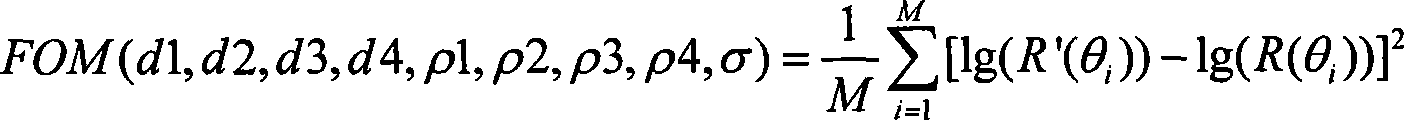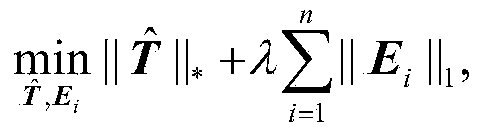Patents
Literature
84 results about "Minimization algorithm" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Minimization Algorithms. The purpose of the minimization algorithm is to detect the minimum of the objective function in the n-dimensional parameter space. In multiphase flow modeling, the calculated system response is a highly non-linear function of the input parameters.
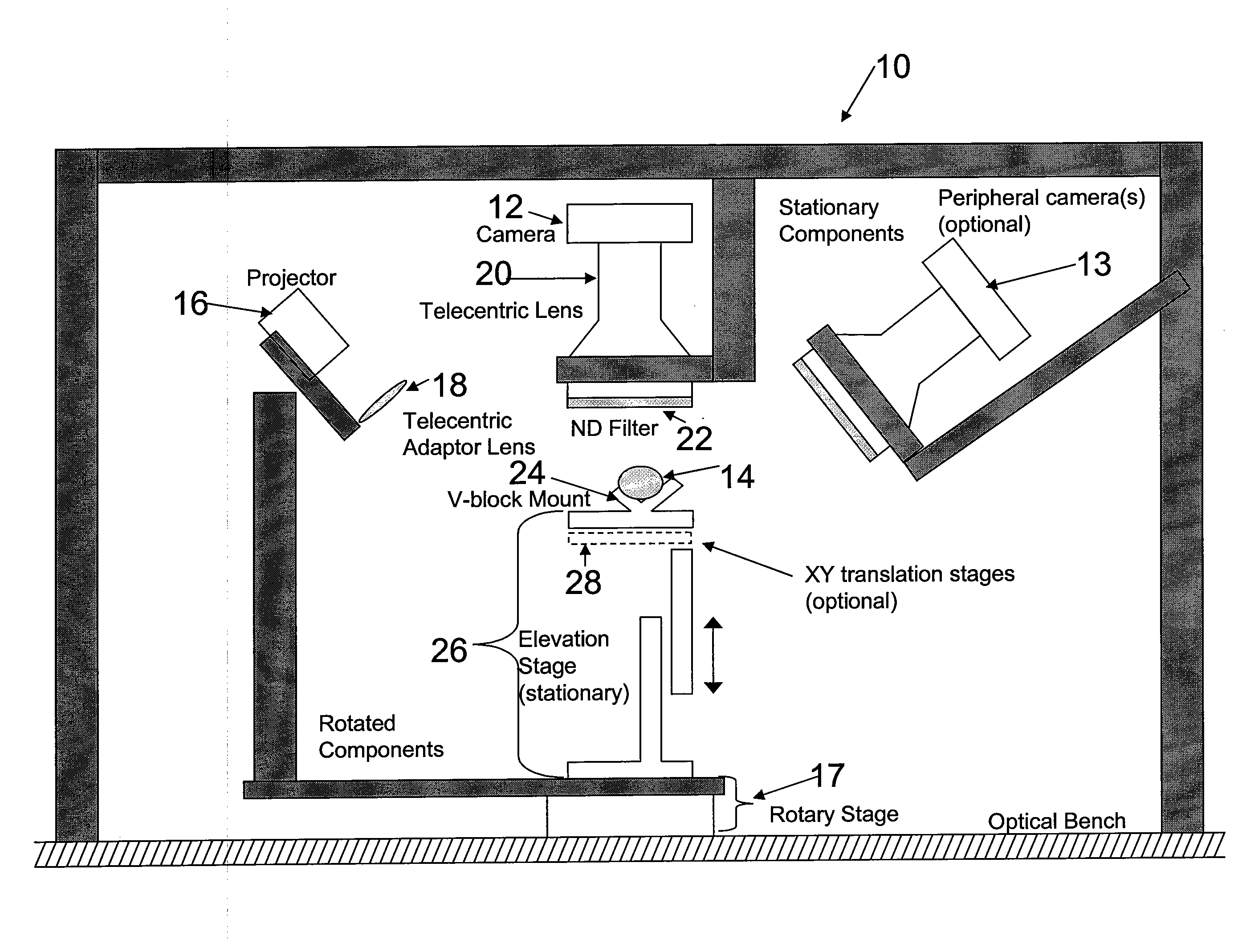
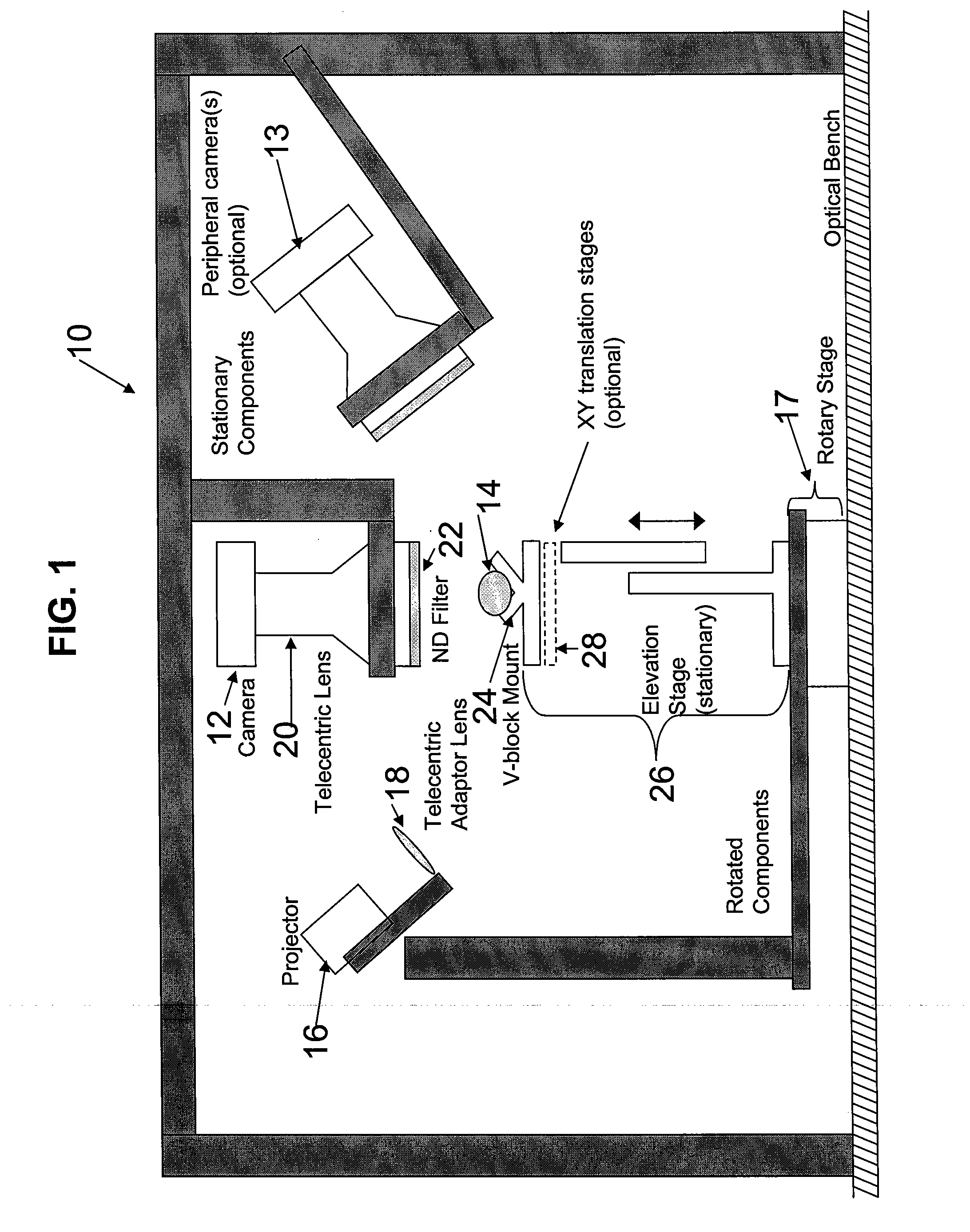
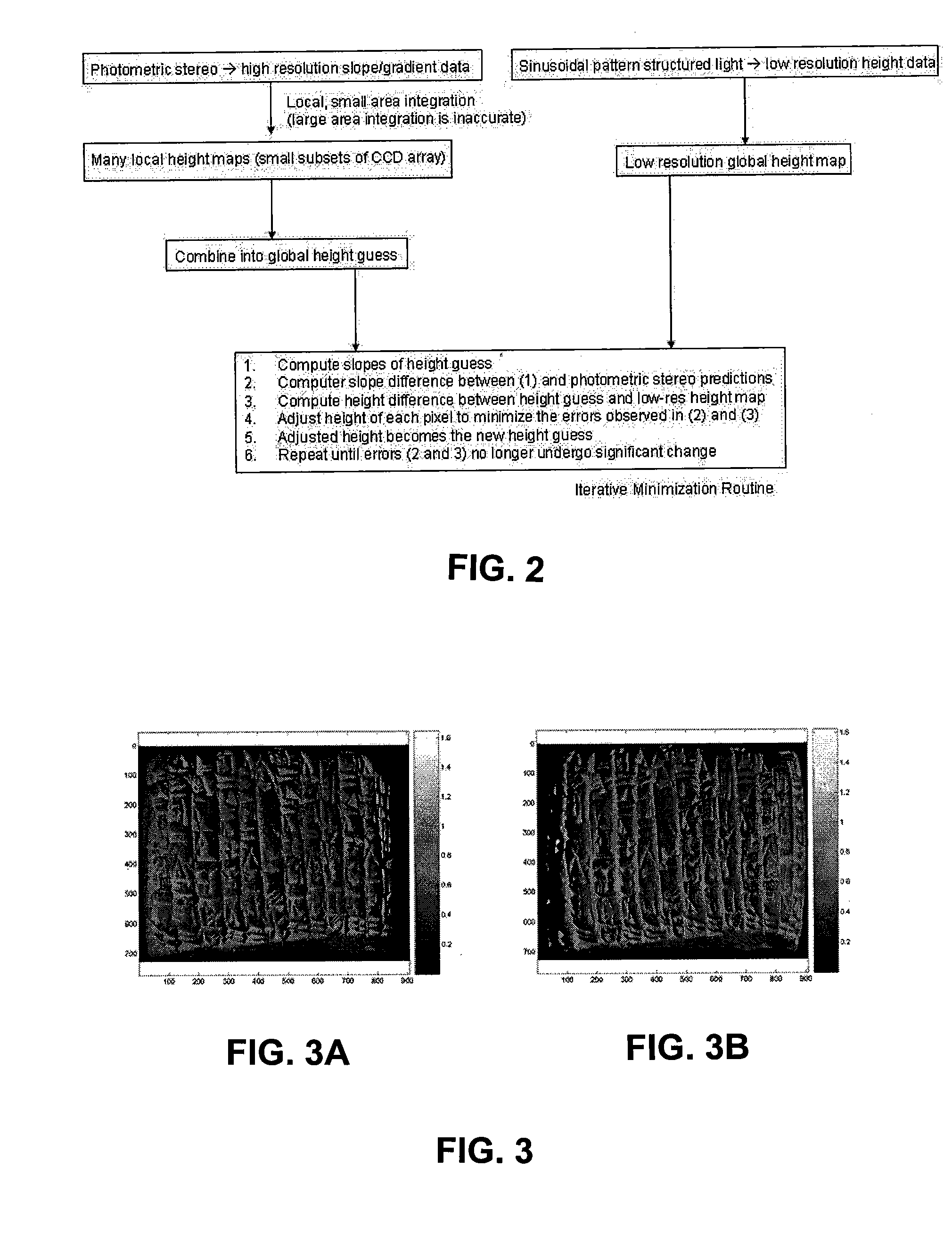
Apparatus and Method for 3-Dimensional Scanning of an Object
InactiveUS20080232679A1High resolution scanningSmall amount of timeCharacter and pattern recognitionMinimization algorithmLuminosity
A 3-dimensional scanner capable of acquiring the shape, color, and reflectance of an object as a complete 3-dimensional object. The scanner utilizes a fixed camera, telecentric lens, and a light source rotatable around an object to acquire images of the object under varying controlled illumination conditions. Image data are processed using photometric stereo and structured light analysis methods to determine the object shape and the data combined using a minimization algorithm. Scans of adjacent object sides are registered together to construct a 3-dimensional surface model.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
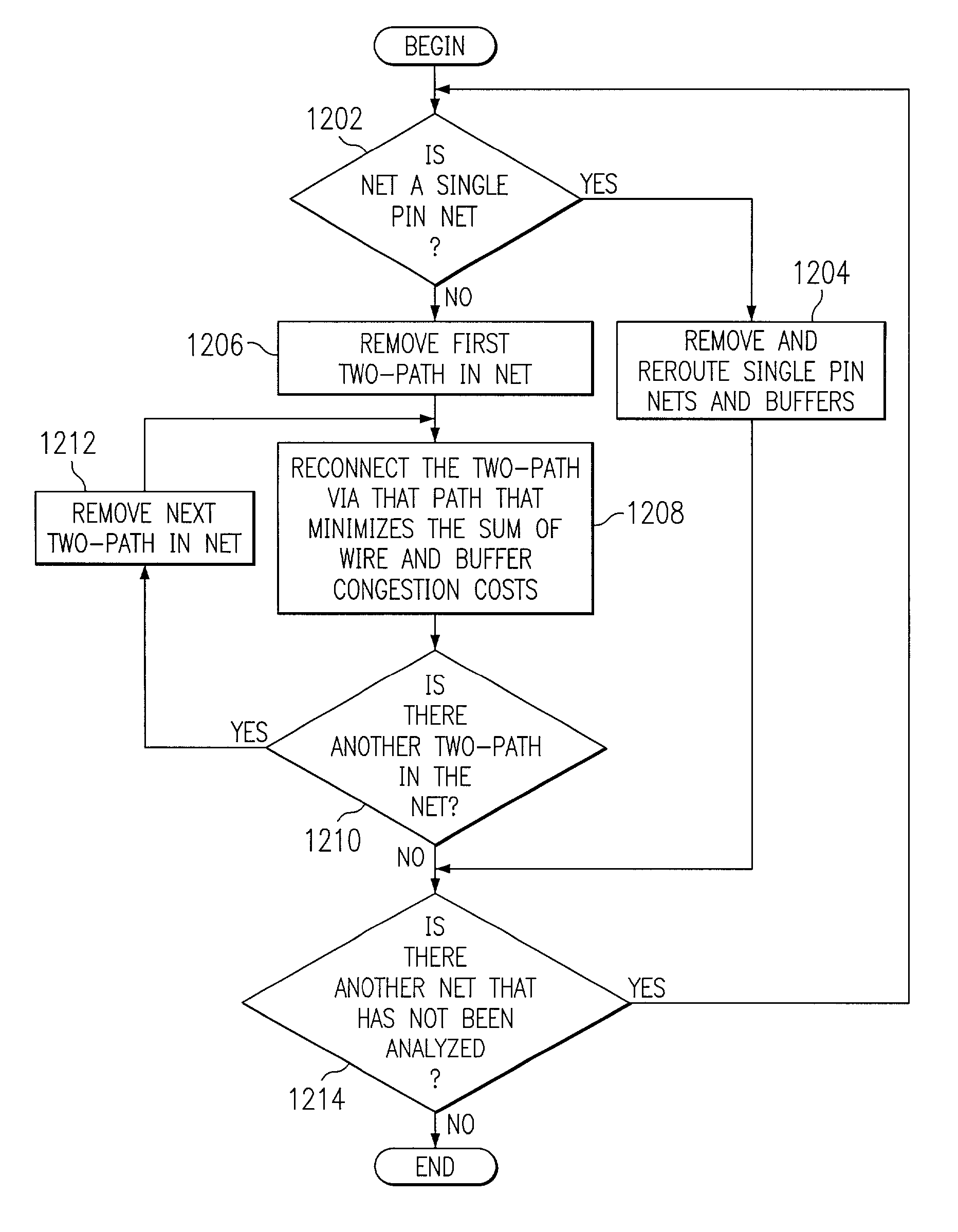
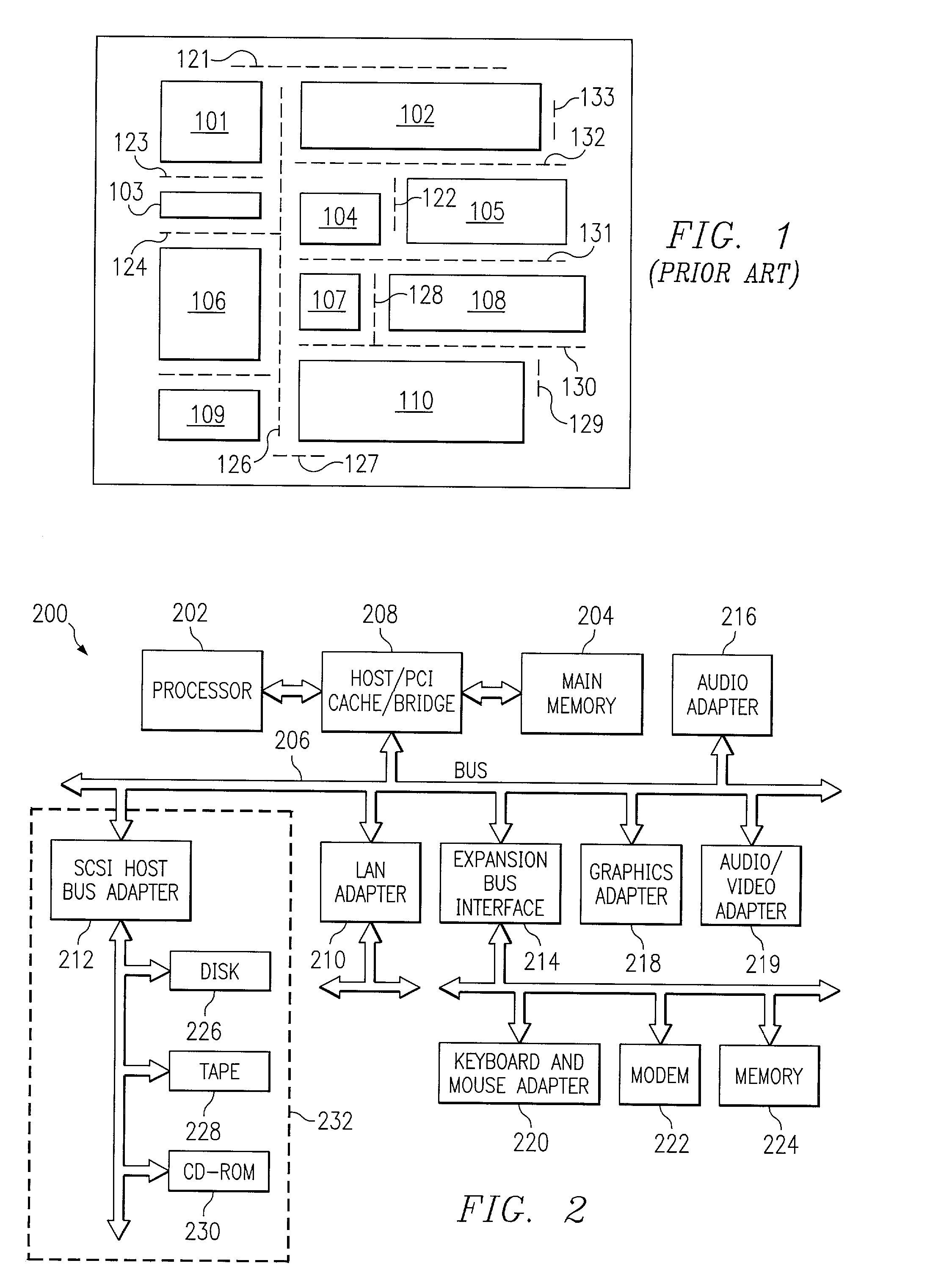
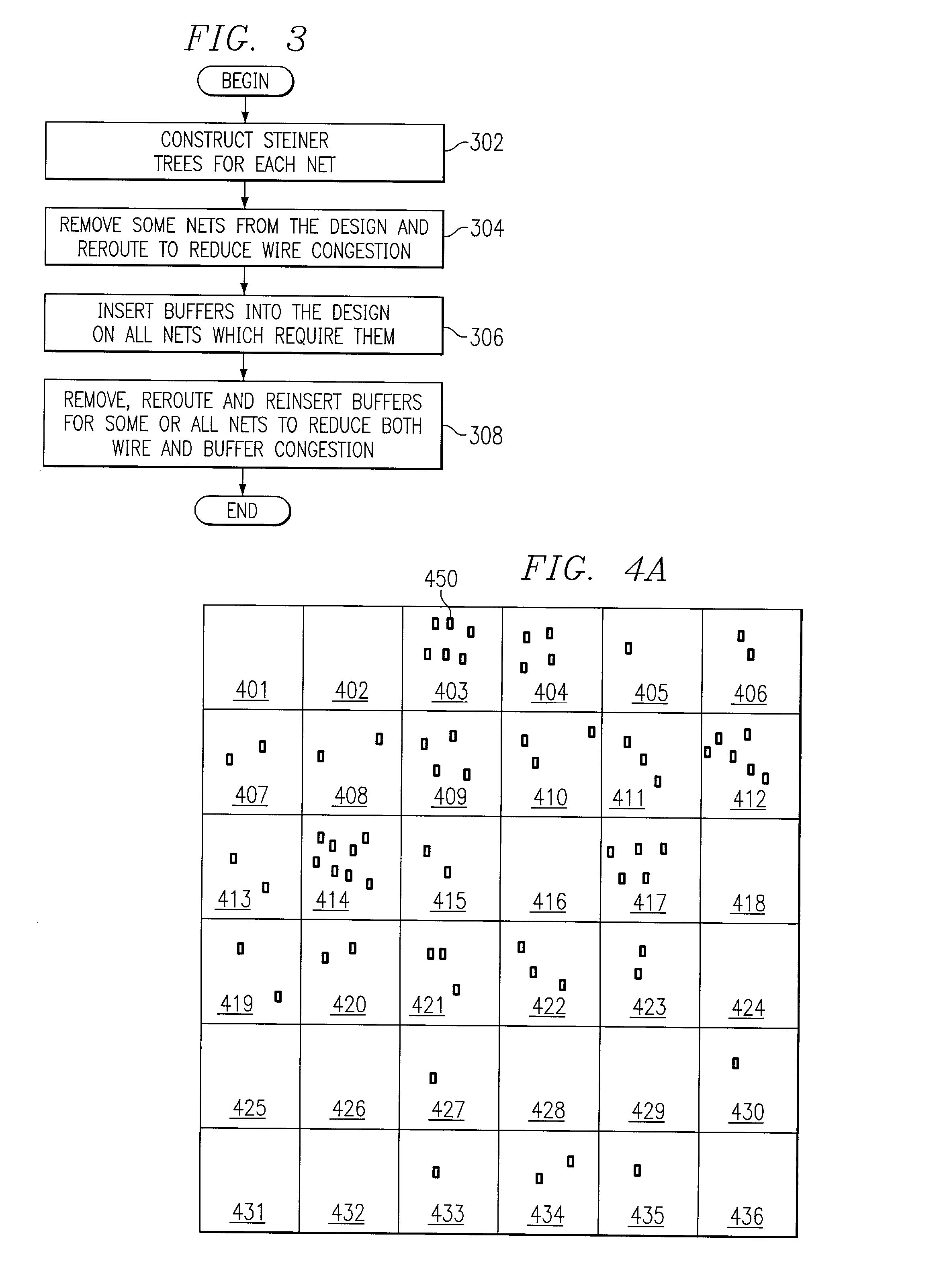
Practical methodology for early buffer and wire resource allocation
InactiveUS6996512B2Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationMinimization algorithmComputer architecture
A method, system, and computer program product for allocating buffer and wire placement in an integrated circuit design is provided. In one embodiment, the surface of a integrated circuit design is represented as a tile graph. Allocation of buffer locations for selected tiles in the tile graph is then received and nets are routed between associated sources and sinks. Buffer locations within selected tiles are then selectively assigned based upon buffer needs of the nets, wherein the nets are routed through selected tiles and assigned buffer locations using a cost minimization algorithm.
Owner:IBM CORP
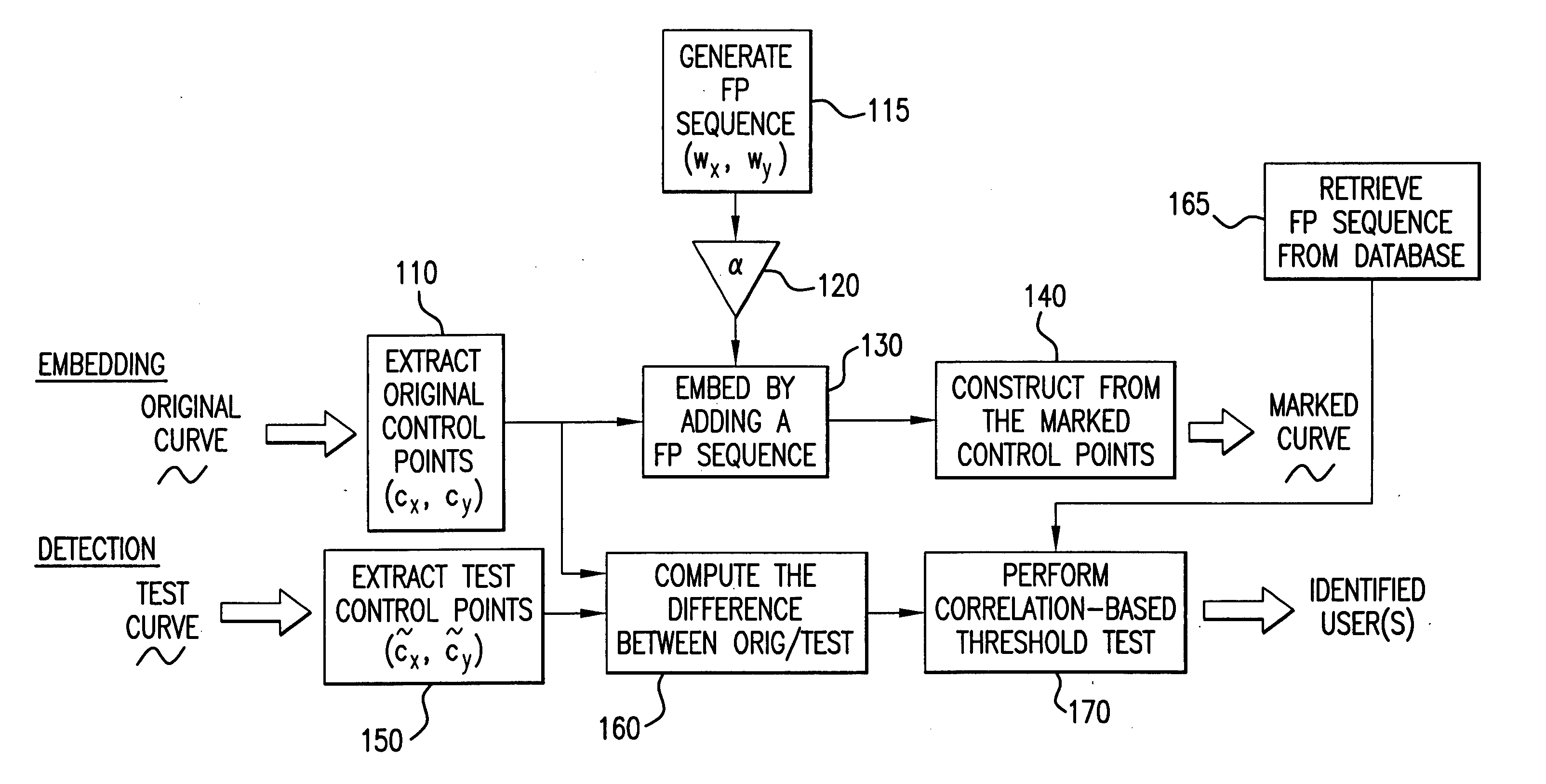
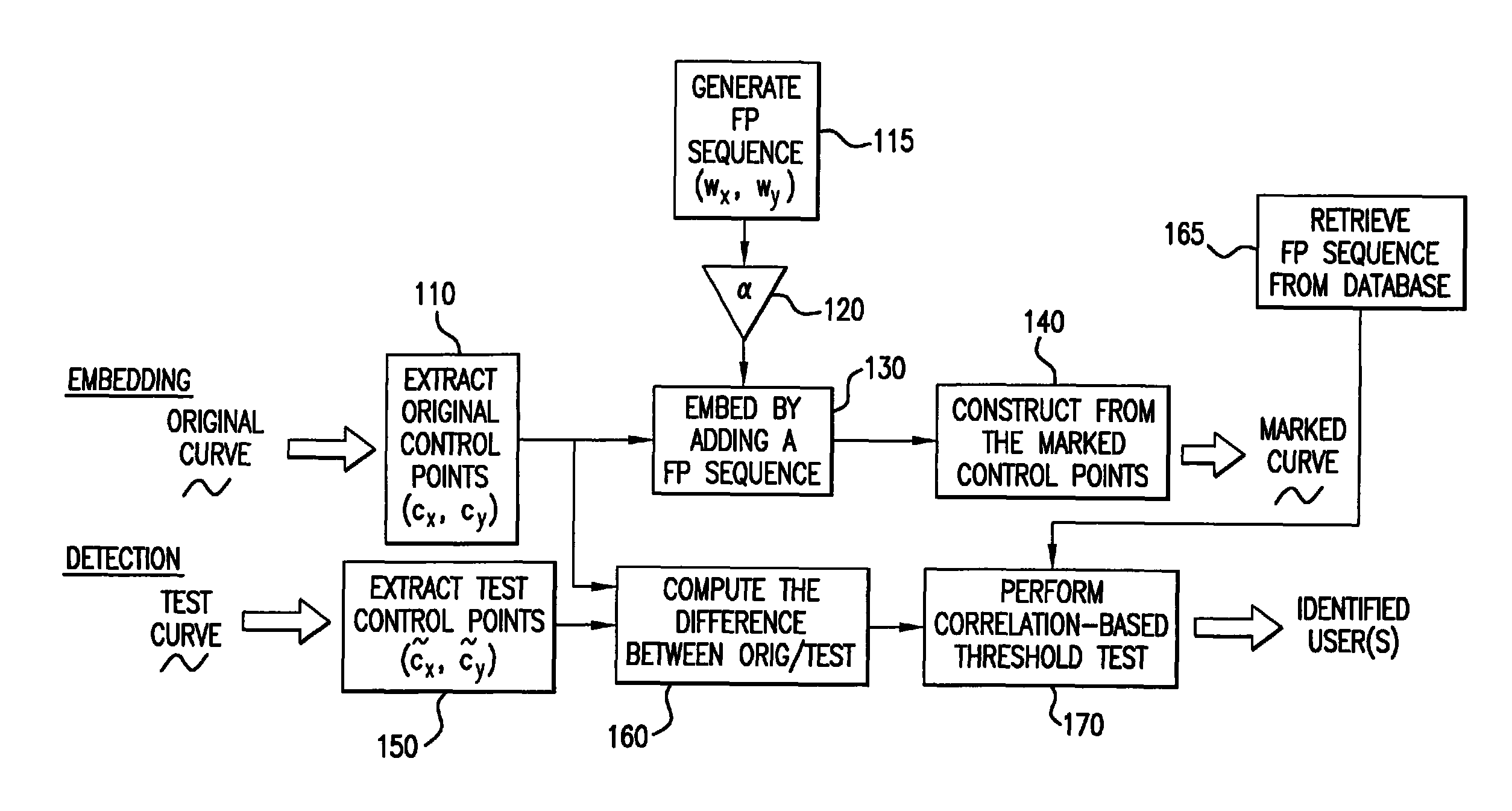
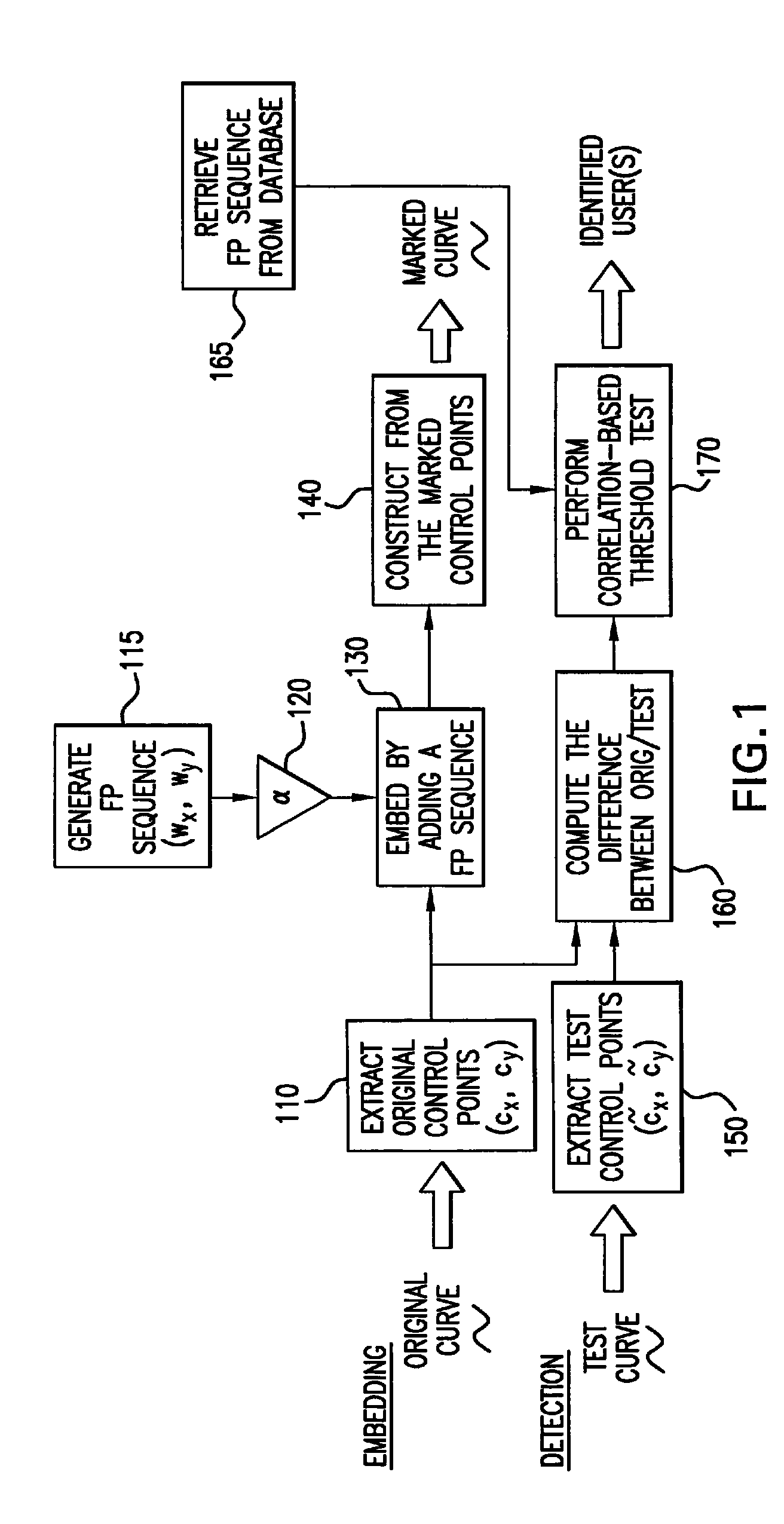
Method for concealing data in curves of an image
InactiveUS20060056695A1Convenient registrationImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionImage watermarkingMinimization algorithmArtificial intelligence
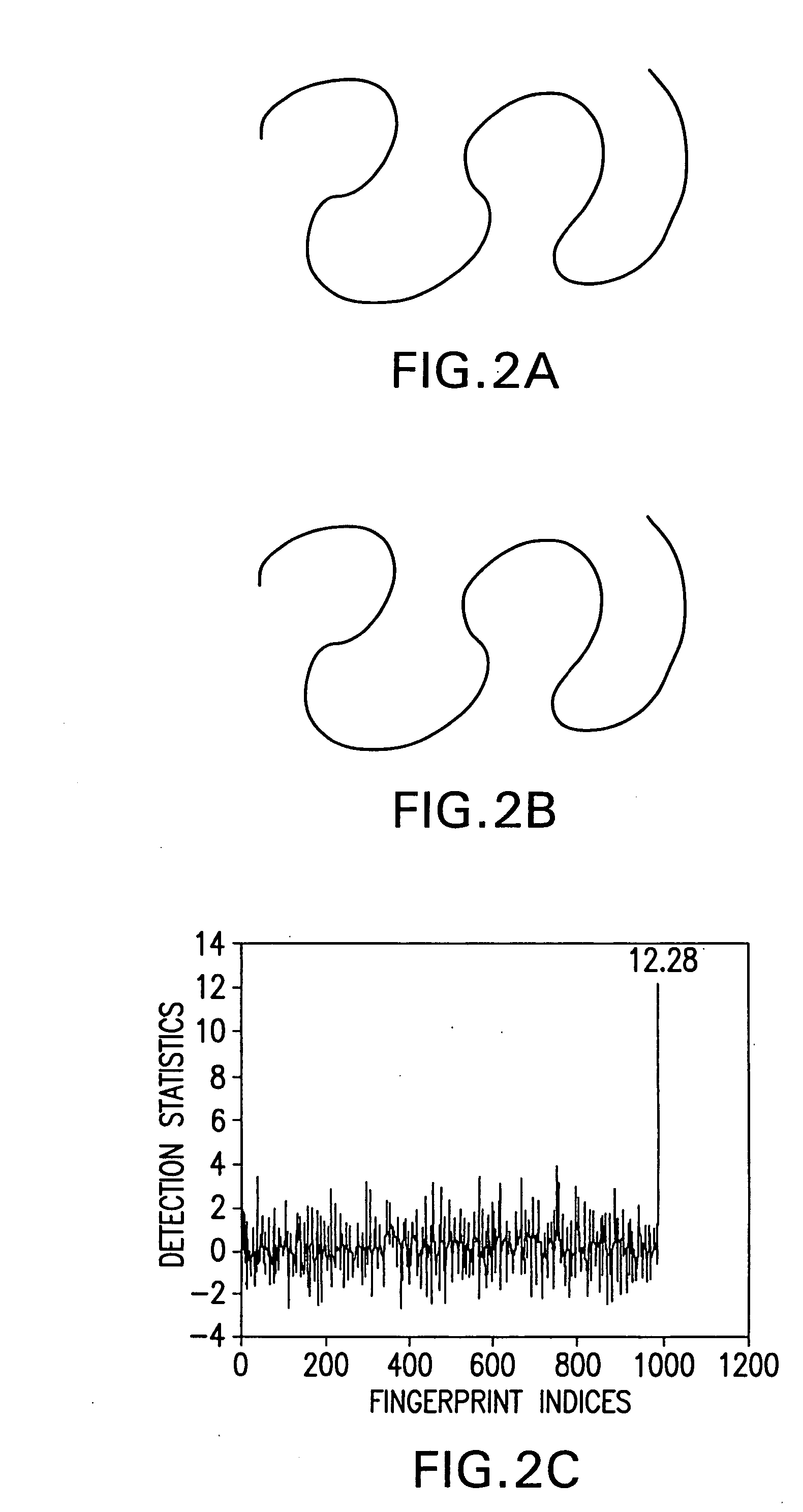
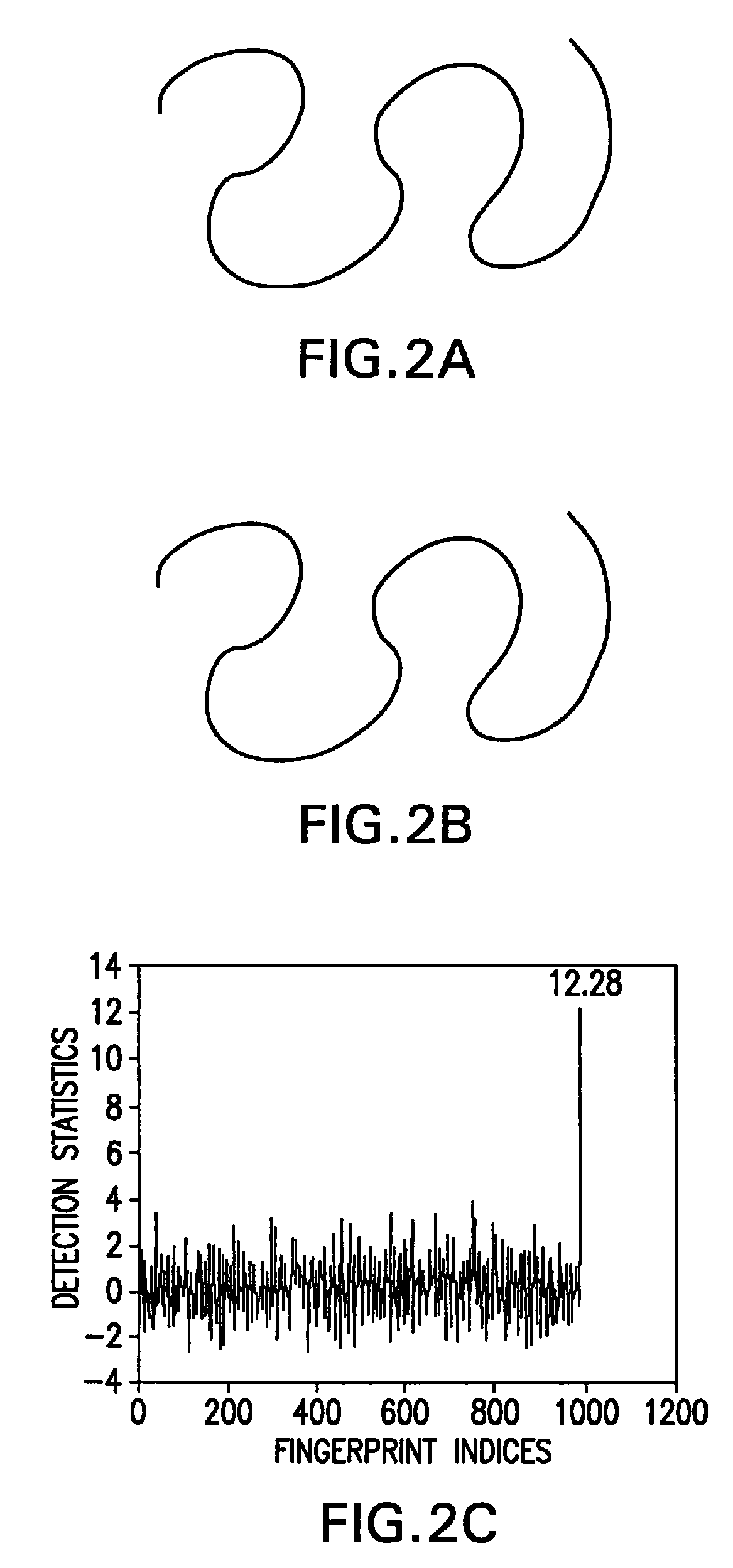
A method of concealing data in images imperceptibly alters curves therein, such as through adding a value representing the data to be hidden to each of a number of B-spline control points representing the original curve. The altered control points characterize the imperceptibly altered curve, which replaces the original curve in the image. The altered control points may be later extracted from the image and compared with the original control points to determine the hidden value. Prudent selection of the values altering the control points as well as an iterative alignment-minimization algorithm in the detection process provides protection against numerous techniques for preventing the hidden values from being recovered.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
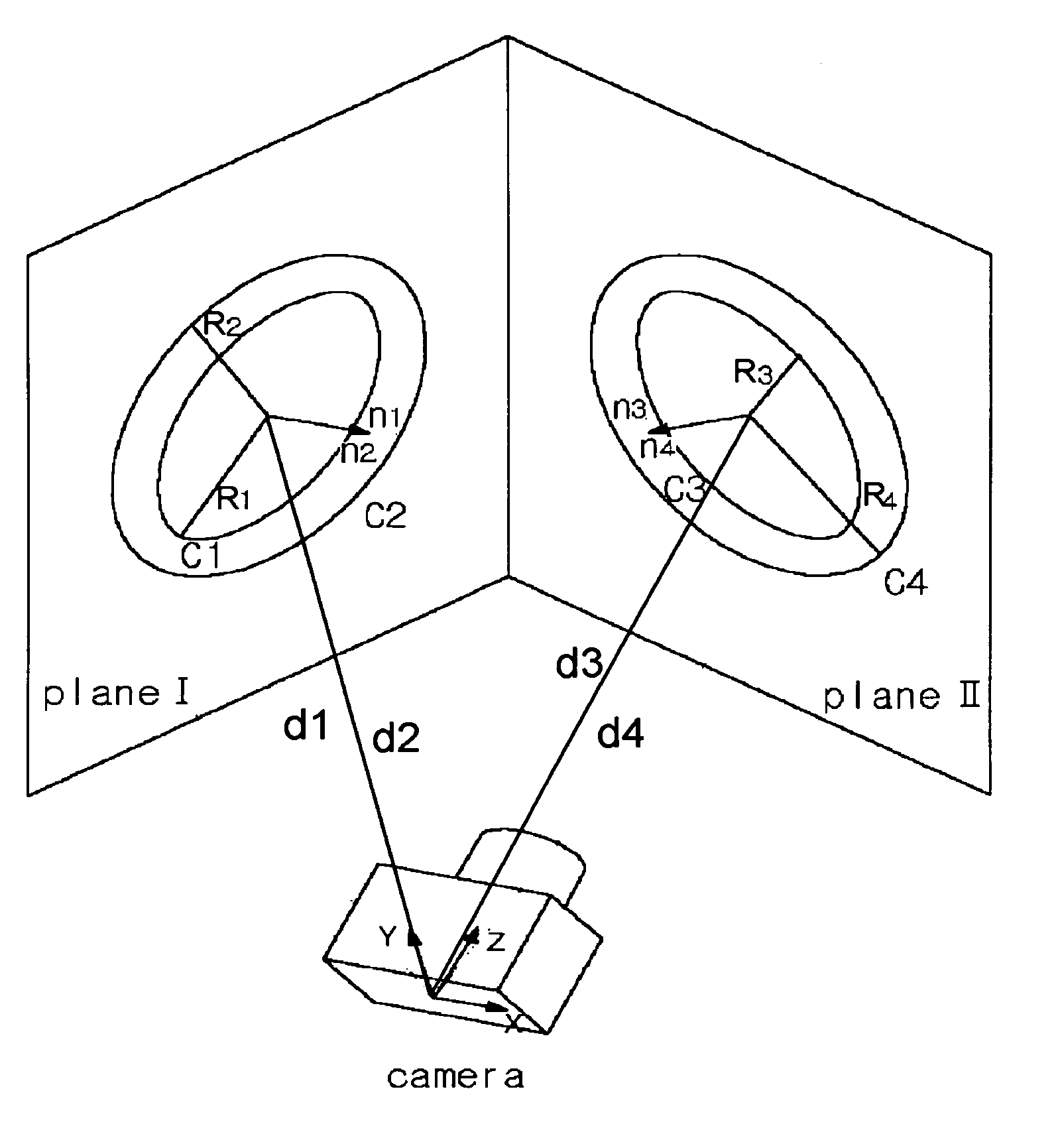
Camera calibration system using planar concentric circles and method thereof
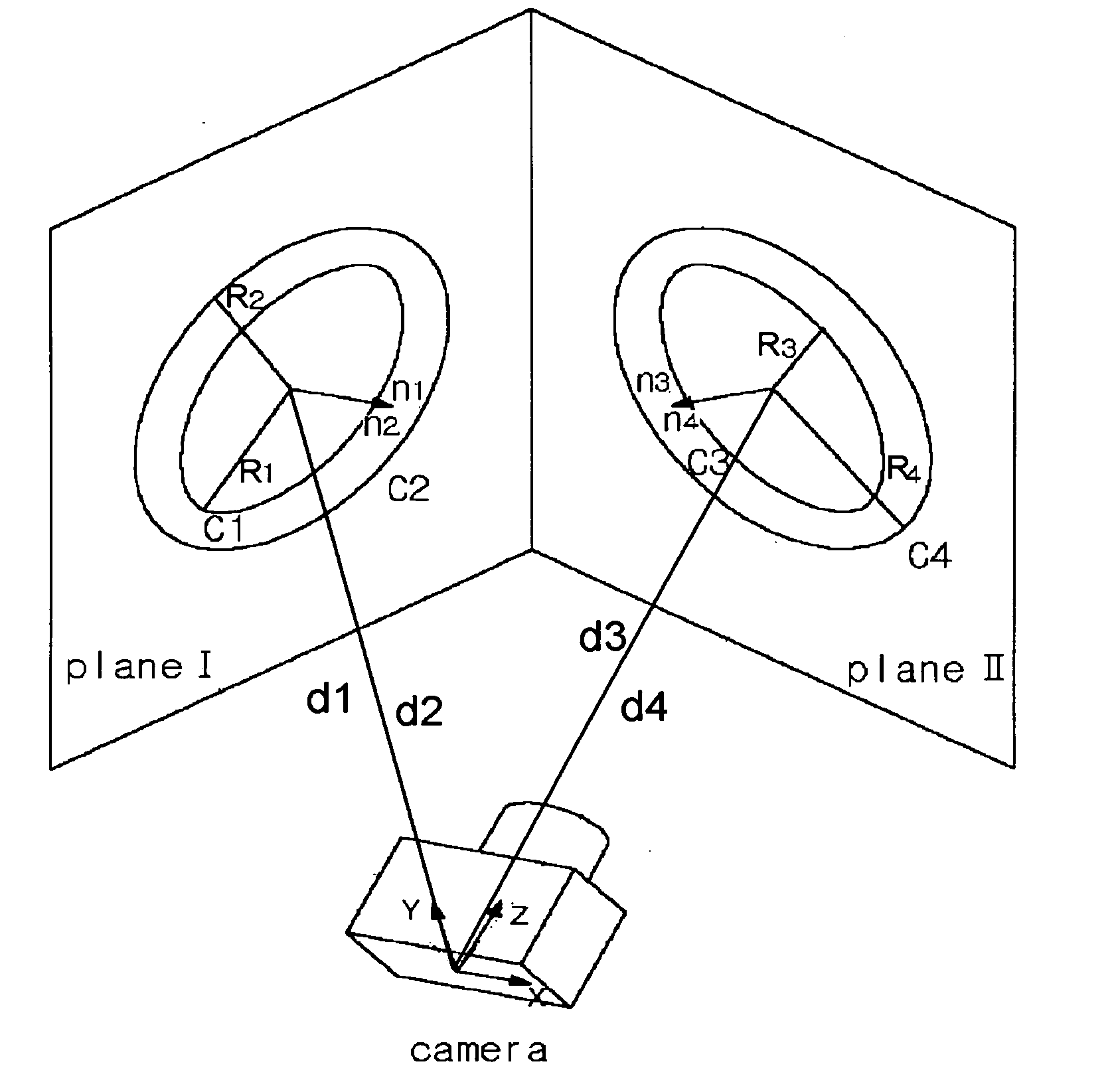
InactiveUS20050207640A1Improve calibration reliabilityTelevision system detailsImage analysisMinimization algorithmProjection image
The invention relates to a camera calibration system and method thereof, which is capable of easily performing camera calibration using a concentric circle pattern. According to the invention, a method of calibrating a camera calibrates the intrinsic parameters of the camera required to measure geometric information of an object using projection invariable characteristics of concentric circles. The method includes the steps of: taking images of the calibration pattern consisting of two or more concentric circles located in the same plane and having different radius at different angles to obtain projected images; calculating the central point of the projected images using a given algorithm, and calculating the principal point and focal point of camera using a nonlinear minimization algorithm based on the central point thus obtained.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
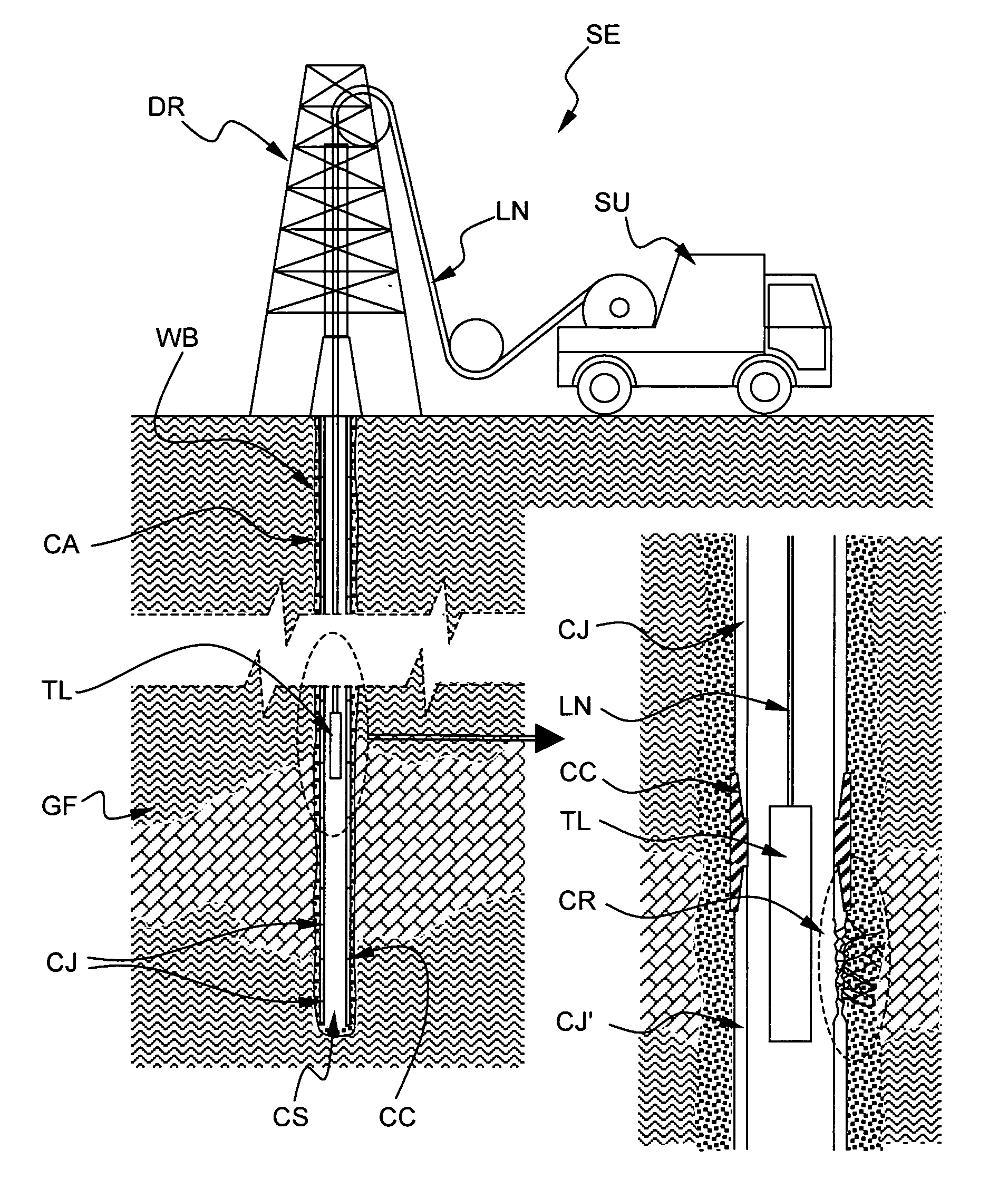
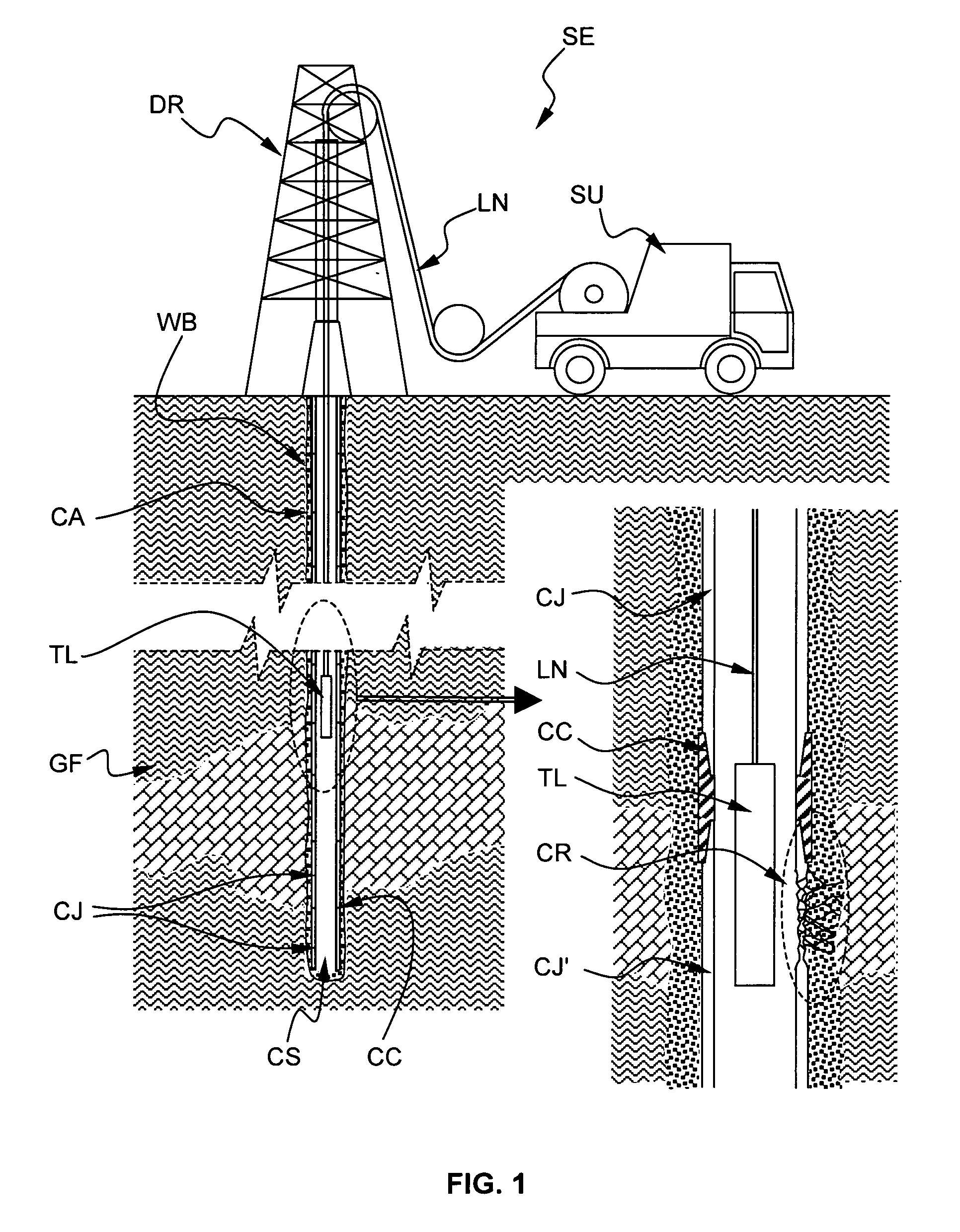
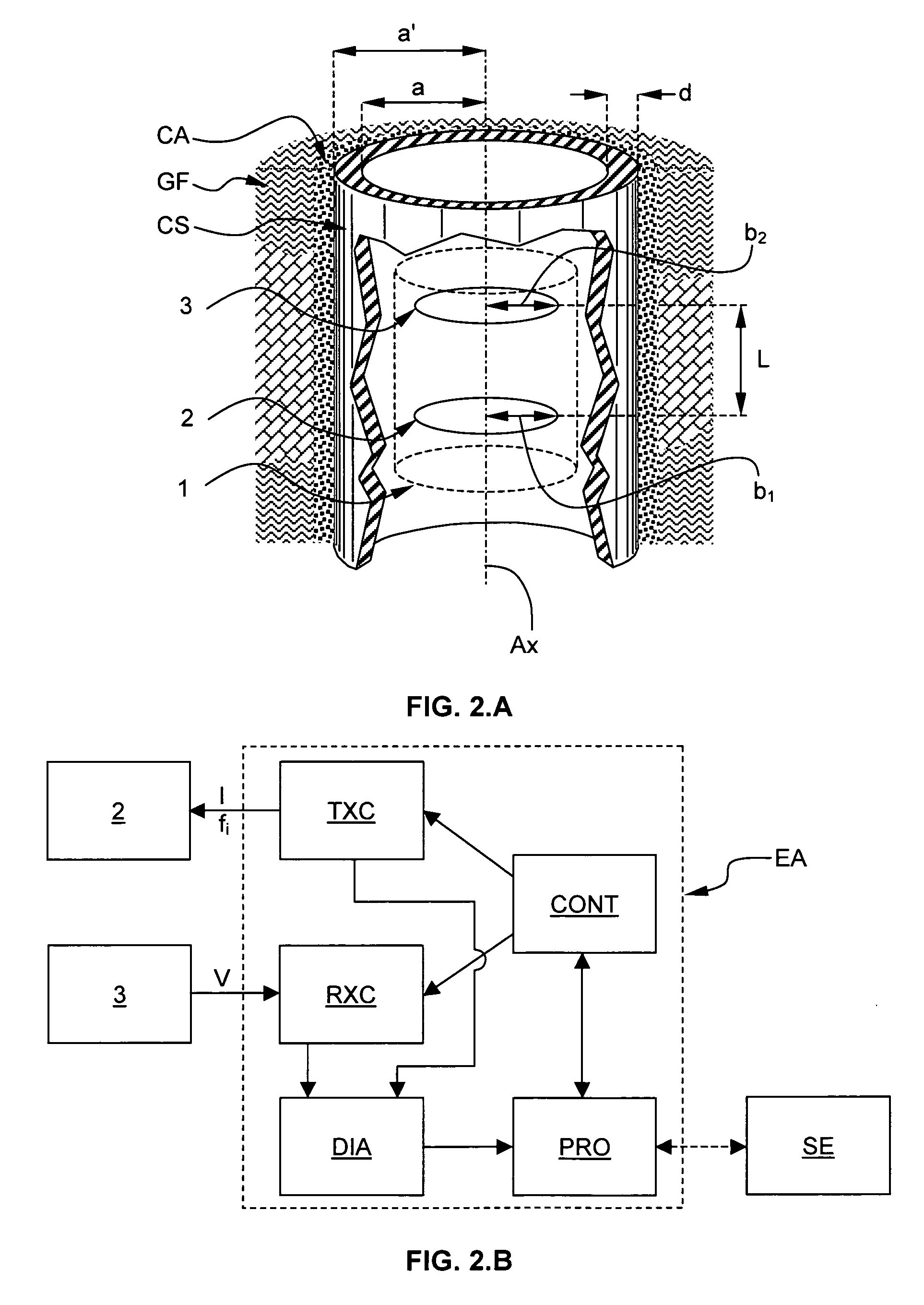
Method for electromagnetically measuring physical parameters of a pipe
ActiveUS20100017137A1Improve accuracyPlug gaugesElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingTransmitter coilPower flow
The method electromagnetically measures a pipe inner diameter ID and a pipe ratio of magnetic permeability to electrical conductivity μ2 / σ2 by means of a measuring arrangement 1 comprising a transmitter coil 2 and a receiver coil 3, both coils being coaxial to and longitudinally spaced from each other, the measuring arrangement 1 being adapted to be positioned into the pipe CS and displaced through the pipe. The method comprises the steps of:a1) exciting the transmitter coil 2 by means of a transmitter current Ii, the transmitter current having a first excitation frequency f1,a2) measuring a receiver voltage Vi at the receiver coil 3, a3) determining a transimpedance Vi / Ii between the transmitter coil 2 and the receiver coil 3 based on the transmitter current Ii and the receiver voltage Vi, and determining a measurement ratio Mi based on said transimpedance,b) repeating the excitation step a1), the measuring step a2), the transimpedance and the measurement ratio determination step a3) for at least a second excitation frequency f2 so as to define a measurement ratio vector [M1, M2, . . . Mn],c) calculating a prediction function vector [G1, G2, . . . Gn] based on the first and at least the second excitation frequency, a plurality of potential pipe ratio of magnetic permeability to electrical conductivity and a plurality of potential pipe inner diameter ID, andd) applying a minimizing algorithm onto the measurement ratio vector [M1, M2, . . . Mn] and the prediction function vector [G1, G2, . . . Gn] and determining the pipe inner diameter and the pipe ratio of magnetic permeability to electrical conductivity corresponding to a maximum solution of the algorithm.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
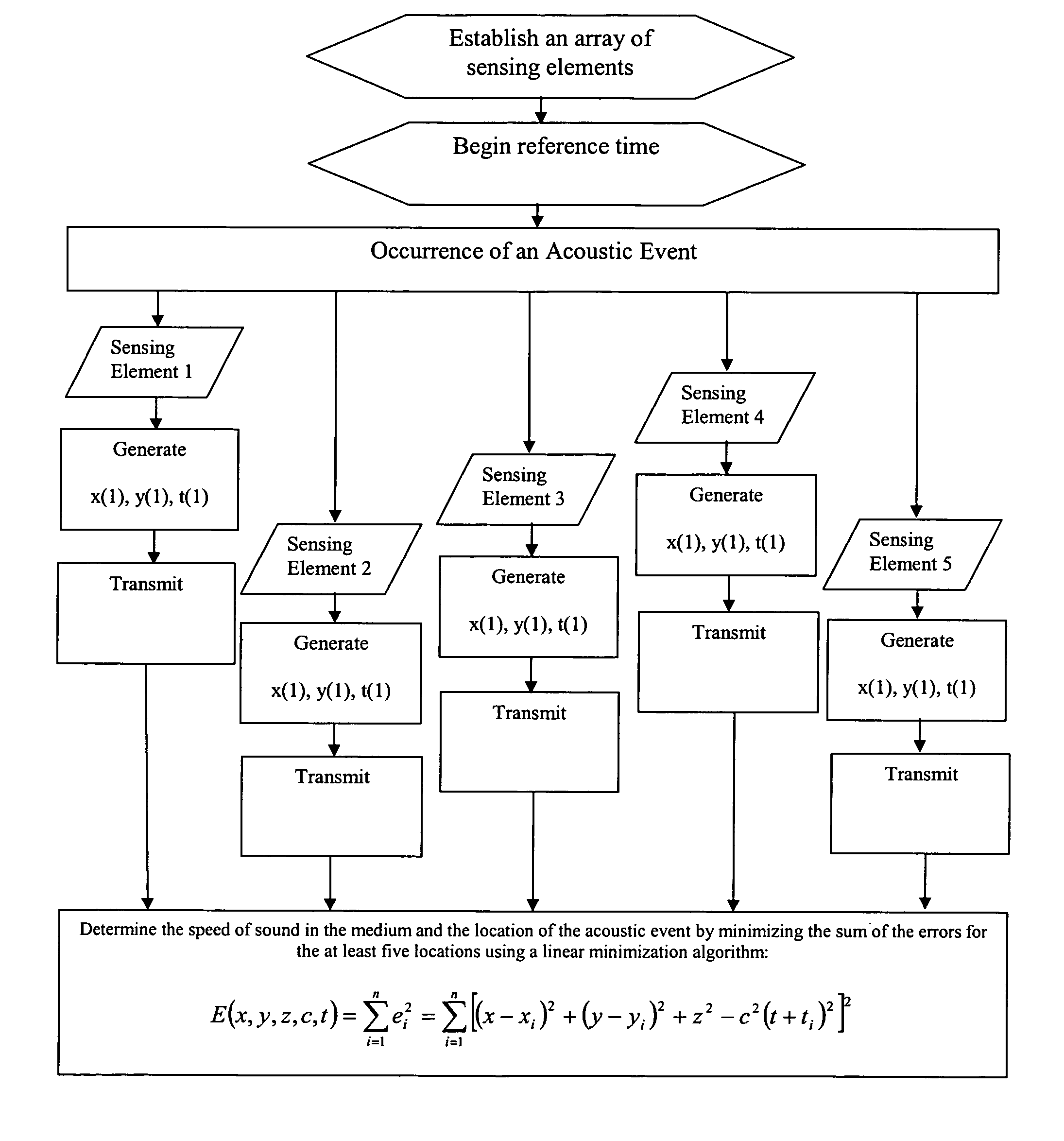
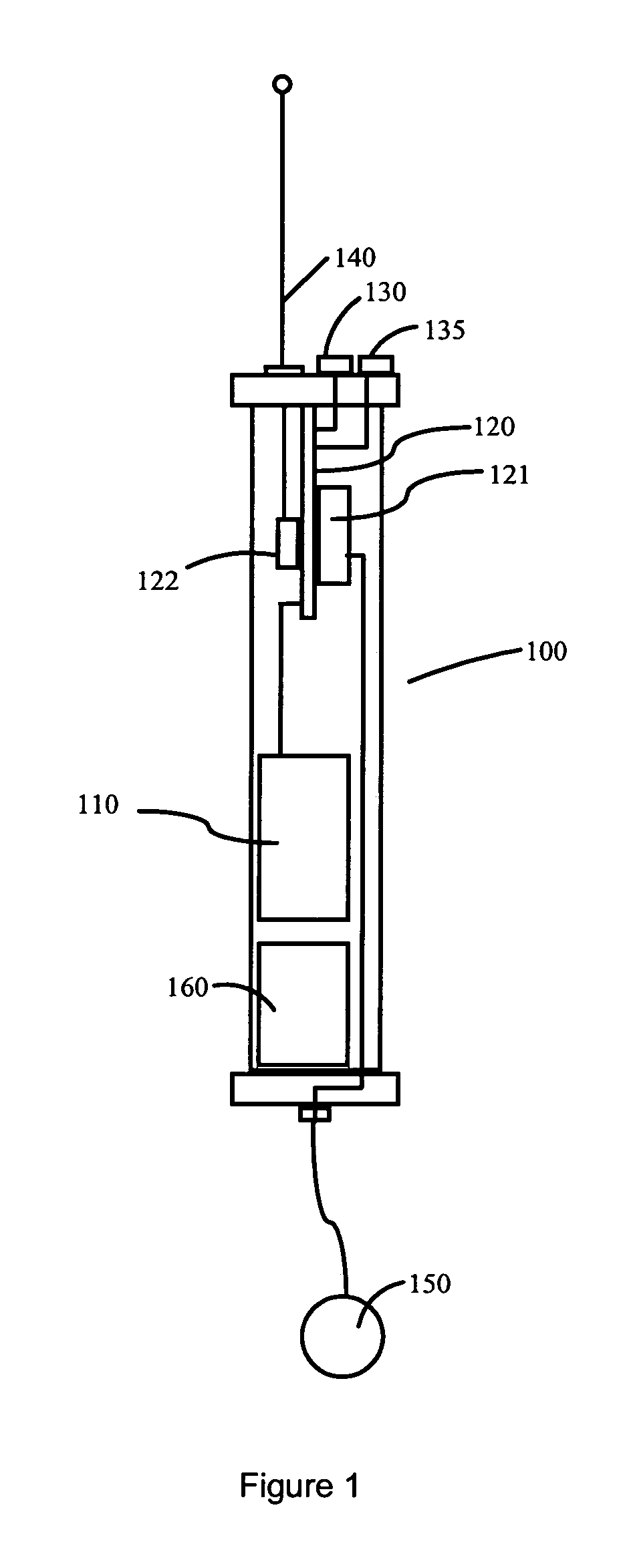
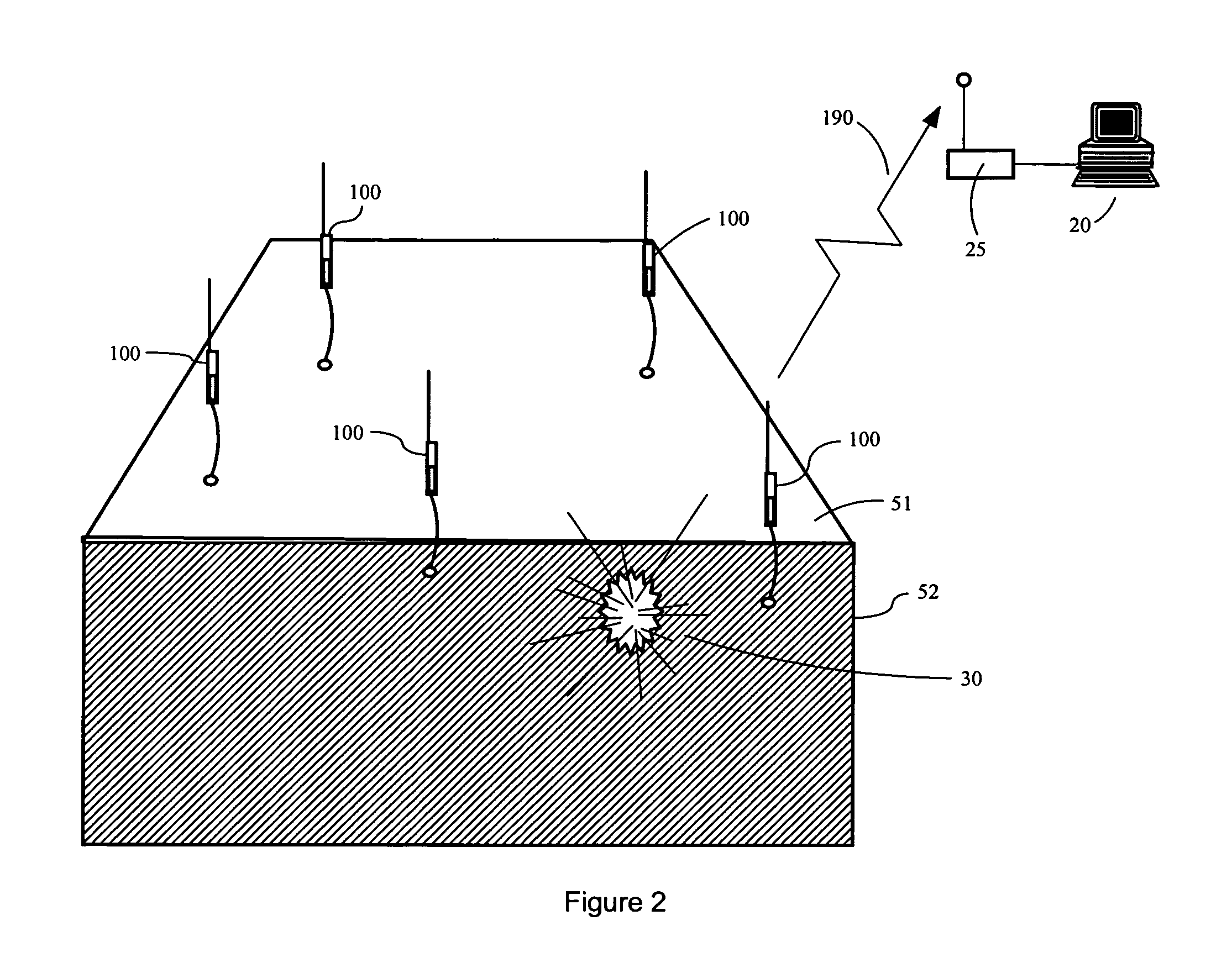
System and method for determining the location of an acoustic event
InactiveUS20060050610A1Error minimizationDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesPosition fixationMinimization algorithmSpeed of sound
A system and method is provided for determining the three dimensional location of an acoustic event using a system of five or more sound sensing elements. The sensing elements are positioned at substantially the same elevation and in spatially distributed locations with respect to the acoustic event. The sensing elements generate notification signals indicating occurrence of the acoustic event. A central processor receives the notification signals, associates the locations of each of the sensing elements with the time at which each sensing element sensed the sound, determines the speed of sound for the medium, and calculates a three dimensional location for the acoustic event using a linear error minimization algorithm. A system of six or more sensing elements enables the processor further to discriminate between near simultaneous acoustic events.
Owner:MCGINN HARVEY HLDG
Method for measuring nano-scale multilayer film structure
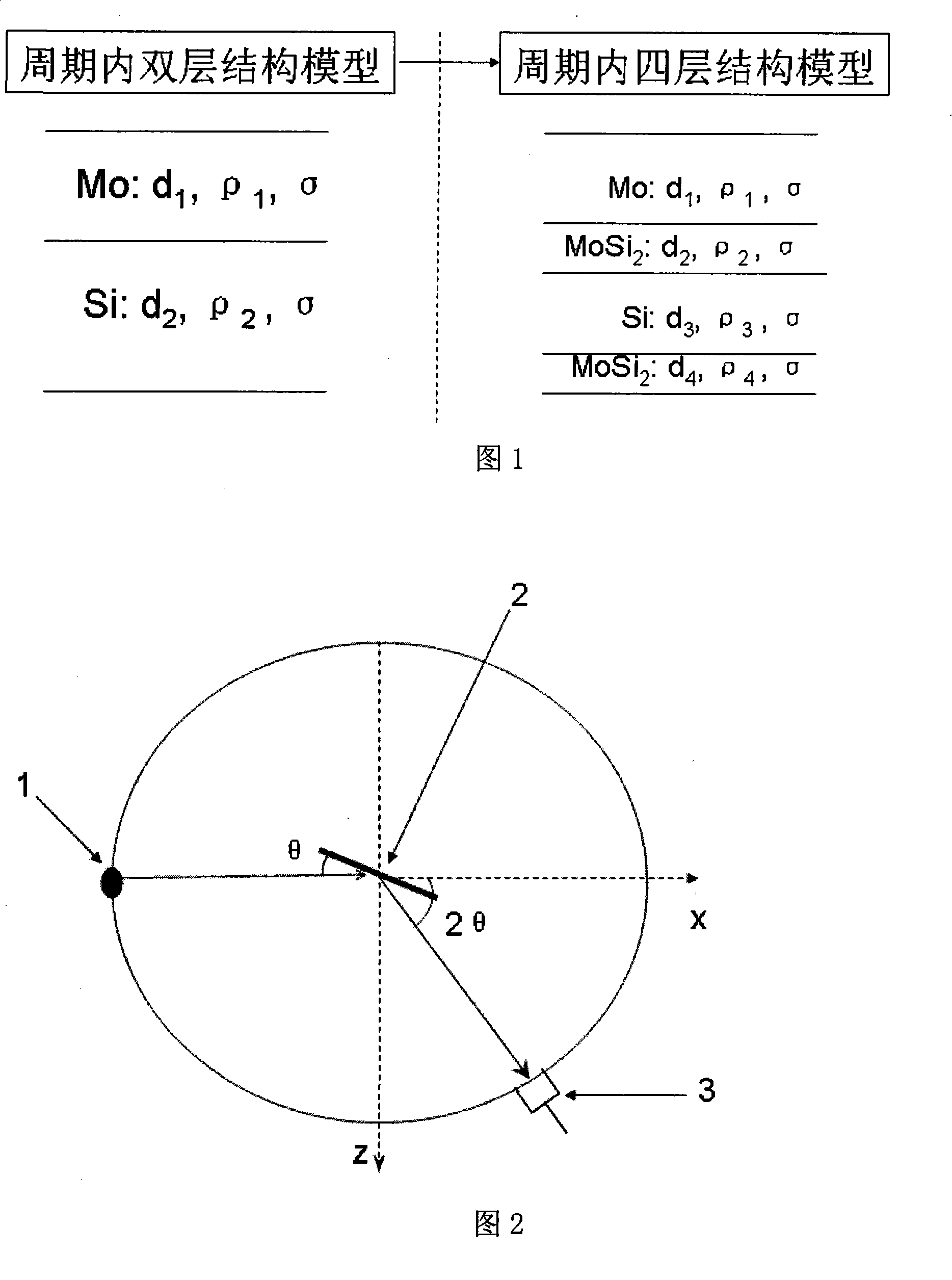
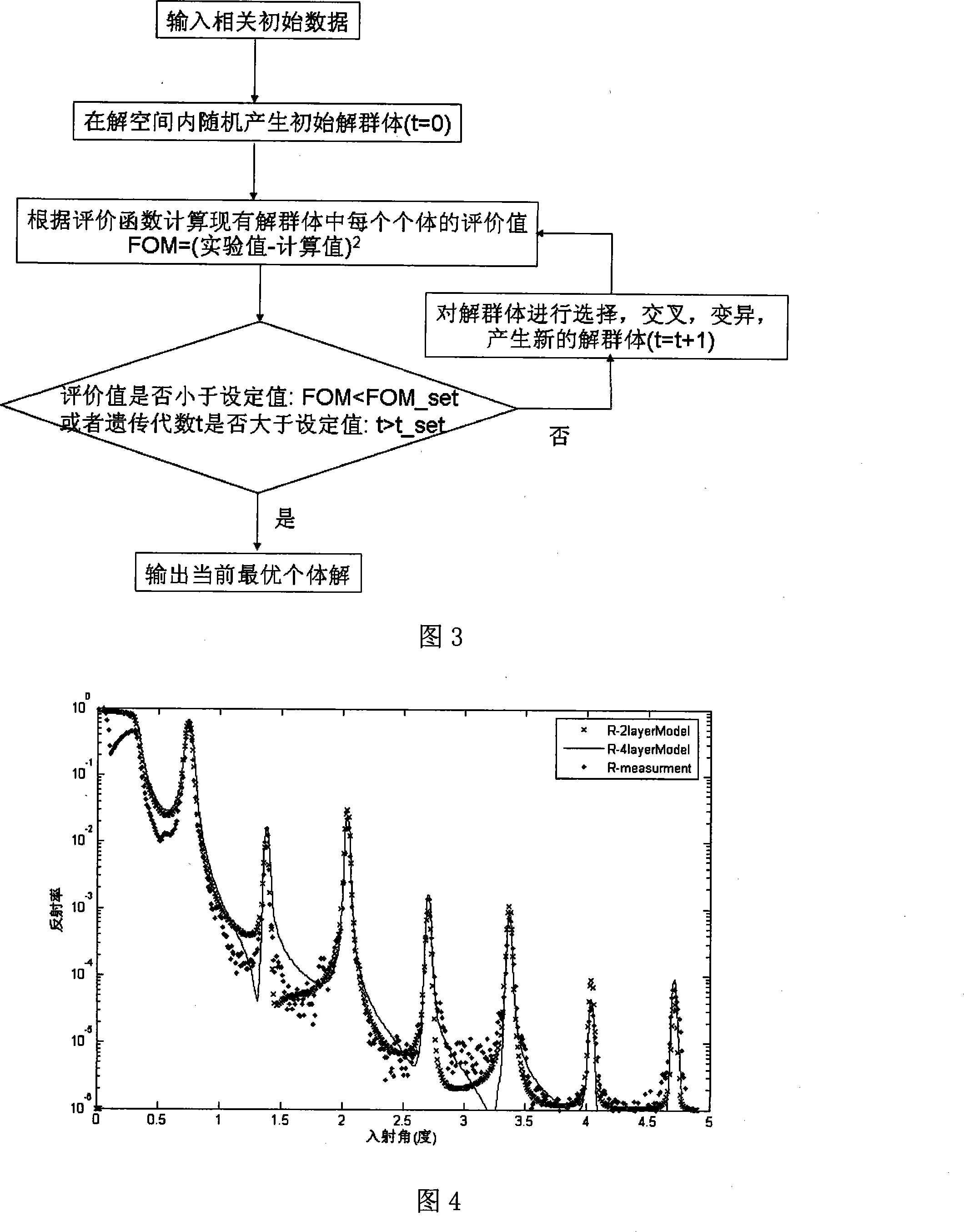
InactiveCN101206112AFit Bias ReductionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationUsing wave/particle radiation meansMinimization algorithmX-ray
The invention discloses a measurement method for a nanometer multi-layer membrane structure and belongs to the optical measurement technical field. The invention establishes a four-layer structural model in the period at first, then measures the X ray grazing incidence reflection rate R' of the multi-layer membrane, calculates the X ray grazing incidence reflection rate R according to the detailed structural model of the multi-layer membrane, and hereby establishes an evaluation function FOM(d1, d2, d3, d4, rho1, rho2, rho3, rho4, sigma)=1 / Msigma [lg(R'(theta))-lg(R(theta))] 2. The detailed structure of the multi-layer membrane can simply be obtained by adopting the Genetic Algorithm to evaluate the maximum value of the evaluation function about each structural parameter. The invention solves the problem that the routine minimization algorithm is easy to be get into a local minimum value when the routine minimization algorithm fits the detailed structural model of the multi-layer membrane, provides a method which can be used for the detailed structure of the representative multi-layer membrane, and is applicable to representative issues of structural parameters of multi-layer membranes with complex structures.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
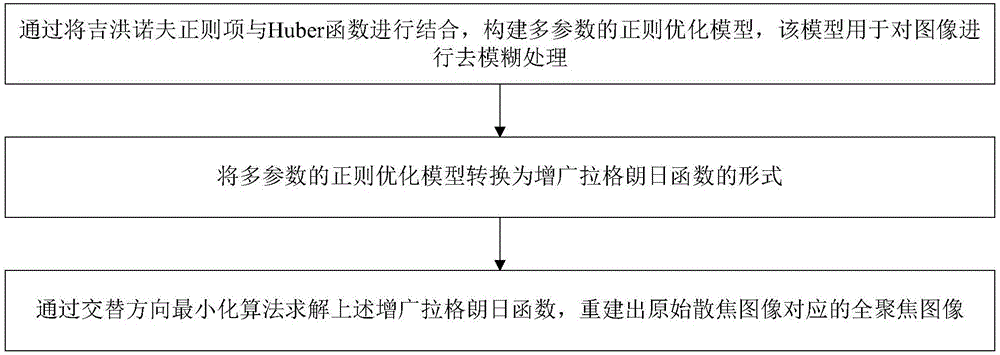
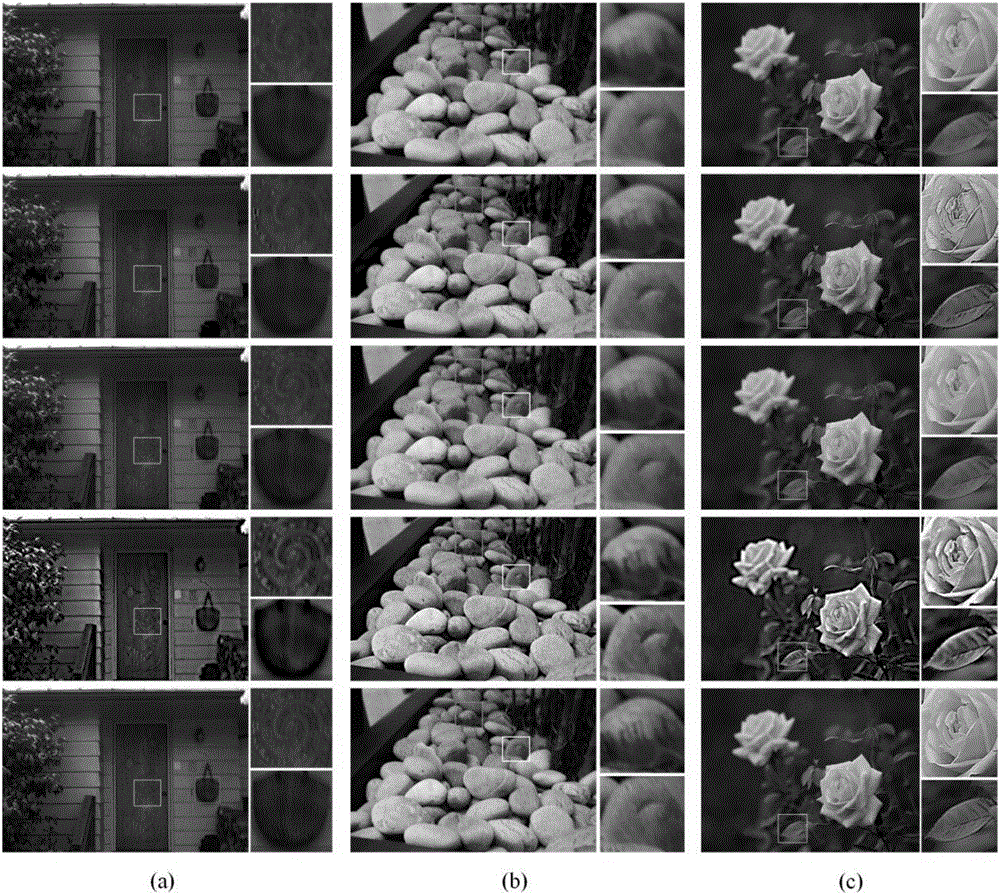
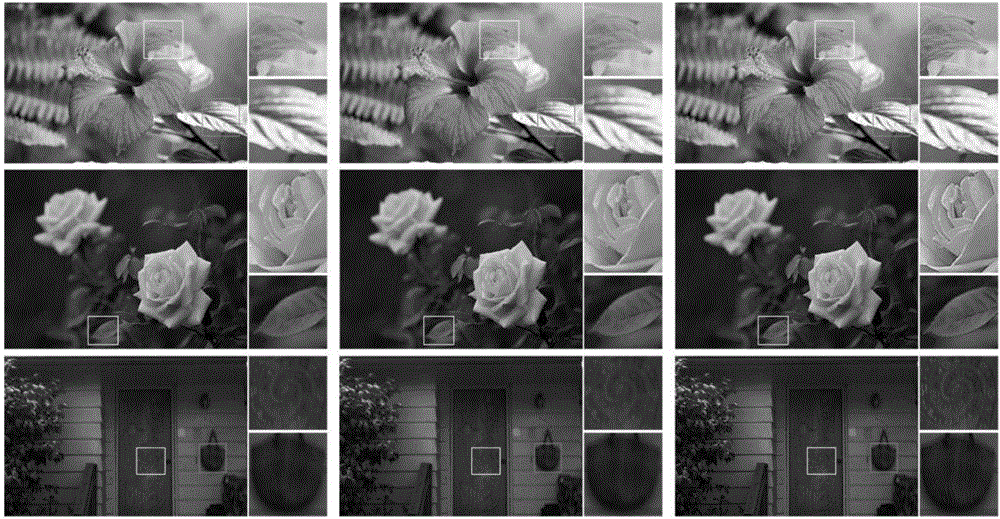
Image deblurring method based on multi-parameter regular optimization model
ActiveCN106709877ARich detail textureSmall distortionImage enhancementInternal combustion piston enginesIlluminanceMinimization algorithm
The invention discloses an image deblurring method based on a multi-parameter regular optimization model. The image deblurring method comprises the following steps that combining a Tikhonov regular item with a Huber function to construct the multi-parameter regular optimization model, wherein the model is used for carrying out deblurring processing on an image; converting the multi-parameter regular optimization model into an augmented Lagrangian function form; and through an alternating direction minimization algorithm, solving the above augmented Lagrangian function, and reconstructing a total focusing image corresponding to an original defocusing image. By use of the image deblurring method which is put forward by the invention, a grayscale image, a text image, a non-text image and a low-illuminance image can be deblurred, and the recovered image contains richer detail textures and less distortion, is free from an artifact phenomenon and is clearer and more natural.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
System and method for determining the location of an acoustic event
InactiveUS7233545B2Error minimizationDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesPosition fixationMinimization algorithmSpeed of sound
A system and method is provided for determining the three dimensional location of an acoustic event using a system of five or more sound sensing elements. The sensing elements are positioned at substantially the same elevation and in spatially distributed locations with respect to the acoustic event. The sensing elements generate notification signals indicating occurrence of the acoustic event. A central processor receives the notification signals, associates the locations of each of the sensing elements with the time at which each sensing element sensed the sound, determines the speed of sound for the medium, and calculates a three dimensional location for the acoustic event using a linear error minimization algorithm. A system of six or more sensing elements enables the processor further to discriminate between near simultaneous acoustic events.
Owner:MCGINN HARVEY HLDG
Method for entity authentication based on secret sharing encryption
InactiveCN101741566AProlong lifeReduce Authentication LatencyEnergy efficient ICTUser identity/authority verificationMinimization algorithmTime delays
The invention discloses a method for entity authentication based on secret sharing encryption, which is suitable for a self-organizing network and relates to the field of safety-related application of a wireless network in an information safety technique. Aiming at the characteristics of limited energy consumption and storage of self-organizing network nodes, the scheme uses a secret sharing technique and a symmetric key algorithm to effectively reduce the authentication time delay and improve the network life time; and simultaneously, a plurality of times of authentications ensure that the safety is not reduced. Besides, when a cluster head is arranged in the self-organizing network, the invention also provides a power consumption minimization algorithm to shorten the distance of transmitted signals between nodes, effectively reduce the node energy consumption and improve the network life time.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Camera calibration system using planar concentric circles and method thereof
InactiveUS7155030B2Improve calibration reliabilityTelevision system detailsImage analysisMinimization algorithmCamera auto-calibration
The invention relates to a camera calibration system and method thereof which is capable of easily performing camera calibration using a concentric circle pattern. According to the invention, a method of calibrating a camera calibrates the intrinsic parameters of the camera required to measure geometric information of an object using projection invariable characteristics of concentric circles. The method includes the steps of taking images of the calibration pattern consisting of two or more concentric circles located in the same plane and having different radius at different angles to obtain projected images calculating the central point of the projected images using a given algorithm, and calculating the principal point and focal point of camera using a nonlinear minimization algorithm based on the central point thus obtained.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
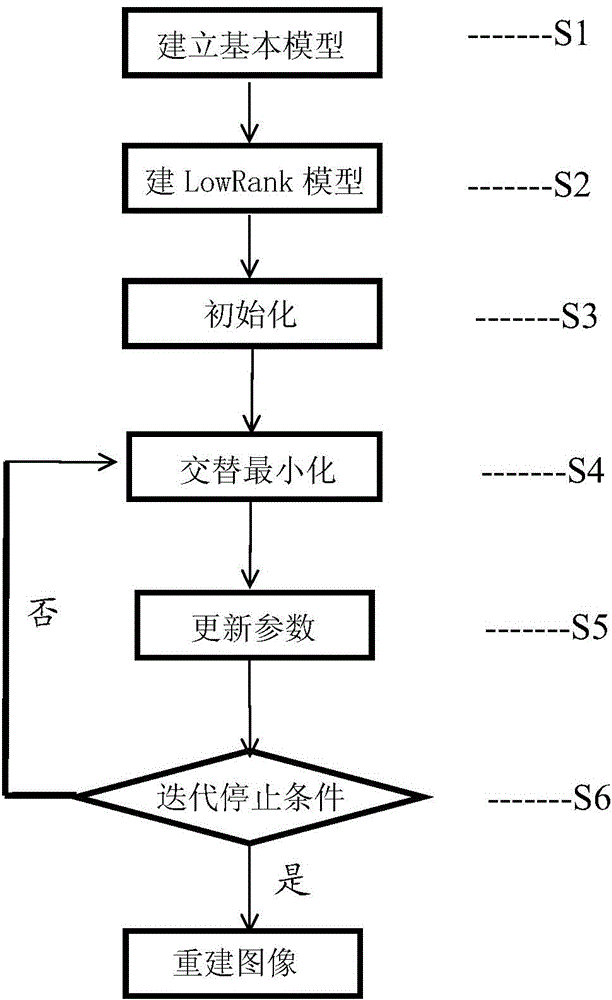
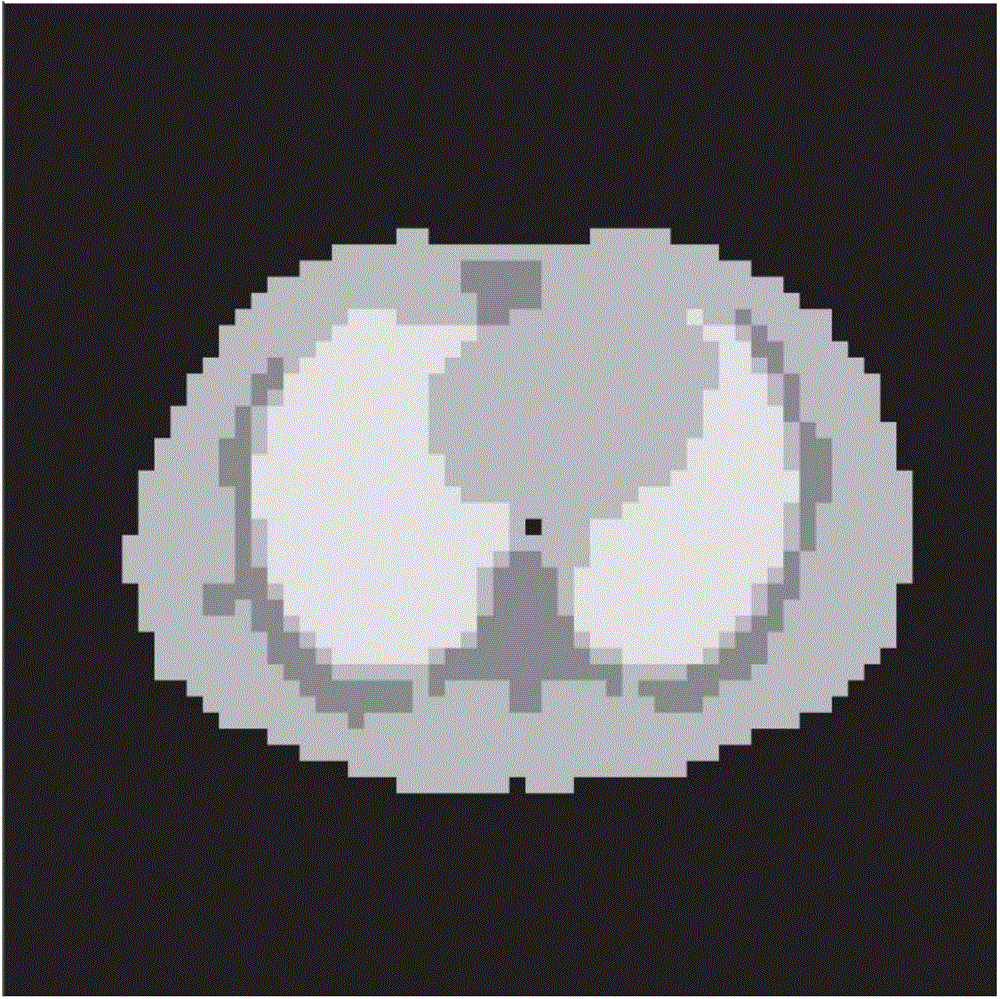
Dynamic PET (positron emission tomography) image reconstruction method based on Poisson TV
ActiveCN104657950AHigh resolutionPromote reconstructionImage enhancementMinimization algorithmAlgorithm
The invention discloses a dynamic PET (positron emission tomography) image reconstruction method based on a Poisson TV. According to the method, PET images are reconstructed through conversion of a reconstruction problem mathematical model and an equivalence problem on the basis of a Low Rank method, and an alternate minimization algorithm is adopted during solution of the equivalence model problem when the PET images are reconstructed in combination with Poisson and Low Rank models. Therefore, the Low-Rank algorithm is utilized effectively, and problems of low resolution and noise interference of results produced during dynamic PET image reconstruction by a computer are solved; compared with existing reconstruction method through tests, the method can realize the better reconstruction effect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
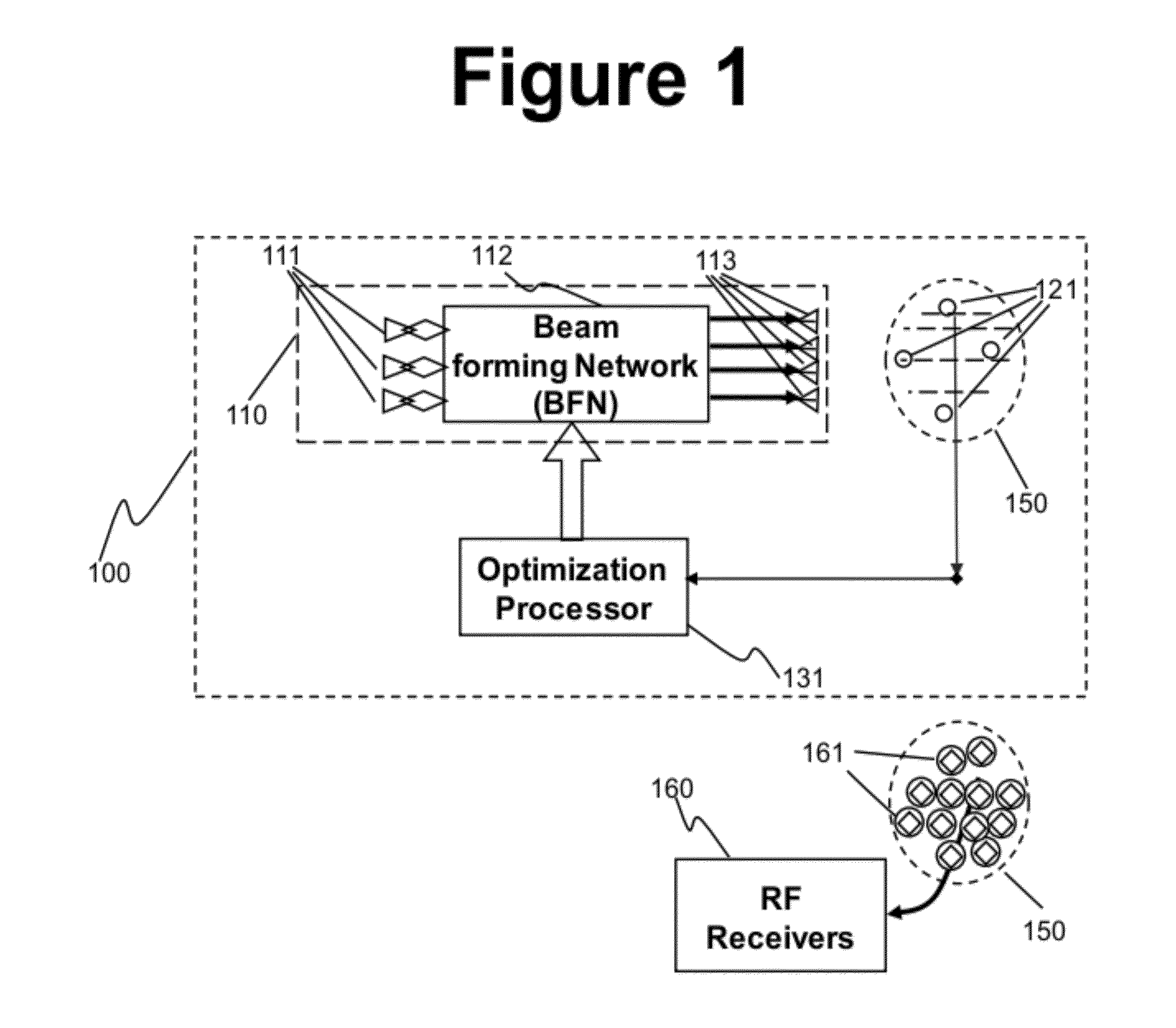
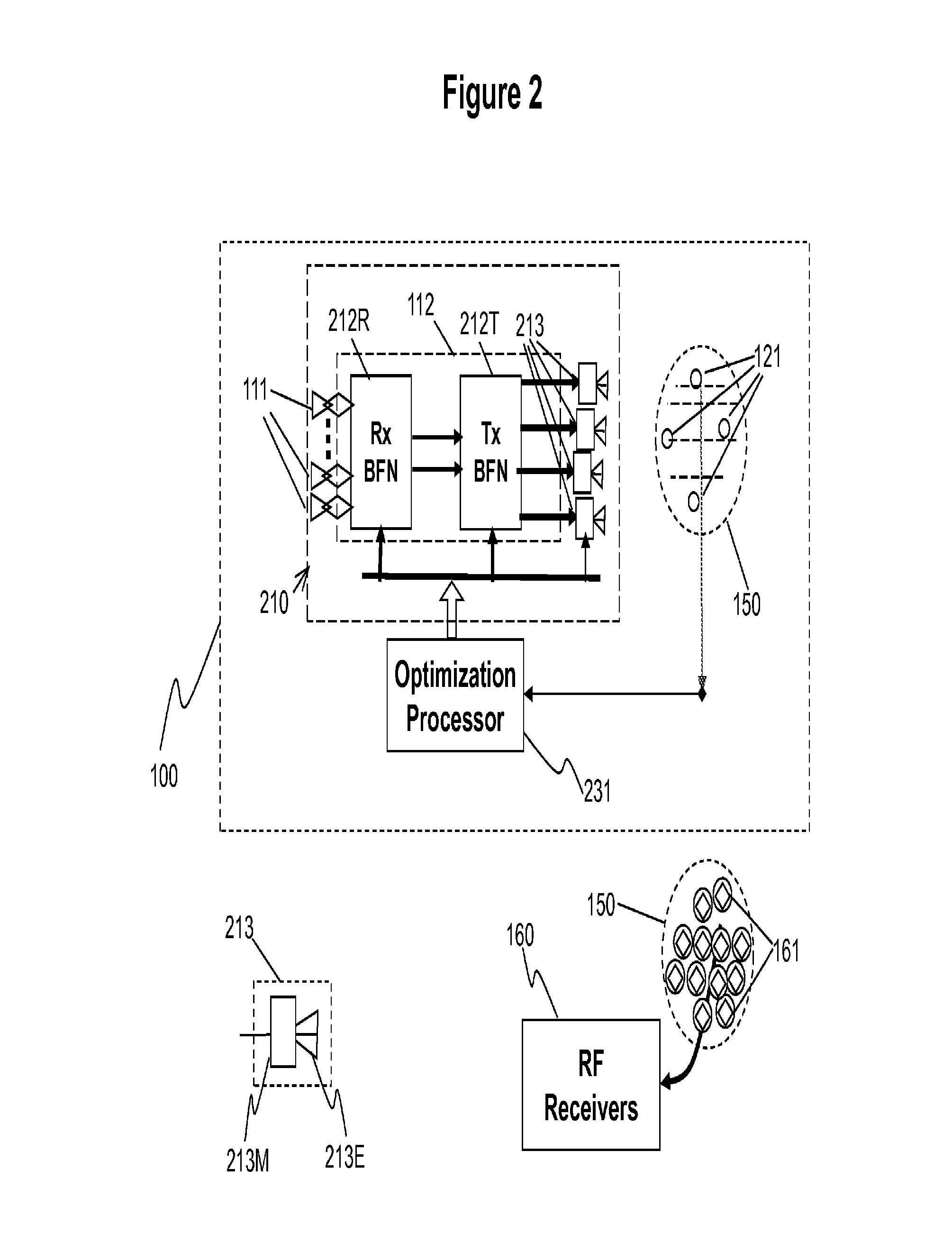
Apparatus and Method of Generating Quiet Zone by Cancellation-Through-Injection Techniques
ActiveUS20120058729A1Reduce and eliminate interferenceMinimize signalingSatellite radio beaconingSound producing devicesMinimization algorithmRadar
A quiet zone generation technique is proposed for interference mitigation for a receive antenna by injecting the very interference signals via iterative processing, generating quiet zones dynamically for receive (RCV) antennas. The receive antenna may feature multiple receiving apertures distributed over a finite area. Optimization loops consist of four cascaded functional blocks; (1) a pick-up array to obtain the interference signals, (2) element weighting and / or repositioning processors, (3) an auxiliary transmit (XMIT) array with optimized element positions, (4) a diagnostic network with strategically located probes, and (5) an optimization processor with cost minimization algorithms.To minimize interferences between transmit (Tx) and receiving (Rx) apertures in limited space of an antenna farm for communications and / or radar applications are very tough problems. Among the tools for solving the problems are many conventional techniques listed in the references [1,2,3]. However, solutions for co-site interference mitigation may not be generic ones but more specific to geometries of antenna farms, Tx apertures and Rx antenna locations, and beam positions of the Tx beams.
Owner:SPATIAL DIGITAL SYST
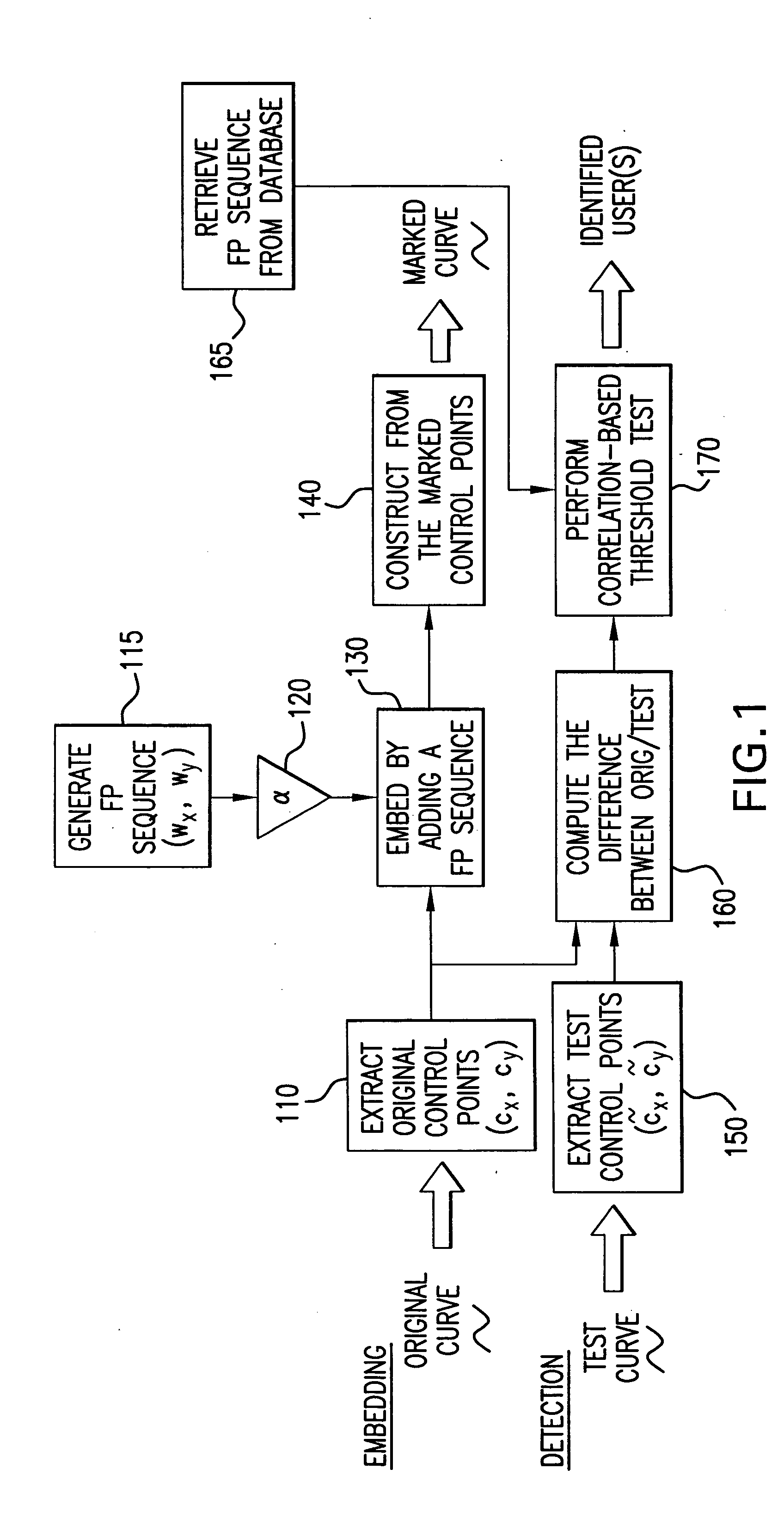
Method for concealing data in curves of an image
InactiveUS7817817B2Convenient registrationImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionImage watermarkingPattern recognitionMinimization algorithm
A method of concealing data in images imperceptibly alters curves therein, such as through adding a value representing the data to be hidden to each of a number of B-spline control points representing the original curve. The altered control points characterize the imperceptibly altered curve, which replaces the original curve in the image. The altered control points may be later extracted from the image and compared with the original control points to determine the hidden value. Prudent selection of the values altering the control points as well as an iterative alignment-minimization algorithm in the detection process provides protection against numerous techniques for preventing the hidden values from being recovered.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
Compressed-sensing-based de-artifact fusion method of high-dynamic-range image
ActiveCN107730479AResolve ArtifactsSolver ambiguityImage enhancementImage analysisDictionary learningComputation complexity
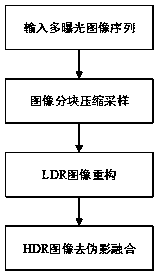
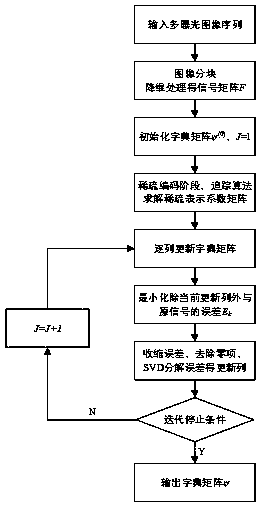
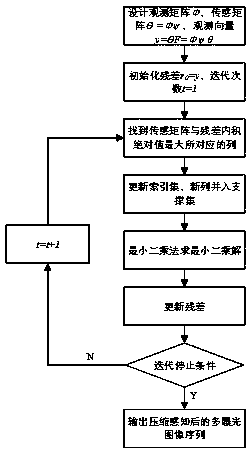
The invention discloses a compressed-sensing-based de-artifact fusion method of a high-dynamic-range image. Compressed sampling is carried out on an inputted multi-exposure image sequence; reconstruction is carried out by using a reconstruction method to obtain multi-exposure image sequence after compressed sensing; and then an image set after compressed sensing is normalized, multi-exposure imagede-artifact fusion based on PatchMatch and a rank minimization algorithm is carried out on the image set to obtain a high-dynamic-range (HDR) image of a target. According to the invention, on the basis of latest research results of K-SVD dictionary learning, compressed sensing and de-artifact fusion, the sampling rate, the storage space and the computational complexity are reduced effectively; and a de-artifact de-blurring HDR image is obtained.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV +2
Design method of classifier for high-precision face recognitio
InactiveCN103268484AEfficient use ofImprove real-time performanceCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionData set
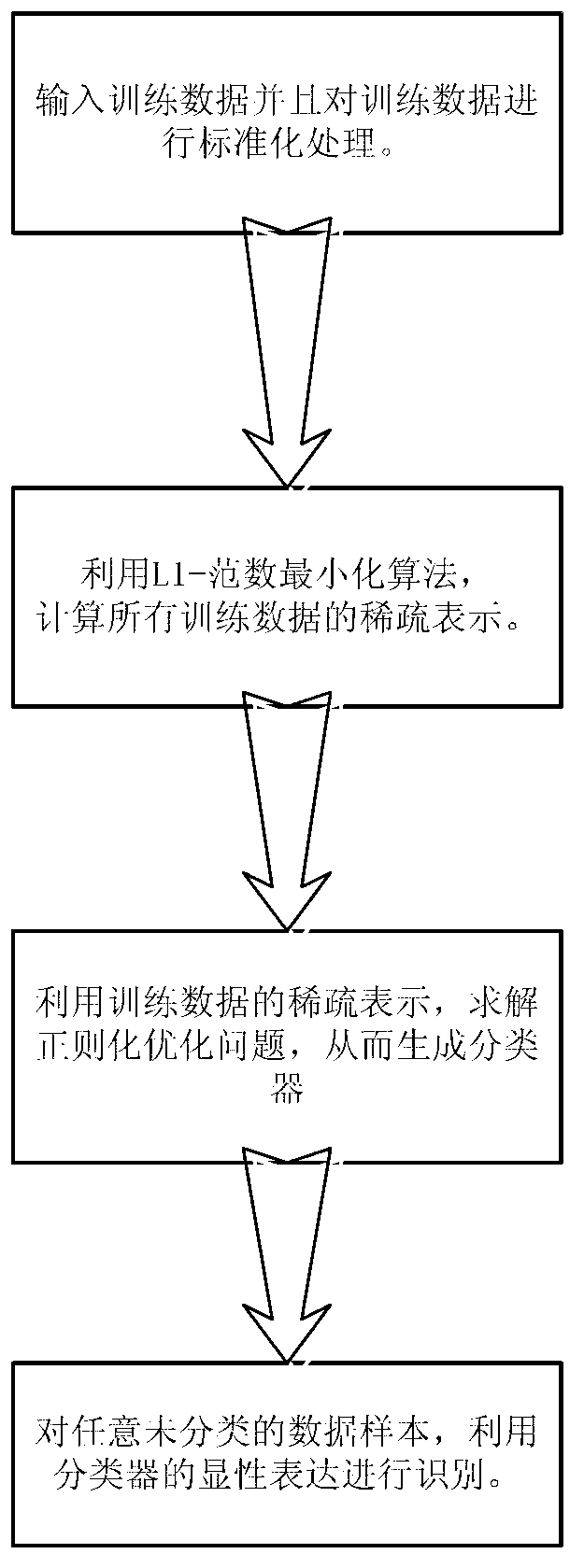
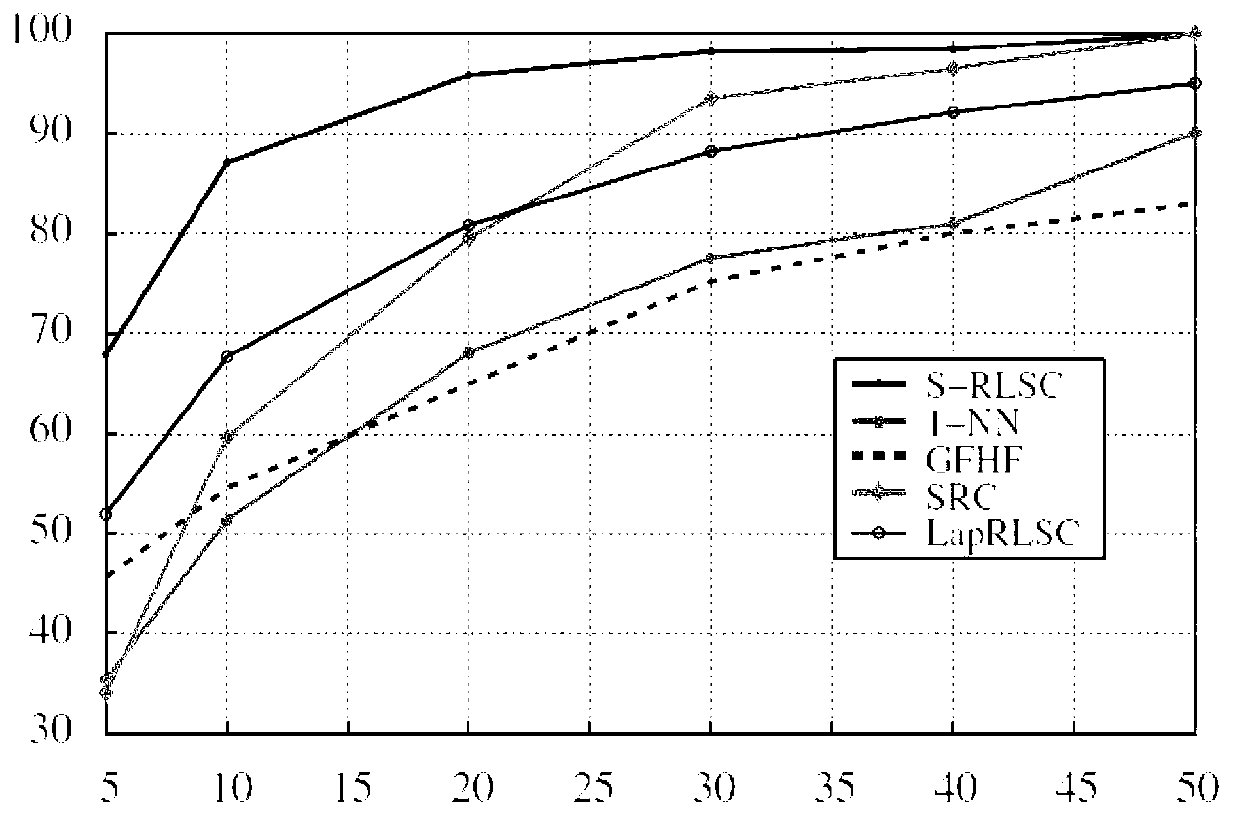
The invention provides a design method of a classifier for high-precision face recognition. The design method comprises the following steps of: (1) inputting a vector type face image data set for standardized processing to obtain a face image sample set, wherein the human face image data set must contain the known classes of face image samples and can contain unknown classes of face image samples; (2) utilizing the L1-minimization algorithm to calculate the sparse representation or sparse coding of each face image sample reconstructed by face image samples except the sample; and (3) utilizing the sparse representation or sparse coding of face image samples and the classification information of the classified face image samples to build the optimal model of the classifier, and solving the regularization optimization problem to obtain a classification function. The design method provided by the invention has an explicit way of expression, so that the real-time performance in face recognition application is obviously improved, and the high-precision face recognition is realized under the condition that an image has a great number of noise pixels.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
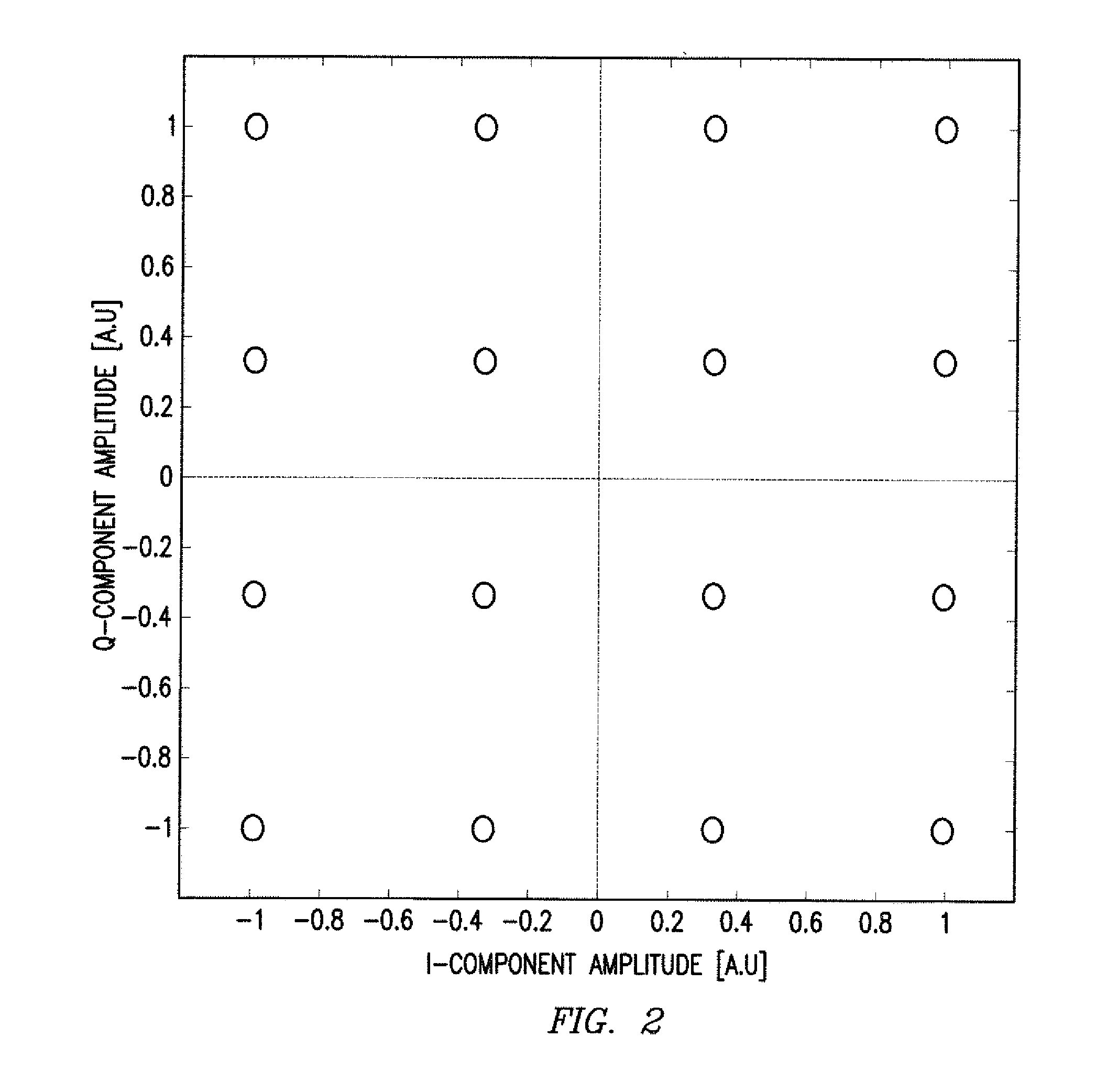
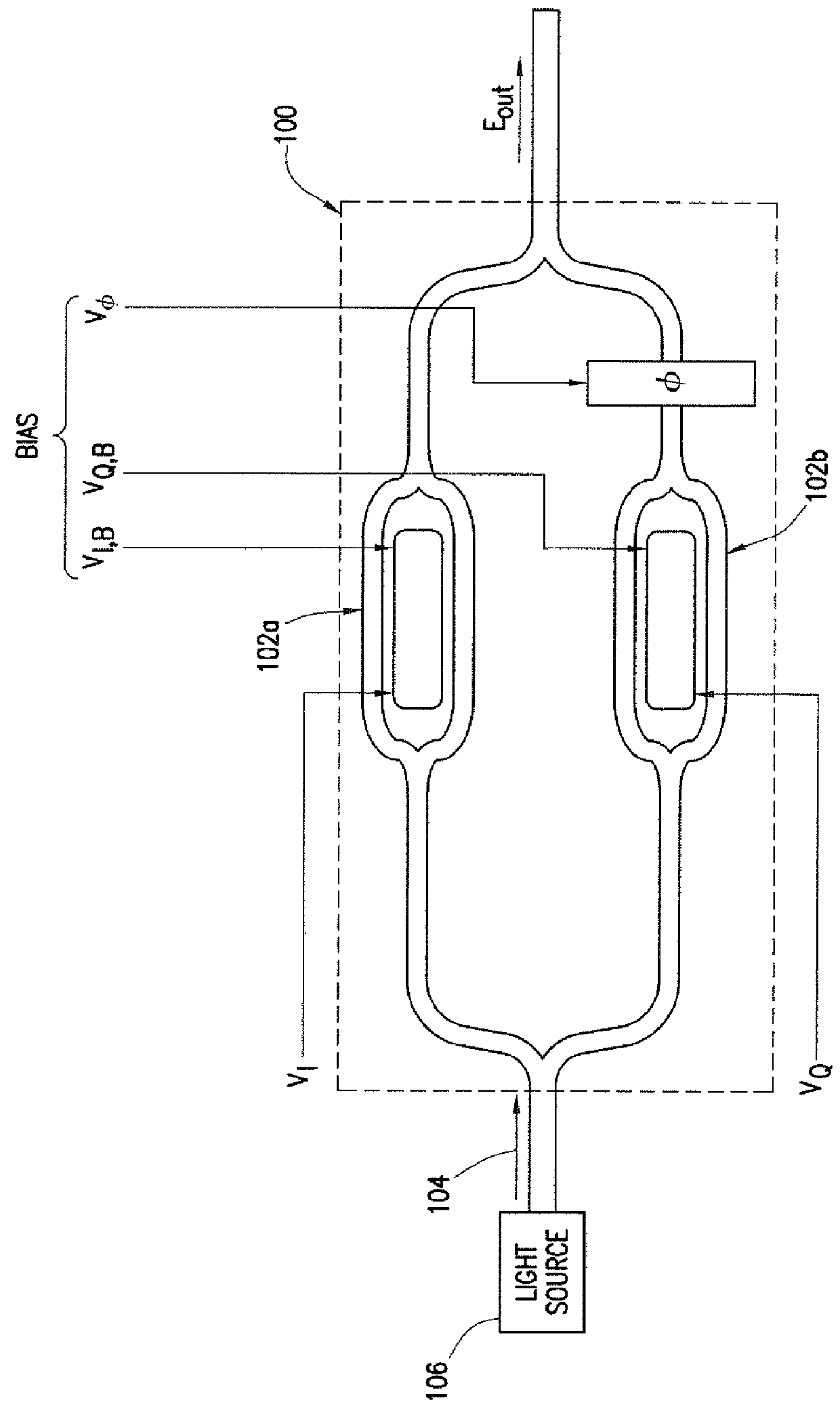
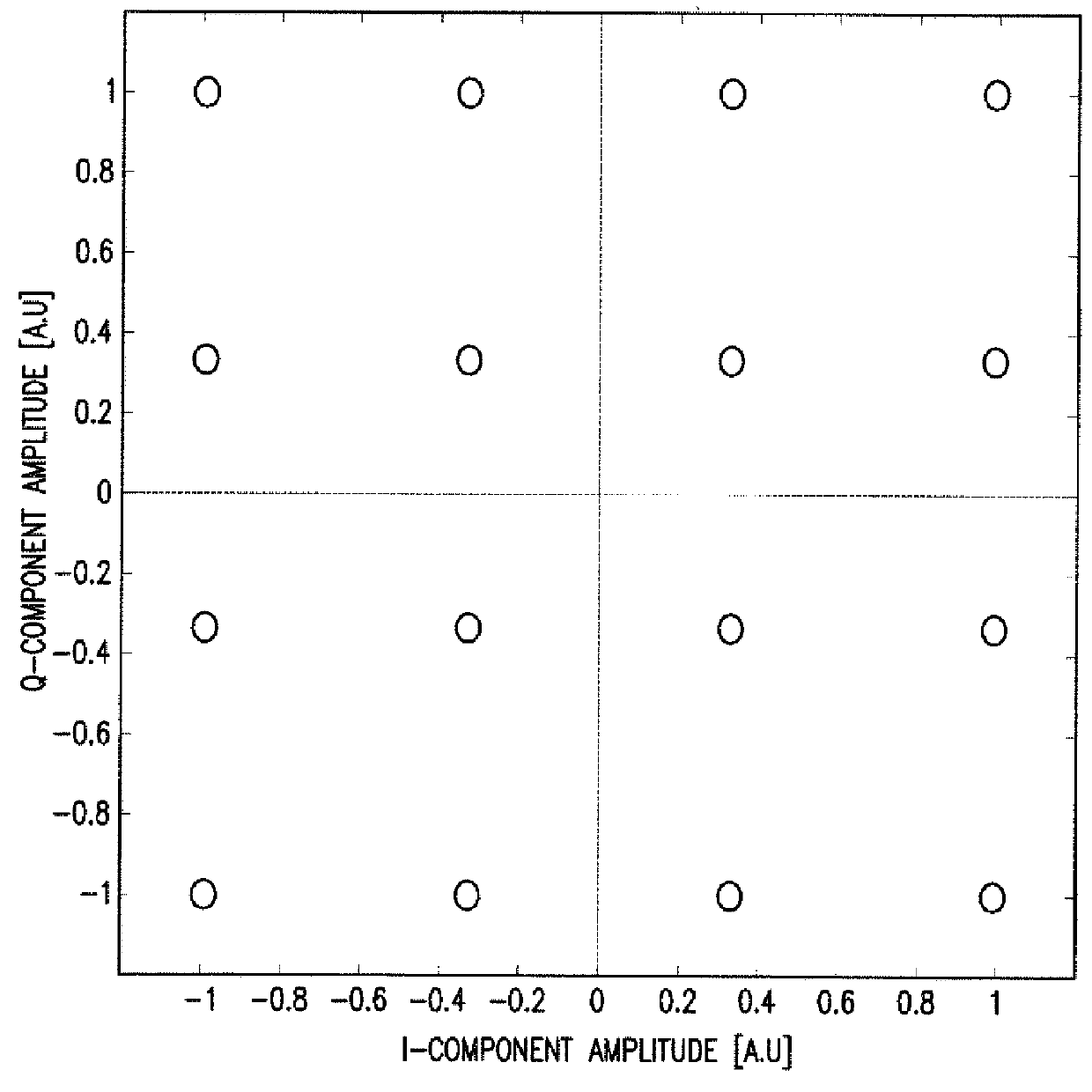
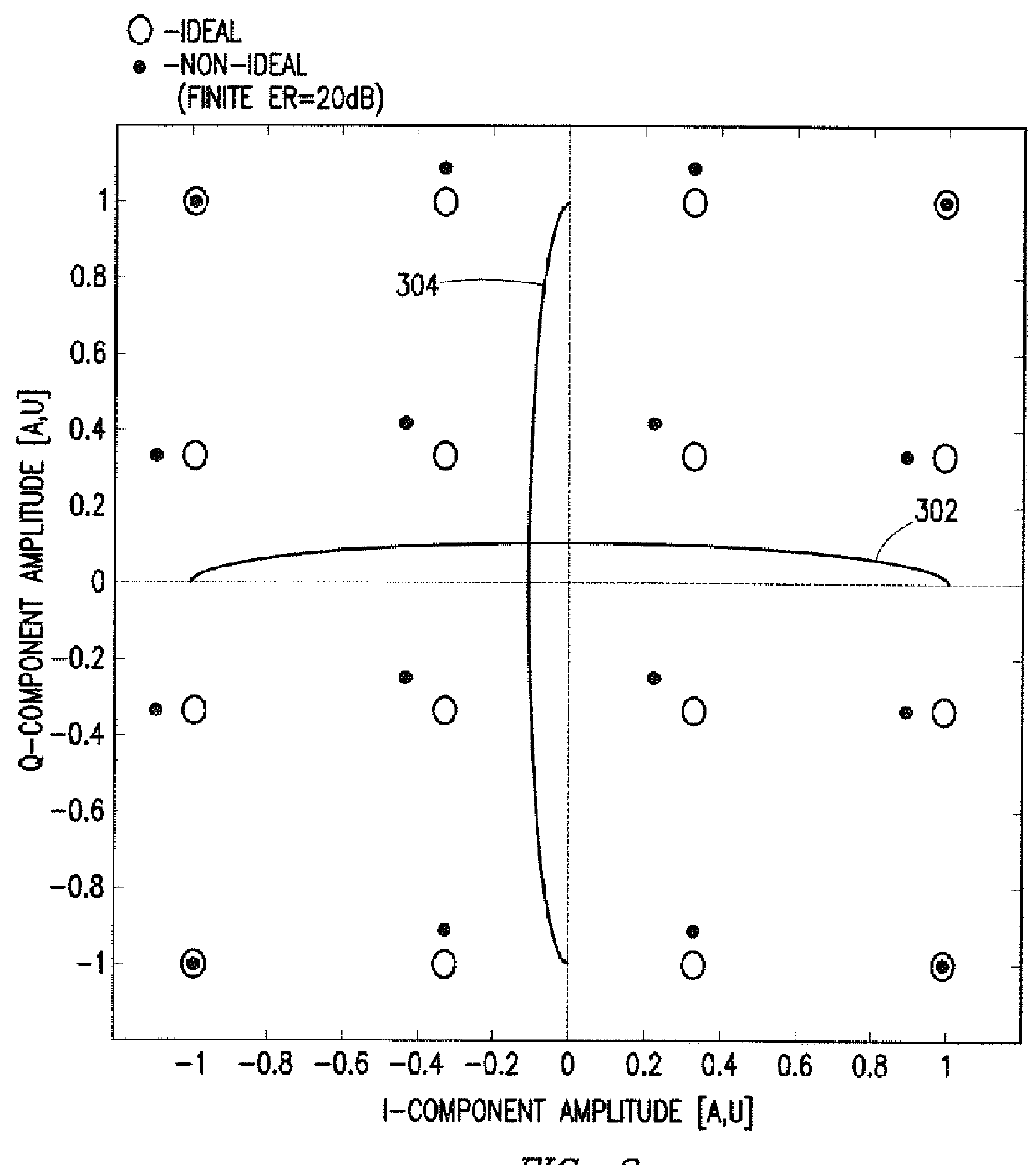
System and Method for Monitoring and Control of an Optical Modulator for an M-QAM Transmitter
ActiveUS20140233965A1Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedProblems be reduced eliminatedElectromagnetic transmittersOptical power meterPhase shifted
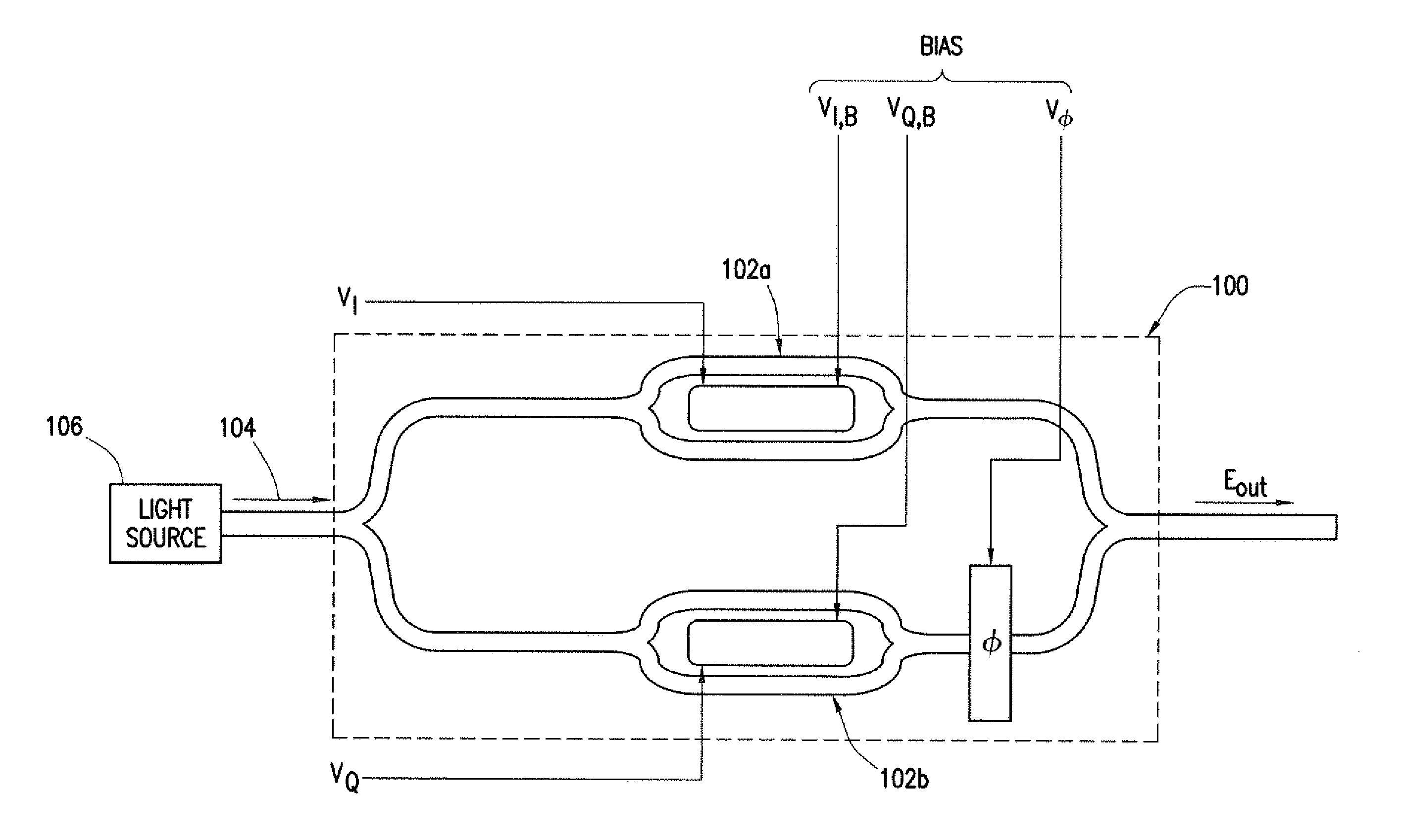
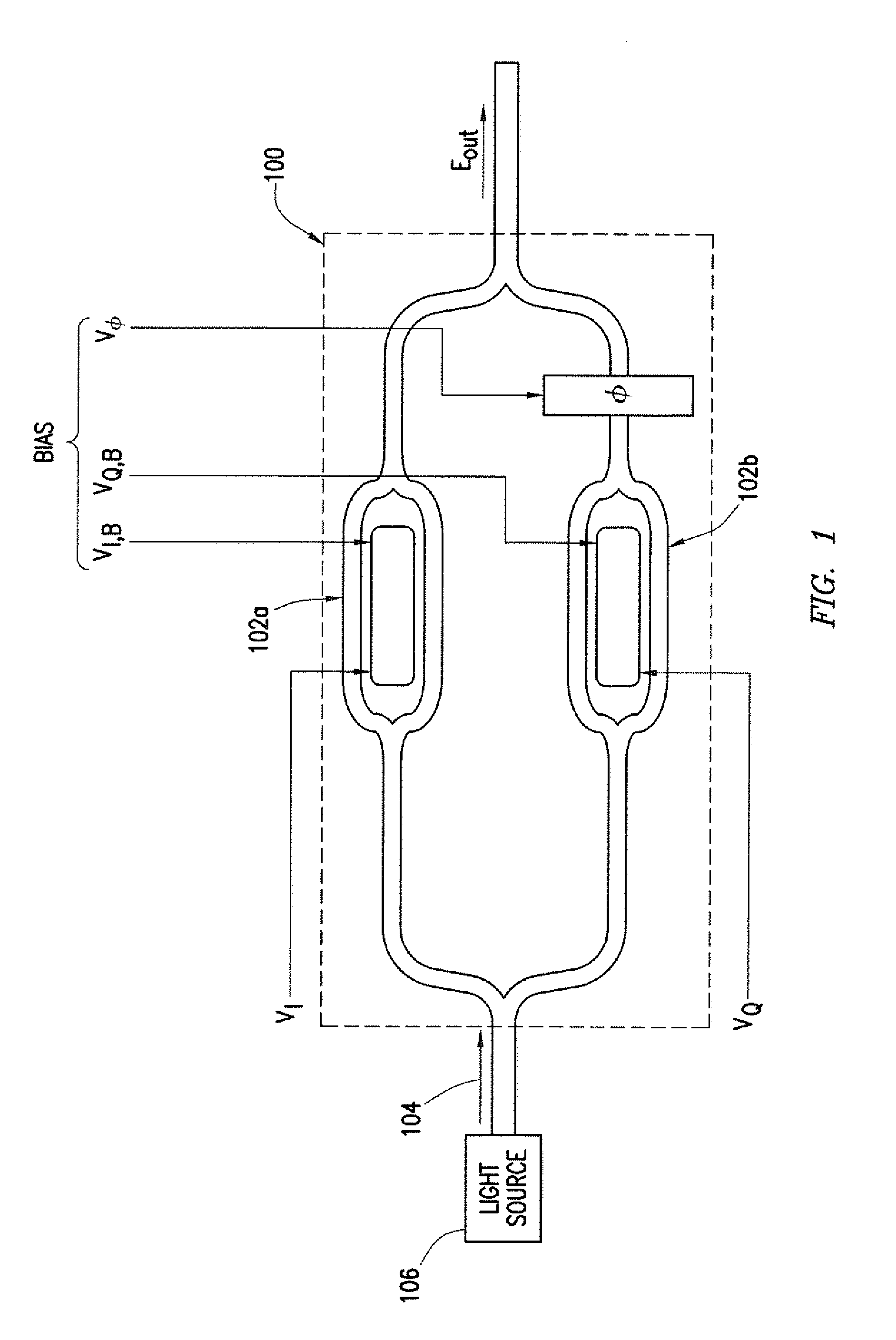
A system includes an optical power meter operable to generate an optical power signal corresponding to the optical power of a received output signal generated by an optical IQ-modulator. The system further includes a processor operable to receive the optical power signal and determine, based on a minimization algorithm and the received optical power signal, a first bias voltage to be applied to a first sub-modulator of the optical IQ-modulator and a second bias voltage to be applied to a second sub-modulator of the optical IQ-modulator. The system may also include a peak power meter operable to generate a peak power signal corresponding to the peak power of the received output signal generated by the optical IQ-modulator, wherein the processor is further operable to determine, based on a minimization algorithm and the received peak power signal, a third bias voltage to be applied to a phase shift component of the optical IQ-modulator.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
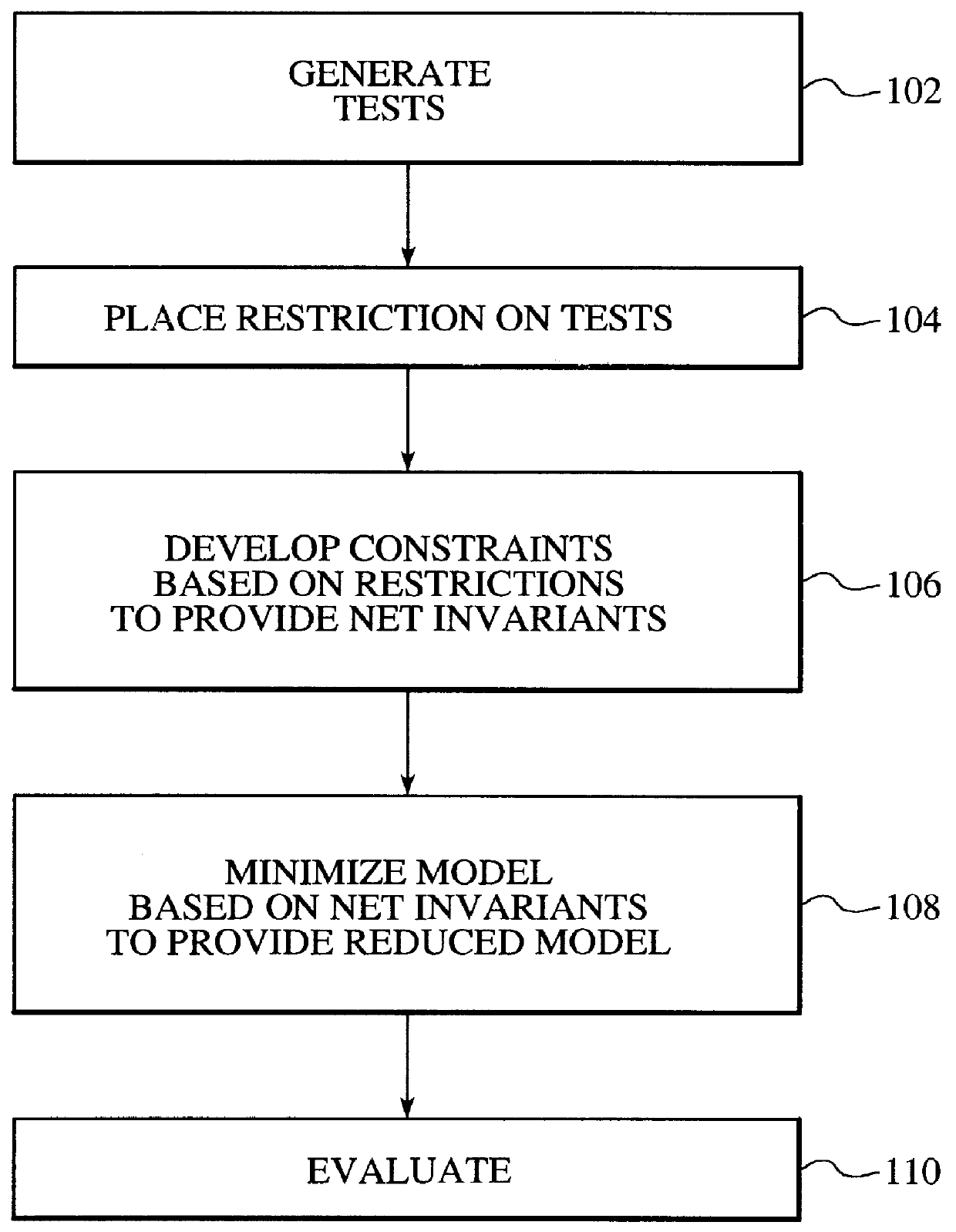
System and method for model size reduction of an integrated circuit utilizing net invariants
InactiveUS6049662AReduce the amount requiredImprove simulation speedDigital circuit testingAnalogue computers for electric apparatusReduced modelMinimization algorithm
The present invention provides a system and method for verifying an integrated circuit model. The model includes a plurality of net variables. The system and method comprises generating a plurality of tests for simulating the integrated circuit, precalculating a reduced model based upon the generated tests, and evaluating the reduced model. In a preferred embodiment, the present invention includes restricting the test that are generated. Then net invariants for the integrated circuit are generated by translating the restricted plurality of tests to a smaller set of possible values for the net variables. Thereafter, a minimization algorithm or procedure is utilized to minimize the logic used in the particular system based upon the latch constraints. This system produces a reduced model which reduces the amount of the integrated circuit that must be simulated thereby increasing the simulation speed thereof. Accordingly, the present invention integrates an event-driven simulation and a cycle simulation in such a manner that the saving can be proportional to the size of the reduction of the model. In many environments this reduction is significant because it allows for a significant reduction in space which has a clear bearing on the verification process.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for quickly measuring precision of reflection face of radiotelescope
InactiveCN103926548ASimple measurement systemReduced measurement timeElectrical measurementsBacksteppingRadiometer
The invention relates to a method for quickly measuring the precision of a reflection face of a radiotelescope. The method can effectively solve the problems that in the large-caliber radiotelescope reflection face precision measurement process, measurement time is long, measurement precision is low, the angle of pitch of measurement is fixed, and external hardware equipment is needed for assistance. According to the method as a special phase retrieval microwave holography method, it is only needed that the amplitude of an antenna aperture field is measured, and the retrieval of the phase of the antenna aperture field is carried out according to a certain method. In the method, any stable astronomical radio source can serve as a signal source, and beam patterns are scanned under the antenna focusing condition or the antenna out-of-focus condition through an astronomic receiving machine and a terminal (power radiometer); an antenna aperture phase model is built according to the Zernike polynomials function, iterative operation is carried out on the residual error of a model value and a measured value through the minimization algorithm, and therefore the optimal solution corresponding to the minimum residual error vector is obtained to obtain a Zernike polynomials coefficient, backstepping is carried out to obtain the hole aperture phase distribution of an antenna, and the precision of the reflection face of the radiotelescope can be obtained.
Owner:XINJIANG ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
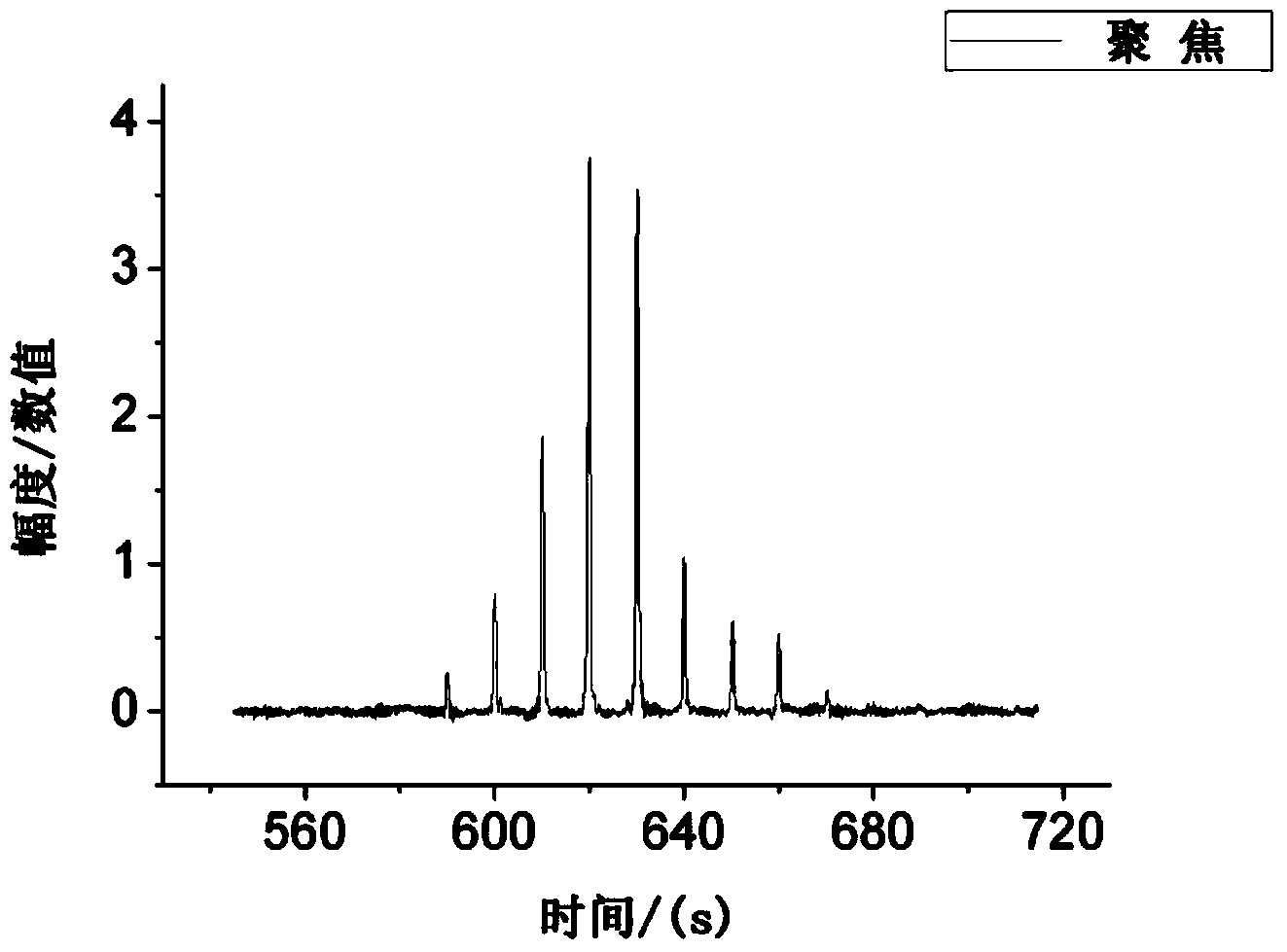
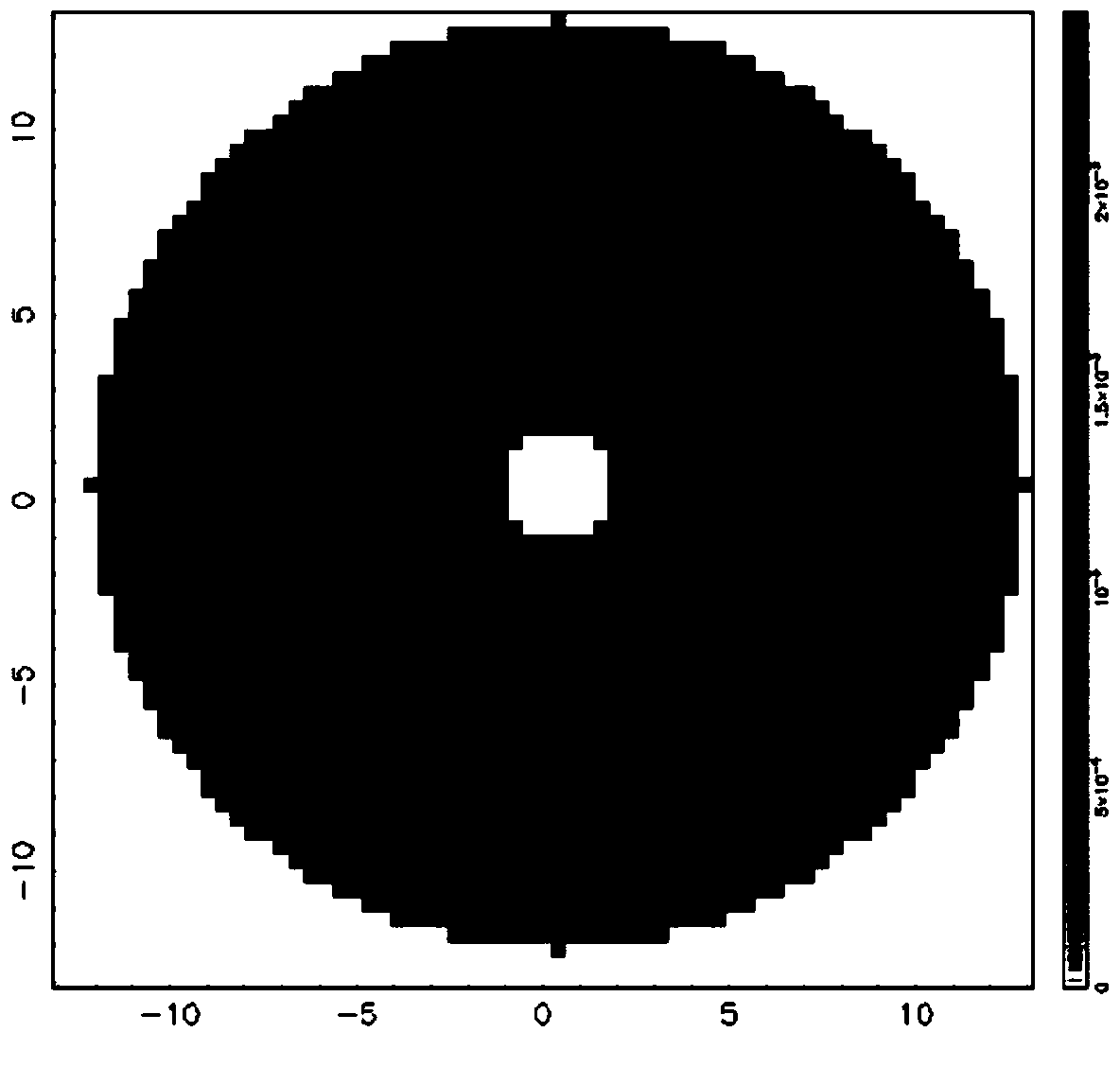
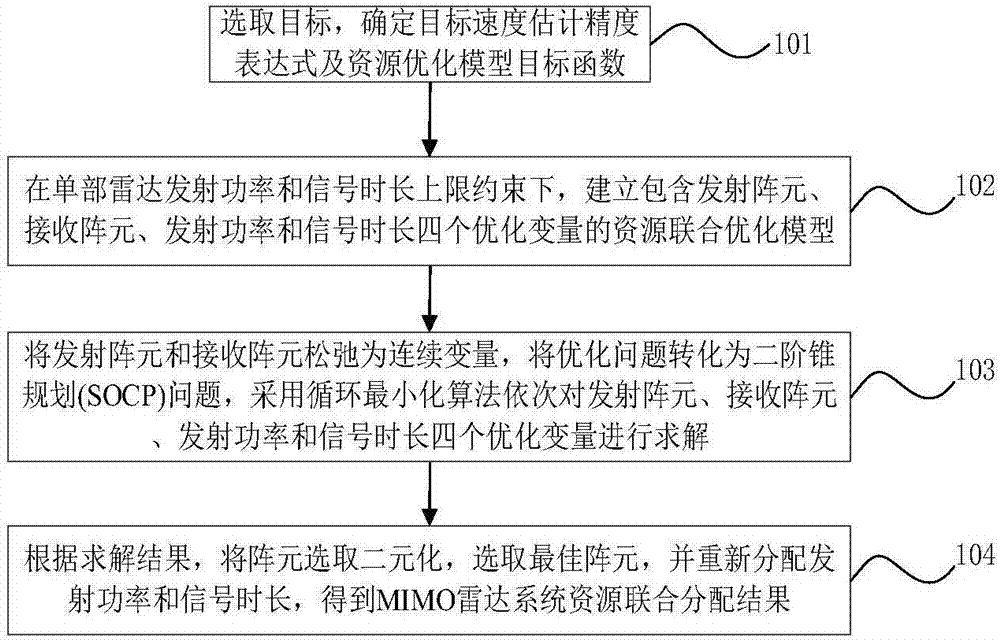
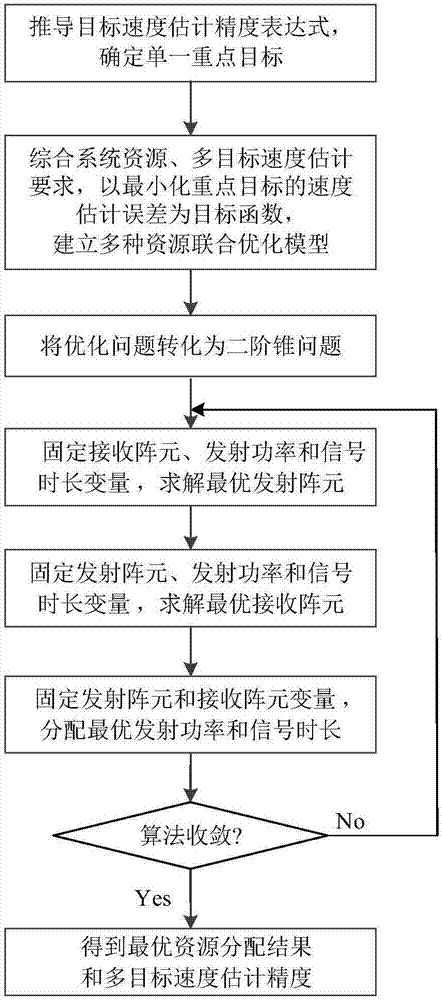
Resource joint optimization method for multi-target velocity estimation of distributed MIMO radar system
ActiveCN107192985ANumber of controlsFlexible control of the numberWave based measurement systemsMinimization algorithmTransmitted power
The invention relates to a resource joint optimization method for the multi-target velocity estimation of a distributed MIMO radar system. The method comprises the following steps that: a target is designated, with minimizing key target velocity estimation error as an objective function, a resource joint optimization model including transmitting array elements, receiving array elements, transmitting power and signal time length is established; an optimization problem is transformed into a second-order cone programming problem, a cyclic minimization algorithm is adopted to solve four optimization variables sequentially; and after the algorithm converges, circulation is terminated, array element selection variables are dualized, an optimal array element is selected, transmitting power and signal time length are re-allocated, so that the result of resource joint allocation is obtained. The method of the invention has high flexibility for the number of tracking targets. With the method adopted, fewest transmitting array elements can be selected under a condition that the requirements of different speed estimation of a plurality of targets are satisfied, key target tracking performance can be improved, and multi-target overall tracking accuracy error is minimum. The method has a high application value.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
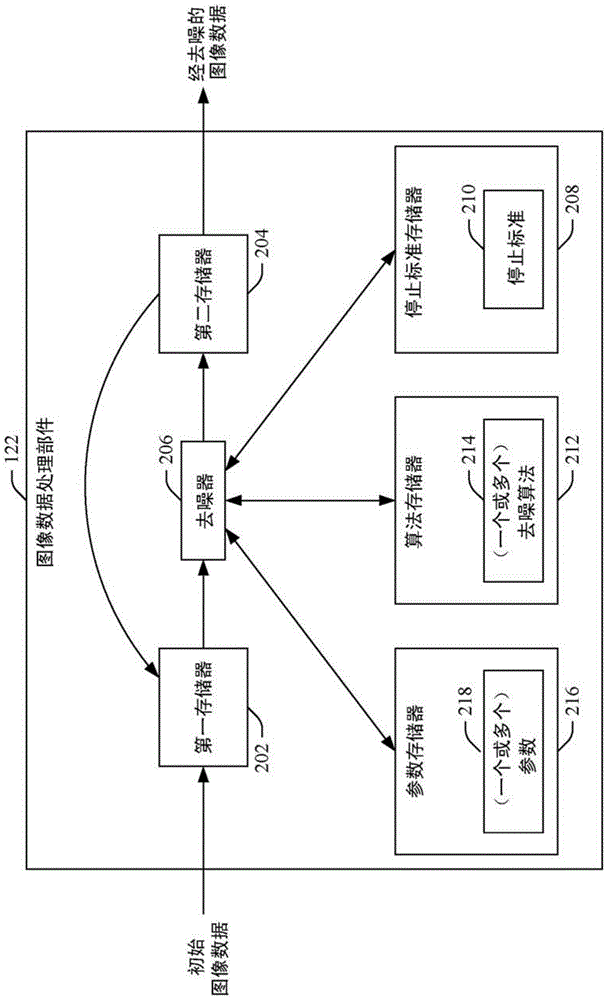
Image domain de-noising
An image data processing component (122) includes algorithm memory (212) including one or more image domain only iterative de-noising algorithms (214) based on the Huber roughness penalty minimization and a processor (206) which de-noises reconstructed image data solely in the image domain based on at least one of the Huber roughness penalty iterative minimization algorithms.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Compression sensing and positioning method
InactiveCN105005024AShorten the timePosition fixationLocation information based serviceL1 minimizationSpace environment
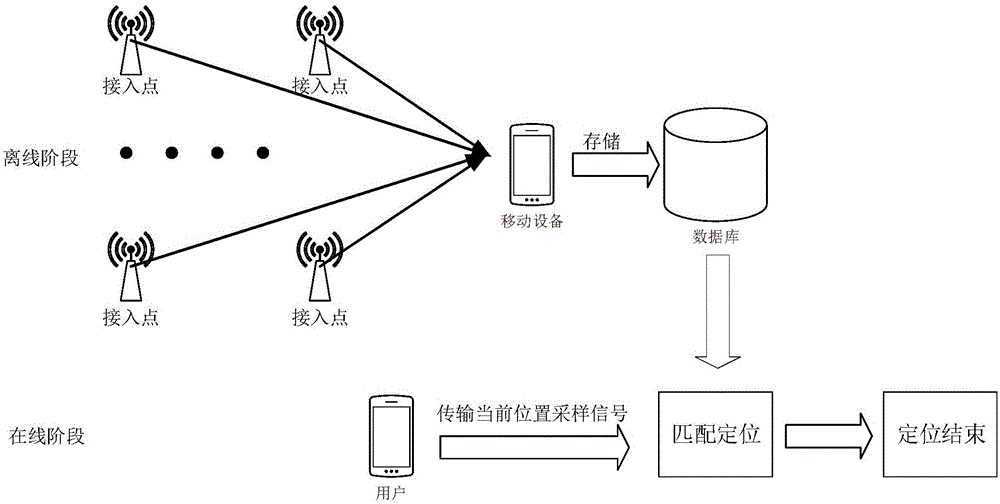
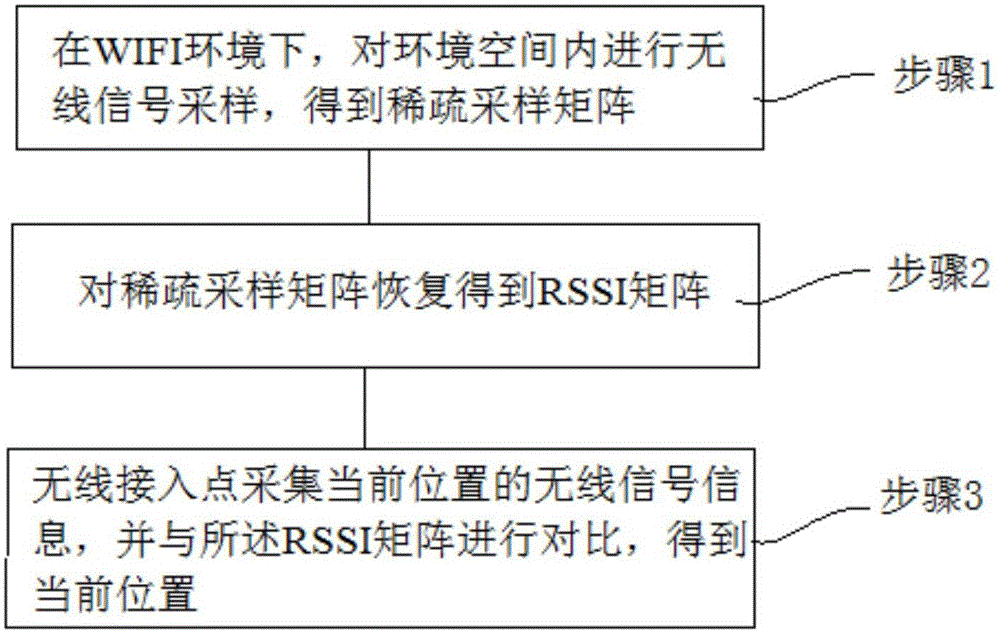
The invention provides a compression sensing and positioning method, which comprises the steps of step 1, sampling wireless signals in the space of a Wifi environment to obtain a sparse sampling matrix; step 2, recovering the sparse sampling matrix to obtain an RSSI matrix; step 3, acquiring the wireless signal information of the current location of a wireless access point, and comparing the wireless signal information with the RSSI matrix to obtain the current location. During the step 1, a sampling model is established and the environment space is sparsely sampled to obtain the sparse sampling matrix. During the step 2, the sparse sampling matrix is recovered based on the minimization algorithm L1 to obtain the RSSI matrix. According to the technical scheme of the invention, a plurality of random reference positions in the space environment are sampled in all directions for multiple times, so that the sparse sampling matrix in the space environment can be obtained. Meanwhile, the RSSI matrix that meets the positioning precision is obtained through recovering the sparse sampling matrix based on the minimization algorithm L1. Therefore, the time period for constructing the RSSI matrix is shortened.
Owner:深圳市西博泰科电子有限公司
Multi-label image annotation result fusion method based on rank minimization
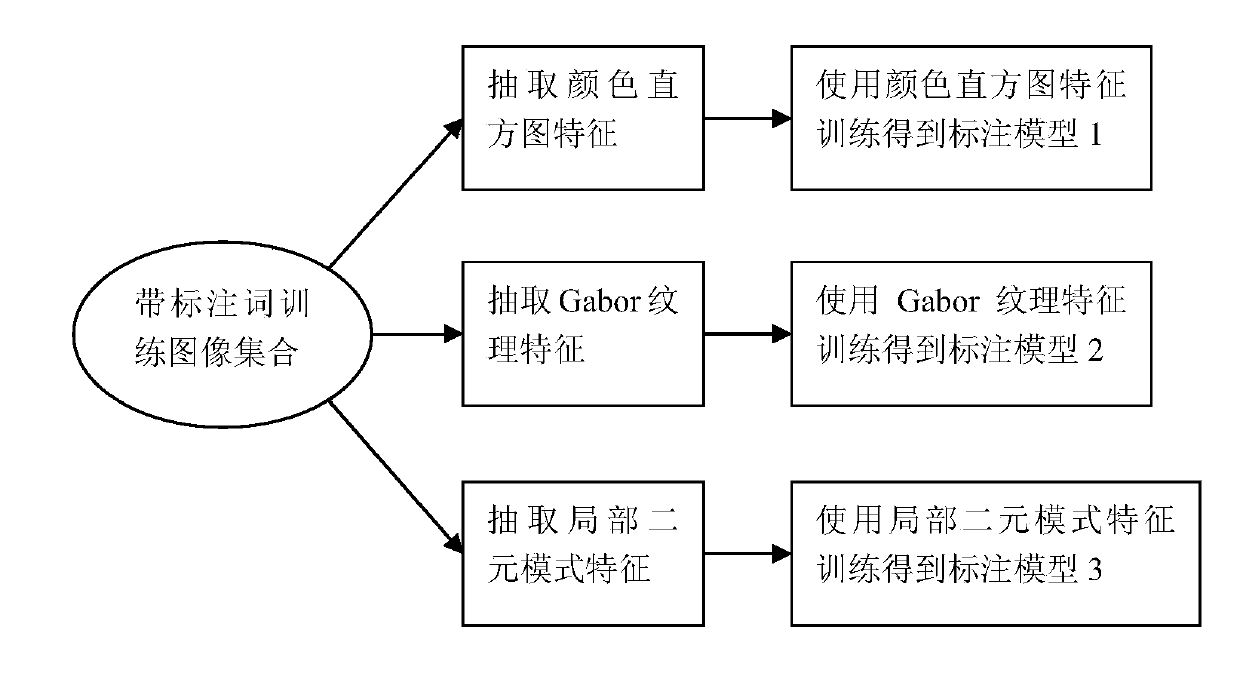
InactiveCN103440651AAvoid the problem of output normalizationAccurately mark the resultsImage analysisSpecial data processing applicationsMinimization algorithmSupervised learning
The invention relates to a multi-label image annotation result fusion method based on a rank minimization optimization algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: (1), extracting various feature representations of a training set image, wherein the training set image has a semantic annotation word which is given in advance; (2) in the various feature representations, training each supervised learning image annotation model; (3) for a new image without a semantic annotation word, using the same method for extracting various features of the image, and using the features for being respectively input to the corresponding supervised learning image annotation models to predict multi-label results; (4) utilizing the rank minimization algorithm for fusing the multi-label results output by the various models to obtain a more accurate annotation result. According to the multi-label image annotation result fusion method based on the rank minimization, the complementarity of the image annotation models under the various feature representations is fully utilized, the rank minimization algorithm is utilized for reducing the number of prediction mistakes in the fused annotation result, and therefore the final image annotation result is more accurate.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
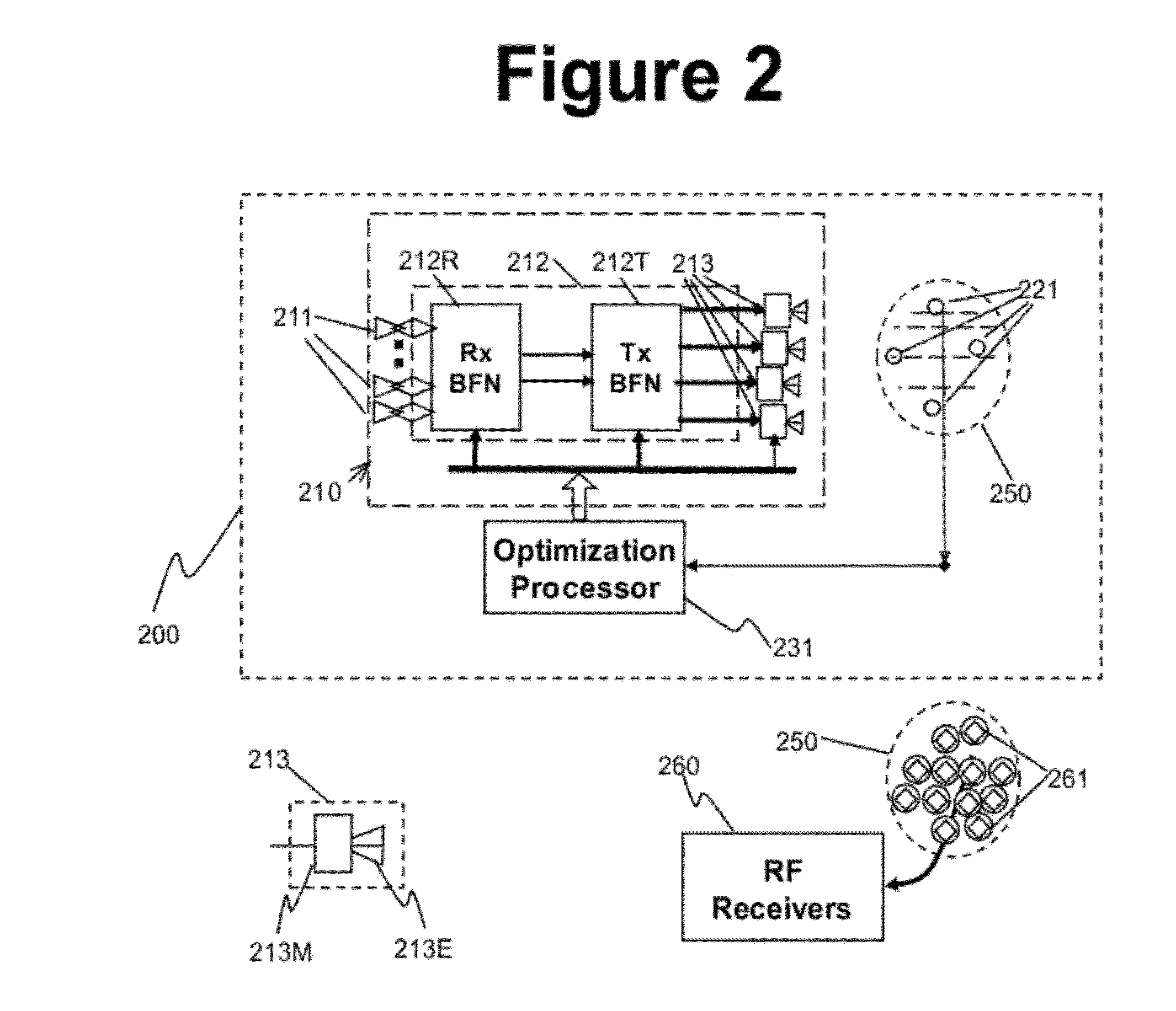
Apparatus and method of generating quiet zone by cancellation-through-injection techniques
ActiveUS9502022B2Reduce and eliminate interferenceMinimize signalingSatellite radio beaconingCommunication jammingMinimization algorithmRadar
A quiet zone generation technique is proposed for interference mitigation for a receive antenna by injecting the very interference signals via iterative processing, generating quiet zones dynamically for receive (RCV) antennas. The receive antenna may feature multiple receiving apertures distributed over a finite area. Optimization loops consist of four cascaded functional blocks; (1) a pick-up array to obtain the interference signals, (2) element weighting and / or repositioning processors, (3) an auxiliary transmit (XMIT) array with optimized element positions, (4) a diagnostic network with strategically located probes, and (5) an optimization processor with cost minimization algorithms. To minimize interferences between transmit (Tx) and receiving (Rx) apertures in limited space of an antenna farm for communications and / or radar applications are very tough problems. However, solutions for co-site interference mitigation may not be generic ones but more specific to geometries of antenna farms, Tx apertures and Rx antenna locations, and beam positions of the Tx beams.
Owner:SPATIAL DIGITAL SYST
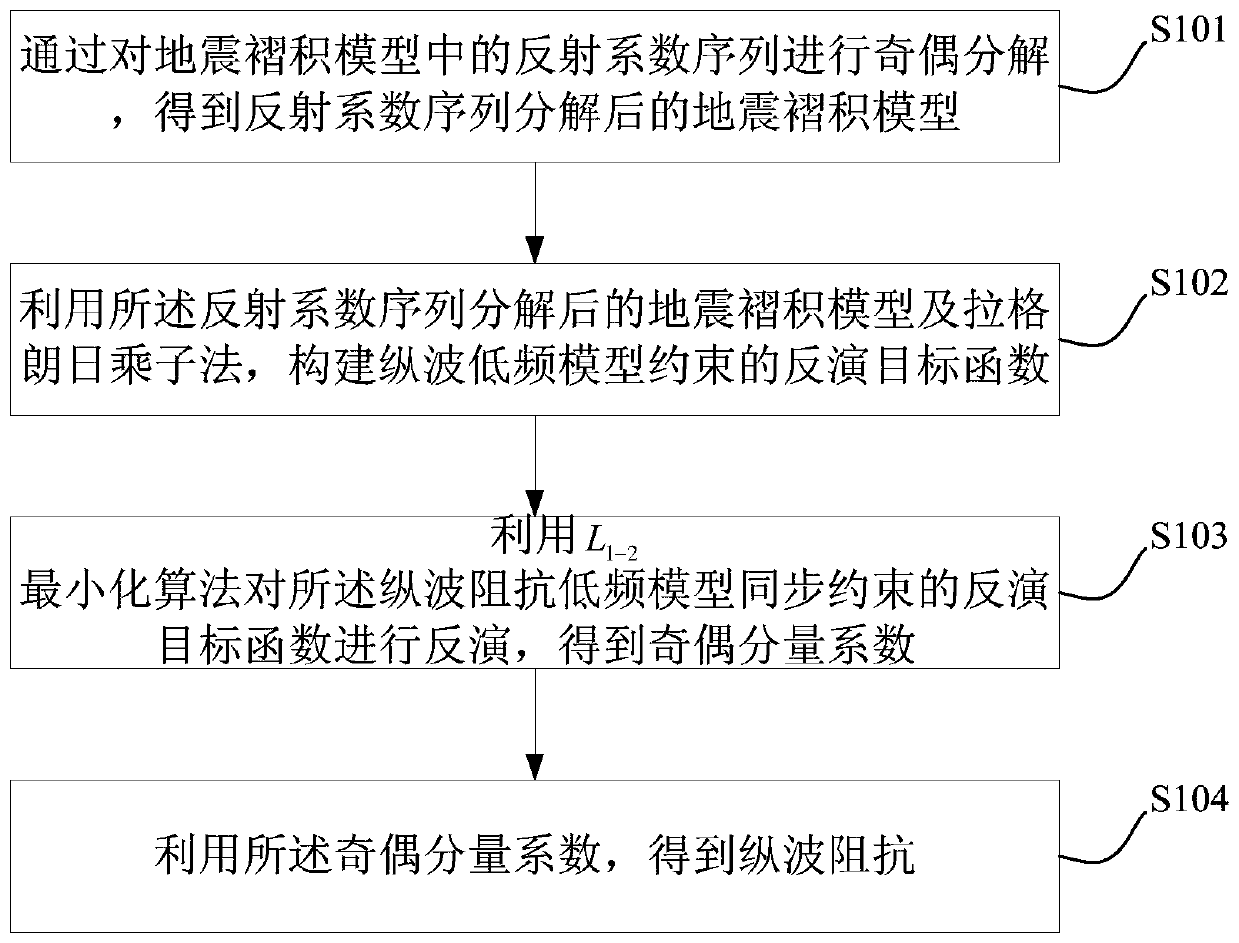
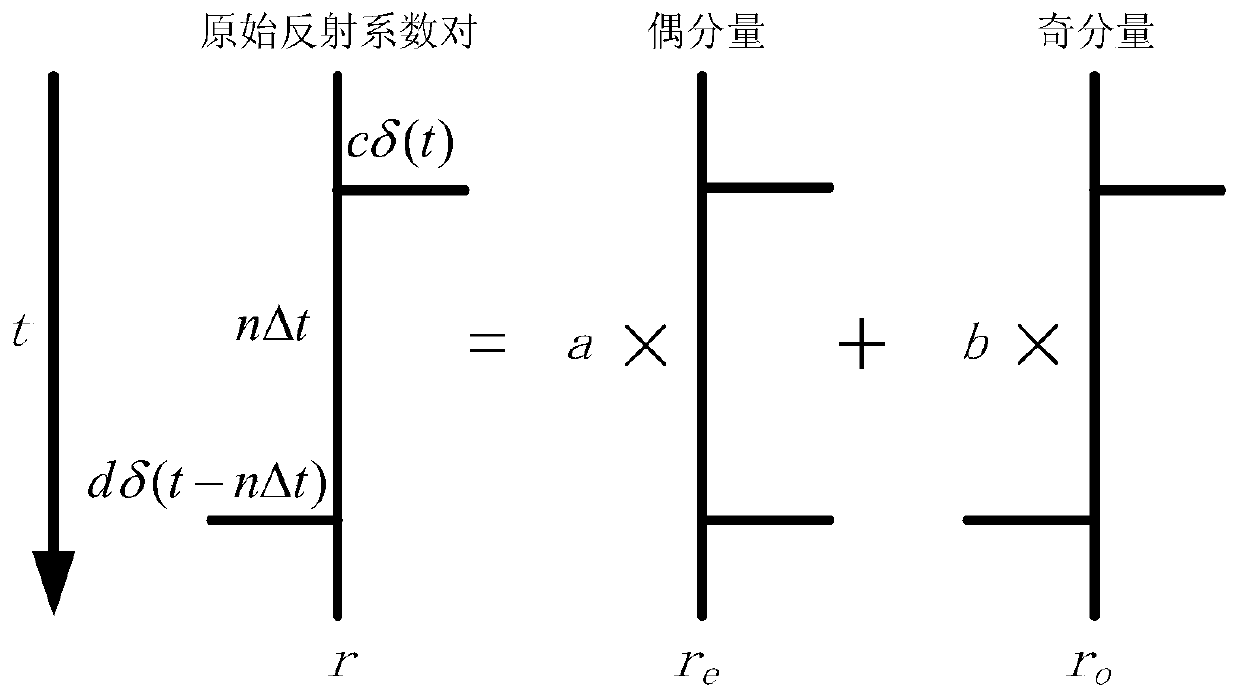
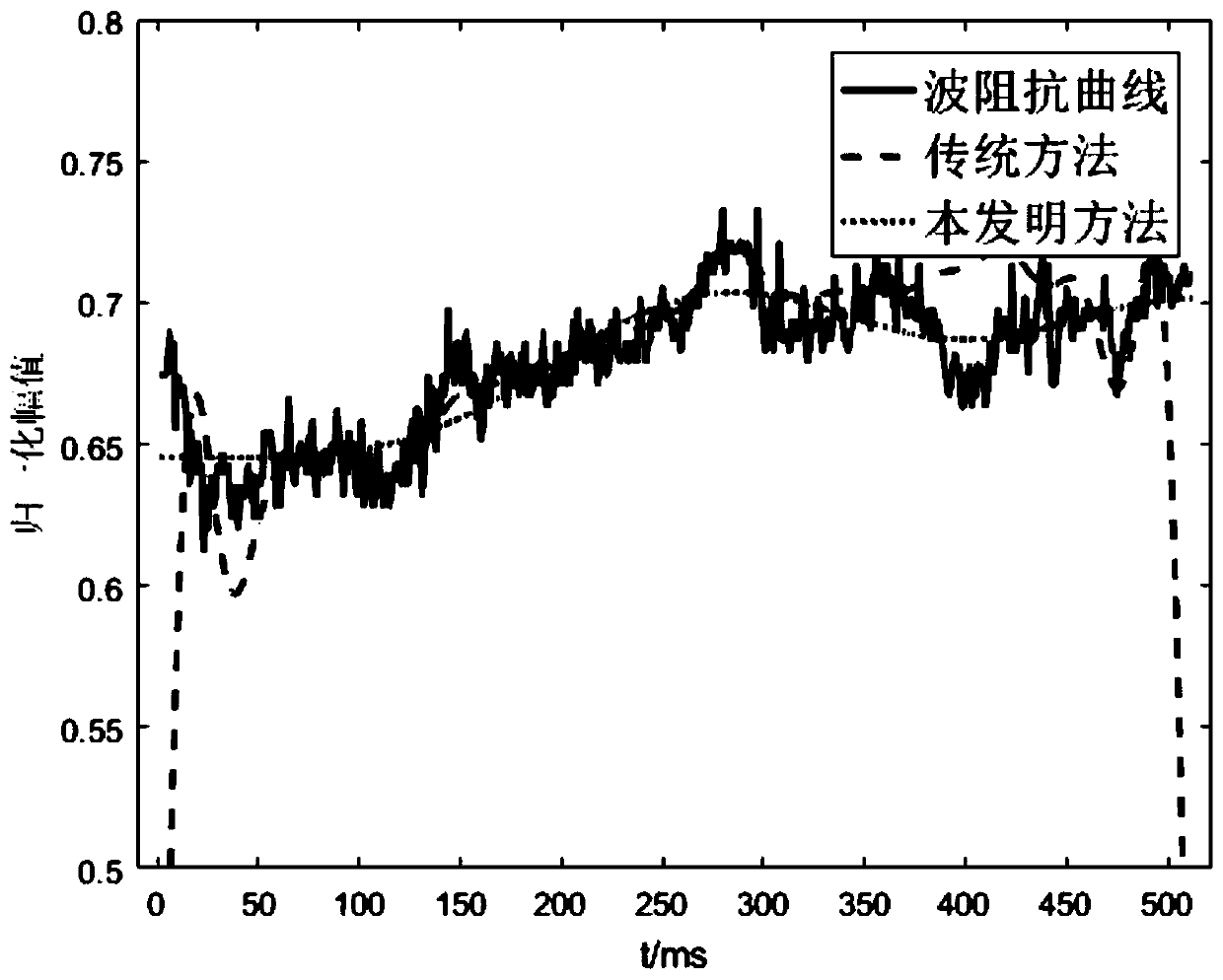
Rapid and high-precision post-stack seismic impedance inversion method
ActiveCN110542923AIncrease vertical resolutionGood horizontal continuitySeismic signal processingMinimization algorithmLongitudinal wave
The invention discloses a rapid and high-precision post-stack seismic impedance inversion method. The method comprises the steps of performing odd-even decomposition on a reflection coefficient sequence in a seismic convolution model to obtain a reflection coefficient sequence decomposed seismic convolution model; constructing an inversion objective function constrained by a longitudinal wave low-frequency model by use of the reflection coefficient sequence decomposed seismic convolution model and a Lagrangian multiplier method; performing inversion on the inversion objective function synchronously constrained by a longitudinal wave impedance low-frequency model by use of an L1-2 minimization algorithm to obtain odd-even component coefficients; and obtaining the longitudinal wave impedanceby use of the odd-even component coefficients.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY +1
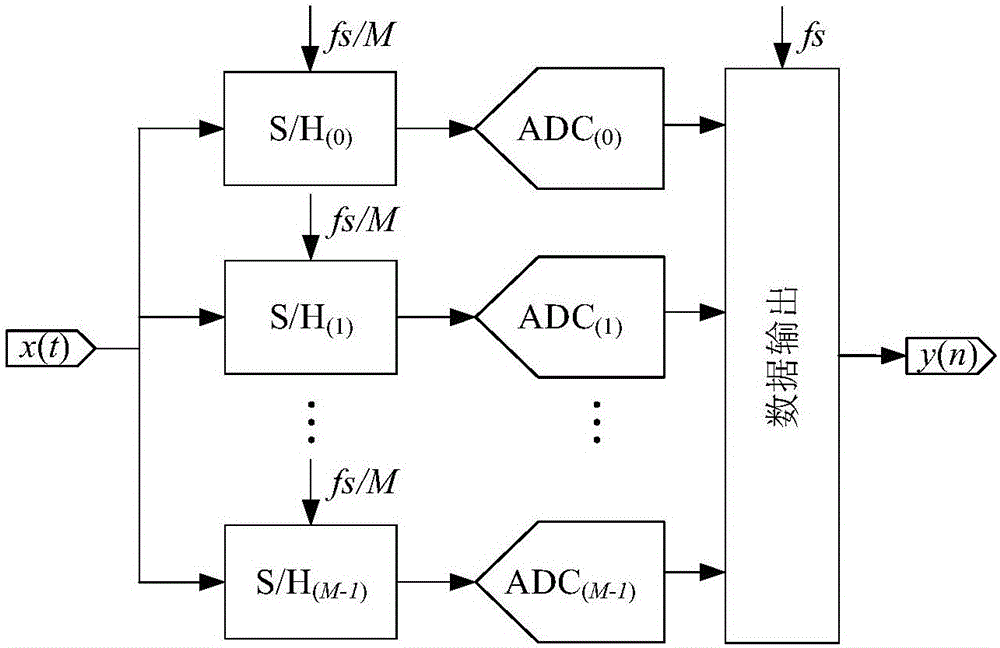
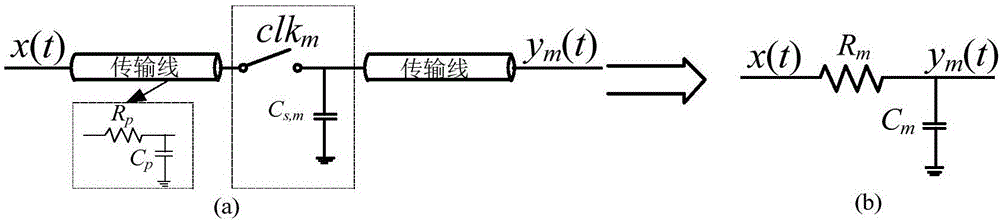
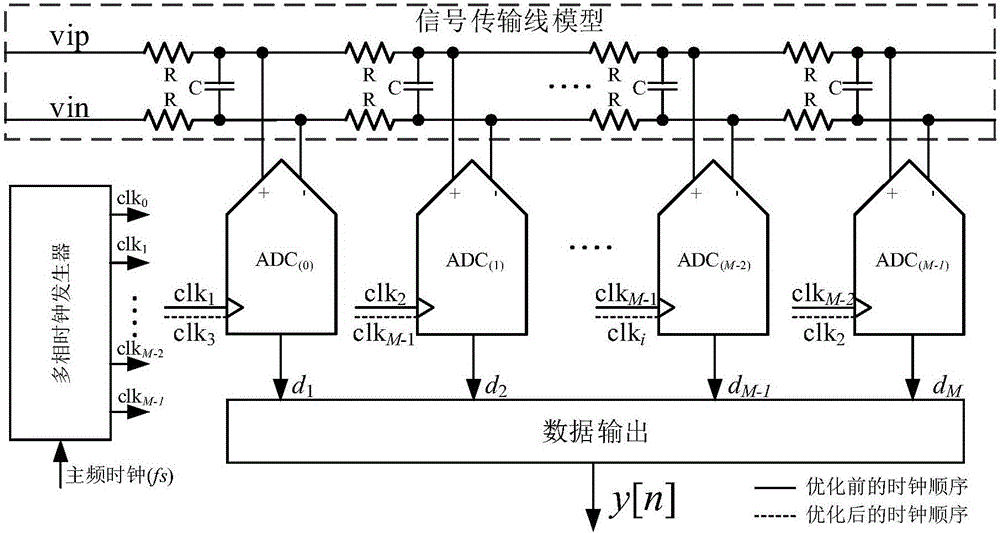
Bandwidth mismatching optimization method for multi-channel time-interleaved analog-to-digital converter
ActiveCN106571823AOptimizing Dynamic Linear PerformanceNo additional overheadAnalogue/digital conversion calibration/testingMinimization algorithmDigital down converter
The invention, which belongs to the technical field of microelectronics, provides a bandwidth mismatching optimization method for a multi-channel time-interleaved analog-to-digital converter. The method comprises: bandwidth parameters of signal transmission paths of all sub channels are extracted, calculation is carried out to obtain bandwidth mismatching values of all channels relative to a reference channel, a vector is formed and is used as an initial bandwidth mismatching vector, the vector is introduced into an objective function, and calculation is carried out to obtain an objective function initial solution; and elements in the bandwidth mismatching vector change randomly to generate a new bandwidth mismatching vector, the new bandwidth mismatching vector is introduced into an objective function, calculation is carried out to obtain a solution of the objective function, a minimum solution of the objective function is updated by using an energy state minimization algorithm until the updating frequency of the minimum solution of the objective function in the energy state minimization algorithm reaches a preset number of times, and then the minimum solution of the objective function is outputted. Therefore, optimization of a dynamic linear performance SFDR of the multi-channel time-interleaved analog-to-digital converter can be realized; no influence on other performances of the device is caused; and no circuit cost increase.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
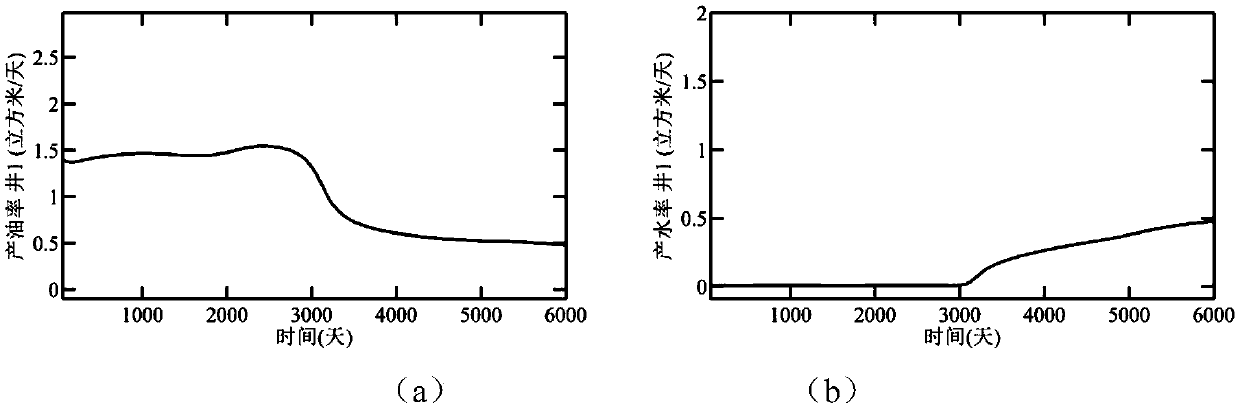
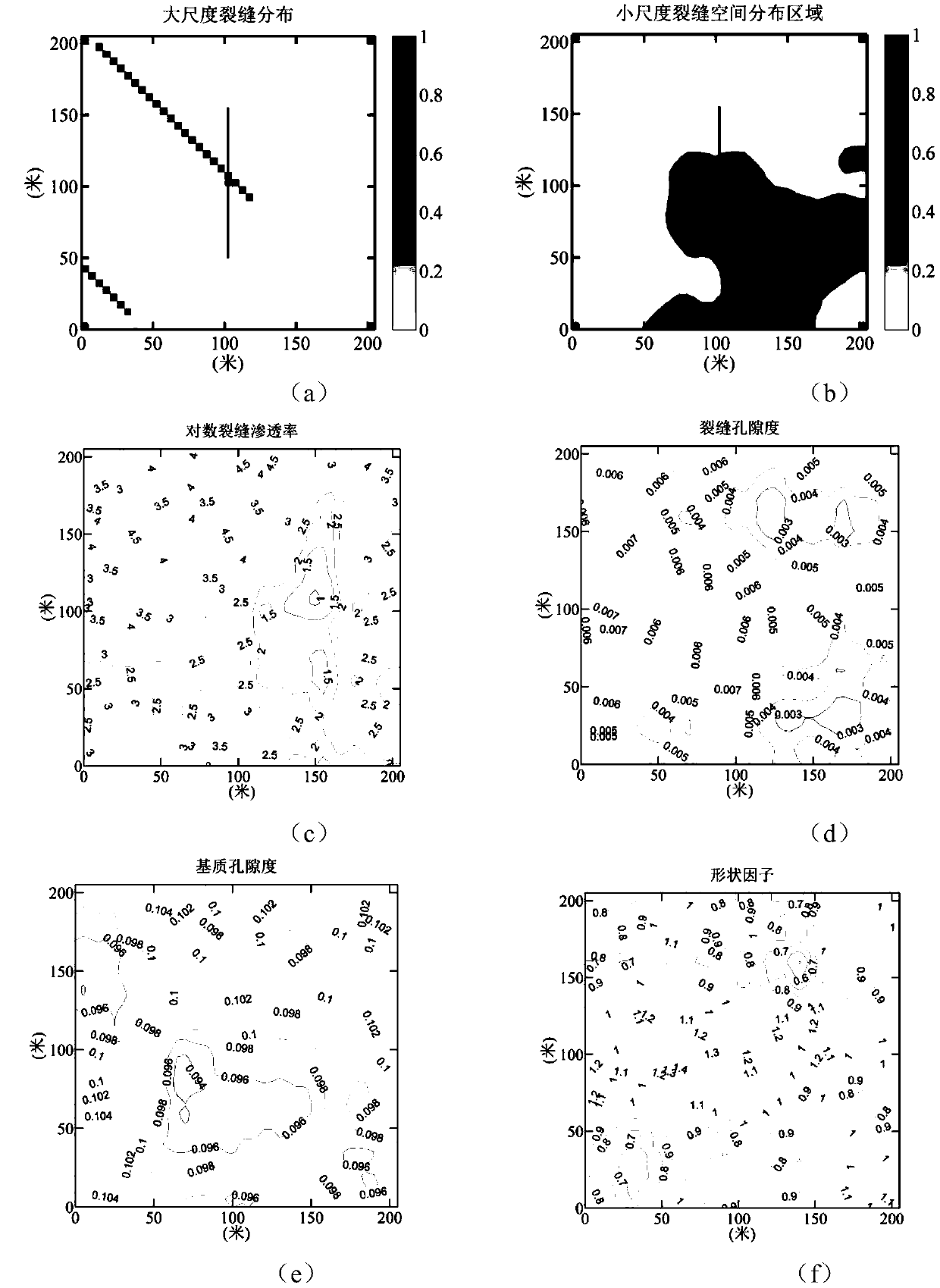
An automatic historical fitting method for a multi-scale fractured medium of a tight oil and gas reservoir
PendingCN109558631AImprove forecast accuracyImprove utilization efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMinimization algorithmTight oil
The invention discloses an automatic historical fitting method for a multi-scale fractured medium of a tight oil and gas reservoir. According to the method, differentiated processing is carried out oncracks of different scales, the multi-scale cracks are characterized by combining an explicit large-scale crack description method and an approximate small-scale crack region description method, namely parameterization is achieved, and an iteration minimization algorithm is adopted on the basis of a proposed parameterization method to form an automatic historical fitting method. According to themethod, the utilization efficiency of the dynamic production data of the tight oil and gas reservoir production well can be improved, the prediction precision of future production of the tight oil andgas reservoir production well is improved, and a foundation can be laid for optimization of a development strategy of the tight oil and gas reservoir.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Low Rank based dynamic PET image reestablishment method
The invention discloses a Low Rank based dynamic PET image reestablishment method. The Low Rank based dynamic PET image reestablishment method reestablishes a PET image by establishing a mathematical model of the reestablishment problem and converting an equivalence problem model based on a Low Rank method. When the Low Rank model is utilized to perform PET image reestablishment, the equivalence problem model adopts an alternating minimization algorithm in the solving process. Therefore, the Low Rank based dynamic PET image reestablishment method effectively utilizes the Low Rank method and solves the problems including low resolution and noise interference of results produced in the dynamic PET image reestablishment process of a computer. Compared with experiments of existing reestablishment methods, the Low Rank based dynamic PET image reestablishment method can obtain good reestablishment effect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
System and method for monitoring and control of an optical modulator for an M-QAM transmitter
ActiveUS9344194B2Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedProblems be reduced eliminatedElectromagnetic transmittersOptical power meterPhase shifted
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Weighted nuclear norm minimization algorithm based on enhanced block matching precision, desert earthquake low-and-intermediate-frequency noise suppression method and application
PendingCN110780349AVerify feasibility and effectivenessSeismic signal processingMinimization algorithmAlgorithm
The invention discloses a weighted nuclear norm minimization algorithm based on enhanced block matching precision. The invention discloses a desert earthquake low-and-intermediate-frequency noise suppression method based on a weighted nuclear norm minimization algorithm. The noise suppression method comprises the following steps: step 1, collecting desert earthquake low-frequency noises; determining an original reference data block and a plurality of common data blocks to obtain a filtered reference data block and a plurality of common data blocks; step 2, calculating the similarity between the filtered reference data block and each common data block, selecting first m filtered common data blocks as blocks similar to the filtered reference data block to form a data matrix by combination; step 3, acquiring an approximate similar block data matrix of an ideal pure similar block data matrix from the data matrix; and S4, acquiring approximate pure earthquake low-frequency noise data afternoise suppression. In addition, the invention further discloses application of the desert low-and-intermediate-frequency noise suppression method to suppression of desert earthquake low-and-intermediate-frequency noises.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com