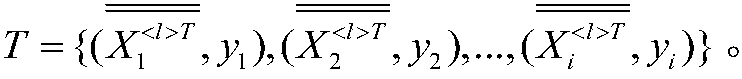Patents
Literature
1301 results about "Feature generation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
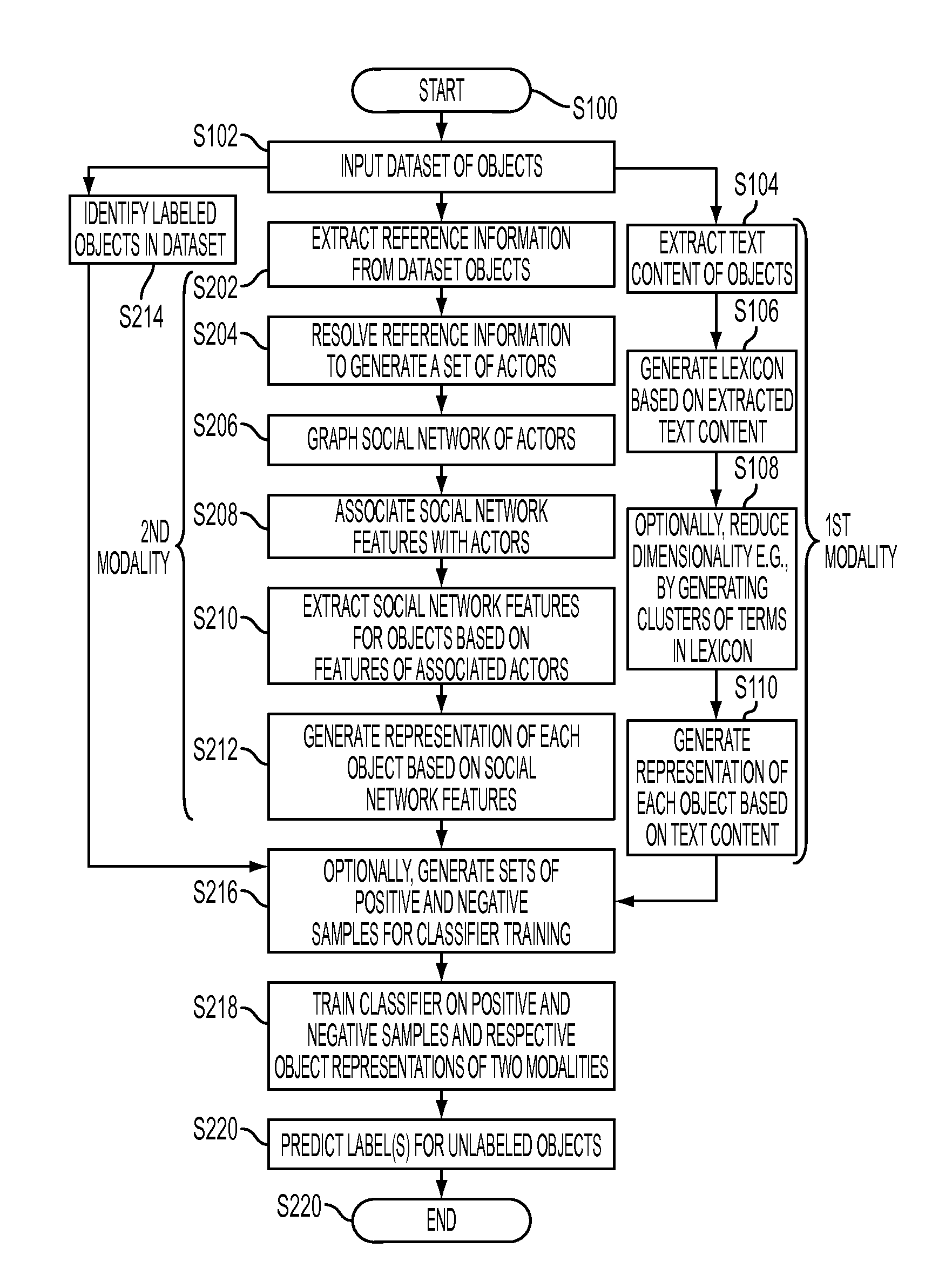
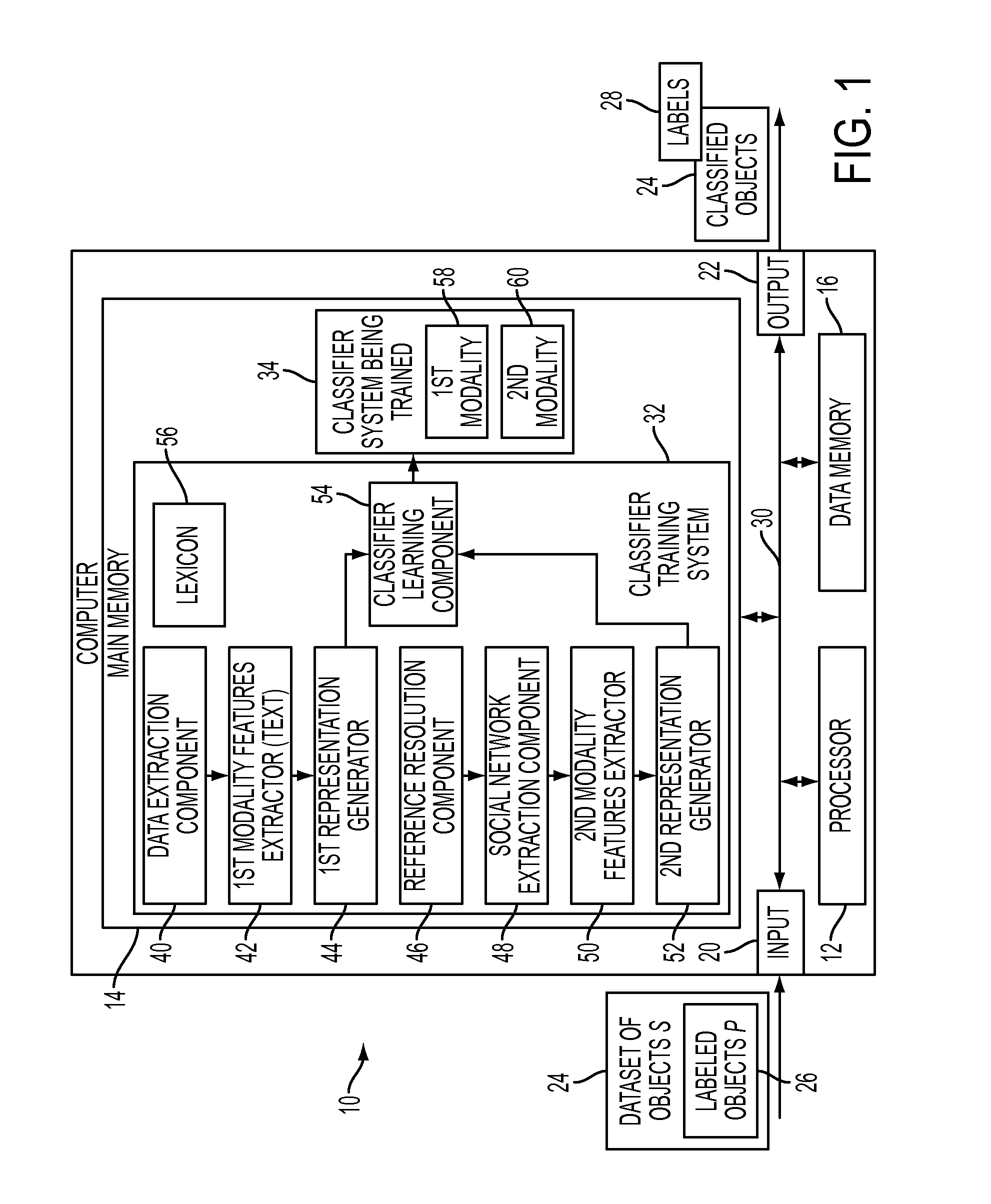
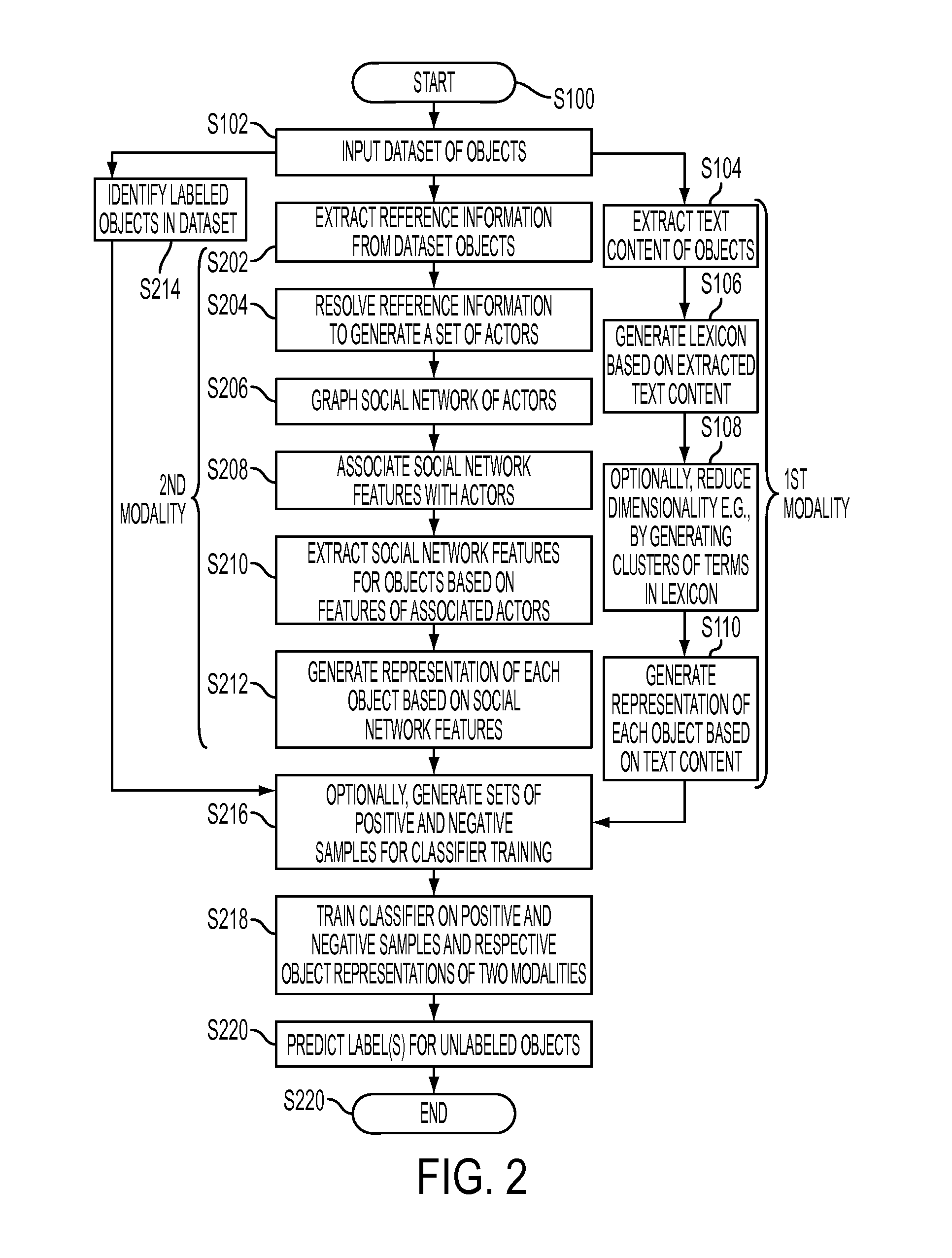
Multi-modality classification for one-class classification in social networks
ActiveUS20110103682A1Character and pattern recognitionData switching networksOne-class classificationData mining
A classification apparatus, method, and computer program product for multi-modality classification are disclosed. For each of a plurality of modalities, the method includes extracting features from objects in a set of objects. The objects include electronic mail messages. A representation of each object for that modality is generated, based on its extracted features. At least one of the plurality of modalities is a social network modality in which social network features are extracted from a social network implicit in the set of electronic mail messages. A classifier system is trained based on class labels of a subset of the set of objects and on the representations generated for each of the modalities. With the trained classifier system, labels are predicted for unlabeled objects in the set of objects.
Owner:XEROX CORP
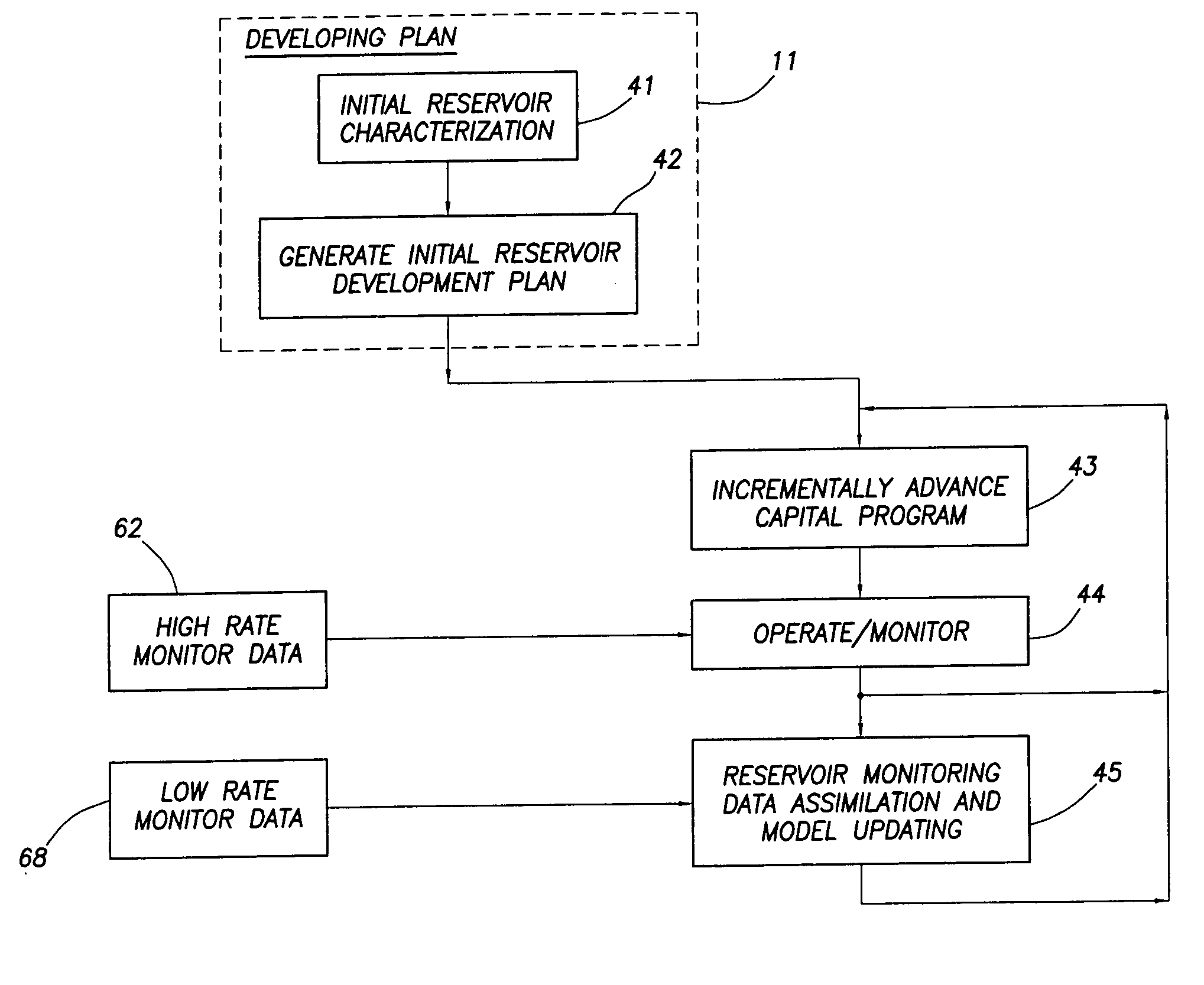
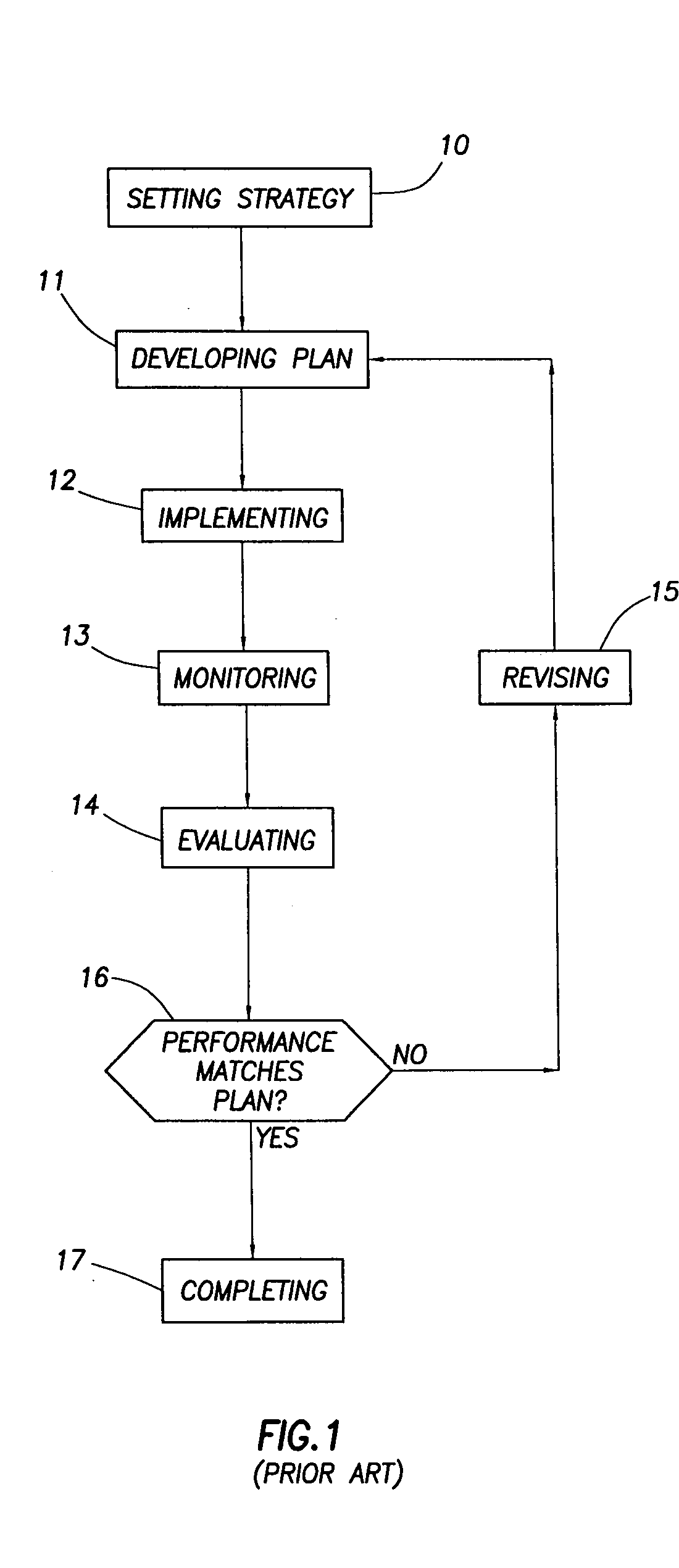
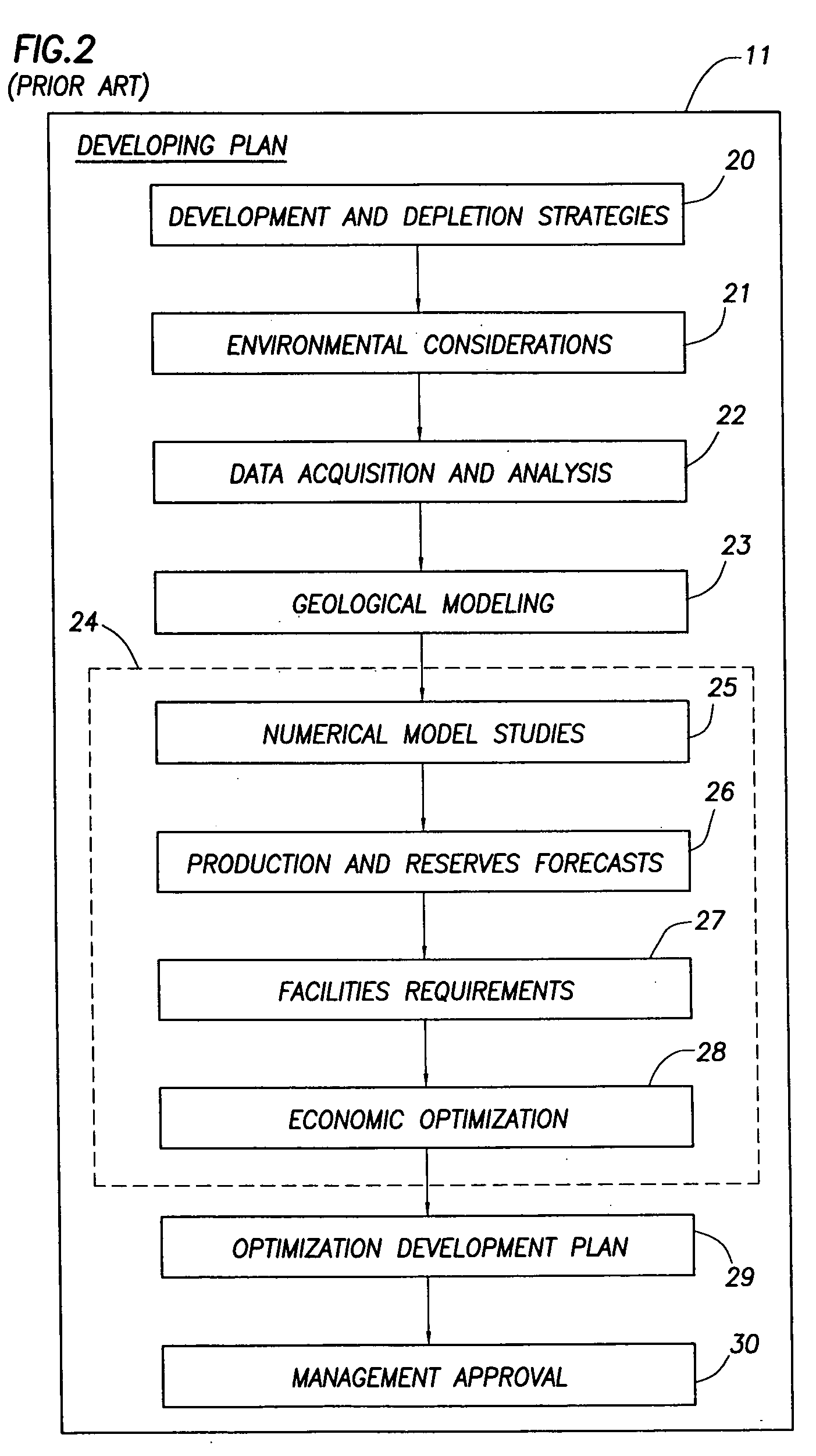
Integrated reservoir optimization
InactiveUS20050149307A1Maximize productionMaximizing value of propertyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyHigh rateAcquisition time
A method of managing a fluid or gas reservoir is disclosed which assimilates diverse data having different acquisition time scales and spatial scales of coverage for iteratively producing a reservoir development plan that is used for optimizing an overall performance of a reservoir. The method includes: (a) generating an initial reservoir characterization, (b) from the initial reservoir characterization, generating an initial reservoir development plan, (c) when the reservoir development plan is generated, incrementally advancing and generating a capital spending program, (d) when the capital spending program is generated, monitoring a performance of the reservoir by acquiring high rate monitor data from a first set of data measurements taken in the reservoir and using the high rate monitor data to perform well-regional and field-reservoir evaluations, (e) further monitoring the performance of the reservoir by acquiring low rate monitor data from a second set of data measurements taken in the reservoir, (f) assimilating together the high rate monitor data and the low rate monitor data, (g) from the high rate monitor data and the low rate monitor data, determining when it is necessary to update the initial reservoir development plan to produce a newly updated reservoir development plan, (h) when necessary, updating the initial reservoir development plan to produce the newly updated reservoir development plan, and (i) when the newly updated reservoir development plan is produced, repeating steps (c) through (h). A detailed disclosure is provided herein relating to the step (a) for generating the initial reservoir characterization and the step (b) for generating the initial reservoir development plan.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
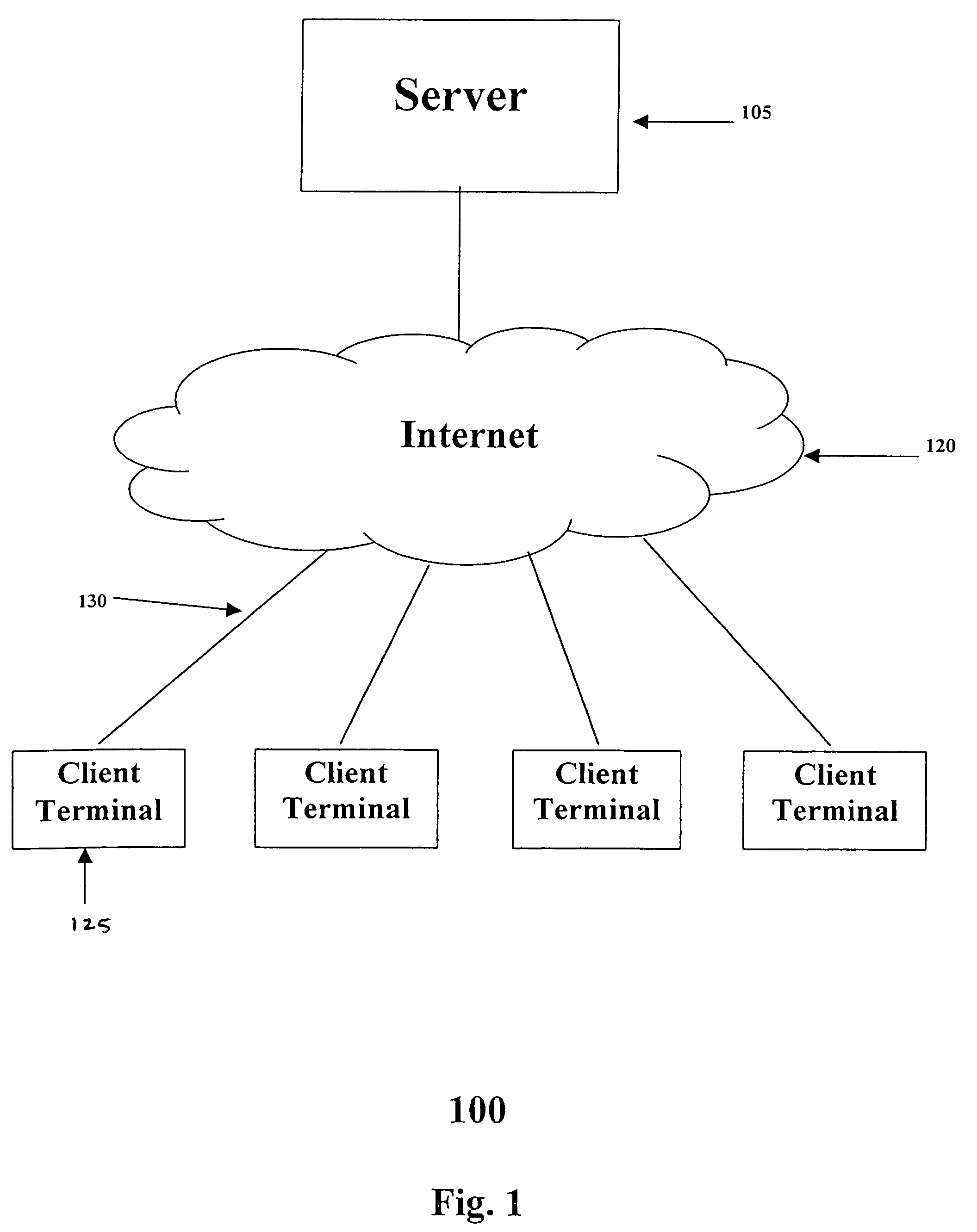
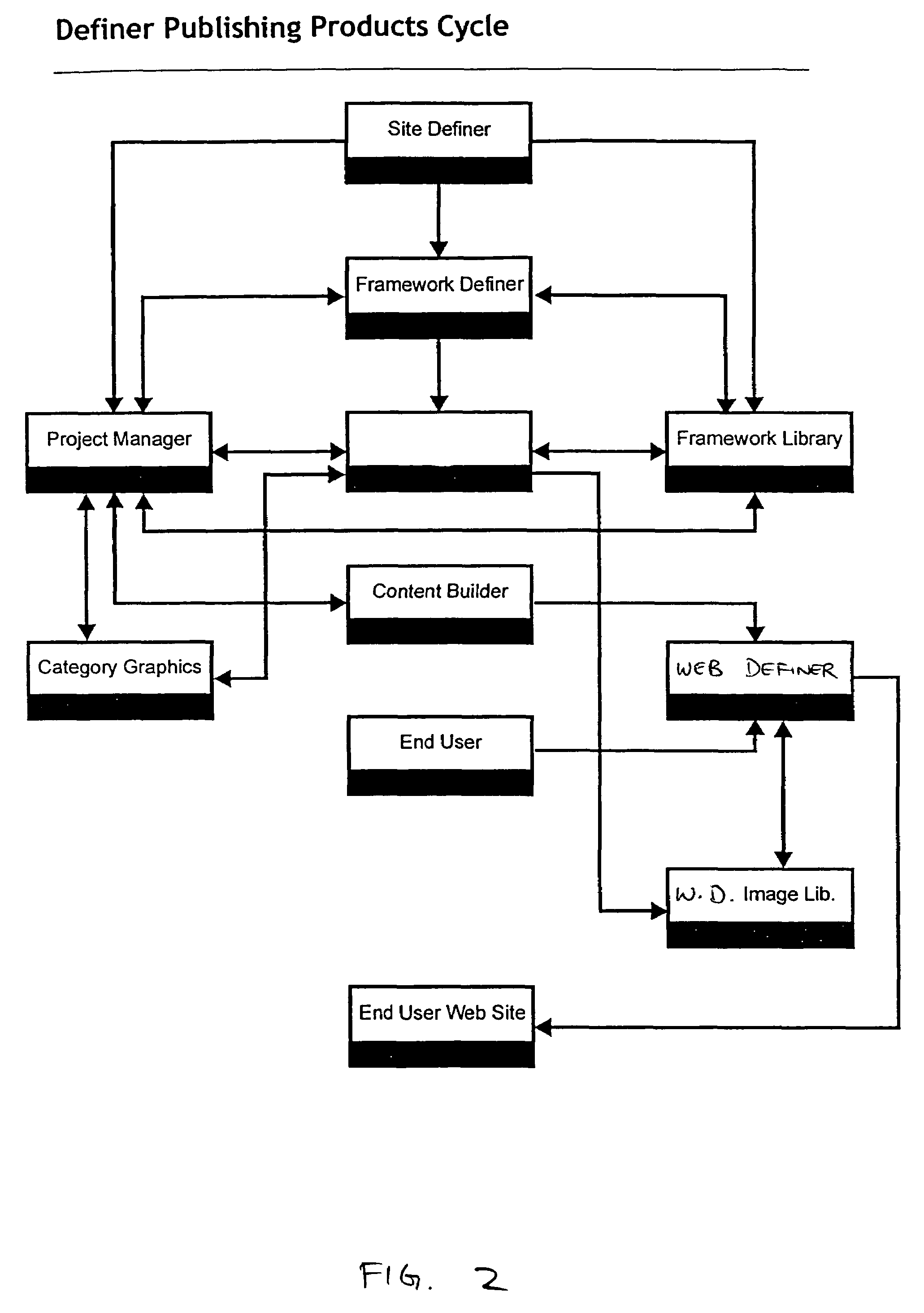
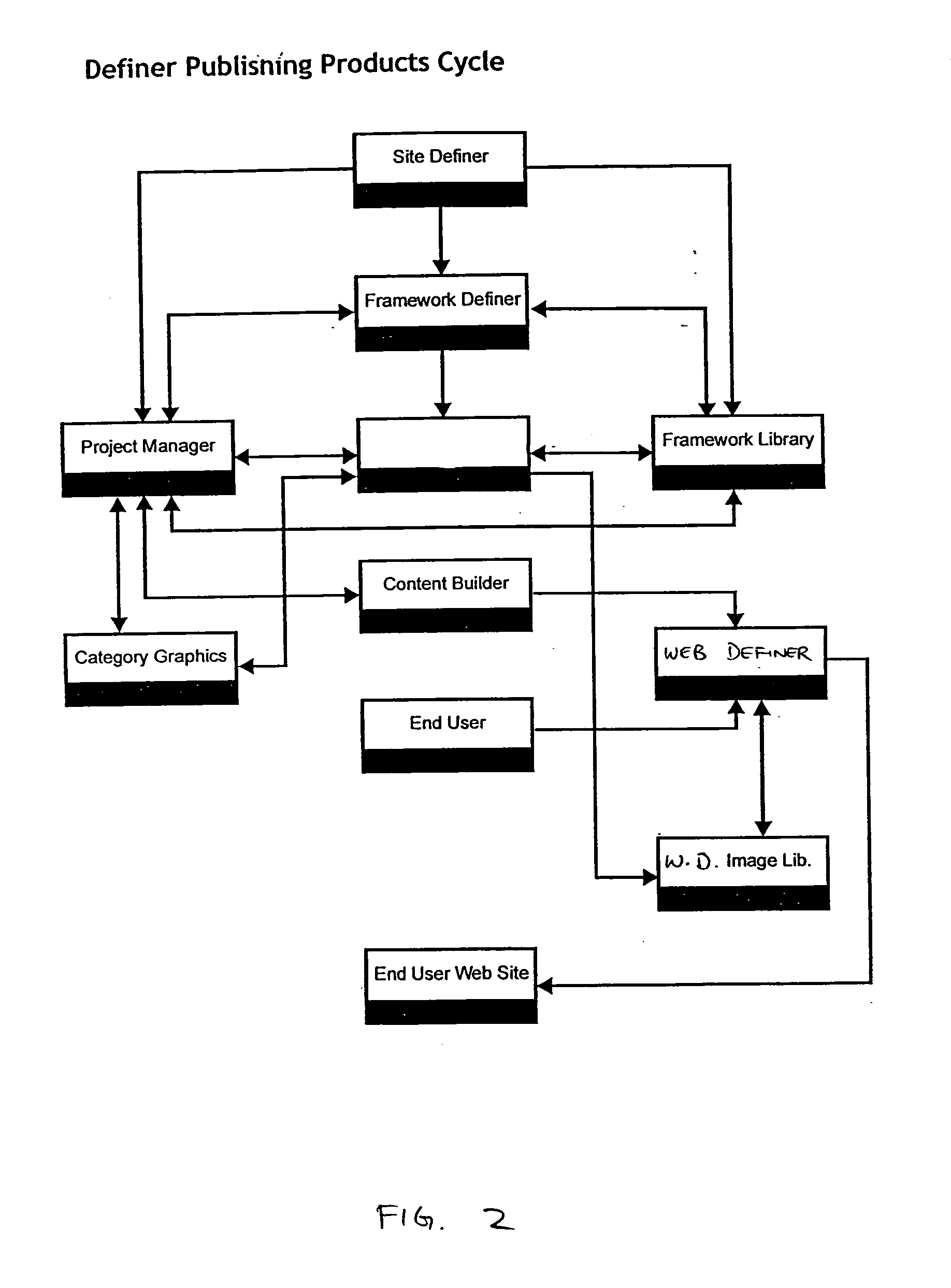
Method and apparatus for providing conditional customization for generating a web site
InactiveUS7152207B1Website content managementSpecial data processing applicationsWeb siteMulti dimensional
A technique for generating a web site in accordance with received data entry by: presenting a prompt for data entry; receiving a data entry in response to the prompt; presenting at least one additional prompt for data entry that is determined at least in part based upon the received data entry; receiving an additional data entry in response to each of the at least one additional prompts; determining at least one characteristic of at least one web site dimension of the web site based on the data entry; generating a multi-dimensional description of the web site based on the determined characteristics; retrieving web site data according to the generated multi-dimensional description of the web site; and generating the web site based upon the generated multi-dimensional description of the web site and the retrieved web site data.
Owner:DECENTRIX
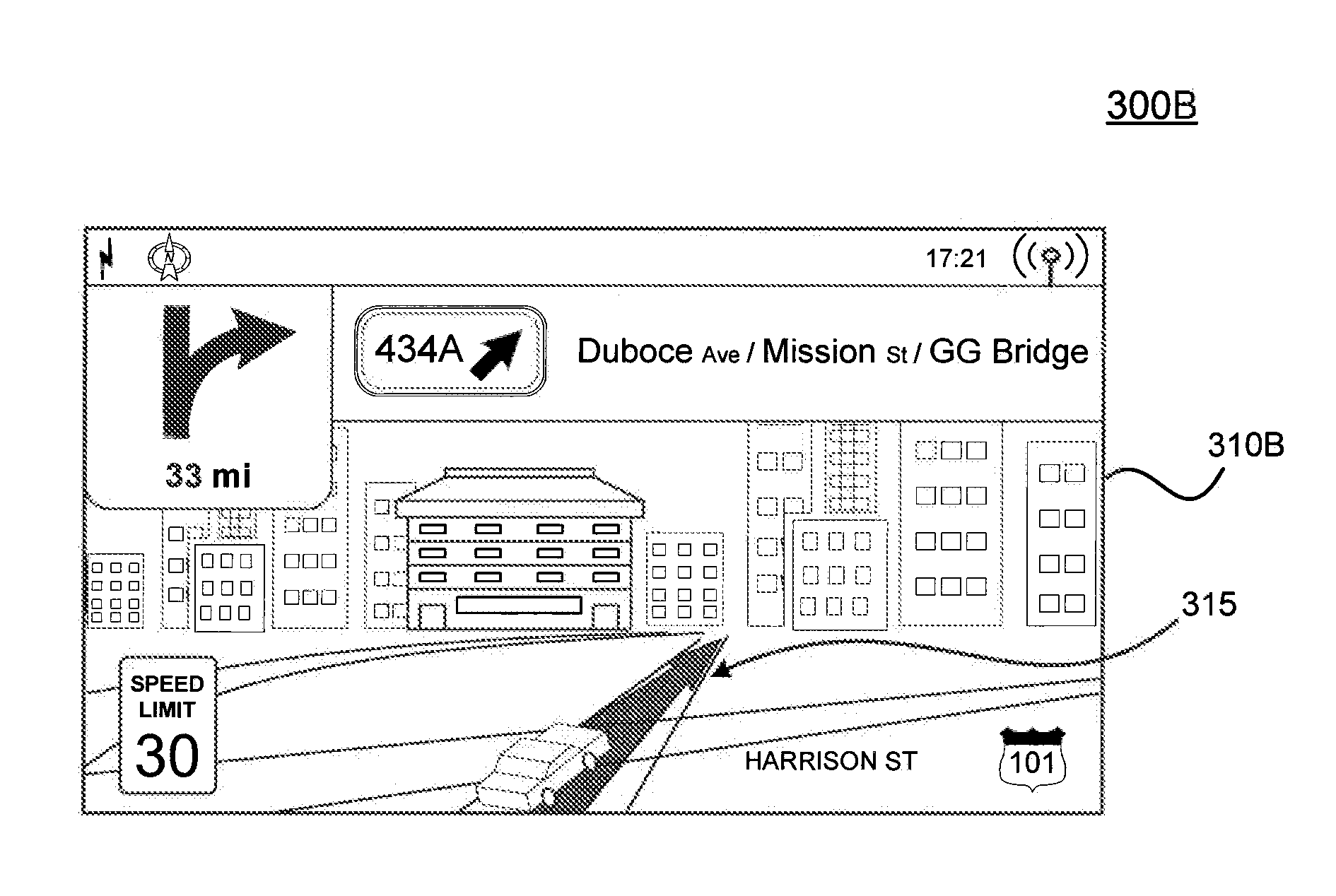
Prominence-Based Generation and Rendering of Map Features
InactiveUS20130035853A1Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlComputer graphics (images)Visual perception
A capability for prominence-based feature generation and rendering for digital maps is provided. More specifically, embodiments relate to rendering map features such as buildings or landmarks in different rendering styles based on signals for how important a particular feature is to a search context. A search context may be, for example and without limitation, a general view of the map or a user-initiated search request for a particular point of interest or driving directions between different points of interest on the map. For example, the different rendering styles may include, but are not limited to, two-dimensional (2D) footprints, two-and-a-half-dimensional (2.5D) extruded polygons, as will be described further below, and full three-dimensional (3D) models. Furthermore, the style could include color and / or visual texture.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
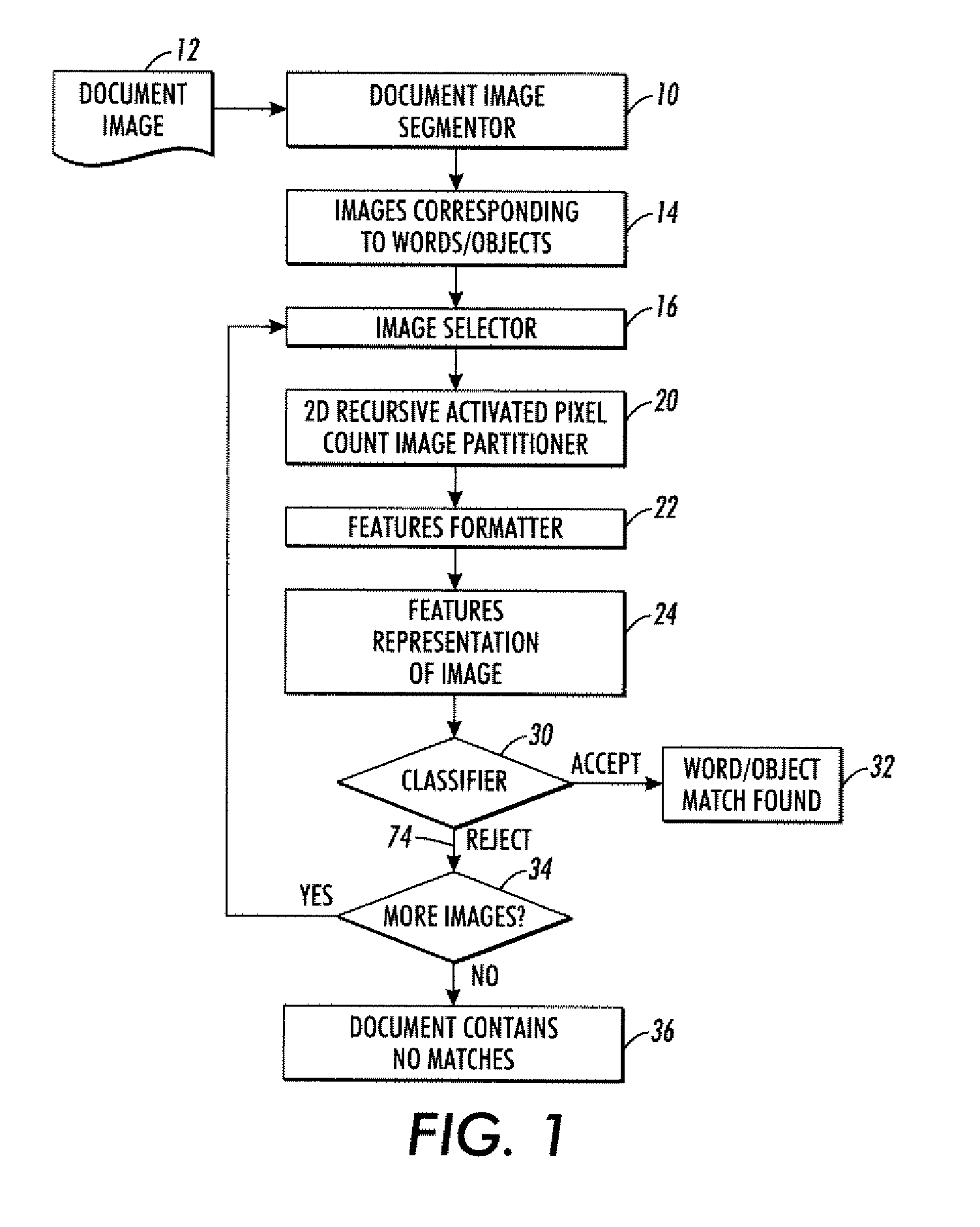
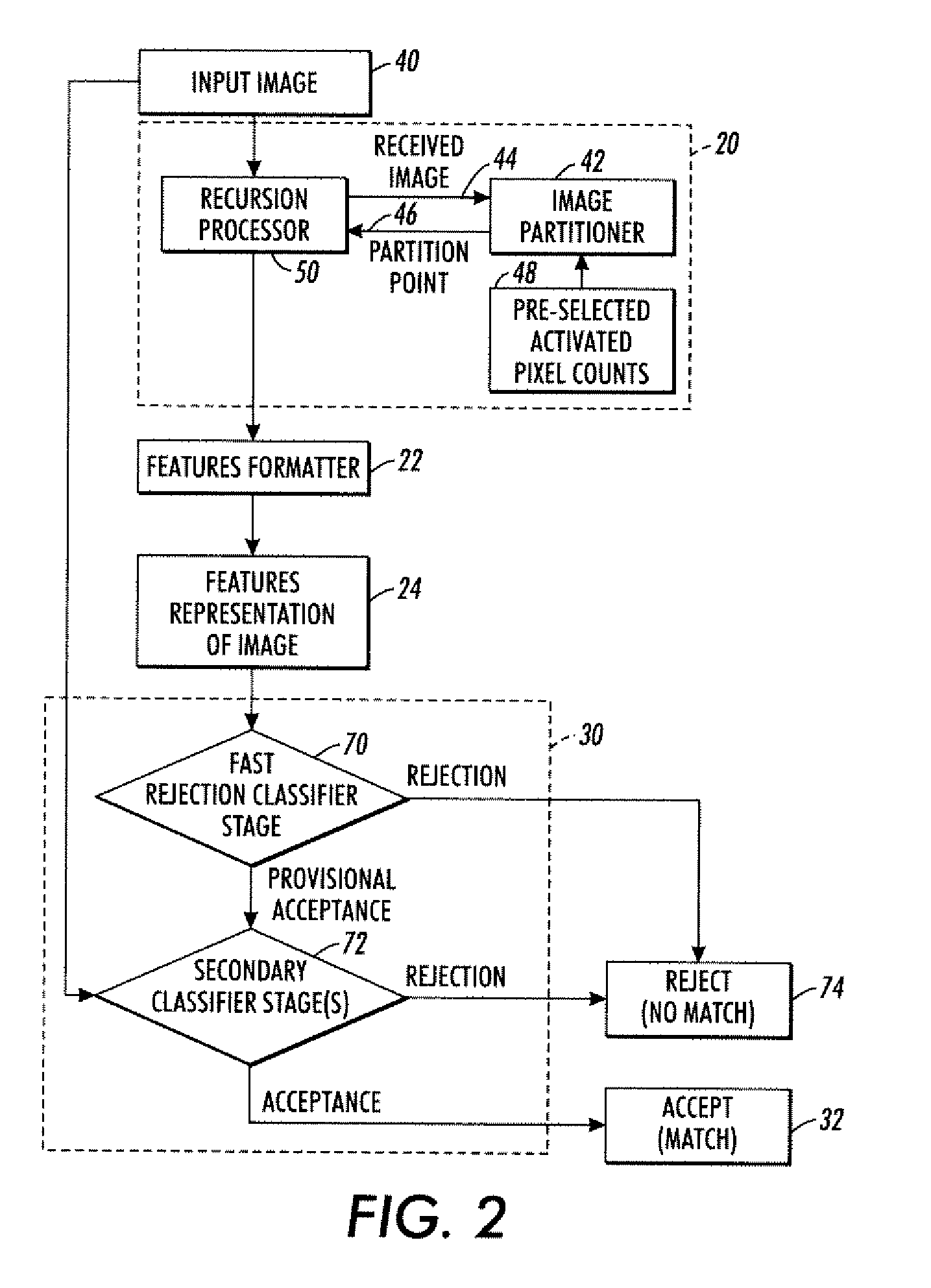
Features generation and spotting methods and systems using same
An image partitioner is configured to find a partition point that divides a received image into four sub-images each having a pre-selected activated pixel count. A recursion processor is configured to (i) apply the image partitioner to an input image to generate a first partition point and four sub-images and to (ii) recursively apply the image partitioner to at least one of the four sub-images for at least one recursion iteration to generate at least one additional partition point. A formatter is configured to generate a features representation of the input image in a selected format. The features representation is based at least in part on the partition points. The features representation can be used in various ways, such as by a classifier configured to classify the input image based on the features representation.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method and apparatus for providing conditional customization for generating a web site
InactiveUS20060200751A1Input/output for user-computer interactionWebsite content managementWeb siteMulti dimensional
A technique for generating a web site in accordance with received data entry by: presenting a prompt for data entry; receiving a data entry in response to the prompt; presenting at least one additional prompt for data entry that is determined at least in part based upon the received data entry; receiving an additional data entry in response to each of the at least one additional prompts; determining at least one characteristic of at least one web site dimension of the web site based on the data entry; generating a multi-dimensional description of the web site based on the determined characteristics; retrieving web site data according to the generated multi-dimensional description of the web site; and generating the web site based upon the generated multi-dimensional description of the web site and the retrieved web site data.
Owner:DECENTRIX
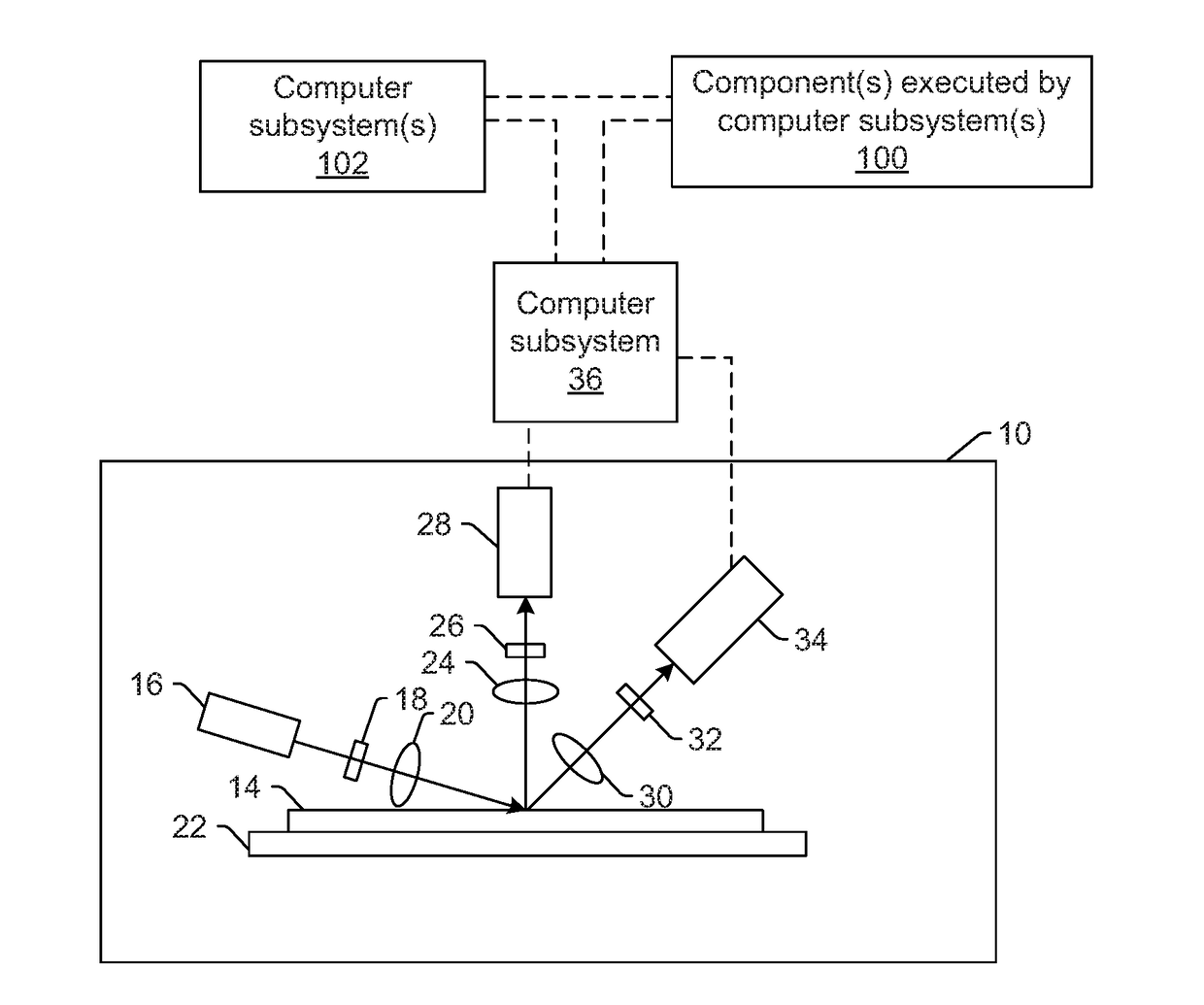
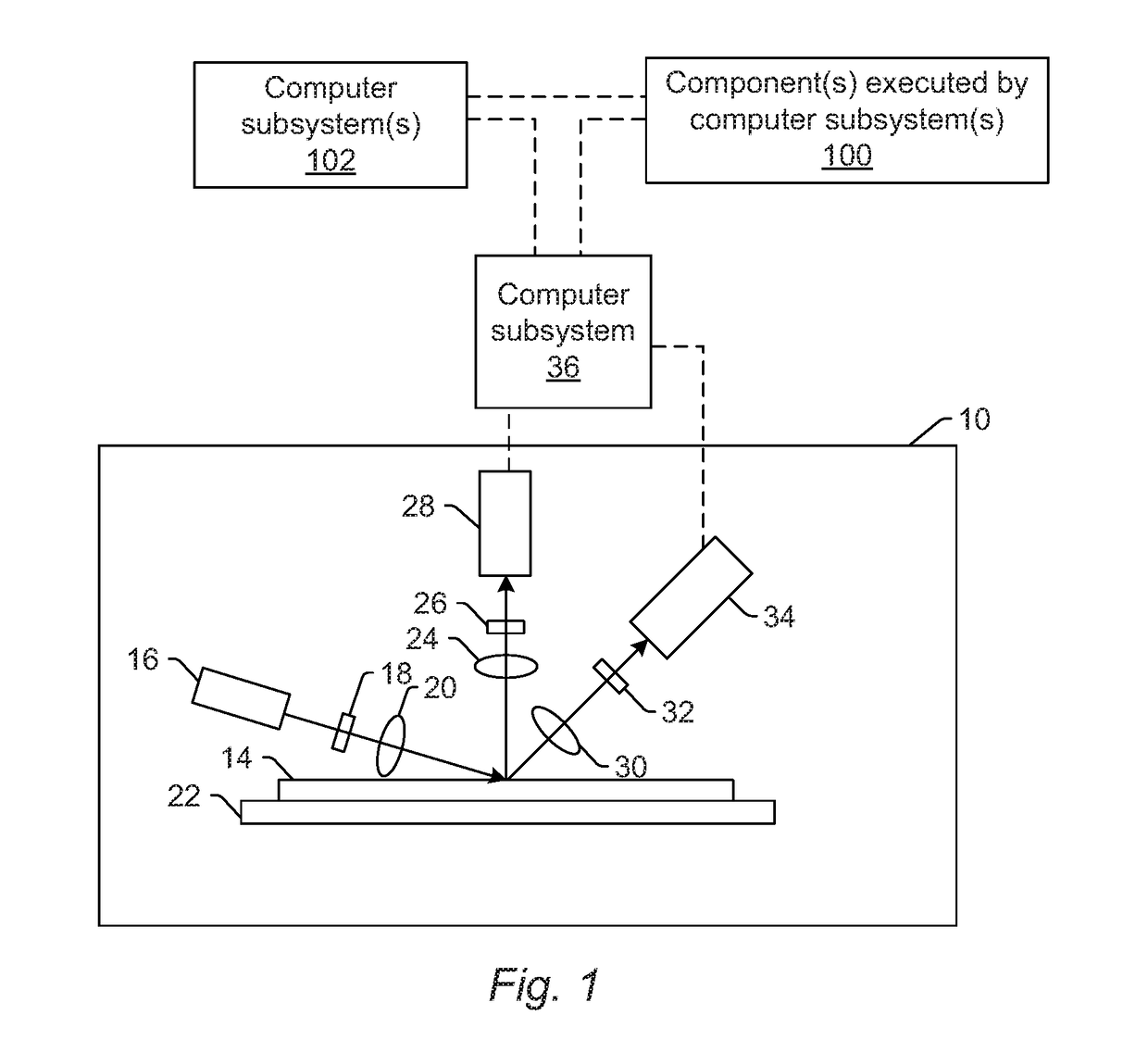
Generating simulated images from design information
ActiveUS20170148226A1Image enhancementDetails involving processing stepsSimulationDesign information
Methods and systems for generating simulated images from design information are provided. One system includes one or more computer subsystems and one or more components executed by the computer subsystem(s), which include a generative model. The generative model includes two or more encoder layers configured for determining features of design information for a specimen. The generative model also includes two or more decoder layers configured for generating one or more simulated images from the determined features. The simulated image(s) illustrate how the design information formed on the specimen appears in one or more actual images of the specimen generated by an imaging system.
Owner:KLA CORP
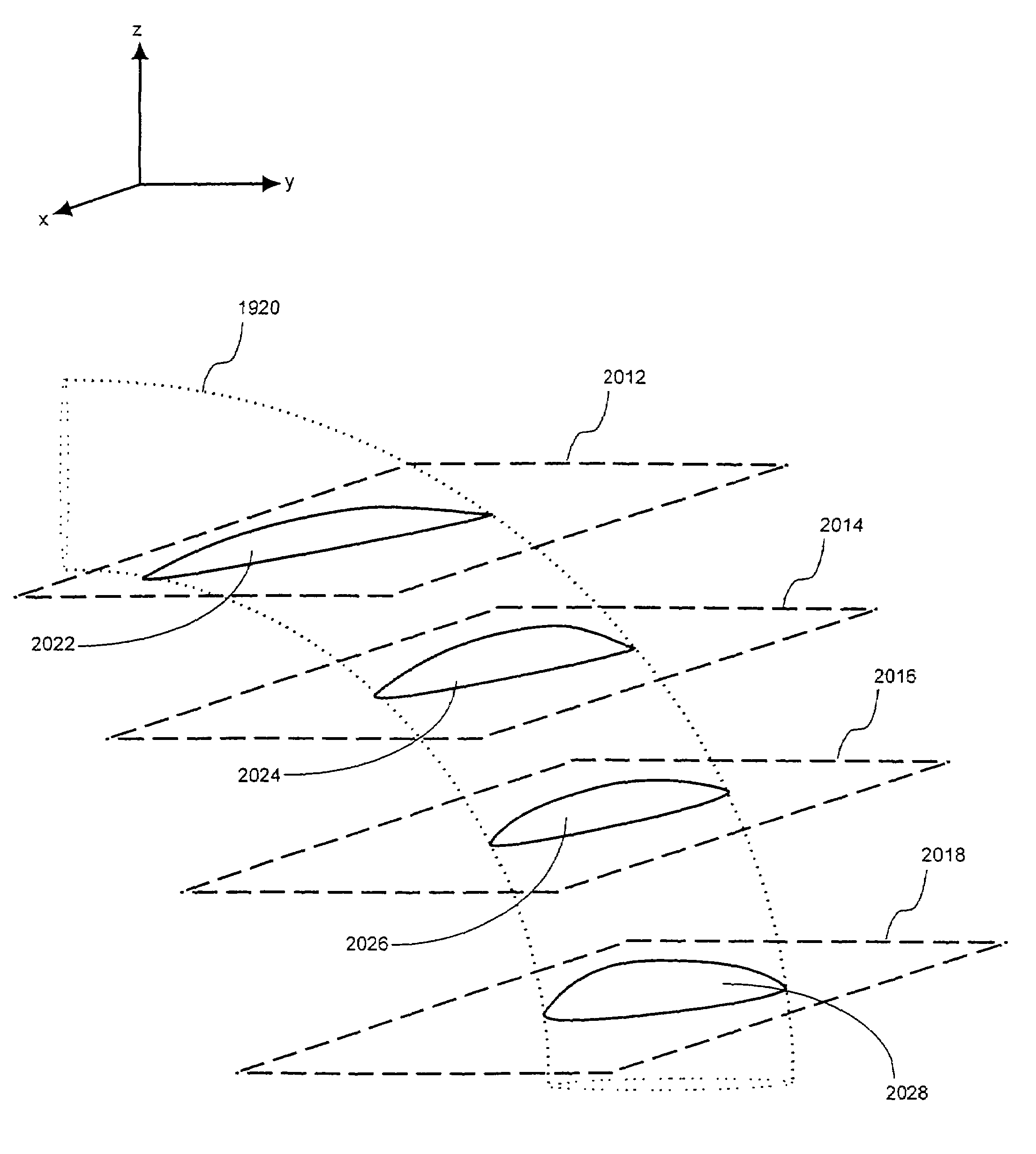
Feature quantification from multidimensional image data
Techniques, hardware, and software are provided for quantification of extensional features of structures of an imaged subject from image data representing a two-dimensional or three-dimensional image. In one embodiment, stenosis in a blood vessel may be quantified from volumetric image data of the blood vessel. A profile from a selected family of profiles is fit to selected image data. An estimate of cross sectional area of the blood vessel is generated based on the fit profile. Area values may be generated along a longitudinal axis of the vessel, and a one-dimensional profile fit to the generated area values. An objective quantification of stenosis in the vessel may be obtained from the area profile. In some cases, volumetric image data representing the imaged structure may be reformatted to facilitate the quantification, when the structural feature varies along a curvilinear axis. A mask is generated for the structural feature to be quantified based on the volumetric image data. A curve representing the curvilinear axis is determined from the mask by center-finding computations, such as moment calculations, and curve fitting. Image data are generated for oblique cuts at corresponding selected orientations with respect to the curvilinear axis, based on the curve and the volumetric image data. The oblique cuts may be used for suitable further processing, such as image display or quantification.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
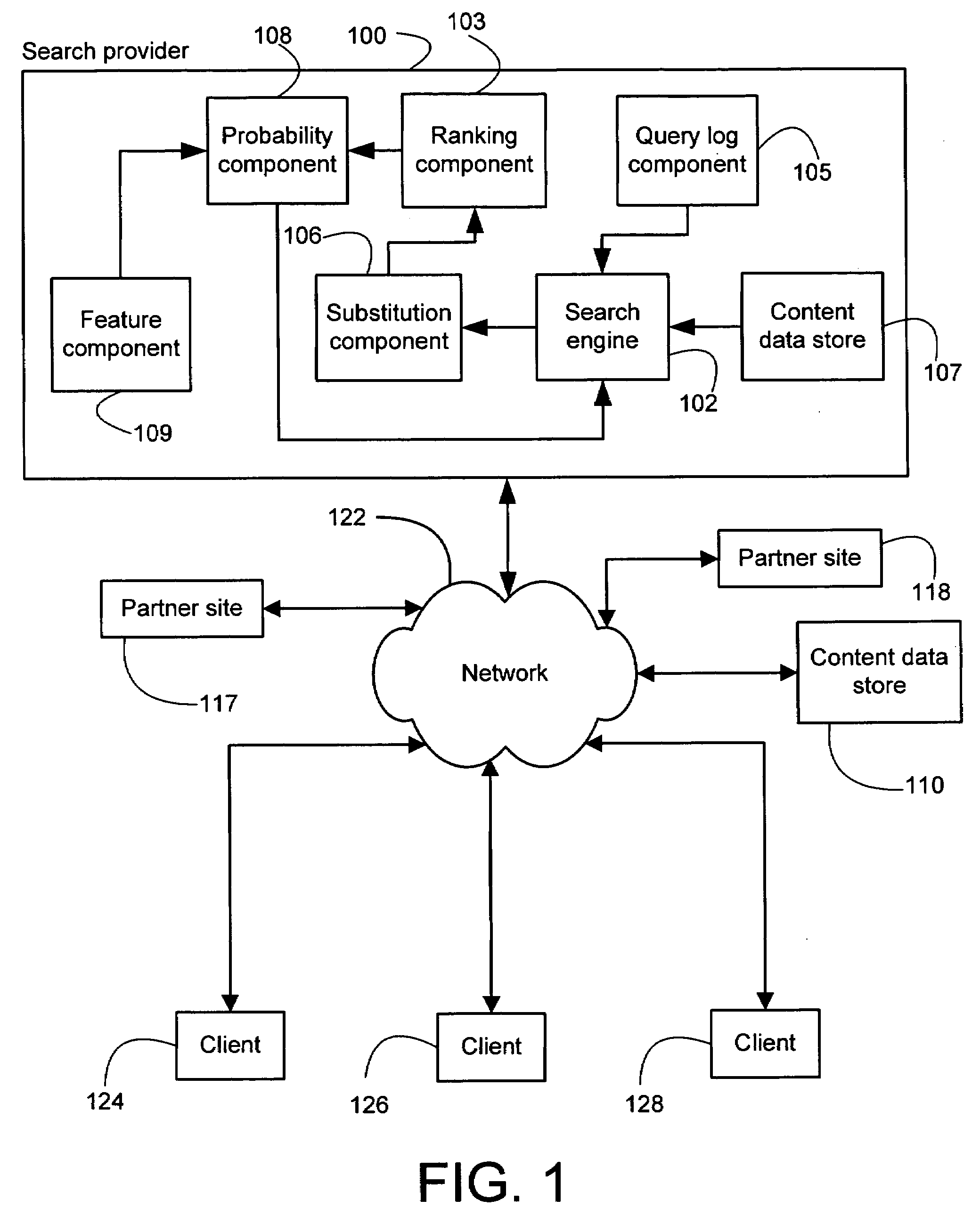
System and method for generating substitutable queries on the basis of one or more features
InactiveUS20080114721A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsTheoretical computer scienceData science
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
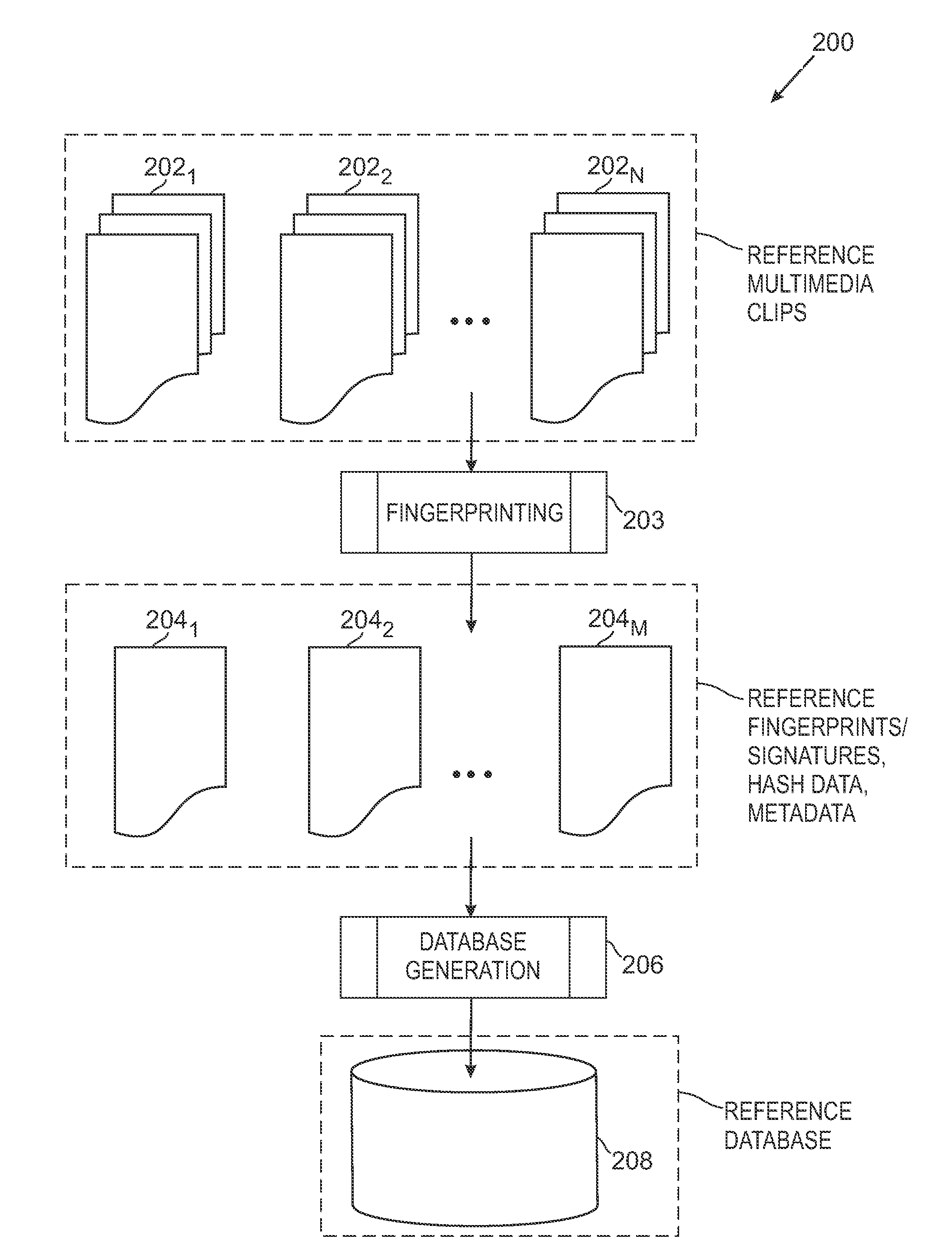
Media fingerprinting and identification system
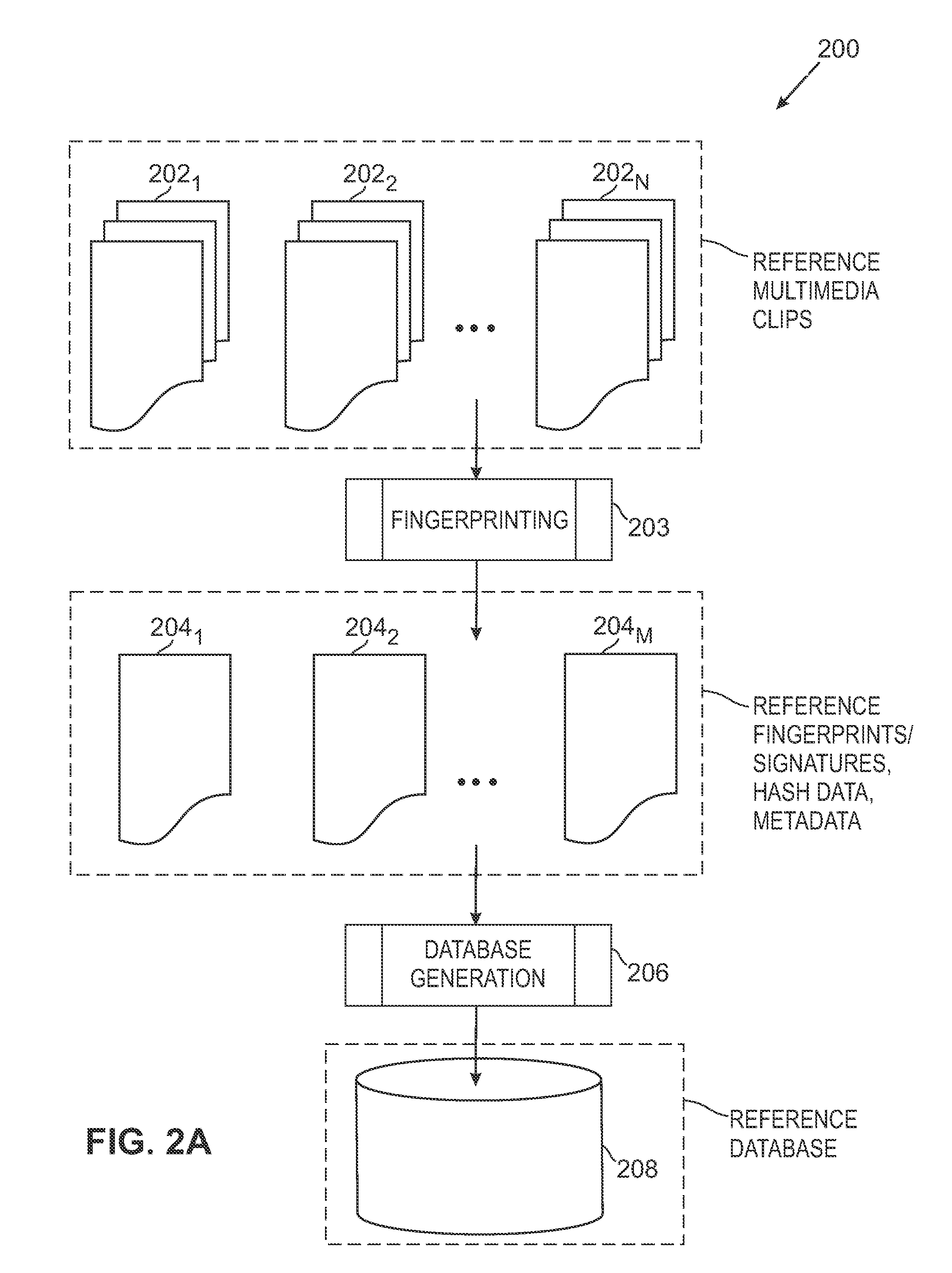
ActiveUS8195689B2Multimedia data indexingData processing applicationsReference databaseNumerical descriptors
The overall architecture and details of a scalable video fingerprinting and identification system that is robust with respect to many classes of video distortions is described. In this system, a fingerprint for a piece of multimedia content is composed of a number of compact signatures, along with traversal hash signatures and associated metadata. Numerical descriptors are generated for features found in a multimedia clip, signatures are generated from these descriptors, and a reference signature database is constructed from these signatures. Query signatures are also generated for a query multimedia clip. These query signatures are searched against the reference database using a fast similarity search procedure, to produce a candidate list of matching signatures. This candidate list is further analyzed to find the most likely reference matches. Signature correlation is performed between the likely reference matches and the query clip to improve detection accuracy.
Owner:ROKU INCORPORATED
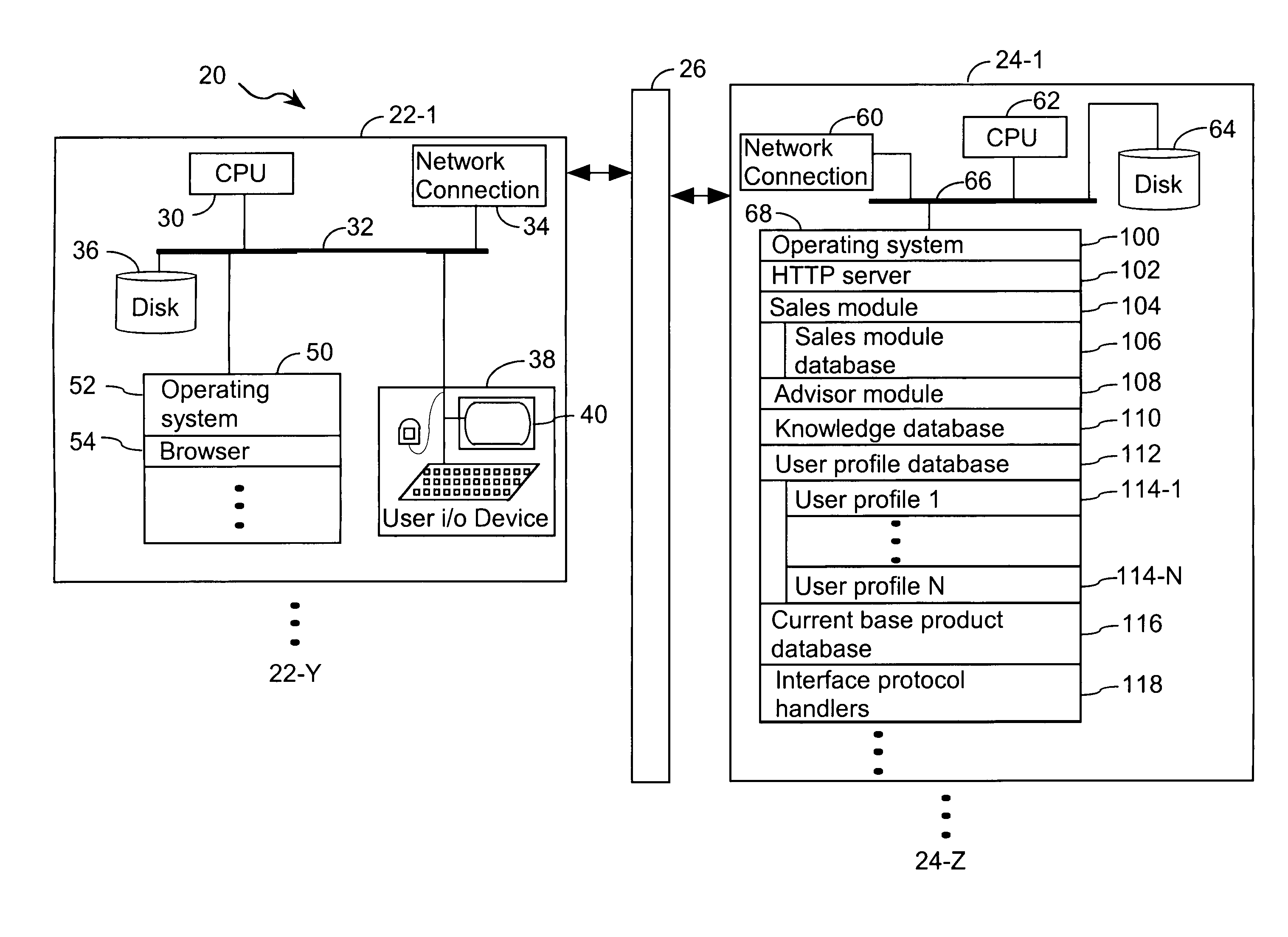
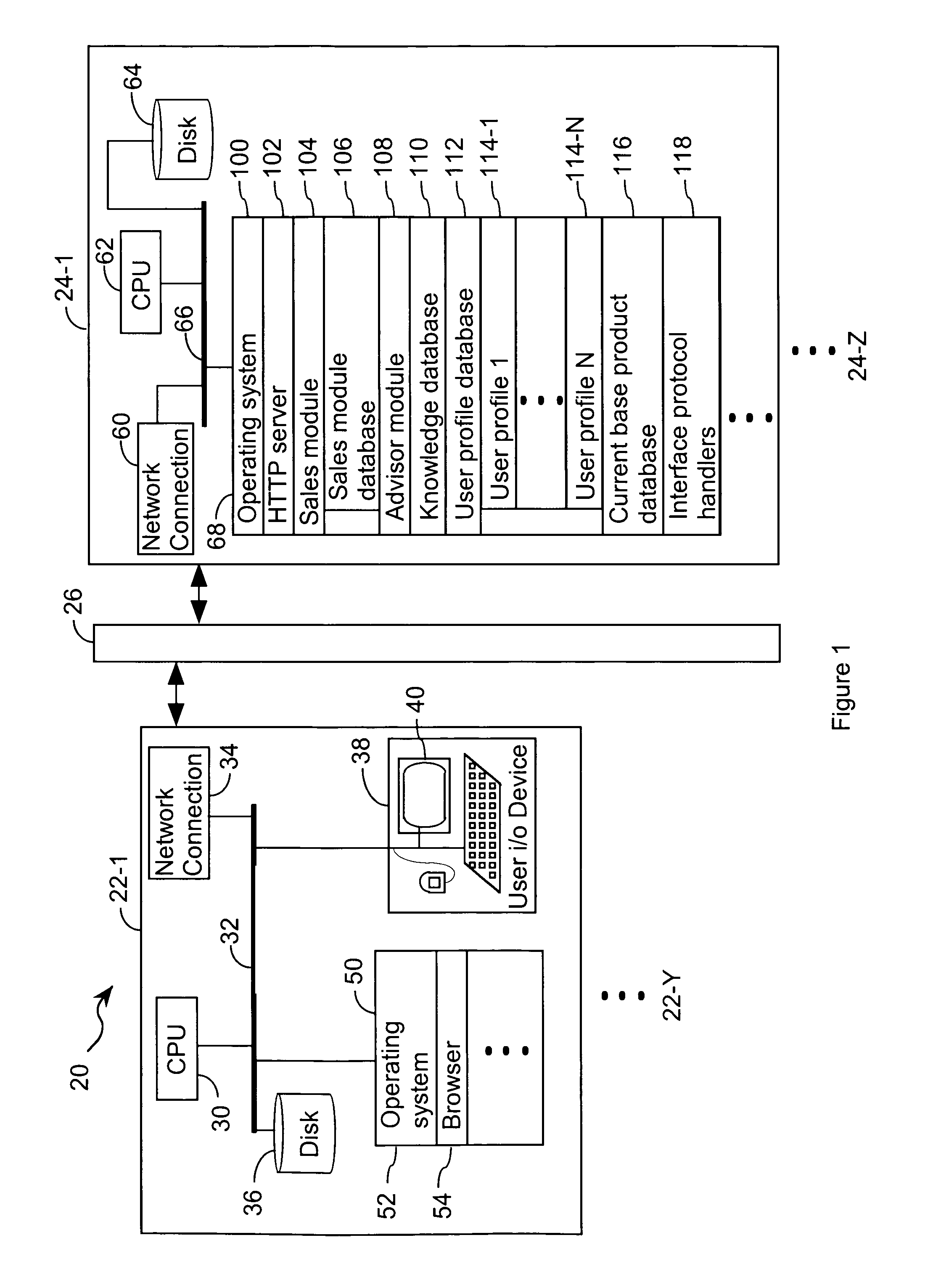
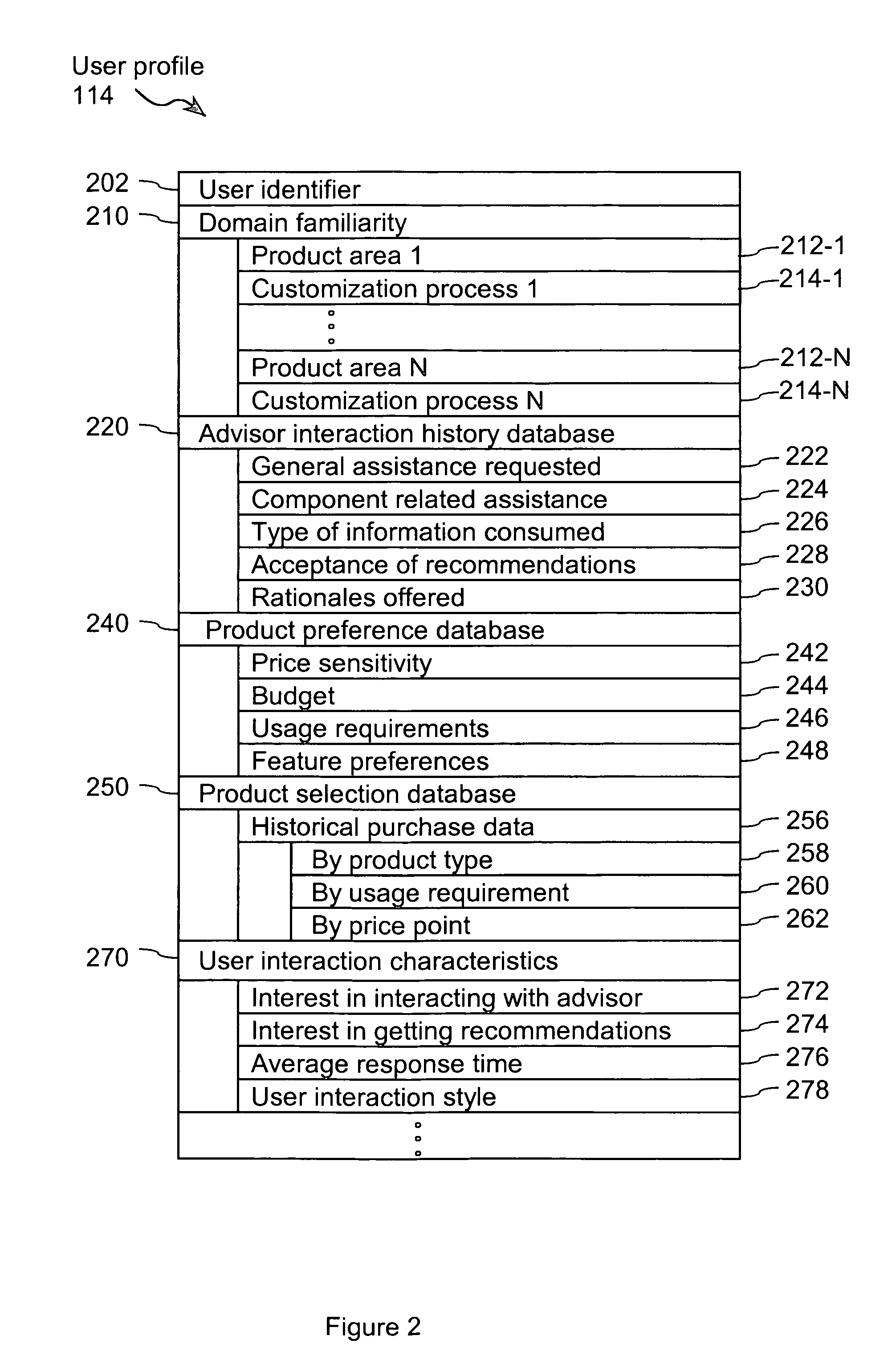
System and method for optimizing a product configuration
A method of optimizing a product includes the step of accessing an event record having a summary of a sequence of events that transpired during a preliminary product selection process. The summary includes an identification of the user and a preliminary designation of the product. A user profile associated with the user includes at least one characteristic corresponding to the user. Based on characteristics in the user profile, a formatted display is generated. User response to formatted displays is used to update characteristics in the user profile. An iterative process, in which the updated user profile is used as a basis for generating subsequent formatted displays to which a user responds, repeats until the user indicates that the product is optimized.
Owner:NETABAGE CORP
Method and apparatus for generating a web site with dynamic content data from an external source integrated therein
InactiveUS7668913B1Natural language data processingMultiple digital computer combinationsWeb siteExternal data
A technique for generating a web site in accordance with received data entry by: determining at least one characteristic of at least one web site dimension of the web site based on the data entry; generating a multi-dimensional description of the web site based on the determined characteristics; retrieving web site data according to the generated multi-dimensional description of the web site; and generating the web site based upon the generated multi-dimensional description of the web site and the retrieved web site data. The web site data includes dynamic content data from an external data source, and the data entry may include a designation of such an external data source.
Owner:DECENTRIX
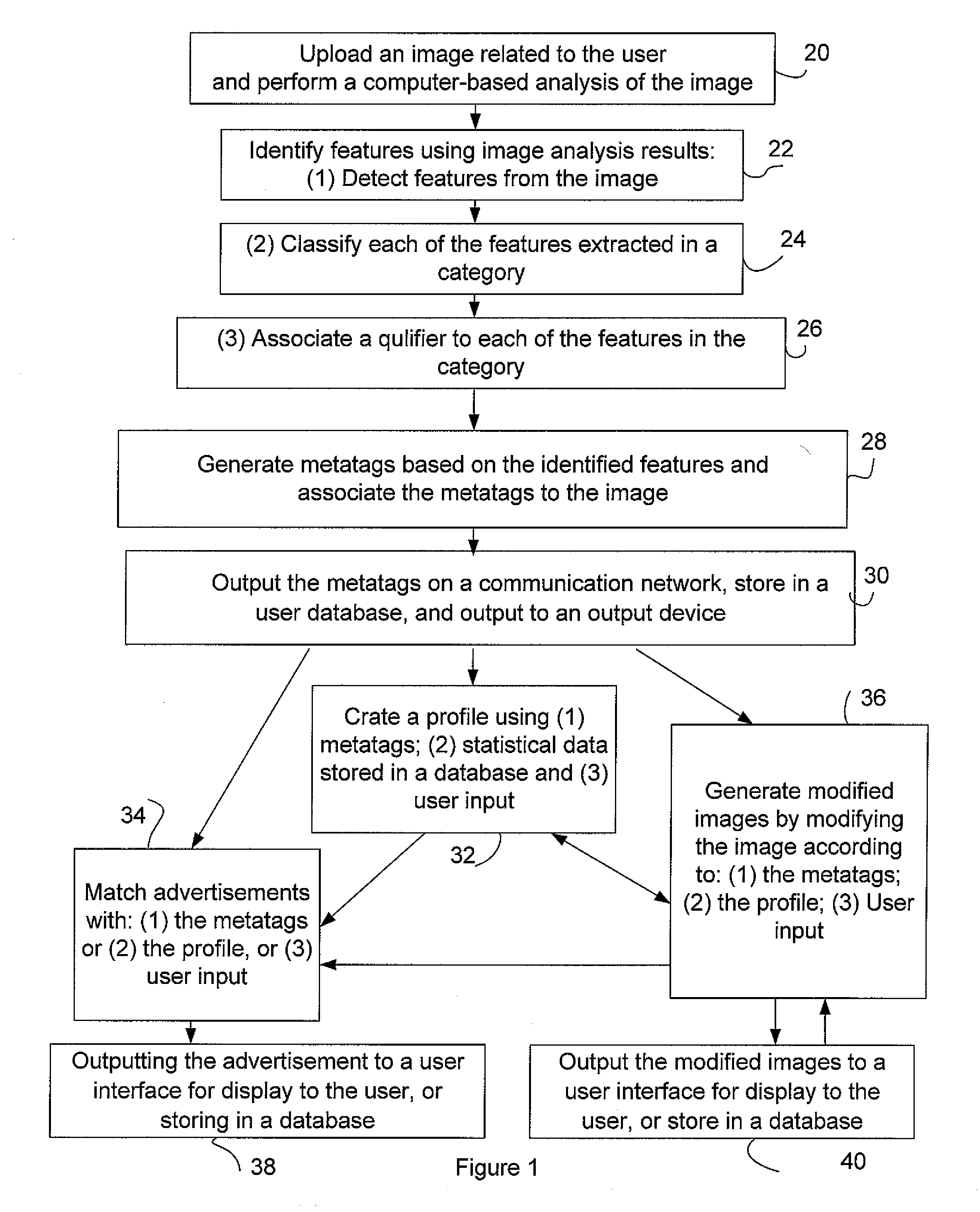
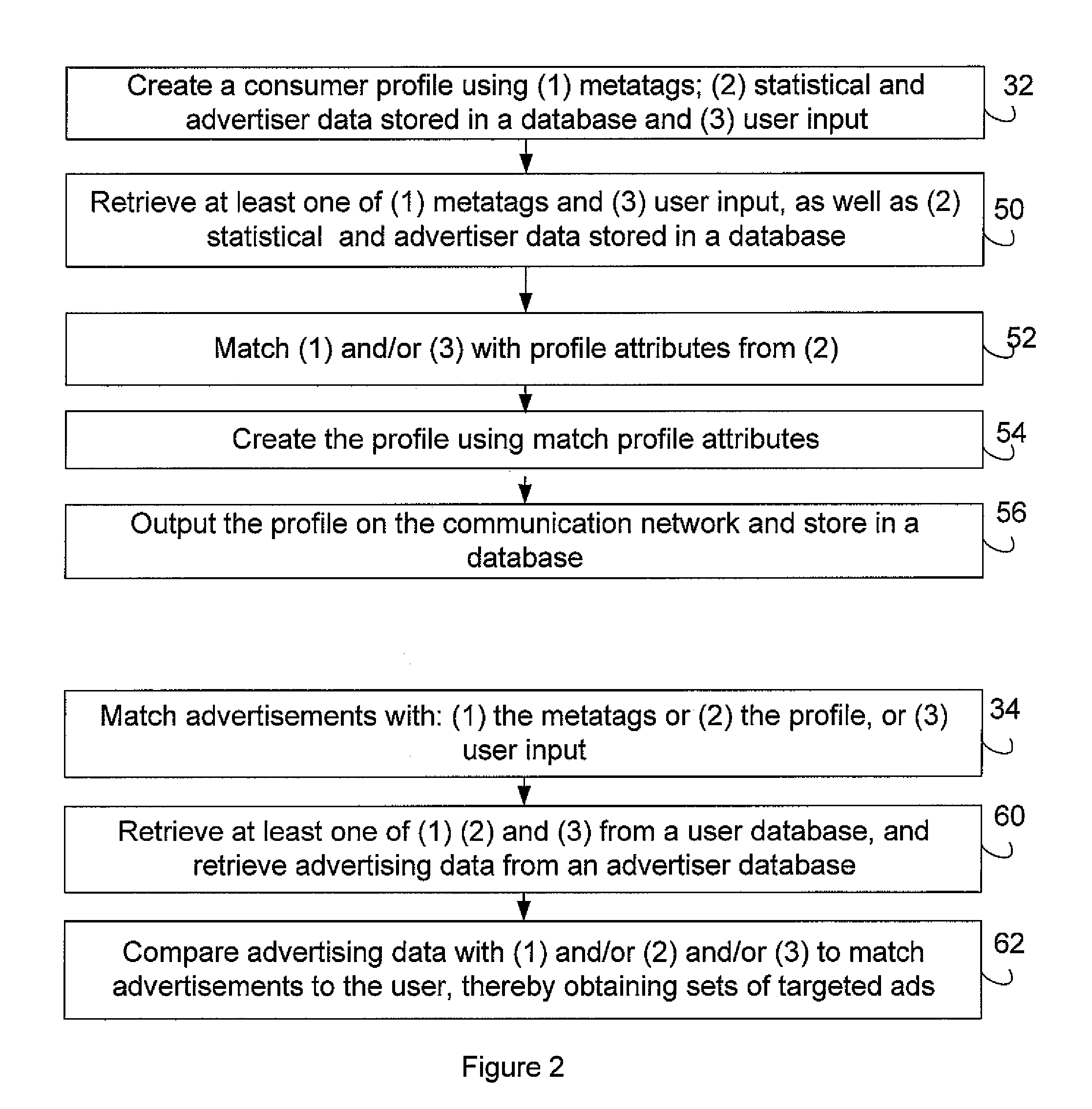
Method and system for image and video analysis, enhancement and display for communication
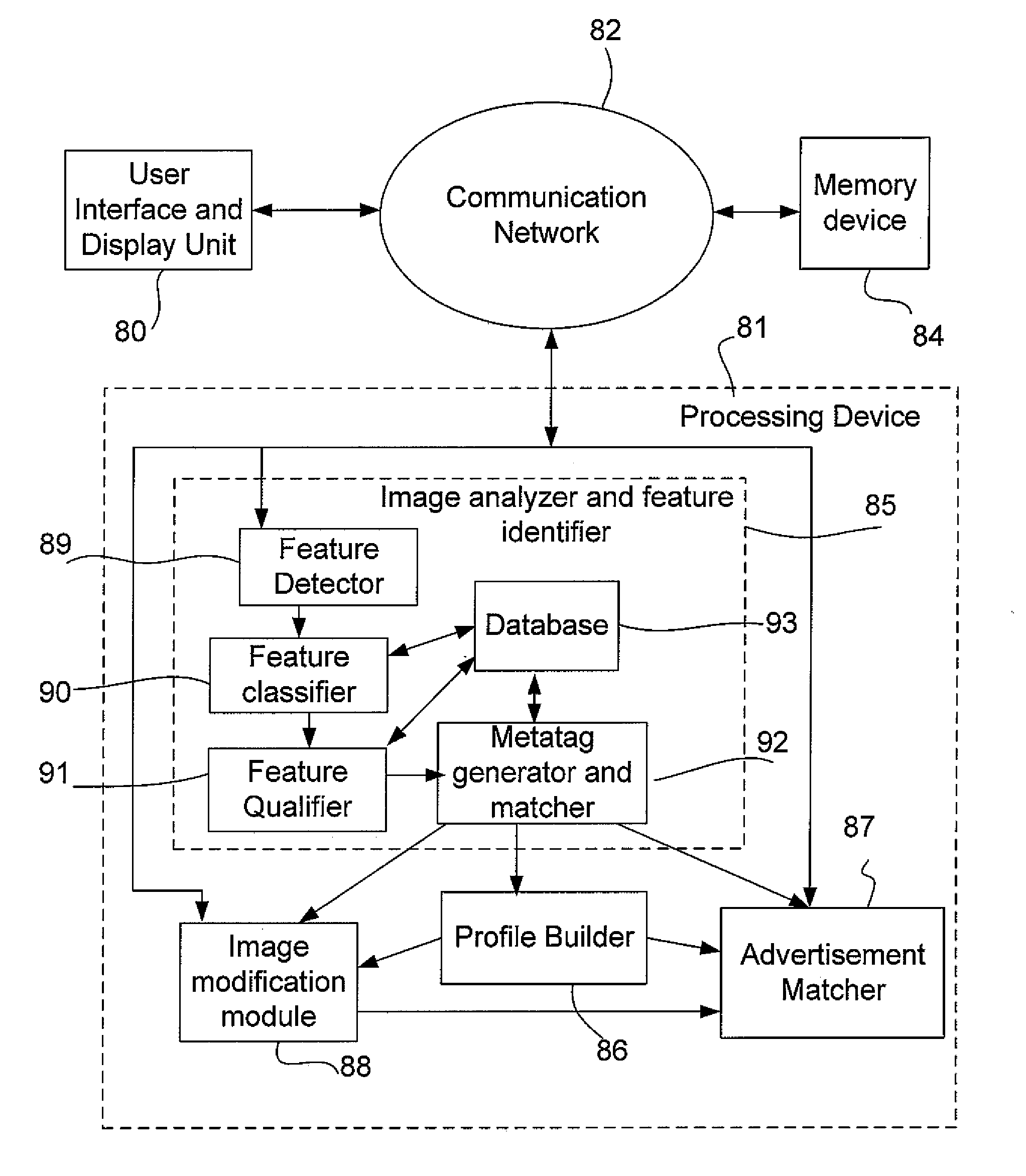
ActiveUS20080002892A1Character and pattern recognitionMetadata still image retrievalFeature generationComputer based
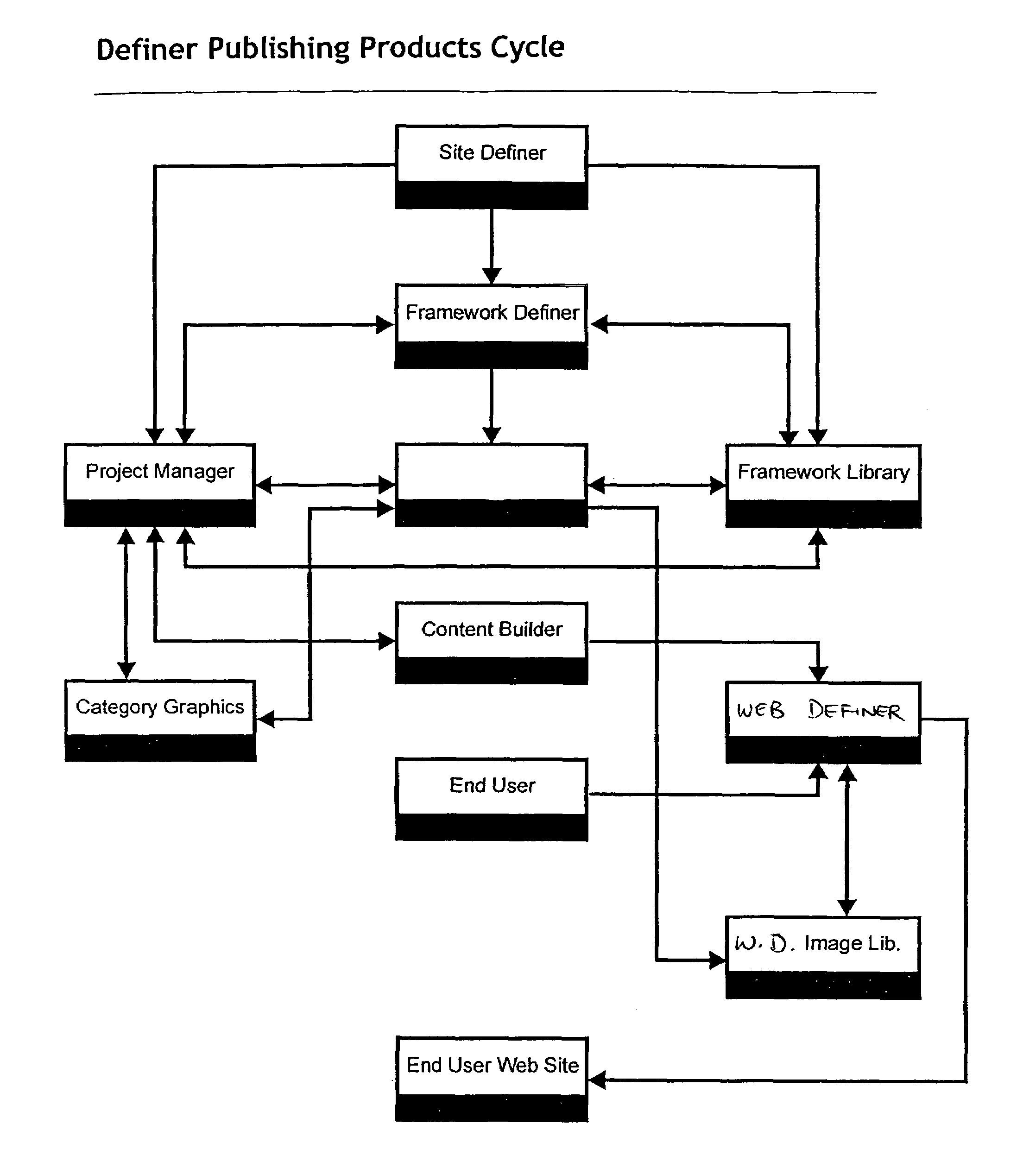
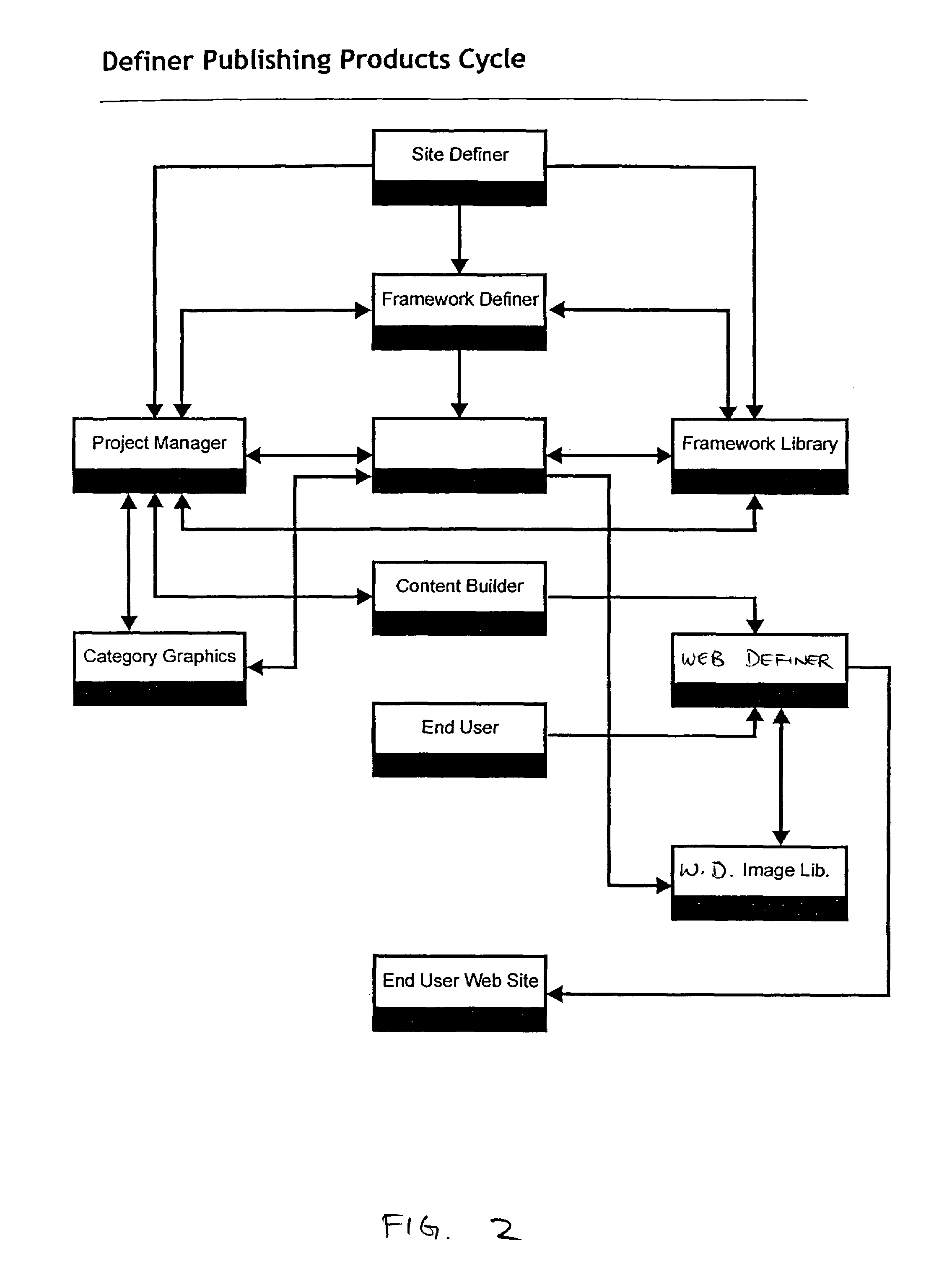
There is described a system and a method for generating a metatag indicative of an attribute of a person represented in an image, the method comprising: performing a computer-based analysis of the image; identifying a feature related to the attribute of the person in the image using results from the computer-based analysis; generating the metatag based on the identified feature; and associating the metatag to the image, the metatag being thereby related to the attribute of the person.
Owner:MOREIDEAS
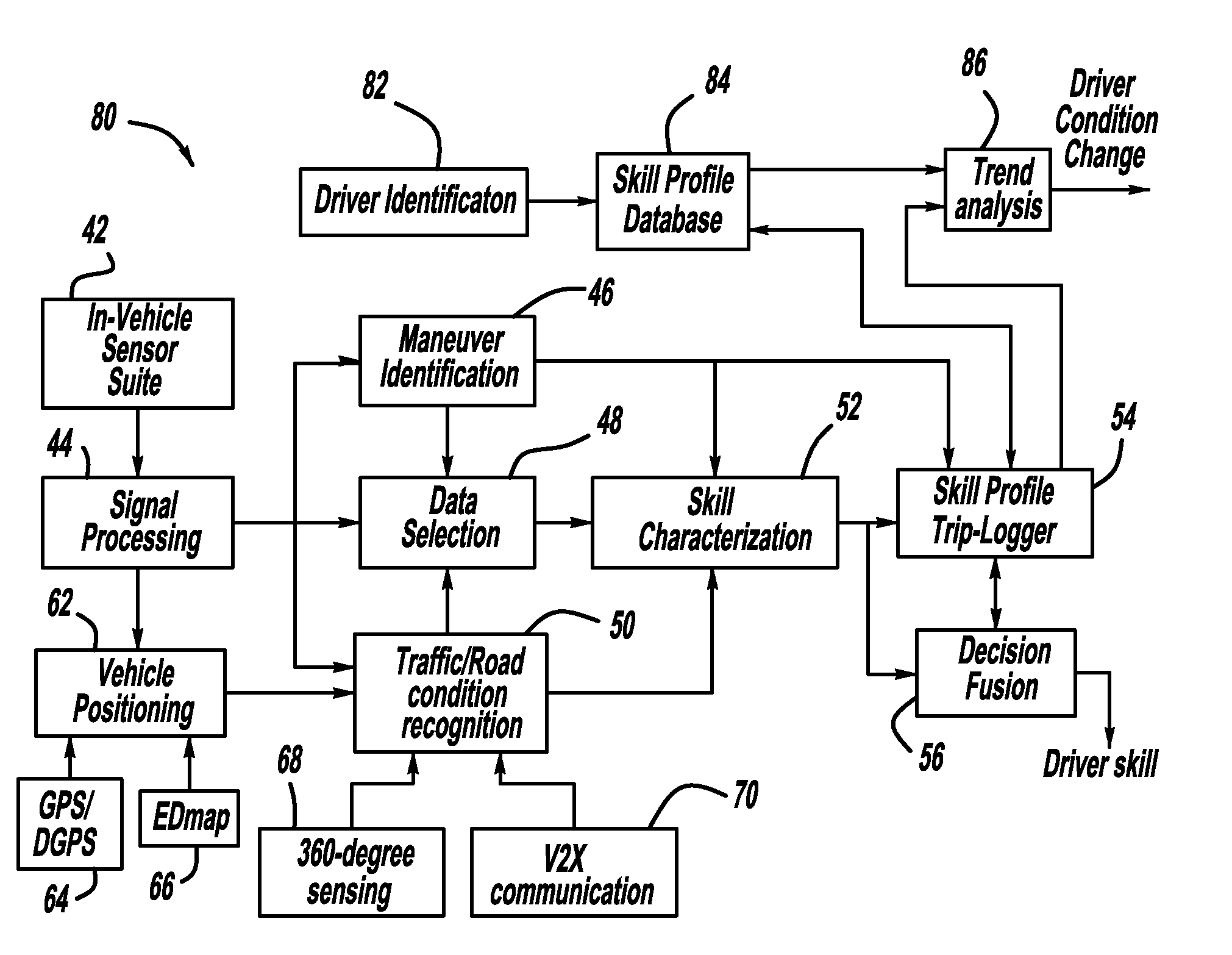
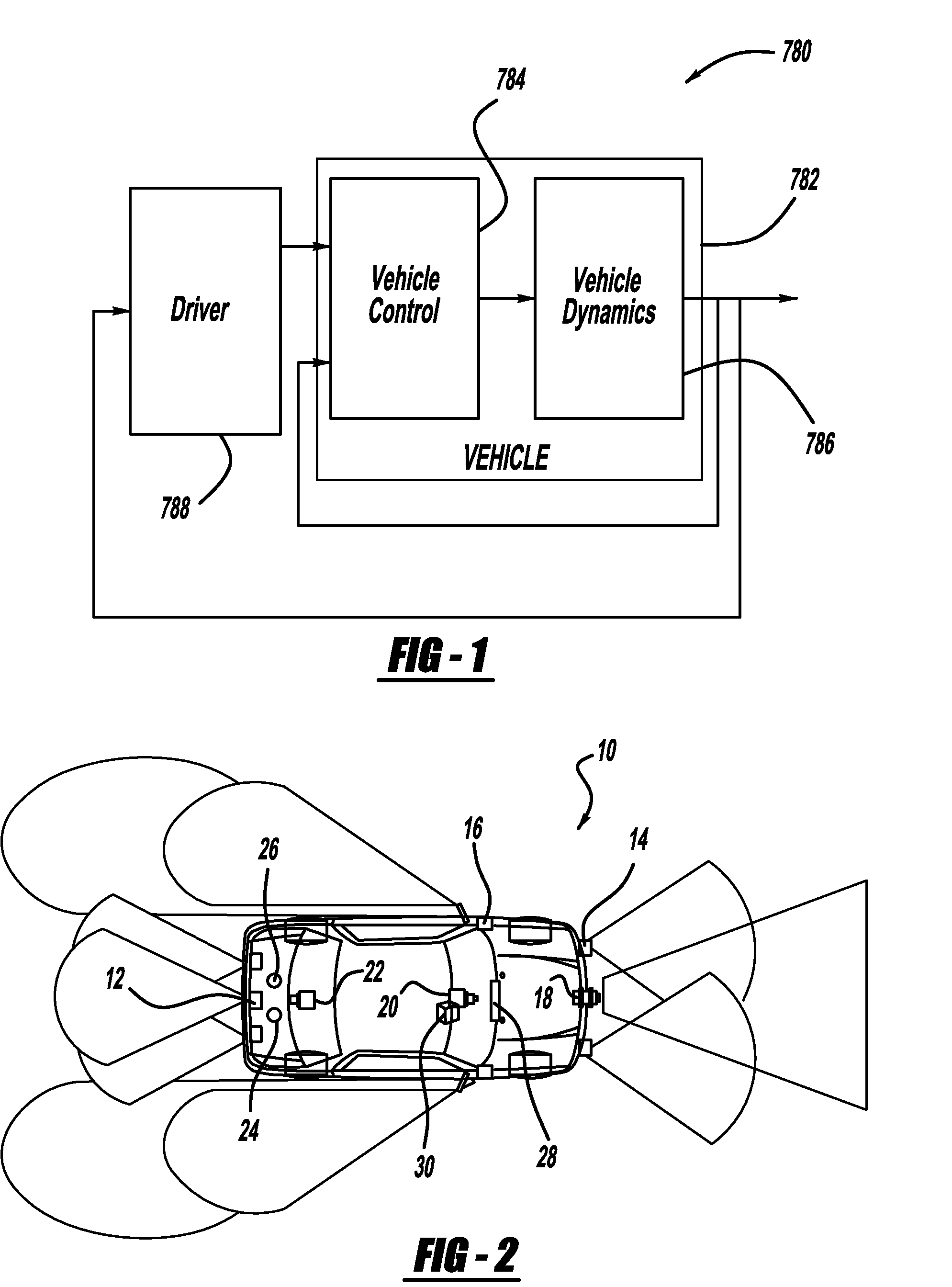
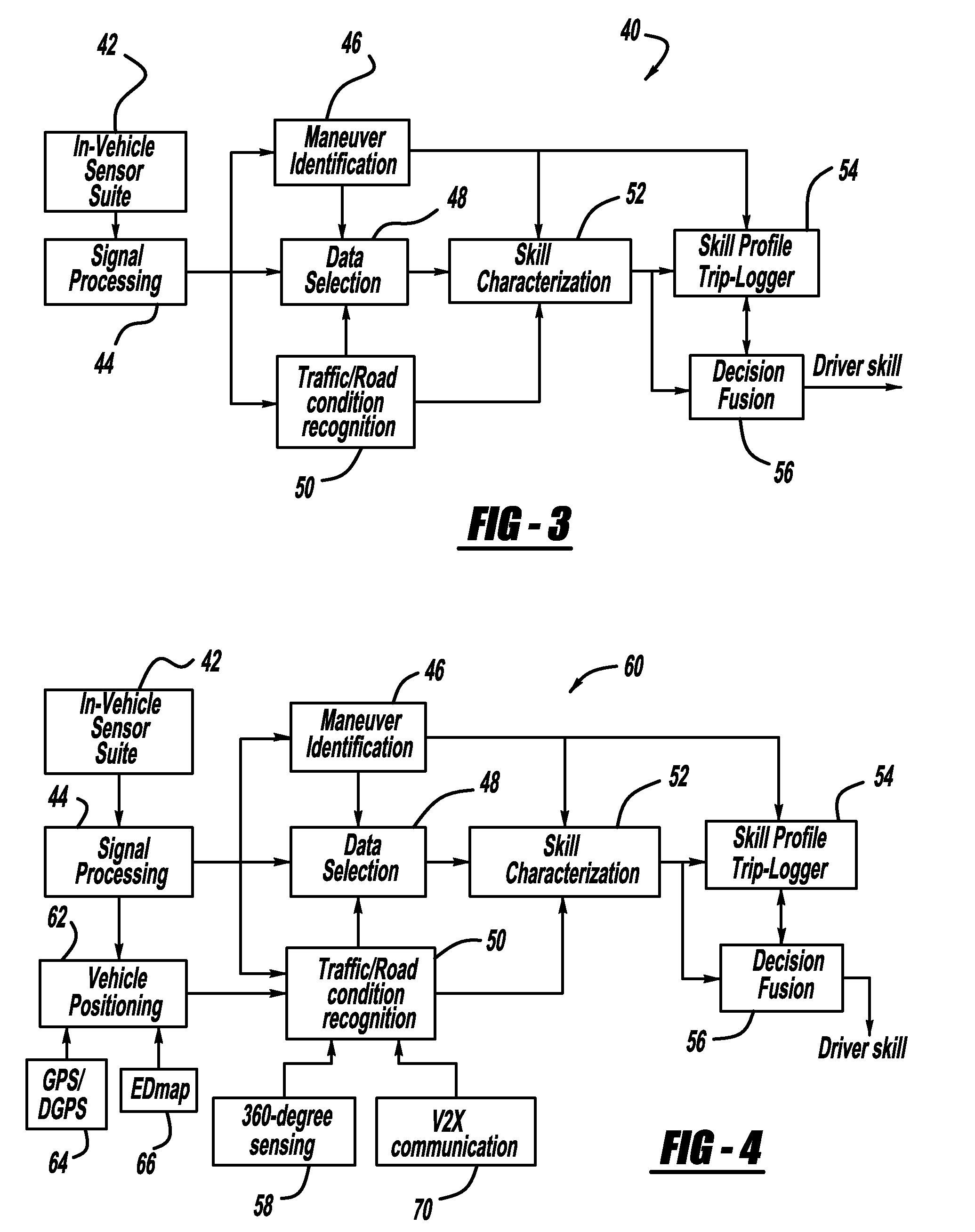
Vehicle stability enhancement control adaptation to driving skill based on multiple types of maneuvers
InactiveUS20100209889A1Cosmonautic condition simulationsRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesFeature extractionDriver/operator
A system and method that classify driver driving skill based on multiple types of maneuvers. An original features generation processor receives signals identifying driving characteristics of the driver of the vehicle and outputs original features from the signals. A features extraction processor extracts certain features from the original features and outputs transformed features. A features selection processor selects certain ones of the transformed features and outputs final features and a classifier classifies the final features to determine the skill level of the vehicle driver.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
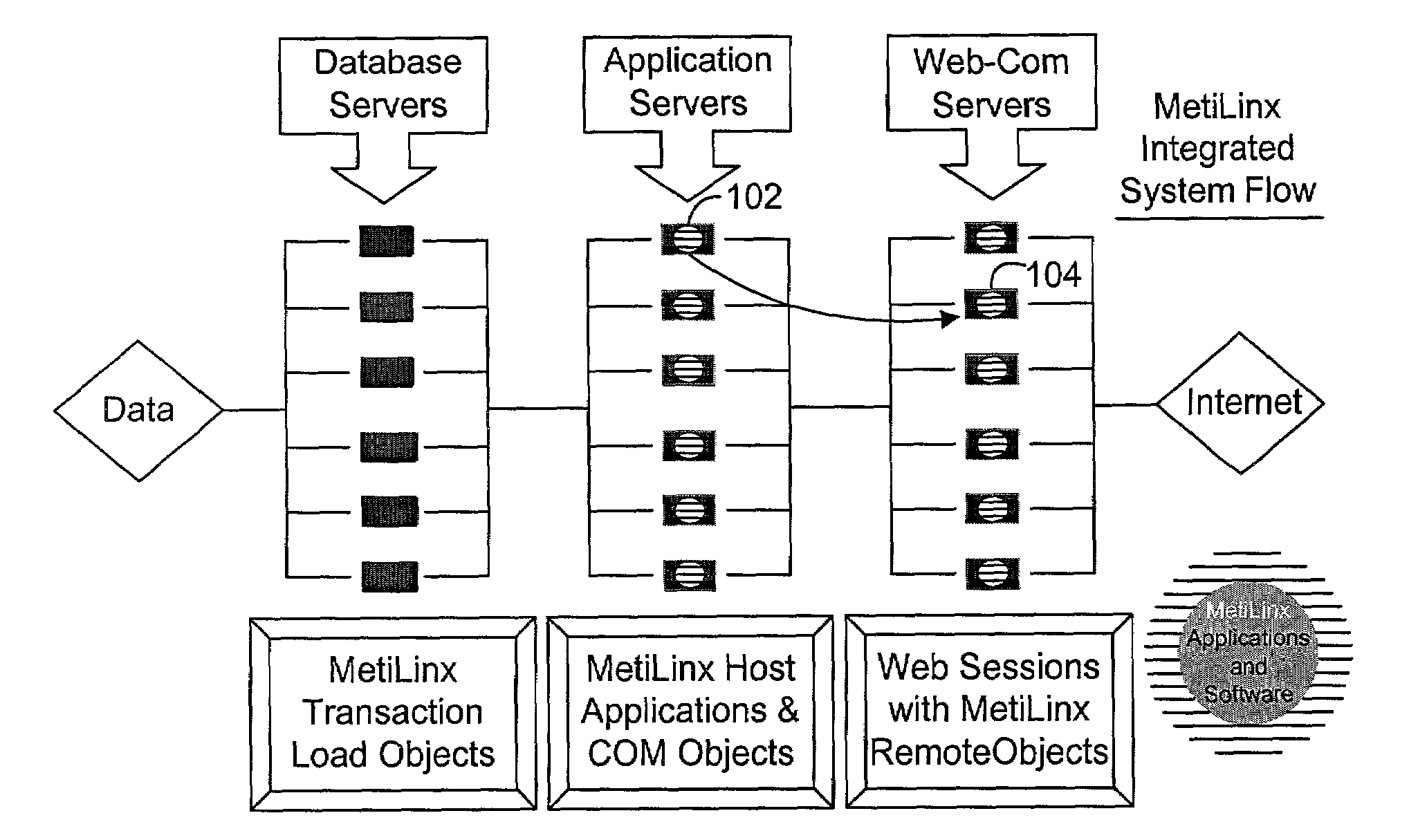
Aggregate system resource analysis including correlation matrix and metric-based analysis
InactiveUS7379994B2Accurately combine valueDigital computer detailsNuclear monitoringResource utilizationDistributed computing
A system for gathering data for purposes of analyzing a network. The data is gathered based on values that are passed from node-to-node within processing devices, such as servers, in a network. The values are generated from characteristics obtained from measuring device performance and resource utilization. Values are passed peer-to-peer and successively combined with values at each receiving system so that, ultimately, a value is obtained that reflects the operation of a group of devices. A correlation matrix is maintained to indicate discrepancies in value meanings from different devices. The correlation matrix is used to more accurately combine values to achieve meaningful composite values.
Owner:METILINX +1
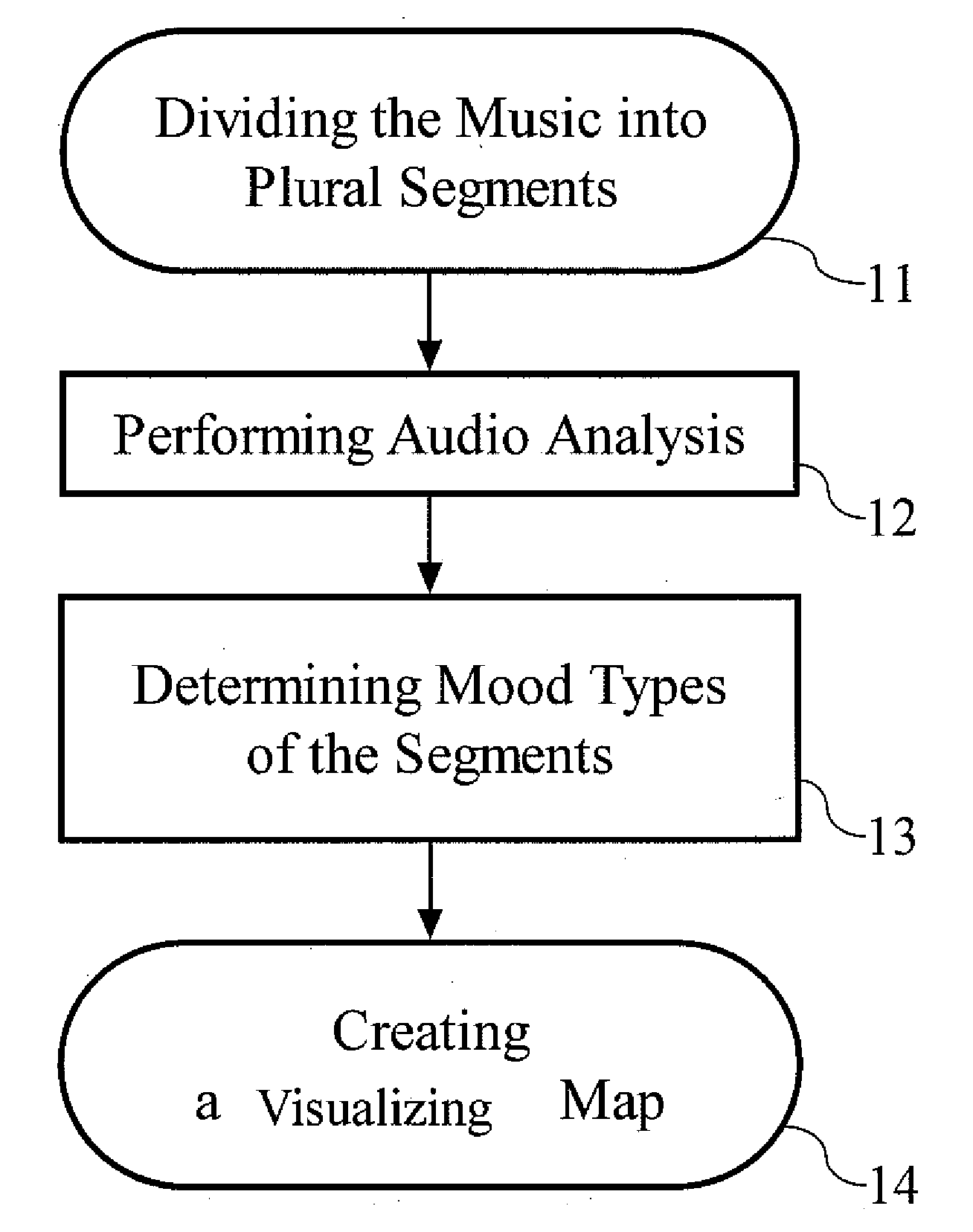
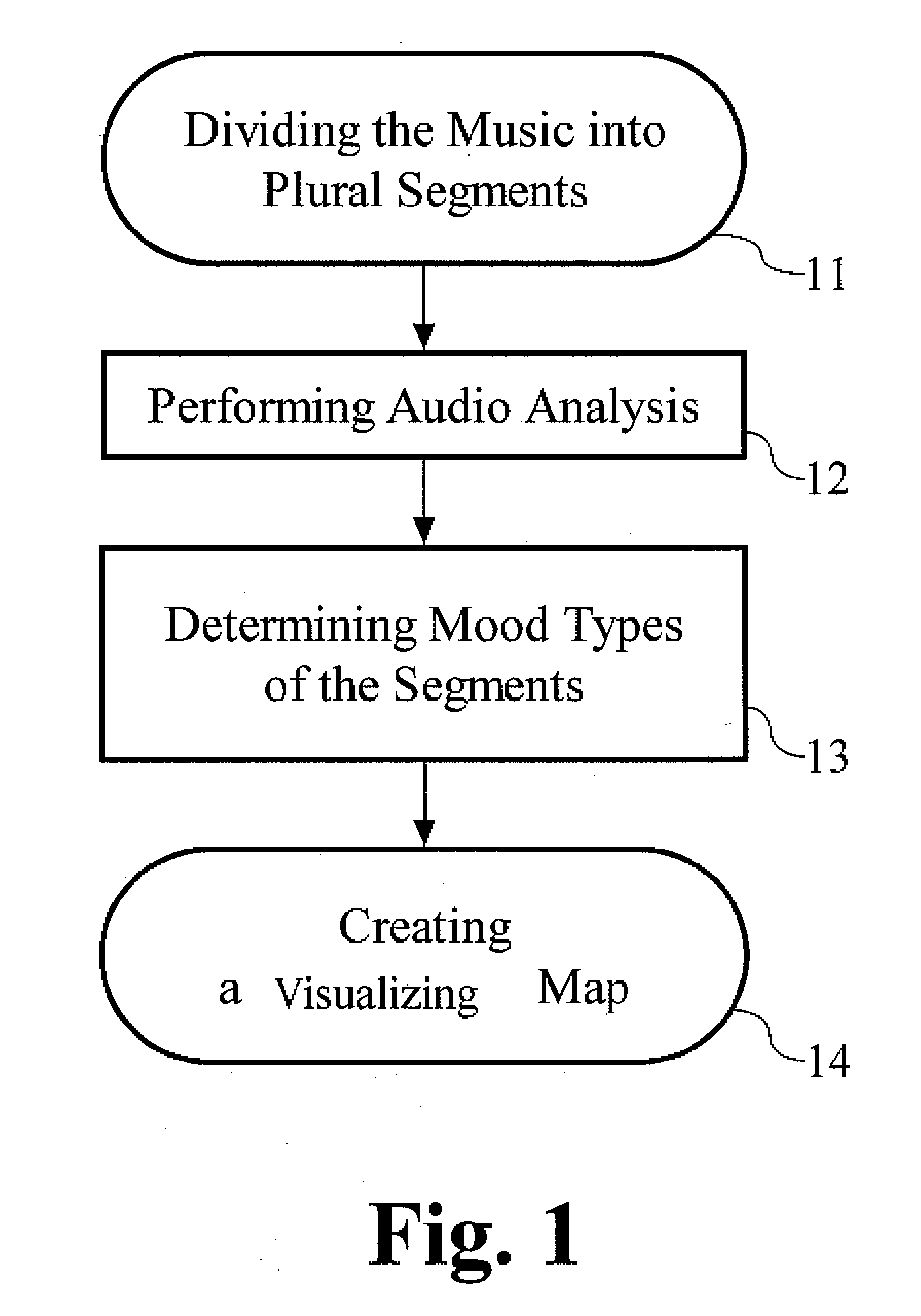
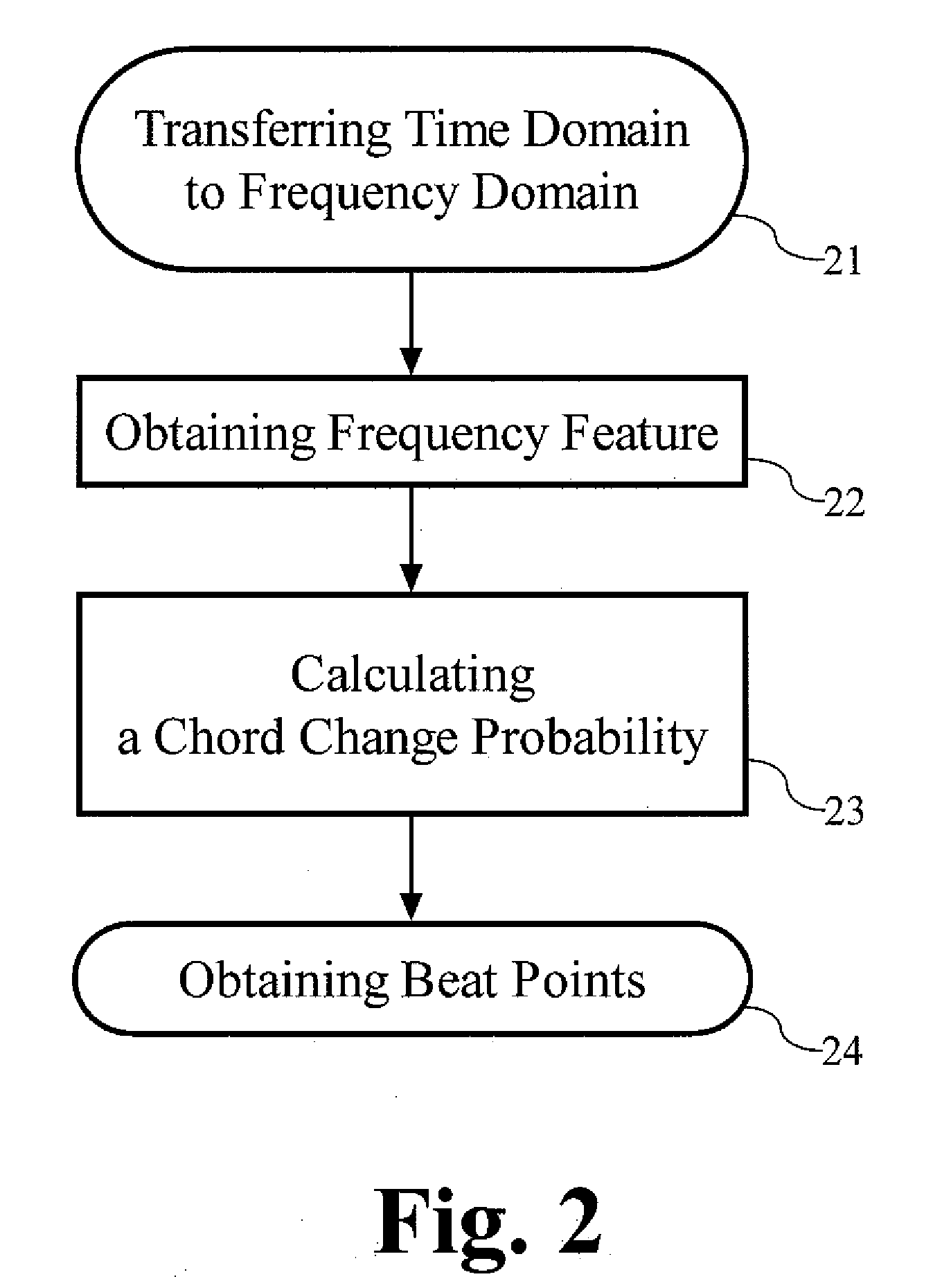
Method for generating a visualizing map of music
InactiveUS20070157795A1Easy to identifyElectrophonic musical instrumentsHuman–computer interactionData science
The present invention provides a method for generating a visualizing map of music in accordance with the identifiable features of the music. First, the music would be divided into plural segments, and the length of each segment is preferably identical. After that, an audio analysis is executed to determine the mood types of these segments. Each mood type may be determined by certain parameters, such as tempo value and articulation type. Besides, every mood type corresponds to a certain visualizing expression, and the correspondence can be defined in advance and looked up in a table for example. Eventually, the visualizing map of the music is generated according to the mood types and the distribution of visualizing expressions.
Owner:COREL TW CORP
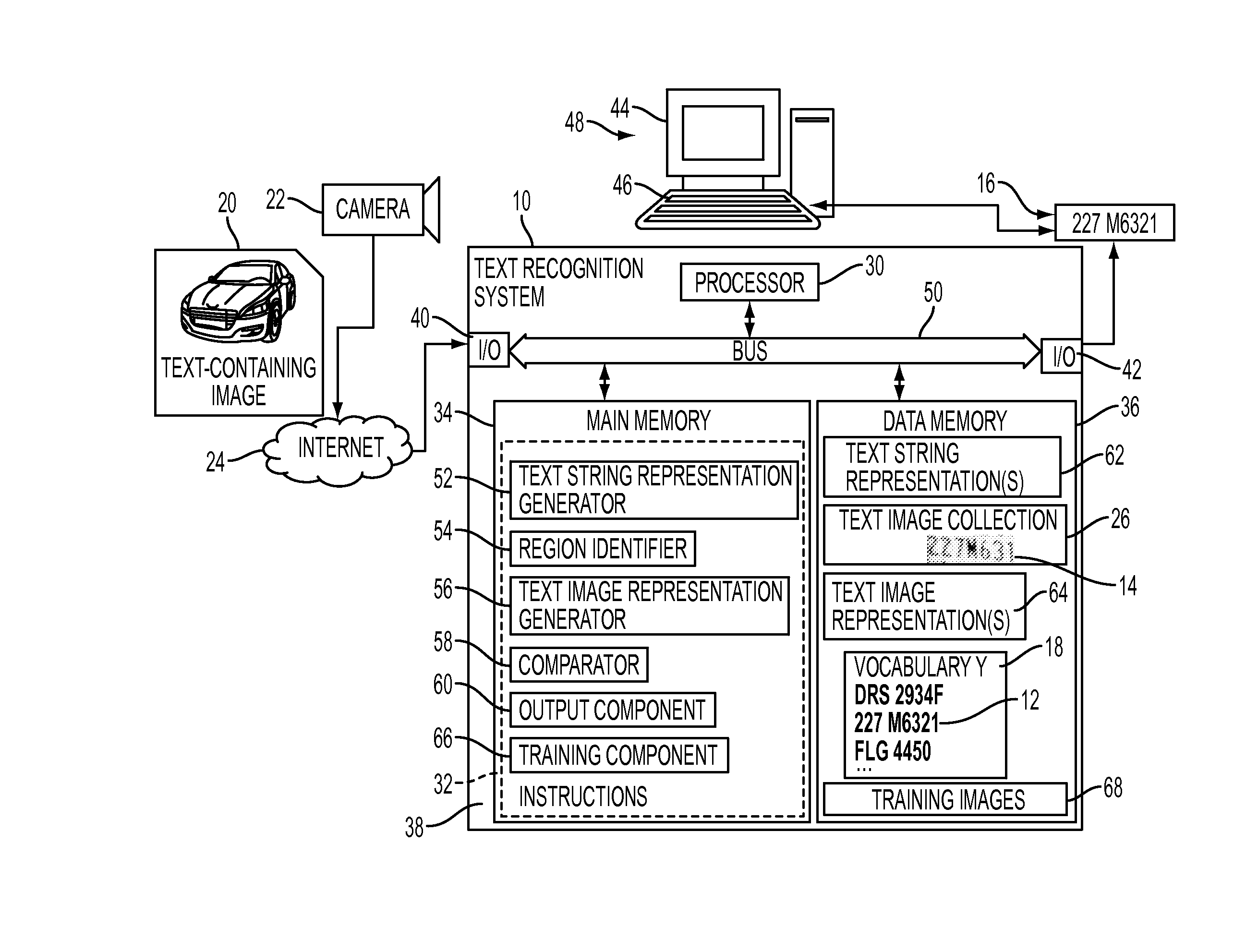
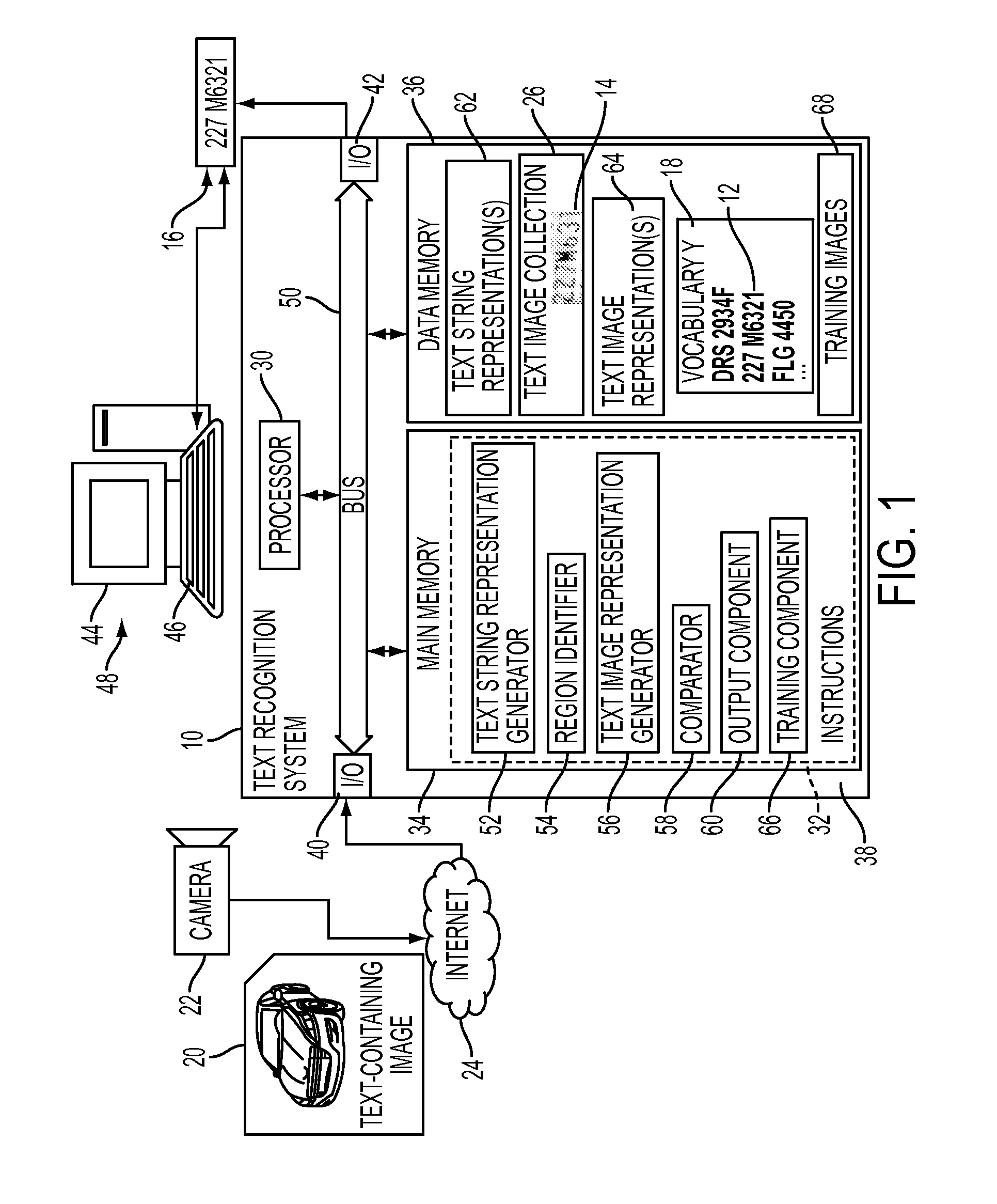
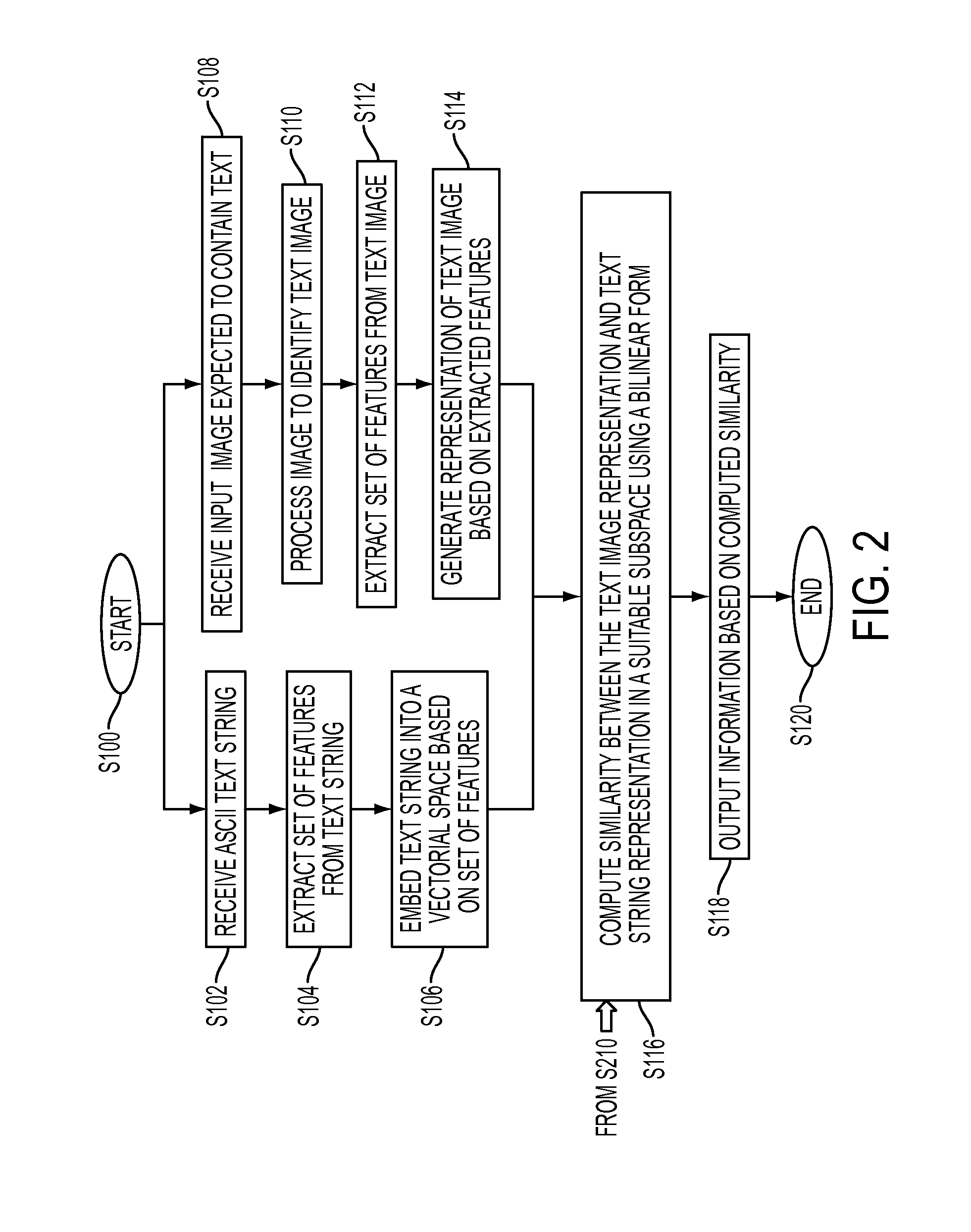
Label-embedding for text recognition
A system and method for comparing a text image and a character string are provided. The method includes embedding a character string into a vectorial space by extracting a set of features from the character string and generating a character string representation based on the extracted features, such as a spatial pyramid bag of characters (SPBOC) representation. A text image is embedded into a vectorial space by extracting a set of features from the text image and generating a text image representation based on the text image extracted features. A compatibility between the text image representation and the character string representation is computed, which includes computing a function of the text image representation and character string representation.
Owner:XEROX CORP
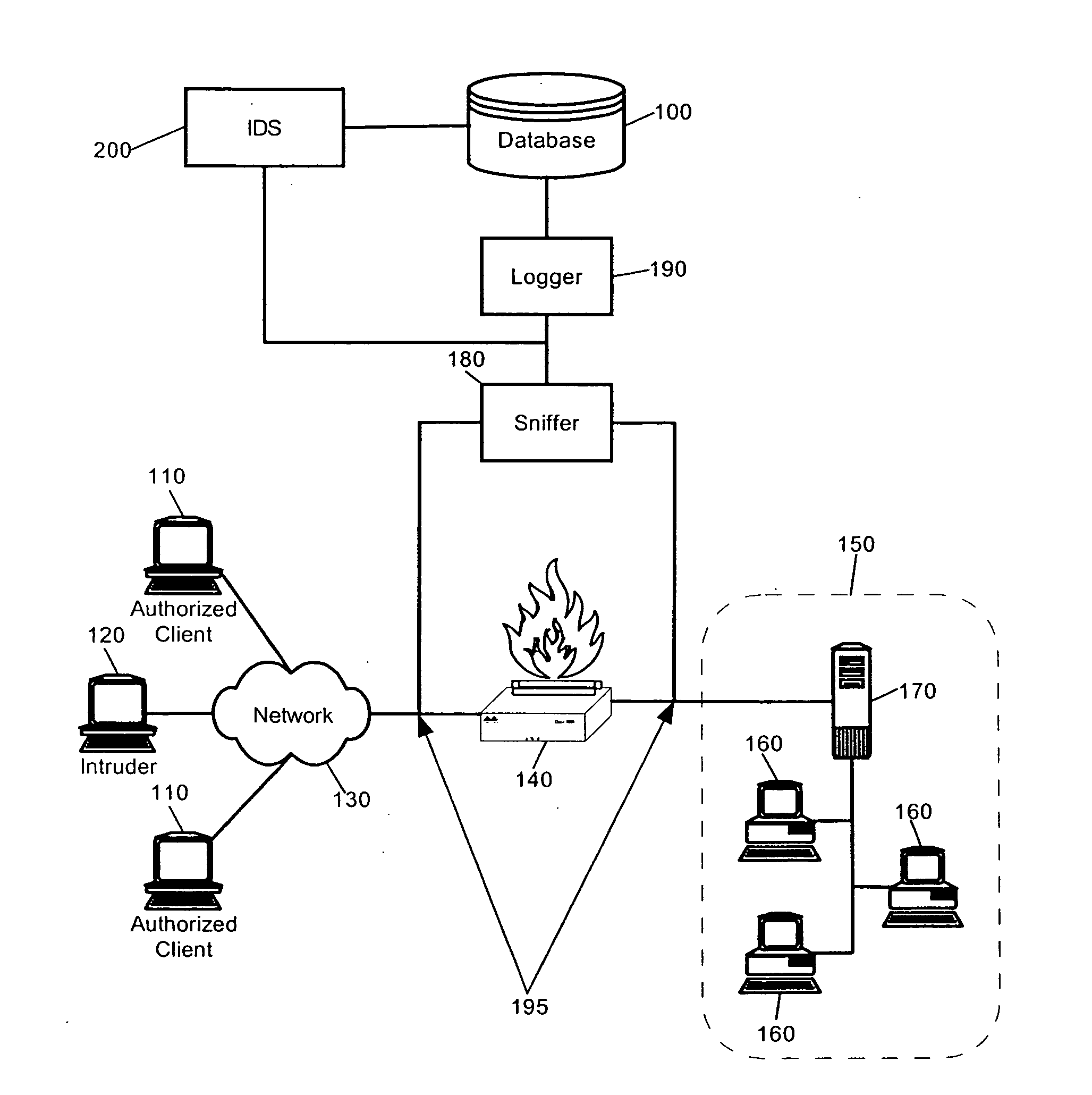
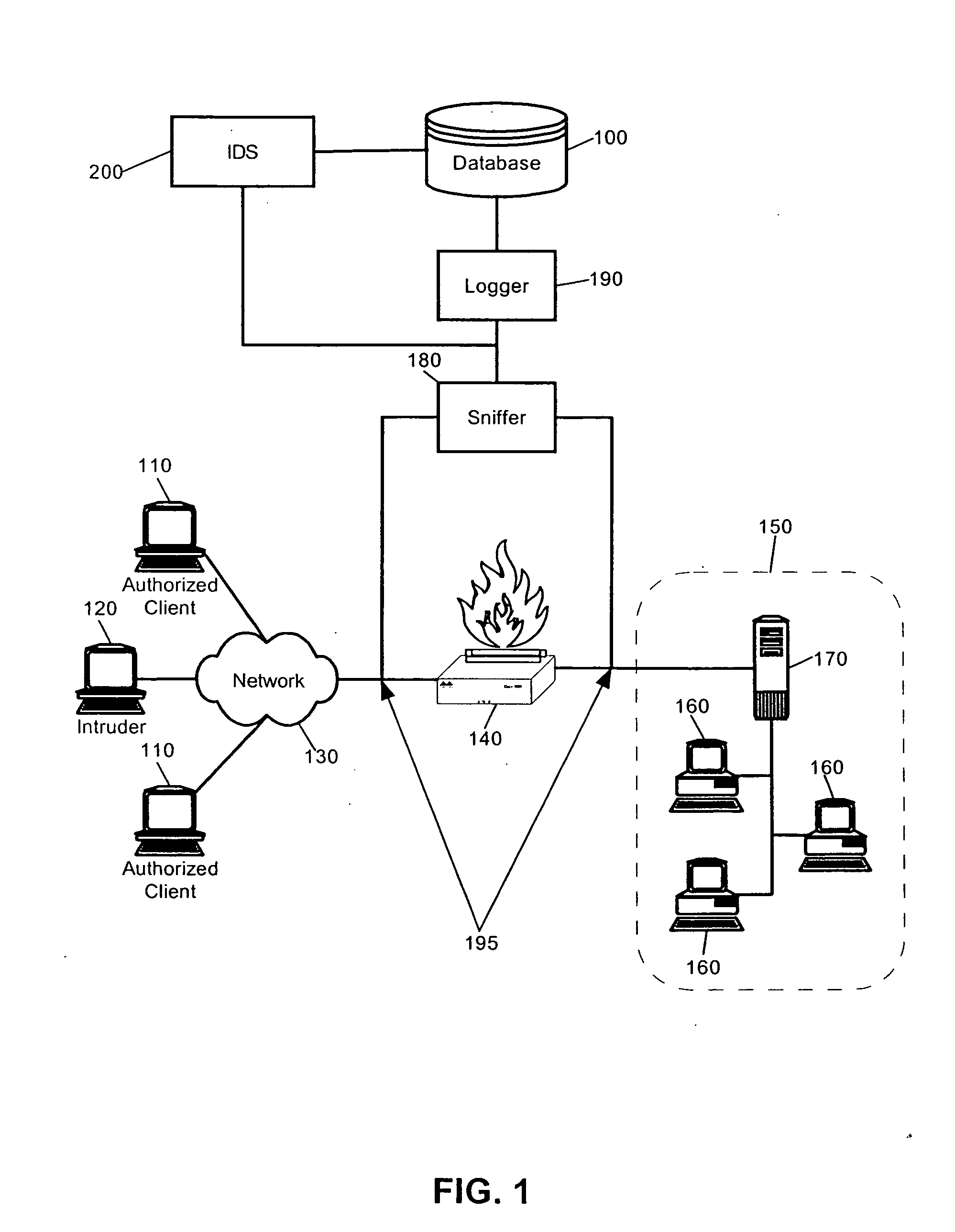
Intrusion detection system
InactiveUS20060156404A1Facilitate robust analysisOvercome limitationsMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsData packInternet traffic
Owner:LONGHORN HD LLC
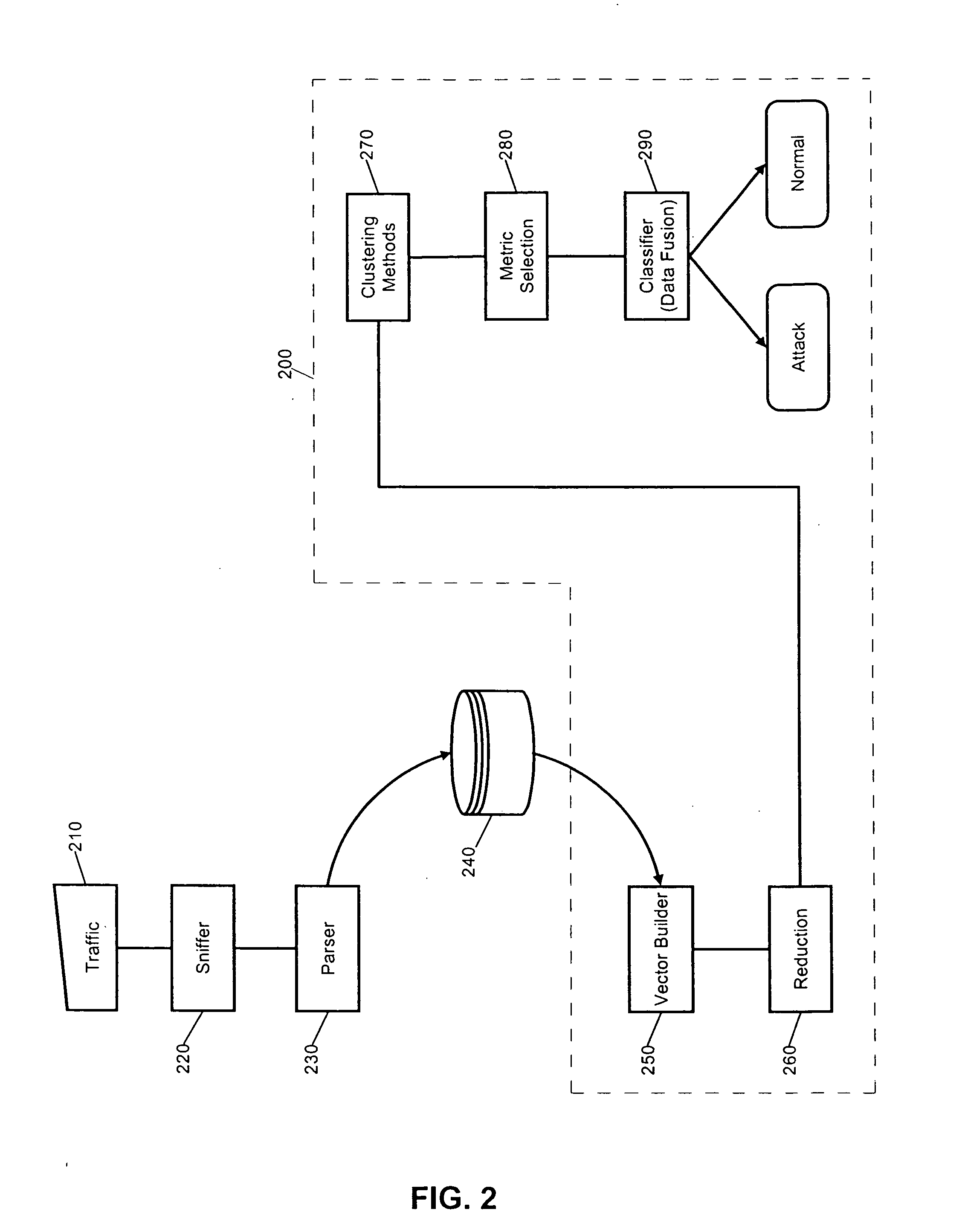
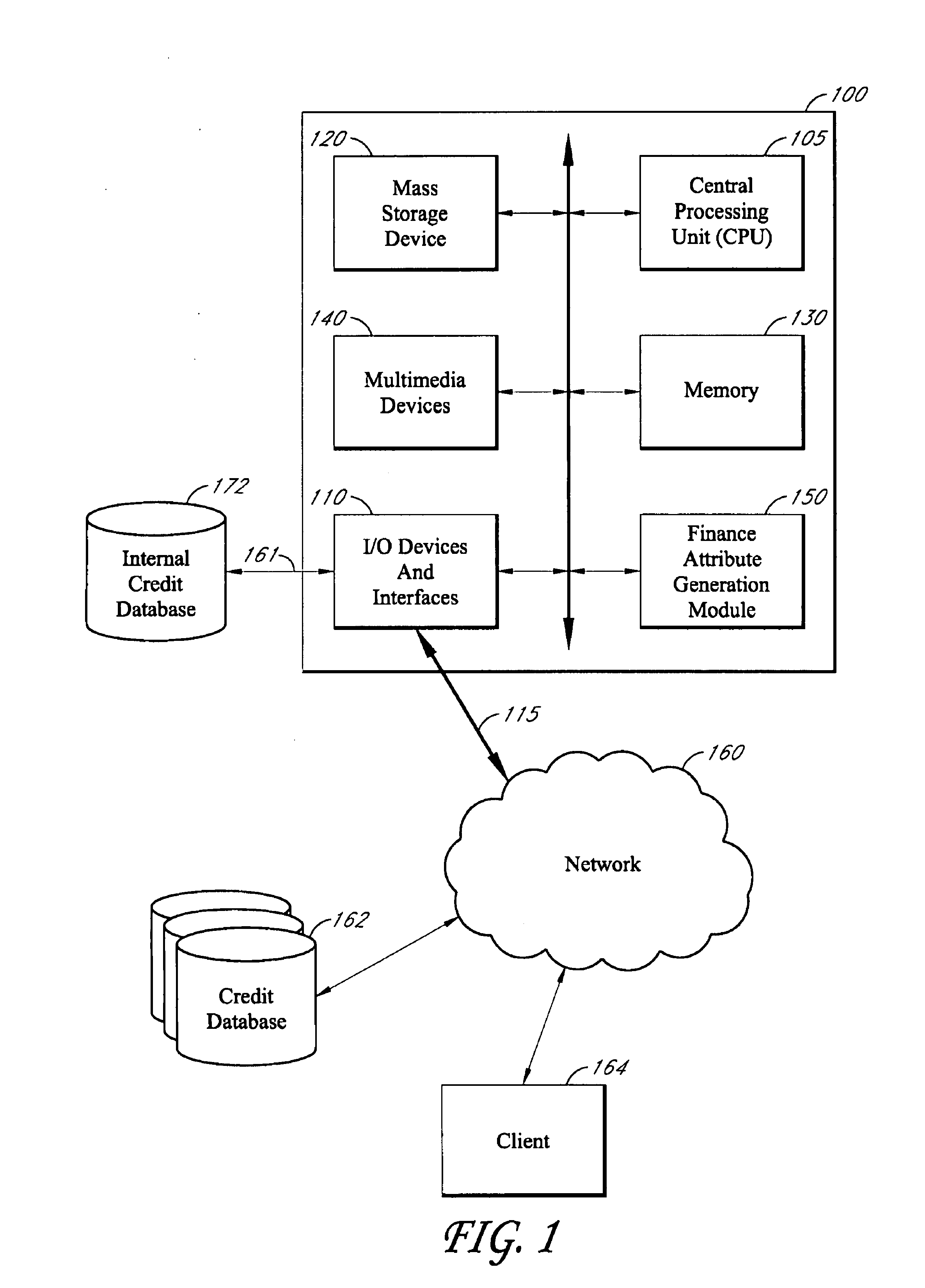
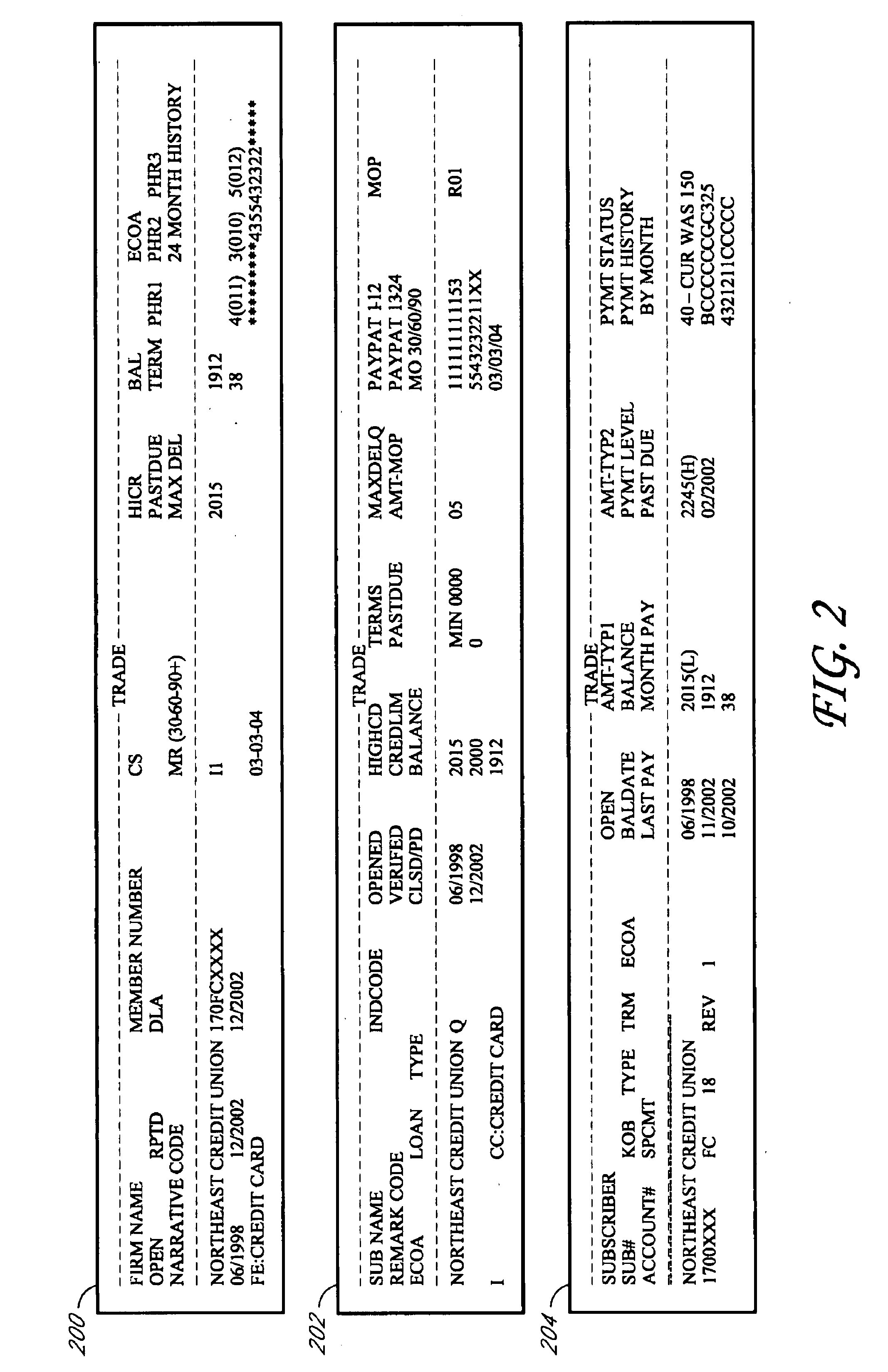
System and method for generating a finance attribute from tradeline data
ActiveUS8036979B1More informed decisionQuickly of creditFinanceForecastingComputer scienceFeature generation
Embodiments of a system and method are described for generating a finance attribute. In one embodiment, the systems and methods retrieve raw tradeline data from a plurality of credit bureaus, retrieve industry code data related to each of the plurality of credit bureaus, determine one or more tradeline leveling characteristics that meet at least one pre-determined threshold, and generate a finance attribute using the selected leveling characteristics.
Owner:EXPERIAN INFORMATION SOLUTIONS
Techniques for navigational query identification
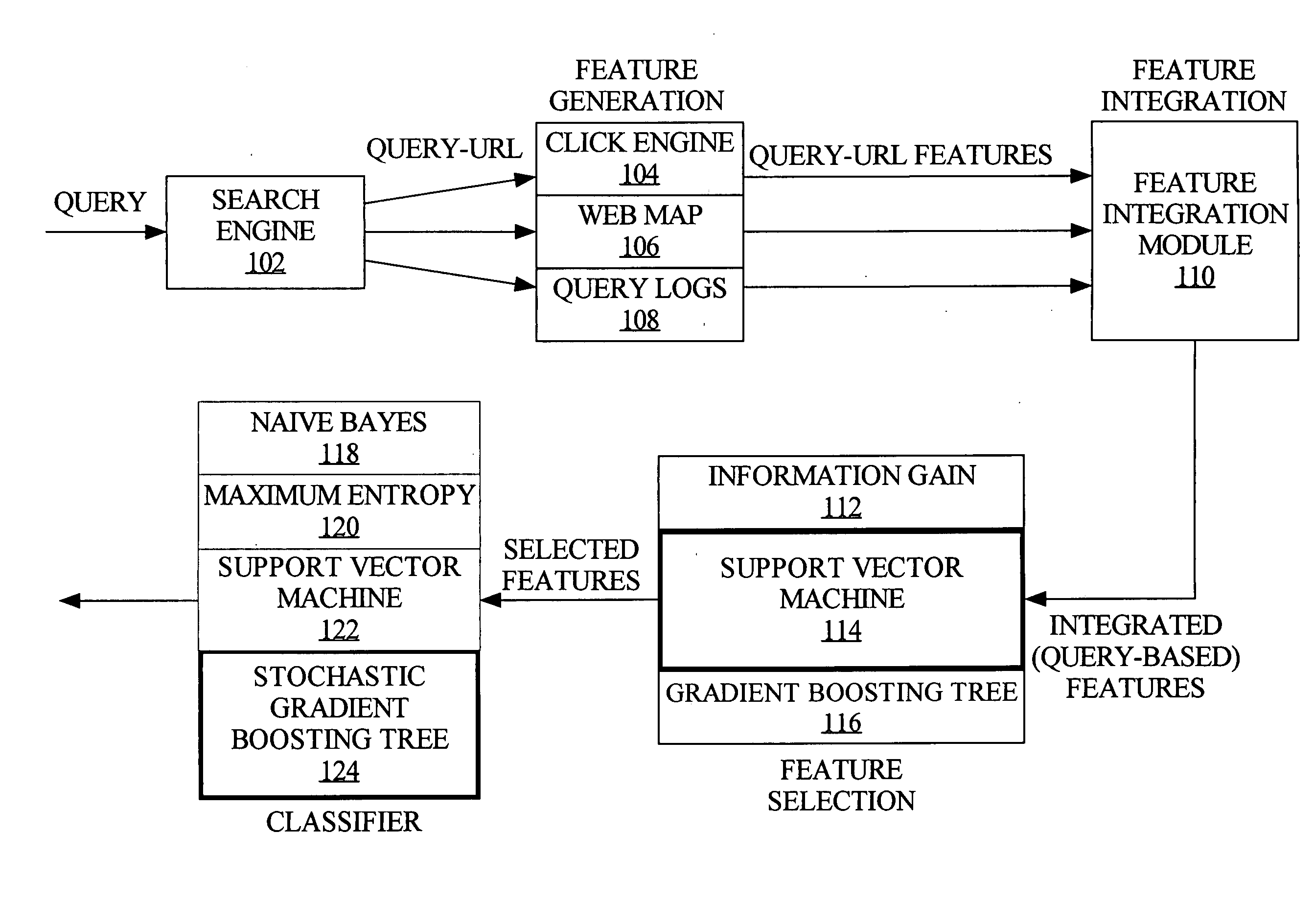
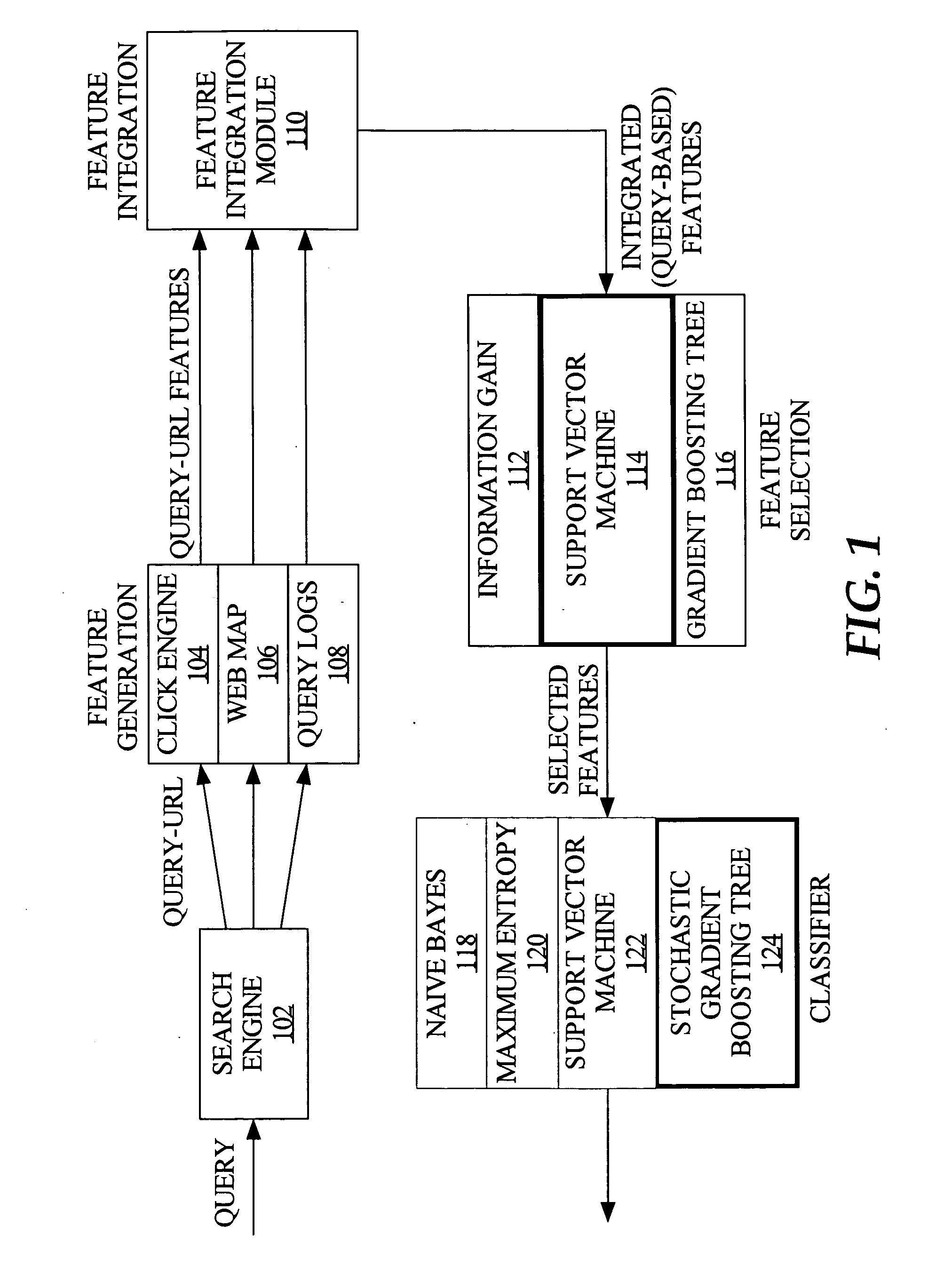
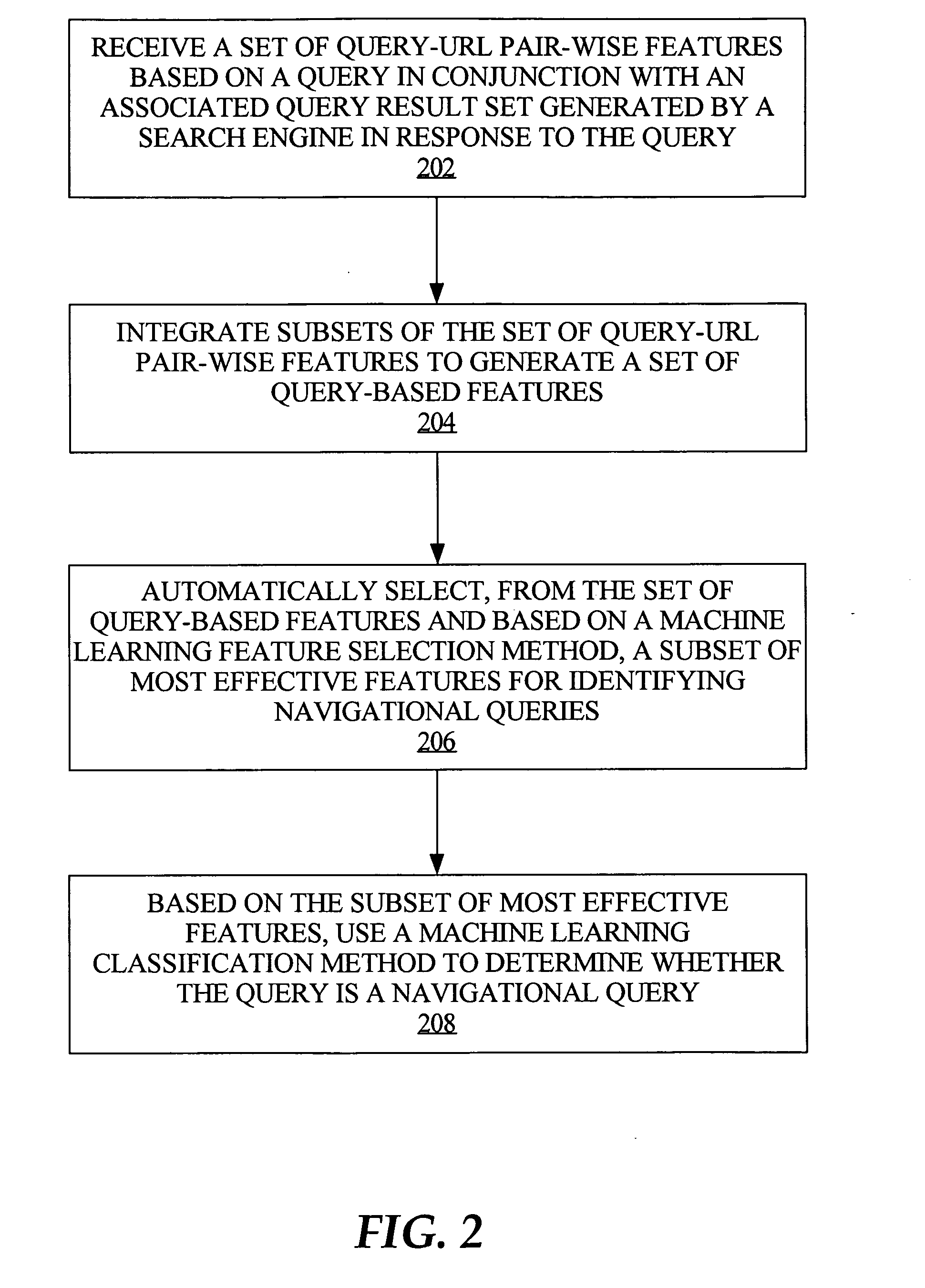
InactiveUS20080059508A1Web data indexingDigital data processing detailsThree levelSupport vector machine
To accurately classify a query as navigational, thousands of available features are explored, extracted from major commercial search engine results, user Web search click data, query log, and the whole Web's relational content. To obtain the most useful features for navigational query identification, a three level system is used which integrates feature generation, feature integration, and feature selection in a pipeline. Because feature selection plays a key role in classification methodologies, the best feature selection method is coupled with the best classification approach to achieve the best performance for identifying navigational queries. According to one embodiment, linear Support Vector Machine (SVM) is used to rank features and the top ranked features are fed into a Stochastic Gradient Boosting Tree (SGBT) classification method for identifying whether or not a particular query is a navigational query.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
Method and apparatus for generating a web site with dynamic content data from an external data source integrated therein
InactiveUS20100205551A1Input/output for user-computer interactionNatural language data processingWeb siteExternal data
A technique for generating a web site in accordance with received data entry by: determining at least one characteristic of at least one web site dimension of the web site based on the data entry; generating a multi-dimensional description of the web site based on the determined characteristics; retrieving web site data according to the generated multi-dimensional description of the web site; and generating the web site based upon the generated multi-dimensional description of the web site and the retrieved web site data. The web site data includes dynamic content data from an external data source, and the data entry may include a designation of such an external data source.
Owner:DECENTRIX
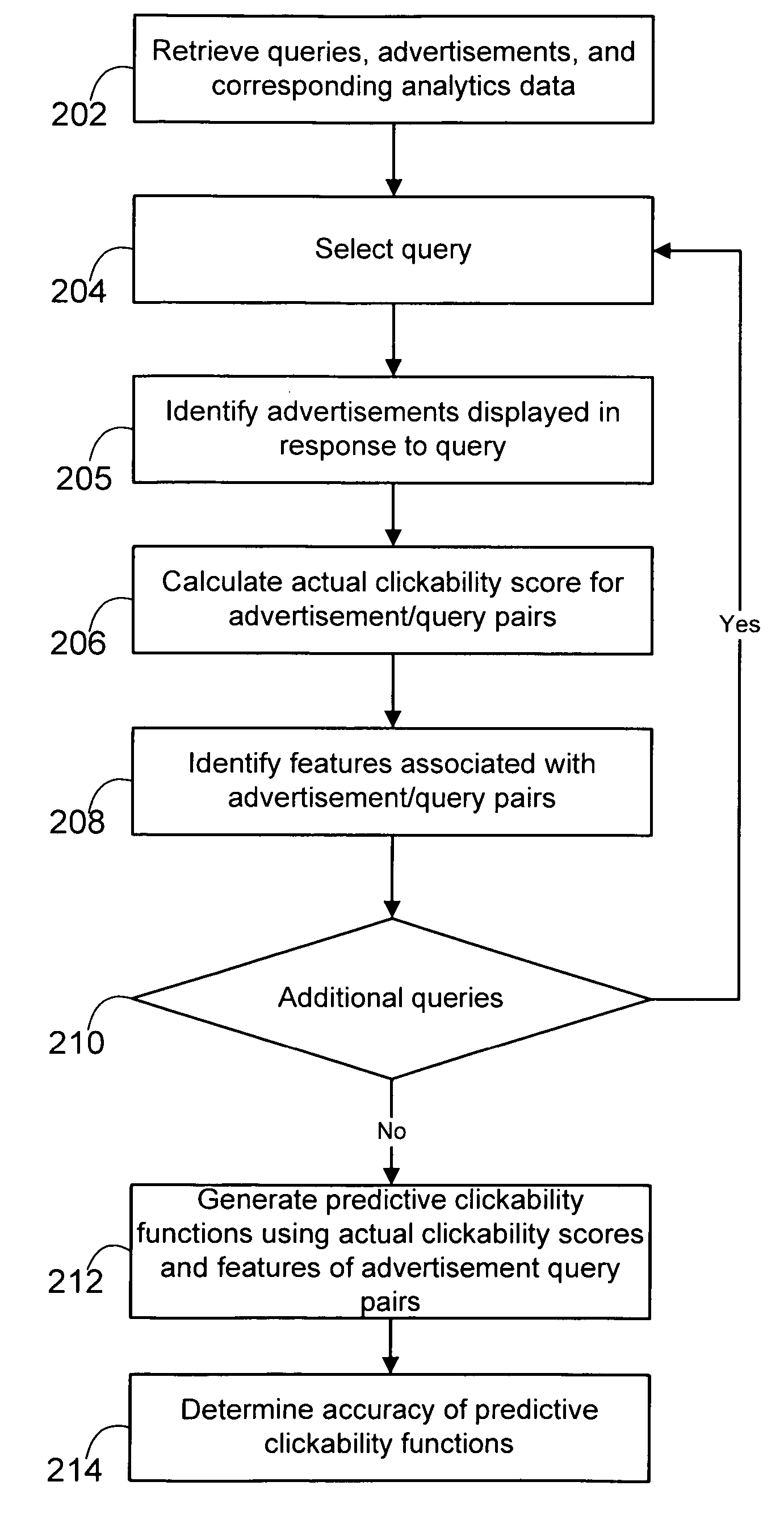
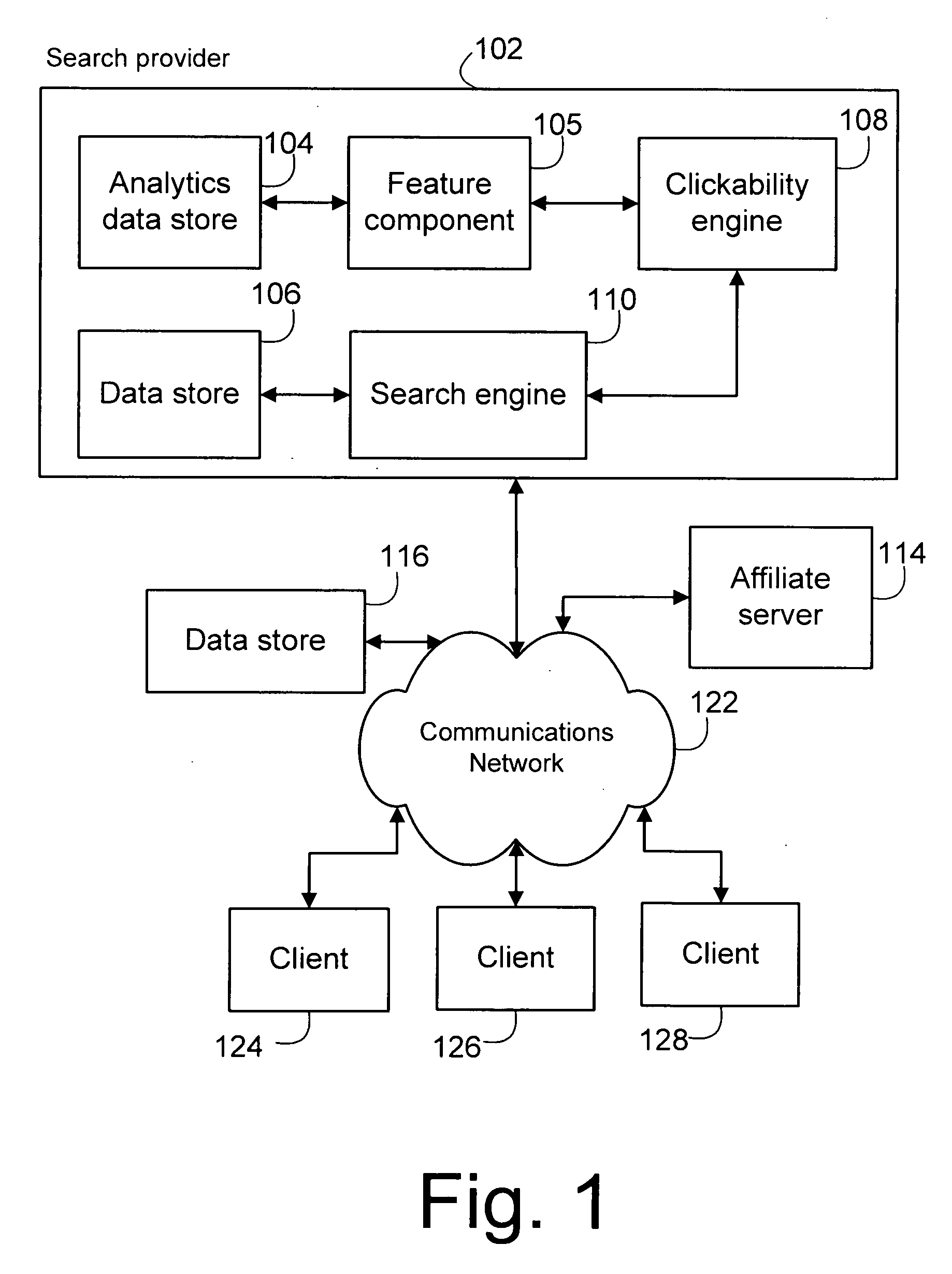
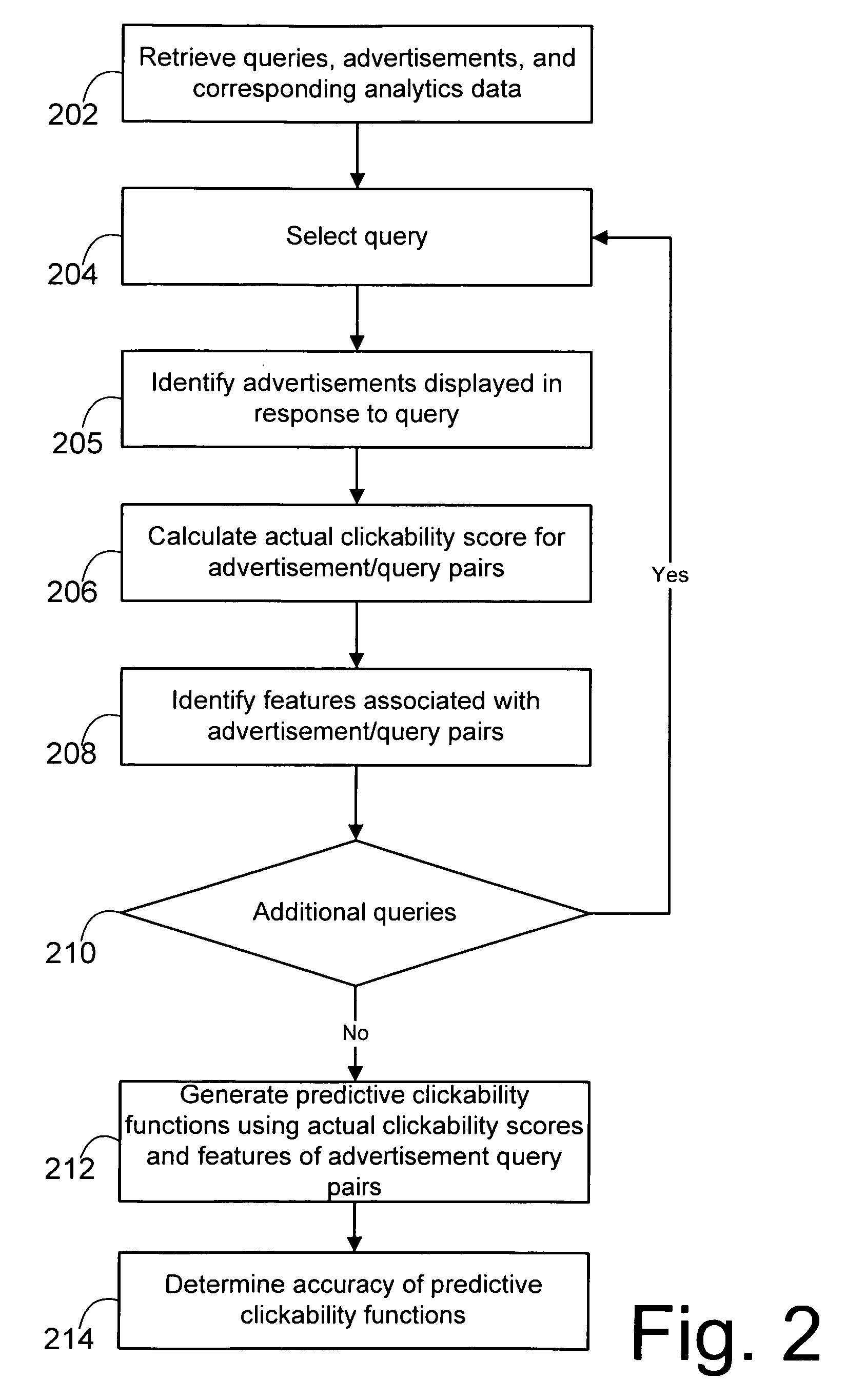
System and method for generating functions to predict the clickability of advertisements
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
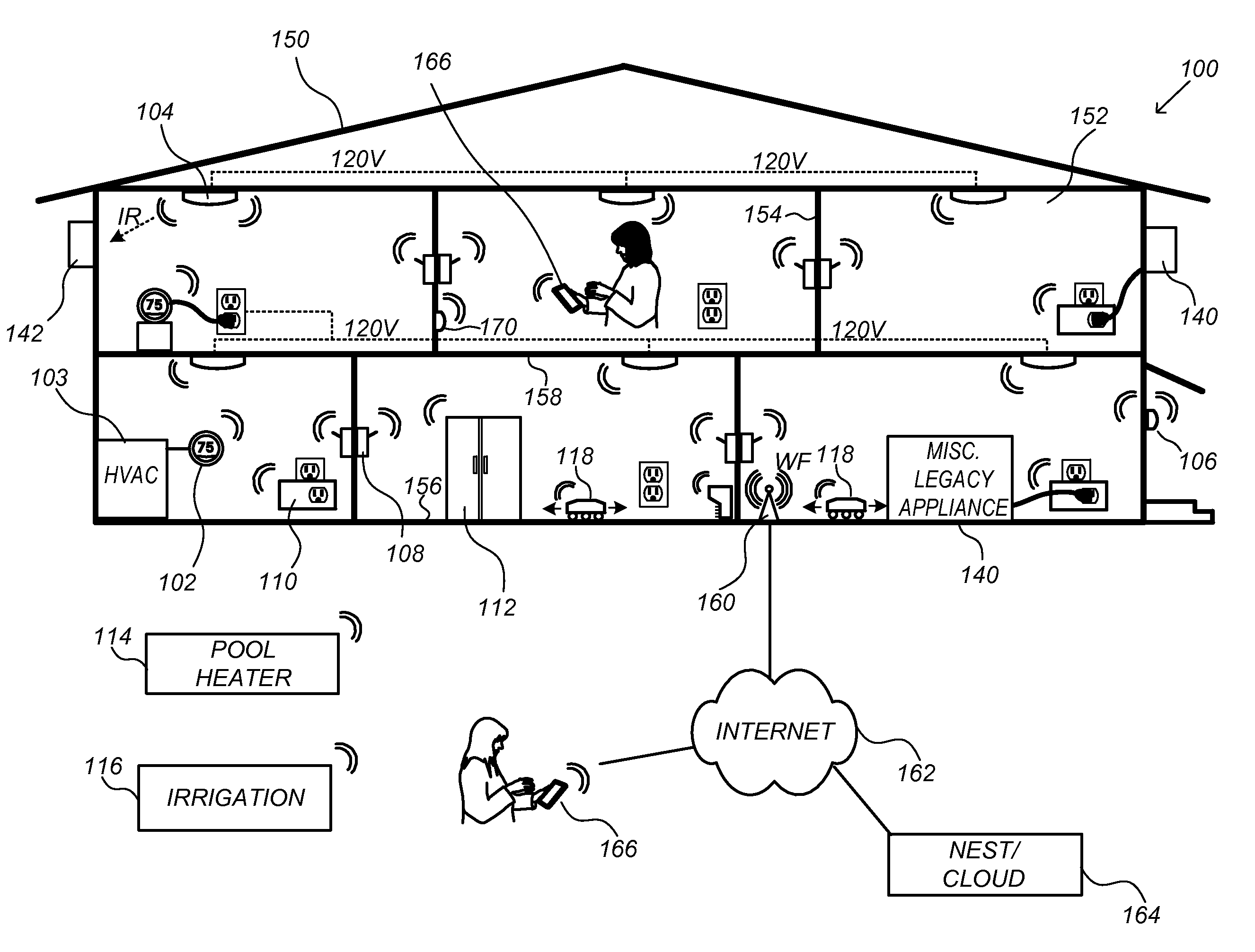
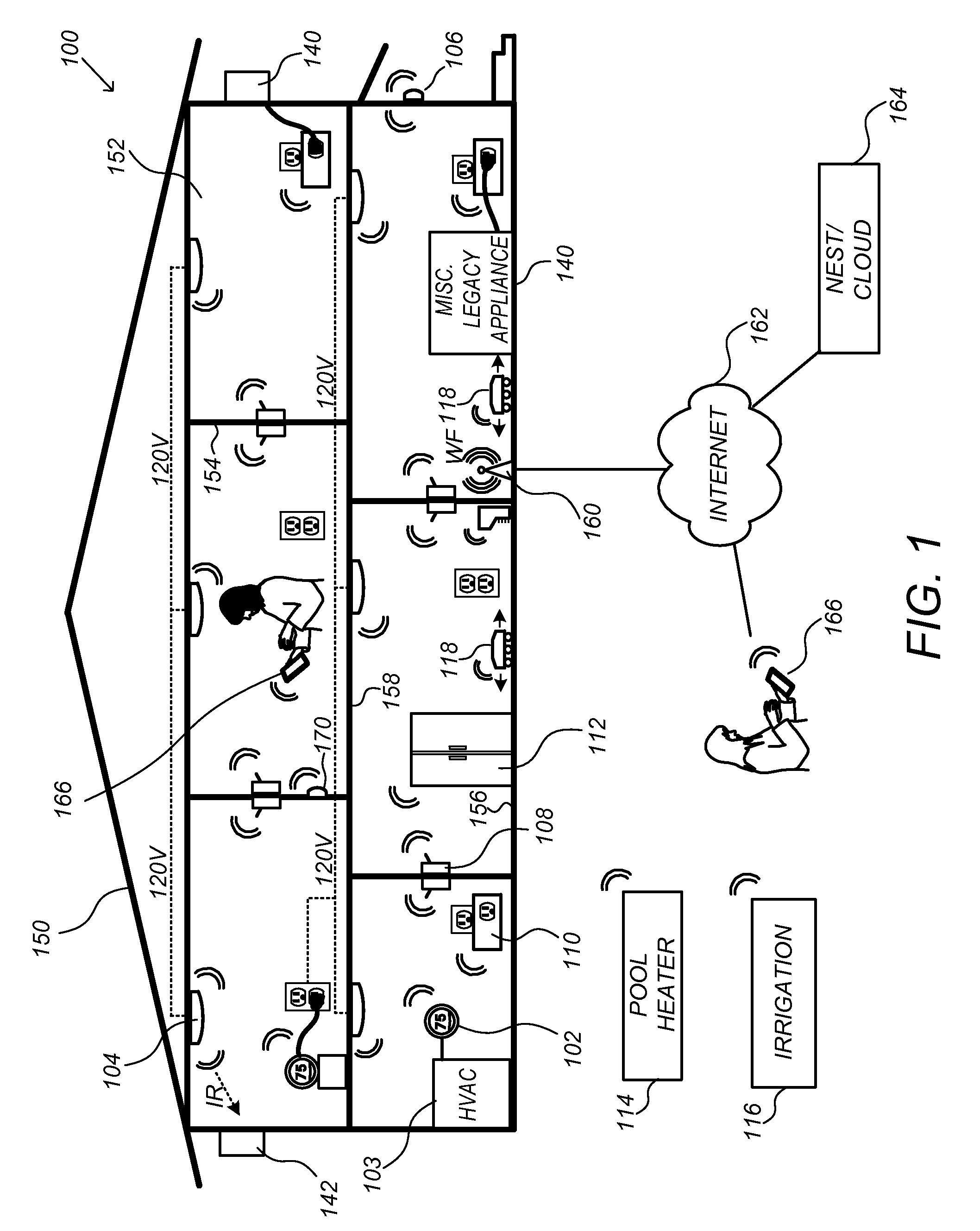
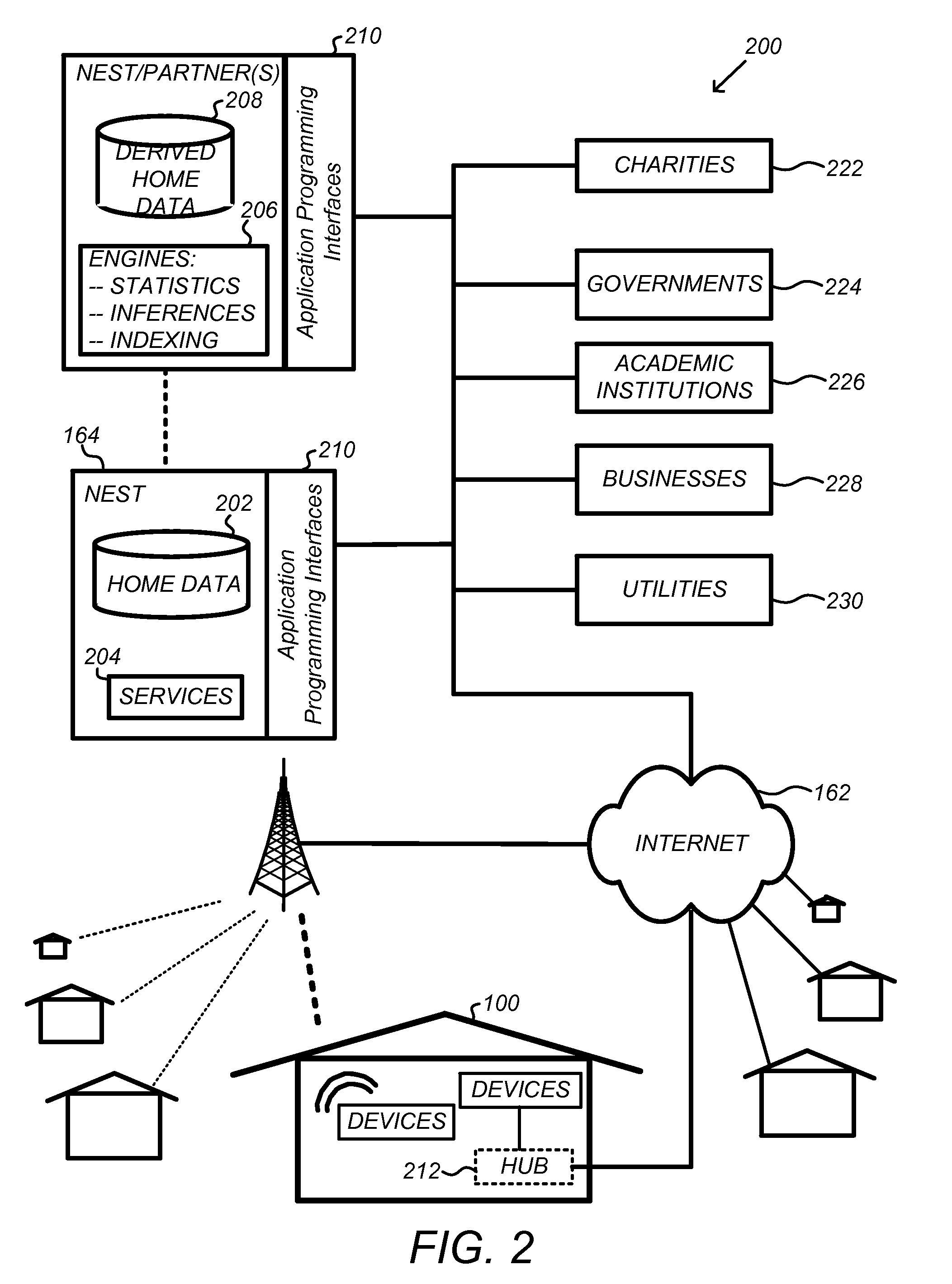
Thermodynamic model generation and implementation using observed HVAC and/or enclosure characteristics
ActiveUS20150300892A1Sampled-variable control systemsSpace heating and ventilationState dependentEngineering
Techniques for determining and using a thermodynamic model that characterizes a thermodynamic response of an enclosure conditioned by an HVAC system are disclosed. To determine a thermodynamic model, temperature information when the HVAC system operates in a first state may first be received. A response interval may then be determined where the response interval indicates an estimated time between when the HVAC system begins operating in the first state and when the temperature within the enclosure begins to change in a direction associated with the first state. Weighting factors corresponding to basis functions may then be determined, where the weighted basis functions characterize the temperature trajectory of the enclosure in response to the HVAC system operating in the first state. The basis functions may include a first basis function that is evaluated from a time that the HVAC system begins operating in the first state until a time when the response interval ends, and a second basis function that is evaluated beginning at the time when the response interval ends.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Internet of things terminal secure access method and system based on edge computing
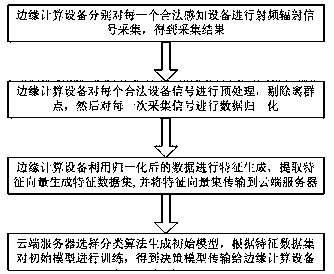
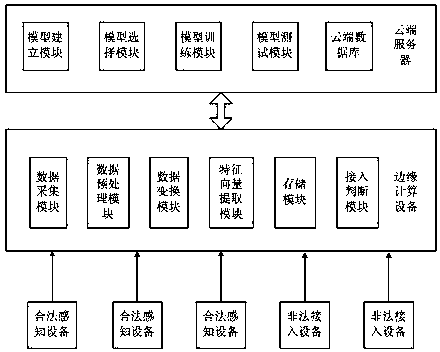
ActiveCN107770263AReduce computational complexityReduce latencyTransmission monitoringSecurity arrangementComputation complexityData set
The invention discloses an Internet of things terminal secure access method and system based on edge computing. The method comprises the steps that an edge computing device carries out radio frequencyradiation signal collection on each legal sensing device, thereby obtaining collection results; the edge computing device preprocesses each legal device signal, removes outliers and carries out datanormalization on collected signals of each time; the edge computing device generates features through utilization of the normalized data, extracts feature vectors to generate feature data sets and transmits the feature vector sets to a cloud server; and the cloud server selects a classification algorithm to generate a data model, trains the data model according to the feature data sets and transmits an obtained decision-making model to the edge computing device. According to the method and the system, the data processing and access judgment are carried out at the edge computing side, and the method and the system are applicable to an Internet of things device interconnection scheme with limited resources and have the advantages of low computing complexity and high authentication accuracy.
Owner:CERTUS NETWORK TECHNANJING
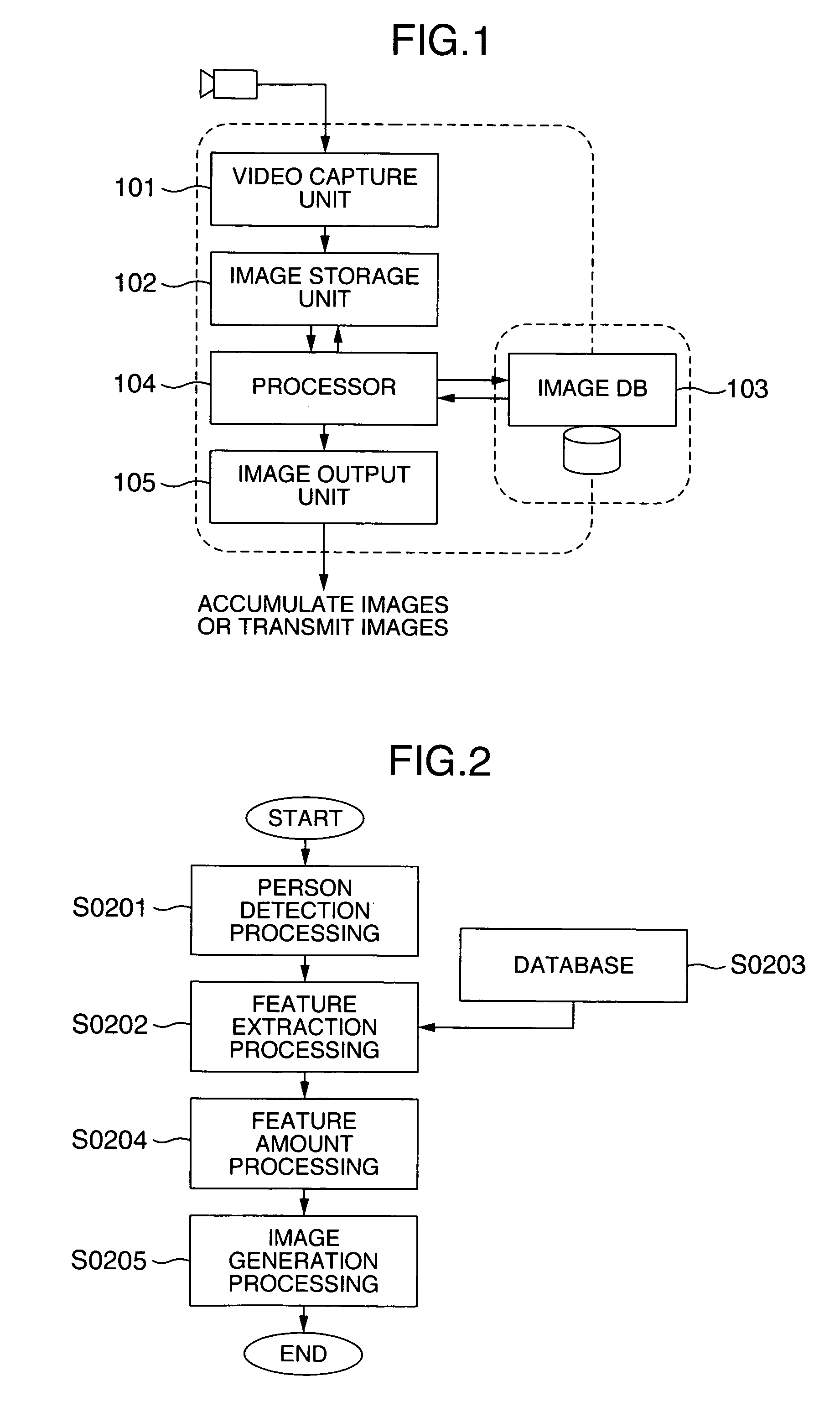
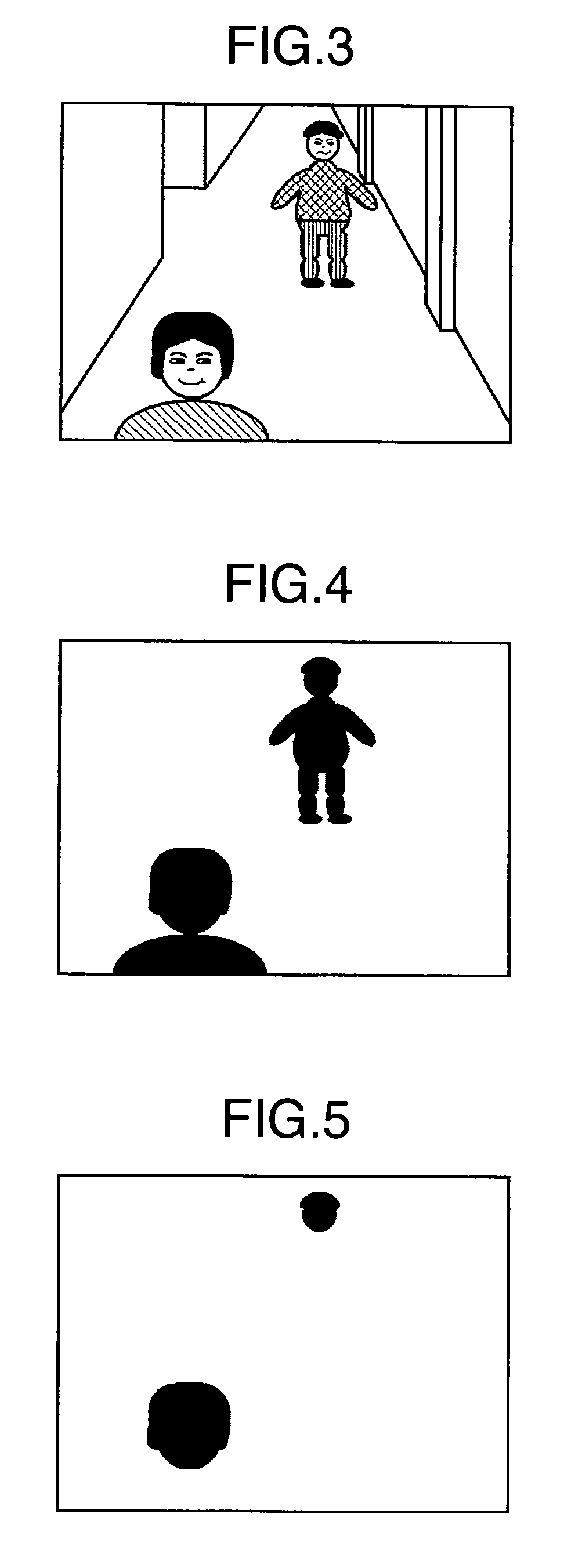
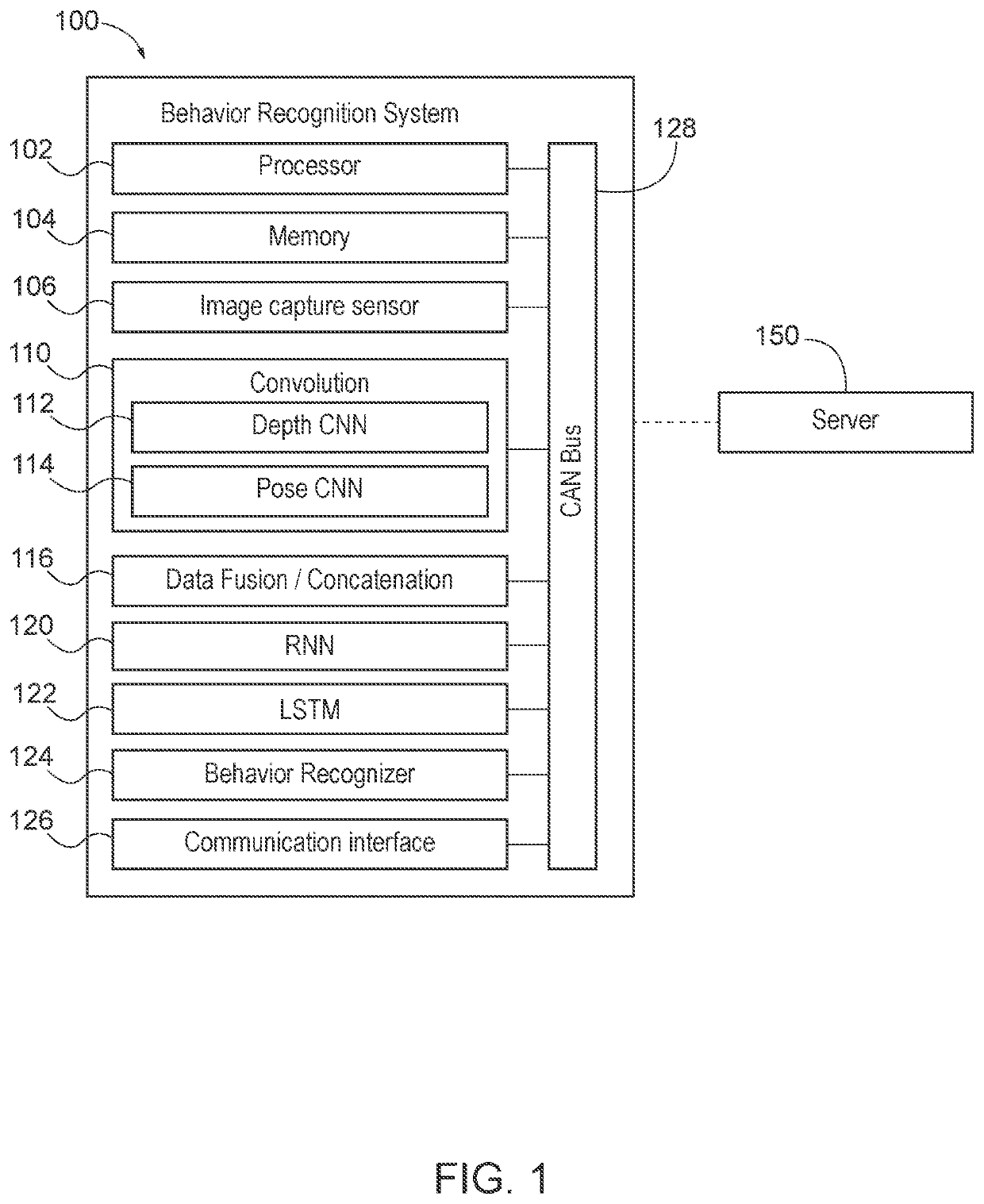
Image processing apparatus, image processing system and recording medium for programs therefor
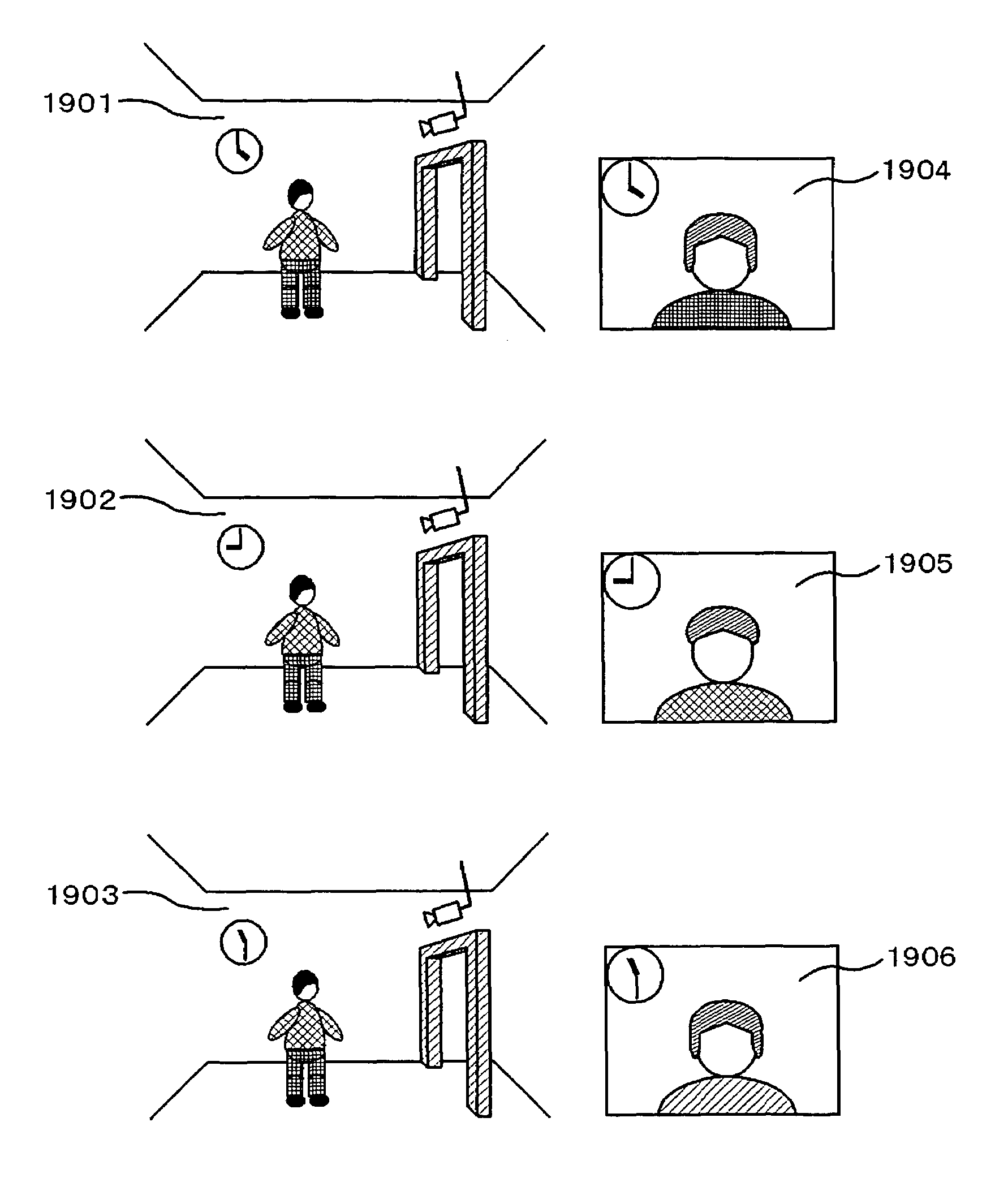
InactiveUS7668345B2Checking apparatusCharacter and pattern recognitionMulti cameraImaging processing
An image processing apparatus, for example, a multi-camera monitoring system is provided for processing images with the intention of protecting the individuals' privacies in accordance with the type of customers in a store which is equipped with the multi-camera monitoring system, and for deleting or modifying individuals' privacy information to protect the individuals' privacies while permitting the identity of a person to be determined among a plurality of cameras. The image processing apparatus processes an image captured by an imager device to output the resulting image. A processor detects a person from an image, and an image database stores feature information on the person. The processor extracts features from the detected person and the database, processes the extracted feature amount in the stored feature information, and generates an output image based on the processed features.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
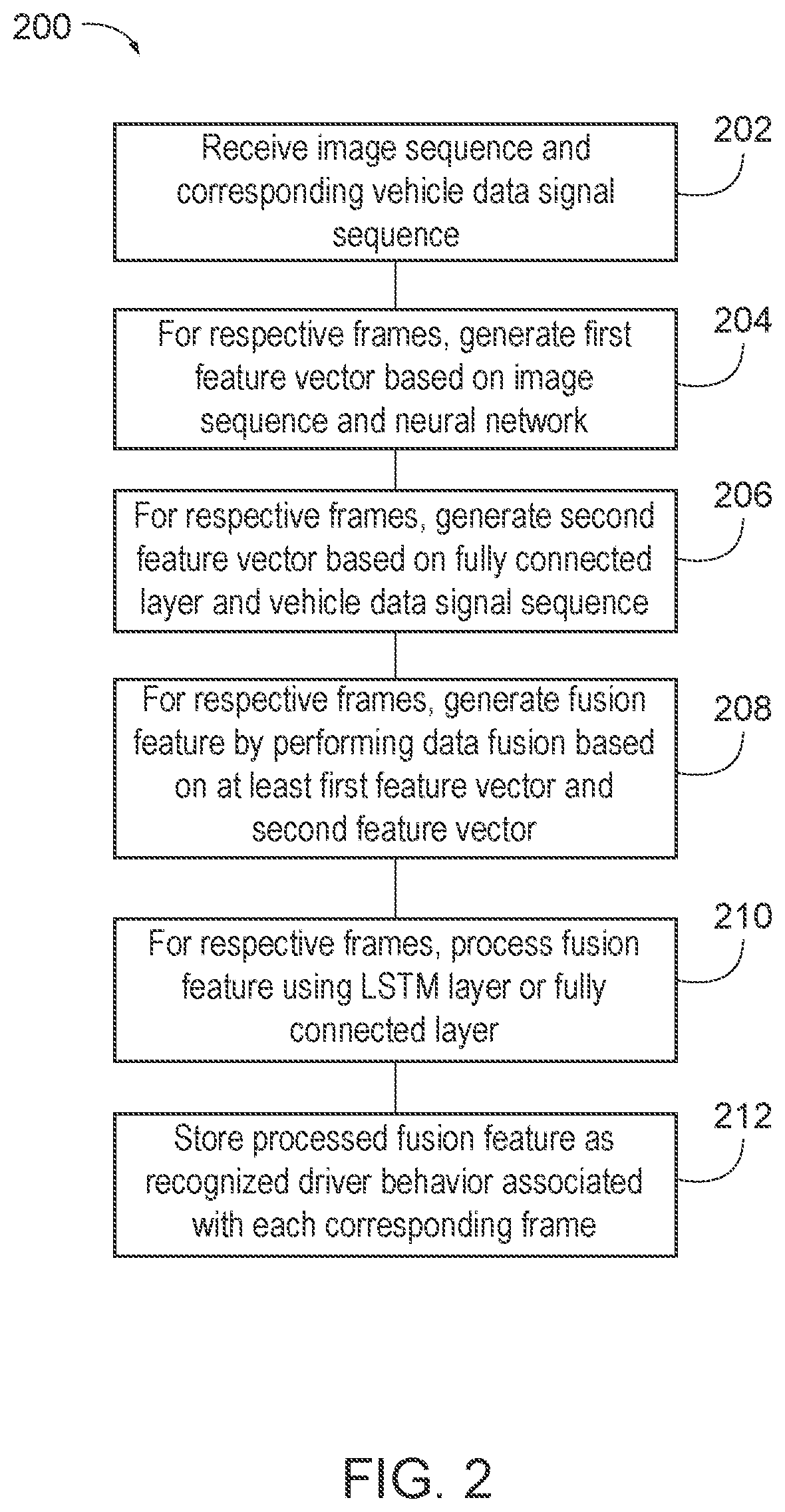
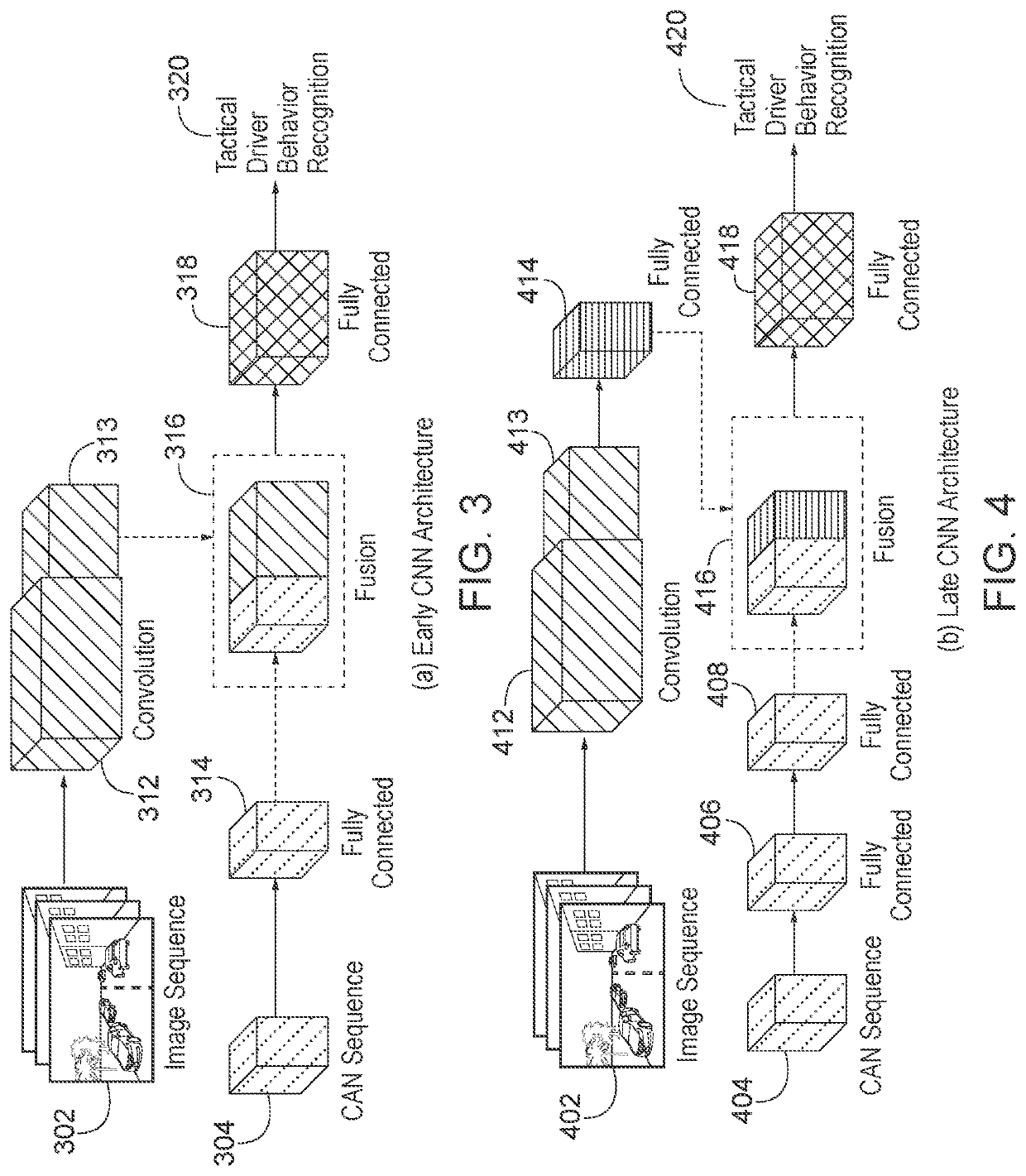
Scene classification prediction
Systems and techniques for scene classification and prediction is provided herein. A first series of image frames of an environment from a moving vehicle may be captured. Traffic participants within the environment may be identified and masked based on a first convolutional neural network (CNN). Temporal classification may be performed to generate a series of image frames associated with temporal predictions based on a scene classification model based on CNNs and a long short-term memory (LSTM) network. Additionally, scene classification may occur based on global average pooling. Feature vectors may be generated based on different series of image frames and a fusion feature vector may be obtained by performing data fusion based on a first feature vector, a second feature vector, a third feature vector, etc. In this way, a behavior predictor may generate a predicted driver behavior based on the fusion feature.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
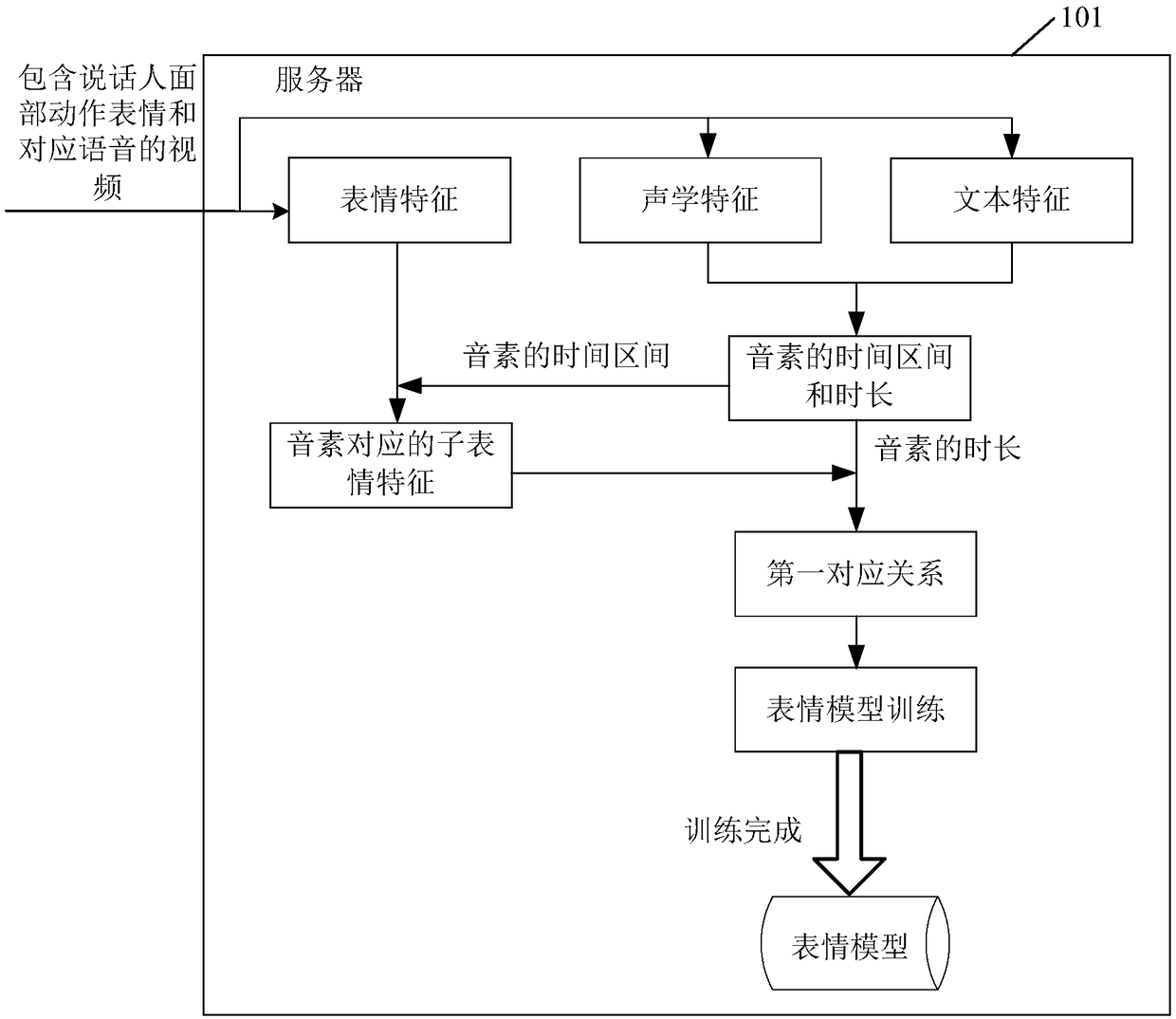
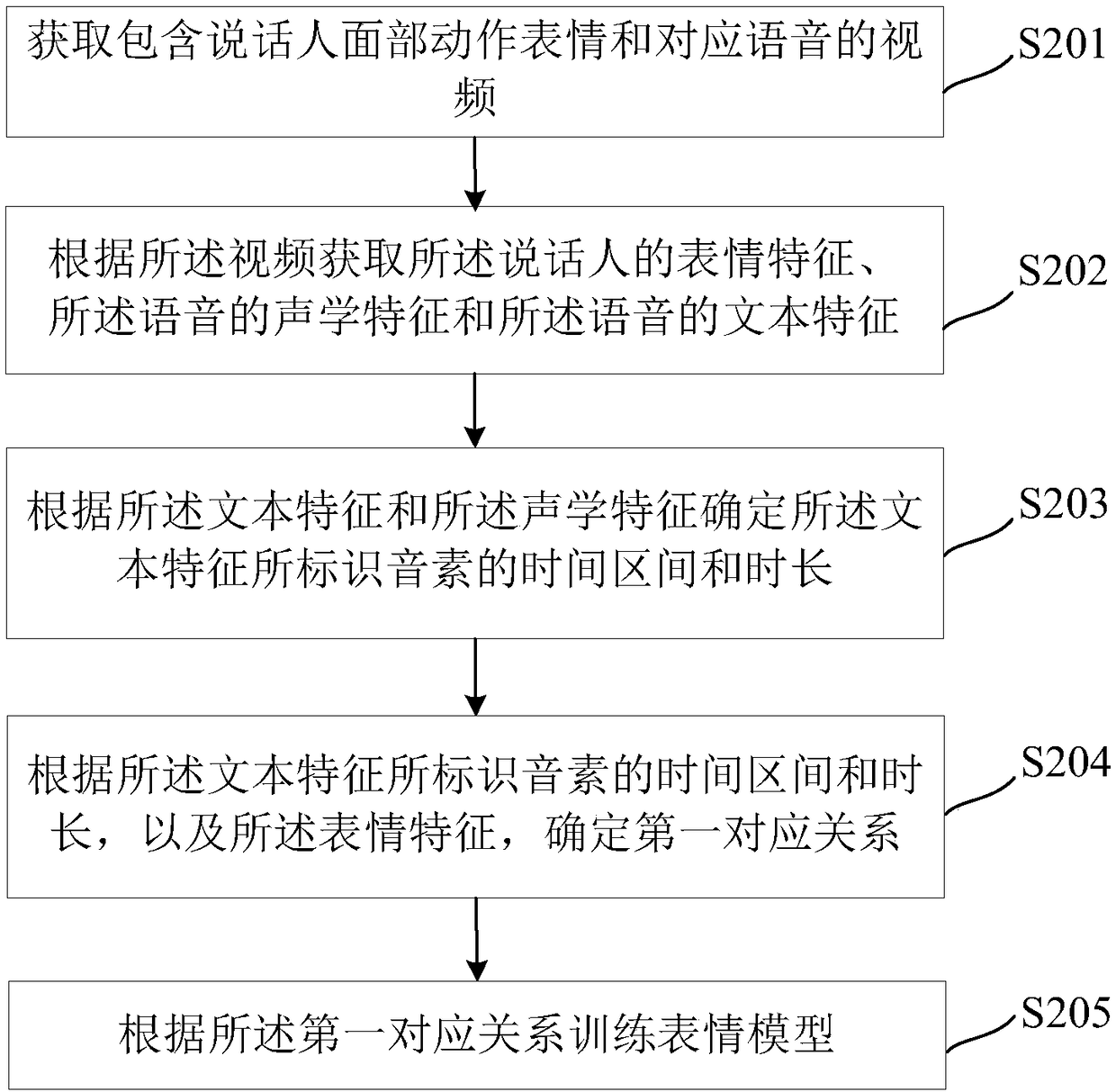
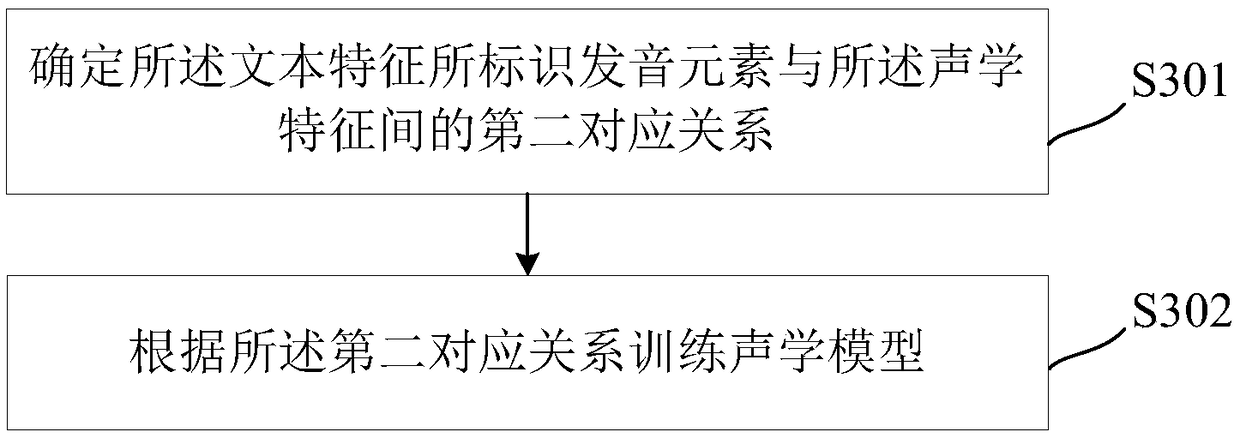
Model training method, method for synthesizing speaking expression and related device
The embodiment of the invention discloses a model training method for synthesizing speaking expressions. Expression characteristics, acoustic characteristics and text characteristics are obtained according to videos containing face action expressions of speakers and corresponding voices. Because the acoustic feature and the text feature are obtained according to the same video, the time interval and the duration of the pronunciation element identified by the text feature are determined according to the acoustic feature. A first corresponding relation is determined according to the time interval and duration of the pronunciation element identified by the text feature and the expression feature, and an expression model is trained according to the first corresponding relation. The expressionmodel can determine different sub-expression characteristics for the same pronunciation element with different durations in the text characteristics; the change patterns of the speaking expressions are added, the speaking expressions generated according to the target expression characteristics is determined by the expression model. The speaking expressions have different change patterns for the same pronunciation element, and therefore the situation that the speaking expressions are excessively unnatural in change is improved to a certain degree.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
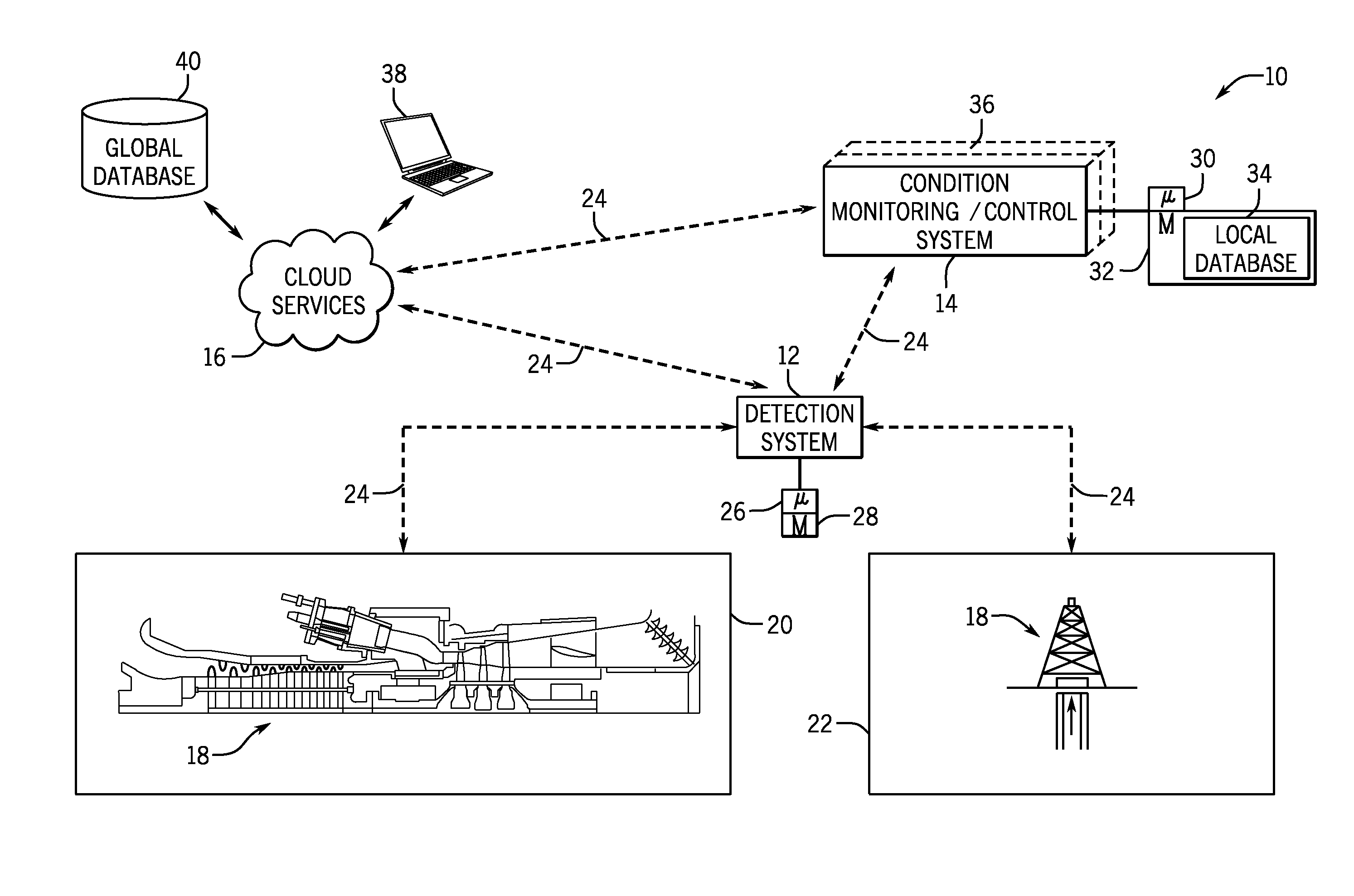
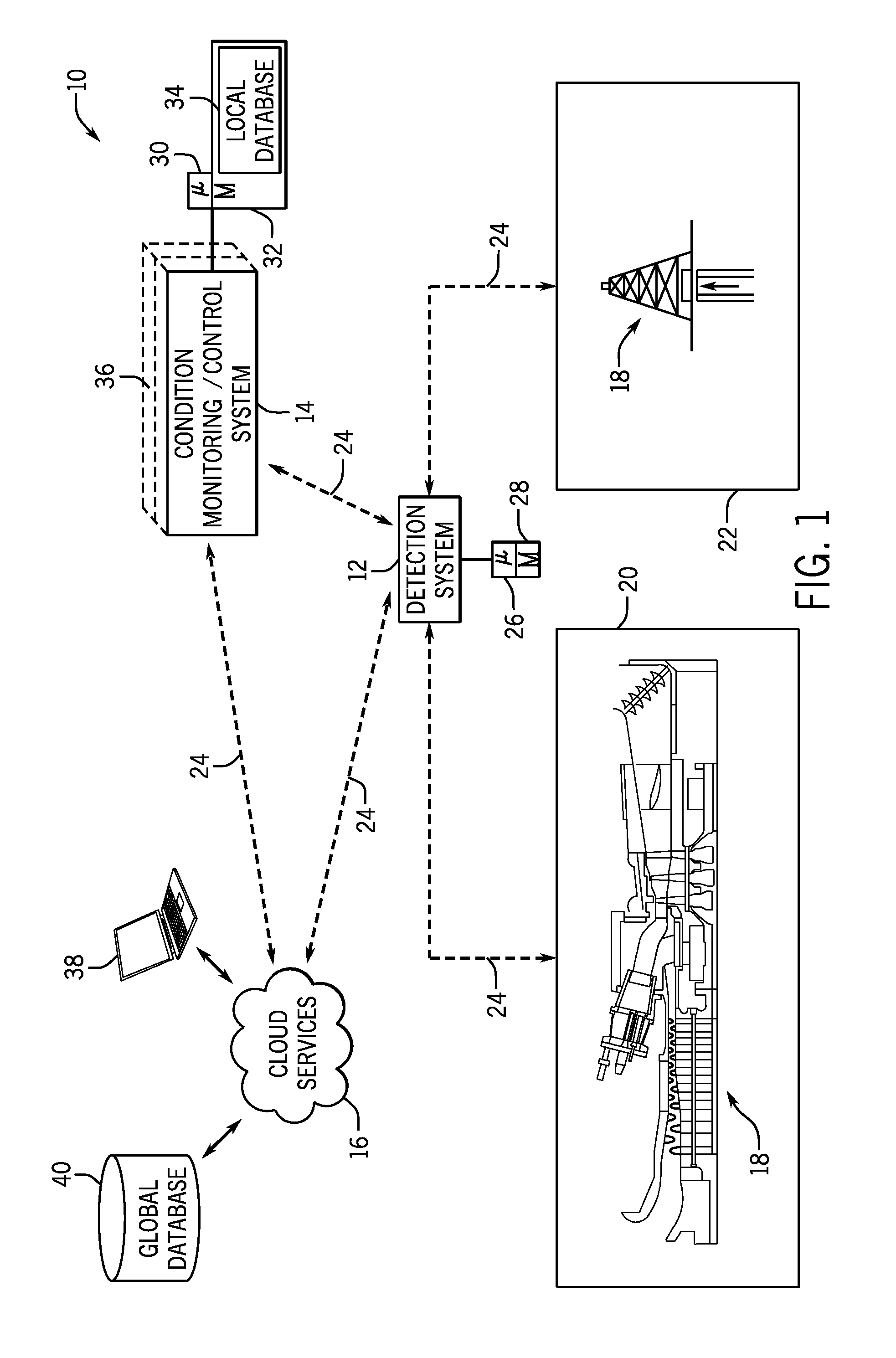
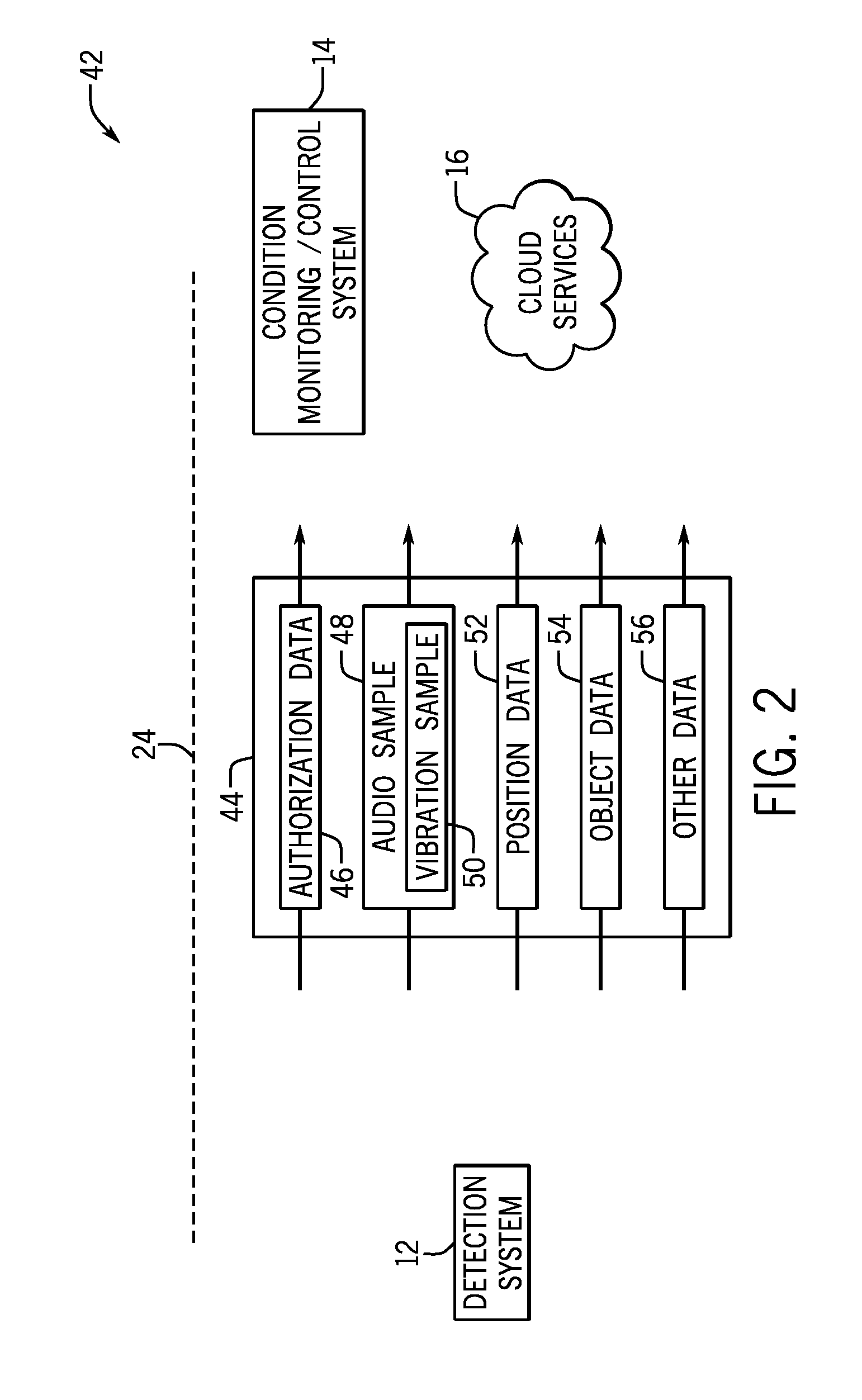
Vibration condition monitoring system and methods
ActiveUS20150039250A1Electrical apparatusMaterial analysis using acoustic emission techniquesContext basedComputing systems
In one embodiment, a diagnostics system is provided. The diagnostics system include a detection system configured to capture acoustic information and contextual information related to a machine component defect. A computing system is coupled to a processor configured to receive the acoustic information and the contextual information from the detection system, select one or more algorithms based at least in part on the contextual information, and retrieve and execute the one or more algorithms to extract one or more characteristic features of the acoustic information. The processor is further configured to generate an acoustic fingerprint based at least in part on the one or more characteristic features of the acoustic information, such that the one or more characteristic features correspond to the machine component defect.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
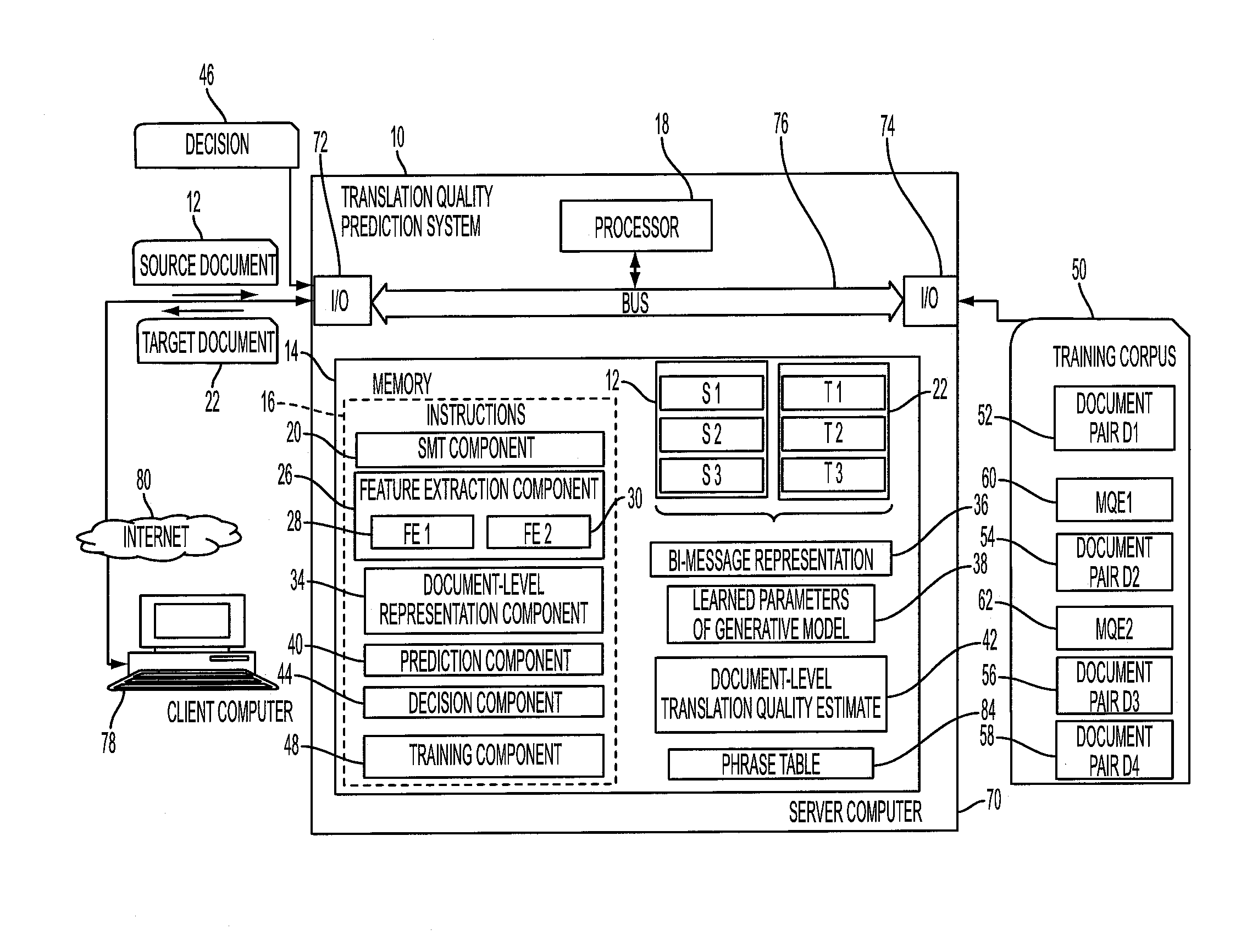
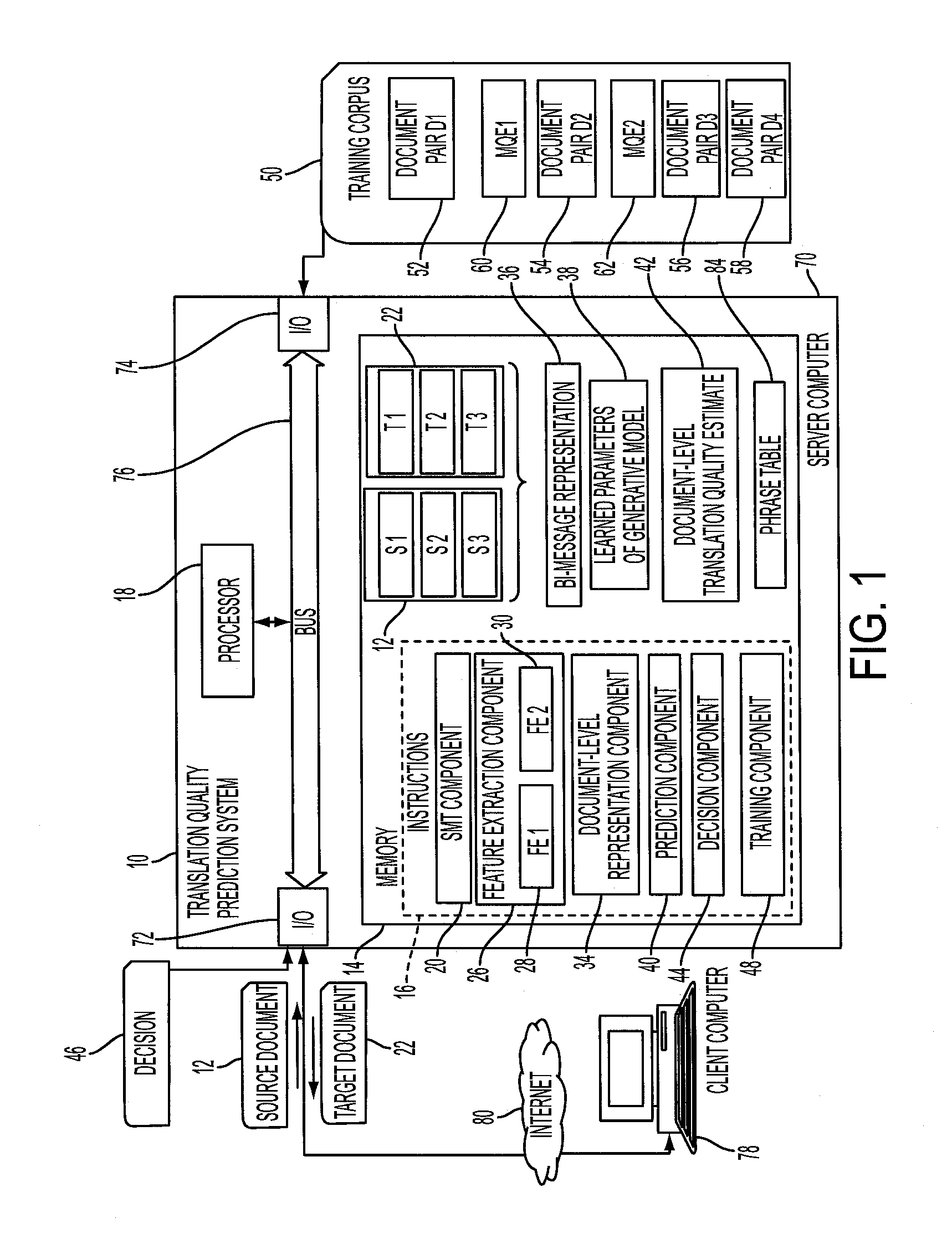
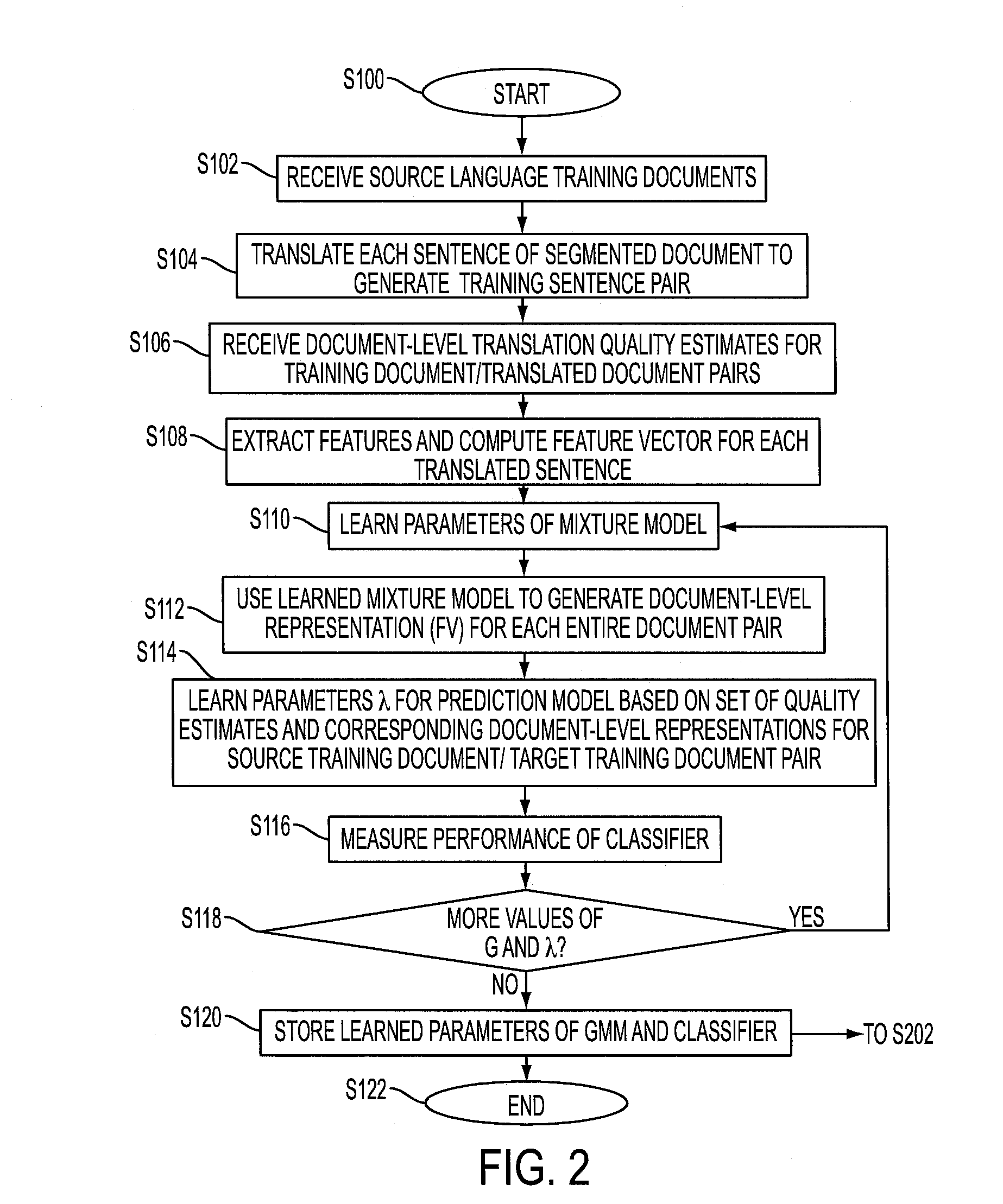
Predicting the quality of automatic translation of an entire document
InactiveUS20160124944A1Natural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsSentence pairSemantic translation
A system and method predict the translation quality of a translated input document. The method includes receiving an input document pair composed of a plurality of sentence pairs, each sentence pair including a source sentence in a source language and a machine translation of the source language sentence to a target language sentence. For each of the sentence pairs, a representation of the sentence pair is generated, based on a set of features extracted for the sentence pair. Using a generative model, a representation of the input document pair is generated, based on the sentence pair representations. A translation quality of the translated input document is computed, based on the representation of the input document pair.
Owner:XEROX CORP
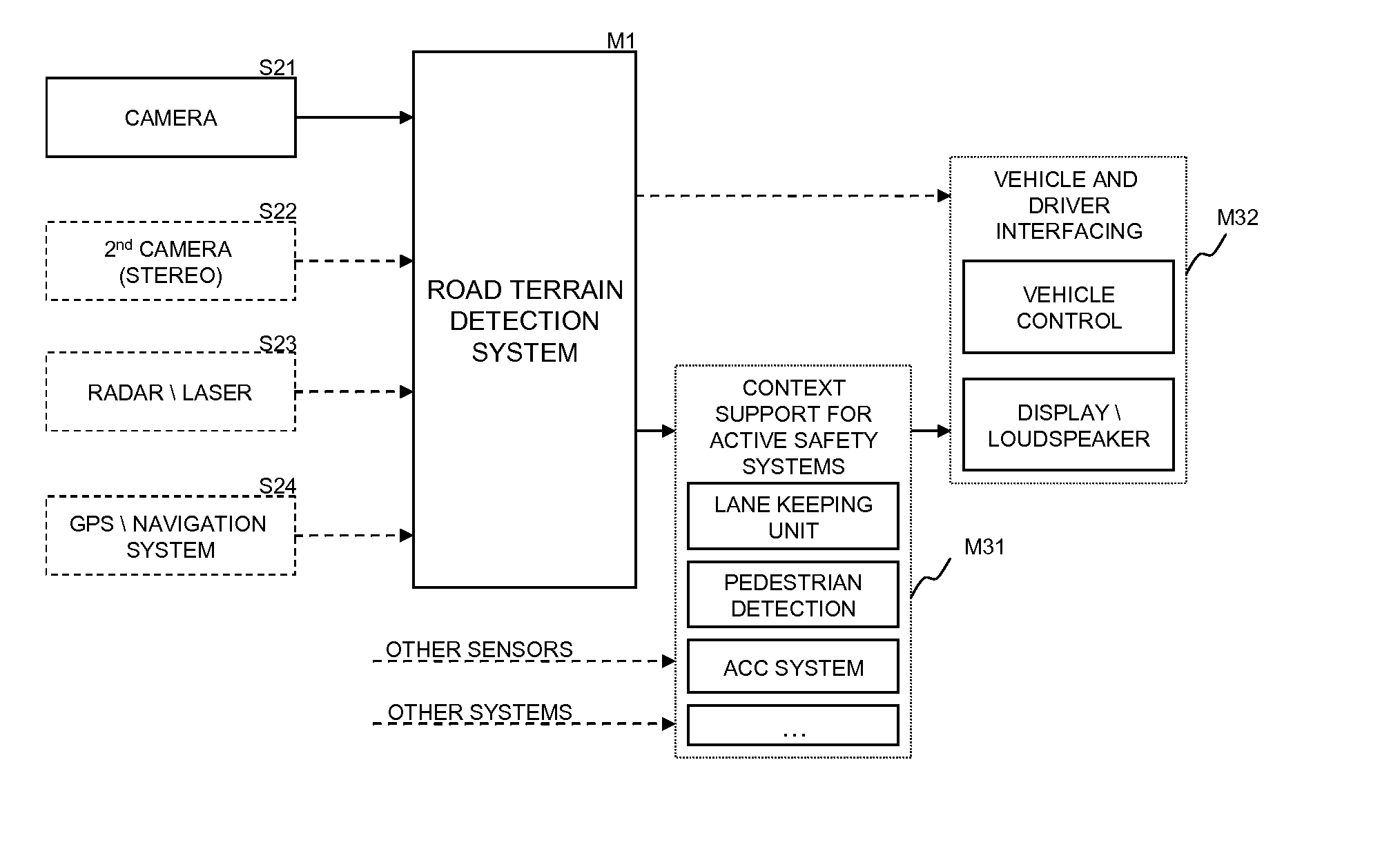
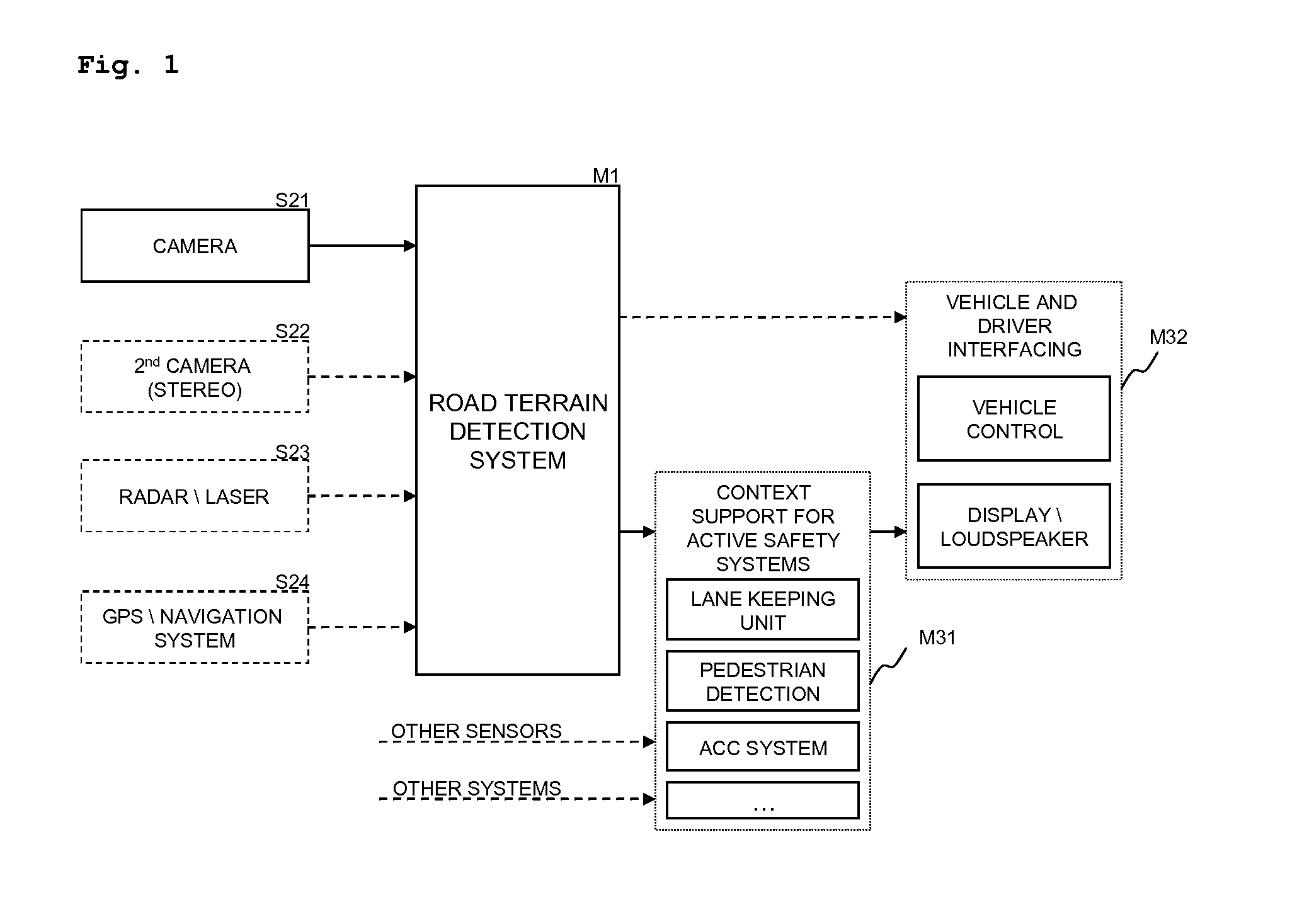
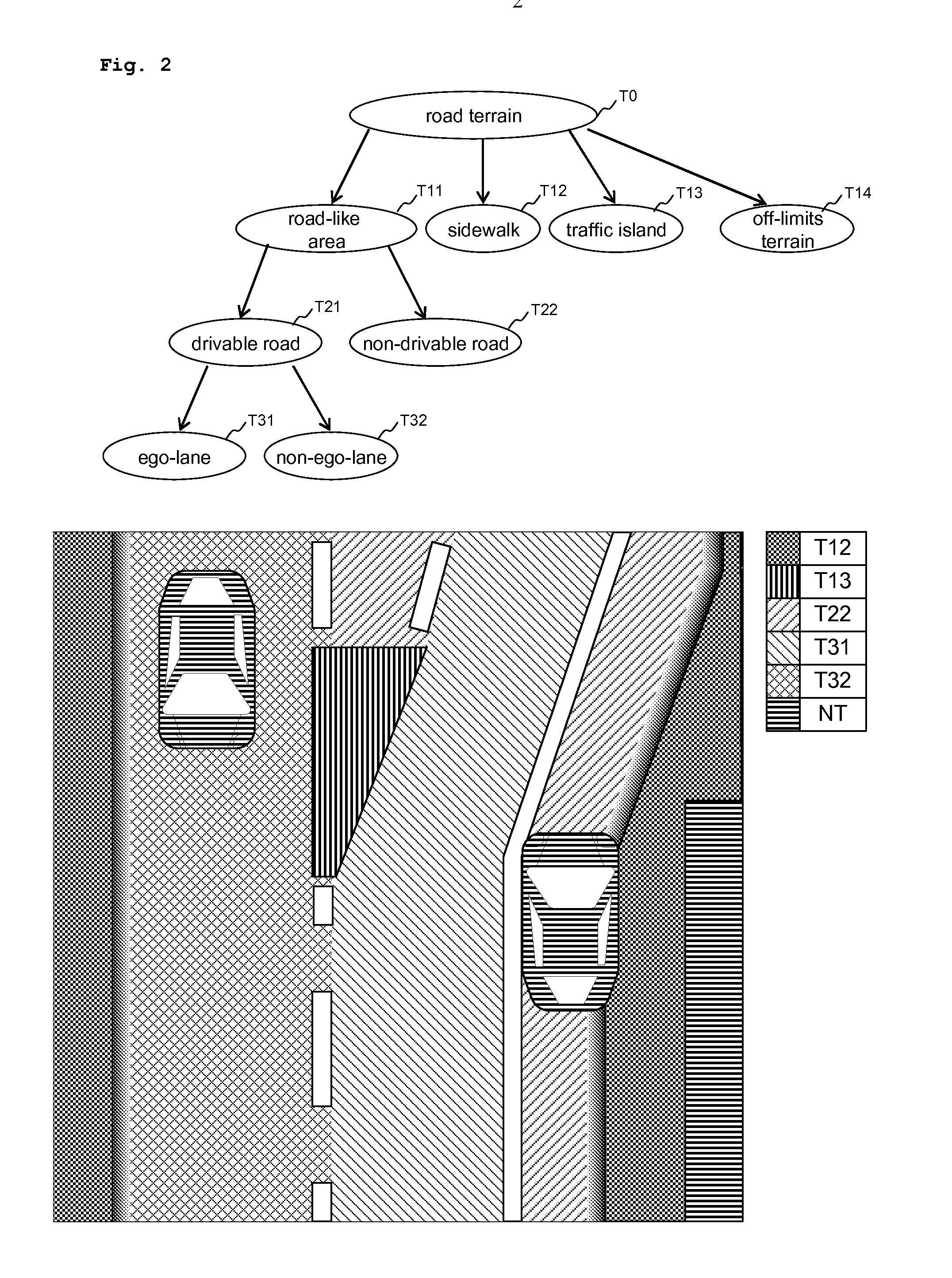
Road-terrain detection method and system for driver assistance systems
ActiveUS20130079990A1Capability of error compensationImprove propertiesImage enhancementImage analysisTerrainCamera image
The present invention describes a road terrain detection system that comprises a method for classifying selected locations in the environment of a vehicle based on sensory input signals such as pixel values of a camera image. The method comprises a high level spatial feature generation for selected locations in the environment called base points. The spatial feature generation of the base points is based on a value-continuous confidence representation that captures visual and physical properties of the environment, generated by so called base classifiers operating on raw sensory data. Consequently, the road terrain detection incorporates both local properties of sensor data and their spatial relationship in a two-step feature extraction process.
Owner:HONDA RES INST EUROPE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com