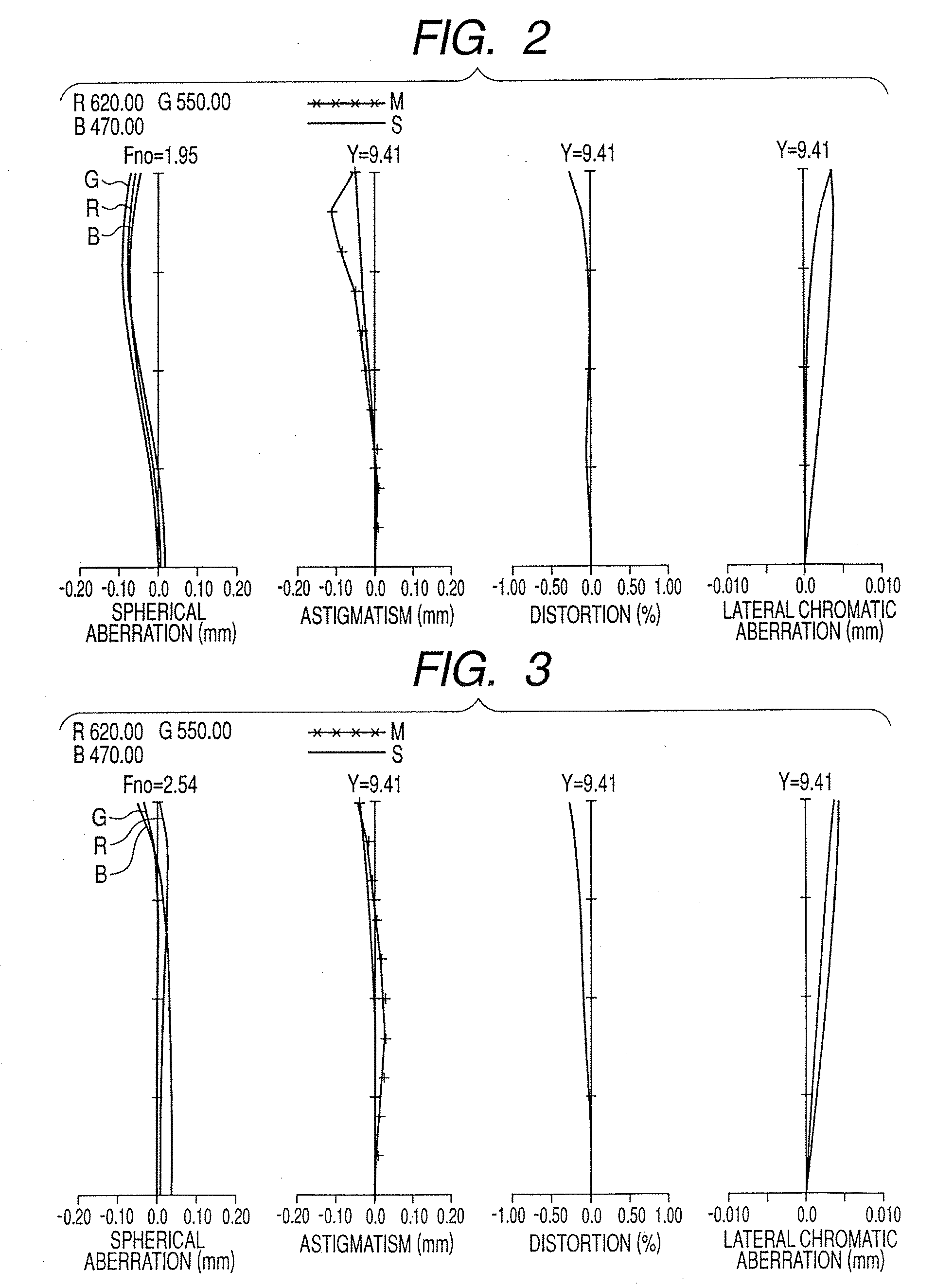
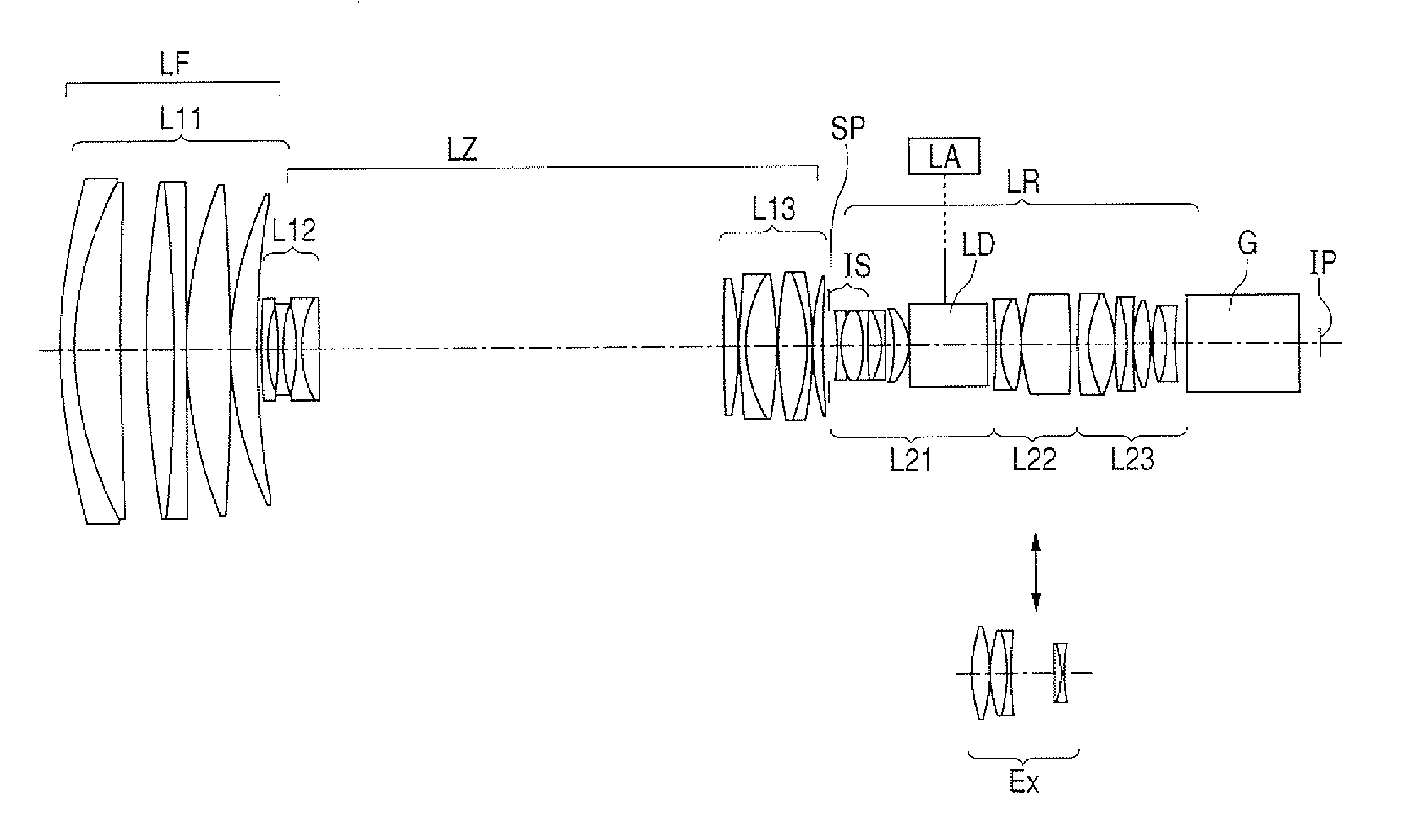
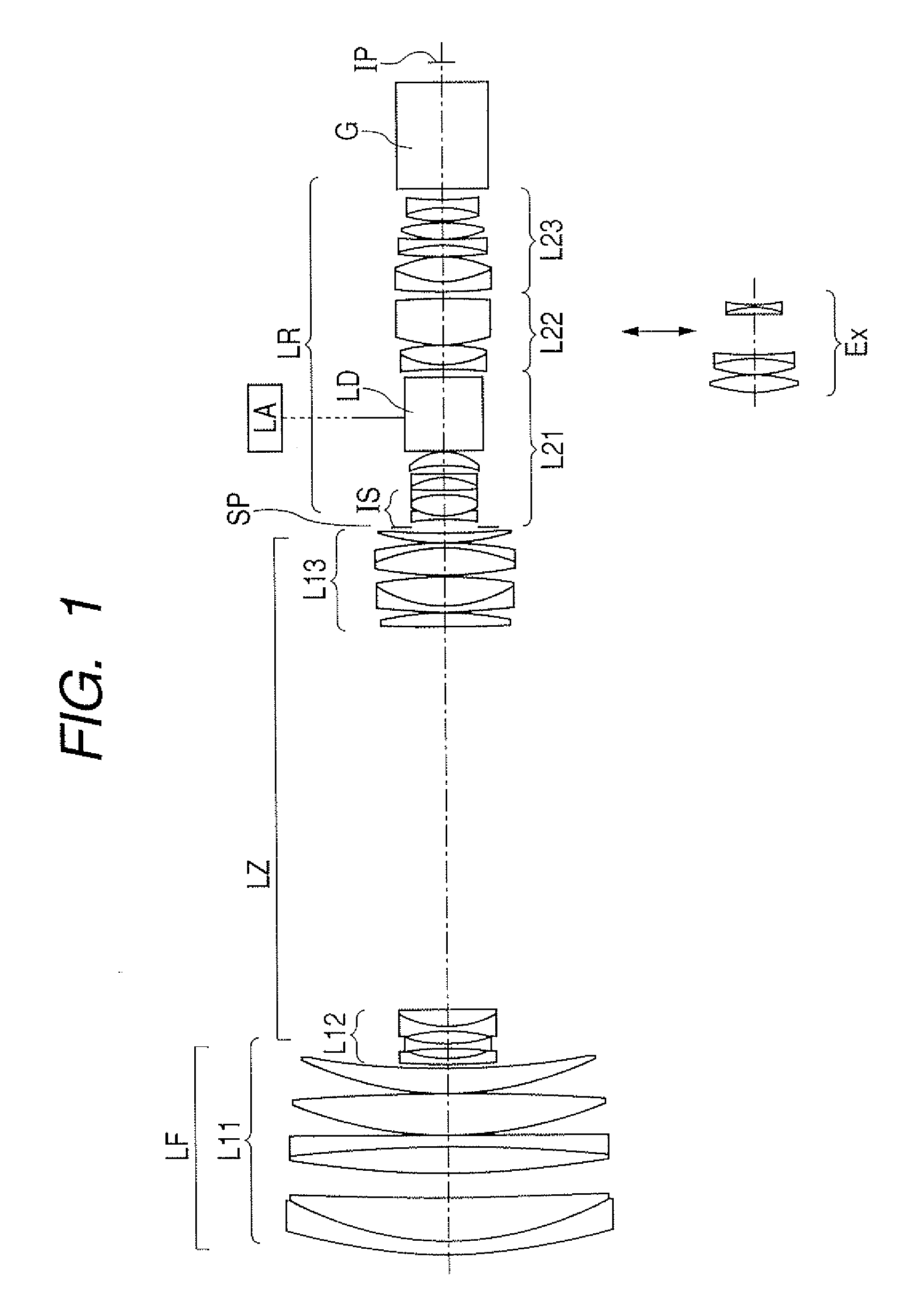
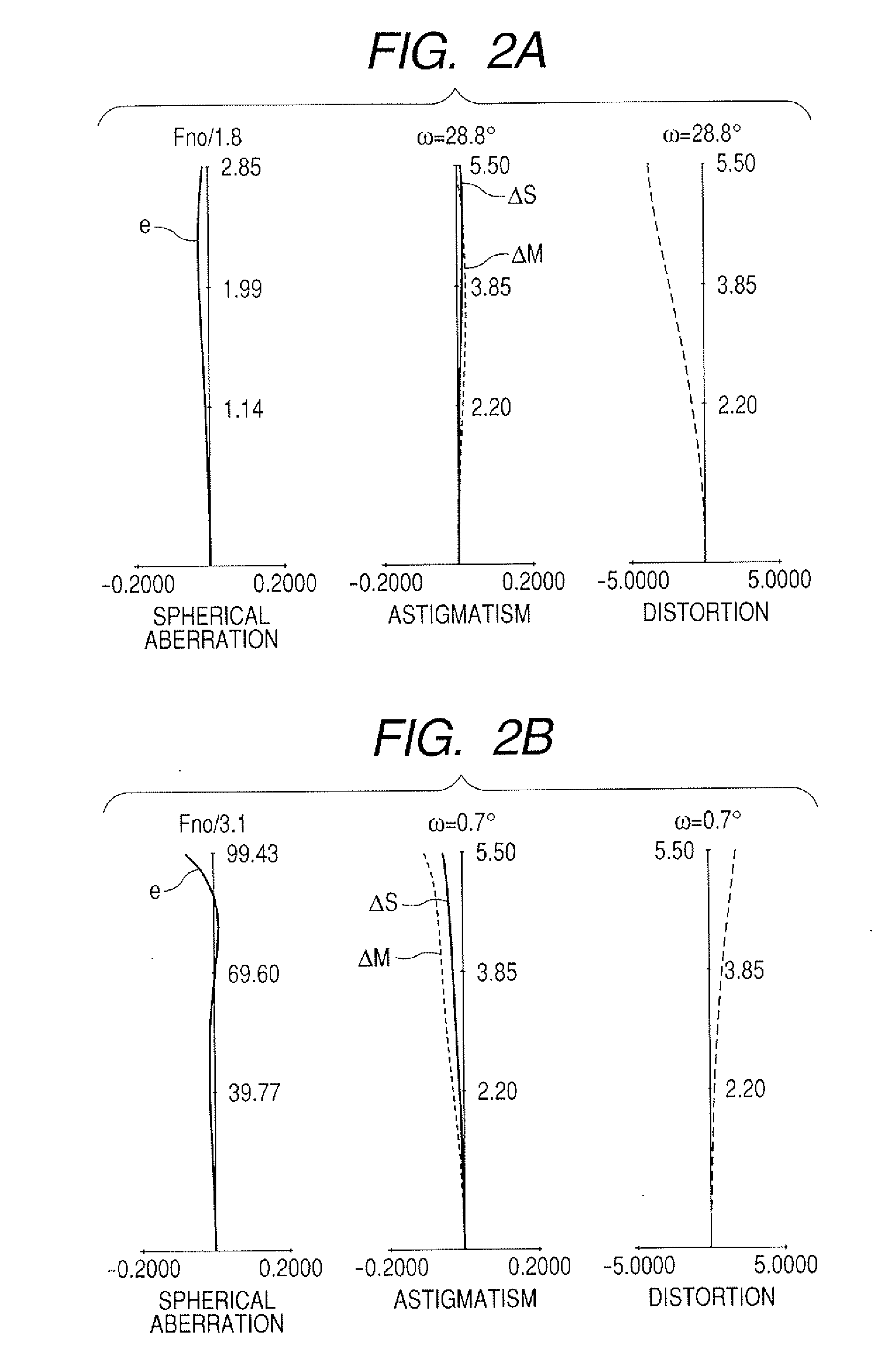
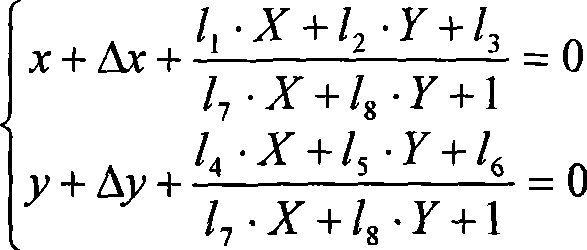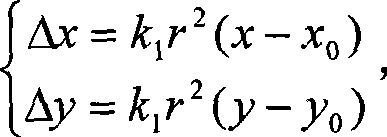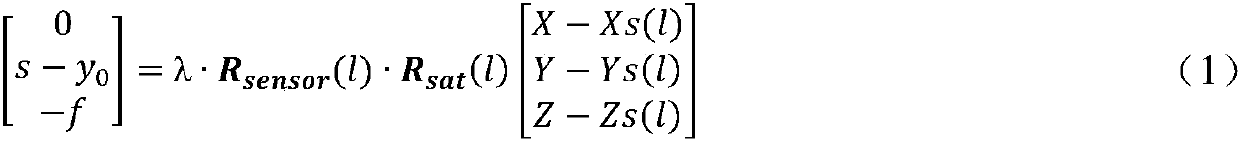Patents
Literature
171 results about "Principal point" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Principal Point was first charted by the French Antarctic Expedition under Charcot, 1903–05. The name, applied by the Argentine Antarctic Expedition, 1953–54, suggests the prominence of the feature. Nearby on the southeast coast is Pursuit Point, an Important Bird Area.
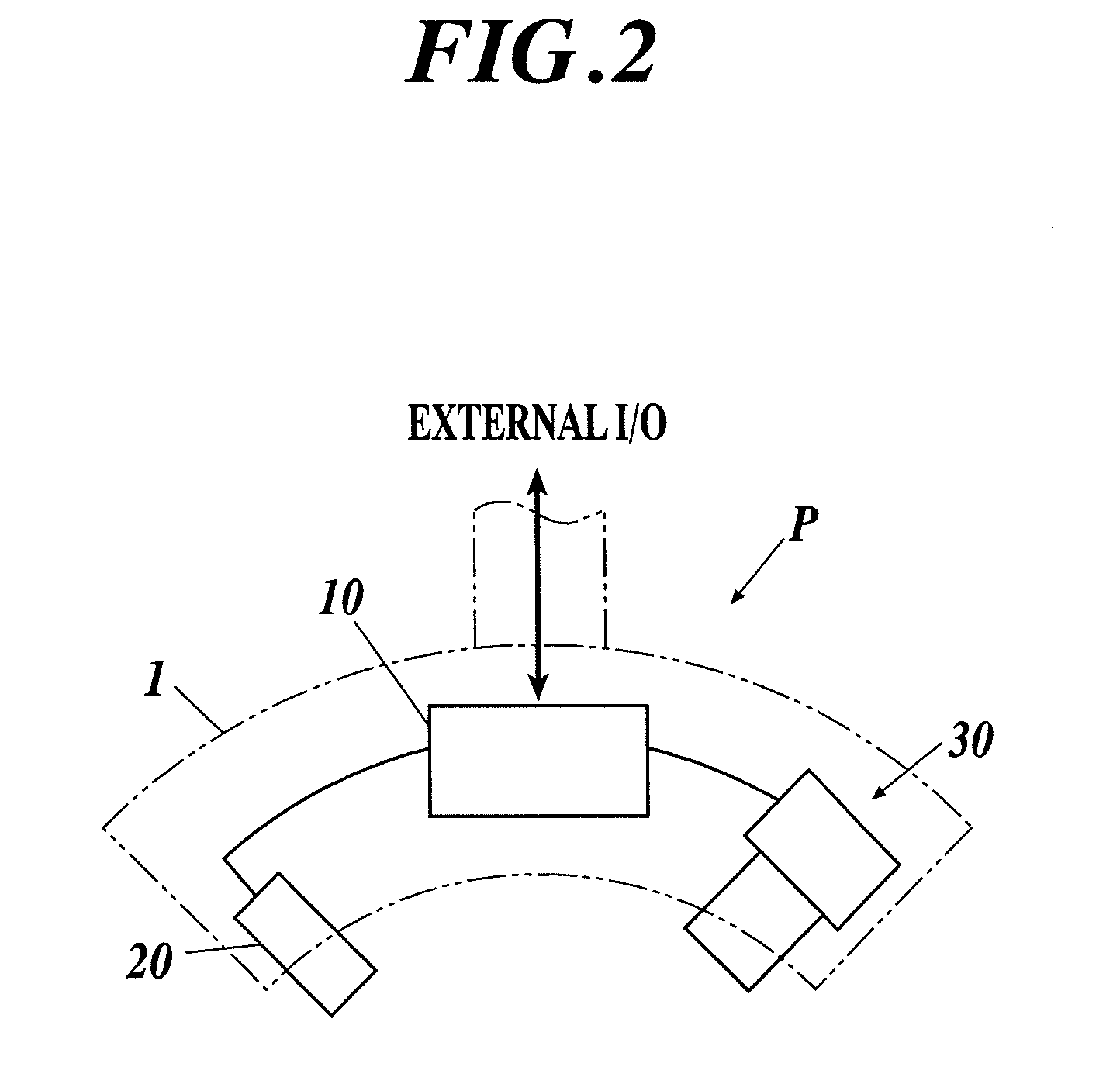
Distance measurement method of binocular stereoscopic gazing monitoring system
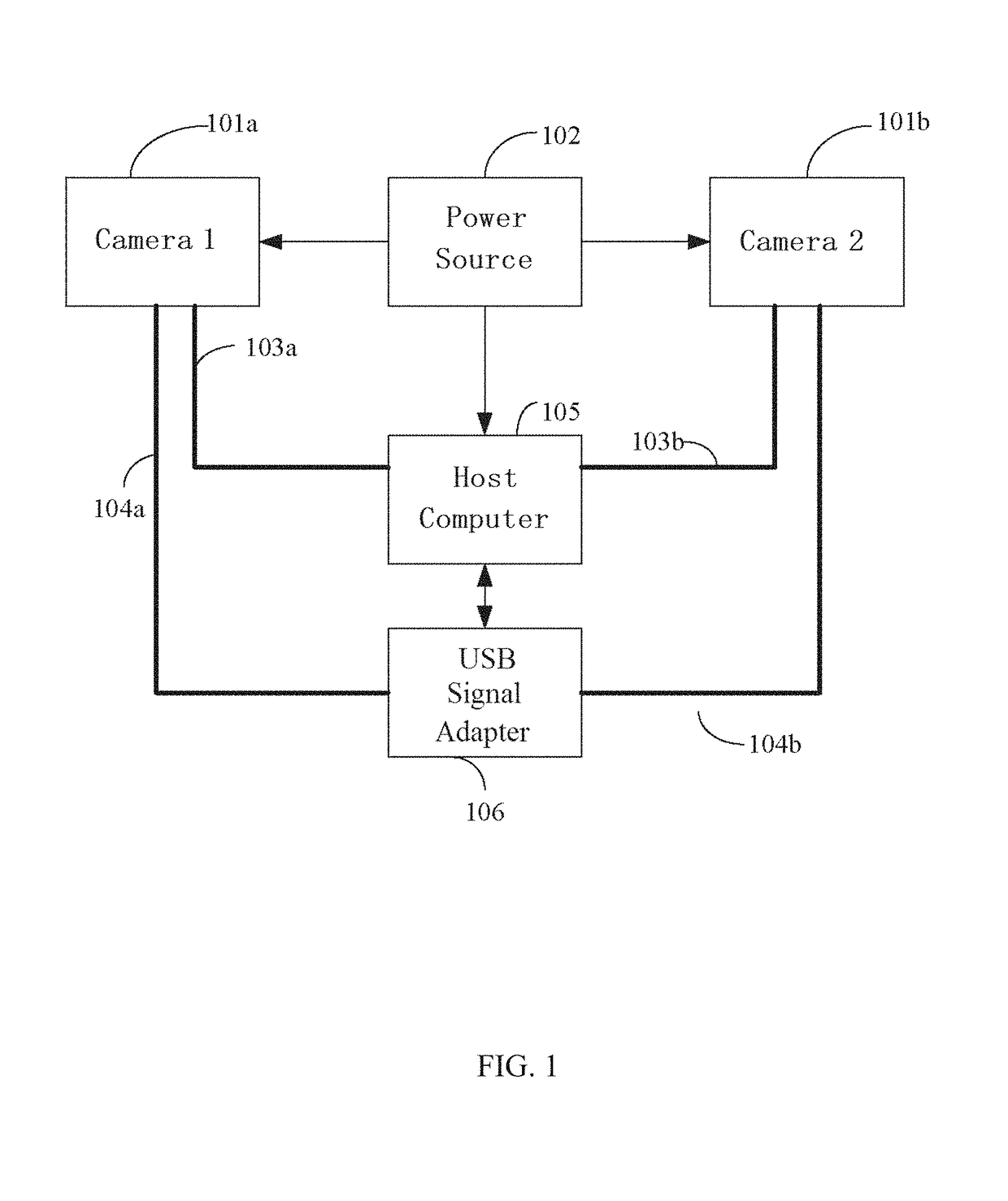
The invention discloses a distance measurement method of a binocular stereoscopic gazing monitoring system. The distance measurement method comprises the following steps that firstly, the coordinates of a principal point of an image, the focal length of a left camera and the focal length of a right camera are determined; secondly, the postures of the binocular cameras are adjusted so as to enable the binocular cameras to gaze at a target point; thirdly, a target distance measurement model based on a rotation angle is established; fourthly, the adjusted binocular convergence cameras are calibrated stereoscopically; fifthly, a transformational relation between the rotation angle and relative external parameters is established; sixthly, target distance measurement and coordinate reestablishment are carried out on the basis of the relative external parameters. On the basis of the distance measurement model, after corresponding parameters are introduced, the distances between the target point and the binocular cameras and the space three-dimensional coordinates of the target point can be worked out. According to the distance measurement method of the binocular stereoscopic gazing monitoring system, the measurement accuracy is high, the detectable distance is long, the result is worked out rapidly and accurately, and the requirement for target positioning of video monitoring can be met.
Owner:ZHONGYUAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE
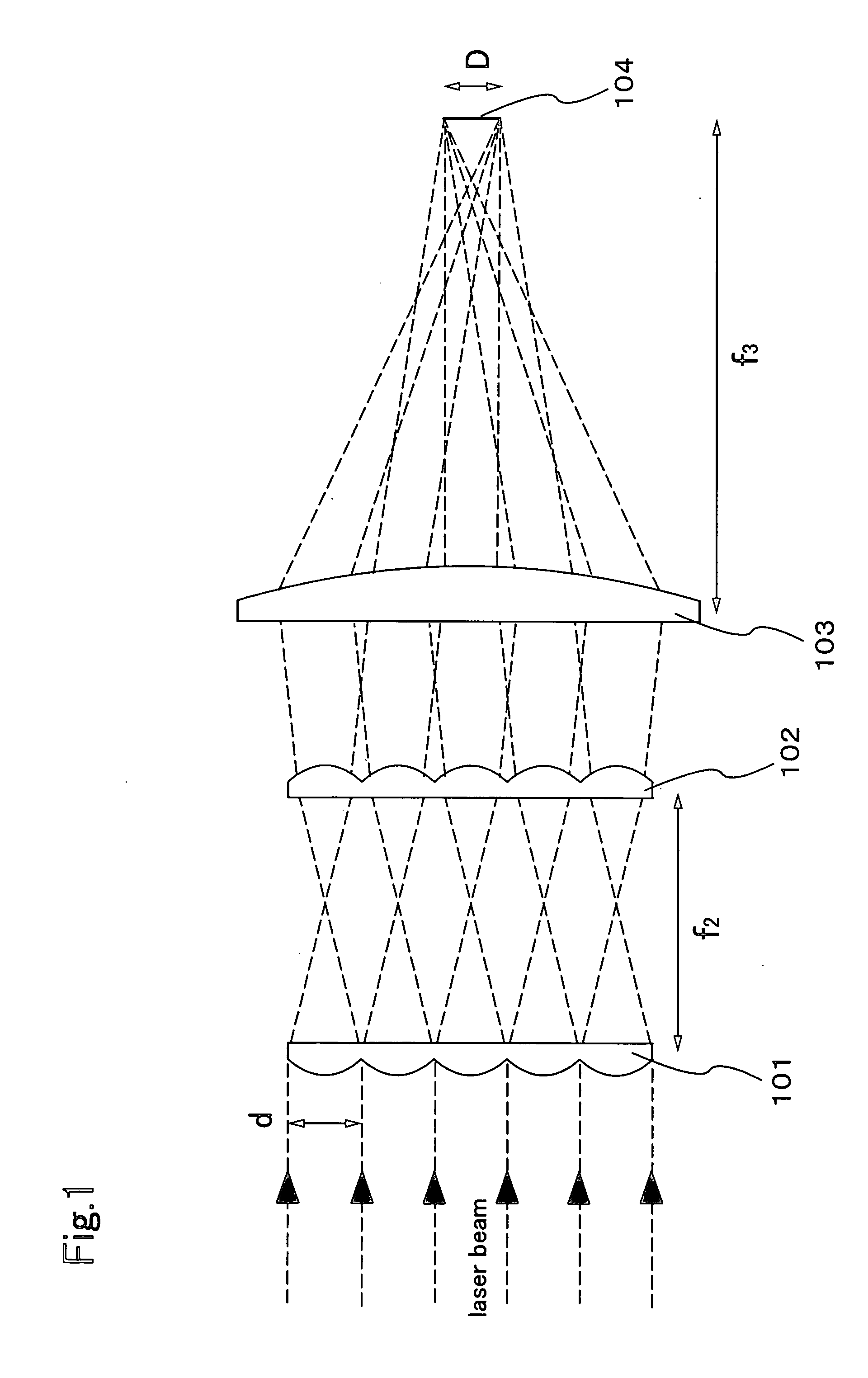
Beam homogenizer and laser irradiation apparatus
ActiveUS20060222041A1Shorten the optical path lengthSmall foot printOptical resonator shape and constructionLaser beam welding apparatusLight beamOptoelectronics
The present invention provides a beam homogenizer for homogenizing energy distribution by making the distance between lenses small to shorten the optical path length with the use of an array lens of an optical path shortened type, and a laser irradiation apparatus using the beam homogenizer. The beam homogenizer is equipped with a front side array lens of an optical path shortened type whose second principal point is positioned ahead on a beam incidence side, a back side array lens of an optical path shortened type whose first principal point is positioned behind on a beam emission side, and a condensing lens, wherein the distance between the second principal point of the front side array lens and the first principal point of the back side array lens is equal to the focal length of the back side array lens.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
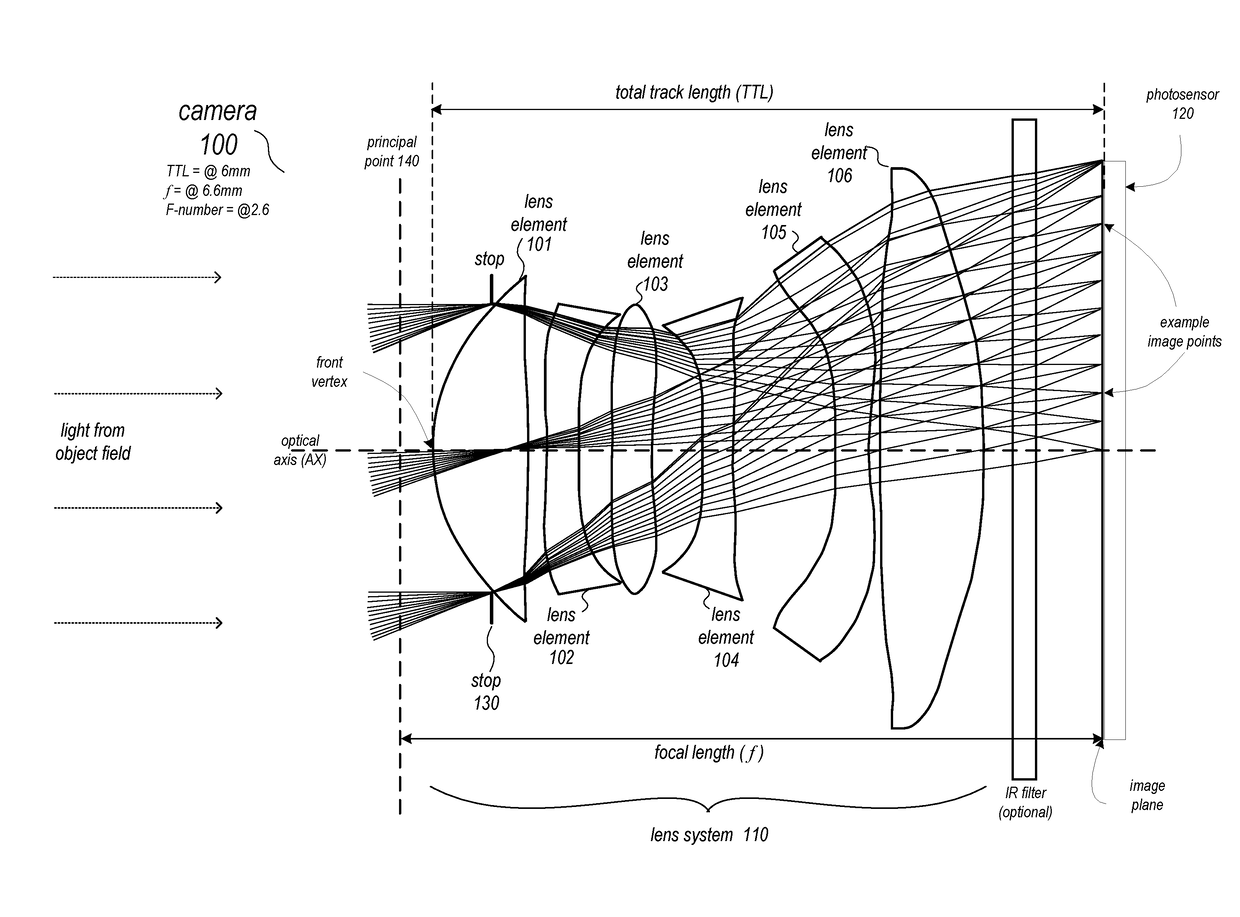
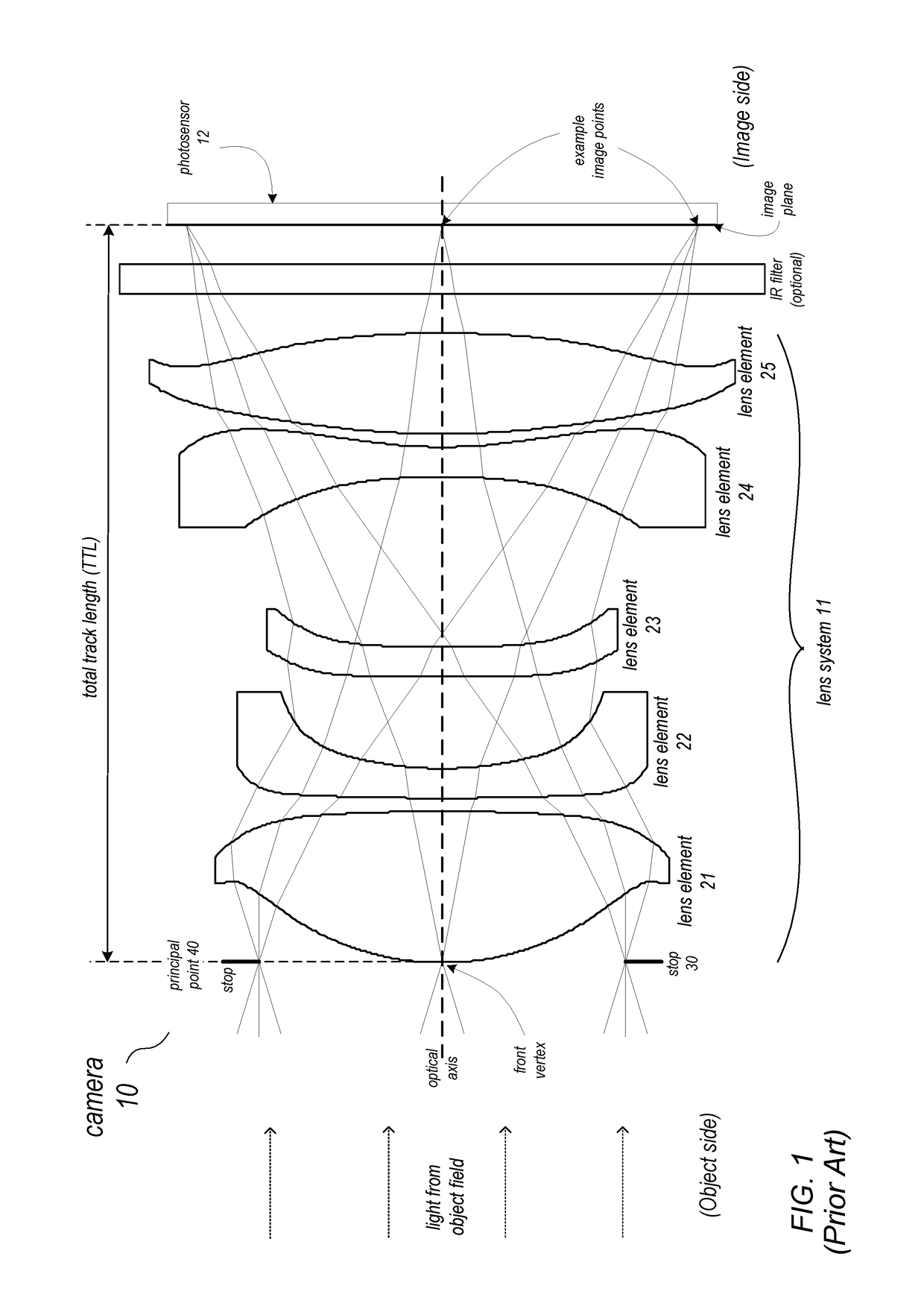
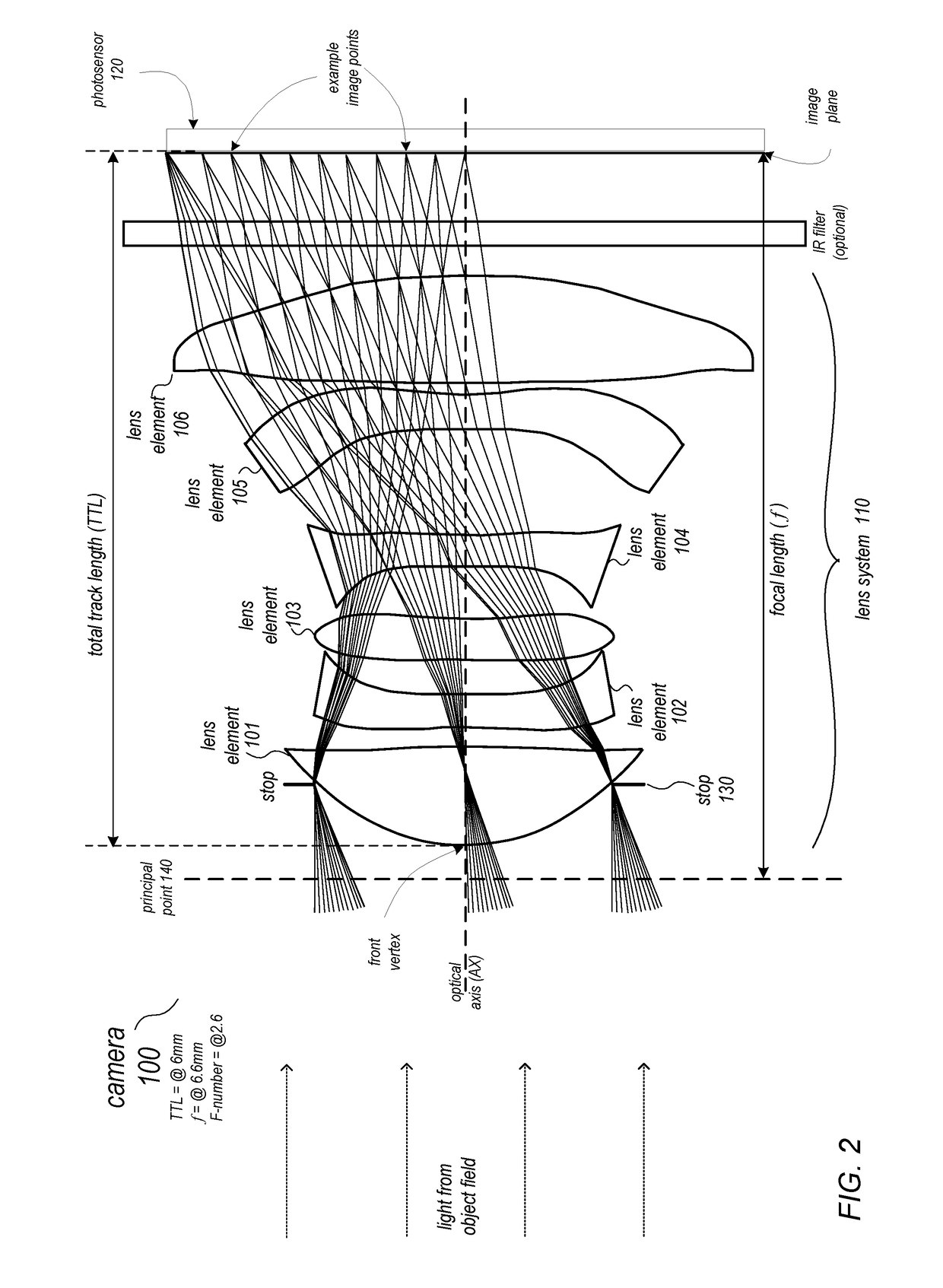
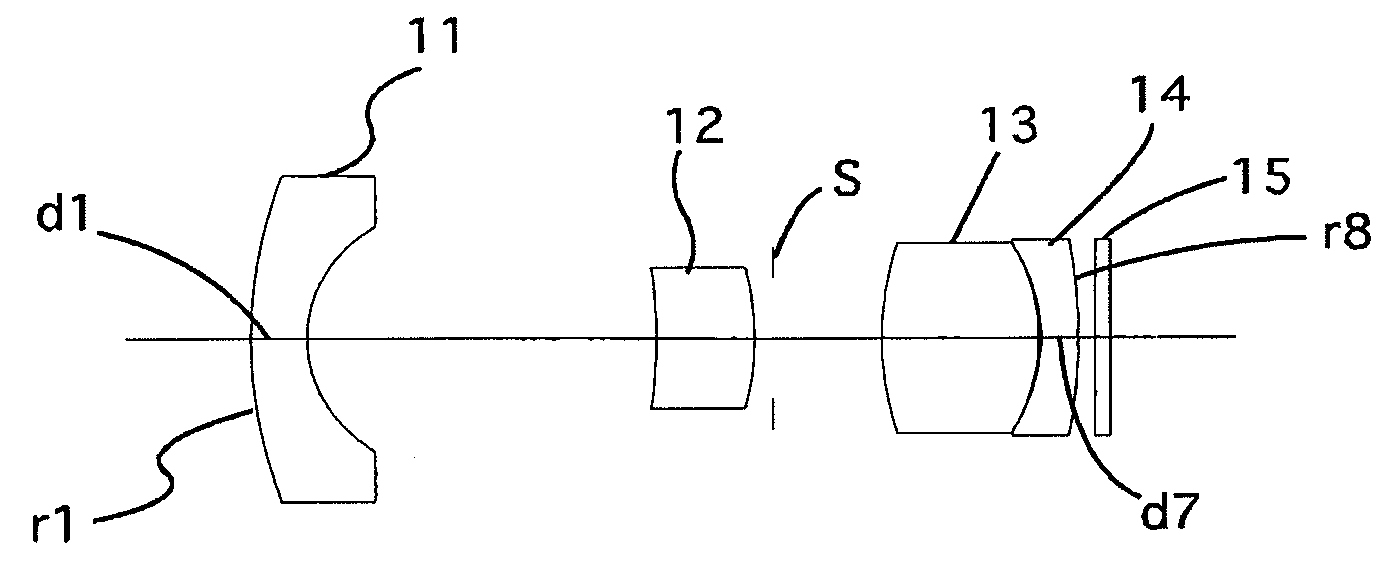
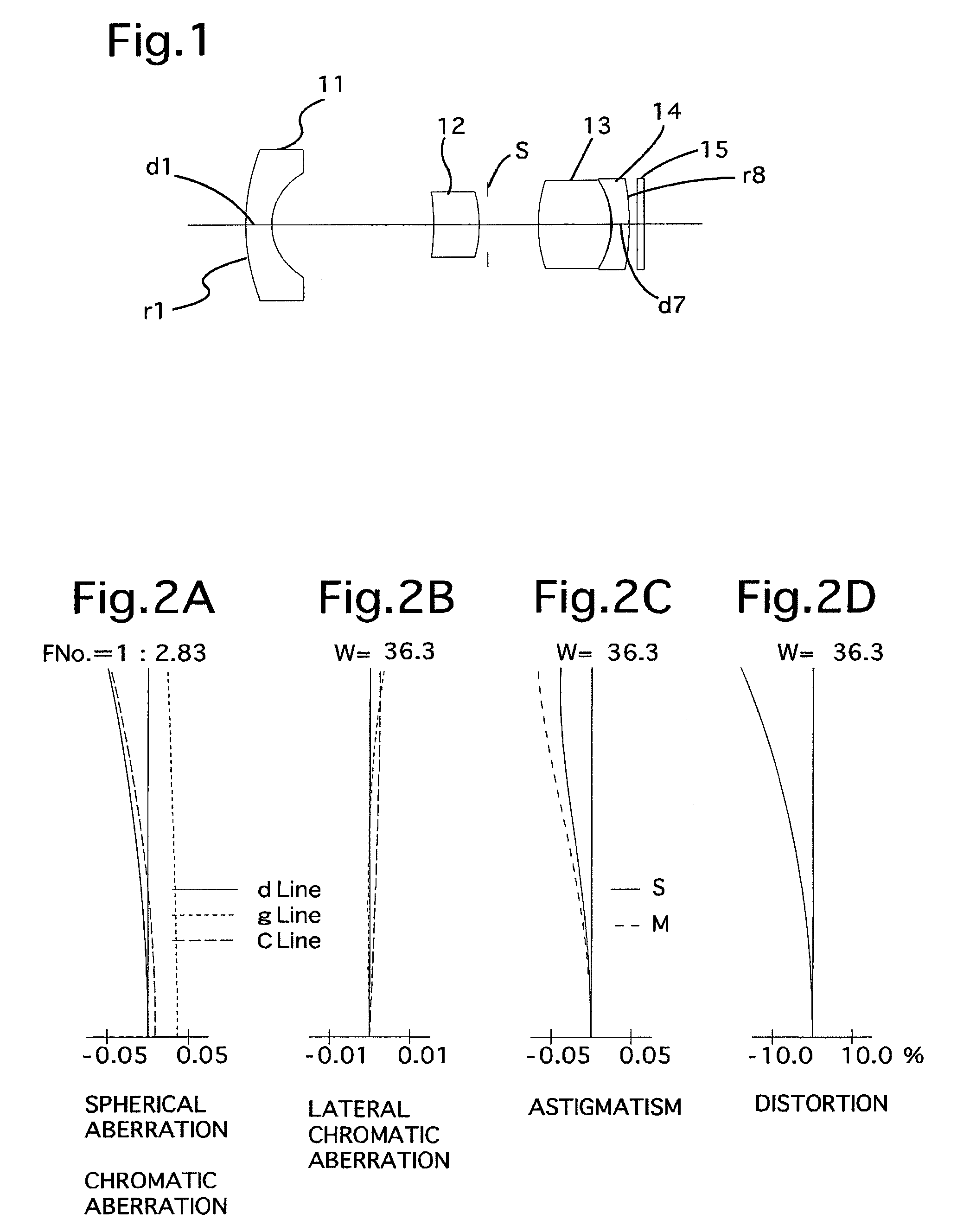
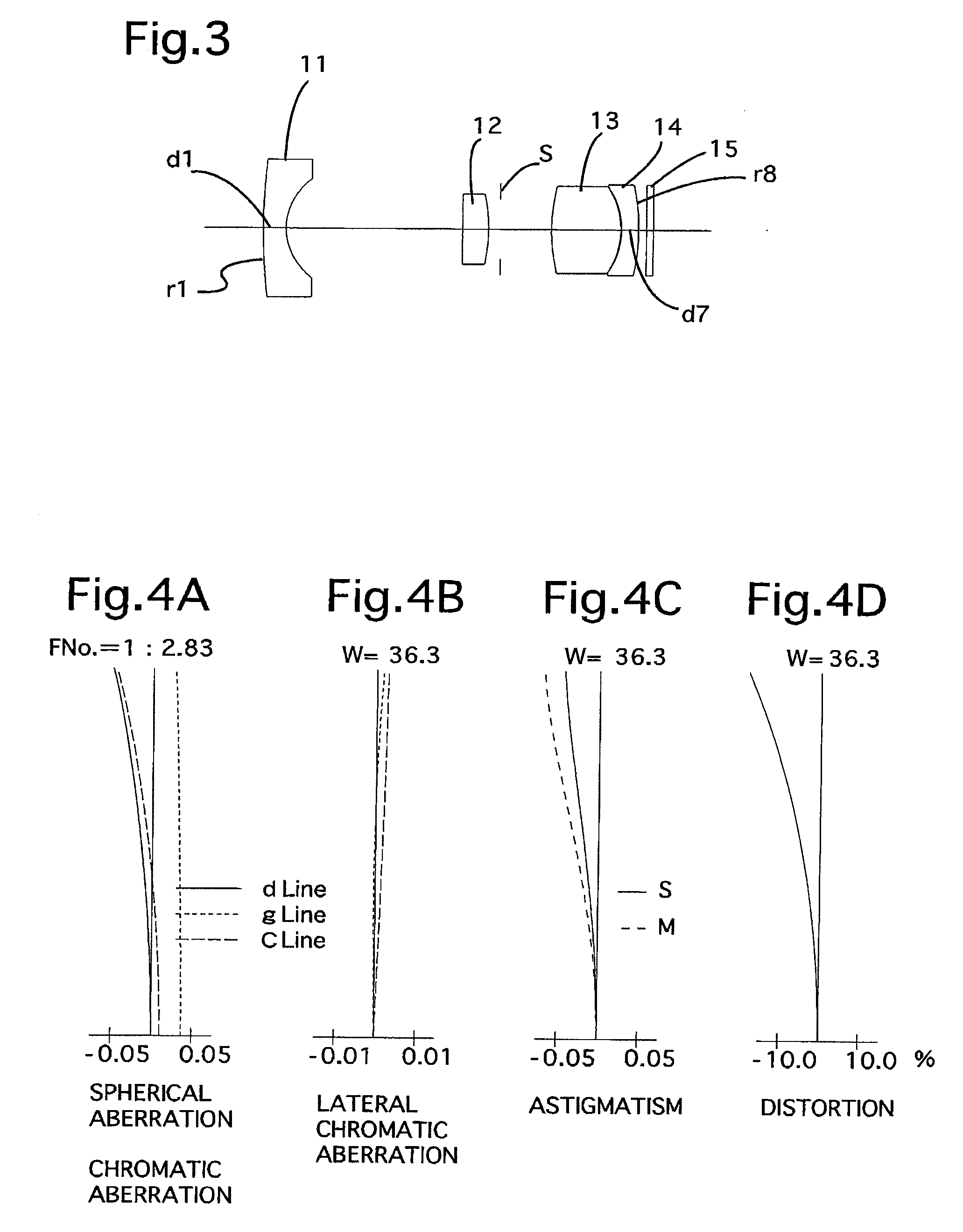
Lens system
ActiveUS20170115471A1Big imageLong effective focal lengthProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementCamera lensImaging quality
Compact narrow angle lens systems that may be used in small form factor cameras. The lens system may include six lens elements with refractive power, and may provide lower F-numbers while maintaining or improving imaging quality and package size when compared to other compact lens systems. Total track length of the lens system may be 6.5 millimeters or less, for example 5.9 or 6 millimeters. Focal length of the lens system may be 7.0 millimeters or less, for example 6.6 millimeters. The lens system may include an aperture stop located behind the front vertex of the lens system, for example between the first and second lens elements, that effectively moves the ideal principal point of the camera to in front of the front vertex. The lens system may provide a focal ratio of 2.8 or less, for example 2.6 or 2.4.
Owner:APPLE INC
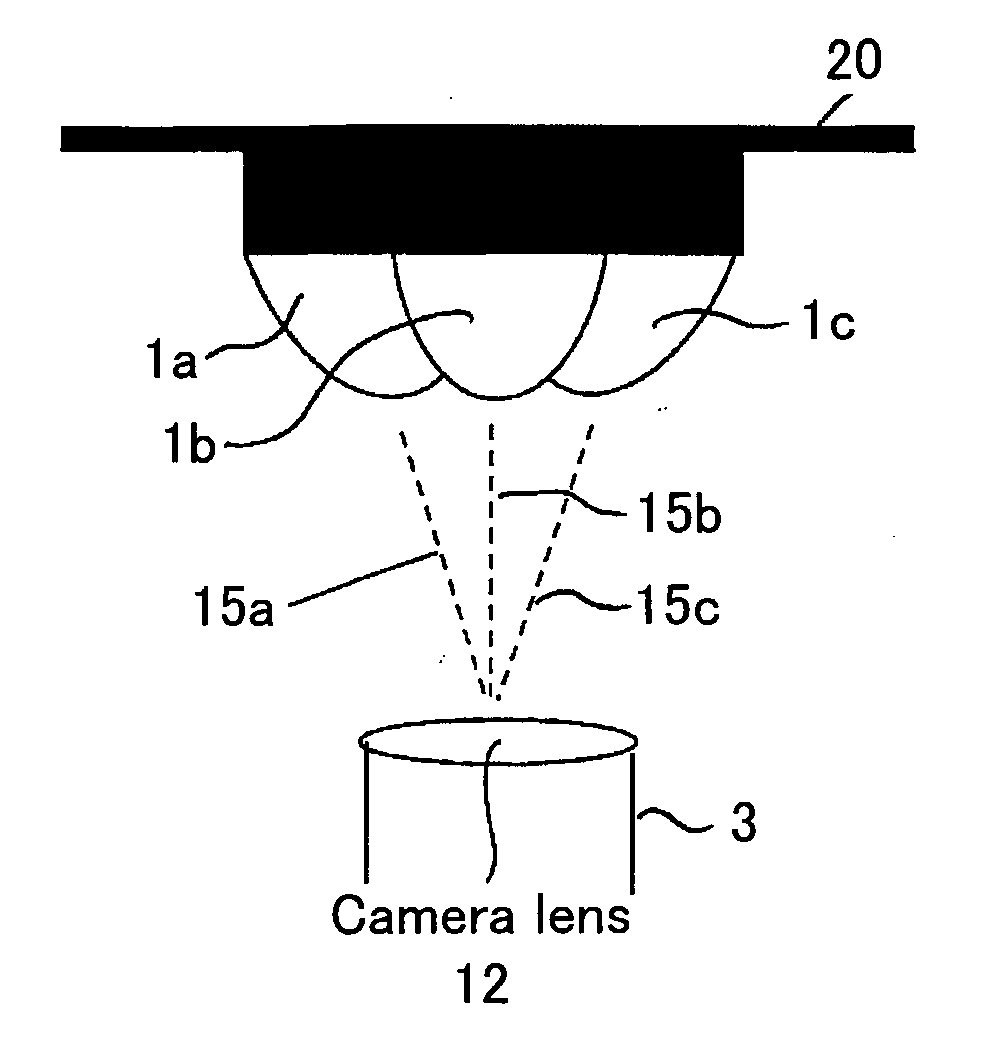
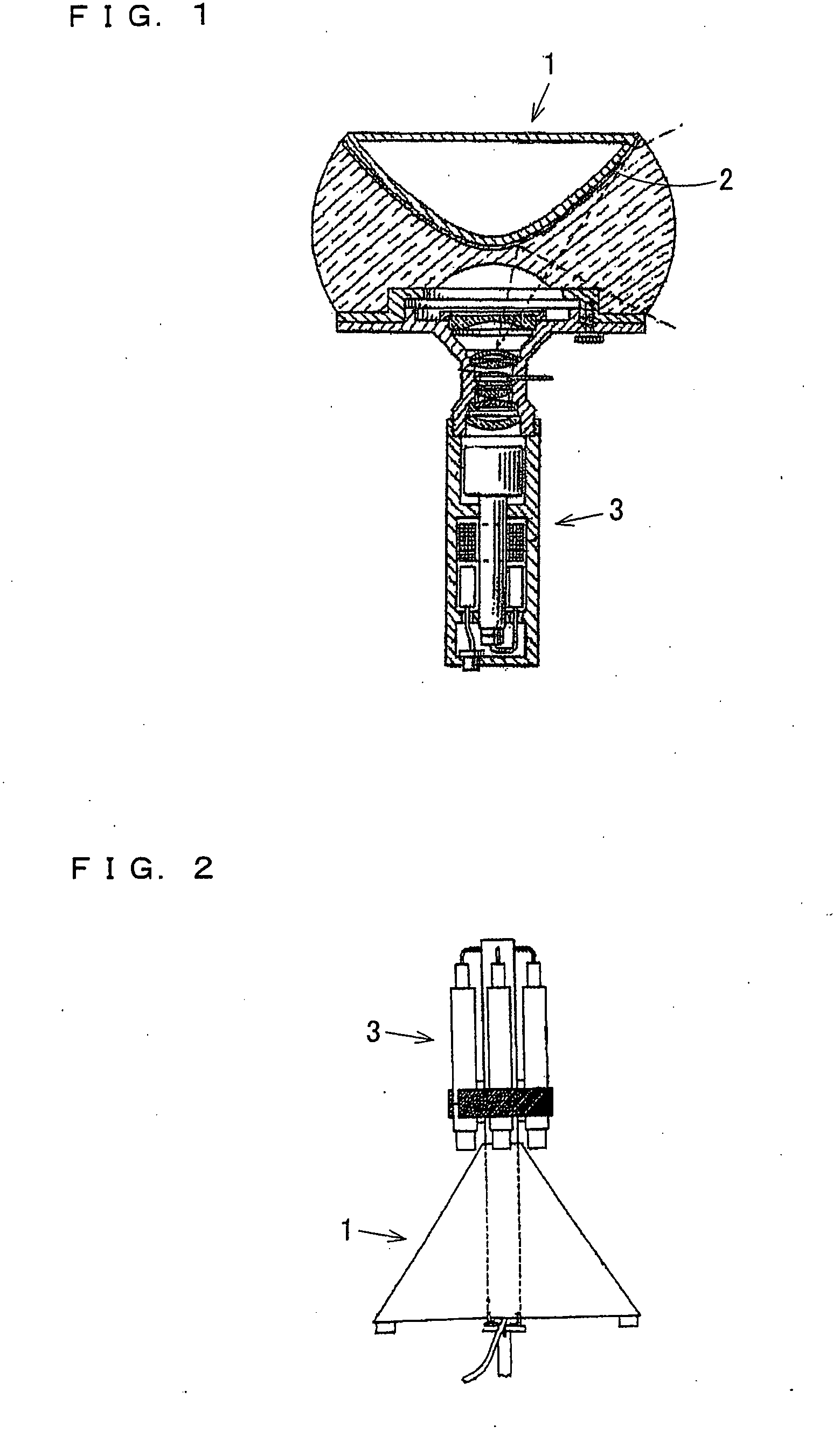
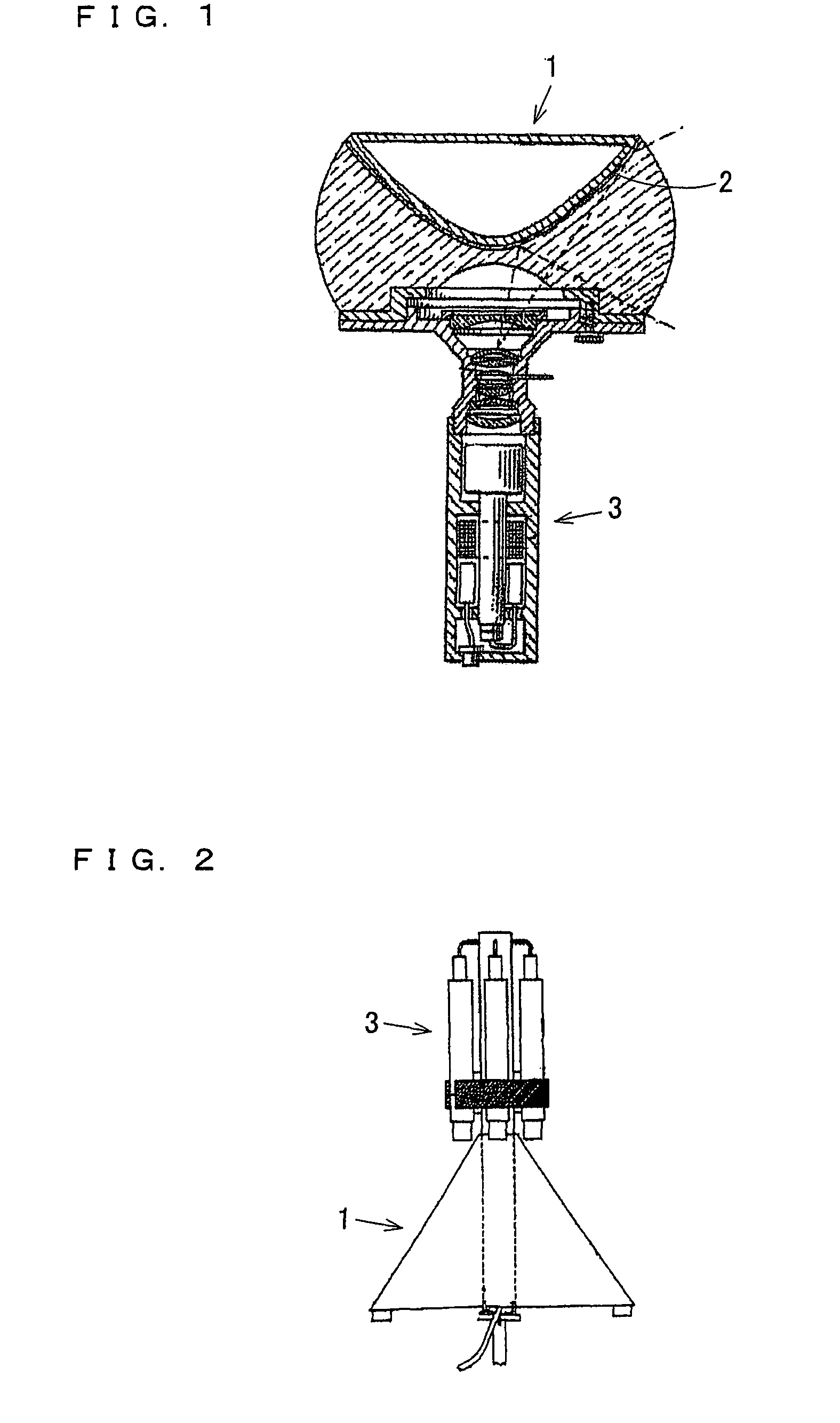
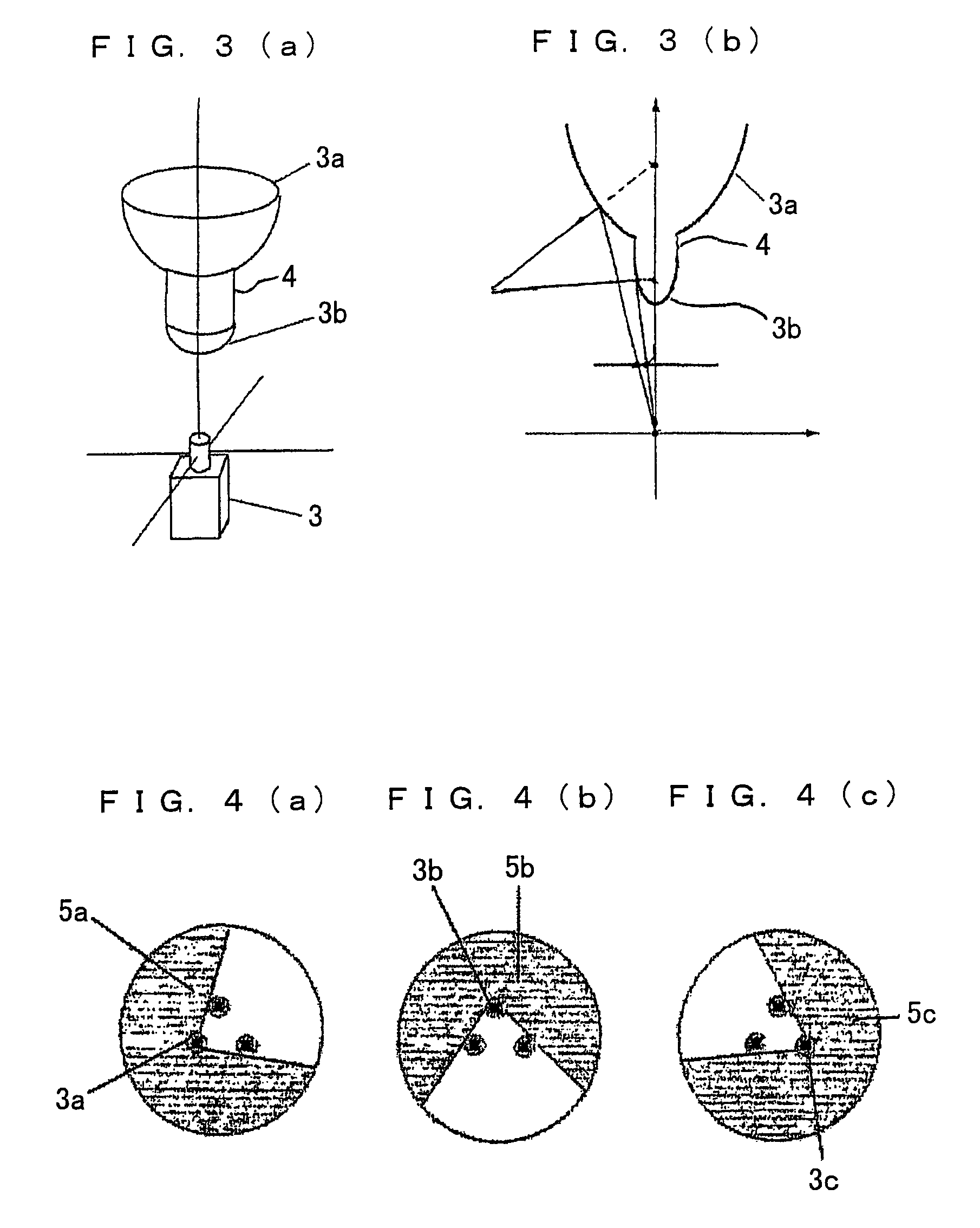
Panoramic three-dimensional adapter for an optical instrument and a combination of such an adapter and such an optical instrument
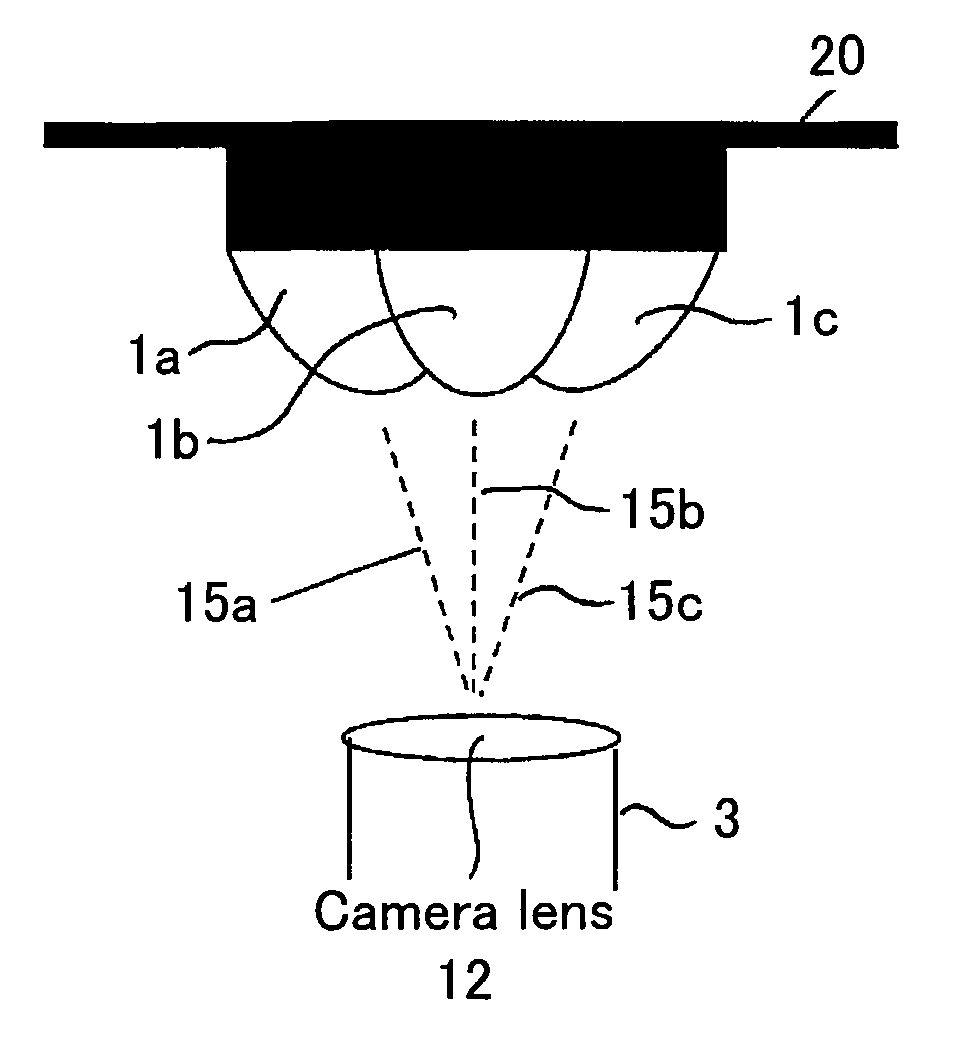
InactiveUS20090034086A1Easy to manufactureSimple processProjectorsTelescopesCamera lensAxis of symmetry
An adapter is provided for adapting an optical instrument, such as a camera (3) or a projector, to capture or display panoramic three-dimensional images. The adapter comprises a plurality of mirrors (1a, 1b, 1c), each of which has a reflective surface which is in the shape of a curved non-circular conic section rotated about an axis of symmetry (15a, 15b, 15c). The reflective surfaces have first foci which are spaced perpendicularly from a longitudinal axis of the adapter and which are angularly spaced around the longitudinal axis. For example, the conic section may be a hyperbola with first foci equidistantly spaced from the longitudinal axis and equiangularly spaced around 15b the longitudinal axis. The axes of symmetry (15a, 15b, 15c) of the mirrors (1a, 1b, 1c) converge to intersect the longitudinal axis at a point which is coincident with the front principal point of, for example, a camera lens (12). Thus, single shot capture of all the image data for the or each panoramic three-dimensional image may be performed.
Owner:SHARP KK
Optical system
InactiveUS6459485B1Angle measurementPhotometry using reference valueCamera lensLiquid-crystal display
An optical system used in an optical measuring apparatus for measuring optical characteristics of, for example, a liquid crystal display panel (LCD panel) guides rays emitted from the LCD panel and having exit angles equal to or smaller than a predetermined maximum exit angle alpha. A lens of the optical system satisfies the following two equations.Hereupon, the symbol "f" designates a focal length of the lens; the symbol "h" designates the maximum height of the photosensitive plane of the photosensor from an optical axis of the lens on the photosensing plane; the symbol "L" designates a distance from a principal point of the lens in the image side to the photosensing plane; and the symbol "H" designates the maximum height of the object from the optical axis of the lens.
Owner:MINOLTA CO LTD
Zoom lens and photographing apparatus having it
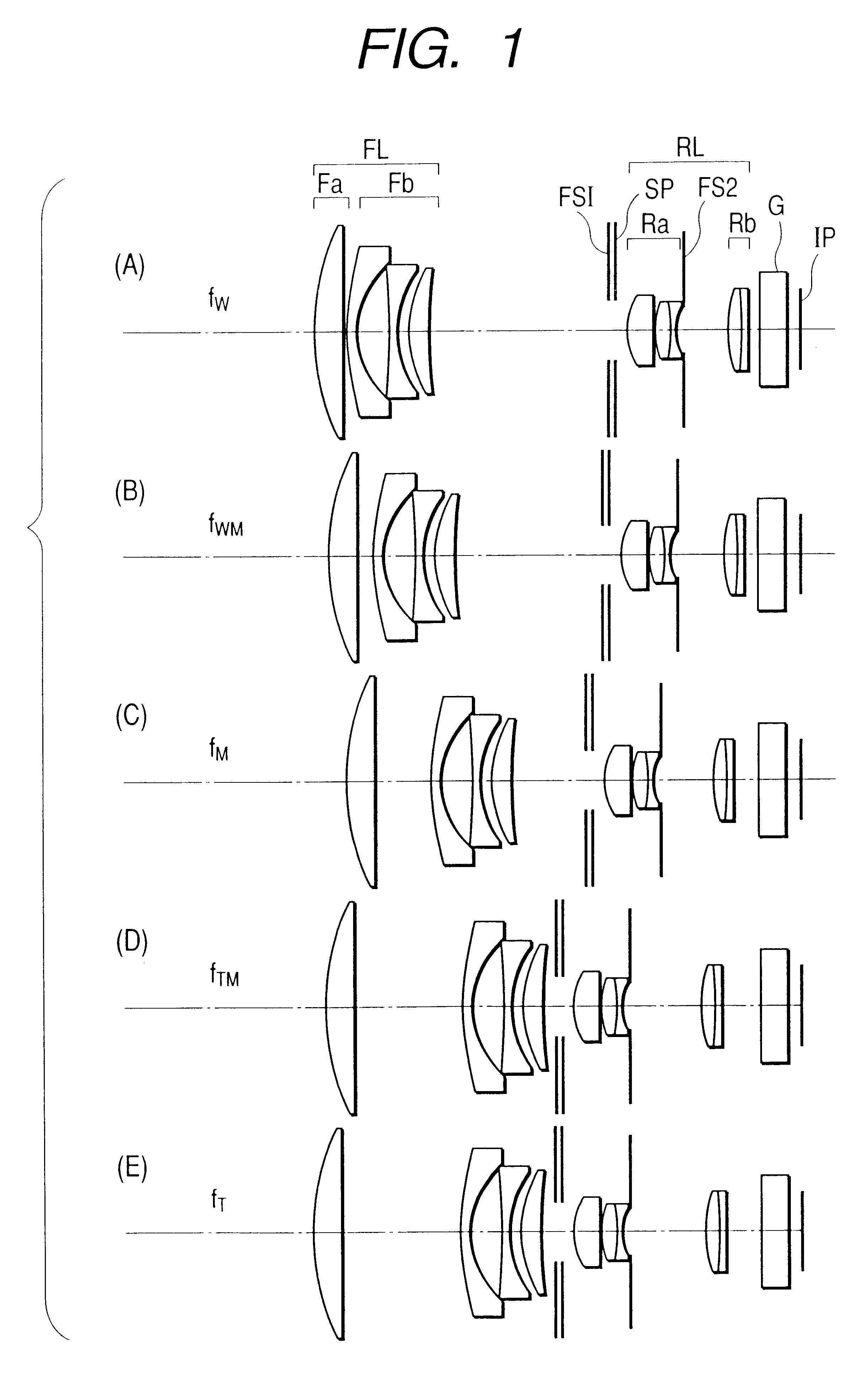
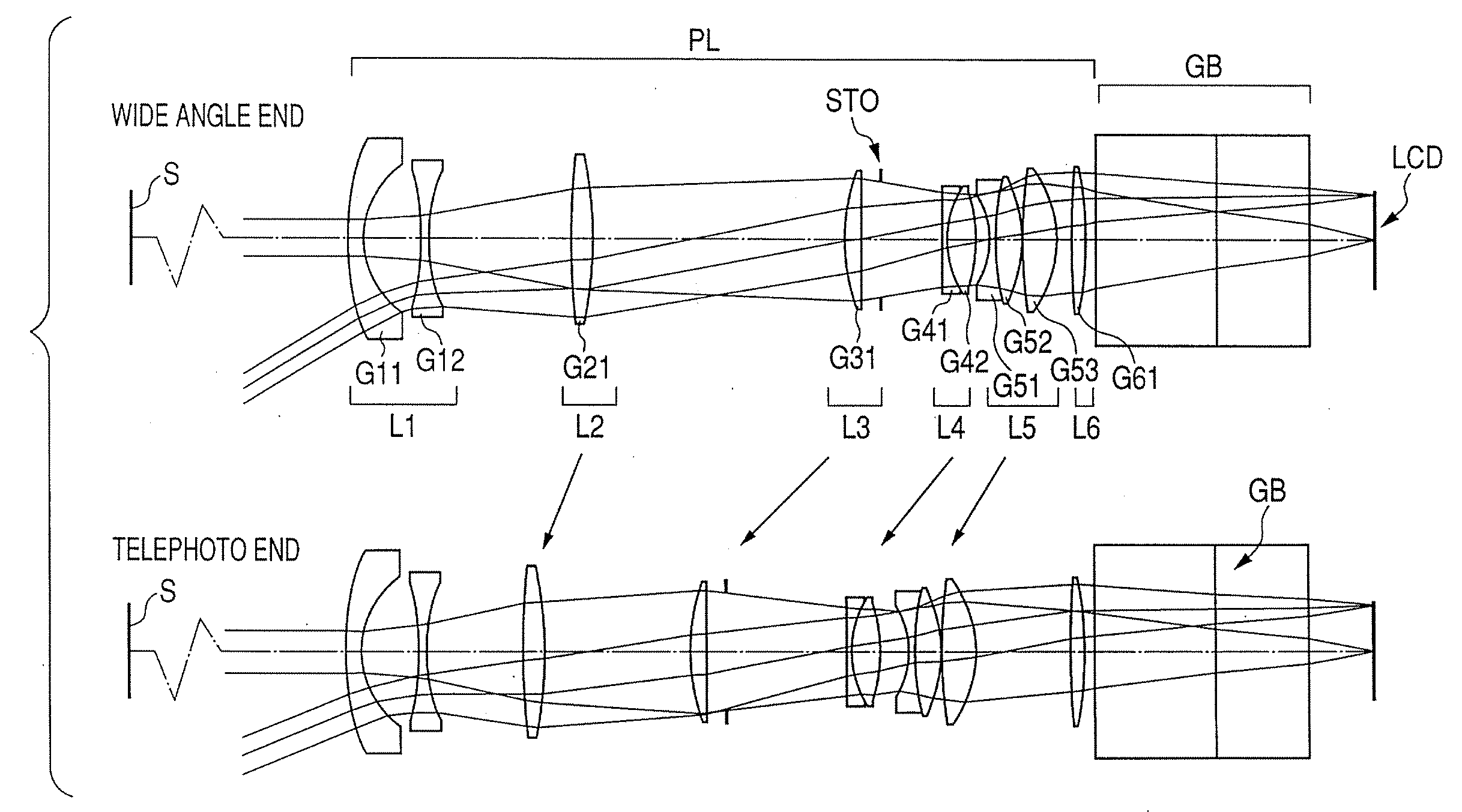
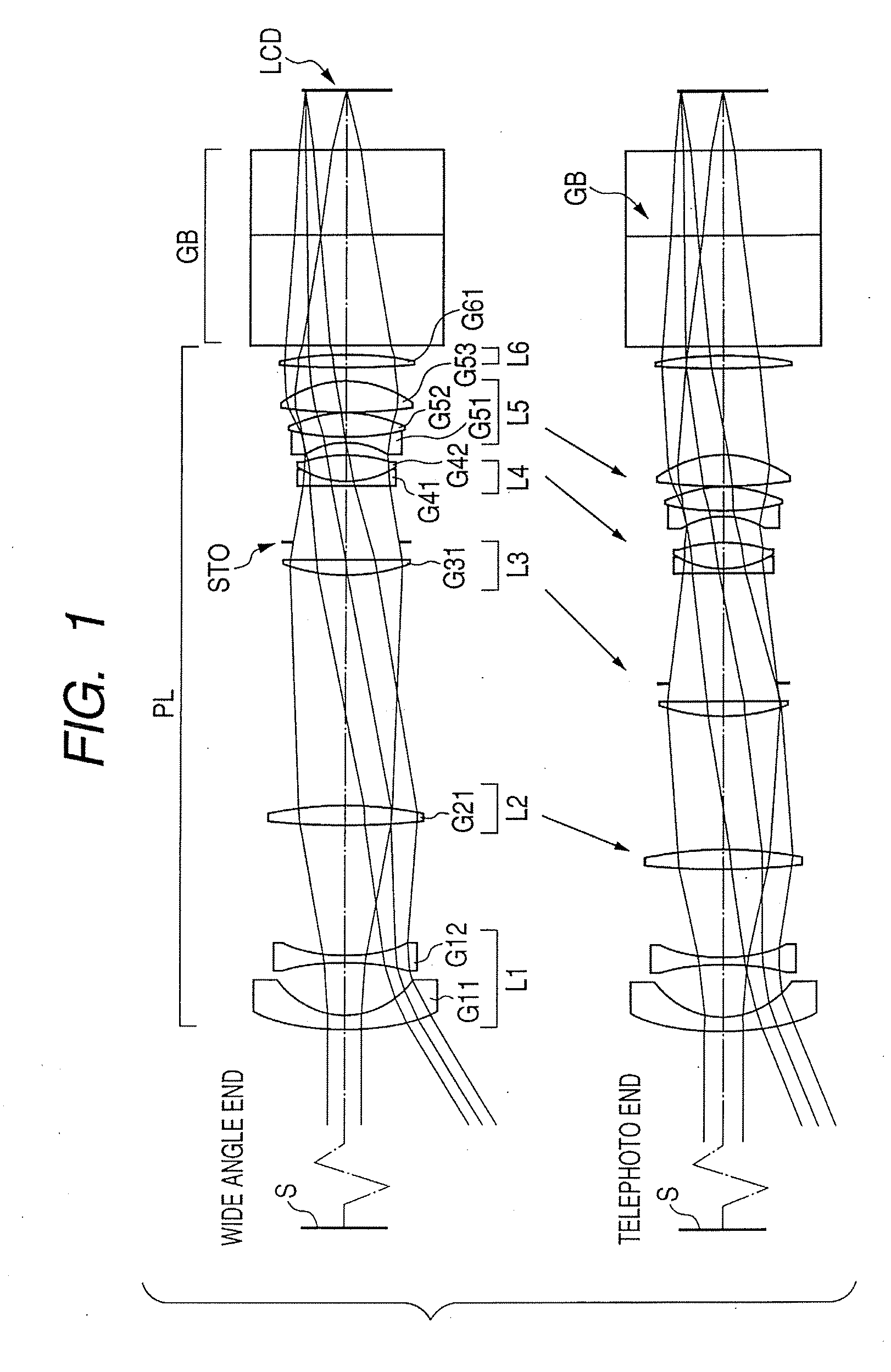
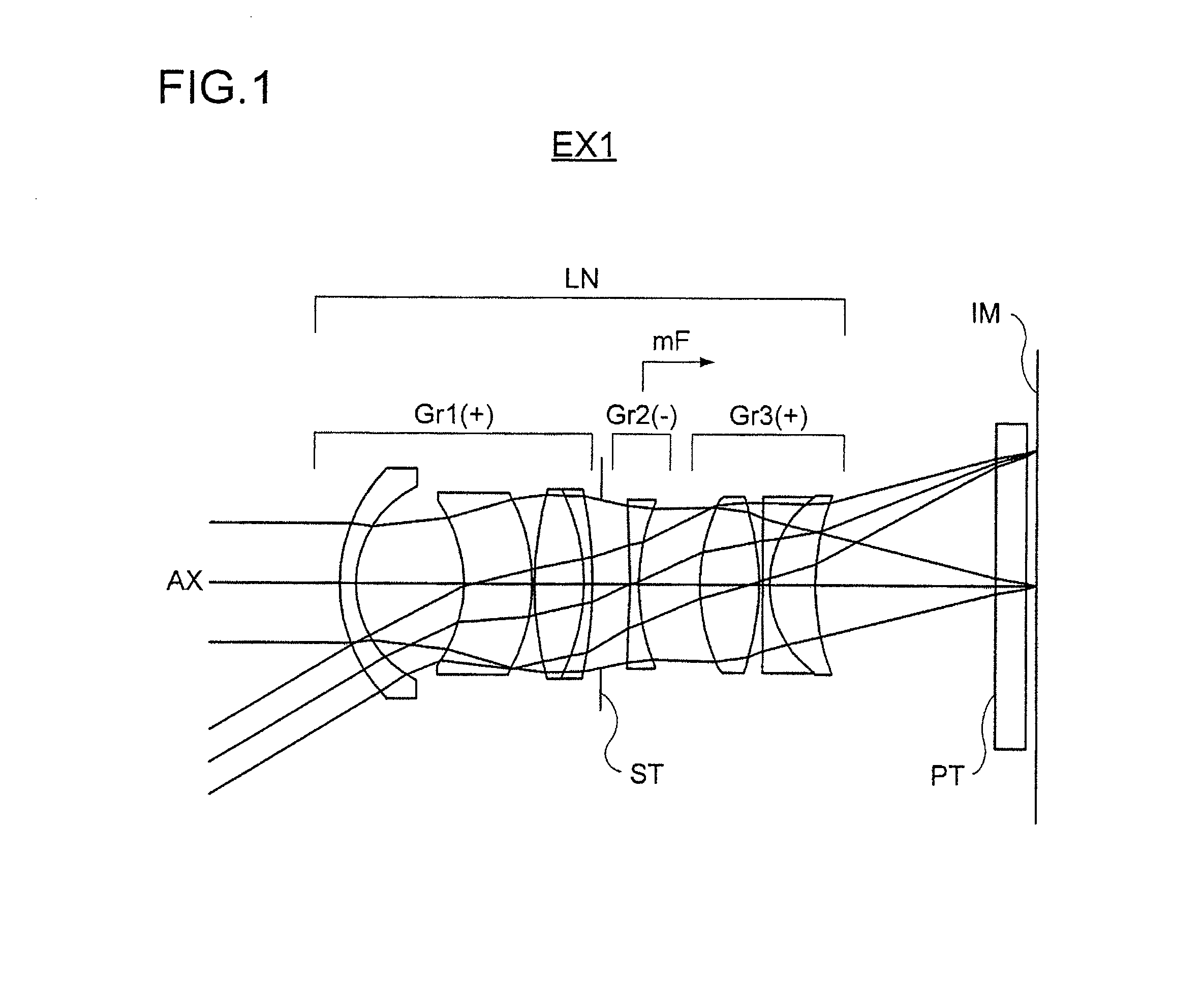
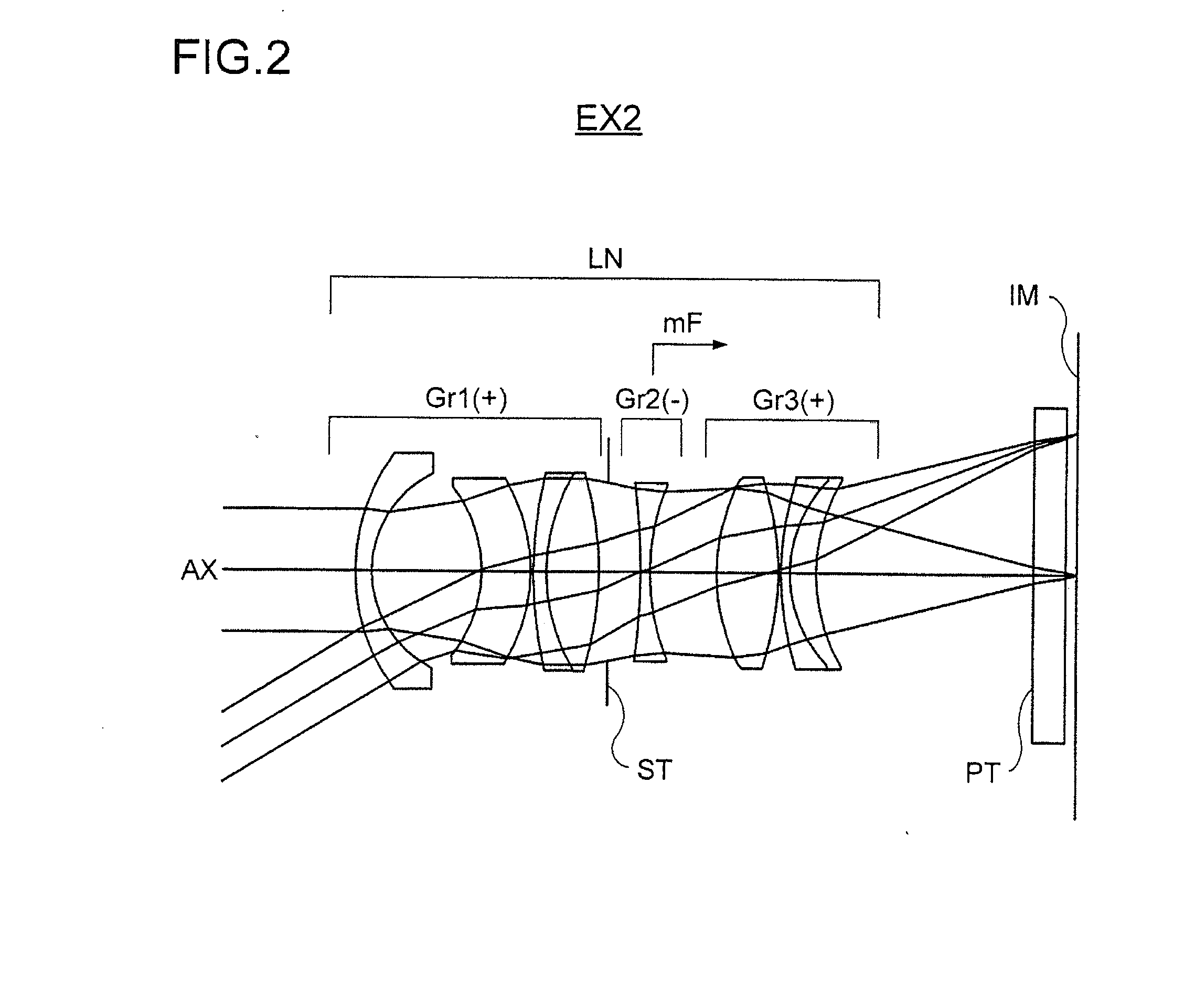
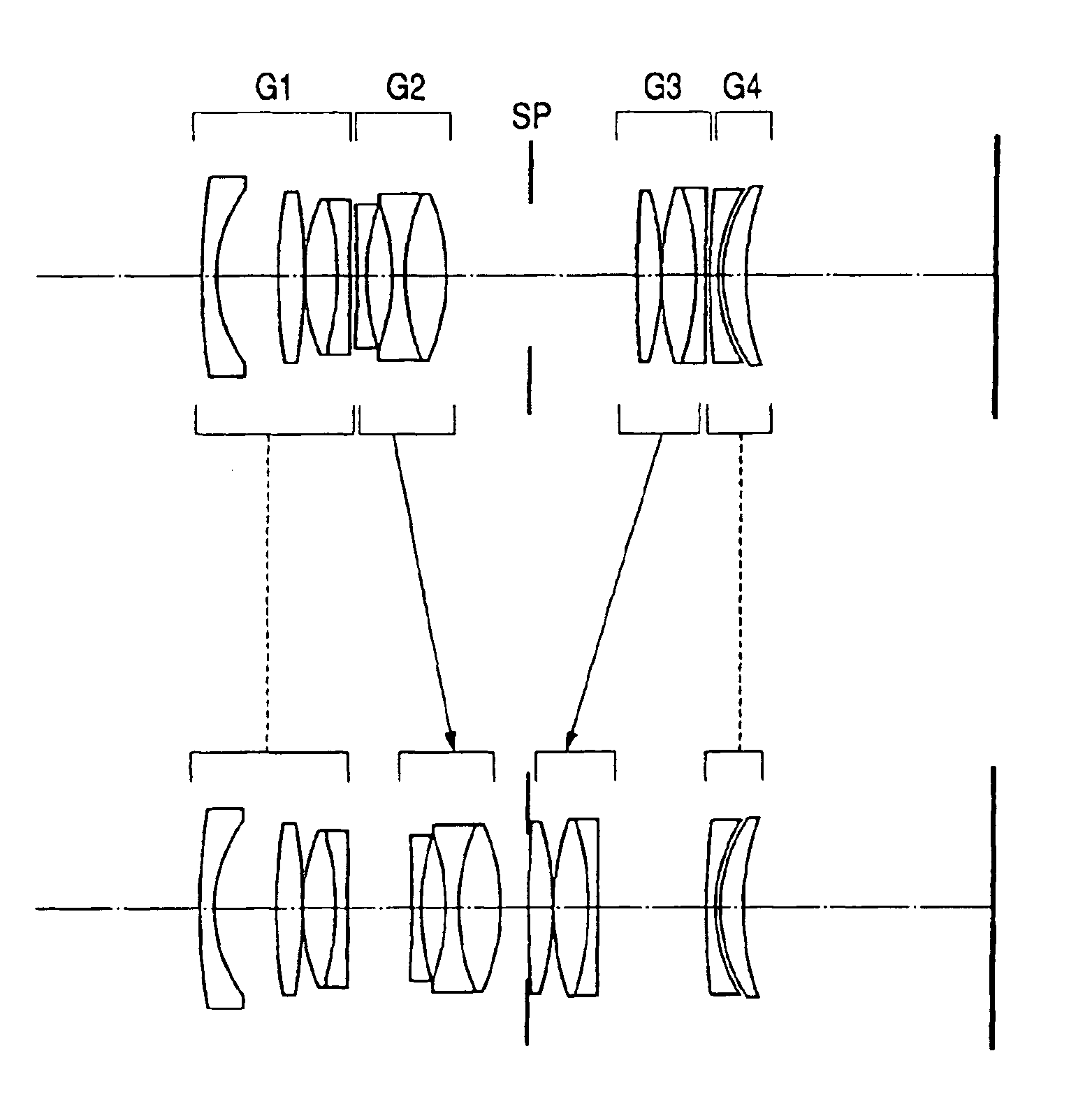
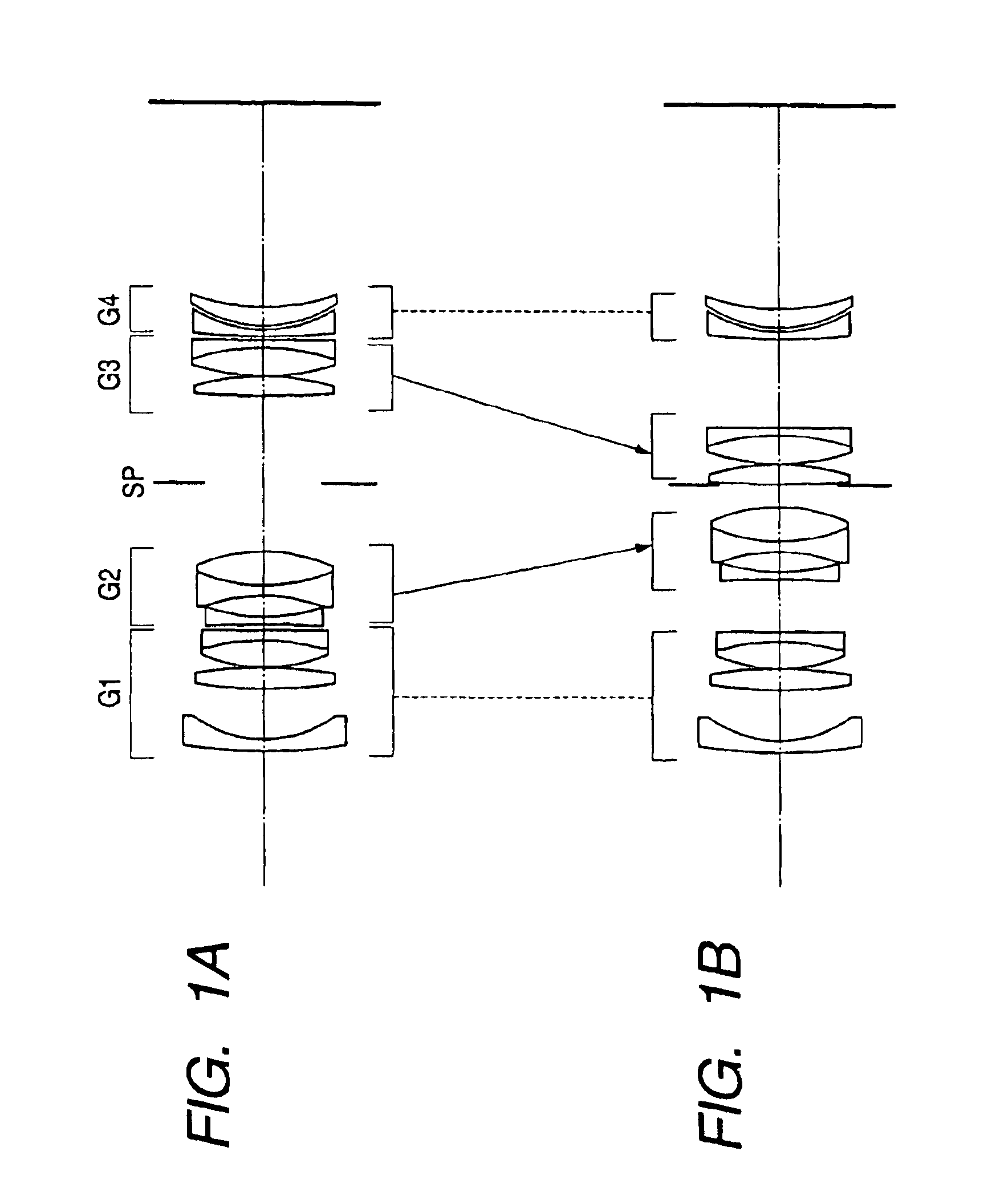
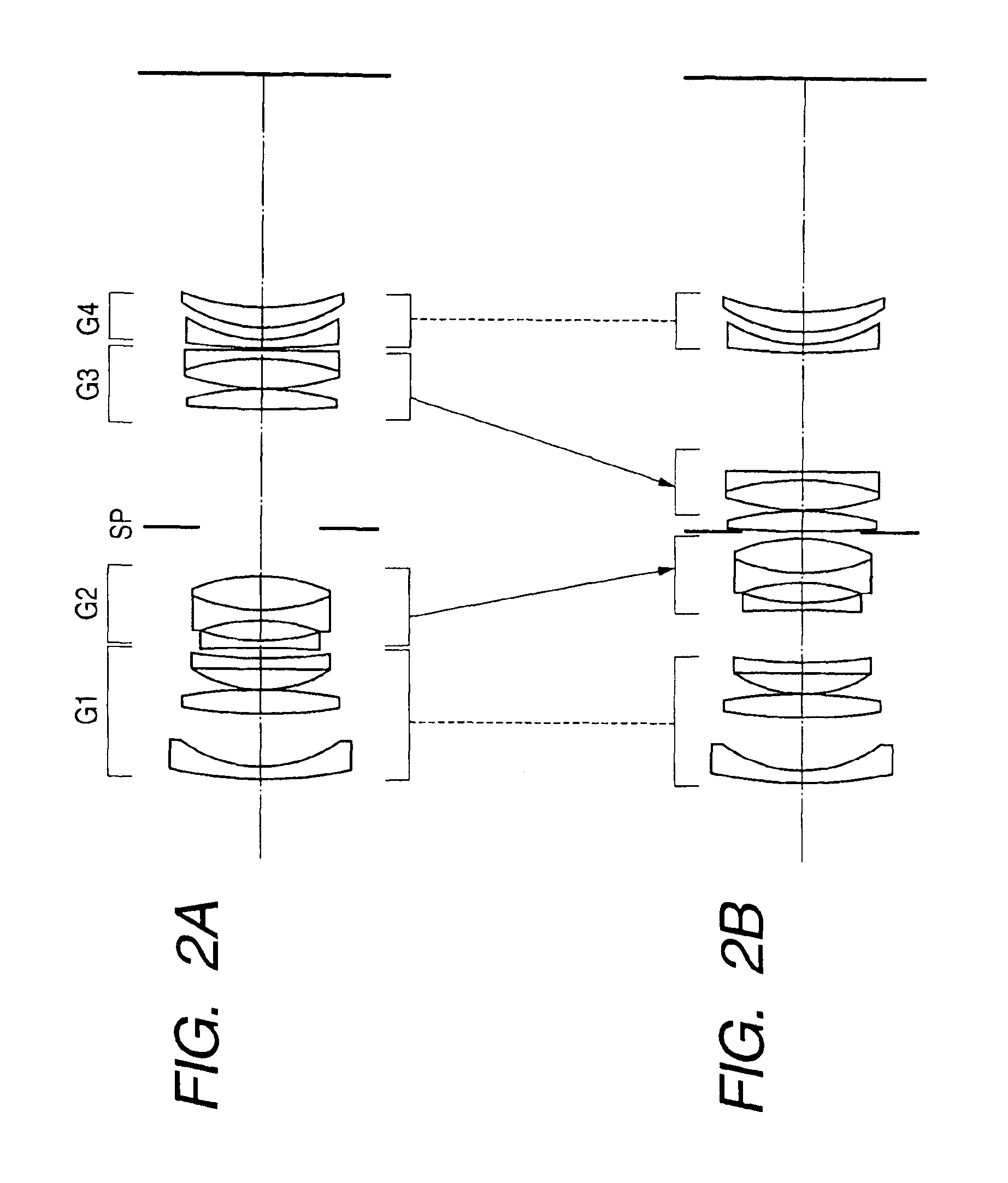
A zoom lens has the following lens components in the order named from the object side: a front lens component of a negative optical power, which has a first lens unit of a positive optical power and a second lens unit of a negative optical power in the order named from the object side; and a rear lens component of a positive optical power, which has a third lens unit of a positive optical power and a fourth lens unit of a positive optical power in the order named from the object side. The zoom lens varies a spacing between principal points of the front lens component and rear lens component by varying a spacing between the first lens unit and the second lens unit and a spacing between the third lens unit and the fourth lens unit, in order to effect zooming. The first lens unit and the fourth lens unit change their moving direction midway through zooming from the wide-angle end to the telephoto end.< / PTEXT>
Owner:CANON KK
3-dimensional image display device and display method thereof
ActiveUS20130307948A1Quality improvementColor television detailsSteroscopic systemsLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
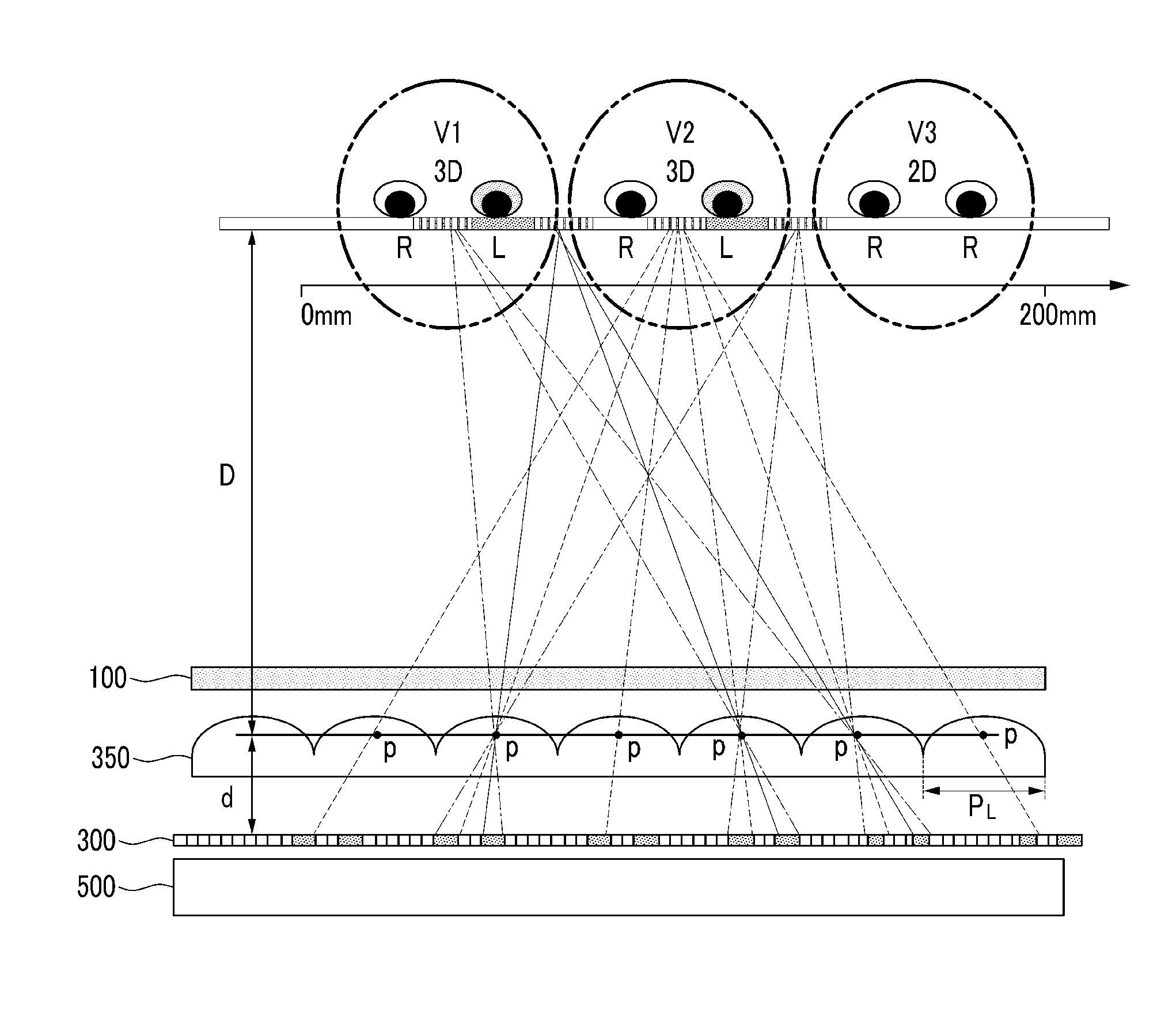
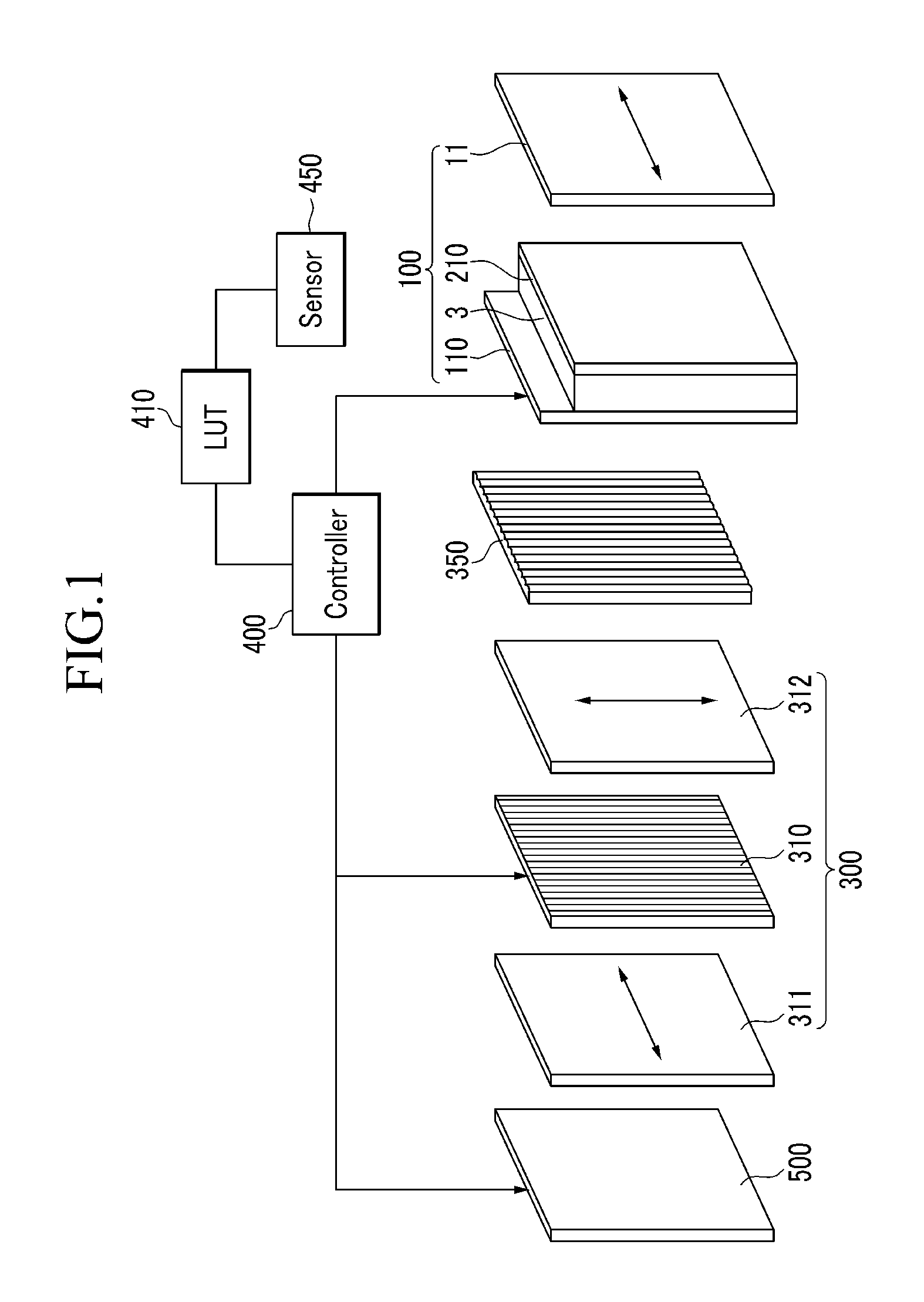
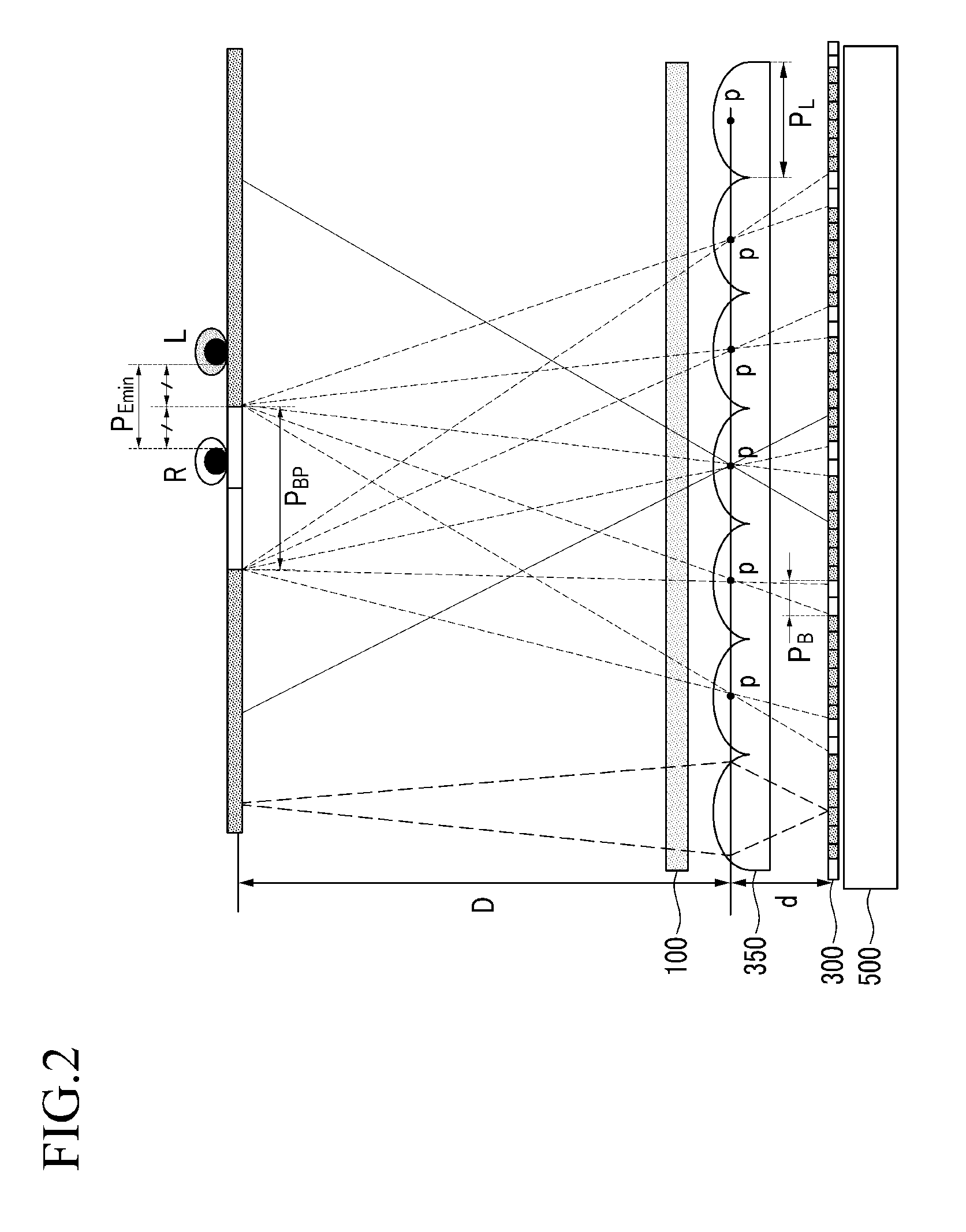
A 3-dimensional image display device includes: a backlight unit; a barrier panel above the backlight unit and including unit barriers which selectively blocks light; a lenticular lens array above the barrier panel and including lenticular lenses, each having a principal point; a liquid crystal panel above the lenticular lens array; an eye tracking sensor which detects a position of eyes of a viewer and a distance between the principal point of the lenticular lenses and the eyes; and a controller which controls the backlight unit, the barrier panel and the liquid crystal panel based on an output of the eye tracking sensor, where the controller turns on and off the unit barriers such that light passes through the principal point of the lenticular lenses to apply a right-eye image to a right eye of the viewer and apply a left-eye image to a left eye of the viewer.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Range finder and method
InactiveUS20050035314A1Prevents deterioration of measurementInhibit deteriorationTelevision system detailsInvestigating moving sheetsPrincipal pointImage capture
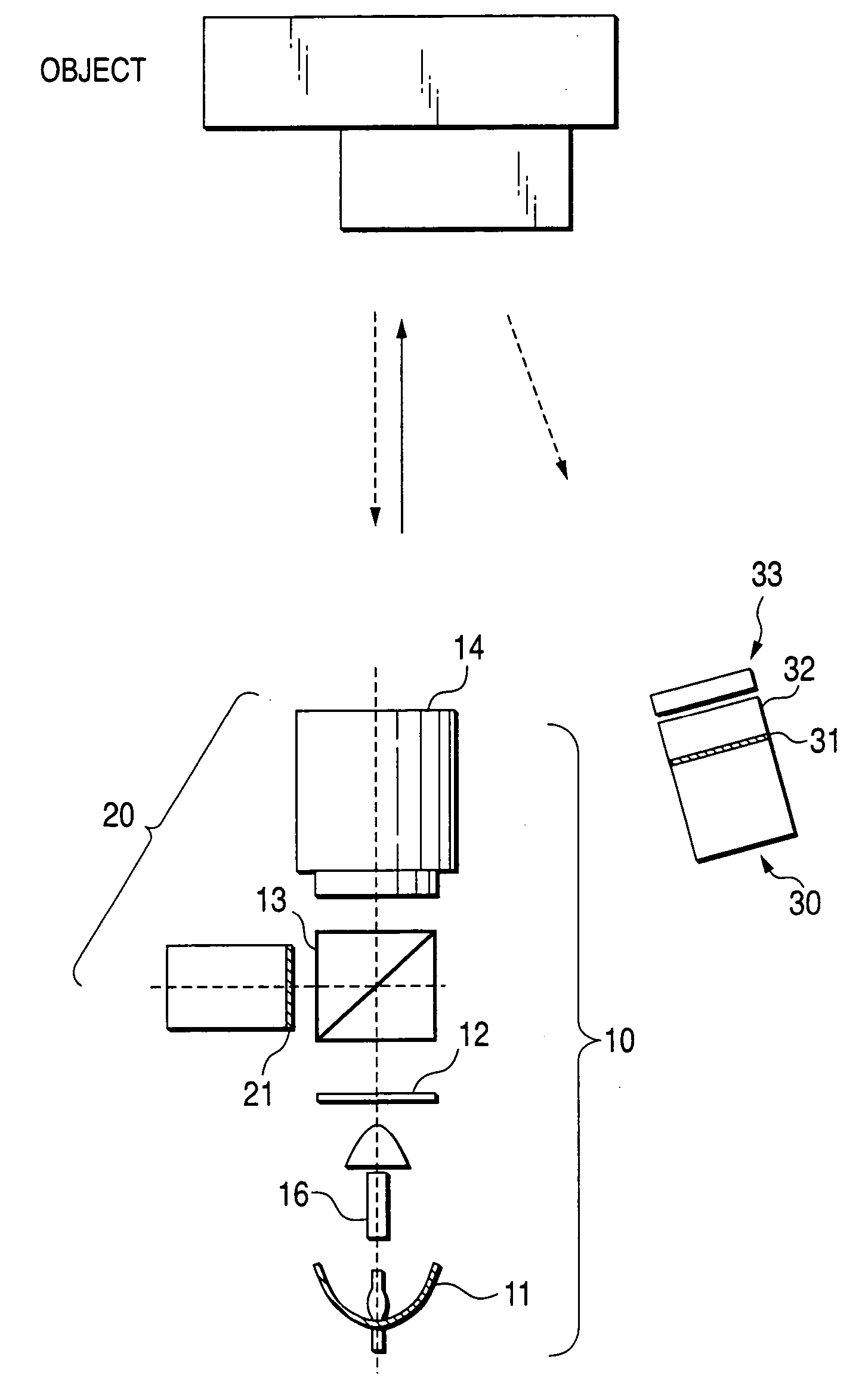
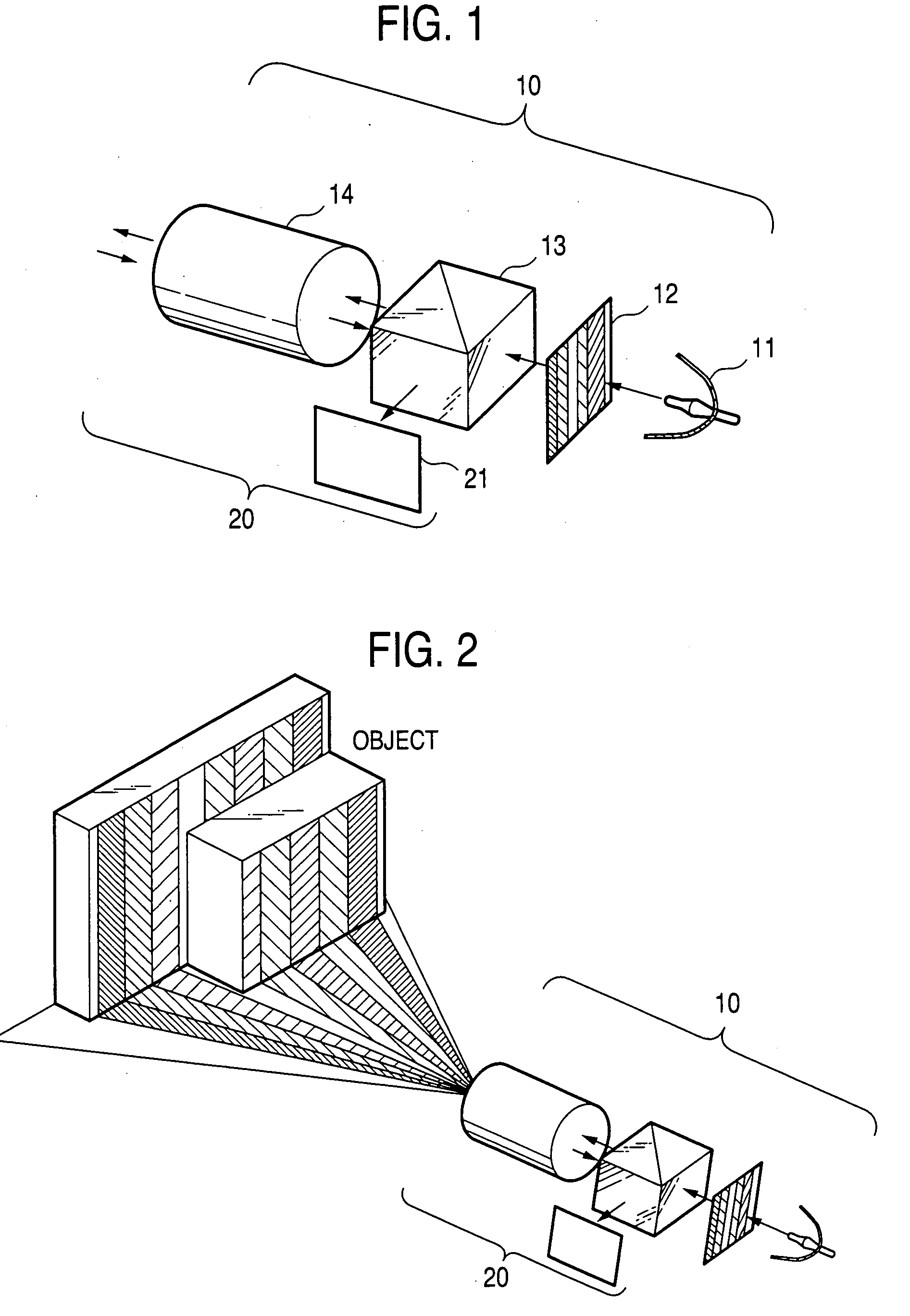
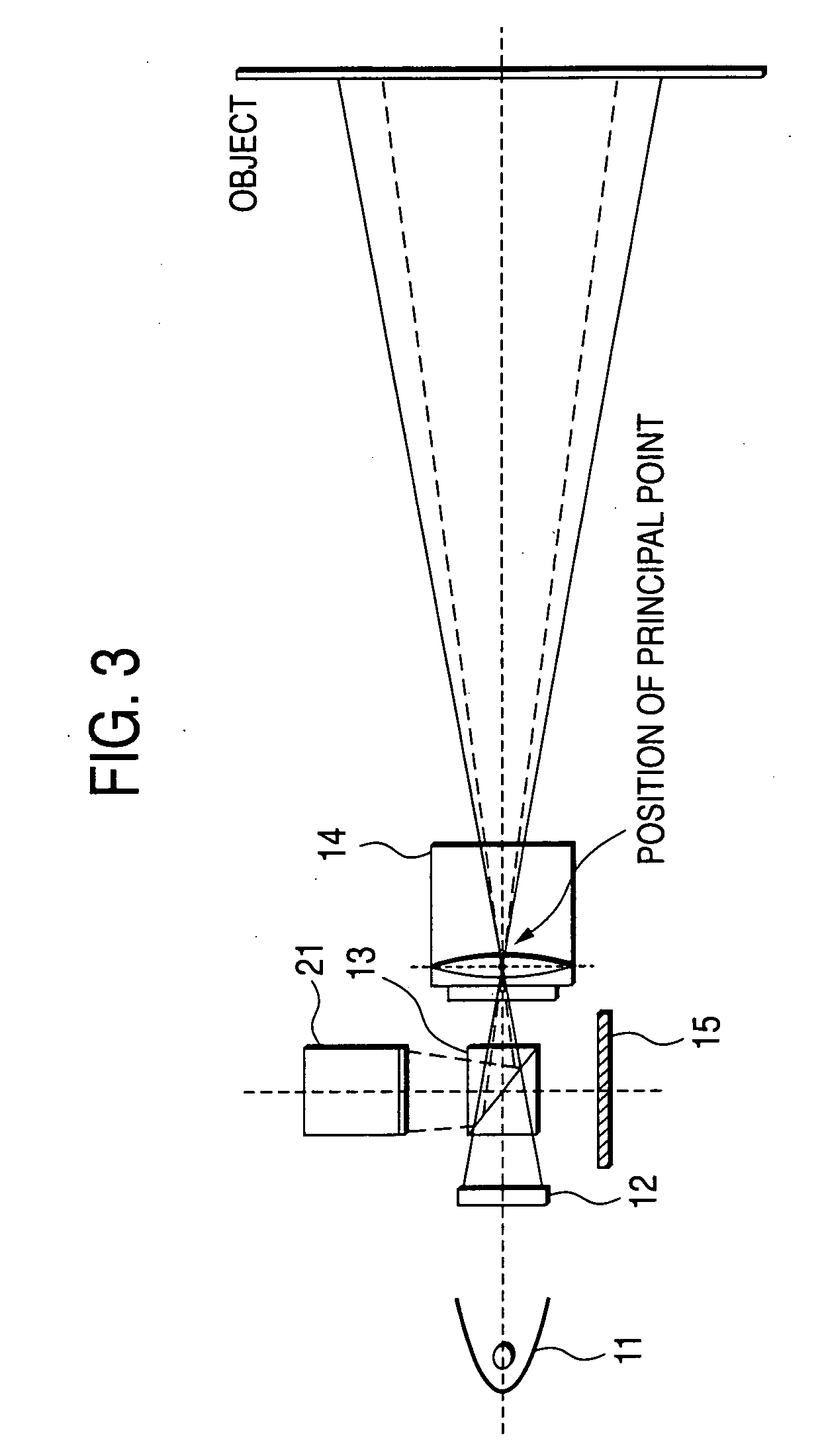
A range finder for measuring a three-dimensional geometry of an object includes a projector unit for projecting the pattern light onto the object, a first image capturing unit for capturing an image reflected from the object, a second image capturing unit for capturing an image reflected from the object, an identical principal point arrangement unit, and an imaging optical system. Preferably, the second image capturing unit is arranged so as to assume a principal point optically differing from that of the first image capturing unit, the identical principal point arrangement unit arranges the projector unit and the first image capturing unit at the position of an optically identical principal point, and the imaging optical system is shared between the projector unit and the first image capturing unit.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
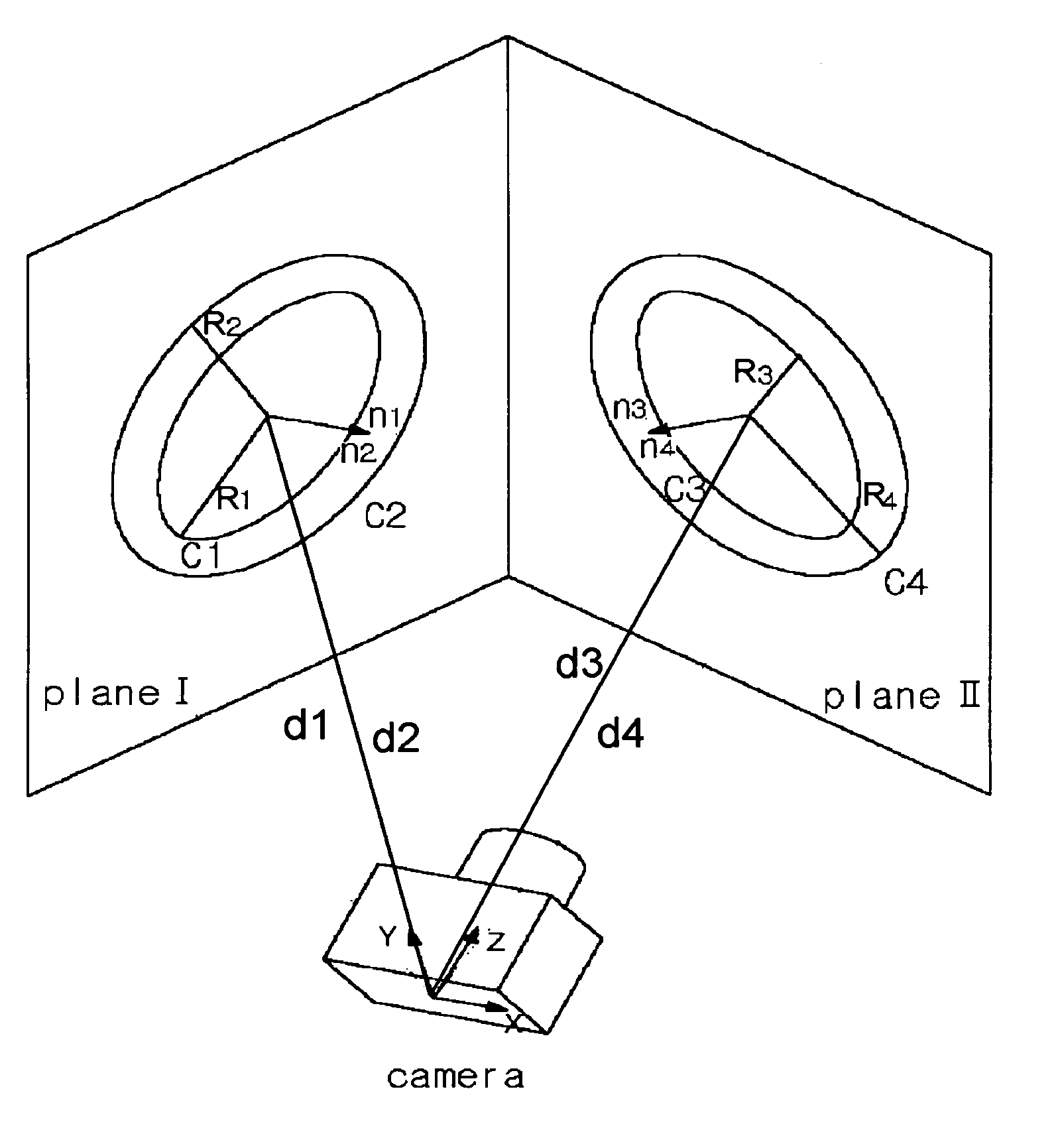
Camera calibration system using planar concentric circles and method thereof
InactiveUS20050207640A1Improve calibration reliabilityTelevision system detailsImage analysisMinimization algorithmProjection image
The invention relates to a camera calibration system and method thereof, which is capable of easily performing camera calibration using a concentric circle pattern. According to the invention, a method of calibrating a camera calibrates the intrinsic parameters of the camera required to measure geometric information of an object using projection invariable characteristics of concentric circles. The method includes the steps of: taking images of the calibration pattern consisting of two or more concentric circles located in the same plane and having different radius at different angles to obtain projected images; calculating the central point of the projected images using a given algorithm, and calculating the principal point and focal point of camera using a nonlinear minimization algorithm based on the central point thus obtained.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
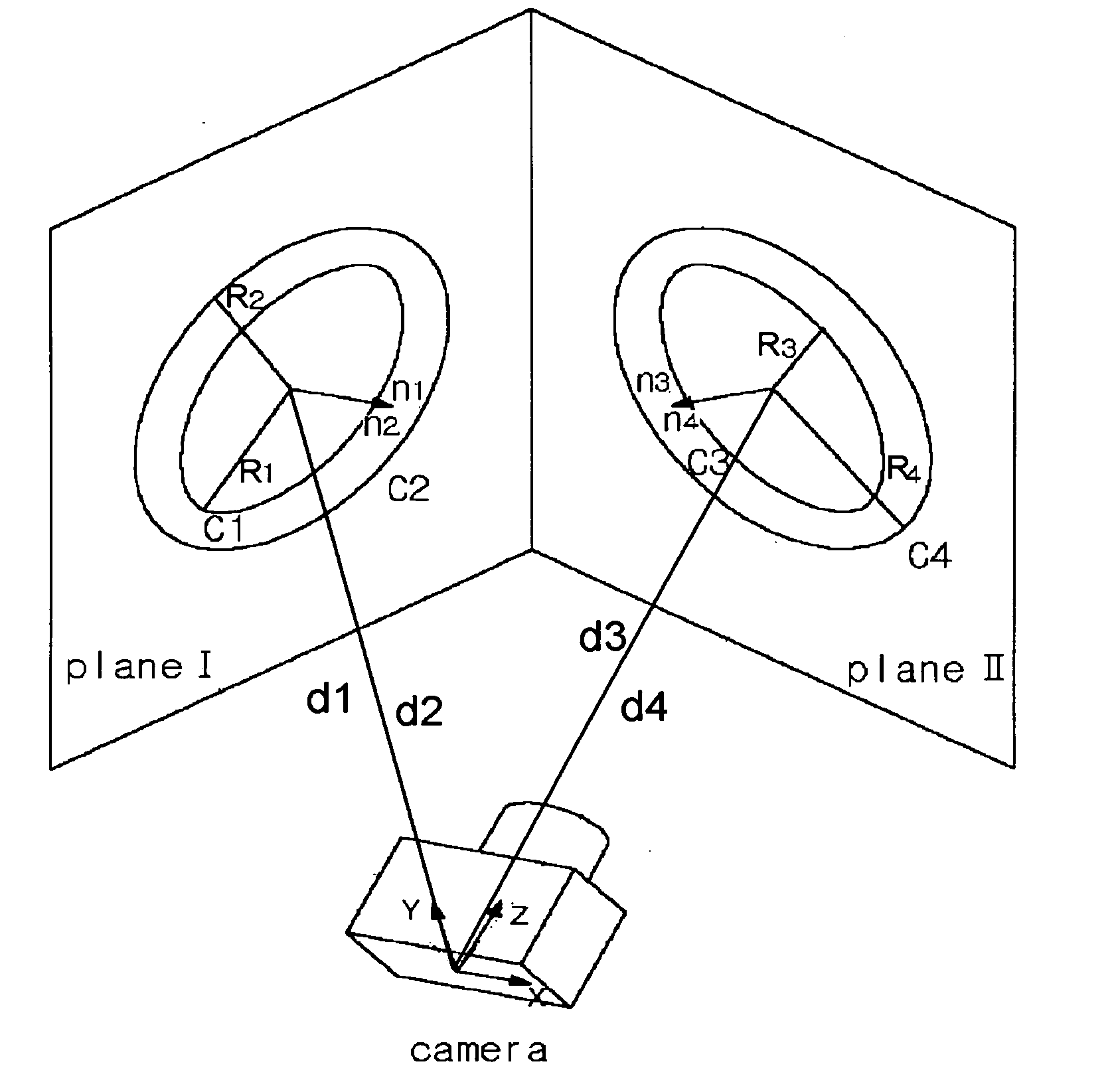
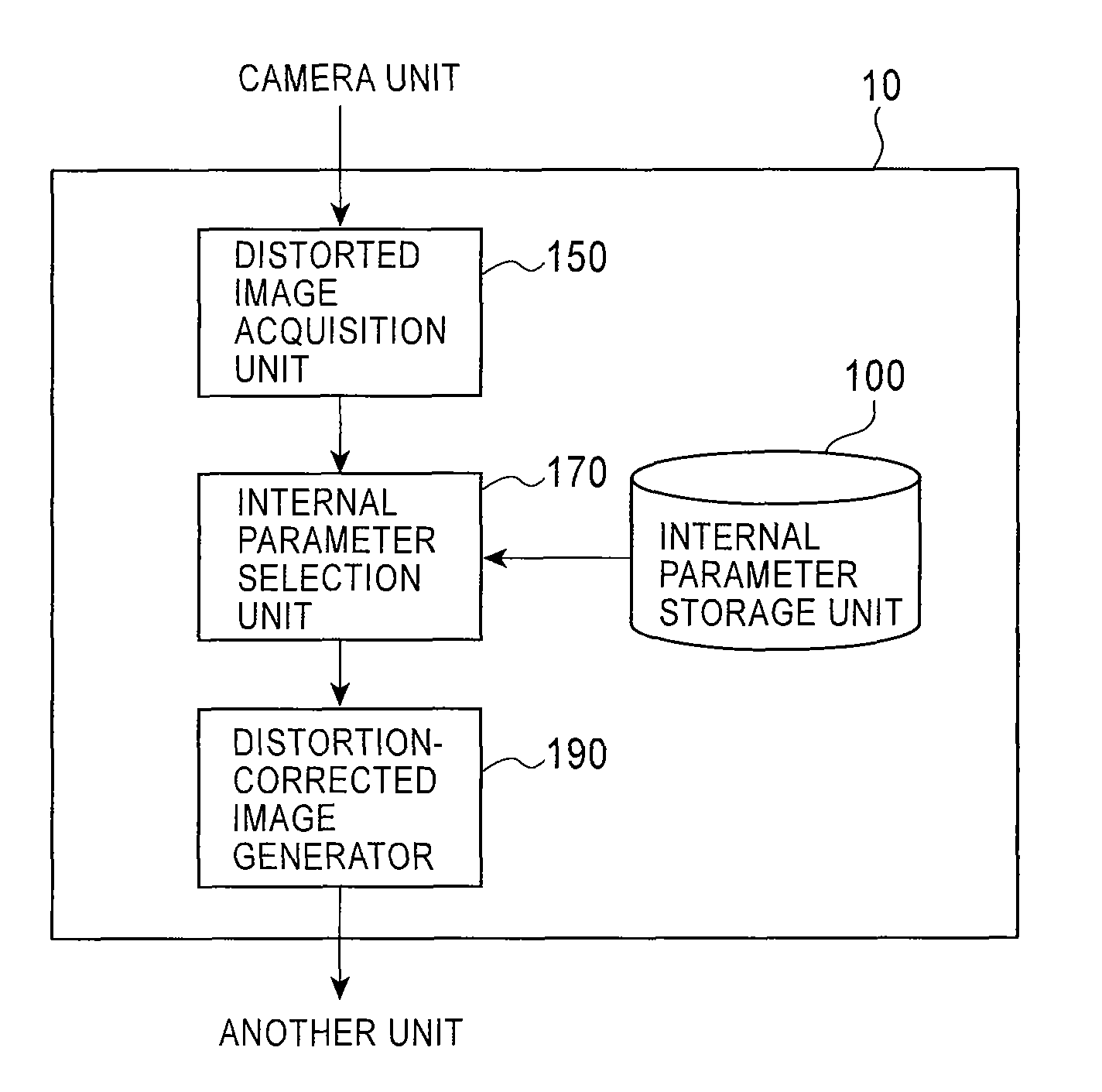
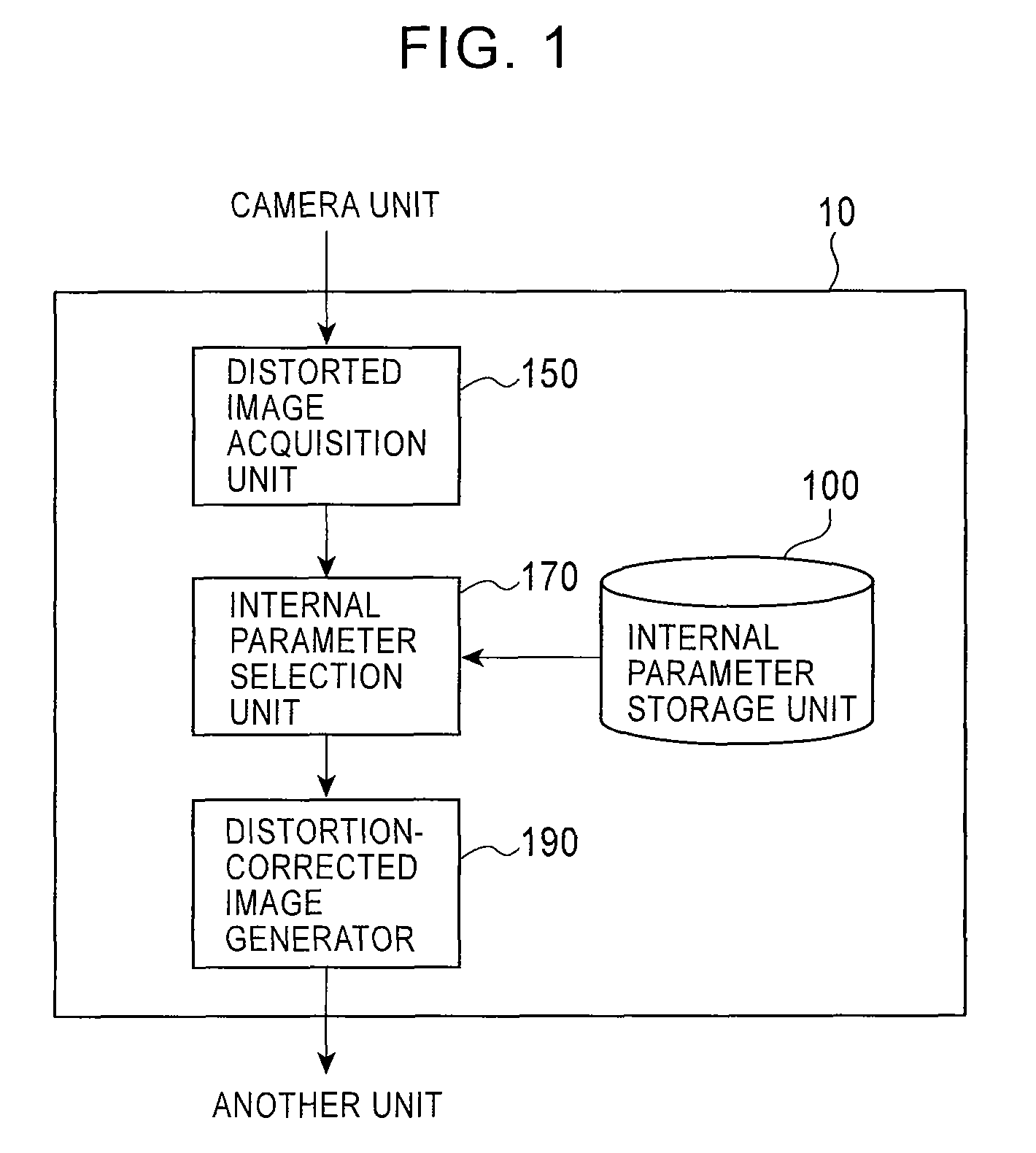
Distortion-corrected image generation unit and distortion-corrected image generation method
ActiveUS7965325B2Superfluous imageAccurate correctionImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPrincipal pointDistortion
Owner:ALPINE ELECTRONICS INC
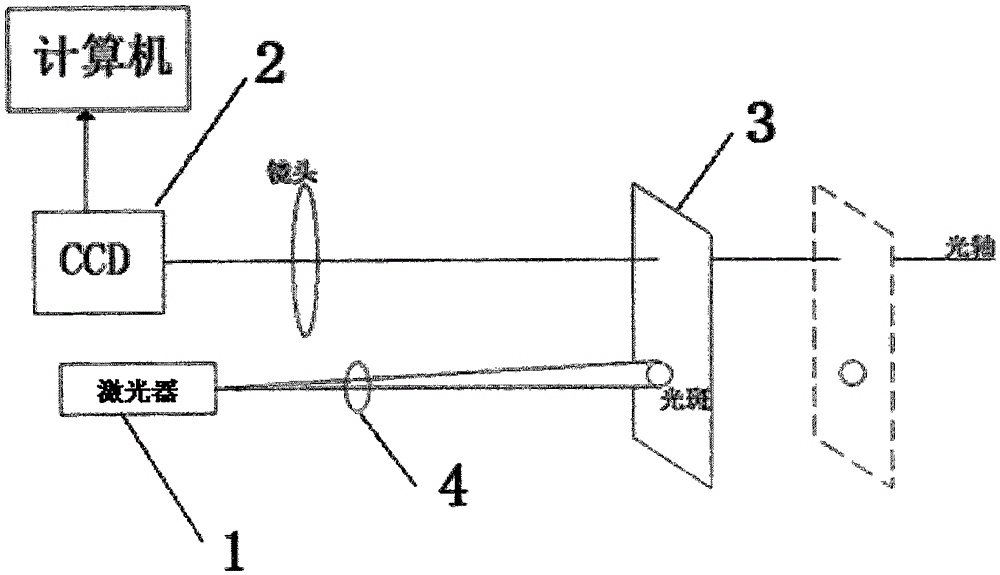
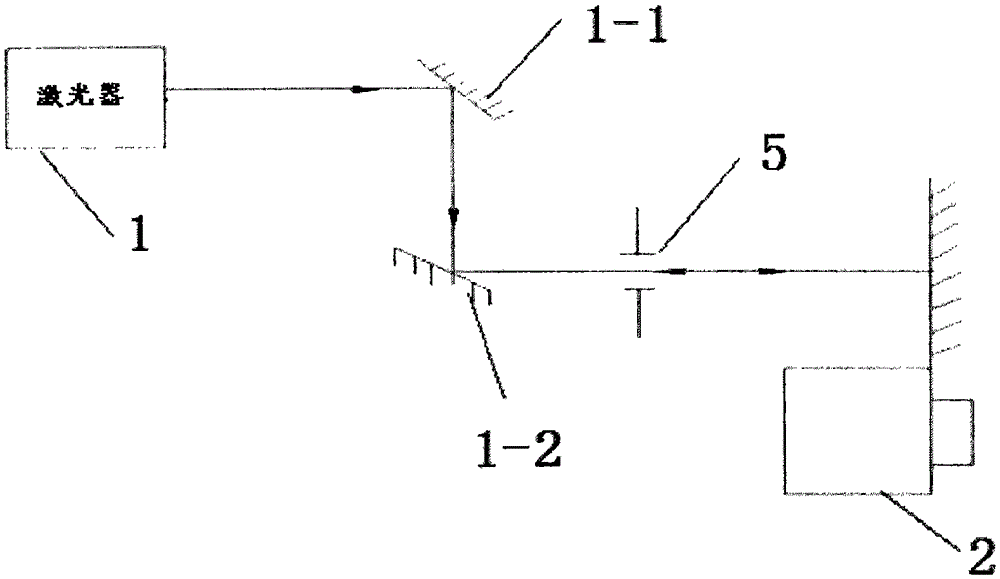
High-precision camera principal point calibration method
InactiveCN105258710AMeet the needs of rapid calibrationHigh precisionMeasurement devicesImaging processingOptical axis
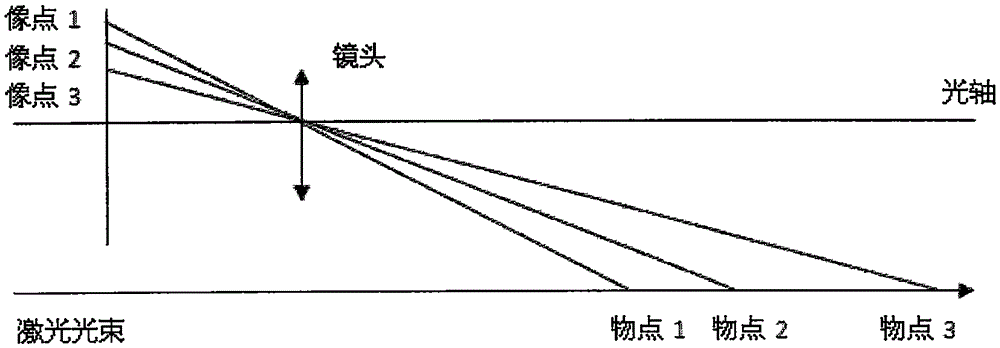
The invention discloses a high-precision camera principal point calibration method, and relates to the technical field of image measurement. The method comprises the following steps: adjusting the direction of laser emitted by a laser device to make the laser direction parallel to the optical axis of a camera and to make laser spots be displayed on a receiving display, moving the receiving display, collecting laser spot images in different positions to obtain a laser spot image set, using an image processing technology to find out the coordinates of the laser spot centers of the laser spot images in different positions, carrying out linear fitting on the obtained laser spot centers to obtain the linear equations of center connecting lines, solving the two linear equations, and finding out the intersection point of the two linear equations, wherein the coordinate of the intersection point is a camera principle point coordinate. The method has the advantages of high calibration precision, simple and easy operation, and strong practicality, and can meet rapid calibration needs of the camera principle point.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for calibrating PTZ camera by using only two scene images
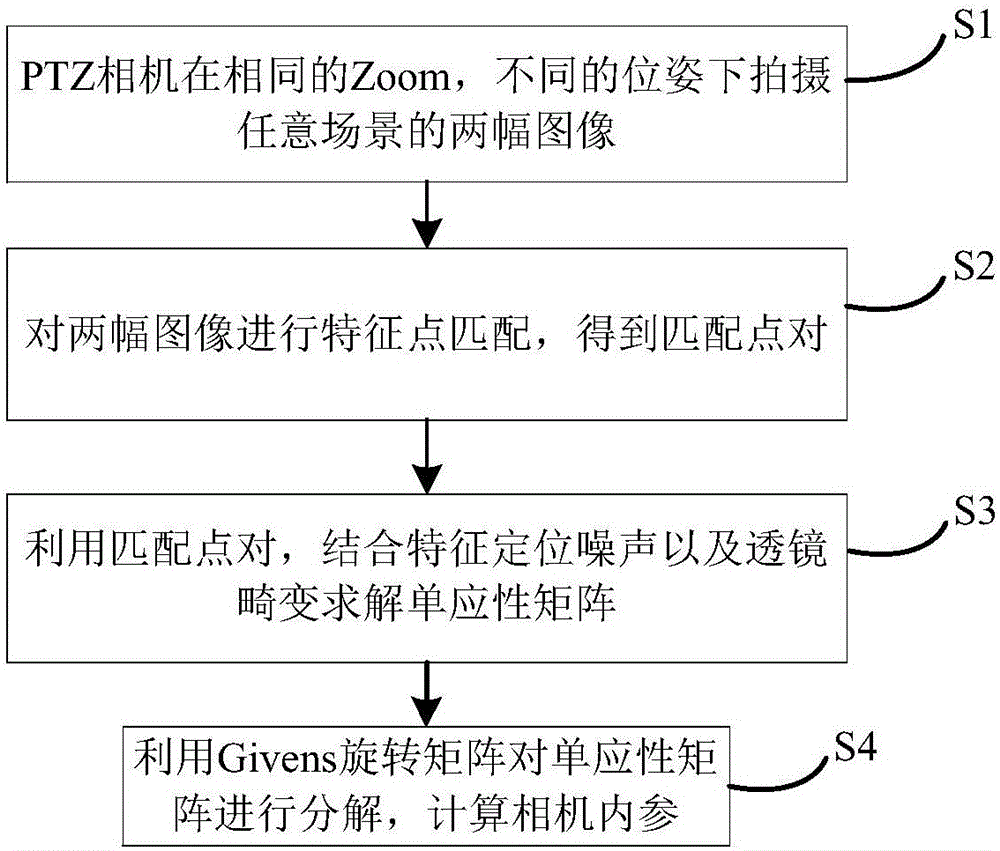
InactiveCN106530358ASimplify the internal calibration processHigh precisionImage analysisCamera lensPrincipal point
The present invention discloses a method for calibrating a PTZ camera by using only two scene images. Firstly, two images with overlapped areas of any scene in a same focal length and different Pan-Tilt angles relative to the PTZ camera are photographed, the two images are subjected to feature point matching, a matching feature point pair between the two images is obtained, the influences of the uncertainty of matching feature point positioning and camera lens distortion are considered, a homography matrix estimation method with the combination of feature point positioning noise and lens distortion is created, the homography matrix between the two images and the radial distortion coefficient of the PTZ camera under the focal length are obtained, finally a Givens rotation matrix is constructed to decompose the obtained homography matrix, and thus the four internal references (focal length, principal point coordinate, and aspect ratio) of the camera is resolved and obtained. According to the method, the online calibration of five parameters of the PTZ camera can be realized.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
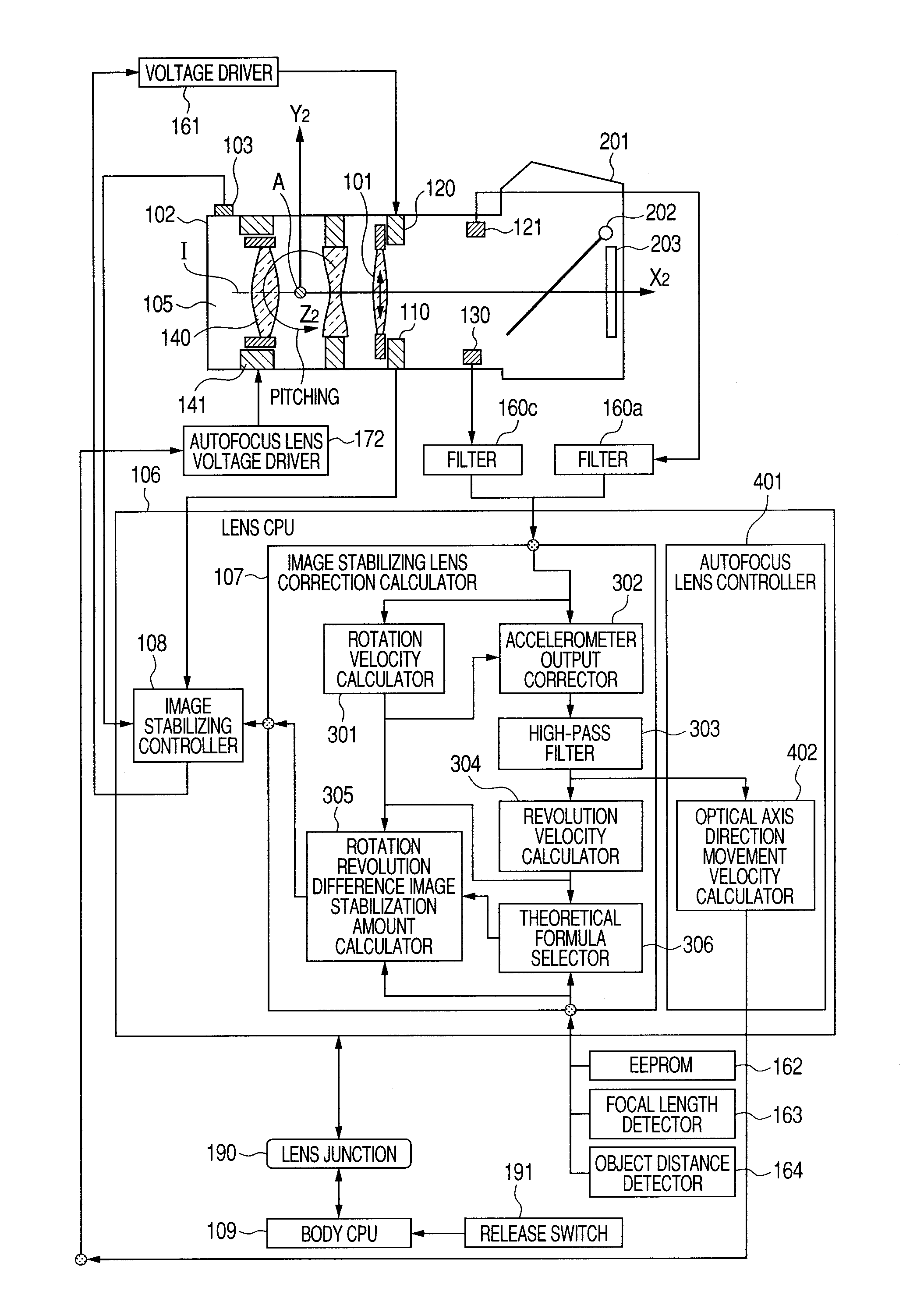
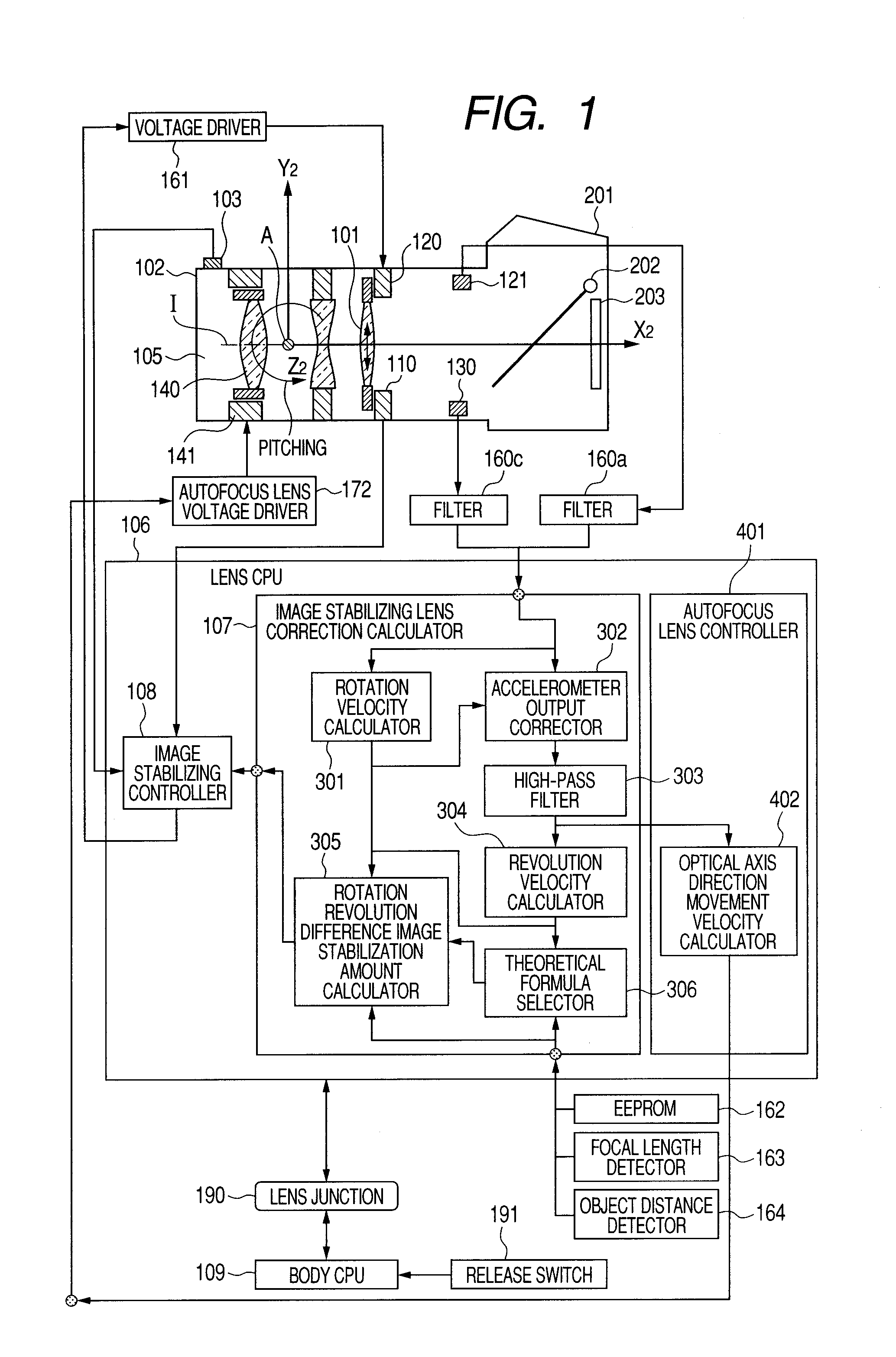
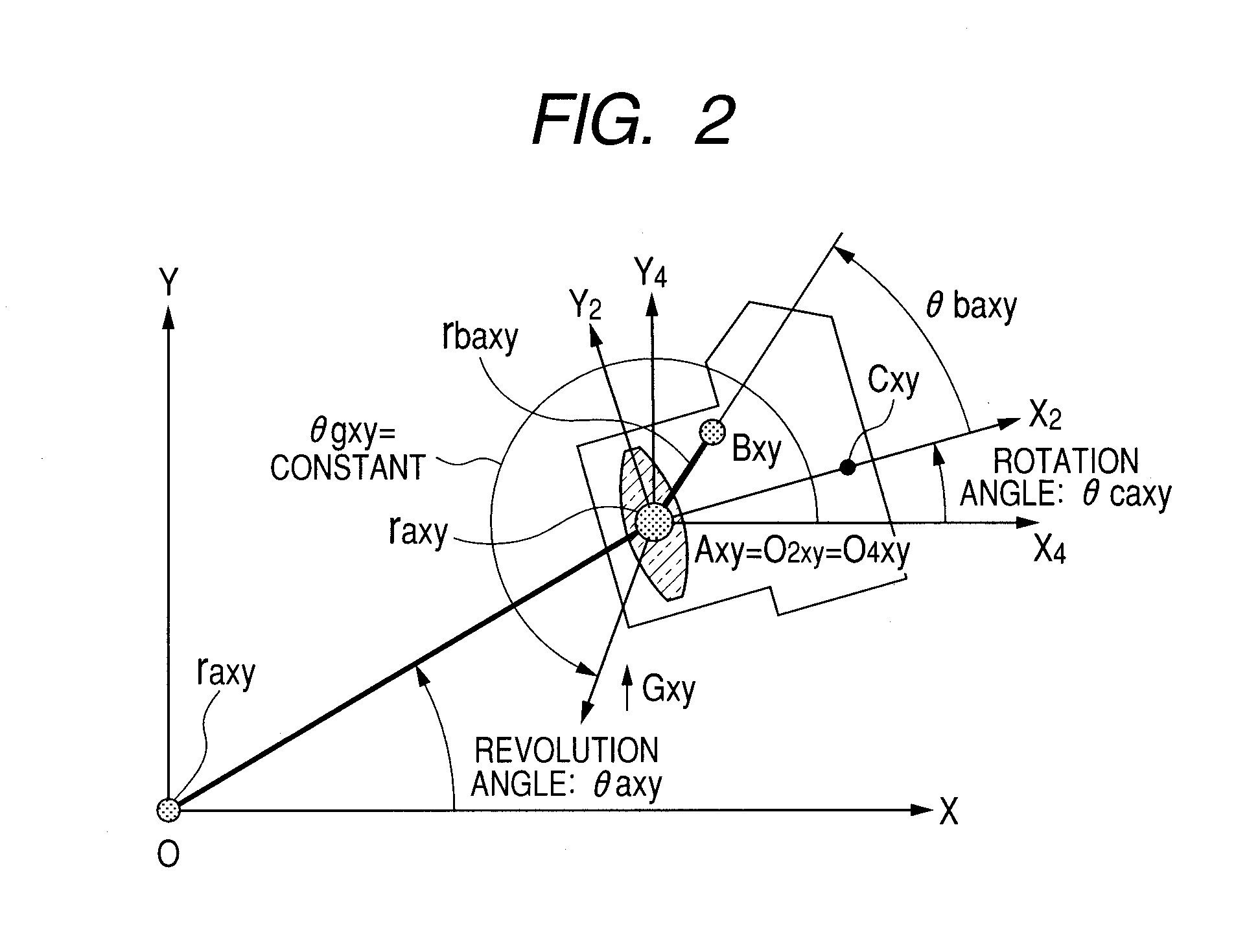
Image shake correction apparatus and image pickup apparatus
InactiveUS20100254688A1Reduce the amount of calculationCamera body detailsAngular velocityPrincipal point
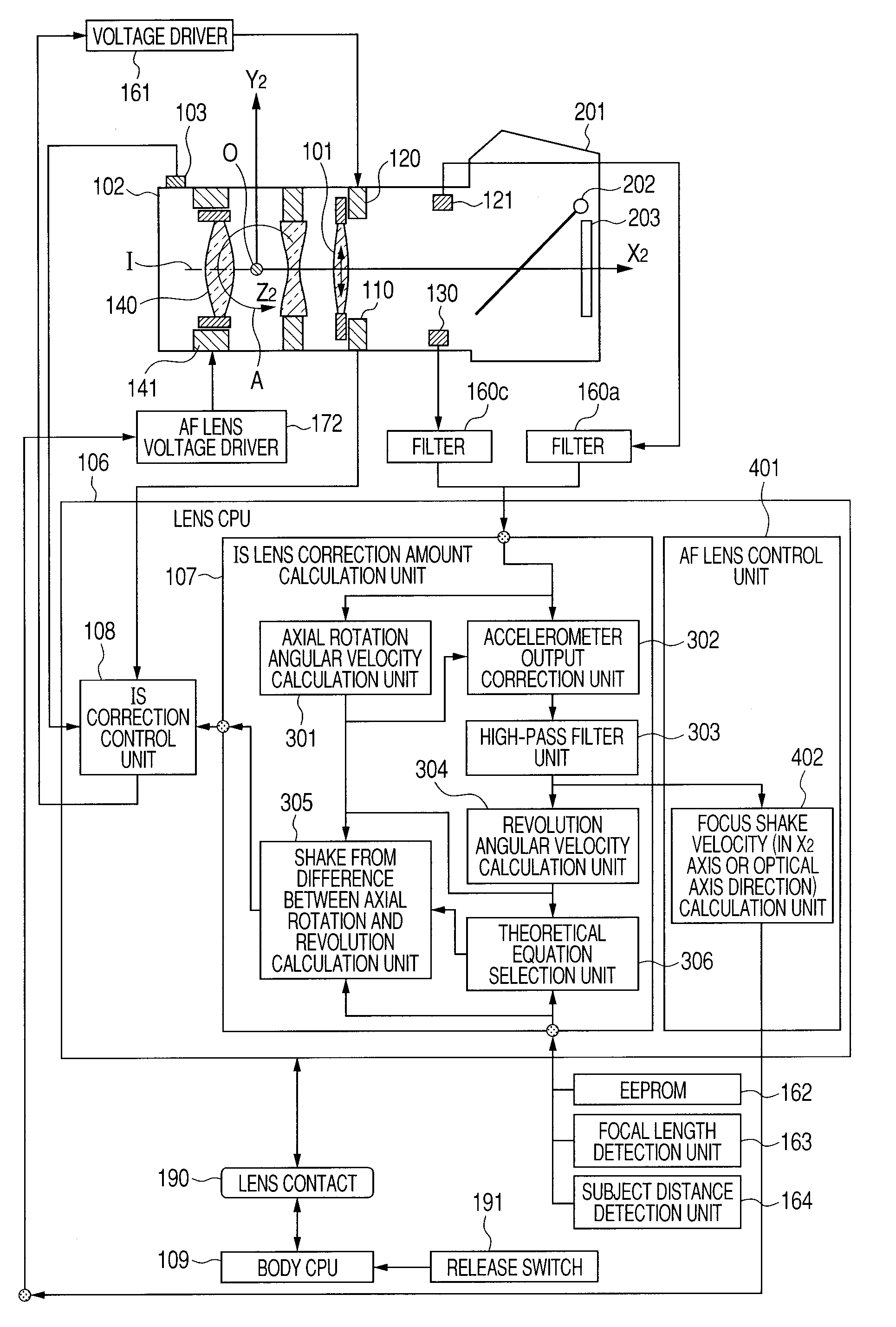
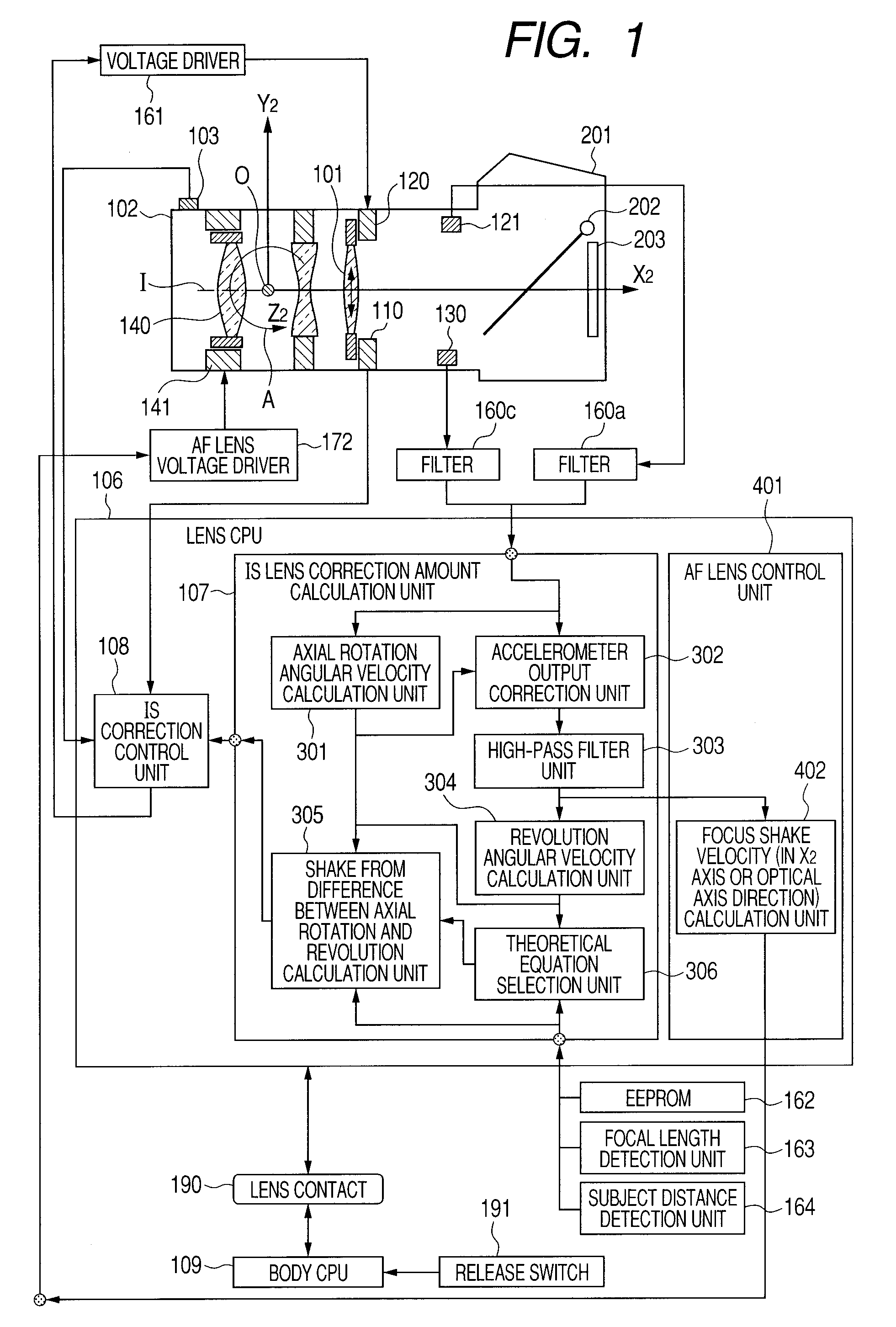
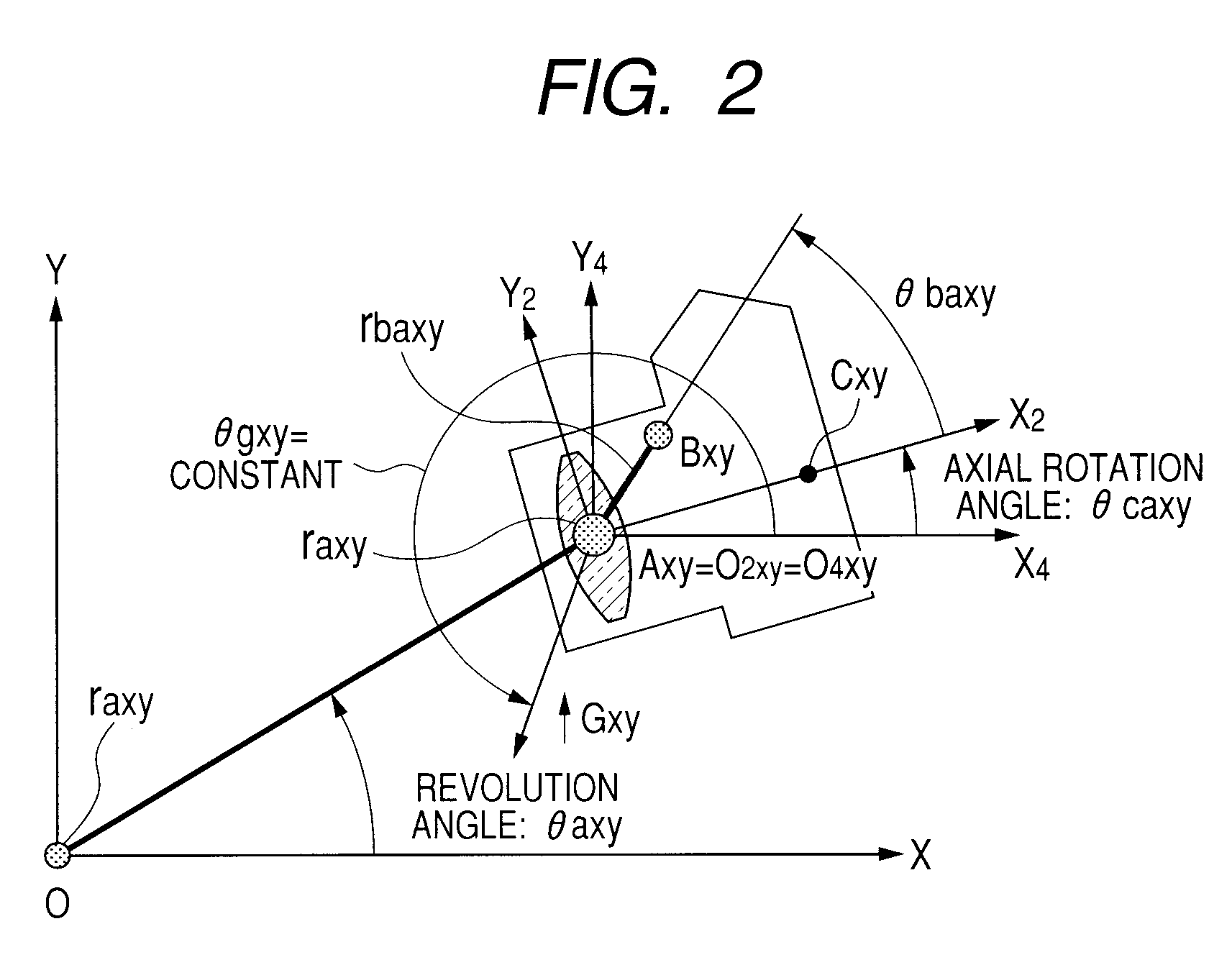
Provided is an image shake correction apparatus including: an image taking optical system for taking an image of a subject; an angular velocity detection unit for detecting an angular velocity applied to the apparatus and outputting a first signal; an acceleration detection unit for detecting an acceleration applied to the apparatus and outputting a second signal; an axial rotation angular velocity calculation unit for calculating an axial rotation angular velocity component about a principal point of the image taking optical system based on the first signal; a revolution angular velocity calculation unit for calculating a revolution angular velocity component about the subject based on the second signal and a result of the calculating by the axial rotation angular velocity calculation unit; and a control unit for performing image shake correction control based on a difference between the axial rotation angular velocity component and the revolution angular velocity component.
Owner:CANON KK
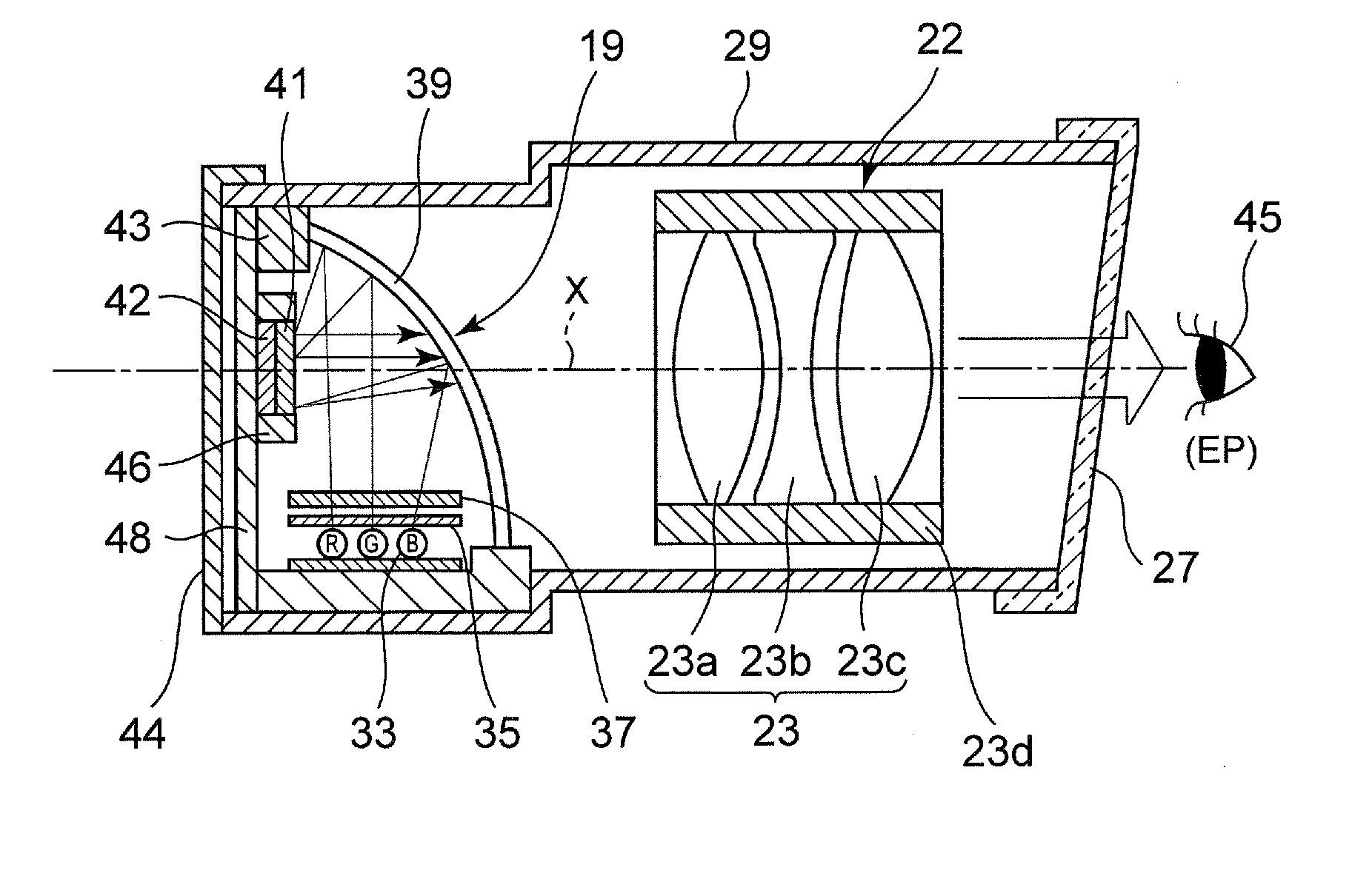
Eyepiece lens system, finder optical system, and electronic viewfinder of imaging apparatus and imaging apparatus
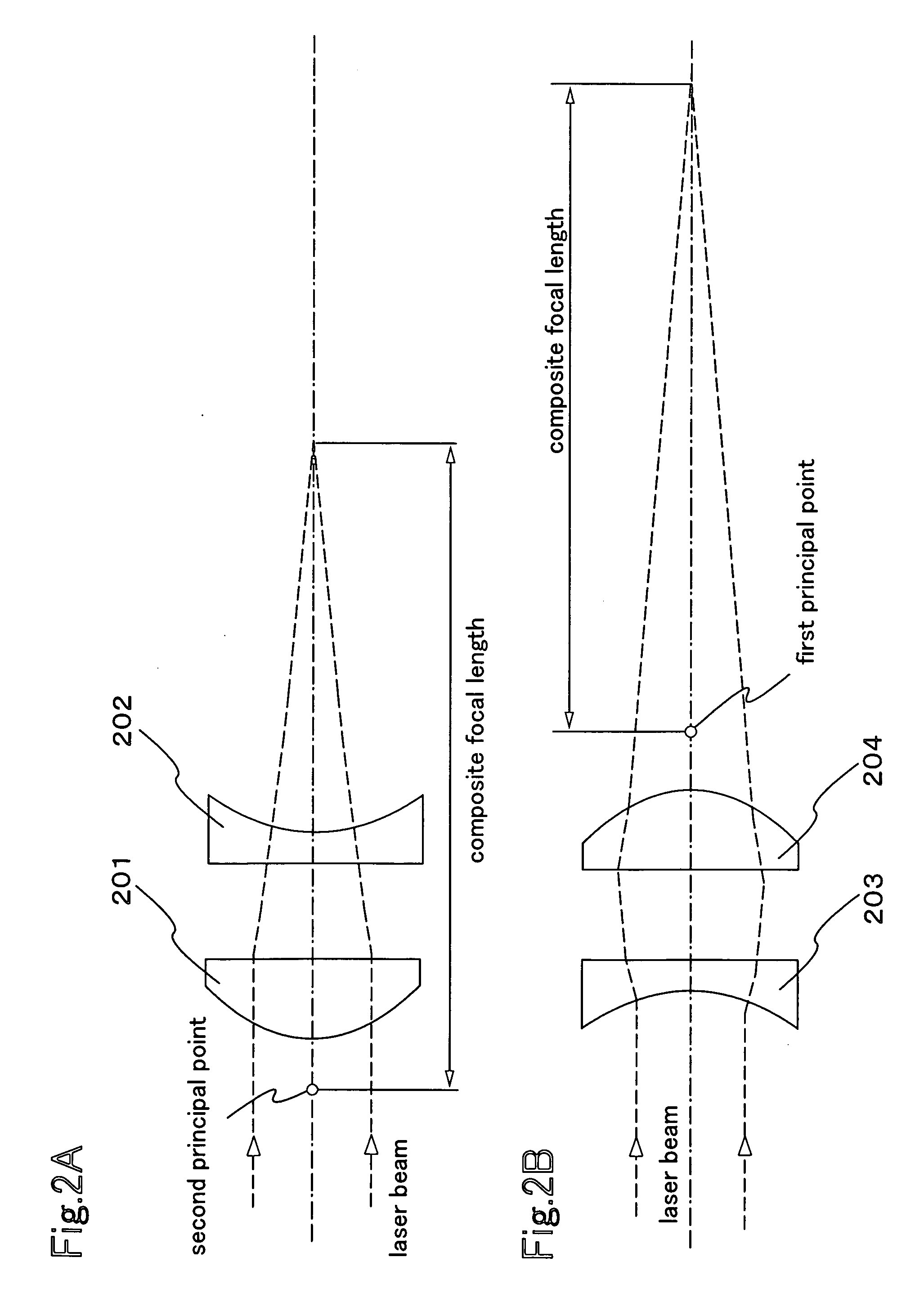
An eyepiece lens system for an electronic viewfinder, usable to be disposed on an optical axis between a reflective LCD of the viewfinder and a last optical surface of the viewfinder, the eyepiece lens system comprising: a first lens having a positive refractive index; a second lens having a negative refractive index; and a third lens having a positive refractive index, wherein the first lens, the second lens, and the third lens are disposed in this order from a side of the LCD to a side of the last optical surface, satisfying the conditions: 18 mm<f1<20 mm, −18 mm<f2<−16 mm, 18 mm<f3<20 mm, 19 mm<f<21 mm, and 0≦̸HH′ / f<+0.13 where f1 is a focal length of the first lens, f2 is a focal length of the second lens, f3 is a focal length of the third lens, f is a combined focal length of the first to the third lenses, and HH′ is distance in an optical axis direction between a rear principal point H and a front principal point H′.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Range finder and method
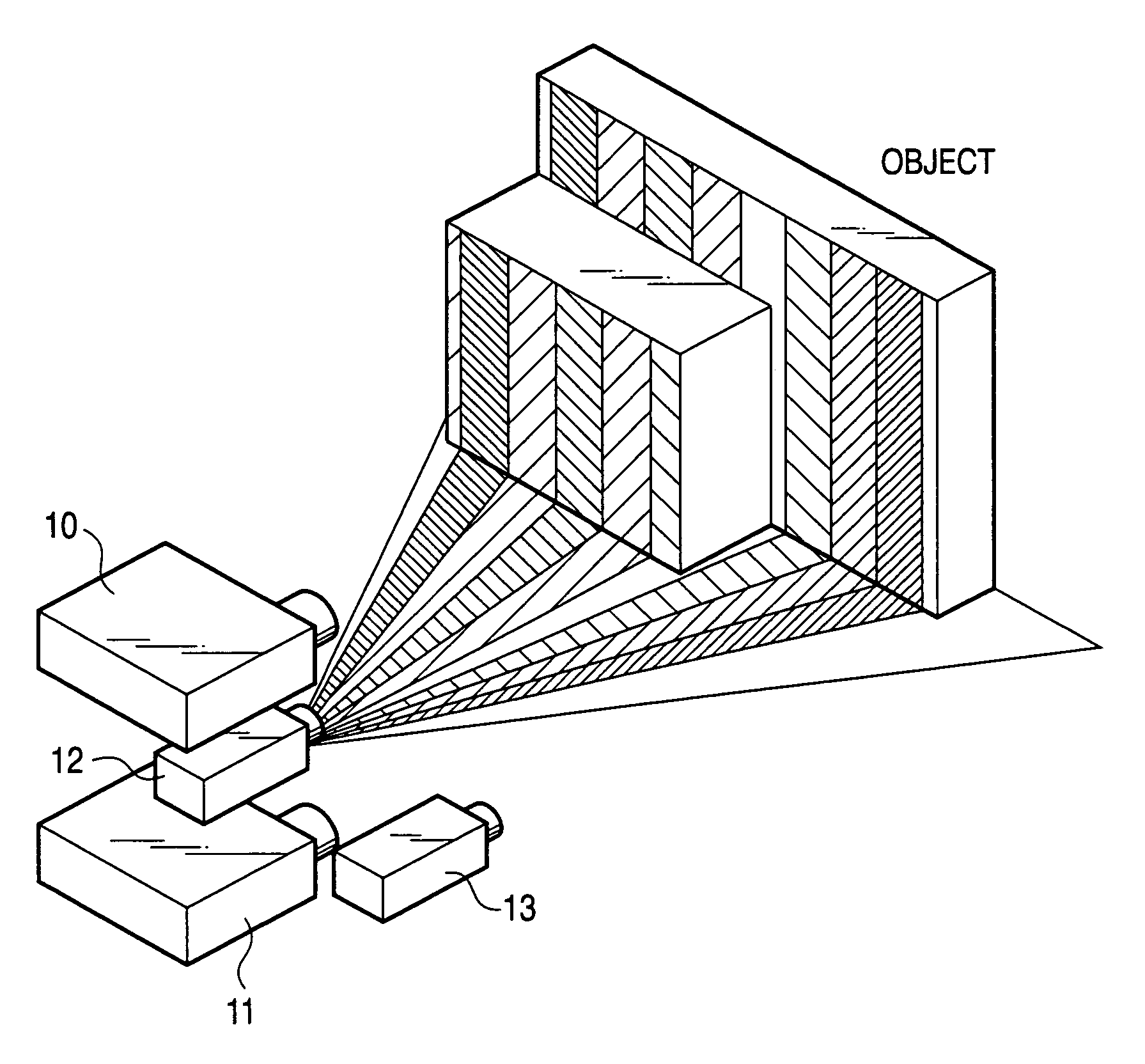
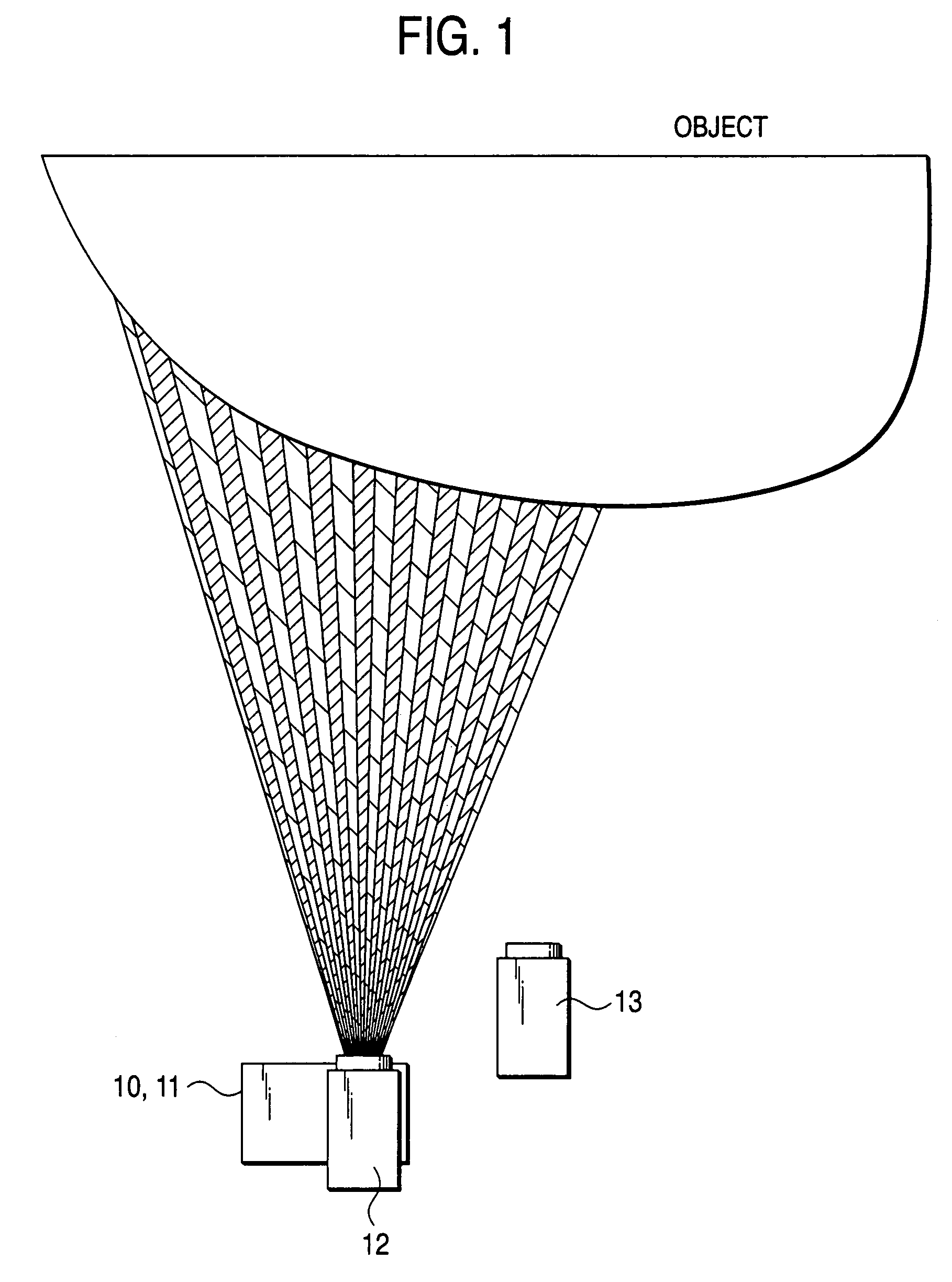
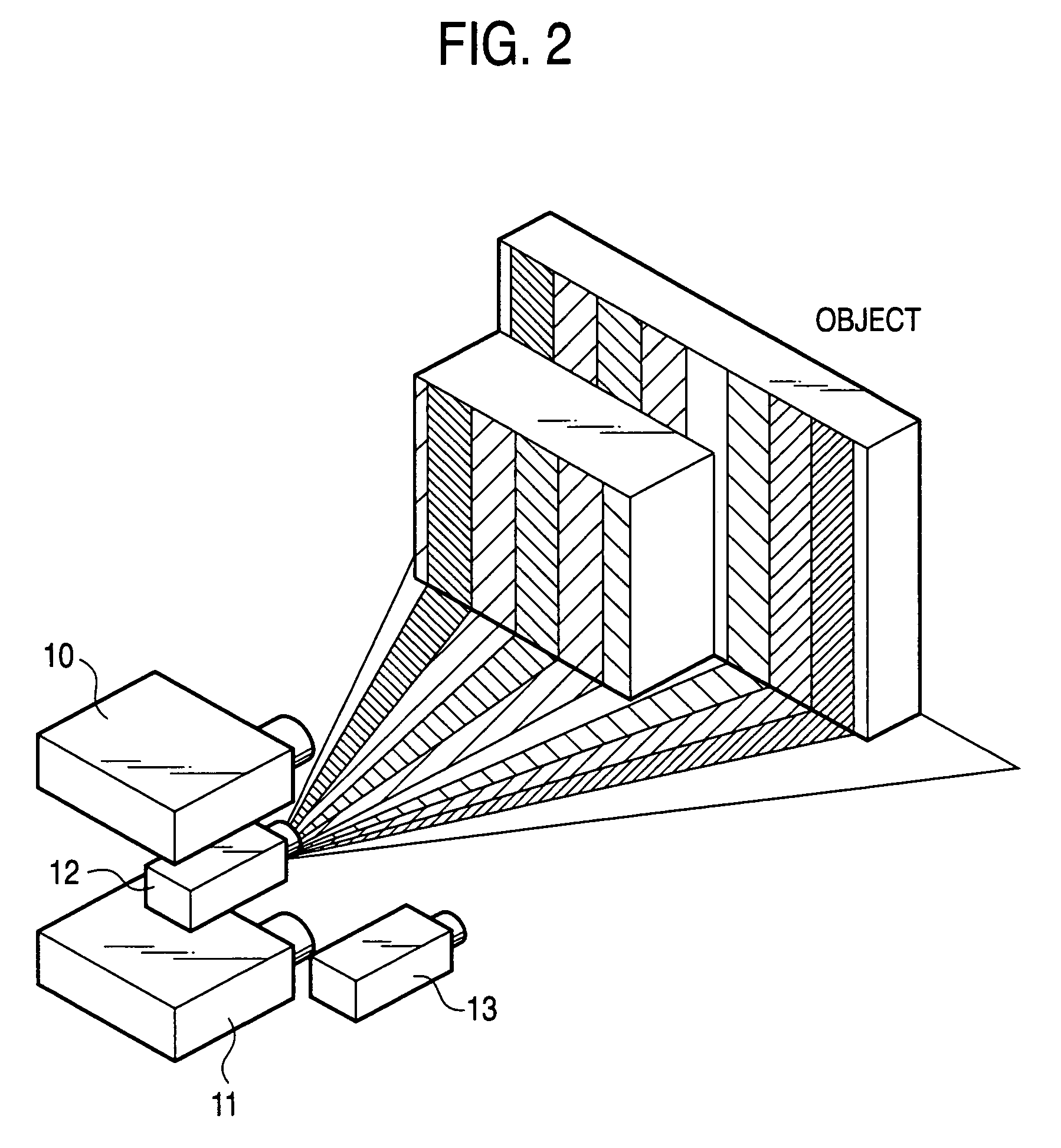
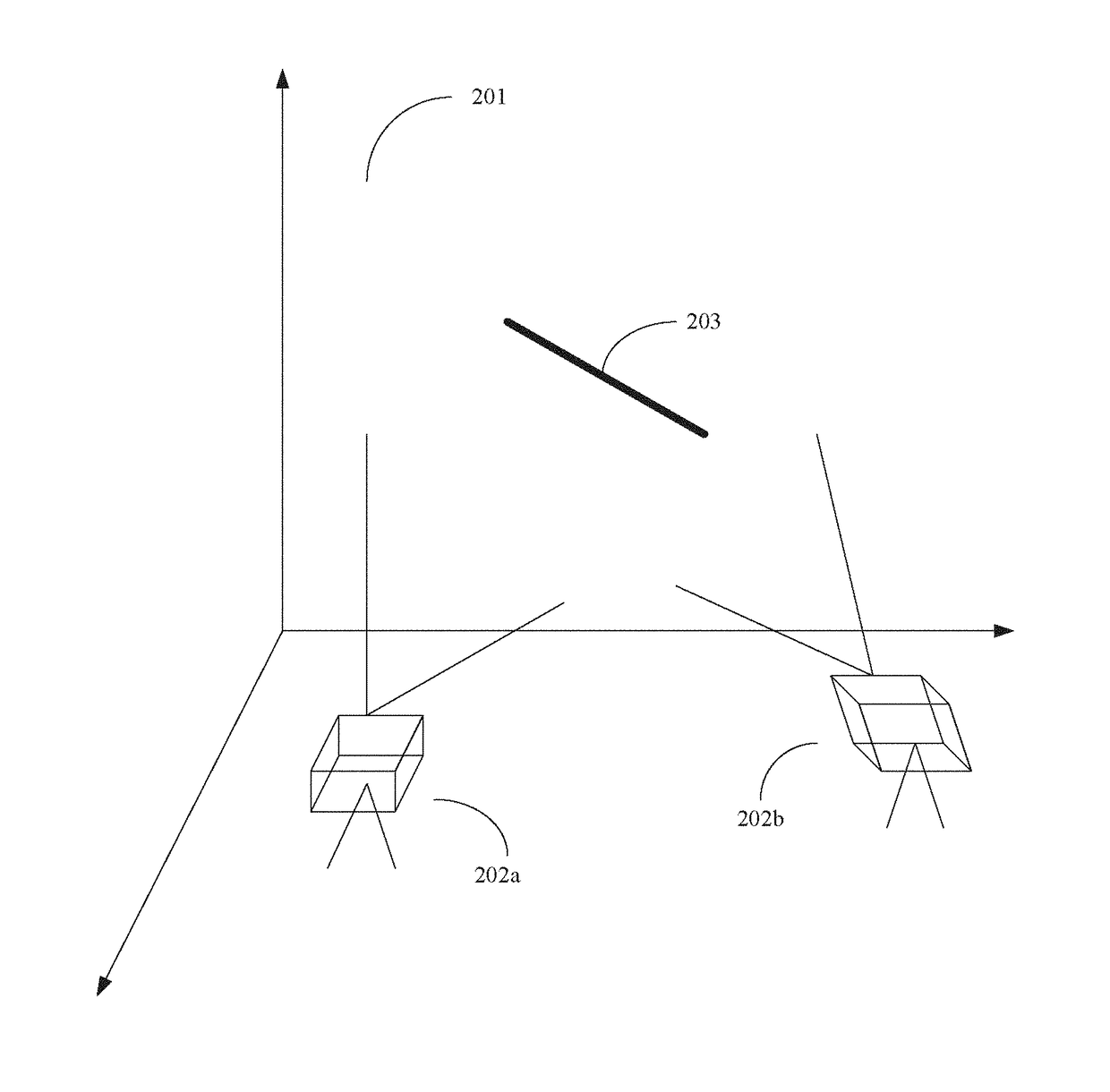
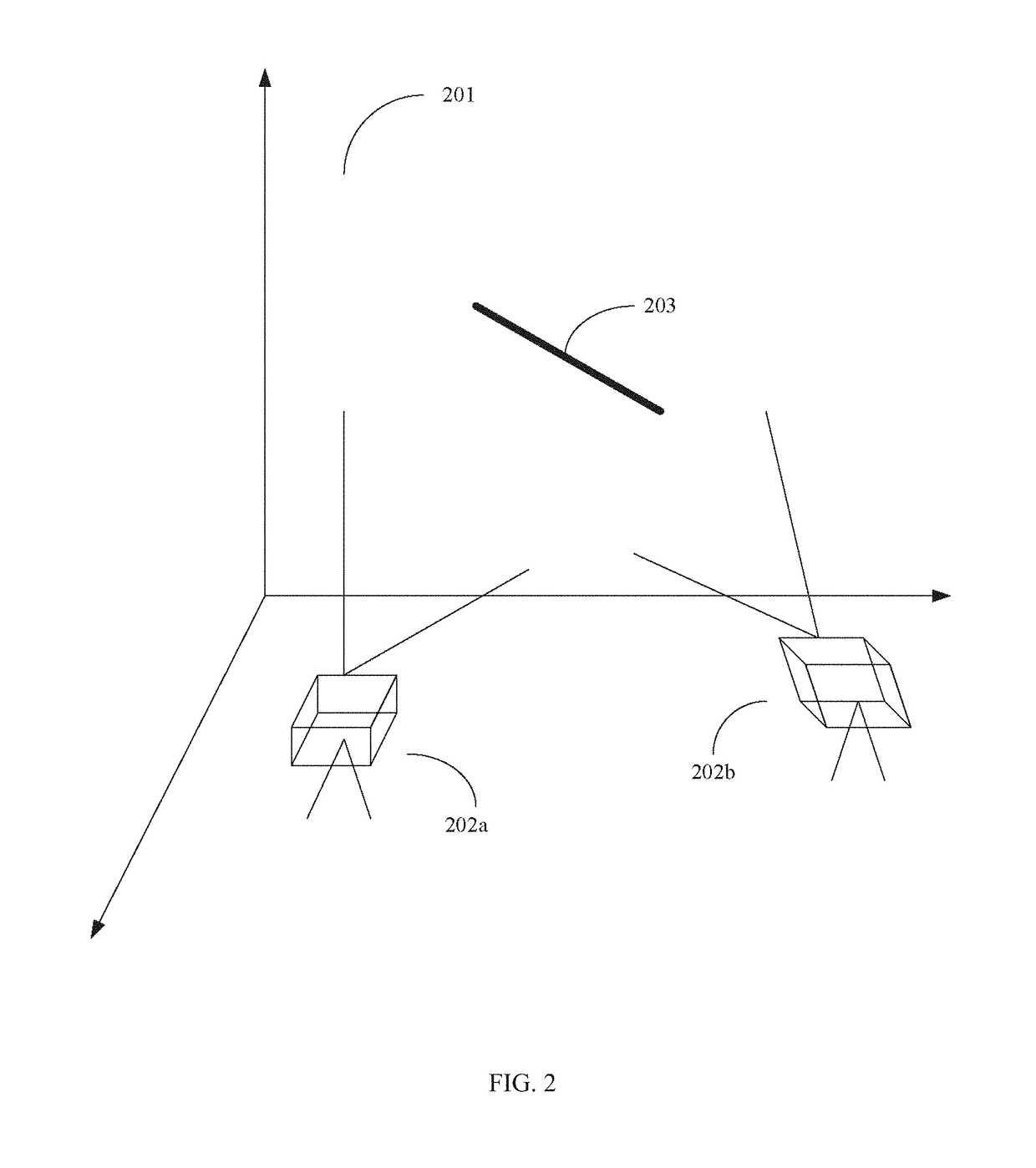
Pattern projection apparatuses are placed on each other in a stack manner in a stripe pattern direction for projecting the same patterns. An image pickup apparatus (camera 1) is placed between the pattern projection apparatuses. The optical axes of the pattern projection apparatuses and the image pickup apparatus are aligned on the same plane parallel with the stripe pattern direction. On the plane, the principal points also become the same. An image of a stripe pattern is picked up directly by the image pickup apparatus without the intervention of a half mirror, etc., and is recoded. An image of the recoded stripe pattern is picked up by an image pickup apparatus (camera 2) and is decoded and the range of an object is measured by triangulation based on image correspondence points.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Image stabilization apparatus and image pickup apparatus
InactiveUS20100315520A1Accurate image stabilizationReduce the amount of calculationTelevision system detailsPrintersObject basedStabilization control
An image stabilization apparatus has an angular velocity detector detecting an angular velocity applied thereto and outputting the angular velocity, an acceleration detector detecting an acceleration applied to the image stabilization apparatus and outputting the acceleration, a principal point calculation unit calculating a principal point position of a shooting optical system, an rotation angular velocity calculation unit calculating a rotation angular velocity component about the principal point of the shooting optical system based on an output of the angular velocity detector, a revolution angular velocity calculation unit calculating a revolution angular velocity component about an object based on the output of the acceleration detector and a calculation result of the rotation angular velocity calculation unit and correcting the calculated revolution angular velocity component according to the principal point position, and a controlling unit performing image stabilization control based on a difference between the rotation and corrected revolution angular velocity components.
Owner:CANON KK
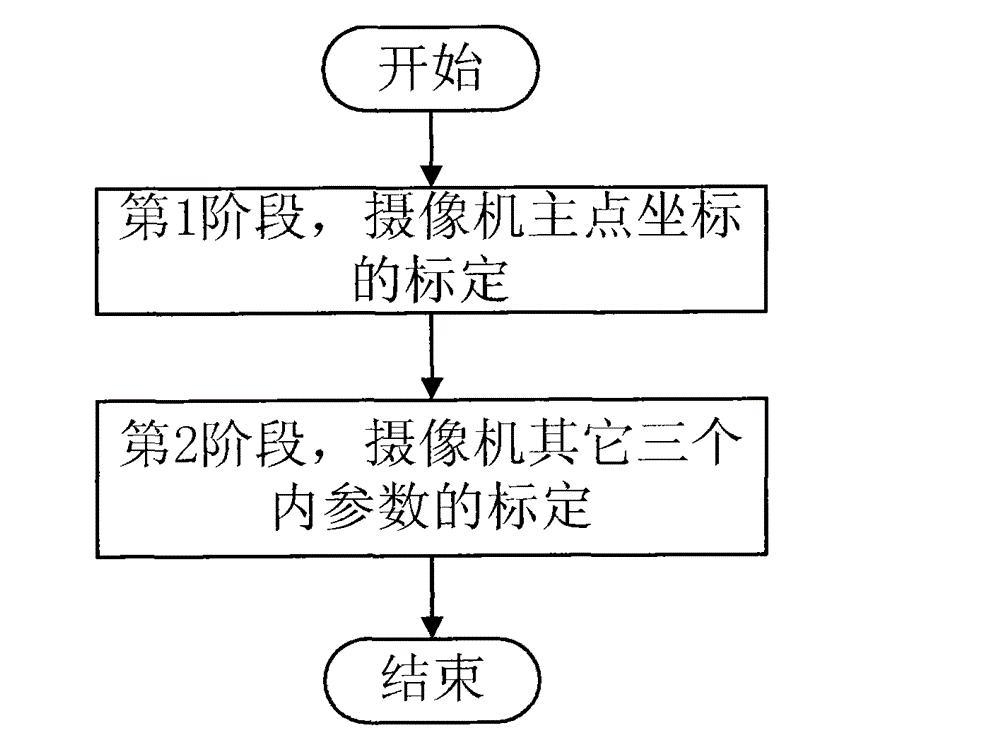
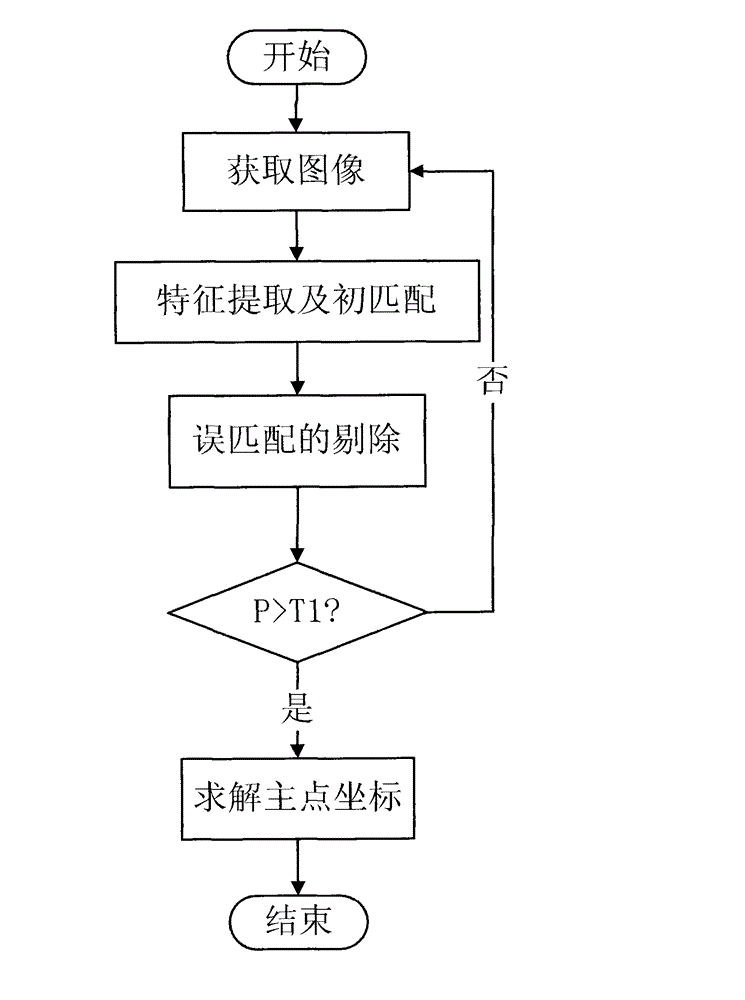
Step-by-step video camera self-calibration method
InactiveCN102750704AImprove calibration accuracyHigh precisionImage analysisFeature extractionThree dimensional measurement
The invention provides a step-by-step video camera self-calibration method, which comprises the following steps: in the first phase, shooting two images of the same scene at different focal lengths, performing feature extraction and matching on the images and eliminating mismatching points, and solving principal point coordinates of the video camera by using matching point pairs; and in the second phase, shooting the same scene from different angles to obtain three images available for matching, and performing feature extraction and matching on the images and eliminating mismatching points, and then based on Kruppa equation, substituting the obtained principal point coordinates into the equation to accomplish solving the three parameters of an obliquity factor, as well as scale factors of the video camera in the directions U and V axes of an imaging plane. By using the method provided by the invention, the calibration accuracy of the principal point coordinates of the video camera is relatively high, and the coefficient matrix size of the Kruppa equation is reduced, the amount of solving computation is reduced, and the method has the characteristic of being real-time. The method is applicable to video camera calibration of a vision system and can be used in the fields of three-dimensional measurement, three-dimensional reconstruction, machine navigation, augment reality and the like.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for implementing high-precision orientation and evaluating orientation precision of large-scale dynamic photogrammetry system
ActiveUS9857172B1Easy to processEasy to measureImage enhancementImage analysisIn planeKinetic photography
The present invention provides a method for implementing high-precision orientation and evaluating orientation precision of a large-scale dynamic photogrammetry system, including steps: a) selecting a scale bar, arranging code points at two ends of the scale bar, and performing length measurement on the scale bar; b) evenly dividing a measurement space into multiple regions, sequentially placing the scale bar in each region, and photographing the scale bar by using left and right cameras; d) limiting self-calibration bundle adjustment by using multiple length constraints, adjustment parameters including principal point, principal distance, radial distortion, eccentric distortion, in-plane distortion, exterior orientation parameter and spatial point coordinate; and e) performing traceable evaluation of orientation precision of the photogrammetry system. The present invention can effectively reduce the relative error in length measurement.
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION SCI & TECH UNIV
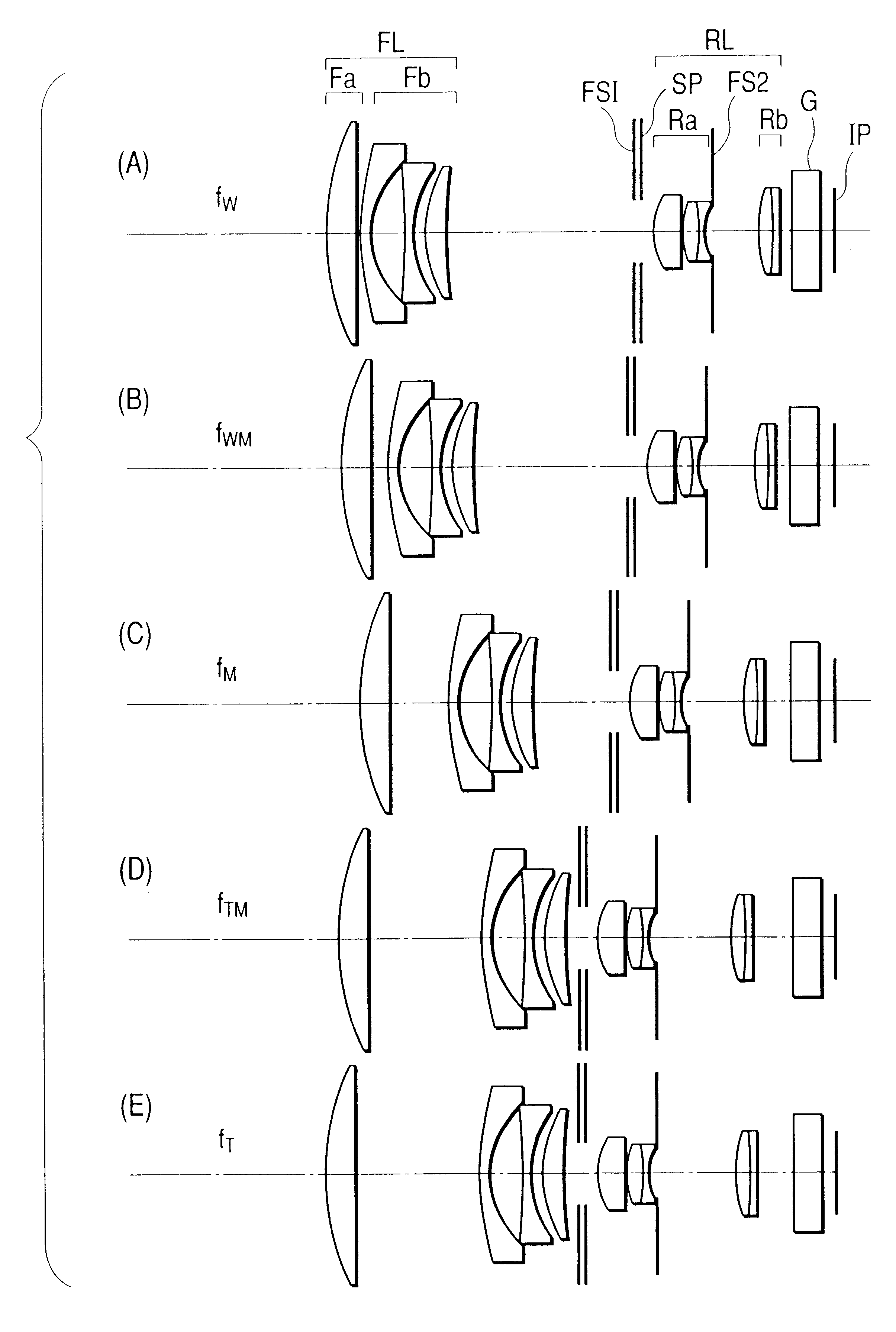
Wide-angle lens system
A wide-angle lens system includes a negative first meniscus lens element, a positive second lens element, a positive third biconvex lens element, and a negative fourth meniscus lens element, in this order from the object;wherein said wide-angle lens system satisfies the following condition: 0.25<H / (p3+p4)<0.60wherein H designates the distance between the second principal point of the positive third biconvex lens element and the first principal point of the negative fourth meniscus lens element, when the focal length of the entire wide-angle lens system is normalized to 1.0;p3 designates the refractive power of the positive third biconvex lens element when the focal length of the entire wide-angle lens system is normalized to 1.0;f3 designates the focal length of the positive third biconvex lens element when the focal length of the entire wide-angle lens system is normalized to 1.0, i.e., p3=1 / f3;p4 designates the refractive power of the negative fourth meniscus lens element when the focal length of the entire wide-angle lens system is normalized to 1.0; andf4 designates the focal length of the negative fourth meniscus lens element wherein the focal length of the entire wide-angle lens system is normalized to 1.0, i.e., p4=1 / f4.
Owner:RICOH IMAGING COMPANY
Camera calibration system using planar concentric circles and method thereof
InactiveUS7155030B2Improve calibration reliabilityTelevision system detailsImage analysisMinimization algorithmCamera auto-calibration
The invention relates to a camera calibration system and method thereof which is capable of easily performing camera calibration using a concentric circle pattern. According to the invention, a method of calibrating a camera calibrates the intrinsic parameters of the camera required to measure geometric information of an object using projection invariable characteristics of concentric circles. The method includes the steps of taking images of the calibration pattern consisting of two or more concentric circles located in the same plane and having different radius at different angles to obtain projected images calculating the central point of the projected images using a given algorithm, and calculating the principal point and focal point of camera using a nonlinear minimization algorithm based on the central point thus obtained.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Zoom lens and image projection apparatus having same
A zoom lens telecentric on a reduction side includes a first negative lens, a second negative lens and a first positive lens arranged from the enlargement side to the reduction side. At least one of the first and second negative lenses has an aspherical surface. The zoom lens satisfies −f12 / fw<1.4, −f12 / (Hwpn−f12)<0.6 and |dn / dt|<1.0×10−5, where f12 is the focal length of the combined optical system composed of the first and second negative lenses, Hwpn is the distance from the rear principal point of the combined optical system composed of the first and second negative lenses to the front principal point of the first positive lens, dn / dt is a change in the refractive index of the material of which said one negative lens is made relative to a change in its temperature from 25° C., and fw is the focal length of the entire lens system at the wide angle end.
Owner:CANON KK
Zoom lens and image pickup apparatus having the same
InactiveUS20070058264A1Reduce image qualityQuality improvementTelevision system detailsOptical elementsCamera lensOptical axis
A zoom lens in which a precise focus detection signal can be detected while a user can observe an image to be shoot without being affected by insertion / removal of an extender lens into an optical axis. A relay lens unit stationary during zooming includes lens unit L21 including a branch element, lens unit L22 interchangeable with extender lens unit insertable into / removable from optical path to change focal length range of the entire system and positive lens unit L23 in order from object side to image side, and the zoom lens satisfies specific conditions among distance from an aperture stop to front principal point of L21, distance from rear principal point of L21 to front principal point of L22, distance from rear principal point of L22 to front principal point of L23, refractive power of L21, and refractive power of the entire system of the zoom lens at wide-angle end.
Owner:CANON KK
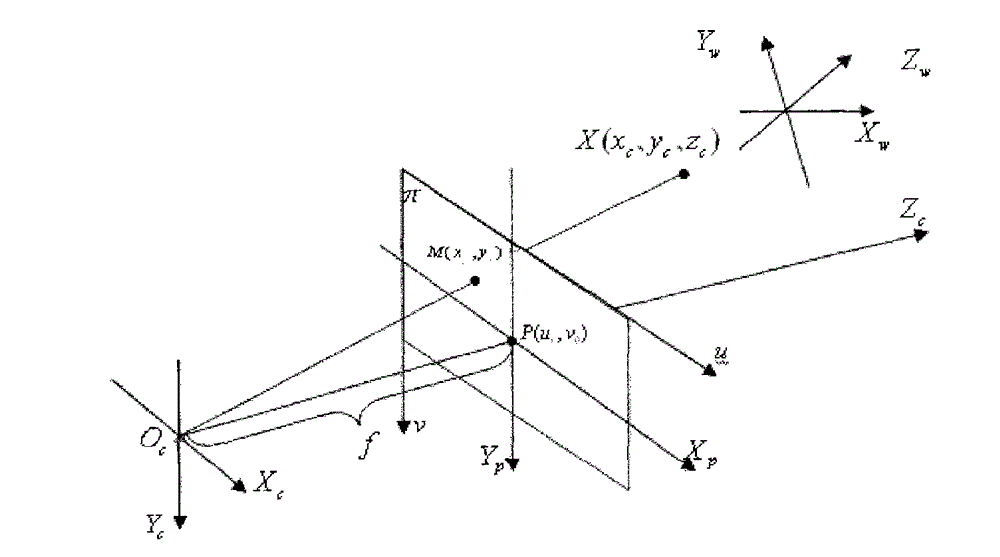
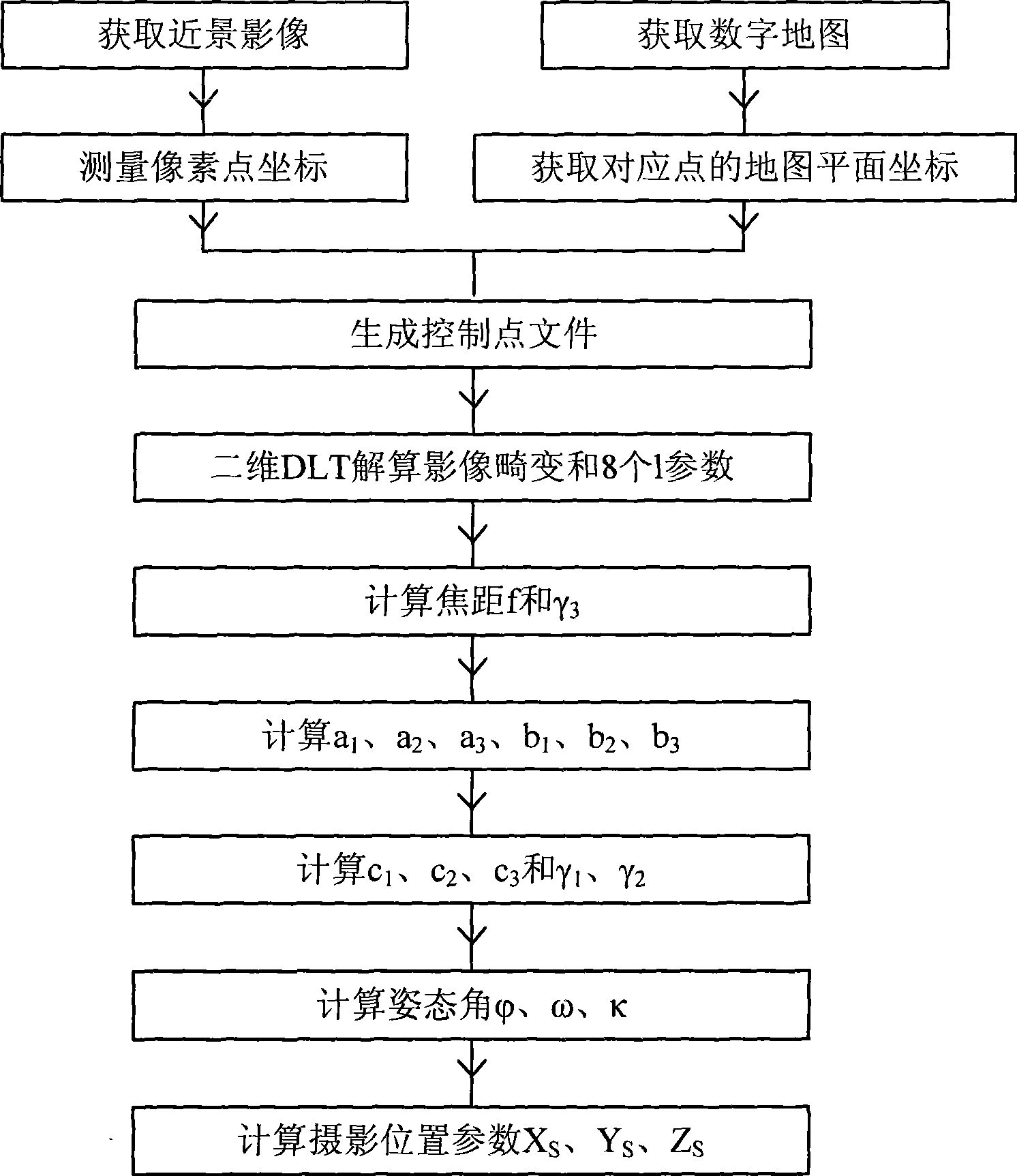
Method for obtaining digital photo orientation elements based on digital map
The invention provides a method for obtaining digital photo orientation elements based on a digital map. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, a digital photo and a digital map corresponding to the digital photo are shot, wherein the digital photo comprises at least five ground object points, and the digital map comprises homologous points corresponding to the ground object points; the ground object points and the homologous points are totally called as control points; the digital photo is provided with a phone two-dimensional coordinate system, and the digital map is provided with a digital map coordinate system; step 2, coordinates of the control points in the digital map coordinate system and the phone two-dimensional coordinate system and coordinates of a photo principal point in the phone two-dimensional coordinate system are obtained, wherein the photo principal point is a perpendicular foot point of a shooting lens center on the photo; and step 3, a photogrammetric coordinate system D-XDYDZD is established. The invention utilizes the prior digital map as a condition to calculate the orientation elements of a common digital image, thereby providing a simple, convenient and rapid low-cost path for obtaining three-dimensional space information and having small field operation workloads and low expense.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Wide-Angle Lens System, Image Sensing Optical Device and Digital Apparatus
InactiveUS20140055558A1Large apertureReduce focusTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptical axisNegative power
A wide-angle lens system is formed, sequentially from an object side, with a first group having a positive power, a second group having a negative power and a third group having a positive power, and at the time of focusing, only the second group is moved on an optical axis. The lens system satisfies conditional formulas of 0.3<BH1 / T1<0.7 and 0.9<f3 / f<1.8 (where BH1 is a distance from the final surface of the first group to a principal point position on the back side of the first group, T1 is a distance on the optical axis from a lens element surface of the first group closest to the side of the object to a lens element surface closest to the side of the image, f3 is the focal length of the third group and f is the focal length of the entire system).
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
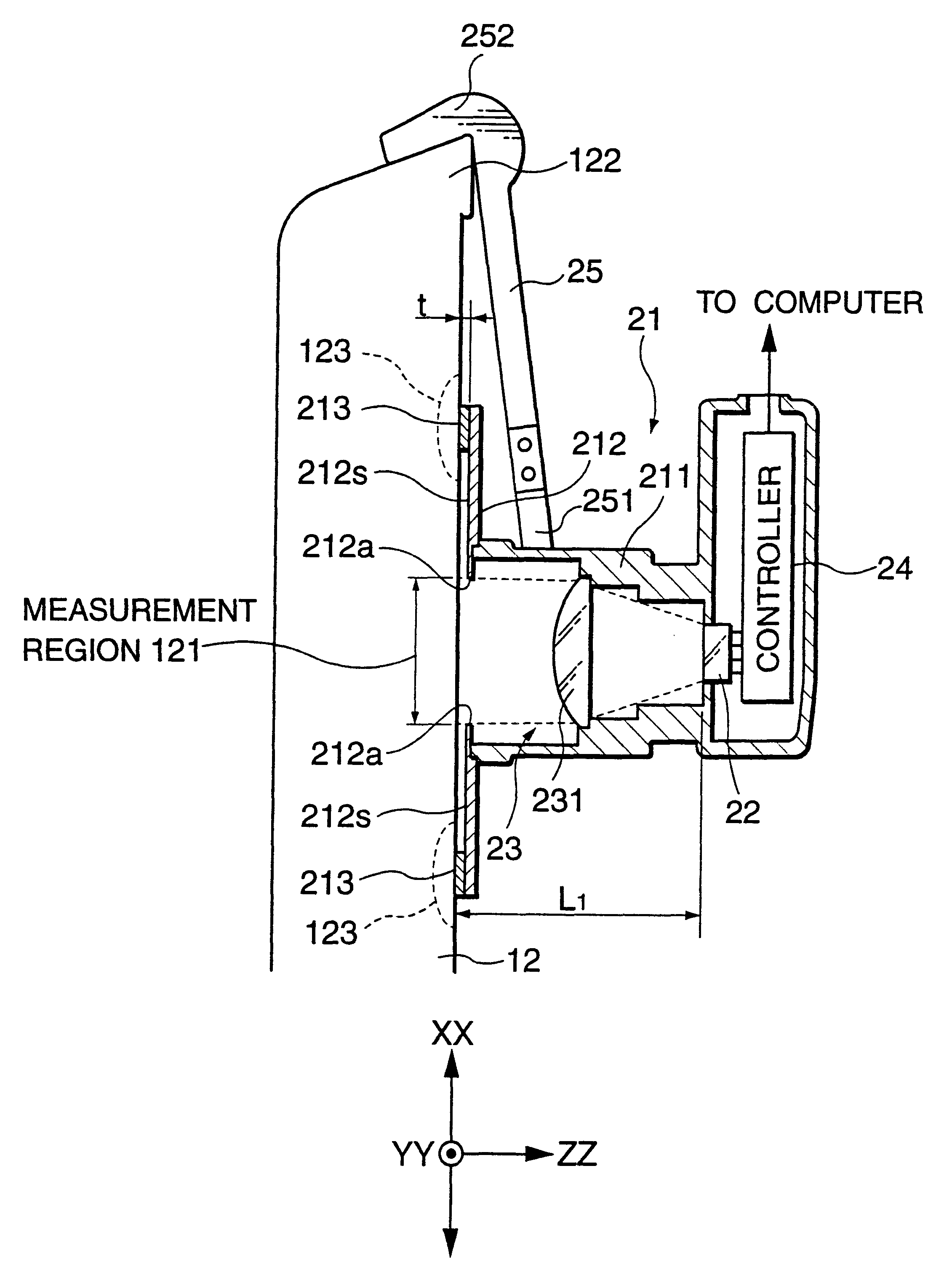
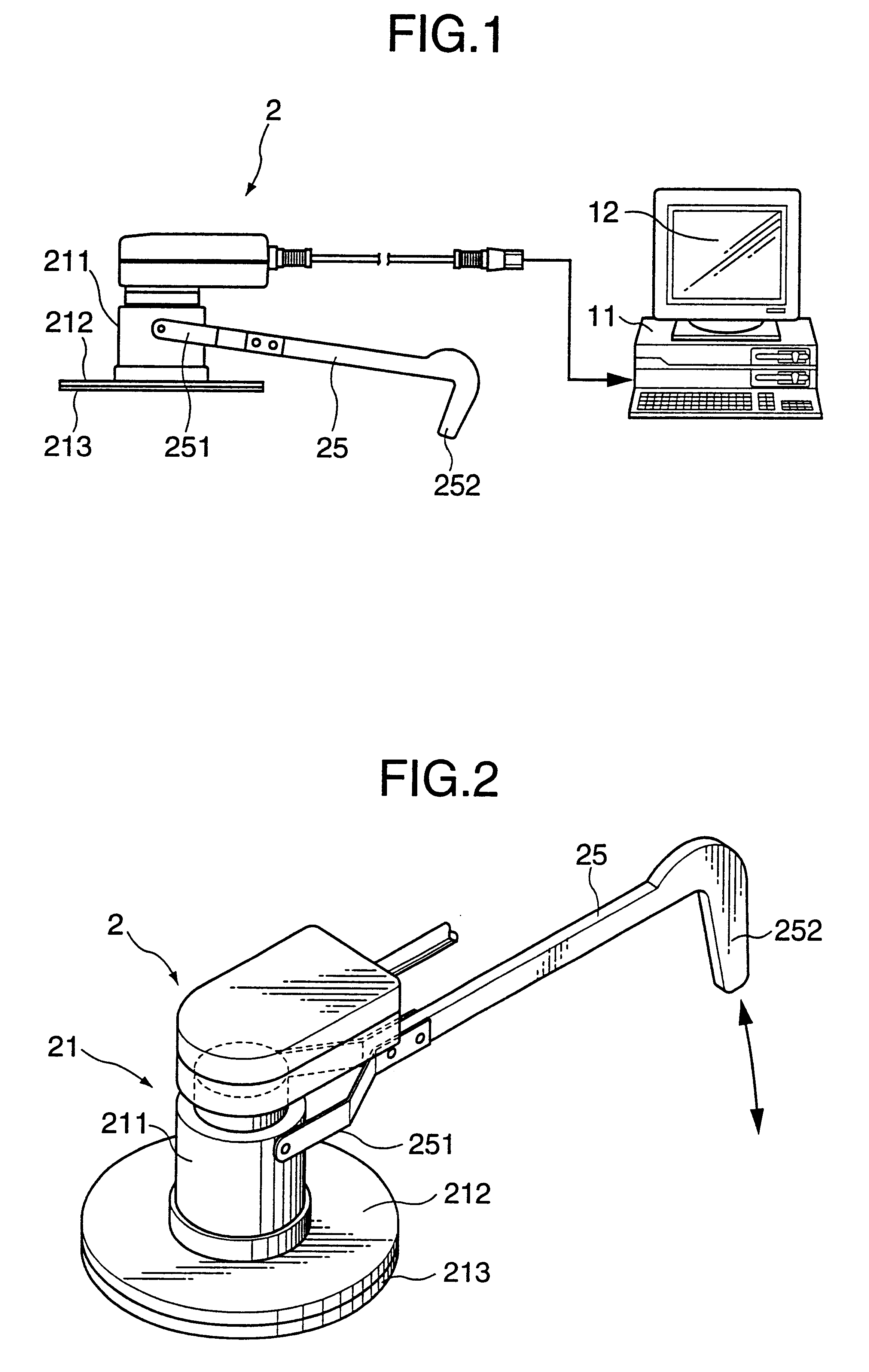
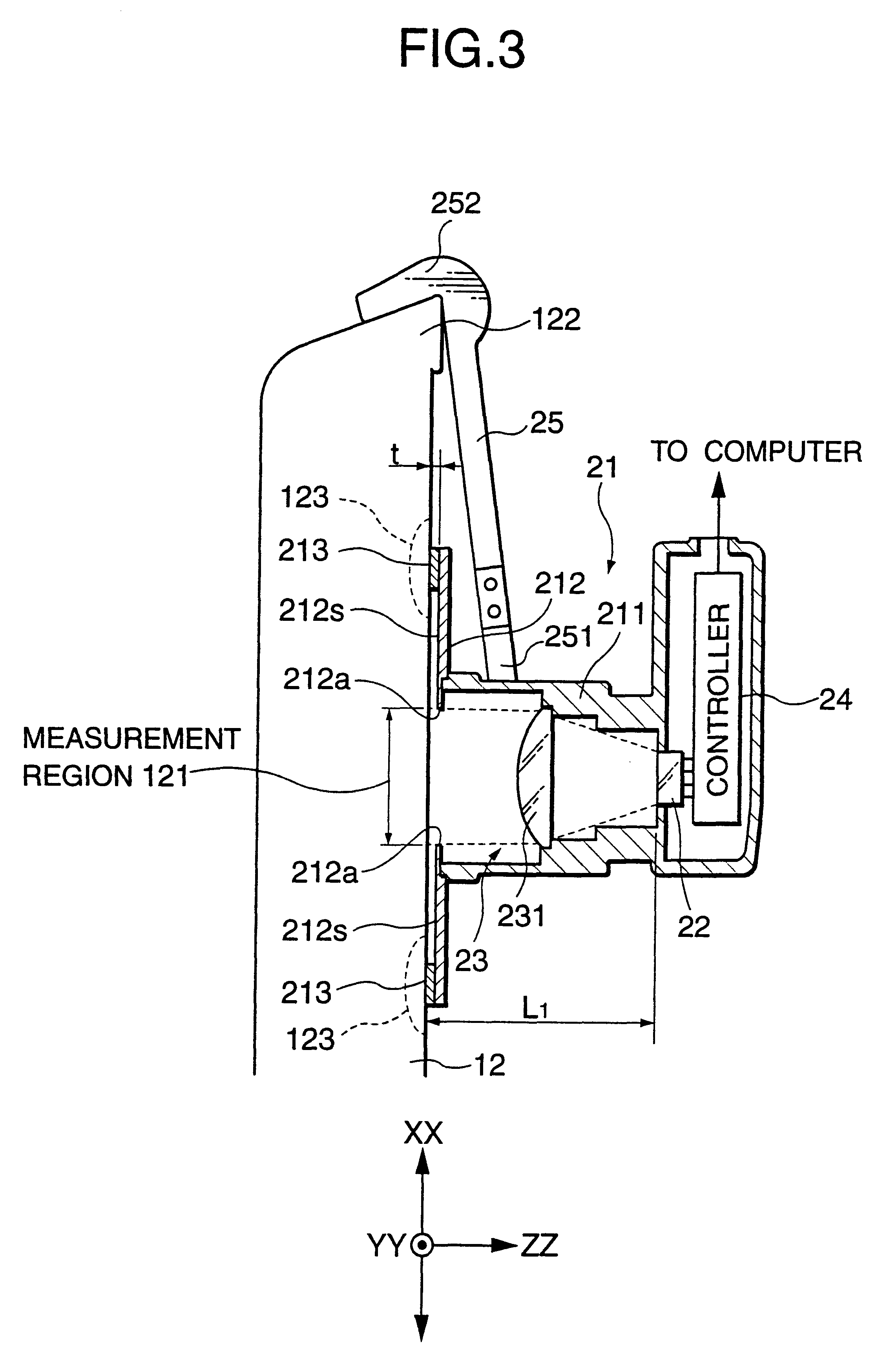
Shape measurement device
Disclosed is a shape measurement device including: a light irradiation unit which irradiates linear light onto a work; an imaging element which images reflected light reflected by the work; and an image-forming lens which forms an image of the reflected light reflected by the work on an imaging plane of the imaging element, and a light irradiation plane of the light irradiation unit, a principal plane including a principal point of the image-forming lens, and the imaging plane of the imaging element satisfy a Scheimpflug principle. The shape measurement device further includes: an image obtaining region selection unit which divides the imaging plane of the imaging element into a plurality of regions, and selects, as an image obtaining region, a region for use in measurement from the plurality of regions in response to at least one of measurement accuracy and a size of a measurement range.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
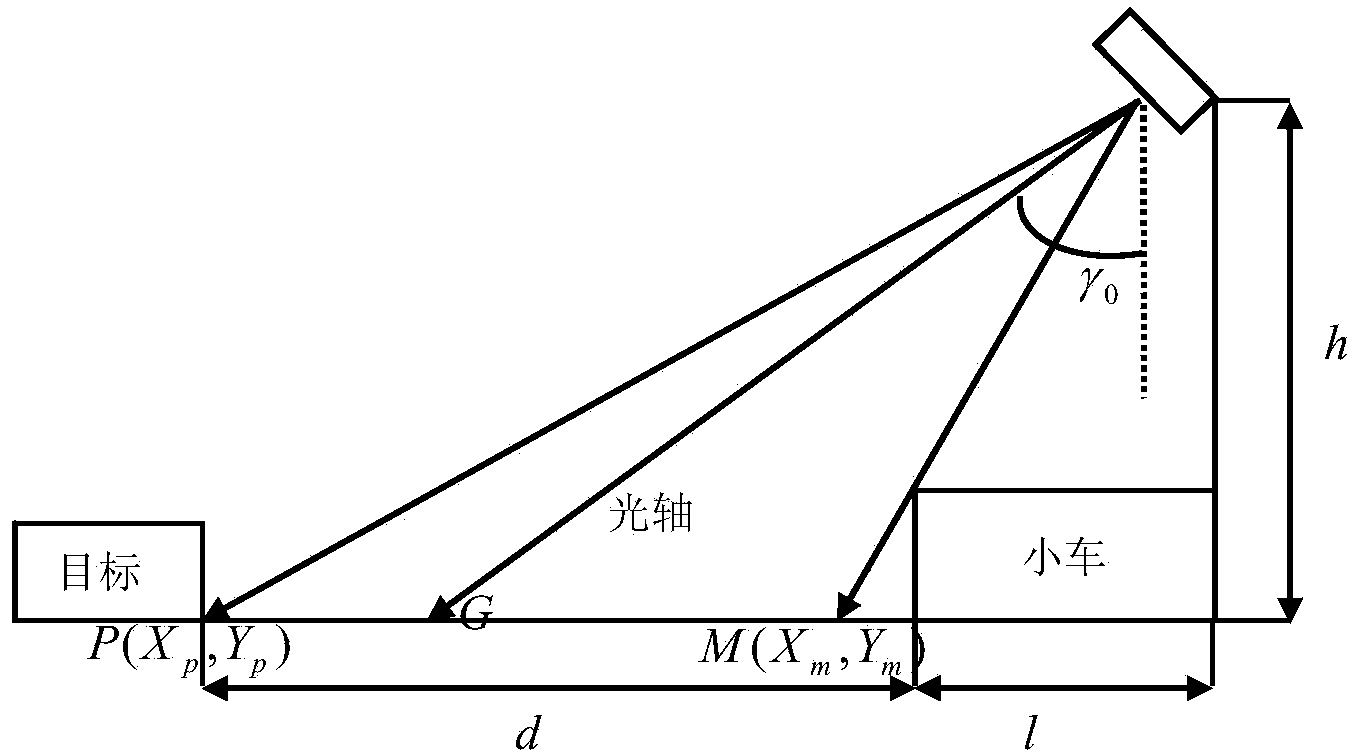
Real-time positioning method based on monocular vision
InactiveCN104034305AHigh measurement accuracyEasy to measureAngle measurementImage analysisPrincipal pointMeasurement precision
The invention relates to a real-time positioning method based on monocular vision. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, calibrating a camera to obtain an inner parameter matrix R; and after calibrating the camera, solving a distance D1 from a ground specified point P to be detected to a reference point M and an angle between a vector (shown in the specification) and a center line of a trolley according a basic pin-hole imaging principle through geometric transformation. According to the method provided by the invention, on the basis of common geometric conversion positioning, a principal point of the camera is commonly not at the center of an image; the geometric correction is carried out and the measurement precision is improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
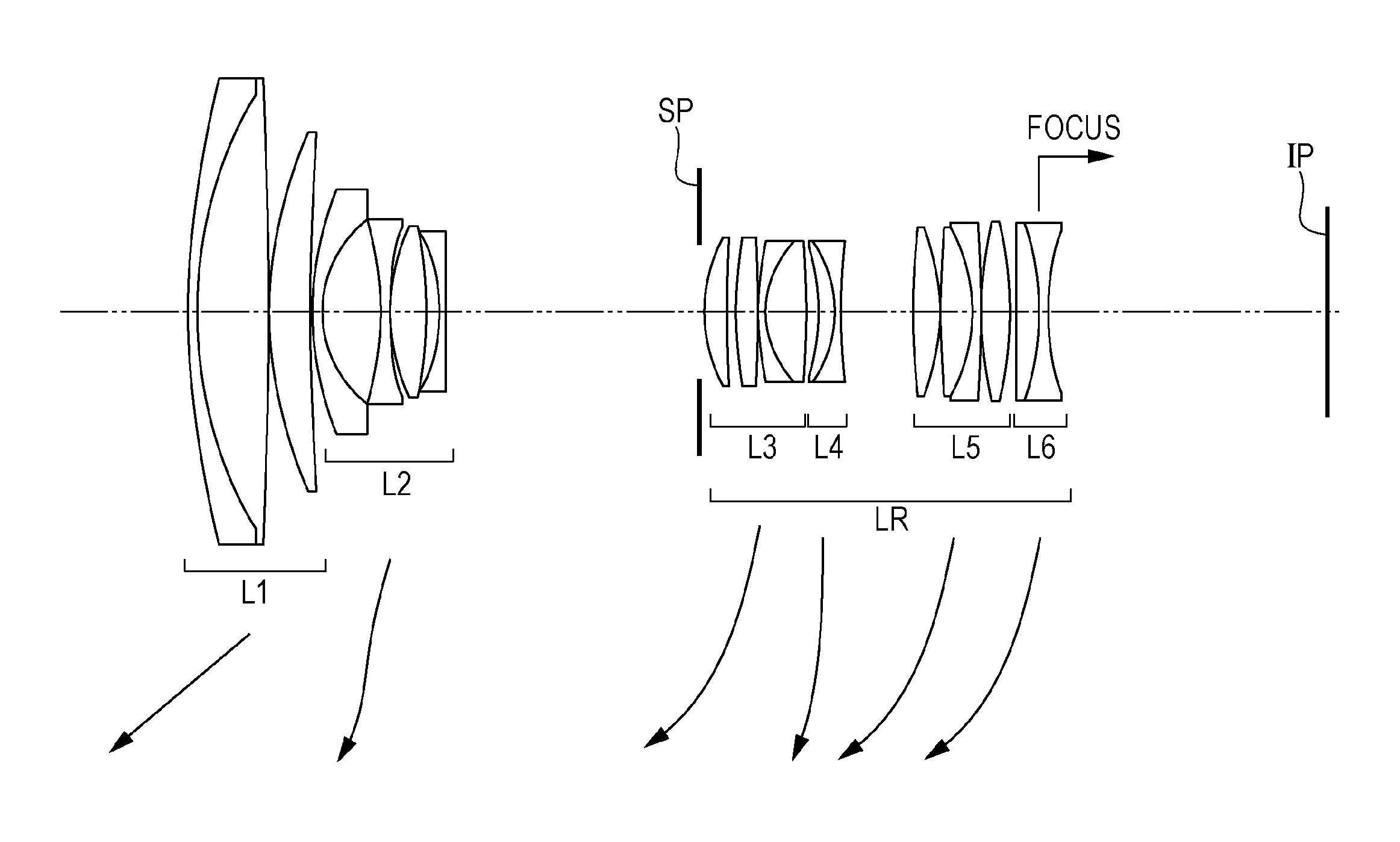
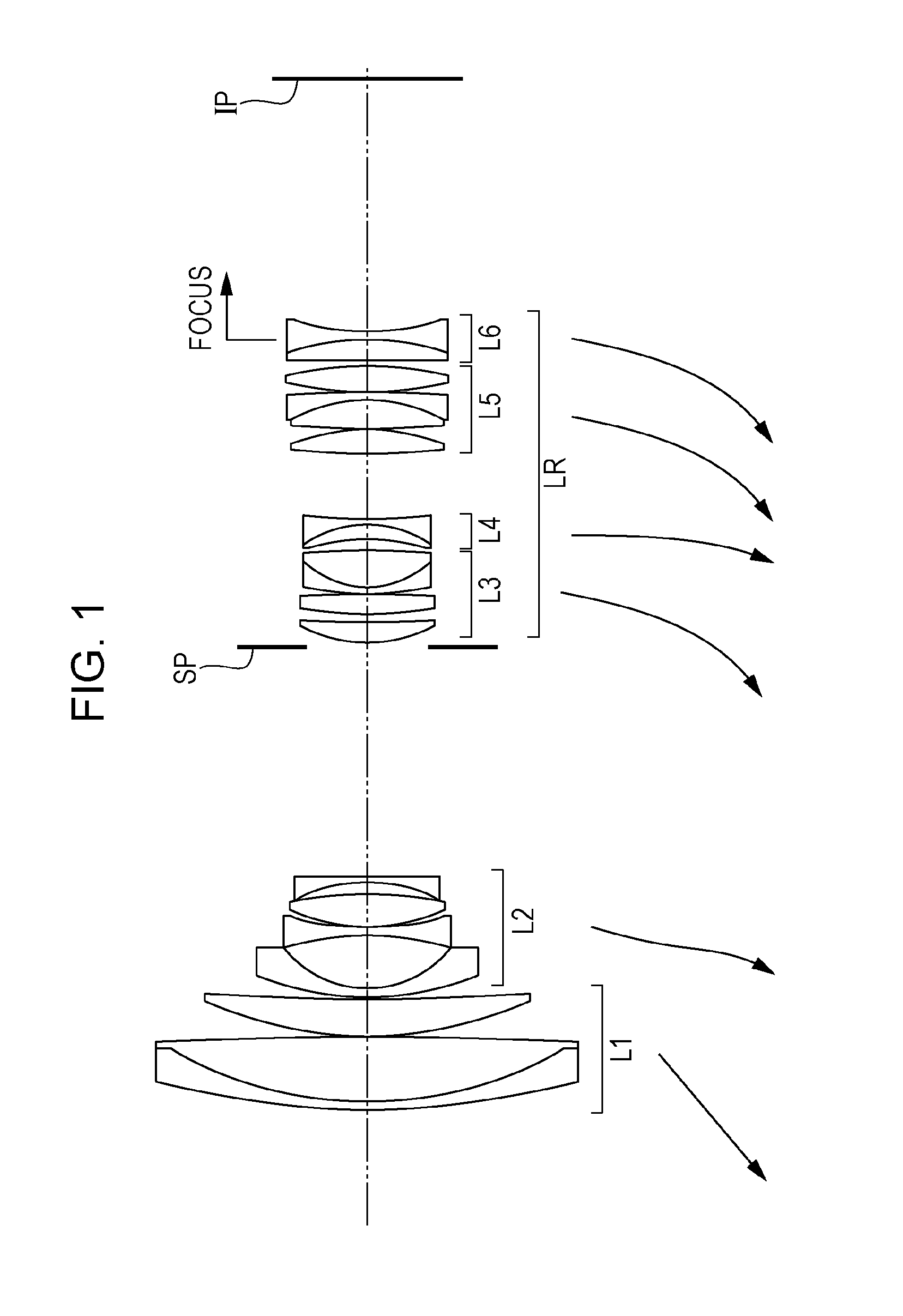
Image taking lens system
This specification discloses an image taking lens system which can quickly effect focusing from an infinity object to a short-distance object. The image taking lens system disclosed in the present specification has, in succession from an object side to an image side, a first lens unit, a second lens unit, a third lens unit and a fourth lens unit. In case of focusing from the infinity object to the short-distance object, the first lens unit is not moved, but the second lens unit is moved to the image side and the third lens unit is moved to the object side. The principal point interval between the first lens unit and the second lens unit is a negative value.
Owner:CANON KK
Panoramic three-dimensional adapter for an optical instrument and a combination of such an adapter and such an optical instrument
An adapter is provided for adapting an optical instrument, such as a camera (3) or a projector, to capture or display panoramic three-dimensional images. The adapter comprises a plurality of mirrors (1a, 1b, 1c), each of which has a reflective surface which is in the shape of a curved non-circular conic section rotated about an axis of symmetry (15a, 15b, 15c). The reflective surfaces have first foci which are spaced perpendicularly from a longitudinal axis of the adapter and which are angularly spaced around the longitudinal axis. For example, the conic section may be a hyperbola with first foci equidistantly spaced from the longitudinal axis and equiangularly spaced around 15b the longitudinal axis. The axes of symmetry (15a, 15b, 15c) of the mirrors (1a, 1b, 1c) converge to intersect the longitudinal axis at a point which is coincident with the front principal point of, for example, a camera lens (12). Thus, single shot capture of all the image data for the or each panoramic three-dimensional image may be performed.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method for establishing equivalent geometric imaging model of high-resolution satellite image by using RPC parameters
ActiveCN110500995AHigh positioning accuracyMutual conversion solutionImage enhancementImage analysisSatellite imageModelling analysis
The invention relates to a method for establishing an equivalent geometric imaging model of a high-resolution satellite image by using RPC parameters. The method comprises: selecting a random scanningline of a high-resolution satellite image and listing a collinear condition equation of a projection center, an image point and a corresponding object square point; on the basis of operating characteristics and geometric characteristics of the high-resolution satellite, abstracting three rotation angles and six orbital numbers in an equivalent principal distance, a principal point coordinate, andan offset matrix and forming 11 independent parameters of an equivalent geometric imaging model; and with RPC parameters, calculating parameters of the equivalent geometric imaging model directly. Therefore, inherent problems of the over-parameterization of the RPC, strong correlation between parameters, and residual error existence of the fitting tight imaging model are solved; the parameters have the obvious geometric and physical meanings; and modeling analysis can be carried out on various imaging error sources conveniently. The mutual conversion of RPC parameters is realized; and the positioning accuracy of high-resolution satellite image is improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Zoom lens and image pickup apparatus having the same
A zoom lens includes, from the object side to the image side, first to sixth lens units having positive, negative, positive, negative, positive, negative refracting powers. In zooming from the wide angle end to the telephoto end, the lens units are moved such that the distance between the first and second lens units increases, the distance between the second and third lens units decreases, the distance between the third and fourth lens units increases, and the distance between the fourth and fifth lens units decreases. In focusing from an infinitely distant object to a near object, the sixth lens unit is moved toward the image side. The distance between the rear principal point of the second lens unit and the front principal point of the rear lens group at the wide angle end, and the focal length of the rear lens group at the wide angle end are appropriately set.
Owner:CANON KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com