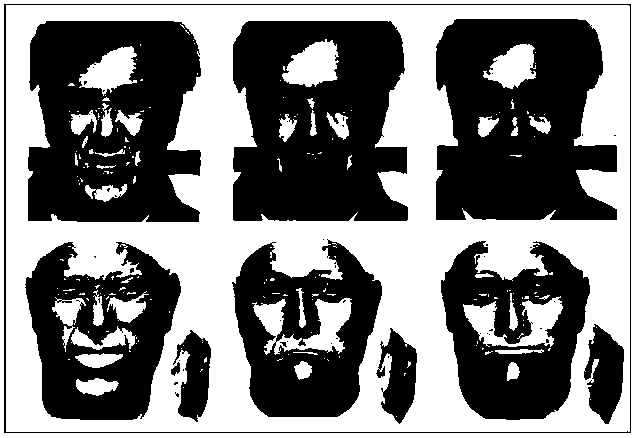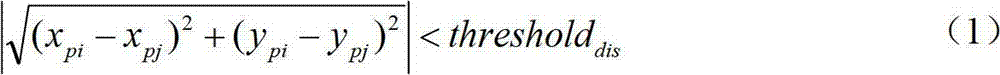Patents
Literature
100 results about "Height field" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
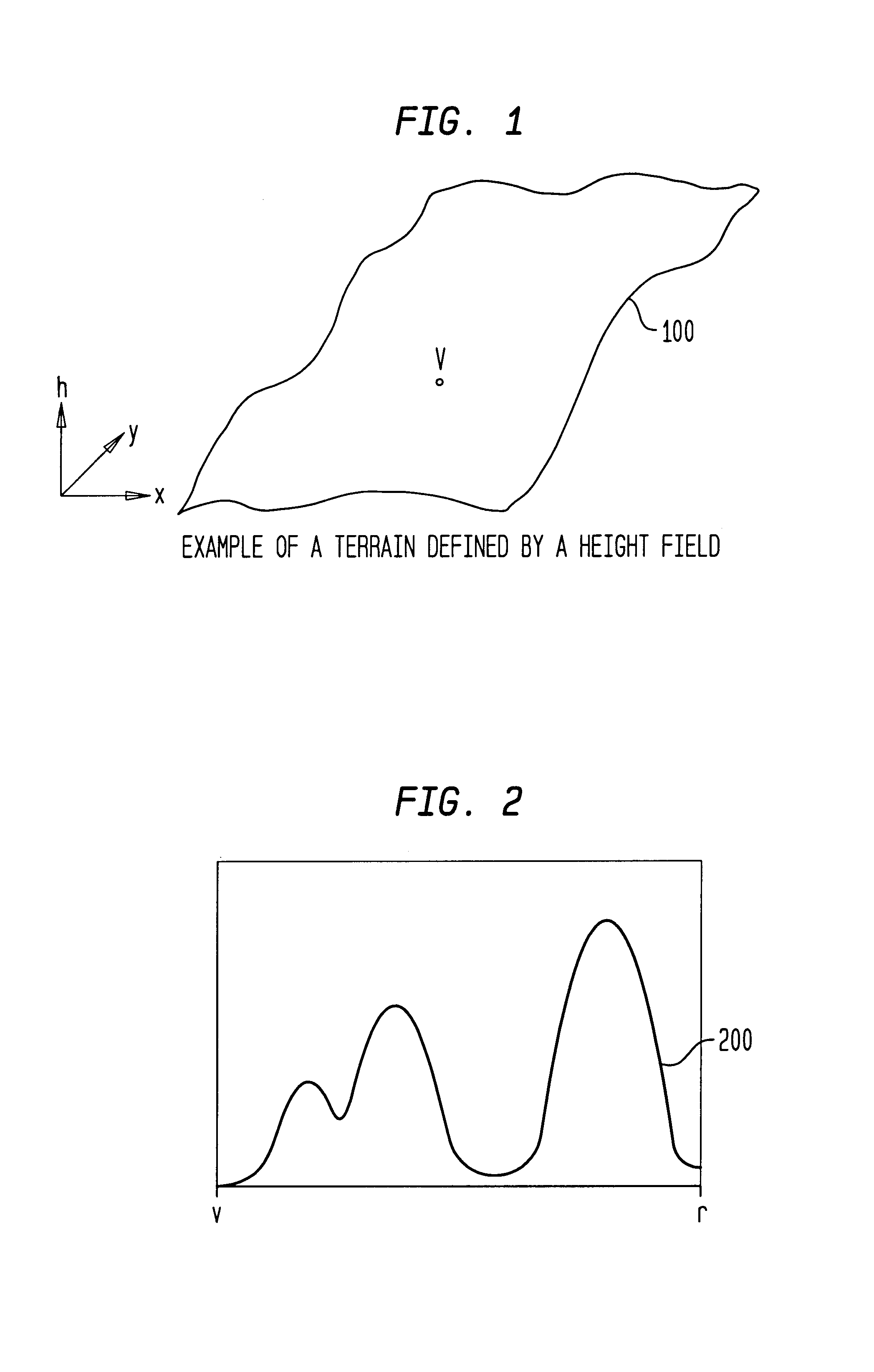
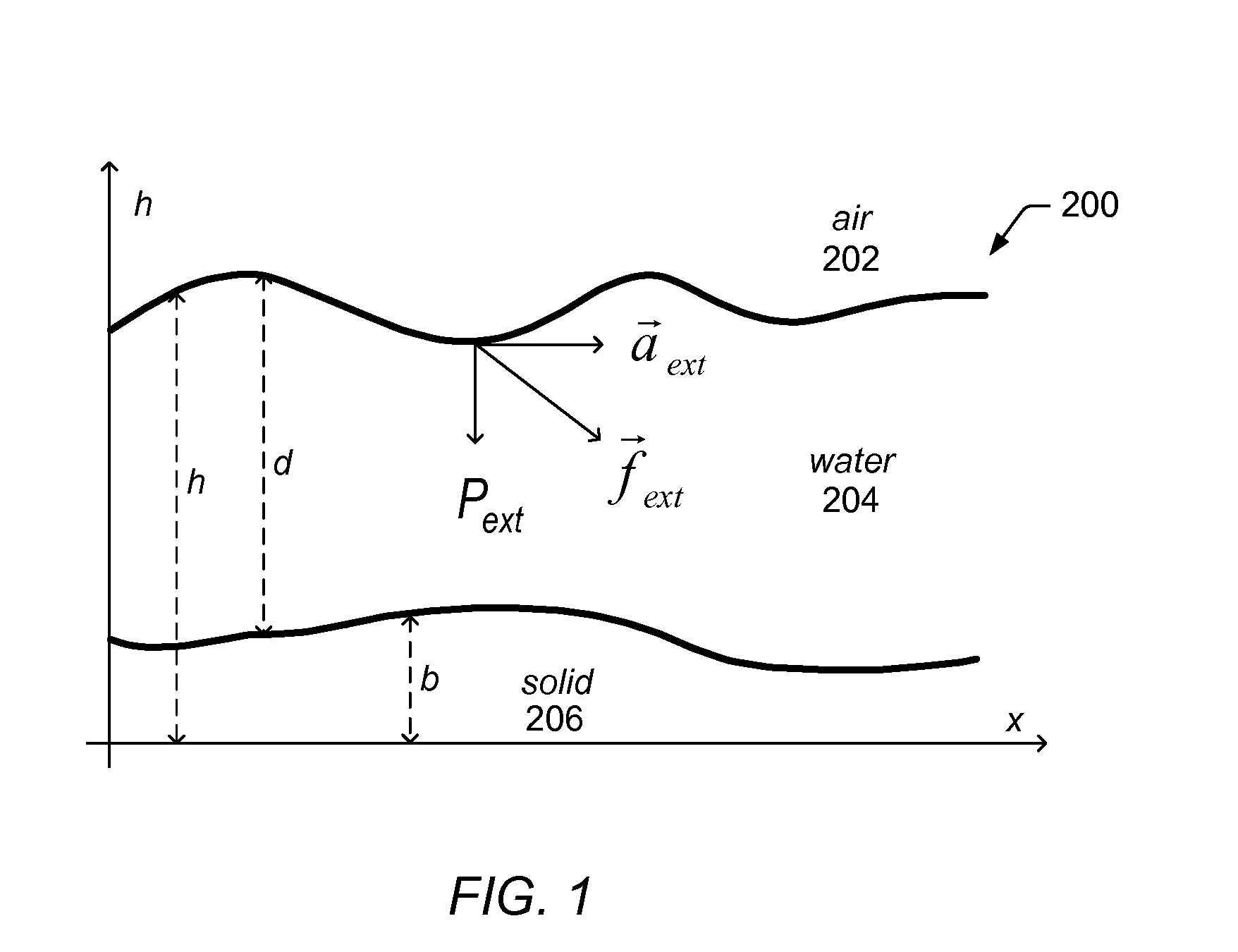
A height field is essentially a one unit wide by one unit long square with a mountainous surface on top. The height of the mountain at each point is taken from the color number or palette index of the pixels in a graphic image file.
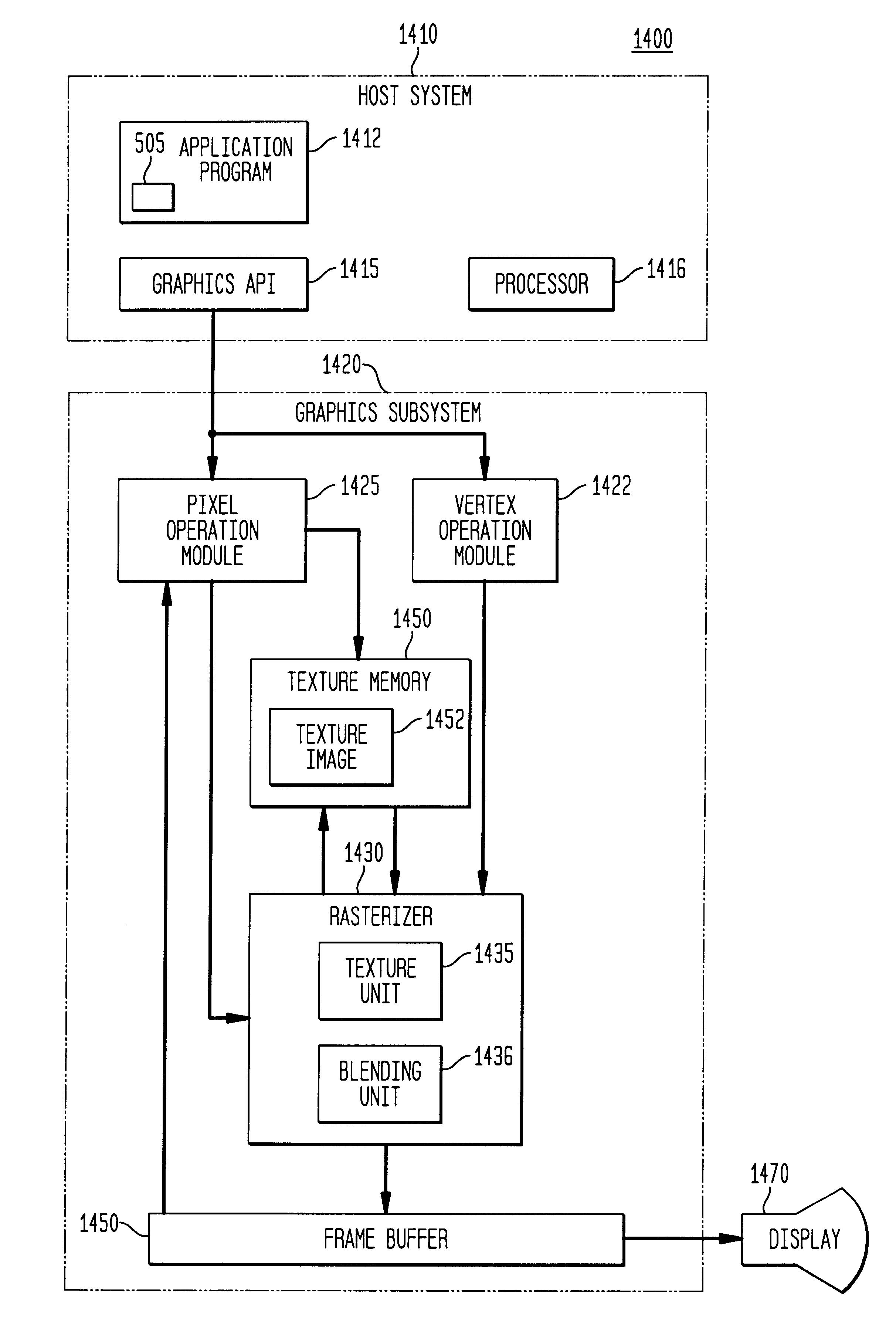
Method, system, and computer program product for visibility culling of terrain
ActiveUS7027046B2Promote reconstructionEasy to adjustCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingTerrainGraphics
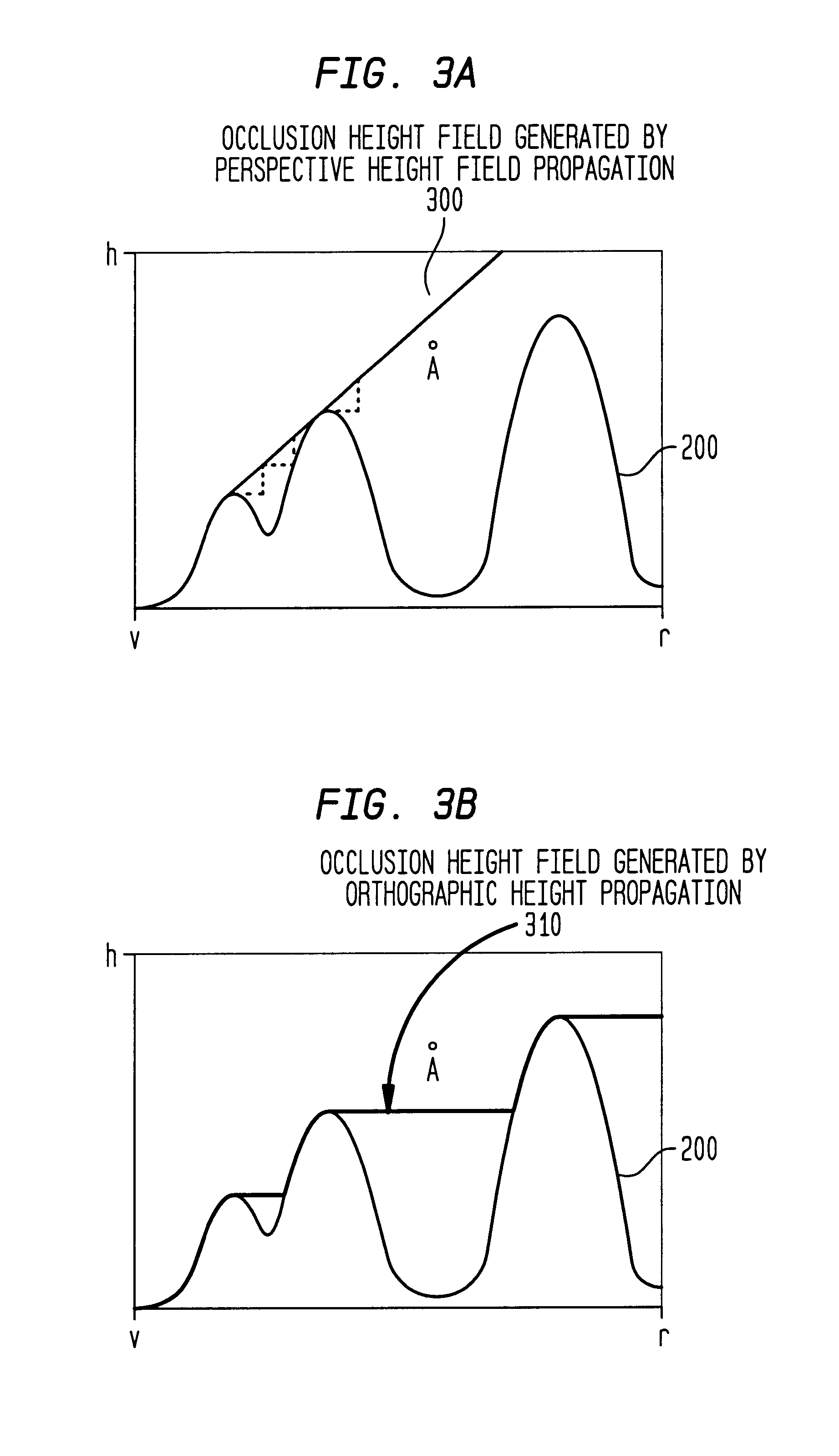
A method, system, and computer program product are provided for visibility culling of terrain. A height field is perspective modulated. An occlusion height field is generated based on an orthographic height propagation of the perspective modulated height field. Graphics data is culled based on the generated occlusion height field. Texturing and blending operations can be used to accelerate the perspective modulation. A perspective modulation disk is used to modulate the first height field along radial slices from a viewpoint. Texture from a one-dimensional texture with distance values is mapped to the radial slices to obtain the perspective modulated height field. Generating an occlusion height field can also be carried out using texturing and blending and can be hardware-accelerated. According to a further feature, a shift disk or shift texture is used.
Owner:ACTIVISION PUBLISHING
System and Method for Simulating Shallow Water Effects on Arbitrary Surfaces
ActiveUS20080177519A1Effective simulationFacilitate real-time fluid controlAnimationImage generationFluid controlWave equation
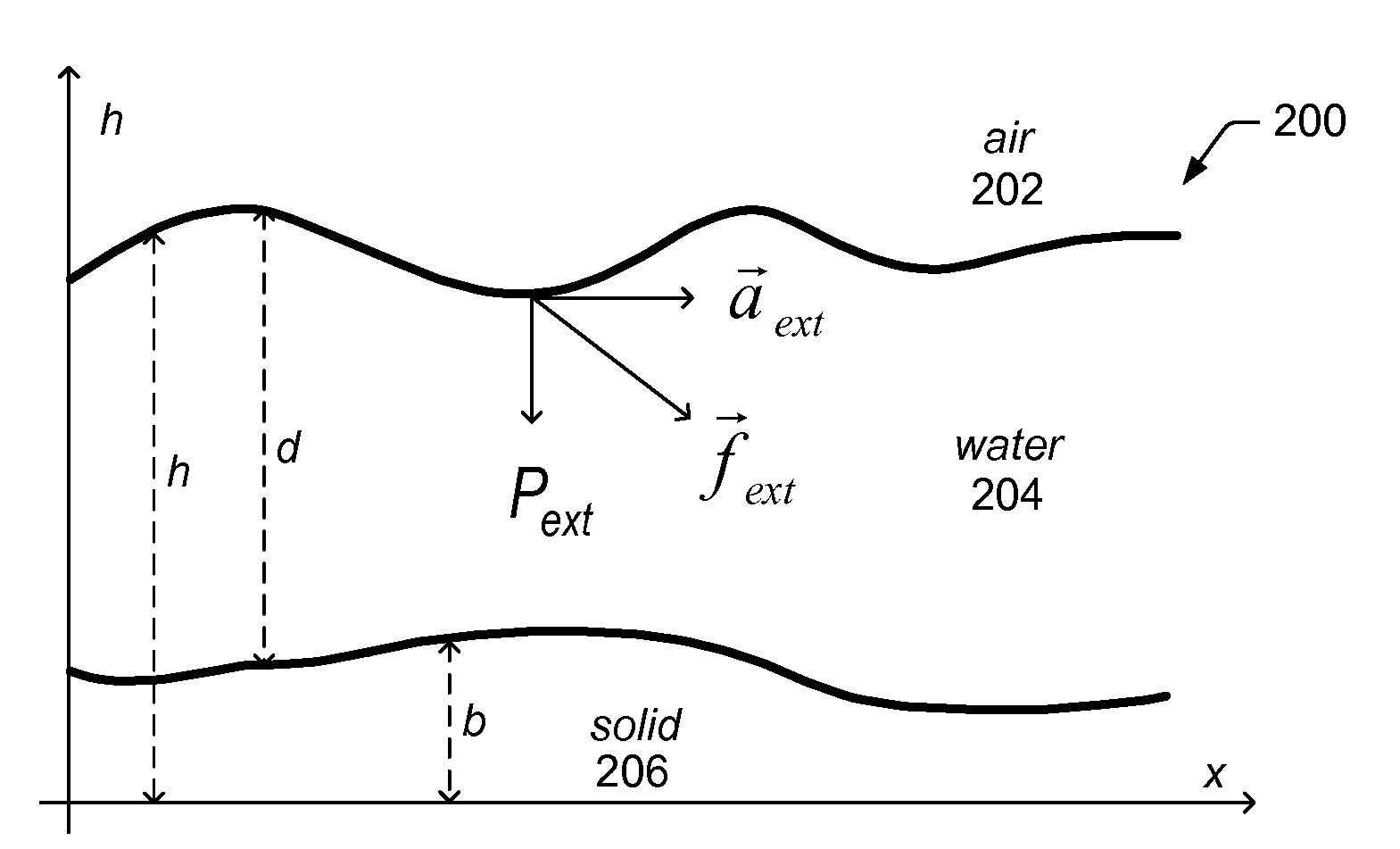
A system and method for shallow water simulation may provide a framework for solving General Shallow Wave Equations (GSWE) to efficiently simulate 3D fluid effects on arbitrary surfaces using a height field representation. The height field representation may include height columns constructed along surface normals, which may be dependent on a condition of boundary cells adjacent to fluid cells and / or artificial viscosity effects. The framework may provide implicit schemes for solving for the effects of external forces applied to the fluid, including gravity and surface tension, and explicit schemes for solving for advection effects. The system and method may be implemented on general-purpose CPU(s) and / or GPU(s) and may be capable of simulating a variety of fluid effects including: waves, rivulets and streams, drops, and capillary events. In some embodiments, the system and method may achieve real-time fluid control and fluid shape design through user-interaction (e.g., in a graphical painting application).
Owner:ADOBE INC
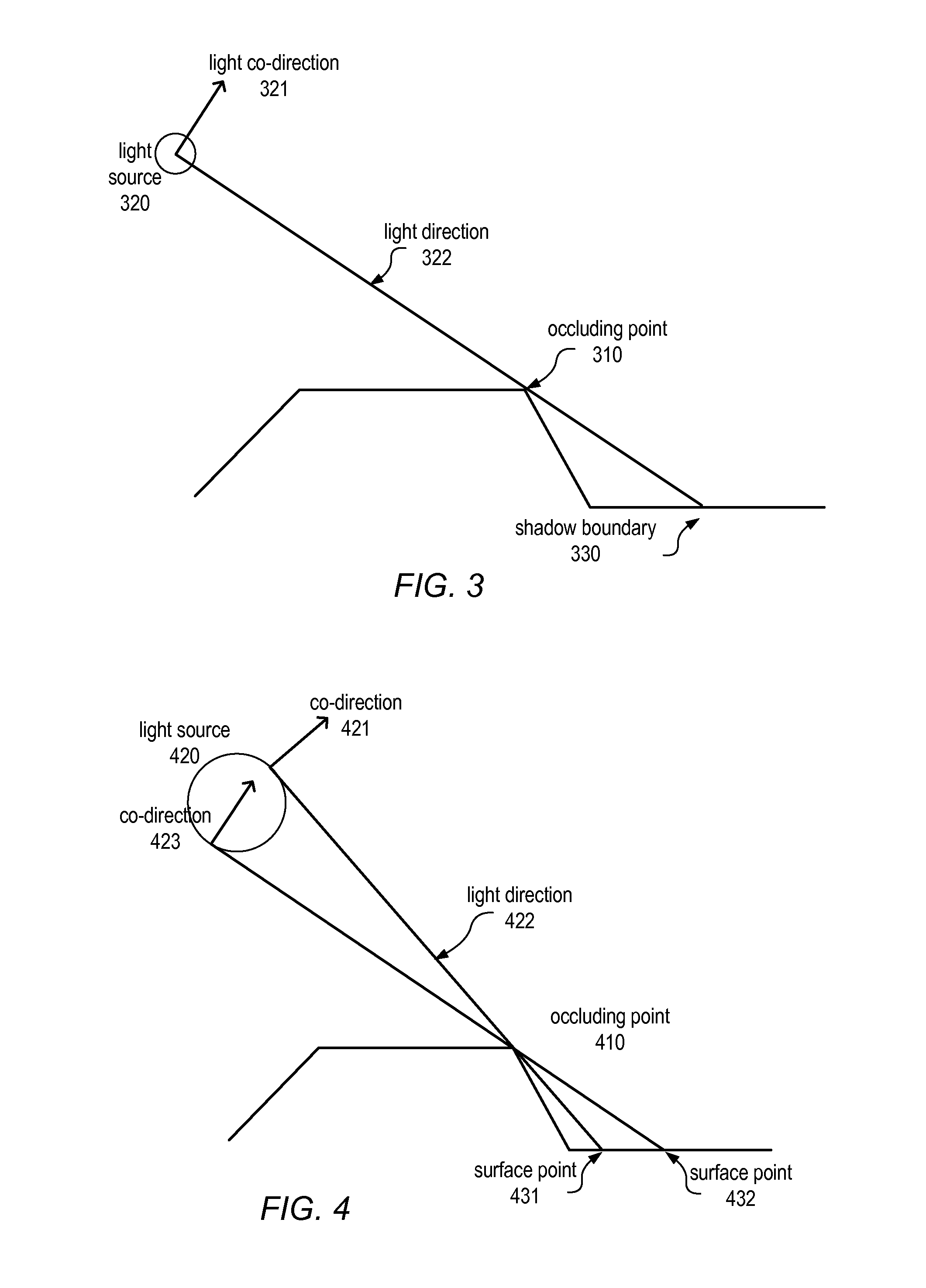
System and methods for rendering height-field images with hard and soft shadows
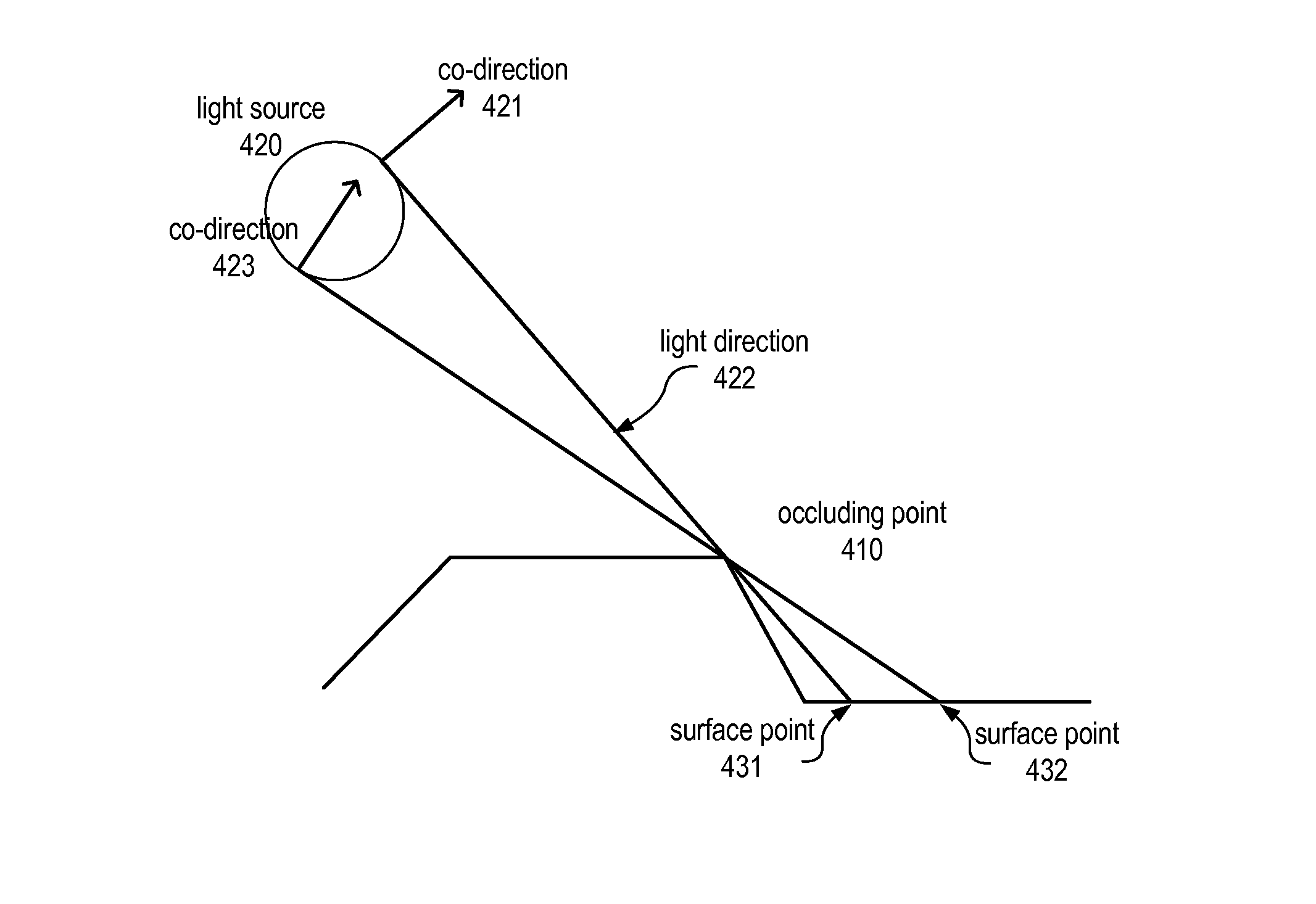
A system, methods, and computer-readable storage media for rendering height-field images that efficiently compute hard and soft shadows are disclosed. The system and methods may utilize a graphics representation comprising bounded 2D shapes with full 3D fill styles that affect shading, and an occlusion priority that determines visibility. The methods may include scan-coherent techniques for computing shadows from height-fields containing depth discontinuities while incrementally updating a convex hull of surface points. The methods may include a sweep-based algorithm for linear light source illumination of 2.5D graphical models across diagonal height-field cross-sections and / or a shear warp algorithm. Pre-computed (weighted) integrals corresponding to the light direction may be stored in tables according to a corresponding horizon angle and may be used in computing the lit intensity. The results may be free of aliasing artifacts. The methods may be implemented as program instructions, stored on computer-readable media, executable by a CPU and / or GPU.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
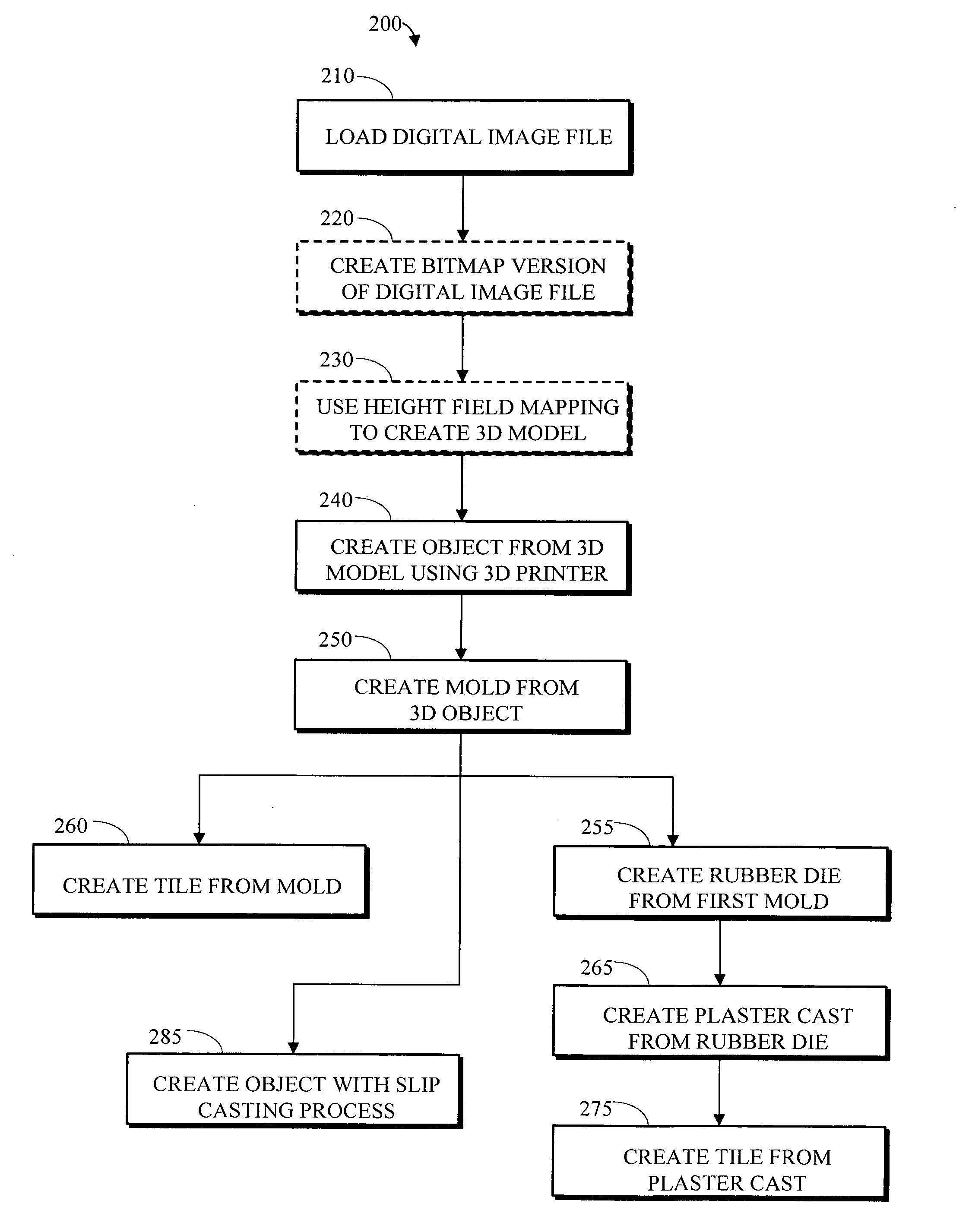
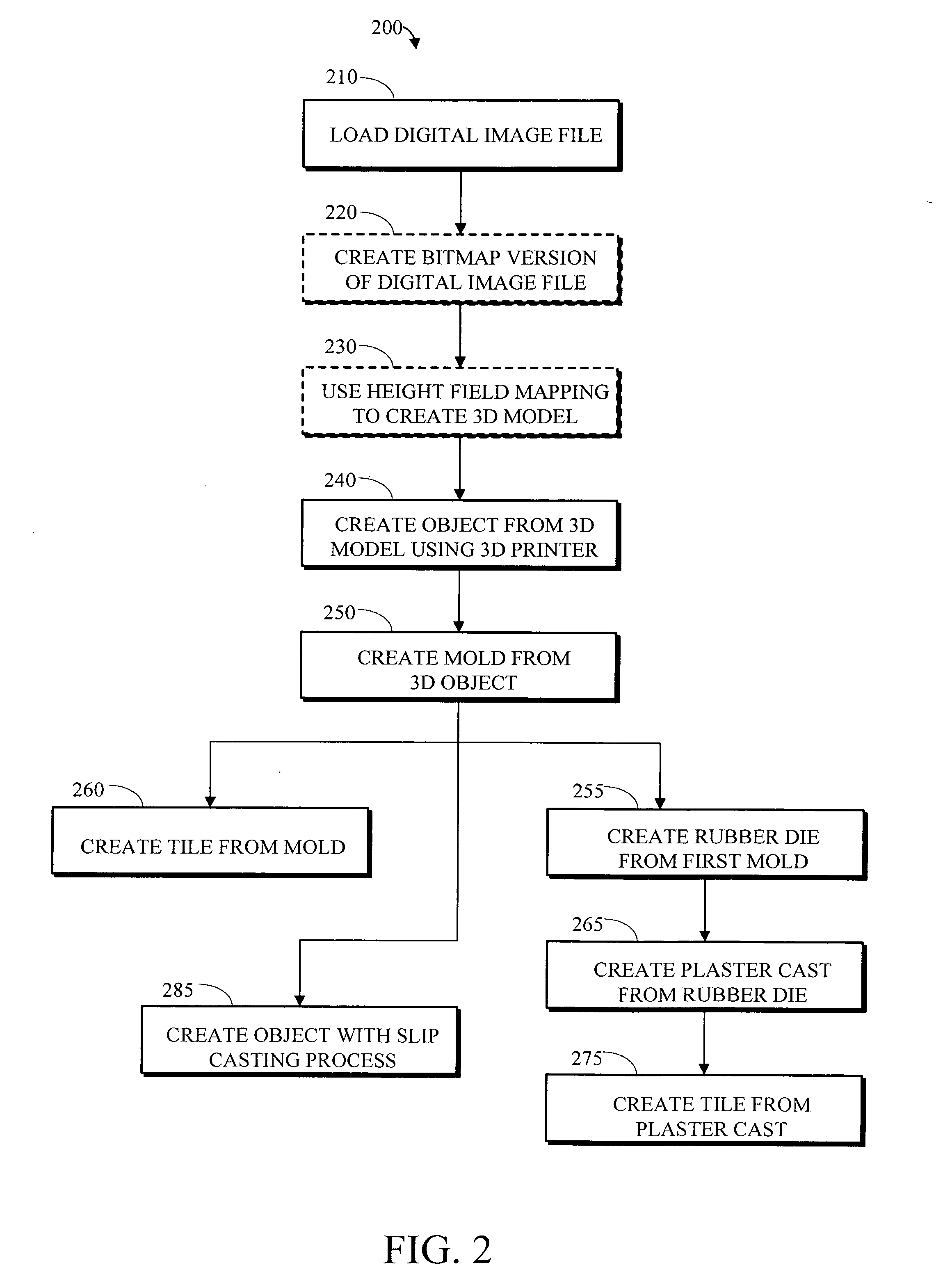
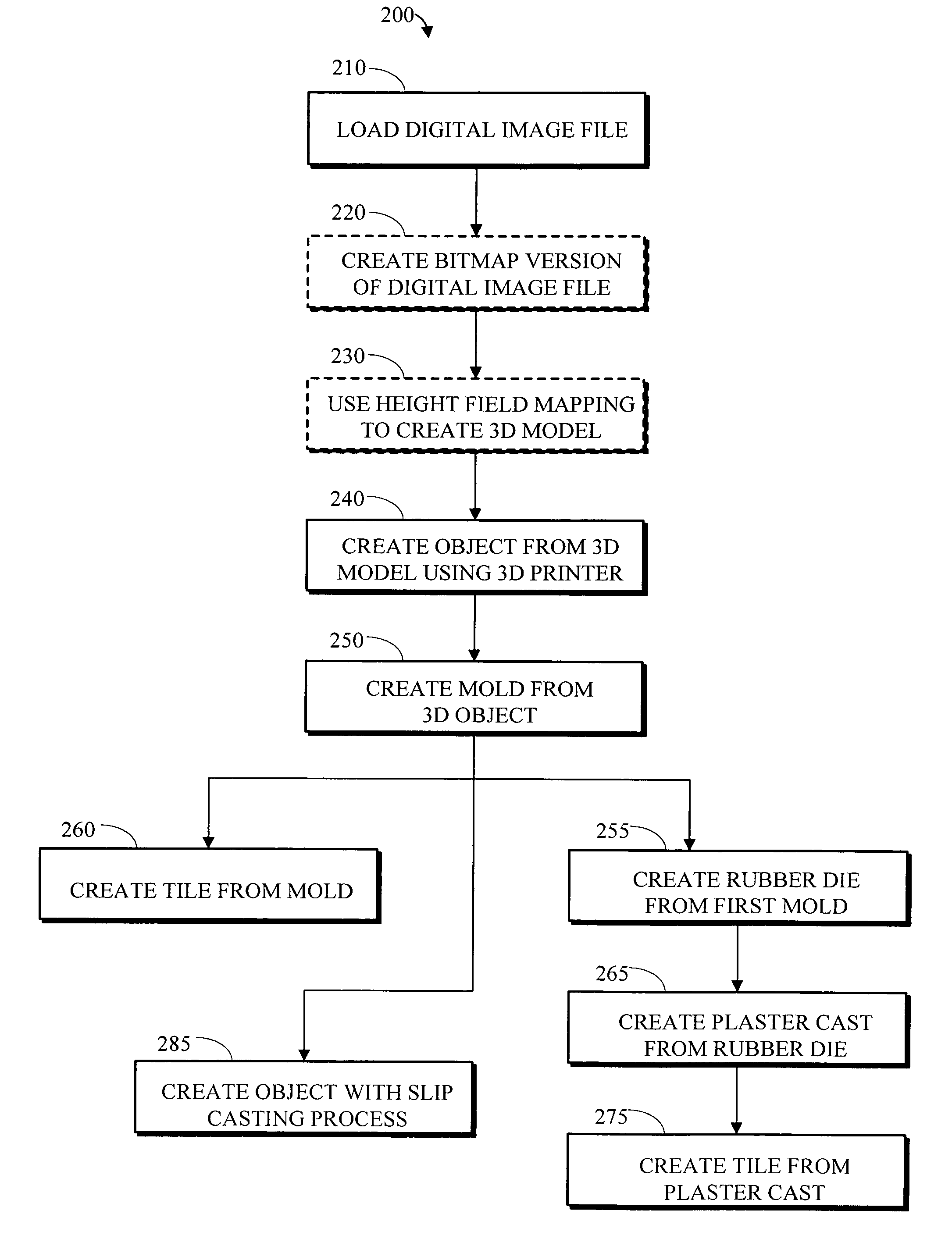
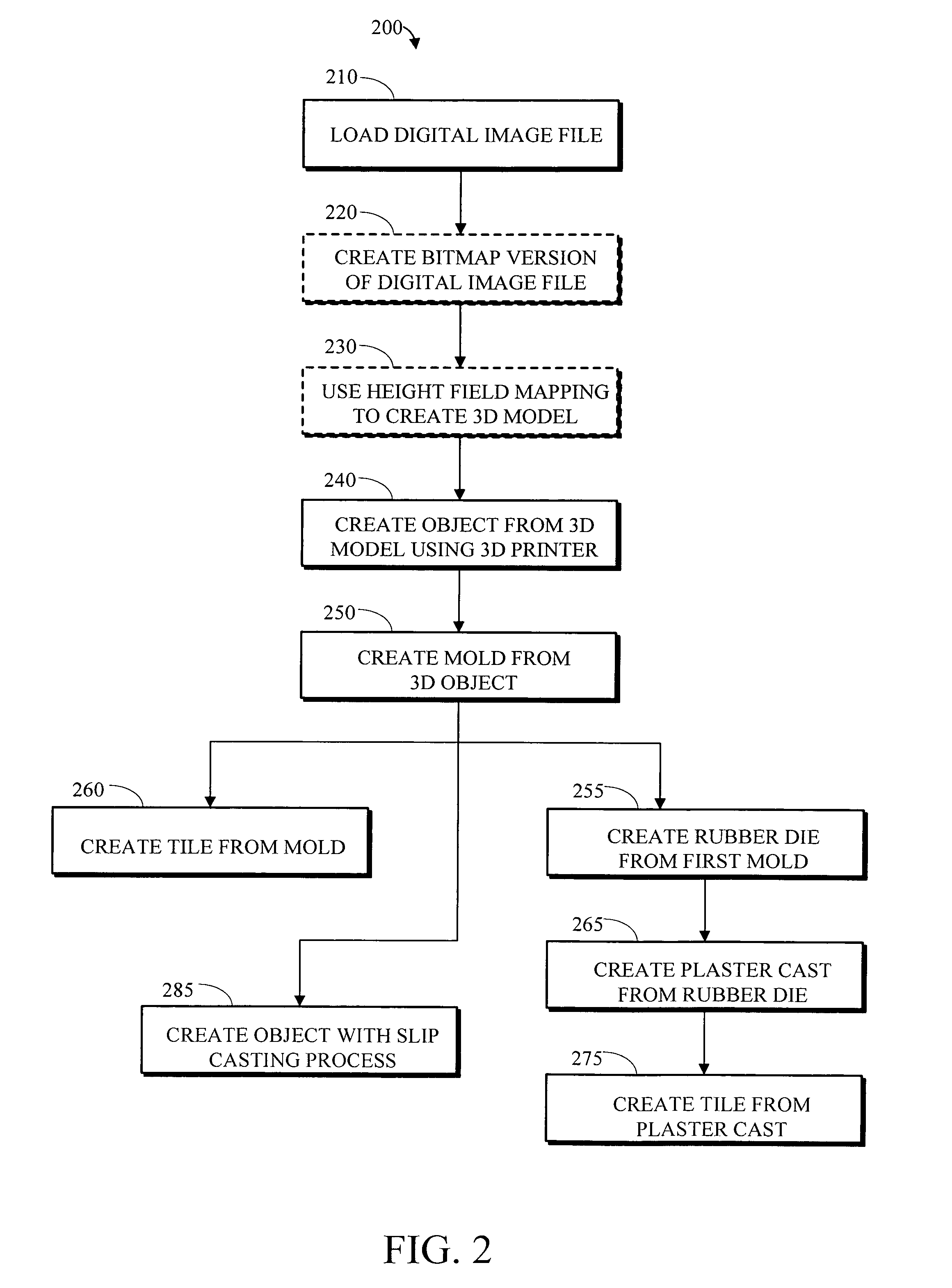
Apparatus and method for creating three dimensional objects
InactiveUS20050251275A1Rapid deploymentProgramme controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusEngineeringBuilding construction
An electronic file containing height field mapping data is output to a specialized printer and used to create one or more three dimensional molds. The molds, in turn, may be used to fabricate bas-relief tiles and similar three-dimensional objects from various materials. The process allows for rapid deployment of customized design elements in many construction applications and environments.
Owner:CARLSON KEITH
Realistic modeling and drawing of shallow water wave
A realistic modeling and drawing method of shallow water wave comprises the following three aspects: using a shallow water equation based on the physical principle to simulate the water face height field; introducing the external force such as the wind force in the shallow water equation; simulating the water face with the ripples; drawing the reflection and refraction effects of the water face, realizing emulation of the optical features of the ripple surface, and improving realistic drawing in the shallow water scene; using the way combined with the shallow water equation to realize interaction of the ripple and the other object, and improving the interaction of the ripple. The invention utilizes the difference method to solve the shallow water equation introduced with the wind force, thereby ensuring simple and valid calculation and long time step stability, and realizing the real-time performance of the ripple simulation. When the realistic drawing is ensured, the calculation performance is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
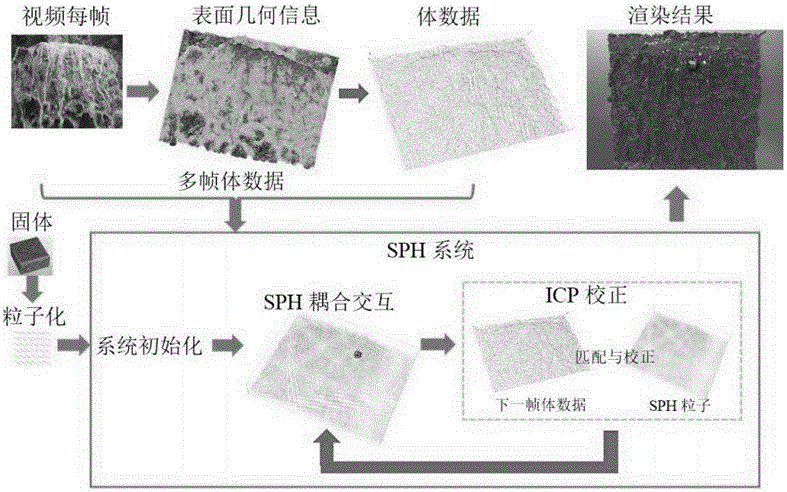
Fluid-solid interaction simulation method based on video reconstruction and SPH model
InactiveCN106446425AOvercome limitationsReal fluid-solid coupling simulation effectDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSimulationSurface level
The invention discloses a fluid-solid interaction simulation method based on video reconstruction and an SPH model. The fluid-solid interaction simulation method includes steps: 1), adopting a bright-dark recovery shape method to quickly reconstruct fluid surface geometric information in video, and acquiring a surface height field of each frame of input image; 2), combining the height fields with a shallow water equation, and calculating to acquire a speed field on the surface of fluid in a form of a minimizing energy equation; 3), using the surface geometric information as a boundary constraint condition to be discretized into a whole three-dimension body to acquire volume data; 4), guiding the volume data reconstructed in the video into an SPH simulation scene to serve as an initial condition of the simulation scene, and interacting with other virtual environment objects in the scene. By the fluid-solid interaction simulation method, high-accuracy data reconstruction can be realized, fluid surface details can be retained, bidirectional interaction simulation is performed on the basis of reconstructed data and a physical simulation model, fluid animation effect closer to real condition is acquired, algorithm complexity is low, and the method has high creativity compared with related algorithms.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
System and method for simulating shallow water effects on arbitrary surfaces
ActiveUS7921003B2Effective simulationEasy to controlAnimationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationFluid controlWave equation
A system and method for shallow water simulation may provide a framework for solving General Shallow Wave Equations (GSWE) to efficiently simulate 3D fluid effects on arbitrary surfaces using a height field representation. The height field representation may include height columns constructed along surface normals, which may be dependent on a condition of boundary cells adjacent to fluid cells and / or artificial viscosity effects. The framework may provide implicit schemes for solving for the effects of external forces applied to the fluid, including gravity and surface tension, and explicit schemes for solving for advection effects. The system and method may be implemented on general-purpose CPU(s) and / or GPU(s) and may be capable of simulating a variety of fluid effects including: waves, rivulets and streams, drops, and capillary events. In some embodiments, the system and method may achieve real-time fluid control and fluid shape design through user-interaction (e.g., in a graphical painting application).
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
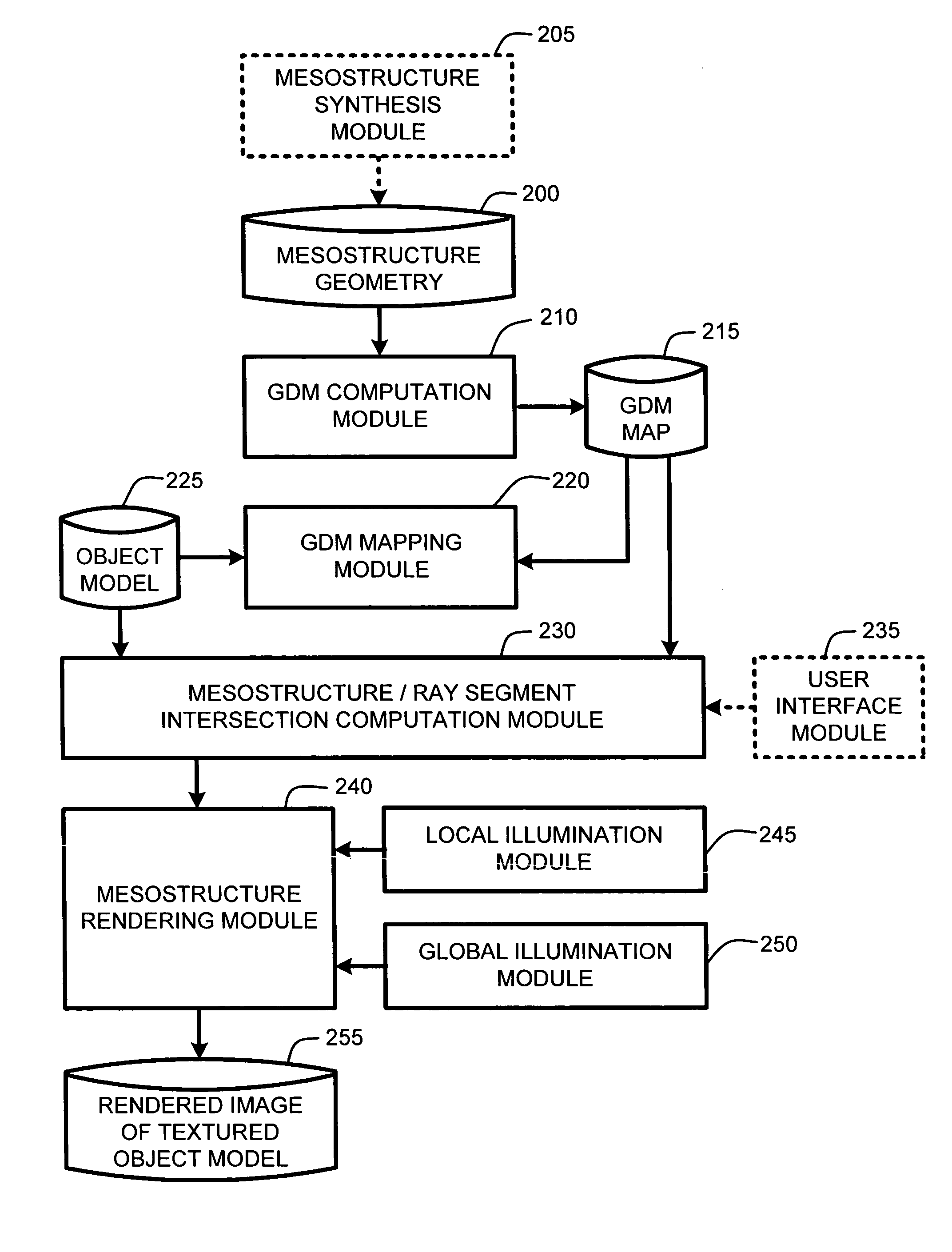
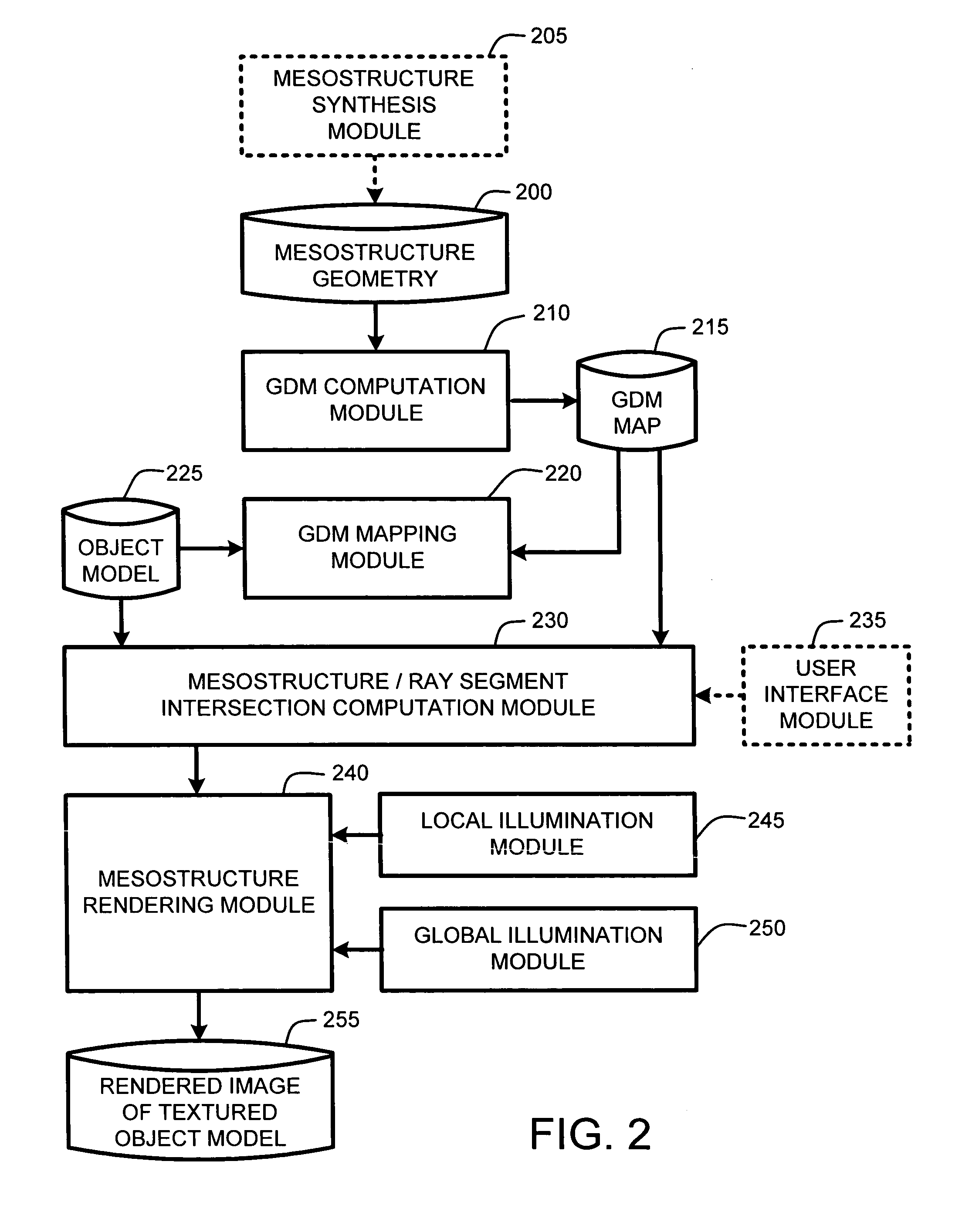
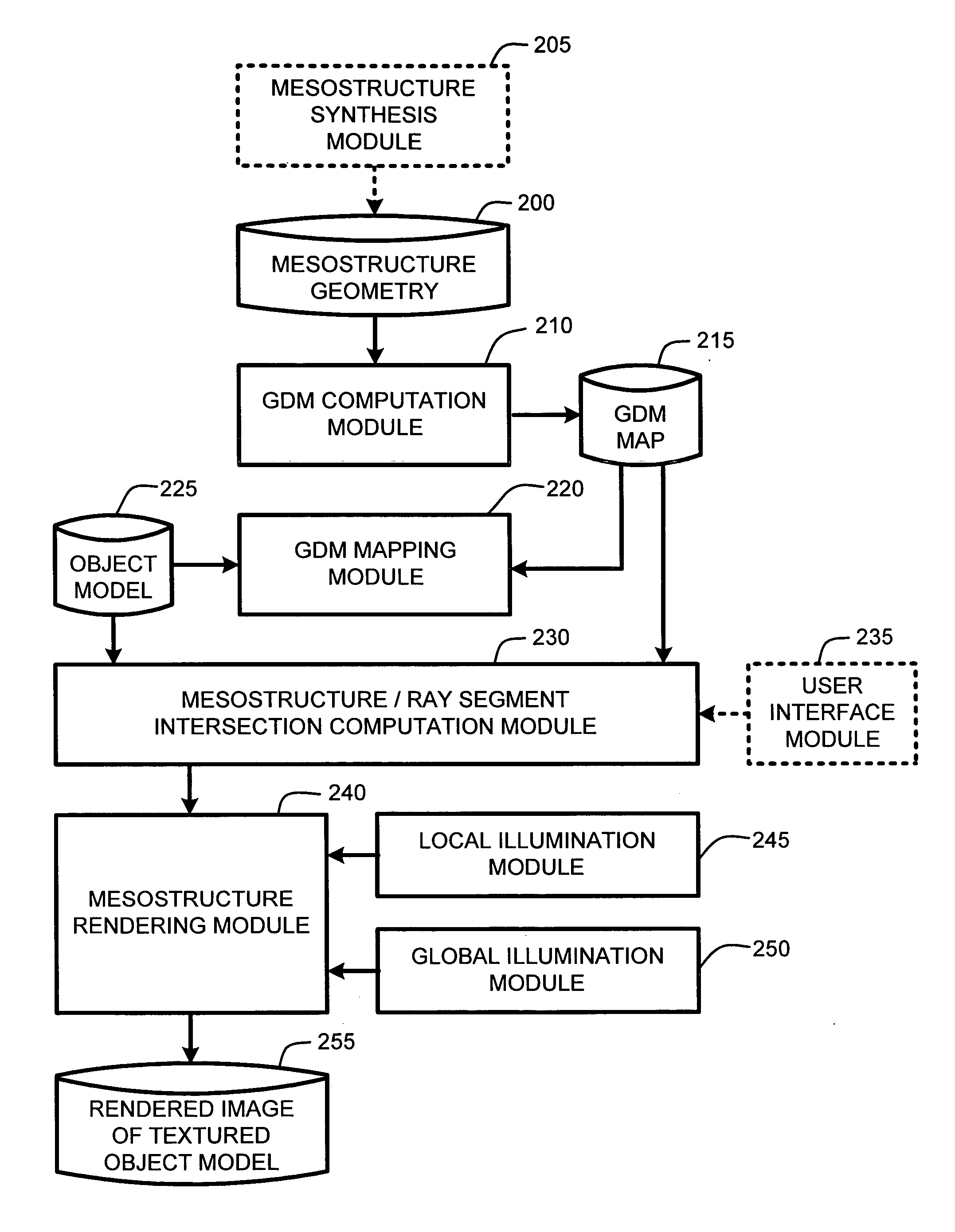
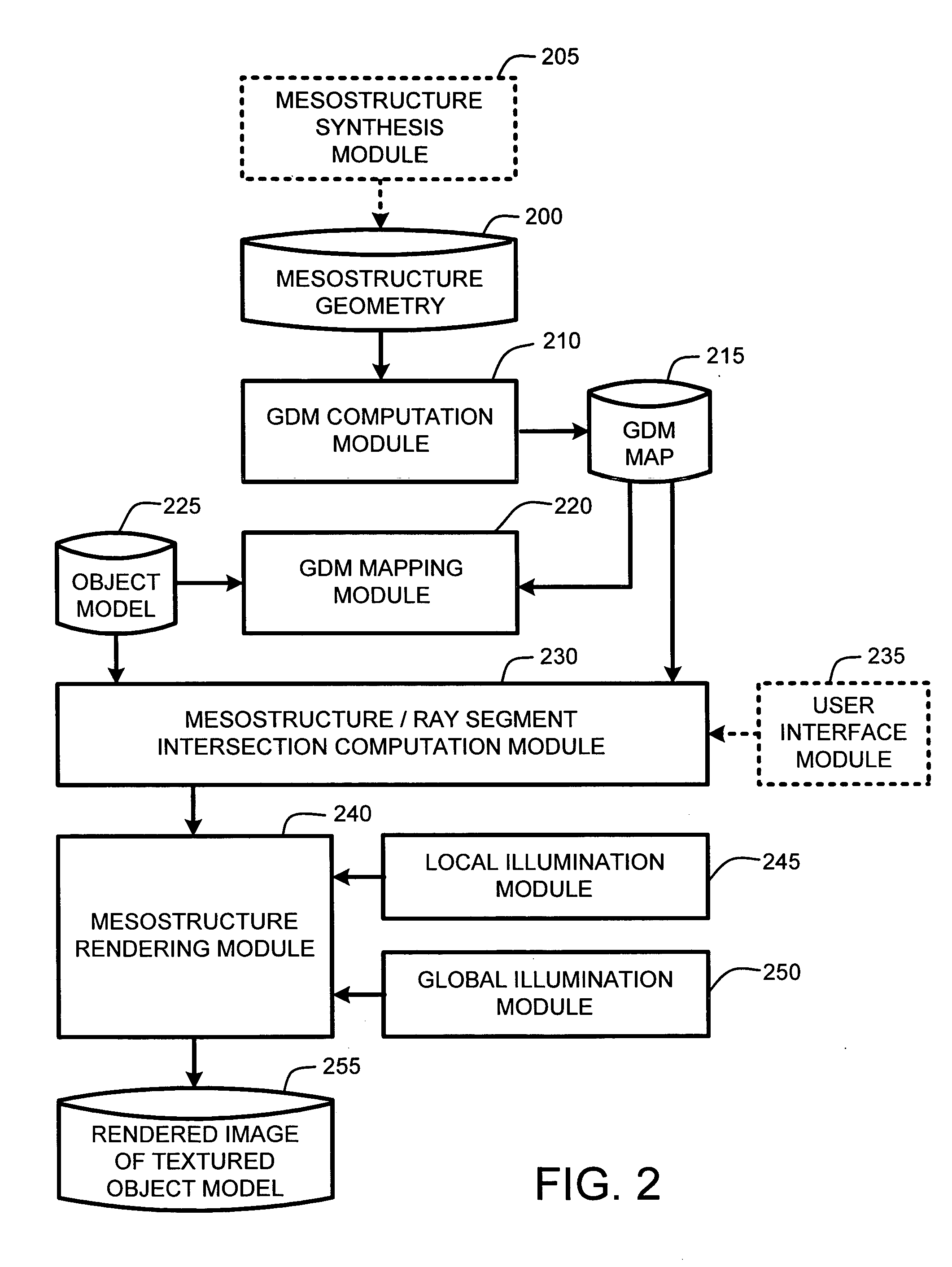
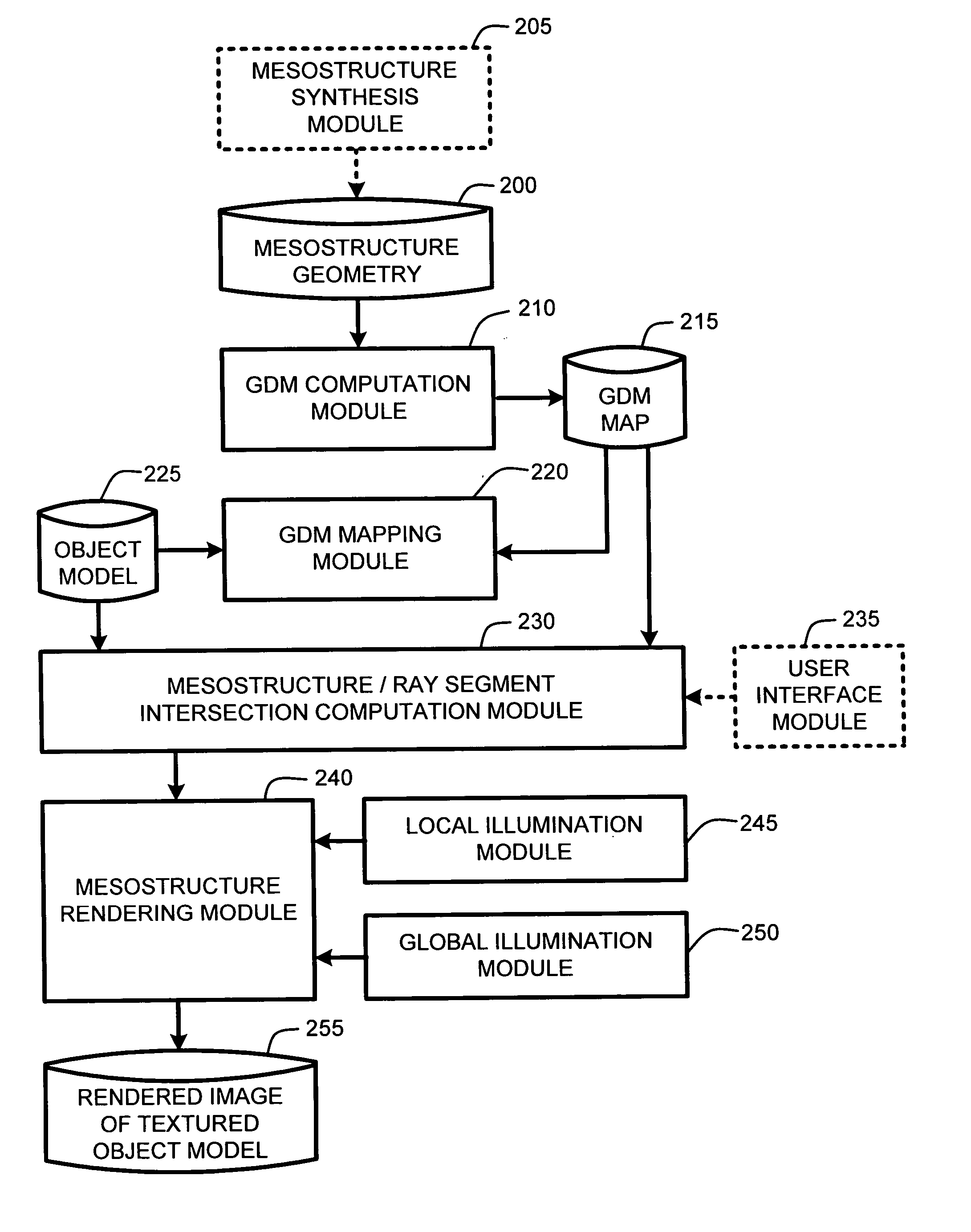
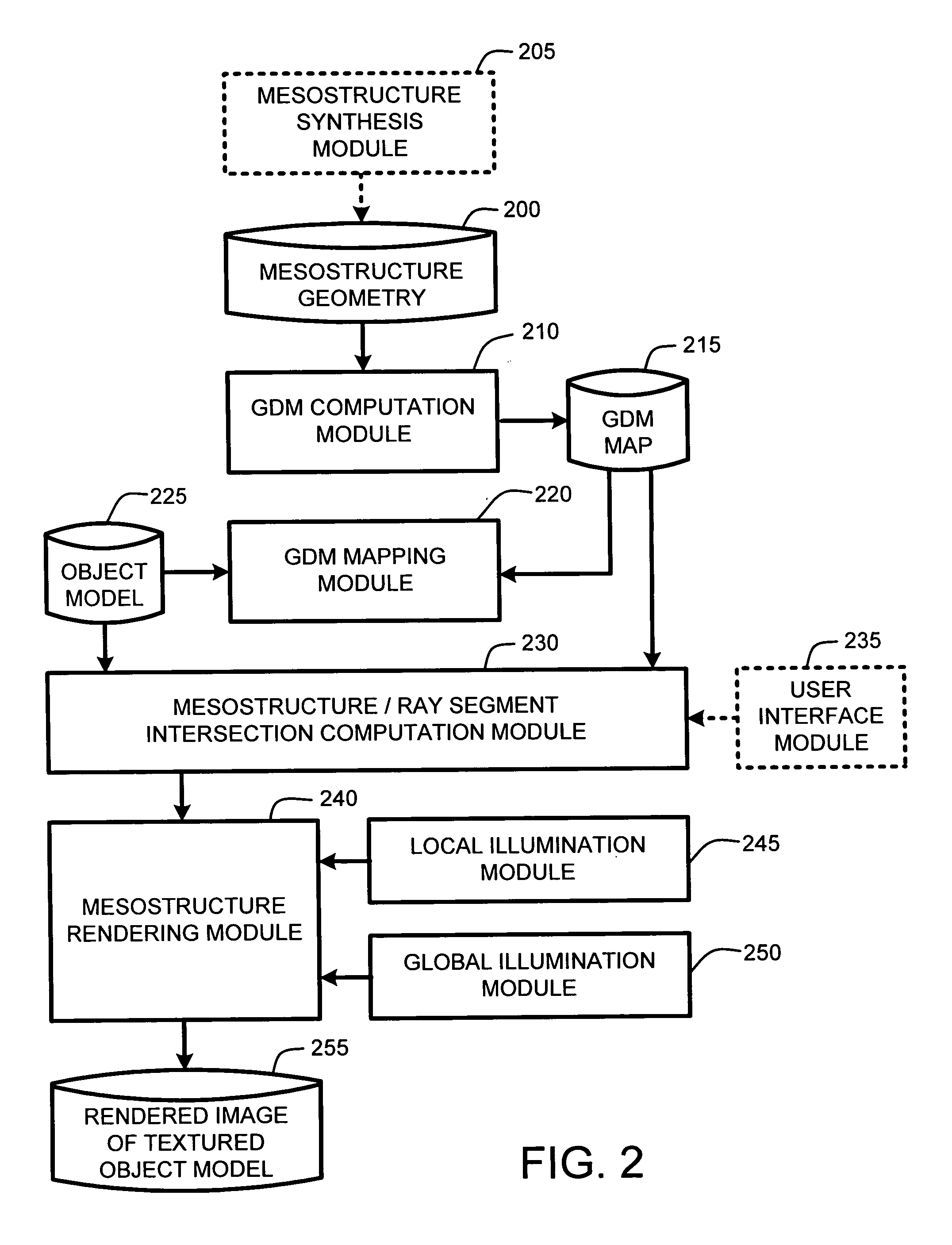
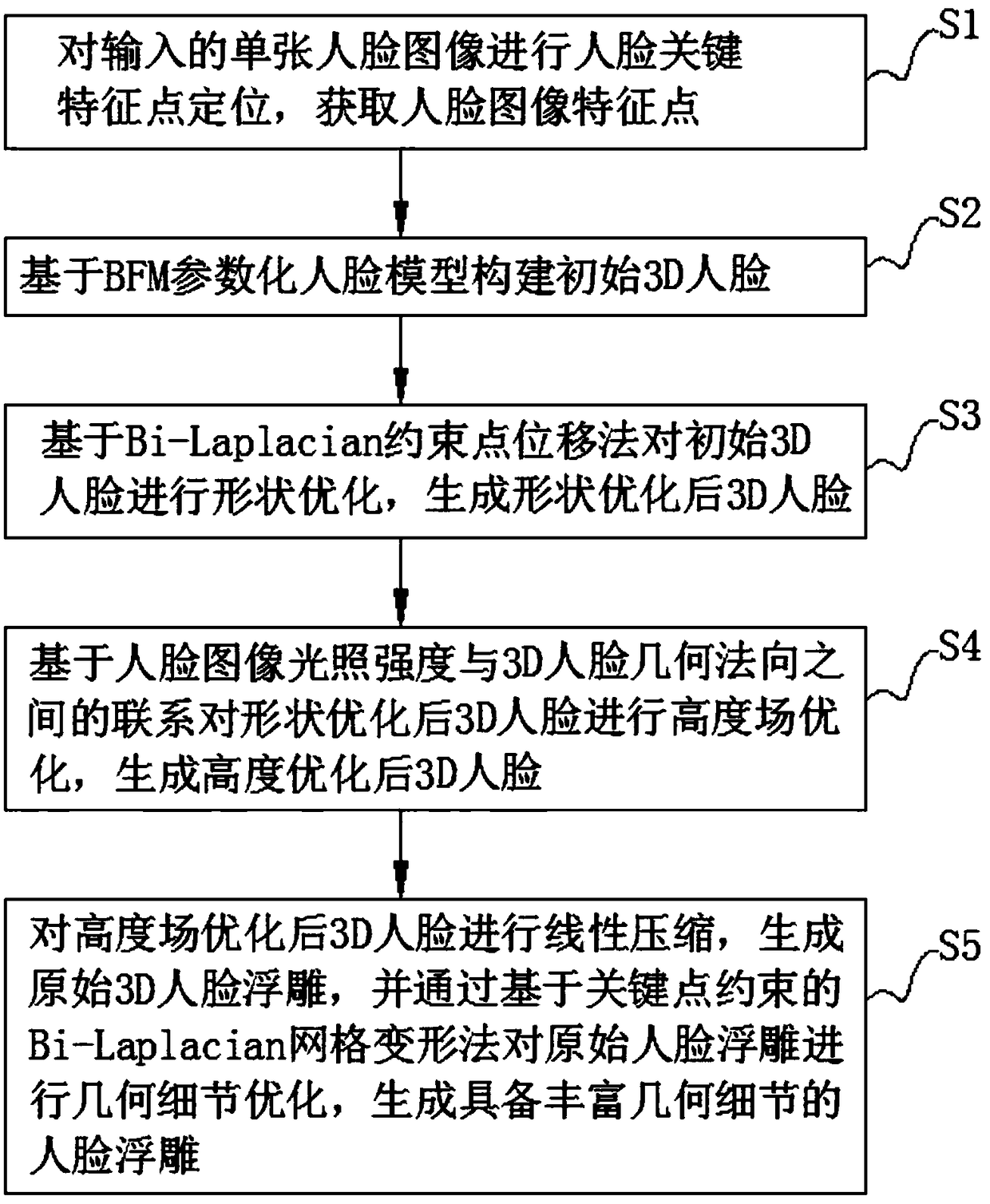
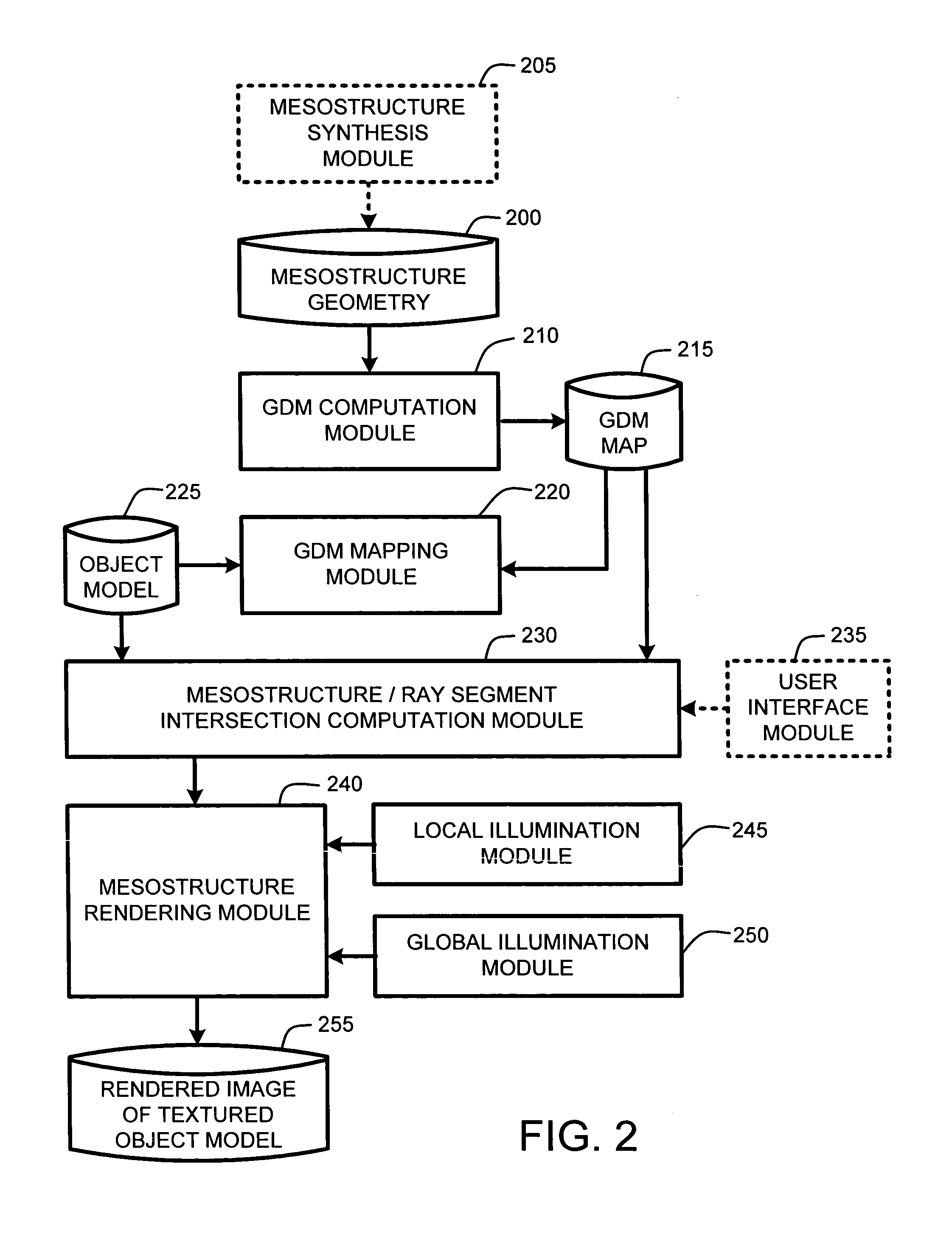
Real-time texture rendering using generalized displacement maps
ActiveUS20050280646A1Facilitate texture coordinate computationAccelerate mesostructure renderingCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingGraphicsVisibility
A “mesostructure renderer” uses pre-computed multi-dimensional “generalized displacement maps” (GDM) to provide real-time rendering of general non-height-field mesostructures on both open and closed surfaces of arbitrary geometry. In general, the GDM represents the distance to solid mesostructure along any ray cast from any point within a volumetric sample. Given the pre-computed GDM, the mesostructure renderer then computes mesostructure visibility jointly in object space and texture space, thereby enabling both control of texture distortion and efficient computation of texture coordinates and shadowing. Further, in one embodiment, the mesostructure renderer uses the GDM to render mesostructures with either local or global illumination as a per-pixel process using conventional computer graphics hardware to accelerate the real-time rendering of the mesostructures. Further acceleration of mesostructure rendering is achieved in another embodiment by automatically reducing the number of triangles in the rendering pipeline according to a user-specified threshold for acceptable texture distortion.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
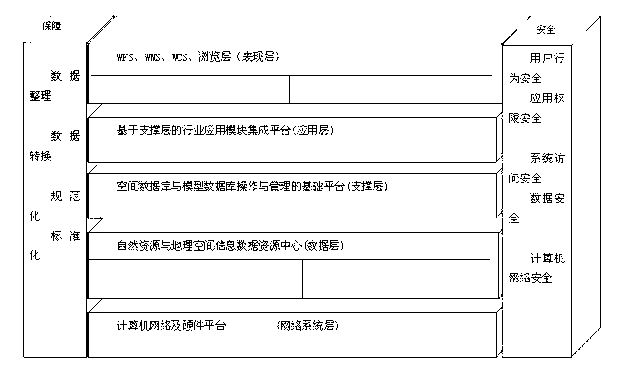
Three-dimensional geographic information platform and topographic data processing method thereof
InactiveCN103309943AQuick buildOptimize browsing efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsResource centerLandform
The invention discloses a three-dimensional geographic information platform and a topographic data processing method thereof. The platform comprises a network system layer, a data layer, a supporting layer, an application layer and a presentation layer; the application layer comprises a computer network and a hardware platform, and the safety of the computer network is guaranteed; the data layer is a natural resource and geographic space information data resource center; the supporting layer is a basic platform for operation and management of a space database and a model database; the application layer is a supporting layer-based industry application module integration platform; the presentation layer comprises WFS, WMS, WCS and a browse layer. A three-dimensional model used in the invention is formed by third-party professional modeling software, and also, the software can be used for forming simple three-dimensional model scenes, namely, a large area of simple three-dimensional scenes can be fast generated by adding a height field and a layer height field into attribute information according to polygon files in data line pictures.
Owner:GUANGDONG SOUTH DIGITAL TECH
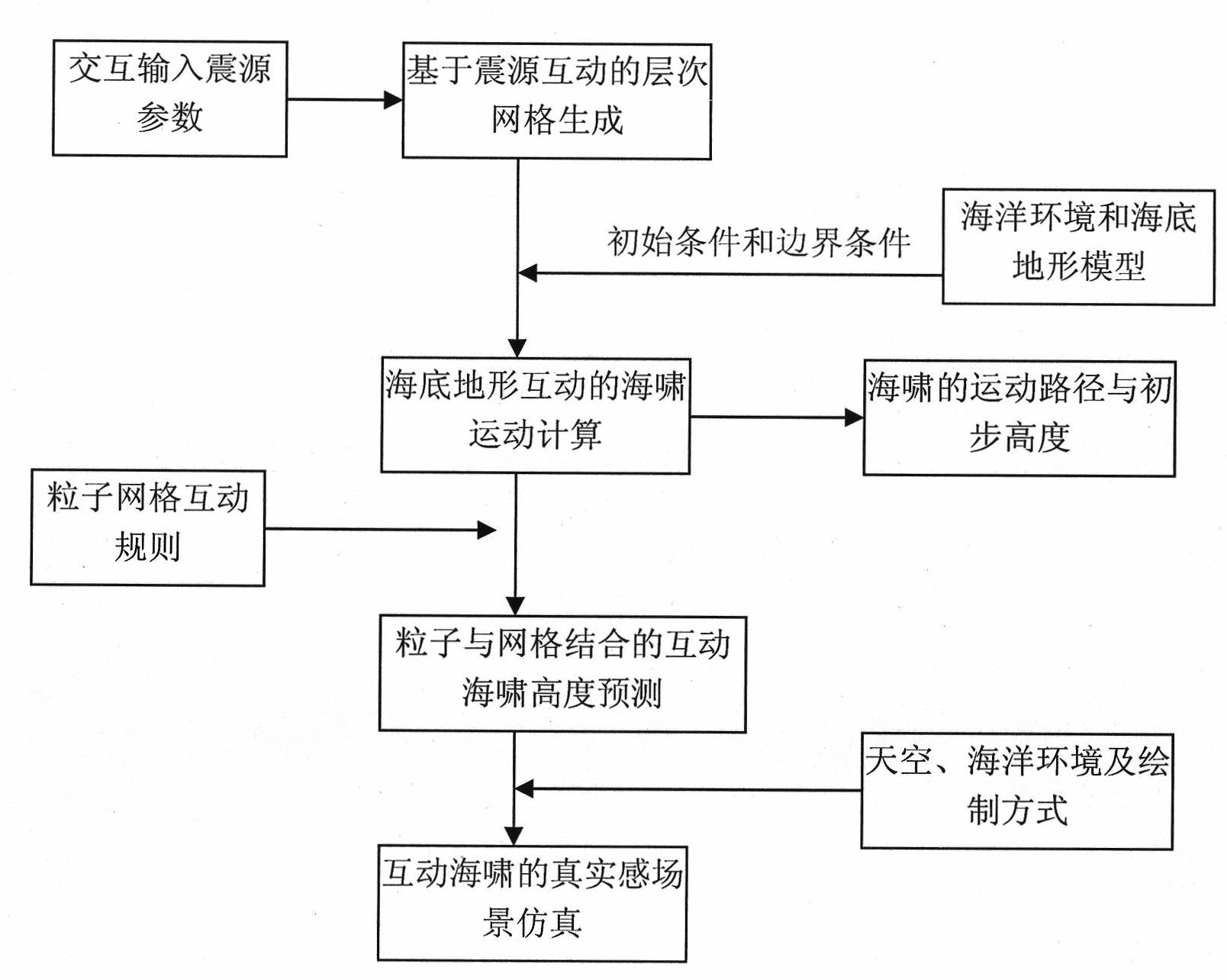
Tsunami motion forecasting method based on multi-hierarchy interaction
InactiveCN101788683AIncrease credibilityGuaranteed accuracySeismologySpecial data processing applicationsWave equationMotion prediction
The invention discloses a tsunami motion forecasting method based on multi-hierarchy interaction, which comprises the following steps: 1) generating hierarchical grids according to the position of an actual tsunami source, establishing corresponding relation between the grids and spherical coordinates, and establishing an interaction mechanism of the hierarchical grids; 2) carrying out sector and square combined dispersion on a tsunami motion equation, setting initial conditions and boundary conditions according to actual conditions, and solving a wave equation to compute flux change of tsunami motion; and 3) setting an initial sea level height field according to the height of a sea level, establishing an interaction mechanism of particles and the grids in the process of tsunami motion, establishing updating and iterating rules of the particles, and then, forecasting the height of tsunami through interaction of the particles and the grids. The method can quickly and vividly forecast the tsunami propagation phenomenon and solves the problems that the existing simulation method only pays attention to numerical simulation, the simulation result is not visual, the computing efficiency is too slow, and the like. The method has certain practical value in the fields of disaster prevention, tsunami early warning, virtual simulation etc.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Methods and systems of comparing face models for recognition
InactiveUS20090244082A1Character and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsFace model
Methods and systems of representation and manipulation of surfaces with perceptual geometric features, using a computer graphics rendering system, include executing algorithmic instructions to compute a plurality of vertices, edges and surfaces in a mesh for the purpose of defining representations of surfaces on grids. Normals and distances are determined for triangular surfaces to be considered. Additionally, height fields of a function are defined. A set of feature curves and a set of feature points are derived, based on the defined function. Infinitesimal movements along the representations of the surfaces are determined, along with derivations of properties of representations of continuous surfaces. Additional determinations of perceptual geometric features include determinations such as zero crossings, parabolic curves, flecnodes, ruffles, gutterpoints, conical points and biflecnodes in a given mesh. After these determinations are made, visual representation are rendered which captures perceptually important features for smoothly varying shapes.
Owner:GOVT OF USA REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY CHIEF OF NAVAL RES OFFICE OF COUNSEL ONR NRL
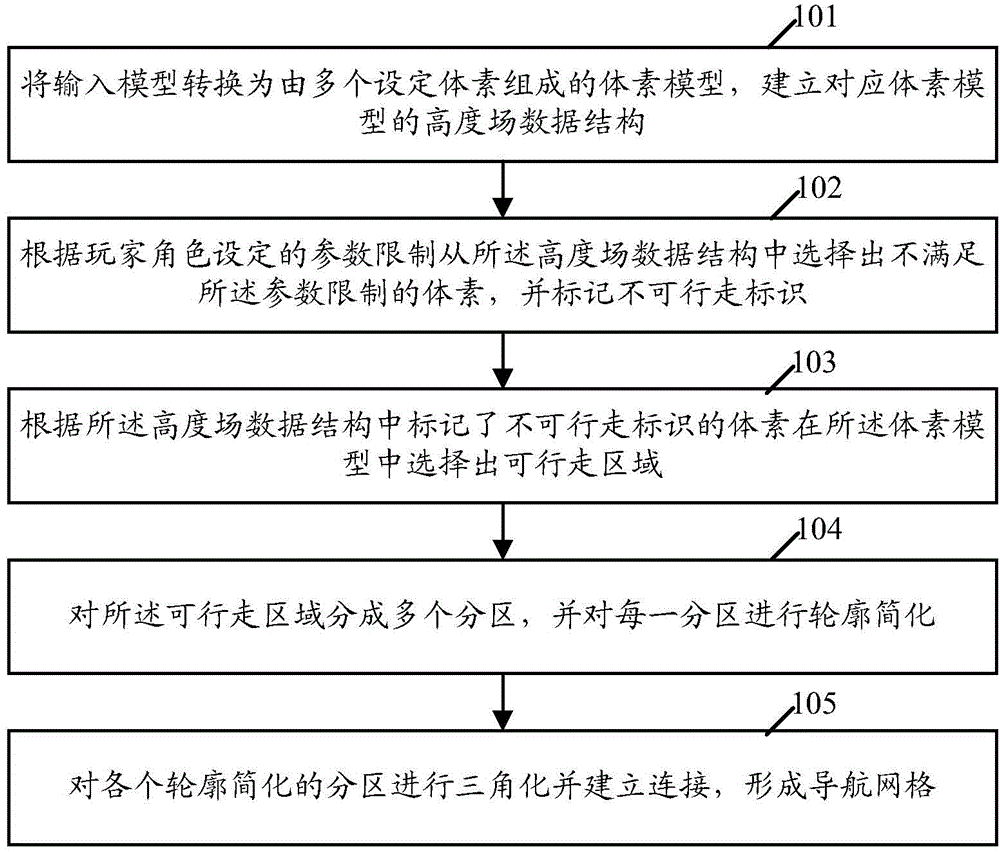
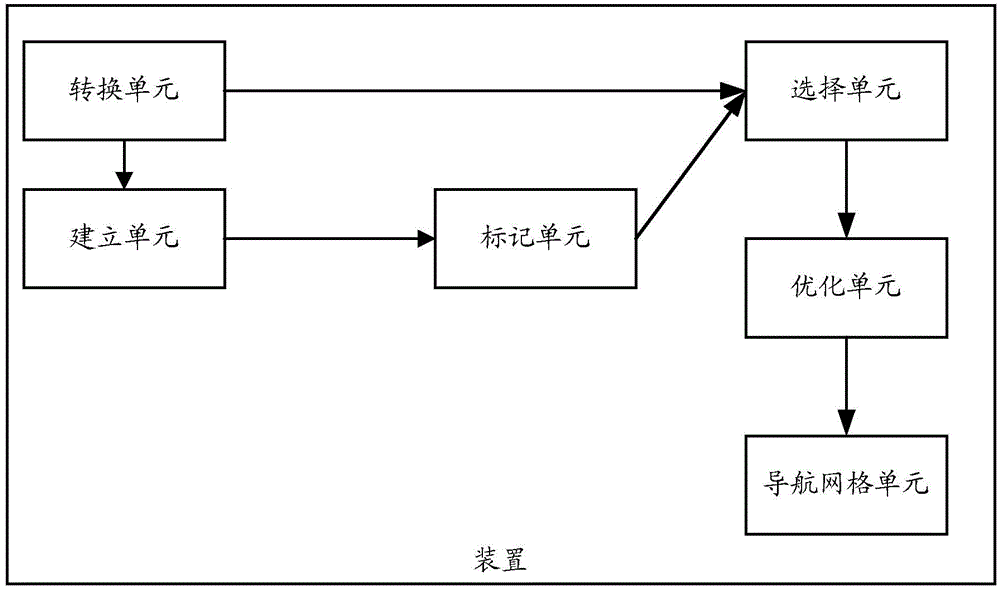
Navigation grid automatic-generation method and navigation grid automatic-generation device
The application provides a navigation grid automatic-generation method and a navigation grid automatic-generation device. The method comprises the following steps: converting an input model into a voxel model which consists of multiple set voxels, and establishing a height field data structure which corresponds to the voxel model; restrictively selecting voxels which doe not meet parameter restrictions from the height field data structure according to parameter restriction set by player roles, and marking non-walkable identifiers; selecting a walkable region from the voxel model according to the voxels marked with the non-walkable identifiers in the height field data structure; dividing the walkable region into multiple subregions, and simplifying the outline of each subregion; triangularizing the subregions with simplified outlines, establishing connection, and forming a navigation grid, thereby realizing automatic generation of the navigation grid.
Owner:BEIJING PIXEL SOFTWARE TECH
System and method for generating generalized displacement maps from mesostructure geometries
InactiveUS20050280647A1Facilitate texture coordinate computationAccelerate mesostructure renderingCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingVisibilityGraphics
A “mesostructure renderer” uses pre-computed multi-dimensional “generalized displacement maps” (GDM) to provide real-time rendering of general non-height-field mesostructures on both open and closed surfaces of arbitrary geometry. In general, the GDM represents the distance to solid mesostructure along any ray cast from any point within a volumetric sample. Given the pre-computed GDM, the mesostructure renderer then computes mesostructure visibility jointly in object space and texture space, thereby enabling both control of texture distortion and efficient computation of texture coordinates and shadowing. Further, in one embodiment, the mesostructure renderer uses the GDM to render mesostructures with either local or global illumination as a per-pixel process using conventional computer graphics hardware to accelerate the real-time rendering of the mesostructures. Further acceleration of mesostructure rendering is achieved in another embodiment by automatically reducing the number of triangles in the rendering pipeline according to a user-specified threshold for acceptable texture distortion.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Optimizing real-time rendering of texture mapped object models relative to adjustable distortion thresholds
InactiveUS20050280648A1Facilitate texture coordinate computationAccelerate mesostructure renderingCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingVisibilityGraphics
A “mesostructure renderer” uses pre-computed multi-dimensional “generalized displacement maps” (GDM) to provide real-time rendering of general non-height-field mesostructures on both open and closed surfaces of arbitrary geometry. In general, the GDM represents the distance to solid mesostructure along any ray cast from any point within a volumetric sample. Given the pre-computed GDM, the mesostructure renderer then computes mesostructure visibility jointly in object space and texture space, thereby enabling both control of texture distortion and efficient computation of texture coordinates and shadowing. Further, in one embodiment, the mesostructure renderer uses the GDM to render mesostructures with either local or global illumination as a per-pixel process using conventional computer graphics hardware to accelerate the real-time rendering of the mesostructures. Further acceleration of mesostructure rendering is achieved in another embodiment by automatically reducing the number of triangles in the rendering pipeline according to a user-specified threshold for acceptable texture distortion.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
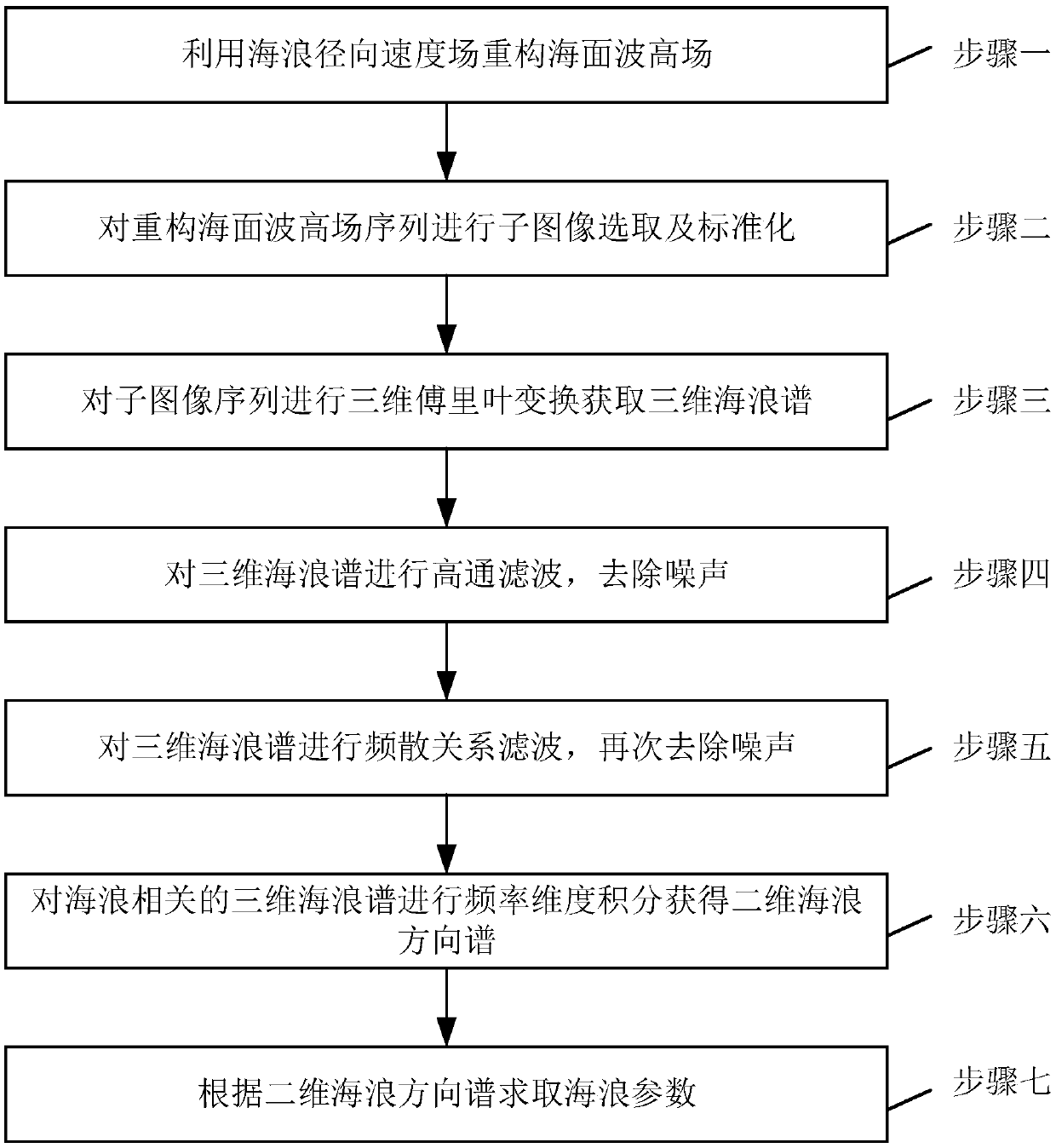
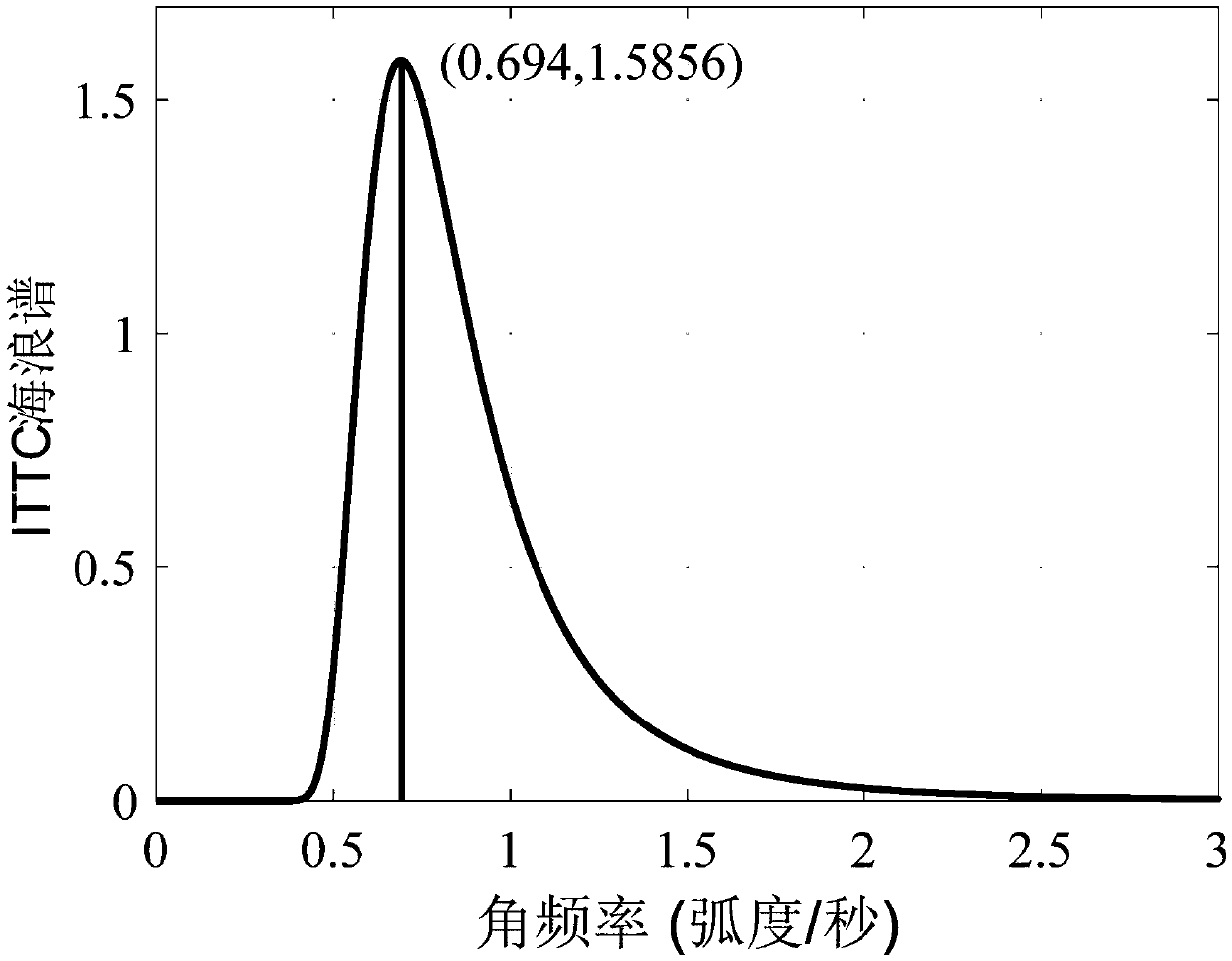
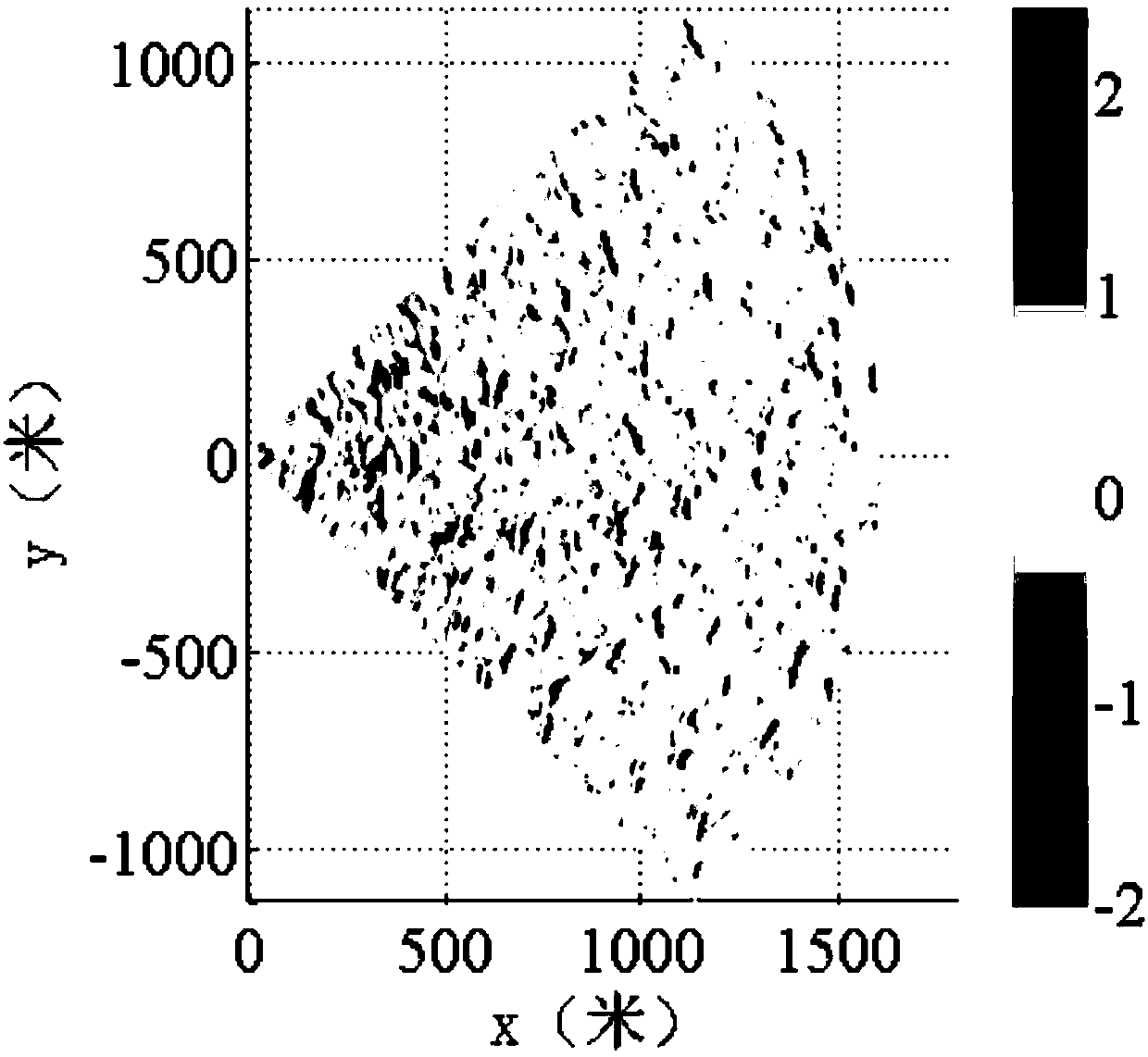
Method for measuring ocean wave parameter based on sea coherent radar
InactiveCN109557538AHigh precisionAvoid Accuracy ImpactRadio wave reradiation/reflectionBandpass filteringWave parameter
The invention provides a method for measuring ocean wave parameters based on sea coherent radar, and relates to a method for measuring ocean wave parameters. The invention aims to solve the problem that the obtained parameter precision is low based on the large calculation complexity of non coherent radar. The method comprises the following steps of: step 1, reconstructing a sea surface wave height field by using the radial velocity of the wave; step 2, performing sub-image selection and standardization on the reconstructed sea surface wave height field sequence; step 3, performing a three-dimensional Fourier transform on the reconstructed sea surface wave height field sub-image sequence to obtain a three-dimensional wave spectrum; step 4, high-pass filtering the three-dimensional wave spectrum to remove noise; step 5, bandpass filtering a three-dimensional wave power spectrum after the noise is removed, again removing the noise, and obtaining a three-dimensional wave spectrum relatedto the ocean wave; step 6, performing frequency dimension integration on the obtained the three-dimensional sea wave spectrum related to the sea waves to obtain a two-dimensional wave direction spectrum; and step 7, obtain the wave parameters according to the two-dimensional wave direction spectrum. The method is used for the field of measuring the sea coherent radar.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Face relief geometric modeling method
ActiveCN108492373ANo manual interventionImage enhancementImage analysisGrid deformationGeometric modeling
The present invention discloses a face relief geometric modeling method, and belongs to the field of relief modeling. The problems are solved that current portrait relief modeling is low in efficiencyand poor in automation. The method comprises the following steps of: performing face key feature point location for an input single face image, and obtaining face image feature points; based on a BFMparameter face model, constructing an initial 3D face; based on a Bi-Laplacian constrained point displacement method to perform shape optimization of the initial 3D face, and generating a 3D face after shape optimization; performing height field optimization of the 3D face after shape optimization based on a relation of the face image illumination intensity and the 3D face geometric normal, and generating a 3D face after height optimization; and performing linear compression of the 3D face after the height field optimization, generating an original 3D face relief, performing geometric detailoptimization of the original face relief through a Bi-Laplacian grid deformation method based on key point constraint, and generating a face relief with rich geometric details.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Real-time texture rendering using generalized displacement maps
ActiveUS7184052B2Facilitate texture coordinate computationAccelerate mesostructure renderingCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingGraphicsVisibility
A “mesostructure renderer” uses pre-computed multi-dimensional “generalized displacement maps” (GDM) to provide real-time rendering of general non-height-field mesostructures on both open and closed surfaces of arbitrary geometry. In general, the GDM represents the distance to solid mesostructure along any ray cast from any point within a volumetric sample. Given the pre-computed GDM, the mesostructure renderer then computes mesostructure visibility jointly in object space and texture space, thereby enabling both control of texture distortion and efficient computation of texture coordinates and shadowing. Further, in one embodiment, the mesostructure renderer uses the GDM to render mesostructures with either local or global illumination as a per-pixel process using conventional computer graphics hardware to accelerate the real-time rendering of the mesostructures. Further acceleration of mesostructure rendering is achieved in another embodiment by automatically reducing the number of triangles in the rendering pipeline according to a user-specified threshold for acceptable texture distortion.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method for extracting and automatically drawing characteristic points of groove and ridge lines
InactiveCN104898186AImplement automatic detectionTimely forecastImage enhancementWeather condition predictionBeam searchBusiness forecasting
The invention discloses a method for extracting and automatically drawing characteristic points of groove and ridge lines, and the method comprises the following steps: enabling grid point meteorological data with 0-degree, 45-degree and 90-degree gradient directions after discretization to serve as the candidate characteristic points of the ridge line according to the direction of the groove ridge line in a temperature / height field; enabling grid point meteorological data with -180-degree, -135-degree and -90-degree gradient directions after discretization to serve as the candidate characteristic points of the groove line; carrying out the error correction and filtering of the characteristic points of the ridge line and the characteristic points of the groove line, and obtaining the final characteristic points of the ridge line and the final characteristic points of the groove line; carrying out beam search according to the final characteristic points of the ridge line and the final characteristic points of the groove line, forming a folded line, enabling the ridge and groove lines, which do not meet conditions, to be eliminated, and obtaining the selected ridge and groove lines; carrying out the smooth axis processing of the selected ridge and groove lines, and obtaining the final smooth ridge and groove lines. The method achieves the automatic detection of the groove and ridge lines, facilitates the forecasting of weather disasters, and reduces the economic loss and persons.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Raster image vectorizing method based on contour line
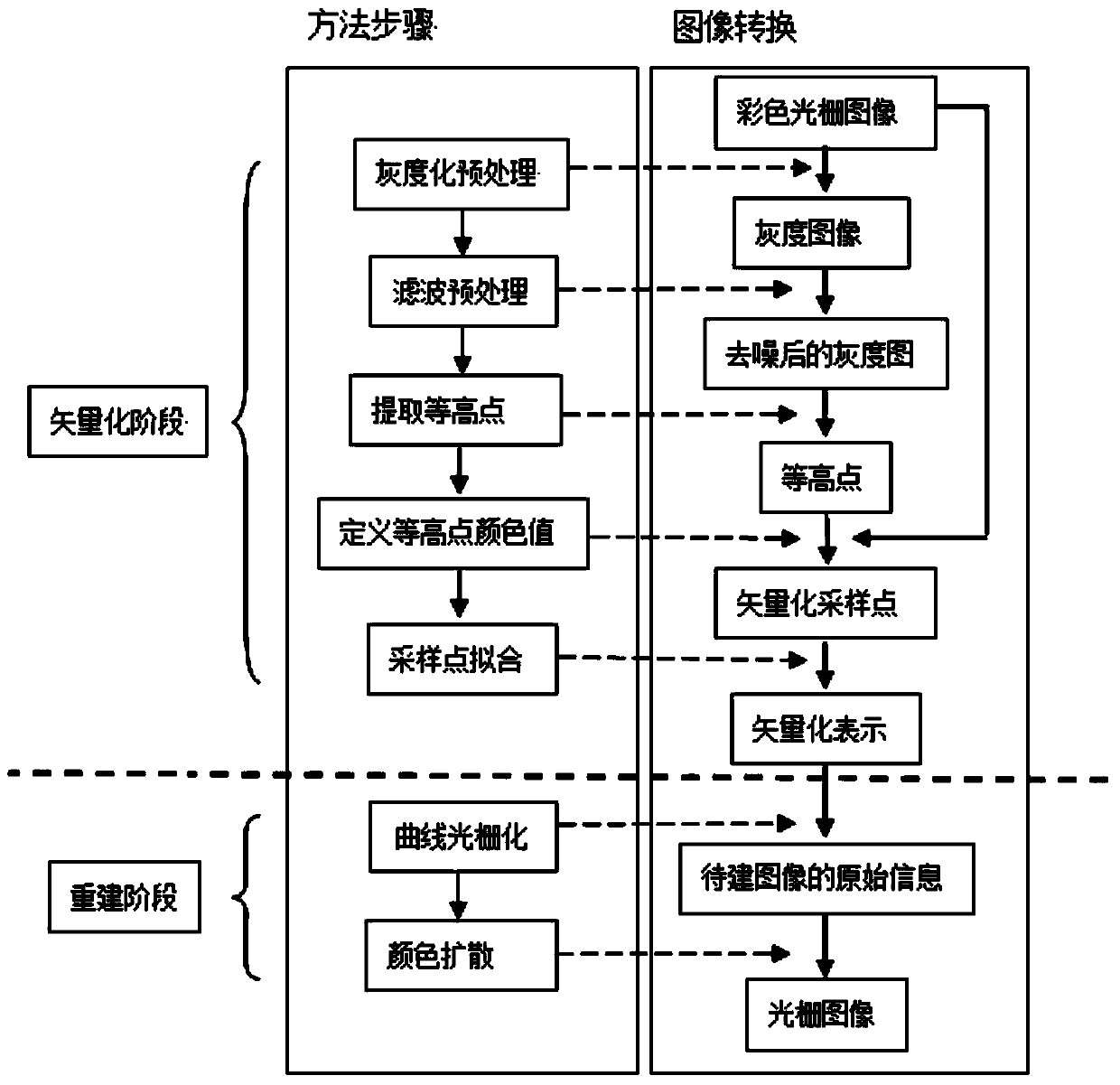
InactiveCN103810729AVectorized implementationThe principle is simpleImage codingGratingComputer vision
The invention discloses a raster image vectorizing method based on a contour line. The raster image vectorizing method based on the contour line includes: generating an intensity image corresponding to a raster image firstly, and then establishing an image height field by using the intensity image after being smoothed; extracting equal altitude points in the image height field, and confirming colors of the equal altitude points; establishing parameter curve math expression of the contour line based on the equal altitude points, and conforming the color of an arbitrary point on the contour line. A parameter curve set with color information is vectorization expression of the raster image. When a reestablishment raster image is expressed in vectorization mode, zooming and discretization operations are performed on a vectorized parameter curve according to the size of the raster image to be established, the position and the color of each pixel occupied by the vectorized parameter curve in the image to be established are confirmed, a coloring pixel is used as initial data, and a color diffusion method is used to reestablish the raster image which is expressed in vectorization mode. The raster image vectorizing method based on the contour line can perform multiple scale vectorization processing on various raster images, can use relative parameters to control the data volume of a vector diagram, and can reestablish the raster image multiple in resolution through vector expression.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
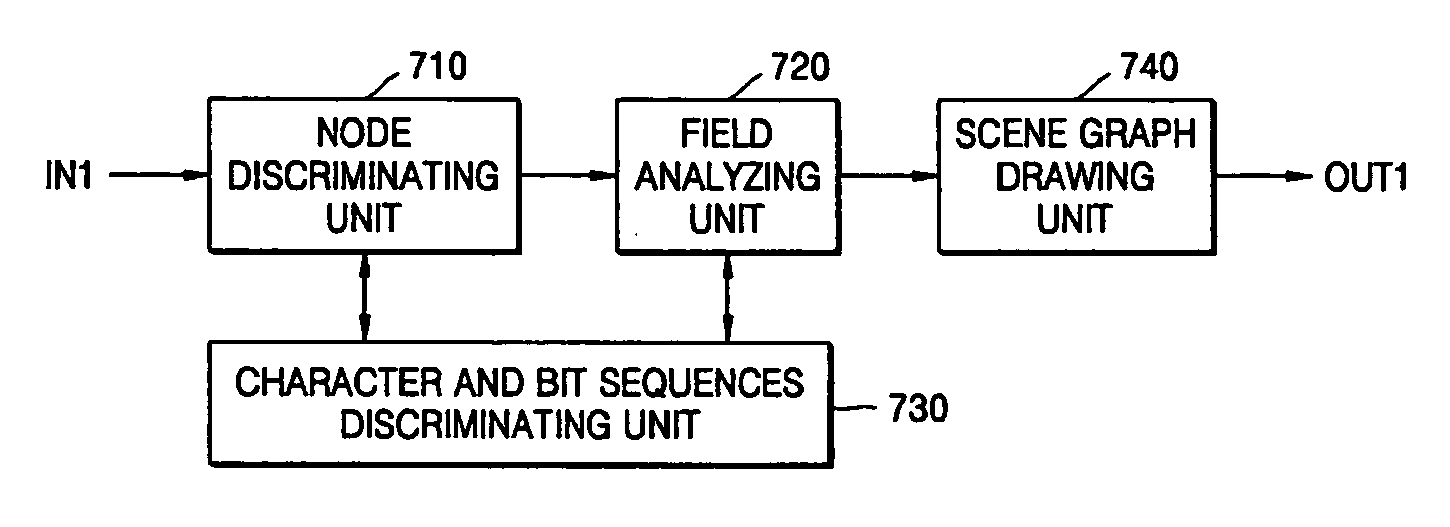
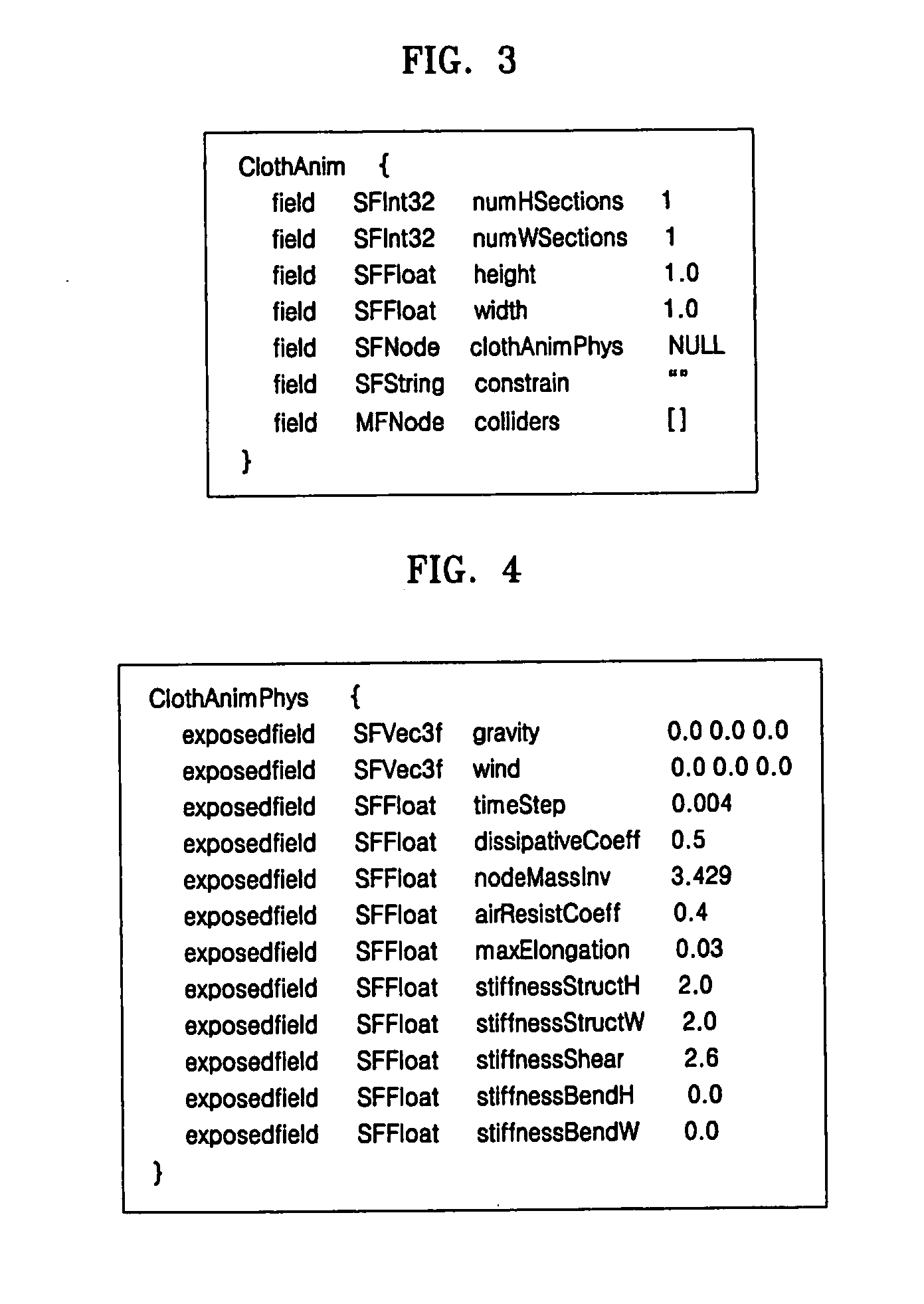
Data structure for cloth animation, and apparatus and method for rendering three-dimensional graphics data using the data structure
A data structure for cloth animation and an apparatus and method of rendering 3D graphics data using the data structure. The data structure for cloth animation comprises a vertical granulation field, a horizontal granulation field, a height field, a width field, and a physical characteristics node which defines values for physical characteristics, a shift position of the cloth due to forces acting on the cloth, and due to a collision of the cloth with an object. The 3D graphics data rendering apparatus comprises an analyzer for outputting a scene graph, a calculator for calculating physical quantities for the cloth animation, and a converter for converting the scene graph comprising the calculated physical quantities into a 2D image and outputting the 2D image.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for partitioning the surface of a three dimentional digital object model in order to map a texture
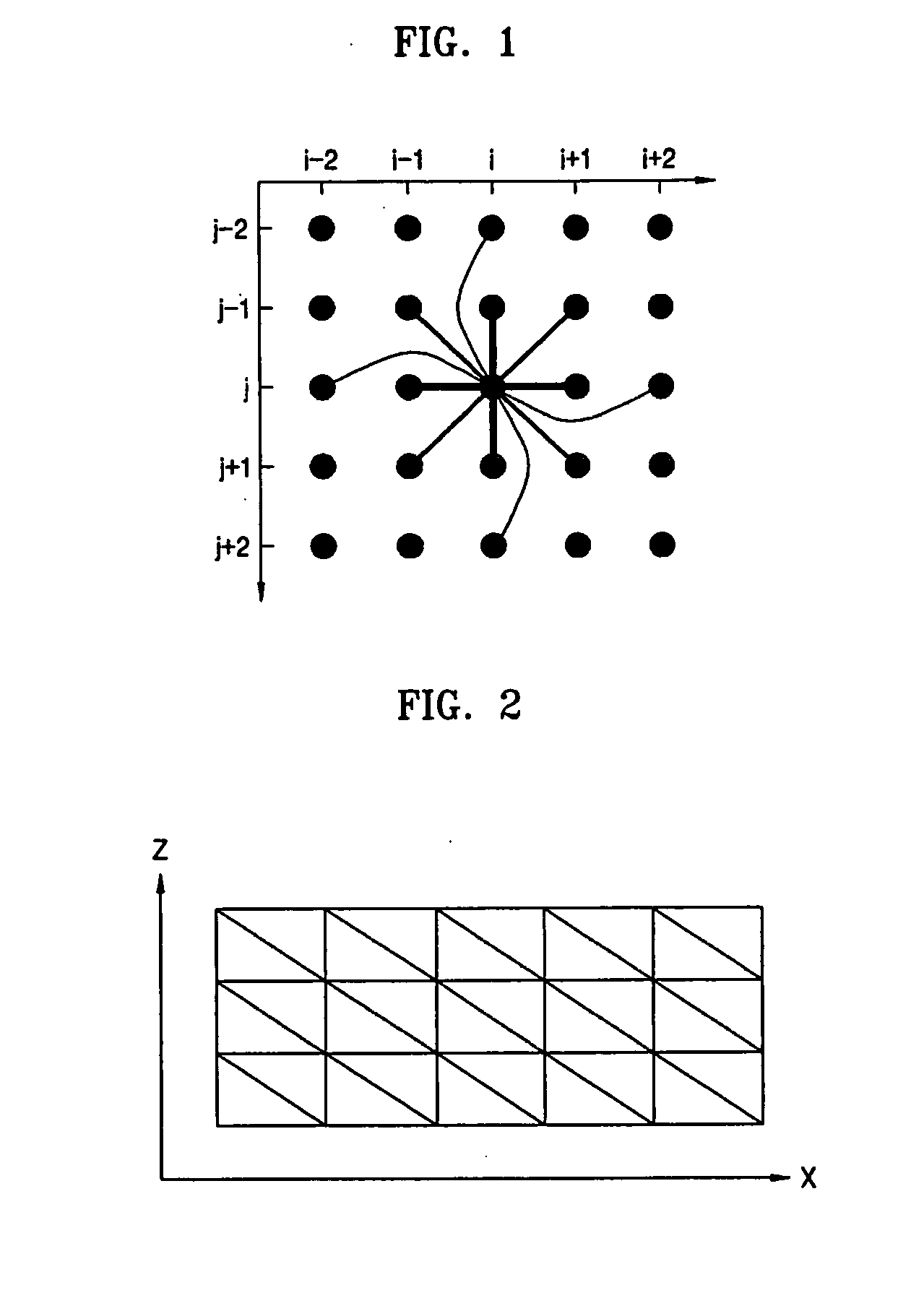
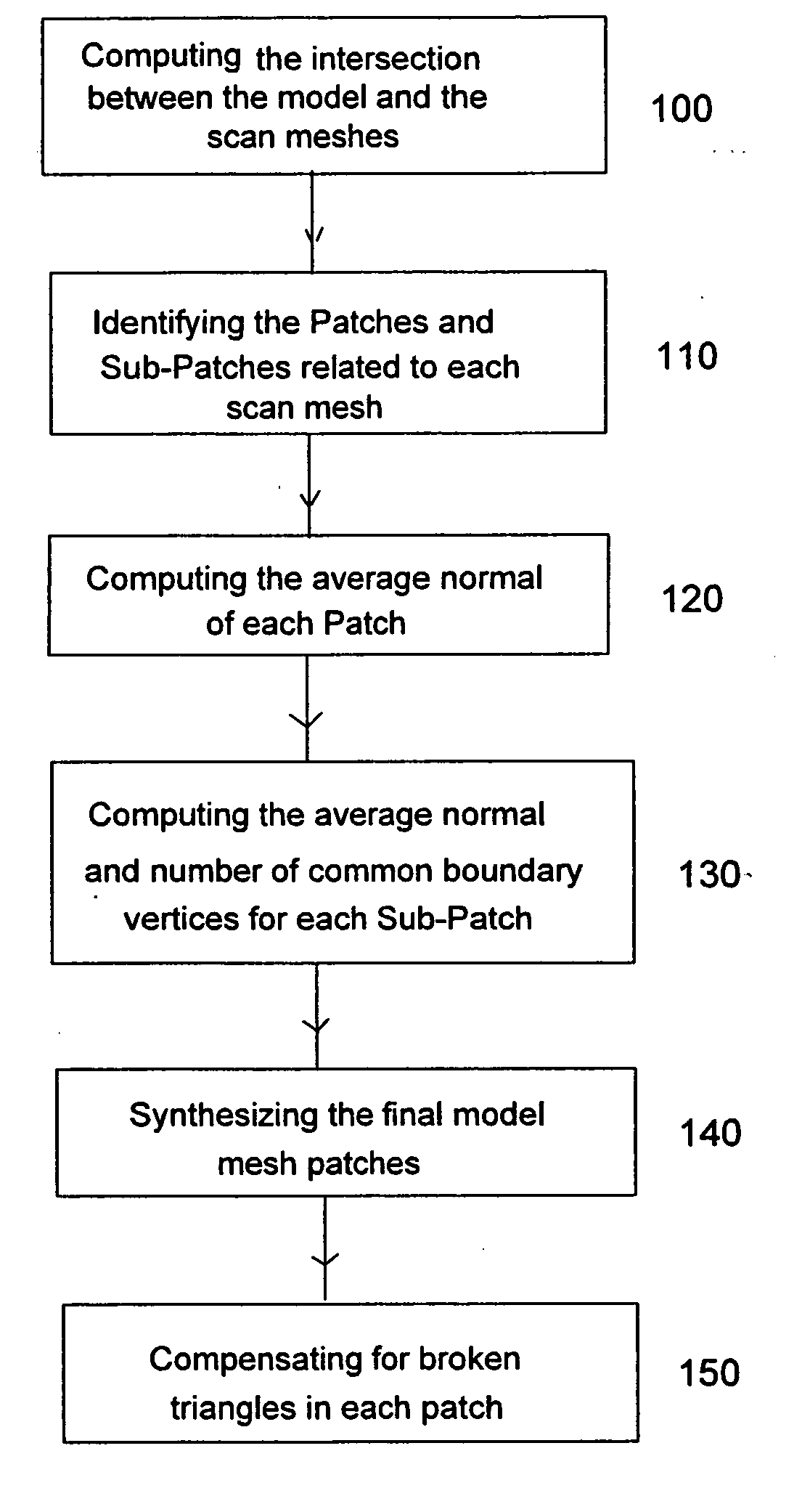
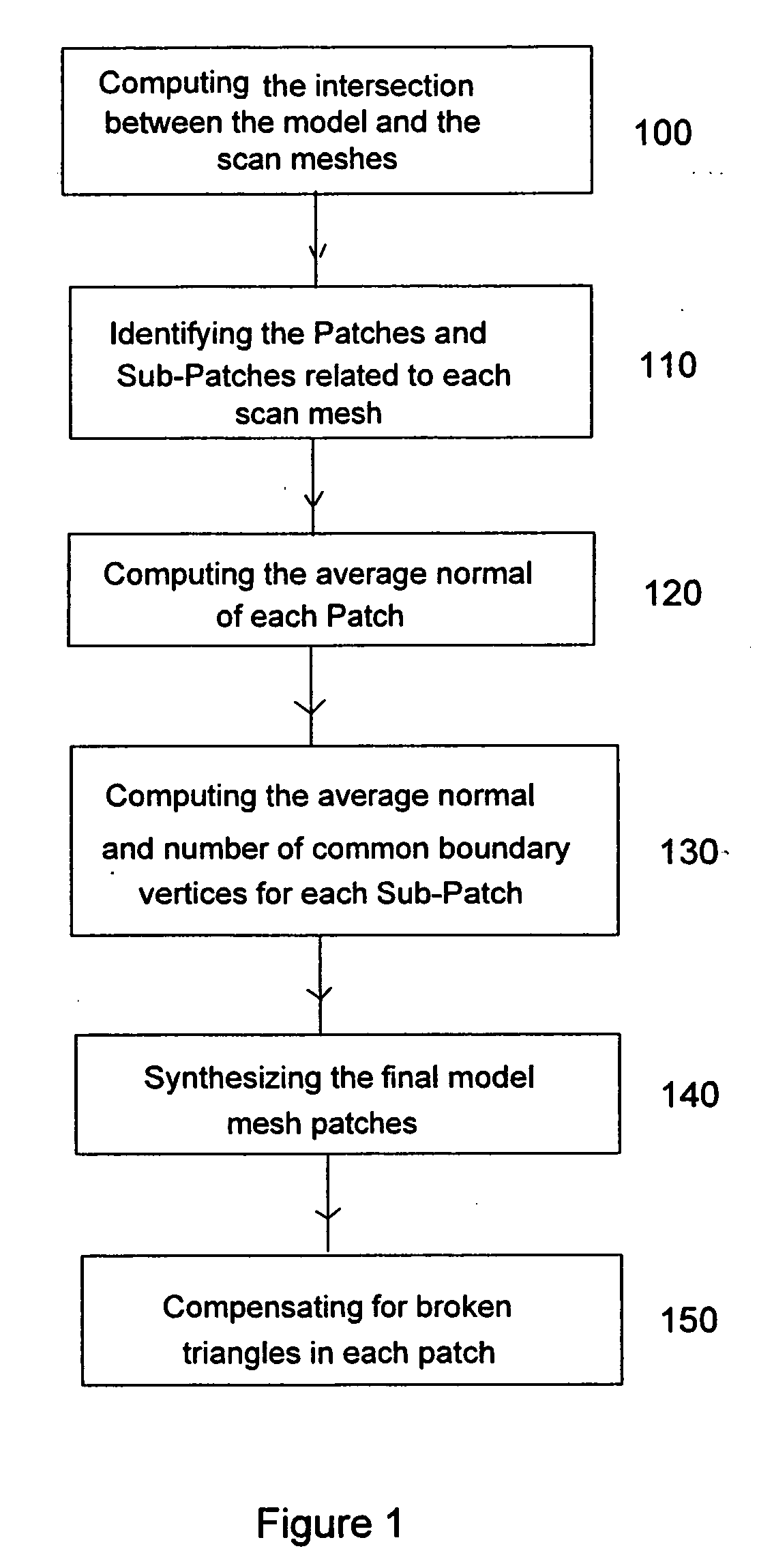
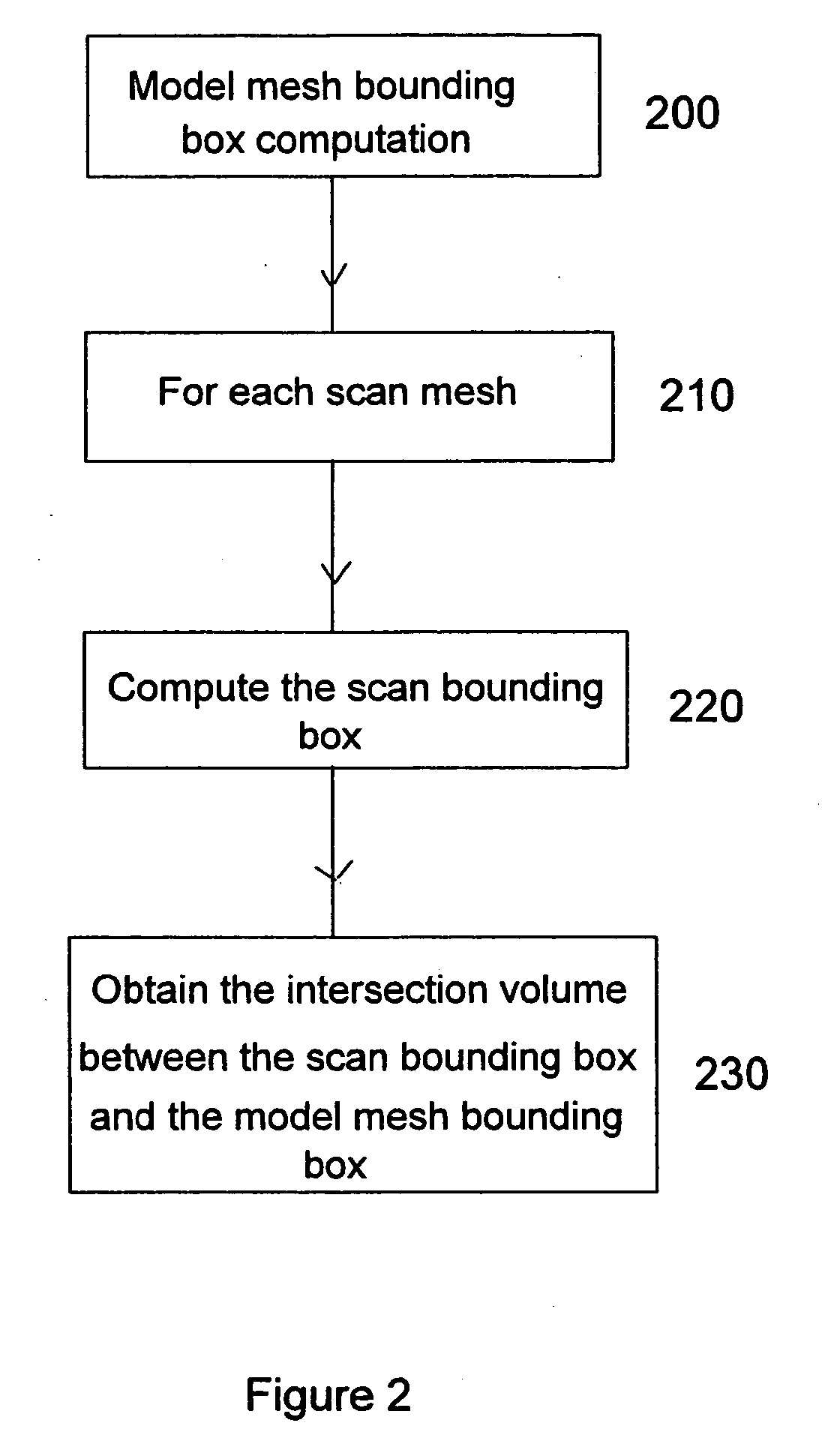
ActiveUS20060066613A1Easy to processTexture can be mapped on the digital object model more efficientlyCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsPresent methodComputer graphics (images)
The present invention is directed to a method and system and computer program for decomposing a triangle mesh representing the surface of a digital object model, reconstructed from 3D scanning data, into a small number of height-field patches (partitions) (in the order of the number of the original scans) with reasonable angular variations with the direction from which the viewer is looking at the digital object and with boundaries as regular as possible, in order to map a texture. The present method uses the original scan information (even when scans are divided into two or more connected meshes), but without selecting a single scan per mesh area.
Owner:WALKER MARK S
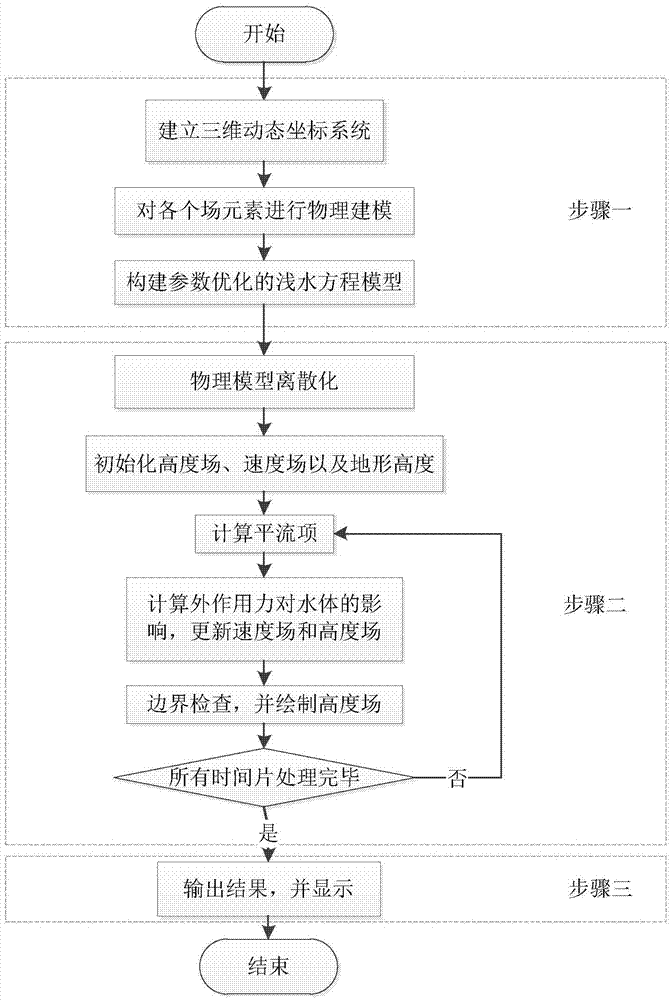
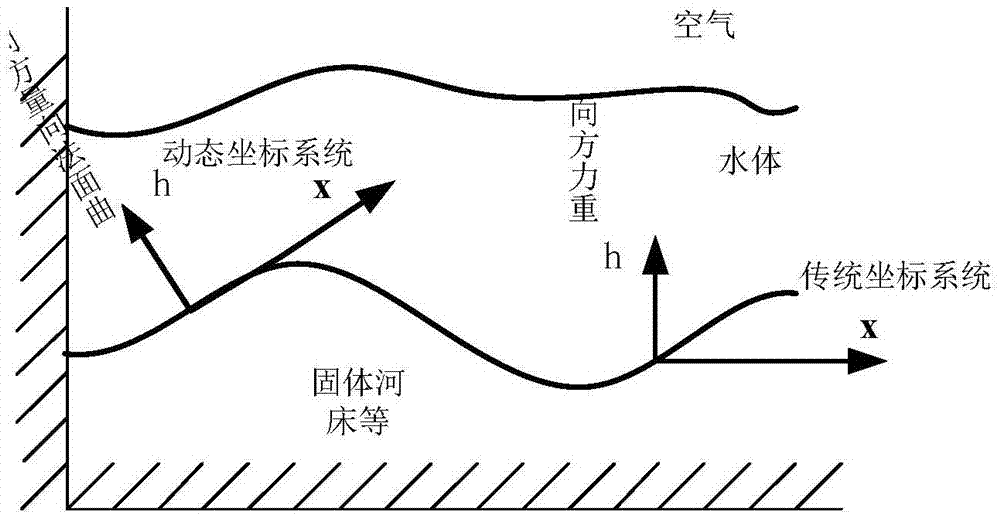
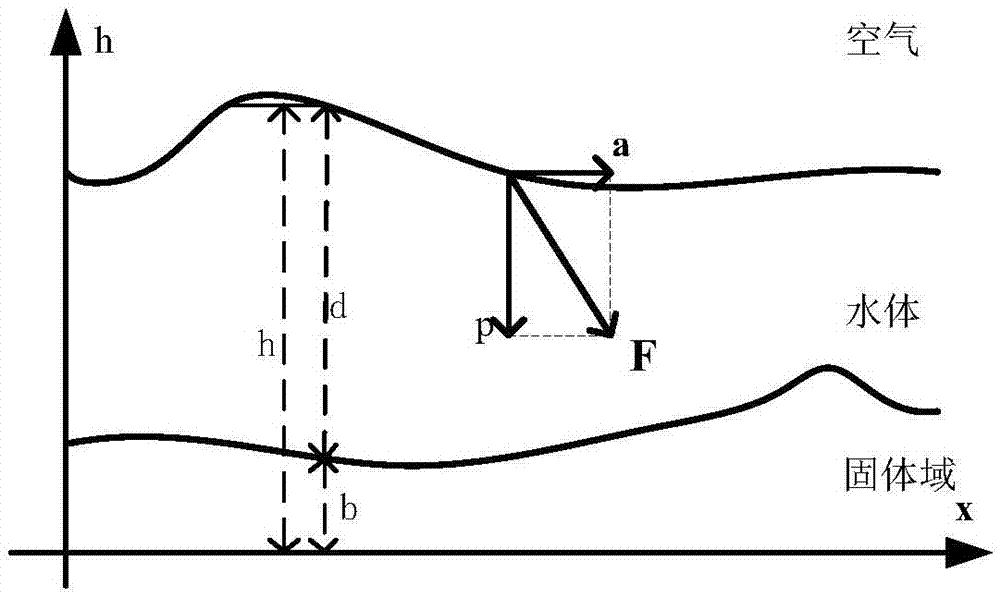
Water body modeling method for shallow water equation model with optimized parameters
ActiveCN106934192AImprove solution rateImprove stabilityInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsReal-time simulationMethod of characteristics
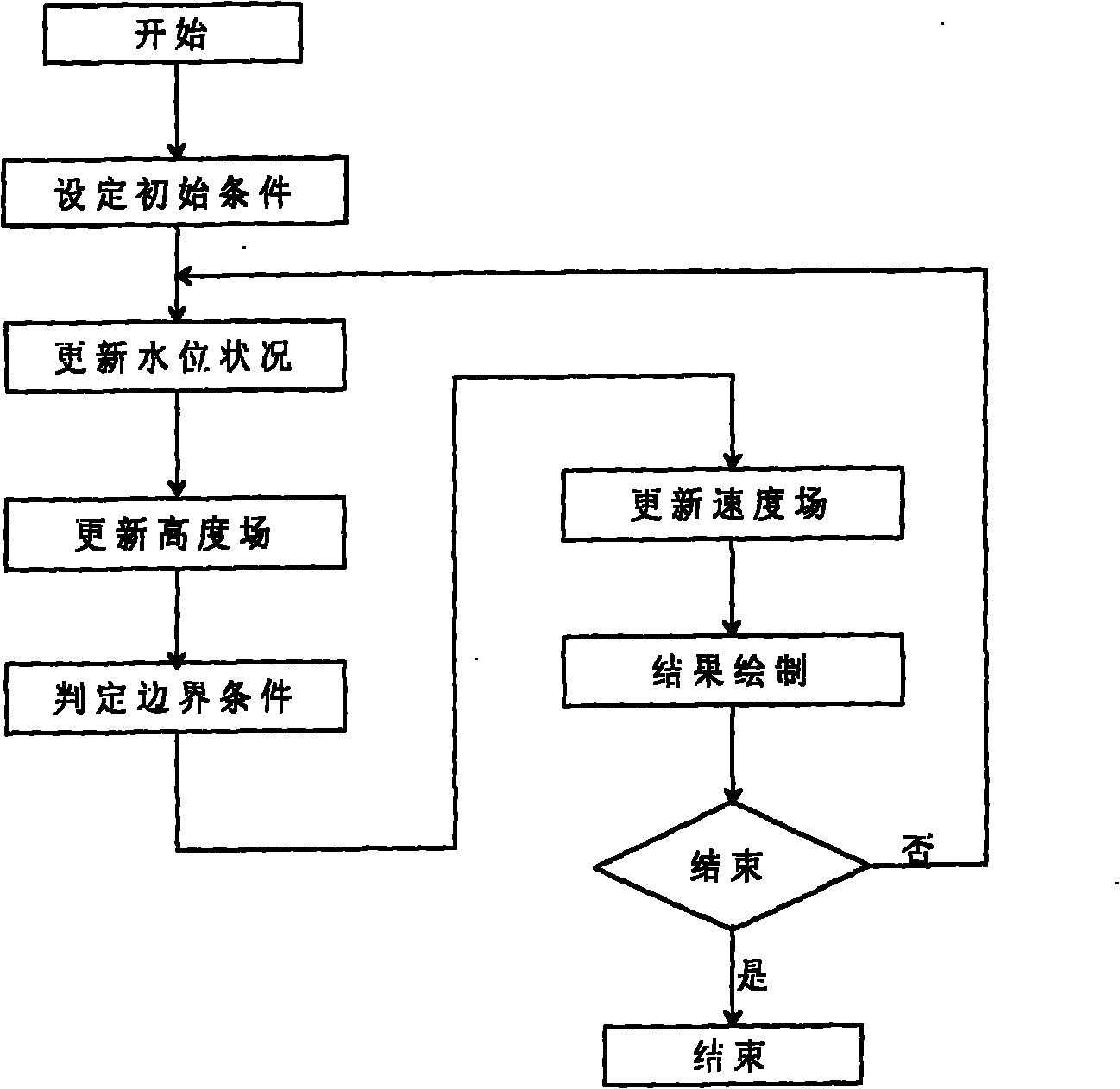
The invention discloses a water body modeling method for a shallow water equation model with optimized parameters. According to the method, first, a three-dimensional dynamic coordinate system is constructed, and the shallow water equation model with optimized parameters is derived; when the model is solved, a reverse path tracking method and a method of characteristics are combined to solve an advective item in an equation, a vector projection method and a Fourier transformation method are combined to solve the effect of external acting force on a water body, and therefore a velocity field and a height field are updated; next, boundary check is performed, a boundary truncation method is adopted to process mesh points beyond a boundary; and last, the height field is drawn, and a next time period is processed cyclically. Compared with a traditional shallow water equation, when the contact surface between the water body and a solid is excessively steep, a water body model can be constructed more vividly and accurately, and the velocity of average 24.9 frame / second can be reached in the water body modeling simulation process; compared with a traditional method, the velocity is increased by 29.016%, and real-time simulation can be realized basically.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Apparatus and method for creating three dimensional relief tiles
InactiveUS7729506B2Rapid deploymentProgramme controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusEngineeringHeight field
An electronic file containing height field mapping data is output to a specialized printer and used to create one or more three dimensional molds. The molds, in turn, may be used to fabricate bas-relief tiles and similar three-dimensional objects from various materials. The process allows for rapid deployment of customized design elements in many construction applications and environments.
Owner:CARLSON KEITH
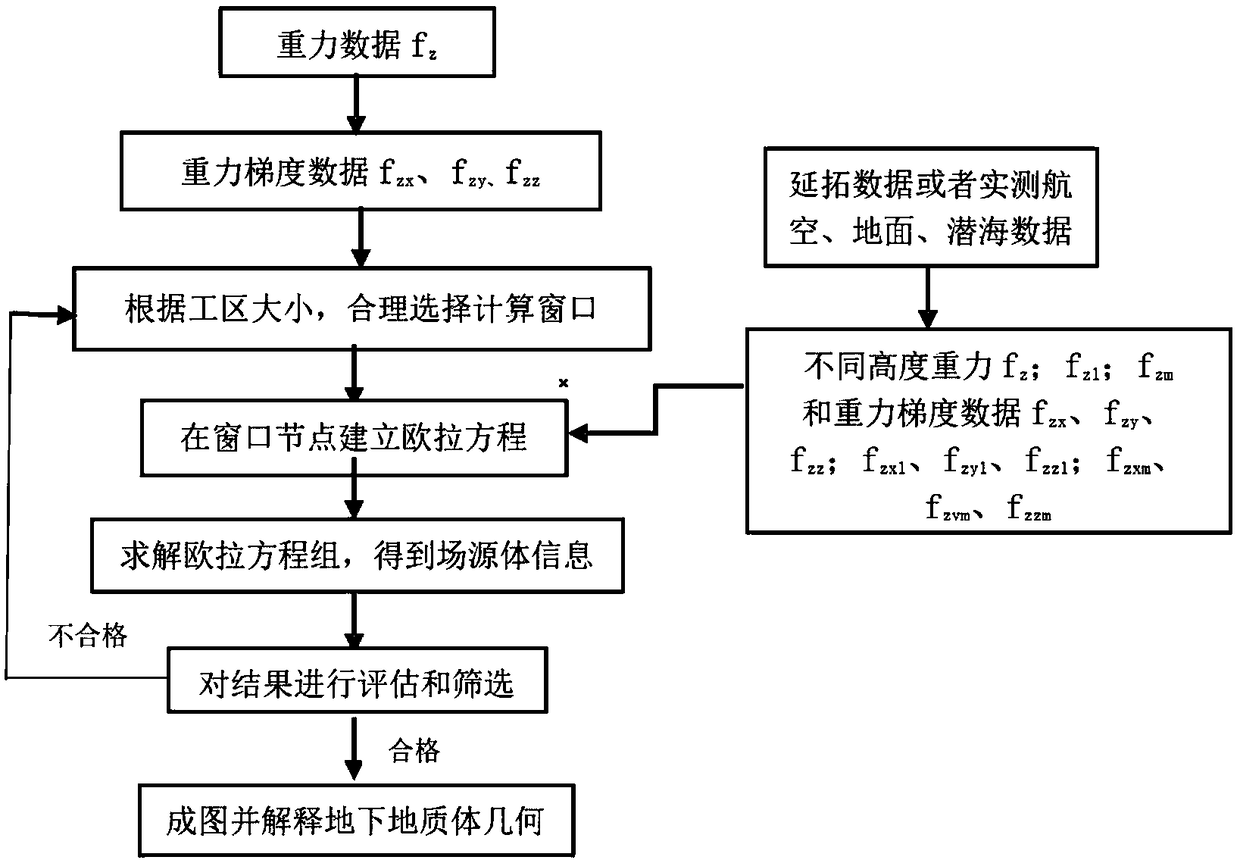
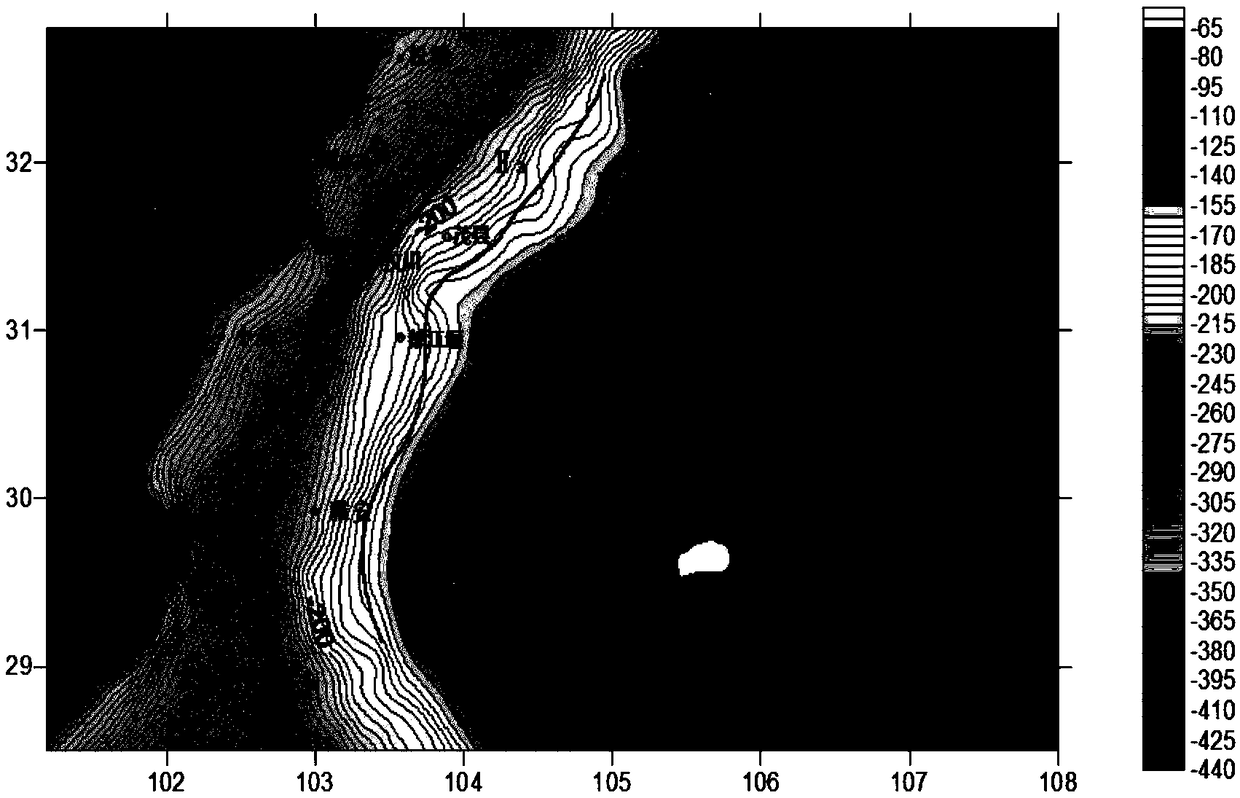
Method for inverting geologic body geometrical morphology by combining data fusion with different heights
InactiveCN108732622AHigh-resolutionImprove solution divergenceSeismic signal processingField dataEuler deconvolution
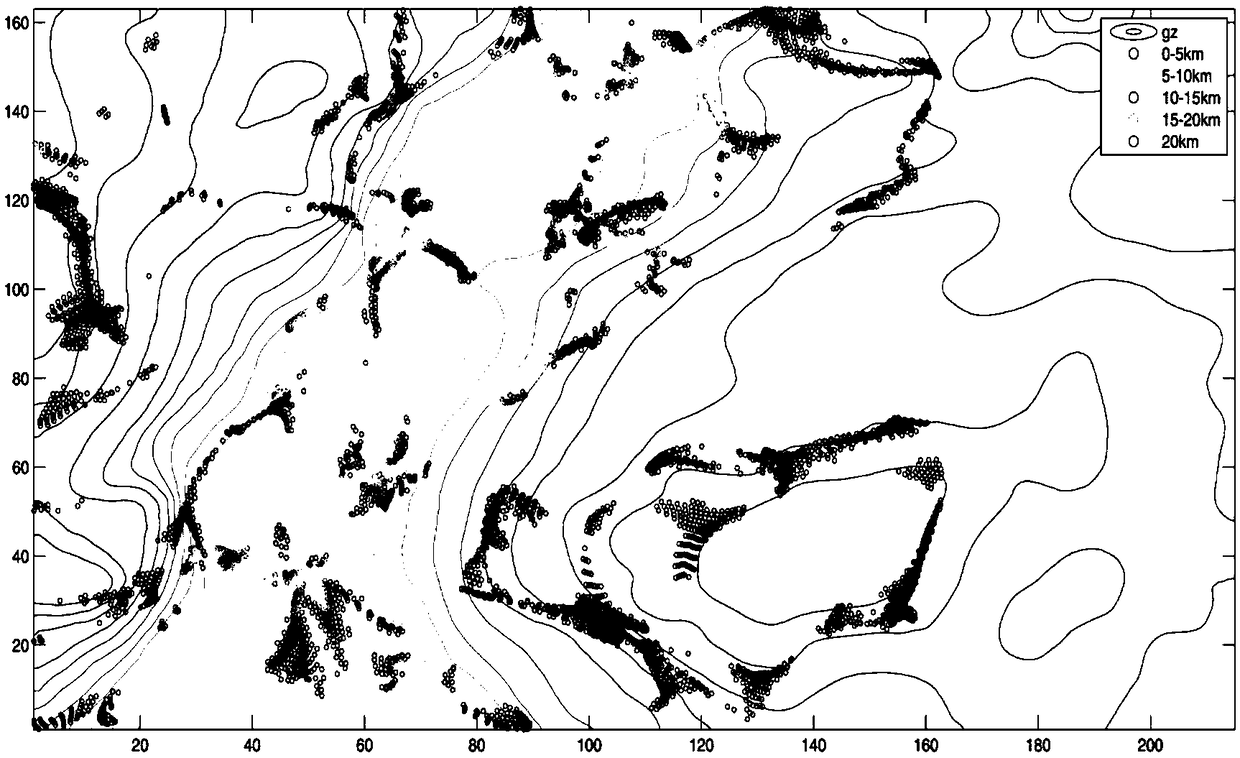
The invention relates to a method for inverting geologic body geometrical morphology by combining data fusion with different heights. The method is to carry out joint processing on the air and groundmeasured data, based on the analysis principle that different height data correspond to the same field source at the same time and is used for inverting the field source, and the application range ofthe field data of different heights in the euler deconvolution method is expanded. The different height field data fusion is combined with the euler deconvolution method, which can solve the scattering problem brought by the single observation surface data calculation, so that the basic contour of the abnormal source can be rapidly and effectively drawn. The method is especially suitable for large-area grid heavy magnetic data calculation and large-depth analysis and interpretation of different height data fusion combined with inversion geologic body geometrical shapes. The thought that a single observation surface data calculation is adopted in the prior art is broken through, the geometrical morphology of the geologic body can be more clearly and accurately divided, and the depth resolution capability of the geologic body is improved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
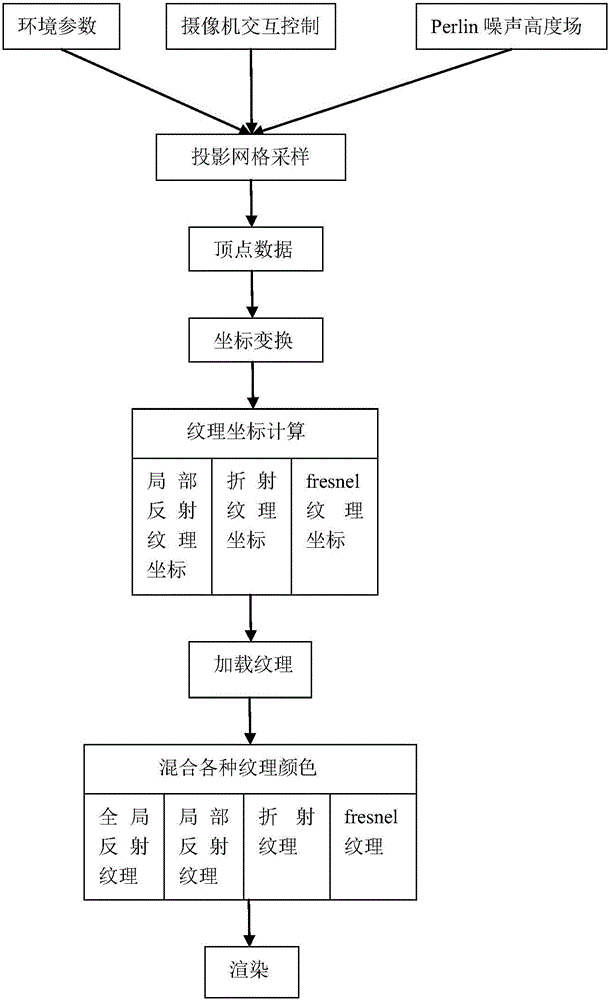
Virtual reality superspeed real-time rendering method
The invention relates to a virtual reality superspeed real-time rendering method, and the method comprises the steps: A, building environmental parameters to build an image model, carrying out the interactive control of a camera, enabling the near peripheral region and far peripheral region of a view field to be divided into three rendering regions with different resolutions, and enabling the built image model to generate a Perlin noise height field; B, carrying out the sampling through a projection grid, and building a virtual figure; C, obtaining the data of top points in the virtual figure; D, enabling the data of all top points to be mapped in a coordinate system; E, calculating texture coordinates; F, loading the texture coordinates; G, mixing various types of texture colors in all rendering regions, and completing the rendering. According to the invention, the method employs the rendering regions and distributes different resolution proportions to match with different visual sensitivity in the view field of a user, reduces the operation cost by several times, saves the operation resources and power of a computer, and achieves the real-time superspeed rendering. The method draws a water surface with a real effect through the pixel rendering and top point rendering.
Owner:江苏奥格视特信息科技有限公司
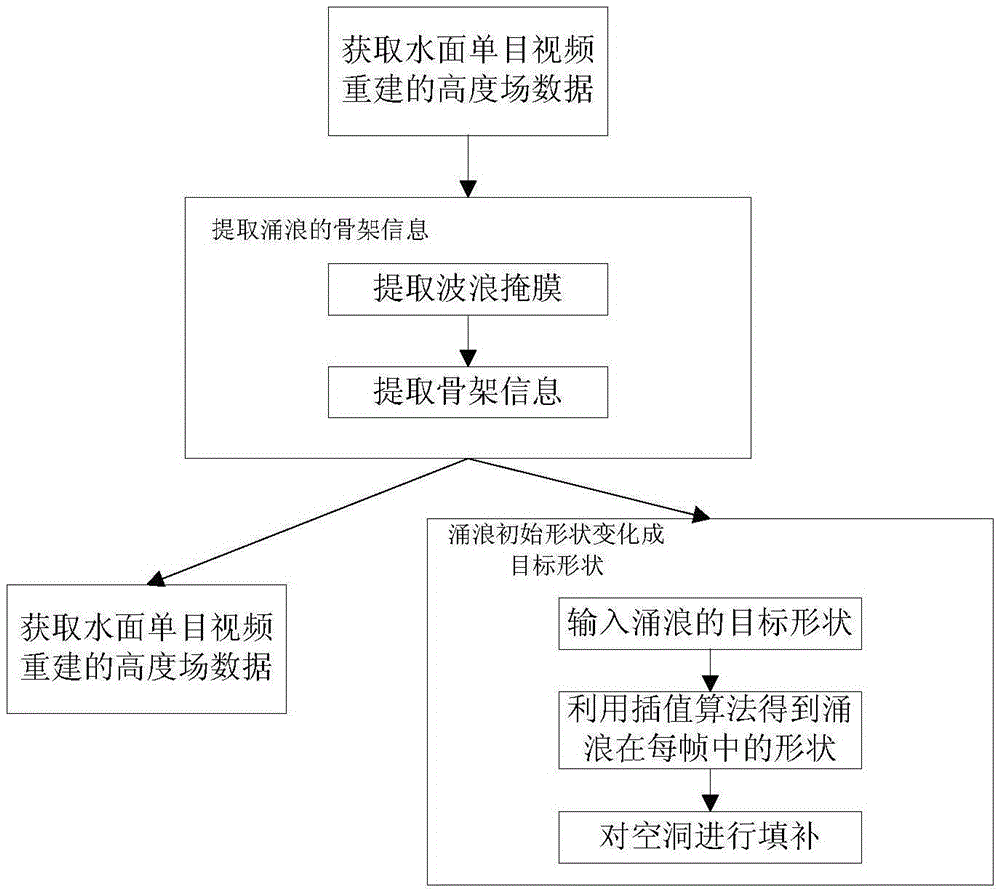
Data driving inshore surge animation synthesis method and system
The invention provides a data driving inshore surge animation synthesis method and a system and belongs to the image processing and computer vision field. The method comprises steps that a monocular video of water surface videos is reconstructed, the height field data of the monocular video is acquired, opening operation reconstruction and closing operation reconstruction for the water surface videos are carried out, surge masks are acquired, the surge masks are processed through a morphological refinement algorithm, and the surge framework information is acquired; according to the surge masks and the surge framework information, a rapid surge height change model is constructed, and a frame sequence graph is acquired according to the rapid surge height change model and the height field data; a target shape of surge inputted by a user is acquired, an initial shape of the surge in the frame sequence graph is changed into the target shape, and the target shape generates animation. Through the method, reusability of the reconstruction data is improved, and the surge information and the control mode are made to be more simple and visual.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Deformation measurement method and device
ActiveCN109029279AObjectively and comprehensively revealFacilitate investigation of oxidation kineticsMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesUsing optical meansReal-time dataClassical mechanics
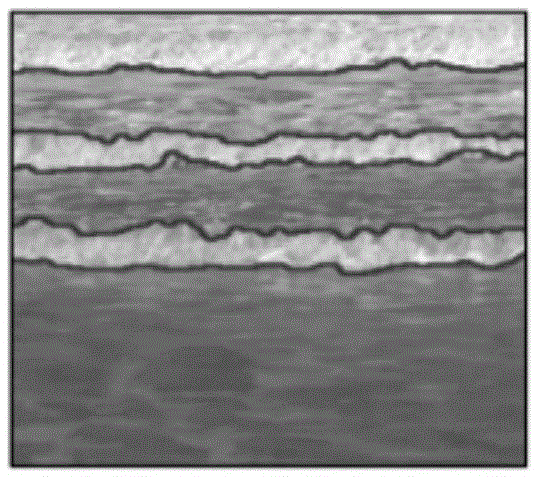
The present disclosure relates to a deformation measurement method and device. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a first height field at a first moment and a second height field at asecond moment of a to-be-tested region on the surface of a to-be- tested member relative to a marker, respectively; and obtaining a first image at the first moment and a second image at the second moment of the to-be-tested region according to the first height field and the second height field, respectively. A force-chemical coupling mechanism is determined according to the first height field, the second height field, the first image and the second image. The deformation measurement method and device in the disclosure carry out analysis according to the characteristics of the height field onthe surface of the to-be-tested member; the operations are simple and easy. In addition, the present disclosure is capable of obtaining real-time data of the to-be-tested member during the process ofhigh-temperature oxidation, thereby obtaining the growth thickness of an oxide film of the to-be-tested member in different regions, which facilitates to investigate the oxidation kinetics process ofmaterials under different stress states and can reveal the force-chemical coupling mechanism more objectively and comprehensively.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for simulating global ocean effect on digital earth
ActiveCN105894563AImprove the display effectEasy transitionDetails involving 3D image data3D-image renderingVisibilitySea waves
The invention provides a method for simulating a global ocean effect on a digital earth. The method includes the steps of first, creating a regular net, projecting the net onto a reference plane in a world coordinate system, outputting a height information map (Heightmap) of a digital earth by using an RTT of orthogonal projection, simulating the movement process of a sea wave according to a height field function, acquiring height information from the Heightmap, calculating the vertex transparency, and finally rendering the net. The method can be used for simulating the global ocean effect on the three-dimensional digital earth; achieves smooth transition between the ocean and the land and excellently shows a coastline effect; exhibits the underwater visibility in a transparent manner and also can be used for simulating an underwater beach effect in offshore; and can well apply the data generated in the simulation to special efficiency simulation of a water surface or underwater target, such as tail waves, side waves and the like.
Owner:THE 28TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
Computing method of video fluid height
InactiveCN102819662ALittle change in heightReal-time interactionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsMotion vectorVisual perception
The invention discloses a computing method of a video fluid height. The computing method comprises the following steps: firstly, initializing motion vectors of a fluid according to fluid motion features; utilizing LBM to compute the height of fluid particles in accordance with a result of the motion vectors; denoising and smoothing the height; utilizing LBM to perform recurrence on the height of continuous multiframes to obtain a height computing result with physical motion features of the fluid according to the continuity of the fluid motion; utilizing a linear interpolation of fluid particle distribution functions to obtain a height result of uniform changes of continuous motion fluids; and finally correcting the fluid height by using intermediate frames. The computing method provided by the invention is simple, convenient and fast. By using the computing method, a fluid height field of continuous changes can be obtained, and a real-time height result is produced. The computing method can be suitable for constructing virtual scenes of natural landscapes and has an application value; and with the adoption of the computing method, the real-time interaction of the fluid motion in the virtual scenes can be realized effectively, and the poor real-time capability in reconstruction based on a vision method is overcome.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
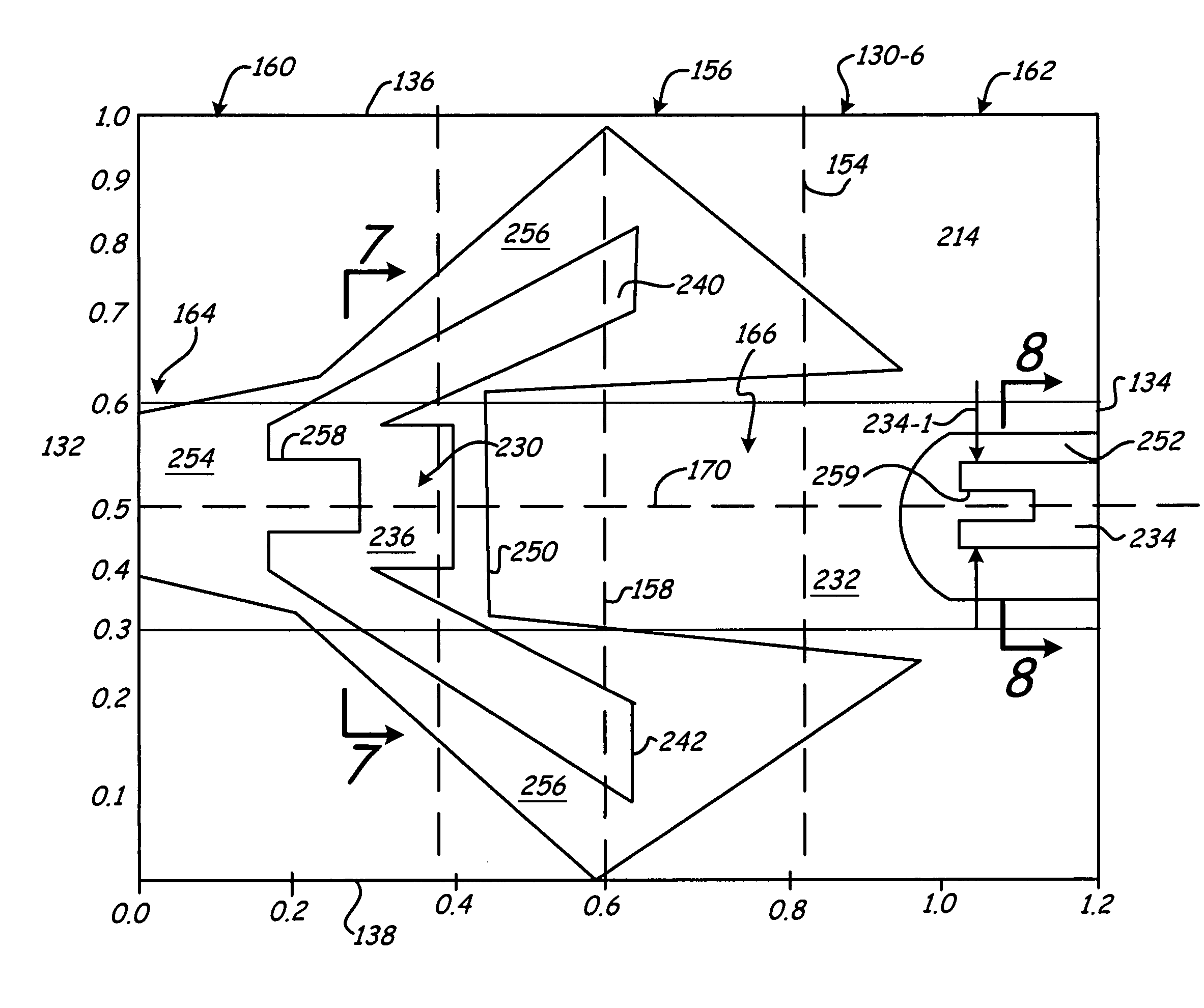
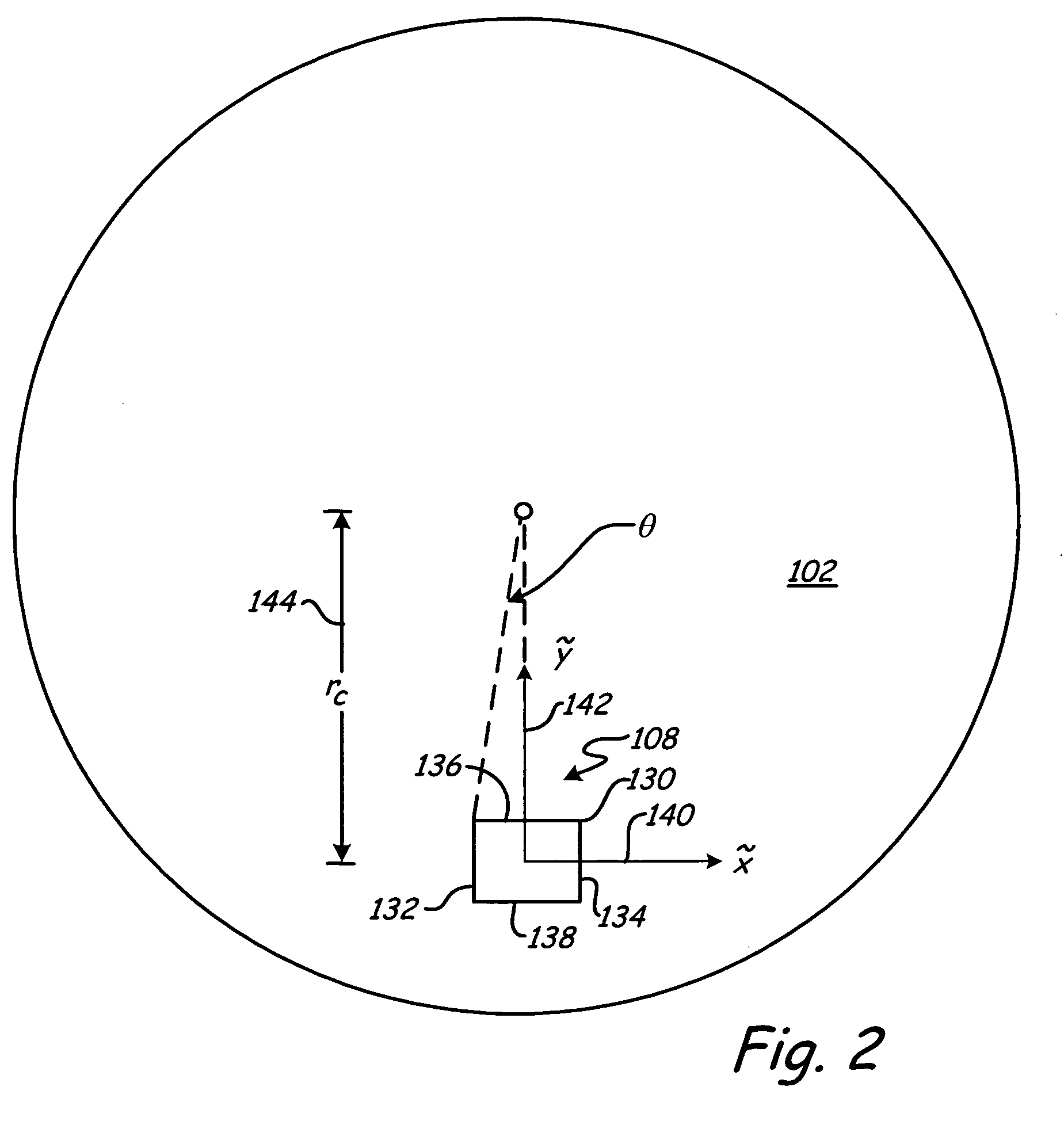
Air bearing slider having a bearing profile contoured for pressurization proximate to nodal regions of a slider-disc interface
InactiveUS7190550B2Limit off-nodal pressurizationLift and roll stabilityFluid-dynamic spacing of headsRecord information storageAir bearingEngineering
An air bearing slider which includes a raised bearing surface or surfaces contoured to limit off nodal pressurization. The air bearing surfaces are located proximate to nodal regions of a height field or profile between the slider and disc surface to limit off-nodal pressurization. The air bearing slider includes a narrow raised bearing surface profile proximate to the trailing edge of the slider body and an expanded intermediate profile along an intermediate portion to provide lift and roll stability proximate to an intermediate nodal region of the slider body to limit off nodal pressurization.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com