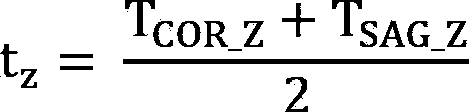Patents
Literature
134 results about "Digital subtraction angiography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
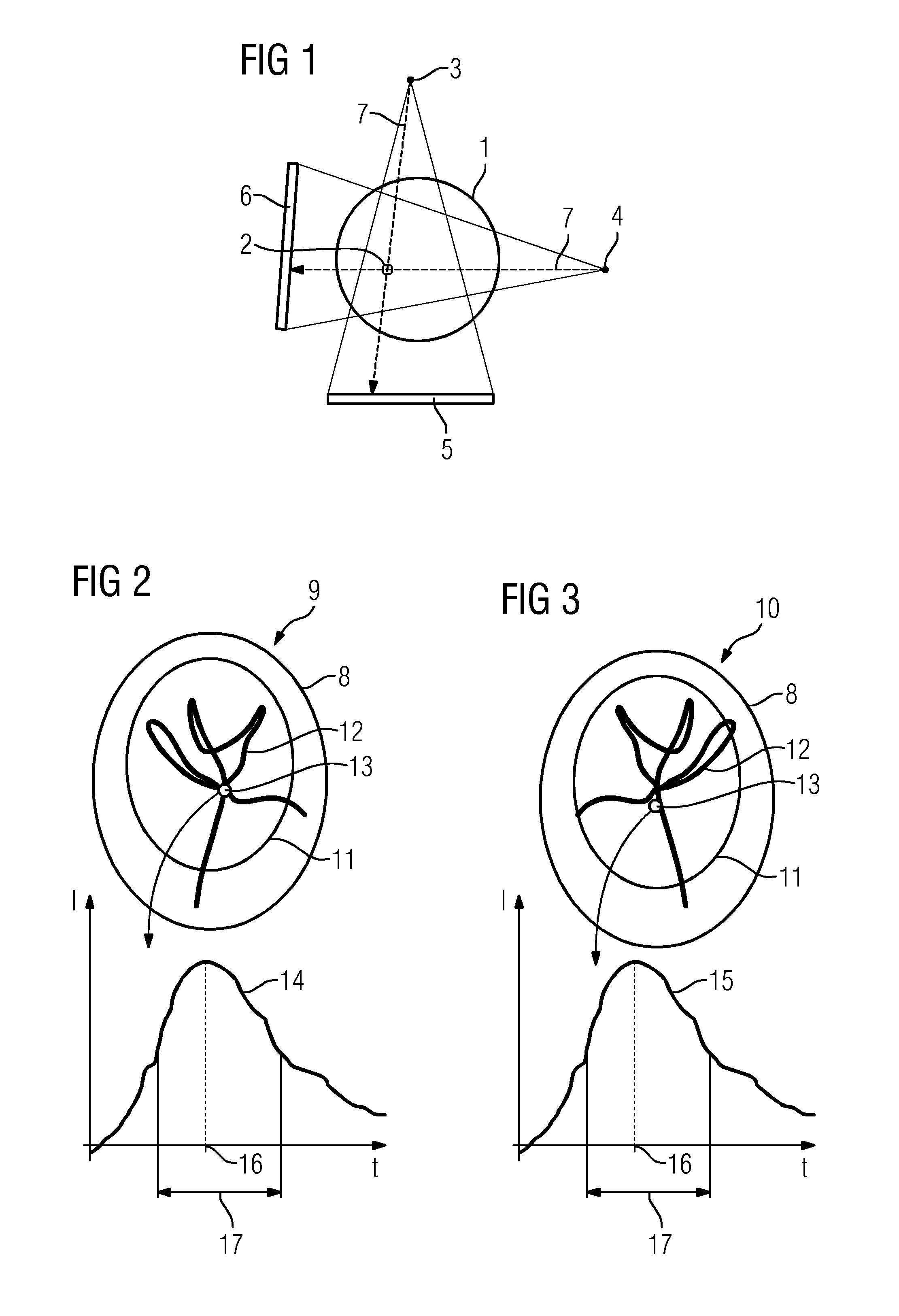
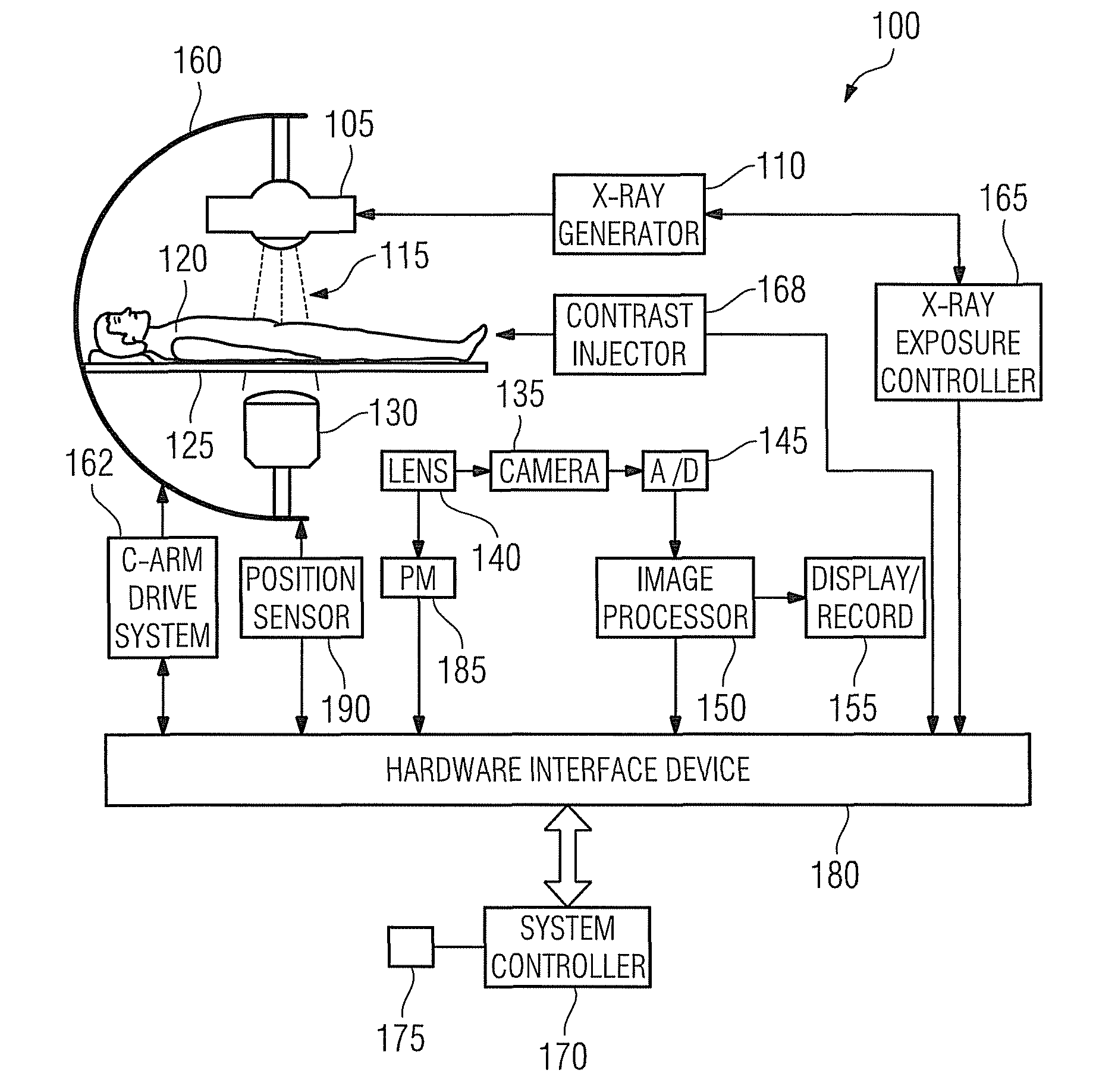
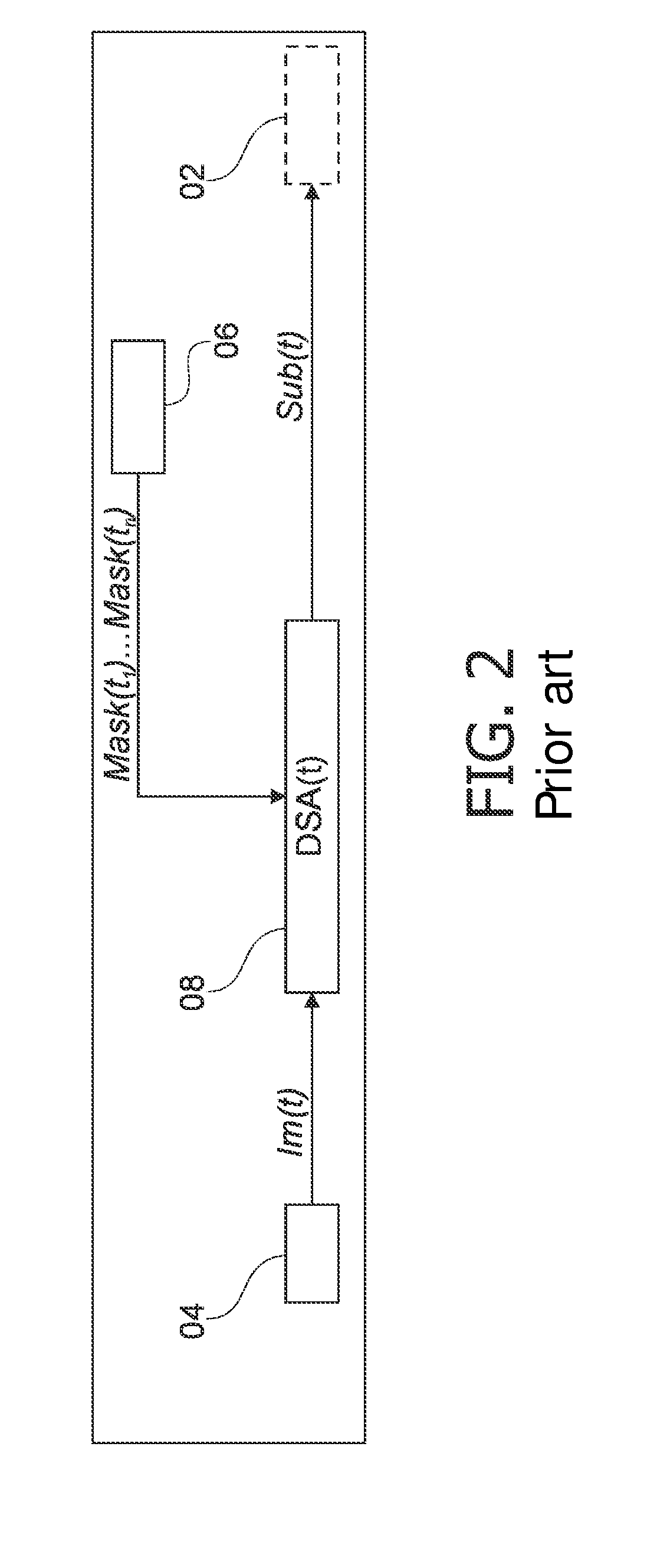
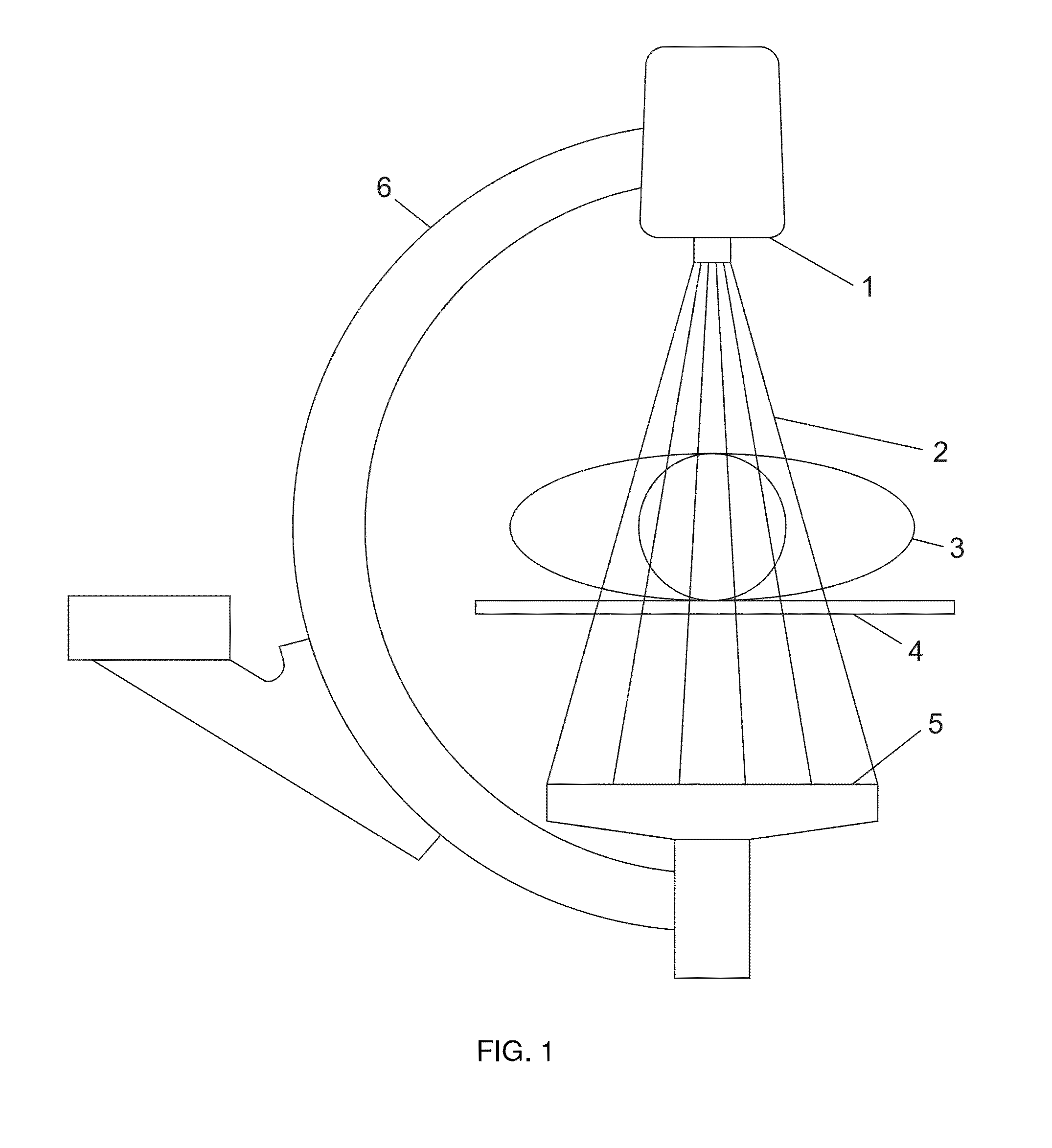
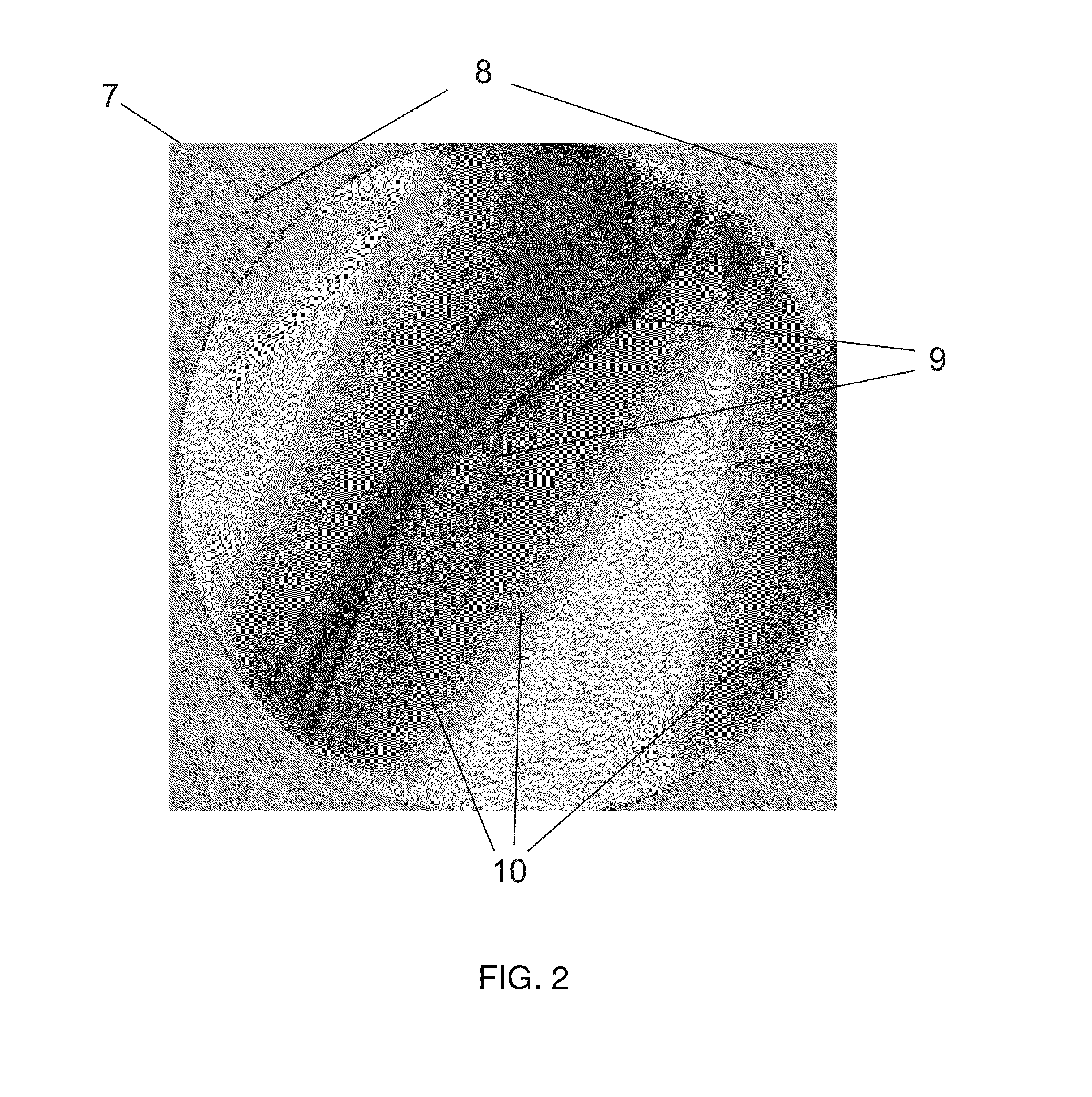
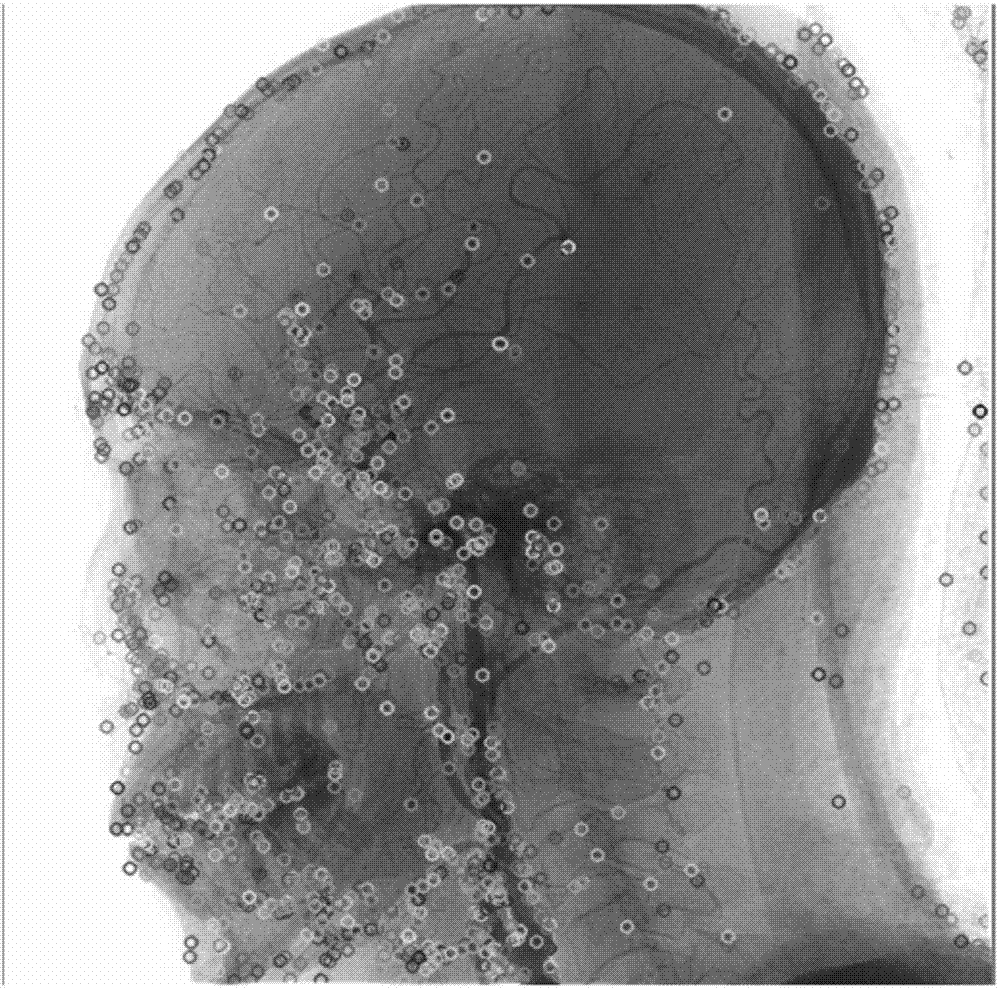
Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) is a fluoroscopy technique used in interventional radiology to clearly visualize blood vessels in a bony or dense soft tissue environment. Images are produced using contrast medium by subtracting a "pre-contrast image" or mask from subsequent images, once the contrast medium has been introduced into a structure. Hence the term "digital subtraction angiography". Subtraction angiography was first described in 1935 and in English sources in 1962 as a manual technique. Digital technology made DSA practical from the 1970s.
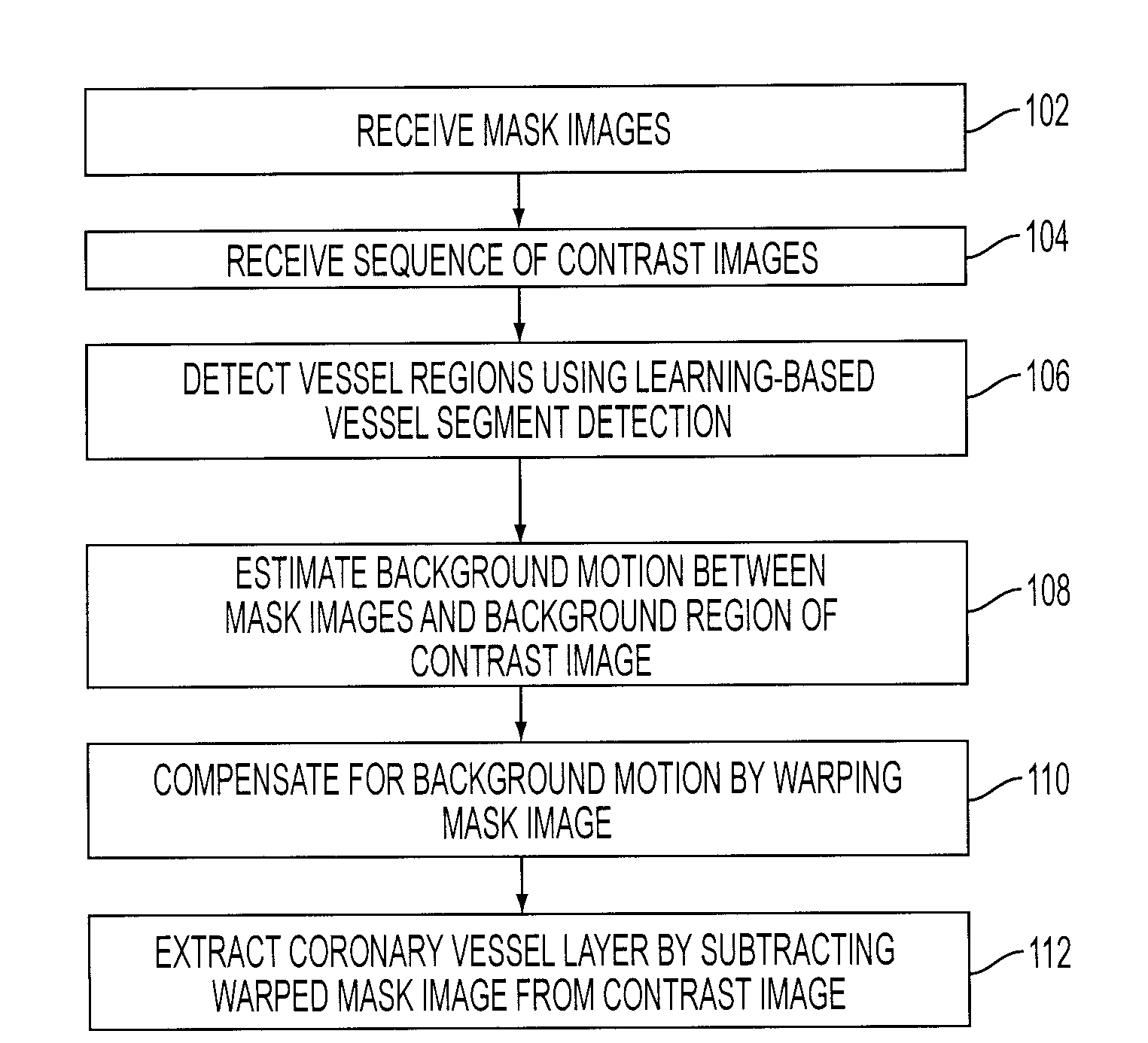
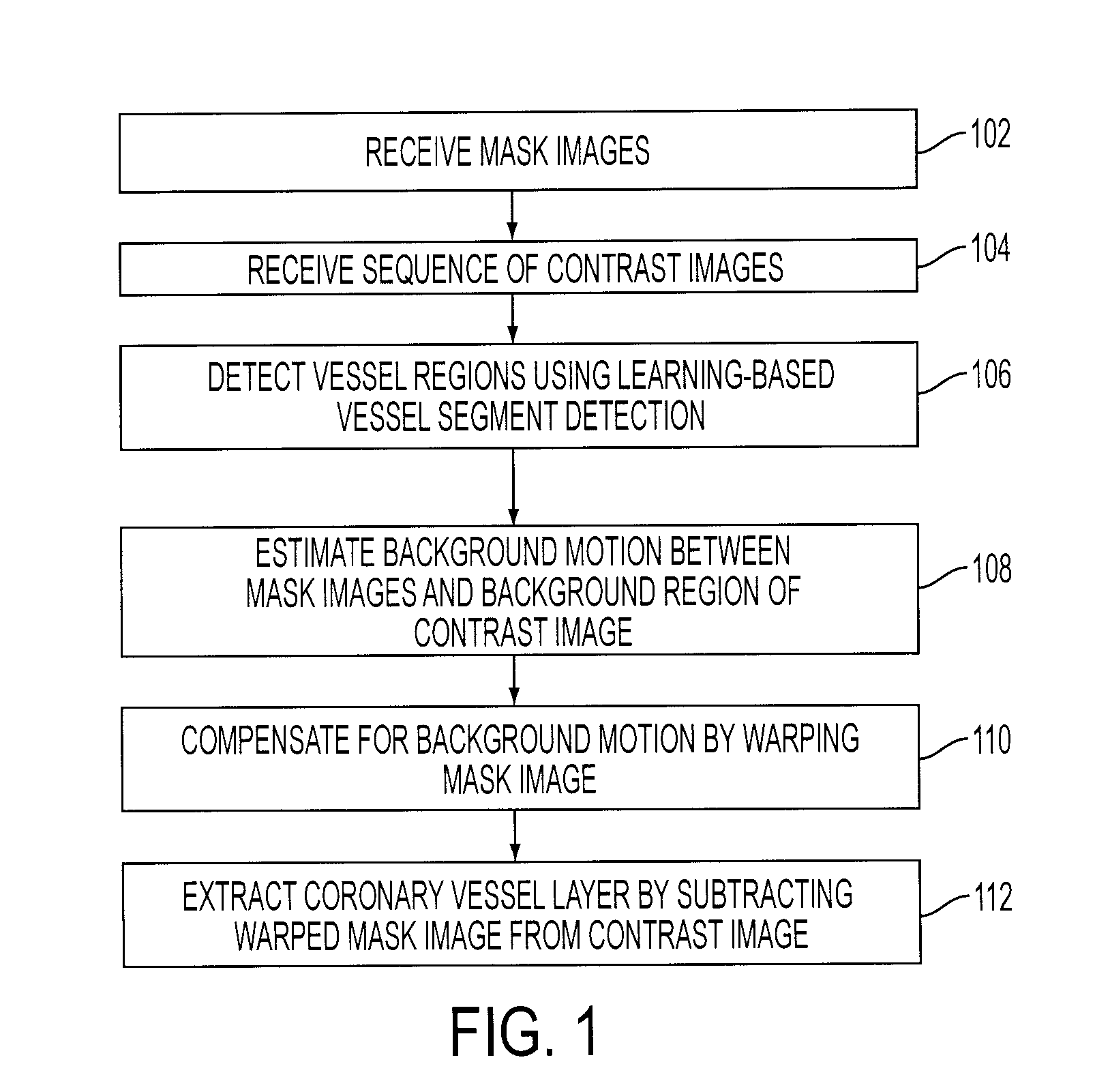
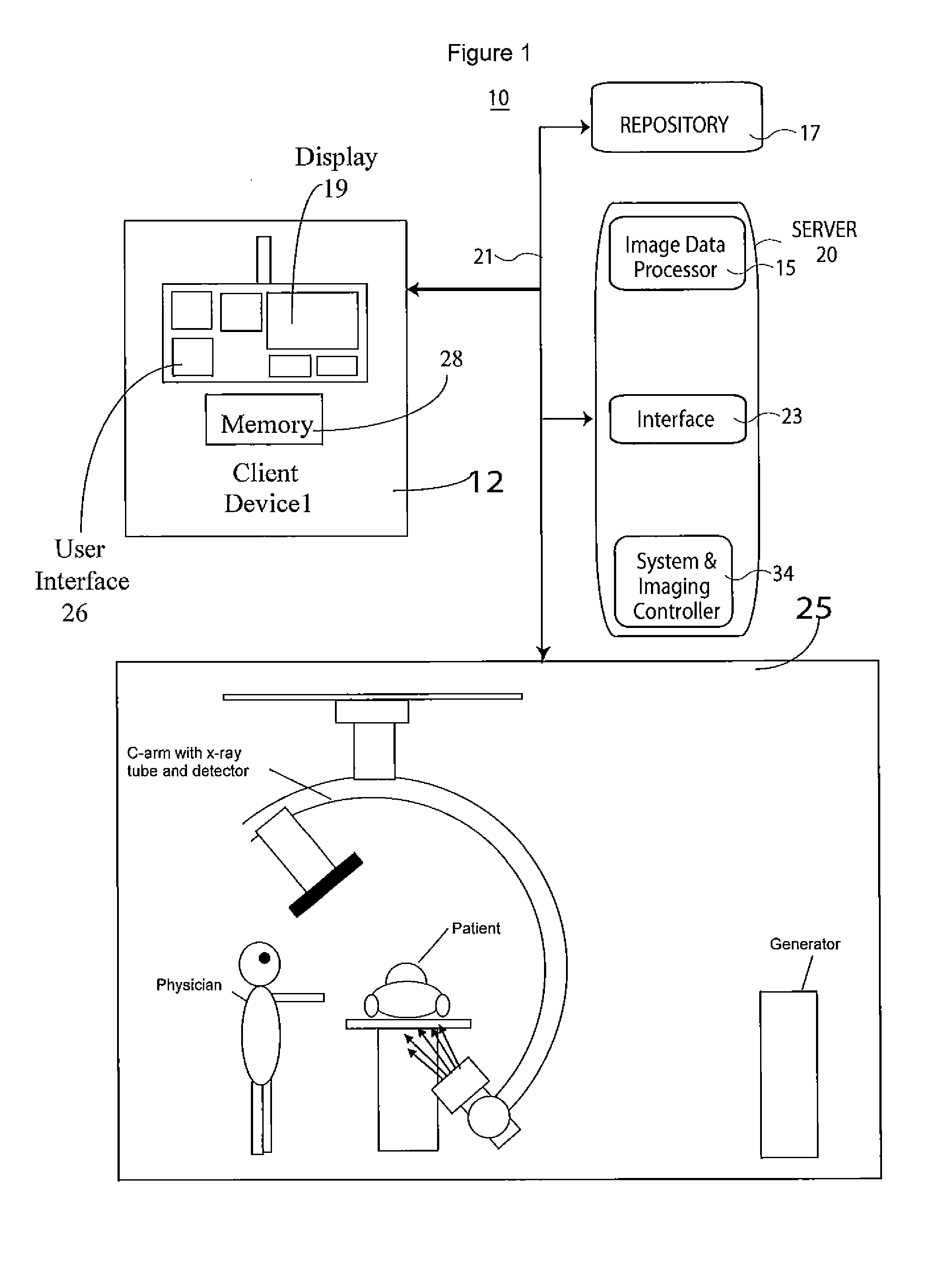
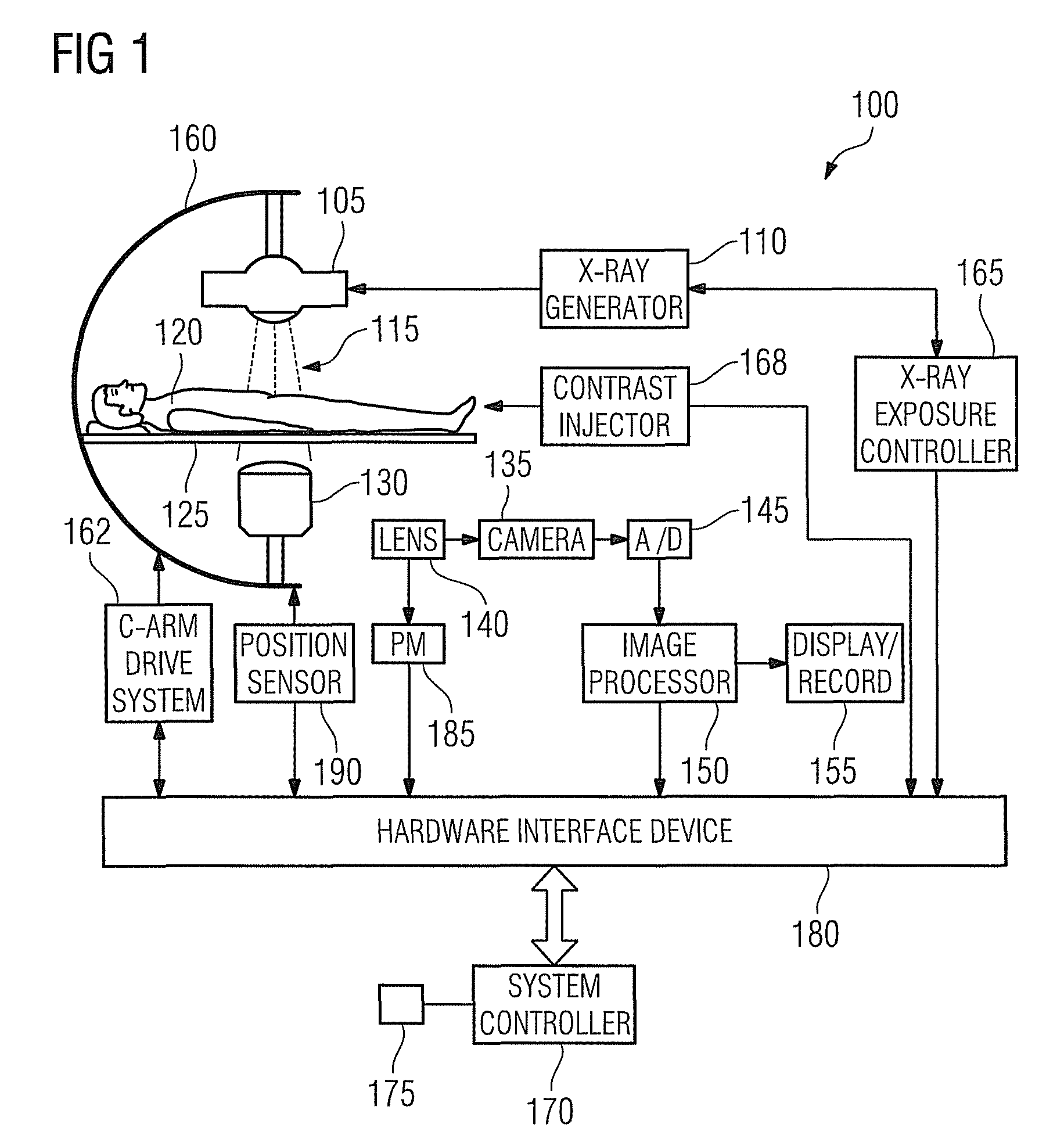
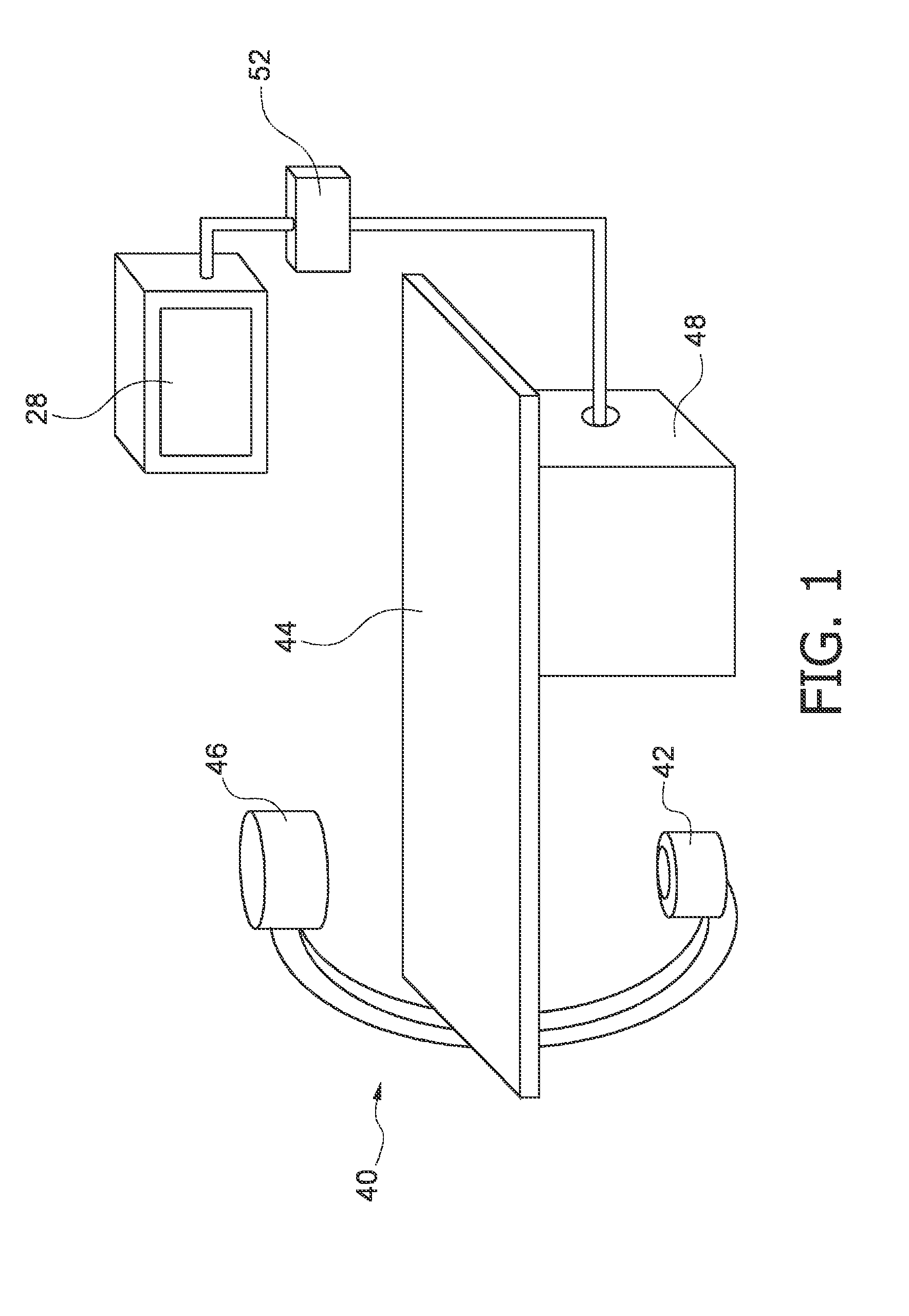
System and Method for Coronary Digital Subtraction Angiography
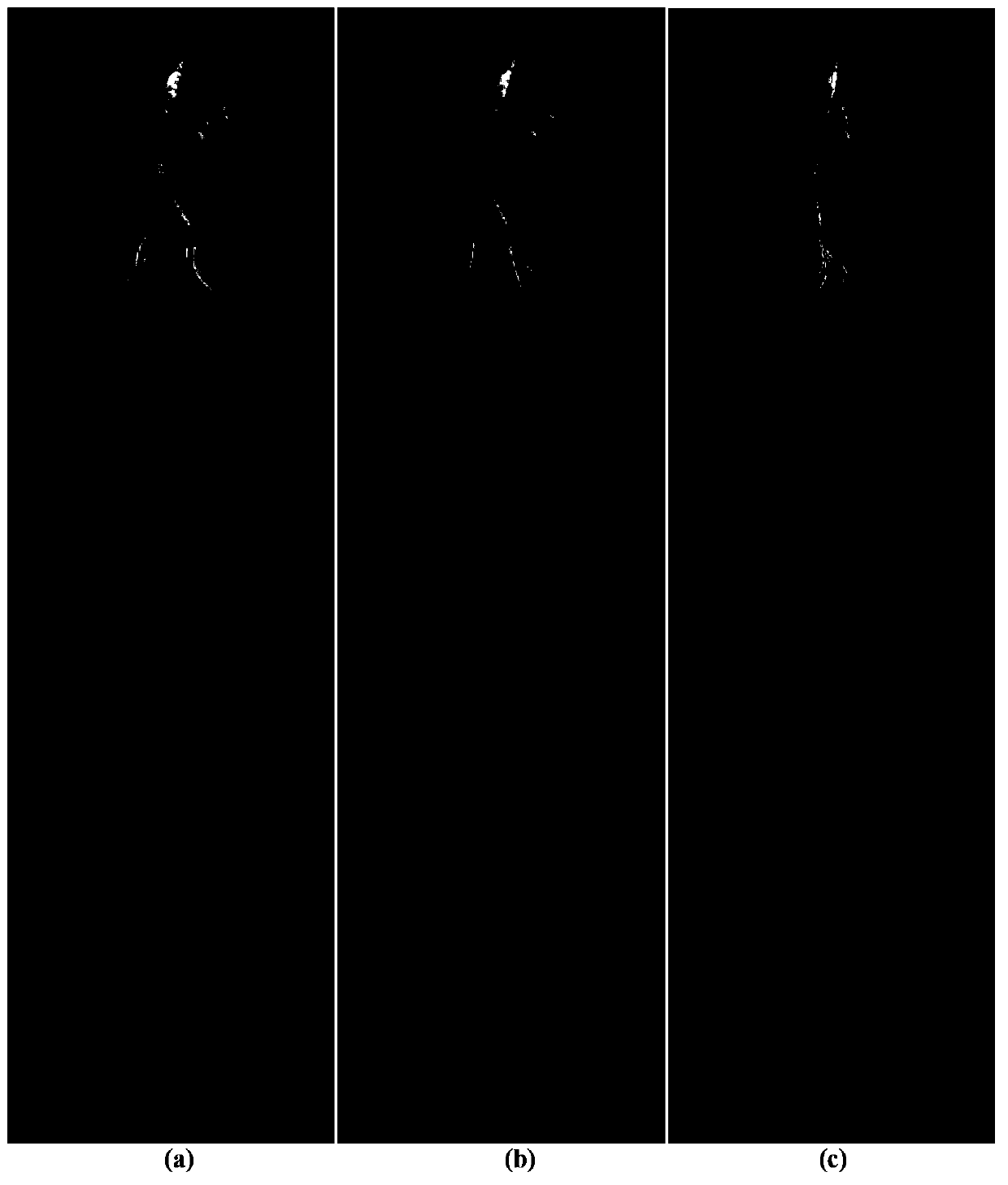
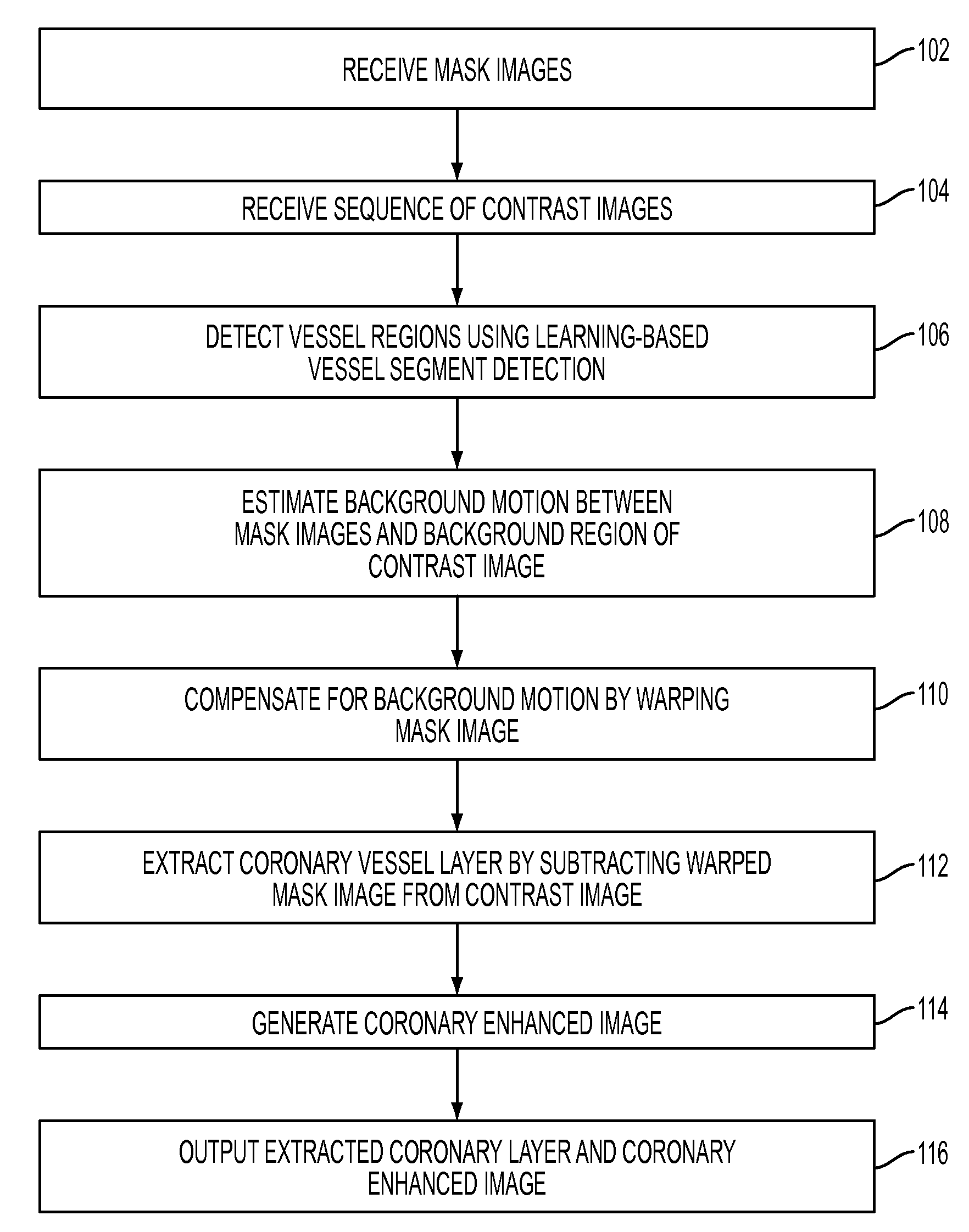
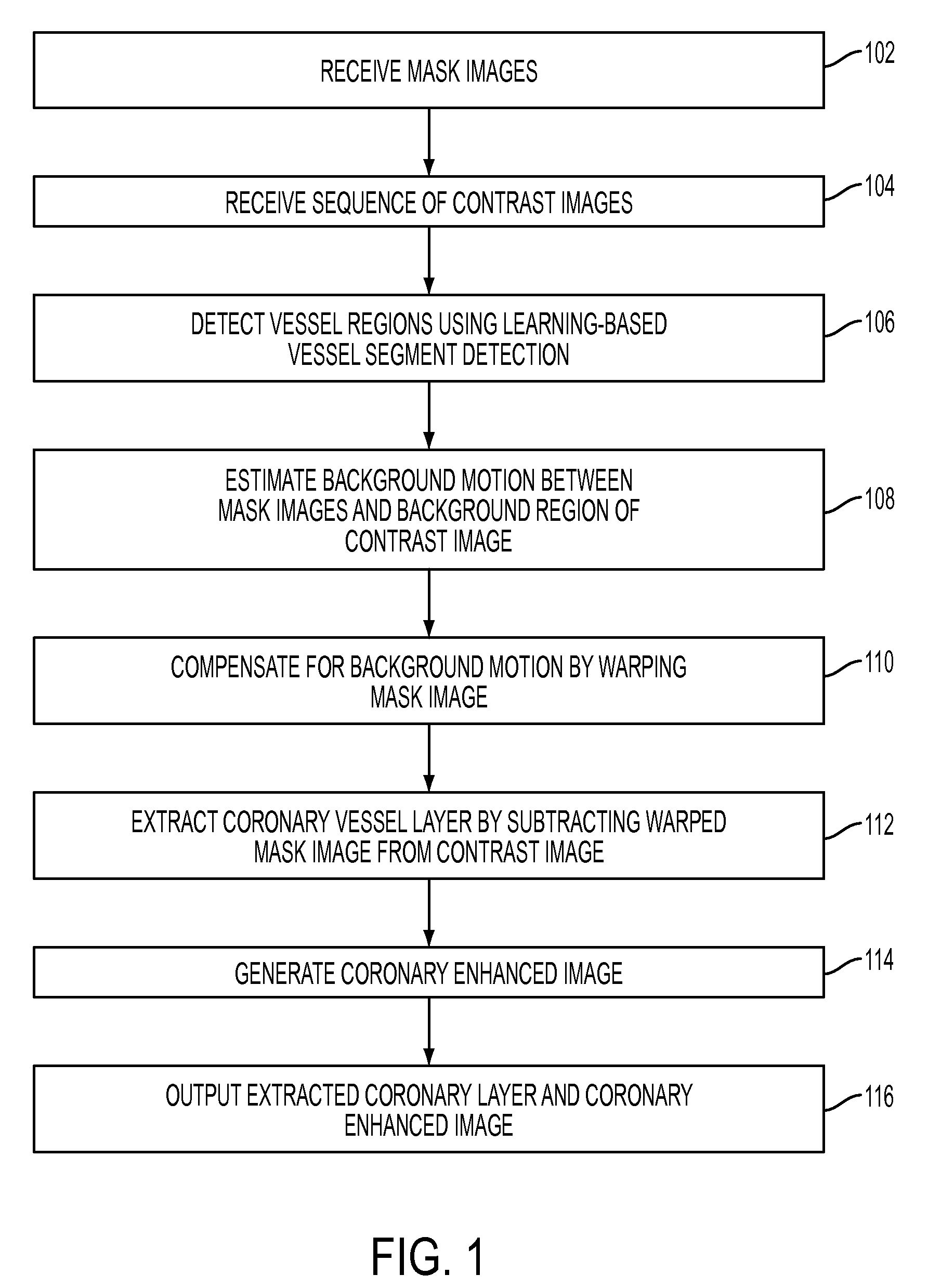
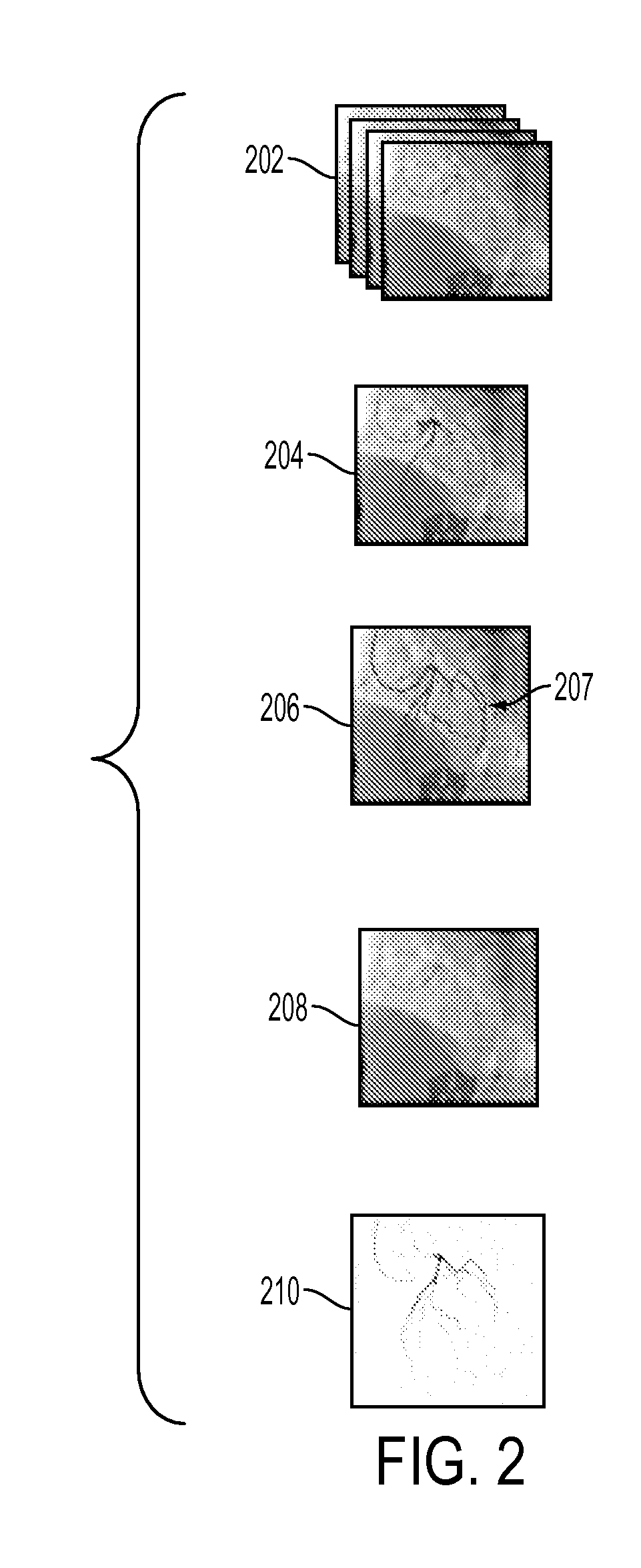
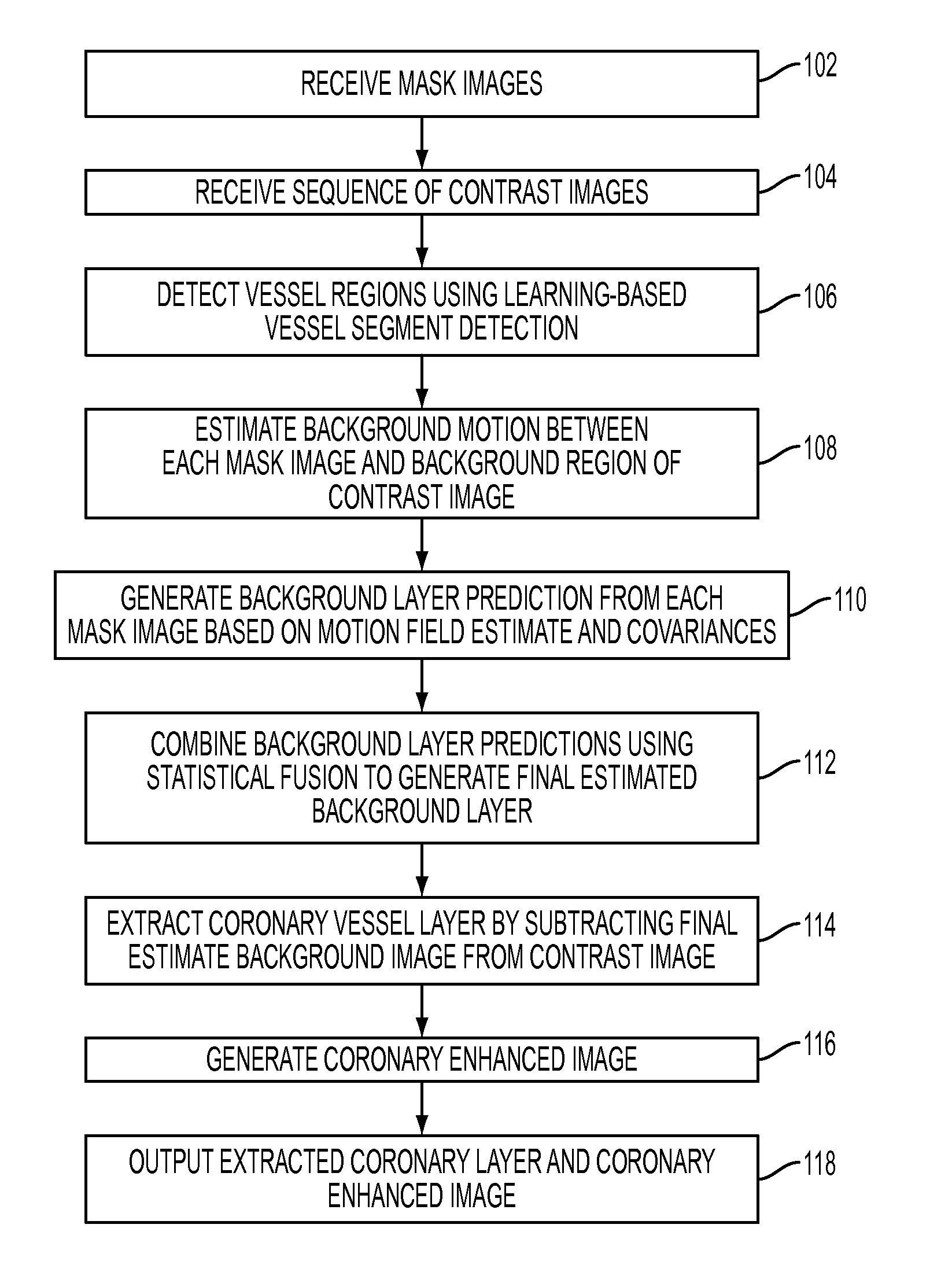
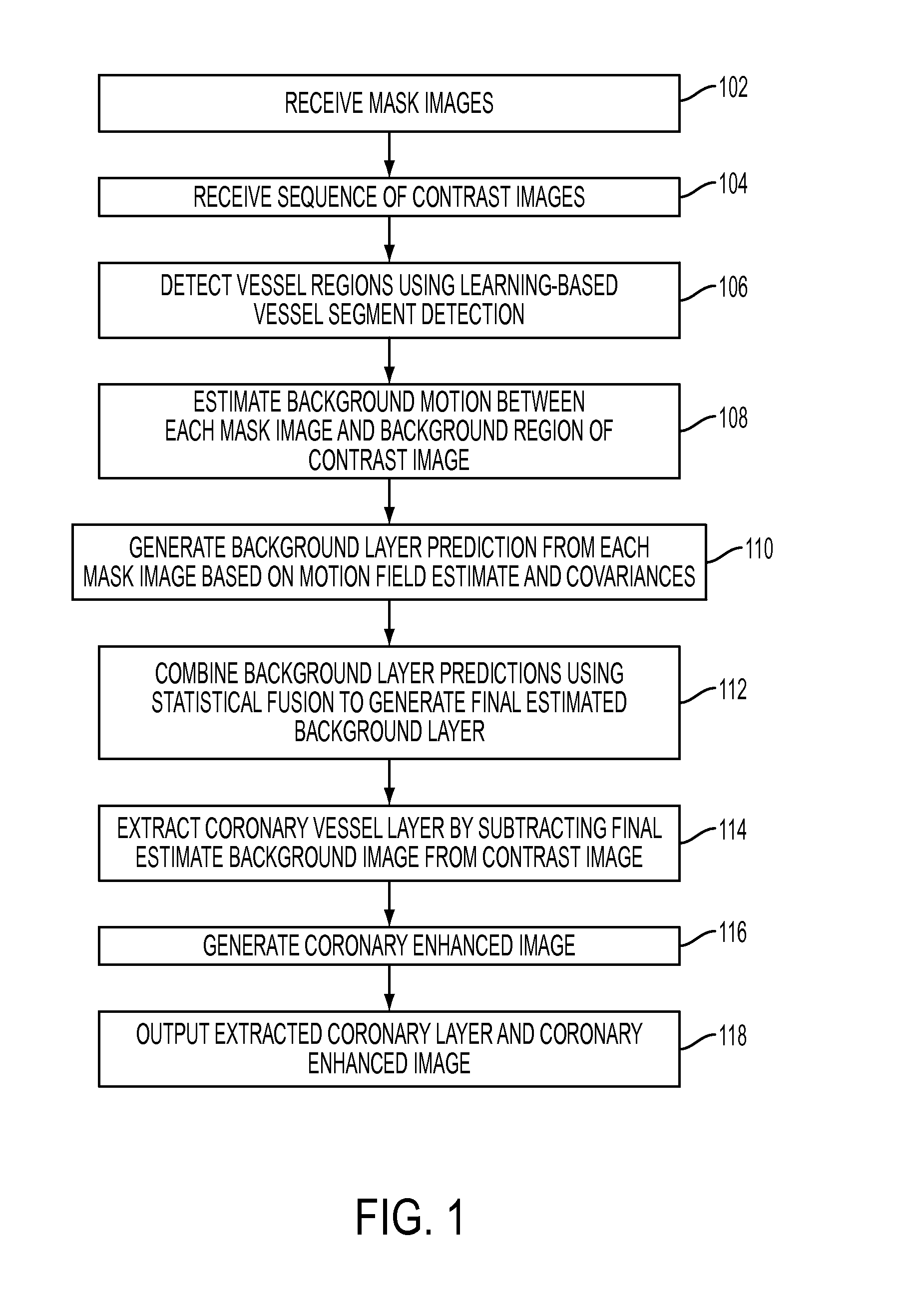
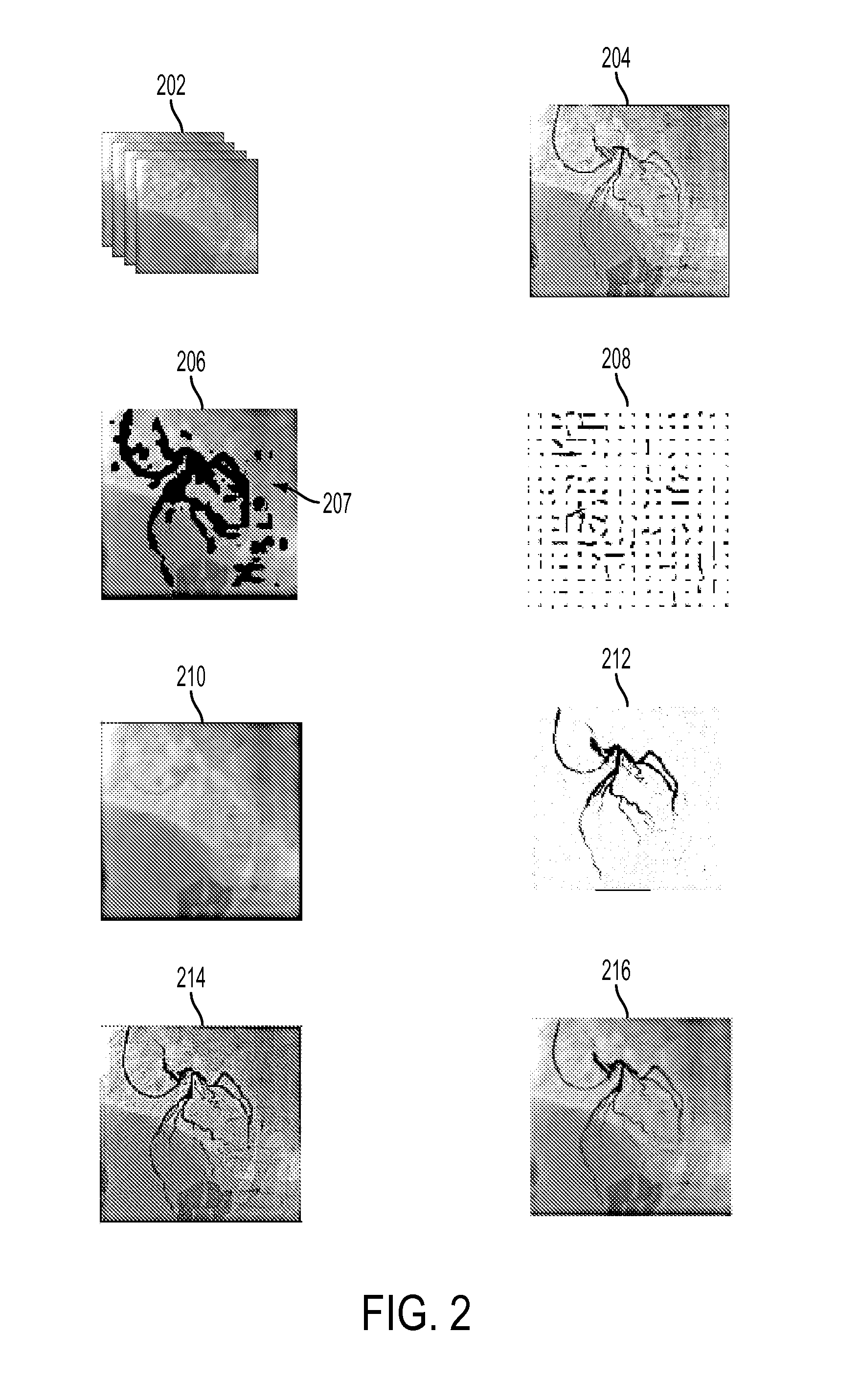
A method and system for extracting coronary vessels fluoroscopic image sequences using coronary digital subtraction angiography (DSA) are disclosed. A set of mask images of a coronary region is received, and a sequence of contrast images for the coronary region is received. For each contrast image, vessel regions are detected in the contrast image using learning-based vessel segment detection and a background region of the contrast image is determined based on the detected vessel regions. Background motion is estimated between one of the mask images and the background region of the contrast image by estimating a motion field between the mask image and the background image and performing covariance-based filtering over the estimated motion field. The mask image is then warped based on the estimated background motion to generate an estimated background layer. The estimated background layer is subtracted from the contrast image to extract a coronary vessel layer for the contrast image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
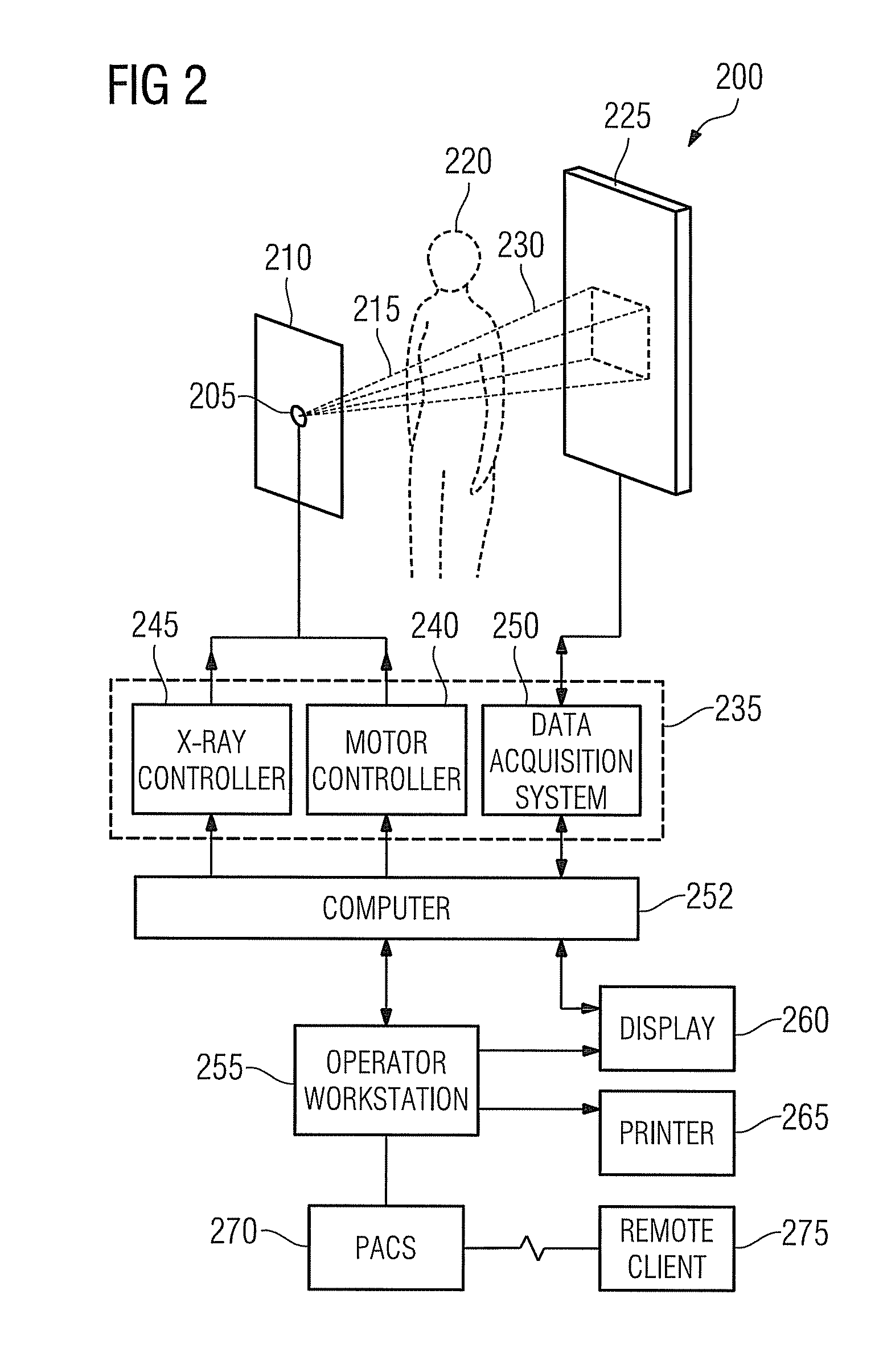
System for Providing Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) Medical Images
A method generates a two dimensional (2D) medical image through a three dimensional (3D) imaged volume of patient anatomy at a desired position, by storing 3D image data representing a 3D imaging volume including vessels in the presence of a contrast agent. The 3D image data comprises, data identifying multiple voxels representing multiple individual volume image element luminance values and luminance distribution data for individual voxels of a vessel in the 3D image data. For multiple individual voxels of a 2D image, the method determines composite luminance distribution data of an individual voxel in the 2D image by combining luminance distribution data of the 3D image data of multiple identified voxels substantially lying on a projection line from a source point to the individual voxel and generating data representing the 2D image using the determined composite luminance distribution data of the multiple individual voxels.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
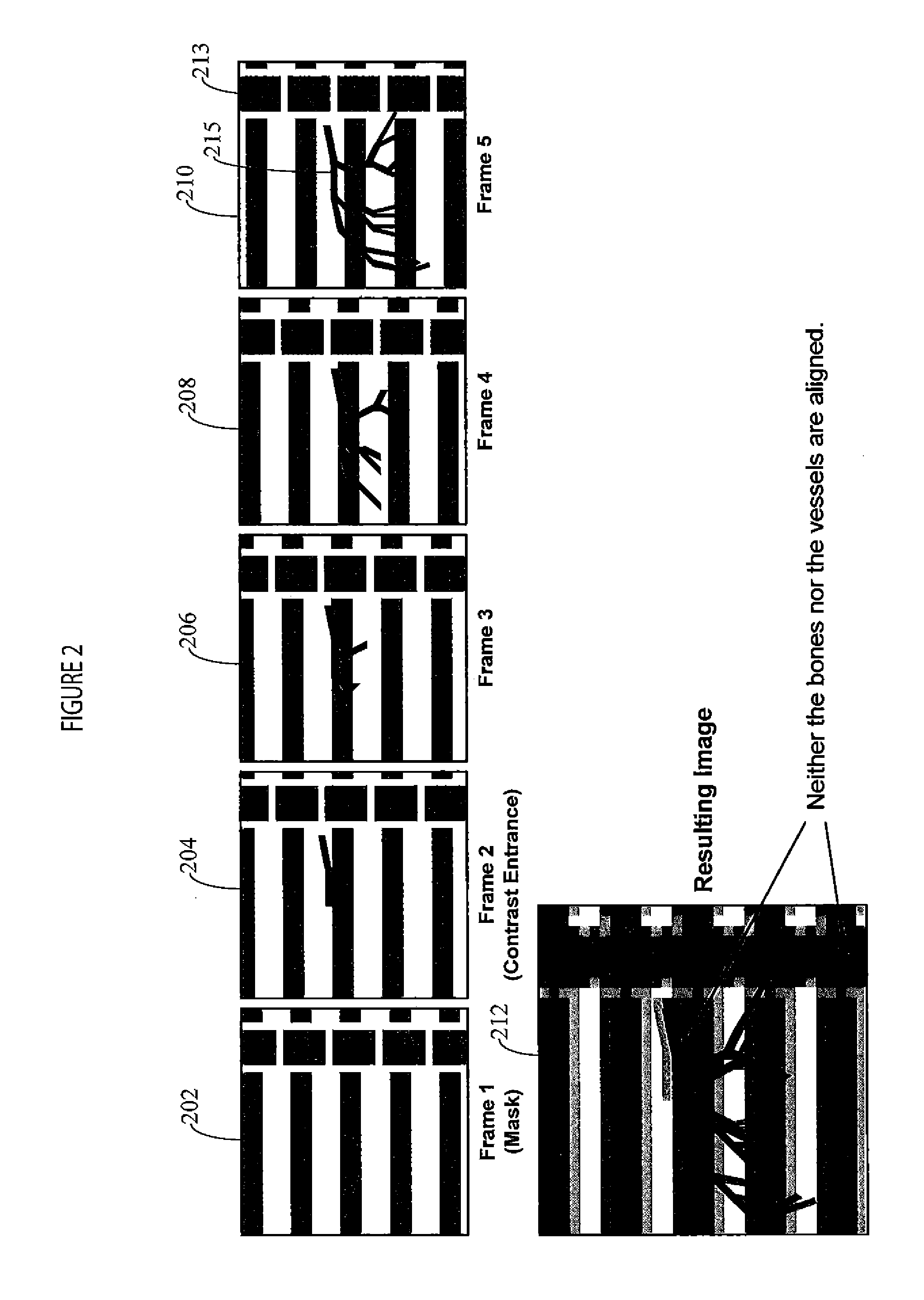
Method for eliminating motion artifacts in digital subtraction angiography and system thereof
InactiveCN101822545ARemove Motion ArtifactsFine image registrationImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingTriangulation
A method for eliminating motion artifacts in digital subtraction angiography comprises the following steps: step 1, reading; step 2, selecting points; step 3, constructing a DSA space body; step 4, carrying out space slicing; step 5, connecting tracks; step 6, analyzing the space motion characteristics of DSA pixel; step 7, carrying out triangulation; step 8, carrying out affine transformation; step 9, carrying out space winding; step 10, optimizing; step 11, registering; step 12, carrying out grey correction; step 13, carrying out logarithmic subtraction angiography. The invention belongs to the technology of image processing. The method of space analysis is used so that the registering of DSA image is more accurate, thereby efficiently eliminating motion artifacts and obtaining clear angiography images. Thus, the diagnostic accuracy of a doctor is improved, and the working efficiency is increased.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Image stitching method and device
ActiveCN104268846AImprove timing performanceShorten the timeImage enhancementImage analysisMaximum intensity projectionImage stitching
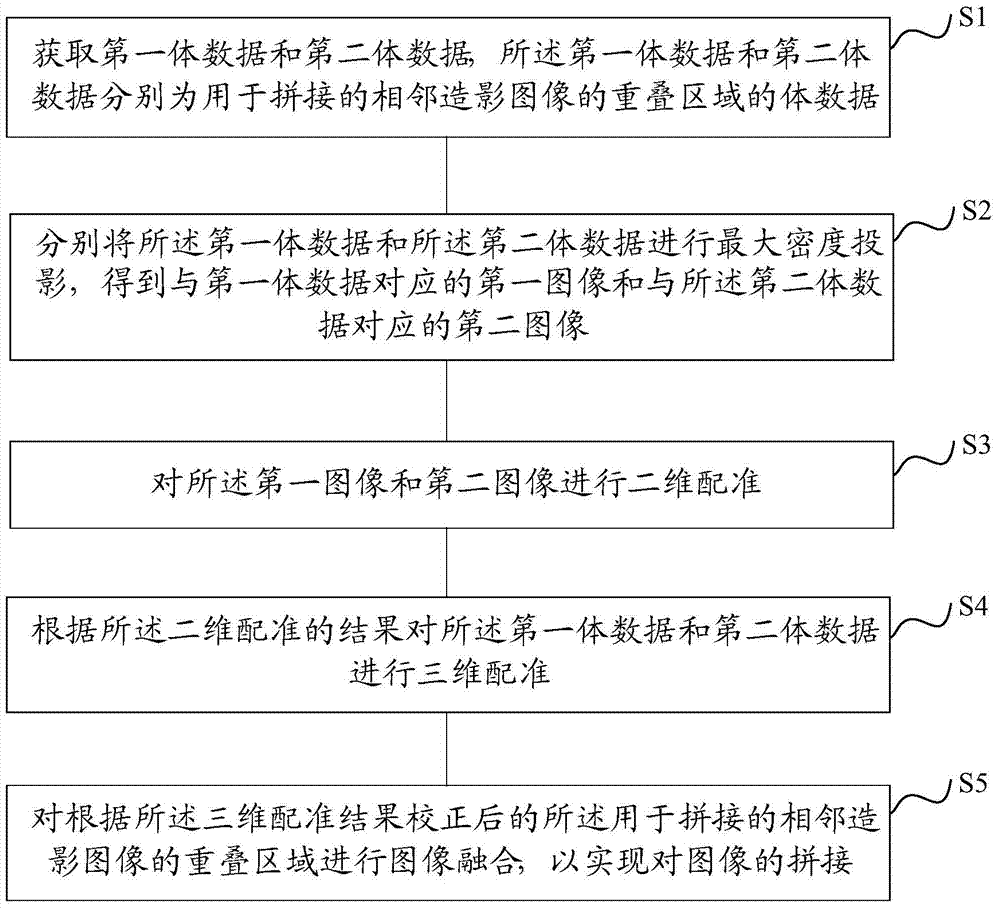
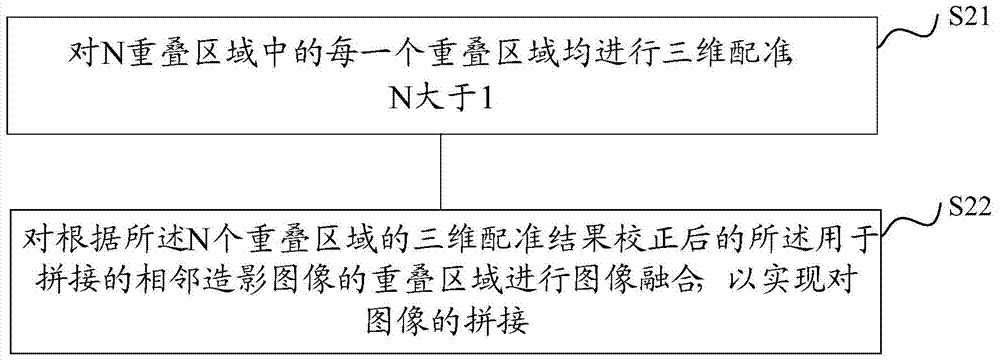
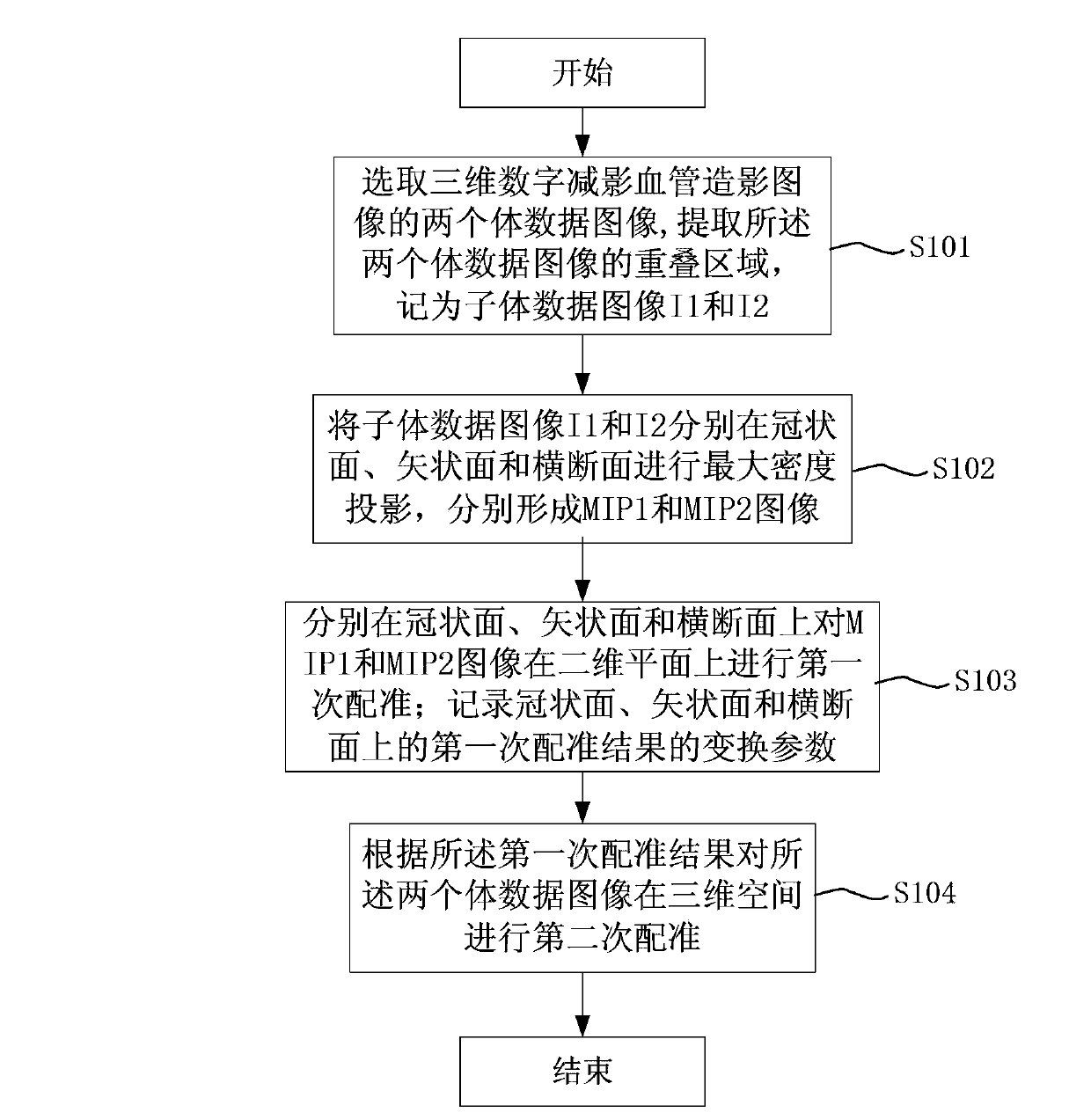
The invention provides an image stitching method and device. The image stitching method and device are used for stitching three-dimensional digital subtraction angiography images. The image stitching method comprises the steps of obtaining first volume data and second volume data, wherein the first volume data and the second volume data are volume data of overlapped areas, used for stitching, of every two adjacent angiography images; maximum intensity projection is conducted on both the first volume data and the second volume data, so that a first image corresponding to the first volume data and a second image corresponding to the second volume data are obtained; two-dimensional registration is conducted on the first image and the second image; according to a registration result, three-dimensional registration is conducted on the first volume data and the second volume data; image fusion is conducted on the overlapped areas, used for stitching, of every two adjacent angiography images after correction is conducted according to a three-dimensional registration result, and therefore stitching of the images is achieved. By the adoption of the image stitching method, the accuracy of a three-dimensional registration algorithm can be effectively improved, and the stitching time of the images can be effectively shortened.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
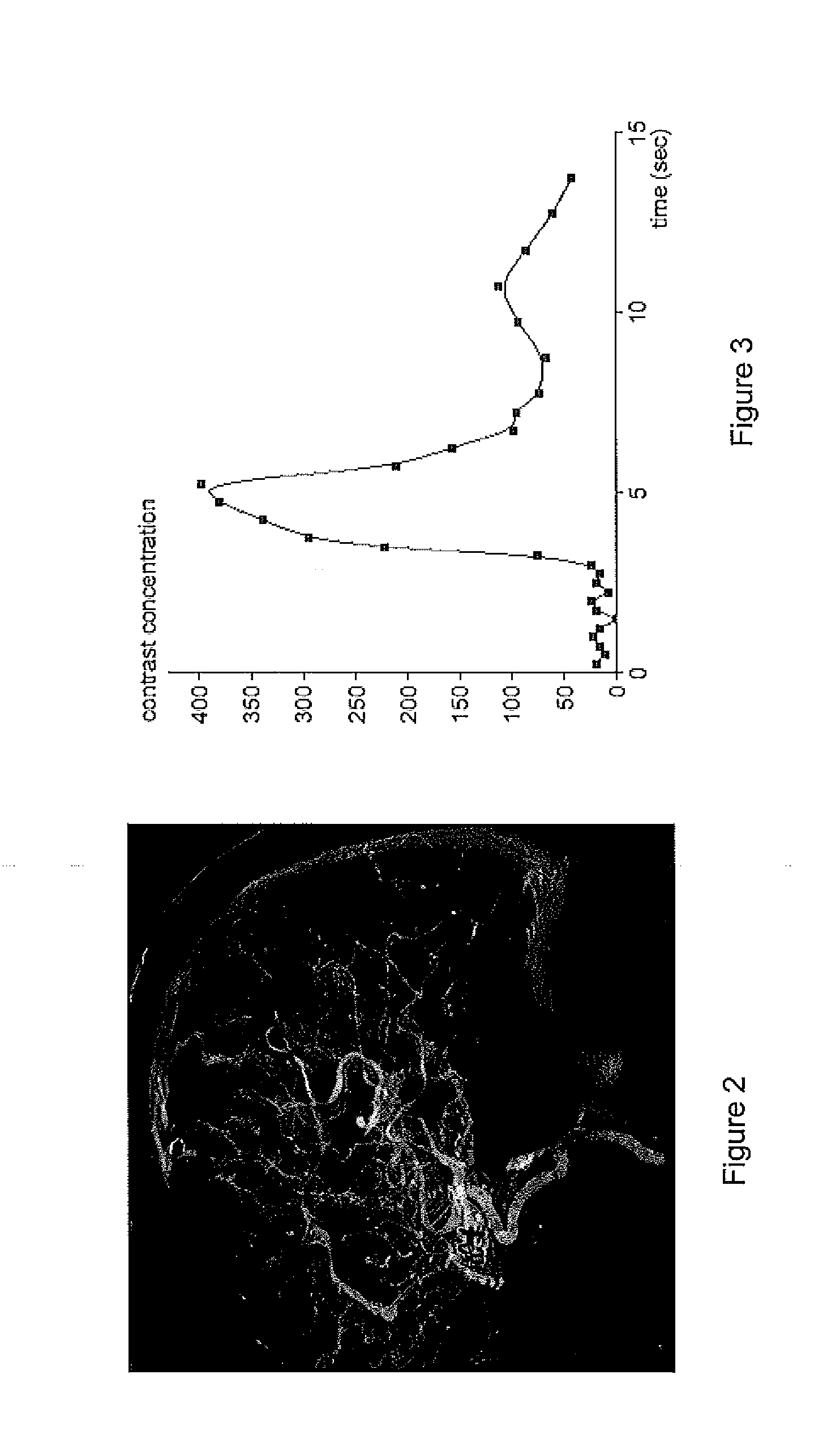
Perfusion digital subtraction angiography
ActiveUS20190015061A1Improve patient outcomesSustain viabilityImage enhancementImage analysisTime density curveVolumetric Mass Density
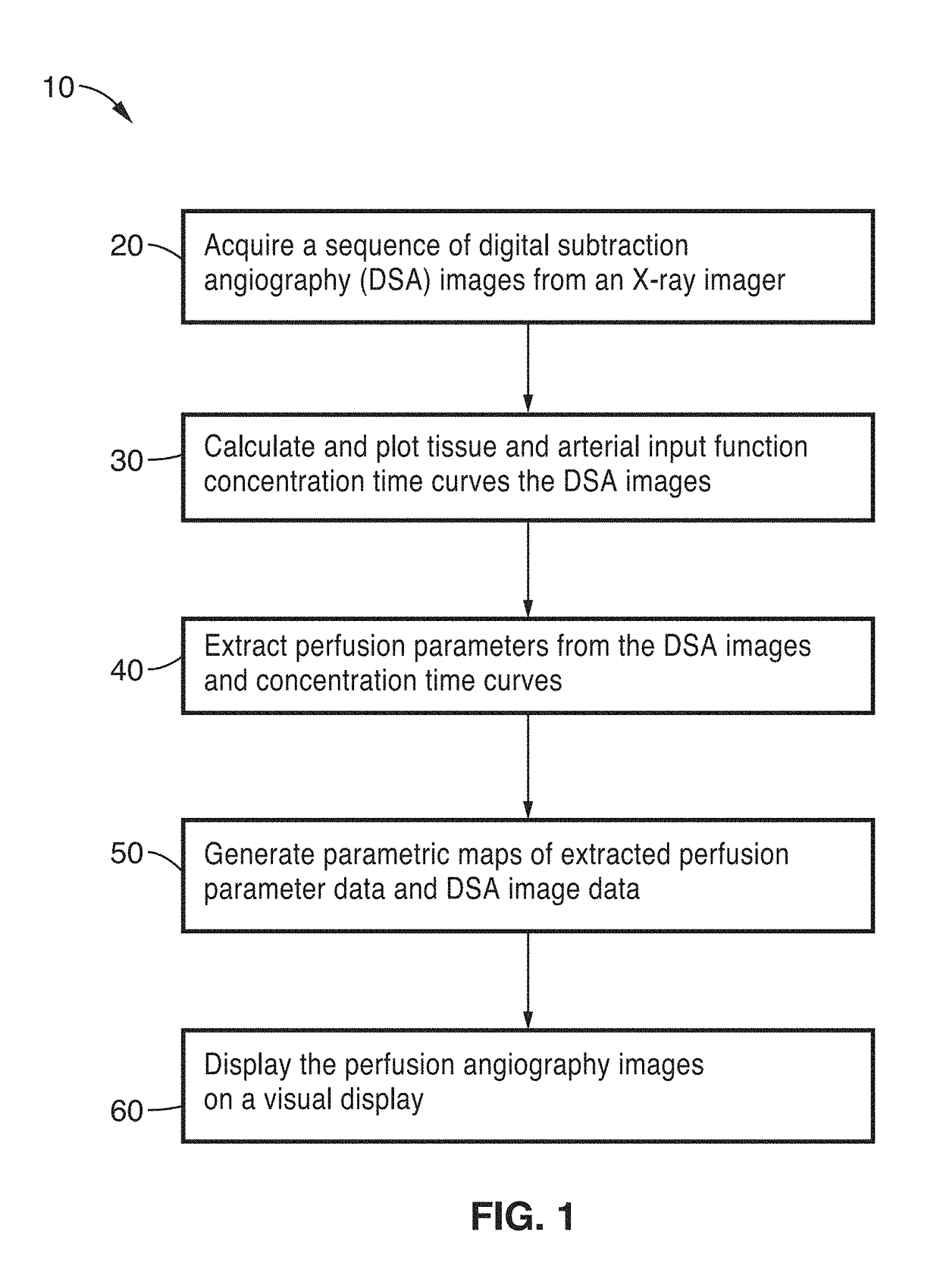
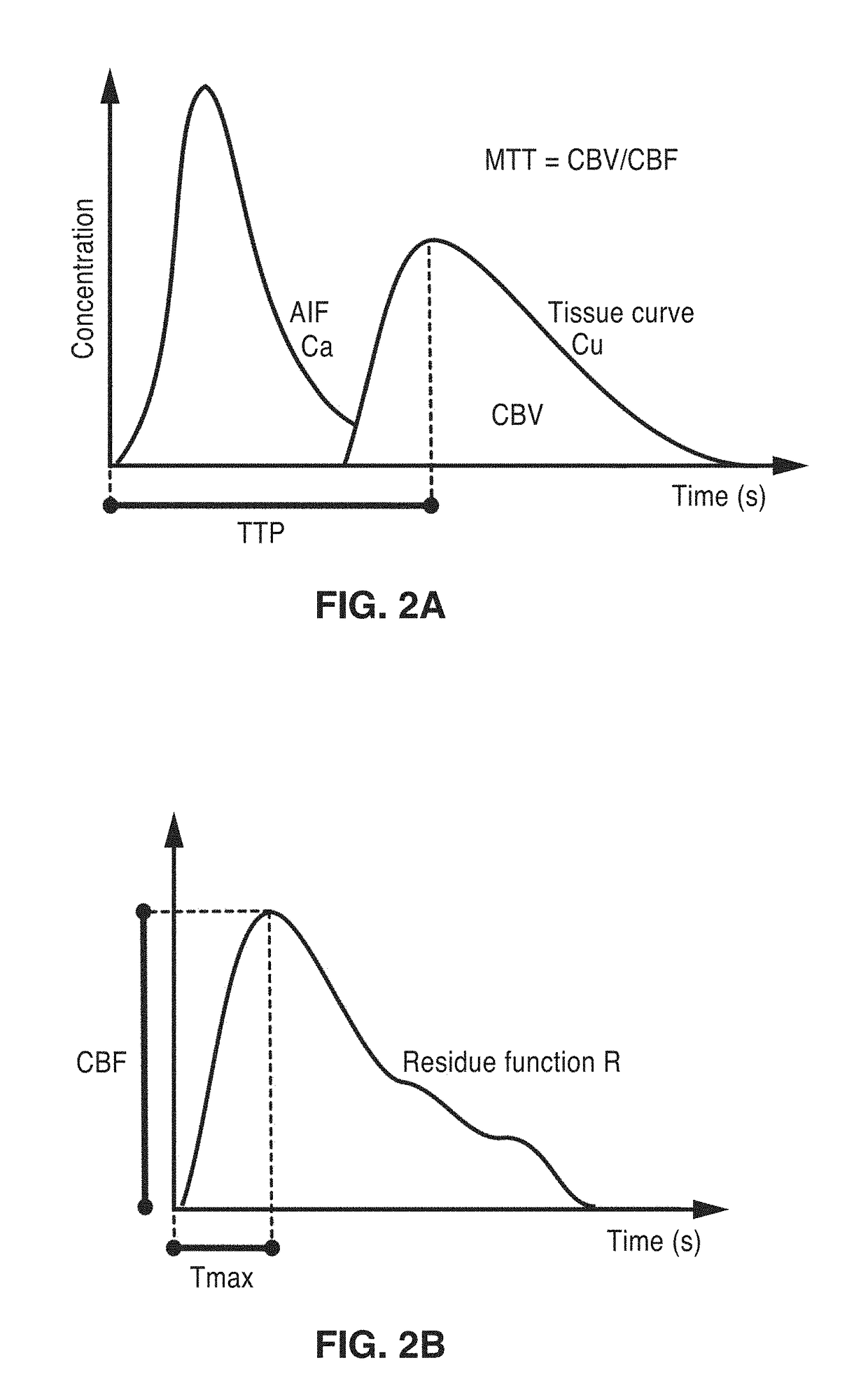
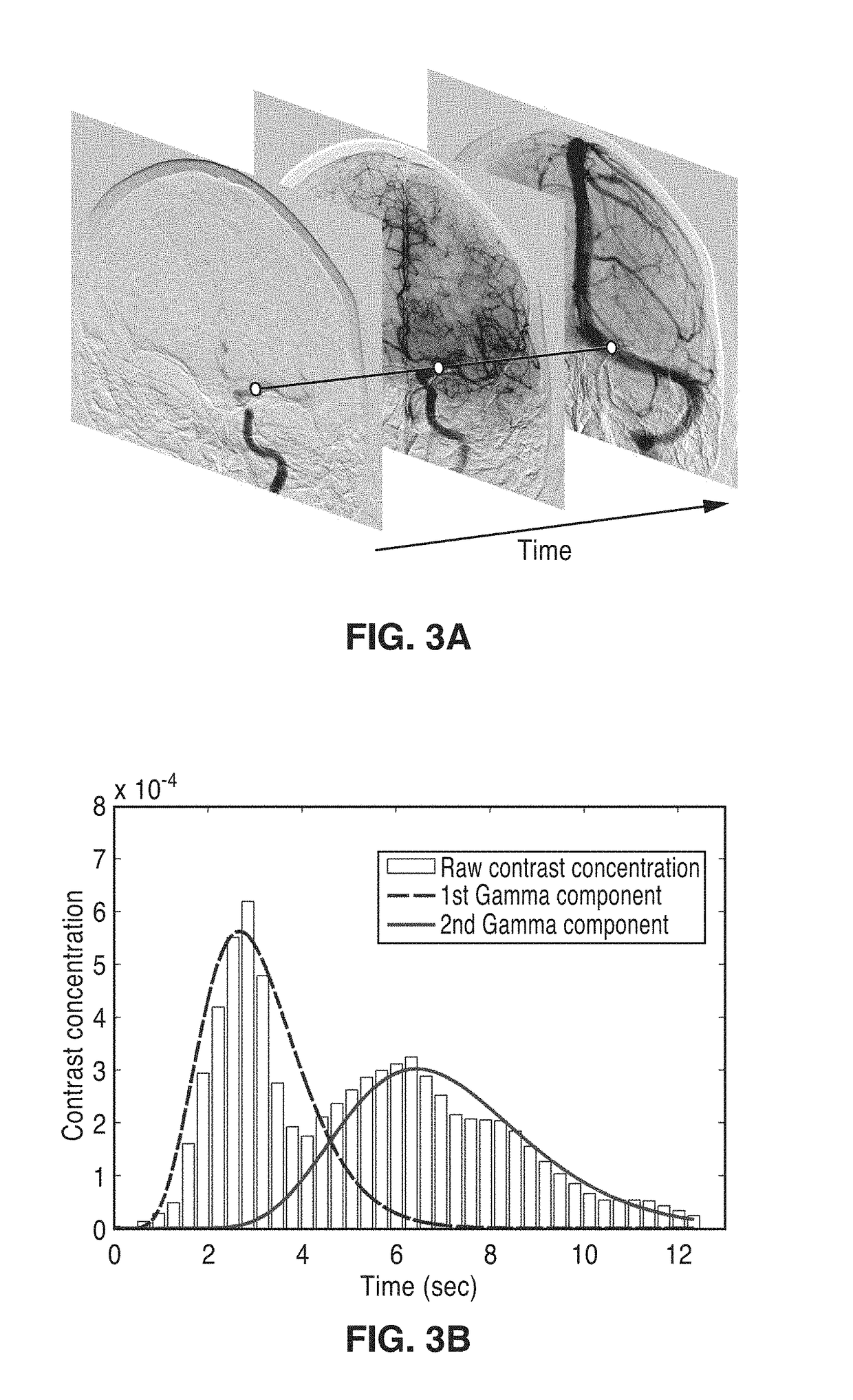
An apparatus and methodological framework are provided, named perfusion angiography, for the quantitative analysis and visualization of blood flow parameters from DSA images. The parameters, including cerebral blood flow (CBF) and cerebral blood volume (CBV), mean transit time (MTT), time-to-peak (TTP), and Tmax, are computed using a bolus tracking method based on the deconvolution of time-density curves on a pixel-by-pixel basis. Individual contrast concentration curves of overlapping vessels can be delineated with multivariate Gamma fitting. The extracted parameters are each transformed into parametric maps of the target that can be color coded with different colors to represent parameter values within a particular set range. Side by side parametric maps with corresponding DSA images allow expert evaluation and condition diagnosis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Electrochemical reactor for processing nitrogenous organic wastewater, and application and processing method thereof
InactiveCN103193301AEfficient removalAmmonium Oxide StrongWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fieldsElectrochemical responseChemical oxygen demand
The invention discloses an electrochemical reactor for processing nitrogenous organic wastewater, and an application and a processing method thereof, and belongs to the field of processing nitrogenous organic wastewater. The device comprises a reaction container, a power supply, a gas outlet pipe, a water outlet pipe, a water outlet pipe valve and a water inlet system, and further comprises a packing material, a negative plate and a positive plate, wherein the packing material is formed by mixing active carbon and magnet particles; the negative plate is connected with the negative electrode of the power supply; the negative plate is a silicon dioxide plate loaded copper-palladium coating electrode, and the coating material consists of Pd and Cu at a mass ratio of 6: 1; and the positive plate is a digital subtraction angiography (DSA) oxide coating electrode Ti / IrO2-PtO2. The reactor is a batch-type operation three-dimensional electrode reactor which adopts a mixture of active carbon particles and magnet particles with similar diameter as the packing material, and has the functions of efficiently removing nitrate nitrogen, ammonia nitrogen and COD (chemical oxygen demand), and is low in energy consumption; and the reactor is capable of achieving a purpose of removing nitrogen and COD in the nitrogenous organic wastewater.
Owner:GUODIAN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION RES INST CO LTD +1
Rapid registering and splicing method used for three-dimensional digital subtraction angiography image
ActiveCN103871036AAvoid registration accuracy impactReduce processing timeImage enhancementGeometric image transformationThree-dimensional spaceMaximum intensity projection
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
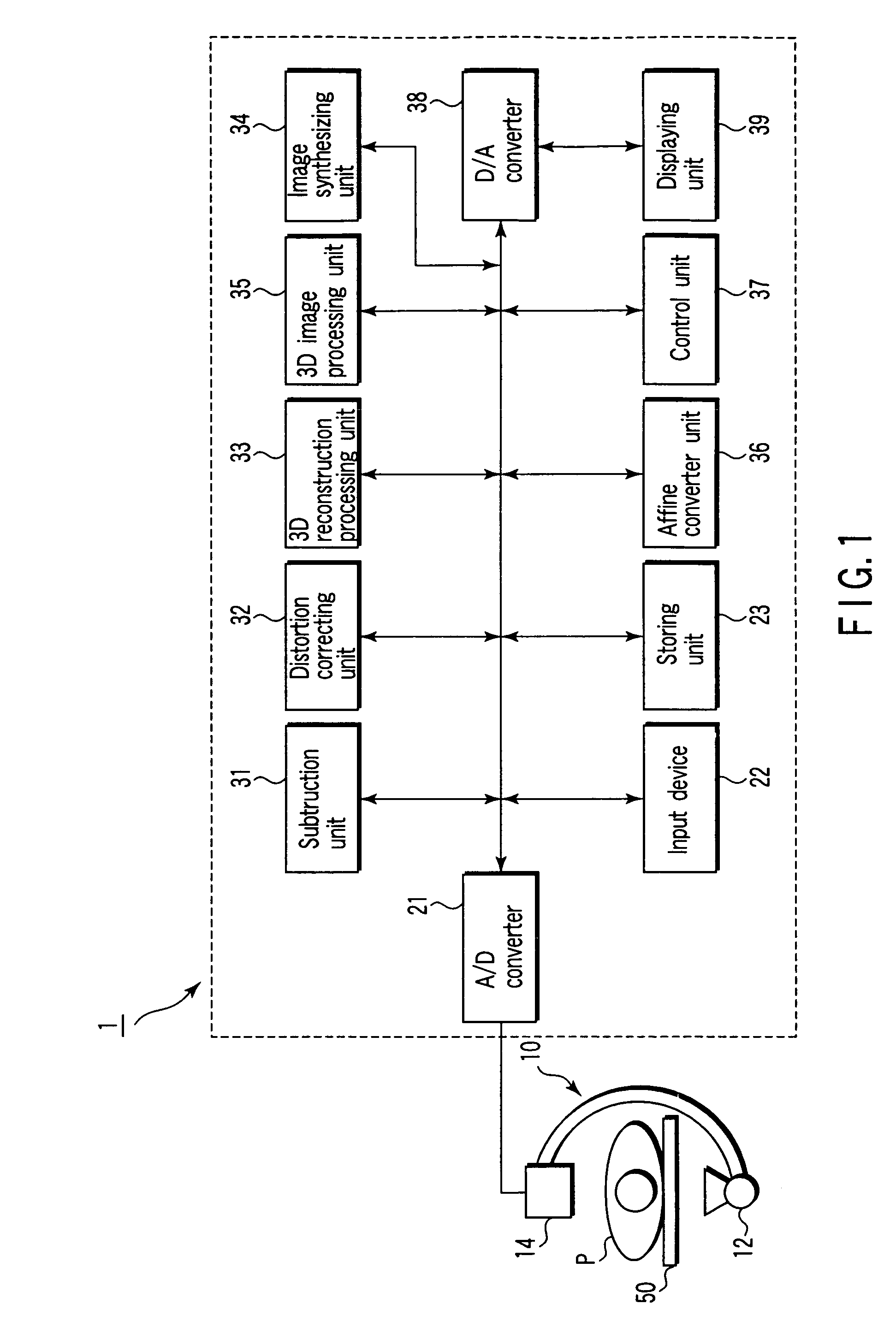
3D digital subtraction angiography image processing apparatus
InactiveUS7432924B2Clear separationTelevision system detailsImage enhancementImaging processingBone structure
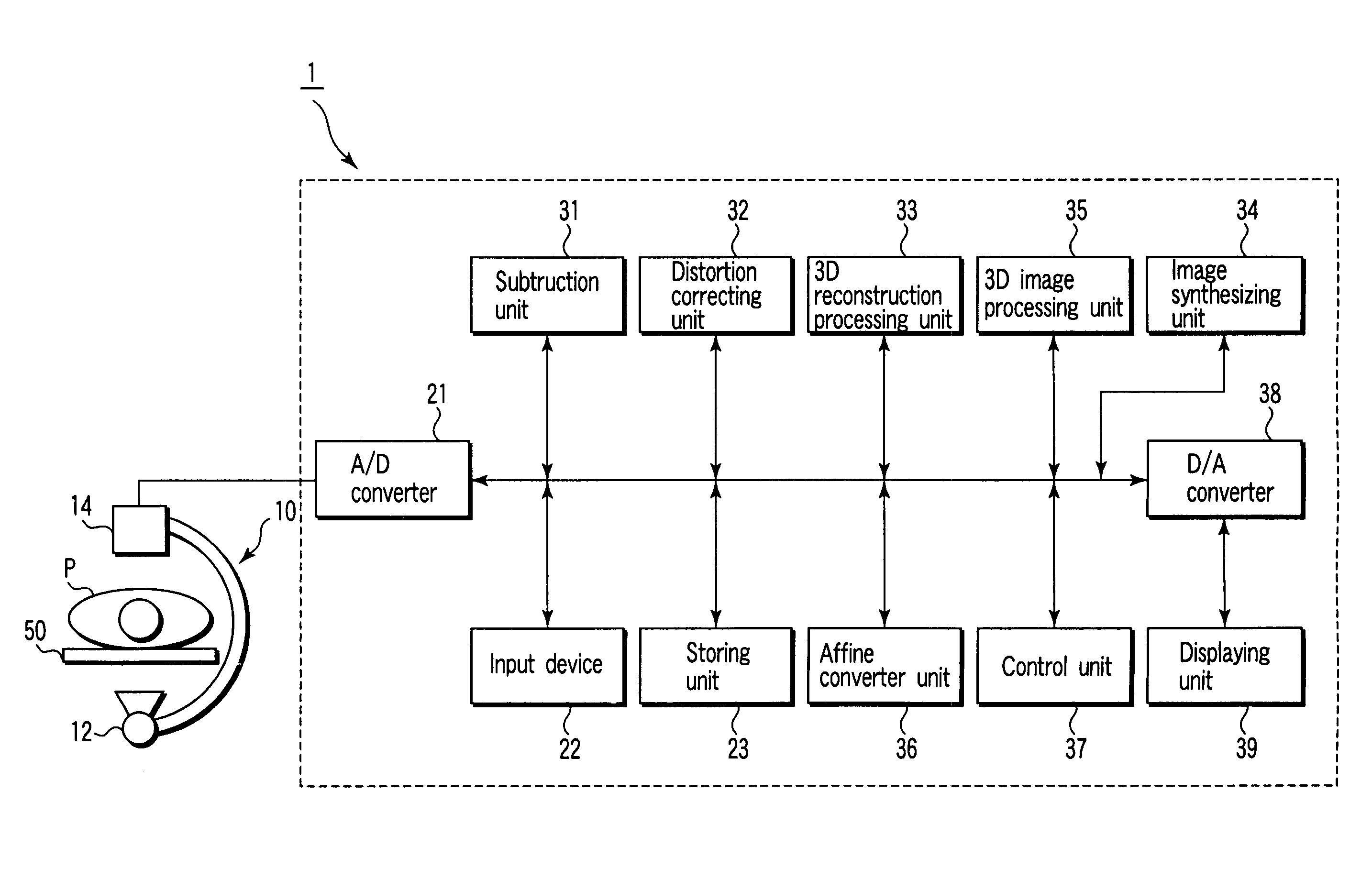
A 3D image processing apparatus comprises a storing unit storing mask images corresponding to projection directions associated with a subject contrast images corresponding to the projection directions, a subtracting unit generating subtraction images by subtracting the mask images from the contrast images, a reconstruction unit reconstructing first volume data from the mask images and reconstructs second volume data from the subtraction images, an image processing unit generating a first 3D image representing a bone structure and / or a soft tissue structure from the first volume data, and generates a second 3D image representing a contrasted blood vessel from the second volume data, an image synthesizing unit generating a synthetic image by synthesizing the first 3D image with the second 3D image, and a displaying unit displaying the synthetic image.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
System and Method For Coronary Digital Subtraction Angiography
InactiveUS20080025588A1SurgeryRecognition of medical/anatomical patternsAnatomical structuresFluoroscopic image
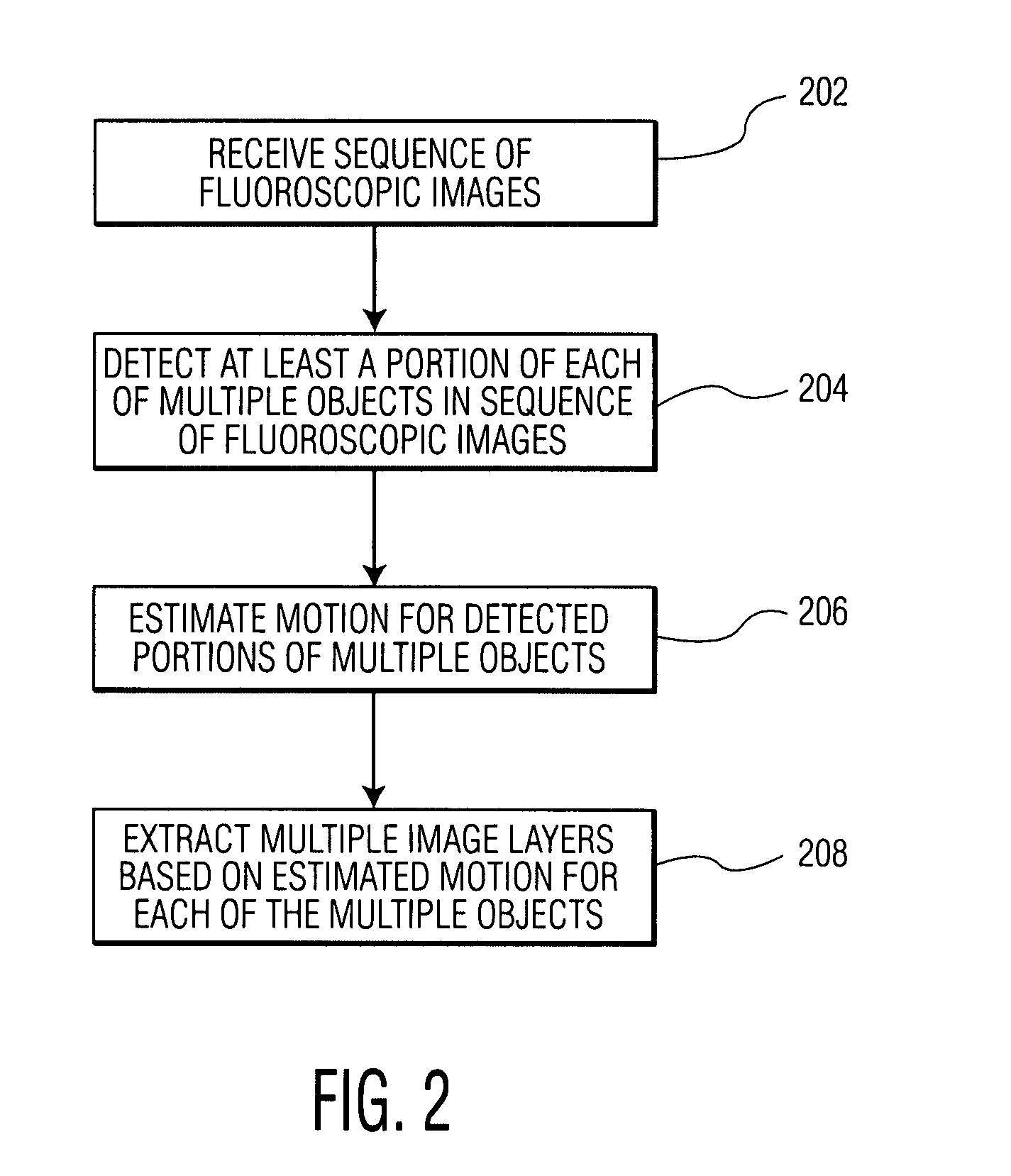
A method and system for extracting motion-based layers from fluoroscopic image sequences are disclosed. Portions of multiple objects, such as anatomical structures, are detected in the fluoroscopic images. Motion of the objects is estimated between the images is the sequence of fluoroscopic images. The images in the fluoroscopic image sequence are then divided into layers based on the estimated motion. In a particular implementation, the coronary vessel tree and the diaphragm can be extracted in separate motion layers from coronary angiograph fluoroscopic image sequence.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC +1
Method for efficient digital subtraction angiography
A system and method for performing DSA (digital subtraction angiography), which does not require a non-enhanced or “mask” image to be obtained.
Owner:PHILIPS MEDICAL SYST TECH
System and method for coronary digital subtraction angiography
A method and system for extracting coronary vessels fluoroscopic image sequences using coronary digital subtraction angiography (DSA) are disclosed. A set of mask images of a coronary region is received, and a sequence of contrast images for the coronary region is received. For each contrast image, vessel regions are detected in the contrast image using learning-based vessel segment detection and a background region of the contrast image is determined based on the detected vessel regions. Background motion is estimated between one of the mask images and the background region of the contrast image, and the mask image is warped based on the estimated background motion to generate an estimated background layer. The estimated background layer is subtracted from the contrast image to extract a coronary vessel layer for the contrast image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
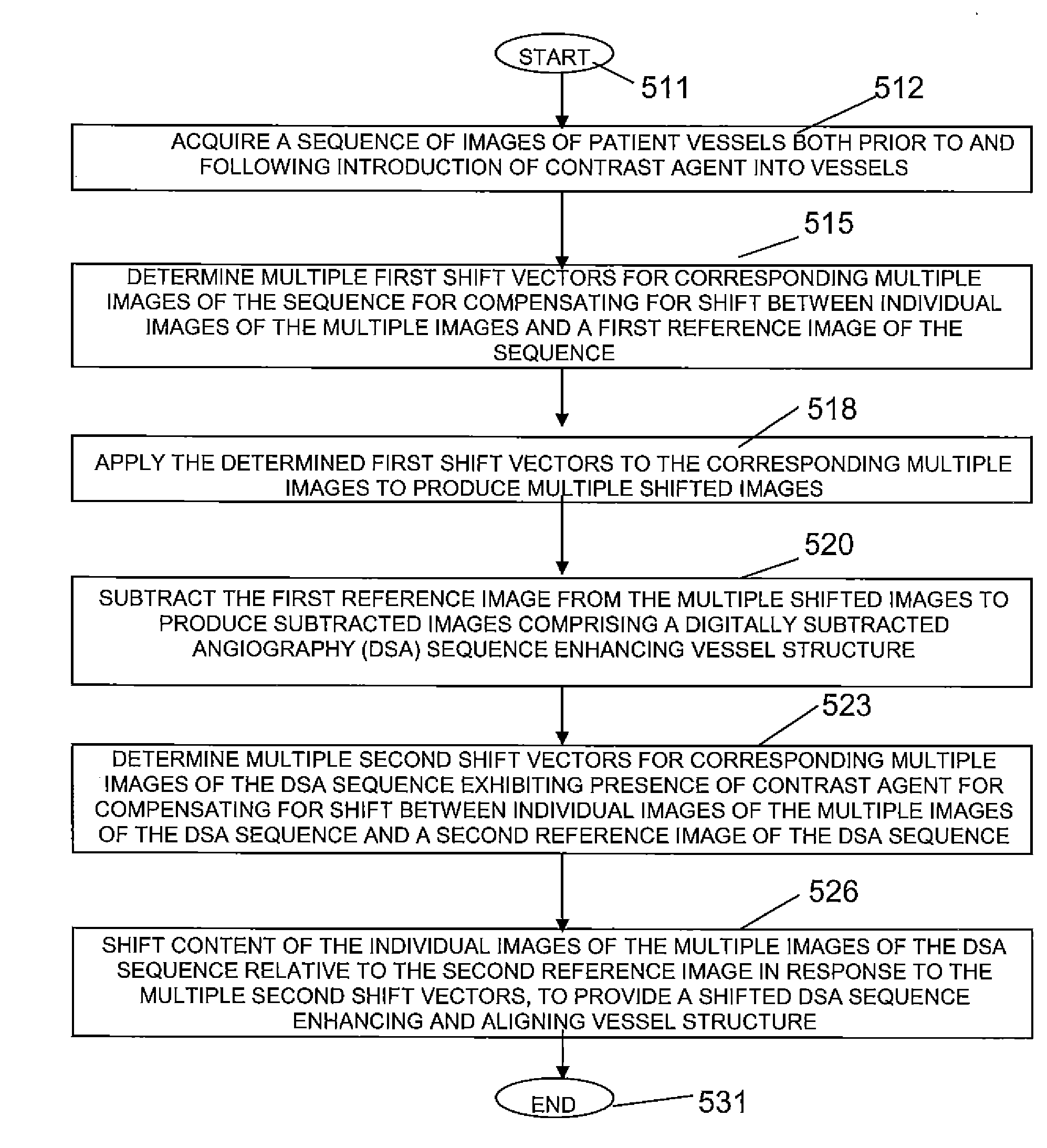
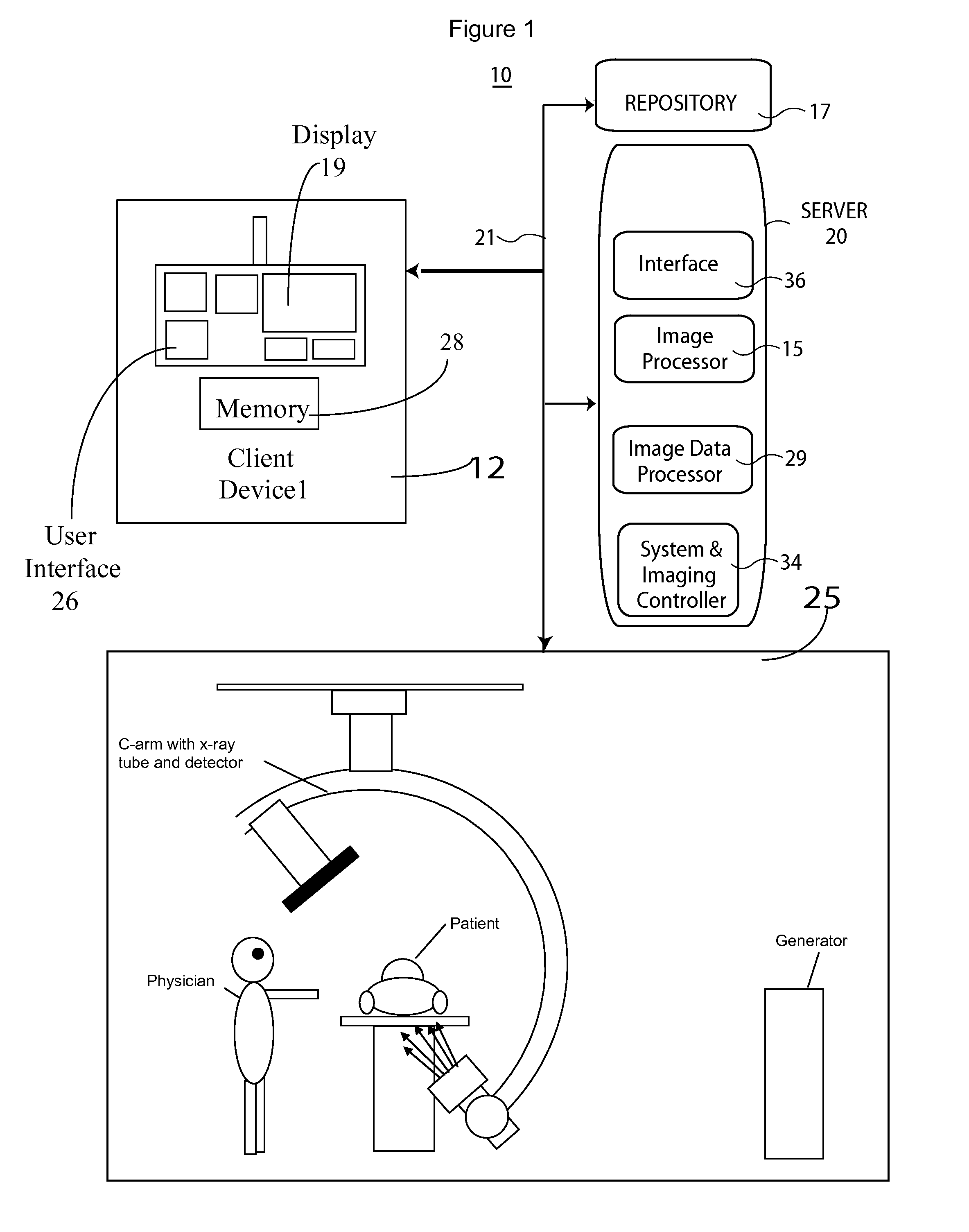
Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) Motion Compensated Imaging System
ActiveUS20120201439A1Improves pixel-shift motion correctionReduce relative motionImage enhancementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationReference imageShift vector
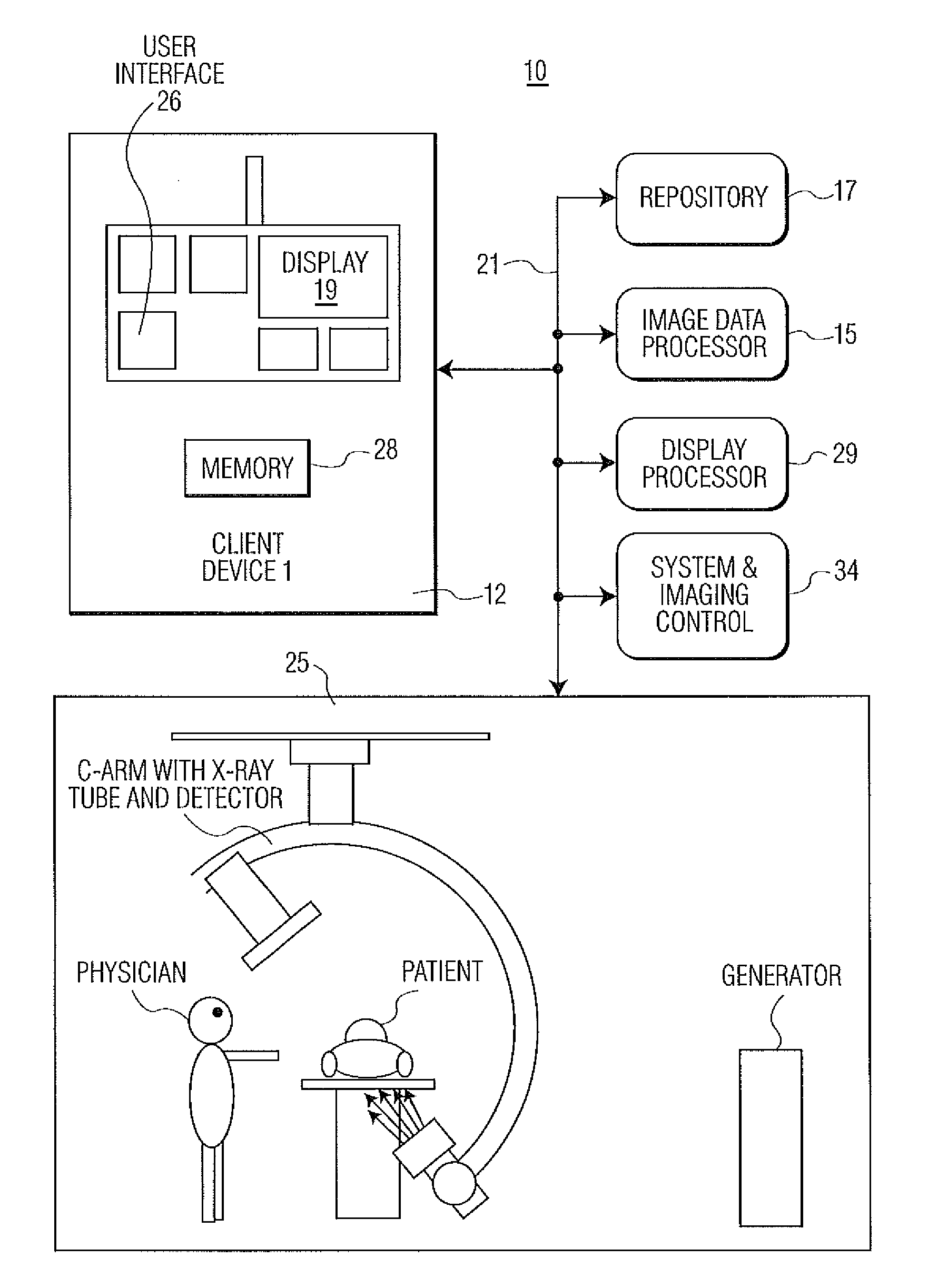
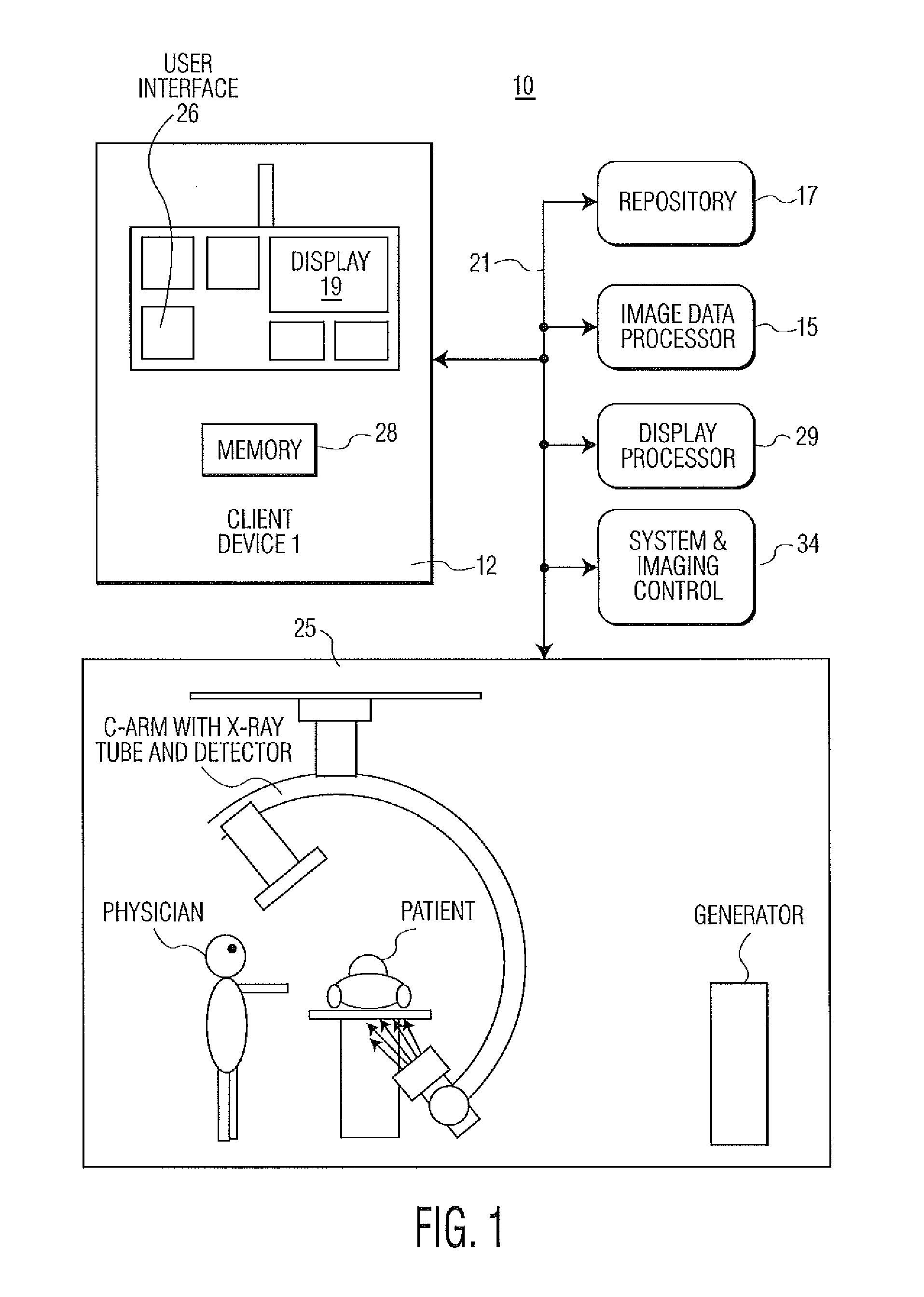
A motion compensated digitally subtracted Angiography (DSA) image processing system includes an interface for acquiring a sequence of images of patient vessels both prior to and following introduction of contrast agent into the vessels. An image data processor automatically, (a) determines a first shift vector for a first image of the sequence for compensating for shift between the first image and a first reference image of the sequence, (b) applies the determined first shift vector to the first image of the sequence to produce a shifted image, (c) subtracts the first reference image from the shifted image to produce a subtracted image enhancing vessel structure, (d) determines a second shift vector for compensating for shift between the subtracted image and a second reference image and (e) shifts content of the subtracted image relative to the second reference image in response to the second shift vector, to provide a shifted subtracted image enhancing and aligning vessel structure.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
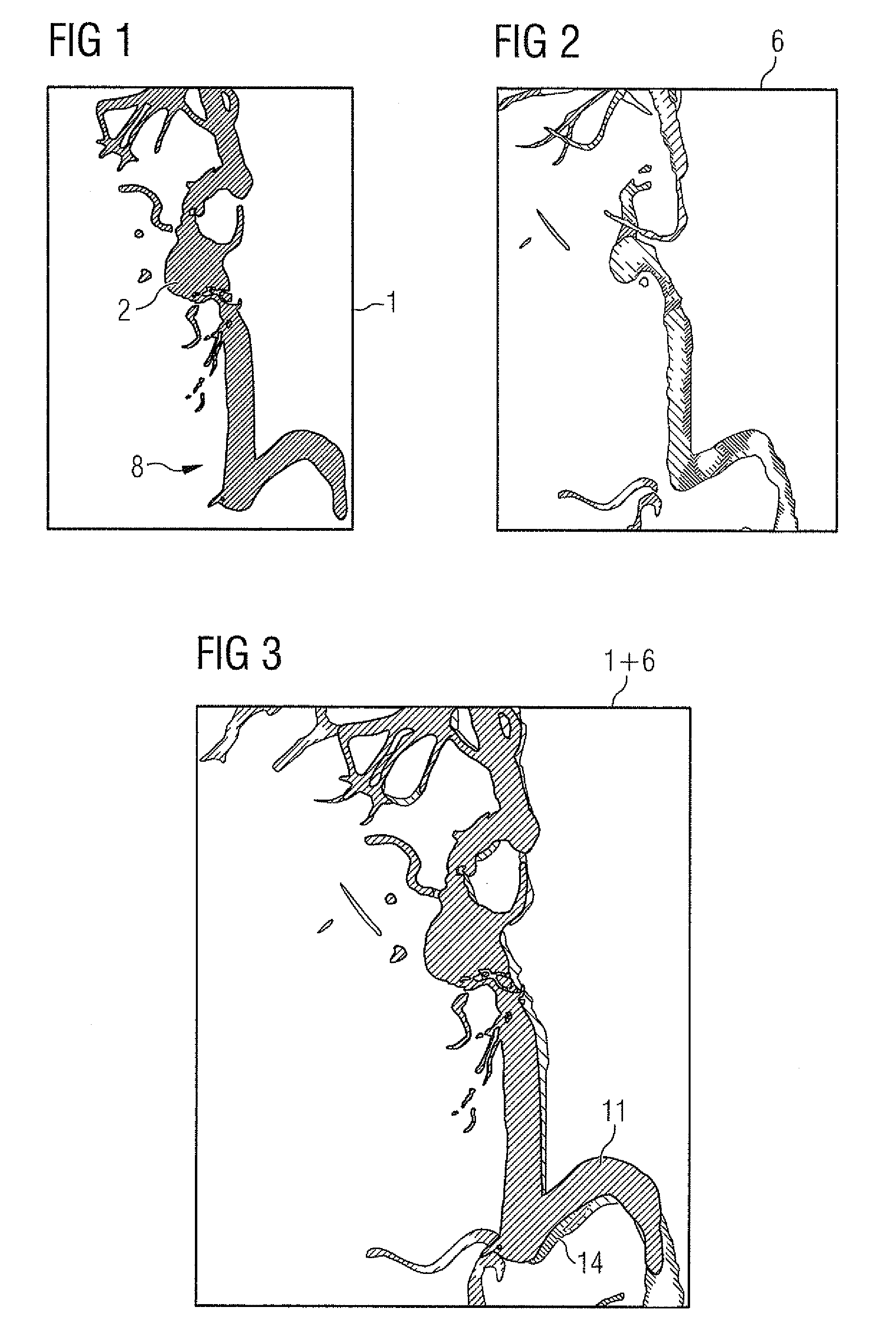
Method for post-processing a three-dimensional image data set of vessel structure
InactiveUS7903856B2Sure easyReduce the differenceImage enhancementImage analysisData setProjection image
The invention relates to a method for post-processing a 3D image data set of a vessel structure of a human or animal body, in which a 2D DSA (Digital Subtraction Angiography) of the vessel structure is recorded and registered with the 3D image data set. The 2D DSA is compared with a corresponding projection image computed from the 3D data set and this is changed, e.g. by changing the segmentation parameters, to adapt it to the 2D DSA. This enables the outstanding local resolution of the 2D DSA to be used for improving the 3D image data set.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Generating an at Least Three-Dimensional Display Data Sheet
ActiveUS20150173699A1Improve directionImproved determinationImage enhancementImage analysisData setX-ray
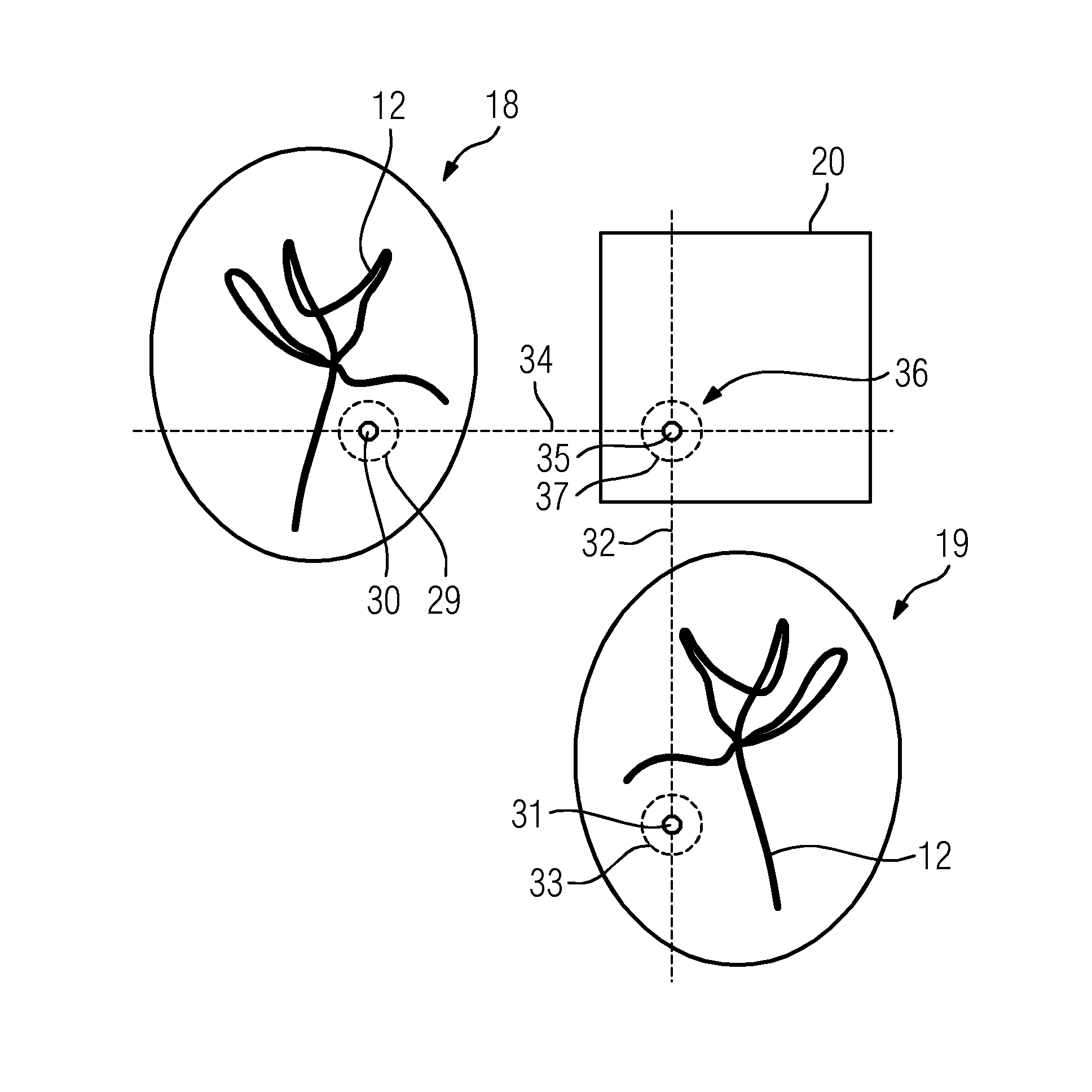
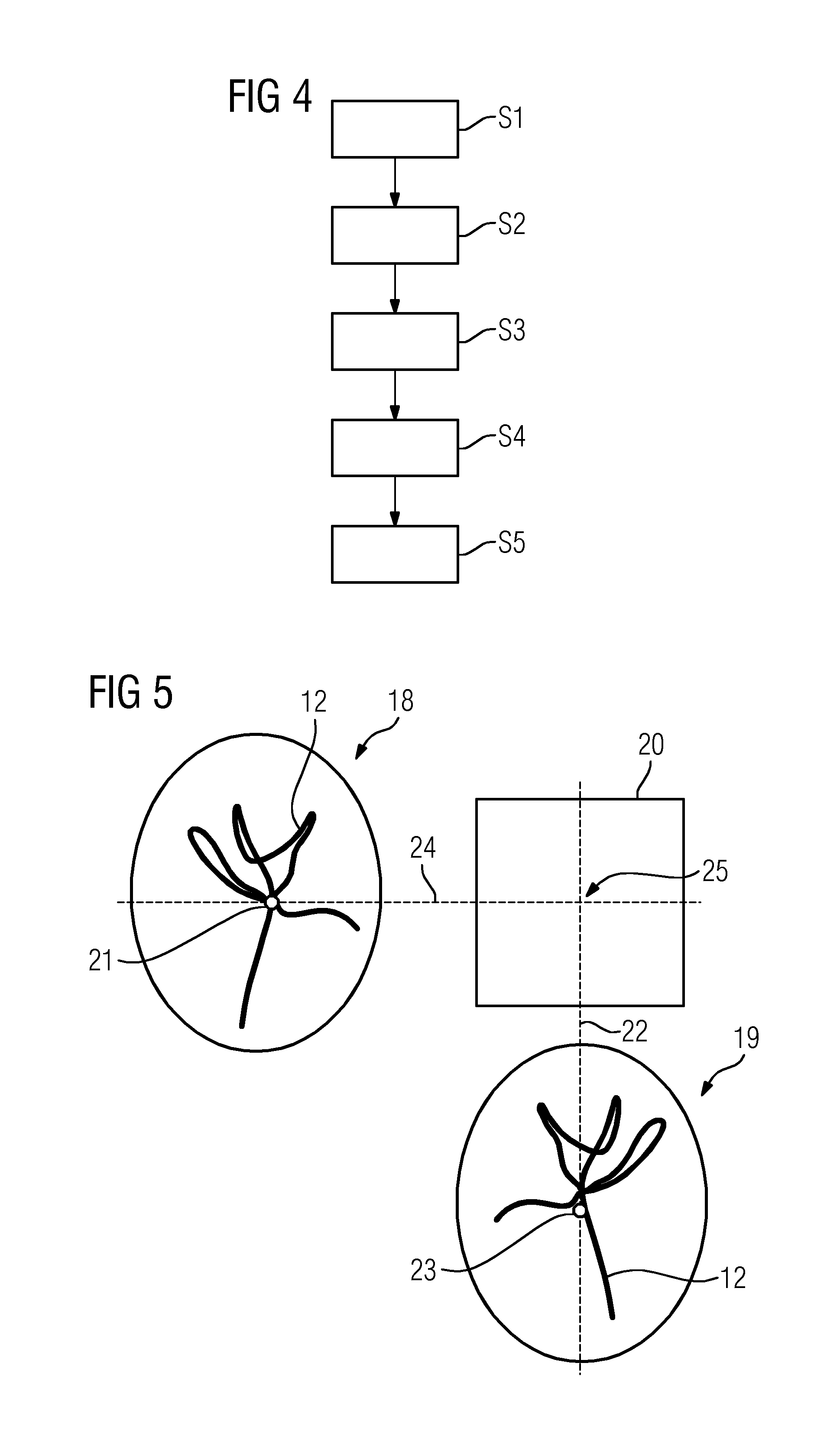
A method for generating an at least three-dimensional display data set of a time parameter relating to the chronological spreading of a contrast medium introduced into a vessel system is provided. A series of chronologically successive x-ray images of digital subtraction angiography from at least two different projection directions showing the chronological spreading of the contrast medium is used. The method includes determining a three-dimensional position for at least one correspondence point and / or correspondence region defined, in each case, in at least one x-ray image of a projection direction. For each three-dimensional position, a time parameter assigned to the three-dimensional position is determined by evaluation of time-intensity curves assigned to the correspondence points or correspondence regions over the series. The display data set formed from the three-dimensional positions is displayed with the assigned time parameters.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
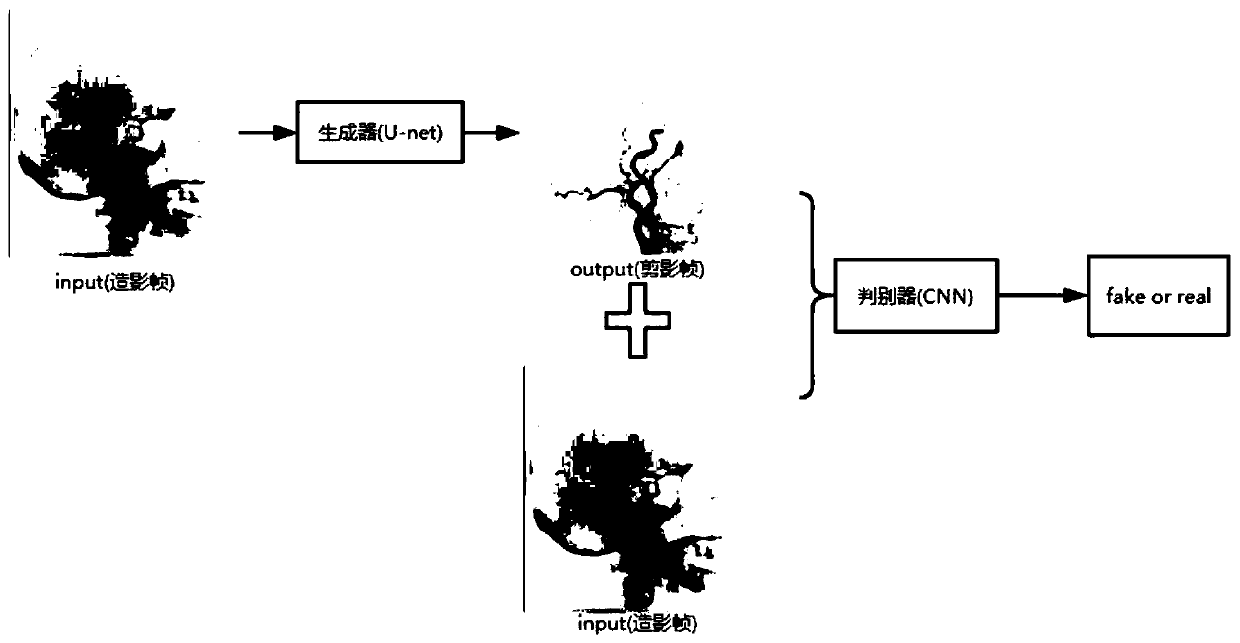
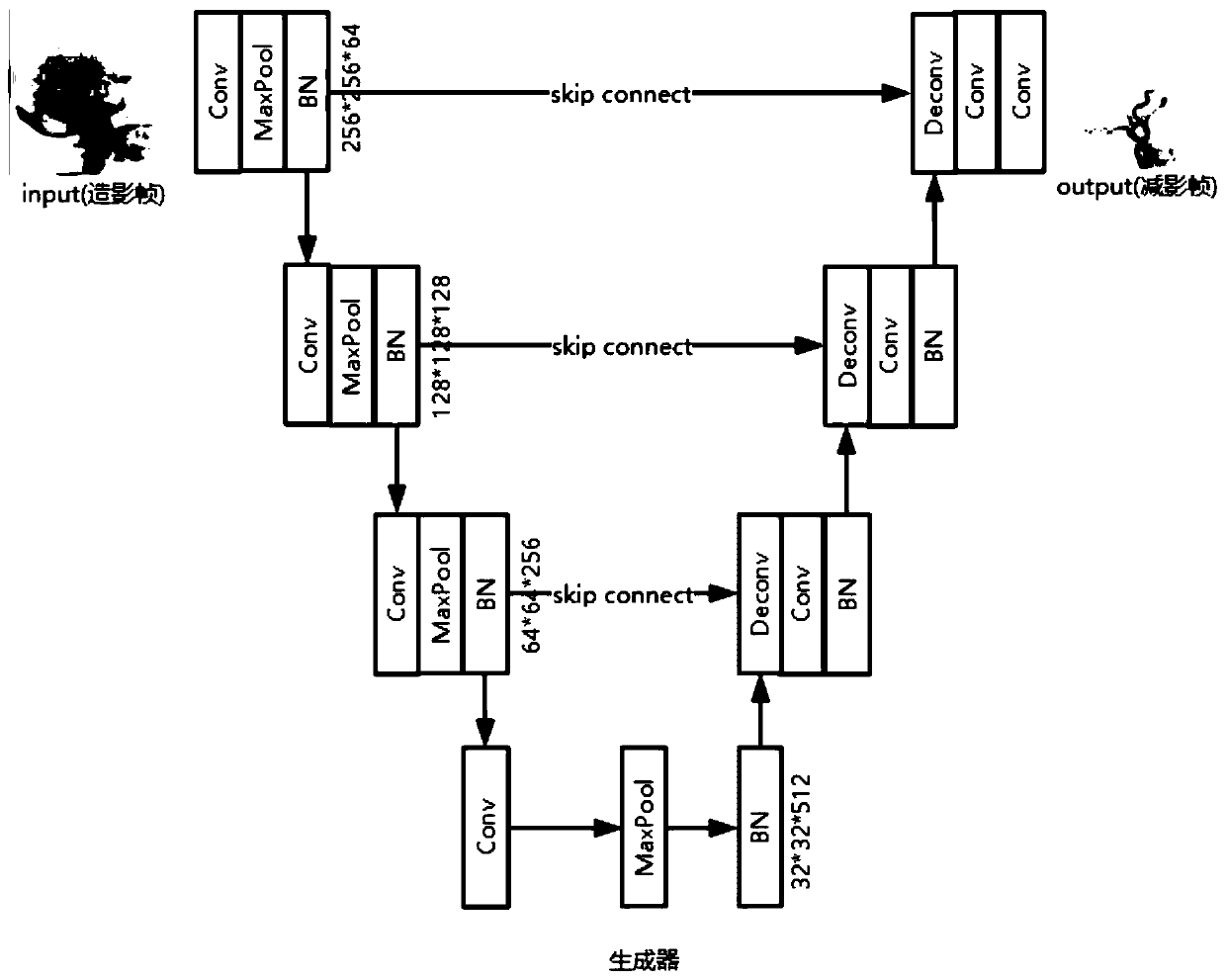
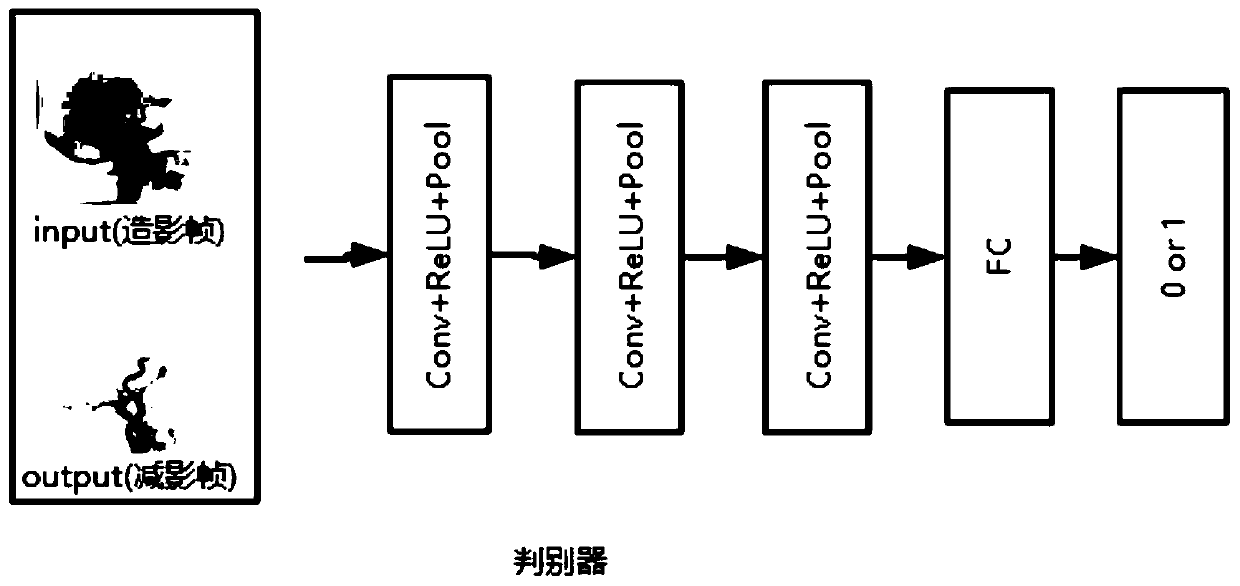
U-net based generation adversarial network DSA imaging method and device
PendingCN110163809AReduce the number of scansEfficient separationImage enhancementImage analysisImaging qualityOriginal data
The invention discloses a U-net based generation adversarial network based digital substration angiography DSA imaging method and device. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, obtaining aplurality of groups of radiography frames and original data corresponding to the subtraction frames; secondly, establishing a U-shaped structure convolutional network, coding and extracting featuresof different scales, and decoding and recovering corresponding features by using a skill connected object, wherein the network inputs a radiography frame and outputs a corresponding subtraction frameto reduce the dependence of DSA generation on a background frame so as to remove motion artifacts generated by motion of a patient; then, by means of generative adversarial training, alternately training the generator and the discriminator, and enhancing the quality of generated digital blood vessel subtraction. According to the method, the motion artifacts in the digital substration angiography (DSA) can be effectively removed, the data quality can meet the requirements of clinical analysis, diagnosis and the like, the DSA imaging quality is improved, and the influence caused by motion of a patient is reduced.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for pixel shift calculation in digital subtraction angiography and X-ray diagnostic imaging system for generating images in digital subtraction angiography
InactiveUS8299413B2Improve display image qualityFlickering is reduced or even completely avoidedImage enhancementImage analysisX-rayContrast enhancement
An X-ray diagnostic imaging system for generating images in digital subtraction angiography is proposed. A mask image frame of a patient and a series of live image frames of the patient acquired in the same imaging position of the mask frame acquisition are accessed. One of the mask and the live image frames is contrast-enhanced. Possible shift vectors in a region of interest are assumed being a difference vector between the mask and a respective live image frame and a scoring is calculated. Possible shift vector with the highest scoring is chosen as an elected shift vector. A likelihood representing a quality value of the elected shift vector is calculated. The mask image frame is shifted with respect to the respective live image frame by a modified shift vector depending on the likelihood. The shifted mask image frame is subtracted from the respective live image frame and is displayed.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method for segmenting blood vessel in digital subtraction angiography (DSA) image sequence
The invention discloses a method for segmenting a blood vessel in a digital subtraction angiography (DSA) image sequence. The method comprises the following steps of: removing noise from a background, performing background separation on an angiography sequence image by a fuzzy C-mean clustering algorithm, and extracting the blood vessel of the angiography sequence image in the angiography image sequence by a background difference method. The method can be used for effectively segmenting the angiography sequence, and is simple in operation and high in segmenting efficiency.
Owner:北京集翔多维信息技术有限公司
Device-based motion-compensated digital subtraction angiography
ActiveUS20170345145A1Display effectFocusImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionImaging processingProjection image
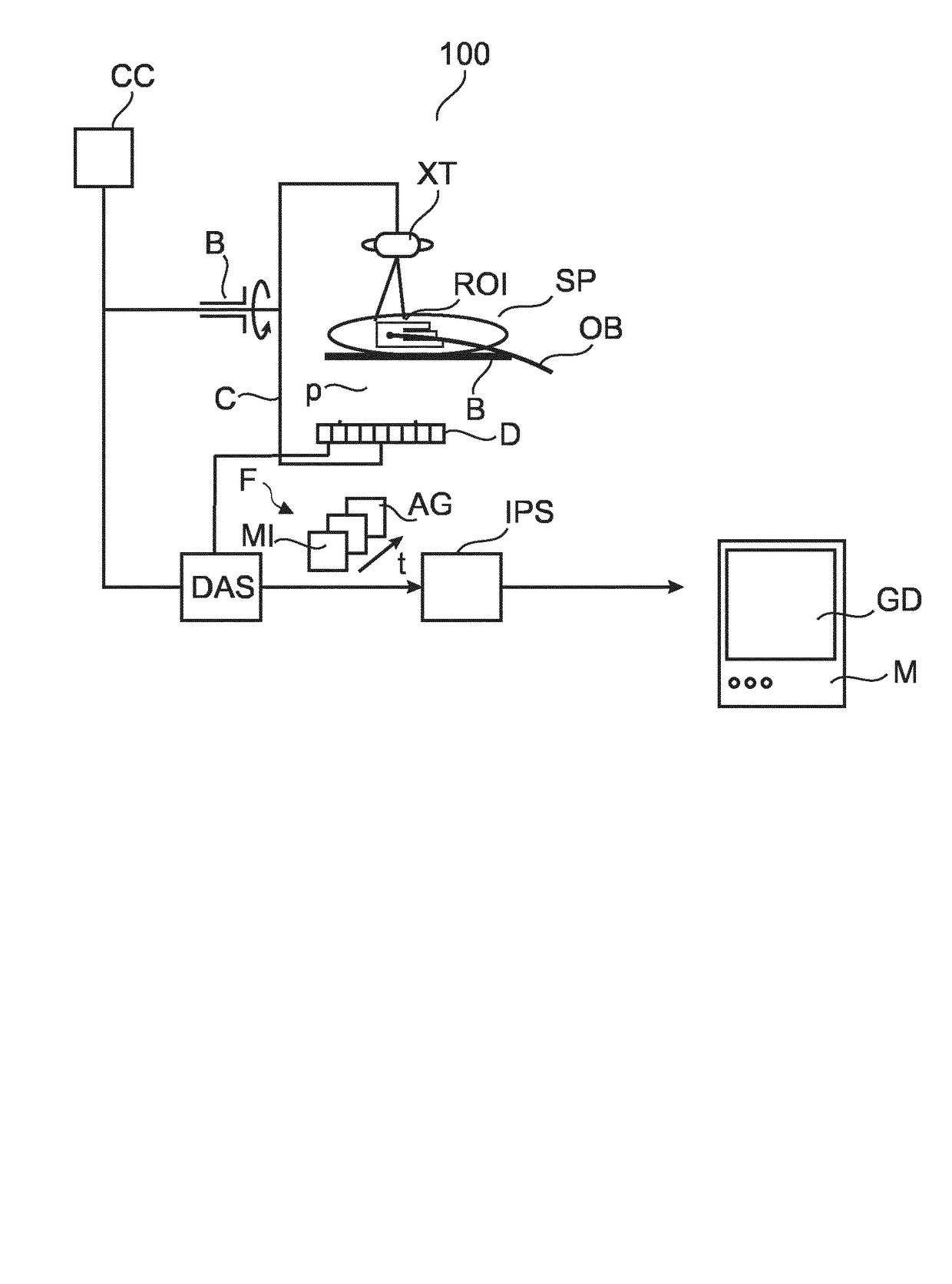
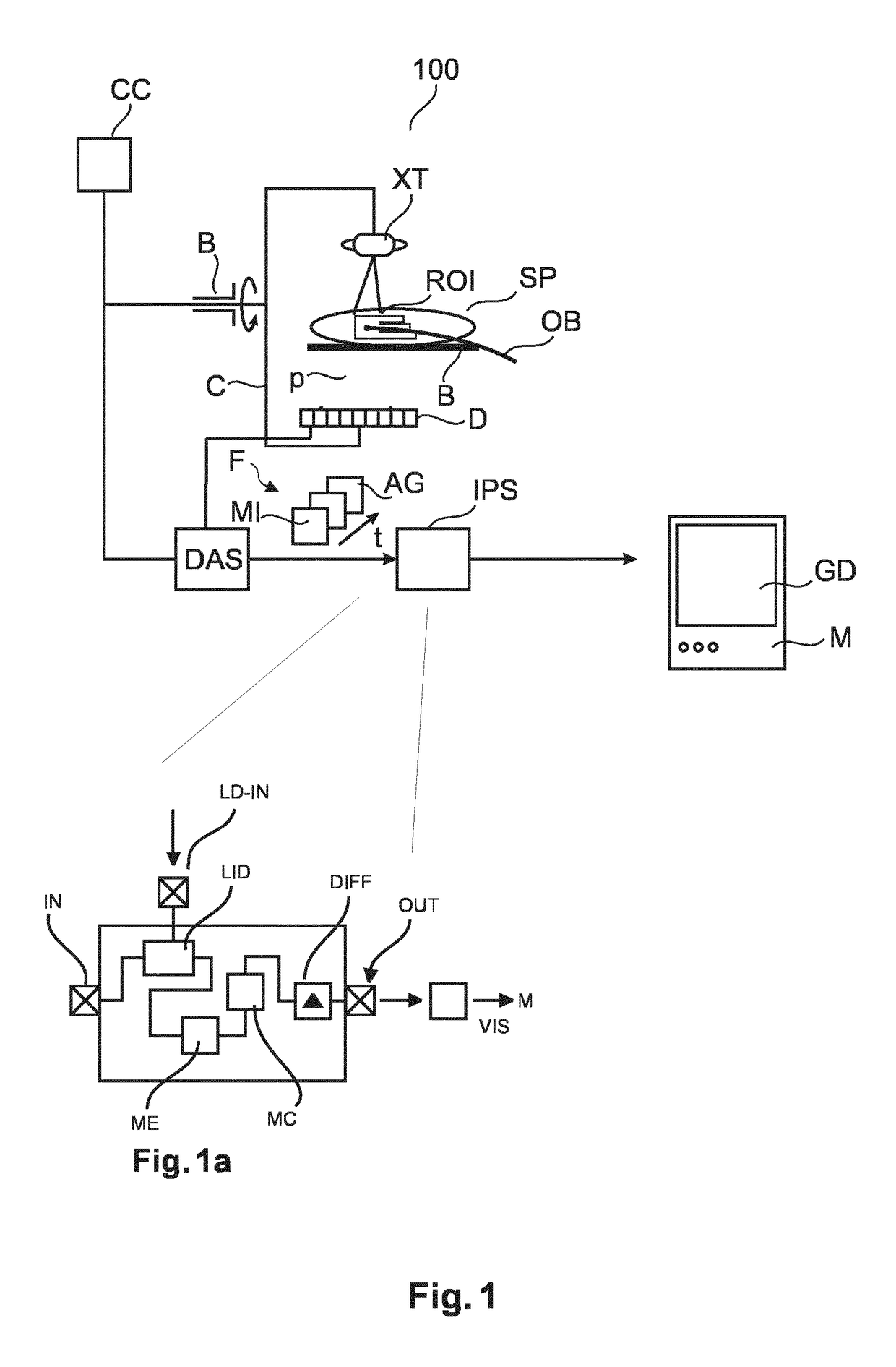
An image processing method and related system to register projection images (AG, MI) only with respect to a motion of a landmark across said images. The motion of the landmark relates to a motion of a region of interest, ROI. The so registered images (AG, MI) are then subtracted from each other to arrive at a difference image that is locally motion compensated and that represents the ROI at good contrast whilst subtraction artifacts can be avoided.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Mask construction for cardiac subtraction
ActiveUS20110305378A1Reduce impactLess motionCharacter and pattern recognitionTomographyDisplay deviceImproved method
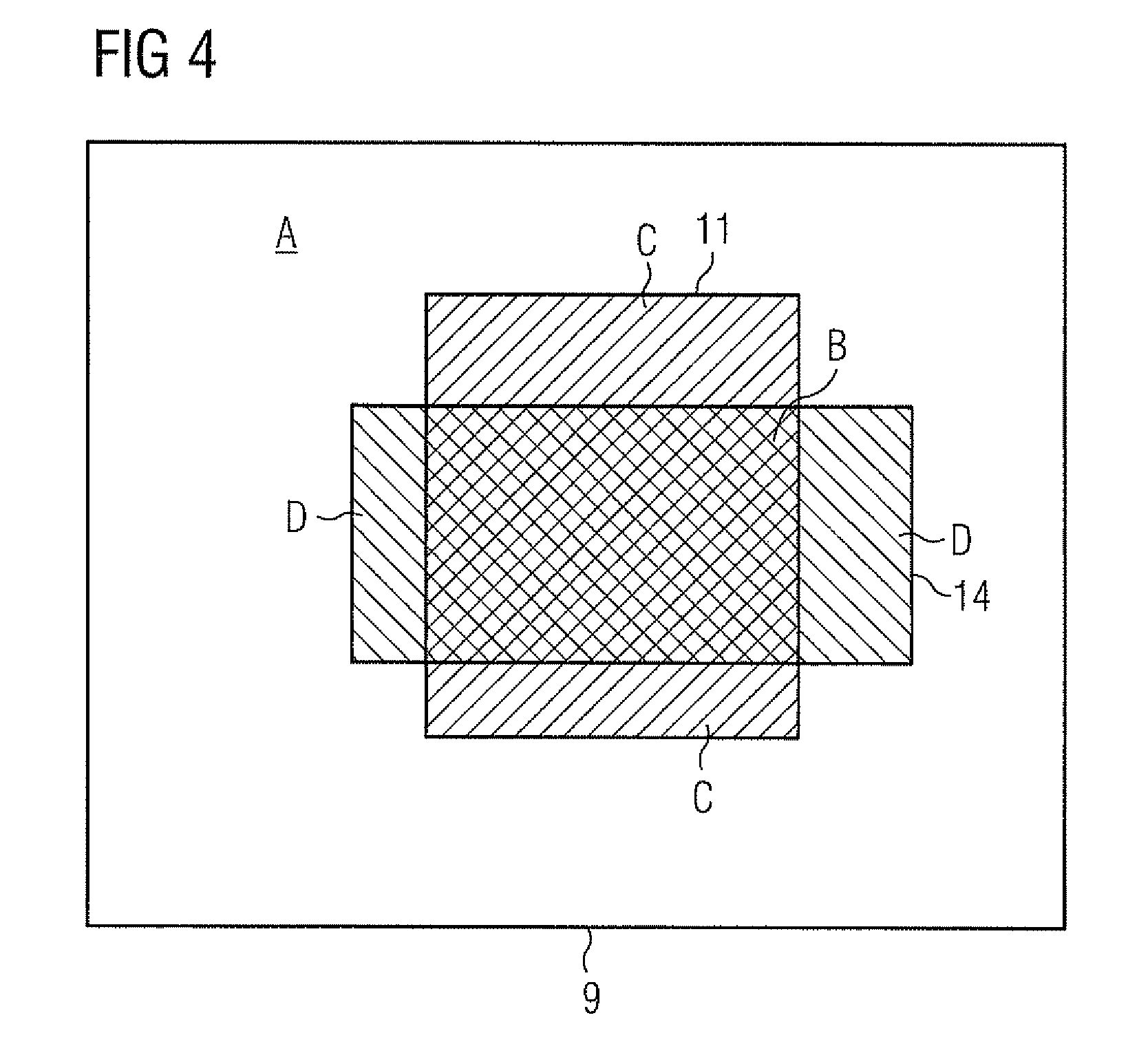
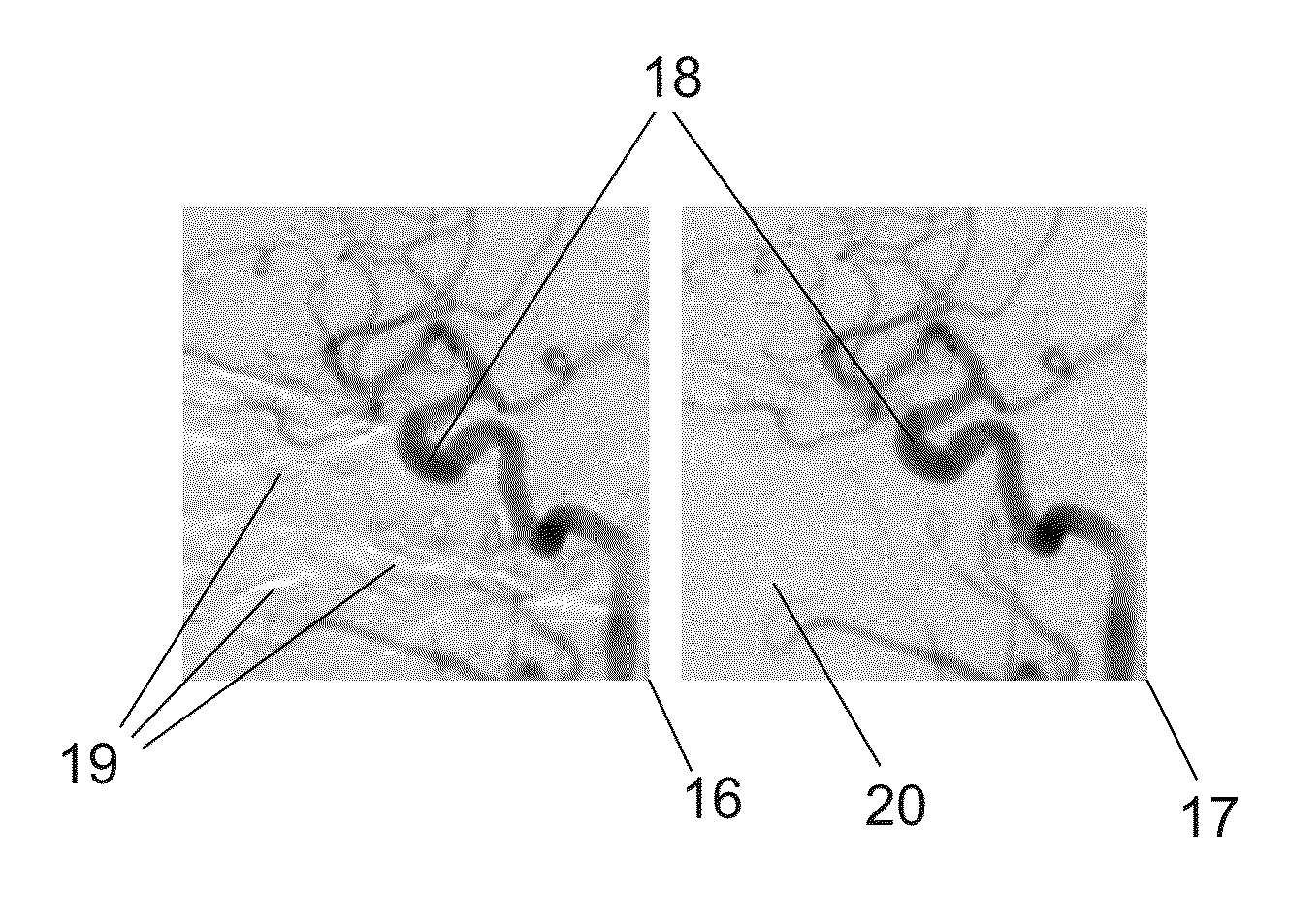
To provide an improved method for achieving DSA images where the effect of residual motions in cardiac DSA during the perfusion phase is reduced and in order to display subtracted images containing less motion artefacts, a method of performing digital subtraction angiography DSA in an imaging apparatus comprises the steps of generating a first image sequence of mask images (10) of a subject to be examined, generating at least one first contrast image (22) at a first phase (16) whereby in the first contrast image part of the subject has a different contrast than in said first image sequence, subtracting the mask images (10) from the at least one first contrast image (22) generating a first DSA image sequence (24), subtracting the DSA images of the first DSA image sequence (24) from the first contrast image (22) within the first phase (16) generating a sequence of extended mask images (32); generating a second contrast image (34) with the imaging system at a second phase (18), said second phase (18) being separated from the first phase (16) by a predetermined phase dividing time limit (20), subtracting the images of the sequence of the extended mask images (32) from the second contrast image (34) generating a second DSA image sequence (38), displaying the second DSA image sequence (38) on a display (28).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
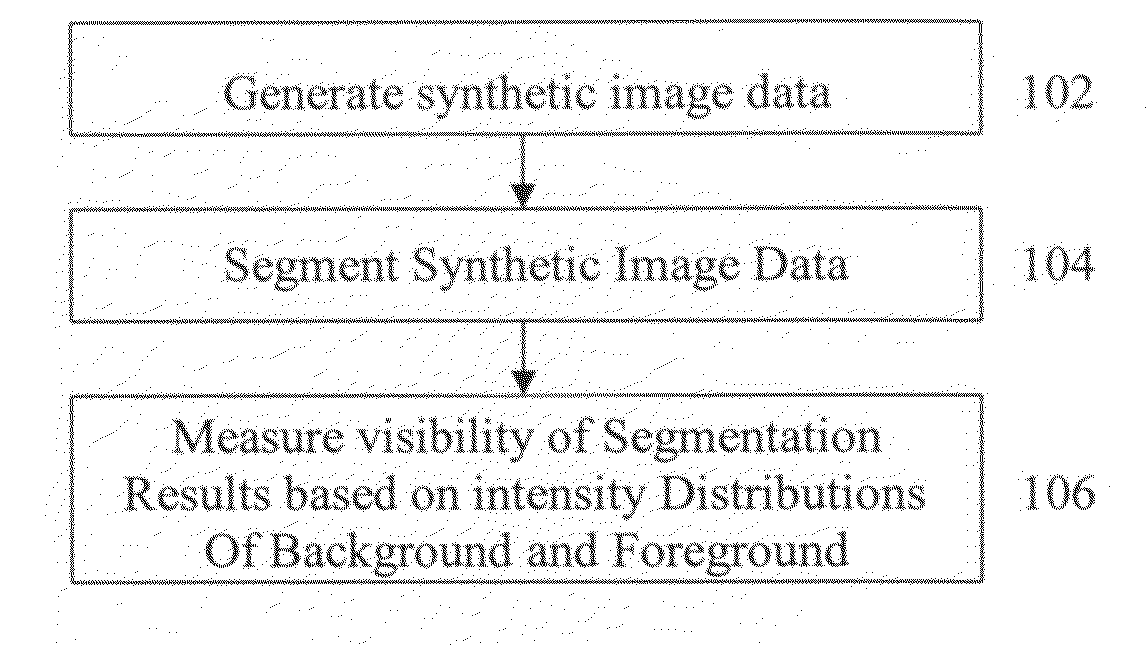
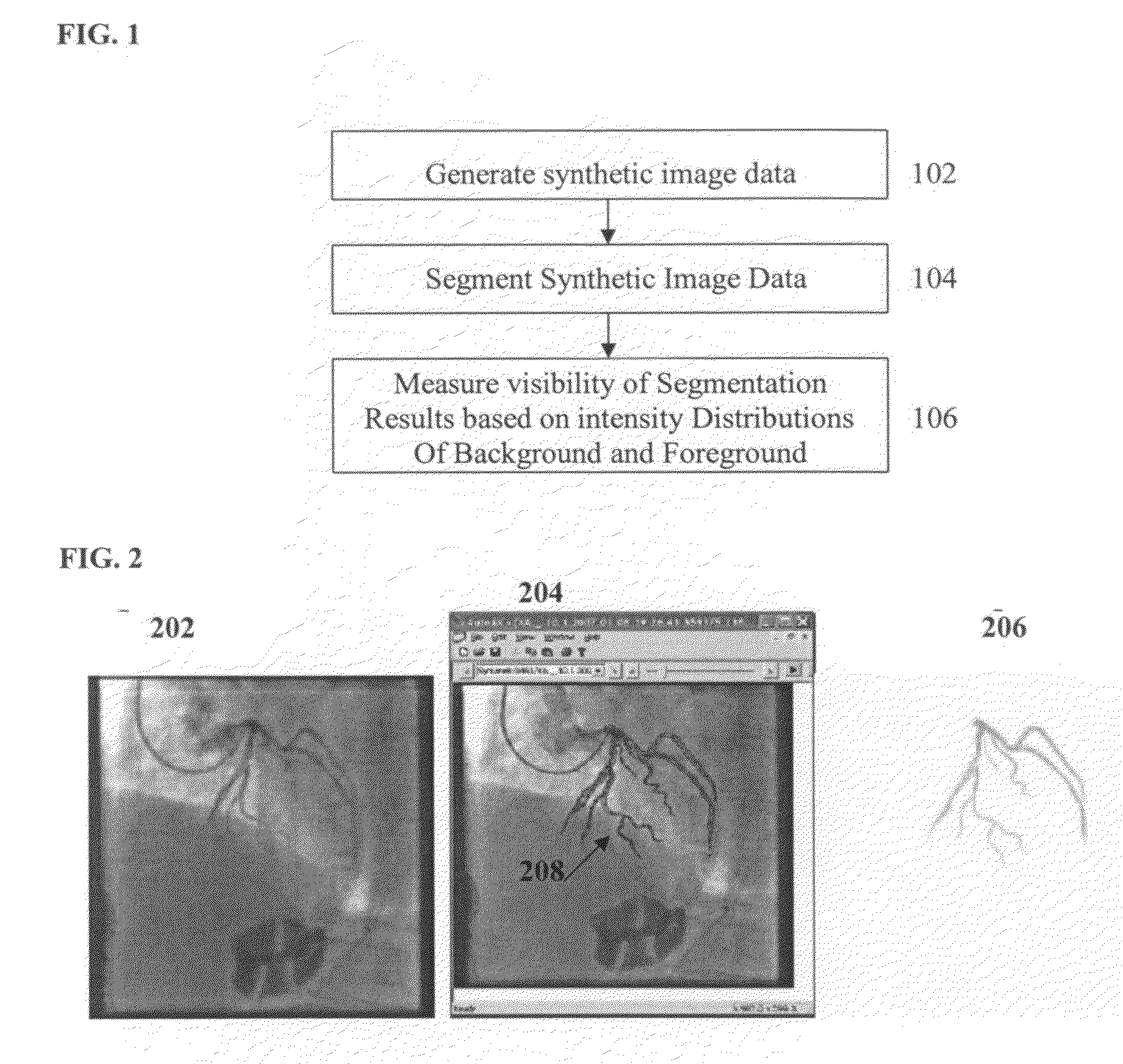
Method and system for evaluating image segmentation based on visibility
A method and system for evaluating image segmentation is disclosed. In order to quantitatively evaluate an image segmentation technique, synthetic image data is generated and the synthetic image data is segmented to extract an object using the segmentation technique. This segmentation results in a foreground containing the extracted object and a background. The visibility of the extracted object is quantitatively measured based on the intensity distributions of the segmented foreground and background. The visibility is quantitatively measured by calculating the Jeffries-Matusita distance between the foreground and background intensity distributions. This method can be used to evaluate segmentation of vessels in fluoroscopic image sequences by coronary digital subtraction angiography (DSA).
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
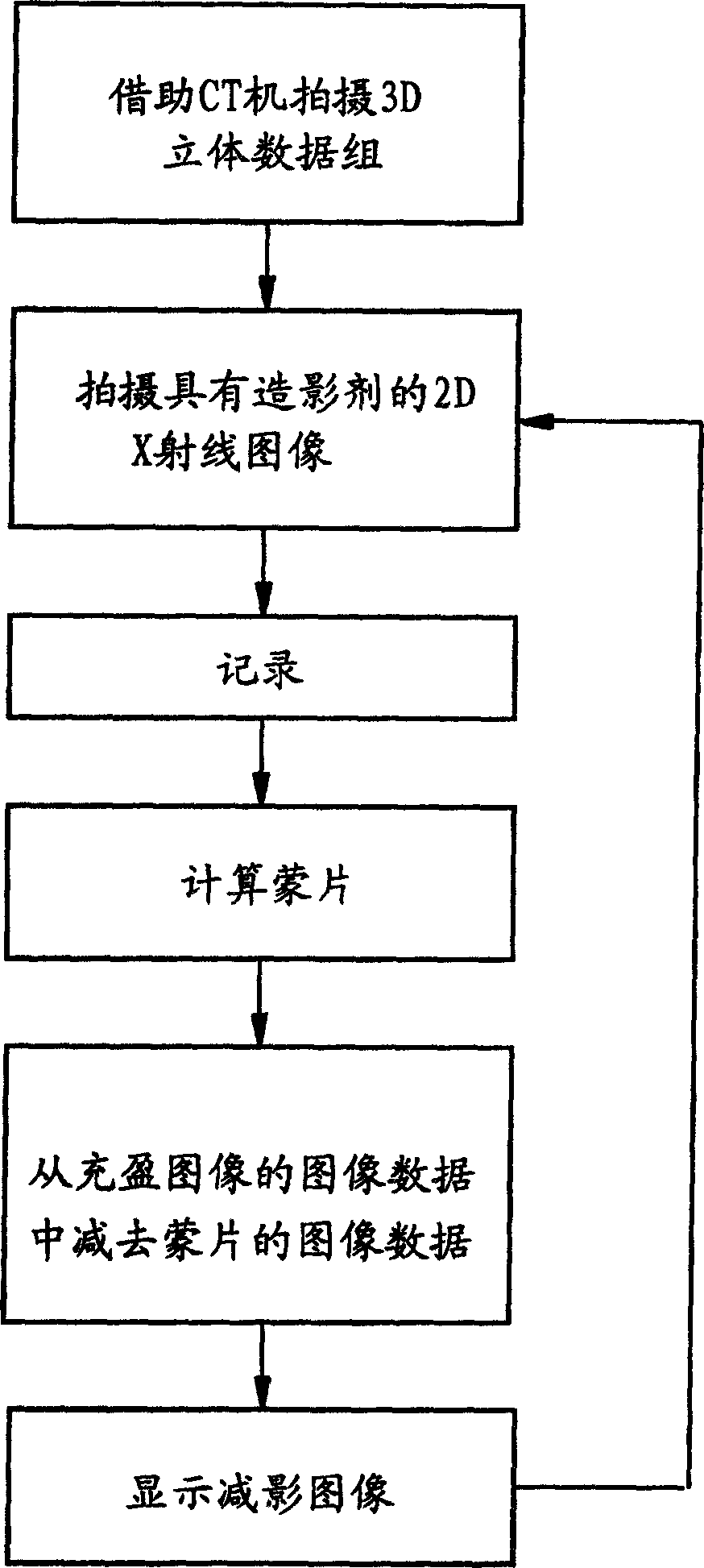
Method for digita image reducing angiography using primary stereo data
In a method to implement digital subtraction angiography, an image of structures (in particular vessels) of a body region is generated by subtraction of image data of a first 2D x-ray image, that is created without enrichment of the structures with contrast agent, from image data of a second 2D x-ray image of the body region that is acquired with contrast agent enrichment of the structures. The image data of the first 2D x-ray image are calculated from a 3D volume dataset of the body region. The x-ray dose applied in the subtraction angiography thus can be reduced.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method for acquisition of subtraction angiograms
InactiveUS20140016844A1Diagnostic value can be improvedIncrease valueImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresMotility
The invention relates to the field of digital processing of x-ray images and can be used in digital subtraction angiography to compensate for impact of involuntary patient movement and movement of internal organs on image of the vascular system. The technical result of the claimed invention is the improvement of diagnostic value of subtraction angiographic images by eliminating artifacts caused by the motility of anatomical structures. Technical result is achieved by the that at the stage of digital images registration a search for characteristic details is performed for each image. According to the shift of the said details determine expectable shift of a patient organs. Then perform segmentation of image from the pre-contrast series in the region of homogenous warping; for each region a geometrical transformation is calculated and corresponding geometrical transformations are performed for each region of a series of pre-contrast digital images.
Owner:ZAKRYTOE AKCIONERNOE OBSHCHESTVO IMPULS
Integrated intravascular OCT (optical coherence tomography) image and DSA (digital subtraction angiography) integrating offline treatment system
ActiveCN103462590AImprove blood vessel treatment effectConvenient researchDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsData acquisitionData acquisition module
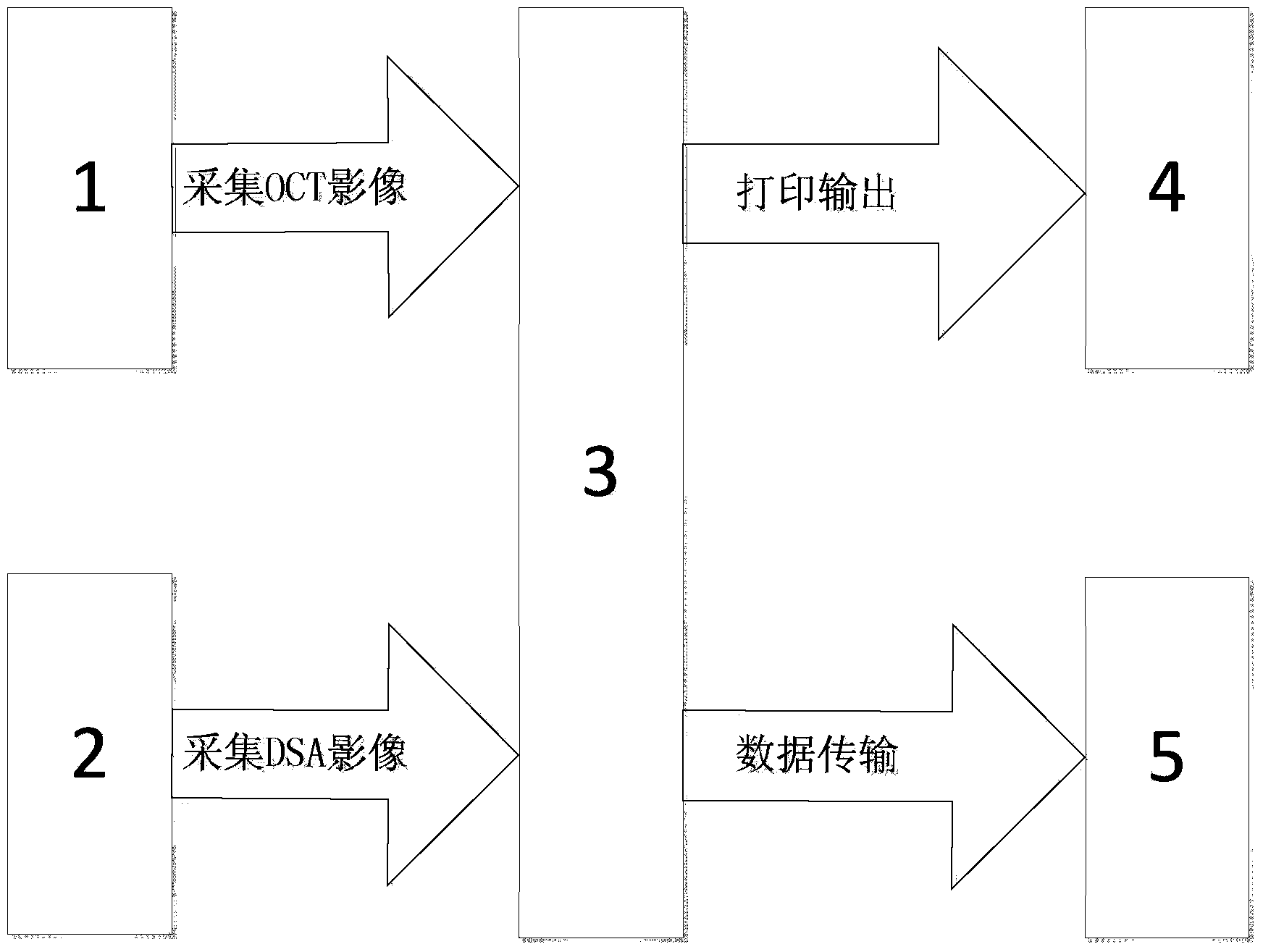
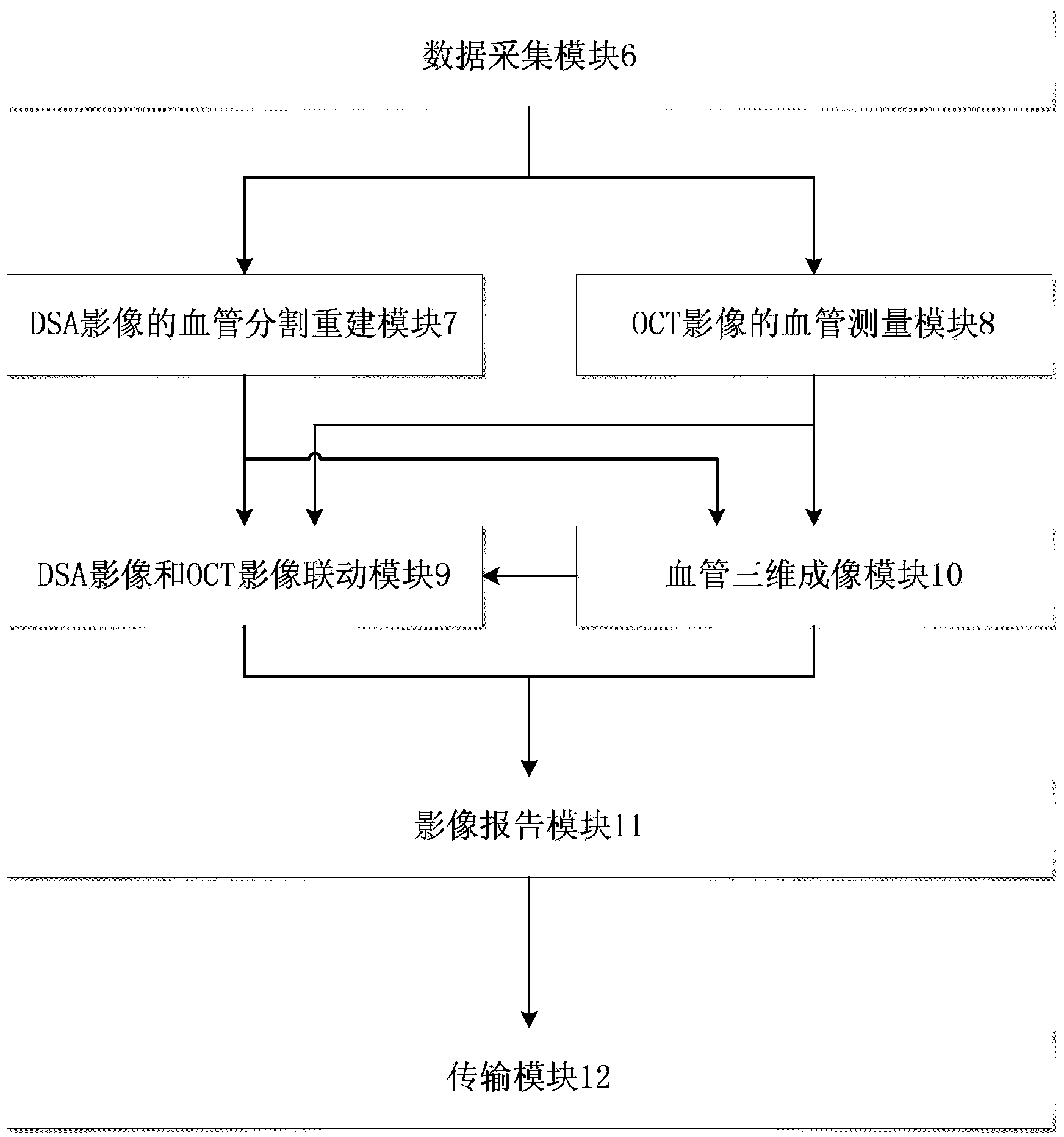
The invention provides an integrated intravascular OCT (optical coherence tomography) image and DSA (digital subtraction angiography) integrating offline treatment system, which comprises a data acquisition module, a DSA-image-based blood vessel segmentation and reconstruction module, an OCT-image-based blood vessel measurement module, a blood vessel three-dimensional imaging module, a DSA image and OCT image linkage module, an image reporting module and a transmission module. According to the system, a blood vessel is multidimensionally treated by combining a DSA image and an OCT image to further facilitate the accurate positioning of an interested blood vessel section; a blood vessel measurement result obtained by the DSA-image-based blood vessel segmentation and reconstruction module is compared with a blood vessel measurement result, obtained by the OCT-image-based blood vessel measurement module, on a cross section, so that the blood vessel treatment research accuracy of a doctor or a researcher after an operation is improved to facilitate the supply of a more perfect therapeutic schedule for an interventional operation in a similar case in the future.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
DSA (digital subtraction angiography) cerebrovascular image auto-segmenting method based on adjacent image feature point sets
ActiveCN104504708AAccurate extractionImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisImage segmentationImaging Feature
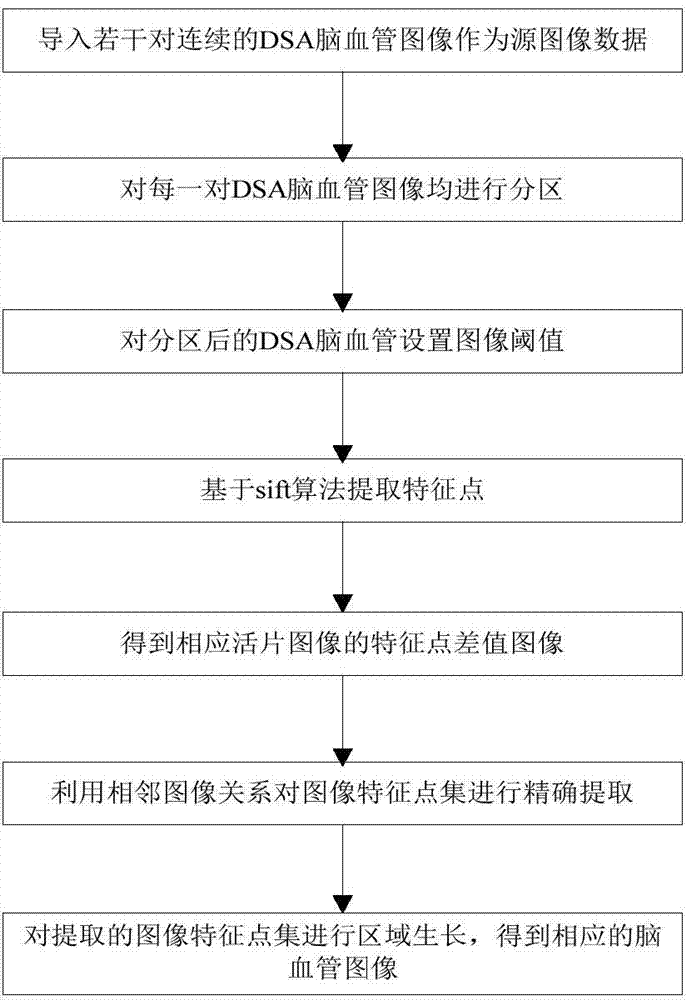
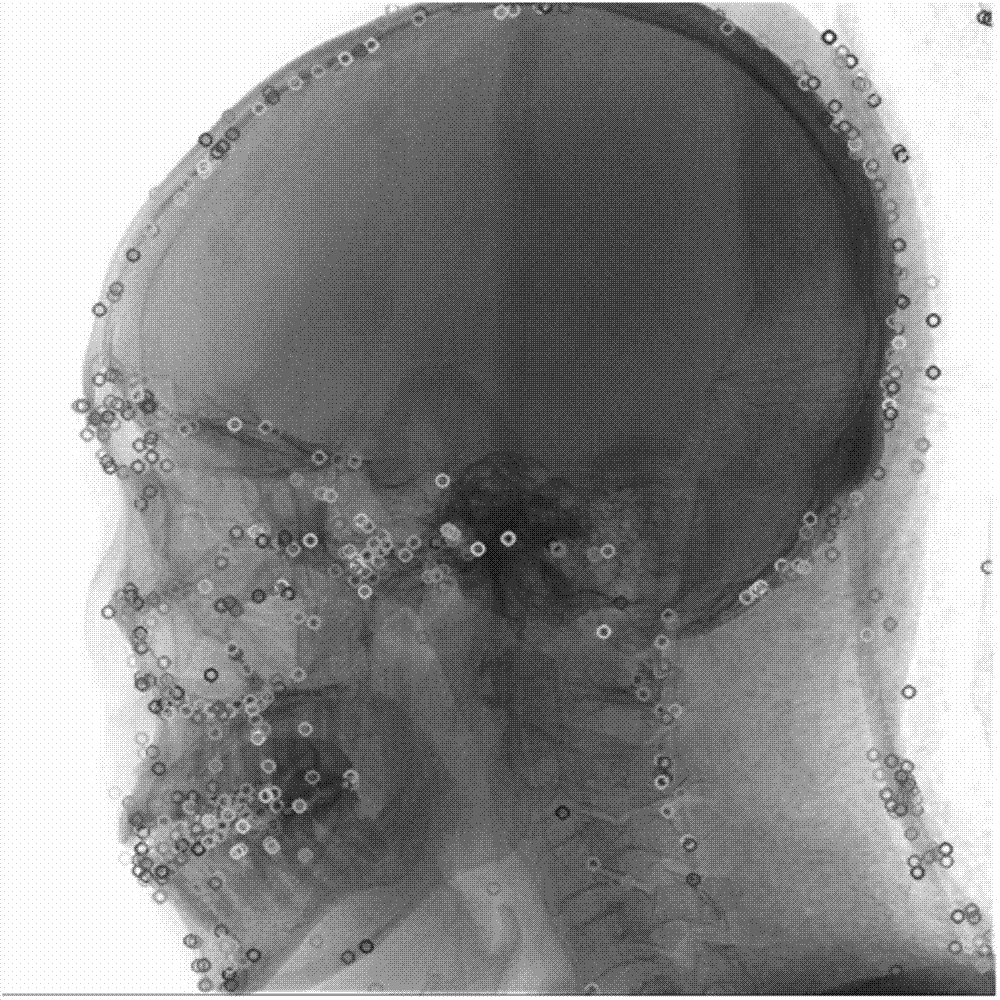
The invention discloses a DSA (digital subtraction angiography) cerebrovascular image auto-segmenting method based on adjacent image feature point sets. The method includes: 1, importing a plurality of pairs of continuous DSA cerebrovascular images as source image data; 2, partitioning each pair of DSA cerebrovascular images; 3, setting an image threshold for each partitioned DSA cerebrovascular image; 4, extracting feature points on the basis of a sift algorithm; 5, acquiring feature point difference images of corresponding live images from mask images and live images in each pair of DSA cerebrovascular images subjected to feature point extraction, by means of the digital subtraction angiography; 6, extracting image feature point sets of all feature point difference images, and precisely extracting the image feature points by means of adjacent image relation; 7, subjecting the extracted image feature points to region growing to obtain corresponding cerebrovascular images. The method has the advantages that pixel information of adjacent domains is integrated through adjacent images by the image segmenting technique, feature point information extraction is more accurate, and noise is effectively decreased.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Medical image processing method
InactiveCN103810754AAccurate guideImage analysisComputerised tomographsFast spin echoFluoroscopic image
Owner:姜卫剑
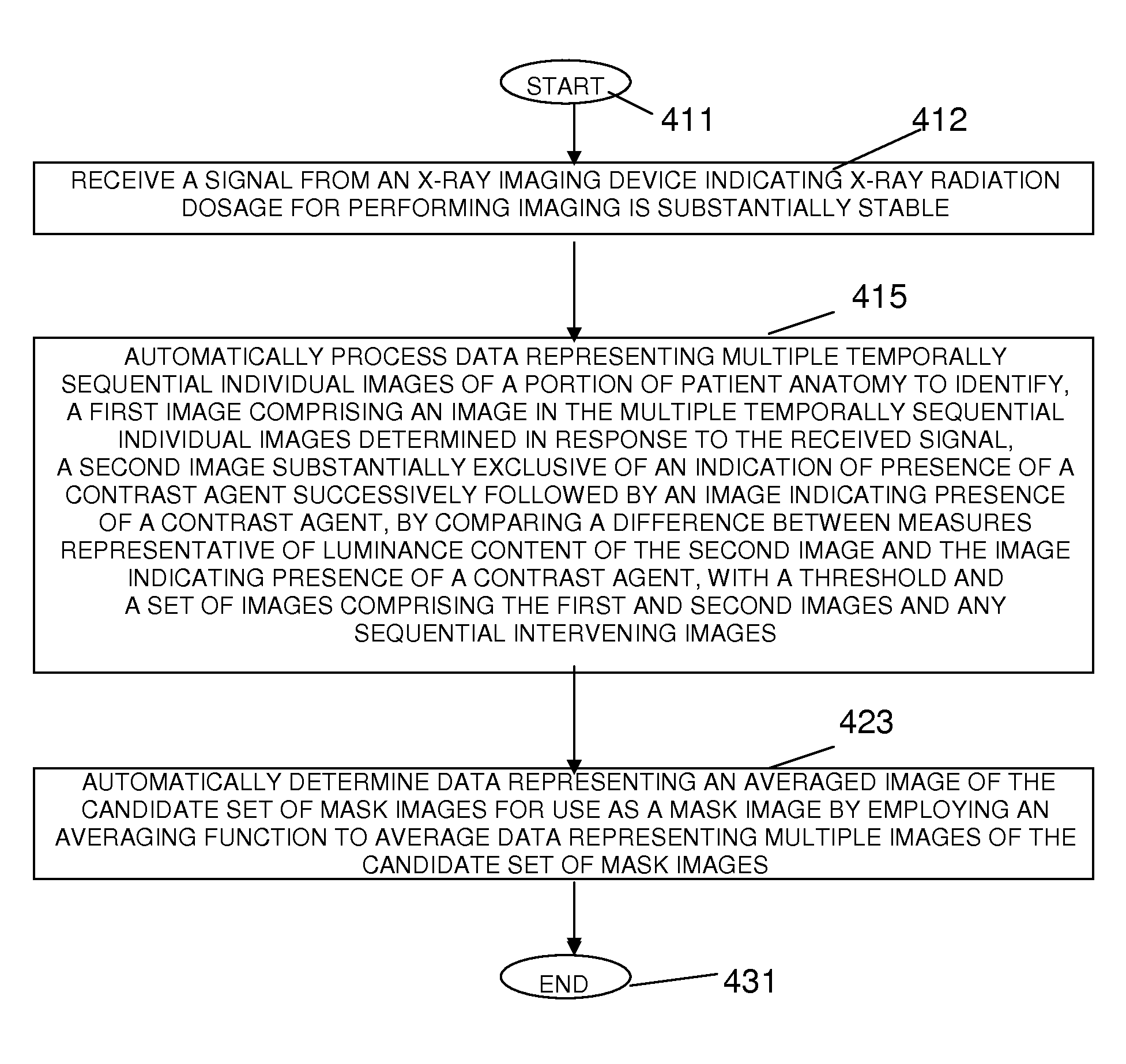
System for Automatically Generating a Mask for Digital Subtraction Angiography
A system automatically generates a mask image. An interface receives a signal from an X-ray imaging device indicating X-ray radiation dosage for performing imaging is substantially stable. An image processor automatically processes data representing multiple temporally sequential individual images of a portion of patient anatomy to identify, a first image comprising an image in the multiple temporally sequential individual images determined in response to the received signal. The image processor identifies a second image substantially exclusive of an indication of presence of a contrast agent successively followed by an image indicating presence of a contrast agent, by comparing a difference between measures representative of luminance content of the second image and the image indicating presence of a contrast agent, with a threshold. The image processor also identifies a set of images comprising the first and second images and any sequential intervening images. An image data processor automatically averages the set of images for use as a mask image.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
System and Method for Coronary Digital Subtraction Angiography
A method and system for extracting coronary vessels fluoroscopic image sequences using coronary digital subtraction angiography (DSA) are disclosed. A set of mask images of a coronary region is received, and a sequence of contrast images for the coronary region is received. For each contrast image, a motion estimate is calculated between each of the mask images and a background region of the contrast image and a covariance is calculated for each motion estimate. Multiple background layer predictions are generated by generating a background layer prediction for each mask image based on the calculated motion estimate and covariance. The multiple background layer estimates are combined using statistical fusion to generate a final estimated background layer. The final estimated background layer is subtracted from the contrast image to extract a coronary vessel layer for the contrast image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
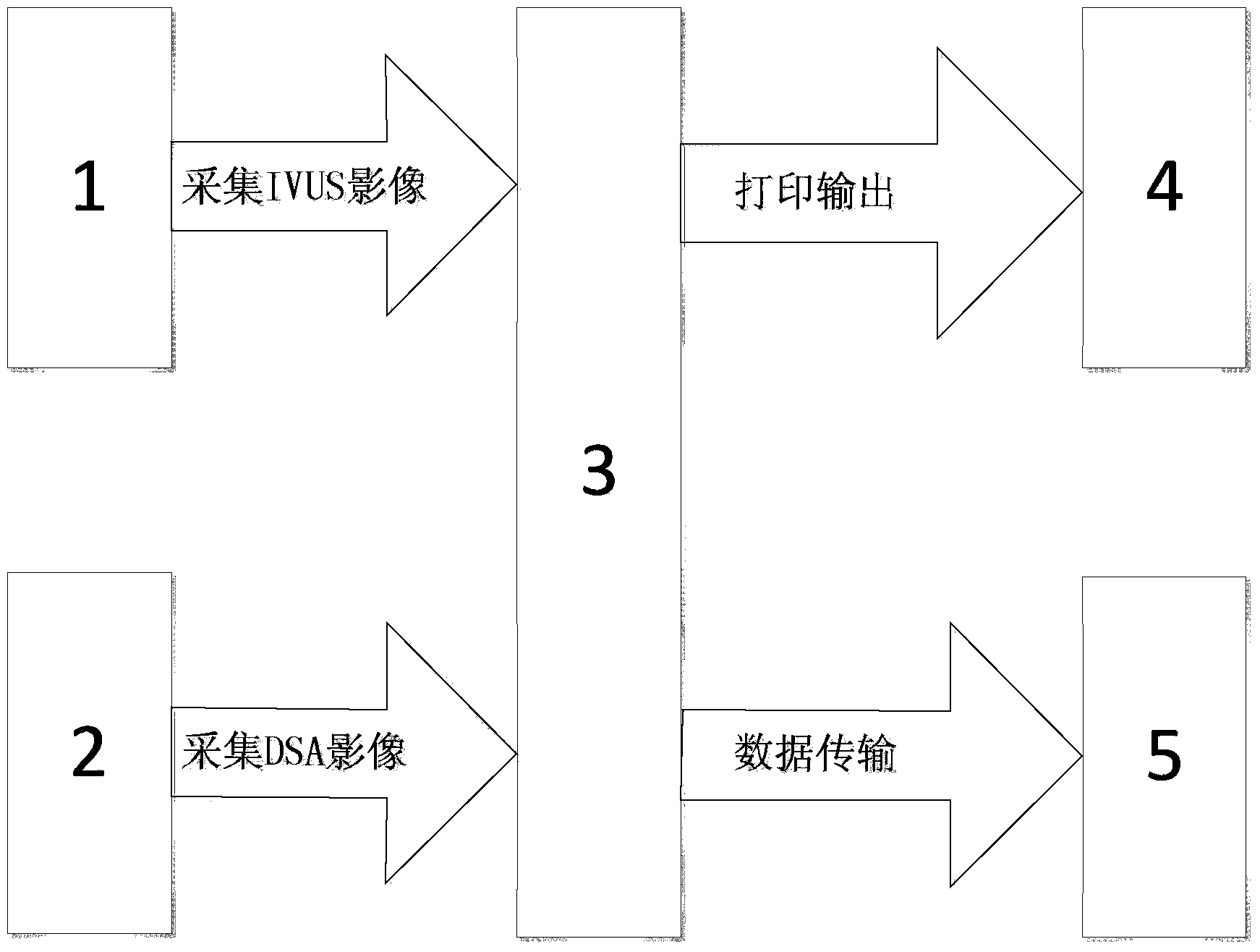
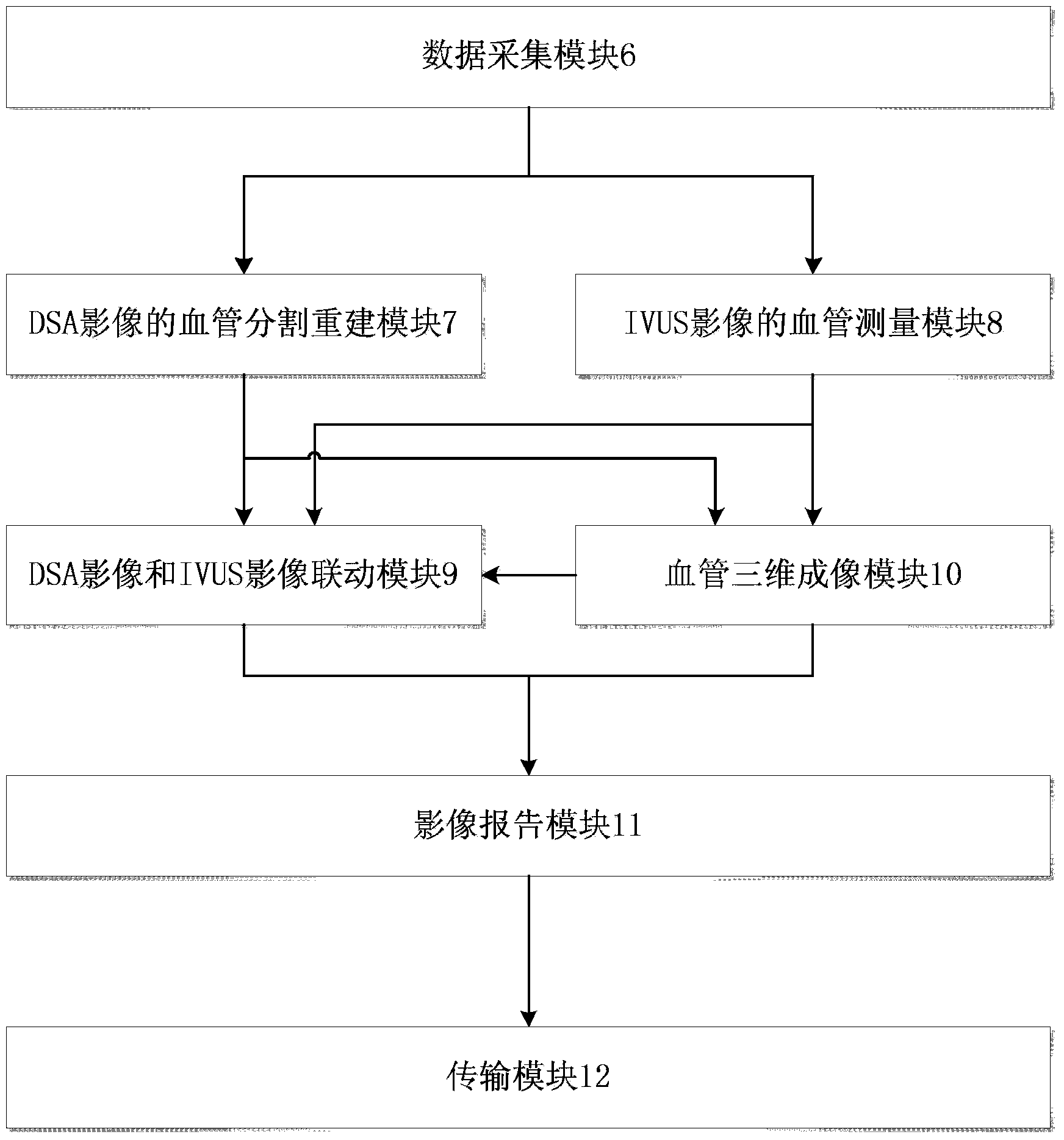
Integrated IVUS (intravascular ultrasound) image and DSA (digital subtraction angiography) image integrating offline-treatment system
ActiveCN103462646AImprove blood vessel treatment effectConvenient researchSurgeryCatheterSonificationData acquisition
The invention provides an integrated IVUS (intravascular ultrasound) image and DSA (digital subtraction angiography) image integrating offline-treatment system, which comprises a data acquisition module, a DSA-image-based blood vessel segmentation and reconstruction module, an IVUS-image-based blood vessel measurement module, a blood vessel three-dimensional imaging module, a DSA image and IVUS image linkage module, an image reporting module and a transmission module. According to the system, a blood vessel is multidimensionally treated by combining a DSA image and an IVUS image to further facilitate the accurate positioning of a selected interested blood vessel section; a blood vessel measurement result obtained by the DSA-image-based blood vessel segmentation and reconstruction module is compared with a blood vessel measurement result, obtained by the IVUS-image-based blood vessel measurement module, on a cross section, so that the blood vessel treatment accuracy of a doctor or a researcher after an operation is improved to facilitate the supply of a more perfect therapeutic schedule for an interventional operation in a similar case in the future.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
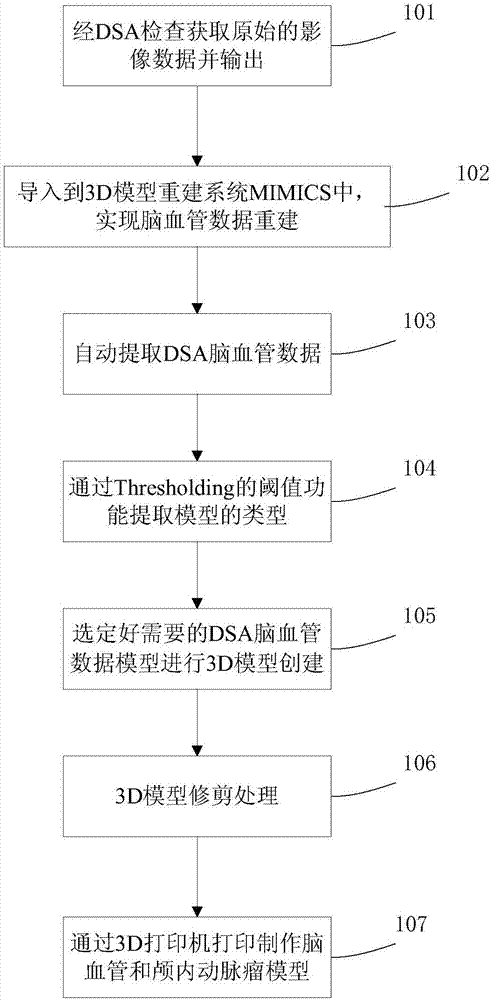
Intracranial aneurysm 3D (three-dimensional) model printing method based on DSA (digital subtraction angiography) data
InactiveCN107049484AFlat surfaceConform to solid modelAdditive manufacturing apparatusComputer-aided planning/modellingEntity modelComputer vision
The invention discloses an intracranial aneurysm 3D (three-dimensional) model printing method based on DSA (digital subtraction angiography) data. The method includes the steps: acquiring original DSA image data and outputting the image date; leading the outputted image date into a medicine 3D model reconstruction system to reconstruct cerebral vascular data; automatically extracting the DSA cerebral vascular data by the 3D model reconstruction system; selecting needed DSA cerebral vascular data model to build a 3D model; trimming the obtained model; printing a cerebral vascular and intracranial aneurysm model by the aid of a 3D printer. The intracranial aneurysm 3D model is more refined and more suitable for an entity model, has a smoother surface and can display tiny branch vessels and provide more important reference for operations.
Owner:SHAOXING PEOPLES HOSPITAL
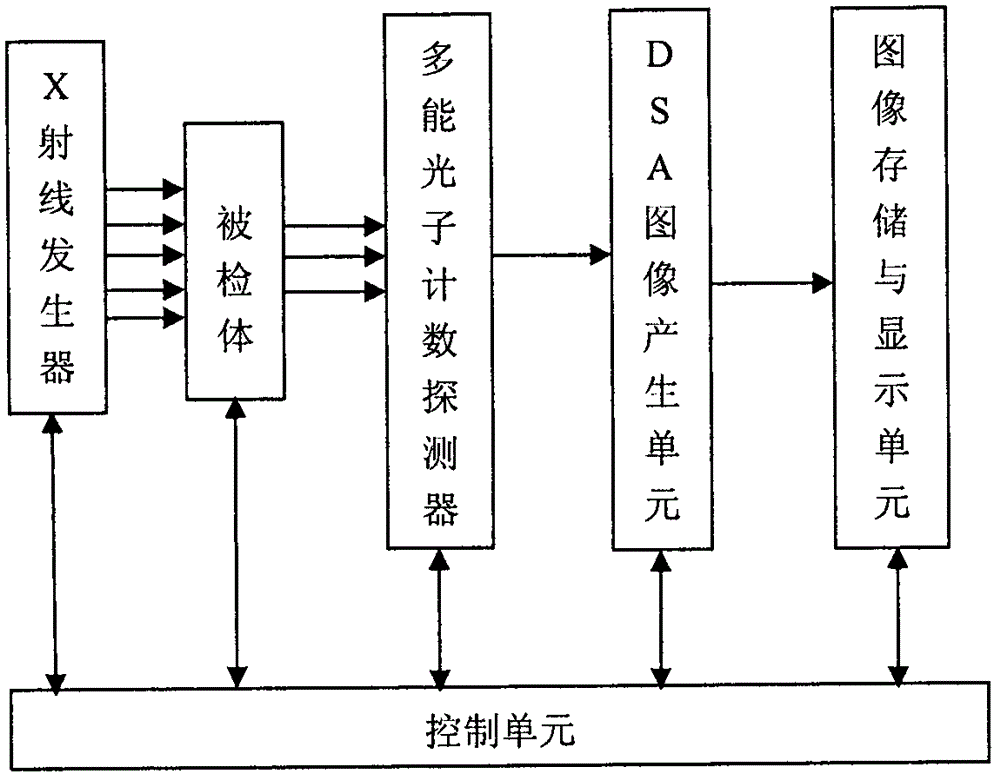
System and method for single-exposure digital subtraction angiography imaging
ActiveCN106562797AReduce radiation doseReduce dosageAngiographyRadiation diagnosticsHigh energyConventional X-Ray
The invention discloses a system and method for single-exposure digital subtraction angiography (DSA) imaging. The system is composed of an x-ray generator, a multi-energy photon counting detector, a DSA image generation unit, a device for image storage and display, a sickbed, a rotary rack and a controller, wherein the x-ray generator can generate continuous energy spectrum x rays; the multi-energy photon counting detector detects x photons which penetrate a human body and can judge and count energy of the x photons respectively; the DSA image generation unit collects output signals of the multi-energy photon counting detector to form data of two transmission images of a high energy zone and a low energy zone; and DSA images are obtained through subtraction computation of the data, and a conventional x-ray image can be obtained through summary computation. The DSA image can be obtained by the system through single exposure, so motion artifacts can be avoided; the contrast medium dosage and the radiation agent dosage can be reduced; equipment efficiency can be increased; more effective approaches can be provided for DSA imaging of dynamic objects; and the system has important values in clinical application.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com