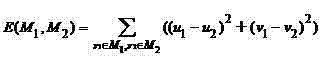Patents
Literature
81 results about "Texture space" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
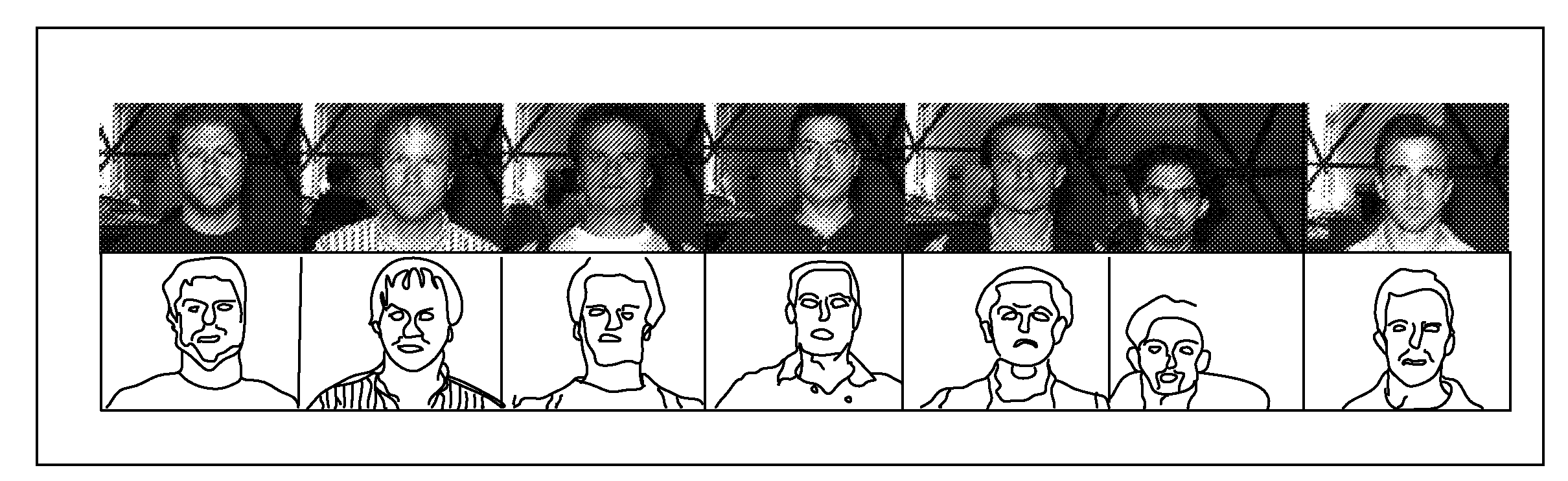
Separating Directional Lighting Variability in Statistical Face Modelling Based on Texture Space Decomposition
ActiveUS20080205712A1Reduce impactAccurately reflectTelevision system detailsImage enhancementPattern recognitionData set
A technique for determining a characteristic of a face or certain other object within a scene captured in a digital image including acquiring an image and applying a linear texture model that is constructed based on a training data set and that includes a class of objects including a first subset of model components that exhibit a dependency on directional lighting variations and a second subset of model components which are independent of directional lighting variations. A fit of the model to the face or certain other object is obtained including adjusting one or more individual values of one or more of the model components of the linear texture model. Based on the obtained fit of the model to the face or certain other object in the scene, a characteristic of the face or certain other object is determined.
Owner:NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND +1
Method, system, and computer program product for updating texture with overscan
A system, method, and computer program product are provided for updating texture on a graphical display object with overscan. A preprocessor stage defines an overscan region representing an extension of an object surface rasterized in texture space. A texture update stage creates a dilated texture map that includes updated mapped texels for a mapped region and updated overscan texels corresponding to the overscan region, such that texture is updated in the mapped region and the overscan region. Texel-based and polygon-based preprocessor stages and texture update stages are provided.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
Separating a Directional Lighting Variability In Statistical Face Modelling Based On Texture Space Decomposition
ActiveUS20090003661A1Reduce impactAccurately reflectImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionData set
A technique for determining a characteristic of a face or certain other object within a scene captured in a digital image including acquiring an image and applying a linear texture model that is constructed based on a training data set and that includes a class of objects including a first subset of model components that exhibit a dependency on directional lighting variations and a second subset of model components which are independent of directional lighting variations. A fit of the model to the face or certain other object is obtained including adjusting one or more individual values of one or more of the model components of the linear texture model. Based on the obtained fit of the model to the face or certain other object in the scene, a characteristic of the face or certain other object is determined.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD +1
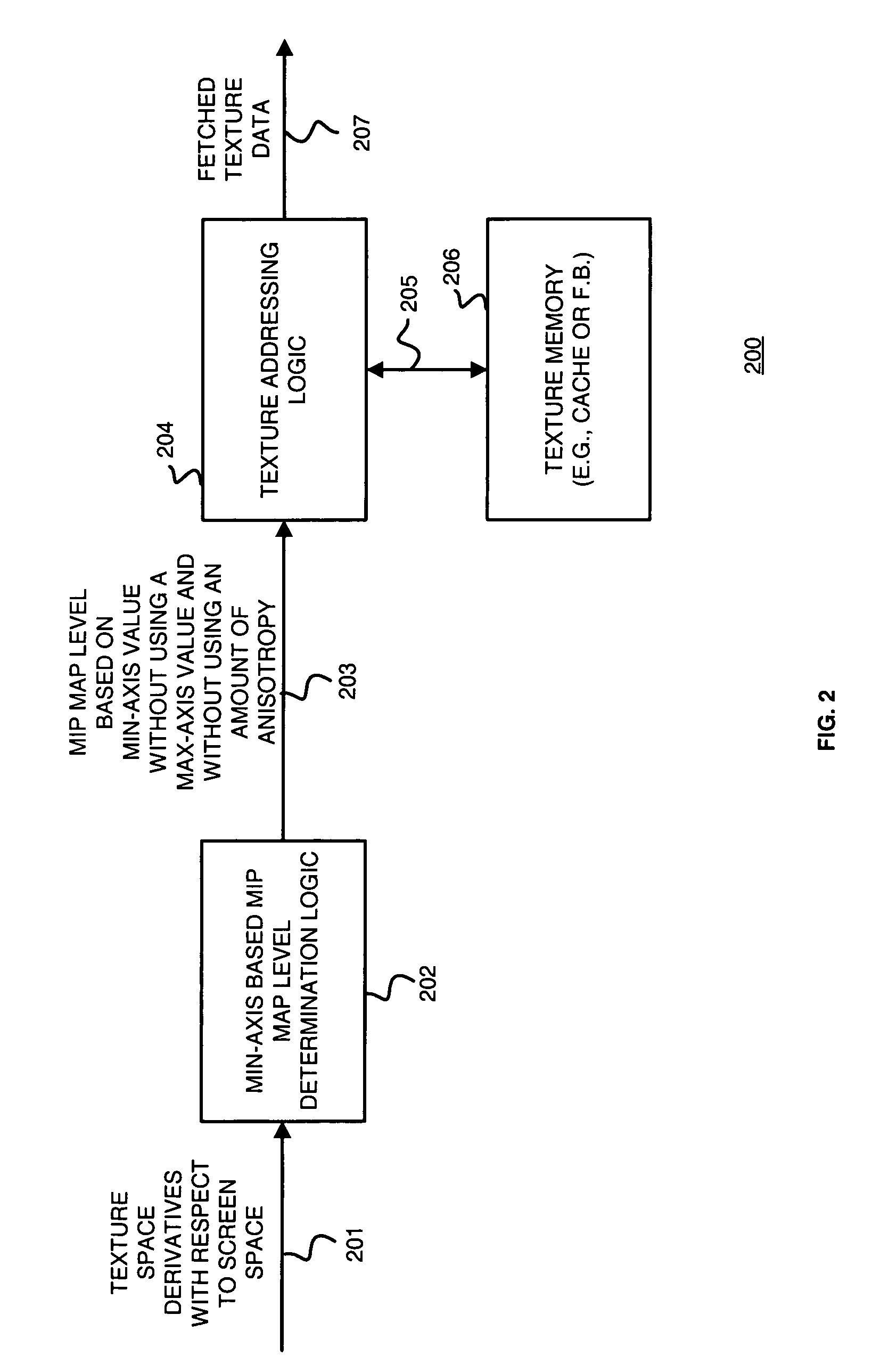
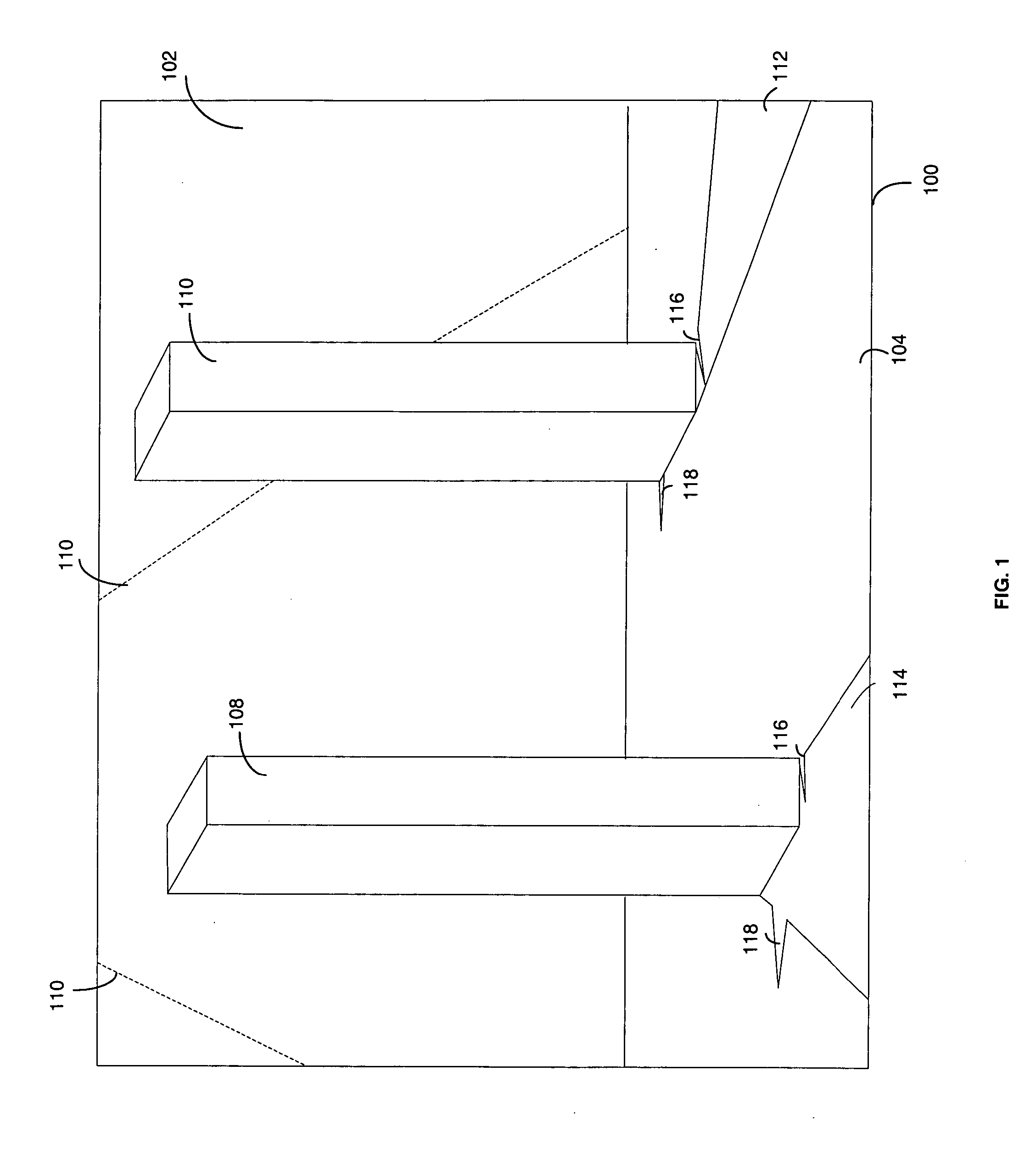
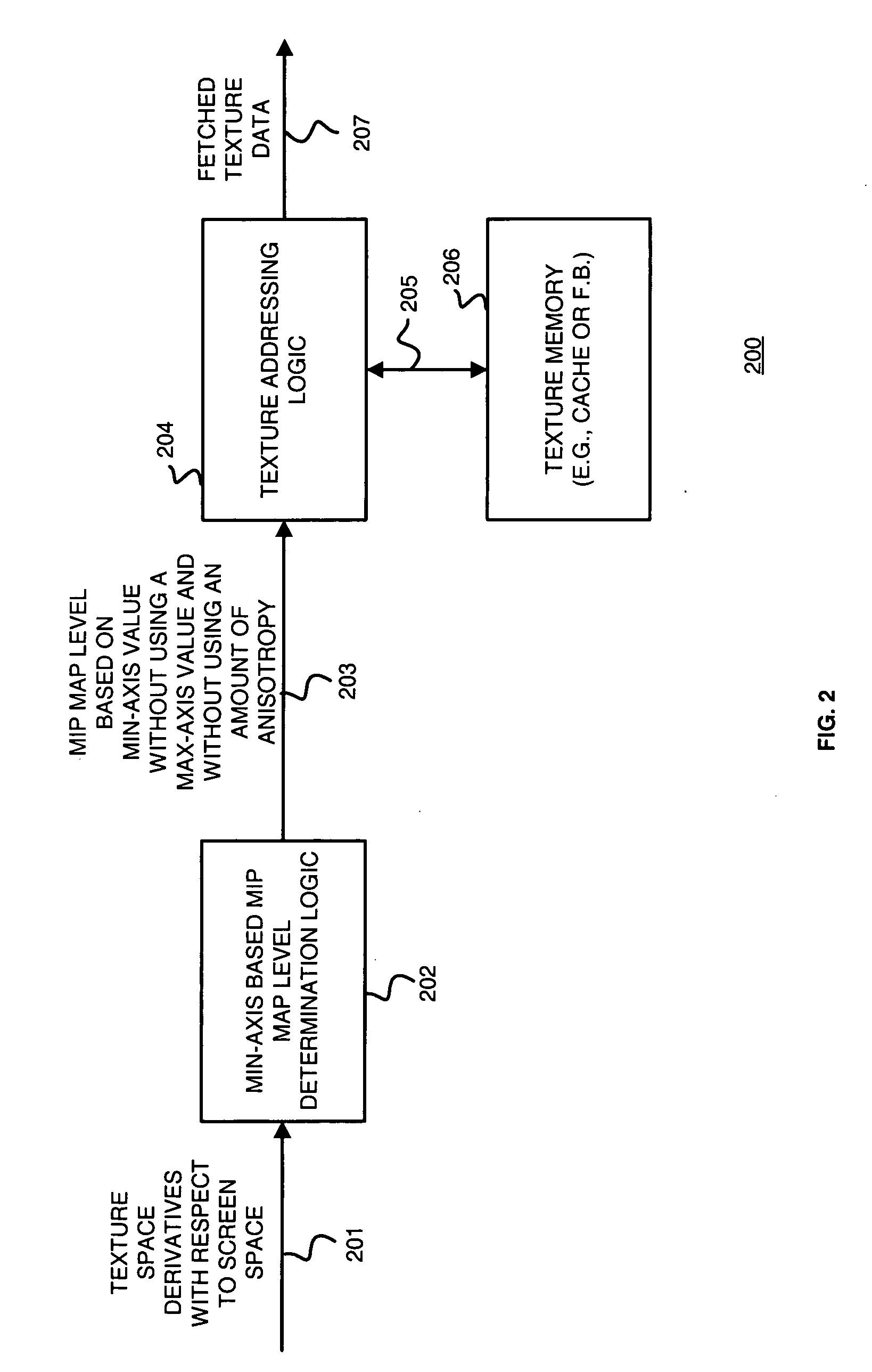
Method and apparatus for selecting a mip map level based on a min-axis value for texture mapping
Min-axis based mip map determination logic receives a plurality of texture space derivatives with respect to screen space for a given pixel and texel location and selects from a plurality of mip map levels a mip map level based on a min-axis without using a max-axis value and without using an amount of anisotropy. The plurality of mip map levels corresponds to mip map levels of a mip chain. The min-axis may be identified as the squares of the texture space derivatives with respect to either the x-axis or the y-axis of screen space. Selecting the mip map level based on the min-axis ensures that each texel of the selected mip map never maps to more than one pixel during texture mapping where the main texture is of sufficient resolution. Thus, using the mip map level based on the min-axis to fetch texture data from memory and render images results in few aliasing artifacts.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
Apparatus and methods for texture mapping
ActiveUS7095418B2Improved allocationImprove textureDrawing from basic elementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsMapping techniques
Owner:3D SYST INC
Content aware texture mapping on deformable surfaces
ActiveUS20140267306A1Reduce distortion problemsMinimizes featureAnimation3D-image renderingAnimationDistortion minimization
A method is disclosed for reducing distortions introduced by deformation of a surface with an existing parameterization. In one embodiment, the distortions are reduced over a user-specified convex region in texture space ensuring optimization is locally contained in areas of interest. A distortion minimization algorithm is presented that is guided by a user-supplied rigidity map of the specified region. In one embodiment, non-linear optimization is used to calculate the axis-aligned deformation of a non-uniform grid specified over the region's parameter space, so that when the space is remapped from the original to the deformed grid, the distortion of the rigid features is minimized. Since grids require minimal storage and the remapping from one grid to another entails minimal cost, grids can be precalculated for animation sequences and used for real-time texture space remapping that minimizes distortions on specified rigid features.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
Apparatus and methods for texture mapping
ActiveUS20050093874A1Improved allocationImprove textureDrawing from basic elementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsPattern recognitionGraphics
The invention provides texture mapping techniques that facilitate interactive painting of a three-dimensional virtual surface by a user in object space, without requiring global parameterization. The texture mapping techniques feature rendering texture for a given virtual object using a plurality of composite textures, each formed by blending collapsible texture layers. Texture coordinates in texture space are derived using information determined at the time of surface mesh generation. The invention features dynamic texture allocation and deallocation, allowing a user to interactively modify the shape of a painted, three-dimensional model. Finally, the invention features an architecture for combined graphical rendering and haptic rendering of a virtual object, allowing a user to experience force feedback during the painting of the object in object space.
Owner:3D SYST INC
Method and apparatus for implementing wash painting style
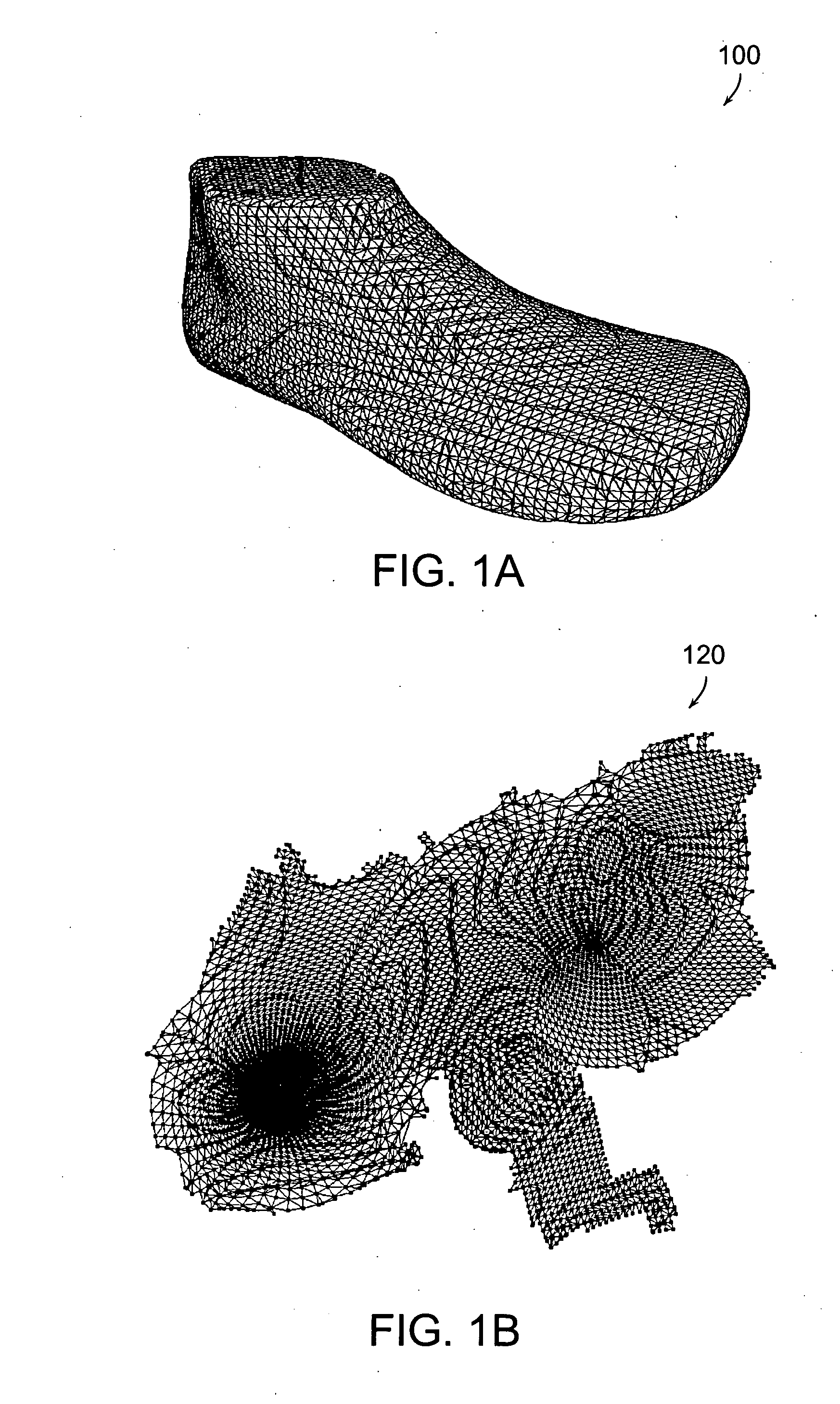
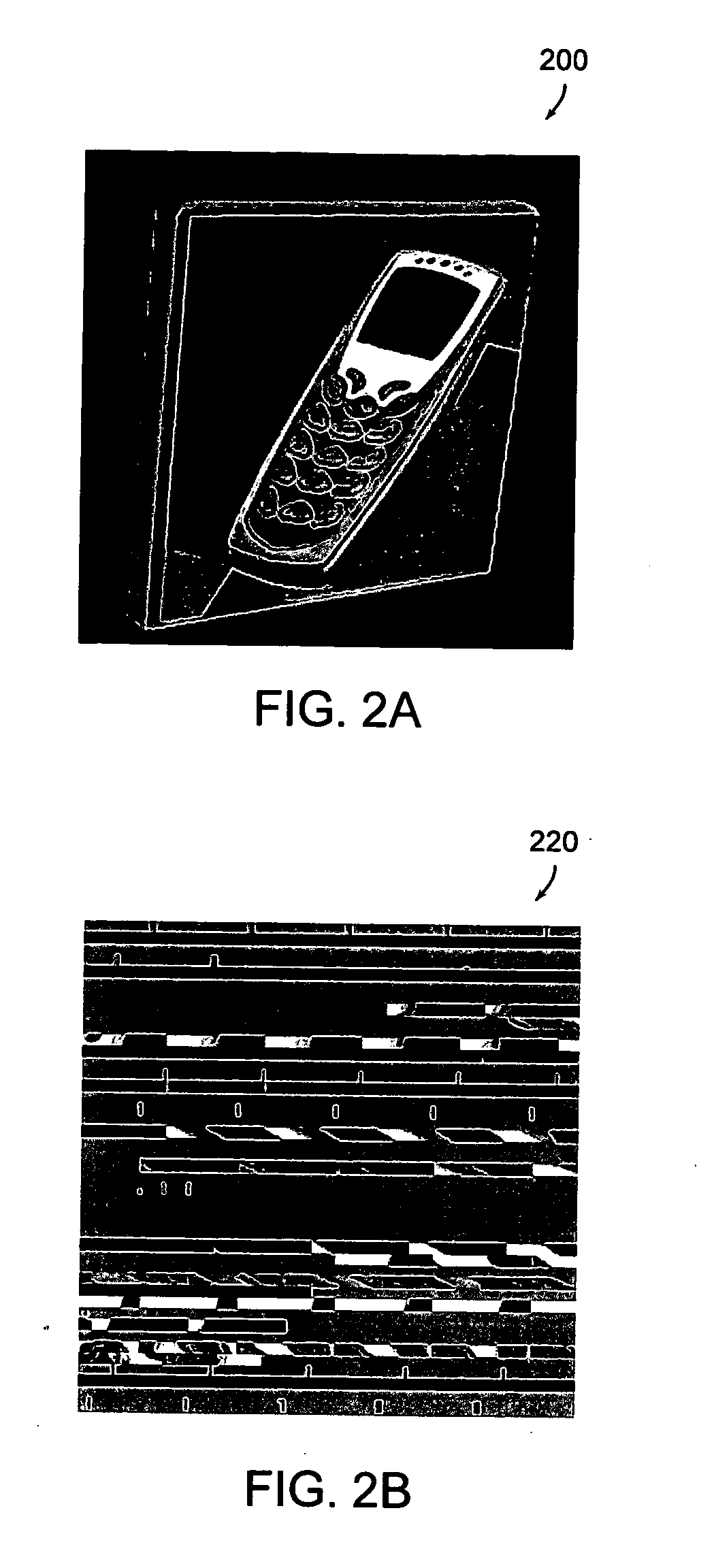
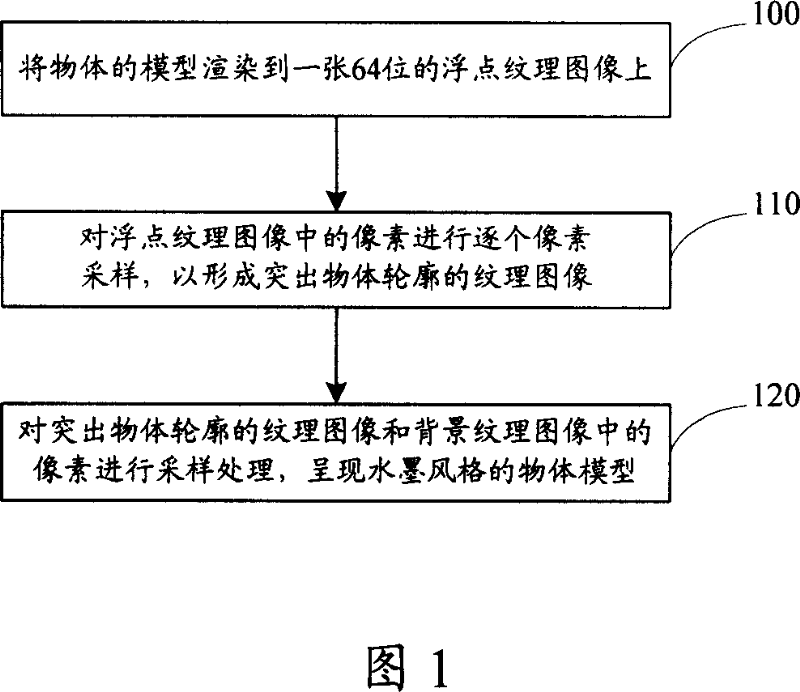
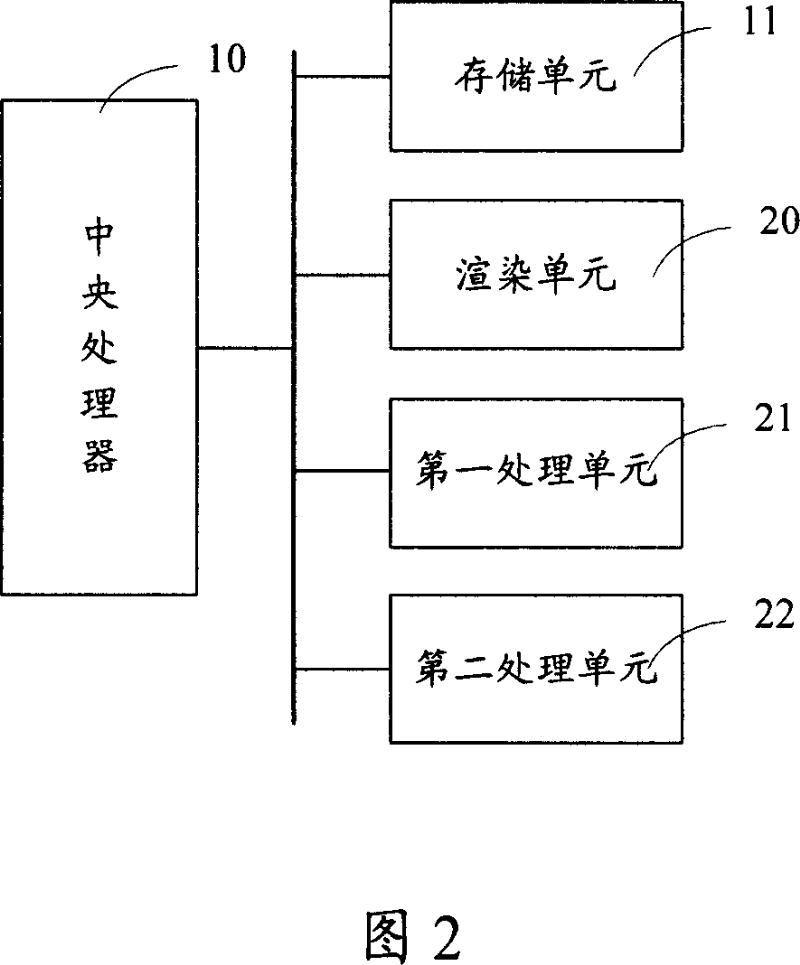
The invention discloses a method for realizing an ink-wash style rendering method which processes via a 2D texture space, the method comprises rendering a model of an object to a first floating-point texture image; sampling respective pixels on the first floating-point texture image and determining the pixels as pixels of an outline of the objcet so as to form a second texture image projecting from the outline of the objcet; sampling respective pixels on the second texture image, sampling the pixels from positions corresponding to a background texture image according to positions of the respective pixels, and mixing the pixels with the corresponding pixels sampled from the second texture image, outputting the mixed pixels to the background texture image to present the model of the object with an ink-wash style. The invention also discloses a device for realizing ink-wash style rendering.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
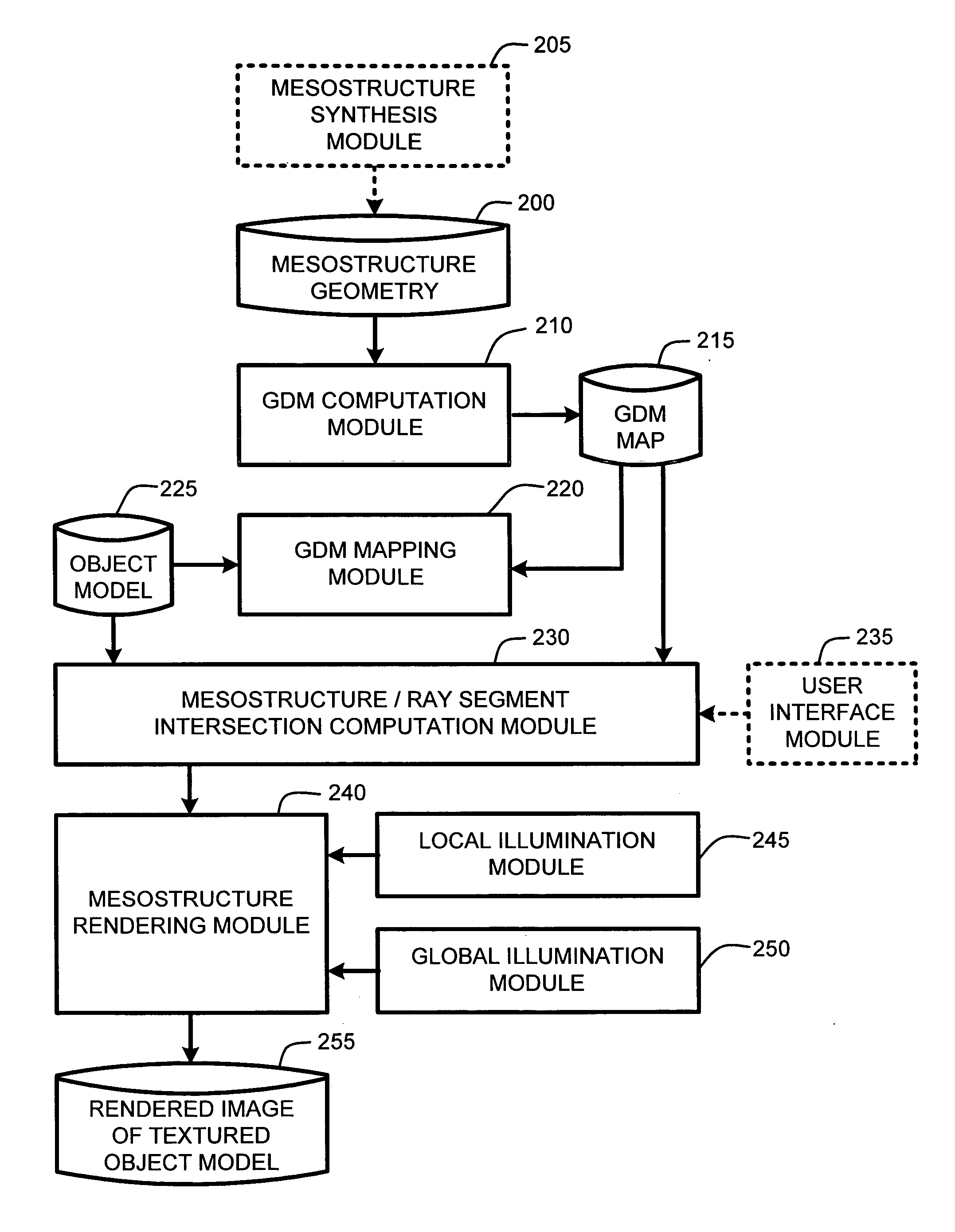
Real-time texture rendering using generalized displacement maps
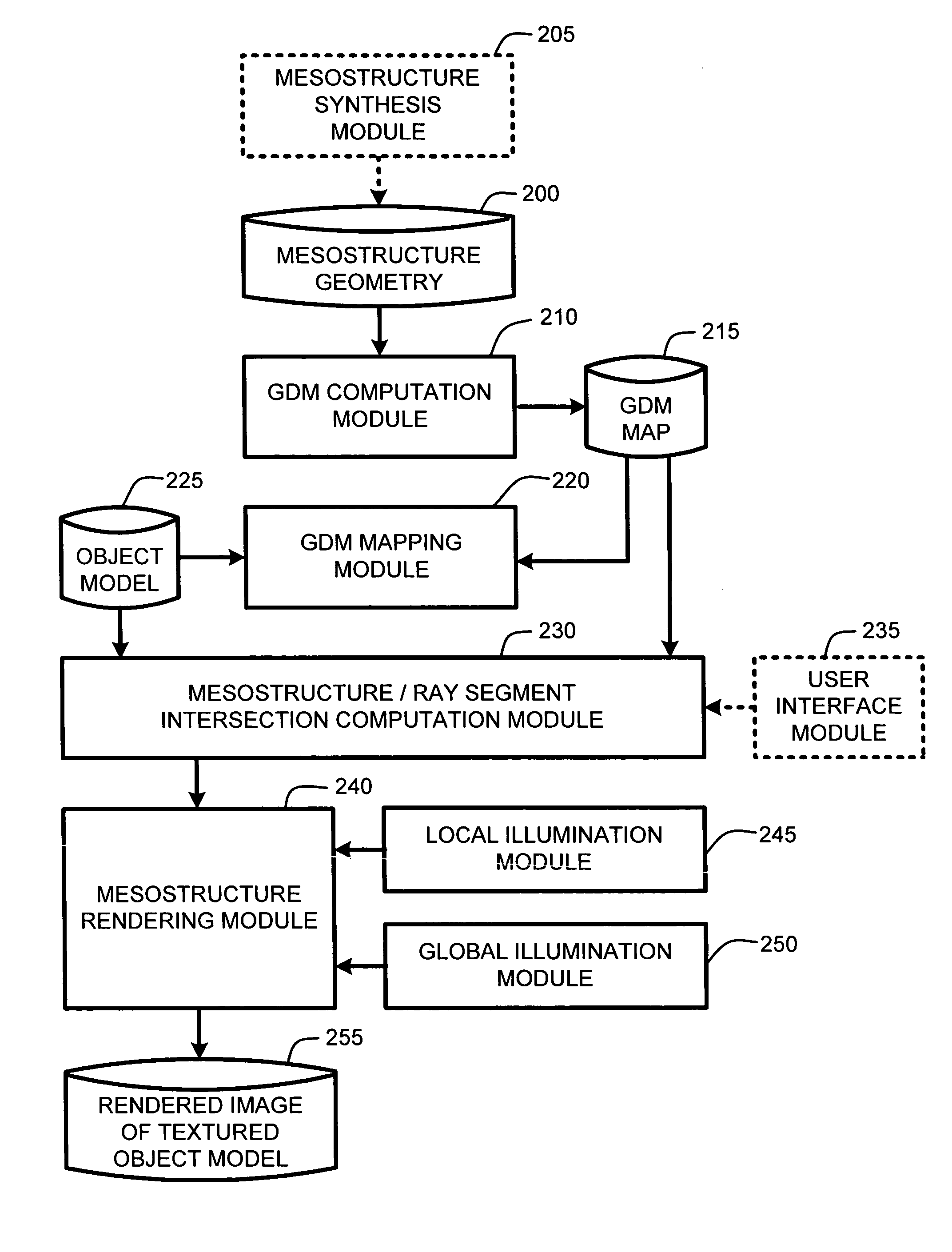
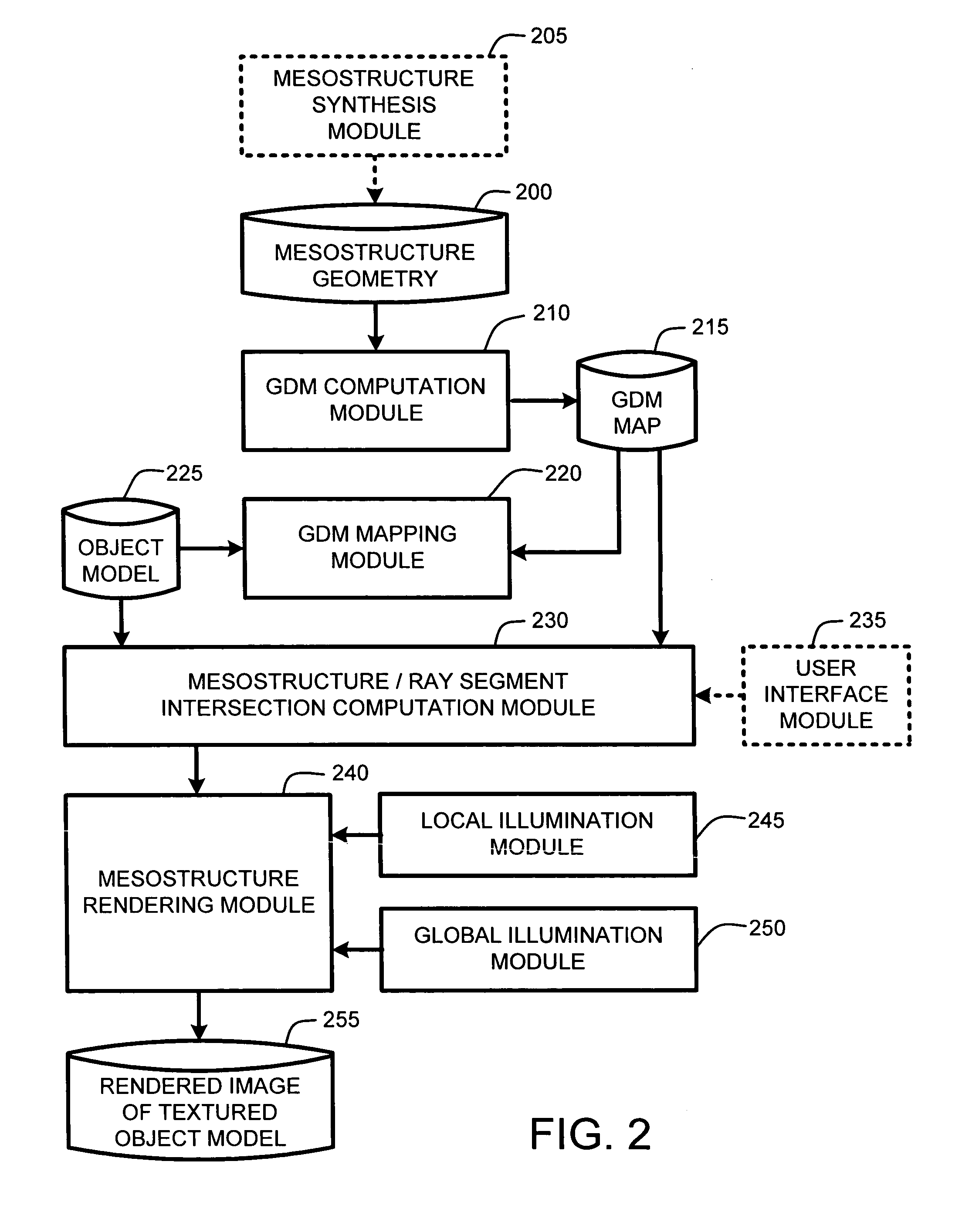
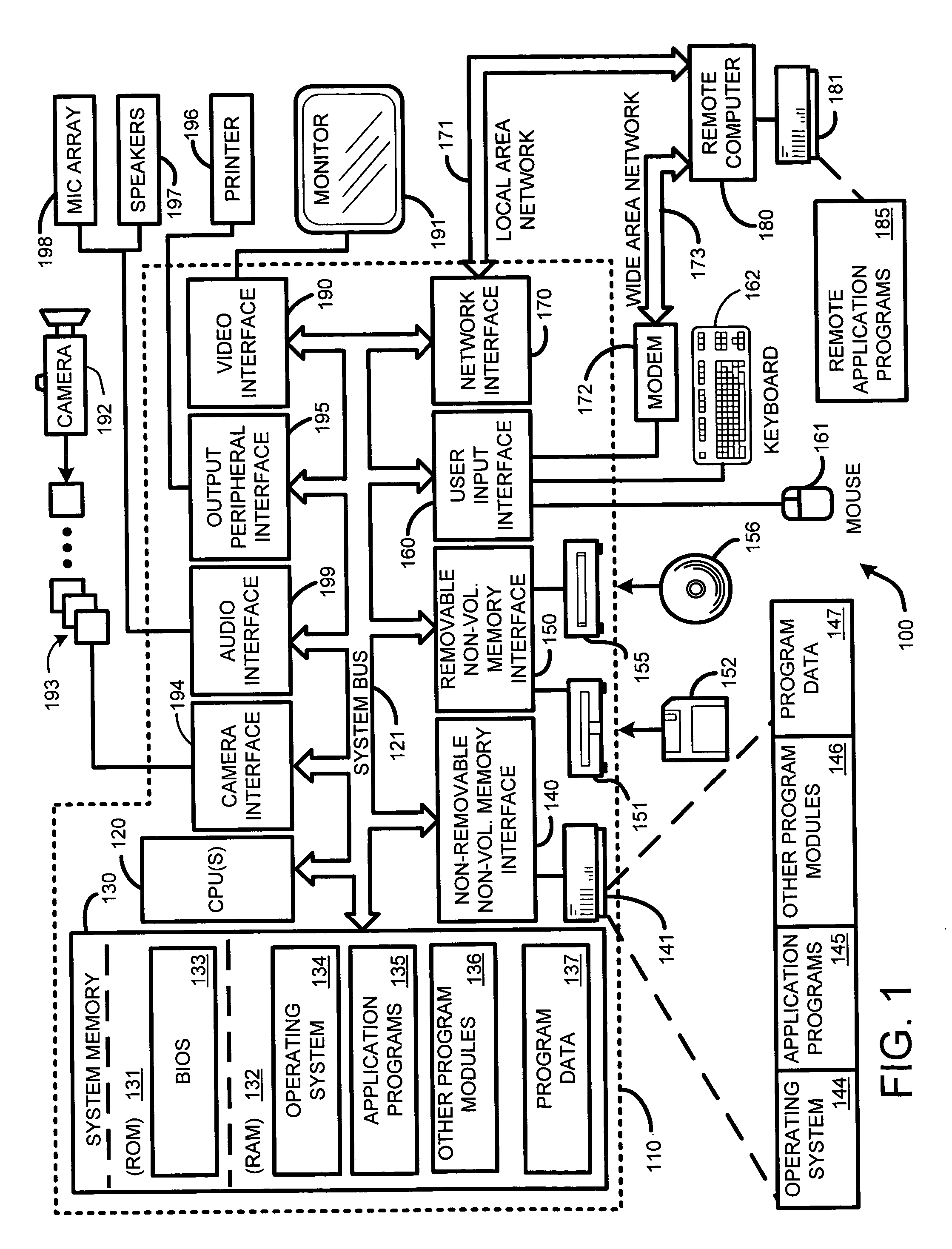
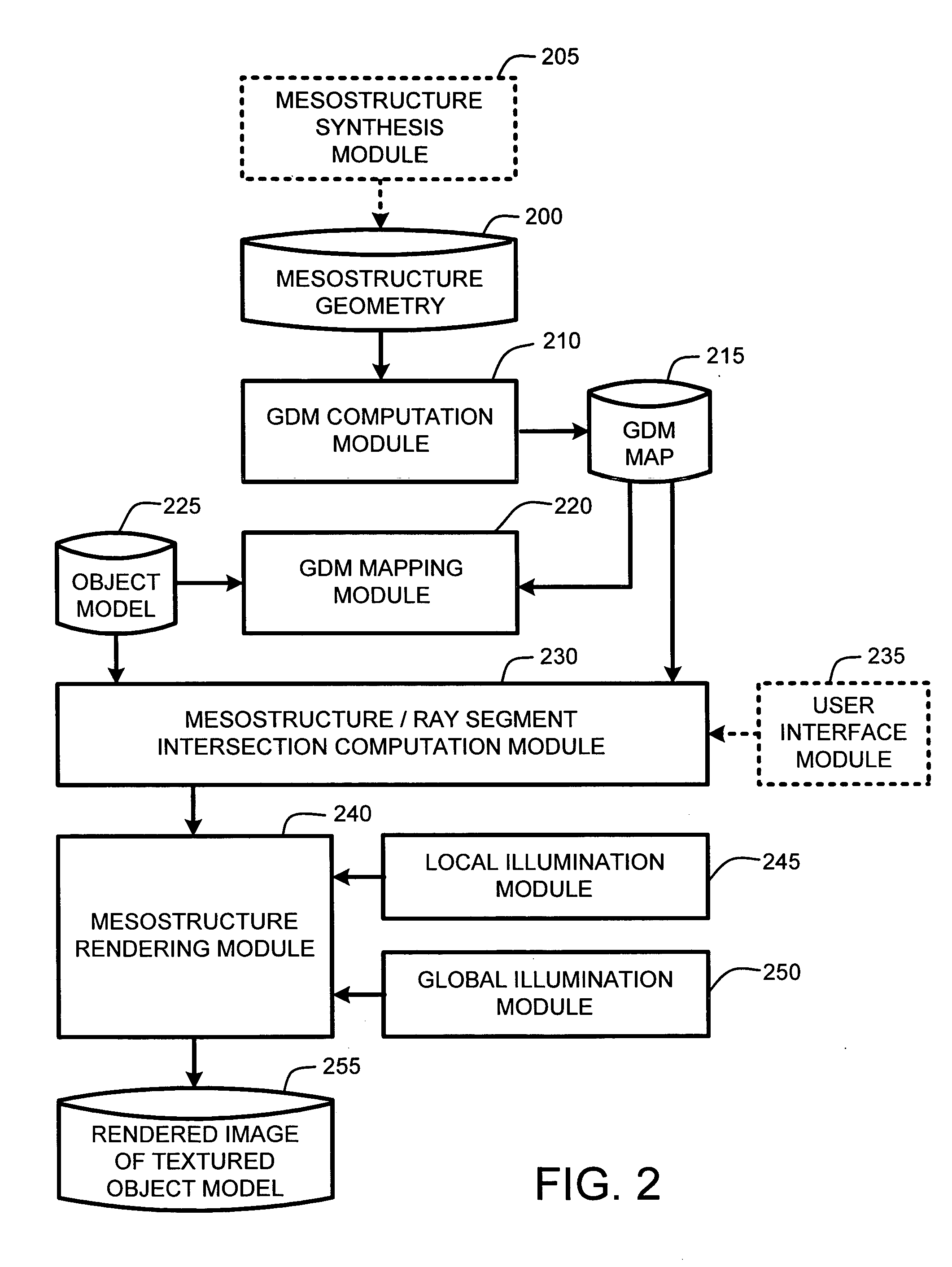
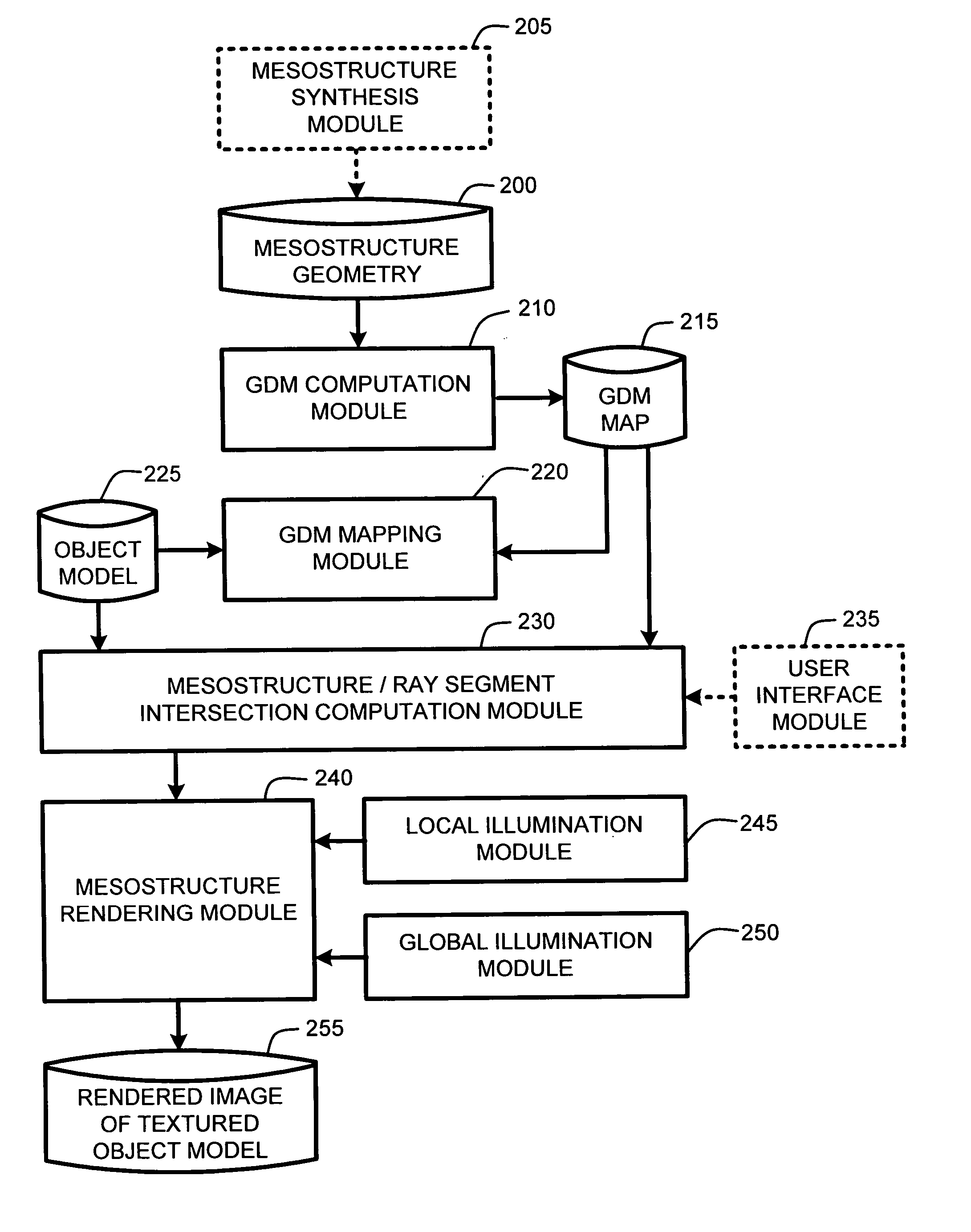
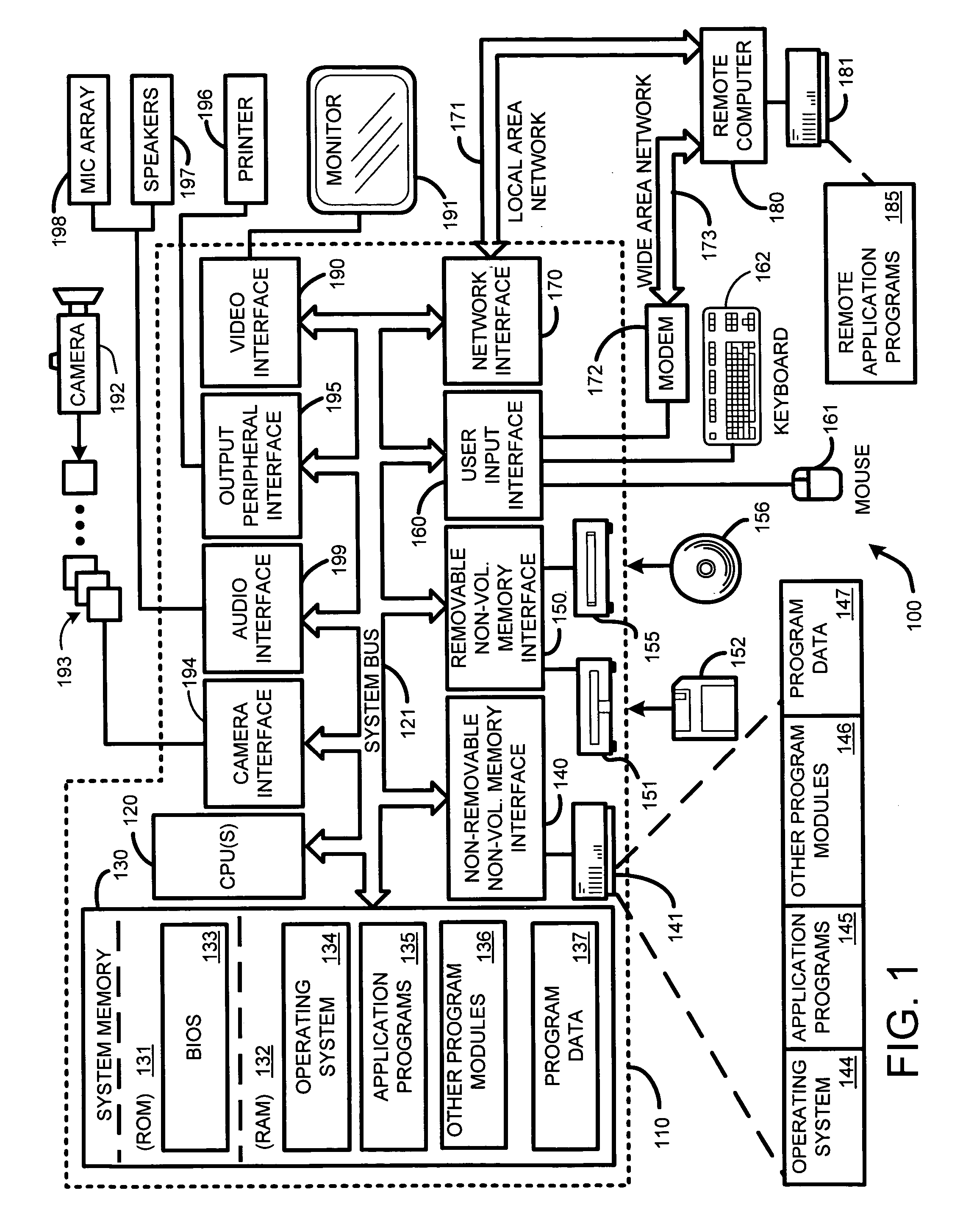
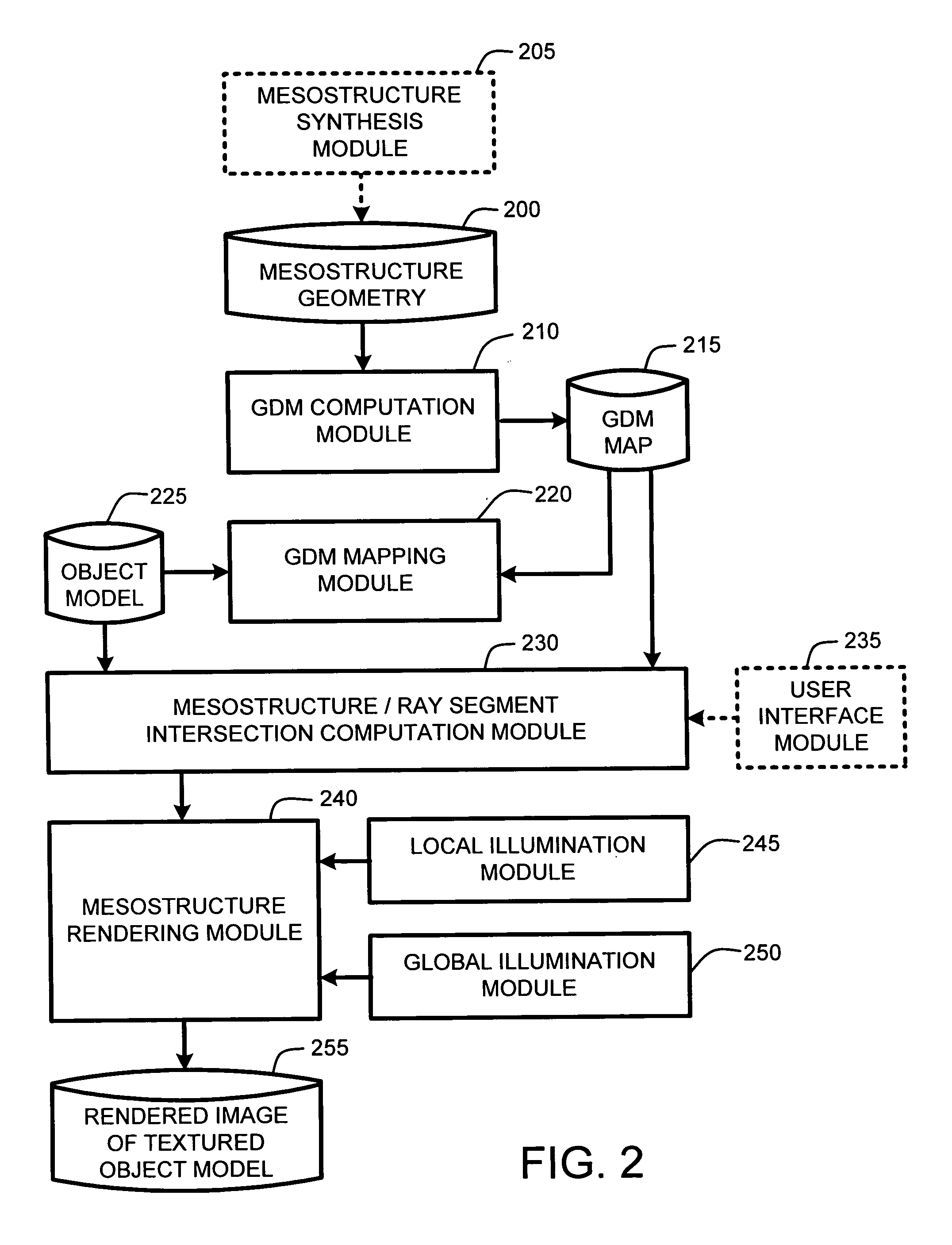
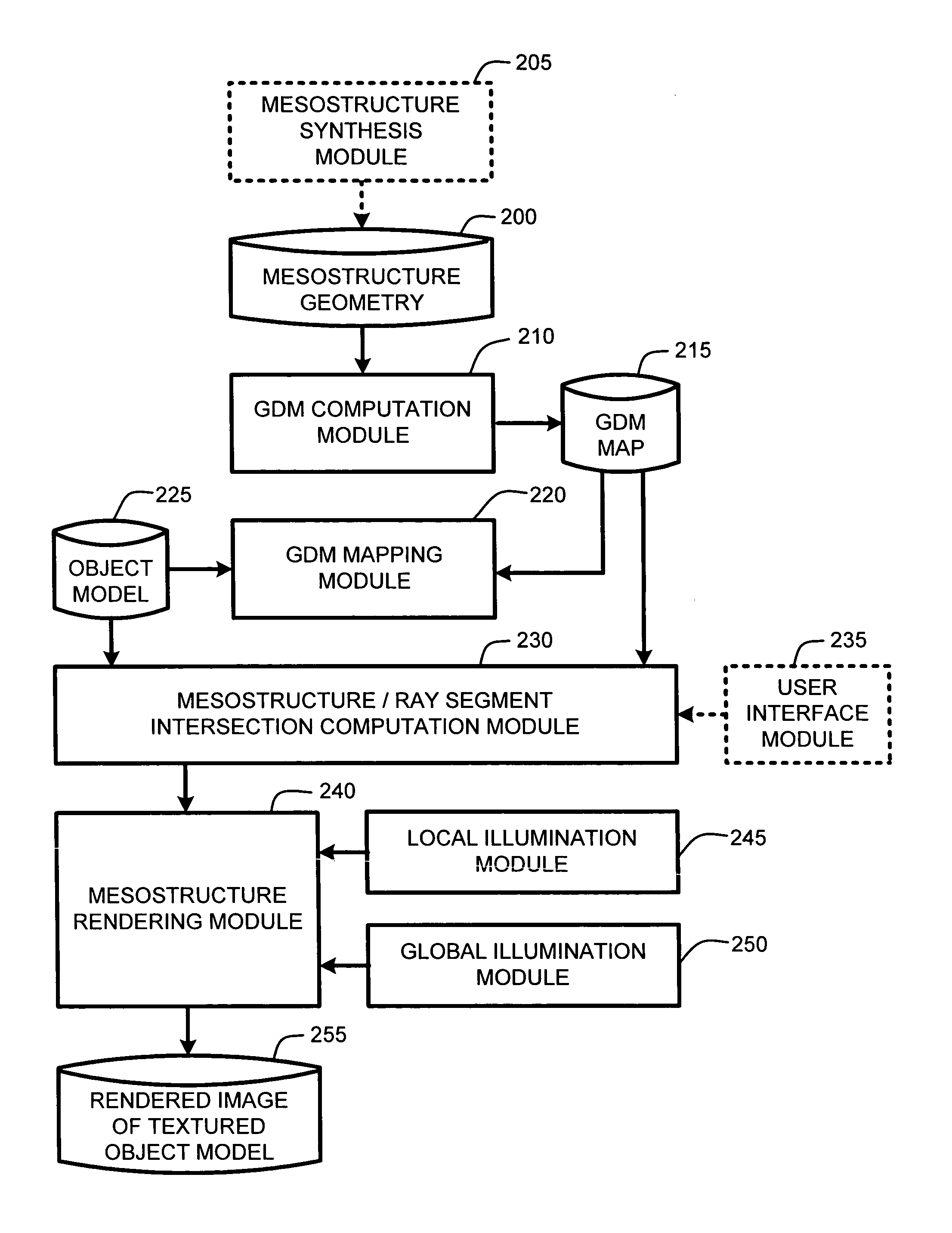
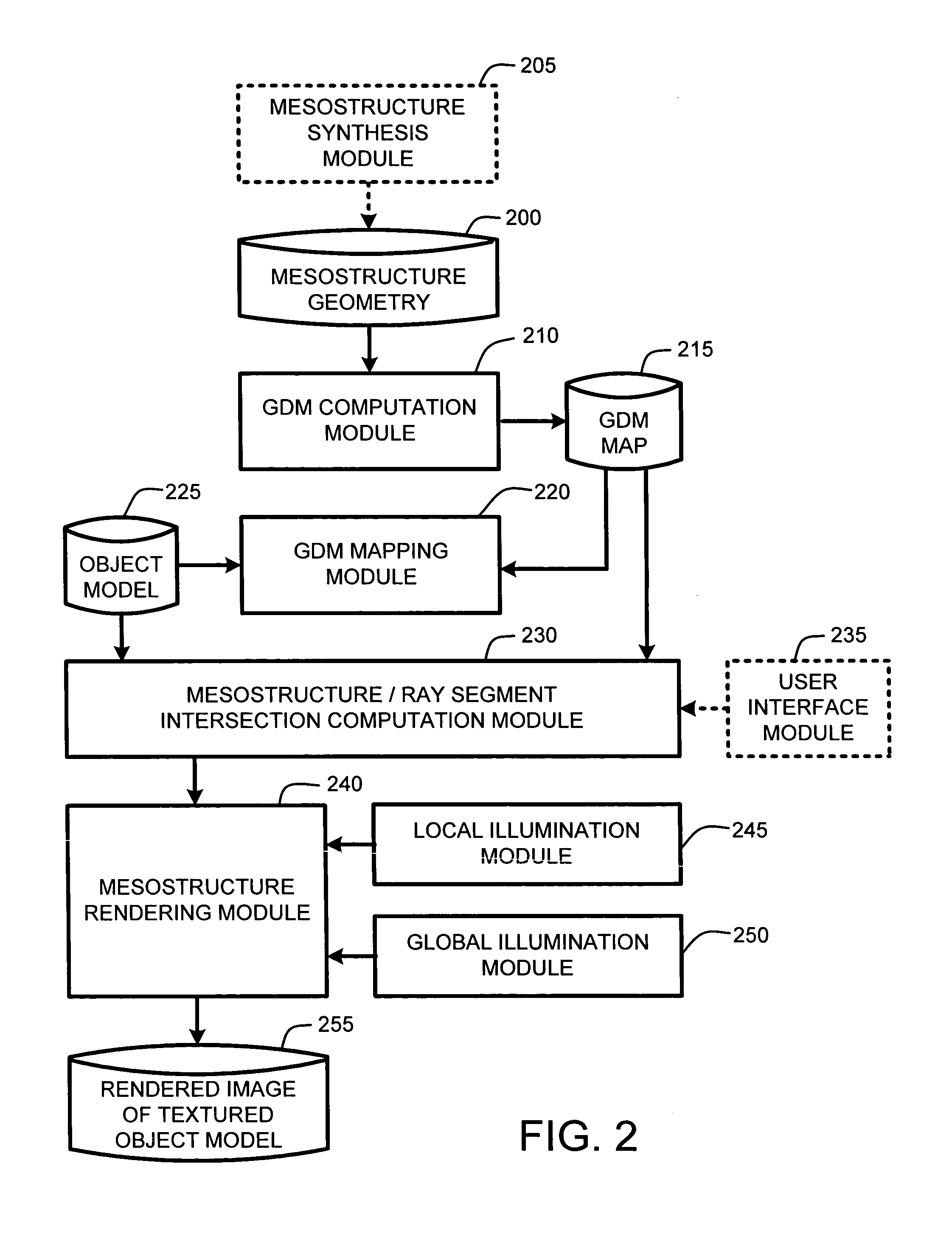
ActiveUS20050280646A1Facilitate texture coordinate computationAccelerate mesostructure renderingCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingGraphicsVisibility
A “mesostructure renderer” uses pre-computed multi-dimensional “generalized displacement maps” (GDM) to provide real-time rendering of general non-height-field mesostructures on both open and closed surfaces of arbitrary geometry. In general, the GDM represents the distance to solid mesostructure along any ray cast from any point within a volumetric sample. Given the pre-computed GDM, the mesostructure renderer then computes mesostructure visibility jointly in object space and texture space, thereby enabling both control of texture distortion and efficient computation of texture coordinates and shadowing. Further, in one embodiment, the mesostructure renderer uses the GDM to render mesostructures with either local or global illumination as a per-pixel process using conventional computer graphics hardware to accelerate the real-time rendering of the mesostructures. Further acceleration of mesostructure rendering is achieved in another embodiment by automatically reducing the number of triangles in the rendering pipeline according to a user-specified threshold for acceptable texture distortion.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus for selecting a mip map level based on a min-axis value for texture mapping
Min-axis based mip map determination logic receives a plurality of texture space derivatives with respect to screen space for a given pixel and texel location and selects from a plurality of mip map levels a mip map level based on a min-axis without using a max-axis value and without using an amount of anisotropy. The plurality of mip map levels corresponds to mip map levels of a mip chain. The min-axis may be identified as the squares of the texture space derivatives with respect to either the x-axis or the y-axis of screen space. Selecting the mip map level based on the min-axis ensures that each texel of the selected mip map never maps to more than one pixel during texture mapping where the main texture is of sufficient resolution. Thus, using the mip map level based on the min-axis to fetch texture data from memory and render images results in few aliasing artifacts.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
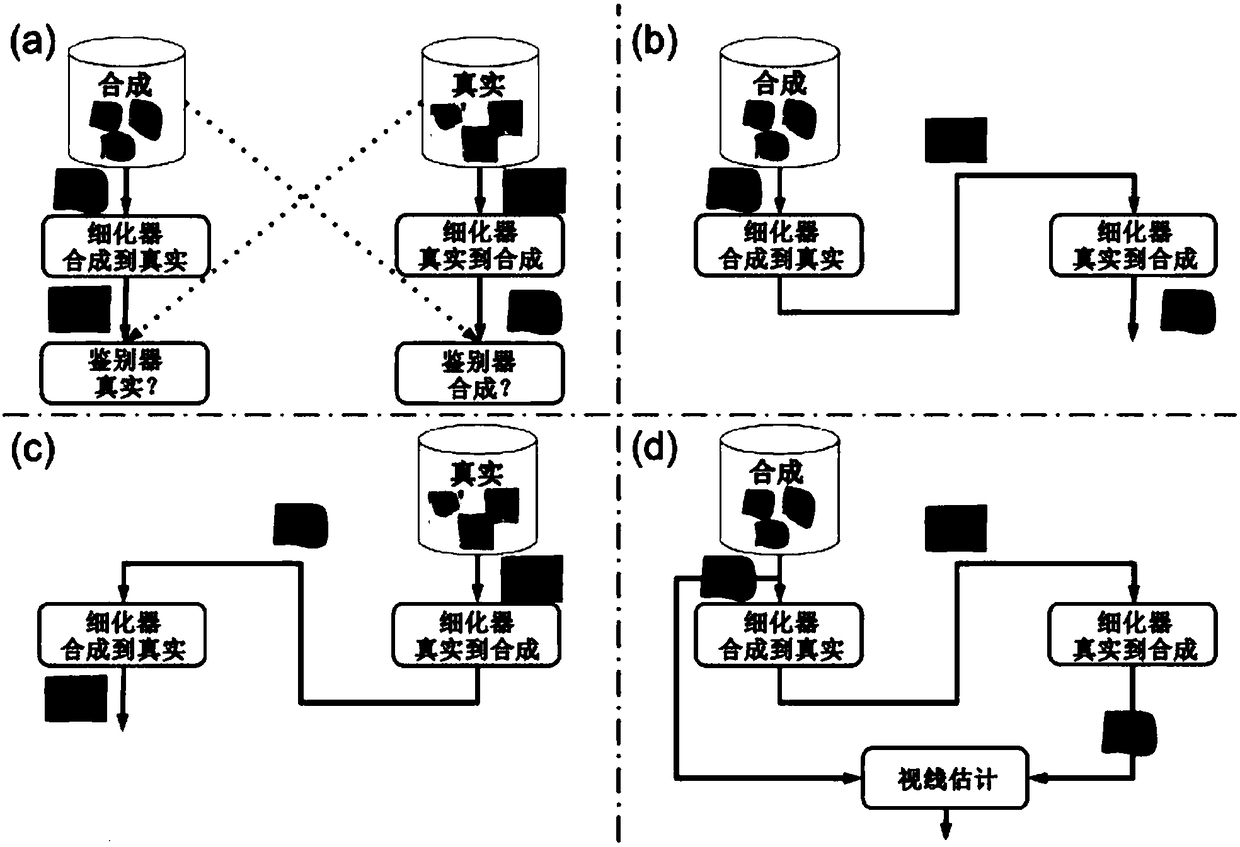
Line of sight estimation method based on generative adversarial network
InactiveCN108334832ALine of sight maintainedInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmGenerative adversarial network
The invention puts forward a line of sight estimation method based on a generative adversarial network. The method comprises the following main contents of generating a texture, generating real data and refining eyes. The method comprises the following processes that: firstly, automatically aligning a face image with the texture space of the horizontal direction and the vertical direction of a 3Dmodel; then, mapping a synthesis image to a true domain by an unpaired pixel level domain adaptive technology; thirdly, using the annotation and synthesis data of a line of sight direction to pre-train a line of sight direction estimator; and finally, in a whole mapping process, executing a refined network to keep a line of sight direction, and using a pre-training network to serve as a conversioncirculation constraint from synthesis to truth to synthesis. By use of the method, a novel adversarial training method is used, the rendered synthesis image is mapped to a vivid domain, and accurateline of sight estimation can be obtained on a practical image without using any piece of additional flag data from a true user. For the situations of extreme head gesture, blur, long distance and thelike, the method can generate line of sight estimation with robustness.
Owner:SHENZHEN WEITESHI TECH
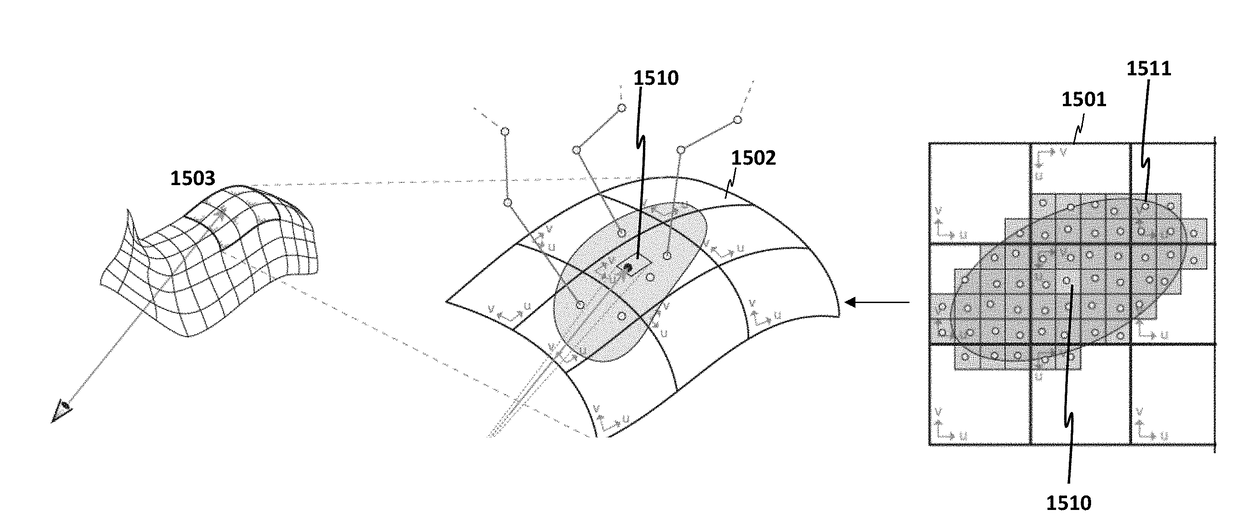
Texture space shading and reconstruction for ray tracing
An apparatus and method are described for texture space shading. For example, one embodiment of a method comprises: performing texture mapping to map one or more textures to surfaces of one or more objects in texture space within a ray tracing architecture; and performing sampling and reconstruction directly on the surfaces of the objects in the texture space.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Apparatus and methods for texture mapping
InactiveUS20070018993A1Improved allocationImprove textureCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsHaptic rendering
The invention provides texture mapping techniques that facilitate interactive painting of a three-dimensional virtual surface by a user in object space, without requiring global parameterization. The texture mapping techniques feature rendering texture for a given virtual object using a plurality of composite textures, each formed by blending collapsible texture layers. Texture coordinates in texture space are derived using information determined at the time of surface mesh generation. The invention features dynamic texture allocation and deallocation, allowing a user to interactively modify the shape of a painted, three-dimensional model. Finally, the invention features an architecture for combined graphical rendering and haptic rendering of a virtual object, allowing a user to experience force feedback during the painting of the object in object space.
Owner:3D SYST INC
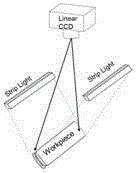
Automatic optic inspection method for surface defects of metal cylindrical workpieces
InactiveCN104156913AEnables automated optical defect detectionLight evenlyImage enhancementTexture extractionEngineering
The invention provides an automatic optic inspection method for surface defects of metal cylindrical workpieces and belongs to the automatic optic inspection methods. The automatic optic inspection method is particularly suitable for detecting surface defects of special metal cylindrical workpieces and comprises the following steps: a linear array CCD acquires the unrolled images of a metal cylindrical workpiece, the local binary pattern (LBP) and the local variance (LVAR) are combined, that is, the image variance intensity serves as the weight value to adjust the local texture extraction and measurement result of the LBP, not only the LBP texture space structure mode but also the texture intensity contrast mode is drawn into consideration, finally, the photoelectric image fault features of metal cylinders are accurately extracted, the sizes, the positions, the ranges, the severities and the like of the defects are determined, and the automatic intelligent detection of the workpiece production quality is realized. Therefore, nonuniform lighting caused by the metal materials of the workpieces per se is avoided, the accuracy in detecting tiny defects is improved, the misjudgement rate is lowered, and automatic optic inspection of the metal cylindrical workpieces is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
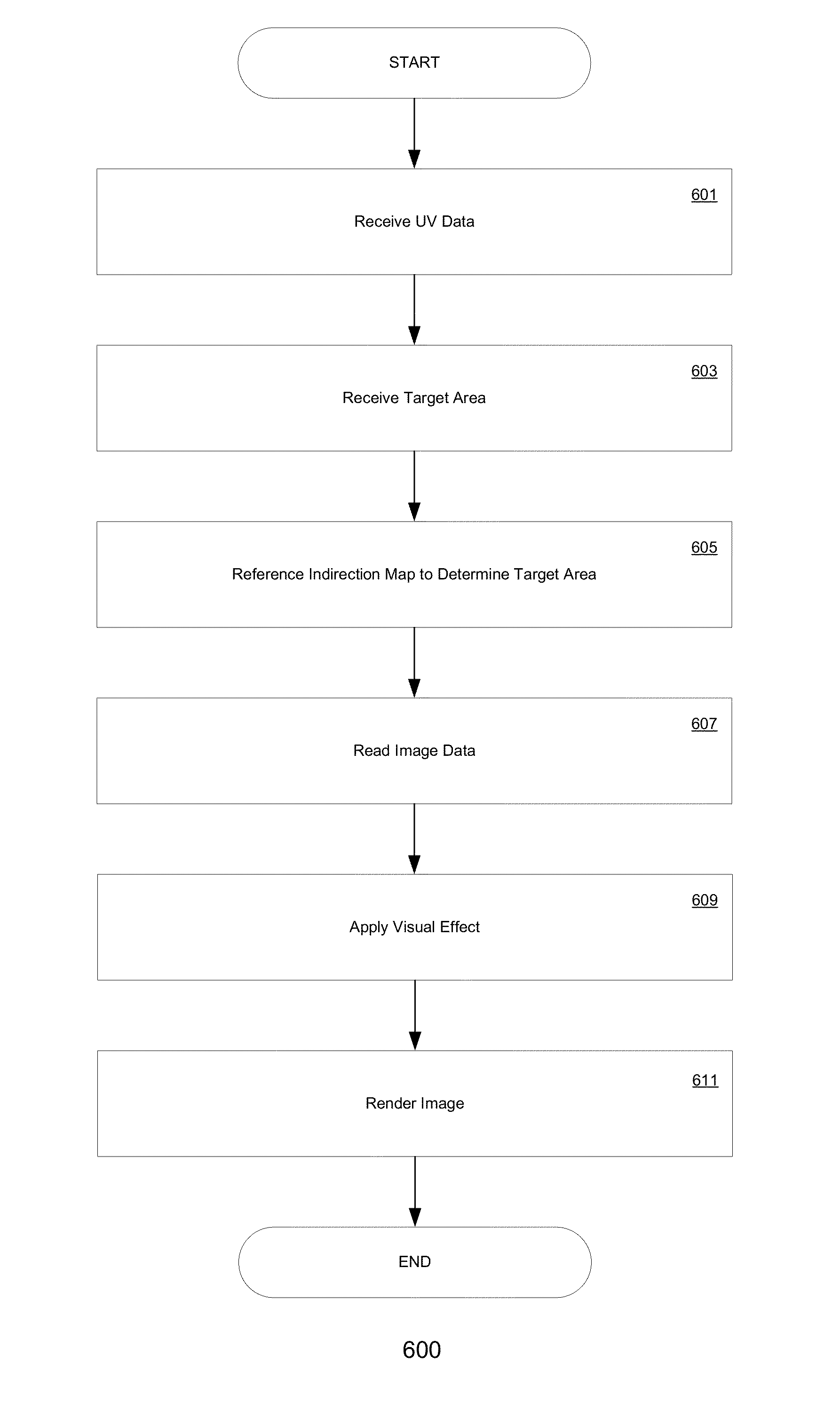
Generating indirection maps for texture space effects
ActiveUS20150187135A1No loss in accuracyWithout producing undesirable artifactsImage generation3D-image renderingGraphicsInvalid Data
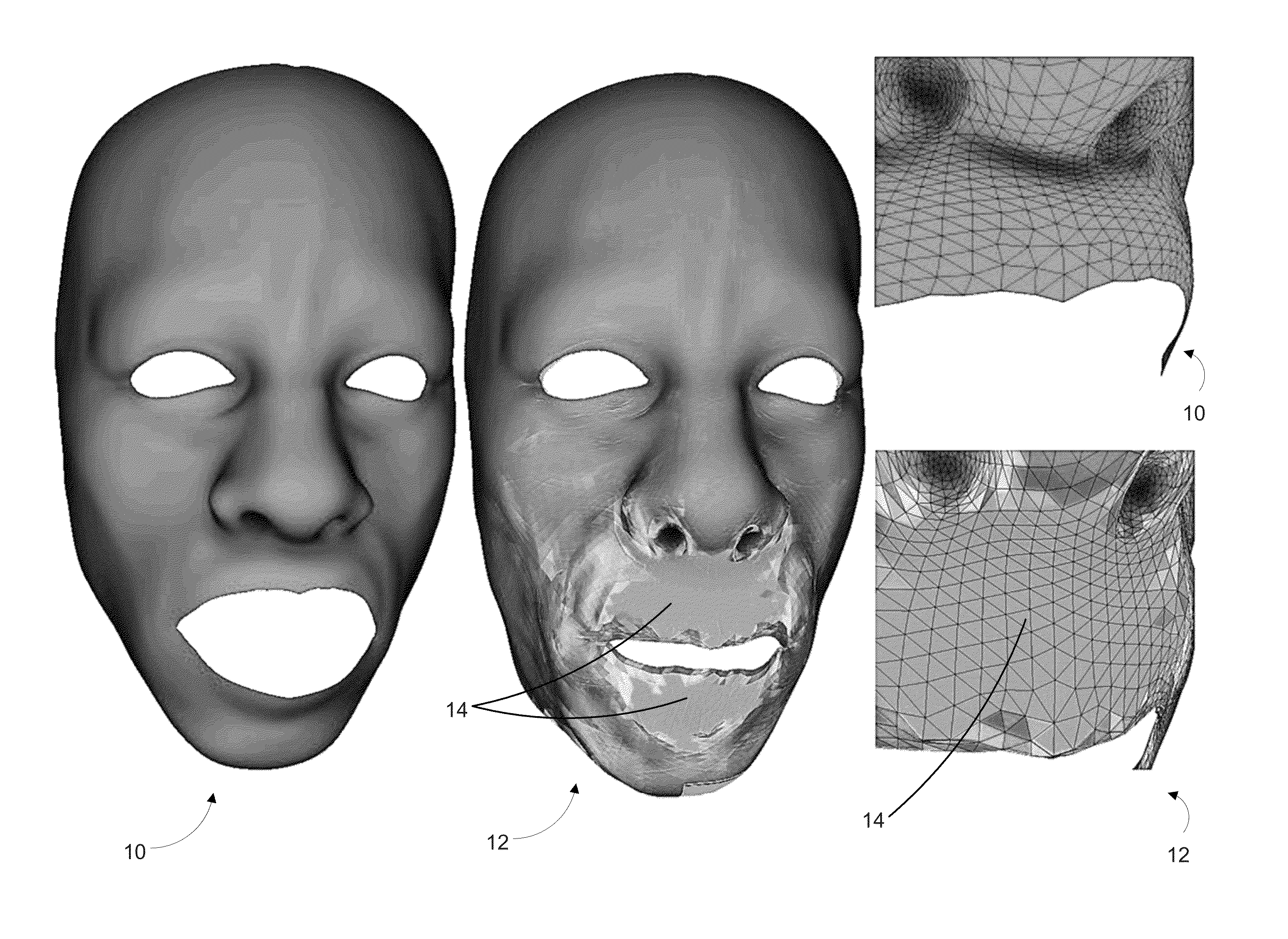
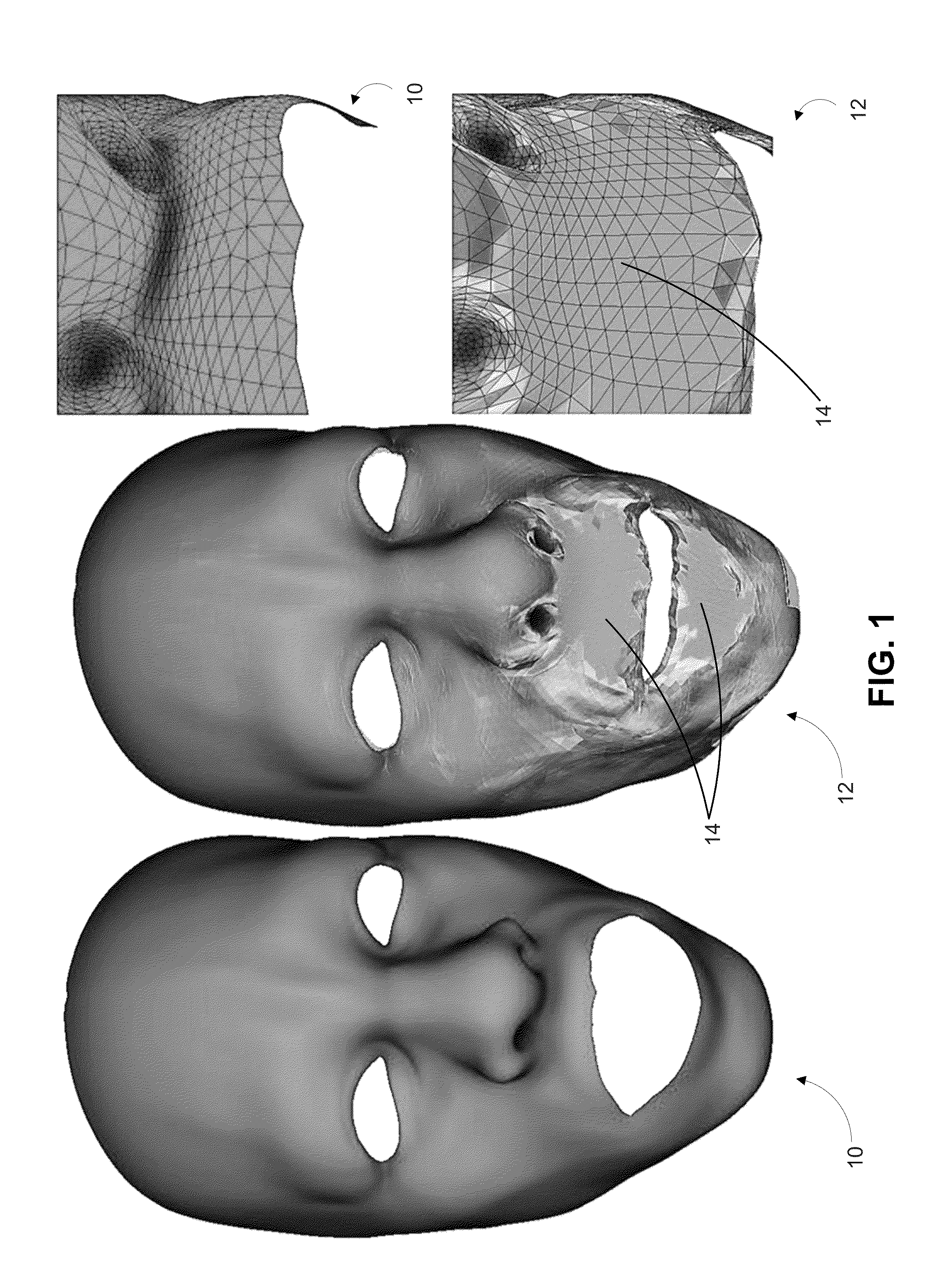
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to a novel approach for realistically modeling sub-surface scattering effects in three-dimensional objects of graphically rendered images. In an embodiment, an indirection map is generated for an image by analyzing the triangle mesh of one or more three-dimensional objects in the image and identifying pairs of edges between adjacent triangles in the mesh that have the same spatial locations in the three-dimensional representations, but which have different locations in the texture map. For each of these edges, the opposite triangle in each pair is projected into their corresponding edge's two-dimensional space. This allows samples which cross a seam in the two dimensional representation that would otherwise sample out into invalid data to be redirected to the spatially correct region of the texture and generate consistent results with non-seam areas.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
System and method for bump mapping setup
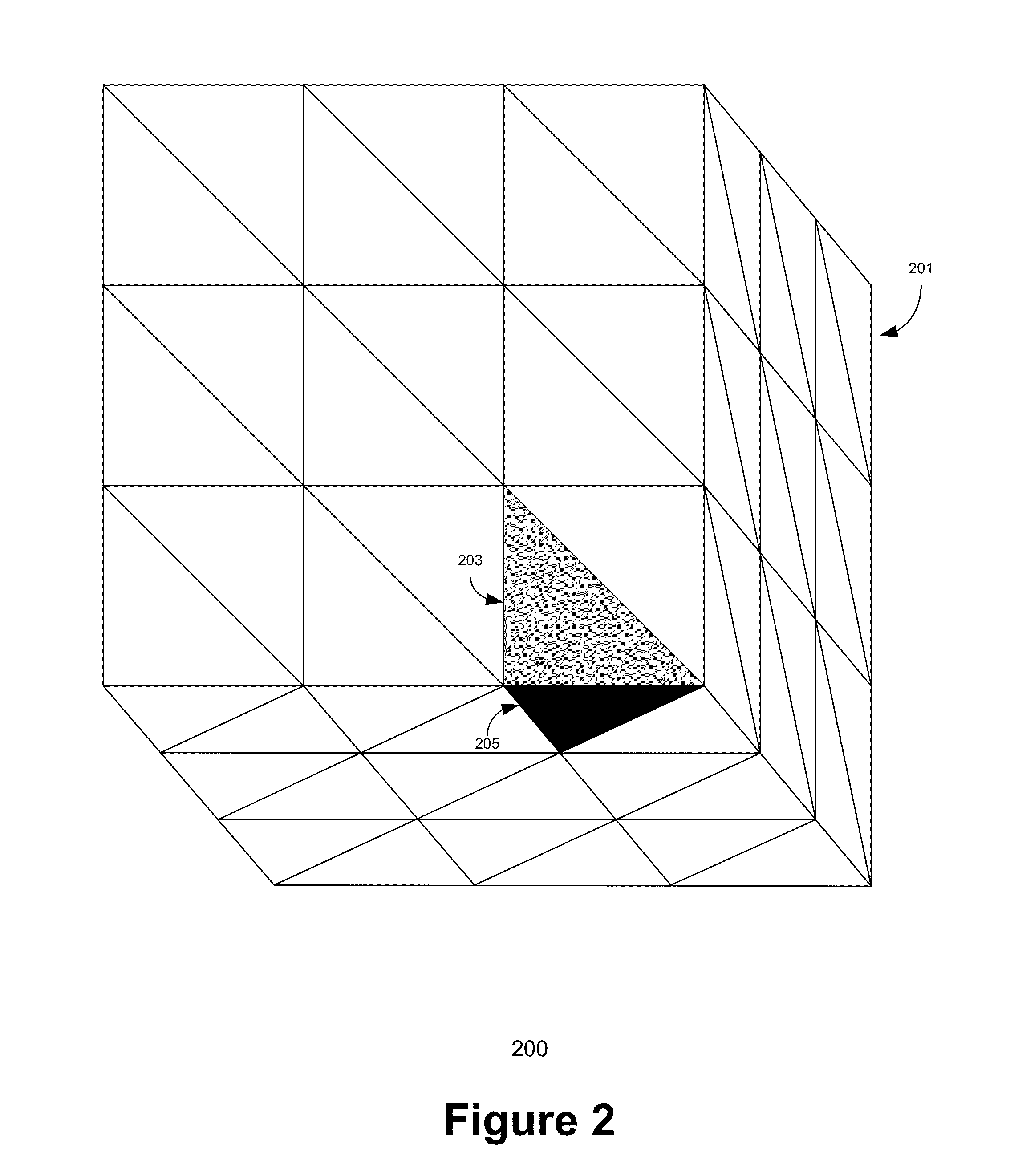
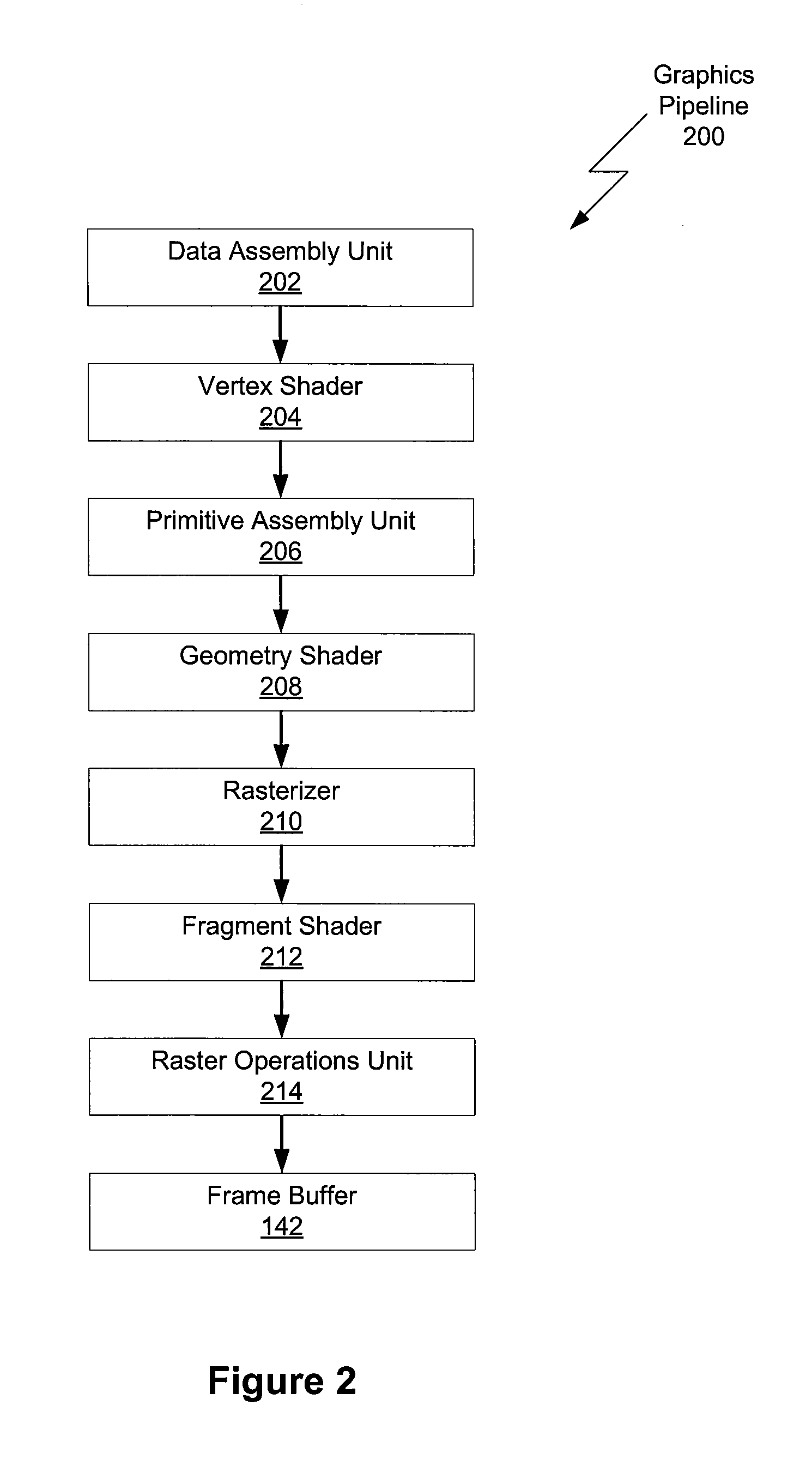
ActiveUS7843463B1Improve processing efficiencyEfficient processingCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsTexture spaceComputer graphics (images)
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth a technique to setup efficient bump mapping using a geometry shader. This approach uses a vertex shader, a primitive assembly unit, and a geometry shader. The vertex shader performs vertex operations, such as calculating a per-vertex normal vector, and emits vertex data. The primitive assembly unit processes the vertex data and constructs primitives. Each primitive includes a series of one or more vertices, each of which may be shared amongst multiple primitives, and state information defining the primitive. The geometry shader processes each primitive, calculating an object-space to texture-space mapping for each vertex of the primitive and, subsequently, using this mapping to transform the object-space view vector and the object-space light vectors associated with each vertex of the primitive to texture-space equivalents. Advantageously, this approach to setting up bump mapping fully utilizes the GPU, thereby optimizing both hardware resources and performance.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
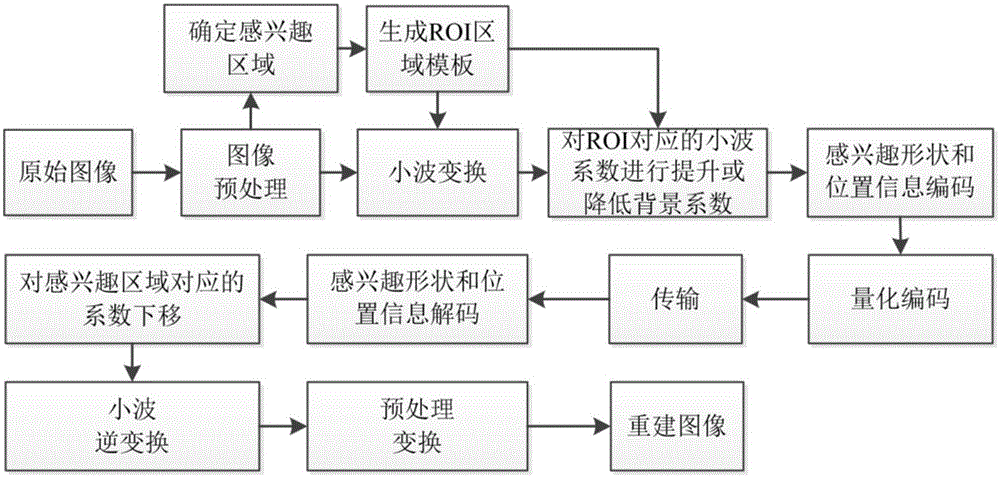
Texture image compression method based on geometric information of three-dimensional model
InactiveCN105141970AWavelet Transform Coefficient LiftingWavelet transform coefficient boosting or loweringDigital video signal modificationVisual presentationMachine vision
The invention provides a texture image compression method based on geometric information of a three-dimensional model in allusion to limitations of traditional product defect detection based on a machine vision method in applicable targets and a problem how a region-of-interest of the human eyes on a texture image is solved in the compression process. According to the invention, a region-of-interest of the human eyes is on a texture image is solved by using model grid data, three-dimensional feature points representing surface detail information of the three-dimensional model after multi-solution re-gridding and mapping points thereof on a texture space are extracted according to a visual presentation mode of the texture so as to act as texture feature points, class aggregation is carried out on the feature points in the image by using a K-means clustering algorithm according to the continuity of an image space, the region-of-interest of the texture image is acquired, and the differentiation precision of the region-of-interest and the background is improved. The method provided by the invention is verified through establishing an ROI based EZW coding and decoding experiment system, and good experiment effects are acquired.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
System and method for generating generalized displacement maps from mesostructure geometries
InactiveUS20050280647A1Facilitate texture coordinate computationAccelerate mesostructure renderingCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingVisibilityGraphics
A “mesostructure renderer” uses pre-computed multi-dimensional “generalized displacement maps” (GDM) to provide real-time rendering of general non-height-field mesostructures on both open and closed surfaces of arbitrary geometry. In general, the GDM represents the distance to solid mesostructure along any ray cast from any point within a volumetric sample. Given the pre-computed GDM, the mesostructure renderer then computes mesostructure visibility jointly in object space and texture space, thereby enabling both control of texture distortion and efficient computation of texture coordinates and shadowing. Further, in one embodiment, the mesostructure renderer uses the GDM to render mesostructures with either local or global illumination as a per-pixel process using conventional computer graphics hardware to accelerate the real-time rendering of the mesostructures. Further acceleration of mesostructure rendering is achieved in another embodiment by automatically reducing the number of triangles in the rendering pipeline according to a user-specified threshold for acceptable texture distortion.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Optimizing real-time rendering of texture mapped object models relative to adjustable distortion thresholds
InactiveUS20050280648A1Facilitate texture coordinate computationAccelerate mesostructure renderingCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingVisibilityGraphics
A “mesostructure renderer” uses pre-computed multi-dimensional “generalized displacement maps” (GDM) to provide real-time rendering of general non-height-field mesostructures on both open and closed surfaces of arbitrary geometry. In general, the GDM represents the distance to solid mesostructure along any ray cast from any point within a volumetric sample. Given the pre-computed GDM, the mesostructure renderer then computes mesostructure visibility jointly in object space and texture space, thereby enabling both control of texture distortion and efficient computation of texture coordinates and shadowing. Further, in one embodiment, the mesostructure renderer uses the GDM to render mesostructures with either local or global illumination as a per-pixel process using conventional computer graphics hardware to accelerate the real-time rendering of the mesostructures. Further acceleration of mesostructure rendering is achieved in another embodiment by automatically reducing the number of triangles in the rendering pipeline according to a user-specified threshold for acceptable texture distortion.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Selection of a mipmap level
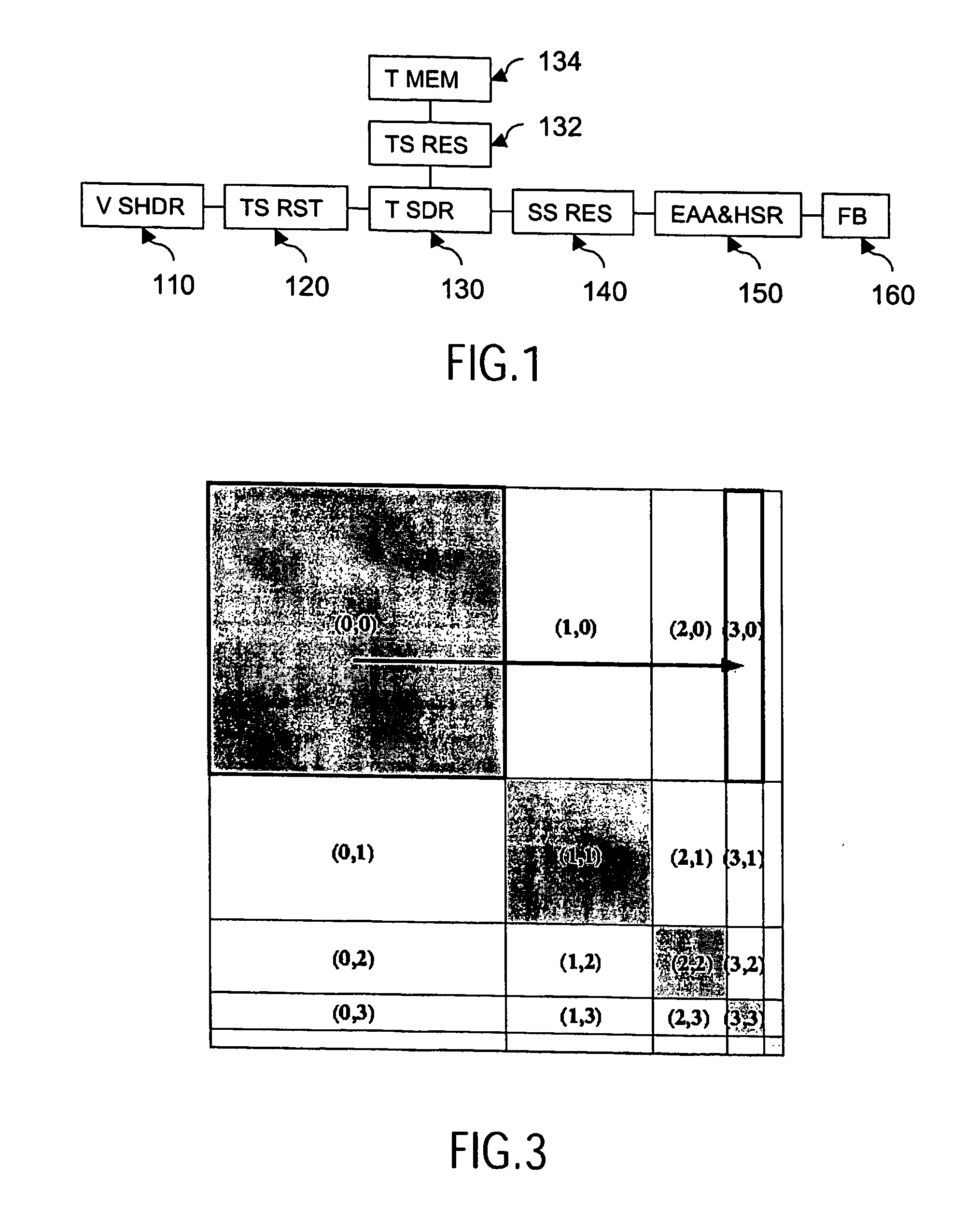
InactiveUS20060158451A1Reduce resolutionAttenuation bandwidthCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingGraphicsMagnification
A computer graphics includes a texture memory (134) storing texture maps in a mipmap structure, texels in a texture map being specified by a pair of u and v coordinates. A rasterizer (120) determines for a texel (u, v) corresponding initial 4D mipmap levels (mmlu, mmlv) and a magnification factor representing a magnification that occurs when the texel is mapped to a corresponding pixel position on the display. It then determines final 4D mipmap levels in dependence on the determined initial 4D mipmap levels mmlu, mmlv, and the magnification factor. A texture space resampler (132) obtains texture data from a texture map identified by the pair off final 4D mipmap levels. A texture mapper (140) maps the obtained texture data to corresponding pixel data defining the display image.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Large-scale-scene indirect illumination algorithm based on scene light map
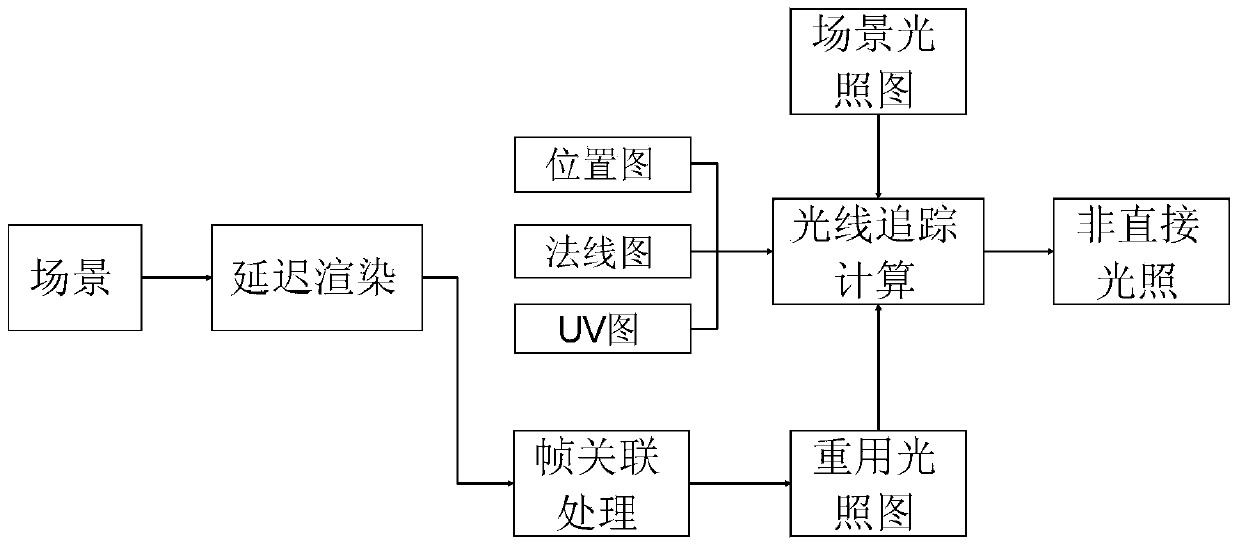
The invention provides a large-scale-scene indirect illumination algorithm based on a scene light map. The large-scale-scene indirect illumination algorithm based on the scene light map comprises the four steps that firstly, parameterization is conducted on a scene in a texture space; secondly, the scene light map is calculated; thirdly, according to the scene light map which is dynamically baked in the second step, indirect illumination is worked out through a light ray tracking algorithm; fourthly, the amount of calculation of indirect illumination is reduced through frame correlation. By the adoption of the large-scale-scene indirect illumination algorithm based on the scene light map, a complicated scene can be well supported, and effects are adjustable and stable. The large-scale-scene indirect illumination algorithm based on the scene light map has high practicable value and broad application prospect in the image processing technical field.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Real-time texture rendering using generalized displacement maps
ActiveUS7184052B2Facilitate texture coordinate computationAccelerate mesostructure renderingCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingGraphicsVisibility
A “mesostructure renderer” uses pre-computed multi-dimensional “generalized displacement maps” (GDM) to provide real-time rendering of general non-height-field mesostructures on both open and closed surfaces of arbitrary geometry. In general, the GDM represents the distance to solid mesostructure along any ray cast from any point within a volumetric sample. Given the pre-computed GDM, the mesostructure renderer then computes mesostructure visibility jointly in object space and texture space, thereby enabling both control of texture distortion and efficient computation of texture coordinates and shadowing. Further, in one embodiment, the mesostructure renderer uses the GDM to render mesostructures with either local or global illumination as a per-pixel process using conventional computer graphics hardware to accelerate the real-time rendering of the mesostructures. Further acceleration of mesostructure rendering is achieved in another embodiment by automatically reducing the number of triangles in the rendering pipeline according to a user-specified threshold for acceptable texture distortion.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
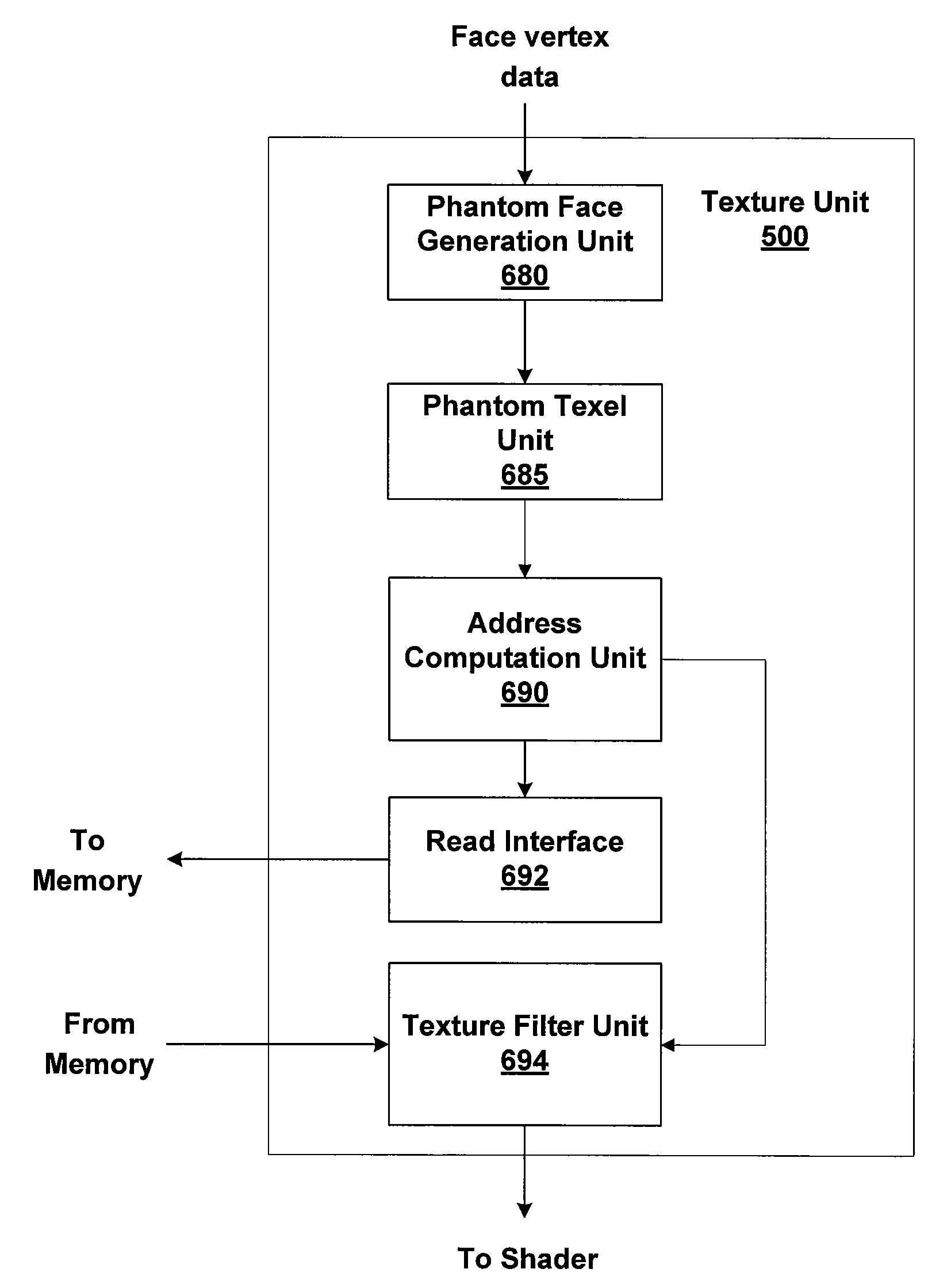
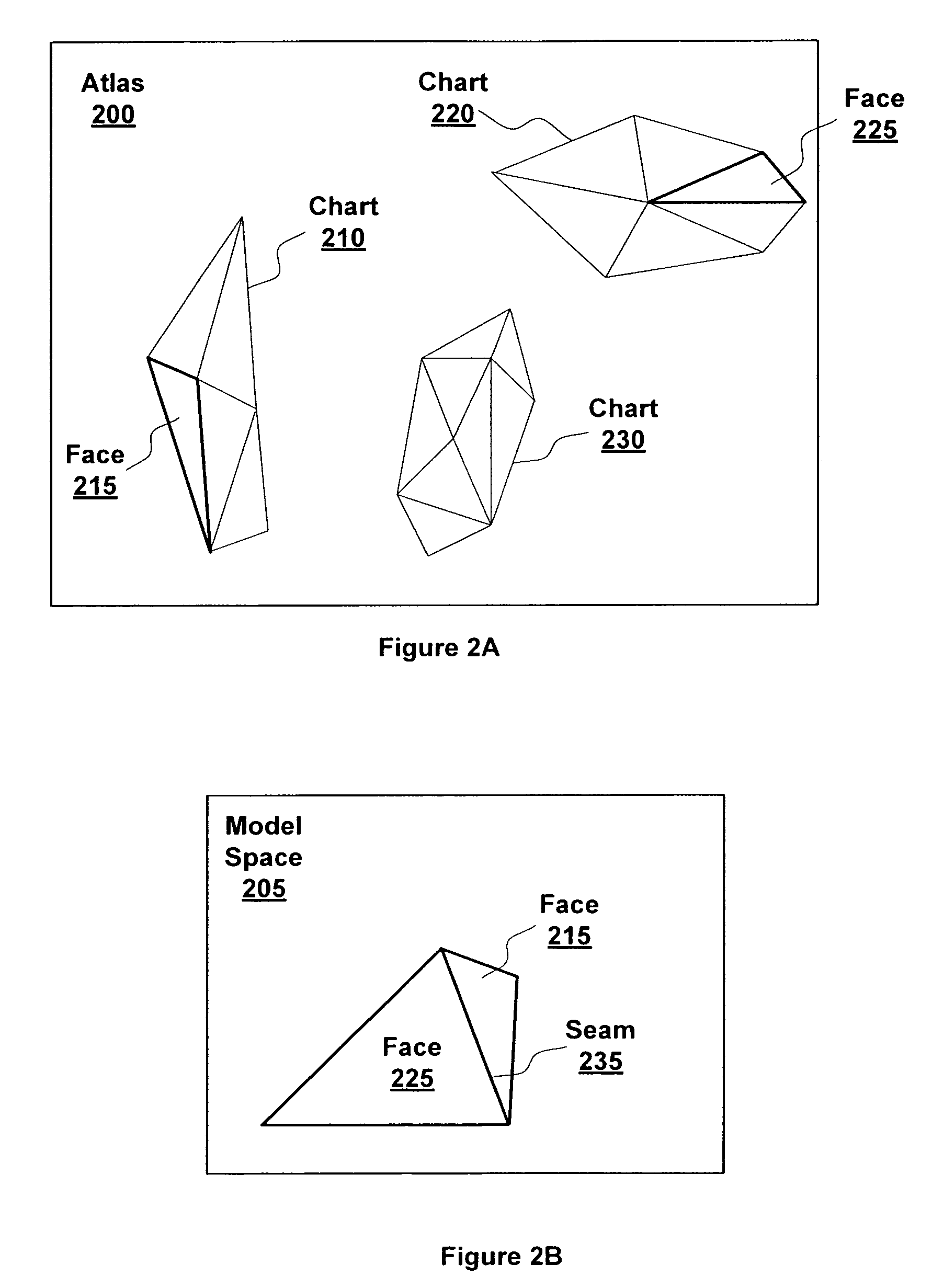
Creating texture data outside of a chart boundary
ActiveUS7605820B1Reduce discontinuitySmooth transitionCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingComputer graphics (images)Three dimensional model
Discontinuities along texture mapped seams of three-dimensional models may be reduced by creating and sampling texture data outside of chart boundaries. When a texel center is not within a chart boundary (a group of connected triangles in texture space) a phantom face is generated that includes the texel center. Phantom texture coordinates are created for each texel center that is covered by the phantom face. The phantom texture coordinates are used to read a texture sample from another chart in texture space that is adjacent to the chart boundary in model space, producing a smooth transition across the seam.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
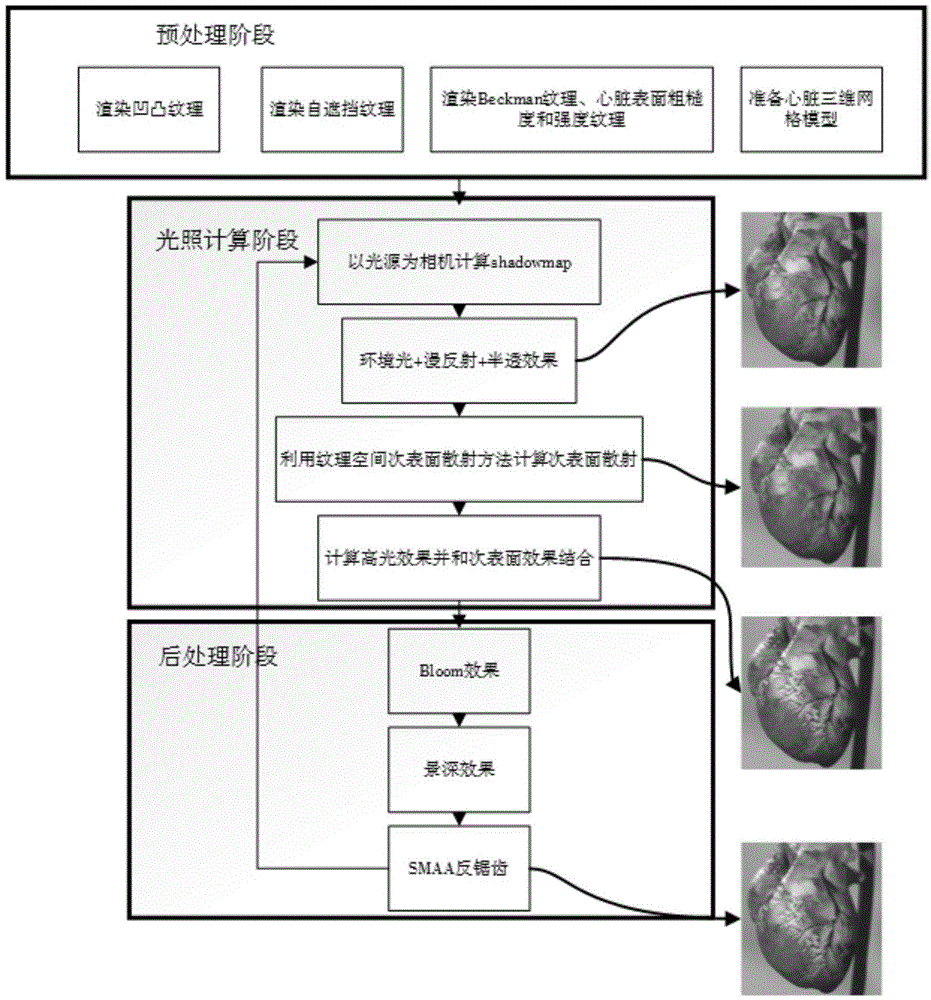
Real-time realistic drawing method of human heart
ActiveCN104599326ARealistic drawingWith subsurface scattering effect3D-image rendering3D modellingSubsurface scatteringMedicine
The invention discloses a real-time realistic drawing method of a human heart. The method comprises the steps of effectively drawing the surface and sub-surface effects by the texture space sub-surface drawing method and the semitransparent transmission method; combining a concave-convex map and a Kelemen / Szirmay-Kalos lighting model, so as to achieve the effect the heart surface is covered with mucus; combining sub-frame scattering, mucus coverage and other foundation effect of the heart surface to obtain the heart surface drawing effect. The experiment result shows that the real-time realistic drawing method of the human heart is relatively high in drawing efficiency and realistic performance.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for simplifying vertex clustering of three-dimensional models with texture constraint
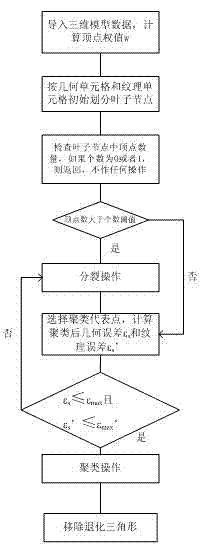
InactiveCN102509339AImprove binding abilityPreserve texture features3D-image renderingGeometric errorAlgorithm
The invention provides a method for simplifying a vertex clustering of three-dimensional models with texture constraint. The method comprises the steps of: expanding the vertexes from a geometric space to a fifth-dimensional space including texture coordinates in consideration of algorithm efficiency in the self-adaptive division processes of the vertexes; dividing the vertexes according to the positions of the vertexes in the geometric space and the texture space in the self-adaptive division processes of the vertexes; in error measurement, respectively computing geometric errors and texture errors, if the error value is more than a given threshold, splitting the current node; and in the self-adaptive division processes of the vertexes, in consideration of saving the storage resources and improving the algorithm efficiency, adopting the relatively important vertex in an original model as a clustering representative instead of computing the geometric position of a new vertex through iteration. The method for simplifying vertex clustering of three-dimensional models with texture constraint organically integrates texture error measurement and geometric simplification, realizes rapid simplification of a mass of complex three-dimensional models and supports efficient three-dimensional visualization of city virtual scenes.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
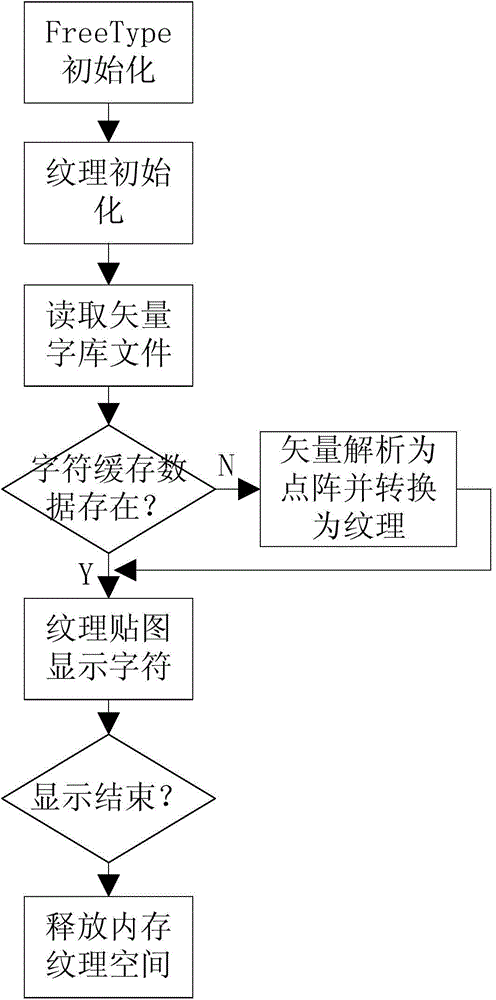
High-performance vector font library display method based on VXWorks system
InactiveCN105718226AImprove operational efficiencyAvoid heavy computationDigital output to display deviceOperational systemAnti-aliasing
The present invention provides a high-performance vector font library display method based on a VXWorks system. The method comprises the following steps: 1) initializing FreeType; 2) performing texture initialization; 3) reading a vector font library file stored in a file system into a memory; 4) determining whether character cache data exists, and if yes, displaying the character cache data as characters via texture mapping, and if no, parsing font vector information into lattice data according to the vector font library file, and displaying the well-parsed lattice data as characters via texture mapping; and 5) determining whether a display process ends, if yes, releasing a memory texture space, and if no, continuing executing the step until the display ends. Based on an OpenGL graphic library based on VXWorks and in combination with TrueType, the high-performance vector font library display method based on a VXWorks system is high in drawing efficiency, good in display effect, capable of supporting zooming, rotating and translation and good in anti-aliasing effects.
Owner:AVIC NO 631 RES INST
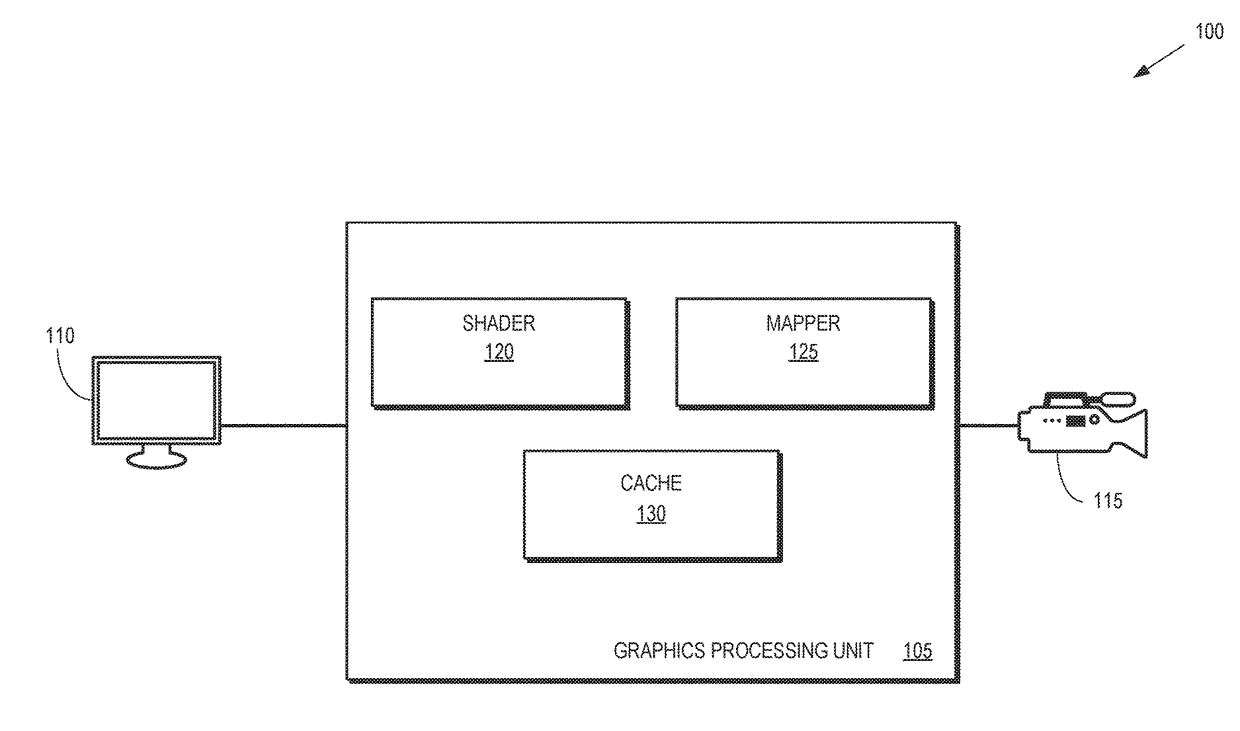
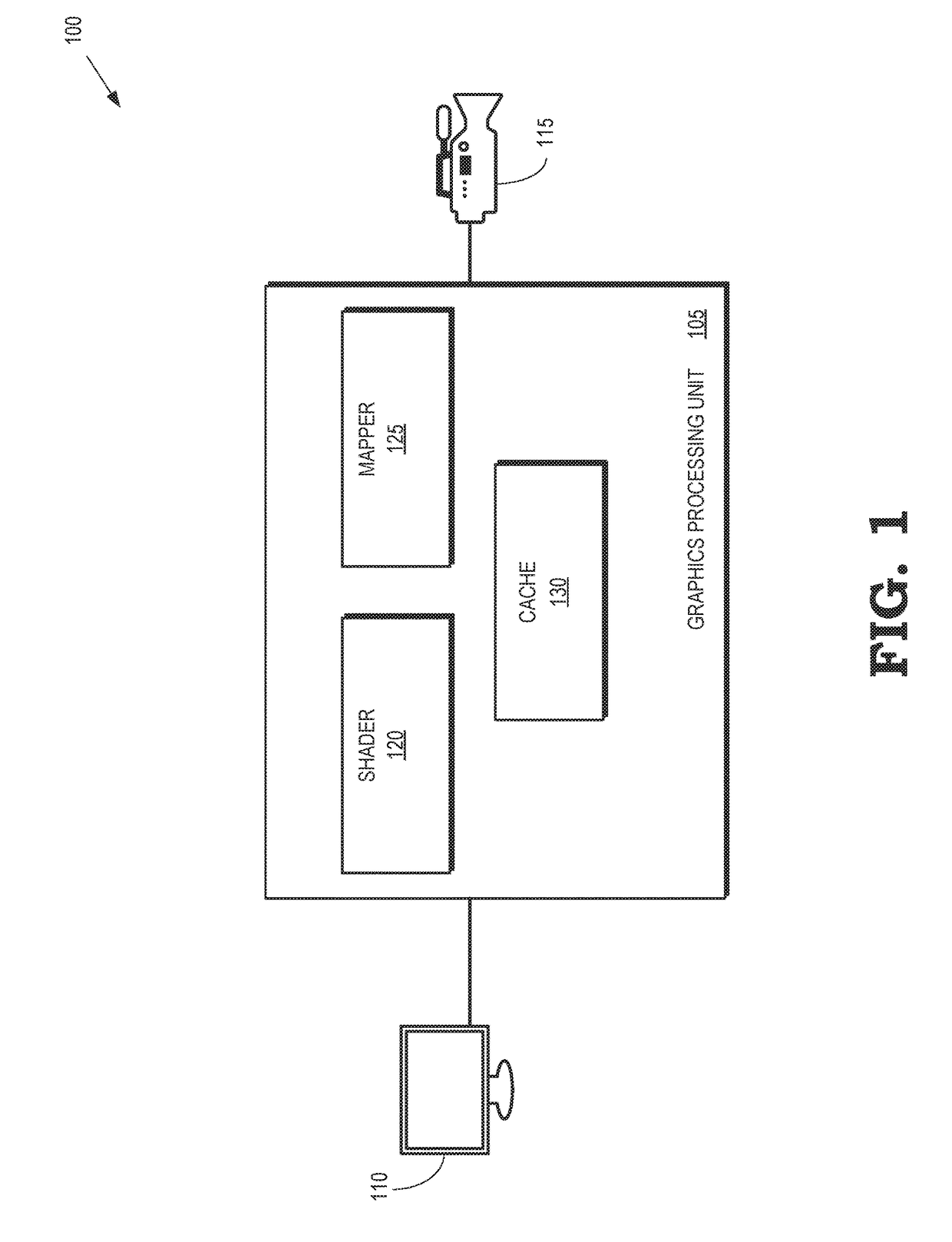
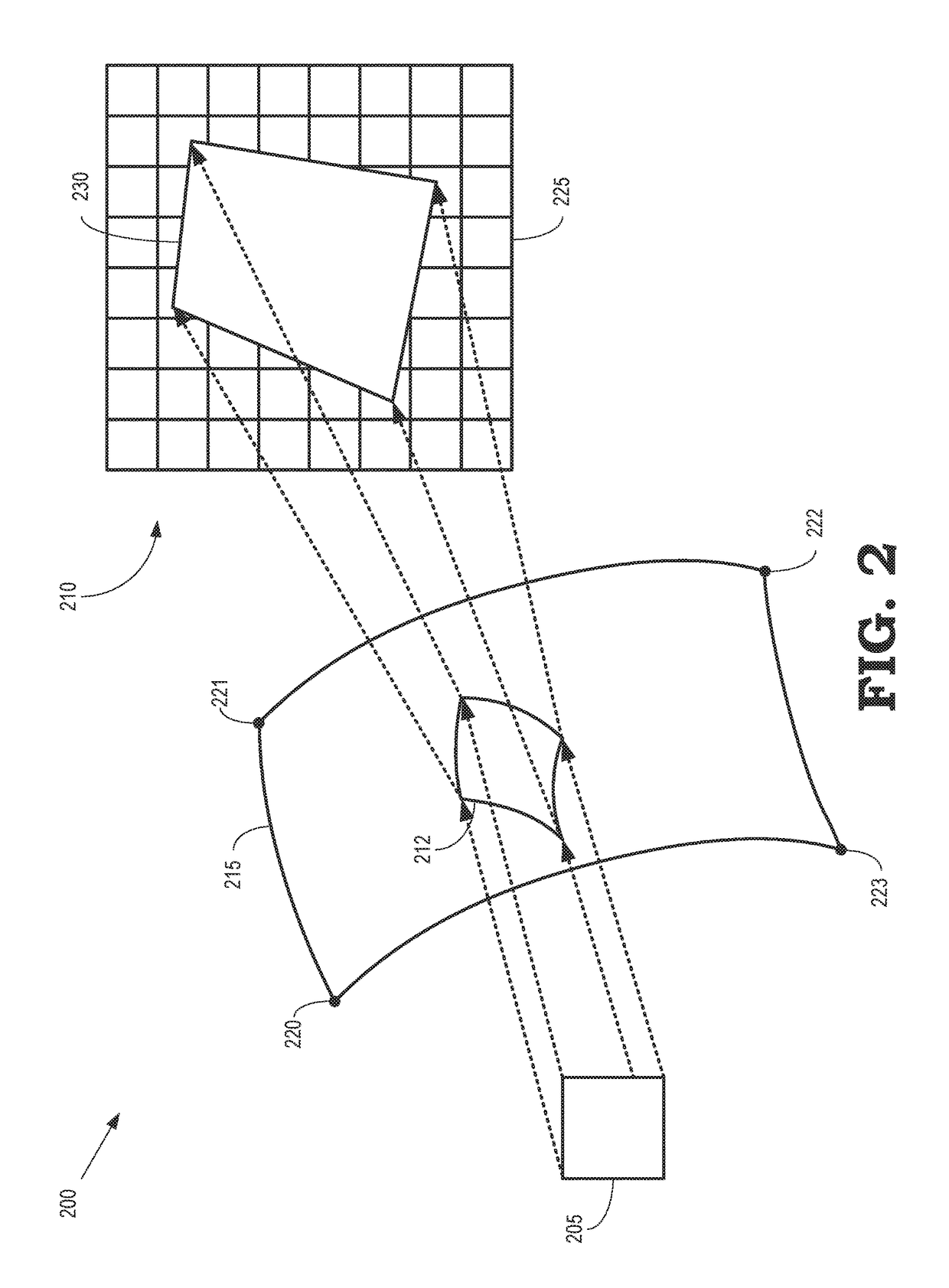
Texel shading in texture space
A graphics processing unit is configured to map pixels of a first frame of a video stream to texels, select a subset of the texels for shading based on previously cached texels that were shaded for a second frame, and shade the subset of the texels. The graphics processing unit is also configured to cache the shaded subset of the texels with the previously cached texels and determine values for the pixels of the first frame based on the cached texels.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Method and apparatus for collating object
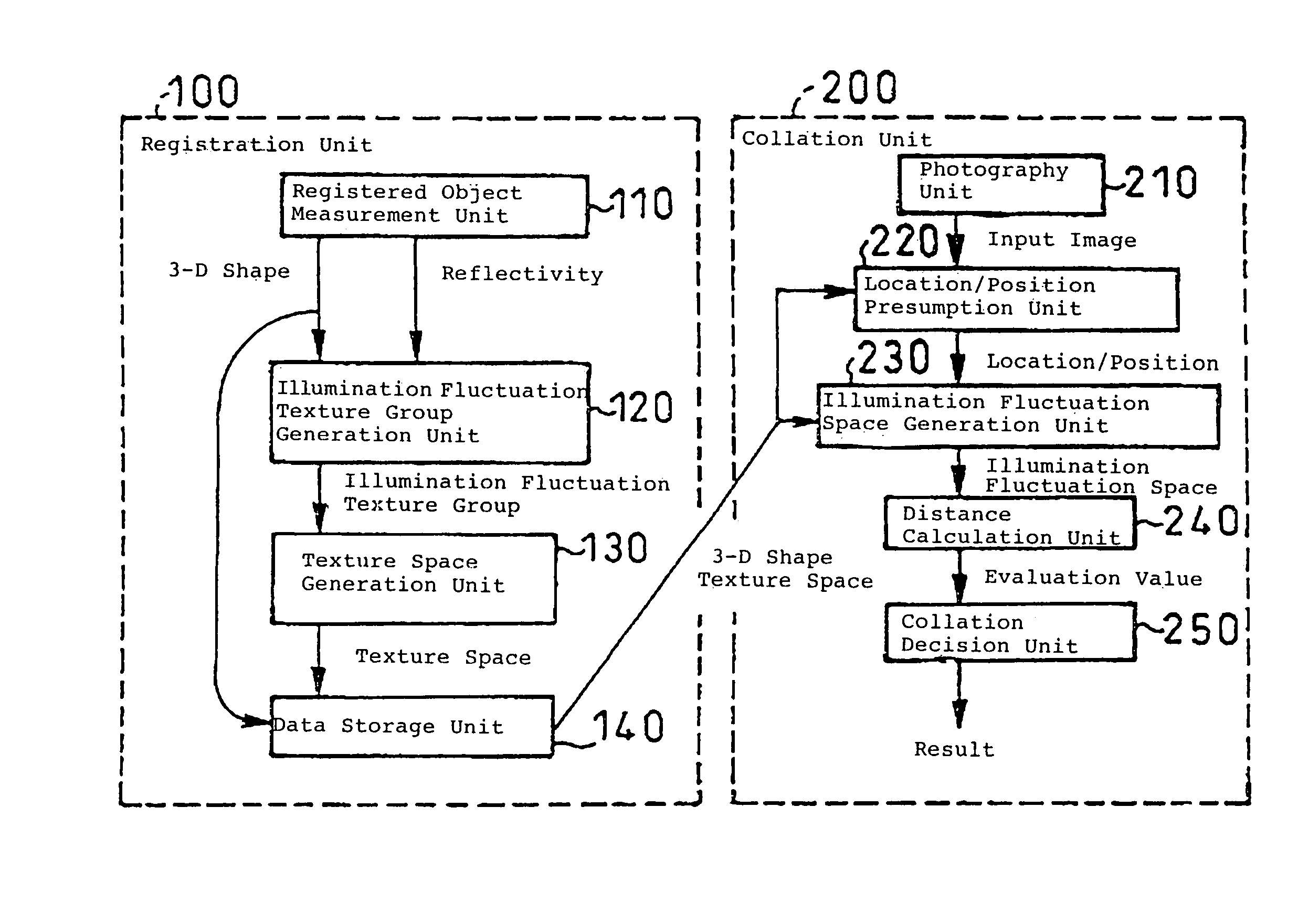
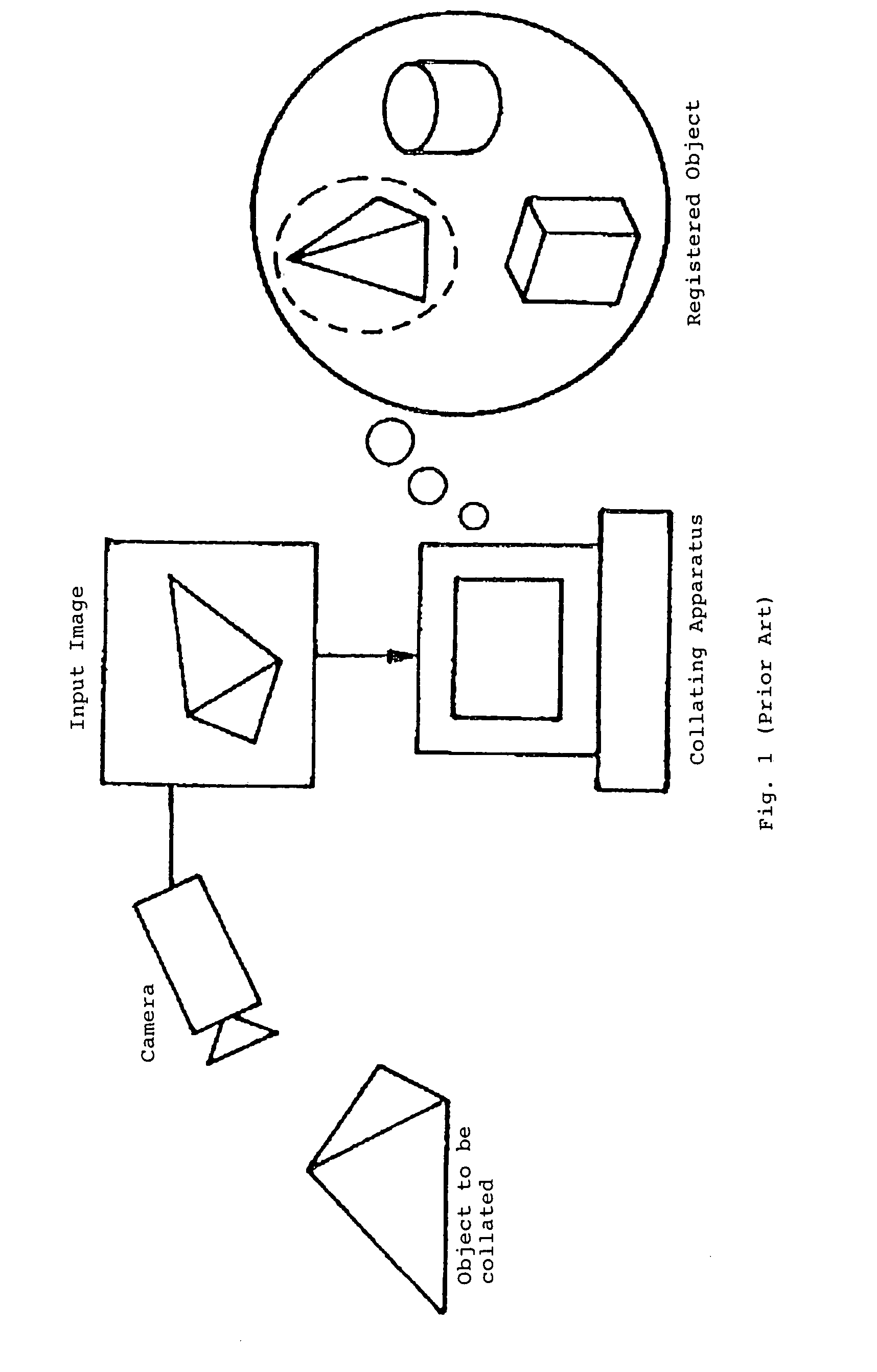
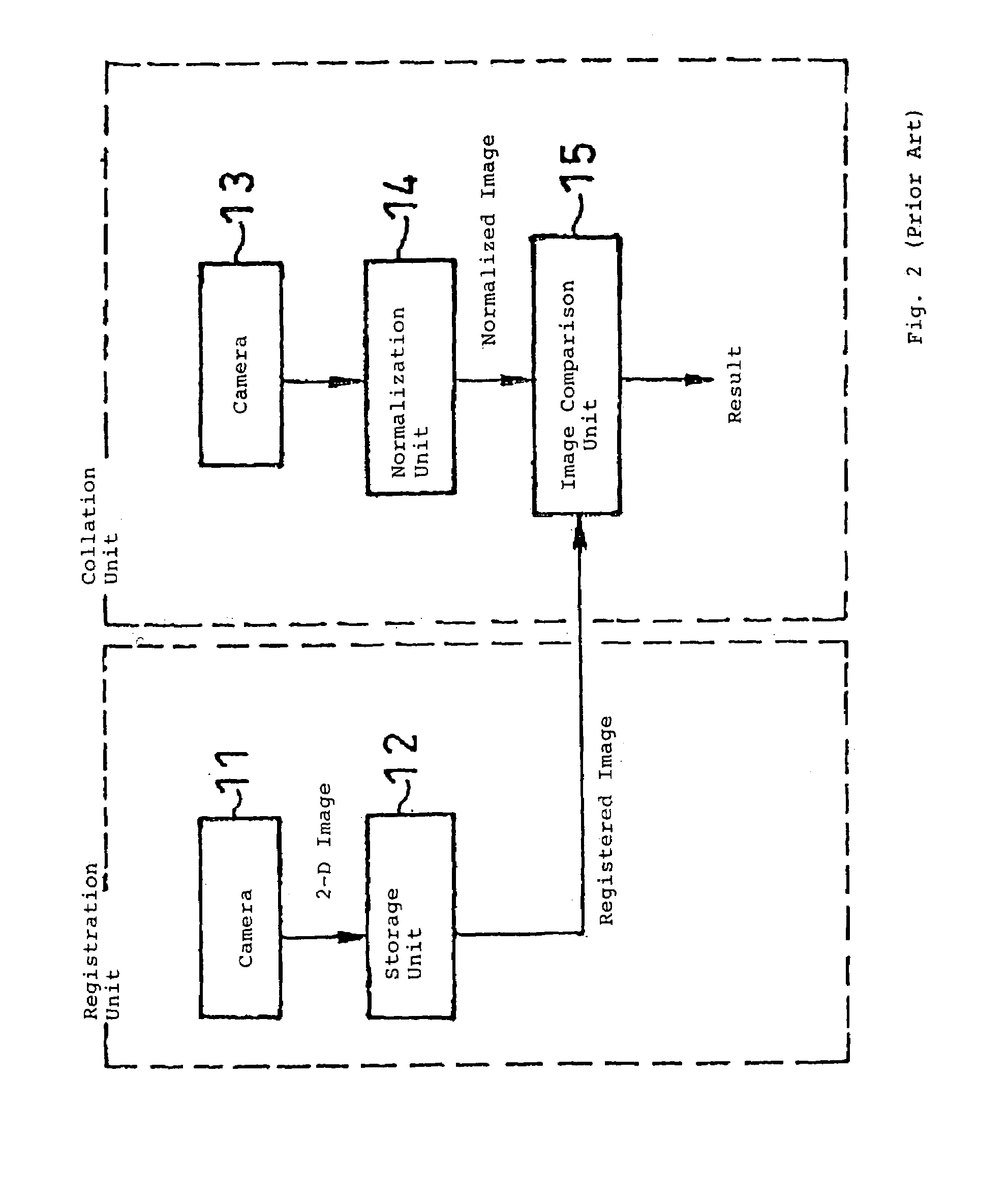
ActiveUS7321370B2Easy to handleImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionThree dimensional shapeTexture space
An object collation method comprising a registration procedure for registering the registered data of a registered object in a database, and a collation procedure for collating the input image of a target object with the registered data. The registration procedure includes a step of storing the three-dimensional shape of the registered object and a texture space defined by a texture group indicating the luminance and / or color information of each position of the object surface under various illumination conditions. The collation procedure includes the steps of: generating an illumination fluctuation space defined by the image group under the various illumination conditions, at the location and position of the target object in the input image from the three-dimensional shape and the texture space; and collating the target object and the registered object based on the distance between the illumination fluctuation space and the input image.
Owner:NEC CORP
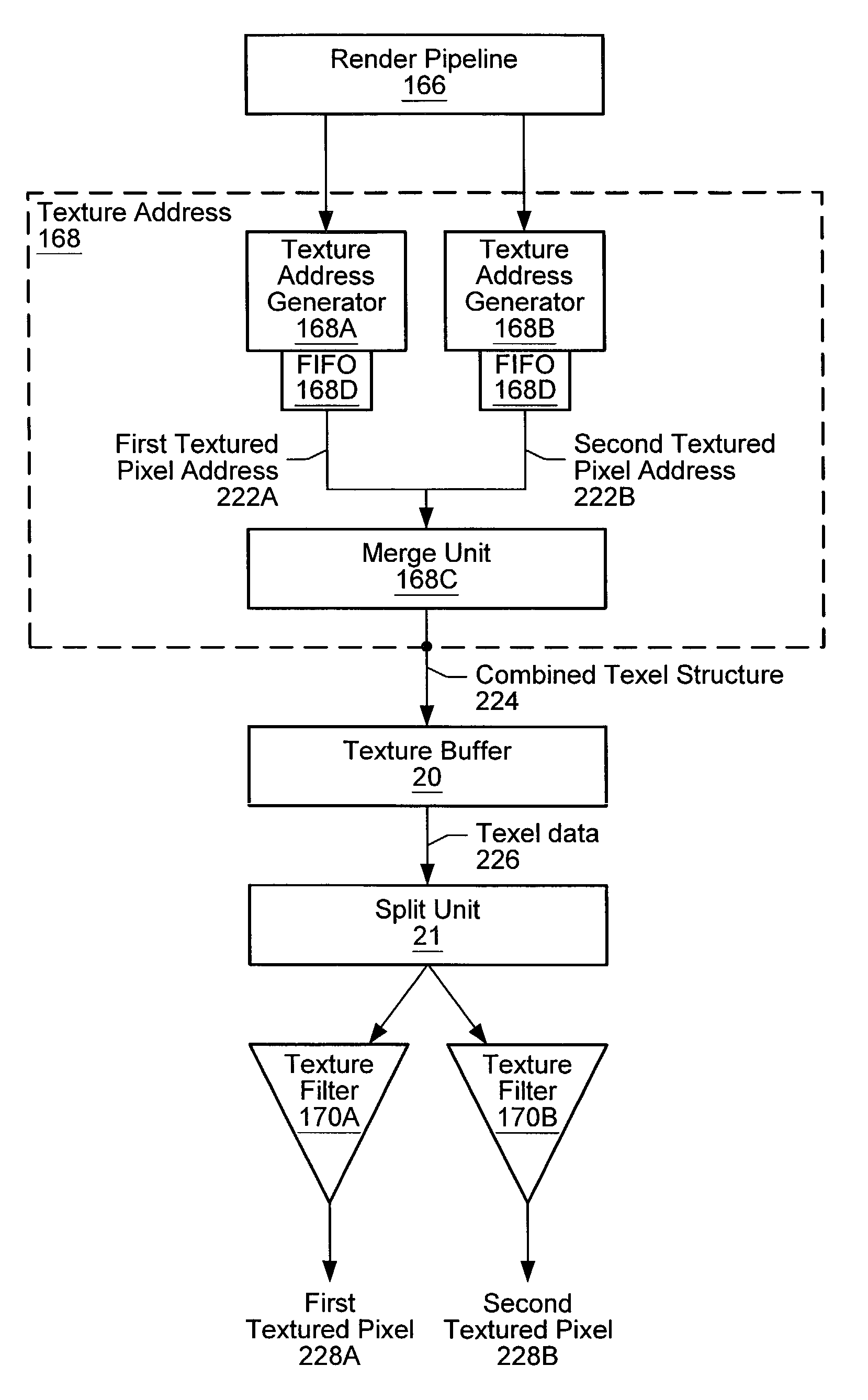
Magnified texture-mapped pixel performance in a single-pixel pipeline
InactiveUS7145570B2Improving magnified texture-mapped pixel performanceImage analysisCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)Single pixel
A system and a method for improving magnified texture-mapped pixel performance in a single-pixel pipeline. A plurality of textured pixel addresses corresponding to a plurality of pixels may be generated. A FIFO or other memory unit may be used to linearly order the plurality of textured pixel addresses. Two consecutive textured pixel addresses out of the plurality of textured pixel addresses may be examined if they map to a common set of texels in texture space. The two consecutive textured pixel addresses may be merged together and propagated down the pipeline if they map to the common set of texels. However, only a first of the two consecutive textured pixel addresses may be propagated down the pipeline if the two consecutive textured pixel addresses do not map to a common set of texels. Texel data may be generated in response to receiving either the combined texel structure or the first of the two textured pixel addresses. The texel data may be filtered using one or more texture filters in order to generate texture values. The next two textured pixel addresses that may be examined by the merge unit include the subsequent two consecutive textured pixel addresses, or a second of the two consecutive textured pixel addresses and a subsequent consecutive textured pixel address.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Using indirection maps for rendering texture space effects
InactiveUS20150187126A1No loss in accuracyWithout producing undesirable artifactsImage enhancementDetails involving 3D image dataGraphicsInvalid Data
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to a novel approach for realistically modeling sub-surface scattering effects in three-dimensional objects of graphically rendered images. In an embodiment, an indirection map is generated for an image by analyzing the triangle mesh of one or more three-dimensional objects in the image and identifying pairs of edges between adjacent triangles in the mesh that have the same spatial locations in the three-dimensional representations, but which have different locations in the texture map. For each of these edges, the opposite triangle in each pair is projected into their corresponding edge's two-dimensional space. This allows samples which cross a seam in the two dimensional representation that would otherwise sample out into invalid data to be redirected to the spatially correct region of the texture and generate consistent results with non-seam areas.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com