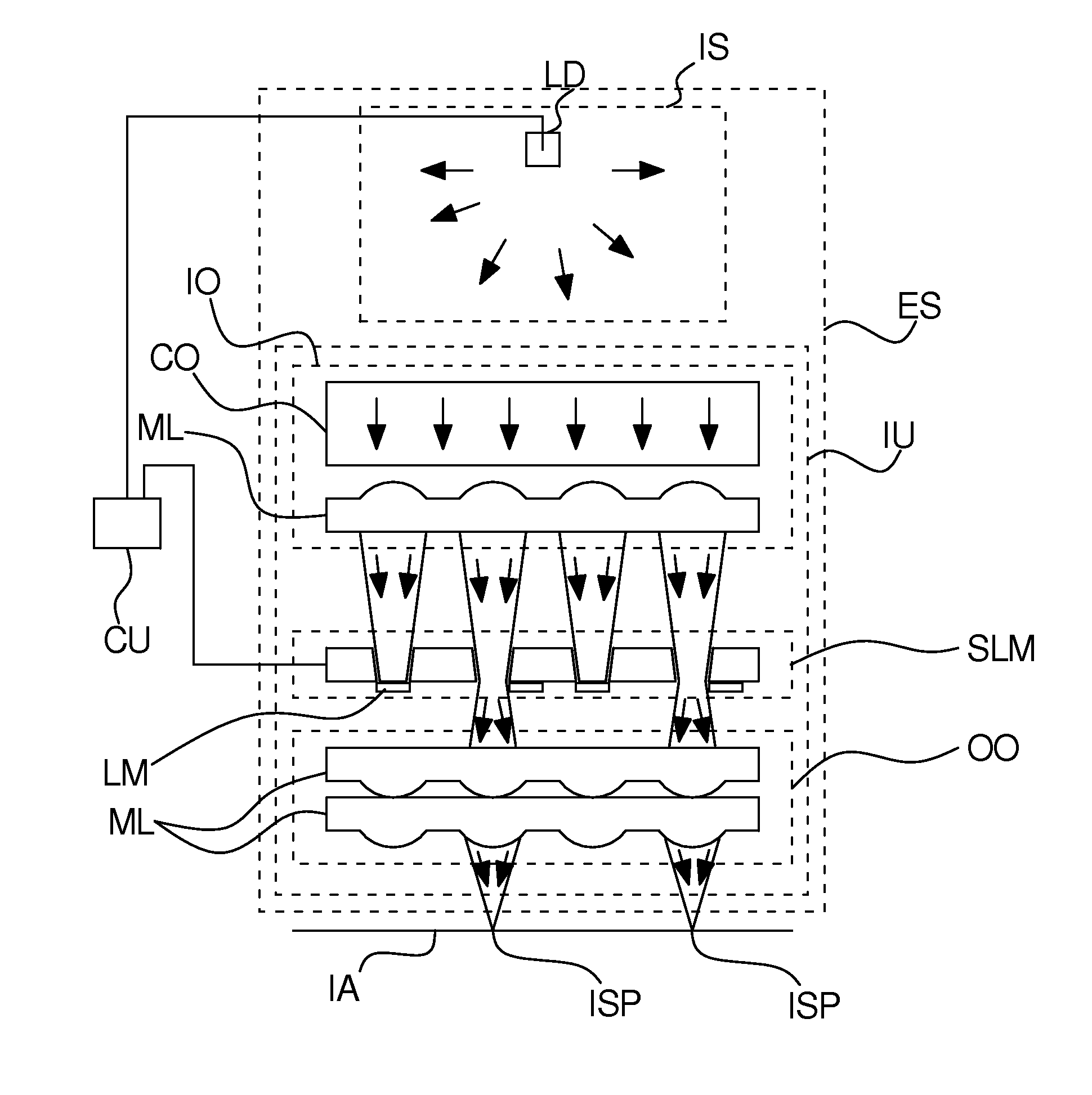
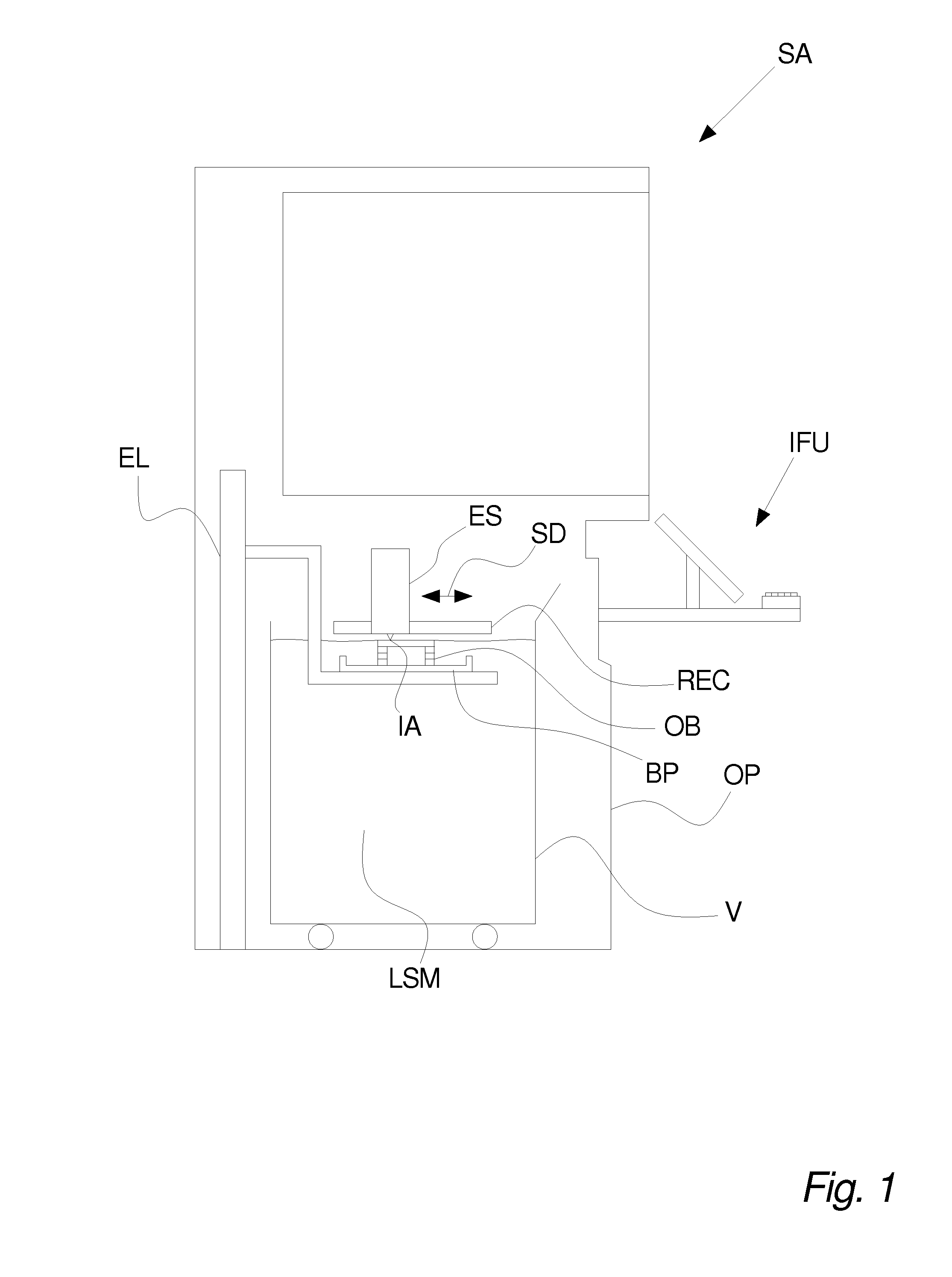
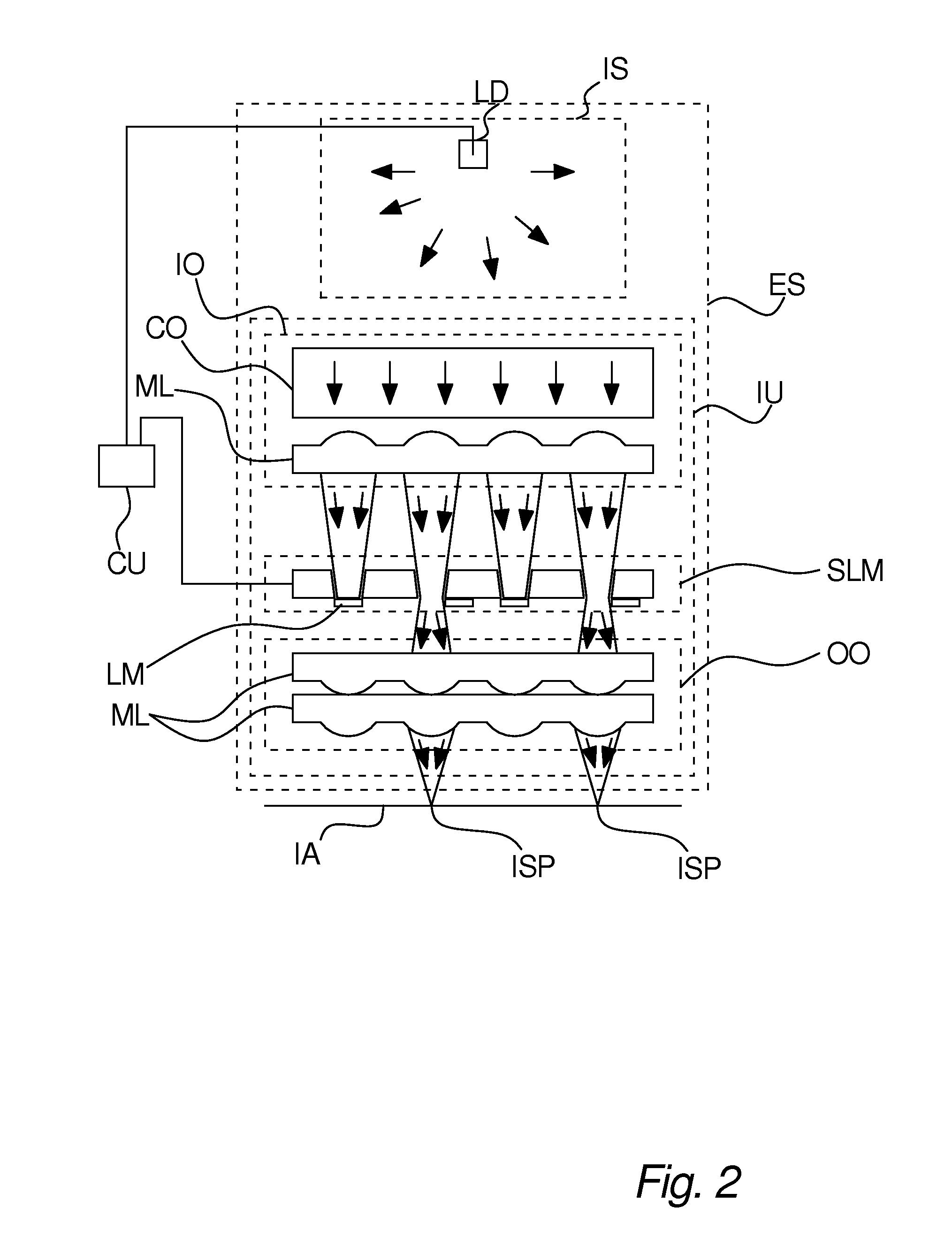
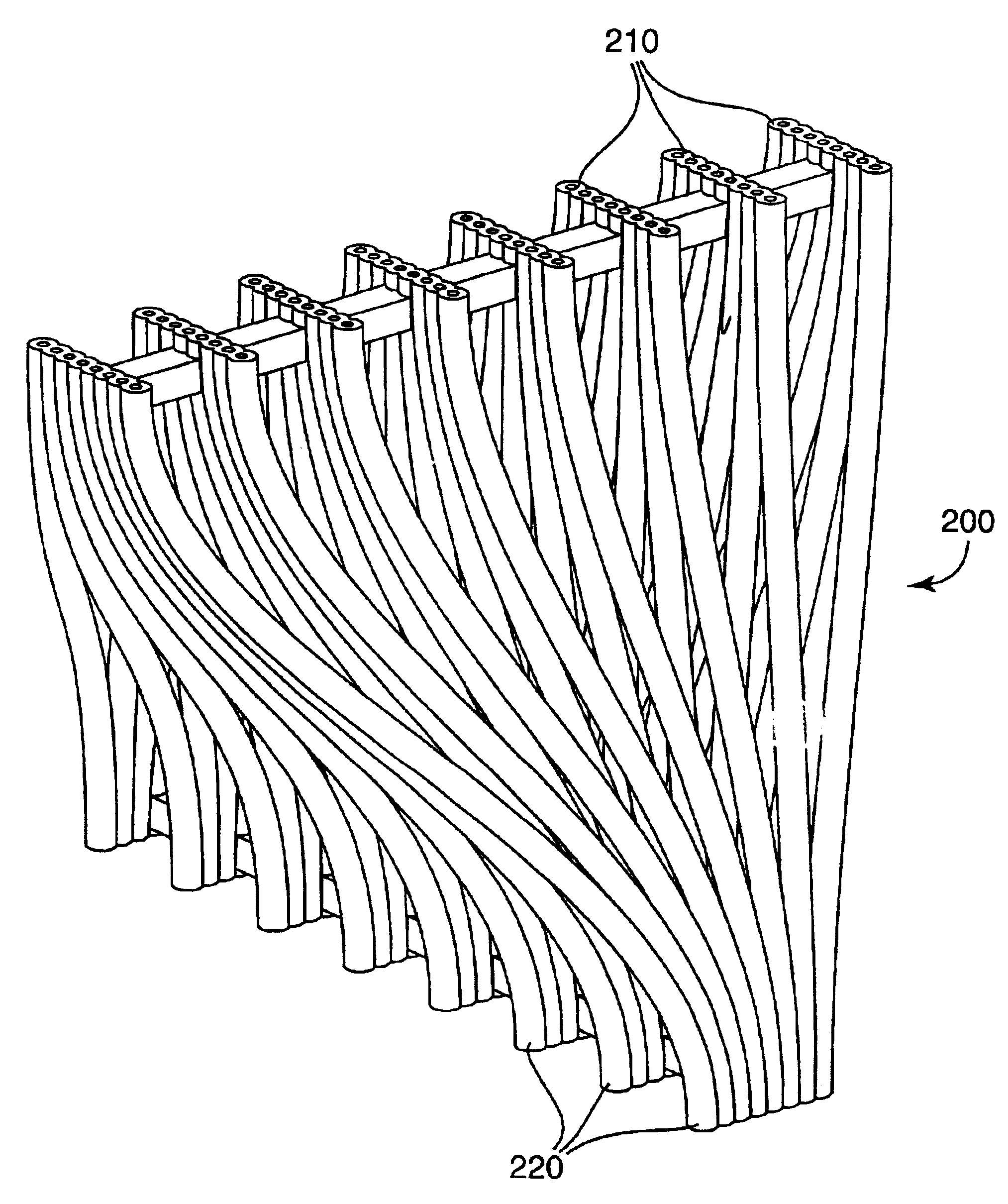
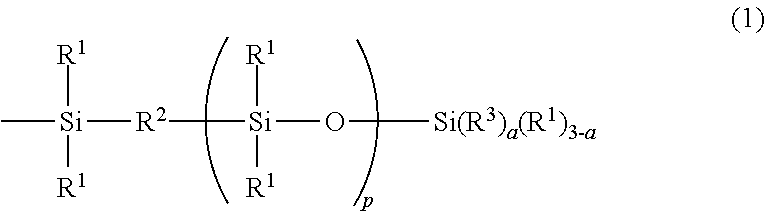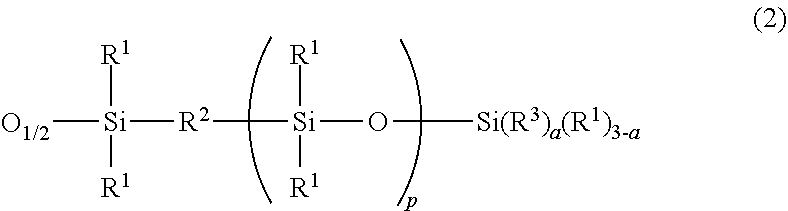Patents
Literature
67 results about "Stereolithographies" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
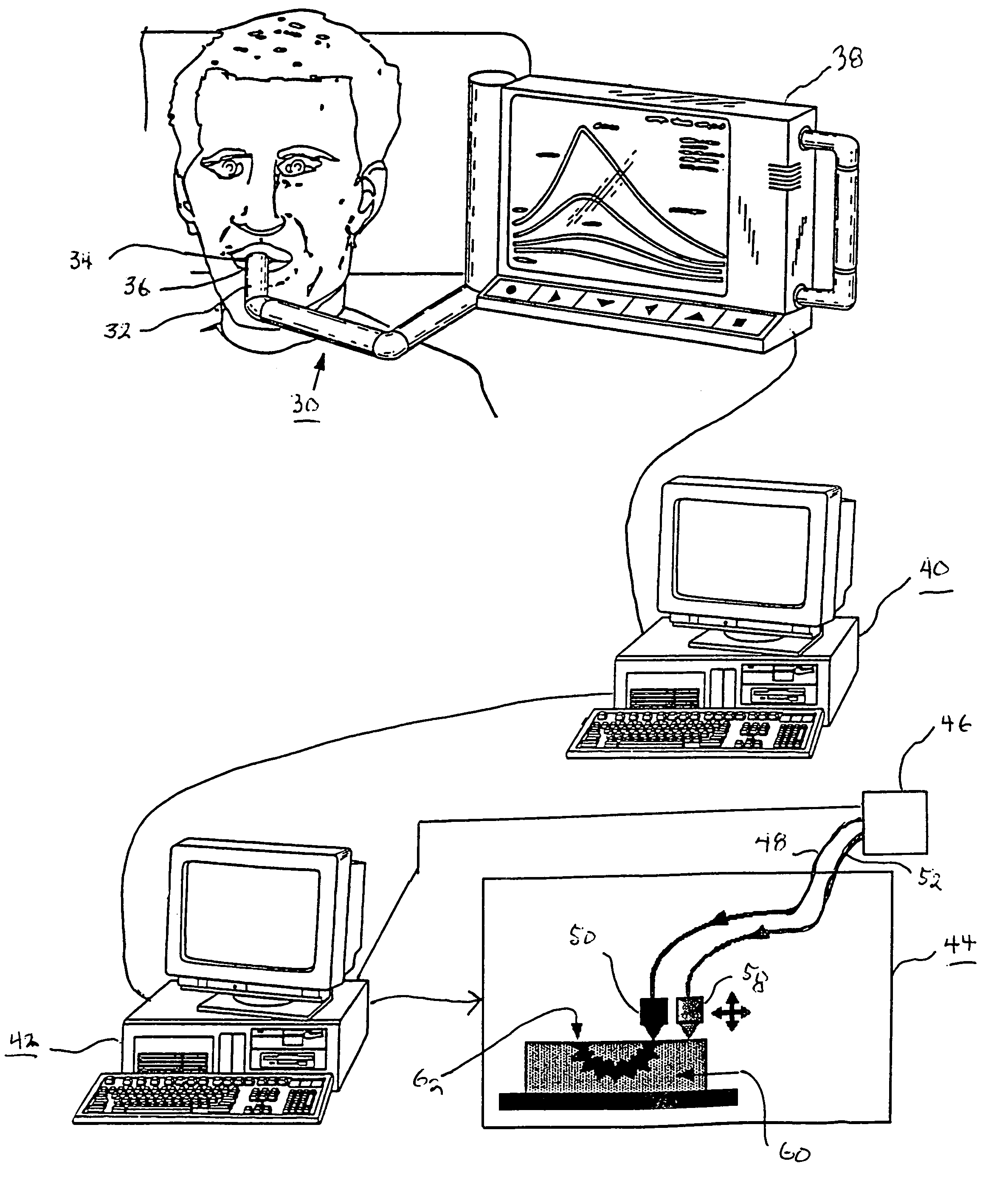
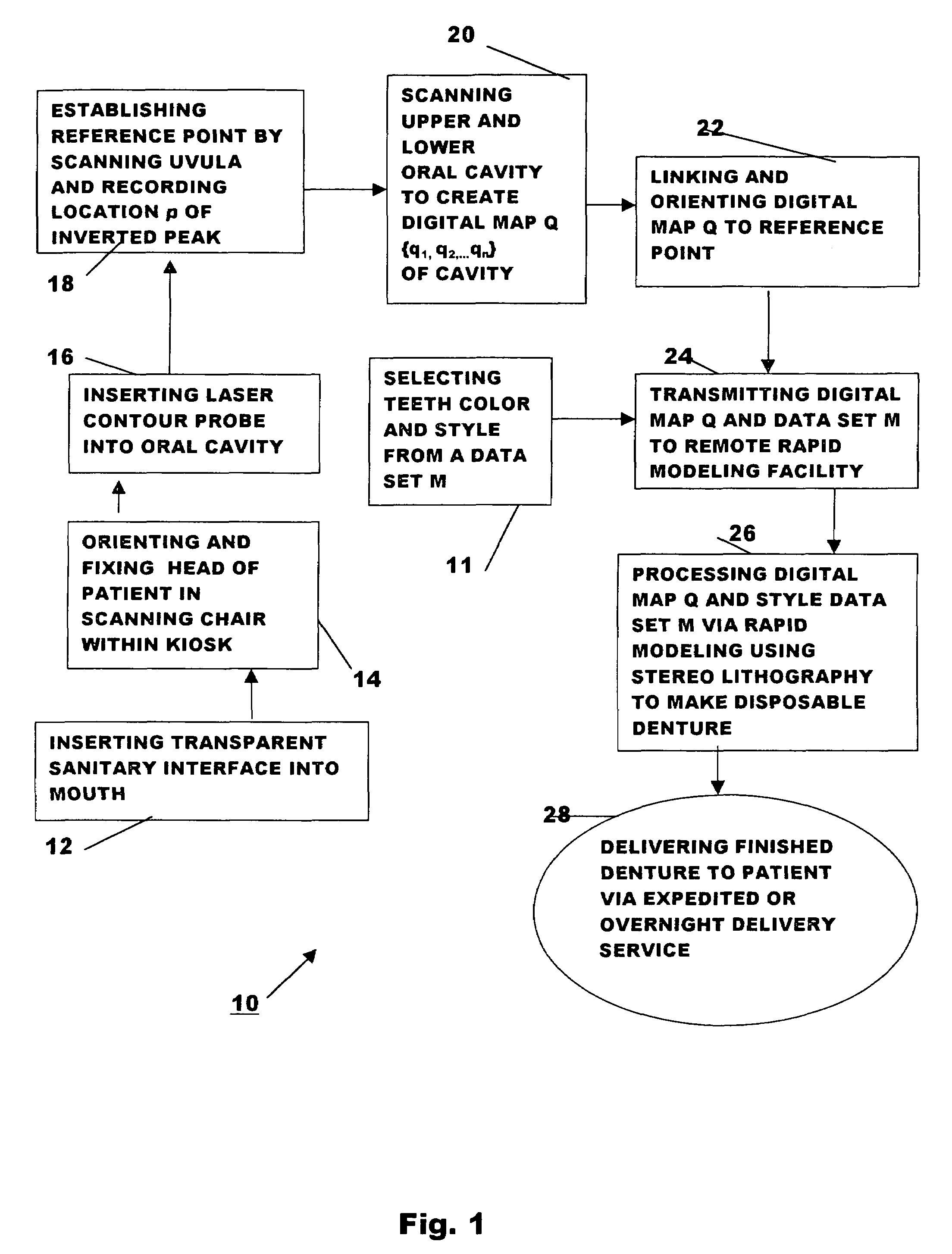
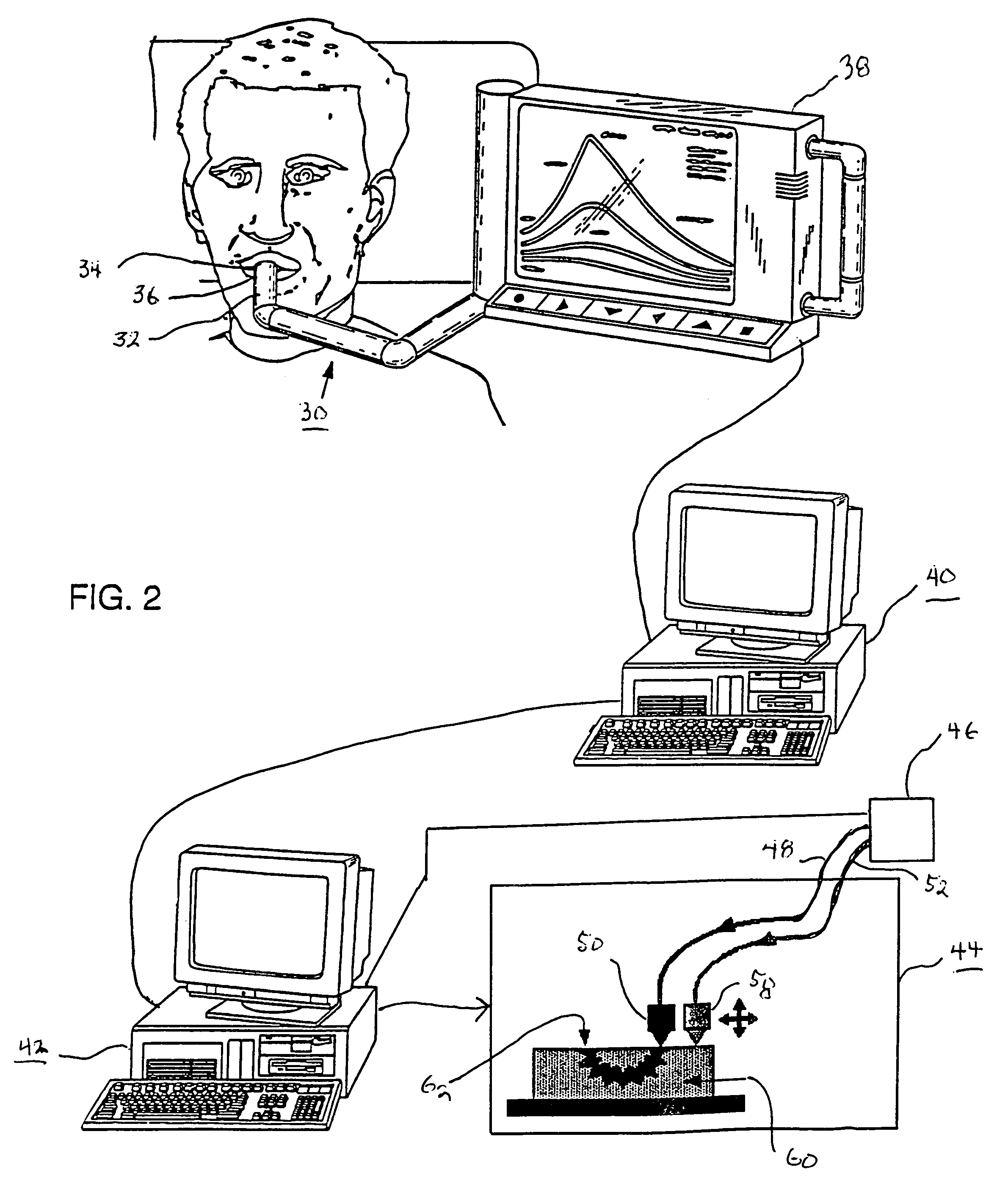
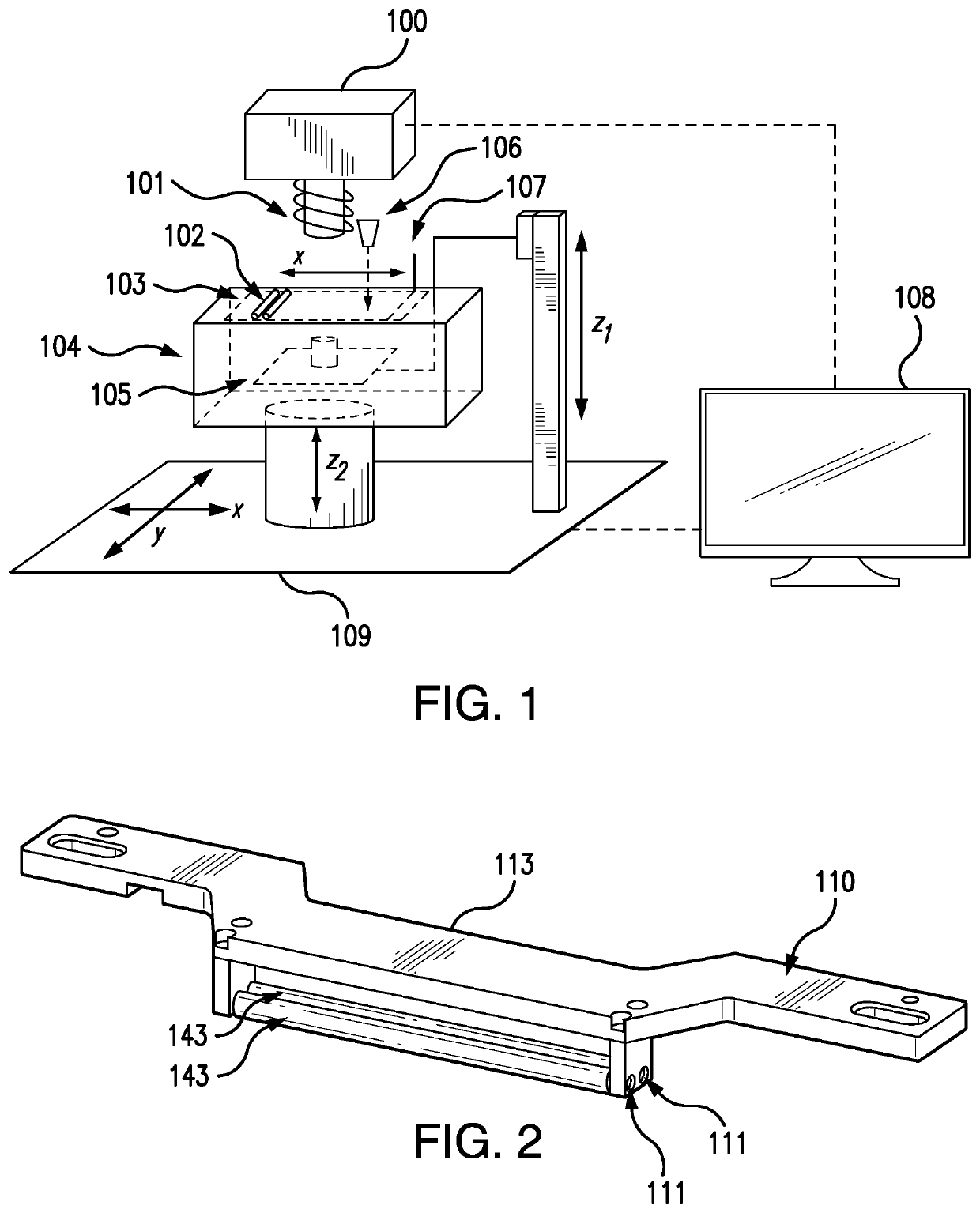
Method for automatically creating a denture using laser altimetry to create a digital 3-D oral cavity model and using a digital internet connection to a rapid stereolithographic modeling machine
InactiveUS7153135B1Low costFit closelyAdditive manufacturing apparatusImpression capsDenturesLaser scanning
A method is presented for rapidly making and delivering directly to a consumer a full upper and / or lower denture on the basis of contemporaneous digital image information laser scanned from the person's oral cavity after all respective upper and / or lower teeth have been removed, the delivery of the denture occurring substantially contemporaneously with the creation of the contemporaneous digital image information and optionally including and based on archived digital image information laser scanned from the person's oral cavity before all respective upper and / or lower teeth have been removed and digitally stored. According to which this contemporaneous digital image information and archival digital image information of the oral cavity is converted, by means of what is called the rapid prototyping technique and thus with a processing step (20) and a combination of an optional laser scanning step (18) solely for archiving the oral cavity when upper and / or lower teeth are present and a repetition of the laser scanning step (18) at a subsequent time when upper and / or lower teeth have been removed, a pre-selected block of plastic is used in a processing step (26) at a remote rapid modeling facility for receiving and processing digital information to form the block of plastic or like material into a denture of which at least a part is formed to substantially perfectly fit in juxtaposed relationship to the corresponding gums of the consumer. At least, pre-selected outer or non-juxtaposing is selected for manufacture of the denture using an arbitrary archived digital image not derived from the consumer's oral cavity image but selected by the consumer for its style, cosmetic characteristics, for example, color of teeth, size and variety of teeth, and / or perceived suitability.
Owner:THOMAS RICHARD J
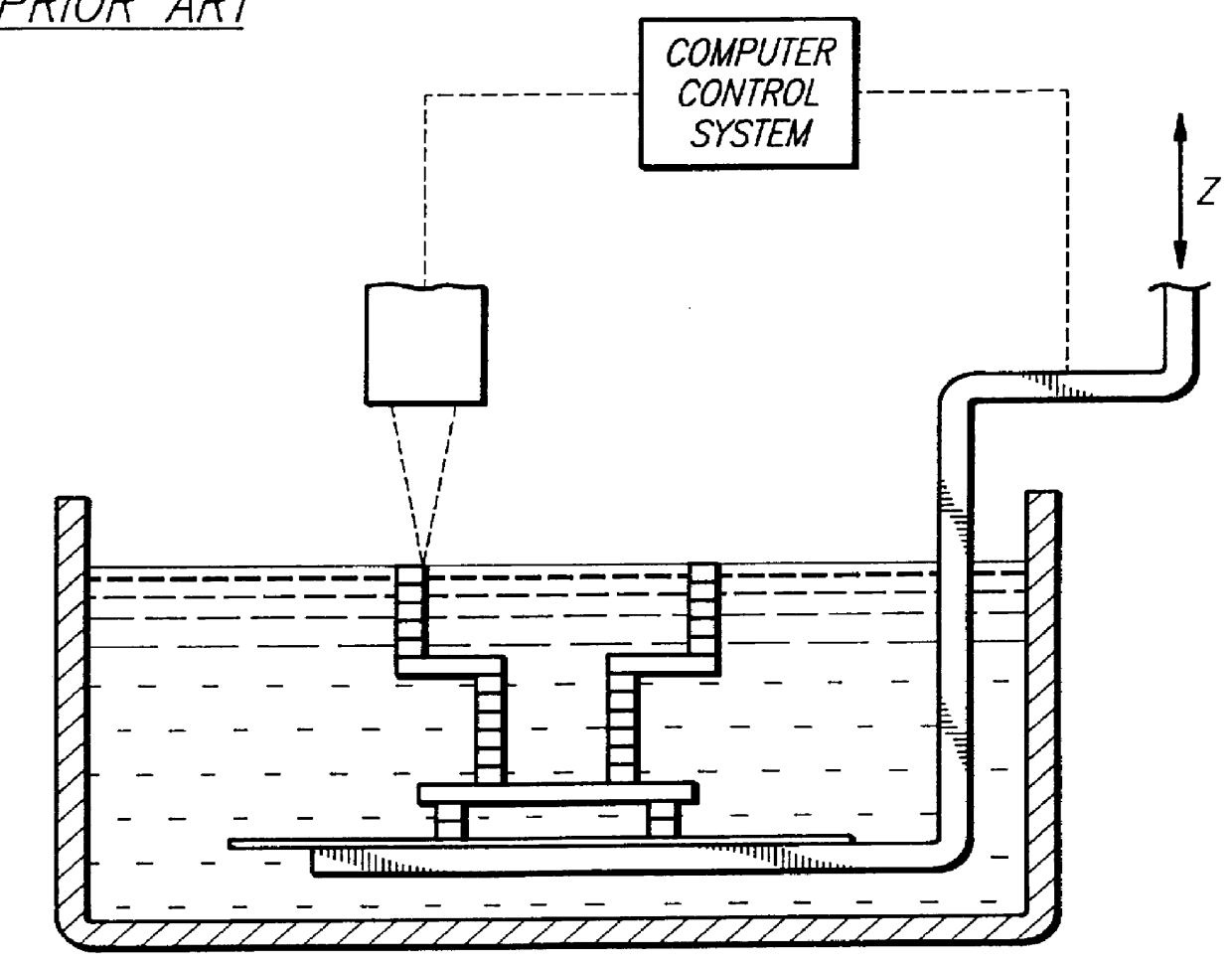
Method and apparatus for identifying surface features associated with selected lamina of a three dimensional object being stereolithographically formed
InactiveUS6029096AEfficient removalEliminate the effects ofAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structuresPattern recognitionStereolithographies
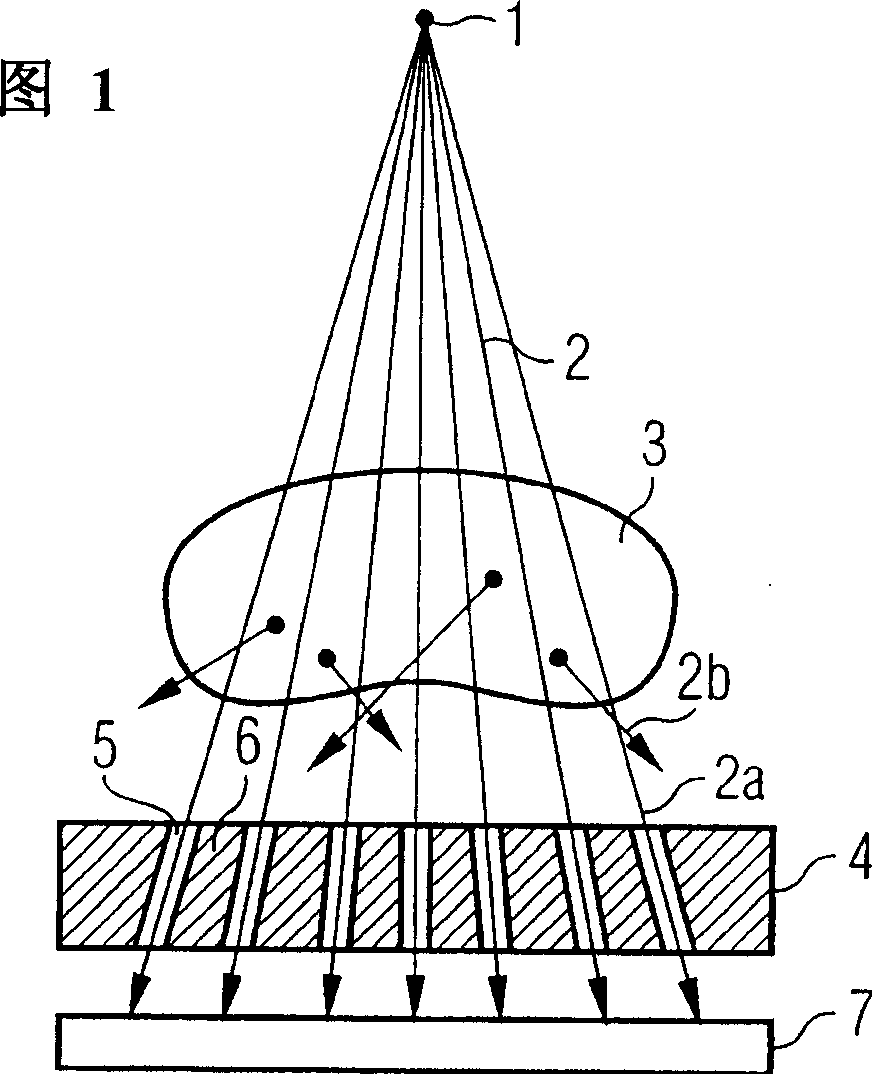
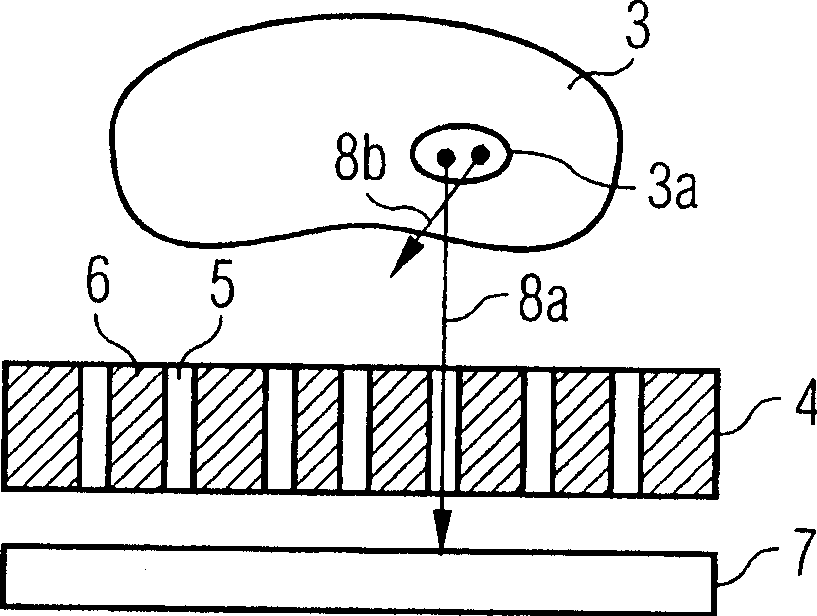
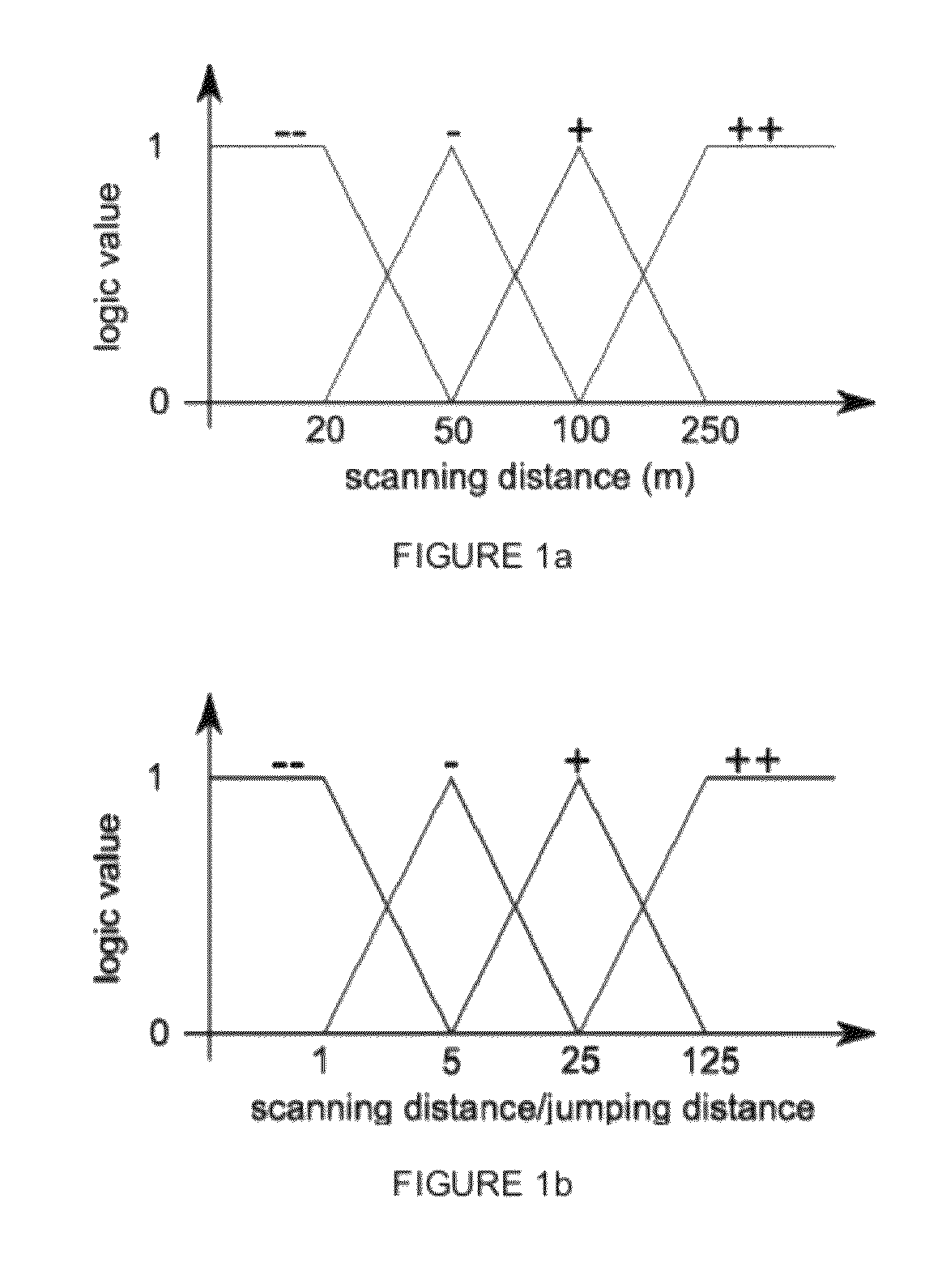
This invention relates to the stepwise layer-by-layer formation of a three-dimensional object through application of the principles of stereolithography and to the automatic detection of surface features of each layer of a three-dimensional object to manufacture parts more reliably, more accurately and more quickly. Automatic detection of trapped volume regions and size of solidified cross-sectional regions are disclosed. Automatic selection of recoating styles is made based on(1) the detected regions, (2) empirically or otherwise determined optimum recoating styles for different types of regions, and (3) a look-up table, other correlation system, or processor for associating recoating style information with laminae containing particular identified regions.
Owner:3D SYST INC
Heat exchanger design and fabrication
A method of forming a heat exchanger for use with a rotating component configured to rotate about an axis of rotation is provided including generating a stereolithography file of the surface geometry of the heat exchanger. The surface geometry of the heat exchanger includes a cylindrical base having a plurality of fins extending generally radially therefrom. The surface geometry defined in the stereolithography file is ‘sliced’ into a plurality of axisymmetric layers, perpendicular to the axis of rotation. Energy from an energy source is applied to a powdered material causing the powdered material to fuse and form the plurality of axisymmetric thin layers. Each of the axisymmetric thin layers is integrally formed with an adjacent axisymmetric thin layer to create a unitary heat exchanger.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Method for making opthalmic devices
ActiveUS7235195B2Easy to adaptCost-effective mannerAdditive manufacturing apparatusOptical articlesSolvent freeEngineering
The present invention provides a method for producing an ophthalmic device by means of stereolithography. The method comprises the steps of: depositing (i) an essentially solvent-free liquid or melt of a device-forming material, or (ii) a solution of said device-forming material, into a container wherein said device-forming material is crosslinkable or polymerizable by actinic radiation; irradiating said device forming material with one or more activation energy beams to obtain a cured layer of polymerized or crosslinked device-forming material; irradiating said device-forming material with said one or more activation energy beams to obtain a cured layer on top of a previously cured layer; and repeating step (c) to obtain additional cured layers until said ophthalmic device is created integrally, wherein each of cured layers corresponds to a pertinent slice of said ophthalmic device.
Owner:ALCON INC
For rapid prototyping apparatus
ActiveUS20110313560A1Good light transmissionPromote disseminationAdditive manufacturing apparatusConfectioneryStereolithographiesEngineering
A stereolithography apparatus and an exposure system for a stereolithography apparatus, wherein light emitting diodes are used as light sources. The invention relates to aligning light from the light emitting diode and to the exchange and control the light emitting diodes.
Owner:3D SYST INC
Three dimensional optical circuits
InactiveUS6847774B2Minimize optical signal lossEasy to manufactureAdditive manufacturing apparatusOptical fibre/cable installationOptical ModuleSelective laser sintering
A three dimensional optical circuit featuring an optical manifold for organizing, guiding and protecting individual optical fibers is shown. One aspect of the present invention is a three dimensional manifold which may be constructed using a rapid prototyping process such as, but not limited to, stereolithography (“SLA”), fused deposition modeling (“FDM”), selective laser sintering (“SLS”), and the like. The manifold has a number of input openings in a first ordered arrangement at one end connected by passageways to a number of output openings in a second ordered arrangement at the opposite end. A plurality of optical fibers may be directed through the passageways of the manifold to produce a three dimensional optical circuit such as a shuffle. Moreover, the optical manifold may be used in conjunction with a number of connections or terminations to form a various optical modules. These modules may be configured for rack mounting within enclosures for electrical components.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Use of free radically curable compositions in additive manufacturing methods
The present invention relates to the use of free-radically curable compositions, comprising chain-like and / or cyclic and / or cage-type polysiloxanes substituted by free-radically polymerizable groups and having at least 3 silicon atoms and / or mixed forms thereof, disiloxanes substituted by free-radically polymerizable groups, optionally one, two, three or more free-radically curable monomers having no silicon atom, fillers, initiators and / or catalysts for free-radical polymerization, and also further customary additives, in additive manufacturing methods, preferably in stereolithography (SL) and digital light processing (DLP). The present invention further relates to the use of the cured free-radically curable compositions, preferably for production of dental products.
Owner:VOCO
Computer-aided system of orthopedic surgery
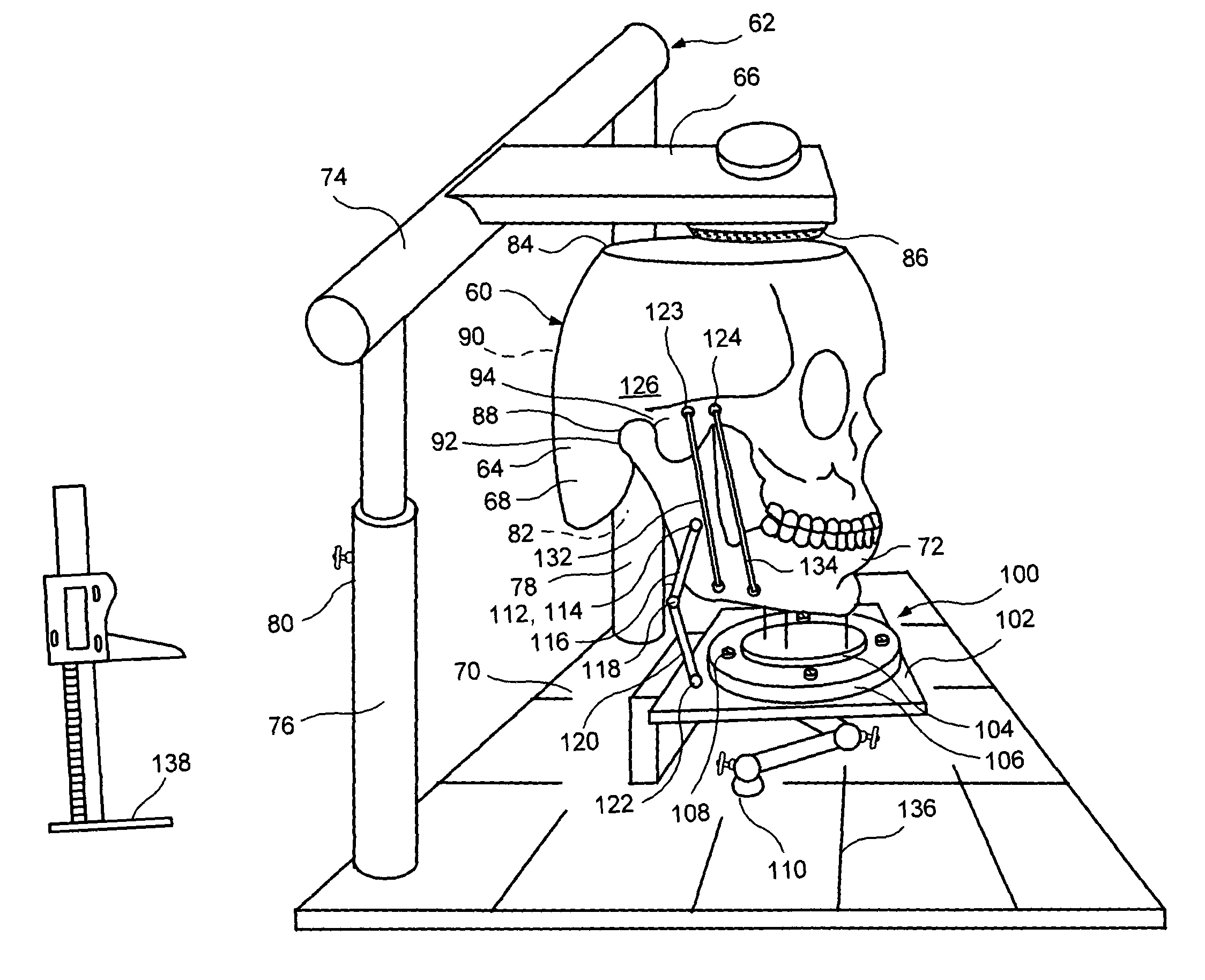
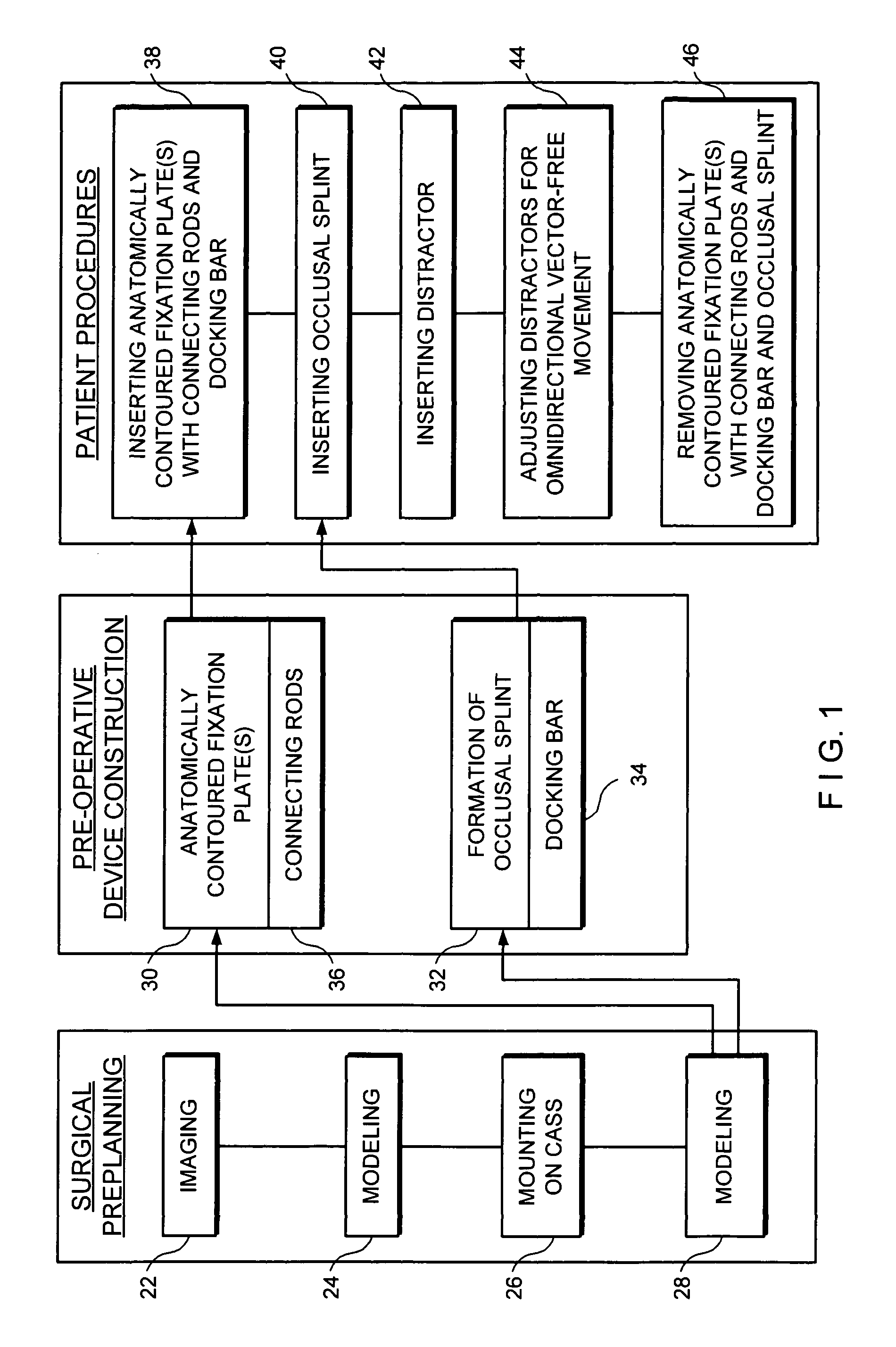
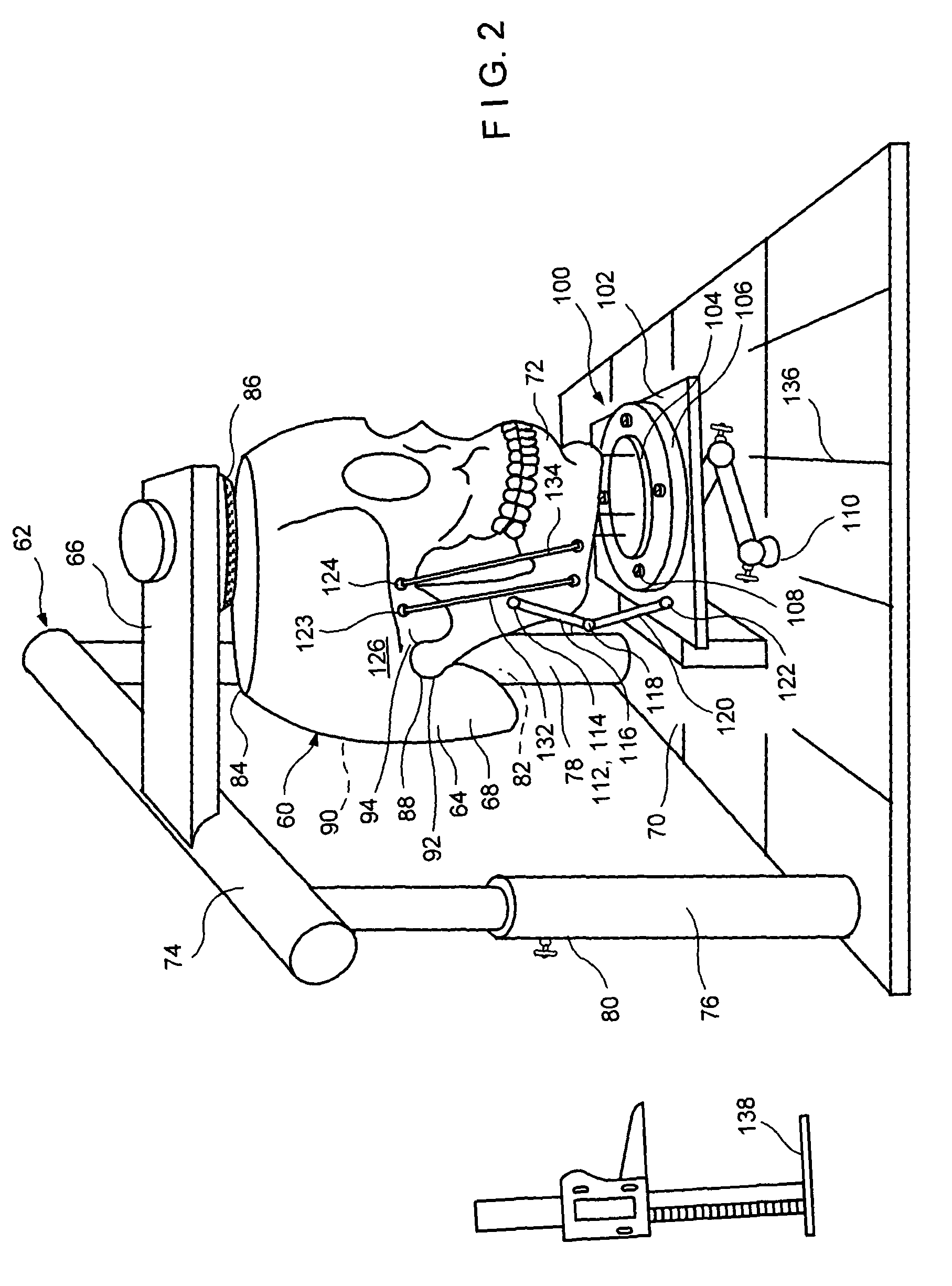
InactiveUS7909610B1Promote formationAvoid difficultyEducational modelsComputer-aided surgerySurgical operationComputer-aided
A computer aided system of orthopedic surgery is disclosed and omnidirectional osteogenesis is provided as an example thereof. To perform this surgery a craniofacial anatomic surgical simulator (CASS) is described, in which simulator a stereolithographic medical model is mounted. The medical model hereof is modified for this purpose so that pre-operative intra-oral devices, including custom-fitted fixation plates, can be crafted. An occlusal splint formed on the stereolithographic model acts as an armature for a docking bar which is, during the surgical operation, rigidly affixed to the fixation plate(s). The CASS, in one embodiment hereof, includes an indexing means for alignment of the stereolithographic model. The CASS also simulates the temporomandibular joint and fixedly mounts segments of the model in a post-operative condition.
Owner:AMATO CRANIOFACIAL ENG
Method for producing scattering ray raster or collimator with ray absorption material
InactiveCN1707699AHigh precision manufacturingReduce processing stepsRadiation measurementHandling using diaphragms/collimetersPresent methodGrating
The invention relates to a method for producing a scattered radiation grating or collimator (4) for a radiation type, the scattered radiation grating or collimator consisting of at least one geometrically predeterminable base body (6) The base body (6) has a channel or a channel groove (5) extending between its two opposing surfaces for the passage of the primary beam of the beam type. The method is characterized in that the base body ( 6 ) is formed by die-casting or stereolithography from a structural material that absorbs strongly this type of radiation. The use of the method allows the production of scattered radiation gratings or collimators with high precision using only a small number of method steps.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method for the manufacture of a spatially varying dielectric material, articles made by the method, and uses thereof
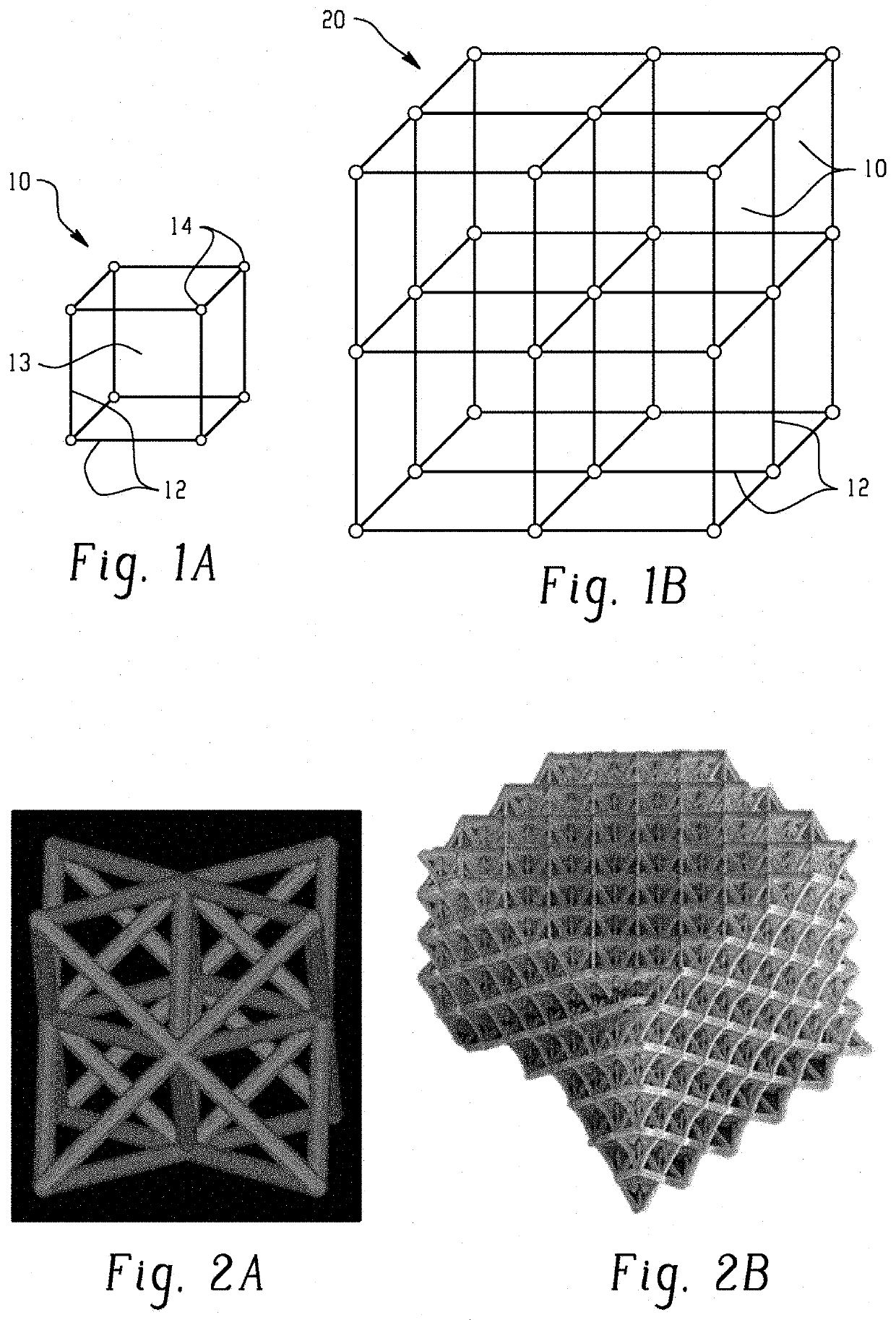
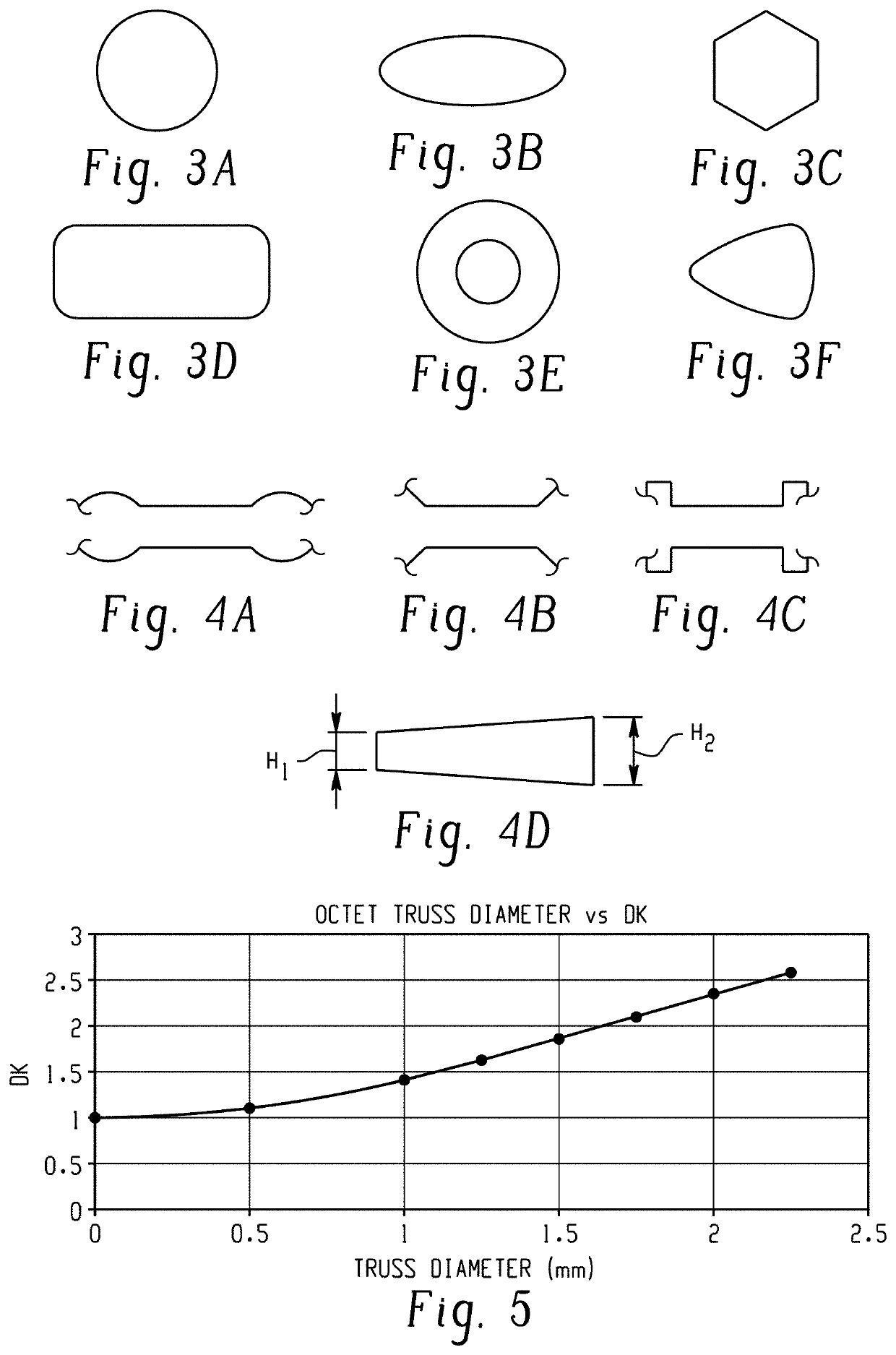
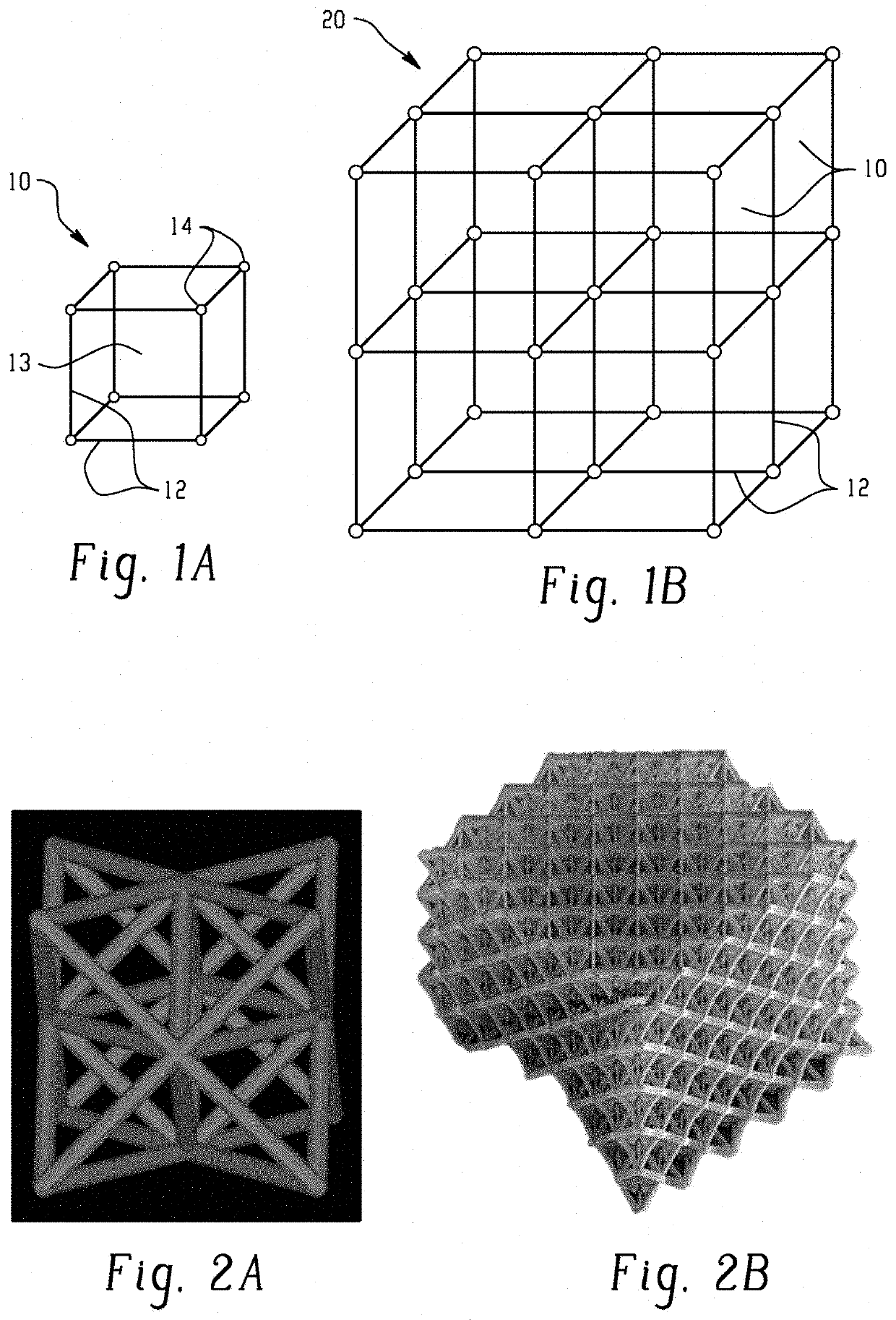
A stereolithography method of manufacture of a polymer structure having a spatially gradient dielectric constant, including: providing a volume of a liquid, radiation-curable composition; irradiating a portion of the liquid, radiation-curable composition with activating radiation in a pattern to form a layer of the polymer structure; contacting the layer with the liquid, radiation-curable composition; irradiating the liquid, radiation-curable composition with activating radiation in a pattern to form a second layer on the first layer; and repeating the contacting and irradiating to form the polymer structure, wherein the polymer structure comprises a plurality of unit cells wherein each unit cell is integrally connected with an adjacent unit cell, each unit cell is defined by a plurality of trusses formed by the irradiation, wherein the trusses are integrally connected with each other at their respective ends, and the trusses of each unit cell are dimensioned to provide the spatially gradient dielectric constant.
Owner:ROGERS CORP
Rapid prototyping resin compositions
ActiveUS8293810B2Improve stabilityLittle viscosity buildupAdditive manufacturing apparatusFibre treatmentPolymer scienceStereolithographies
A resin composition suited for rapid prototyping is provided comprising (I) an actinic energy radiation-curable silicone composition, (II) an actinic energy radiation-sensitive polymerization initiator, and (III) an actinic energy radiation absorber. The resin composition experiences little viscosity buildup and maintains fluidity during long-term storage at elevated temperature, and is effective in rapid prototyping or shaping by stereolithography using any actinic energy radiation.
Owner:CMET +1
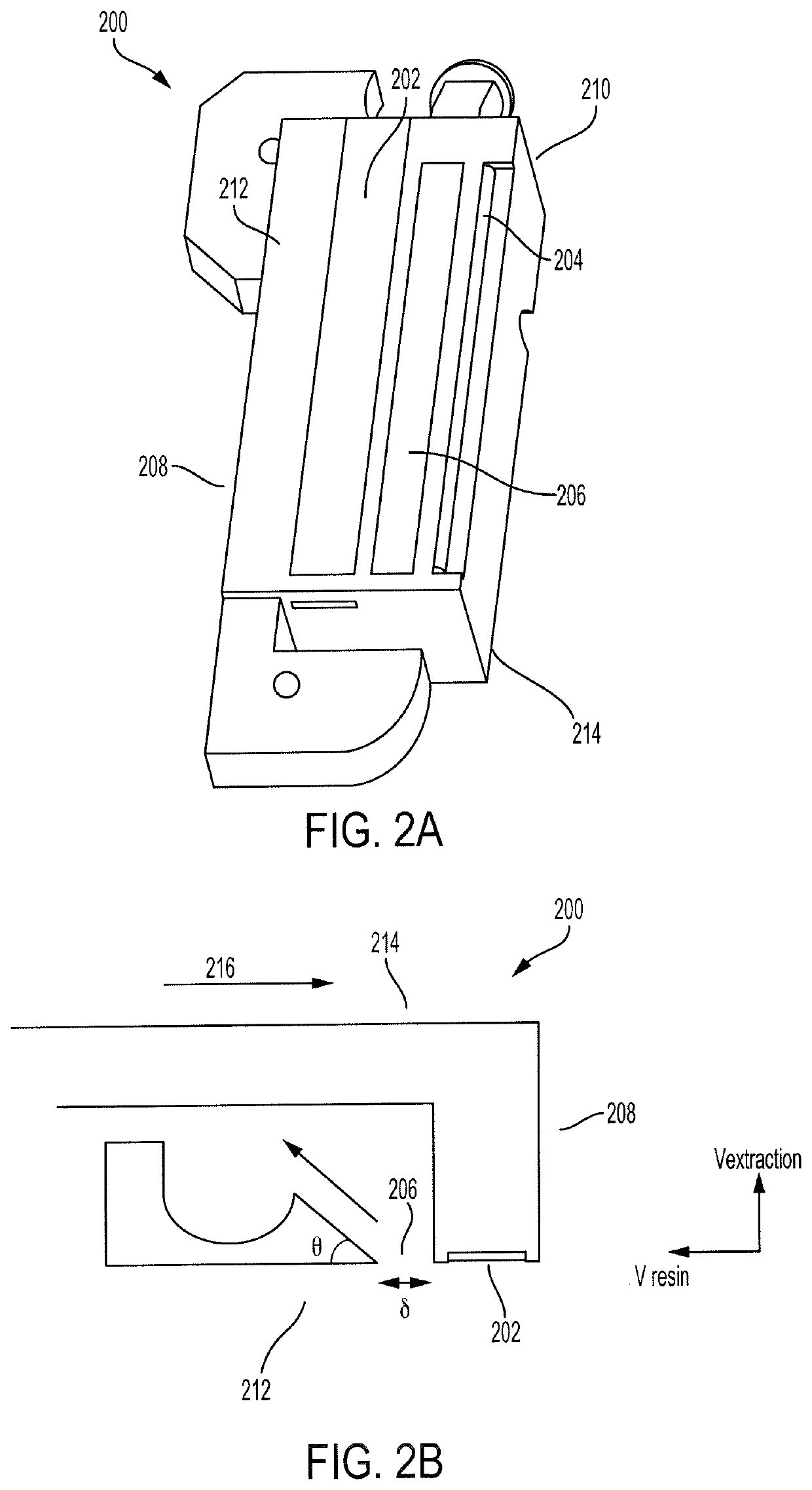
Resin extractor for additive manufacturing
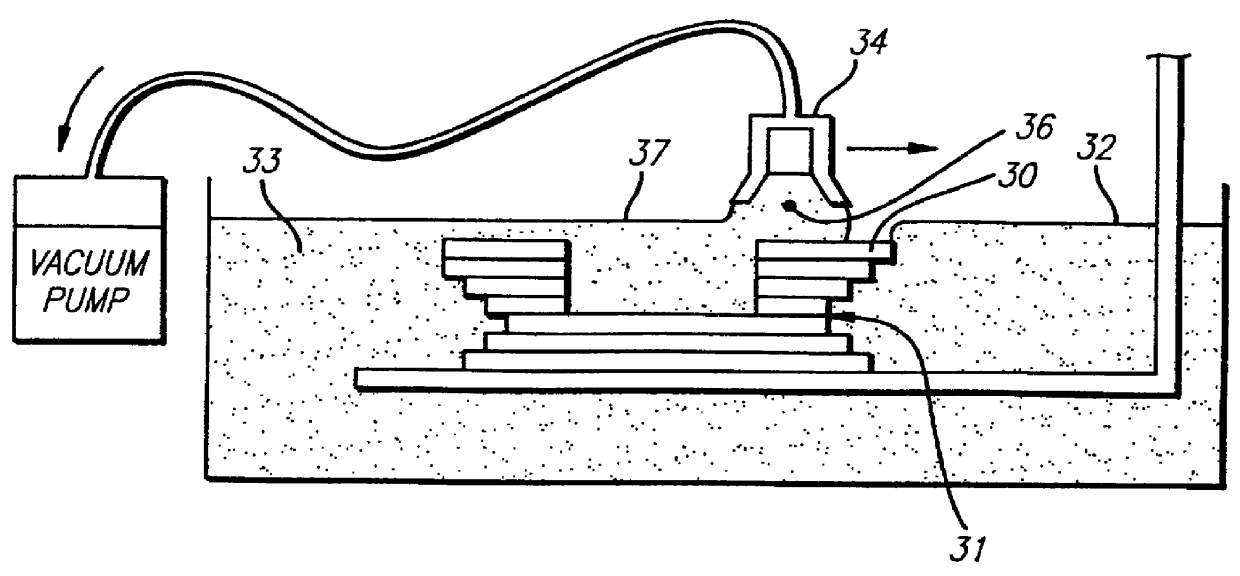
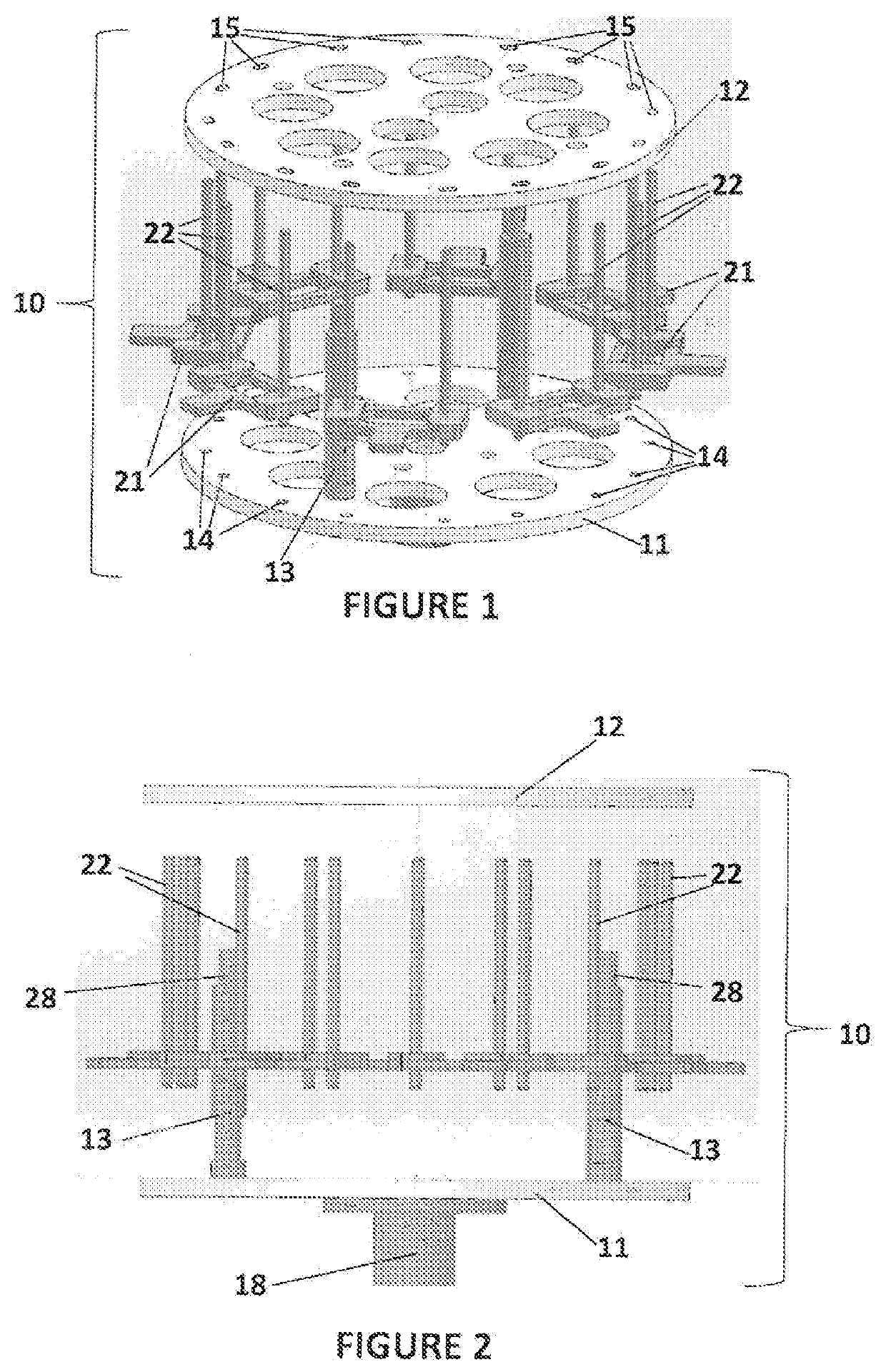
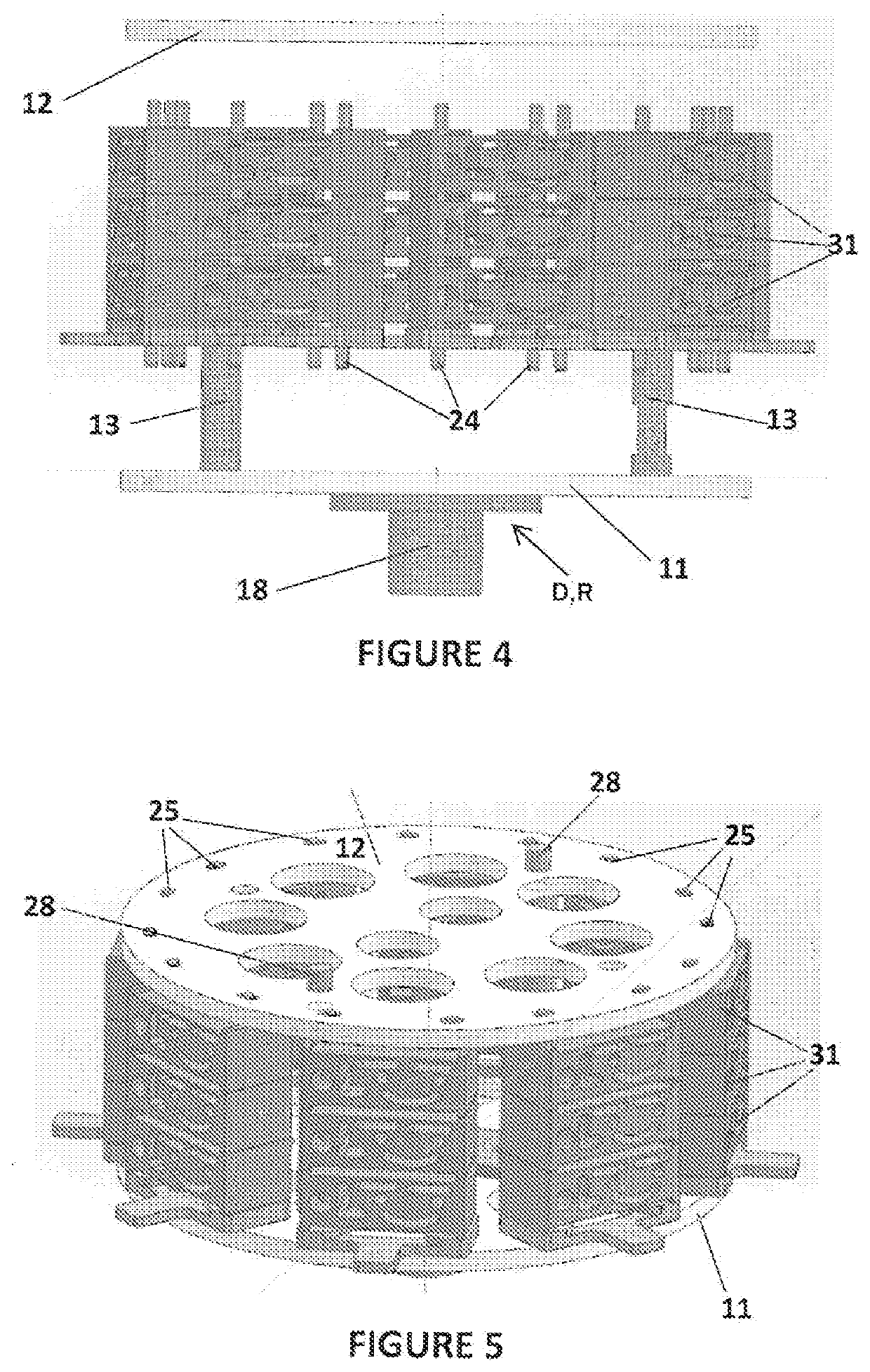
ActiveUS20210086450A1Low viscosityReduce resistanceManufacturing platforms/substrates3D object support structuresStereolithographiesResin extraction
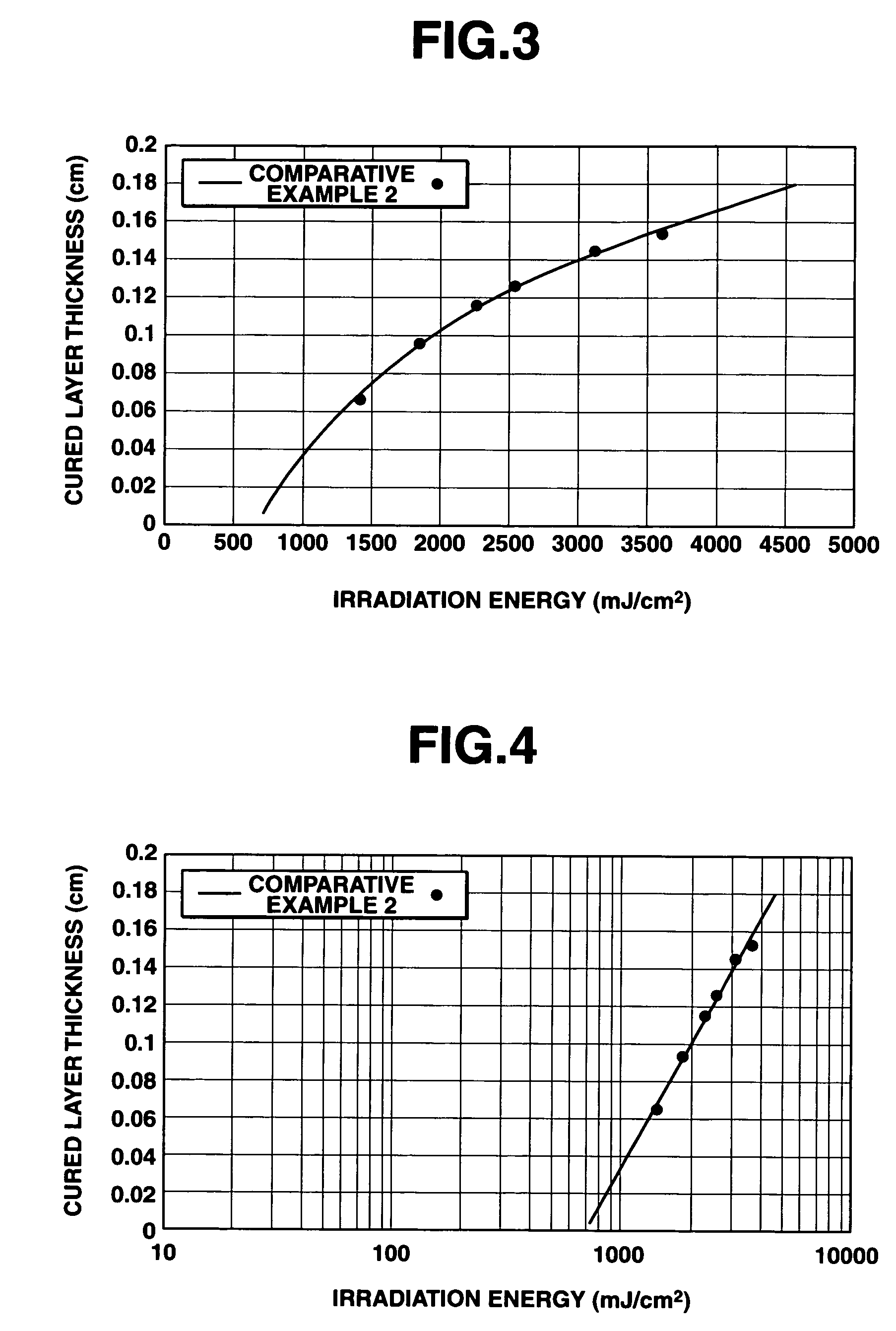
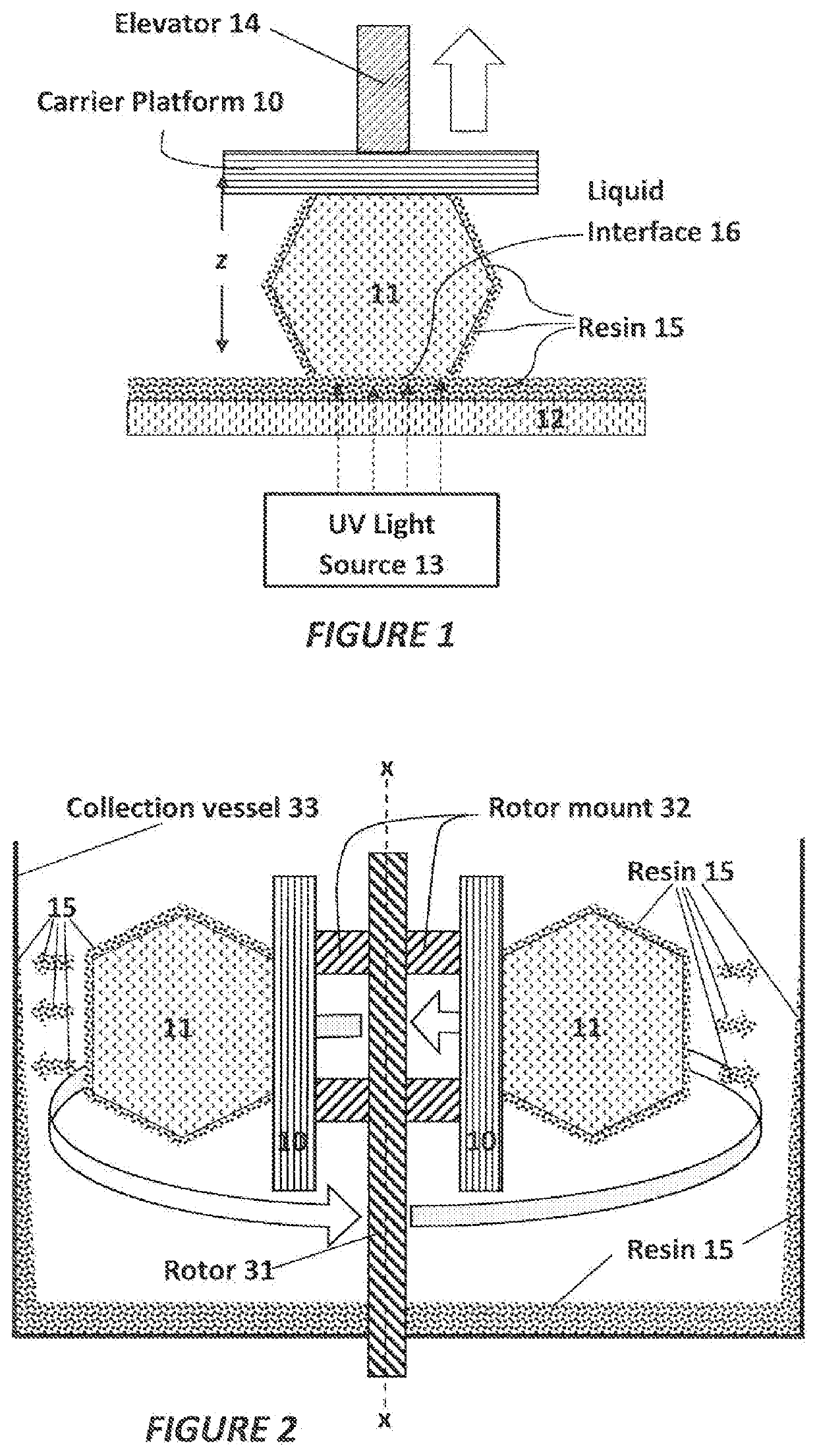
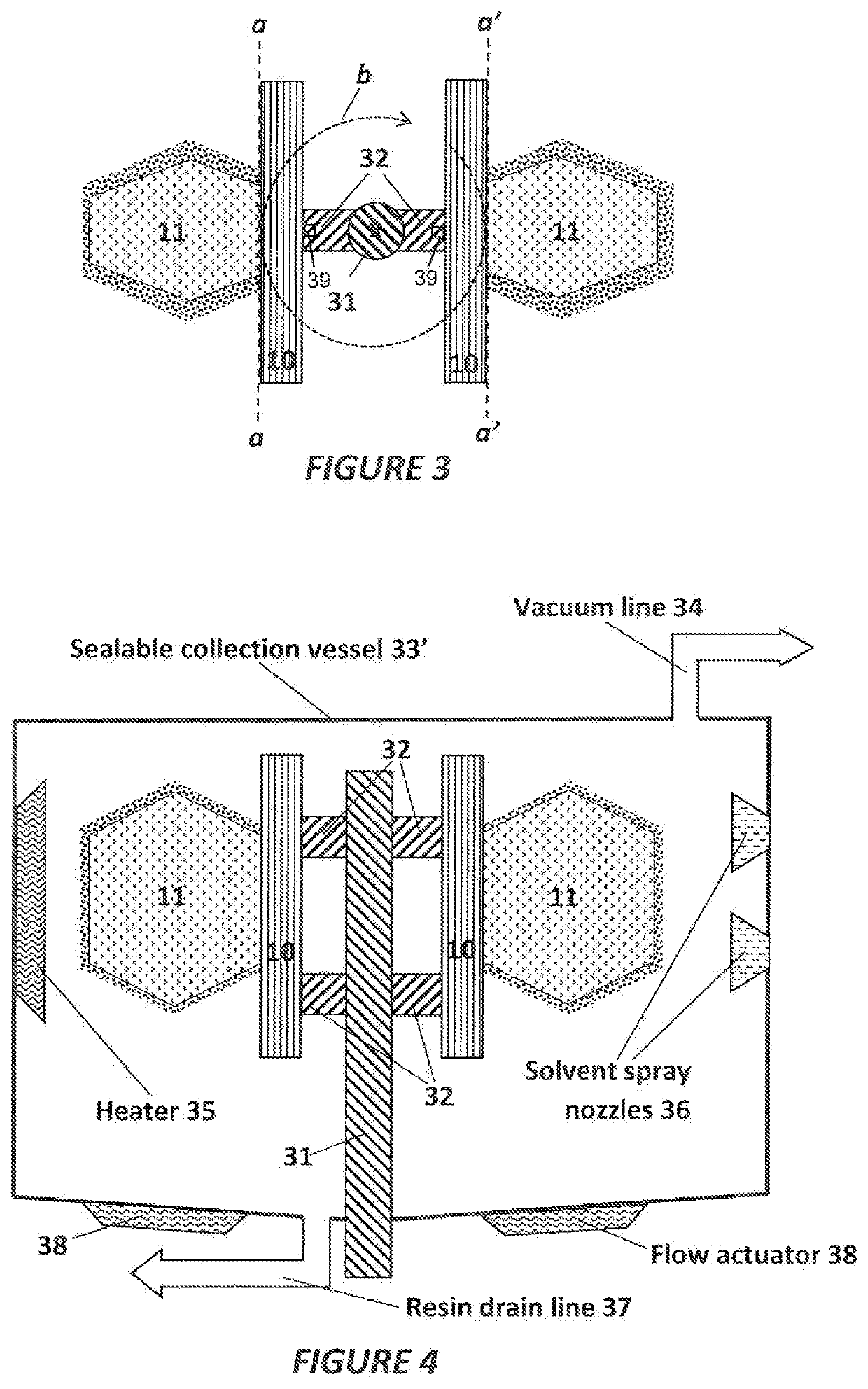
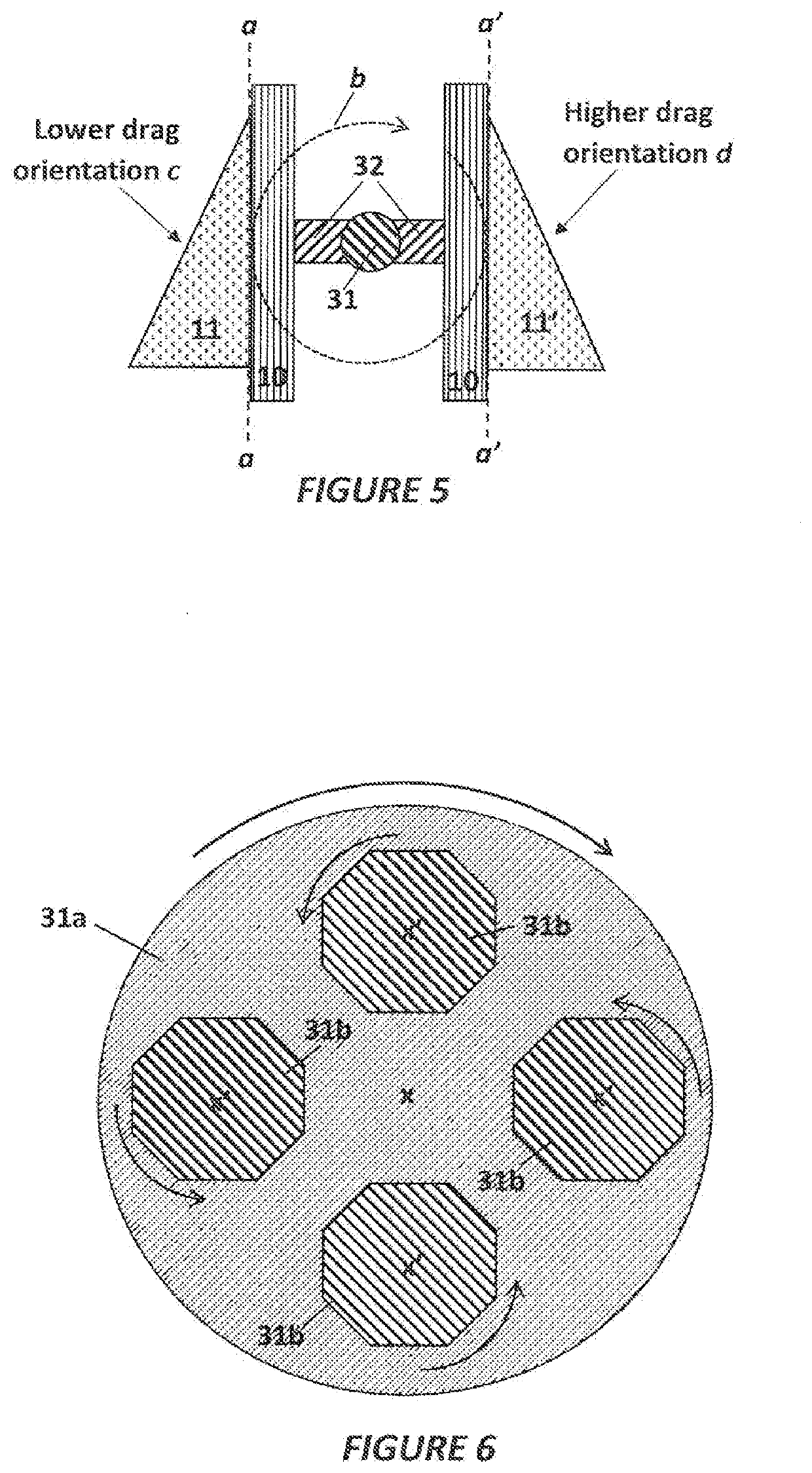
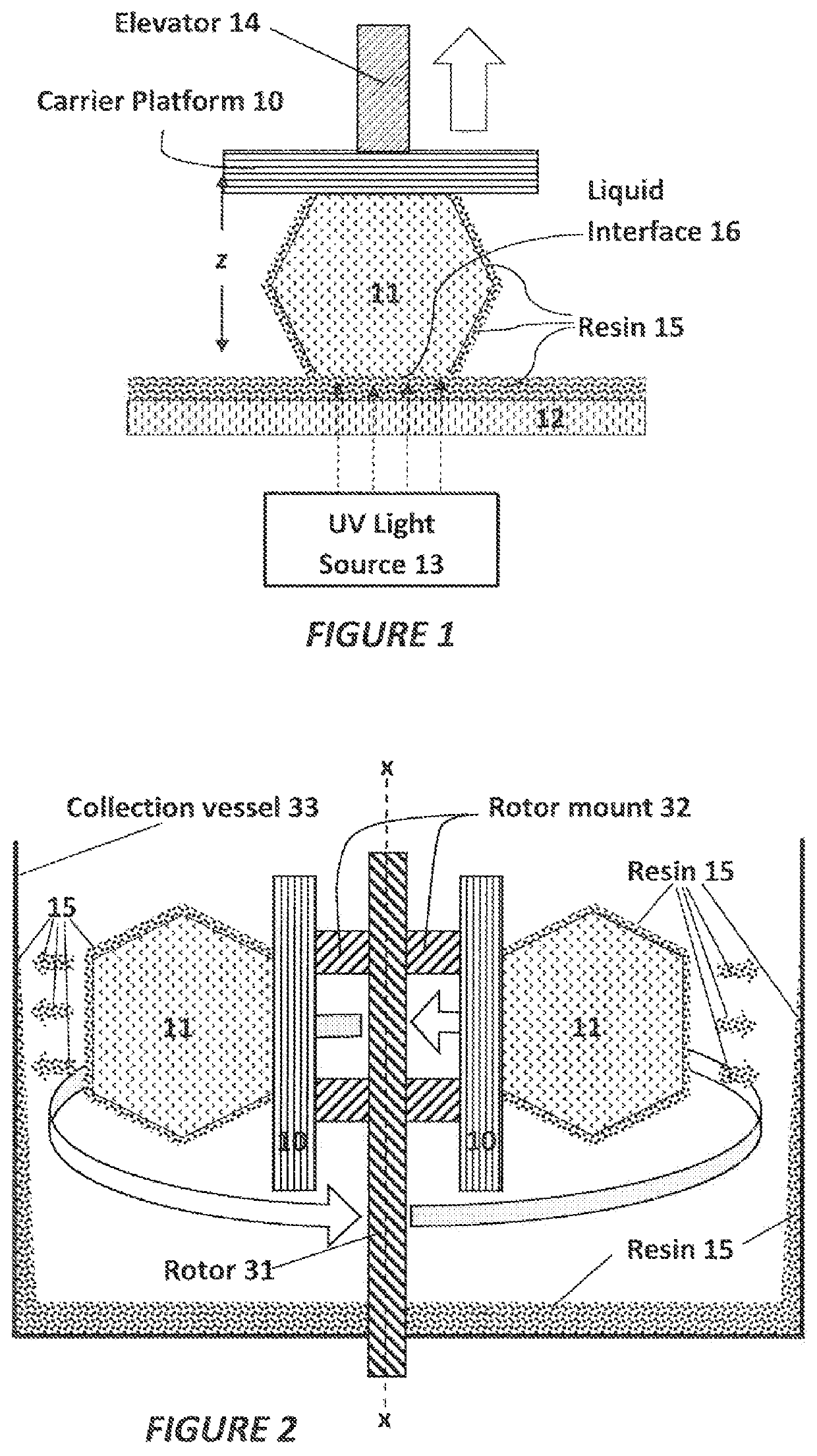
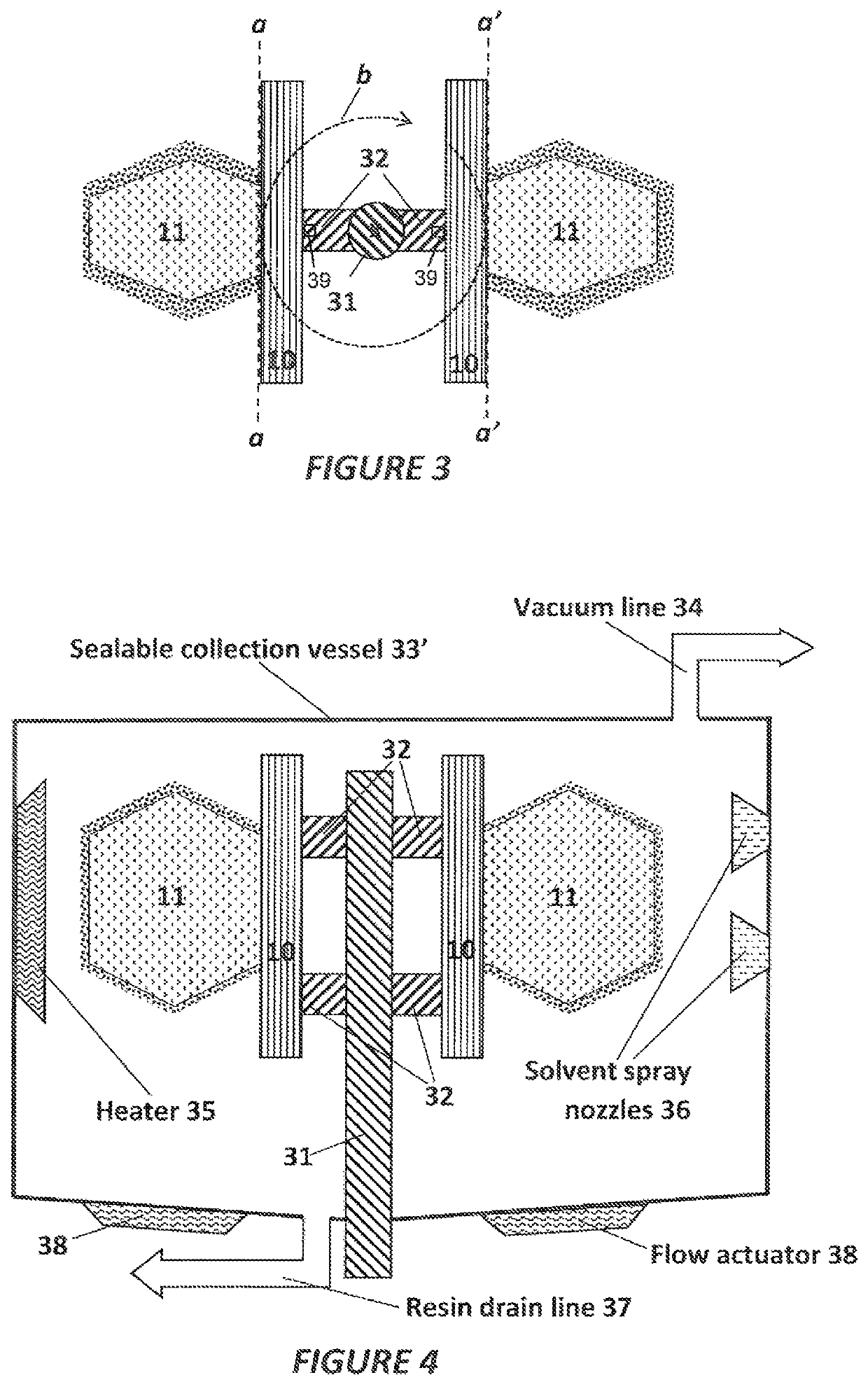
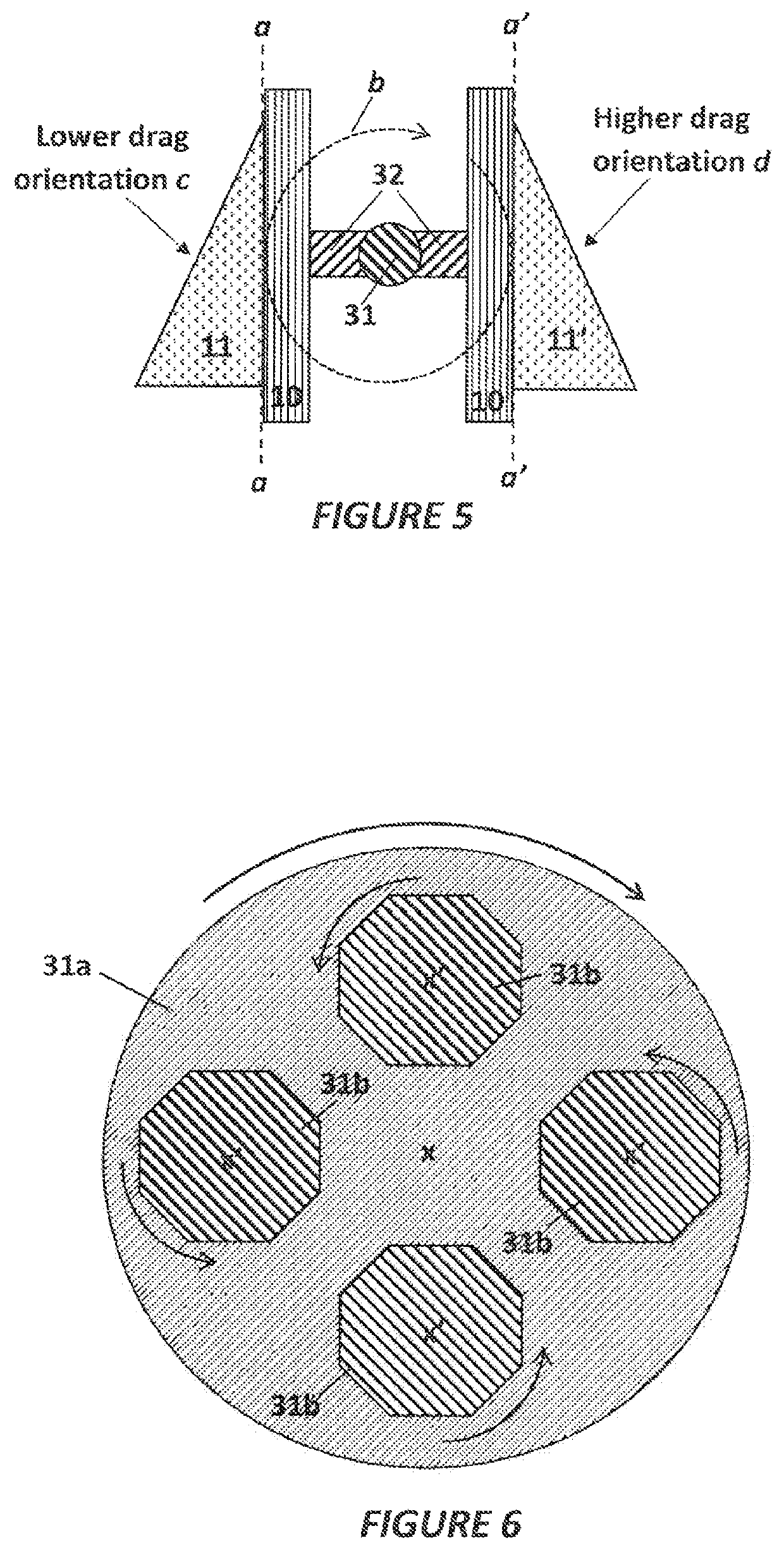
A method of separating excess resin (15) from at least one object (11), includes: (a) stereolithographically producing at least one object (11) on at least one carrier platform (10), each carrier platform (10) having a planar build surface to which at least one object (11) is connected, each object (11) carrying excess resin (15) on a surface thereof; then (b) mounting each carrier platform (10) to a rotor (31); (c) centrifugally separating excess resin (15) from each object (11) by spinning the rotor (31) with each carrier platform (10) connected thereto while each object (11) remains connected to each carrier platform (10); and then (d) removing each carrier platform (10) from the rotor (31) with each object (11) thereon, with excess resin (15) separated therefrom.
Owner:CARBON INC
Resin extractor for additive manufacturing
ActiveUS11084216B2Low viscosityReduce resistanceManufacturing platforms/substrates3D object support structuresStereolithographiesResin extraction
A method of separating excess resin (15) from at least one object (11), includes: (a) stereolithographically producing at least one object (11) on at least one carrier platform (10), each carrier platform (10) having a planar build surface to which at least one object (11) is connected, each object (11) carrying excess resin (15) on a surface thereof; then (b) mounting each carrier platform (10) to a rotor (31); (c) centrifugally separating excess resin (15) from each object (11) by spinning the rotor (31) with each carrier platform (10) connected thereto while each object (11) remains connected to each carrier platform (10); and then (d) removing each carrier platform (10) from the rotor (31) with each object (11) thereon, with excess resin (15) separated therefrom.
Owner:CARBON INC
Method for forming all-ceramic dental crown by stereolithography of zirconia ceramic slurry
InactiveCN112390646ASmall mechanical propertiesAchieving Precise FormingAdditive manufacturing apparatusStereolithographiesSlurry
The invention relates to the technical field of dental restorations, particularly to a method for forming an all-ceramic dental crown by stereolithography of zirconia ceramic slurry. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring three-dimensional data of a dental crown; according to the three-dimensional data of the dental crown, forming zirconia ceramic slurry into a green body on a supporting structure by adopting a digital light processing method; polishing to remove the supporting structure, and degreasing the green body; directly sintering the degreased green body or dyeing the degreased green body by using a dyeing solution, and then sintering to obtain the all-ceramic dental crown; and carrying out surface treatment on the sintered all-ceramic dental crown. According to the invention, zirconium oxide dental crown forming is achieved in an additive manufacturing mode, compared with a subtractive manufacturing method, materials can be saved by 90%, no dust is formed, the method is environmentally friendly, the machining process of the method is not limited by the appearance of the dental crown, and accurate forming of the dental crown with the more complex appearance canbe achieved; and no mechanical cutting exists, and the situation that the overall mechanical property of the dental crown is reduced due to micro-cracks caused by cutting is avoided.
Owner:江苏乾度智造高科技有限公司
Stereolithographic Resins Containing Selected Oxetane Compounds
InactiveUS20090239175A1Improve impact resistanceHigh modulusPhotosensitive materialsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusCompound aCationic polymerization
A liquid radiation-curable composition that comprises(A) at least one cationically polymerizing organic substance;(B) at least one free-radical polymerizing organic substance;(C) at least one cationic polymerization initiator;(D) at least one free-radical polymerization initiator;(E) at least one hydroxyl-functional compound; and(F) at least one hydroxyl-functional oxetane compound;
Owner:3D SYST INC
Method of making surfaces smooth or flat for 3D printing
InactiveUS20200070411A1Reduce defectsEnhance physical fitnessAdditive manufacturing apparatusPhotomechanical exposure apparatusStereolithographiesComputer printing
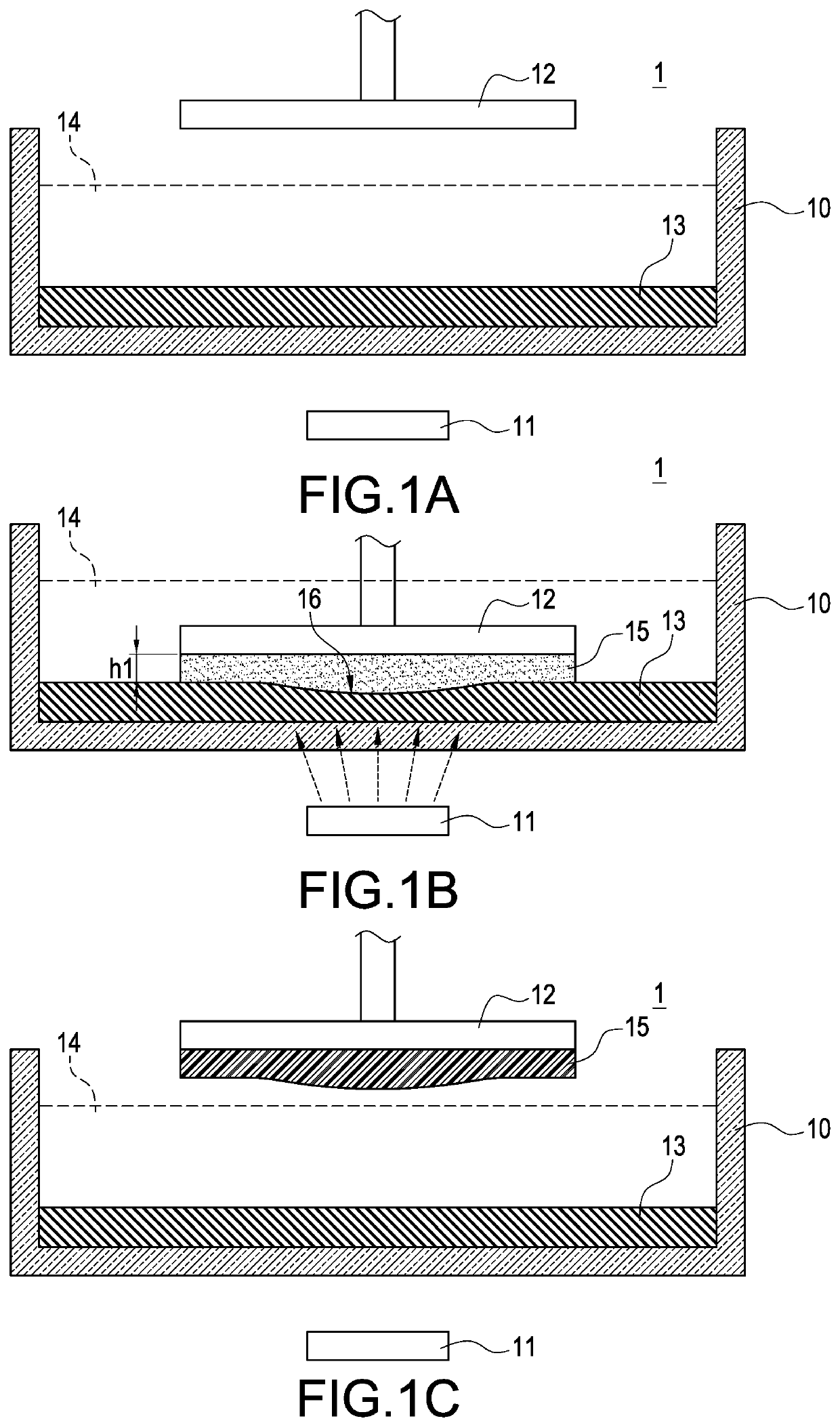
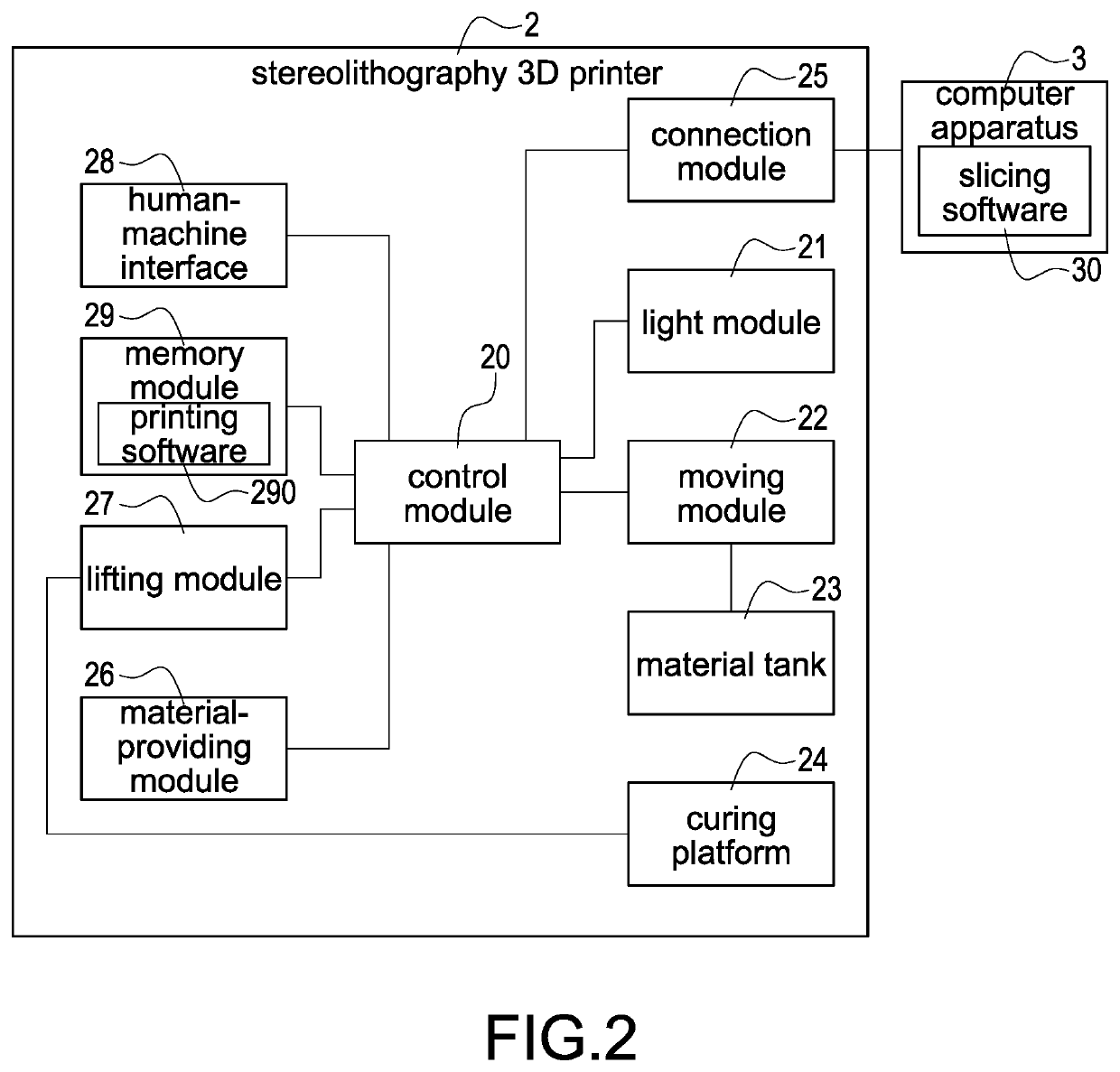
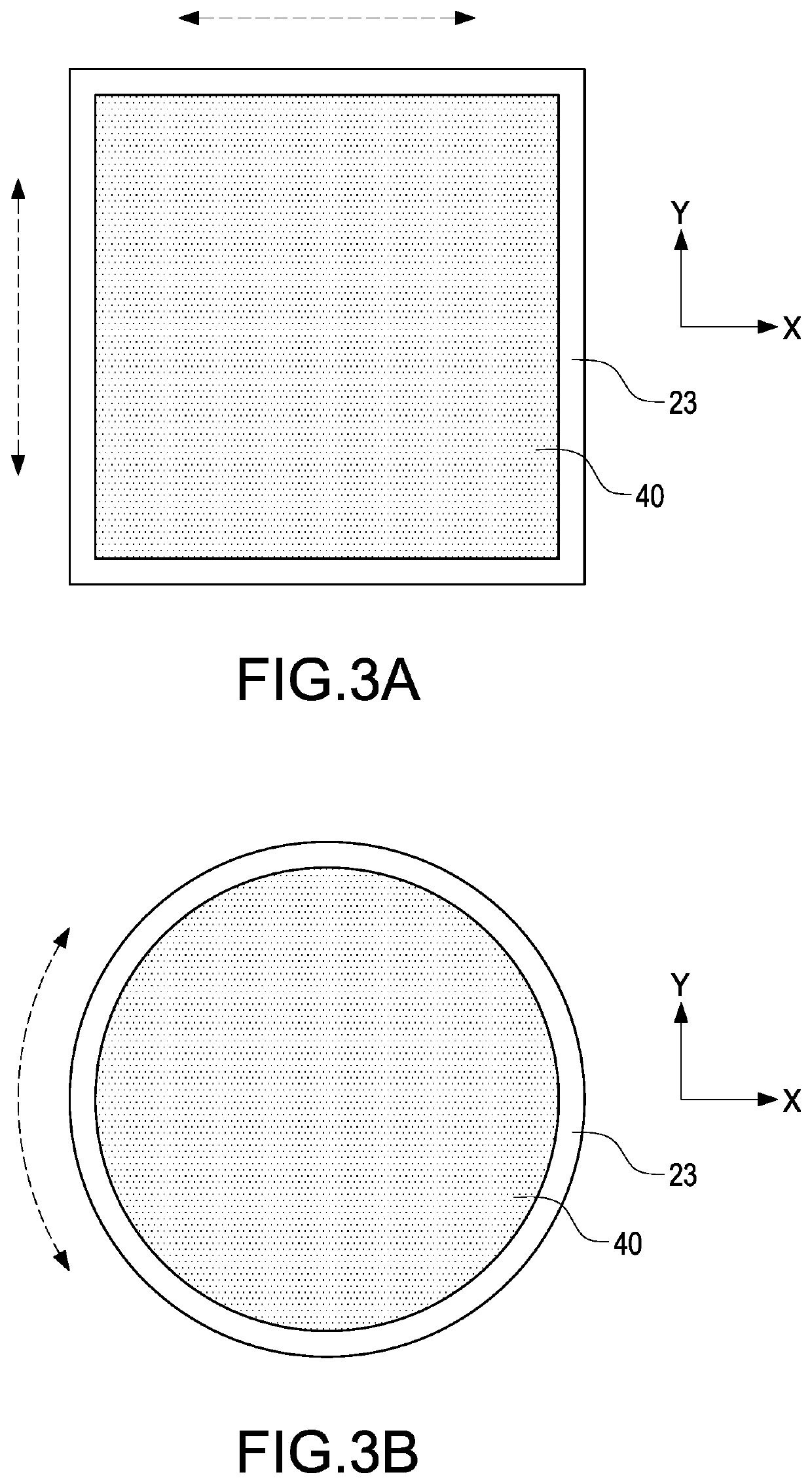
A method of making surfaces smooth or flat for 3D printing applied to a stereolithography 3D printer (2) is provided. The method is to control a modeling plane of a curing platform (24) to contact light-curable materials (41) in a material tank (23), moving the modeling tank (23) by a moving module (22) for making the light-curable materials (41) in the modeling tank (23) flow, and control a light module (21) to irradiate the curing platform (24) according to print data for manufacturing one layer of slice physical model on the modeling plane. The method can effectively reduce the defects on the surface of a physical model, and improve a printing quality of the physical models.
Owner:XYZPRINTING +1
Method for reducing differential shrinkage in stereolithography
InactiveUS8845949B2Low shrinkageHigh strengthAdditive manufacturing apparatusTailstocks/centresStereolithographiesEngineering
The present invention relates to a new and improved stereolithography method and system for generating a three-dimensional object by forming successive, adjacent, cross-sectional laminae of that object, thereby providing an object being specially processed to reduce differential shrinkage.
Owner:MATERIALISE NV
Spin cleaning method and apparatus for additive manufacturing
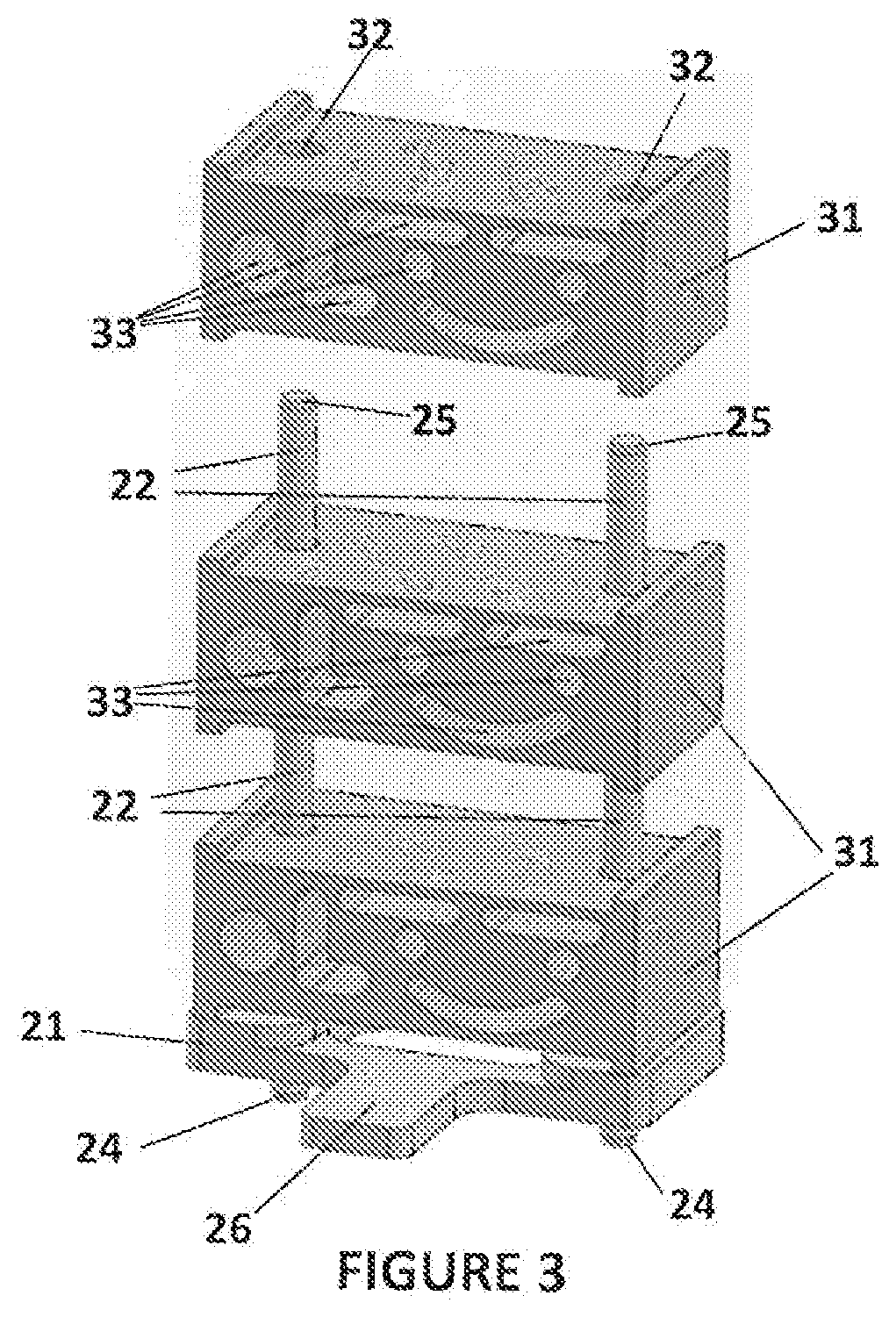
PendingUS20210323234A1Low viscosityAdditive manufacturing apparatusManufacturing recyclingStereolithographiesEngineering
A method of separating excess resin from at least one object includes: (a) stereolithographically producing at least one object, each object having at least one retention feature (32) formed thereon, each object carrying excess resin on a surface thereof; then (b) mounting each object on at least one transfer frame (21), each transfer frame having at least one retention member (22) that mates with the retention feature; (c) connecting each transfer frame to a rotor with the at least one object carried thereon; (d) centrifugally separating excess resin from each object by spinning the rotor with each transfer frame connected thereto while the at least one object remains connected to each transfer frame by the retention feature; then (e) removing each transfer frame from the rotor, with excess resin separated from each at least one object thereon.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Methods, apparatuses, and systems for creating 3-dimensional representations exhibiting geometric and surface characteristics of brain lesions
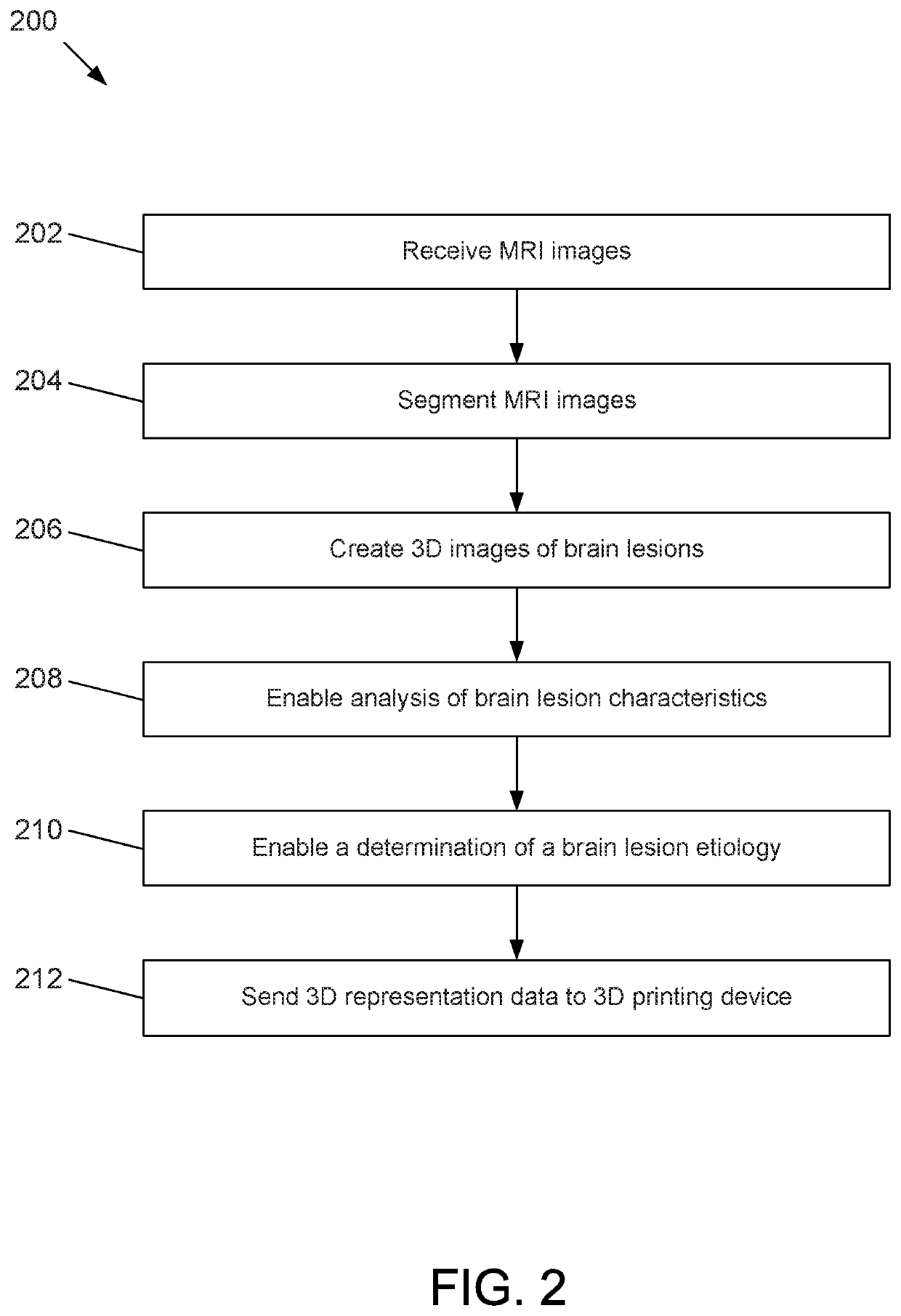
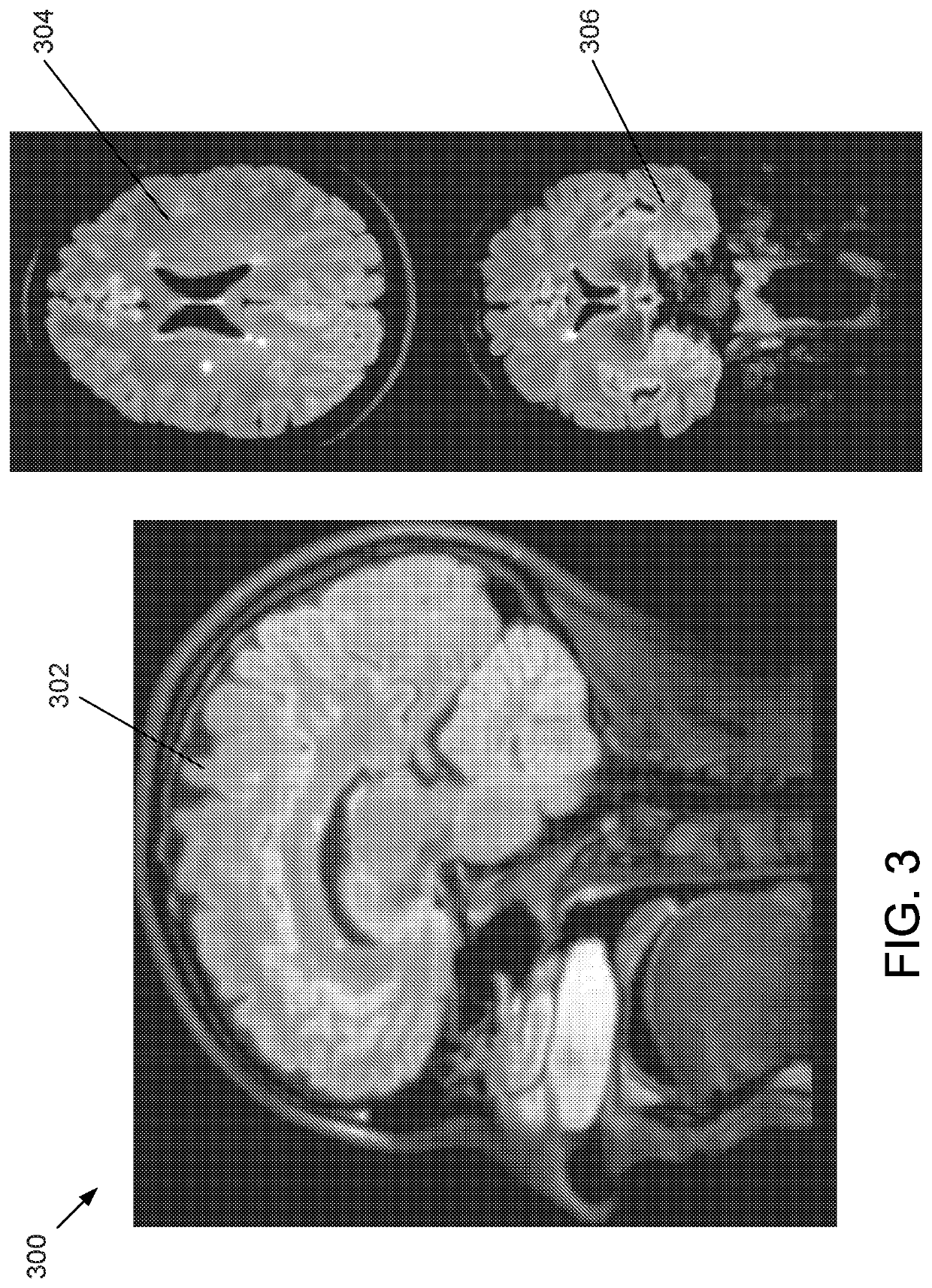
ActiveUS11093787B2Accurate assessmentOverall shapeImage enhancementImage analysisStereolithographiesProjection image
Methods, apparatuses, systems, and implementations for creating 3-dimensional (3D) representations exhibiting geometric and surface characteristics of brain lesions are disclosed. 2D and / or 3D MRI images of the brain may be acquired. Brain lesions and other abnormalities may be identified and isolated with each lesion serving as a region of interest (ROI). Saved ROI may be converted into stereolithography format, maximum intensity projection (MIP) images, and / or orthographic projection images. Data corresponding to these resulting 3D brain lesion images may be used to create 3D printed models of the isolated brain lesions using 3D printing technology. Analysis of the 3D brain lesion images and the 3D printed brain lesion models may enable a more efficient and accurate way of determining brain lesion etiologies.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Roller-membrane layering micro stereolithography
PendingUS20210299952A1Improve accuracyIncrease speedManufacturing platforms/substrates3D object support structuresStereolithographiesEngineering
The speed and control over layer thickness in multi-layer 3-D printing is enhanced when producing a sample layer by projecting an image of the layer from light engine onto an optically clear membrane in contact with a printing material to prepare a sample layer in contact with the membrane, followed by moving the sample away from the membrane to separate the two, then moving the sample back toward the membrane to a point where the distance between the membrane and sample, as measured by a laser displacement sensor, is equal to the thickness of the next layer. While the sample moves back toward the membrane a dual-roller spreader or rotary roller spreader oscillates on the membrane to simultaneously to drive away printing material and flatten the membrane. A bubble scrapper is employed to remove bubbles from the printing material as they form.
Owner:BMF NANO MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
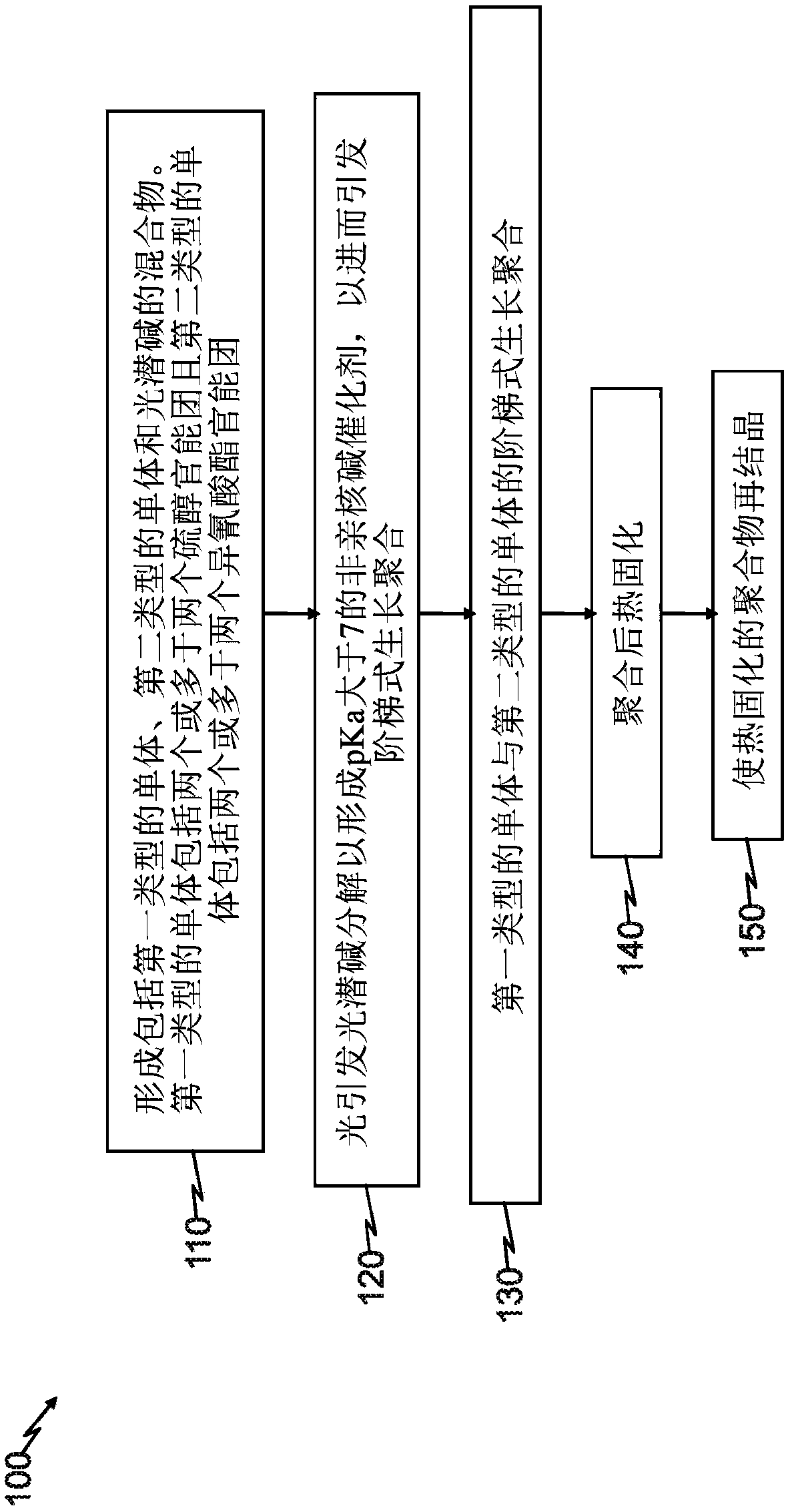
Thiourethane polymers, method of synthesis thereof and use in additive manufacturing technologies
ActiveCN108779225AAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structuresThiocarbamatePolymer science
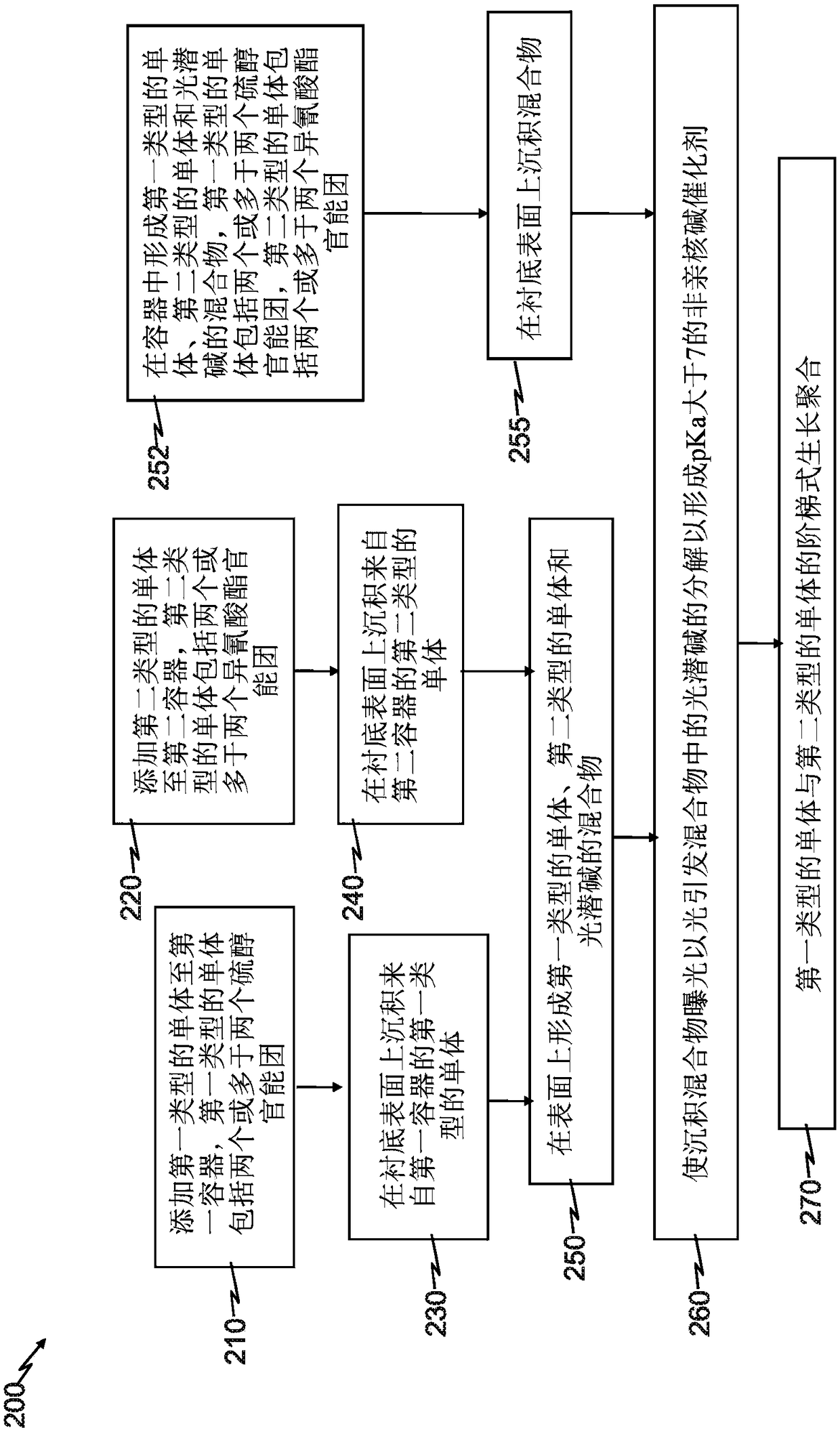
A semi-crystalline thiourethane polymer. The semi-crystalline thiourethane polymer comprises a sequential chain of a first type of monomer covalently bonded to a second type of monomer via thiourethane linkages. Each of the first type of monomer includes two or more thiol functional groups and each of the second type of monomer includes two or more isocyanate functional groups. The first and second types of monomers are polymerized together in an anionic step-growth polymerization reaction that is catalyzed by a non-nucleophillic base having a pKa greater than 7, produced by photo-initiated decomposition of a photolatent base. A method of synthesizing, and polymer jetting and stereolithography methods of manufacturing a polymer part, are also disclosed.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
Glass scintillators and methods of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS10940639B1Reduce needImprove homogeneityAdditive manufacturing apparatusGlass shaping apparatusDopantStereolithographies
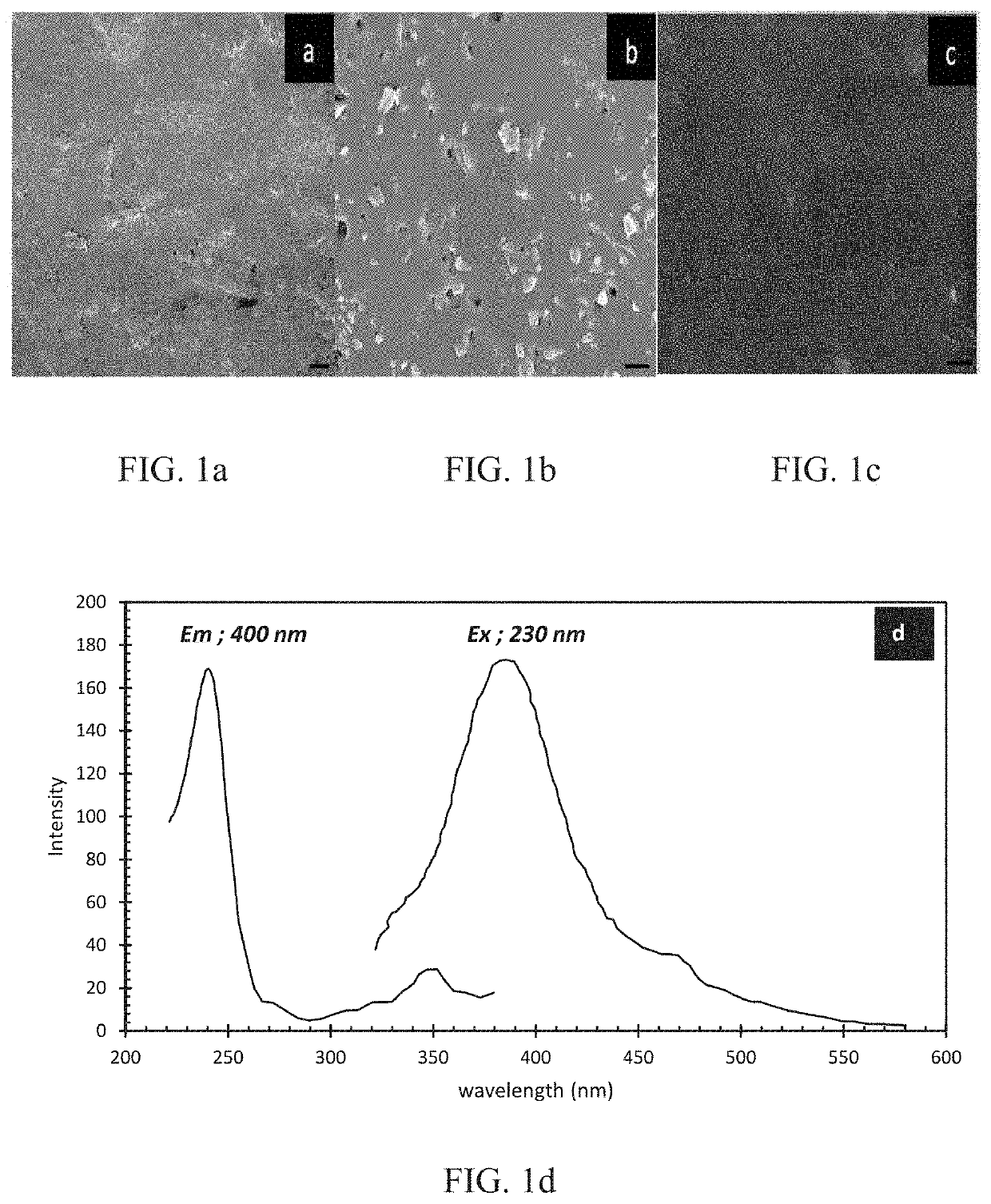
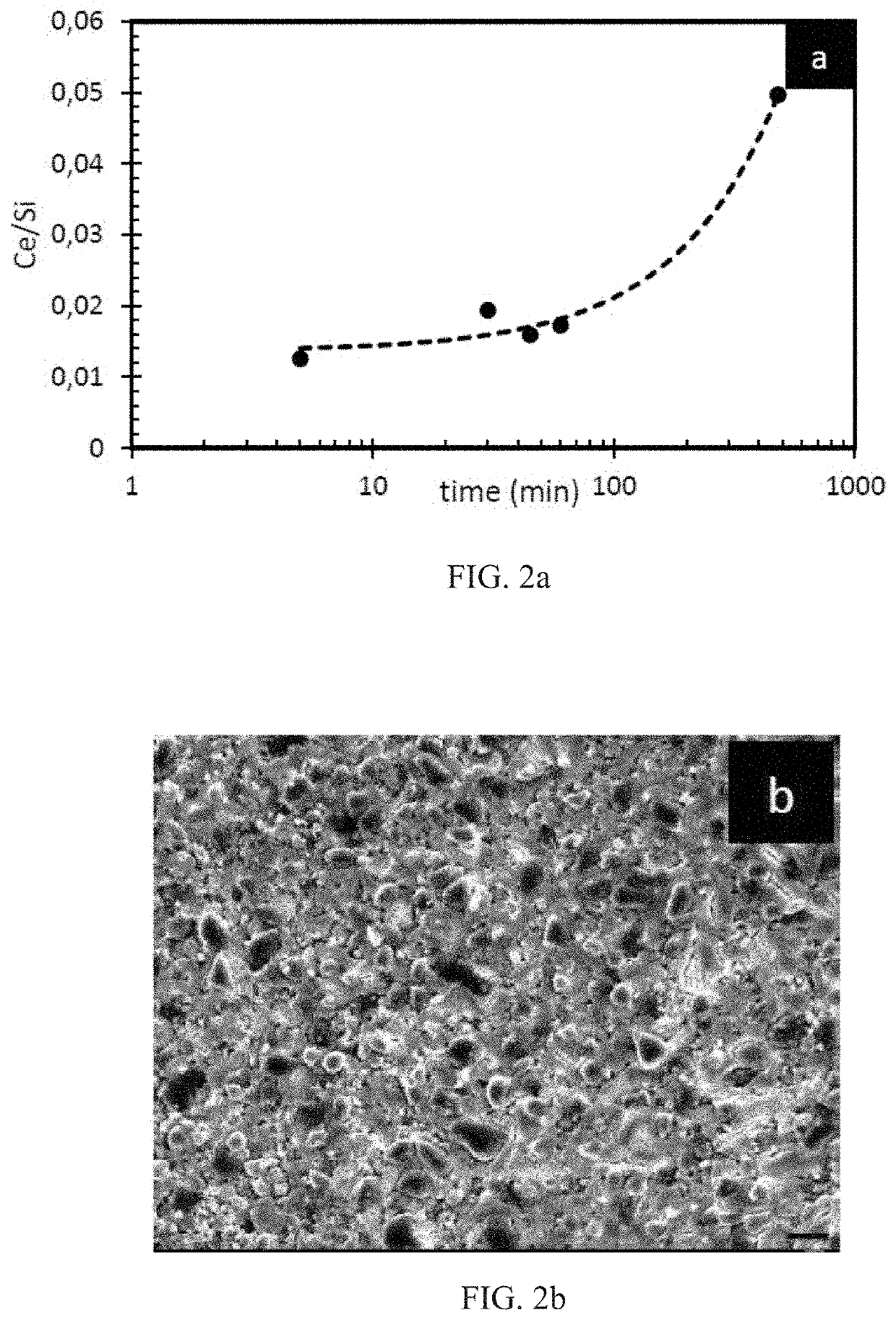
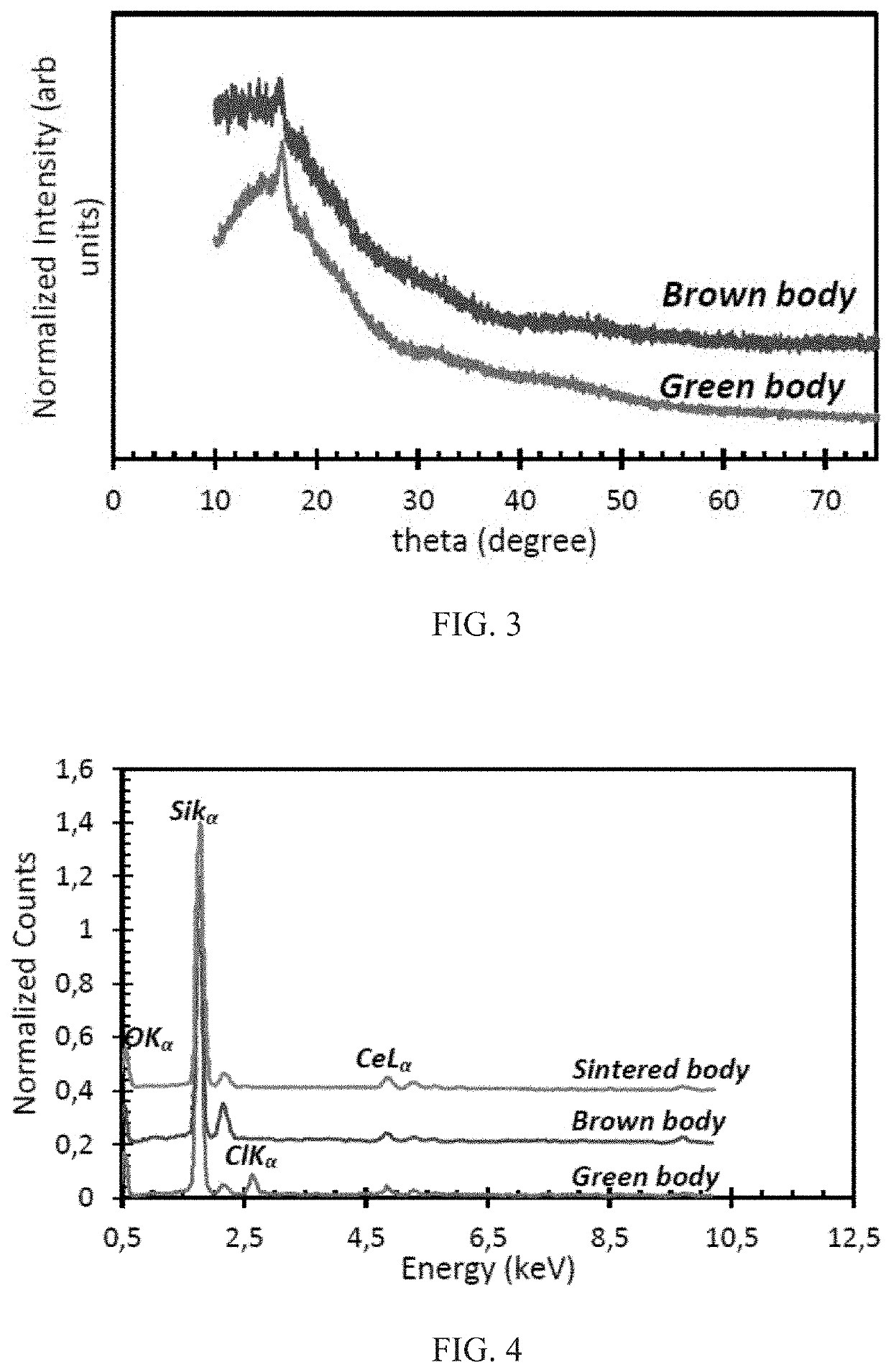
Doped glass scintillators and methods of fabricating the same are provided. Doped glass scintillators can be fabricated by a stereolithography process, and doping can be carried out before the green body composite formation so that homogeneity of the dopant is improved. The structures retain an amorphous structure through the fabrication process, and the vacuum sintering process assists with keeping the dopants in their luminescence-producing oxidation state.
Owner:FLORIDA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY
Method for producing a three-dimensional object and stereolithography machine
PendingCN108357096AEasy to useSmall sizeManufacturing platforms/substratesManufacturing enclosuresStereolithographiesEngineering
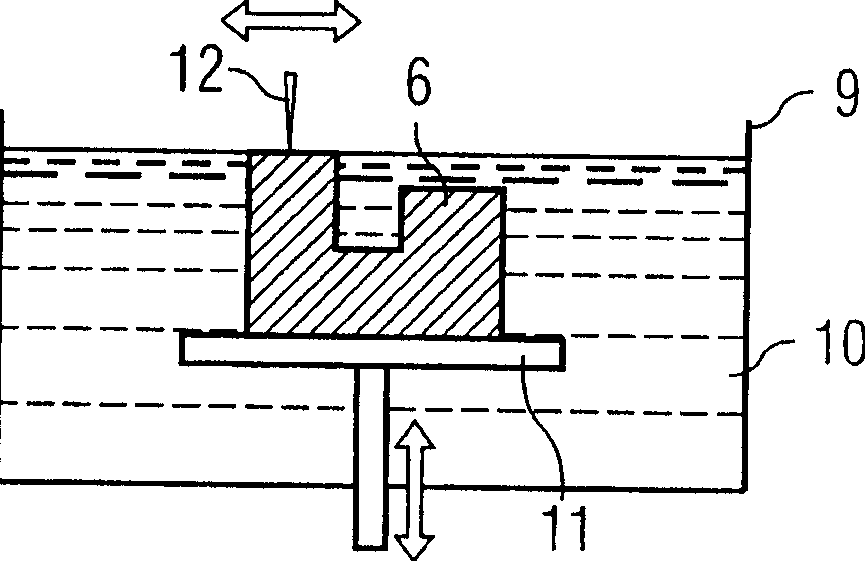
The invention is a method for producing a three-dimensional object in layers by means of a stereolithography machine comprising: a container containing a fluid substance suited to solidify through exposure to predefined radiation; a device suited to emit the predefined radiation and to solidify a layer of the fluid substance adjacent to the bottom of the container; a modeling plate suited to support the solidified layer and associated with an actuator device suited to move it perpendicular to the bottom of the container; a leveling device arranged in contact with the fluid substance, the leveling device comprising a paddle developed according to a longitudinal direction and having an edge facing the container's bottom and arranged inside the container. The method comprises the following operations: selectively irradiating the layer of fluid substance to obtain the solidified layer; extracting the solidified layer from the fluid substance; redistributing the fluid substance in the container by moving the leveling device so that they are passed between the modeling plate and the container.
Owner:DWS SRL
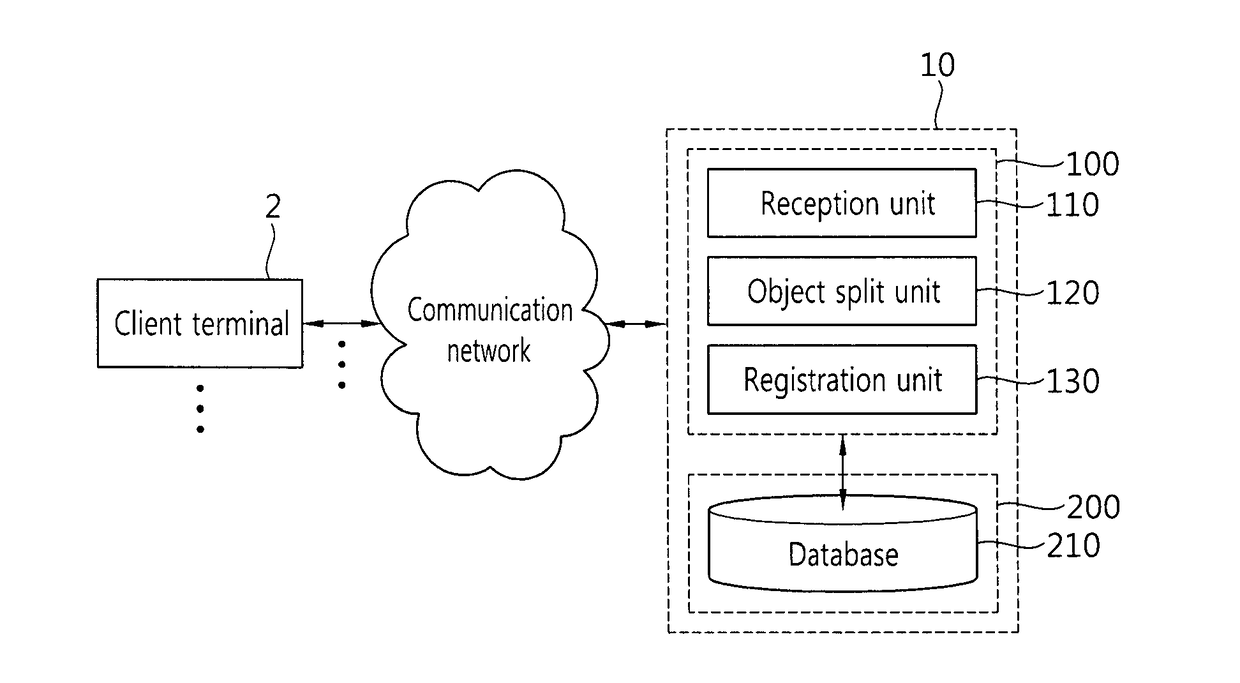
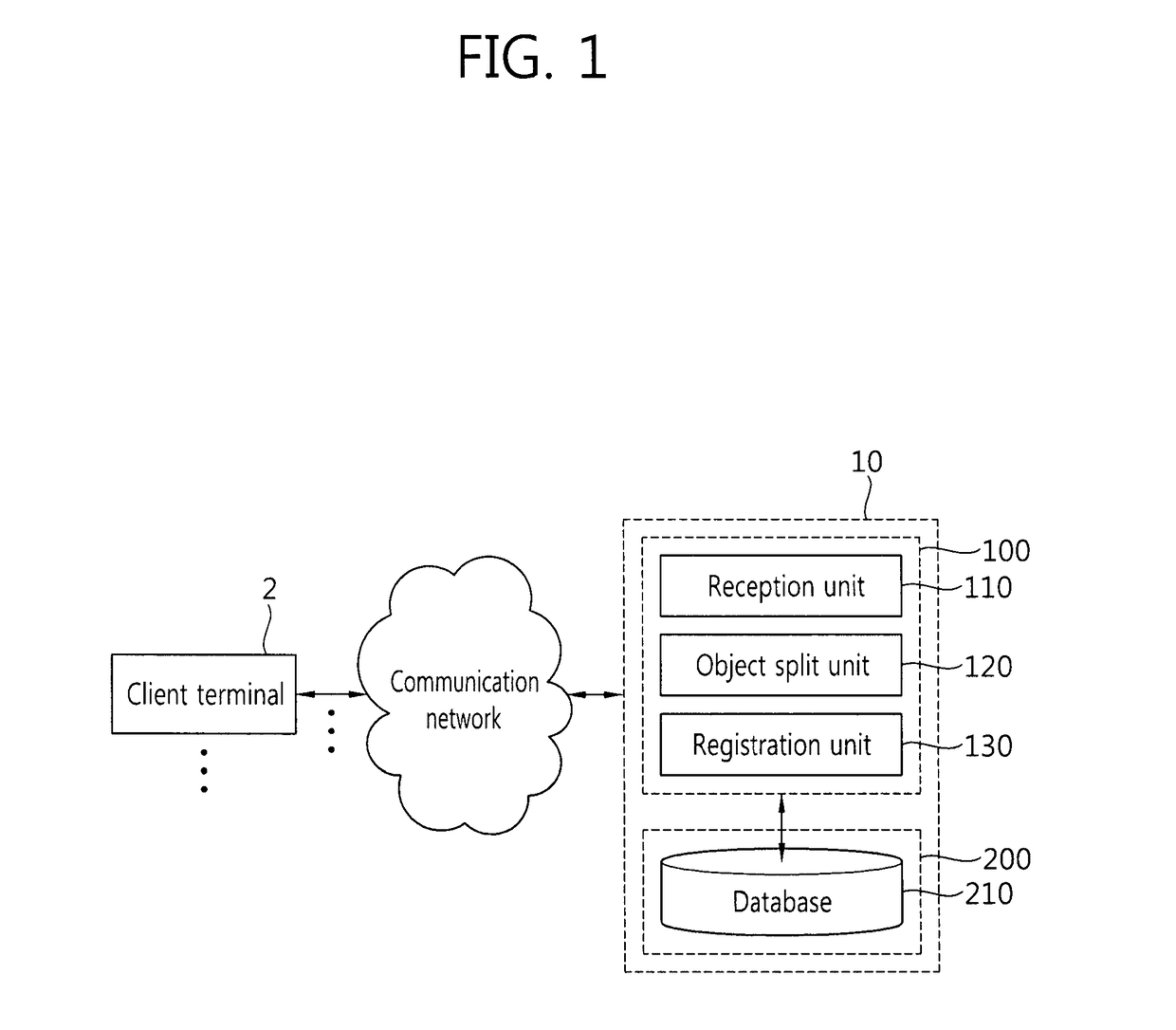
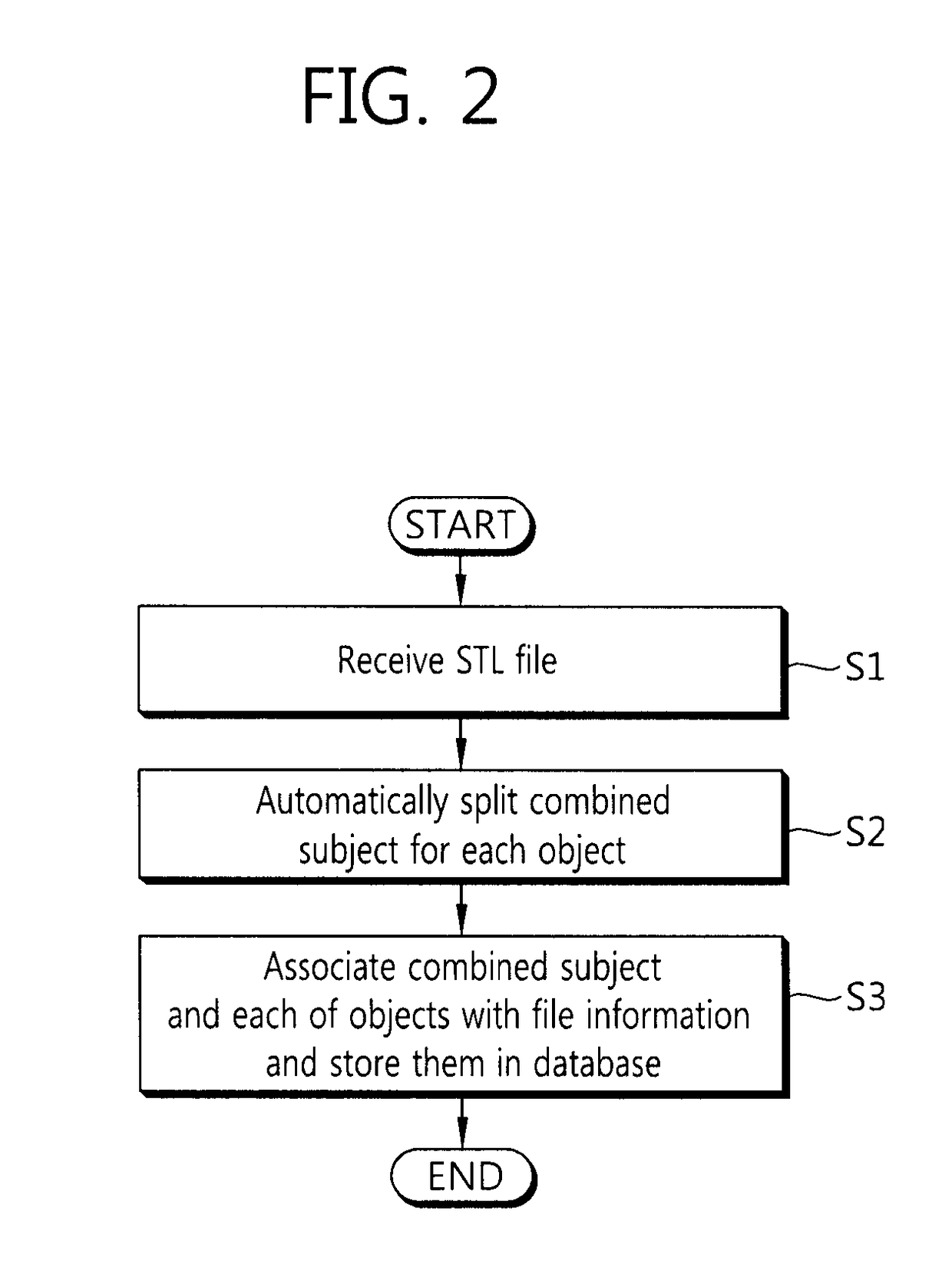
Method and apparatus for automatically splitting object and method, apparatus, and system for registering file
ActiveUS20170161959A1Easily splitting an STL planAutomatically split easily for each objectAdditive manufacturing apparatusImage data processingComputer graphics (images)3d image
Provided are a method and apparatus for automatically splitting an object and a method, apparatus, and system for registering a file. The method for splitting an object includes receiving the data of a stereolithography (STL) file representing a 3D image, tagging vertex coordinates corresponding to objects included in the 3D image so that the vertex coordinates are classified for each object, and splitting each of the objects included in the 3D image based on the tagged vertex coordinates.
Owner:MARKANY
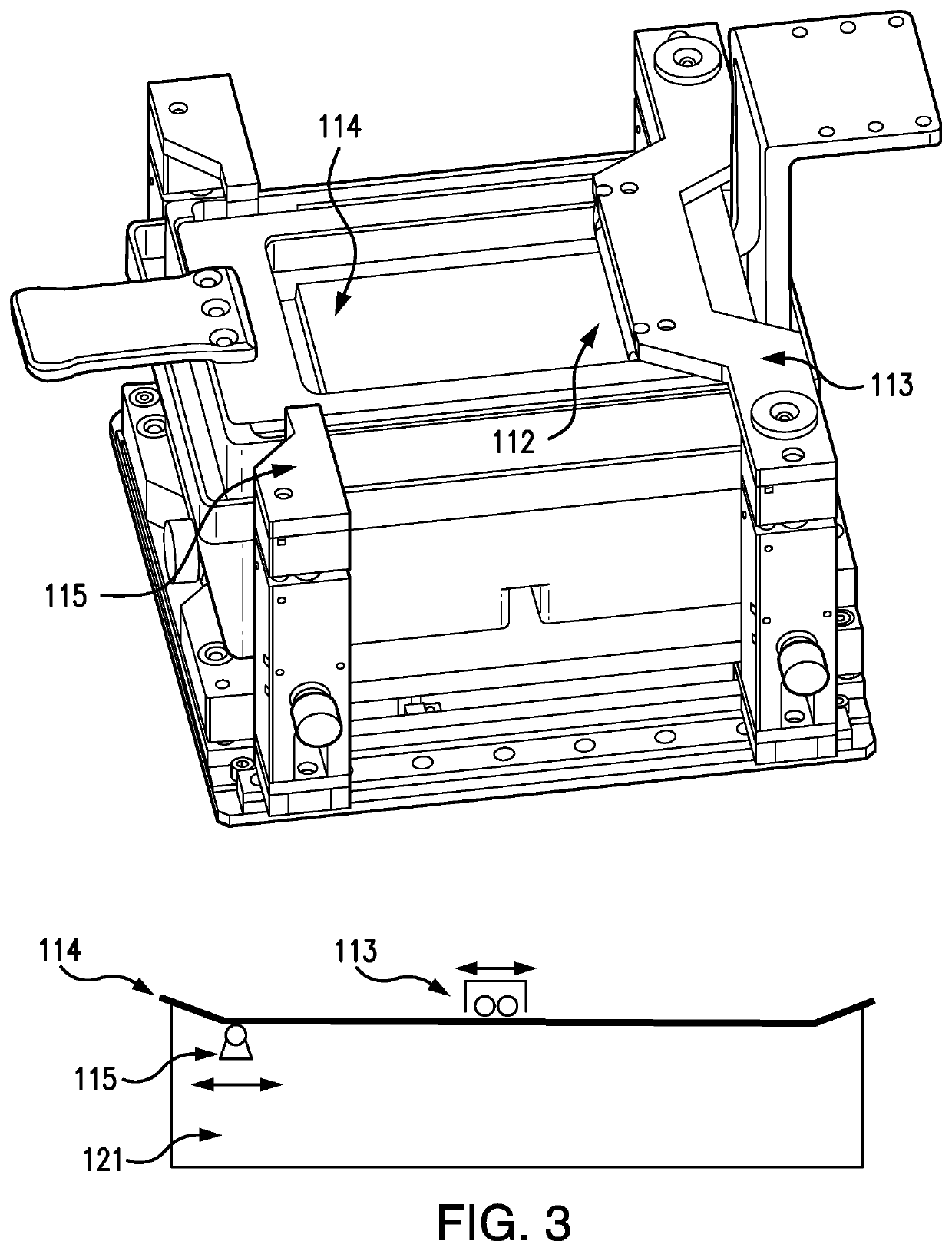
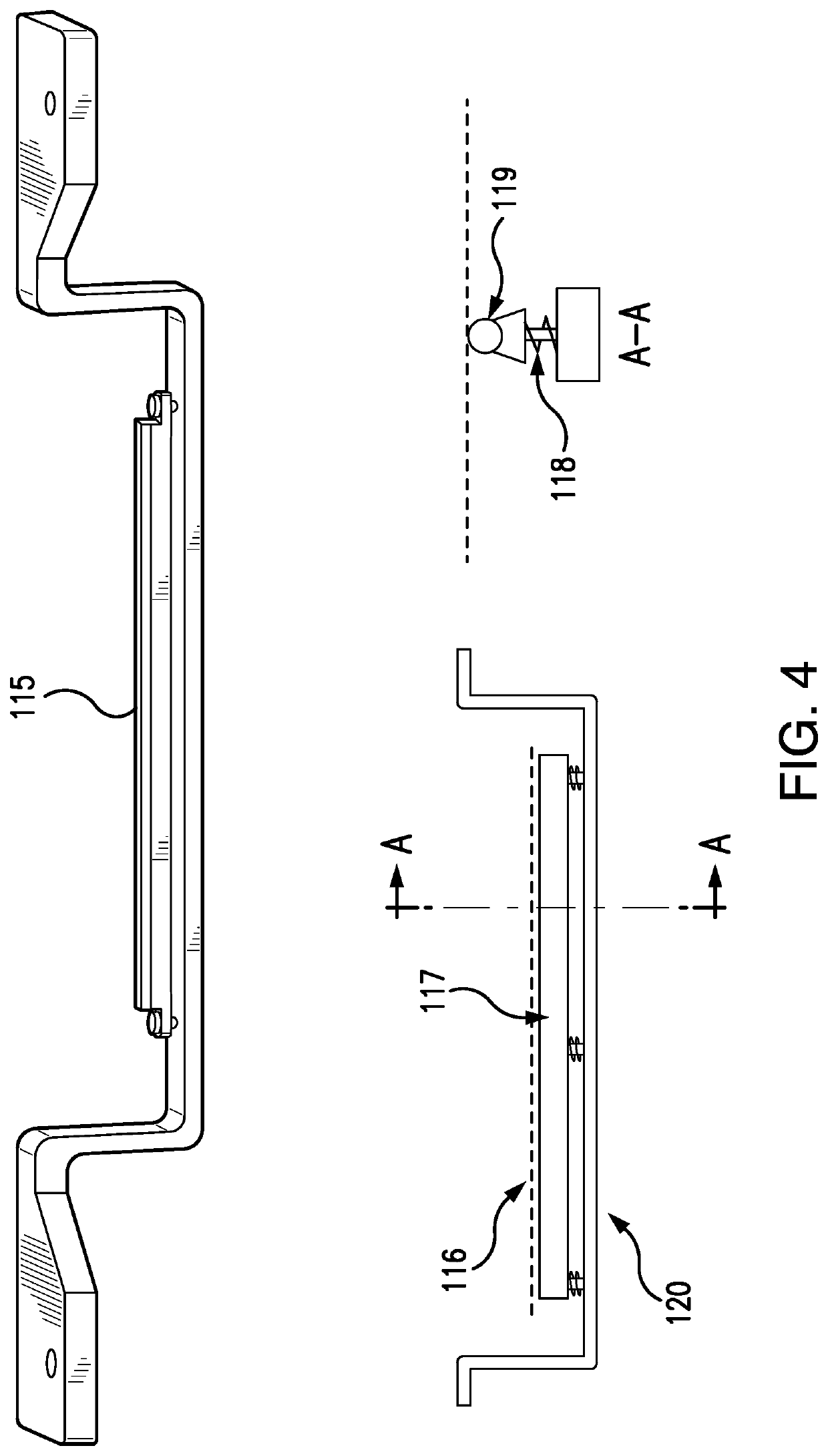
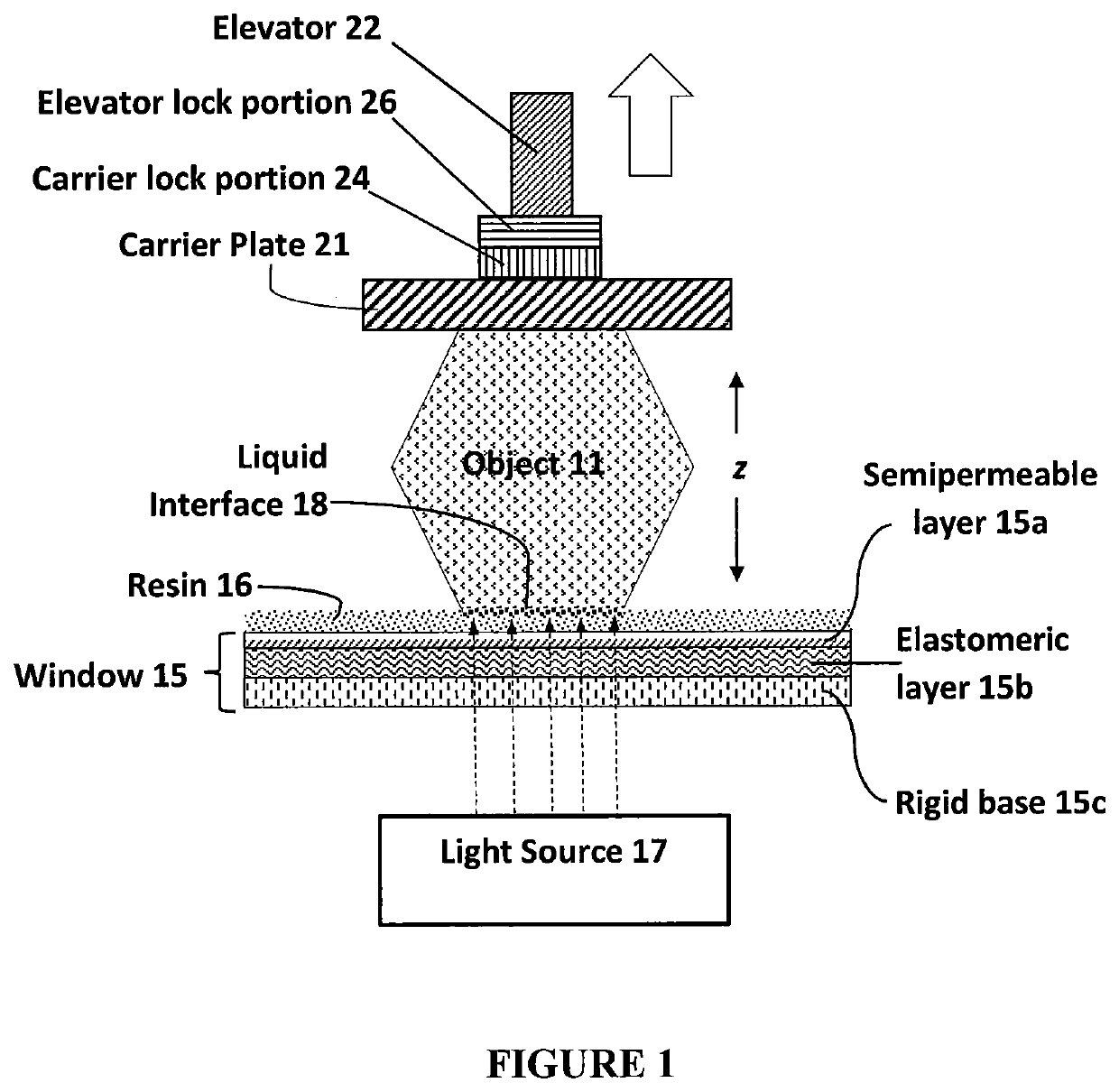
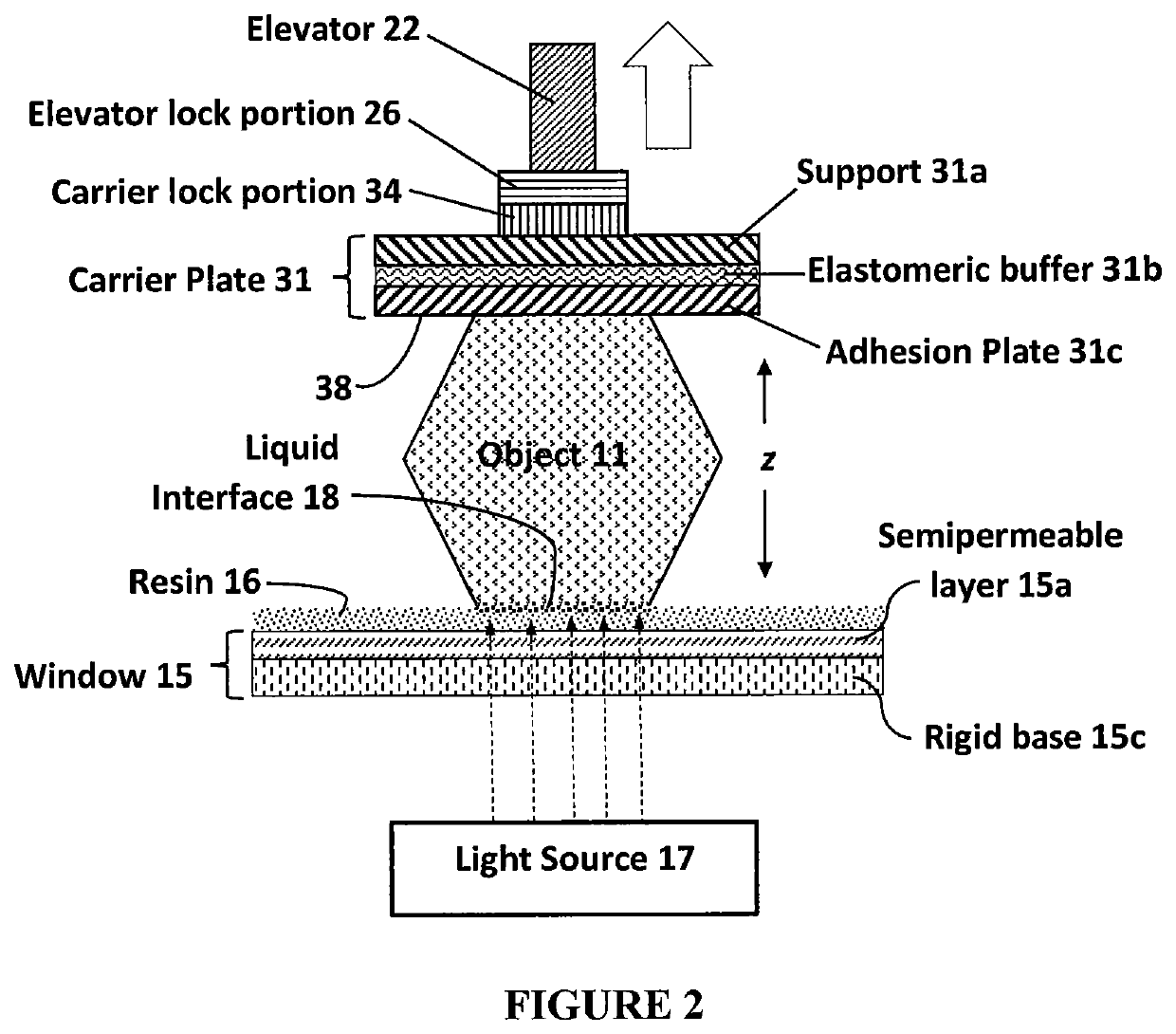
Additive manufacturing carrier platform with window damage protection features
ActiveUS11117315B2Manufacturing platforms/substrates3D object support structuresStereolithographiesEngineering
A carrier plate assembly for use in producing a three-dimensional object by bottom-up stereolithography includes: (a) an upper support; (b) an adhesion plate having a substantially flat planar lower adhesion surface, on which surface the three-dimensional object can be formed; (c) at least one energy absorber interconnecting the upper support and the adhesion plate; and (d) a carrier lock portion connected to the upper support.
Owner:CARBON INC
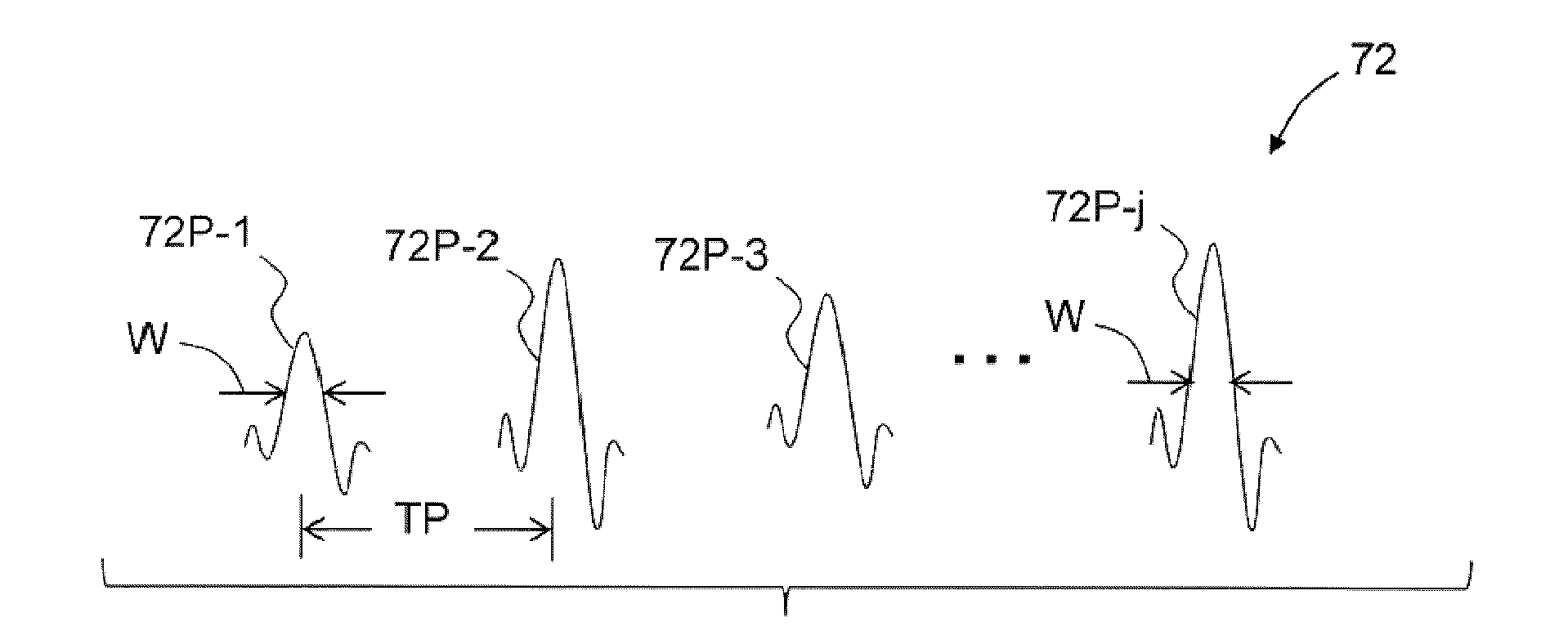
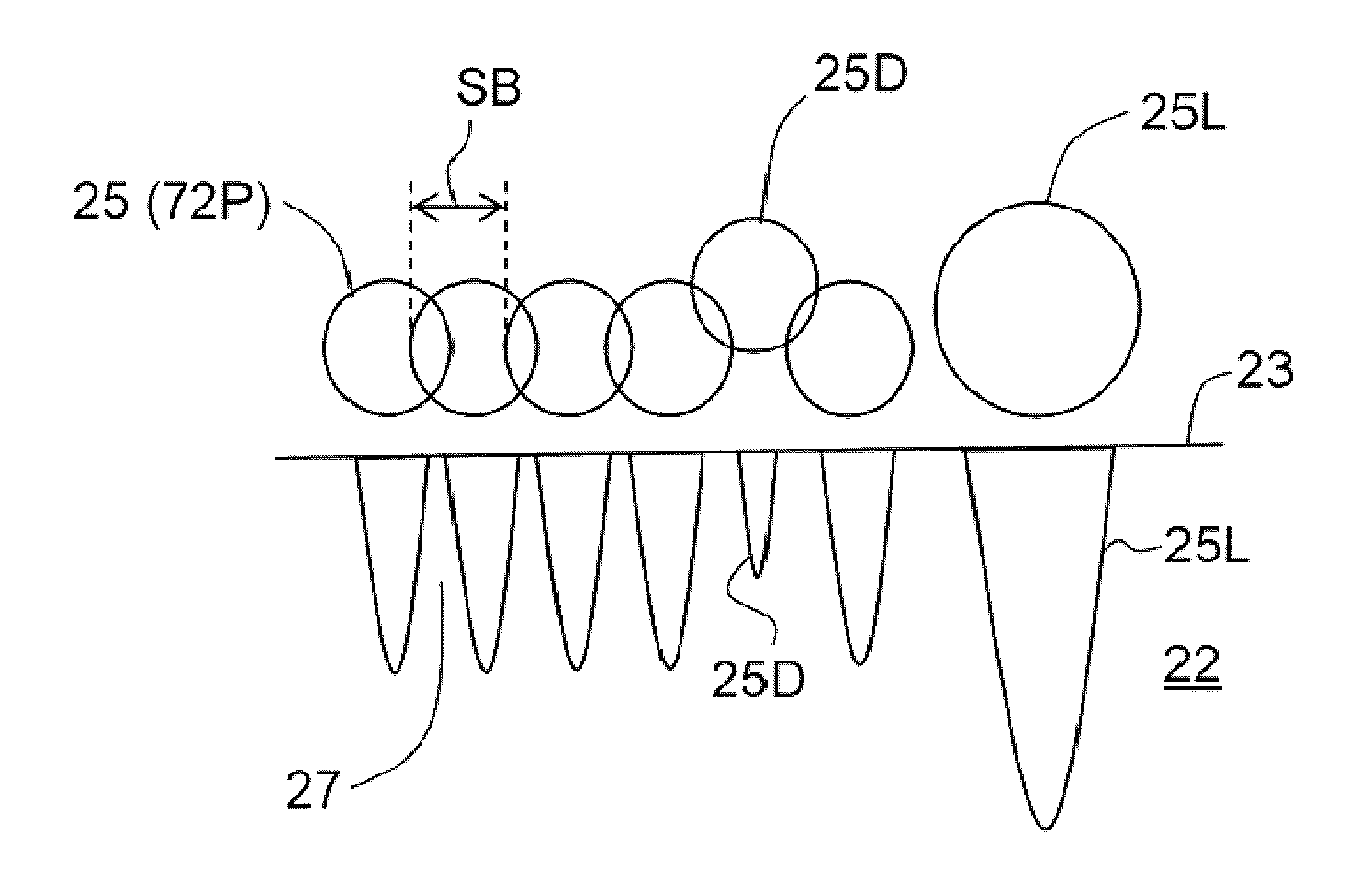
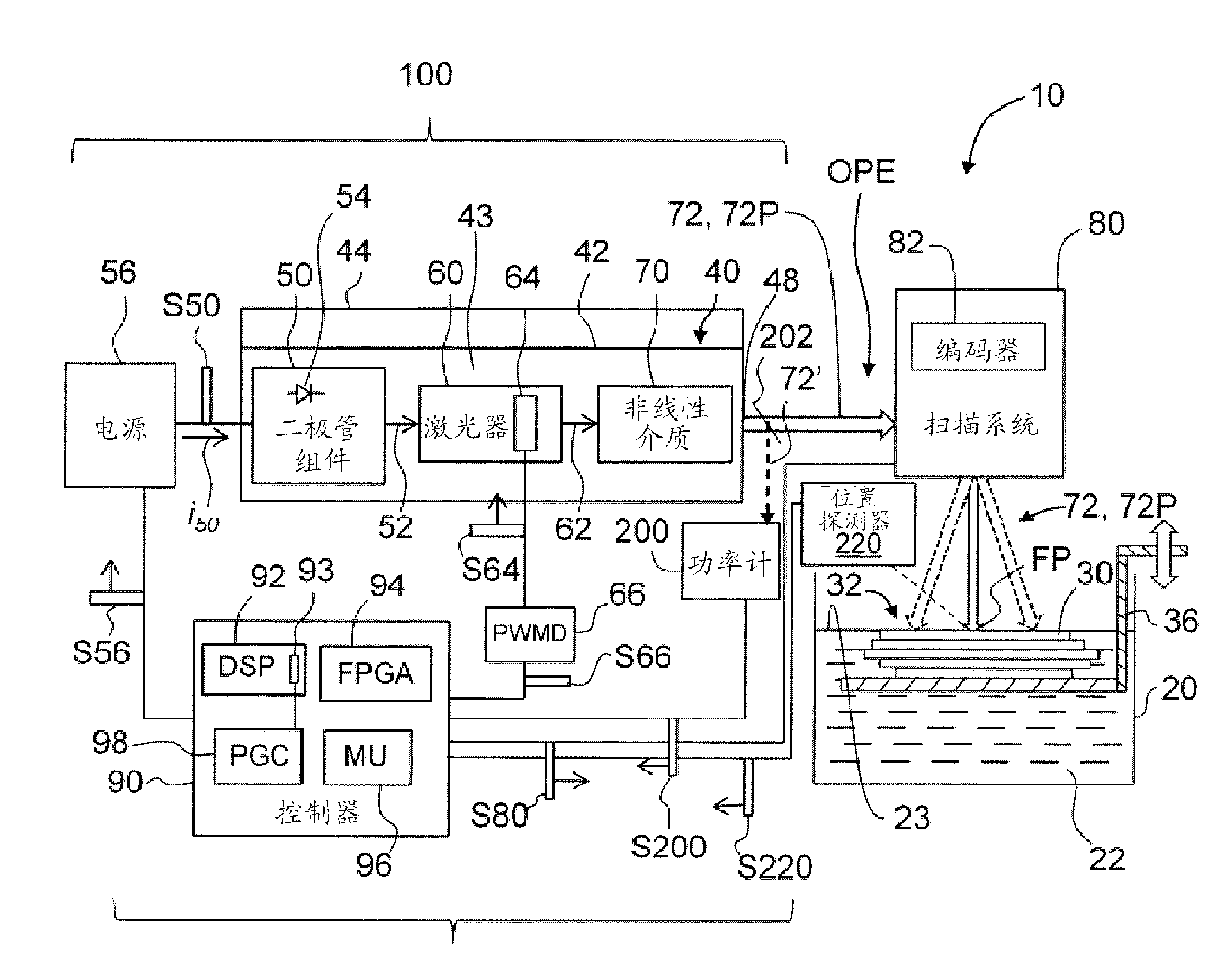
Stereolithography systems and methods using internal laser modulation
Stereolithography systems (10) and methods using internal laser modulation are disclosed. The system includes an internally modulated diode-pumped frequency-multiplied solid-state (DPFMSS) laser 40. There is no external modulation system (EMS) within an external optical path (OPE) between the laser and a scanning system (80). The scanning system directs a laser beam (72) with laser pulses (72P) to a focus position (FP) on surface (23) of a build material (22) to form bullets (25) therein to define a build layer (30) based on build instructions for forming a three-dimensional object (32).
Owner:3D SYST INC
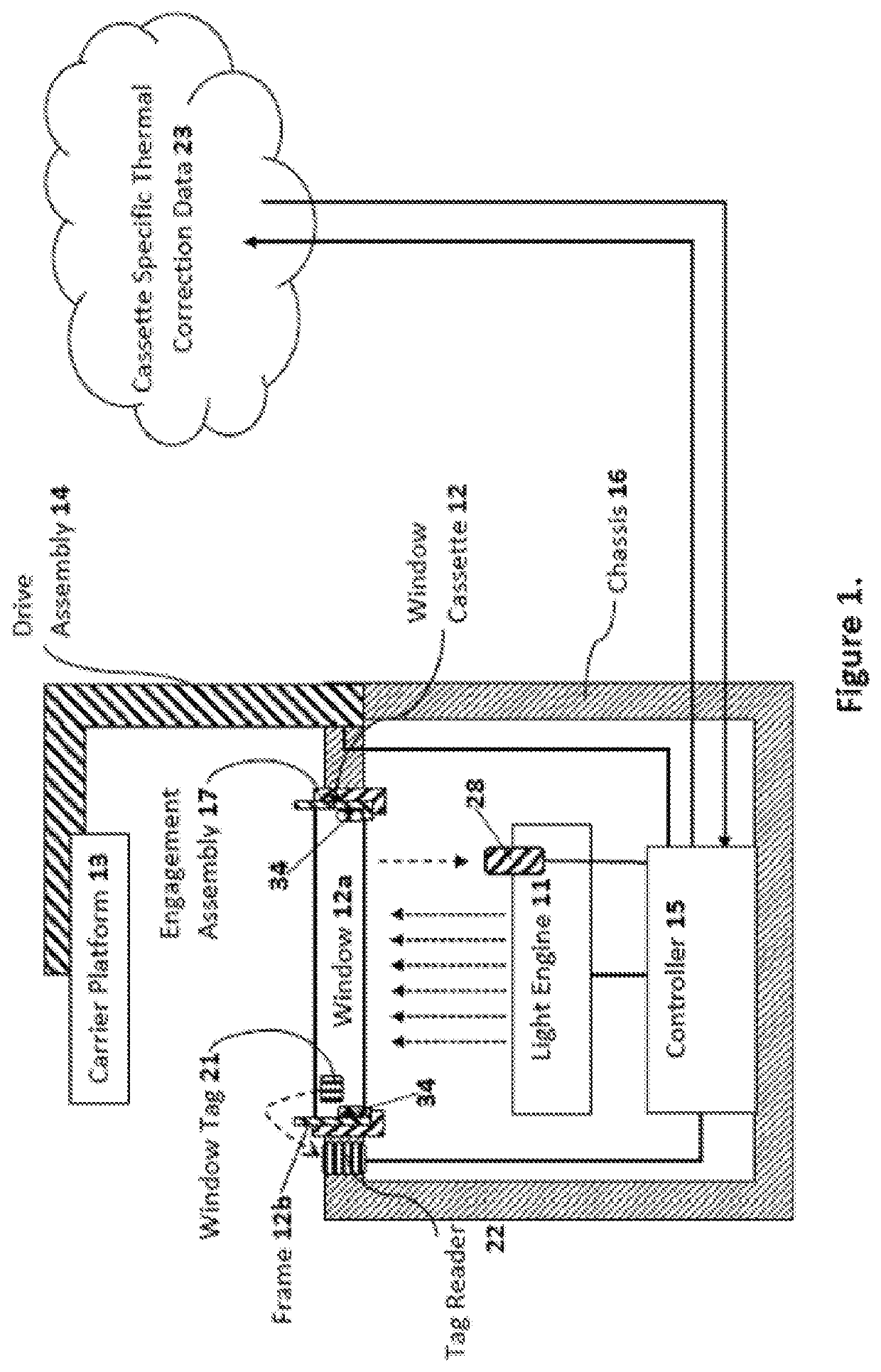
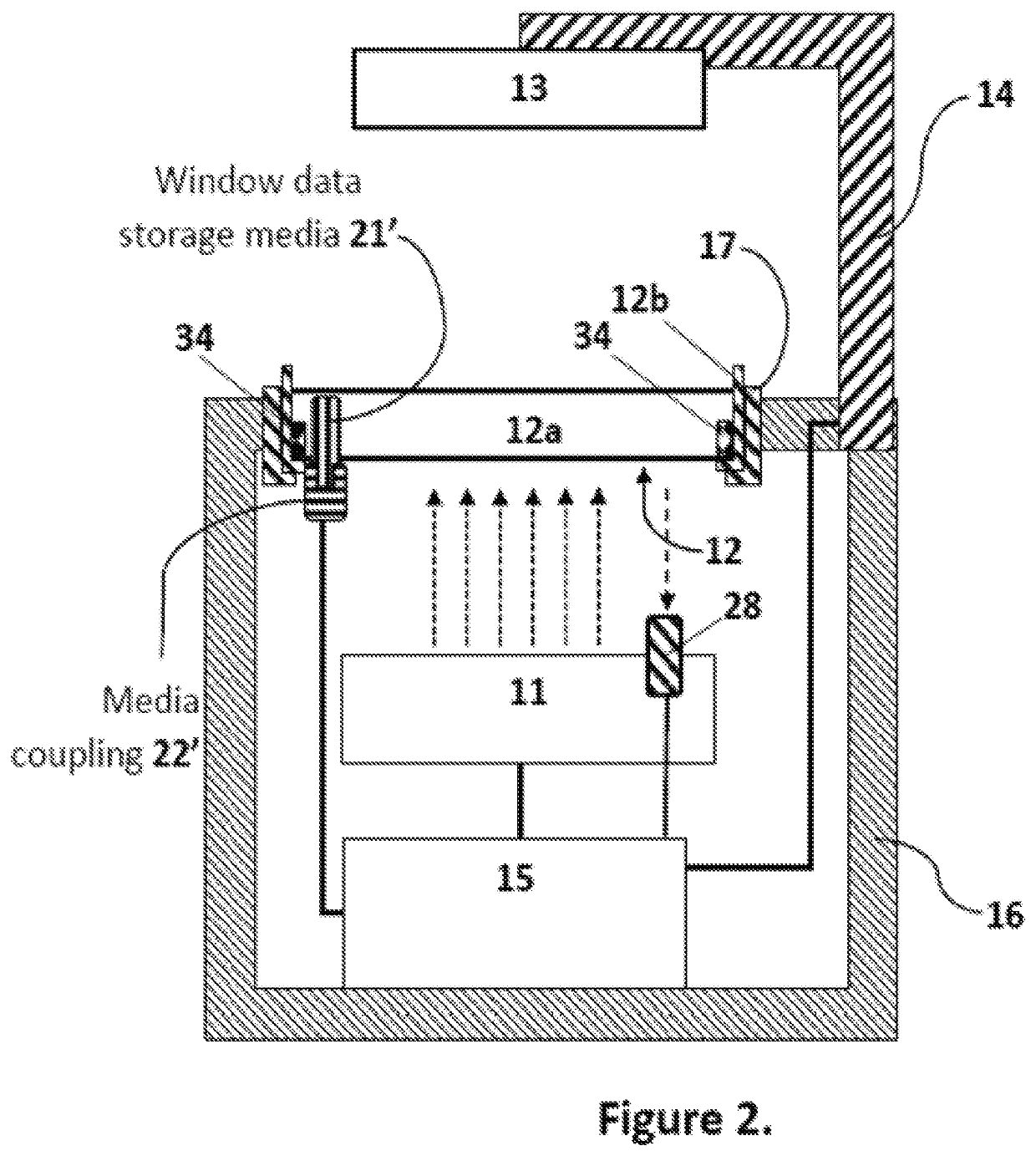
Window thermal profile calibration in additive manufacturing
ActiveUS11498274B2Improve performanceIncrease rate increaseManufacturing platforms/substratesManufacturing enclosuresStereolithographiesPolymeric liquid
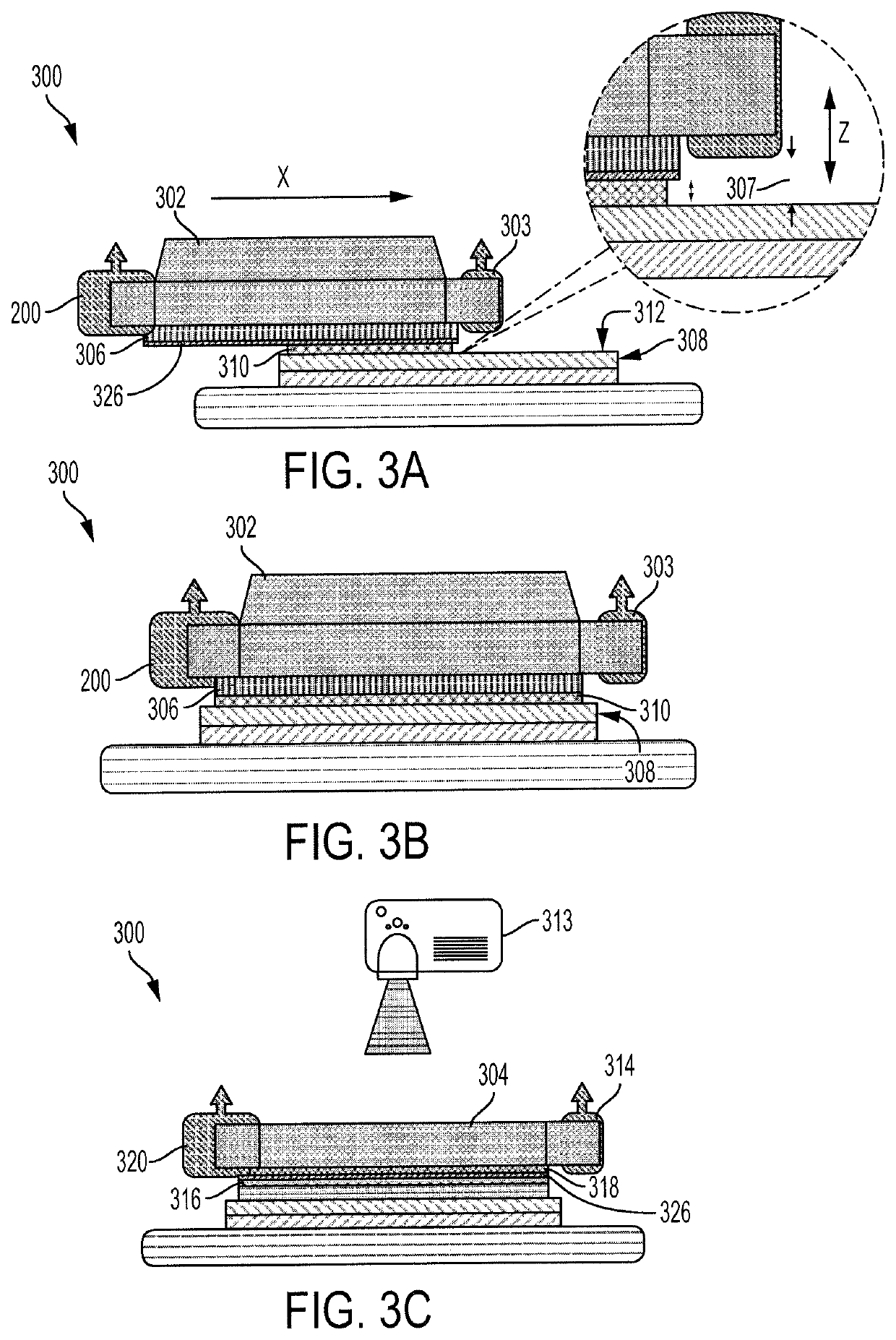
Methods, systems, and / or apparatuses for making an object on a bottom-up stereolithography apparatus that includes a light source (11), a drive assembly (14), optionally a heater (34) and / or cooler (34), and a controller (15). The light source, optional heater and / or cooler, and / or the drive assembly have at least one adjustable parameter that is adjustable by said controller. An example method comprises (a) installing a removable window cassette (12) on said apparatus in a configuration through which said light source projects, said window cassette comprising an optically transparent member (12a) having a build surface on which an object can be produced, and with said optically transparent member having at least one thermal profile associated therewith; and then (b) modifying said at least one adjustable parameter by said controller based on said at least one thermal profile of said optically transparent member; and then (c) producing the object on said build surface from a light-polymerizable liquid by bottom-up stereolithography.
Owner:CARBON INC
SLA additive manufacturing using frozen supports of non-SLA material
ActiveUS10894354B2Manufacturing platforms/substratesManufacturing heating elementsStereolithographiesEngineering
Methods and apparatuses for additive manufacturing using stereolithography (“SLA”) materials. The apparatus includes a platform for holding an assembly of SLA resin layers. The apparatus also includes a platform for holding an assembly of SLA resin layers. The apparatus also includes a first movable stage for depositing and curing a portion of the liquid SLA resin on the platform, forming a pattern of cured SLA resin. The apparatus also includes a second movable stage for depositing a low-viscosity non-SLA material in voids in the pattern of cured SLA resin. The apparatus also includes a cooler for cooling the low-viscosity non-SLA material below its freezing point until solidified.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Method for the manufacture of a spatially varying dielectric material, articles made by the method, and uses thereof
A stereolithography method of manufacture of a polymer structure having a spatially gradient dielectric constant, including: providing a volume of a liquid, radiation-curable composition; irradiating a portion of the liquid, radiation-curable composition with activating radiation in a pattern to form a layer of the polymer structure; contacting the layer with the liquid, radiation-curable composition; irradiating the liquid, radiation-curable composition with activating radiation in a pattern to form a second layer on the first layer; and repeating the contacting and irradiating to form the polymer structure, wherein the polymer structure comprises a plurality of unit cells wherein each unit cell is integrally connected with an adjacent unit cell, each unit cell is defined by a plurality of trusses formed by the irradiation, wherein the trusses are integrally connected with each other at their respective ends, and the trusses of each unit cell are dimensioned to provide the spatially gradient dielectric constant.
Owner:ROGERS CORP
Ultraviolet curable silicone composition for stereolithography and cured product of same
ActiveUS11370869B2Good rubber performanceSuitable for useAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structuresPolymer scienceStereolithographies
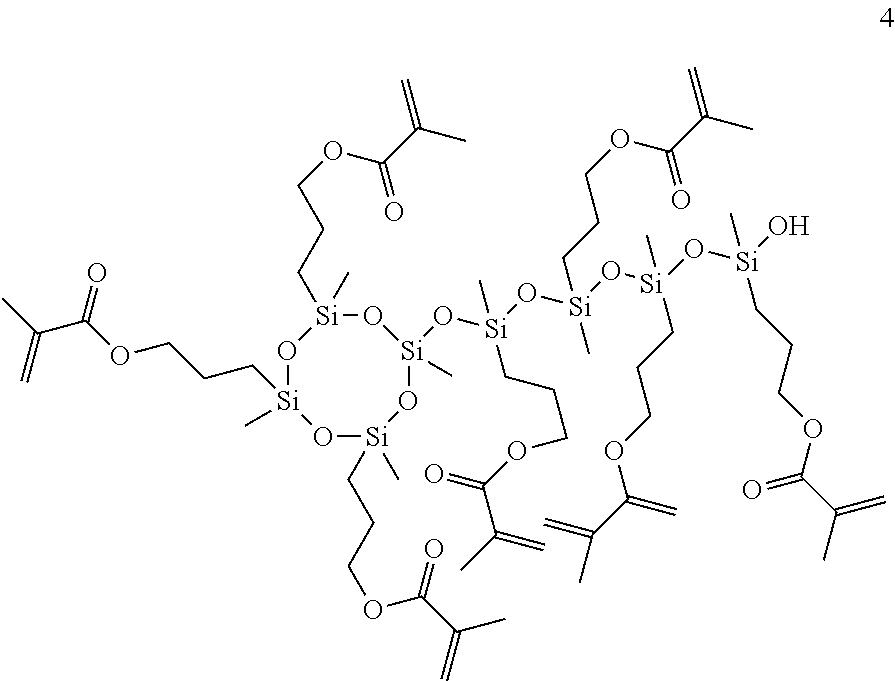
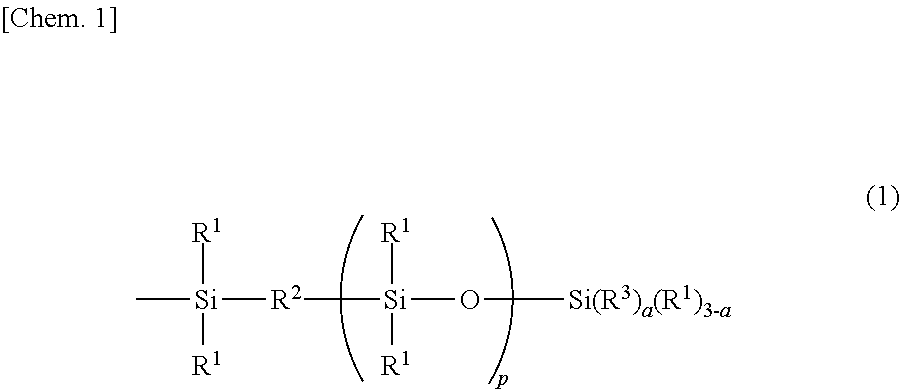
According to the present invention, an ultraviolet curable silicone composition for stereolithography, which contains(A) an organopolysiloxane that has two groups represented by formula (1)(wherein each R1 independently represents a monovalent hydrocarbon group having 1-20 carbon atoms; R2 represents an oxygen atom or the like; R3 represents an acryloyloxyalkyl group or the like; p represents a number satisfying 0≤p≤10; and a represents a number satisfying 1≤a≤3) in each molecule,(B) an organopolysiloxane resin that is composed of (a) a unit represented by formula (2)(wherein R1-R3, a and p are as defined above), (b) an R43SiO1 / 2 unit (wherein each R4 independently represents a monovalent hydrocarbon group having 1-10 carbon atoms) and (c) an SiO4 / 2 unit, and wherein the molar ratio of the total of the unit (a) and the unit (b) to the unit (c) is within the range of 0.6-1.2:1 and(C) a photopolymerization initiator has a viscosity that is applicable to a stereolithography system such as lifting system and forms a cured product which has excellent physical properties of rubber.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com