Patents
Literature
171 results about "Ray casting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
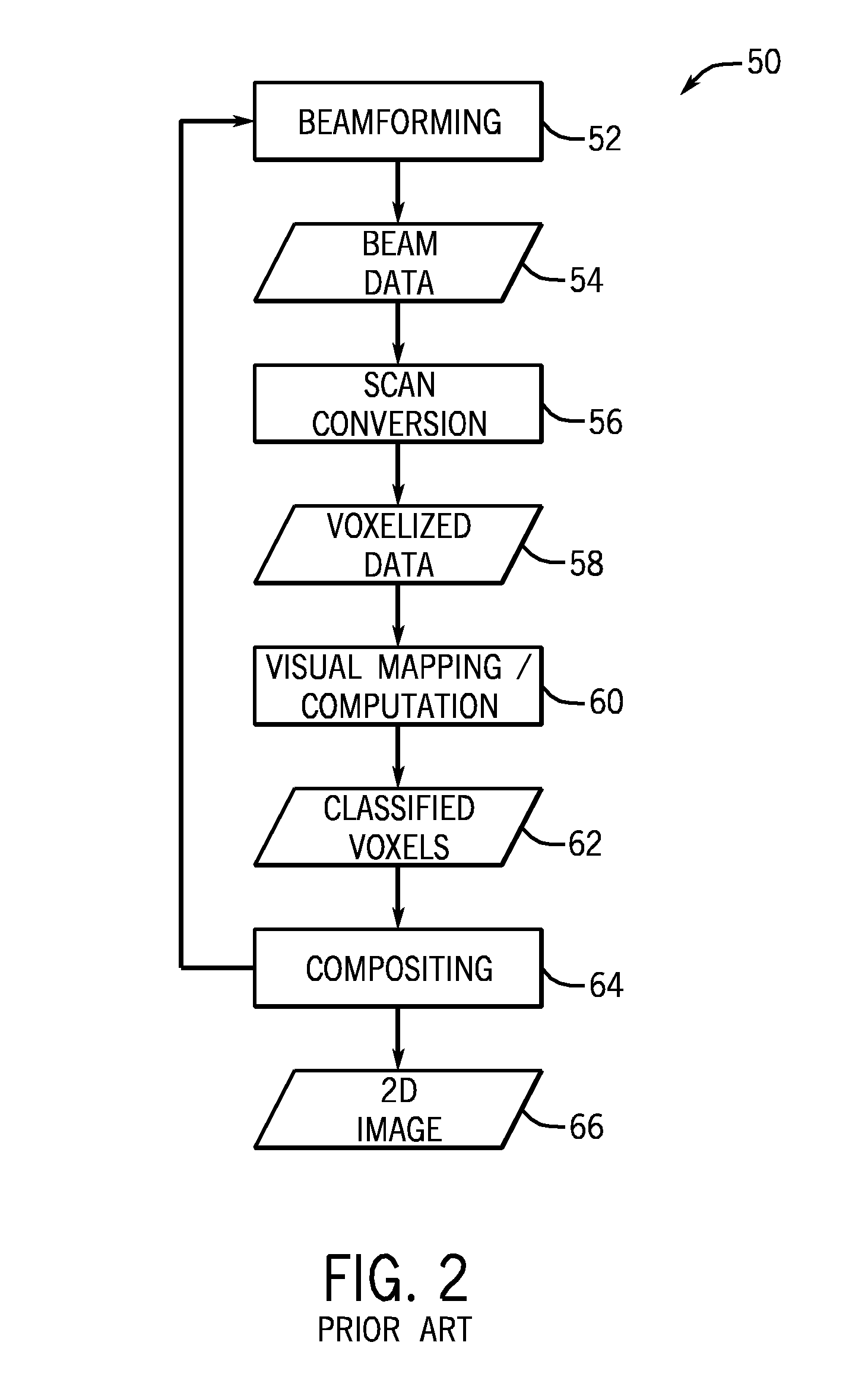
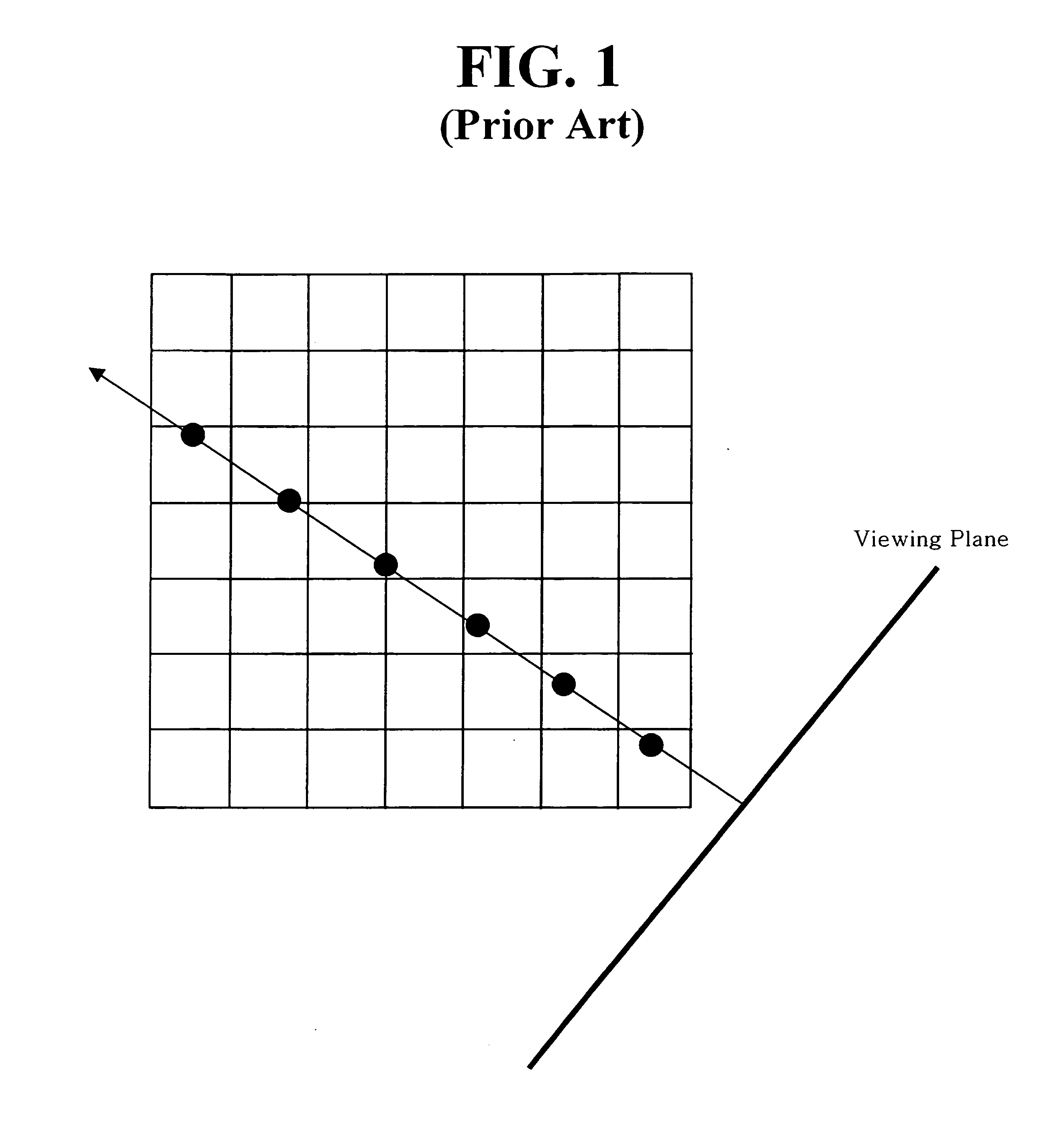
Ray casting is the use of ray–surface intersection tests to solve a variety of problems in 3D computer graphics and computational geometry. The term was first used in computer graphics in a 1982 paper by Scott Roth to describe a method for rendering constructive solid geometry models.
Indoor scene 3D reconstruction method based on Kinect
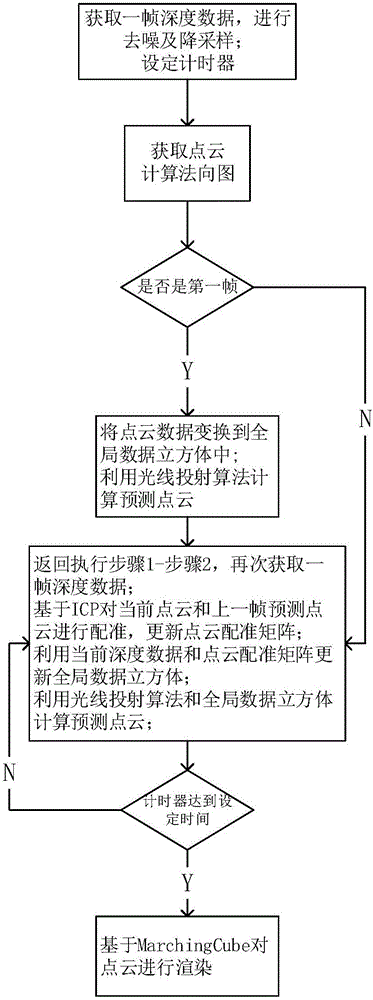
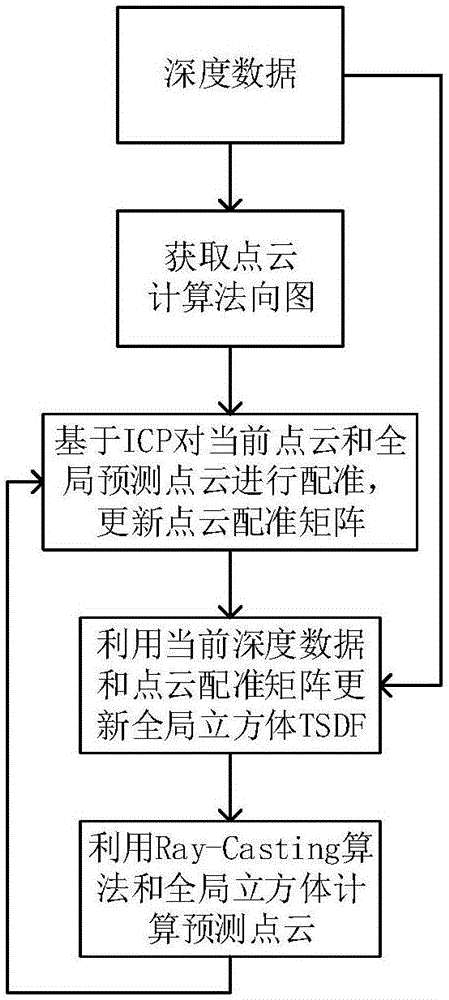
ActiveCN106803267ALess redundancyImprove real-time performanceDetails involving processing stepsImage enhancementPoint cloudRay casting
The invention discloses an indoor scene 3D reconstruction method based on Kinect and solves the technical problem of the real-time reconstruction of an indoor scene 3D model and avoidance of excessive redundant points. The method comprises steps of: obtaining the depth data of an object by using Kinect and de-nosing and down-sampling the depth data; obtaining the point cloud data of a current frame and calculating the vector normal of each point in the frame; using a TSDF algorithm to establish a global data cube, and using a ray casting algorithm to calculate predicted point cloud data; calculating a point cloud registration matrix by using an ICP algorithm and the predicted point cloud data, fusing the obtained point cloud data of each frame into the global data cube, and fusing the point cloud data frame by frame until a good fusion effect is obtained; rendering the point cloud data with an isosurface extraction algorithm and constructing the 3D model of the object. The method improves the registration speed and the registration precision, is fast in fusion speed and few in redundancy points, and can be used for real-time reconstruction of the indoor scene.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
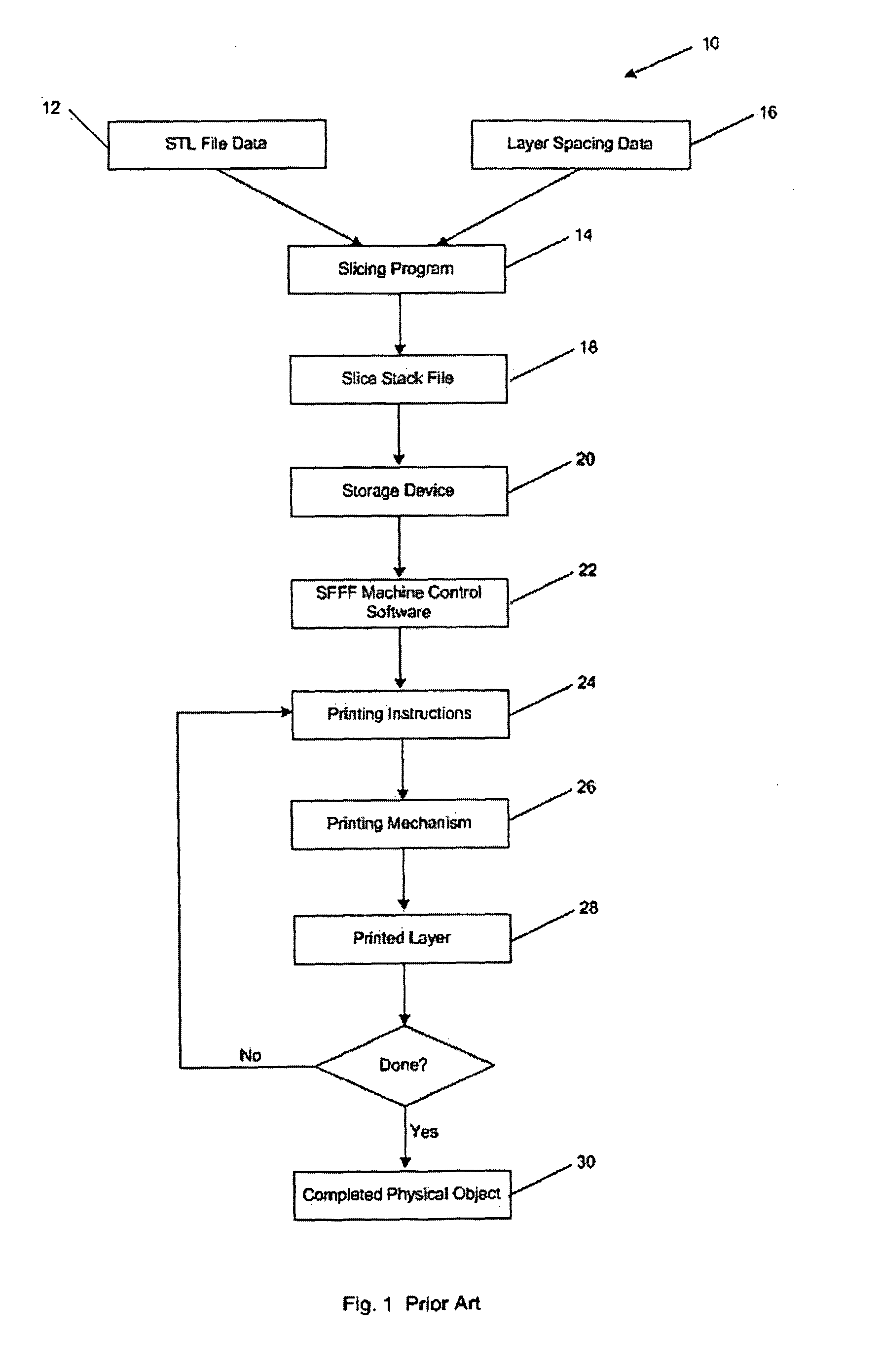
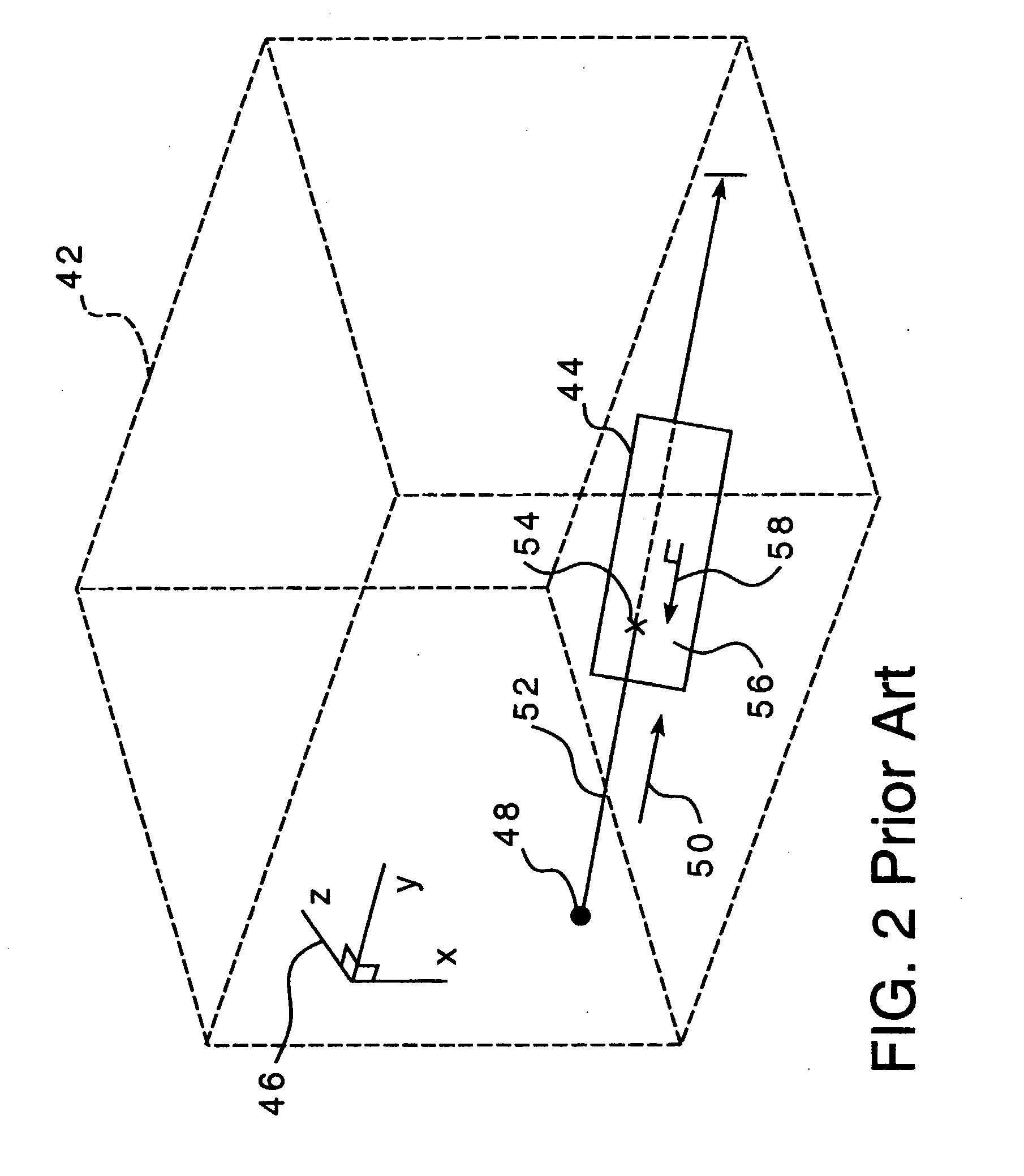
Apparatus, method and article for direct slicing of step based nurbs models for solid freeform fabrication
InactiveUS20060155418A1Reduce eliminateImprove modeling accuracyProgramme controlTotal factory controlFeasibility studyGrating
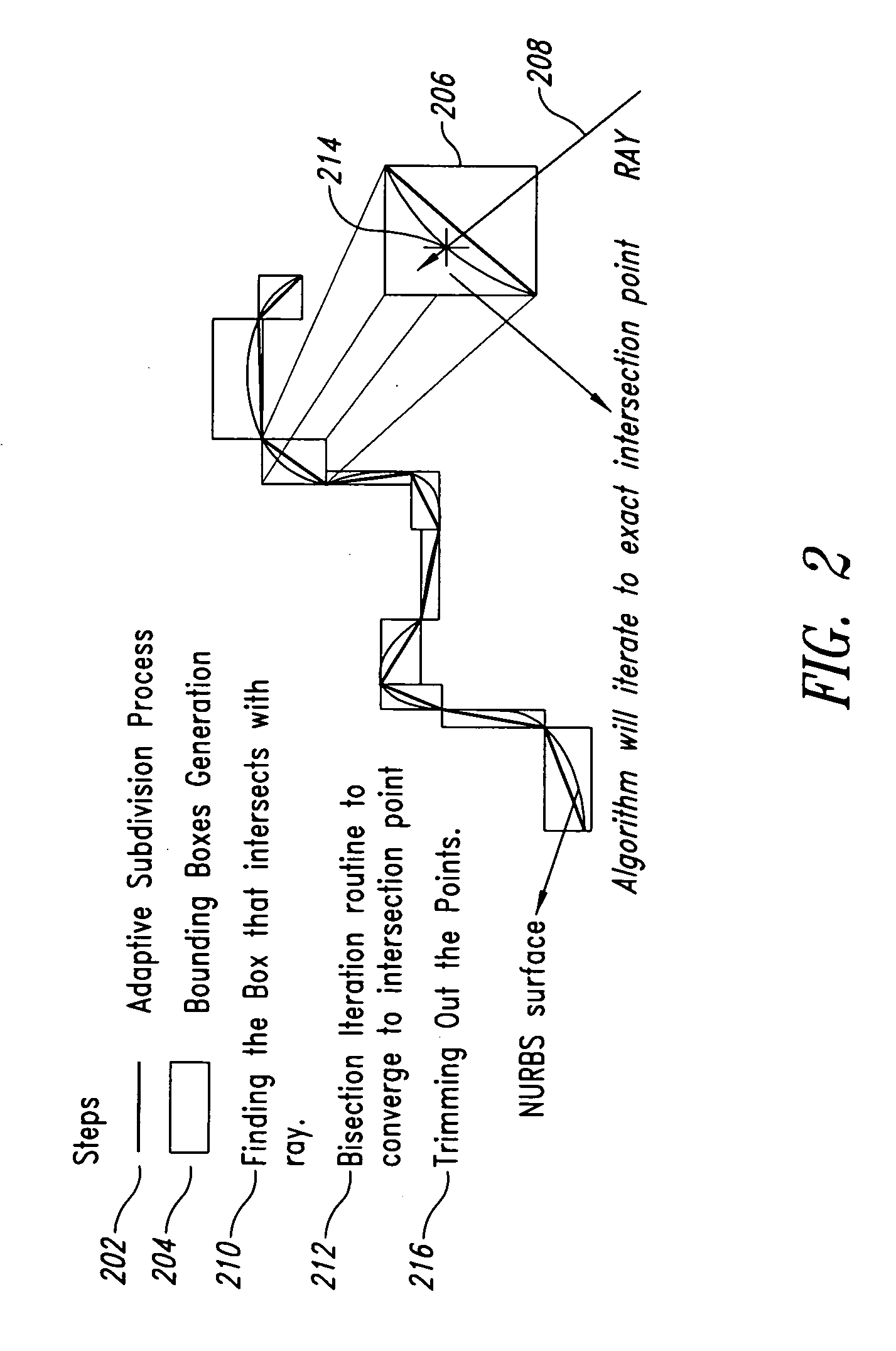
Direct slicing of CAD models to generate process planning instructions for solid freeform fabrication may overcome inherent disadvantages of using STL format in terms of the process accuracy, ease of file management, and incorporation of multiple materials. This paper will present the results of our development of a direct slicing algorithm for layered freeform fabrication. The direct slicing algorithm was based on a neutral, international standard (ISO 10303) STEP-formatted NURBS geometric representation and is intended to be independent of any commercial CAD software. The following aspects of the development effort will be presented: 1) Determination of optimal build direction based upon STEP-based NURBS models; 2) Adaptive subdivision of NURBS data for geometric refinement; and 3) Ray-casting slice generation into sets of raster patterns. Feasibility studies applying the direct slicing algorithm to example models and the generation of fabrication planning instructions involving multi-material structures will also be presented.
Owner:THERICS
Variable resolution virtual reality display system
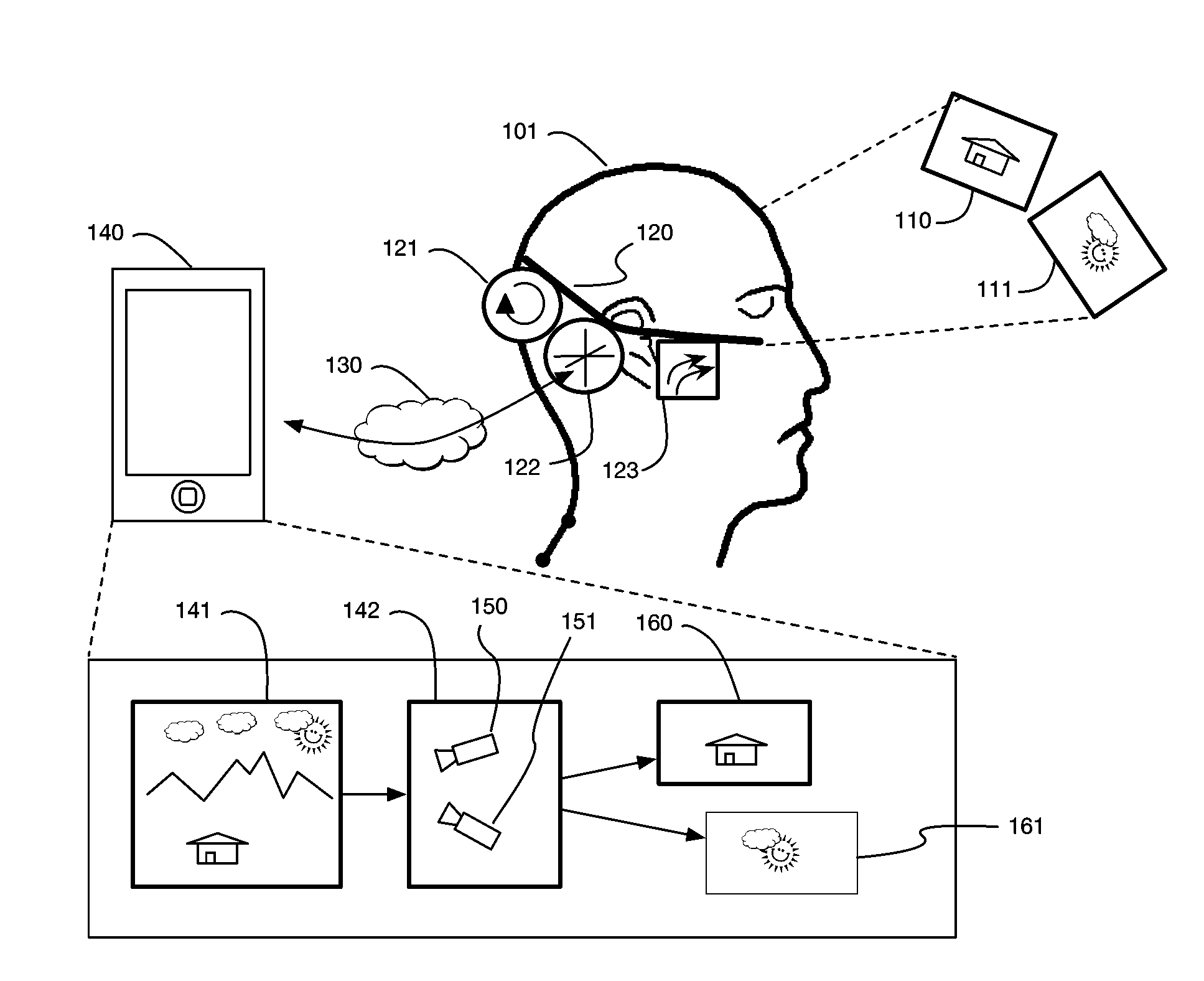
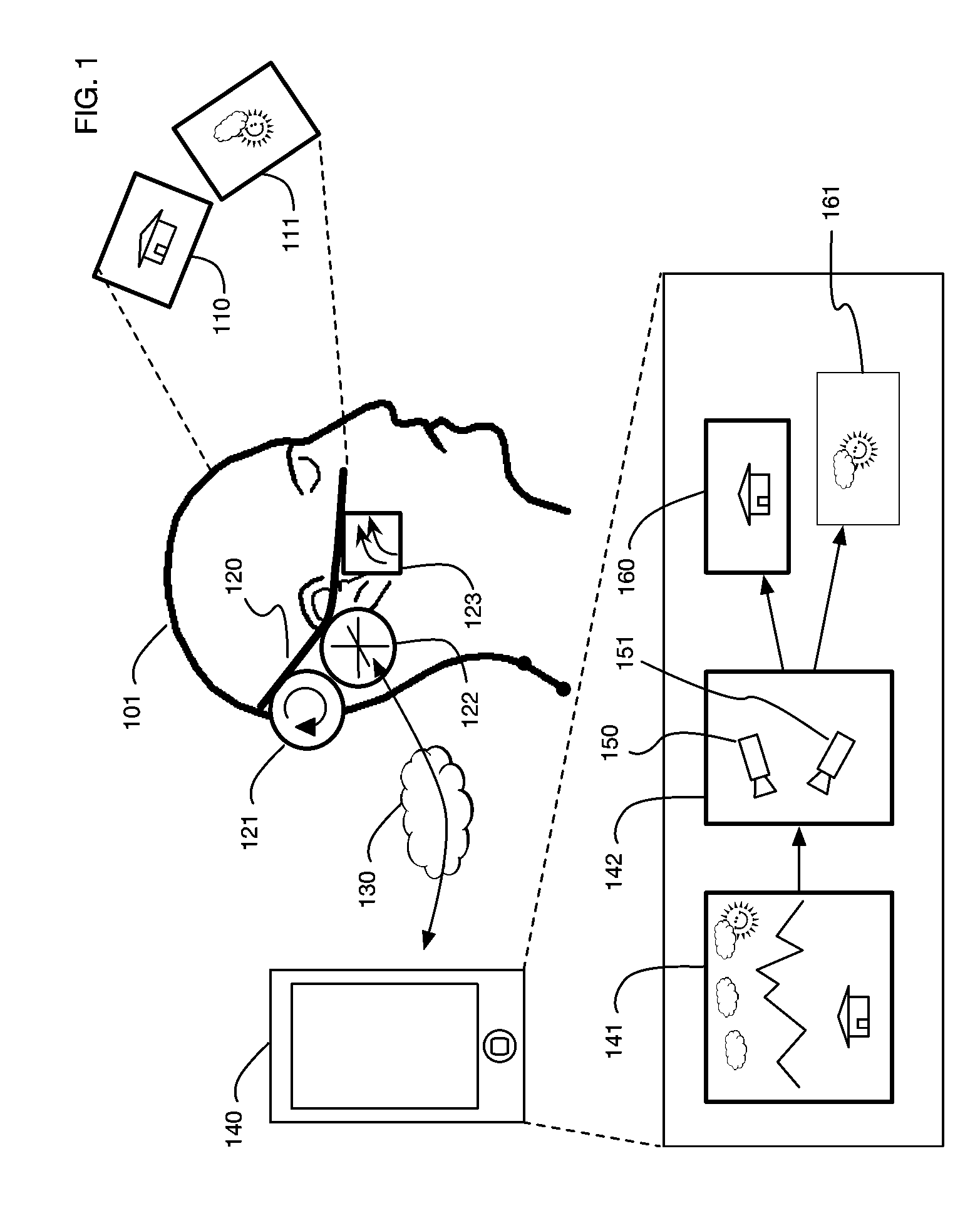
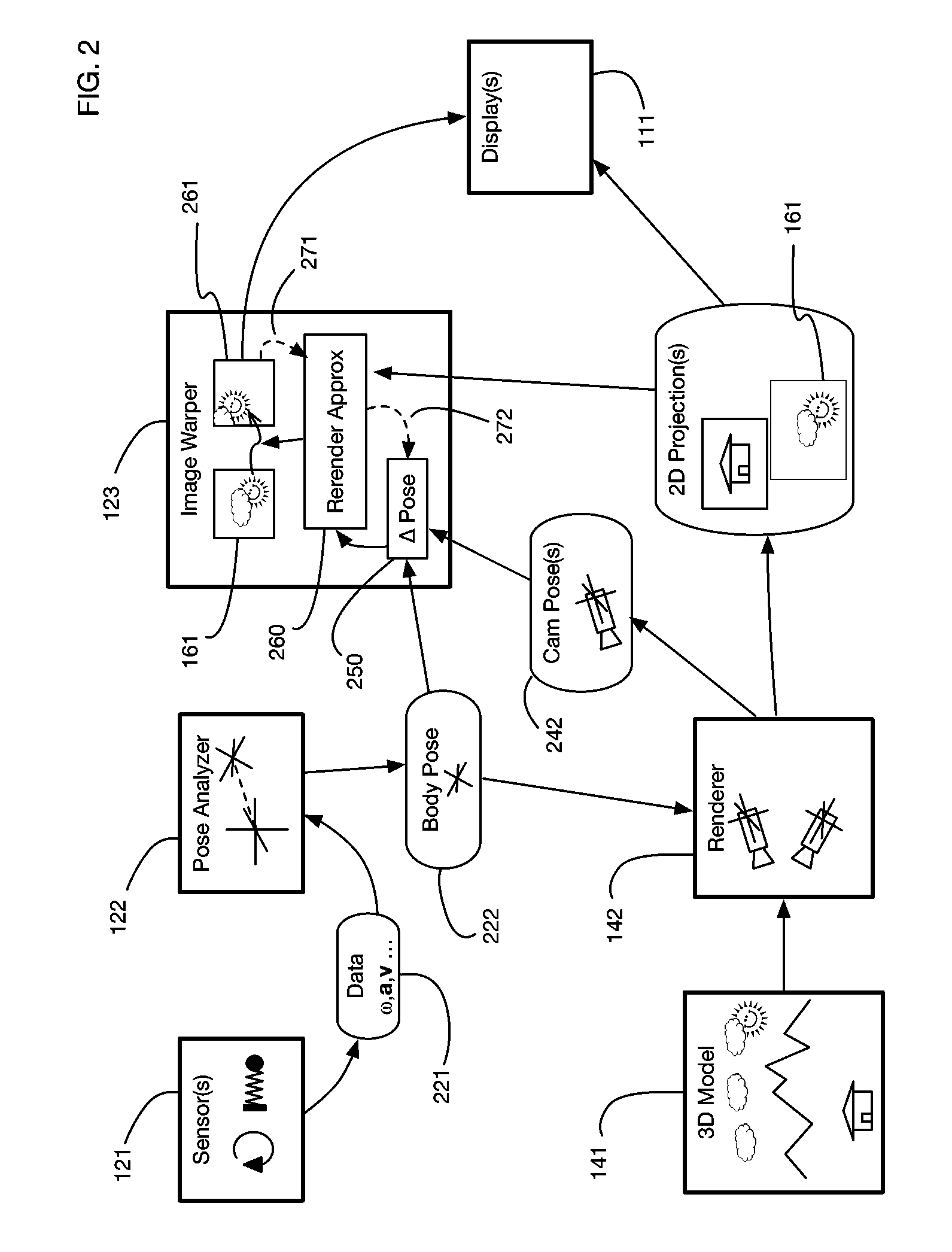
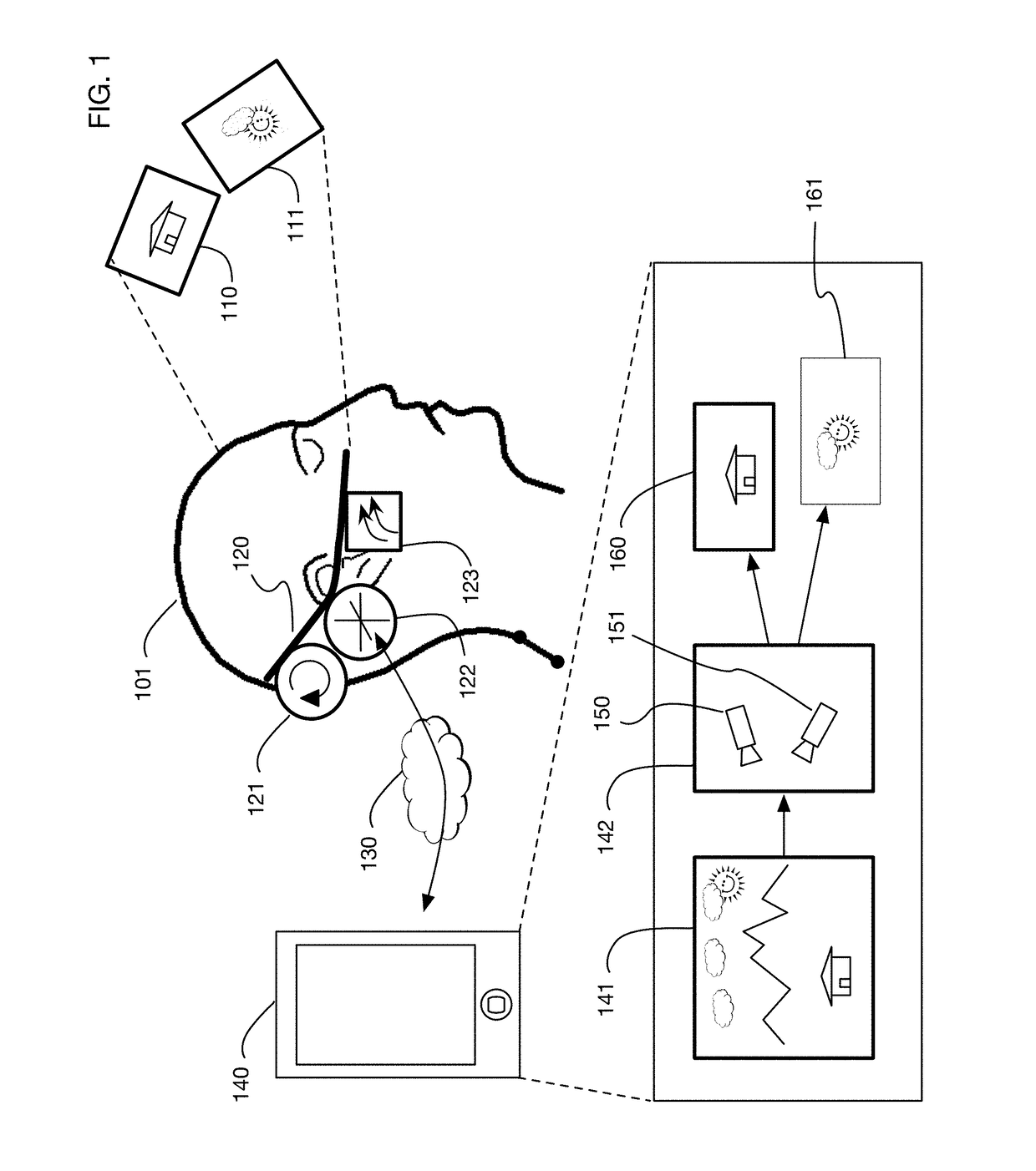
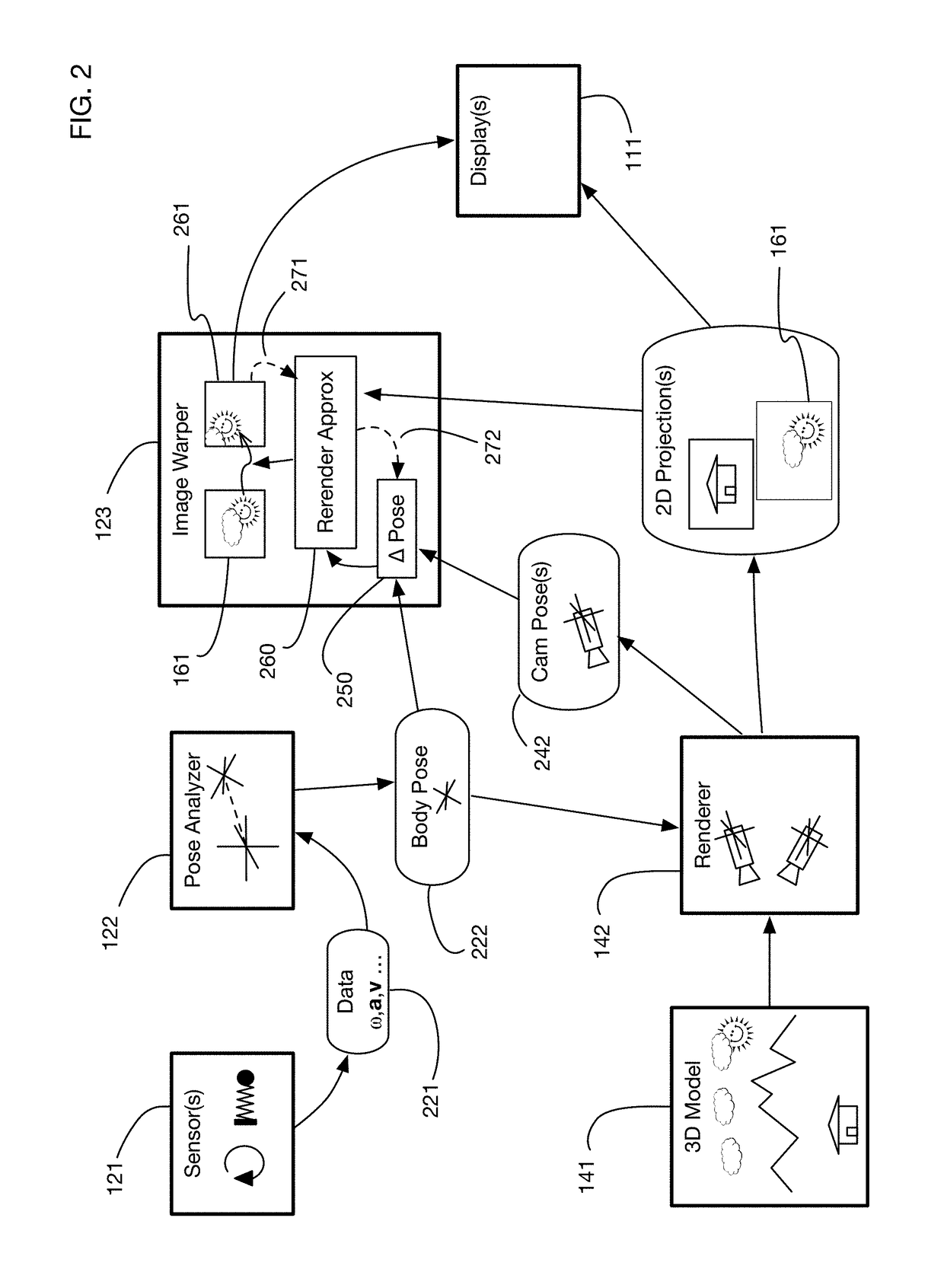
ActiveUS9607428B2Enhance the virtual reality experienceEfficient and rapid rerendering reduces latencyInput/output for user-computer interactionGeometric image transformationImage resolutionLevel of detail
Owner:LI ADAM
Variable resolution virtual reality display system
ActiveUS20170004648A1Enhance the virtual reality experienceEfficient and rapid rerendering reduces latencyInput/output for user-computer interactionGeometric image transformationImage resolutionLevel of detail
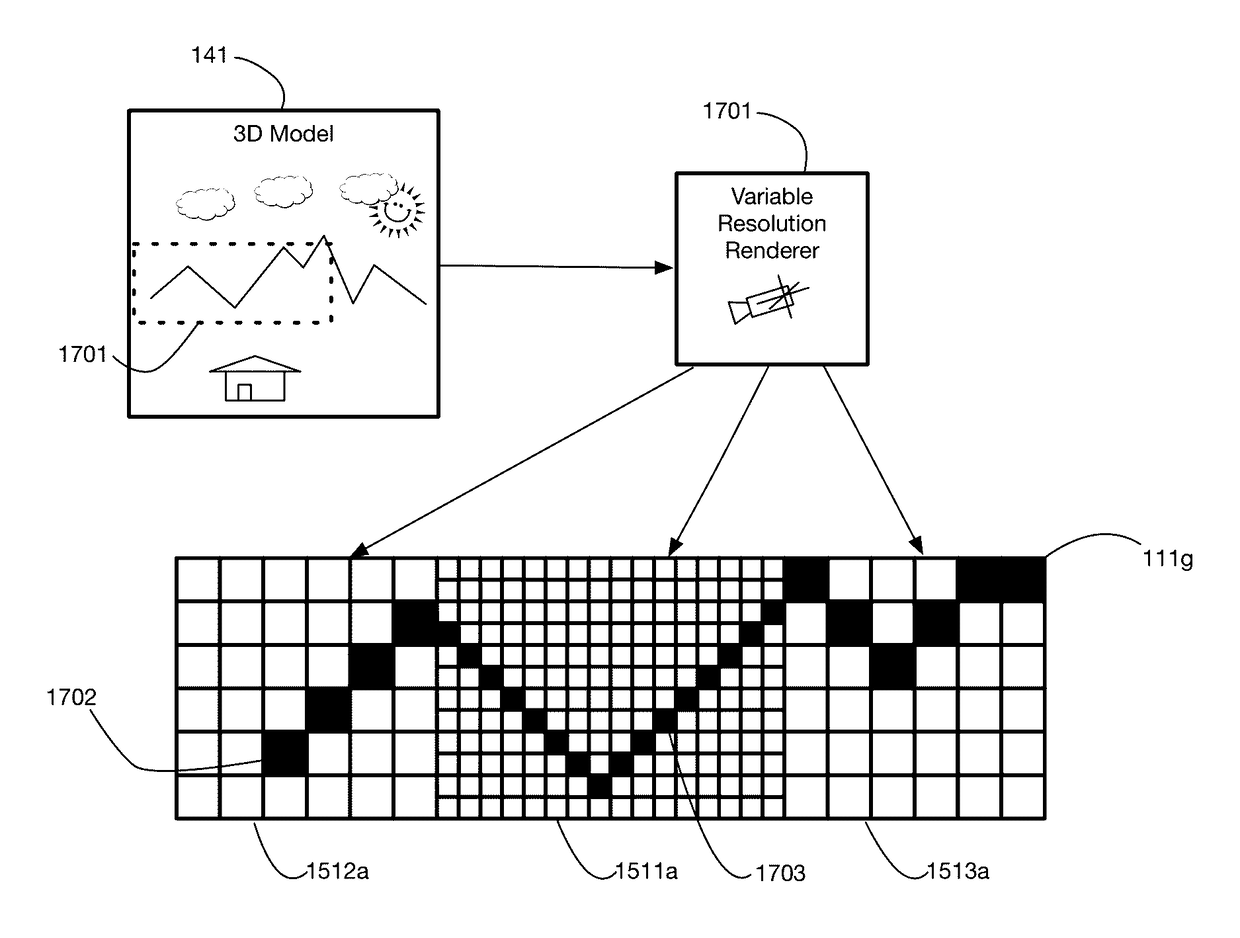
A virtual reality display system that renders images at different resolutions in different parts of a display. Reduces rendering latency by rendering at a lower resolution in selected regions, for example on the sides of a display where human vision has lower resolution than in the center. Pixels in low resolution regions are combined into grid elements, and rendering may generate grid element values rather than individual pixel values. Rendering may use ray casting, rasterization, or both. Variable resolution rendering may be combined with variable level of detail geometry models to further reduce rendering time. Selected objects may be designed as high resolution objects that are rendered at a high resolution even in low resolution display regions.
Owner:LI ADAM
Using Ray Tracing to Enhance Artificial Intelligence Character Behavior
Embodiments of the invention provide use ray-tracing to simulate vision for a artificial intelligence controlled character within a three-dimensional scene. According to one embodiment of the invention, an artificial intelligence system may cast rays into the three-dimensional scene from a viewpoint of the character and may perform ray-tracing with the rays to determine if objects are within a field of view of the character. Furthermore, according to embodiments of the invention, the artificial intelligence system may determine behavior for the character based on whether or not objects are within the field of view, and may determine the behavior for the character based on the objects which are within the field of view.
Owner:IBM CORP
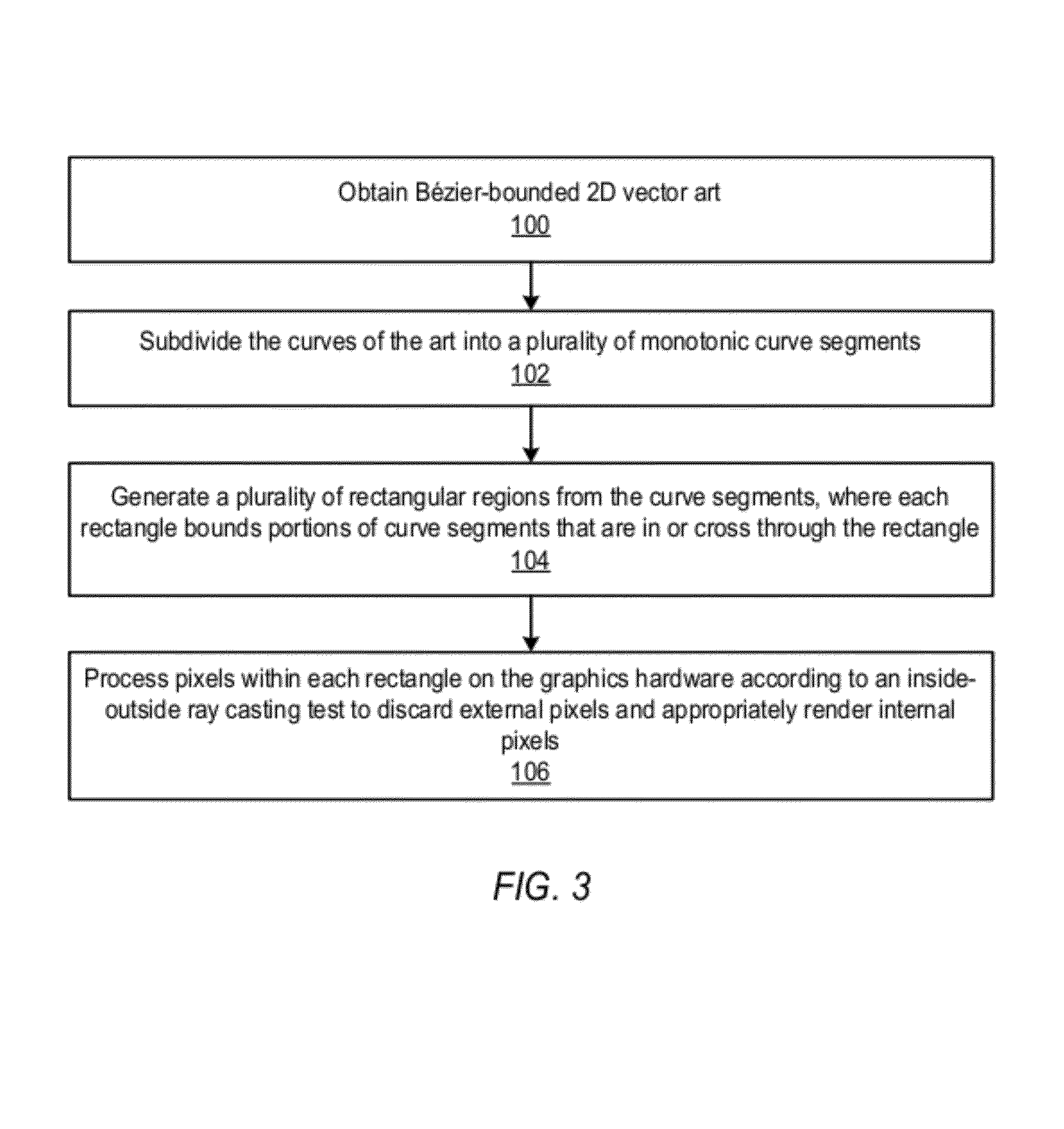
Methods and apparatus for rendering vector art on graphics hardware
ActiveUS8379025B1Reduce CPU overheadEfficiently render quadratic2D-image generation3D-image renderingComputational scienceAnimation
Methods and apparatus for ray-casting 2D animated vector art on graphics hardware. Embodiments maintain curves in their analytic form when transmitted to the GPU. On the CPU, the curves in the vector art may be subdivided into a plurality of monotonic curve segments. A plurality of intervals may be generated from the curve segments. Further subdivision may be applied on the CPU to any interval that includes more than n curves, where n is the maximum number of curves that can be processed in parallel in the pixel shader. On the GPU, the pixels are evaluated to determine whether each pixel is inside or outside of the curve network. The technique used in the GPU may be based on a point-in-polygon algorithm that casts rays from points under test and counts the number of curve crossings before the rays exit the shape using a modified implicit formula.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
Automatic coronary isolation using a n-MIP ray casting technique
A novel method is presented for detecting coronary arteries as well as other peripheral vessels of the heart. After finding the location of the myocardium through a segmentation method, such as a graph theoretic segmentation method, the method models the heart with a biaxial ellipsoid. For each point of the ellipsoid, a collection of intensities are computed that are normal to the surface. This collection is then filtered to detect the cardiovascular structures. Ultimately, vessel centerline points are detected using a vessel tracking method, and linked together to form a complete coronary artery tree.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
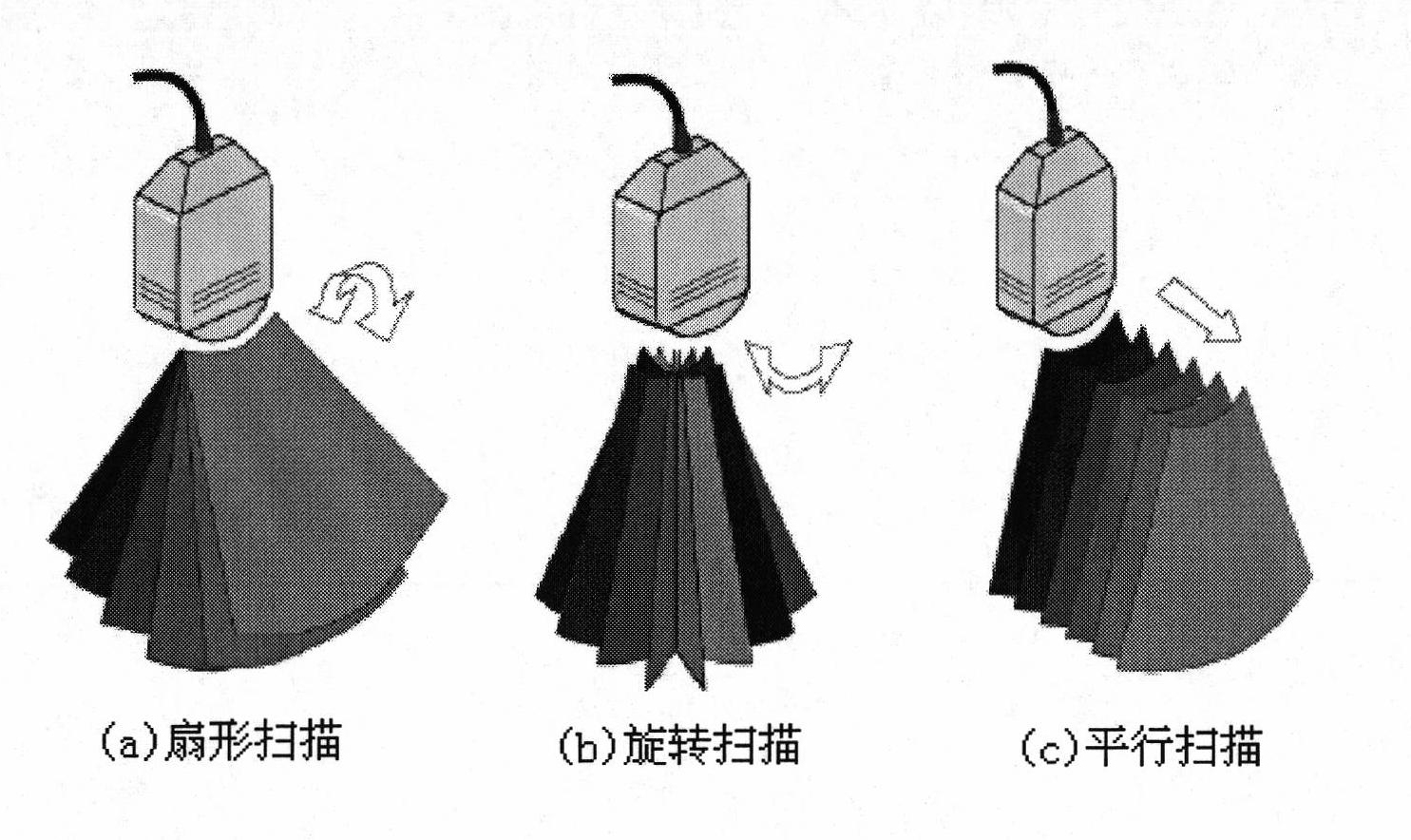
Three-dimensional reconstruction method for two-dimensional ultrasonic image
InactiveCN102106741AFast imagingImprove image qualityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage analysisSonificationData information
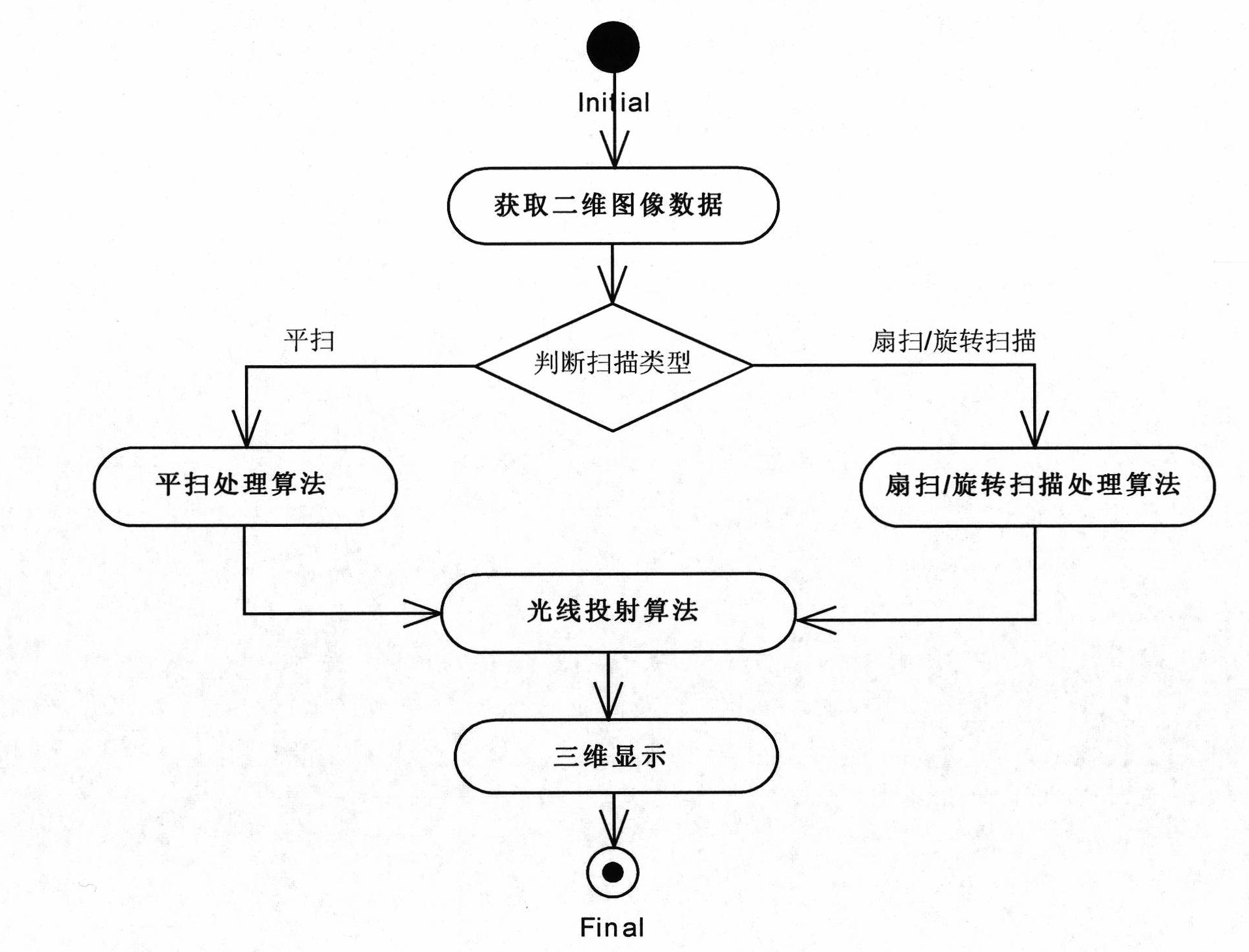
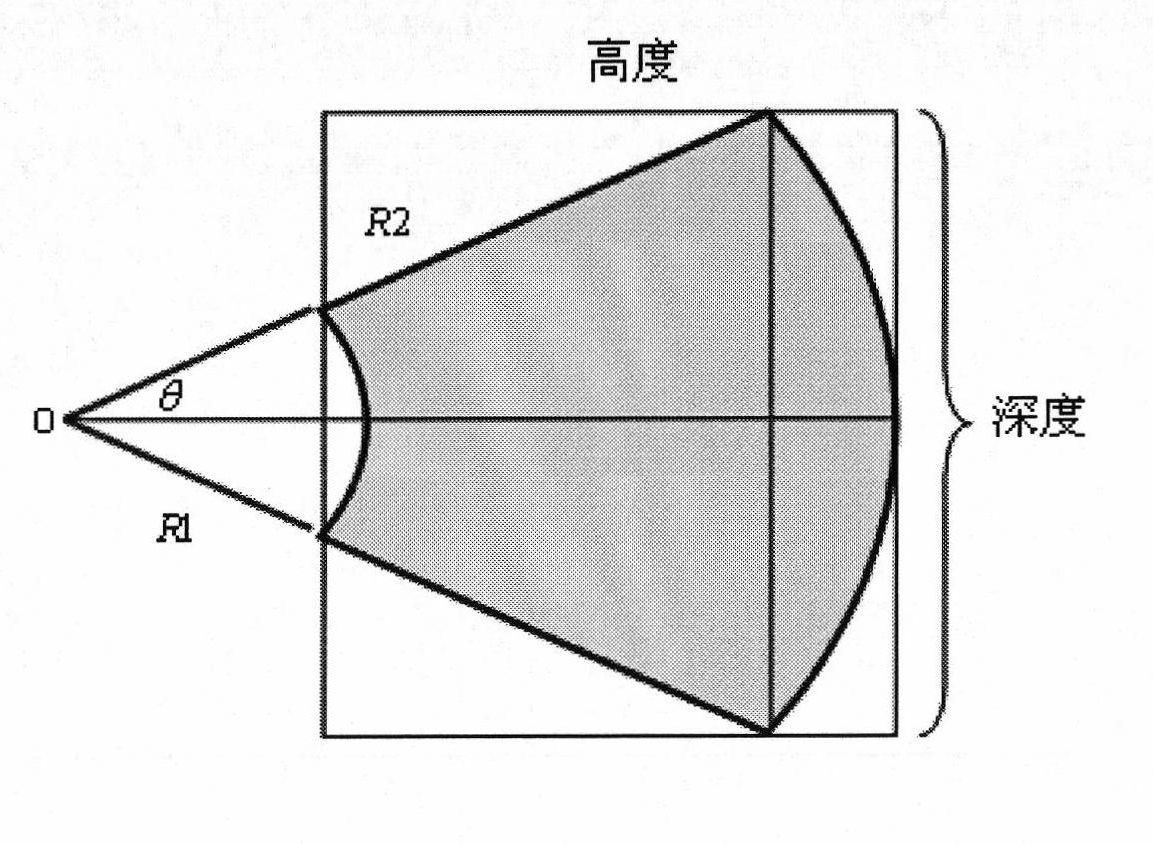
The invention relates to a three-dimensional reconstruction method for a two-dimensional ultrasonic image. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring data of a two-dimensional image in a mechanically-driven scanning mode; judging a scanning type, and processing the data of the two-dimensional image by adopting a sector scanning / rotary scanning processing algorithm to generate a regular data field if the scanning is sector scanning or rotary scanning; and displaying a three-dimensional image by utilizing the regular data field through a ray casting algorithm. The sector scanning processing algorithm comprises the processing steps of: extracting interesting areas, namely rejecting unwanted data information; calculating the size of the regular data field to obtain the length, width and height of the regular data field; improving coordinate conversion and an interpolation algorithm to obtain a grey value of a current pixel; and performing filtering processing. In the method, the three-dimensional reconstruction is performed on the data of the two-dimensional ultrasonic image which are acquired in different scanning modes; and the method has the advantages of clear reconstructed images, strong sense of reality, high imaging speed and the like.
Owner:PHILIPS CHINA INVESTMENT
Three-dimensional reconstruction method for concrete CT (computed tomography) image
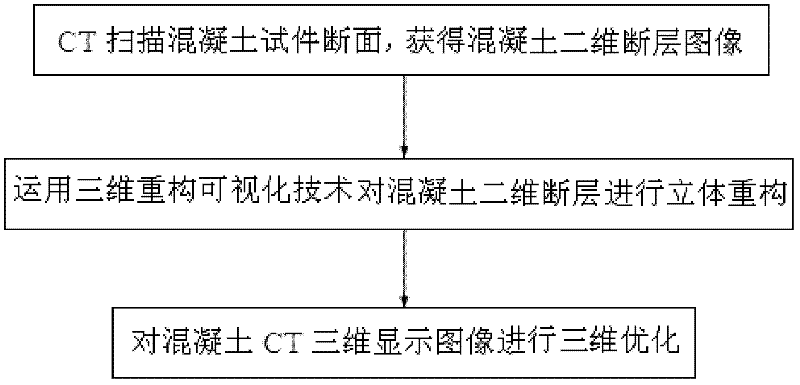
The invention discloses a three-dimensional reconstruction method for a concrete CT (computed tomography) image, comprising the following steps of: firstly, performing tomography on a concrete test sample by a CT machine; secondly, performing three-dimensional reconstruction on the concrete CT image by using a ray-casting algorithm, so as to obtain real images of aggregates, mortar and holes; and finally, performing three-dimensional stereo reconstruction on the concrete CT image by using a visualization tool VTK (visualization tool kit). The three-dimensional reconstruction method for the concrete CT (computed tomography) image, disclosed by the invention, has the advantages of being strong in real-time performance, high in operation efficiency, and capable of clearly and reliably distinguishing the aggregates, the mortar and the holes. A real meso-structure model of concrete can be obtained through a three-dimensional reconstruction result, the three-dimensional reconstruction result can be subjected to a test comparison with a concrete mesoscopic numerical simulation result, and a numerical analysis model is corrected.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY +1
Method and system for adaptive maximum intensity projection ray casting
ActiveUS20070040833A1Reduce computing costQuality improvement3D-image rendering3D modellingData setComputer graphics (images)
The adaptive MIP ray casting system first fragments a 3-D dataset into multiple sub-volumes and constructs an octree data structure with each sub-volume being associated with one node of the octree data structure. The system then establishes a 2-D image plane and selectively launches a plurality of rays towards the 3-D dataset, each ray adaptively interacting with a subset of the sub-volumes and identifies the maximum data value along the ray path. The maximum data value is then converted into a pixel value on the 2-D image plane. Finally, the system interpolates pixel values at those locations where no pixel value is generated by ray casting and thereby generates a 2-D image of the 3-D dataset.
Owner:FOVIA
Method for manufacturing oral implant positioning guiding template based on CBCT data
InactiveCN102626347AGuaranteed accurate reconstructionImprove production accuracyDental implantsAnatomical structuresModel reconstruction
The invention discloses a method for making oral implant positioning guiding template based on CBCT data. The method comprises the steps: 1) scanning patient jaw bones through CBCT to mainly obtain jaw bone three-dimensional anatomic structure information of a implant region; 2) analyzing and processing CBCT data; 3) using the processed CBCT data to reconstruct a three-dimensional jaw bone model; 4) processing the reconstructed three-dimensional jaw bone model; 5) designing an oral implant positioning guiding template based on the three-dimensional jaw bone model; and 6) carrying out rapid prototype processing; Amount of influence data is effectively reduced through carrying out resampling, anisotropic diffusion filtering to original image data obtained through CBCT scanning, carrying out volume rendering through a ray-casting method, and noise of the data is further removed, thereby accurate reconstruction of the three-dimensional jaw bone model is guaranteed. Furthermore, accuracy of manufacturing the oral implant positioning guiding template is substantially improved through removing model fragments caused by image artifact and non-implant region models in the process of three dimensional jaw bone model reconstruction.
Owner:UNIVERSAL ENTERPRISES GRP CO LTD
System and method for computer aided polyp detection
ActiveUS20100215226A1Easy to distinguishSure easyInput/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementPattern recognitionPresent method
In the present methods, the automatic detection of polyps is converted into a 2D pattern recognition problem using conformal mapping and direct volume rendering. The colon surface is first segmented and extracted from the CT data set of the abdomen, which is then mapped to a 2D plane using conformal mapping. Ray casting is used to determine sub-surface density values and the flattened image is rendered using a volume rendering technique with a translucent electronic biopsy transfer function. Polyp candidates are detected by a clustering method which identifies regions of elevated sub-surface density. The potential for false positives is reduced by analyzing the volumetric shape and texture features of the polyp candidate regions.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
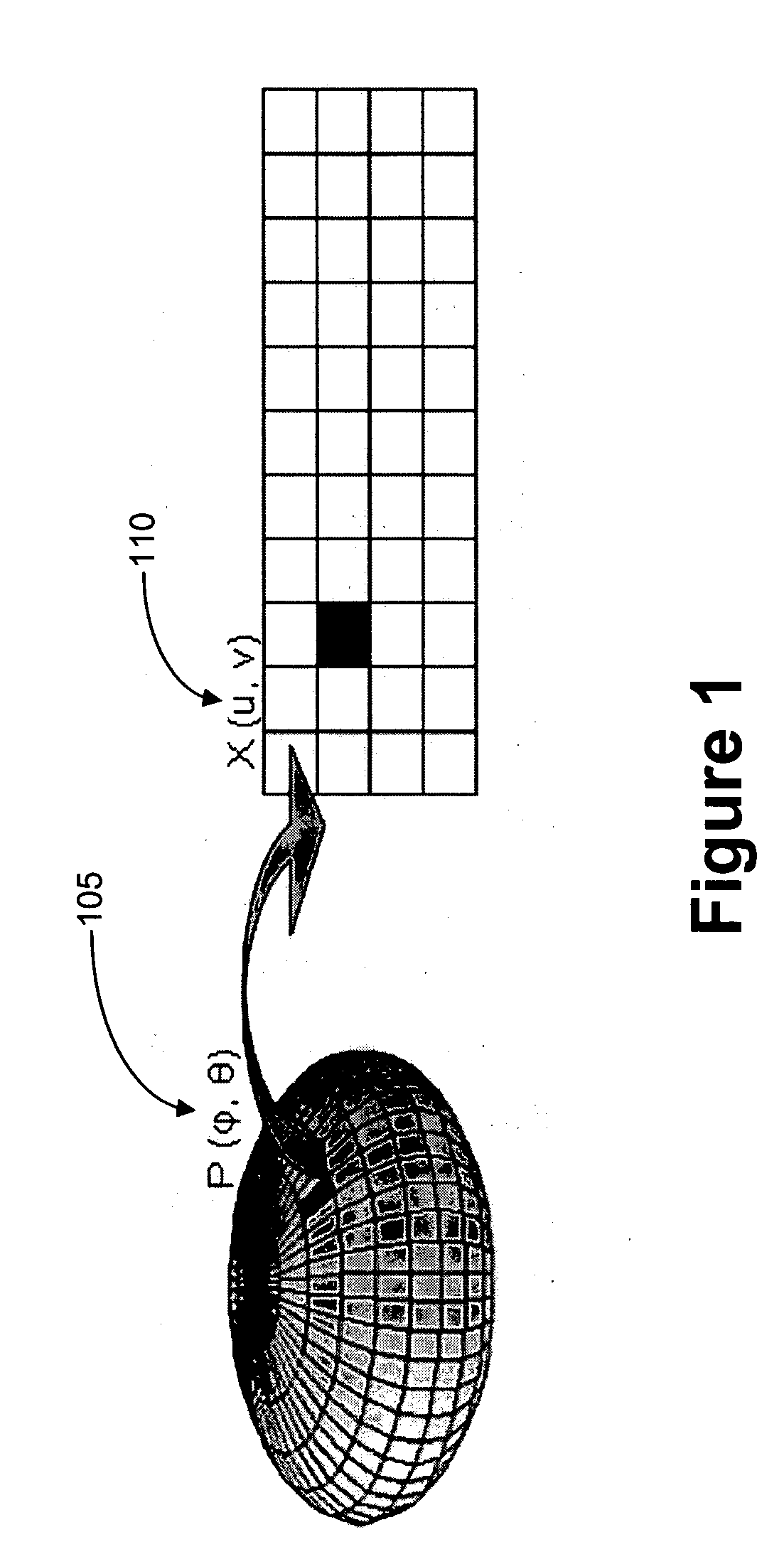
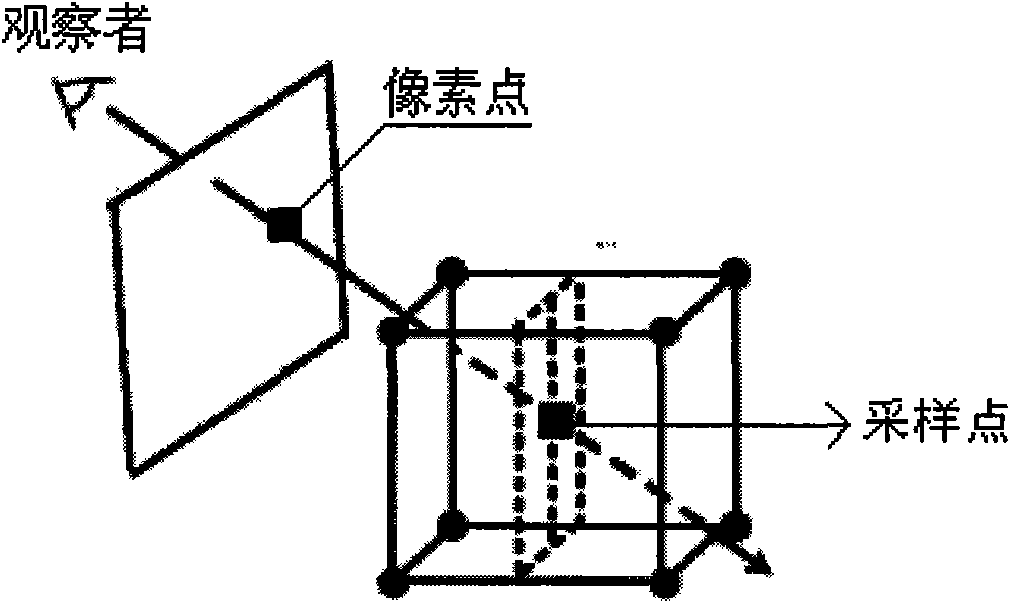
Method of forming a perspective rendering from a voxel space
InactiveUS6999078B1Improve spatial resolutionMinimize extent3D-image rendering3D modellingVoxel volumeImage resolution
A method for forming a high spatial resolution perspective rendering from a low spatial resolution voxel space is disclosed. The method comprises steps of: a) initializing a virtual window of predetermined resolution pixels, and placing the virtual window in or near the voxel space; b) sparsely ray-casting a plurality of vectors from a predetermined vantage-point through the virtual window into the voxel space; and c) calculating a visualization-value at a series of positions along each vector. In a position ordering of steps from the vantage-point to the pixel, an accumulated transparency-value threshold is calculated. Values of proximate voxels are interpolated into an interpolated voxel value for each position. The interpolated voxel values are then transformed into a derived visualization-value and transparency value.
Owner:ALGOTEC SYST
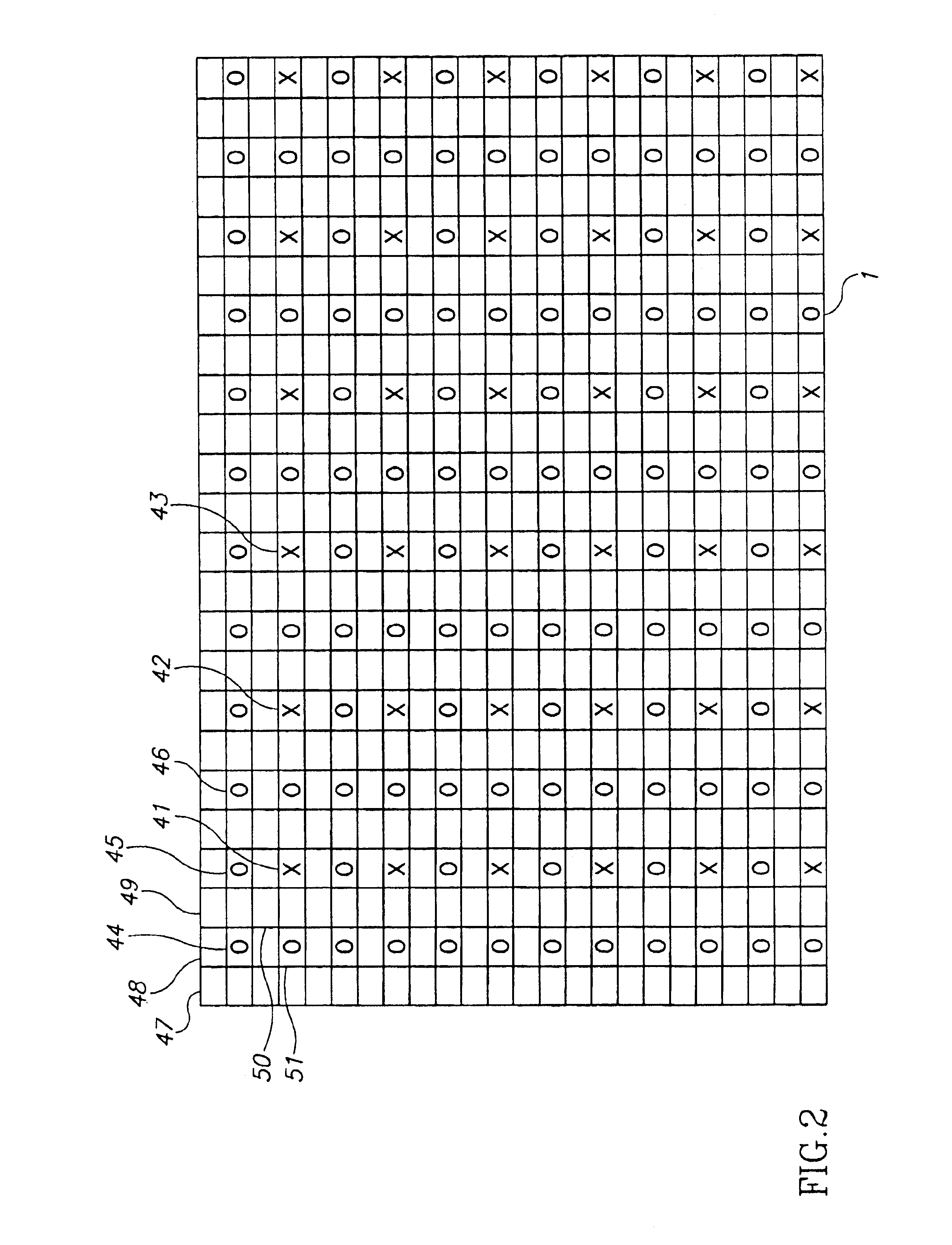
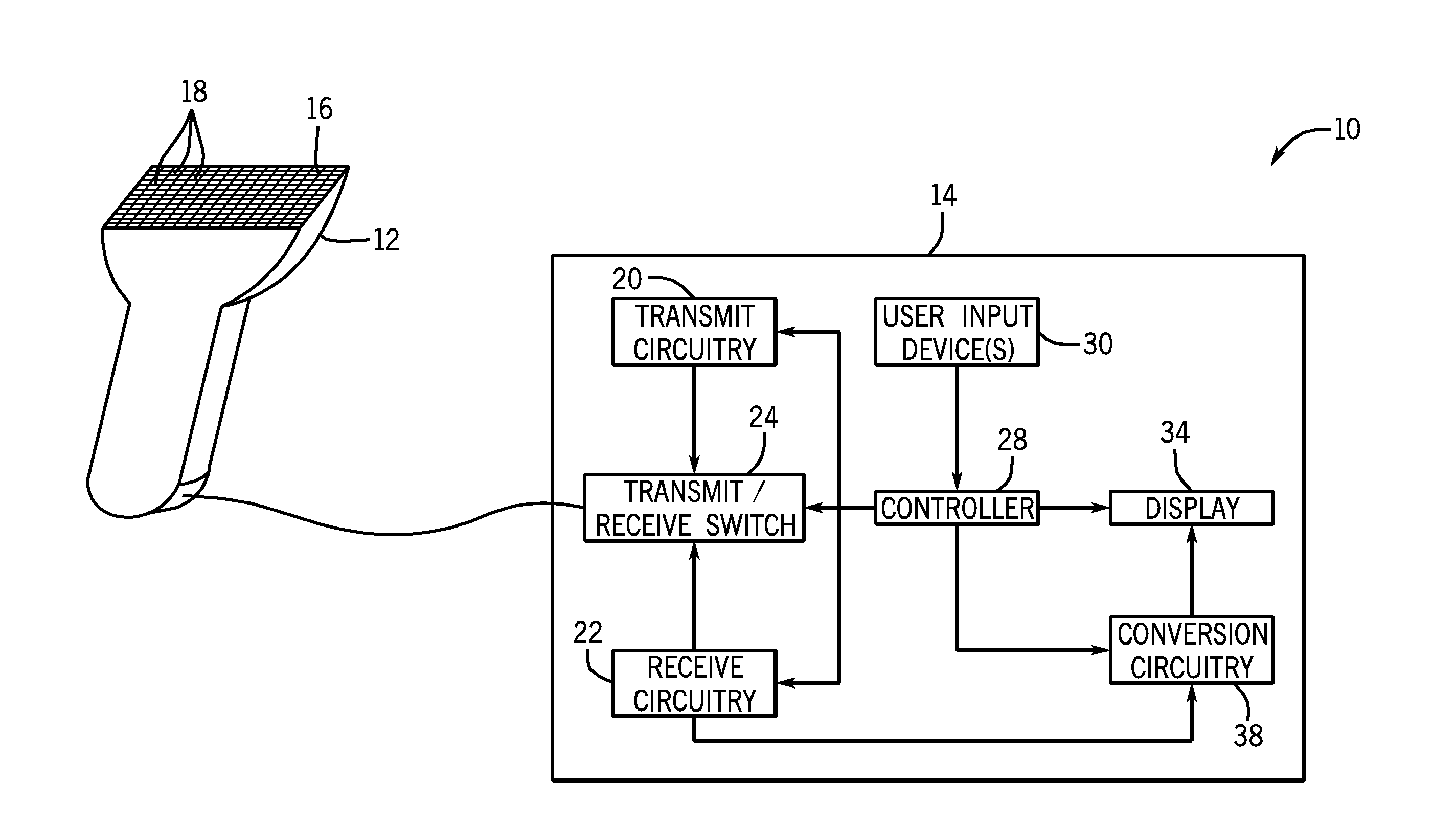
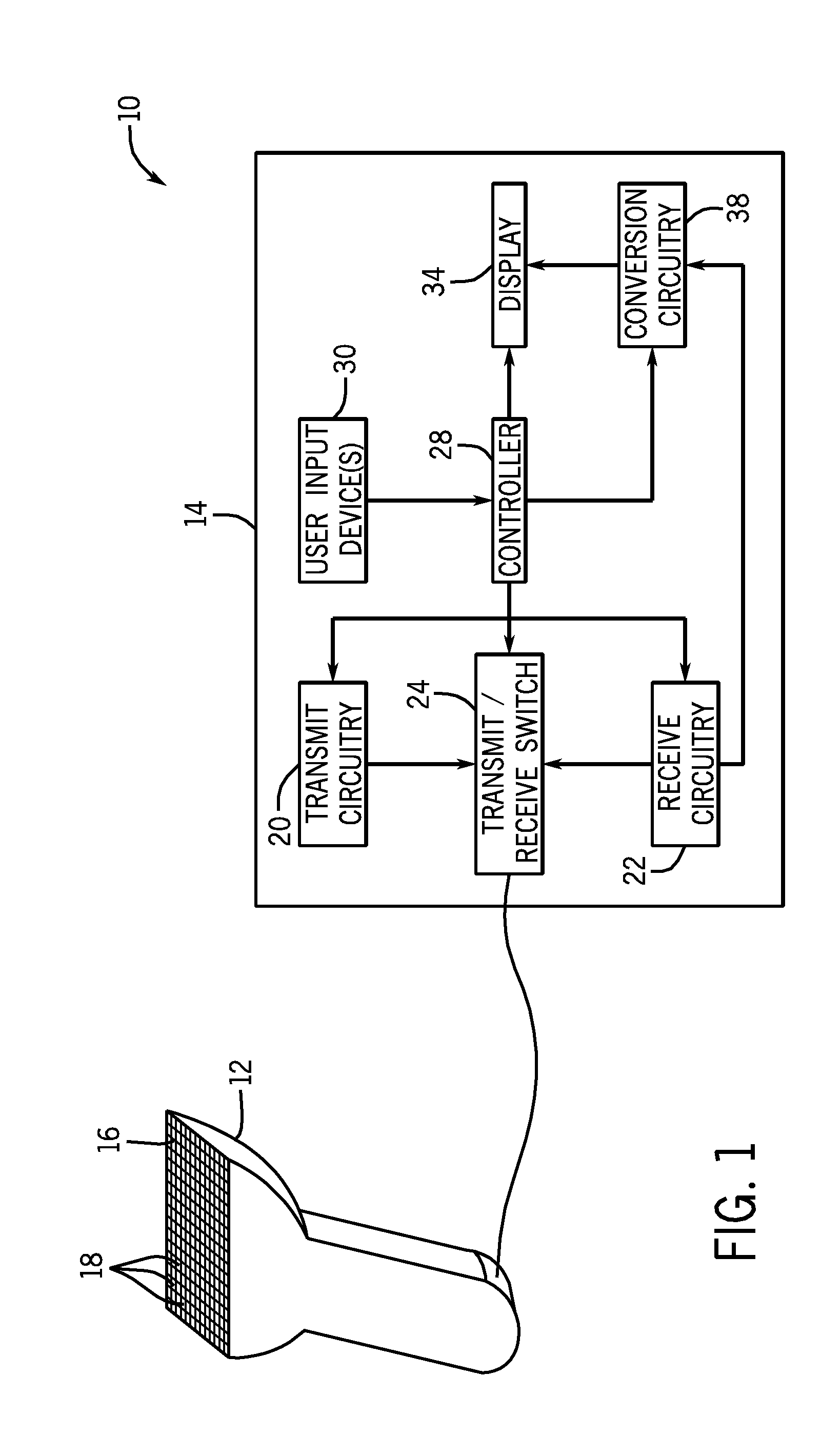
Ultrasound imaging with ray casting and software-based image reconstruction
ActiveUS20110270086A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCharacter and pattern recognitionSonificationData set
Systems and methods are presented for increasing the frame rate of real-time 3D ultrasound imaging. In one embodiment, the frame rate for generating a pseudo-shaded 2D projection image may be increased by controlling the image reconstruction process. Rather than beamforming, scan converting, and interpolating a 3D voxelized data set of an entire scanned volume, only samples required for generating the 2D projection image may be reconstructed. The element data measured from each transducer array element may be combined to directly reconstruct those 3D image samples required by the volume rendering algorithm to generate the 2D projection image.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Clipping geometries in ray-casting
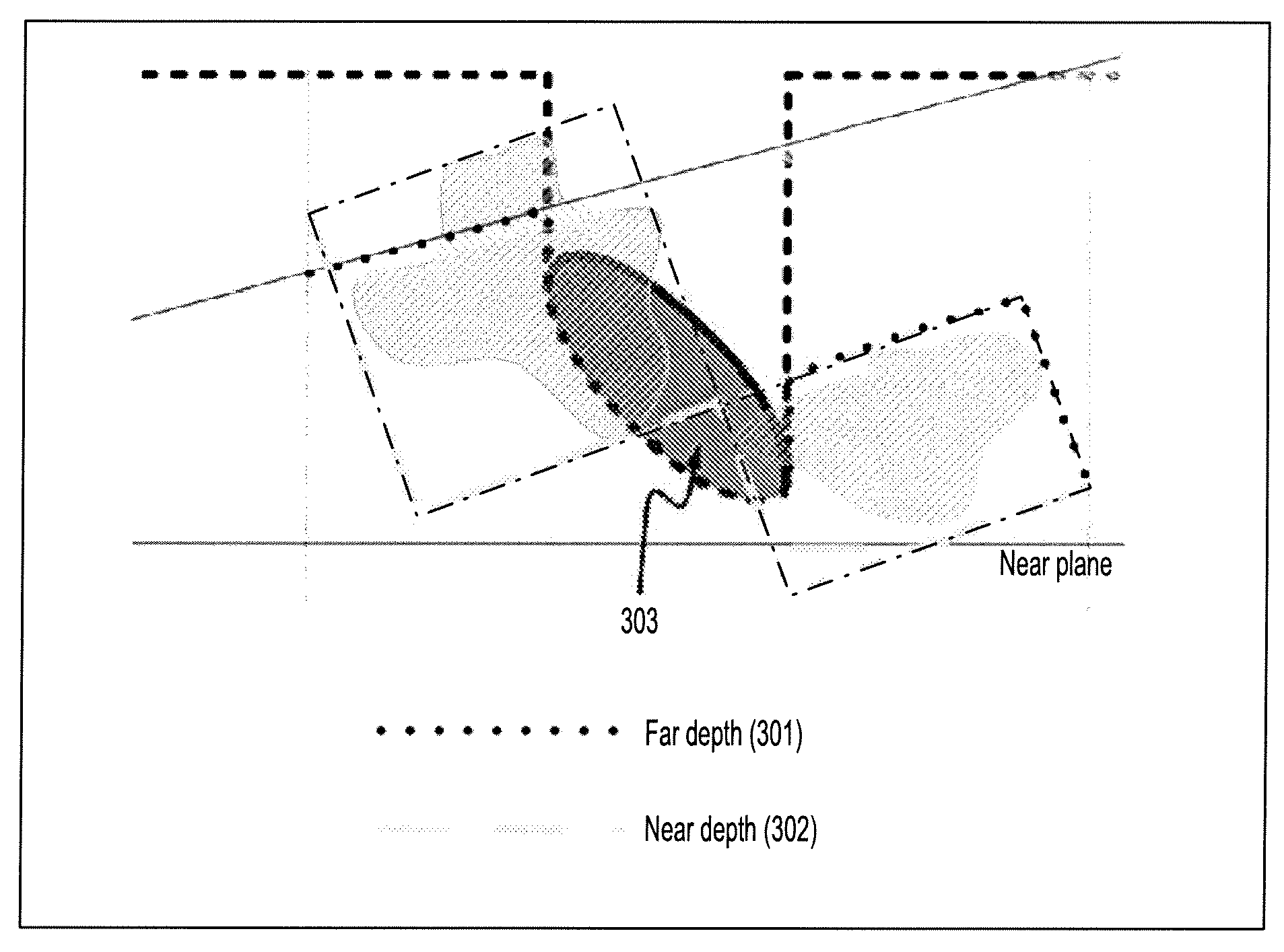
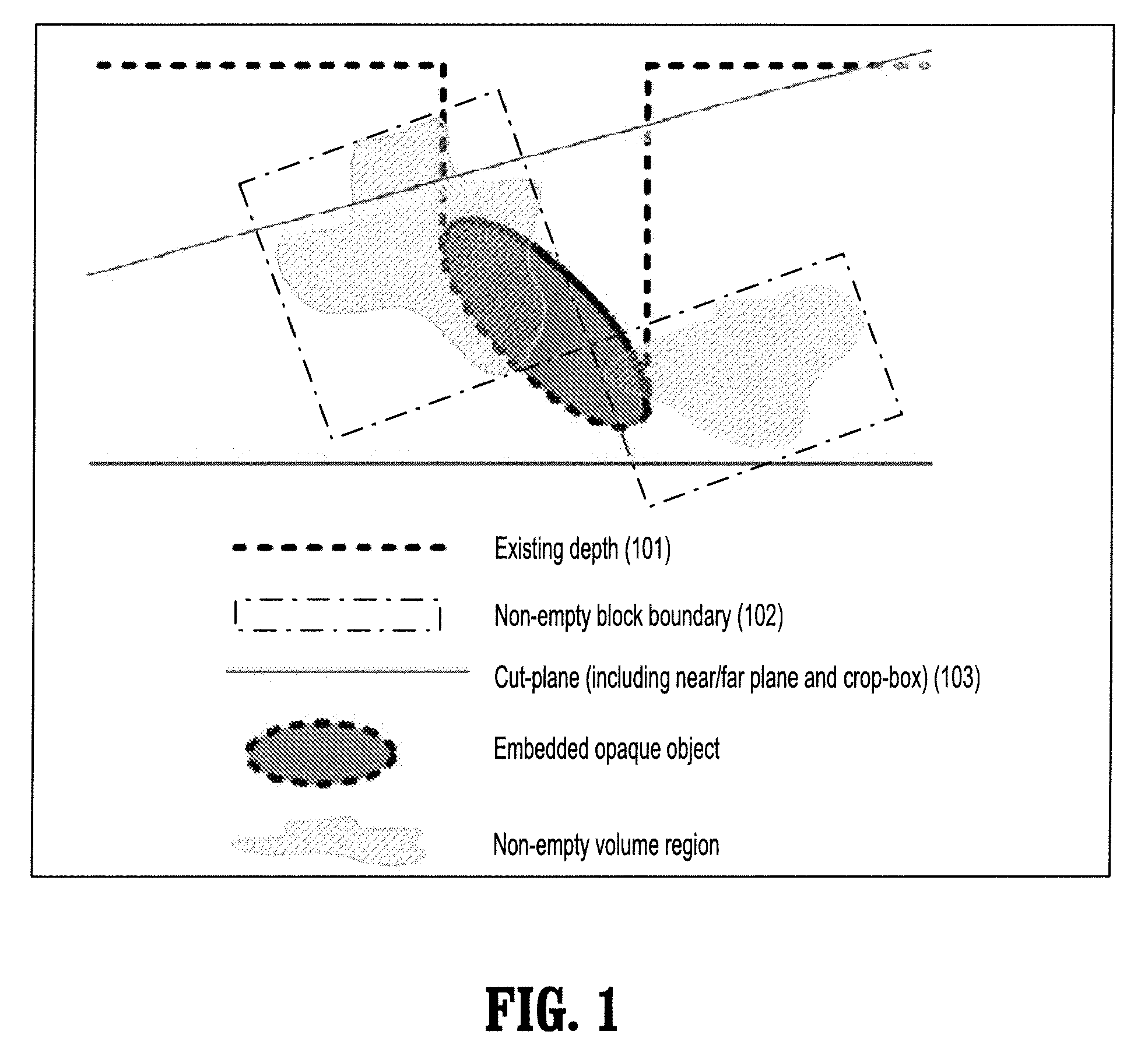
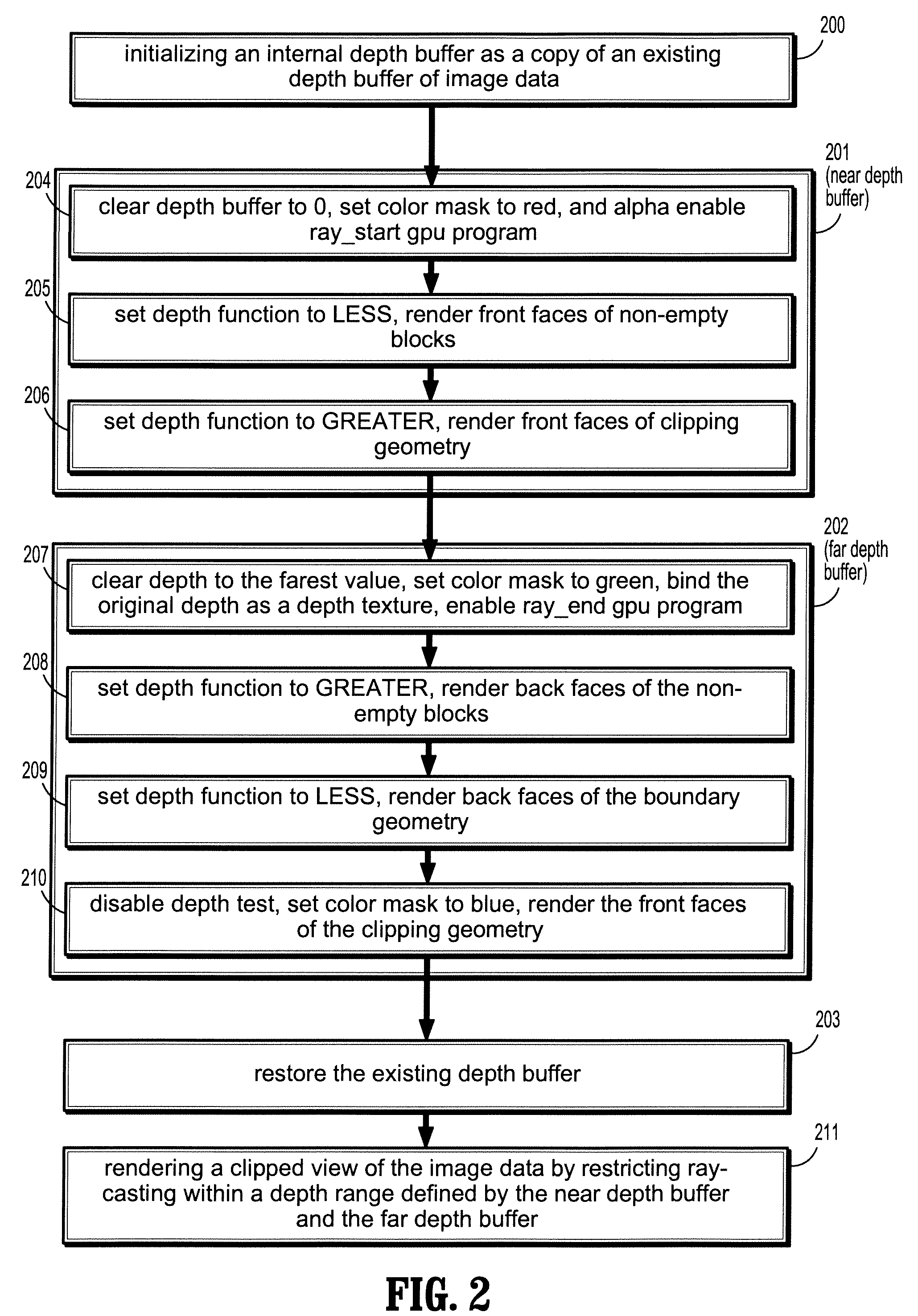
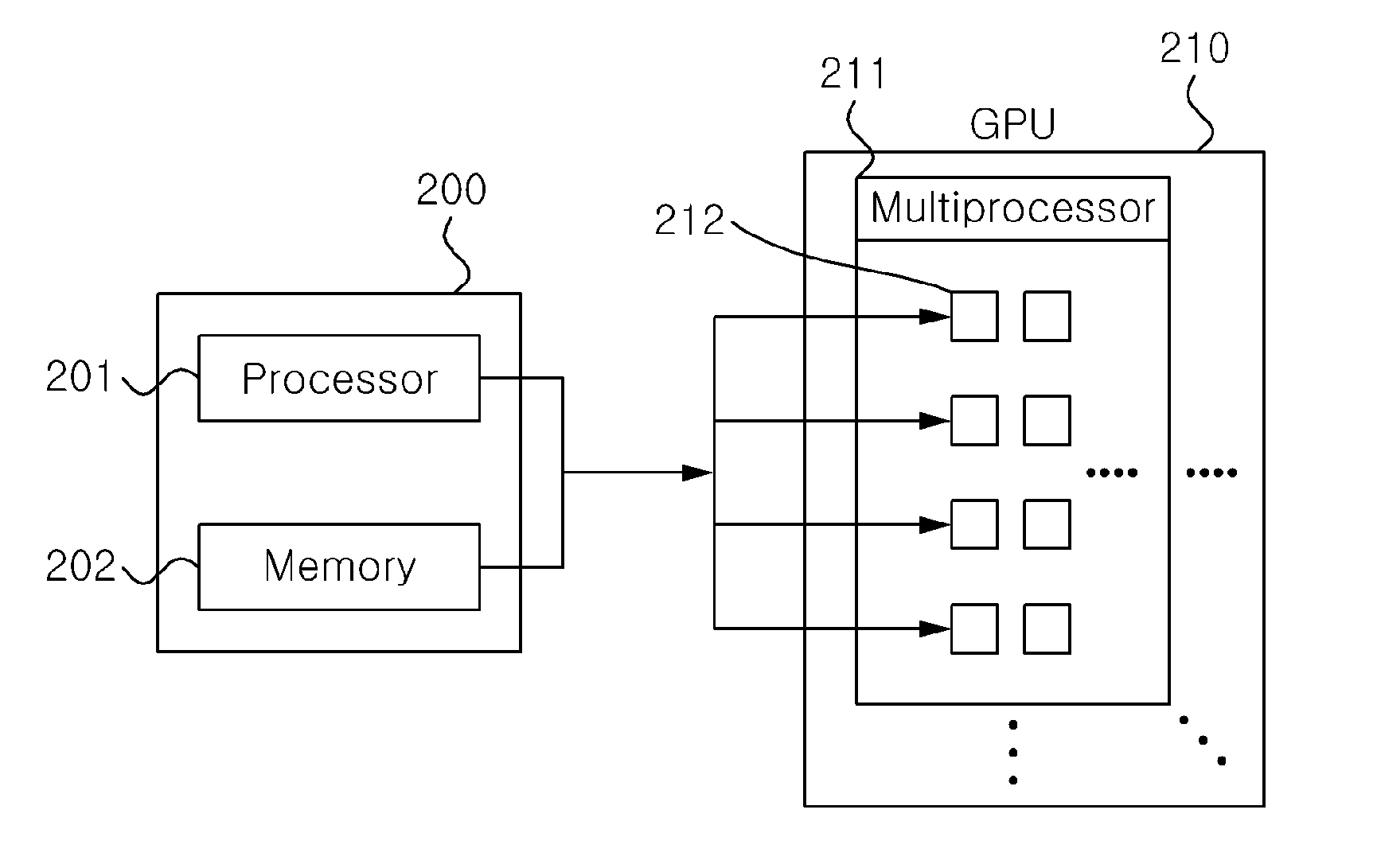
A computer implemented method for creating a depth range buffer for supporting clipping geometries for ray-casting includes inputting image data, establishing a depth range buffer for specifying a start and an end point of each ray, computing a near depth of the image data corresponding to the start point of each ray, computing a far depth of the image data corresponding to the end point of each ray, clipping the volume by restricting ray-casting within the start and end points of the depth range buffer, and rendering a portion of the image data corresponding to the visible depth range.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
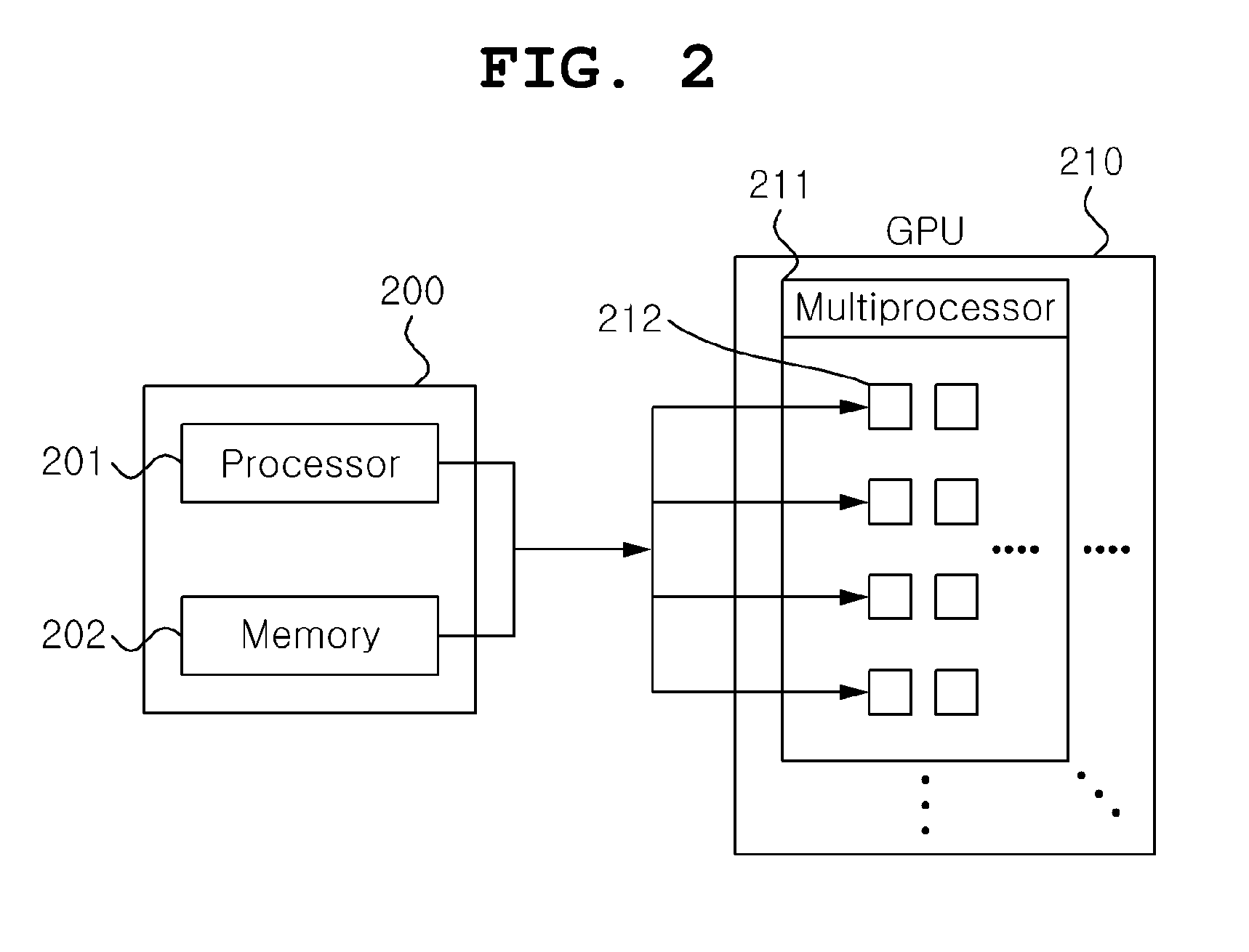
Processor and method for accelerating ray casting
ActiveUS20160350960A1Increase speedImage analysisImage generationViewpointsComputer graphics (images)
A processor and method for accelerating ray casting are disclosed herein. The processor for accelerating ray casting includes a computation unit, a sorting unit, an allocation unit, and an execution control unit. The computation unit calculates the length information of a section in which a ray corresponding to each of the pixels of a two-dimensional (2D) scene corresponding to a viewpoint intersects an effective volume in order to apply ray casting to the pixel. The sorting unit sorts the ray based on the length information of the section in which the ray intersects the effective volume. The allocation unit allocates the sorted rays to respective thread groups having a parallel multiprocessor structure in order of the sorting. The execution control unit transfers control instructions to the allocated thread groups so that the allocated thread groups execute ray casting for the sorted rays.
Owner:CORELINE SOFT
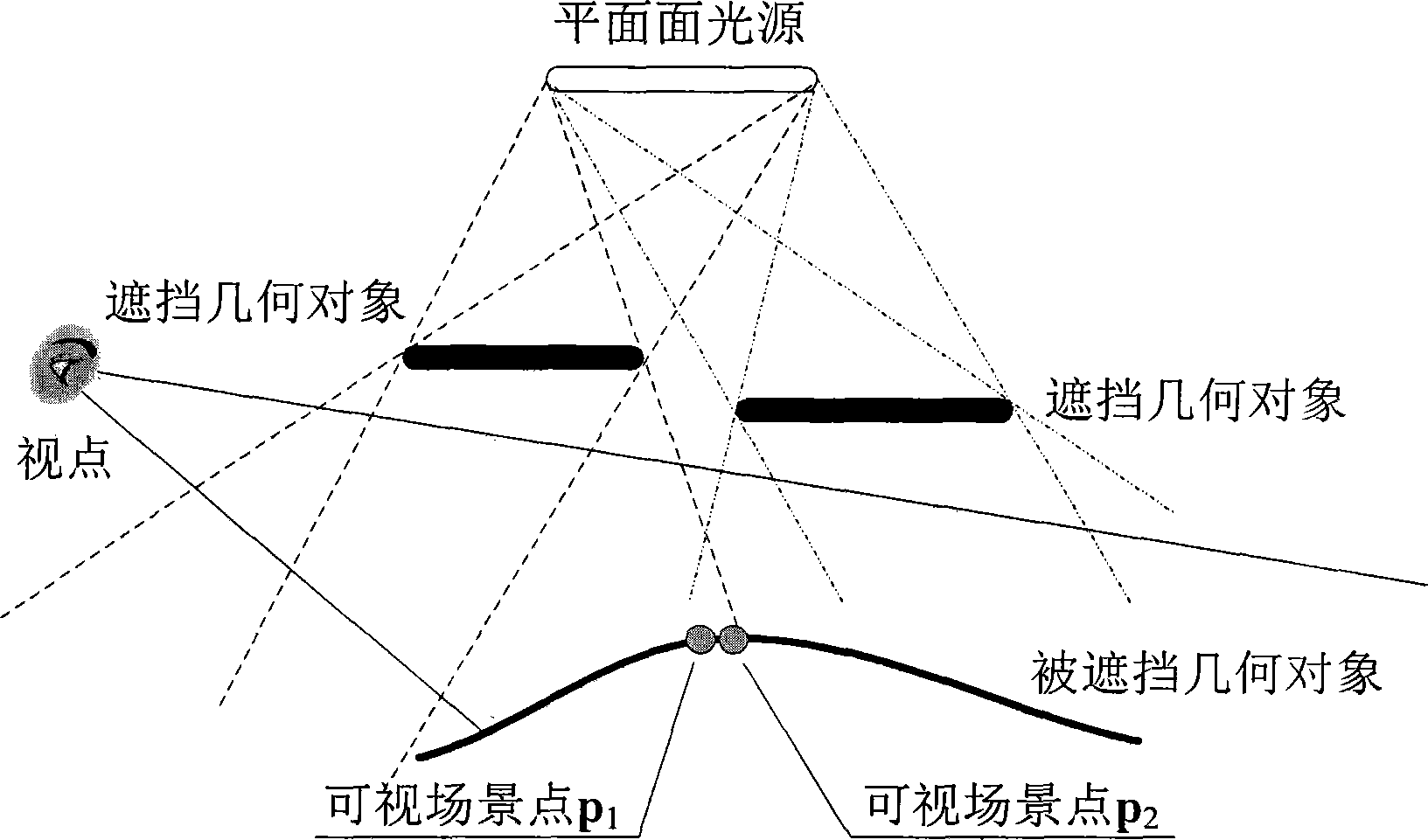
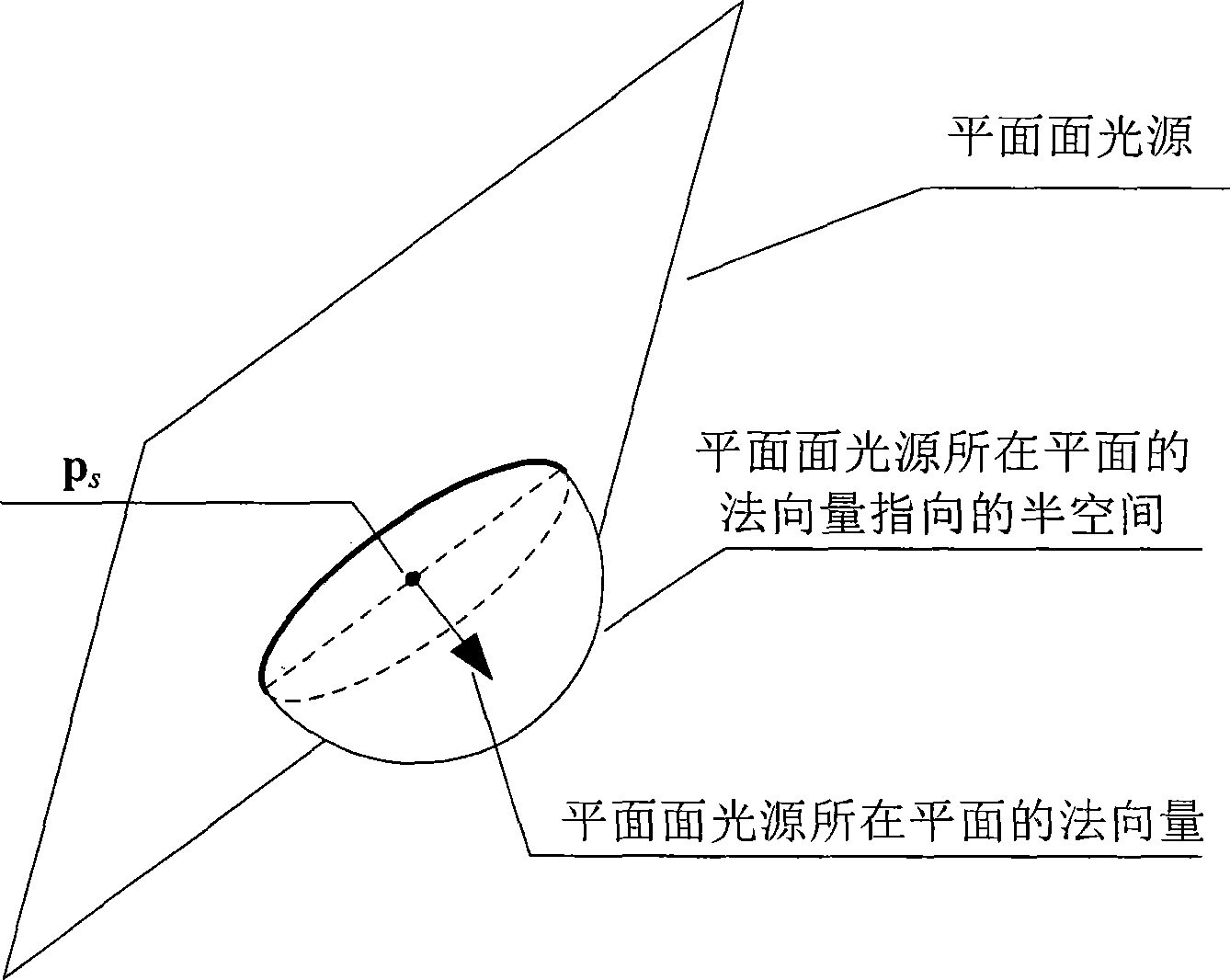
Method for approximately drawing soft shadow of three-dimensional scene
ActiveCN104346831AQuality improvementReduce noise3D-image rendering3D modellingVisibilityComputer graphics (images)
The invention provides a method for approximately drawing a soft shadow of a three-dimensional scene. The method comprises the following steps of estimating planar surface light source visibility in a visible scene area by randomly sampling planar surface light sources, and reducing planar surface light source visibility noise introduced through random sampling by utilizing spatial convolution smooth denoising and filtering; utilizing a ray casting technology, calculating illumination contribution of the planar surface light sources visibility data to a visible scene point according to the obtained planar surface light source visibility data of the visible scene point, finally calculating a color value of the visible scene point based on the illumination contribution, and drawing a three-dimensional scene picture comprising the soft shadow. According to the method, the drawing quality of the three-dimensional scene picture can be ensured, and the drawing speed is improved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
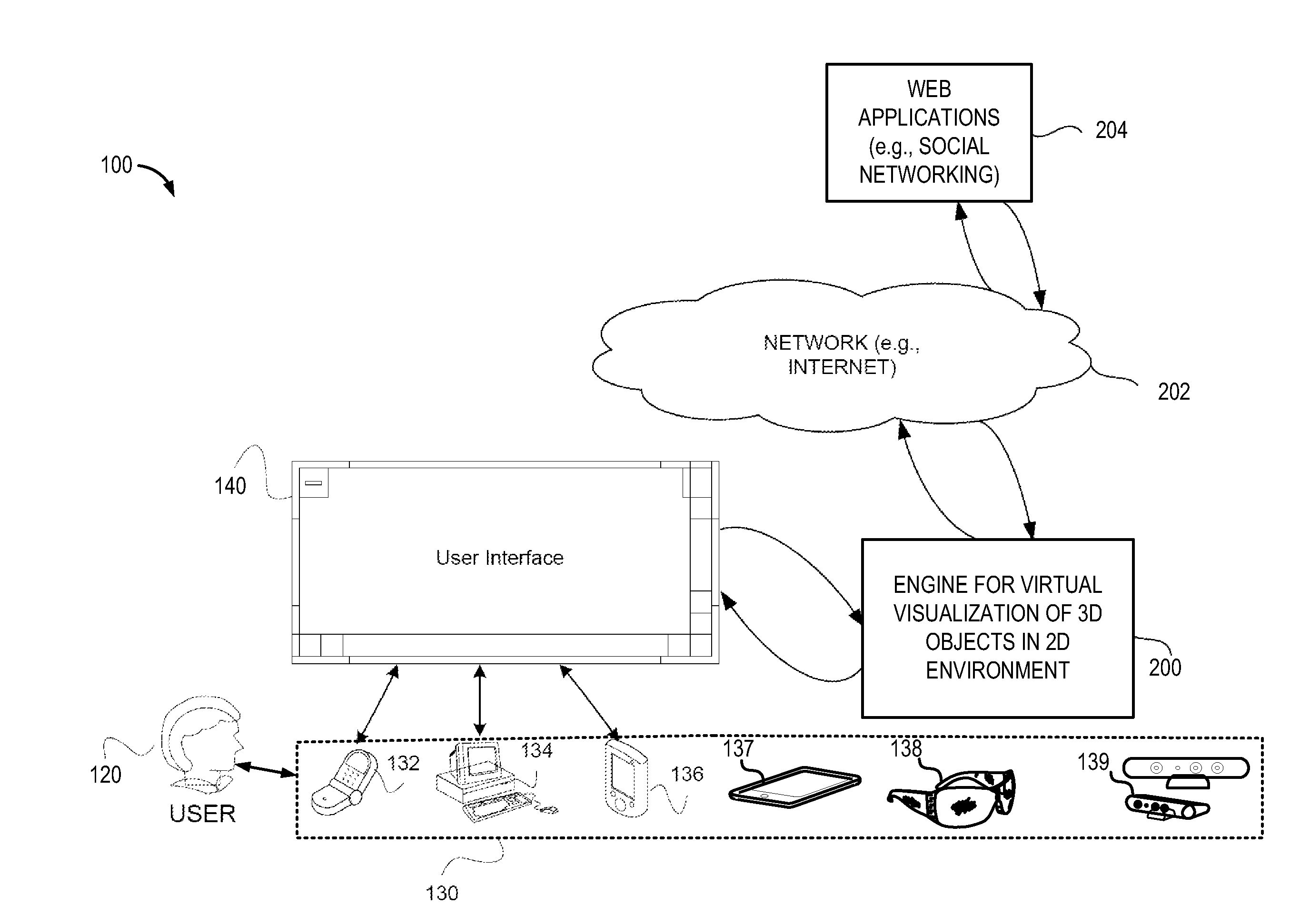
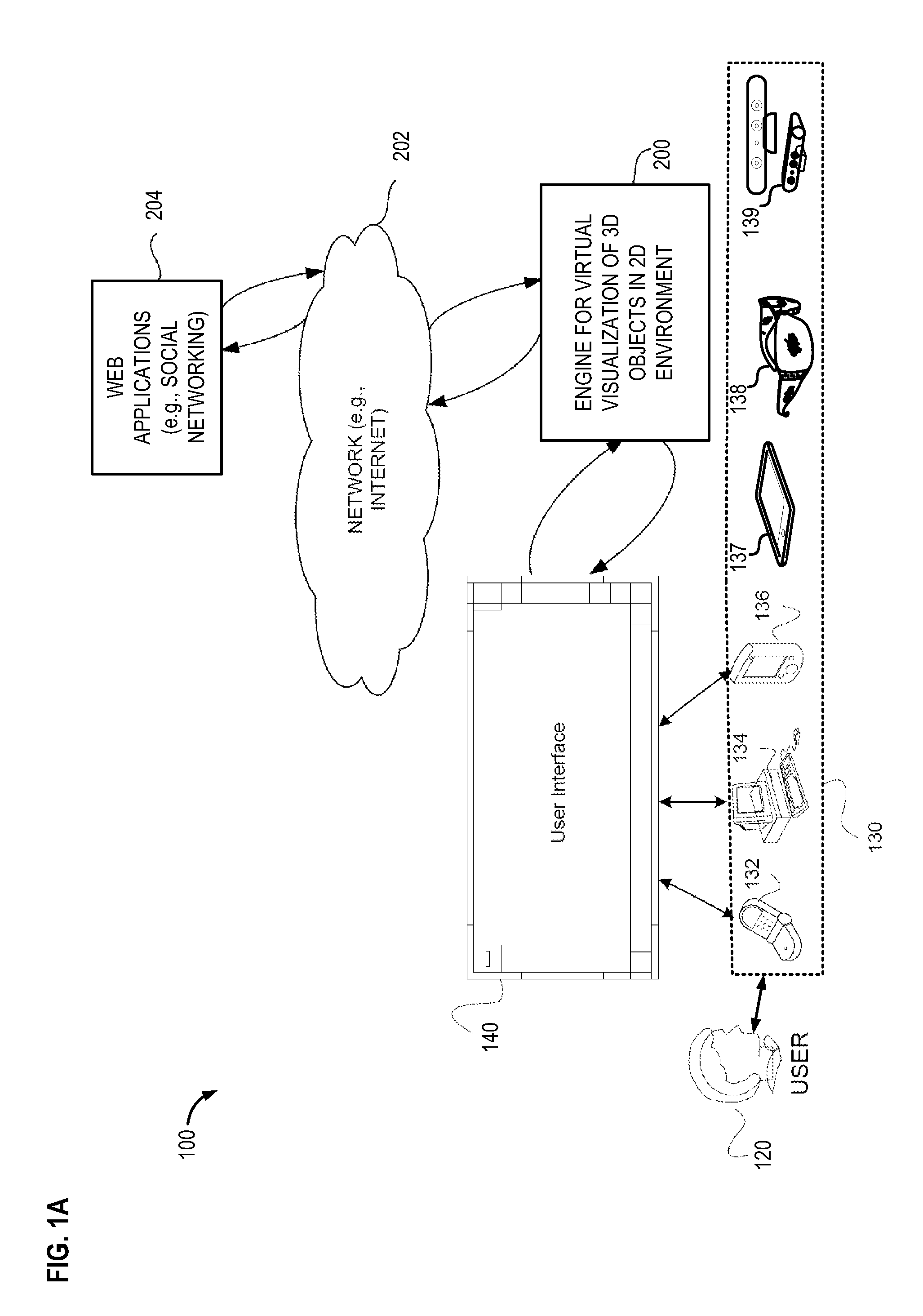
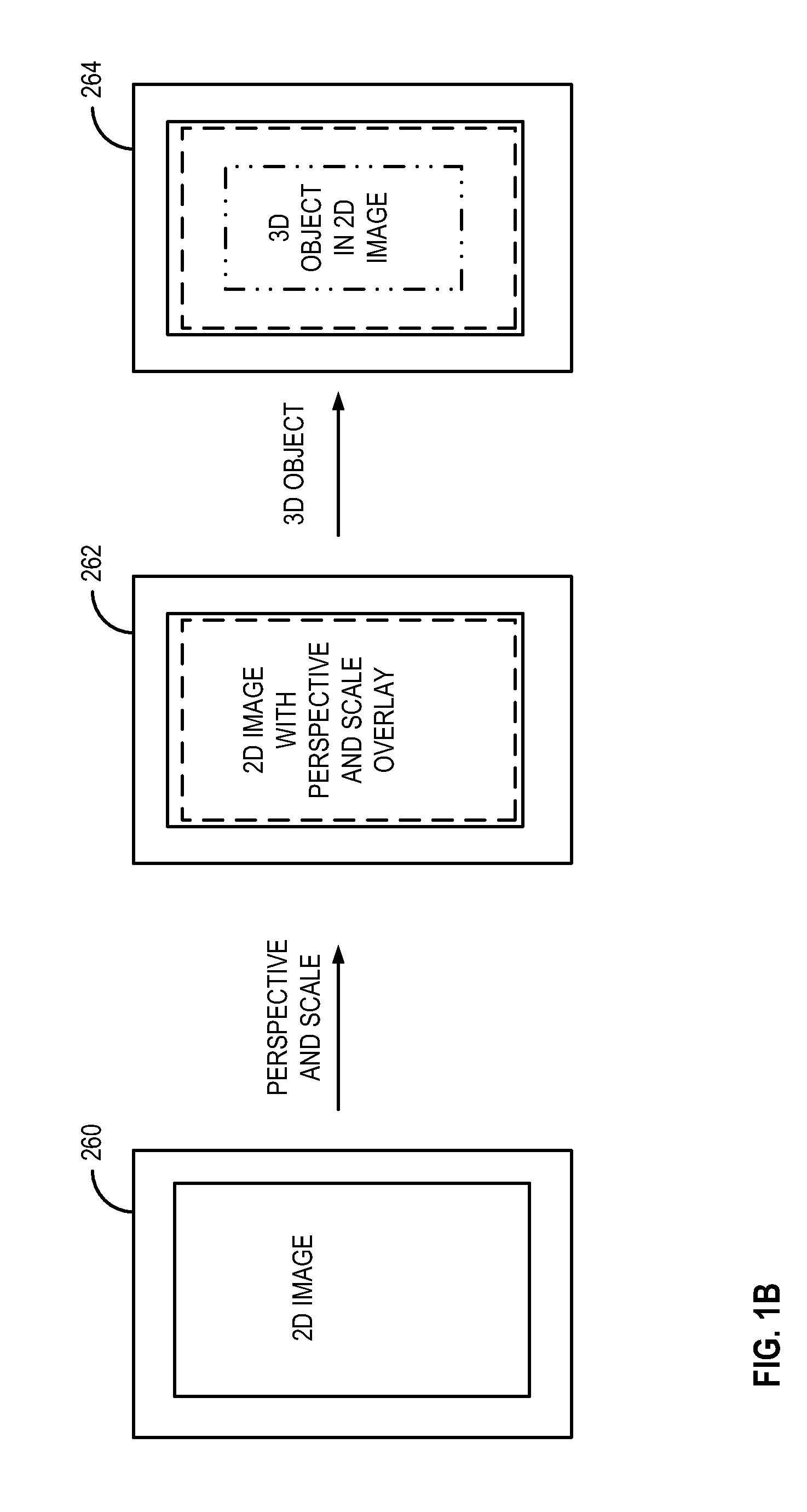
Method for providing scale to align 3D objects in 2d environment
ActiveUS20150243071A1Data processing applicationsImage generationUser deviceComputer graphics (images)
Example systems and methods for virtual visualization of a three-dimensional (3D) model of an object in a two-dimensional (2D) environment. The method may include projecting a ray from a user device to a ground plane and determining an angle at which the projected ray touches the ground plane. The method further helps determine a level for the ground plane for positioning the 3D model of the object in the 2D environment.
Owner:WEST TEXAS TECH PARTNERS LLC
Volumetric rendering of image data
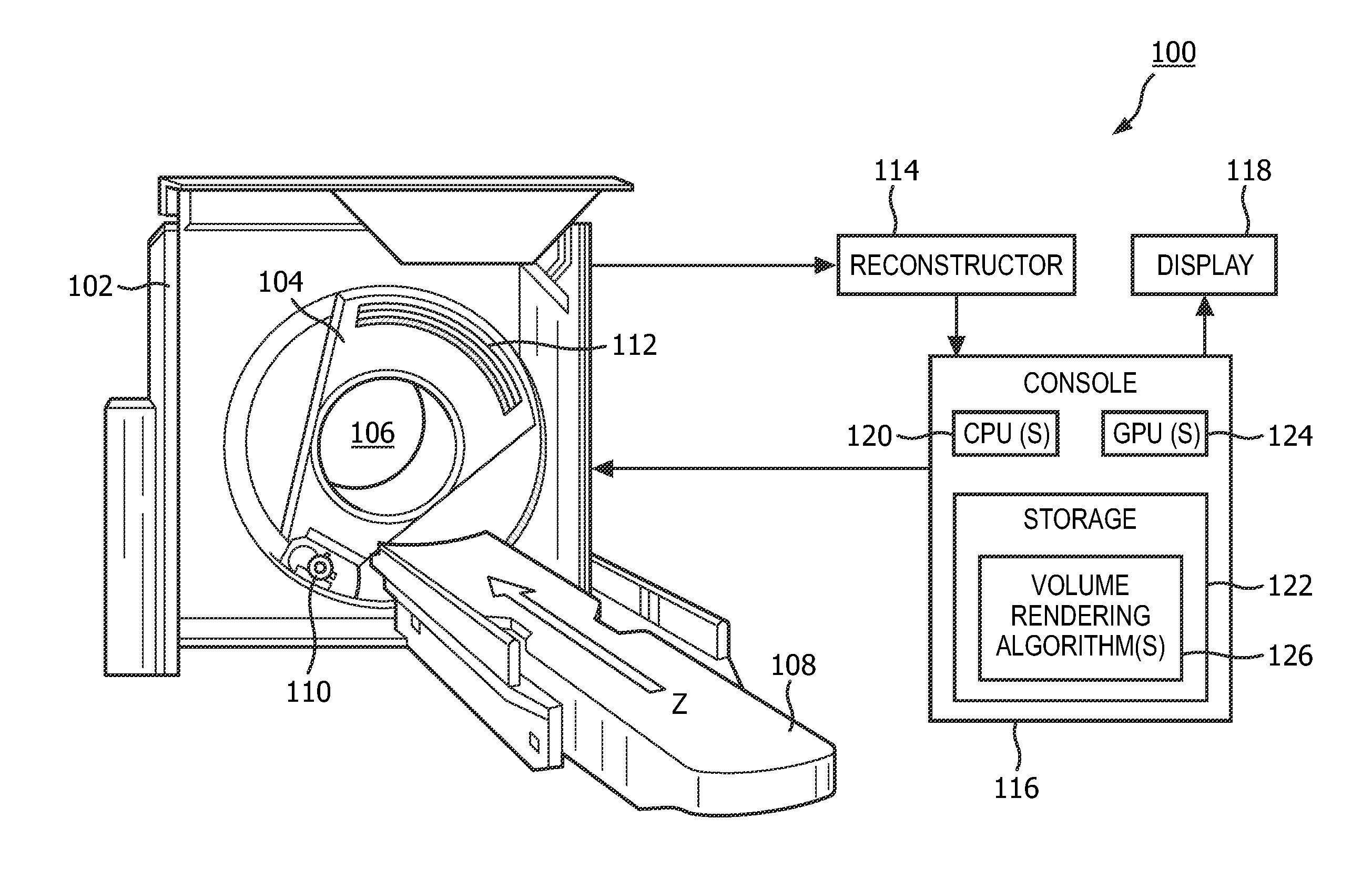
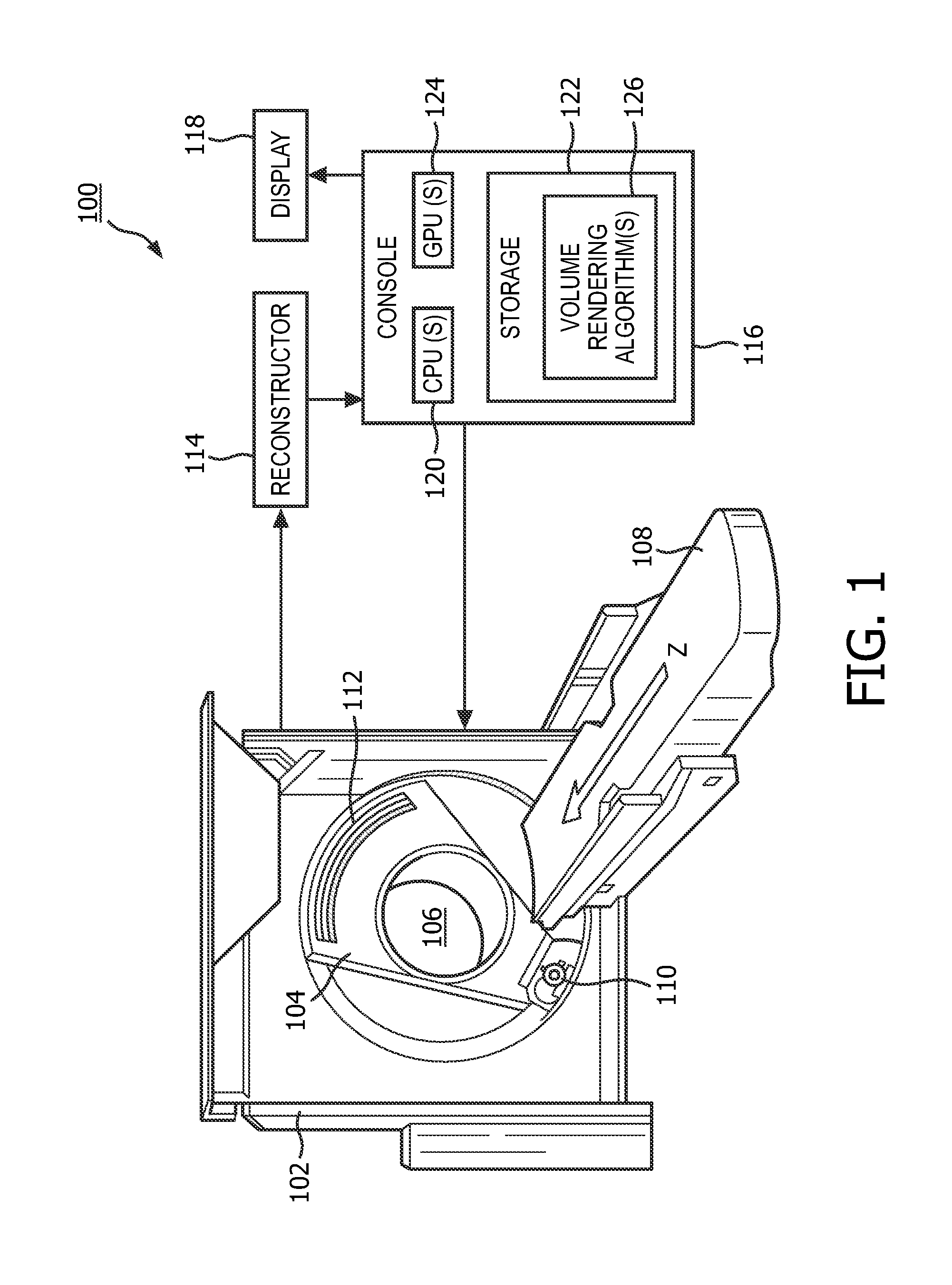
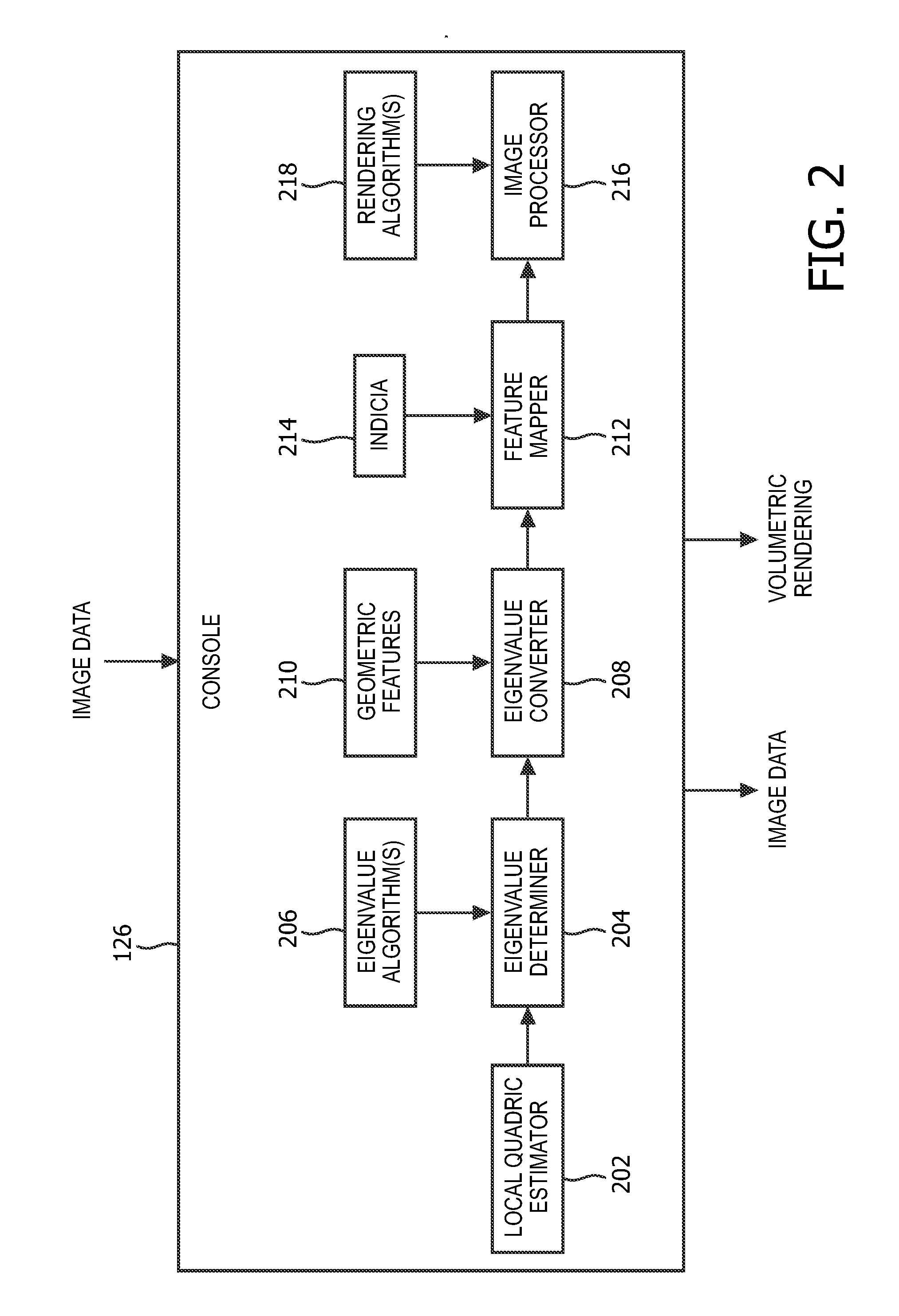
A method includes obtaining image data generated by an imaging system (100), generating data indicative of a degree to which each of a plurality of voxels of the image data corresponds to one or more predetermined geometrical features, wherein each geometrical feature is assigned a different color, generating a signal indicative of a single color value for each of the plurality of voxels based on the degree and the colors, generating a volumetric rending of the image data based on the signal, generating a link between voxels of the volumetric rendering and voxels of the image data, and visually presenting the image data and the volumetric rendering concurrently. The geometrical features represent local shape features which are determined by ray casting with the rays being used for the computation of a quadric represented by a matrix and with the eigenvalues of said matrix determine the degree to which voxels correspond to some local geometric shape features (i.e. blobness, tubularness).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Automatic coronary isolation using a n-MIP ray casting technique
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
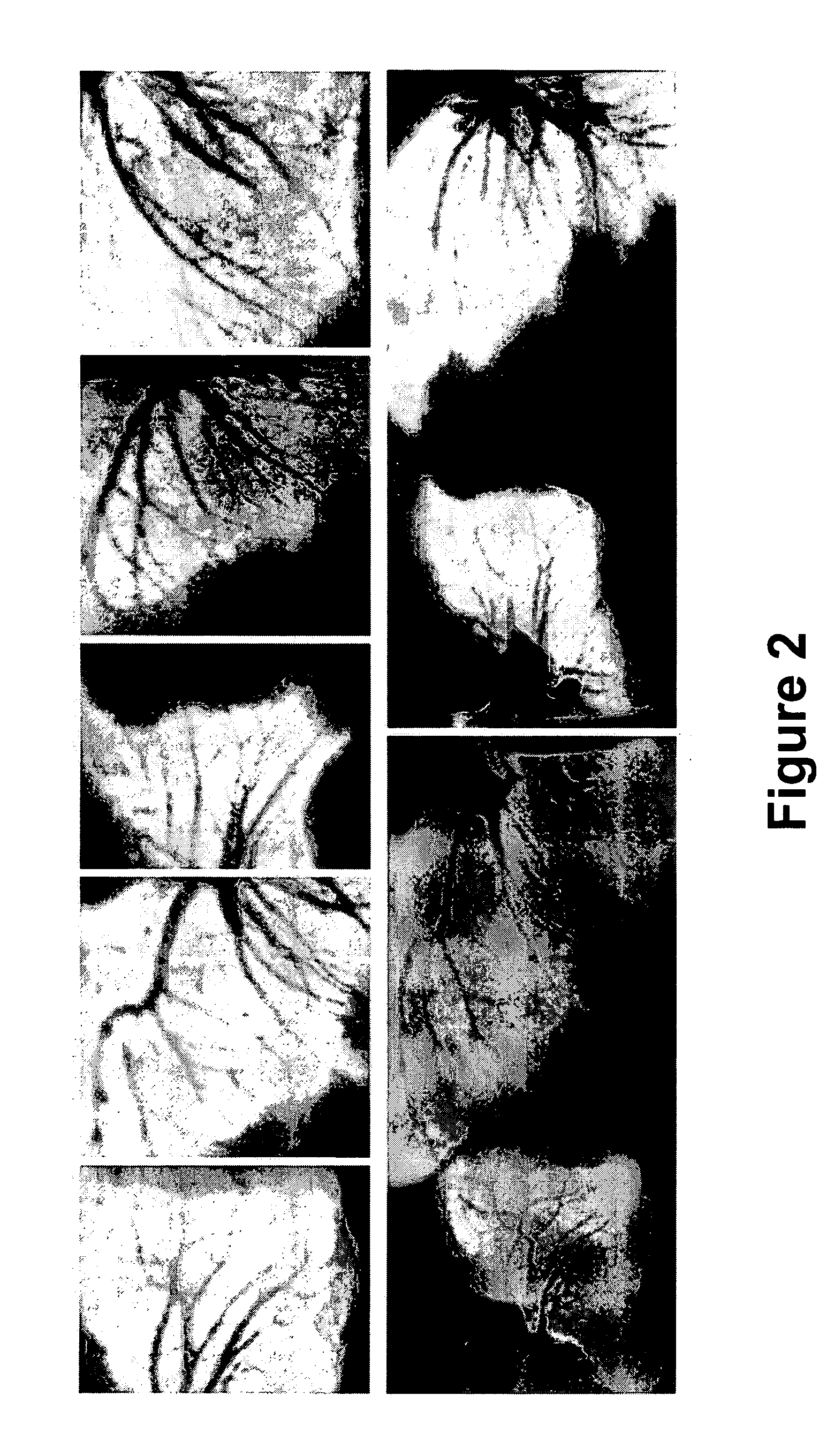
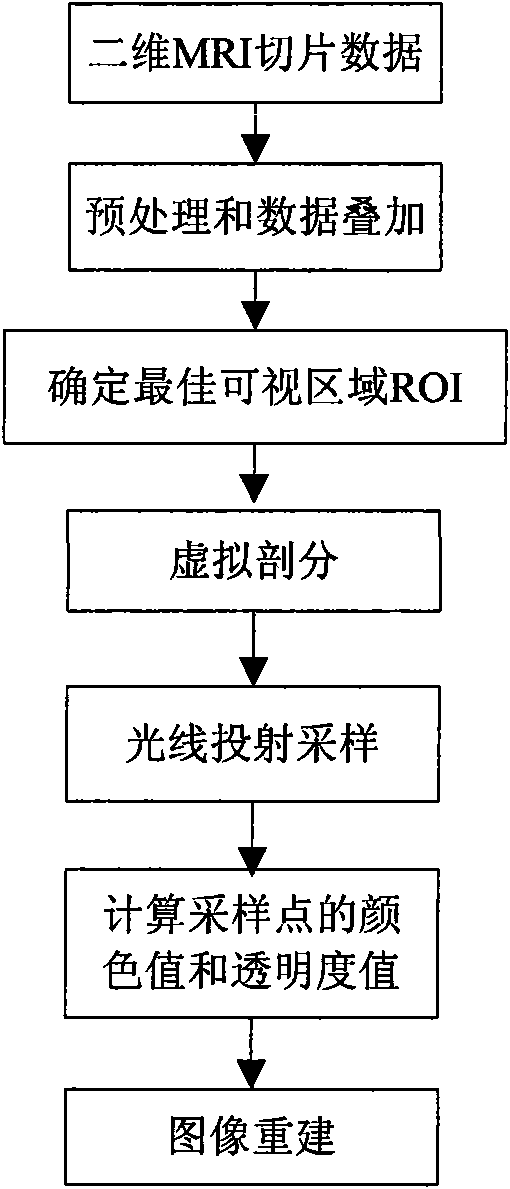
Partition method of three dimensional medical images based on ray casting volume rendering algorithm
InactiveCN101577001AEasy to observe in real timeWith human-computer interaction functionImage analysis3D-image renderingImaging processingRay casting
A partition method of three dimensional medical images based on ray casting volume rendering algorithm belongs to the technical field of image processing and relates to the physical partition method of three dimensional medical images. The method includes the following steps of: first converting a two dimensional MRI slice image sequence into three dimensional cuboid data Volume1, revolving the three dimensional cuboid data Volume1 to obtain an optimal visible area ROI; then adopting a regular geometry Volume2 with space size less than that of Volume1 to conduct virtual partition on the Volume1 and to obtain a space geometry Volume3 after the Volume1 is partitioned from the Volume2; subsequently conducting ray casting sampling on the space geometry Volume3; and finally conducting image reconstruction on the space geometry Volume3. Different from a common partition method which first partitions the three dimensional medical images and then reconstructs images, the partition method conducts the partition and three dimensional reconstruction simultaneously, thus increasing arithmetic speed greatly, having high real-time and being capable of observing the required regions at real time through methods of rotation, light illumination and the like so as to find out the association among tissues and facilitate accurate medical analysis and judgment.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
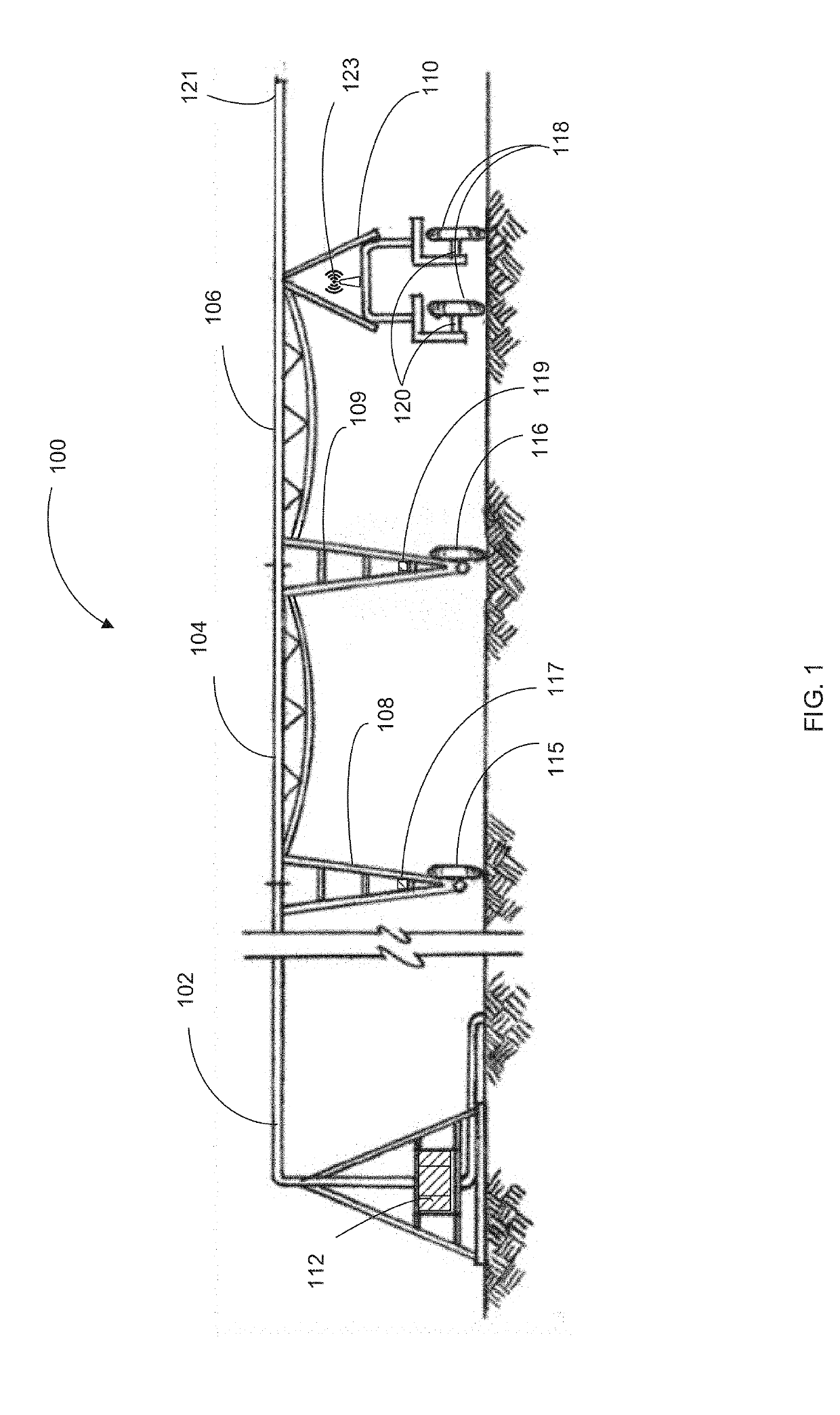
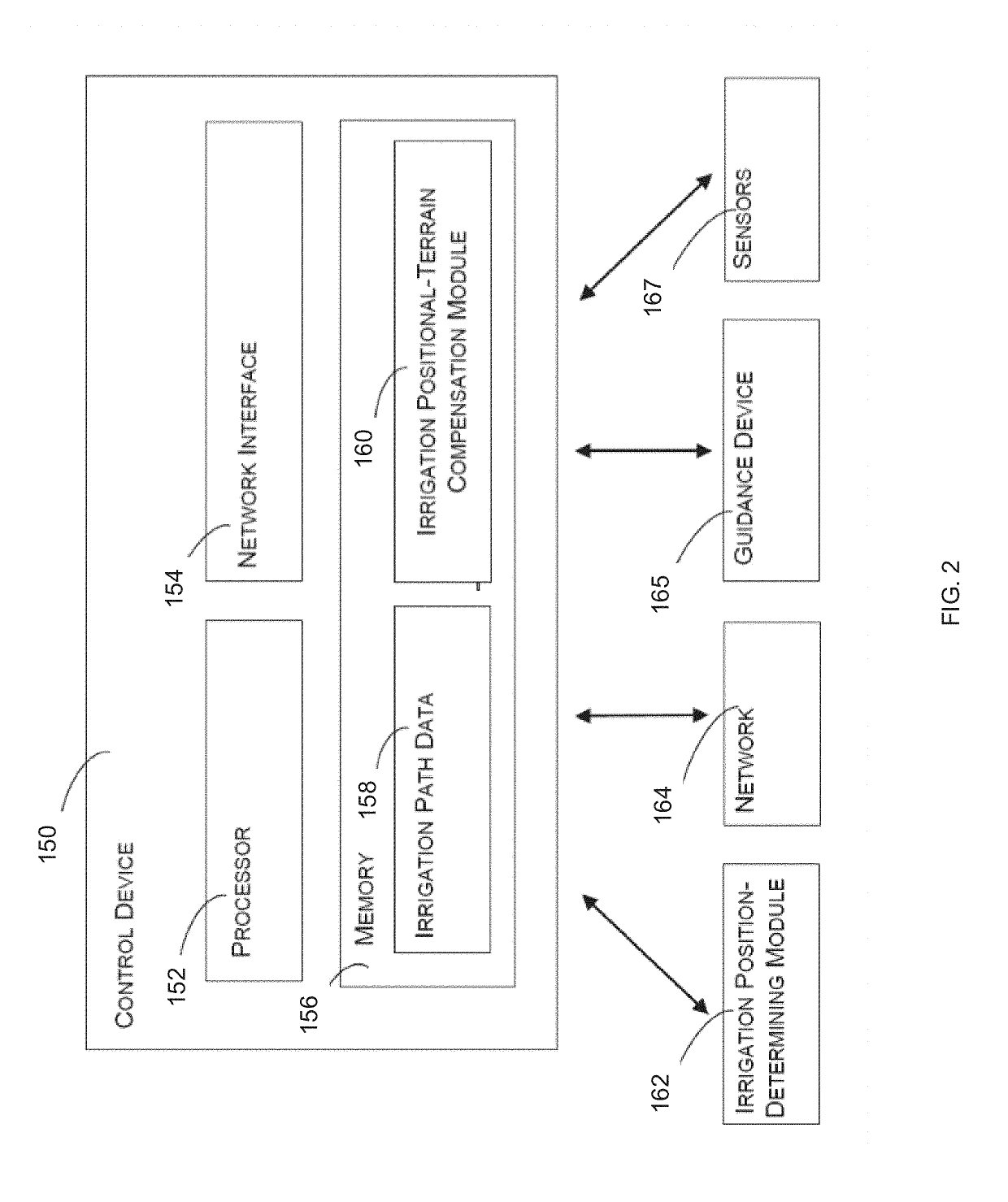
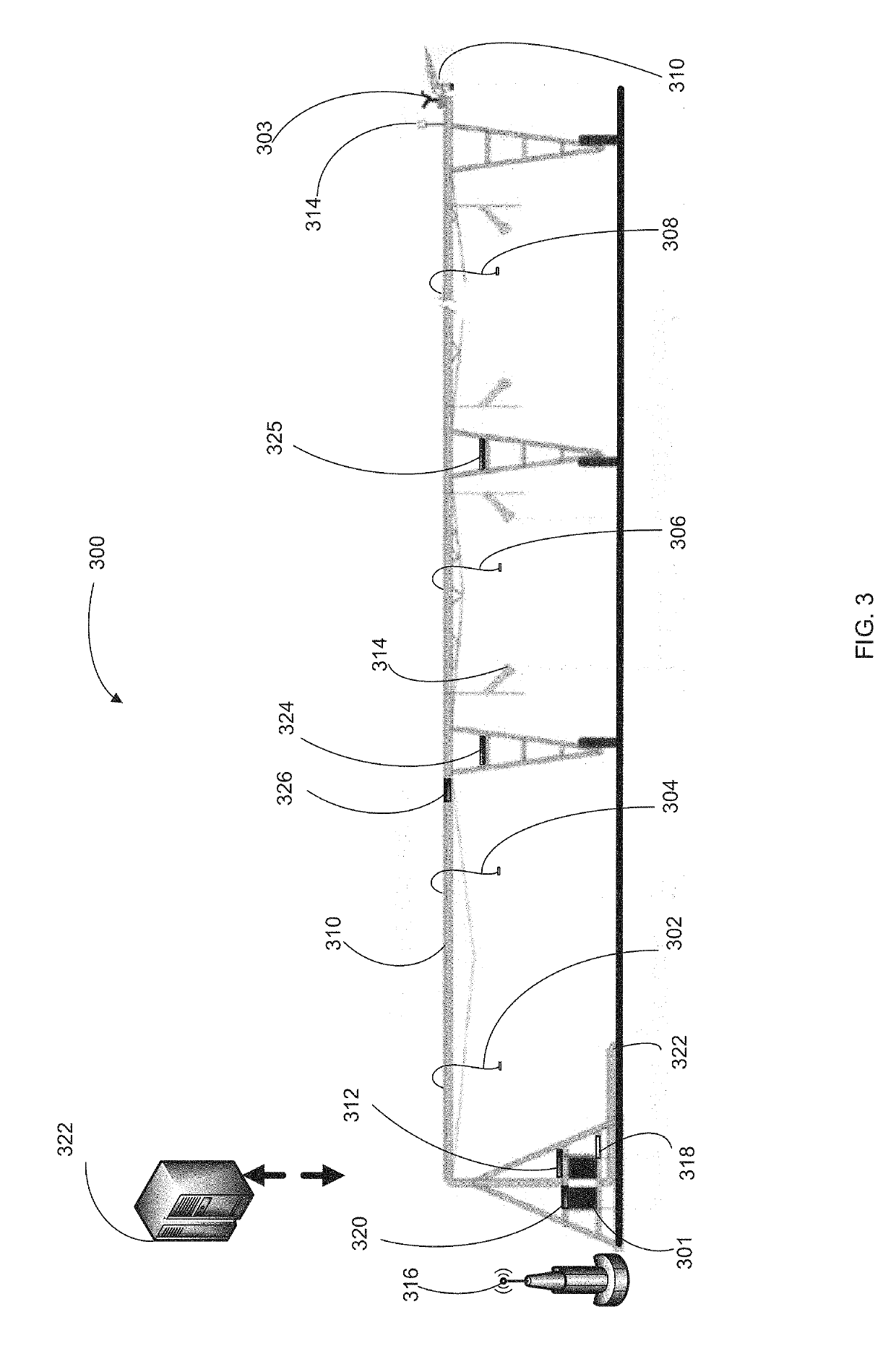
System and method for irrigation management using vri ray casting algorithms within irrigation machine workflows
The present invention discloses a system and method for irrigation management using VRI ray casting algorithms within irrigation machine workflows. According to an exemplary preferred embodiment, the present invention may preferably include: a position sensor which determines a position of the irrigation system; a memory system storing a prescribed watering plan for a field; and a variable rate mapping program using VRI ray casting algorithms.
Owner:VALMONT INDUSTIES INC
Variable resolution virtual reality display system
ActiveUS20170200304A1Enhance the virtual reality experienceEfficient and rapid rerendering reduces latencyGeometric image transformationImage renderingImage resolutionLevel of detail
A virtual reality display system that renders images at different resolutions in different parts of a display. Reduces rendering latency by rendering at a lower resolution in selected regions, for example on the sides of a display where human vision has lower resolution than in the center. Pixels in low resolution regions are combined into grid elements, and rendering may generate grid element values rather than individual pixel values. Rendering may use ray casting, rasterization, or both. Variable resolution rendering may be combined with variable level of detail geometry models to further reduce rendering time. Selected objects may be designed as high resolution objects that are rendered at a high resolution even in low resolution display regions.
Owner:LI ADAM
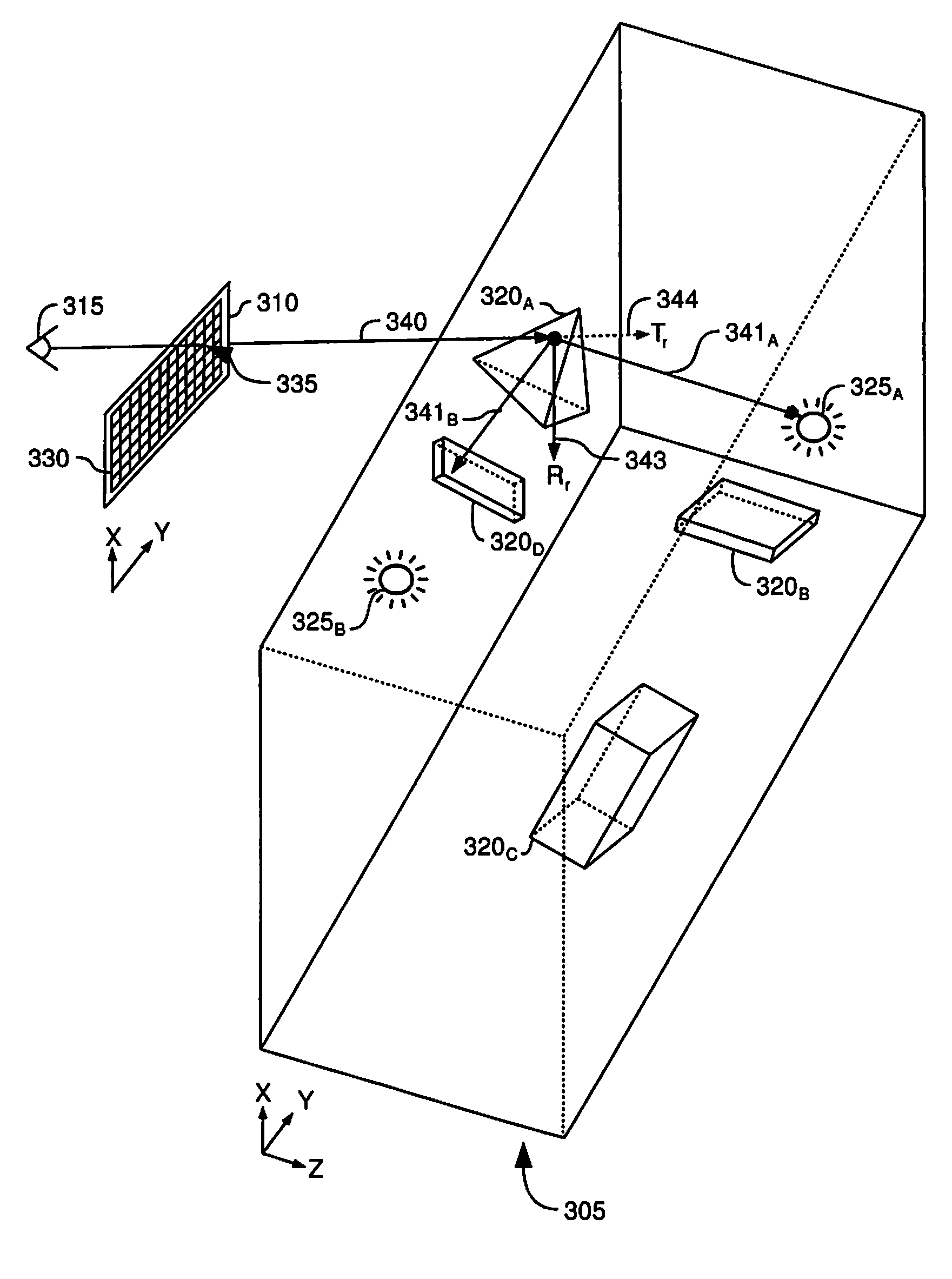
Point of view selection in virtual 3D environment
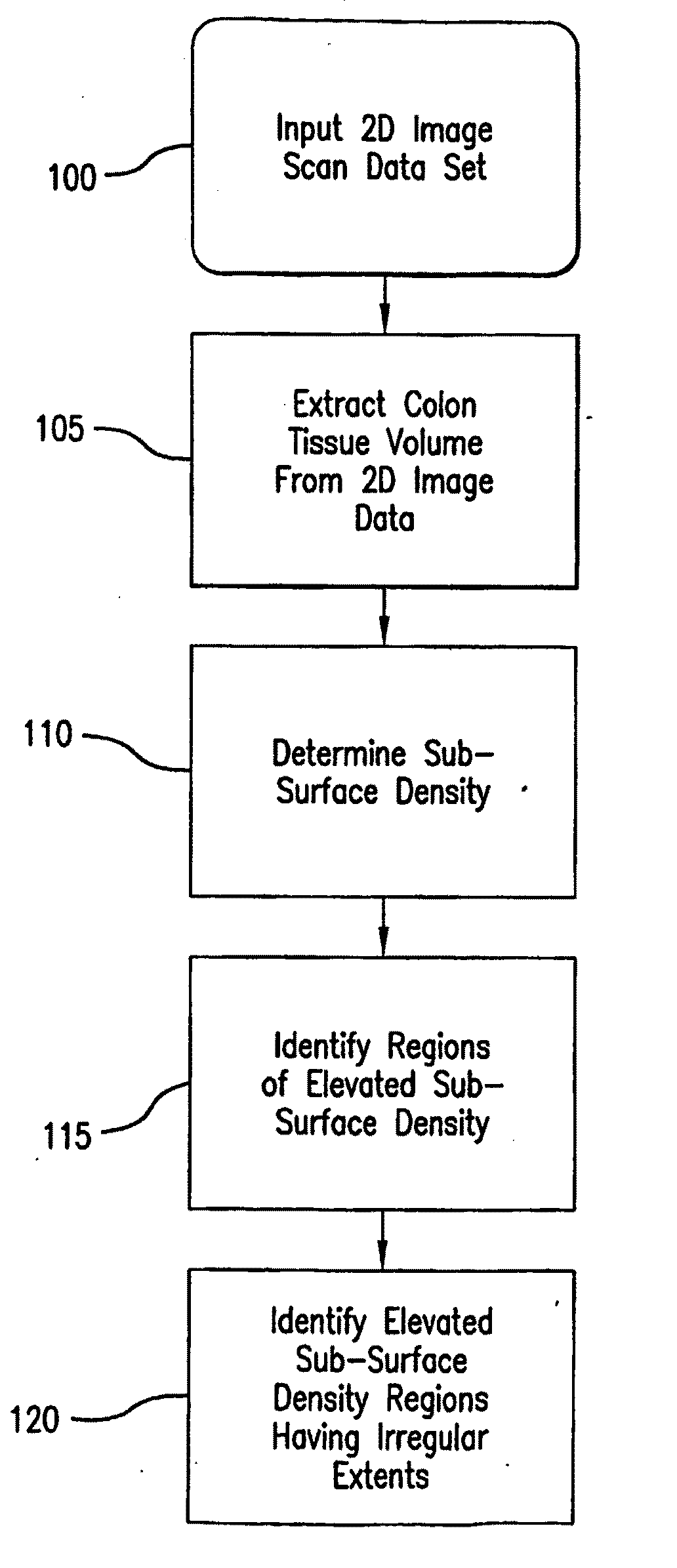
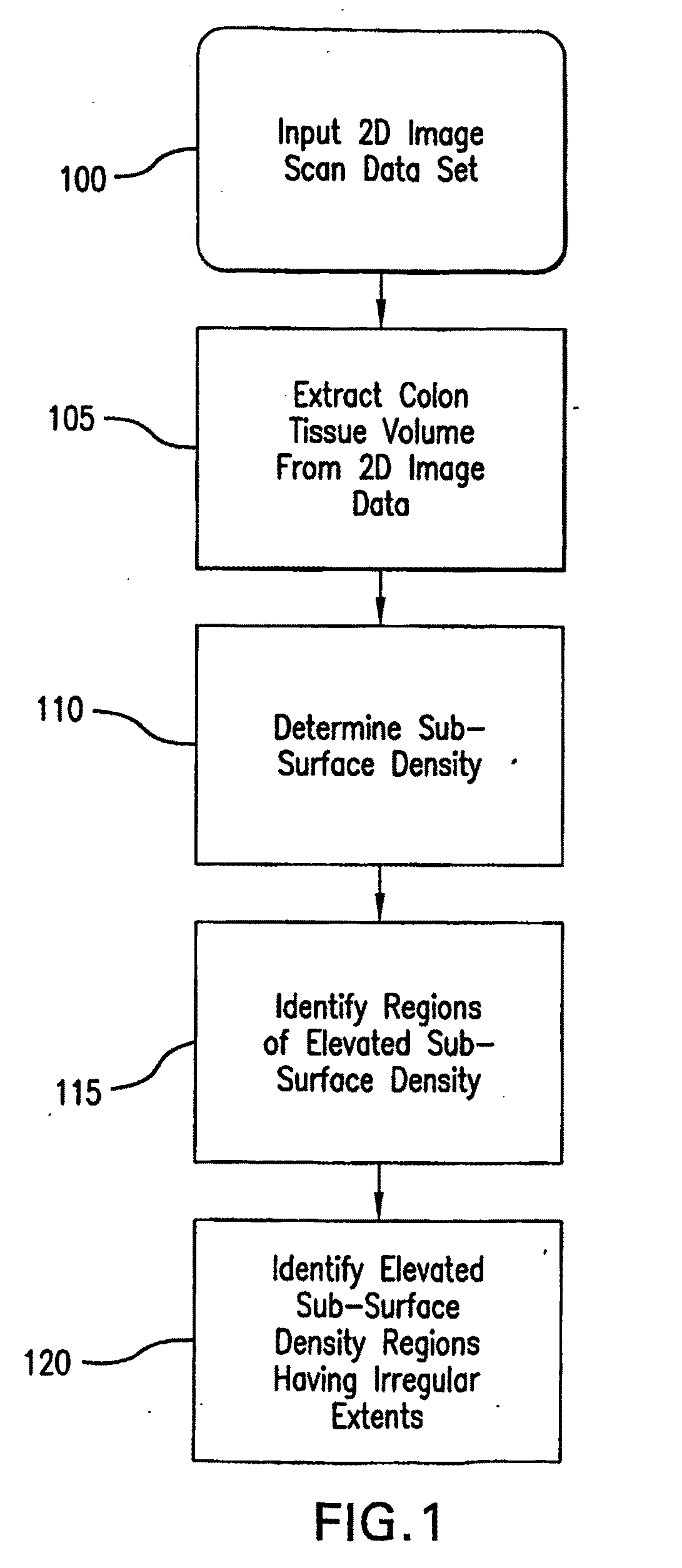
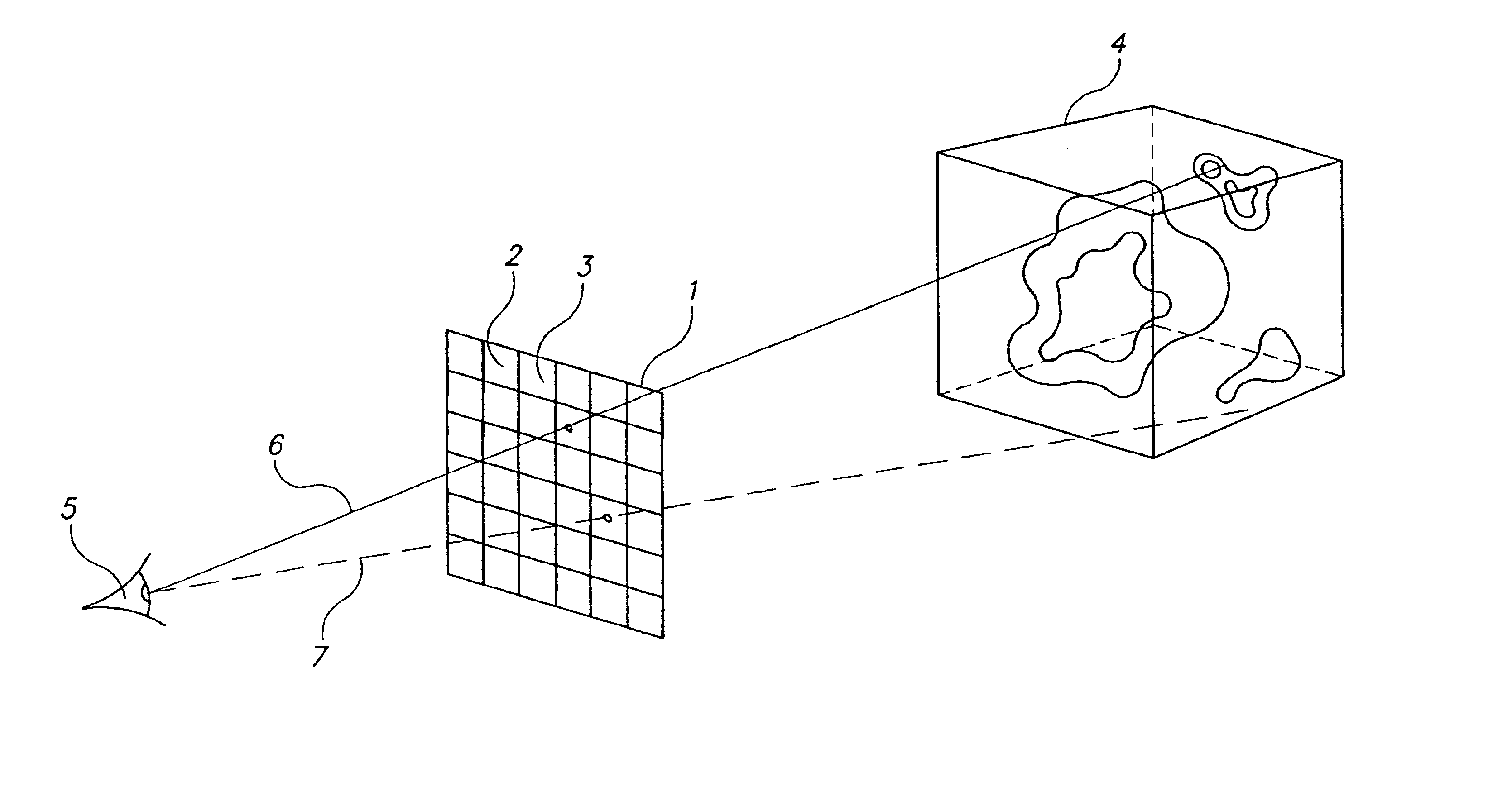
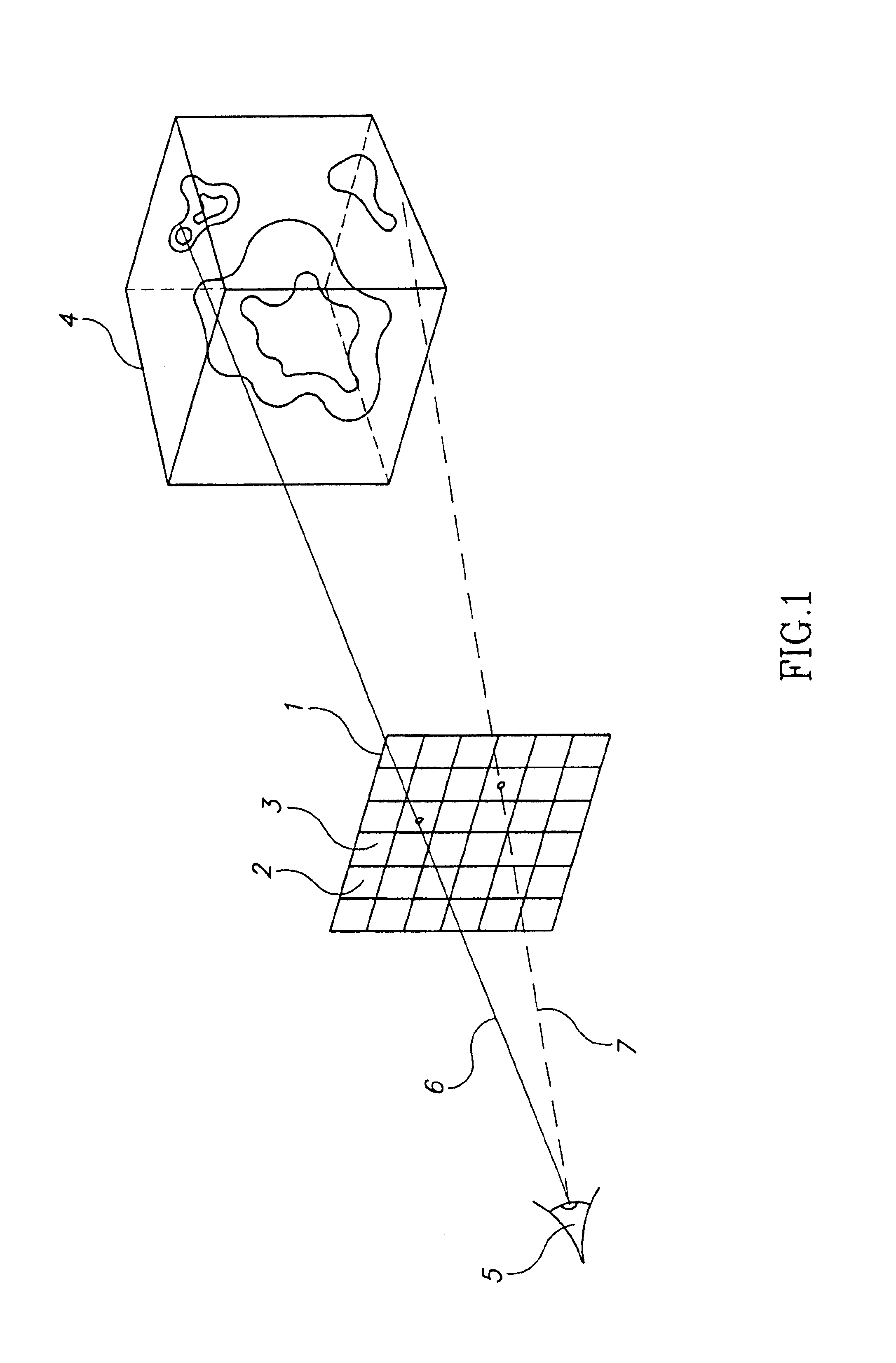
ActiveUS20170278300A1Drain can be reducedReduce demand3D-image renderingMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionVoxelThree-dimensional space
In a crowded representation of a virtual three dimensional space defined in terms of voxels, an object of interest will often be occluded by one or more objects of varying densities between the virtual camera defining the user's point of view, and the object of interest. To automatically identify an optimal camera position, an number of candidate positions are considered, for example situated at the vertices of a regular polyhedron centred on the object of interest. For each of these candidate positions, a ray is cast towards the object of interest, and the occlusion for each intervening voxel is determined as the product of that voxel's density, and a density transfer function. The virtual camera position corresponding to the least occluded path is then selected as the new point of view.
Owner:FRENCH CIVIL AVIATION UNIVERSITY
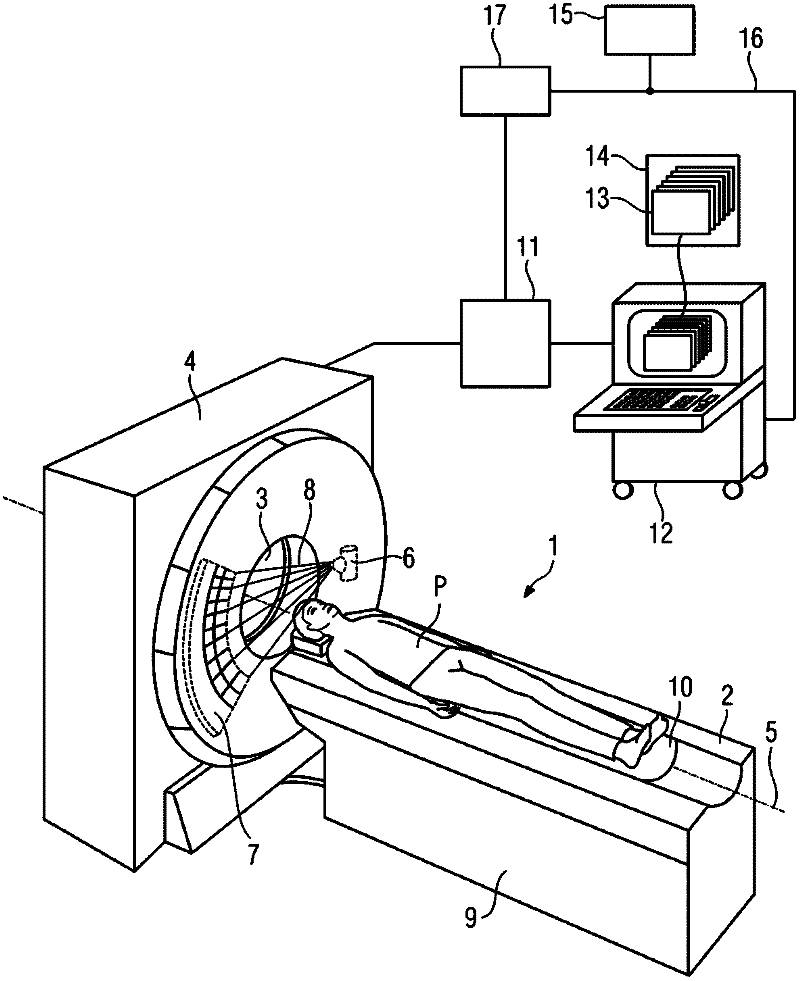
Medical image generating apparatus and method, and program
ActiveUS20050065425A1Character and pattern recognitionComputerised tomographsImaging processingVoxel
An image processing apparatus acquires voxel data obtained by imaging an interior of a living body by a modality and generates a three-dimensional medical image by volume rendering using a ray casting method. The image processing apparatus generates the three-dimensional medical image wherein shade of a surface of an inner wall of an intestinal tract is clearly displayed and an abnormal region invasively developed in the interior of the inner wall is distinguishably displayed based on color information corresponding to voxel data placed at a position shifted from the surface by a predetermined distance.
Owner:ZIOSOFT
Apparatus and method for rendering volume data
ActiveUS20060250395A1Increase speedUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCharacter and pattern recognitionVoxelSonification
The present invention relates to an apparatus and a method for rendering volume data in an ultrasound diagnostic system. A method for rendering volume data including an object space and an empty space acquired from ultrasound data, comprises the following steps: a) casting a virtual ray from at least one pixel comprising a viewing plane into the volume data; b) sampling voxels of the volume data along the virtual ray in a first sampling interval; c) checking whether a currently sampled voxel corresponds to the object space or the empty space by using opacity based on a voxel value of a sampled voxel; d) at step c), if it is determined that the currently sampled voxel corresponds to the object space, then returning to the previously sampled voxel and sampling voxels in a second sampling interval shorter than the first sampling interval; e) checking whether accumulated opacity calculated based on the sampled voxels along the virtual ray is greater than a critical value; f) at step e), if it is determined that the accumulated opacity is greater than the critical value, then completing the sampling process for the current virtual ray and calculating a rendering value by using the voxel values and the opacity of the sampled voxels; and g) repeating the steps a) to f) until the sampling process for the pixels comprising the viewing plane is completed.
Owner:MEDISON CO LTD
Three-Dimensional Data Extraction Using Ray Casting
InactiveUS20100168890A1Good precisionCorrection for variationAdditive manufacturing apparatusAdditive manufacturing with solidsImage resolutionFree form
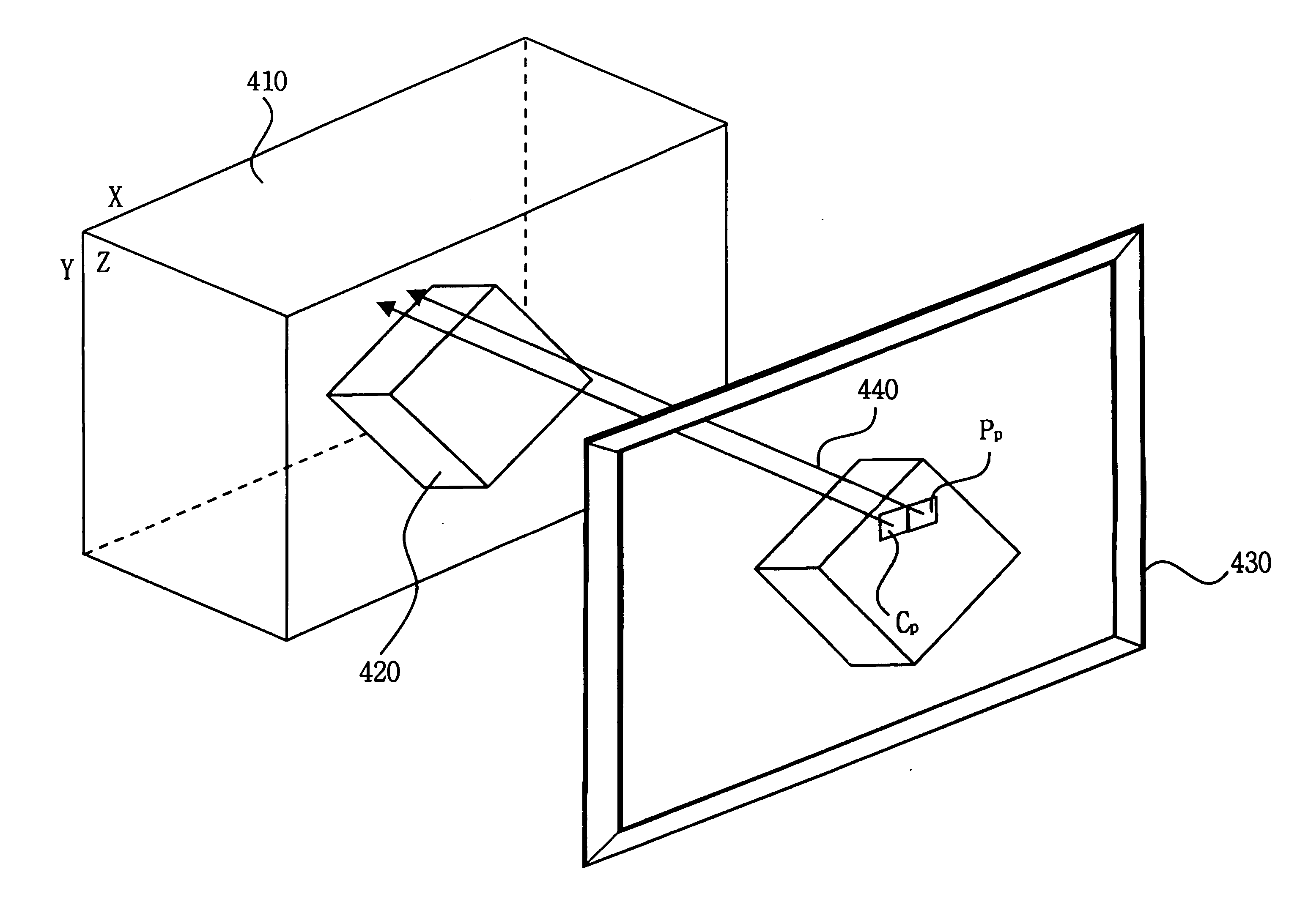
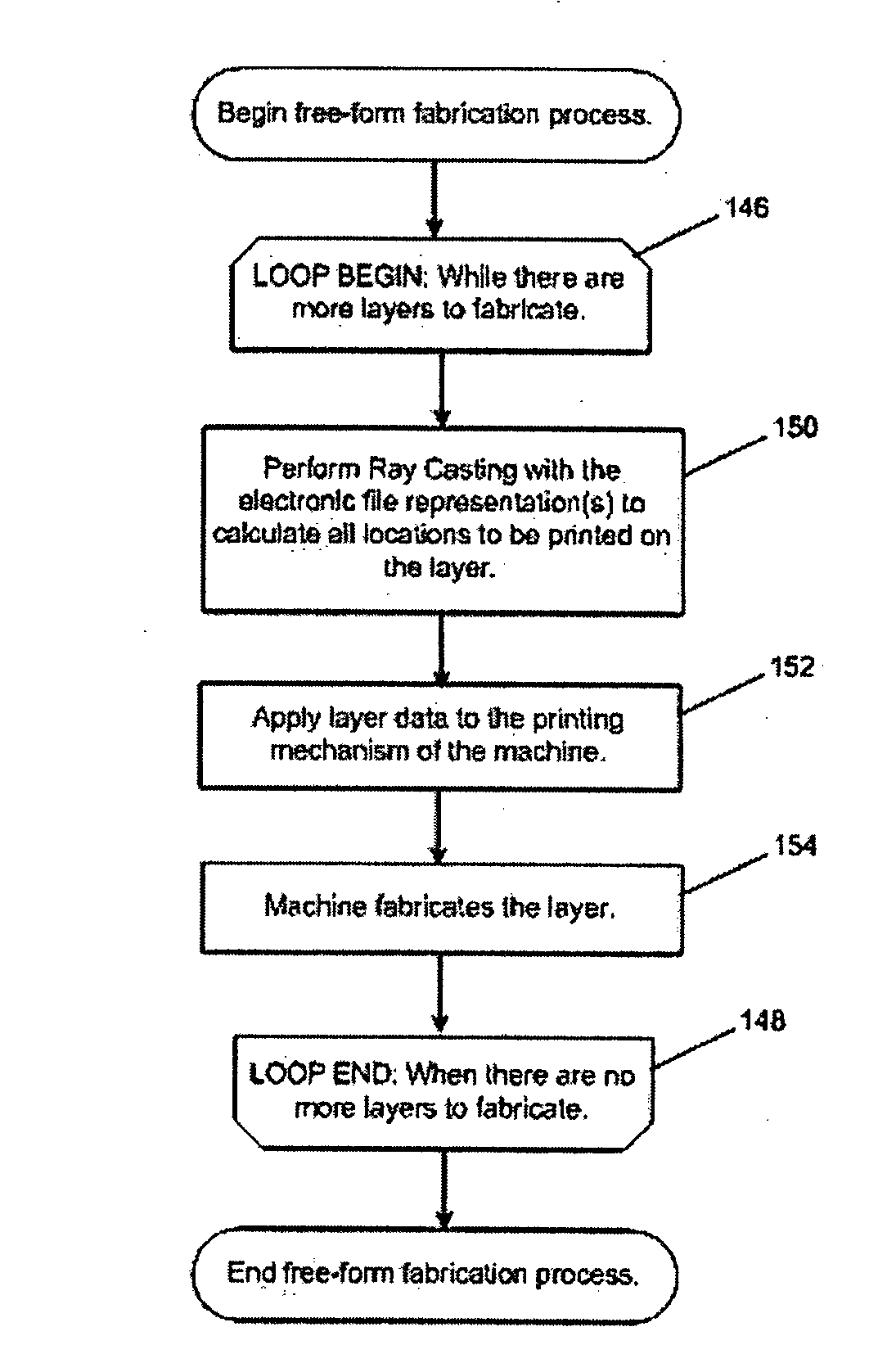
Methods are provided for solid free-form fabrication of an article without using a slice stack file. These apply ray casting a number of times to an electronic representation of the article to create data objects for use directly as printing instructions or which are convertible into printing instructions. The data objects may be utilized as they is generated or after they are created for a portion or all of the article. After utilization, the data objects may be discarded or stored for later use. Layer-specific layer thickness and other-direction resolution parameters may be input and utilized in selecting the number of rays to be cast, their origination points, and their directions, thus permitting controllable variation in detail precision in any direction. Error diffusion techniques may be used to improve fabricated part integrity. Improved intermachine portability is provided. Method, system, code, and media claims are included.
Owner:THE EX ONE
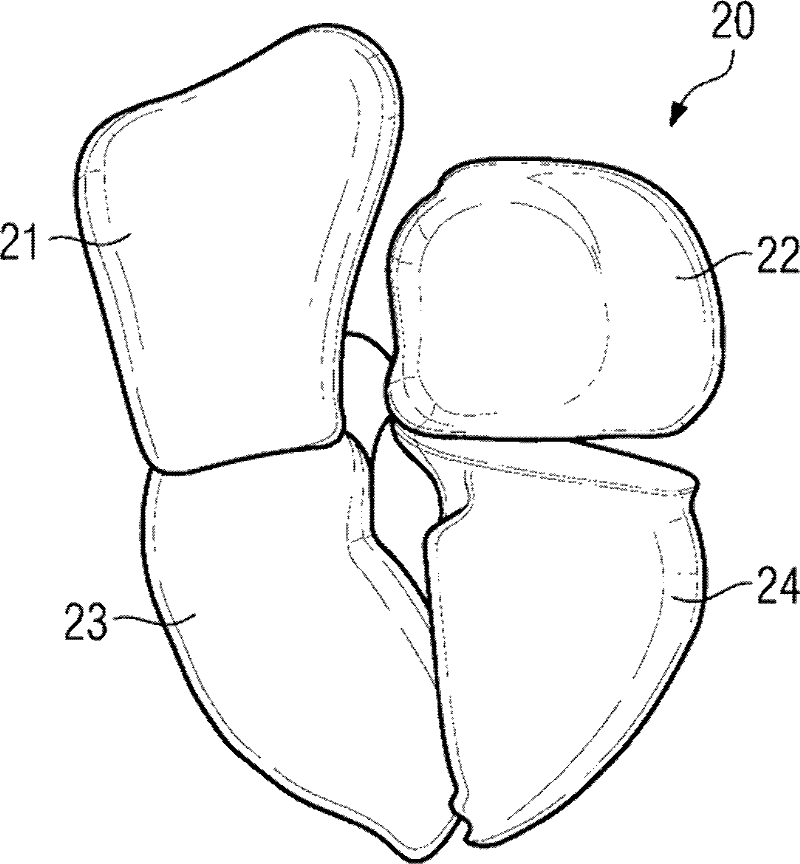
Method for visualizing an atrium of the heart in a patient
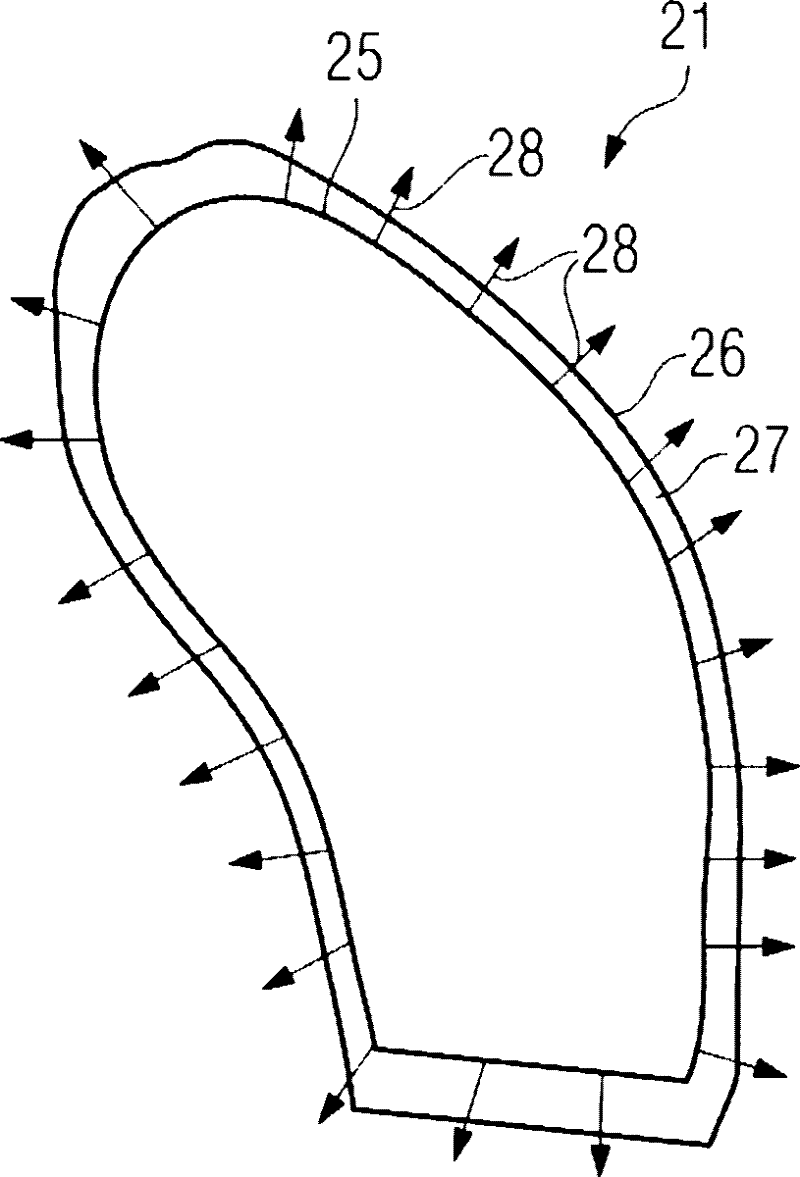
A method is disclosed for visualizing at least one section of the wall of an atrium (21) of the heart in a patient (P) after an ablation for treating atrial fibrillation, in which, based on a volume data record of the heart in the patient (P) obtained after the ablation, at least the treated atrium (21) of the heart in the patient (P) is segmented, wherein those voxels are established that can be considered part of the inner surface (25), the outer surface (26), and the volume (27) situated between the inner (25) and outer surfaces (26) of the wall of the treated atrium (21). Further, in at least one embodiment of the method, there is volume rendering or ray casting such that only the voxel values of those voxels that lie on the inner surface (25), in the volume (27), or on the outer surface (26) of the wall of the treated atrium (21) are used for visualizing at least the section of the wall of the treated atrium (21) of the heart. At least one embodiment of the invention moreover relates to a computational program (13) that executes the method, a computational unit (12) that carries out the computational program, and / or a data medium (14, 15) with the computational program.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Real-time medical ultrasonic three-dimensional imaging method
InactiveCN102254339ASolve the problem of intersecting positionsImproving the efficiency of parallelization implementationsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationRay casting
The invention provides a real-time medical ultrasonic three-dimensional imaging method, which is applicable to real-time acquisition of three-dimensional medical ultrasonic volume data which may be stored. Aiming at the characteristics of a current central processing unit (CPU) and the characteristics of a three-dimensional ultrasonic image, storage and access modes of three-dimensional data are optimized, and the conventional ray casting method is improved in combination with the knowledge of image morphology, so that the reconstruction and visualization of the three-dimensional data are quickly realized.
Owner:SHENZHEN LANDWIND IND
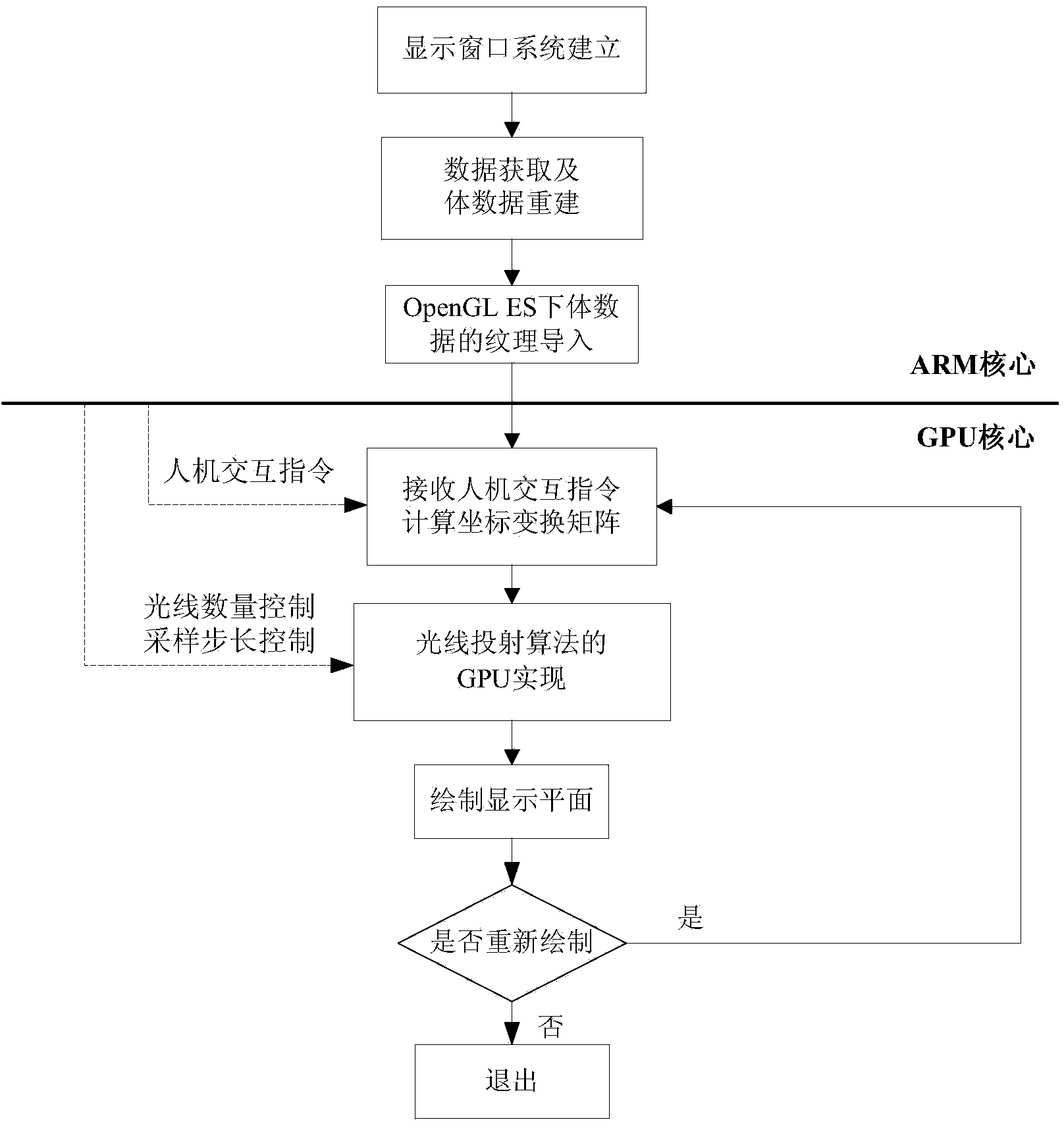
OpenGL ES (open graphics library for embedded system) implementation method for ray casting algorithm under ARM+GPU (advanced RISC machine+graphic processing unit) heterogeneous architecture
ActiveCN103971396AReduce development costsSolve limited problems3D-image renderingGraphic cardGraphics processing unit
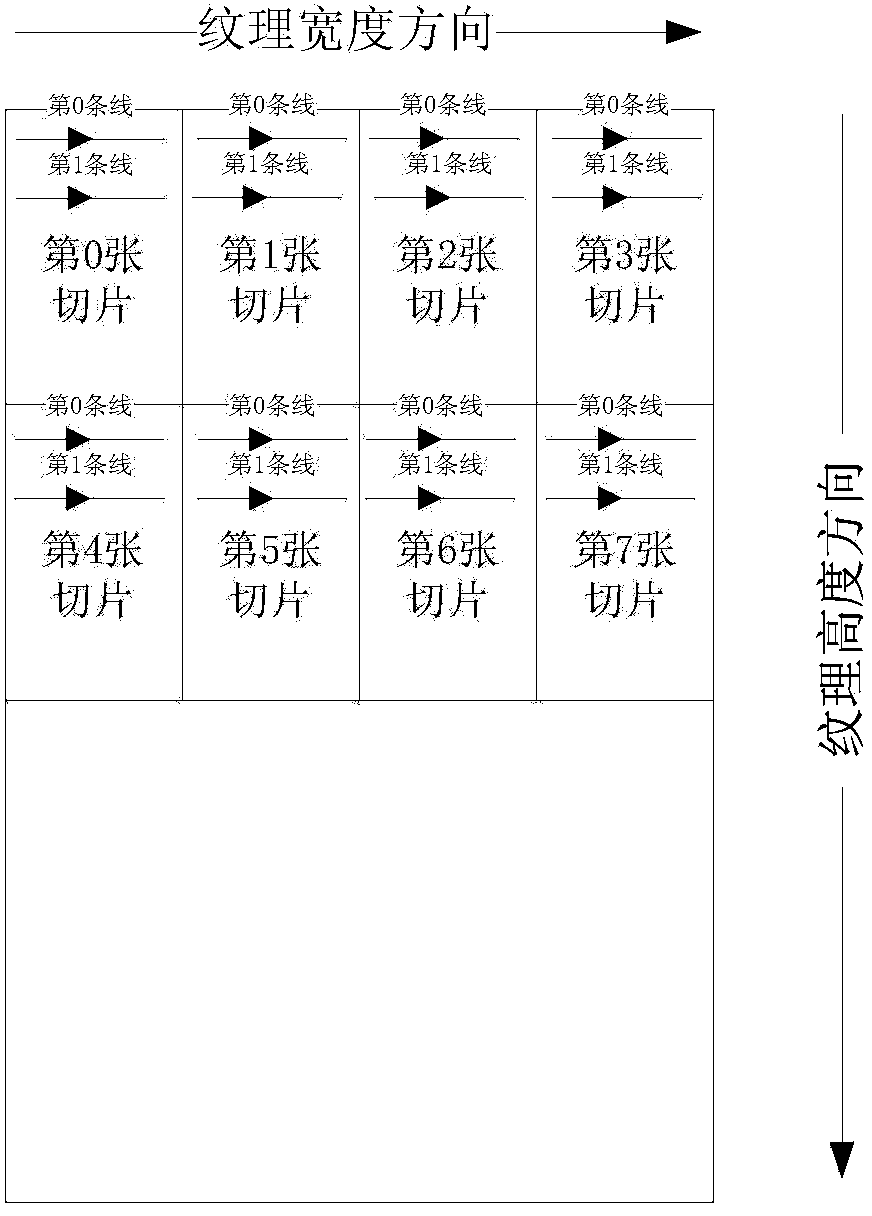
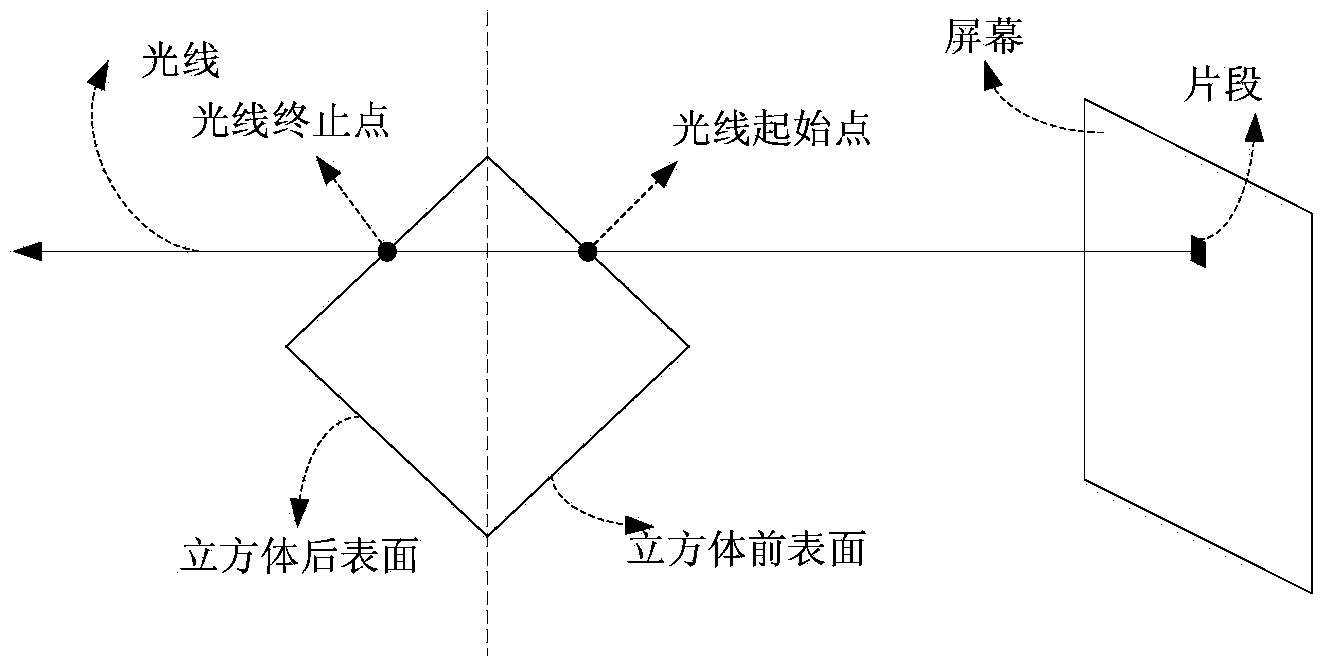
The invention discloses an OpenGL ES (open graphics library for embedded system) implementation method for a ray casting algorithm under an ARM+GPU (advanced RISC machine+graphic processing unit) heterogeneous architecture. The method comprises the following steps of 1, establishing a display window system in an ARM; 2, acquiring initial body data from the ARM, and recreating the initial body data to a three-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system; 3, arranging two-dimensional textures by using the ARM, and importing three-dimensional ultrasonic body data in a two-dimensional texture way by using an OpenGL ES interface; 4, receiving a human-computer interaction instruction by using a GPU, and calculating a coordinate transformation matrix to realize a human-computer interaction function in three-dimensional imaging; 5, performing OpenGL ES implementation on the ray casting algorithm by using the GPU, and controlling the calculated amount; and 6, drawing a display plane by using the GPU. According to the method, a conventional ray casting algorithm based on a graphics card and an Intel processor is implemented under an embedded platform, so that the system development cost is lowered.
Owner:哈尔滨工业大学人工智能研究院有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com