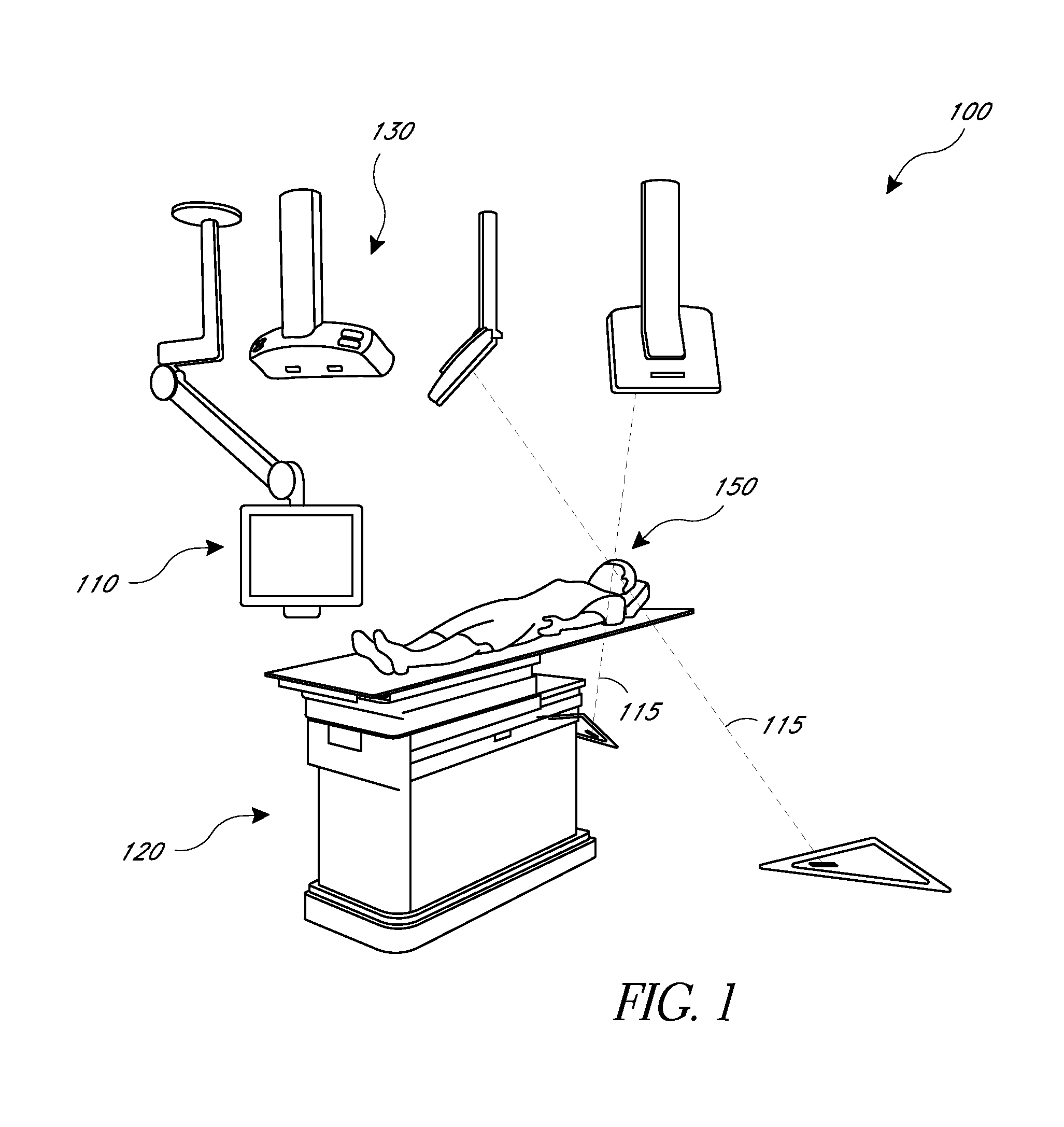
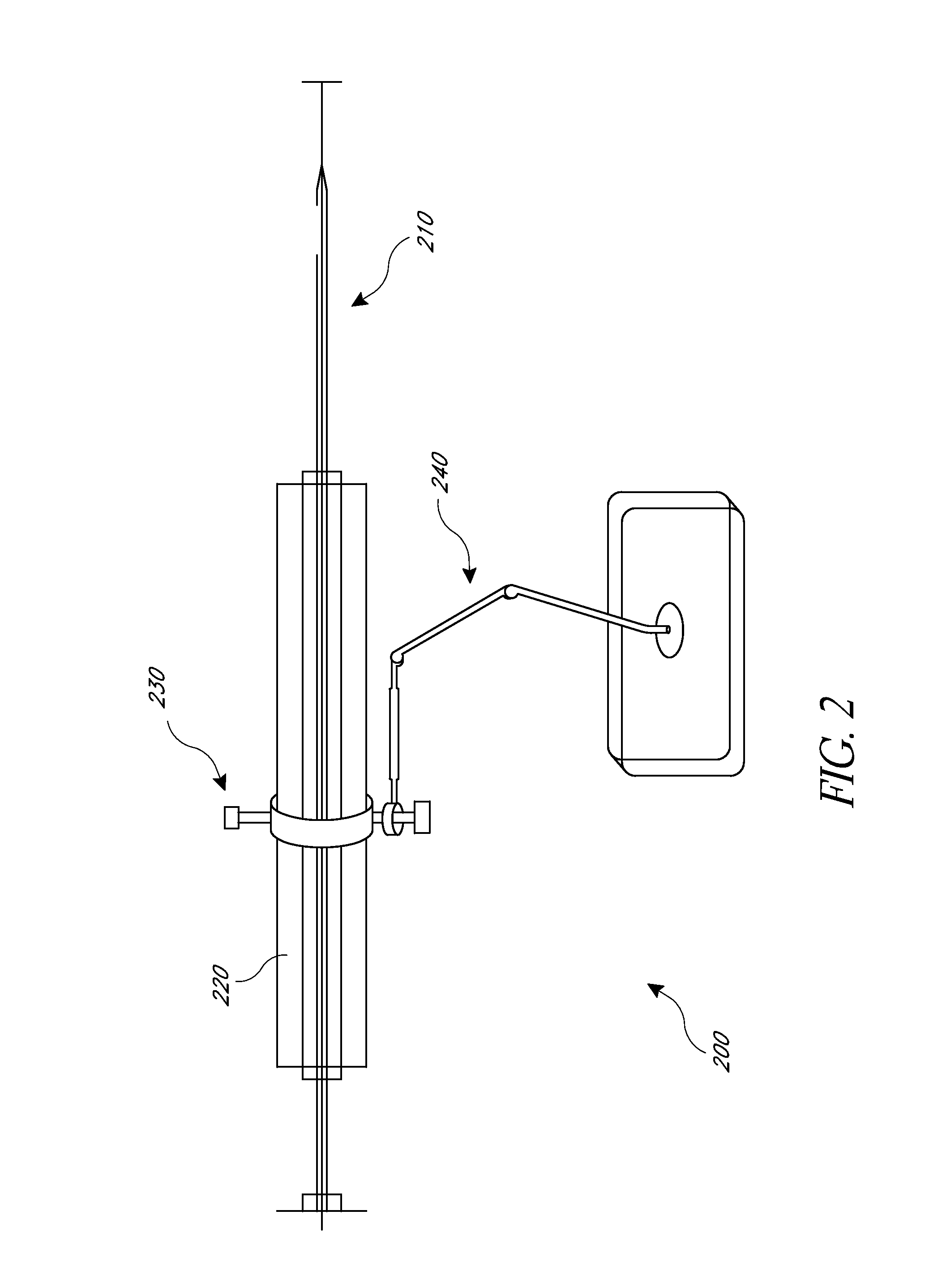
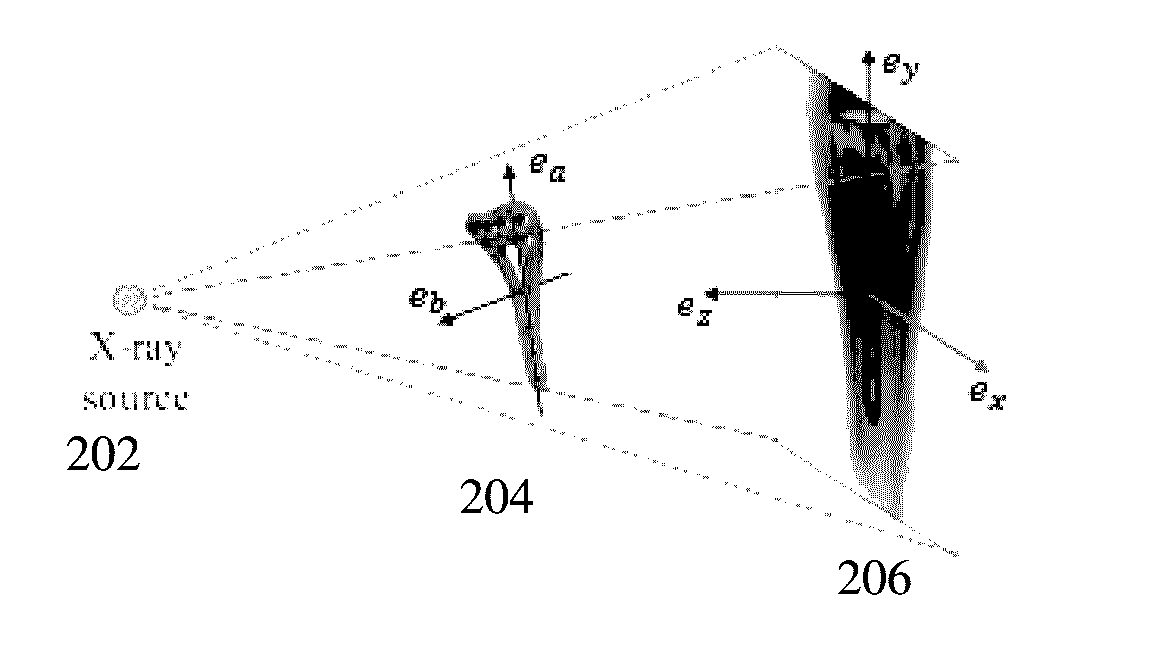
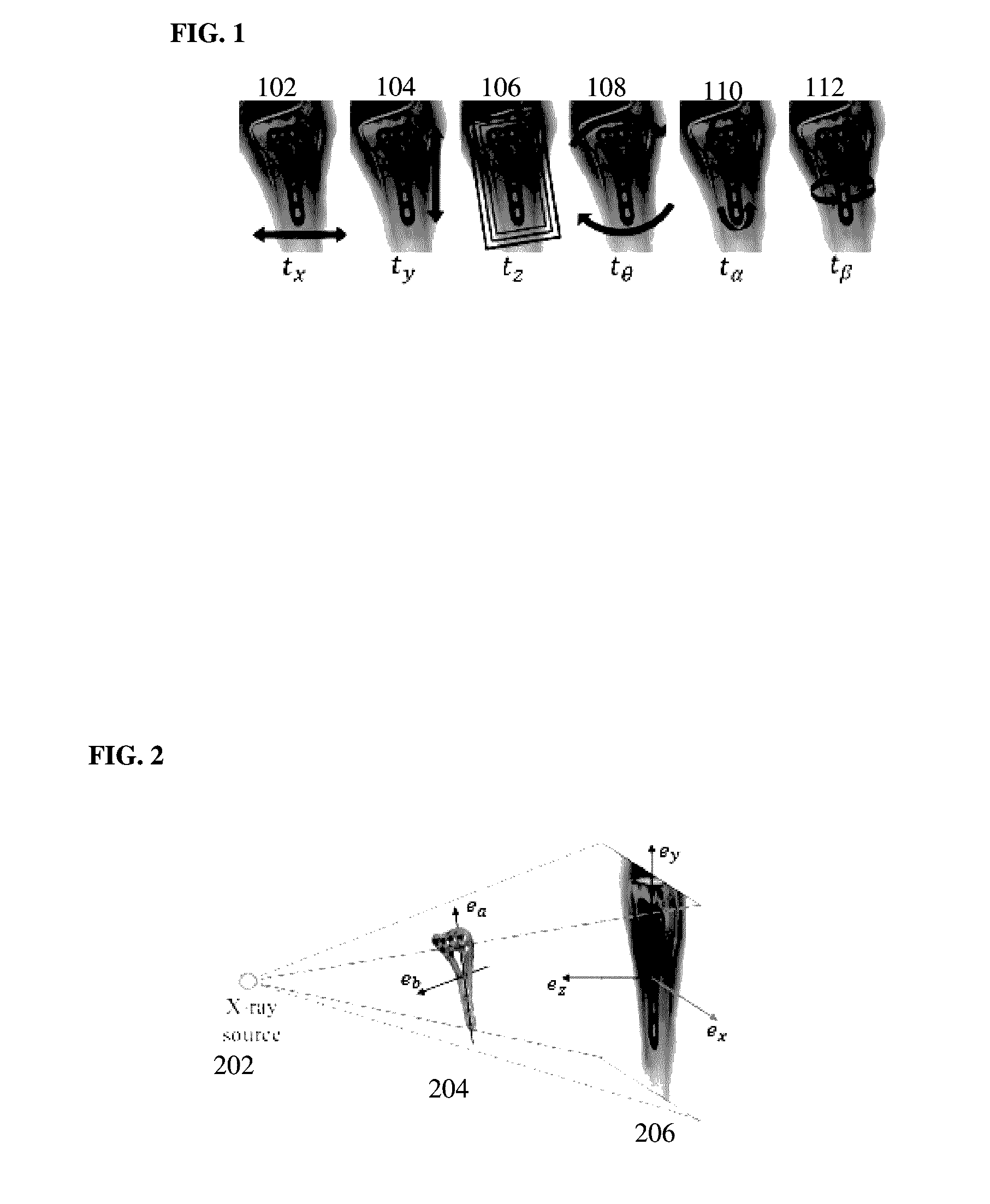
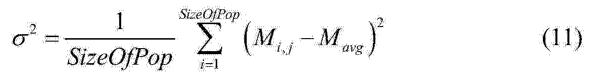Patents
Literature
34 results about "Digitally reconstructed radiographs" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
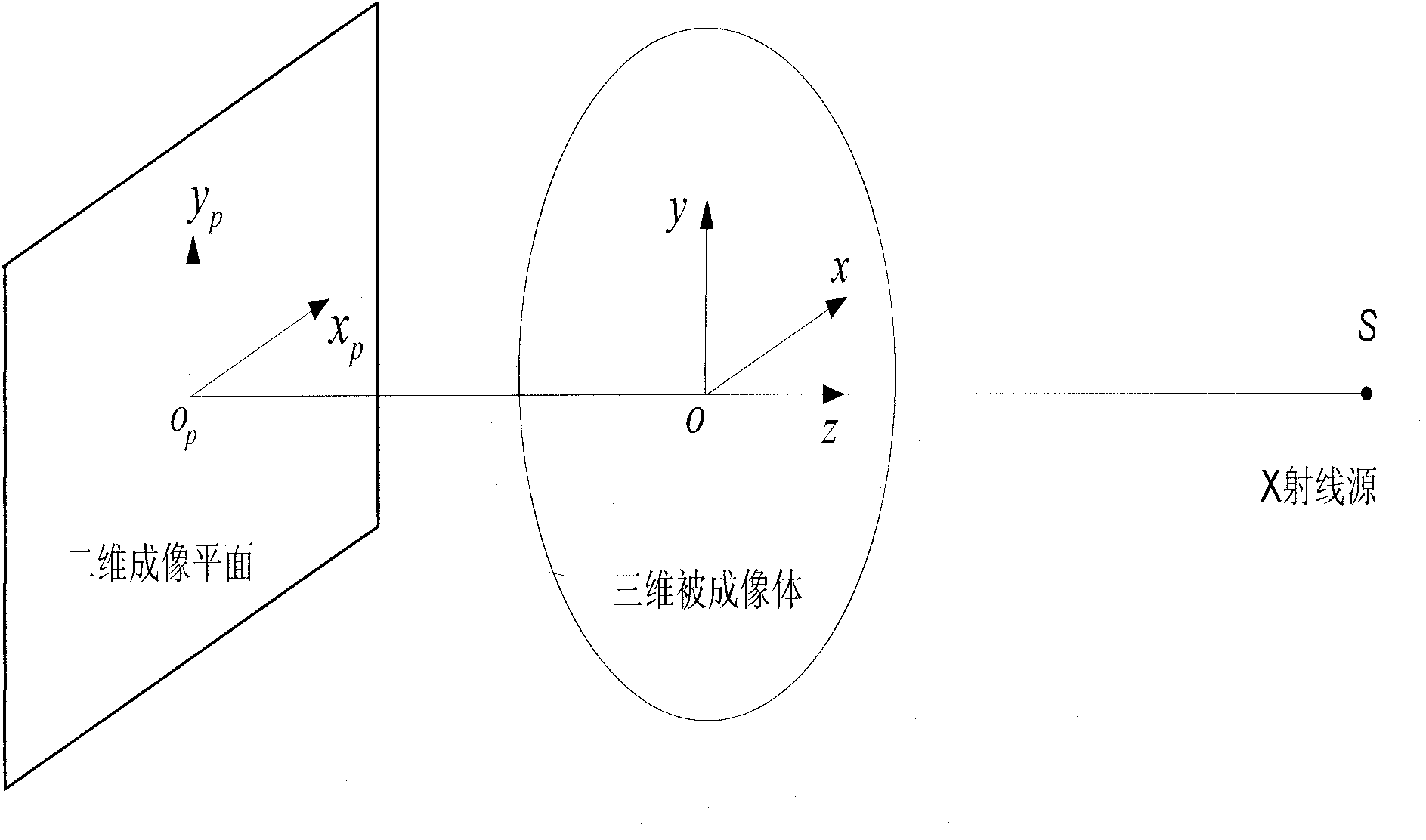
Digitally Reconstructed Radiograph. A Digitally Reconstructed Radiograph (DRR) is a simulation of a conventional 2D x-ray image, created from computed tomography (CT) data. A radiograph, or conventional x-ray image, is a single 2D view of total x-ray absorption through the body along a given axis.
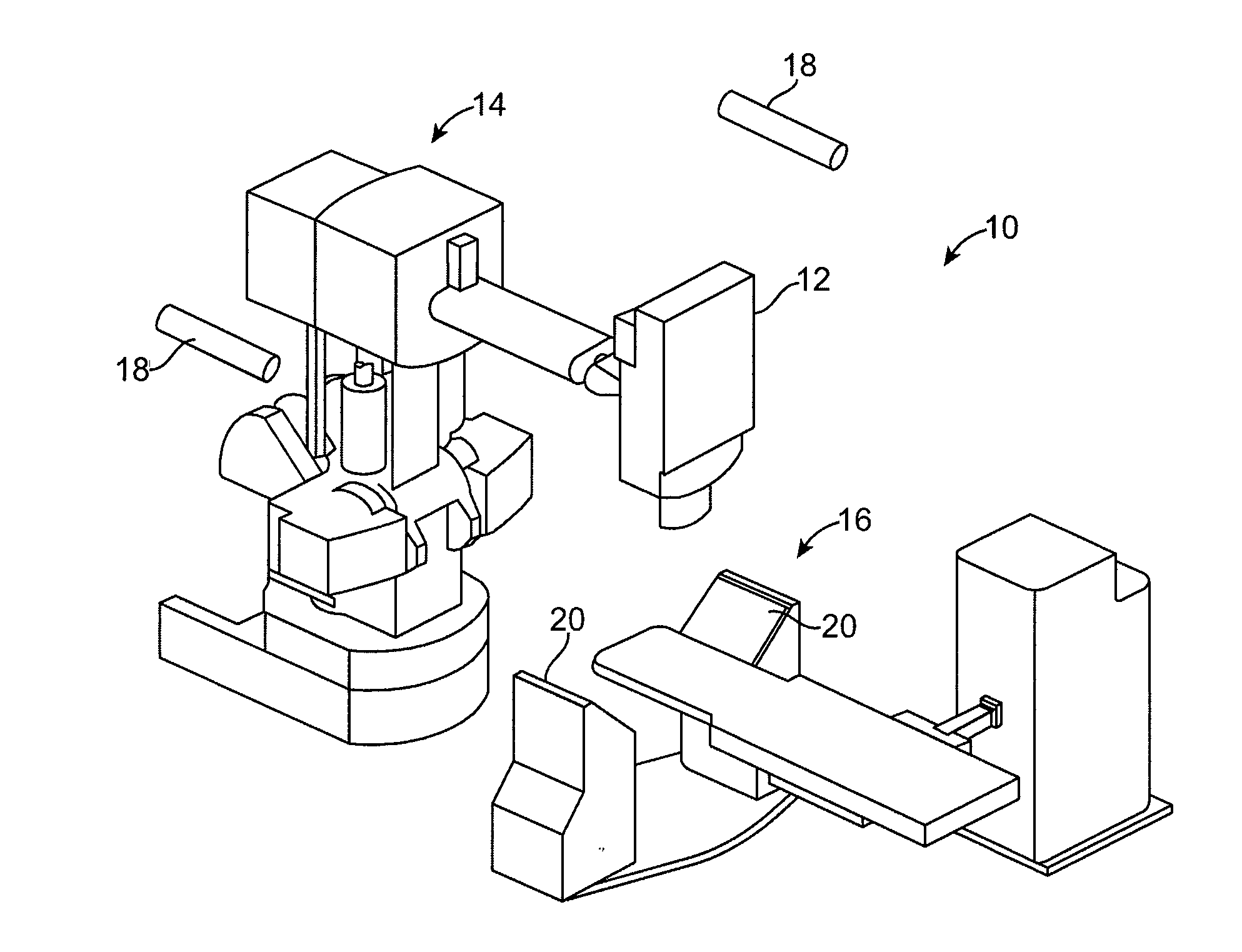
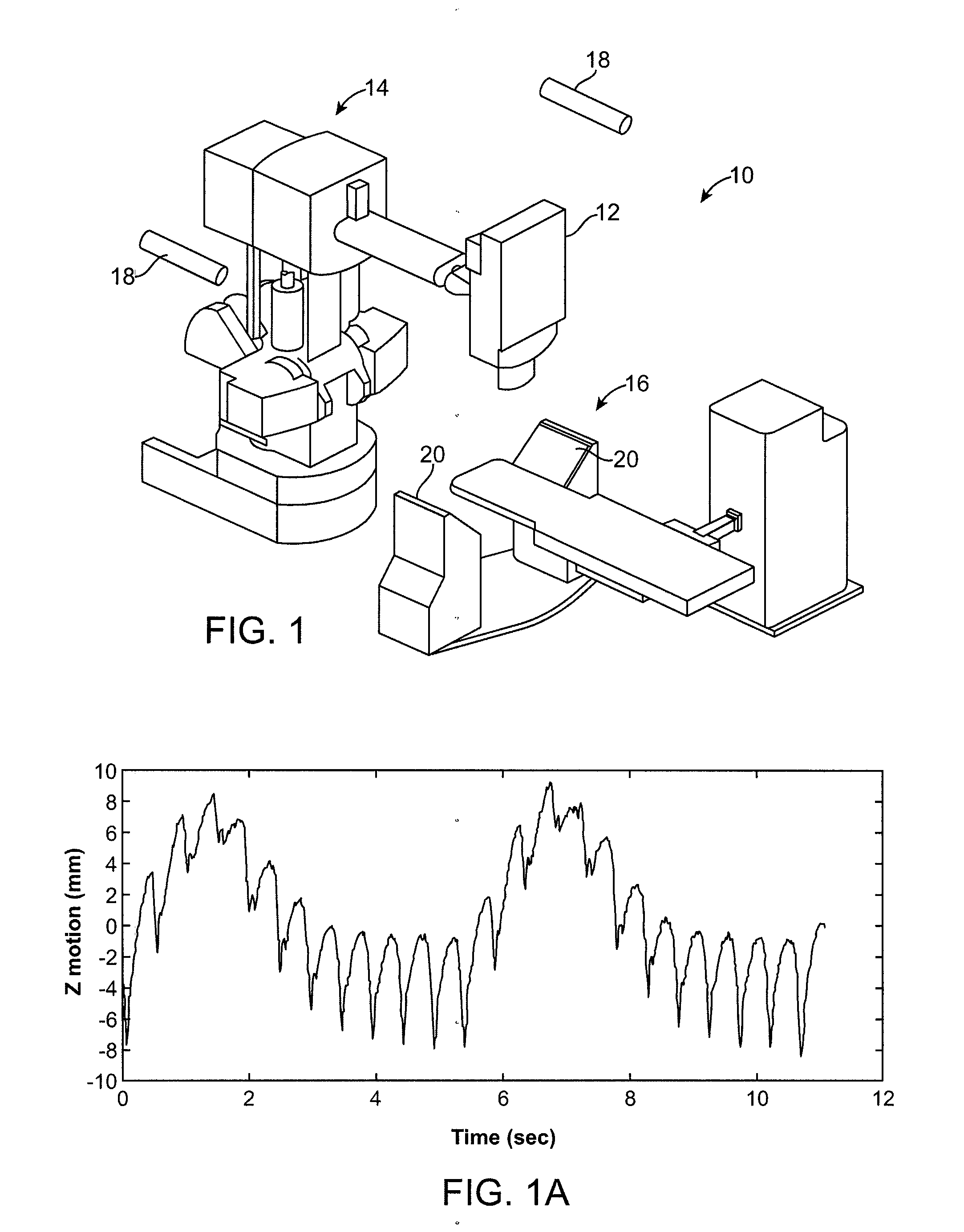
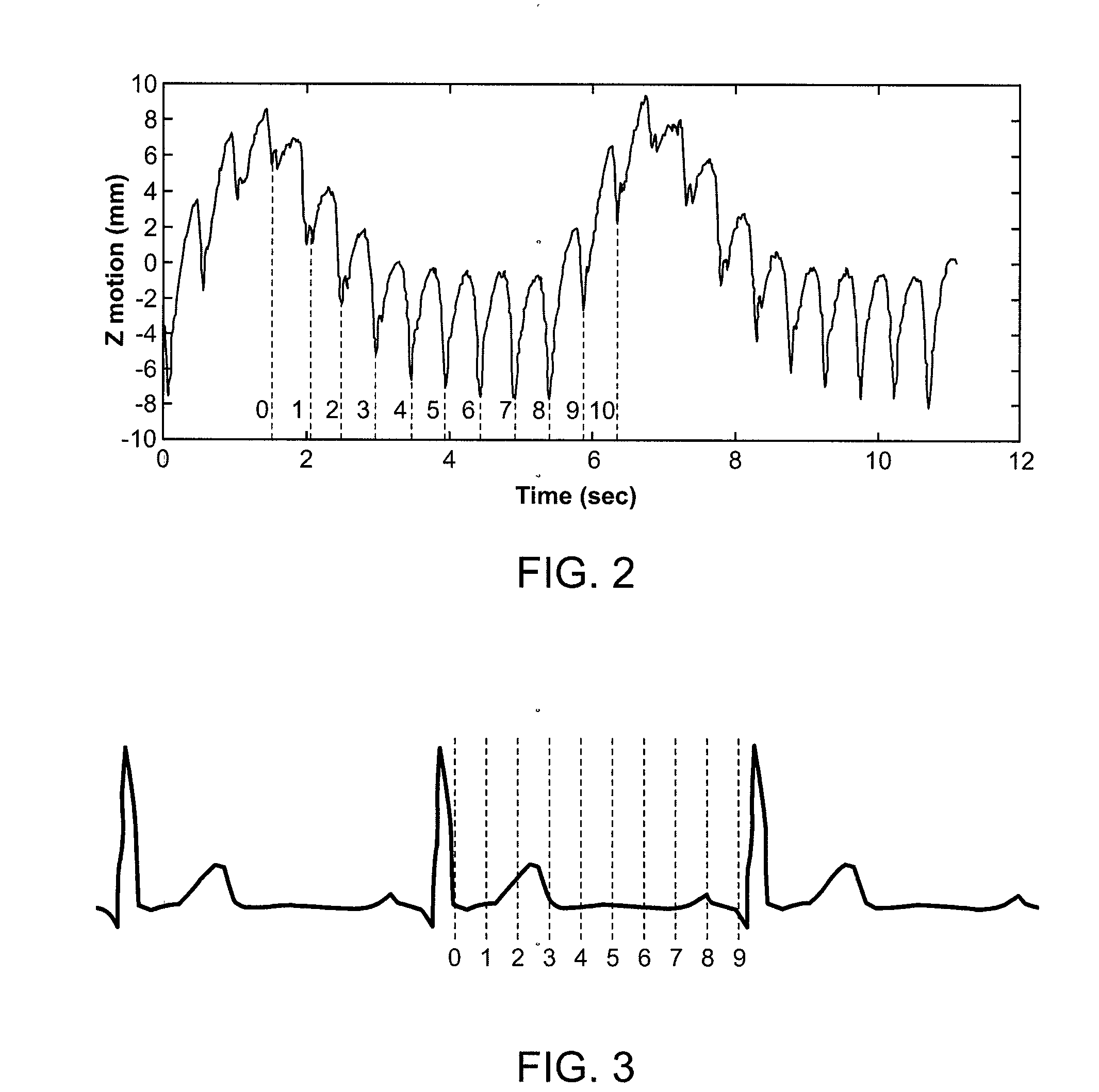
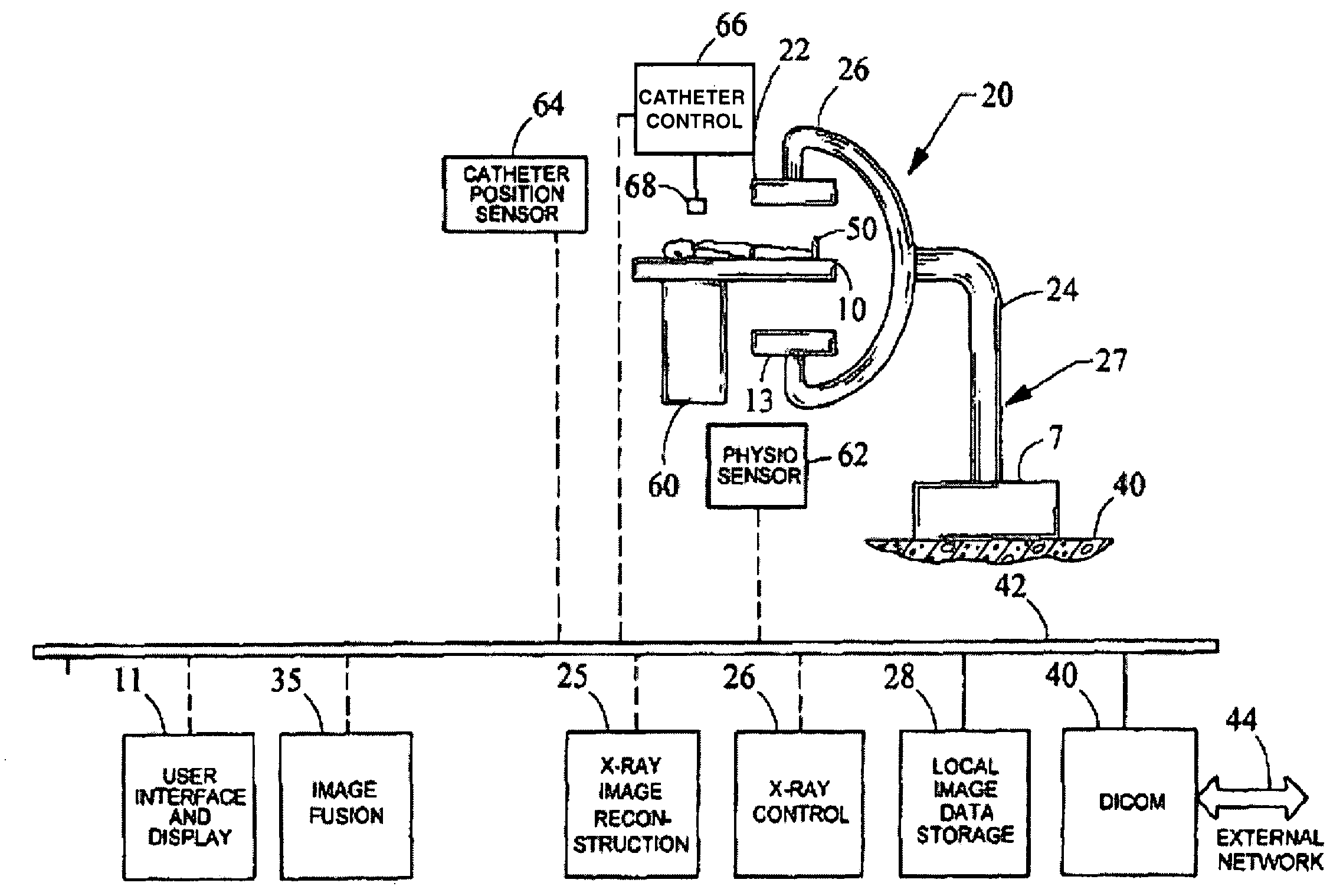
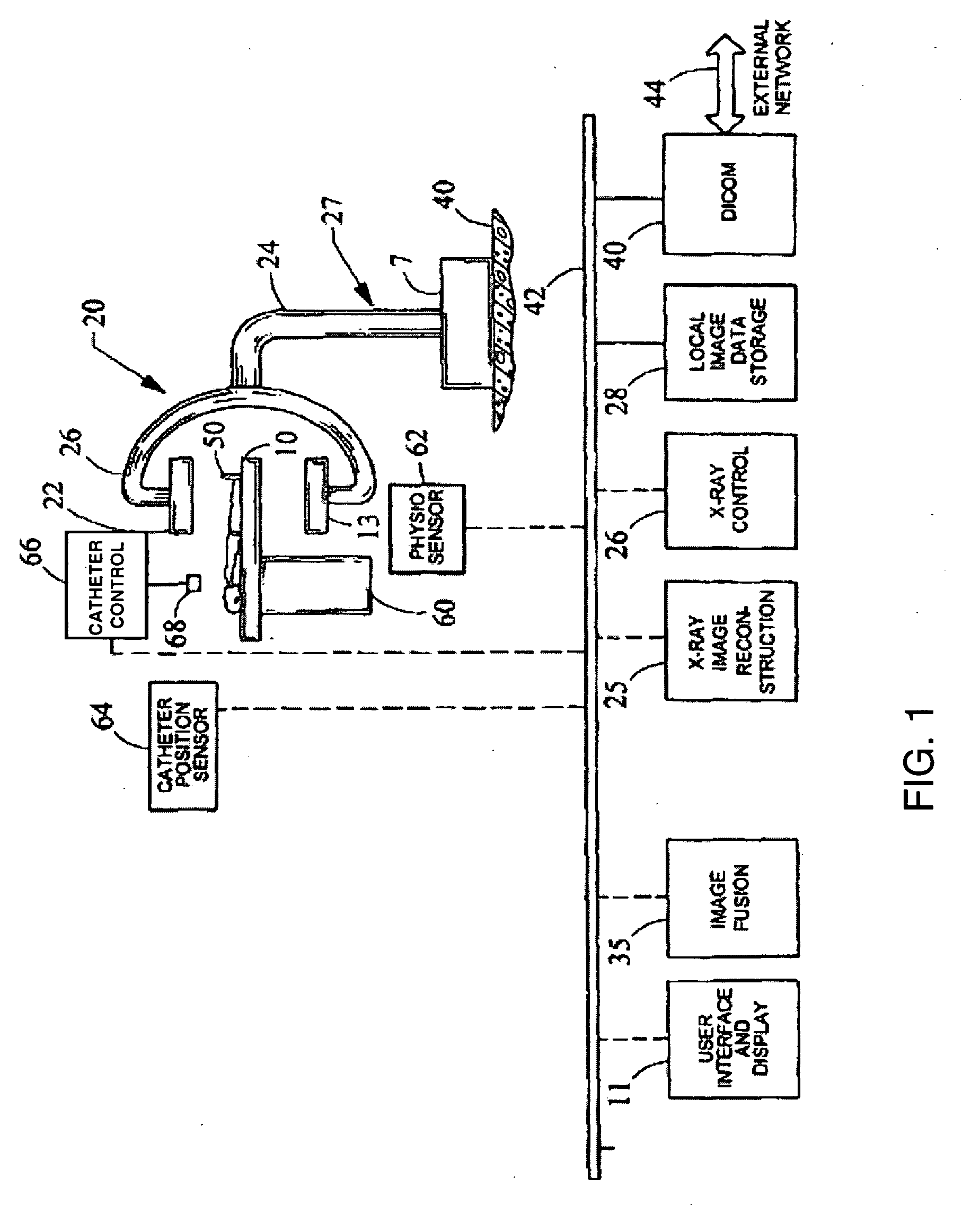
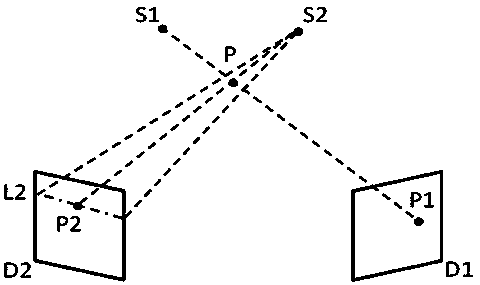
Image guided radiosurgery method and apparatus using registration of 2D radiographic images with digitally reconstructed radiographs of 3D scan data
ActiveUS20050049478A1Rapid and accurate methodThe process is fast and accurateImage enhancementImage analysisIn plane3d image
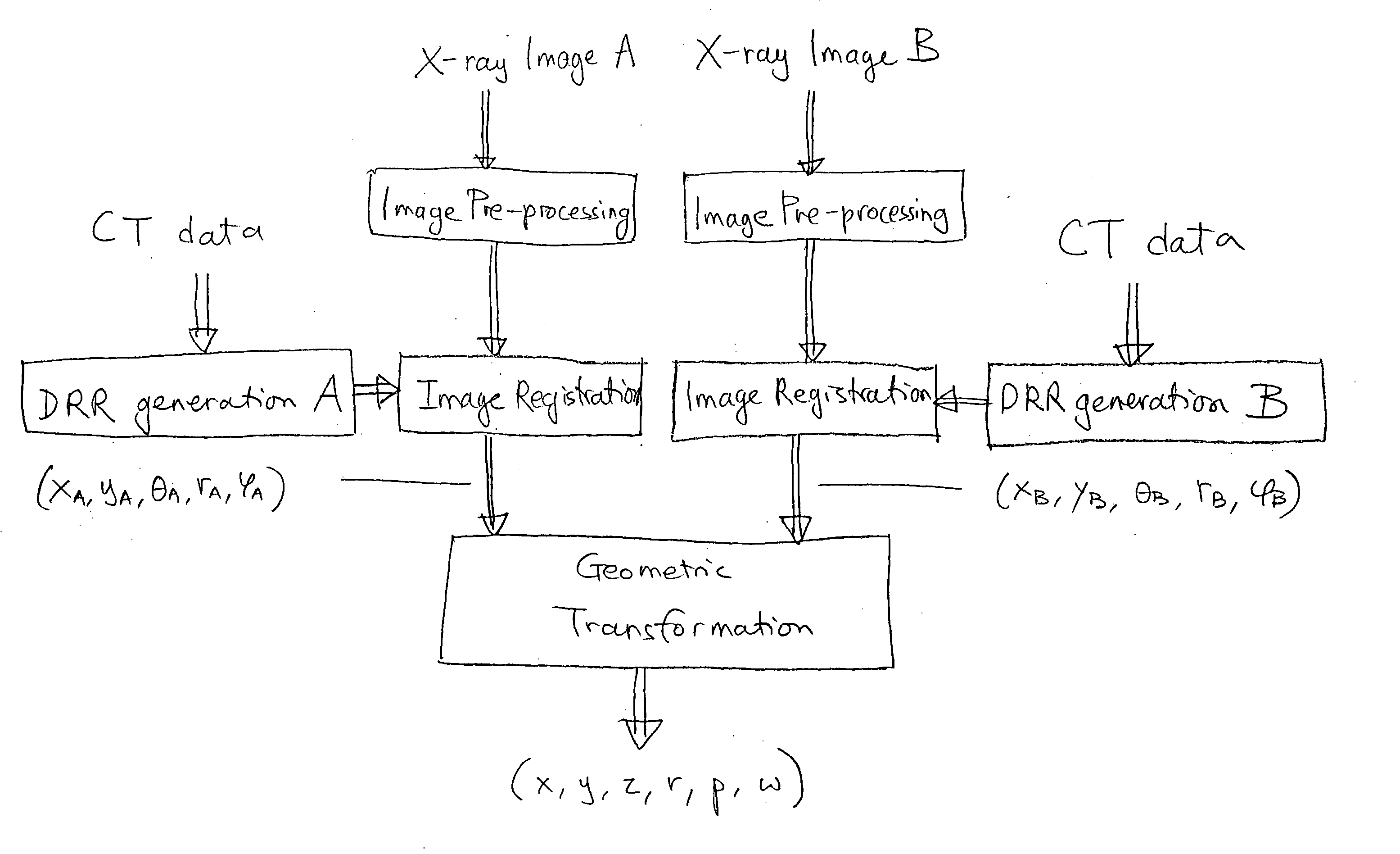
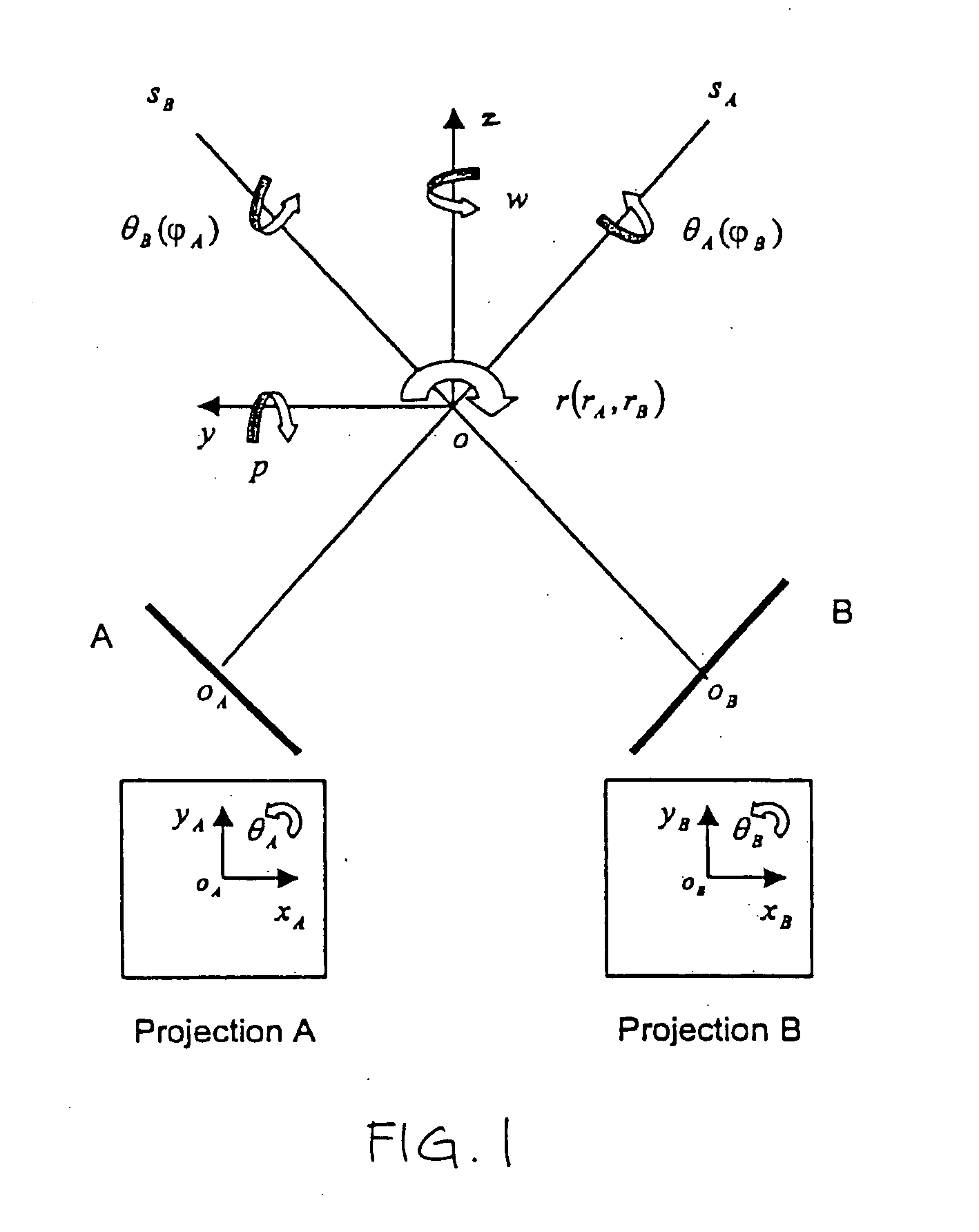
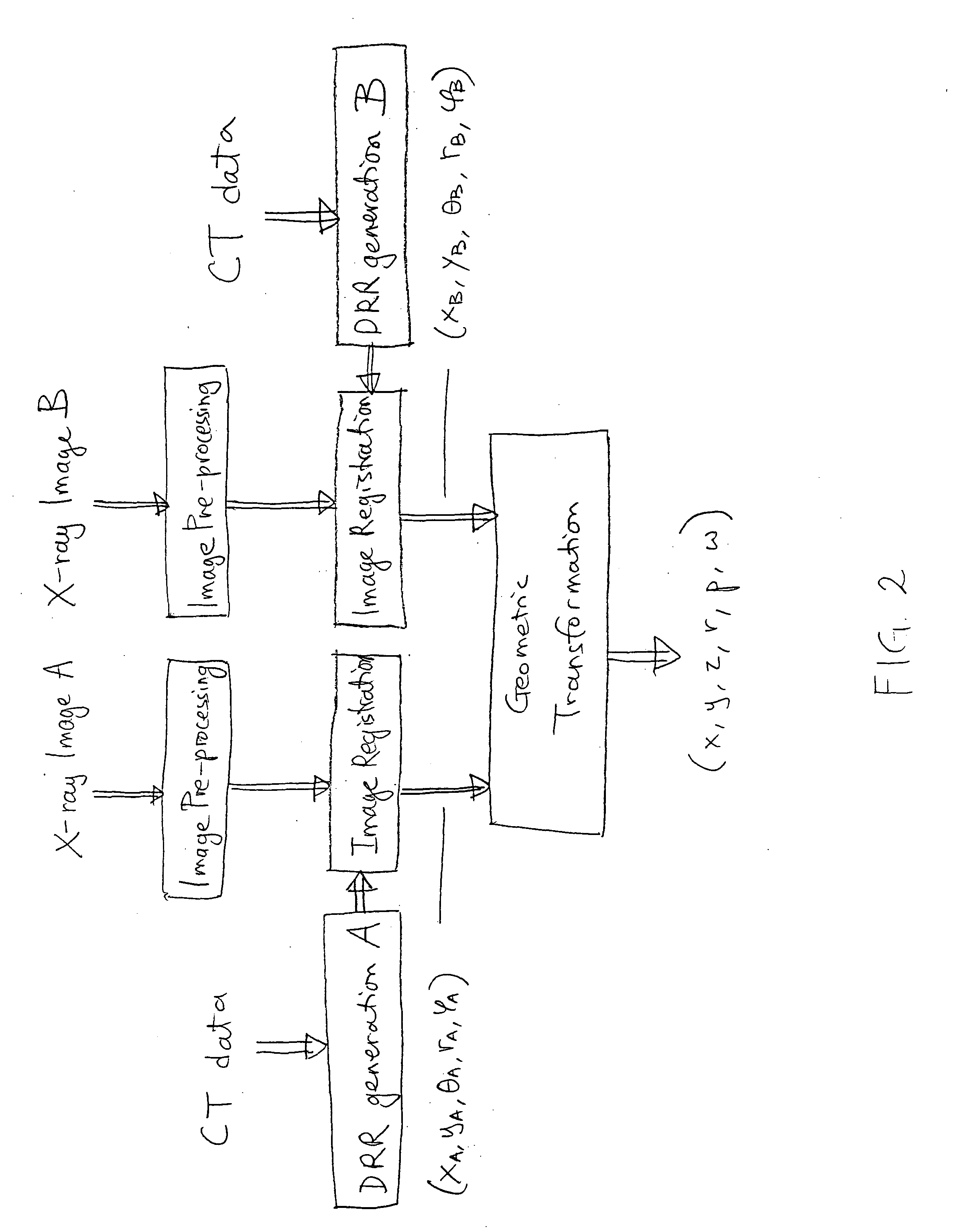
An image-guided radiosurgery method and system are presented that use 2D / 3D image registration to keep the radiosurgical beams properly focused onto a treatment target. A pre-treatment 3D scan of the target is generated at or near treatment planning time. A set of 2D DRRs are generated, based on the pre-treatment 3D scan. At least one 2D x-ray image of the target is generated in near real time during treatment. The DRRs are registered with the x-ray images, by computing a set of 3D transformation parameters that represent the change in target position between the 3D scan and the x-ray images. The relative position of the radiosurgical beams and the target is continuously adjusted in near real time in accordance with the 3D transformation parameters. A hierarchical and iterative 2D / 3D registration algorithm is used, in which the transformation parameters that are in-plane with respect to the image plane of the x-ray images are computed separately from the out-of-plane transformation parameters.
Owner:ACCURAY
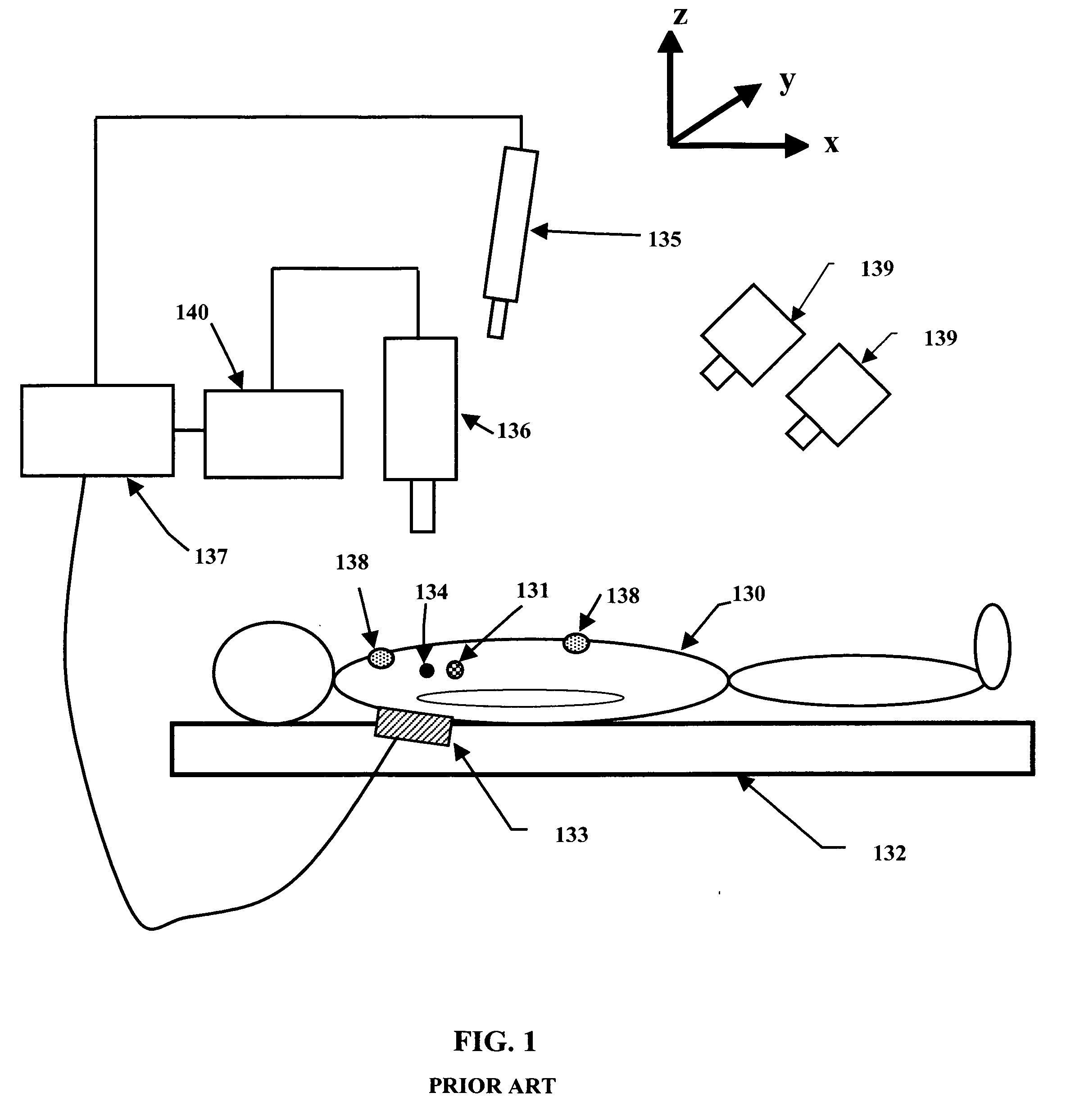
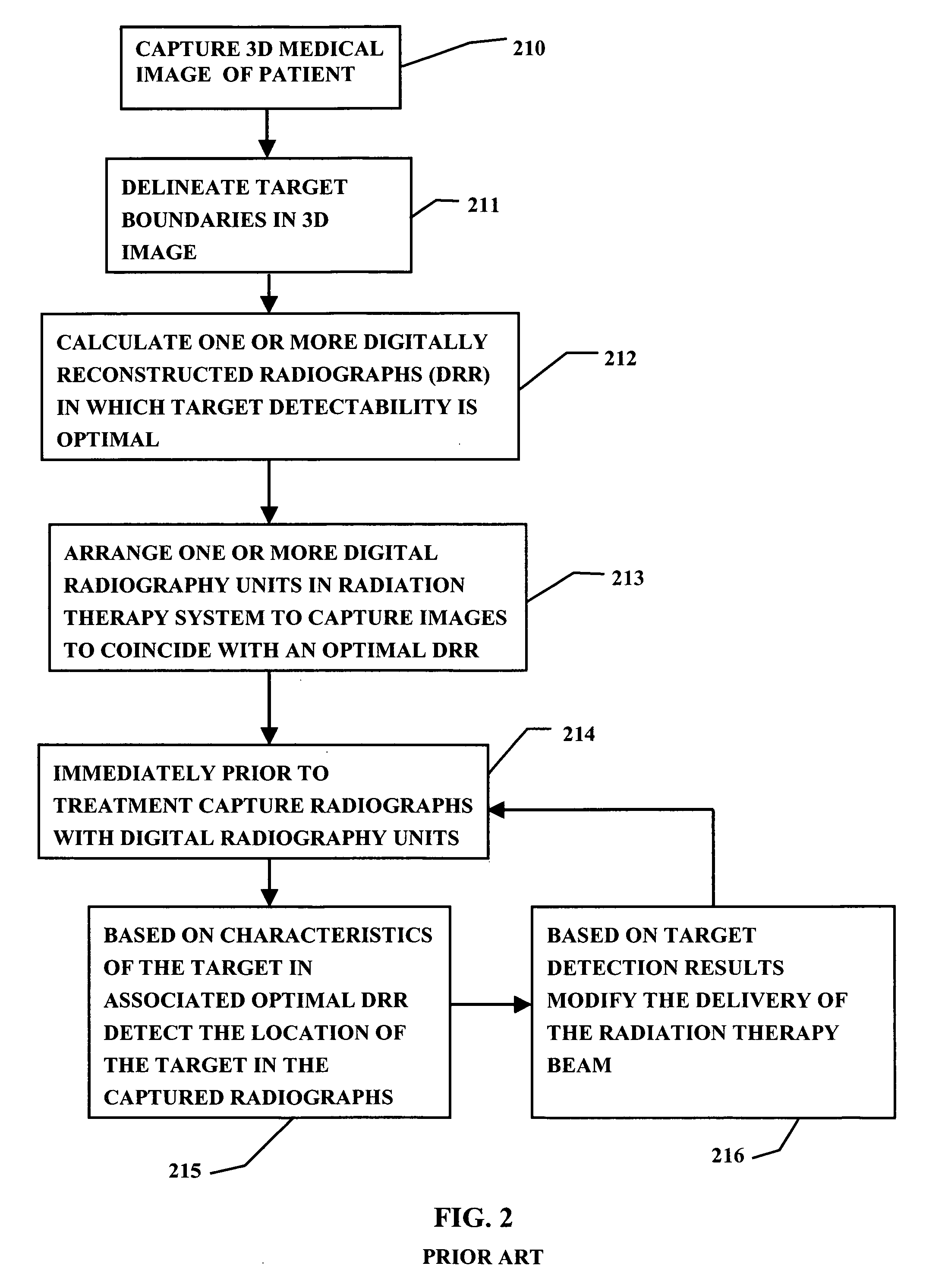
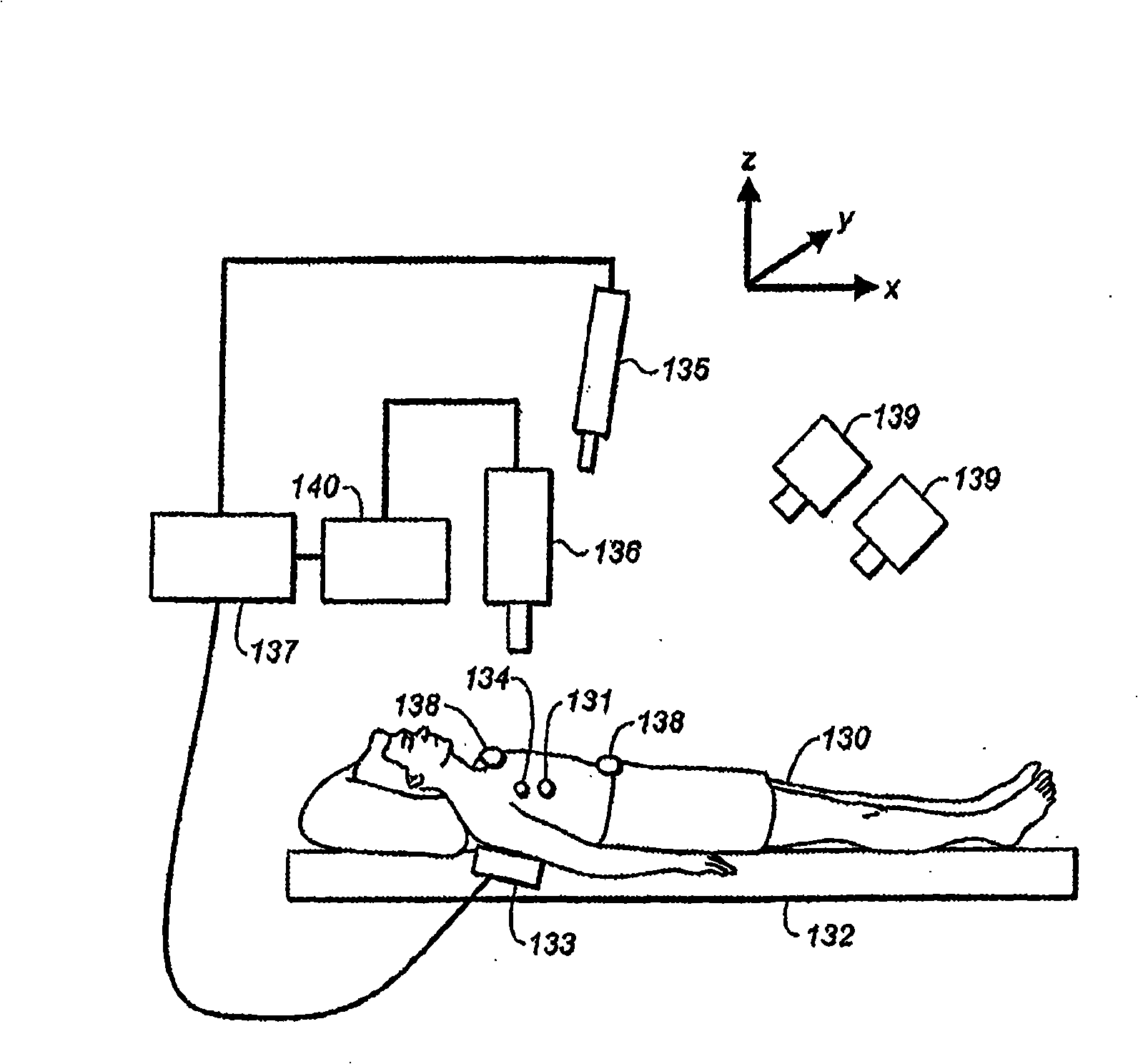
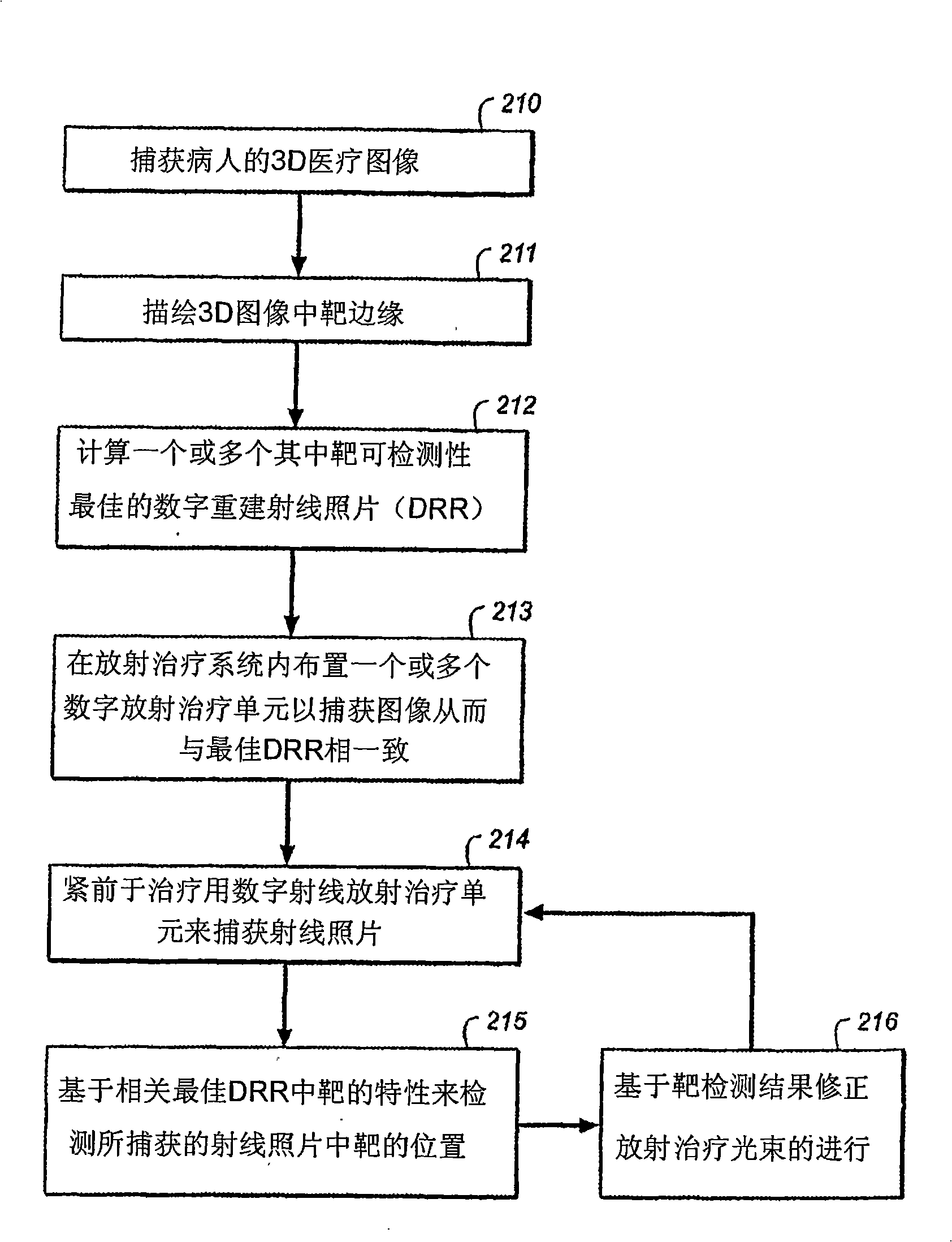
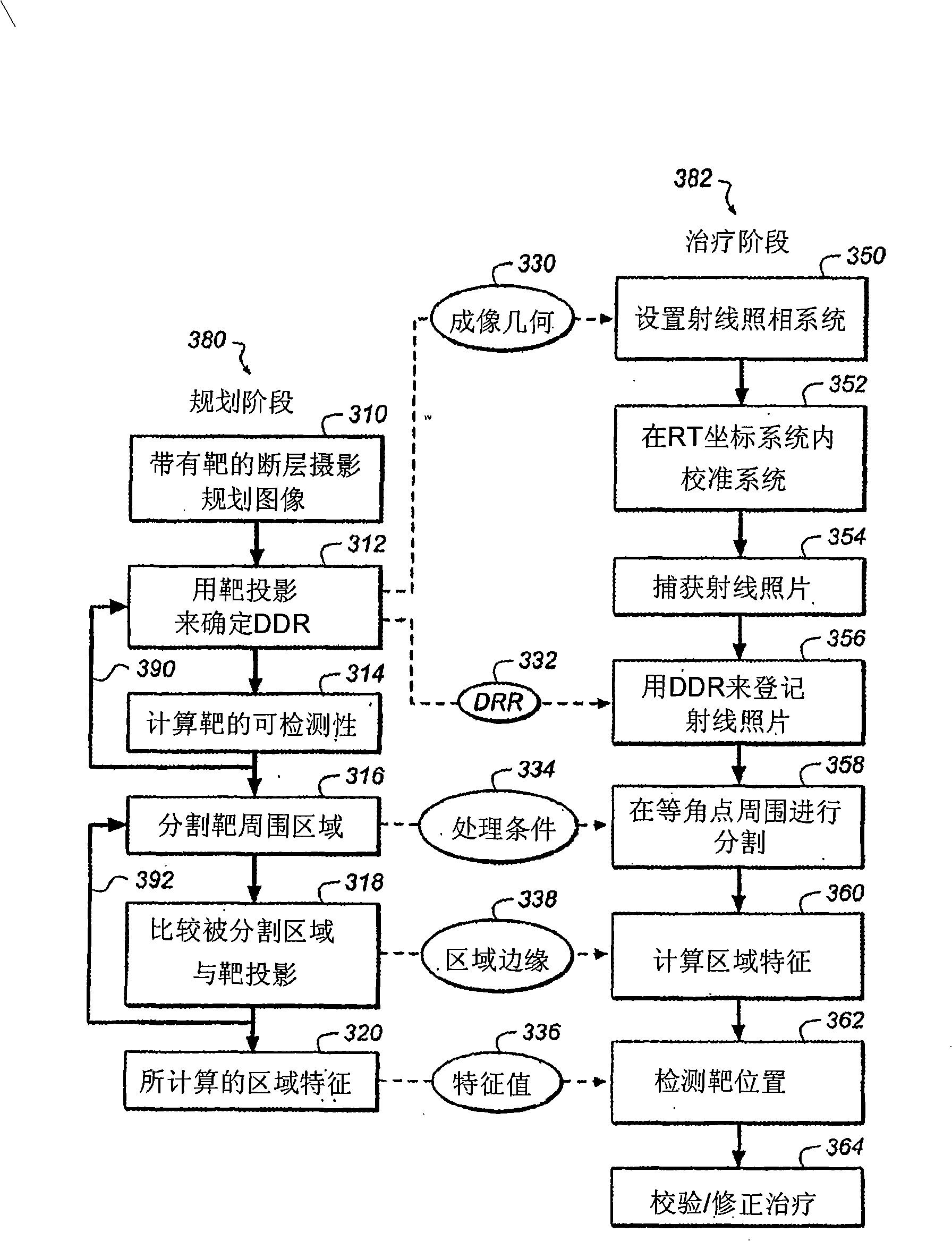
Adaptive radiation therapy method with target detection
InactiveUS20070053491A1Image enhancementImage analysisAdaptive radiotherapyThree dimensional planning
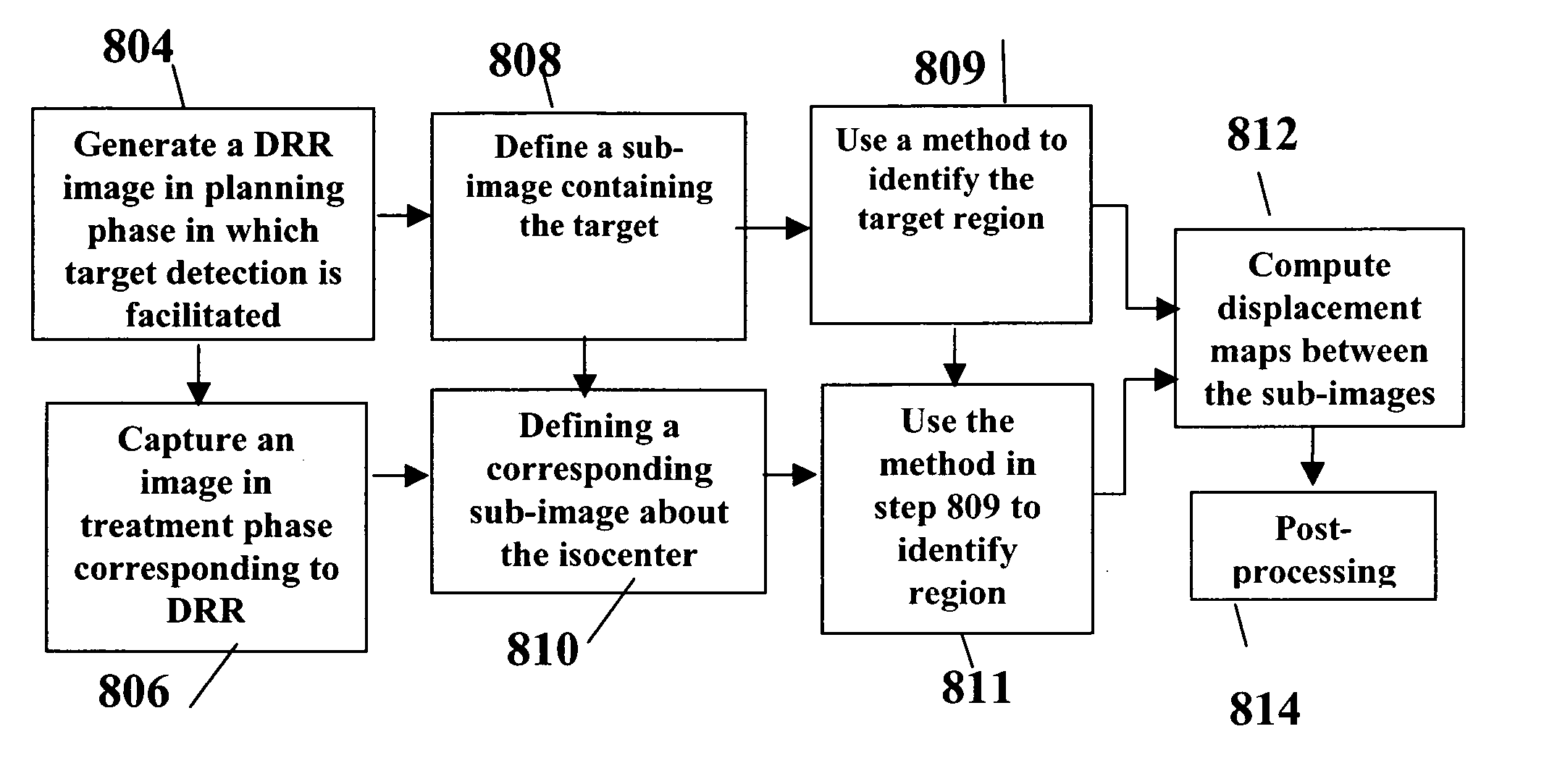
A method for delivering radiation therapy to a patient using a three-dimensional planning image for radiation therapy of the patient wherein the planning image includes a radiation therapy target includes the steps of: determining a digitally reconstructed radiograph from the planning image; identifying a region of the target's projection in the digitally reconstructed radiograph; capturing a radiographic image corresponding to the digitally reconstructed radiograph; identifying a region in the captured radiographic image; comparing the region of the target's projection in the digitally reconstructed radiograph with the identified region in the captured radiographic image; and determining a delivery of the radiation therapy in response to this comparison.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
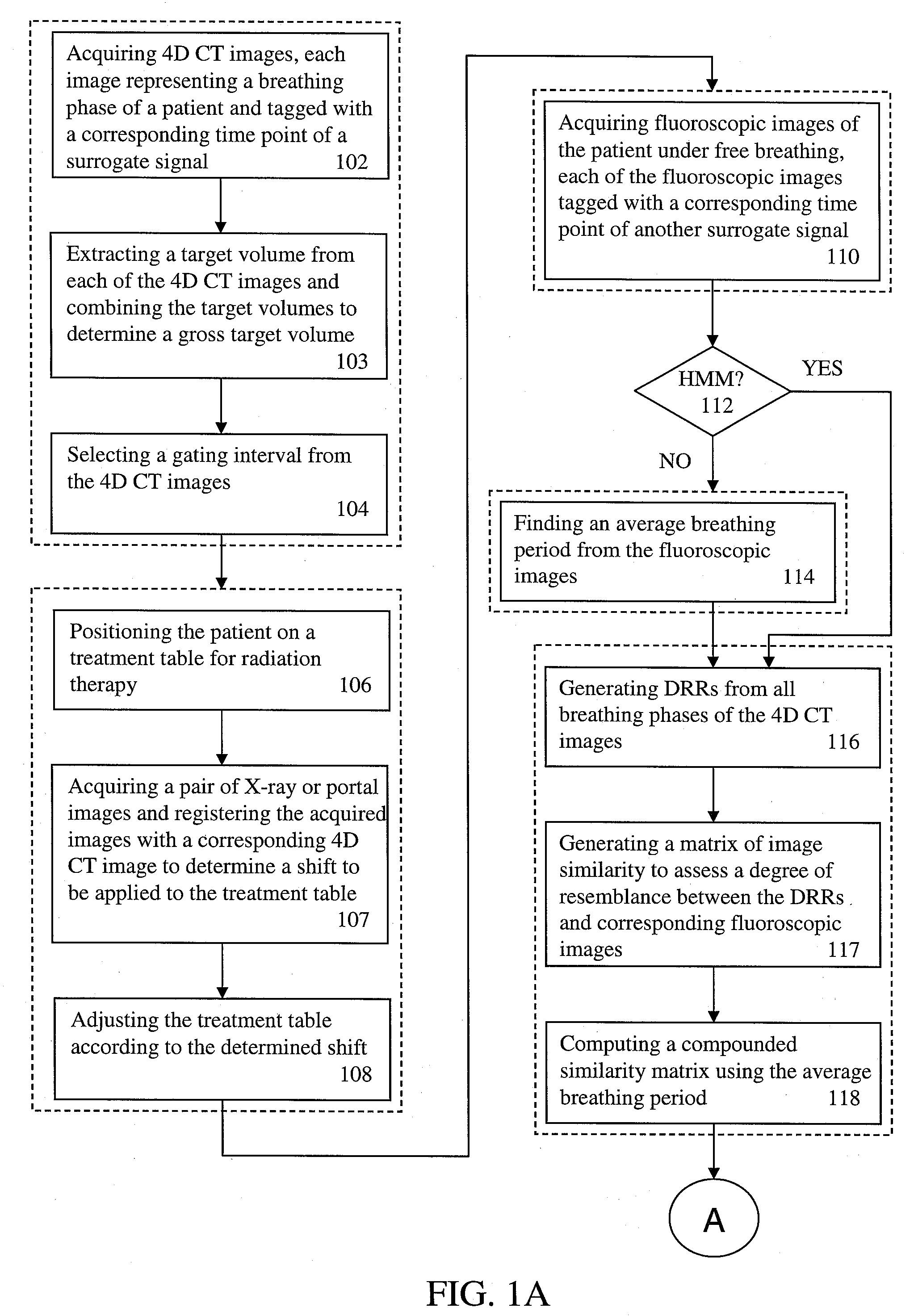
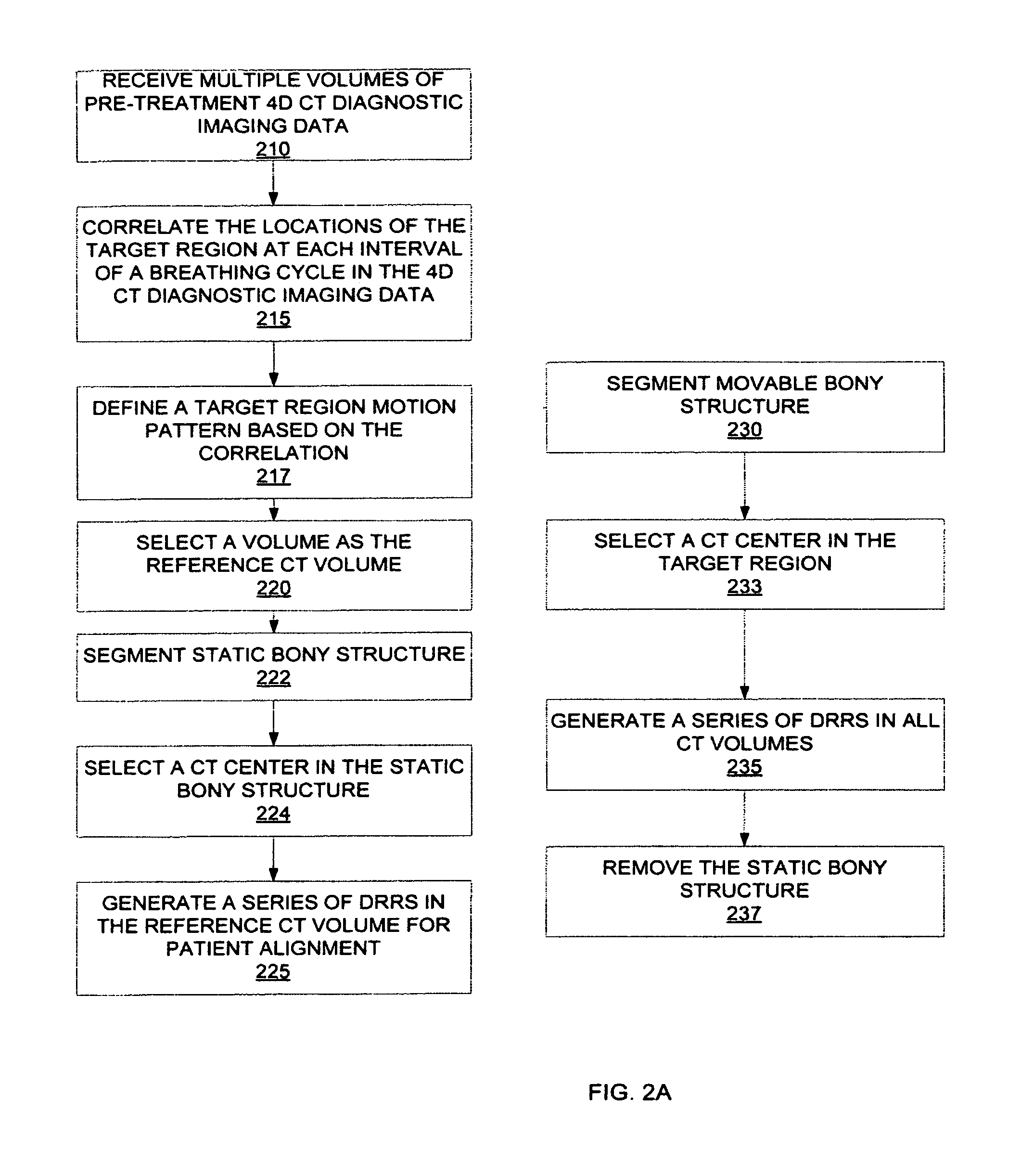
Four-dimensional (4D) image verification in respiratory gated radiation therapy
ActiveUS20080031404A1X-ray/infra-red processesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationFluoroscopic image4D Computed Tomography
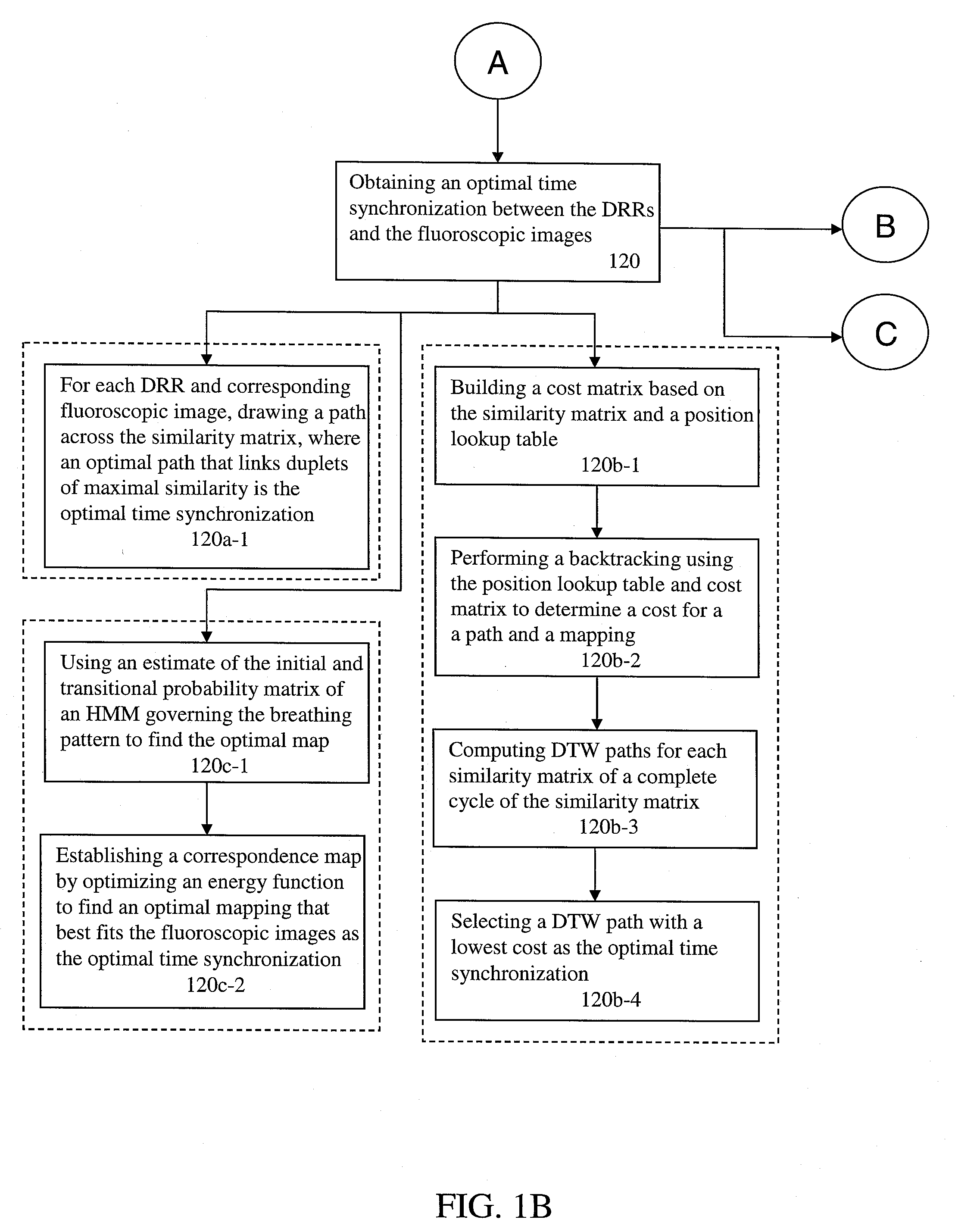
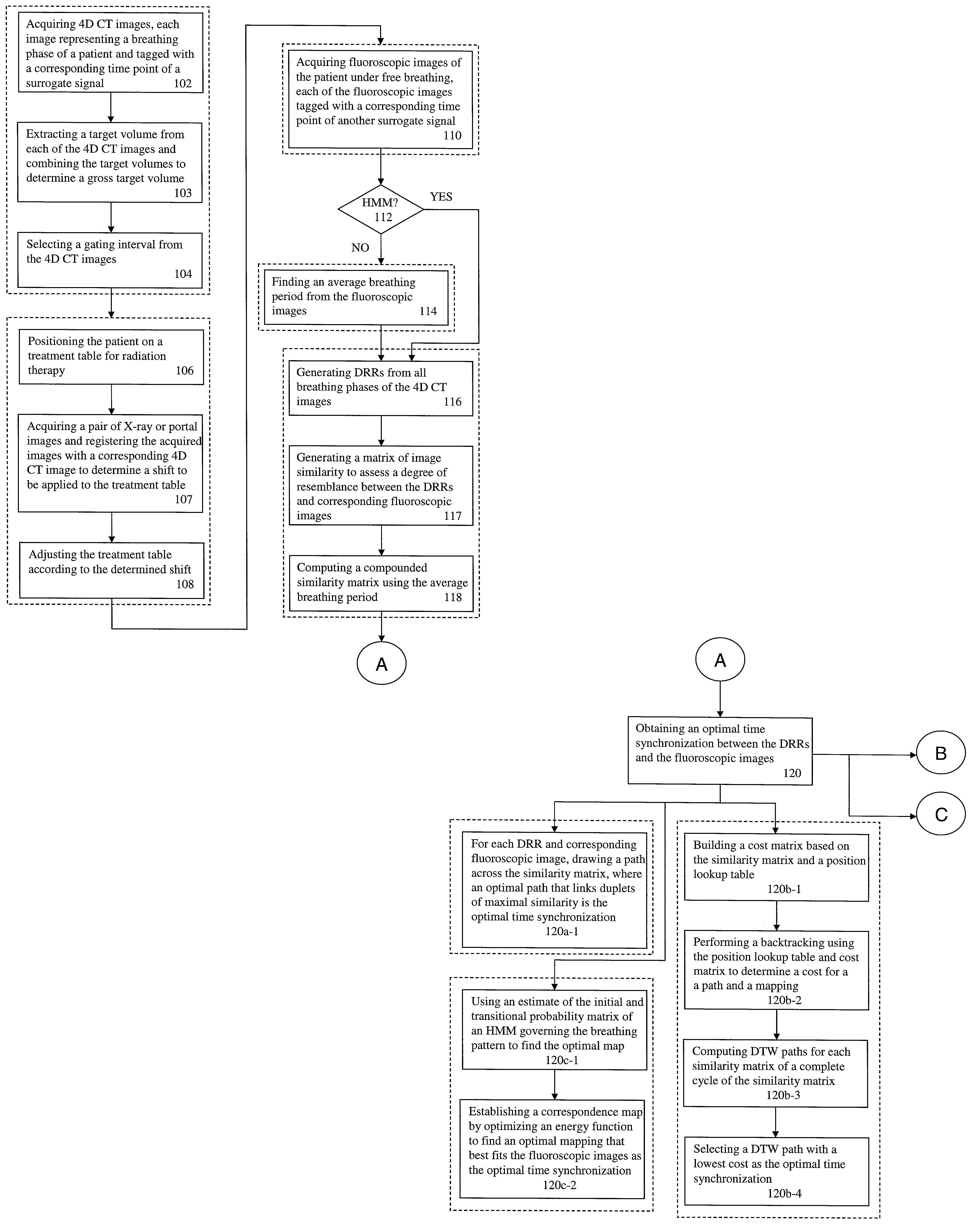
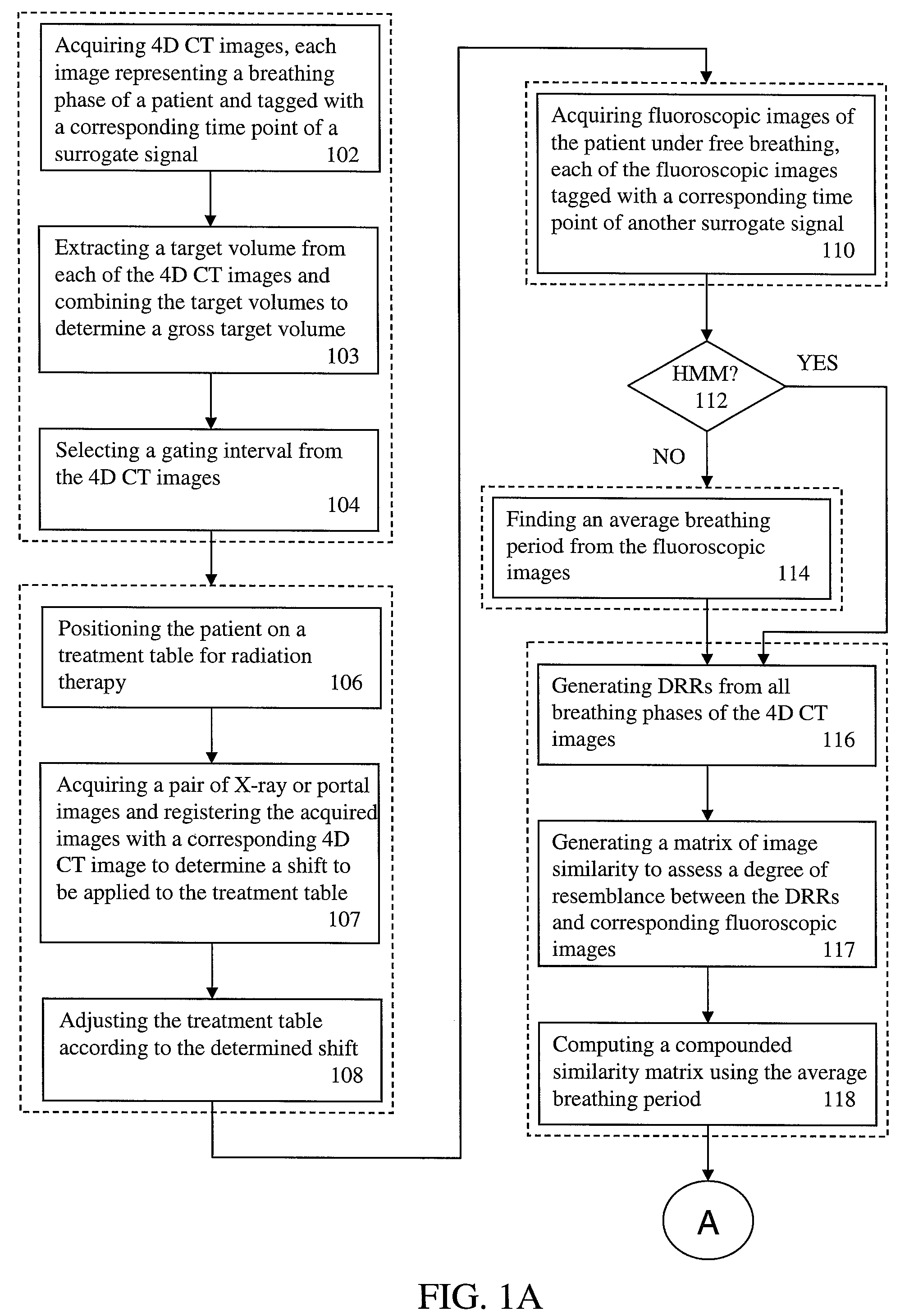
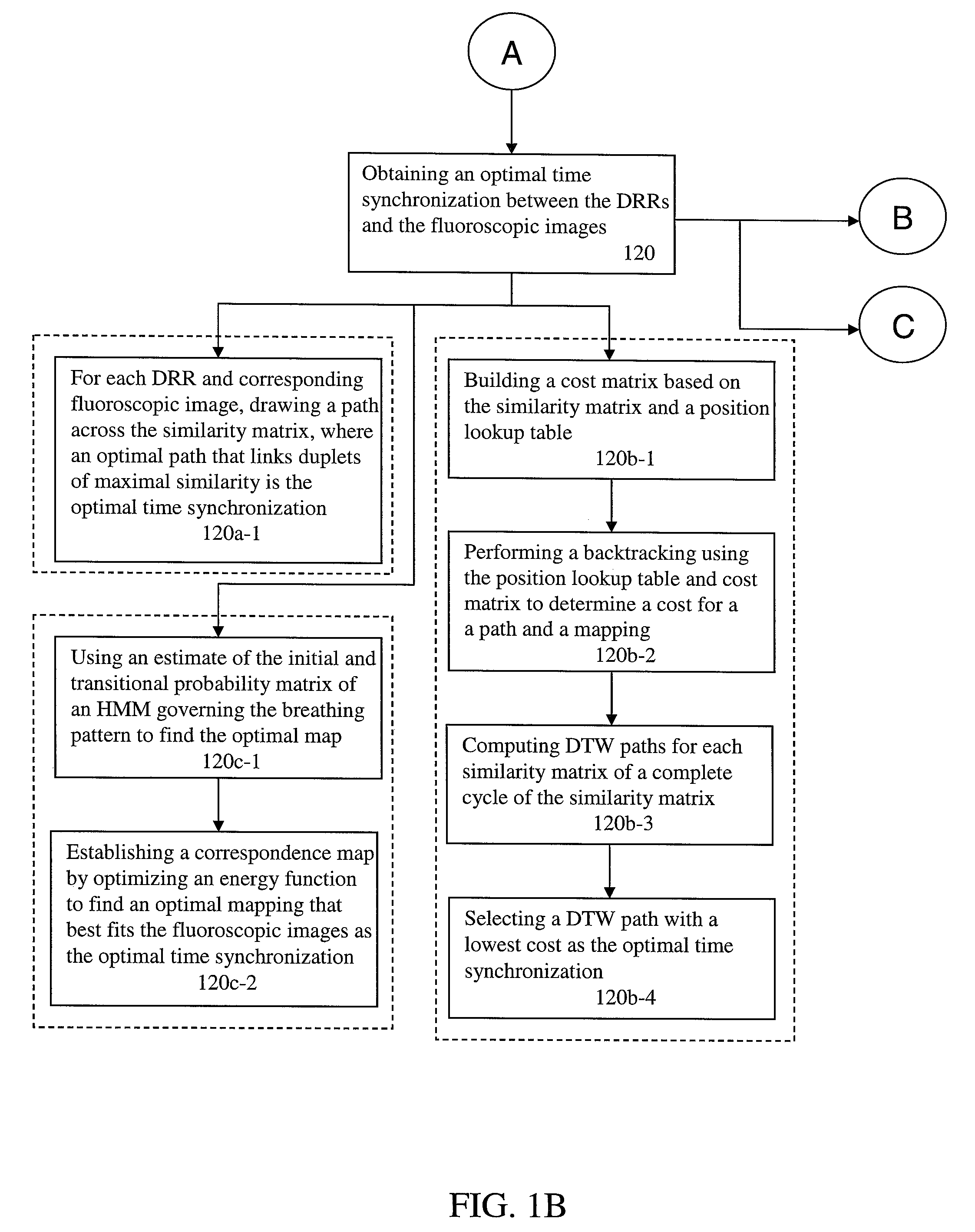
A method for four-dimensional (4D) image verification in respiratory gated radiation therapy, includes: acquiring 4D computed tomography (CT) images, each of the 4D CT images representing a breathing phase of a patient and tagged with a corresponding time point of a first surrogate signal; acquiring fluoroscopic images of the patient under free breathing, each of the fluoroscopic images tagged with a corresponding time point of a second surrogate signal; generating digitally reconstructed radiographs (DRRs) for each breathing phase represented by the 4D CT images; generating a similarity matrix to assess a degree of resemblance in a region of interest between the DRRs and the fluoroscopic images; computing a compounded similarity matrix by averaging values of the similarity matrix across different time points of the breathing phase during a breathing period of the patient; determining an optimal time point synchronization between the DRRs and the fluoroscopic images by using the compounded similarity matrix; and acquiring a third surrogate signal and turning a treatment beam on or off according to the optimal time point synchronization.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
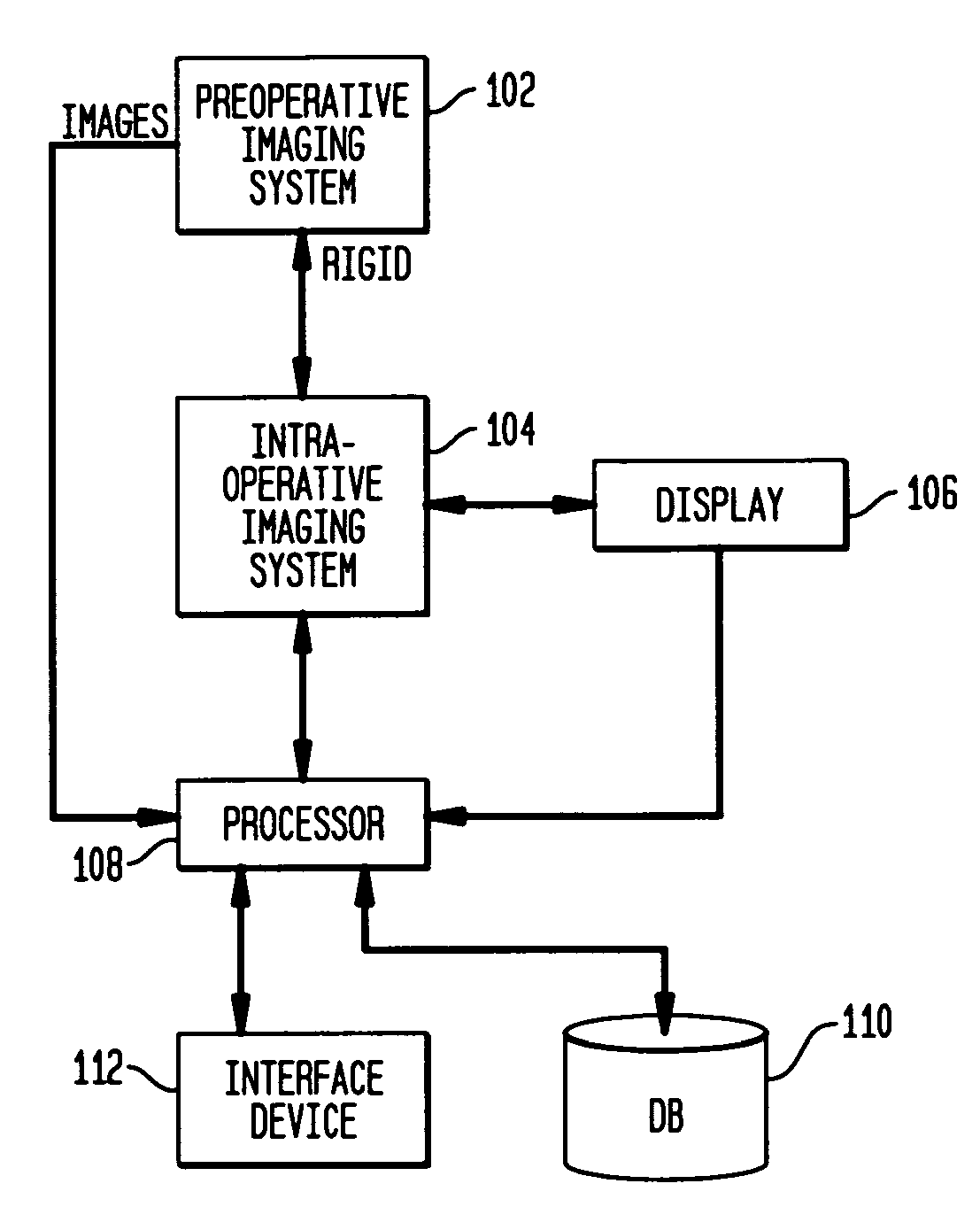
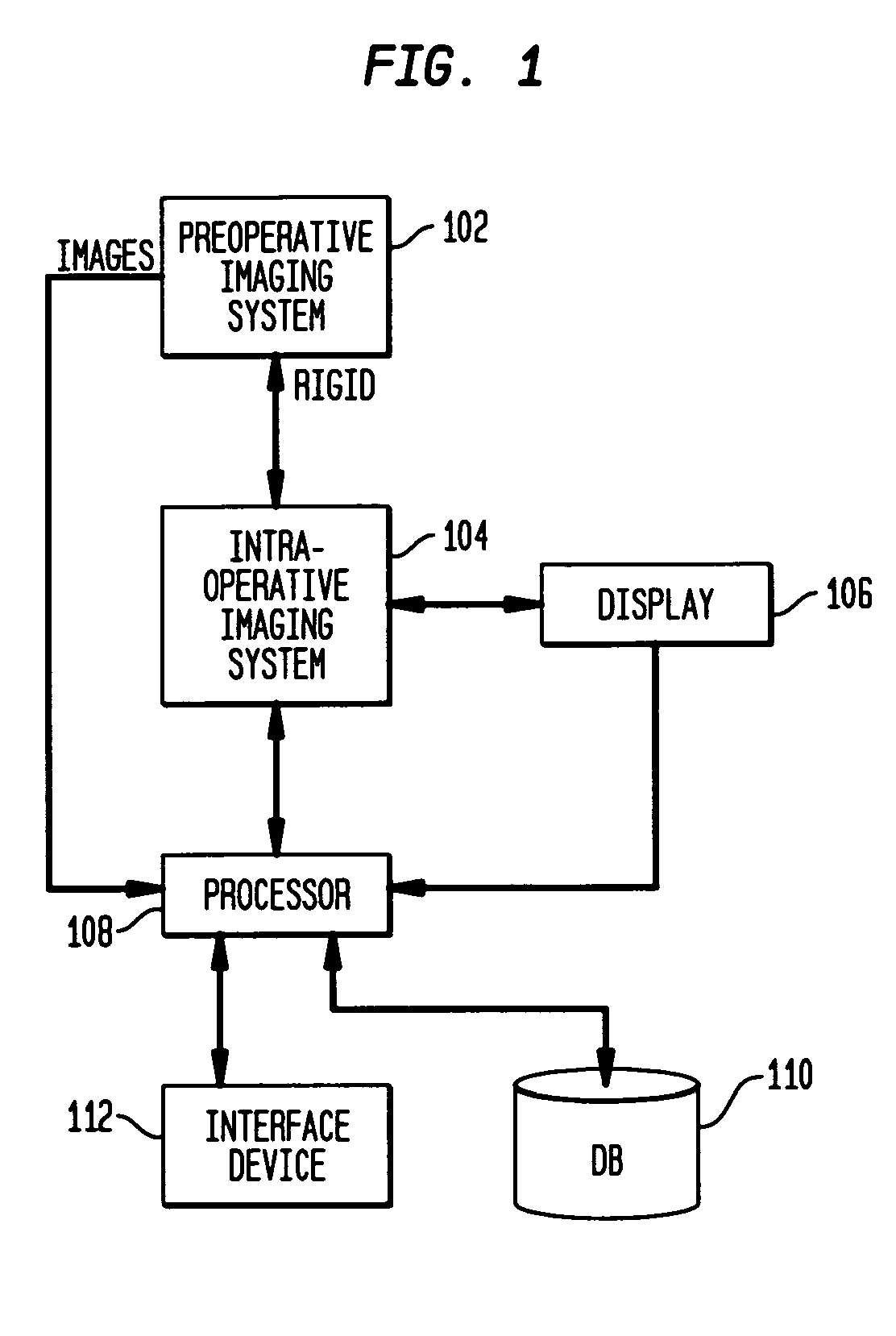
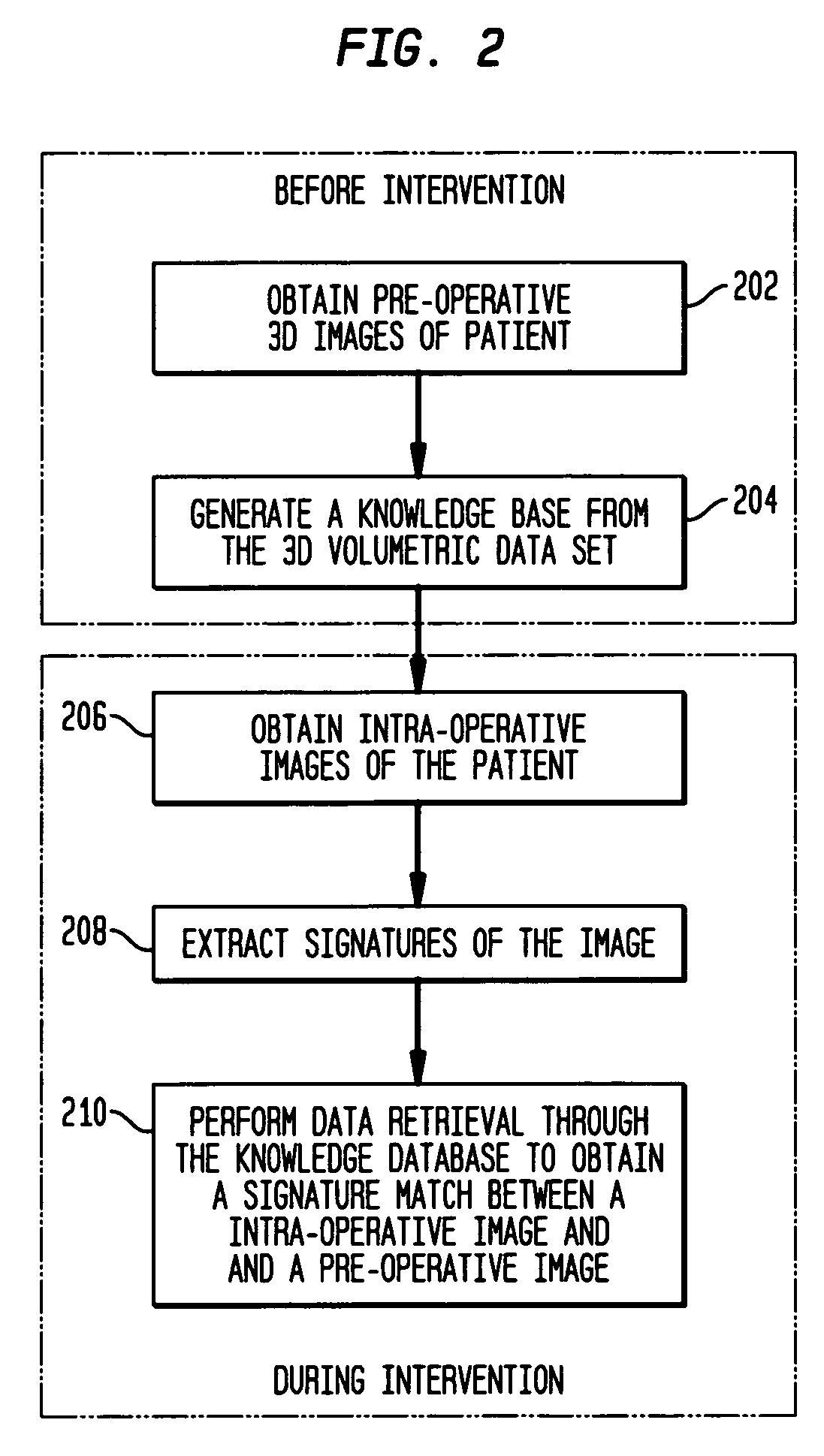
Method and system for registering pre-procedural images with intra-procedural images using a pre-computed knowledge base
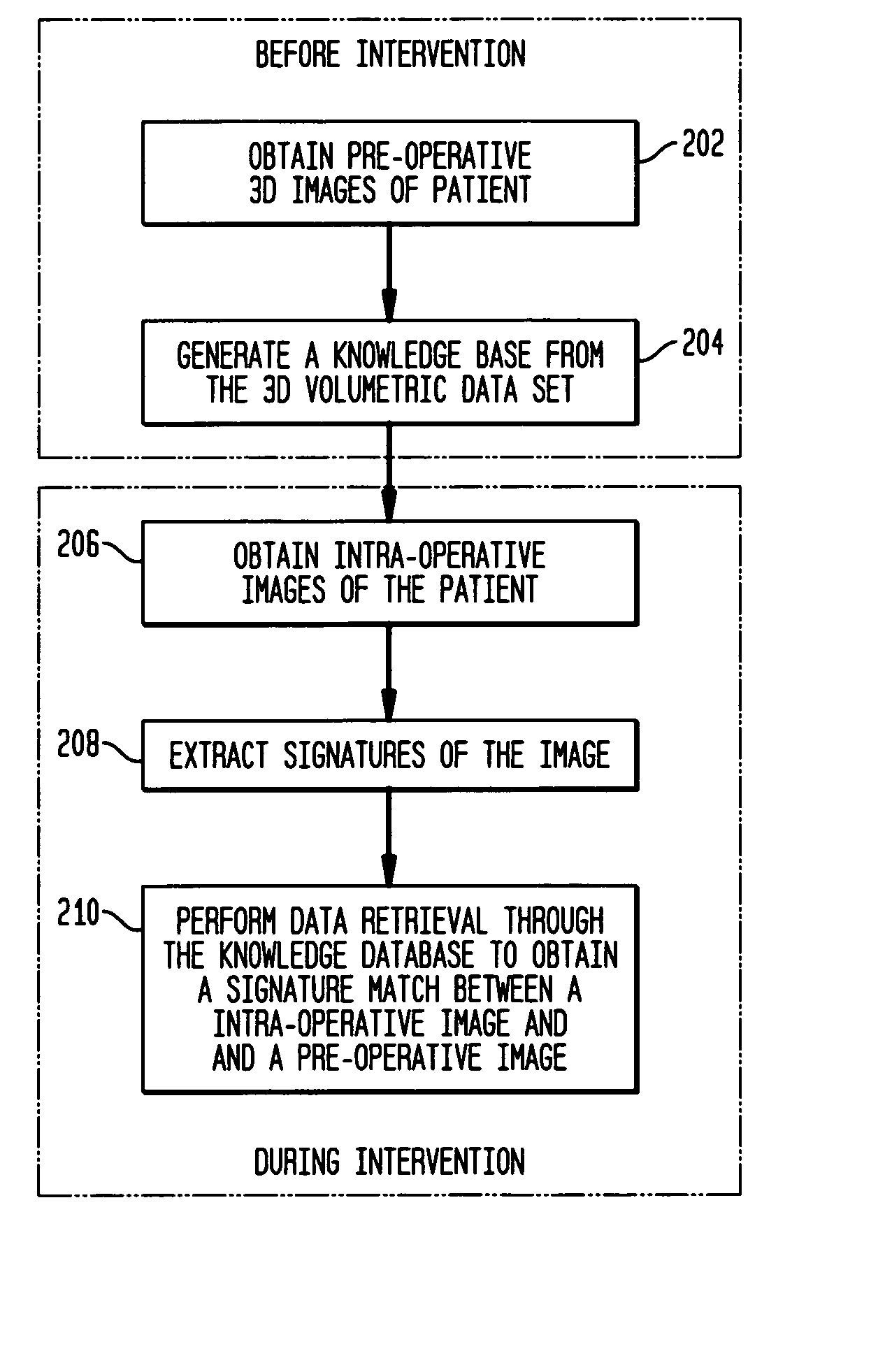
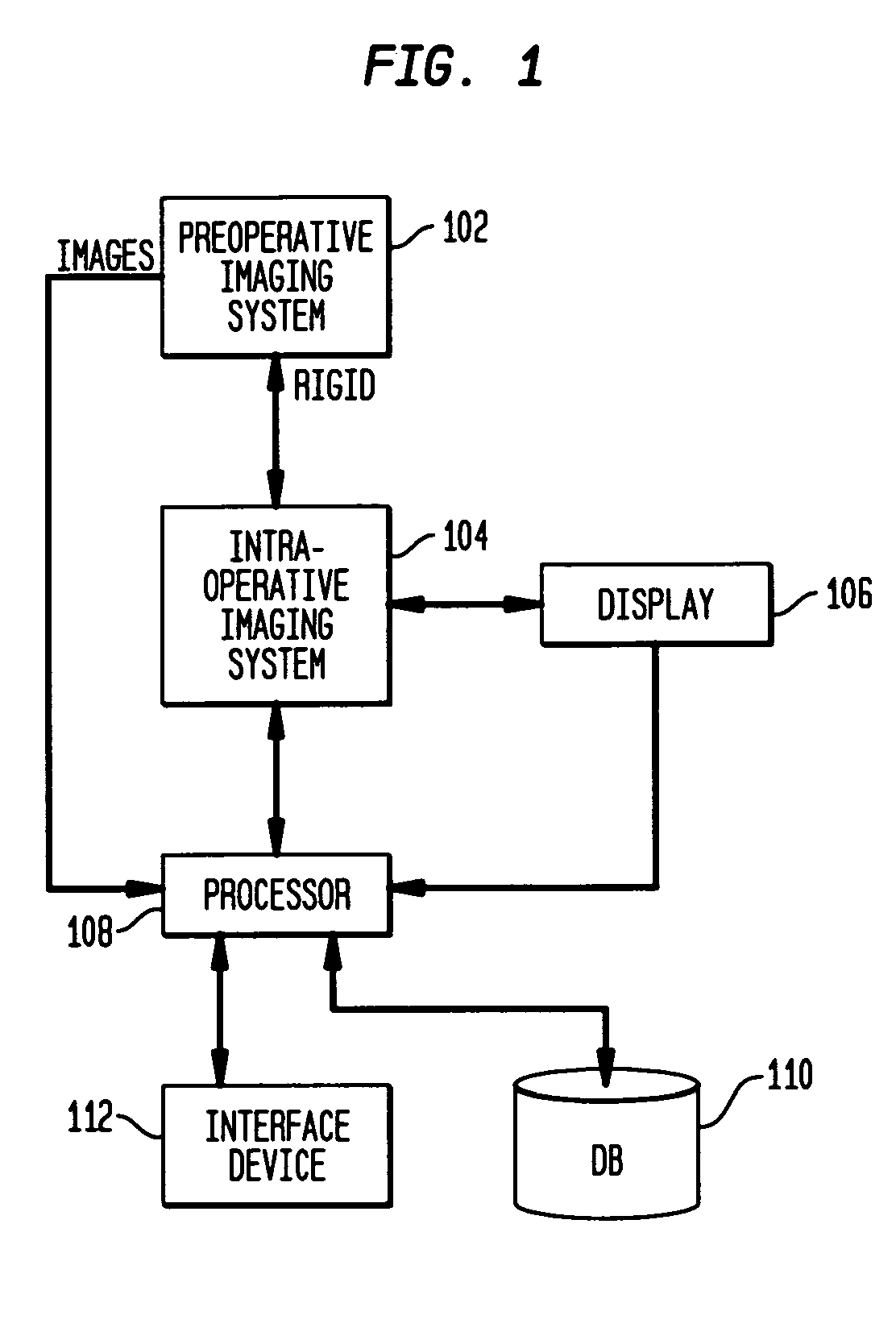
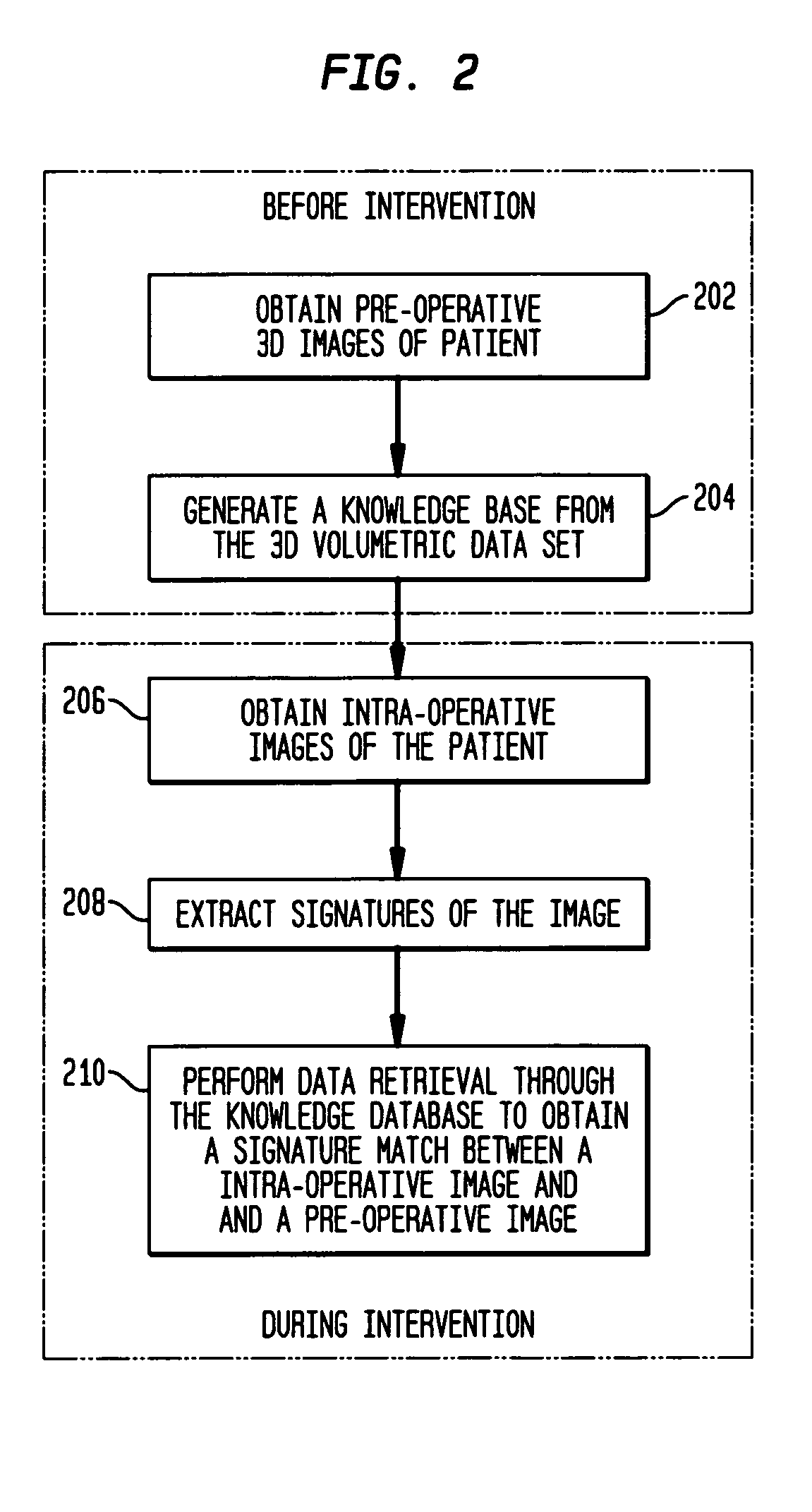
A system and method for registering pre-operative images of an object with an intra-operative image of the object is disclosed. Prior to an operative procedure, Digitally Reconstructed Radiographs (DRRs) are generated for the pre-operative images of each individual patient. Signatures are extracted from the DRRs. The signatures are stored in a knowledge base. During the operative procedure, a signature is extracted from the intra-operative image. The intra-operative signature is compared to the stored pre-operative signatures. A pre-operative image having a best signature match to the intra-operative signature is retrieved. The retrieved pre-operative image is registered with the intra-operative image.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Method for Depositing Radiation in Heart Muscle
InactiveUS20080177280A1Improved radiosurgical treatment of tissueReduce arrhythmiaComputer-aided planning/modellingDiagnostic recording/measuringX-raySurgical department
Radiosurgical treatment of tissues of the heart to mitigate arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation or the like. Radiosurgical targeting of the relatively rapid movement of heart tissues may be enhanced by generating a moving model volume using a time-sequence of three dimensional acquired tissue volumes. A digitally reconstructed radiograph (DRR) may be generated from the model at a desired cardiac and / or respiration motion phase and compared to an X-ray or the like taken immediately before or during treatment. When a series of radiation beams will be directed to a heart tissue to alleviate an arrhythmia, the treatment system may alter the radiation beam series in response to the type of the arrhythmia.
Owner:CYBERHEART
Systems and methods for frameless image-guided biopsy and therapeutic intervention
ActiveUS8758263B1Enhances patient comfortEliminate riskSurgical navigation systemsVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsComputed tomographyStereotaxy
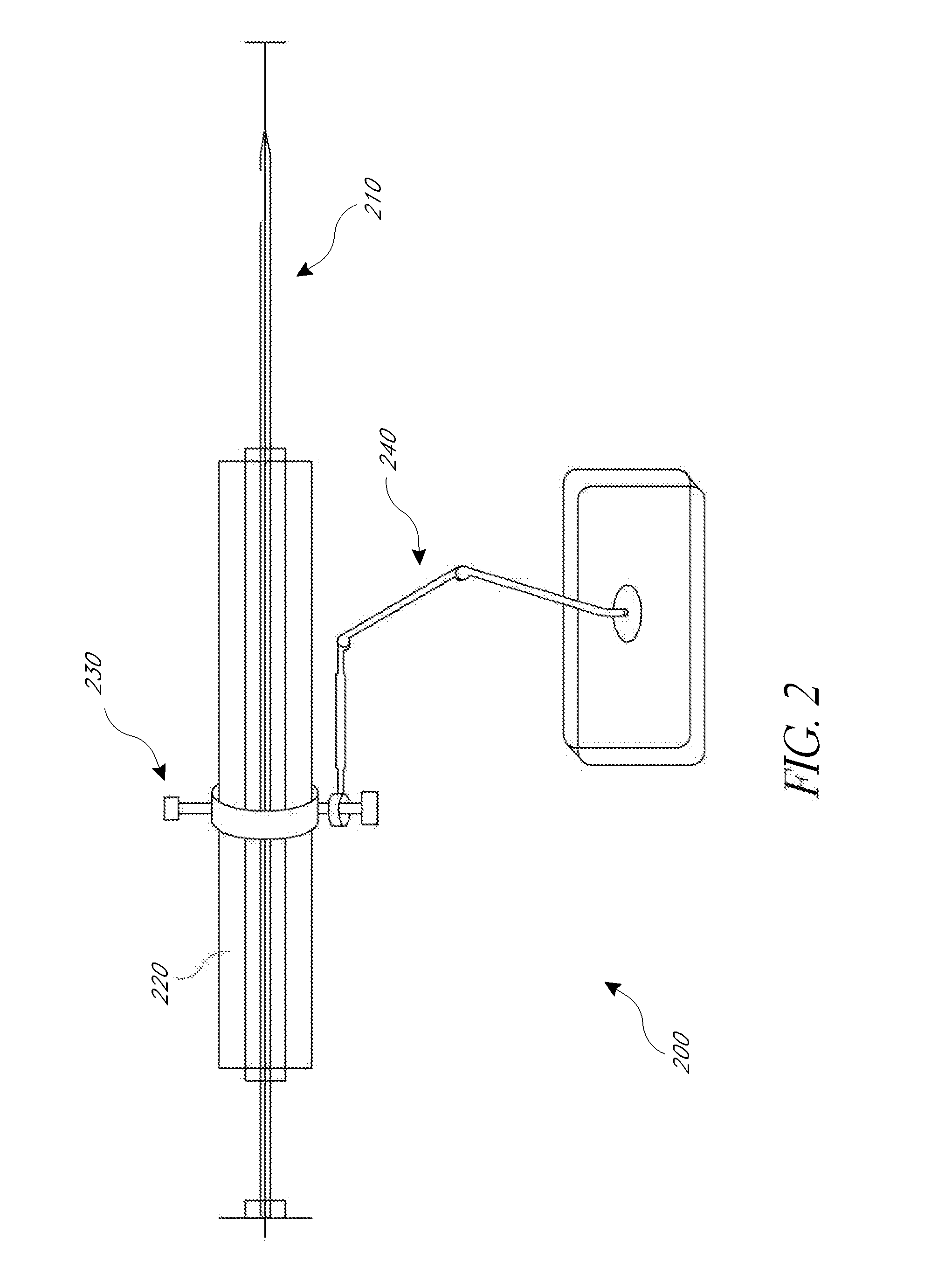
A system and a method of performing a frameless image-guided biopsy uses imaging, a six-dimensional robotic couch system, a laser guidance system, an optical distance indicator, and a needle control apparatus. A planning CT scan is made of the patient with stereotactic fiduciary markers to localize and produce digitally reconstructed radiographs. Two stereoscopic images are generated using an imaging device to visualize and identify a target tumor. The images are fused with the digitally reconstructed radiographs of the planning CT scan to process tumor location. The tumor location data are communicated to the movable robotic couch to position the target tumor of the patient at a known isocenter location. A biopsy needle is guided with a laser alignment mechanism towards the isocenter at the determined depth using a needle positioning apparatus and an Optical Distance Indicator, and a biopsy sample of the target tumor is obtained.
Owner:VOXEL RAD
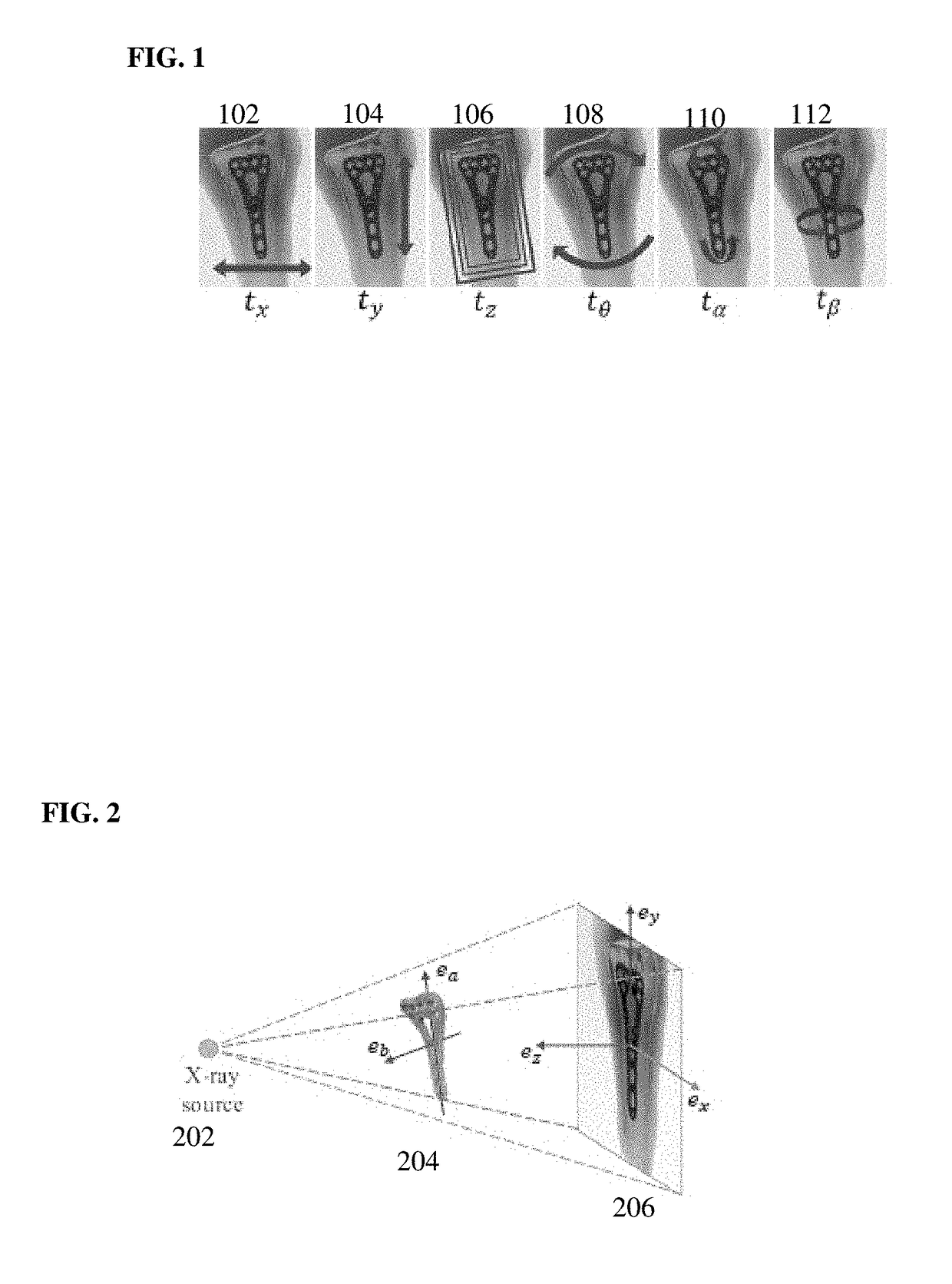
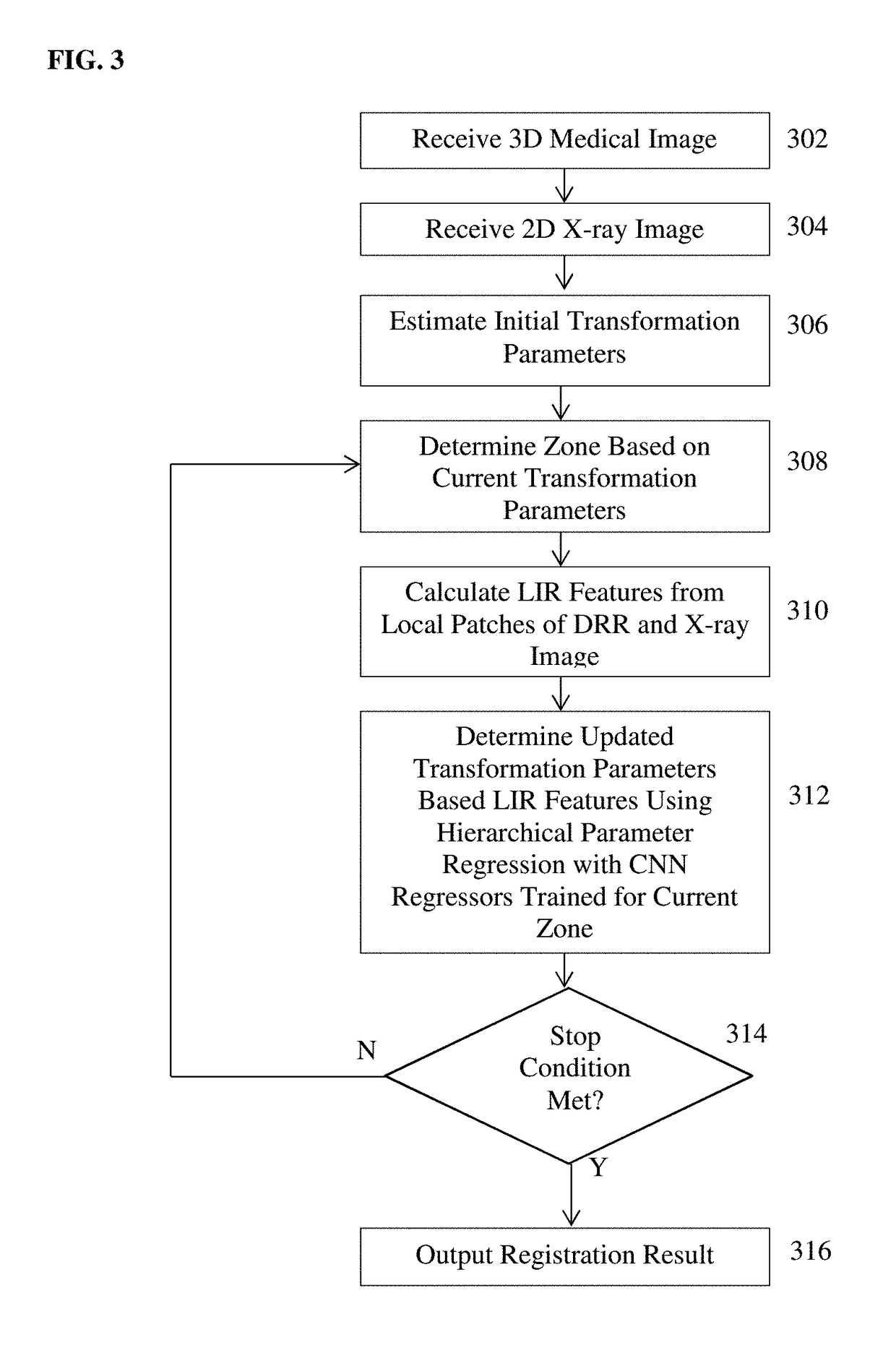
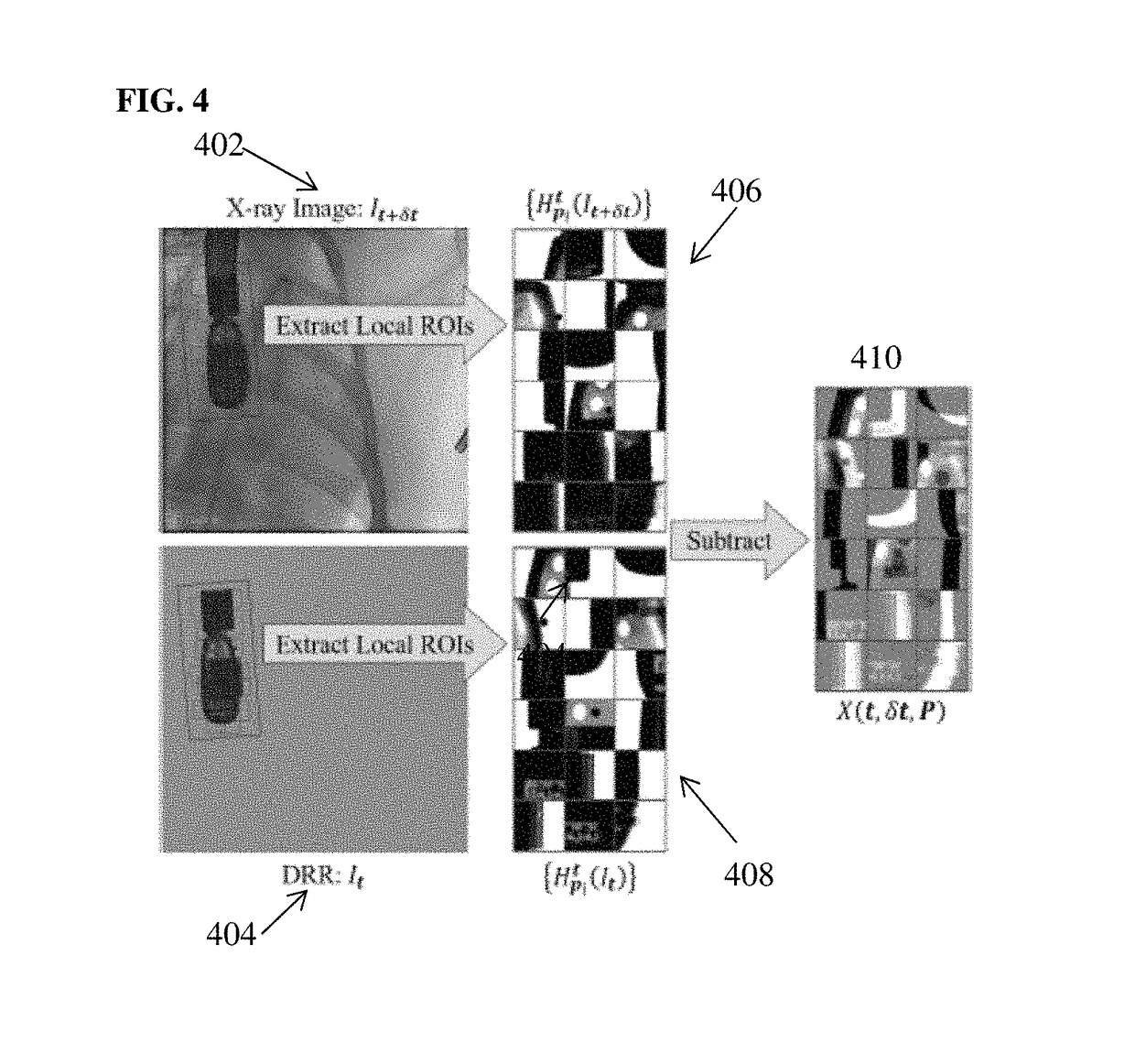
Method for 2-D/3-D registration based on hierarchical pose regression
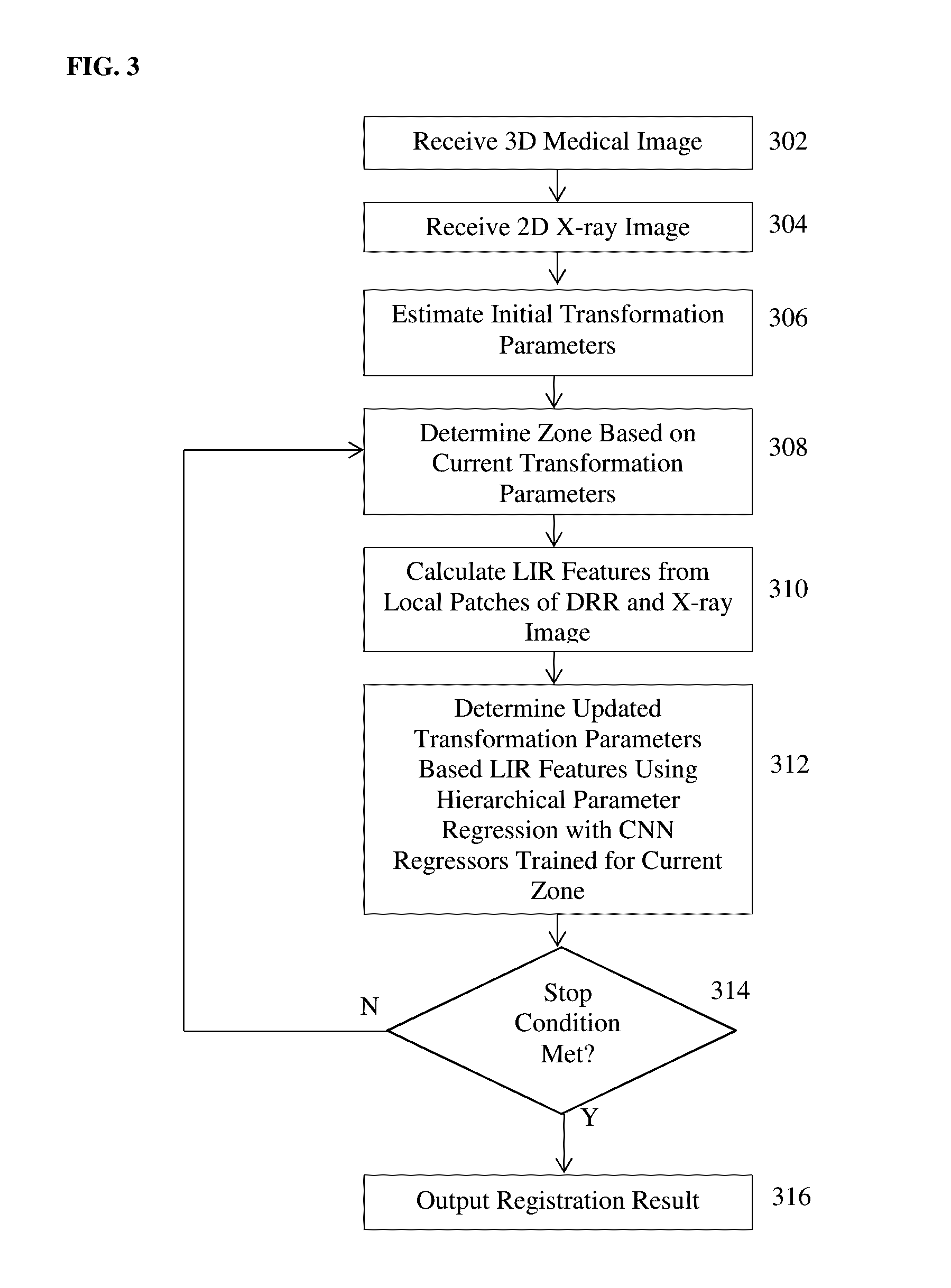
ActiveUS20170024634A1Large capture rangeImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisTransformation parameterX ray image
A method and apparatus for convolutional neural network (CNN) regression based 2D / 3D registration of medical images is disclosed. A parameter space zone is determined based on transformation parameters corresponding to a digitally reconstructed radiograph (DRR) generated from the 3D medical image. Local image residual (LIR) features are calculated from local patches of the DRR and the X-ray image based on a set of 3D points in the 3D medical image extracted for the determined parameter space zone. Updated transformation parameters are calculated based on the LIR features using a hierarchical series of regressors trained for the determined parameter space zone. The hierarchical series of regressors includes a plurality of regressors each of which calculates updates for a respective subset of the transformation parameters.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
Four-dimensional (4D) image verification in respiratory gated radiation therapy
ActiveUS7570738B2X-ray/infra-red processesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationFluoroscopic image4D Computed Tomography
A method for four-dimensional (4D) image verification in respiratory gated radiation therapy, includes: acquiring 4D computed tomography (CT) images, each of the 4D CT images representing a breathing phase of a patient and tagged with a corresponding time point of a first surrogate signal; acquiring fluoroscopic images of the patient under free breathing, each of the fluoroscopic images tagged with a corresponding time point of a second surrogate signal; generating digitally reconstructed radiographs (DRRs) for each breathing phase represented by the 4D CT images; generating a similarity matrix to assess a degree of resemblance in a region of interest between the DRRs and the fluoroscopic images; computing a compounded similarity matrix by averaging values of the similarity matrix across different time points of the breathing phase during a breathing period of the patient; determining an optimal time point synchronization between the DRRs and the fluoroscopic images by using the compounded similarity matrix; and acquiring a third surrogate signal and turning a treatment beam on or off according to the optimal time point synchronization.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
Two-dimensional and three-dimensional medical image registration method
InactiveCN104637061AFast and Accurate Guided TreatmentFast and accurate registrationImage enhancementImage analysisIn planeThree dimensional ct
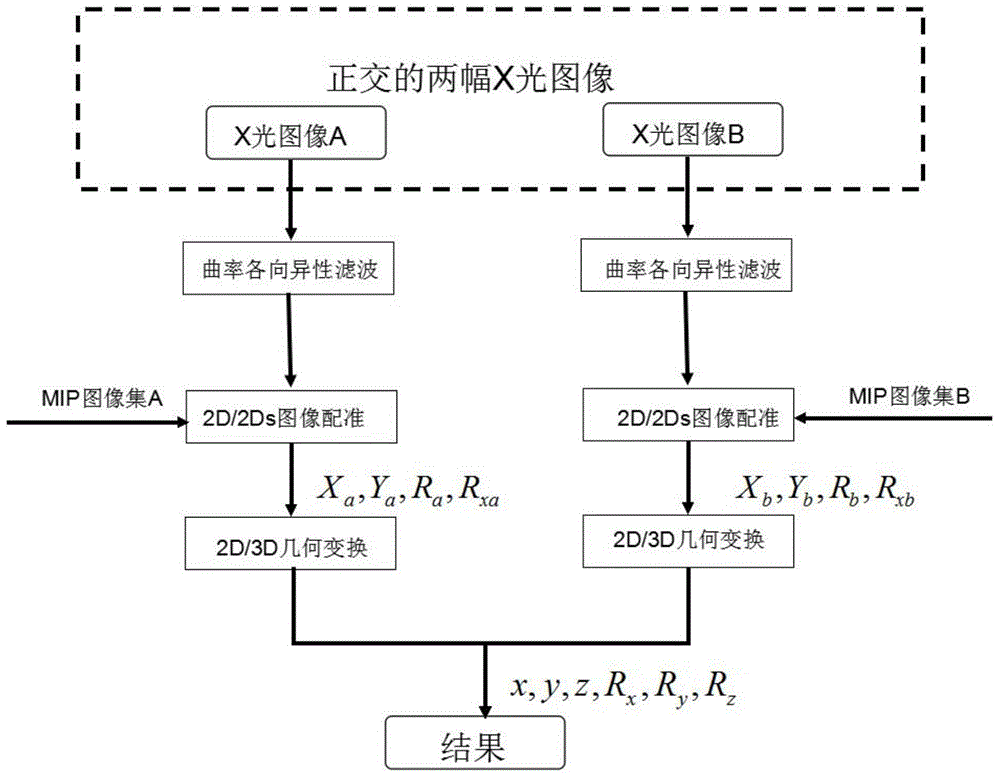
The invention provides a two-dimensional and three-dimensional medical image registration method, which can quickly carry out registration on an intra-operative two-dimensional X-ray image and a preoperative three-dimensional CT (Computed Tomography) image. The two-dimensional and three-dimensional medical image registration method comprises the following steps: carrying out filtering preprocessing on the three-dimensional CT image, projecting the three-dimensional CT image in two mutually-orthogonal plane systems to obtain two corresponding digitally reconstructed radiograph (DRR) sets according to a maximum intensity projection (MIP) algorithm; obtaining two two-dimensional X-ray images on another two orthogonal planes, and carrying out the filtering preprocessing on the two-dimensional X-ray image; carrying out traversal on the two DRR sets, and carrying out registration on the two DRR sets and another two orthogonal two-dimensional X-ray images so as to determine a corresponding most similar DRR as well as the in-plane position coordinate, the in-plane rotation angle and an out-of-plane rotation angle of the DRR; converting the coordinate and the angles to be under a three-dimensional CT image coordinate system to obtain six registration parameters. According to the method, the X-ray image and the CT image which is generated in advance can be subjected to accurate and quick real-time registration.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
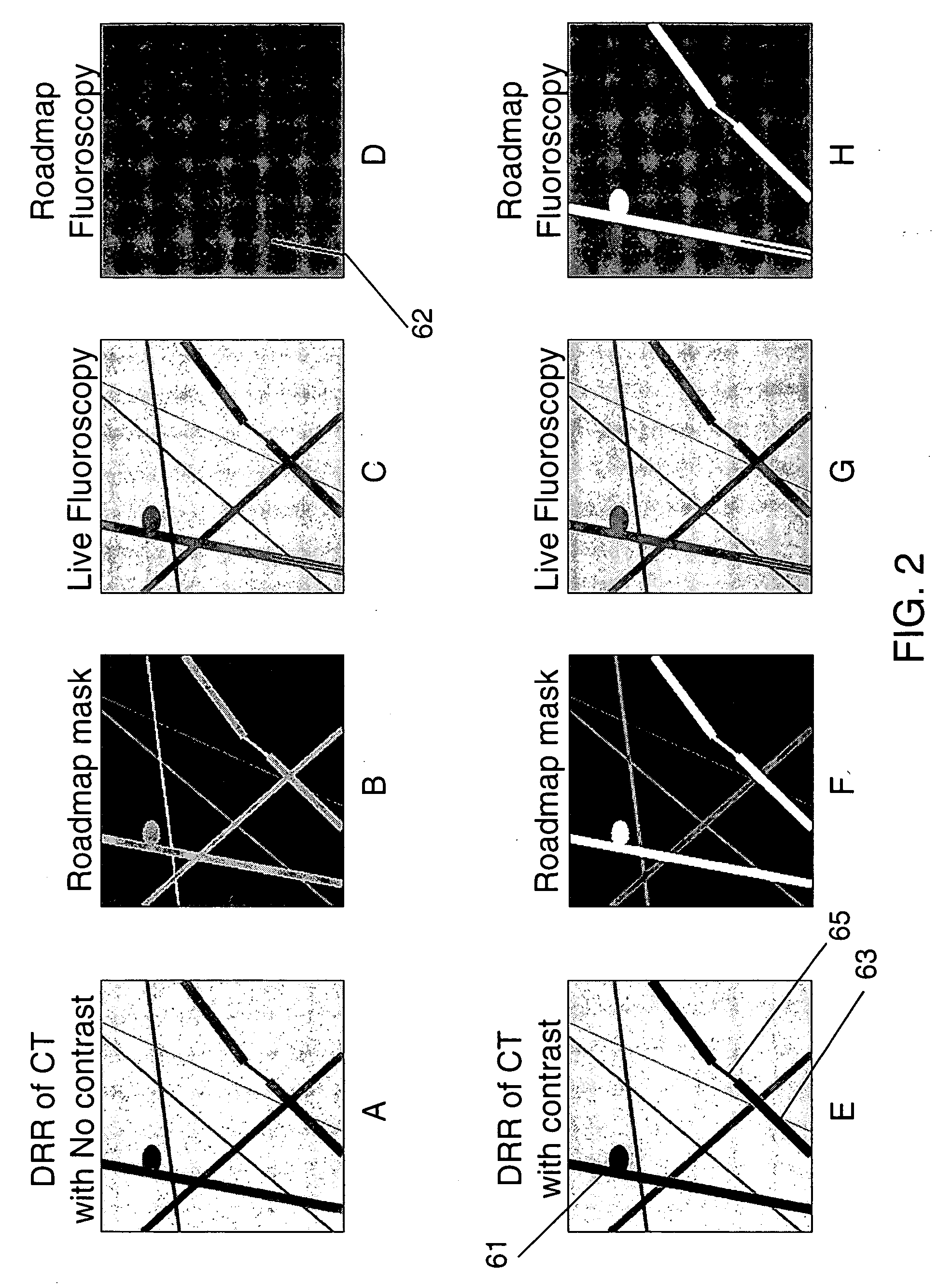
Method and system for virtual roadmap imaging
InactiveUS20090192385A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsFluoroscopic imageX-ray
A system and method of producing virtual roadmap image of a patient is described. CT-like image data may be obtained for a patient, with or without a contrast agent, and differenced so as to form a roadmap mask. The roadmap mask is in the form of a 2-dimensional digitally reconstructed radiograph from the same orientation as that of a fluoroscopic X-ray device which takes real-time images of the patient during treatment. The fluoroscopic image may be subtracted from the roadmap mask so as to more clearly visualize the position of a catheter introduced into the patient for treatment. When the orientation of the fluoroscopic image is changed during the course of treatment, the roadmap mask image for the corresponding orientation is used.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
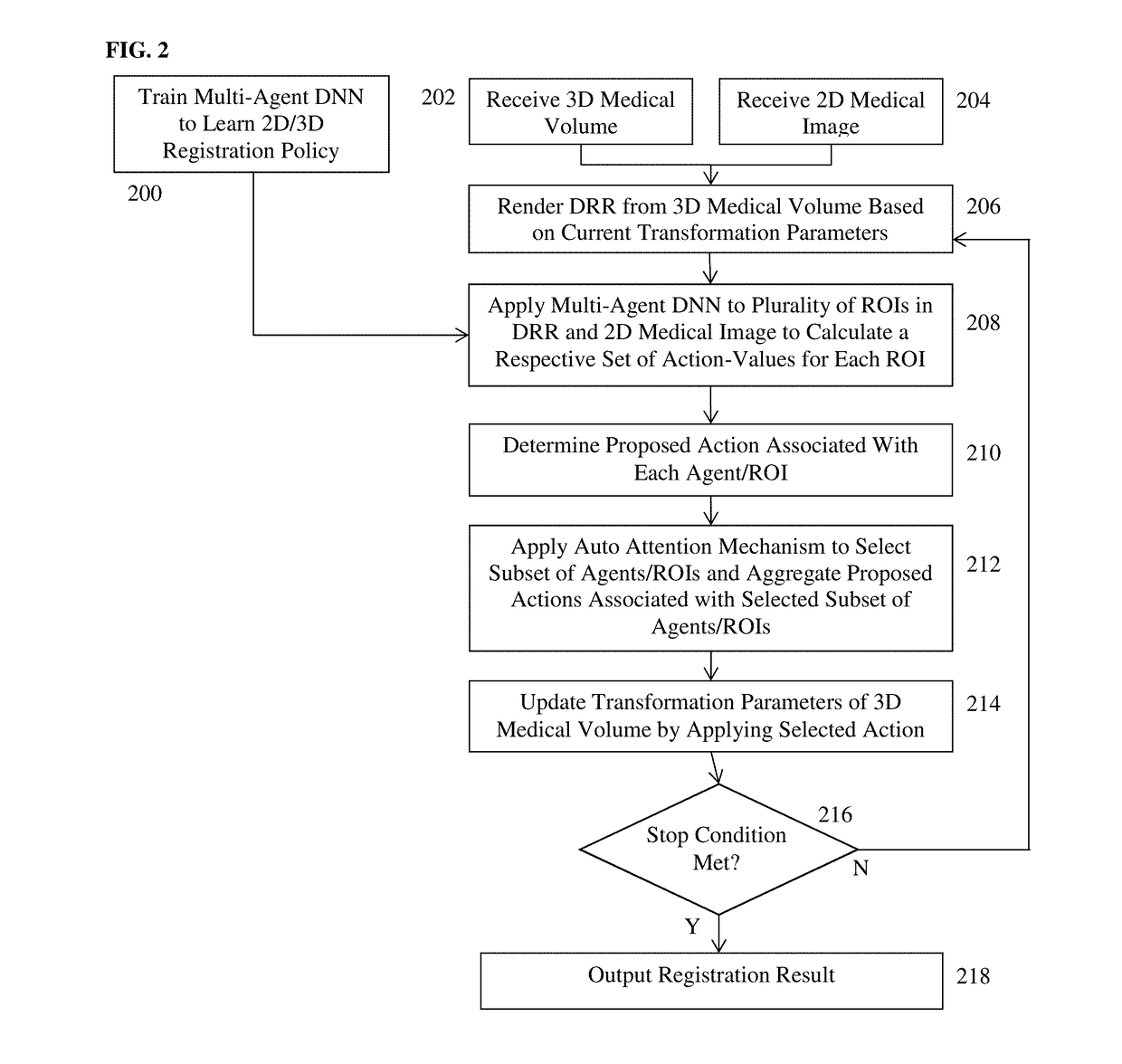
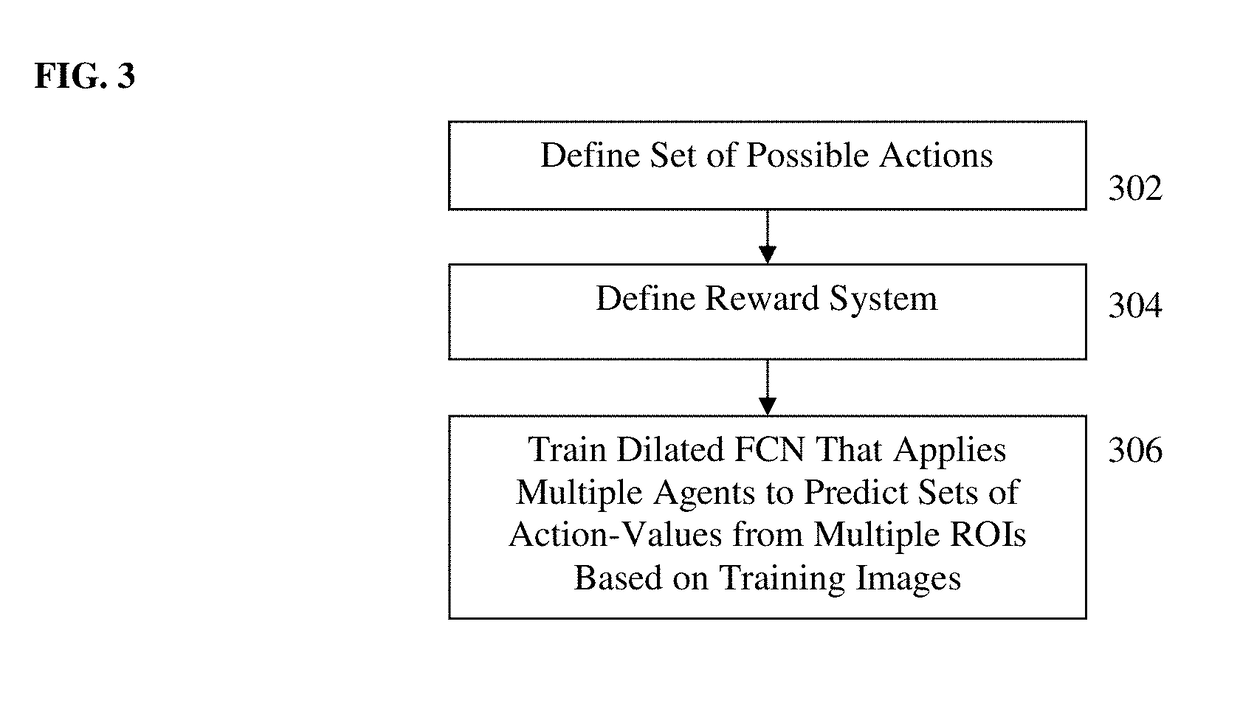
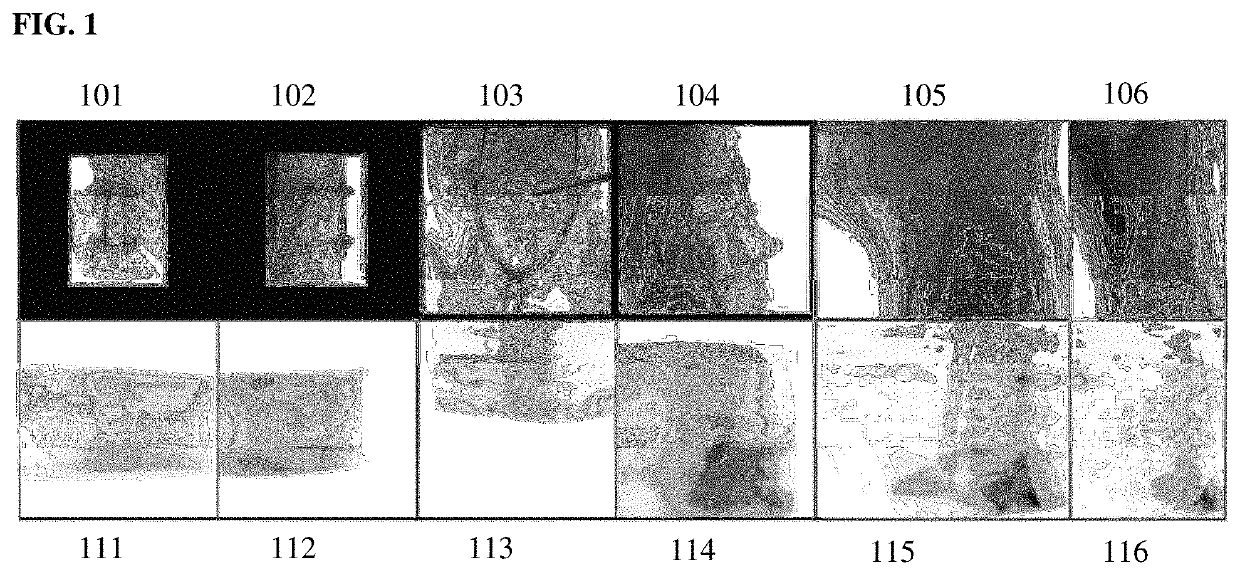
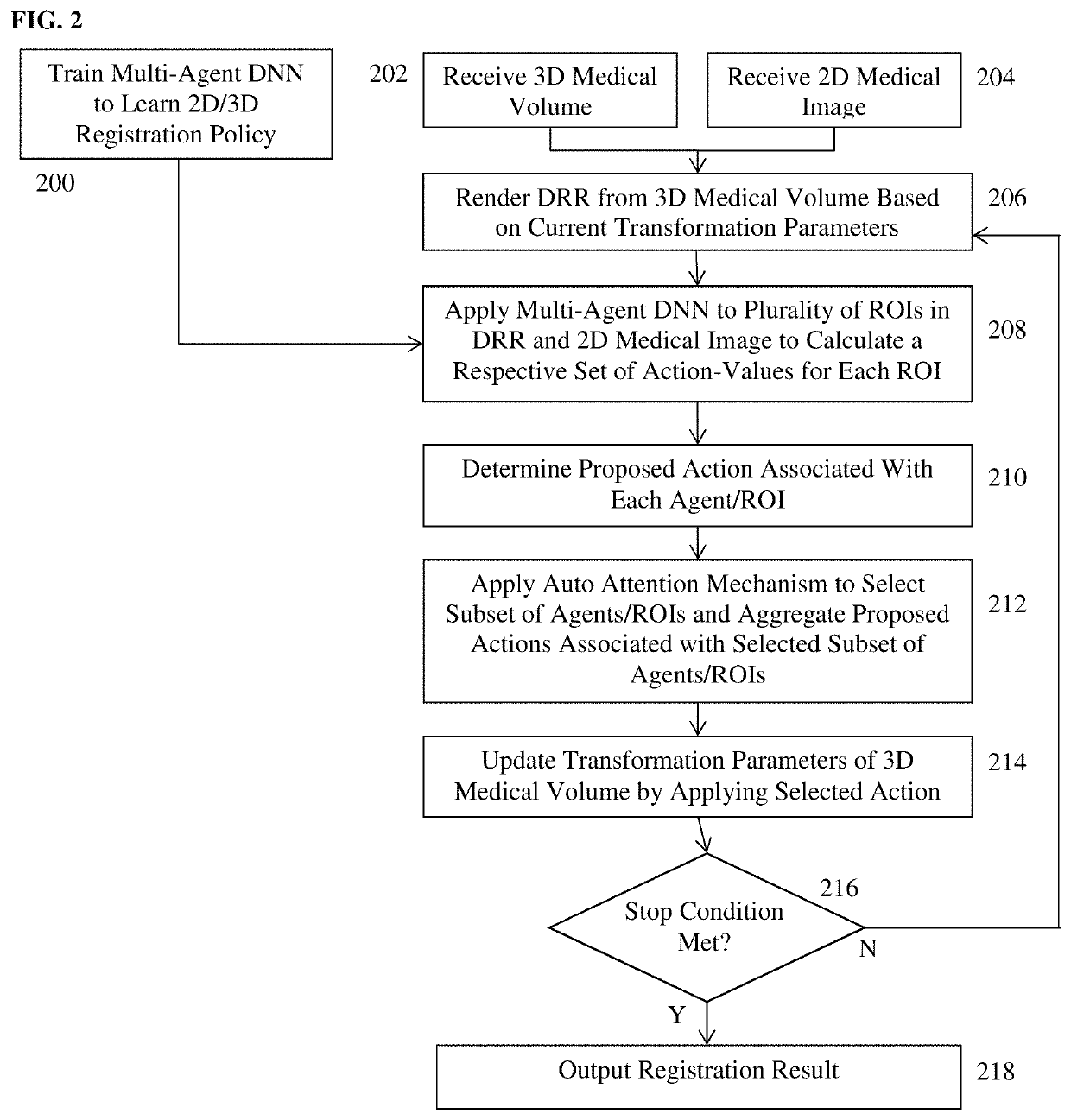
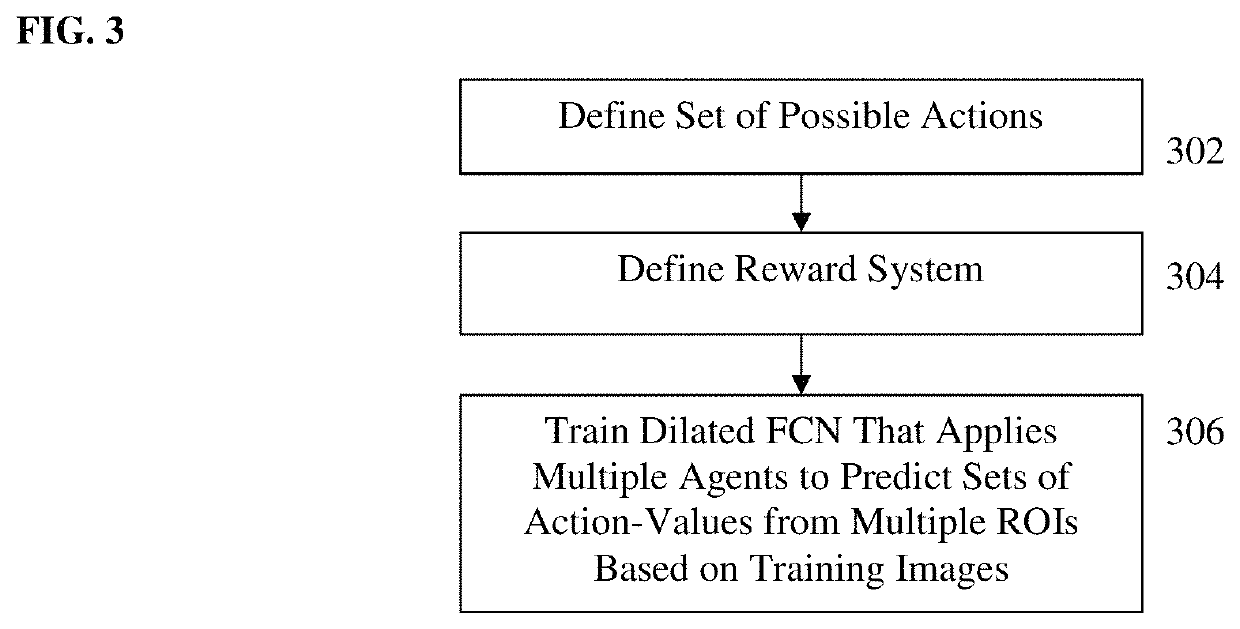
Dilated Fully Convolutional Network for Multi-Agent 2D/3D Medical Image Registration
A method and system for 3D / 3D medical image registration. A digitally reconstructed radiograph (DRR) is rendered from a 3D medical volume based on current transformation parameters. A trained multi-agent deep neural network (DNN) is applied to a plurality of regions of interest (ROIs) in the DRR and a 2D medical image. The trained multi-agent DNN applies a respective agent to each ROI to calculate a respective set of action-values from each ROI. A maximum action-value and a proposed action associated with the maximum action value are determined for each agent. A subset of agents is selected based on the maximum action-values determined for the agents. The proposed actions determined for the selected subset of agents are aggregated to determine an optimal adjustment to the transformation parameters and the transformation parameters are adjusted by the determined optimal adjustment. The 3D medical volume is registered to the 2D medical image using final transformation parameters resulting from a plurality of iterations.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and system for registering pre-procedural images with intra-procedural images using a pre-computed knowledge base
A system and method for registering pre-operative images of an object with an intra-operative image of the object is disclosed. Prior to an operative procedure, Digitally Reconstructed Radiographs (DRRs) are generated for the pre-operative images of each individual patient. Signatures are extracted from the DRRs. The signatures are stored in a knowledge base. During the operative procedure, a signature is extracted from the intra-operative image. The intra-operative signature is compared to the stored pre-operative signatures. A pre-operative image having a best signature match to the intra-operative signature is retrieved. The retrieved pre-operative image is registered with the intra-operative image.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
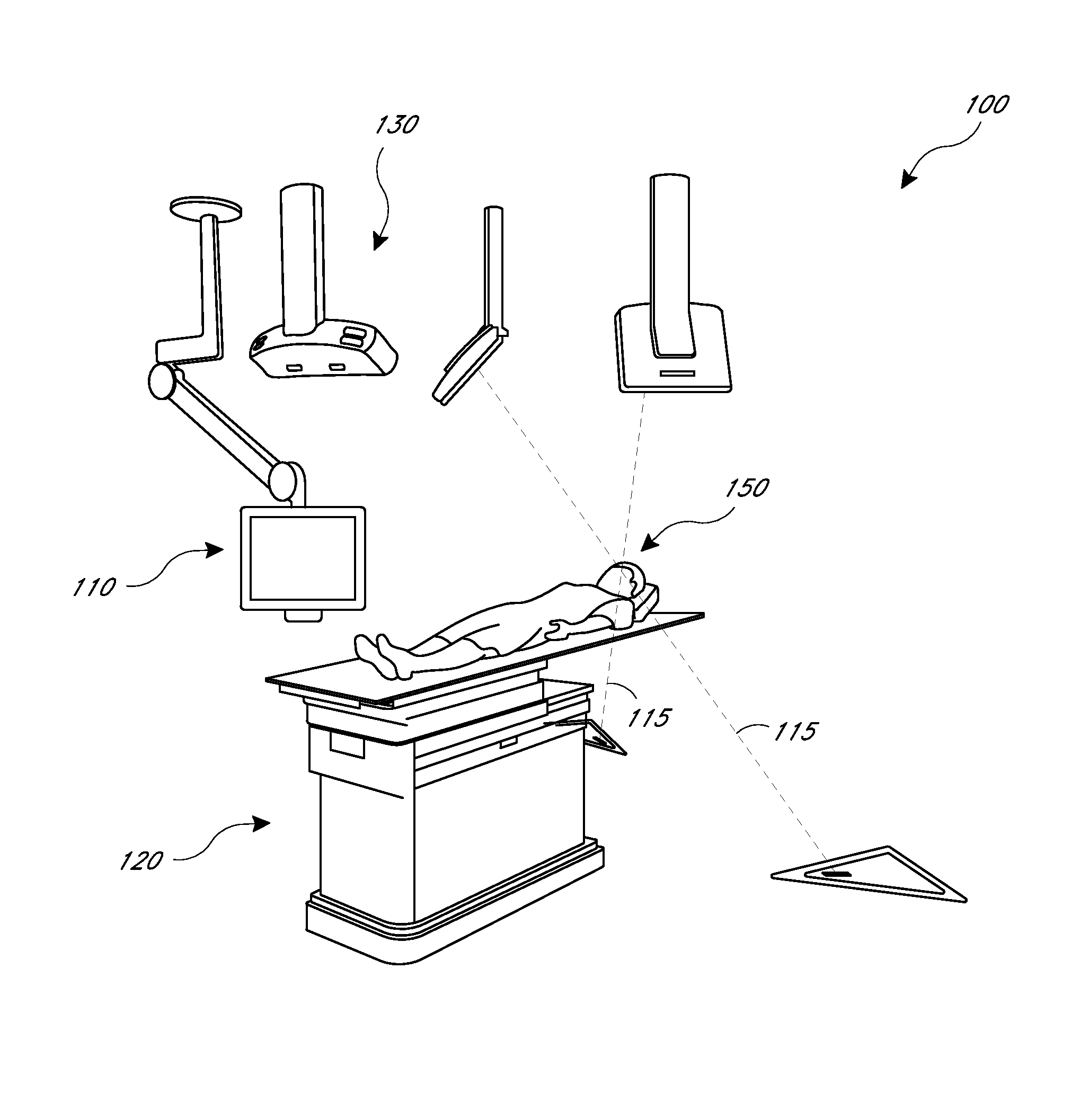
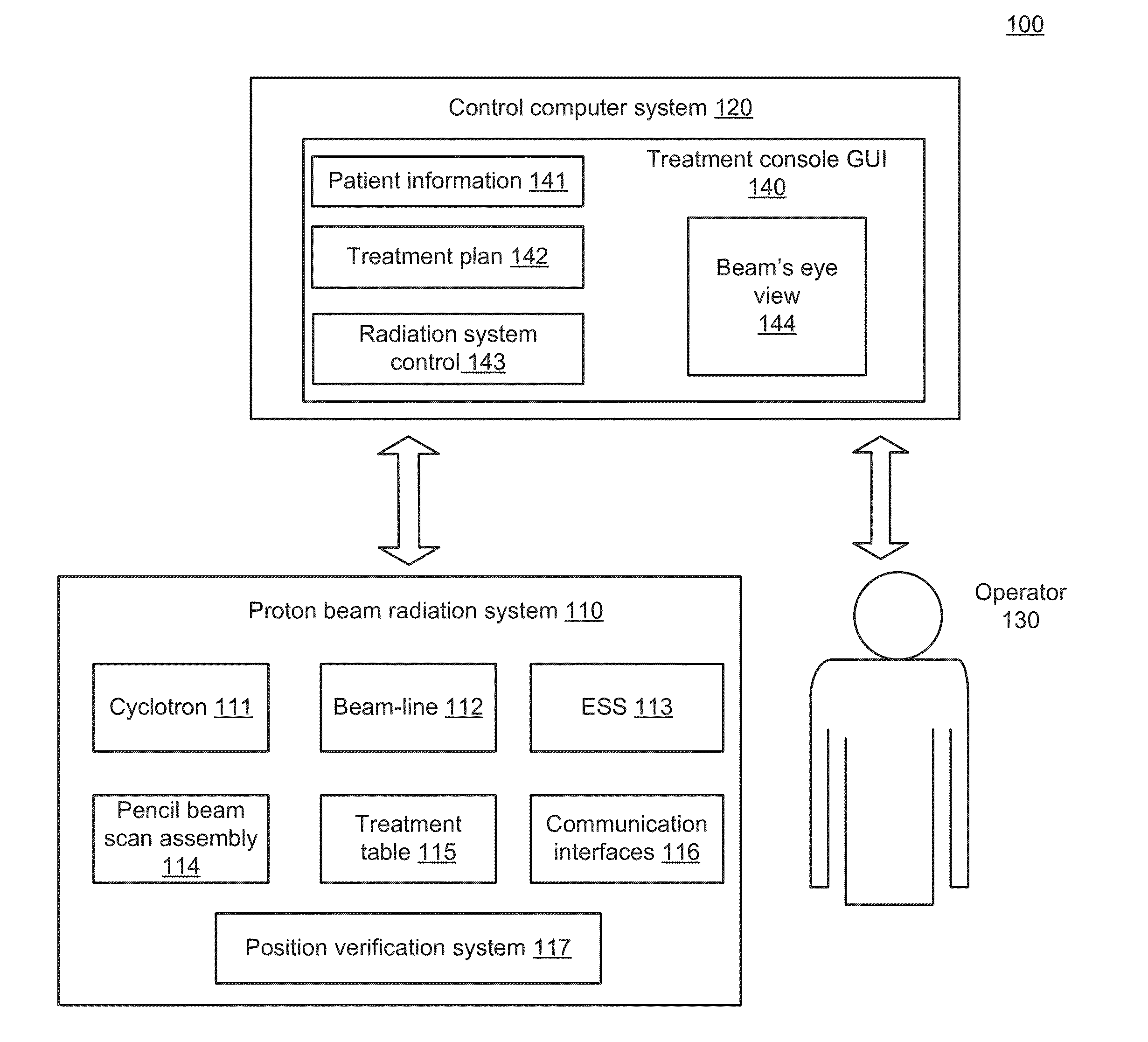
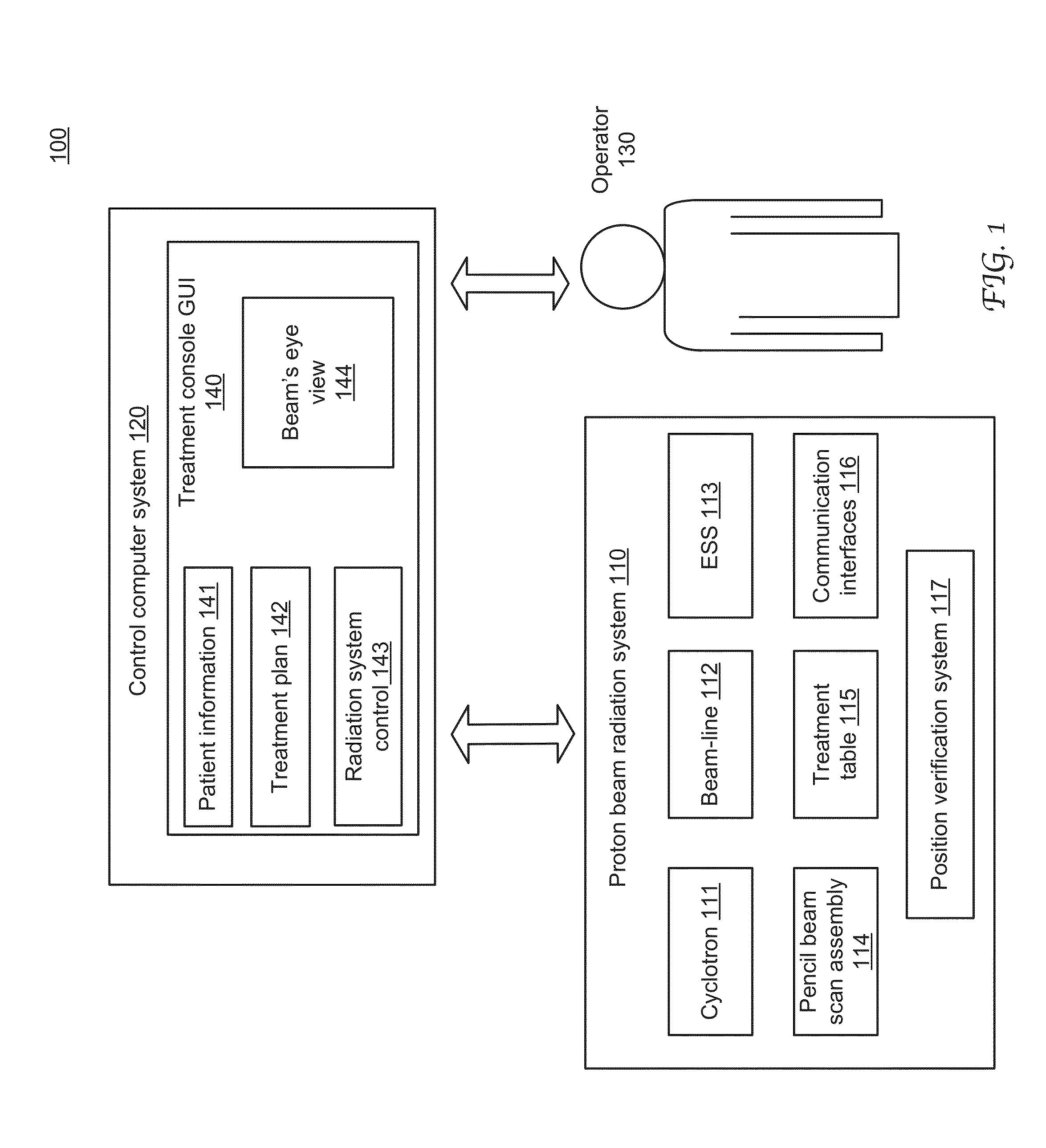
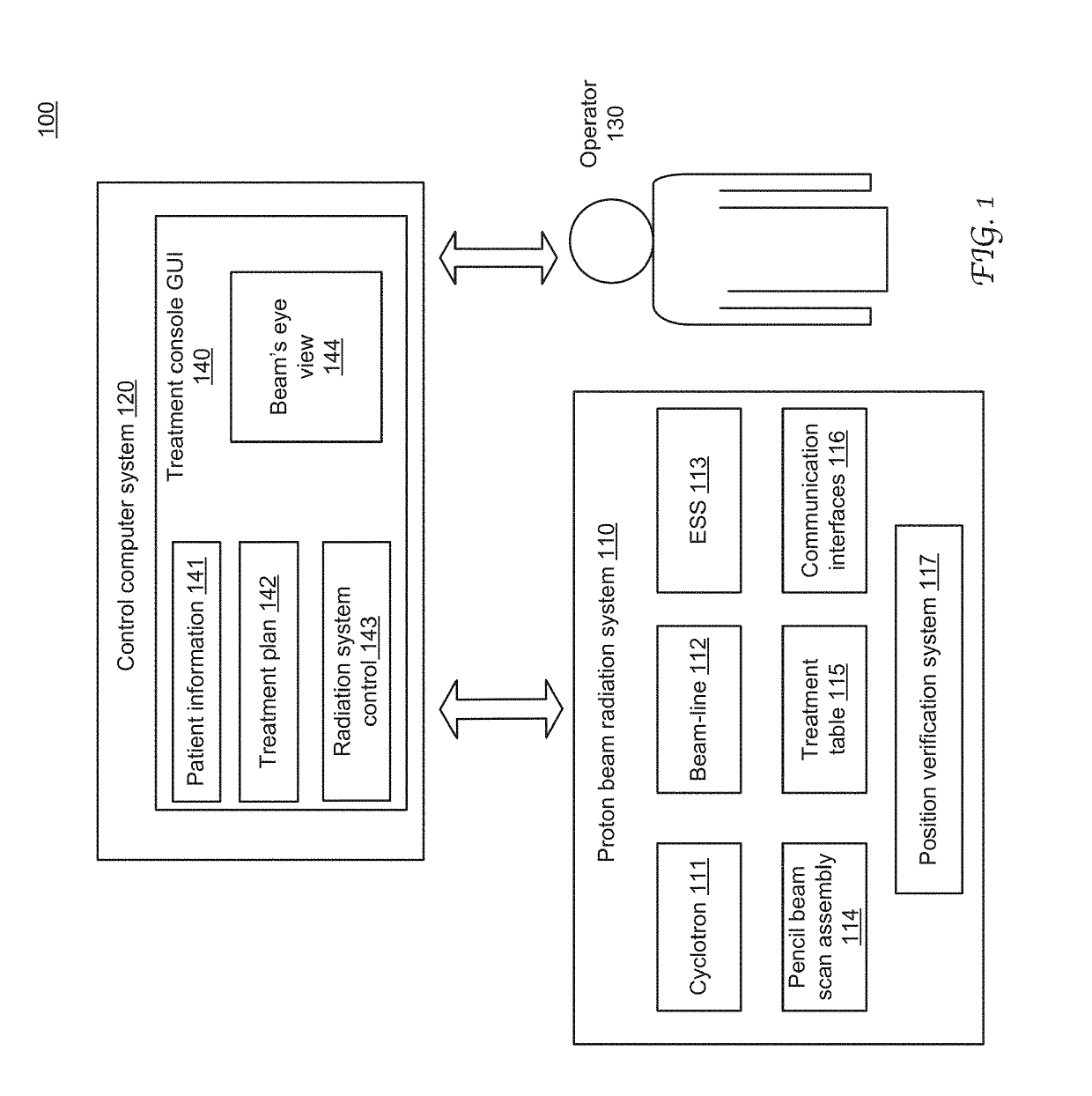
Dynamic beam's eye view of proton therapy irradiation shown in anatomical context
ActiveUS20160175617A1Facilitate quality assuranceFacilitate therapy planningX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyVisual perceptionUser interface
System and method of dynamically presenting visual representations of a target volume in an anatomical context to an operator-user of a charged particle radiation therapy system. The visual representations are integrated as a part of a treatment console graphical user interface (GUI) and presented as a part of a holistic view of treatment information. The visual representations are digitally reconstructed radiographs (DRRs) constructed based on anatomical images captured before the therapy session, or alternatively during a treatment session using an imaging system attached to the radiation treatment system. In an online mode, the on-screen visual representations are rendered in synchronization with the irradiation delivery process.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
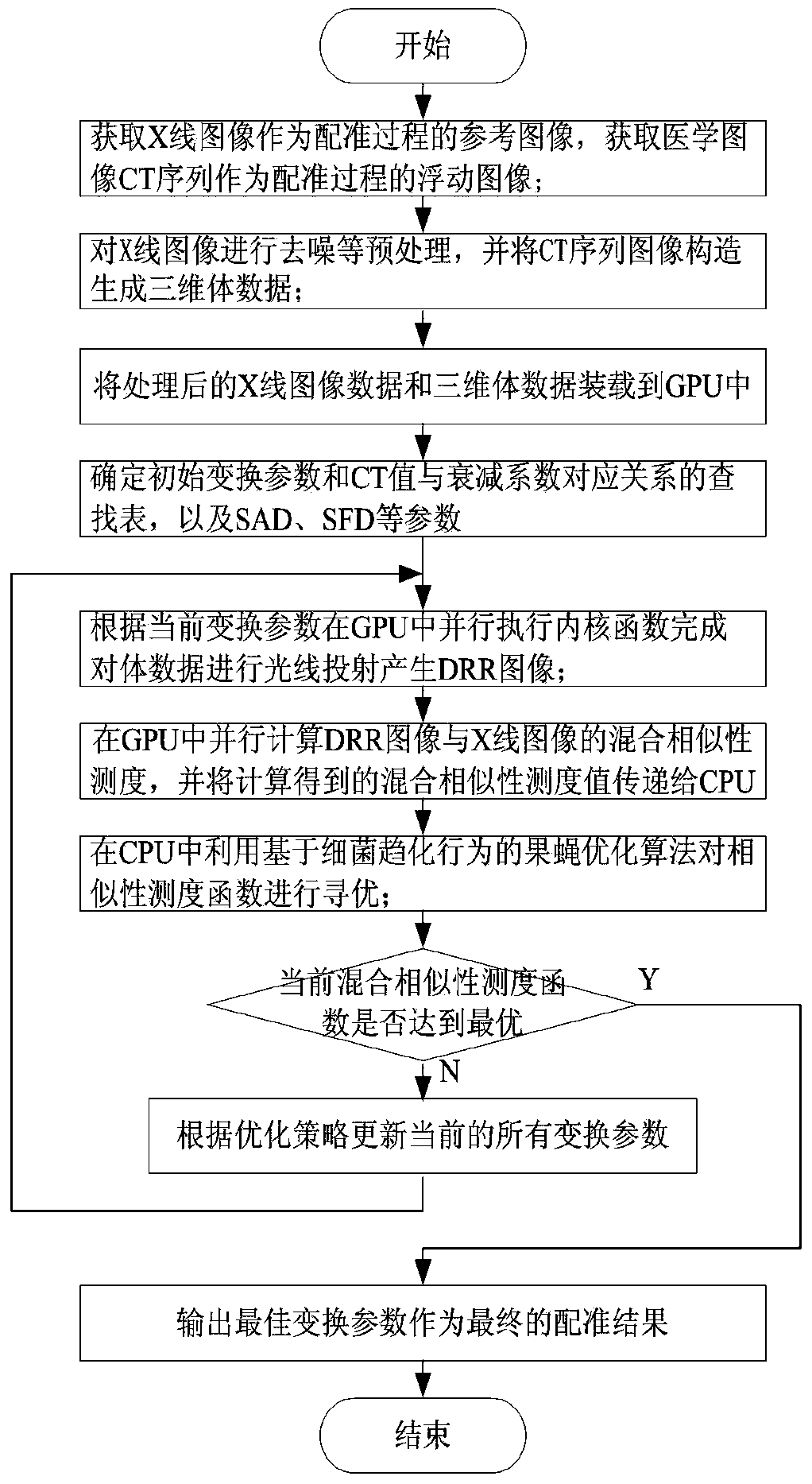
2D-3D medical image parallel registration method based on combination similarity measure
InactiveCN104134210ASimple calculationHigh precisionImage analysisGeneration processParallel programming model
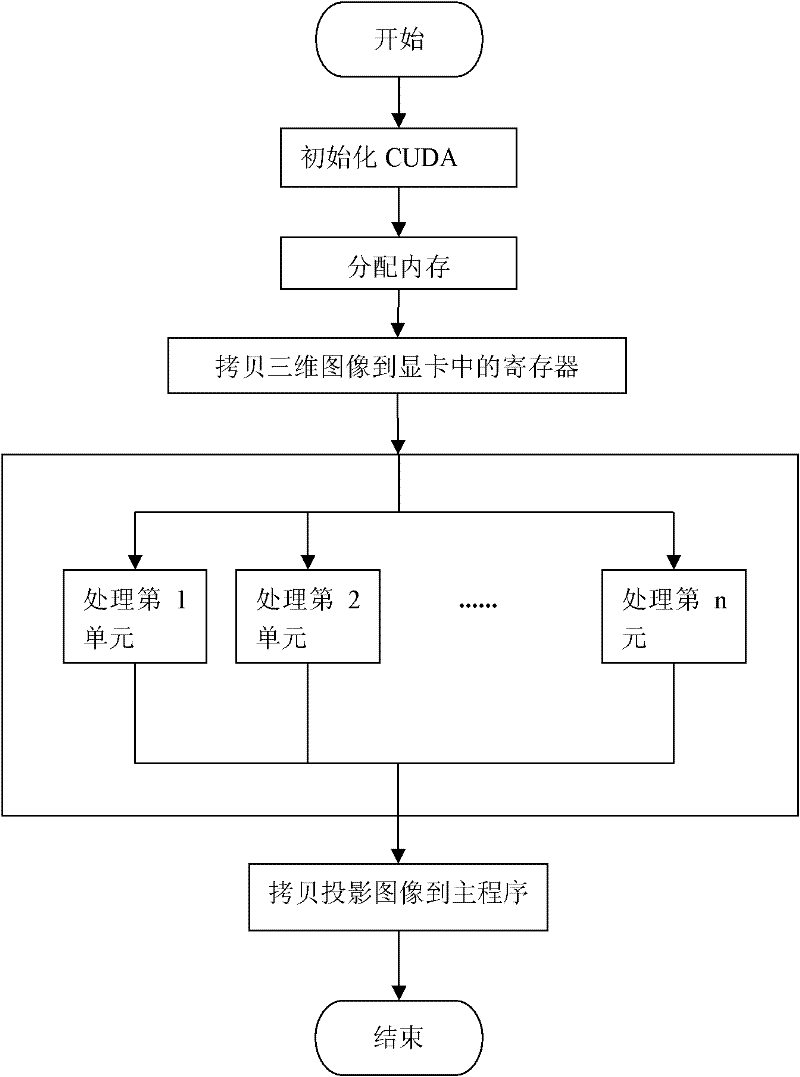
The invention discloses a 2D-3D medical image parallel registration method based on combination similarity measure. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, using a CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture) parallel computing model to finish a quick generation process of a DRR (Digitally Reconstructed Radiograph) image; combining a SAD (Sum of Absolute Difference) with PI (pattern intensity) as new similarity measure to carry out parallel computation on GPU (Graphics Processing Unit); and finally, transferring a combination similarity measure value to CPU (Central Processing Unit), and adopting a fruit fly optimization algorithm based on bacterial chemotaxis behaviors to optimize for looking for an optimal registration parameter. An experiment verifies the performance of the method to show that the execution speed of the method is effectively improved since DRR high-speed generation and the mixed similarity measure are realized in the GPU. Meanwhile, compared with the single similarity measure, the invention adopts the mixed similarity measure to improve the accuracy of a registration result.
Owner:LANZHOU JIAOTONG UNIV
Fiducial-less tracking of a volume of interest
ActiveUS8831706B2Health-index calculationCharacter and pattern recognitionNuclear medicineImaging data
A method and an apparatus for fiducial-less tracking of a volume of interest (VOI) have been presented. In some embodiments, a pair of intra-operative images of a portion of a patient is generated during treatment of a target region in the patient to show a bony structure of the patient. The bony structure shown is movable responsive to respiration of the patient. Then the pair of intra-operative images is compared with a set of digitally reconstructed radiograph (DRR) pairs, generated from volumes of four-dimensional (4D) diagnostic imaging data, to determine a location of the movable bony structure that corresponds to a particular volume of the 4D diagnostic imaging data.
Owner:ACCURAY
Method and system for convolutional neural network regression based 2D/3D image registration
ActiveUS10235606B2Large capture rangeImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisTransformation parameterX ray image
A method and apparatus for convolutional neural network (CNN) regression based 2D / 3D registration of medical images is disclosed. A parameter space zone is determined based on transformation parameters corresponding to a digitally reconstructed radiograph (DRR) generated from the 3D medical image. Local image residual (LIR) features are calculated from local patches of the DRR and the X-ray image based on a set of 3D points in the 3D medical image extracted for the determined parameter space zone. Updated transformation parameters are calculated based on the LIR features using a hierarchical series of regressors trained for the determined parameter space zone. The hierarchical series of regressors includes a plurality of regressors each of which calculates updates for a respective subset of the transformation parameters.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
Systems and methods for frameless image-guided biopsy and therapeutic intervention
ActiveUS20150018842A1High precisionAdverse effectSurgical needlesSurgical navigation systemsComputed tomographyLocation Equipment
A system and a method of performing a frameless image-guided biopsy uses imaging, a six-dimensional robotic couch system, a laser guidance system, an optical distance indicator, and a needle control apparatus. A planning CT scan is made of the patient with stereotactic fiduciary markers to localize and produce digitally reconstructed radiographs. Two stereoscopic images are generated using an imaging device to visualize and identify a target tumor. The images are fused with the digitally reconstructed radiographs of the planning CT scan to process tumor location. The tumor location data are communicated to the movable robotic couch to position the target tumor of the patient at a known isocenter location. A biopsy needle is guided with a laser alignment mechanism towards the isocenter at the determined depth using a needle positioning apparatus and an Optical Distance Indicator, and a biopsy sample of the target tumor is obtained.
Owner:VOXEL RAD
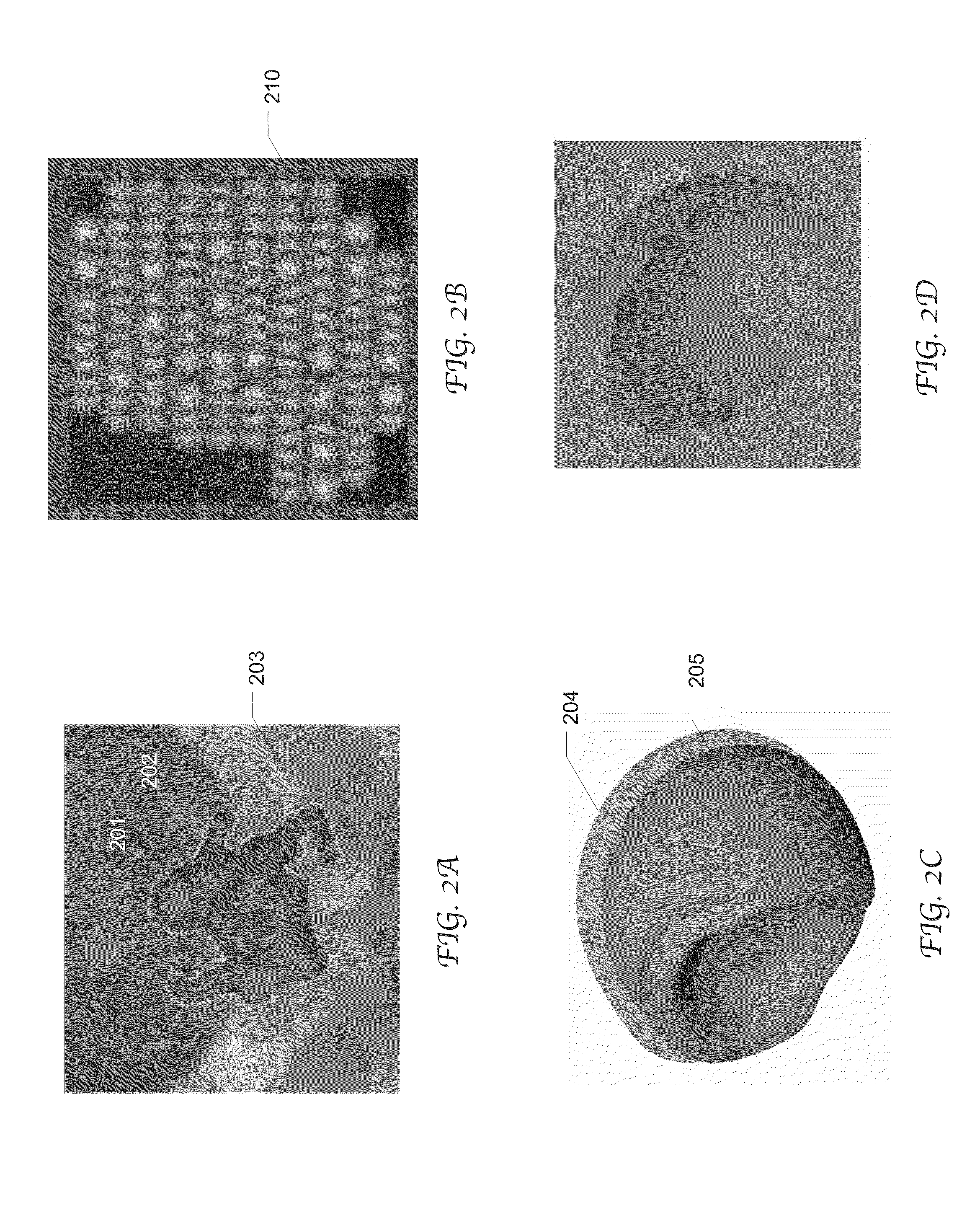
Simulated projection DRR( digitally reconstructed radiograph) generating method based on CUDA (compute unified device architecture) technology
InactiveCN102542600AEliminate couplingImprove robustness3D-image renderingProjection imageScale variation
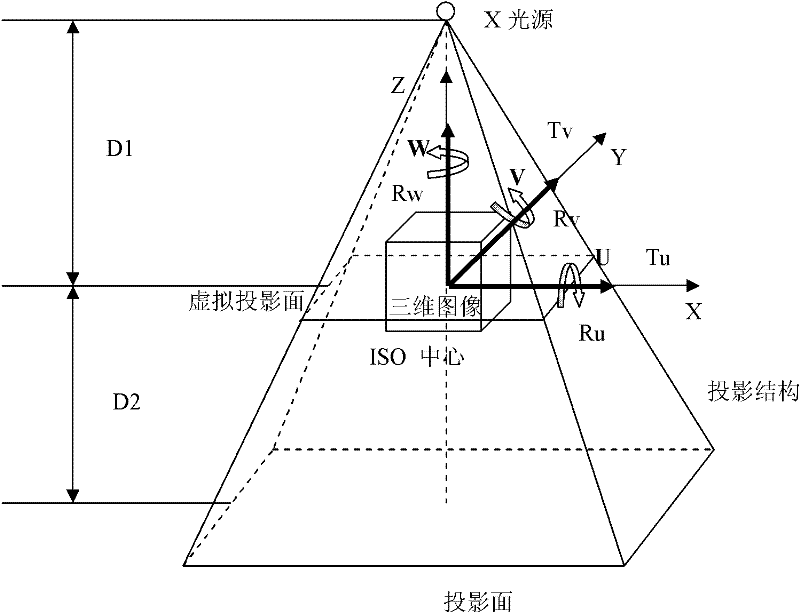
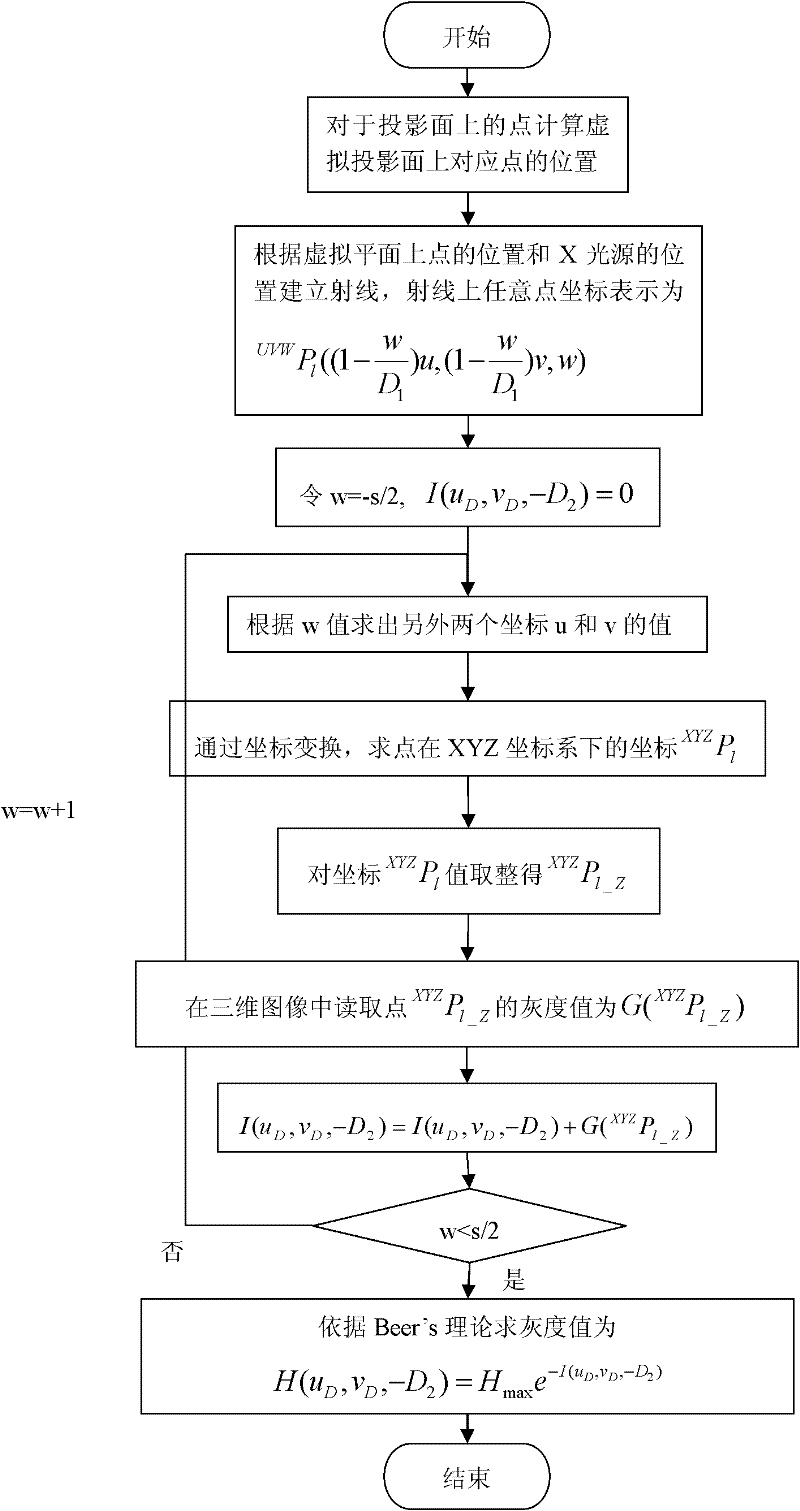
The invention discloses a simulated projection DRR ( digitally reconstructed radiograph) generating method based on a CUDA (compute unified device architecture) technology. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a new projection model; back-projecting each pixel point of a two-dimensional image; and finally generating a simulated projection image required by image registration through computing the sum of grey values of three-dimensional images on a back-projection line. Besides, based on the model, the invention also discloses a hardware acceleration method based on the CUDA technology. By using the method disclosed by the invention, the coupling between the projection distortion and scale variation can be effectively eliminated, the robustness and the accuracy of two-dimensional and three-dimensional image registration are increased, and the real-time and the efficiency of the algorithm are improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Dynamic beam's eye view of proton therapy irradiation shown in anatomical context
ActiveUS10342997B2Quality improvementFacilitate therapyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyVisual perceptionUser interface
System and method of dynamically presenting visual representations of a target volume in an anatomical context to an operator-user of a charged particle radiation therapy system. The visual representations are integrated as a part of a treatment console graphical user interface (GUI) and presented as a part of a holistic view of treatment information. The visual representations are digitally reconstructed radiographs (DRRs) constructed based on anatomical images captured before the therapy session, or alternatively during a treatment session using an imaging system attached to the radiation treatment system. In an online mode, the on-screen visual representations are rendered in synchronization with the irradiation delivery process.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
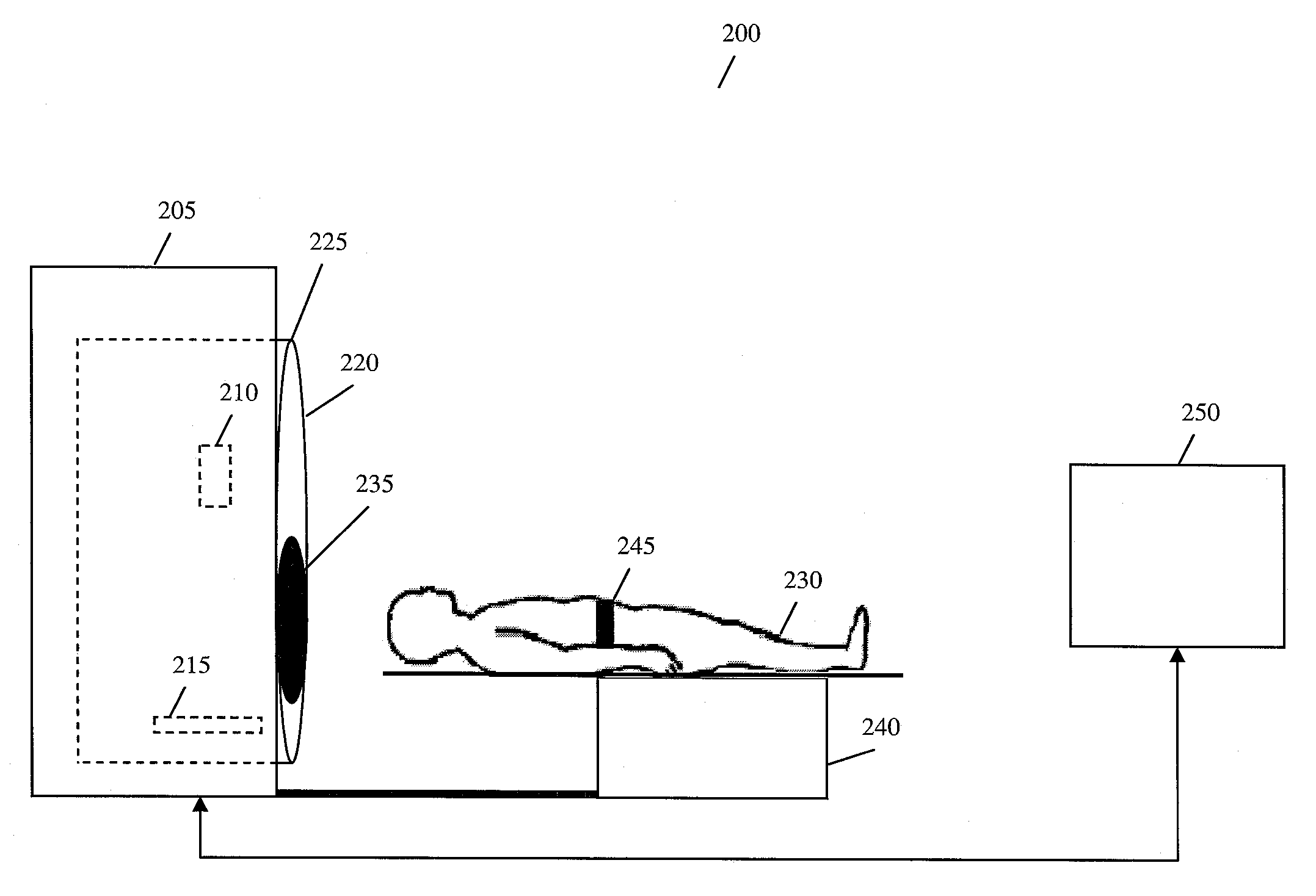
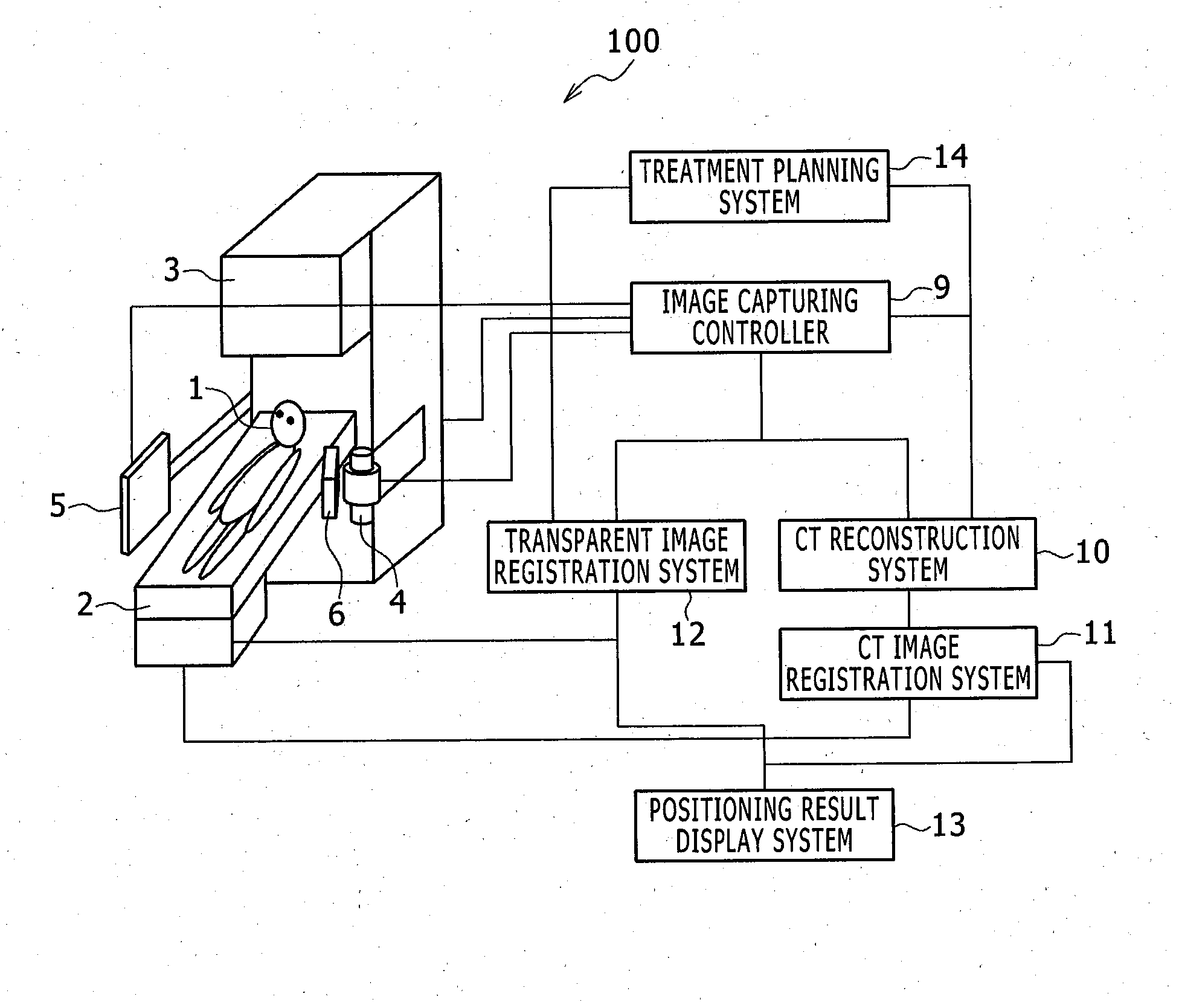
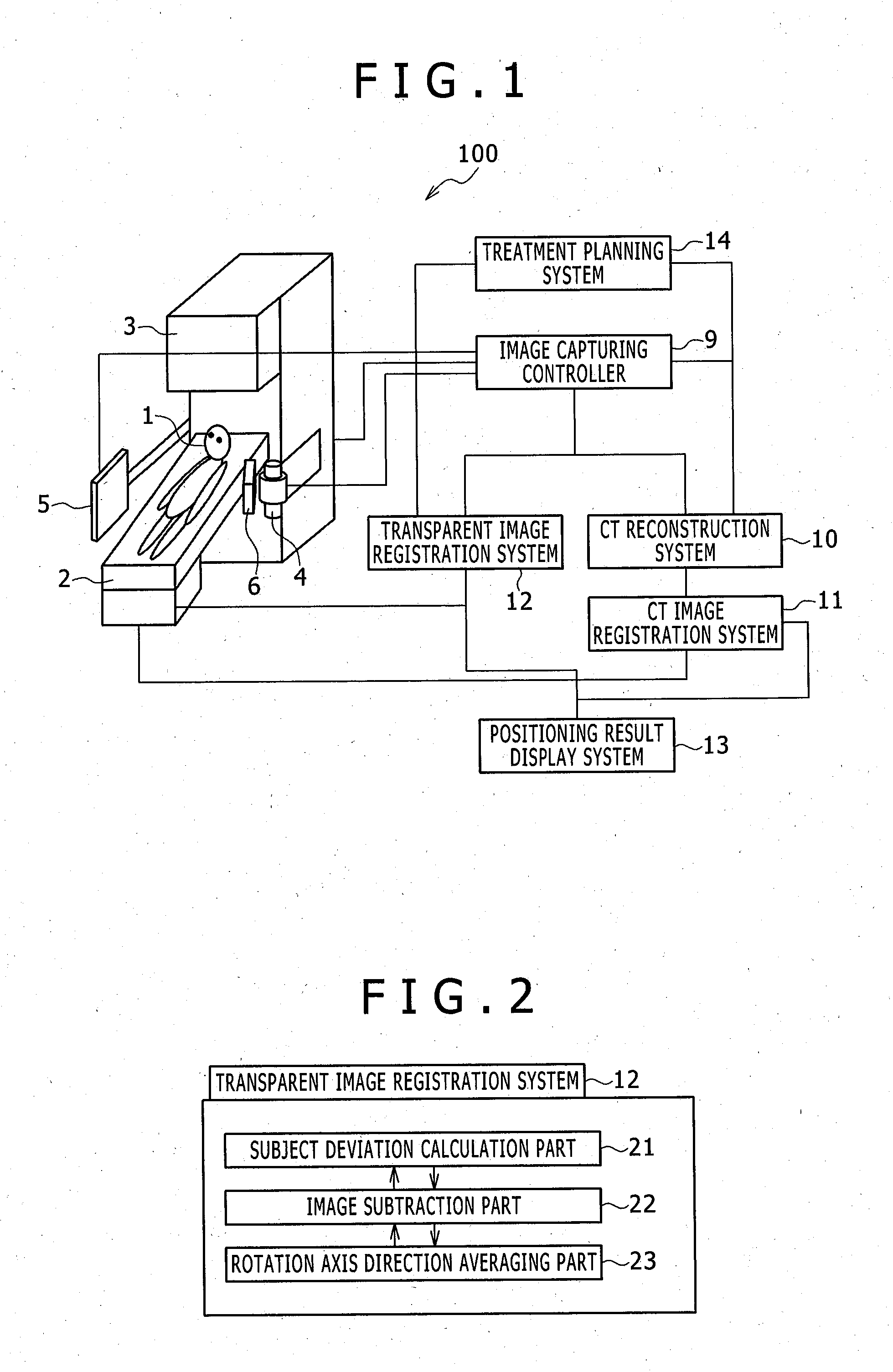
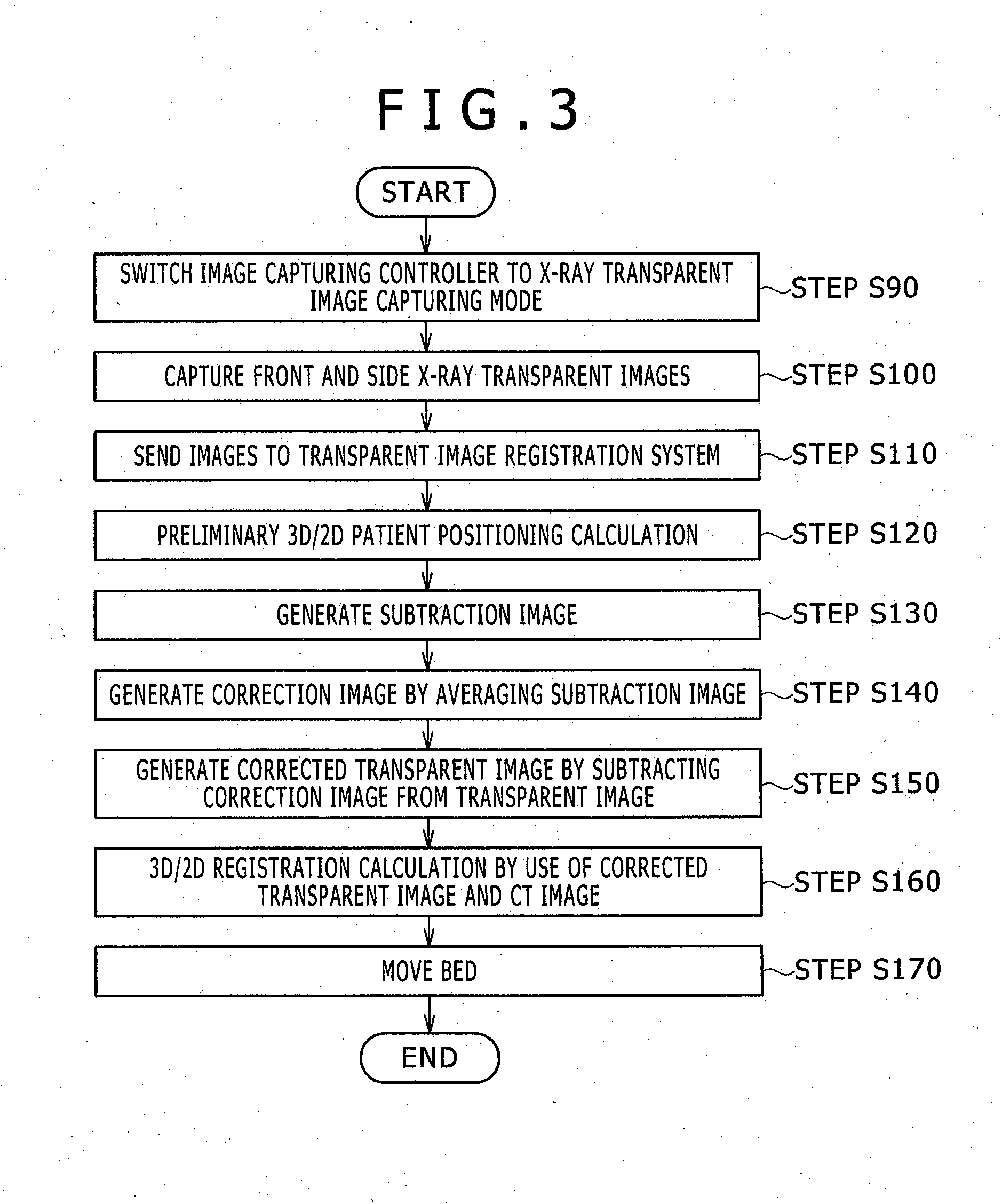
Bed positioning system for radiation therapy
ActiveUS20150272530A1High-accuracy bed positioningMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayPositioning system
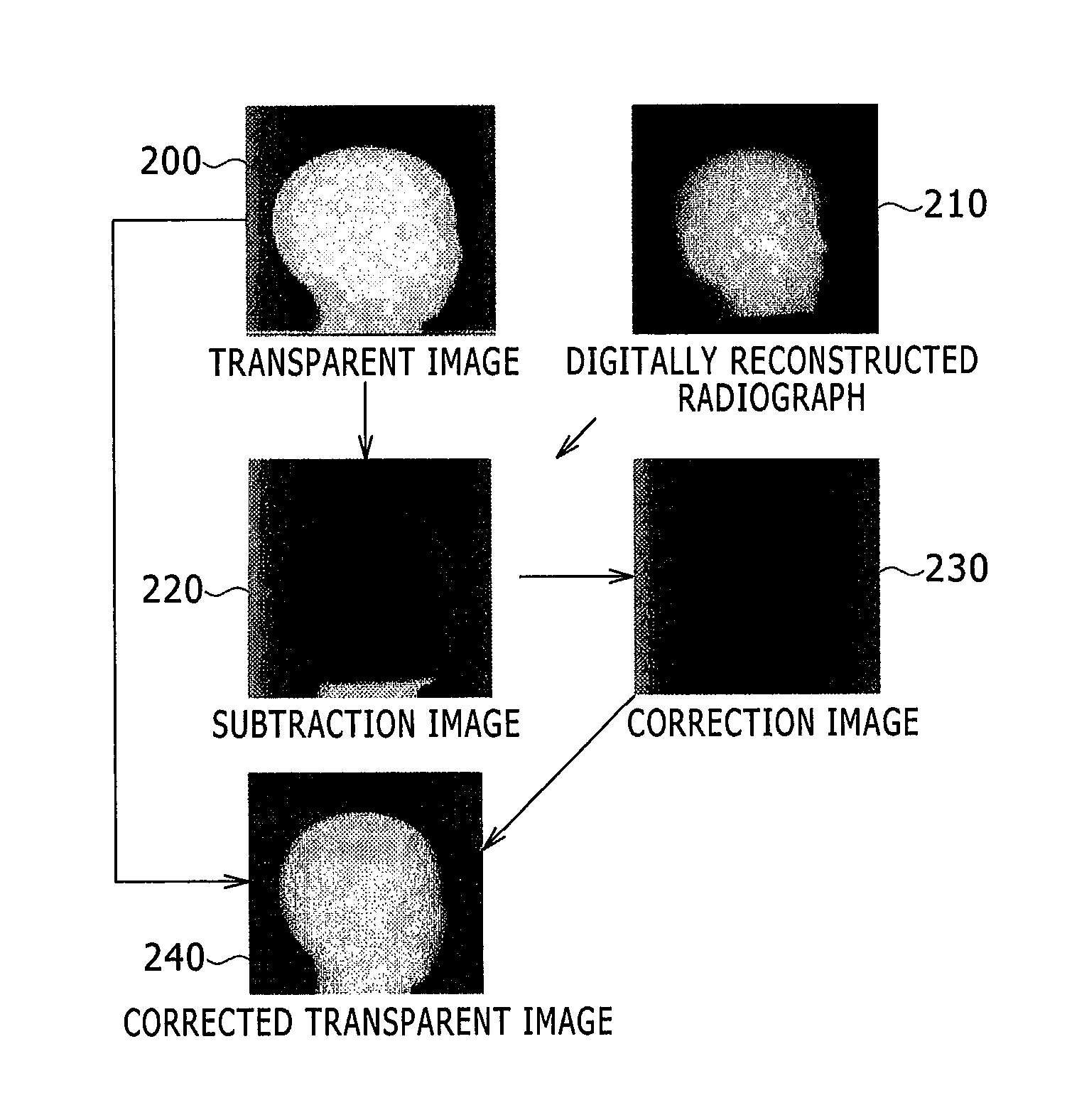
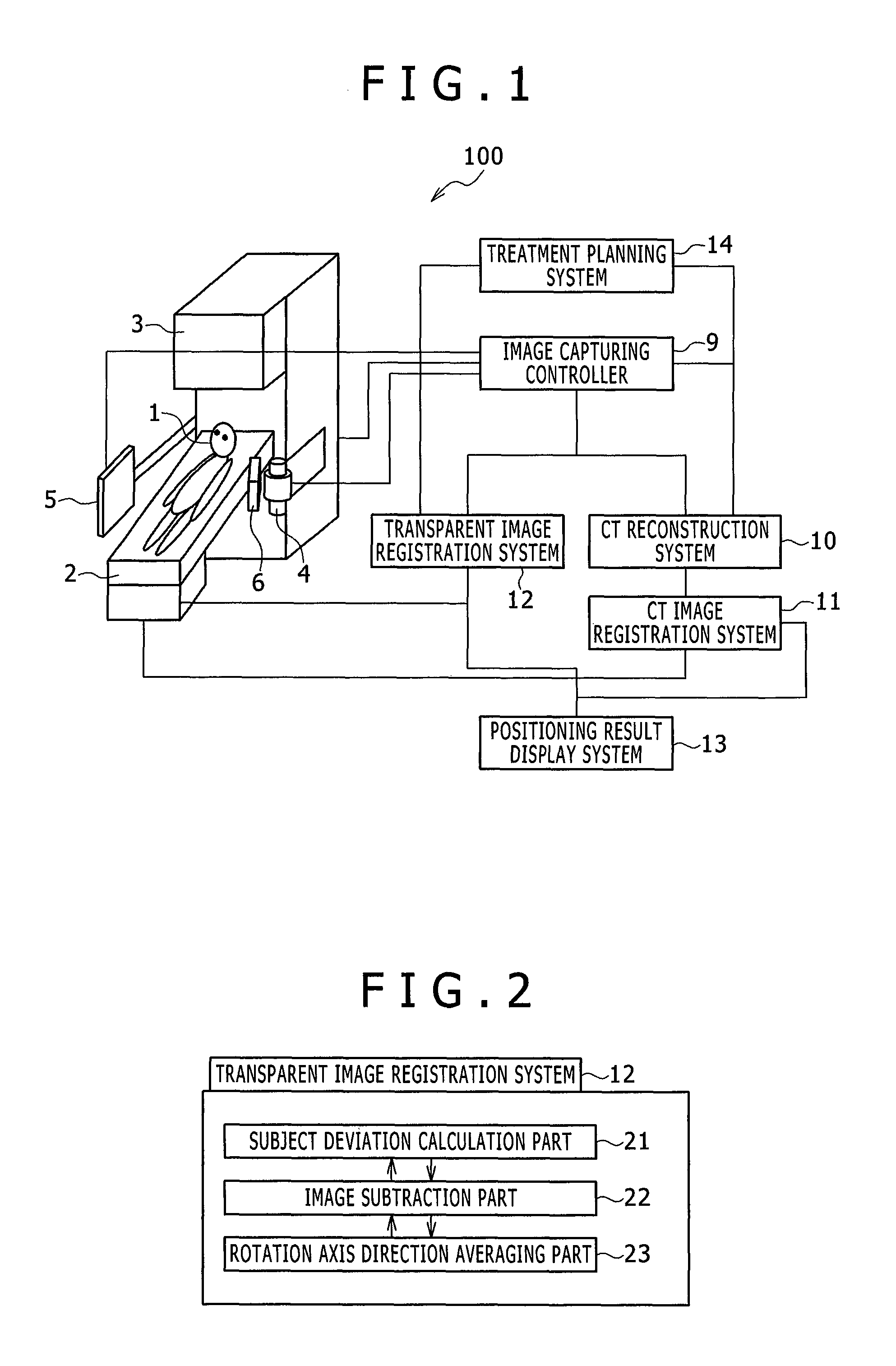
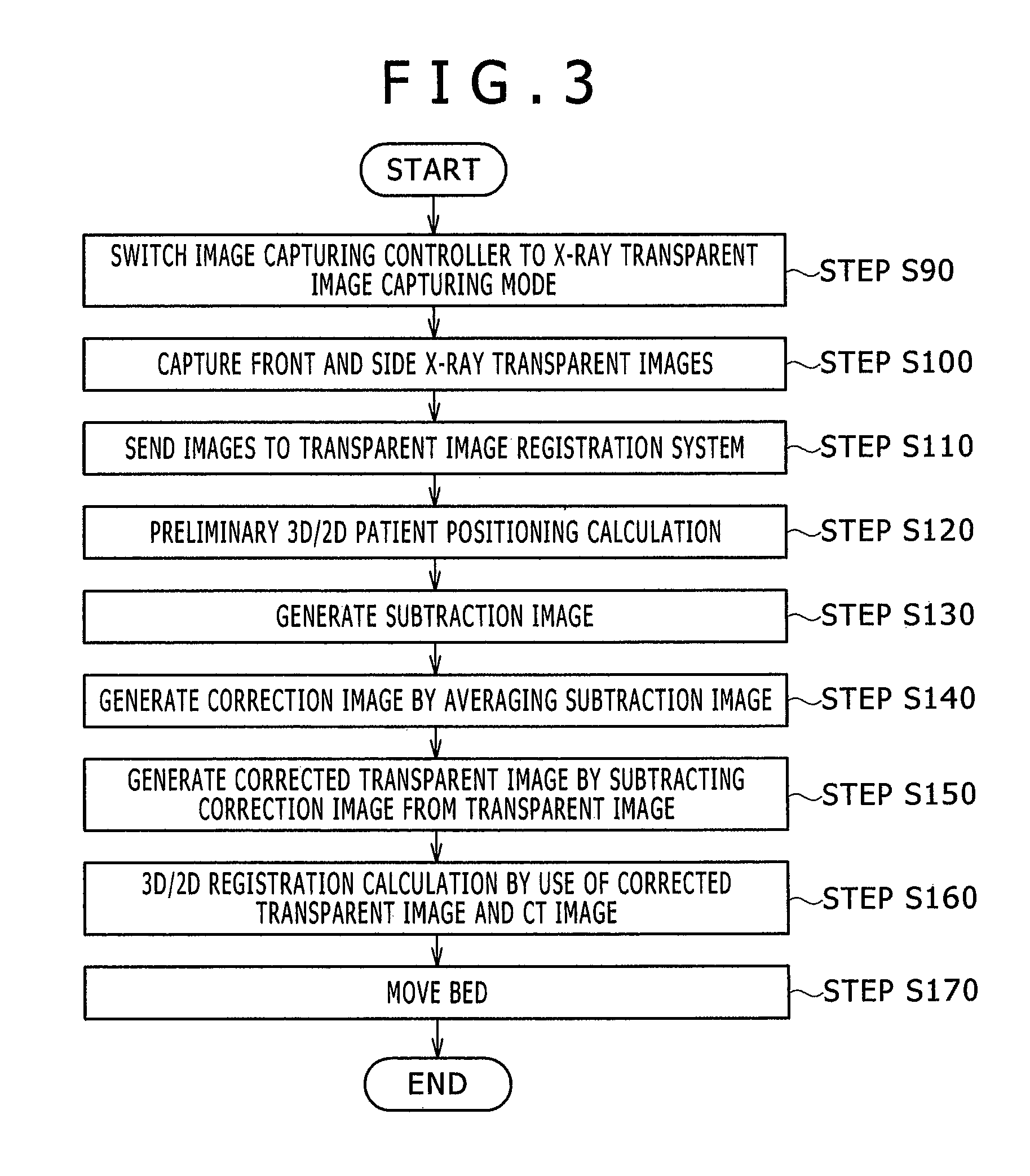
Provided is a bed positioning system for a radiation therapy system capable of capturing X-ray transparent images and CT images by rotating an X-ray tube and an X-ray detector around a subject on a bed, comprising: a transparent image registration system which generates a subtraction image from a first X-ray transparent image captured by the X-ray tube and the X-ray detector and a digitally reconstructed radiograph generated from a treatment plan CT image, corrects the first X-ray transparent image by use of a correction image generated by processing the subtraction image in a previously specified direction, and compares the first X-ray transparent image after the correction and the digitally reconstructed radiograph to determine a movement amount of the bed.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
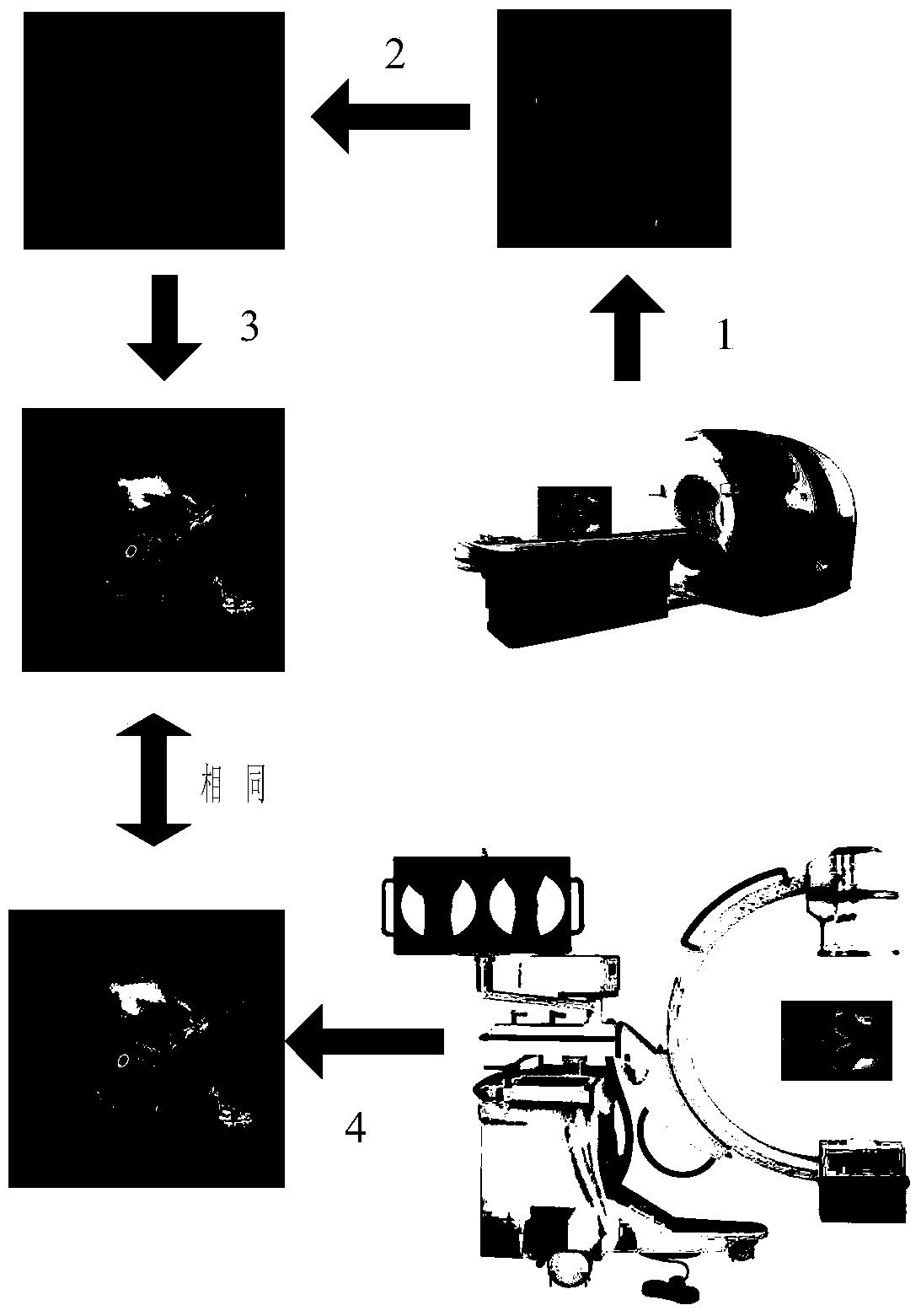
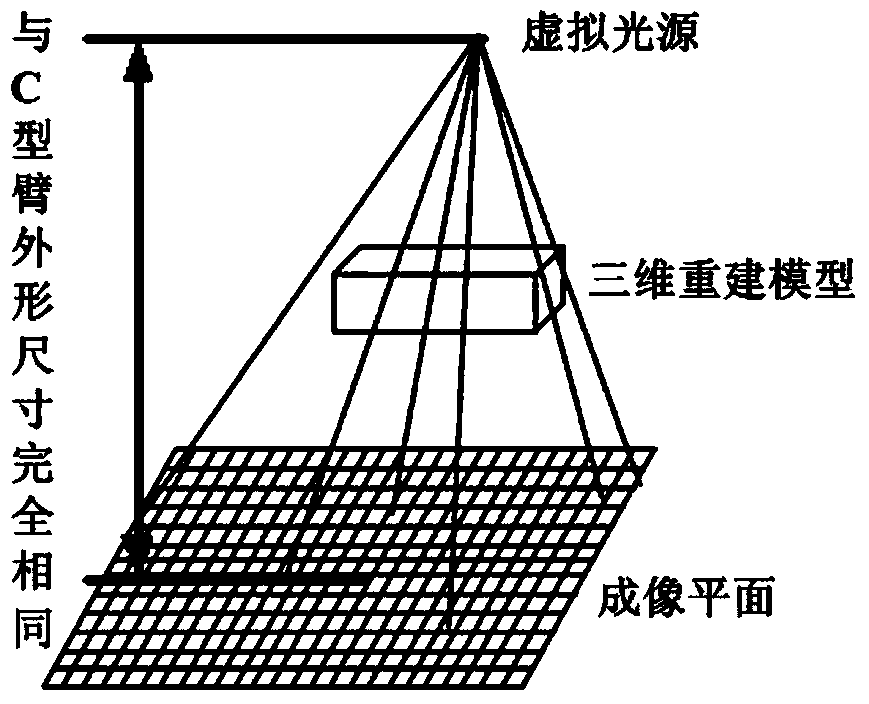
Method for fully corresponding fusion of pre-operation CT data and intraoperative X-ray radiograph
InactiveCN103479376AAvoid deformationAvoid blurComputerised tomographsTomographyGeneration processImaging processing
The invention provides a method for fully corresponding fusion of pre-operation CT data and intraoperative X-ray radiograph, and belongs to the field of medical image processing. Three-dimensional reconstruction of a focal part is carried out by using pre-operation CT 3D data of a patient and an MC algorithm; by taking the three-dimensional reconstructed model as information input, an digitally reconstructed three-dimensional radiograph, namely a DRR (digitally reconstructed radiograph) is simulated and generated on the basis of known boundary dimensions of a C-shaped arm type X-ray machine to be applied; a simulation emission source generated by the DRR is arranged at the position of a true emission source of the C-shaped arm type X-ray machine; an imaging plane is arranged at a true imaging plane position of the C-shaped arm type X-ray machine; the three-dimensional reconstructed focal model is arranged at the position of the patient during photographing; thus, the generation process of the DRR truly simulates the imaging process of the C-shaped arm type X-ray machine applied by the system; accordingly the CT 3D data and the X-ray radiograph are fully correspondingly fused, and the DRR is used for simulating the true X-ray radiograph.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Image guide method implemented by aid of two-dimensional images
InactiveCN103876763ARelieve painReduce treatment riskComputerised tomographsTomographyComputer visionLesion
The invention discloses an image guide method implemented by the aid of two-dimensional images. The image guide method includes steps of selecting and screening reference feature regions; searching real-time feature regions; performing positioning and computing on the basis of the reference feature regions and the real-time feature regions; estimating deformation and errors, and the like. The image guide method has the advantages that two-dimensional DRRs (digitally reconstructed radiographs) need to be generated according to three-dimensional images of lesions of patients when image guide is carried out by the aid of two-dimensional images, and then the feature regions in real-time images which are acquired in real time are compared to feature regions in the two-dimensional DRRs, so that deviation among current locations and preset locations can be determined; markers do not need to be implanted in the patients when the patients are examined by the aid of the image guide method, accordingly, suffering can be relieved for the patients, and treatment risks and the treatment cost can be reduced for the patients.
Owner:WEIDU MEDICAL SYST
Adaptive radiation therapy method with target detection
InactiveCN101258524AResolve detectionImage enhancementImage analysisAdaptive radiotherapyRadiography
The present invention provides a method for delivering radiation therapy to a patient using a three-dimensional planning image for radiation therapy of the patient wherein the planning image includes a radiation therapy target includes the steps of: determining a digitally reconstructed radiograph from the planning image; identifying a region of the target's projection in the digitally reconstructed radiograph; capturing a radiographic image corresponding to the digitally reconstructed radiograph; identifying a region in the captured radiographic image; comparing the region of the target's projection in the digitally reconstructed radiograph with the identified region in the captured radiographic image; and determining a delivery of the radiation therapy in response to this comparison.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Dilated fully convolutional network for multi-agent 2D/3D medical image registration
A method and system for 3D / 3D medical image registration. A digitally reconstructed radiograph (DRR) is rendered from a 3D medical volume based on current transformation parameters. A trained multi-agent deep neural network (DNN) is applied to a plurality of regions of interest (ROIs) in the DRR and a 2D medical image. The trained multi-agent DNN applies a respective agent to each ROI to calculate a respective set of action-values from each ROI. A maximum action-value and a proposed action associated with the maximum action value are determined for each agent. A subset of agents is selected based on the maximum action-values determined for the agents. The proposed actions determined for the selected subset of agents are aggregated to determine an optimal adjustment to the transformation parameters and the transformation parameters are adjusted by the determined optimal adjustment. The 3D medical volume is registered to the 2D medical image using final transformation parameters resulting from a plurality of iterations.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
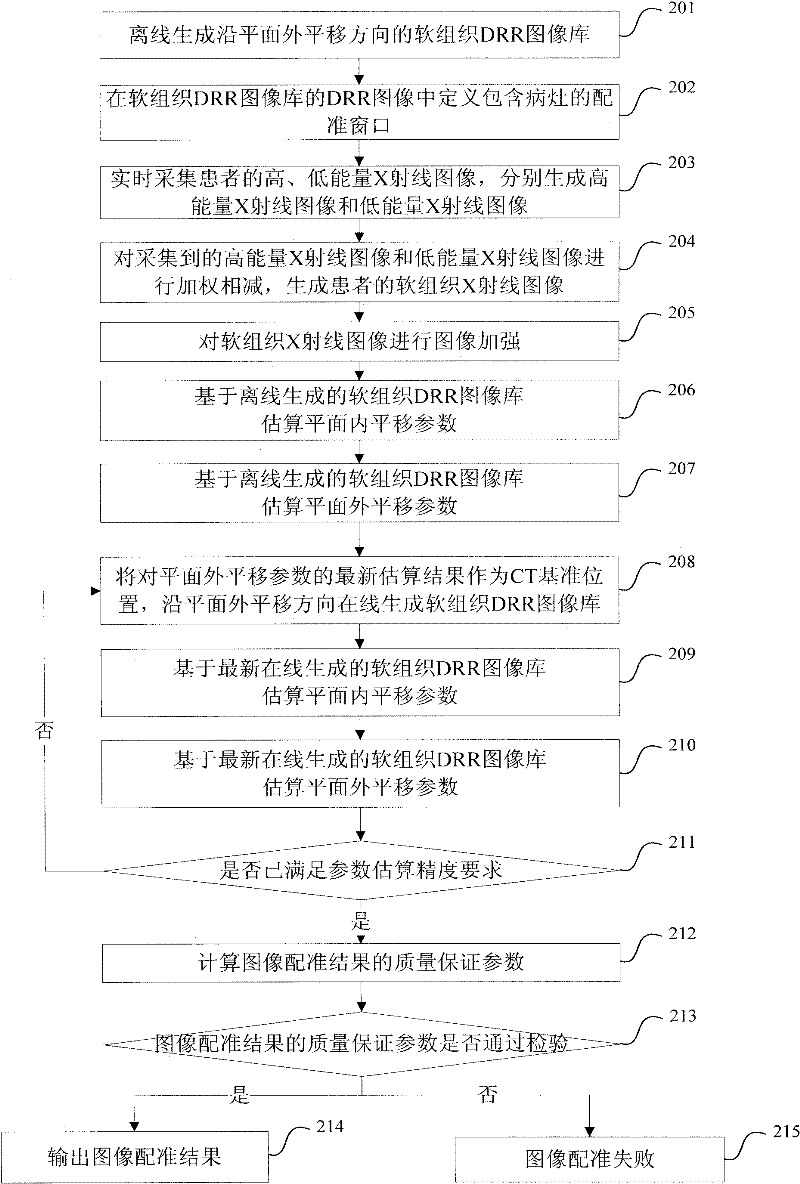
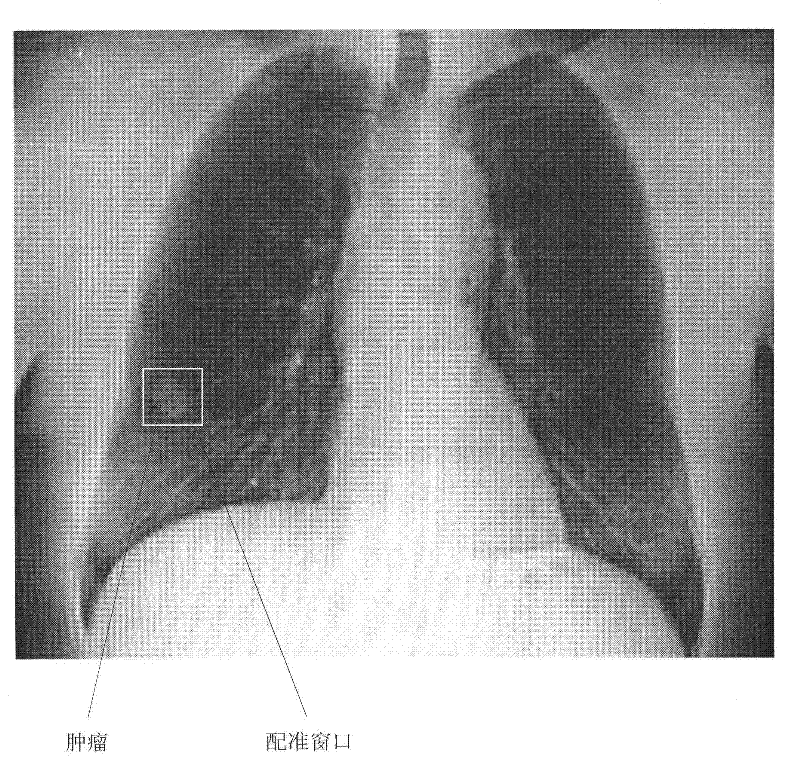
Method and system for positioning soft tissue lesion based on dual-energy X-ray images
The invention discloses a method and system for positioning a soft tissue lesion based on dual-energy X-ray images. The method comprises the following steps of: generating a three-dimensional image of a patient and offline generating a soft tissue DRR (Digitally Reconstructed Radiograph) image library along a plane inside translation direction; acquiring high- and low-energy X-ray images of the patient and generating a soft tissue X-ray image of the patient; taking the soft tissue X-ray image as a registered image and estimating values of a plane inside translation parameter and a plane outside translation parameter by using a registering window including the lesion in the DRR image in the soft tissue DRR image library generated offline; adjusting the three-dimensional image by a newest parameter estimation result for the plane outside translation parameter and generating the soft tissue DRR image library along the plane outside translation direction on line; and taking the soft tissue X-ray image as the registered image and further estimating the values of the plane inside translation parameter and the plane outside translation parameter by using the registering window including the lesion in the DRR image in the soft tissue DRR image library generated on line.
Owner:江苏瑞尔医疗科技有限公司
Bed positioning system for radiation therapy
ActiveUS9566039B2High-accuracy bed positioningPatient positioning for diagnosticsComputerised tomographsX-rayPositioning system
Provided is a bed positioning system for a radiation therapy system capable of capturing X-ray transparent images and CT images by rotating an X-ray tube and an X-ray detector around a subject on a bed, comprising: a transparent image registration system which generates a subtraction image from a first X-ray transparent image captured by the X-ray tube and the X-ray detector and a digitally reconstructed radiograph generated from a treatment plan CT image, corrects the first X-ray transparent image by use of a correction image generated by processing the subtraction image in a previously specified direction, and compares the first X-ray transparent image after the correction and the digitally reconstructed radiograph to determine a movement amount of the bed.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
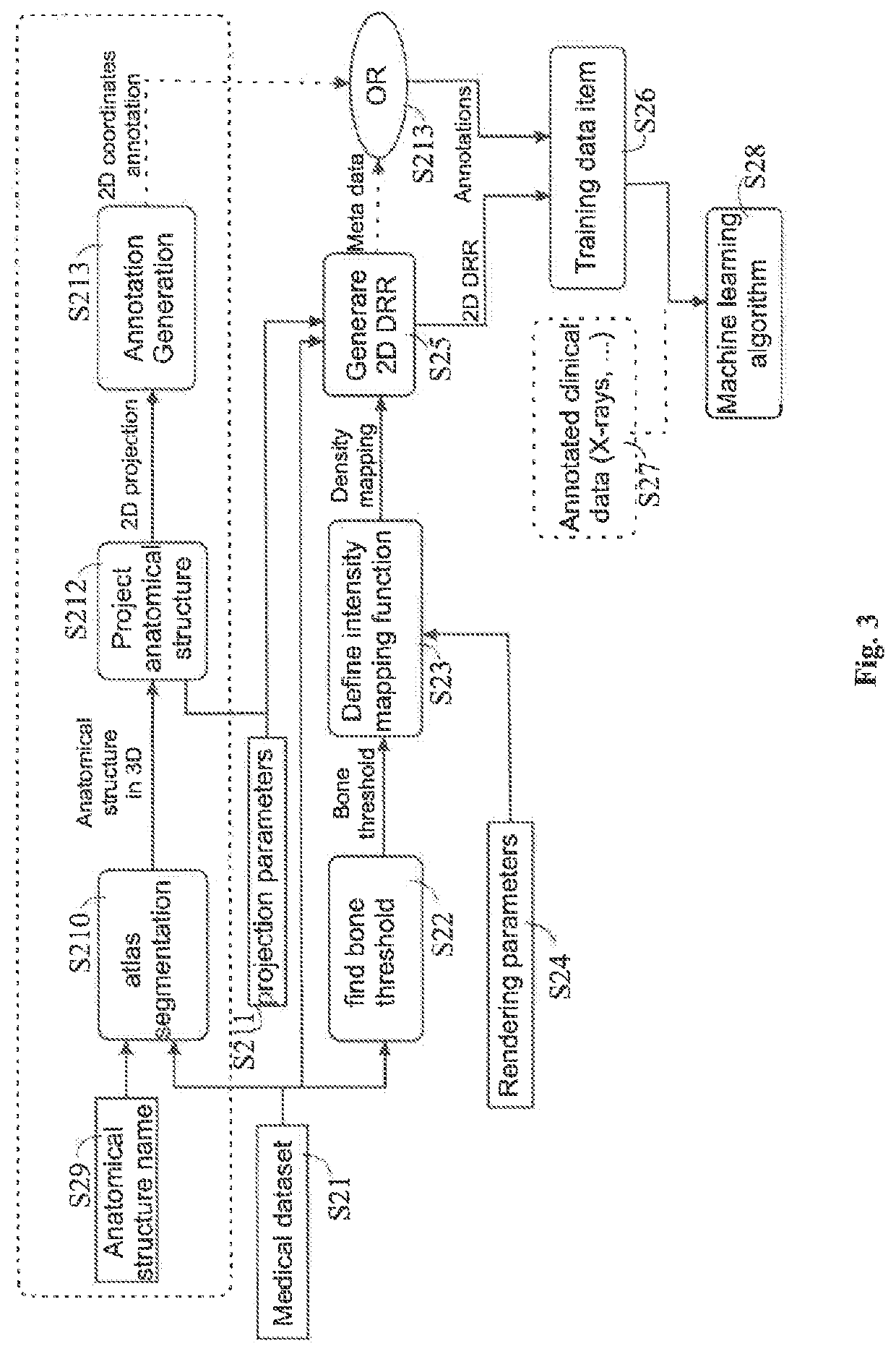
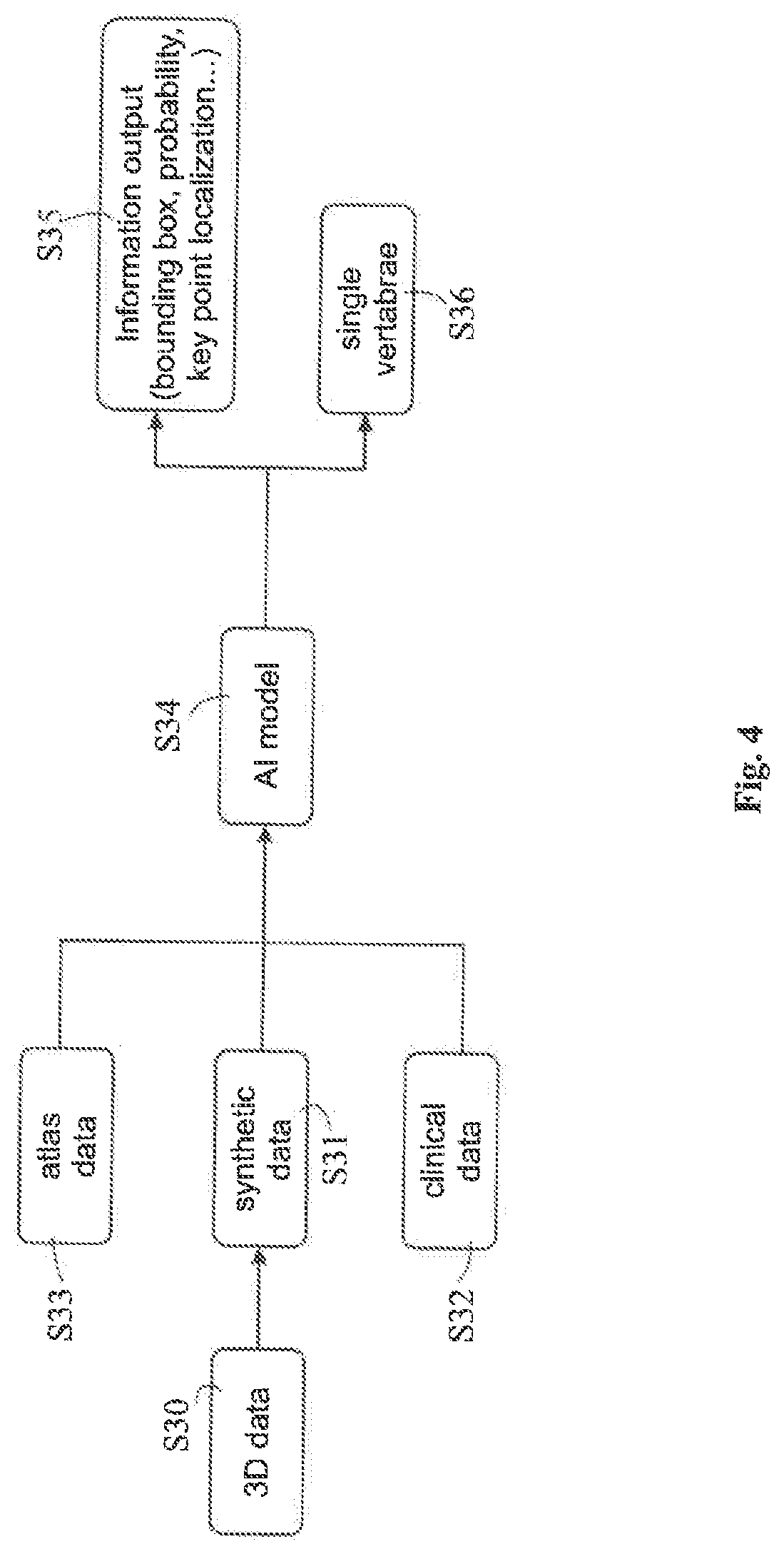
Training a machine learning algorithm using digitally reconstructed radiographs
Disclosed is a computer-implemented method of training a likelihood-based computational model for determining the position of an image representation of an annotated anatomical structure in a two-dimensional x-ray image, wherein the method encompasses inputting medical DRRs together with annotation to a machine learning algorithm to train the algorithm, i.e. to generate adapted leamable parameters of the machine learning model. The annotations may be derived from metadata associated with the DRRs or may be included in atlas data which is matched with the DRRs to establish a relation between the annotations included in the atlas data and the DRRs. The thus generated machine learning algorithm may then be used to analyse clinical or synthesized DRRs so as to appropriately add annotations to those DRRs and / or identify the position of an anatomical structure in those DRRs.
Owner:BRAINLAB
Method for dynamically generating an adaptive multi-resolution image from algorithms selected based on user input
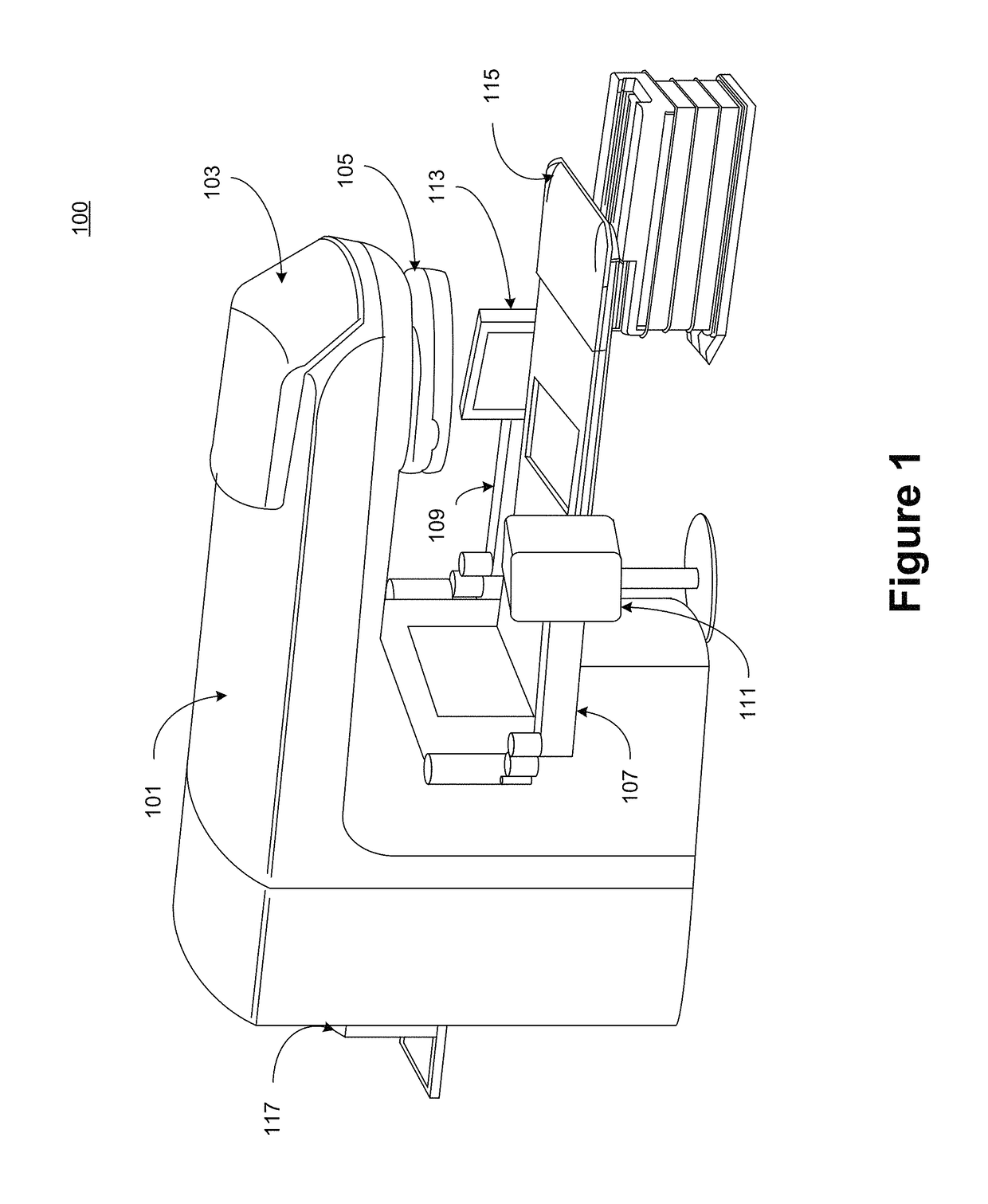
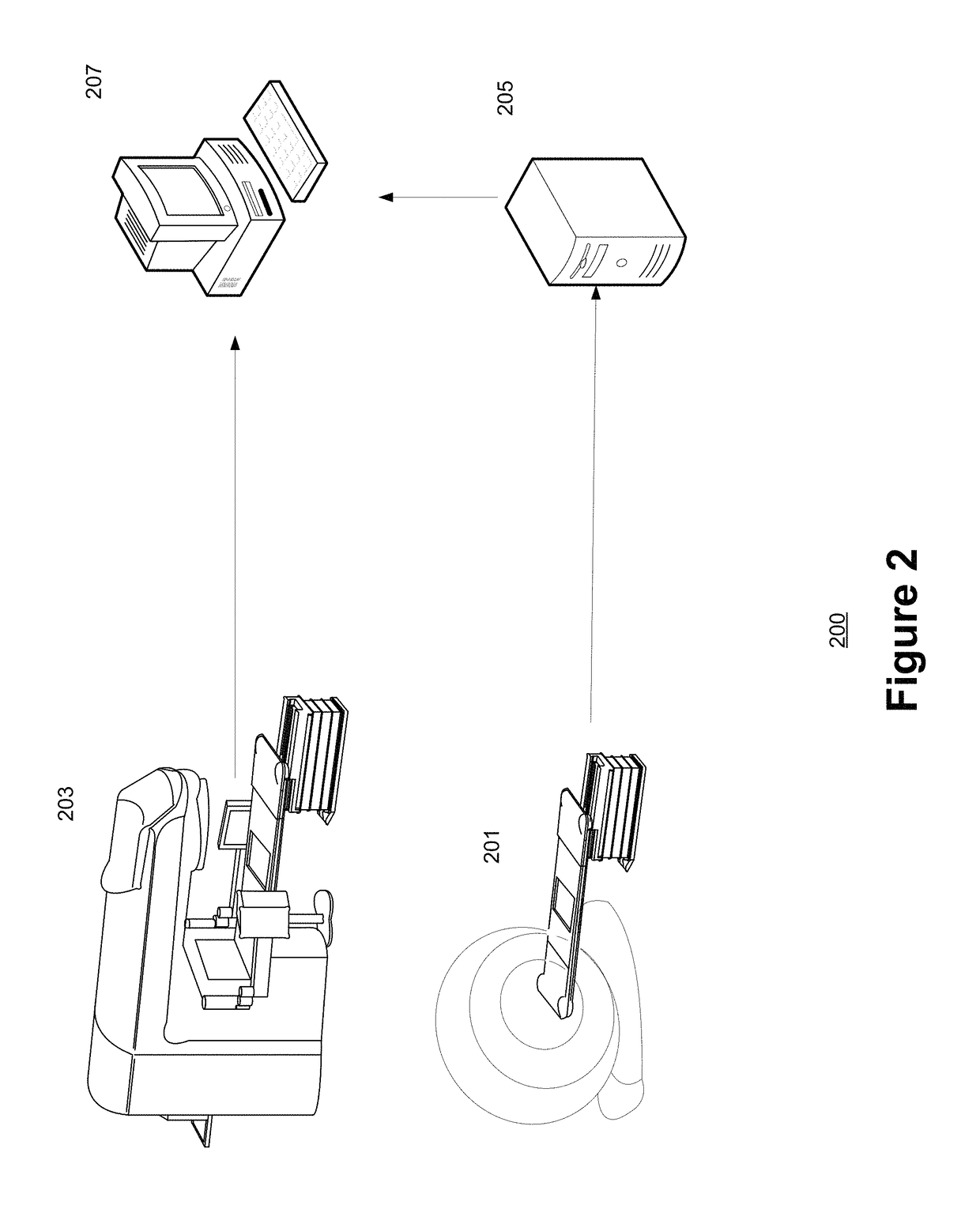
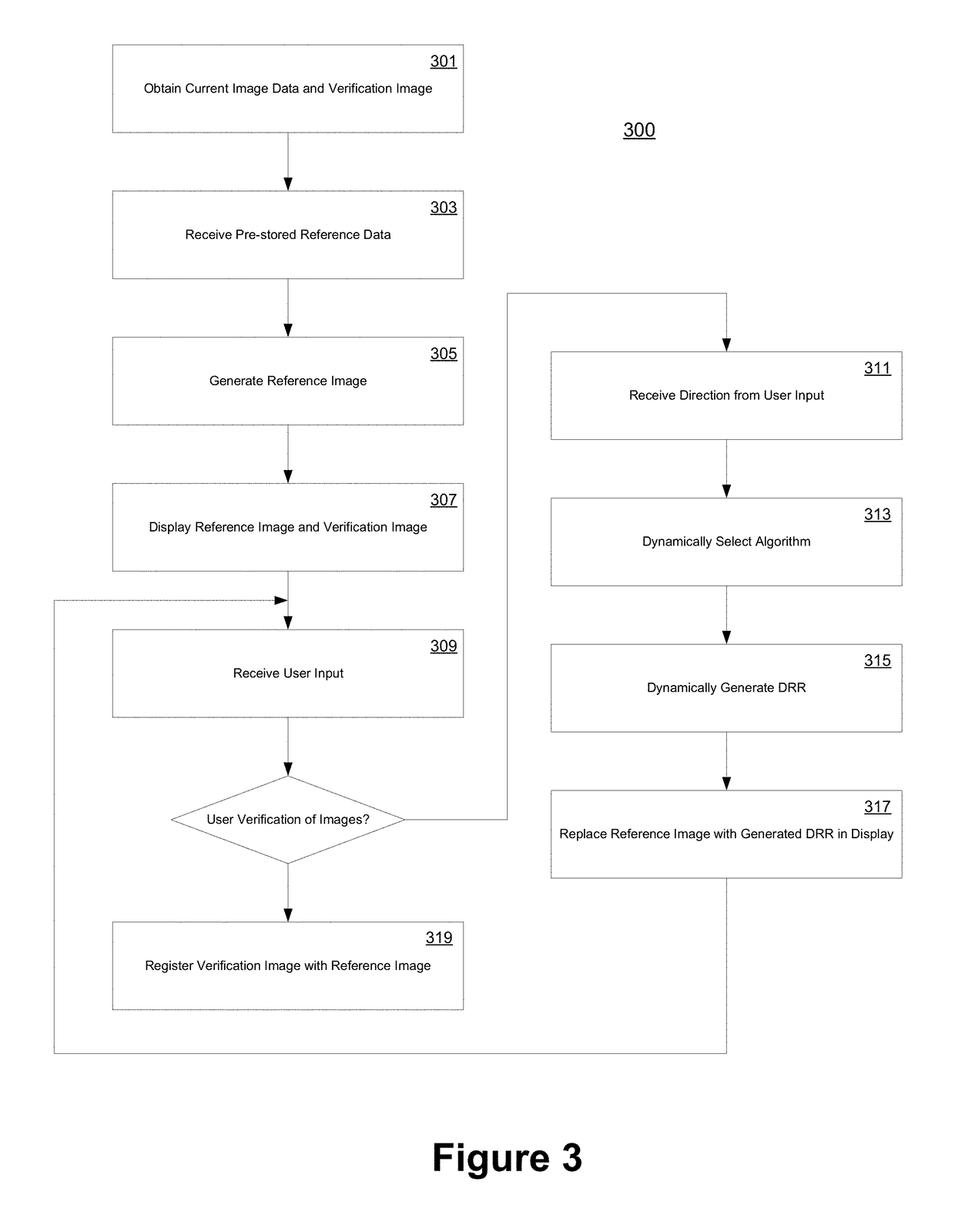
ActiveUS20170316589A1Efficient executionImprove efficiencyReconstruction from projectionComputerised tomographsUser inputComputer graphics (images)
Methods and systems are proposed herein for generative adaptive, multi-resolution images efficiently without intensive processing and / or memory consumption or hardware requirements. According to one aspect of the claimed subject matter, a system is provided that includes a computing workstation, communicatively coupled to both a data storage device and an image acquisition device. Real time images acquired by the image acquisition device are presented to the user along with one or more digitally reconstructed radiographs (DRRs)—generated using dynamically selected rendering techniques—from previously acquired image data. The user is able to verify the DRRs as a match to the verification image, and subsequently to dynamically generate additional DRRs more suitable by actuating a portion of the generated DRR. Based on the user actuation, a new DRR is generated and presented to the user for verification.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST INT AG
Method and system for positioning soft tissue lesion based on dual-energy X-ray images
Owner:JIANGSU RAYER MEDICAL TECH GO LTD
Method for dynamically generating an adaptive multi-resolution image from algorithms selected based on user input
ActiveUS10062186B2Efficient executionGenerate efficientlyReconstruction from projectionComputerised tomographsUser inputComputer graphics (images)
Methods and systems are proposed herein for generative adaptive, multi-resolution images efficiently without intensive processing and / or memory consumption or hardware requirements. According to one aspect of the claimed subject matter, a system is provided that includes a computing workstation, communicatively coupled to both a data storage device and an image acquisition device. Real time images acquired by the image acquisition device are presented to the user along with one or more digitally reconstructed radiographs (DRRs)—generated using dynamically selected rendering techniques—from previously acquired image data. The user is able to verify the DRRs as a match to the verification image, and subsequently to dynamically generate additional DRRs more suitable by actuating a portion of the generated DRR. Based on the user actuation, a new DRR is generated and presented to the user for verification.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST INT AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com