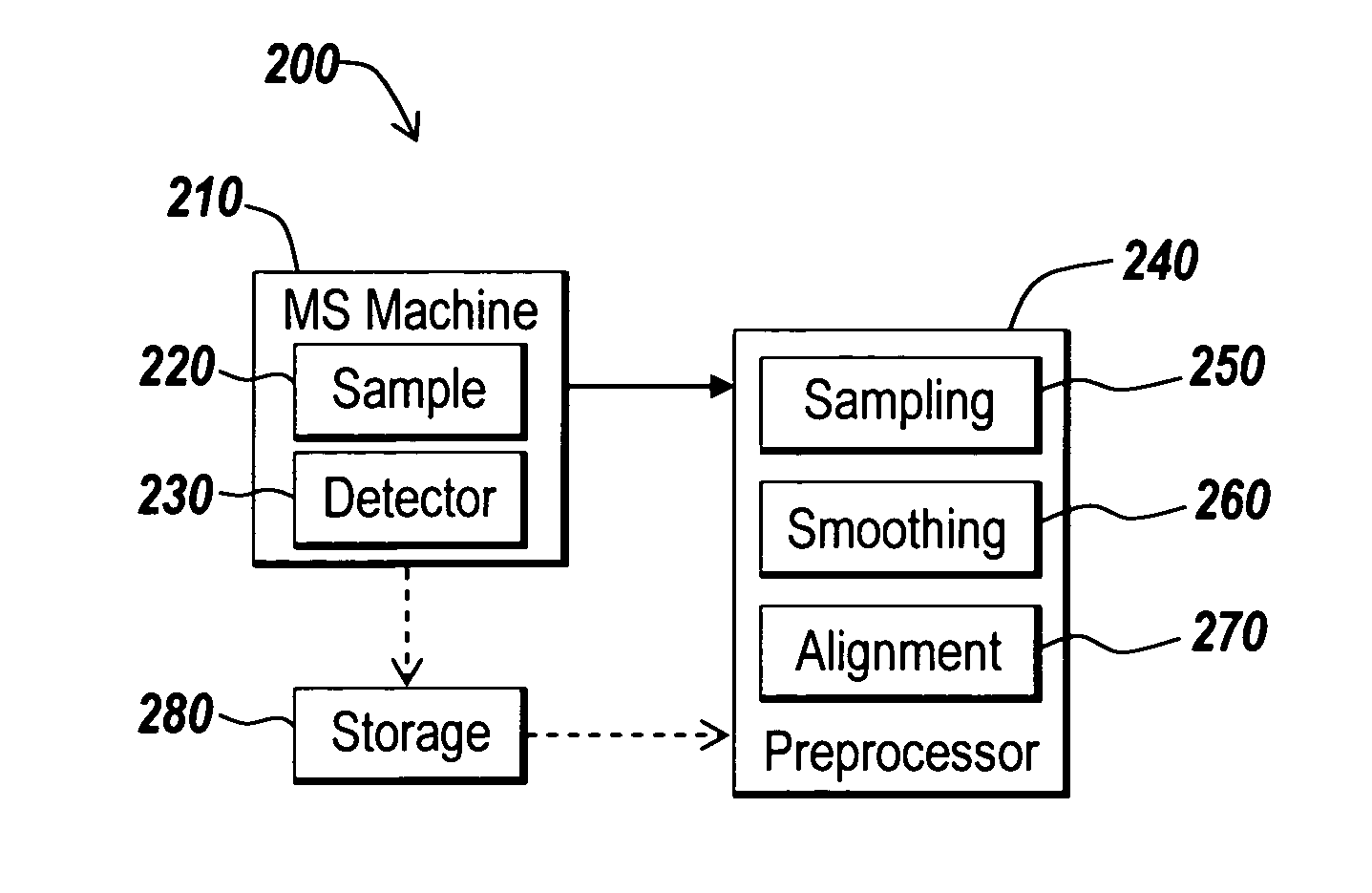
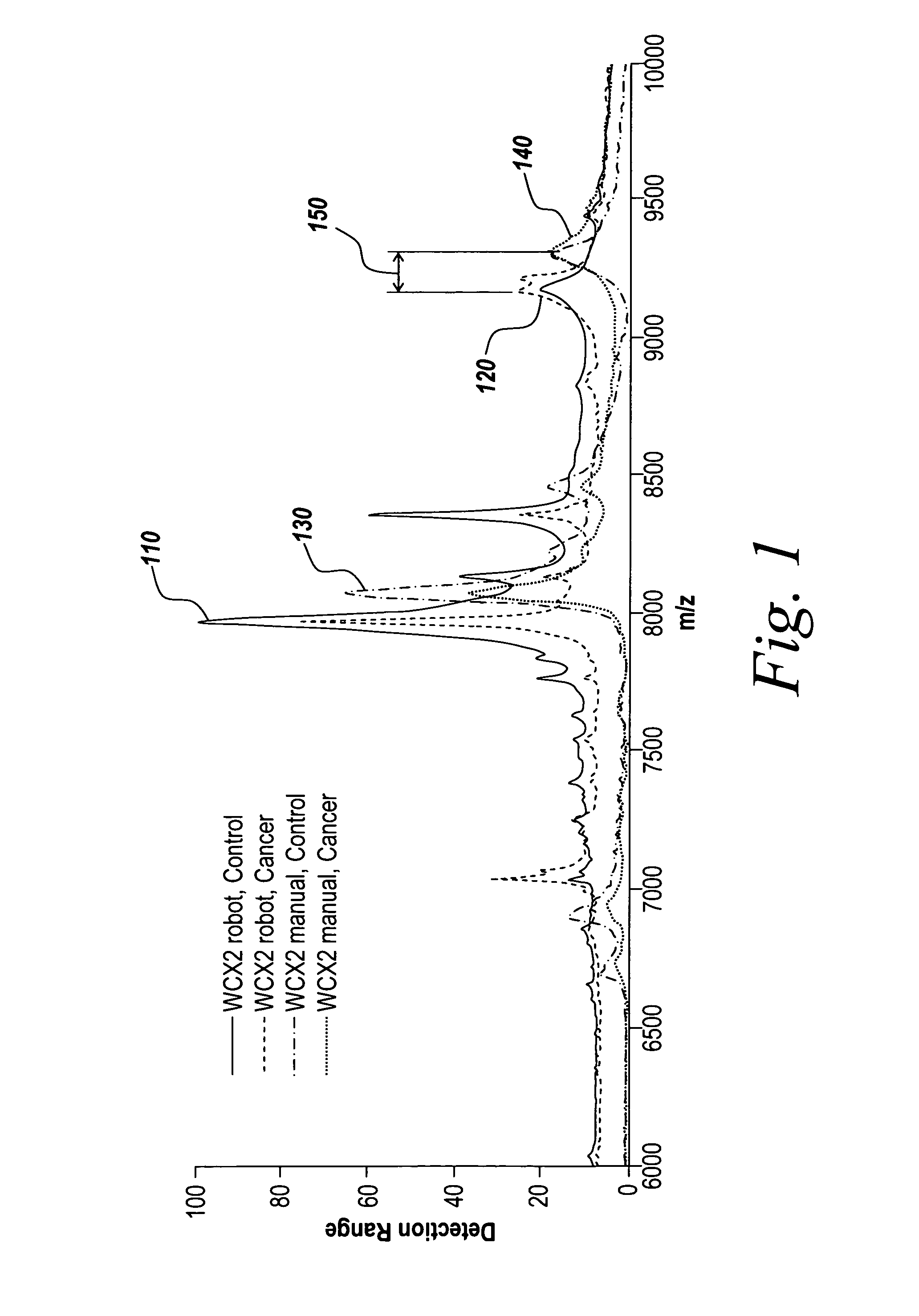
Alignment of mass spectrometry data
InactiveUS7365311B1Prevents failure of alignmentSpectral/fourier analysisParticle separator tubesSpectral patternWarping function
Methods, systems and mediums are disclosed for aligning mass spectrometry data before the analysis of the mass spectrometry data. The mass spectrometry data may be received from a mass spectrometry machine, and re-sampled using a smooth warping function. To estimate the warping function, a synthetic signal is build using, for example, Gaussian pulses centered at a set of reference peaks. The reference peaks may be designated by users or calculated after observing a group of spectrograms. The synthetic signal is shifted and scaled so that the cross-correlation between the mass spectrometry data and the synthetic signal reaches its maximum value.
Owner:THE MATHWORKS INC
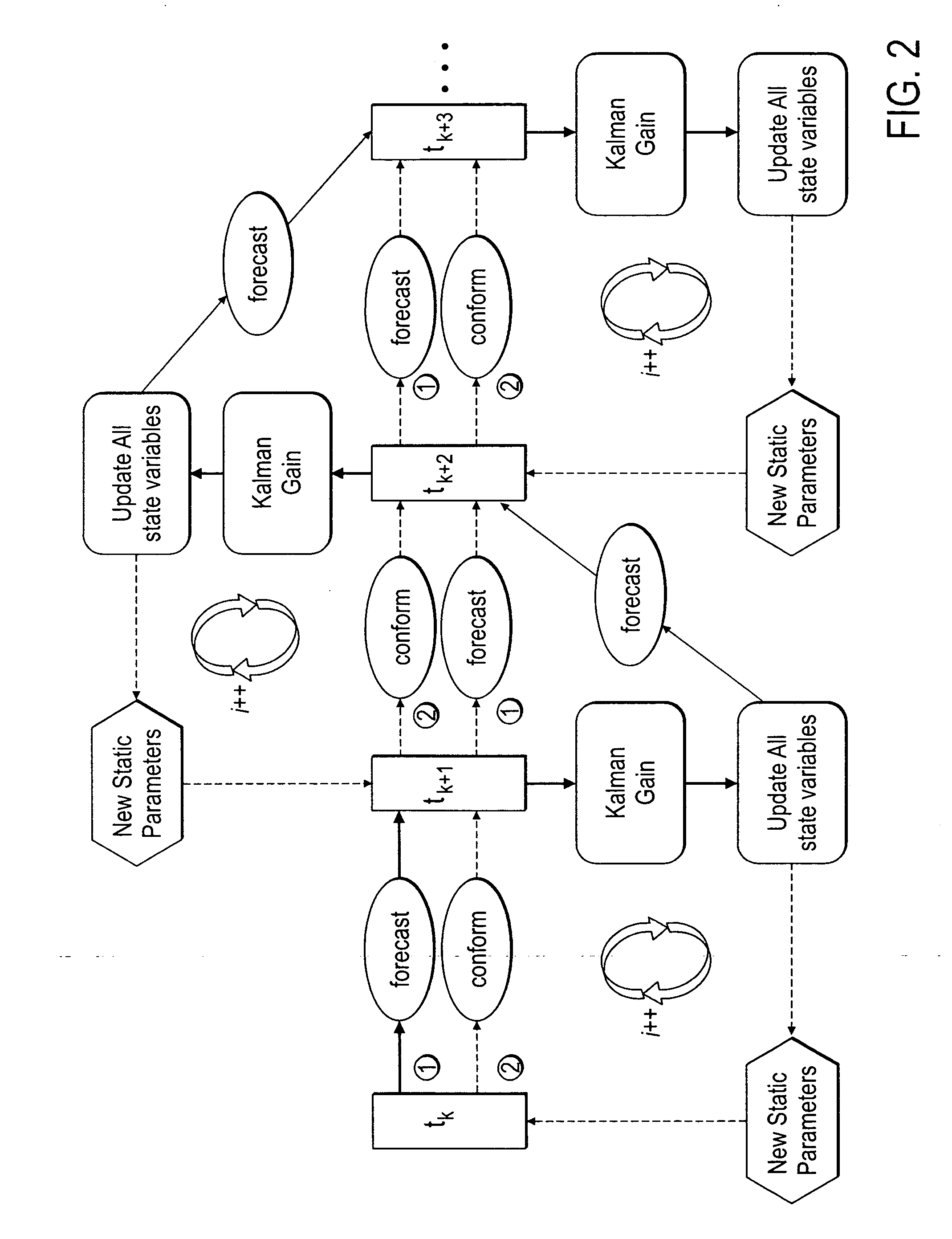
Method, system and apparatus for real-time reservoir model updating using ensemble kalman filter
ActiveUS7584081B2Reduce problem sizeReduce in quantityFluid removalComputation using non-denominational number representationState variableCombined use
A method, system and apparatus for real-time reservoir model updating using ensemble Kalman filters is described. The method includes a conforming step for bring bringing static and dynamic state variables into conformance with one another during a time step of the updating. Also, an iterative damping method is used in conjunction with the conformance step to account for nonGaussian and nonlinear features in a system. Also, a re-sampling method is described which reduces the ensemble size of reservoir models which are to be updated.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
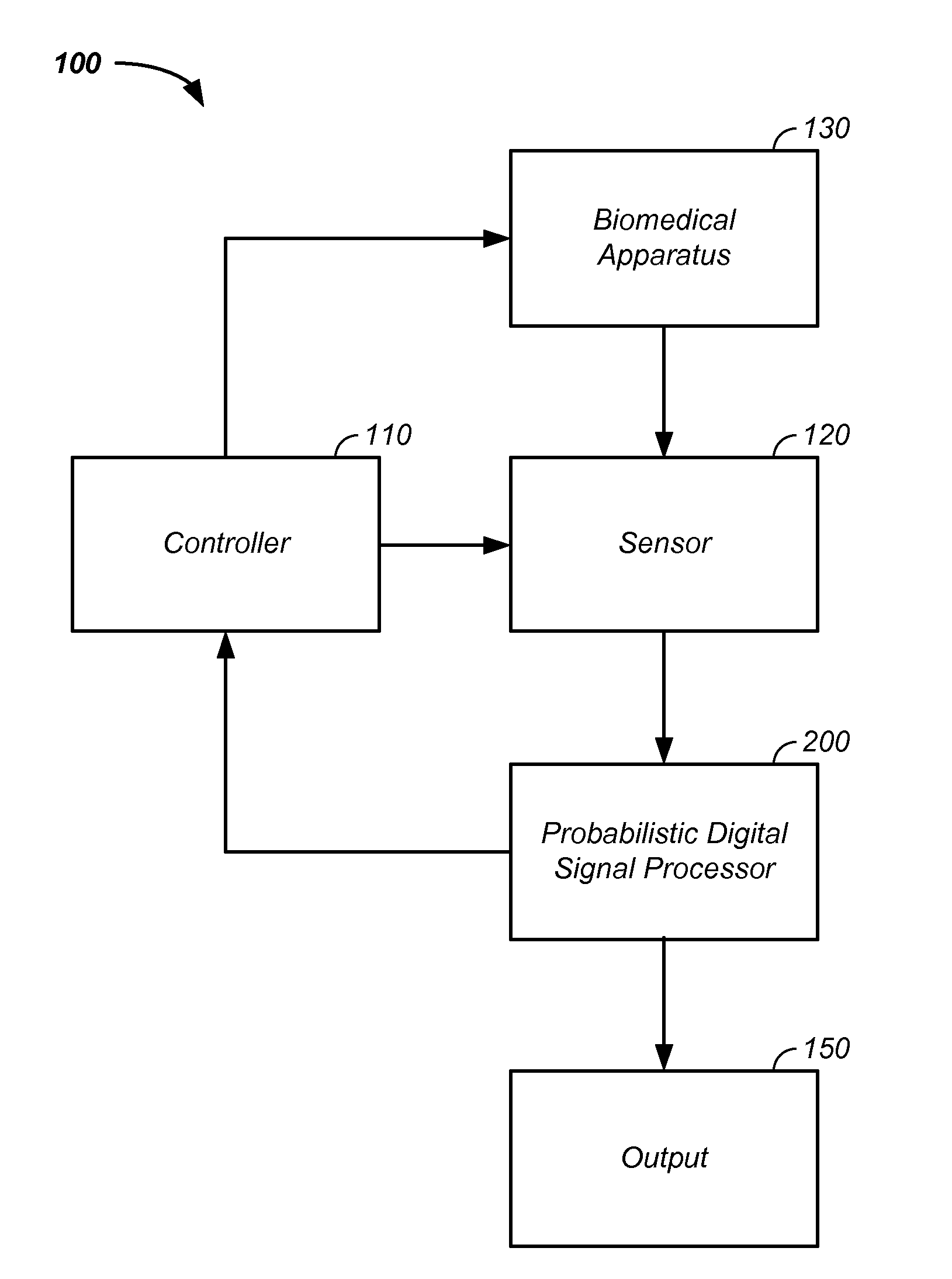
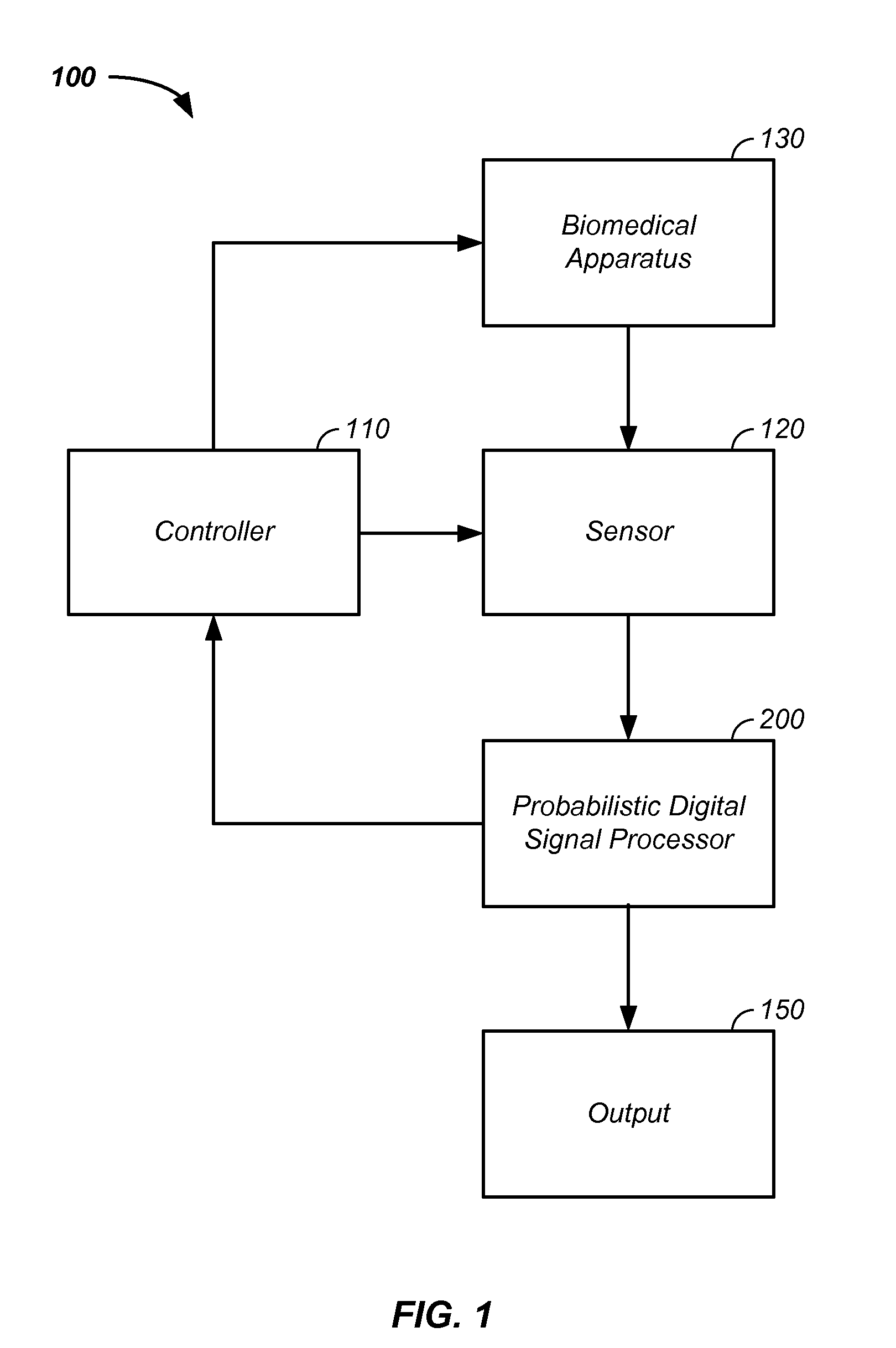
Probabilistic biomedical parameter estimation apparatus and method of operation therefor
A probabilistic digital signal processor for medical function is described. Initial probability distribution functions are input to a dynamic state-space model, which operates on state and / or model probability distribution functions to generate a prior probability distribution function, which is input to a probabilistic updater. The probabilistic updater integrates sensor data with the prior to generate a posterior probability distribution function passed to a probabilistic sampler, which estimates one or more parameters using the posterior, which is output or re-sampled in an iterative algorithm. For example, the probabilistic processor operates using a physical model on data from a medical meter, where the medical meter uses a first physical parameter, such as blood oxygen saturation levels from a pulse oximeter, to generate a second physical parameter not output by the medical meter, such as a heart stroke volume, a cardiac output flow rate, and / or a blood pressure.
Owner:VITAL METRIX INC
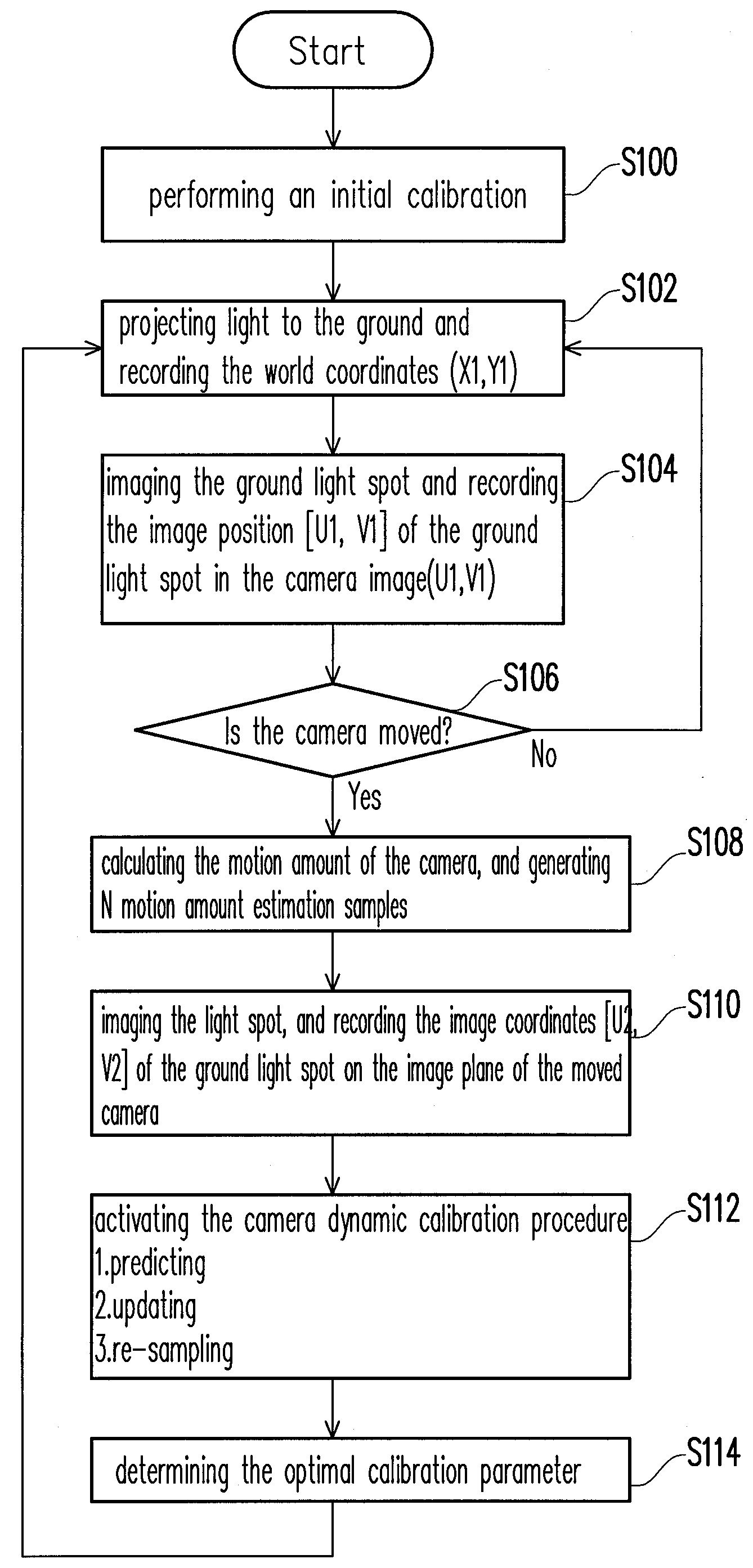
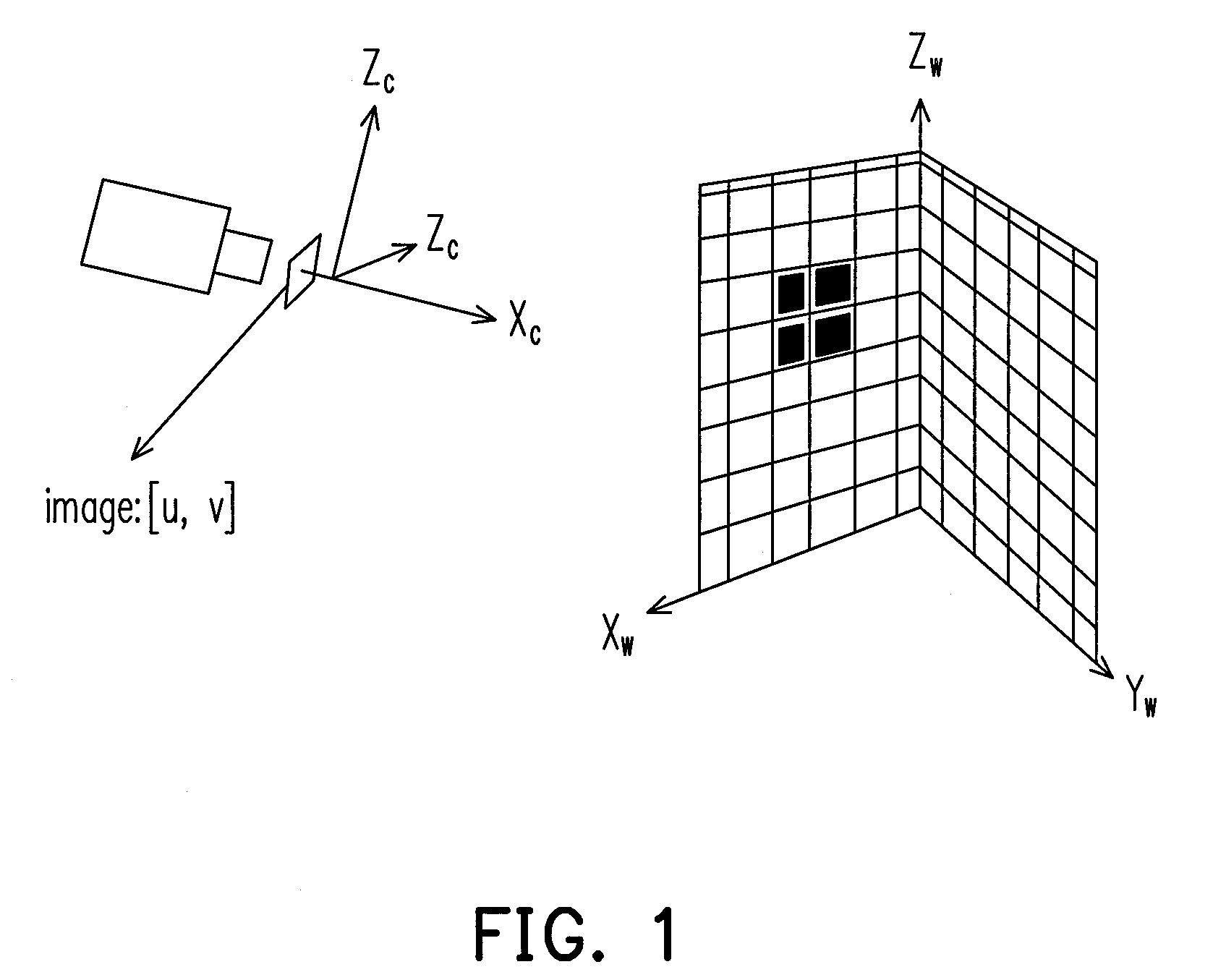
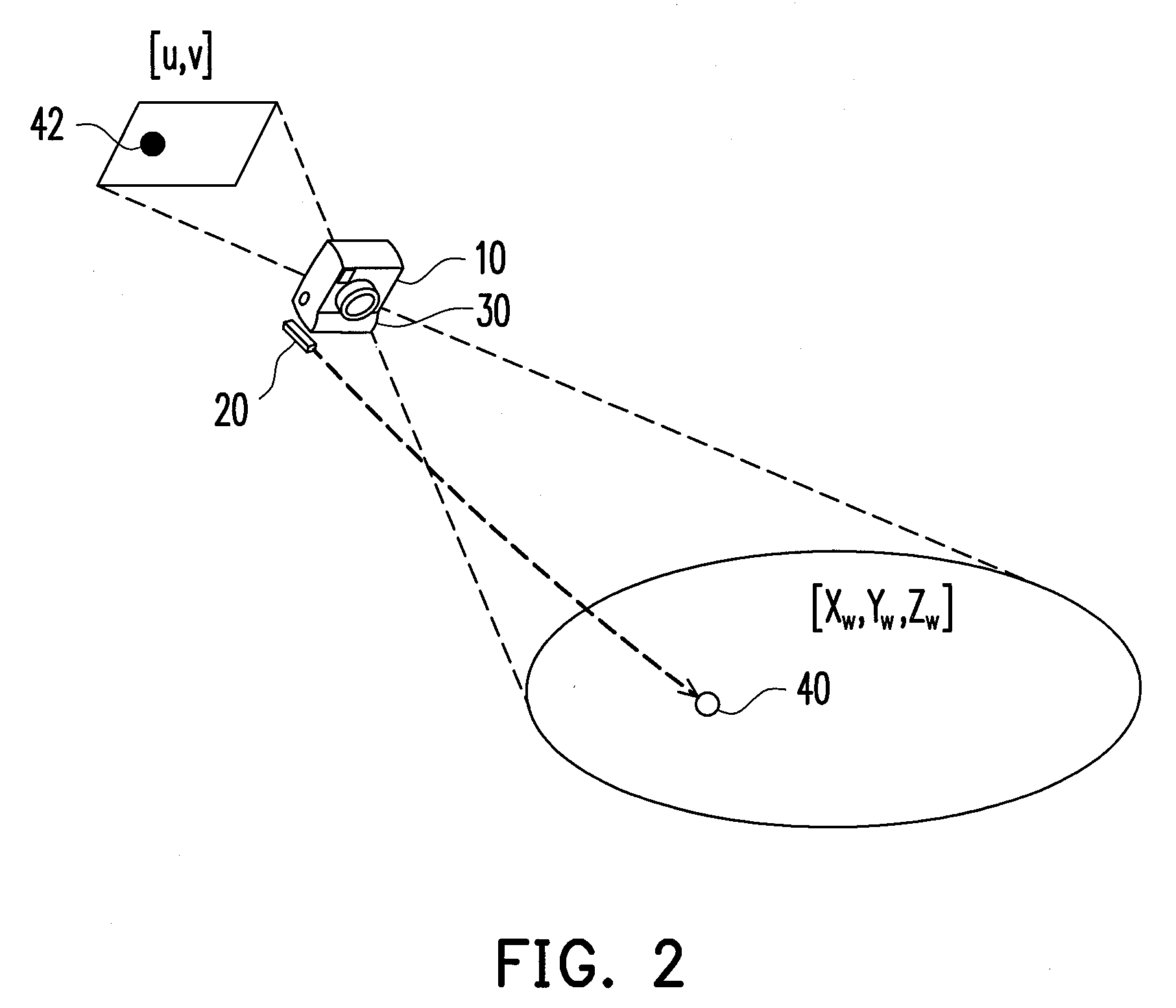
Camera with dynamic calibration and method thereof
InactiveUS20100165116A1Improve portabilityLow costTelevision system detailsImage enhancementComputer visionRe sampling
A camera with dynamic calibration and a method thereof is provided. The camera is first subject to an initial calibration. Then, a motion amount of the camera is calculated, and a plurality of motion amount estimation samples of the camera is generated according to the motion amount. Then, a weight of each of the motion amount estimation samples is calculated. Thereafter, the plurality of motion amount estimation samples is re-sampled based on the weights, and the camera is calibrated by the re-sampled estimated motion samples.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
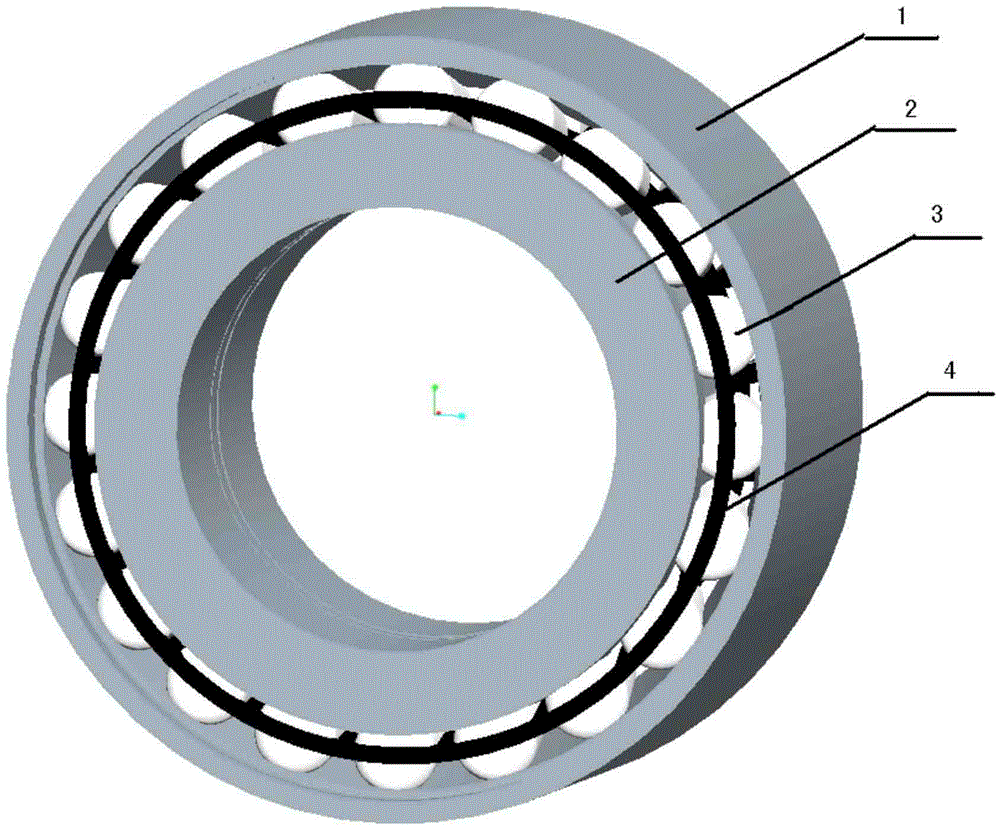
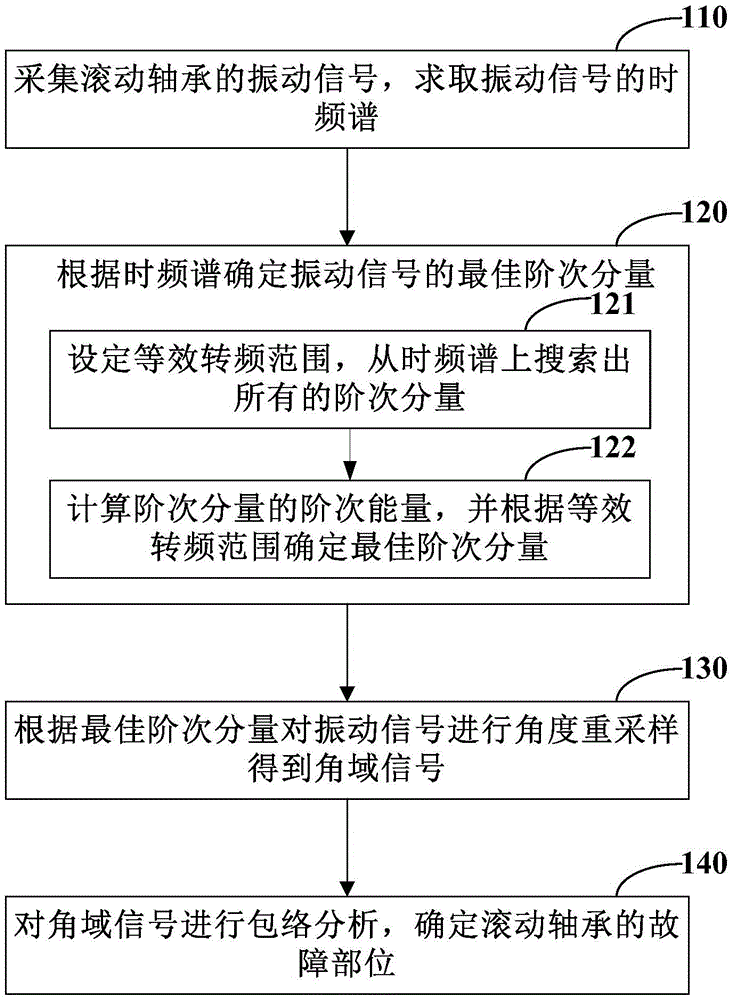
Fault diagnosis method and apparatus for rolling bearing
ActiveCN105547698AOK automaticallyQuick fixMachine bearings testingFrequency spectrumFrequency conversion
The embodiments of the invention provide a fault diagnosis method and apparatus for a rolling bearing. The fault diagnosis method for the rolling bearing comprises the following steps: acquiring vibration signals of the rolling bearing, and solving a time-frequency spectrum of the vibration signals; according to the time-frequency spectrum, determining an optimal order component of the vibration signals; according to the optimal order component, performing angle re-sampling on the vibration signals to obtain angle domain signals; and performing envelope analyzing on the angle domain signals, and determining fault positions of the rolling bearing, wherein determination of the optimal order component comprises: setting an equivalent frequency conversion scope and searching for all order components from the time-frequency spectrum; and calculating order energy of the order components and determining the optimal order component from the equivalent frequency conversion scope. The fault diagnosis method and apparatus for the rolling bearing realize automatic and rapid determination of the optimal order component so as to provide a basis for fault diagnosis of the rolling bearing, improve the fault diagnosis accuracy and avoid interference of manual factors.
Owner:XINJIANG GOLDWIND SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com