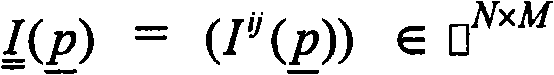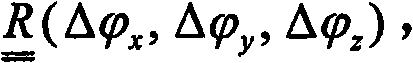Detection and tracking of interventional tools
一种工具、对象的技术,应用在图像处理和绘制系统领域,能够解决遮蔽自由可见性等问题
Inactive Publication Date: 2010-08-18
KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
View PDF2 Cites 36 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
To overcome the problem of undesired structures obscuring the free visibility of interventional tools used in X-ray-guided interventions, a reference image obtained without the interventional tool and e.g. at the beginning of the procedure can be subtracted from the acquired X-ray sequence
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
Embodiment Construction
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
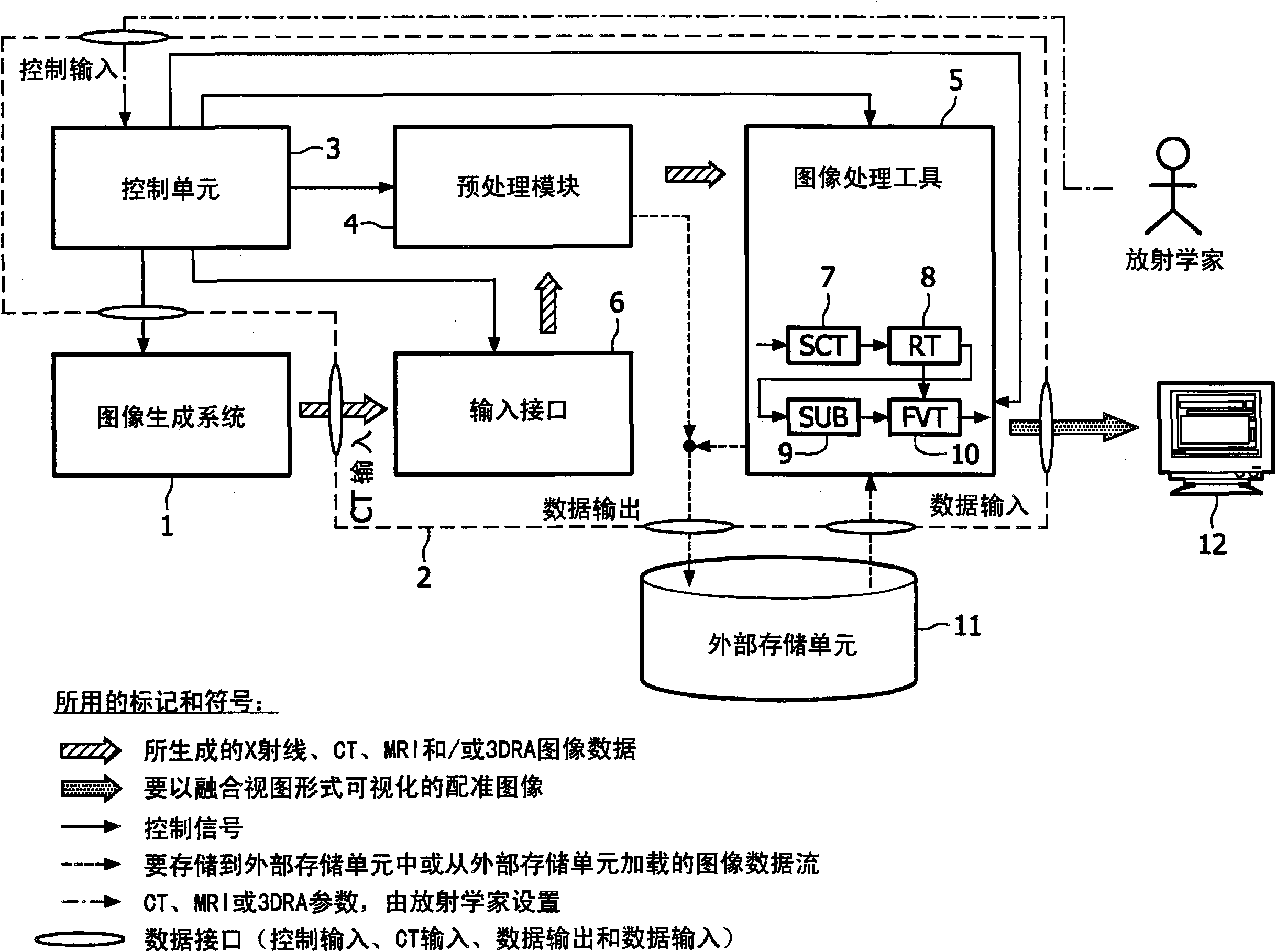
The present invention relates to minimally invasive X-ray guided interventions, in particular to an image processing and rendering system and a method for improving visibility and supporting automatic detection and tracking of interventional tools that are used in electrophysiological procedures. According to the invention, this is accomplished by calculating differences between 2D projected image data of a preoperatively acquired 3D voxel volume showing a specific anatomical region of interest or a pathological abnormality (e.g. an intracranial arterial stenosis, an aneurysm of a cerebral, pulmonary or coronary artery branch, a gastric carcinoma or sarcoma, etc.) in a tissue of a patient's body and intraoperatively recorded 2D fluoroscopic images showing the aforementioned objects in the interior of said patient's body, wherein said 3D voxel volume has been generated in the scope of a computed tomography, magnet resonance imaging or 3D rotational angiography based image acquisition procedure and said 2D fluoroscopic images have been co-registered with the 2D projected image data. After registration of the projected 3D data with each of said X-ray images, comparison of the 2D projected image data with the 2D fluoroscopic images - based on the resulting difference images - allows removing common patterns and thus enhancing the visibility of interventional instruments which are inserted into a pathological tissue region, a blood vessel segment or any other region of interest in the interior of the patient's body. Automatic image processing methods to detect and track those instruments are also made easier and more robust by this invention. Once the 2D-3D registration is completed for a given view, all the changes in the system geometry of an X-ray system used for generating said fluoroscopic images can be applied to a registration matrix. Hence, use of said method as claimed is not limited to the same X-ray view during the whole procedure.
Description
technical field The present invention relates to minimally invasive X-ray guided interventions, and more particularly to an image processing and rendering system and method for improving the visibility and supporting automatic detection and tracking of interventional tools used in electrophysiological procedures. According to the invention, this is achieved by computing the differences between the co-registered X-ray images and the 2D projection image data of the 3D voxel volume acquired pre-procedurally and using these differences to enhance the contrast and visibility of the interventional tool. Background technique Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) such as arteriosclerosis, hypertension and ischemia remain the leading cause of death in most developed countries as they cause permanent damage to the heart and blood vessels which can lead to chronic heart failure, angina or myocardial infarction (heart attack). For patients showing symptoms of cardiovascular disease, initial di...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More Patent Type & Authority Applications(China)
IPC IPC(8): G06T5/50G06T17/50G06T17/05
CPCG06T2207/10116G06T2207/30021G06T5/50G06T2207/30101G06T2207/10072G06T7/32
Inventor N·F·维兰C·A·M·皮卡尔N·P·B·戈金
Owner KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com