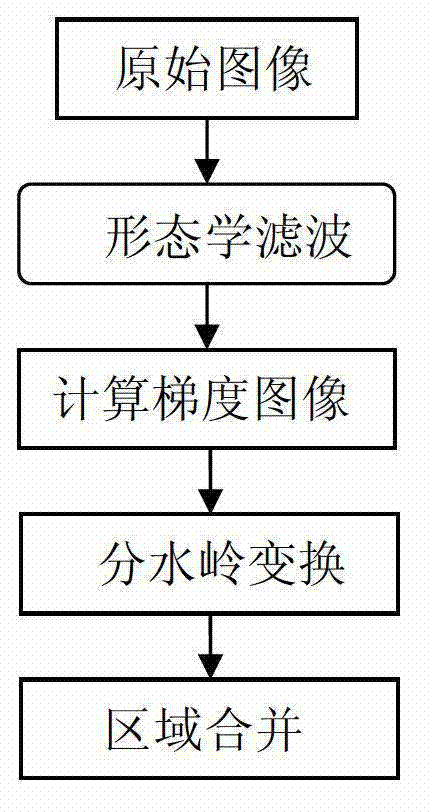
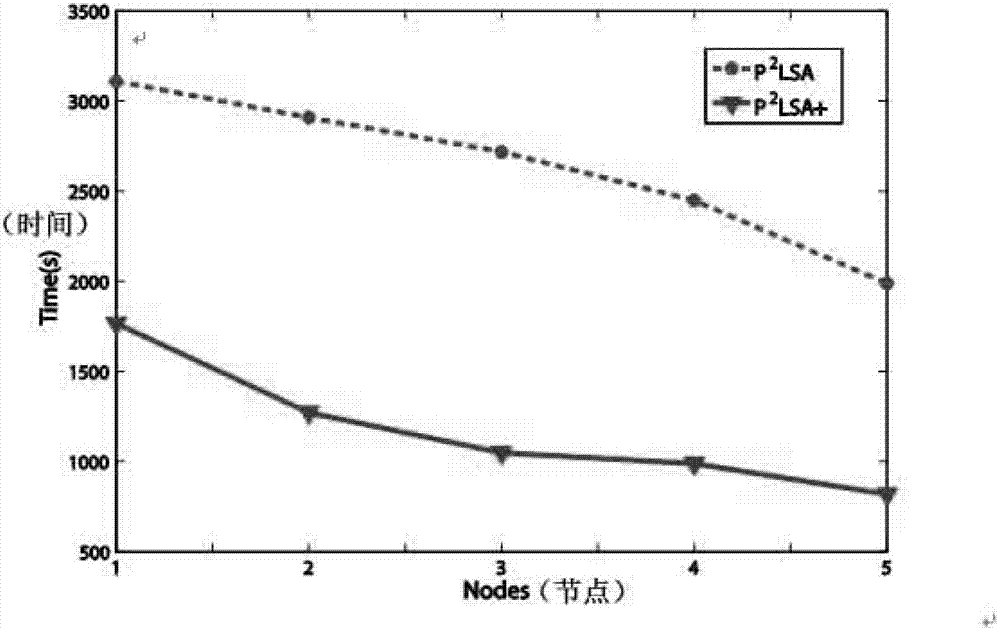
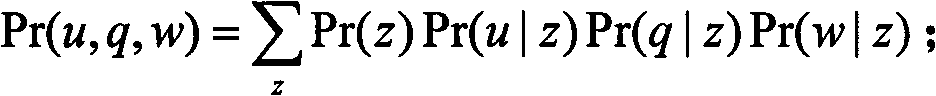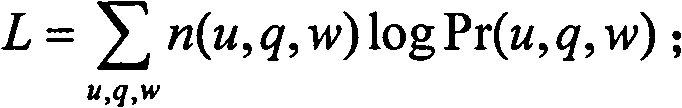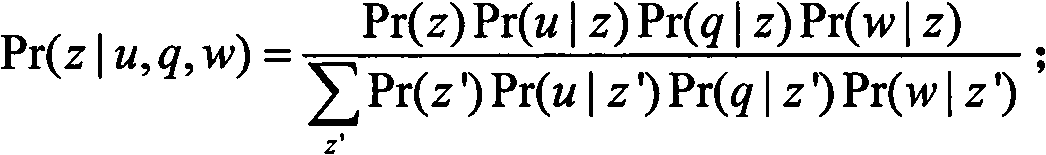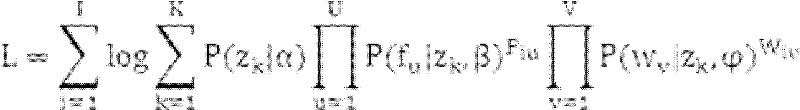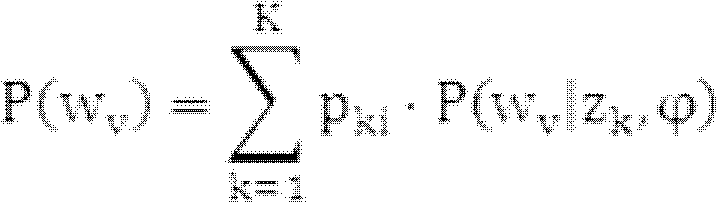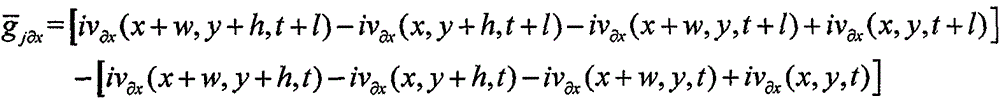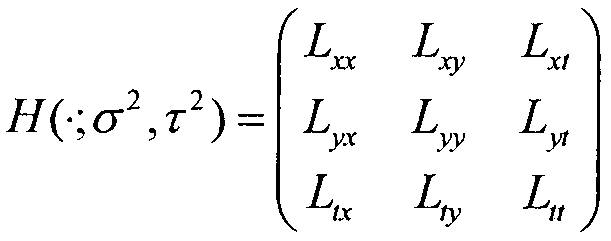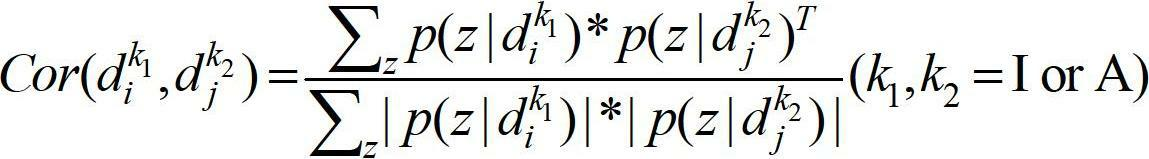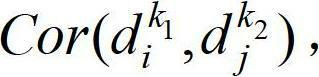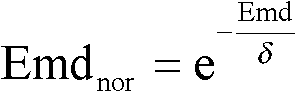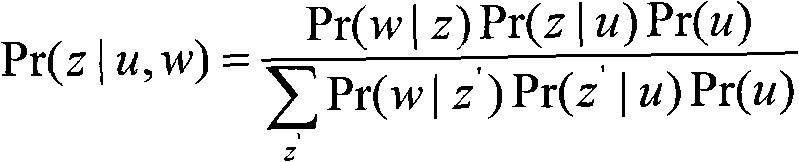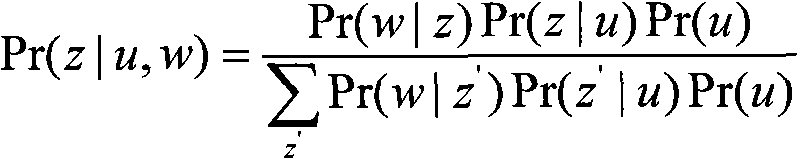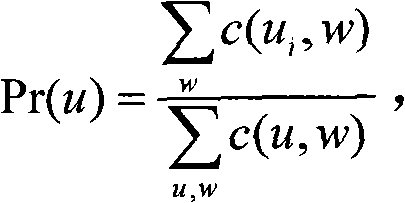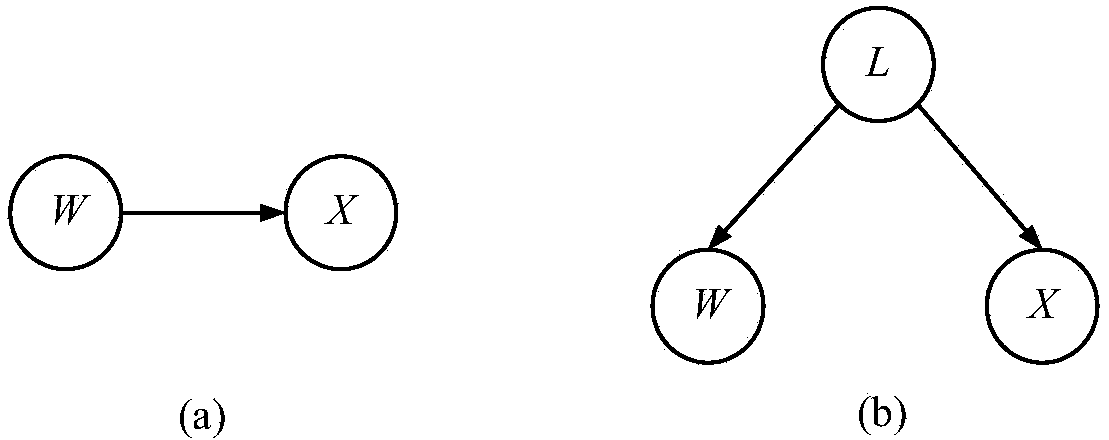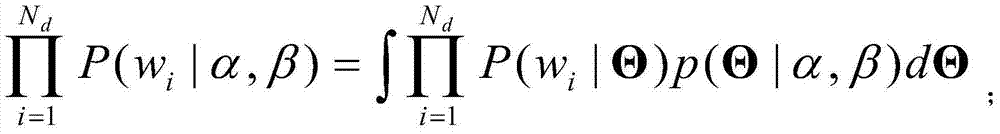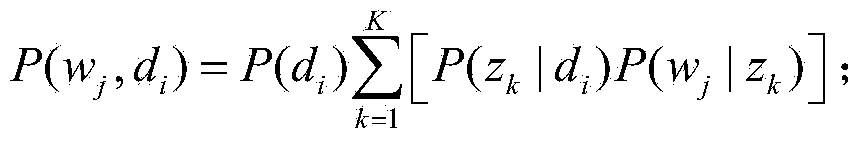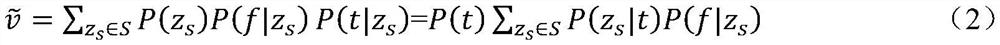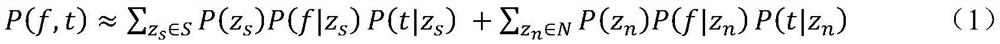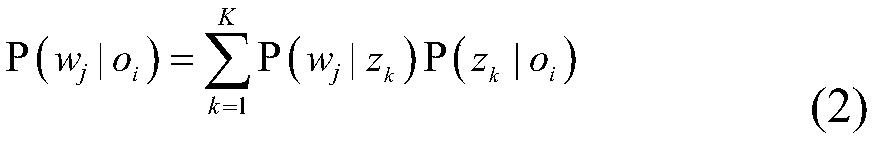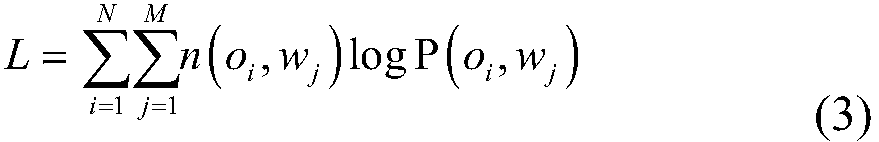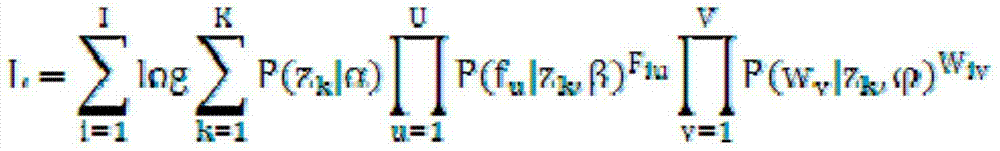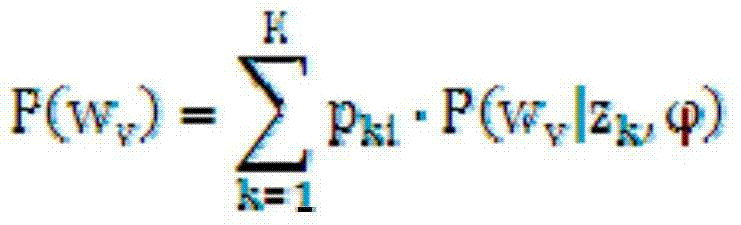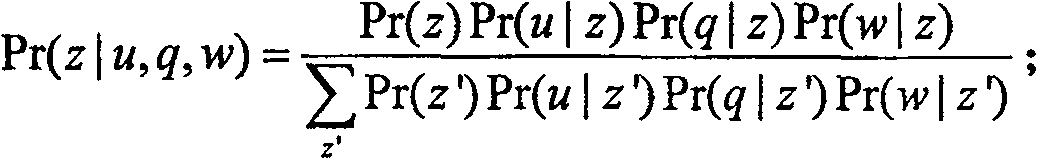Patents
Literature
36 results about "Probabilistic latent semantic analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
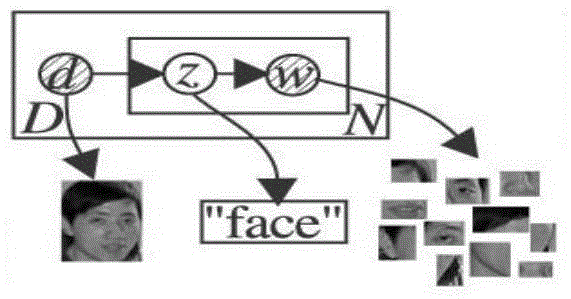
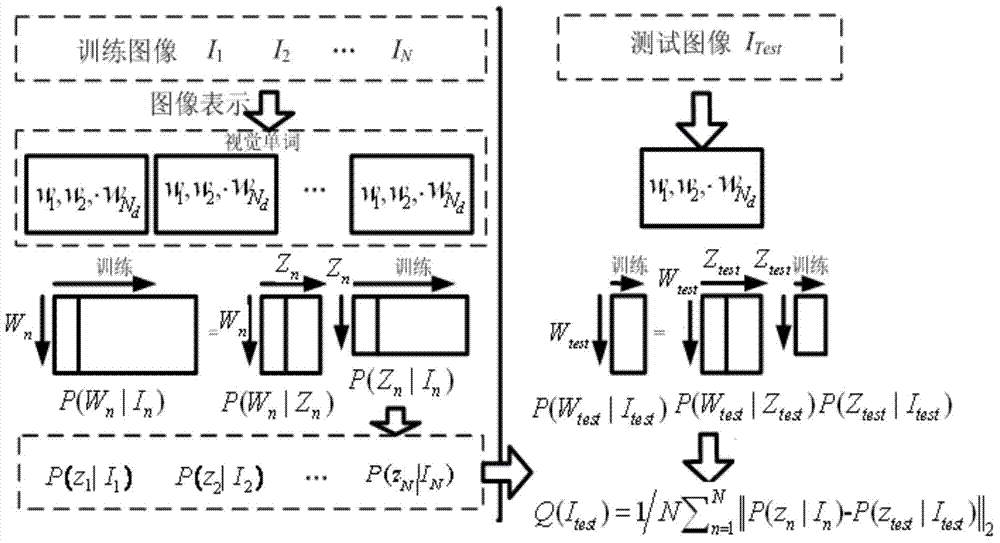
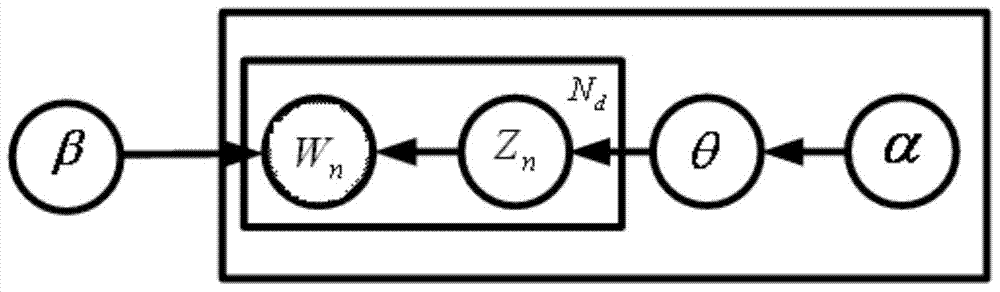
Probabilistic latent semantic analysis (PLSA), also known as probabilistic latent semantic indexing (PLSI, especially in information retrieval circles) is a statistical technique for the analysis of two-mode and co-occurrence data. In effect, one can derive a low-dimensional representation of the observed variables in terms of their affinity to certain hidden variables, just as in latent semantic analysis, from which PLSA evolved.
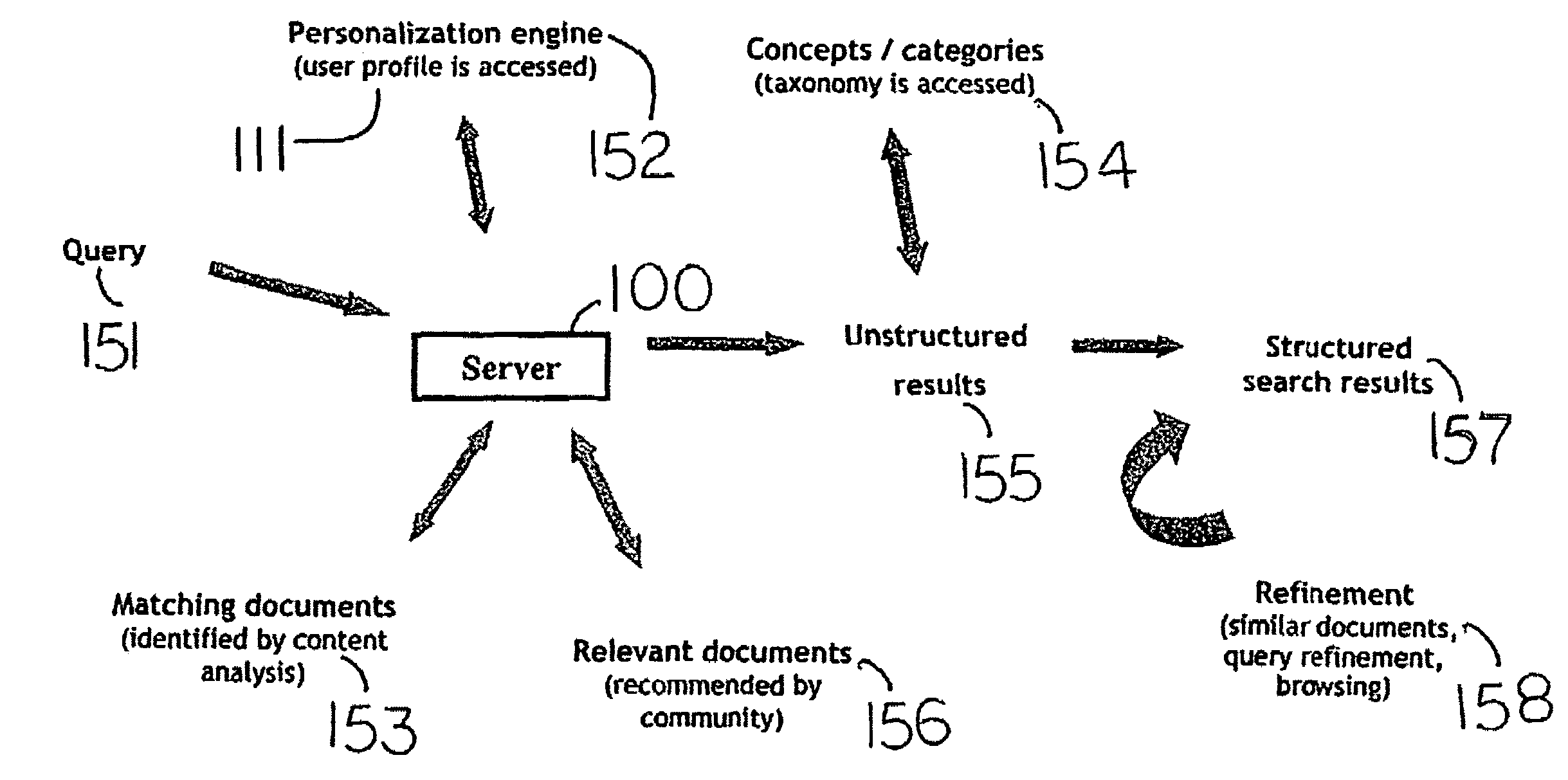
System and method for personalized search, information filtering, and for generating recommendations utilizing statistical latent class models
InactiveUS7328216B2Easy to collect informationHigh precisionData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalPersonalized searchAmbiguity
The system implements a novel method for personalized filtering of information and automated generation of user-specific recommendations. The system uses a statistical latent class model, also known as Probabilistic Latent Semantic Analysis, to integrate data including textual and other content descriptions of items to be searched, user profiles, demographic information, query logs of previous searches, and explicit user ratings of items. The system learns one or more statistical models based on available data. The learning may be reiterated once additional data is available. The statistical model, once learned, is utilized in various ways: to make predictions about item relevance and user preferences on un-rated items, to generate recommendation lists of items, to generate personalized search result lists, to disambiguate a users query, to refine a search, to compute similarities between items or users, and for data mining purposes such as identifying user communities.
Owner:OPEN TEXT HLDG INC
Multi-level-point-set characteristic extraction method applicable to ground laser radar point cloud classification
InactiveCN104091321AEfficient acquisitionImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPoint cloudRadar
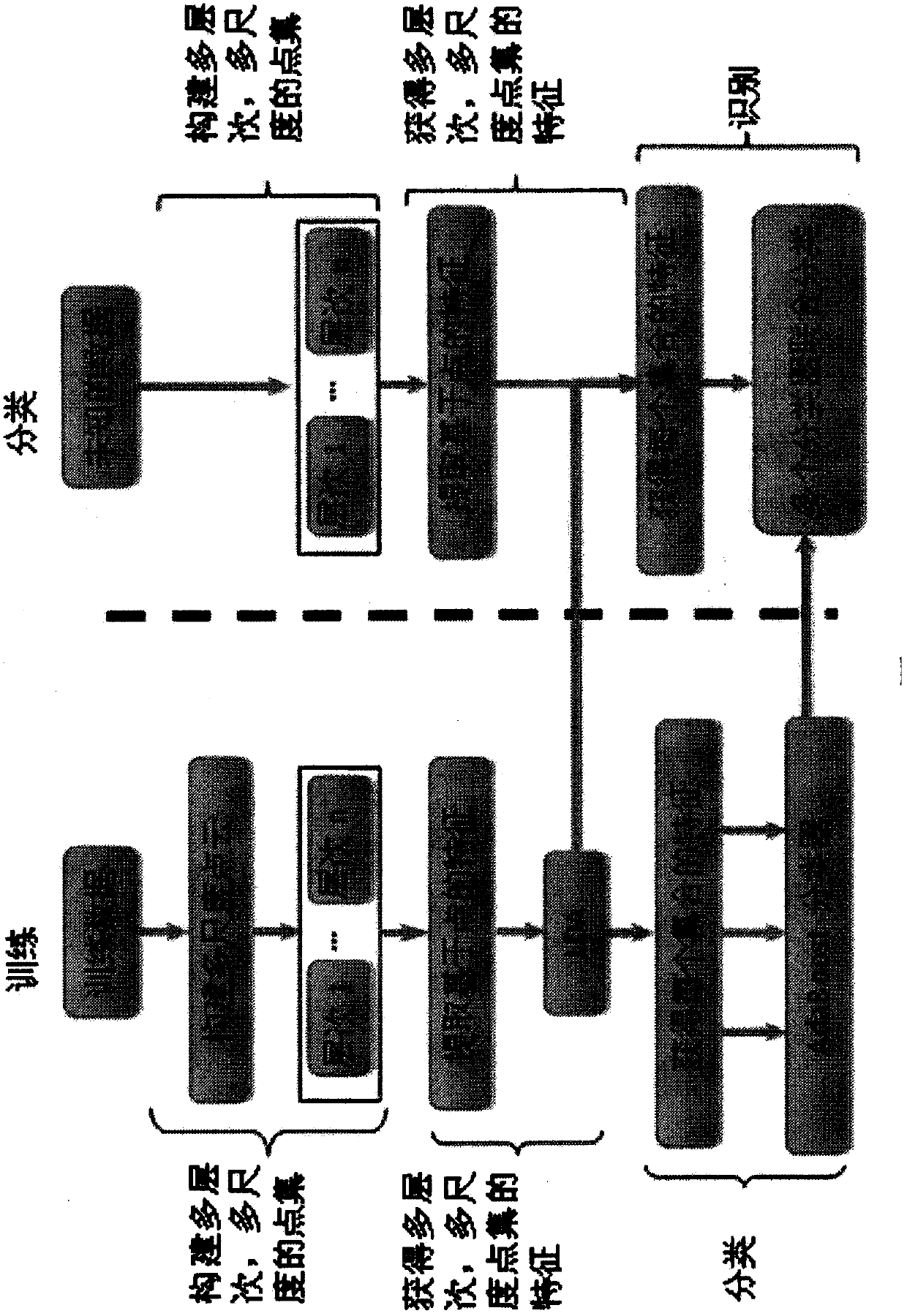
The invention relates to a multi-level-point-set characteristic extraction method applicable to ground laser radar point cloud classification. Based on point set characteristics, high-precision classification of four kinds of common ground features including pedestrians, trees, buildings and automobiles and the like in a scene is realized. Firstly, point sets are constructed and a point cloud is re-sampled into a point cloud of different scales and thus point sets which are different in size and provided with layered structures are formed through clustering and characteristics of each point in the point sets are obtained; next, an LDA (Latent Dirichlet Allocation ) method is adopted to synthesizing point-based characteristics of all points in each point set into shape characteristics of the point sets; and at last, based on the shape characteristics of the point set, an Adaboost classifier is adopted to train the point sets of different levels so as to obtain a classification result of the whole point cloud. The multi-level-point-set characteristic extraction method has a higher classification precision and has a classification precision, which is far higher than that of point-based characteristics, Bag-of-Word-based characteristics and characteristics based on probabilistic latent semantic analysis (PLSA), in aspect of pedestrians and vehicles.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Object-oriented high-resolution remote-sensing image classification method
InactiveCN102902978AImprove classification accuracyImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionSupport vector machineLocal optimum
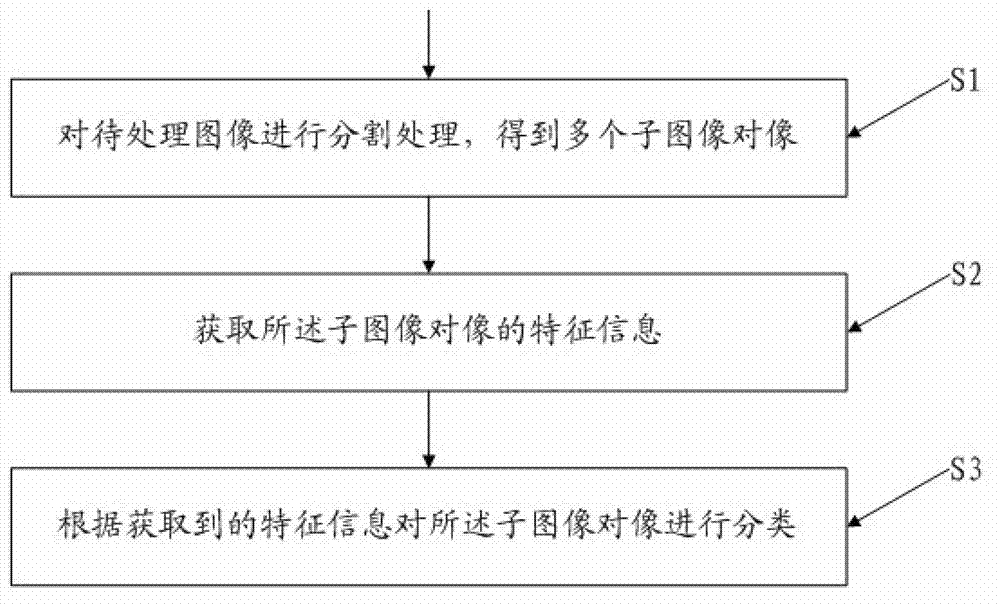
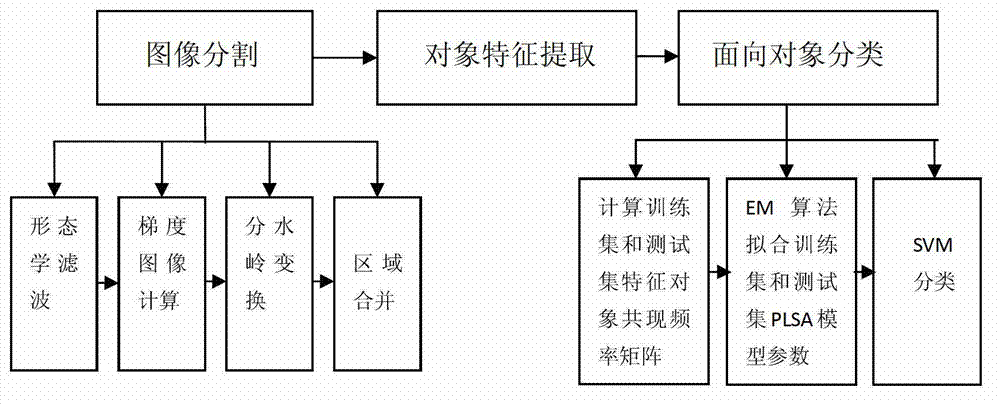
The invention provides an object-oriented high-resolution remote-sensing image classification method. The method comprises the steps of S1, conducting segmentation processing on images to be processed to obtained a plurality of subimage objects; S2, obtaining feature information of subimage objects; and S3, classifying subimage objects according to the obtained feature information, wherein images to be processed are high-resolution remote-sensing images, the feature information of subimage objects comprises spectral information, shape information and texture information of subimage objects. According to the method, on the basis of object-oriented classification, a classification method combining probabilistic latent semantic analysis and a support vector machine is introduced, the problem that 'the same features with different classifications' and 'the same classifications with different features' are not high in identification ratio in the prior art is solved, the classification precision of high-resolution remote-sensing images is greatly improved, advantages of latent semantic analysis (LSA) and advantages of probabilistic latent semantic analysis (PLSA) are combined, and the problems of overfitting and local optimum which are caused by random initialization are effectively solved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for recommending problem based on probability latent semantic analysis
InactiveCN101354714AImprove accuracyWide applicabilitySpecial data processing applicationsPersonalizationState model
The invention discloses a recommended method for analyzing the latent semantic problem based on the probability. The method describes the interest of a user through a state model in the latent semantic analysis on the probability and provides the compatible problem recommendation for the user interactive type question-answering system. The method adopts a ternary state model, has the advantages of two recommended ways based on the content and collaborative filtering, performs problem recommendation according to the personalized information of the user, and has high accuracy and good applicability in the user interactive type question-answering system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
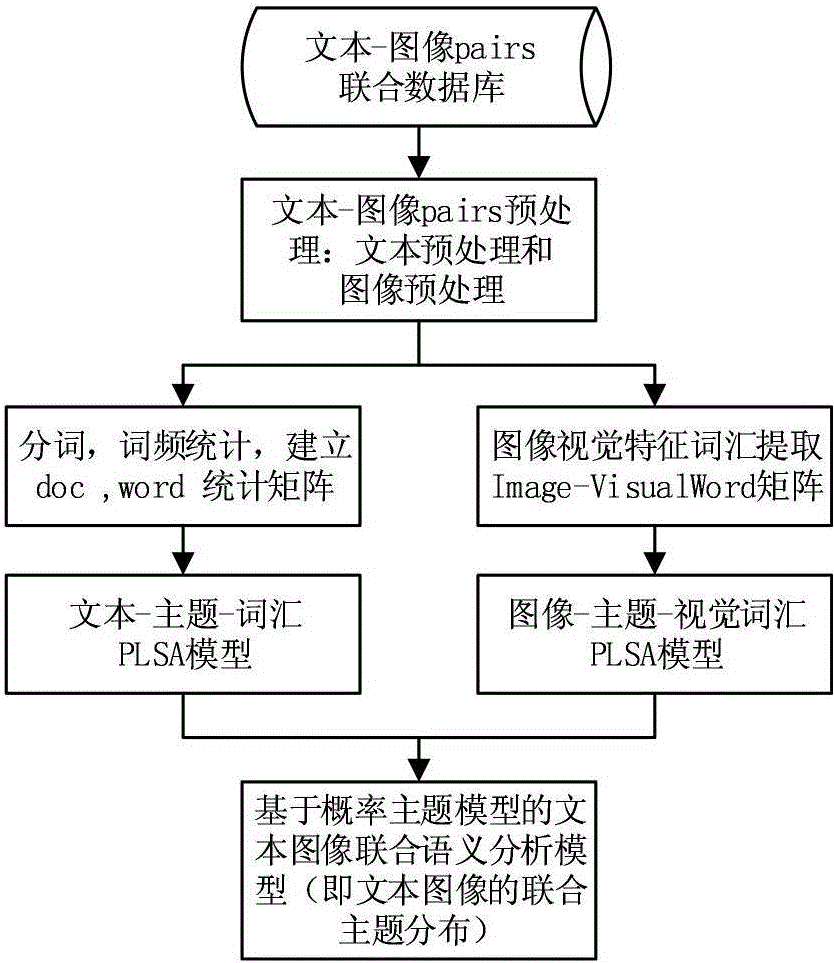
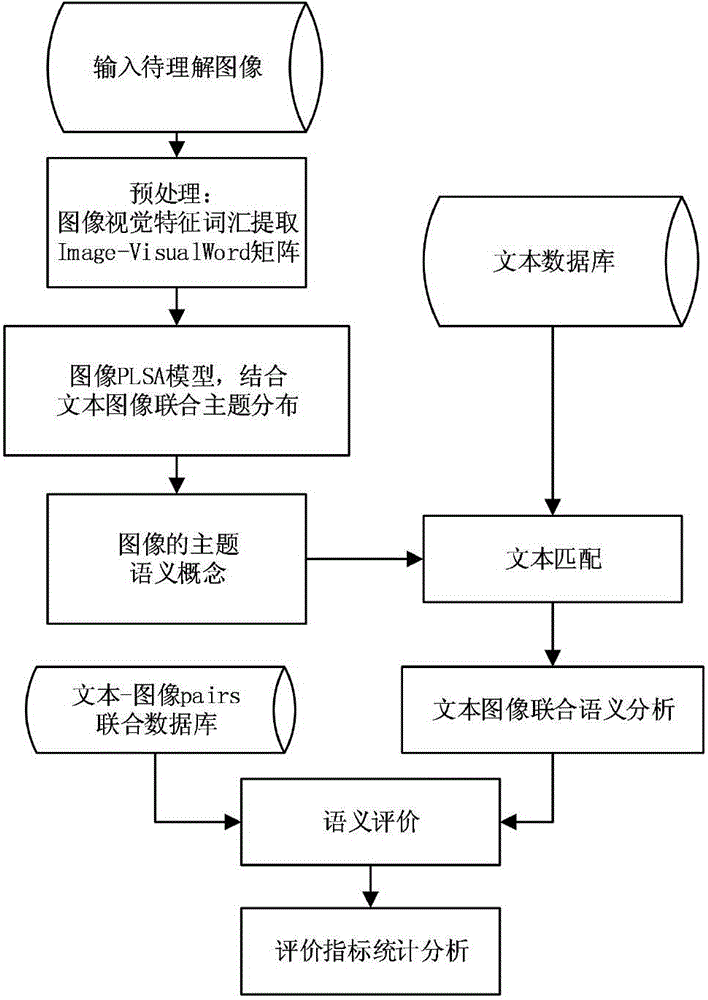
Text image joint semantics analysis method based on probability theme model
InactiveCN104933029ARich semantic informationSpecial data processing applicationsPattern recognitionSemantics
The invention provides a text image joint semantics analysis method based on a probability theme model. The text image joint semantics analysis method comprises the following steps: collecting a great quantity of texts comprising images, carrying out proper processing on the texts and the images, and forming an image-text pairs database in an image and text one-to-one way; utilizing samples to train to obtain a joint theme distribution model used for the text image semantics analysis; for an input image to be analyzed, extracting a visual characteristic vocabulary; applying a PLSA (Probabilistic Latent Semantic Analysis) model to the image and the visual characteristic vocabulary, and combining with text image joint theme distribution to obtain theme semantics of the image to be analyzed; matching the theme semantics obtained tin the previous step with the theme of the text in the image-text pairs database to select an optimal matching text; and for the obtained matching text, combining with an input image to carry out semantics evaluation. The text image joint semantics analysis method can obtain more semantics knowledge in addition to visualized scene object information.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
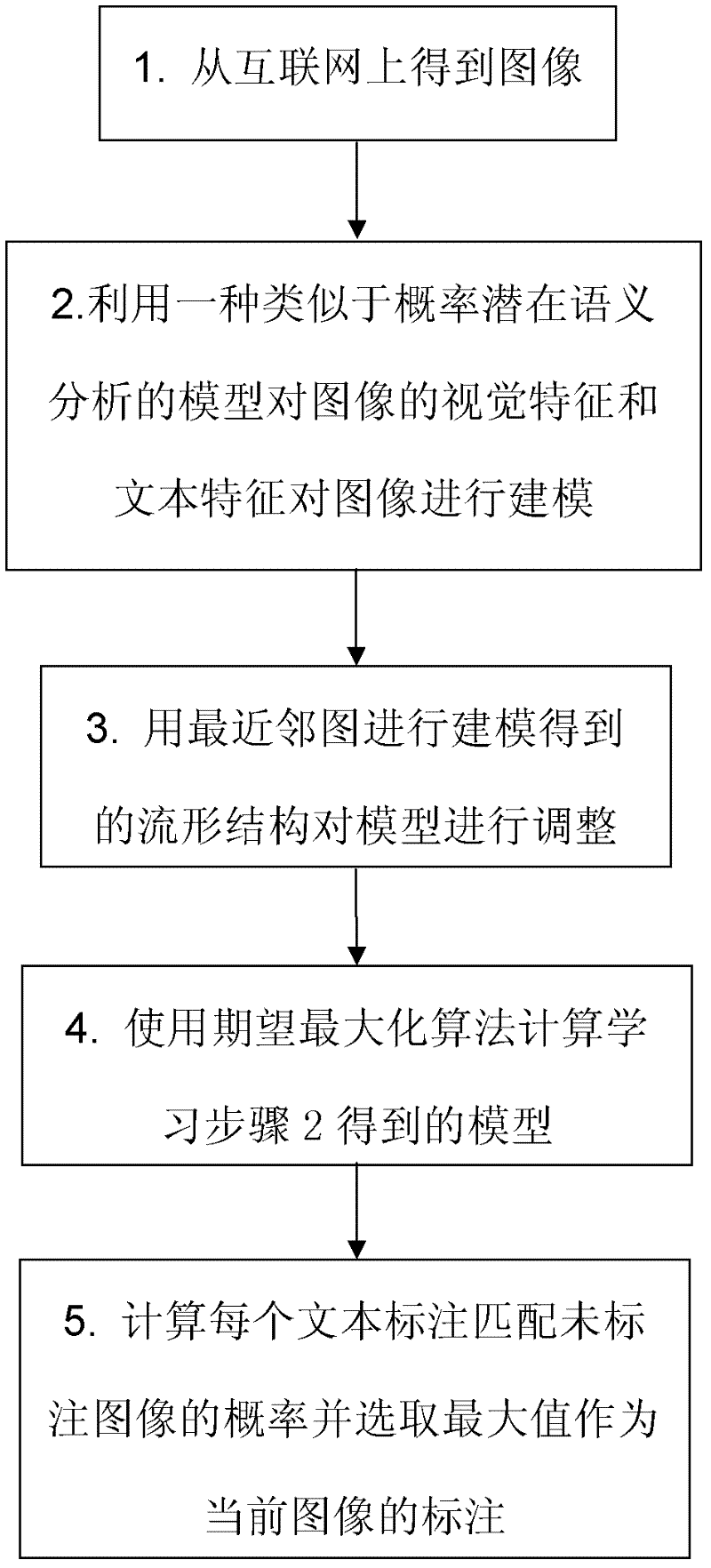
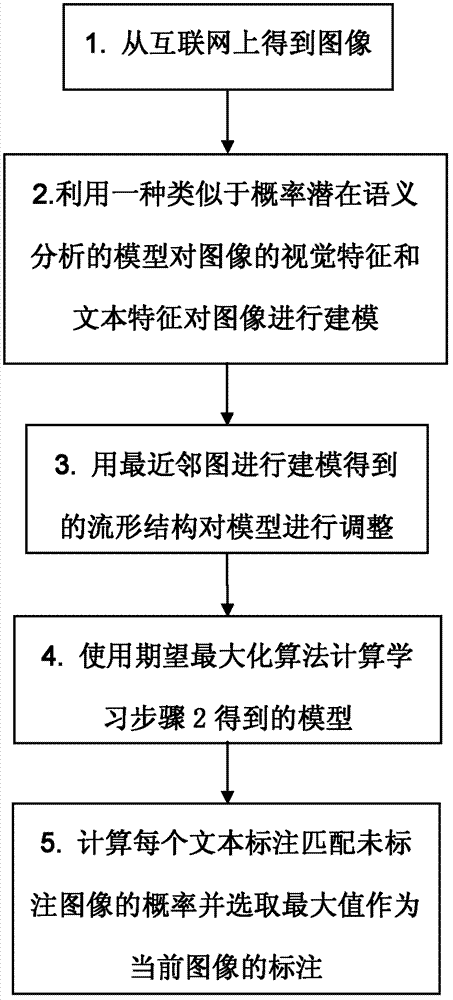
Image marking method based on semi-supervised subject modeling
InactiveCN102637199ASpecial data processing applicationsExpectation–maximization algorithmHigh probability
The invention discloses an image marking method based on semi-supervised subject modeling. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, obtaining images from the Internet, including images with text marks and unmarked images; then, modeling the relation between the visual features and text marks of all images through latent subjects by use of a model similar to probabilistic latent semantic analysis; establishing the nearest-neighbor graphs of all images, and adjusting the model according to the manifold structure obtained by modeling the nearest-neighbor graphs; learning the model by an expectation maximization algorithm, and calculating the probability of matching the latent subjects with the images respectively; and finally, calculating the probability of matching each text mark with the unmarked images according to the probability of matching the latent subjects with the images, and selecting the text mark with the highest probability to mark the unmarked images.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Pedestrian abnormity identification method based on probabilistic latent semantic analysis
InactiveCN106650617AAdaptableOvercome the problem that the extraction is affected by the background environmentCharacter and pattern recognitionHuman bodyVideo monitoring
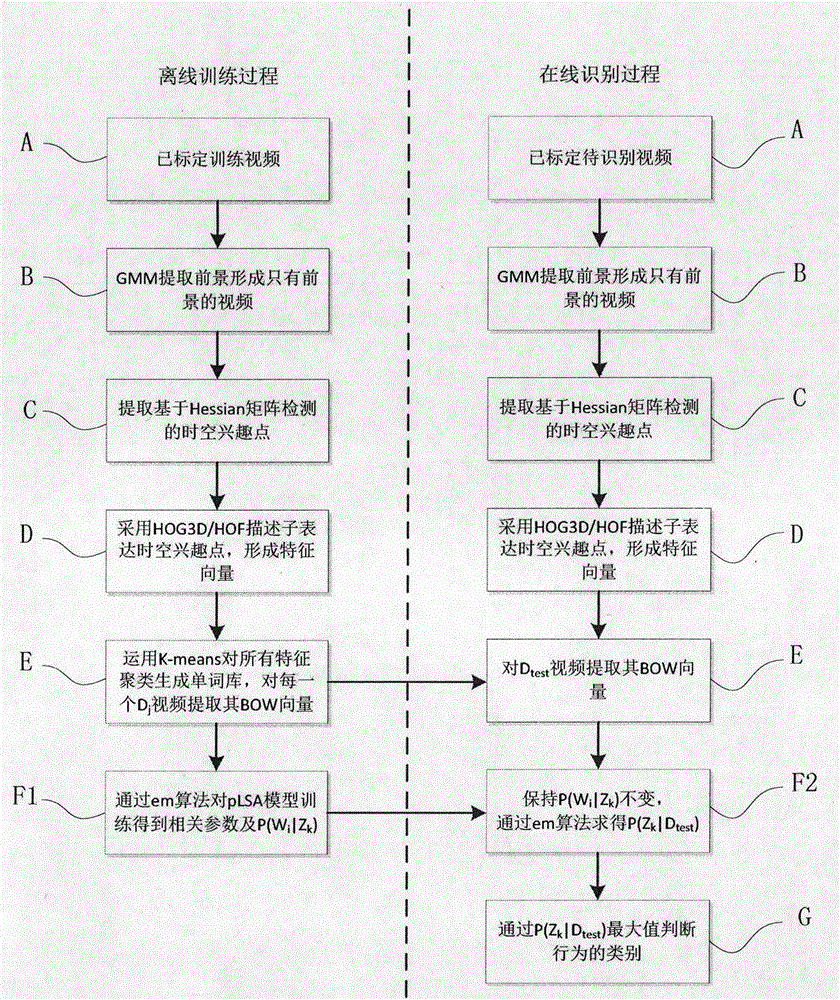
The invention provides a pedestrian abnormity identification method based on probabilistic latent semantic analysis, which is mainly used for solving the problems of poor feature representation capability and not accurate classification in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps: extracting a human body moving object from a video file; extracting space-time interest points in an object region, and representing the space-time interest points through HOG3D / HOF descriptors; carrying out classification on all descriptor feature vectors through a K-means clustering method, generating video dictionary and establishing a bag-of-word model; and then, training a probabilistic latent semantic analysis model to realize classification of test videos. The method can accurately identify human body motion, has a certain robustness for environment scene motion and human body shape change, can be used for pedestrian video monitoring.
Owner:JIANGSU XINTONGDA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECHCO
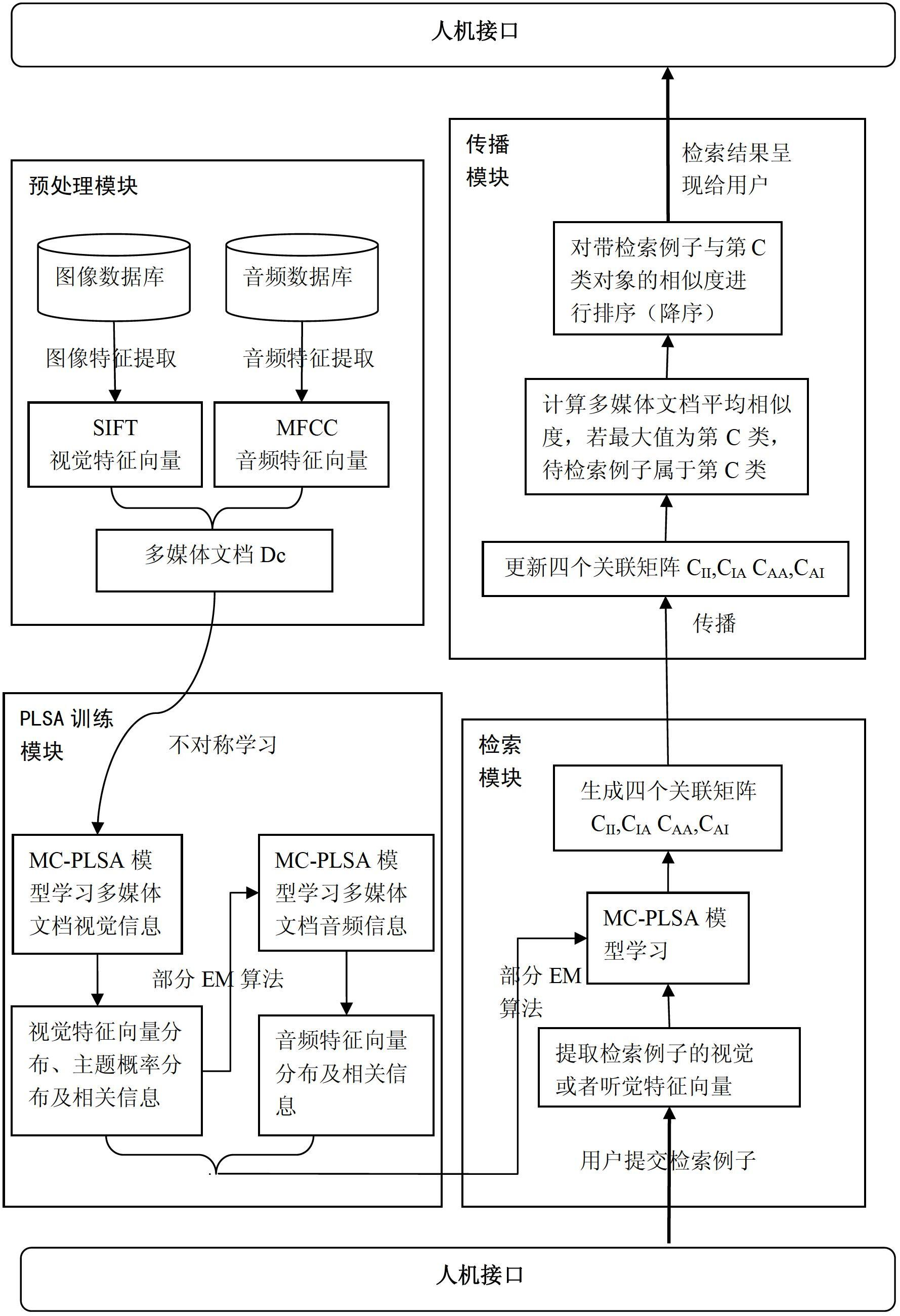
Cross-media information analysis and retrieval method
InactiveCN102693321AAlleviate the problem of excessive space complexitySolve the problem of feature heterogeneitySpecial data processing applicationsFeature vectorInformation analysis
The invention provides a cross-media information analysis and retrieval method, which comprises the following steps of: performing semantic integration processing on multimode information; performing expansion according to a probability latent semantic analysis model to obtain a multilayer continuous probability latent semantic analysis model for processing a continuous feature vector; learning the multilayer-continuous probability latent semantic analysis model by adopting an asymmetric learning method, and calculating the visual feature vector distribution of an image, the visual feature vector distribution of an audio and topic probability distribution; submitting a training set and a tested media object which serves as a retrieval example by a user, and calculating intra-mode and inter-mode initial similarity values of the image and the audio in the retrieval sample; constructing a propagation model, and updating the intra-mode and inter-mode similarity values according to the propagation model; and performing secondary retrieval according to the updated similarity values.
Owner:CHANGZHOU HIGH TECH RES INST OF NANJING UNIV
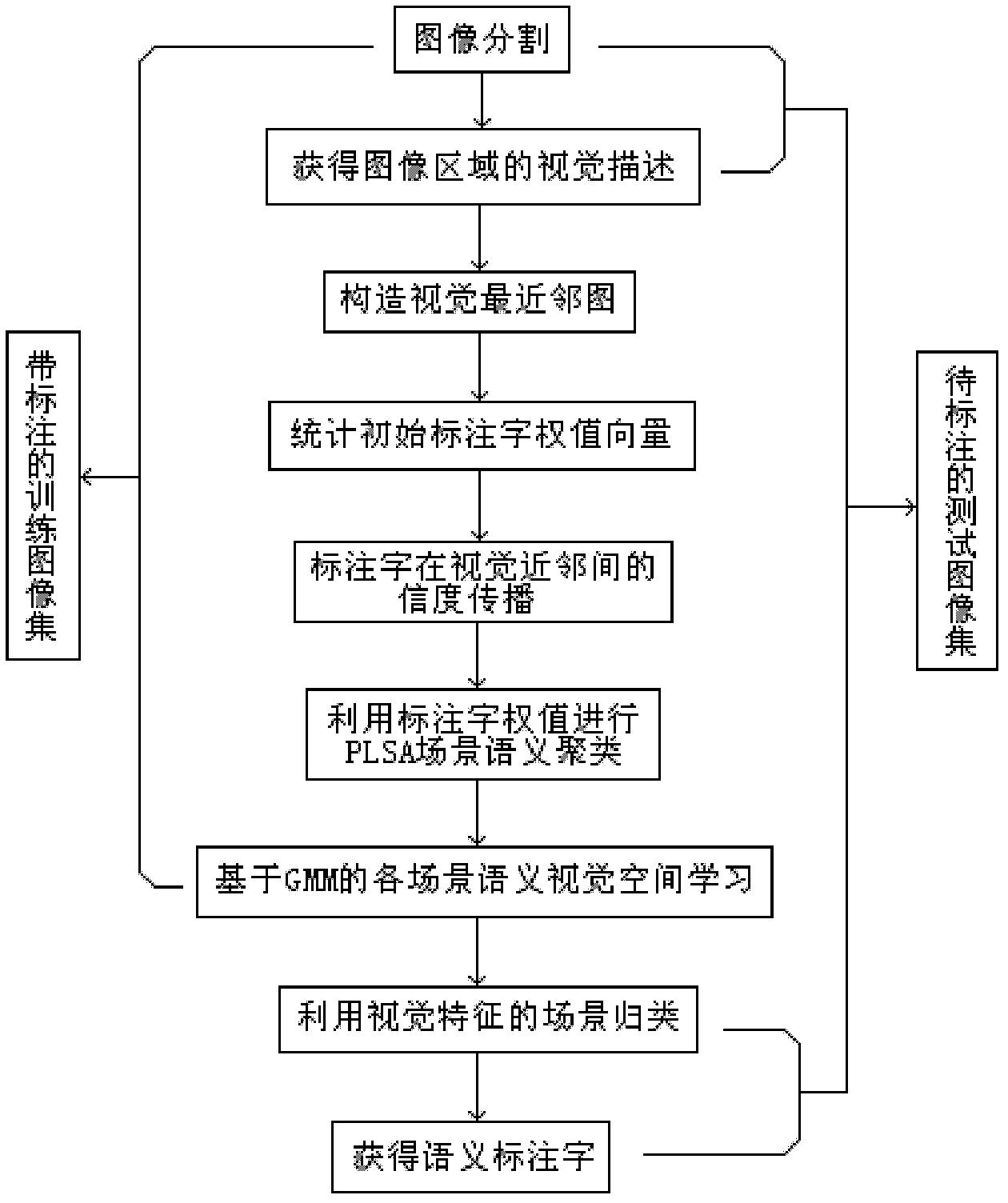
Labelling image scene clustering method based on vision and labelling character related information
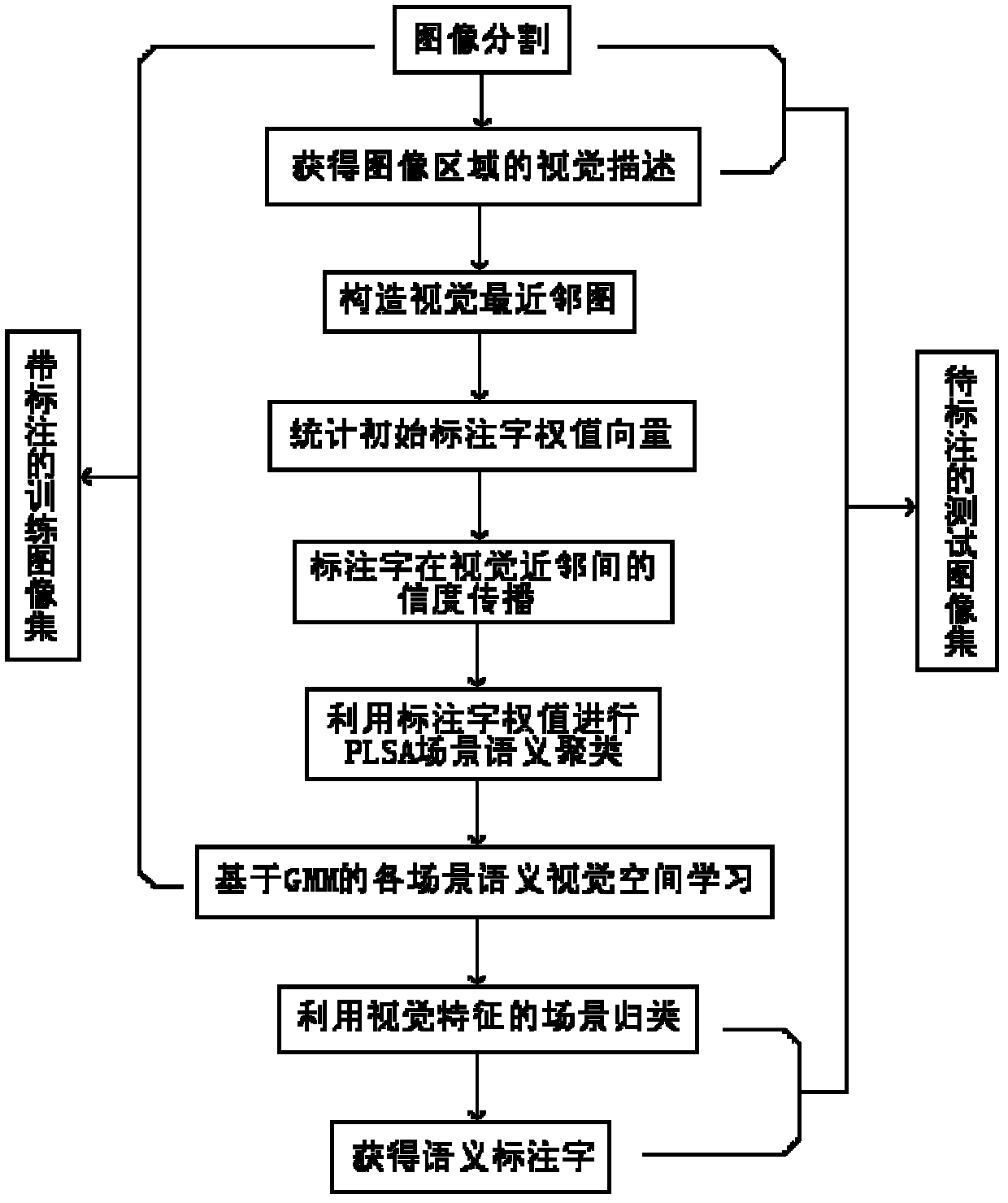
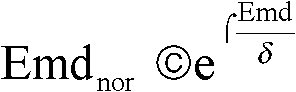
InactiveCN102222239AAvoid sparsityDetermining the weight distribution problemCharacter and pattern recognitionEarth mover's distanceRelevant information
The invention provides a labelling image scene clustering method based on vision and labelling character related information. The method comprises the following steps of: dividing a training image and a test image respectively by using a NCut (Normalized Cut) image dividing algorithm; constructing a vision nearest-neighbour graph G(C)(V, E) of all images {J1, ., Jl} PCtrain for learning, wherein in a training image set, each image has one group of initial normalized labelling character weight vectors; spreading the labelling character of each training image among the vision nearest neighbours, receiving the accepted images according to the degree of normalized EMD (Earth Mover's Distance) among the accepted images; for each training image, normalizing the accumulated labelling character weights; after the vision characteristics of the image are converted into a group of labelling characters with weights, carrying out the scene semantic clustering by using a PLSA (Probabilistic Latent Semantic Analysis) model; learning each scene semantic vision space by using a Gaussian mixture model; and carrying out the scene classification by using the vision characteristics. With the invention, the coupling precision between the vision characteristics of the image and the labelling character can be increased, and the method can be directly used for the automatic semantic labelling of the image.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
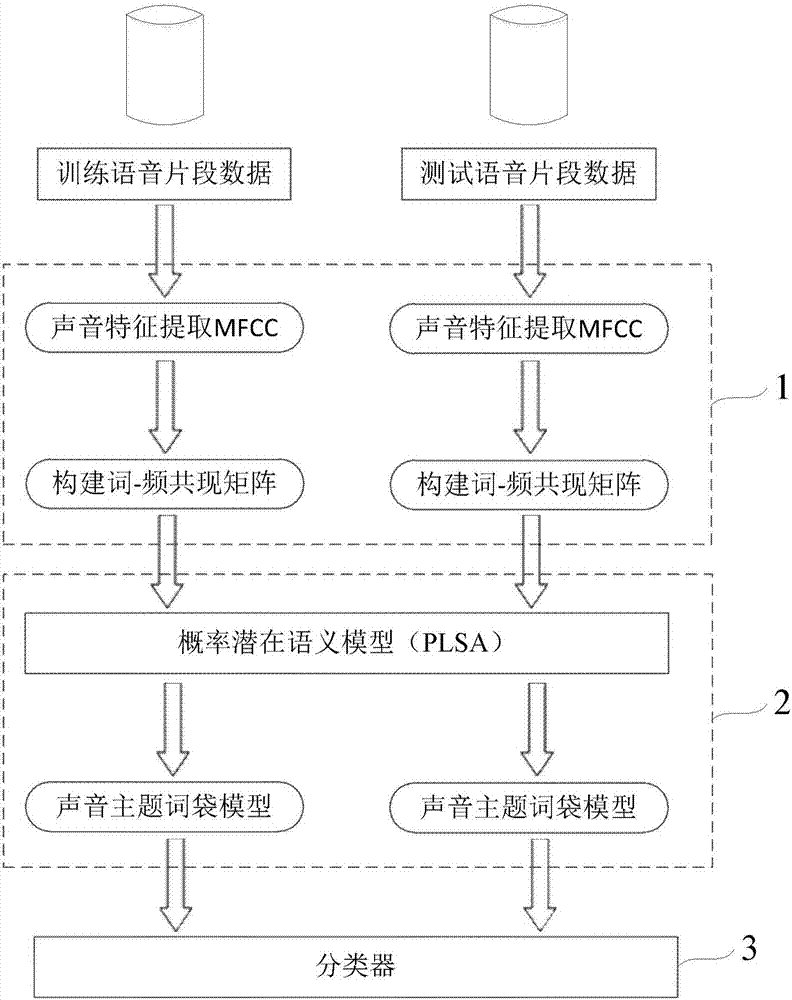
Audio classification system and method applied to abnormal sound detection
InactiveCN106910495AImprove performanceImprove accuracySpeech recognitionSound detectionFeature vector
The invention discloses an audio classification system and method applied to abnormal sound detection. Audio classification is an important module in an abnormal sound detection system. Existing audio classification methods like a Gaussian mixed model and a K-nearest neighbor are low in detection rate and cannot meet actual needs. Aiming at this situation, the audio classification system which uses a Probabilistic Latent Semantic Analysis (PLSA) model and a K-nearest neighbor classifier is put forward. In the system, firstly a signal feature vector is sent into the Probabilistic Latent Semantic Analysis model to be trained so as to obtain a sound subject term bag model, and then the K-nearest neighbor classifier (KNN) is utilized to conduct classification, and finally the system obtains a classified audio file. Compared with a traditional audio classification system which uses the K-nearest neighbor classifier, the audio classification system and method achieve a better classification effect.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Parallel PLSA (Probabilistic Latent Semantic Analysis) method based on Hadoop
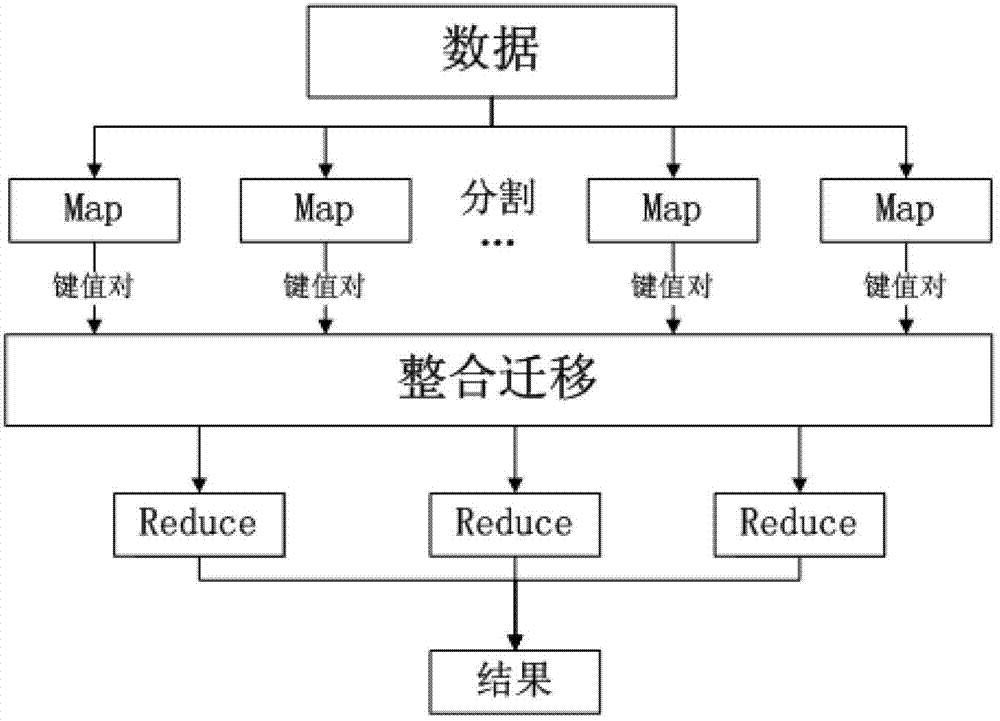
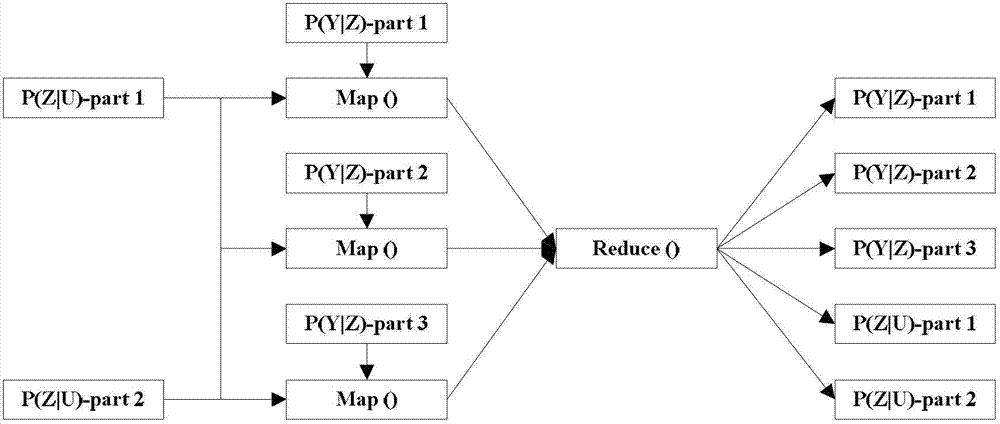
InactiveCN102779025AShorten the timeImprove computing efficiencyConcurrent instruction executionSpecial data processing applicationsProbit modelTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses a parallel PLSA (Probabilistic Latent Semantic Analysis) method based on Hadoop. The method comprises the following steps: data is stored in a distributed data storage environment; a probabilistic model file needing to be subjected to calculation updating is segmented to be used as the input of each mapper; each iteration updating process in the whole EM (expectation-maximization) process is calculated through mapreduce, and each iteration updating process in the EM process is calculated through the sending of a map function at a mapper end, a reduce function at a reducer end and a key value pair; the iteration result updated each time is used as the input of the next iteration; and the iteration is carried out until all the results are converged. By the parallelization carried out through mapreduce, the PLSA can be applied into a large amount of data, the entire operation time is reduced, and the calculation efficiency is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
Selection method of network answers based on probabilistic latent semantic analysis
InactiveCN101751454AImprove accuracyWide applicabilitySpecial data processing applicationsSubject matterQuestion answer
A selection method of network answers based on probabilistic latent semantic analysis comprises the following steps: a problem set C, constructing a probabilistic latent semantic analysis model by using a user set u and a word set w as variables, and using the probabilistic latent semantic analysis model to dig the latent theme information of each user u; obtaining problems q newly raised in a question-answering community and the words w forming the questions, determining the joint probability of the current problems and candidate answers, and calculating the joint probability of the current questions and the users answering the current problems; linearly weighting the joint probability of the current problems and the candidate answers and the joint probability of the current questions and the users answering the current problems to obtain candidate answer scores, arranging the candidate answer scores in the manner of descending order, and sending the answers to the user raising the problem according to an arranged order. The invention has the advantages of capability of adequately using the abundant user information in the question-answering community, high accuracy and wide applicability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
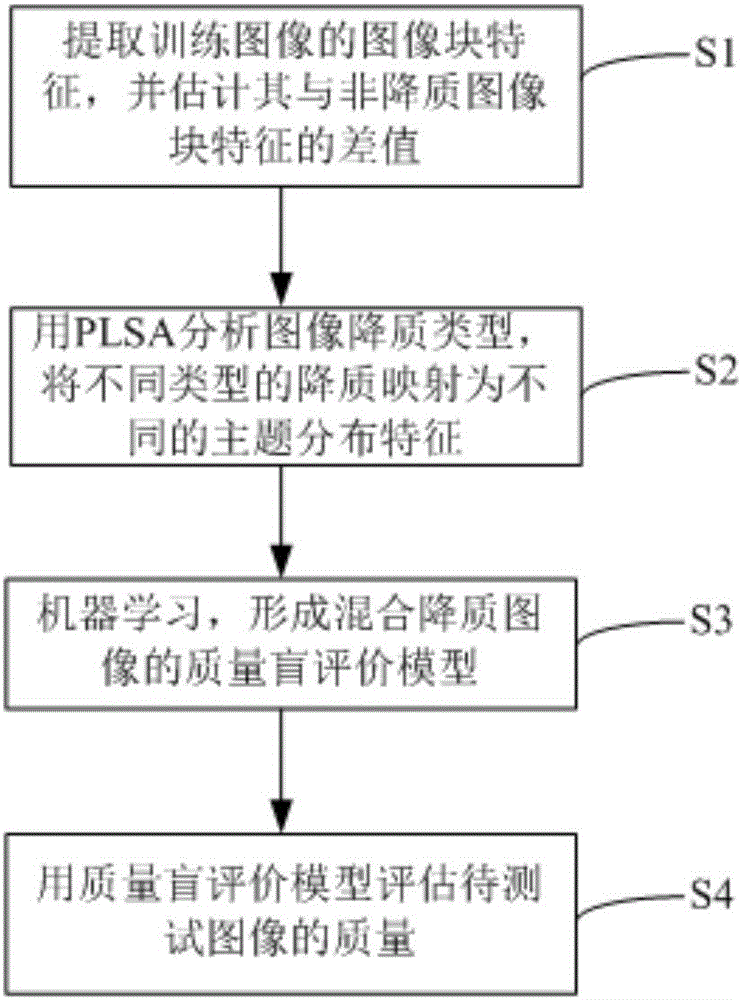
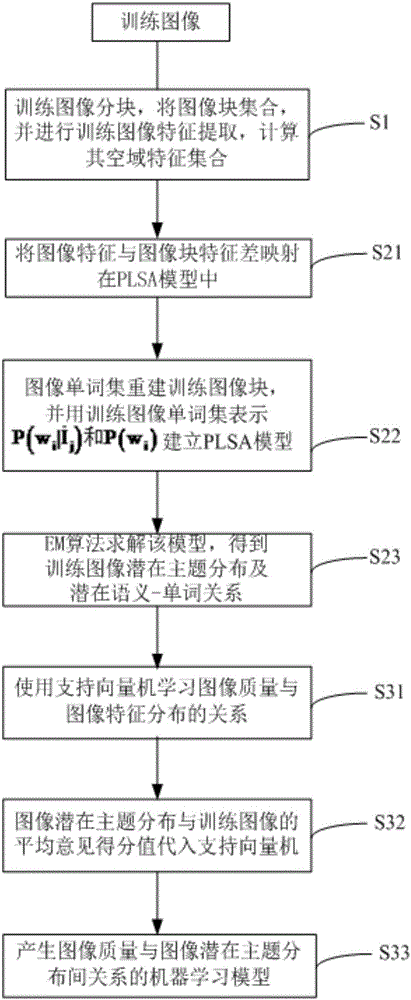
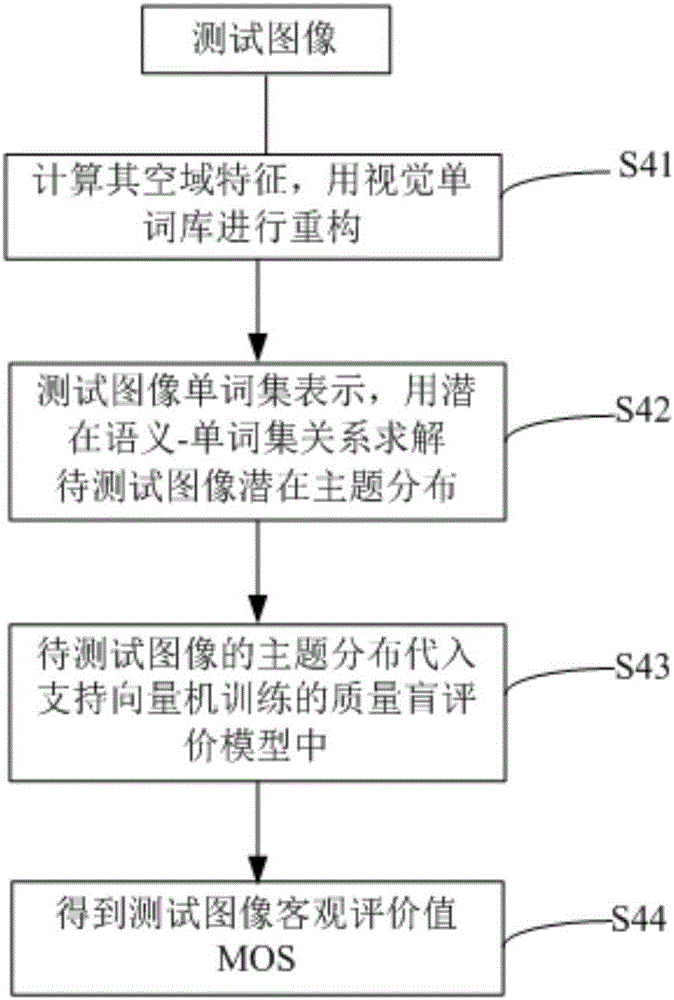
Image quality blind evaluation method
ActiveCN106815839AImprove accuracySolve evaluation problemsImage enhancementImage analysisImaging qualityAlgorithm
The invention provides an image quality blind evaluation method. The image quality blind evaluation method comprises the steps of 1), extracting a characteristic of a quality-reduced image block in a training image, and estimating an offset between the characteristic of the image block and the characteristic of a non-quality-reduced image block; 2), analyzing different types of quality reduction in a probability latent semantic analysis method, and mapping the different types of quality reduction to different theme distribution characteristics, wherein the different types of quality reduction comprise single quality reduction and hybrid quality reduction; 3), establishing a relation between an image theme distribution characteristic and the image quality based on the image training set according to a machine learning method, thereby forming a quality blind evaluation model for a hybrid quality reduction image; and 4), evaluating the quality of the quality reduction image outside the training set by means of the quality blind evaluation model. The image quality blind evaluation method has advantages of improving accuracy in no-parameter quality evaluation, setting a problem of evaluating the hybrid quality reduction image in engineering, and realizing high suitability of comprehensive evaluation for image acquisition, compression and transmission performance in a multimedia system on the condition that an original image cannot be acquired.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
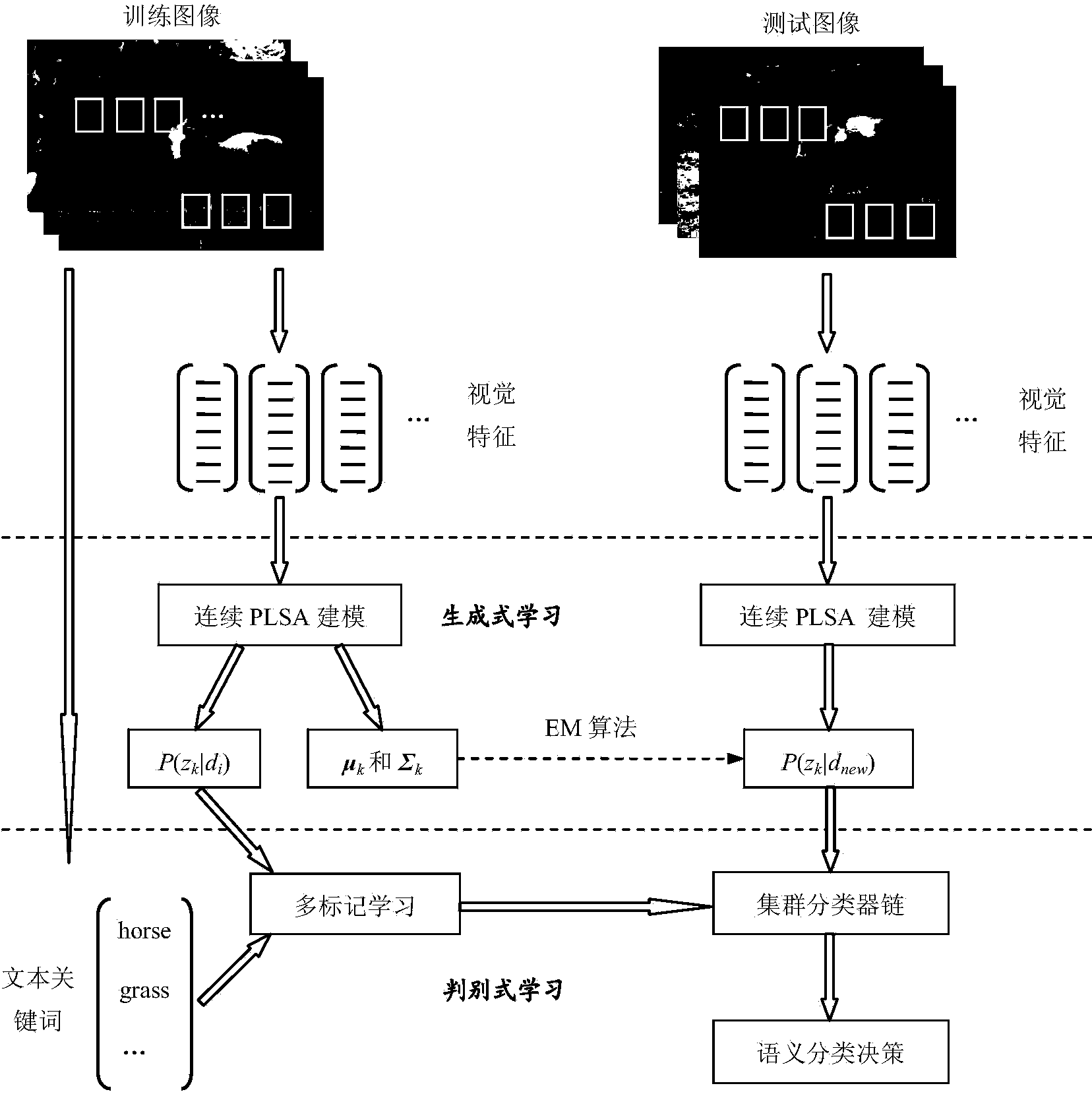
Method for semantically annotating images on basis of hybrid generative and discriminative learning models
InactiveCN104036021AScalableSolve the weak labeling problemSpecial data processing applicationsDiscriminantModel parameters
The invention discloses a method for semantically annotating images on the basis of hybrid generative and discriminative learning models. The method includes generatively building models of the images by means of continuous PLSA (probabilistic latent semantic analysis) at generative learning stages, acquiring corresponding model parameters and subject distribution of each image, and utilizing the corresponding subject distribution as an intermediate representation vector of each image; constructing cluster classifier chains to discriminatively learn from the intermediate representation vectors of the images at discriminative learning stages, creating the classifier chains and integrating contextual information among annotation keywords; automatically extracting visual features of each given unknown image at annotation stages, acquiring representation of subject vectors of the given unknown images by the aid of a continuous PLSA parameter estimation algorithm, classifying the subject vectors by the aid of trained cluster classifier chains and semantically annotating the images by a plurality of semantic keywords with the highest confidence. The method has the advantage that the annotation and retrieval performance of the method are superior to the annotation and retrieval performance of most current typical methods for automatically annotating images.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Image quality assessment method based on probabilistic graphical model
InactiveCN104766299AAvoid defectsGood image quality assessmentImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionProbability estimation
The invention discloses an image quality assessment method based on a probabilistic graphical model to overcome the defect of a probabilistic latent semantic analysis model. Topic probability distribution of a test image is estimated based on a probabilistic graphical model, the perceived quality score of the test image is calculated by comparing the topic probability distribution of the test image with topic probability estimation of an undistorted image, and a good image quality assessment result can be obtained without the need for distorted image information.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Method for simultaneously detecting various residues of veterinary drug in meat food
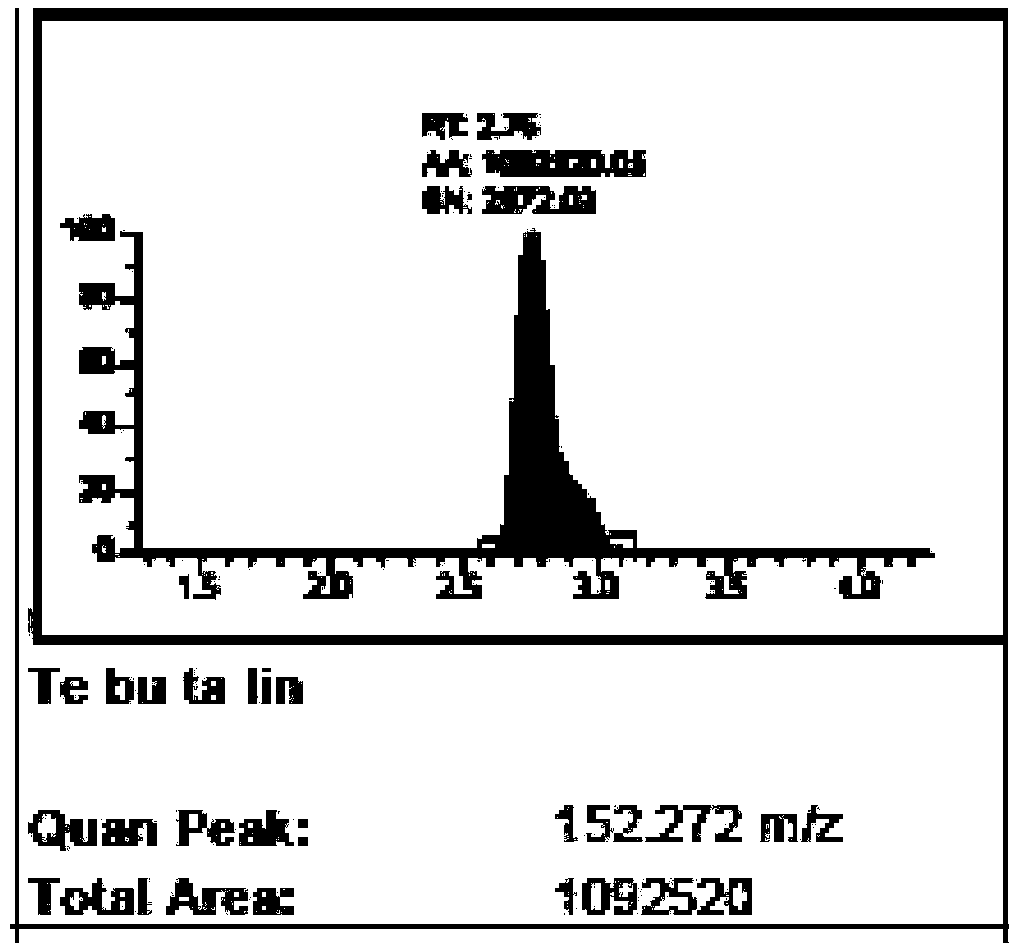
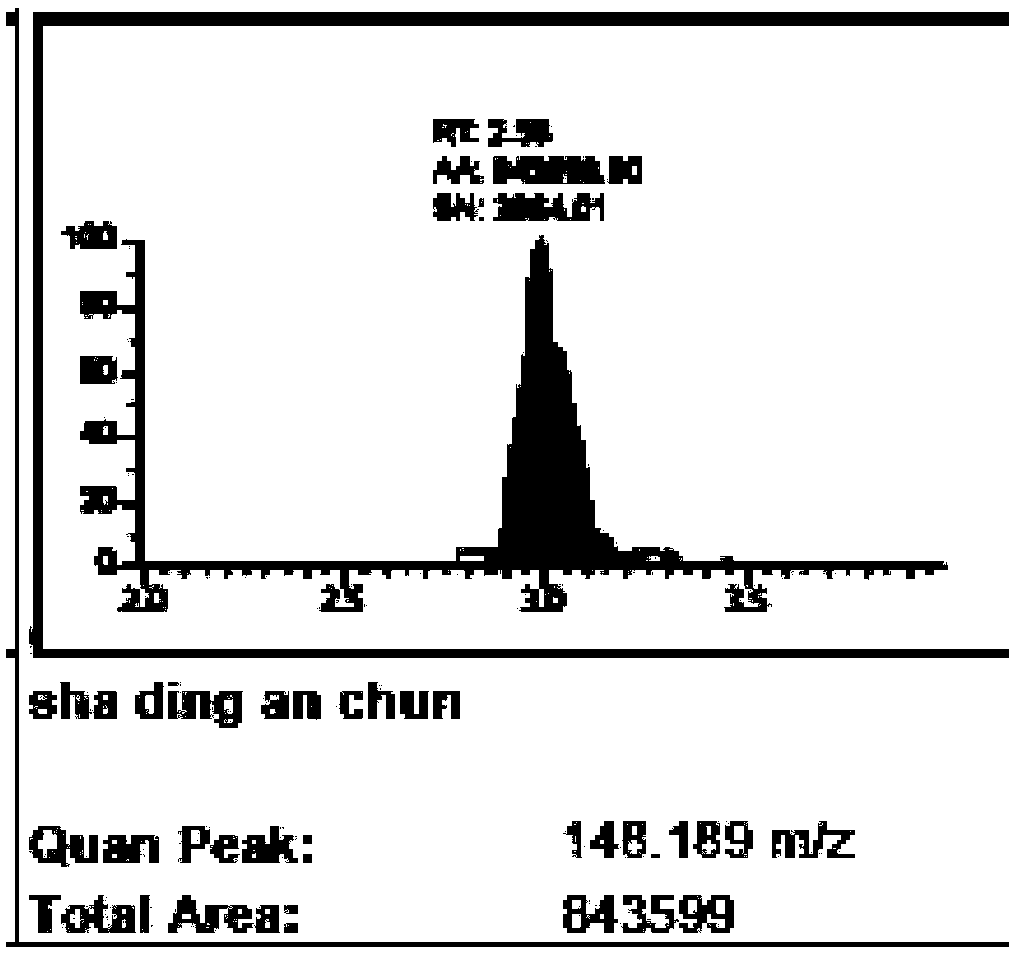
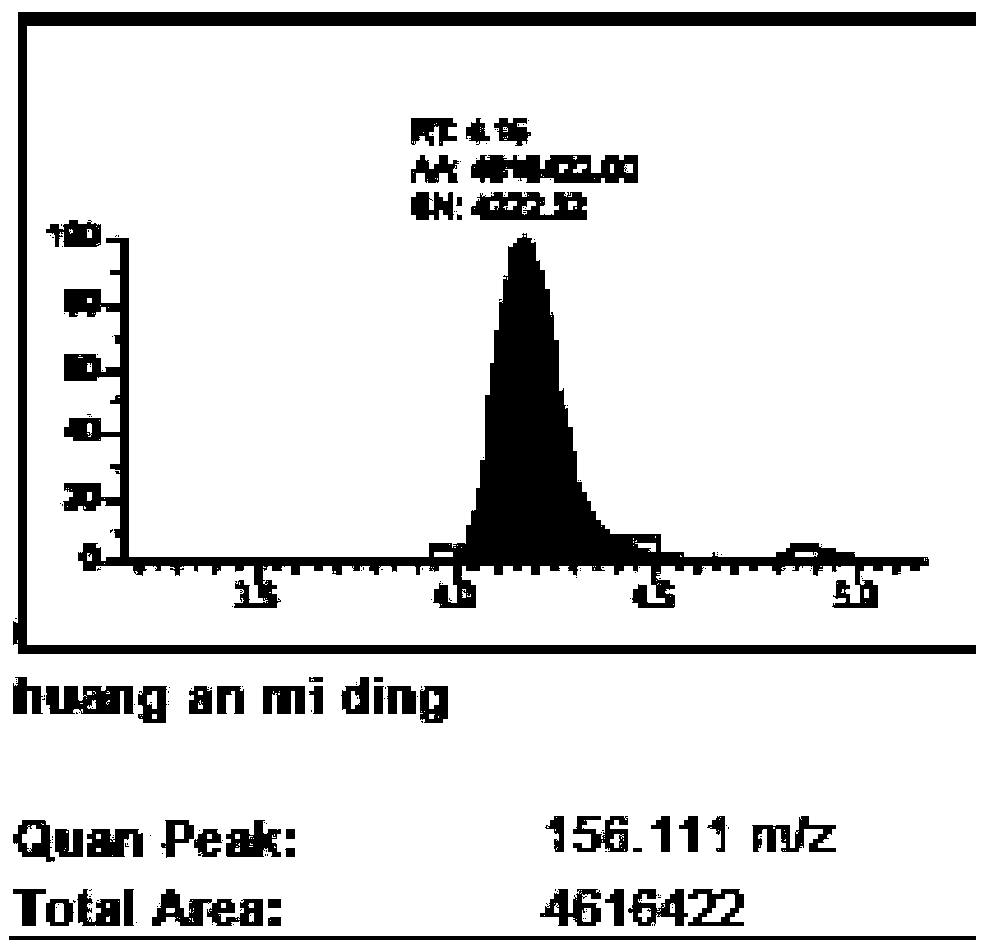
InactiveCN109298109ASimplify preprocessing stepsReduce preprocessing timeComponent separationPhospholipidVeterinary Drugs
The invention relates to the technical field of the detection of residues of veterinary drug, and provides a method for simultaneously detecting various residues of veterinary drug in meat food. The method comprises the following steps of treating a sample, establishing a standard curve and calculating the content of each residue of veterinary drug in the detected sample, and the detection methodis an HPLC-MS (Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry) method. Therefore, a PLS-A (Probabilistic Latent Semantic Analysis) solid phase extraction small column is adopted, activationand balance steps are not required, more than 95% of matrix disturbance substances, including protein, salt, phospholipid and the like, can be removed after extraction liquid directly passes throughthe small column, most veterinary drugs can directly pass without being retained, and therefore, different categories of residues of veterinary drug can be completely extracted only through preliminary treatment for one time. A preliminary treatment step is simplified, a solid phase extraction column does not need to be activated, in addition, various categories of residues of veterinary drug canbe simultaneously detected, preliminary treatment time is greatly shortened, and detection cost is lowered. A result indicates that the method is accurate, quick, convenient and reliable in quantitative results and is very suitable for simultaneously processing multiple batches of samples.
Owner:昌邑市检验检测中心
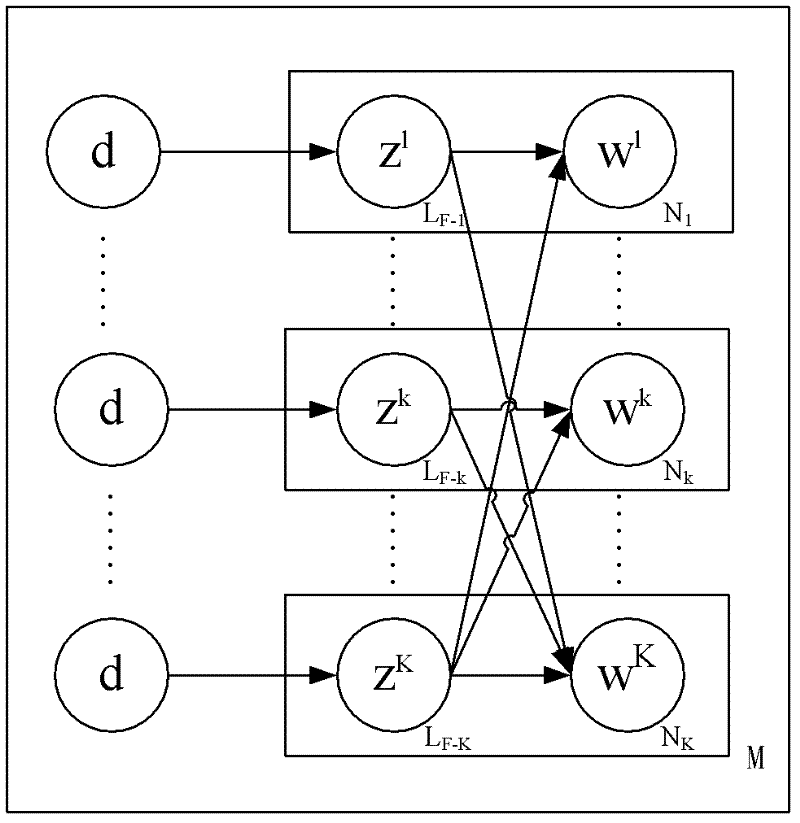
Method for analyzing latent semantics of fusion probability of multi-modality data
InactiveCN102289430AReasonable analysis resultsThe analysis result is accurateSpecial data processing applicationsSemanticsSemantic space
The invention discloses a method for analyzing latent semantics of the fusion probability of multi-modality data in the technical field of latent semantics analysis of probability. By starting from the essence of the multi-modality data and introducing a crossed structure, a standard probability latent semantic analysis model which is only applicable to single-modality is expanded to multi-modality, and difference between contributes of each modality to a latent semantic space and relevance of contents of each modality are modeled, so more accurate analysis and description are provided for the multi-modality data. The method has the advantages that: more accurate parameter estimation is realized by global parameter updating; reference is provided for selection of a proper subject number value range for each modality; and the working load of manual selection is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Land cover classification method and land cover classification system based on crowdsourced geographic data spatial clustering
ActiveCN107066572ACharacter and pattern recognitionGeographical information databasesLand coverClassification methods
The invention discloses a land cover classification method and a land cover classification system based on crowdsourced geographic data spatial clustering. The land cover classification method comprises the following steps: acquiring crowdsourced geographic data, and using the crowdsourced geographic data as land cover classification data; carrying out spatial clustering on data points by using coordinate information for expressing spatial positions in the data points of the acquired crowdsourced geographic data, and clustering the data points into a plurality of groups of data points; obtaining the plurality of groups of data points by using the spatial clustering, and delimiting land cover areas containing all the groups of data points; inputting text information of each land cover area into a probabilistic latent semantic analysis model, outputting a land cover theme and a theme weight which consist of terms in the text information of each land cover area by the probabilistic latent semantic analysis model, screening the land cover type corresponding to a theme with highest weight in the text information of the land cover area as a basis for judging the land cover type, and judging the land cover type of a to-be-detected land cover area according to the basis for judging the land cover type.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Semi-supervised probabilistic latent semantic analysis based software change log classification method
ActiveCN103984756AImprove accuracyFast convergenceSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmClassification methods
The invention provides a semi-supervised probabilistic latent semantic analysis based software change log classification method. A word dictionary determined through prior knowledge is combined, classification is performed on software change logs objectively according to probabilistic dependencies between words, probabilistic dependencies between the words and change log categories and probabilistic dependencies between the software change logs and the change log categories, and accordingly the classification on the software change logs according to weight values of the word frequency characteristics is avoided, the accuracy of the classification can be improved, and the problems that errors are produced and the accuracy is low in the process of the classification on the software change logs due to the fact that the weight values are set artificially in the prior art are effectively solved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Underwater target signal feature extraction method based on probabilistic latent semantic analysis
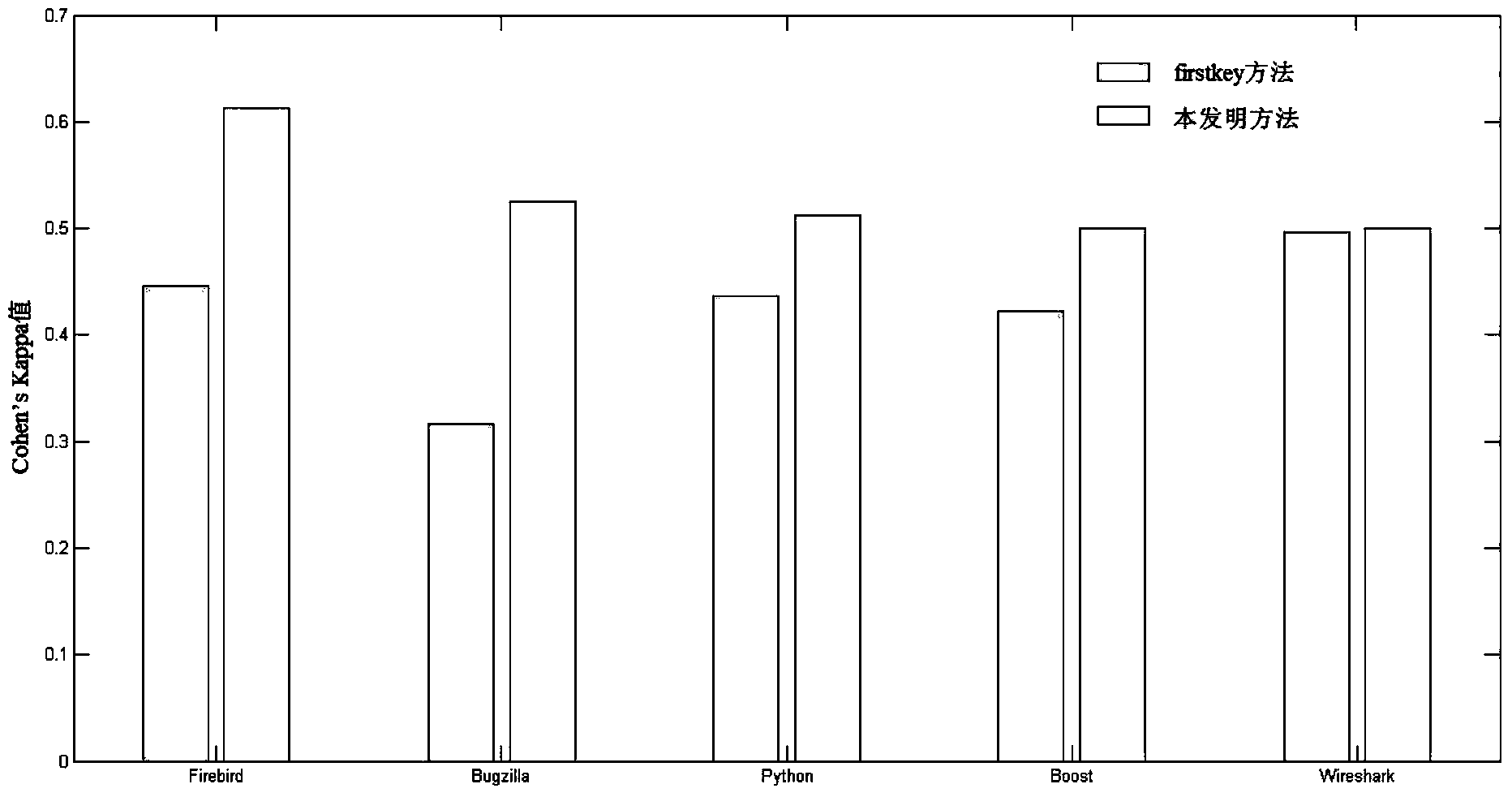
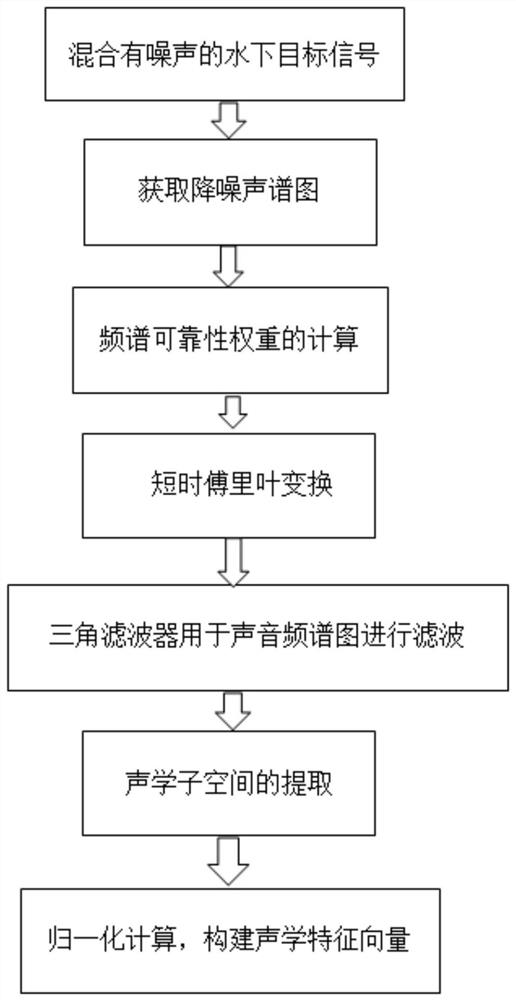
ActiveCN112183225AAchieve separationReduce the impact of accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionLow noiseFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses an underwater target signal feature extraction method based on probability latent semantic analysis, and the method comprises the following steps: processing an underwater target signal mixed with noise to obtain a noise reduction spectrogram, and carrying out the spectrum reliability weight calculation through an original spectrogram v and the noise reduction spectrogram;obtaining a noise reduction spectrogram Sn of the nth frequency band after weighting; carrying out short-time Fourier transform on Sn to obtain a signal pair, filtering the signal pair by using a frequency spectrum triangular filter, carrying out matrix decomposition on the whole frequency spectrum pair after filtering, and extracting first L feature vectors with the highest contribution rate to form an acoustics subspace; performing normalization calculation on the extracted first L feature vectors, and connecting the normalized L feature vectors to construct an acoustic feature vector. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the characteristics of the sound signal are reflected by combining time and frequency, and the noise pollution can be reduced, so that the sound signal can be more effectively represented.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
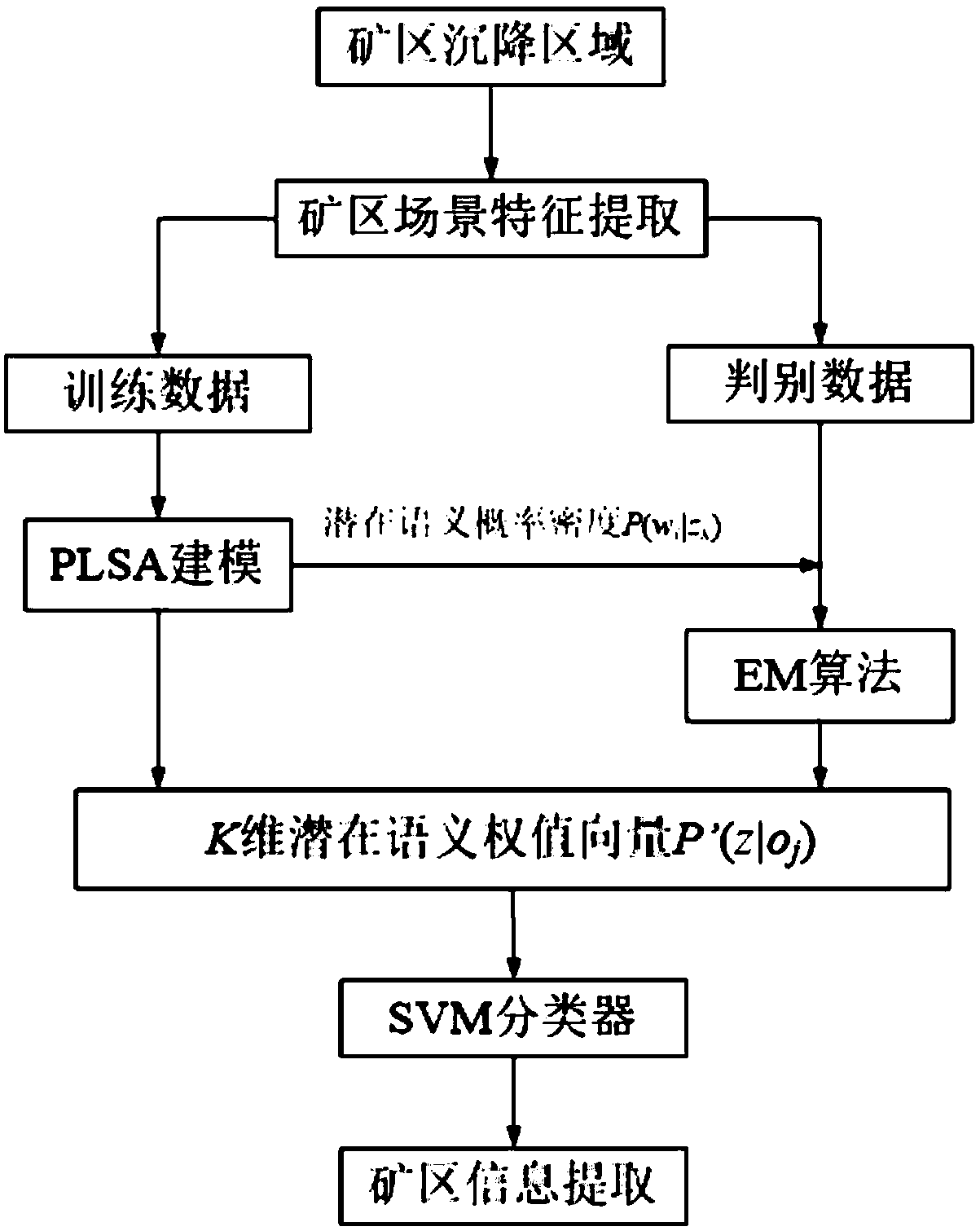
Mining area distribution thematic information extraction method based on multi-source remote sensing images
The invention provides a mining area distribution thematic information extraction method based on multi-source remote sensing images, comprising extracting land subsidence information, calculating uplift information characteristics of target area according to radiant value of remote sensing image interferogram of target area, dividing possible mining area according to sudden change characteristicsof uplift, and further identifying combined with radar image, extracting land subsidence information; establishing a thematic semantic model of mining area, and adopting the probabilistic latent semantic analysis method to model the latent semantics, and the scene of mining area is expressed by the feature vector of latent semantics; extracting information from multi-source remote sensing imagesof mining area. The invention not only greatly reduces the cost, but also is convenient to operate and greatly improves the working efficiency by using the mode of combining the multi-source optical images and the radar images. For the influence of vegetation, the vegetation index is used to extract the thematic information from the non-vegetation-covered area.
Owner:STATE GRID ECONOMIC TECH RES INST CO +2
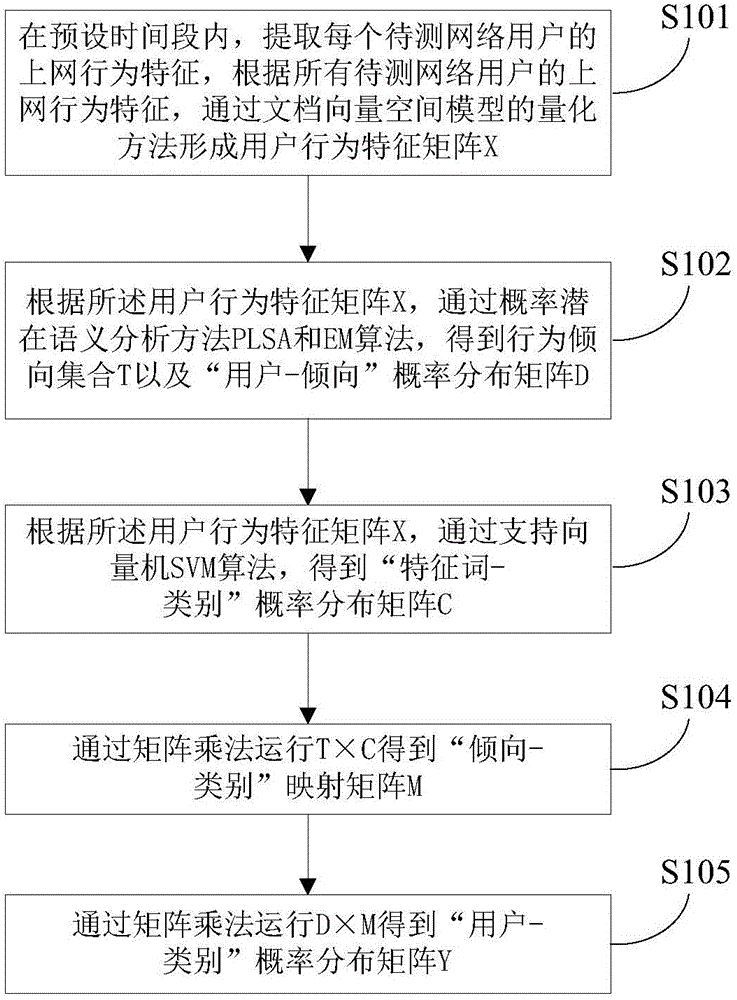
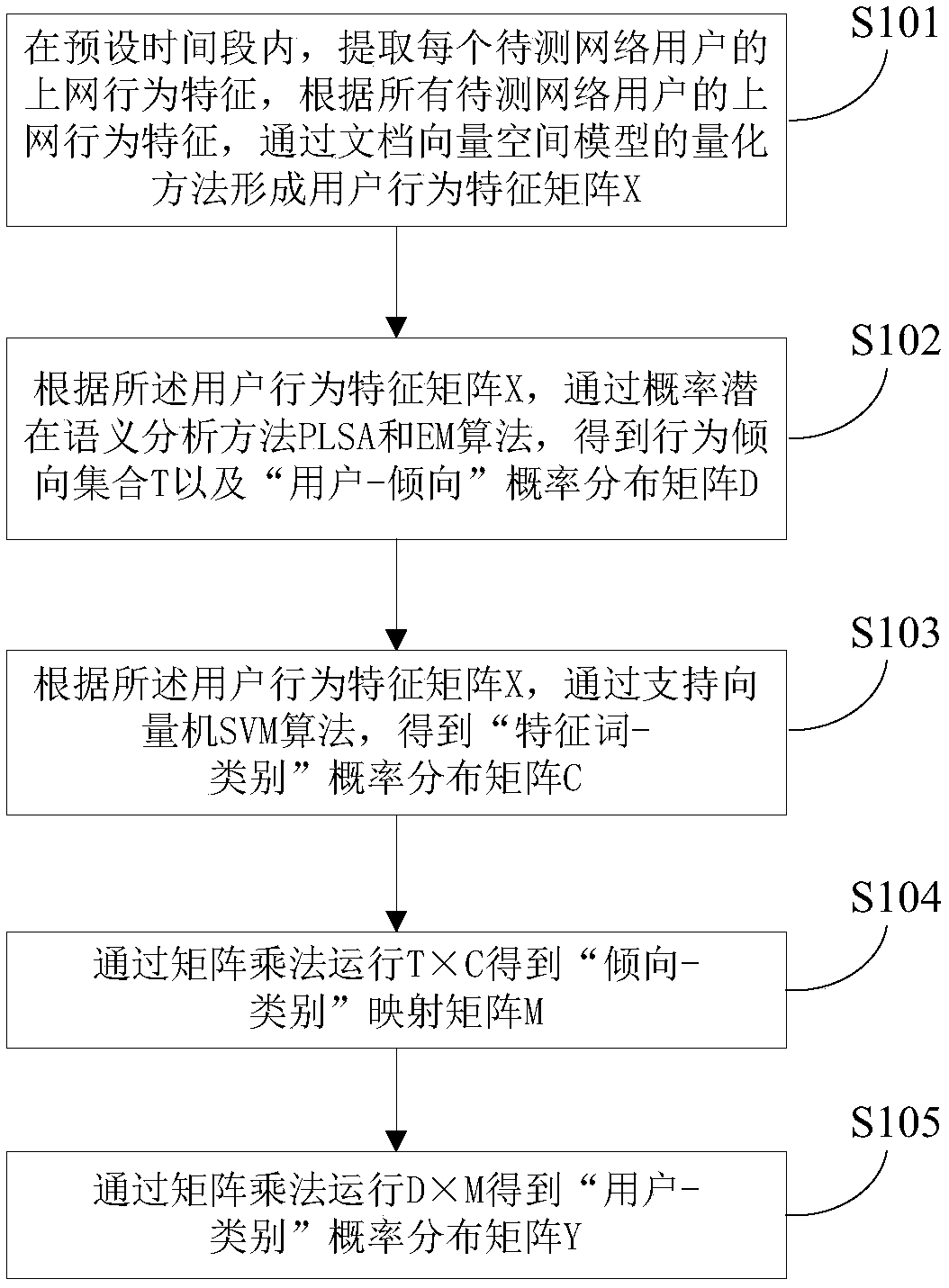
Method for determining Internet surfing behavior categories of network users
The invention provides a method for determining Internet surfing behavior categories of network users. The method comprises the steps that Internet surfing behavior features of all the network users to be detected are extracted, and a user behavior feature matrix X is formed through a quantitative method of a document vector space model; according to the user behavior feature matrix X, a behavior tendency set T and a user-tendency probability distribution matrix D are obtained through a probability latent semantic analysis PLSA and an EM algorithm; according to the user behavior feature matrix X, a feature word-category probability distribution matrix C is obtained through a support vector machine (SVM) algorithm; T*C runs through matrix multiplication to obtain a tendency-category mapping matrix M; D*M runs through matrix multiplication to obtain a user-category probability distribution matrix Y; according to the probability distribution situation of any network user to be detected in the categories, the network user to be detected is classified into the category with the maximum probability value.
Owner:NAT COMP NETWORK & INFORMATION SECURITY MANAGEMENT CENT
Labelling image scene clustering method based on vision and labelling character related information
InactiveCN102222239BHigh connection precisionReduce ambiguityCharacter and pattern recognitionEarth mover's distanceRelevant information
The invention provides a labelling image scene clustering method based on vision and labelling character related information. The method comprises the following steps of: dividing a training image and a test image respectively by using a NCut (Normalized Cut) image dividing algorithm; constructing a vision nearest-neighbour graph G(C)(V, E) of all images {J1, ., Jl} PCtrain for learning, wherein in a training image set, each image has one group of initial normalized labelling character weight vectors; spreading the labelling character of each training image among the vision nearest neighbours, receiving the accepted images according to the degree of normalized EMD (Earth Mover's Distance) among the accepted images; for each training image, normalizing the accumulated labelling character weights; after the vision characteristics of the image are converted into a group of labelling characters with weights, carrying out the scene semantic clustering by using a PLSA (Probabilistic Latent Semantic Analysis) model; learning each scene semantic vision space by using a Gaussian mixture model; and carrying out the scene classification by using the vision characteristics. With the invention, the coupling precision between the vision characteristics of the image and the labelling character can be increased, and the method can be directly used for the automatic semantic labelling of the image.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
A method for determining the online behavior category of network users
The present invention proposes a method for determining the online behavior category of network users, the method comprising: extracting the online behavior characteristics of each network user to be tested, and forming a user behavior characteristic matrix X through the quantization method of the document vector space model; The user behavior feature matrix X, through the probabilistic latent semantic analysis method PLSA and EM algorithm, obtains the behavior tendency set T and the "user-tendency" probability distribution matrix D; according to the user behavior feature matrix X, through the support vector machine SVM algorithm , to get the probability distribution matrix C of "characteristic word-category"; run T×C through matrix multiplication to get the mapping matrix M of "propensity-category"; run D×M through matrix multiplication to get the probability distribution matrix Y of "user-category"; according to any A probability distribution of network users to be tested in each category, and any network user to be tested is classified into the category with the highest probability value.
Owner:NAT COMP NETWORK & INFORMATION SECURITY MANAGEMENT CENT
Land Cover Classification Method and System Based on Spatial Clustering of Crowdsource Geographic Data
ActiveCN107066572BCharacter and pattern recognitionGeographical information databasesCrowd sourcingLand cover
The invention discloses a land cover classification method and system based on the spatial clustering of crowd-source geographic data; the crowd-source geographic data is obtained, and the crowd-source geographic data is used as the land cover classification data; The coordinate information of the spatial position is used to carry out the spatial clustering of the data points, and the data points are clustered into several groups of data points; the several groups of data points obtained by the spatial clustering are used to delineate the land cover area containing each group of data points; The text information in each land cover area is input into the probabilistic latent semantic analysis model, and the probabilistic latent semantic analysis model outputs the land cover topics and topic weights composed of the words in the text information in each land cover area, and filters the text information in the land cover area The land cover type corresponding to the topic with the highest weight is used as the basis for judging the land cover type, and the land cover type is judged for the land cover area to be detected according to the basis for judging the land cover type.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Document Topic Mining Method and Device
ActiveCN105243083BExcavate accuratelyImprove relevanceNatural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsDocumentationProbabilistic latent semantic analysis
Owner:BAIDU ONLINE NETWORK TECH (BEIJIBG) CO LTD
Image marking method based on semi-supervised subject modeling
InactiveCN102637199BSpecial data processing applicationsExpectation–maximization algorithmHigh probability
The invention discloses an image marking method based on semi-supervised subject modeling. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, obtaining images from the Internet, including images with text marks and unmarked images; then, modeling the relation between the visual features and text marks of all images through latent subjects by use of a model similar to probabilistic latent semantic analysis; establishing the nearest-neighbor graphs of all images, and adjusting the model according to the manifold structure obtained by modeling the nearest-neighbor graphs; learning the model by an expectation maximization algorithm, and calculating the probability of matching the latent subjects with the images respectively; and finally, calculating the probability of matching each text mark with the unmarked images according to the probability of matching the latent subjects with the images, and selecting the text mark with the highest probability to mark the unmarked images.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
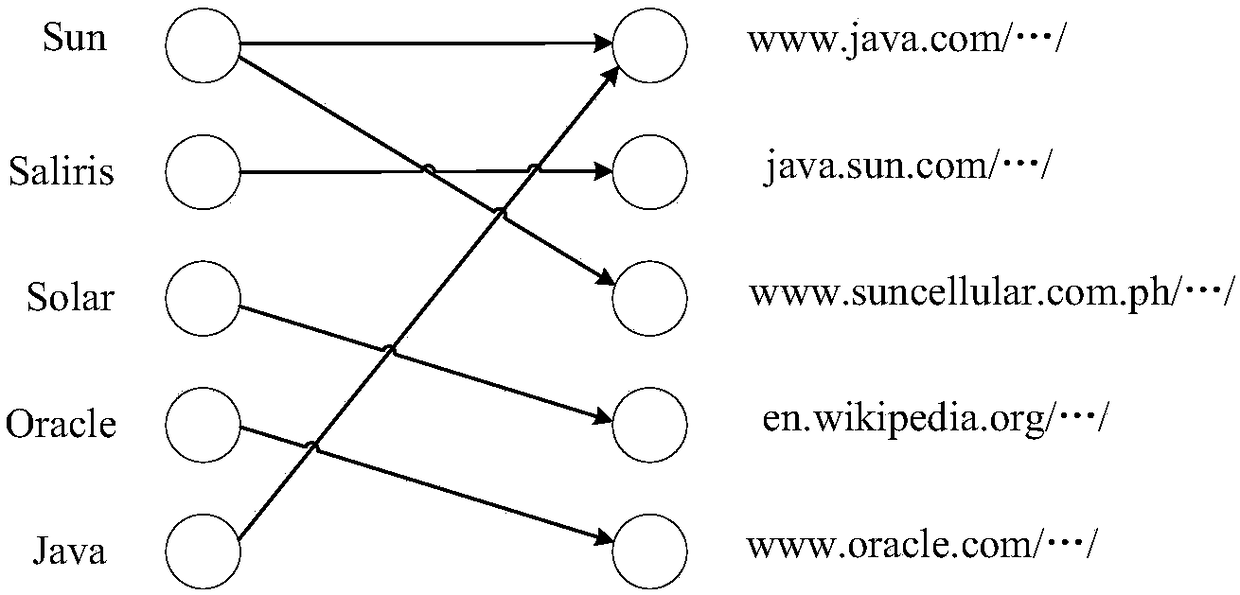
Method and device for achieving website navigation
InactiveCN105117482AWeb data navigationSpecial data processing applicationsThe InternetProbabilistic latent semantic analysis
Owner:BEIJING QIHOO TECH CO LTD +1
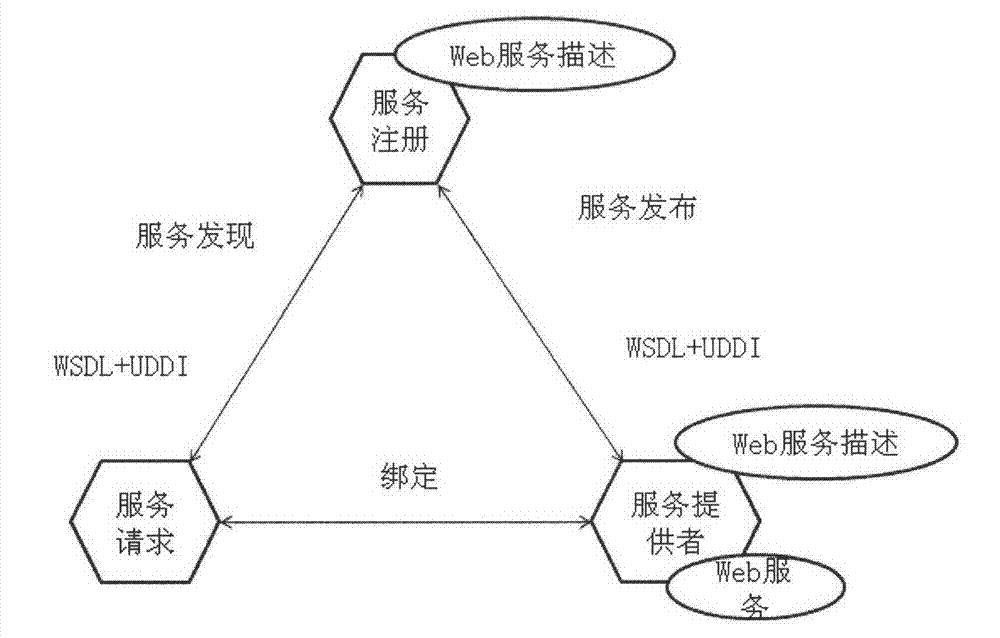
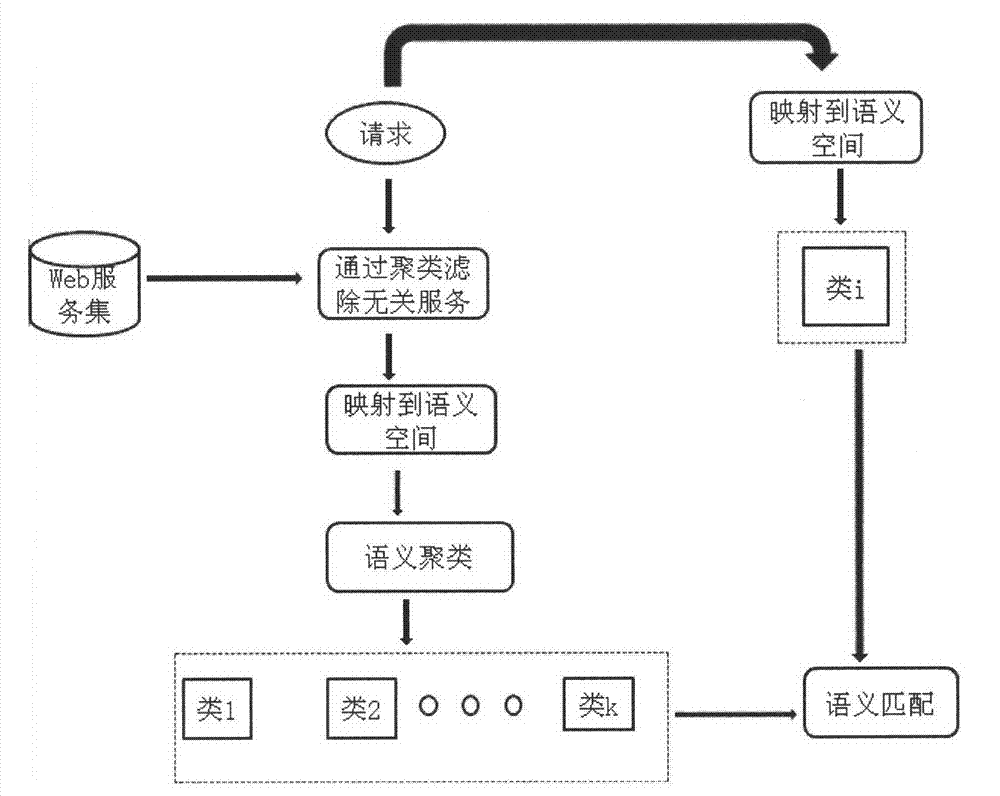
World wide web service discovery method based on probabilistic latent semantic analysis model
InactiveCN102129479BImprove precisionImprove recallSpecial data processing applicationsComputation complexityData set
The invention discloses a Web service discovery method based on a probabilistic latent semantic analysis model, wherein the probabilistic latent semantic analysis model is utilized to perform modeling analysis on analyzed Web service descriptive documents, semantic concepts hidden behind service description are dug out for semantic clustering, demand service and service-centralized service are subjected to similarity matching at the relatively advanced concept hierarchy, and in combination with spectral clustering on semantic hierarchy, a service data set is subjected to irrelevant data filtration by a spectral clustering-based algorithm prior to the semantic clustering, thereby compressing the computation complexity. As proved by tests, the method is quite superior in both precision ratio and recall ratio of service discovery.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for recommending problem based on probability latent semantic analysis
InactiveCN101354714BImprove accuracyWide applicabilitySpecial data processing applicationsPersonalizationState model
The invention discloses a recommended method for analyzing the latent semantic problem based on the probability. The method describes the interest of a user through a state model in the latent semantic analysis on the probability and provides the compatible problem recommendation for the user interactive type question-answering system. The method adopts a ternary state model, has the advantages of two recommended ways based on the content and collaborative filtering, performs problem recommendation according to the personalized information of the user, and has high accuracy and good applicability in the user interactive type question-answering system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com