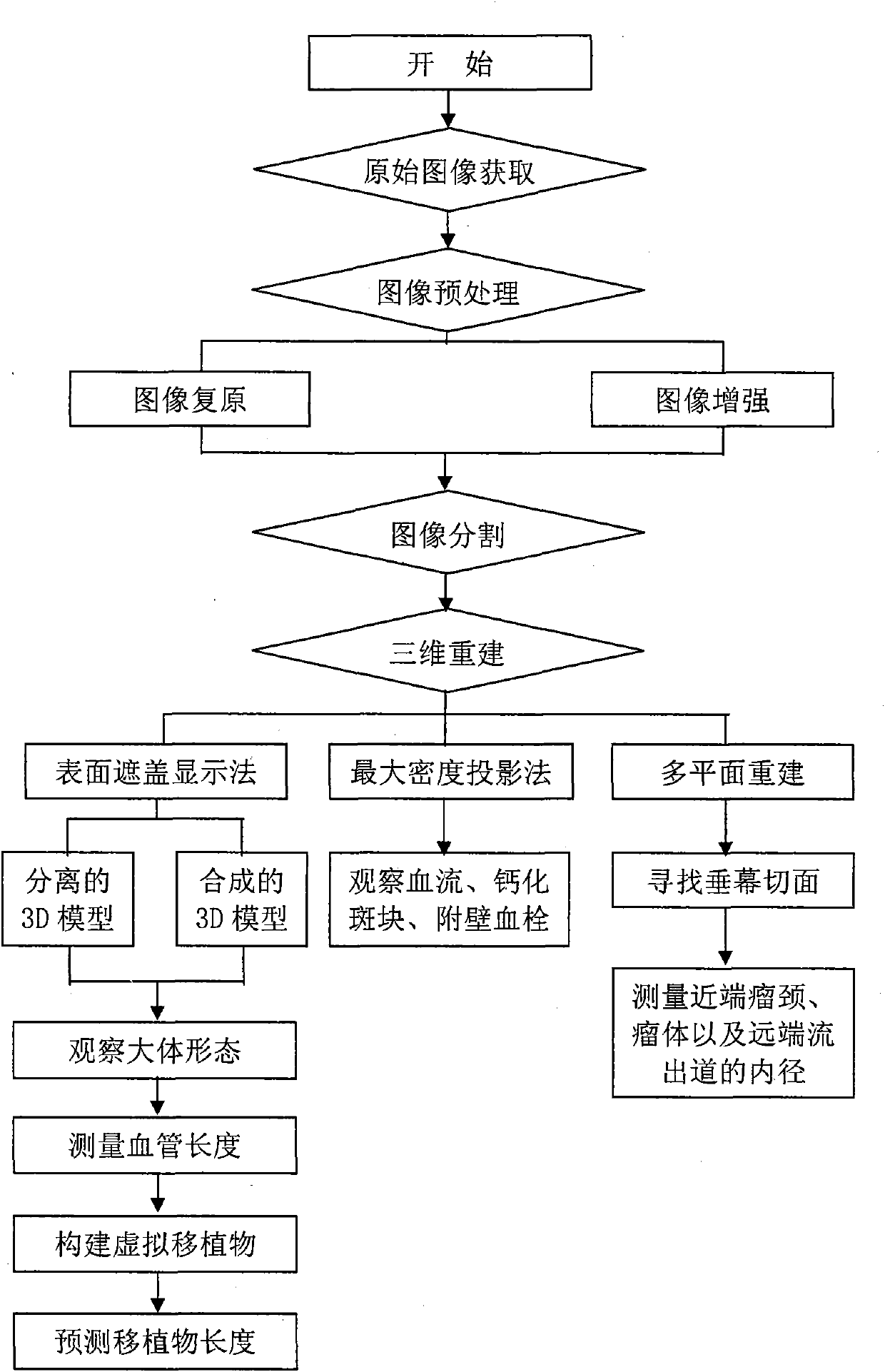
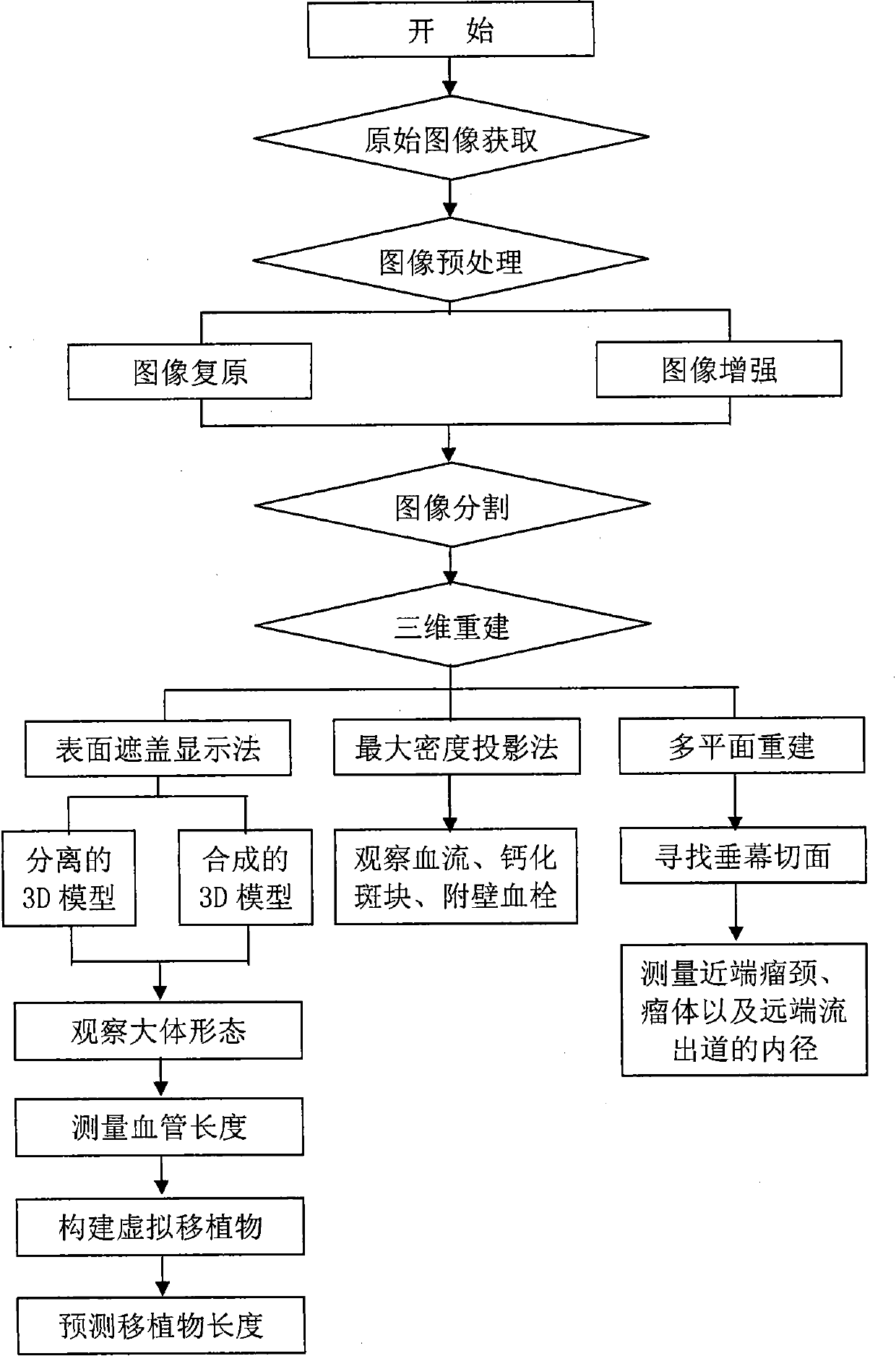
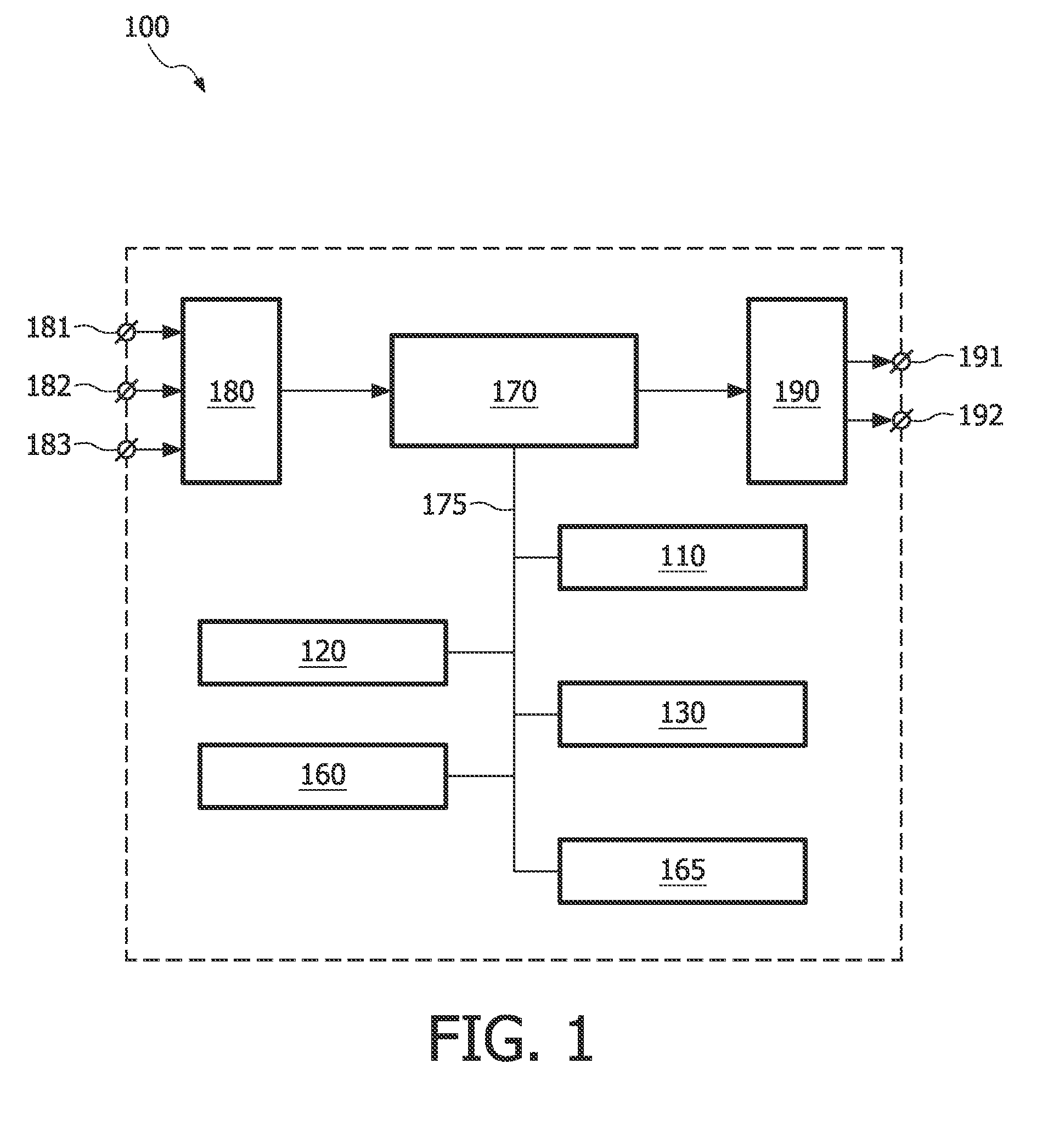
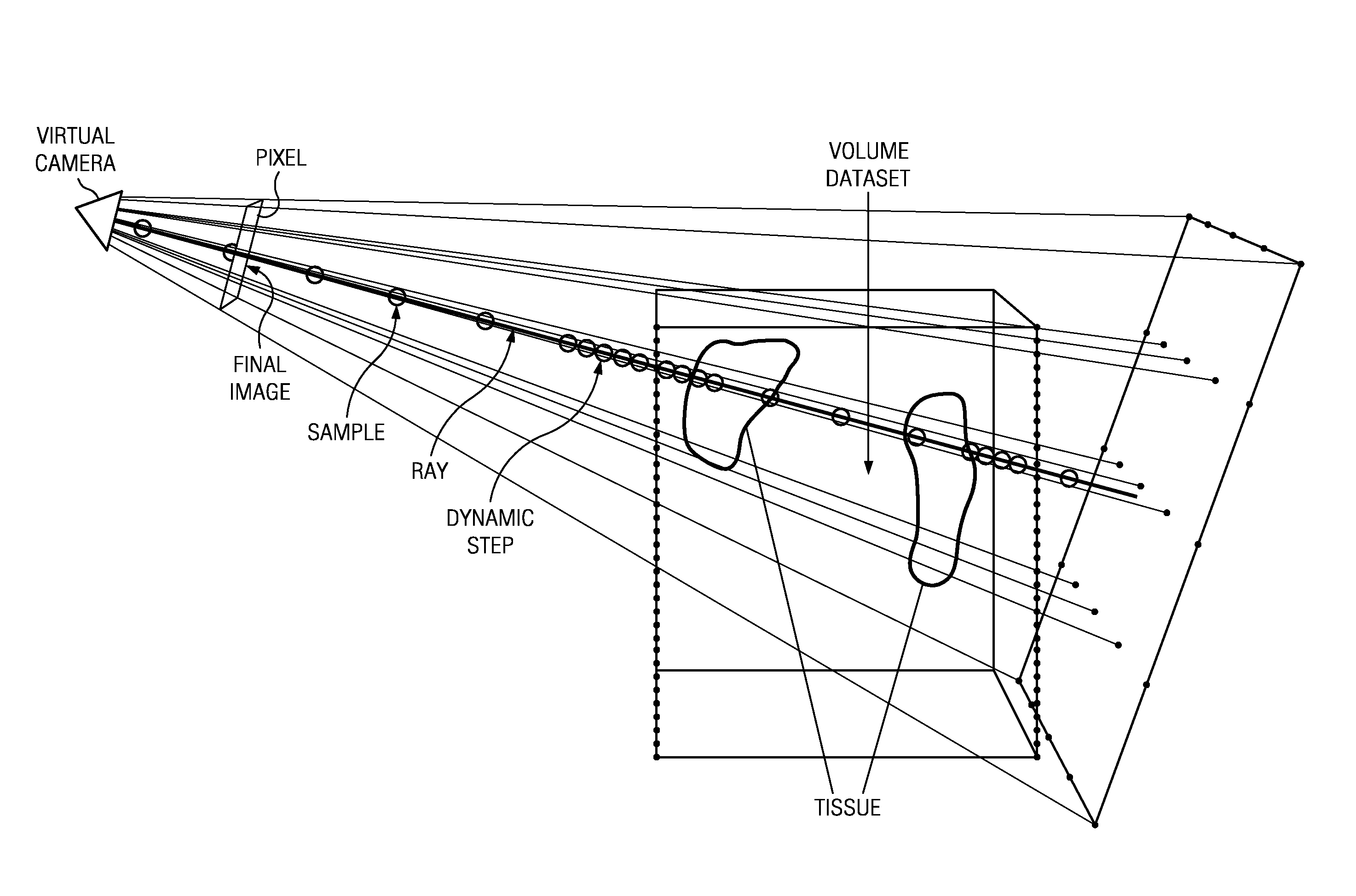
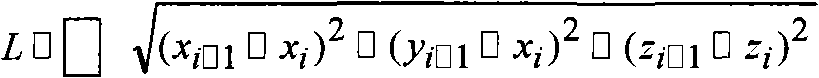Patents
Literature
86 results about "Maximum intensity projection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
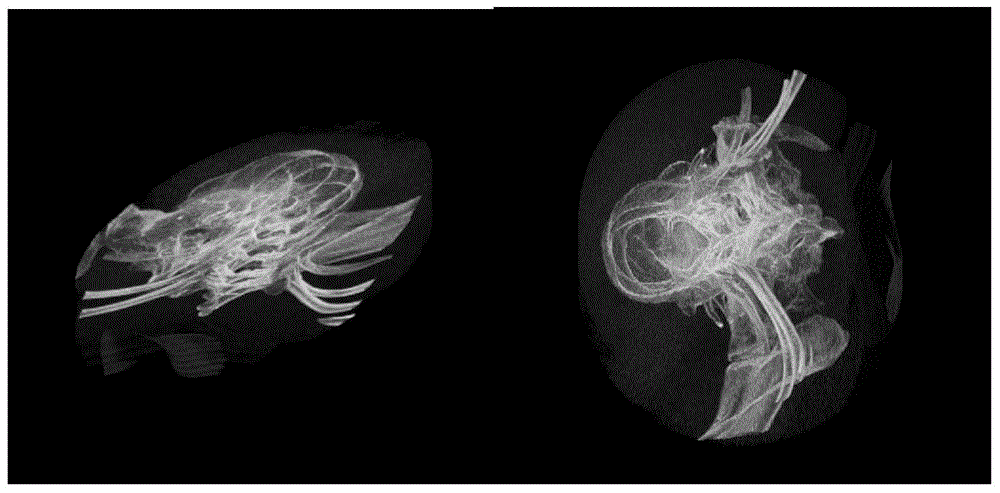
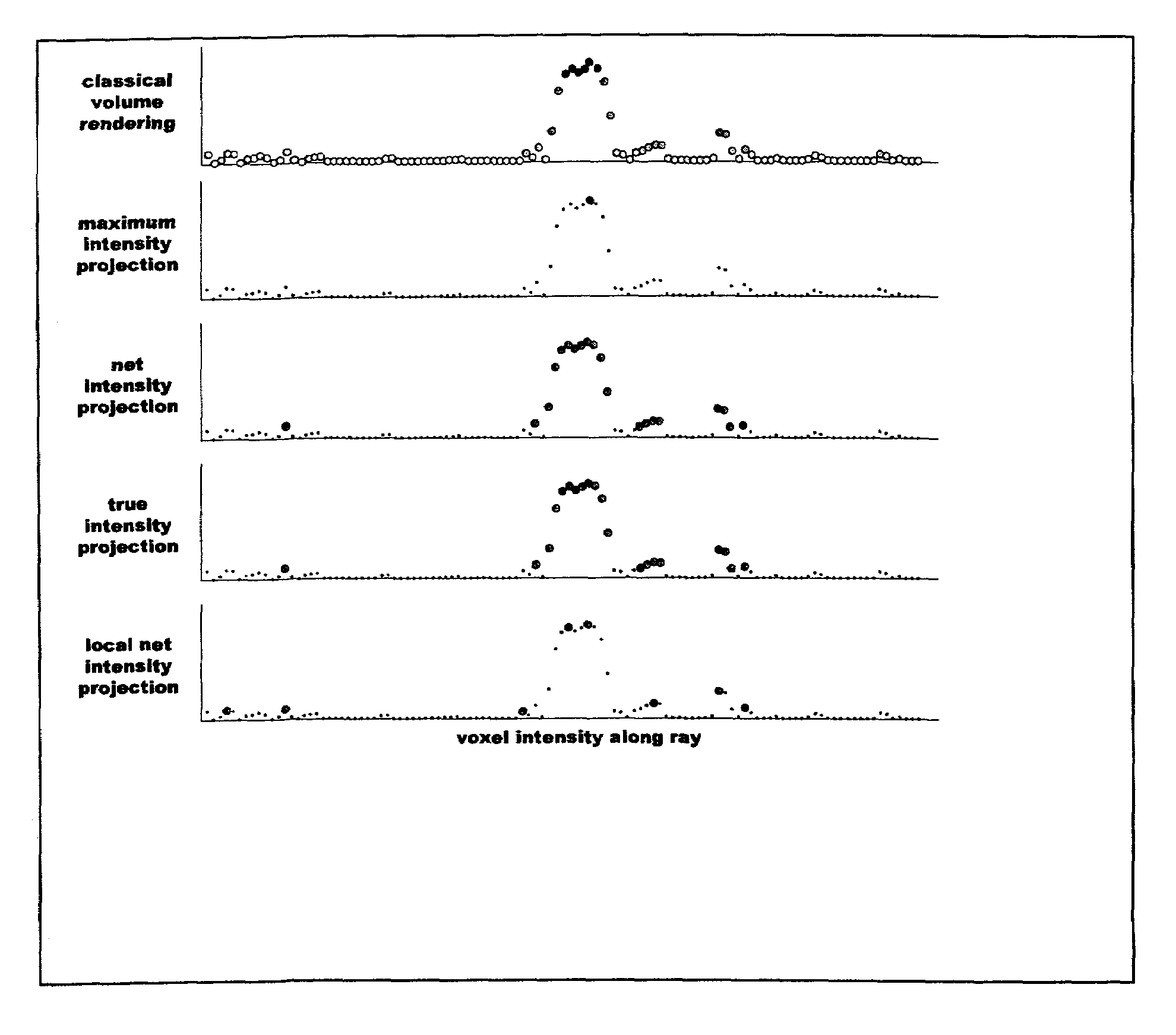
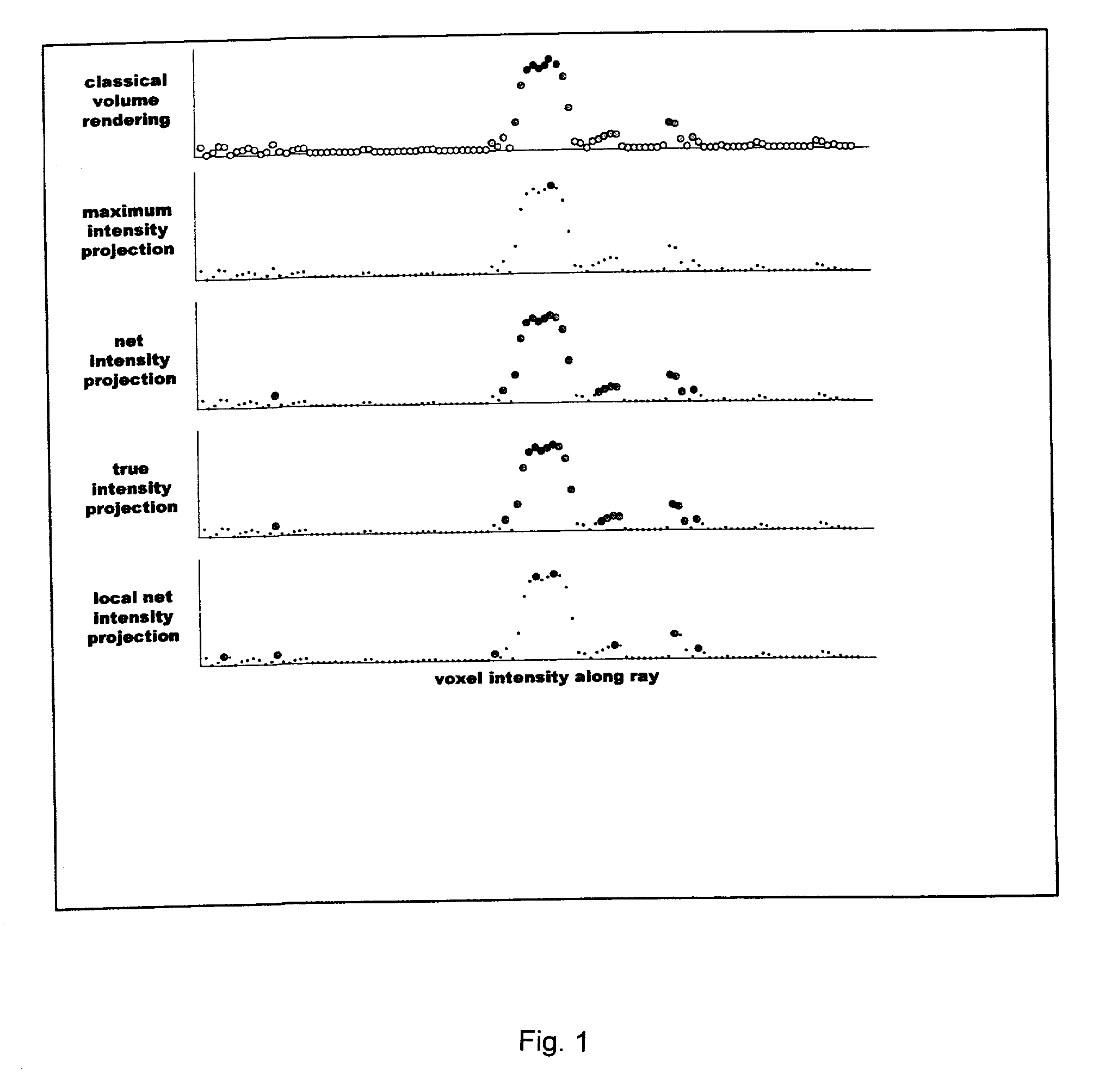
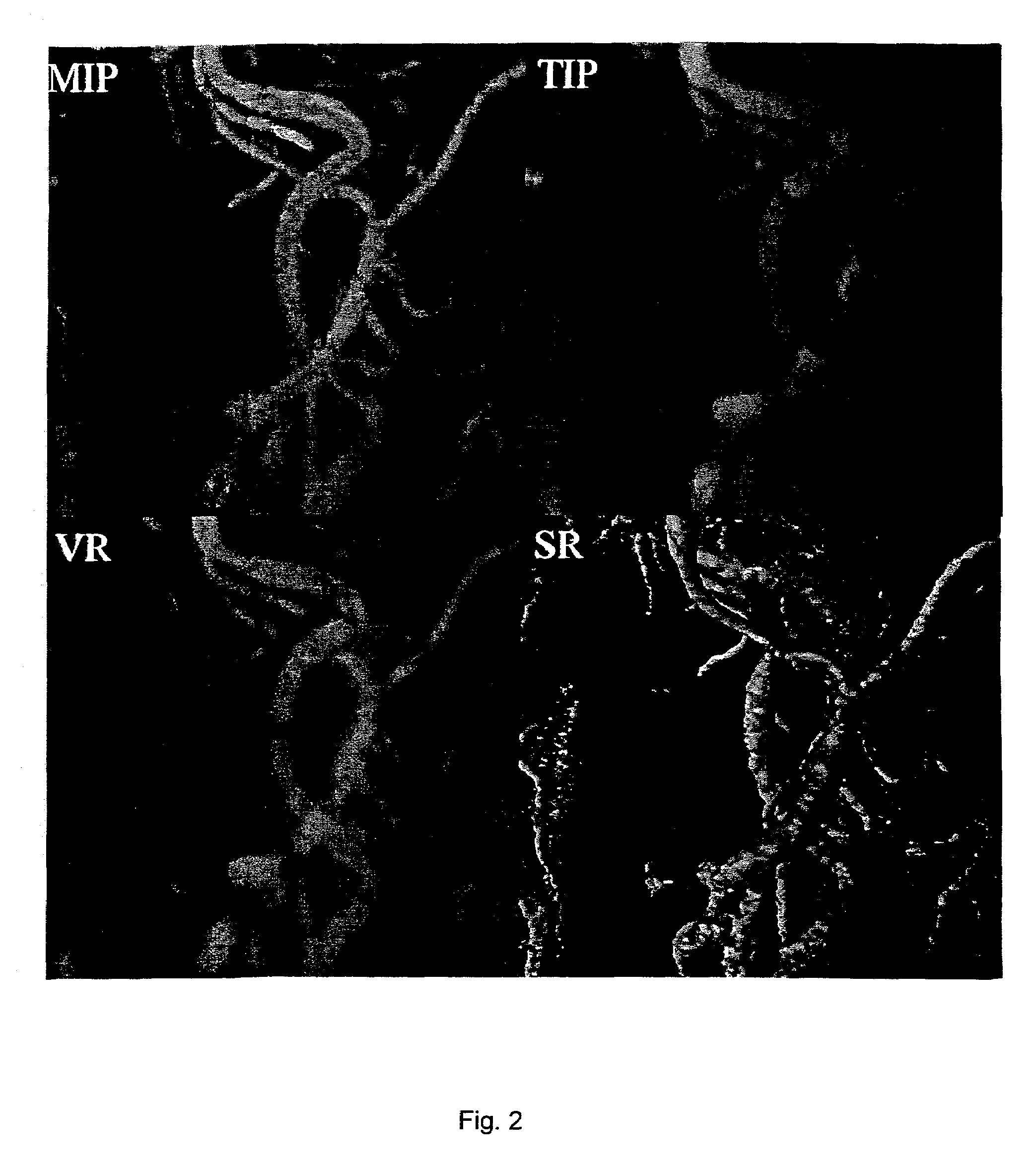
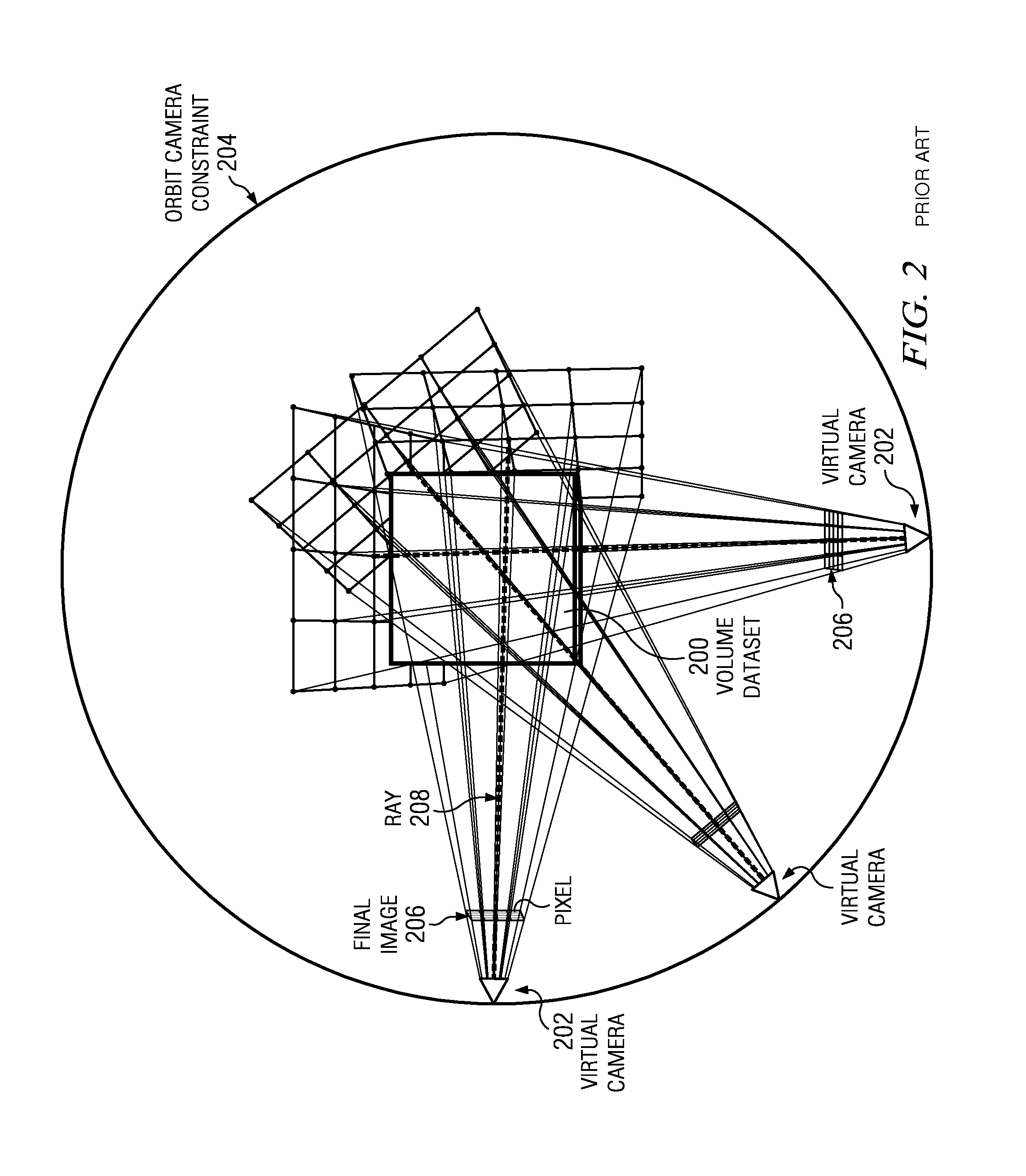
In scientific visualization, a maximum intensity projection (MIP) is a method for 3D data that projects in the visualization plane the voxels with maximum intensity that fall in the way of parallel rays traced from the viewpoint to the plane of projection. This implies that two MIP renderings from opposite viewpoints are symmetrical images if they are rendered using orthographic projection.
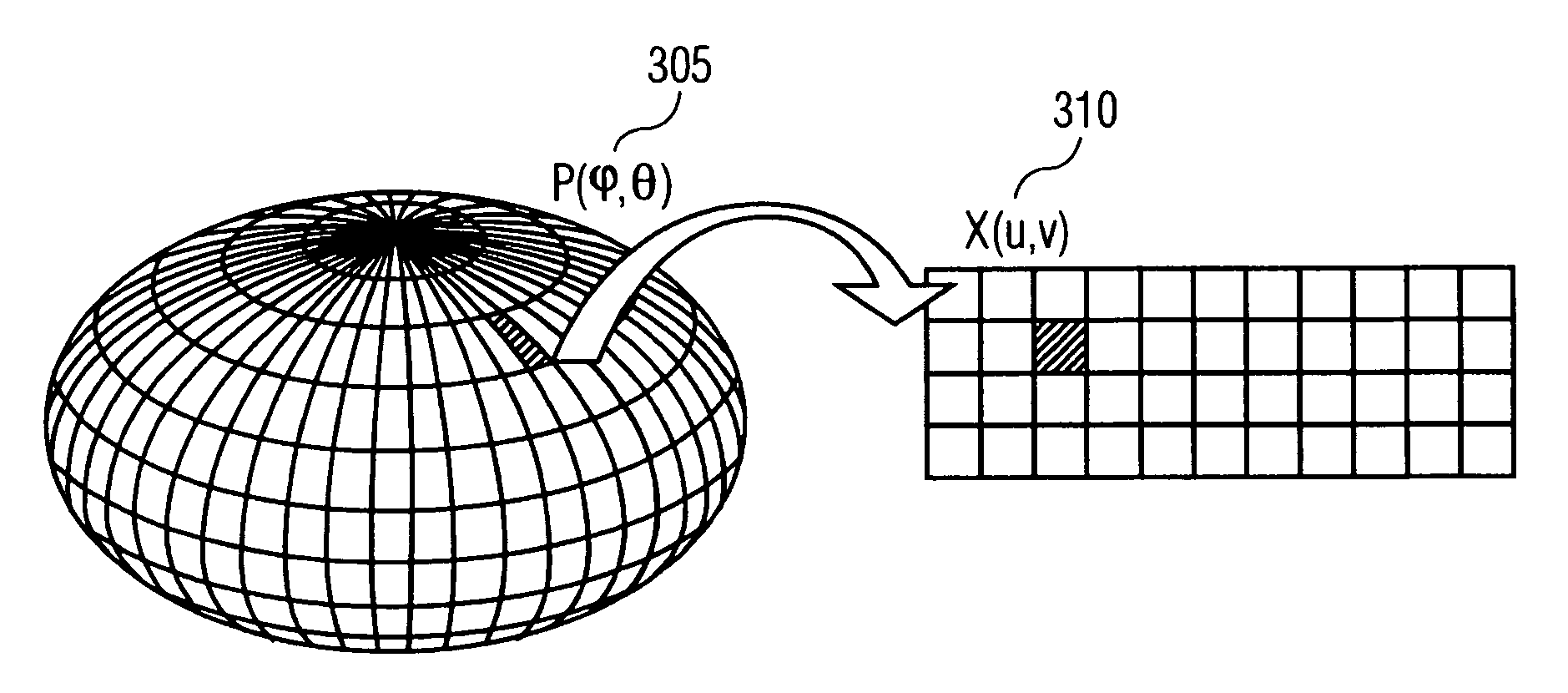
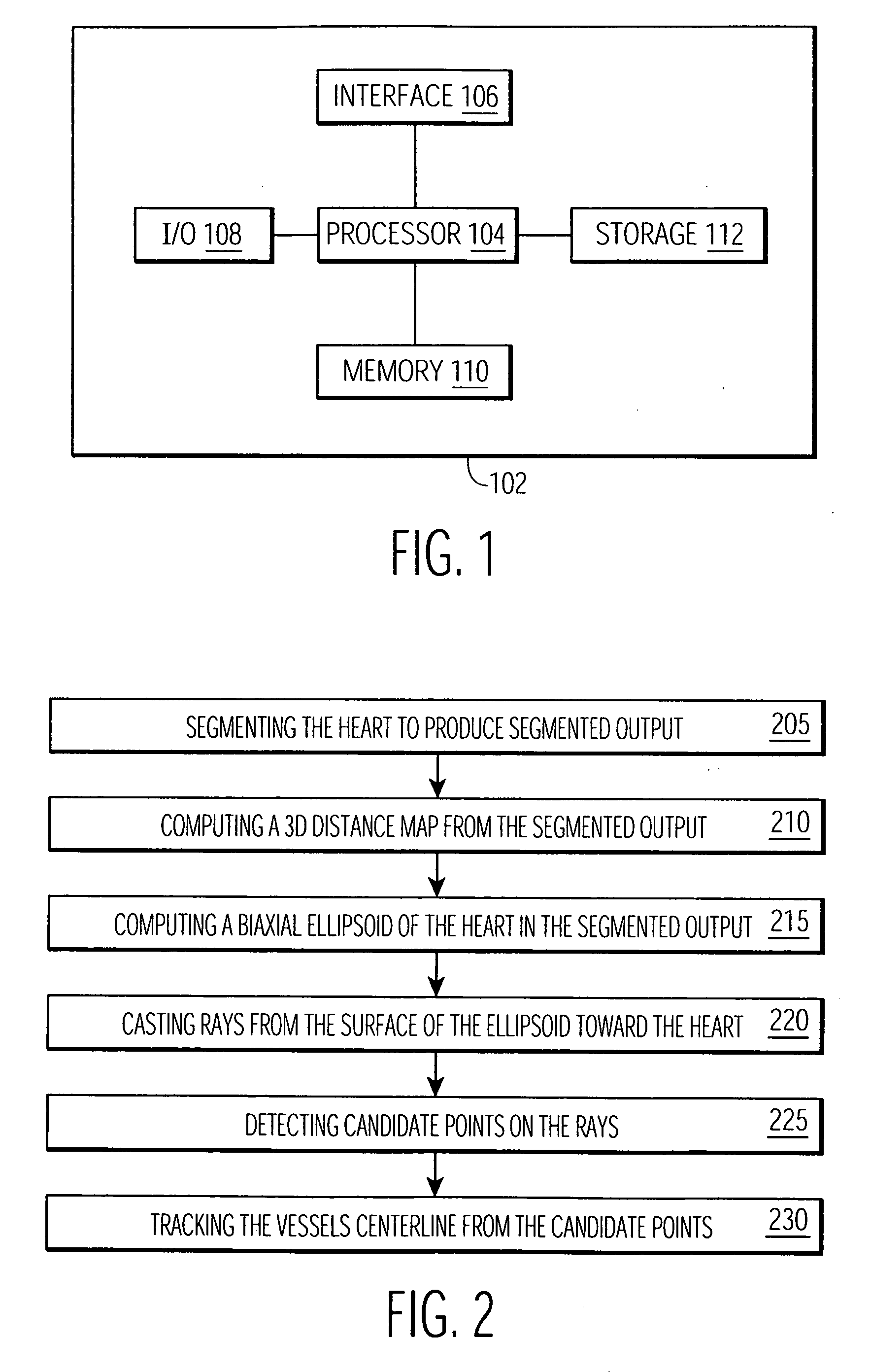
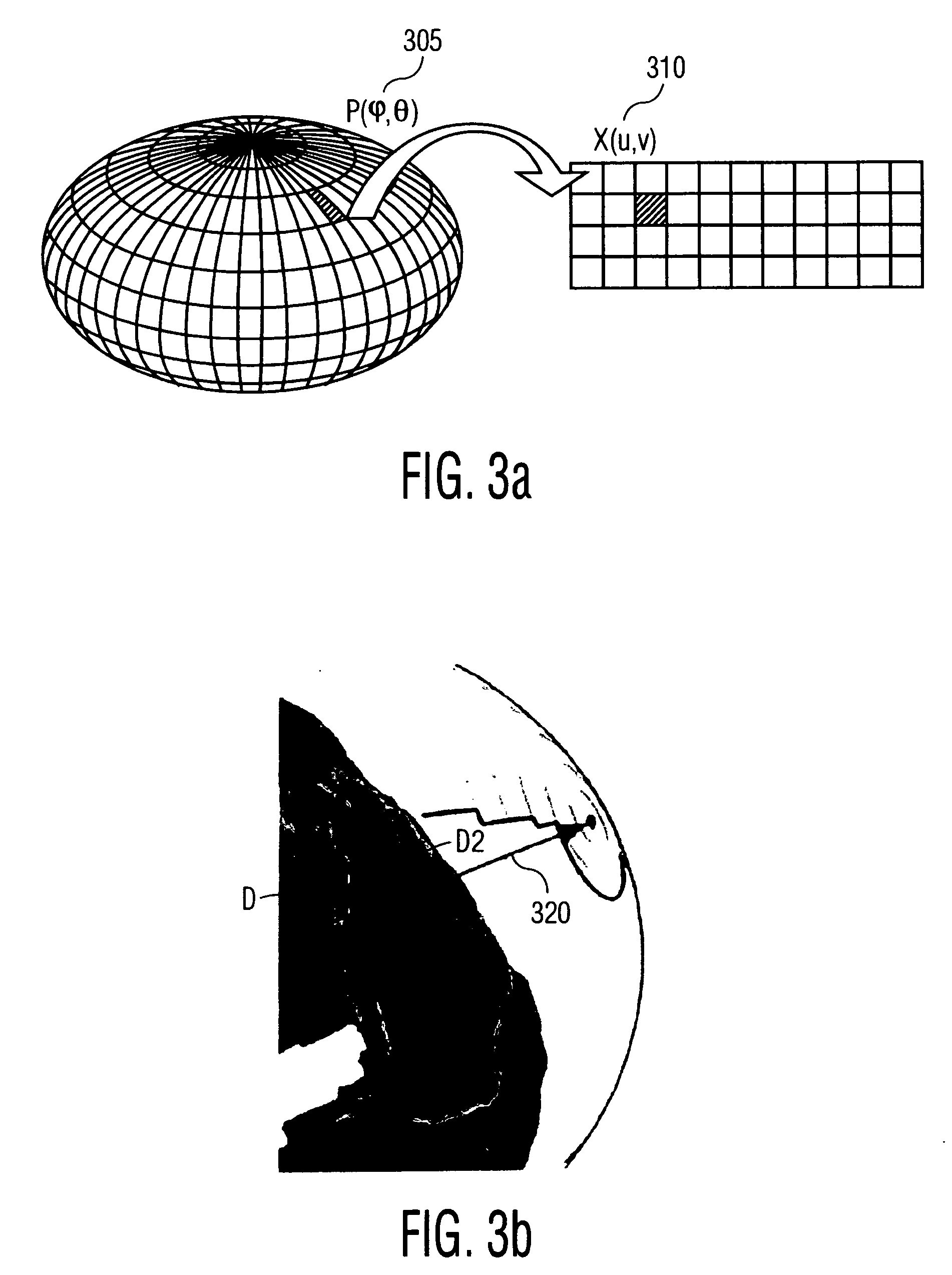
Method and apparatus for generating a 2D image having pixels corresponding to voxels of a 3D image
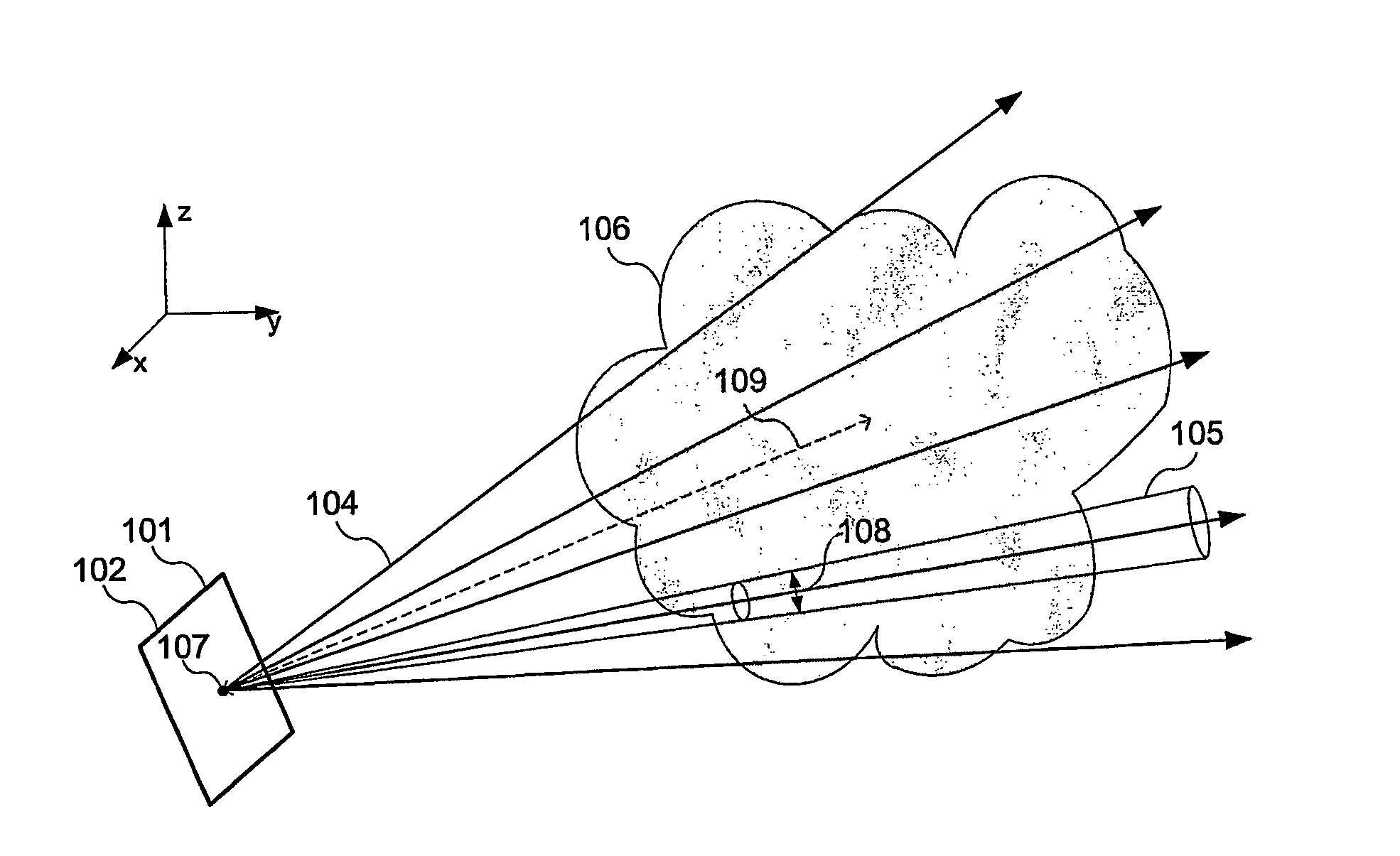
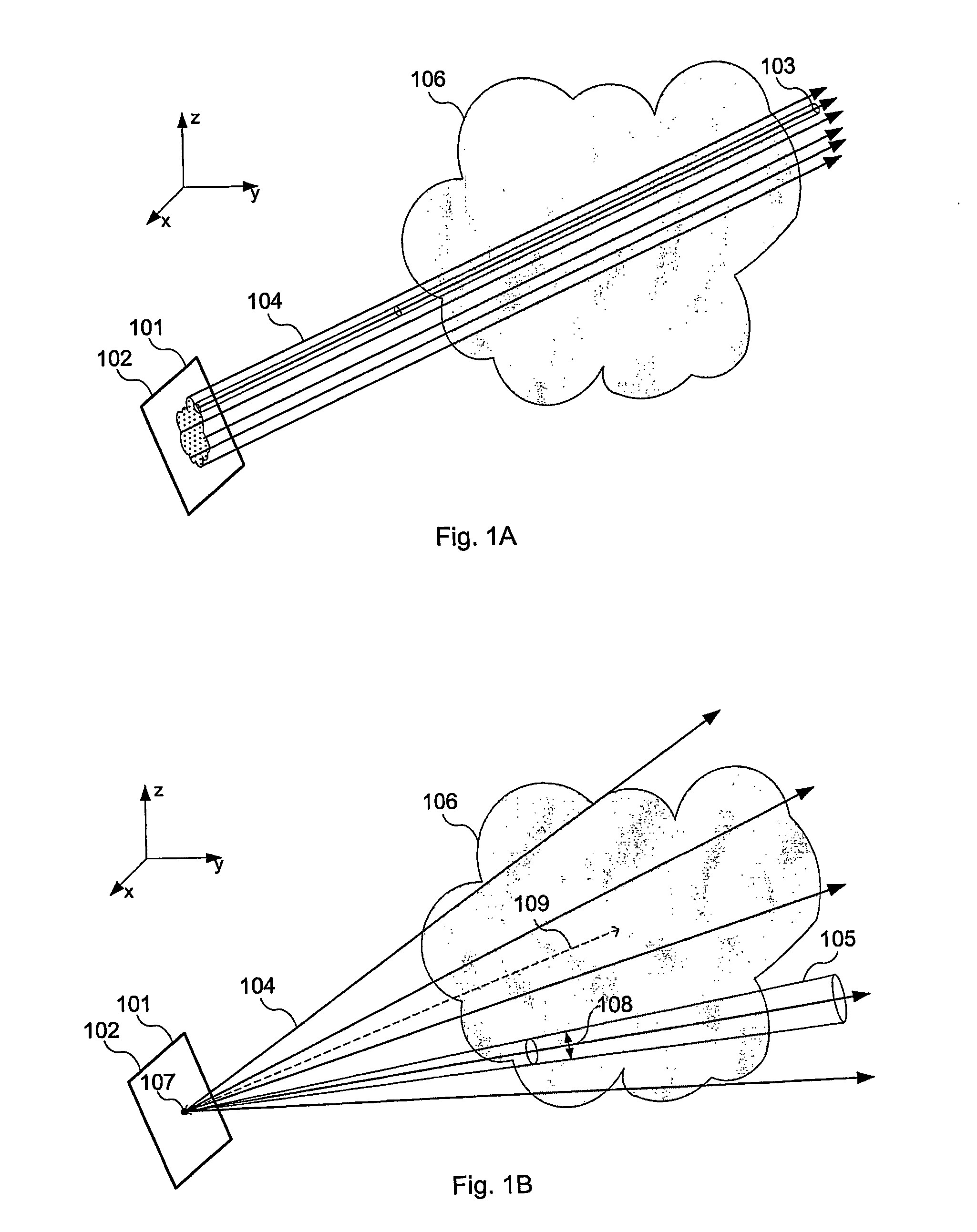
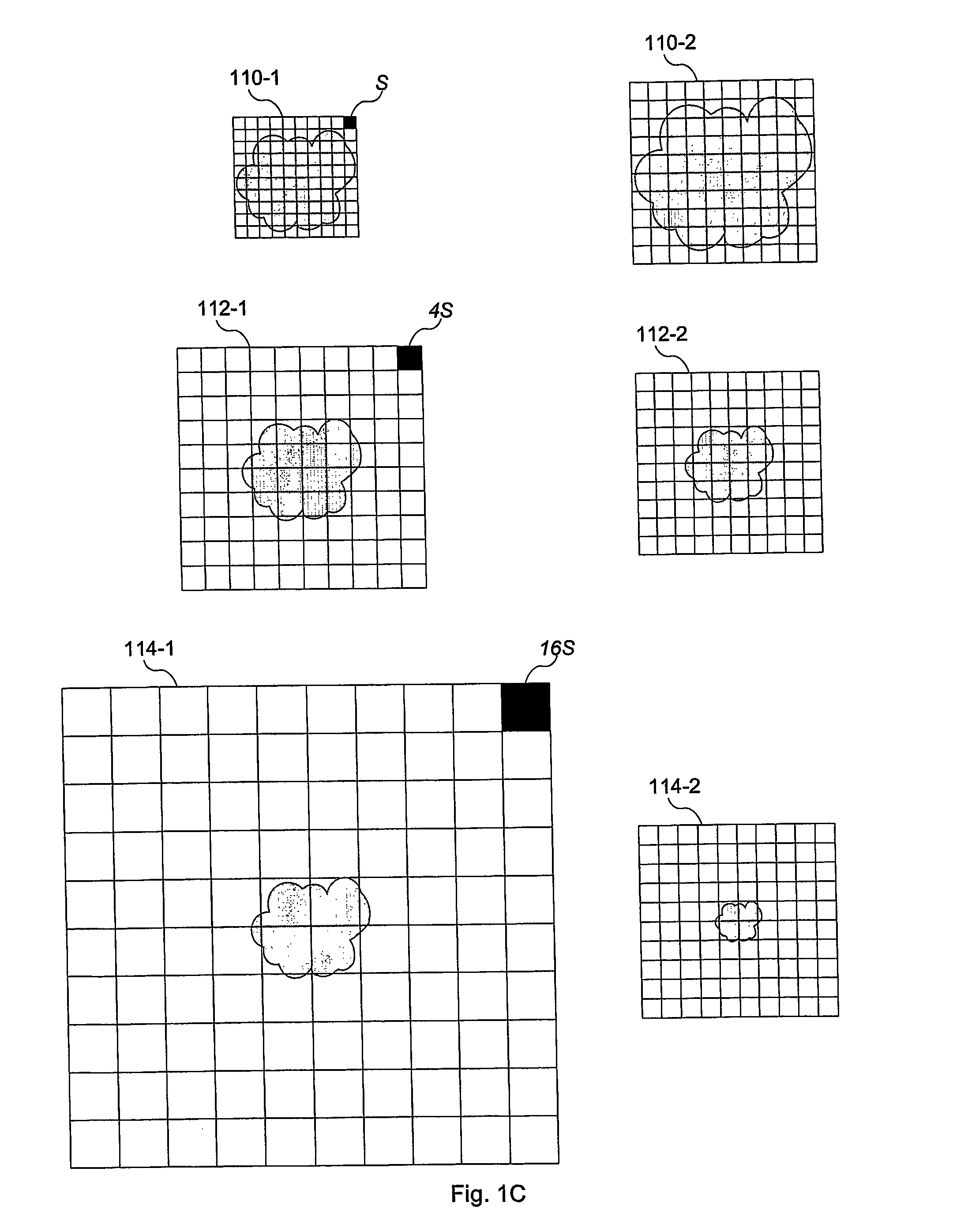
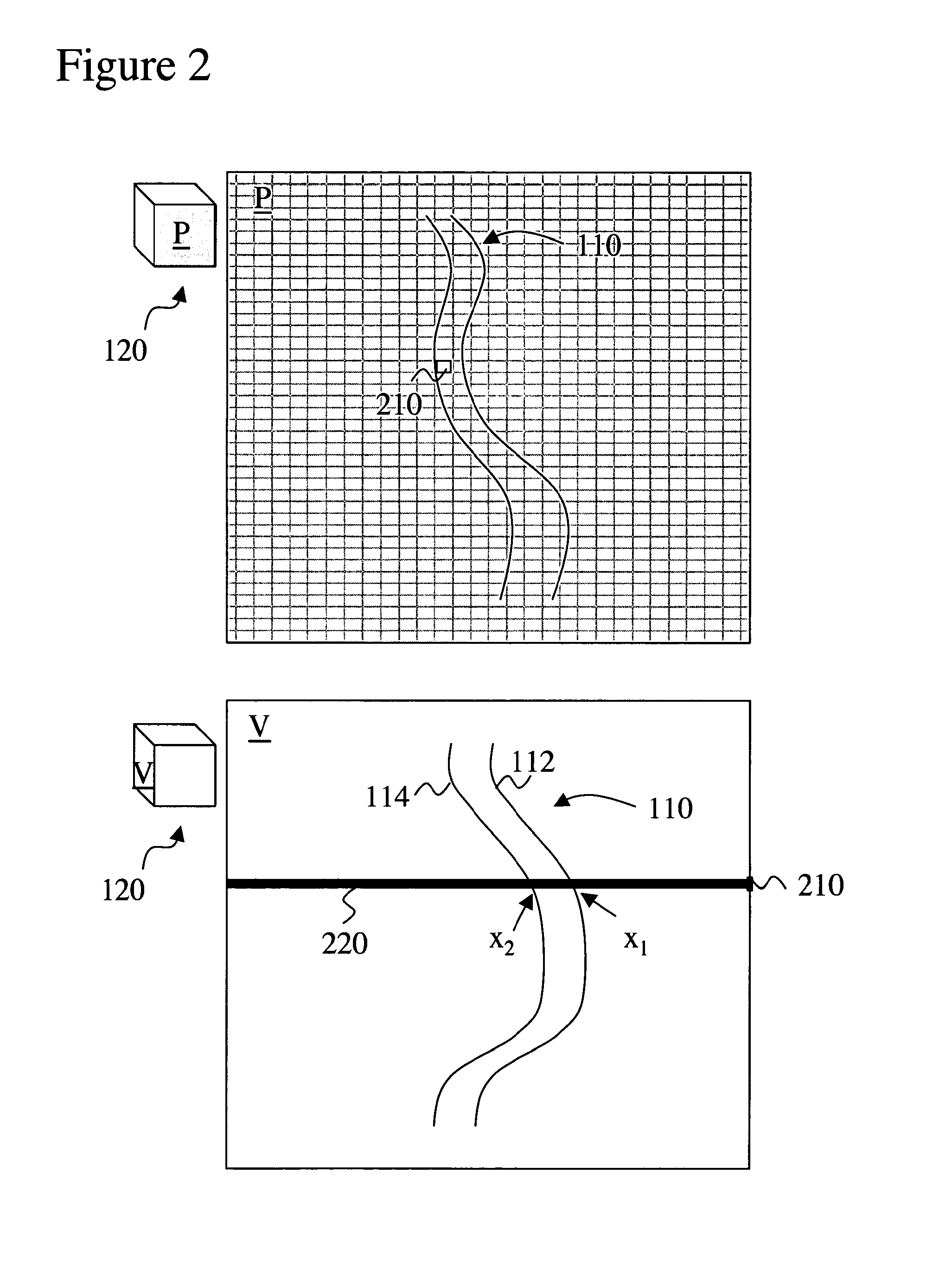
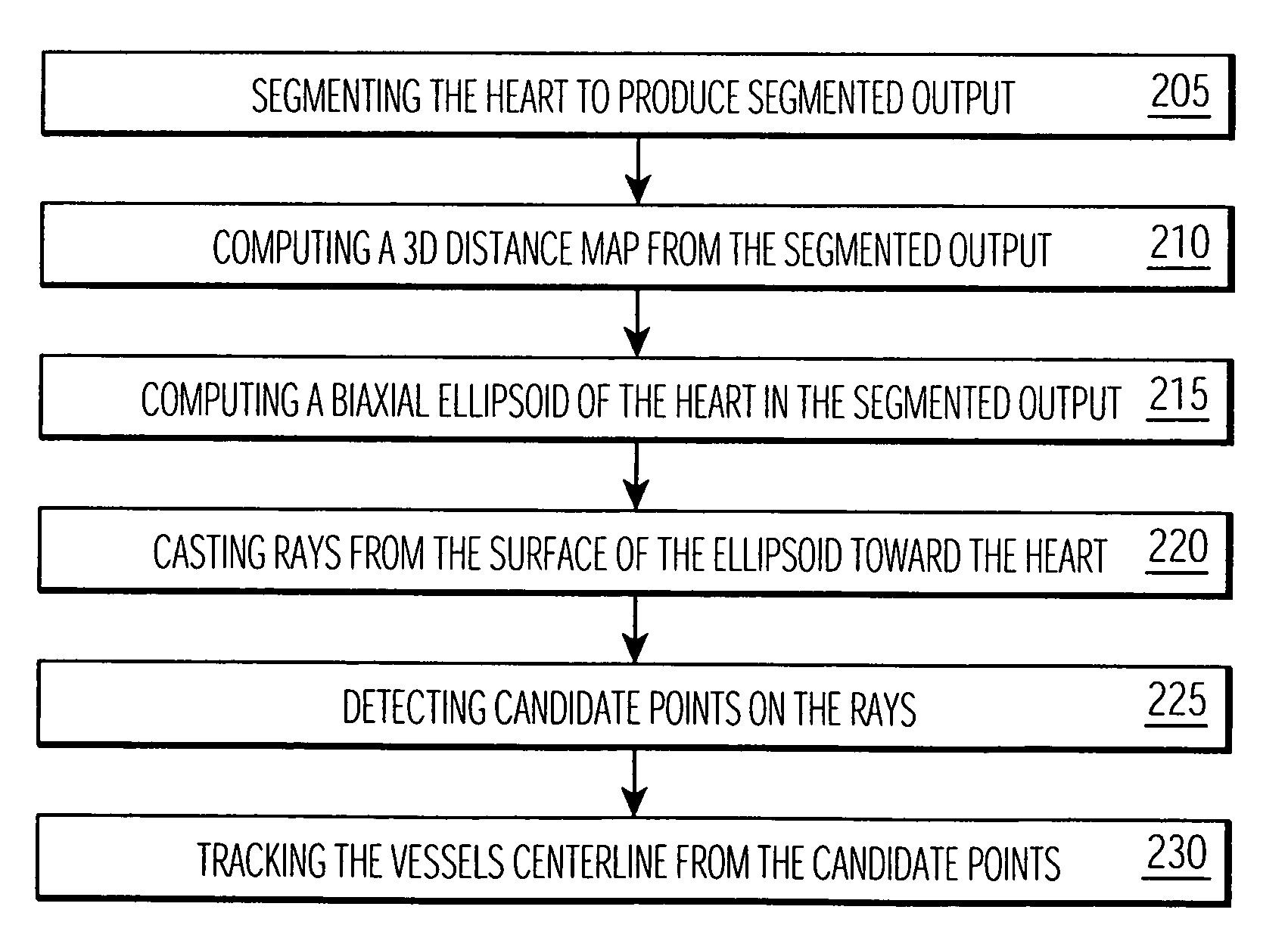
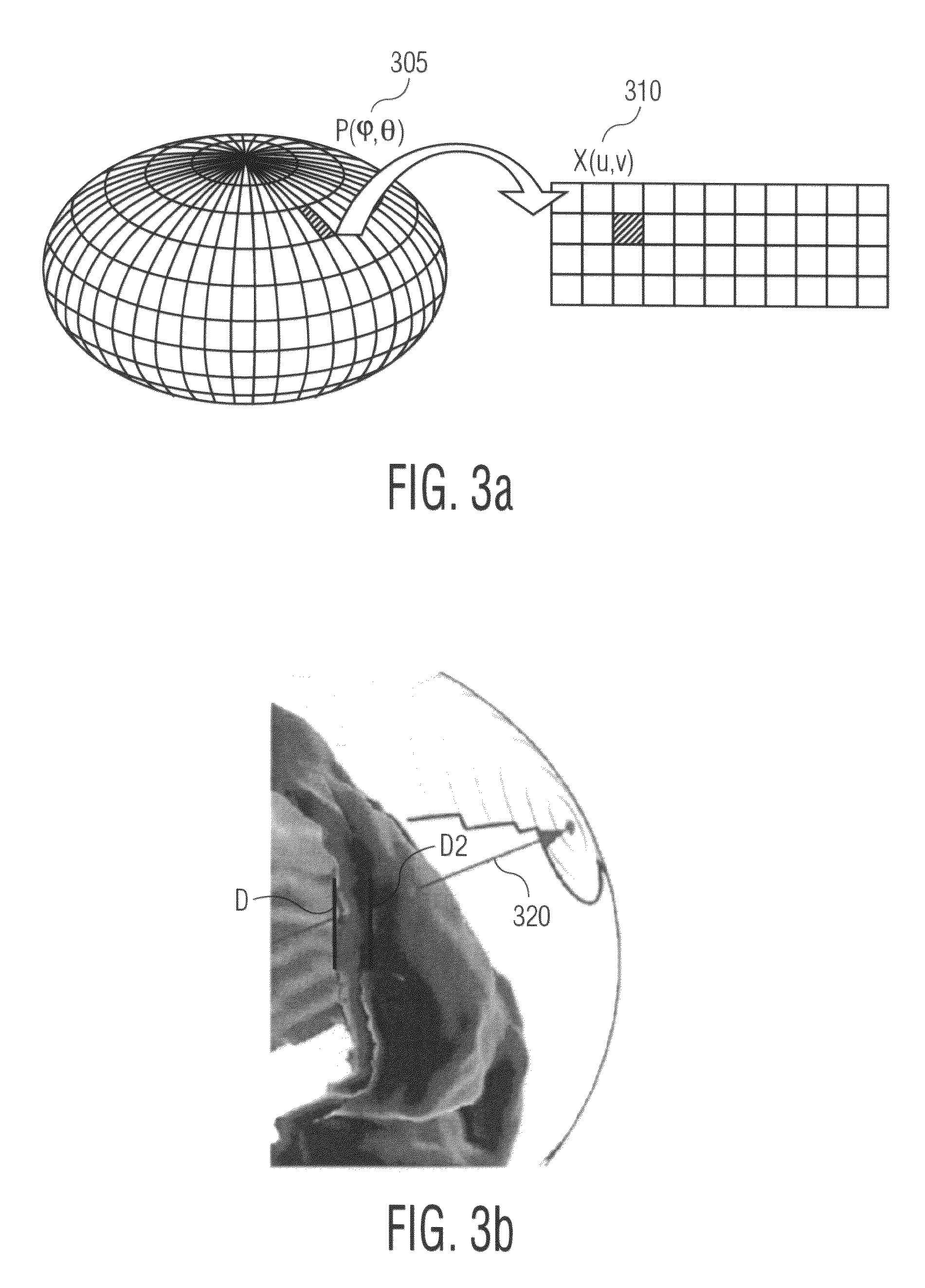
Disclosed is a method and apparatus for generating a two dimensional (2D) image of a structure (e.g., an organ) that has at least one pixel corresponding to at least one voxel of a three dimensional (3D) image of the structure. First, the surface of the structure in the 3D image is modeled by a geometrical volume such as an ellipsoid. Next, normal maximum intensity projection (MIP) rays are cast (i.e., projected) for voxels of the geometrical volume. The 2D image is then generated using the rays. The 2D image has at least one pixel that corresponds to at least one voxel of the 3D image.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
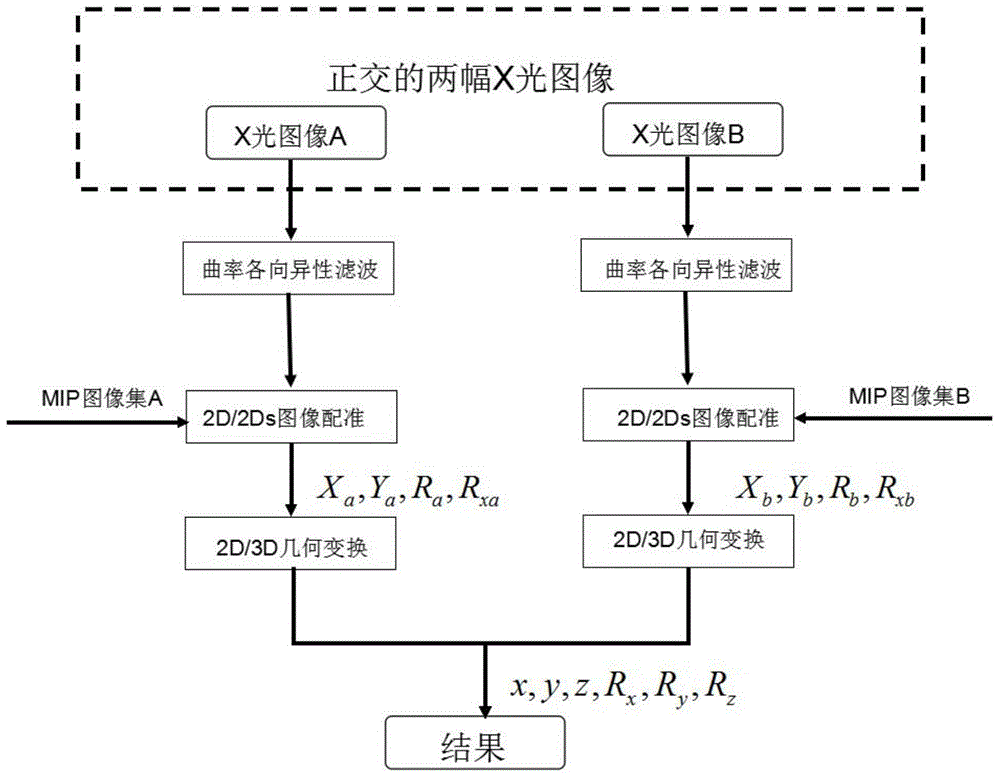
Two-dimensional and three-dimensional medical image registration method
InactiveCN104637061AFast and Accurate Guided TreatmentFast and accurate registrationImage enhancementImage analysisIn planeThree dimensional ct
The invention provides a two-dimensional and three-dimensional medical image registration method, which can quickly carry out registration on an intra-operative two-dimensional X-ray image and a preoperative three-dimensional CT (Computed Tomography) image. The two-dimensional and three-dimensional medical image registration method comprises the following steps: carrying out filtering preprocessing on the three-dimensional CT image, projecting the three-dimensional CT image in two mutually-orthogonal plane systems to obtain two corresponding digitally reconstructed radiograph (DRR) sets according to a maximum intensity projection (MIP) algorithm; obtaining two two-dimensional X-ray images on another two orthogonal planes, and carrying out the filtering preprocessing on the two-dimensional X-ray image; carrying out traversal on the two DRR sets, and carrying out registration on the two DRR sets and another two orthogonal two-dimensional X-ray images so as to determine a corresponding most similar DRR as well as the in-plane position coordinate, the in-plane rotation angle and an out-of-plane rotation angle of the DRR; converting the coordinate and the angles to be under a three-dimensional CT image coordinate system to obtain six registration parameters. According to the method, the X-ray image and the CT image which is generated in advance can be subjected to accurate and quick real-time registration.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and system for adaptive maximum intensity projection ray casting
ActiveUS20070040833A1Reduce computing costQuality improvement3D-image rendering3D modellingData setComputer graphics (images)
The adaptive MIP ray casting system first fragments a 3-D dataset into multiple sub-volumes and constructs an octree data structure with each sub-volume being associated with one node of the octree data structure. The system then establishes a 2-D image plane and selectively launches a plurality of rays towards the 3-D dataset, each ray adaptively interacting with a subset of the sub-volumes and identifies the maximum data value along the ray path. The maximum data value is then converted into a pixel value on the 2-D image plane. Finally, the system interpolates pixel values at those locations where no pixel value is generated by ray casting and thereby generates a 2-D image of the 3-D dataset.
Owner:FOVIA
Blood vessel computer aided iconography evaluating system
InactiveCN101923607AEasy to importAccurate measurementSpecial data processing applications3D modellingSurface displayReconstruction method
The invention relates to a blood vessel computer aided iconography evaluating system. The system comprises the following contents: (A) transmission of CTA (Computed Tomography Angiography) from a CT (Computed Tomography) working station to a PC (Personal Computer), wherein a transmission way comprises network card connection, CD burning and CT film scanning; (B) CTA three-dimensional reconstruction, wherein a three-dimensional reconstruction method comprises shaded surface display (SSD), maximum intensity projection (MIP) and multiplane reformation (MPR), obtains various real and clear three-dimensional models and images and can be used for observing a blood vessel three-dimensional space structure anytime and anywhere and lay the foundation for the three-dimensional measurement of various blood vessel geometric parameters; (C) blood vessel structure three-dimensional measurement; and (D) aneurysm endovascular graft exclusion virtual graft. The invention provides the computer aided iconography evaluating system which is suitable for people to use at random and is more accurate. In addition, the invention plays a role in blood vessel surgical scientific research, teaching, surgery training, and the like. The system realized by the invention is stable and reliable and is suitable for being popularized and used in blood vessel surgery centers of various large, medium and small hospitals.
Owner:冯睿
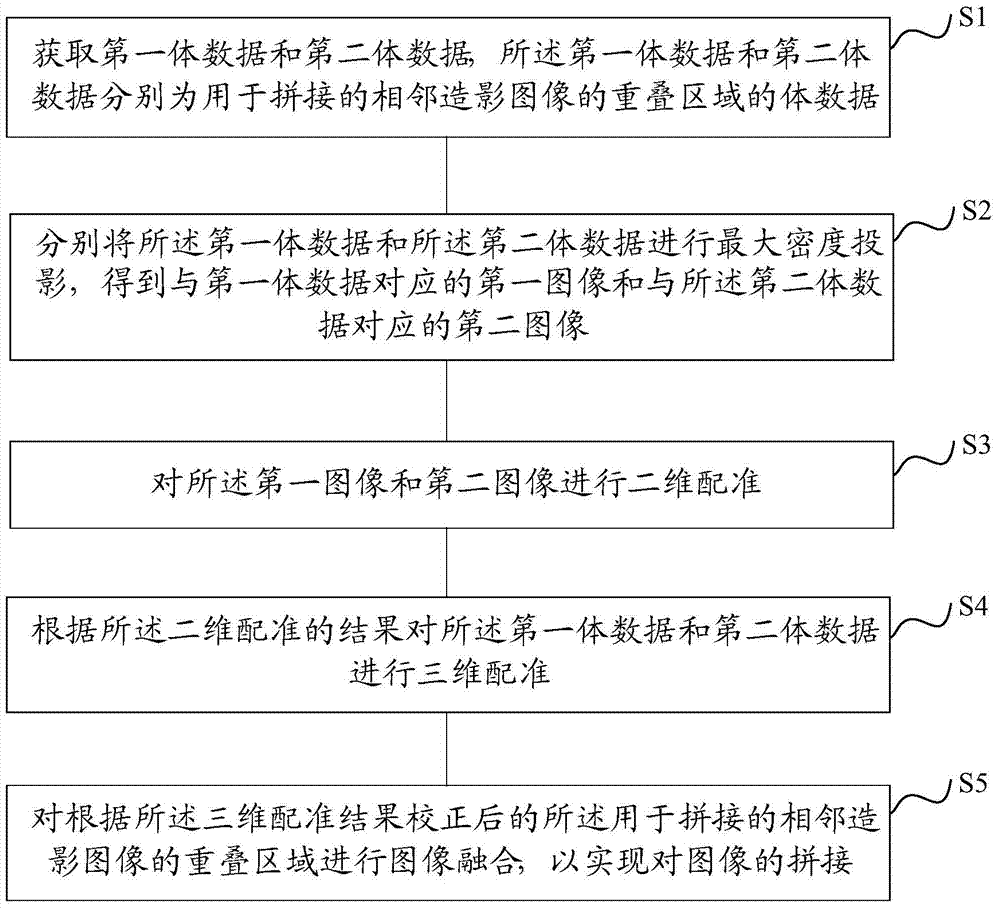
Image stitching method and device
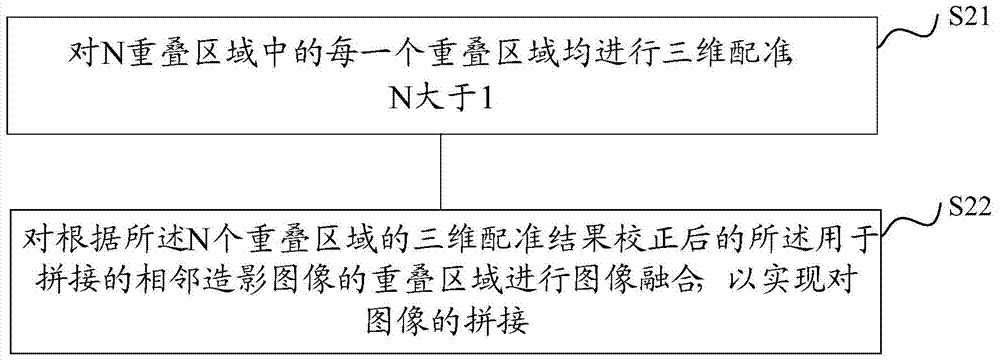
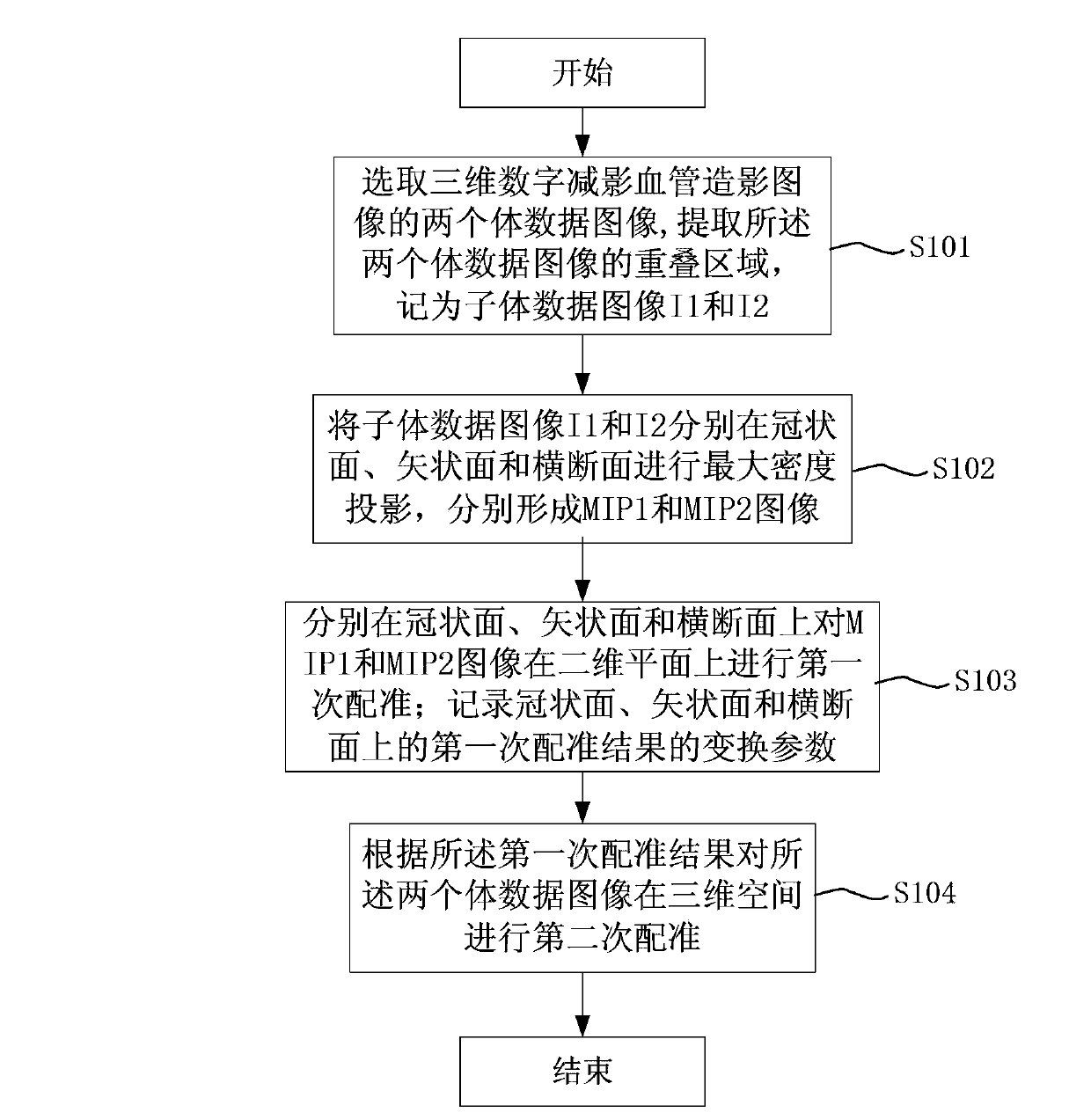
ActiveCN104268846AImprove timing performanceShorten the timeImage enhancementImage analysisMaximum intensity projectionImage stitching
The invention provides an image stitching method and device. The image stitching method and device are used for stitching three-dimensional digital subtraction angiography images. The image stitching method comprises the steps of obtaining first volume data and second volume data, wherein the first volume data and the second volume data are volume data of overlapped areas, used for stitching, of every two adjacent angiography images; maximum intensity projection is conducted on both the first volume data and the second volume data, so that a first image corresponding to the first volume data and a second image corresponding to the second volume data are obtained; two-dimensional registration is conducted on the first image and the second image; according to a registration result, three-dimensional registration is conducted on the first volume data and the second volume data; image fusion is conducted on the overlapped areas, used for stitching, of every two adjacent angiography images after correction is conducted according to a three-dimensional registration result, and therefore stitching of the images is achieved. By the adoption of the image stitching method, the accuracy of a three-dimensional registration algorithm can be effectively improved, and the stitching time of the images can be effectively shortened.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Rapid registering and splicing method used for three-dimensional digital subtraction angiography image
ActiveCN103871036AAvoid registration accuracy impactReduce processing timeImage enhancementGeometric image transformationThree-dimensional spaceMaximum intensity projection
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Translucent intensity projection imaging
InactiveUS7020318B2Eliminate bad effectsPromote resultsSurgeryCharacter and pattern recognitionImage contrastProjection image
MR imaging produces a projection image showing better image contrast between small blood vessels and background than traditional net intensity projection (NIP) images but more visual clues to vessel depth than traditional maximum intensity projection (MIP) images.
Owner:ADVANCED MRI TECH
Curved-slab maximum intensity projections
InactiveUS7170517B2Increase overall arterial contrastReduction in apparent vessel narrowingImage enhancementImage analysisMedicineTransverse plane
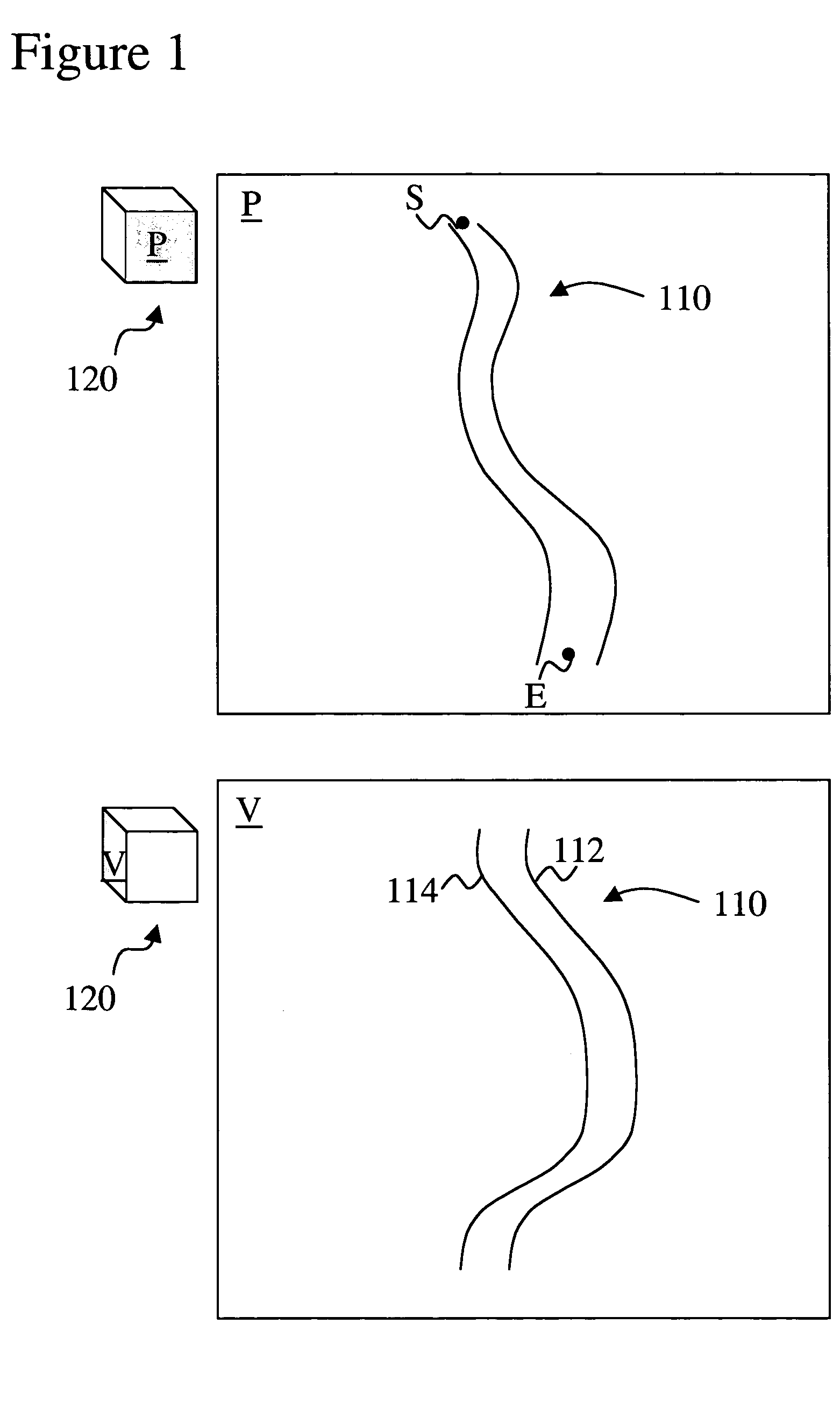
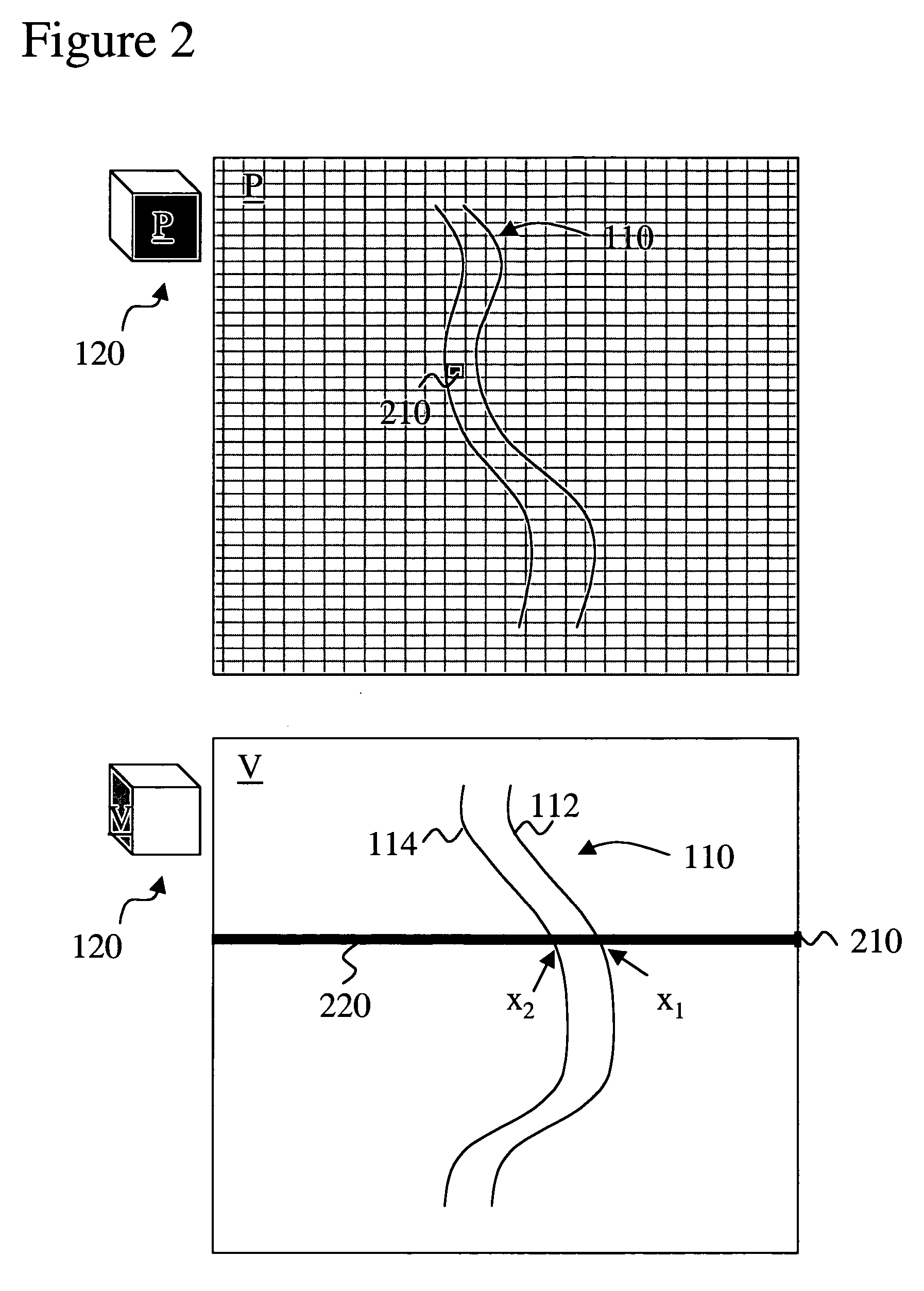
A method to define a curved slab region of interest that includes vessels while maximally excluding surrounding soft tissue and bone is provided. The thickness of the curved slab is automatically adapted to the thickness of the vessel and follows the tortuous vessel(s) so that an increase in tortuousity does not result in a disproportionate increase in the region of interest required to enclose the vessel. A plurality of boundary pairs is determined in the view plane to define a vessel. Vessel-intensities are determined for each one of the boundary pairs. The boundary pairs with associated intensities define the view of the vessel in the projection plane. Context-intensity could be defined in the area surrounding the boundary pairs in the projection and / or transverse plane. The method also includes several steps that will result in a better boundary outline and view of the vessel.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
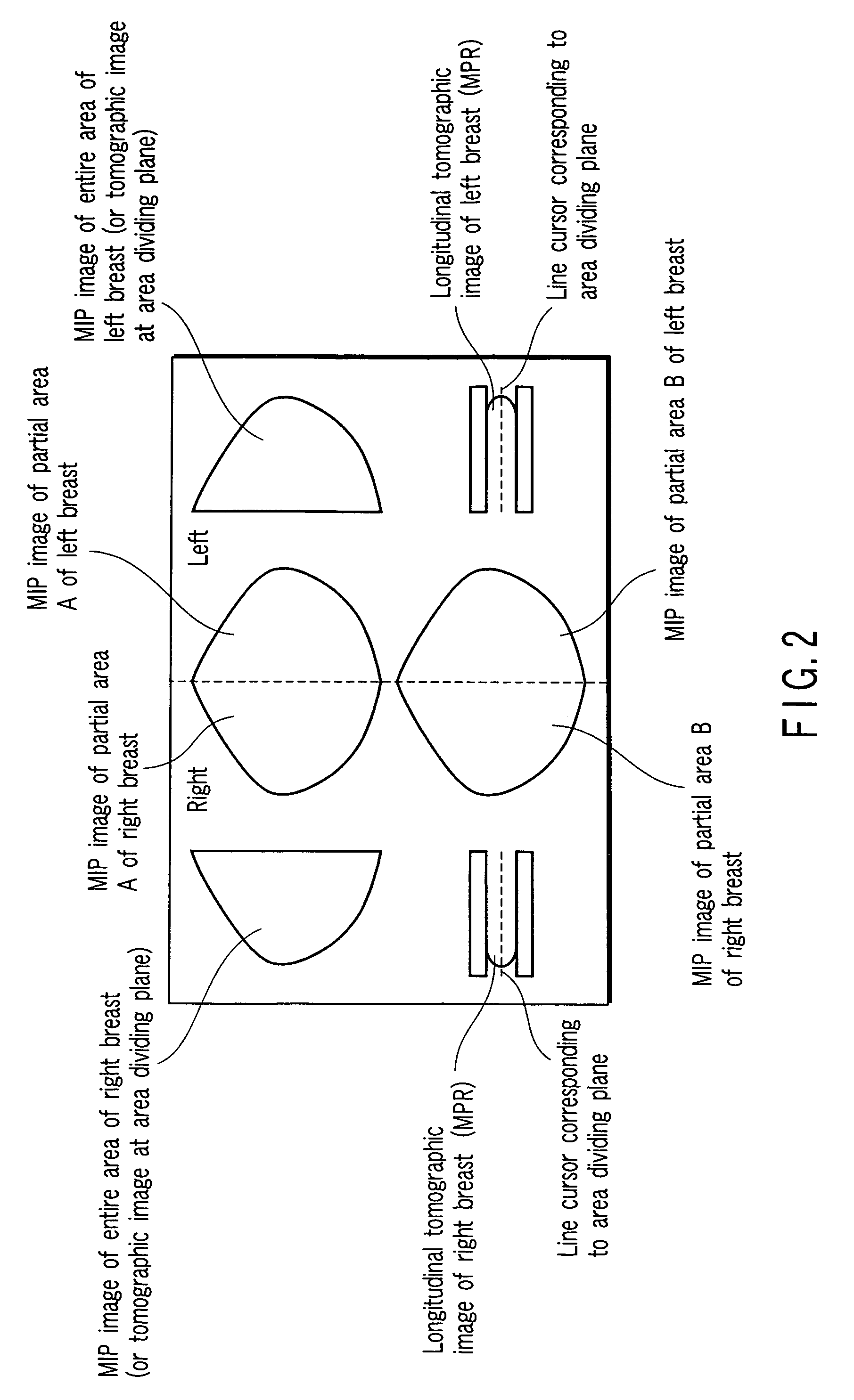
Image displaying apparatus, image displaying method, and computer readable medium for displaying an image of a mammary gland structure without overlaps thereof
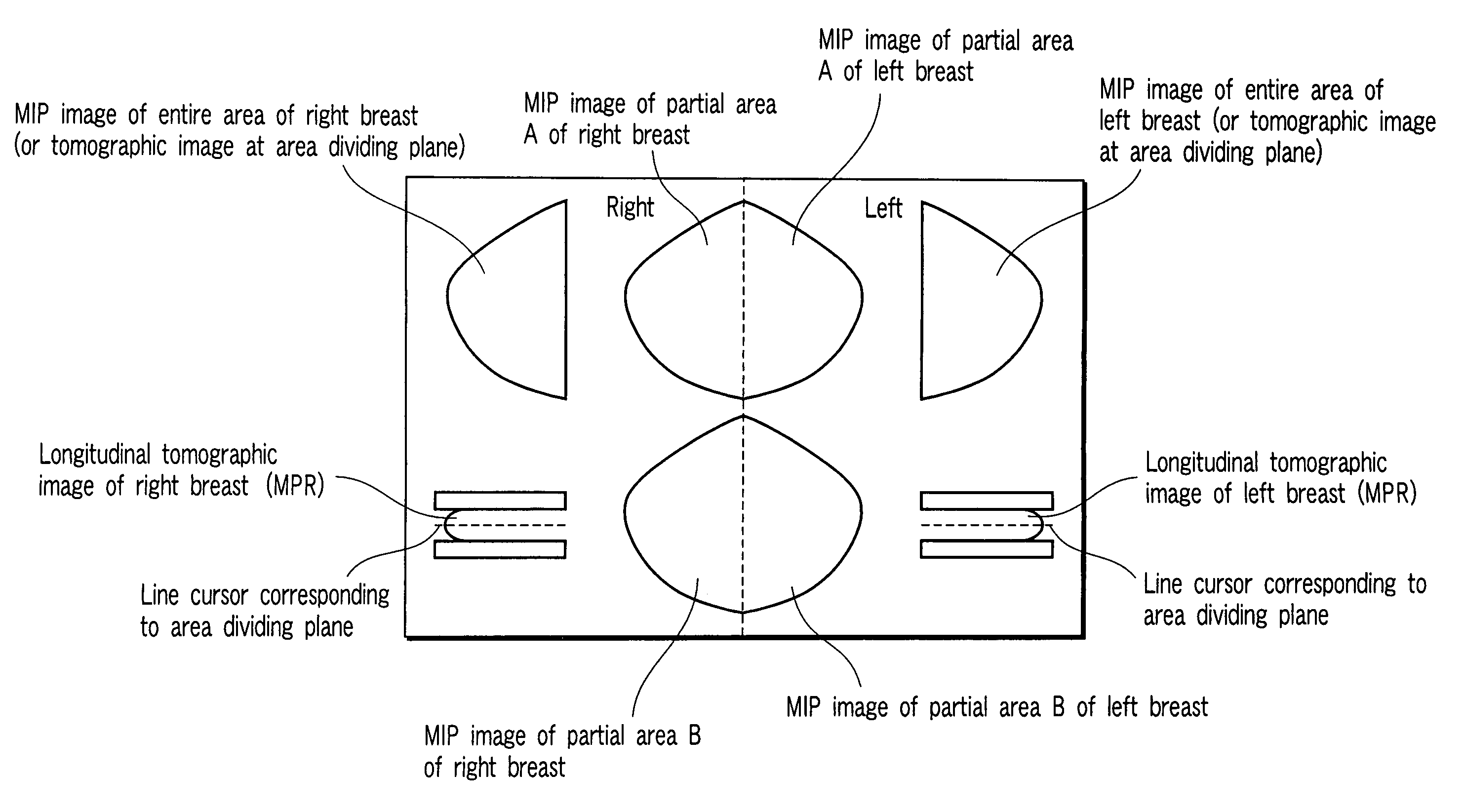
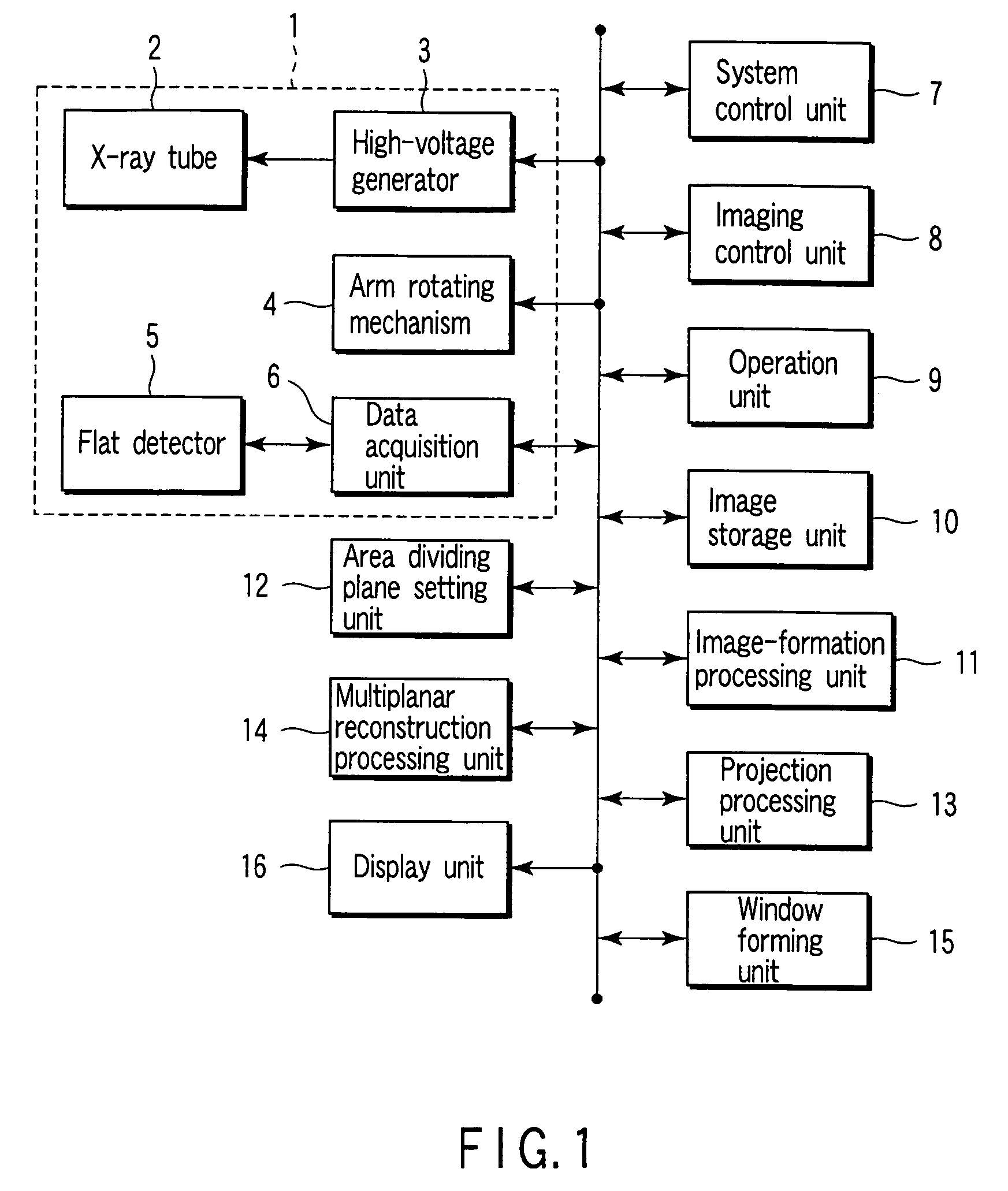
ActiveUS9098935B2Easy to understandEliminating overlaps of mammary glandsReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionLeft breastProjection image
Three-dimensional data is associated with a first imaging area including a left breast of a subject to be examined and a second imaging area including a right breast of the subject. An image displaying apparatus includes a specifying unit that specifies a nipple position of the left breast on the basis of positional information of pressure plates from the three-dimensional data. The image displaying apparatus also includes a generating unit that generates, by a maximum intensity projection, four projection images from the three-dimensional data. Two of the projection images respectively correspond to a plurality of divided areas of the left breast in the first imaging area divided on the basis of the specified nipple position. Two of the projection images respectively correspond to a plurality of divided areas of the right breast in the second imaging area. The four projection images are simultaneously displayed.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Image processing method and image processing apparatus
The present invention provides an image display method and an image display apparatus, which solve the three-dimensional cueing confliction problem of the maximum intensity projection in the stereoscopic display method, while enabling users to select and render with emphasis the maximum intensity projection of the objects of interest, so that to realize the stereoscopic display. In accordance with the present invention, a three-dimensional surface which has equal distance to a sight-point is utilized as a reference surface, and the distances from all of the local maximum intensity points to this reference surface are calculated, then, the weighting factor of each local maximum intensity point is calculated according to the distances and predetermined weighting function, afterwards, the values of local maximum intensity points are adjusted according to the obtained weighting factors, and finally, the maximum intensity projection value is produced by synthesizing all of the adjusted values of local maximum intensity points.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
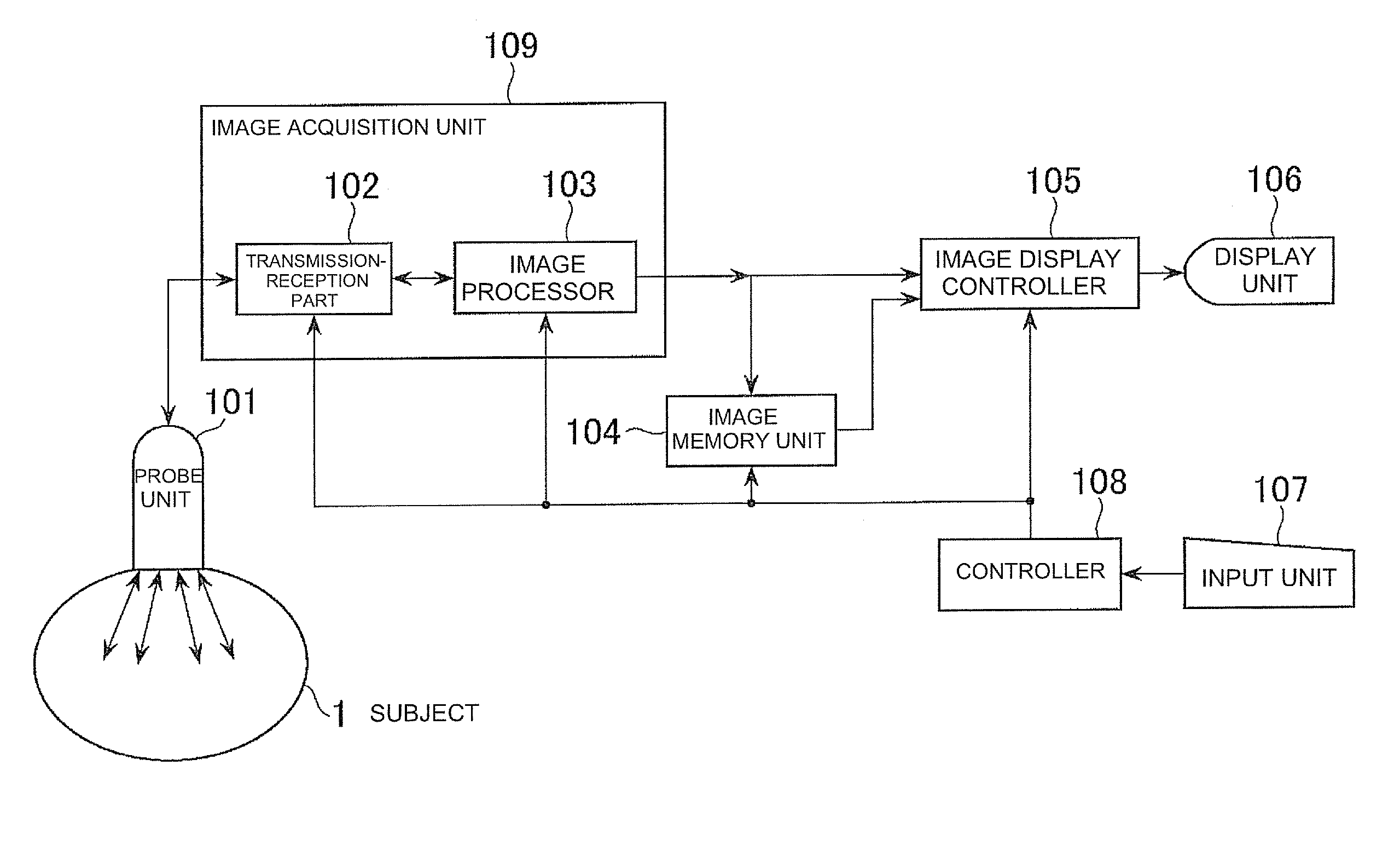
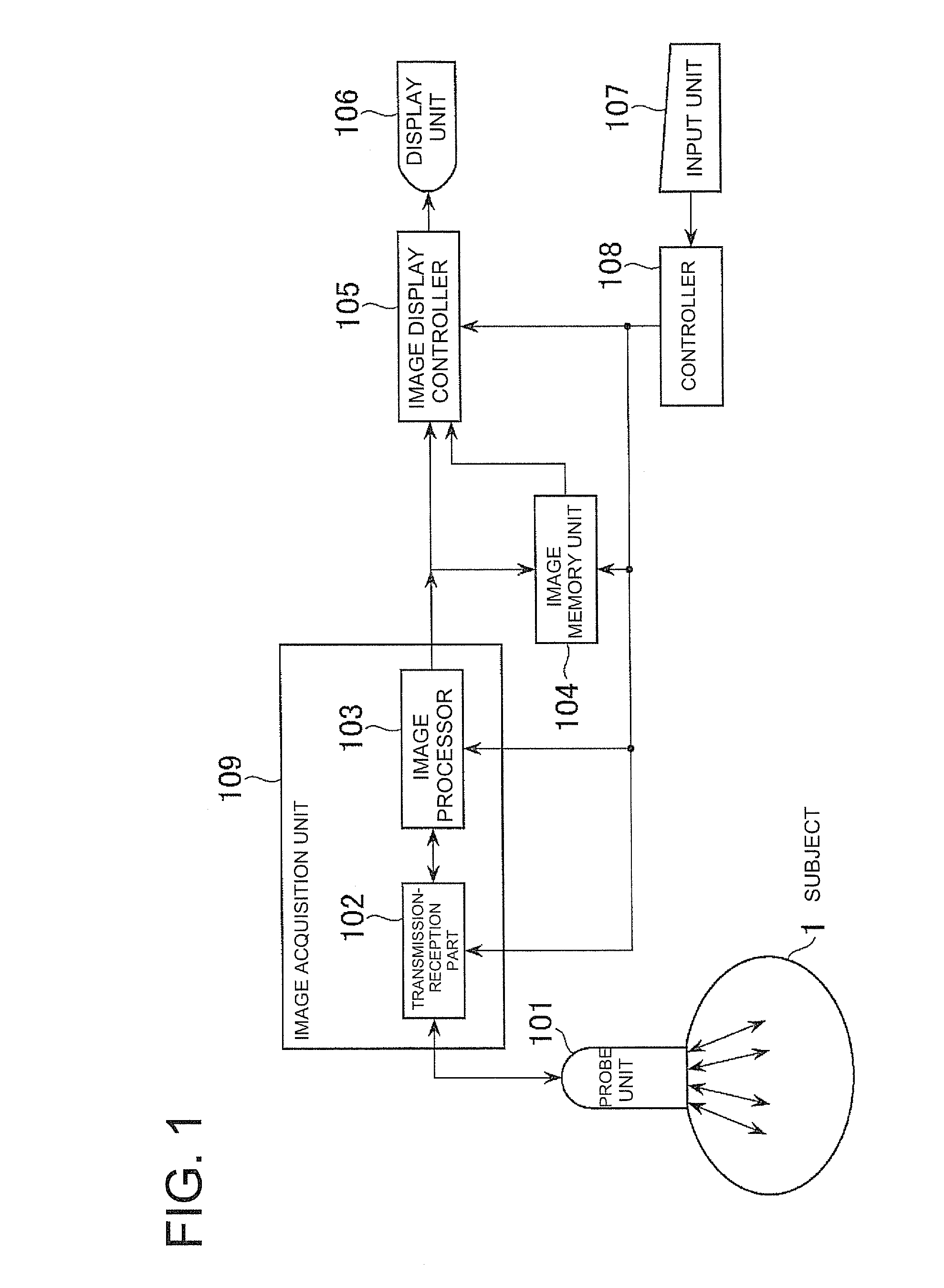
Ultrasonic imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20090099452A1Easy to seeEasy to understandUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsWave based measurement systemsTime rangeUltrasonic imaging
An ultrasonic imaging apparatus includes an image acquisition device for administering a contrast agent and acquiring B-mode image information, an image storing device for storing the B-mode image information during a predetermined imaging time range from after the administration, a first maximum intensity projection device for forming first maximum intensity projection image information using the B-mode image information acquired in a first time range contained in the imaging time range, a second maximum intensity projection device for forming second maximum intensity projection image information using the B-mode image information acquired in a second time range contained in the first time range, a second image formation device for forming a second image based on the second maximum intensity projection image information, an overlaid image generation device for generating an overlaid image in which the second image is overlaid on a first image of the first maximum intensity projection image information.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
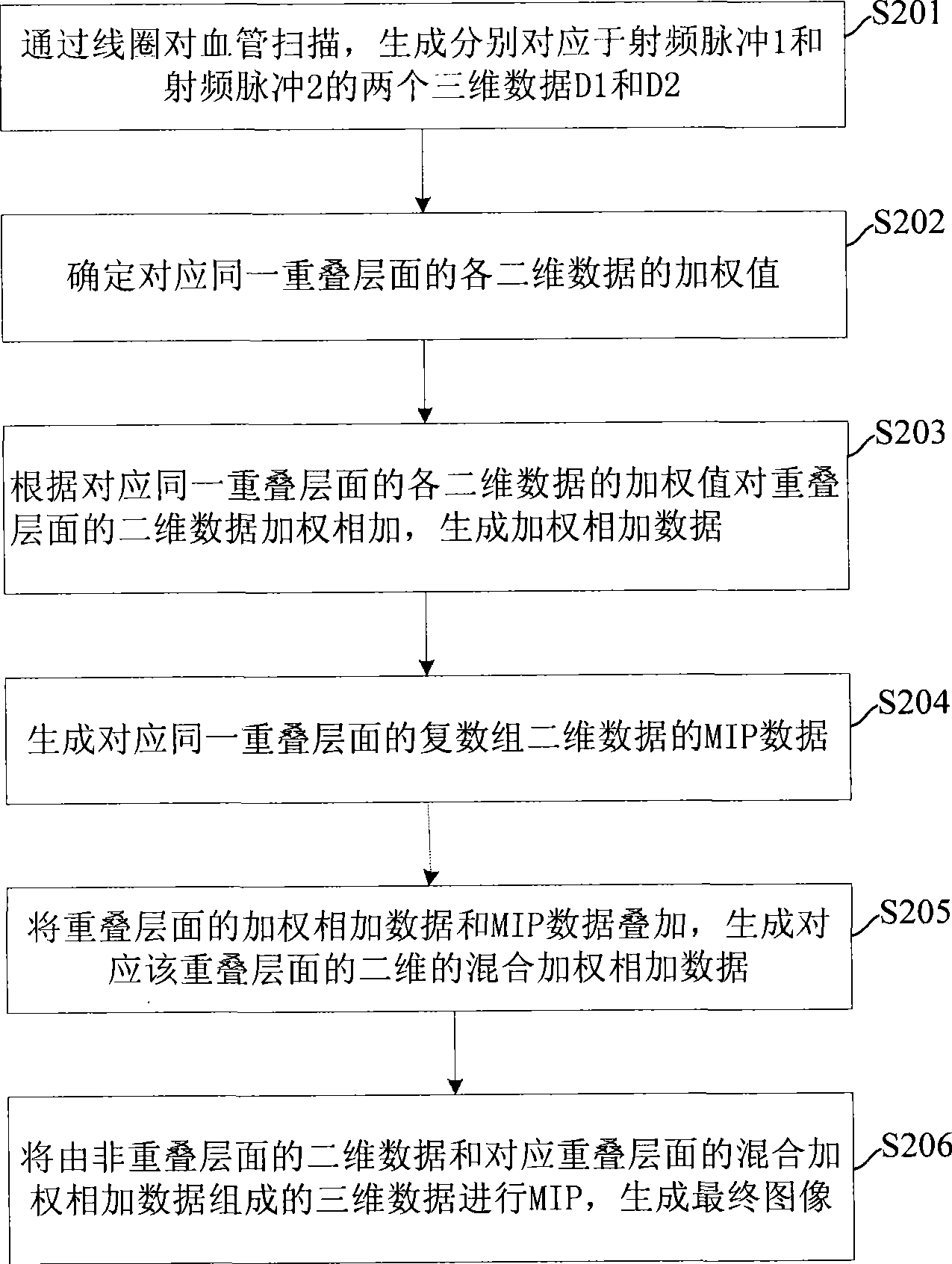
Method and device for removing artifacts in magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveCN101520499AImprove reliabilityDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMedical diagnosisMaximum intensity projection
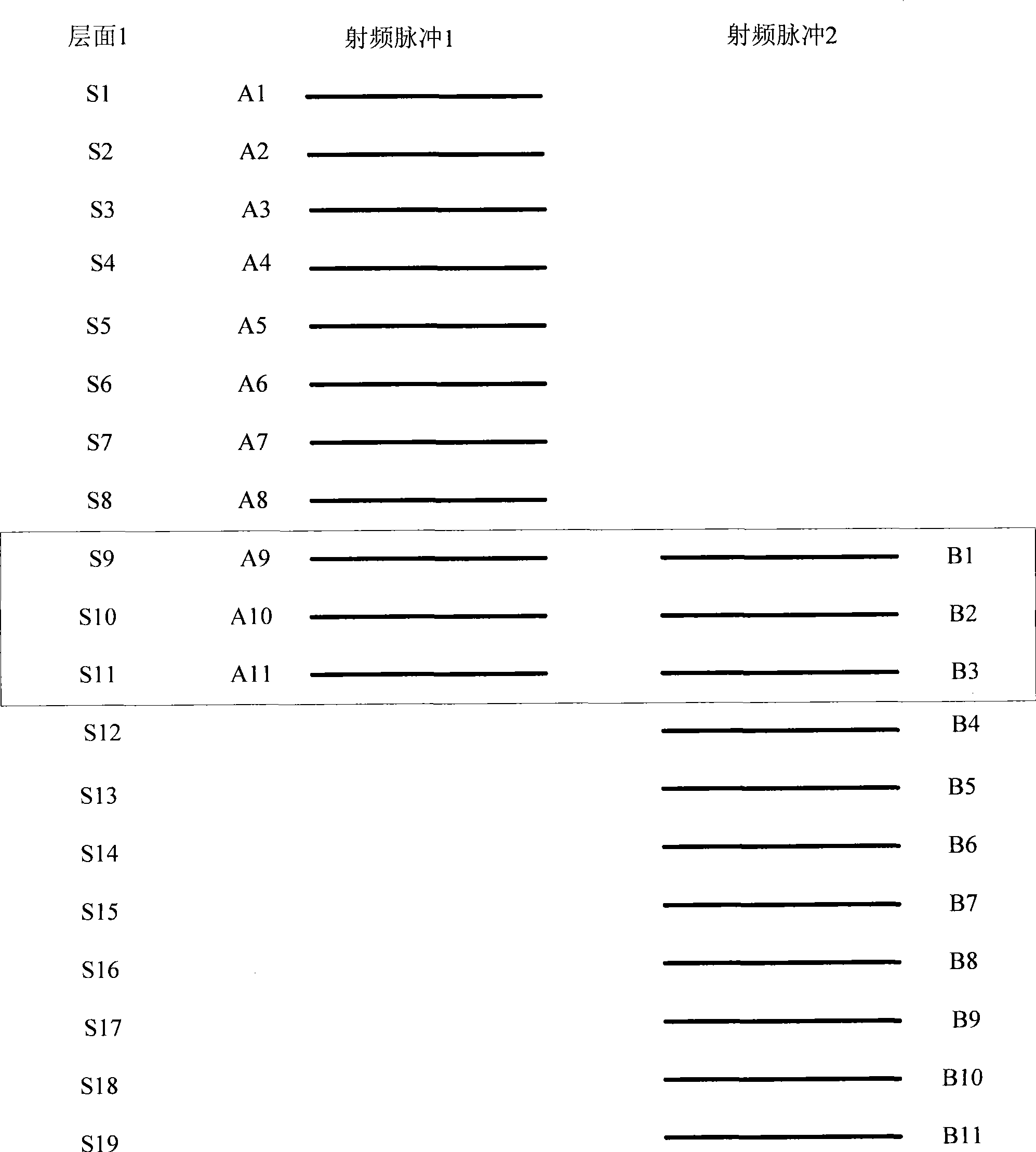
The invention discloses a method for removing artifacts in magnetic resonance imaging, which comprises the steps: plural groups of three-dimensional data are generated through scanning and each group of three-dimensional data comprise plural groups of two-dimensional data; all two-dimensional data corresponding to the same overlapping layer surface are subjected to weighting addition and maximum intensity projection, the data of weighting addition and the data of maximum intensity projection are superposed so as to generate two-dimensional data corresponding to the overlapping layer surface; and the tree-dimensional data consisting of the two-dimensional data of non-overlapping layer surface and the data corresponding to the overlapping layer surface are subjected to maximum intensity projection so as to generate a final image. The invention also discloses a device for removing the artifacts in magnetic resonance imaging. As all the tow-dimensional data corresponding to the same overlapping layer surface are subjected to mixed weighting addition instead of simple adoption of MIP for processing the data of the overlapping layer surface, important information of medical diagnosis in the data on the layer surface of each radio-frequency pulse edge can be retained maximally, while background signals can be smoothed effectively.
Owner:西门子数字医疗科技(上海)有限公司
Maximum intensity projection performing method and apparatus
InactiveUS20070237379A1Reduce functionCharacter and pattern recognitionComputerised tomographsUltrasound attenuationMaximum intensity projection
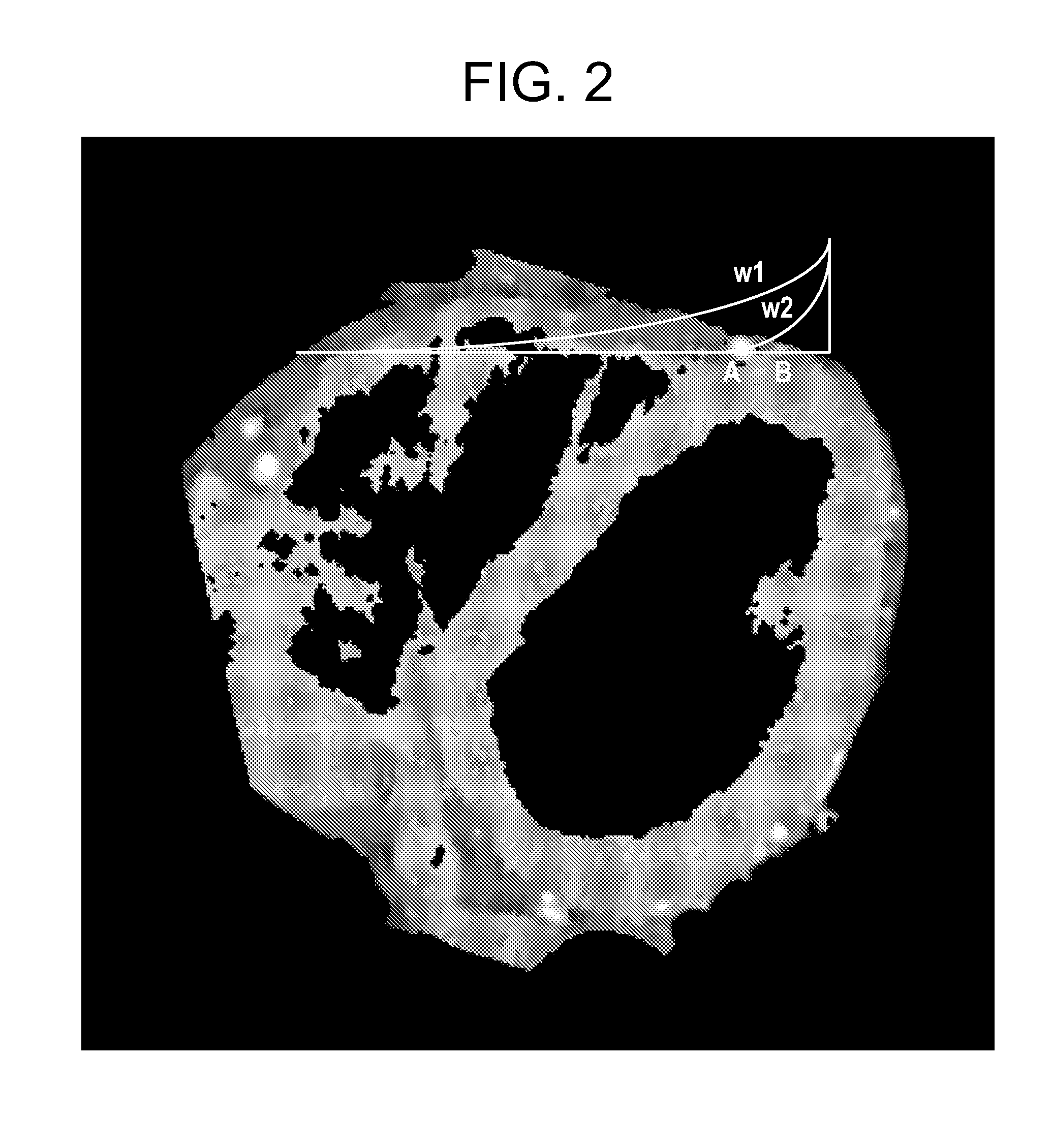
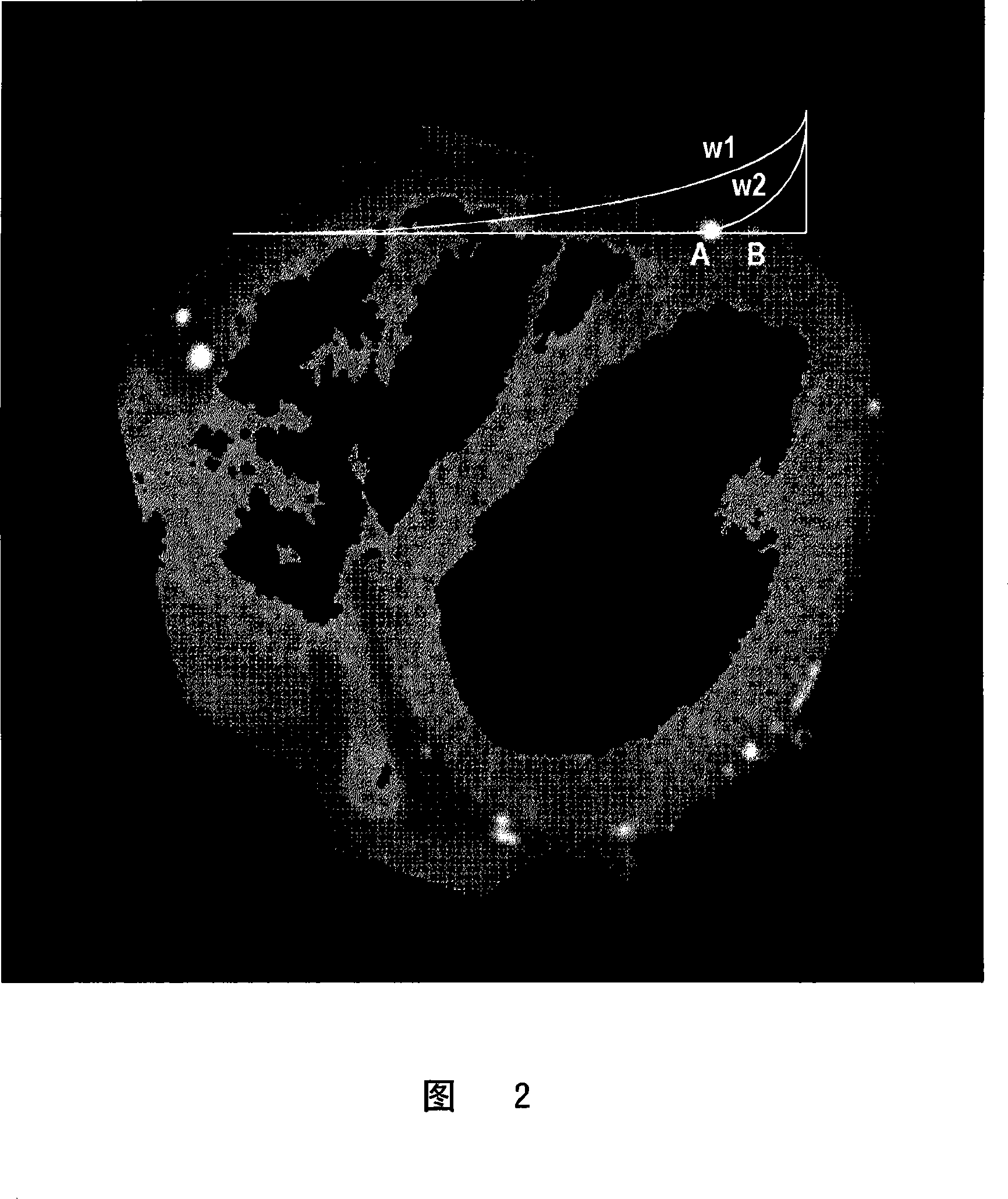
In order to visualize a narrow blood vessel overlapping a thick blood vessel, at the time of performing a maximum intensity projection on three-dimensional image data, three-dimensional image data is weighted with a plurality of weighting functions of different attenuation characteristics along a projection line. Maximum intensity projections are performed on the plurality of pieces of the weighted three-dimensional image data, and results of all of the maximum intensity projections are summed. The weight of the weighting function is zero until the projection line reaches the surface of an image and, after the reach, gradually decreases from an initial value. Alternatively, the weight of the weighting function is zero to some midpoint of the projection line and, after the midpoint, gradually decreases from the initial value. The midpoint is adjustable. The attenuation characteristic is given by an exponential function. Parameters of the exponential function are adjustable.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Intracranial aneurysm detection method and system based on convolutional neural network
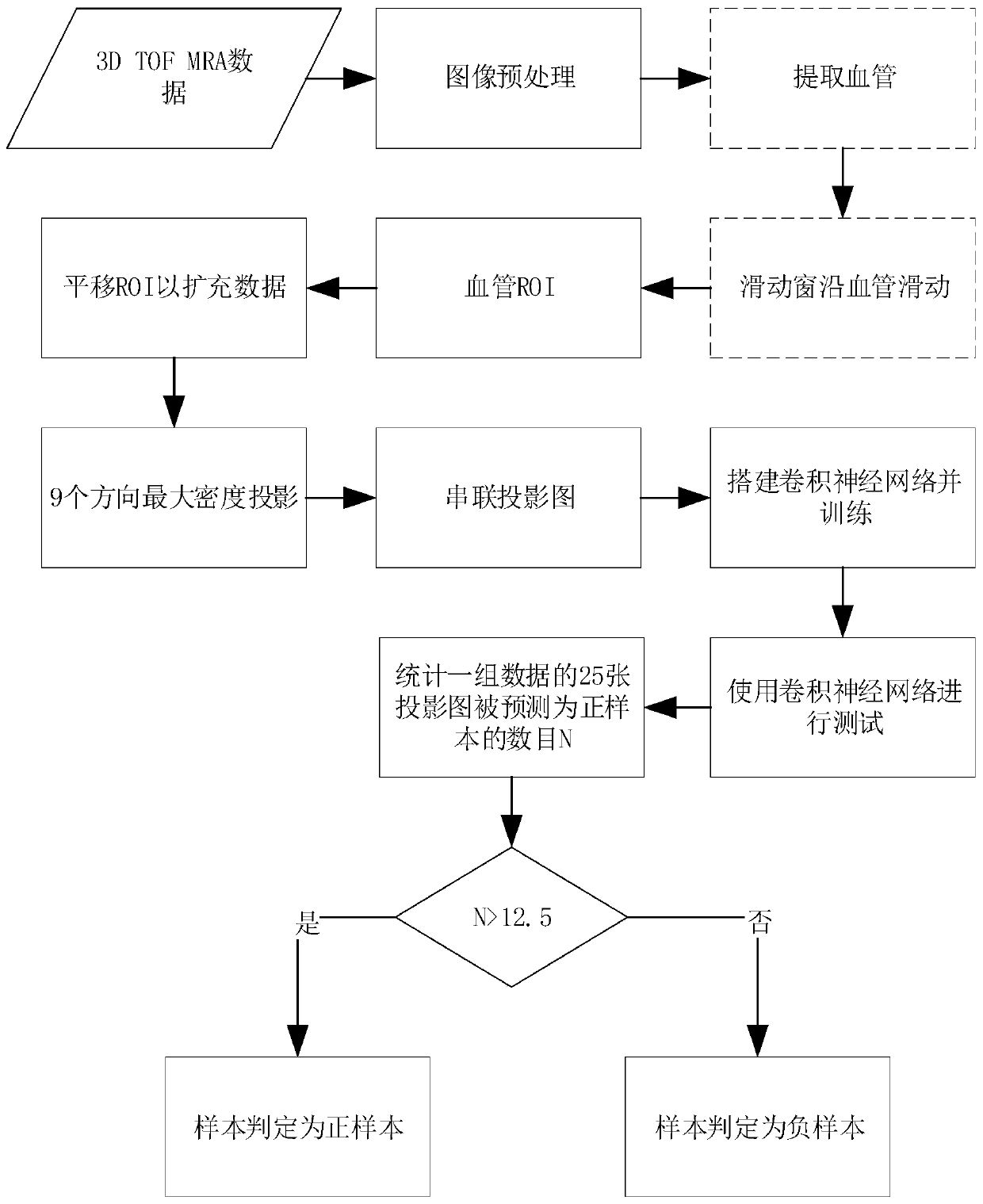
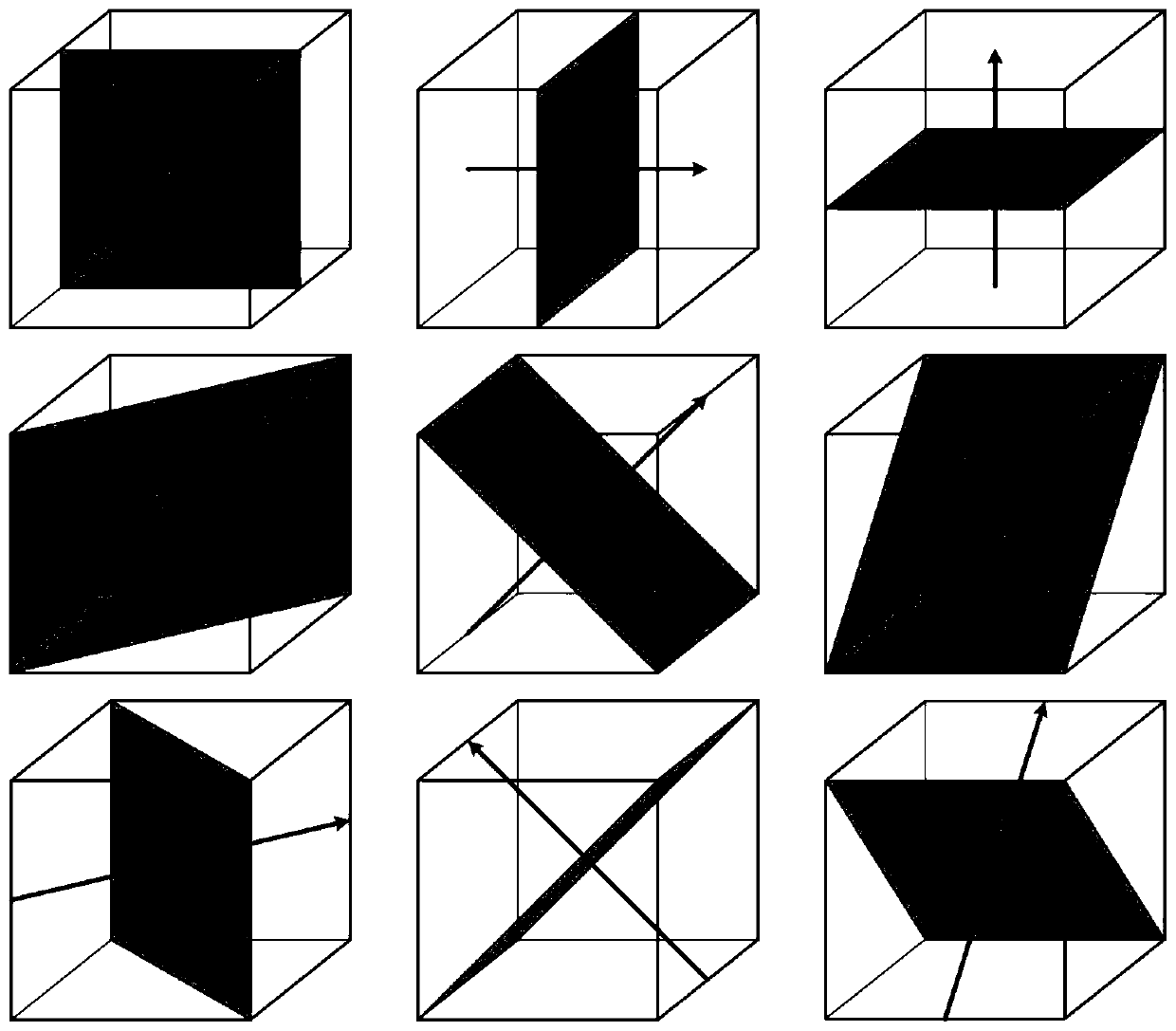
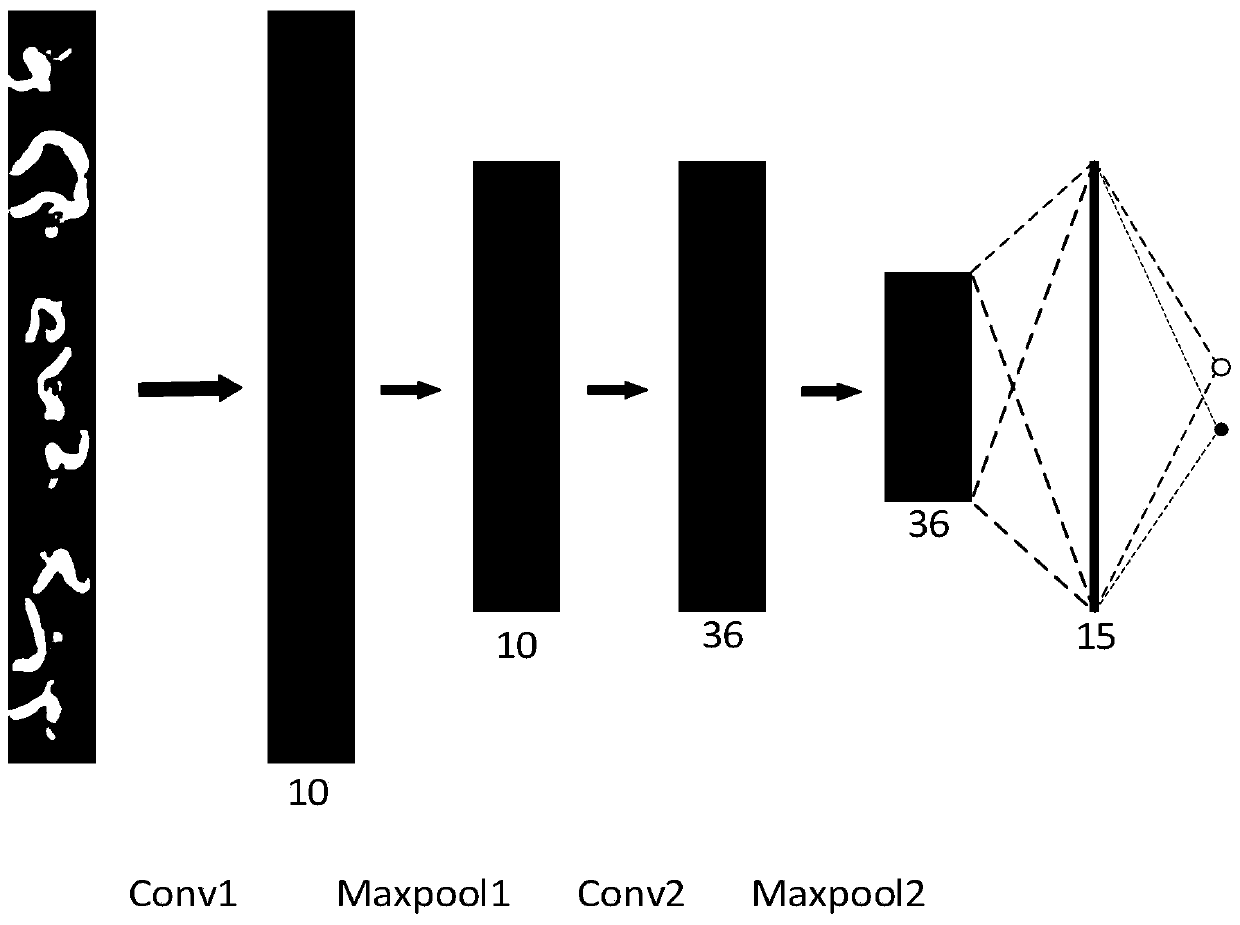
ActiveCN110827242ARealize the detection functionImprove classification accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisVoxelBlood vessel
The invention belongs to the field of medical image processing. The invention discloses an intracranial aneurysm detection method and system based on a convolutional neural network. The detection method is based on a three-dimensional time leap magnetic resonance angiography image (3D Time-of-Flight MR Angiography, 3D TOF MRA), and is characterized in that first of all, blood vessels are extracted, a series of cubic voxel blocks are extracted as ROIs (Region of Interest) along the central line of the blood vessel; maximum density projection is performed on each ROI (Region of Interest) in a plurality of directions to obtain a MIP (Maximal Intensity Projection) by taking the MIP as the ROI; the MIP graph is used as input, the trained convolutional neural network is used for classifying theMIP graph, an obtained classification result reflects whether the ROI contains the aneurysm or not, and then whether the intracranial aneurysm exists in the to-be-detected object or not is judged. According to the method and the system, the whole process of the method is processed, and the setting mode of each functional module component in the corresponding system device is improved, so that thedetection method and the detection system have relatively high classification accuracy and sensitivity.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method, medium and device for reconstructing special image for performing image omics feature extraction based on lung tumor 4DCT image
ActiveCN110880195AEasy extractionImprove predictive performanceReconstruction from projectionRadiation diagnosticsImage extractionTime domain
The invention relates to the technical field of 4DCT image reconstruction, in particular to a reconstruction method, a medium and a device for reconstructing a special image for performing image omicsfeature extraction based on a lung tumor 4DCT image. The objective of the invention is to solve the problem of how to extract iconomics characteristic parameters close to a static CT image from a reconstructed image of a 4DCT image and how to influence modeling of a prediction model by the iconomics characteristic parameters. A concept and a mathematical model (MGDPM) for reconstructing an imageon the basis of a minimum gradient density projection matrix are provided by analyzing the time domain gradient of a tumor centroid motion curve, and the concept and the mathematical model are used for reconstructing the image on the basis of the minimum gradient density projection matrix. Compared with the existing traditional average density projection, the invention provides the prediction capability of MIP (Maximum Intensity Projection) image extraction characteristics in NSCLC (Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer) early metastasis, in particular to a prediction capability of MIP (Maximum IntensityProjection) image extraction characteristics in NSCLC early metastasis.
Owner:李夏东
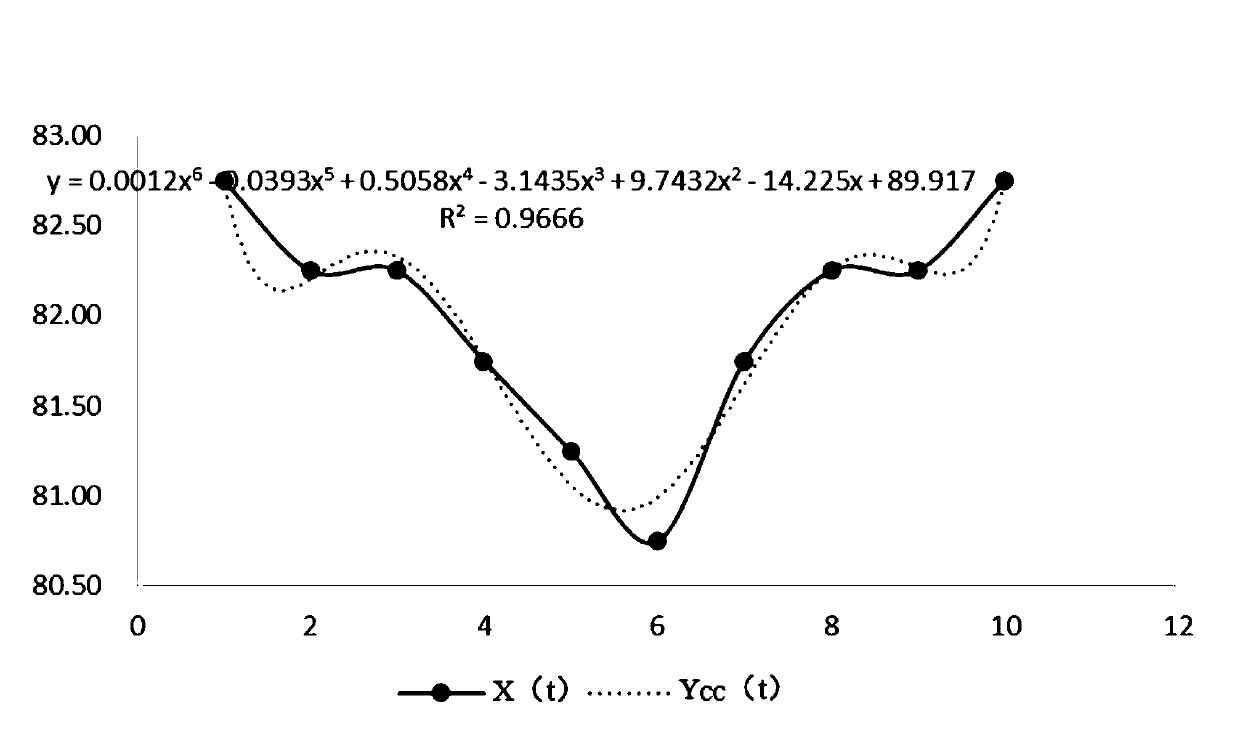
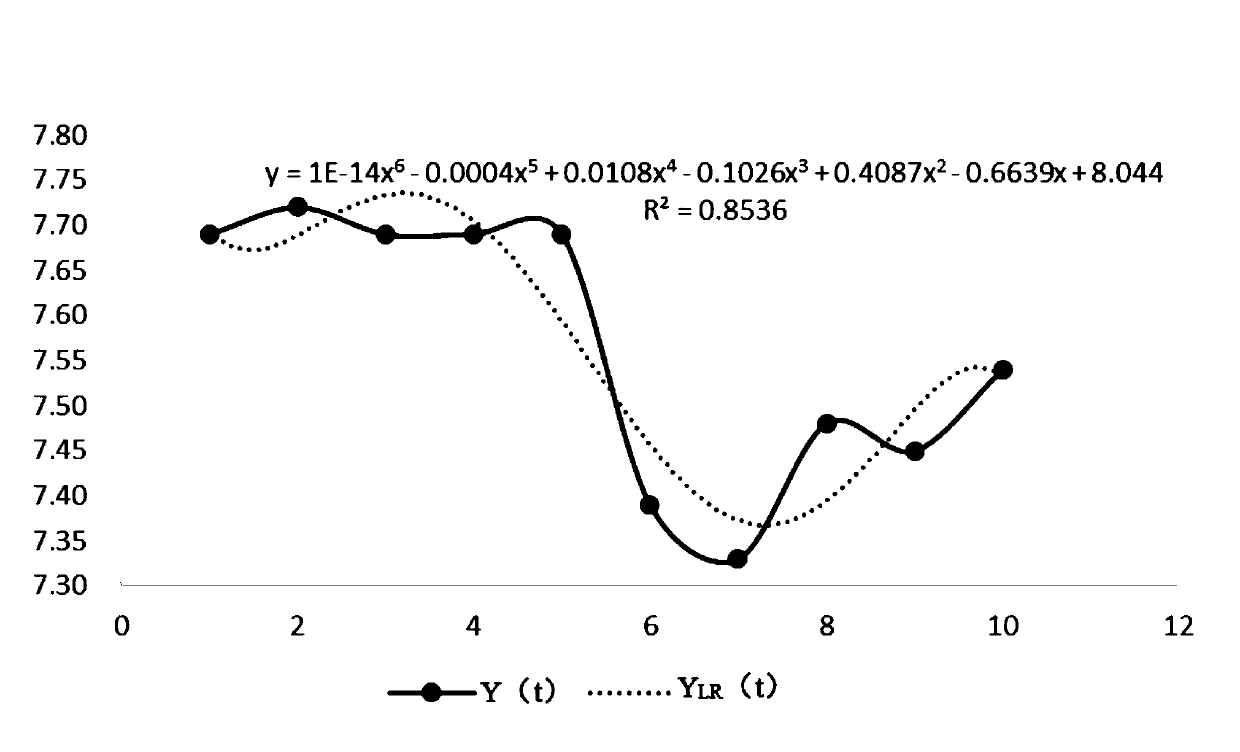
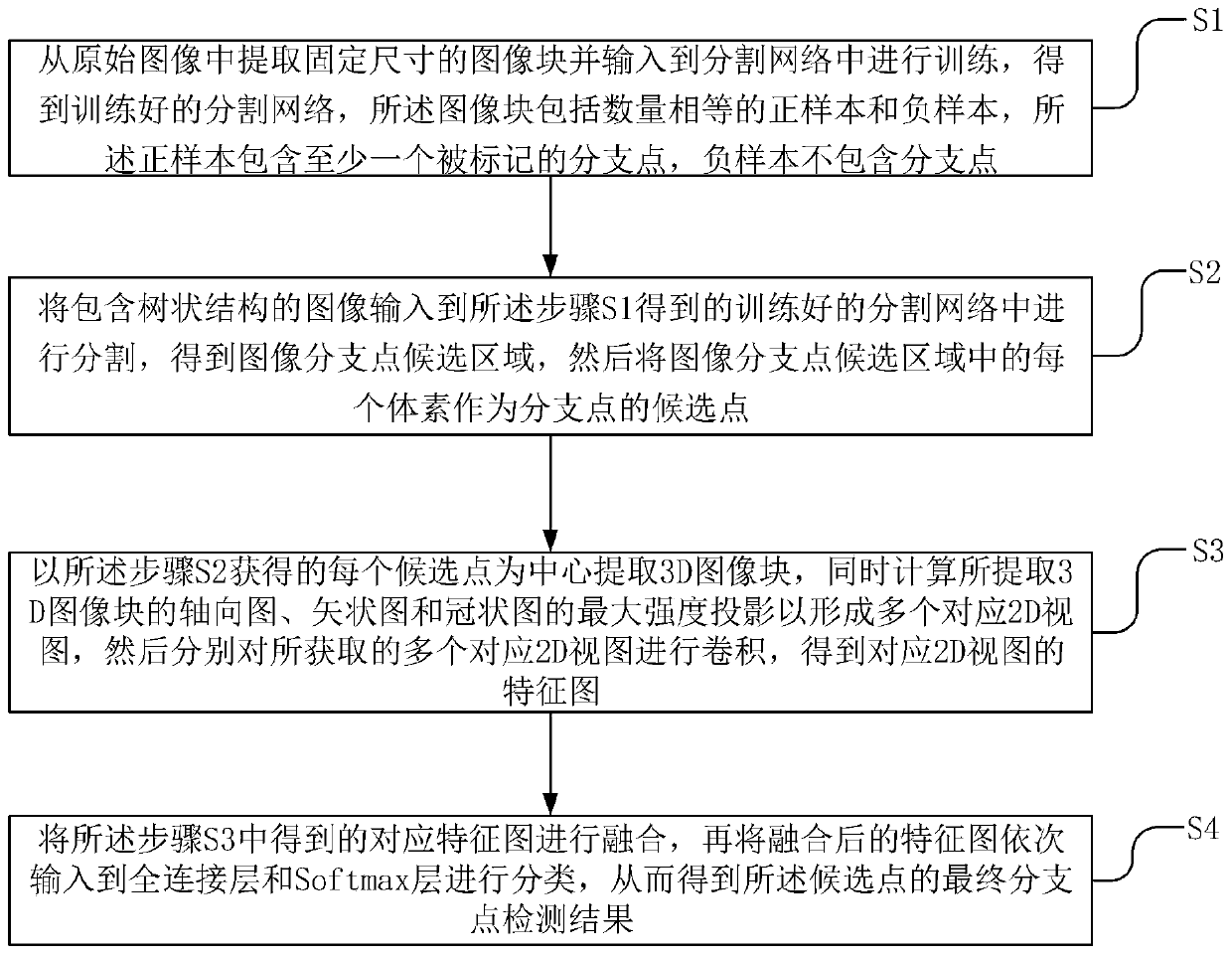
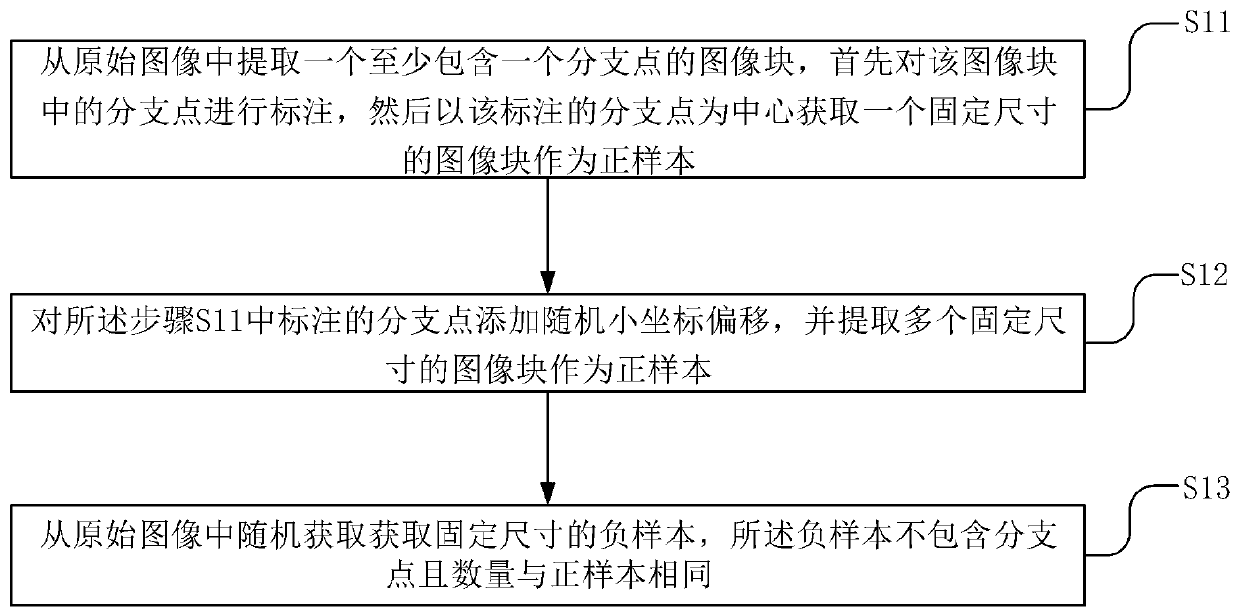
Method for detecting branch points of tree structure in digital image
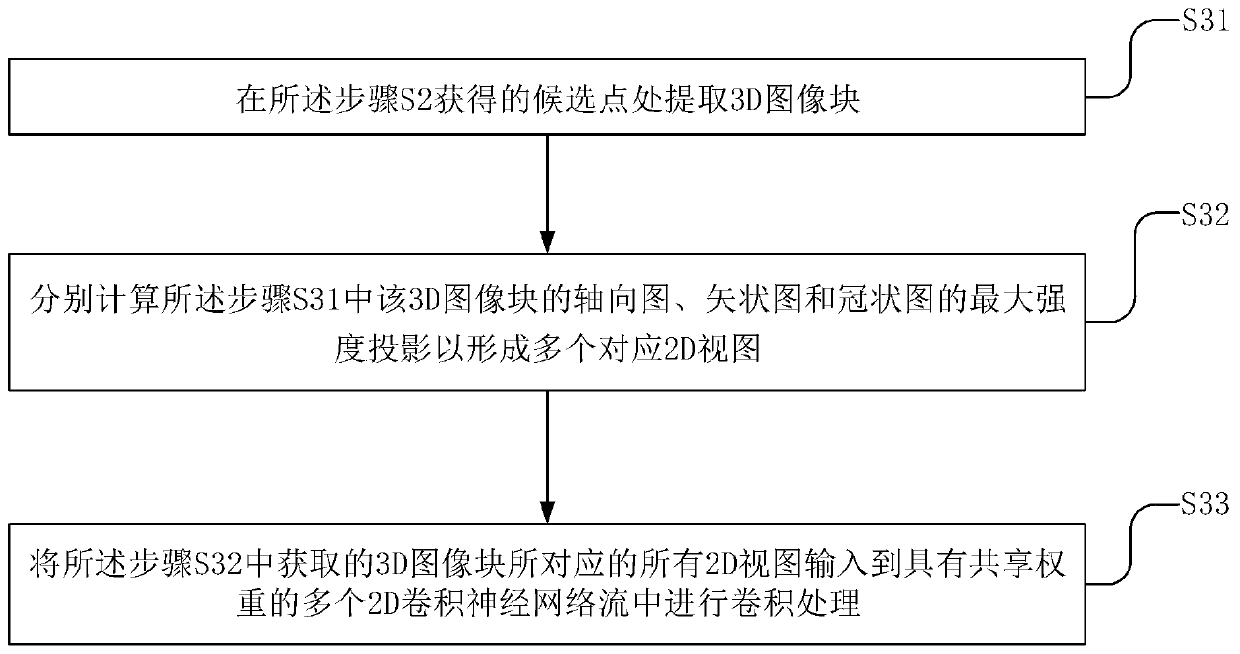
ActiveCN110533113AReduce computing costReduce false detection rateImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognition3d image
The invention discloses a branch point detection method for a tree structure in a digital image, and the method is a depth branch point detection model based on a two-stage cascaded convolutional network, i.e., a candidate region segmentation network and a false detection elimination network. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, extracting a sample with a fixed size from an originalimage to train a three-dimensional U-shaped segmentation network of an anisotropic convolution kernel, then inputting an image containing a tree structure into the trained segmentation network for segmentation to obtain branch point candidate regions, and taking each point of the candidate regions as a candidate point of a branch point; extracting three 3D image blocks of the candidate points according to three proportions, and calculating the maximum intensity projection of three views of each 3D image block to form nine corresponding 2D views; meanwhile, inputting the 2D views into the stacks of the five convolution layers respectively, finally, fusing the features, corresponding to the candidate points, of the 2D views after convolution, a final branch point detection result is obtained, and the method has the advantages of being low in calculation cost, low in false detection rate and high in detection efficiency.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
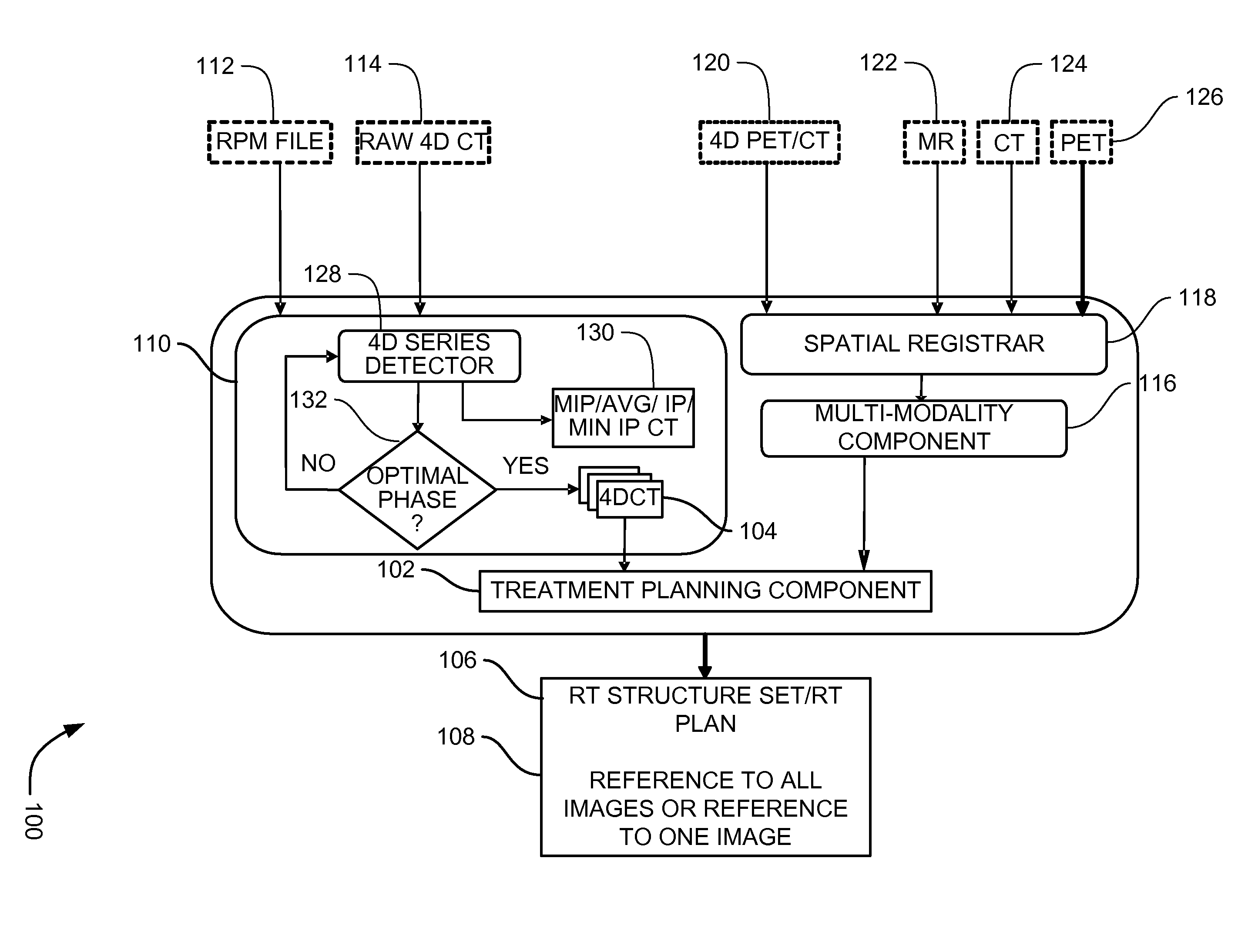
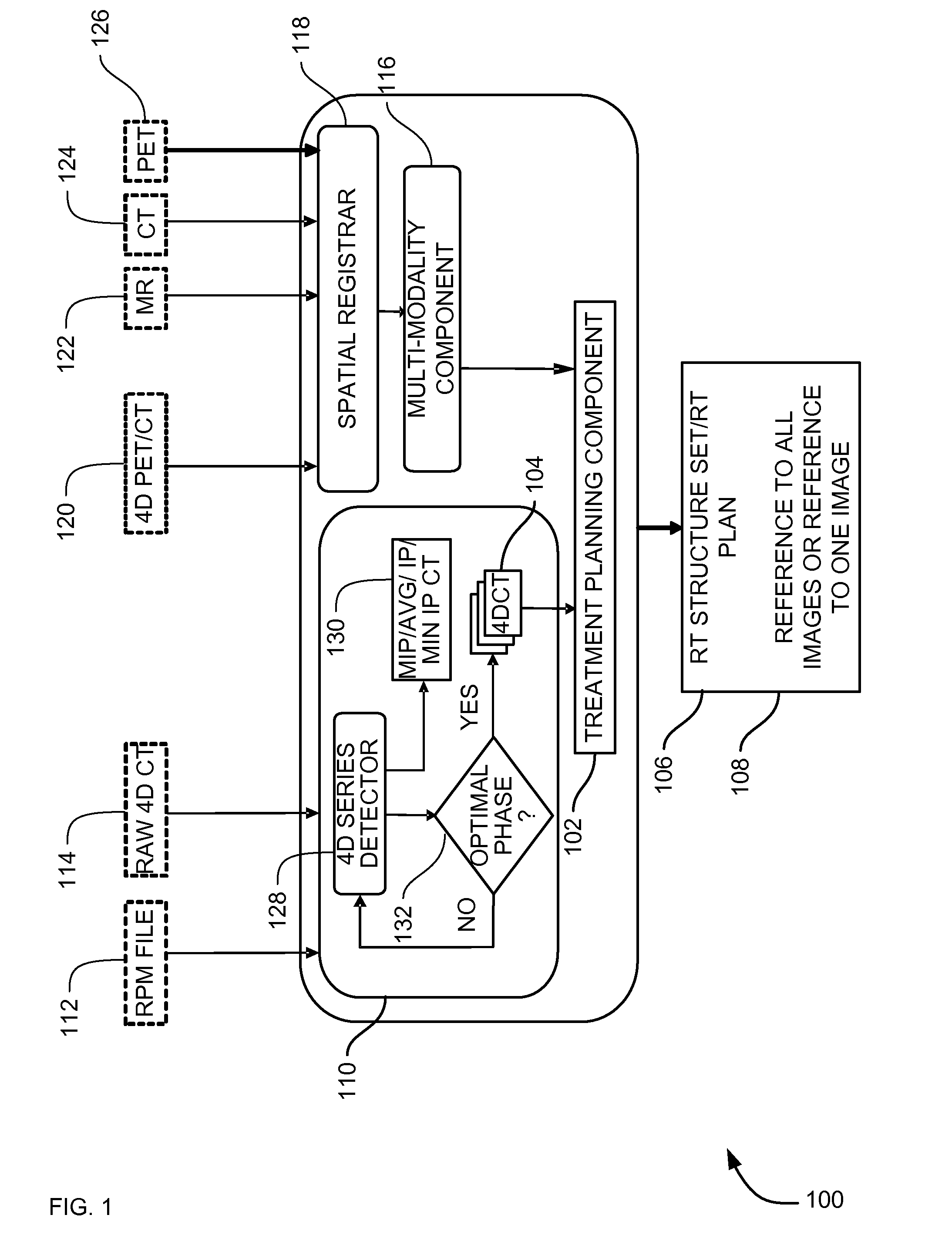
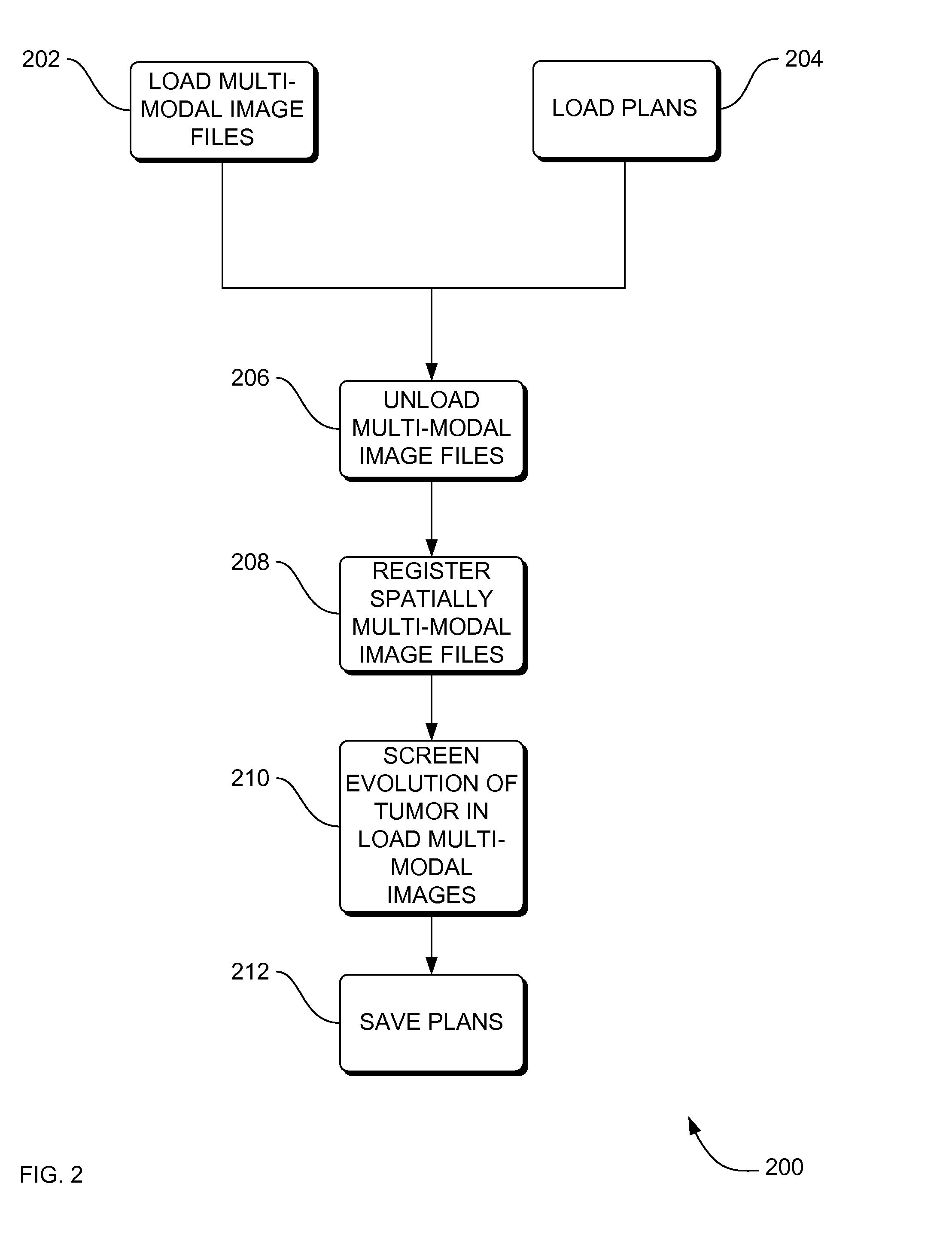
Systems, methods and apparatus for oncology workflow integration
ActiveUS7907990B2Easy to identifyReduce riskDiagnostic recording/measuringTomographyRespiratory phaseMaximum intensity projection
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
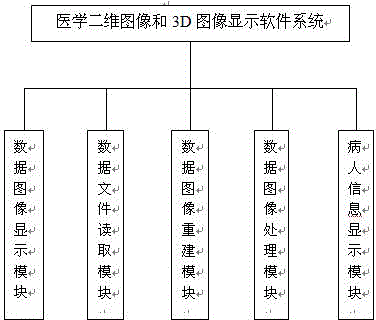
Medical two-dimensional image and 3D image display software system
InactiveCN105321202AImprove the level of auxiliary diagnosisClear structure3D modellingSoftware system3d image
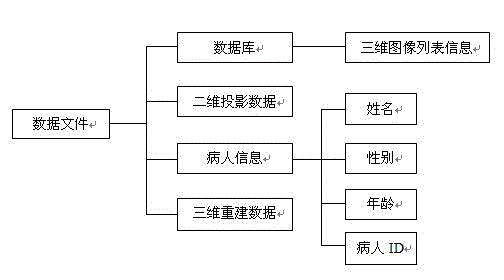
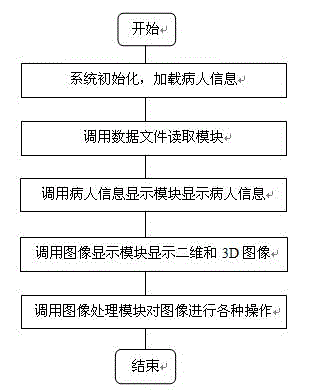
The invention relates to a medical two-dimensional image and 3D image display software system, and belongs to the technical field of medical instruments. The system comprises a data image display module, a data file reading module, a data image reconstruction module, a data image processing module and a patient information display module, and is characterized in that the data image display module has a function of displaying two-dimensional images and 3D images; the data file reading module has a function of reading 3D reconstruction data; the image reconstruction module has a function of reading 3D projection data; the data image processing module has functions of two-dimensional image cross line marking, image distance measurement and image zooming, 3D image rotation, movement, zooming, an MIP (Maximum Intensity Projection) technology and a VRT (Volume Rendering Technology), and a function of two-dimensional and 3D image window width and window level regulation; and the patient information display module has functions of displaying patient names, the gender, the age and patient ID numbers and displaying patient 3D reconstruction data in a list. The medical two-dimensional image and 3D image display software system has the advantages of clear architecture, simple and easily understood operation, and wide application range.
Owner:NANJING PERLOVE RADIAL VIDEO EQUIP
Maxim intensity projection method based on enhanced visual perception
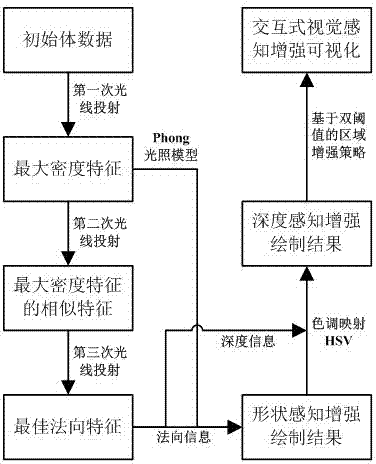
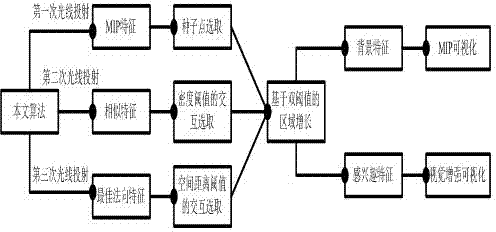
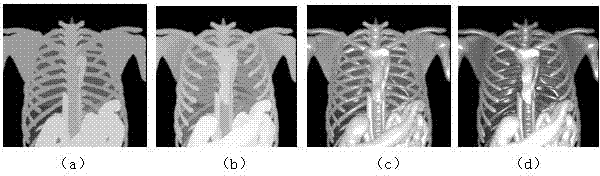
ActiveCN103035026AImprove visual effectsGuaranteed Density3D-image renderingLight treatmentVision based
The invention discloses a maxim intensity projection method based on enhanced visual perception. The maxim intensity projection method based on the enhanced visual perception comprises the following steps: getting volume data of a target object, a first light projection of the volume data is conducted so that maxim intensity characteristics of a current line-of-sight direction is obtained and a drawing result image of the volume data is also obtained; taking the spatial position of the maxim intensity characteristics as an end, a second light projection of the volume data along the current line-of-sight direction is conducted, similar characteristics before the maxim intensity characteristics is obtained according to a similar threshold which is alternatively set by users and a drawing result image of the similar characteristics is obtained; taking the location of the similar characteristics as a start, a third light projection of the volume data along an opposite direction of the current line-of-sight is conducted, finding a sampling point which owns the maxim gradient model and taking the sampling point as the best normal characteristics of the maxim intensity characteristics, and obtaining a drawing result image of the best normal characteristics; and utilizing normal information of the best normal characteristics, a light treatment of the maxim intensity characteristics is conducted so that a shaping perception enhanced image of the maxim intensity characteristics is obtained.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Reprocessing method for maximum-density projection image data
ActiveCN101295406ATissue texture details are clearWill not deform2D-image generation3D-image renderingProjection imageMaximum intensity projection
The invention discloses a post-processing method for the image data of the maximum intensity projection, comprising the following steps of: A1 before the maximum intensity projection of an image sequence, selecting a vertex at the same position of each image, making a calculation in accordance with an ascending order or a descending order of the image sequence, and keeping records for coordinating deviation of vertexes of the adjacent two images on the projection plane; A2 after the maximum intensity projection of the image sequence, recording the coordinates and gray values of each pixel in the projection data, the marks of the image where the pixels are arranged and the relations between the pixels and the image, and conducting a post-processing for the pixels.
Owner:LANWON TECH
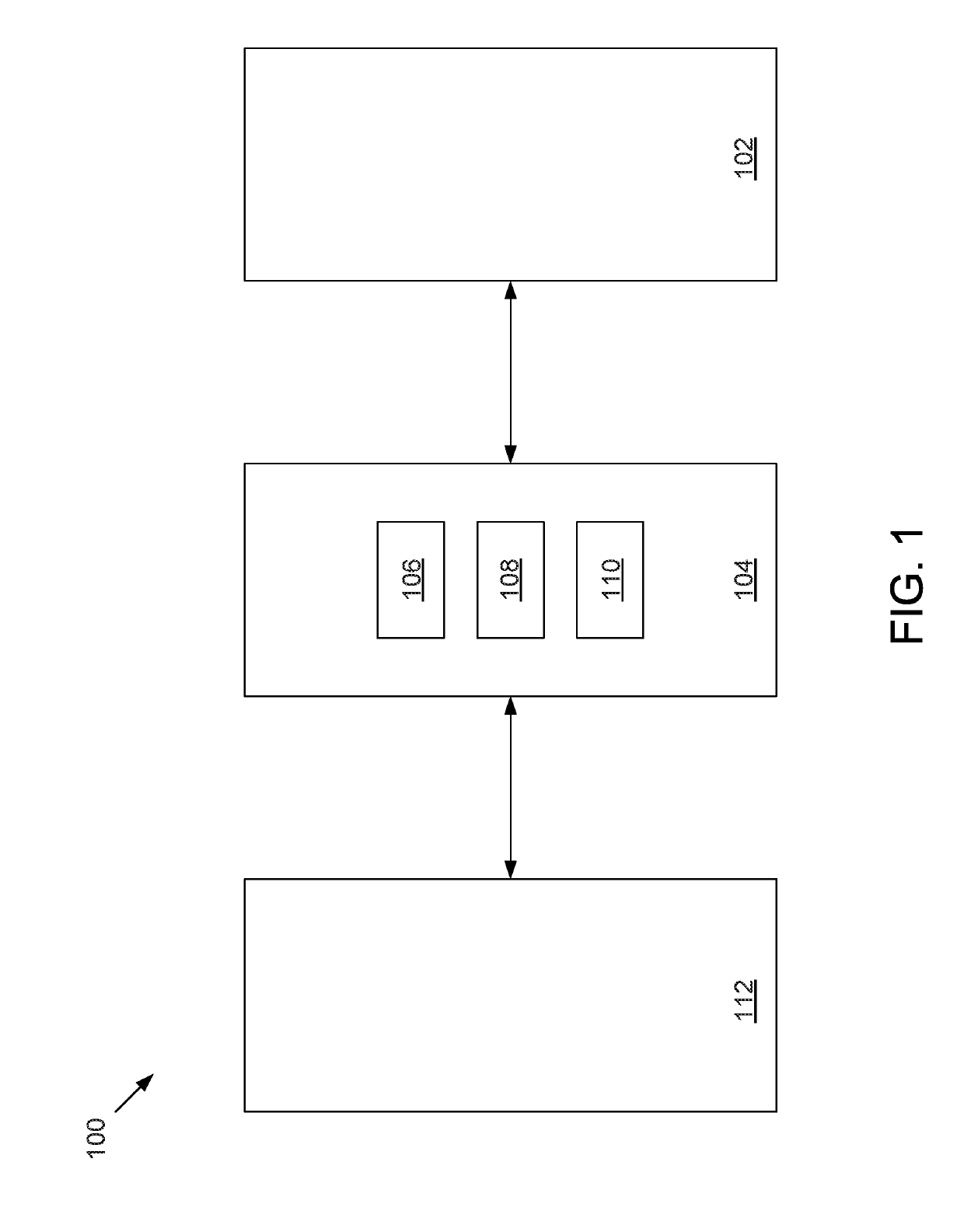
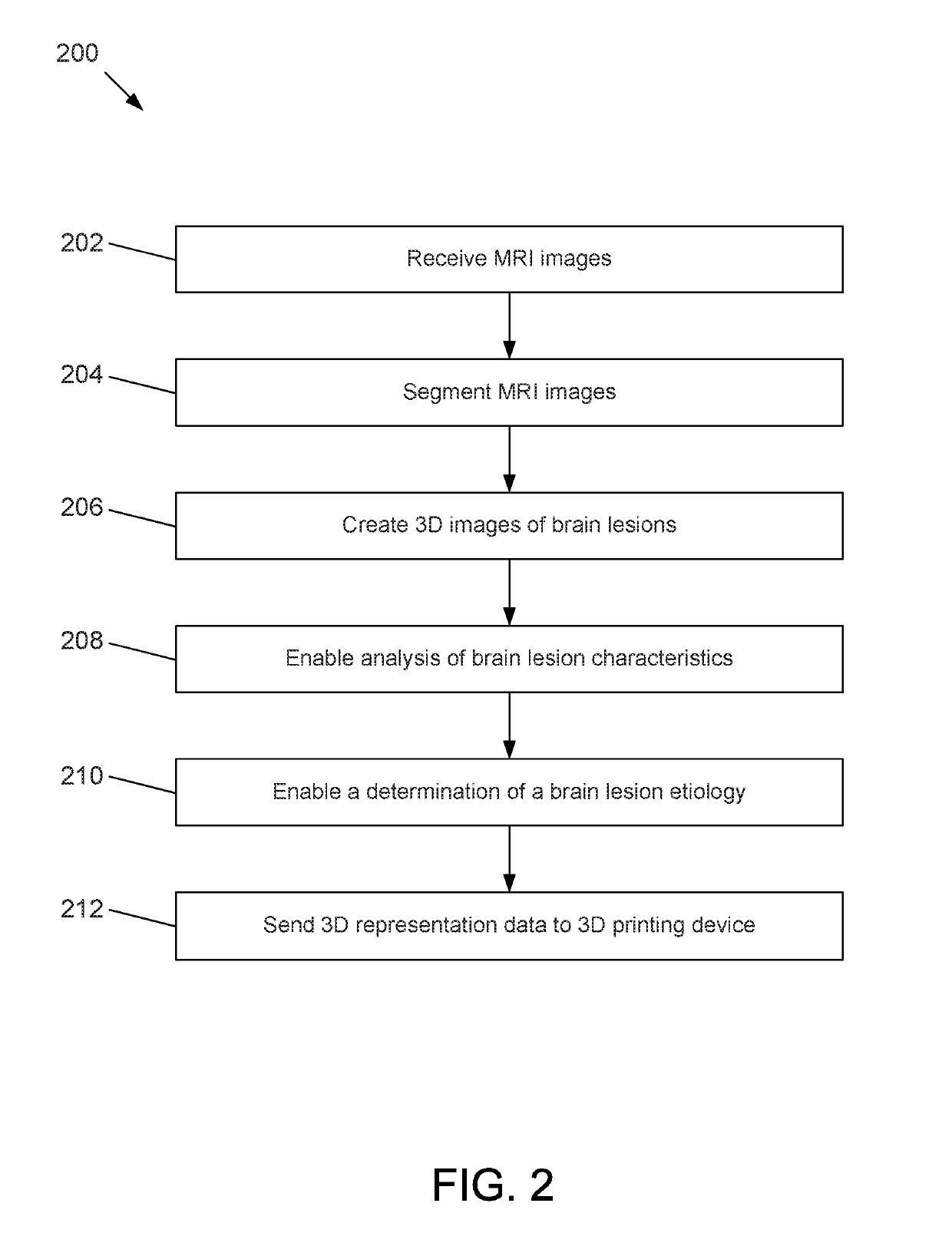
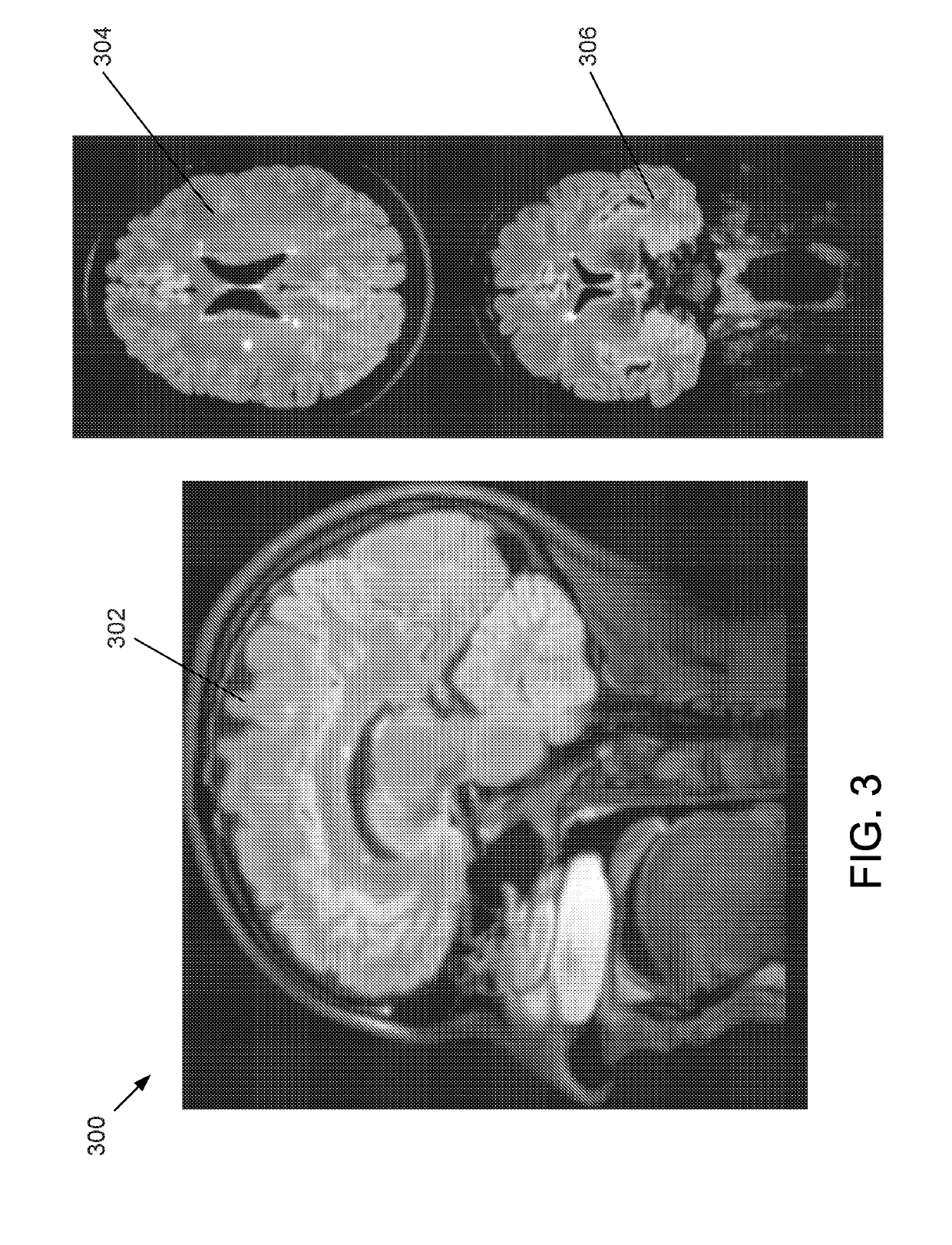
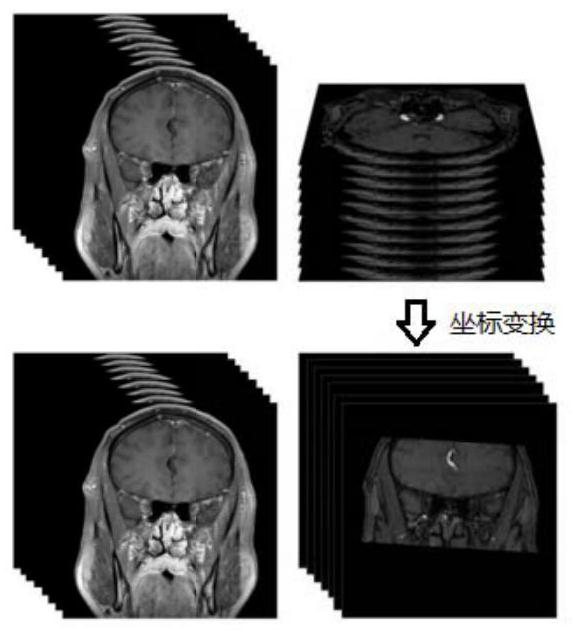
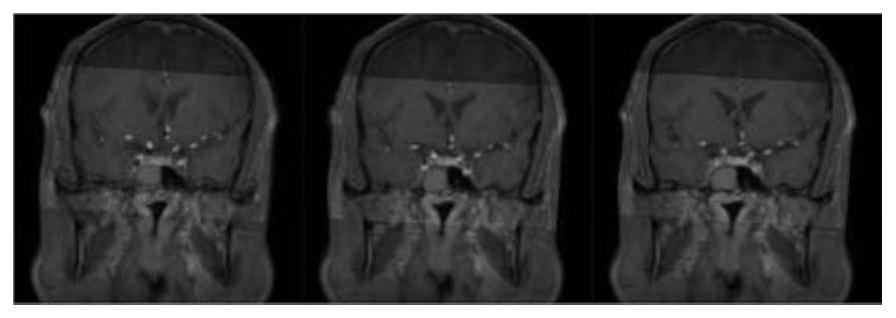
Methods, apparatuses, and systems for creating 3-dimensional representations exhibiting geometric and surface characteristics of brain lesions
ActiveUS20190197347A1Accurate assessmentOverall shapeImage enhancementImage analysisEtiologyProjection image
Methods, apparatuses, systems, and implementations for creating 3-dimensional (3D) representations exhibiting geometric and surface characteristics of brain lesions are disclosed. 2D and / or 3D MRI images of the brain may be acquired. Brain lesions and other abnormalities may be identified and isolated with each lesion serving as a region of interest (ROI). Saved ROI may be converted into stereolithography format, maximum intensity projection (MIP) images, and / or orthographic projection images. Data corresponding to these resulting 3D brain lesion images may be used to create 3D printed models of the isolated brain lesions using 3D printing technology. Analysis of the 3D brain lesion images and the 3D printed brain lesion models may enable a more efficient and accurate way of determining brain lesion etiologies.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Anatomy-defined automated cpr generation
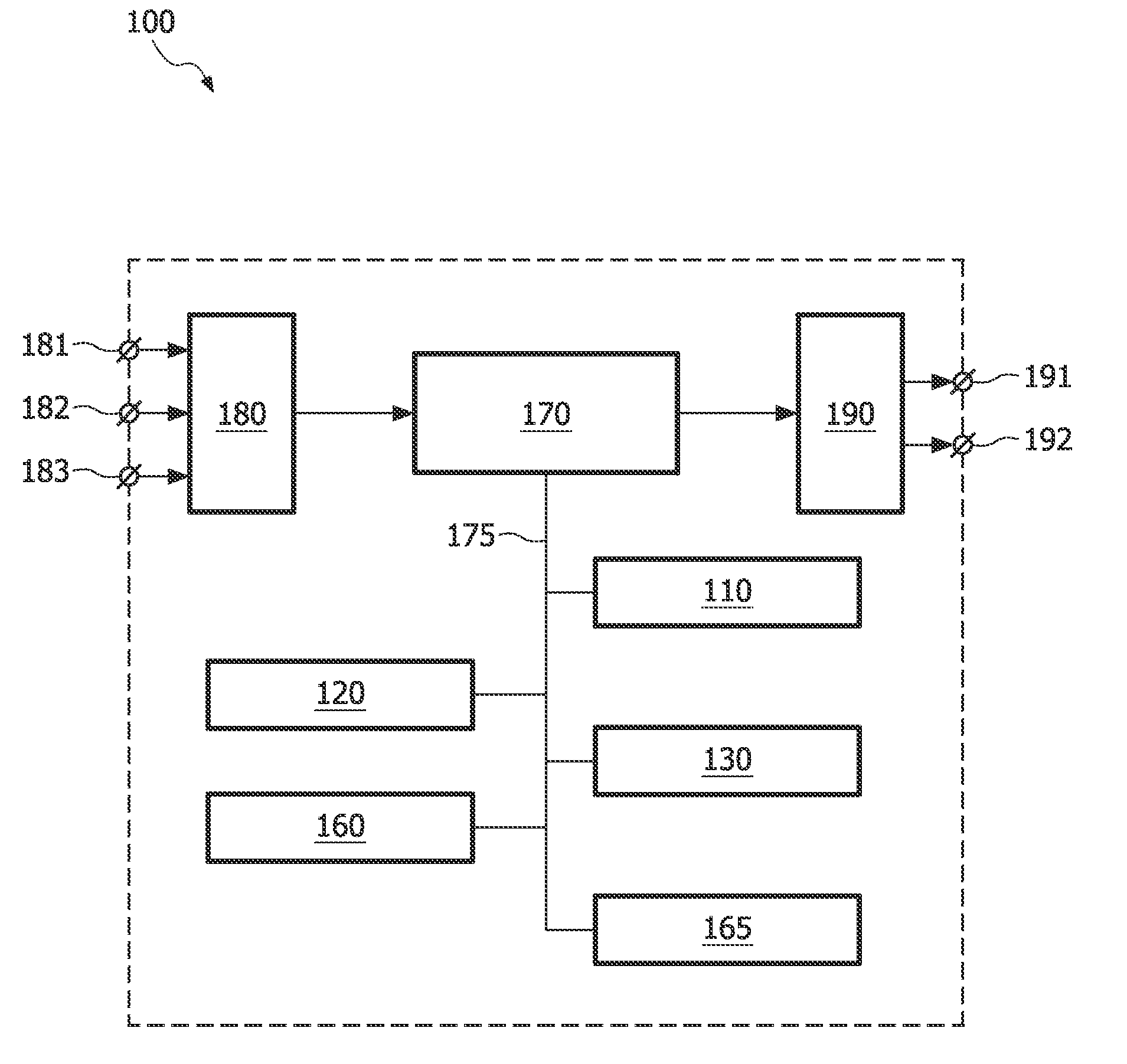
ActiveUS20110175909A1Less reliableLess accurateImage generation3D-image renderingObject basedCoupling
The invention relates to a system (100) for visualizing an object in image data using a first cross-section surface coupled to a model of the object, the system comprising a model unit for adapting a model to the object in the image data, a surface unit for adapting the first cross-section surface to the adapted model on the basis of the coupling between the first cross-section surface and the model, and a visualization unit for computing an image from the image data on the basis of the adapted first cross-section surface. The first cross-section surface may be used to define a slice of the image data for visualizing useful features of the object. Any suitable rendering technique, e.g. maximum intensity projection, can be used by the visualization unit to compute the image based on the slice of the image data defined by the first cross-section surface. Because the first cross-section surface of the invention is coupled to the model, the position, orientation and / or shape of the surface is determined by the model adapted to the object in the image data. Advantageously, adapting the model to the object in the image data and the coupling between the first cross-section surface and the model enable the first cross-section surface to be adapted to the image data. Thus, the shape, orientation and / or position of the adapted first cross-section surface is / are based on the shape, orientation and / or position of the adapted model. Adapting the first cross-section surface directly to the object based on features in the image data would be less reliable and less accurate because the surface comprises fewer features of the object than the model.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Relative maximum intensity projection
A machine-implemented display method that, with respect to a volume dataset being rendered, enables a user to navigate to any position in space and look in any direction. An enhanced display method for this type of dataset improves upon known Maximum Intensity Projection (MIP) techniques. The enhanced method, “Relative MIP,” uses a different approach to pixel value rendering. Relative MIP draws information from an amount of difference present between a current pixel and its neighbors, and then visualizes the maximum intensity of this difference.
Owner:AUTHENTIC
Maximum intensity projection performing method and apparatus
InactiveCN101051391ALarge initial valueComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringUltrasound attenuationMaximum intensity projection
In order to visualize a narrow blood vessel overlapping a thick blood vessel, at the time of performing a maximum intensity projection on three-dimensional image data, three-dimensional image data is weighted with a plurality of weighting functions of different attenuation characteristics along a projection line. Maximum intensity projections are performed on the plurality of pieces of the weighted three-dimensional image data, and results of all of the maximum intensity projections are summed. The weight of the weighting function is zero until the projection line reaches the surface of an image and, after the reach, gradually decreases from an initial value. Alternatively, the weight of the weighting function is zero to some midpoint of the projection line and, after the midpoint, gradually decreases from the initial value. The midpoint is adjustable. The attenuation characteristic is given by an exponential function. Parameters of the exponential function are adjustable.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
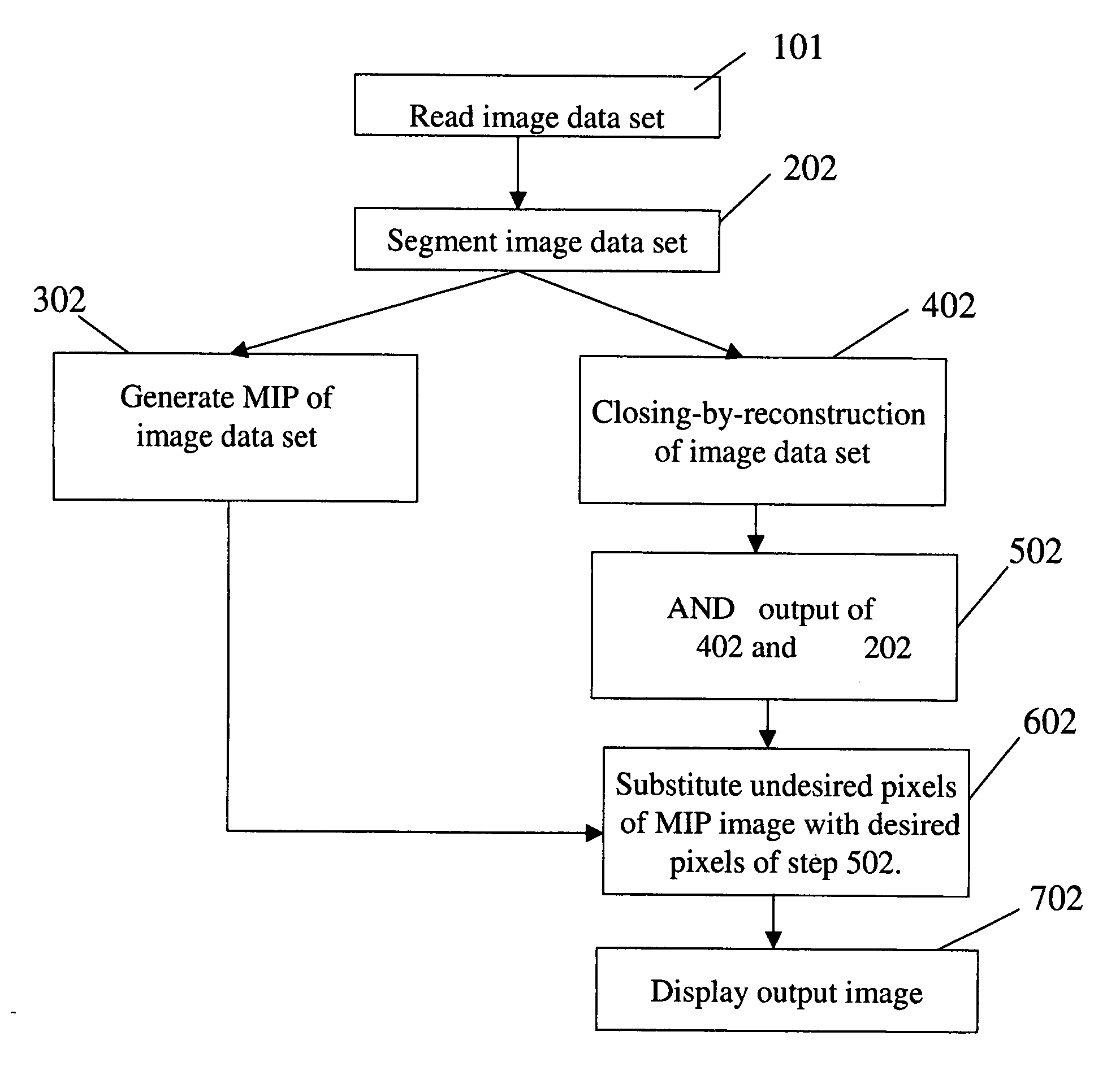
Method and system for digital image processing
In an embodiment, a method of digital image processing is provided wherein the method includes the actions of (i) segmenting a data set of an image to be processed, based on predetermined conditions (ii) generating a maximum intensity projection of the segmented data set (iii) closing-by-reconstruction of said data set in parallel to action (ii) (iv) combining the result of action (i) with result of action (iii) by a logical AND function, and (v) replacing pixels of undesired intensity in result of action (ii) by pixels of desired intensity from result of action (iv).
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Curved-slab maximum intensity projections
InactiveUS7471814B2Increase overall arterial contrastReduce intensityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementMedicineTransverse plane
A method to define a curved slab region of interest that includes vessels while maximally excluding surrounding soft tissue and bone is provided. The thickness of the curved slab is automatically adapted to the thickness of the vessel and follows the tortuous vessel(s) so that an increase in tortuousity does not result in a disproportionate increase in the region of interest required to enclose the vessel. A plurality of boundary pairs is determined in the view plane to define a vessel. Vessel-intensities are determined for each one of the boundary pairs. The boundary pairs with associated intensities define the view of the vessel in the projection plane. Context-intensity could be defined in the area surrounding the boundary pairs in the projection and / or transverse plane. The method also includes several steps that will result in a better isolation and removal of non-vessel structures and view of the vessel(s) and its(their) branches.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method and apparatus for generating a 2D image having pixels corresponding to voxels of a 3D image
InactiveUS7746340B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsReconstruction from projectionVoxel3d image
Disclosed is a method and apparatus for generating a two dimensional (2D) image of a structure (e.g., an organ) that has at least one pixel corresponding to at least one voxel of a three dimensional (3D) image of the structure. First, the surface of the structure in the 3D image is modeled by a geometrical volume such as an ellipsoid. Next, normal maximum intensity projection (MIP) rays are cast (i.e., projected) for voxels of the geometrical volume. The 2D image is then generated using the rays. The 2D image has at least one pixel that corresponds to at least one voxel of the 3D image.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
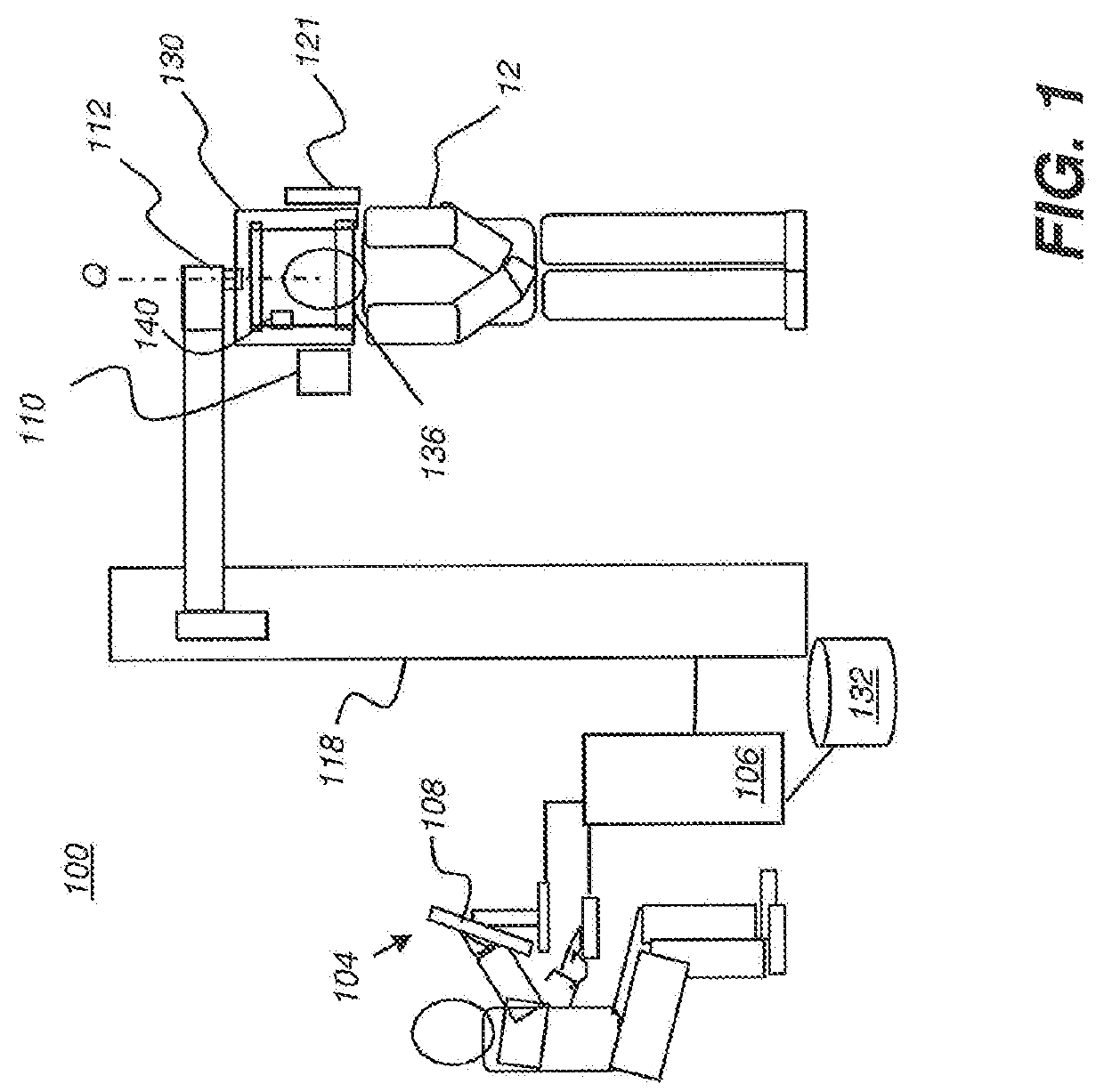
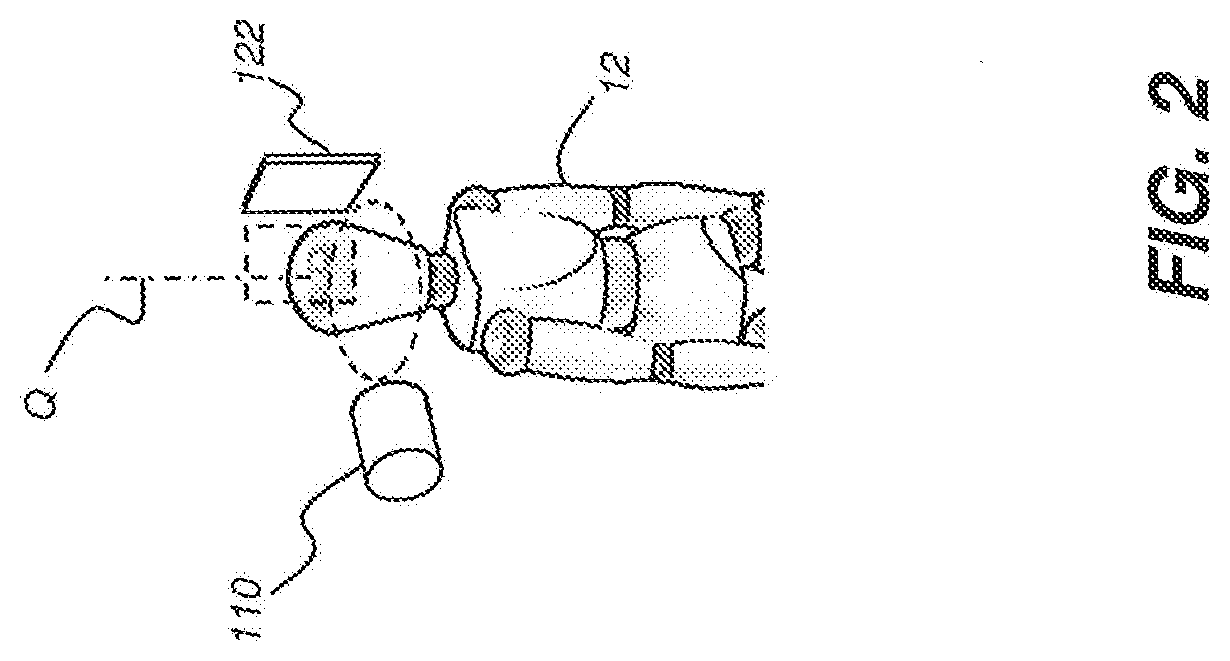
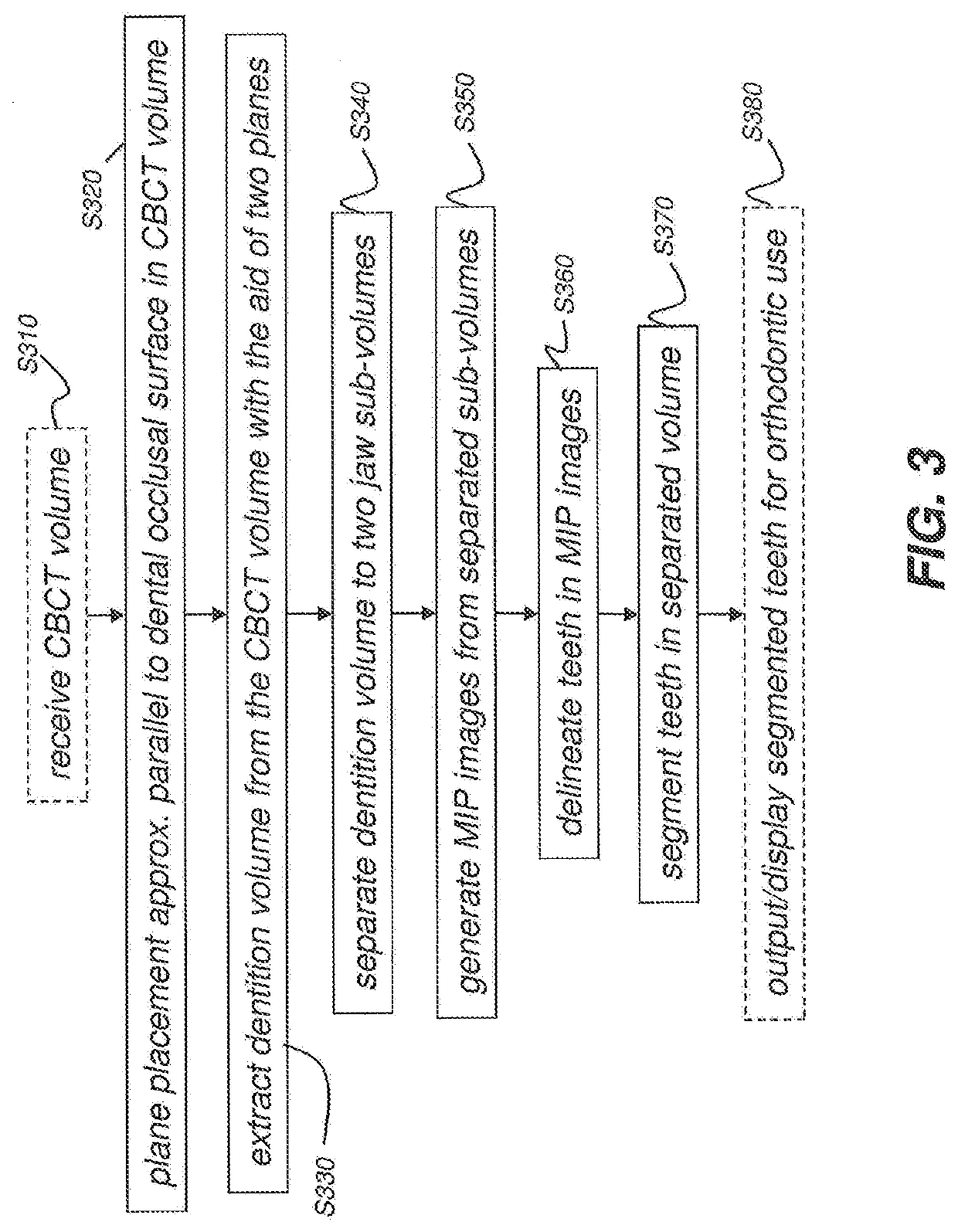
Methods and system for autonomous volumetric dental image segmentation
The present disclosure describes a system and methods for autonomous segmentation of volumetric dental images, such as those produced by an imaging system, The methods, implemented by the system, acquire a volume image of a patient and extract a volume of interest comprising patient dentition from the acquired volume image. A first plane is extended through maxillary portions of the patients jaw and a second plane through mandibular portions of the patients jaw. A maxillary sub-volume is generated from the volume of interest according to the first plane and a mandibular sub-volume from the volume of interest according to the second plane. Maximum intensity projection images are formed for each sub-volume and teeth are delineated from these images. Teeth are segmented within each sub-volume according to the tooth delineation for their respective sub-volume.
Owner:CARESTREAM DENTAL LLC
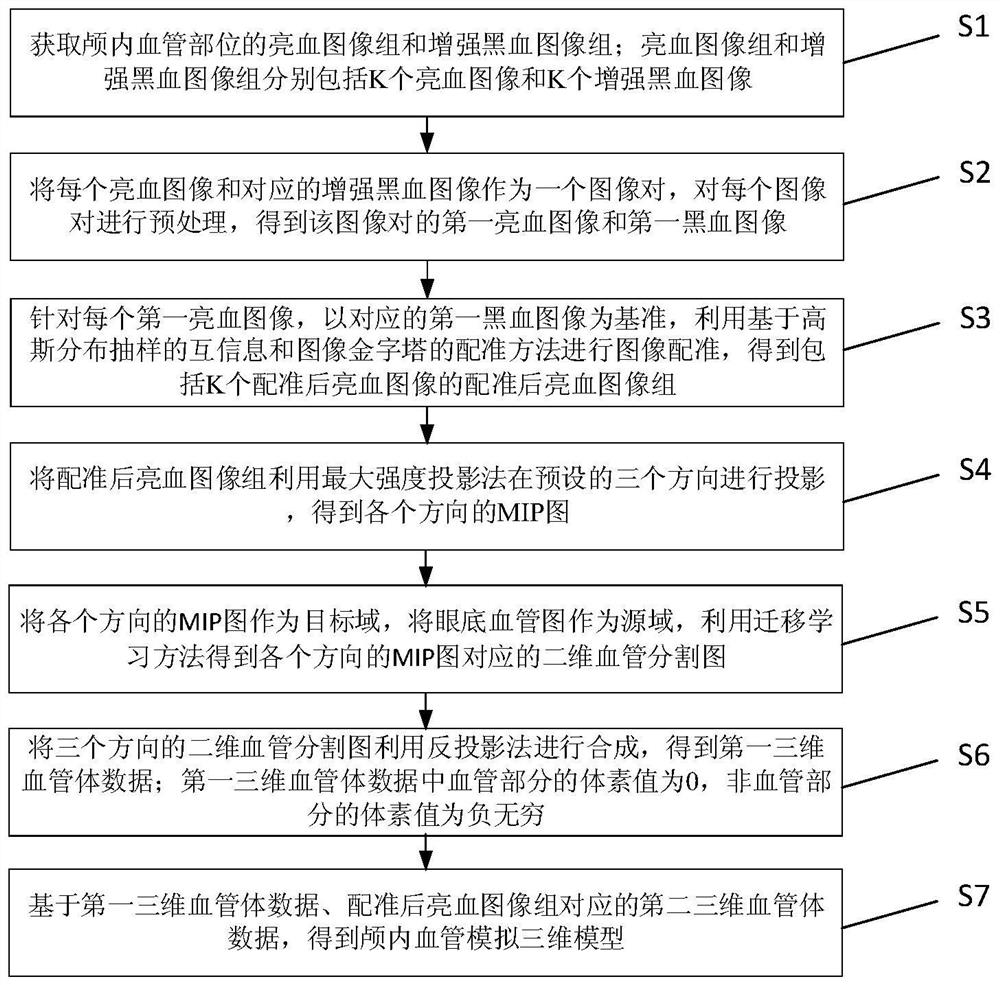
Method for quickly establishing intracranial vessel simulation three-dimensional model based on transfer learning
PendingCN112562058ARealize 3D visualizationImprove registration efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisVascular bodyBlack blood
The invention discloses a method for quickly establishing an intracranial blood vessel simulation three-dimensional model based on transfer learning. The method comprises the following steps: collecting a bright blood image group and an enhanced black blood image group of an intracranial blood vessel part; preprocessing each bright blood image and the corresponding enhanced black blood image to obtain a first bright blood image and a first black blood image; performing image registration on the first bright blood image by using mutual information based on Gaussian distribution sampling and a registration method of an image pyramid; utilizing a maximum intensity projection method to obtain MIP images in all directions from the registered bright blood image groups; taking the MIP image as atarget domain, taking the fundus blood vessel image as a source domain, and obtaining a two-dimensional blood vessel segmentation image by using a transfer learning method; performing back projectionsynthesis on the two-dimensional blood vessel segmentation images in the three directions to obtain first three-dimensional blood vessel body data; and obtaining an intracranial blood vessel simulation three-dimensional model by utilizing the second three-dimensional blood vessel body data corresponding to the registered bright blood image group. According to the method, the whole state of the intracranial blood vessel can be simply, conveniently, quickly and visually obtained clinically.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Methods, apparatuses, and systems for creating 3-dimensional representations exhibiting geometric and surface characteristics of brain lesions
ActiveUS11093787B2Accurate assessmentOverall shapeImage enhancementImage analysisStereolithographiesProjection image
Methods, apparatuses, systems, and implementations for creating 3-dimensional (3D) representations exhibiting geometric and surface characteristics of brain lesions are disclosed. 2D and / or 3D MRI images of the brain may be acquired. Brain lesions and other abnormalities may be identified and isolated with each lesion serving as a region of interest (ROI). Saved ROI may be converted into stereolithography format, maximum intensity projection (MIP) images, and / or orthographic projection images. Data corresponding to these resulting 3D brain lesion images may be used to create 3D printed models of the isolated brain lesions using 3D printing technology. Analysis of the 3D brain lesion images and the 3D printed brain lesion models may enable a more efficient and accurate way of determining brain lesion etiologies.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com