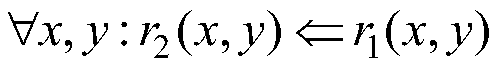Patents
Literature
272 results about "Energy equation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
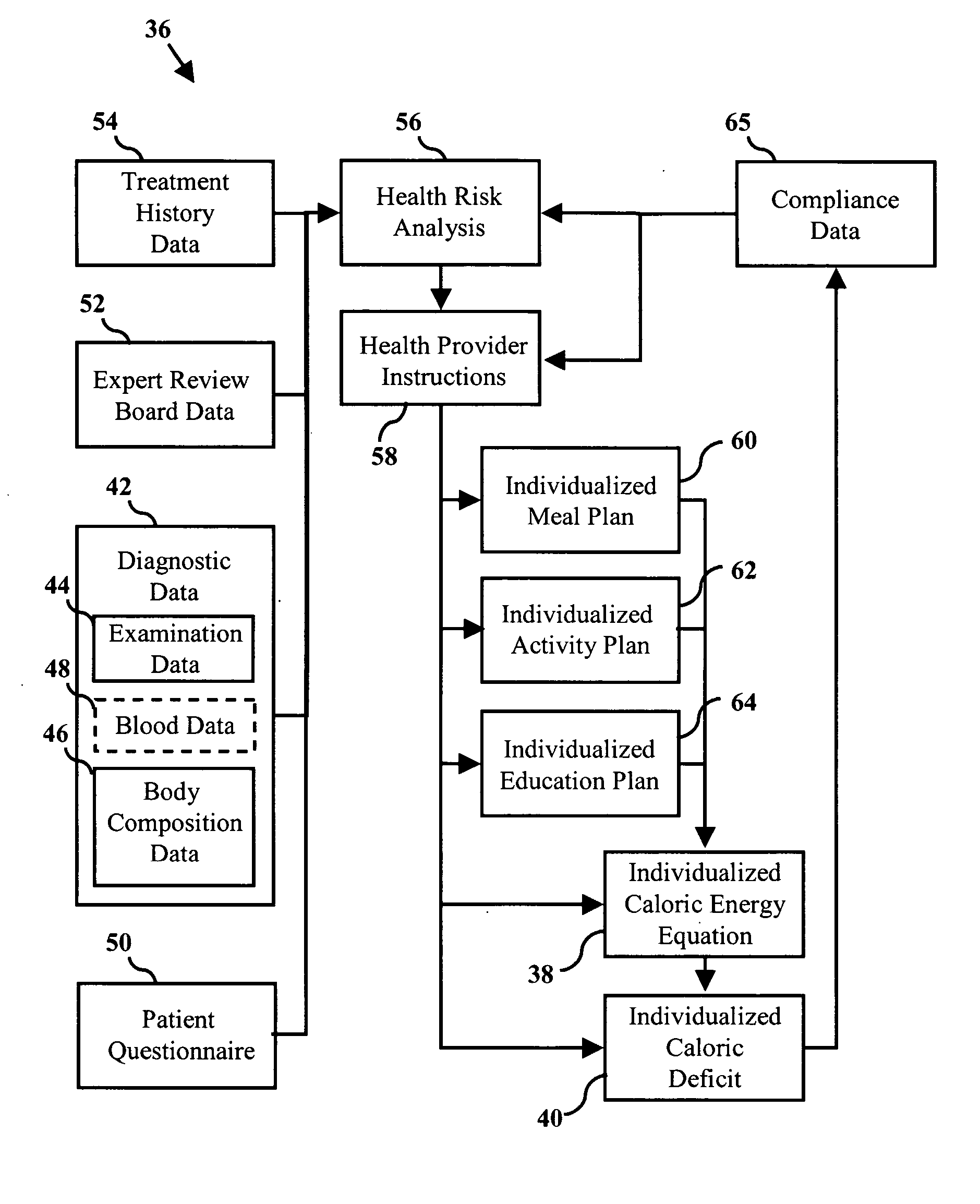
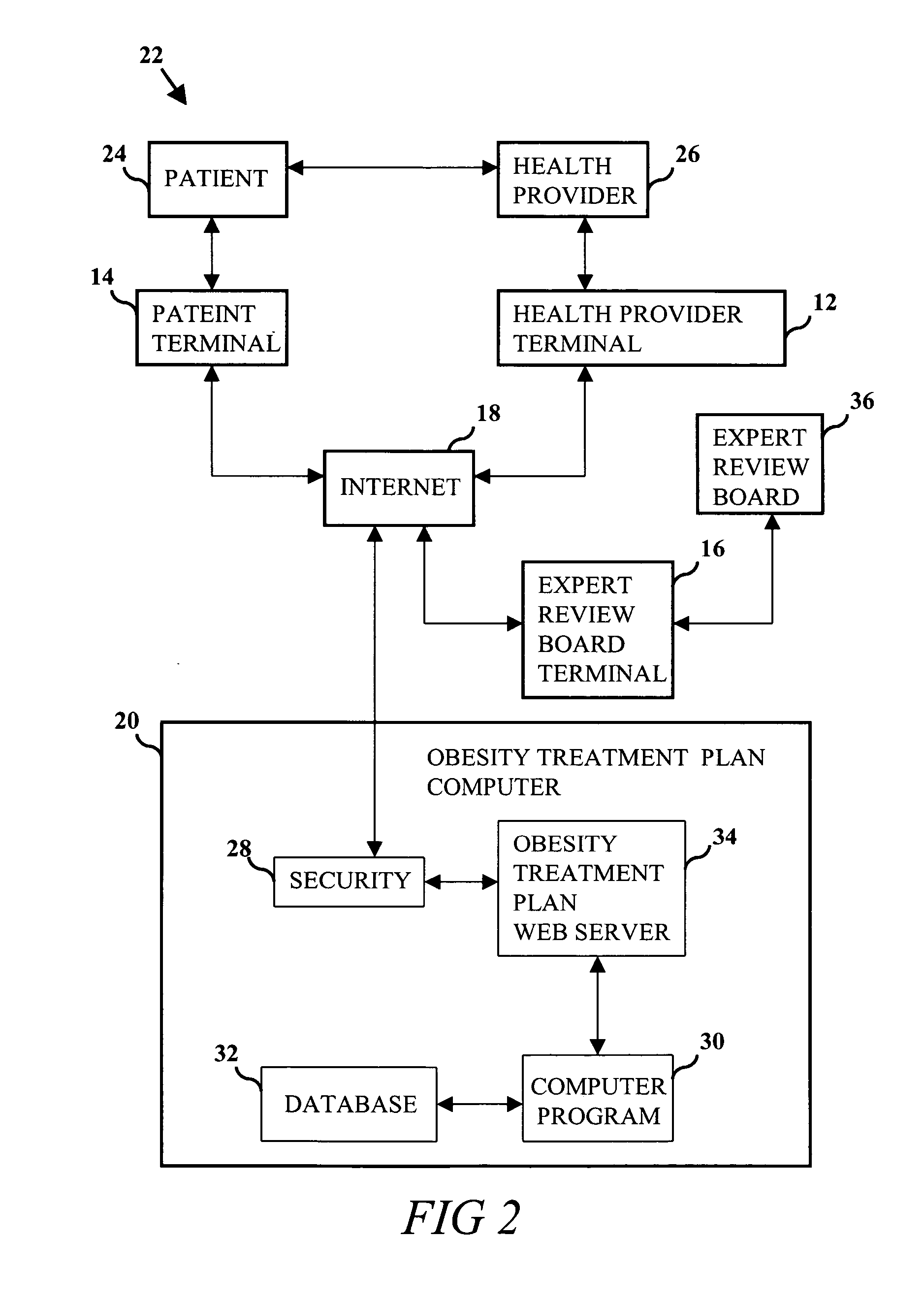
System and method of individualized mass diagnosis and treatment of obesity
InactiveUS20050240444A1Medical communicationPhysical therapies and activitiesPatient compliancePatient data
An individualized system and method of mass diagnosis and treatment of obesity that is optionally configurable for a plurality of patients and health providers. Computer and relational data storage systems are used for operating a computer program and a secure web site on an internet. User profiles are assigned for accessing the secure web site using a plurality of computer terminals. Patient data and information are gathered for use in a health risk analysis to determine values for variables in a caloric energy equation. An individualized health provider web page is used to administer a meal plan, an exercise plan and an education plan to influence variables in the caloric energy equation to derive an individualized caloric energy deficit and a starvation response threshold in the patient. Patient compliance information is gathered for use in the health risk analysis and for correlation with the stored data to re-derive the variables.
Owner:HEALTHPORT
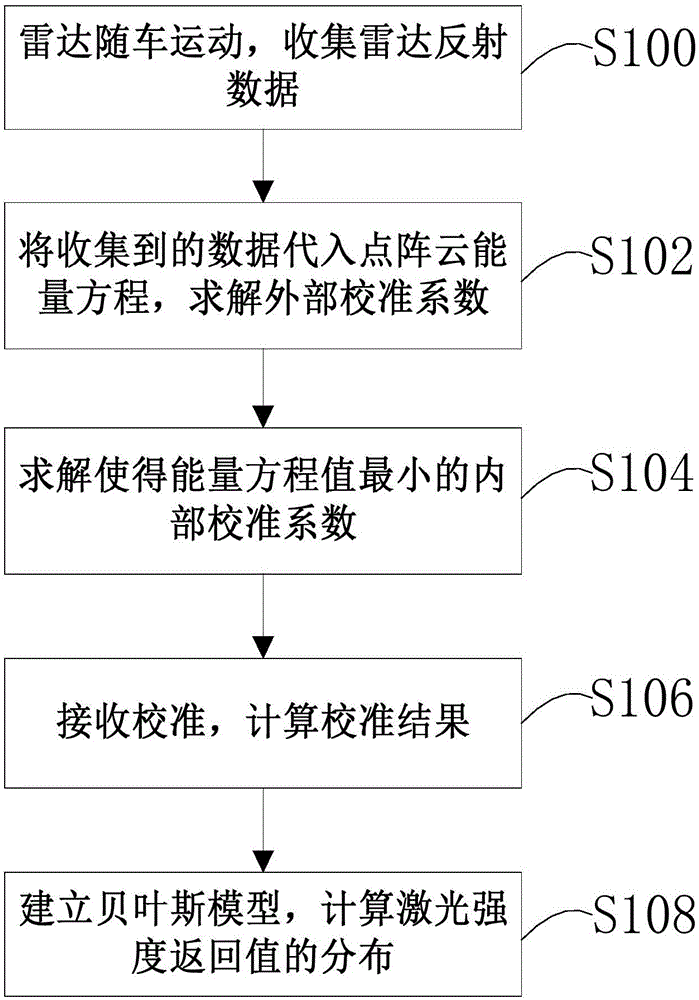
Laser-radar automatic calibration method and device thereof
ActiveCN105866762AQuick correctionImprove accuracyWave based measurement systemsEnergy equationComputer science
A laser-radar calibration method and a device thereof are disclosed. The method comprises the step of external parameter calibration, wherein the external parameter calibration includes steps that a radar moves along with a vehicle; radar reflection data is collected; the collected data is substituted into a lattice cloud energy equation and an energy equation value is a minimum external calibration parameter through solving. Compared to the prior art, by using the above technical scheme, data returned by the laser radar in real time can be analyzed; a parameter of the laser radar itself can be initiatively corrected so that effects of rapidly correcting the laser radar, increasing scanning data accuracy and increasing a scanning image differentiation degree are reached.
Owner:FUZHOU HUAYING HEAVY IND MACHINERY
Image stretching distortion adaptive correction method
InactiveCN105046657ANot subject to bendingUncut imaginationImage enhancementImage analysisFace detectionAlgorithm
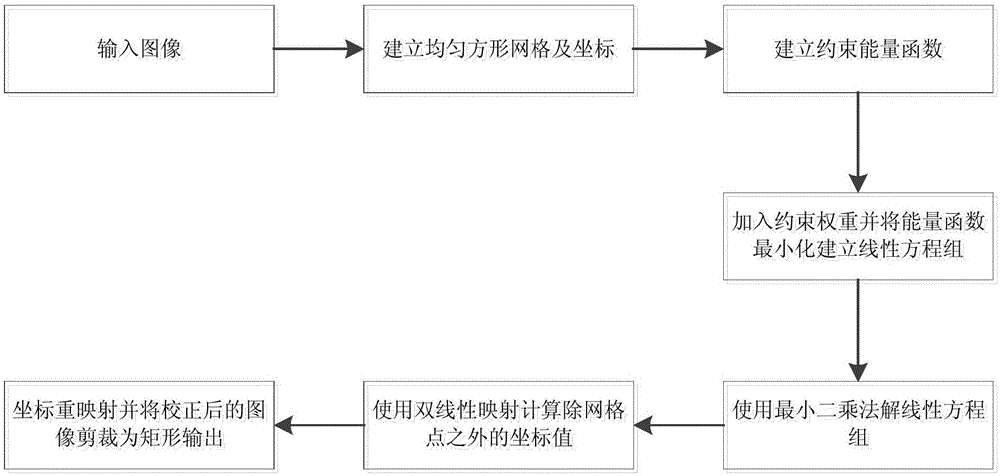
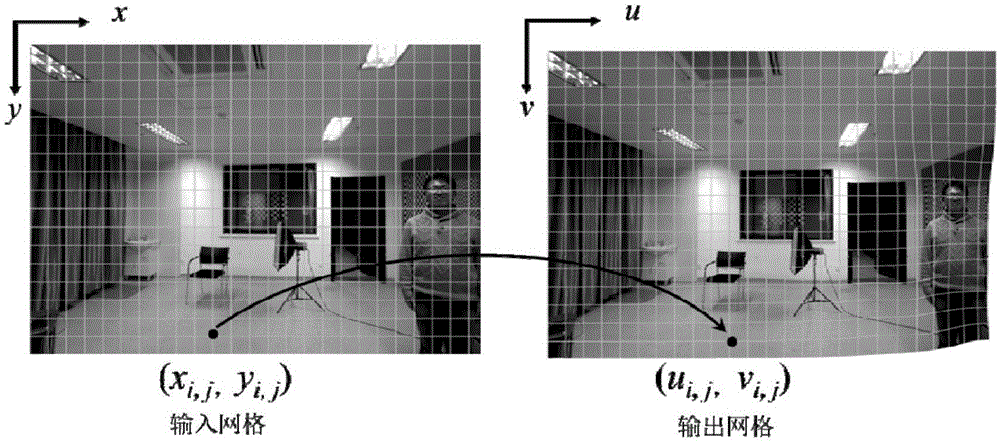
The invention provides an image stretching distortion adaptive correction method comprising: dividing an image into uniform square grids and establishing an input-output coordinate; determining a person area and a background area by using a face detection algorithm, establishing homographic constraint for each grid in order to correct the stretching distortion appearing in the person area, establishing homographic compatible constraint for adjacent grids in order to guarantee the continuity of the grids; determining a linear area by using a linear detection algorithm and establishing linear maintaining constraint for the linear area in order to protect a corrected line against bending; guaranteeing the uniform continuity of the whole image by means of global coordinate smoothness and uniformity constraint; using an energy function to express the constraint, adding weights and adding the energy equations, computing a coordinate value with the minimum energy by using a least square method so as to obtain a corrected image coordinate value; performing rendering by using bilinear mapping to obtain a final corrected image.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Flight icing numerical value simulation method of helicopter rotor wing
InactiveCN102682144AAccurate captureGuaranteed calculation accuracySpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringRotary wing
The invention relates to a flight icing numerical value simulation method of a helicopter rotor wing. The flight icing numerical value simulation method is mainly characterized by comprising the following steps that: a vorticity compensation force algorithm is added into a momentum equation and an energy equation in a single fluid model used for vortex movement used for simulating air-super cold water drop two-phase flows under a rotating coordinate system in rotor wing trail traces, and a centrifugal force and geostrophic force algorithm is added into a super cold water drop sliding velocity equation; a water film movement and icing model of the centrifugal force and the geostrophic force is considered; and the algorithms and the models are used for carrying out the flight icing numerical value simulation flow process of the helicopter rotor wing, wherein the model of single fluid two-phase flowing used for simulating the simulating air-super cold water drop movement is realized by a partial differential equation group for describing the movement of air and air-super cold water drop binary mixtures in a rotor wing tail trace flow field, and a two-phase flow slipping speed model. The condition that the quality and energy changes are generated in water films and ice layers because of the rotary movement of the rotor wing is considered in the model of the water film movement and icing process on the rotor wing surface, and the icing shape of the rotor wing surface is obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN AEROCODE ENG APPL SOFTWAREDEV
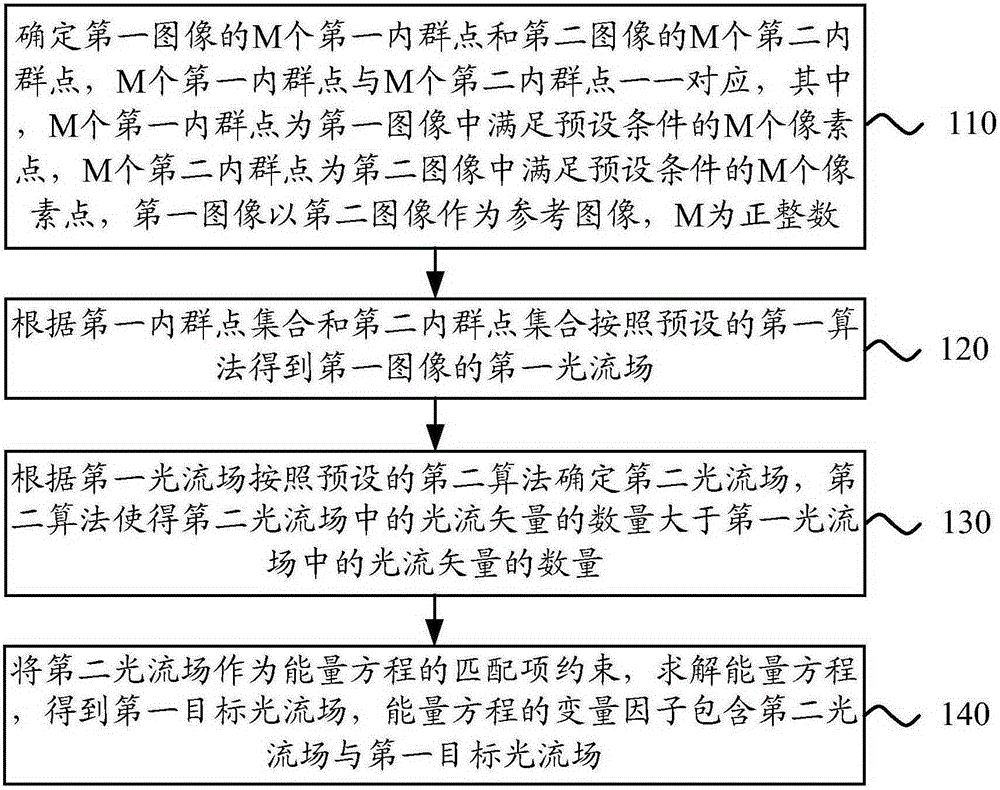
Optical flow estimation method and apparatus
InactiveCN105261042AAccurate Optical Flow EstimationImage enhancementImage analysisReference imageEnergy equation
The embodiment of the invention provides an optical flow estimation method and apparatus. The method comprises: determining M first inliers of a first image and M second inliers of a second image, wherein the M first inliers and the M second inliers are corresponding one-to-one, the M first inliers are M pixels in the first image meeting preset conditions, the M second inliers are M pixels in the second image meeting preset conditions, and the first image employs the second image as a reference image; obtaining a first optical flow field of the first image according to the M first inliers and the M second inliers; determining a second optical flow field according to a second algorithm based on the first optical flow field, wherein the second algorithm makes the optical flow vector quantity in the second optical flow field greater than the optical flow vector quantity in the first optical flow field; and using the second optical flow field as the coupling item constraint of an energy equation to solve the energy equation and obtain an object optical flow field. The optical flow estimation method and apparatus can realize more accurate optical flow estimation under large displacement scenes.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
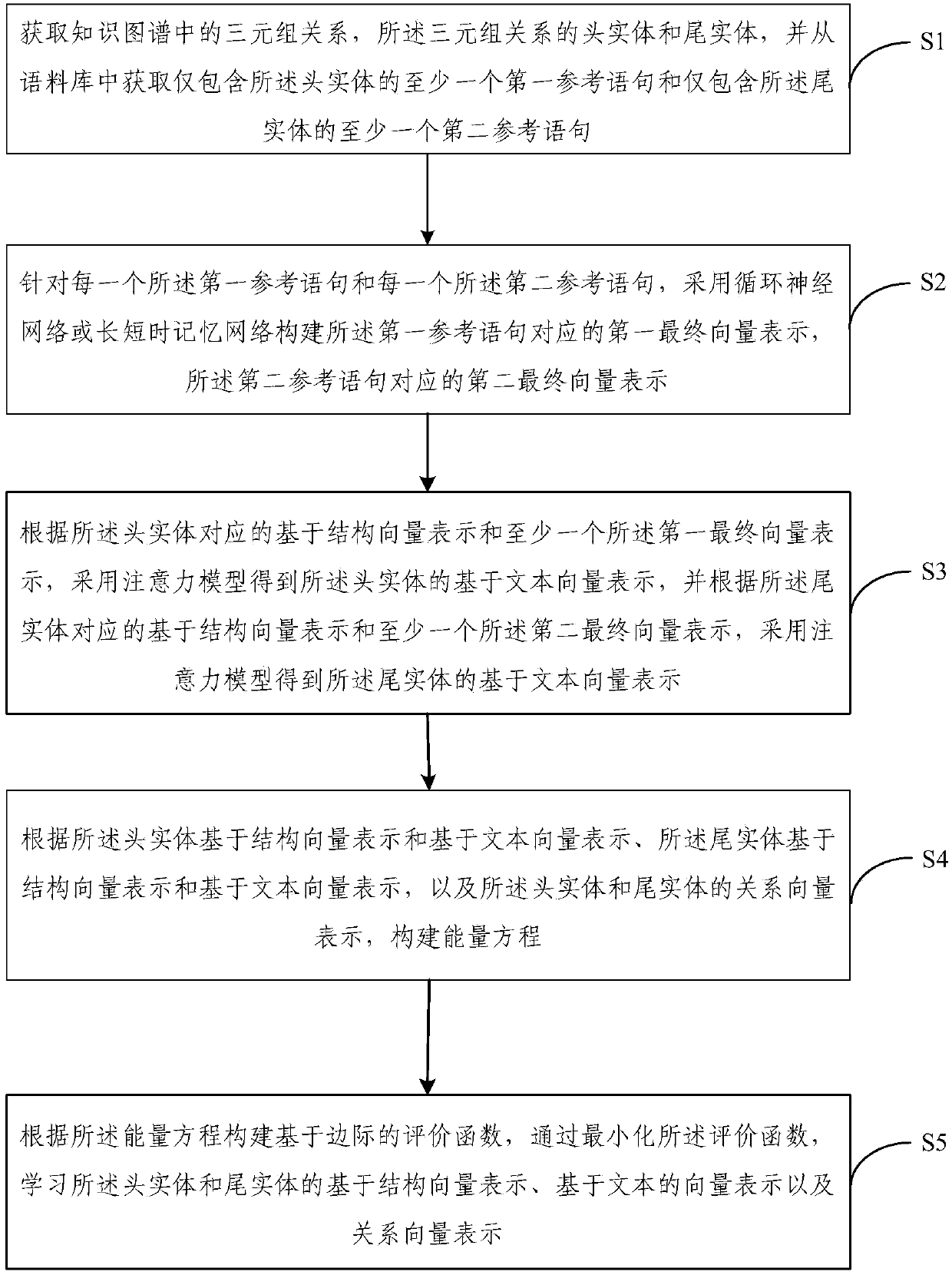
Sequence text information-combined knowledge graph expression learning method and device
InactiveCN107871158AEnhance representation learning abilityEnhance expressive abilitySemantic analysisNeural architecturesRelation classificationGraph spectra
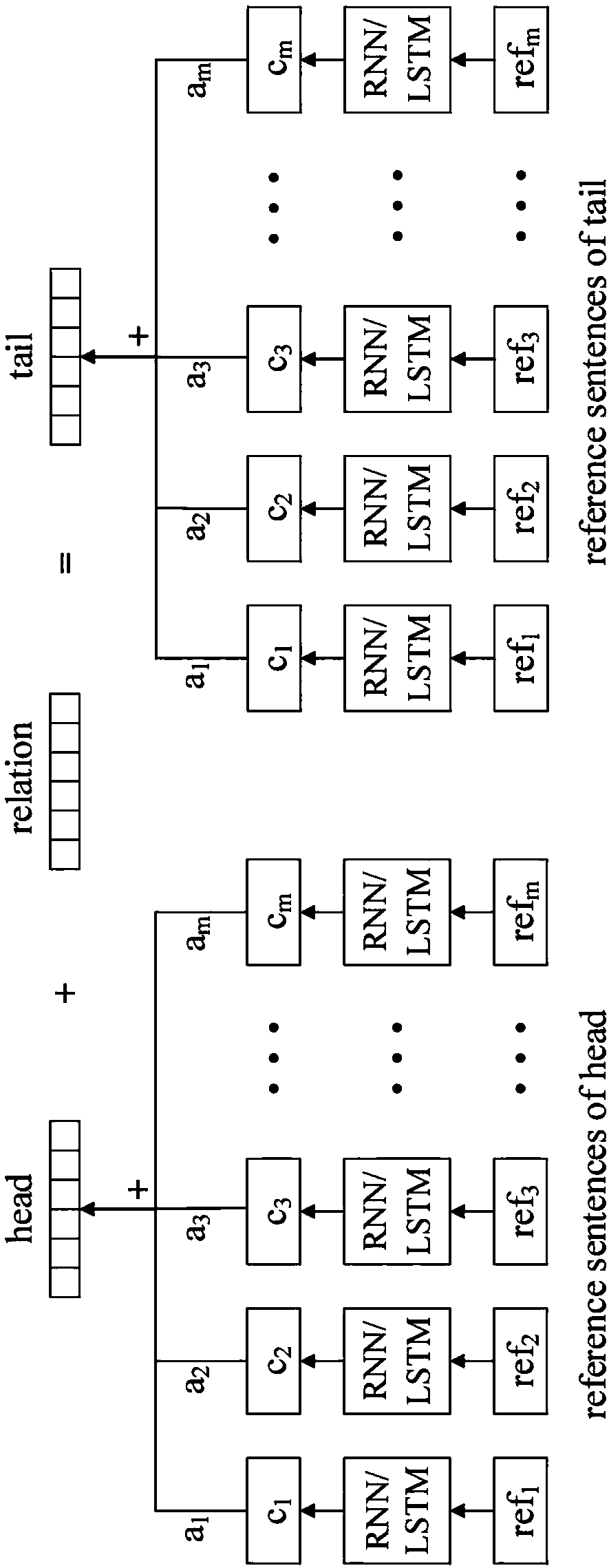
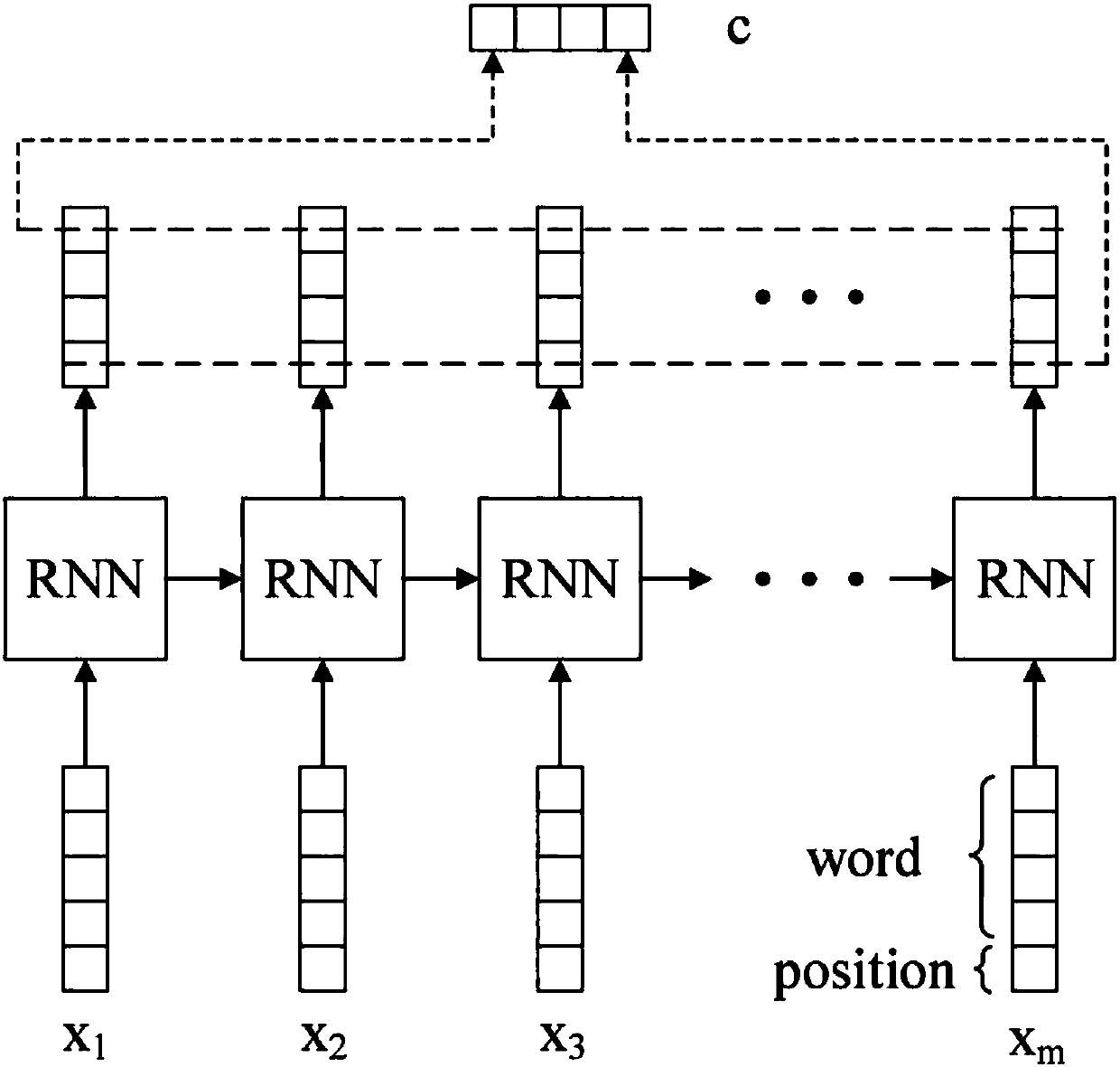
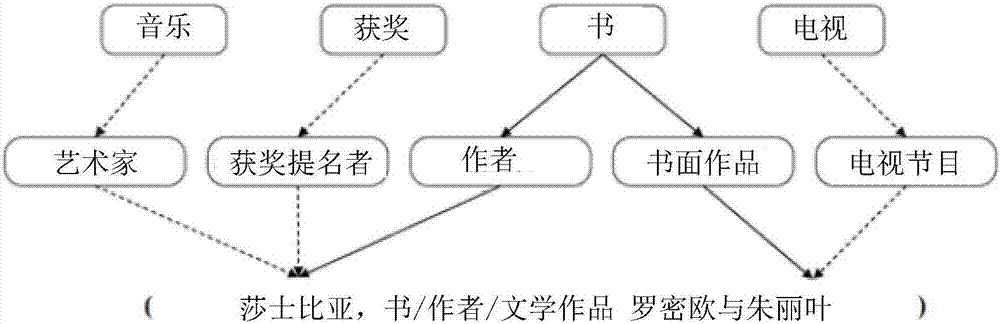
The invention provides a sequence text information-combined knowledge graph expression learning method and a knowledge graph expression learning device. According to the method, not only the ternary relation group information between entities is utilized, but also the sequence text information containing the entities in a designated corpus is fully utilized. An energy equation is constructed, so that the entities have different expression vectors in the structured ternary relation group information and the non-structured text information. Meanwhile, a marginal-based evaluation function is minimized, and the expression of structure-based entity vectors, text-based entity vectors and relation vectors is learned. Therefore, the expression learning effect of a knowledge graph is remarkably improved. According to the method and the device, the learned knowledge graph expression fully utilizes the sequence text information of entities contained in the corpus. Therefore, the higher accuracy can be obtained in the tasks such as ternary group relation classification, ternary group head and tail entity prediction and the like. The good practicability is achieved, and the expression performance of the knowledge graph is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
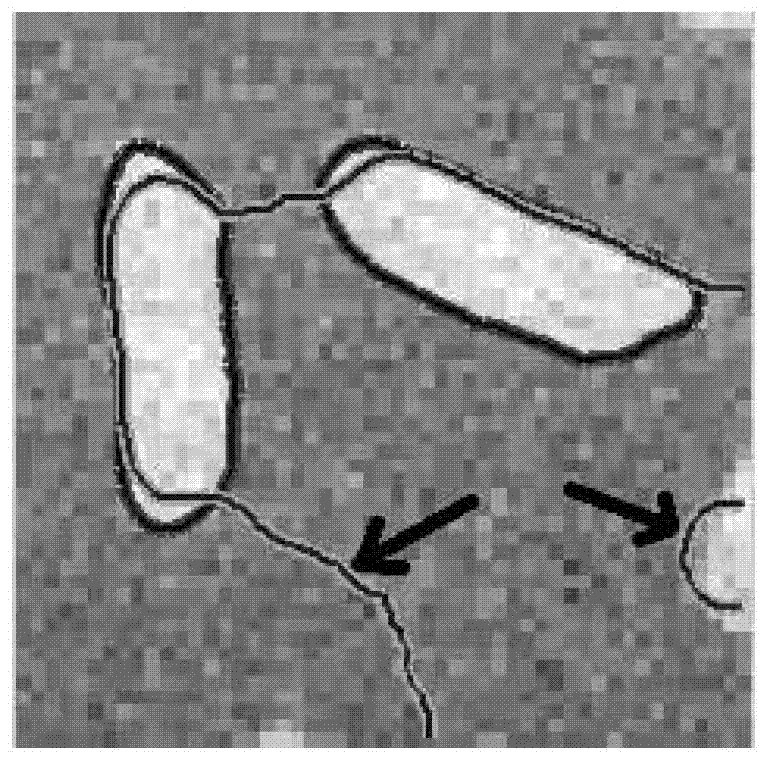
Shadow detection and removal algorithm based on image segmentation
InactiveCN104463853AAccurate segmentationEasy to detectImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingImage segmentation algorithm
The invention discloses a shadow detection and removal algorithm based on image segmentation, and relates to the technical field of image processing. The algorithm mainly solves the problems about how to judge whether shadows exist in a region or not or whether an edge is a shadow or not and how to remove corresponding shadows. The algorithm includes the steps that firstly, through texture and brightness characteristics, the probability that each pixel point is a shadow edge is estimated through the combination of local information and overall information; an image is segmented through a watershed algorithm and contour information shown in the specification; a shadow region and a non-shadow region in the image are segmented through a region fusion algorithm based on edges, and meanwhile the shadow region and the non-shadow region are segmented into multiple sub-regions respectively; then classifiers SVM are trained respectively for recognizing shadows; then, a shadow detection energy equation is solved through an image segmentation algorithm, and then a final shadow detection result is acquired; finally, according to the shadow detection result, shadow labels are calculated through an image matting algorithm, the shadow region is lightened through the marks, and illumination of the shadow region is restored.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Heat front capture in thermal recovery simulations of hydrocarbon reservoirs
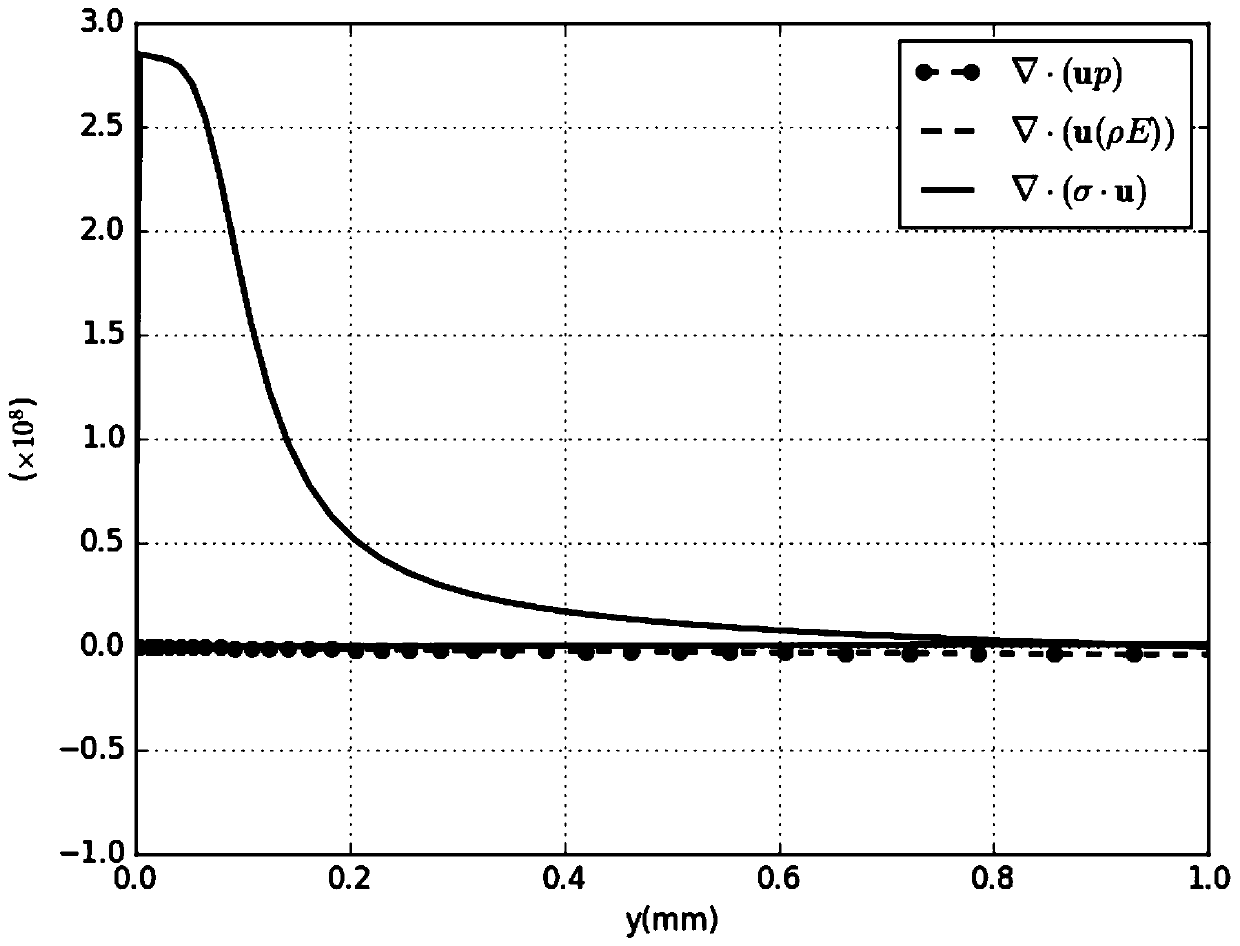
ActiveUS20130041633A1Improve stabilityHigh temperature accuracyFluid removalComputation using non-denominational number representationEnergy balancingMathematical model
A numerical procedure is disclosed to improve the prediction of heat fronts when simulating hot fluid injection in viscous hydrocarbon reservoirs. The mathematical model is composed of the conventional governing equations that describe multiphase fluid flow and energy balance. The reservoir geometry can be partitioned into a regular Cartesian grid or an irregular corner-point geometry grid. The numerical procedure uses the finite different (FD) method to solve the flow equations and the discontinuous Galerkin (DG) method to solve the energy balance equation. The proposed FD-DG method is an alternative to the traditional solution procedure that uses the FD method to solve both the flow and the energy equations. The traditional method has the deficiency that it may require excessive number of grid cells to achieve acceptable resolution of the heat fronts. The proposed FD-DG method significantly reduces numerical dispersion near discontinuities in the solution of the energy equation and therefore provides a better capture of the heat fronts. To obtain a desired accuracy in the energy equation solution, the FD-DG method can be orders of magnitude faster than the traditional method. The superiority of the FD-DG method is that it converges on coarser grids while the traditional method requires much finer grids.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Asymptotic variational method-based method for simulating and optimizing composite material laminated plate
InactiveCN102096736AIncreased buckling critical loadHigh speedSpecial data processing applicationsTensor decompositionEngineering
The invention relates to an asymptotic variational method-based method for simulating and optimizing a composite material laminated plate, which belongs to the field of analysis of material mechanics. The method specifically comprises the following steps of: constructing a three-dimensional plate energy equation represented by a one-dimensional generalized strain and warping function on the basisof a rotation tensor decomposition concept; strictly splitting the original three-dimensional problem analysis into nonlinear two-dimensional plate analysis and cross-section analysis along a thickness direction on the basis of an asymptotic variational method; asymptotically correcting an approximate energy functional of a reduced-order model to a second order by using the inherent small parameter of the plate and converting the approximate energy functional into the form of Reissner model for practical application through an equilibrium equation; accurately reconstructing a three-dimensional stress / strain / displacement field by using an obtained global response asymptotic correction warping function; and optimizing the composite material laminated plate by using an optimization strategy of bending and torsion rigidity coefficients obtained by maximization cross-section analysis. The method has high practicability and high generality, and the resolving speed and efficiency of this type of problems can be remarkably increased.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
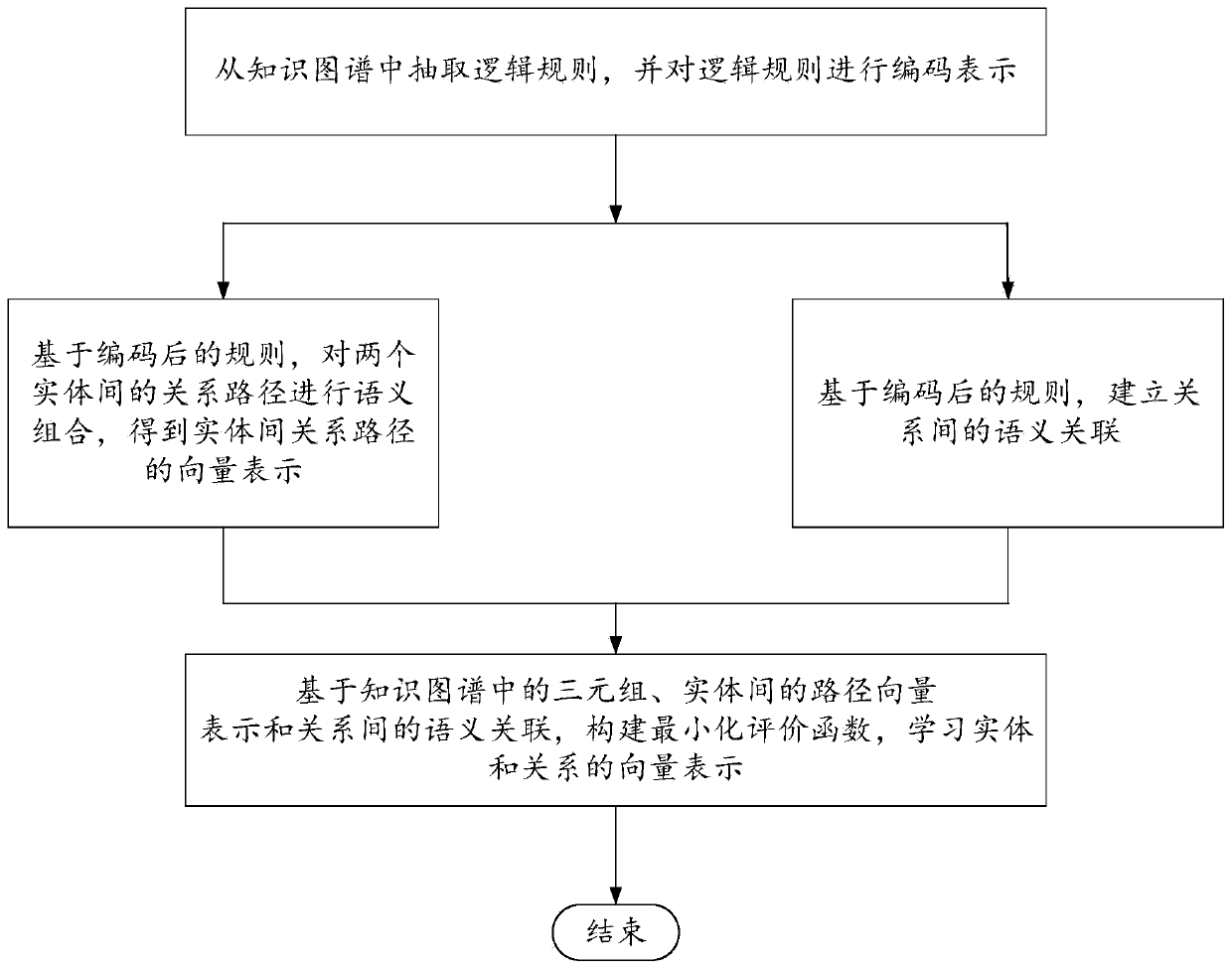
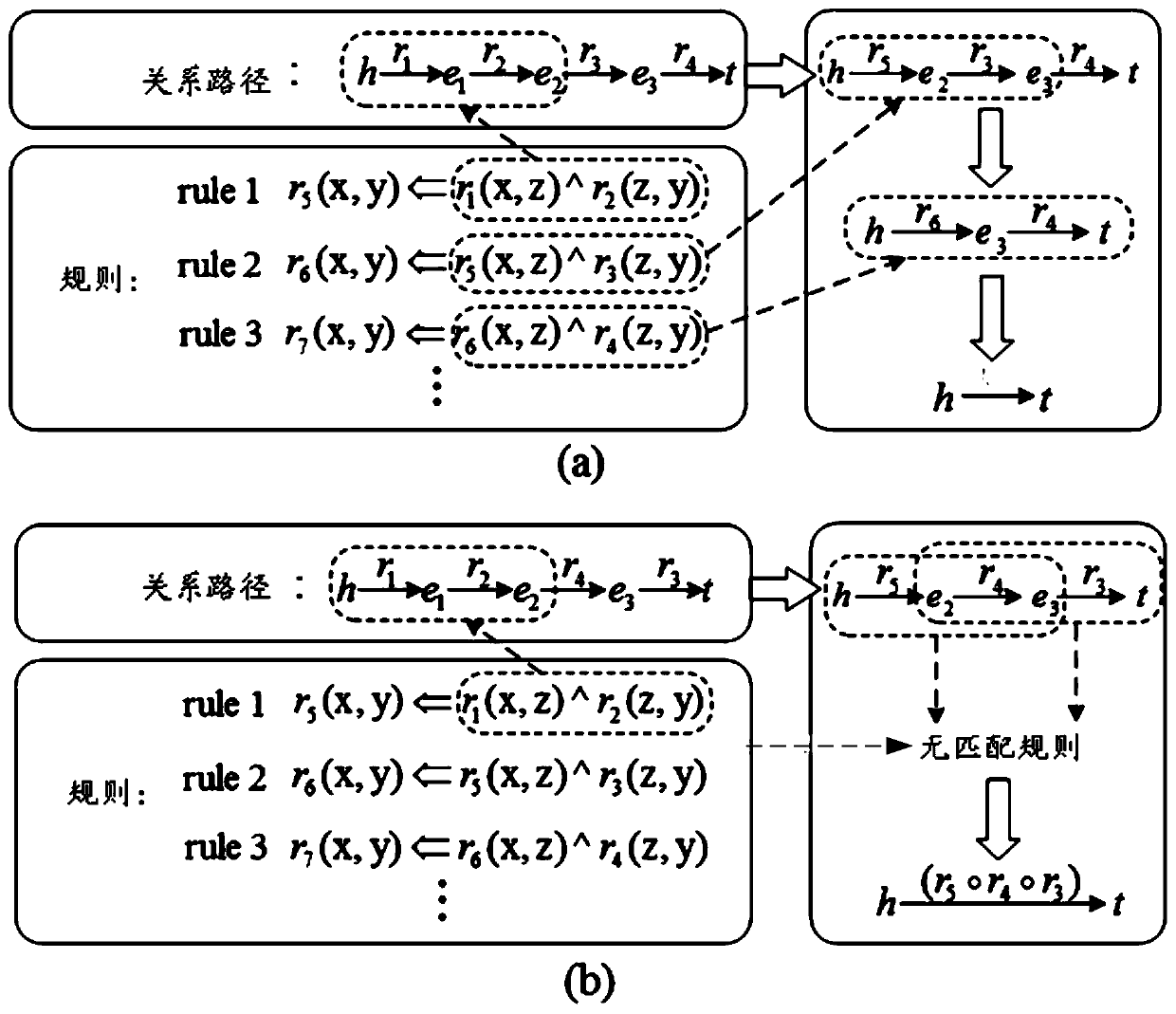
Rule and path combined knowledge graph representation learning method
ActiveCN110069638AImprove accuracyHigh precisionNatural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsGraph spectraStudy methods
The invention discloses a rule and path combined knowledge graph representation learning method, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, extracting a logic rule from a knowledge graph, and encoding and representing the logic rule; then, on the basis of the rule subjected to encoding representation, completing a relation semantic combination operation in the relation path and establishingsemantic association between the relation pairs; and finally, in combination with the triplet, the relation path vector representation between the entities and the semantic association constraint between the relation vectors, jointly constructing an energy equation, and obtaining a minimum evaluation function. The method has the advantages that not only is the accuracy of relation representation improved, but also semantic association among the relations is established by the aid of rules, vector representation of the relations with the semantic association is constrained, more semantic information is added into the vector representation of the relations, and the precision of the vector representation of the relations is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
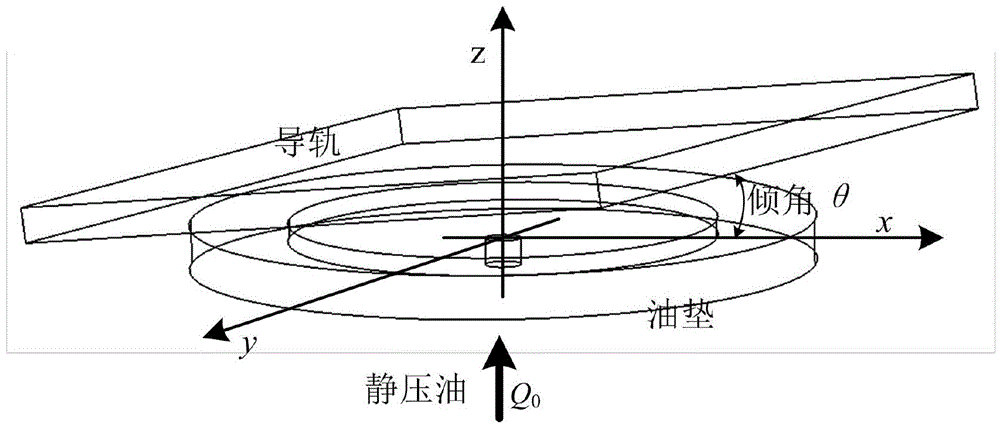
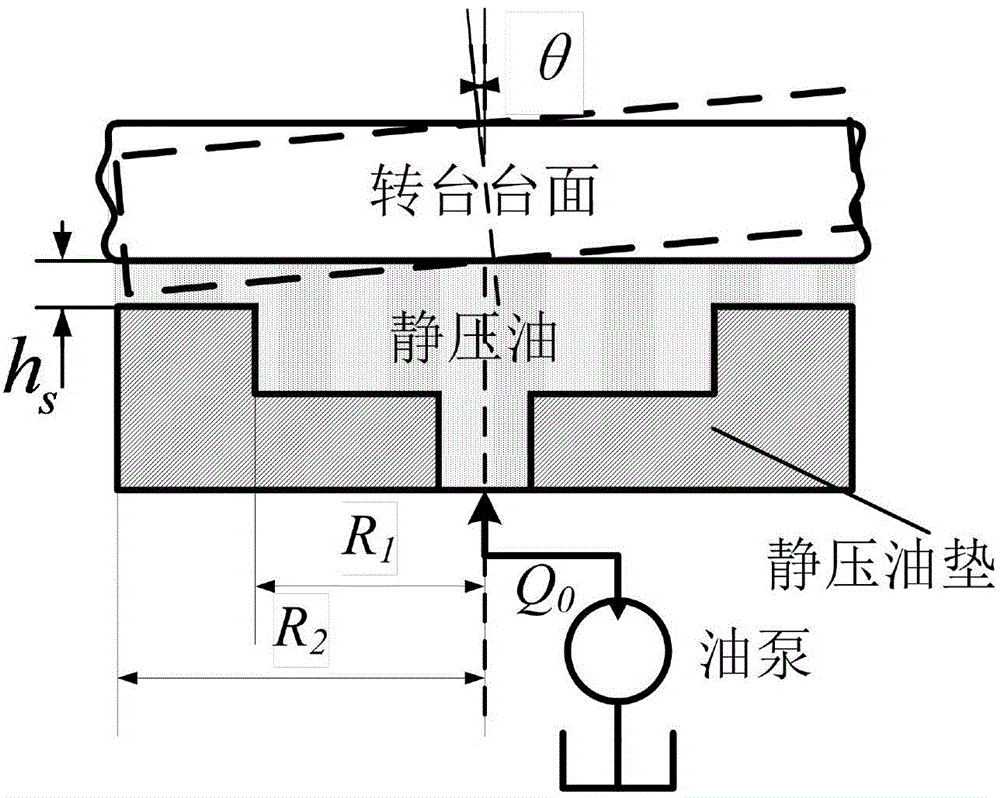
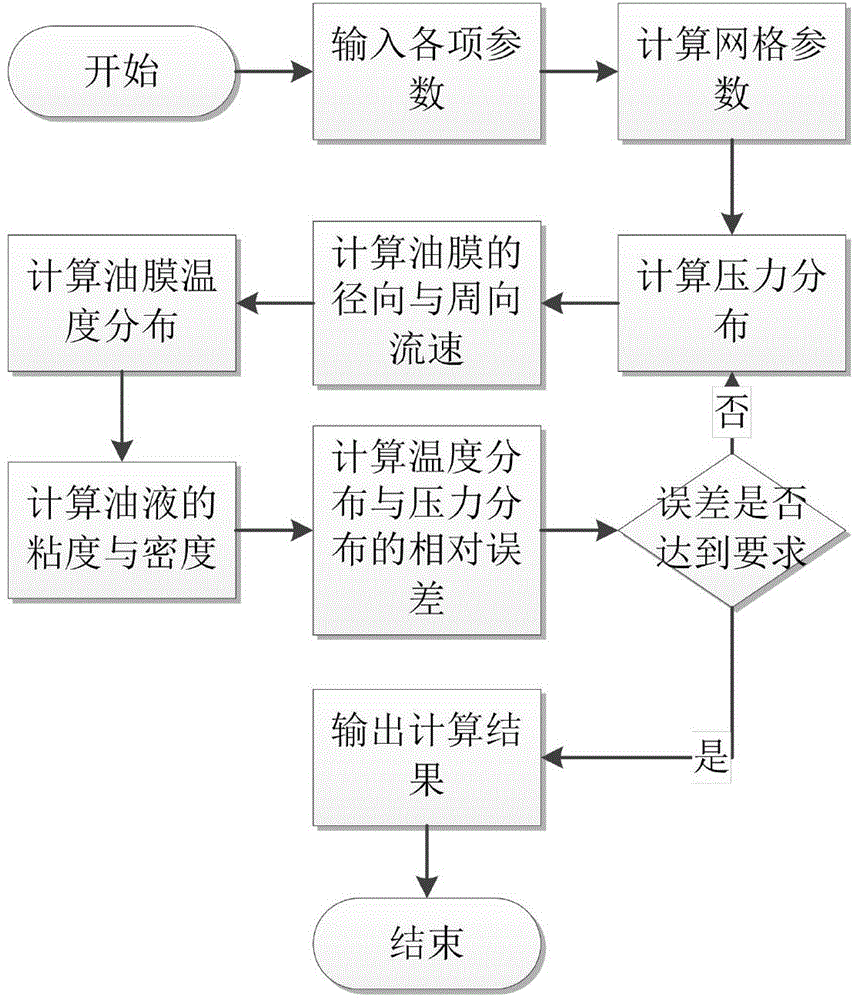
Method for calculating properties of hydrostatic oil pad by considering inclination and heat
The invention discloses a method for calculating various properties of a hydrostatic oil pad by considering inclination and heat. According to the method, influences from inclination and the heat are considered, and pressure distribution and temperature distribution of the oil pad are calculated through the finite difference method. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, an N-S equation and an energy equation are simplified and a two-dimension Reynolds equation is deduced; secondly, dimensionless processing is conducted on the equations; thirdly, the bearing capacity, rigidity and damping of the oil pad are calculated; finally, on the basis of the finite difference method, a calculation program is written through Matlab so as to obtain parameters of the properties of the oil pad. The method is characterized in that the simplified N-S equation is used for deducing the Reynolds equation, and the energy equation and the Reynolds equation are coupled with each other through a viscosity-temperature equation and a density-temperature equation. The coupled equation is solved through the finite difference method, the bearing capacity of the oil pad is obtained through the bearing surface integral, and the rigidity and the damping are obtained by deriving the bearing capacity. The method can provide guidance for use and design of a rotary table.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
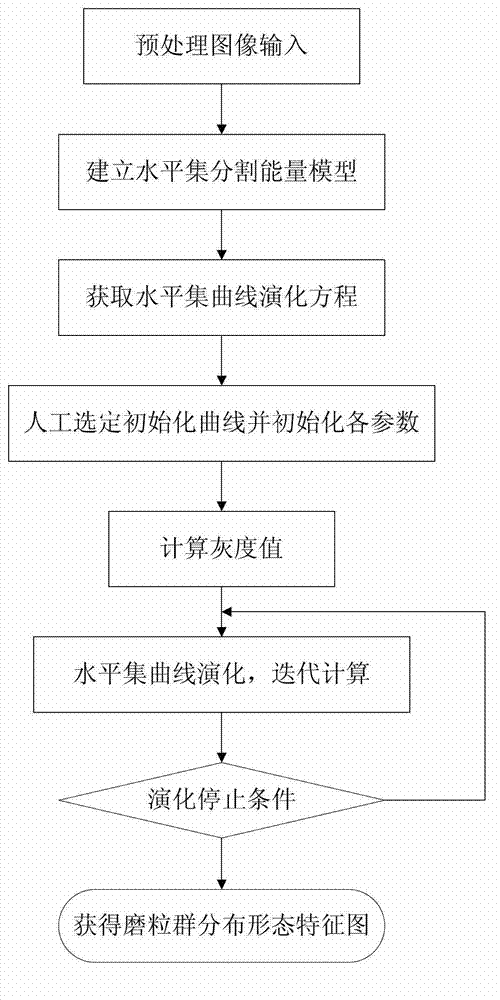
Real-time detection method of soft abrasive flow abrasive group
InactiveCN102830121AEfficient detectionAccurate extractionInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsField functionRunge–Kutta method
A real-time detection method of a soft abrasive flow abrasive group comprises the following steps: 1) establishing a phase-field model two-phase interface mixed energy equation according to the distribution condition of the soft abrasive flow abrasive group, also establishing a control equation of the phase-field function evolution, finally approximating a viscous phase and a surface pressure phase by a traditional second order center difference scheme, performing spatial discretization reconstruction of the control equation by a fifth order WENO scheme, performing discretization in the time direction by a Runge-Kutta method with a TVD property, and thus solving the two-phase interface to obtain a theoretical model of the abrasive group distribution; 2) performing real-time image processing of the distribution area of the abrasive group in a constraint channel obtained by a soft abrasive flow image acquisition device according to the obtained theoretical model of the abrasive group distribution, and thus extracting a contour feature of the abrasive group distribution area to obtain the change condition of the abrasive group dynamic boundary. The invention effectively detects the distribution condition of the soft abrasive flow abrasive group.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
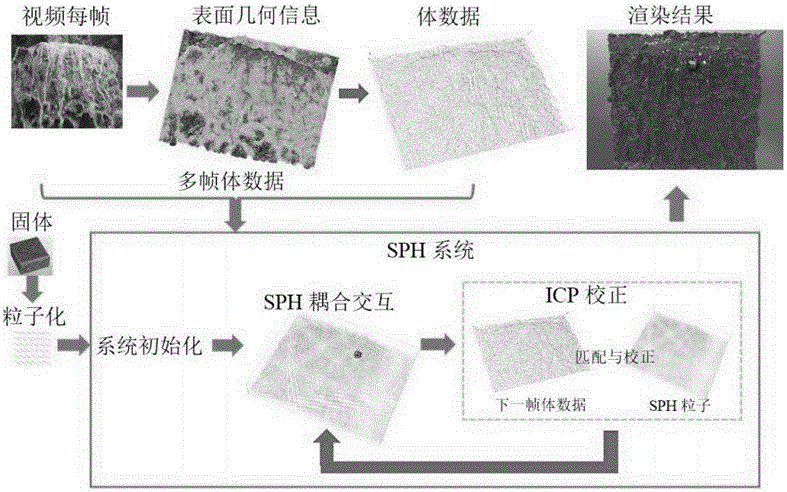
Fluid-solid interaction simulation method based on video reconstruction and SPH model
InactiveCN106446425AOvercome limitationsReal fluid-solid coupling simulation effectDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSimulationSurface level
The invention discloses a fluid-solid interaction simulation method based on video reconstruction and an SPH model. The fluid-solid interaction simulation method includes steps: 1), adopting a bright-dark recovery shape method to quickly reconstruct fluid surface geometric information in video, and acquiring a surface height field of each frame of input image; 2), combining the height fields with a shallow water equation, and calculating to acquire a speed field on the surface of fluid in a form of a minimizing energy equation; 3), using the surface geometric information as a boundary constraint condition to be discretized into a whole three-dimension body to acquire volume data; 4), guiding the volume data reconstructed in the video into an SPH simulation scene to serve as an initial condition of the simulation scene, and interacting with other virtual environment objects in the scene. By the fluid-solid interaction simulation method, high-accuracy data reconstruction can be realized, fluid surface details can be retained, bidirectional interaction simulation is performed on the basis of reconstructed data and a physical simulation model, fluid animation effect closer to real condition is acquired, algorithm complexity is low, and the method has high creativity compared with related algorithms.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
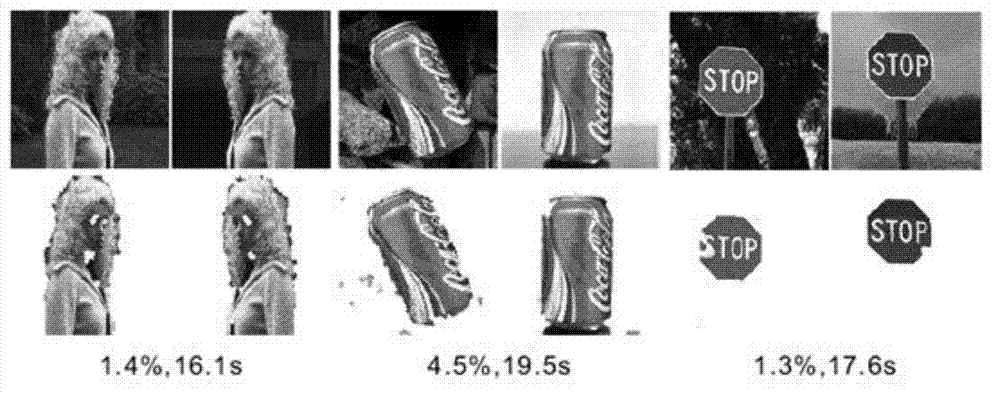
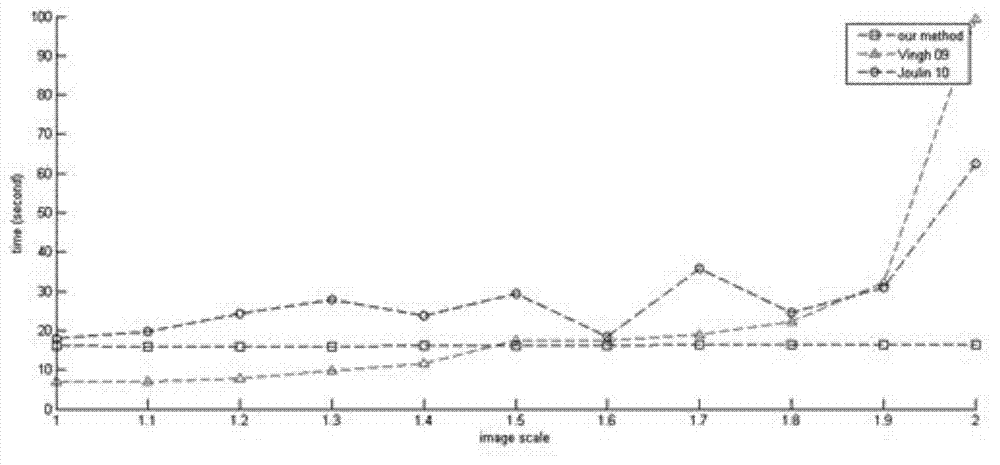
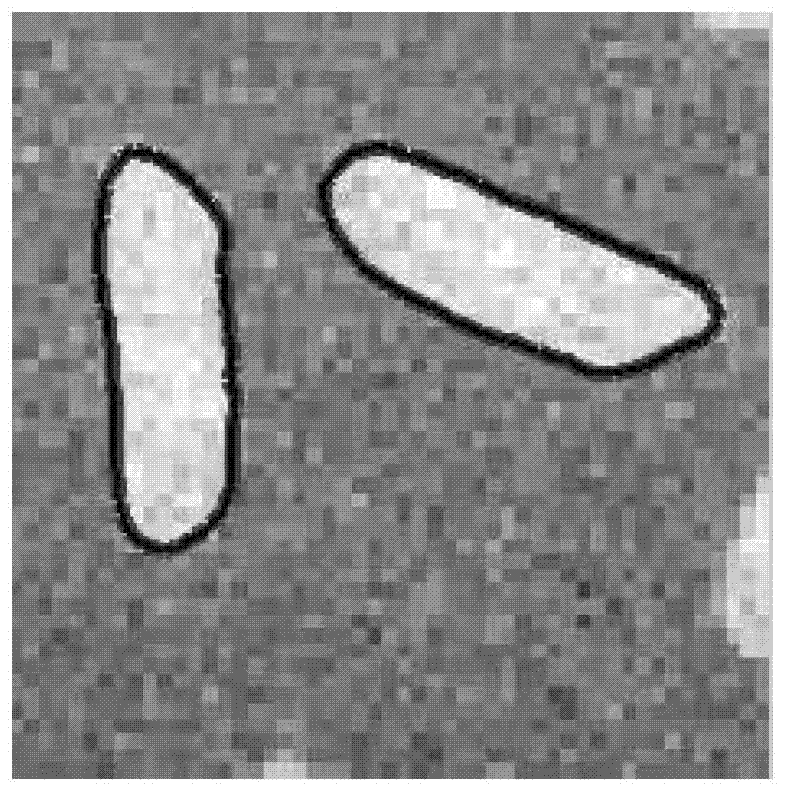
Rapid multi-modal image synergy segmentation method with unrelated scale feature
The invention discloses a rapid multi-modal image synergy segmentation method with scale unrelated feature. The method includes the following steps: firstly, opening inputted image set files, extracting superpixel in sequence by the image in the current input image set by utilizing a subscriber line interface circuit (SLIC), and extracting the superpizel of each image; calculating color characteristics of the superpizel and the regional covariance matrix, and initializing the foreground region and the background region of the image; secondly, building superpixel multi-modal features and models of the foreground and background regions; thirdly, optimizing and saluting. The rapid multi-modal image synergy segmentation method with the unrelated scale feature has the advantages that the multi-modal features are further introduced into an energy equation of the image synergy segmentation. The higher accuracy rate is guaranteed and the operating speed of the algorithm is improved. In addition, scenes which are capable of being processed by the image synergy segmentation are greatly expanded due to the introduction of the multi-modal features, and the method has certain robustness over the complicated image background.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Unsteady measurement algorithm based image segmentation method of improved rule distance level set
The invention discloses an unsteady measurement algorithm based image segmentation method of an improved rule distance level set, belongs to the field of digital image processing and aims to more precisely segment images of gaussian noise and salt and pepper noise interference. The method includes: firstly, constructing a mean operator, and setting a stopping function by the constructed operator; secondly, manually setting an initial contour, and initializing a level set function according to the contour; and thirdly, importing the stopping function set in the first step into an energy equation of a DRLSE model, minimizing the energy equation by the aid of a central difference method, and iterating by taking the initialized level set obtained in the second step as an initial condition to obtain a zero level set of a steady state solution, namely the final segmentation results. The method is more precise in segmentation of the images of the gaussian noise and salt and pepper noise interference as compared with a traditional geometric Snake model method.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
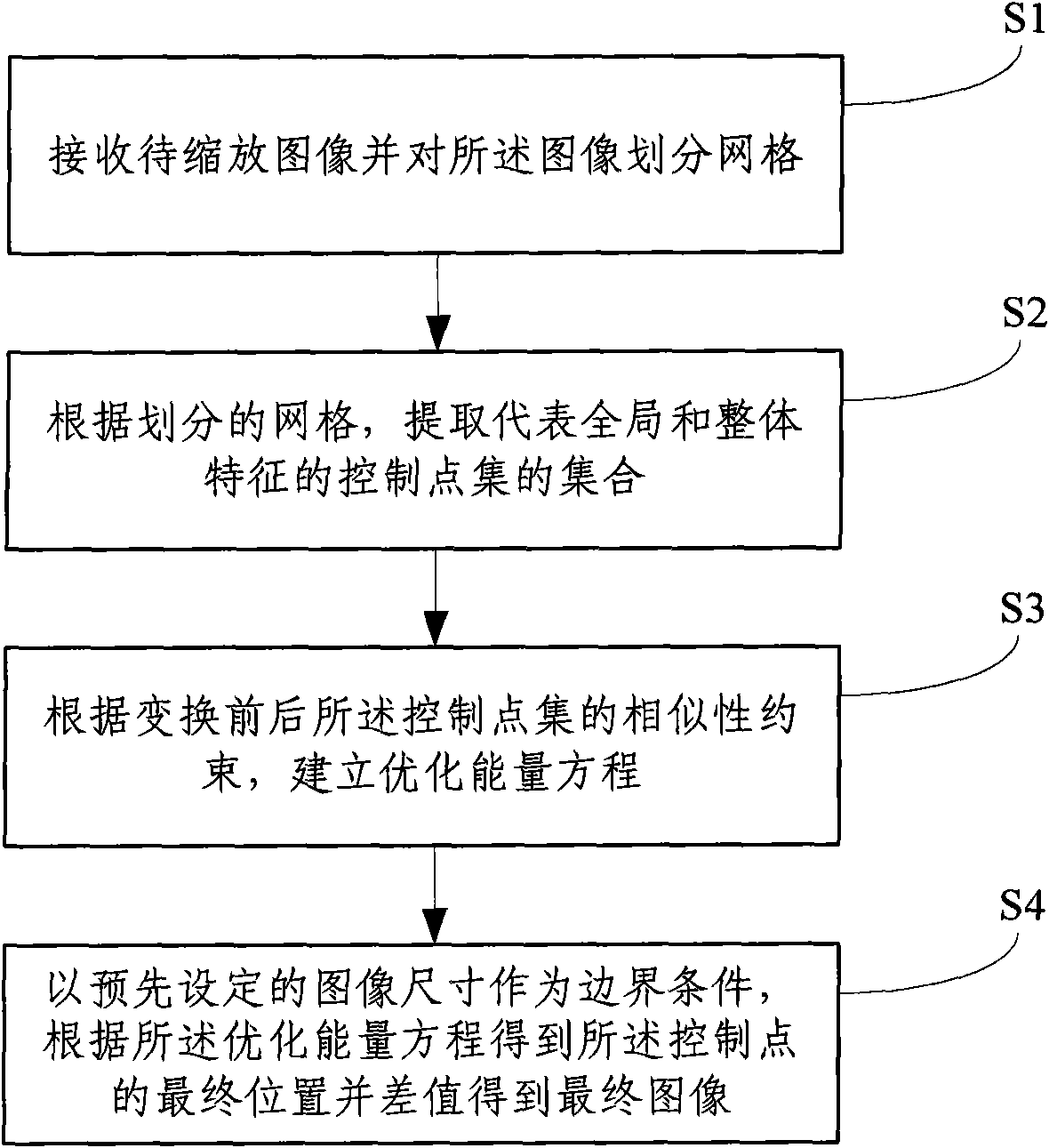
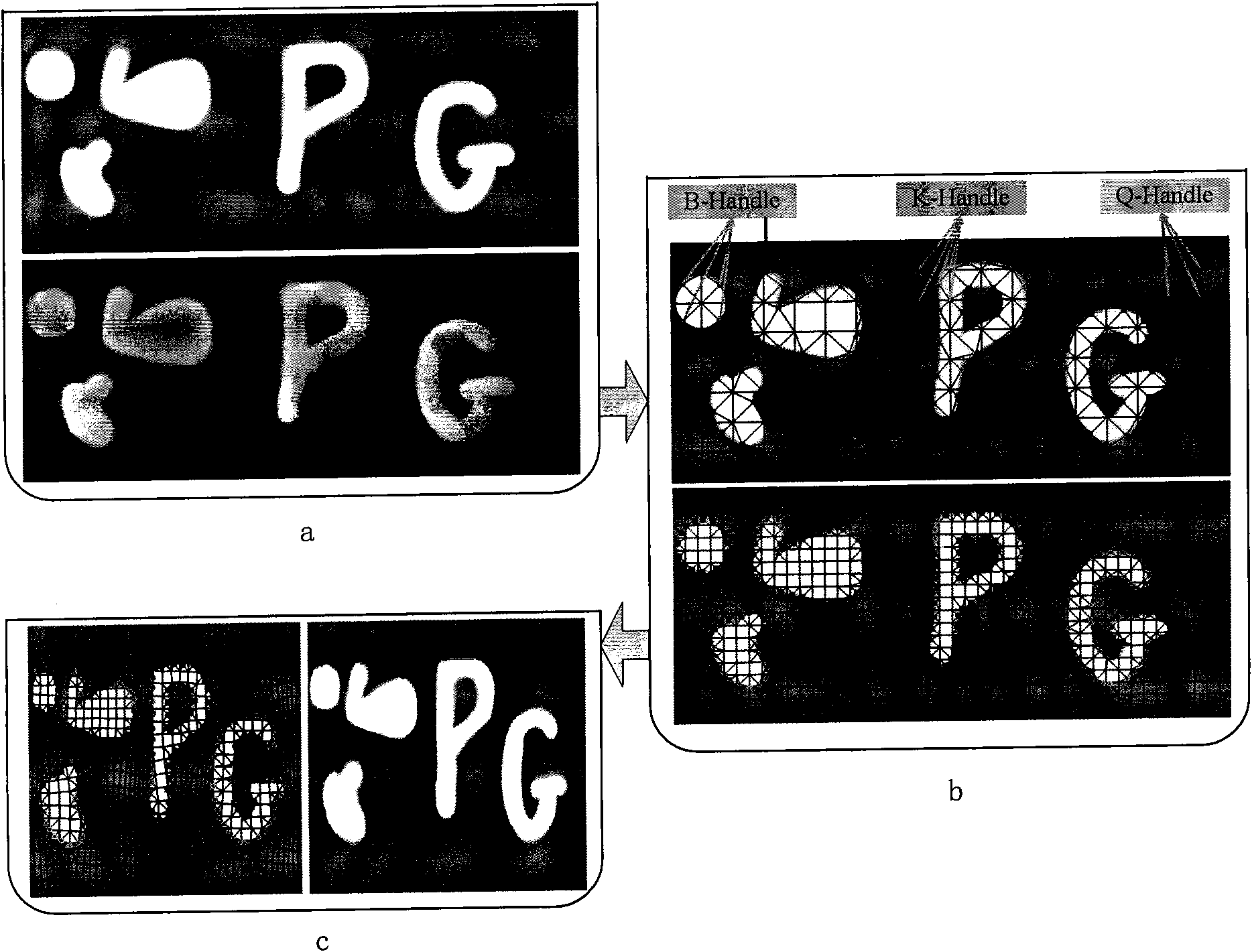
Content erotic image zooming method based on conformal energy
ActiveCN101650824AReduce distortionGuaranteed similarityGeometric image transformationComputer visionEnergy equation
The invention relates to a content erotic image zooming method based on conformal energy. The method comprises the following steps: S1. receiving an image to be zoomed, and dividing the image into grids; S2. extracting a control dot set representing local and integral characters according to the divided grids; S3. establishing an optimized energy equation according to similar constraint of the control dot set before and after being changed; and S4. using the preset image dimension as the border condition to obtain final positions of control dots by the optimized energy equation and obtain thefinal image by difference value. When the content erotic image zooming method is used for zooming the image, the image can be adjusted to any dimension and aspect ratio, and meanwhile, the distortionof important objects in the image is minimized.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
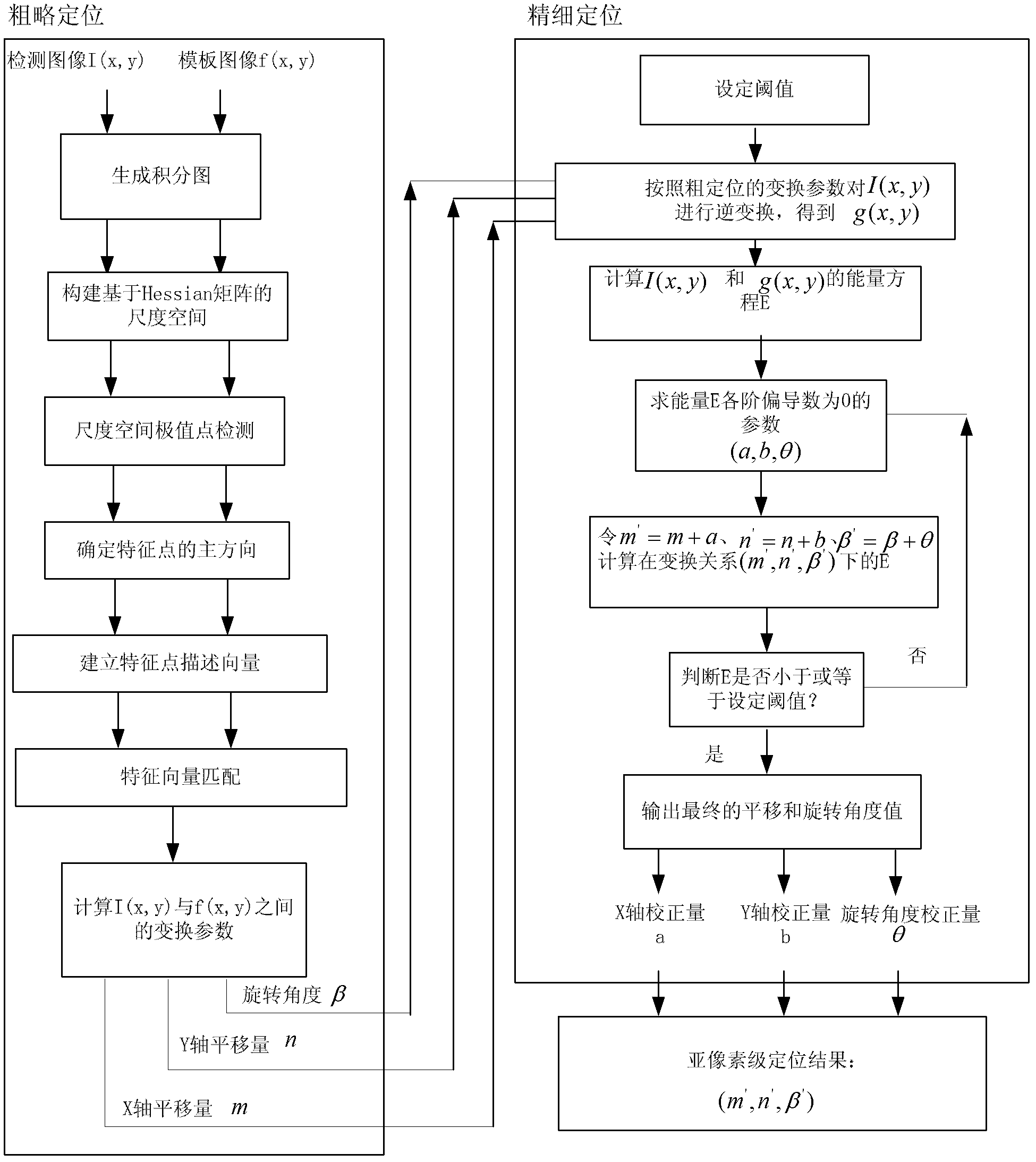
High-density packaged element positioning method based on speeded up robust features (SURFs)
ActiveCN102661708ARealize high-precision sub-pixel positioningImprove robustnessUsing optical meansHigh densityTransformation parameter
The invention discloses a high-density packaged element positioning method based on speeded up robust features (SURFs), which comprises the following steps: (1), coarse positioning: coarse transformation parameters (m, n and Beta) are obtained by adopting a SURF registration method; (2) fine positioning: an image I (x, y) to be registered is inversely transformed by utilizing the coarse transformation parameters (m, n and Beta) to obtain an image g (x and y), the minimum energy equation E of the image g (x and y) and a template image f (x and y) is calculated, each partial derivative of the E is solved and enabled to be zero, and transformation parameters (a, b and Theta) are solved; m' is enabled to be equal to m plus a, n' is enabled to be equal to n plus b, and Beta' is enabled to be equal to Beta plus Theta; the energy equation E under a transformation relation (m', n' and Beta') is calculated; whether the E is smaller than a set value or not is judged, and if no, next iteration is conducted; and if yes, the iteration process is finished, m' is taken as the final translation parameter in an x direction, n' is taken as the final translation parameter in a y direction, and Beta' is taken as the final rotation angle. Compared with the prior art, the high-density packaged element positioning method realizes high-precision sub-pixel positioning and has great robustness on illumination transformation and noise.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Manhattan structure building automatic modeling method based on cuboid fitting scanning three-dimensional point cloud
InactiveCN107657659AEvasion of independent responsesImprove computing efficiencyDetails involving processing stepsImage generationPoint cloudGlobal optimization
The invention provides a Manhattan structure building automatic modeling method based on cuboid fitting scanning three-dimensional point cloud. The method carried out modeling through plane extraction, cuboid-based space division and binary classification based on a graph-cut algorithm. The method enables modeling work to be converted into the binary classification problem based on a cuboid element structure; the method establishes coverage index for reflecting fitting efficiency and establishes a global optimization target energy equation by utilizing a point set on a plane and space relativeposition relation of each cuboid; the method solves the target equation through the graph-cut algorithm to obtain binary classification of the cuboids, and operation processing efficiency is high; each surface of the model is flat, the overall structure is compact and a comfortable visual effect is achieved; and since the model result only keeps cuboid vertexes and facet structure, compared withinput dense three-dimensional point cloud, data volume is compressed greatly, and model achieves obvious light weight, which has a good support function for modeling work in a large-scale building scene.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
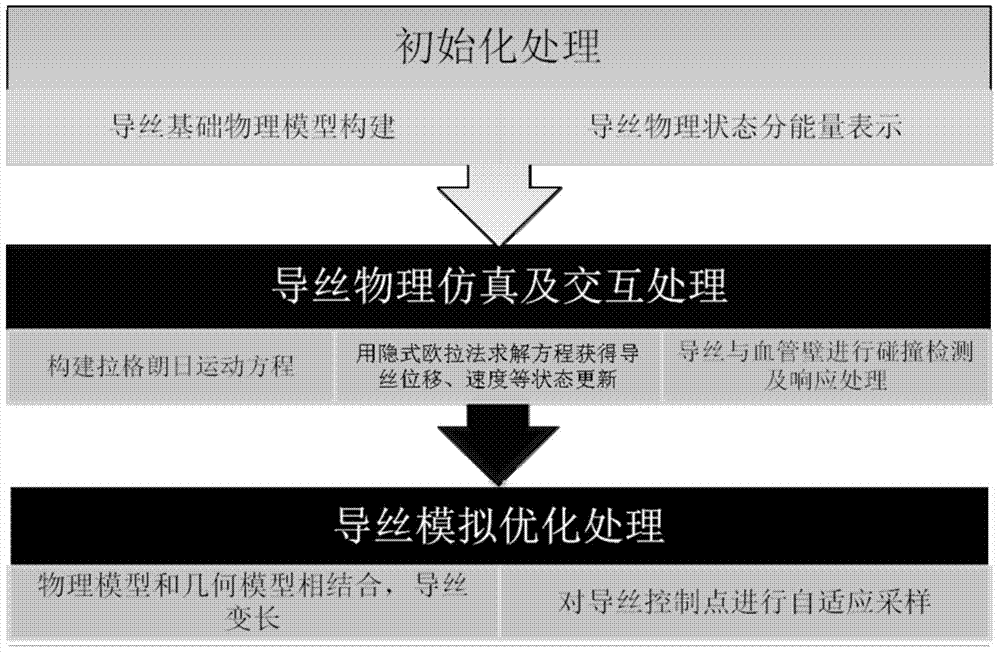
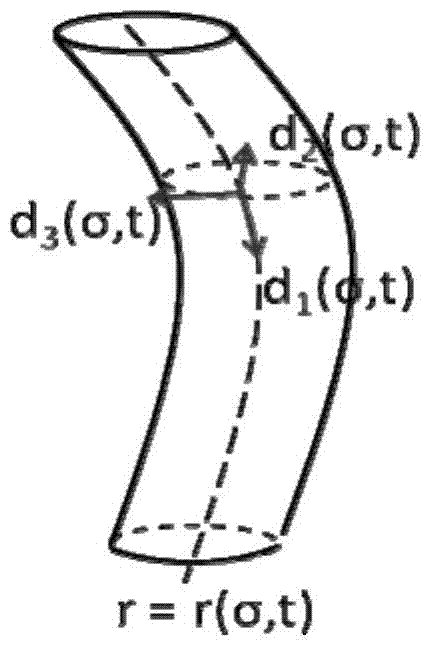
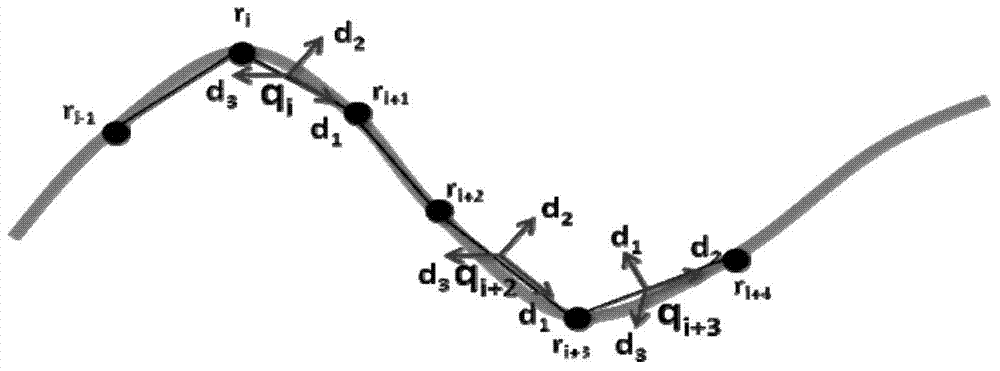
Guide wire simulation method facing cardiovascular interventional surgery emulation
InactiveCN103699776AObtain visually realistic interactive simulation effectsHave physical realitySoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationSpecial data processing applicationsPhysical realityPhysical model
The invention provides a guide wire simulation method facing cardiovascular interventional surgery emulation. The method comprises four steps that: an initialization stage is used for initializing each kind of basic physical information of a guide wire and the initial state of the guide wire and constructing a guide wire physical model; in a guide wire model physical emulation stage, a guide wire motion equation is solved according to external force and energy equations to obtain the displacement and state updating of the guide wire; in the guide wire and ambient environment interaction stage, the guide wire generates interaction with the ambient environment in the inserting process in a blood vessel, so the physical state of the guide wire is influenced; in a guide wire simulation optimization stage, the guide wire emulation is subjected to optimization treatment according to the state characteristics of the current guide wire. The guide wire simulation method has the advantages that the hidden method physical simulation emulation is carried out on the guide wire, in addition, the interaction with the ambient environment is also realized, the method is applied to the cardiovascular interventional surgery, and the characteristics that the stability is high, the real-time performance is good, the physical reality sense is high, and the high fidelity is realized are realized.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
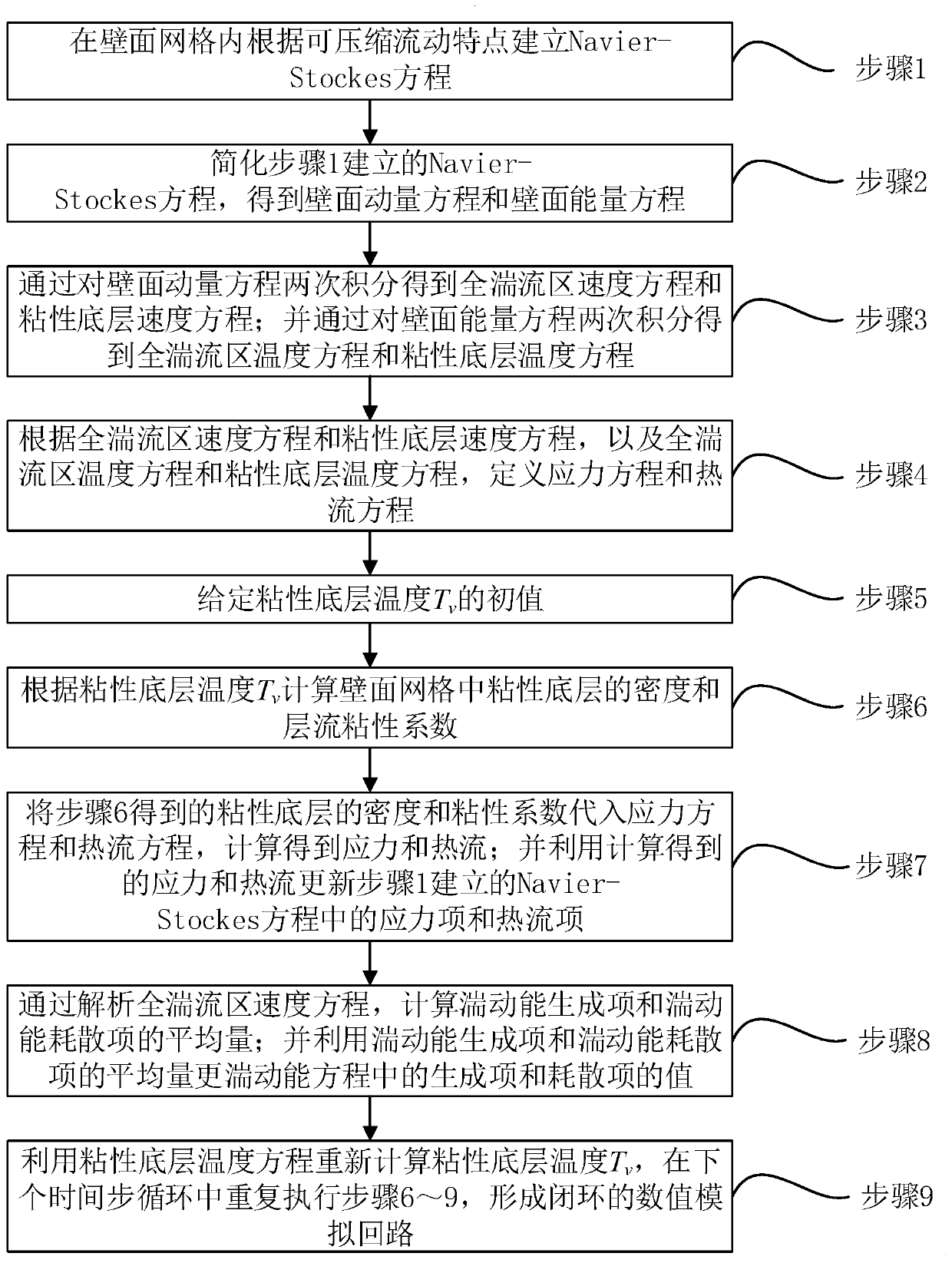
Compressible flow-based numerical simulation method for analyzing wall surface function
ActiveCN110489709ATightly coupledAccurate predictionComplex mathematical operationsSpeed of soundKinetic energy
The invention discloses a numerical simulation method for analyzing a wall surface function based on compressible flow. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a Navier-Stokes equationaccording to compressible flow characteristics, simplifying the Navier-Stokes equation, analyzing the Navier-Stokes equation to obtain a full turbulence zone speed equation, a viscous bottom layer speed equation, a full turbulence zone temperature equation and a viscous bottom layer temperature equation, and further defining a stress equation and a heat flow equation; giving an initial value of the temperature Tv of the viscous bottom layer, and calculating according to the Tv to obtain stress and heat flow; updating a stress item and a heat flow item by utilizing the calculated stress and heat flow; updating the values of a generation item and a dissipation item in the turbulence energy equation by calculating the average quantity of the turbulence energy generation item and the turbulence energy dissipation item; and finally, recalculating Tv by utilizing a viscous bottom layer temperature equation, and repeatedly updating in the next time step cycle. Based on the compressible flow characteristic, the method is particularly suitable for hypersonic flow, and the wall surface heat flow can be predicted more accurately.
Owner:CALCULATION AERODYNAMICS INST CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
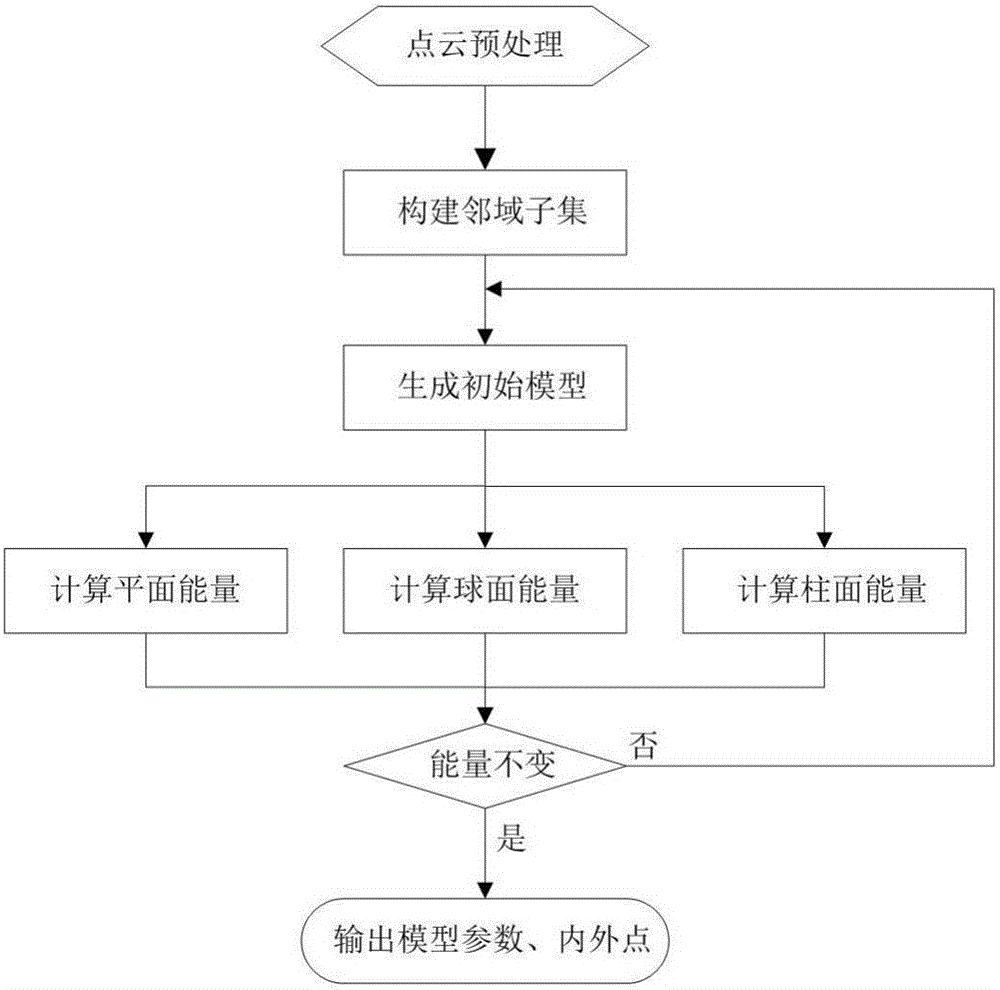
Method for automatically recognizing various types of geometric elements in three-dimensional point cloud
ActiveCN106228539AAccurate estimateAccurate and reasonable divisionImage enhancementImage analysisNeighbor relationVoxel
The invention discloses a method for automatically recognizing various types of geometric elements in a three-dimensional point cloud, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the preprocessing of an inputted three-dimensional point cloud, i.e., voxel filtering, building a neighbor structure based on a Kd tree, and estimating a normal vector of points; carrying out the determining of a neighbor relation of the point cloud, and carrying out the sampling of the point cloud; calculating a covariance matrix of sample point neighbor, analyzing the size relation among three characteristic values, and generating a corresponding initial geometric element model according to a coplanar rule; respectively building a corresponding energy equation according to the initial geometric element models, and carrying out the planar, spherical and cylindrical surface energy calculation according to an energy optimization frame; carrying out the loop iteration of the above steps, minimizing the energy of various types of geometric elements, solving geometric element parameters under optimal significance through employing an optimization algorithm, thereby achieving the refining of the parameters of geometric element models; and finally outputting the parameters and inner points of a plurality of types of geometric elements. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the method is wide in application range, is accurate in parameter estimation, is strong in anti-interference capability, and greatly improves the recognition and analysis capability of the three-dimensional point cloud.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Equivalent mass based spatial manipulator continuous collision dynamics modeling method
ActiveCN104537151ASimple modeling methodSpecial data processing applicationsKinematics equationsCollision dynamics
The invention discloses an equivalent mass based spatial manipulator continuous collision dynamics modeling method and belongs to the manipulator modeling technical field. The equivalent mass based spatial manipulator continuous collision dynamics modeling method comprises calculating the equivalent mass of the tail end of a spatial manipulator on the basis of the establishment of a spatial manipulator kinematics equation, dynamic equation and energy equation; deducing the collision force, the duration of the collision and the amount of the compression through a continuous collision Hertz damping model between monomers, wherein the collision force, the duration of the collision and the amount of the compression are produced by monomer collision; combining with the equivalent mass of the tail end of the spatial manipulator and the monomer continuous collision Hertz damping model, establishing a spatial manipulator continuous collision dynamics model and calculating the collision force, the duration of the collision and the maximum amount of the compression in the spatial manipulator collision process. According to the equivalent mass based spatial manipulator continuous collision dynamics modeling method, the problem of spatial manipulator continuous collision dynamics modeling is solved, the modeling process by the equivalent mass based spatial manipulator continuous collision dynamics modeling method is simple and easy to understand, and the collision force, the duration of the collision and the maximum amount of the compression in the collision process can be expressed explicitly.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Super-pixel-level image global matching method
ActiveCN104318576AThe result is robustRich in detailsImage enhancementImage analysisParallaxBinocular stereo
A super-pixel-level image global matching method comprises the steps of obtaining an input image pair corrected by polar lines through a binocular stereo camera, calculating a self-adaption cross of each pixel of the input image pair so as to obtain a self-adaption window of the current pixel, calculating the matching cost of the pixel, adopting a replacement strategy to process a coverage area and adopting a suboptimum strategy to process an image boundary; establishing super-pixels for images, conducting planar fitting on a parallax value of each super-pixel area to determine reliable pixels and deleting obvious wrong planes so as to determine initial parallax plane set; calculating the matching cost of the super-pixels according to the obtained matching cost of the pixel, establishing a data item and a smoothing item and utilizing a Graph-Cut optimization algorithm to conduct continuous iteration on an energy equation so as to obtain a final parallax plane. The super-pixel-level image global matching method can effectively avoid the problem that image noise, distortion or pixel value abnormity and other situations easily occur in a weak texture area, a discontinuous-parallax area and the coverage area, is good in robustness and can obtain depth information more approximating to real scenes.
Owner:中城绿建科技有限公司
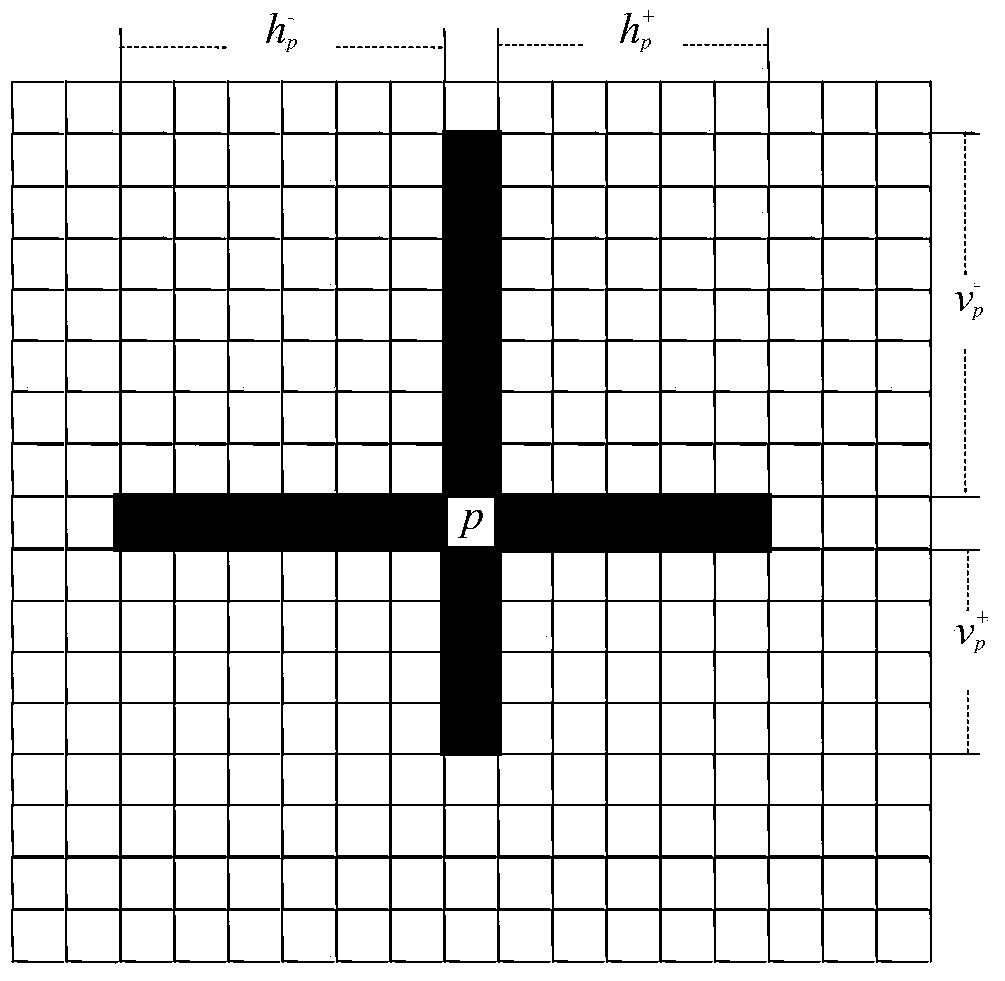
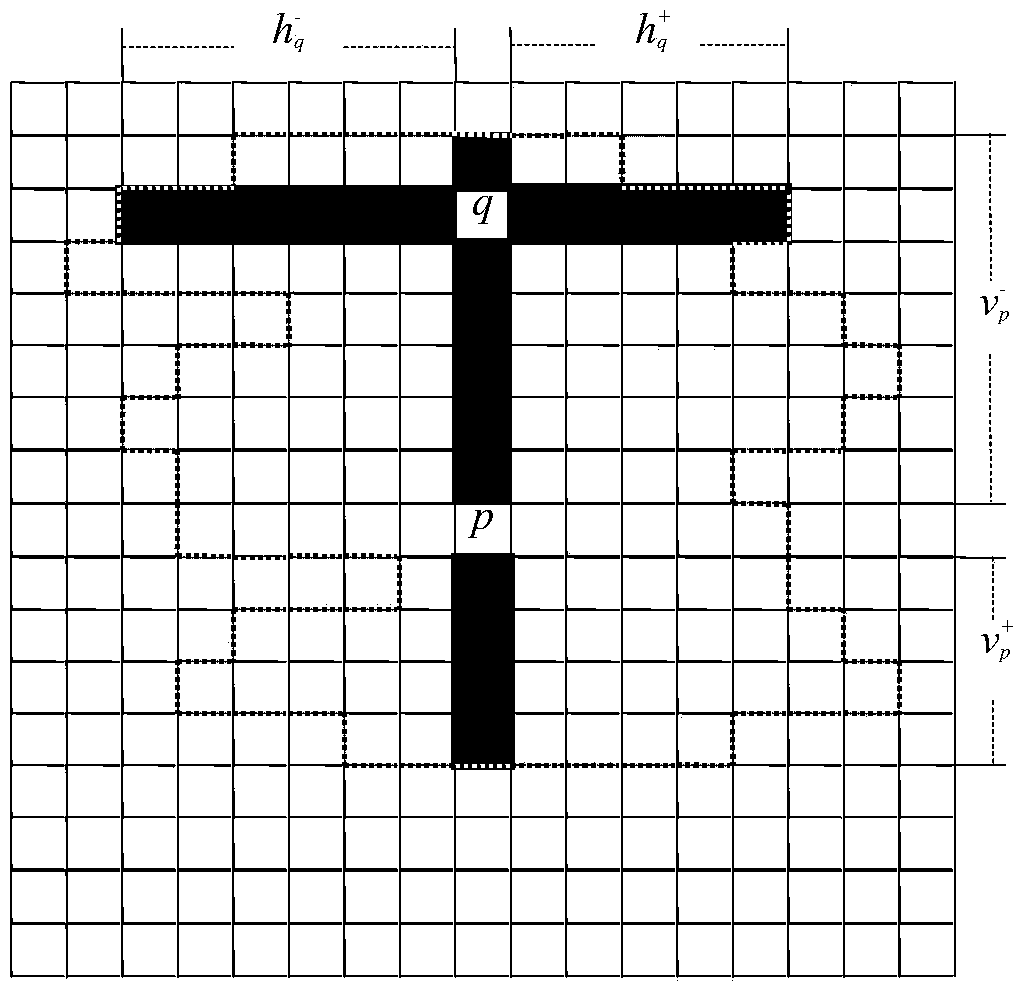
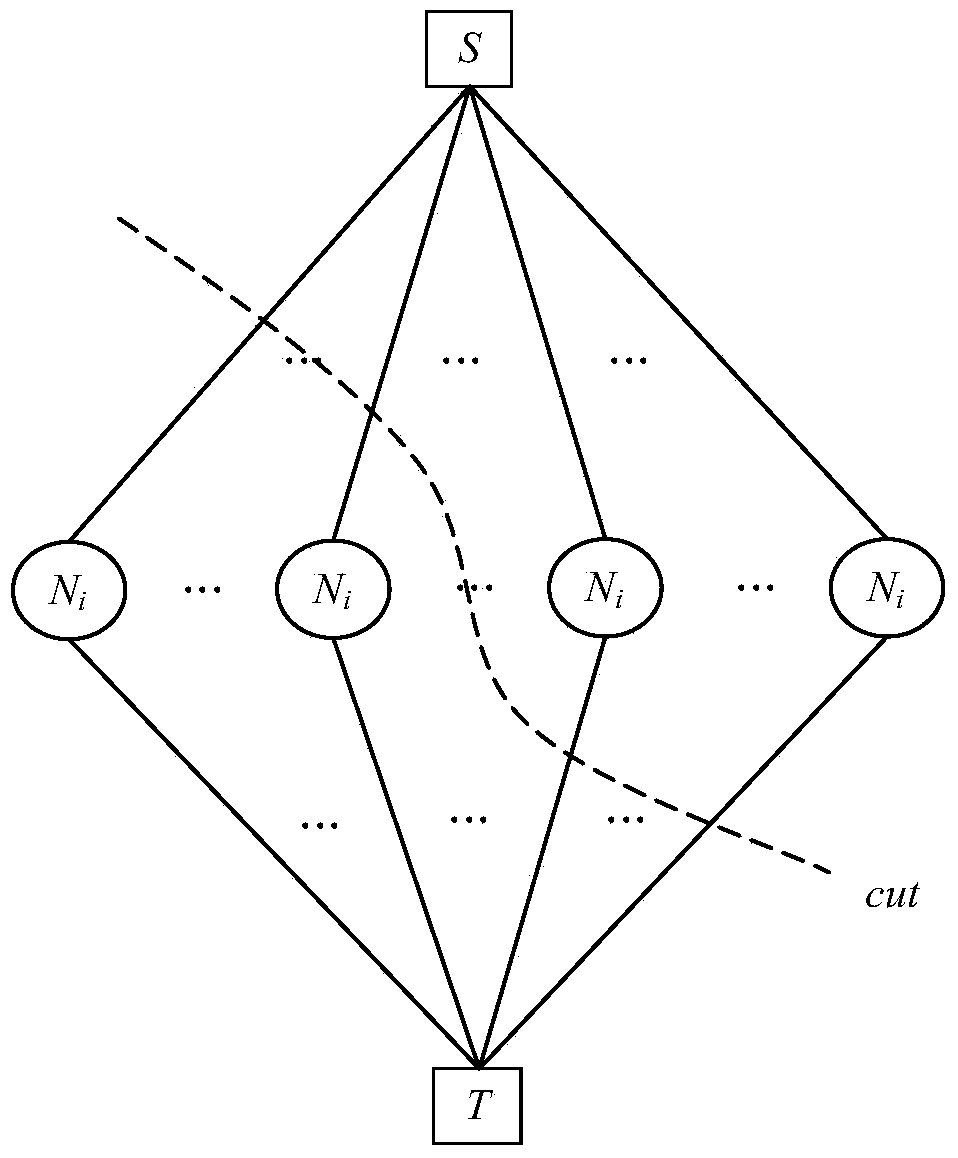
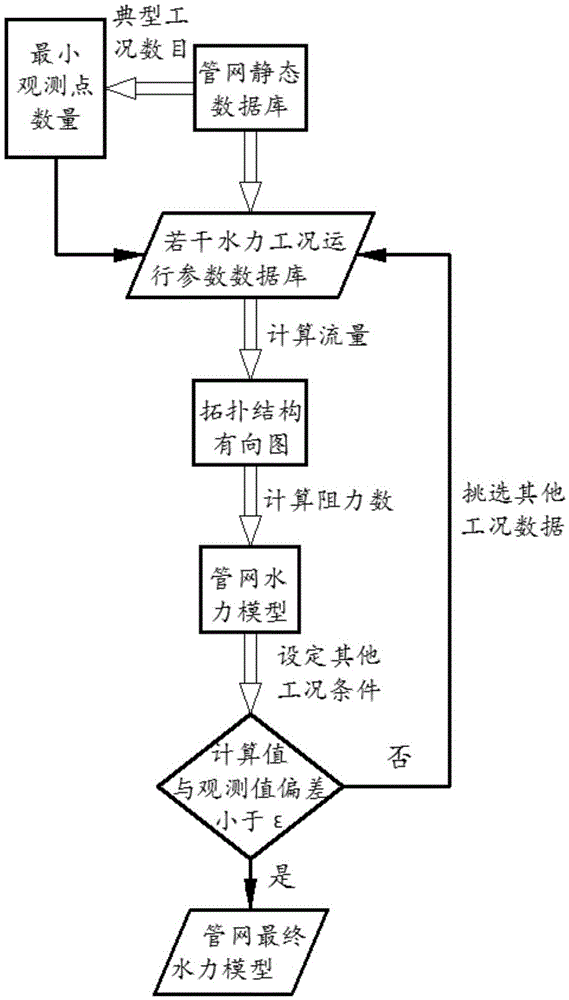
Method for building municipal pipeline hydraulic model
InactiveCN105550405AReduce computing timeFacilitate the analysis of the impact on credibilityComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsDirected graphObservation data
The invention relates to a method for building a municipal pipeline hydraulic model, relates to the technical field of municipal engineering information, and in particular relates to a method for building a pipeline hydraulic model. According to the method, the problem that the existing method for building the pipeline hydraulic model is long in computing time and difficult to estimate result error is solved. According to the method, a pipeline static database is built through obtaining the design information of a pipeline system; the number of minimal observation points is determined according to a pipeline flow equation and a pipeline energy equation; the node pressures and pipe section flow observation data under multiple working conditions are collected; the flow direction in each pipe section is determined and a directed graph which can represent the flow directions is obtained; then the resistance parameter of each pipe section is extracted, the directed graph is endowed with the values of the resistance parameters of the pipe sections, thus the building of the pipeline hydraulic model is completed and the reliability of the pipeline hydraulic model is verified until the pipeline hydraulic model meeting the requirement of pipeline analysis is obtained. The method is applicable to building the pipeline hydraulic model in the field of municipal engineering information technology.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
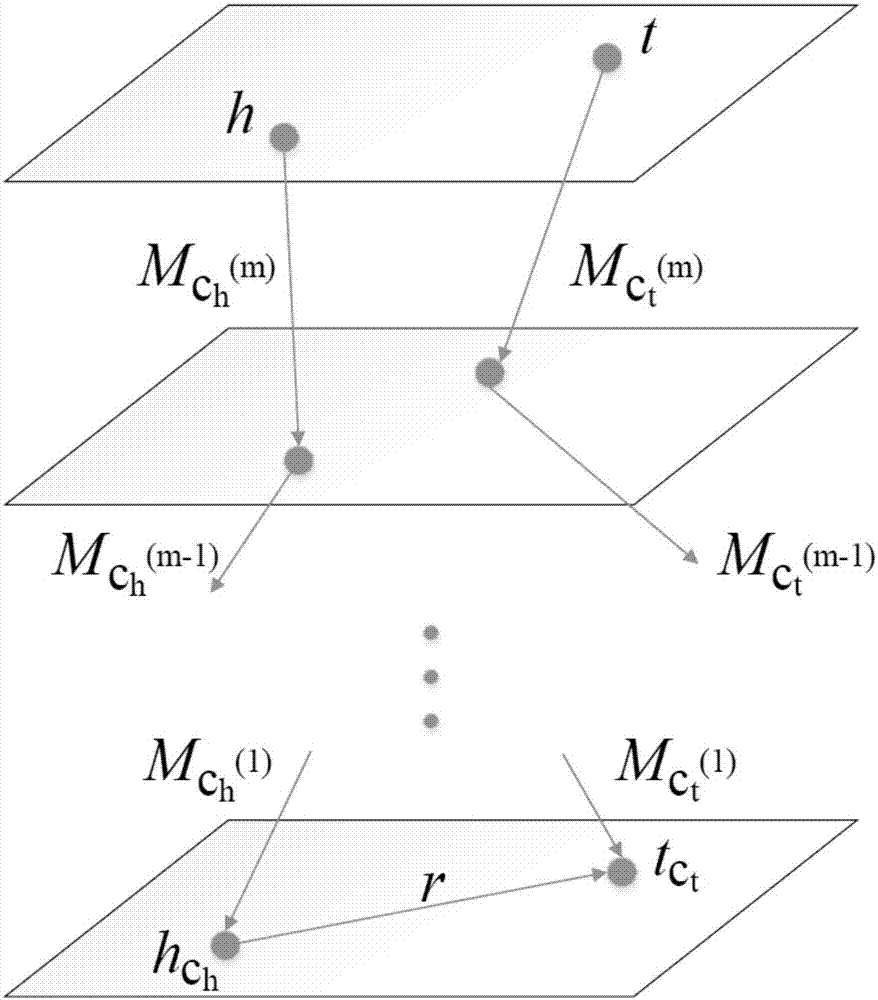
Knowledge graph representation learning method through combination of entity hierarchy category
ActiveCN107423820AEnhance representation learning abilityImprove accuracyKnowledge representationGraph spectraAlgorithm
The invention relates to a knowledge graph representation learning method through combination of the entity hierarchy category. The knowledge graph representation learning method comprises the steps that the trituple relationship of a knowledge graph and the hierarchical structure category information of the entity are acquired; the category mapping matrix of the entity under the preset trituple is constructed according to the hierarchical structure category information of the entity; an energy equation is constructed according to the entity vector and the relationship vector of the trituple relationship and the category mapping matrix; and a margin-based evaluation function is constructed according to the energy equation, and representation of the entity vector, the relationship vector and the category mapping matrix is learnt by minimizing the evaluation function. According to the knowledge graph representation learning method through combination of the entity hierarchy category, the representation learning effect can be enhanced by fully utilizing the category information of the entity having the hierarchical structure, the higher accuracy can be obtained in the task of knowledge graph completion and trituple relationship classification and effect enhancement is especially prominent in the low frequency trituple relationship having long-tailed distribution so that the method has great practicality.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Numerical simulation method for the flight-icing of helicopter rotary-wings
InactiveUS20140257770A1Practical and reliable and efficientAccurate captureGeometric CADComputation using non-denominational number representationMomentumEngineering
The present invention is related to a numerical simulation method for the flight-icing of helicopter rotary-wings. This invention includes the algorithm of adding the voracity compensation force term to the momentum and energy equations describing the air-supercooled water droplets two-phase rotational flows in the single fluid two-phase flow system in wake domain of helicopter-rotary wings; the algorithm of adding the centrifugal and Coriolis force to the slip velocity equation; the models describing the water film and icing progress containing the effect of the centrifugal and Coriolis force; and the procedure using the above algorithms and models to do simulation.
Owner:XIAN VIRTUAL DYNAMICS SIMULATION TECH
Image foreground matting method based on neighborhood and non-neighborhood smoothness priors
ActiveUS20150220805A1Improve performanceImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisGraphicsPattern recognition
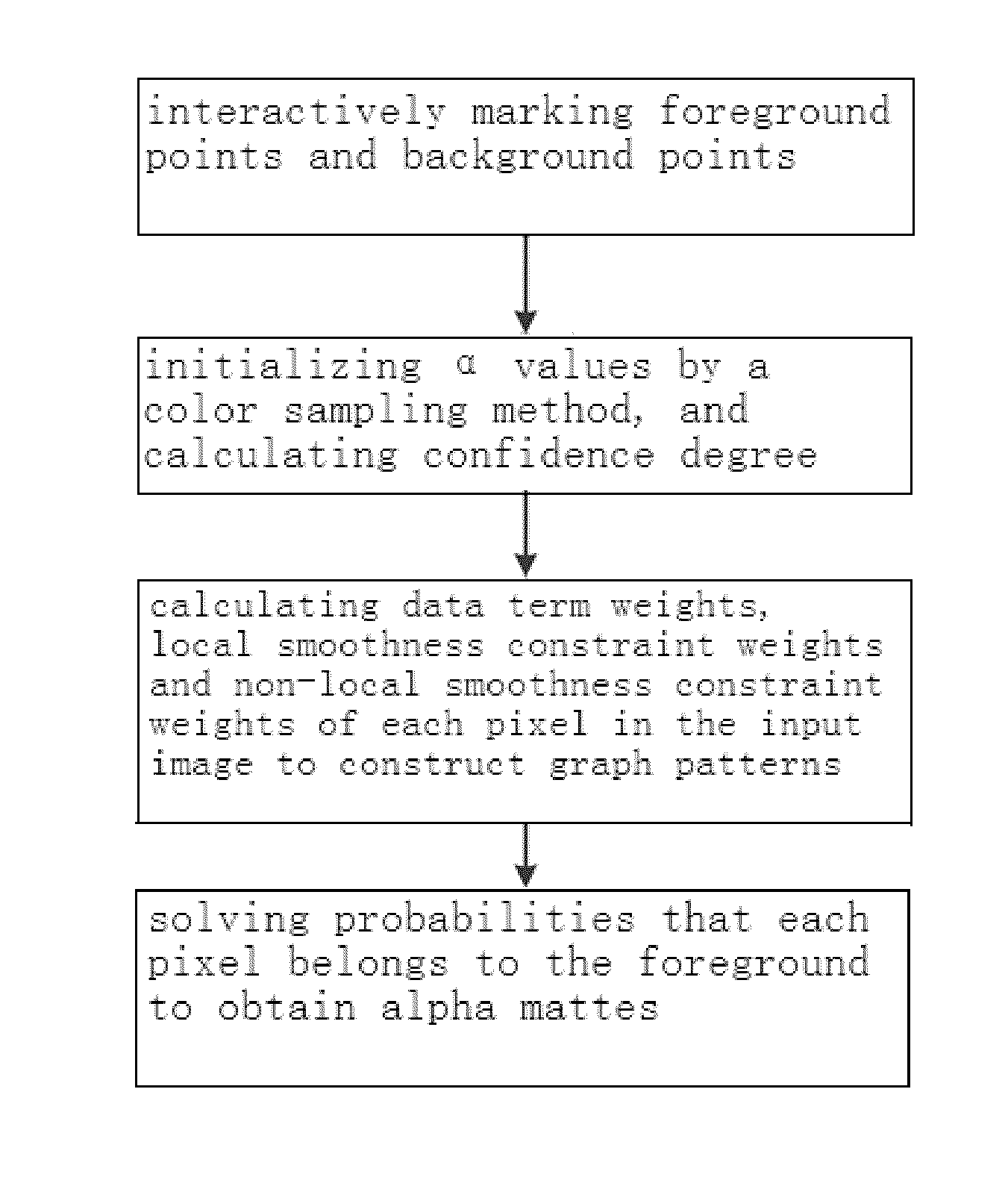
The present invention discloses an image foreground matting method based on neighborhood and non-neighborhood smoothness priors. The method primarily comprises the steps of: interactively marking foreground points and background points; initializing α values of each unmarked pixel of the input image by a color sampling method, calculating confidence degree of the pixel, and admitting α values of pixels of which confidence degree is larger than a given threshold as known pixels; calculating data term weights, neighborhood smoothness constraint term weights and non-neighborhood smoothness constraint term weights of each pixel in the input image to construct graph patterns of all pixels of the input image; and according to a values of the known pixels, under the constraint of the graph patterns, solving probabilities that each pixel belongs to the foreground by minimizing the energy equation so as to obtain alpha mattes.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
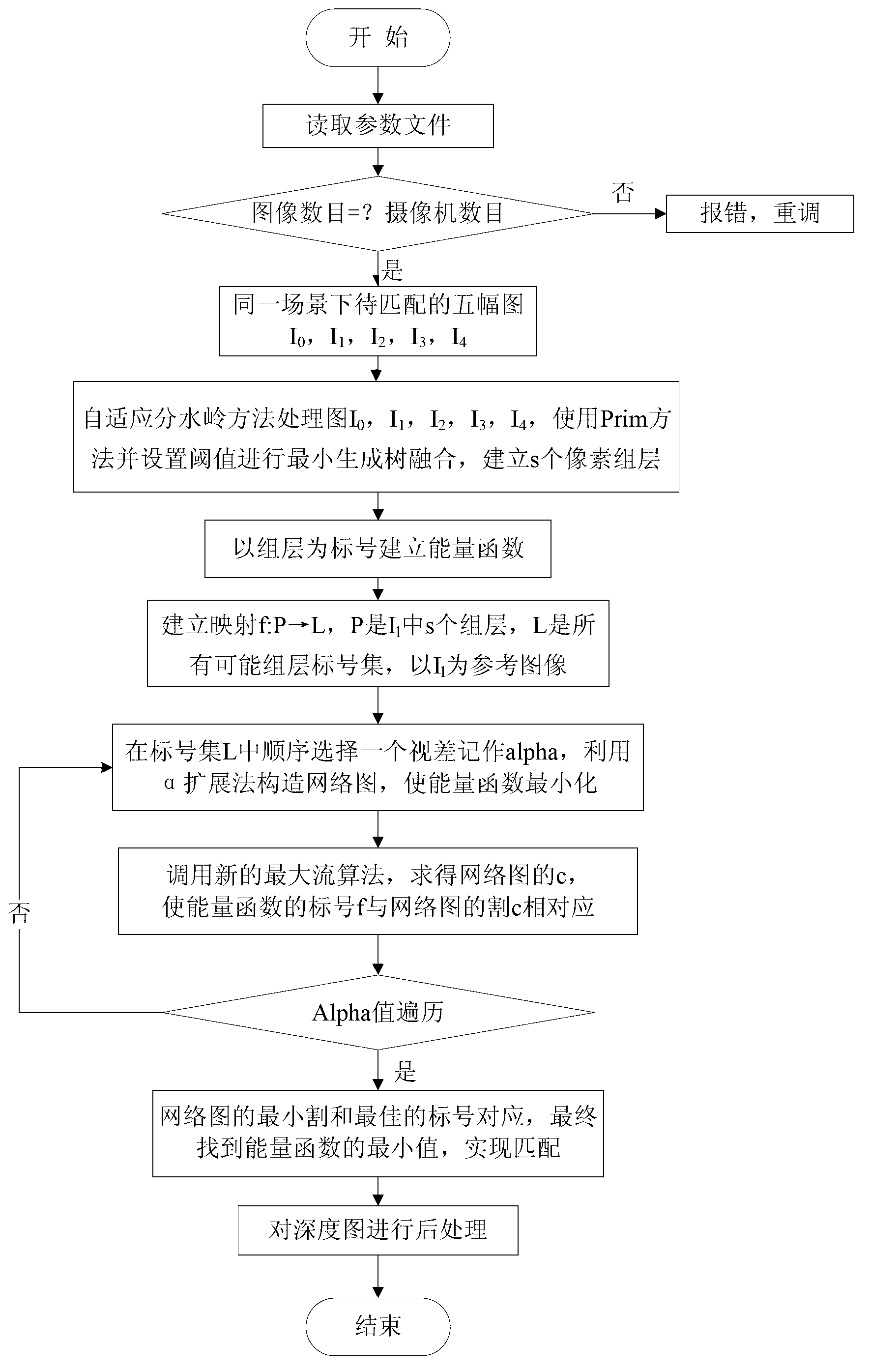
Multi-view stereo matching method based on self-adaptive watershed image segmentation
The invention provides a multi-view stereo matching method based on self-adaptive watershed image segmentation, provides a new self-adaptive local threshold method, and applies the method to region fusion of a watershed combined with a Prim method. The method comprise the following steps: processing an image using a self-adaptive watershed, so that pixels in the picture segment the image into different regions in a certain relation, allocating mark numbers to set up an energy equation, and providing a new large-region parameter-free smoothing constraint model; and finally through an optimized alpha-expansion method, searching by using a pixel range in a minimum spanning tree region for region pixels within the range to find a matching point, otherwise not performing the search. A neighborhood enables the method to more flexibly obtain a better target boundary, thus achieving very good effect at a discontinuous boundary and in a high folding texture region. While not affecting the quality of an synthesized view, the method solves the problem of contraction between a static image and a motion video, and discontinuous jumping phenomenon does not occur in the result of depth estimation.
Owner:SHENZHEN XIAOLAJIAO TECH CO LTD
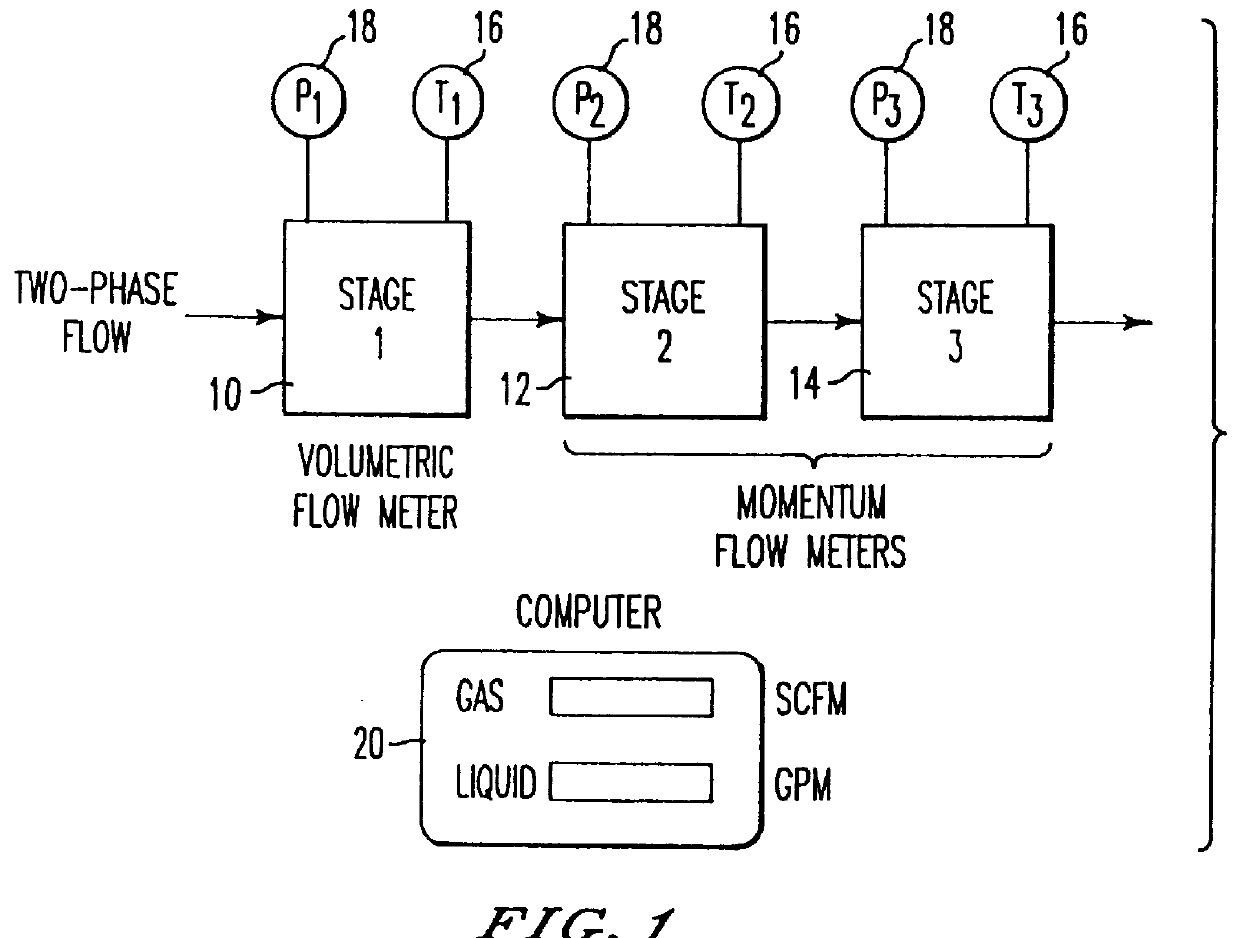
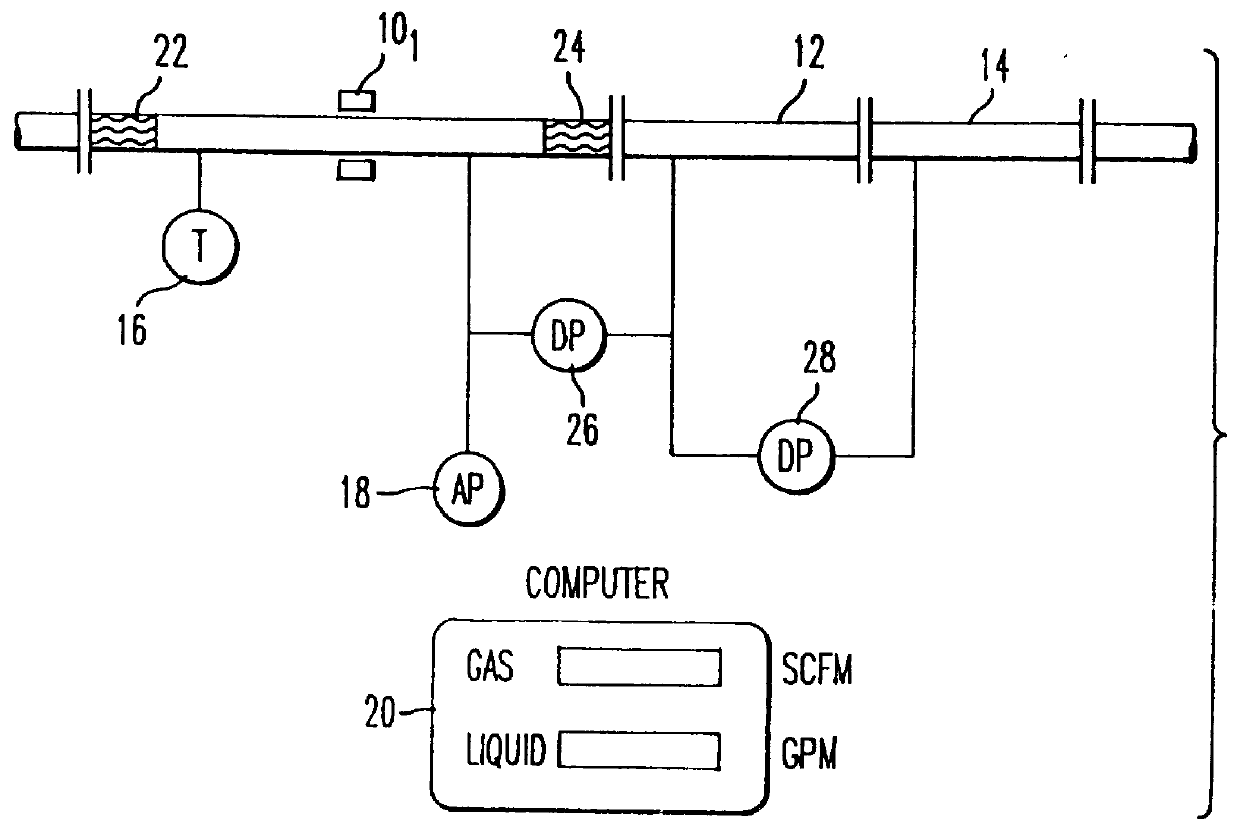
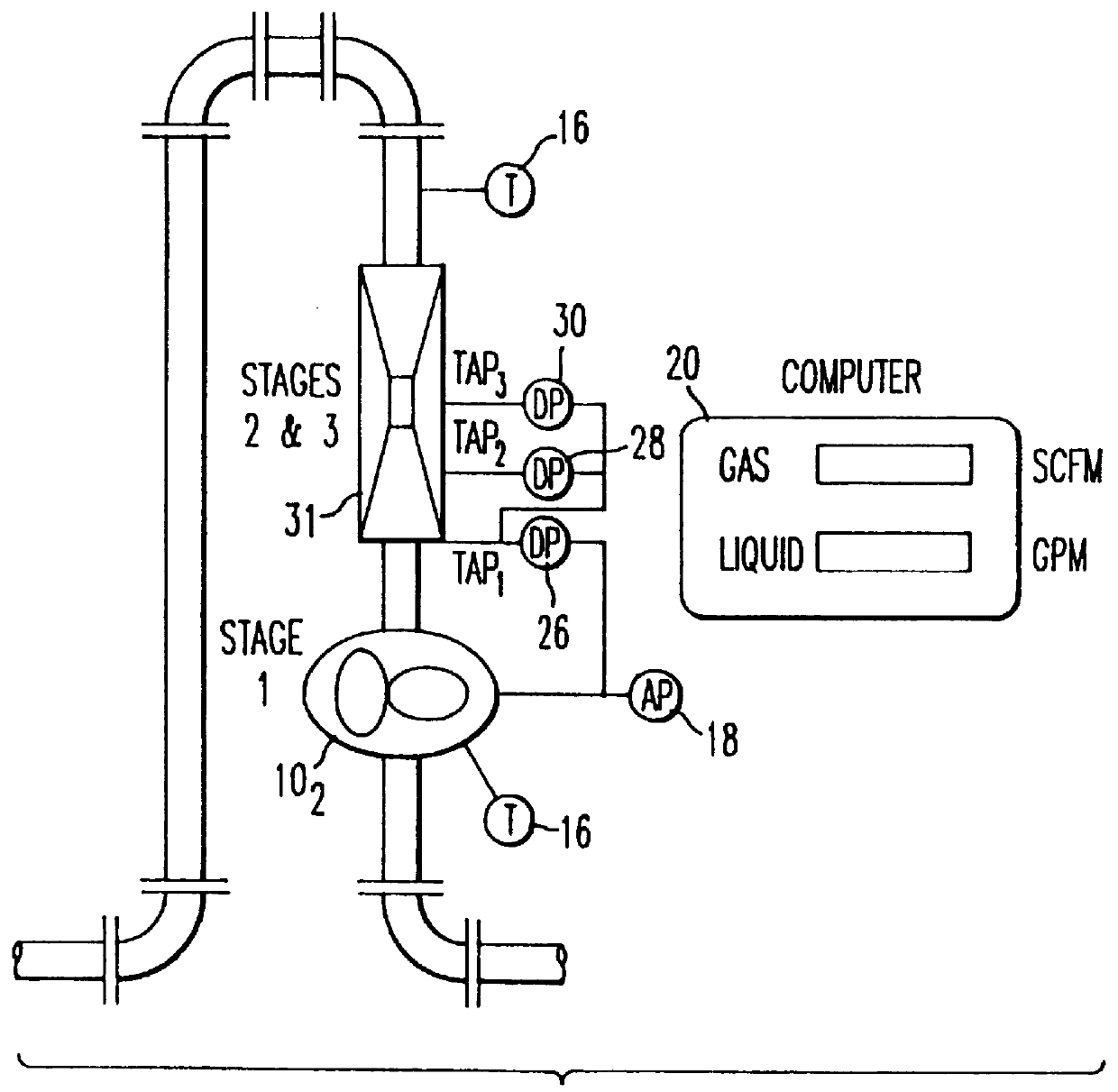
Apparatus and method for measuring two- or three-phase fluid flow utilizing one or more momentum flow meters and a volumetric flow meter
InactiveUSRE36597E1Low costHigh measurement accuracyVolume/mass flow by differential pressureMomentumDifferential pressure
An apparatus and method for measuring the flow rates of each component of two-phase flow consisting of a gas and a liquid or three-phase flow consisting of water, oil and gas, including a first volumetric flow meter stage, and second and third momentum flow meter stages coupled in a series flow path with the volumetric flow meter stage and in which a velocity ratio between the gas and the liquid in the series flow path is maintained to be one. A processor calculates flow rates of the components of flow by solving volumetric flow and momentum or energy equations defining flow through the first through third stages utilizing a volumetric flow output from the first stage and momentum flux outputs from said second and third stages, and an indicator displays flow of liquid and gas or oil, water and gas components of the flow. To measure three-phase flow, a water-cut meter is provided to determine the amount of water flow, which is then used by the processor to determine the flow of the rest of the liquid. The second and third momentum flow meter stages can be implemented by two separate momentum flow meters or by a single momentum flow meter, such as a venturi flow meter having a venturi nozzle including pressure taps for obtaining at least two differential pressure measurements. In the event that the density of the liquid component is known, a single momentum flow meter stage is sufficient.
Owner:AGAR CORP
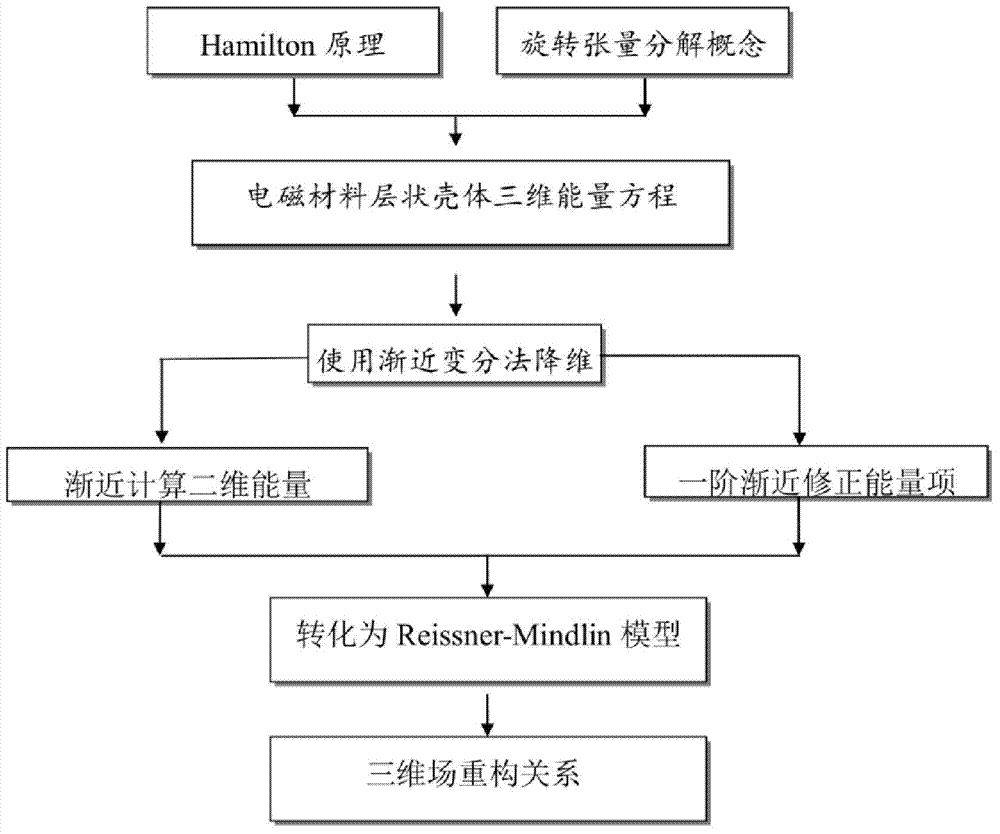
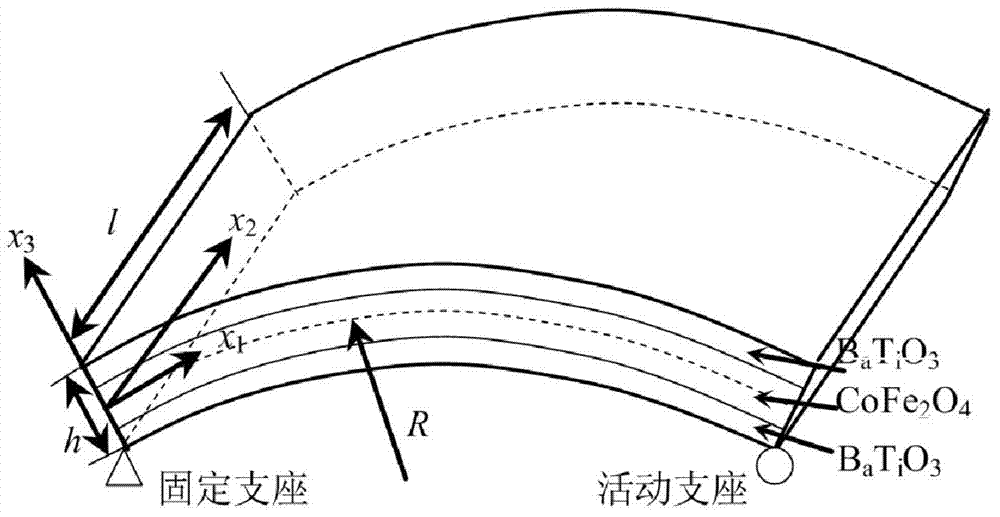
Analogue simulation method for electromagnetic elastic coupling of layering shell made of electromagnetic materials
InactiveCN103886165AHigh accuracy of 3D field distributionSmall amount of calculationSpecial data processing applicationsComputer resourcesExtension principle
The invention provides an analogue simulation method for electromagnetic elastic coupling of a layering shell made of electromagnetic materials. A three-dimensional energy equation including the electricity-magnetism-elastic coupling effect is established based on the Hamilton extension principle; three-dimensional energy is asymptotically extended into serial two-dimensional recursion energy based on the variation asymptotic method, a leading variation item in the two-dimensional recursion energy is corrected asymptotically through inherent small parameters of the shell, and therefore a correction model close to the original three-dimensional energy as much as possible is obtained and is converted into the Reissner-Mindlin model form commonly used in the engineering; a three-dimensional variation reconstruction relation is inferred based on the obtained two-dimensional overall response and all levels of warping functions. The apriority hypothesis is not needed in the model, the structural electromagnetic elastic coupling performance under the function of various fields can be accurately predicted, the calculated amount is small, calculating efficiency is higher than that of the high-order set theory and the three-dimensional finite element solution, and the number of resources occupied in a computer is small.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com