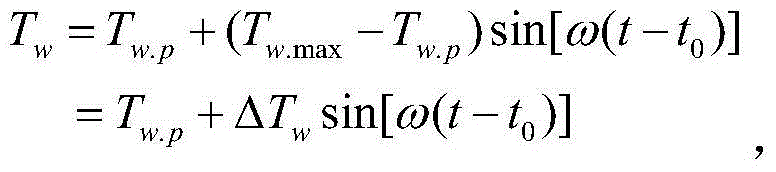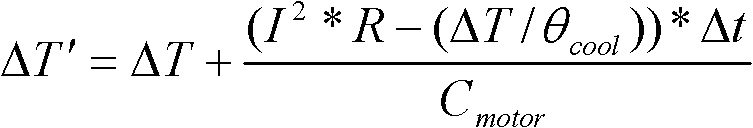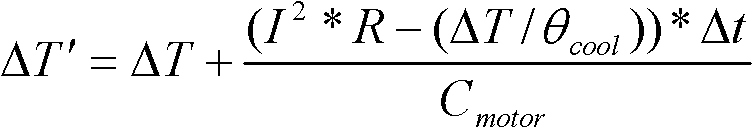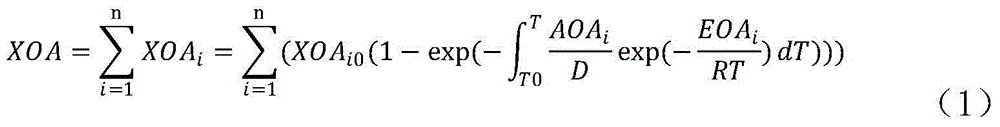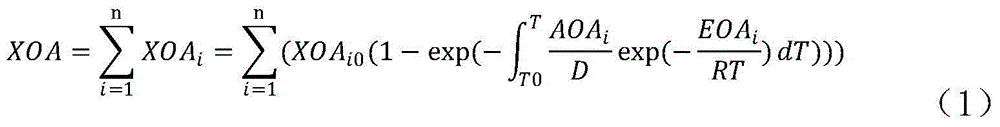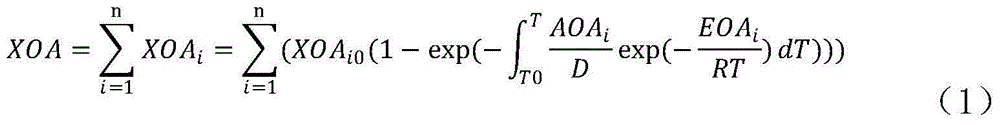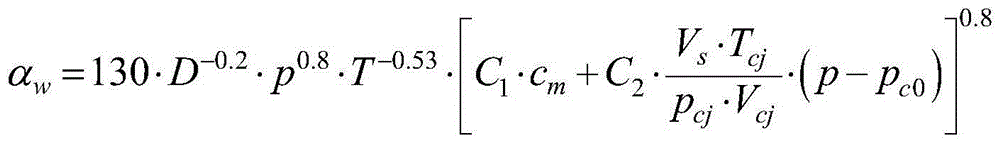Patents
Literature
217 results about "Thermodynamic model" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A thermodynamic model is a set of equations that permit the estimation of pure component and mixture properties.
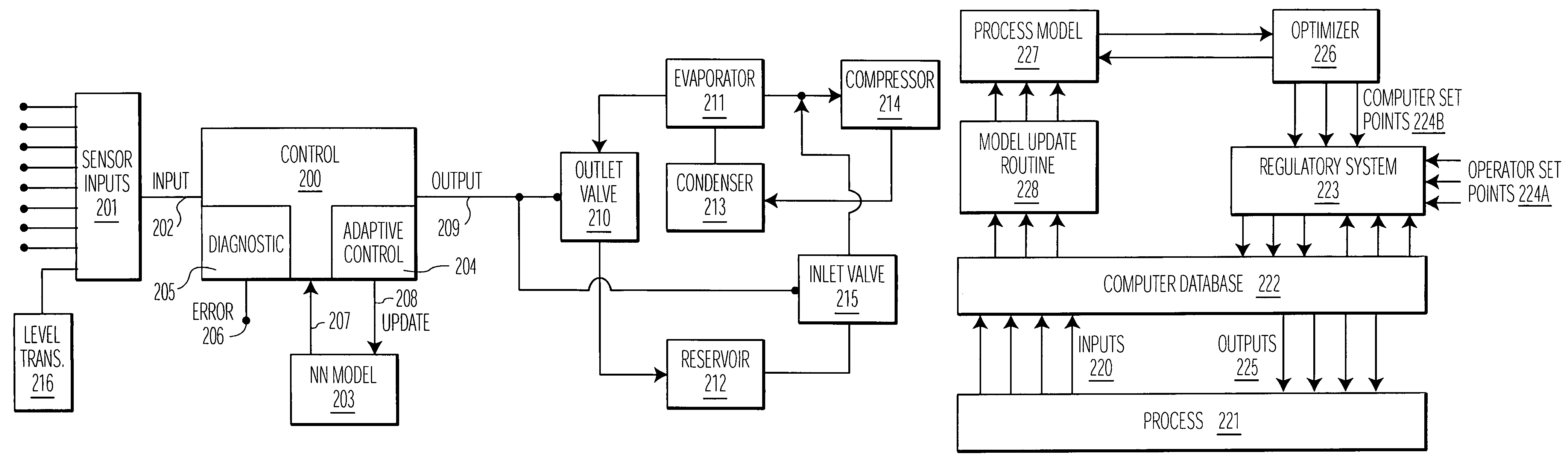
Method and apparatus for optimizing refrigeration systems
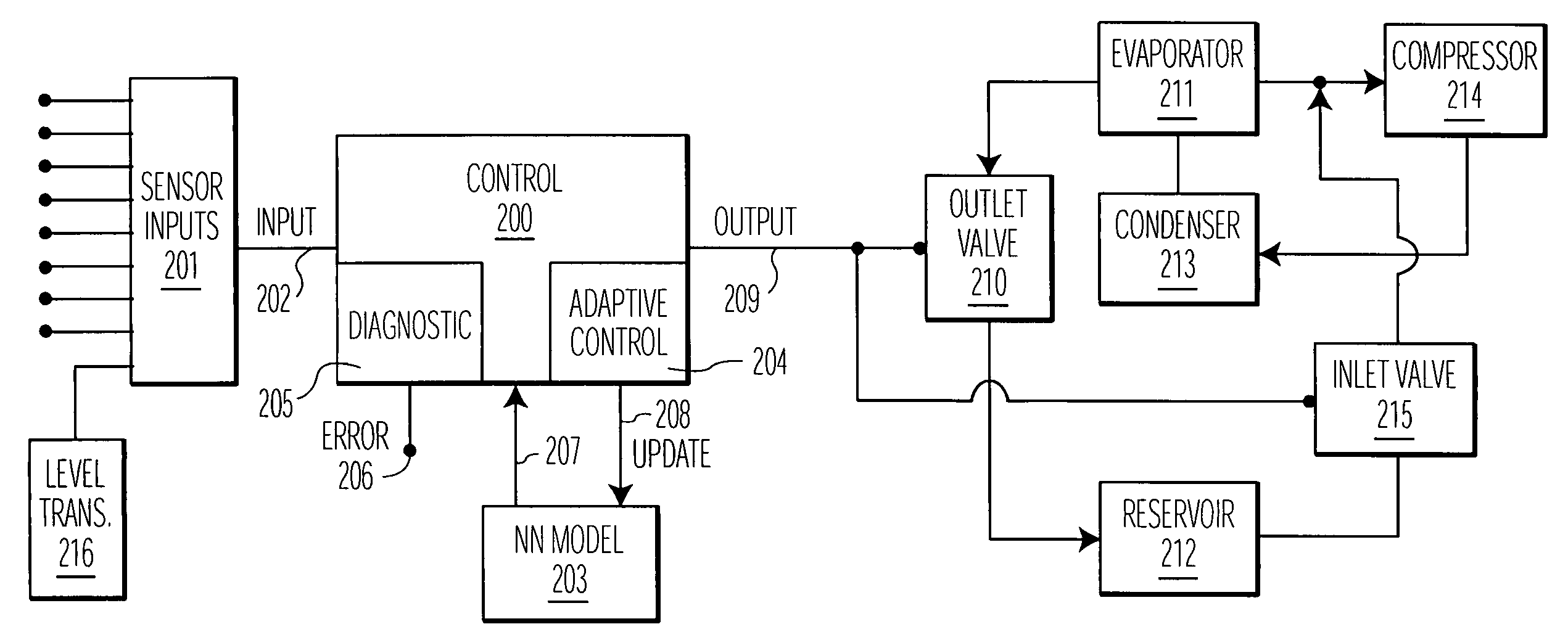
ActiveUS20070256432A1Lower Level RequirementsDecrease in heat removal capacitySampled-variable control systemsComputer controlCost effectivenessEngineering
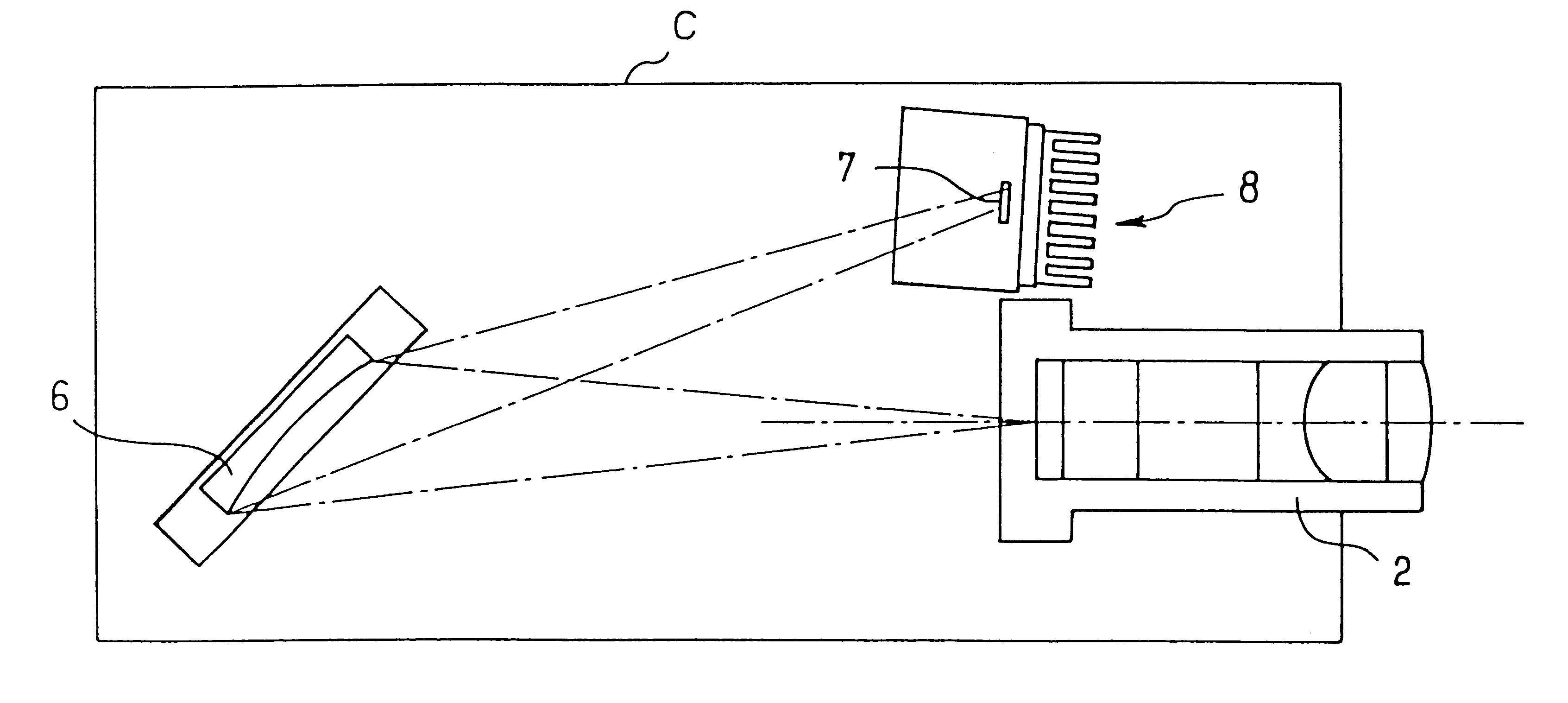
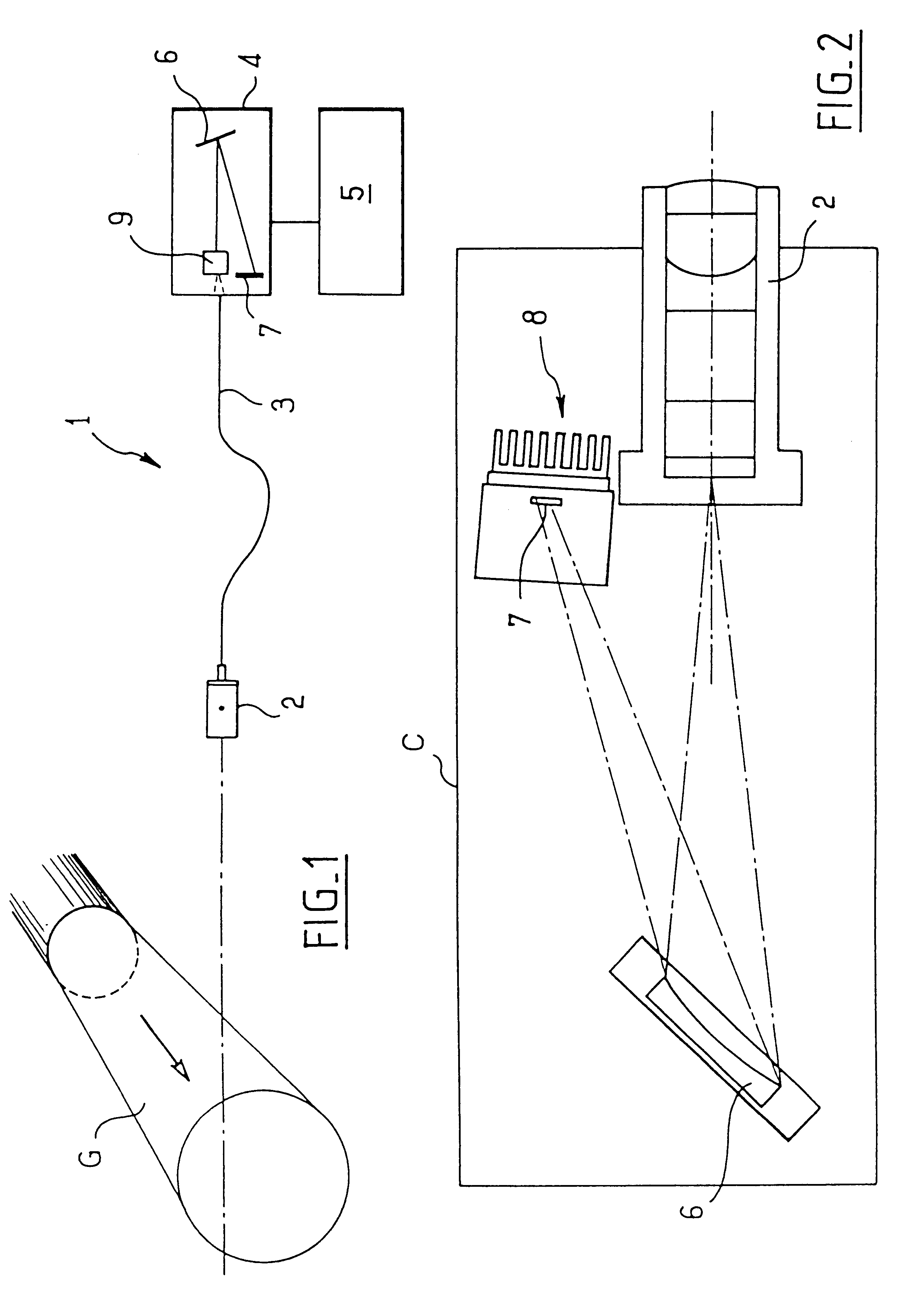
A refrigeration system comprising a compressor for compressing a refrigerant, a condenser for condensing refrigerant to a liquid, an evaporator for evaporating liquid refrigerant from the condenser to a gas, an inner control loop for optimizing a supply of liquid refrigerant to the evaporator, and an outer control loop for optimizing a level of refrigerant in the evaporator, said outer control loop defining a supply rate for said inner control loop based on an optimization including measurement of evaporator performance, and said inner control loop optimizing liquid refrigerant supply based on said defined supply rate. Independent variables, such as proportion of oil in refrigerant, amount of refrigerant, contaminants, non-condensibles, scale and other deposits on heat transfer surfaces, may be estimated or measured. A model of the system and / or a thermodynamic model approximating the system, for example derived from temperature and pressure gages, as well as power computations or measurements, is employed to determine or estimate the effect on efficiency of deviance from an optimal state. Various methods are provided for returning the system to an optimal state, and for calculating a cost-effectiveness of employing such processes.
Owner:HUDSON TECHNOLOGIES
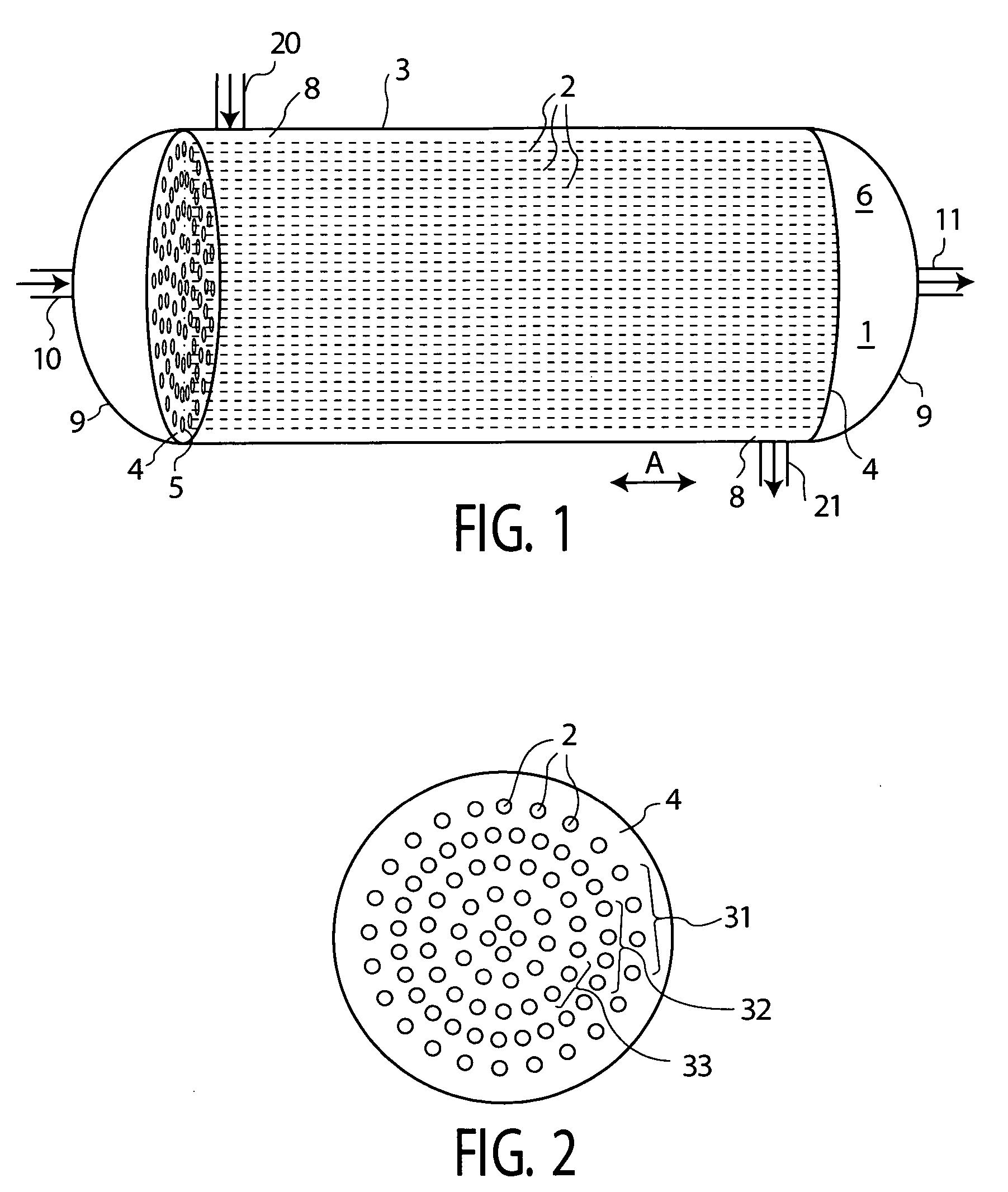
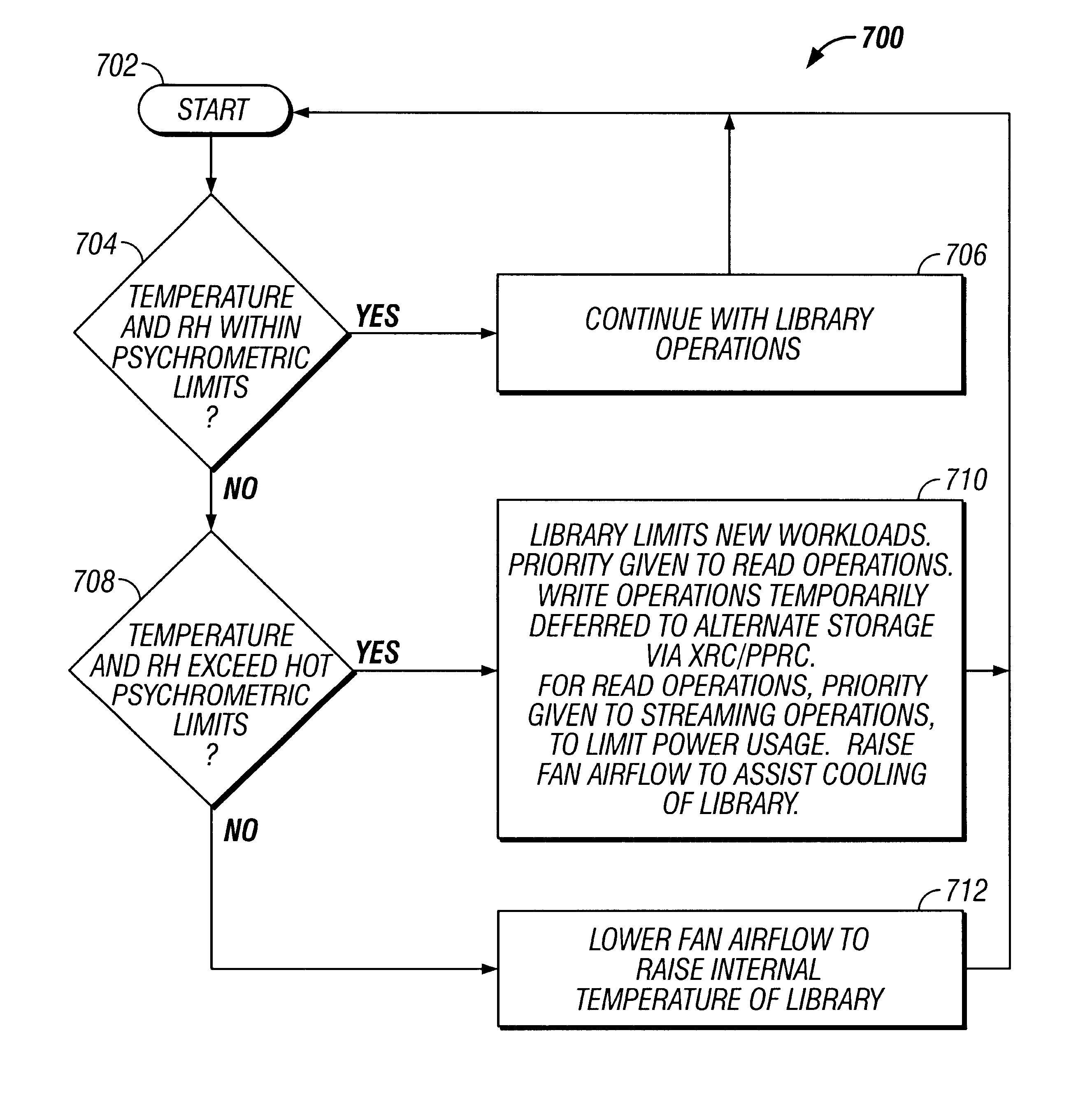
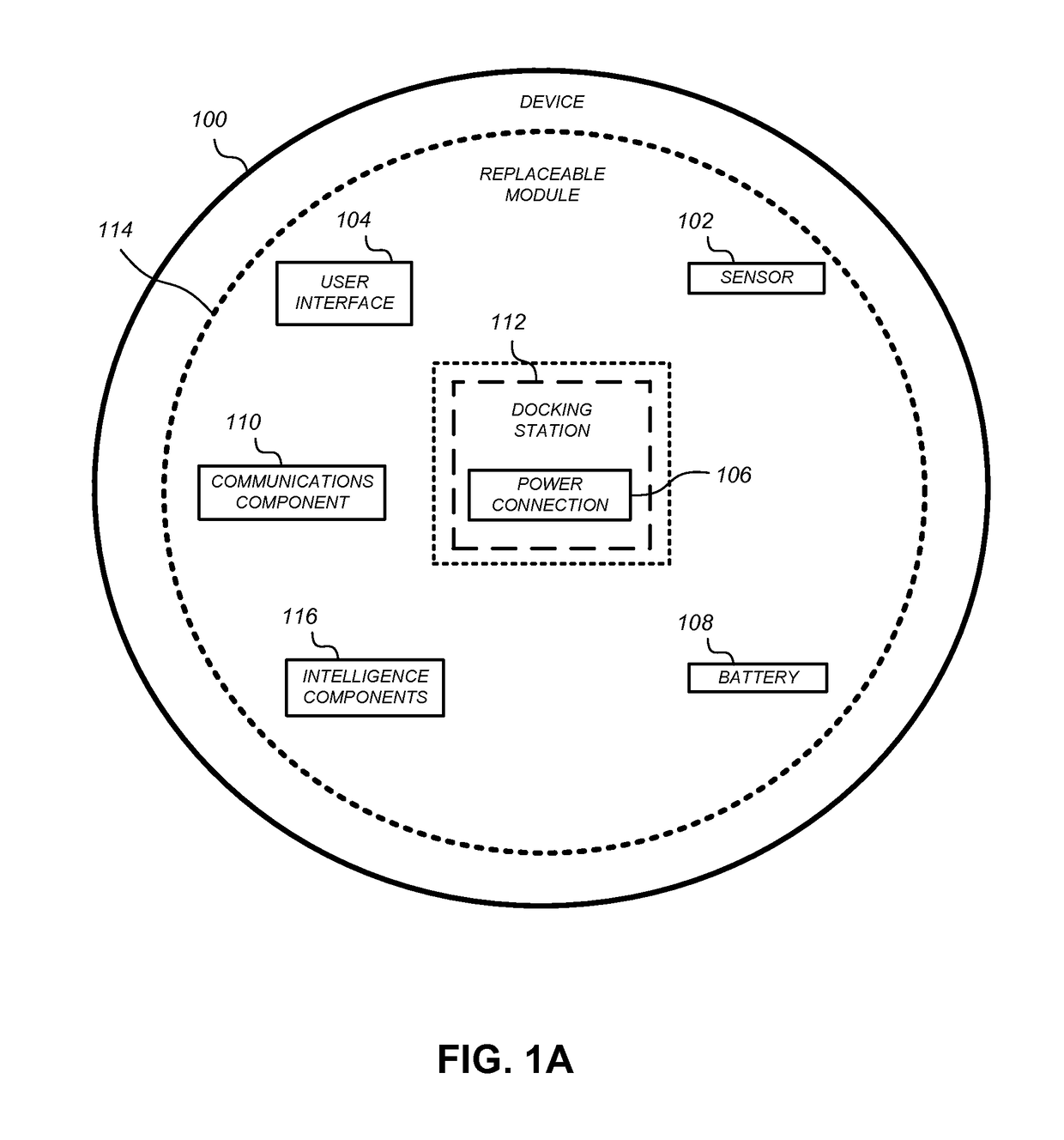
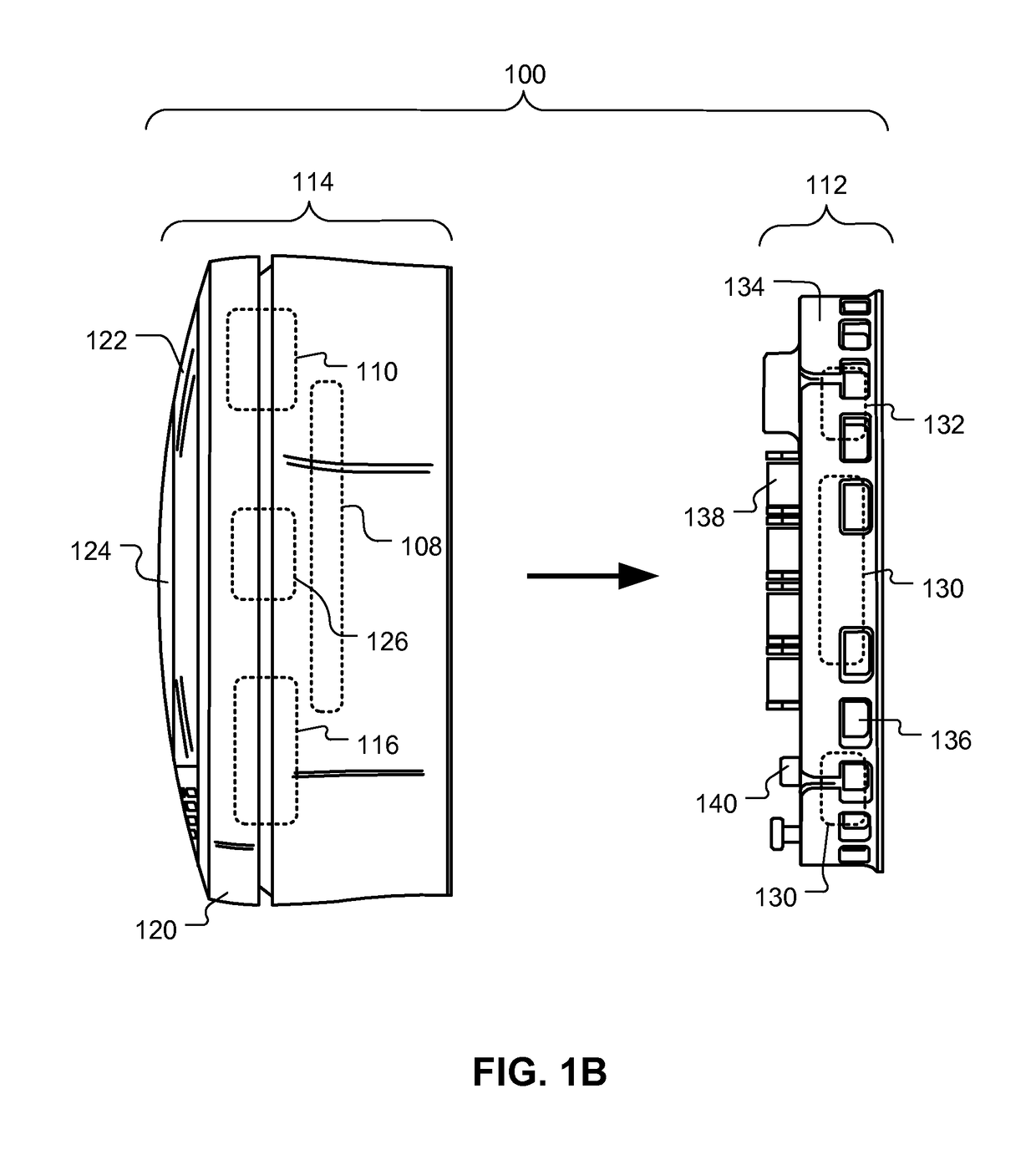
System and method for autonomic environmental monitoring, adjusting, and reporting capability in a remote data storage and retrieval device
InactiveUS6676026B1Reducing temperature influence on carrierAir-treating devicesComputer data storageEngineering
A data storage and retrieval system such as a robotic library has a large plurality of removable storage media, such as tape cartridges, for purposes of I / O. To enhance performance and reliability of the library, a thermodynamic model of the library is constructed and stored in the library, and environmental conditions such as the temperature, humidity, and flow rate of cooling air coming into, flowing through, and leaving the library are monitored. The thermodynamic model of the library includes an acceptable operating range for the library in a psychrometric chart; and the product of the effective thermodynamic mass and specific heat of the library.
Owner:IBM CORP
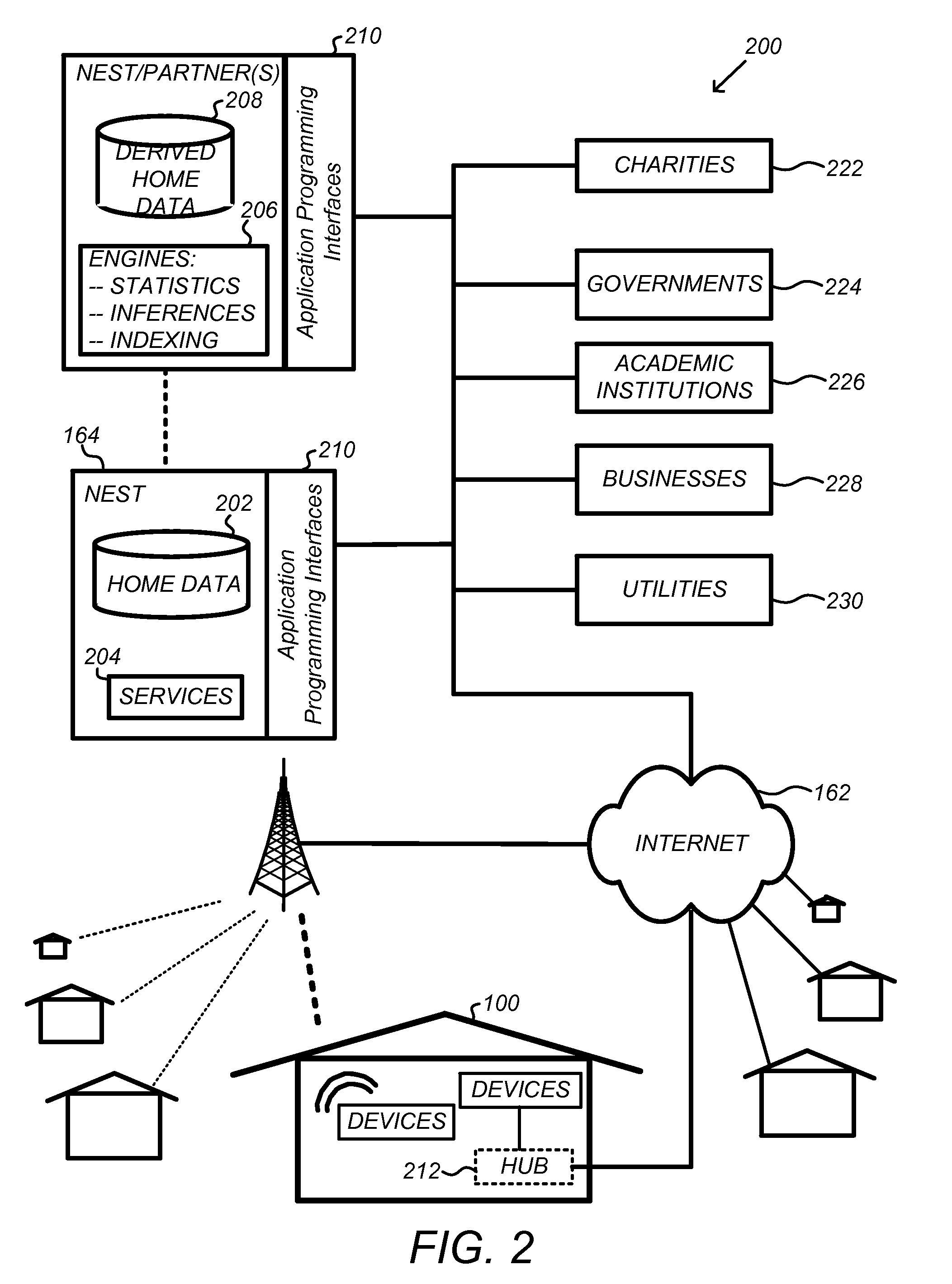
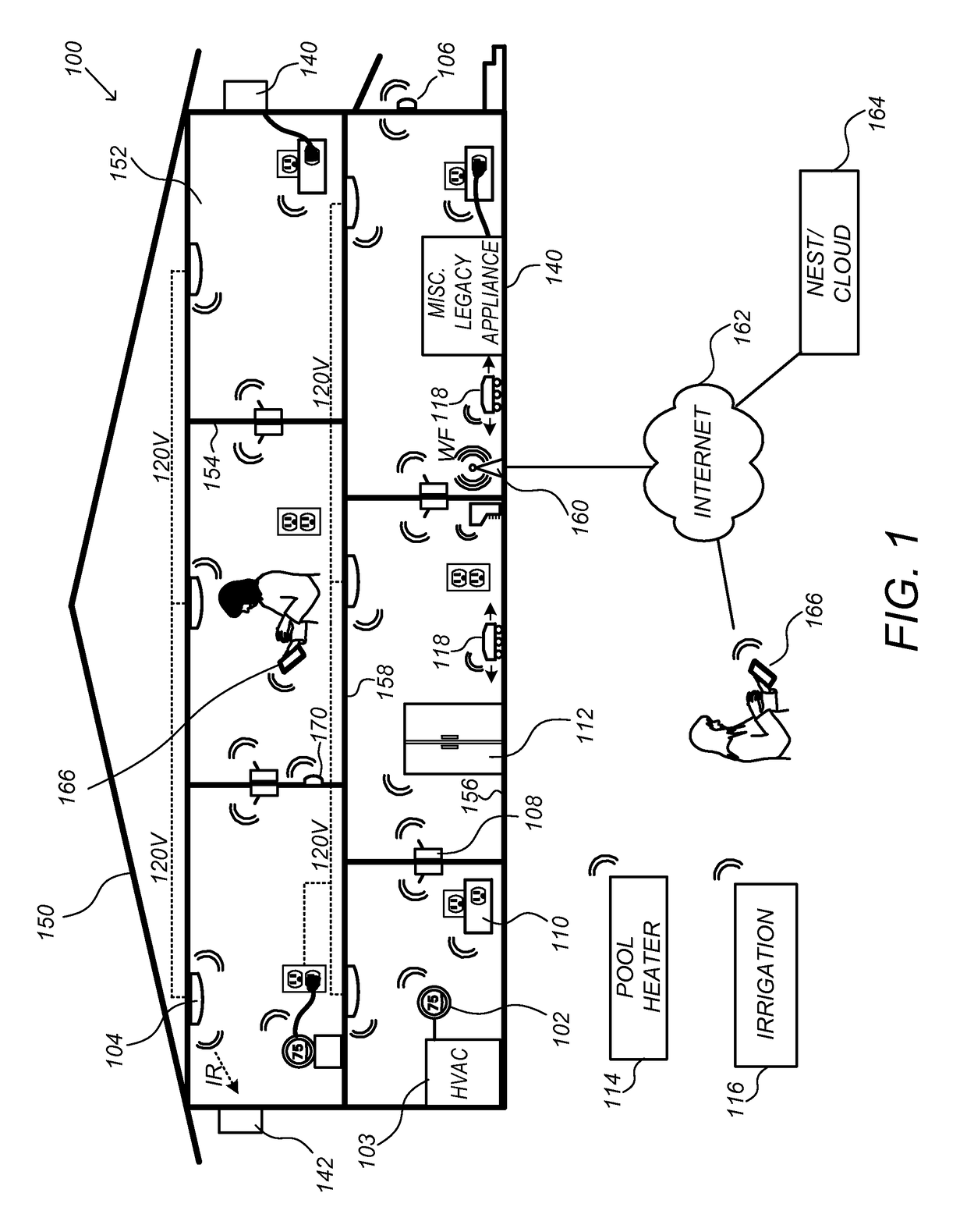
Thermodynamic model generation and implementation using observed HVAC and/or enclosure characteristics
ActiveUS20150300892A1Sampled-variable control systemsSpace heating and ventilationState dependentEngineering
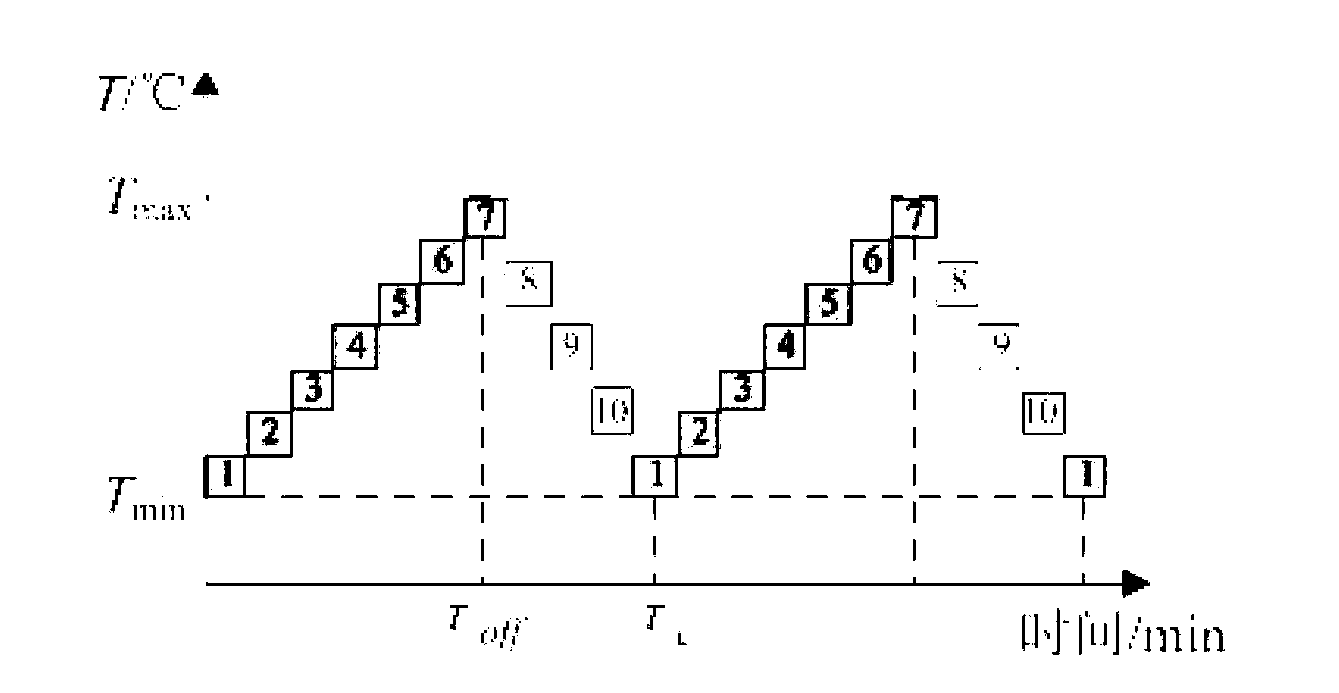
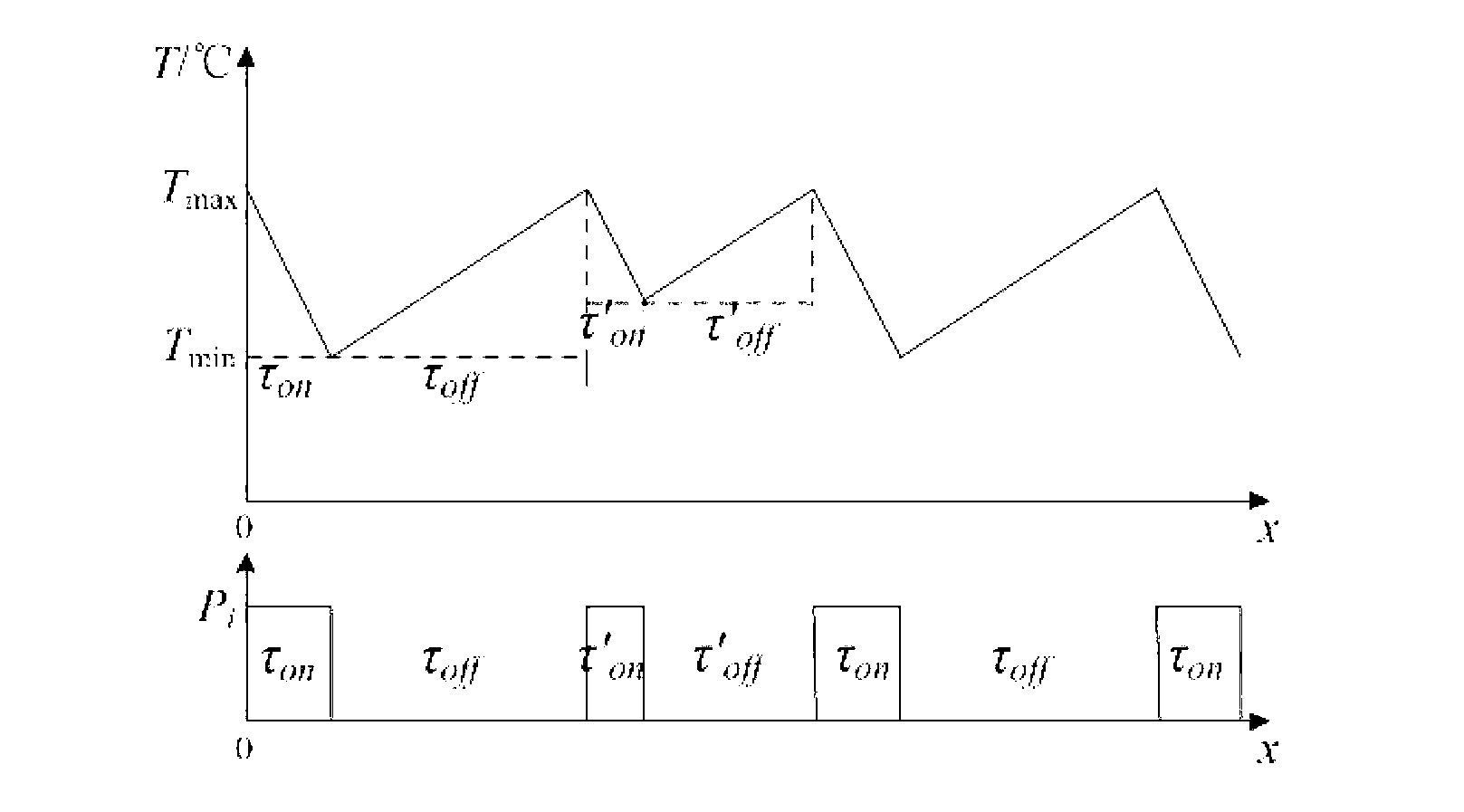
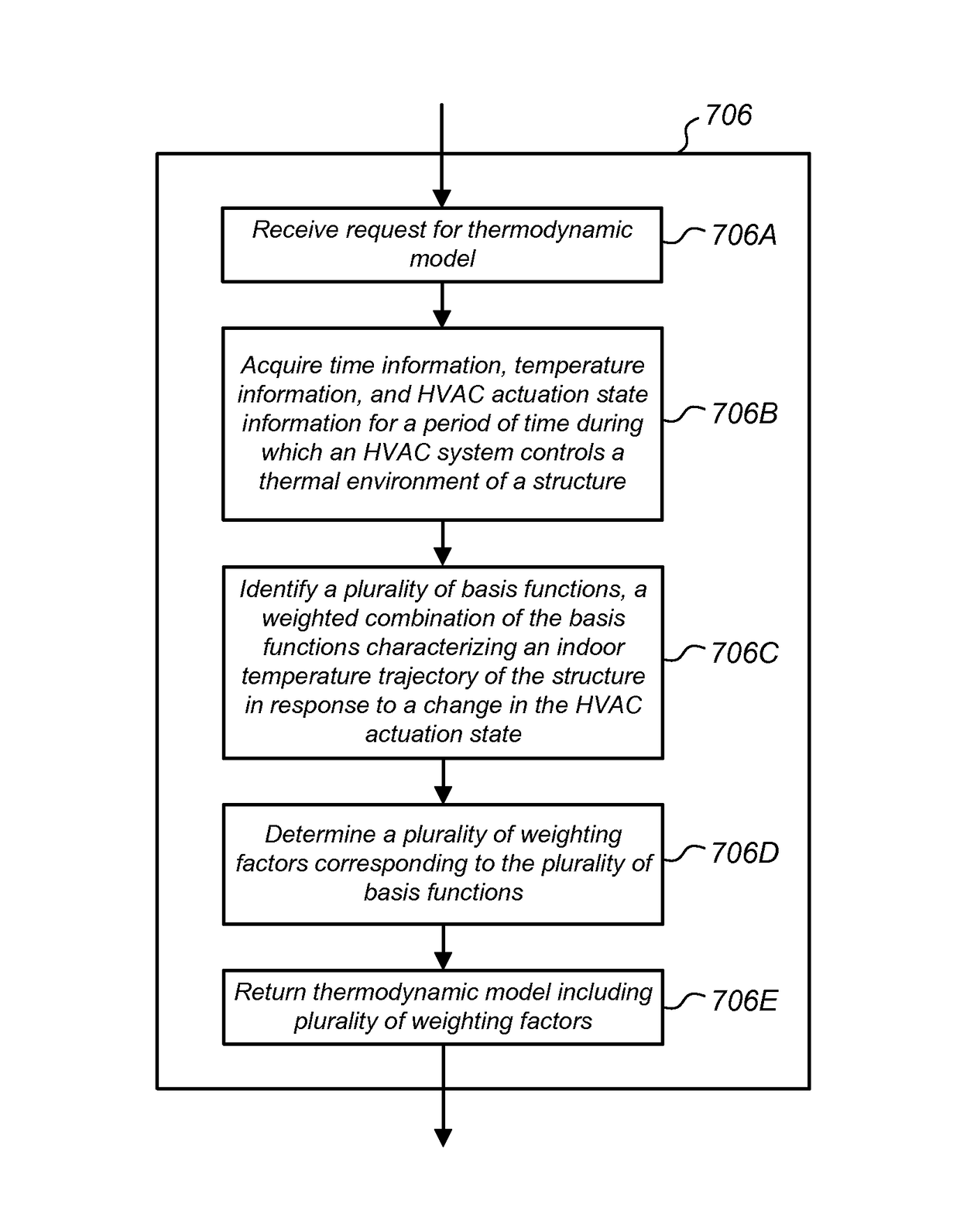
Techniques for determining and using a thermodynamic model that characterizes a thermodynamic response of an enclosure conditioned by an HVAC system are disclosed. To determine a thermodynamic model, temperature information when the HVAC system operates in a first state may first be received. A response interval may then be determined where the response interval indicates an estimated time between when the HVAC system begins operating in the first state and when the temperature within the enclosure begins to change in a direction associated with the first state. Weighting factors corresponding to basis functions may then be determined, where the weighted basis functions characterize the temperature trajectory of the enclosure in response to the HVAC system operating in the first state. The basis functions may include a first basis function that is evaluated from a time that the HVAC system begins operating in the first state until a time when the response interval ends, and a second basis function that is evaluated beginning at the time when the response interval ends.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Generating and implementing thermodynamic models of a structure
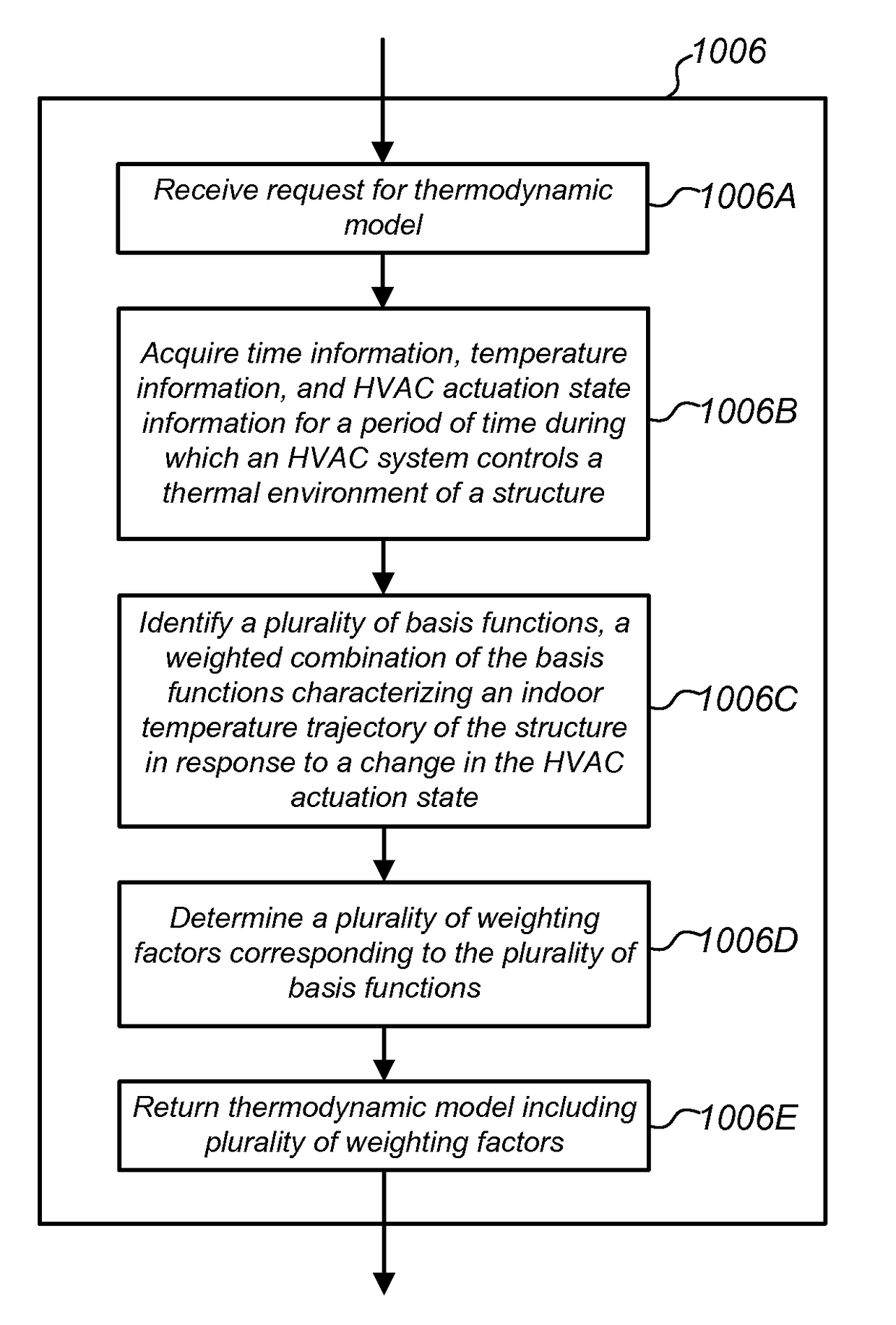
Apparatus, systems, methods, and related computer program products for generating and implementing thermodynamic models of a structure. Thermostats disclosed herein are operable to control an HVAC system. In controlling the HVAC system, a need to determine an expected indoor temperature profile for a particular schedule of setpoint temperatures may arise. To make such a determination, a thermodynamic model of the structure may be used. The thermodynamic model may be generated by fitting weighting factors of a set of basis functions to a variety of historical data including time information, temperature information, and HVAC actuation state information. The set of basis functions characterize an indoor temperature trajectory of the structure in response to a change in HVAC actuation state, and include an inertial carryover component that characterizes a carryover of a rate of indoor temperature change that was occurring immediately prior to the change in actuation state.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
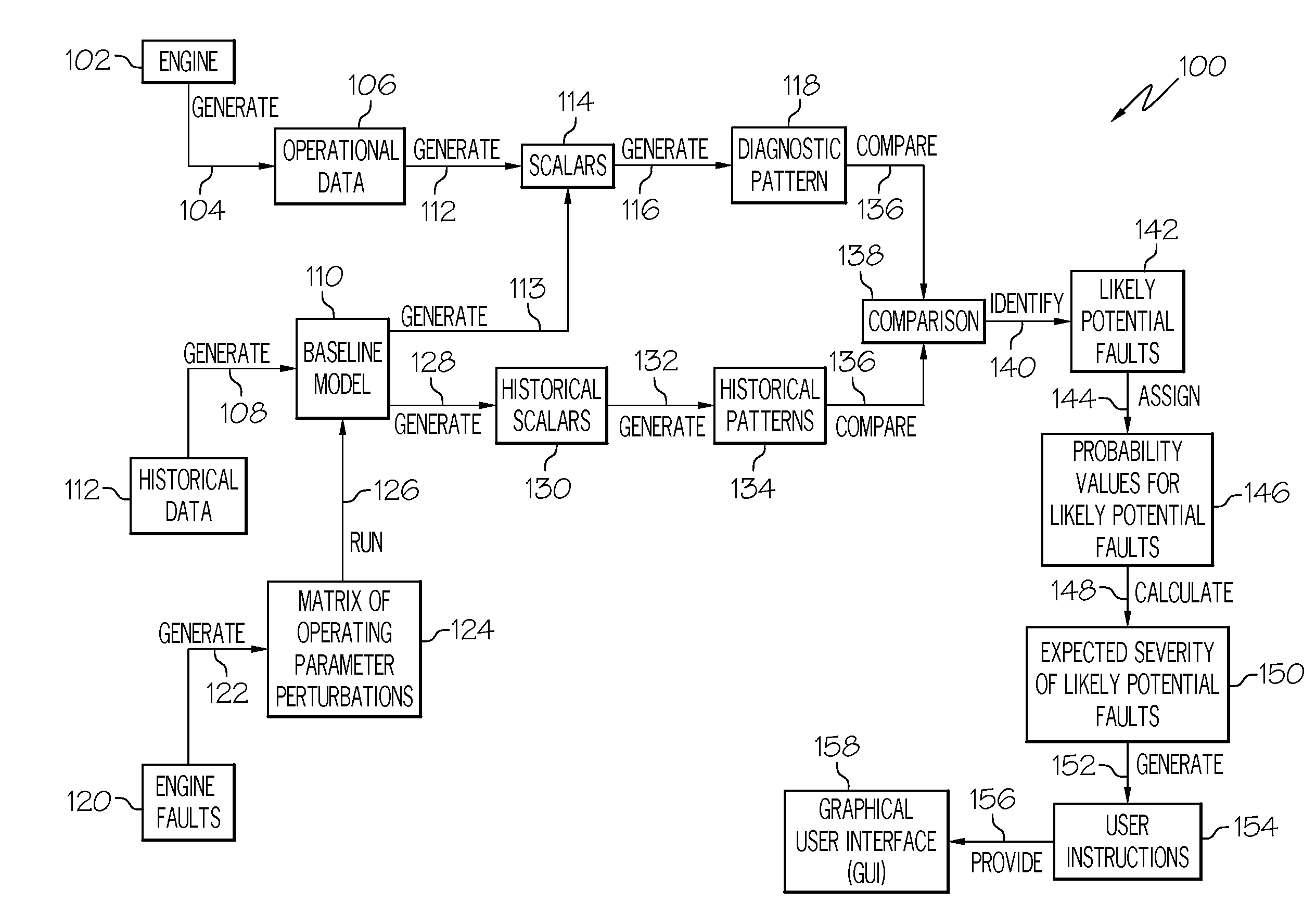
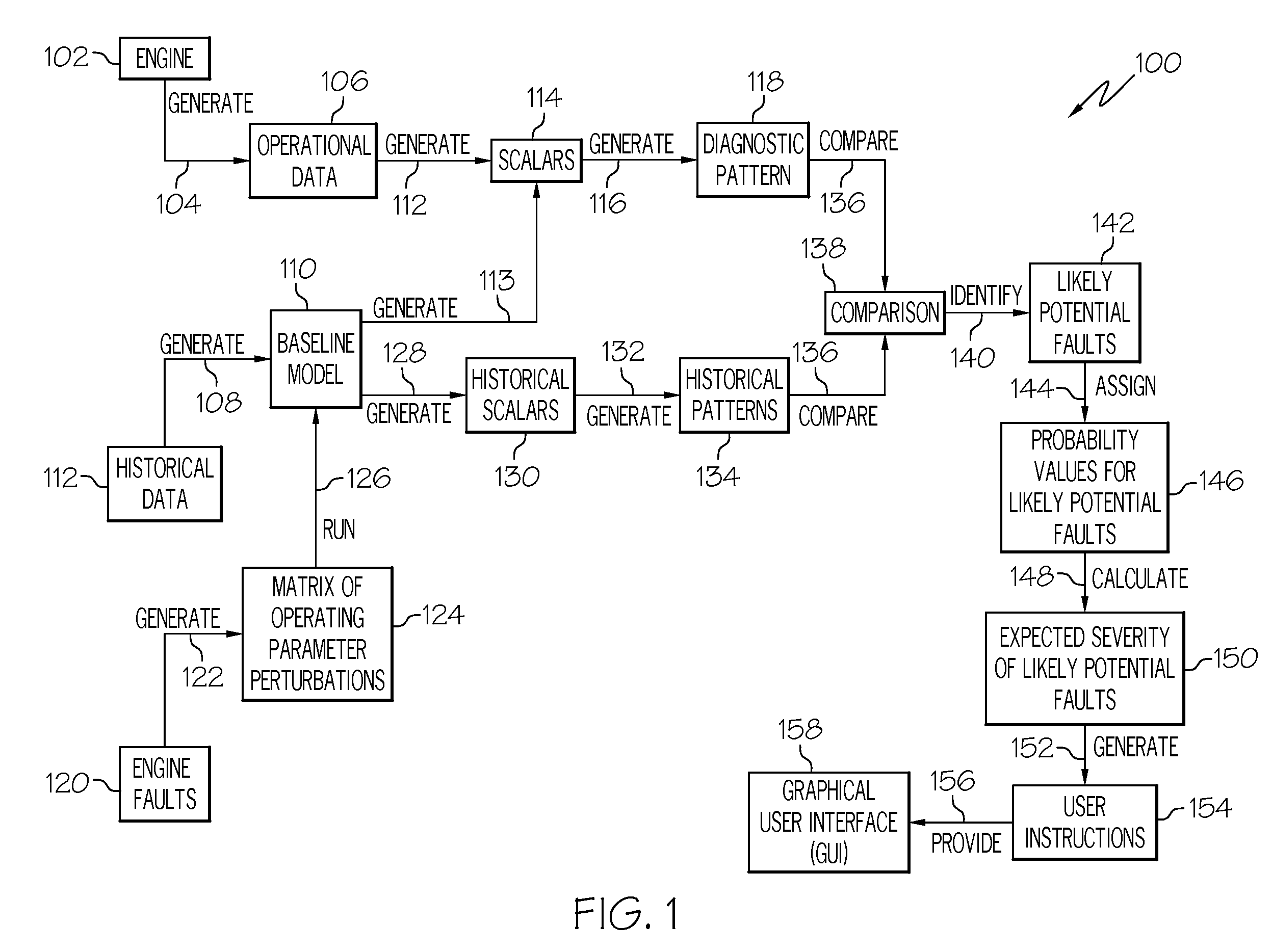
Automated engine data diagnostic analysis
InactiveUS20080228338A1Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDiagnostic modalitiesData mining
A method for diagnosing potential faults reflected in operational data for a turbine engine includes the steps of generating a diagnostic pattern for the operational data and comparing the diagnostic pattern with a plurality of historical patterns, to thereby identify one or more likely potential faults reflected in the operational data. The diagnostic pattern comprises a plurality of scalars. Each scalar represents an arithmetic relationship between values of the operational data and values predicted by a baseline thermodynamic model. Each historical pattern is linked to one or more specific faults.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
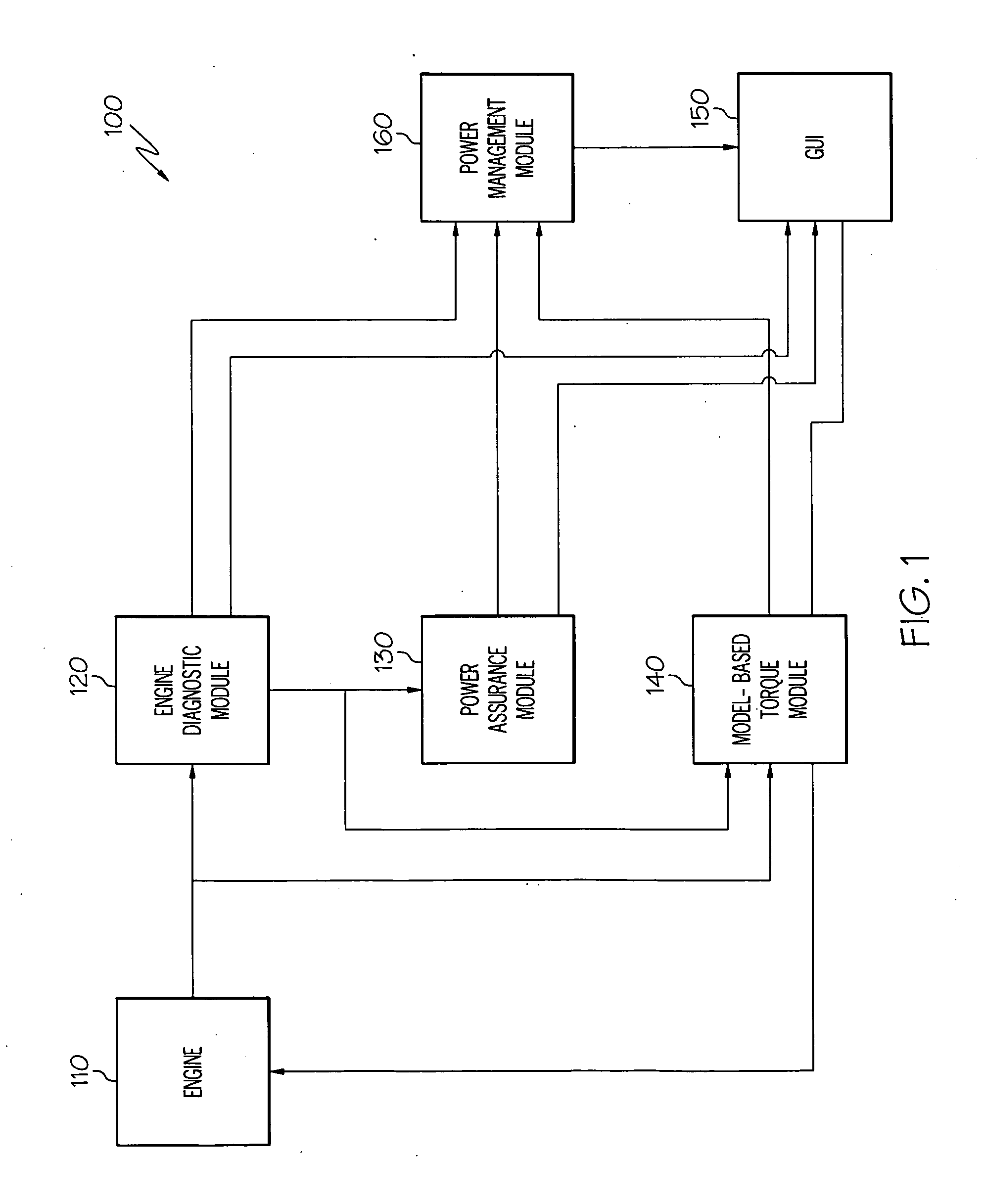
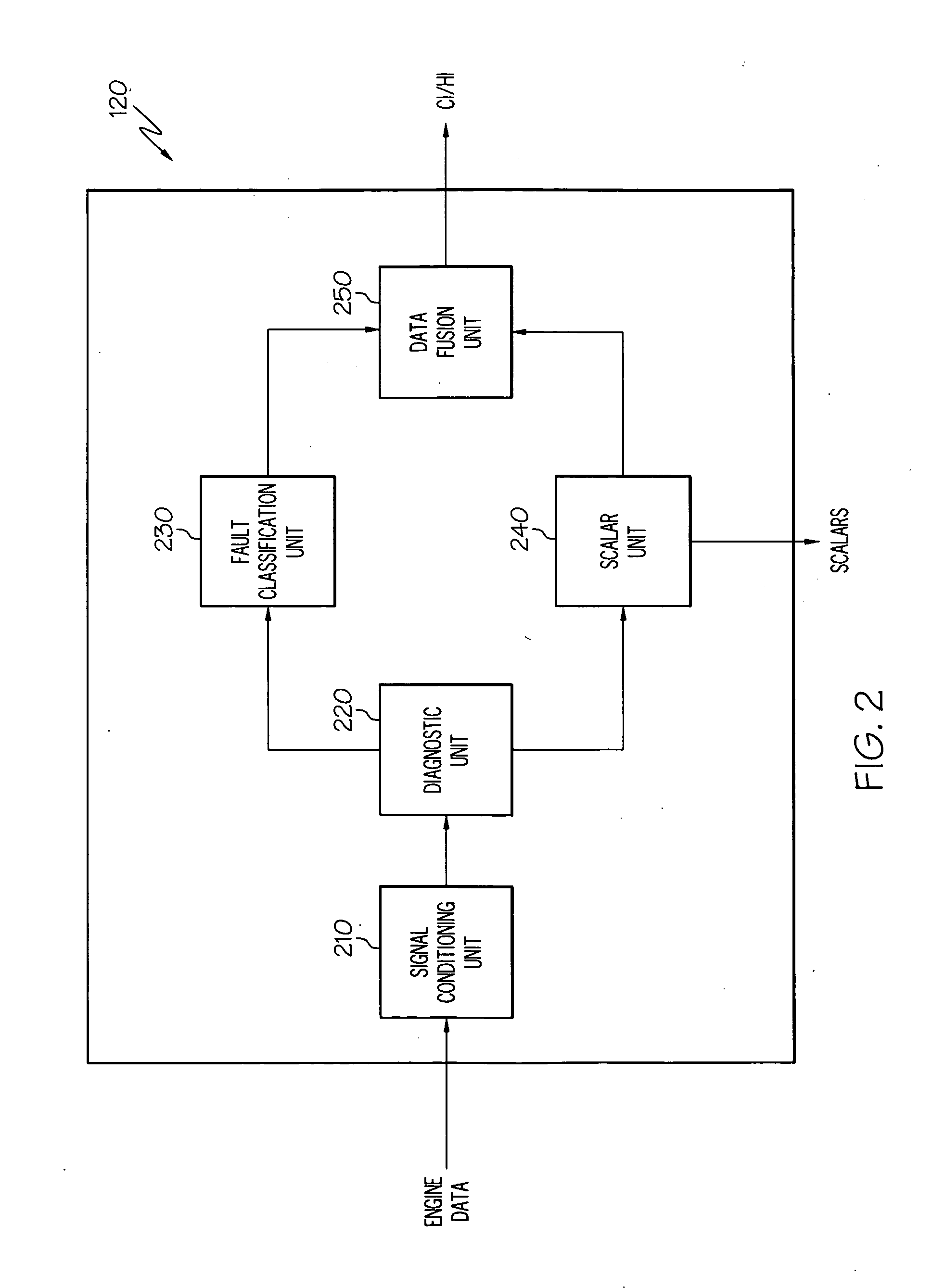
Operations support systems and methods with engine diagnostics
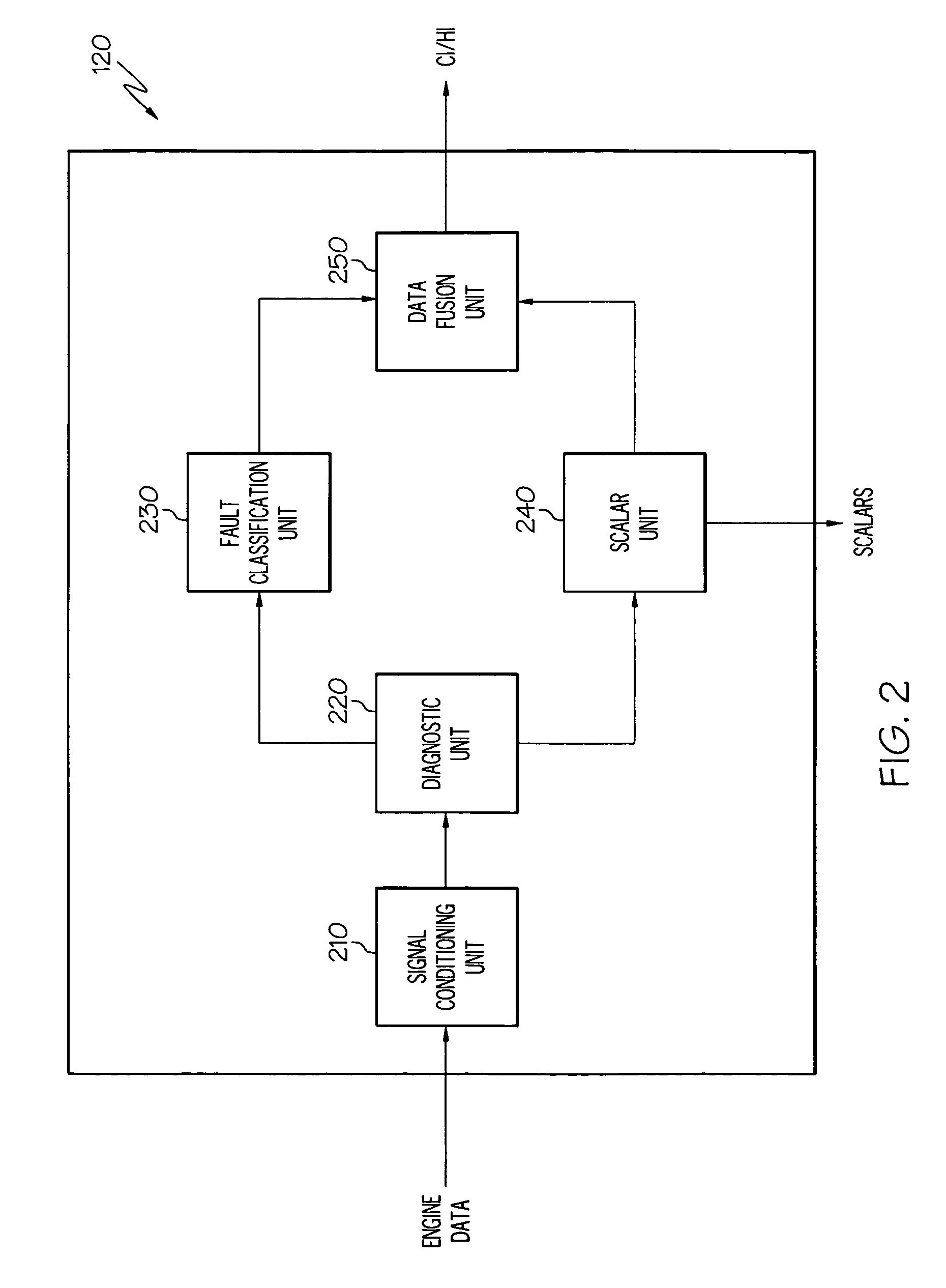
InactiveUS20100161196A1Analogue computers for vehiclesDigital data processing detailsEngineeringHealth indicator
An operations support system for an engine includes a diagnostics unit configured to receive engine data from the engine and to generate condition indicators based on the engine data using a thermodynamic model. The thermodynamic model is based on component maps associated with the engine. The system further includes a fault classification unit coupled to the diagnostic unit and configured to generate health indicators based on the condition indicators.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
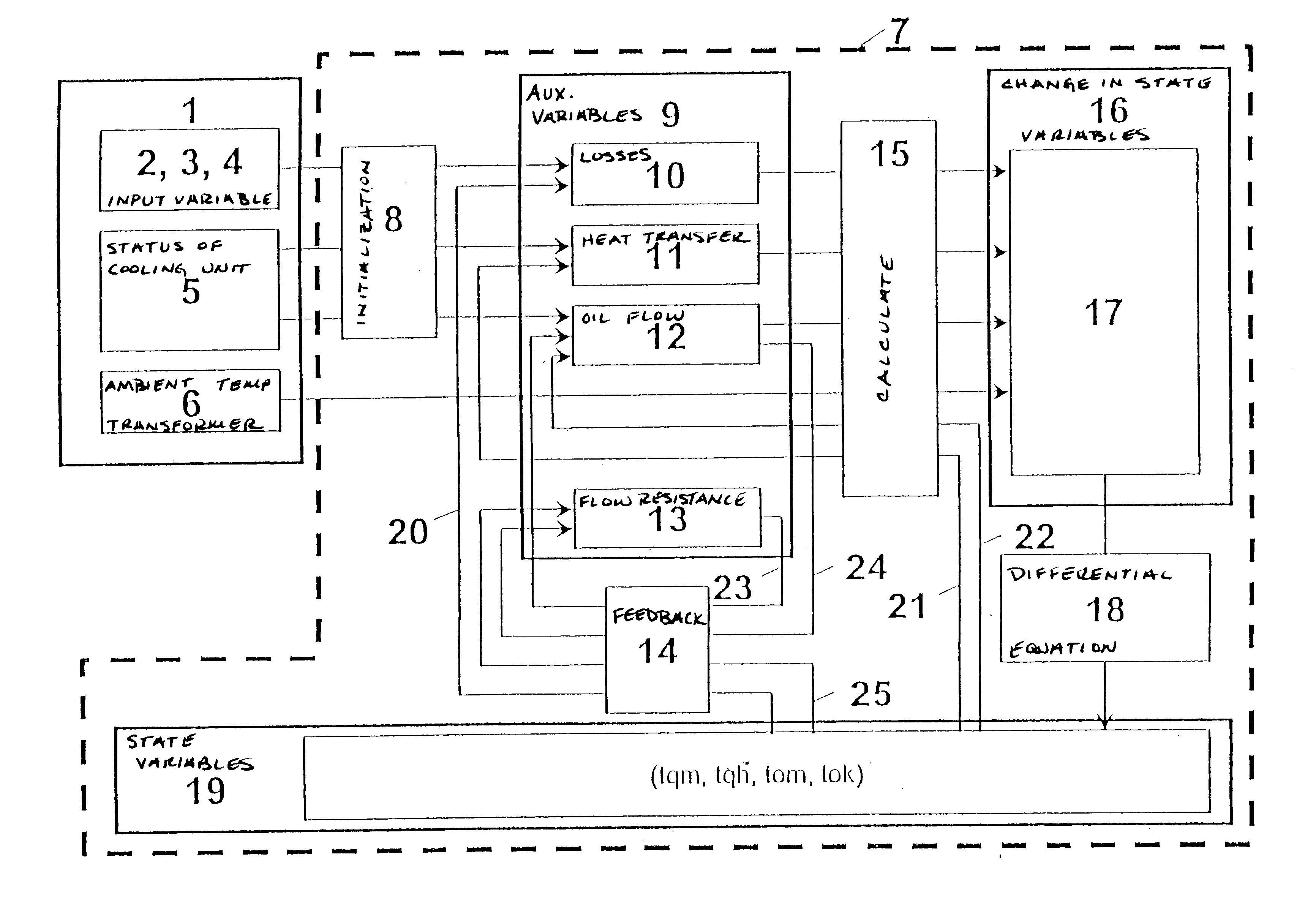
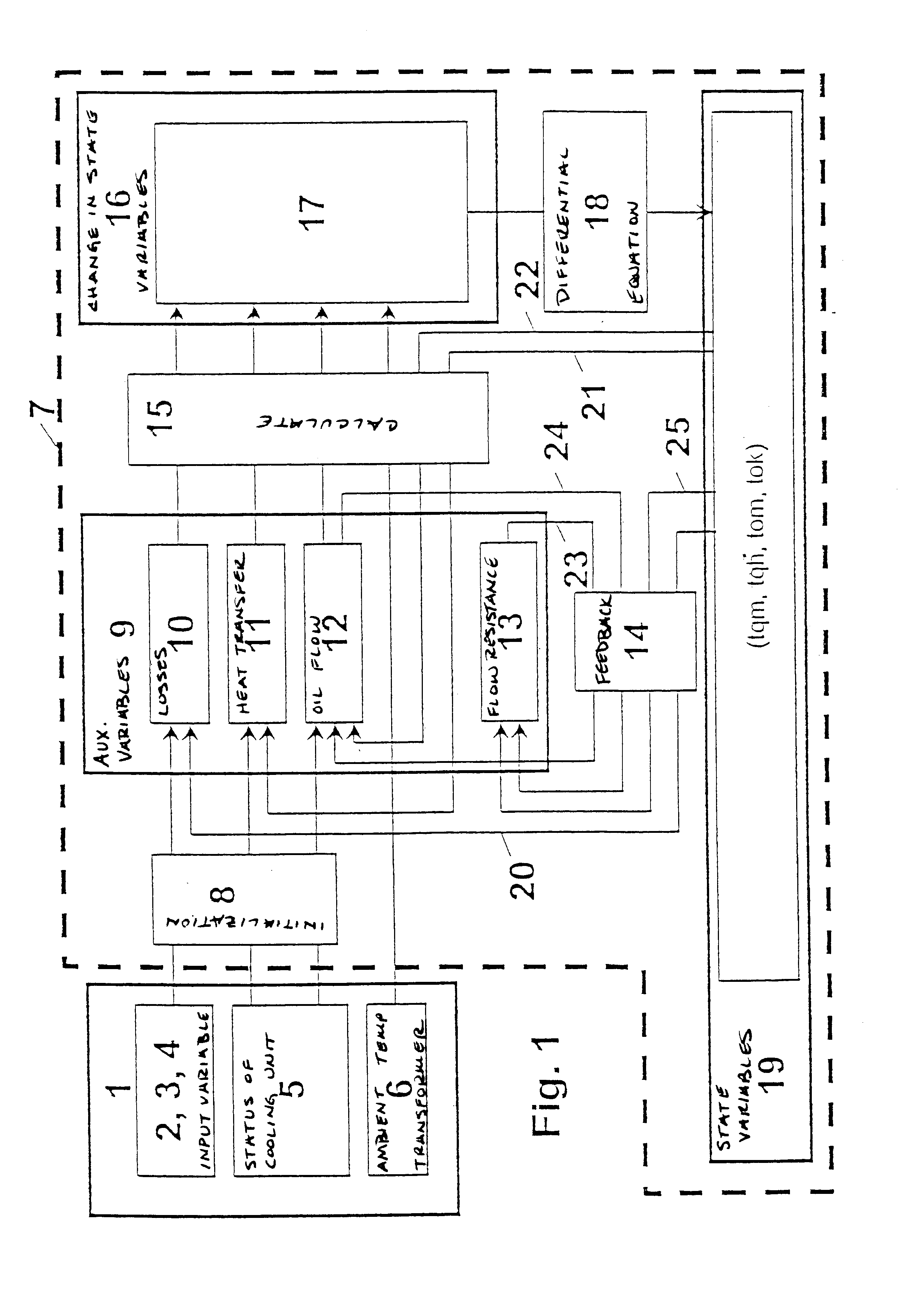
Method and arrangement for ascertaining state variables
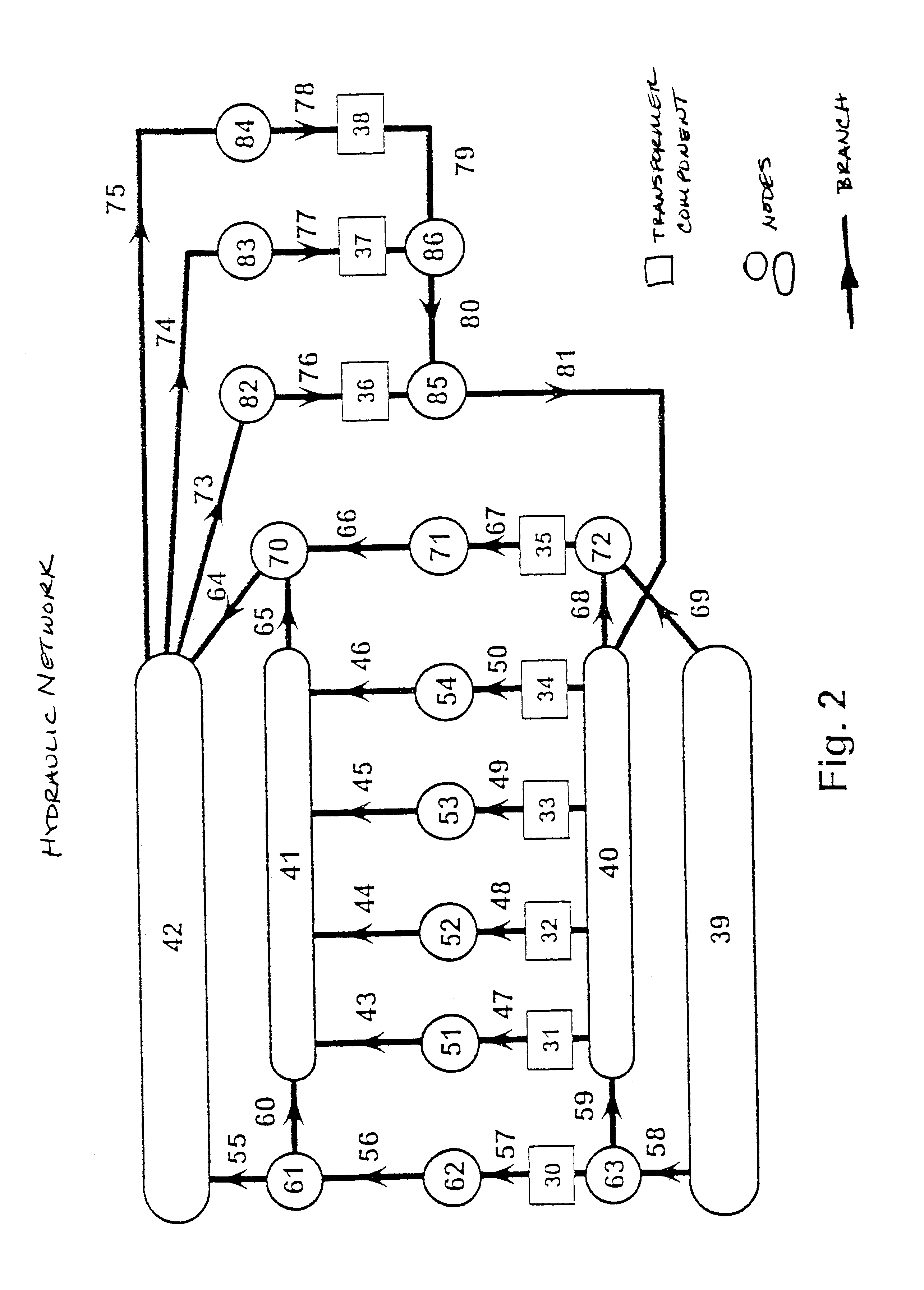
In a method for ascertaining temperatures (tqm, tqh, tom, tok) in an oil-cooled transformer, the transformer terminal voltages (2), the winding currents (3) and the ambient temperature (6) are measured. Furthermore, the status (5) of fans and pumps and the switch position (4) of a stepping switch are established. The measured and established variables (2, 3, 4, 5, 6) are fed to a thermohydraulic model (7), in which state variables (19) are calculated with auxiliary variables (9), which are losses (10) in the transformer, heat transfer parameters (11), flow resistances (13) and the oil flow (12), and a hydraulic network of the oil circuit, which has branches and nodes. The state variables (19) are the average temperatures (tqm) and the hotspot temperatures (tqh) in loss-producing parts of the transformer and the average oil temperatures in branches (tom) and in nodes (tok) of the hydraulic network of the oil circuit. When there is a change in the variables measured and established (2, 3, 4, 5, 6), the auxiliary variables (9) are adapted appropriately, and the rate of change of the state variables (19) is subsequently ascertained and new state variables (19) are consequently calculated. With this method, temperatures (tqm, tqh, tom, tok) and their changes in the transformer are ascertained without temperature sensors, whereby the optimum operation of the transformer is ensured, an early detection of errors and risks takes place and the optimum point in time for service work can be established.
Owner:VA TECH ELIN TRANSFORMATOREN
Diesel aftertreatment systems
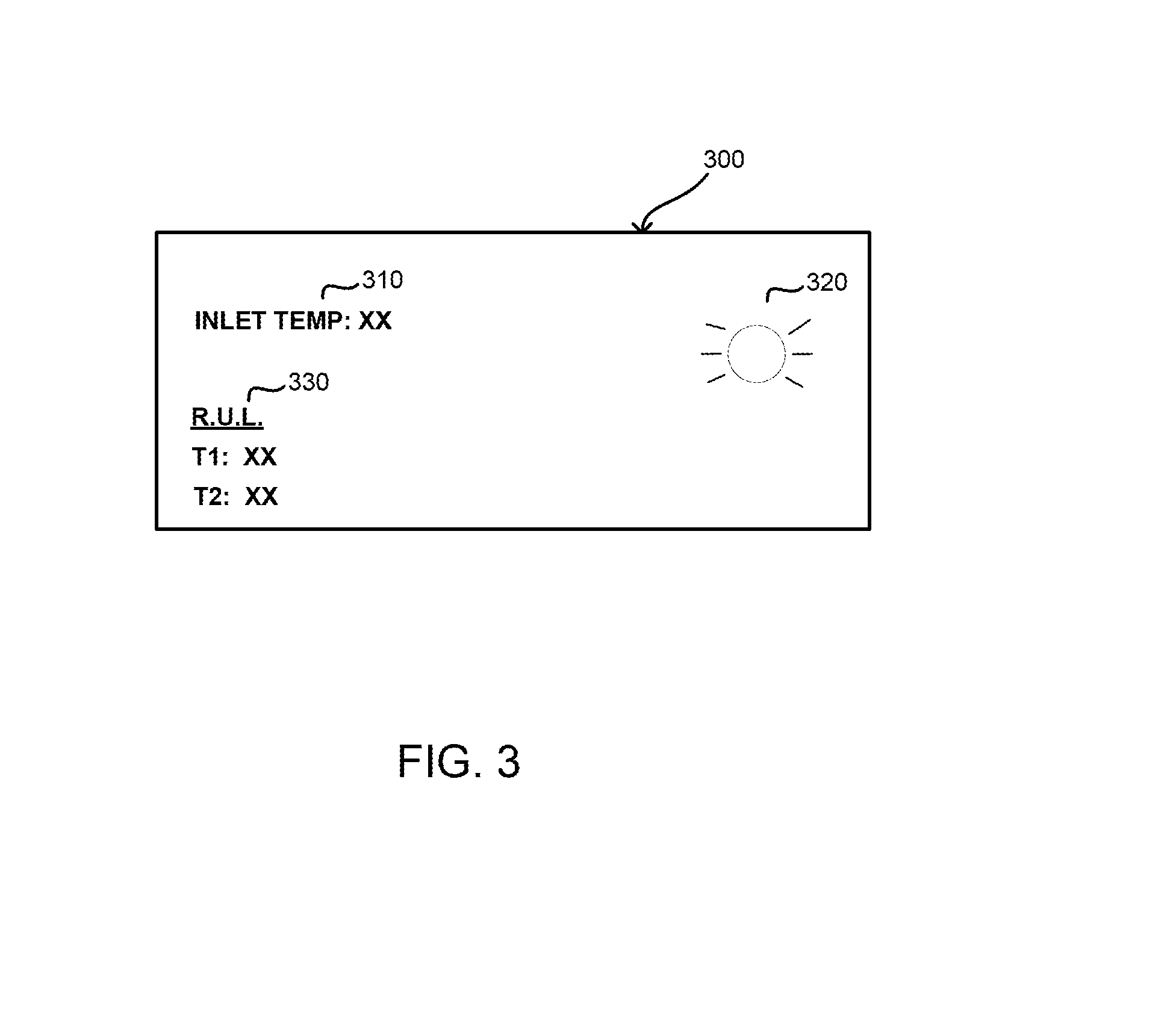
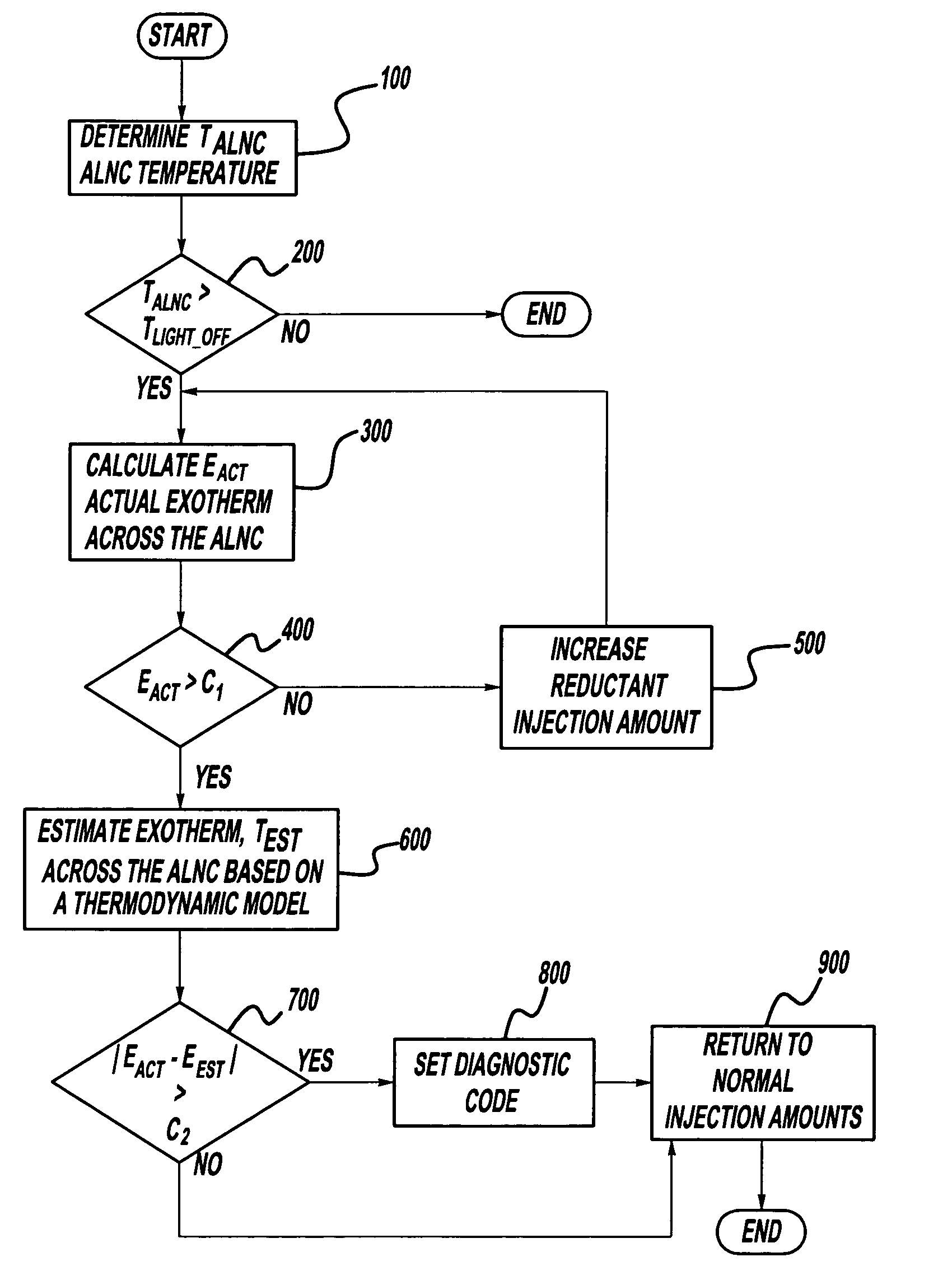
ActiveUS20050103099A1Improved system diagnosticsImprove diagnostic accuracyElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesHydrocotyle bowlesioidesCompound (substance)
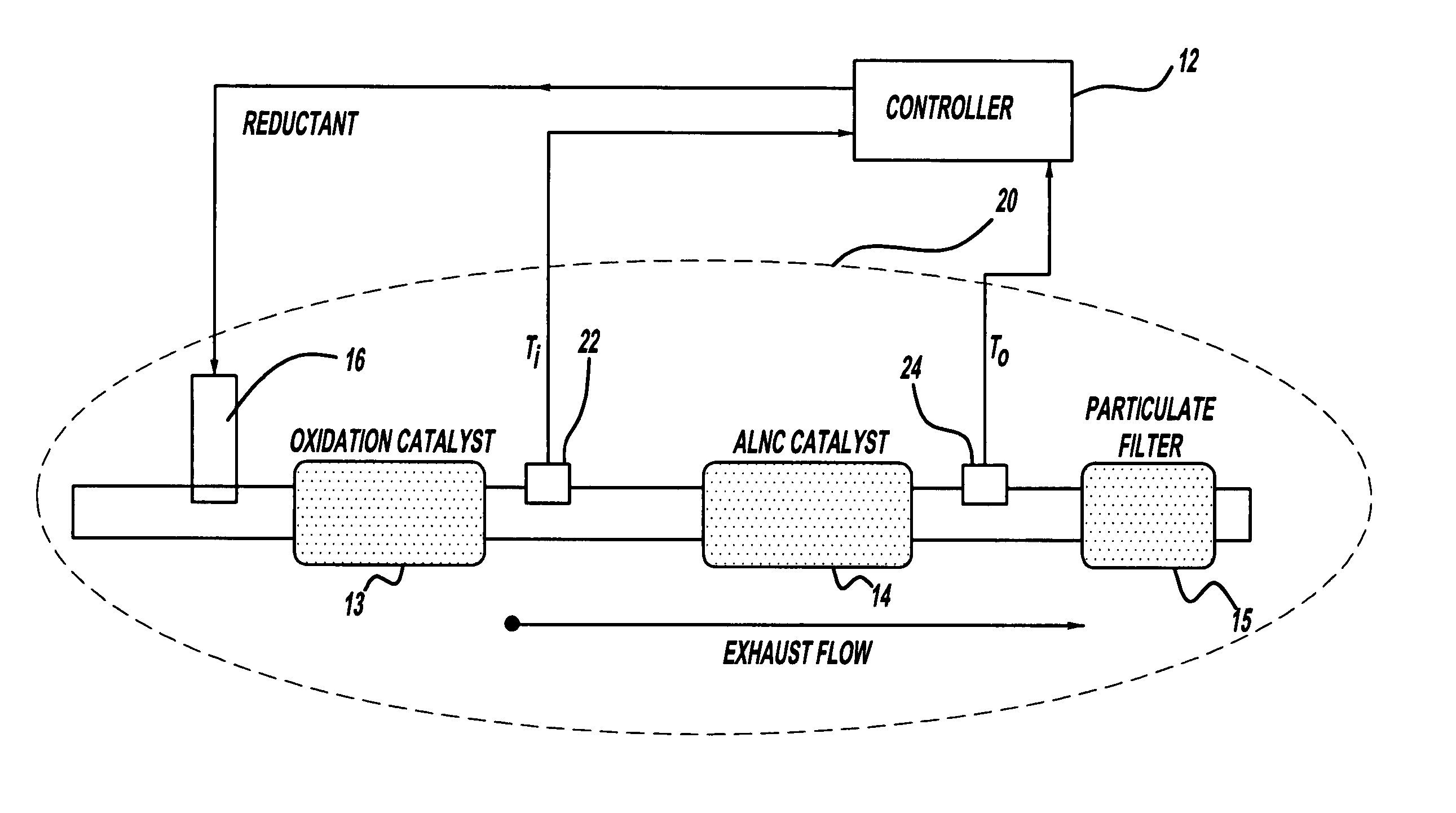
An accurate thermodynamic model of an Active Lean NOx (ALNC) Catalyst is presented. The model takes into account hydrocarbon storage and release mechanisms of the ALNC, as well as the degradation in the ALNC hydrocarbon conversion efficiency due to ageing, and thus provides a more accurate estimate of an exotherm generated by hydrocarbon combustion in the ALNC. The estimated exotherm can them be used to detect system degradation and identify components responsible for the degradation.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
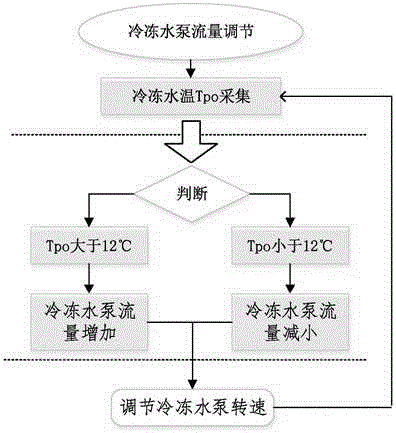
Method for optimized setting of air conditioner temperature in office building
InactiveCN104896660AReduce energy consumptionGood thermal comfort levelMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsNatural ventilationThermal comfort
The invention discloses a method for optimized setting of air conditioner temperature in an office building and relates to a dynamic setting method for changing a set value of the air conditioner temperature in real time according to indoor and outdoor environmental factors. To improve the dynamic setting of the air conditioner temperature, a simplified room thermodynamic model is established; in the model, the air conditioning opening is performed in the daytime, and natural ventilation is performed at night. The dynamic relations between the air conditioner load and environmental variables such as outdoor temperature, hot material temperature and the indoor temperature set value are established through the analysis of the room model. With the air conditioner load as an objective function and according to the limiting conditions that the human comfort index PMV value is within the regulated range, an optimized model of the air conditioner temperature set value is established; and optimization solution is performed on the model, so as to obtain the optimal air conditioner temperature set value at each moment. The obtained dynamic temperature set value can guarantee the good thermal comfort level for indoor workers and can effectively reduce energy consumption of the air conditioner.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
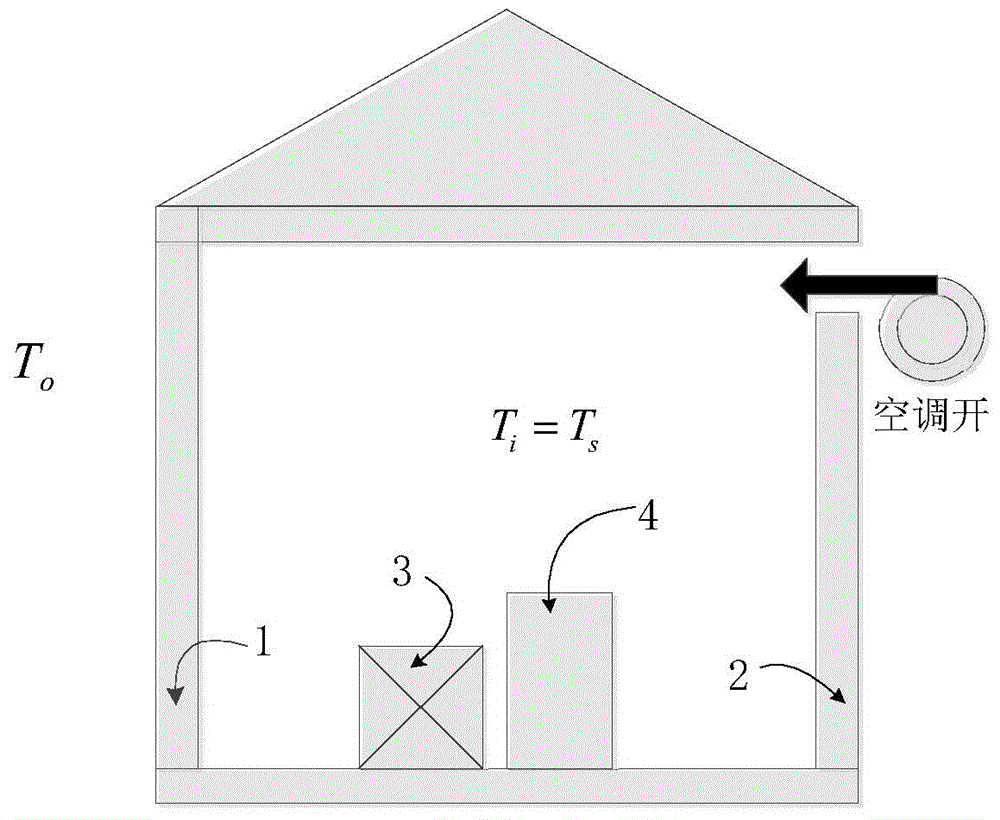
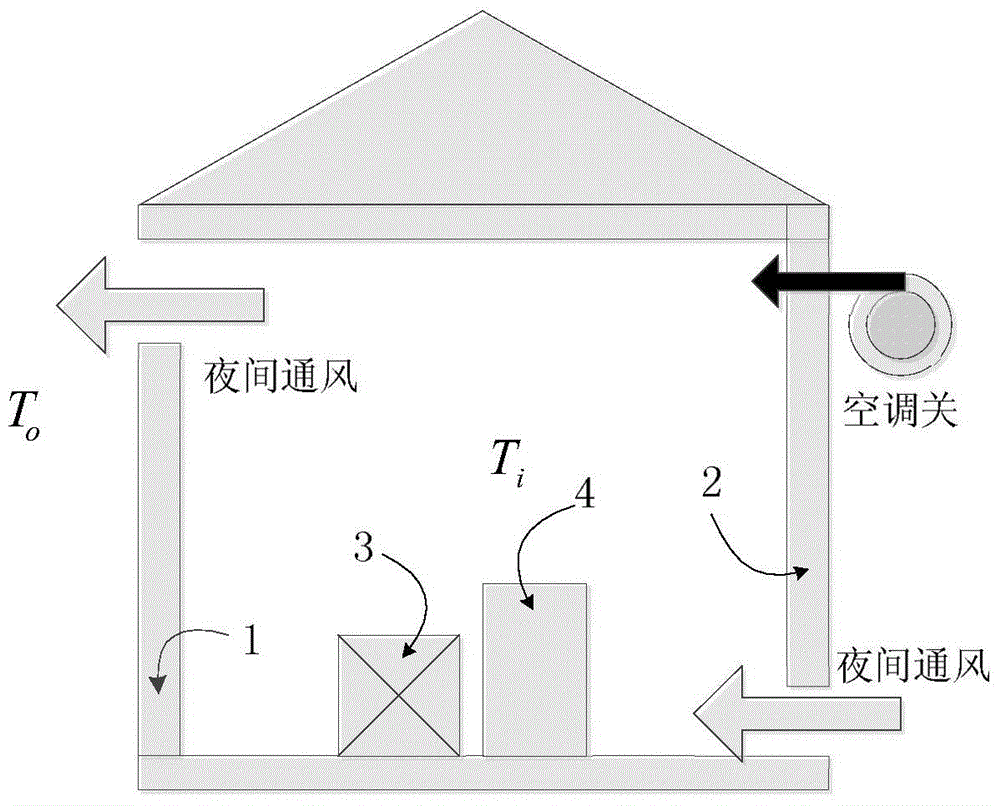
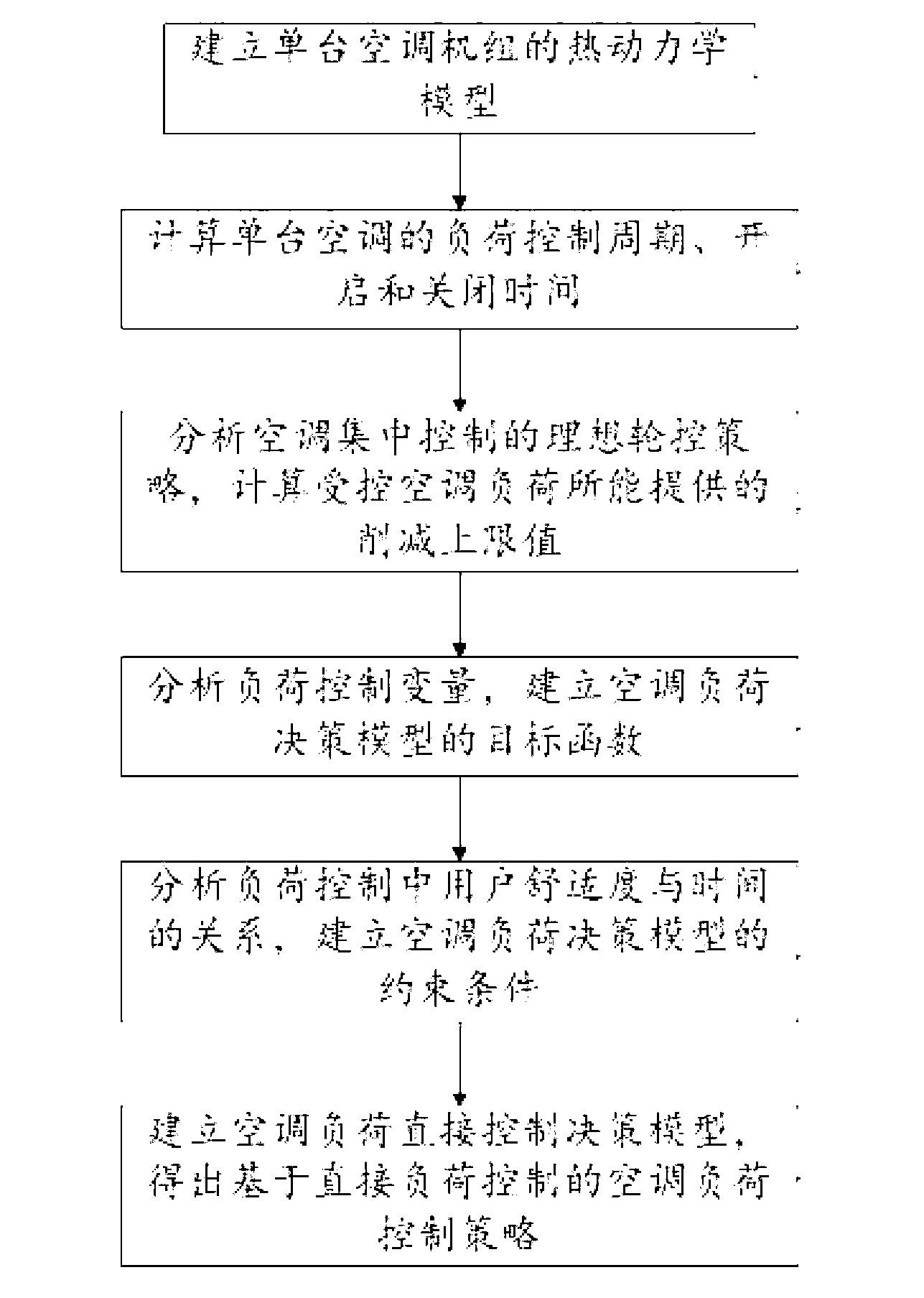
Air conditioning load control strategy making method based on direct load control
ActiveCN103257571AReduce investmentAlleviate tension in power supply and demandAdaptive controlElectric power systemRoom temperature
The invention discloses an air conditioning load control strategy making method based on direct load control. According to the air conditioning load control strategy making method, a thermodynamic model of a single air conditioning unit is established and used for representing the relation among air conditioning power, temperature and time; an ideal in-turn control strategy for centralized control of air conditioning loads is analyzed according to the thermodynamic model of the single air conditioner unit and requirements of users for comfort level specified in a direct load control contract, and reduced upper limit values which can be provided by all the air conditioning loads under control are calculated. A decision-making model for the direct control of the air conditioning loads in actual electric power system operation is established. Through optimization of the control strategy of all the air conditioning loads under control, the deviation between actual force exerted by the air conditioning loads and ideal reduction quantity is minimized. Moreover, continuous starting and closing time of the air conditioning loads is used for replacing constraint conditions of a real-time room temperature representation air conditioning in-turn control strategy.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Thermodynamic model generation and implementation using observed HVAC and/or enclosure characteristics
ActiveUS9857238B2Mechanical apparatusTemperature control using digital meansState dependentEngineering
Techniques for determining and using a thermodynamic model that characterizes a thermodynamic response of an enclosure conditioned by an HVAC system are disclosed. To determine a thermodynamic model, temperature information when the HVAC system operates in a first state may first be received. A response interval may then be determined where the response interval indicates an estimated time between when the HVAC system begins operating in the first state and when the temperature within the enclosure begins to change in a direction associated with the first state. Weighting factors corresponding to basis functions may then be determined, where the weighted basis functions characterize the temperature trajectory of the enclosure in response to the HVAC system operating in the first state. The basis functions may include a first basis function that is evaluated from a time that the HVAC system begins operating in the first state until a time when the response interval ends, and a second basis function that is evaluated beginning at the time when the response interval ends.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
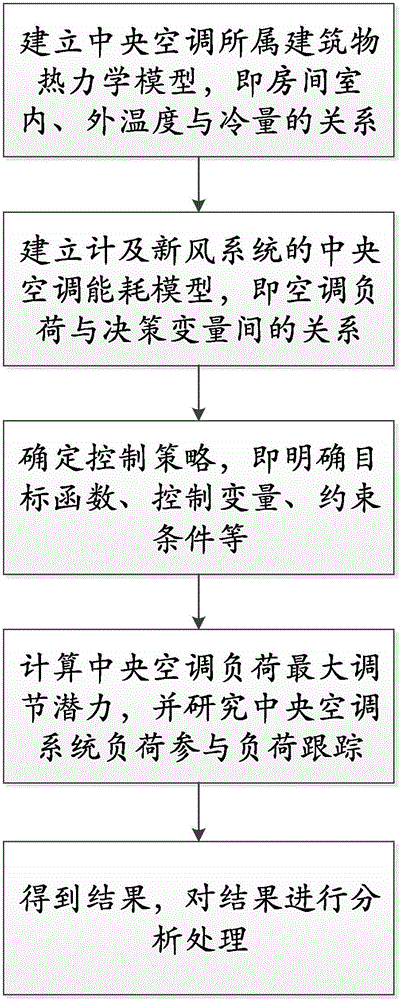
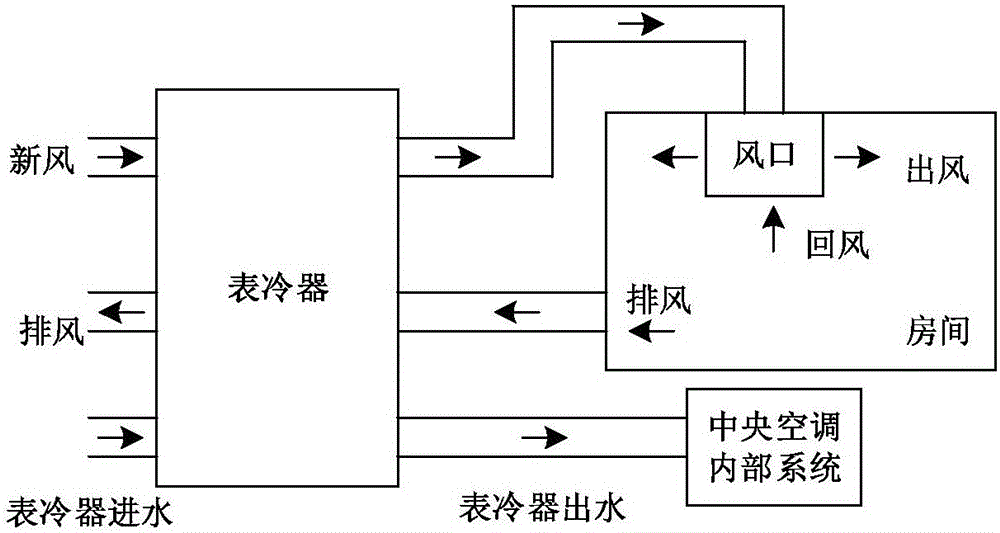
Modeling and controlling strategy for central air conditioner with fresh air system
ActiveCN105841300AMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsScientific theoryElectric power system
The invention discloses a modeling and controlling strategy for a central air conditioner with a fresh air system. The modeling and controlling strategy includes the following steps of building a thermodynamic model of a building where the central air conditioner is installed, namely, the relation between indoor and outdoor temperatures and the cold capacity of the building; building an energy consumption model of the central air conditioner with the fresh air system, namely the relation between the air conditioner load and decision variables; determining a control strategy, namely determining the target function, control variables, constraint conditions and the like; and working out the highest adjusting potential of the load of the central air conditioner, comparing the adjusting results of different control modes, researching the system load of the central air conditioner and participating in load tracing. By finely building the model and determining the cooperative optimization strategy of the control variables, a scientific theory support is provided for the central air conditioner with the fresh air system to participate in operation of a power system.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
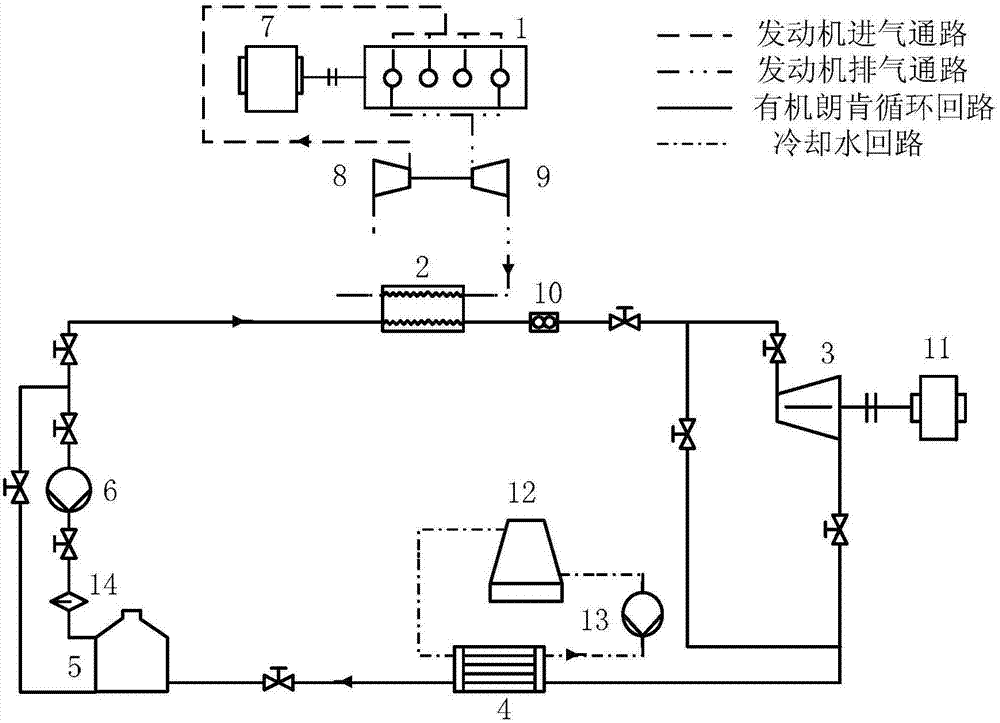
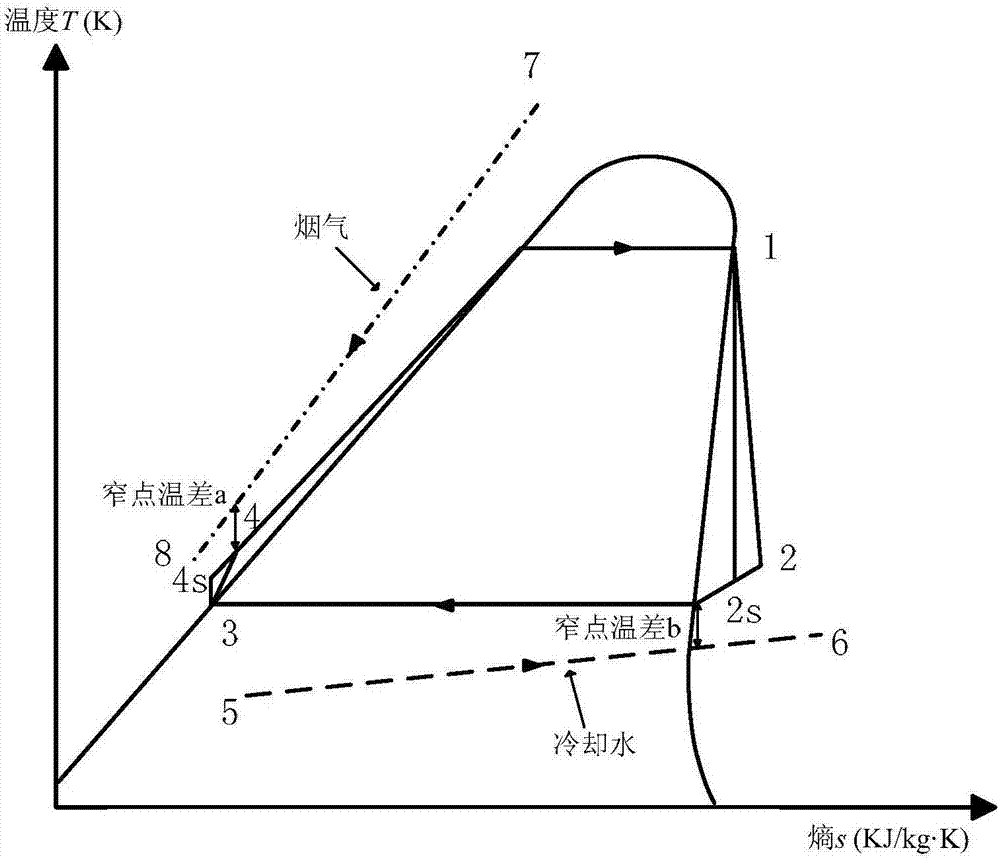
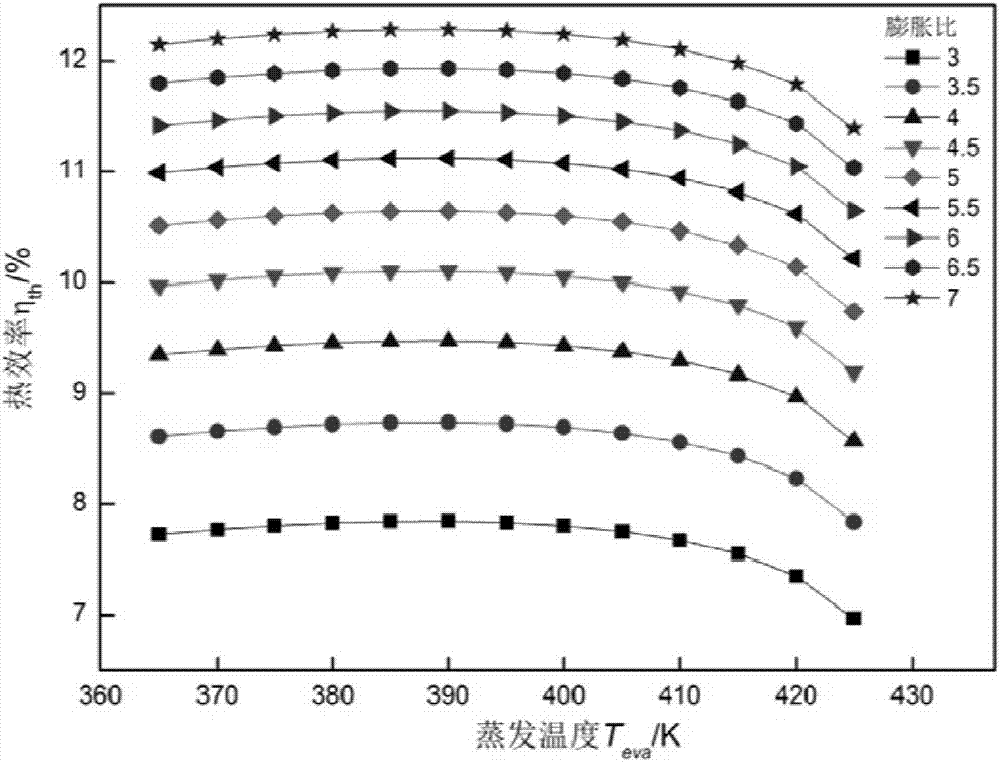
Optimization method for determining flue gas excess heat organic Rankine cycle system parameter
InactiveCN107016187AIncrease profitEmission reductionGeneral water supply conservationForecastingOrganic Rankine cycleSecond law of thermodynamics
The invention provides an optimization method for determining a flue gas excess heat organic Rankine cycle system parameter. The optimization method comprises the steps of taking into account of a cooling water cycle to establish a thermodynamic model; through a first law of thermodynamics and a second law of thermodynamics, obtaining system net output power, water pump waste power, heat efficiency, (the formula is shown in the description) efficiency and irreversible loss, and according to the influence of an evaporation temperature and an expansion ratio on system thermodynamic performance, determining an optimal evaporation temperature; under the optimal evaporation temperature, calculating heat exchange areas of an evaporator and a condenser, wherein it is defined that an economical objective function is the ratio of the system net output power to the area of the evaporator to the area of the condenser, and the comprehensively evaluation function is the weighted sum the economical objective function (the formula is shown in the description) and the efficiency; with the comprehensive evaluation function being an optimization target, determining an optimal condensation temperature; according to the optimal evaporation temperature and the optimal condensation temperature, determining system parameters of work medium mass, cooling water mass, evaporation pressure, condensation pressure, an expansion ratio, the net output power, the heat efficiency and the irreversible loss. According to the optimization method for determining the flue gas excess heat organic Rankine cycle system parameter, the optimal evaporation temperature and the condensation temperature can be determined, and thus the optimal system parameter is determined.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
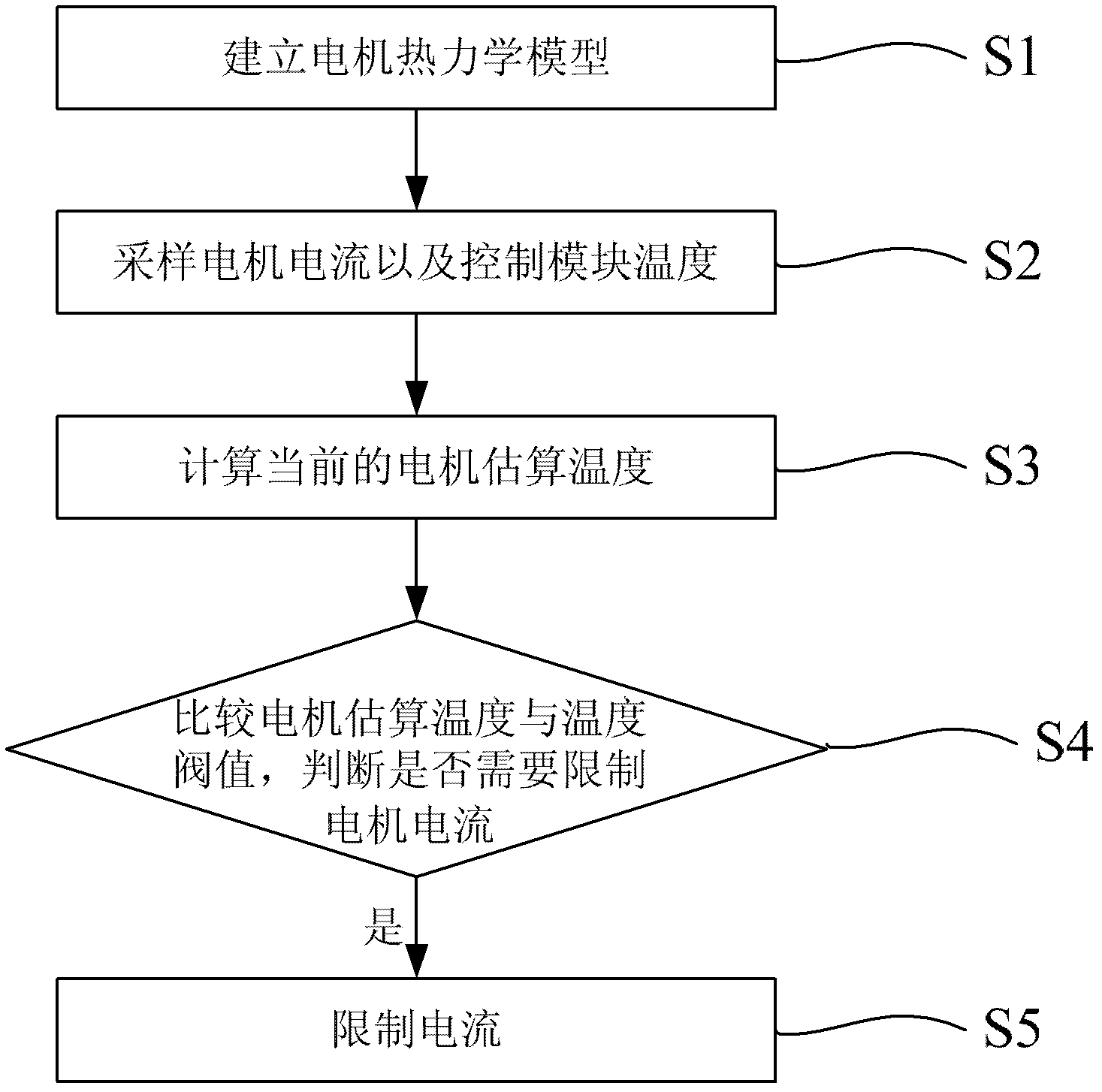
Motor thermodynamic model-based over-temperature protection method for electric power-assisted steering system
InactiveCN102566434ALow implementation costSimple technologyElectrical steeringThermometer applicationsElectric power steeringElectric machine
The invention provides a motor thermodynamic model-based over-temperature protection method for an electric power-assisted steering system. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a motor thermodynamic model which represents a relationship between heat which is generated and dissipated during operation of a motor and the temperature of the motor; sampling the current of the motor and the temperature of a control module; calculating the current estimation temperature of the motor by using the current of the motor, the temperature of the control module and the motor thermodynamic model; comparing the calculated estimation temperature of the motor with the range of a normal operation temperature threshold value of the motor; and limiting the current of the motor if the estimation temperature of the motor is not in the range of the temperature threshold value. The method has the advantages of low implementation cost, simple technology and high accuracy.
Owner:范示德汽车技术(上海)有限公司
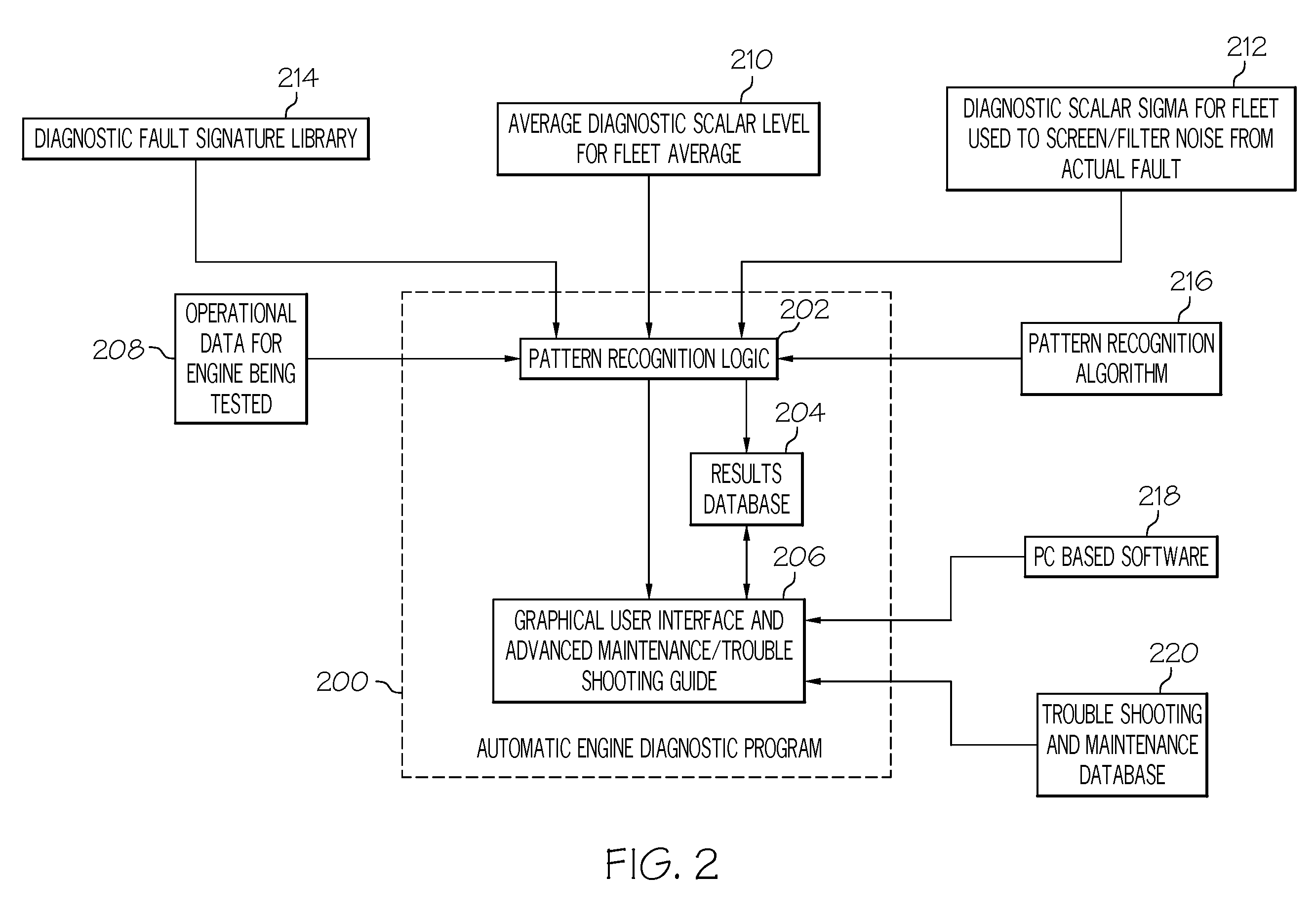
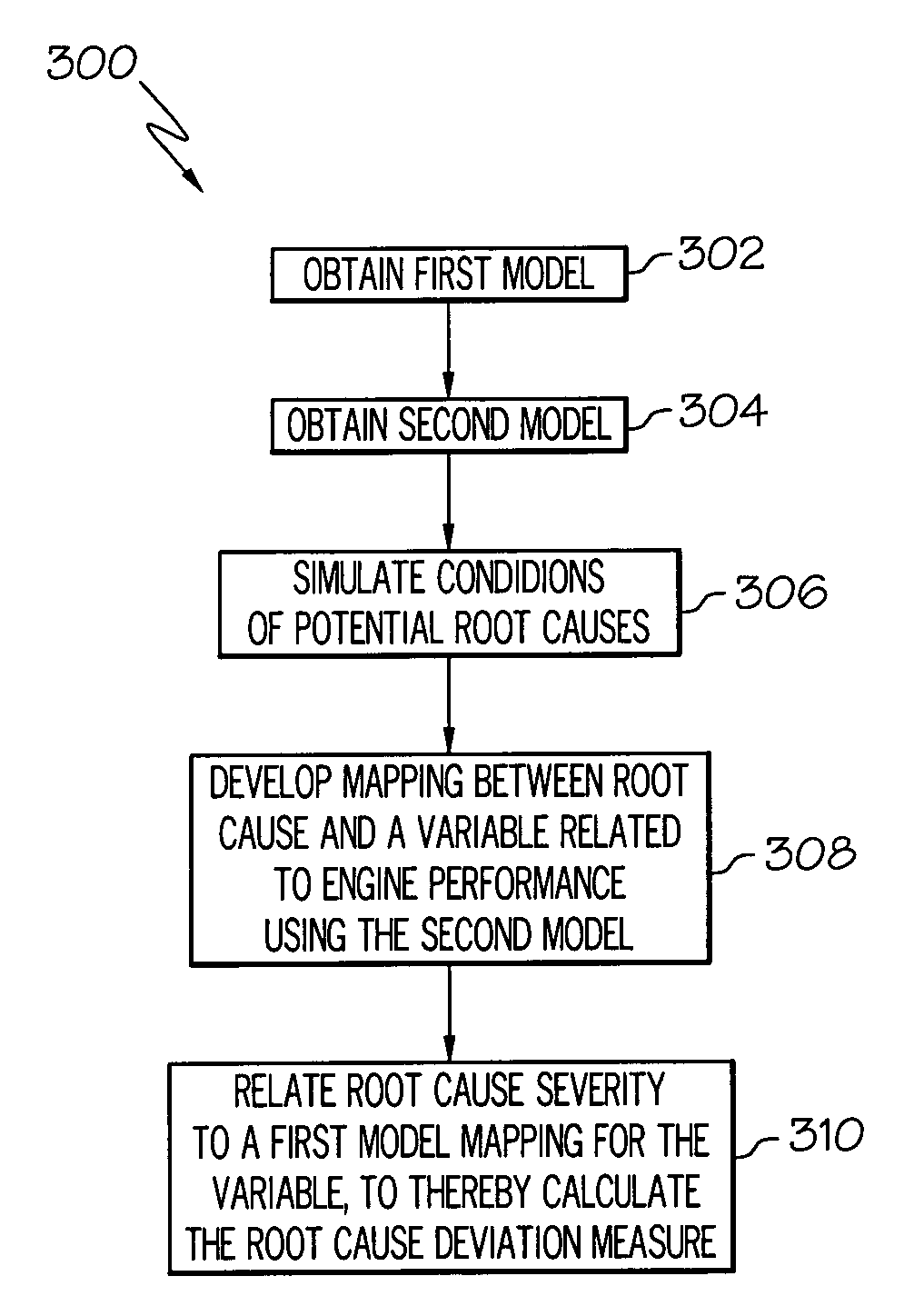
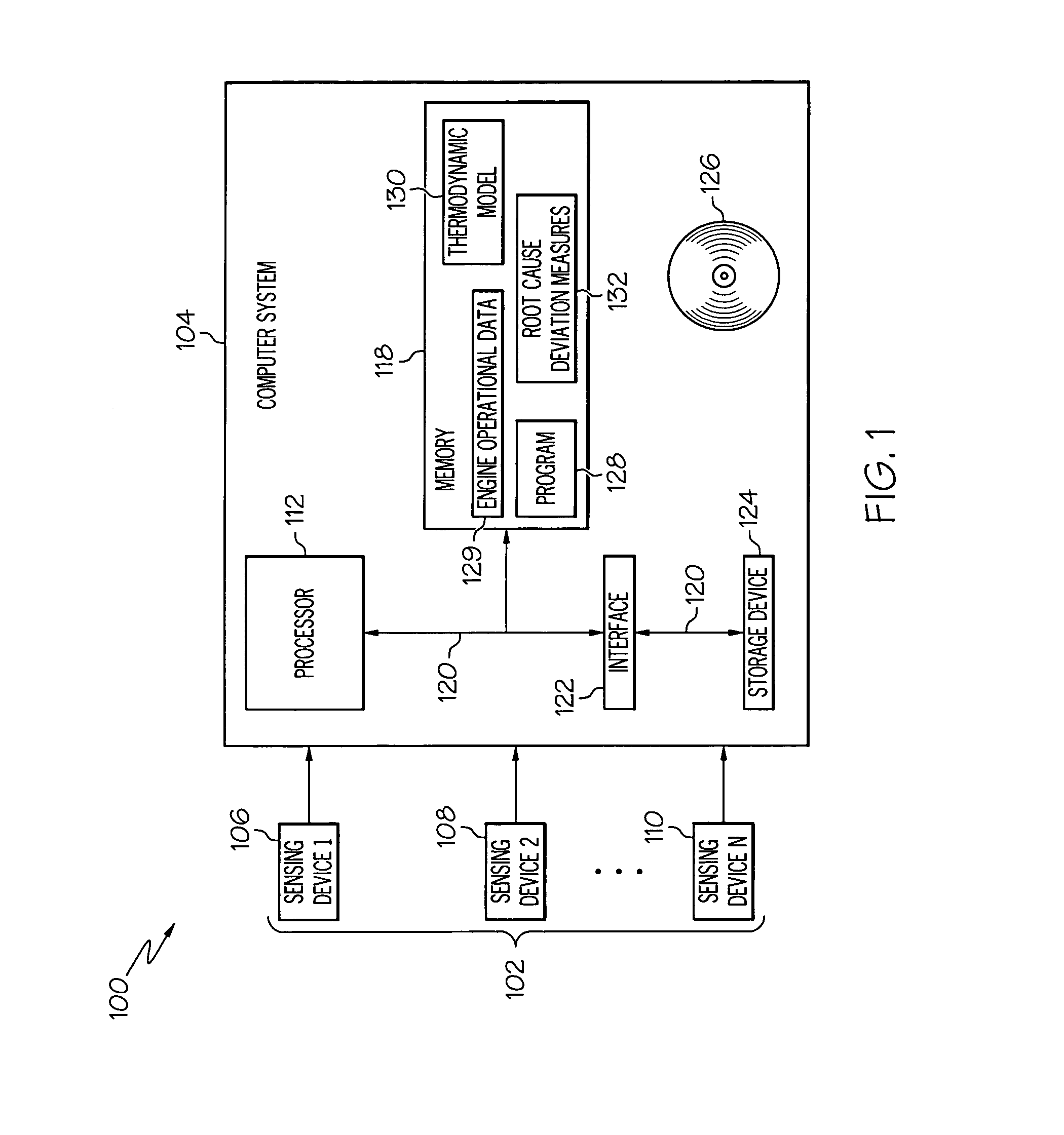
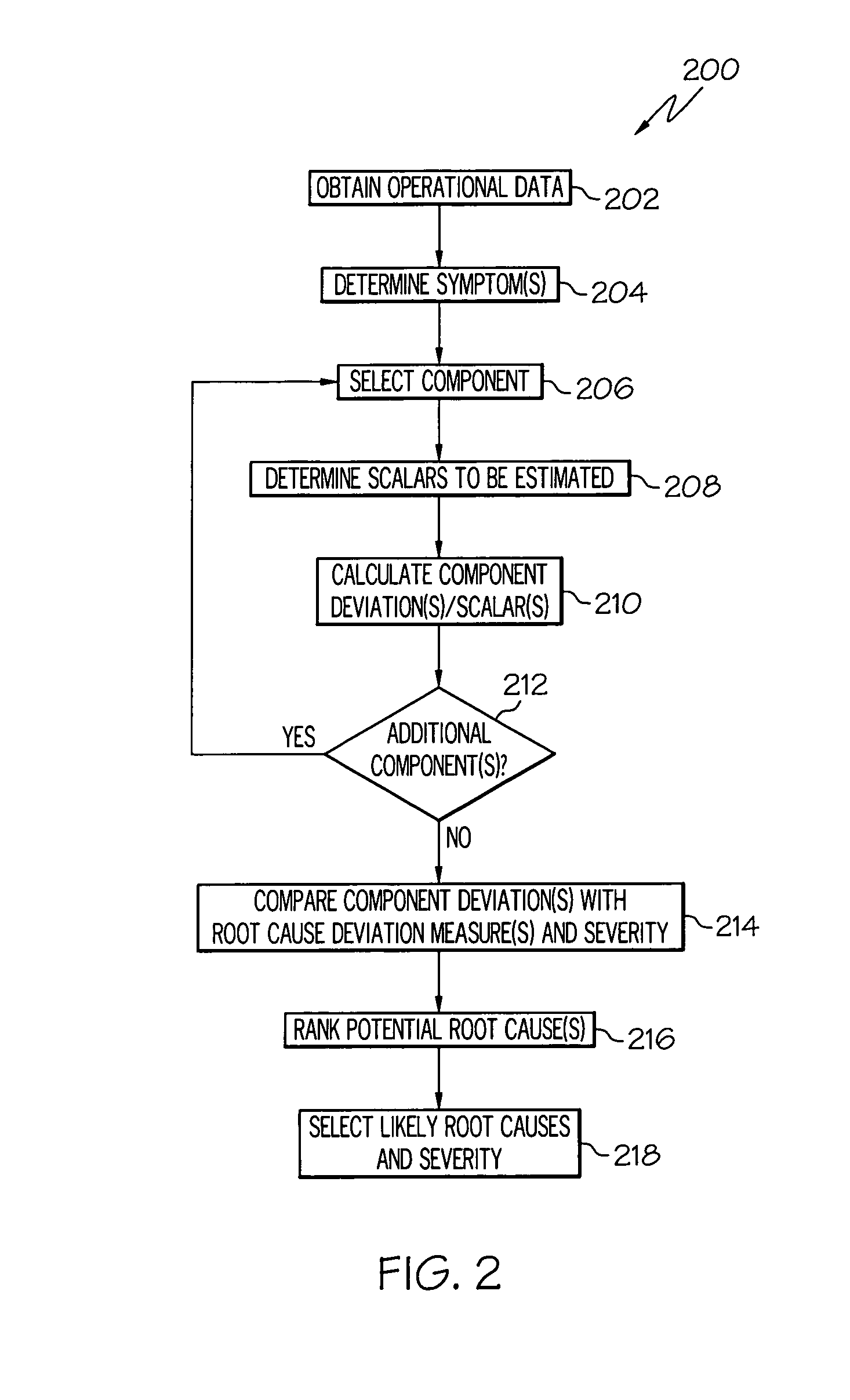
Methods and systems for performing diagnostics regarding underlying root causes in turbine engines
ActiveUS8090559B2Testing/monitoring control systemsAnalogue processes for specific applicationsEngineeringRoot cause
A method for performing diagnostics for an engine comprises the steps of identifying an engine component as potentially being related to operational data of an engine, calculating a deviation from a thermodynamic model, and comparing the deviation with root cause deviation measures. The deviation relates the engine component to an adjustment to the thermodynamic model with respect to a variable of the thermodynamic model, based at least in part on the operational data. Each root cause deviation measure relates one of a plurality of potential root causes to the thermodynamic model with respect to the variable of the thermodynamic model.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Method and apparatus for optimizing refrigeration systems
A refrigeration system comprising a compressor for compressing a refrigerant, a condenser for condensing refrigerant to a liquid, an evaporator for evaporating liquid refrigerant from the condenser to a gas, an inner control loop for optimizing a supply of liquid refrigerant to the evaporator, and an outer control loop for optimizing a level of refrigerant in the evaporator, said outer control loop defining a supply rate for said inner control loop based on an optimization including measurement of evaporator performance, and said inner control loop optimizing liquid refrigerant supply based on said defined supply rate. Independent variables, such as proportion of oil in refrigerant, amount of refrigerant, contaminants, non-condensibles, scale and other deposits on heat transfer surfaces, may be estimated or measured. A model of the system and / or a thermodynamic model approximating the system, for example derived from temperature and pressure gages, as well as power computations or measurements, is employed to determine or estimate the effect on efficiency of deviance from an optimal state. Various methods are provided for returning the system to an optimal state, and for calculating a cost-effectiveness of employing such processes.
Owner:HUDSON TECHNOLOGIES
Sensor for measuring temperature and/or concentration
InactiveUS6341890B1Low costImprove reliabilityThermometer detailsSensing radiation from gases/flamesAviationPhotovoltaic detectors
A sensor used to measure temperature or concentration of a combustible gas. The sensor includes an optical head that picks up infrared information emitted by the combustible gas. The infrared information is conveyed from the optical sensor through a diffracting device onto a strip of photodetectors. A processor receives the information garnered by the photodetectors and determines the concentration and temperature profile of the combustible gas based on a stored thermodynamic model, radiation behavior, varying the thermodynamic parameters, and comparing a calculated spectrum with the measured spectrum. The sensor additionally has elements, such as cooling devices and casing to make it suitable for use with aviation where altitude creates problems with known methods of gas temperature analysis.
Owner:AUXITROL
Commercial building HVAC control method based on multi-agent deep reinforcement learning
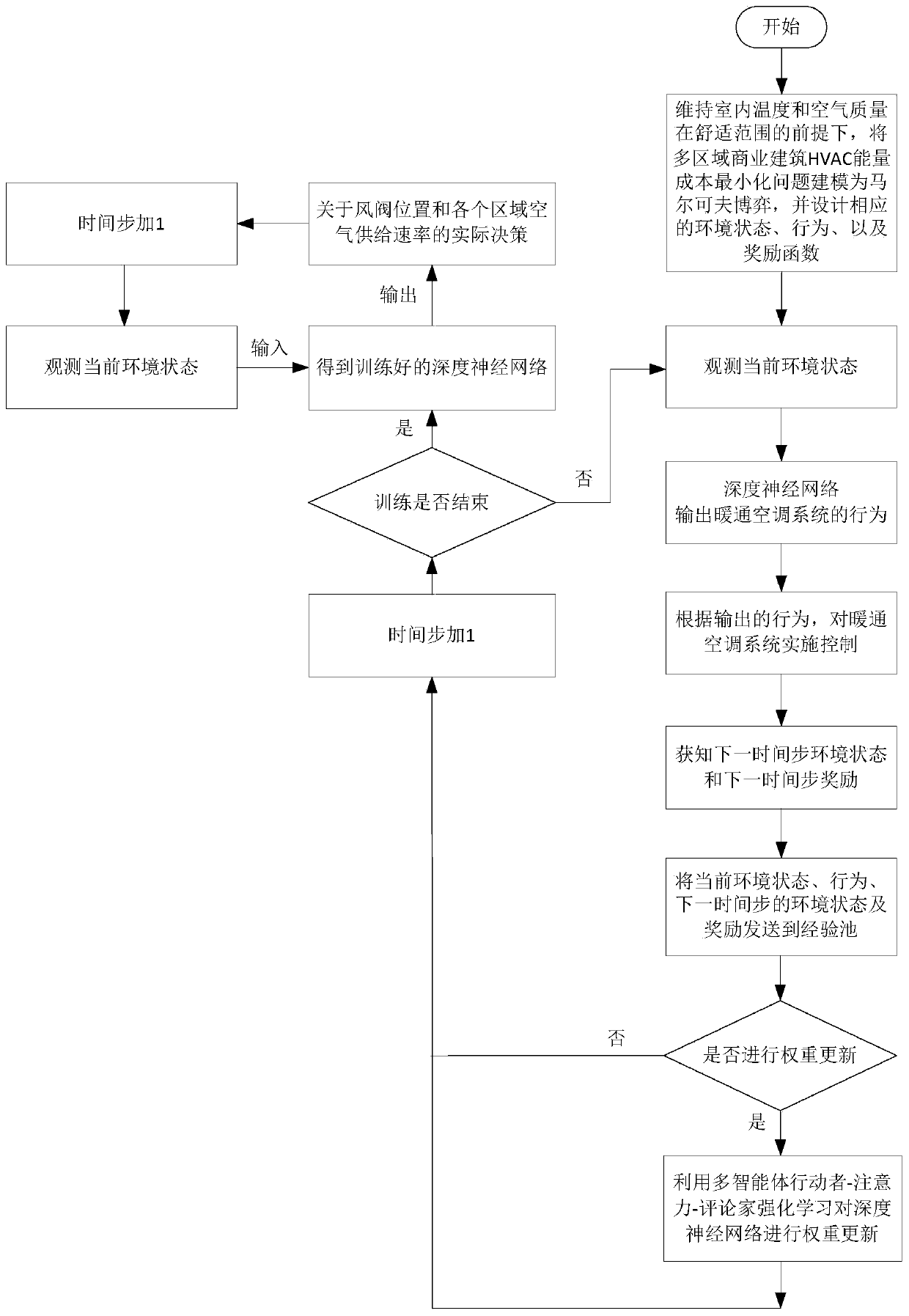
ActiveCN111144793AWide applicabilityImprove scalabilityResourcesNeural learning methodsControl engineeringReinforcement learning algorithm
The invention discloses a commercial building HVAC control method based on multi-agent deep reinforcement learning. The method comprises the following steps: (1) on the premise of maintaining indoor temperature and air quality in a comfortable range, modeling a multi-region commercial building HVAC energy cost minimization problem into a Markov game, and designing a corresponding environment state, behavior and award function; (2) training a deep neural network by using a multi-agent actor-attention-reviewer reinforcement learning algorithm; and (3) in practical application, obtaining decisions about the position of an HVAC air valve and the air supply rate of each region according to the trained deep neural network and new environment state input. Compared with an existing method, the method provided by the invention does not need to know any priori information of a building thermodynamic model and uncertainty parameters, and has greater energy cost saving potential and higher expandability.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
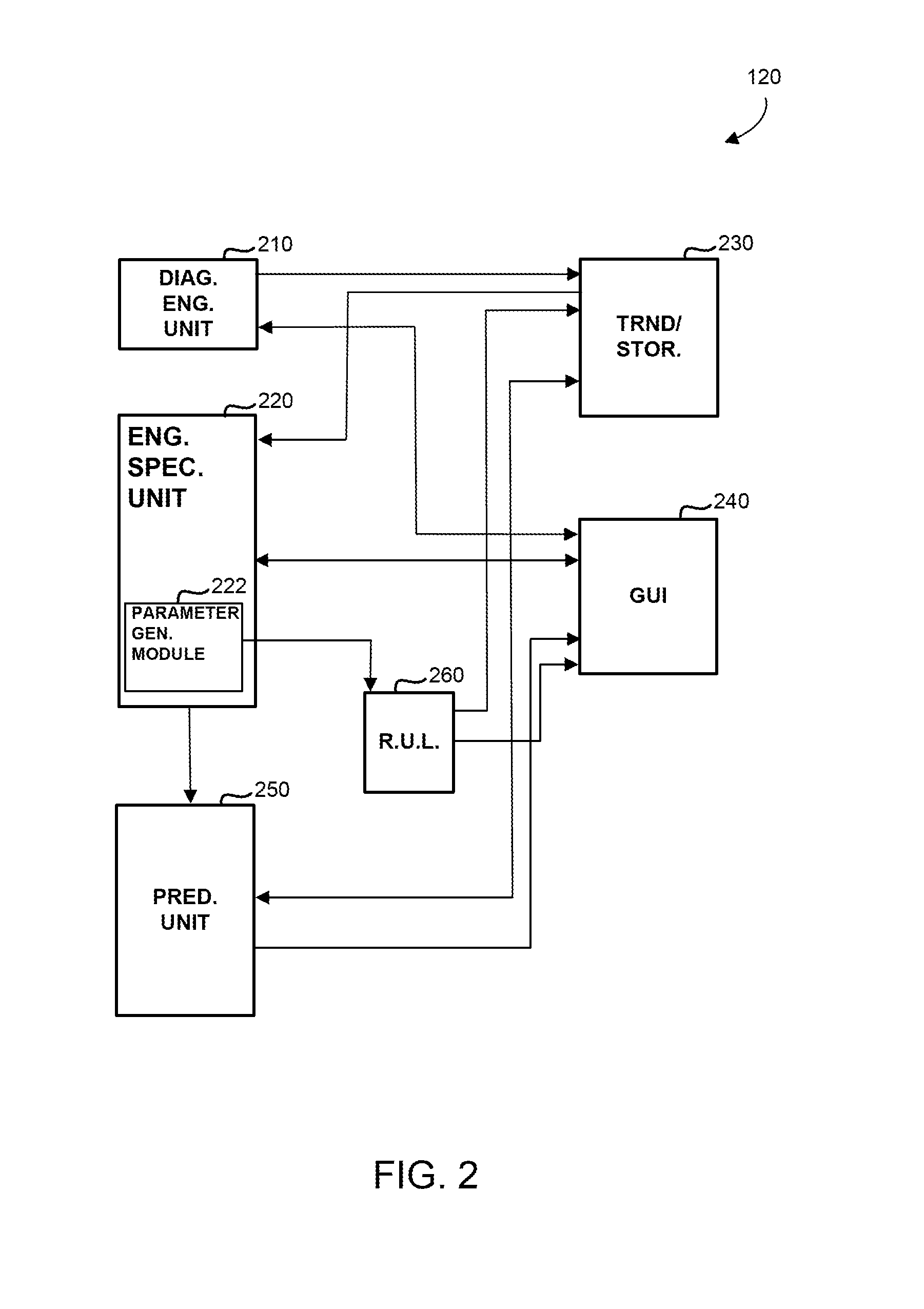
Operations support systems and methods for calculating and evaluating turbine temperatures and health
ActiveUS20140163838A1Analogue computers for vehiclesDigital data processing detailsDiagnostic dataSpecific model
An operations support system is provided for an engine with a turbine having a turbine inlet. The system includes a diagnostic engine model unit configured to receive engine data from the engine and to generate diagnostics data based on the engine data, the diagnostics data including scalars. The system further includes an engine-specific model unit coupled to the diagnostic engine model unit and configured to receive the scalars from the diagnostic engine model unit and configured to generate turbine inlet temperature information for the engine using a thermodynamic model. The thermodynamic model is based on component maps associated with the engine. The system further includes a storage unit coupled to the engine-specific model unit and configured to store the turbine inlet temperature information.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Active lean NOx catalyst diagnostics
InactiveUS6990854B2Improved system diagnosticsIncreases magnitudeElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesHydrogen compoundsHydrocarbon
An accurate thermodynamic model of an Active Lean NOx (ALNC) Catalyst is presented. The model takes into account hydrocarbon storage and release mechanisms of the ALNC, as well as the degradation in the ALNC hydrocarbon conversion efficiency due to ageing, and thus provides a more accurate estimate of an exotherm generated by hydrocarbon combustion in the ALNC. The estimated exotherm can them be used to detect system degradation and identify components responsible for the degradation.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Experimental method of organic acid generation and erosion effect of organic acid on tight oil reservoir
InactiveCN104390881ARealize quantitative evaluationWeighing by removing componentWeather/light/corrosion resistanceClay mineralsDynamic models
The invention discloses an experimental method of organic acid generation and an erosion effect of the organic acid on a tight oil reservoir. The experimental contents include (1) a hot simulation experiment for proportioning kerogen and a clay mineral to form a sample and generating an organic acid; (2) a hot simulation experiment for generating the organic acid by virtue of thermal evolution of shale; (3) a hot simulation experiment for the erosion effect of the organic acid on tight sandstone and monomineral; and (4) a hot simulation experiment for artificially proportioning the sample. The mechanism and influence factors of the development of the tight reservoir, especially erosion pores of the shale reservoir can be clarified by analyzing the experimental data, and a dynamics model of the organic acid generation and a thermodynamic model of the decarboxylation and erosion reaction of the organic acid can be established; the geological application can be realized by combining the models with the sedimentary and burial history, thermal history and mineral association characteristics of the reservoir in a research area, the development situation of a secondary erosion pore in different geologic periods can be quantitatively evaluated, and a foundation can be set for predicting a tight oil exploration sweet spot area.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
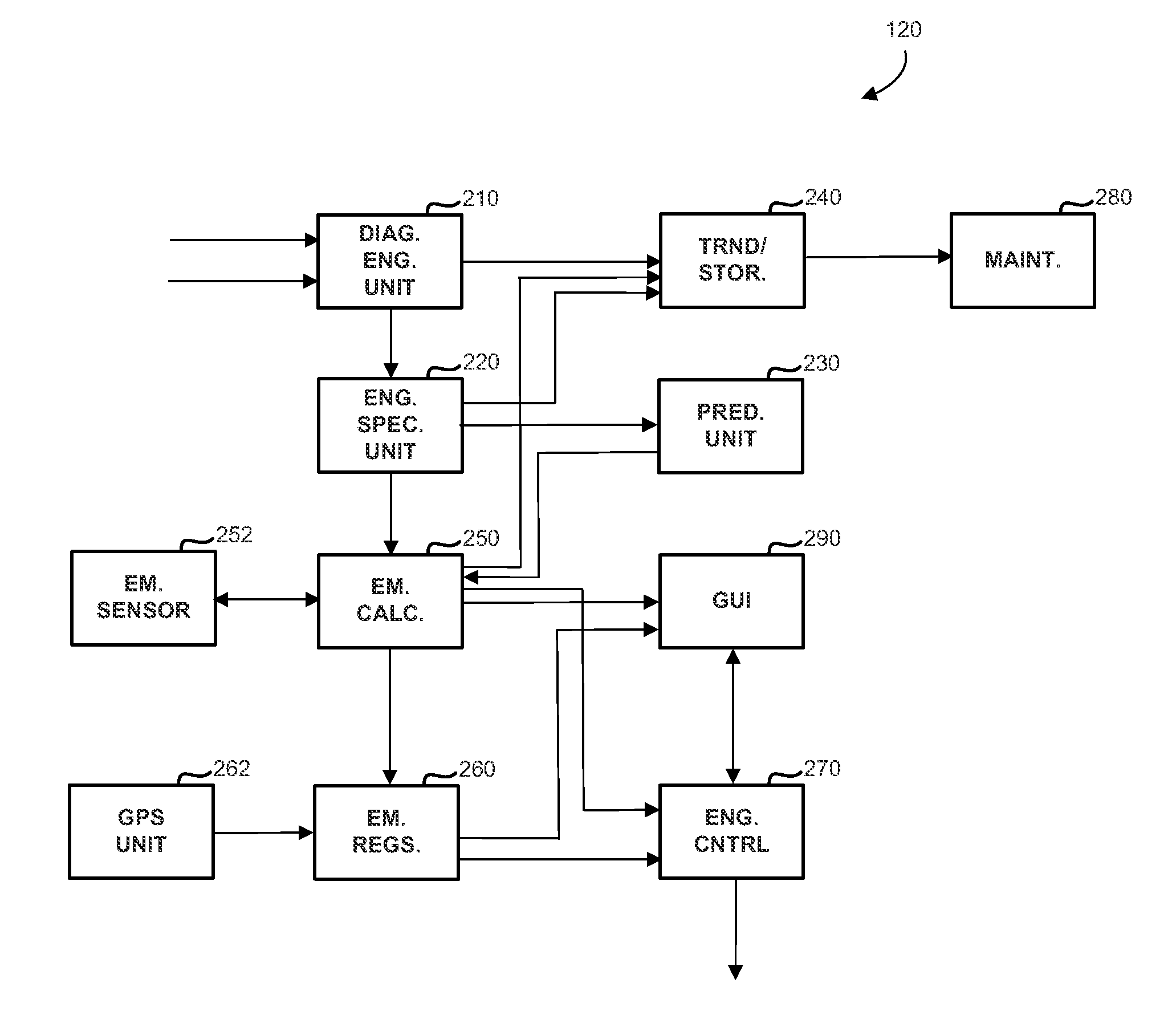
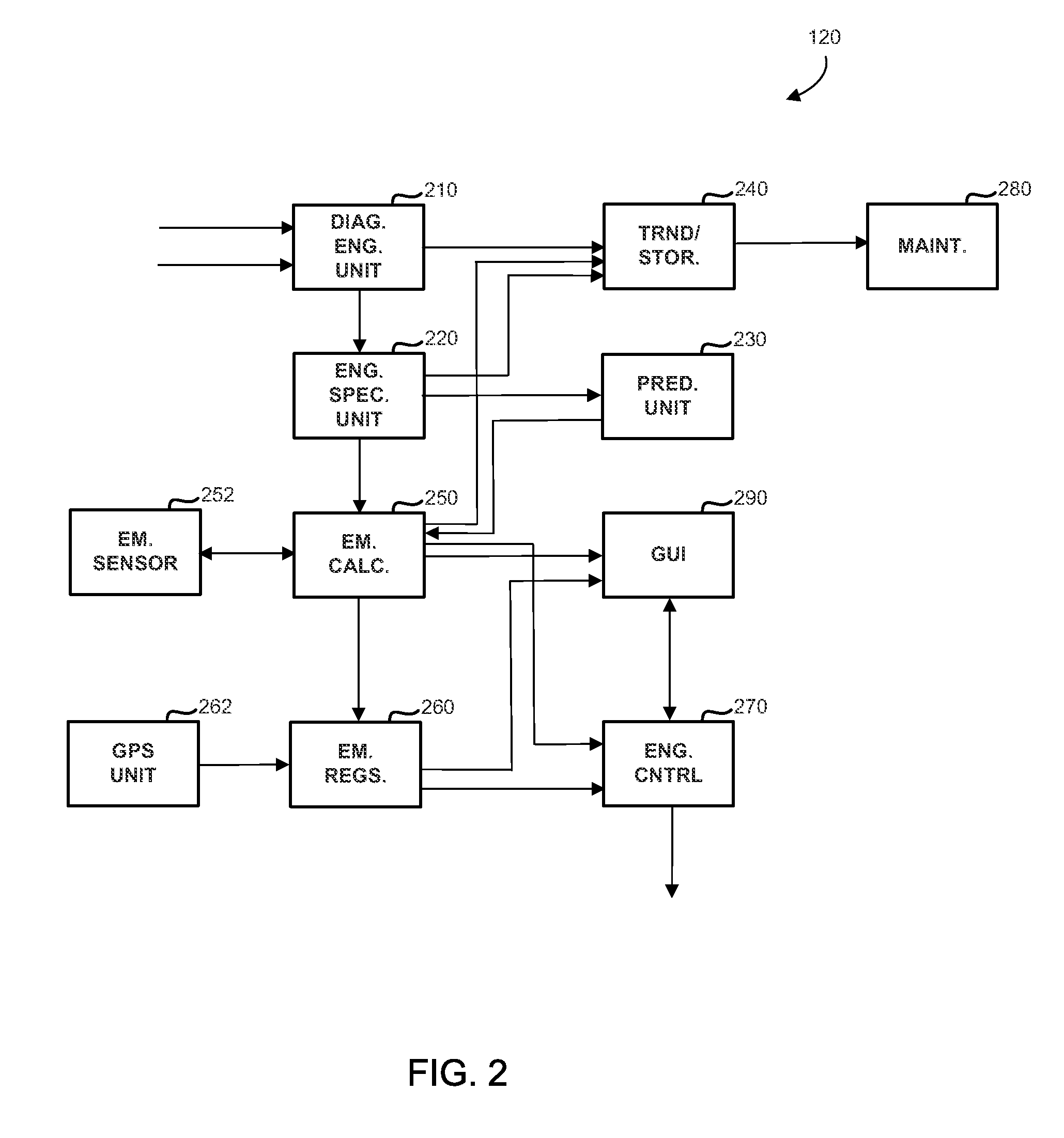
Operations support systems and methods for calculating and evaluating engine emissions
ActiveUS20130158832A1Improve engine operationReduce complianceInternal-combustion engine testingAnalogue computers for vehiclesGraphicsGraphical user interface
In accordance with an exemplary embodiment, an operations support system for an engine is provided. A diagnostics unit is configured to receive engine data from the engine and to generate condition indicators based on the engine data using a thermodynamic model, the thermodynamic model being based on component maps associated with the engine. An emissions calculation unit is coupled to the diagnostic unit and configured to calculate emissions information for the engine based on the condition indicators. A graphical user interface is coupled to the emissions calculation unit and configured to display the emissions information.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
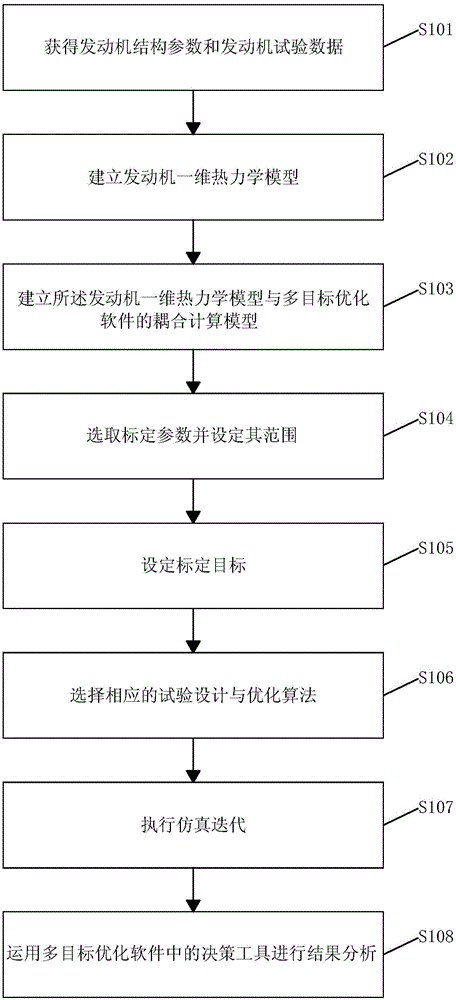
Engine thermodynamic simulation model calibration method based on multi-objective optimization
InactiveCN104951628AQuick calibrationImprove development efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsTest designThermodynamic simulation
The invention discloses an engine thermodynamic simulation model calibration method based on multi-objective optimization. The method comprises steps as follows: S101, acquiring engine structure parameters and engine test data; S102, establishing a one-dimensional engine thermodynamic model; S103, establishing a coupling calculation model of the one-dimensional engine thermodynamic model and multi-objective optimization software; S104, selecting calibration parameters and setting ranges of the calibration parameters; S105, setting a calibration objective; S106, selecting a corresponding test design and optimization algorithm; S107, executing simulation iteration; S108, performing result analysis by using decision-making tools in the multi-objective optimization software. The method is based on computer simulation analysis, a multi-objective optimization algorithm and a numerical simulation technique are combined, automation of the calibration process is realized, accurate models can be calibrated quickly, the follow-up engine development is supported, the development efficiency is improved, the development cost is saved, and the development cycle is shortened.
Owner:WUXI WOERFU AUTO TECH CO LTD
Solar heat pump hot water system control strategy optimization method based on machine learning
ActiveCN110906571AAvoid insufficient heatingAvoid wastingSolar heating energyFluid heatersProcess engineeringSupervised learning
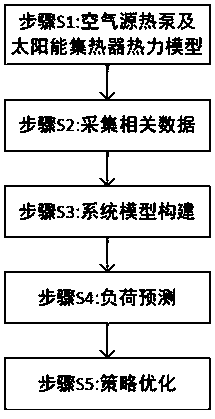
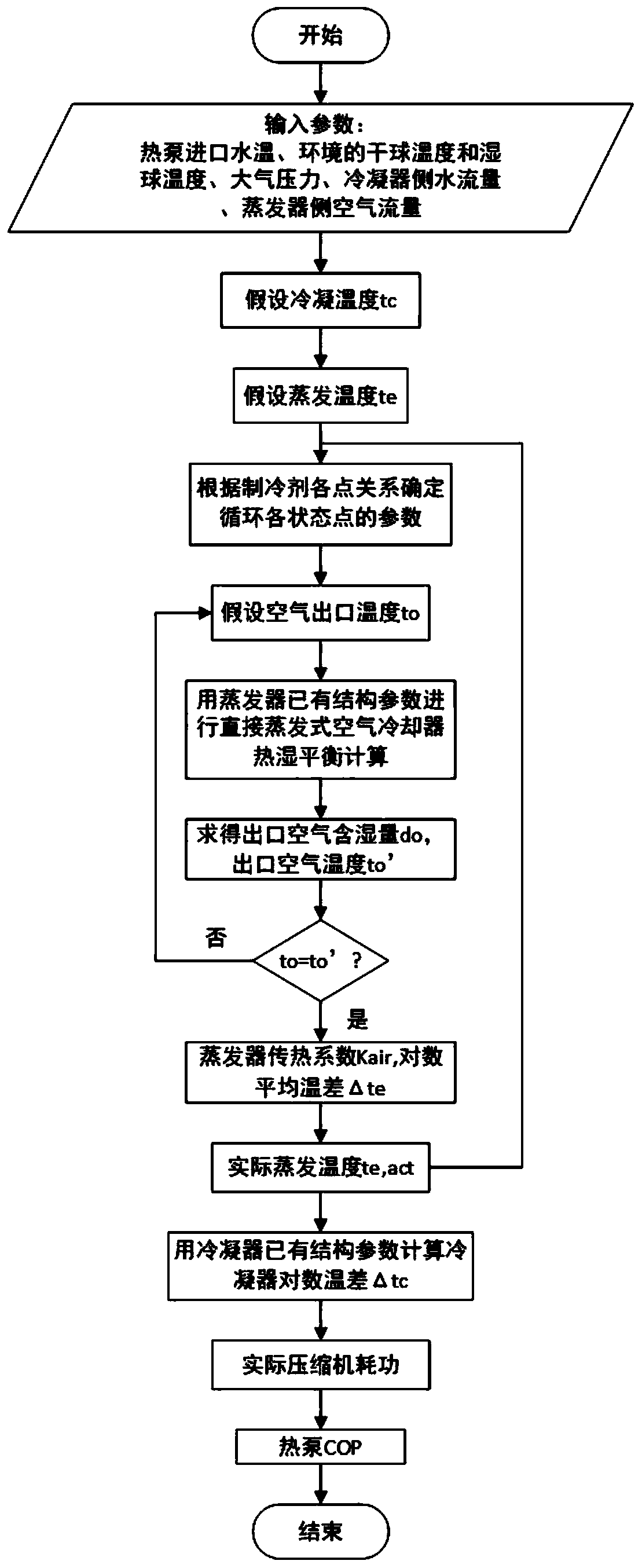
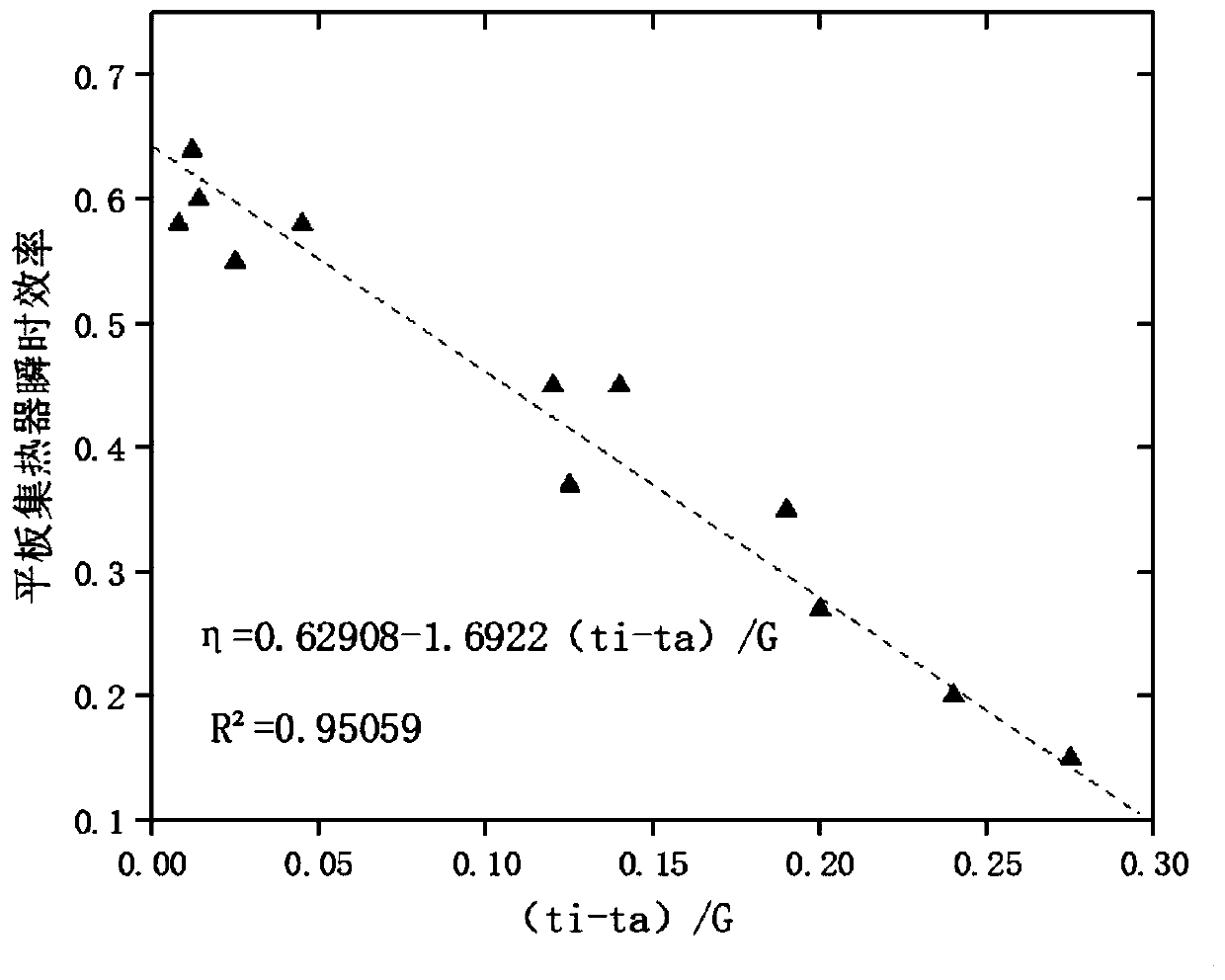
The invention discloses a solar heat pump hot water system control strategy optimization method based on machine learning. The method includes the steps that an air source heat pump thermal model anda solar collector thermal model are constructed; related data are collected; a hot water system model is constructed; load prediction is conducted; and strategy optimization is conducted. According tothe solar heat pump hot water system control strategy optimization method, a thermodynamic model of a system is constructed, an input-output relationship of a heat collection process of an air sourceheat pump and a solar collector is established, a KNN(K-Nearest Neighbor) supervised learning algorithm in machine learning is utilized to realize hourly prediction of a hot water load, a predicted value is used as a demand load value, the established thermal models are utilized to analyze an optimal control strategy and the energy saving rate of the system, thus a theoretical basis is provided for engineers, and it is ensured that the hot water system operates more stably and energy-efficiently.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
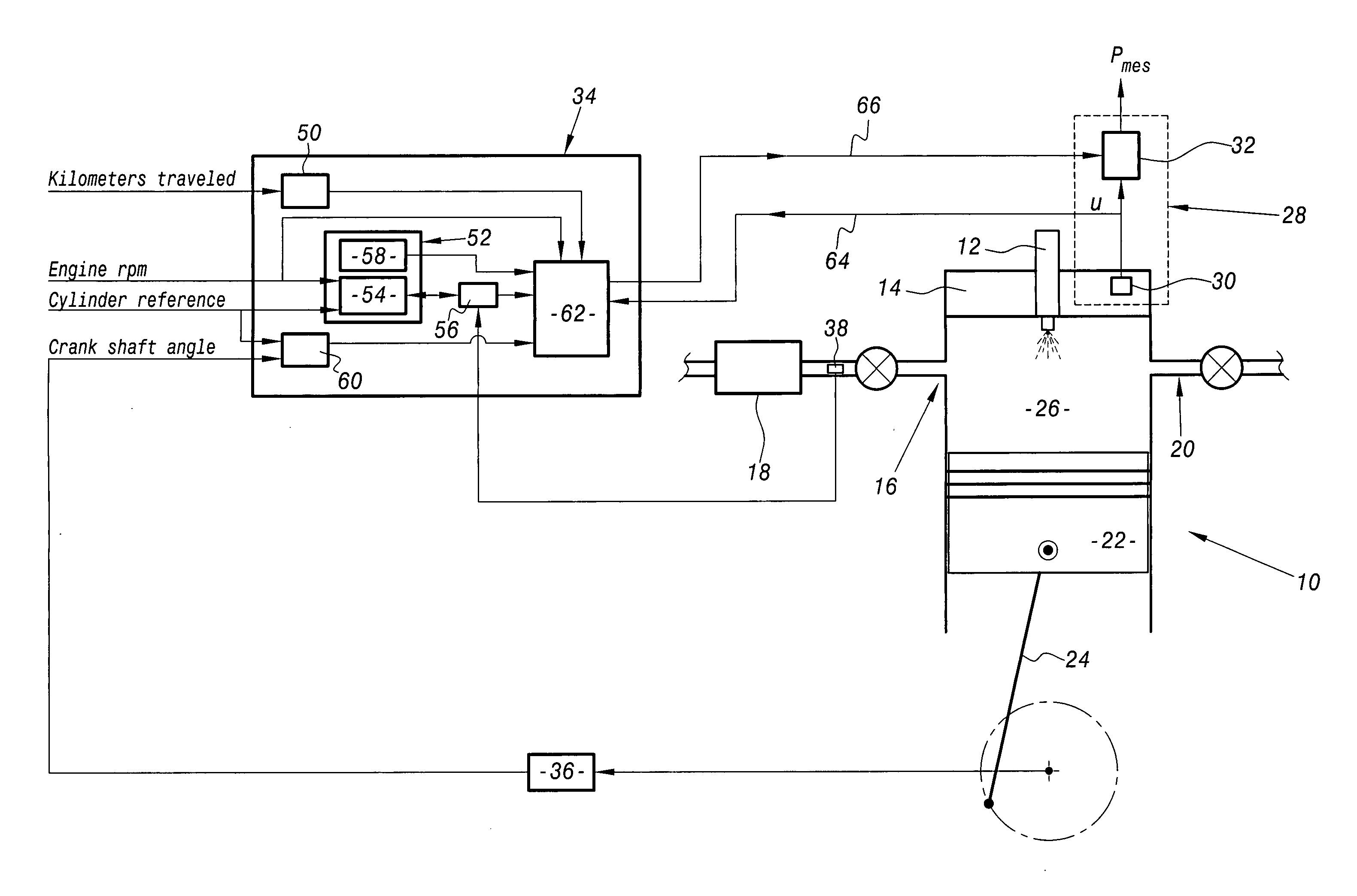
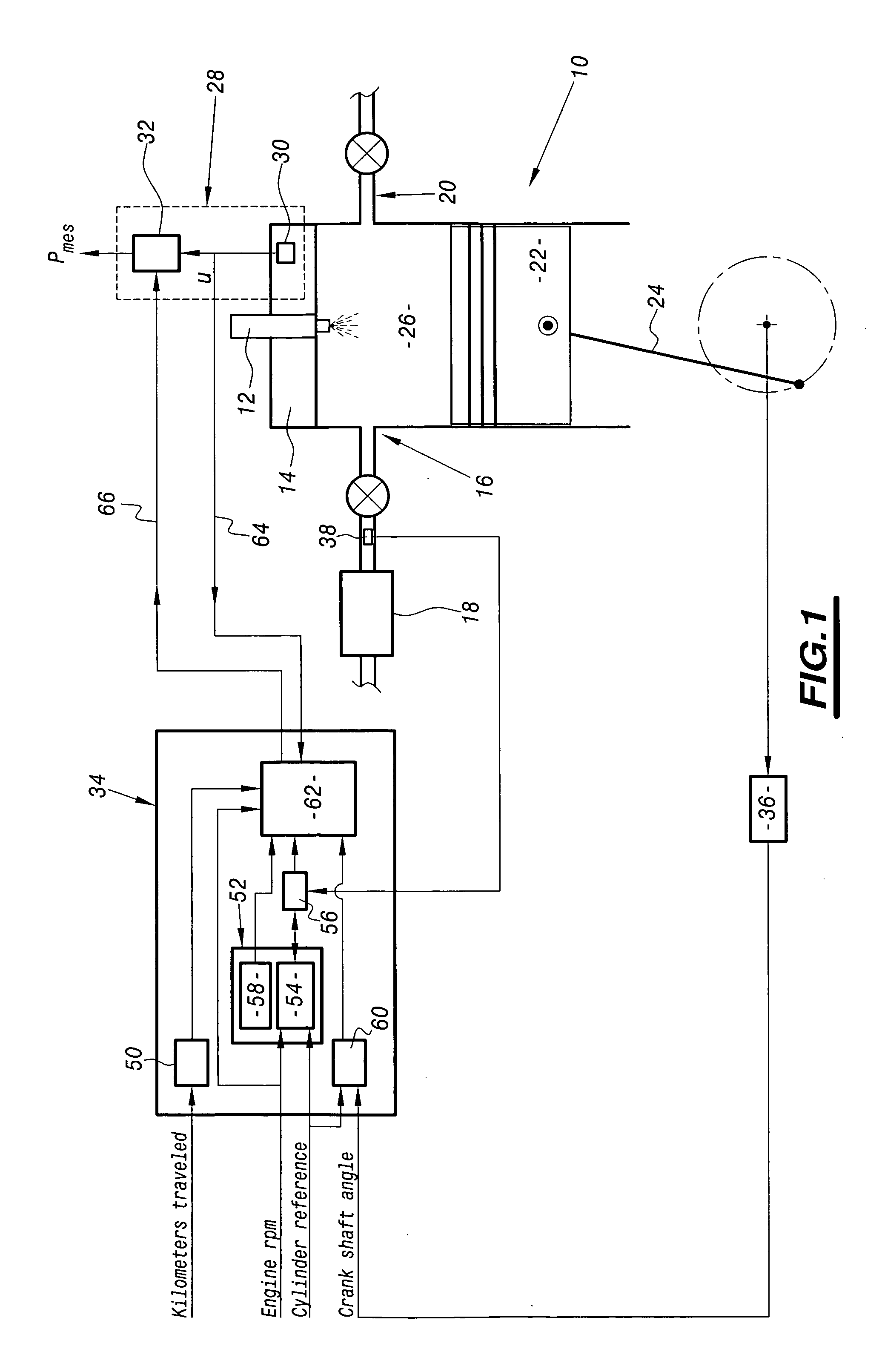
System for calibrating apparatus for acquiring the pressure in a motor vehicle diesel engine cylinder
InactiveUS20050125140A1Analogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlInformation processingAcquisition apparatus
The invention relates to a system for calibrating apparatus (28) for acquiring the pressure in a cylinder (10) of a motor vehicle diesel engine, of the type comprising a cylinder pressure sensor (30) associated with the cylinder and means (32) for conditioning the signal delivered by the sensor (30) as a function of conditioning parameters. The calibration system comprises means (64) for collecting a signal delivered by the cylinder pressure sensor (30), an information processing unit (34) adapted to determine the values of the conditioning parameters as a function of a polytropic thermodynamic model of the evolution of the pressure in the cylinder, a reference pressure of the pure compression phase of the cycle of the cylinder, and the signal delivered by the pressure sensor (30) and collected by the collecting means (64), and means (66) for modifying the values of the conditioning parameters in the acquisition apparatus (28) as a function of the values of the conditioning parameters determined by the information processing unit (34).
Owner:PEZHO SITROEN AUTOMOBILS SA +1
Generating and implementing thermodynamic models of a structure
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
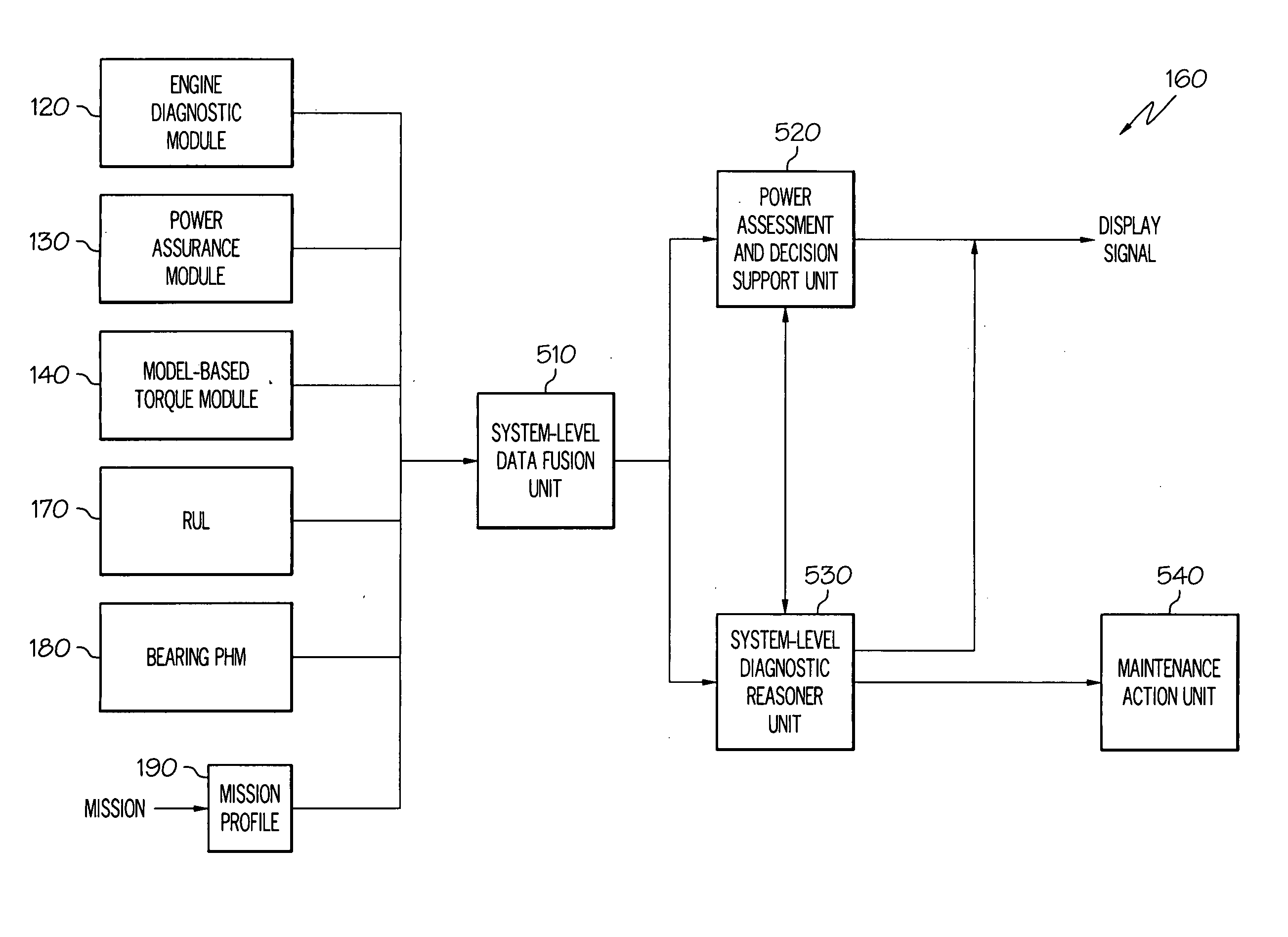
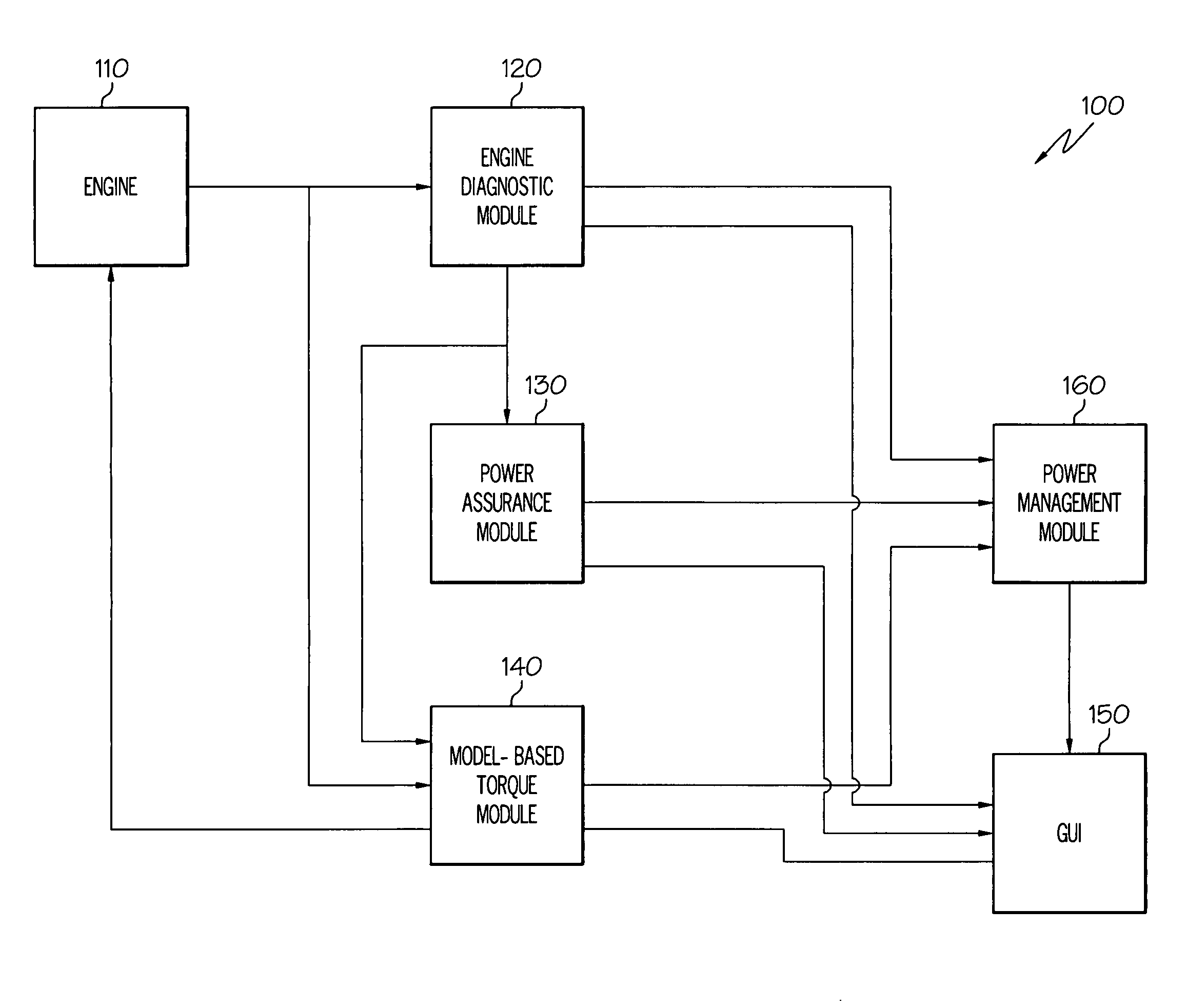
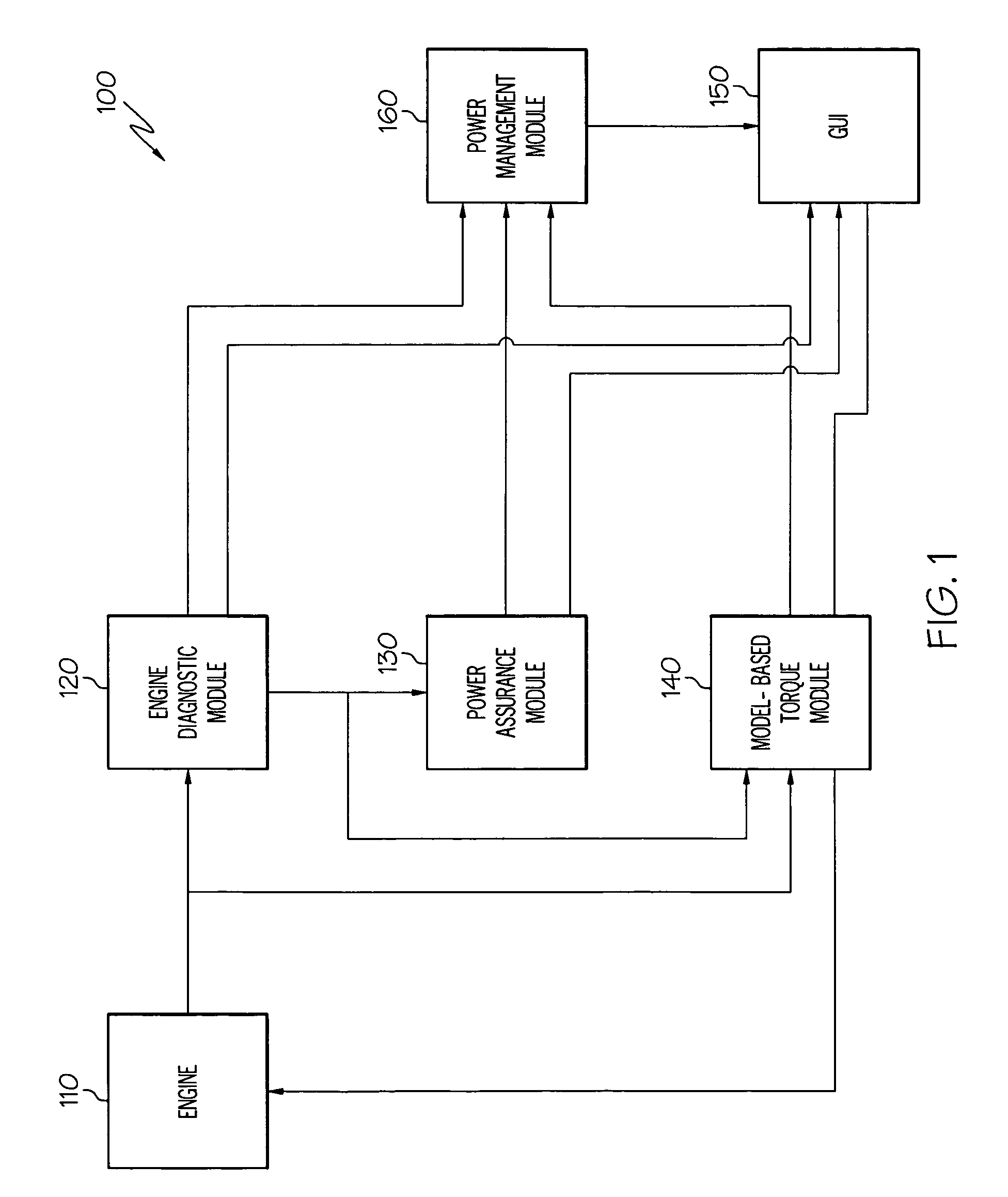
Operations support systems and methods with model-based torque estimates
ActiveUS7801695B2Testing/calibration apparatusDigital data processing detailsEngineeringOperations support system
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Modeling method for heterogeneous azeotropic rectification solvent dehydrating tower of industrial purified terephthalic acid (PTA) device
ActiveCN101986320AAvoid blind operationReduce optimization costsSpecial data processing applicationsCarboxylic compound separation/purificationVapor liquidProcess mechanism
The invention relates to a modeling method for a heterogeneous azeotropic rectification solvent dehydrating tower of an industrial purified terephthalic acid (PTA) device. In the method, the vapor-liquid balance experimental data of an acetic acid, n-propyl acetate, water, p-xylene and methyl acetate quinary mixture system are associated and fitted with the binary interaction parameters of the quinary mixture system according to a thermodynamic property model; and according to the process data of the solvent dehydrating tower under the actual device design condition, a heterogeneous azeotropic rectification solvent dehydrating tower model of the industrial PTA device under the design condition is established, the accuracies of the thermodynamic model and parameters thereof of the quinary mixture system in a laboratory and a rectification tower mathematical steady model are verified, key parameters representing the separating property of the solvent dehydrating tower under the actual condition are acquired, the model is corrected and a process mechanism steady model capable of accurately describing the operating characteristics of the solvent dehydrating tower under the actual condition is established.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
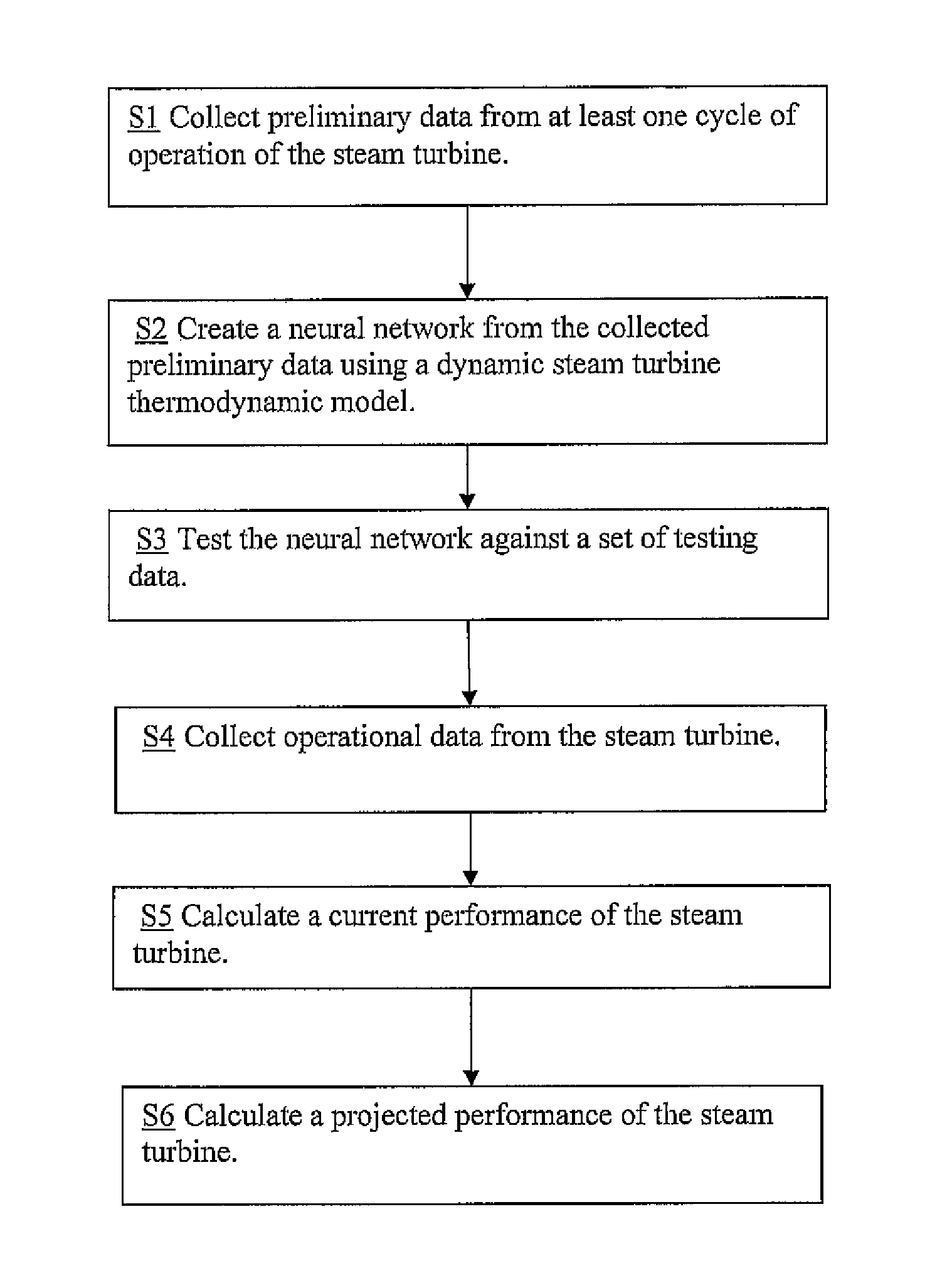
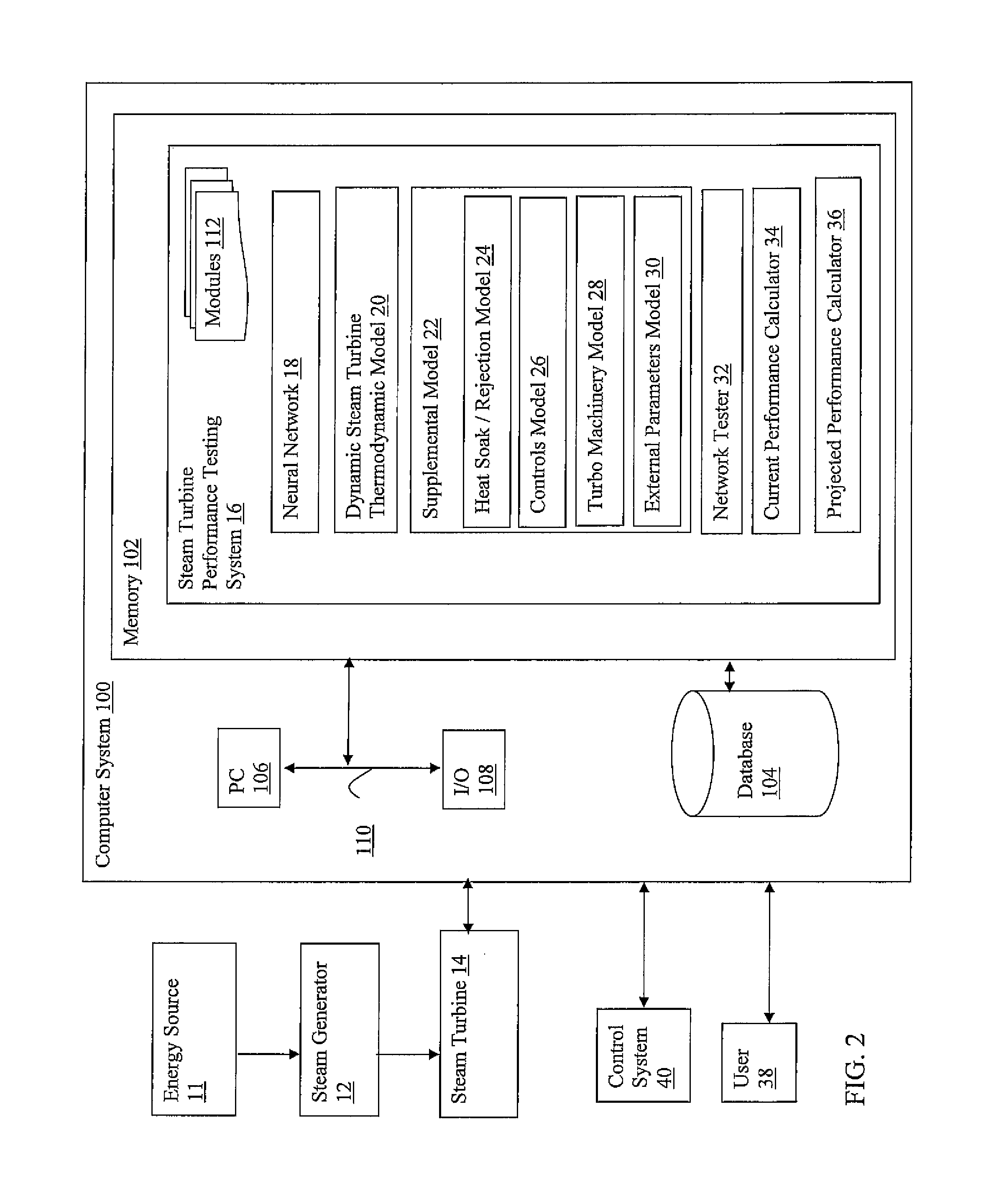
Steam turbine performance testing
A steam turbine performance testing system, including at least one computer hardware device, including a neural network created using a dynamic steam turbine thermodynamic model and preliminary data collected from a steam turbine; a network tester for testing the neural network with testing data; a current performance calculator for calculating a current performance of the steam turbine from operation data of the steam turbine; and a projected performance calculator for calculating a projected performance of the steam turbine from the current performance.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for motor vehicle interior climate control
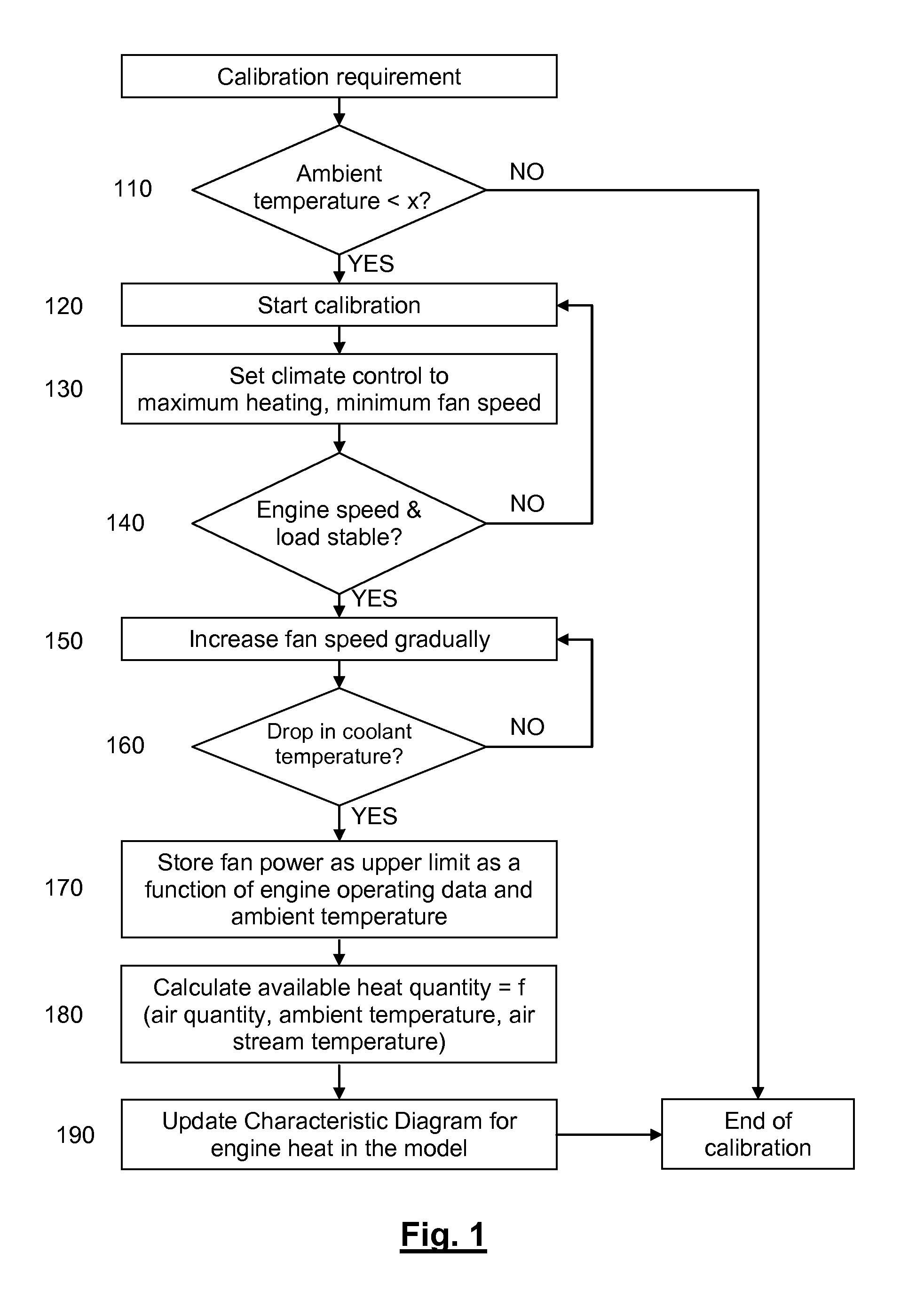
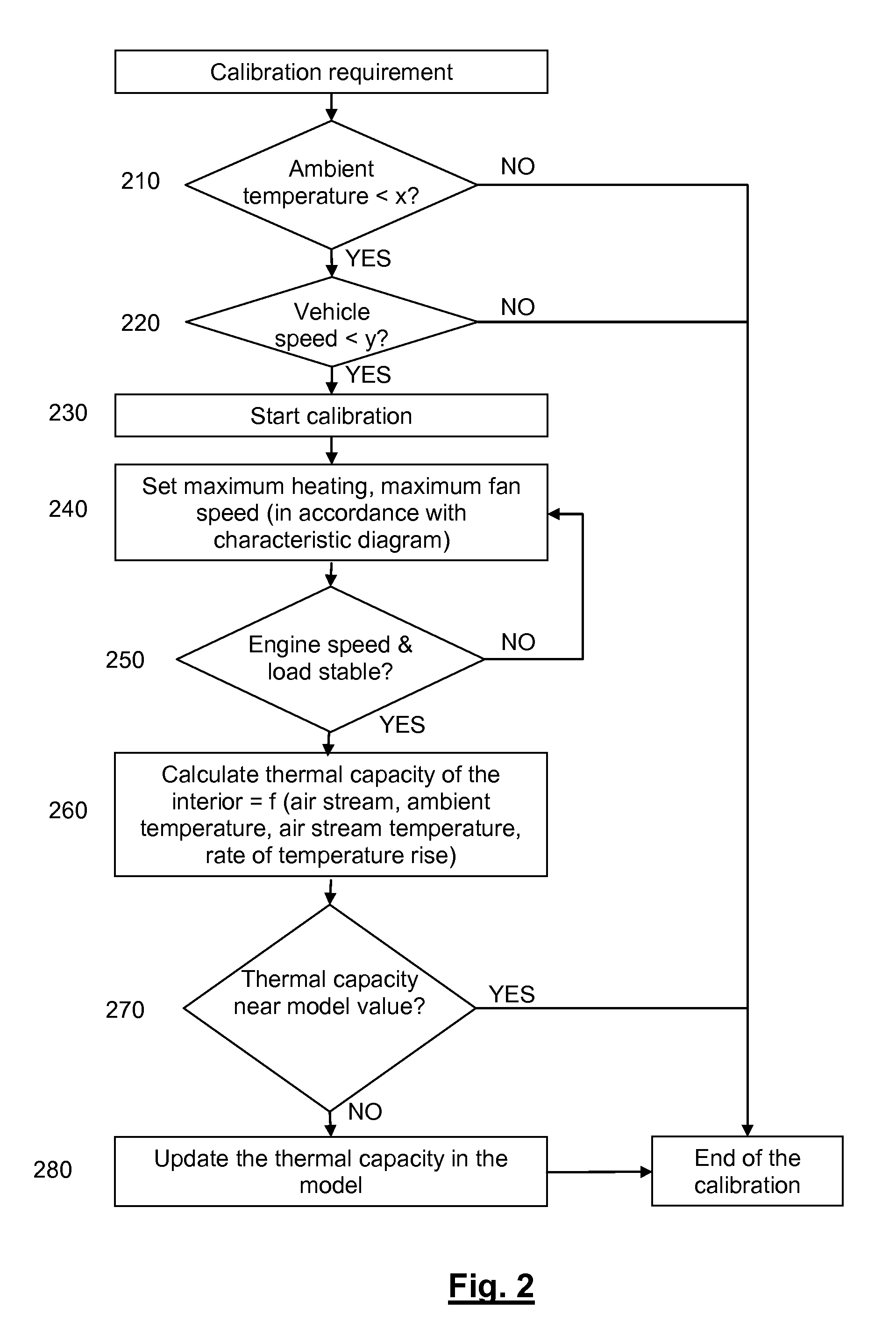
ActiveUS20110166711A1Easy temperature controlAvoid substantial outlaySampled-variable control systemsAir-treating devicesMobile vehicleEngineering
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com