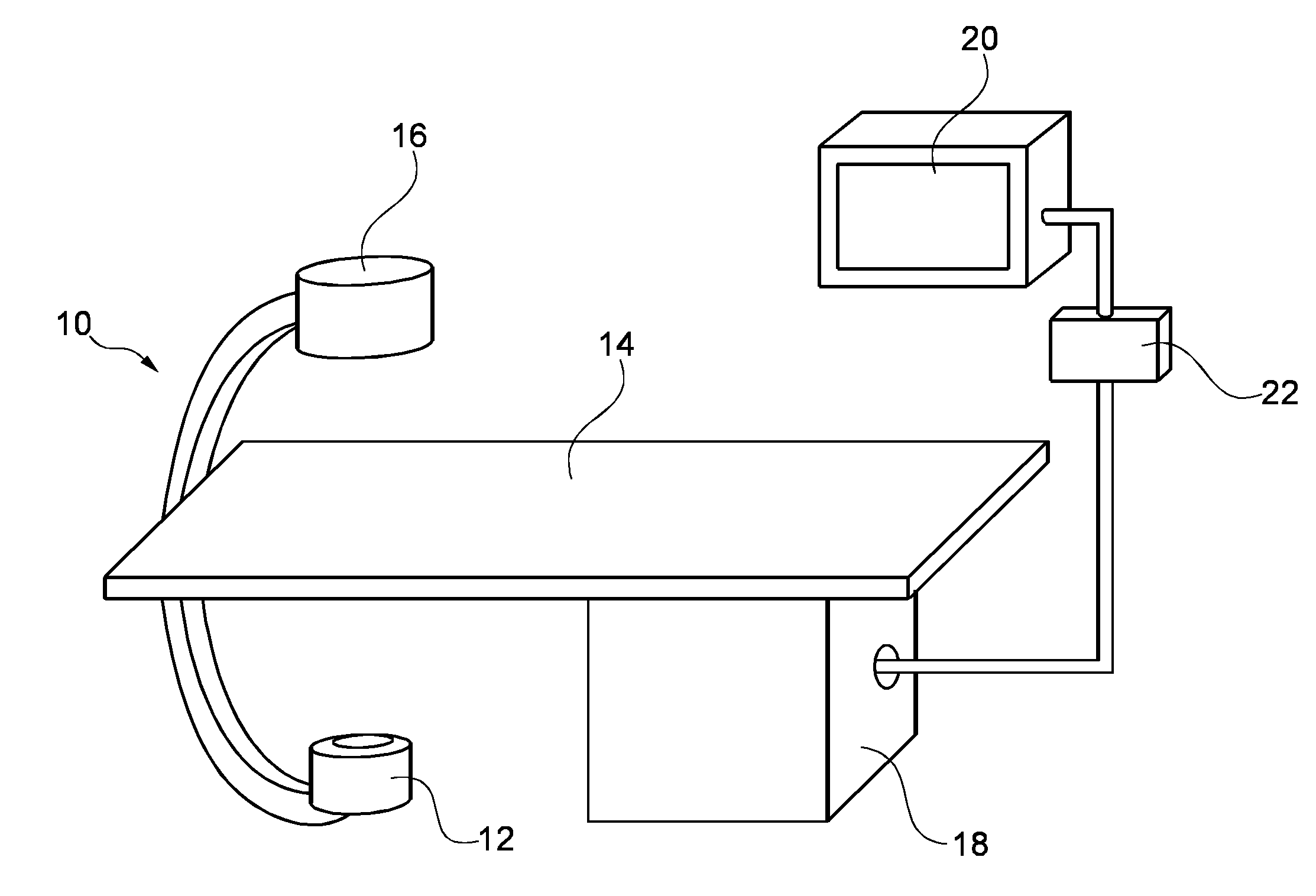
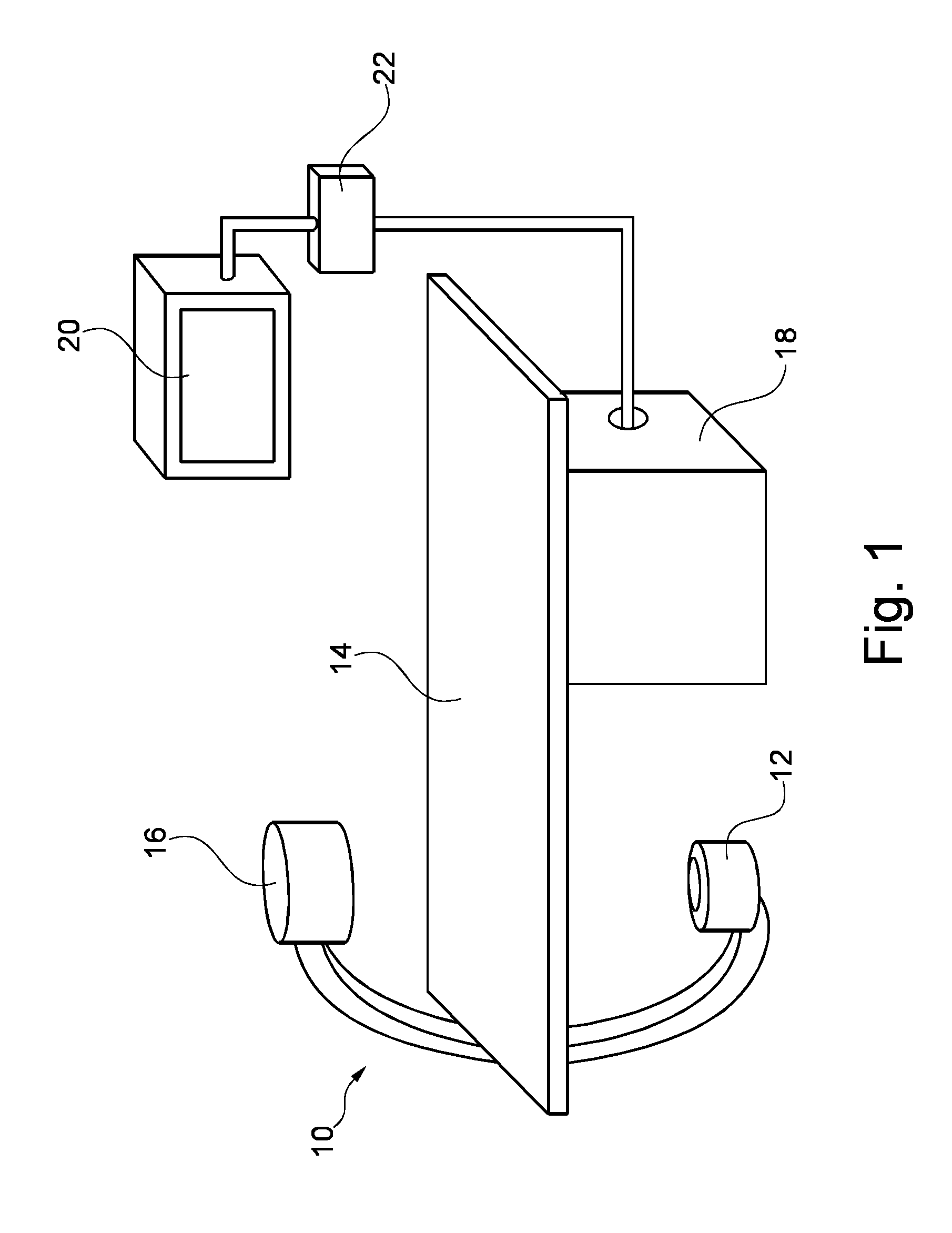
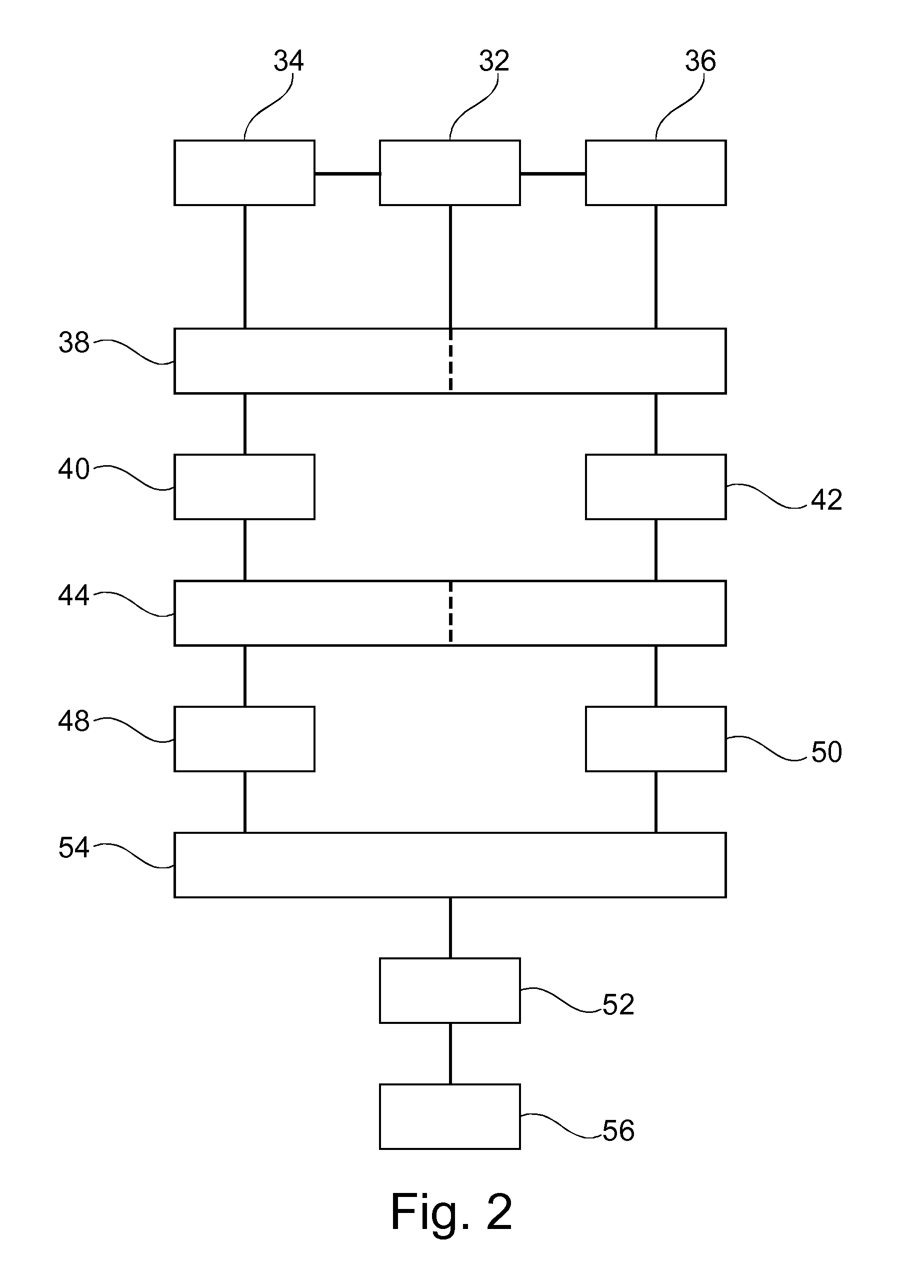
Patents
Literature
41 results about "Coronary arterial tree" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
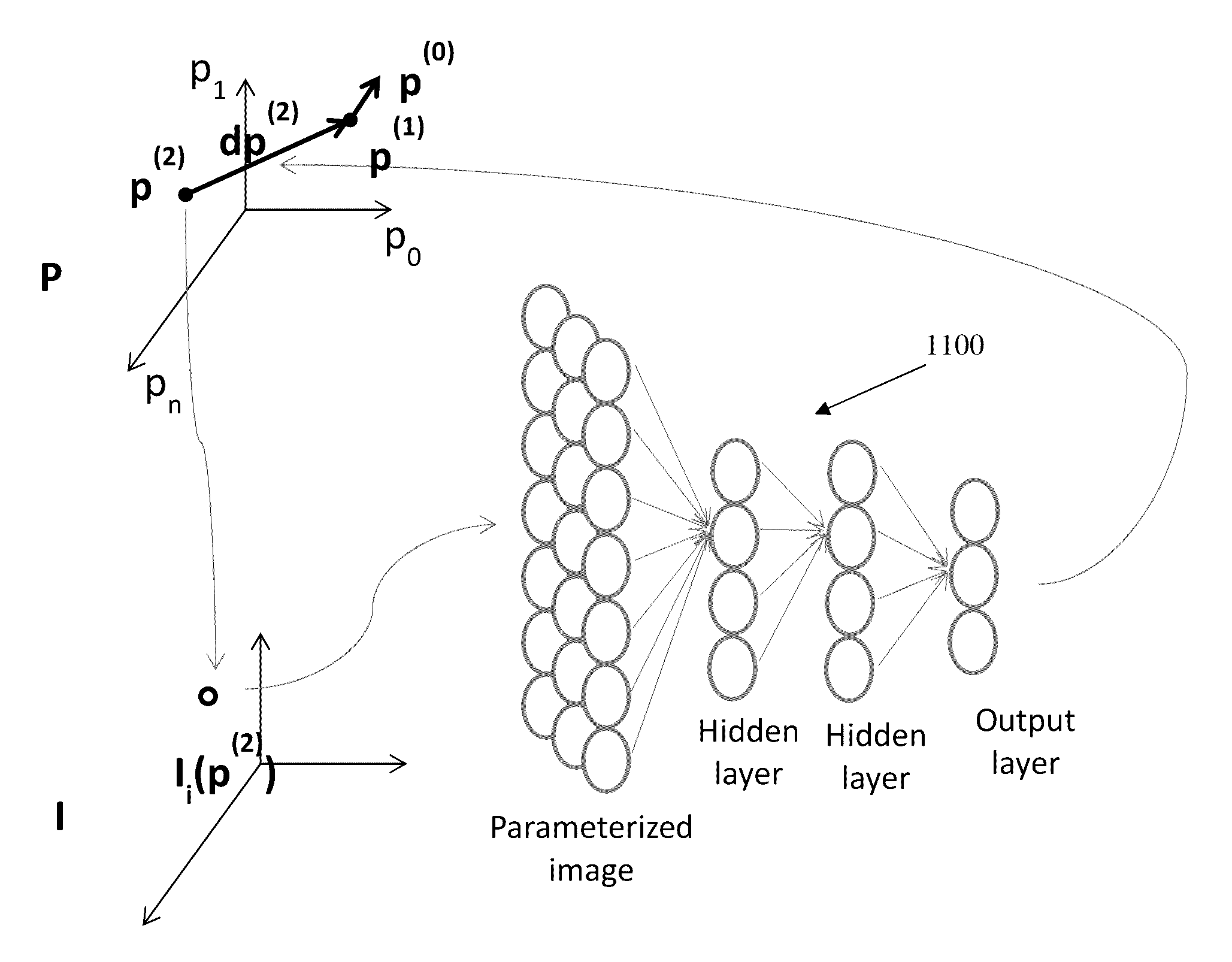
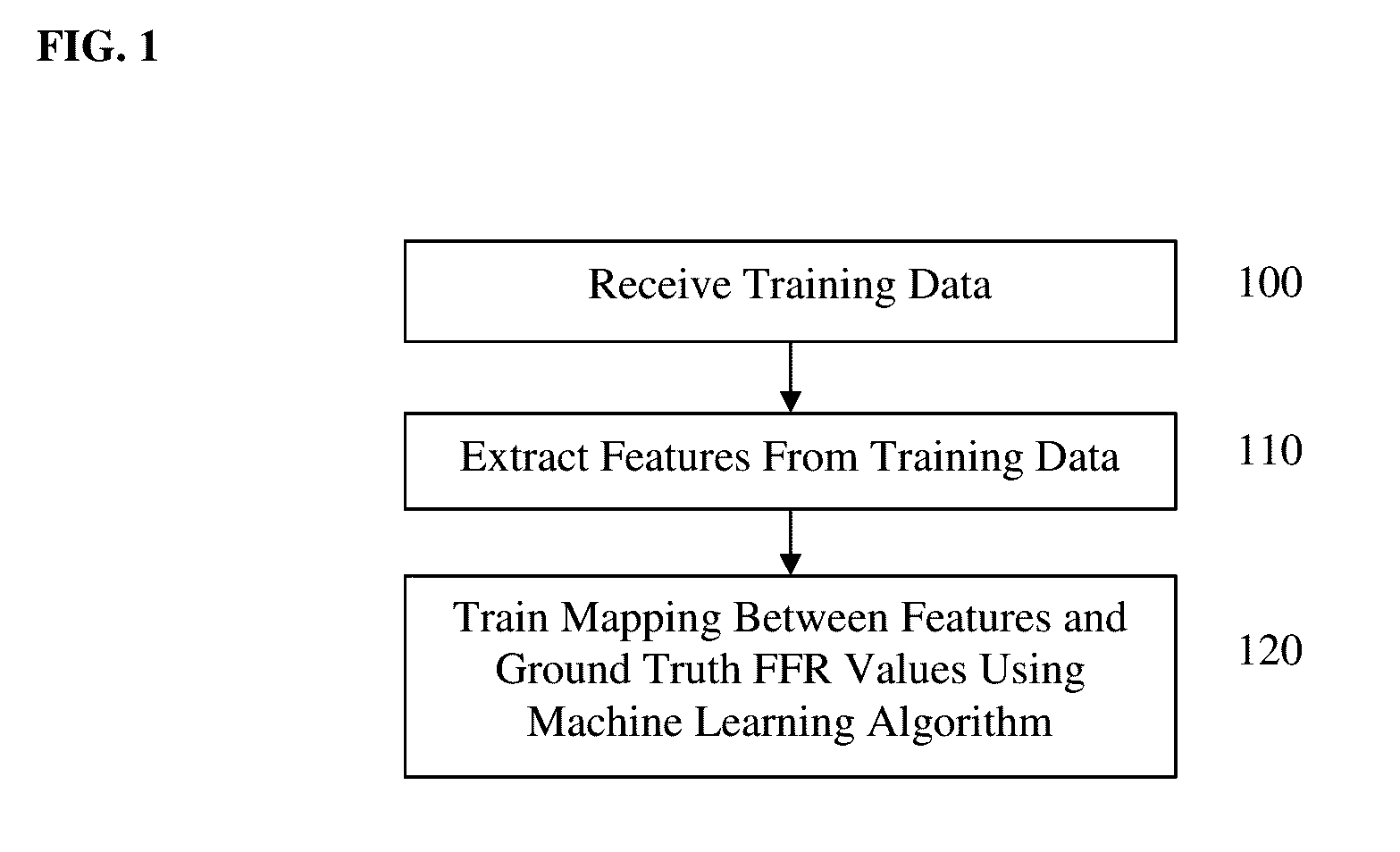
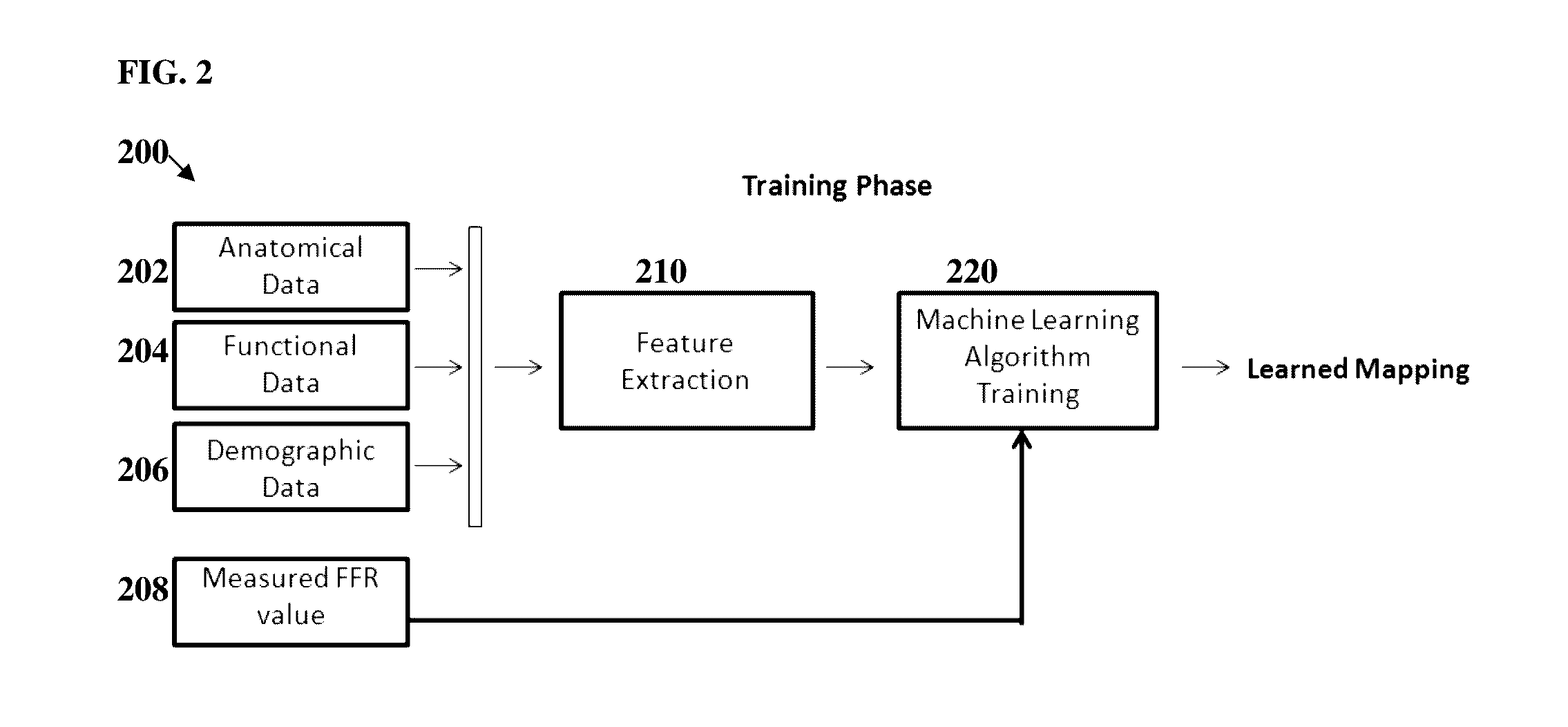
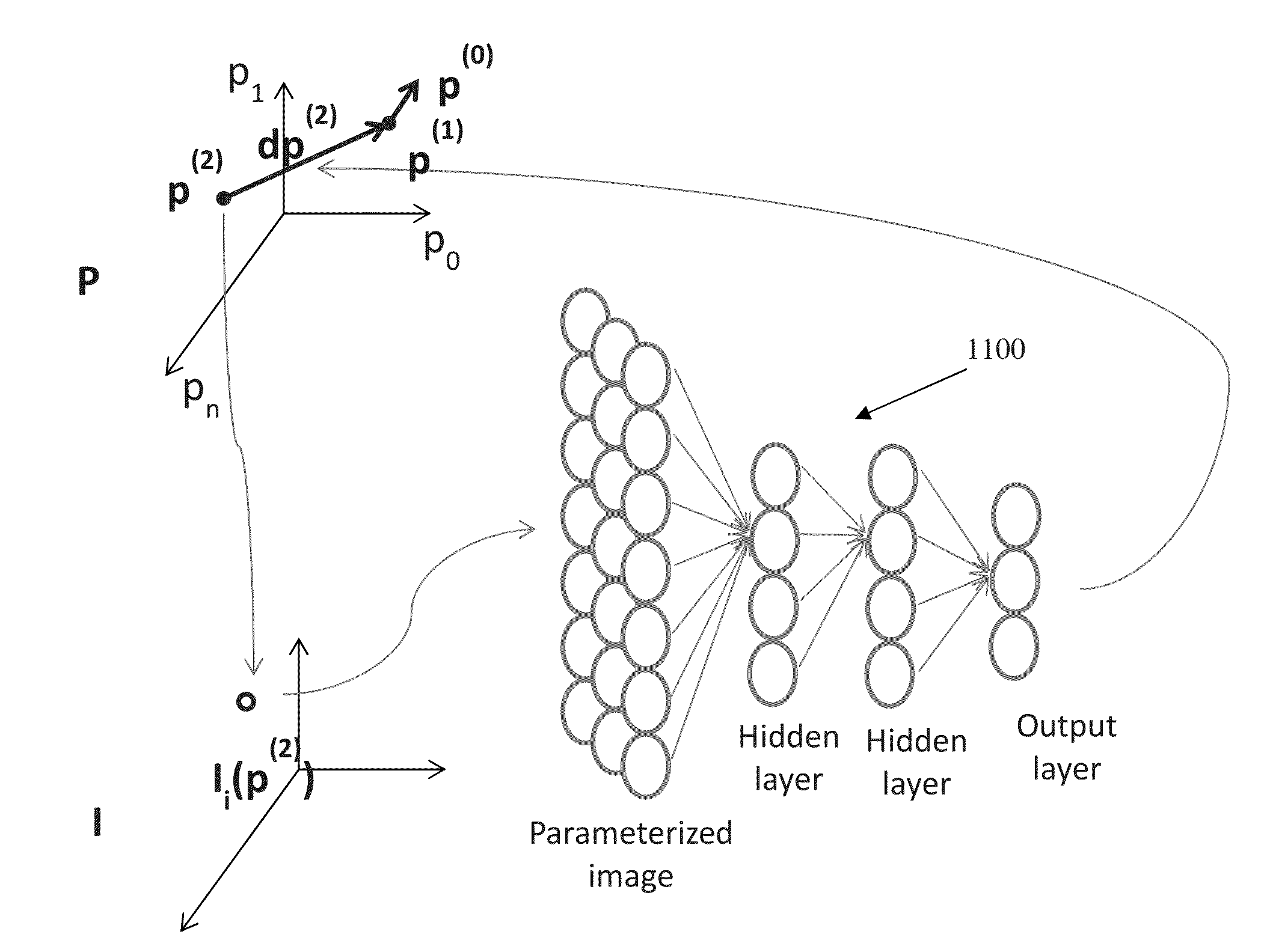
Method and System for Machine Learning Based Assessment of Fractional Flow Reserve
A method and system for determining fractional flow reserve (FFR) for a coronary artery stenosis of a patient is disclosed. In one embodiment, medical image data of the patient including the stenosis is received, a set of features for the stenosis is extracted from the medical image data of the patient, and an FFR value for the stenosis is determined based on the extracted set of features using a trained machine-learning based mapping. In another embodiment, a medical image of the patient including the stenosis of interest is received, image patches corresponding to the stenosis of interest and a coronary tree of the patient are detected, an FFR value for the stenosis of interest is determined using a trained deep neural network regressor applied directly to the detected image patches.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
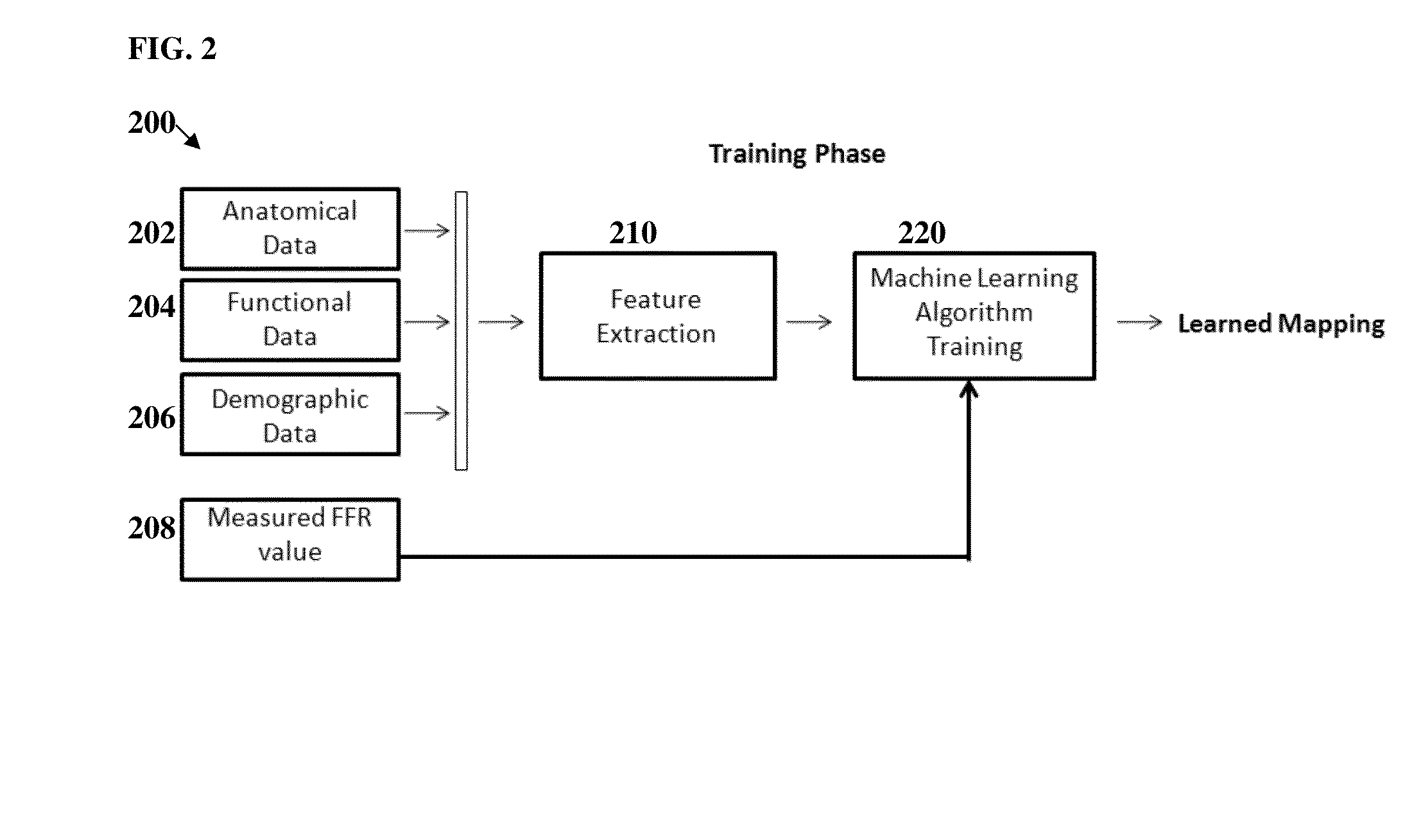
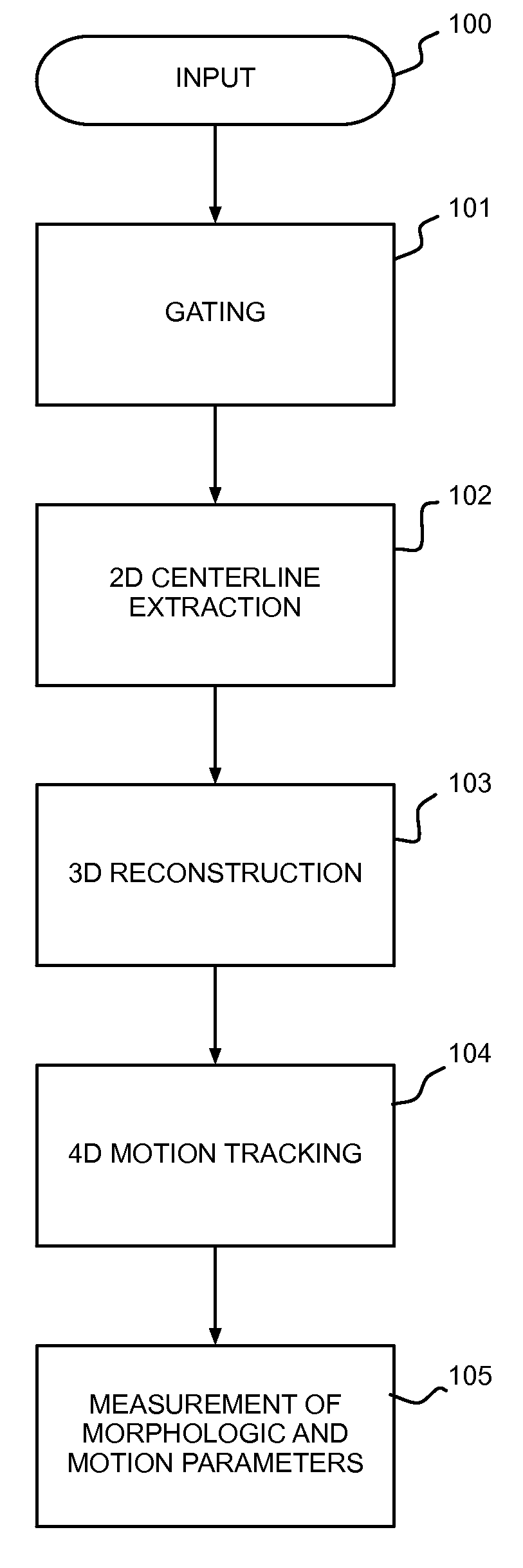
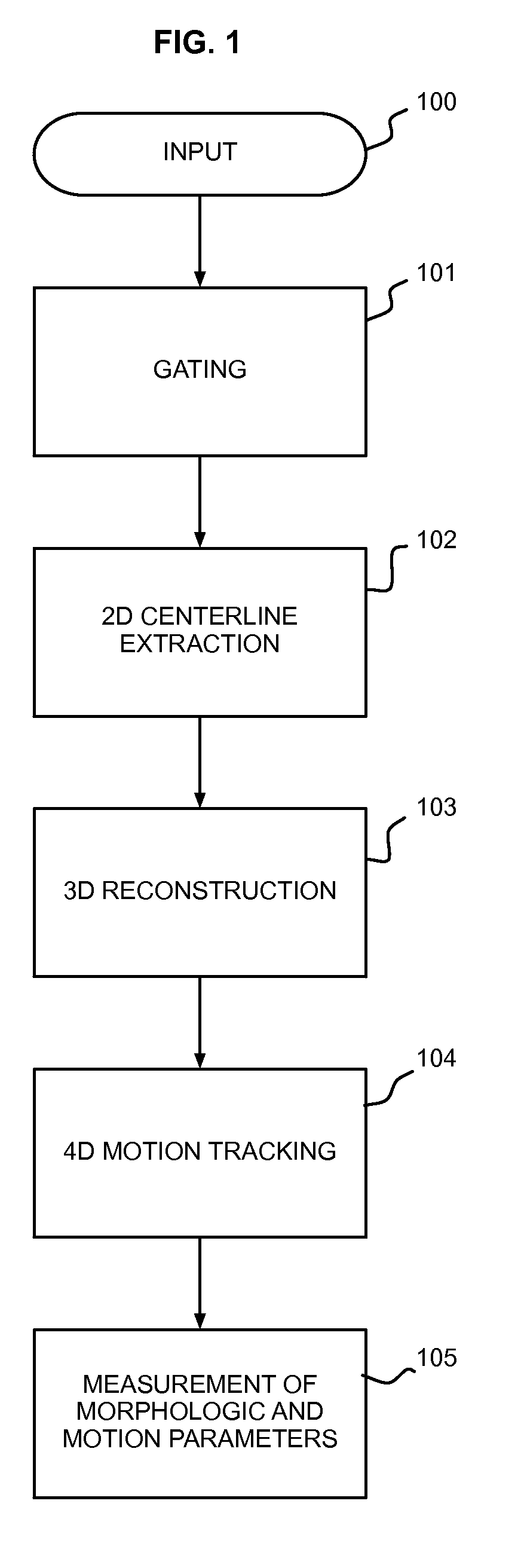
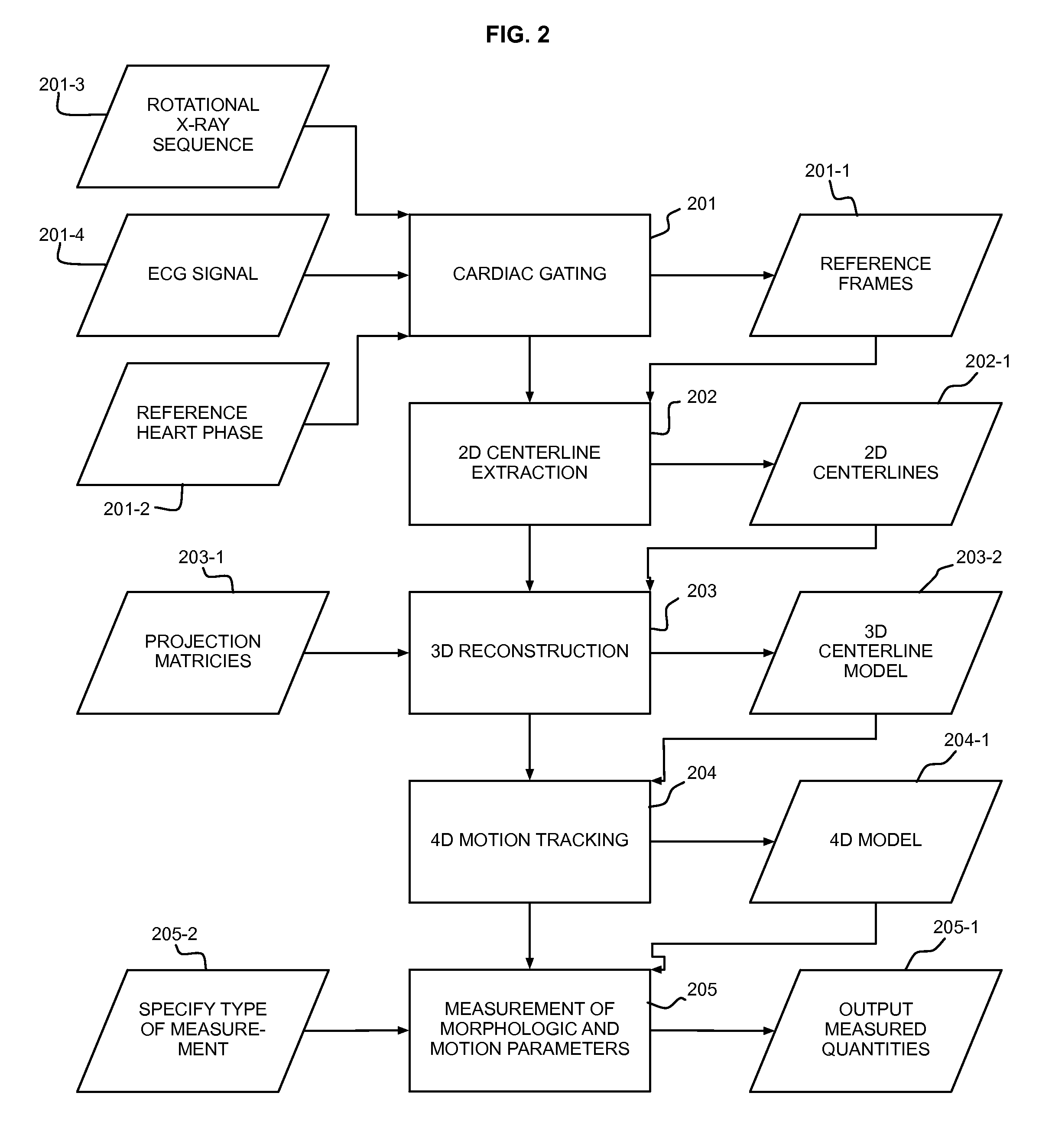
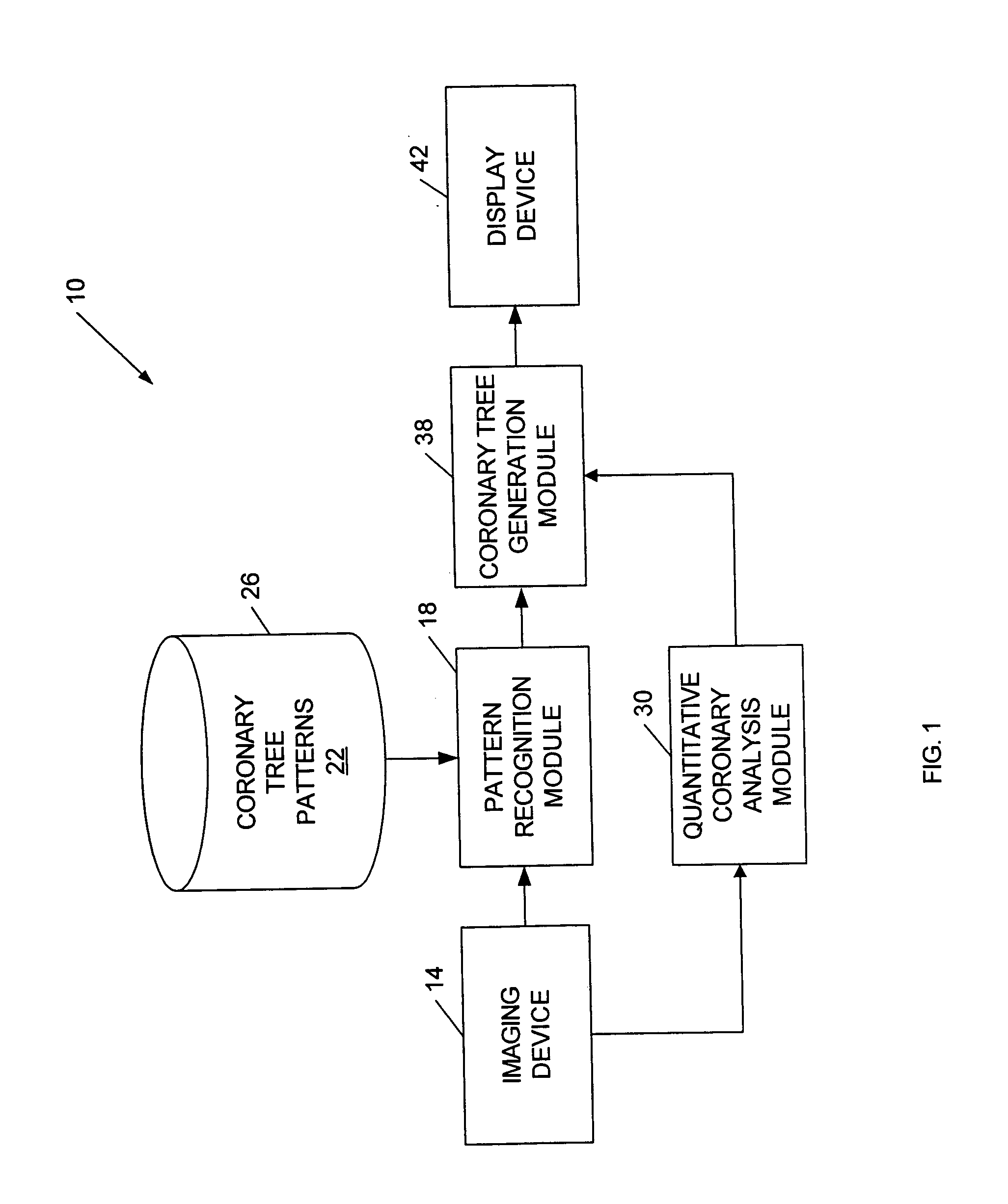
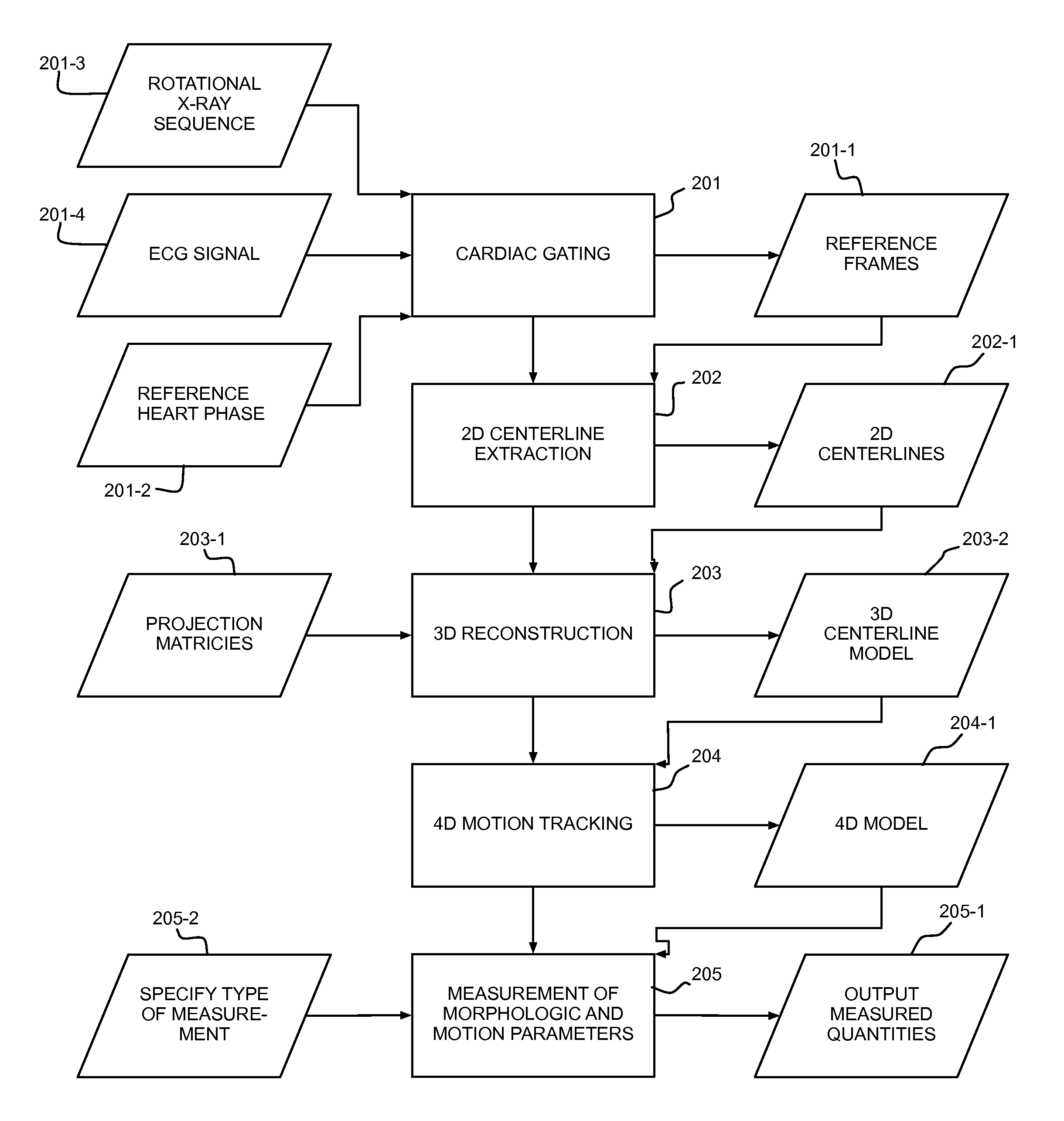
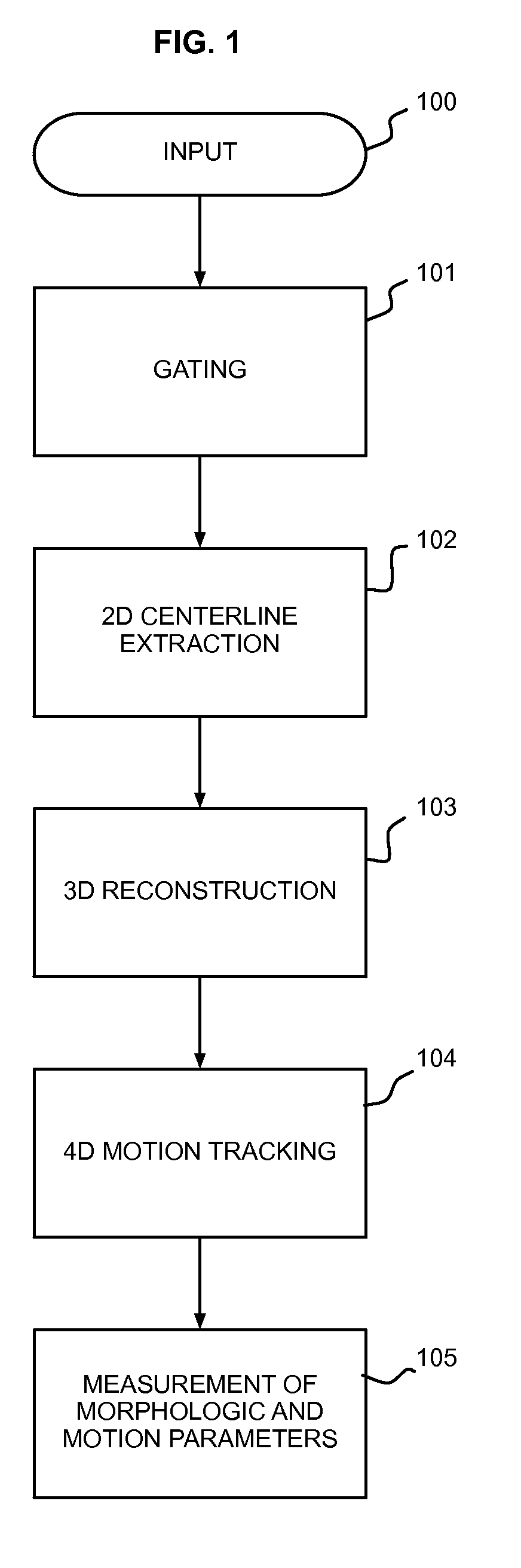
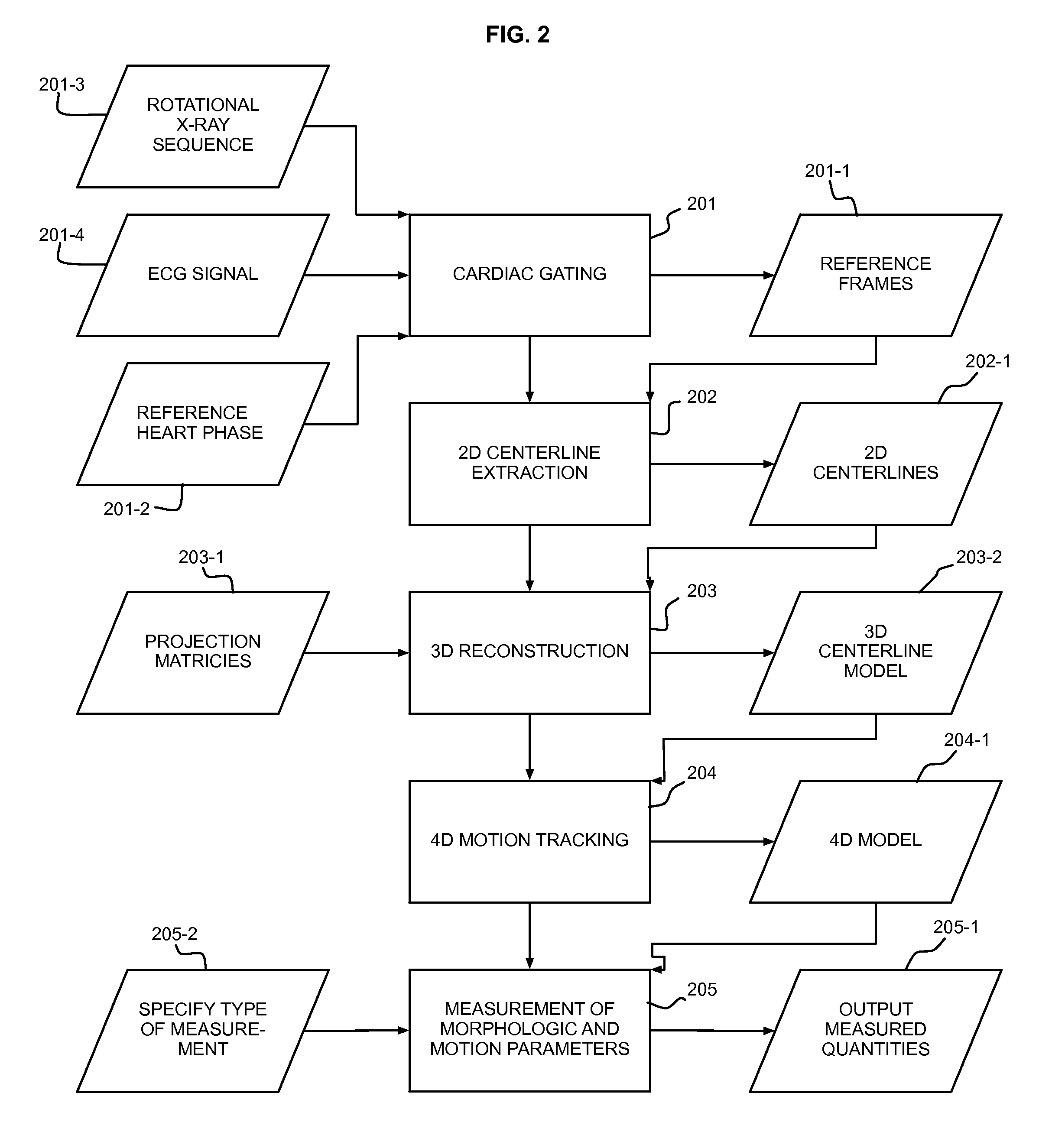
Automatic Measurement of Morphometric and Motion Parameters of the Coronary Tree From A Rotational X-Ray Sequence
Automatic measurement of morphometric and motion parameters of a coronary target includes extracting reference frames from input data of a coronary target at different phases of a cardiac cycle, extracting a three-dimensional centerline model for each phase of the cardiac cycle based on the references frames and projection matrices of the coronary target, tracking a motion of the coronary target through the phases based on the three-dimensional centerline models, and determining a measurement of morphologic and motion parameters of the coronary target based on the motion.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
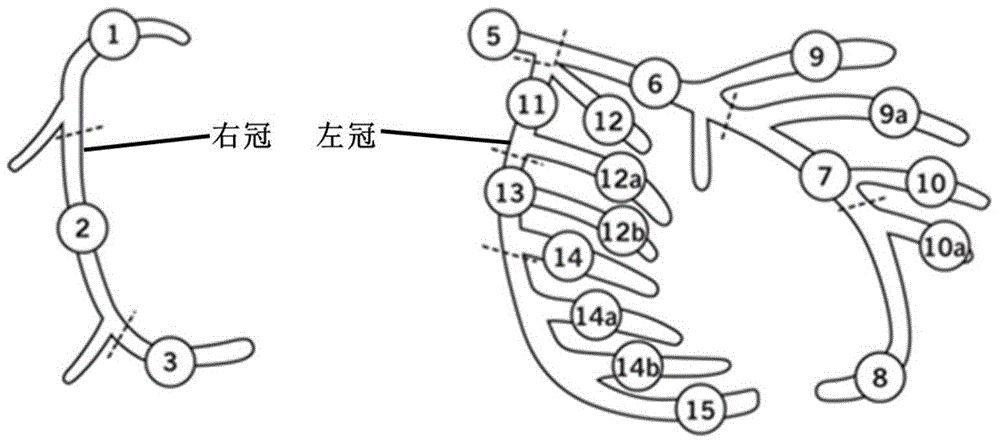
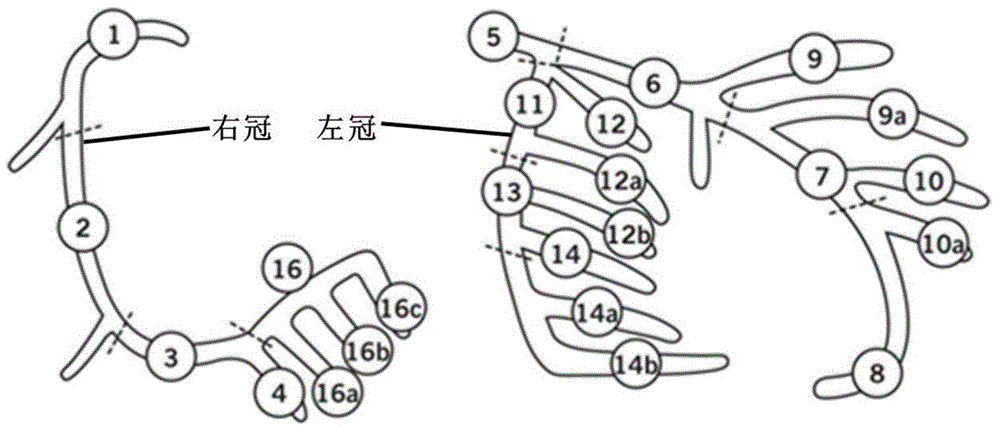
SYNTAX automatic scoring method based on coronary angiogram image segmentation
InactiveCN104867147AReduce workloadShorten the timeImage enhancementImage analysisUltrasound attenuationCoronary arterial tree
An SYNTAX automatic scoring method based on coronary angiogram image segmentation segments and extracts a coronary arterial tree and central line based on coronary angiogram images of a patient and employs a blood vessel side branch separation, reconnection and K main curve method, and generates a binary image of the coronary arterial tree The blood vessel segment numbers are automatically matched based on the SYNTAX scoring standard by employing a central line direction tracking method, and coronary artery pathological changes and adverse characteristics are identified and scored by selecting a coronary left (right) advantageous type in combination with the width attenuation degree of the cross section of the blood vessel and the curvature change of the center line, and the scores are calculated to give a reasonable score result to allow a doctor to employ optimal operation scheme. The method overcomes the problems of great computation amount, tedious calculating steps, complex scoring standard and long calculating time of artificial calculating SYNTAX scoring in conventional clinics.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method and system for machine learning based assessment of fractional flow reserve
A method and system for determining fractional flow reserve (FFR) for a coronary artery stenosis of a patient is disclosed. In one embodiment, medical image data of the patient including the stenosis is received, a set of features for the stenosis is extracted from the medical image data of the patient, and an FFR value for the stenosis is determined based on the extracted set of features using a trained machine-learning based mapping. In another embodiment, a medical image of the patient including the stenosis of interest is received, image patches corresponding to the stenosis of interest and a coronary tree of the patient are detected, an FFR value for the stenosis of interest is determined using a trained deep neural network regressor applied directly to the detected image patches.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHINEERS AG
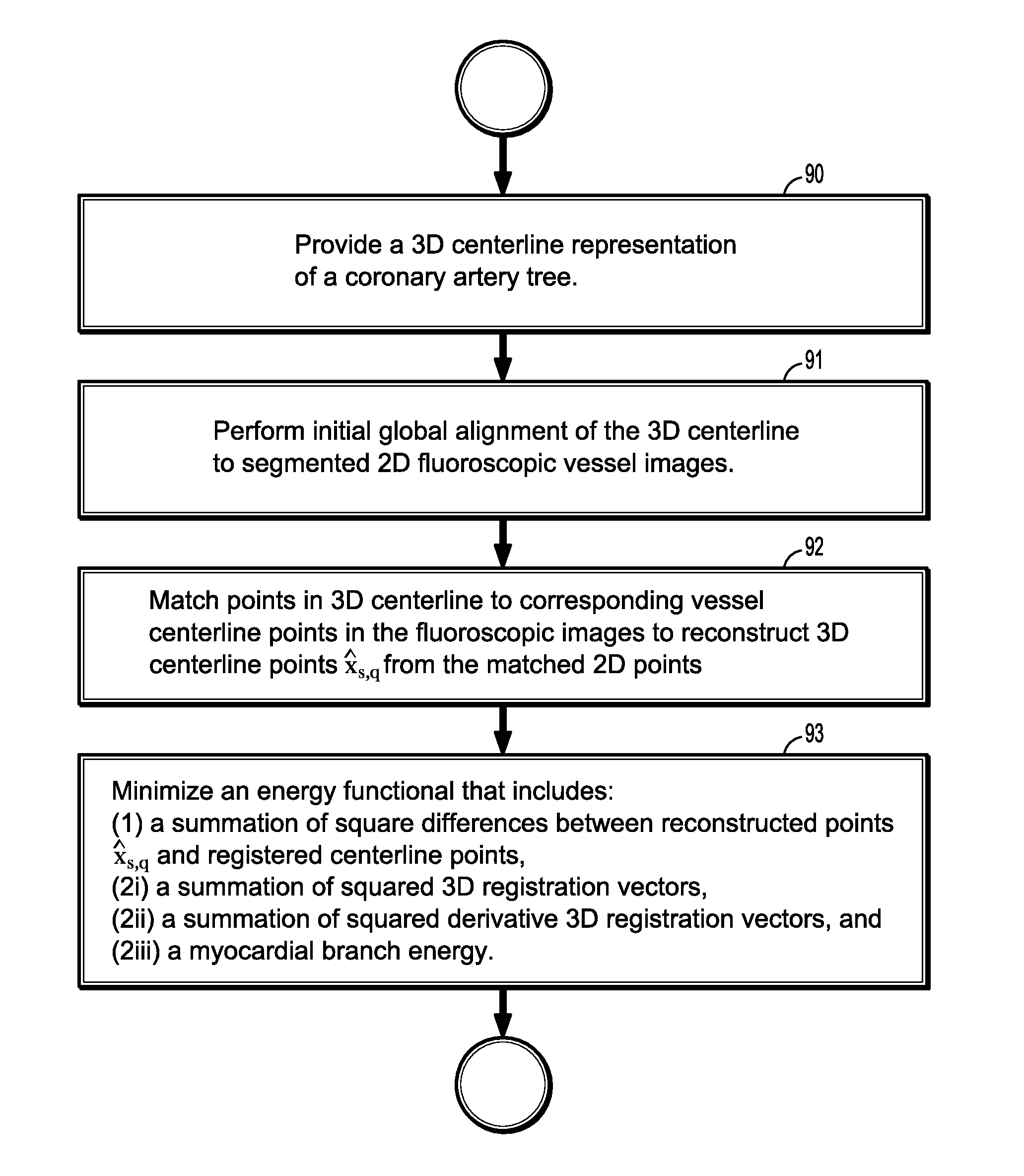
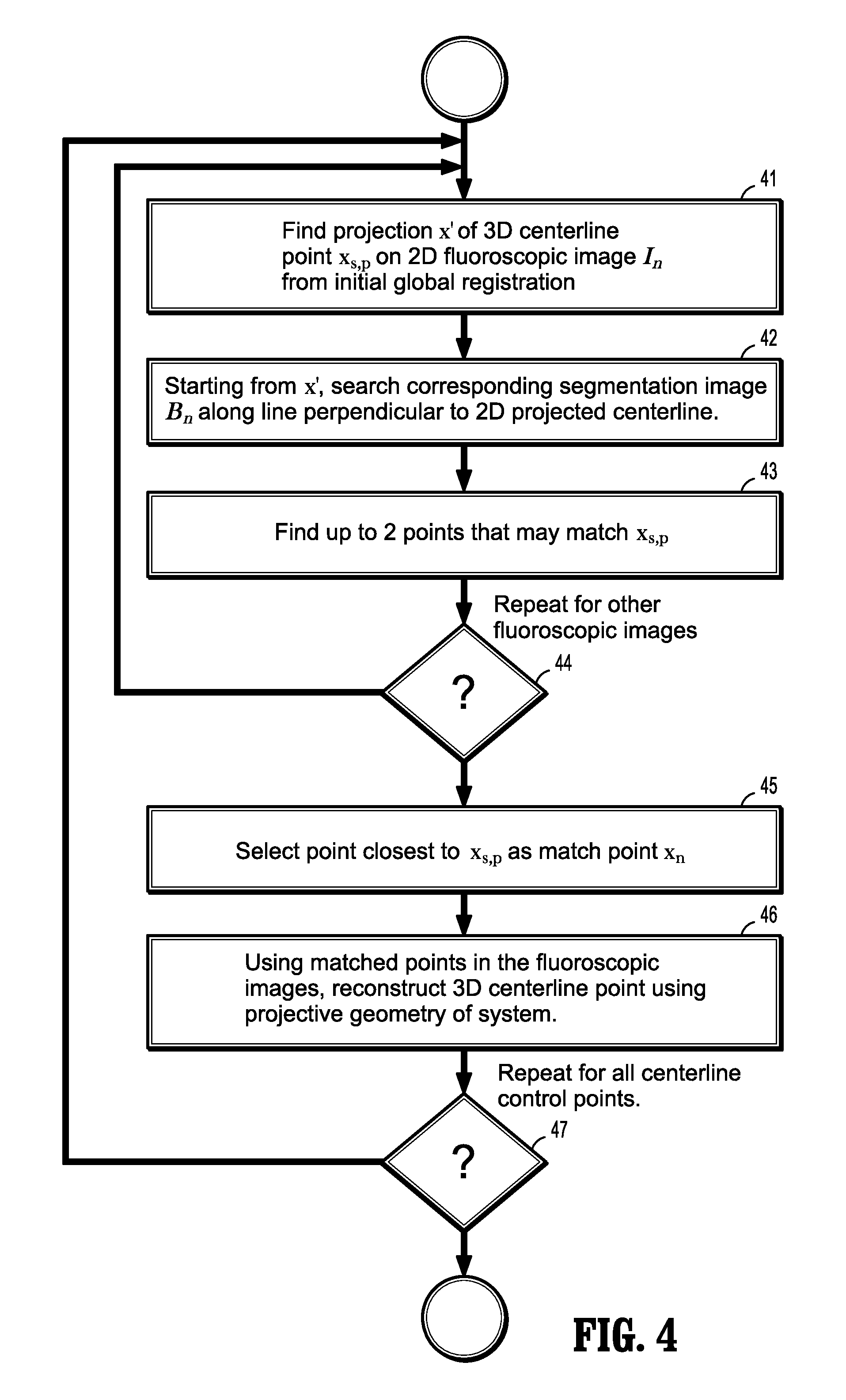
Non-rigid 2d/3d registration of coronary artery models with live fluoroscopy images
ActiveUS20130094745A1Increase heightReduce uncertaintyImage enhancementImage analysisFluoroscopic imageCoronary arterial tree
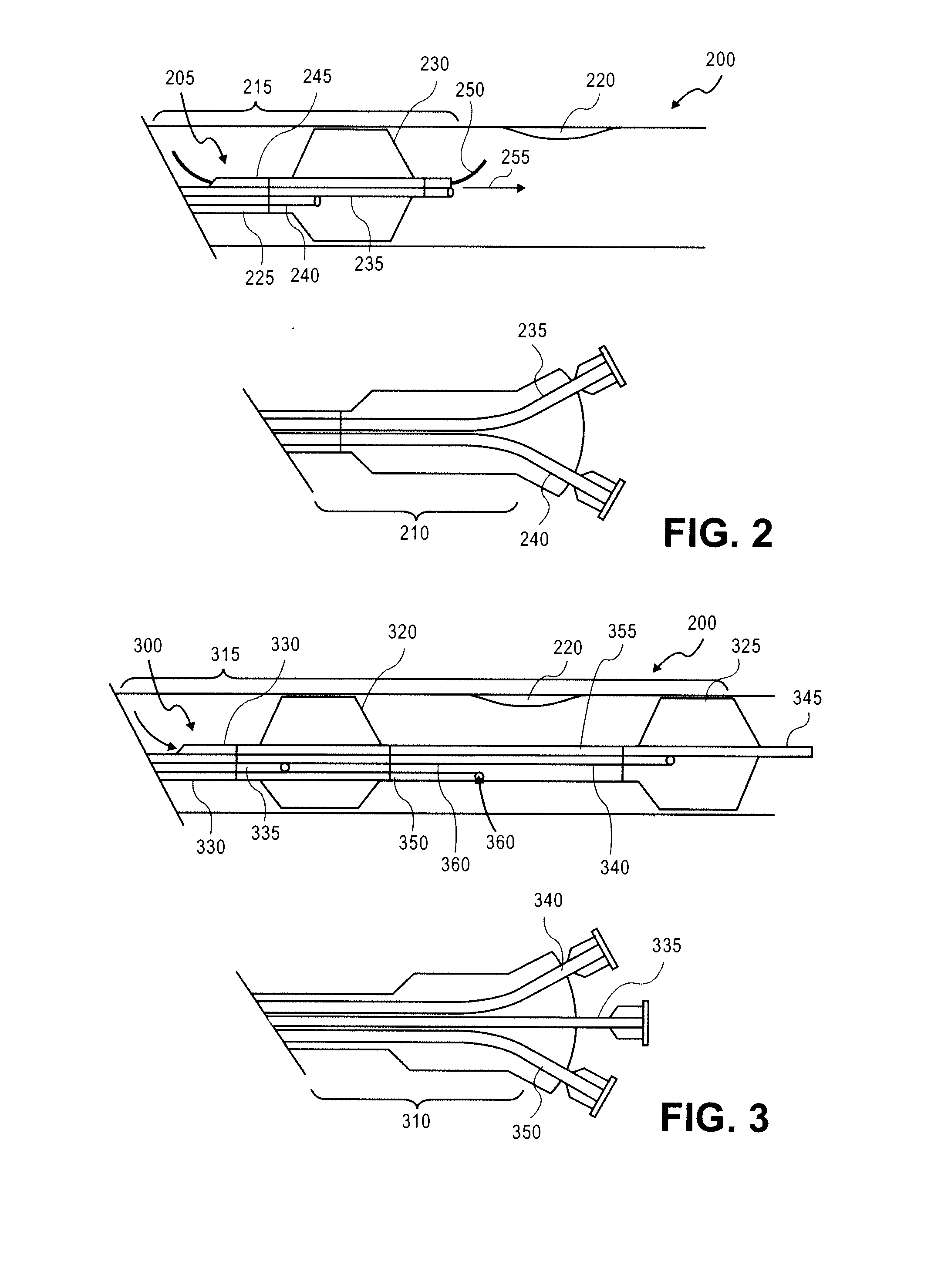
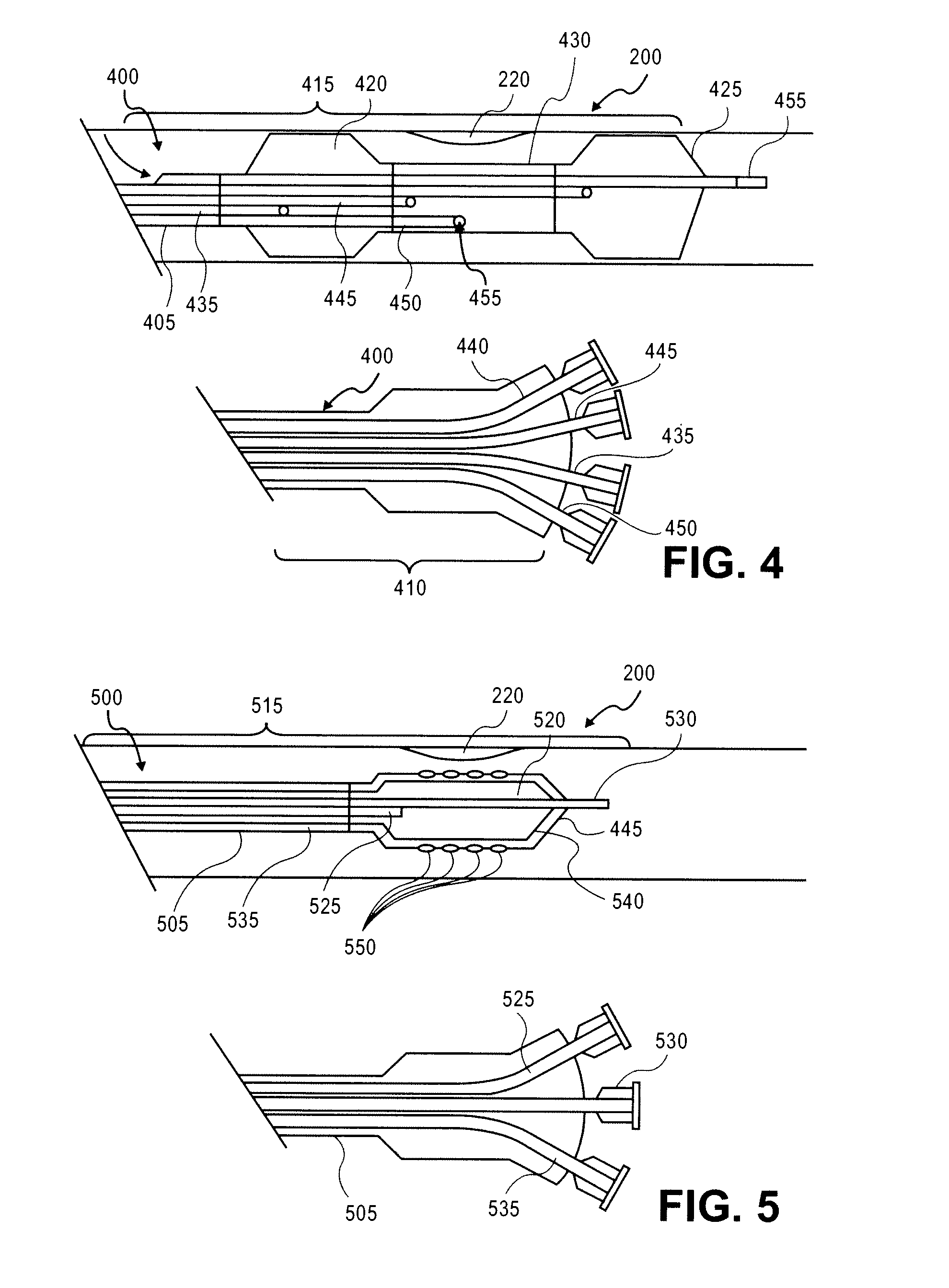
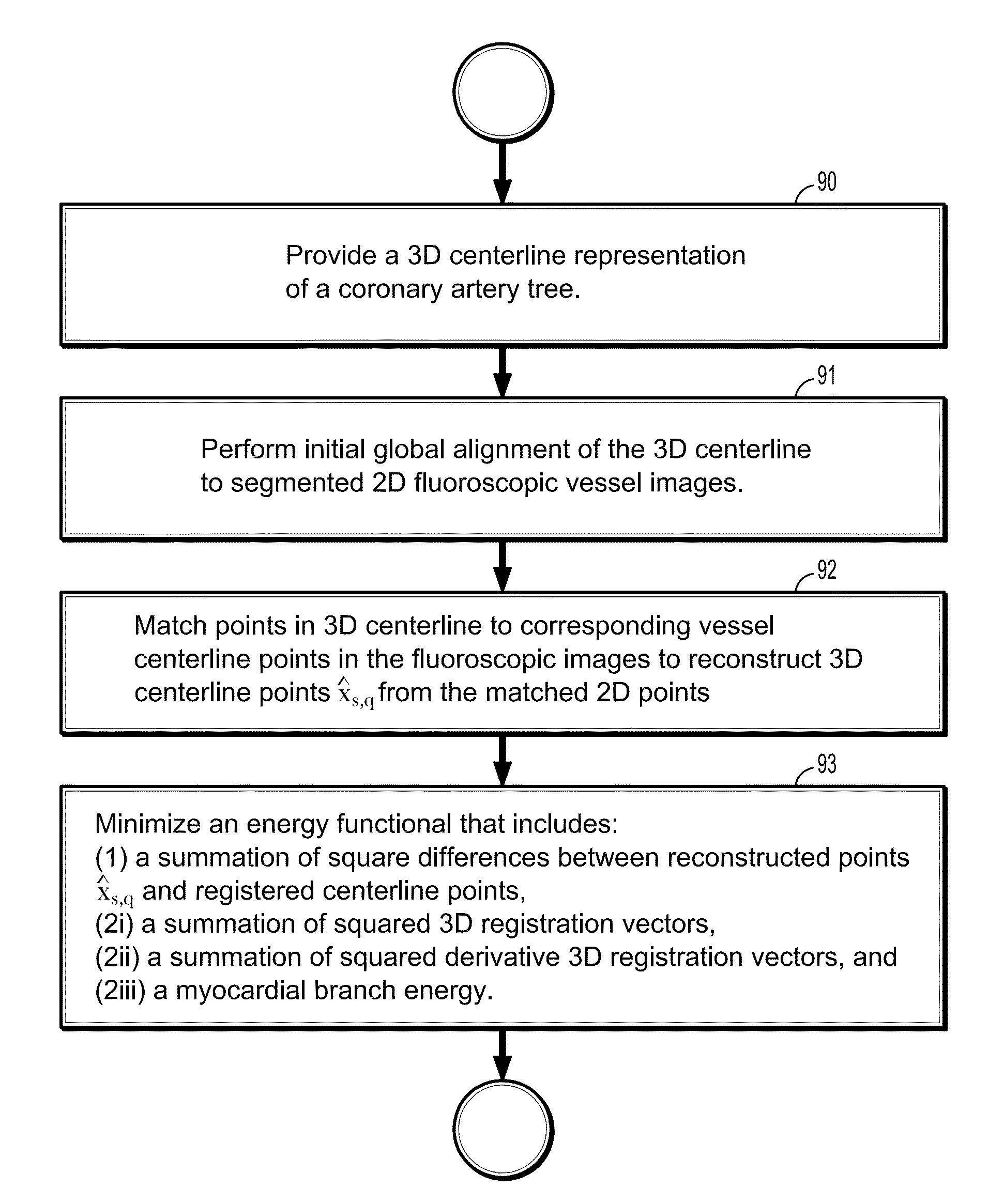
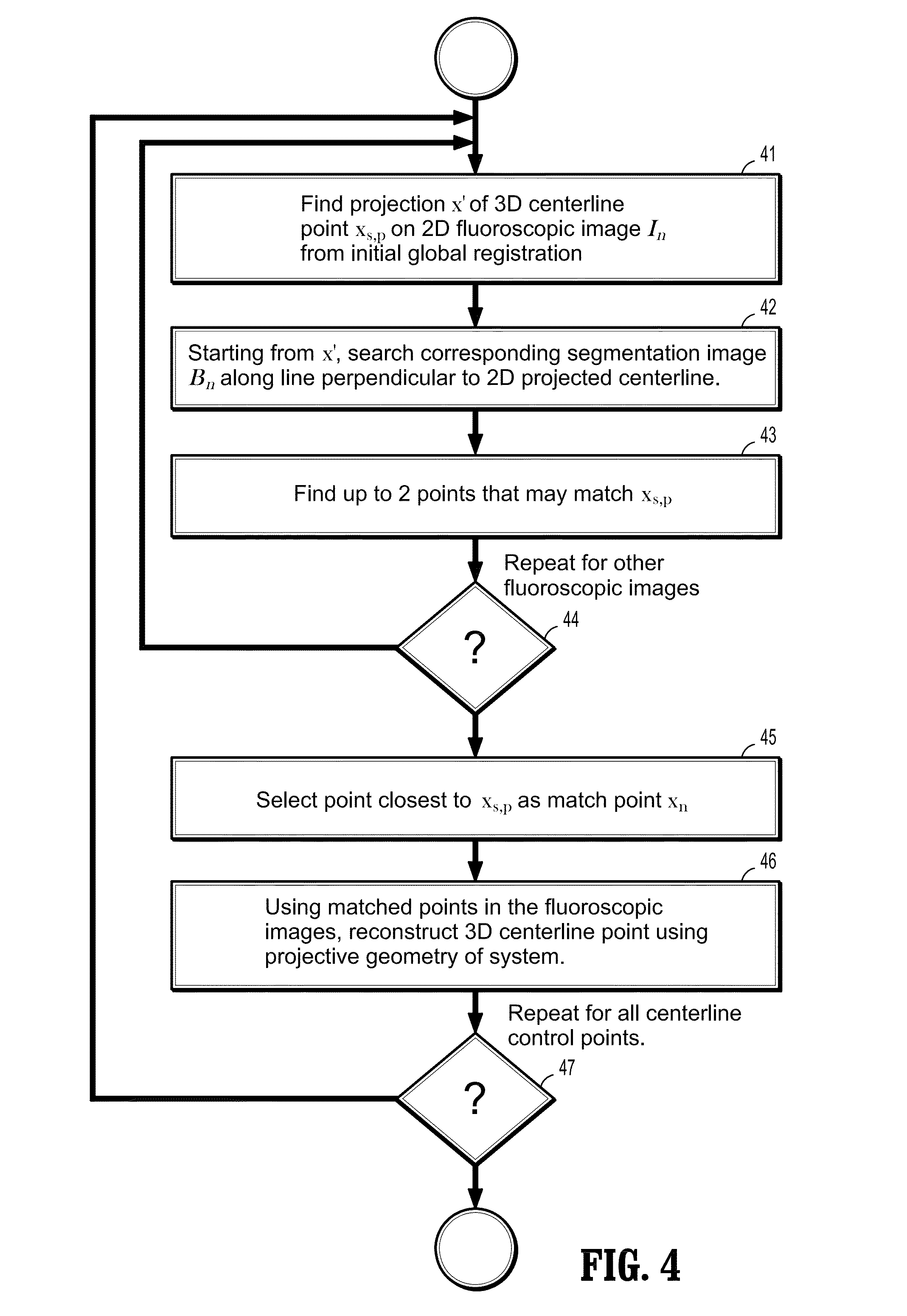
A method for non-rigid registration of digital 3D coronary artery models with 2D fluoroscopic images during a cardiac intervention includes providing a digitized 3D centerline representation of a coronary artery tree that comprises a set of S segments composed of QS 3D control points, globally aligning the 3D centerline to at least two 2D fluoroscopic images, and non-rigidly registering the 3D centerline to the at least two 2D fluoroscopic images by minimizing an energy functional that includes a summation of square differences between reconstructed centerline points and registered centerline points, a summation of squared 3D registration vectors, a summation of squared derivative 3D registration vectors, and a myocardial branch energy. The non-rigid registration of the 3D centerline is represented as a set of 3D translation vectors rs,q that are applied to corresponding centerline points xs,q in a coordinate system of the 3D centerline.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and System for Machine Learning Based Assessment of Fractional Flow Reserve
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Automatic coronary isolation using a n-MIP ray casting technique
A novel method is presented for detecting coronary arteries as well as other peripheral vessels of the heart. After finding the location of the myocardium through a segmentation method, such as a graph theoretic segmentation method, the method models the heart with a biaxial ellipsoid. For each point of the ellipsoid, a collection of intensities are computed that are normal to the surface. This collection is then filtered to detect the cardiovascular structures. Ultimately, vessel centerline points are detected using a vessel tracking method, and linked together to form a complete coronary artery tree.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Method and apparatus for classification of coronary artery image data
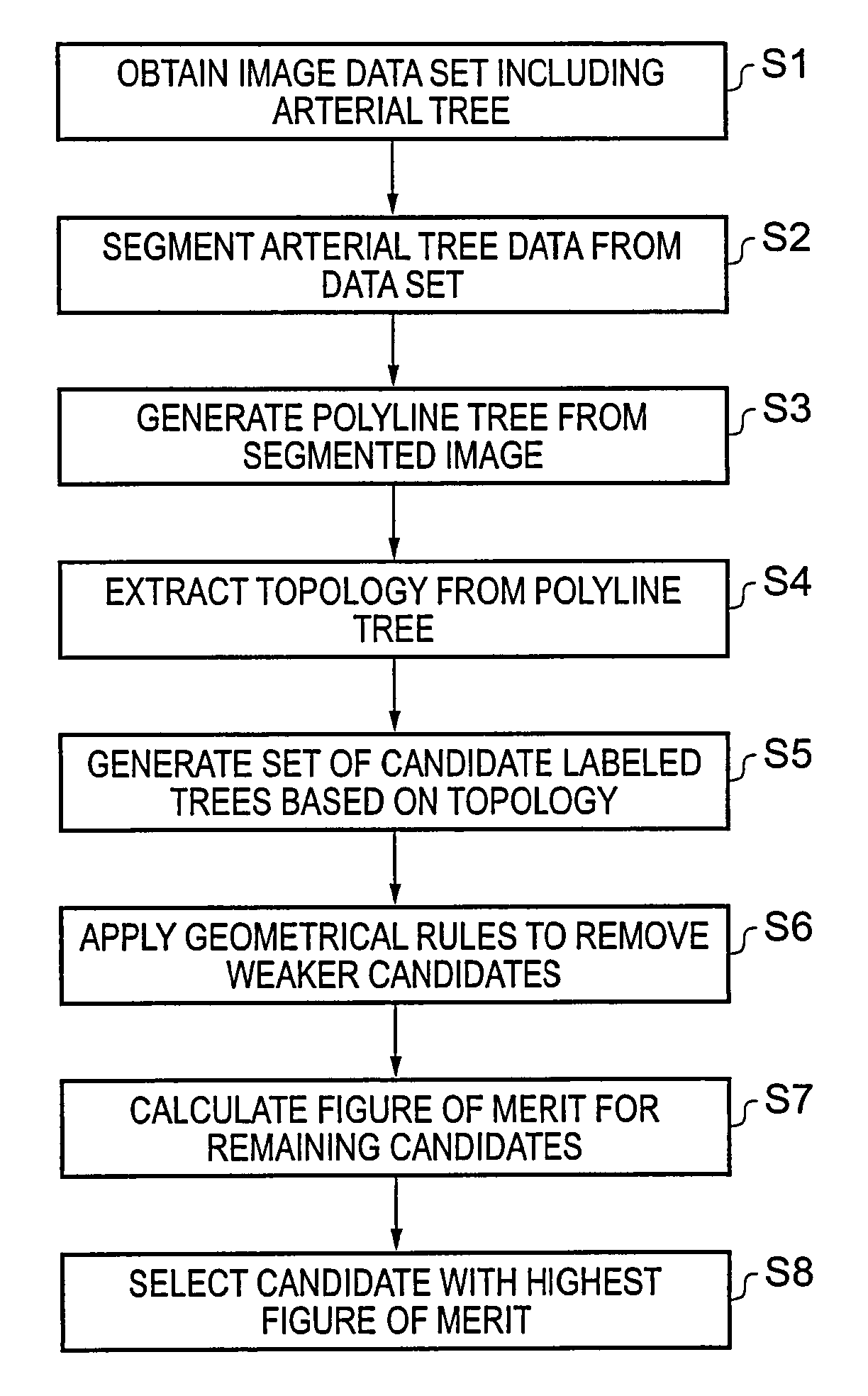
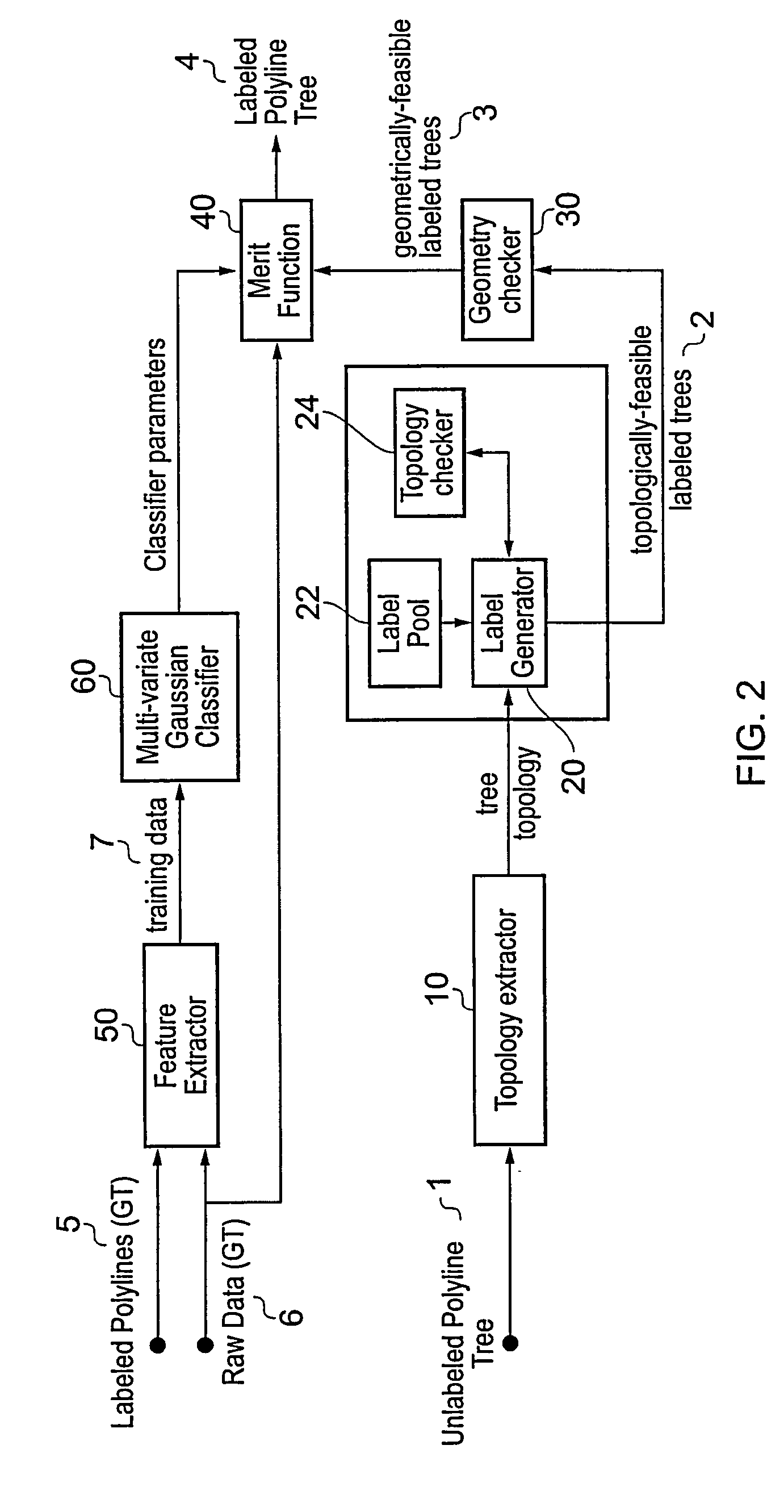
InactiveUS20100082692A1Accurate and computationally efficient techniqueIncrease speedImage enhancementMedical data miningCoronary arterial treeBlood vessel feature
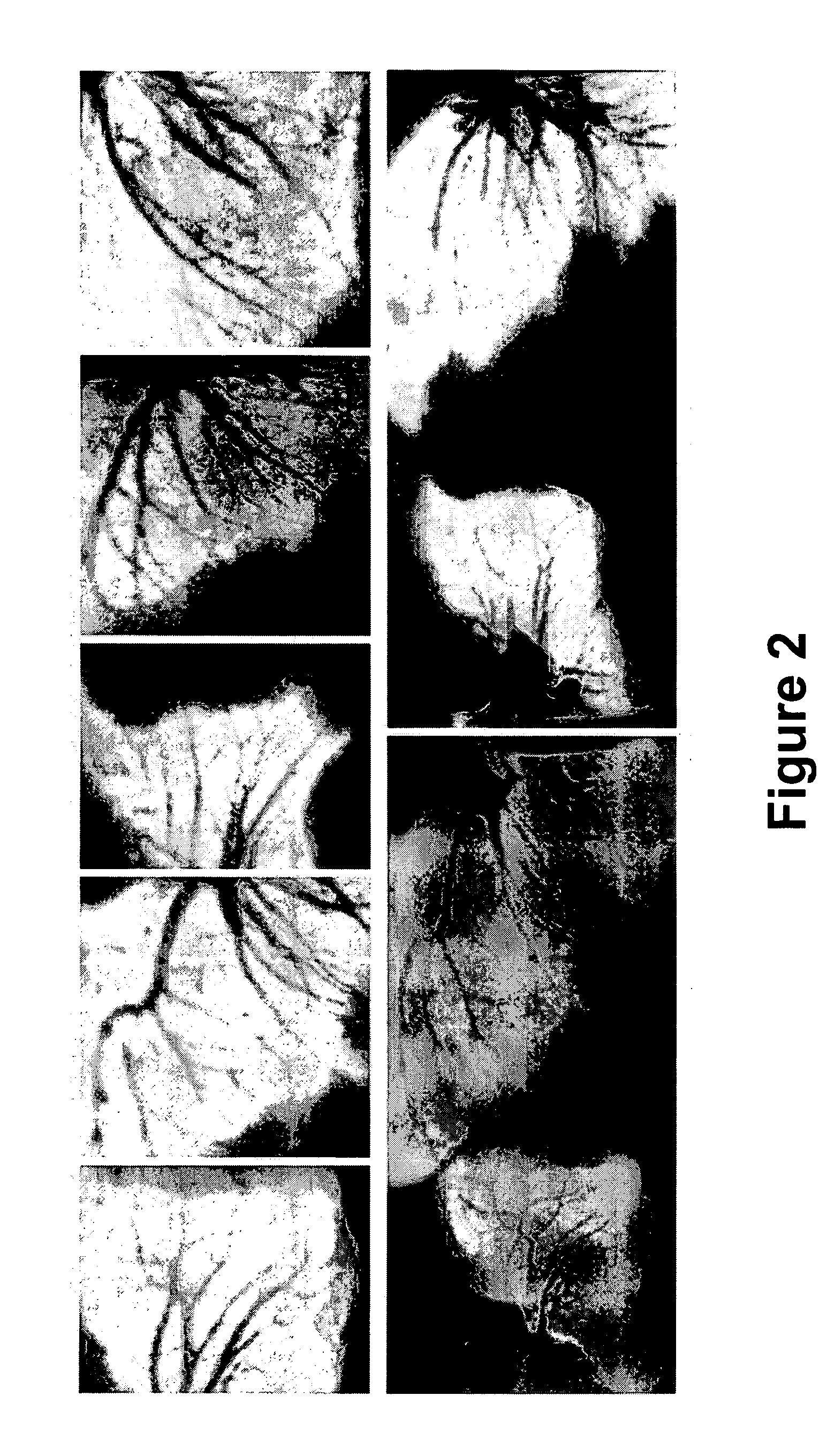
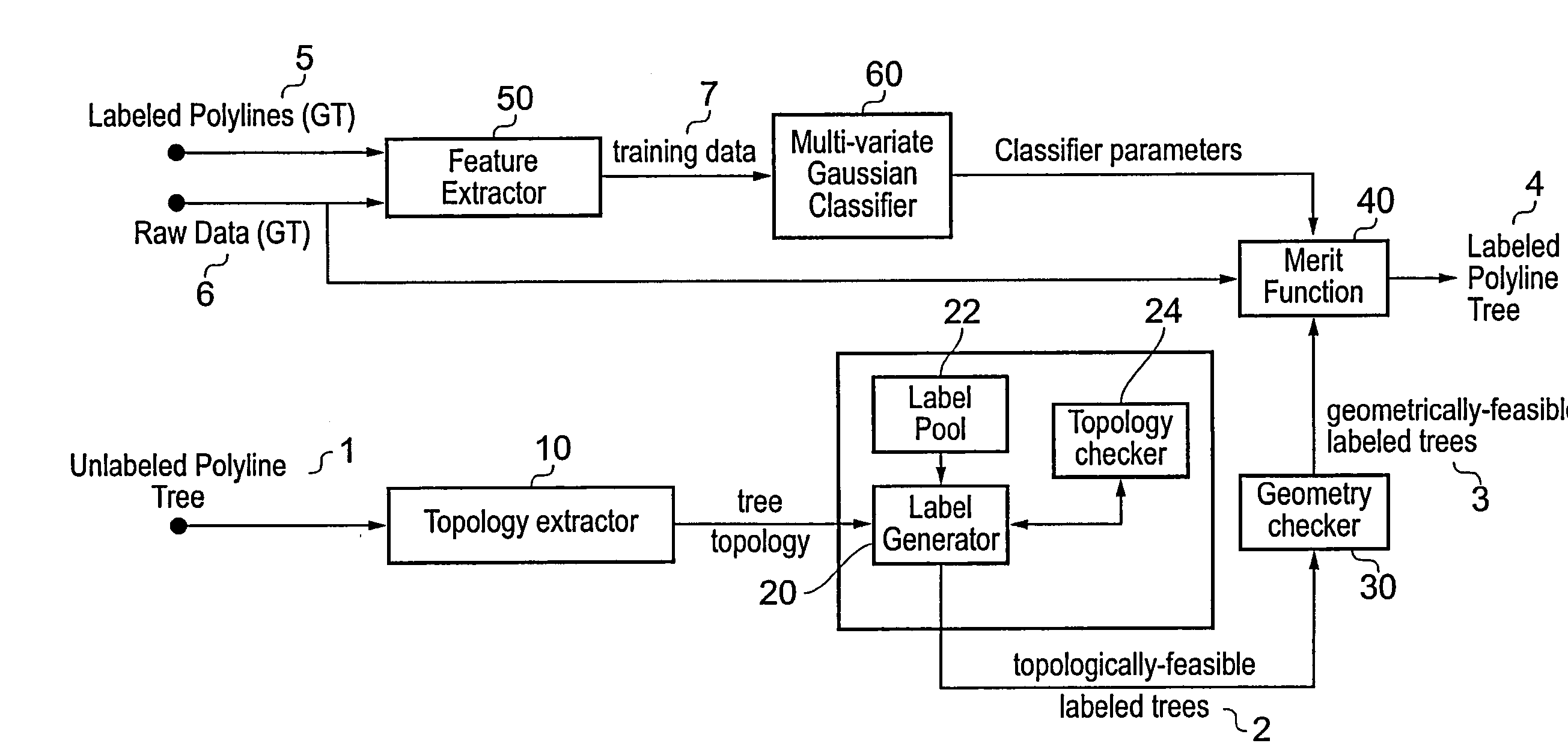
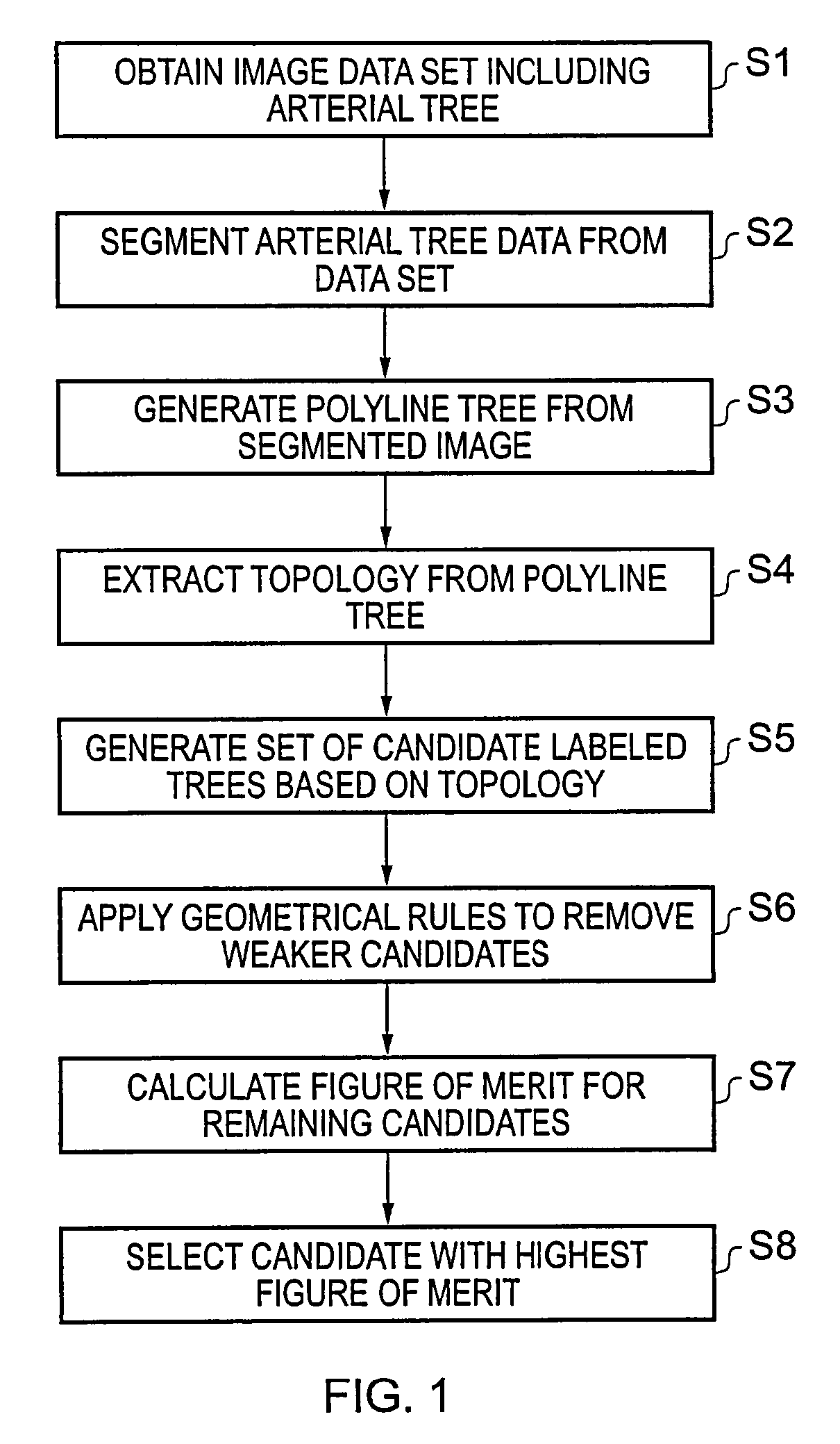
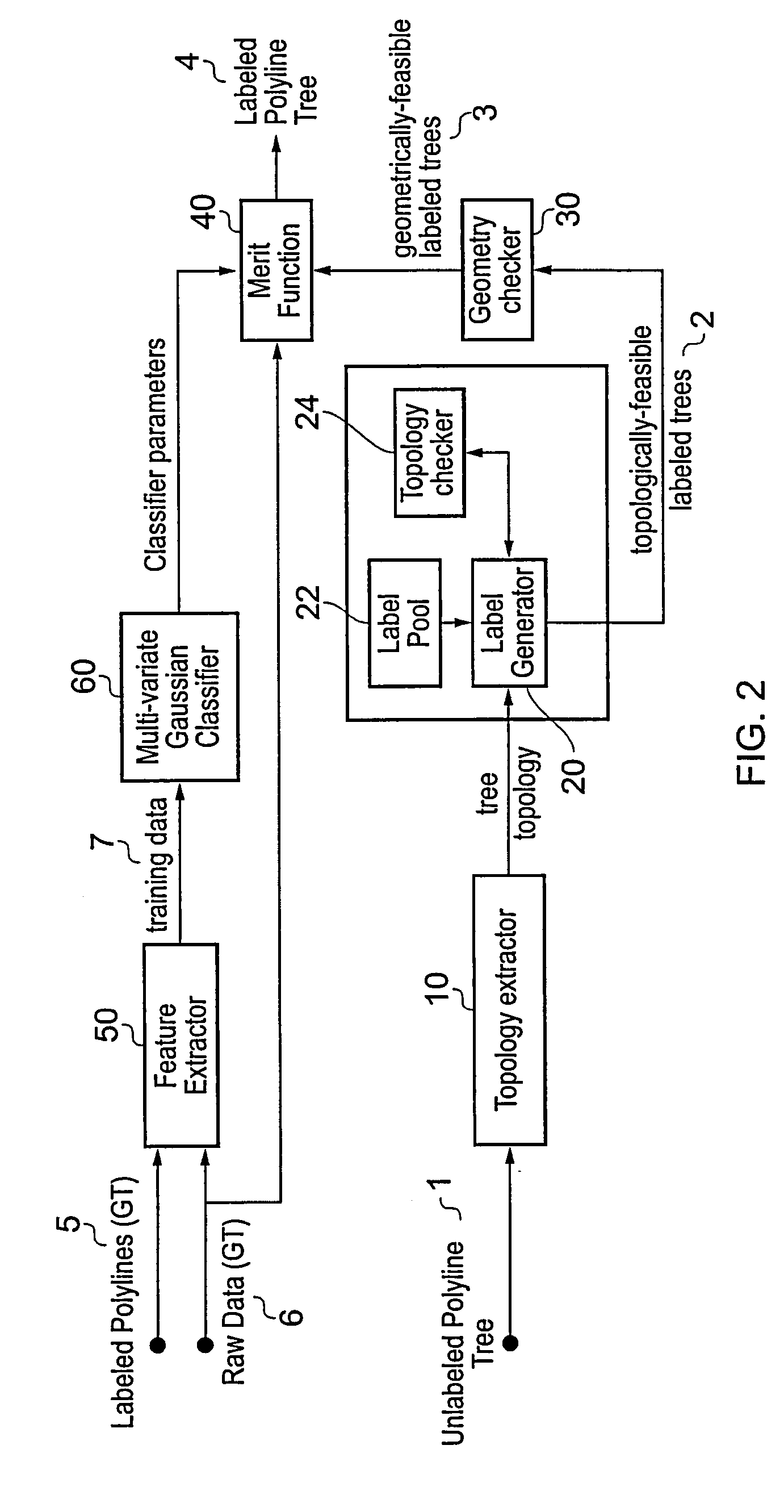
A polyline tree representation of a coronary artery tree imaged in a volume data set is obtained, and its topology is extracted to give a topological representation indicating the relative positions of vessels in the tree. The topological representation is compared with a set of topological rules to find possible anatomical classifications for each vessel, and a set of candidate labeled polyline trees is generated by labeling the polyline tree with labels showing each combination of possible anatomical classifications. Each candidate labeled tree is filtered according to a set of geometric rules pertaining to spatial characteristics of vessels in arterial trees, and any labeled tree not satisfying the geometric rules is rejected A figure of merit is calculated for each remaining candidate by comparing features of the vessels measured from the polyline tree and from the volume data set with features of correctly classified vessels in other data sets to determine the probable correctness of the labeling of each candidate, and the candidate with the best figure of merit is selected as showing the proper classification of the vessels.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL VISUALIZATION SYST EURO
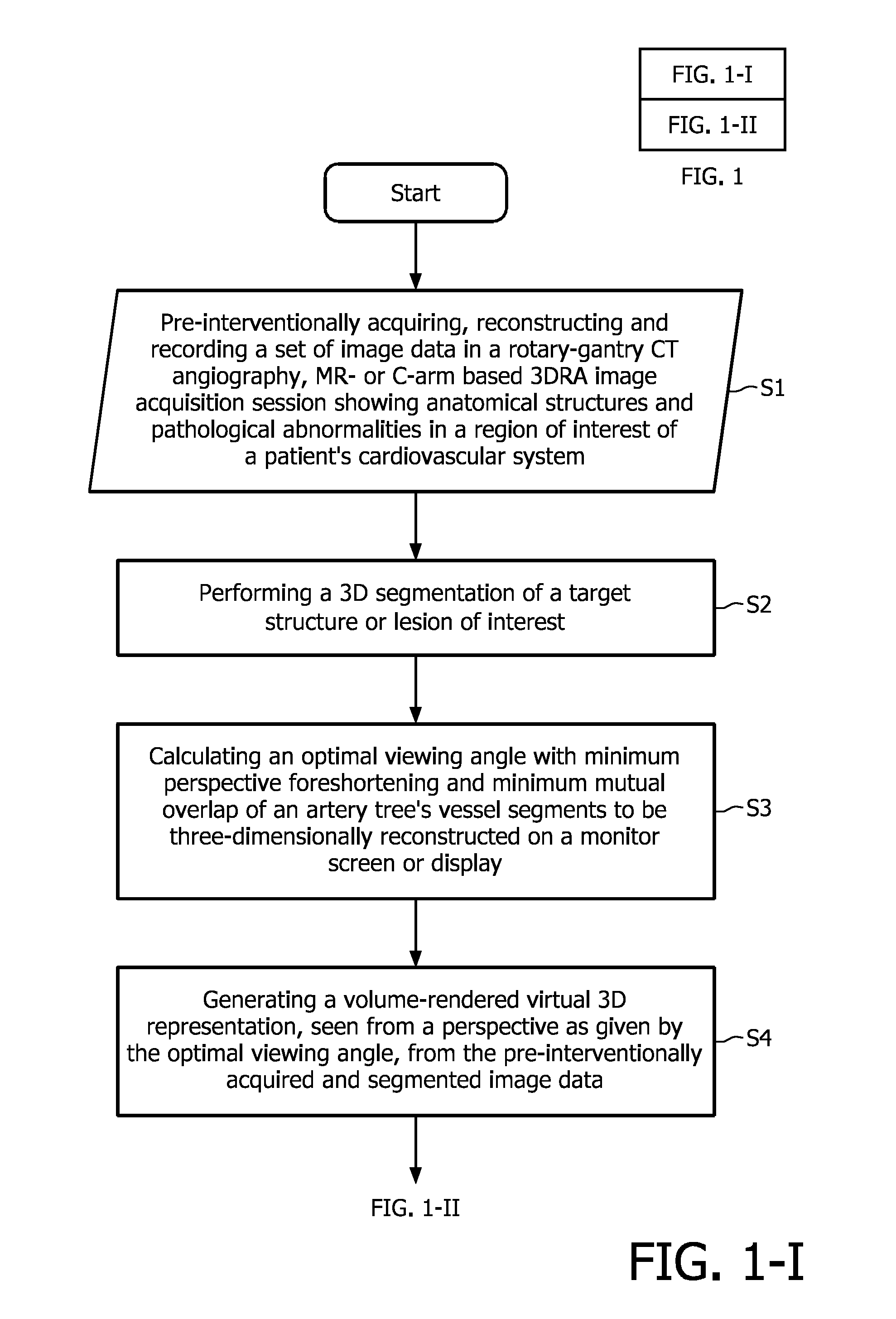
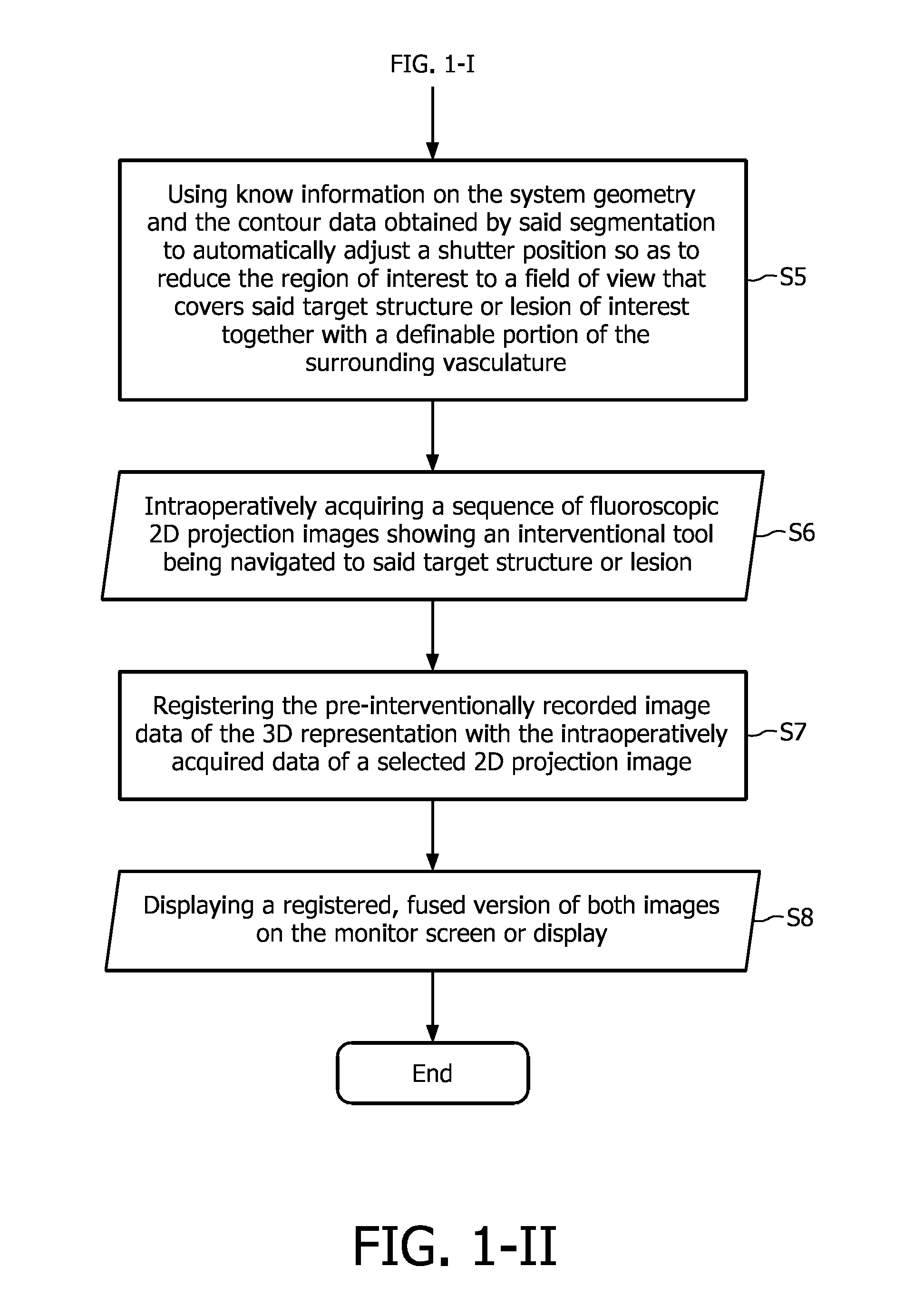
Angiographic image acquisition system and method with automatic shutter adaptation for yielding a reduced field of view covering a segmented target structure or lesion for decreasing X-radiation dose in minimally invasive X-ray-guided interventions
ActiveUS9280837B2Reduce radiation doseImprove directionCharacter and pattern recognitionTomography3d rotational angiography3d segmentation
The present invention refers to an angiographic image acquisition system and method which can beneficially be used in the scope of minimally invasive image-guided interventions. In particular, the present invention relates to a system and method for graphically visualizing a pre-interventionally virtual 3D representation of a patient's coronary artery tree's vessel segments in a region of interest of a patient's cardiovascular system to be three-dimensionally reconstructed. Optionally, this 3D representation can then be fused with an intraoperatively acquired fluoroscopic 2D live image of an interventional tool. According to the present invention, said method comprises the steps of subjecting the image data set of the 3D representation associated with the precalculated optimal viewing angle to a 3D segmentation algorithm (S4) in order to find the contours of a target structure or lesion to be examined and interventionally treated within a region of interest and automatically adjusting (S5) a collimator wedge position and / or aperture of a shutter mechanism used for collimating an X-ray beam emitted by an X-ray source of a C-arm-based 3D rotational angiography device or rotational gantry-based CT imaging system to which the patient is exposed during an image-guided radiographic examination procedure based on data obtained as a result of said segmentation which indicate the contour and size of said target structure or lesion. The aim is to reduce the region of interest to a field of view that covers said target structure or lesion together with a user-definable portion of the surrounding vasculature.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
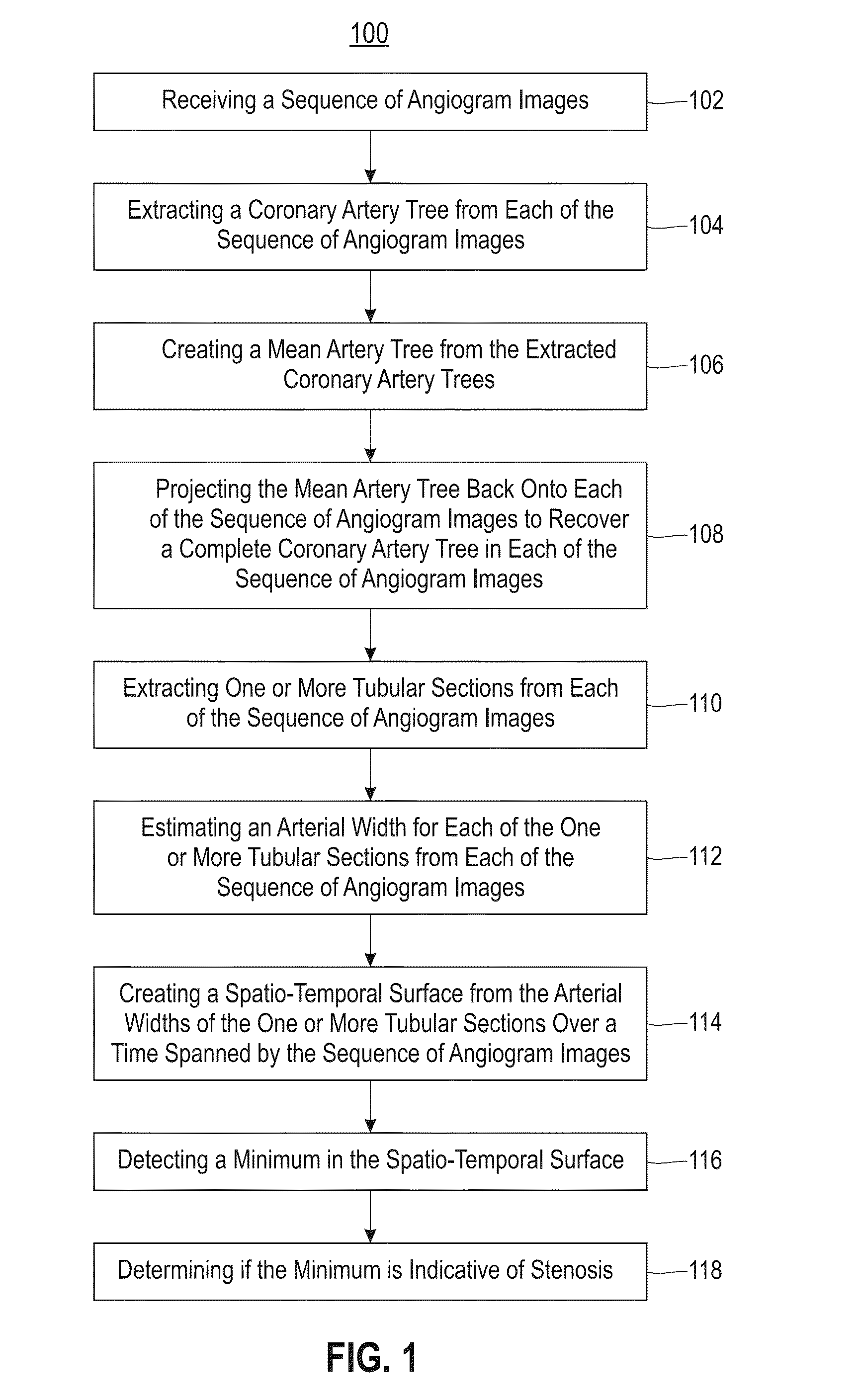
Detecting coronary stenosis through spatio-temporal tracking
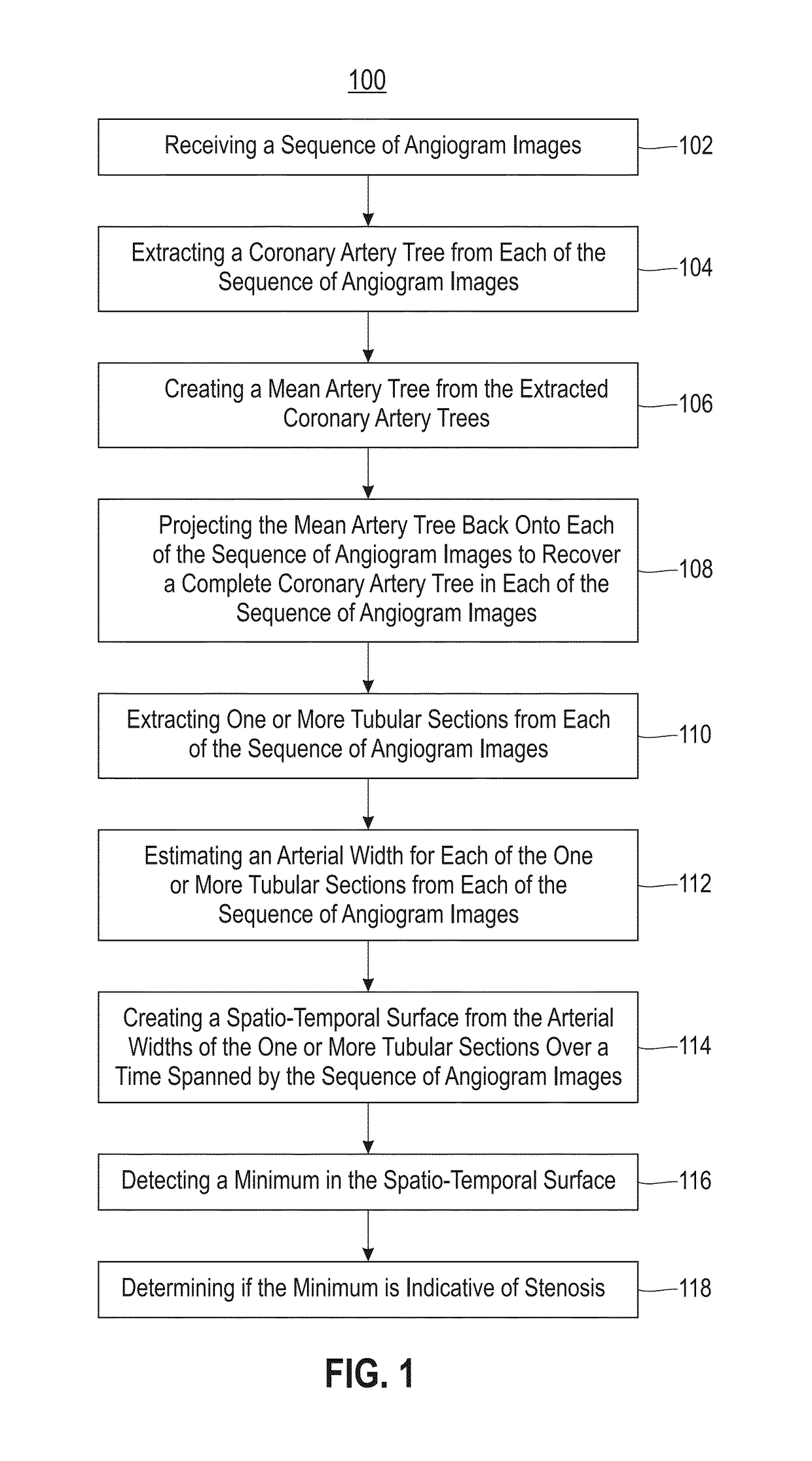
Embodiments relate to detecting coronary stenosis through spatio-temporal tracking. Aspects include extracting a coronary artery tree from each of a sequence of angiogram images, creating a mean artery tree from the extracted coronary artery trees, and projecting the mean artery tree back onto each of the sequence of angiogram images to recover a complete coronary artery tree for each of the sequence of angiogram images. Aspects also include extracting one or more tubular sections from each of the sequence of angiogram images, estimating an arterial width for each of the one or more tubular sections from each of the sequence of angiogram images, and creating a spatio-temporal surface from the arterial widths of the one or more tubular sections over a time spanned by the sequence of angiogram images. Aspects further include detecting a minimum in the spatio-temporal surface and determining if the minimum is indicative of stenosis.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for classification of coronary artery image data
InactiveUS7941462B2Accurate and computationally efficient techniqueIncrease speedImage enhancementMedical data miningData setCoronary arterial tree
A polyline tree representation of a coronary artery tree imaged in a volume data set is obtained, and its topology is extracted to give a topological representation indicating the relative positions of vessels in the tree. The topological representation is compared with a set of topological rules to find possible anatomical classifications for each vessel, and a set of candidate labeled polyline trees is generated by labeling the polyline tree with labels showing each combination of possible anatomical classifications. Each candidate labeled tree is filtered according to a set of geometric rules pertaining to spatial characteristics of vessels in arterial trees, and any labeled tree not satisfying the geometric rules is rejected A figure of merit is calculated for each remaining candidate by comparing features of the vessels measured from the polyline tree and from the volume data set with features of correctly classified vessels in other data sets to determine the probable correctness of the labeling of each candidate, and the candidate with the best figure of merit is selected as showing the proper classification of the vessels.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL VISUALIZATION SYST EURO
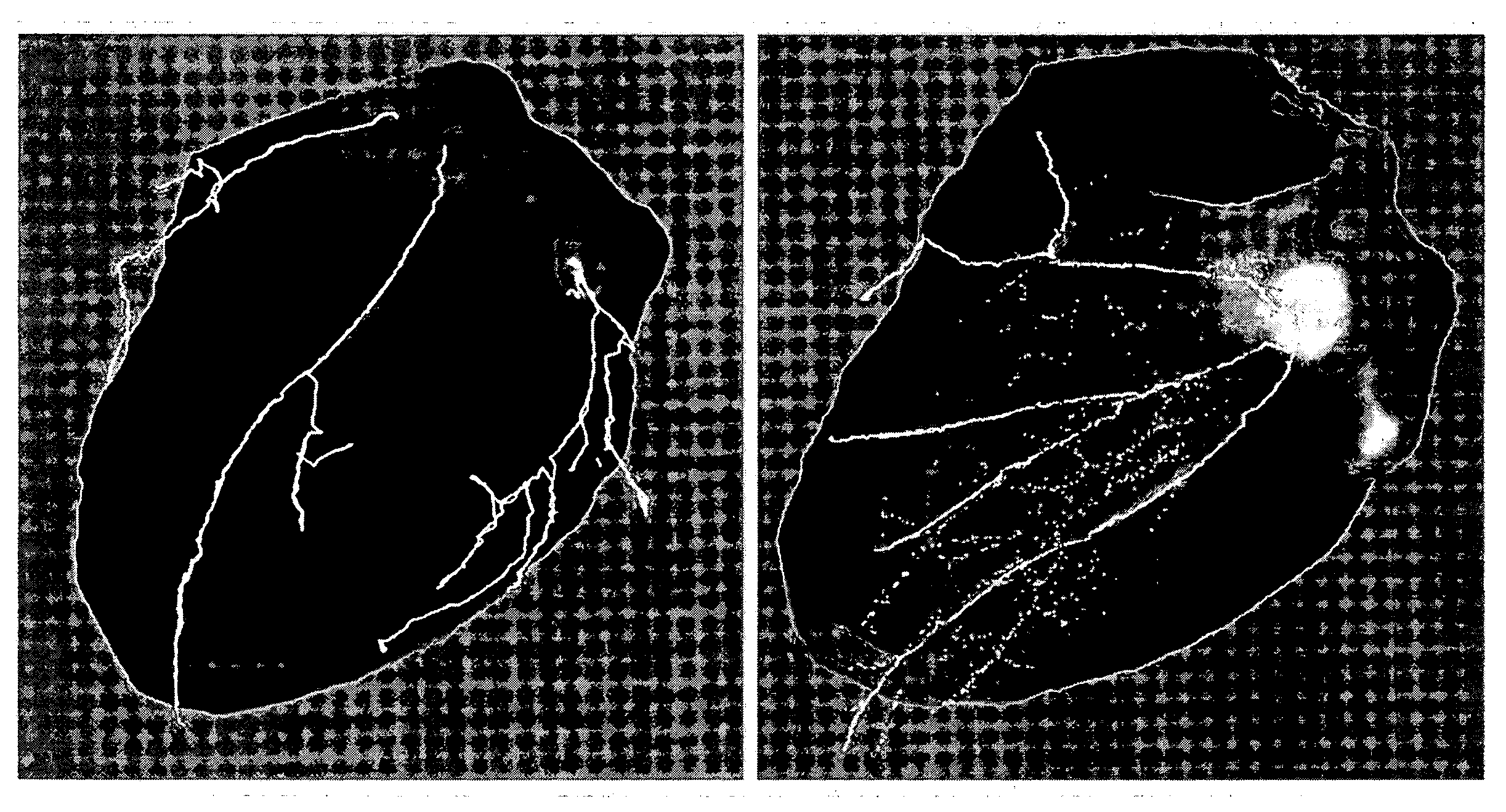
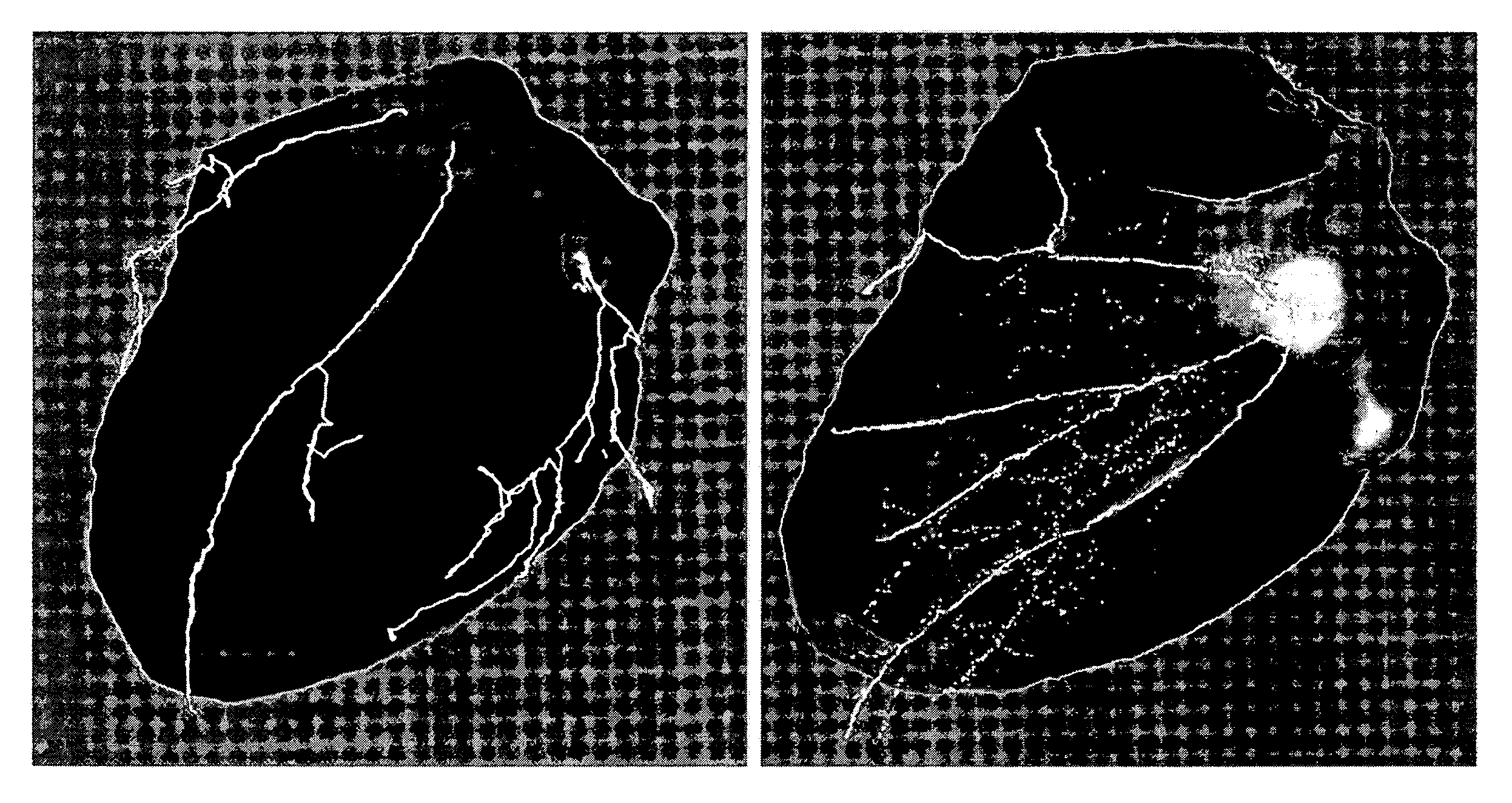
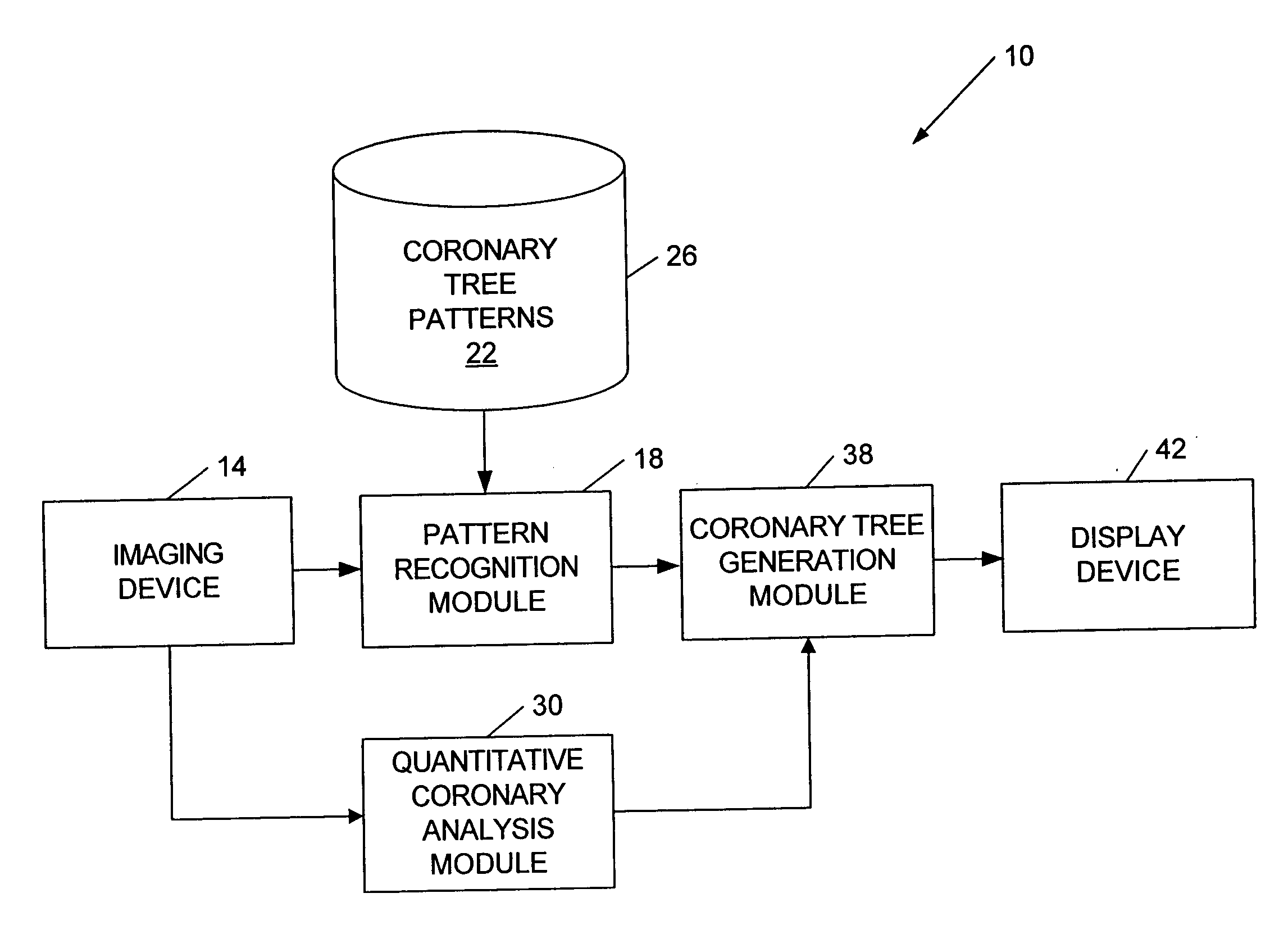
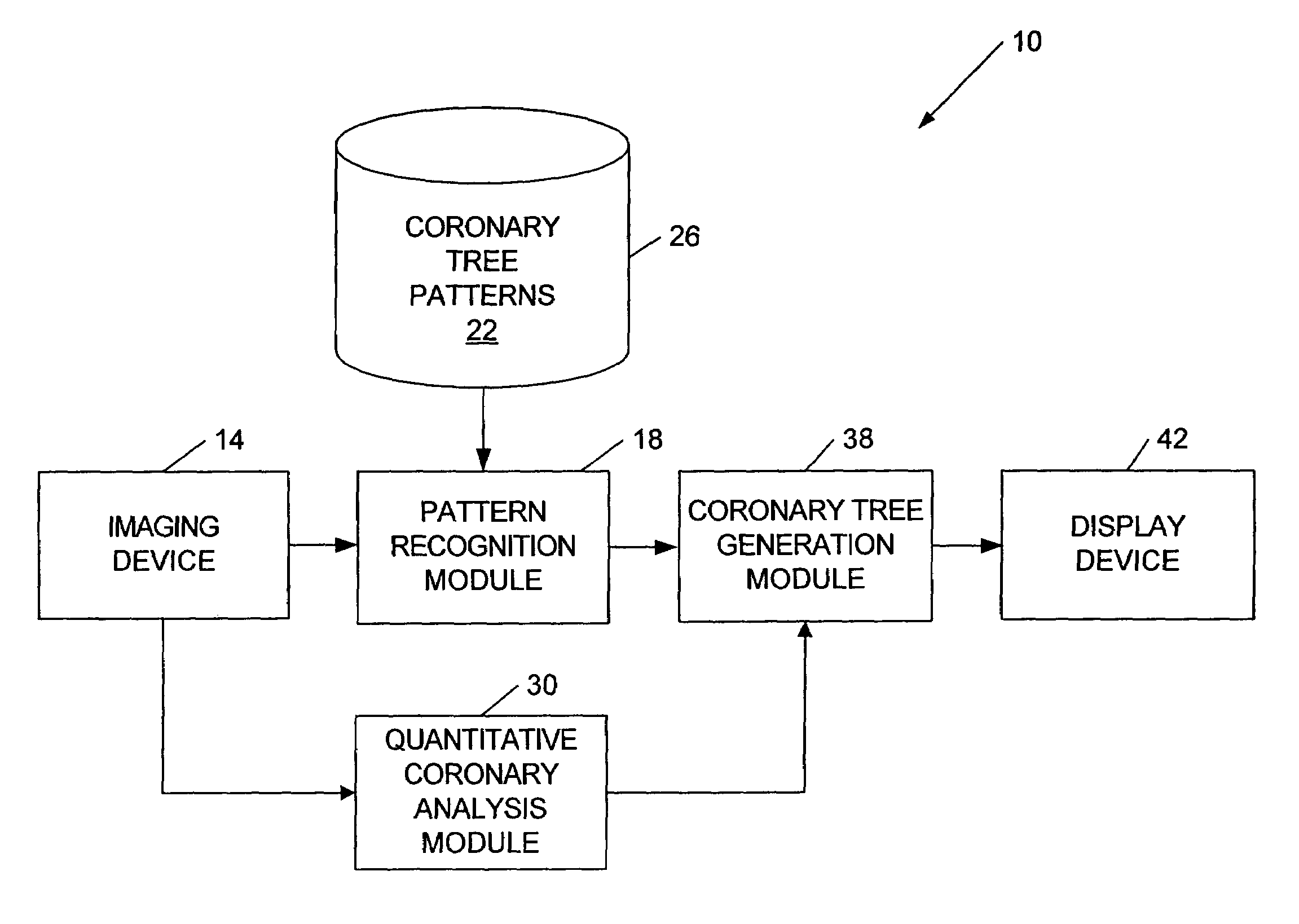
Coronary artery tree imaging system and method
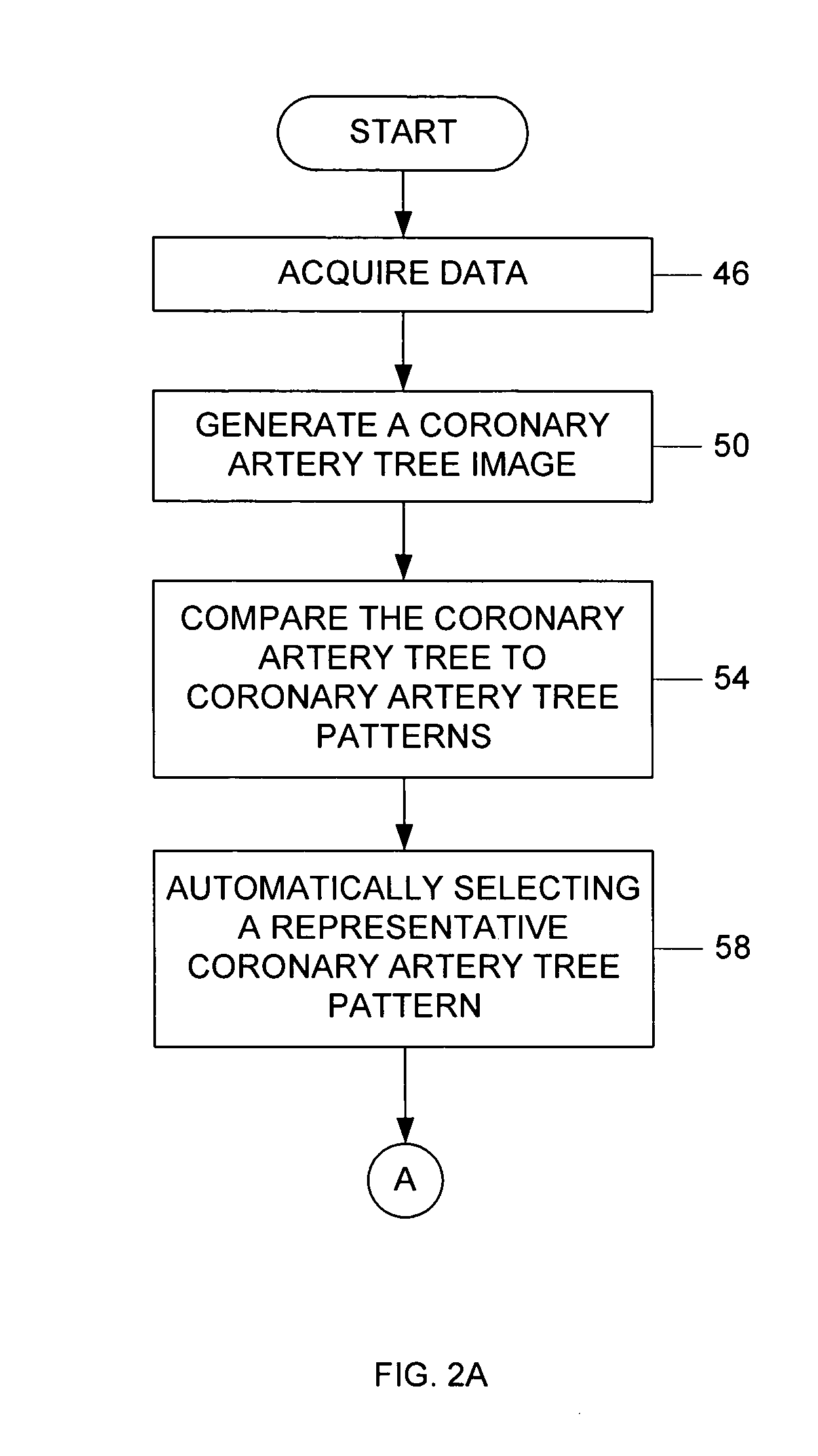
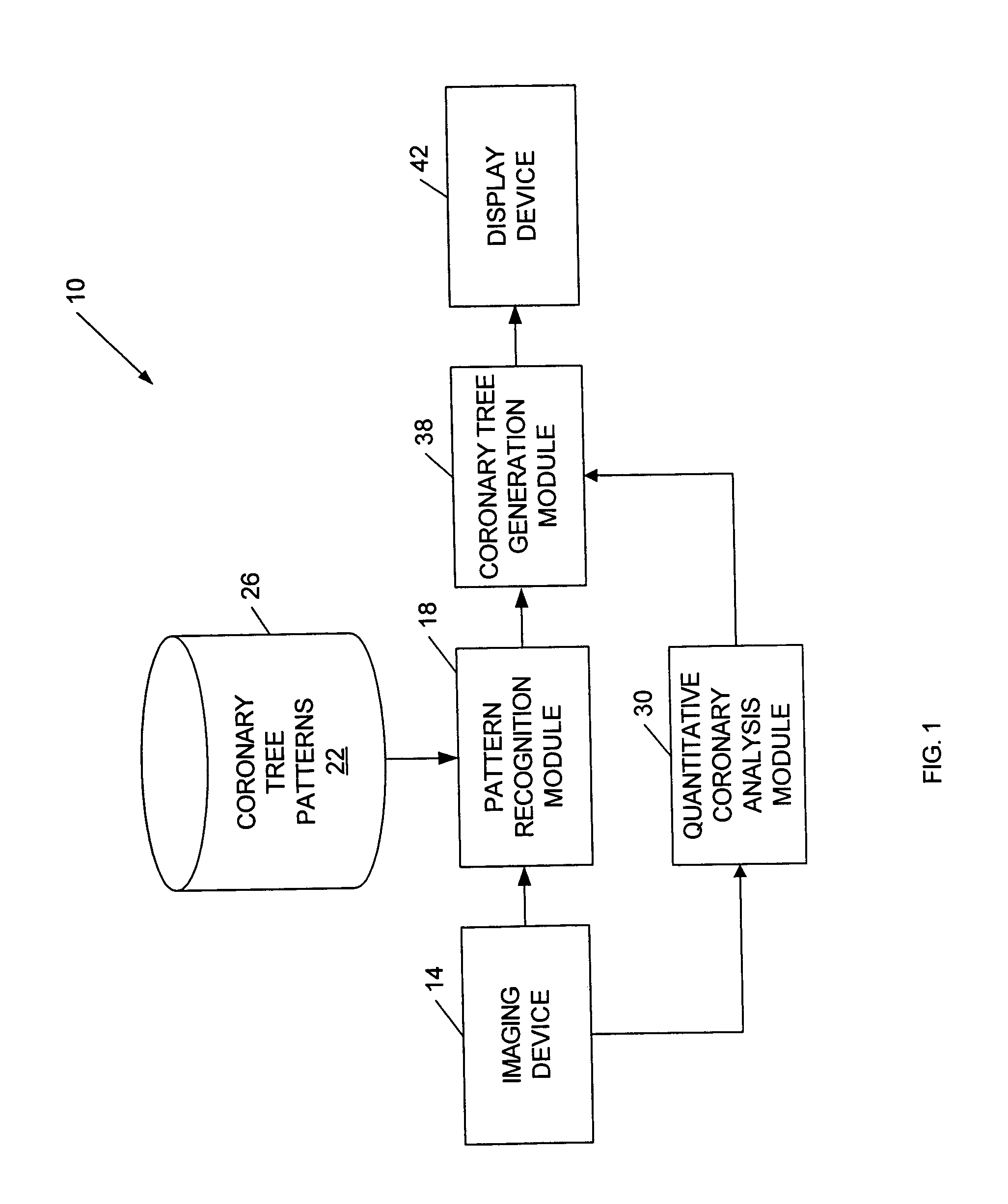
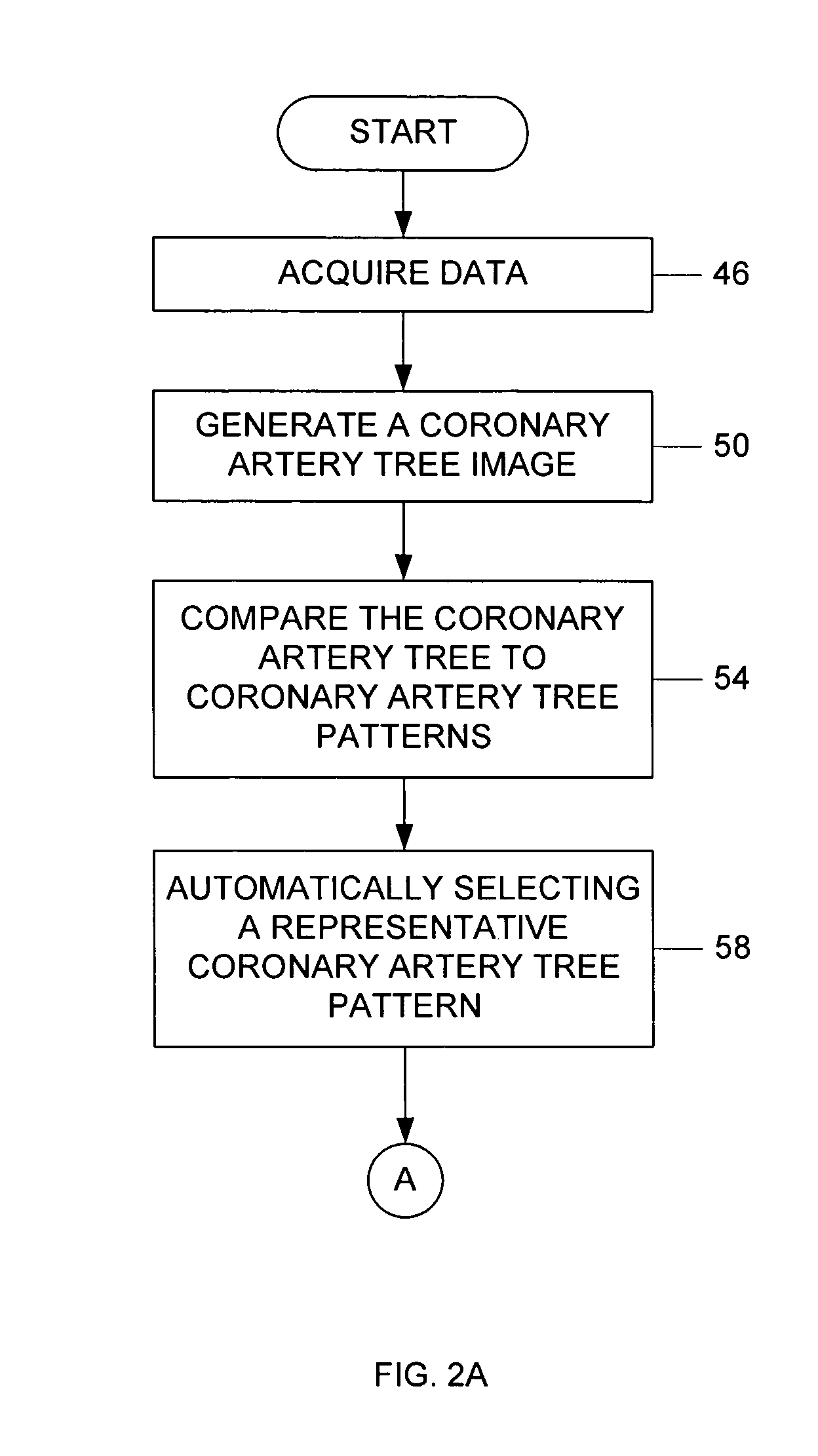
ActiveUS20060050941A1Improve accuracyImprove efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisCoronary arterial treeRadiology
A method of generating an image of a coronary artery tree for a patient. The method can include acquiring data from the patient for coronary artery segments and generating a coronary artery tree image including the coronary artery segments. The method can also include accessing coronary artery tree patterns, comparing the coronary artery tree image to the coronary artery tree patterns, and automatically selecting one of the coronary artery tree patterns as a representative coronary artery tree image for the patient. The method can further include measuring lesions and automatically adding the lesion measurements to the coronary artery tree image for the patient.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST INFORMATION TECH
Automatic measurement of morphometric and motion parameters of the coronary tree from a rotational X-ray sequence
Automatic measurement of morphometric and motion parameters of a coronary target includes extracting reference frames from input data of a coronary target at different phases of a cardiac cycle, extracting a three-dimensional centerline model for each phase of the cardiac cycle based on the references frames and projection matrices of the coronary target, tracking a motion of the coronary target through the phases based on the three-dimensional centerline models, and determining a measurement of morphologic and motion parameters of the coronary target based on the motion.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Automatic coronary isolation using a n-MIP ray casting technique
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Stimulus-release carrier, methods of manufacture and methods of treatment
Compositions, methods of fabrication and methods of treatment for the controlled release of a therapeutic substance to a treatment region are disclosed herein. In some embodiments, block copolymer-based release platforms (modified or unmodified) can be used to deliver a therapeutic substance to an inflamed site in, for example, the coronary tree or the kidney glomeri. The platforms can be carriers of at least one therapeutic substance. An external “trigger”, or stimulus, such as radiation, ultrasound, temperature, a magnetic field, a change in pH, a change in ionic strength or release of an enzyme, can be used to destabilize the platform in order to release its payload in a controlled manner once at a treatment site. Delivery devices can include a syringe, an infusion catheter, a porous balloon catheter, a double balloon catheter and the like.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
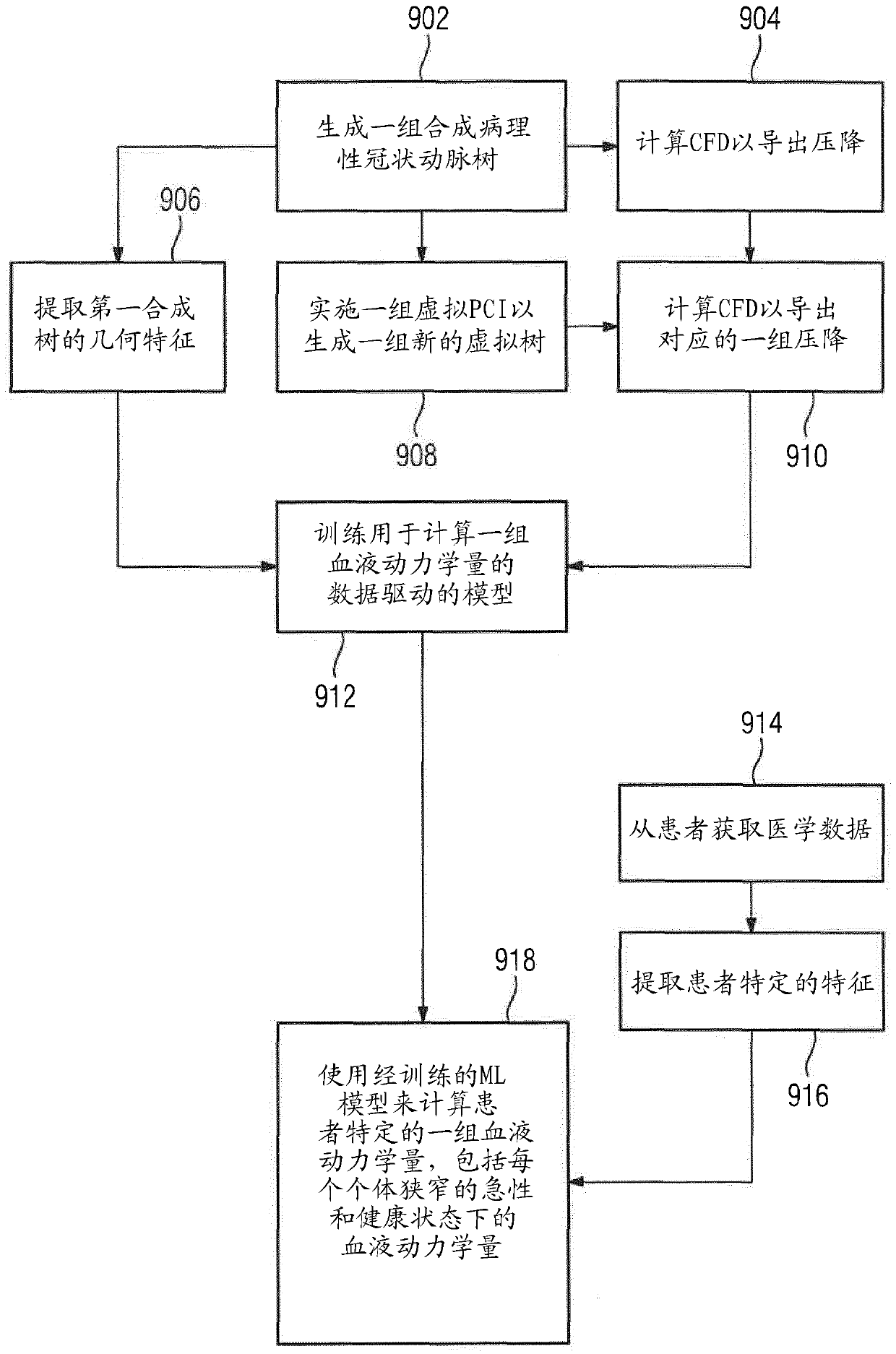
Method and system for purely geometric machine learning based fractional flow reserve
A method and system for determining hemodynamic indices, such as fractional flow reserve (FFR), for a location of interest in a coronary artery of a patient are disclosed. Medical image data of a patient is received. Patient-specific coronary arterial tree geometry of the patient is extracted from the medical image data. Geometric features are extracted from the patient-specific coronary arterial tree geometry of the patient. A hemodynamic index, such as FFR, is computed for a location of interest in the patient-specific coronary arterial tree based on the extracted geometric features using a trained machine-learning based surrogate model. The machine-learning based surrogate model is trained based on geometric features extracted from synthetically generated coronary arterial tree geometries.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
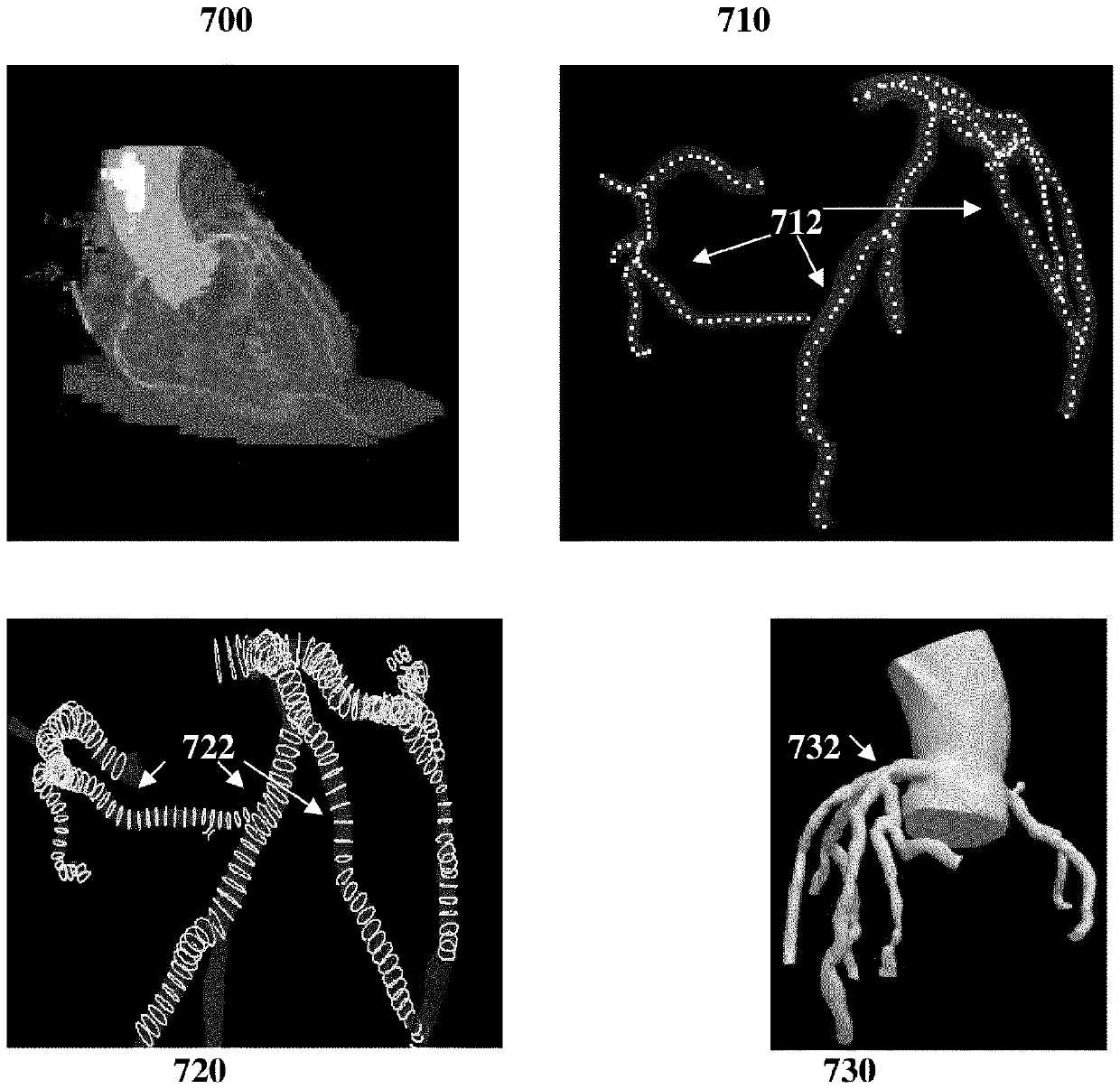
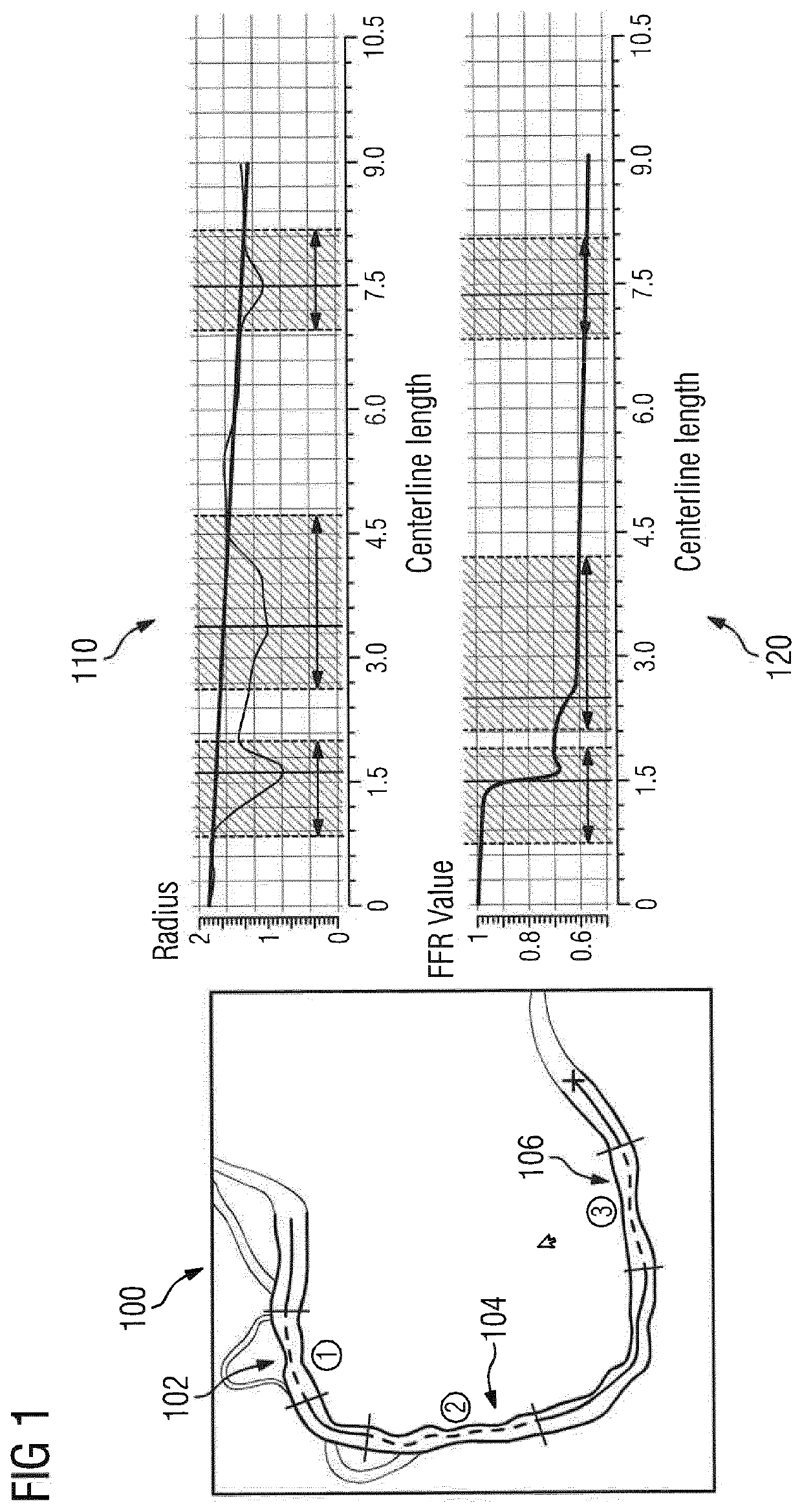
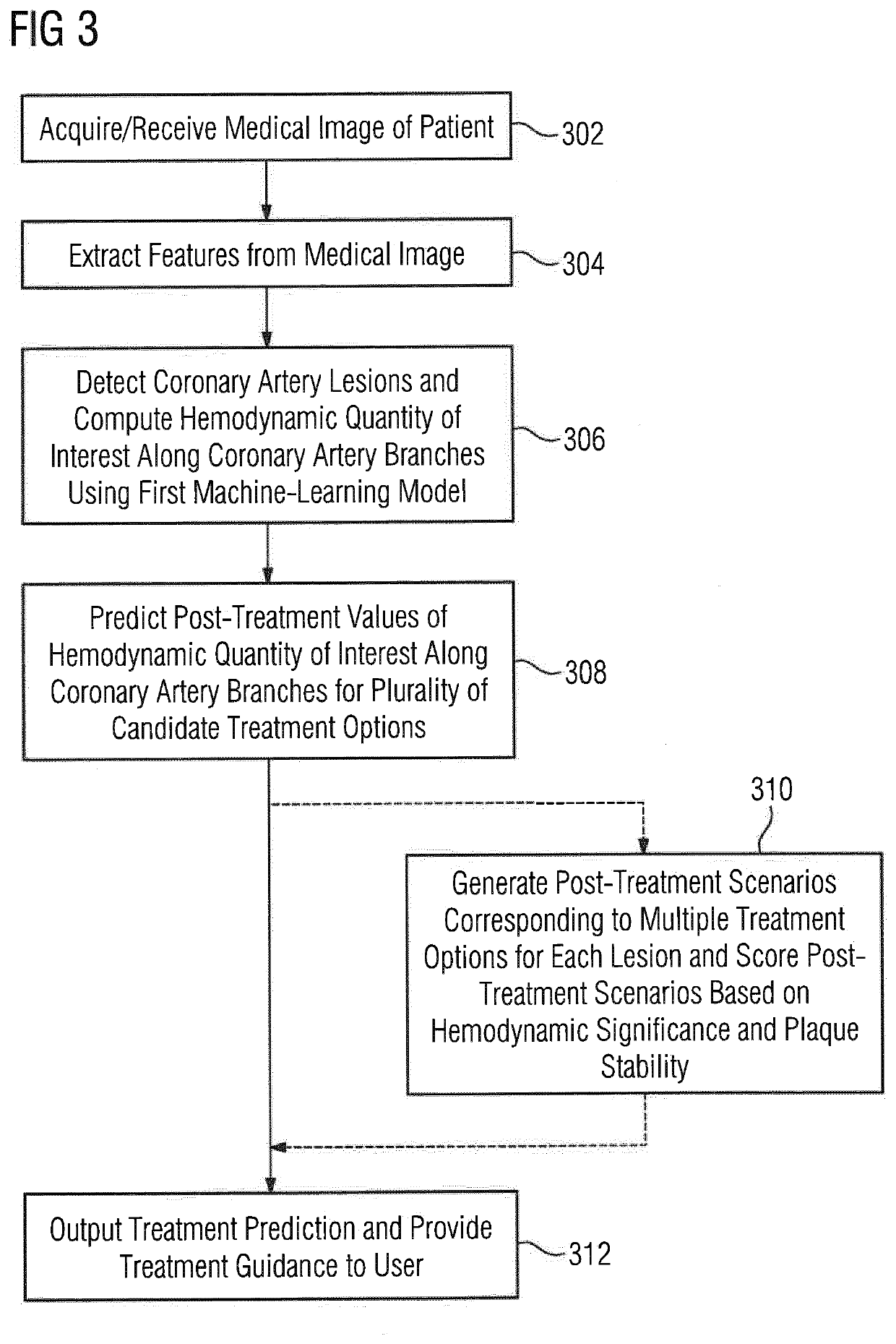
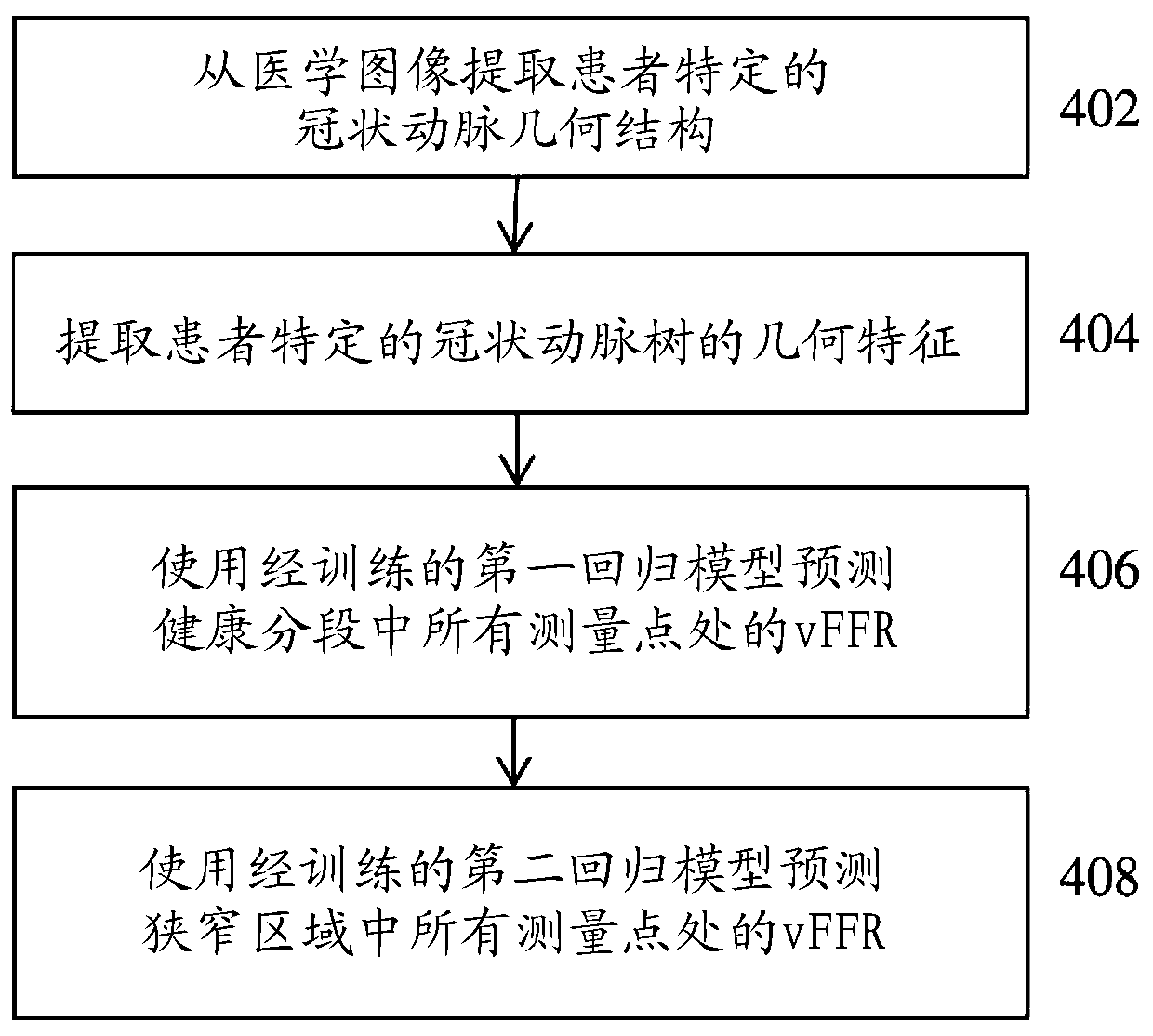
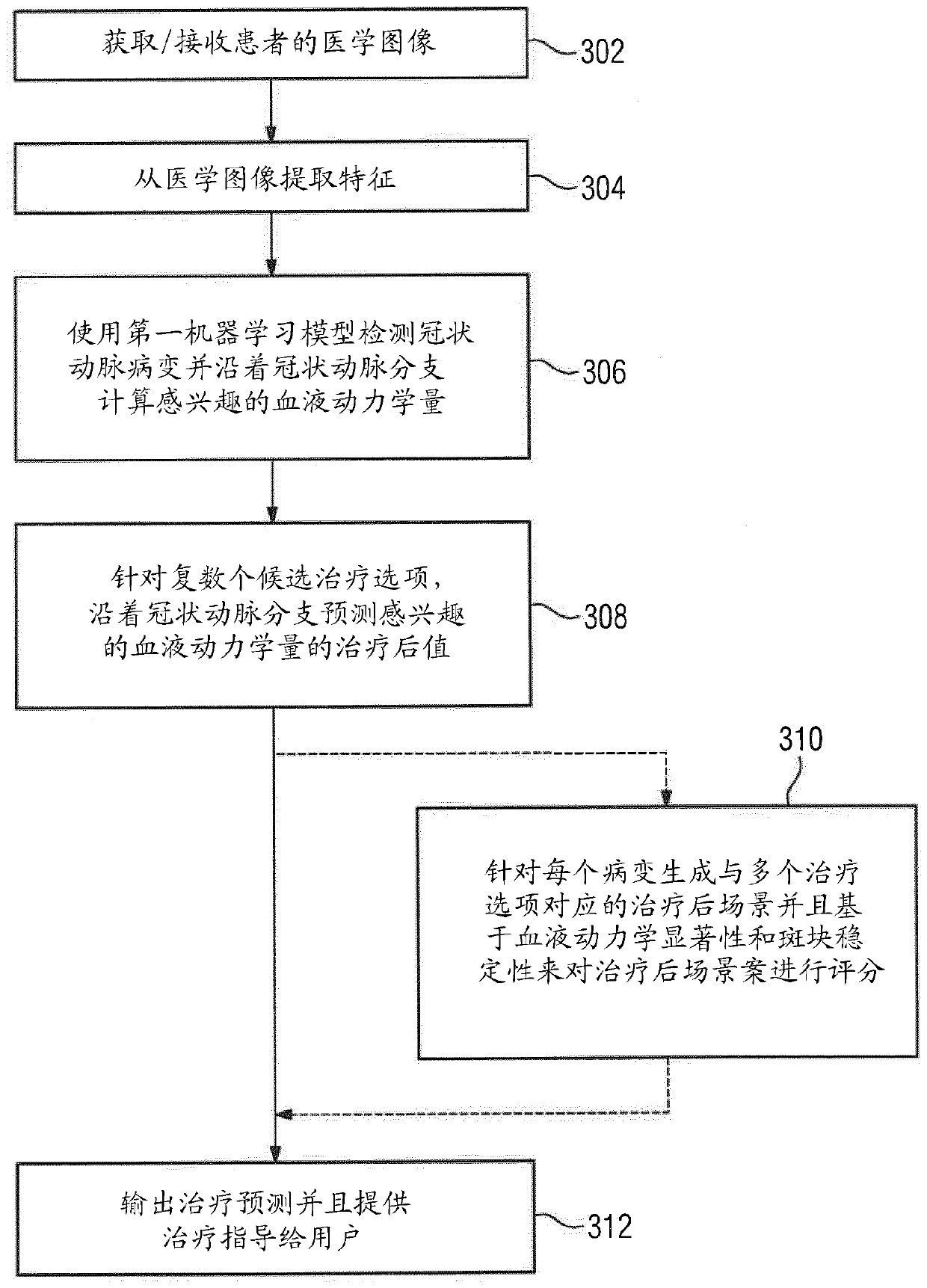
Non-invasive assessment and therapy guidance for coronary artery disease in diffuse and tandem lesions
ActiveUS20210085397A1Improve accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisCoronary artery diseaseCoronary arterial tree
A method and system for non-invasive assessment and therapy planning for coronary artery disease from medical image data of a patient is disclosed. Geometric features representing at least a portion of a coronary artery tree of the patient are extracted from medical image data. Lesions are detected in coronary artery tree of the patient and a hemodynamic quantity of interest is computed at a plurality of points along the coronary artery tree including multiple points within the lesions based on the extracted geometric features using a machine learning model, resulting in an estimated pullback curve for the hemodynamic quantity of interest. Post-treatment values for the hemodynamic quantity of interest are predicted at the plurality of points along the coronary artery tree including the multiple points within the lesions for each of one or more candidate treatment options for the patient, resulting in a respective predicted post-treatment pullback curve for the hemodynamic quantity of interest for each of the one or more candidate treatment options. A visualization of a treatment prediction for at least one of the candidate treatment options is displayed.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and system for hemodynamic computation in coronary arteries
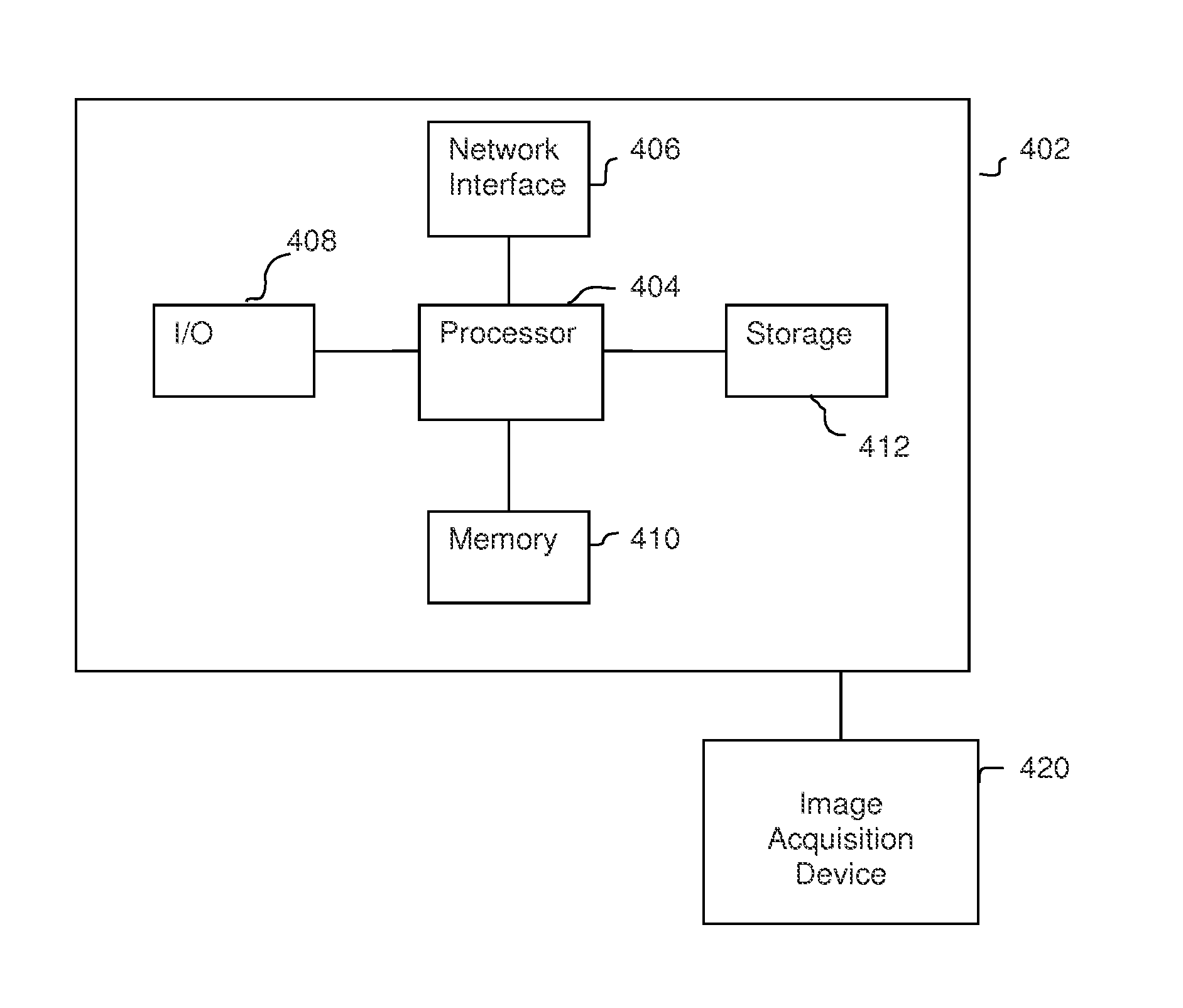
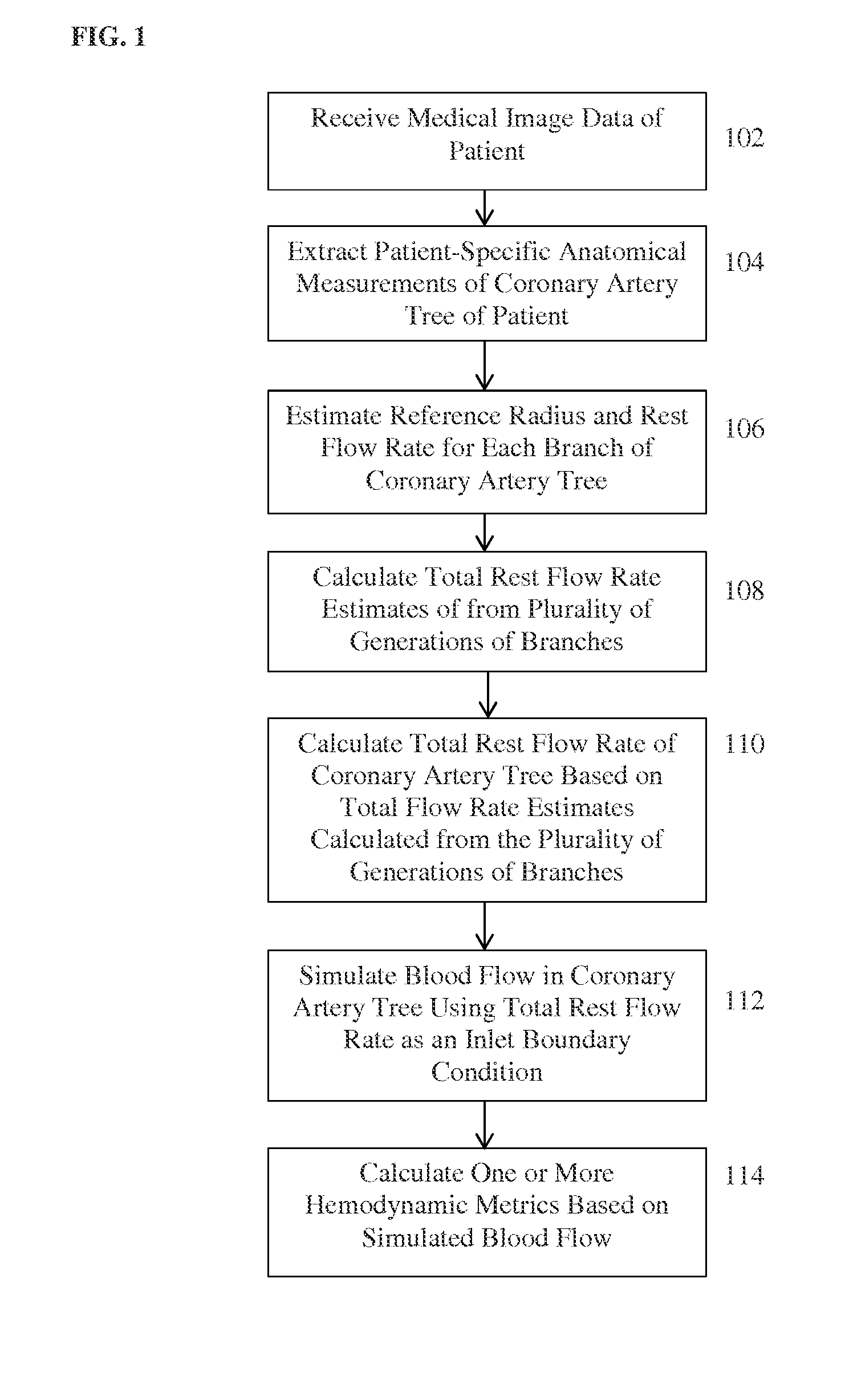
ActiveUS20170046834A1Medical simulationImage enhancementCoronary arterial treeAnatomical measurement
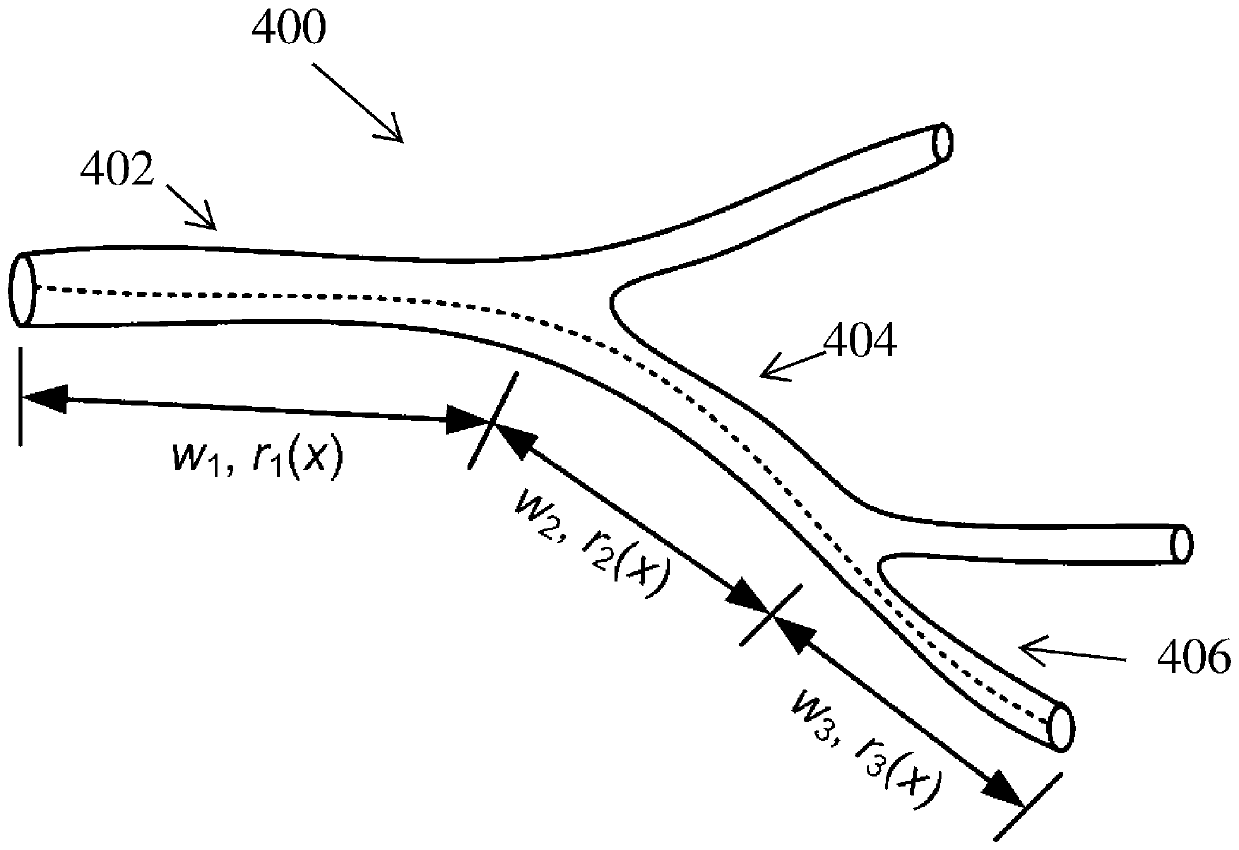
A method and system for computing blood flow in coronary arteries from medical image data disclosed. Patient-specific anatomical measurements of a coronary artery tree are extracted from medical image data of a patient. A reference radius is estimated for each of a plurality of branches in the coronary artery tree from the patient-specific anatomical measurements of the coronary artery tree. A flow rate is calculated based on the reference radius for each of the plurality of branches of the coronary artery tree. A plurality of total flow rate estimates for the coronary artery tree are calculated. Each total flow rate estimate is calculated from the flow rates of branches of particular generation in the coronary artery tree. A total flow rate of the coronary artery tree is calculated based on the plurality of total flow rate estimates. The total flow rate of the coronary artery tree can be used to derive boundary conditions for simulating blood flow in the coronary artery tree.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
A framework for personalization of coronary flow computations during rest and hyperemia
Embodiments relate to non-invasively determining coronary circulation parameters during a rest state and a hyperemic state for a patient. The blood flow in the coronary arteries during a hyperemic state provides a functional assessment of the patient's coronary vessel tree. Imaging techniques are used to obtain an anatomical model of the patient's coronary tree. Rest boundary conditions are computed based on non-invasive measurements taken at a rest state, and estimated hyperemic boundary conditions are computed. A feedback control system performs a simulation matching the rest state utilizing a model based on the anatomical model and a plurality of controllers, each controller relating to respective output variables of the coronary tree. The model parameters are adjusted for the output variables to be in agreement with the rest state measurements, and the hyperemic boundary conditions are accordingly adjusted. The hyperemic boundary conditions are used to compute coronary flow and coronary pressure variables.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
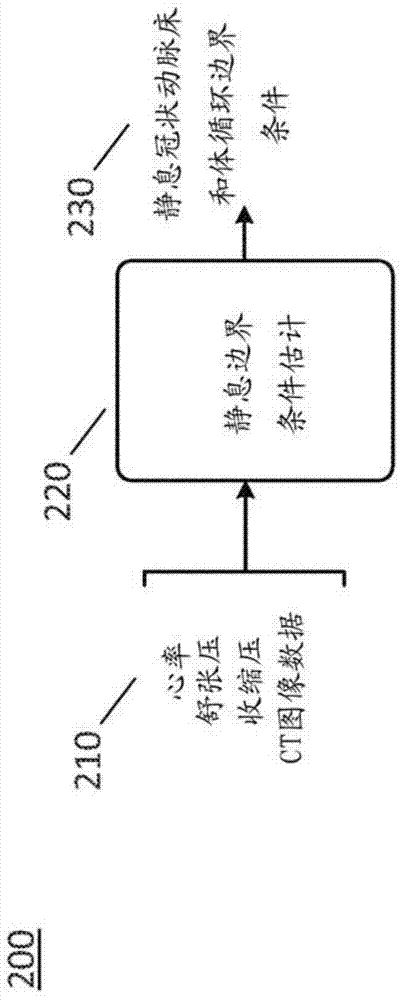
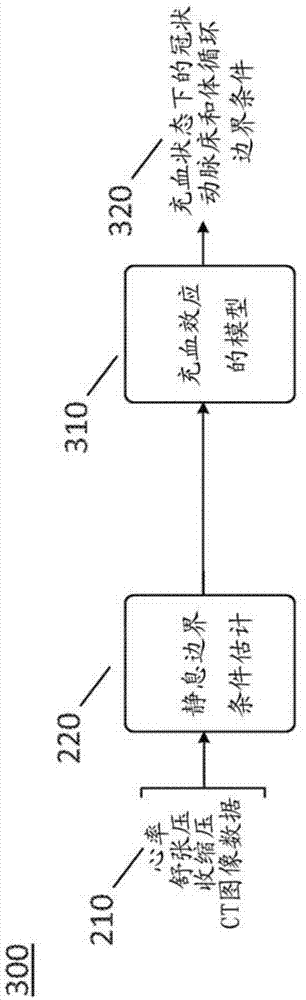
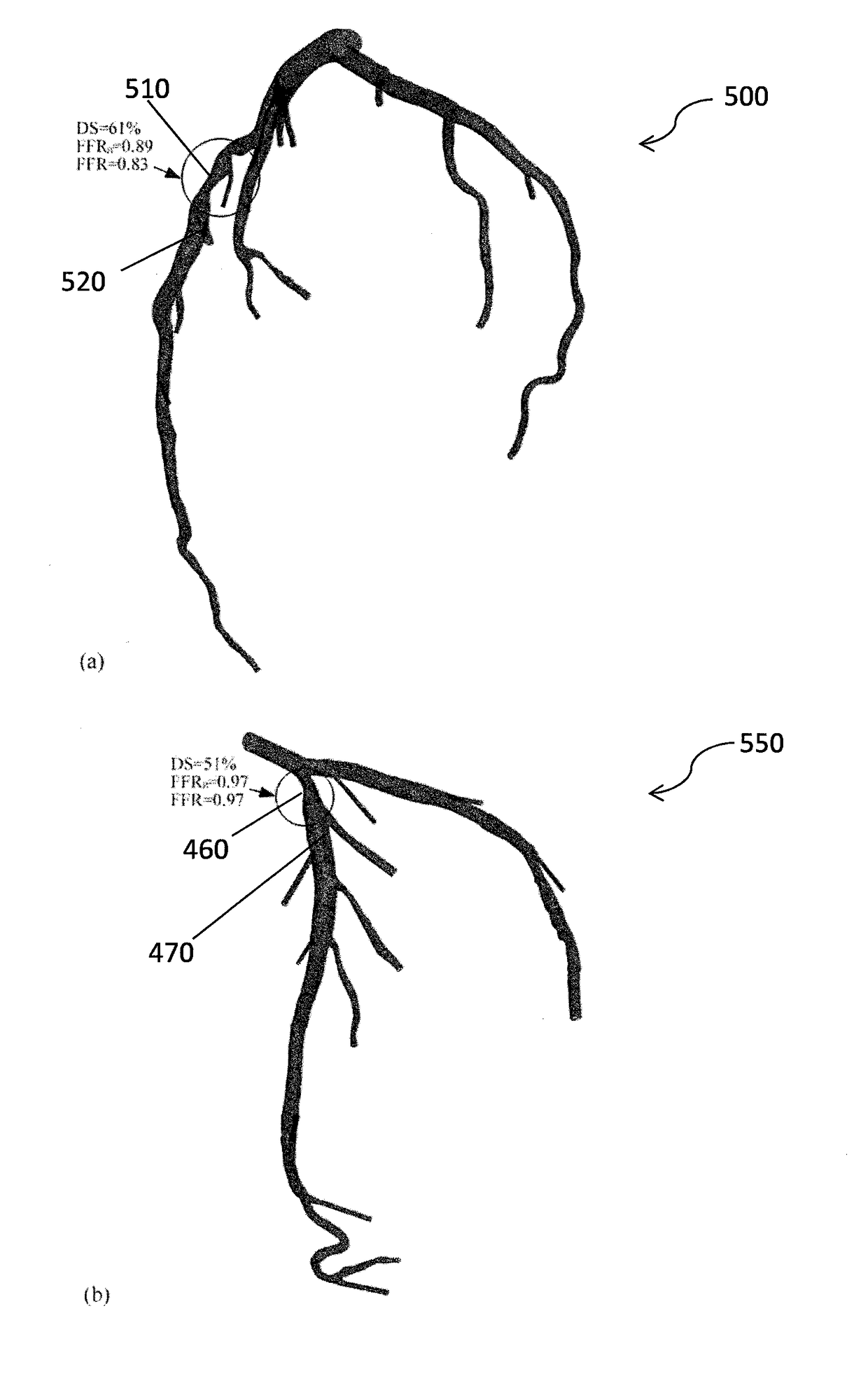
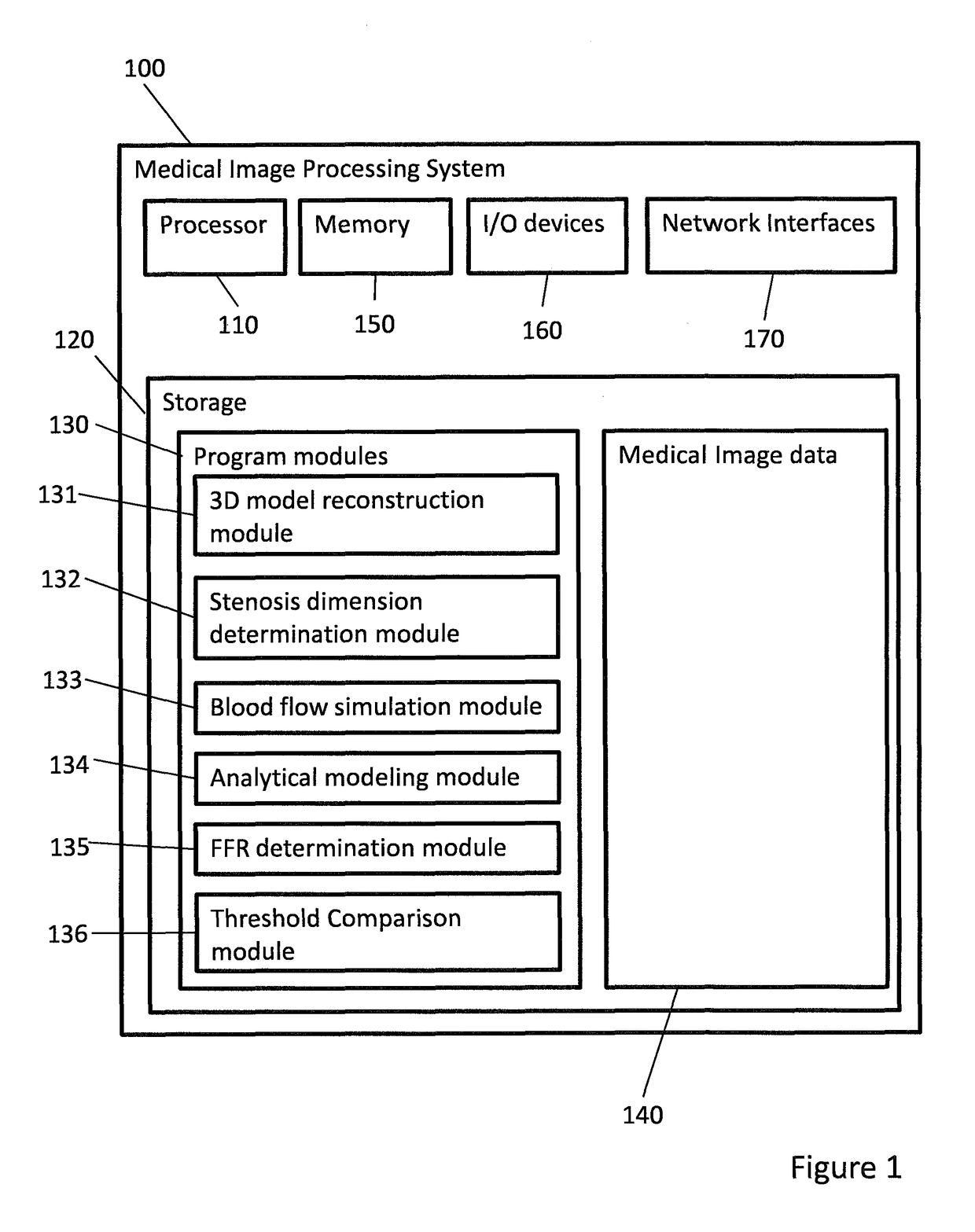
Medical image processing methods and systems
ActiveUS20180089829A1Reduce complexityMedical simulationDetails involving processing stepsCoronary arterial treeRadiology
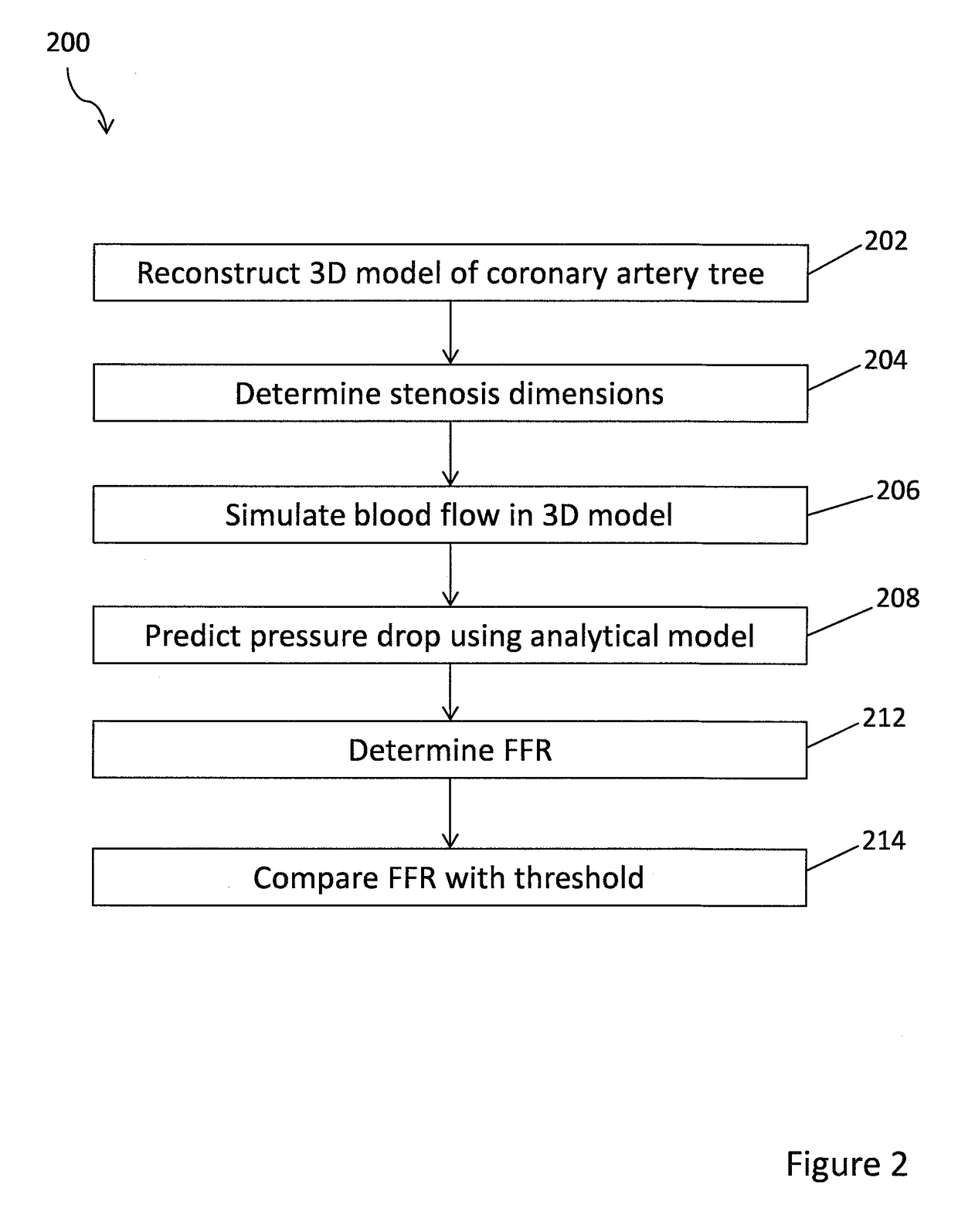
A medical image processing method of determining a fractional flow reserve through a stenosis of a coronary artery from medical image data is disclosed. The medical image data comprises a set of images of a coronary region of a patient. The coronary region includes the stenosis. The method comprises: reconstructing a three dimensional model of a coronary artery tree of the patient from the medical image data; determining stenosis dimensions from the three dimensional model of the coronary artery tree of the patient; simulating blood flow in the three dimensional model of the coronary artery tree of the patient to determine modeled flow rates; using an analytical model depending on the stenosis dimensions to predict a modeled pressure drop over the stenosis from the modeled flow rates; and determining the fractional flow reserve through the stenosis from the modeled pressure drop.
Owner:SINGAPORE HEALTH SERVICES PTE
Non-rigid 2D/3D registration of coronary artery models with live fluoroscopy images
ActiveUS8948487B2Reduce uncertaintyEnhance the imageImage enhancementImage analysisFluoroscopic imageCoronary arterial tree
A method for non-rigid registration of digital 3D coronary artery models with 2D fluoroscopic images during a cardiac intervention includes providing a digitized 3D centerline representation of a coronary artery tree that comprises a set of S segments composed of QS 3D control points, globally aligning the 3D centerline to at least two 2D fluoroscopic images, and non-rigidly registering the 3D centerline to the at least two 2D fluoroscopic images by minimizing an energy functional that includes a summation of square differences between reconstructed centerline points and registered centerline points, a summation of squared 3D registration vectors, a summation of squared derivative 3D registration vectors, and a myocardial branch energy. The non-rigid registration of the 3D centerline is represented as a set of 3D translation vectors rs,q that are applied to corresponding centerline points xs,q in a coordinate system of the 3D centerline.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Non-invasive assessment and therapy guidance for coronary artery disease in diffuse and tandem lesions
PendingCN110998744AImage enhancementMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesCoronary artery diseaseCoronary arterial tree
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Coronary artery tree imaging system and method
ActiveUS7639847B2Improve accuracyImprove efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisCoronary arterial treeRadiology
A method of generating an image of a coronary artery tree for a patient. The method can include acquiring data from the patient for coronary artery segments and generating a coronary artery tree image including the coronary artery segments. The method can also include accessing coronary artery tree patterns, comparing the coronary artery tree image to the coronary artery tree patterns, and automatically selecting one of the coronary artery tree patterns as a representative coronary artery tree image for the patient. The method can further include measuring lesions and automatically adding the lesion measurements to the coronary artery tree image for the patient.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST INFORMATION TECH
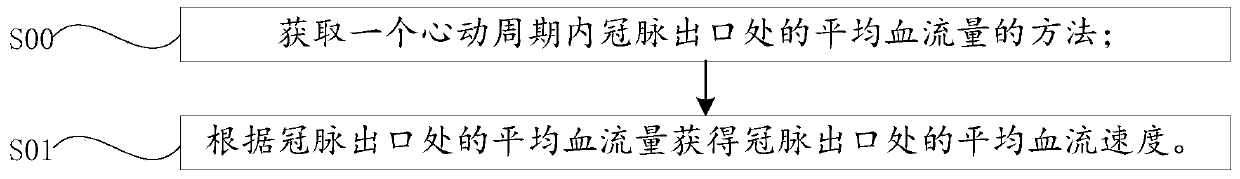
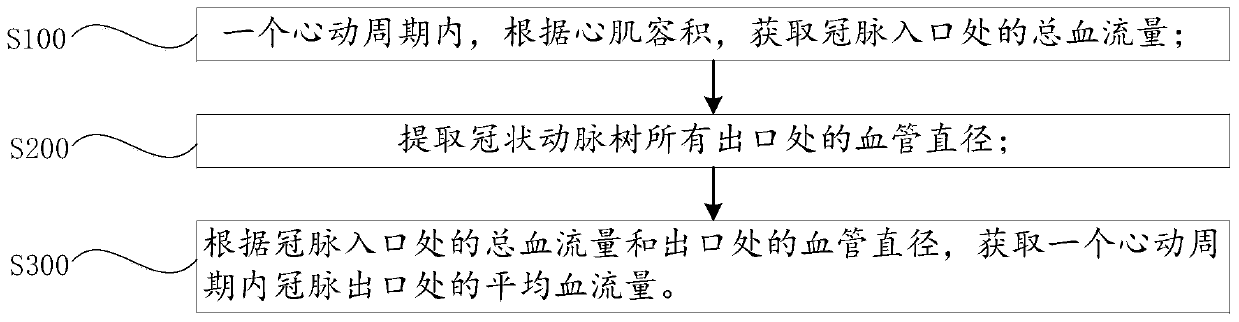
Method and device for obtaining average blood flow and flow rate at outlet of coronary artery, and system
InactiveCN110432886AEasy to operateAccurate measurementComputerised tomographsTomographyFine structureCoronary arterial tree
The application provides a method and device for obtaining average blood flow and flow rate at an outlet of a coronary artery, and a system. The method for obtaining the average blood flow at the outlet of the coronary artery in a cardiac cycle comprises the following steps of in one cardiac cycle, according to the volume of cardiac muscles, obtaining the total blood flow of an inlet of the coronary artery; extracting the blood vessel diameter of each of all the outlets of a corona arterial tree; and according to the total blood flow at the inlet of the coronary artery and the blood vessel diameter of the outlet of the coronary artery, obtaining the average blood flow at the outlet of the coronary artery in the cardiac cycle. The method disclosed by the application is a new non-invasive detection means, measuring the blood flow does not need to rely on a coronary artery ultrasonic technique, and according to the total blood flow at the inlet of the coronary artery and the blood vesseldiameter at the outlet, the average blood flow at the outlet of the coronary artery in one cardiac cycle can be obtained, so that the operation is easy, fine structure images can be distinguished, andthe measuring is more accurate.
Owner:SUZHOU RAINMED MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Myocardial CT perfusion image synthesis
PendingCN110461235ARealize detailed evaluationMedical imagingImage analysisComputed tomographyCoronary arterial tree
The present invention relates to image processing devices and related methods. The image processing device (10) comprises a data input (11) for receiving spectral computed tomography volumetric imagedata organized in voxels. The image data comprises a contrast-enhanced volumetric image of a cardiac region in a subject's body and a baseline volumetric image of that cardiac region, e.g. a virtual non-contrast image, wherein the contrast-enhanced volumetric image conveys anatomical information regarding coronary artery anatomy of the subject. The device comprises a flow simulator (12) for generating, or receiving as input, a three-dimensional coronary tree model based on the volumetric image data and for simulating a coronary flow based on the three-dimensional coronary tree model. The device comprises a perfusion synthesis unit (13) for generating a perfusion image representative of a blood distribution in tissue at at least one instant in time taking at least the baseline volumetric image and said coronary flow simulation into account.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Visualization of the coronary artery tree
ActiveUS20120020462A1Enhanced informationQuick and reliable diagnosisReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionCoronary arterial treeRadiology
The present invention is related to a method for reconstruction of the coronary arteries and an examination apparatus for reconstruction of the coronary arteries. To provide improved coronary artery information, an apparatus and a method are provided where a gating signal is provided (32) and a first gated X-ray image sequence of one of the left or right branches of the coronary arteries is acquired (34) with injected contrast agent into the one of the left or right branches of the coronary arteries. Further, a second gated X-ray image sequence of the other branch of the coronary arteries is acquired (36) with injected contrast agent into said other branch. Then, a gated reconstructing (38) of the left and the right coronary artery is suggested and a volume data (40, 42) of the coronary arteries is generated. The volume data of the left and right coronary arteries is registered (44) in relation to time and space. Further; the registered volume data (48, 50) of the left and the right coronary arteries is combined and a combined coronary artery tree volume data set (52) is generated (54). Finally, the combined coronary tree volume data set is visualized (56).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Application of Morindae officinalis oligosaccharide 6 glycan in preparation of myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury resistance medicines
ActiveCN103665180AImprove protectionProtection formOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesReperfusion injuryOfficinalis
The invention discloses an application of a Morindae officinalis extract product and Morindae officinalis oligosaccharide 6 glycan in the preparation of medicines for resisting myocardial ischemia and / or reperfusion injury and promoting therapeutic angiogenesis. The myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury are body injuries caused by the afresh circulation establishment and the blood supply recovery during the stopping or abnormality of the myocardial blood perfusion, like ischemic and anoxic injuries. The Morindae officinalis oligosaccharide 6 glycan has a protect effect on an in-vivo rat myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury model and an in-vitro purify-cultured mouse myocardial cell reoxygenation injury model, can substantially reduces the myocardial infarction area, can mitigate the reperfusion arrhythmia, can effectively protect the form of myocardial cells, and can mitigate the injuries of anoxic reoxygenation to the myocardial cells. The therapeutic angiogenesis promotion is characterized in that the ischemic myocardial blood supply recovery and the cardiac function improvement are realized by increasing the functional coronary arterial tree or coronary collateral through some irradiations comprising the treatment effects of some medicines.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Detecting coronary stenosis through spatio-temporal tracking
Embodiments relate to detecting coronary stenosis through spatio-temporal tracking. Aspects include extracting a coronary artery tree from each of a sequence of angiogram images, creating a mean artery tree from the extracted coronary artery trees, and projecting the mean artery tree back onto each of the sequence of angiogram images to recover a complete coronary artery tree for each of the sequence of angiogram images. Aspects also include extracting one or more tubular sections from each of the sequence of angiogram images, estimating an arterial width for each of the one or more tubular sections from each of the sequence of angiogram images, and creating a spatio-temporal surface from the arterial widths of the one or more tubular sections over a time spanned by the sequence of angiogram images. Aspects further include detecting a minimum in the spatio-temporal surface and determining if the minimum is indicative of stenosis.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Initialization independent approaches towards registration of 3D models with 2D projections
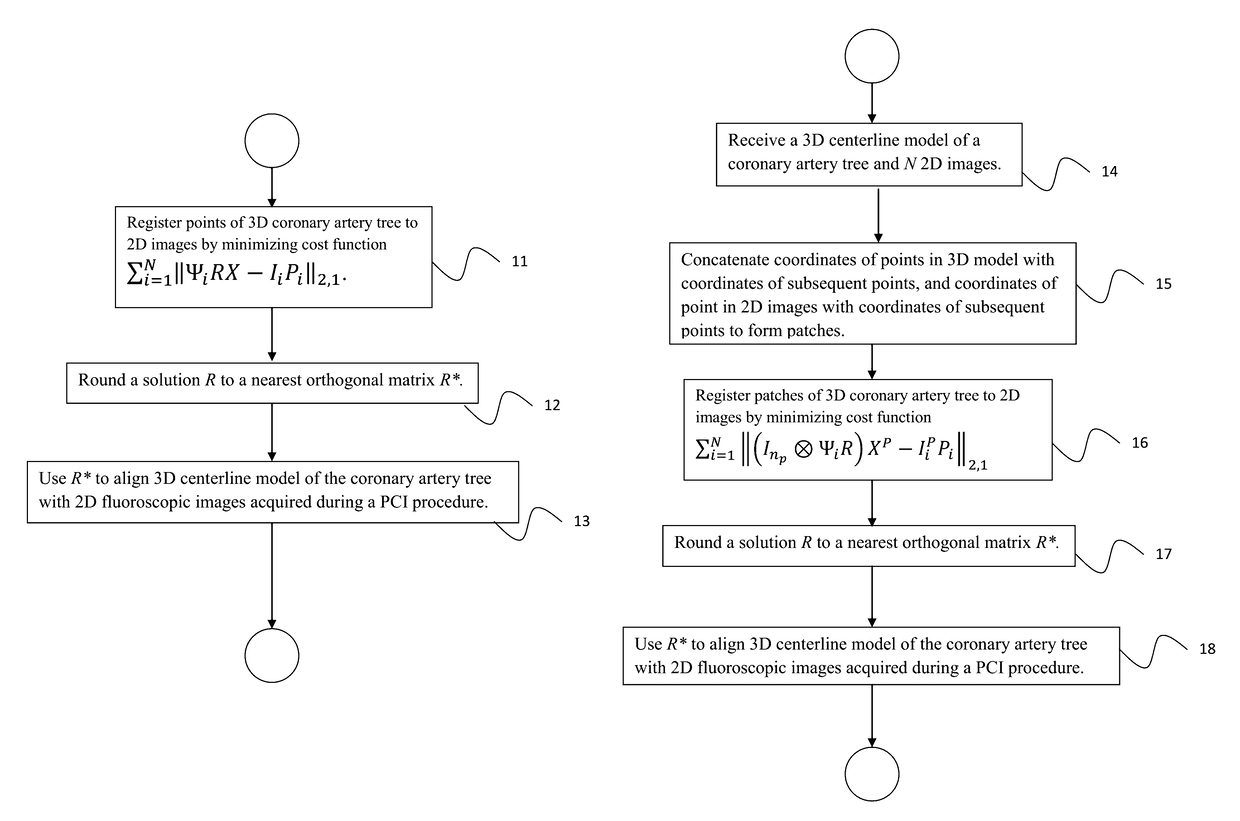
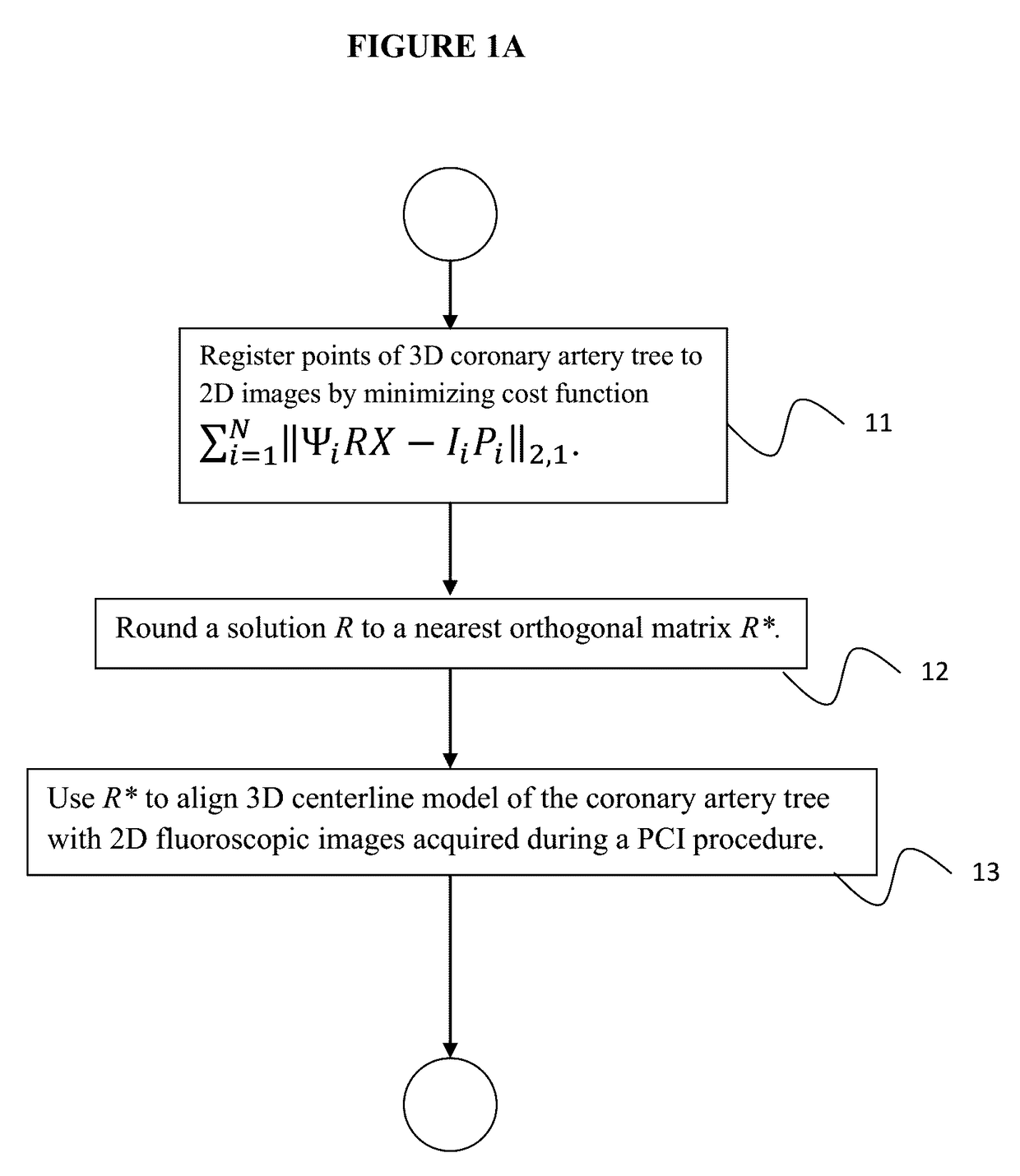
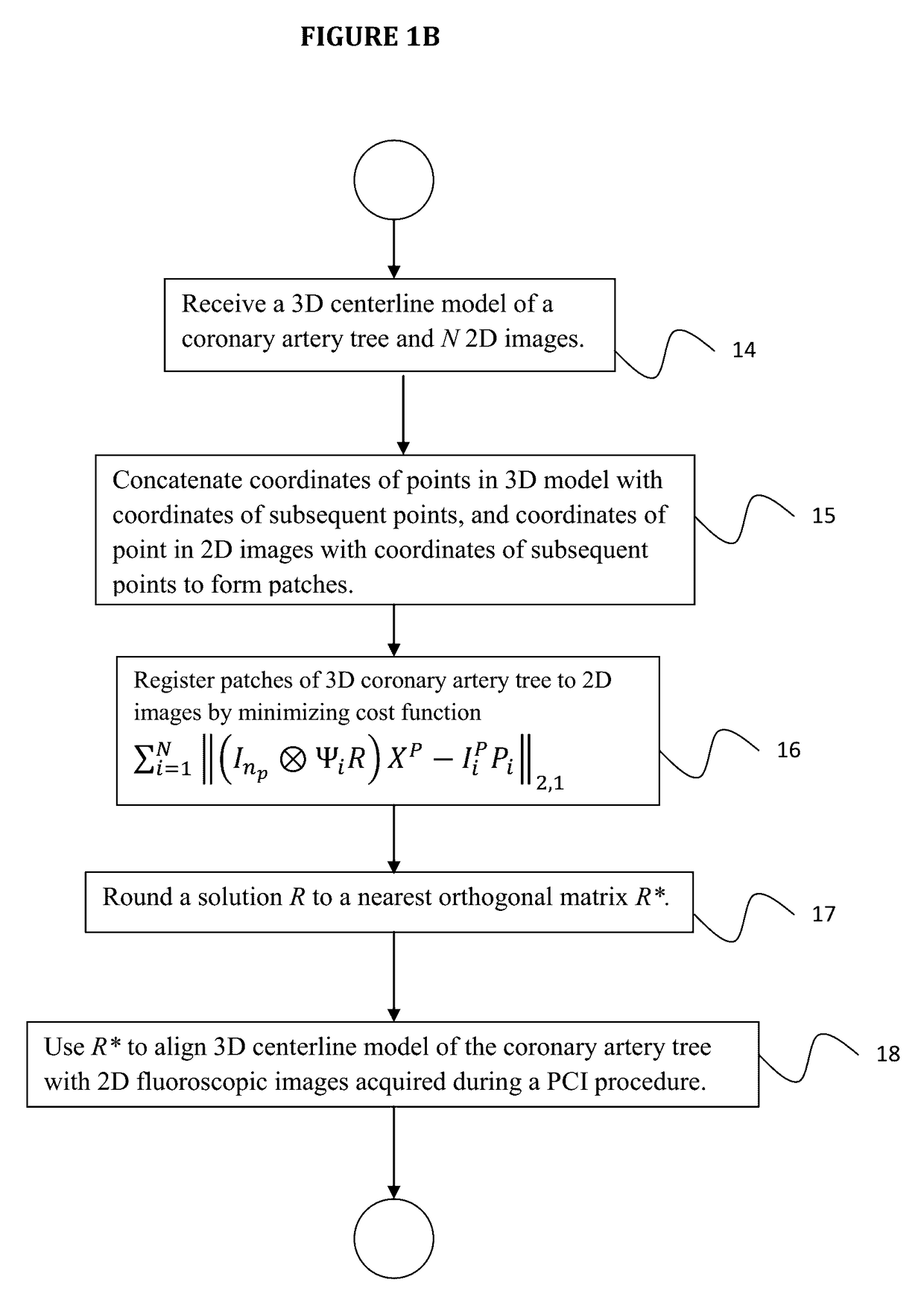
ActiveUS9646361B2Efficient searchImage enhancementImage analysisFluoroscopic imageCoronary arterial tree
A method of registering a 3-dimensional (3D) model of a coronary artery tree with 2-dimensional (2D) images includes solving for matrices R, Pi, i=1, . . . , N, that minimize a cost function Σi=1N∥ΨiRX−IiPi∥2,1 subject to constraints that R∈conv(SO(3)), Pi∈[0,1]n<sub2>i< / sub2>×m, and Pi1≦1, 1TPi=1, for i∈{1, N}, where N is a number of 2D images, R is a rotation matrix, conv(SO(3)) denotes a convex hull of the special orthogonal group in 3 dimensions, X denotes a 3D centerline model of a coronary artery tree, Ii denotes the ith 2D image, Ψi denotes a transformation between the 3D centerline model X and the ith 2D image Ii, 1 is an all-ones vector, Pi is a permutation matrix, and rounding a solution R to a nearest orthogonal matrix R* in SO(3), where R* aligns the 3D centerline model X of the coronary artery tree with 2D fluoroscopic images acquired during a percutaneous coronary intervention procedure.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
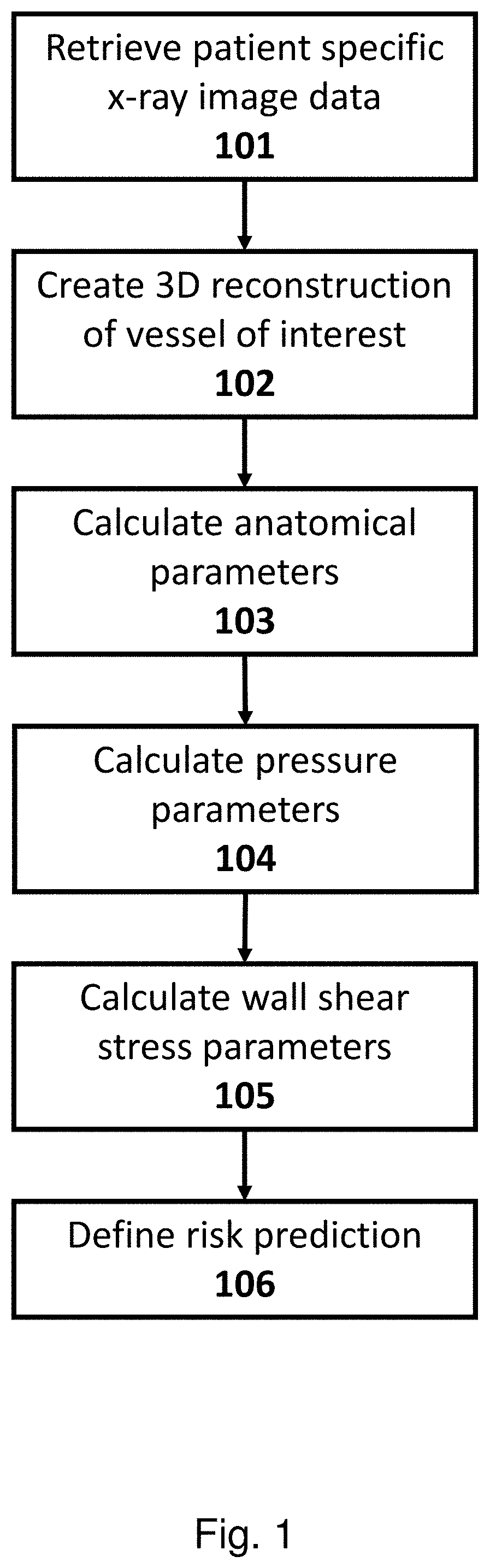
Method and system for calculating myocardial infarction likelihood based on lesion wall shear stress descriptors
Method and systems are described that create a 3D reconstruction of a vessel of interest that represents a subset of a coronary tree that includes a lesion; calculate at least one of pressure parameters or anatomical parameters based at least in part on a portion of the 3D reconstruction that includes the lesion; calculate a wall shear stress (WSS) descriptor, based on the 3D reconstruction, for a segment of a surface of the vessel that includes the lesion, wherein the WSS descriptor includes information regarding an amount of variation in contraction or expansion applied at surface elements within the segment during at least a portion of a cardiac cycle; and calculate a myocardial infarction (MI) index based on the WSS descriptor and the at least one of the pressure or anatomical parameters, the MI index representing a likelihood that the lesion will result in an MI.
Owner:PIE MEDICAL IMAGING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com