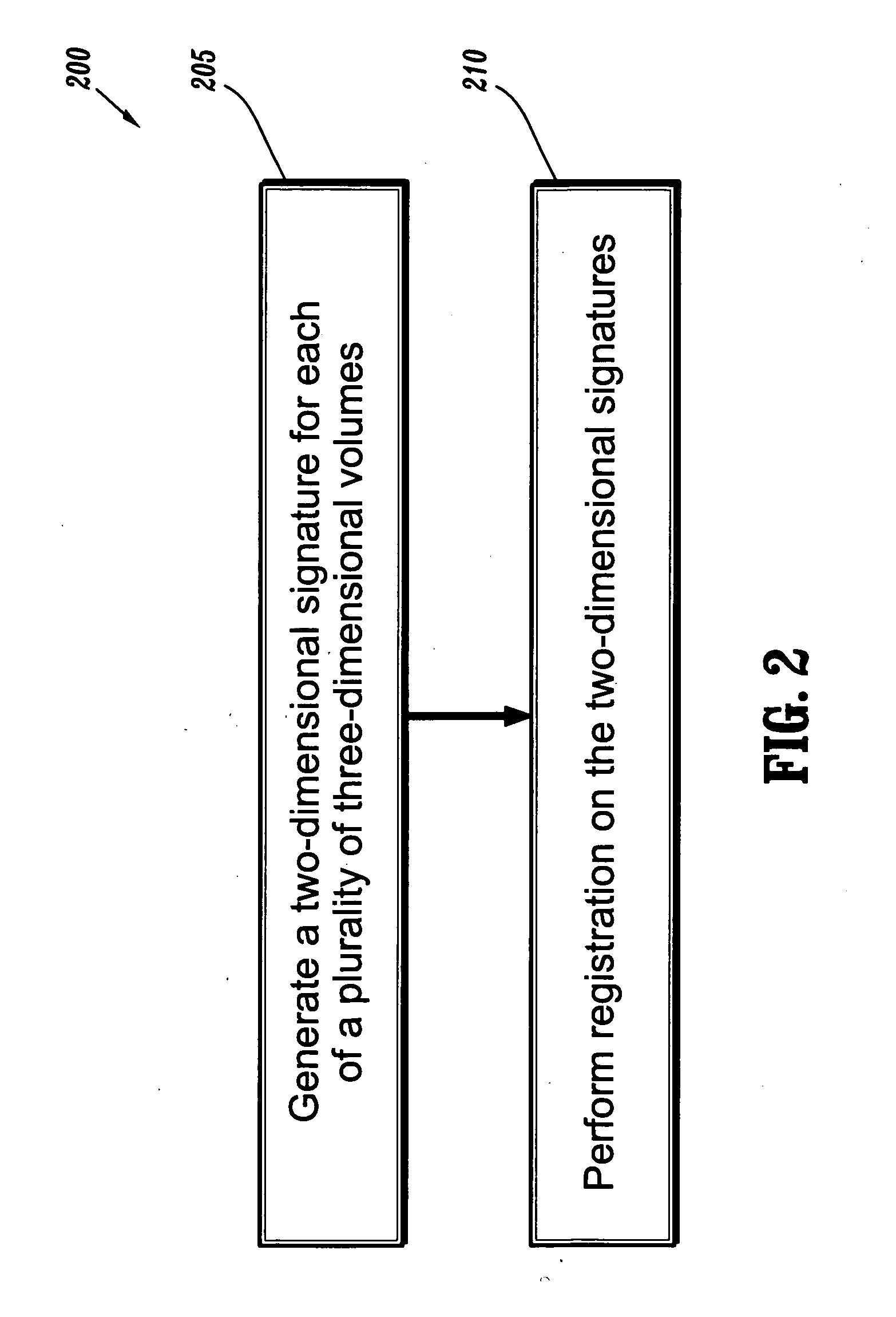
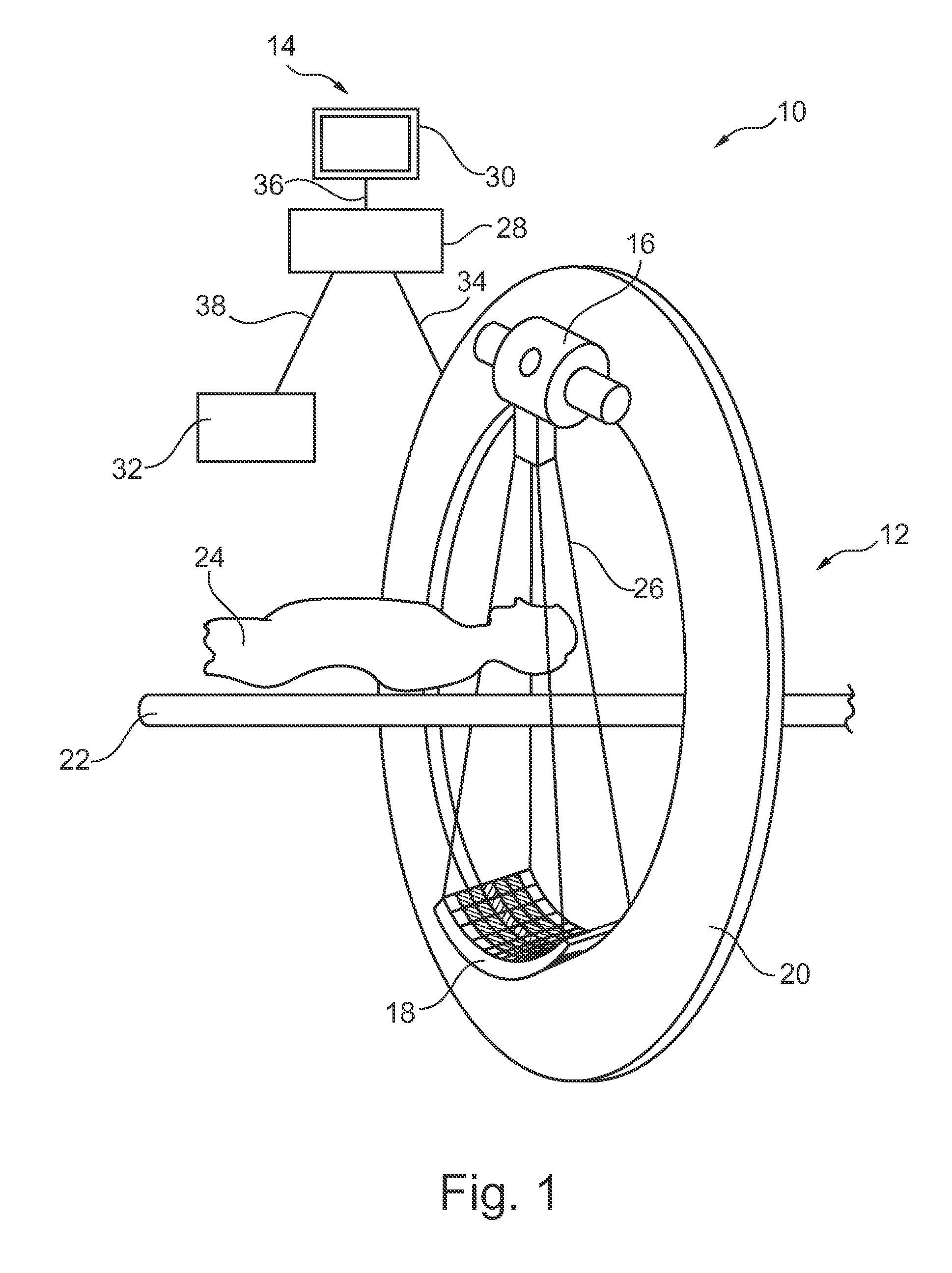
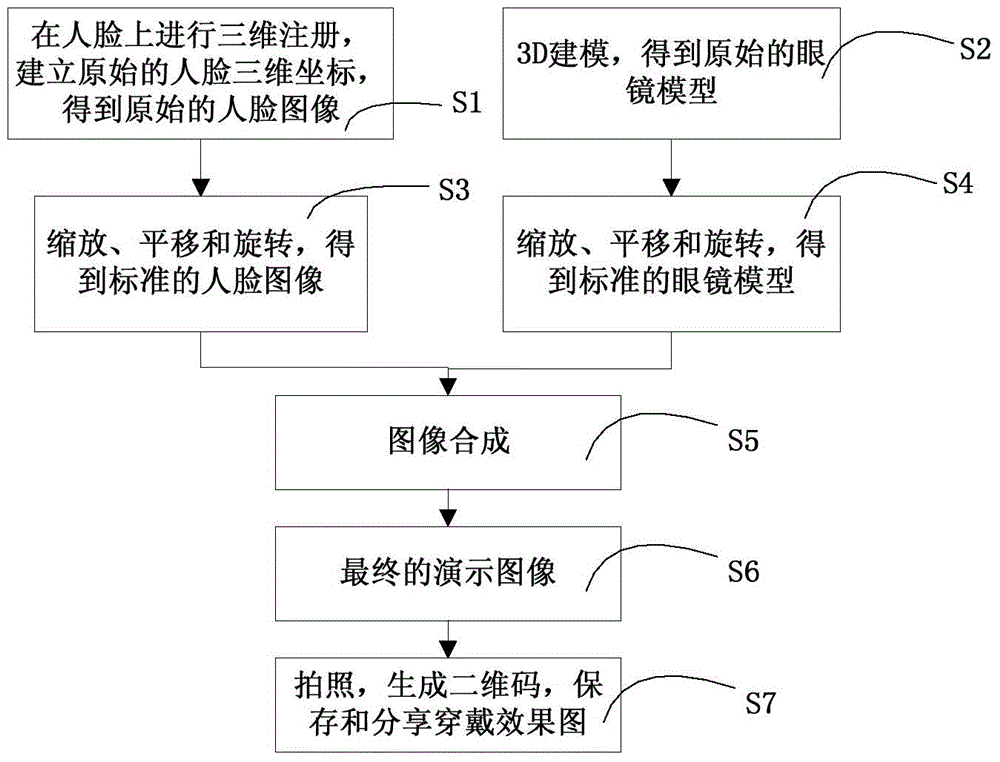
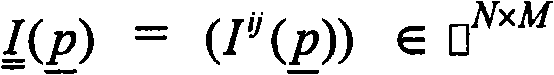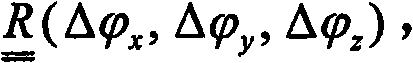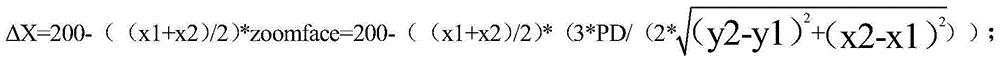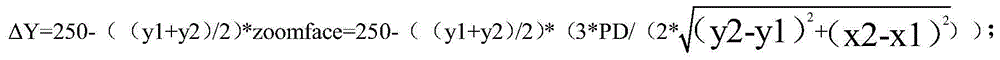Patents
Literature
85 results about "3d registration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
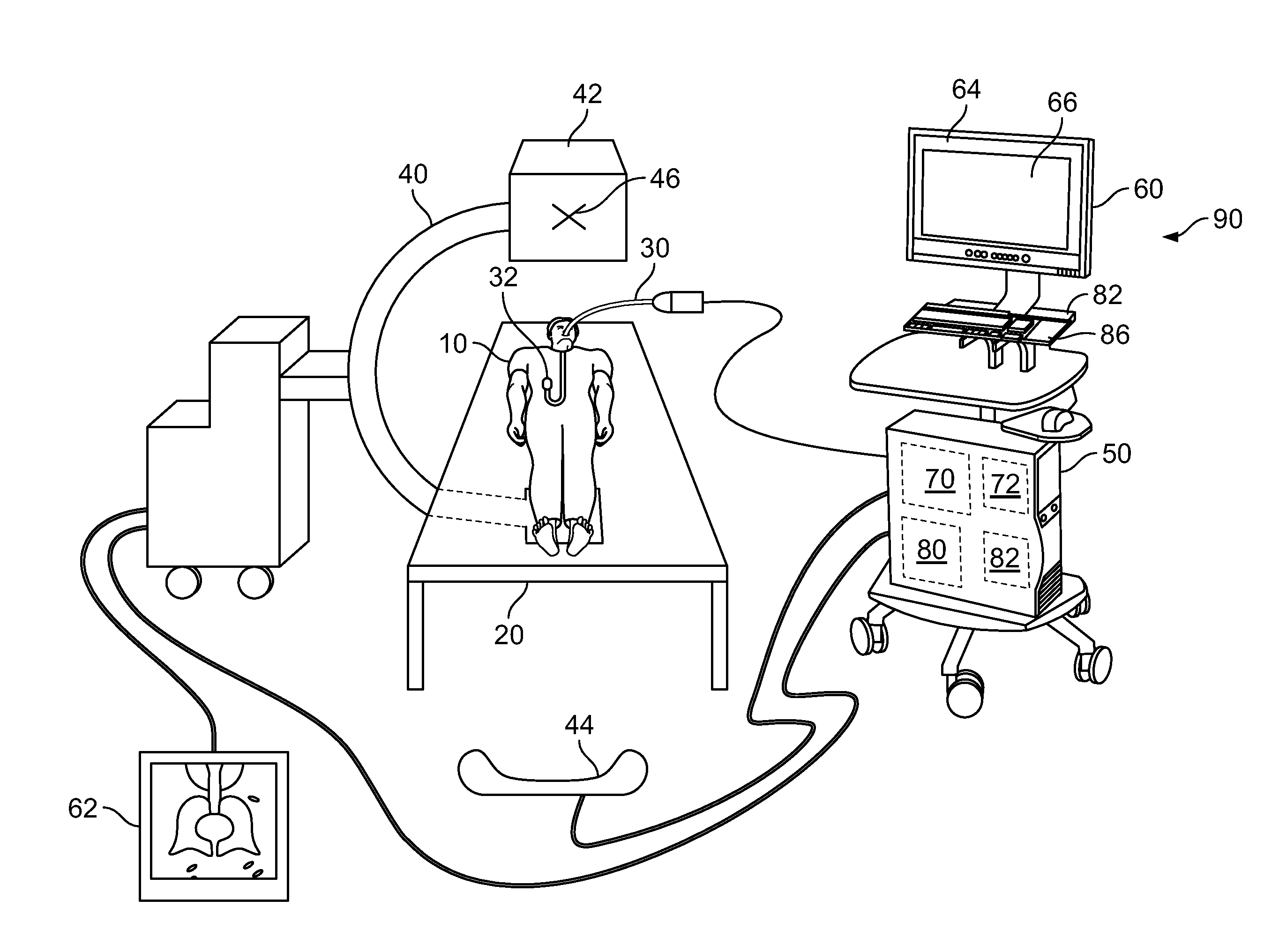
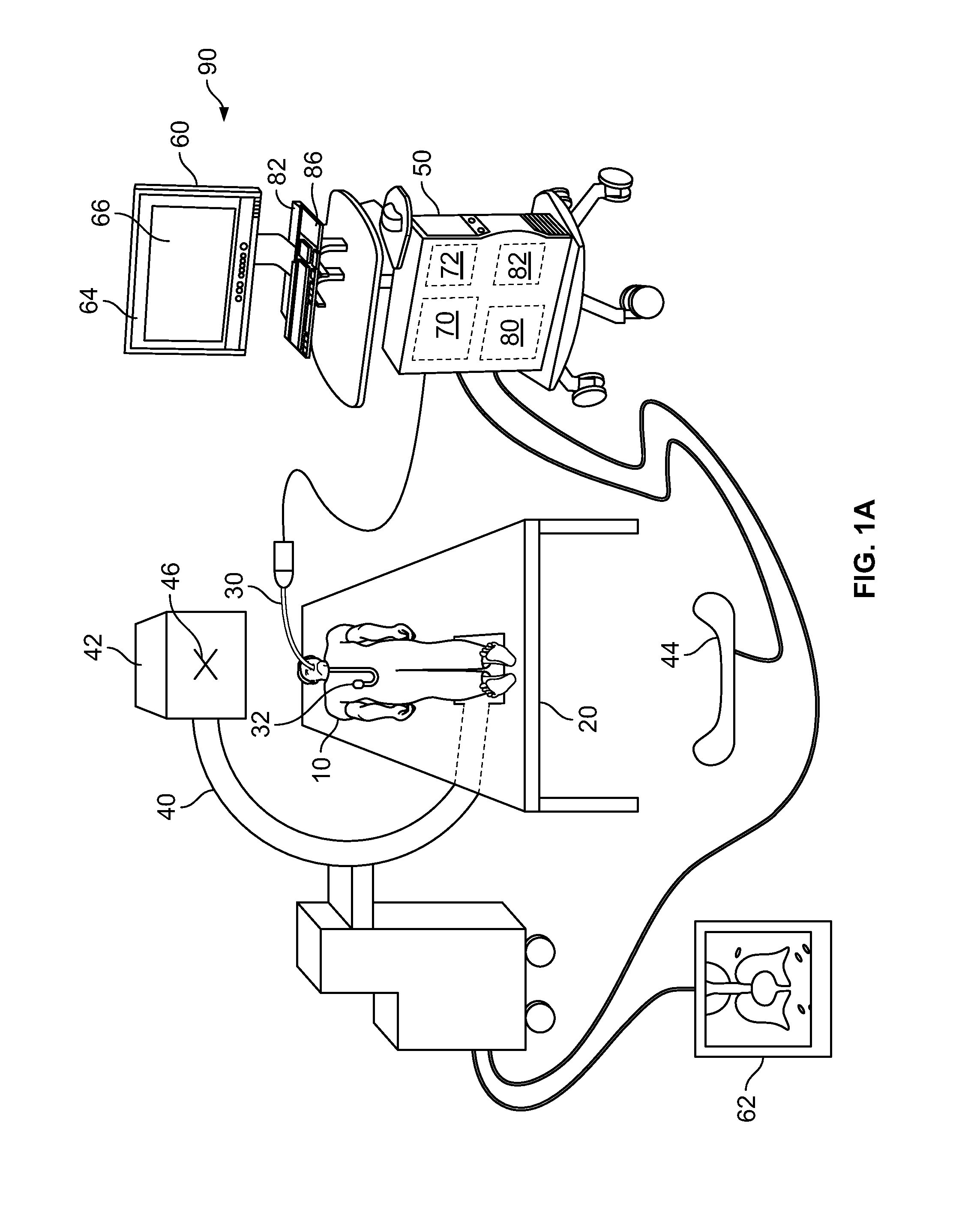
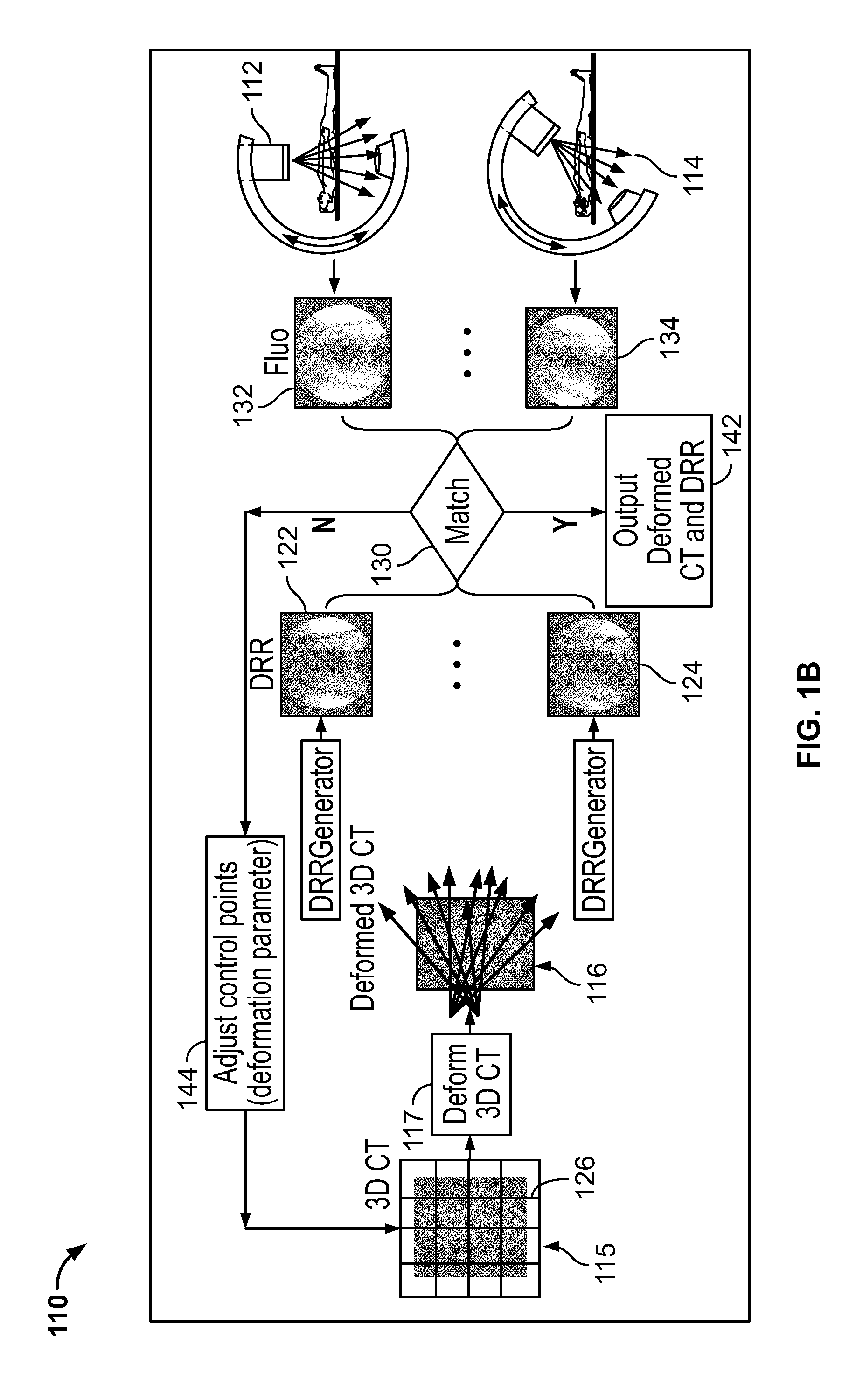
Image guided radiosurgery method and apparatus using registration of 2D radiographic images with digitally reconstructed radiographs of 3D scan data
ActiveUS20050049478A1Rapid and accurate methodThe process is fast and accurateImage enhancementImage analysisIn plane3d image
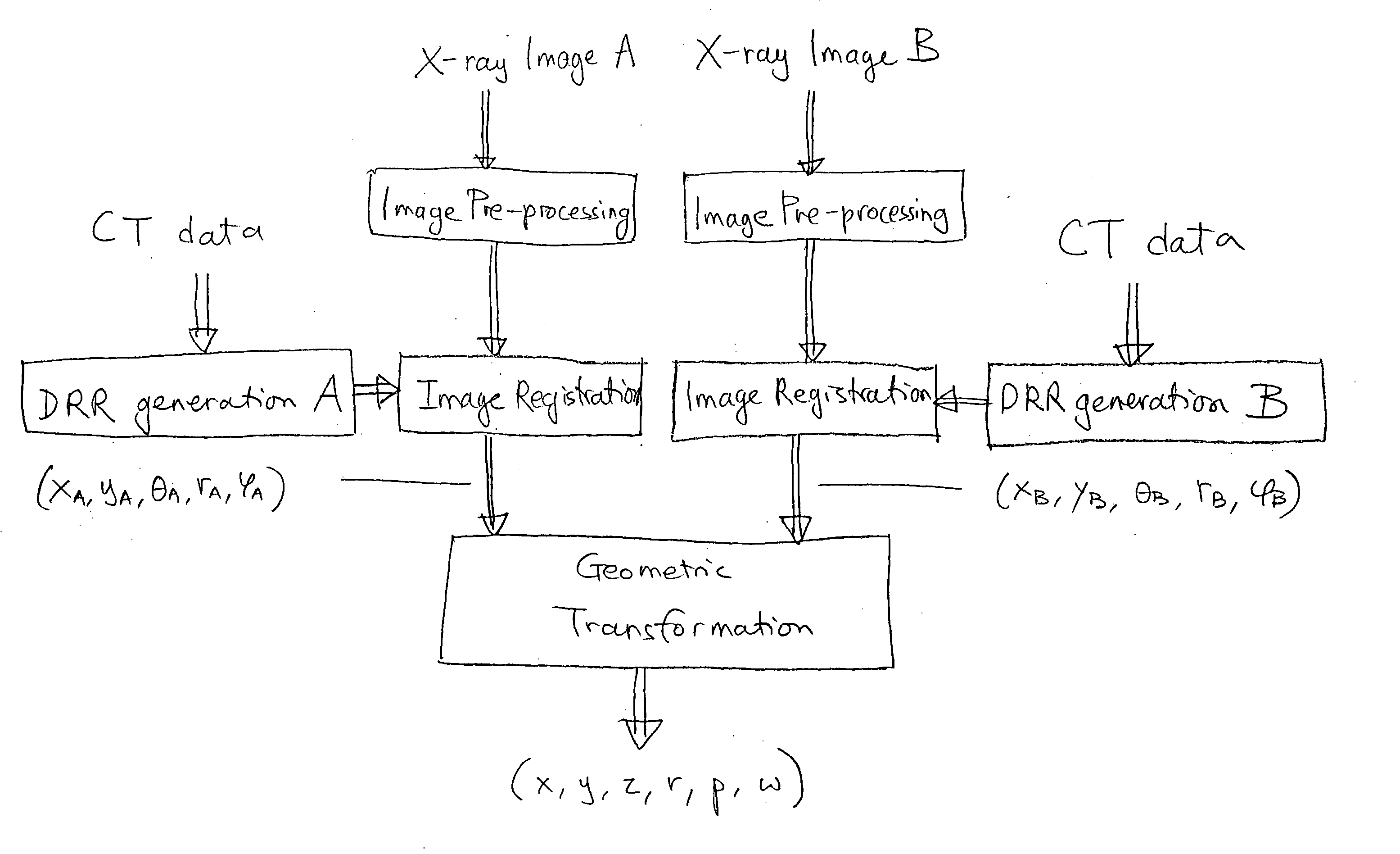
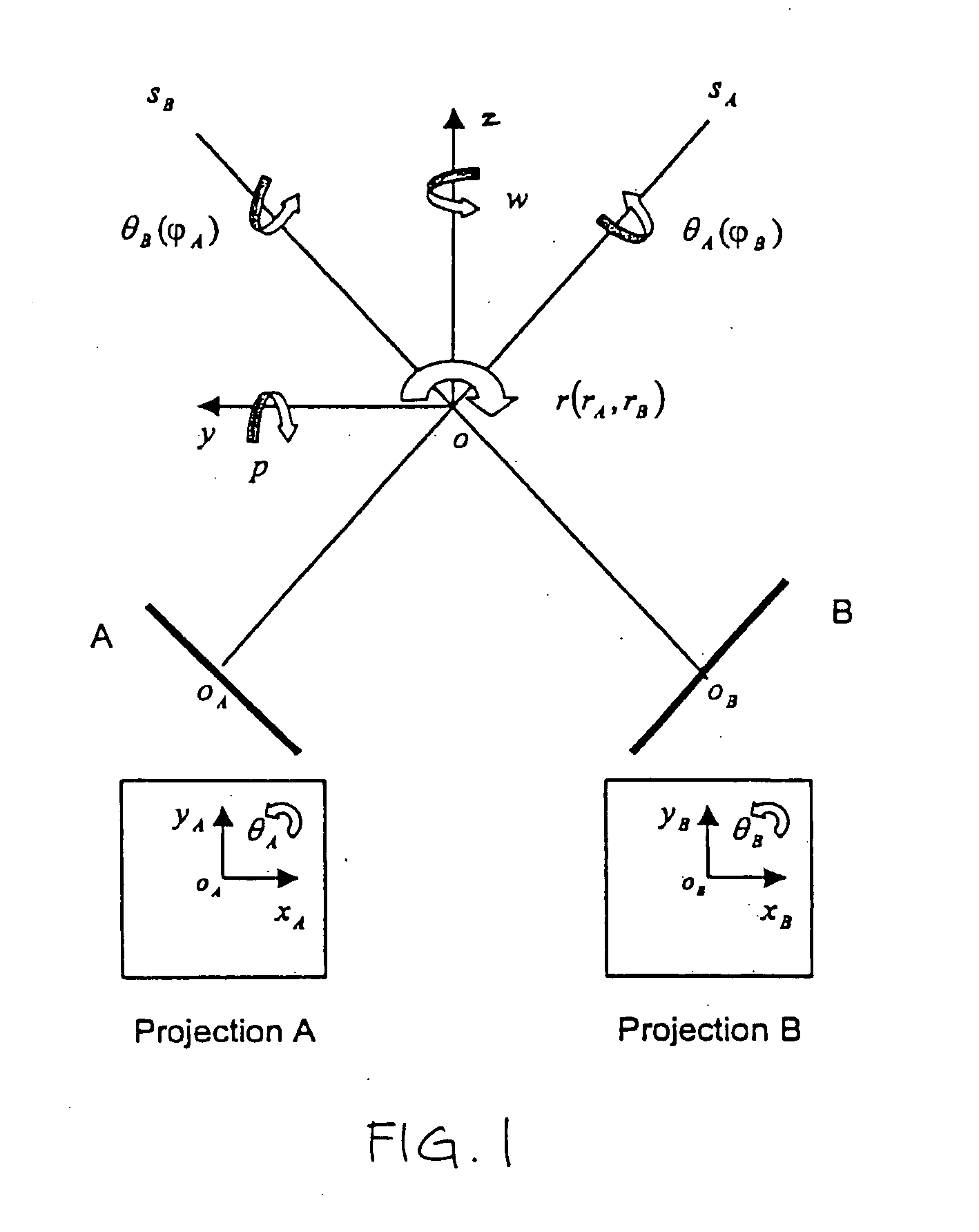
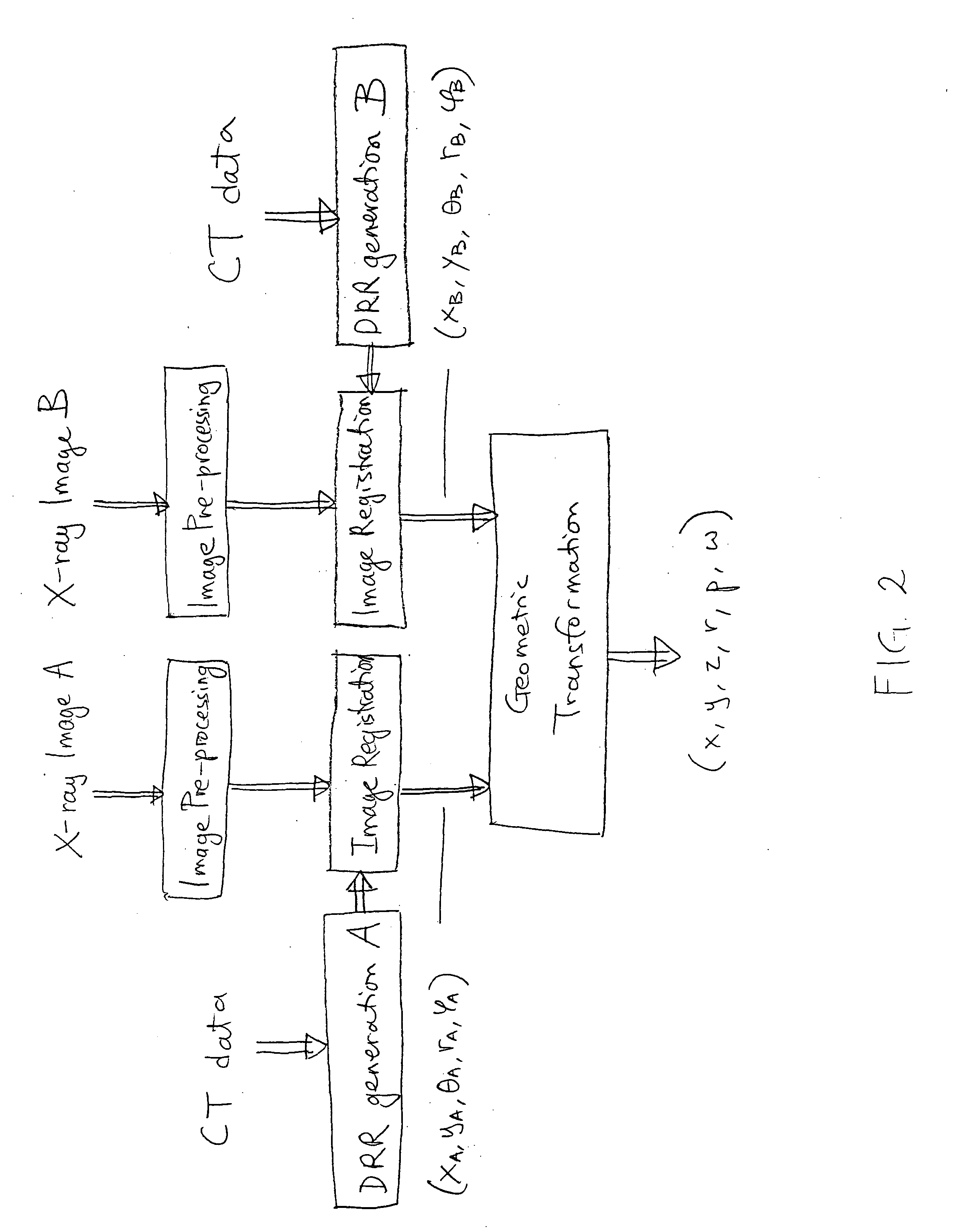
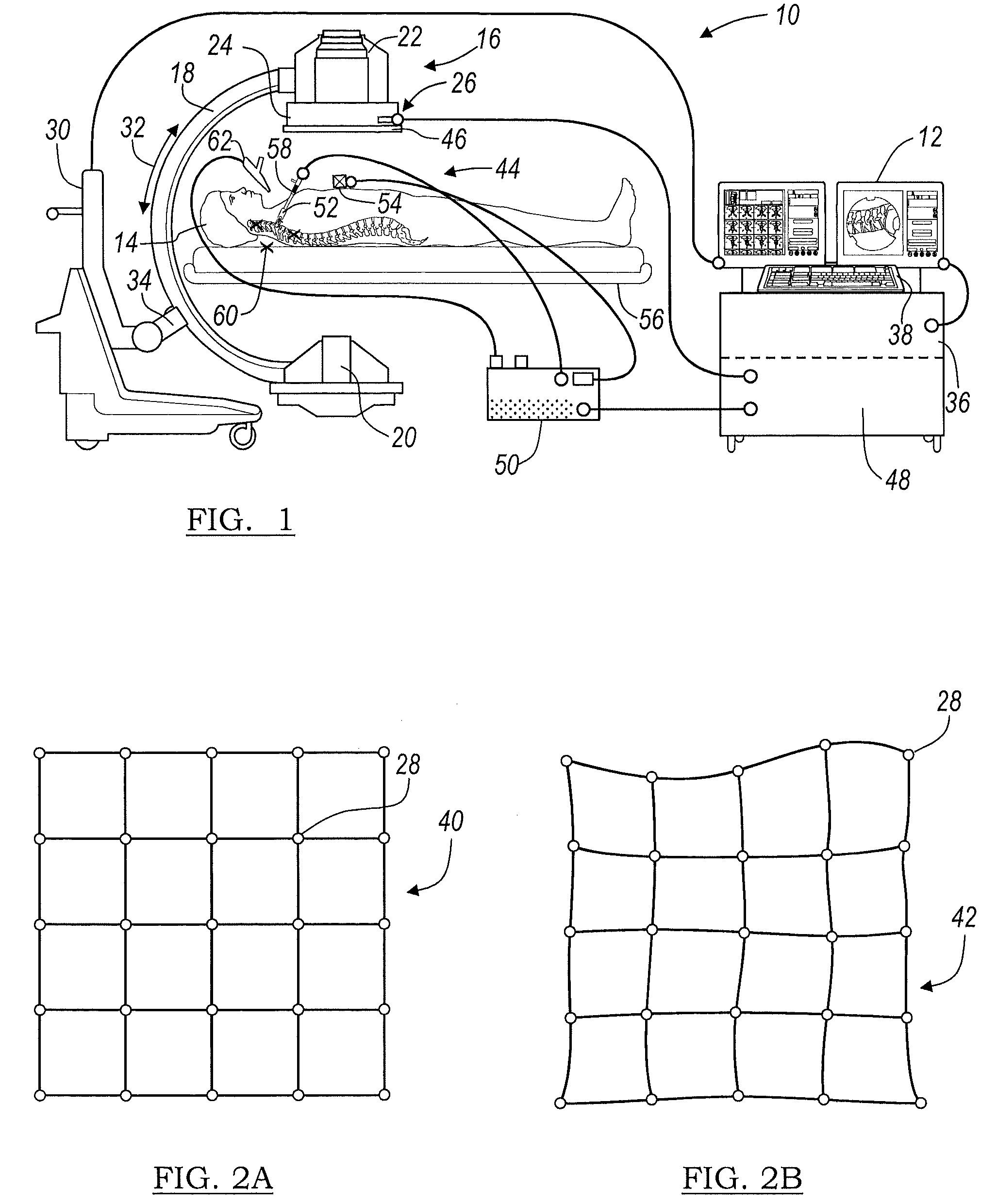
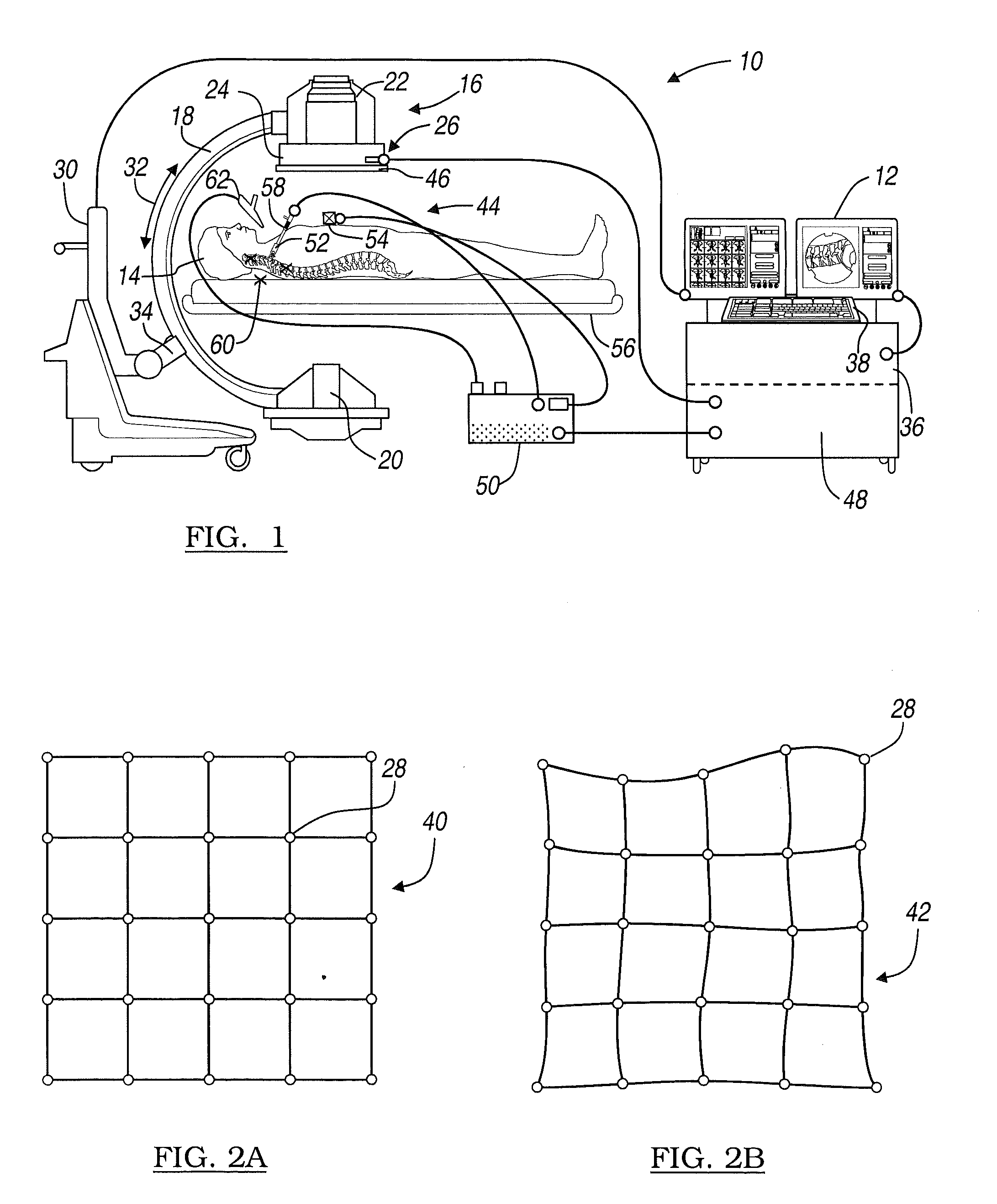
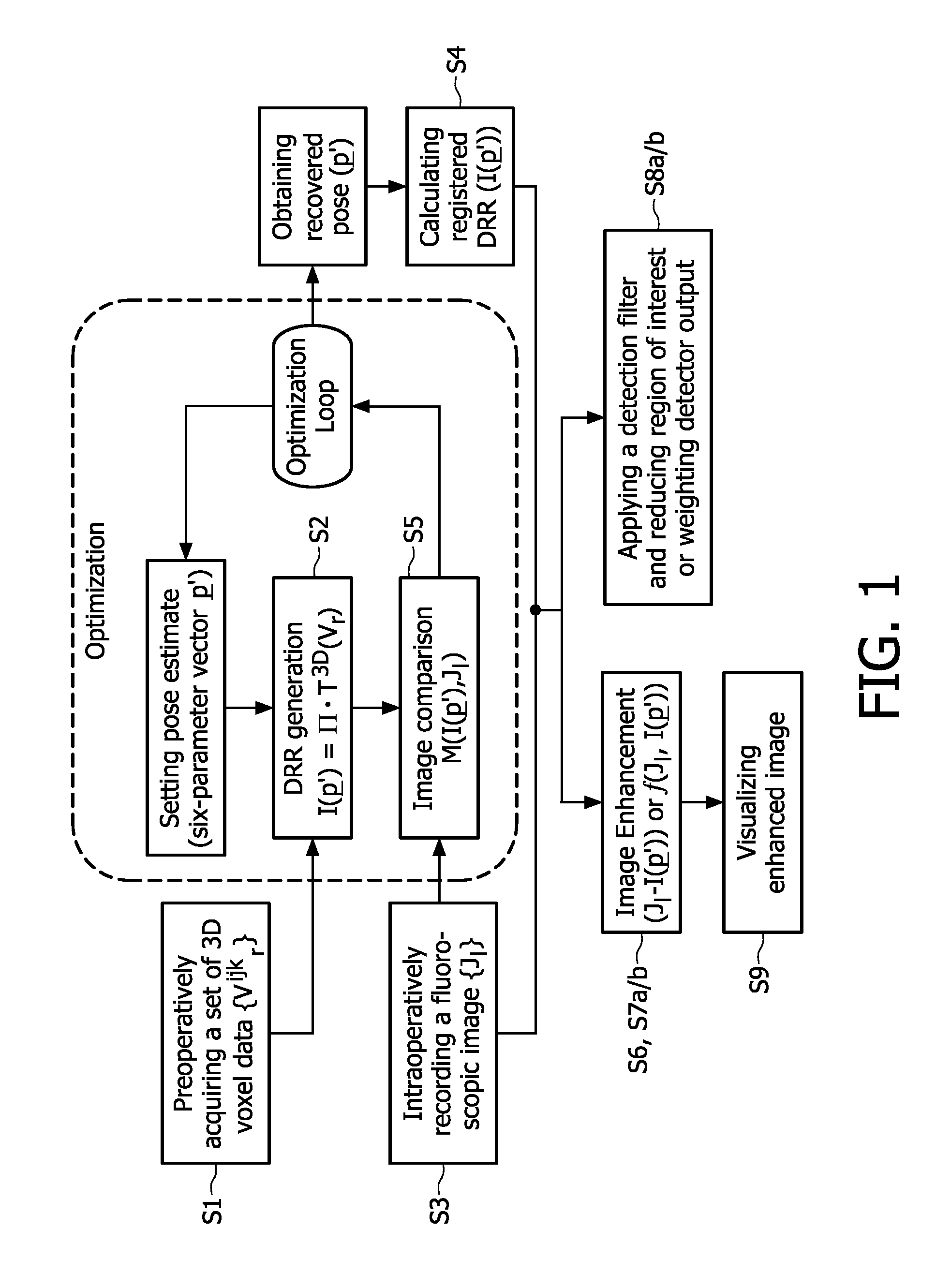
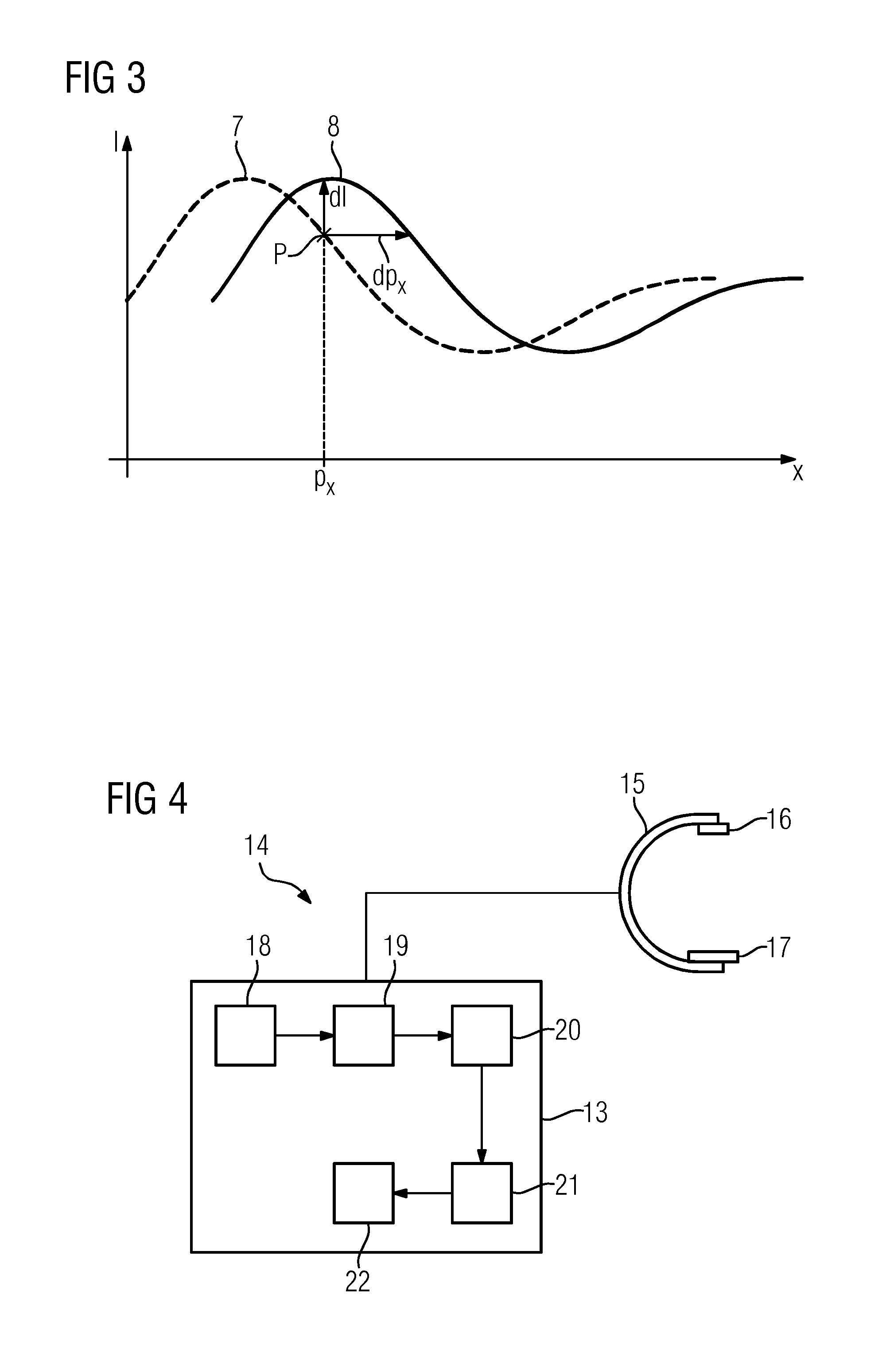
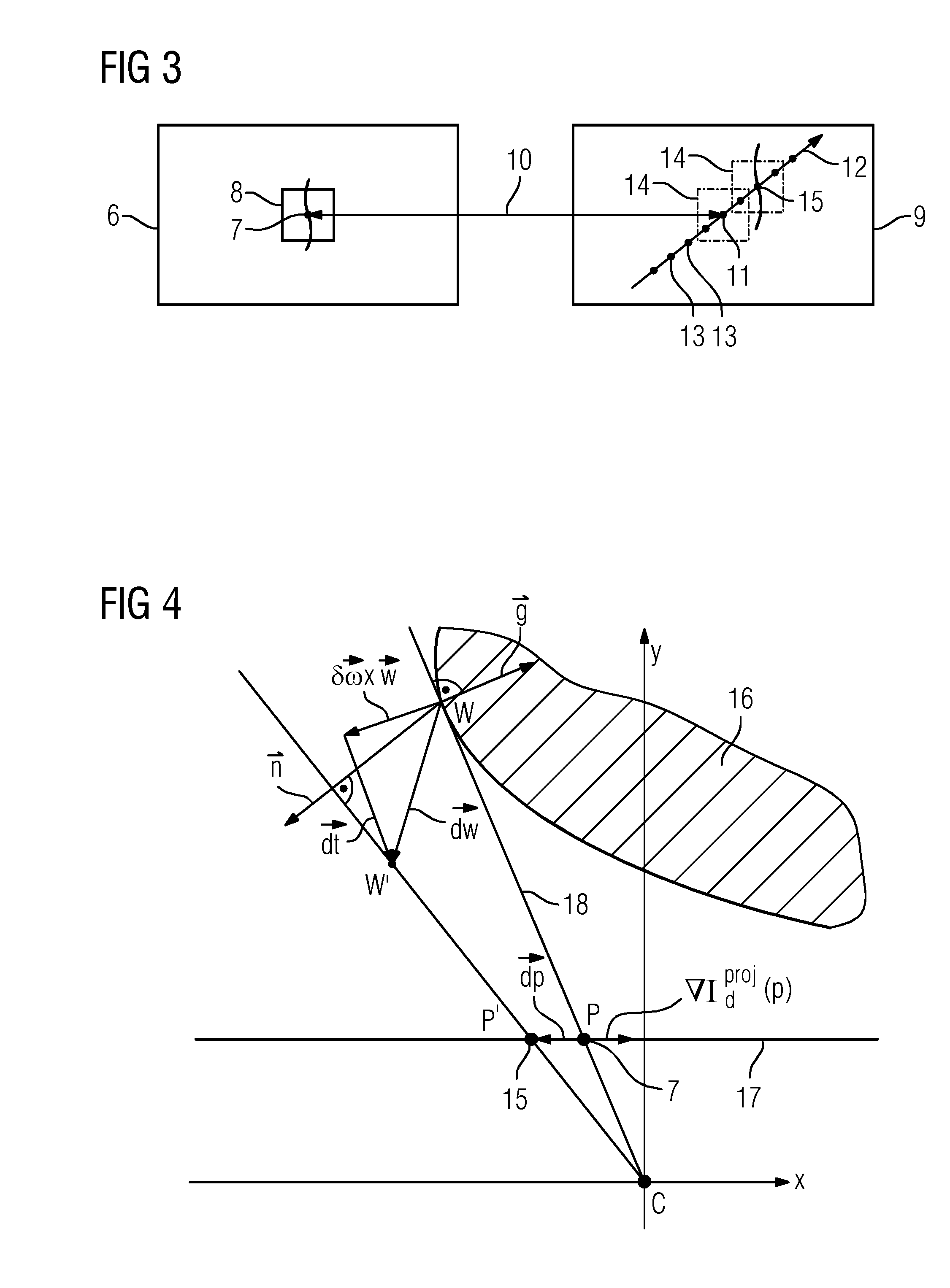
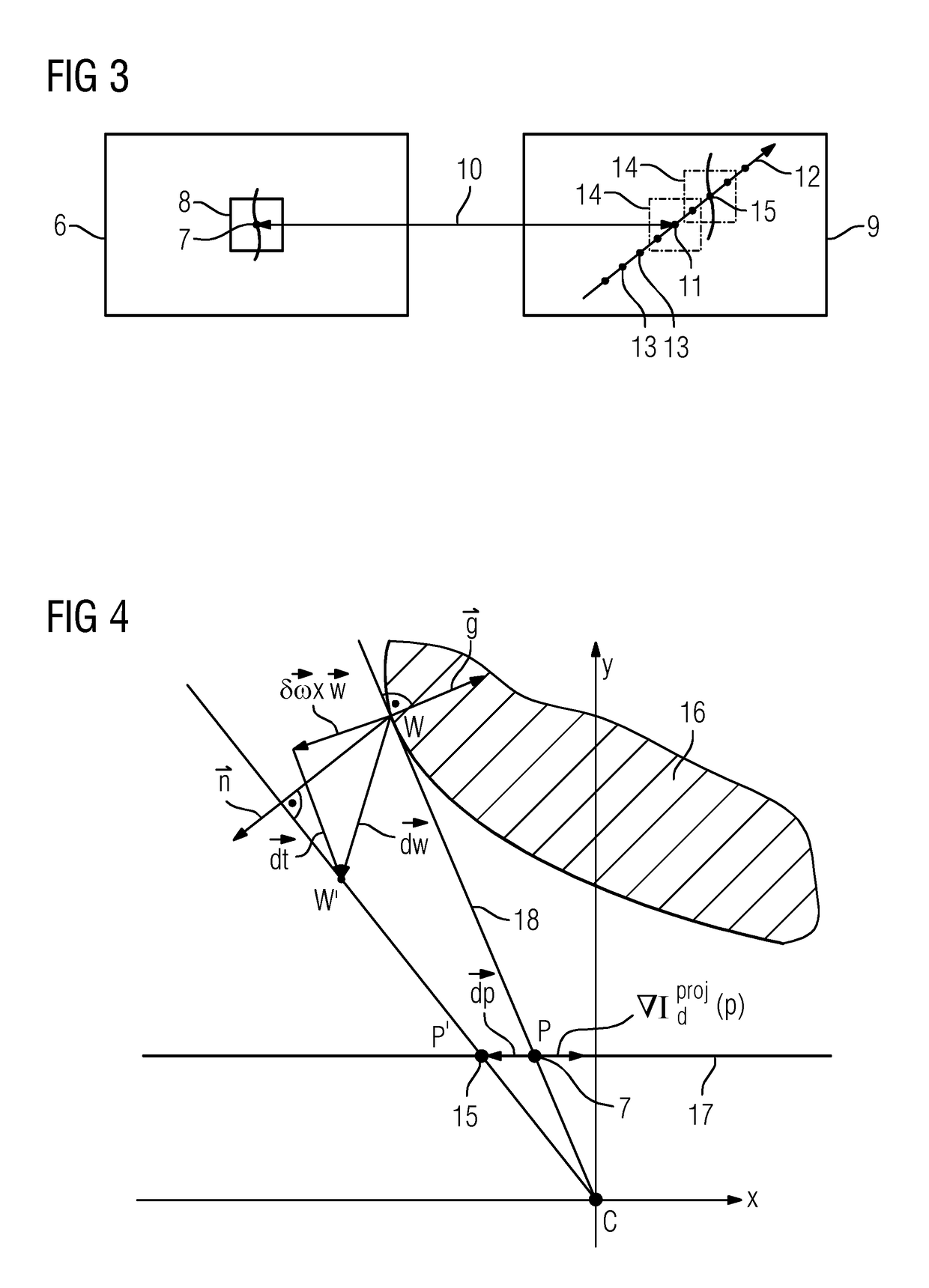
An image-guided radiosurgery method and system are presented that use 2D / 3D image registration to keep the radiosurgical beams properly focused onto a treatment target. A pre-treatment 3D scan of the target is generated at or near treatment planning time. A set of 2D DRRs are generated, based on the pre-treatment 3D scan. At least one 2D x-ray image of the target is generated in near real time during treatment. The DRRs are registered with the x-ray images, by computing a set of 3D transformation parameters that represent the change in target position between the 3D scan and the x-ray images. The relative position of the radiosurgical beams and the target is continuously adjusted in near real time in accordance with the 3D transformation parameters. A hierarchical and iterative 2D / 3D registration algorithm is used, in which the transformation parameters that are in-plane with respect to the image plane of the x-ray images are computed separately from the out-of-plane transformation parameters.
Owner:ACCURAY
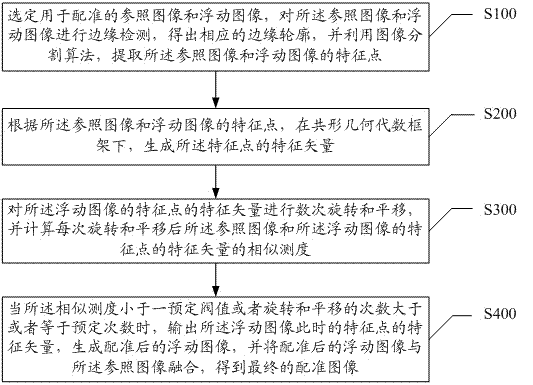
Method and apparatus for performing 2D to 3D registration
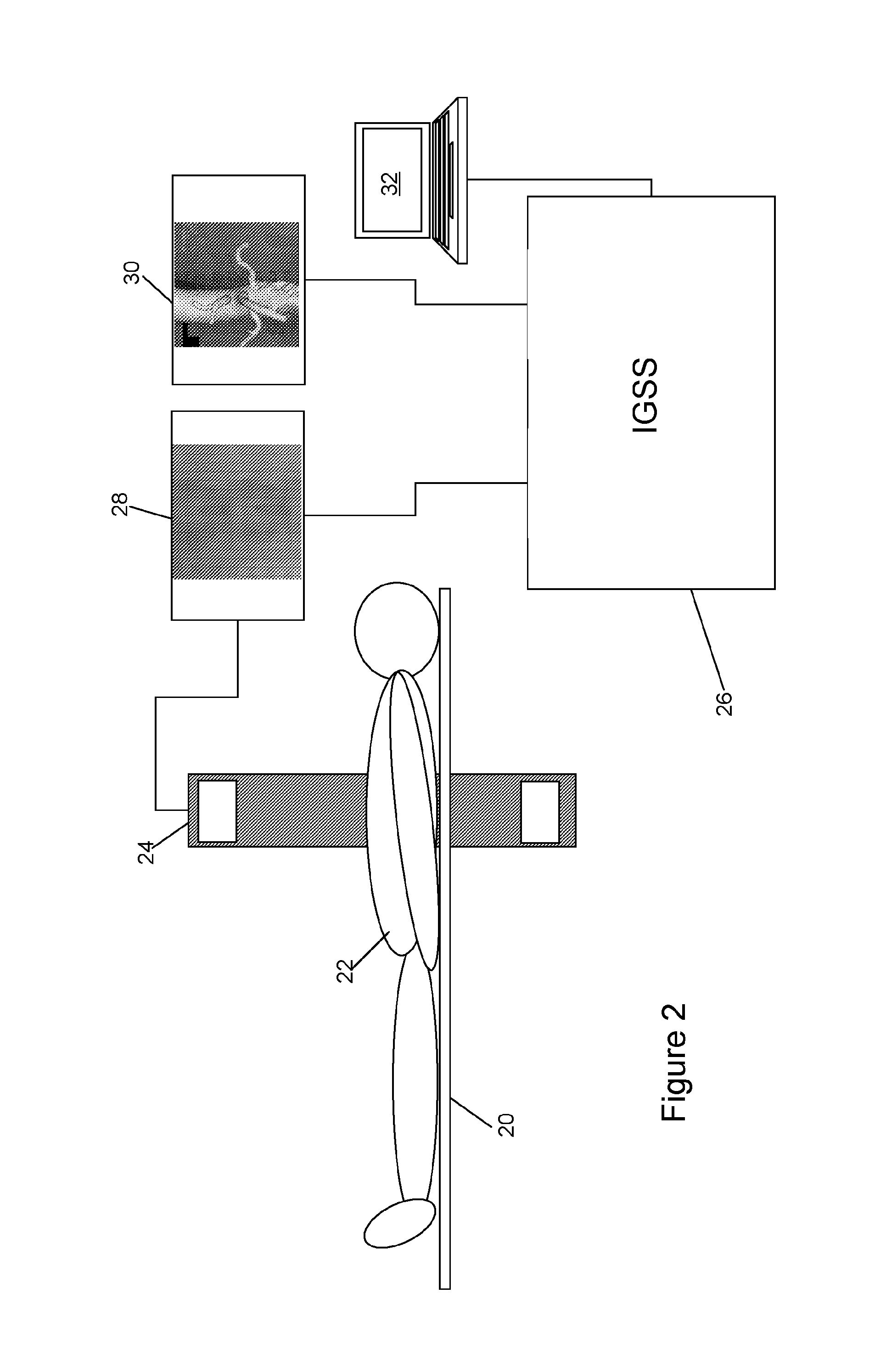
ActiveUS7570791B2Reduce the impactReduce impactSurgeryCharacter and pattern recognitionNormalized mutual informationNormalize mutual information
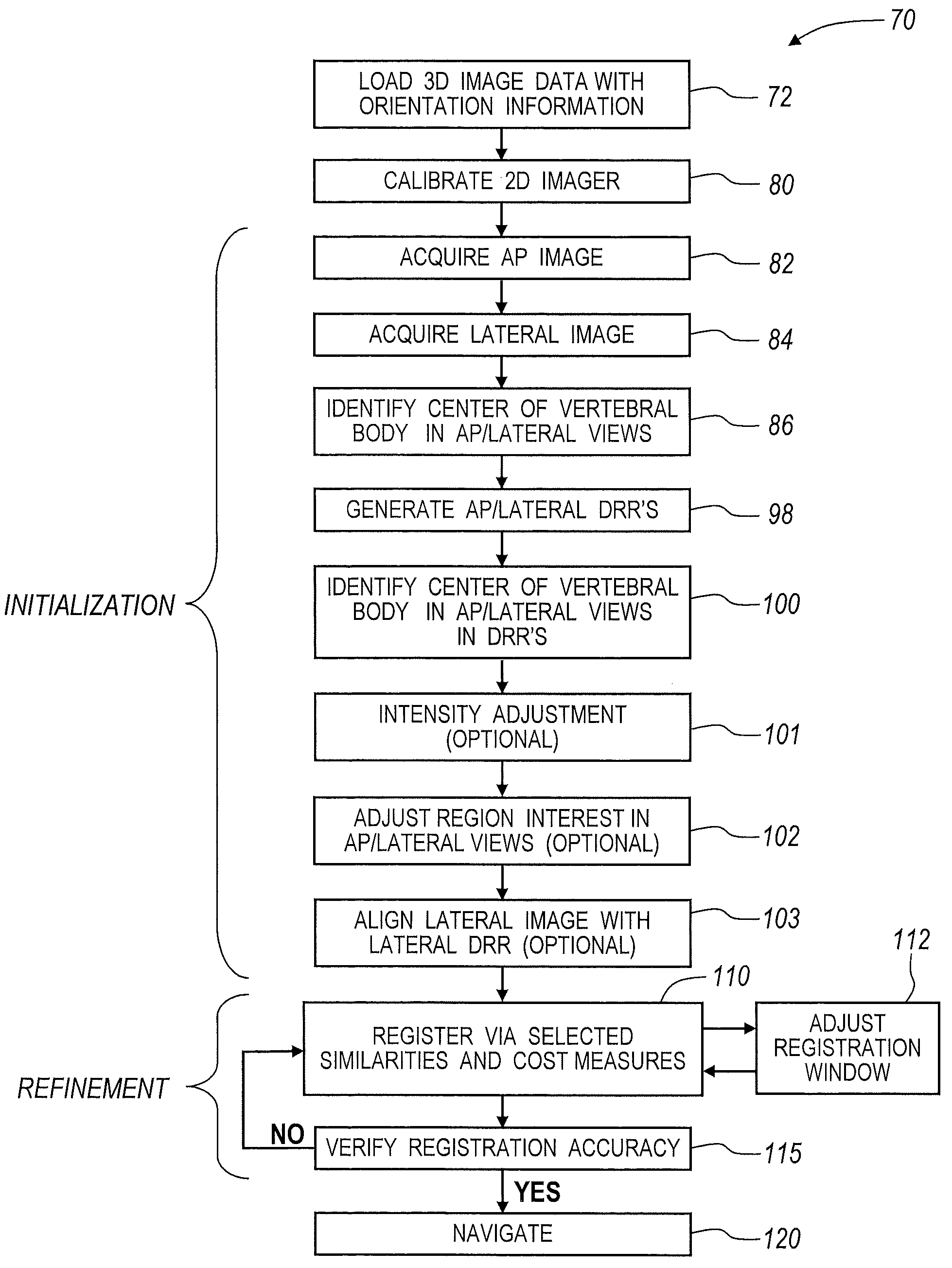
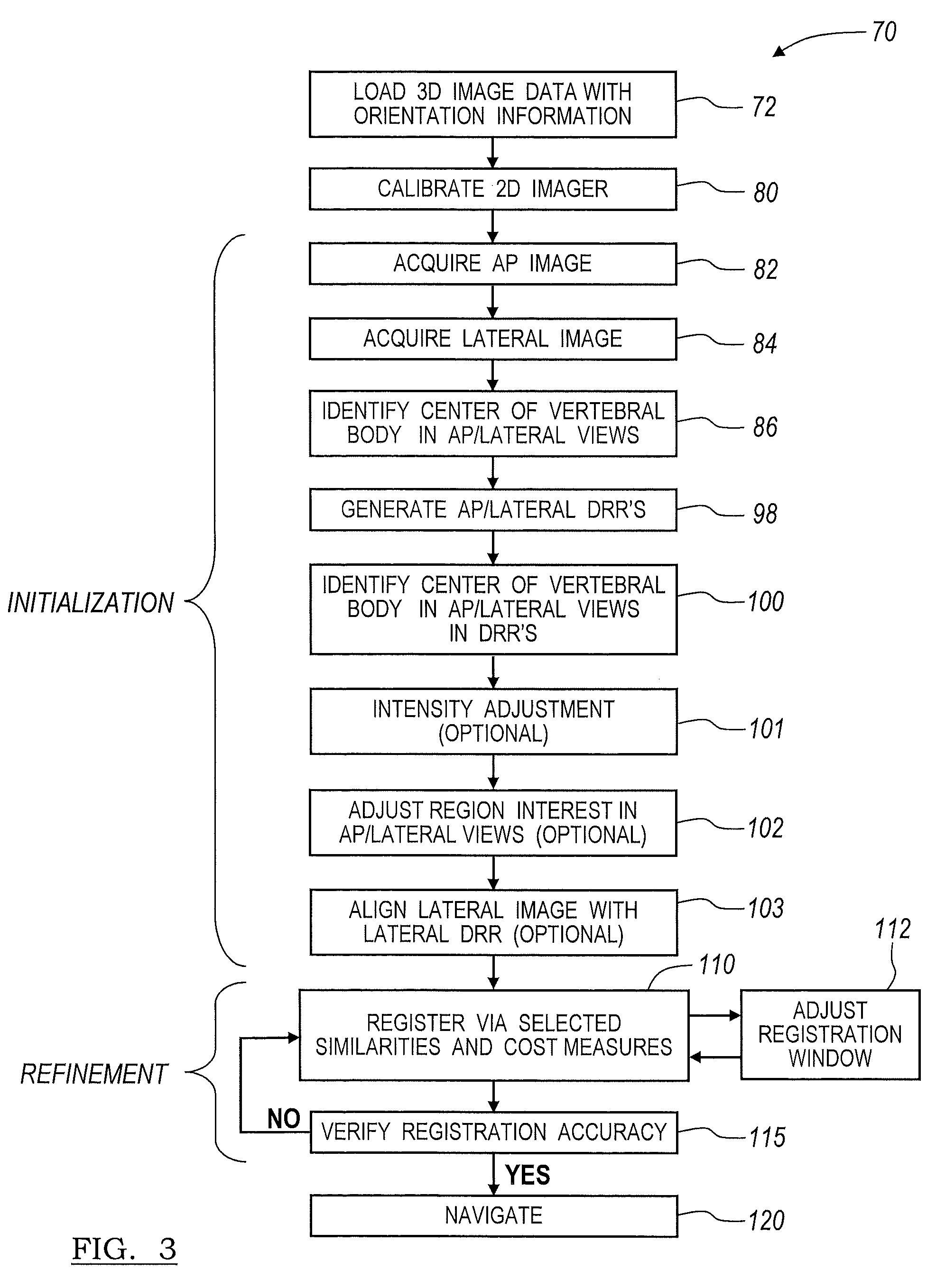
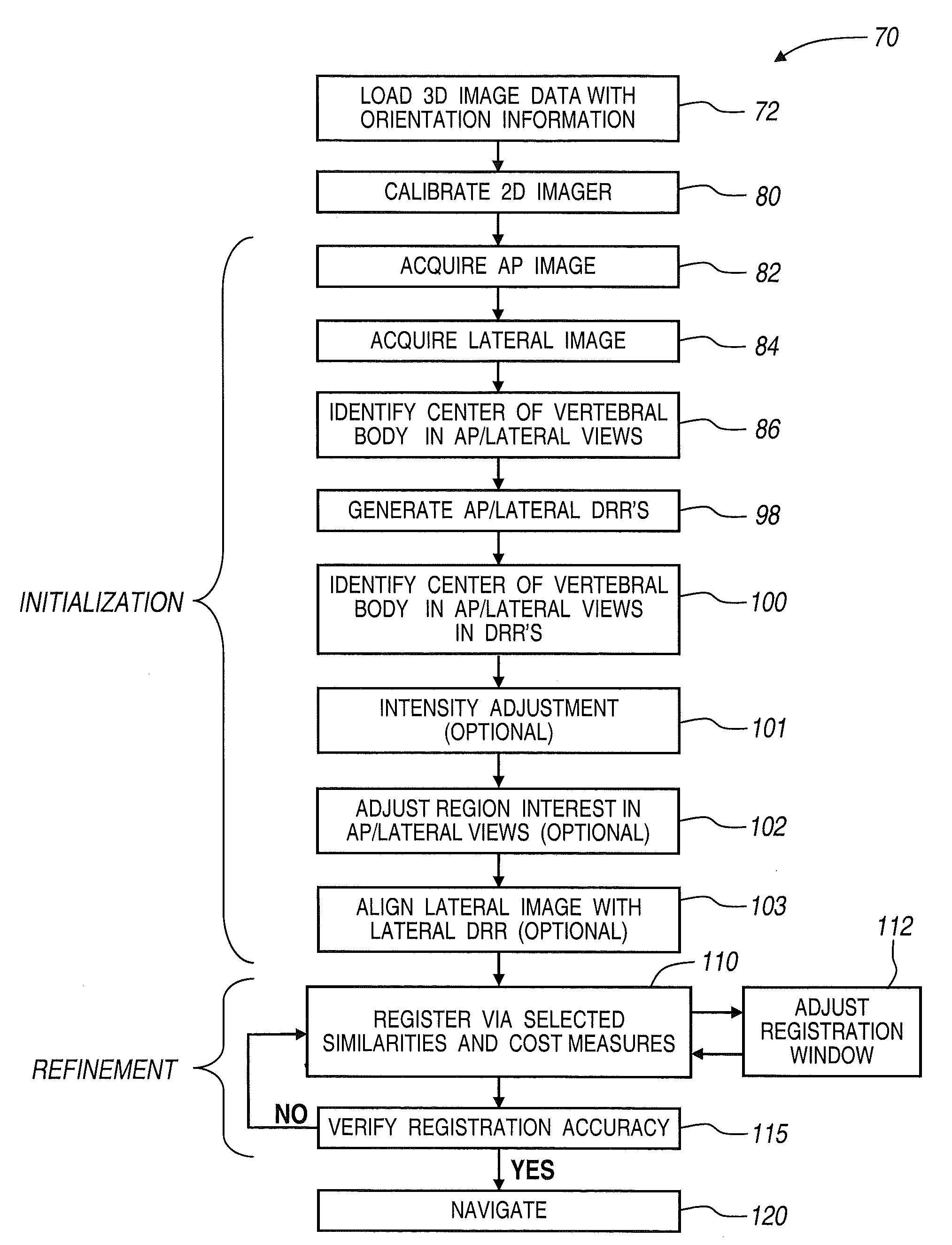
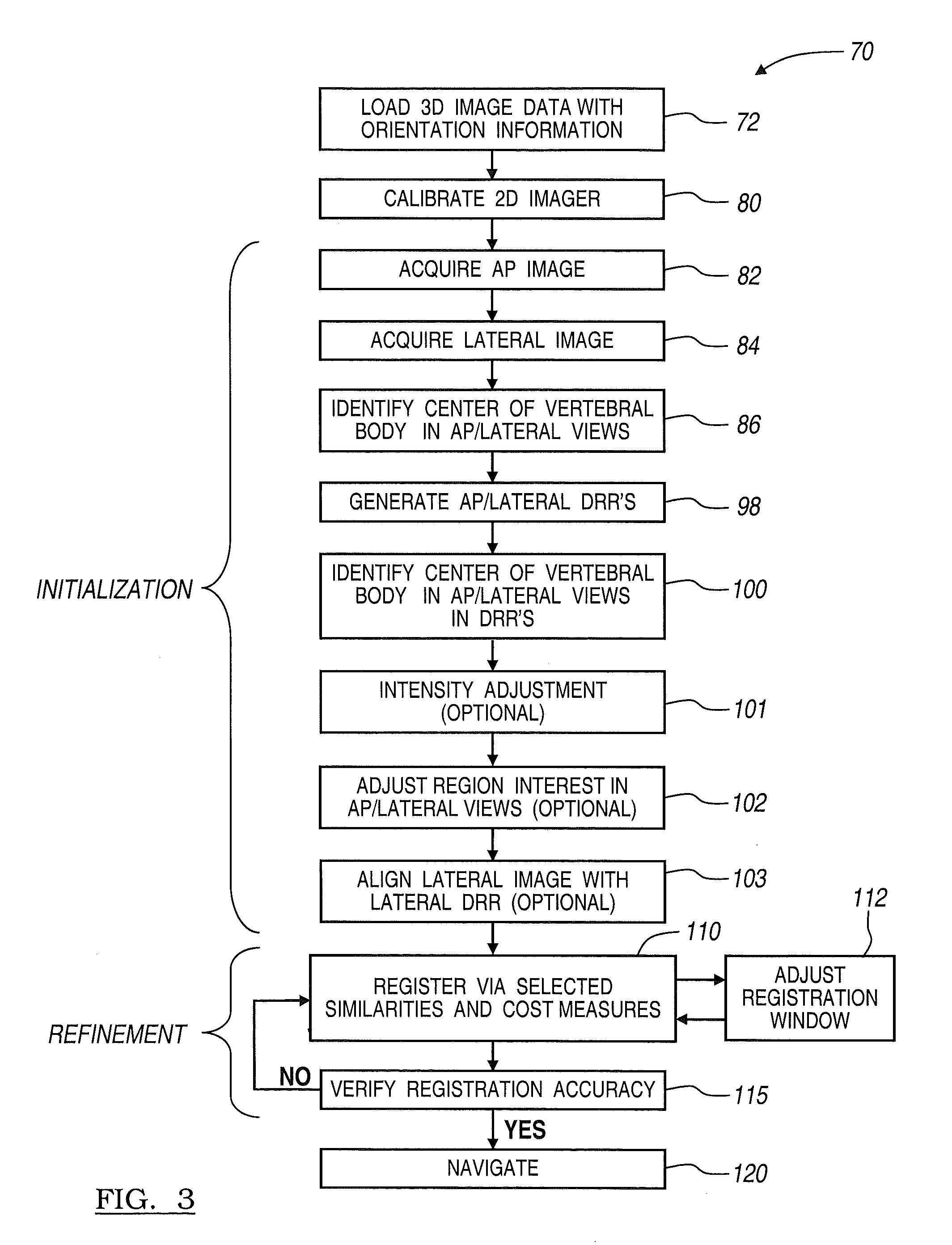
A method and apparatus for performing 2D to 3D registration includes an initialization step and a refinement step. The initialization step is directed to identifying an orientation and a position by knowing orientation information where data images are captured and by identifying centers of relevant bodies. The refinement step uses normalized mutual information and pattern intensity algorithms to register the 2D image to the 3D volume.
Owner:MEDTRONIC NAVIGATION
Rapid and robust 3D/3D registration technique
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
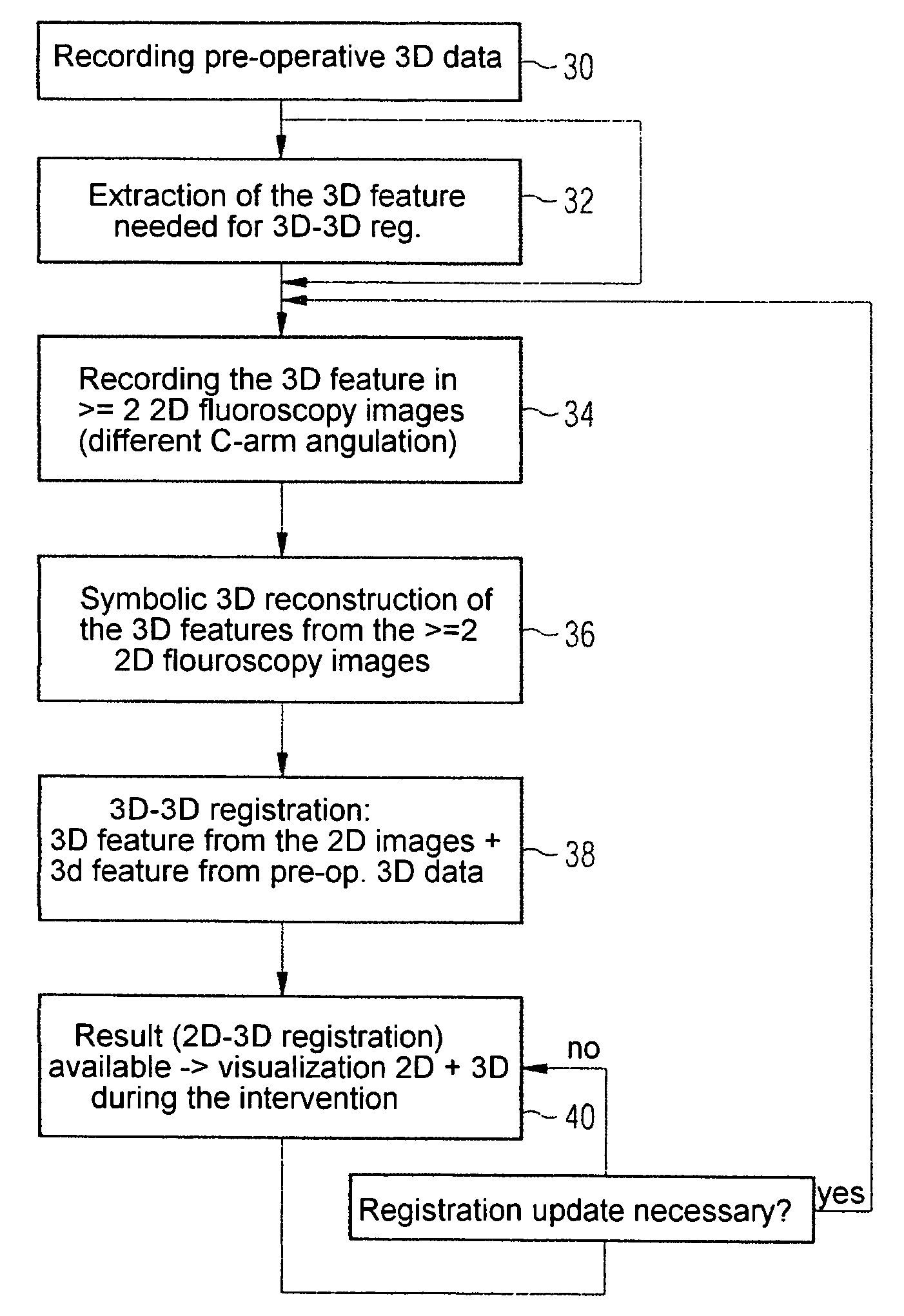
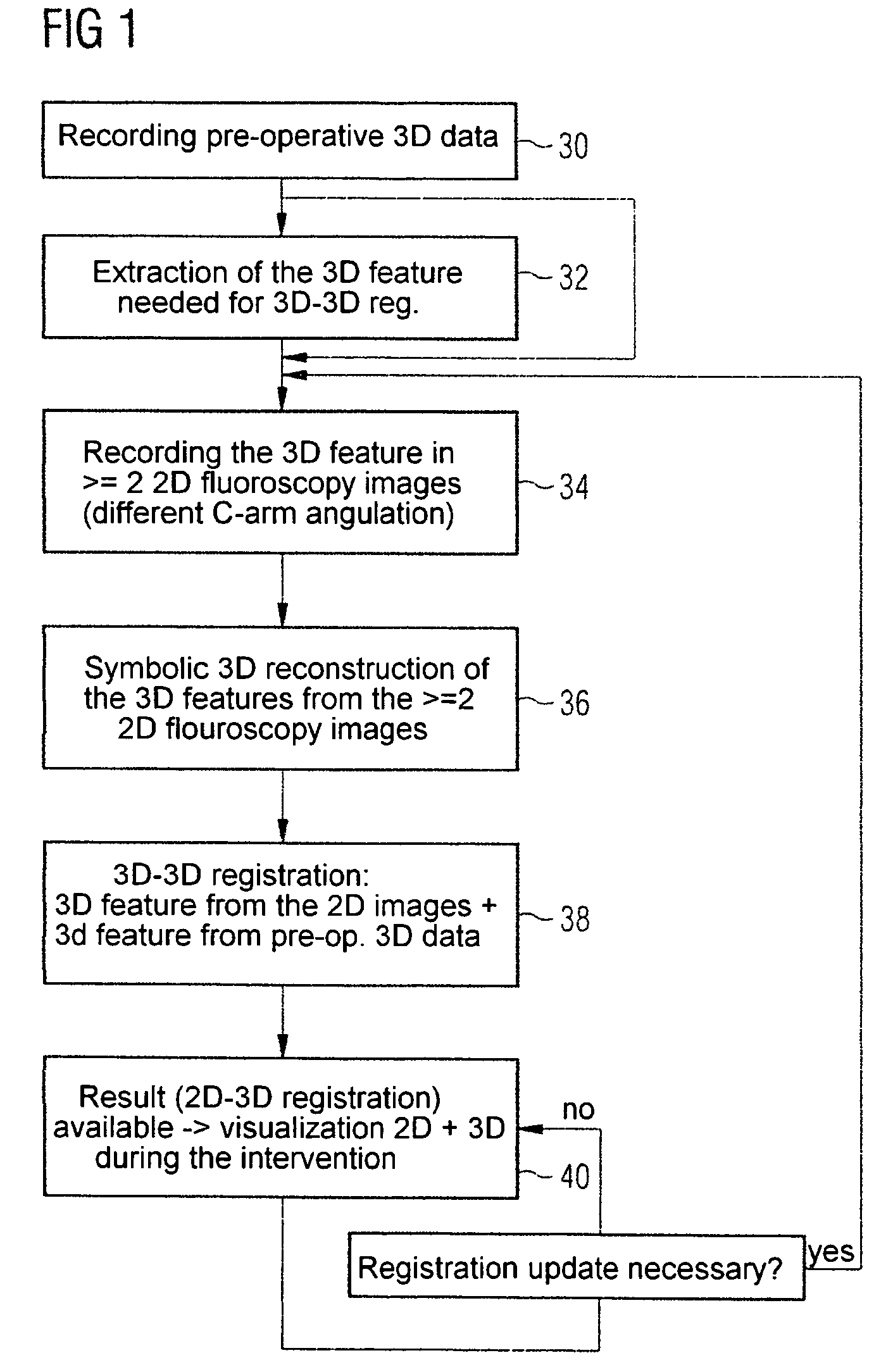
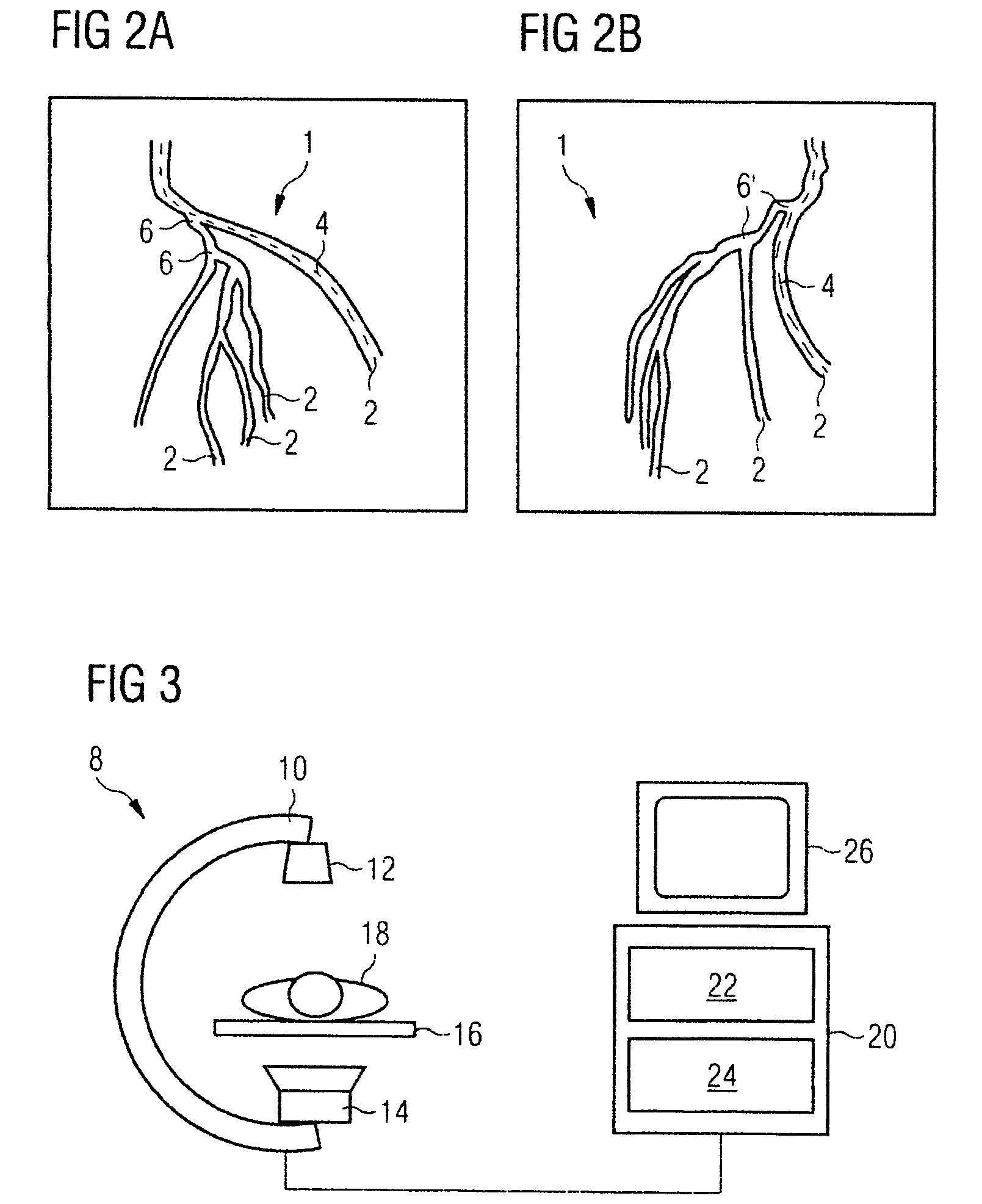
Method and device for registering 2D projection images relative to a 3D image data record
ActiveUS7689019B2Simplify the rebuild processImage enhancementImage analysis3d imageComputer graphics (images)
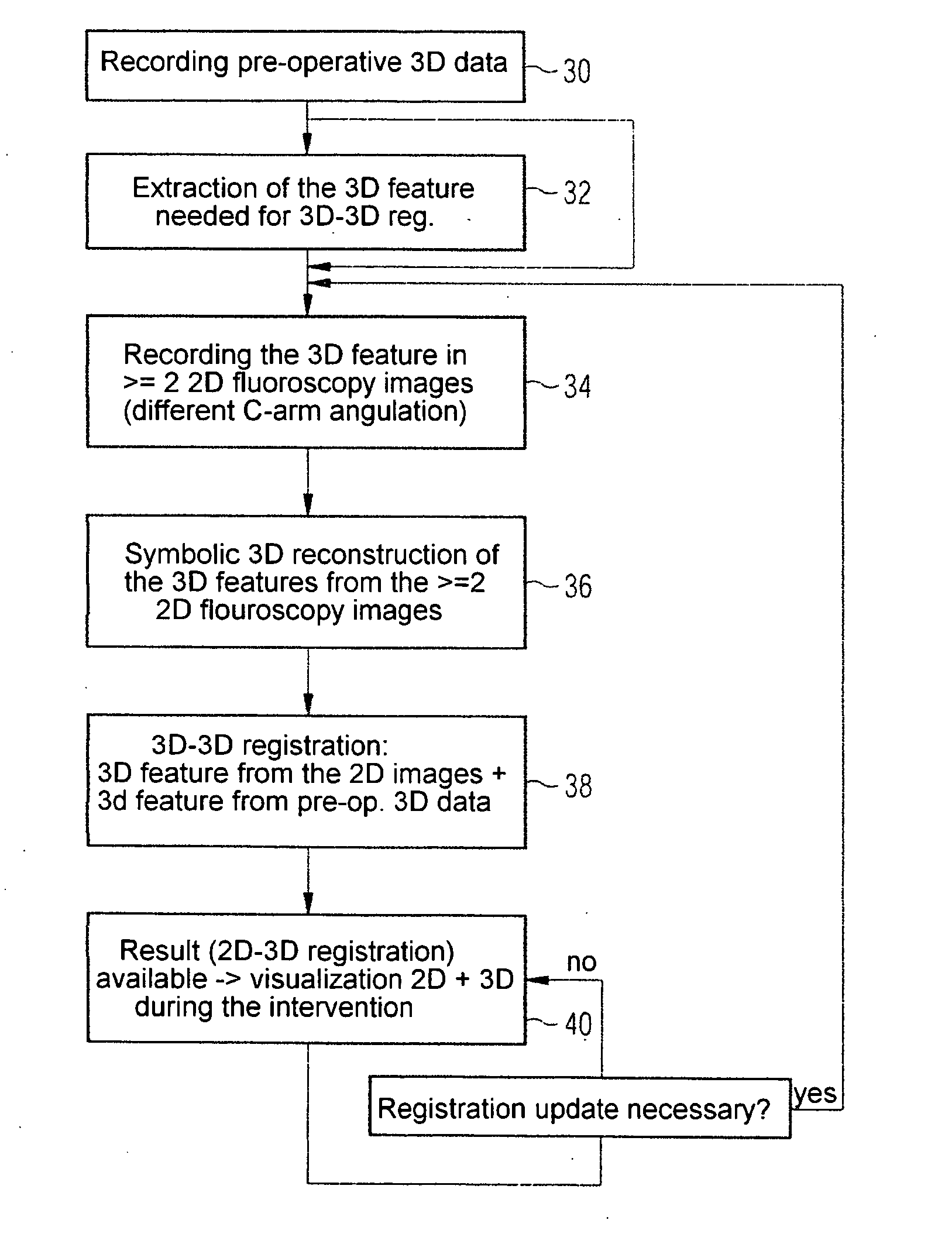
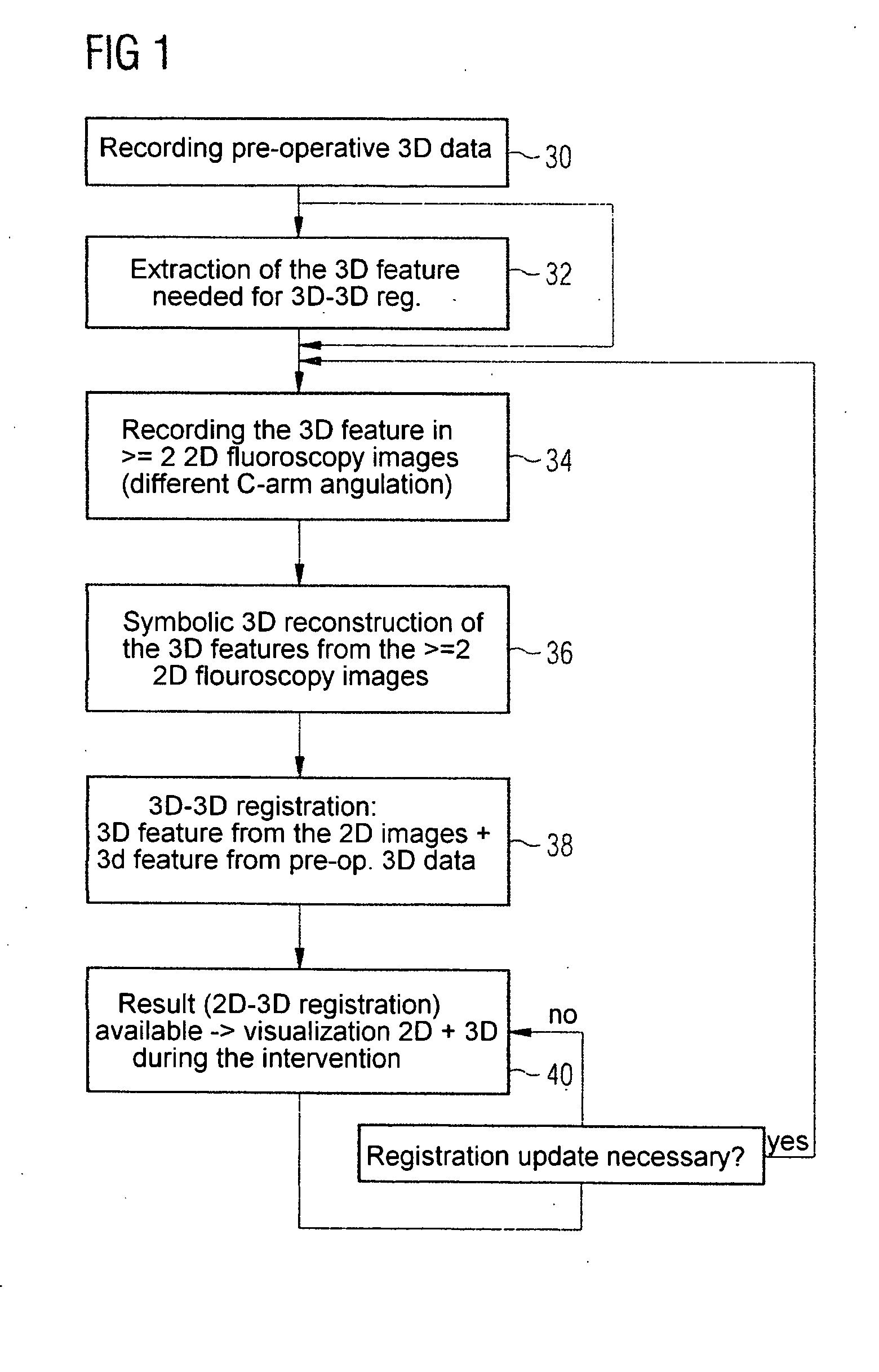
The invention relates to a method and a device for registering 2D projection images of an object relative to a 3D image data record of the same object, in which, from just a few 2D projection images, a 3D feature contained in an object, which is also identifiable in the 3D images, is symbolically reconstructed. The 3D feature obtained in this way is then registered by 3D-3D registration with the 3D image data record.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and device for registering 2D projection images relative to a 3D image data record
ActiveUS20060262970A1Simple methodSimplify the rebuild processImage enhancementImage analysis3d imageProjection image
The invention relates to a method and a device for registering 2D projection images of an object relative to a 3D image data record of the same object, in which, from just a few 2D projection images, a 3D feature contained in an object, which is also identifiable in the 3D images, is symbolically reconstructed. The 3D feature obtained in this way is then registered by 3D-3D registration with the 3D image data record.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
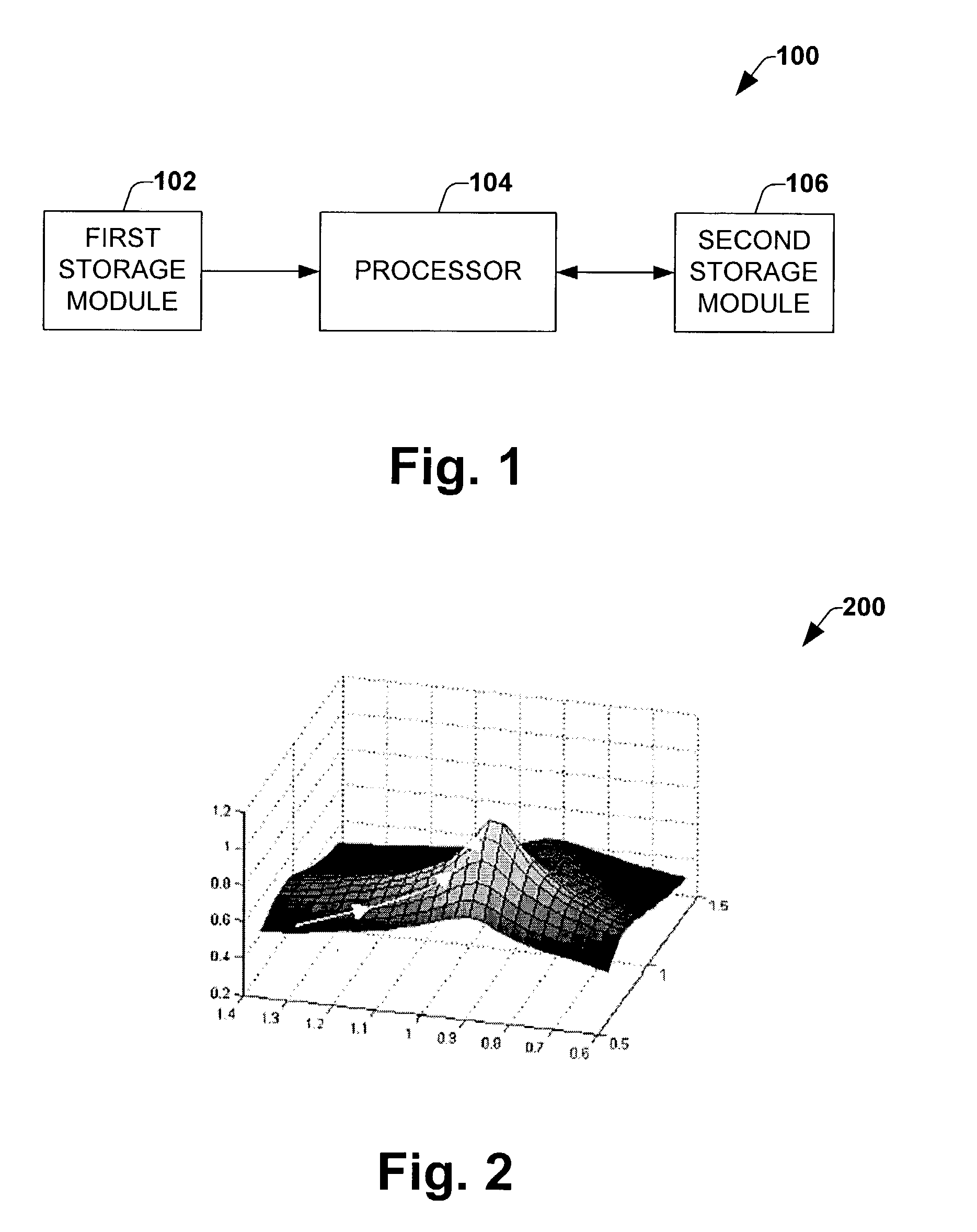
Architecture for real-time 3D image registration
InactiveUS7280710B1Facilitates fast executionMaximizing mutual informationImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognition3d imageMutual information
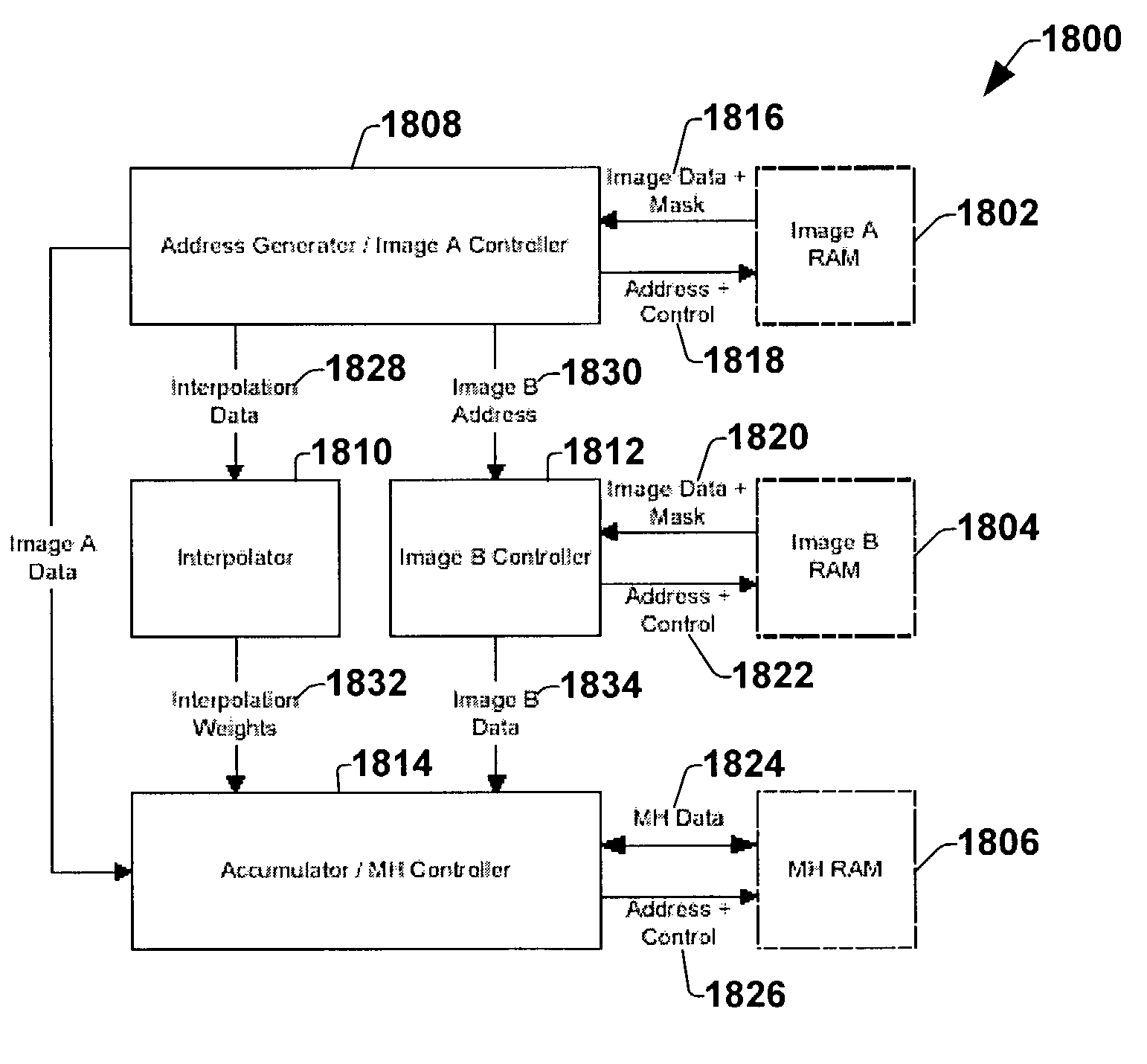
A system architecture is disclosed that facilitates rapid execution of 3D registration or alignment algorithms. A first image module (e.g., RAM) is included to store data corresponding to images to be registered. A processor coupled to the first storage module accesses the data and determined mutual histogram (MH) values which are then used to compute mutual information (MI) between the images. The processor accumulates the MH values in a second image module. The second storage module is accessible so that registered images can be displayed. The architecture is scalable facilitating distributed calculations to speed-up the registration process.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
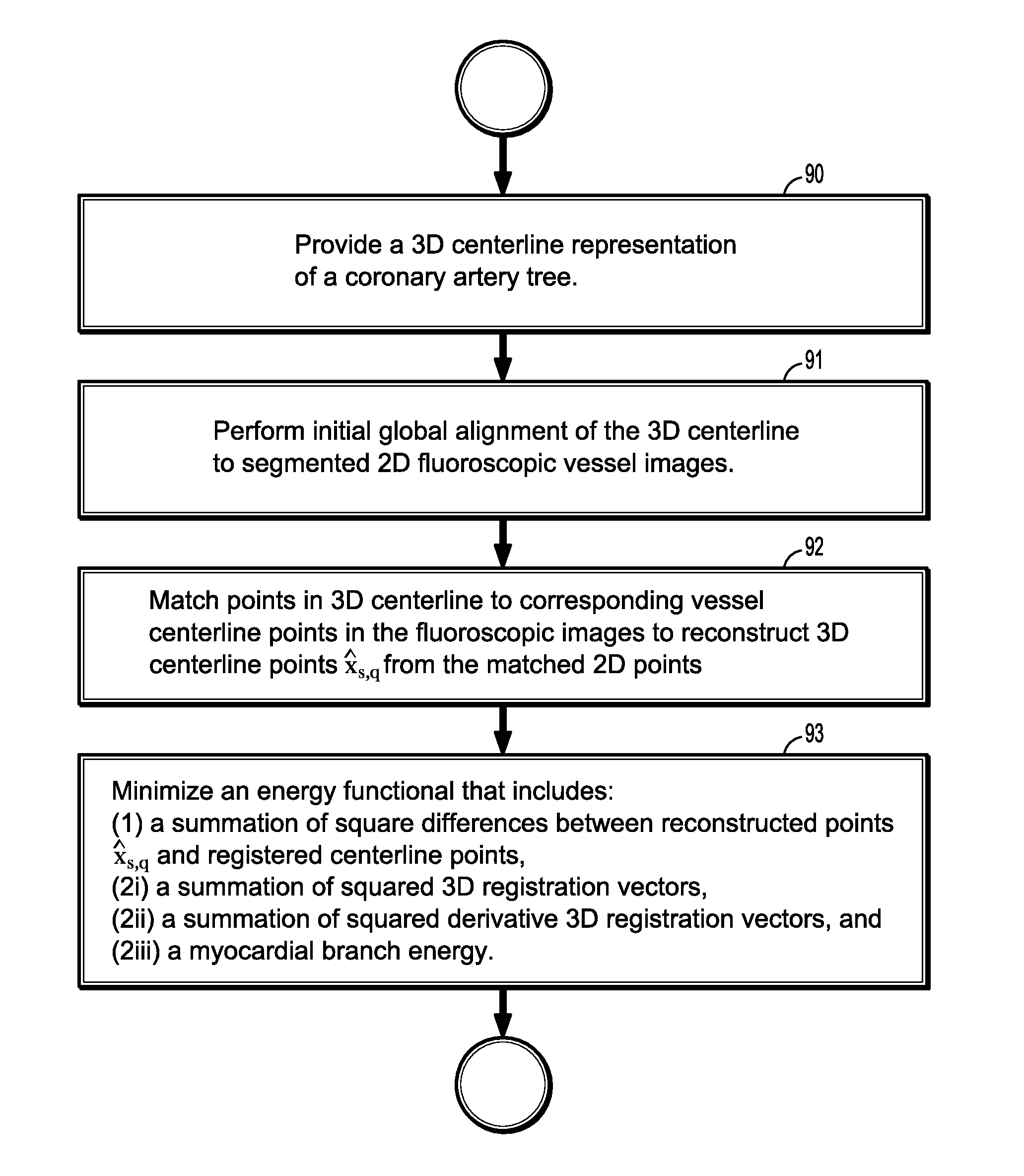
Non-rigid 2d/3d registration of coronary artery models with live fluoroscopy images
ActiveUS20130094745A1Increase heightReduce uncertaintyImage enhancementImage analysisFluoroscopic imageCoronary arterial tree
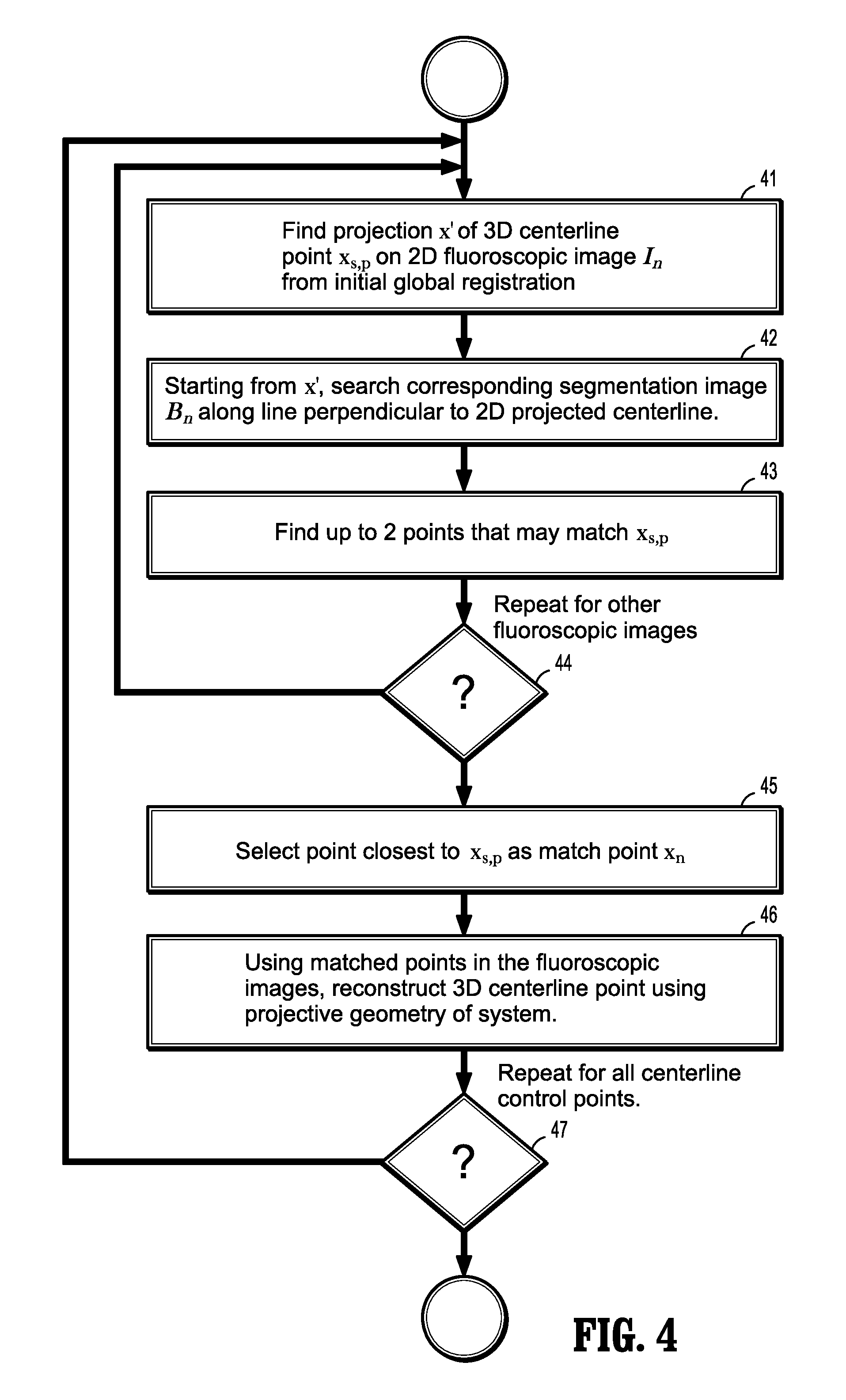
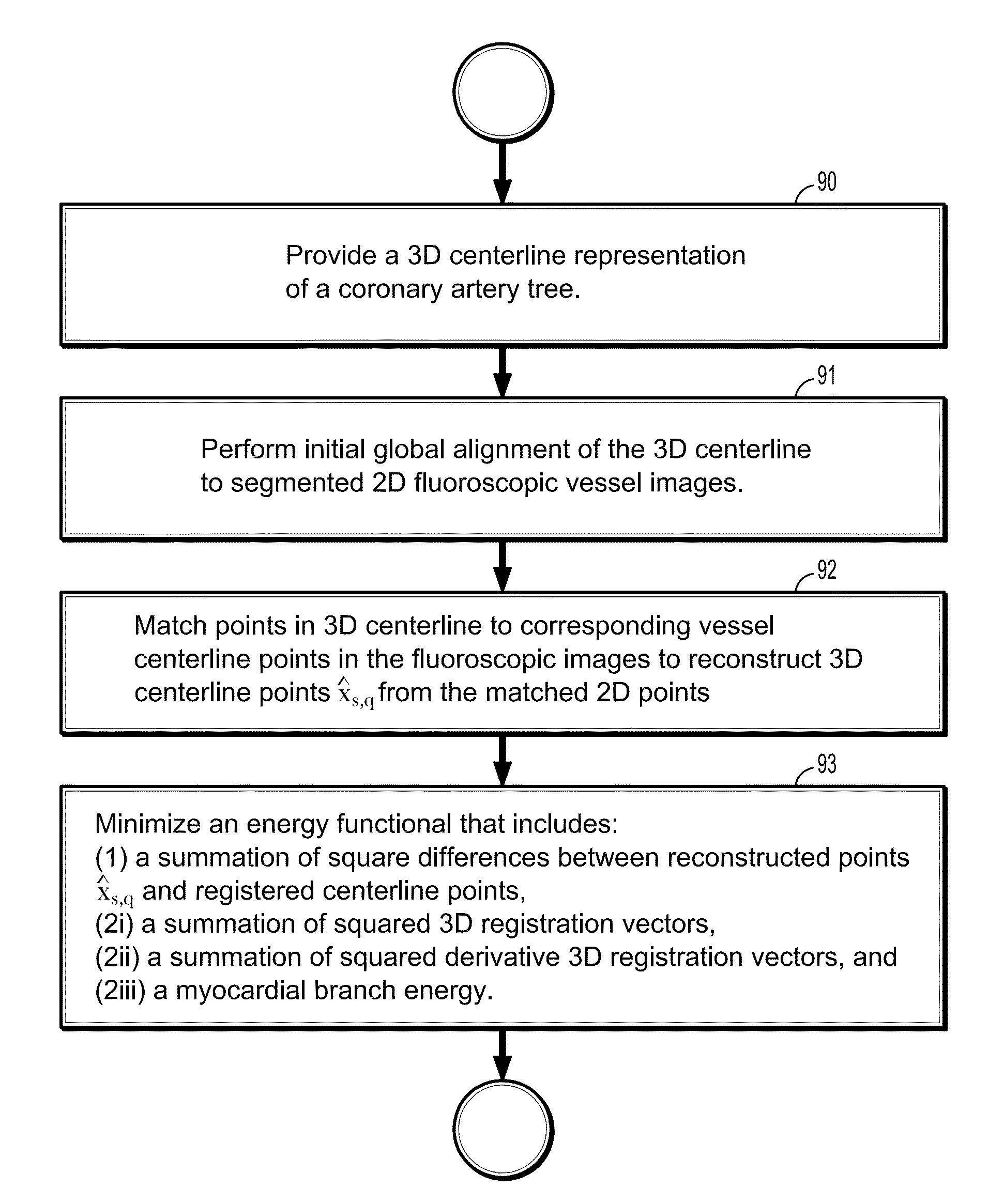
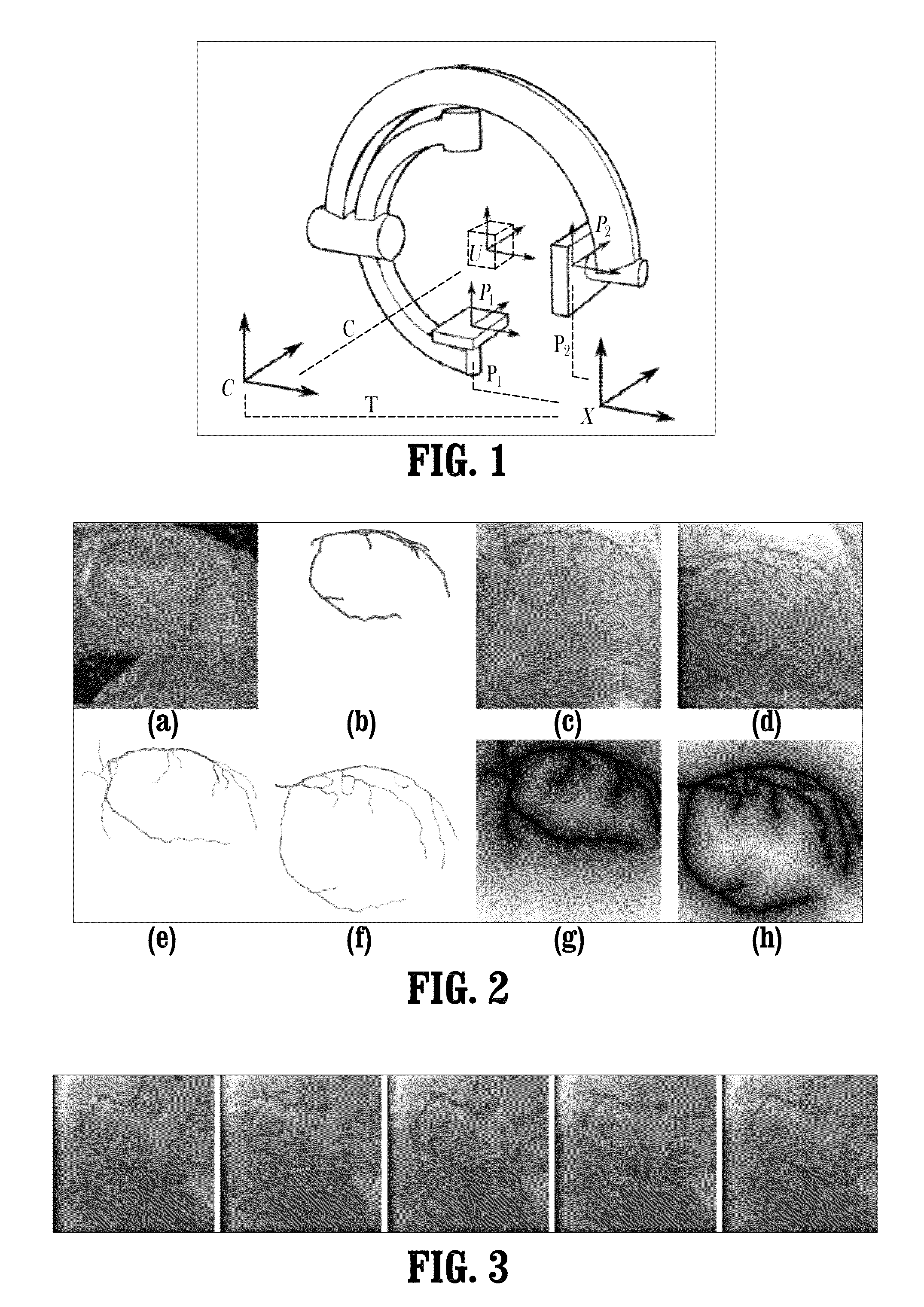
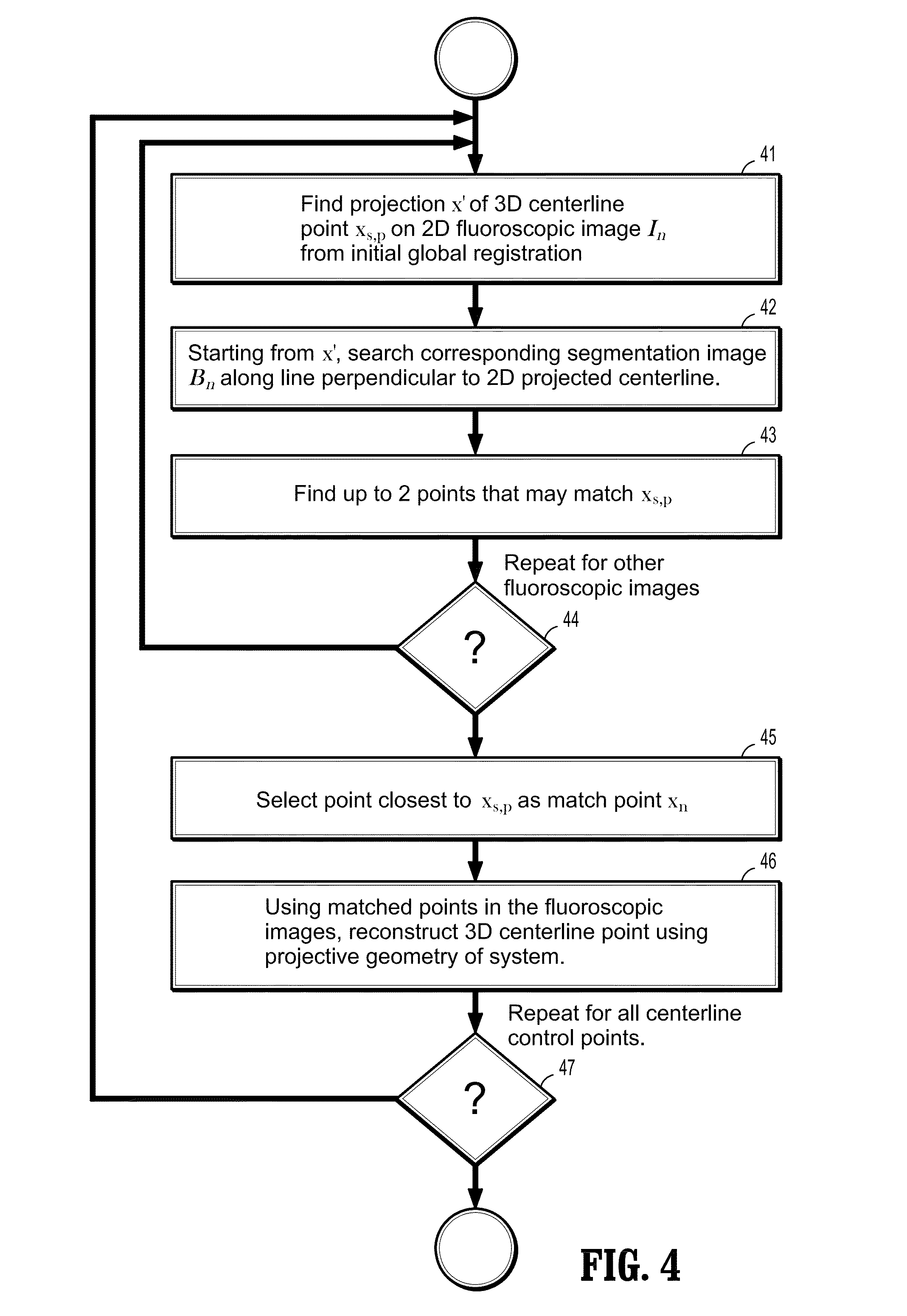
A method for non-rigid registration of digital 3D coronary artery models with 2D fluoroscopic images during a cardiac intervention includes providing a digitized 3D centerline representation of a coronary artery tree that comprises a set of S segments composed of QS 3D control points, globally aligning the 3D centerline to at least two 2D fluoroscopic images, and non-rigidly registering the 3D centerline to the at least two 2D fluoroscopic images by minimizing an energy functional that includes a summation of square differences between reconstructed centerline points and registered centerline points, a summation of squared 3D registration vectors, a summation of squared derivative 3D registration vectors, and a myocardial branch energy. The non-rigid registration of the 3D centerline is represented as a set of 3D translation vectors rs,q that are applied to corresponding centerline points xs,q in a coordinate system of the 3D centerline.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
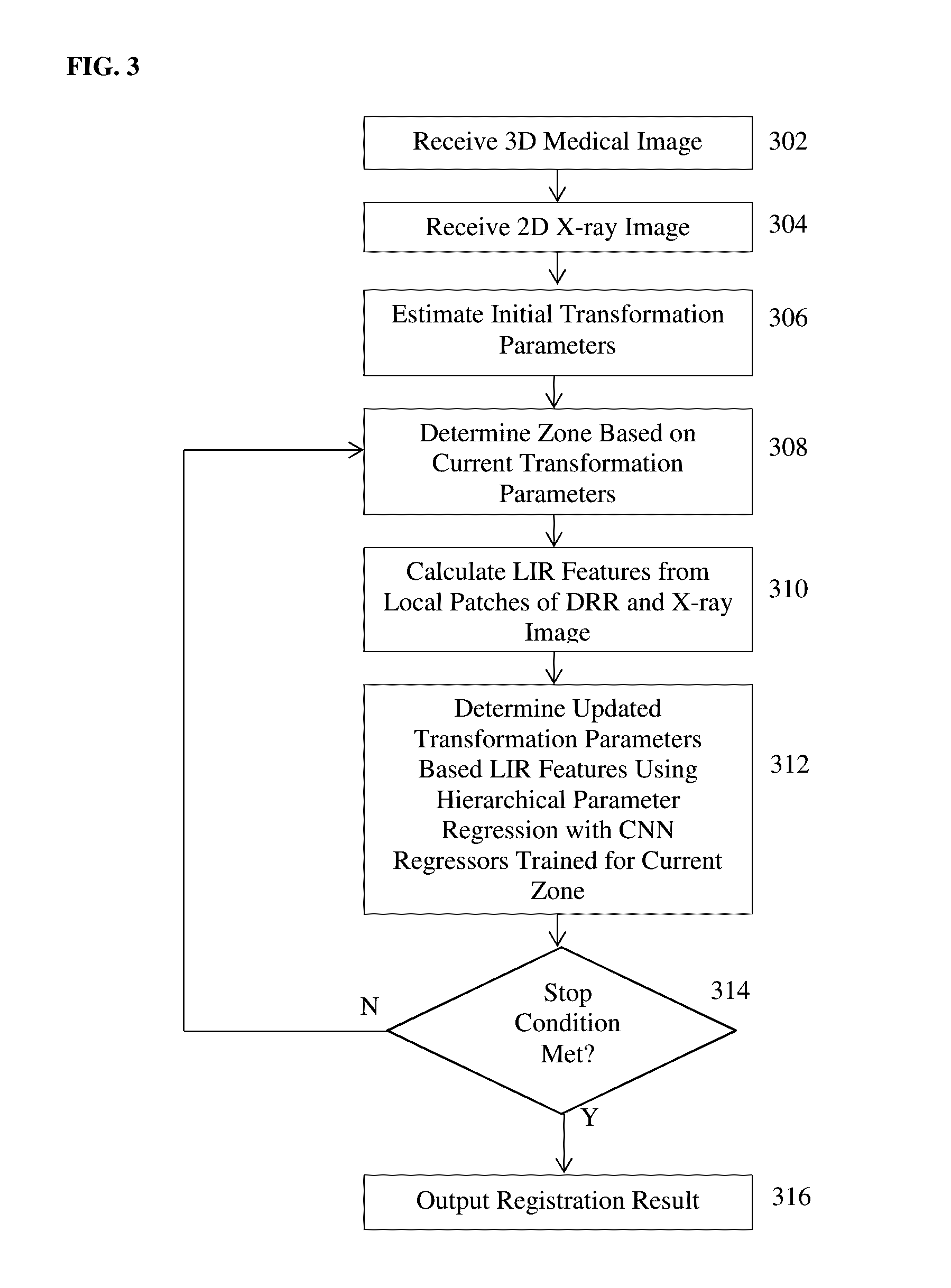
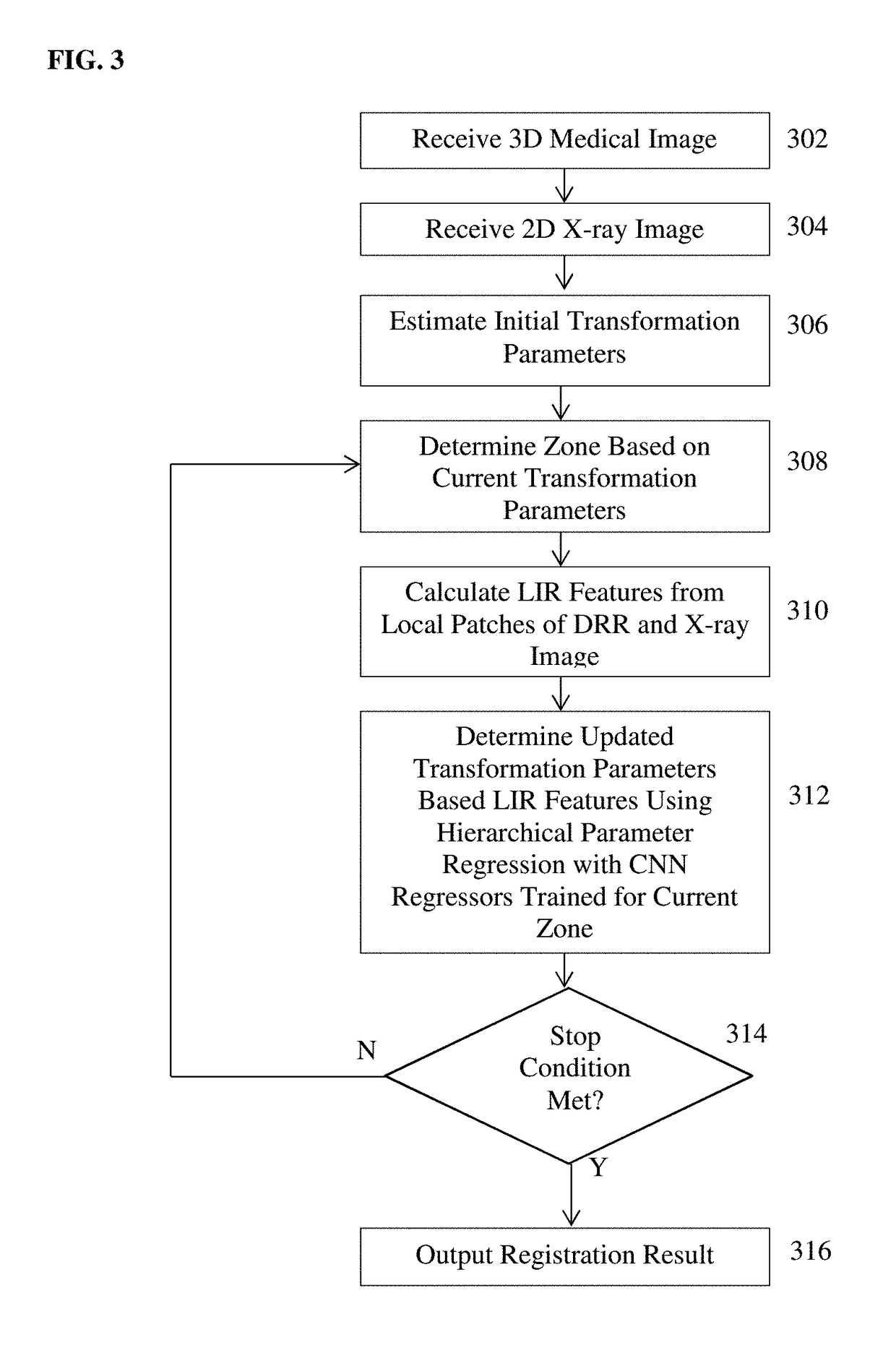
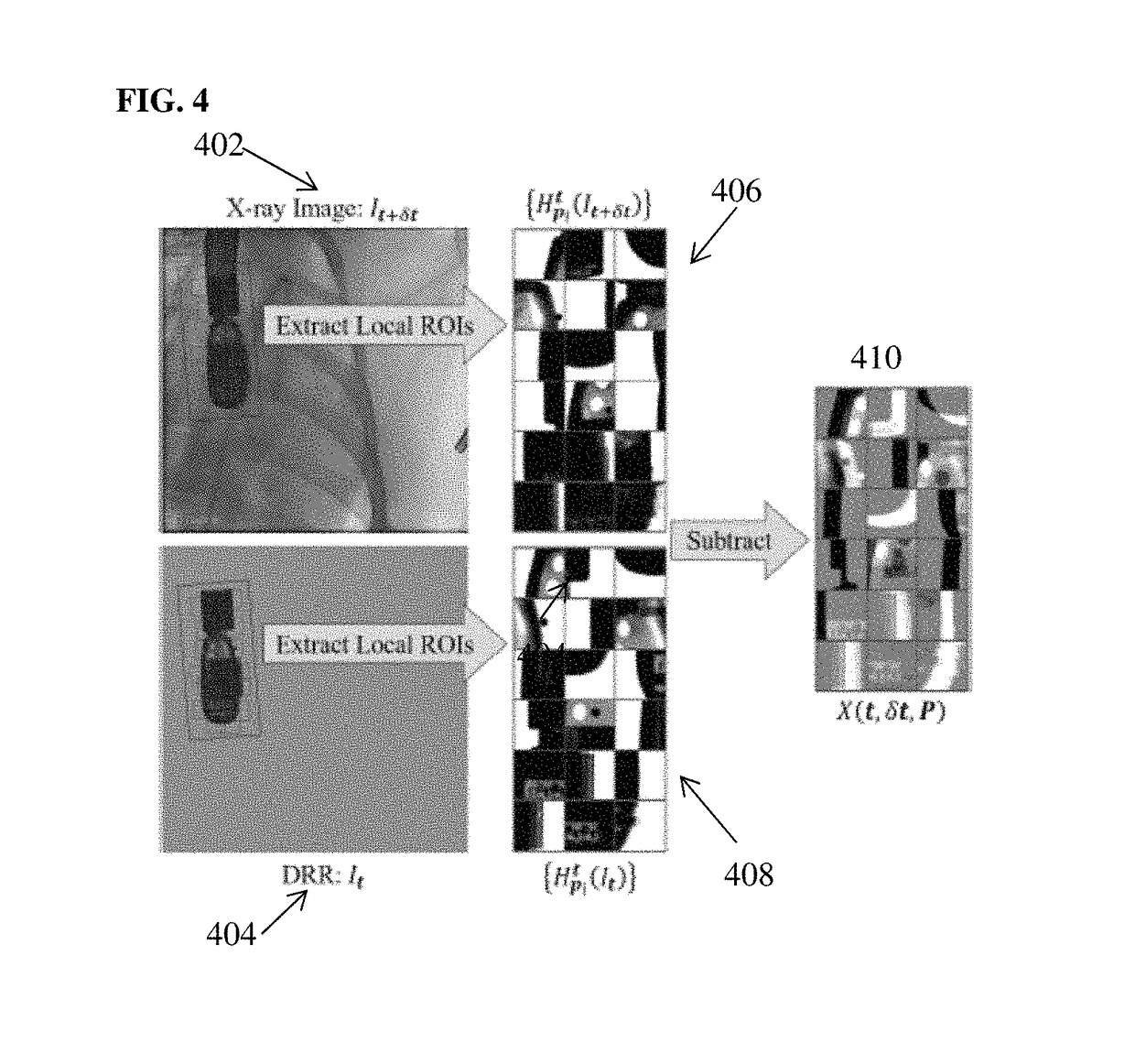
Method for 2-D/3-D registration based on hierarchical pose regression
ActiveUS20170024634A1Large capture rangeImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisTransformation parameterX ray image
A method and apparatus for convolutional neural network (CNN) regression based 2D / 3D registration of medical images is disclosed. A parameter space zone is determined based on transformation parameters corresponding to a digitally reconstructed radiograph (DRR) generated from the 3D medical image. Local image residual (LIR) features are calculated from local patches of the DRR and the X-ray image based on a set of 3D points in the 3D medical image extracted for the determined parameter space zone. Updated transformation parameters are calculated based on the LIR features using a hierarchical series of regressors trained for the determined parameter space zone. The hierarchical series of regressors includes a plurality of regressors each of which calculates updates for a respective subset of the transformation parameters.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
Method and Apparatus for Performing 2D to 3D Registration
InactiveUS20090290771A1Reduce impactSurgeryCharacter and pattern recognitionNormalized mutual informationNormalize mutual information
A method and apparatus for performing 2D to 3D registration includes an initialization step and a refinement step. The initialization step is directed to identifying an orientation and a position by knowing orientation information where data images are captured and by identifying centers of relevant bodies. The refinement step uses normalized mutual information and pattern intensity algorithms to register the 2D image to the 3D volume.
Owner:MEDTRONIC NAVIGATION INC
Detection and tracking of interventional tools
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
2D/3D image registration
2D images are registered with 3D volume data. In order to provide 2D / 3D registration with a facilitated workflow 3D volume data (112) of an object, having a frame of reference is received. A transformation plane (116) is defined in relation to the 3D volume data. A 2D image of the object with an image plane is received. The transformation plane is projected on the image plane. The frame of reference is aligned with the 2D image. At least one alignment interaction value (128) is projected (130) on the transformation plane to determine (134) at least one transformed interaction value (132). The frame of reference is translated with the at least one transformed interaction value.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Laser guided tip approach with 3D registration to a surface
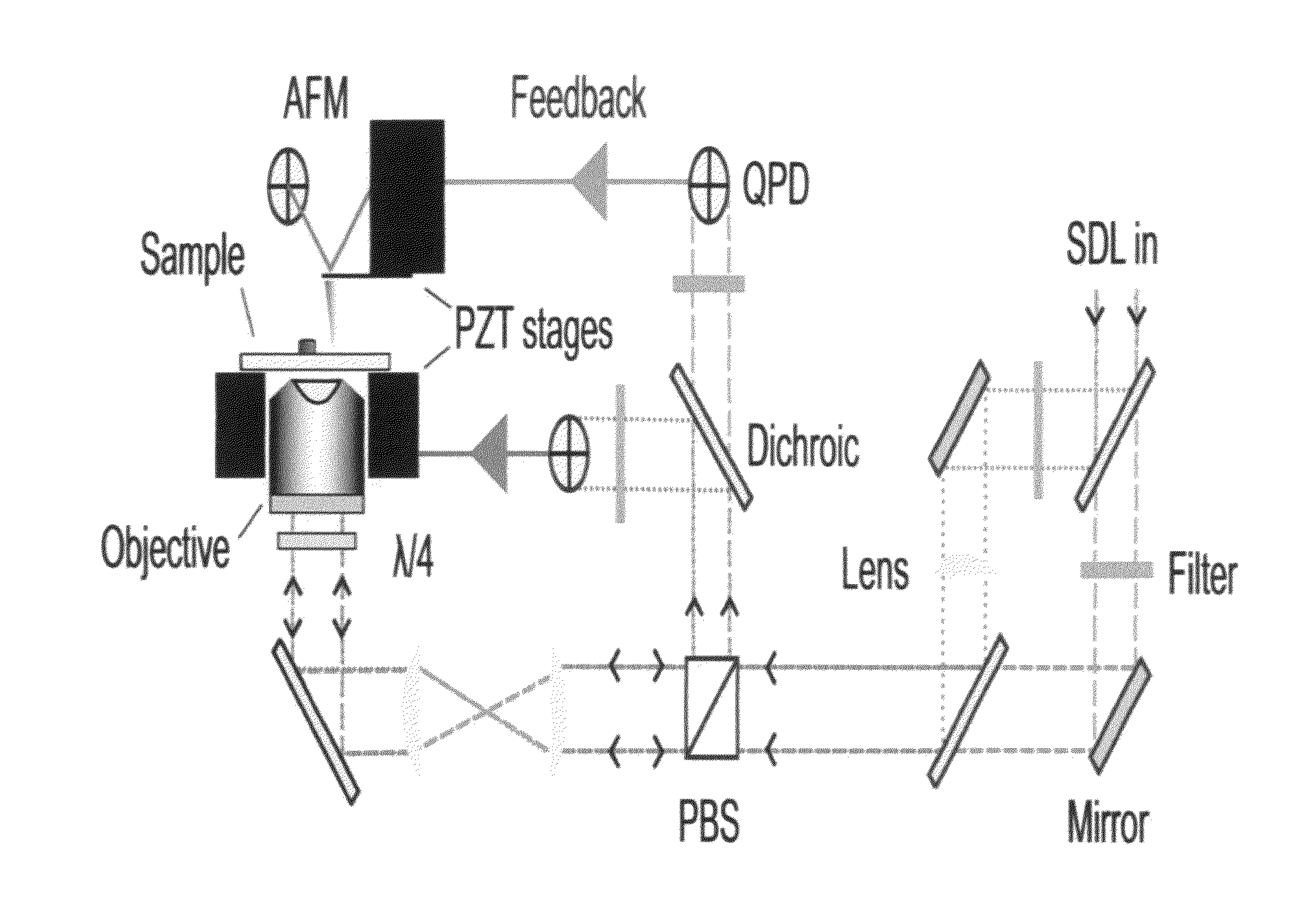
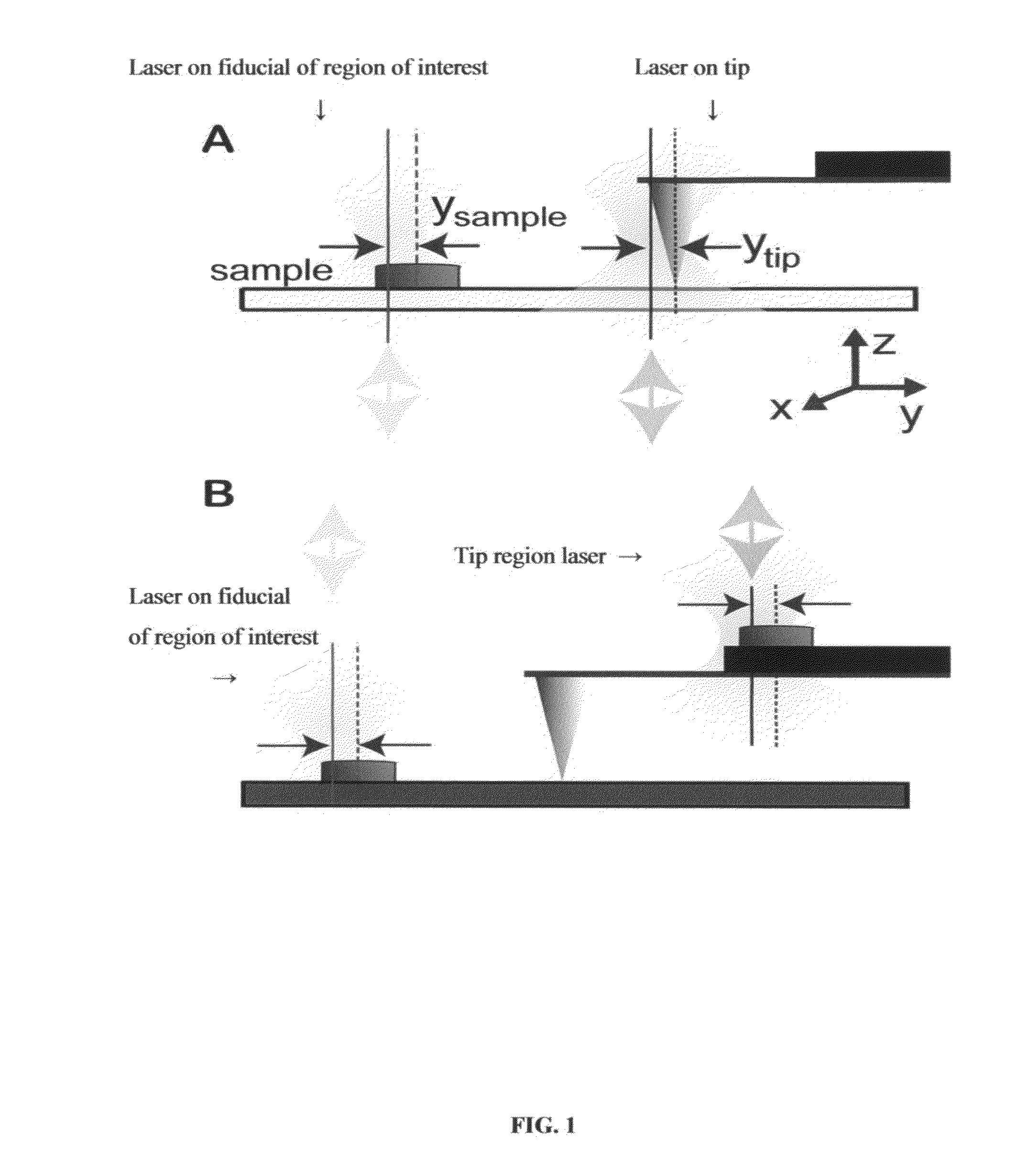
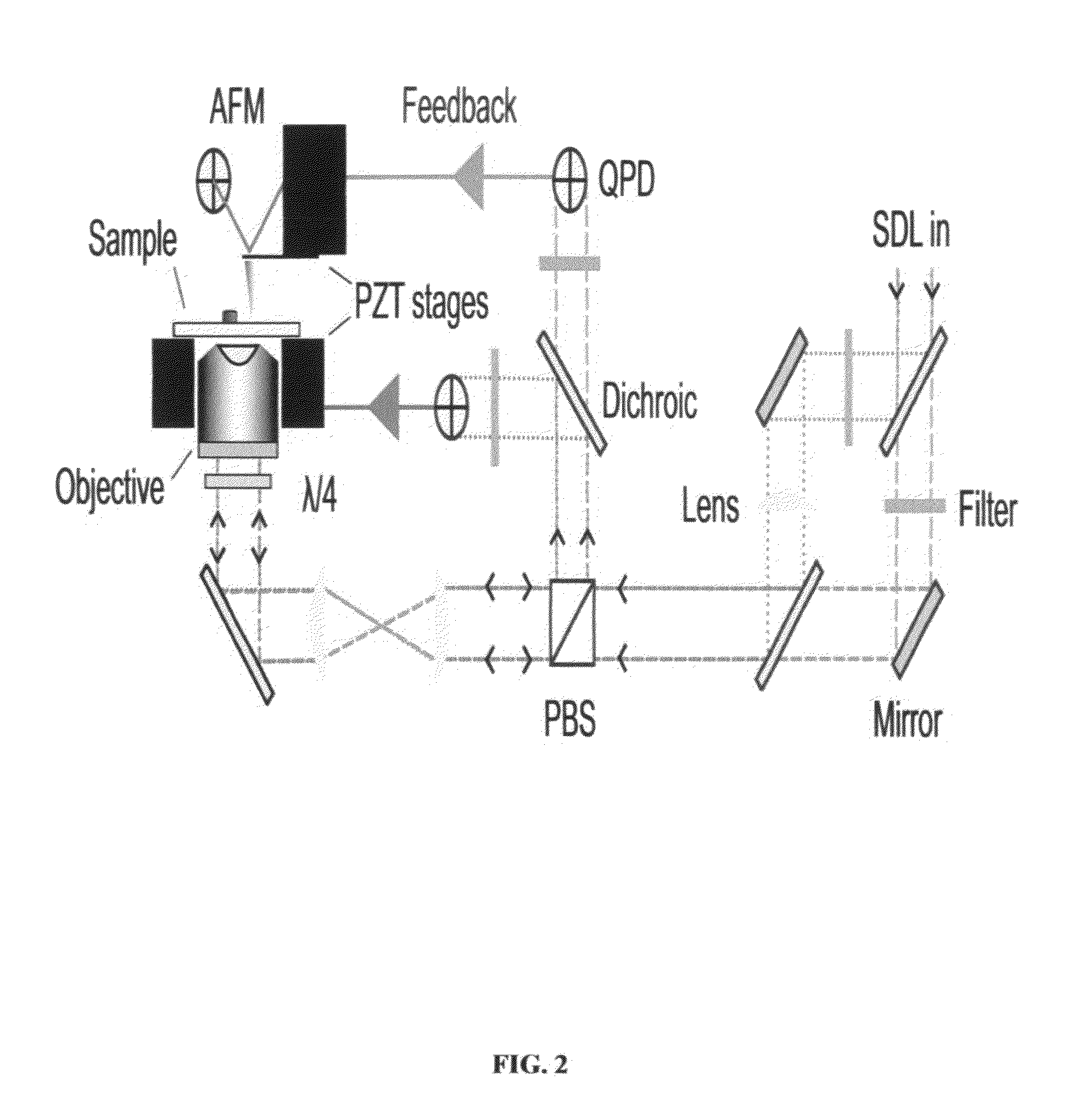
ActiveUS20110035848A1Reduce driftEnhance the imageNanotechnologyScanning probe microscopyLaserRegion of interest
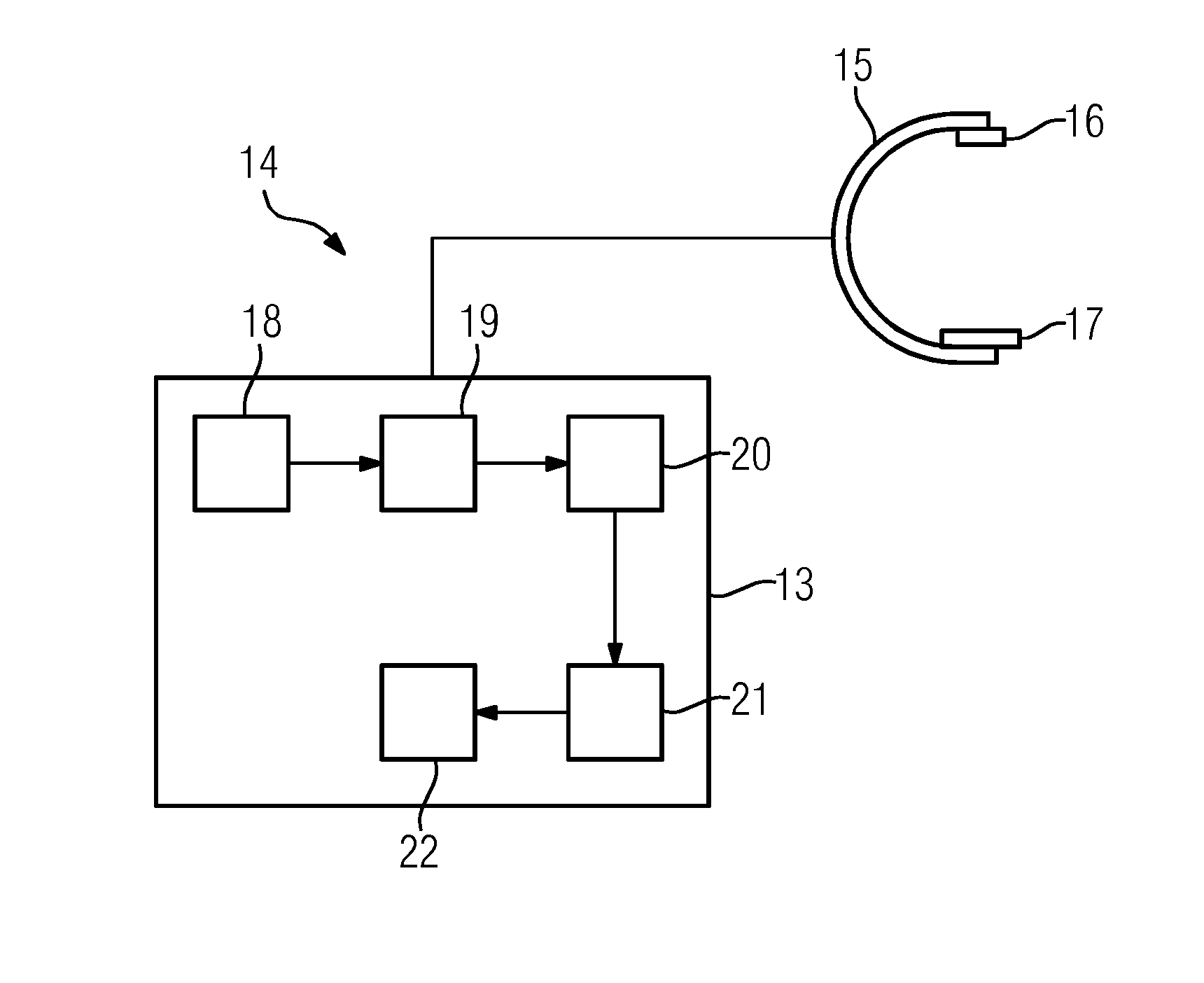
The present invention relates to a method of rapidly and repeatably bringing sharp objects into close proximity to a particular region of interest of a sample with high precision and accuracy in two or three dimensions using a laser guided tip approach with three dimensional registration to the surface.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
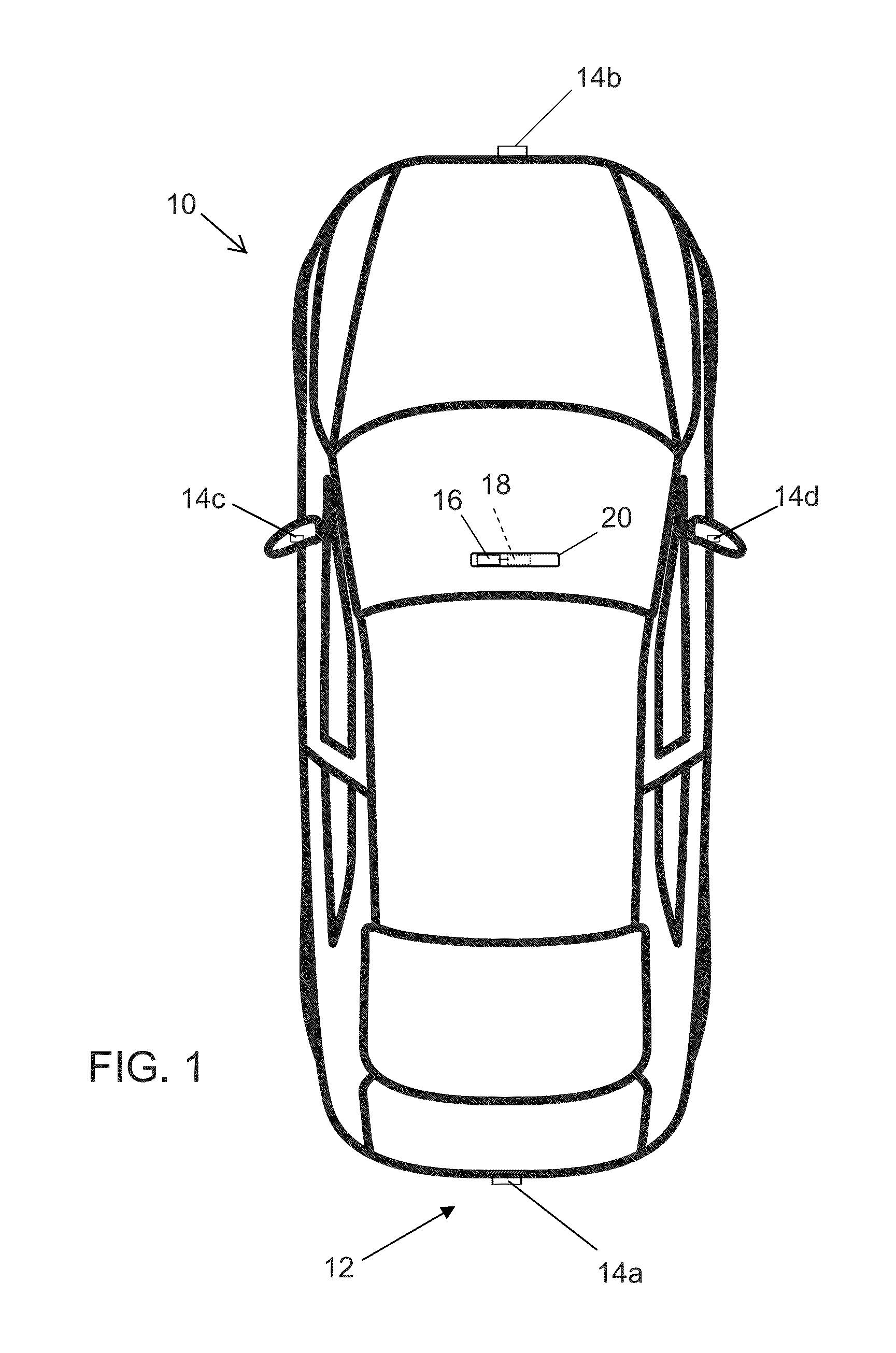
Vehicle vision system with 3D registration for distance estimation
ActiveUS20160180182A1Reliable distance estimationStable outputImage enhancementImage analysisTriangulationVisual perception
A vision system of a vehicle includes at least one camera configured to be disposed at a vehicle so as to have a field of view exterior of the vehicle. Responsive to image processing of captured image data and with the at least one camera disposed at the vehicle, the image processor determines a three dimensional object present in the field of view of the camera and determines a point of interest on the determined object. The vision system uses triangulation to determine an estimated location in three dimensional space of the determined point of interest. The vision system processes additional frames of captured image data to enhance the estimation of the location in three dimensional space of the determined point of interest. The image processor is operable to estimate a distance to the determined object by comparing multiple frames of captured image data.
Owner:MAGNA ELECTRONICS
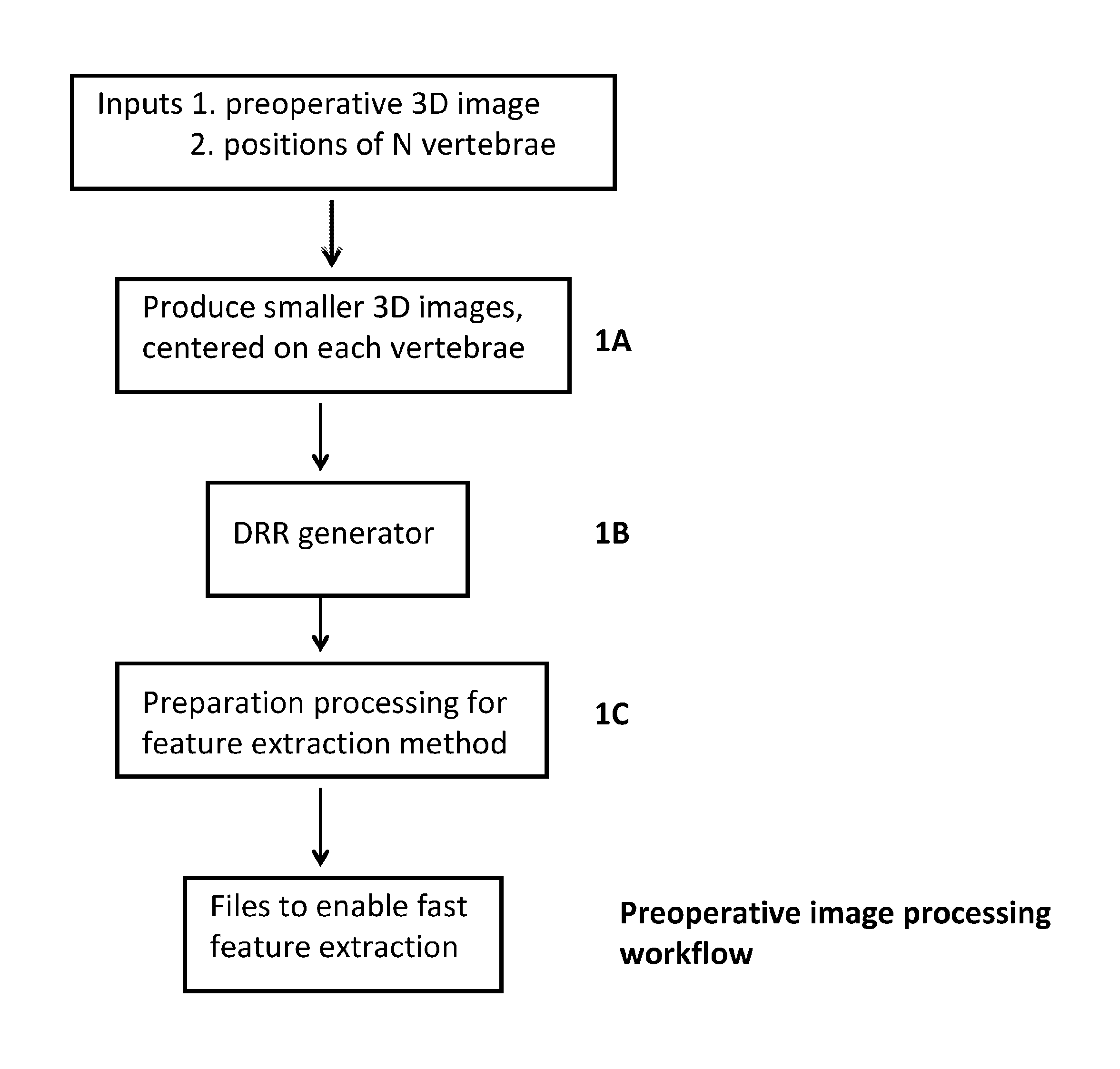
Method and system to assist 2D-3D image registration
Embodiments of the invention provide a system and method that is able to automatically provide a starting point for 2D to 3D image registration, without relying on human recognition of features shown in the 2D image. This is achieved by pre-processing the 3D data to obtain synthetically generated 2D images of those parts of the 3D data volume which will be used for registration purposes. Many different synthetically generated 2D images of the or each part of the 3D volume are produced, each from a different possible viewing direction. Each of these synthetic images is then subject to a feature extraction process to extract characterizing feature data of the registration feature shown in the images. Once the feature extraction has been undertaken for each image, when registration is to be performed the real-time 2D image is processed by applying each of the sets of extracted features thereto, to try and identify which set best matches the registration features in the 2D image. For example, where a generalized Hough transform was used in the feature extraction, the R tables would be applied to the 2D image to obtain respective accumulation images. The accumulation images may then be ranked to identify which registration feature is shown in the 2-D image, and from which view direction. This gives the required information of which registration feature is being shown in the 2D image, and also the in-plane location and orientation. This information can then be used as a starting point for the 2D to 3D registration procedure.
Owner:CYDAR LTD
Multimodal carotid MRI registration method based on physical alignment and contour matching
ActiveCN108053433AAccurate 3D RegistrationAchieving alignmentImage enhancementImage analysisDiagnostic Radiology ModalityContour matching
The invention relates to a multimodal carotid MRI registration method based on physical alignment and contour matching. The method comprises steps that 1), image space physical coordinates are calculated; 2), body pixel spacing conversion image formats are unified; 3), the alignment relationship of multi-modal image layers is determined; 4), inner wall segmentation of multi-modal 2D images of eachsequence is carried out, a sequence of MRI images is sequentially selected, segmentation start and termination layers of the sequence images are determined, the ROI where a carotid is located in thestart layer image is selected, and the segmentation method is utilized to realize continuous automatic segmentation of the entire sequence; and 5), 3D registration based on the inner wall contour is carried out, and the clear inner wall contour segmentation result is utilized to carry out three-dimensional continuous registration. The method is advantaged in that carotid multimodal sequence imagesin various types are effective, alignment registration among pixels is excellently realized, and doctors are facilitated to carry out subsequent diagnosis and treatment determination and patch composition analysis.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Detection and tracking of interventional tools
InactiveUS20100226537A1Improve visibilityEasy to detectImage enhancementImage analysisFluorescence3d rotational angiography
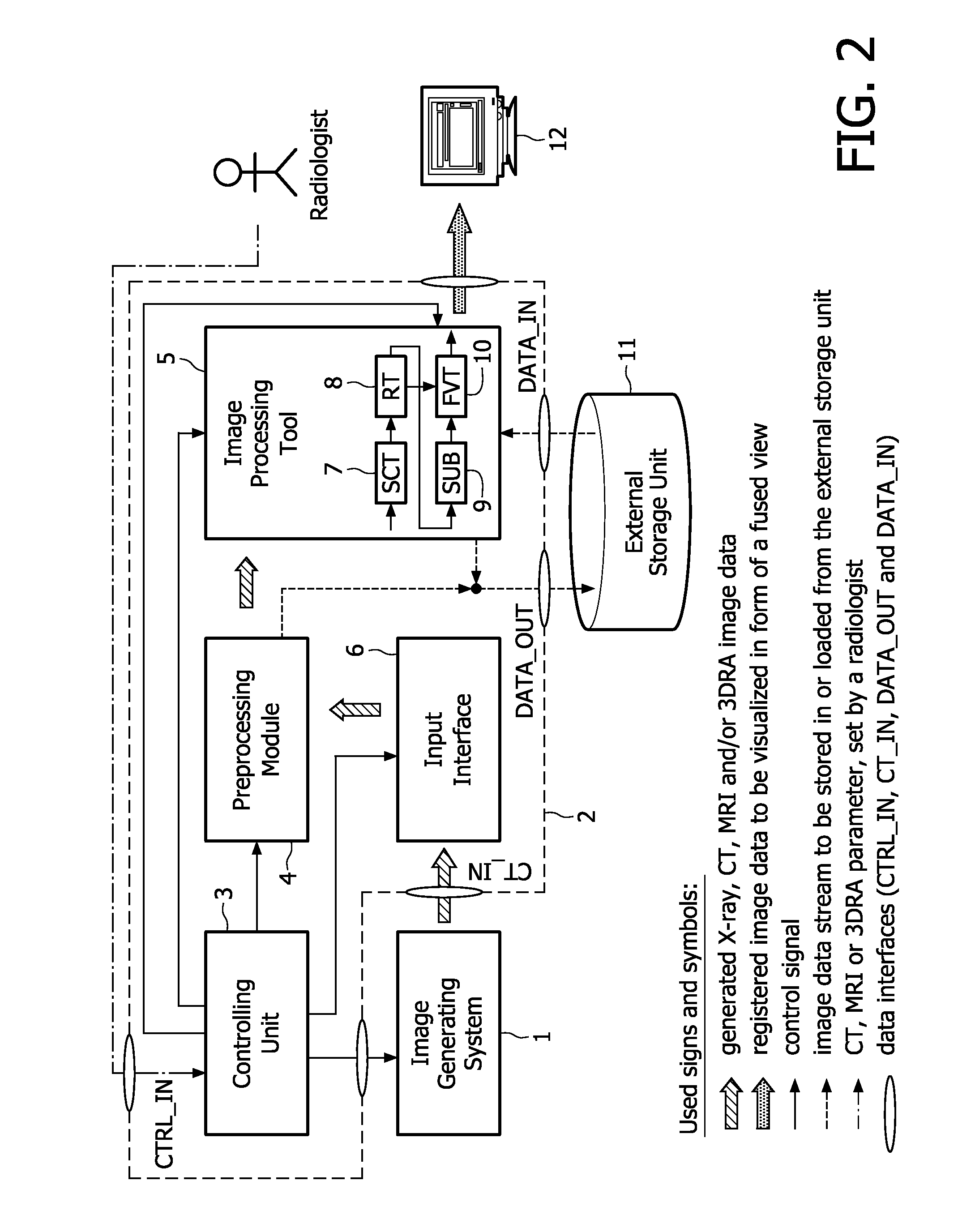
The present invention relates to minimally invasive X-ray guided interventions, in particular to an image processing and rendering system and a method for improving visibility and supporting automatic detection and tracking of interventional tools that are used in electrophysiological procedures. According to the invention, this is accomplished by calculating differences between 2D projected image data of a preoperatively acquired 3D voxel volume showing a specific anatomical region of interest or a pathological abnormality (e.g. an intracranial arterial stenosis, an aneurysm of a cerebral, pulmonary or coronary artery branch, a gastric carcinoma or sarcoma, etc.) in a tissue of a patient's body and intraoperatively recorded 2D fluoroscopic images showing the aforementioned objects in the interior of said patient's body, wherein said 3D voxel volume has been generated in the scope of a computed tomography, magnet resonance imaging or 3D rotational angiography based image acquisition procedure and said 2D fluoroscopic images have been co-registered with the 2D projected image data. After registration of the projected 3D data with each of said X-ray images, comparison of the 2D projected image data with the 2D fluoroscopic images—based on the resulting difference images—allows removing common patterns and thus enhancing the visibility of interventional instruments which are inserted into a pathological tissue region, a blood vessel segment or any other region of interest in the interior of the patient's body. Automatic image processing methods to detect and track those instruments are also made easier and more robust by this invention. Once the 2D-3D registration is completed for a given view, all the changes in the system geometry of an X-ray system used for generating said fluoroscopic images can be applied to a registration matrix. Hence, use of said method as claimed is not limited to the same X-ray view during the whole procedure.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Methods for Updating 2D/3D Registration on Movement and Computing Device
ActiveUS20150030229A1Easy to observeMinimize confusionImage enhancementStentsData setProjection image
Methods for updating a 2D / 3D registration between a three-dimensional image data set corresponding to a target area subjected to a movement and a plurality of two-dimensional projection images of the target area include: selecting a plurality of contour points along a contour, the contour being visible in a first projection image and a three-dimensional image data set registered therewith, the plurality of contour points being associated with a rigid object in the target area; determining a displacement of each contour point of the plurality of contour points between the first projection image and a successively captured second projection image; obtaining movement information for each contour point of the plurality of contour points based on the determined displacement, the movement information describing a movement of the rigid object; and updating the registration based on the obtained movement information.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
3D (three-dimensional) image registration method and device based on conformal geometric algebra
The invention discloses a 3D (three-dimensional) image registration method and device based on conformal geometric algebra. The 3D image registration method comprises the following steps of: rebuilding a position relation restrain problem of a 3D medical image by using the conformal geometric algebra, analyzing conformal geometric transformation of the medical image, constructing a new 3D medical image registration similarity measure, and proposing a 3D medical image registration algorithm for 3D registration of CT (Computed Tomography) and MR_T1 (Magnetic Resonance) images. According to the three-dimensional image registration method and the three-dimensional image registration device, the direct alignment of 3D data is realized, the 3D positions of tissues and organs can be better positioned, the registration result is more direct, the image after registration is clearer, and the registration precision is higher.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Angle rotation real-time matching method based on try wearing of 3D (three dimensional) glasses
ActiveCN104881114AEasy to useLow costInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingEyewearMatching methods
Owner:深圳新视代眼健康科技有限公司
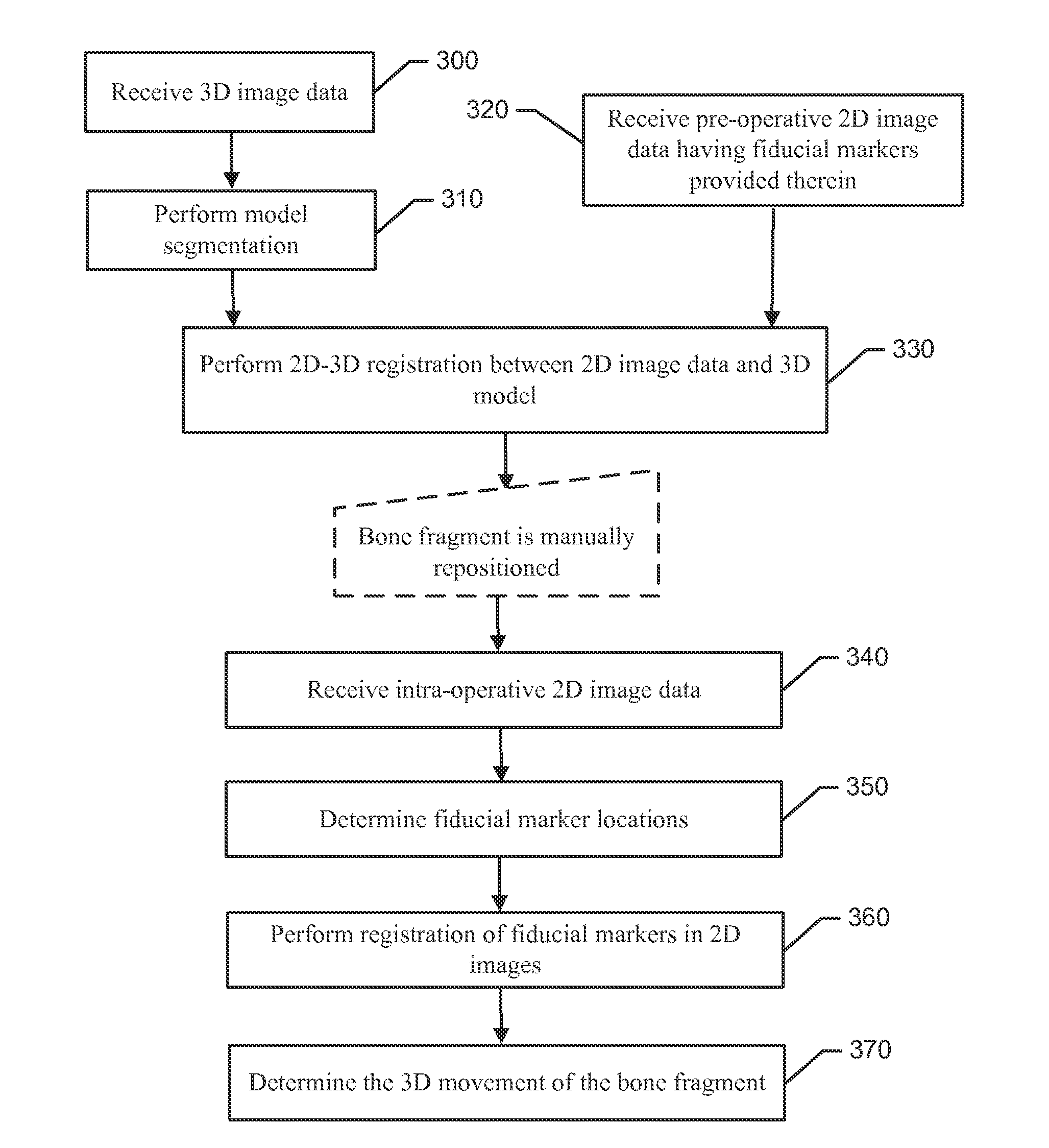
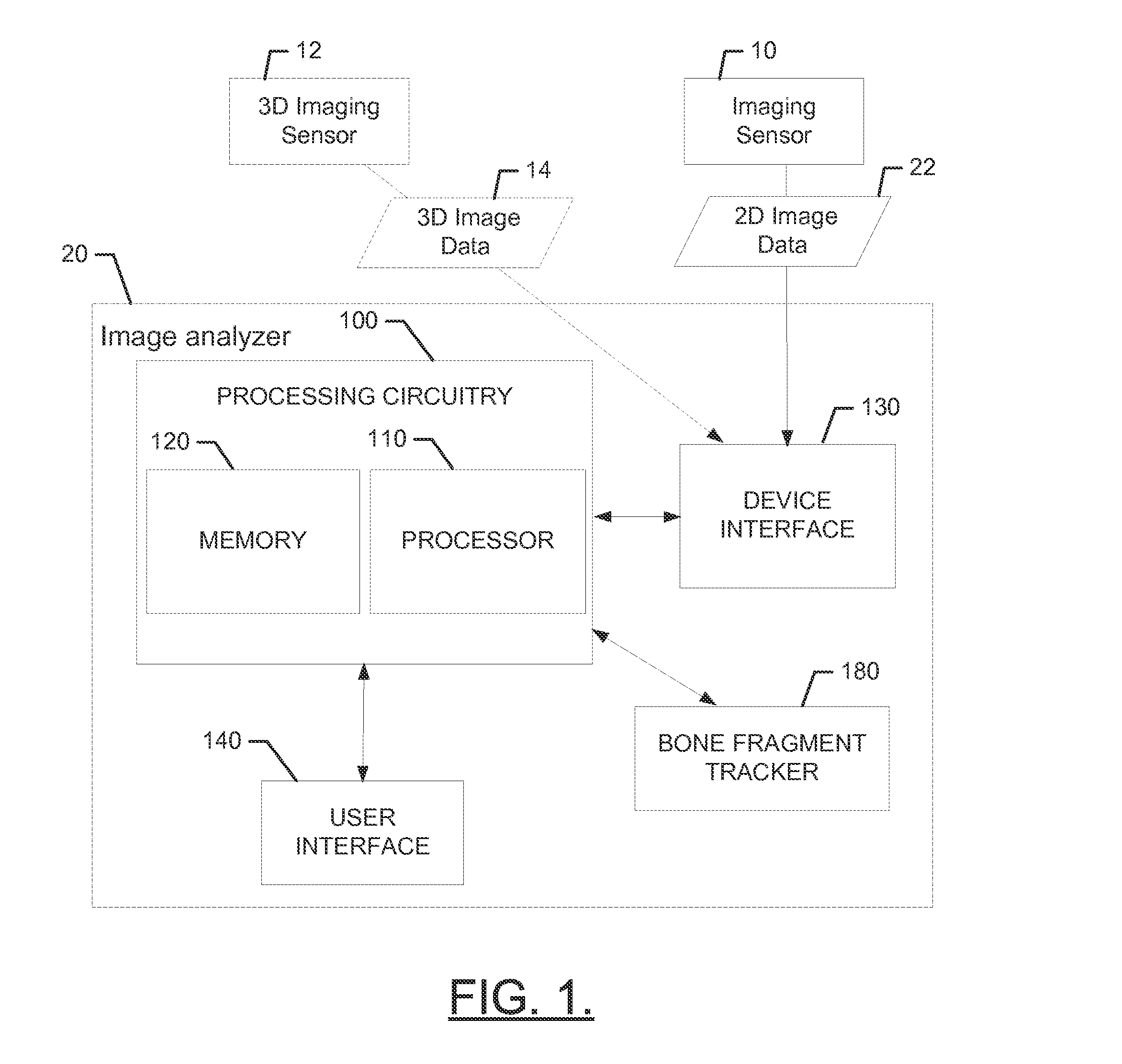
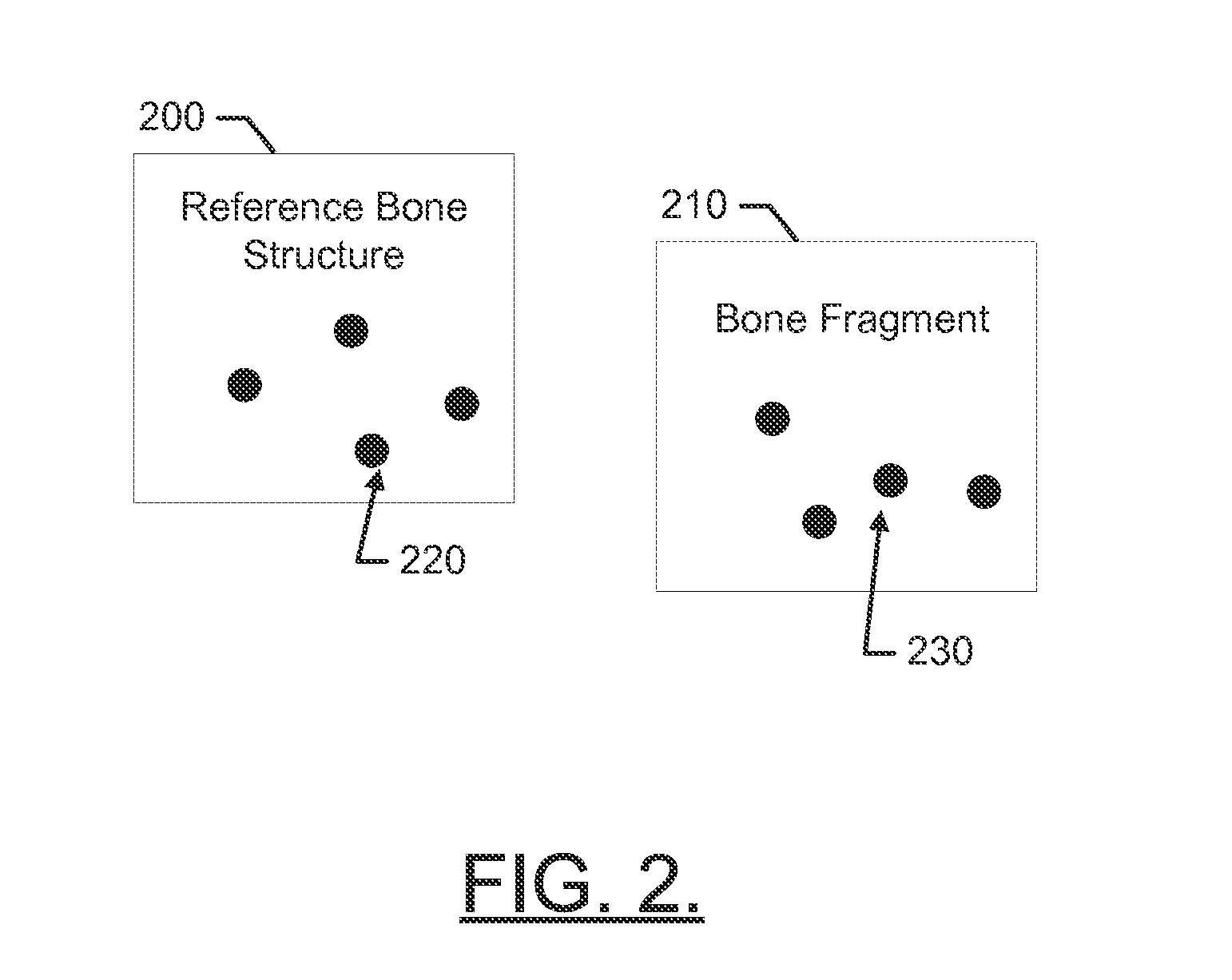
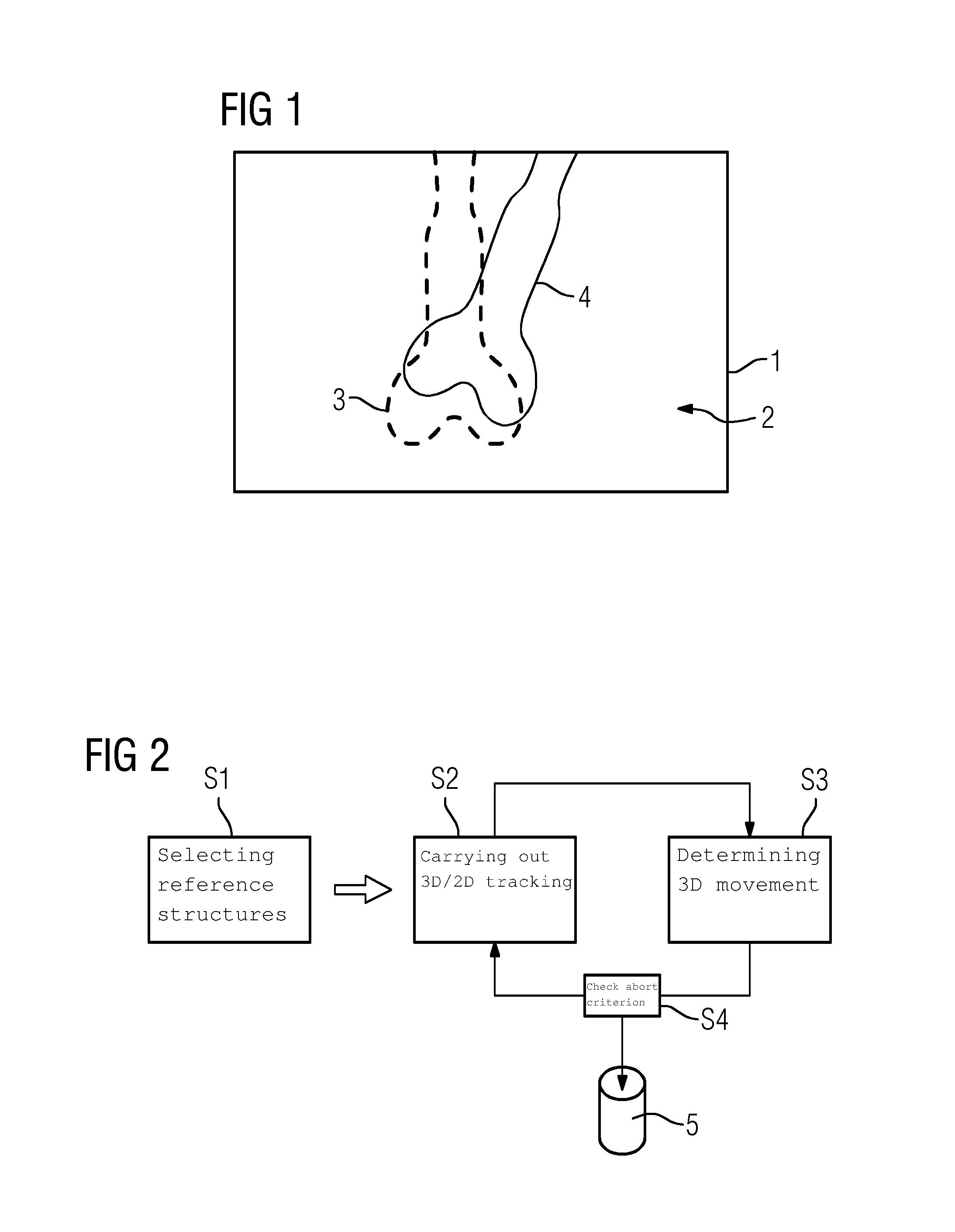
Bone fragment tracking
A method of determining bone fragment navigation may include receiving pre-operative 2D image data of a reference bone structure and a bone fragment. The reference bone structure may include a first set of fiducial markers provided thereon, and the bone fragment may include a second set of fiducial markers provided thereon. The method may further include performing a 2D-3D registration between the pre-operative 2D image data and a 3D model of the reference bone structure and the bone fragment, after manual repositioning of the bone fragment, receiving second 2D image data, performing 2D-2D registration of the first set of fiducial markers and the second set of fiducial markers between the pre-operative 2D image data and the second 2D image data, and determining 3D movement of the bone fragment based at least in part on the 2D-2D registration.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
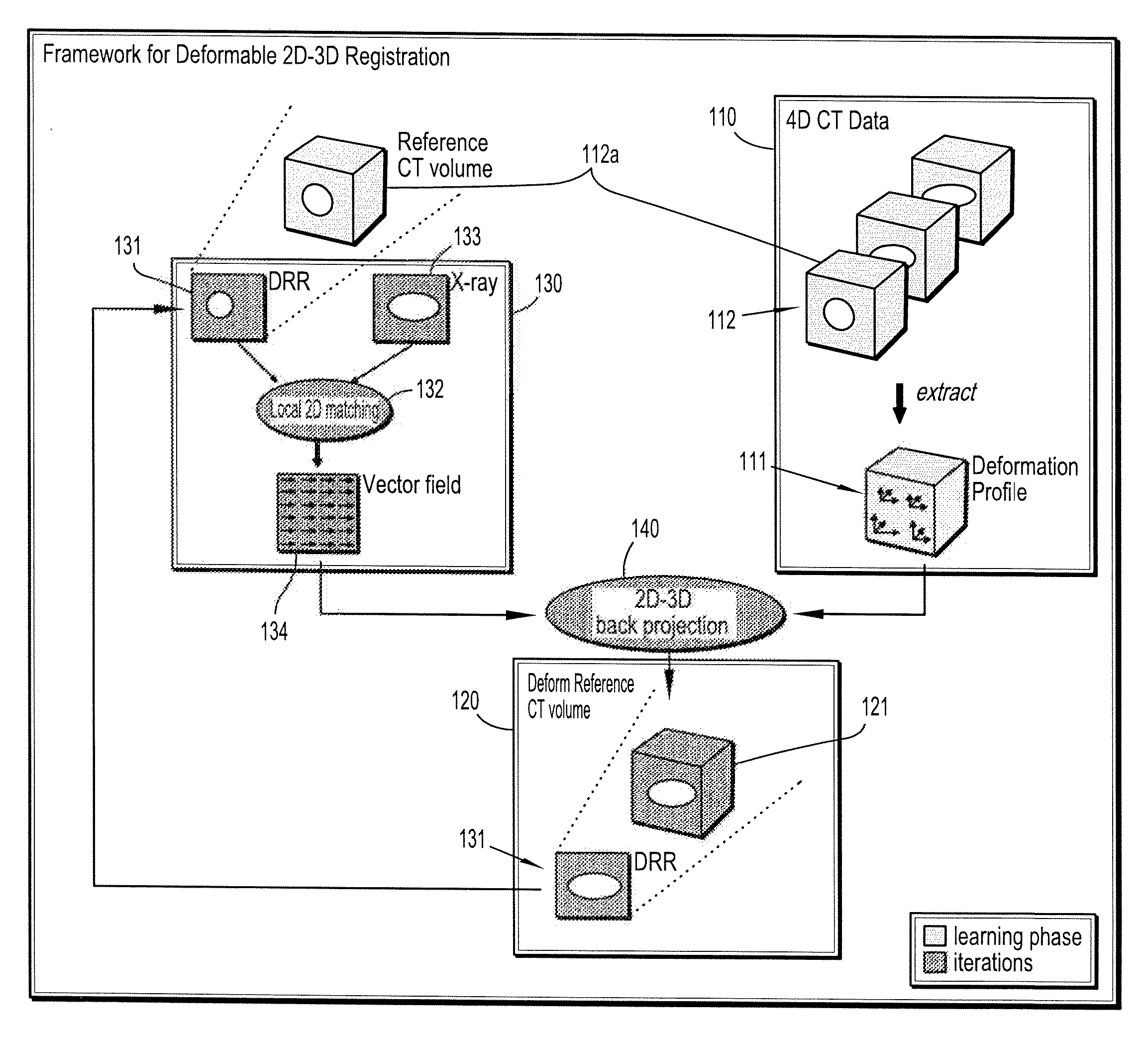
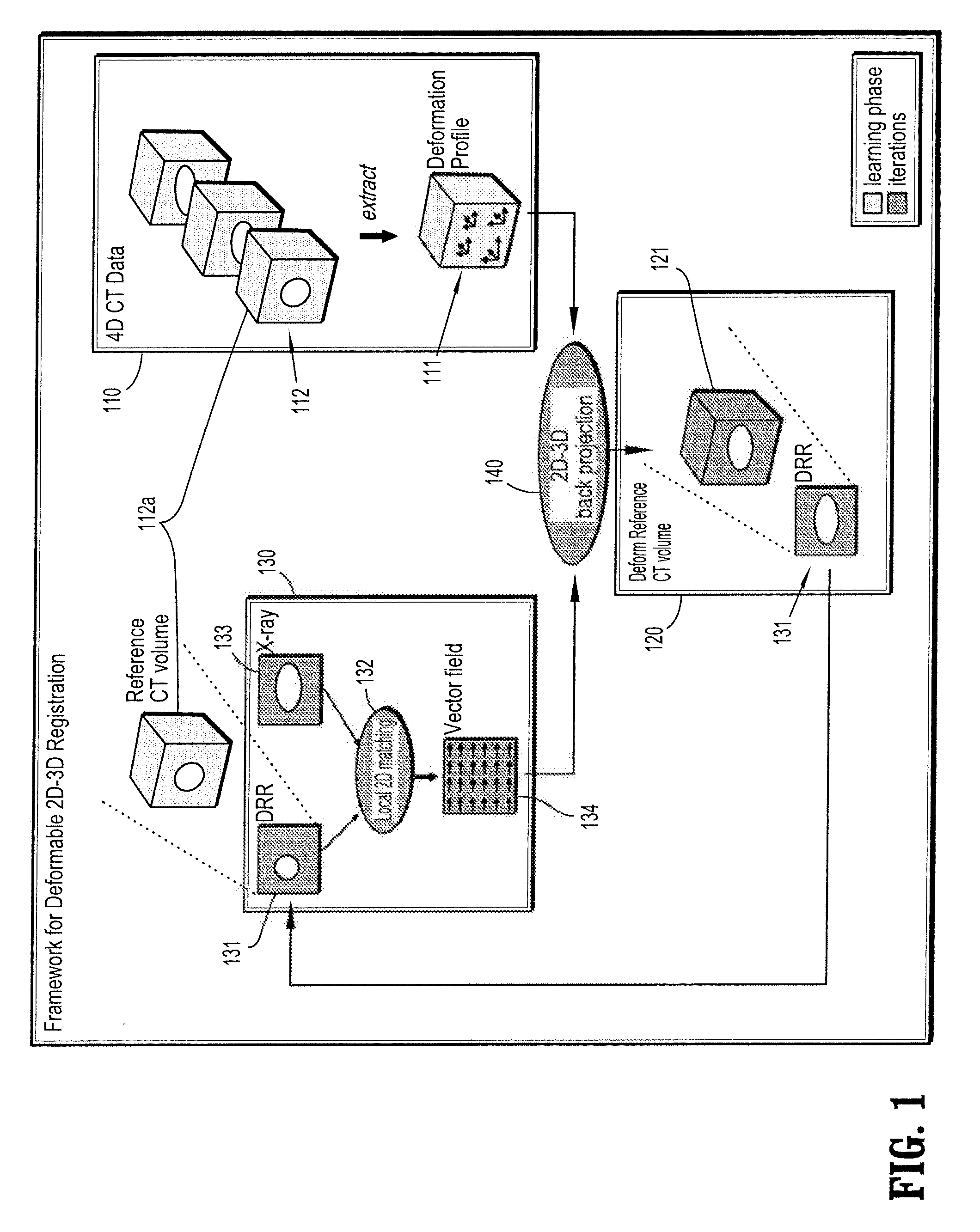
Deformable 2d-3d registration
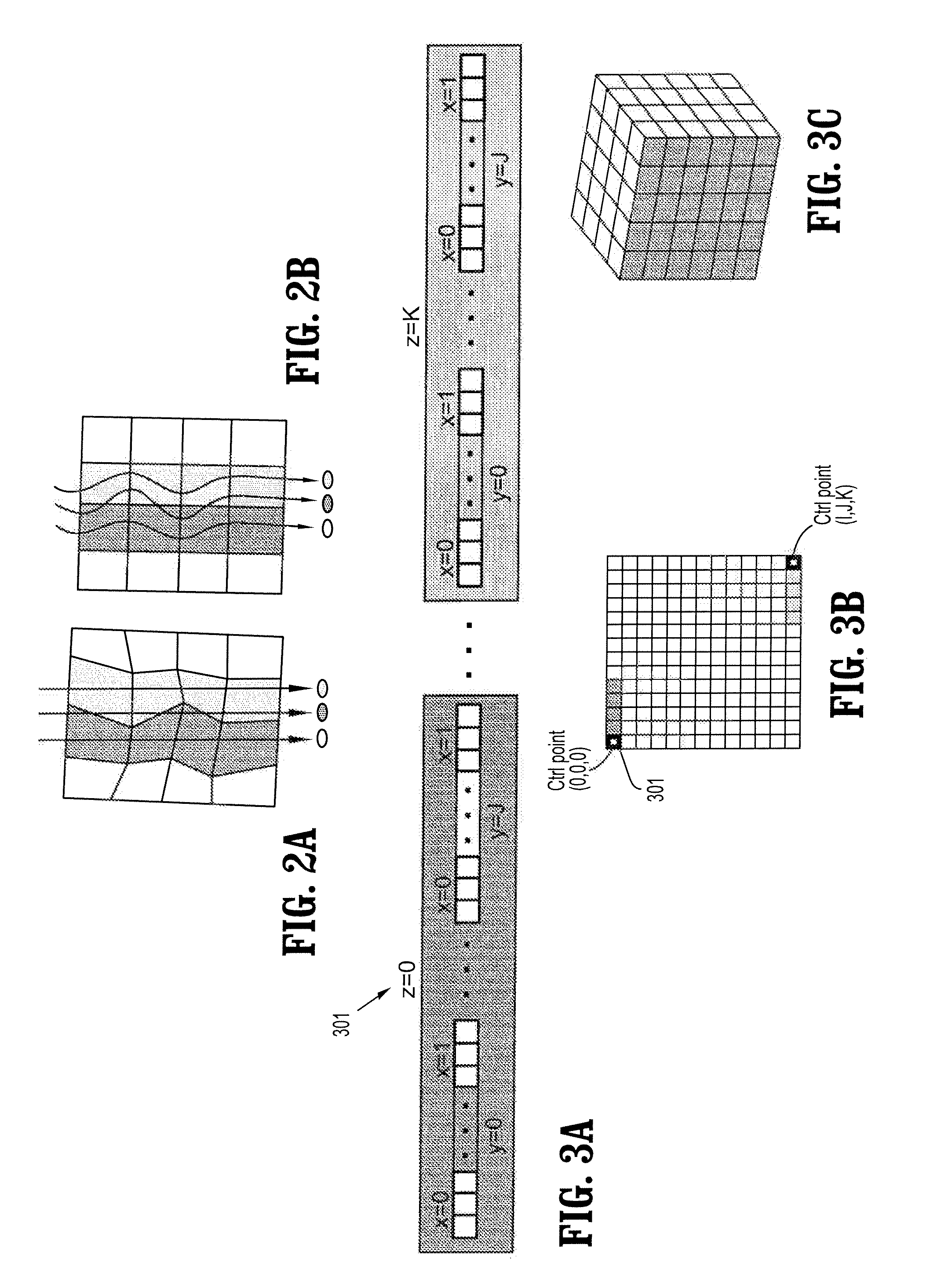
A method for deformable registration including determining a vector field from a two-dimensional matching of a volume of an object of interest and a two-dimensional image of the object of interest, providing a deformation profile, and finding a volume deformation that maps to a state of the two-dimensional image, wherein the deformation is parameterized by the vector field and control points of the deformation profile to find a control point configuration of the volume deformation.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Geographic grid and image identification combination-based outdoor mobile augmented reality method
ActiveCN107833280ASolve problems that are prone to mismatchesQuick matchImage analysisImage generationData acquisitionGeographic information system
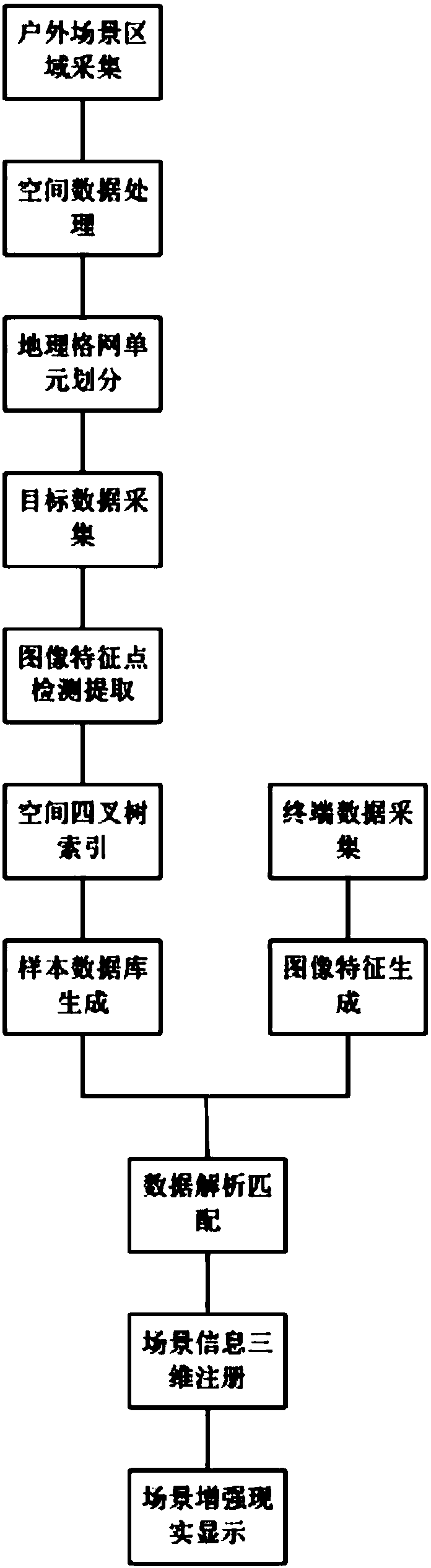
The present invention relates to the augmented reality field, in particular relates to a geographic grid and image identification combined outdoor mobile augmented reality method. The outdoor mobile augmented reality method comprises the following steps of the outdoor scene area acquisition, the spatial data processing, the geographic grid unit division, the target data acquisition, the image feature point detection and extraction, the spatial quadtree index, the sample database generation, the terminal data acquisition, the image feature generation, the data analysis and matching, the scene information 3D registration and the scene augmented reality display. The outdoor mobile augmented reality method of the present invention can better overcome the influence of the factors during an image identification process, such as the translation, the rotation, the scale zooming, the brightness change, etc., at the same time, by adding the color information in a descriptor, the problem that thegray change similar areas generate the mismatching problem easily is solved, by combining a geographic information technology, the image features having the similar textures can be distinguished according to the positions, by utilizing the division of the geographic grids, the sample point information quadtree indexes are established, and the rapid and accurate matching can be carried out in a mass feature database.
Owner:TIANJIN RES INST FOR WATER TRANSPORT ENG M O T
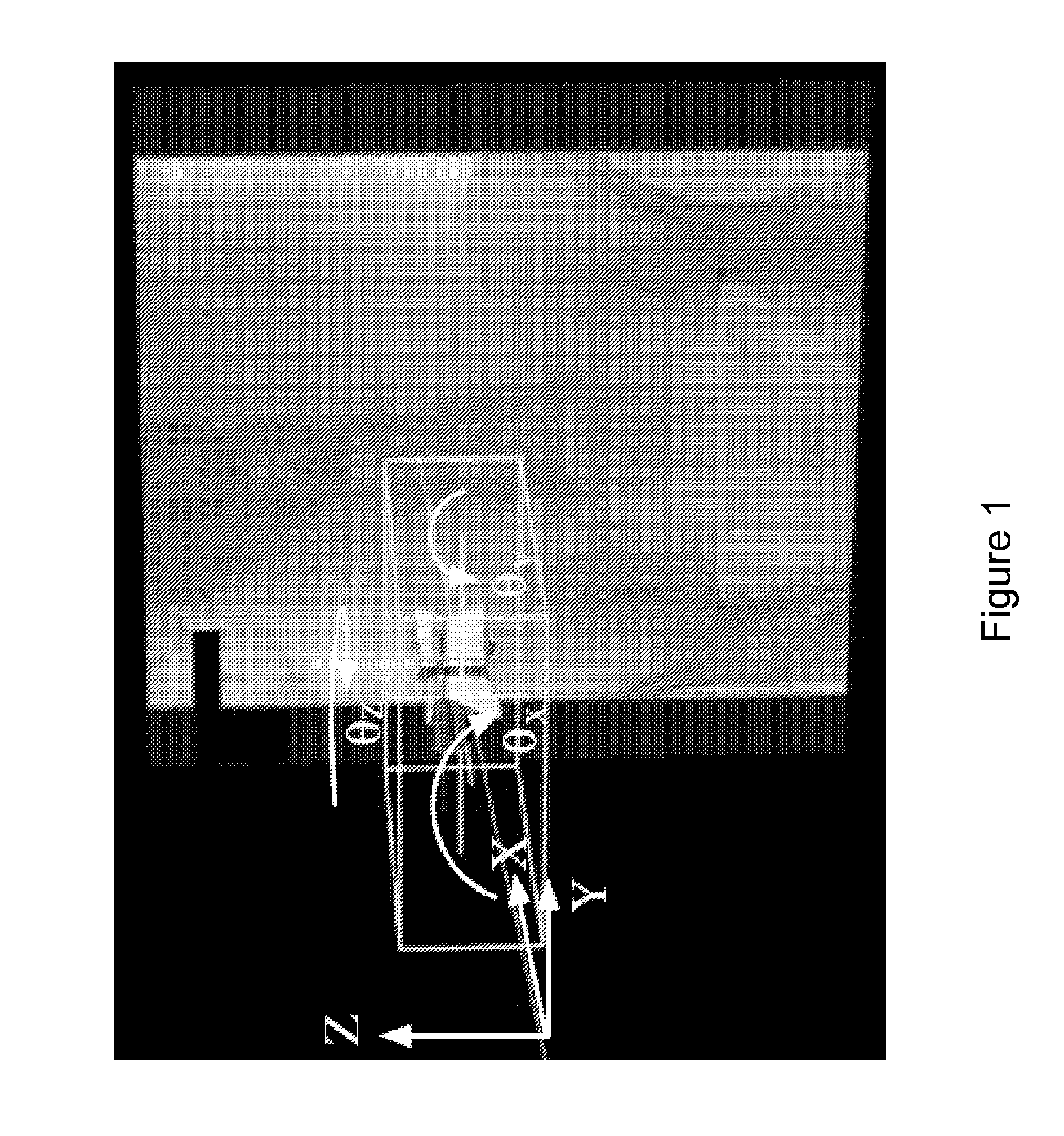
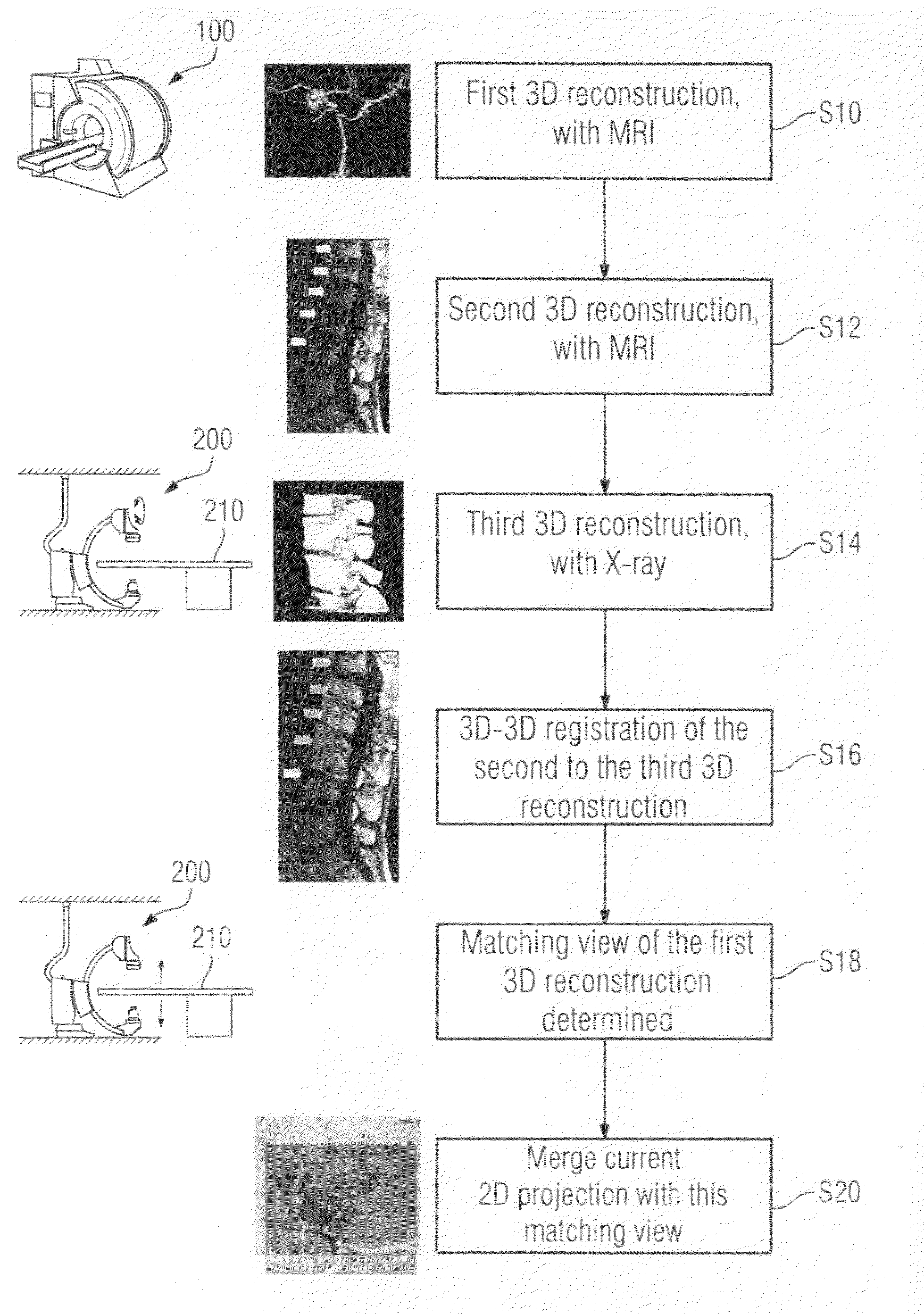
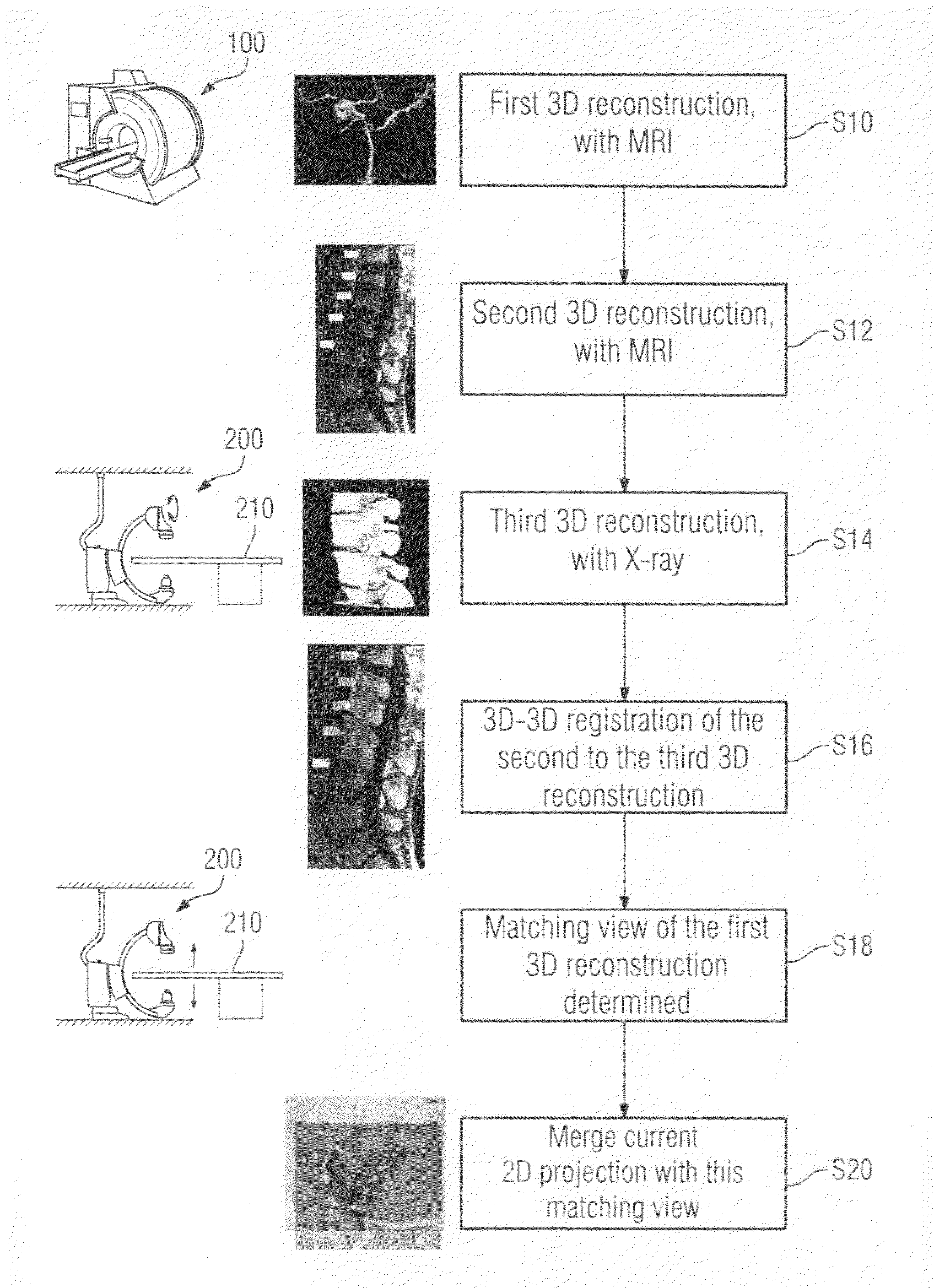
Method for image registration processes and X-ray angiography system
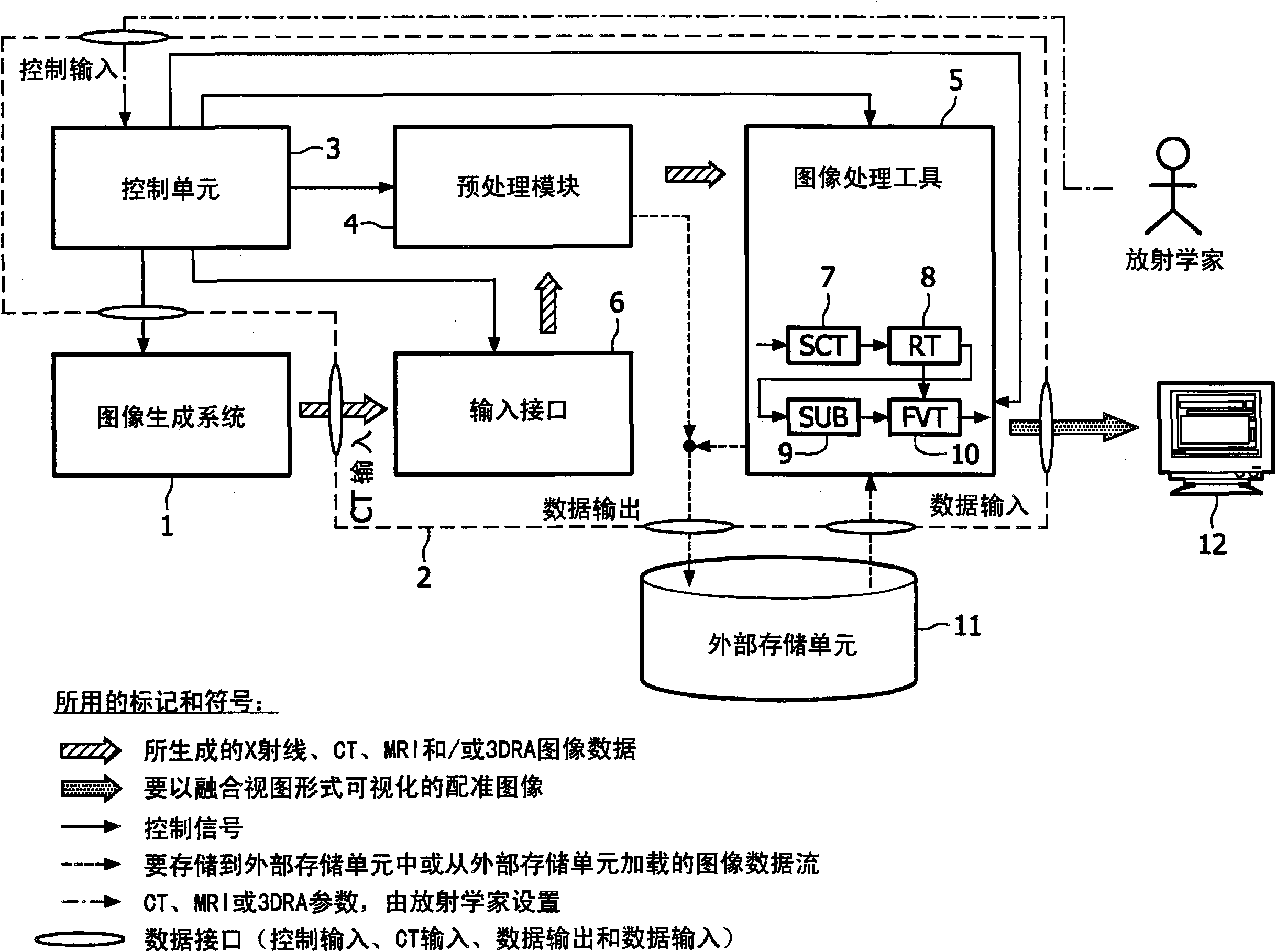
Registration of preoperatively acquired MRI images of soft parts to intraoperatively acquired X-ray images of soft parts is not possible. The invention shows a way of nevertheless using such preoperatively acquired images for superimposition with 2D projections of the soft parts, taking an indirect route via 3D / 3D registration of images of the spinal column. For this purpose, 3D image data sets of the spinal column must be obtained separately on the one hand using MRI and on the other using the X-ray imaging system so that the 3D / 3D registration produces a mapping rule which then also applies to the preoperatively acquired images of the soft part if the soft part images and the spinal images are acquired without intervening change in the patient position in the MRI scanner.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Gpu-based system for performing 2d-3d deformable registration of a body organ using multiple 2d fluoroscopic views
ActiveUS20160260220A1Precise motionThe result is accurateImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionGraphicsBody organs
Systems and methods for assisting a physician in a medical intervention comprises performing a 2D-3D deformable registration, and more particularly, performing a 2D-3D registration based on multiple live 2D fluoroscopic views, and implemented on a multi-core processing framework such as a Graphics Processing Unit.
Owner:BRONCUS MEDICAL
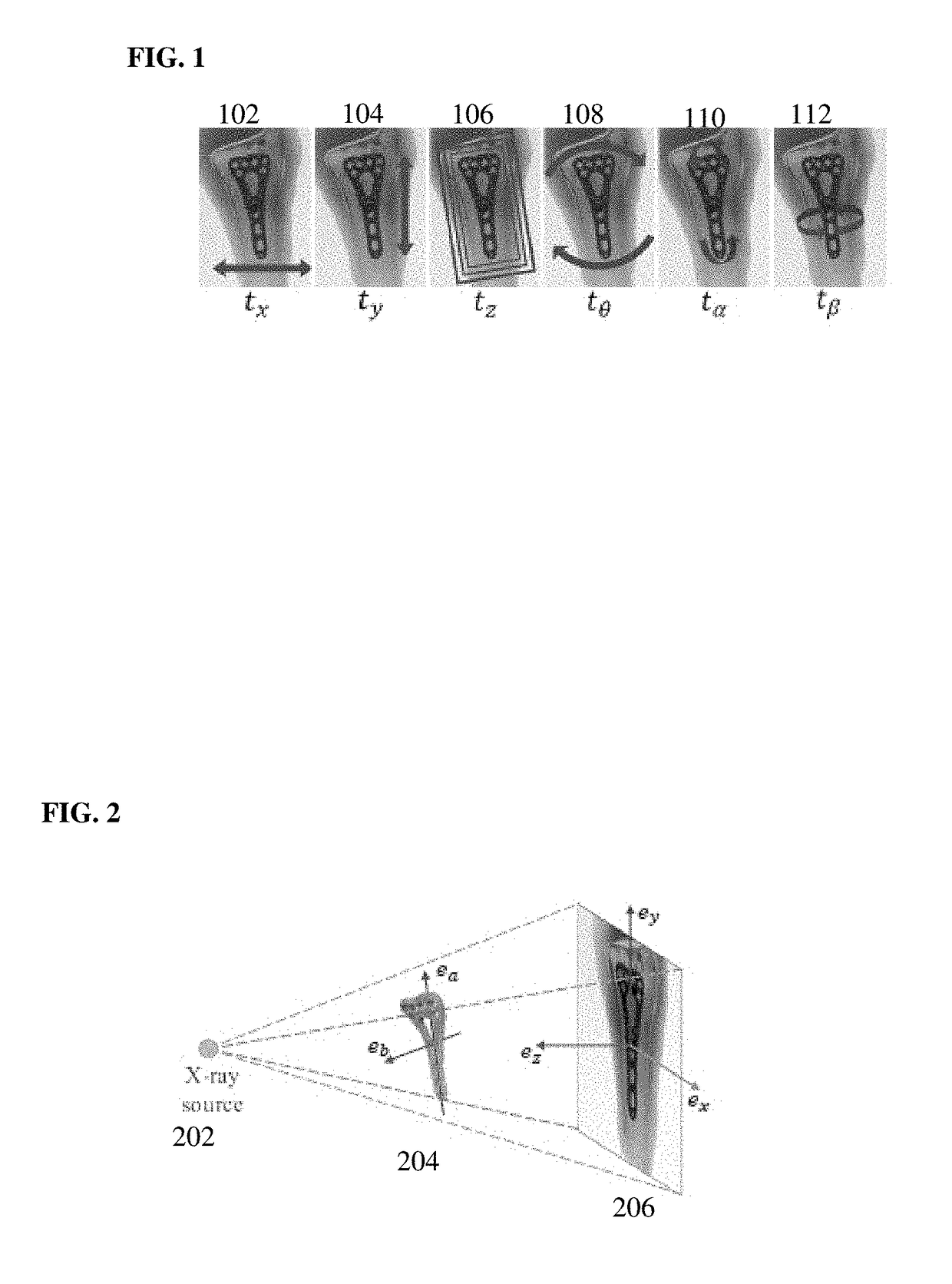
Method and system for convolutional neural network regression based 2D/3D image registration
ActiveUS10235606B2Large capture rangeImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisTransformation parameterX ray image
A method and apparatus for convolutional neural network (CNN) regression based 2D / 3D registration of medical images is disclosed. A parameter space zone is determined based on transformation parameters corresponding to a digitally reconstructed radiograph (DRR) generated from the 3D medical image. Local image residual (LIR) features are calculated from local patches of the DRR and the X-ray image based on a set of 3D points in the 3D medical image extracted for the determined parameter space zone. Updated transformation parameters are calculated based on the LIR features using a hierarchical series of regressors trained for the determined parameter space zone. The hierarchical series of regressors includes a plurality of regressors each of which calculates updates for a respective subset of the transformation parameters.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
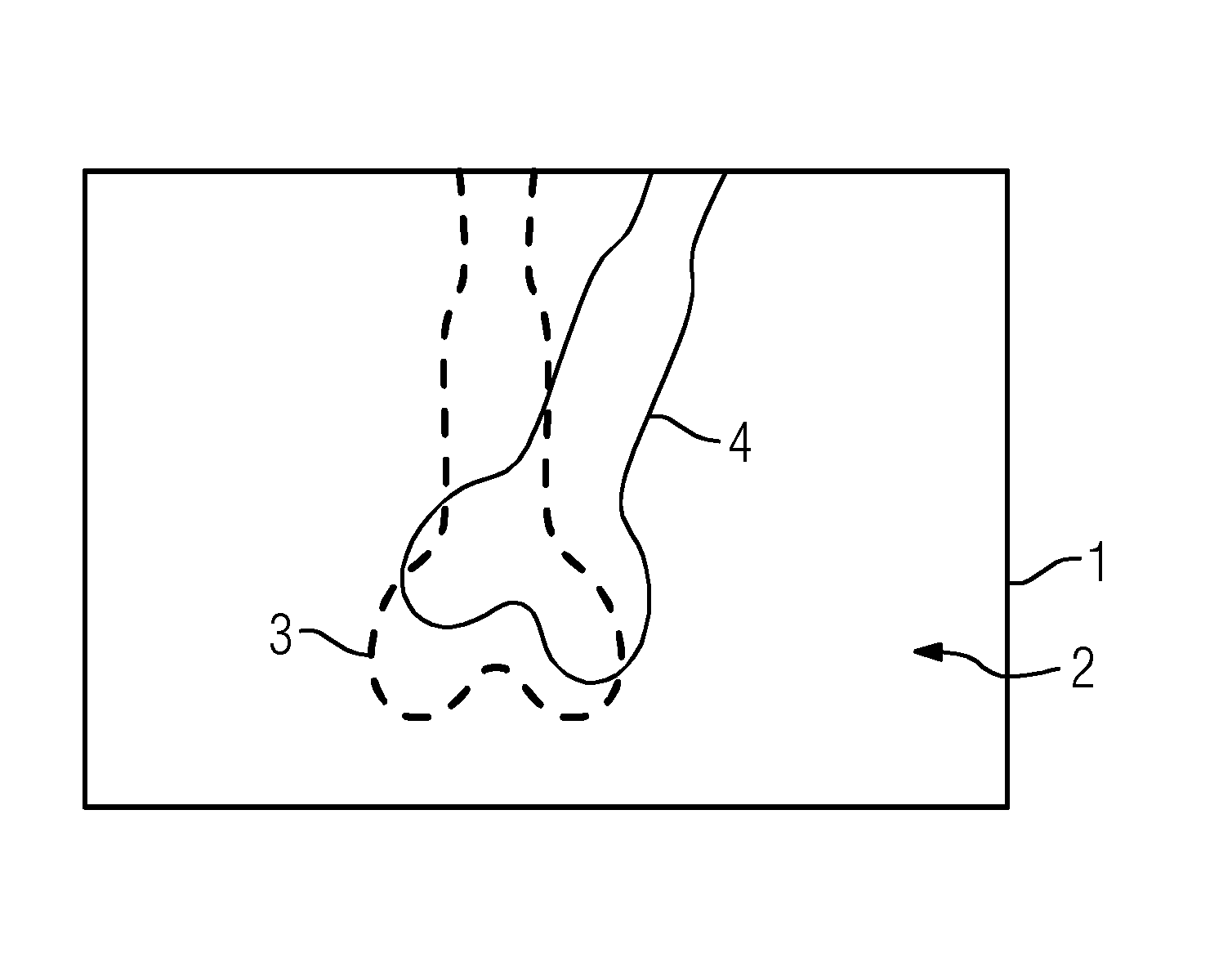
Method for 2D/3D Registration, Computational Apparatus, and Computer Program
ActiveUS20160335777A1Robust and accurate registrationReduce computational overheadImage enhancementImage analysisX-rayMotion parameter
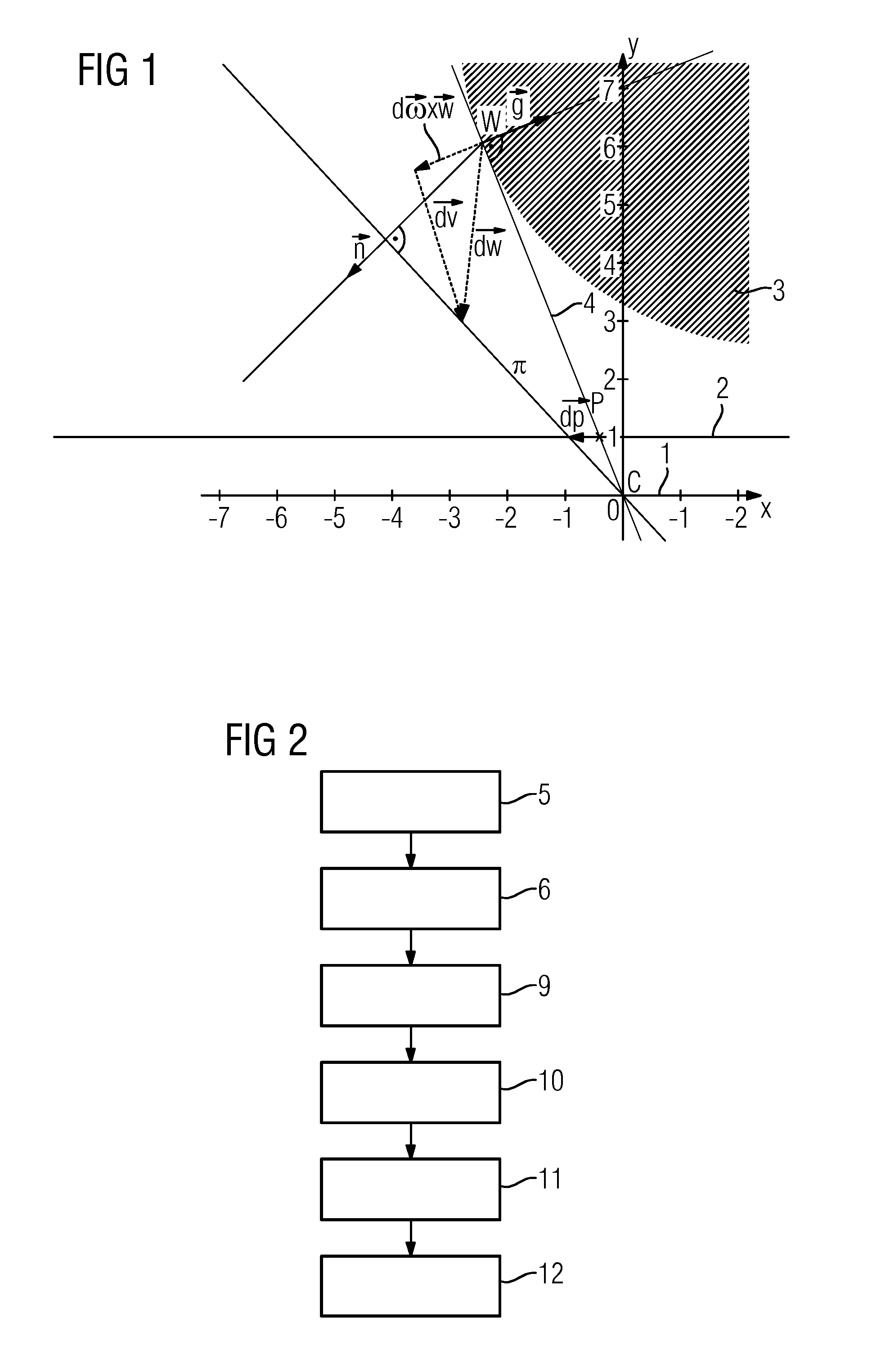
A method for registering a three-dimensional image data record of a target region of a patient with a two-dimensional x-ray image is provided. The method includes selecting at least one rigid reference structure with an associated contour; establishing a two-dimensional gradient x-ray image and a three-dimensional gradient data record of the image data record; finding a neighborhood in the gradient x-ray image from a plurality of neighborhoods extending about test points for a plurality of contour points; establishing local two-dimensional displacement information by comparison of the contour points with the associated comparison points; establishing movement parameters of a three-dimensional movement model describing a movement of the target region between recording of the image data record and the x-ray image from the local two-dimensional displacement information; and establishing a registration transformation describing the registration by correcting the test transformation based on the movement parameters.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
2D/3D Registration
ActiveUS20170243361A1High resolutionIncrease in sizeImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionData setMotion parameter
A method includes, following specification of an initial transformation as a test transformation that is to be optimized, determining a 2D gradient x-ray image and a 3D gradient dataset of the image dataset, carrying out, for each image element of the gradient comparison image, a check for selection as a contour point, and determining an environment best corresponding to a local environment of the contour point and extending around a comparison point in the gradient x-ray image for all contour points in the at least one gradient comparison image. Local 2D displacement information is determined by comparing the contour points with the associated comparison points, and motion parameters of a 3D motion model describing a movement of the target region between the acquisition of the image dataset and the x-ray image are determined from the displacement information and a registration transformation describing the registration.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
A method for automatically adjust a three-dimensional human face model
InactiveCN109389682AClear methodFriendly interfaceDetails involving processing steps3D modellingComputer animationFace model
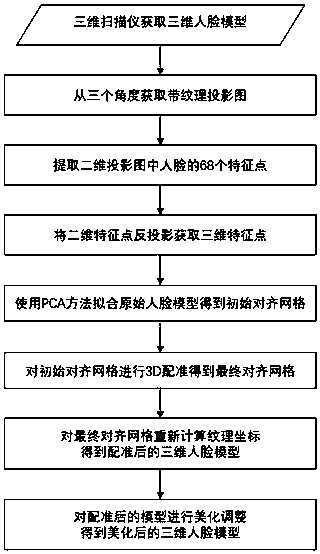
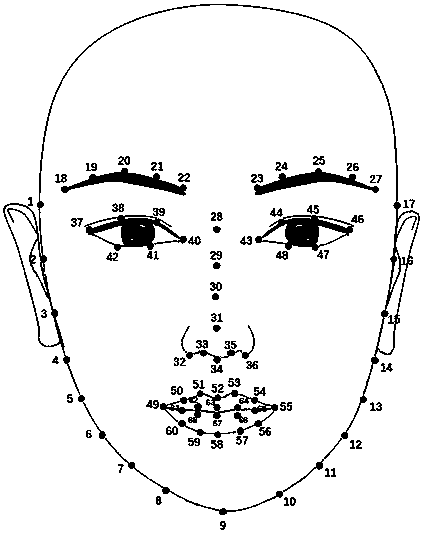
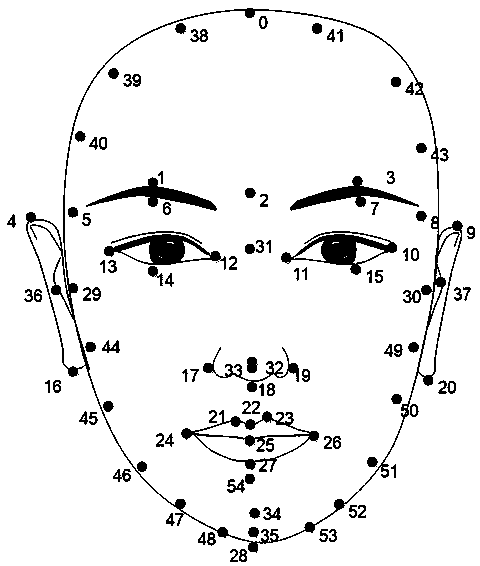
The invention discloses an automatic adjustment method of a three-dimensional human face model, comprising the following steps: a three-dimensional scanner obtains a three-dimensional human face modeland obtains a projection map of the three-dimensional human face with texture from three angles; the three-dimensional scanner obtains a projection map of the three-dimensional human face with texture from three angles; 2D feature point detection of projection map; 2D feature point are backprojected into 3D to obtain 3D feature point; The PCA facial model is used to fit the original 3D facial model. 3D registration of that initially align mesh is performed to solve the energy equation; Recalculating texture coordinates for the final aligned mesh; After the registration of the three-dimensional face adjustment, get the adjusted three-dimensional face model. The invention adopts a set of technology for automatically recognizing three-dimensional human face characteristic points and adjusting the human face on the basis of the technology, It can beautify 3D face captured by 3D scanner with one button, simple and convenient, and has clear algorithm, friendly interface and robust results.It can be used in virtual face plastic surgery, computer animation and computer games and other fields.
Owner:上海影子智能科技有限公司
Non-rigid 2D/3D registration of coronary artery models with live fluoroscopy images
ActiveUS8948487B2Reduce uncertaintyEnhance the imageImage enhancementImage analysisFluoroscopic imageCoronary arterial tree
A method for non-rigid registration of digital 3D coronary artery models with 2D fluoroscopic images during a cardiac intervention includes providing a digitized 3D centerline representation of a coronary artery tree that comprises a set of S segments composed of QS 3D control points, globally aligning the 3D centerline to at least two 2D fluoroscopic images, and non-rigidly registering the 3D centerline to the at least two 2D fluoroscopic images by minimizing an energy functional that includes a summation of square differences between reconstructed centerline points and registered centerline points, a summation of squared 3D registration vectors, a summation of squared derivative 3D registration vectors, and a myocardial branch energy. The non-rigid registration of the 3D centerline is represented as a set of 3D translation vectors rs,q that are applied to corresponding centerline points xs,q in a coordinate system of the 3D centerline.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Image real-time registration method and system
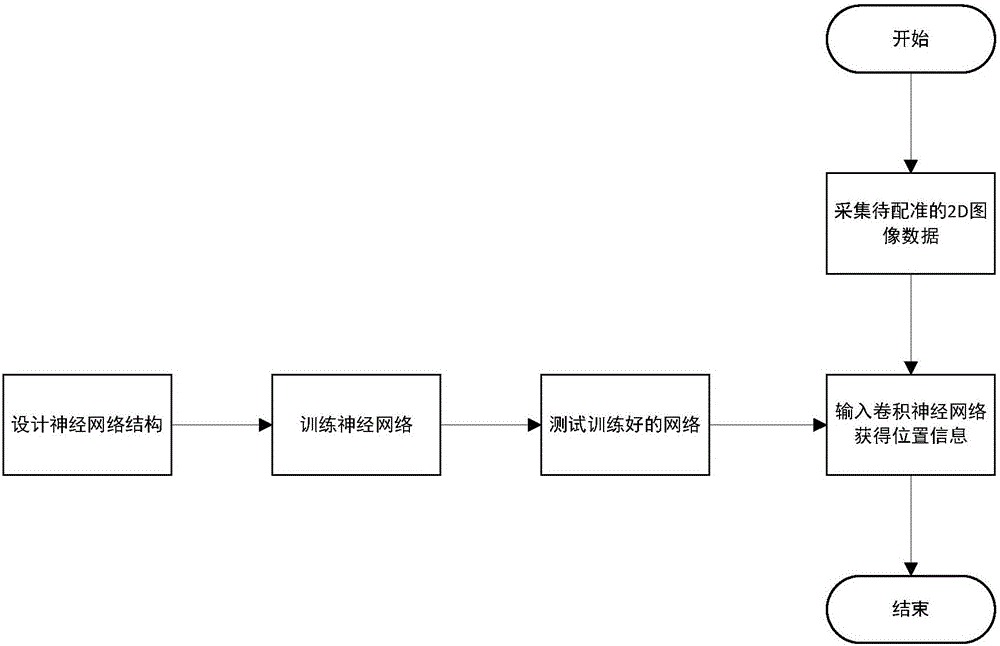
ActiveCN106447707ATo achieve the purpose of real-time registrationShorten the timeImage analysisBiological neural network modelsElevation angleFeature vector
The invention discloses an image real-time registration method and system. The method comprises the following steps of (1) acquiring data of a to-be-registered 2D image; and (2) inputting the data to a registration neural network obtained according to training of a target 3D image, and obtaining position information of the 2D image in the target 3D image, wherein the position information comprises an eigenvector of the to-be-registered 2D image in a coordinate system of the target 3D image and a distance between the to-be-registered 2D image and an origin of the coordinate system, and the eigenvector is a vector passing through the origin of the coordinate system and perpendicular to a 2D image plane, and comprises two parameters including an elevation angle and an azimuth angle. The system comprises an image acquisition module and a registration module. According to the method and the system, deep learning is introduced in the 2D-3D registration problem, a corresponding relationship between 2D and 3D is expressed as a deep convolutional neural network, and a policy for solving the exhaustion calculation problem is explored theoretically, so that the purpose of real-time registration is achieved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com